Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
53 results about "Esophageal wall" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
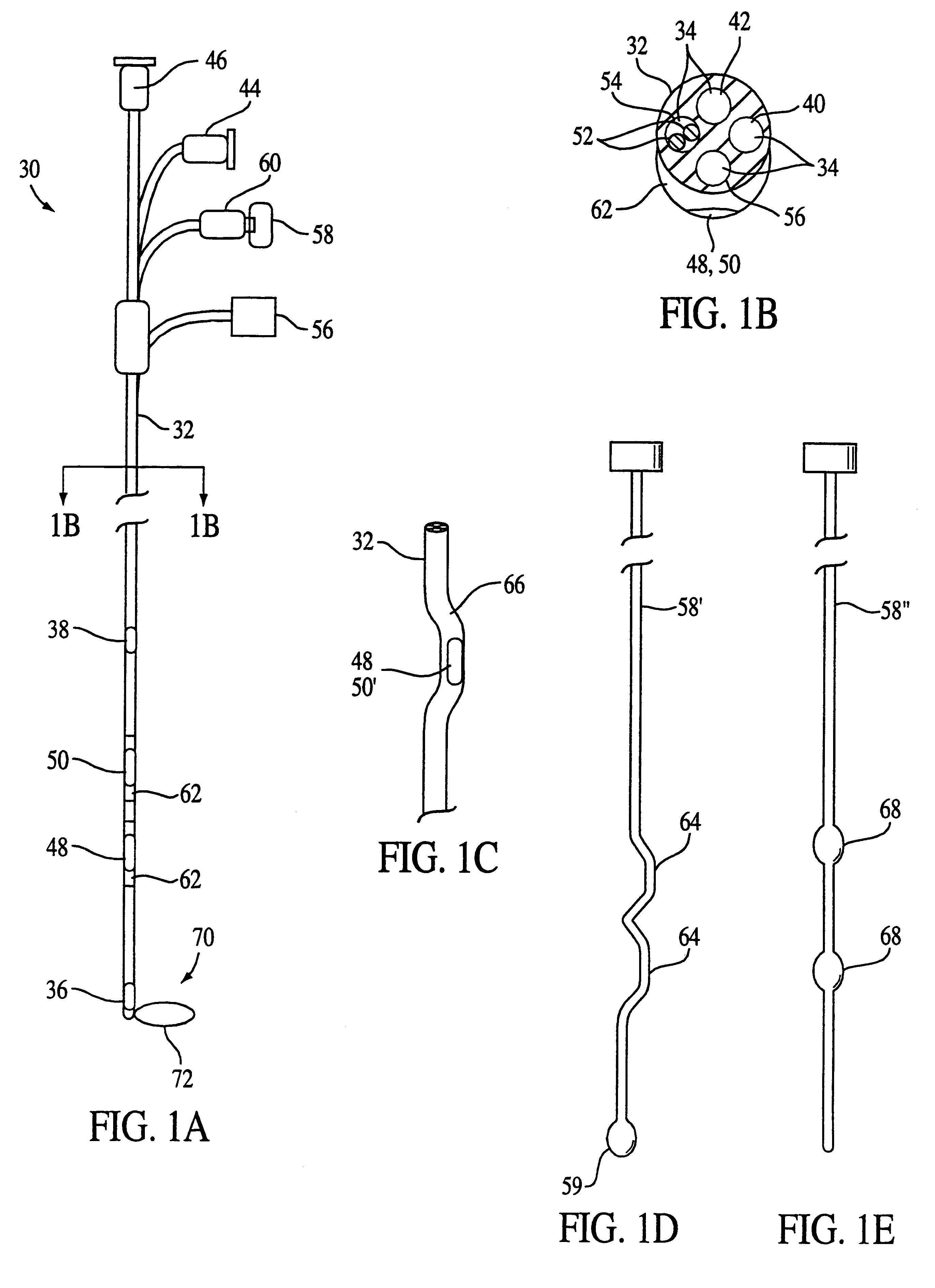
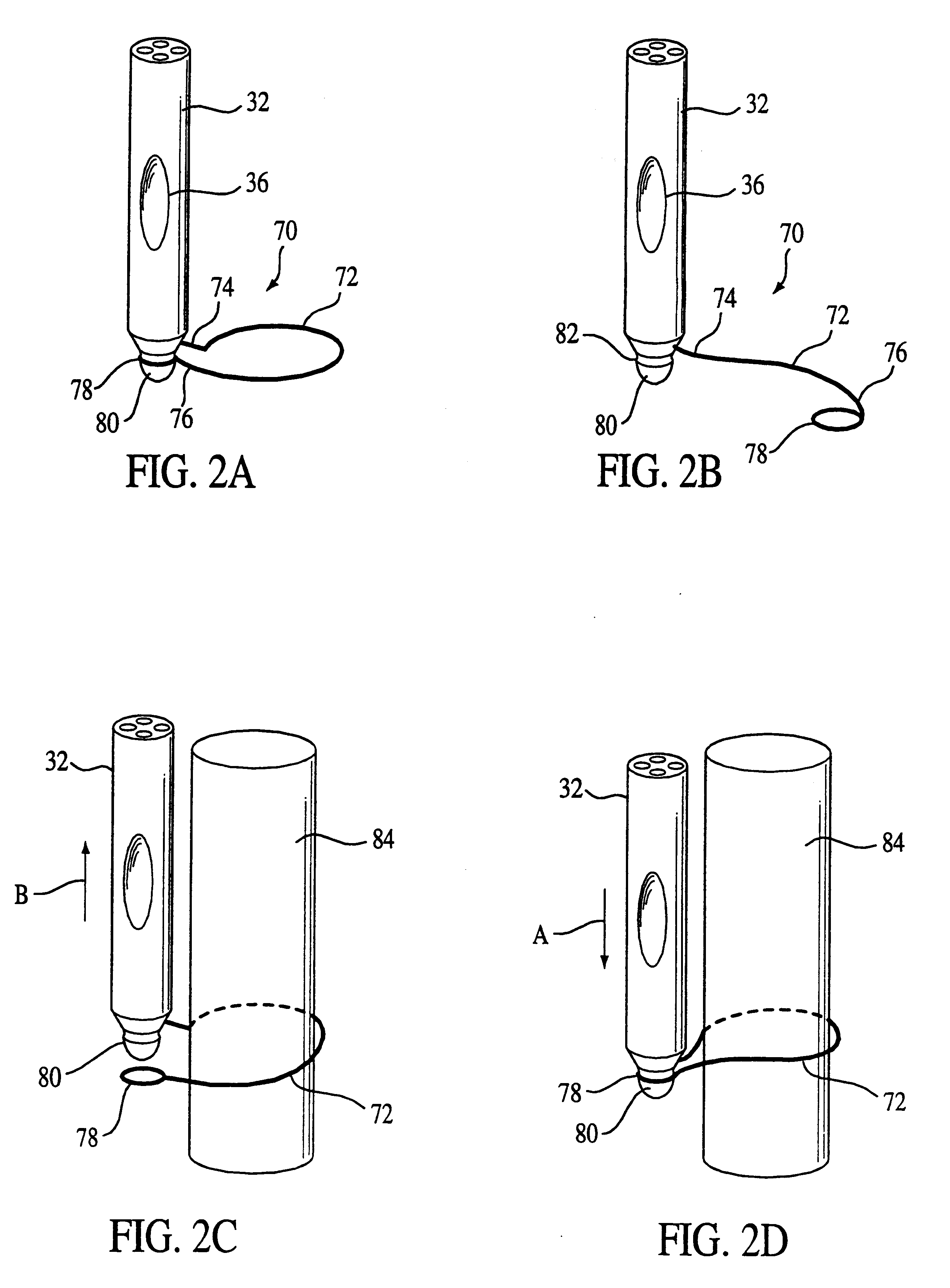
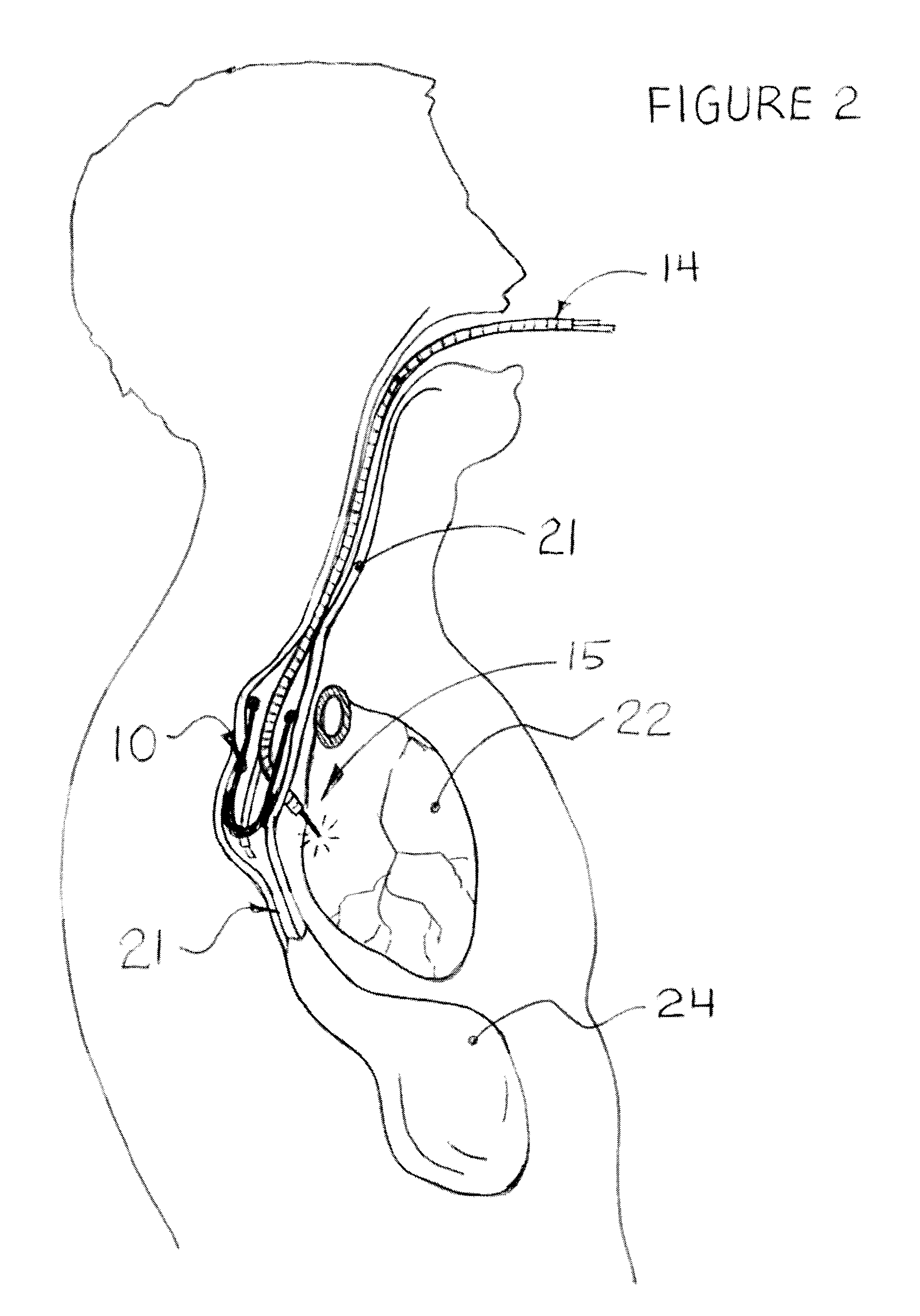
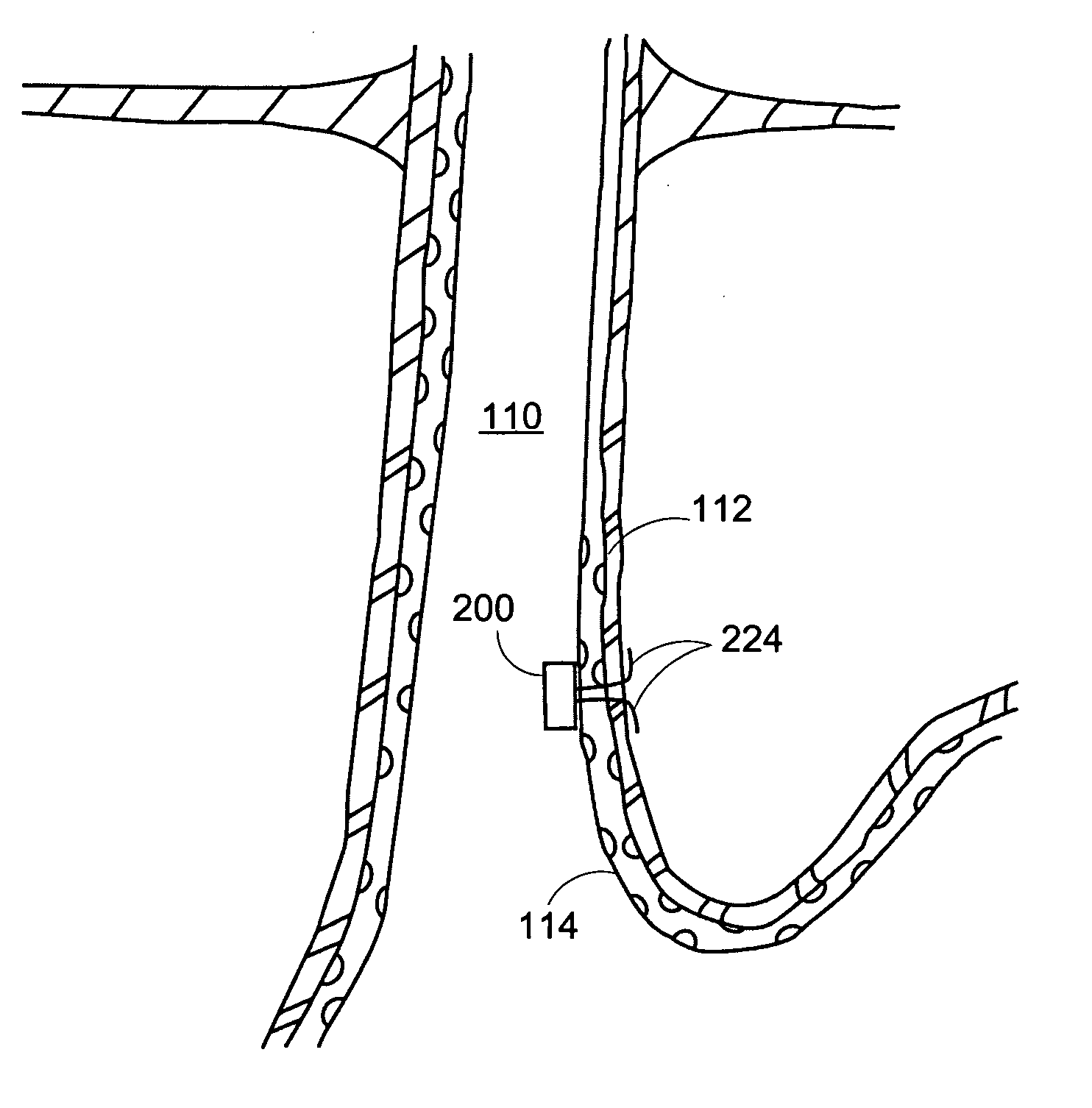
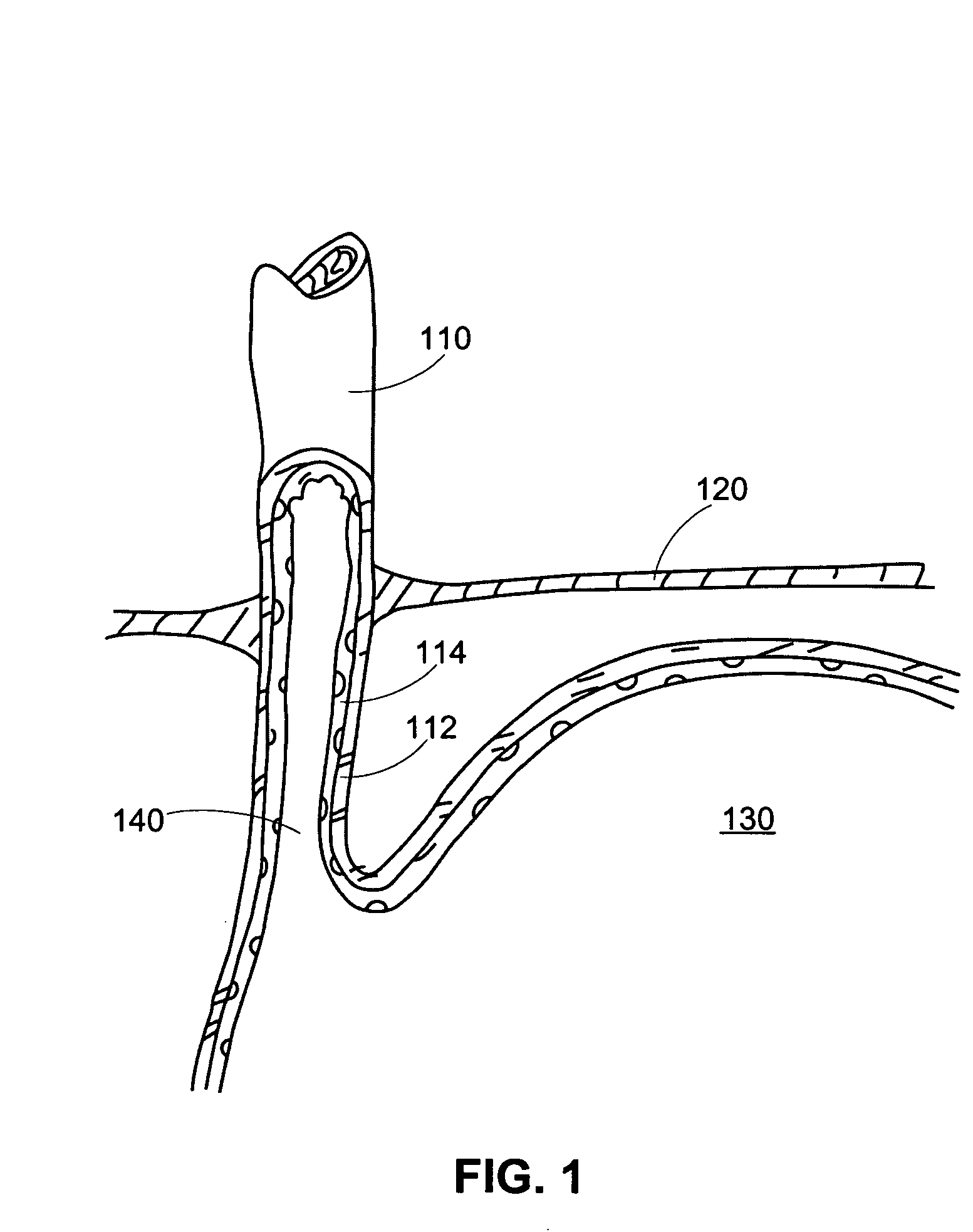
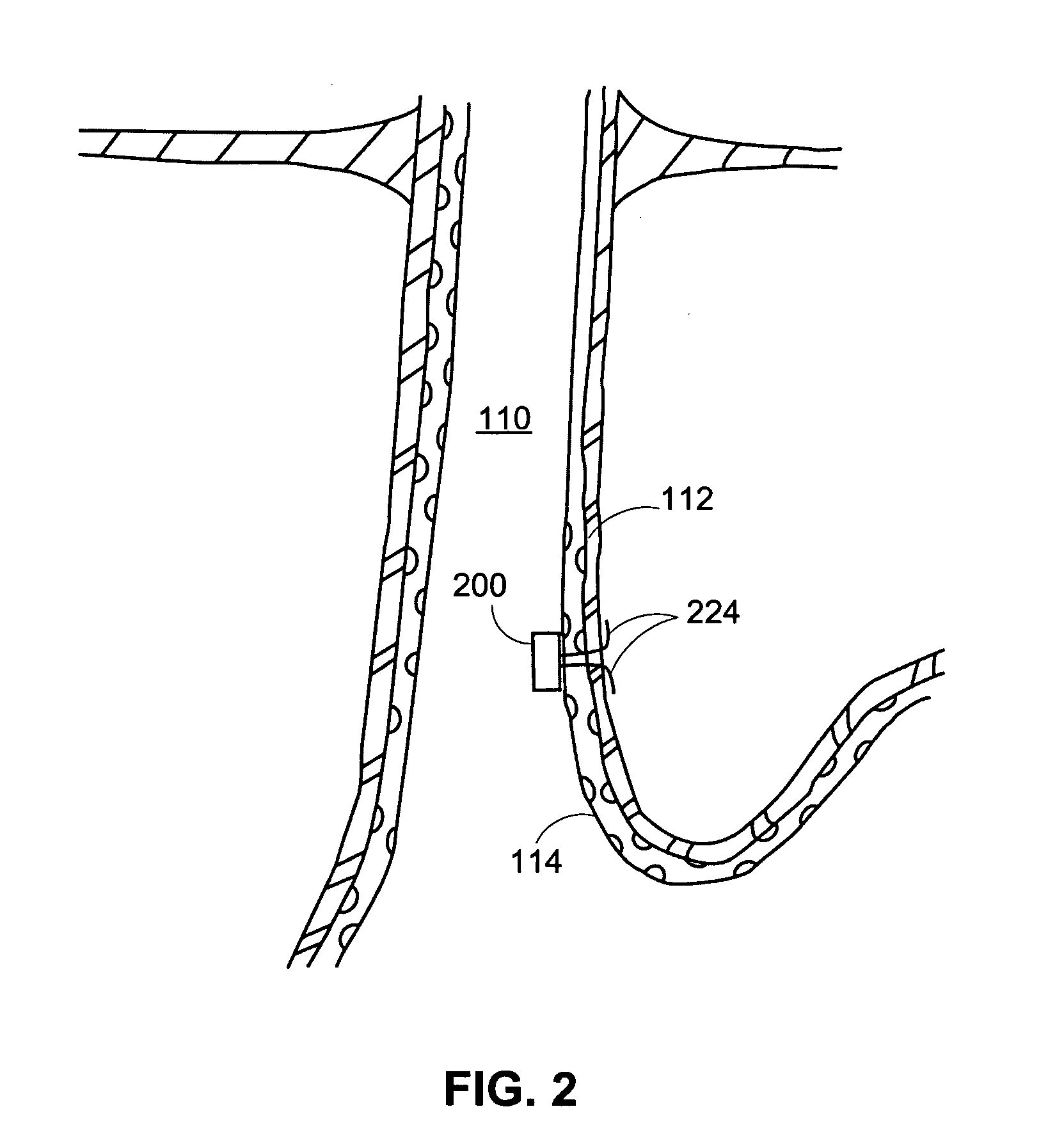
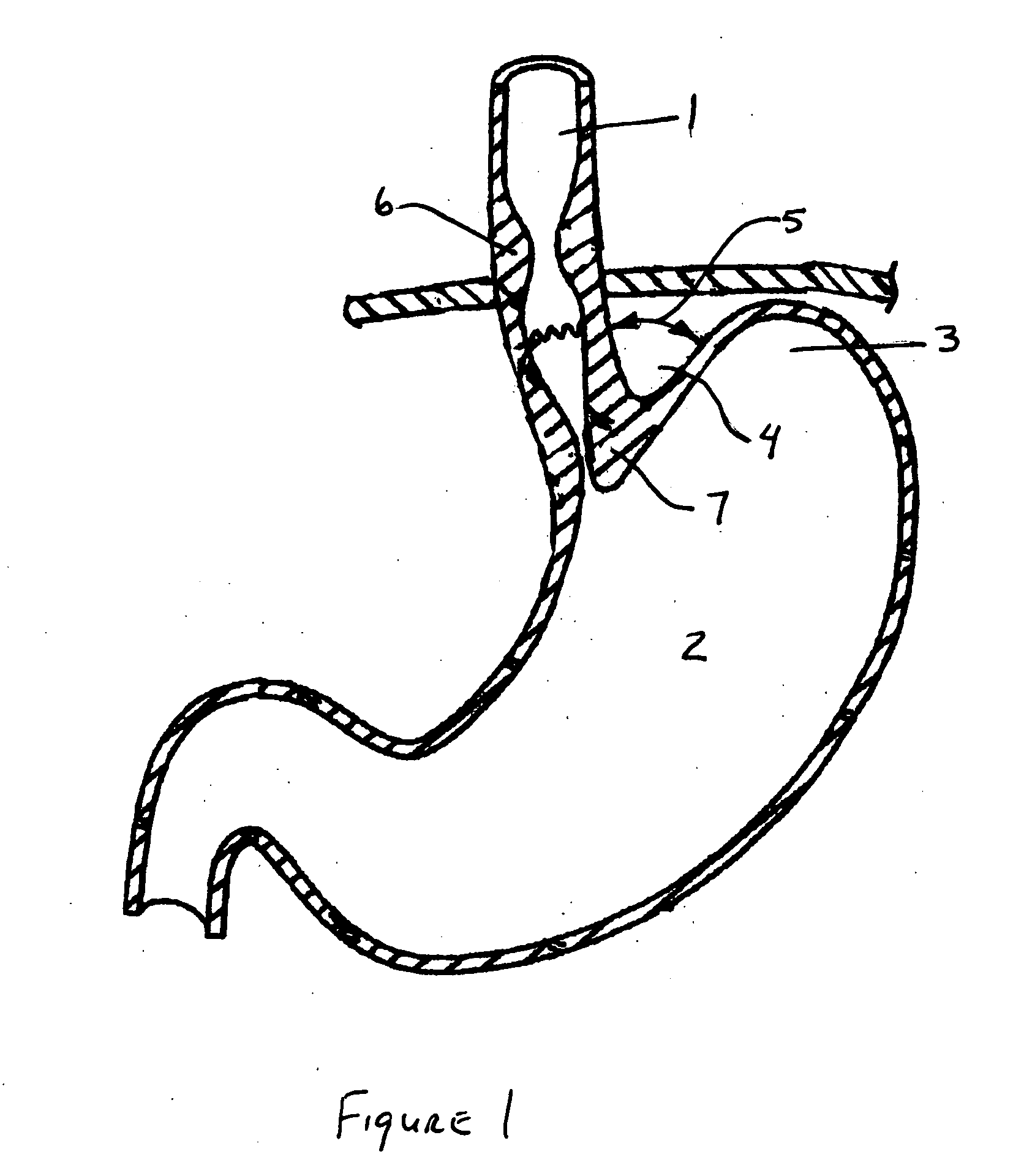
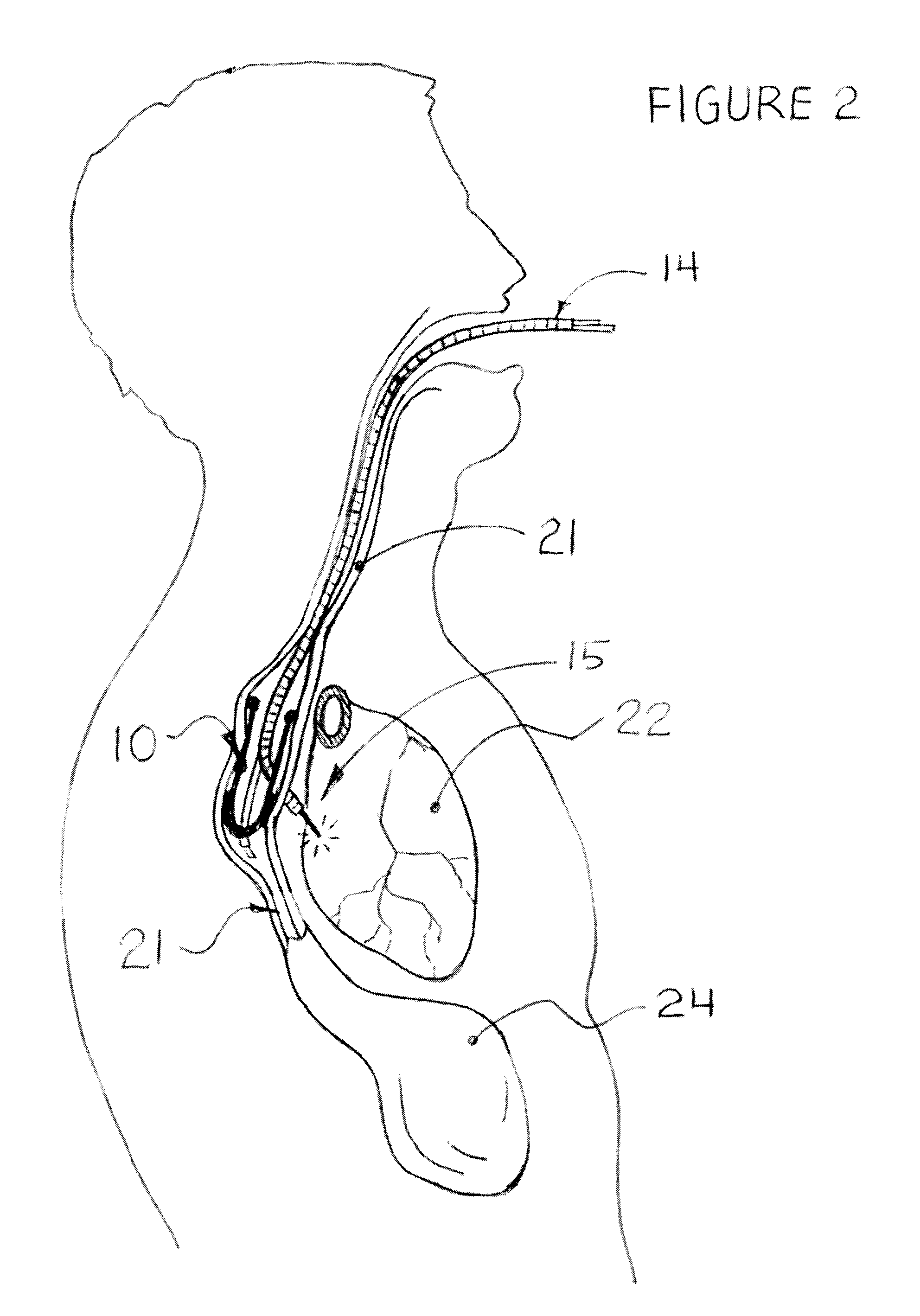
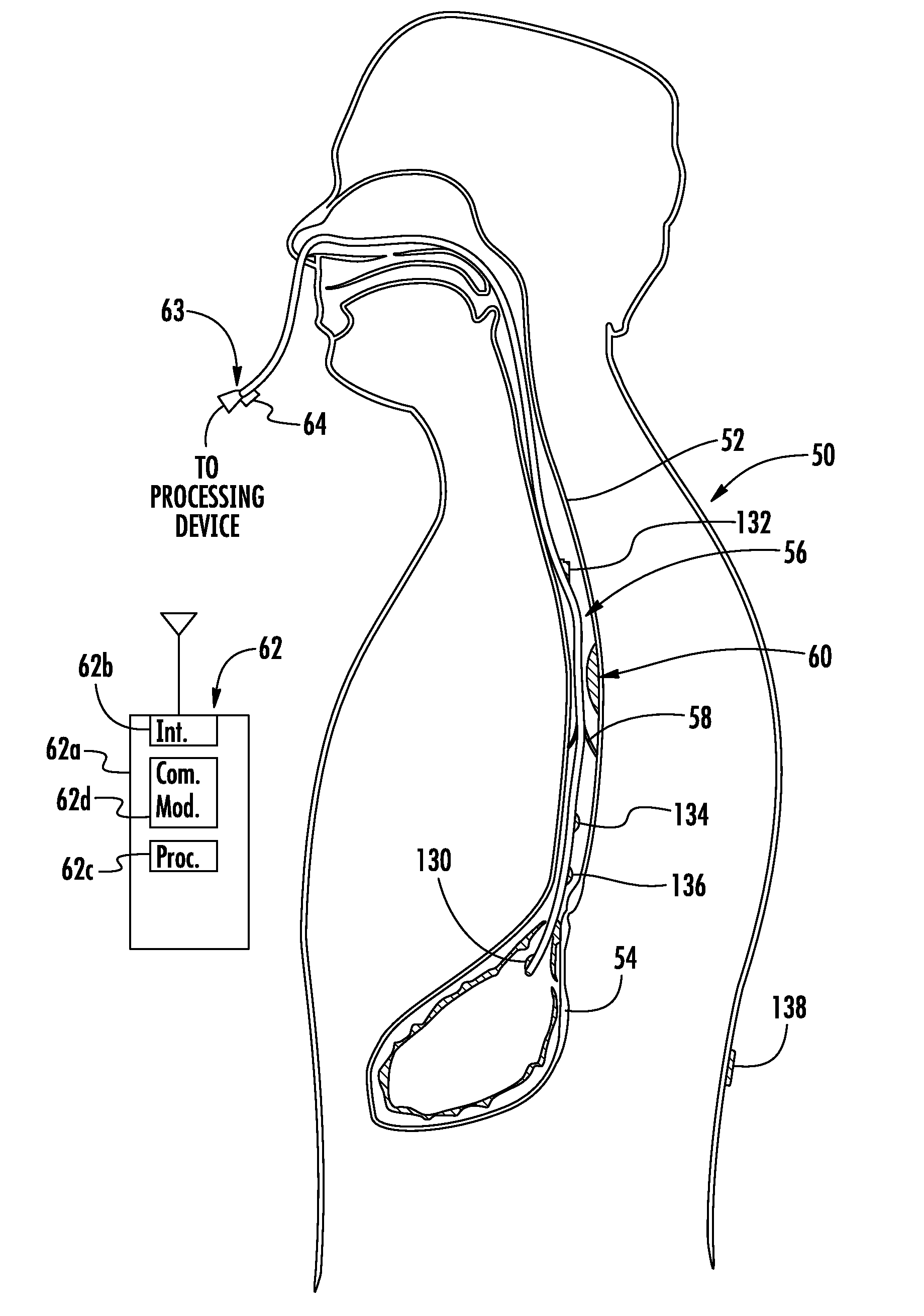
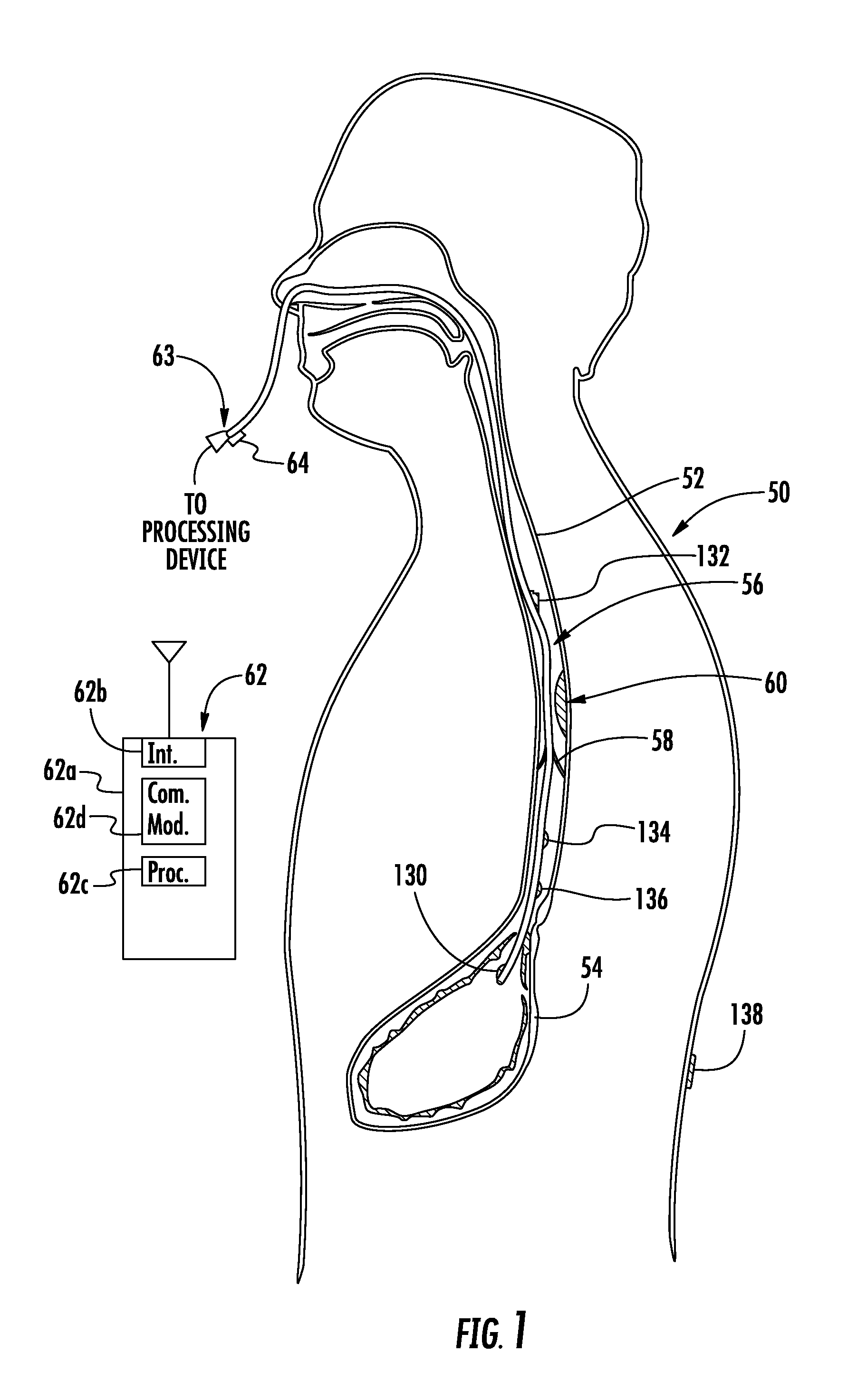
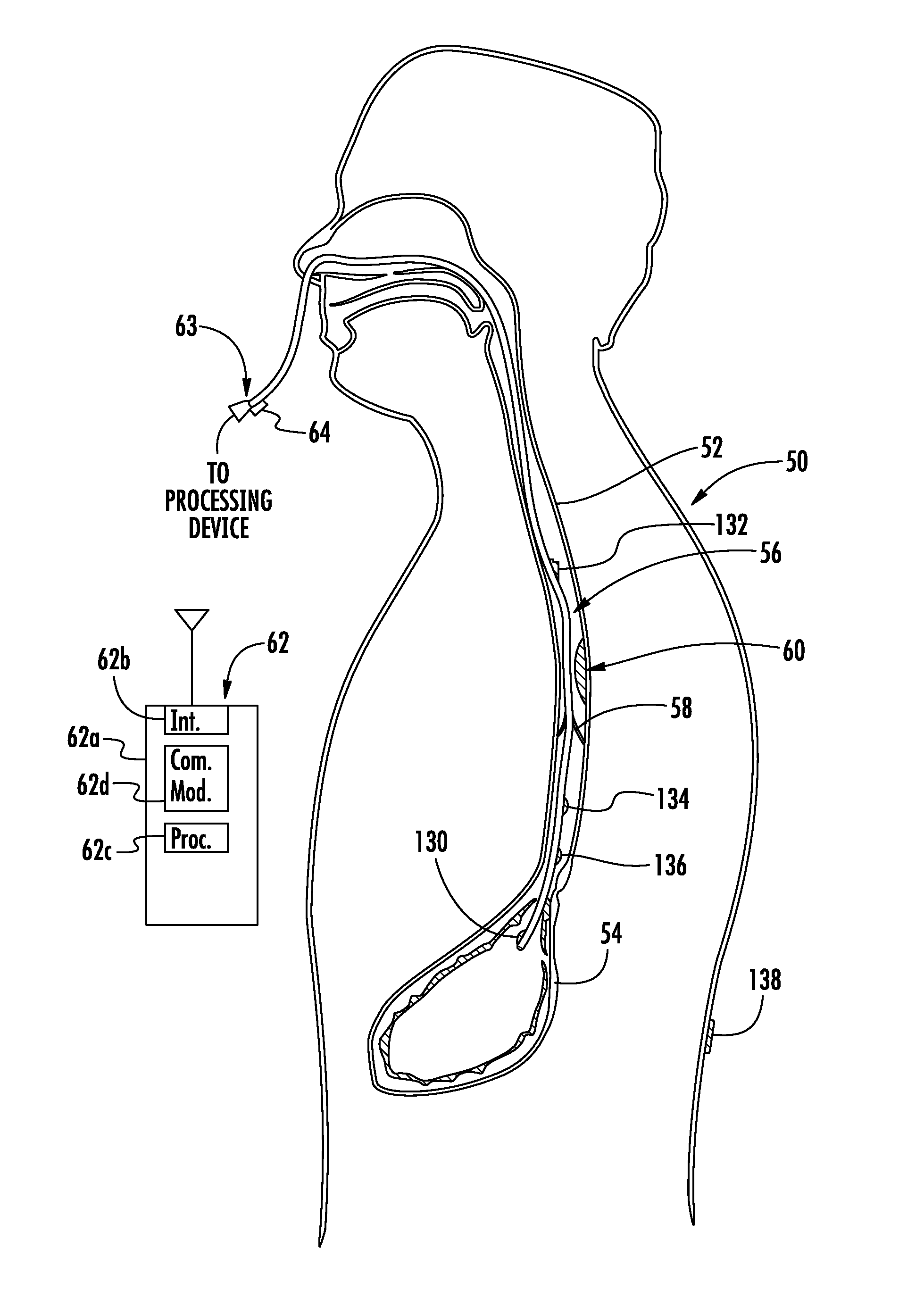
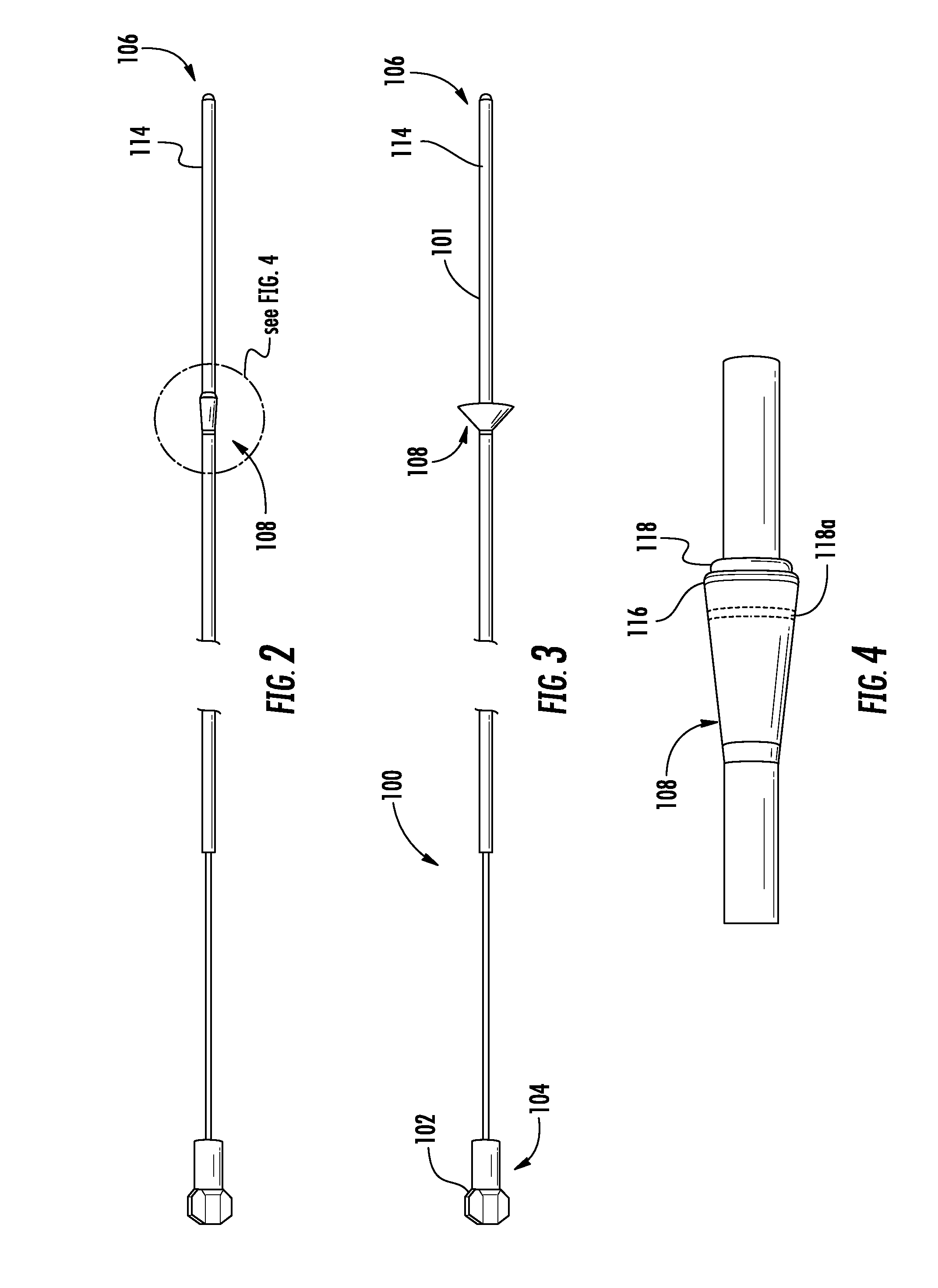
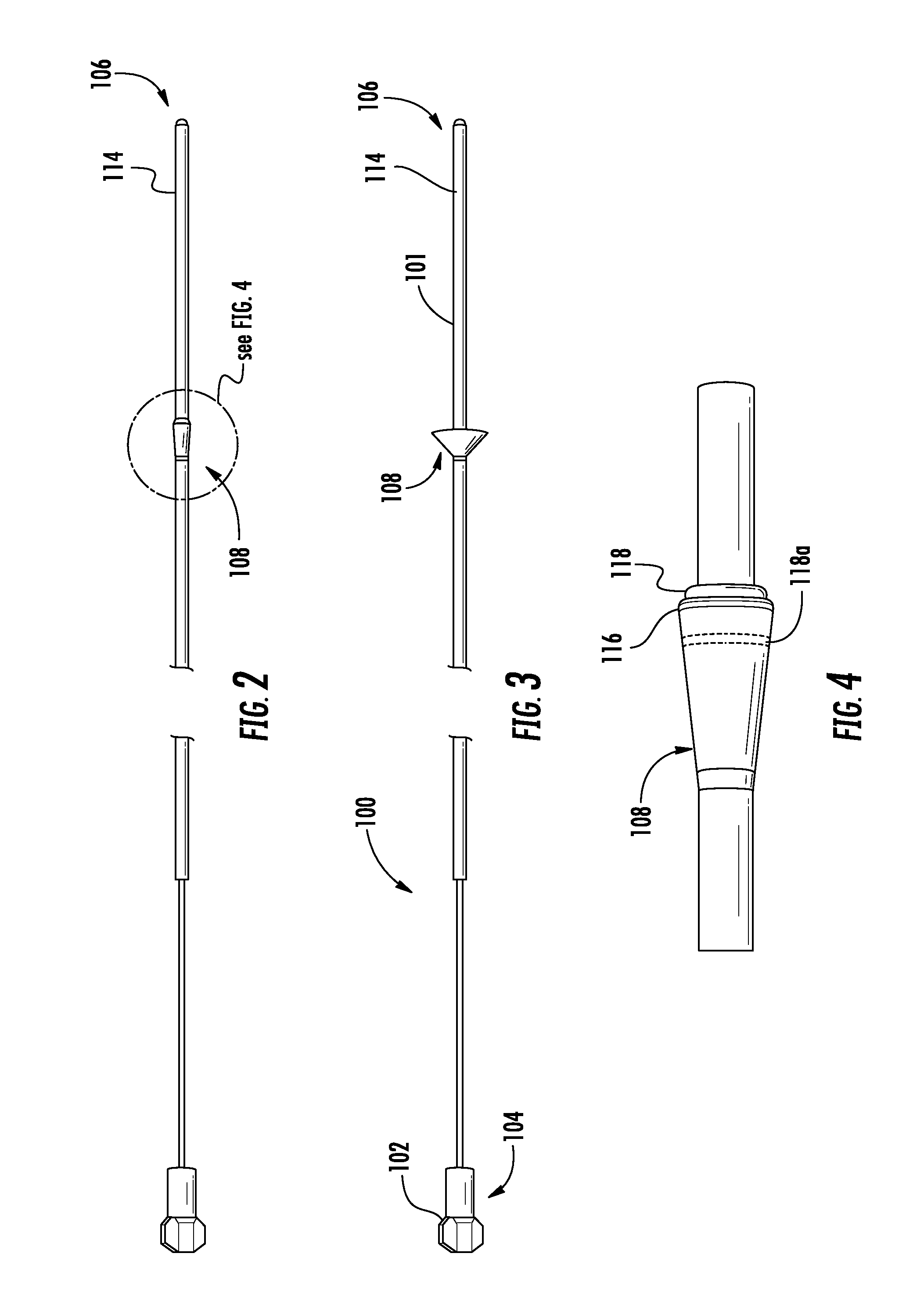
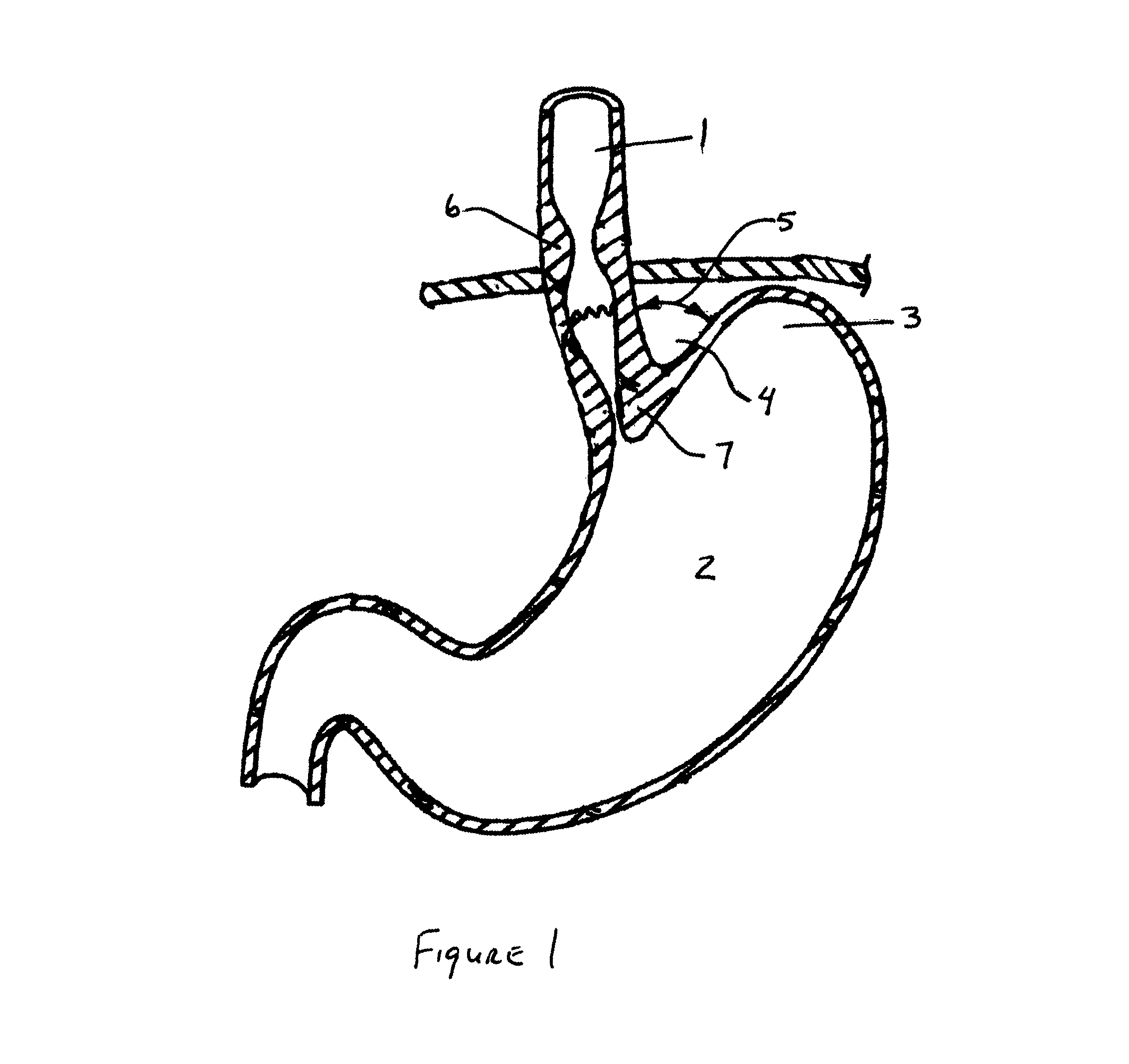
Methods and apparatus for improving the function of biological passages
ActiveUS6960233B1Reduces the hiatal herniaStrengthens the function of the lower esophageal sphincterTubular organ implantsInsertion stentEsophageal wall
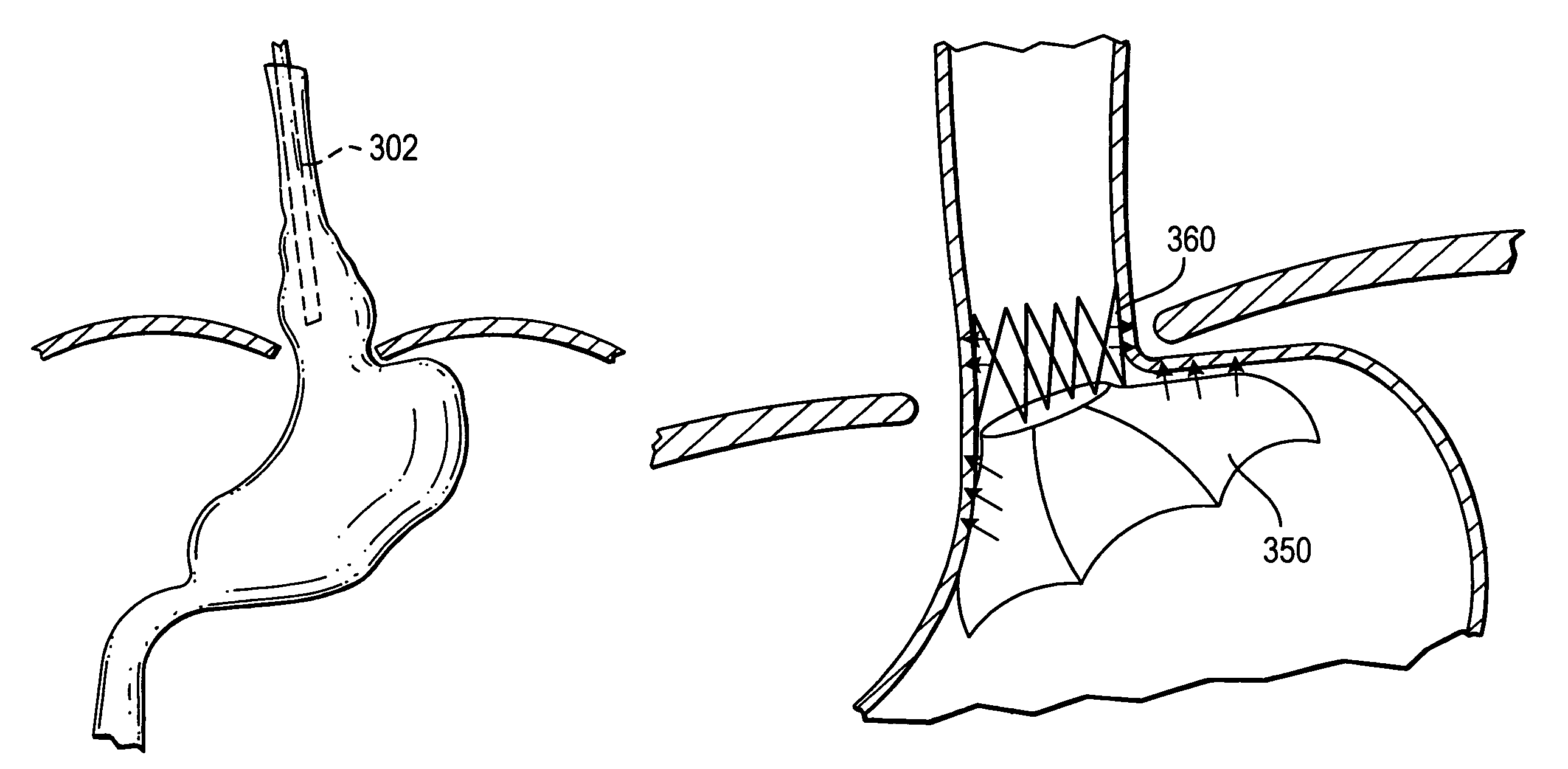
Several methods and apparatus are available for treating patients that suffer from both gastro-esophageal reflux disorder and hiatal hernias. In order to treat these patients, an endoscopic probe may be used to push the herniated stomach below the diaphragm. In some embodiments, a two-part stent comprising a funnel stent and a reverse stent may be deployed to prevent a future re-herniation of the stomach and to reduce the annulus of the lower esophageal sphincter. In some embodiments, a reverse stent with perforating barbs may be deployed, in which the barbs penetrate the esophageal wall and attach to the diaphragm. In some embodiments, the crus muscles may be sutured together to reduce the hiatus size and a reverse stent may be deployed to reduce the annulus of the lower esophageal sphincter.
Owner:TORAX MEDICAL
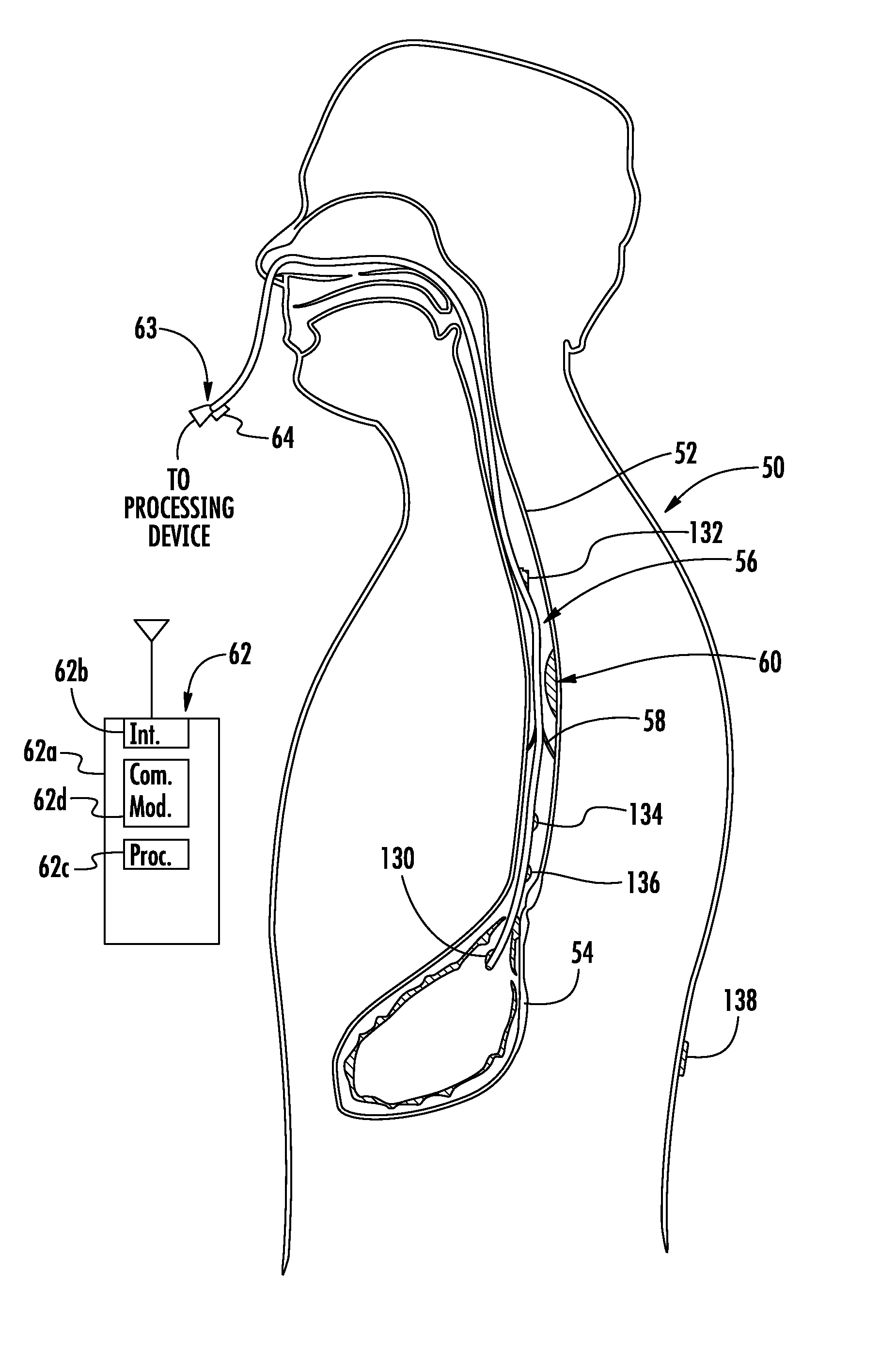
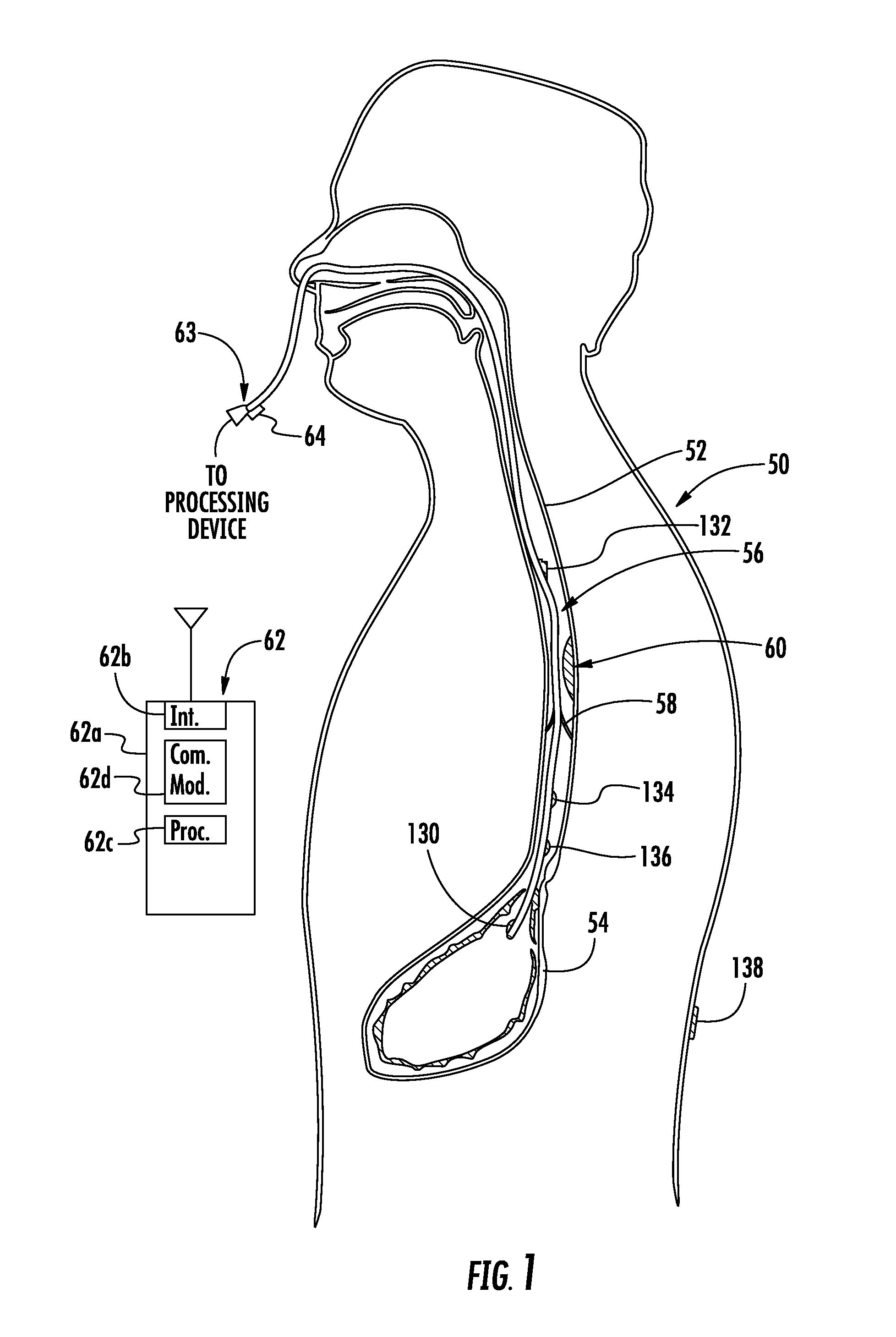
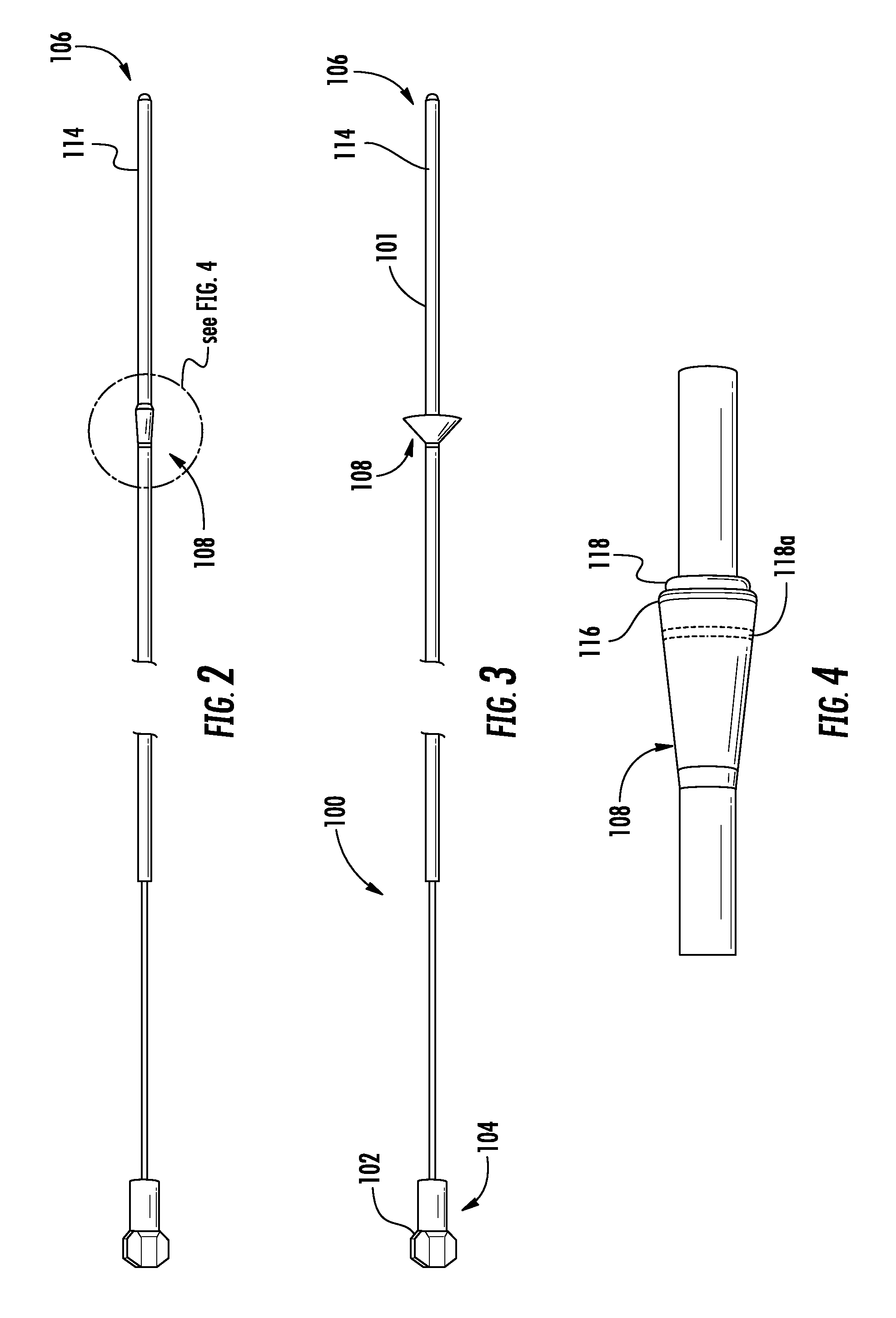
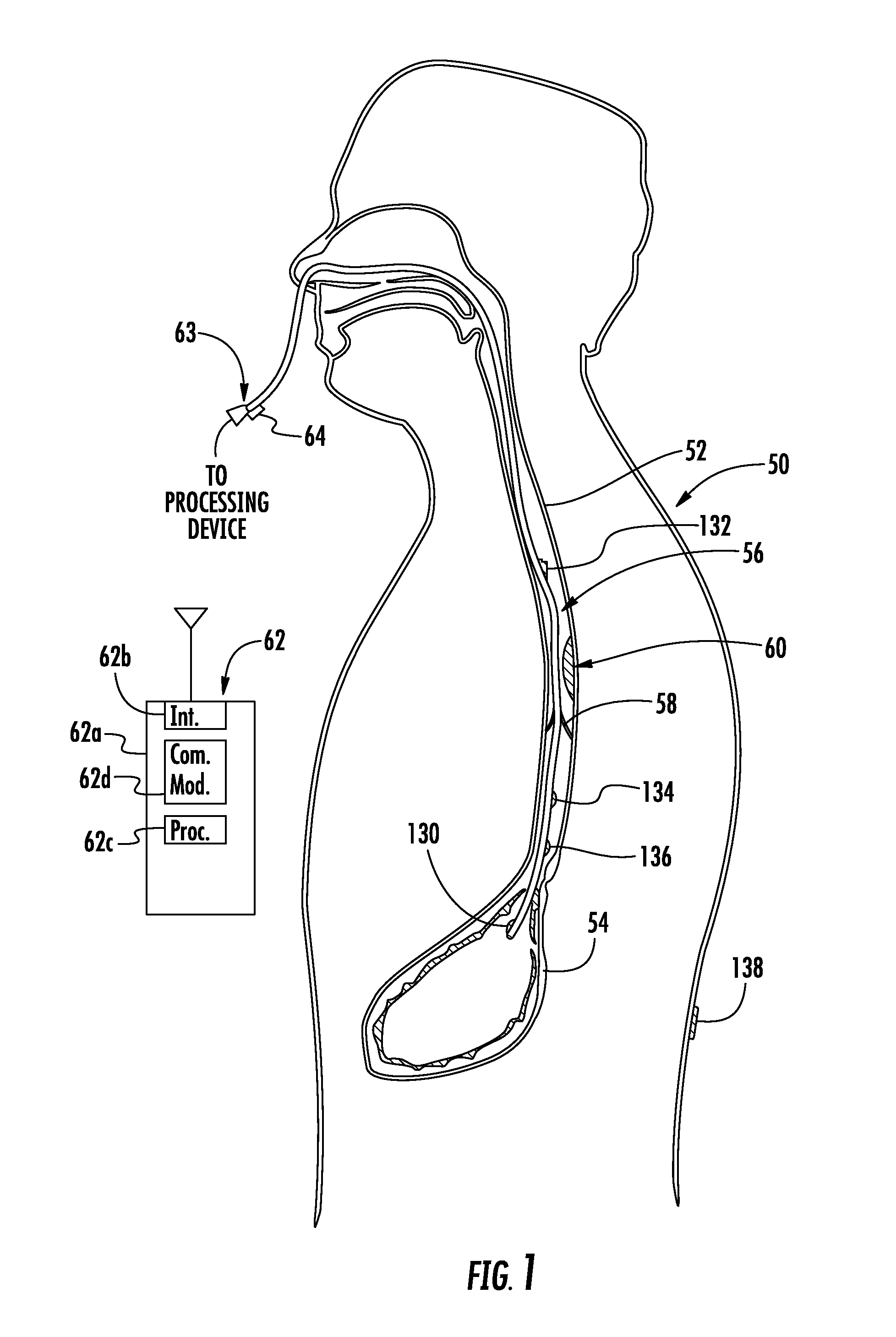
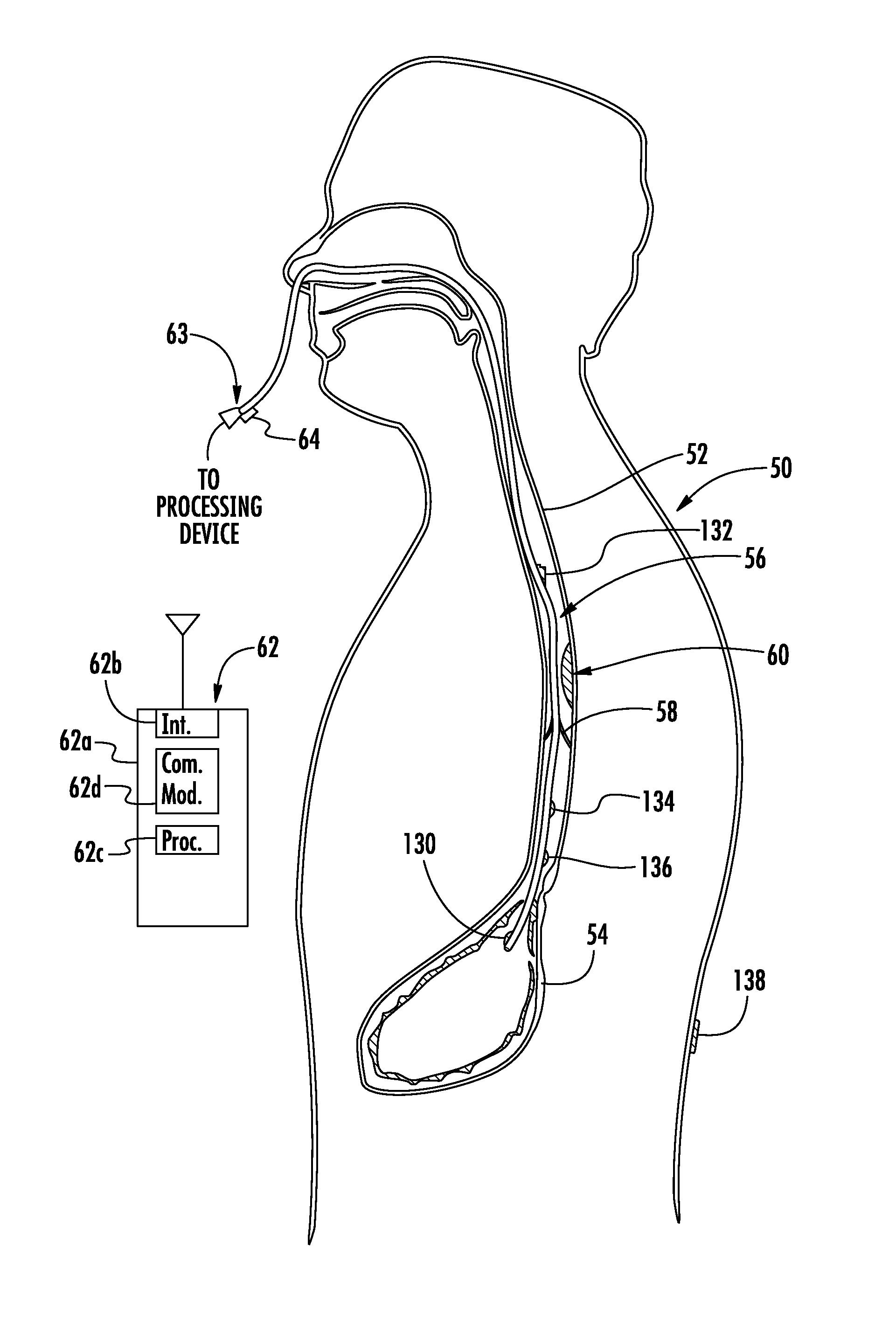
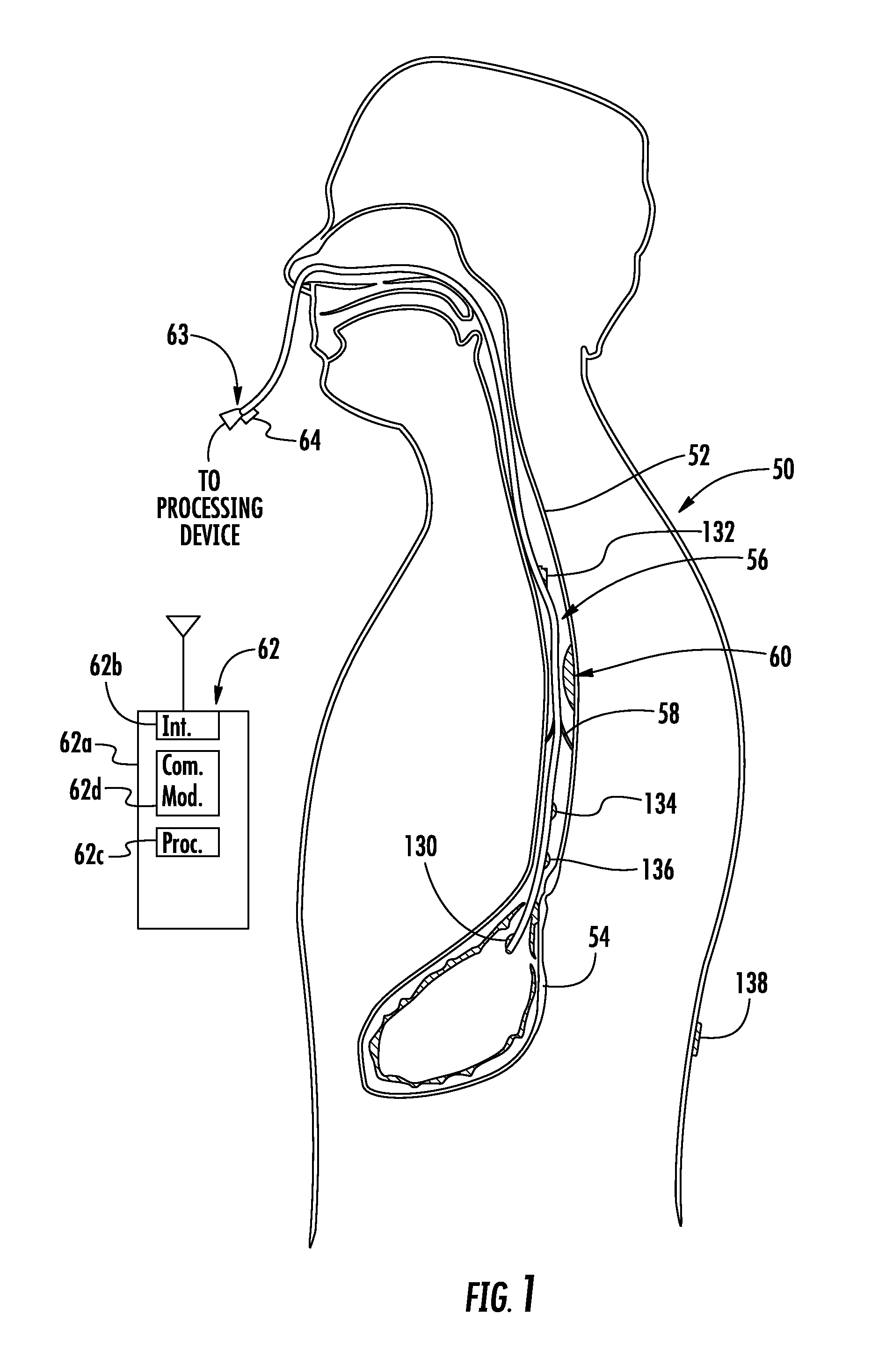
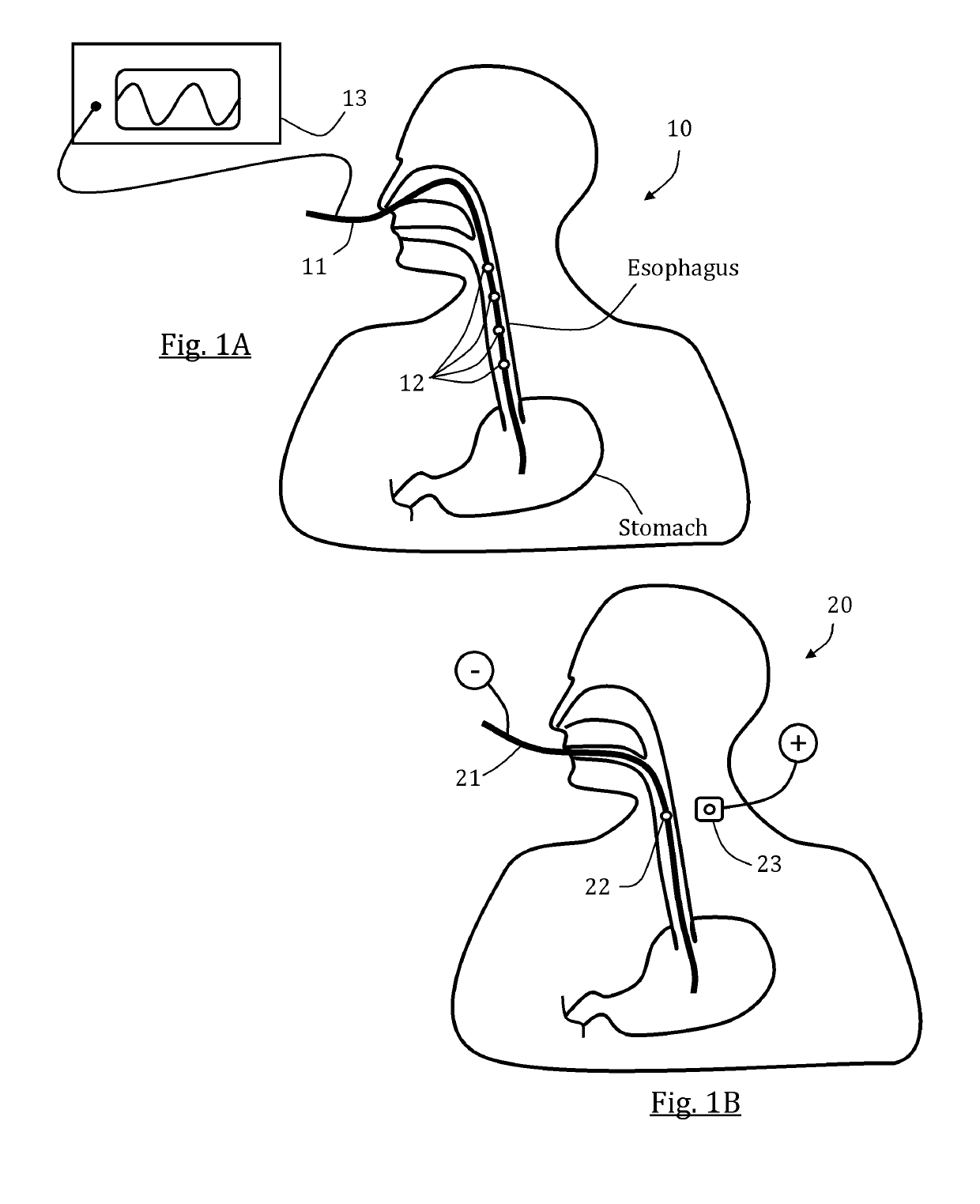
Monitoring catheter and method of using same
A monitoring catheter that inserts into the patient's esophagus alone or in combination with an existing catheter, such as a feeding or aspiration tube. The monitoring catheter includes a pair of EMG electrodes on an exposed surface that contact the patient's esophageal wall to measure the activity of the diaphragm and / or a pair of pressure detecting mechanisms that measure the pressures within the patient at separate locations. The electrodes are sized and spaced from one another so as to maximize detection of diaphragm muscle activity while minimizing detection of noise. The pressure detecting mechanisms are sized and spaced apart to measure the patient's esophageal and gastric pressures, for example. If necessary, an attaching mechanism secures at least a portion of the monitoring catheter to the existing catheter so that the monitoring catheter uses the existing catheter as a tracking guide.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
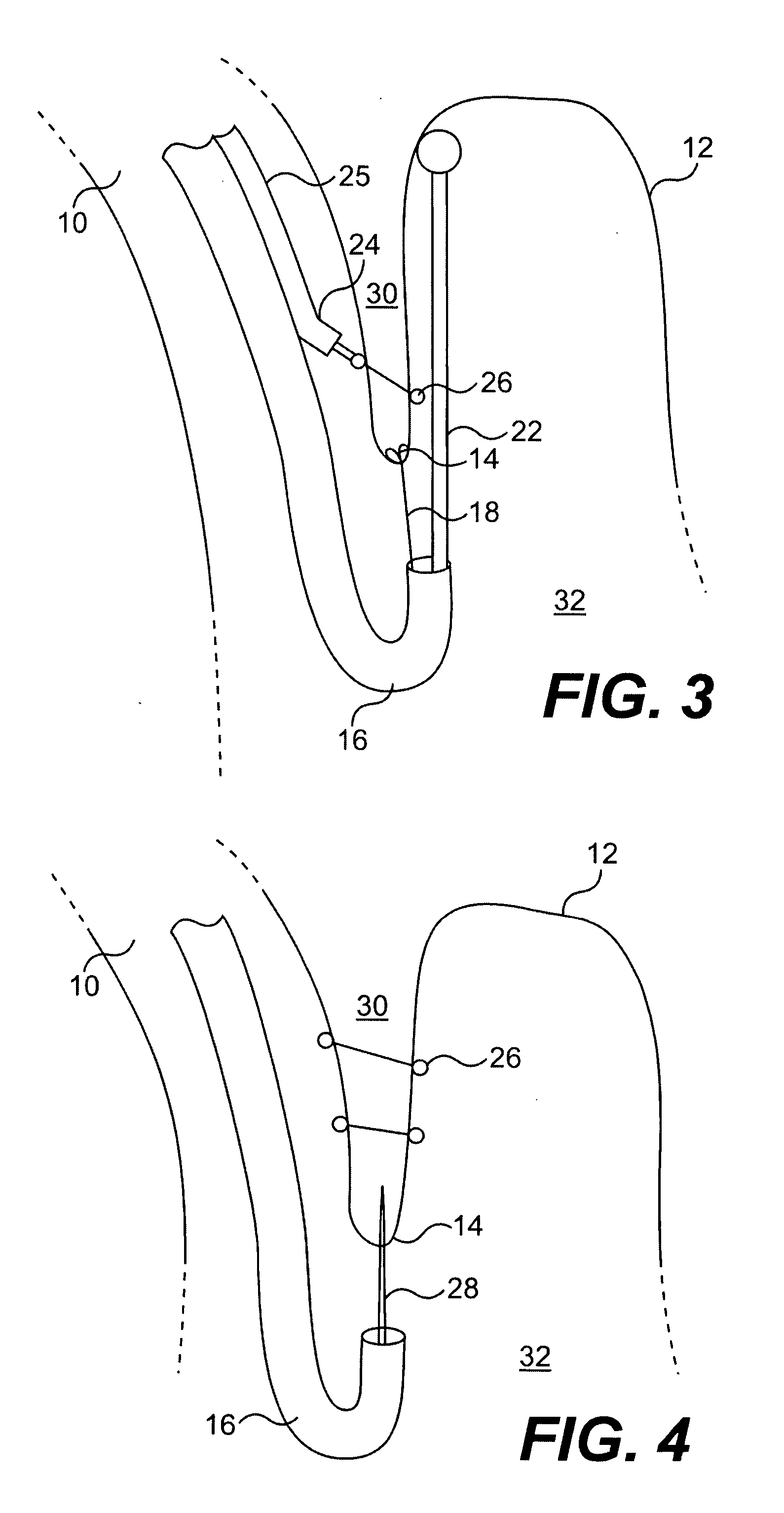
Methods and apparatus for transesophageal microaccess surgery
The current invention describes methods of transesophageal access to the neck and thorax to perform surgical interventions on structures outside the esophagus in both the cervical and the thoracic cavity. It describes a liner device made of a complete or partial tubular structure, or a flat plate, the liner having means to facilitate creation of a side opening, which may include a valve. The liner with its side opening form a port structure inside the esophageal lumen. The port structure allows elongated surgical devices to pass through a perforation across the full thickness of the esophageal wall to outside location, in a controlled way. The elongated surgical devices can be diagnostic scopes, therapeutic scopes, manual elongated surgical devices, robotic arms or the like. After being deployed outside the esophagus, the surgical devices can access structures outside the esophagus, in the neck and thorax in 360 degrees of freedom around the esophageal circumference. These structures can be bony, cartilaginous, spinal, vascular, soft tissue, deep tissues, lymph nodal, cardiac, pulmonary, tracheal, nervous, muscular or diaphragmatic, skin and subcutaneous tissues of the neck, skin and subcutaneous tissues of the anterior chest wall, skin and subcutaneous tissues of the skin of the back, and skin and layers of the breast.
Owner:MICROACCESS
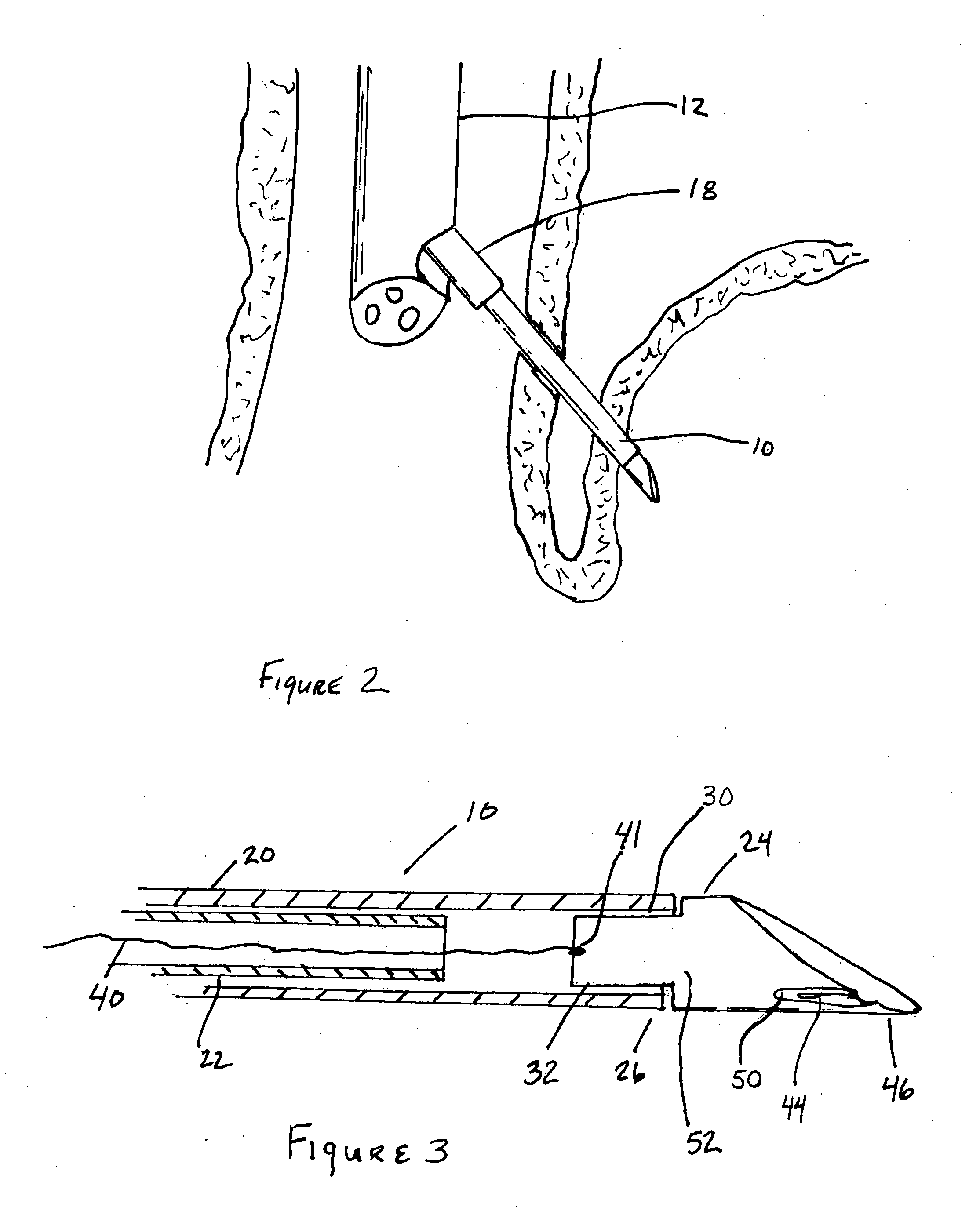
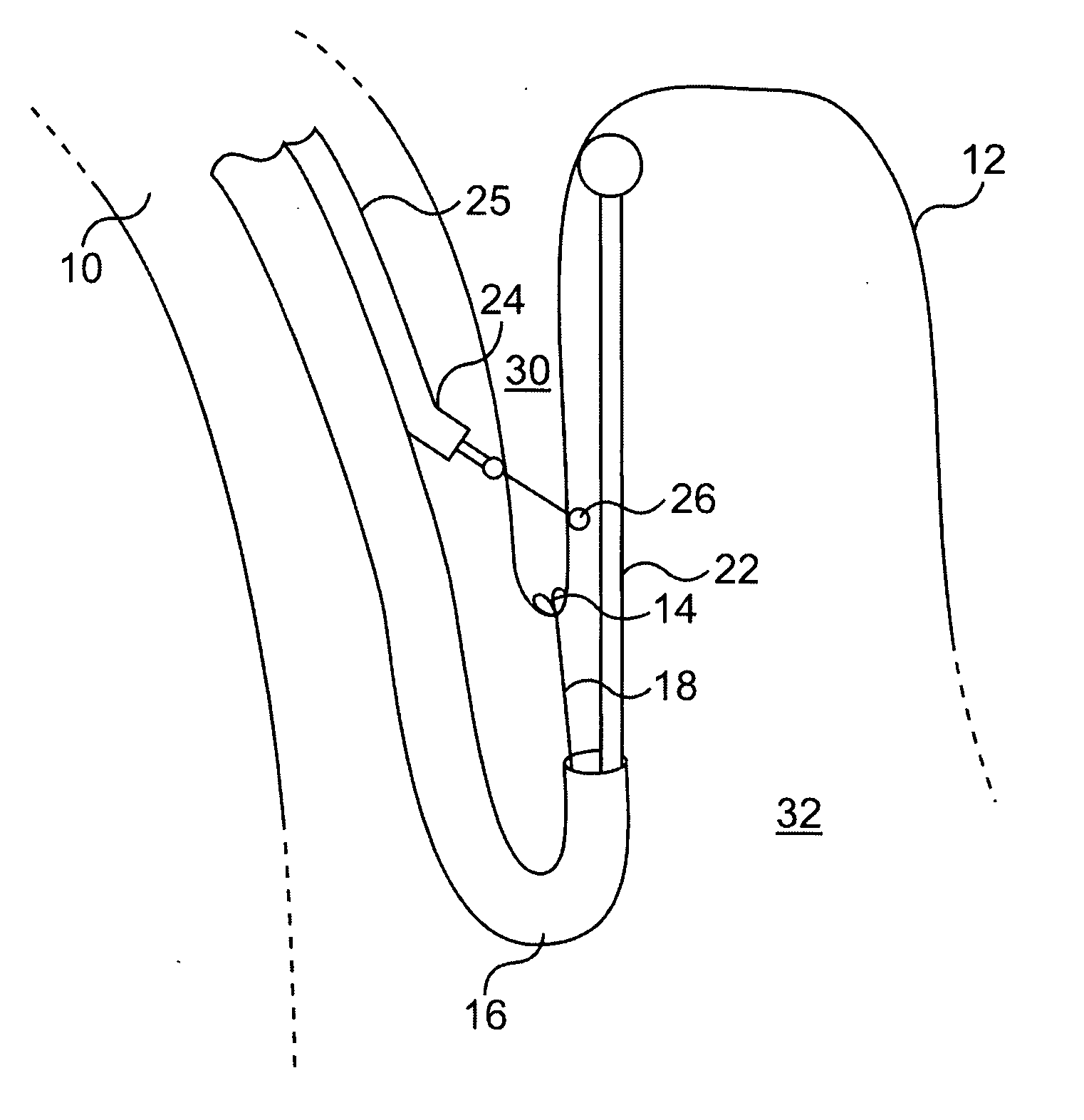
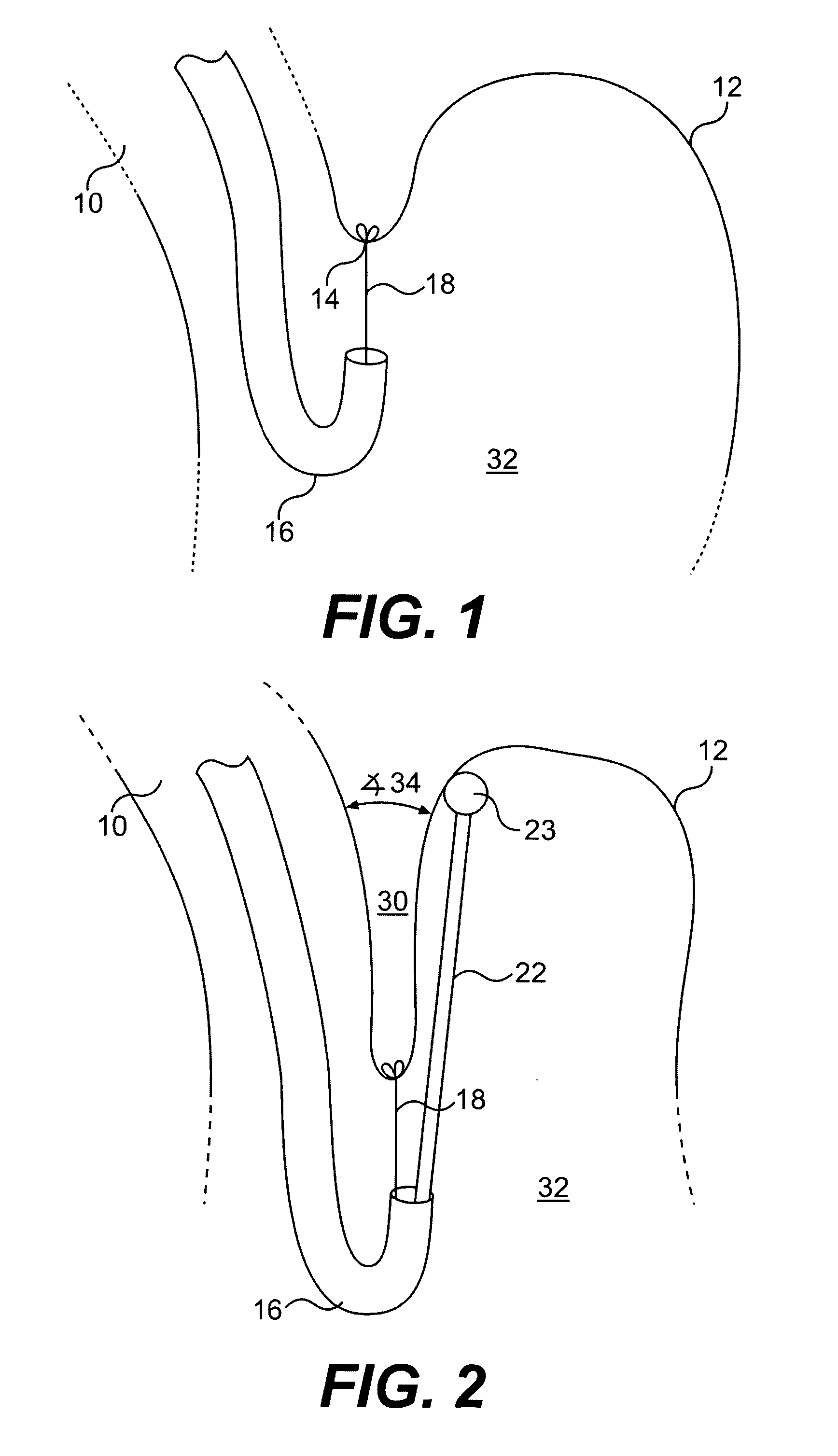
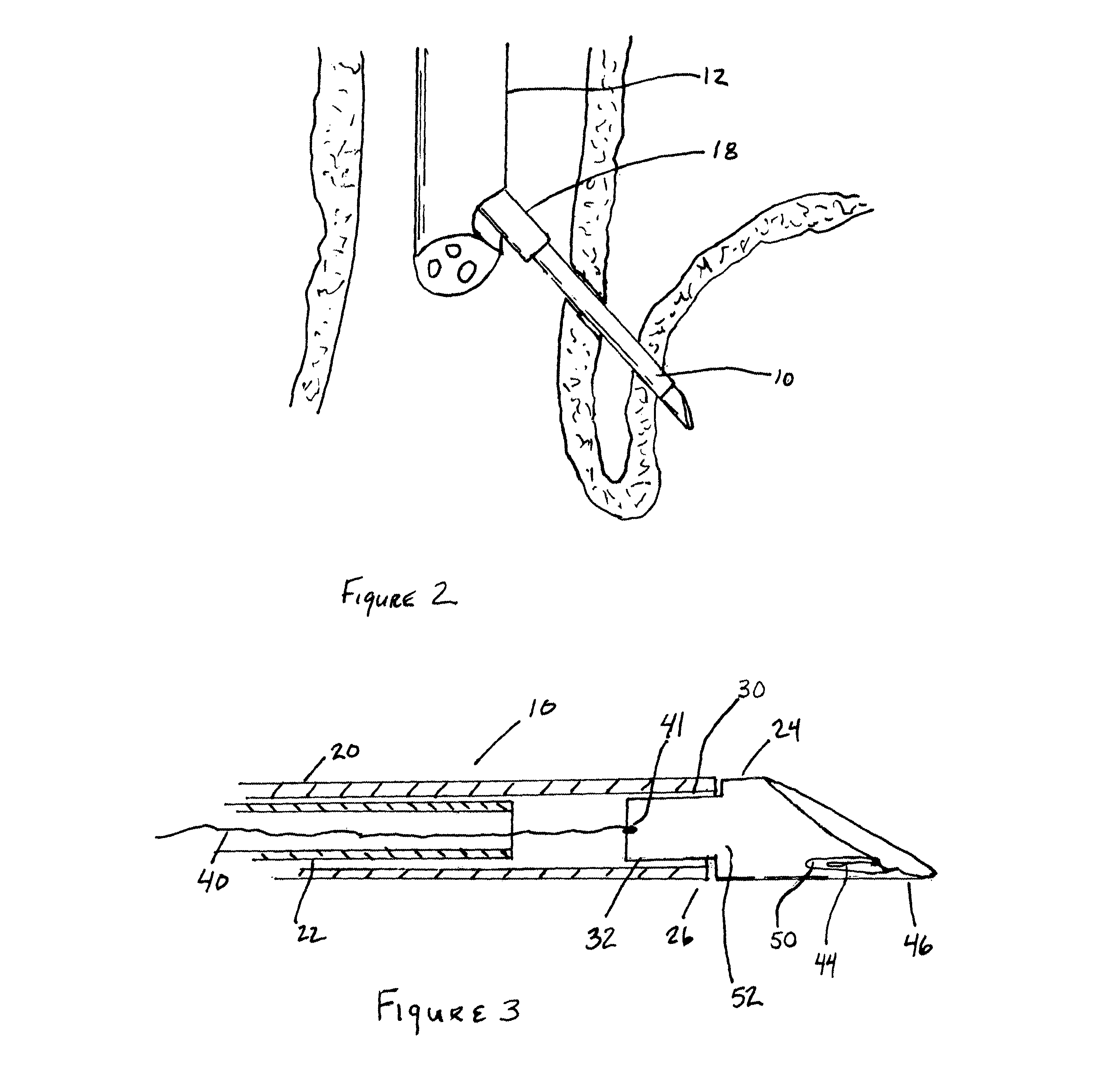
Method and apparatus for adjusting body lumens
Disclosed is a device and method for accessing the lower esophageal sphincter through the esophagus. In one embodiment, a catheter is inserted through the mouth or nose of a patient and advanced to the region of the diaphragm. Under fluoroscopy or endoscopy, a hollow needle at the distal end of the catheter punctures the wall of the esophagus from the inside so that the distal end of the needle is positioned outside the esophagus. An implant is next advanced out through the hollow needle to the region outside the sphincter where it is deflected and coerced to bluntly dissect around the circumference of the esophagus, where the implant is left in place to heal. The hollow needle is removed and the esophageal wall is allowed to heal. Subsequent diametric adjustment of the implant allows for tightening or loosening of the sphincter to minimize gastric reflux. The device and method can also be used to treat the pyloric or other body sphincters, hollow organs, or ducts.
Owner:ELLIPSE TECH
Methods and apparatus for implanting devices into non-sterile body lumens or organs
InactiveUS20050197715A1Minimize infectionImprove sealingSuture equipmentsMammary implantsSterile environmentDevice implant
Implantable devices for use in a non-sterile environment of a patient's anatomy are medicated or include medication. For example, the housing of the device and / or members for securing the device to the patient's anatomy (e.g., the muscular esophageal wall) may be medicated to, among other things, prevent a rejection mechanism from being triggered, to prevent or reduce bacterial infection, or to promote tissue ingrowth. The medication may be for medicating tissue at the implant site, or for medicating some other portion of the patient's anatomy.
Owner:TORAX MEDICAL
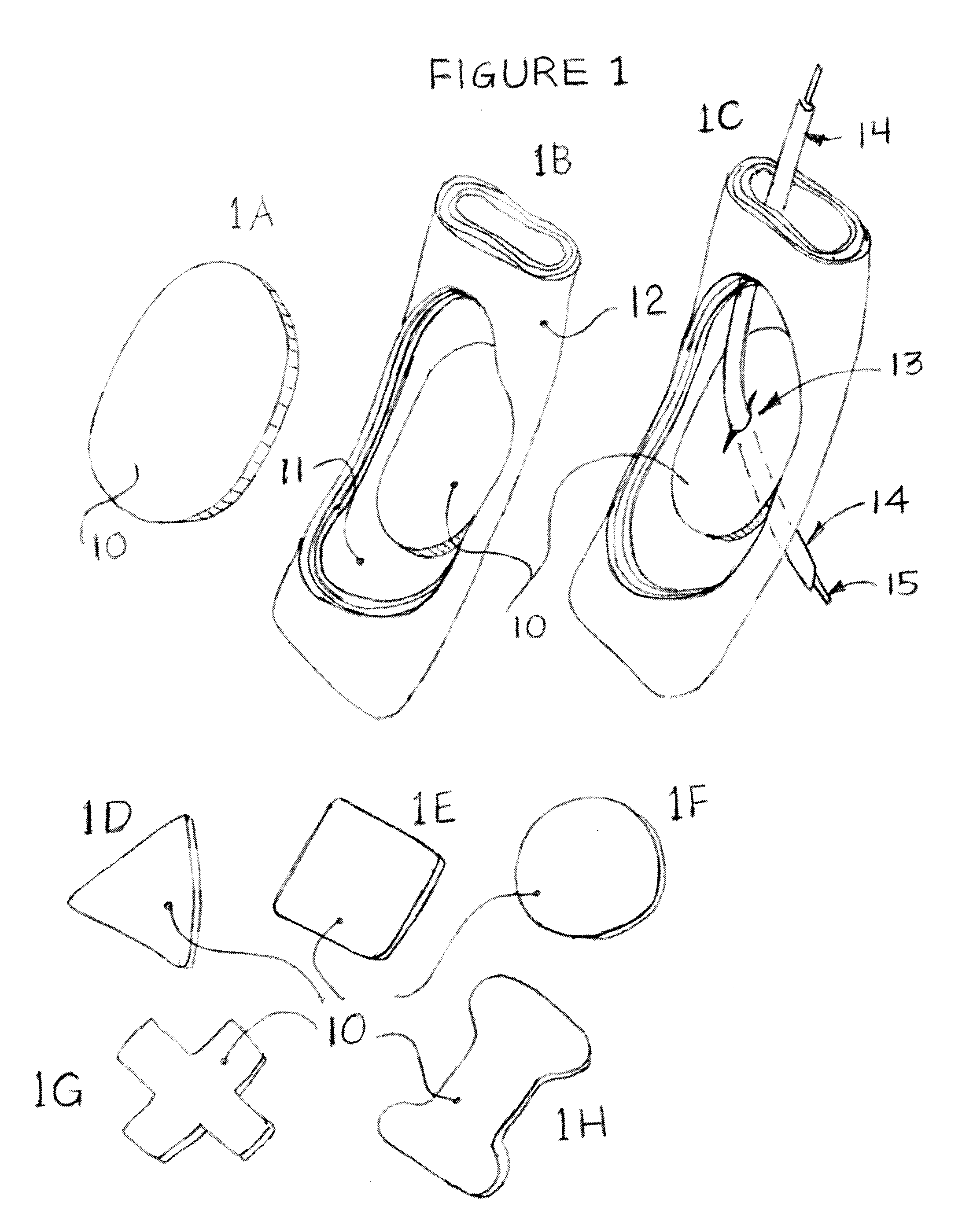
Methods and devices for endosonography-guided fundopexy
ActiveUS20060282087A1Reduce gastroesophageal refluxEasily drawnSuture equipmentsWound clampsFlexible endoscopeEsophageal wall
The present invention relates to a tissue securement system, device and method for endoscopy or endosonography-guided transluminal interventions whereby a ligation or anchor is placed and secured into soft tissue. An objective of this invention is to provide a method to reduce gastroesophageal reflux by endosonography-guided intervention. Specifically, endosonography is used to insert a ligation element through the esophageal wall, through the diaphragmatic crus and into the fundus of the stomach. This ligation element placed from the esophagus and around the angle of His that may create a barrier to gastroesophageal reflux.
Owner:ADVENT MEDICAL
Methods and apparatus for transesophageal microaccess surgery
InactiveUS20100036197A1Avoid pollutionPrecise positioningBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesNODALOesophageal tube
The current invention describes methods of transesophageal access to the neck and thorax to perform surgical interventions on structures outside the esophagus in both the cervical and the thoracic cavity. It describes a liner device made of a complete or partial tubular structure, or a flat plate, the liner having means to facilitate creation of a side opening, which may include a valve. The liner with its side opening form a port structure inside the esophageal lumen. The port structure allows elongated surgical devices to pass through a perforation across the full thickness of the esophageal wall to outside location, in a controlled way. The elongated surgical devices can be diagnostic scopes, therapeutic scopes, manual elongated surgical devices, robotic arms or the like. After being deployed outside the esophagus, the surgical devices can access structures outside the esophagus, in the neck and thorax in 360 degrees of freedom around the esophageal circumference. These structures can be bony, cartilaginous, spinal, vascular, soft tissue, deep tissues, lymph nodal, cardiac, pulmonary, tracheal, nervous, muscular or diaphragmatic, skin and subcutaneous tissues of the neck, skin and subcutaneous tissues of the anterior chest wall, skin and subcutaneous tissues of the skin of the back, and skin and layers of the breast.
Owner:MICROACCESS
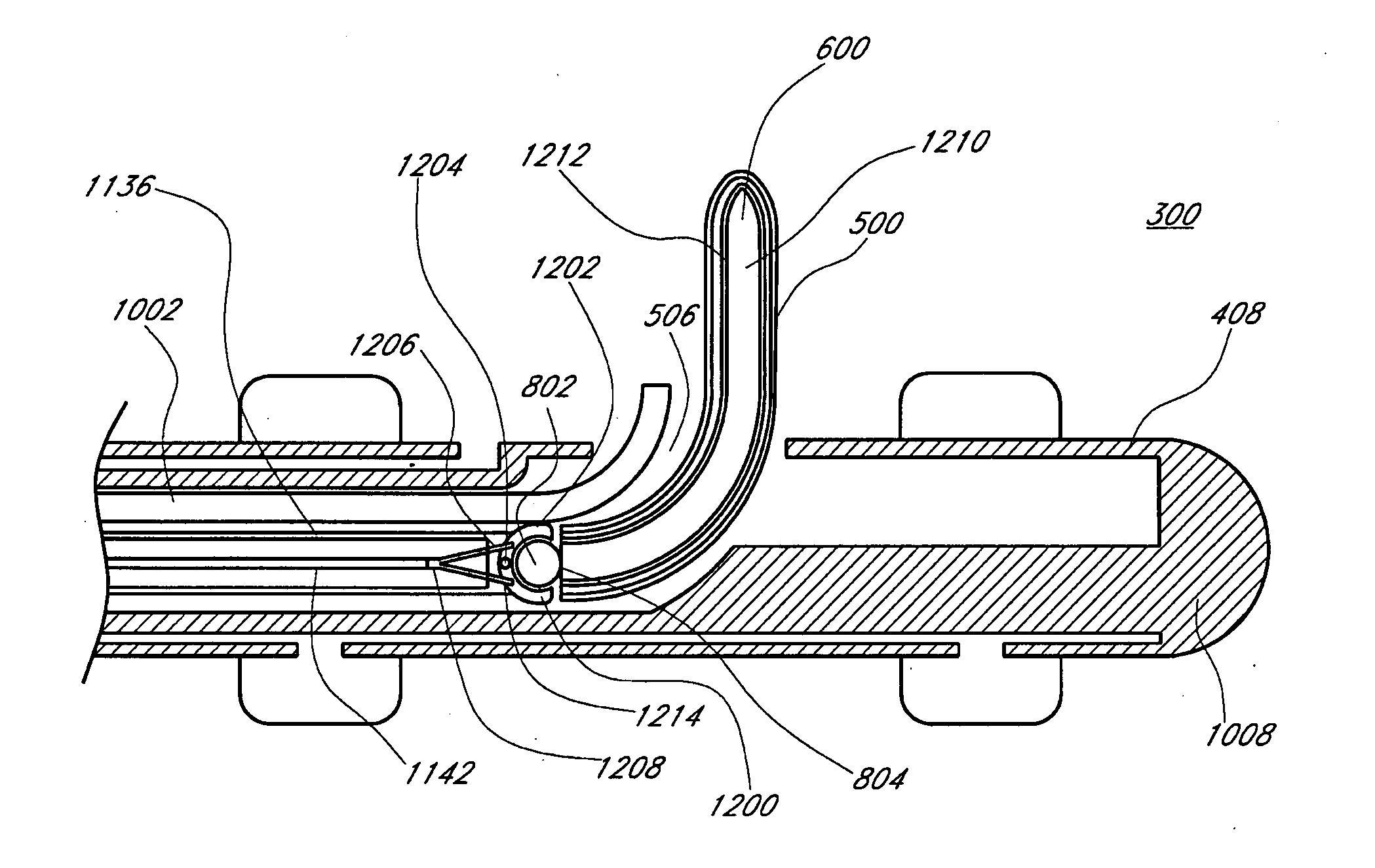
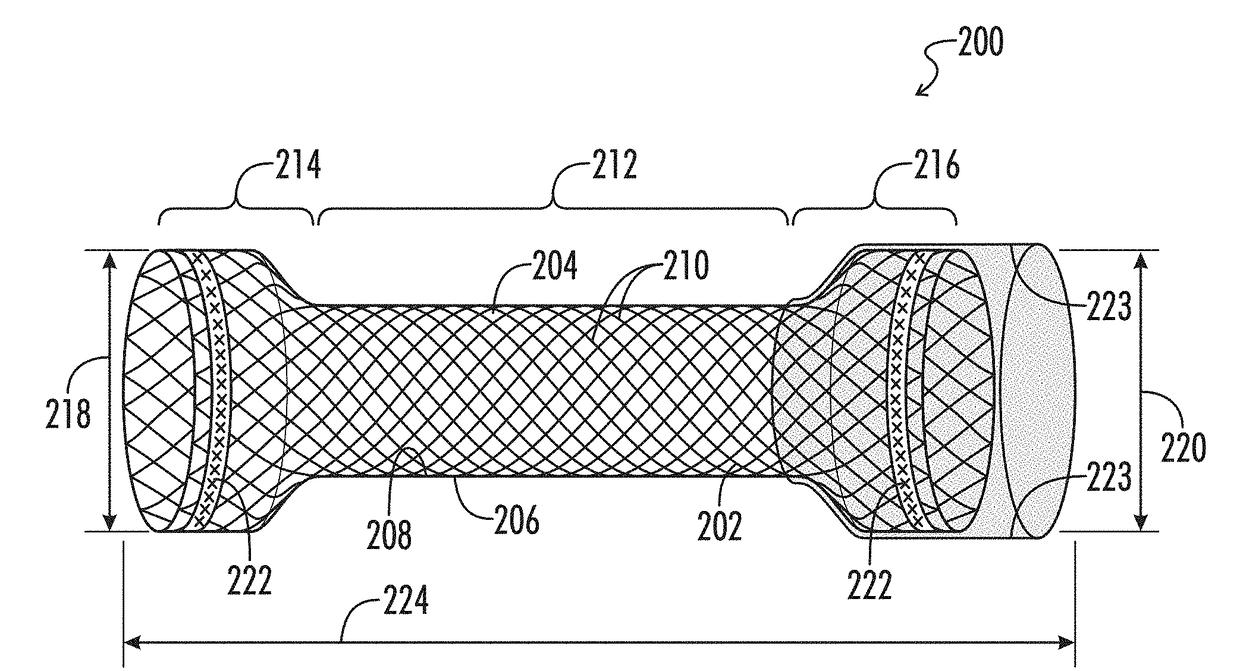
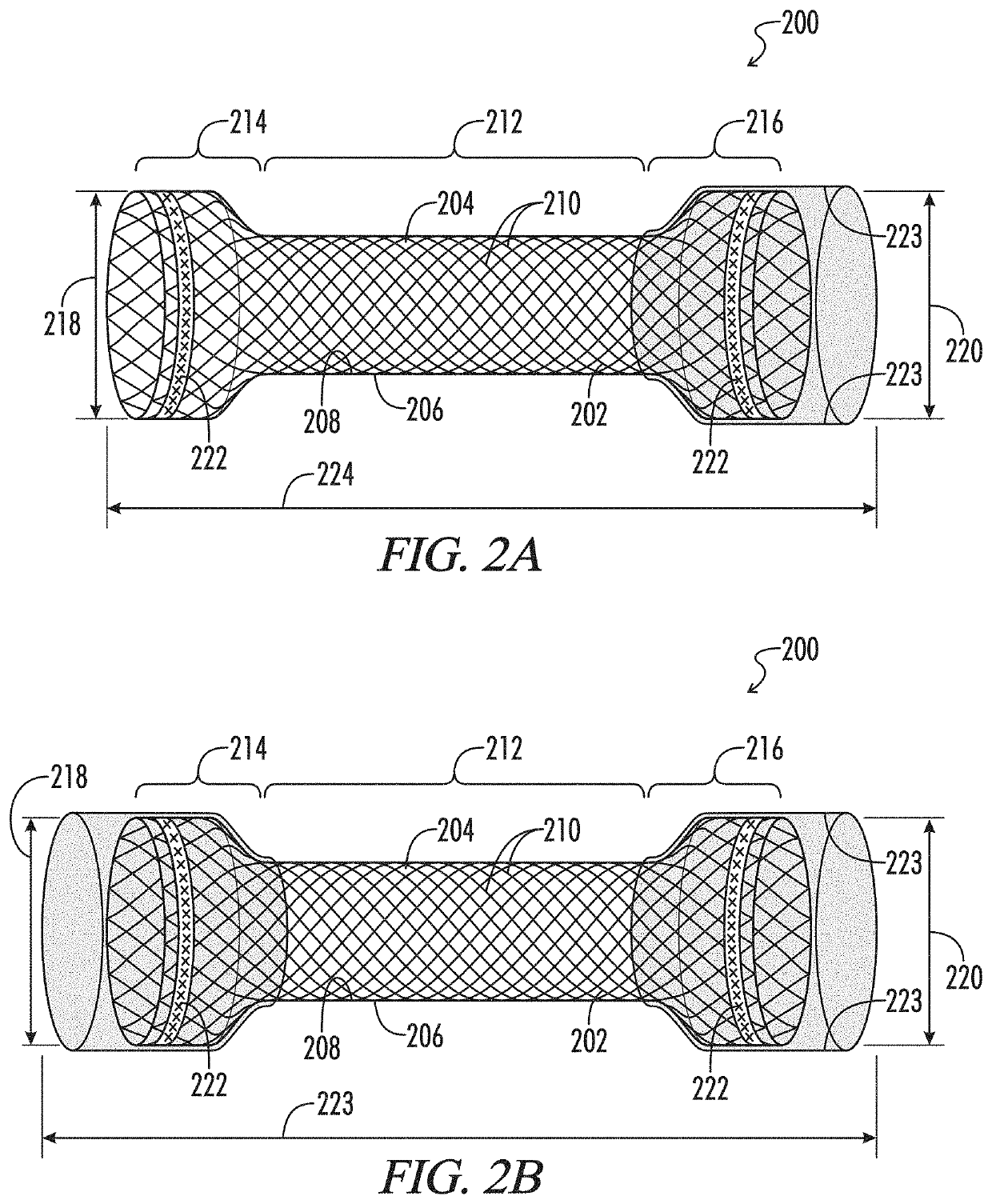
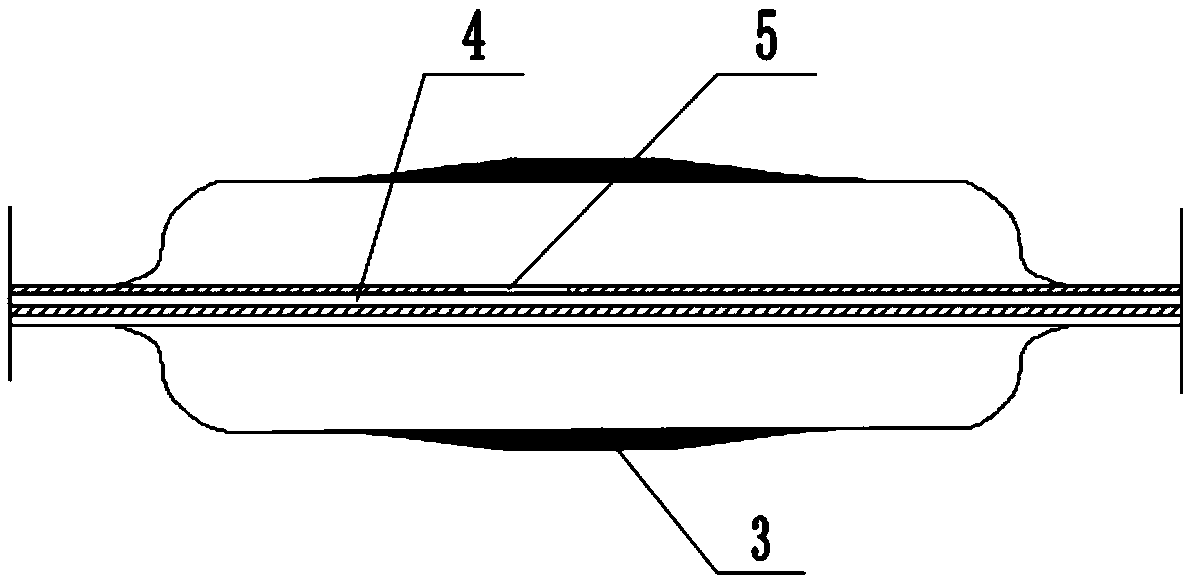
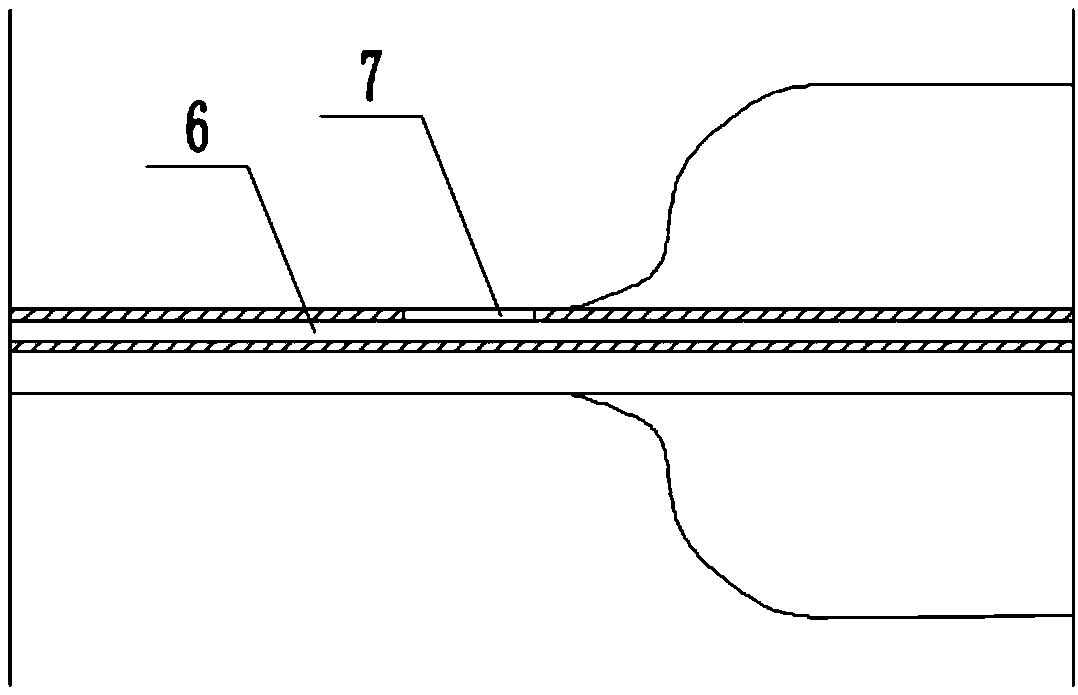
Stents with improved fixation
ActiveUS20180193175A1Prevent stent migrationInhibit migrationStentsOesophagiElastomerSurface pattern
The present disclosure provides stents, particularly self-expanding stents, useful for the GI tract, and more particularly, useful for treating esophageal strictures. The stents provided herein include a medial region and proximal and distal cuffs having external diameters greater than the medial region diameter when the stent is in the deployed state. The medial region comprises an open weave wire construction. An elastomeric coating circumscribes the medial region, while the may be an extension of the wire construction or separate elements. Preferably, the cuffs have a textured surface for contact with the esophageal wall tissue to resist stent migration. The elastomer coated medial region provides a barrier to tissue ingrowth, and has an enhanced radial restoring force to maintain an open passageway in a body lumen. Optionally, the stent includes an exterior sheath with a surface pattern, to which the stent couples. A low durometer sleeve, between the stent and body lumen, axial positioning of the stent relative to the body lumen. Consequently, precision in stent placement is provided without tissue damage that could result if positioning motion occurred between the surface texture and the body lumen.
Owner:BVW HLDG
Method for performing endoluminal fundoplication and apparatus for use in the method
A method and device for performing endoluminal fundoplication are described. A device is inserted in the patient's stomach through the esophagus, including an unit adapted to grasp and pull a portion of the gastroesophageal junction into the stomach, and an unit adapted to move a portion of the fundus towards the esophagus. The device also can place fasteners to hold the gastric wall and the esophageal wall secured together, thus forming a valve between esophagus and stomach. An adhesive compound can be used to stabilize the juncture of the two walls.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Degradable magnesium alloy esophageal stent for infants
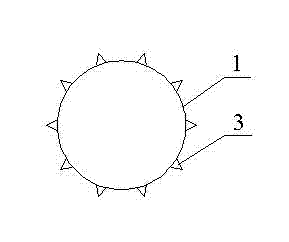
The invention discloses a degradable magnesium alloy esophageal stent for infants. The esophageal stent comprises annular single bodies, connecting points and projections, wherein each annular single body is formed in the way that a magnesium alloy metal wire is folded in the shape of W and connected to form a cylindrical shape; the annular single bodies have elasticity; bending parts are formed at the two ends of each annular single body; the annular single bodies are axially connected with one another in series by the connecting points; the bottom of each projection is positioned at each connecting point; the top end of each projection is positioned on the outer side of the esophageal stent; and after the magnesium alloy esophageal stent is expanded and released, the projections can be embedded into the esophageal wall and are used for fixing the stent. The degradable magnesium alloy esophageal stent for infants is formed by connecting a plurality of annular single bodies and the length of the esophageal stent can be determined by the number of the connected annular single bodies, so the requirements of the infants suffering from esophageal stenosis are met; the projections on the outer surface of the stent can be embedded into the inner wall of the esophagus and are used for fixing the stent to prevent the stent from moving or slipping off; and the stent can be degraded and absorbed by a human body and the degradation products have no toxicity, so growth and development of infantile patients are not influenced.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Endoscopic esophageal variceal ligation apparatus
The invention discloses an endoscopic esophageal variceal ligation apparatus which comprises a ligation outer tube and an endoscope connecting base. The ligation outer tube is in a cone shape of which the front part is thin and the rear part is thick; a ligation inner tube is arranged in the ligation outer tube; the front end of the ligation inner tube is in sealing connection with the front end of the ligation outer tube; the rear end of the ligation inner tube is connected with a negative pressure suction tube; a plurality of positioning holes are distributed at an equal interval front and back on the side wall of the ligation outer tube; a positioning pin is arranged in each positioning hole; a pulling ring is arranged at the inner end of each positioning pin; the pulling rings of a plurality of positioning pins are fixedly connected with a stay wire; the ligation outer tube is sleeved with rubber rings of which the number is equal to that of the positioning pins; each rubber ring is respectively limited by one positioning pin to be prevented from sliding forwards by the self. The endoscopic esophageal variceal ligation apparatus has a simple, small and compact structure, can be used for continuously carrying out ligation and is high in efficiency; the endoscopic esophageal variceal ligation apparatus is convenient and rapid to operate and works stably and ligation success efficiency is improved; moreover, the esophageal wall cannot be contused, so that pain of a patient is reduced and the infection risk is reduced.
Owner:王维国
Device with passive valve to block emesis and/or reflux and associated system and method
A device to block emesis and / or reflux includes a tube insertable into the esophagus. A valve is carried by the tube and includes a flexible sheath having an upper edge secured onto the tube and an unsecured lower circumferential edge and configured such that upon contact with emesis and / or reflux from the stomach, the flexible sheath opens in a concave configuration towards the stomach and the unsecured lower circumferential edge engages the esophageal wall and blocks emesis and / or reflux from the stomach passing into the esophagus past the valve.
Owner:PNEUMOFLEX SYST
Device with active valve to block emesis and reflux blockage device and associated system and method
ActiveUS20140235958A1Minimize damageBalloon catheterMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesReflexReflux
A device blocks emesis and / or reflex and includes a tube insertable into the esophagus. The tube includes an inflation lumen. A valve is carried by the tube and includes a flexible sheath having an upper edge secured onto the tube and a lower circumferential edge. An inflatable balloon is associated with the flexible sheath and in communication with the inflation lumen. Upon inflation of the balloon, the flexible sheath opens in a concave configuration towards the stomach and the unsecured lower circumferential edge engages the esophageal wall and blocks emesis and / or reflux from the stomach passing into the esophagus past the valve.
Owner:PNEUMOFLEX SYST
Device with passive valve to block emesis and/or reflux and associated system and method
ActiveUS20140235957A1Minimize damageMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesSurgeryRefluxEsophageal wall
A device to block emesis and / or reflux includes a tube insertable into the esophagus. A valve is carried by the tube and includes a flexible sheath having an upper edge secured onto the tube and an unsecured lower circumferential edge and configured such that upon contact with emesis and / or reflux from the stomach, the flexible sheath opens in a concave configuration towards the stomach and the unsecured lower circumferential edge engages the esophageal wall and blocks emesis and / or reflux from the stomach passing into the esophagus past the valve.
Owner:PNEUMOFLEX SYST
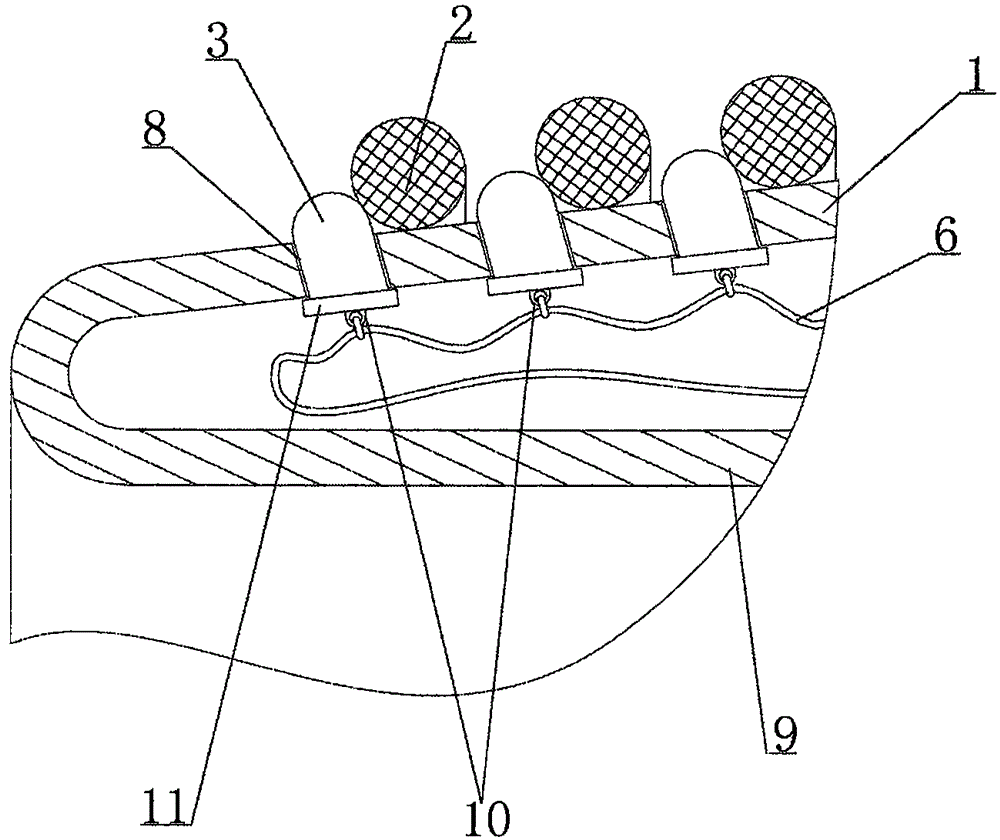
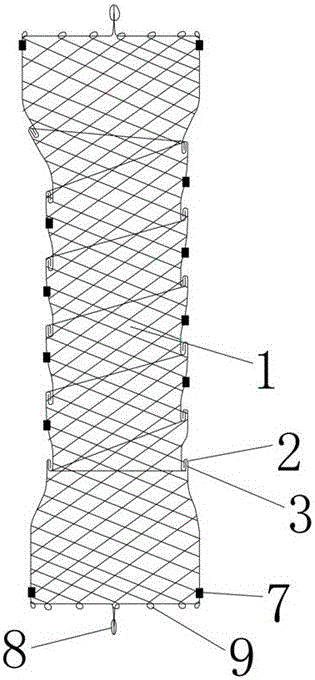
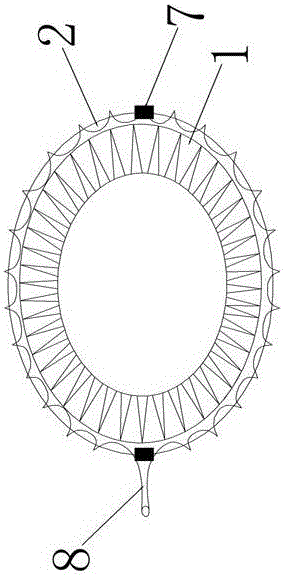
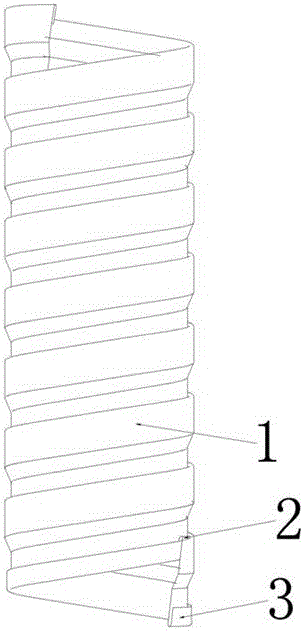
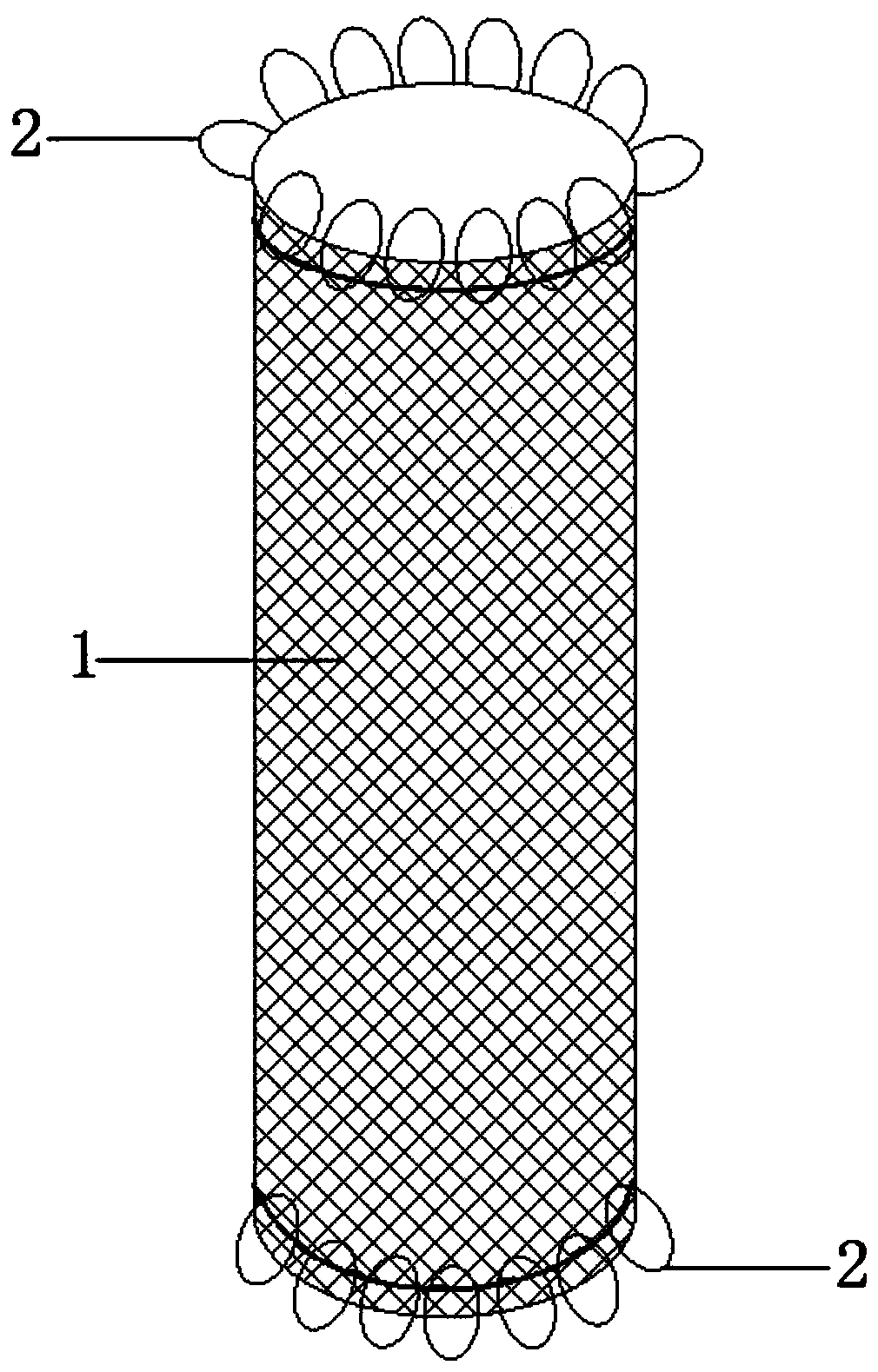
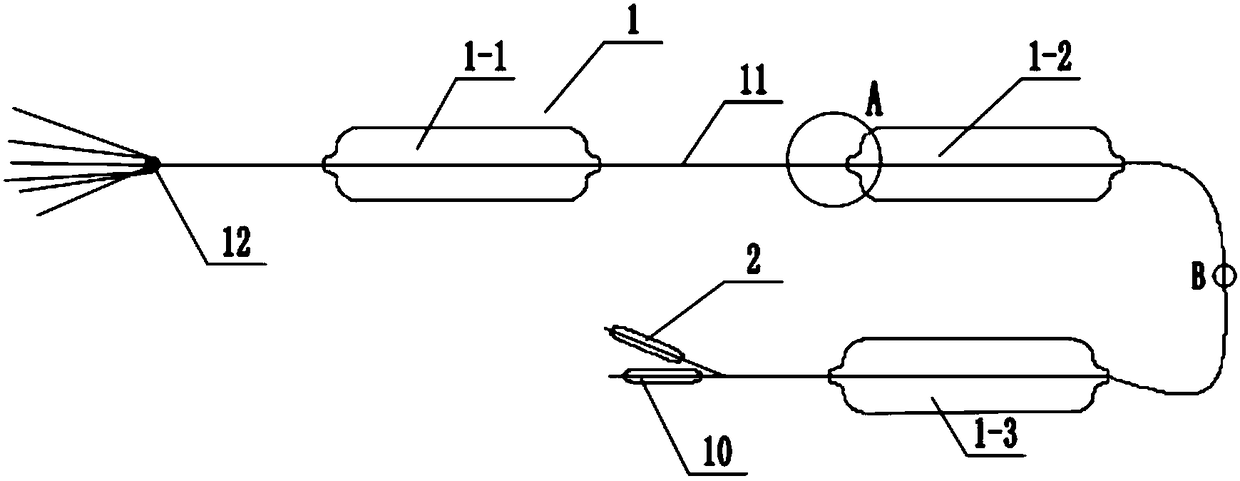
Fully fitting esophageal stent complying with esophageal peristalsis
InactiveCN106420127AEnhanced displacement resistanceAvoid pushingStentsProsthesisInsertion stentEsophageal function
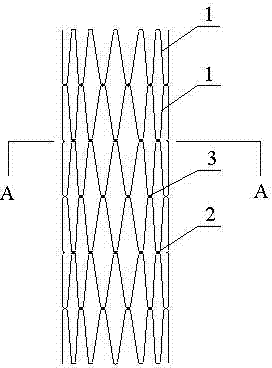
The invention relates to a fully fitting esophageal stent complying with esophageal peristalsis. The esophageal stent is composed of three sections in smooth connection with each other, wherein the sections at the two ends are thick and the section in the middle is thin; the two end sections have a shape of cylinder encircled by a single-layer net; the middle section is formed by spirally winding a bar-shaped screen mesh in equal width; an upper hook is arranged at the upper end of the bar-shaped screen mesh; a lower hook is arranged at the lower end of the bar-shaped screen mesh; the upper hook and the lower hook are buckled with each other when the bar-shaped screen mesh is spirally wound; the cross section of the bar-shaped screen mesh is of step shape. The esophageal stent is formed by spirally winding the bar-shaped screen mesh in equal width, so that the esophageal stent has flexibility and following capacity, the esophageal peristalsis can be extremely transferred to the food and the food can be more easily swallowed; the displacement resistance of the esophageal stent can be further enhanced by the following capacity of the esophageal stent; the influences of the stent on the esophageal function and structure are greatly improved; the stent is more comfortable for the patient and is fully fit with human esophageal wall; the trachea is extremely prevented from being pressed by the stent.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Device with active valve to block emesis and reflux blockage device and associated system and method
Owner:PNEUMOFLEX SYST
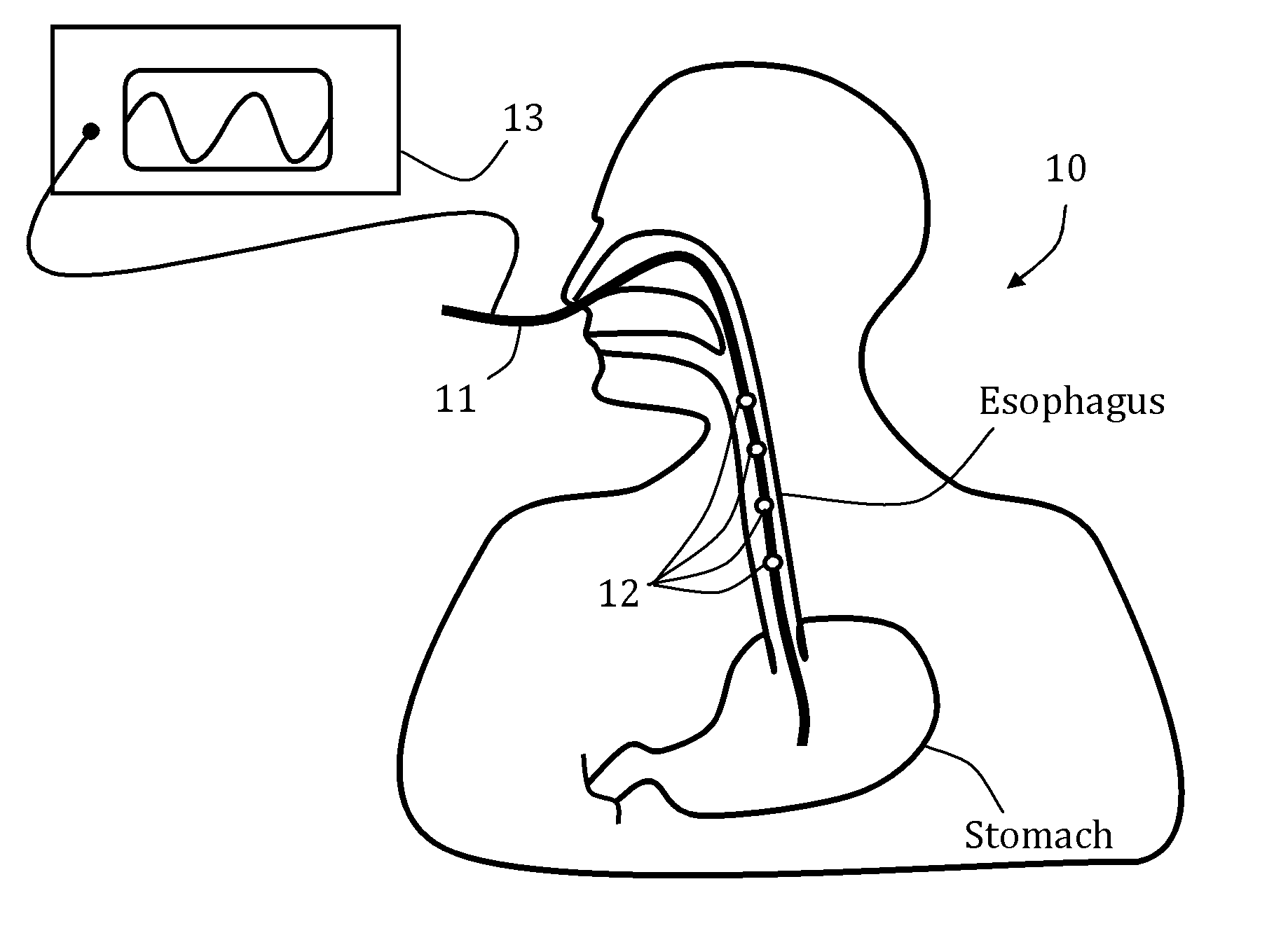
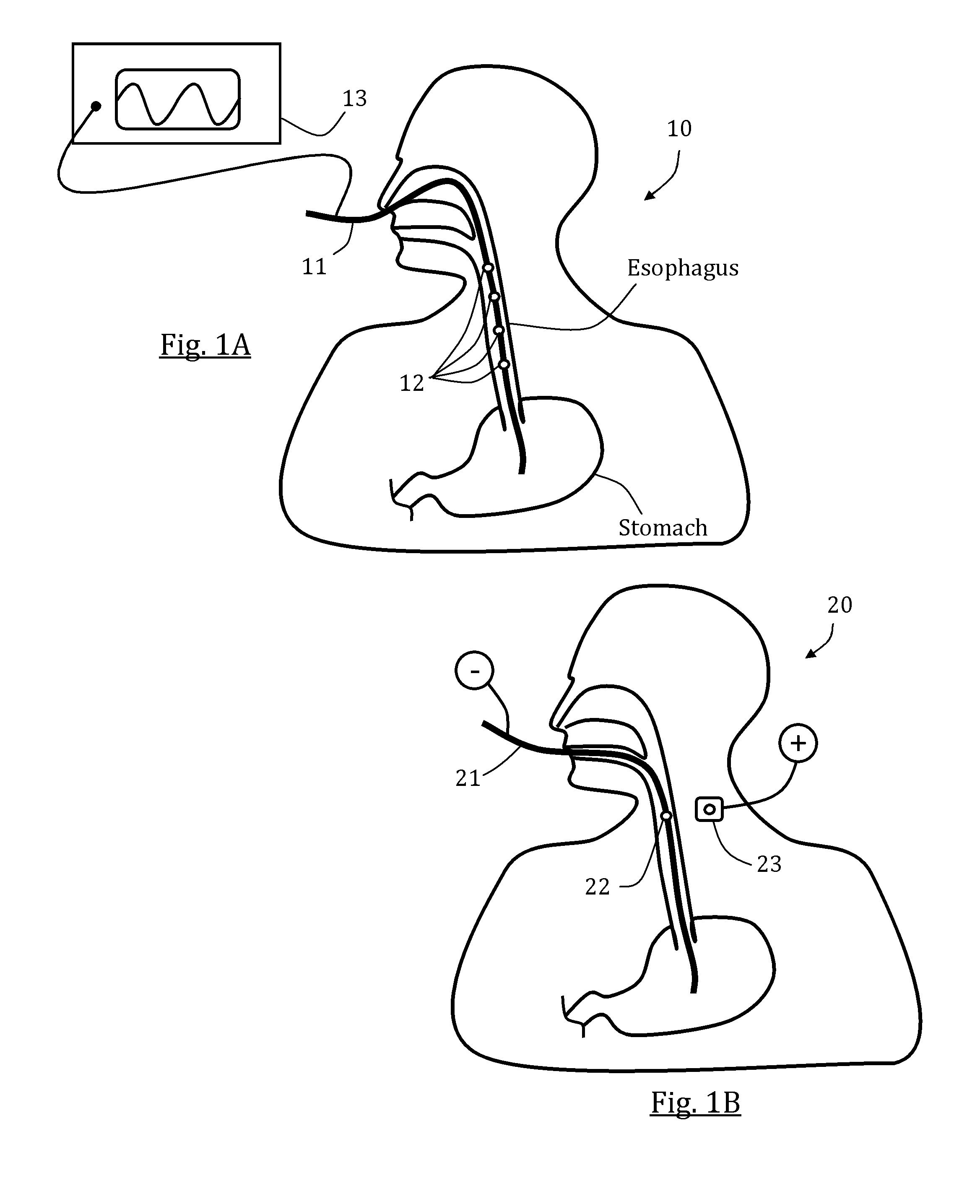
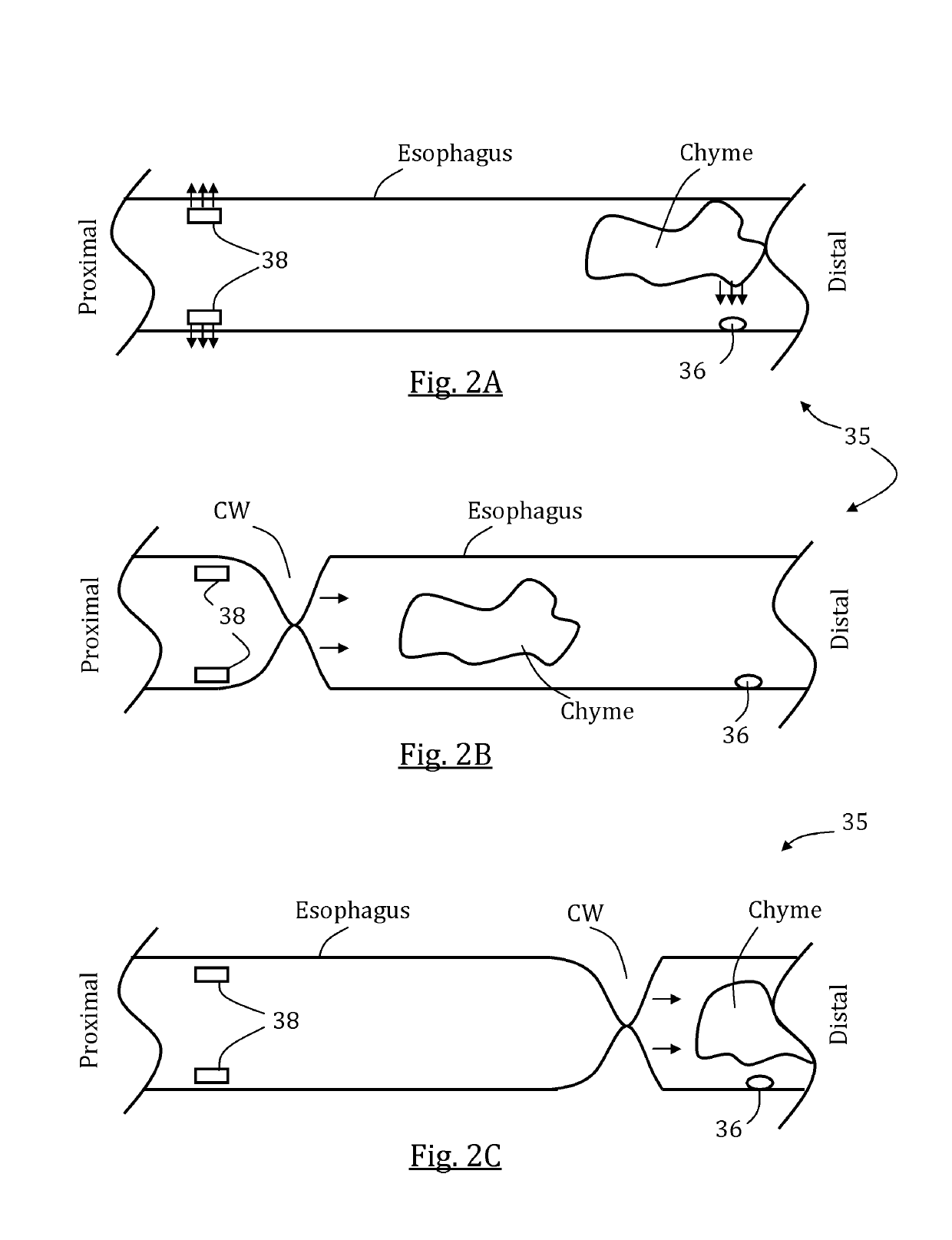
Gi tract stimulation devices and methods
ActiveUS20150343211A1Inhibit stimulusImprove energy efficiencyExternal electrodesEsophageal electrodesCardioesophageal sphincterEsophageal wall
Systems, methods and devices, for stimulating one or more esophageal muscle contractions are provided. The system, methods, and devices may be designed to evoke motion and / or restore function in one or more organs that are located distal to the lower esophageal sphincter. A controller and a generator may be used to transmit signals to one or more electrodes in a tube placed in a patient's GI tract. In some aspect, the generator is configures to generate a series of pulses for one or more periods of time. In some aspects, a preliminary pulse is transmitted to narrow and esophageal portion such that an esophageal wall is in contact with at least one electrode thus lowering the nominal stimulation threshold.
Owner:E MOTION MEDICAL
Esophagus-stomach anastomotic fistula occluder and application thereof
The invention relates to an esophagus-stomach anastomotic fistula occluder which is composed of a stomach tube, a columnar balloon, an annular balloon and a support, wherein the support is circular-barrel-shaped as well as is sleeved and fixed on the stomach tube; the columnar balloon is a circular-barrel-shaped air balloon as well as is attached and fixed on the outer surface of the support; the annular balloon is an annular air balloon and is fixed on the surface of the lower end of the support; a gap is disposed between the annular balloon and the columnar balloon; and a columnar balloon pipeline communicated with the columnar balloon and an annular balloon pipeline communicated with the annular balloon are disposed in the tube wall of the stomach tube. The invention further provides an application of the occluder. The esophagus-stomach anastomotic fistula occluder disclosed by the invention has the following advantages that: when the esophagus-stomach anastomotic fistula occluder is in use, a function of accurate location can be realized, and the tension of anastomosis can also be reduced to promote the union of anastomosis; the sealing performance of occlusion is greatly improved, and injury on esophageal wall is greatly reduced; the operation is simple, fistula can be completely isolated from stomach and esophageal cavity, and the pain and mucosal injury caused by the compression of the support can be reduced; and the support has no displacement and is easy to take out.
Owner:XIN HUA HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
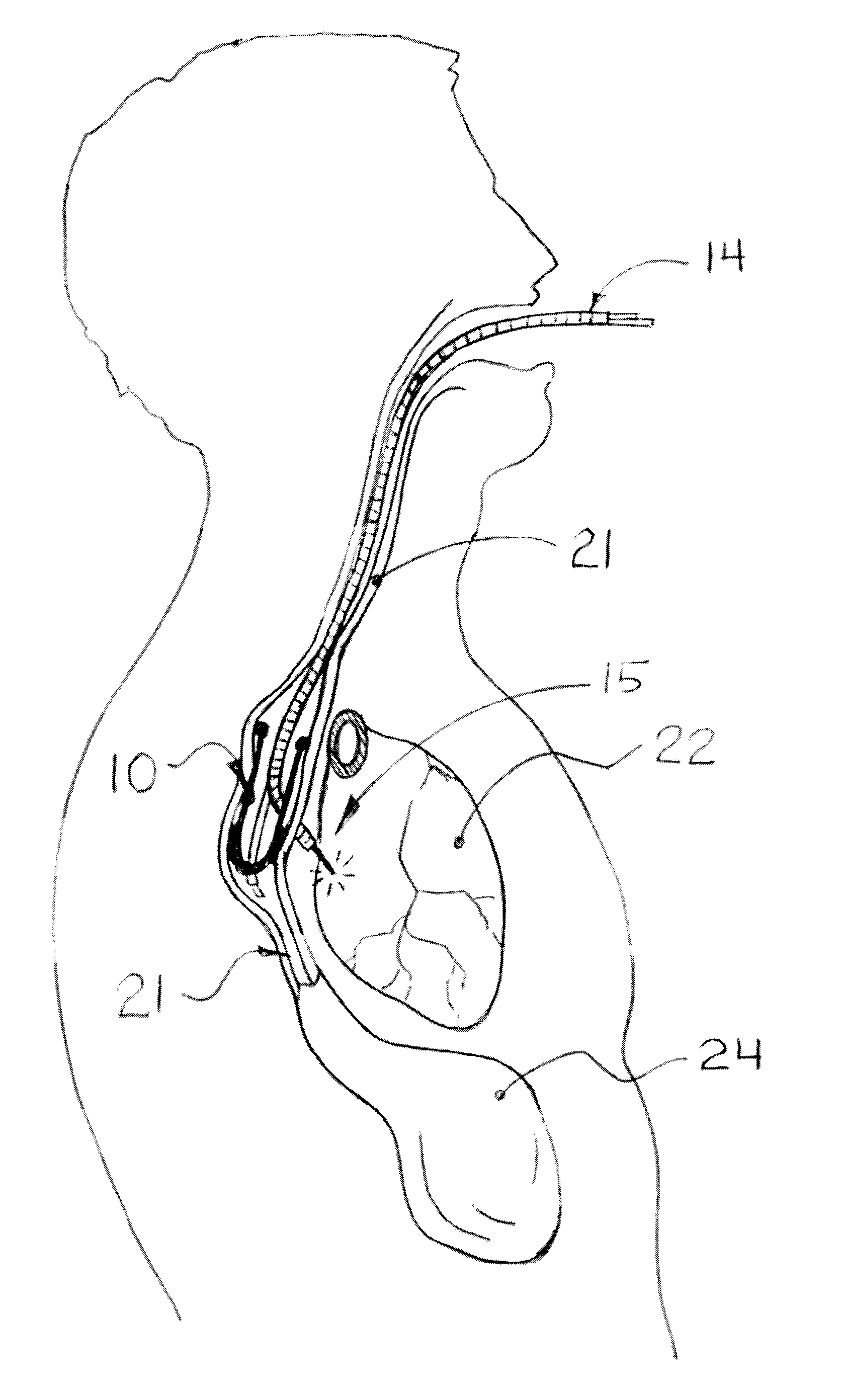
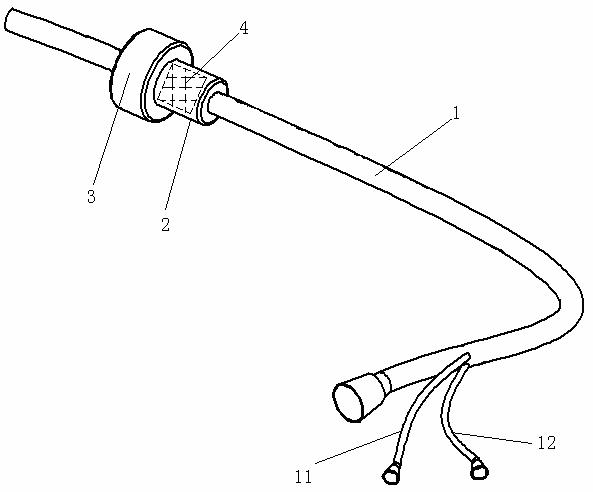
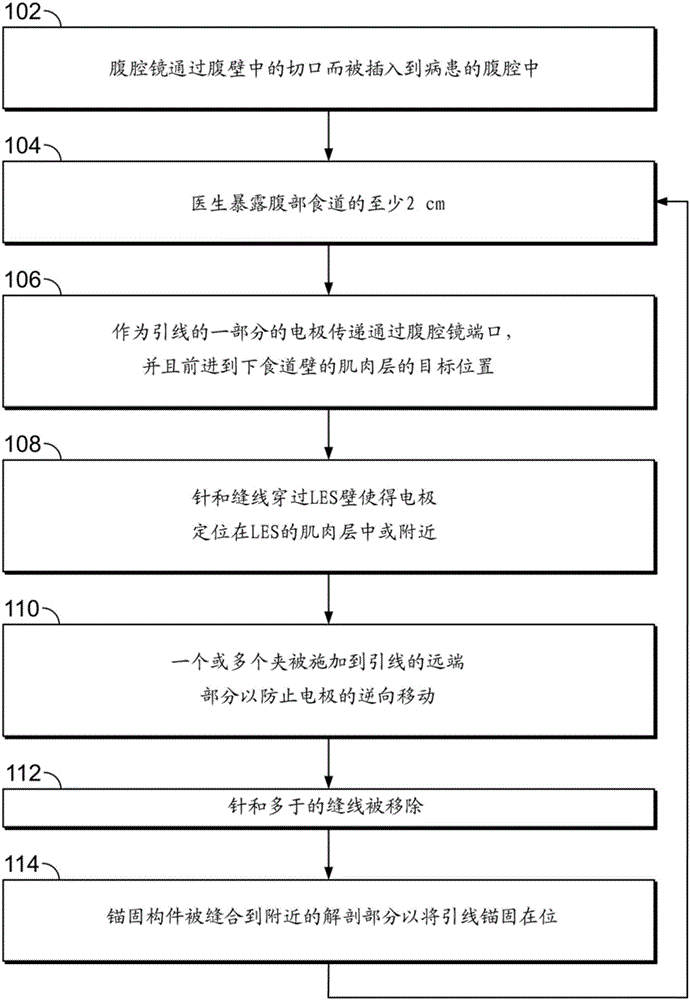
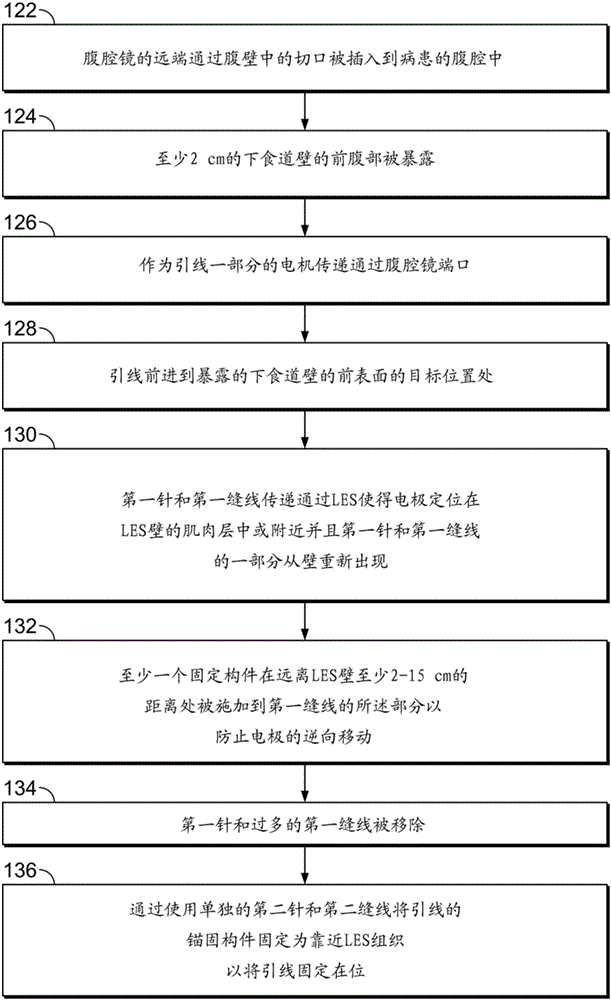
Lead implantation method
A method of laparoscopically implanting an electrically stimulating lead proximate the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) of a patient includes delivering the lead through a port of a laparoscope inserted into the abdominal cavity of the patient through an incision in the abdominal wall. The stimulating electrode is implanted in or proximate the muscularis layer of the lower esophageal wall to treat esophageal reflux disease (GERD). The lead includes a needle and suture at its distal end for pulling the electrode into the muscular wall of the LES. Clips are applied to the suture attached to the distal end of the lead to prevent retrograde movement of the electrode. The lead also includes an anchoring member for anchoring the portion of the lead proximal to the electrode. The method and lead used with the method allow the surgeon to work within the confined anatomy present at the gastroesophageal junction and prevents backwards movement and dislodgment of the electrode. The implantation procedure can be combined with a hiatal hernia repair to repair the hernia and prevent recurrence of a hiatal hernia.
Owner:ENDOSTIM INC
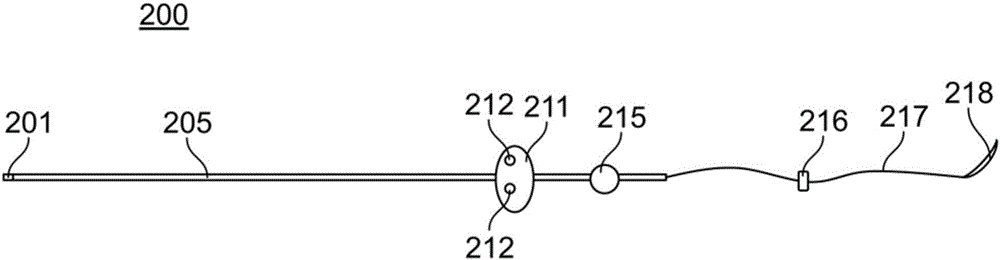
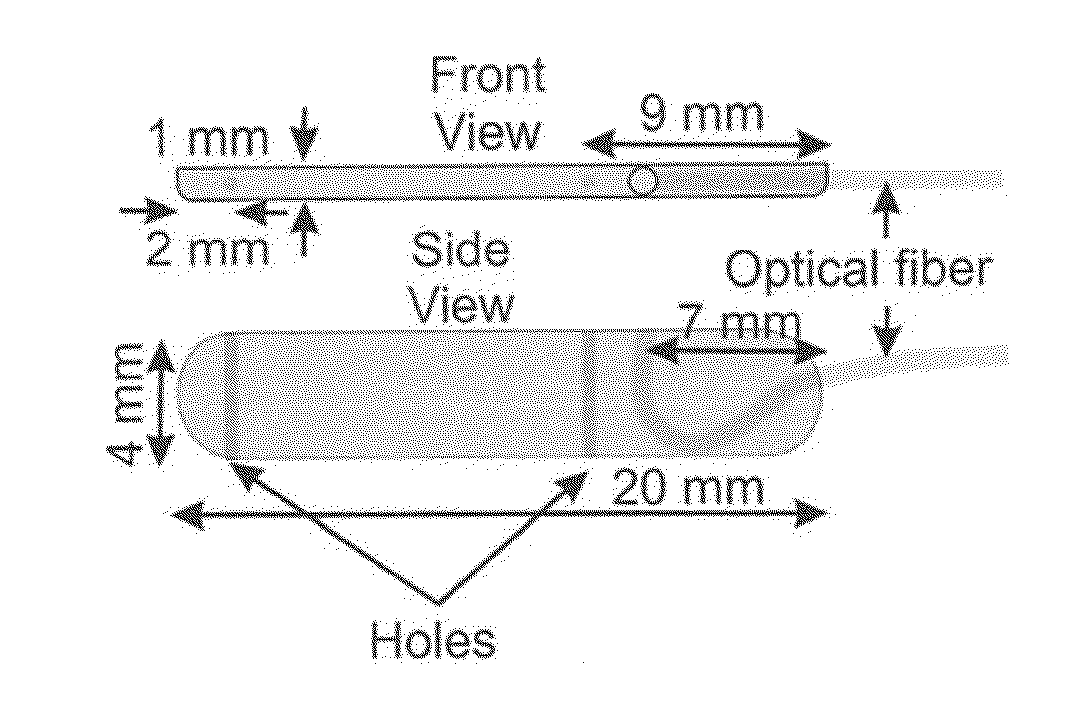
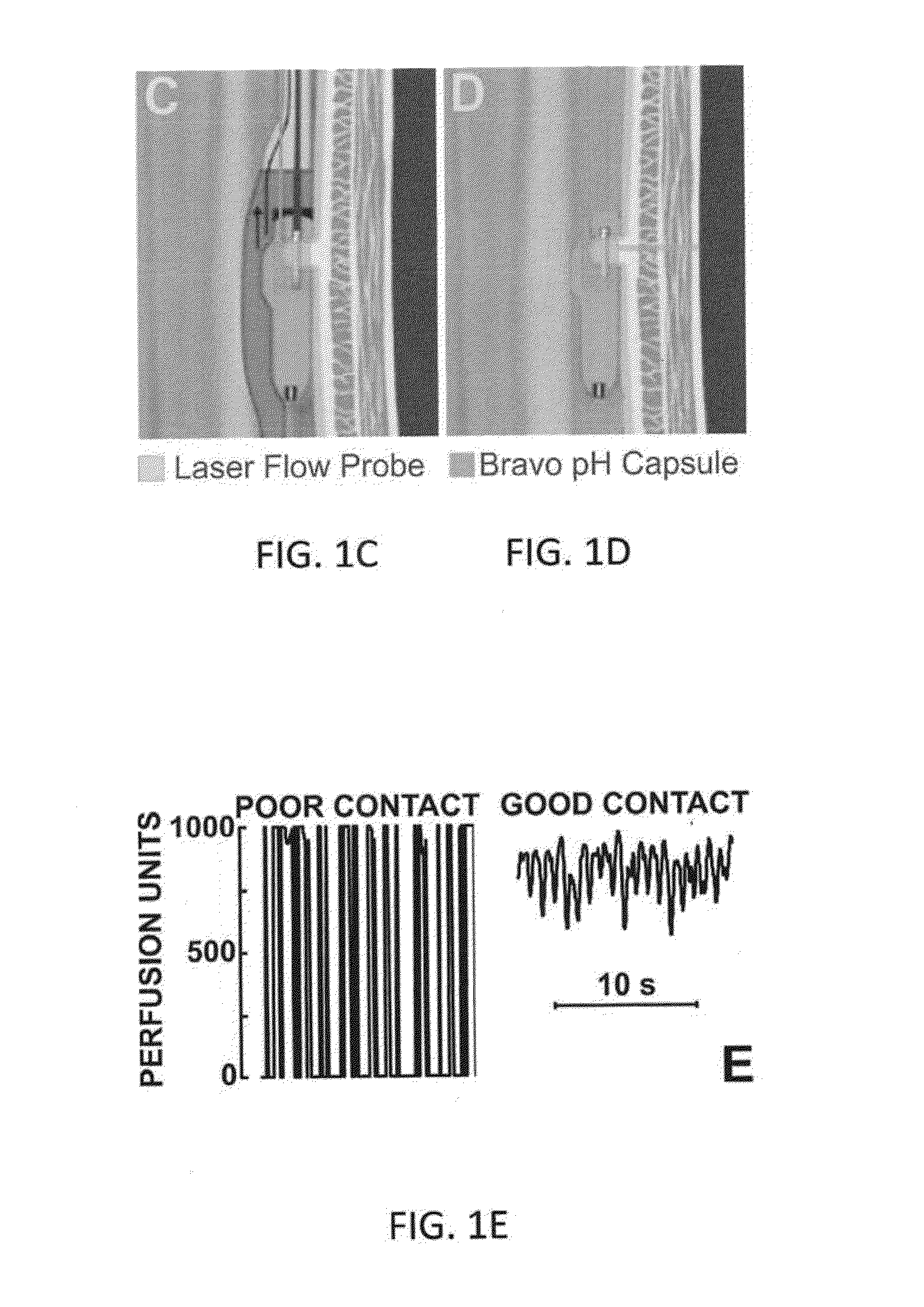
System, device and method for measurement of esophageal wall blood perfusion
InactiveUS20150051450A1Reduce decreaseReduce swallow-induced esophageal contraction amplitudeSurgical needlesCatheterDiagnostic modalitiesEtiology
The present invention provides a device and system useful as a new diagnostic modality to differentiate the etiology of heartburn / chest pain by measuring esophageal blood flow. Furthermore, the device and system of the present invention can be used as a new diagnostic modality to differentiate the etiology of abdominal pain by measuring blood in the wall of gastrointestinal tract including rectum and colon blood flow.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Novel fixed, recyclable and anti-displacement esophagus metal stent
The invention relates to a novel fixed, recyclable and anti-displacement esophagus metal stent. The esophagus metal stent comprises a main body part, fixing rings, anti-skidding wires and fixing clips. The main body part is tubular. The surface of the main body part is covered by a film. Additionally, edge at upper and lower ends of the main body part are covered by a skirt film formed from the film. Positions, approaching end openings, of the upper and lower ends of the main body part are equipped with shallow grooves. The multiple fixing rings are respectively arranged on the anti-skidding wires. The anti-skidding wires which are fixedly equipped with the multiple fixing rings in a penetrating manner are respectively fixed into the shallow grooves at upper and lower ends of the main bodypart. The fixing clips are arranged onto the fixing rings. The novel fixed, recyclable and anti-displacement esophagus metal stent has following advantages: the recovered fixing clips are used for fixing the stent; the stent has more reliable fixation effect without depending on friction force between the stent and an esophageal wall; the diameter of the main body part is properly reduced; pressure on the esophageal wall is minimized; discomfort of a patient is relived; hyperplasia of esophageal mucosa is avoided; and the stent is convenient to recover subsequently.
Owner:SHANGHAI FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Stents with improved fixation
The present disclosure provides stents, particularly self-expanding stents, useful for the GI tract, and more particularly, useful for treating esophageal strictures. The stents provided herein include a medial region and proximal and distal cuffs having external diameters greater than the medial region diameter when the stent is in the deployed state. The medial region comprises an open weave wire construction. An elastomeric coating circumscribes the medial region, while the may be an extension of the wire construction or separate elements. Preferably, the cuffs have a textured surface for contact with the esophageal wall tissue to resist stent migration. The elastomer coated medial region provides a barrier to tissue ingrowth, and has an enhanced radial restoring force to maintain an open passageway in a body lumen. Optionally, the stent includes an exterior sheath with a surface pattern, to which the stent couples. A low durometer sleeve, between the stent and body lumen, axial positioning of the stent relative to the body lumen. Consequently, precision in stent placement is provided without tissue damage that could result if positioning motion occurred between the surface texture and the body lumen.
Owner:BVW HLDG
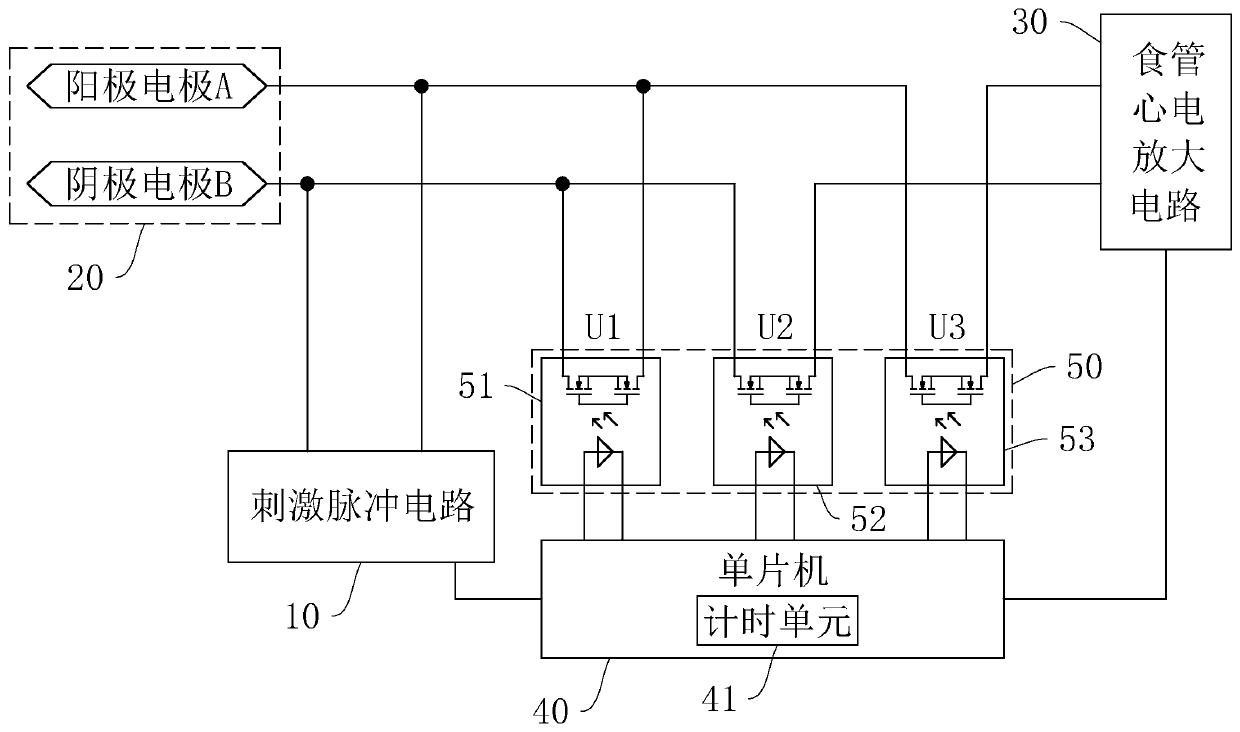
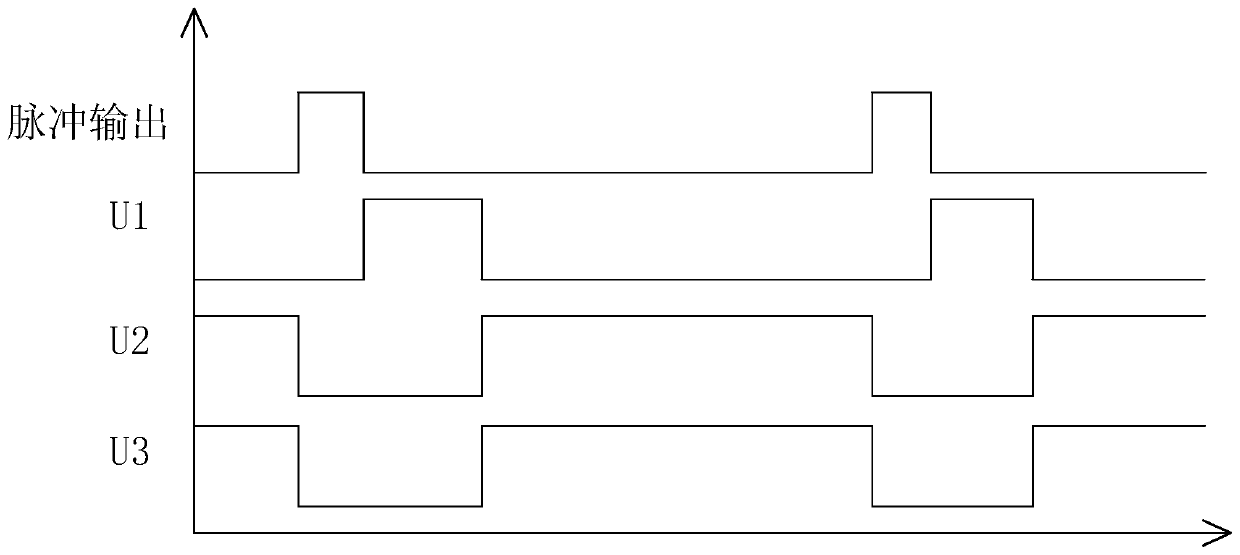
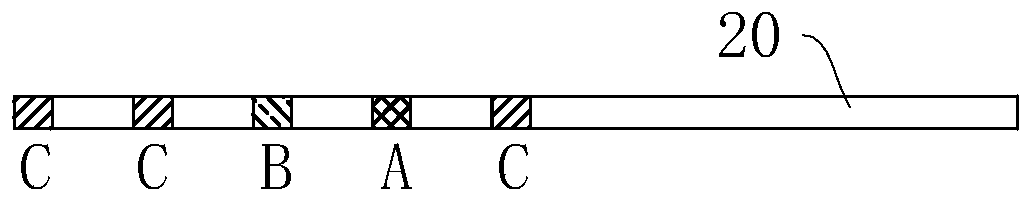
Technique for sharing of stimulating electrode and recording electrode in esophageal cardiac electrophysiology catheter
PendingCN111387970ARealize multiplexingHigh resolutionHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringHemt circuitsLeft atrium
The invention relates to a technique for sharing of a stimulating electrode and a recording electrode in an esophageal cardiac electrophysiology catheter. According to the technical scheme the technique is mainly characterized in that an anode electrode A and a cathode electrode B are simultaneously connected to a stimulating pulse circuit and an esophageal electrocardiogram amplification circuit;when the stimulating pulse circuit carries out electrical pulse output, connection between the esophageal electrocardiogram amplification circuit and the electrodes is cut off; when electrical pulseoutput is ended, the anode electrode A and the cathode electrode B are controlled to communicate; and when the communicating time of the anode electrode A and the cathode electrode B reaches a set first time threshold, connection between the anode electrode A and the cathode electrode B is cut off, and meanwhile, the esophageal electrocardiogram amplification circuit communicates with the anode electrode A and the cathode electrode B. By multiplexing the stimulating electrode and the recording electrode, the technique can make a signal of the recording electrode closer to a left atrium nearbyan esophageal wall to guarantee the waveform quality of the esophageal electrocardiogram.
Owner:苏州市东方电子仪器厂
Instrument capable of preventing esophageal stenosis for ESD (endoscopic submucosal dissection) post-operation
PendingCN109498965ARelieve pressureImprove the quality of lifeBalloon catheterMulti-lumen catheterEsophageal stenosisNutrition
The invention discloses an instrument capable of preventing esophageal stenosis for ESD (endoscopic submucosal dissection) post-operation. The instrument is used for later period heal of esophagus cancer submucosal dissection and prevention of the esophageal stenosis. The instrument comprises three balloons, an inflation tube is arranged in each balloon, the three inflation tubes are not communicated each other, a through hole is formed in each inflation tube and communicated with the inflation tube and the corresponding balloon, the balloons are positioned on the upper portion, and the middleand the low portion of a chest to support a whole esophageal wall. The instrument is additionally provided with a drainage tube, a stomach tube and a duodenal tube, the drainage tube is used for leading out saliva, the stomach tube is used for sucking out gas or liquid in a gastrointestinal tract, and the duodenal tube is used for conveying nutrition to a patient. The instrument is simple in structure and applicable to industrial production.
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL OF HEBEI MEDICAL UNIV
Methods and devices for endosonography-guided fundoplexy
ActiveUS8784437B2Reduce gastroesophageal refluxEasily drawnSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesEsophageal wallGuided intervention
The present invention relates to a tissue securement system, device and method for endoscopy or endosonography-guided transluminal interventions whereby a ligation or anchor is placed and secured into soft tissue. An objective of this invention is to provide a method to reduce gastroesophageal reflux by endosonography-guided intervention. Specifically, endosonography is used to insert a ligation element through the esophageal wall, through the diaphragmatic crus and into the fundus of the stomach. This ligation element placed from the esophagus and around the Angle of His to create a barrier to gastroesophageal reflux.
Owner:ADVENT MEDICAL
Self-service esophageal stenosis dilator with gradually-increased expanding diameter and method
ActiveCN113018654ADiameter changeThe diameter is gradually changed by changing the volume of air or saline injected into the dilated balloonBalloon catheterSurgeryInjection portEsophageal wall
The invention discloses a self-service esophageal stenosis dilator capable of gradually increasing the expanding diameter and a method, and belongs to the technical field of medical instruments. The self-service esophageal stenosis dilator with the gradually-increased expanding diameter comprises a dilation mechanism which comprises an air guide pipe, a positioning air bag and a dilation air bag, wherein the air guide pipe is provided with a first through hole, a second through hole, a first air vent and a second air vent, one end of the first through hole is communicated with the positioning air bag through the first air vent, the other end of the first through hole is communicated with the dilation air bag through the second air vent, and one end of the second through hole is communicated with the expansion airbag through the second vent; an injector which is provided with scales; and an air valve mechanism which is used for switching the injection port to be communicated with the first through hole or the second through hole. By using the esophageal dilator provided by the invention, the stenosis of the esophagus can be easily and accurately positioned. The esophageal dilator can ensure that the pressure applied by the air bag to the esophageal wall is within the maximum dilation pressure capable of being borne by the esophageal wall.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Lifting device convenient to use in anastomosis
The invention discloses a lifting device convenient to use in anastomosis. The lifting device comprises a supporting unit, a connecting rod and an operating unit, the connecting rod comprises a connecting rod first end and a connecting rod second end which are located in the extending direction of the connecting rod; the supporting unit is of a hard structure arranged at the connecting rod first end; the operating unit is arranged at the connecting rod second end; the supporting unit is movably connected with the connecting rod; the supporting unit moves relative to the connecting rod to enable the supporting unit to have at least two switchable locking states; the operation unit is connected with the supporting unit to control the supporting unit to be switched and locked between the twolocking states; and the middle part of the supporting unit protrudes towards one side of the supporting plane. The lifting device disclosed by the invention is simple to operate and is good in liftingstability and accuracy; an obvious hole is formed between the lower side of the supporting unit and a esophagus wall; and through formation of the hole, an operating forceps / clamp can be used to conveniently pull out a stomach tube from an esophagus, or an anastomat can conveniently enter the esophagus, so that clinical operation is facilitated.
Owner:王冬
GI tract stimulation devices and methods
InactiveUS10384052B2Improving motility of esophagealEffectively function disregardingExternal electrodesEsophageal electrodesCardioesophageal sphincterEsophageal wall
Systems, methods and devices, for stimulating one or more esophageal muscle contractions are provided. The system, methods, and devices may be designed to evoke motion and / or restore function in one or more organs that are located distal to the lower esophageal sphincter. A controller and a generator may be used to transmit signals to one or more electrodes in a tube placed in a patient's GI tract. In some aspect, the generator is configures to generate a series of pulses for one or more periods of time. In some aspects, a preliminary pulse is transmitted to narrow and esophageal portion such that an esophageal wall is in contact with at least one electrode thus lowering the nominal stimulation threshold.
Owner:E MOTION MEDICAL
Detachable esophageal foreign matter clamping assistance device under endoscope
The invention discloses a detachable esophageal foreign matter clamping assistance device under an endoscope, which comprises a clamping assistance device, wherein the clamping assistance device body comprises an expansion valve, an expansion valve delivery device, a mantle compression bolt, a mantle compression gasket, expansion valve connecting rods, a connecting guide wire, an upper fixator and a lower fixator, the upper fixator and the lower fixator are both in a ring shape and are coaxial, the expansion valve delivery device is in a circular tube shape, the number of the expansion valve connecting rods is at least three, one ends of the expansion valve connecting rods are fixedly connected with the expansion valve delivery device, the other ends of the expansion valve connecting rods penetrate through the lower fixator to be fixedly connected with the expansion valves, and the expansion valves correspond to the expansion valve connecting rods in a one-to-one mode. The device is firm, durable and high in practicability, can be used in cooperation with a digestive endoscope to reduce damage of jujube-pit-shaped foreign matter to the esophageal wall, and assists the medical staff in safely and effectively clamping the foreign matter in the esophagus.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Esophageal local drug delivery device for acute radiation esophagitis
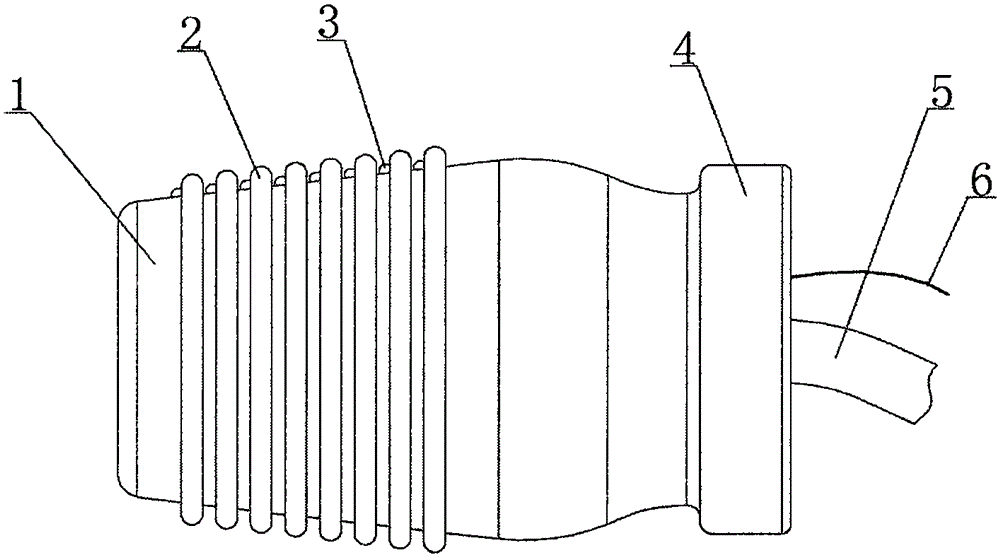
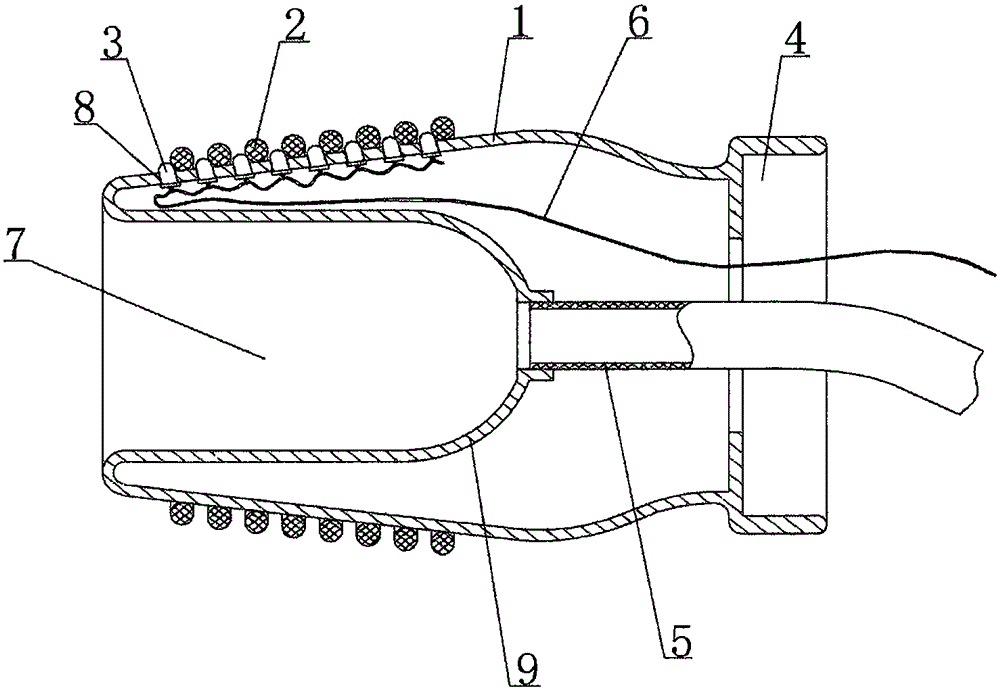
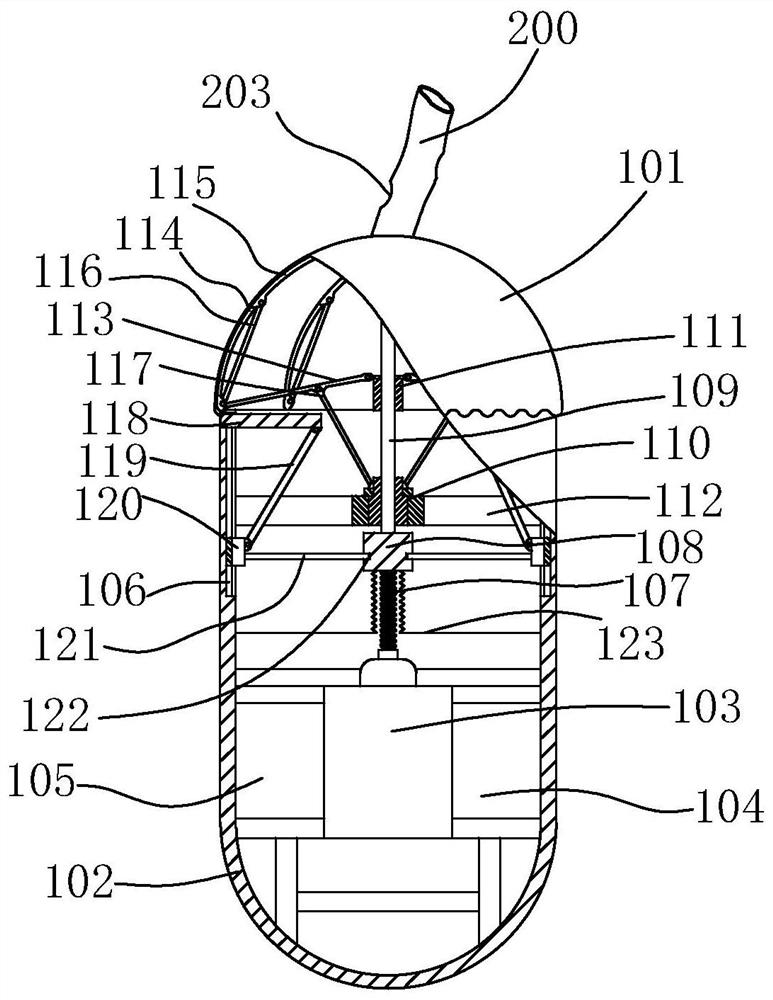
ActiveCN112741955AStable positionExtension of timeMedical devicesFeeding-tubesEsophageal wallEsophageal mucosa
The invention discloses an esophageal local drug delivery device for acute radiation esophagitis, and aims to solve the problems that liquid medicine is difficult to stay on the surface of esophageal mucosa or stays for a short time, and the liquid medicine is difficult to take and eat by swallowing. The drug delivery device comprises a capsule, a hose and a fixator, wherein the fixator comprises an ear hook, one end of the hose is connected with the capsule, an adaptive connecting piece is connected between the other end of the hose and the ear hook, the capsule comprises a capsule shell and a micro-transmission mechanism fixed in the capsule shell, the capsule shell comprises an elastic head membrane and a capsule body, A micro-motor in the micro-transmission mechanism is electrically connected with a power supply and a microcontroller, the micro-transmission mechanism comprises a spiral mechanism and a stretching mechanism, and the spiral mechanism drives the stretching mechanism to stretch the elastic head membrane, so that a gap between the periphery of the elastic head membrane and an esophageal wall is reduced, a liquid medicine column is formed, and the retention time of medicine acting on the surface of the esophageal mucosa is prolonged.
Owner:AFFILIATED CANCER HOSPITAL OF SHANDONG FIRST MEDICAL UNIV SHANDONG CANCER INST (SHANDONG CANCER HOSPITAL)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com