Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
95 results about "Esophageal stent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
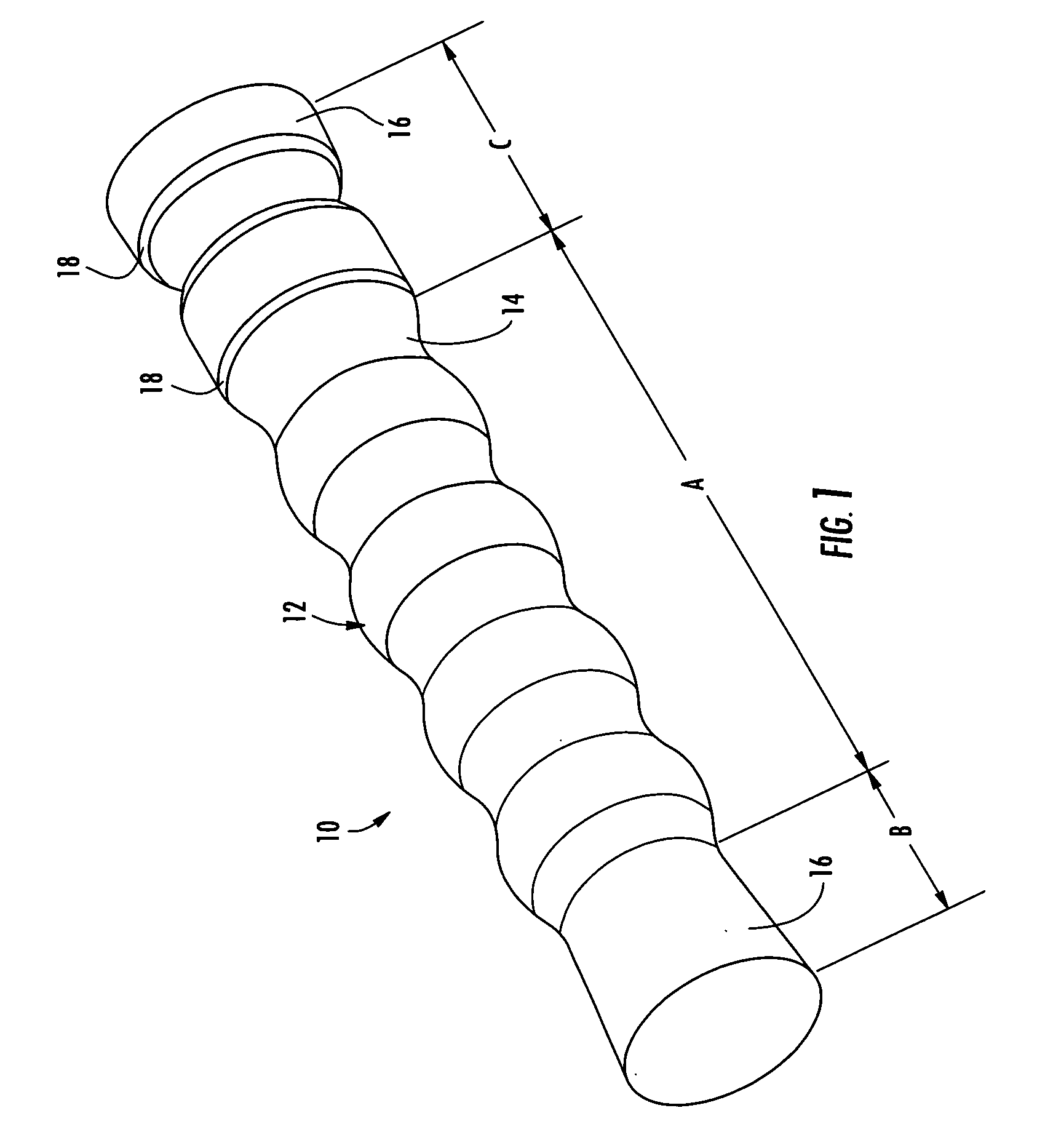
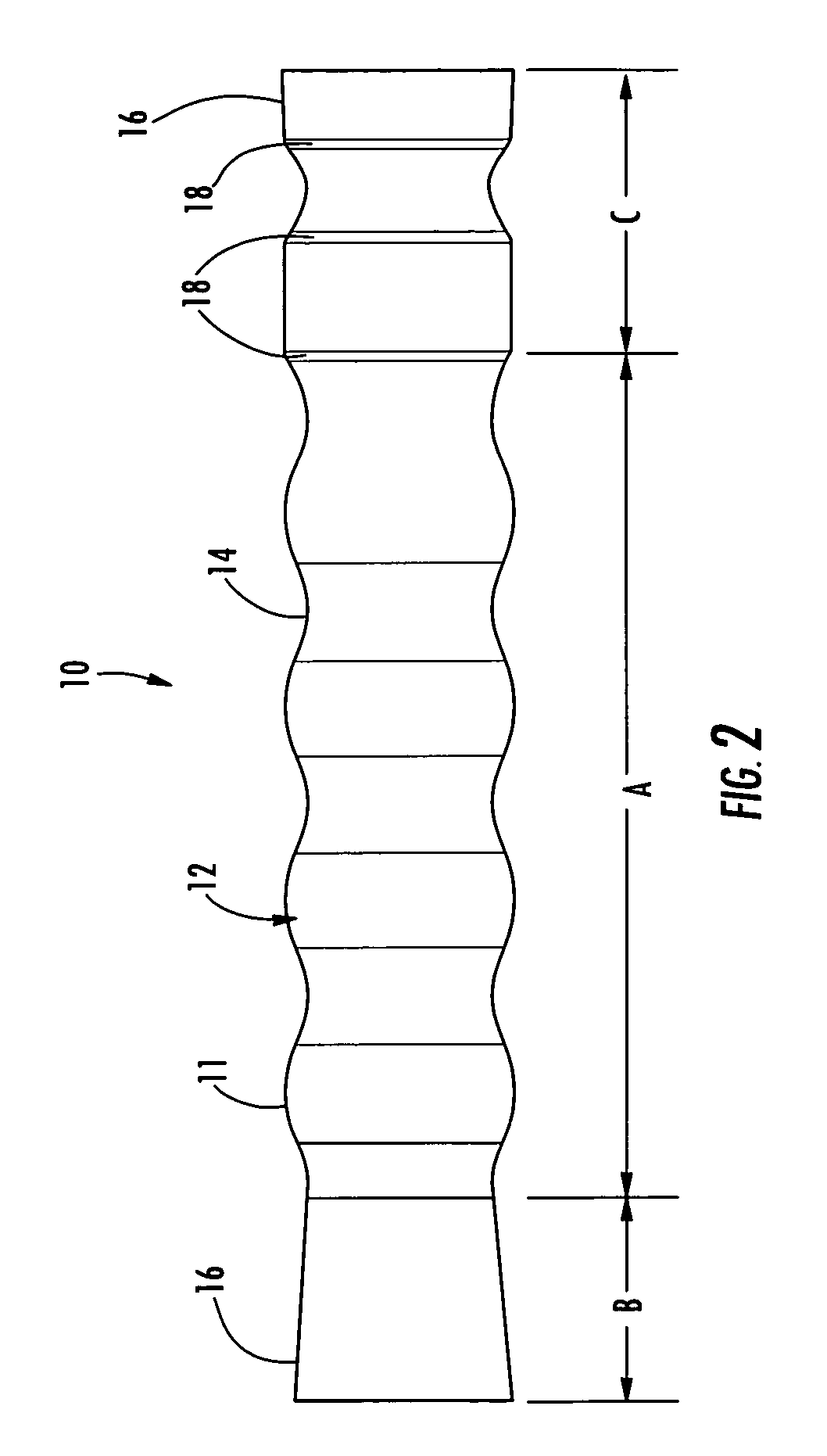
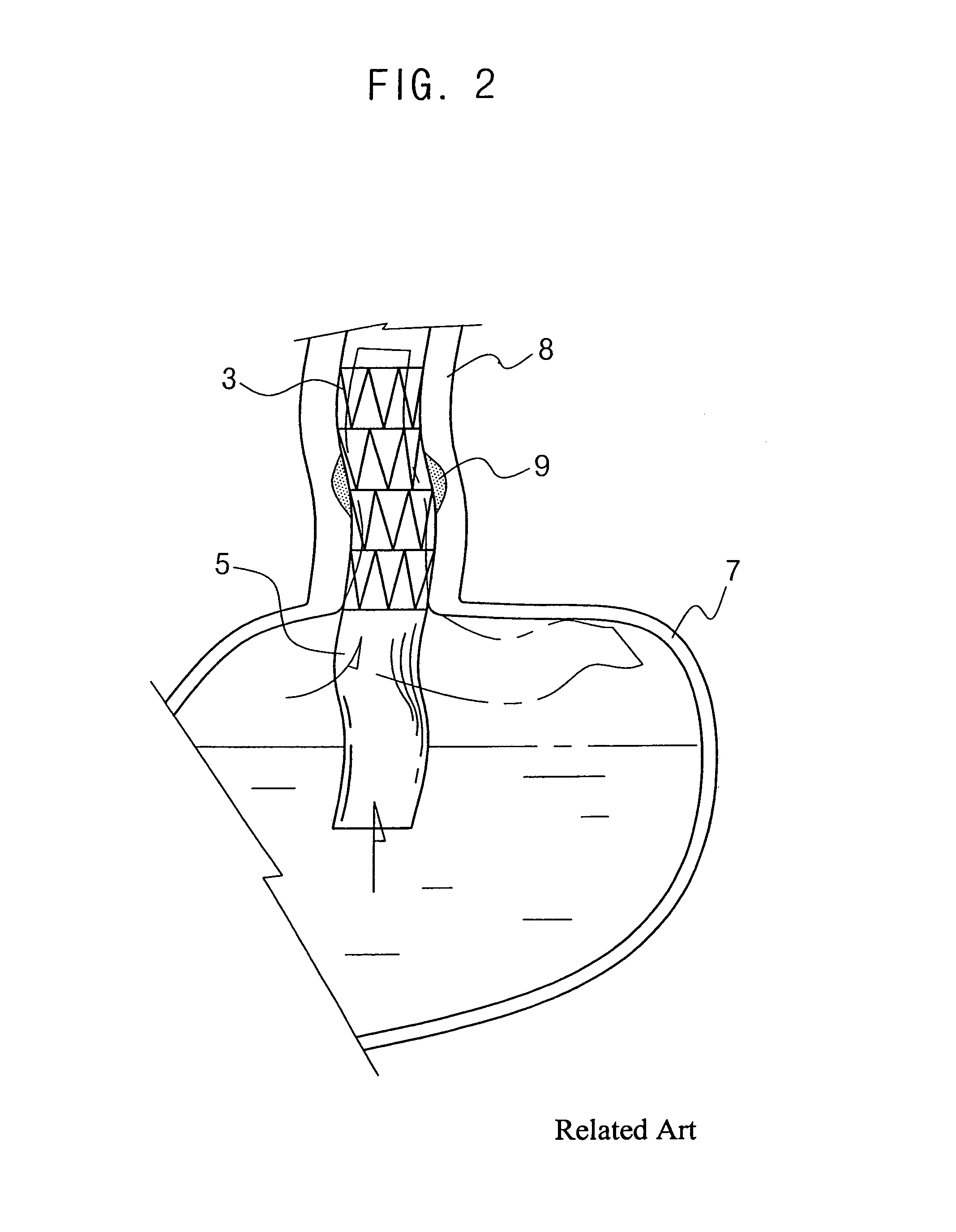
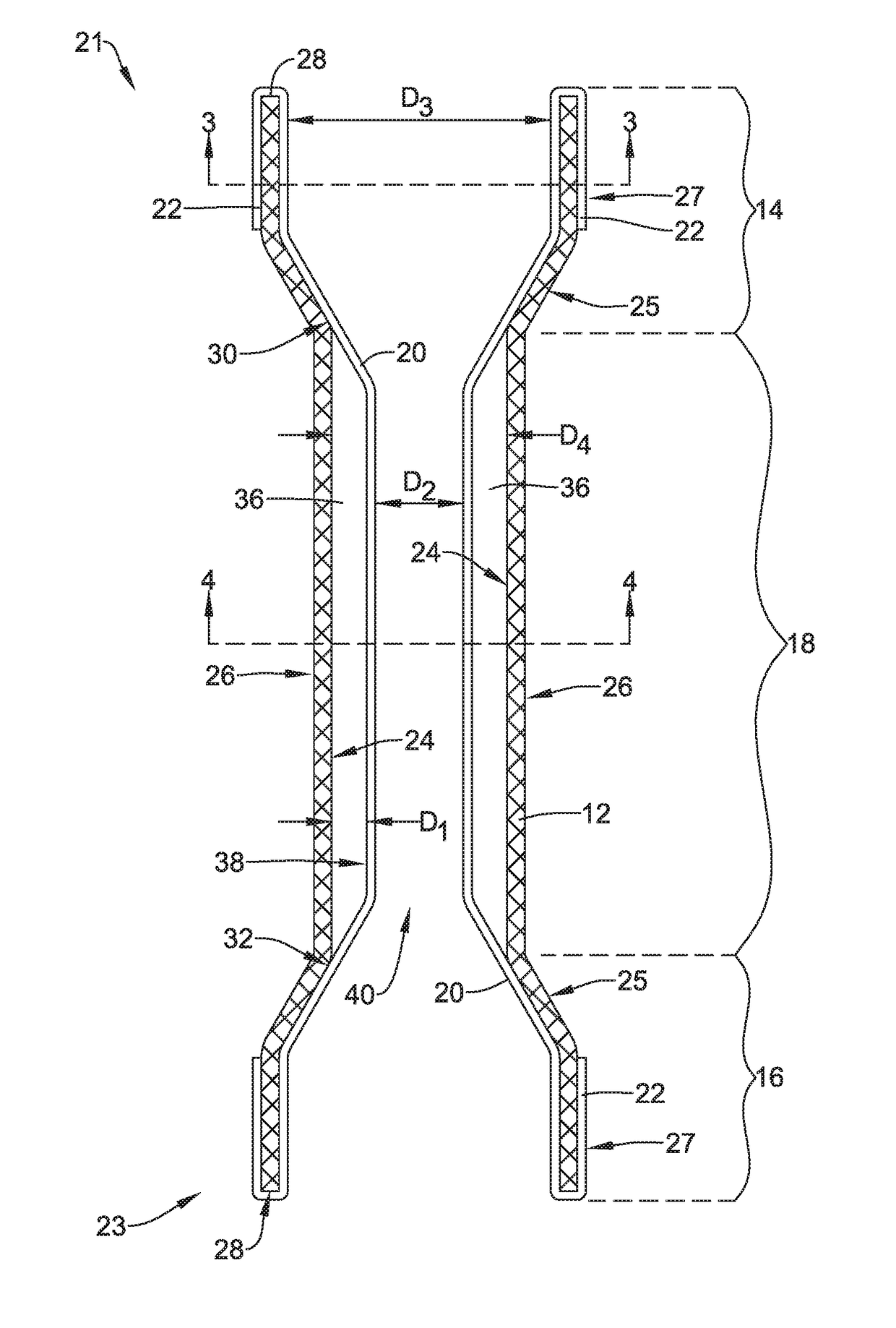
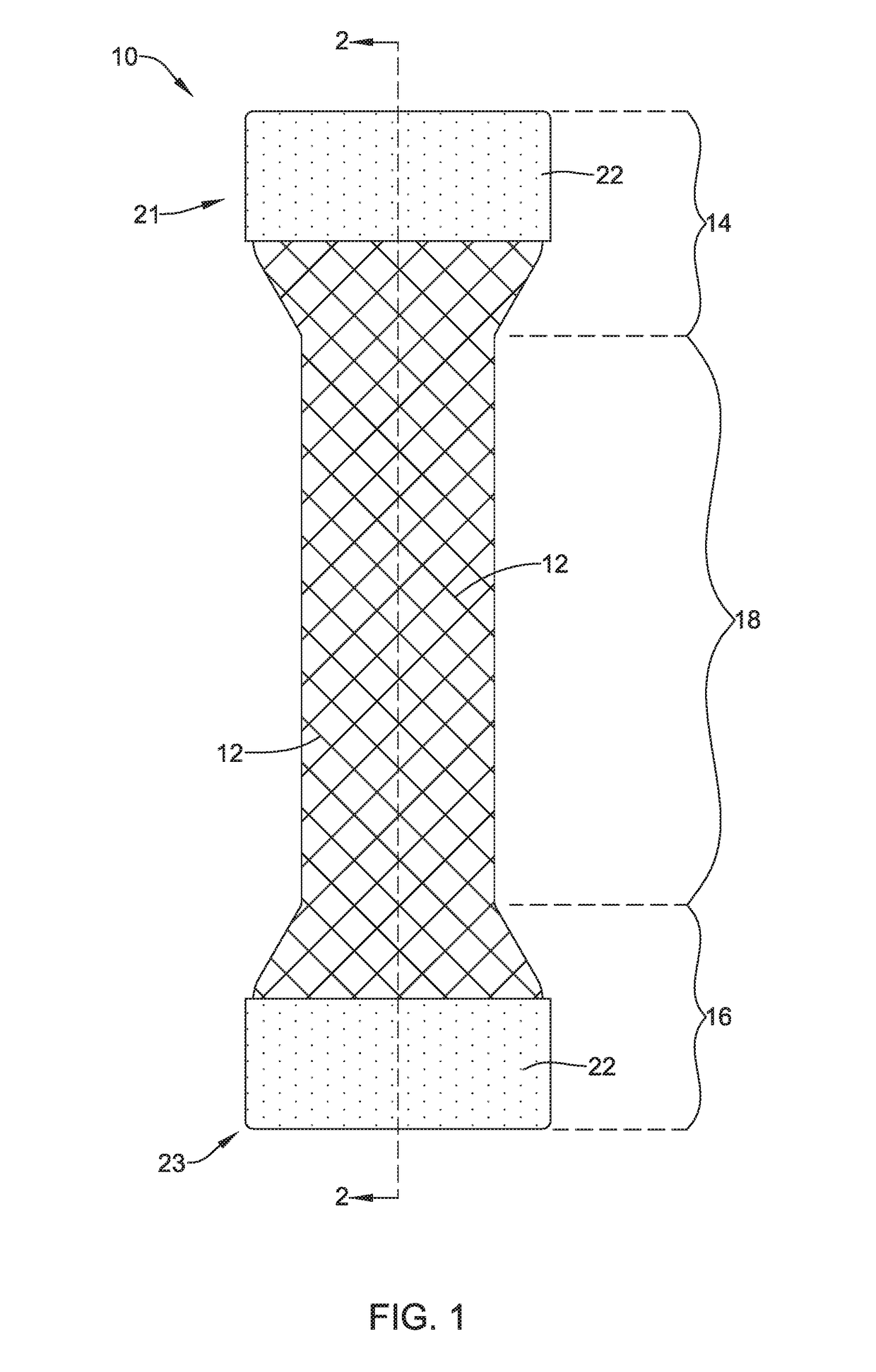
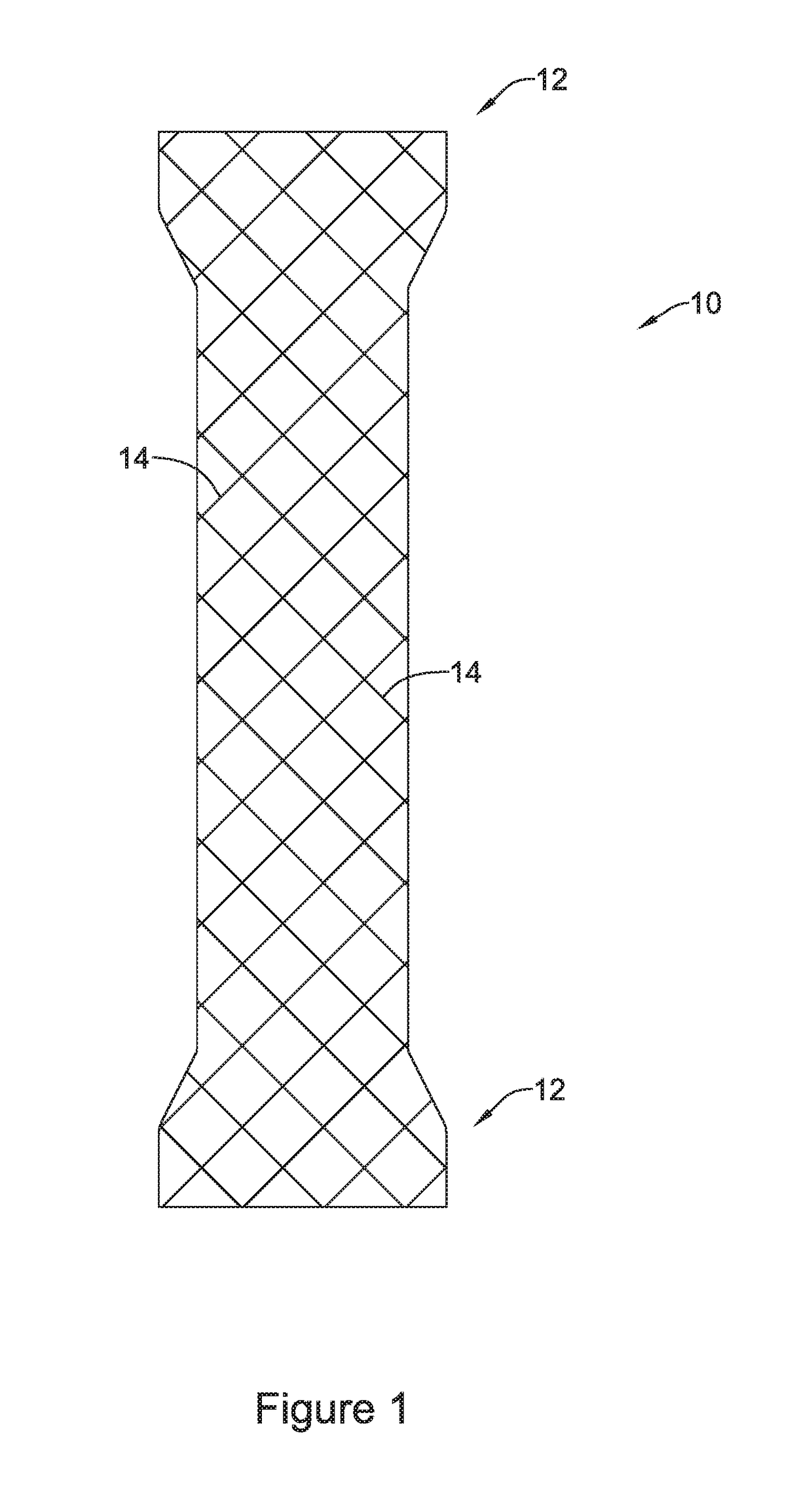
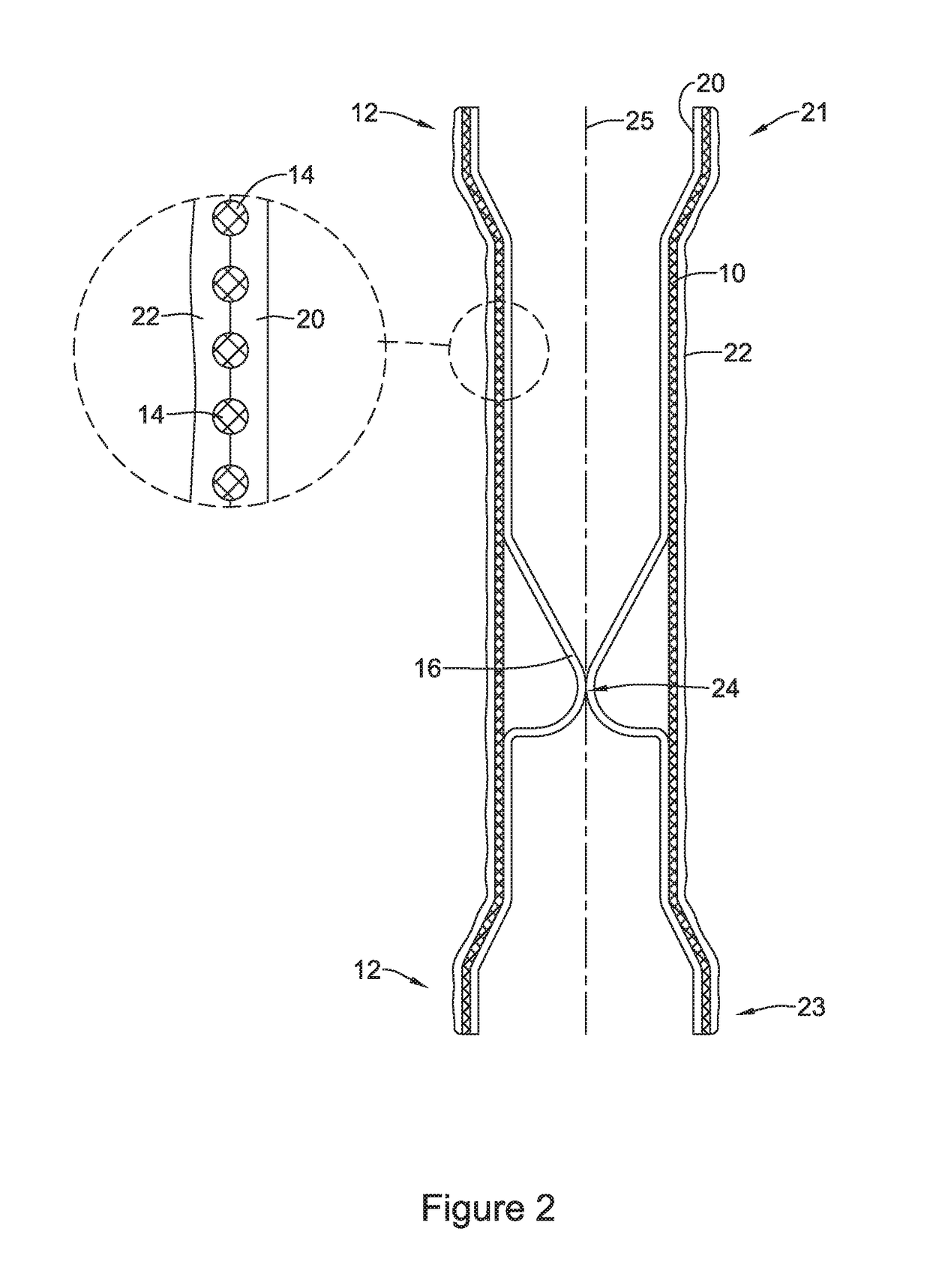
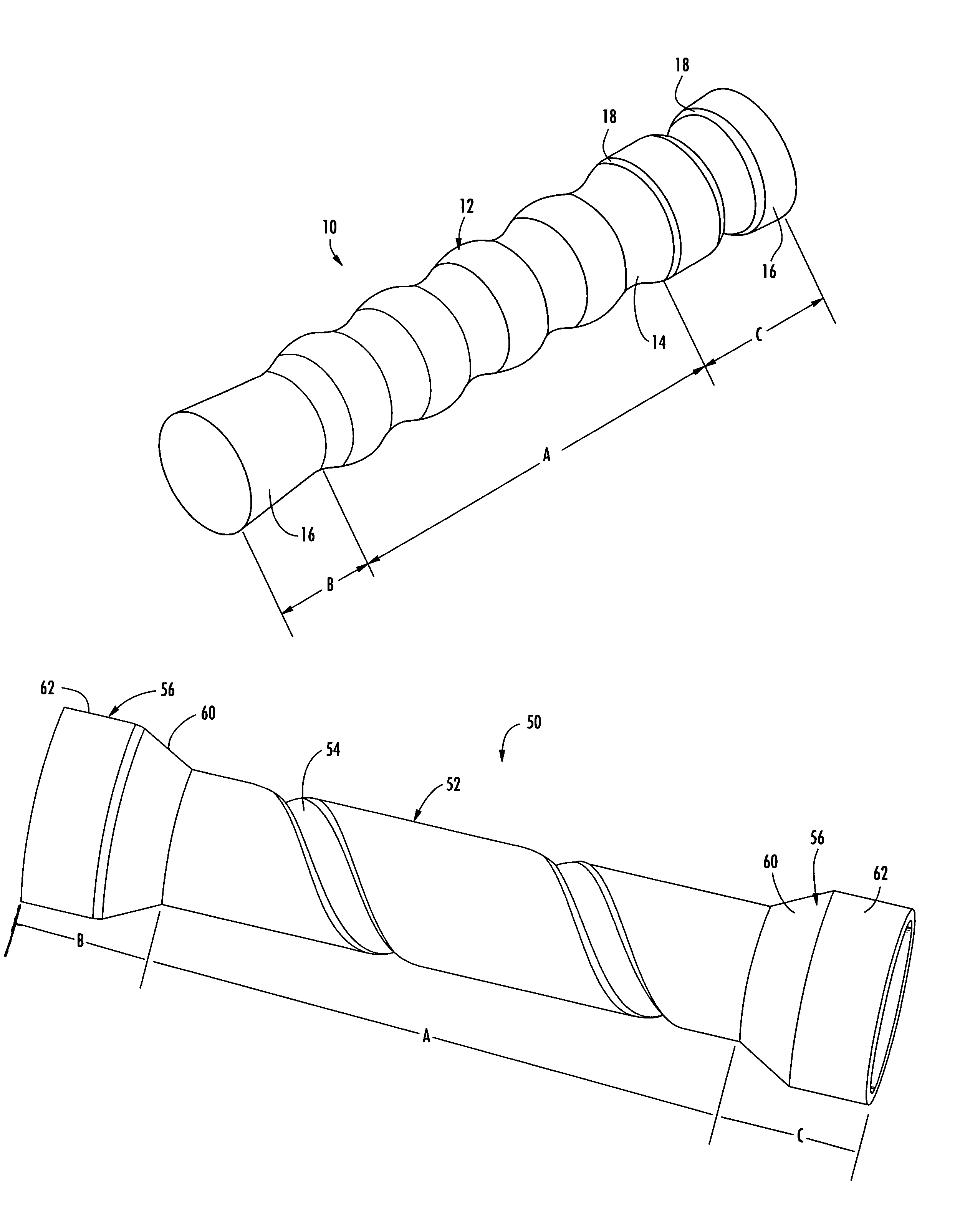
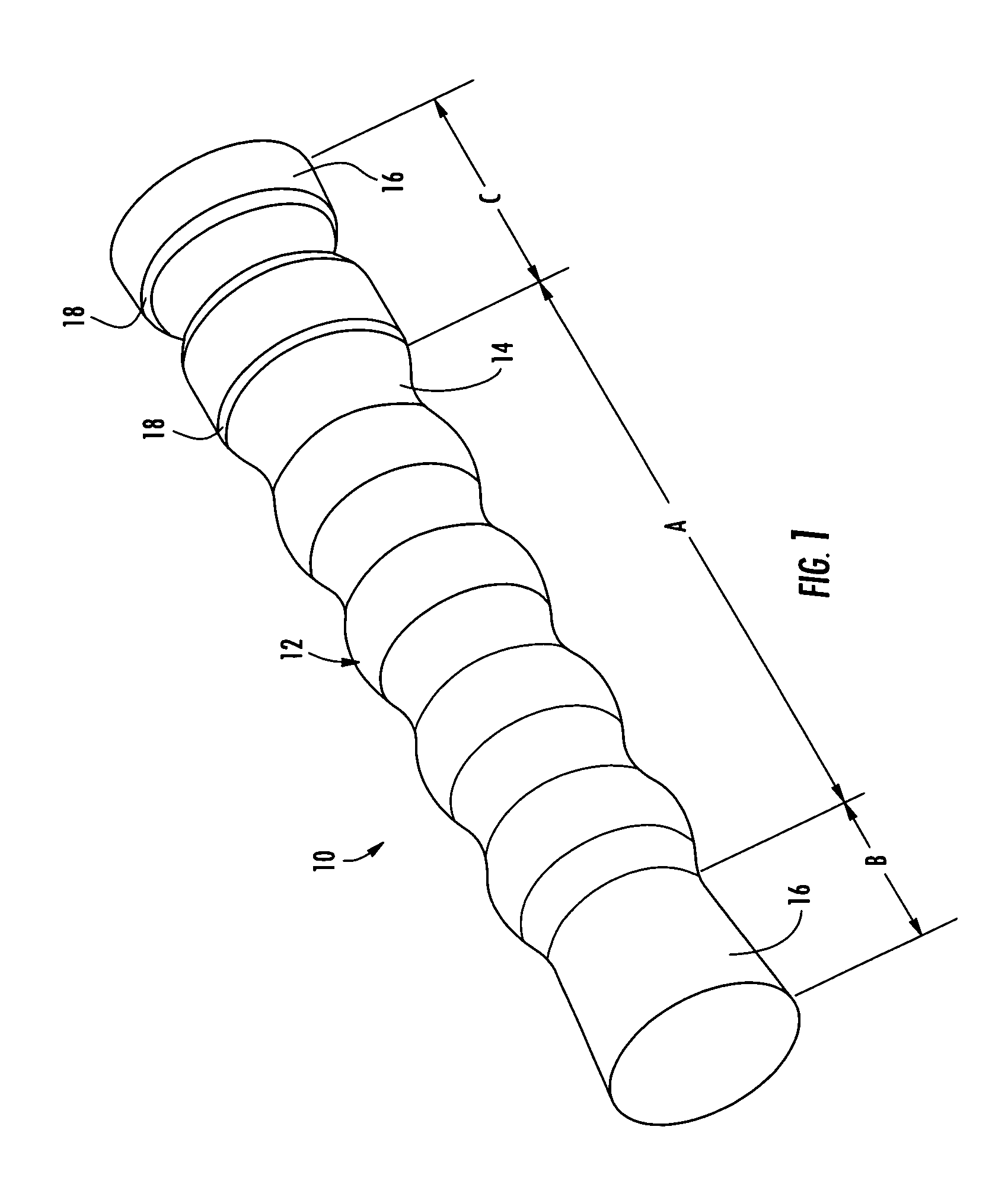
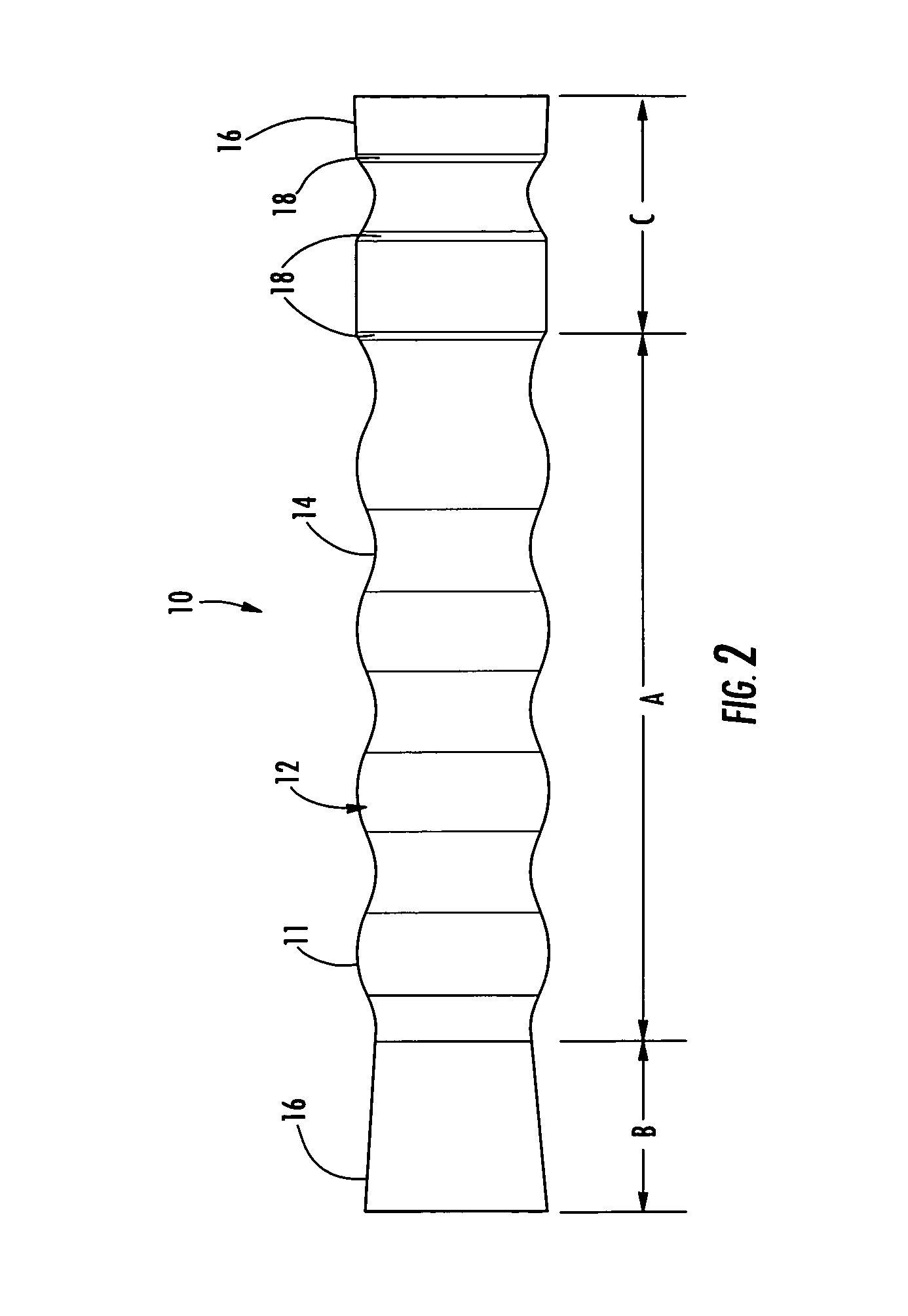
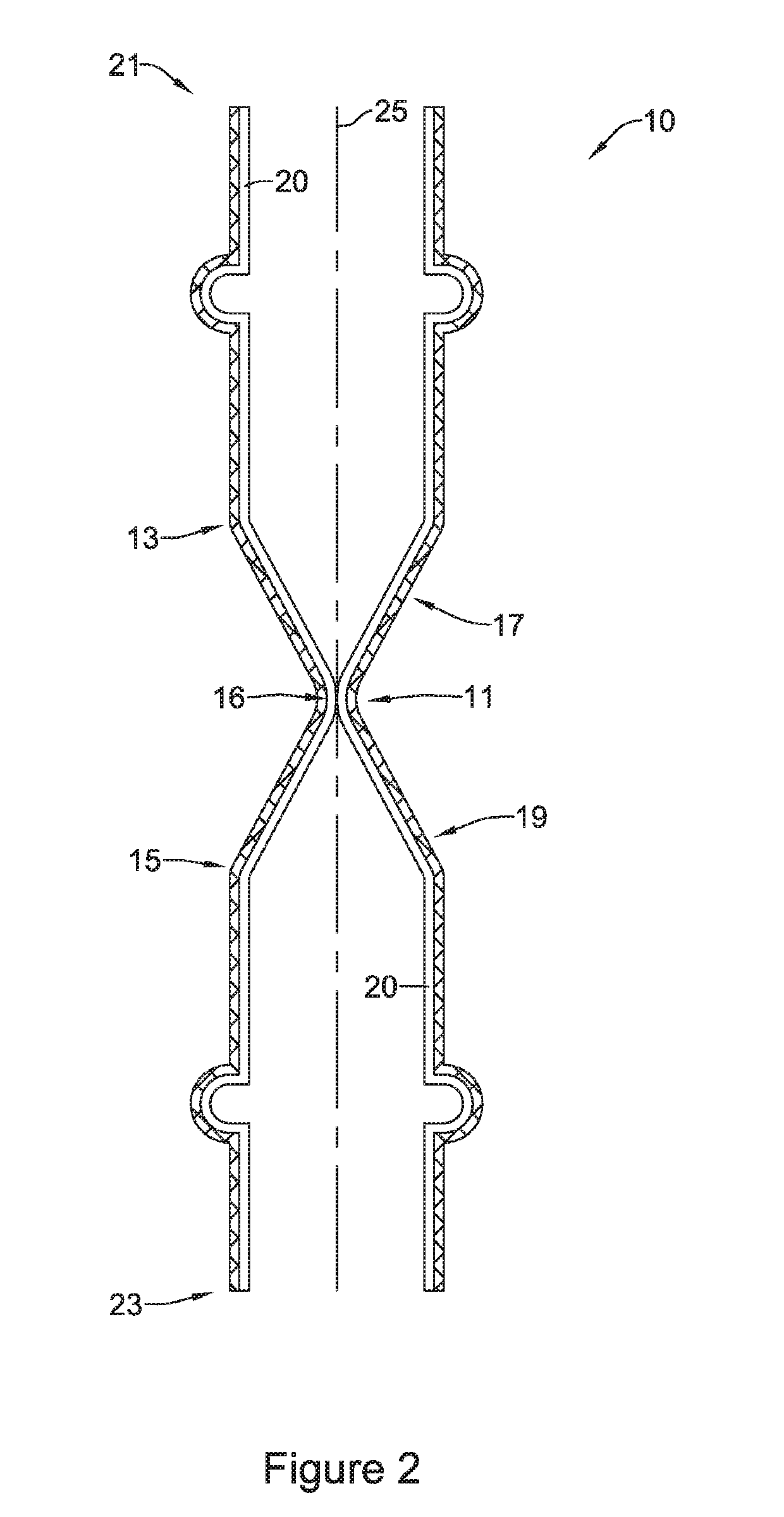
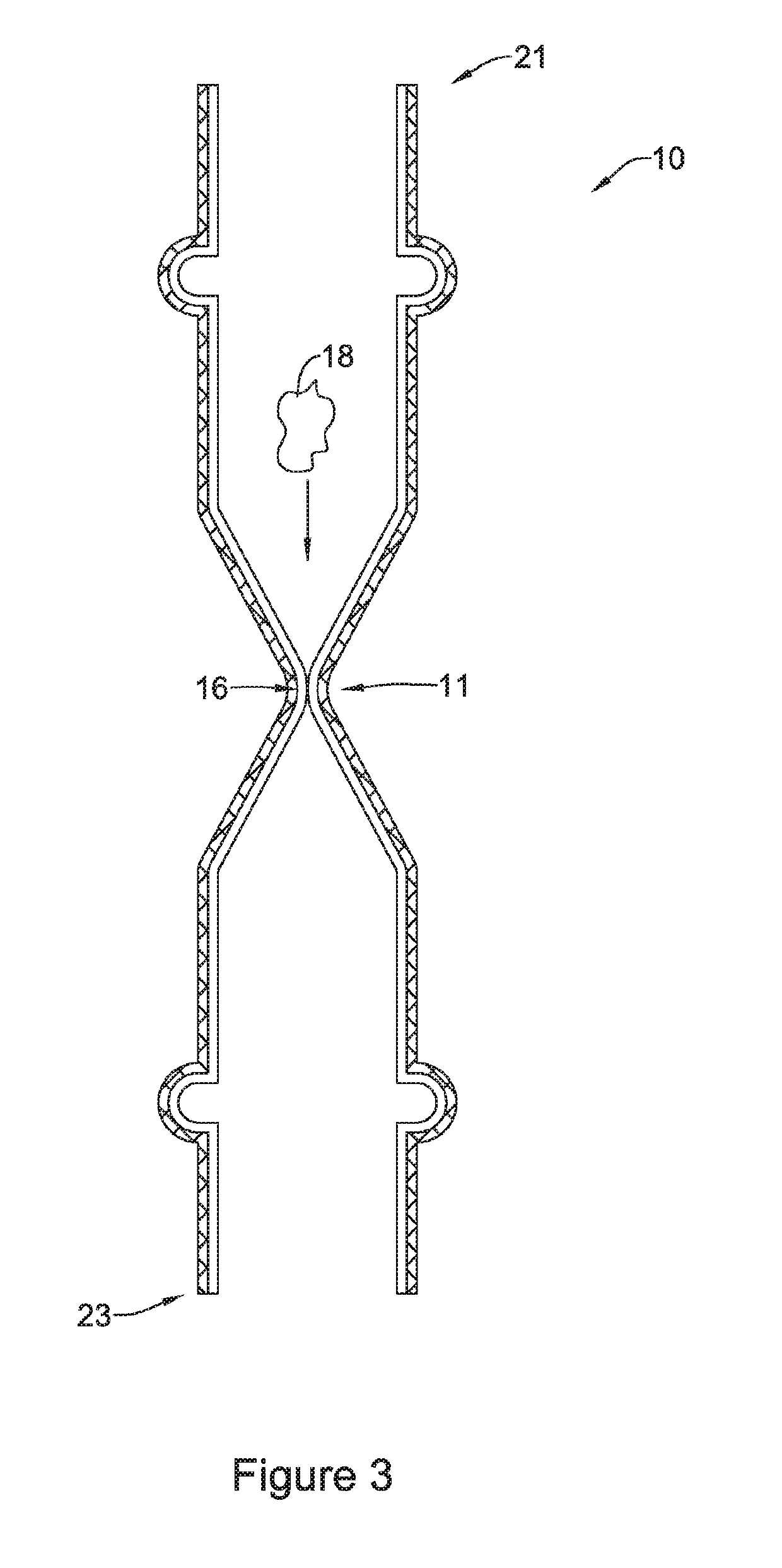
An esophageal stent is a stent (tube) placed in the esophagus to keep a blocked area open so the patient can swallow soft food and liquids. Esophageal stents may be self-expandable metallic stents, or made of plastic, or silicone, and may be used in the treatment of esophageal cancer.
Esophageal stent
ActiveUS20060212052A1Prevent backflowMaximizes operational reliabilityStentsHeart valvesTunica intimaGastric Content
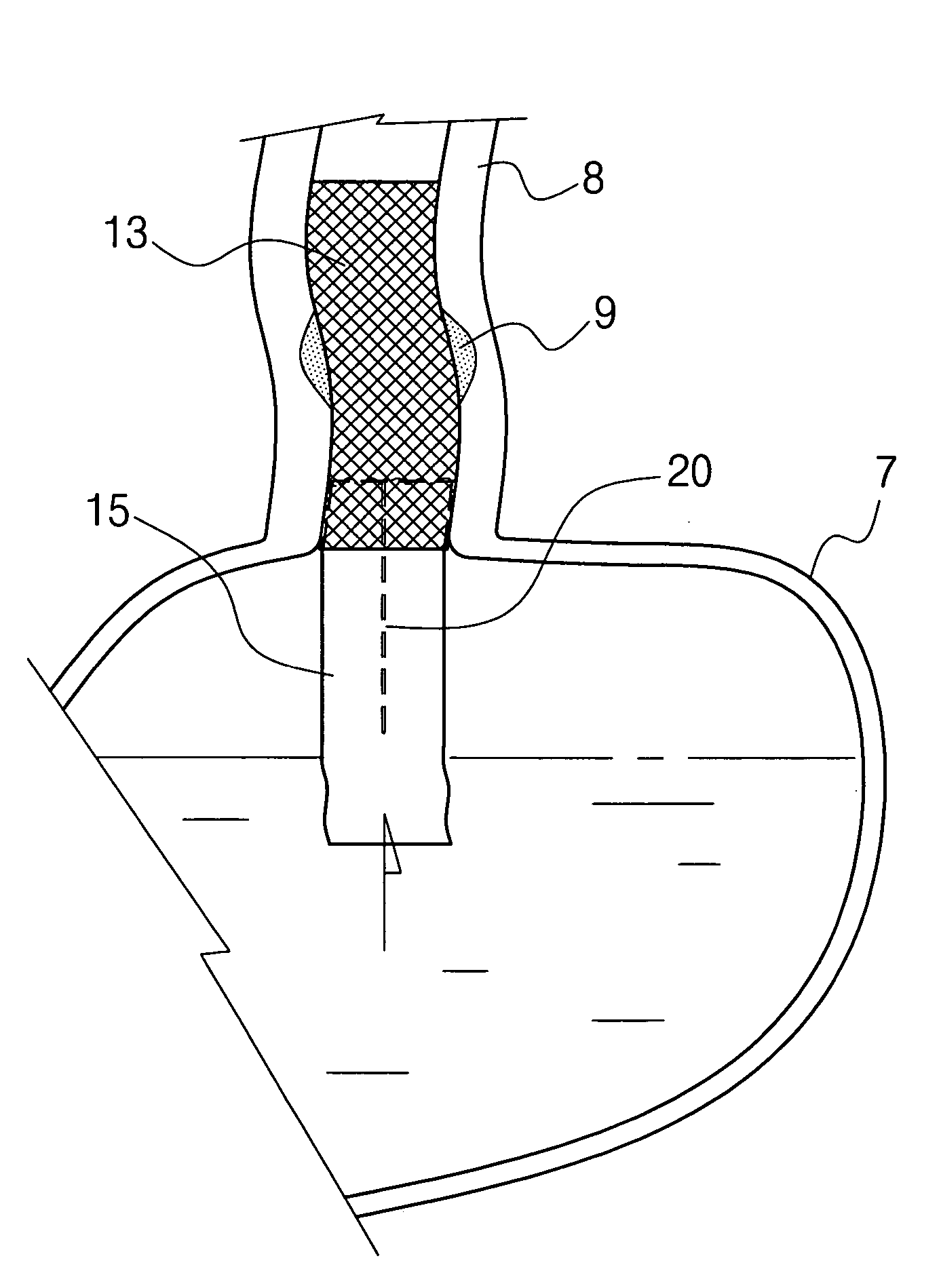
Disclosed is an esophageal stent placed in a stenosed part of the esophagus having a flexible tube to prevent the reverse flow of gastric contents from the stomach is coupled to the lower end of the esophageal stent. The flexible tube has an inside membrane and an outside membrane adhered to each other, thus having a twofold structure with at least one core longitudinally placed between the adhered inside and outside membranes while the core extends from the upper end toward the lower end of the flexible tube. Thus, the flexible tube is prevented from being inverted, and prevents the reverse flow of the gastric contents, and maximizes the operational reliability of the esophageal stent. The flexible tube does not cause a patient pain or discomfort due to frictional contact of the tube with the inner surface of the stomach when the tube moves in the stomach.
Owner:TAEWOONG MEDICAL CO LTD
Esophageal stent and associated method
ActiveUS20060259113A1Promote migrationReduce incidenceOesophagiBlood vesselsProximateInsertion stent
A flexible stent and method for performing a stent within a lumen proximate to a target area is provided. The stent includes a tubular member having proximal and distal ends, where at least a portion of the tubular member is capable of being positioned proximate to the target area. The stent also includes a plurality of stabilization members defined circumferentially about at least a portion of the tubular member, wherein each stabilization member extends inwardly to define an inner diameter that is less than an inner diameter of the tubular member within the tubular member. As a result, the stabilization members are capable of reducing migration of the stent within the lumen and the incident of infolding of the tubular member.
Owner:MERIT MEDICAL SYST INC
Esophageal stent
ActiveUS7993410B2Prevent backflowMaximizes operational reliabilityStentsHeart valvesTunica AdventitiaInsertion stent
Disclosed is an esophageal stent placed in a stenosed part of the esophagus having a flexible tube to prevent the reverse flow of gastric contents from the stomach is coupled to the lower end of the esophageal stent. The flexible tube has an inside membrane and an outside membrane adhered to each other, thus having a twofold structure with at least one core longitudinally placed between the adhered inside and outside membranes while the core extends from the upper end toward the lower end of the flexible tube. Thus, the flexible tube is prevented from being inverted, and prevents the reverse flow of the gastric contents, and maximizes the operational reliability of the esophageal stent. The flexible tube does not cause a patient pain or discomfort due to frictional contact of the tube with the inner surface of the stomach when the tube moves in the stomach.
Owner:TAEWOONG MEDICAL CO LTD
Esophageal stent including an inner liner
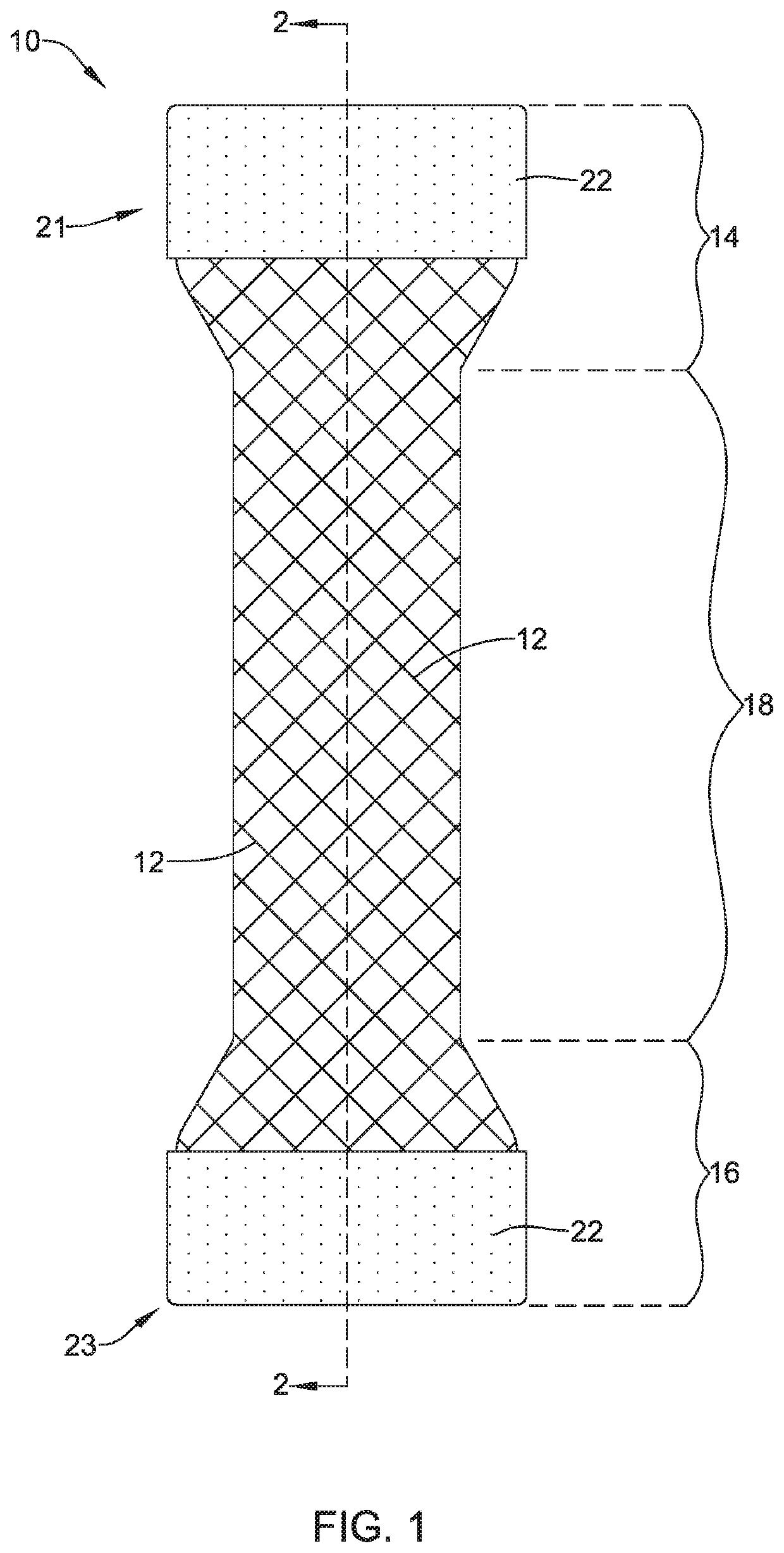
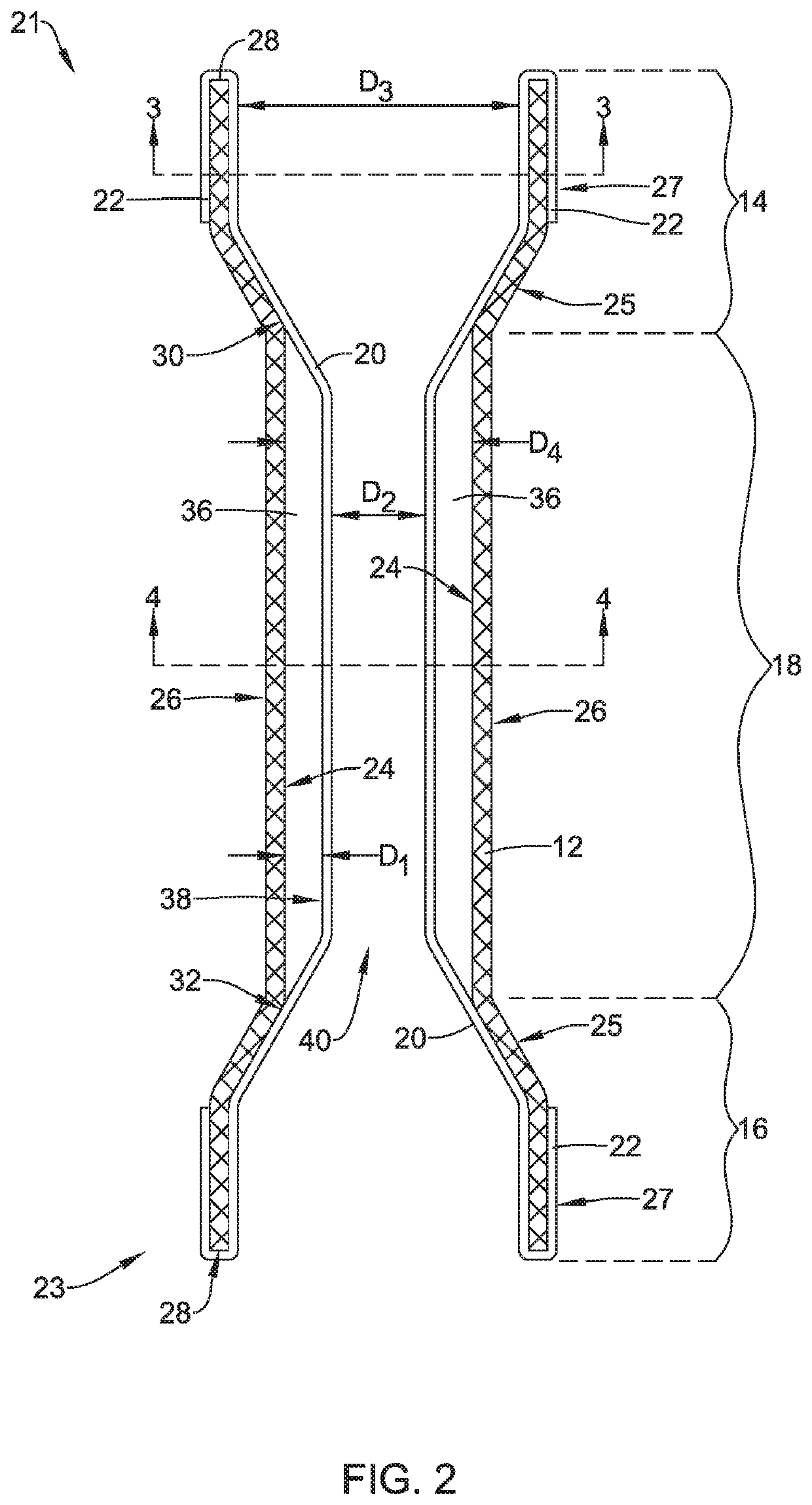
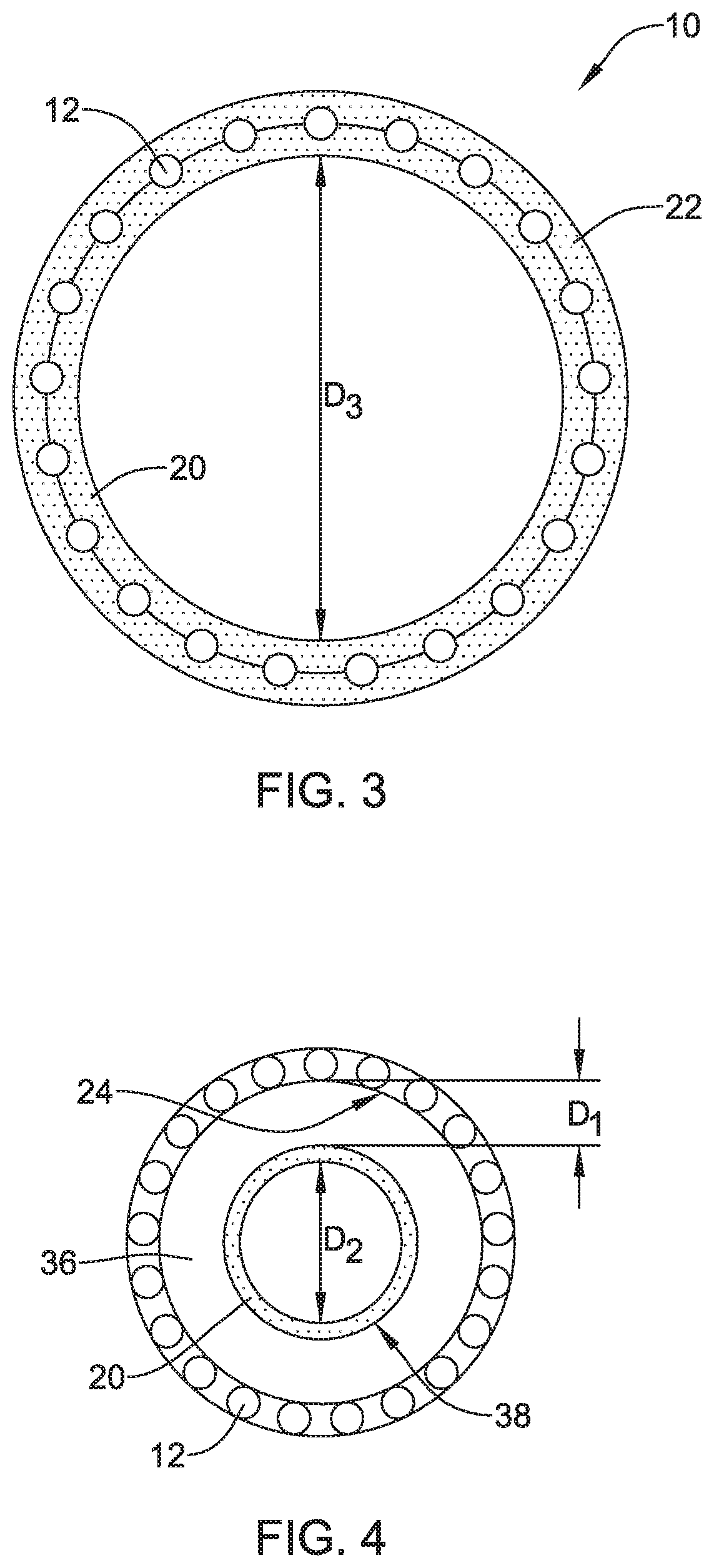
An example medical device is disclosed as an expandable stent. The stent includes a tubular scaffold having an inner surface, an outer surface, and a lumen extending therein. The expandable stent also includes a liner disposed within the lumen of the tubular scaffold. Further, the liner is radially spaced from a medial region of the tubular scaffold to define a tissue ingrowth region along an uncovered portion of the medial region. Additionally, the liner extending along the tissue ingrowth region is configured to limit the amount of tissue ingrowth along the medial region of the scaffold.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES +1
Gradient degradable polymeric material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103374208AIdeal degradation timeGood biocompatibilitySuture equipmentsStentsPolyesterPolymer science
A polymer material capable of gradient degradation. The polymer material is formed by at least two types of aliphatic polyesters having different degradation velocities, the aliphatic polyesters being arranged in an ascending order or descending order of the degradation velocities and fused together. The polymer material may be manufactured as thread materials, barrier materials, tube materials, and controlled drug release carriers, which specifically comprise sutures, medical dressings, adhesion prevention material, hemostasis material, guided tissue regeneration barriers, tissue repair materials, enhancement surgical meshes, drug carriers, cartilage tissue culture scaffolds, scaffolds, and especially urethral scaffolds.
Owner:山东省新征程工业科技有限公司
Placing and recovering device of non-memory alloy esophageal stent
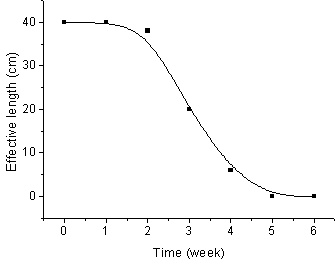
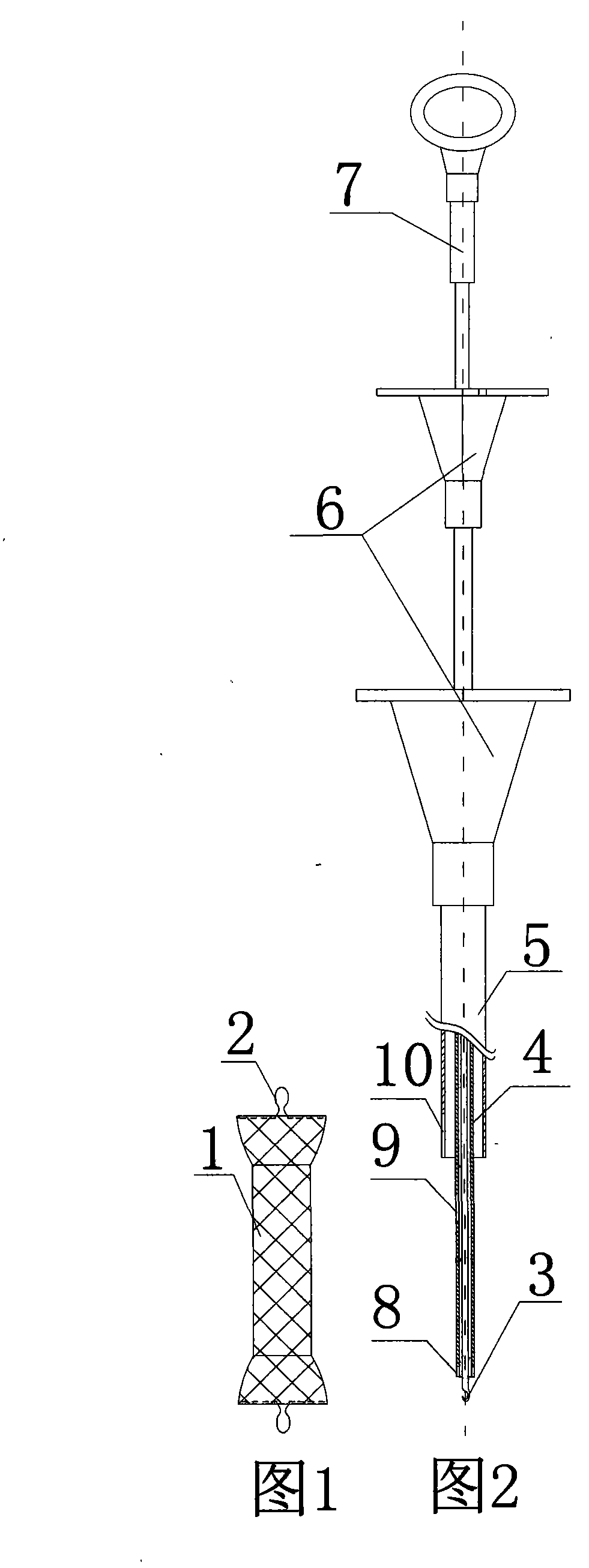
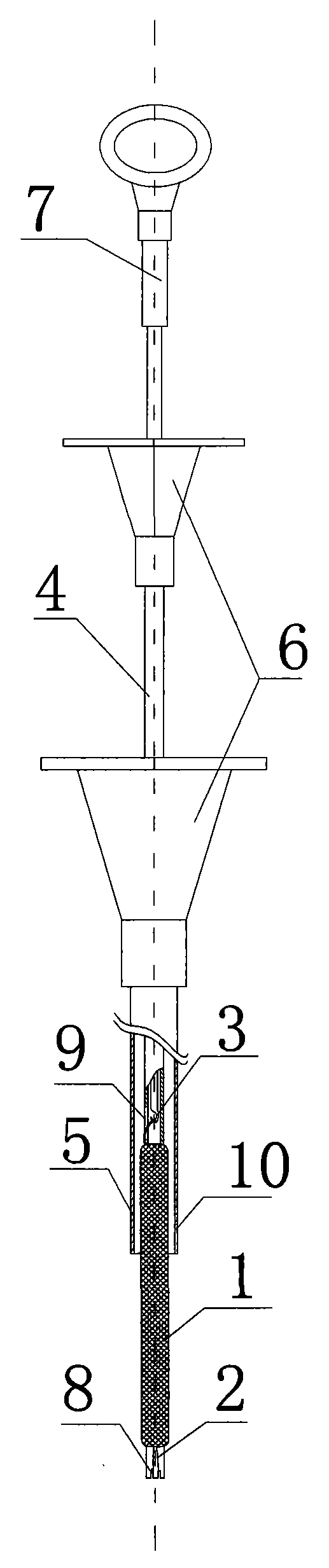
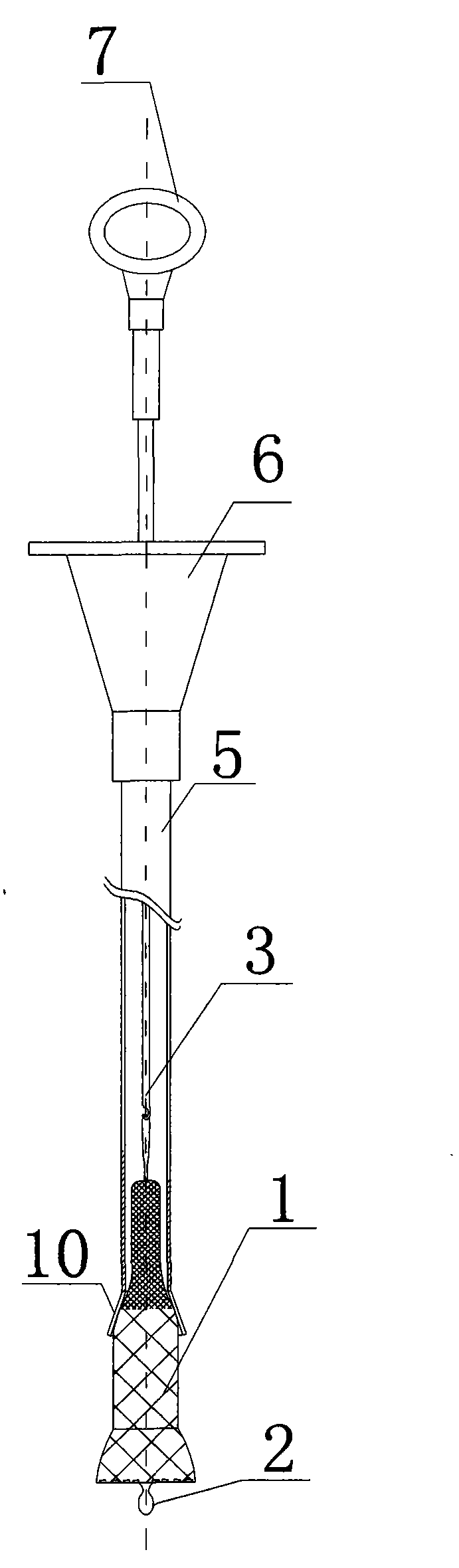
The invention provides a placing and recovering device of a non-memory alloy esophageal stent. The placing and recovering device of the non-memory alloy esophageal stent structurally comprises an outer sleeve, an inner sleeve, a recovering drag hook and the non-memory alloy esophageal stent. A drag hook handle is arranged at the rear end of the recovering drag hook, a hook head is arranged at the front end of the recovering drag hook, the hook head portion is inserted into the inner sleeve in a penetrating mode, and the inner sleeve is inserted into the outer sleeve. At least one opening is formed in the front end of the inner sleeve, at least one slot hole is formed in the middle of the inner sleeve, and at least three open seams are formed in the front end of the outer sleeve. The rear end of the outer sleeve and the rear end of the inner sleeve are respectively provided with a horn-shaped handle, and the upper end and the lower end of the non-memory alloy esophageal stent are respectively provided with an annular metallization tightening string. One annular metallization tightening string penetrates through the slot hole in the middle of the inner sleeve and is hooked together with the hook head, the annular metallization tightening string at the lower end of the non-memory alloy esophageal stent is hooked together with the opening in the front end of the inner sleeve, and the non-memory alloy esophageal stent is made to cover the front end of the inner sleeve through stretching of the recovering drag hook. The placing and recovering device of the non-memory alloy esophageal stent has the advantages that the structure is simple, placing and recovering can both be achieved, and a common stainless steel non-memory alloy esophageal stent can be used for replacing a traditional expensive nickel-titanium memory alloy esophageal stent.
Owner:SHANDONG PROVINCIAL HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANDONG FIRST MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Esophageal stent including a valve member
An example medical device is disclosed. The example medical device includes a tubular scaffold. The scaffold includes a longitudinal axis, an inner surface and an outer surface. The medical device also includes a flexible valve extending radially inward from the inner surface of the scaffold. The valve includes an annular chamber extending circumferentially around the inner surface of the scaffold and is configured to shift from a closed configuration to an open configuration.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Esophageal stent and associated method
ActiveUS8834558B2Promote migrationReduce incidenceOesophagiBlood vesselsInsertion stentEsophageal stent
A flexible stent and method for performing a stent within a lumen proximate to a target area is provided. The stent includes a tubular member having proximal and distal ends, where at least a portion of the tubular member is capable of being positioned proximate to the target area. The stent also includes a plurality of stabilization members defined circumferentially about at least a portion of the tubular member, wherein each stabilization member extends inwardly to define an inner diameter that is less than an inner diameter of the tubular member within the tubular member. As a result, the stabilization members are capable of reducing migration of the stent within the lumen and the incident of infolding of the tubular member.
Owner:MERIT MEDICAL SYST INC
Degradable magnesium alloy esophageal stent for infants
The invention discloses a degradable magnesium alloy esophageal stent for infants. The esophageal stent comprises annular single bodies, connecting points and projections, wherein each annular single body is formed in the way that a magnesium alloy metal wire is folded in the shape of W and connected to form a cylindrical shape; the annular single bodies have elasticity; bending parts are formed at the two ends of each annular single body; the annular single bodies are axially connected with one another in series by the connecting points; the bottom of each projection is positioned at each connecting point; the top end of each projection is positioned on the outer side of the esophageal stent; and after the magnesium alloy esophageal stent is expanded and released, the projections can be embedded into the esophageal wall and are used for fixing the stent. The degradable magnesium alloy esophageal stent for infants is formed by connecting a plurality of annular single bodies and the length of the esophageal stent can be determined by the number of the connected annular single bodies, so the requirements of the infants suffering from esophageal stenosis are met; the projections on the outer surface of the stent can be embedded into the inner wall of the esophagus and are used for fixing the stent to prevent the stent from moving or slipping off; and the stent can be degraded and absorbed by a human body and the degradation products have no toxicity, so growth and development of infantile patients are not influenced.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Method for coating esophageal stent through melt electrospinning
InactiveCN103225174AGood biocompatibilityLess irritatingFilament/thread formingNon-woven fabricsHigh pressureMelt electrospinning
The invention discloses a method for coating an esophageal stent through melt electrospinning and belongs to the fields of medical instruments and electrospinning. Devices adopted by the method comprise a melt-electrospinning device, a stent coating device and the like, wherein the melt-electrospinning device comprises a capillary tube, a nozzle, a heating ring, a hopper, a piston shaft with an end cover, a temperature sensor, a high-voltage electrostatic generator and the like; the stent coating device comprises a stent, a metal-coated insulating rod, a slip ring, a guide rod and a linear stepping motor; and a polymer can be thermoplastic resin used in a living body; and a spinning raw material can be polymer particles, or powder, or slices or melt. The method can be used for melt-electrospinning coating of metallic or nonmetallic stent.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Expandable esophageal stent
The invention discloses an expandable esophageal stent. The expandable esophageal stent comprises a stent body, an expansion air bag and a hung tube, wherein the stent body is in a cylindrical tube shape, the expansion air bag is arranged on the outer cylindrical surface of the stent body in a covering mode, the hung tube is connected with one end of the stent body, and the hung pipe is communicated with the expansion air bag. The expandable esophageal stent can be well matched with the esophageal cavity of a human body in shape, an expansion part simulating the esophagus and a spike part simulating the esophagus do not exist, and high tolerance is achieved; the hung pipe penetrates out of the nasal cavity of a patient, and is fixedly arranged outside the human body through adhesive tape and the like, and therefore the problem that due to physiological peristalsis of the esophagus, an esophageal stent moves and falls off can be solved; after the expandable esophageal stent is implanted into the esophagus for a period of time, and the expandable esophageal stent deforms due to growth of tissue around the stent body, the expansion air bag can be inflated through the hung pipe, the tissue around the expandable esophageal stent is expanded, the original shape of the stent body can be automatically recovered, and therefore the problem that the expandable esophageal stent is pressed to deform due to growth of the tissue around the expandable esophageal stent can be solved; the service life of the esophagus is long, and the treatment effect is good.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIV
Degradable self-expandable esophageal stent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102000366AGood tissue compatibilityLess prone to inflammatory reactionsStentsSurgeryEsophageal diseaseX-ray
The invention relates to the technical field of medical appliances, and in particular discloses a degradable self-expandable esophageal stent and a preparation method thereof. The degradable self-expandable esophageal stent is characterized in that: the degradable self-expandable esophageal stent has anticancer and developing effects and is obtained by mixing a degradable polymer and other auxiliary agents uniformly to obtain a mixture, melting and extruding the mixture by using an extruder to obtain degradable filaments, weaving the degradable filaments into a mesh esophageal stent on a mould which has a certain shape, and performing film-coating treatment on the stent. The degradable self-expandable esophageal stent not only overcomes the shortcomings of a metal stent, but also reinforces the treatment and the diagnosis of esophageal diseases by coating an anti-cancer medicament or an X-ray developing agent, so the degradable self-expandable esophageal stent has a broad application prospect.
Owner:苏州同科生物科技有限公司
Nanogold film memory alloy esophageal stent and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN105030393ASimplified coating processNo radioactive contaminationStentsTherapeutic coolingNitinol stentTitanium alloy
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical instruments and relates to a nanogold film memory alloy esophageal stent with a photo-thermal therapy function. A nanogold film is prepared by conducting in-situ surface chloroauric acid reduction on a high polymer material with a reduction function used for modifying the surface of a memory alloy wire under the alkaline condition. According to the preparing method, a unique nanogold surface coating method is adopted, the nanogold material is safe and free of toxicity, and the coating process is simple and quick; photo-thermal efficiency is high, and repeated use is realized. The method can be applied to nickel-titanium alloy stents in various shapes and types such as a biliary stent, an intestinal tract stent, a urinary tract stent and a tracheal stent.
Owner:SHANGHAI THERANOSTICS BIOTECH CO LTD
Nickel-titanium memory alloy esophageal stent placing and recycling device used in X-ray perspective
The invention provides a nickel-titanium memory alloy esophageal stent placing and recycling device used in X-ray perspective. The nickel-titanium memory alloy esophageal stent placing and recycling device used in X-ray perspective comprises an outer sleeve, an inner sleeve, sampling pincers and a nickel-titanium memory alloy esophageal stent, wherein the head of a jaw of the sampling pincers is inserted in the inner sleeve; the inner sleeve is inserted in the outer sleeve; a latex ring is sleeved on the outer wall of the lower end of the inner sleeve; trumpet-shaped handles are arranged at the rear end of the outer sleeve and the rear end of the inner sleeve; the upper end of the nickel-titanium memory alloy esophageal stent is sleeved on the latex ring; the lower end of the nickel-titanium memory alloy esophageal stent is sleeved at the lower end of the inner sleeve; and a metalized annular tightening line is arranged at one end of the esophageal stent. The nickel-titanium memory alloy esophageal stent placing and recycling device used in X-ray perspective has the advantages that the nickel-titanium memory alloy esophageal stent placing and recycling device is simple in structure, can be placed or recycled and facilitates surgery; the surgery time is short, the paining of a patient is low, the labor intensity of doctors is low, the esophageal stent can be reused after being recycled, and the treatment cost of the patient can be greatly reduced.
Owner:泰州威普检测技术有限公司
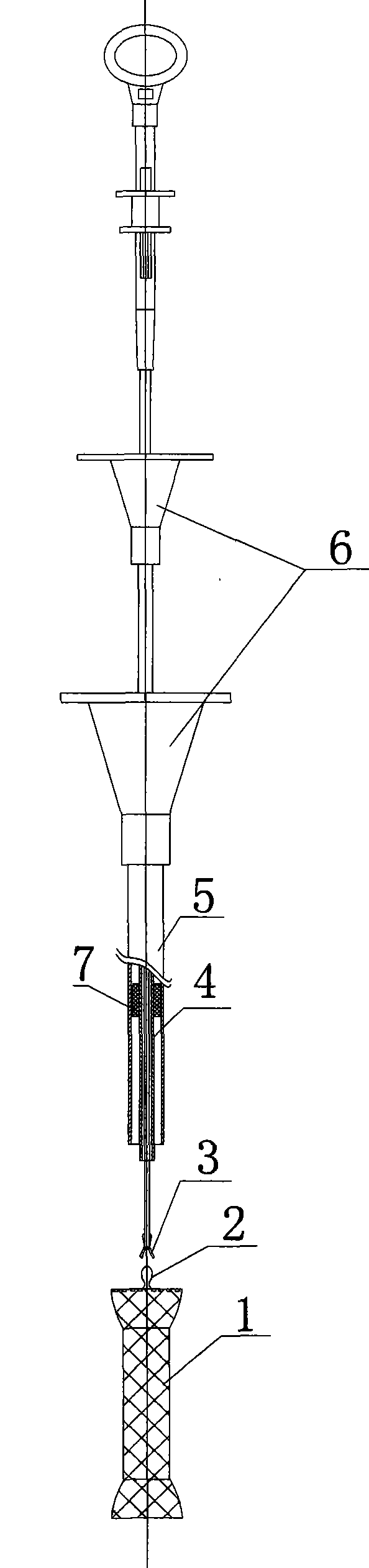
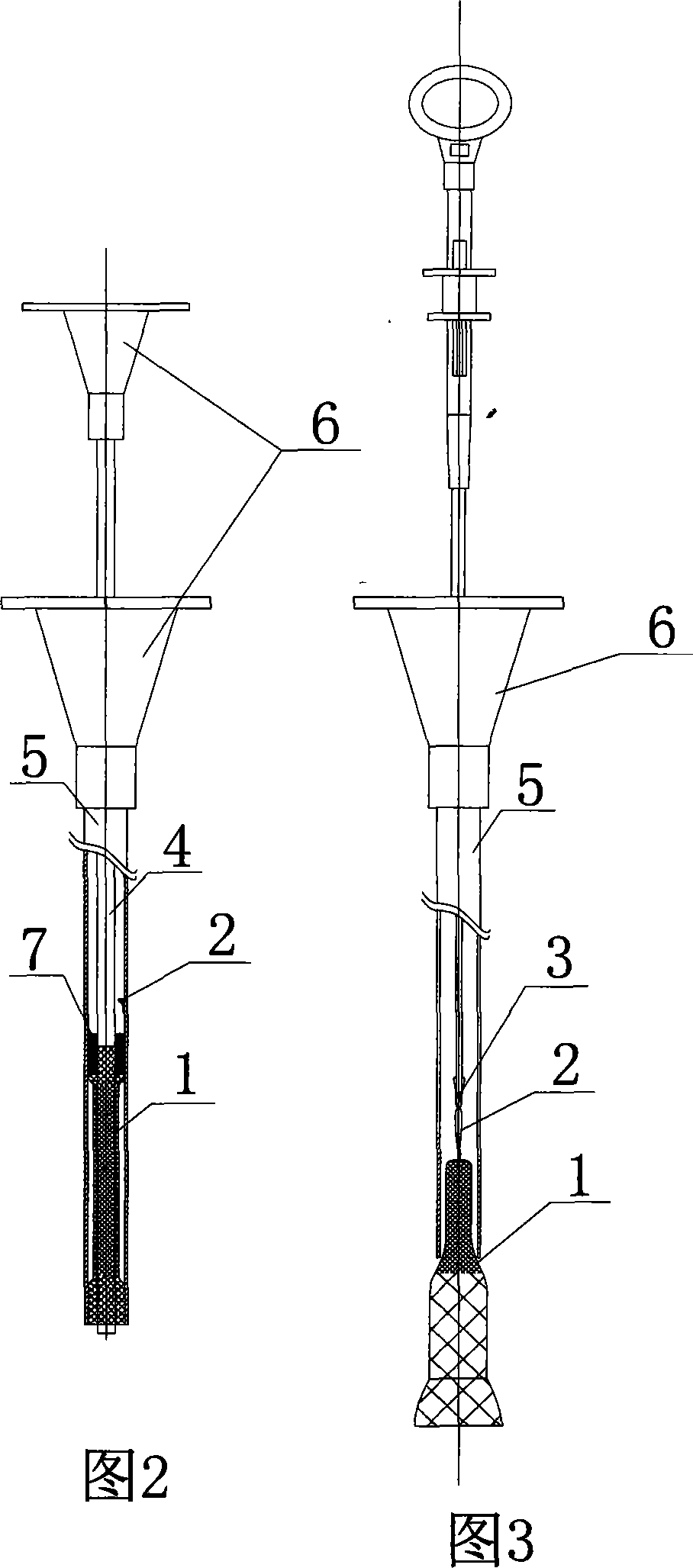
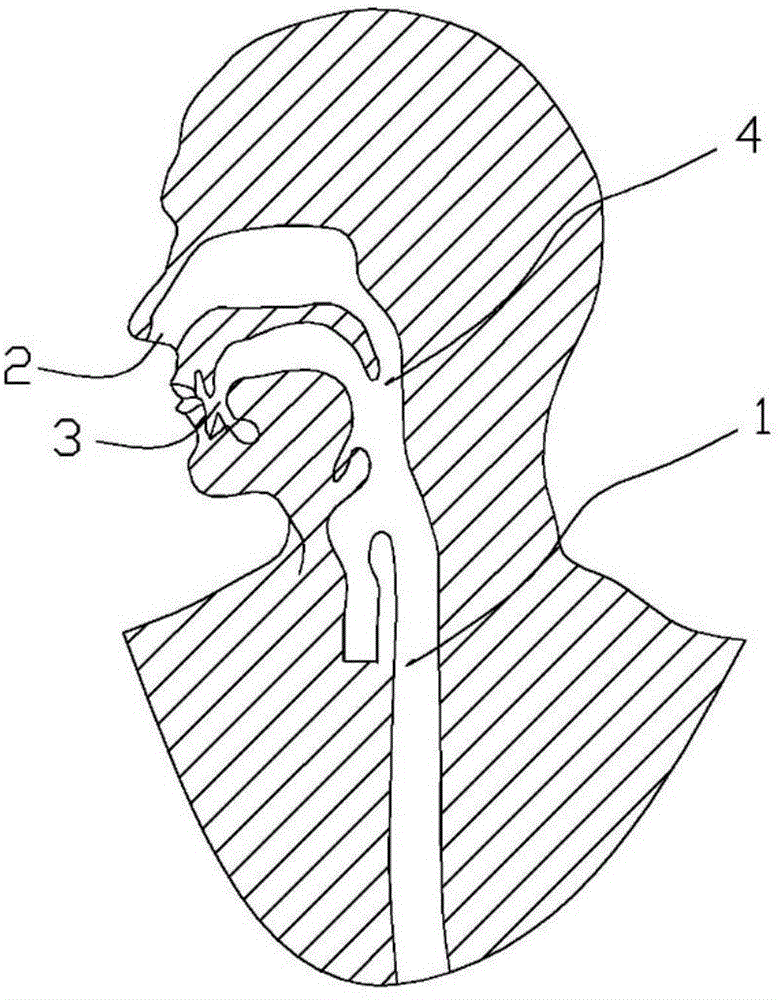
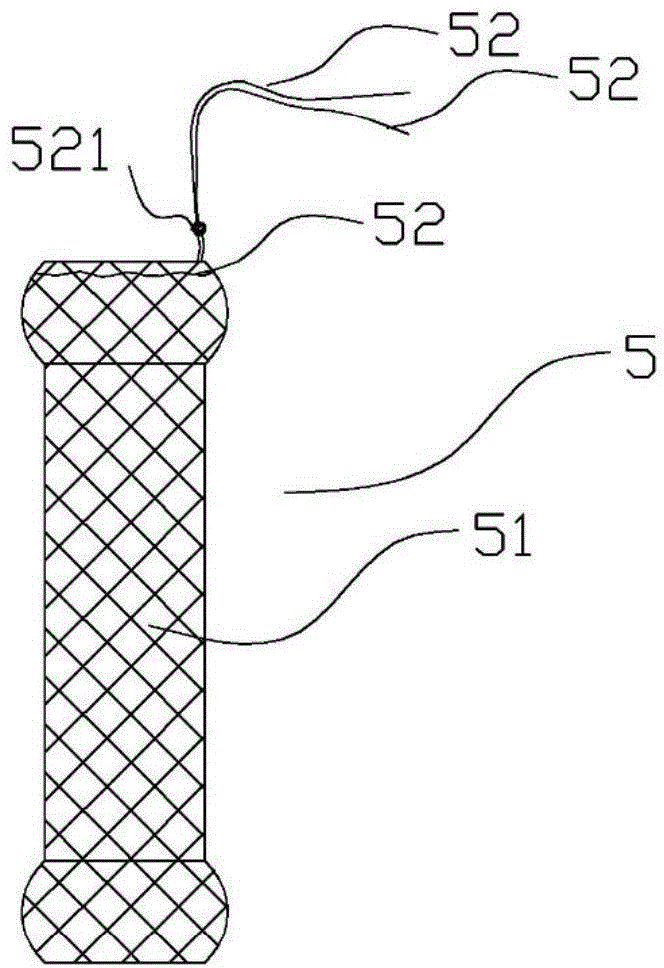
Anti-displacement esophageal stent apparatus bag
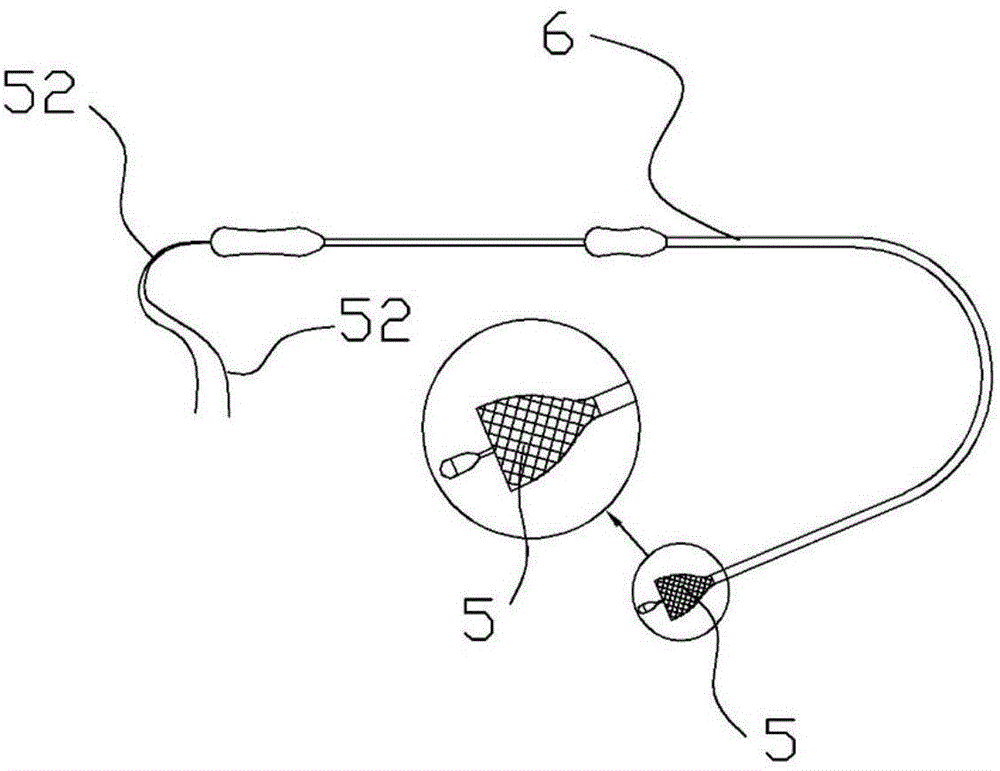
The invention relates to an anti-displacement esophageal stent apparatus bag. The esophageal stent apparatus bag comprises an esophageal stent, a conveyor, a threading apparatus and a buffer fixing pipe. A fixed line, on the esophageal stent, implanted into a diseased region is withdrawn outside a body, namely a portion of naris, through the threading apparatus, the fixed line is fixed on the buffer fixing pipe, and the purposes of the esophageal stent not shifting and not falling out are achieved.
Owner:KOSSEL MEDTECH SUZHOU
Esophageal stent including an inner liner
An example medical device is disclosed as an expandable stent. The stent includes a tubular scaffold having an inner surface, an outer surface, and a lumen extending therein. The expandable stent also includes a liner disposed within the lumen of the tubular scaffold. Further, the liner is radially spaced from a medial region of the tubular scaffold to define a tissue ingrowth region along an uncovered portion of the medial region. Additionally, the liner extending along the tissue ingrowth region is configured to limit the amount of tissue ingrowth along the medial region of the scaffold.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES +1
Multi-thermoplastic shape memory polymer 4D printing method
ActiveCN111907055AEasy to drawImprove qualityAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structuresPolymer scienceSolid structure
The invention discloses a multi-thermoplastic shape memory polymer 4D printing method. According to the multi-thermoplastic shape memory polymer 4D printing method, two or more thermoplastic shape memory polymers are adopted as a raw material, a solid structure is finally obtained through multiple steps of raw material wire drawing, target structure modeling and step-by-step fused deposition printing, initial structure modeling, programming mold manufacturing, shape programming and the like, and under the effect of the gradually-increased temperature, the solid structure can be recovered to atarget structure through step deformation. The multi-thermoplastic shape memory polymer 4D printing method can be widely applied to medical instruments such as tracheal stents and esophageal stents, gradually expands tissues such as trachea and esophagus, recovers organ functions and helps rehabilitation, and has important practical value.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
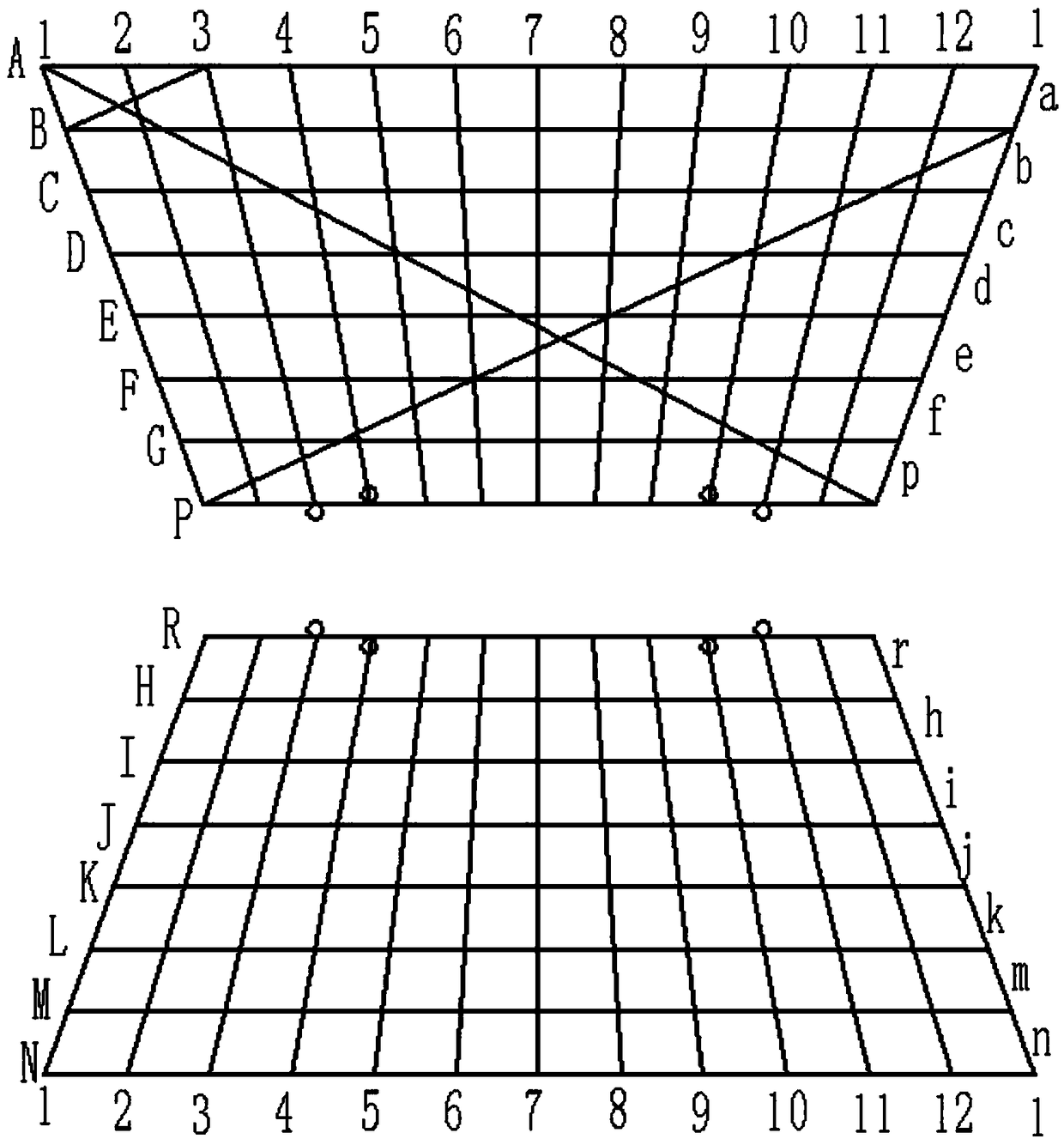
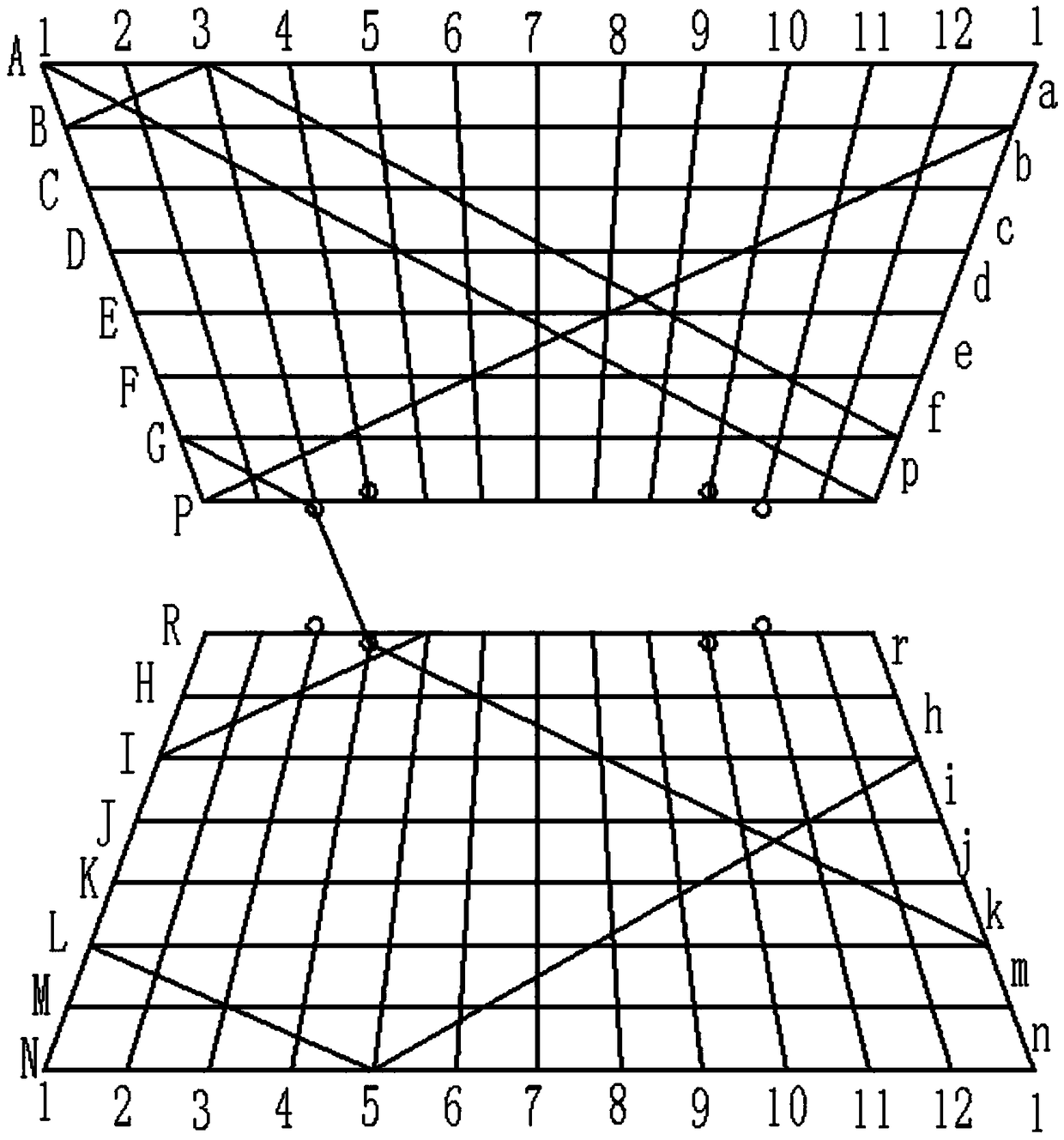
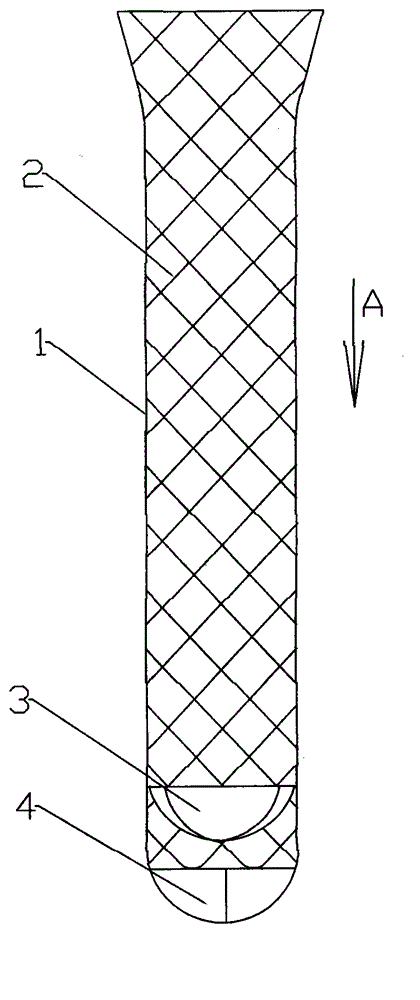
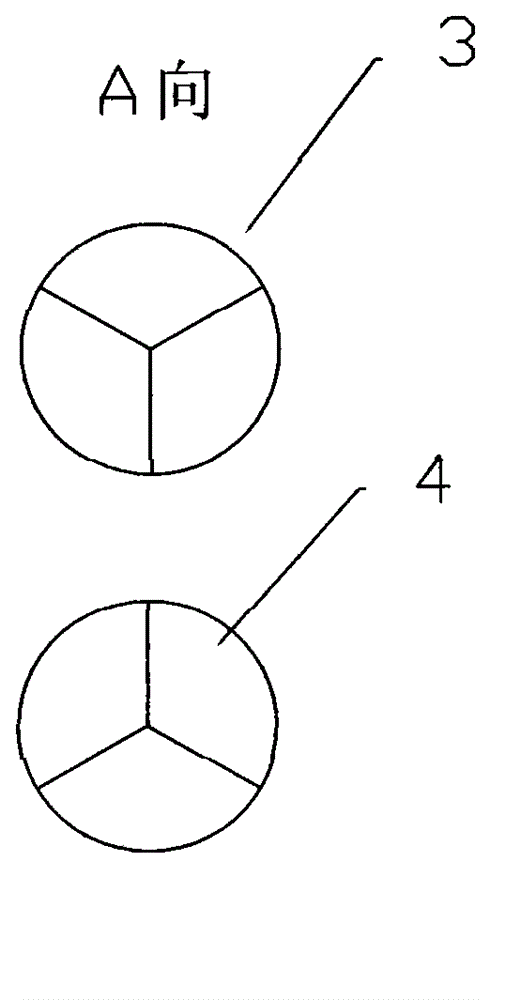
Sectional type esophageal stent and weaving method thereof
The invention provides a sectional type esophageal stent and a weaving method thereof. The sectional type esophageal stent is a cylindrical net-shaped stent formed by weaving a monofilament, wherein two ends of the cylindrical net-shaped stent are respectively of a horn mouth shape, and the cylindrical net-shaped stent comprises an upper horn mouth section and a lower horn mouth section which areconnected through a plurality of hasp structures. Compared with existing hooking type hasps, the sectional type esophageal stent adopting a cross-shaped hasp structure has the advantages that the support force of the whole esophageal stent can be enhanced, and the esophageal stent has relatively good rigidity; two ends of the cylindrical net-shaped stent are respectively of horn mouth design, after the esophageal stent is inserted into the esophagus, the horn mouth in the upper part is beneficial to the pass of foods, the displacement of the stent can be prevented by virtue of the horn mouth in the lower part, and the stent can be well and accurately fixed; and the weaving process of the whole stent is finished by virtue of one filament, so that the rigidity of the esophageal stent is improved, meanwhile, the axial compression deformation of the esophageal stent can be reduced, and the normal use of the esophageal stent can be guaranteed.
Owner:SHANGHAI ELITEK BIOSCI CO LTD
Fully fitting esophageal stent complying with esophageal peristalsis
InactiveCN106420127AEnhanced displacement resistanceAvoid pushingStentsProsthesisInsertion stentEsophageal function
The invention relates to a fully fitting esophageal stent complying with esophageal peristalsis. The esophageal stent is composed of three sections in smooth connection with each other, wherein the sections at the two ends are thick and the section in the middle is thin; the two end sections have a shape of cylinder encircled by a single-layer net; the middle section is formed by spirally winding a bar-shaped screen mesh in equal width; an upper hook is arranged at the upper end of the bar-shaped screen mesh; a lower hook is arranged at the lower end of the bar-shaped screen mesh; the upper hook and the lower hook are buckled with each other when the bar-shaped screen mesh is spirally wound; the cross section of the bar-shaped screen mesh is of step shape. The esophageal stent is formed by spirally winding the bar-shaped screen mesh in equal width, so that the esophageal stent has flexibility and following capacity, the esophageal peristalsis can be extremely transferred to the food and the food can be more easily swallowed; the displacement resistance of the esophageal stent can be further enhanced by the following capacity of the esophageal stent; the influences of the stent on the esophageal function and structure are greatly improved; the stent is more comfortable for the patient and is fully fit with human esophageal wall; the trachea is extremely prevented from being pressed by the stent.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZHENGZHOU UNIV
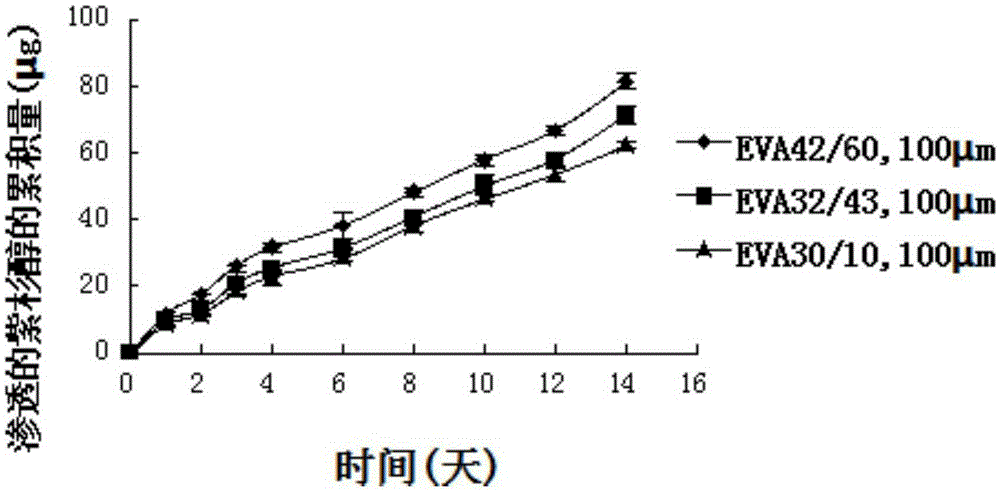
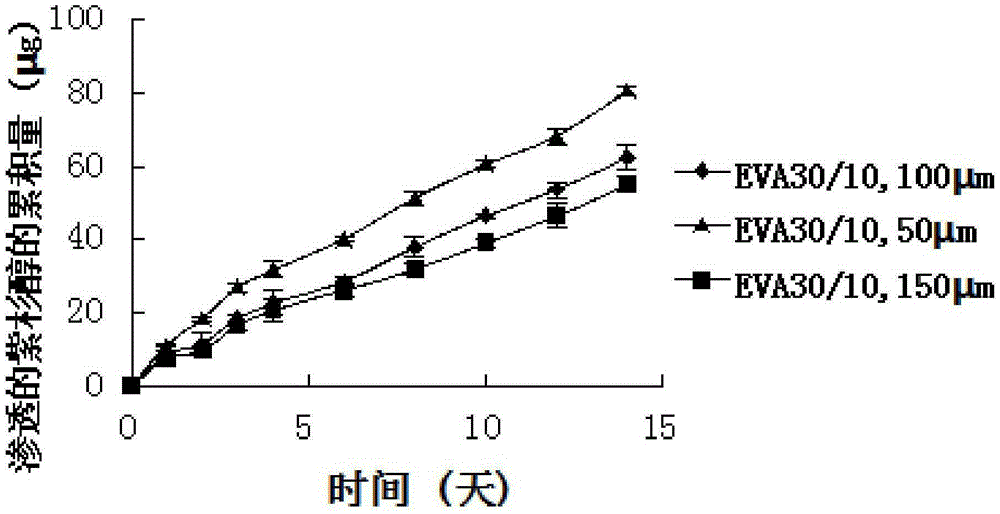
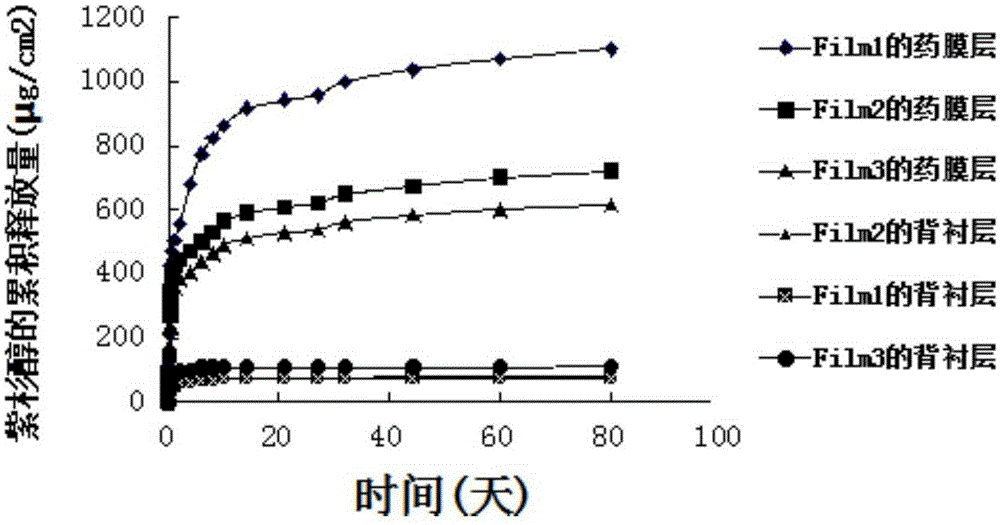
Paclitaxel-loaded ethylene-vinyl acetate esophageal stent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105232182AGood mechanical supportImprove mechanical propertiesSurgeryTubular organ implantsBare-metal stentMechanical property
The invention pertains to the field of medical instruments and discloses a paclitaxel-loaded ethylene-vinyl acetate esophageal stent and a preparation method thereof. The stent is composed of a bare metal stent and a covering film covering the bare metal stent. The covering film comprises an ethylene-vinyl acetate esophageal backing layer and a paclitaxel medicine film layer. The inside of the ethylene-vinyl acetate esophageal backing layer is closely adhered to the bare metal stent. The outside of the ethylene-vinyl acetate esophageal backing layer is adhered to the paclitaxel medicine film layer. The stent is 50% in the theoretical drug-loading amount ranges from 48.26% -50.81% in the measured drug-loading amount. Within 80d, paclitaxel ranges from 615.274-1101.368 [mu]m / cm2 in the accumulative releasing amount and ranges from 57.93-108359 [mu]m / cm2 and also ranges from 57.93-108359 [mu]m / cm2 in the infiltration amount from the backing layer. The paclitaxel-loaded ethylene-vinyl acetate esophageal stent and the preparation method thereof have following beneficial effects: the preparation method is easily and conveniently applied; the good mechanical property is obtained; the slow release function can be fulfilled for a long time; and the stent has good functions of mechanical support and prevention against growth inside of tumors.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Drug-injectable anti-shift esophageal stent
ActiveCN107007378AAvoid displacementSolve the shiftMedical devicesOesophagiDrug injectionDrug Storage
The invention relates to a drug-injectable anti-shift esophageal stent which comprises an esophageal bracket body and a liner membrane. The drug-injectable anti-shift esophageal stent further comprises a drug injection device for injecting a drug into the esophagus; the esophageal stent body comprises a plurality of bracket units which are connected through suture lines and closed skirt membranes; the liner membrane is located in the esophageal stent body, the lower end edge of the liner membrane extends outward radially to form an annular bottom membrane, and an annular drug storage chamber is formed between the liner membrane and the inner wall of the esophagus; the drug-injection device is separately connected to the upper end edges of the liner membrane and the esophageal stent body and communicates with the drug storage chamber. The drug-injectable anti-shift esophageal stent provided by the invention can effectively solve the problem of shift of the esophageal stent and also can directly inject the drug into the diseased region of the esophagus through the drug injection device.
Owner:令狐恩强 +1
Esophageal stent including a valve member
An example medical device is disclosed. An example medical device includes an expandable stent. The stent includes a tubular scaffold formed of one or more interwoven filament. The tubular scaffold includes an inner surface and a flexible valve extending radially inward from the inner surface of the scaffold. Further, the valve is configured to shift between a closed configuration and an open configuration and the one or more filaments of the scaffold bias the valve to the closed configuration while in a nominally deployed state.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
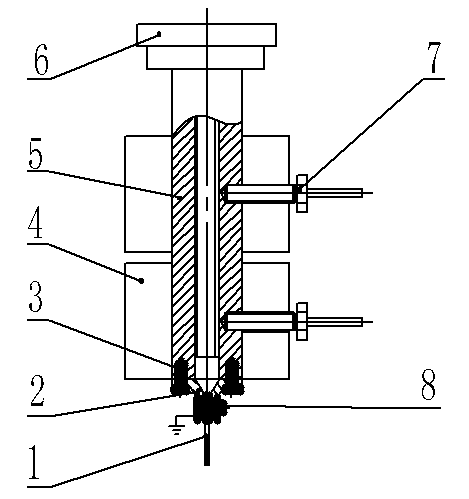
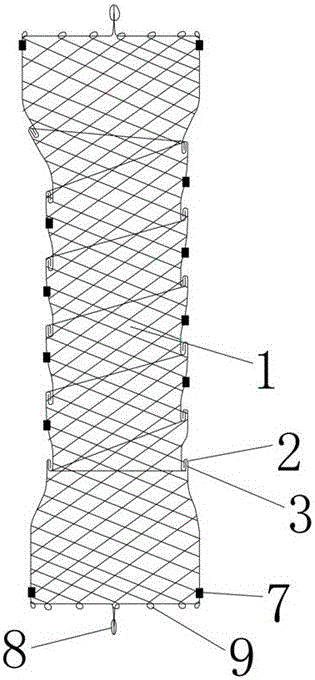
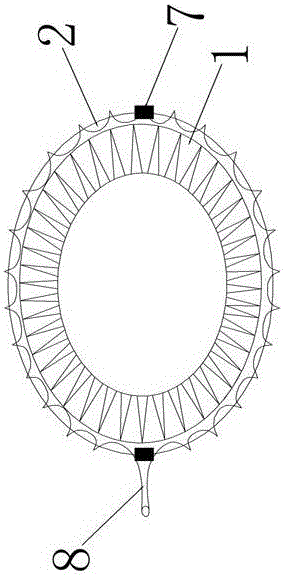
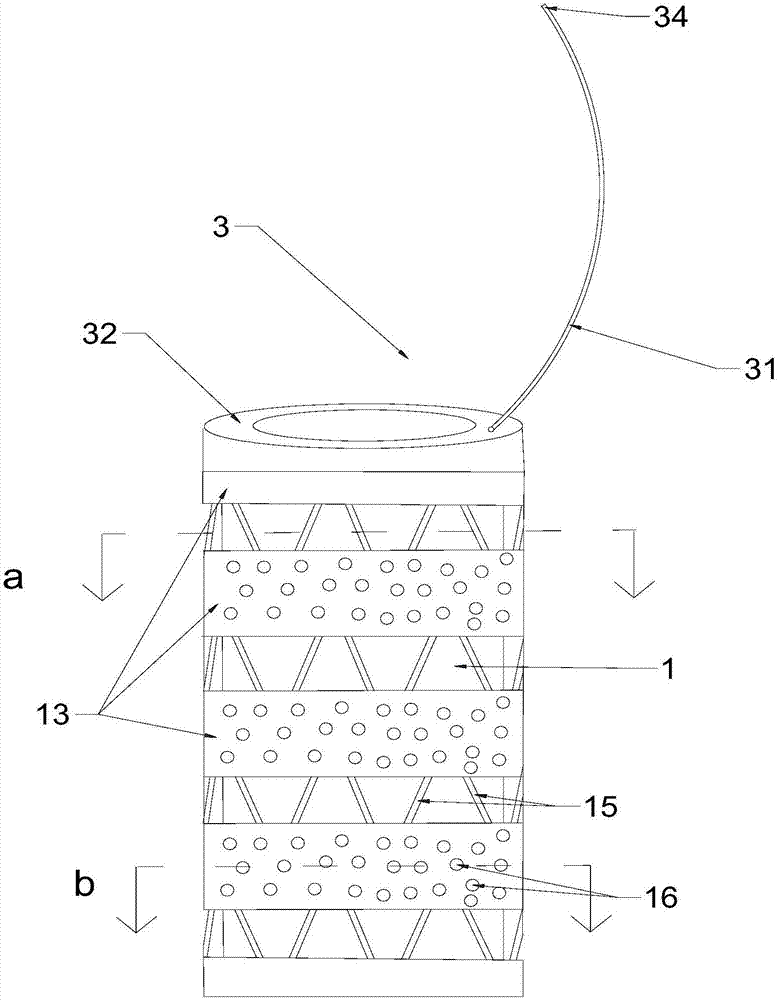
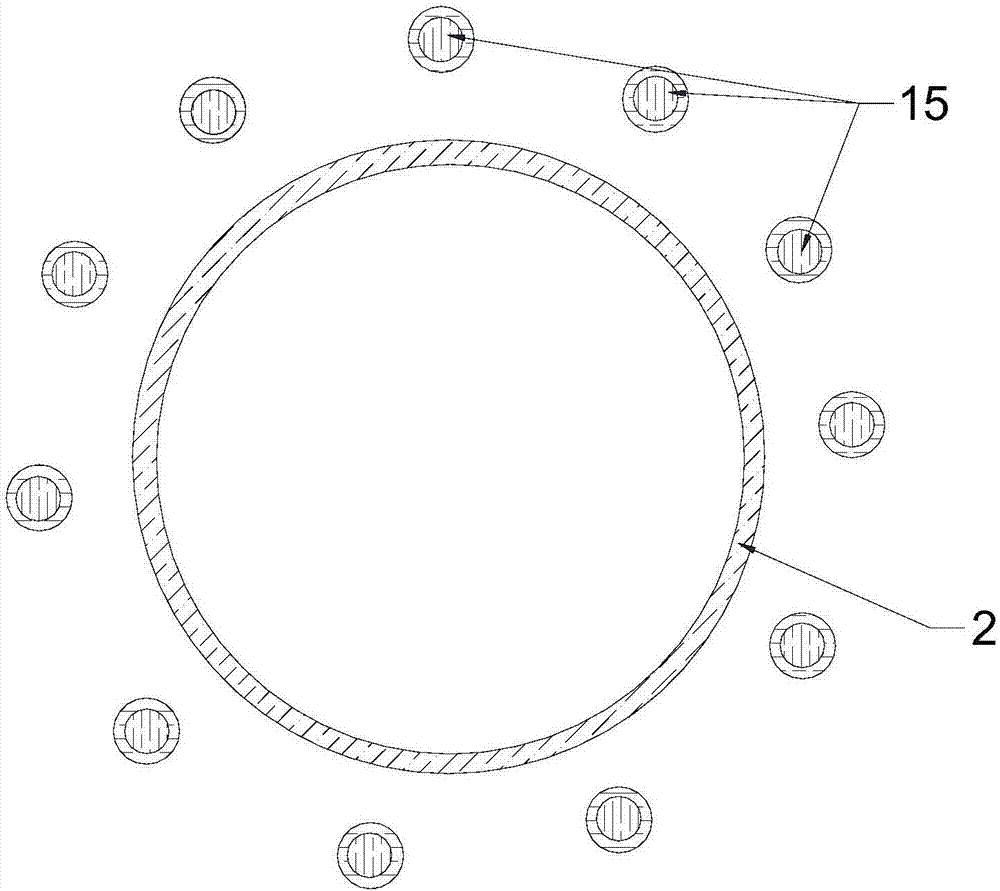
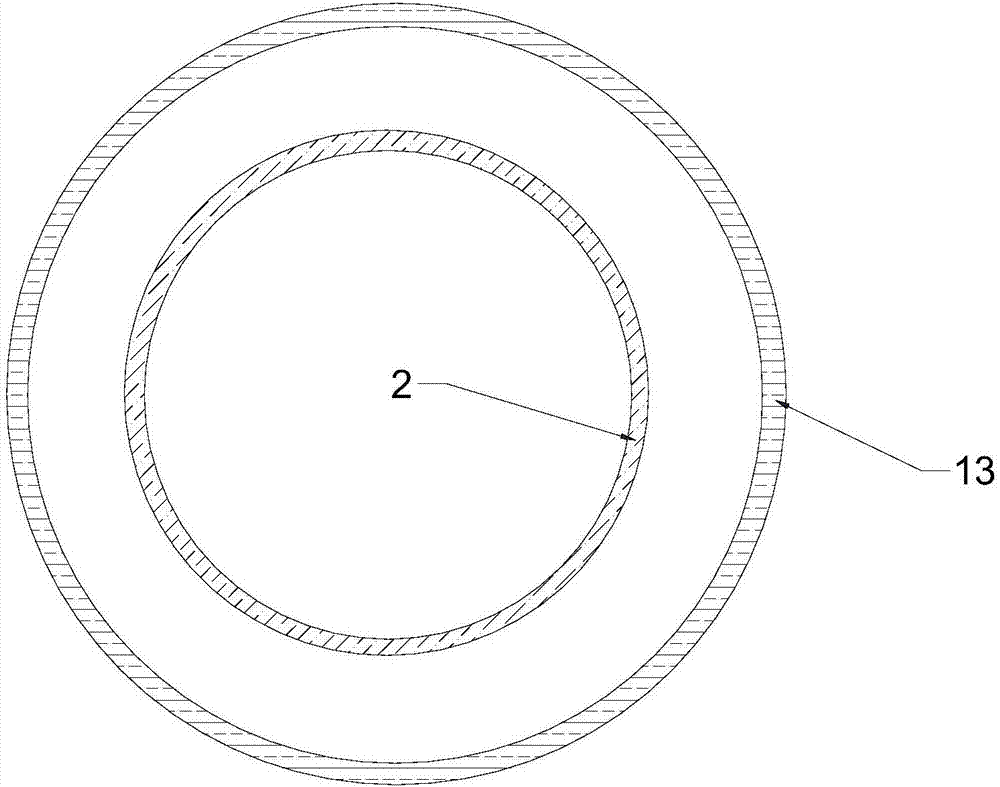
Membrane-coverage bivalve anti-backflow nickel-titanium memory alloy esophageal stent
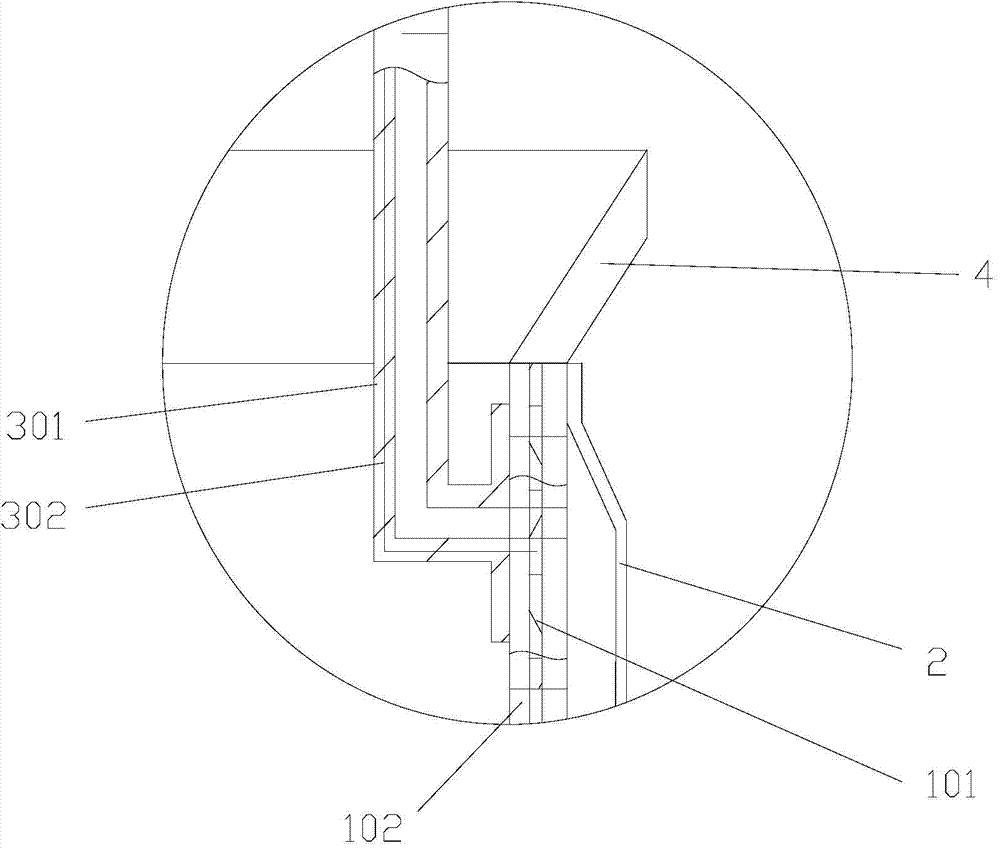
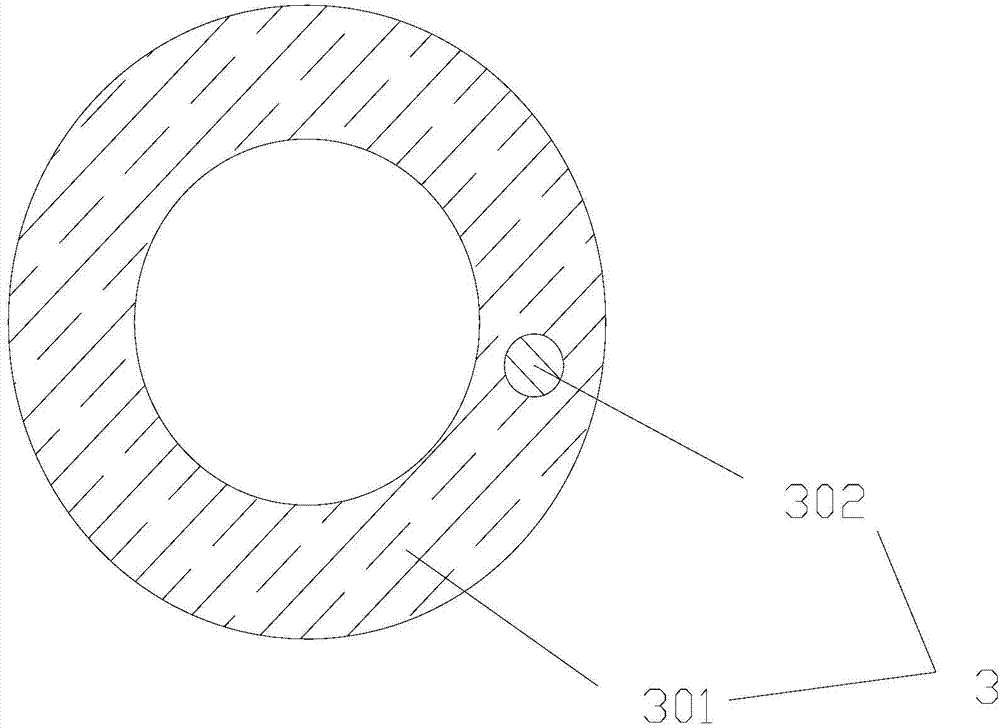
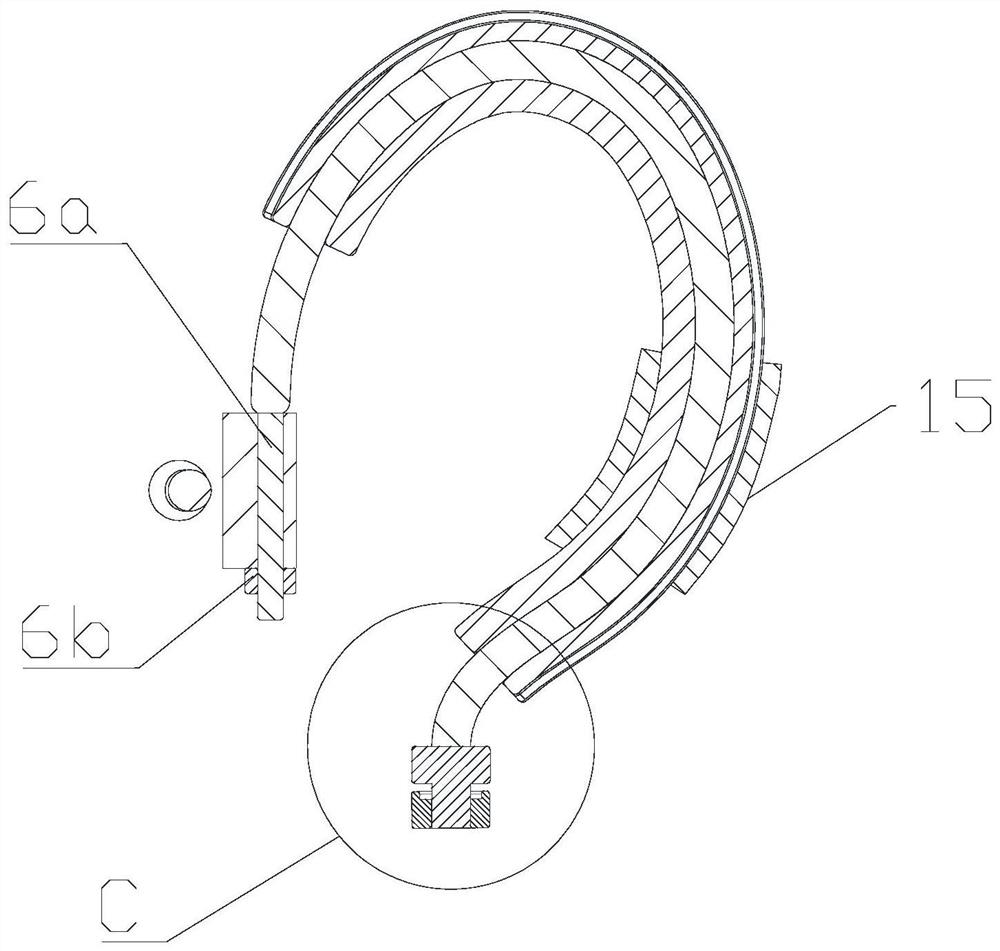
The invention relates to a medical apparatus and particularly relates to a membrane-coverage bivalve anti-backflow nickel-titanium memory alloy esophageal stent. A medical silicone rubber membrane (1) is arranged on a tubular mesh support (2) woven through titanium-nickel alloy wires and an elastic valve A (4) is arranged at the lower end of the tubular mesh support (2). The esophageal stent is characterized in that a layer of elastic valve B (3) is arranged at the upper end of the elastic valve A (4). The esophageal stent has the advantages that backflow of food, in particular to liquids, can be well prevented.
Owner:杨廷旭
Biodegradable anti-displacement esophageal stent and preparing method
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Stents combined with paclitaxel derivatives
ActiveUSH2260H1Reduce fibrosisInhibit scar developmentStentsSurgeryOtolaryngology/ENTOesophageal tube
Stents are used in combination with a paclitaxel derivative in order to inhibit scarring that may otherwise occur when the implant is placed within an animal. Suitable implants include vascular stents, esophageal stents, tracheal or bronchial stents, gastrointestinal stents, genital-urinary stents, nasal and sinus stents, and ENT stents.
Owner:ANGIOTECH INT AG (CH)
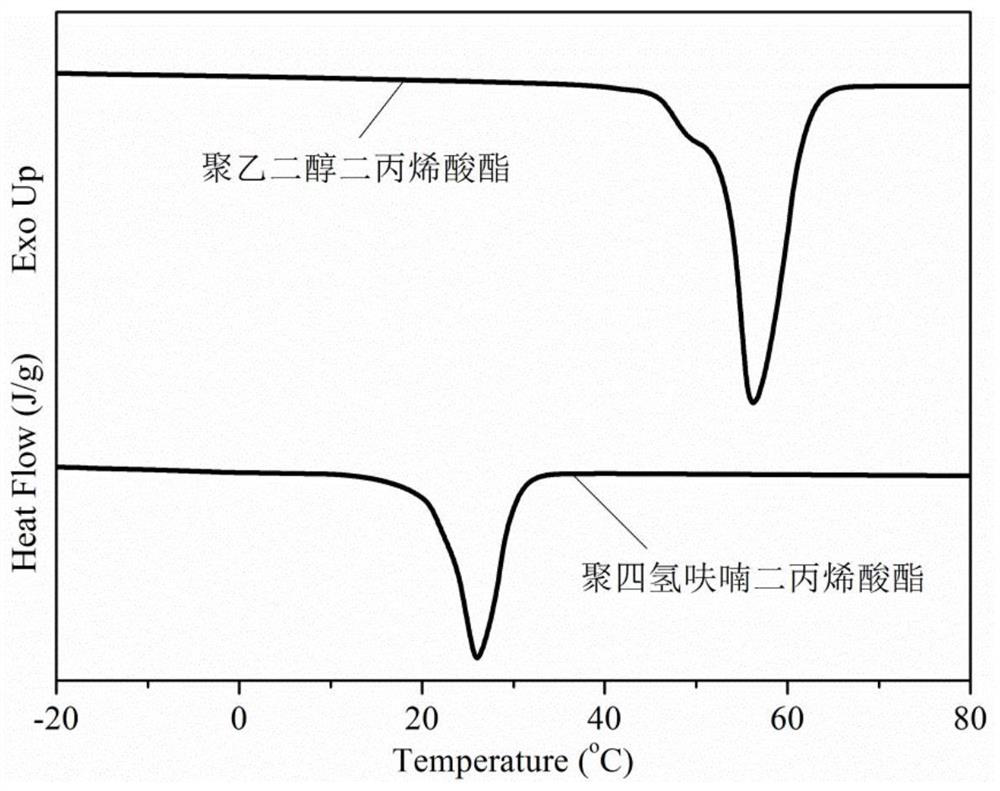
Shape memory polymer material for esophageal stent, preparation method and application method
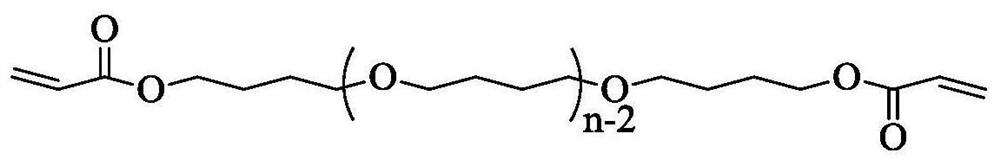
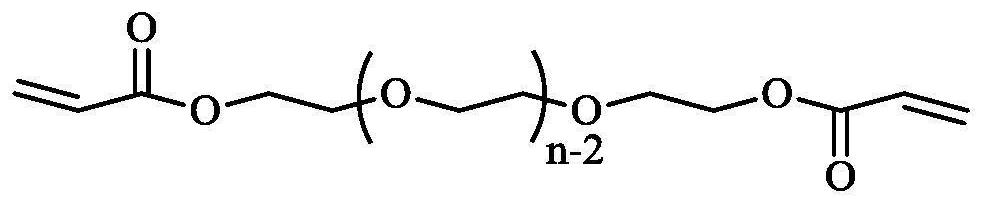
ActiveCN112245664ASolve the shortcomings that are difficult to apply to the human bodySimple preparation processSurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPolymer sciencePolythylene glycol
The invention discloses a shape memory polymer material for an esophageal stent and a preparation method thereof. The shape memory polymer material is prepared from, by mass, 30-60 parts of hydrophilic crystallizable macromonomer, 40-70 parts of hydrophobic crystallizable macromonomer and 1-10 parts of cross-linking agent through a polymerization reaction, wherein the hydrophilic crystallizable macromonomer is polyethylene glycol diacrylate, the hydrophobic crystallizable macromonomer is polytetrahydrofuran diacrylate, and the cross-linking agent is pentaerythritol tetra-3-mercaptopropionate.The material is simple to prepare, light and soft in texture and degradable, has the self-unfolding, adjustable and drug sustained-release capacity in a human body environment when serving as an esophageal stent material and shows a higher application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
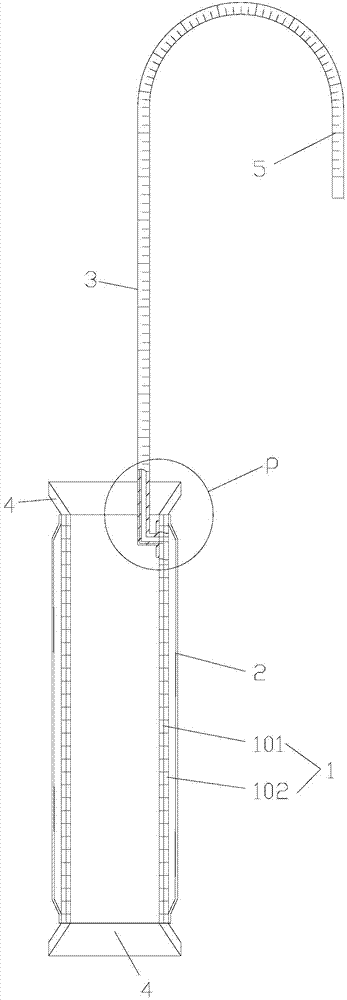
Recyclable esophageal stent
Disclosed is a recyclable esophageal stent. The recyclable esophageal stent is structurally composed of a meshed esophageal stent body and an annular opening tightening line. The annular opening tightening line penetrates into mesh buckles at the two ends of the meshed esophageal stent body. The recyclable esophageal stent has the advantages that the structure is simple, the recyclable esophageal stent can be placed and can also be recycled, the cost is low, the recyclable esophageal stent can be made of common stainless steel wires to replace traditional expensive nickel-titanium memory alloy, and no refrigeration memory needs to be carried out on the recyclable esophageal stent before an operation; once the meshed esophageal stent body falls into the stomach, the meshed esophageal stent body can be dragged out and recycled through a pair of biopsy forceps under the monitoring of an X-ray machine, the meshed esophageal stent body can be repeatedly used after being recycled, the operation is conveniently carried out, the operation time is short, the pain of a patient is small, labor intensity of a doctor is low, and the treatment expenses of the patient can be greatly reduced.
Owner:JINAN GAODA INFORMATION TECH
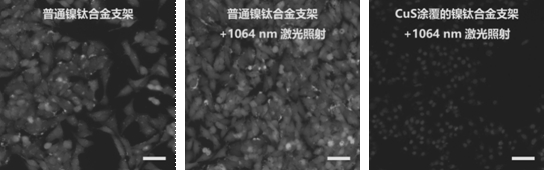
Memory alloy esophageal stent modified by nano copper sulfide coating and preparation method of memory alloy esophageal stent
ActiveCN113499483AStable in natureNot easy to decomposeStentsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismUrethral stentsNitinol stent
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical instruments, and relates to a memory alloy esophageal stent with a uniform nano copper sulfide film and an efficient photo-thermal physiotherapy function and a preparation method of the memory alloy esophageal stent. The stent is prepared by reducing dopamine under an alkaline condition to obtain a polydopamine-coated memory alloy stent, and then efficiently adsorbing copper ions through polydopamine under a heating condition to grow copper sulfide in situ. According to the method, a unique method for in-situ growth of nano CuS particles on the surface of the stent is adopted, the nano CuS material is safe and non-toxic, and the growth process is simple and rapid; photo-thermal conversion is efficient, and repeated use can be achieved; the method can be applied to nickel-titanium alloy stents of various shapes and other types, such as biliary tract stents, intestinal tract stents, urinary tract stents and tracheal stents.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
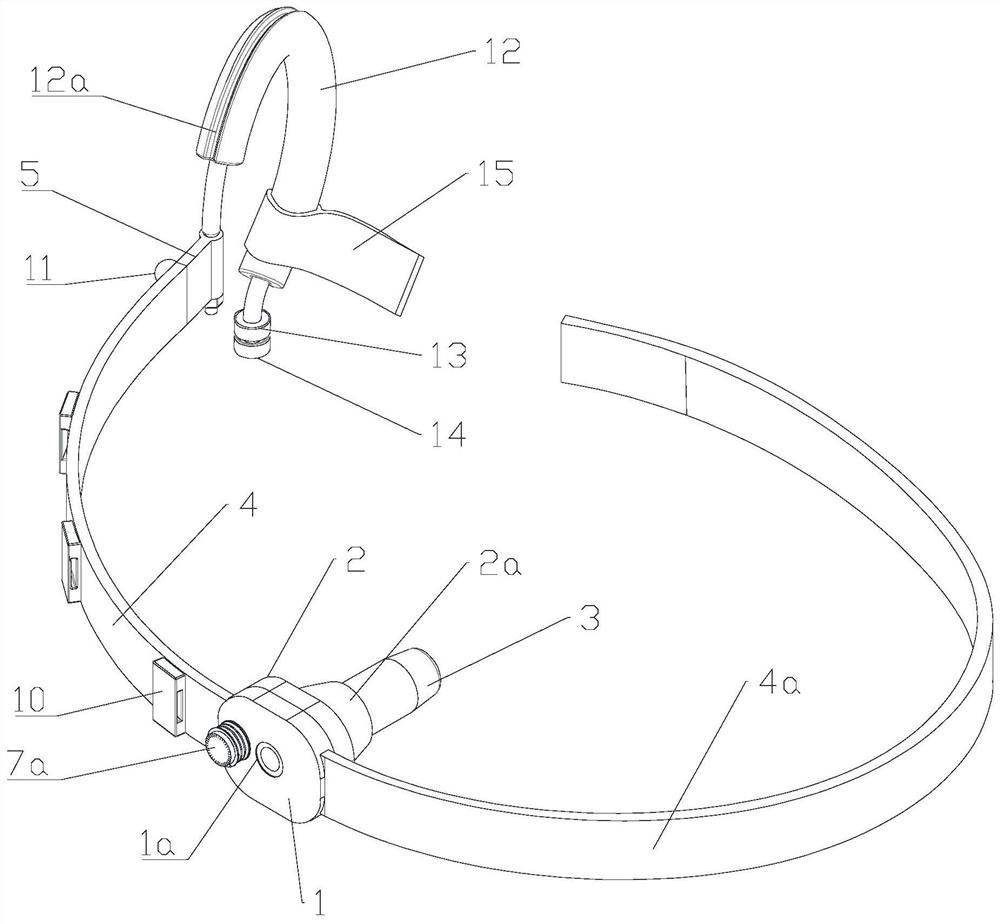
Pull wire skidproof and antiskid device for medical esophageal stent
ActiveCN111773108AAvoid displacementPrevent slippageFeeding-tubesAgainst vector-borne diseasesNasal passagesNasal congestion
The invention discloses a pull wire skidproof and antiskid device for a medical esophageal stent. The pull wire skidproof and antiskid device comprises a nose fixing device and an ear fixing device, wherein the nose fixing device and the ear fixing device are connected through an elastic band; the nose fixing device comprises a fixing plate, a nose stuffing pad is arranged on the fixing plate, anda graduation label plate is also rotatably connected to the fixing plate; the ear fixing device comprises a curved stent being conjunctive with the ear outline of a patient, and a rubber soft pad isarranged on the curved stent; and a pull wire locking device is also arranged at one end of the curved stent. The nose fixing device, the ear fixing device and the elastic band are in cooperation, thepull wire skidproof and antiskid device is simple in structure, the pull wire of the esophageal stent of the patient can be fixed, the condition that while in use, the esophageal stent displaces andslips can be avoided, the fine sliding of the pull wire can be shown in a quantification manner, and besides, the pull wire can be prevented from causing pressure sores on the nose and the faces of the patient.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE HOSPITAL THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL WITH NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Temporary esophageal stent extractor
The invention relates to an extractor, in particular to a temporary esophageal stent extractor which comprises a guide head, an inner cannula, an outer cannula and a handle. An inner core is arranged in the inner cannula and is of a hollow structure, and the outer cannula is arranged on the outer side of the inner cannula and is connected onto the handle. The temporary esophageal stent extractor has the advantages that the integral cannulas can be pushed into the esophagus of a patient by a push rod, injury to the esophagus of the patient can be reduced under the guide effects of a withdrawing line and the guide head, the guide head can reach a level of the upper end of a temporary esophageal stent under a fluoroscopic monitoring effect, the outer cannula is withdrawn, stent claws are opened, the inner core is withdrawn, the temporary esophageal stent withdrawing line is pulled, the temporary esophageal stent is contracted by the aid of the stent claws and is completely withdrawn into the inner cannula, the outer cannula is pushed, then the stent claws are withdrawn into the outer cannula, the stent extractor can be withdrawn via the esophagus of the patient, and accordingly injury to the esophagus of the patient can be reduced to the greatest extent in stent extraction procedures.
Owner:LISHUI CENT HOSPITAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com