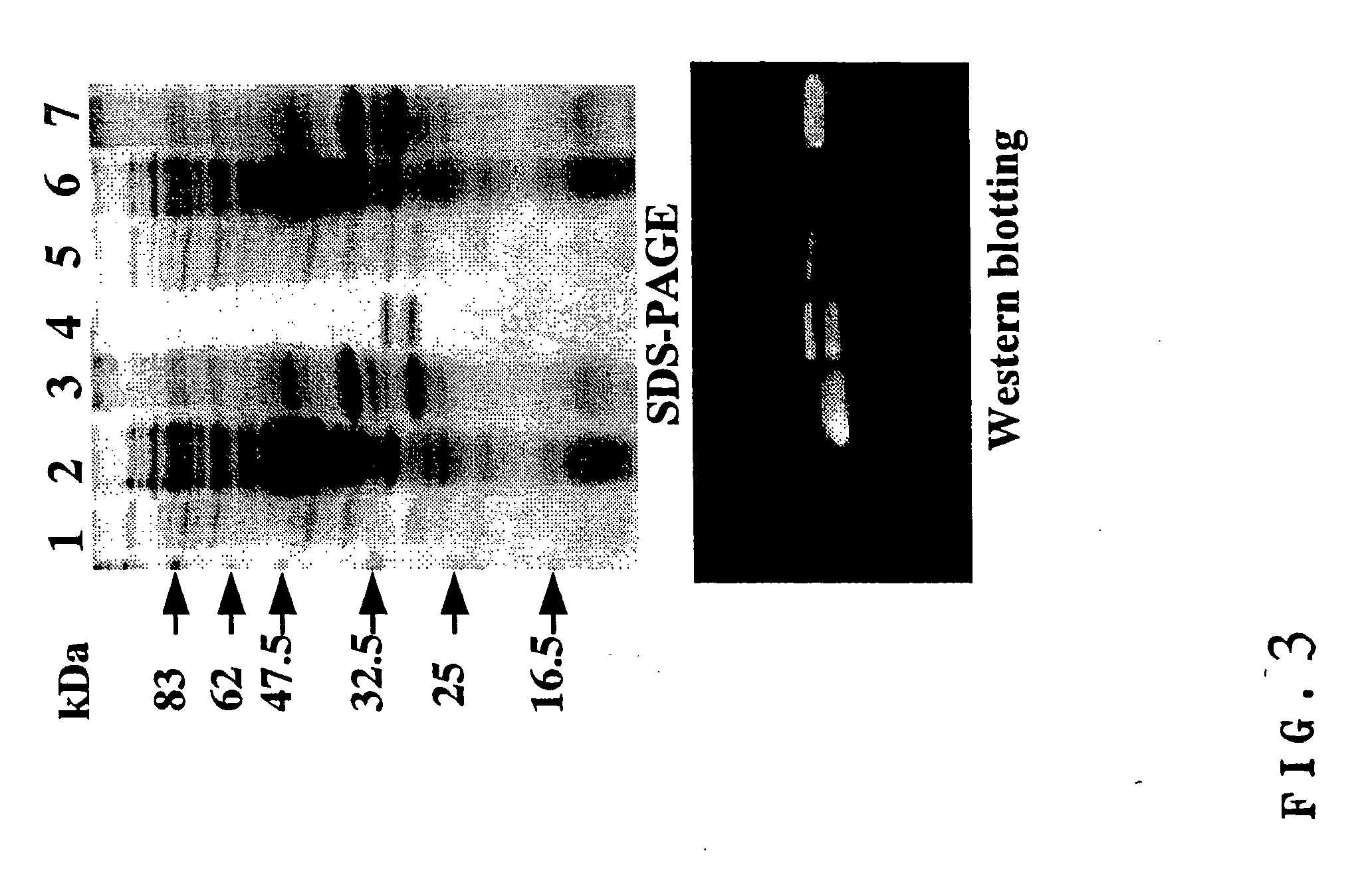
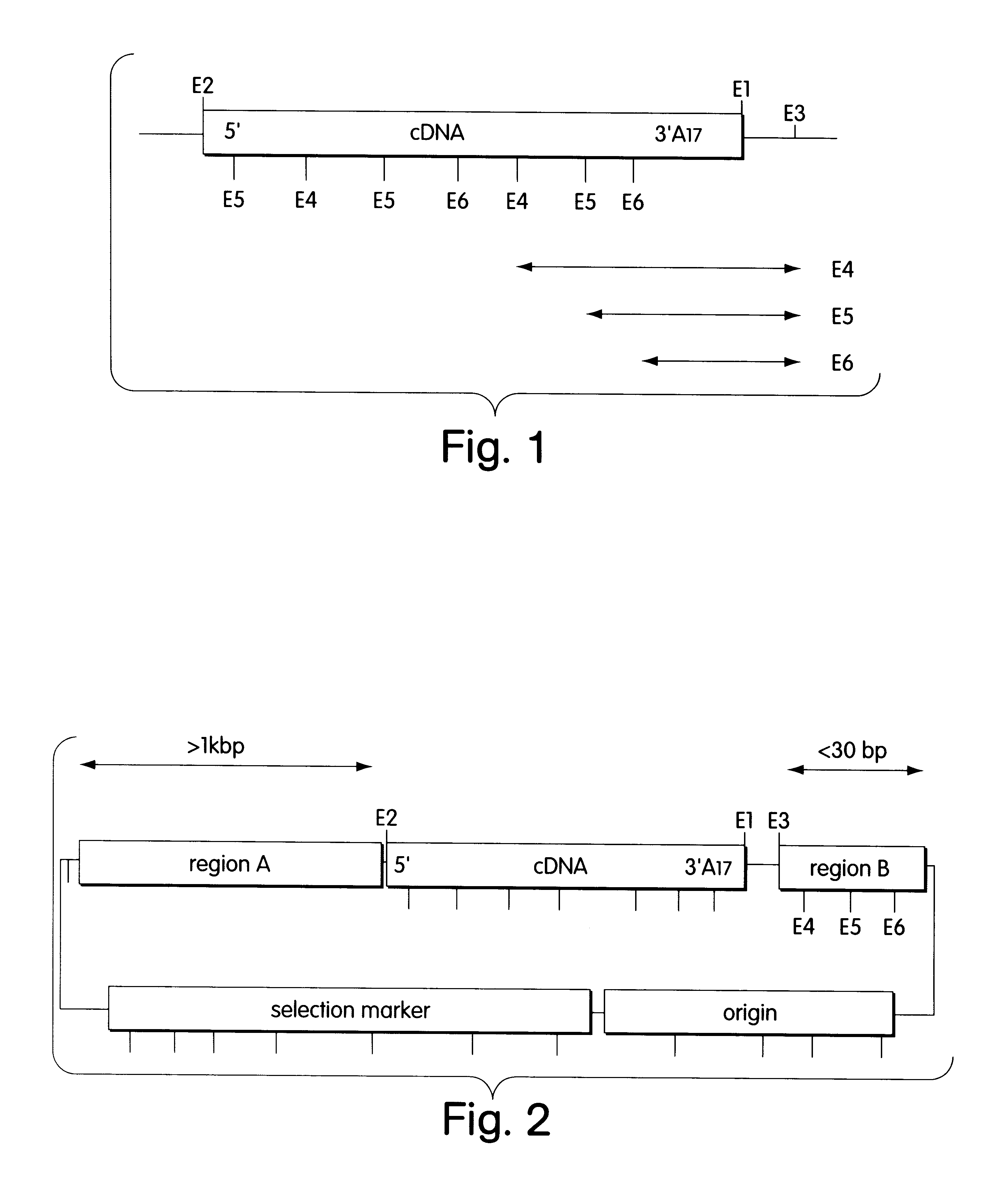
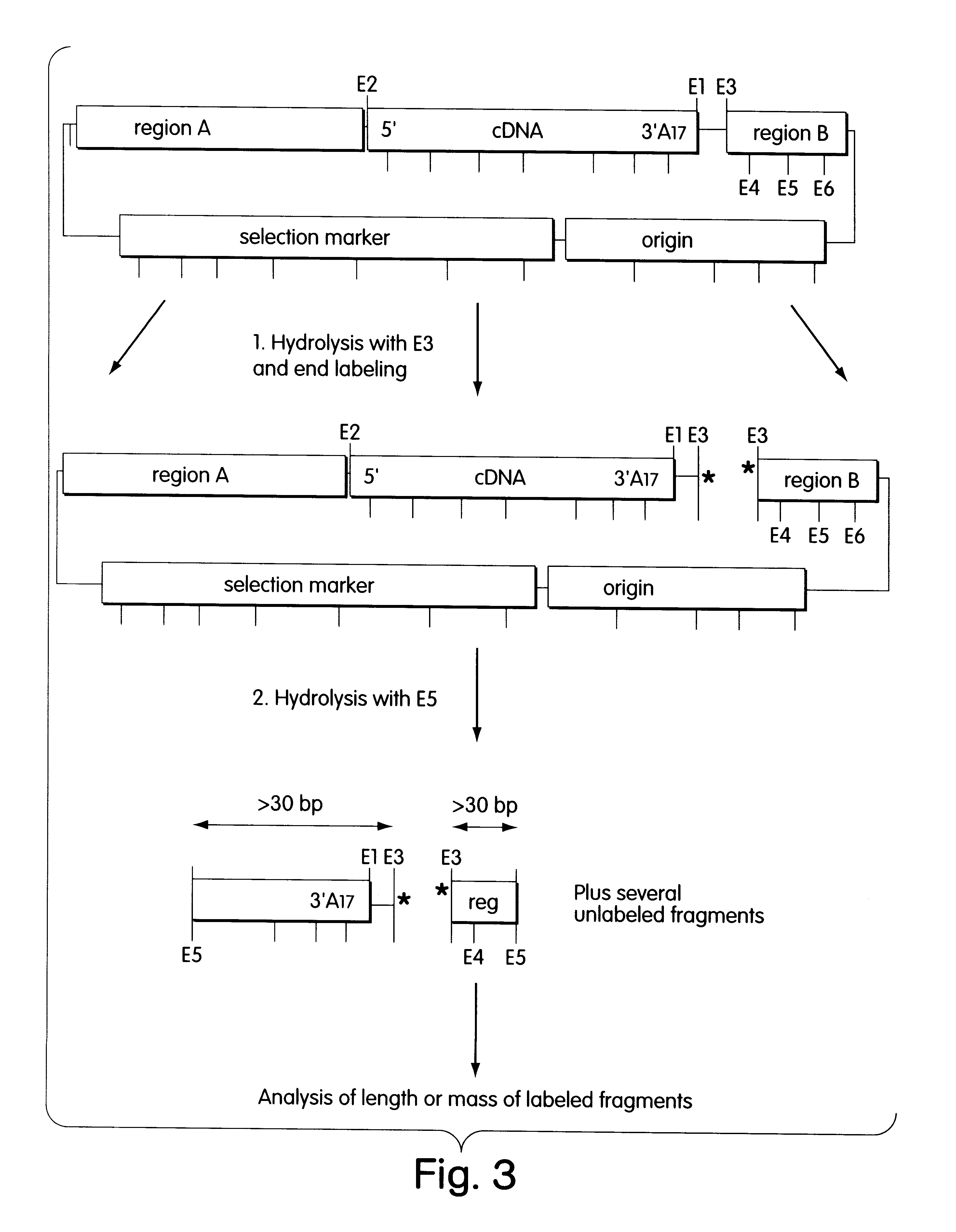
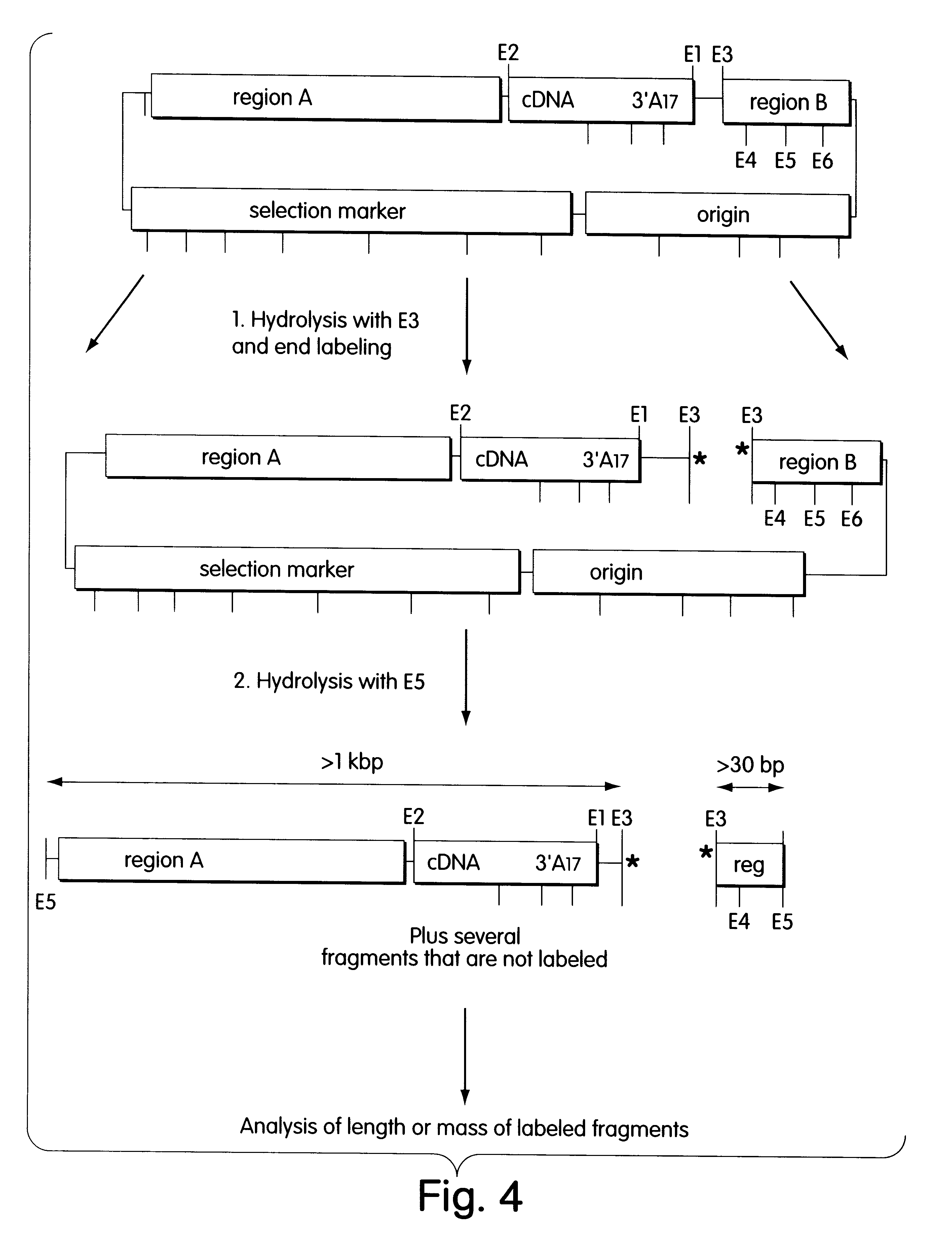
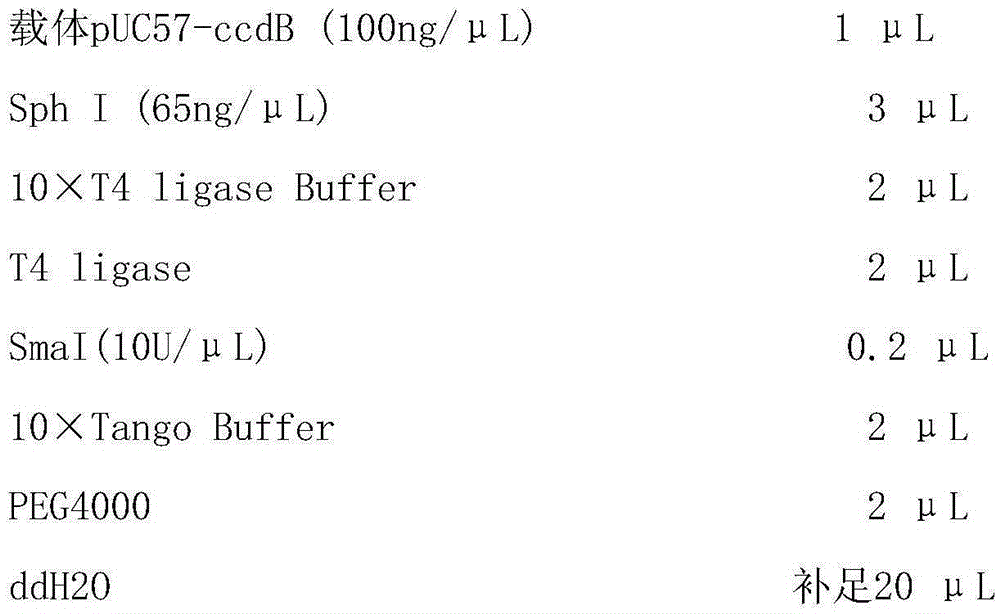Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
423 results about "Cloning vector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A cloning vector is a small piece of DNA that can be stably maintained in an organism, and into which a foreign DNA fragment can be inserted for cloning purposes. The cloning vector may be DNA taken from a virus, the cell of a higher organism, or it may be the plasmid of a bacterium. The vector therefore contains features that allow for the convenient insertion or removal of a DNA fragment to or from the vector, for example by treating the vector and the foreign DNA with a restriction enzyme that cuts the DNA. DNA fragments thus generated contain either blunt ends or overhangs known as sticky ends, and vector DNA and foreign DNA with compatible ends can then be joined together by molecular ligation. After a DNA fragment has been cloned into a cloning vector, it may be further subcloned into another vector designed for more specific use.
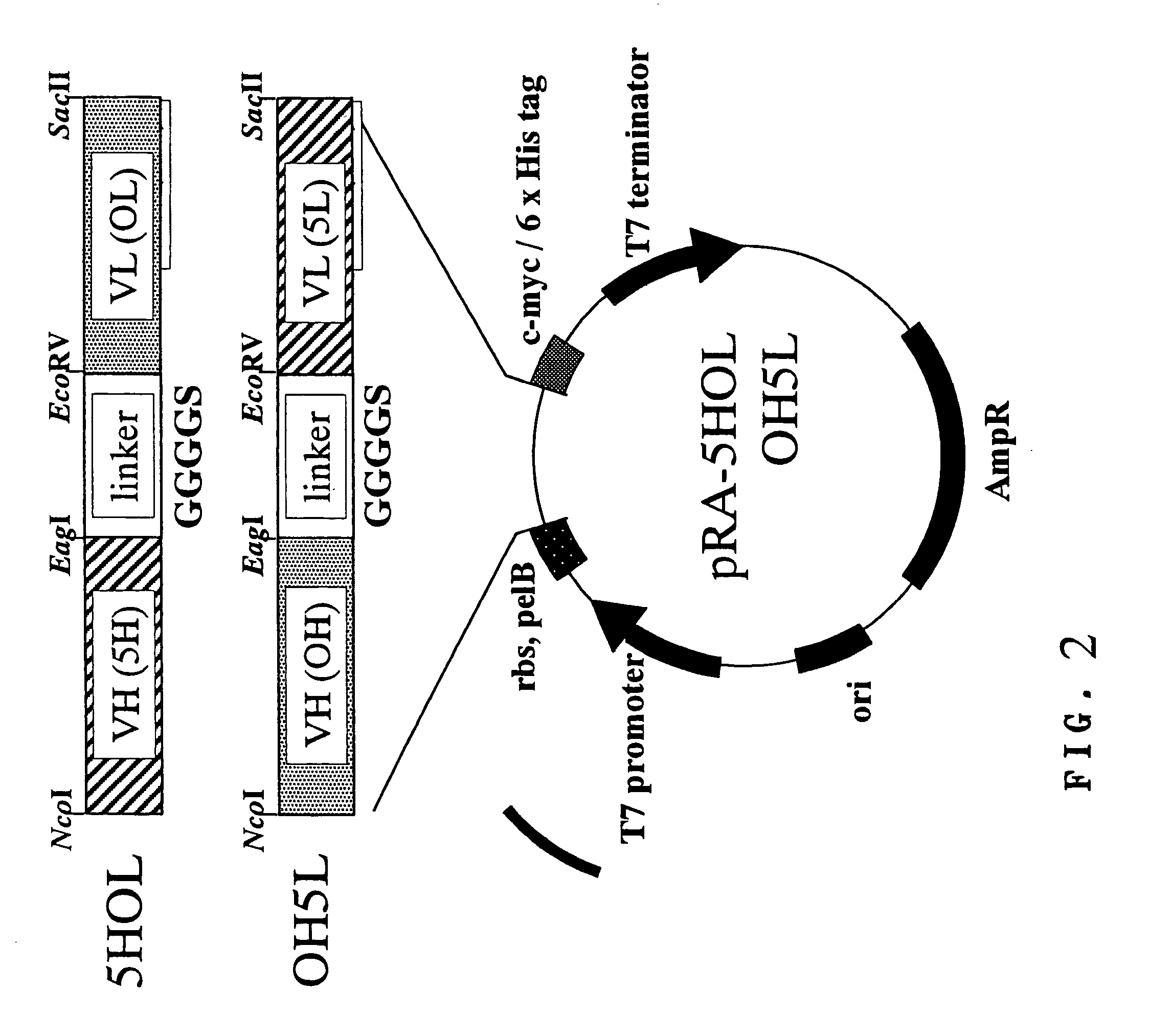
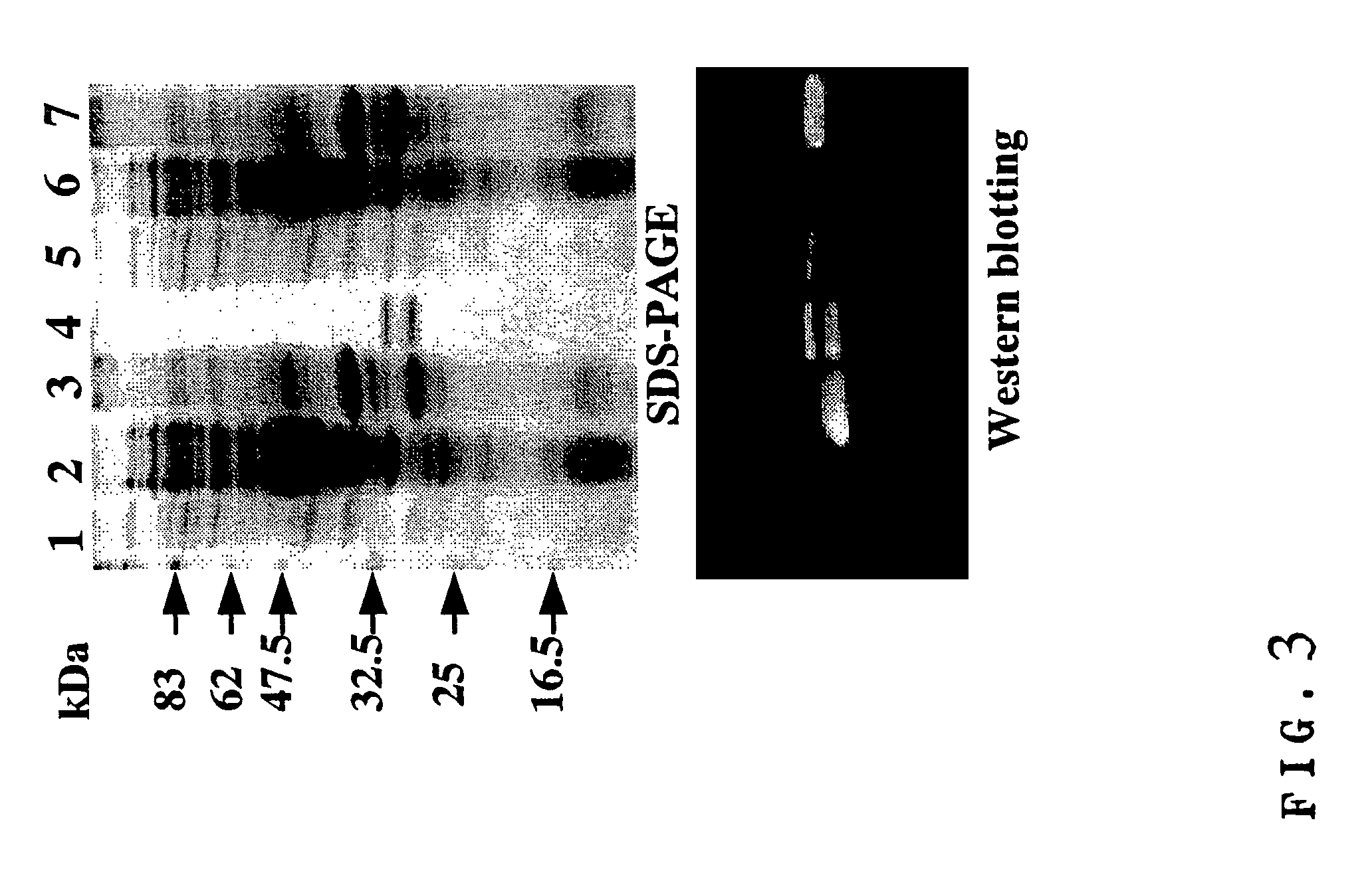
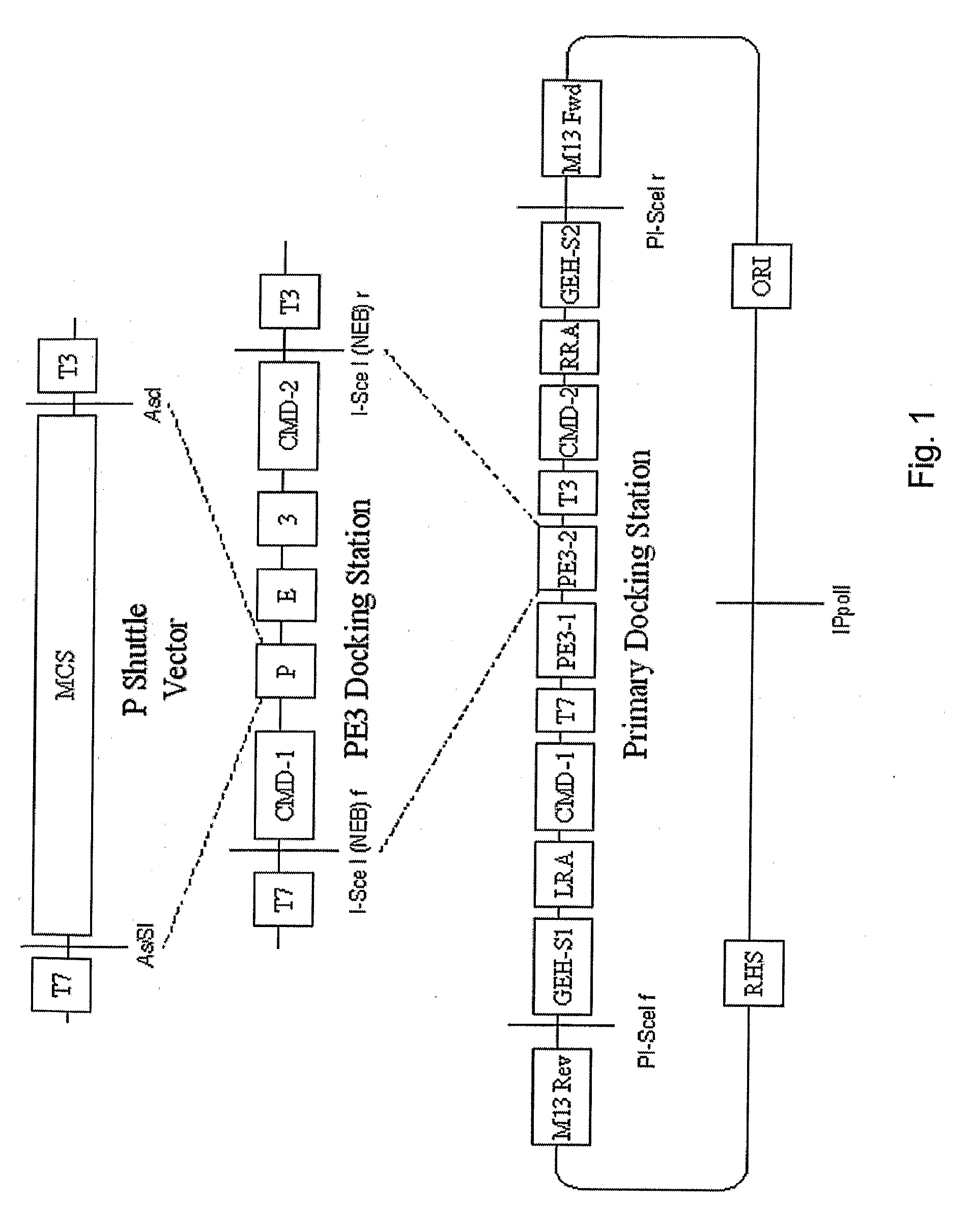
DNA modular cloning vector plasmids and methods for their use
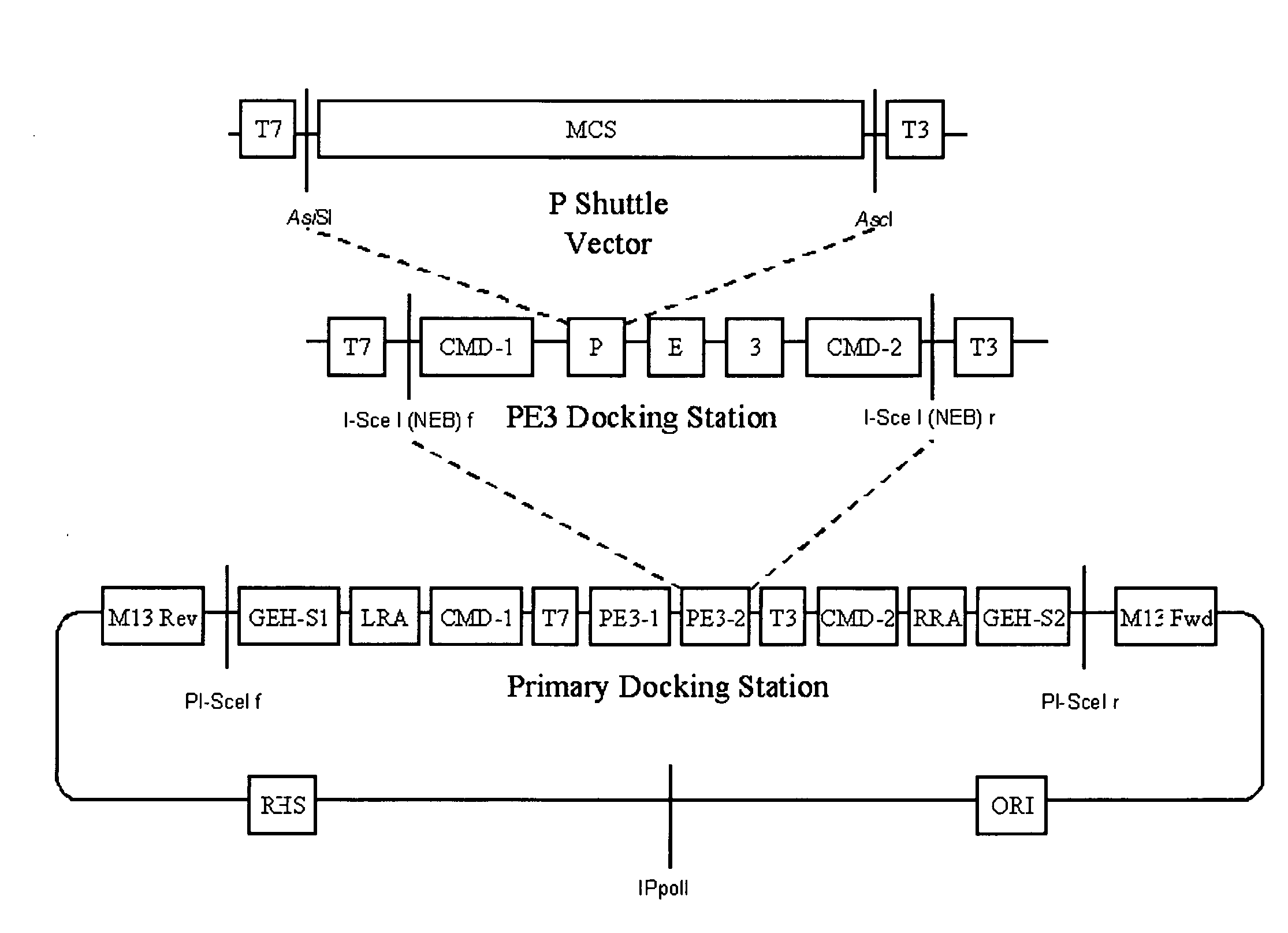
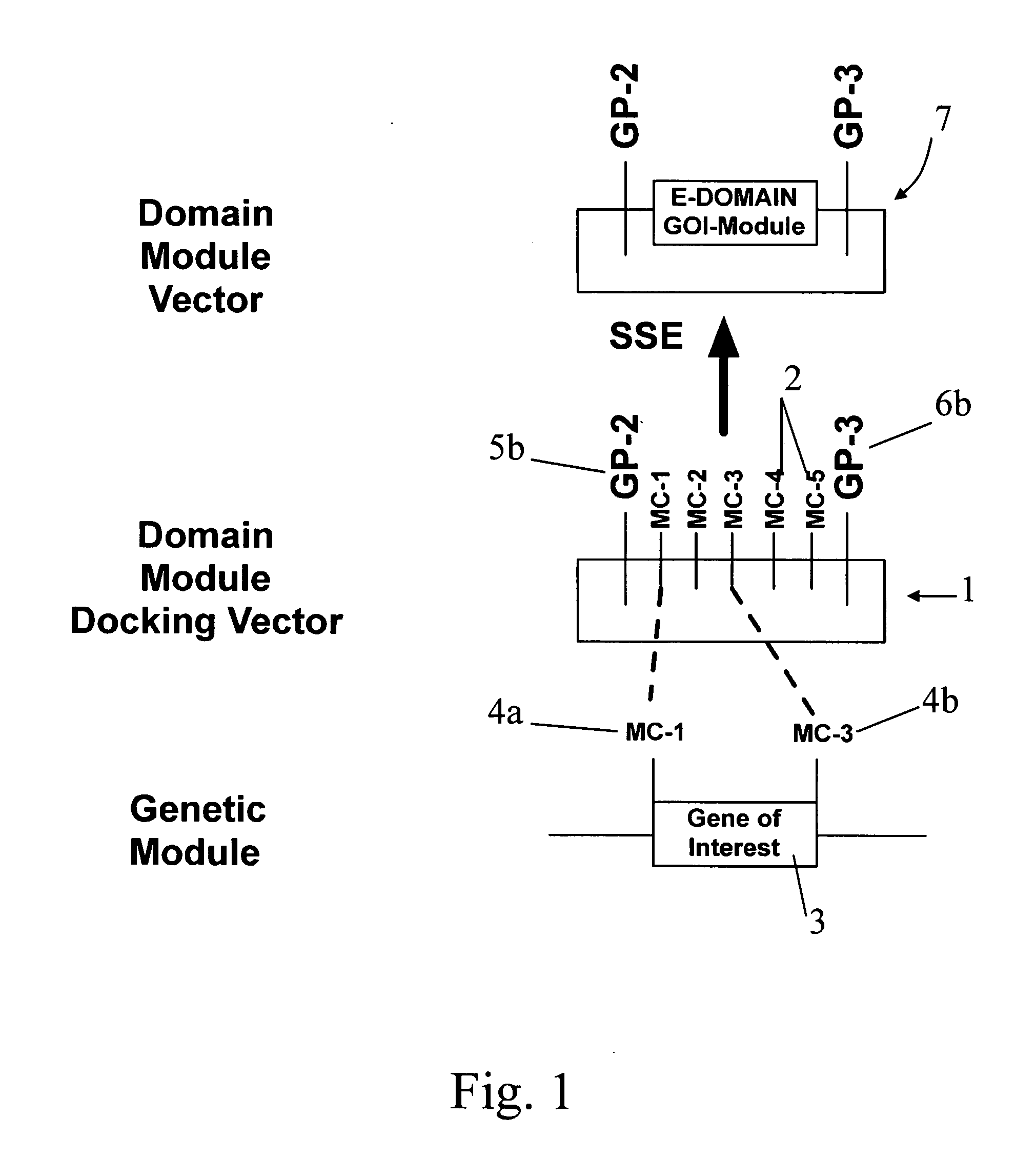
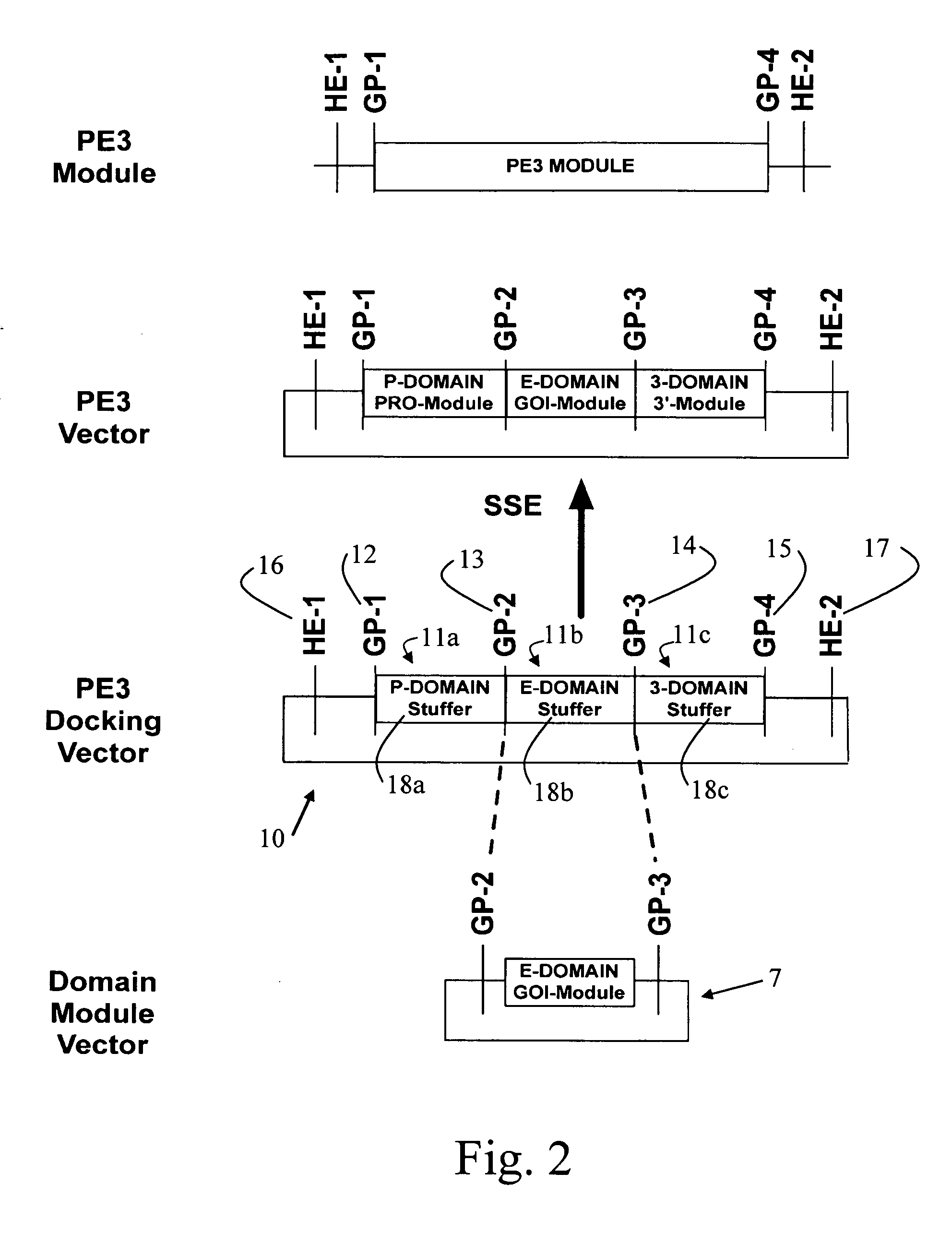
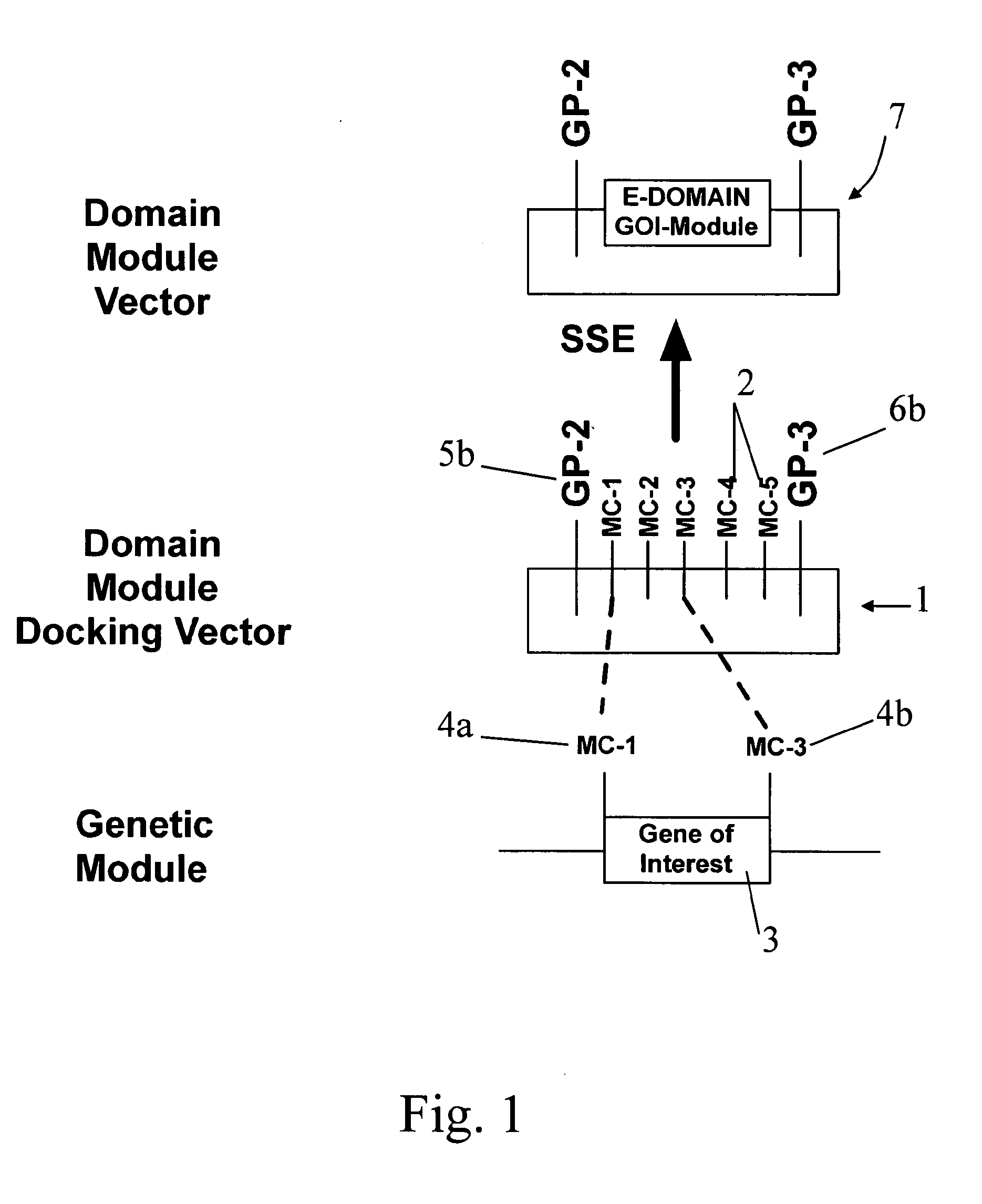
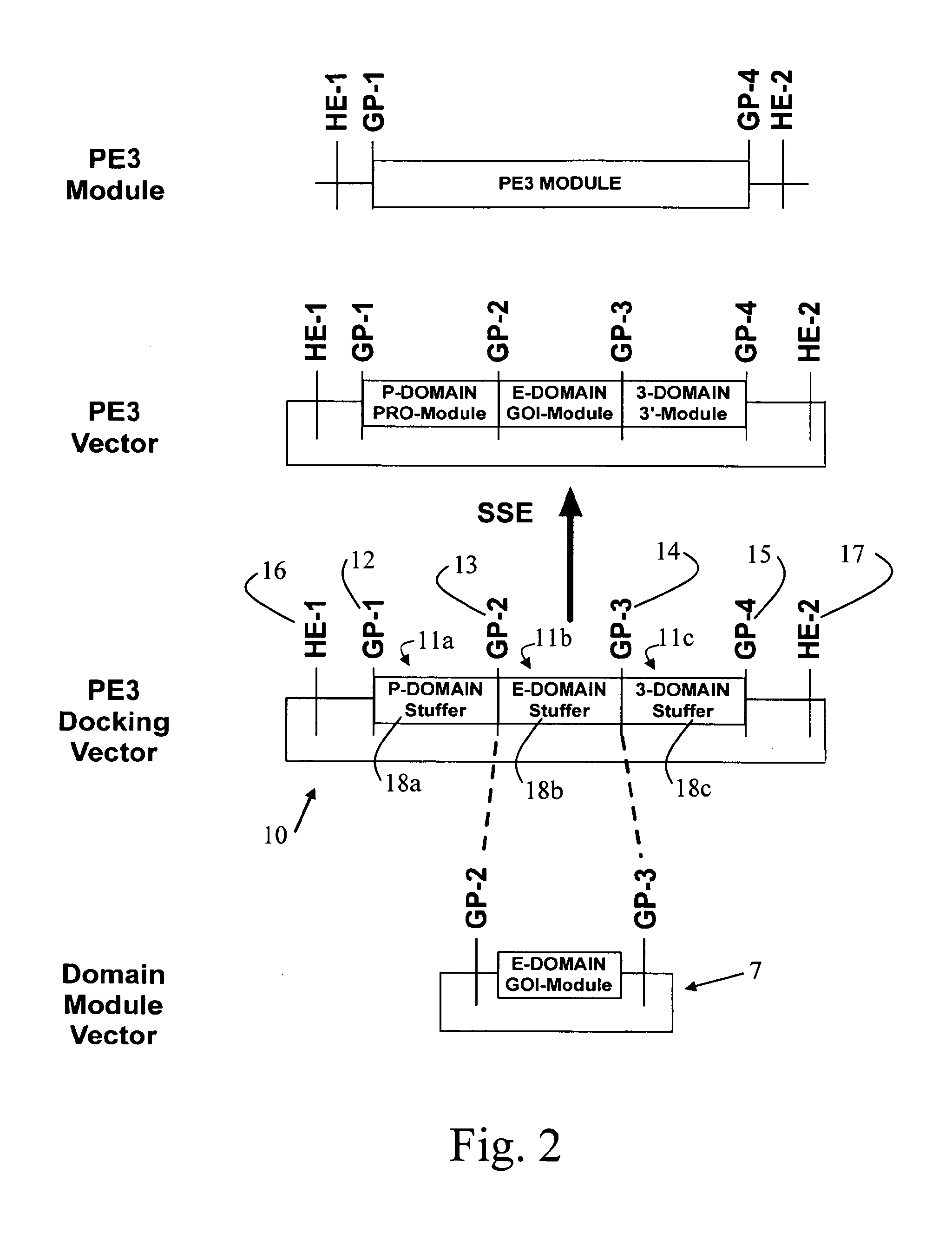
A group of modular cloning vector plasmids for the synthesis of a transgene or other complicated DNA construct, by providing a backbone having docking points therein, for the purpose of gene expression or analysis of gene expression. The invention is useful for assembling a variety of DNA fragments into a de novo DNA construct or transgene by using cloning vectors optimized to reduce the amount of manipulation frequently needed. The module vector contains at least one multiple cloning site (MCS) and multiple sets of rare restriction and / or unique homing endonuclease (“HE”) sites, arranged in a linear pattern. This arrangement defines a modular architecture that allows the user to place domain modules or inserts into a PE3 transgene vector construct without disturbing the integrity of DNA elements already incorporated into the PE3 vector in previous cloning steps. The PE3 transgenes produced using the invention may be used in a single organism, or in a variety of organisms including bacteria, yeast, mice, and other eukaryotes with little or no further modification.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
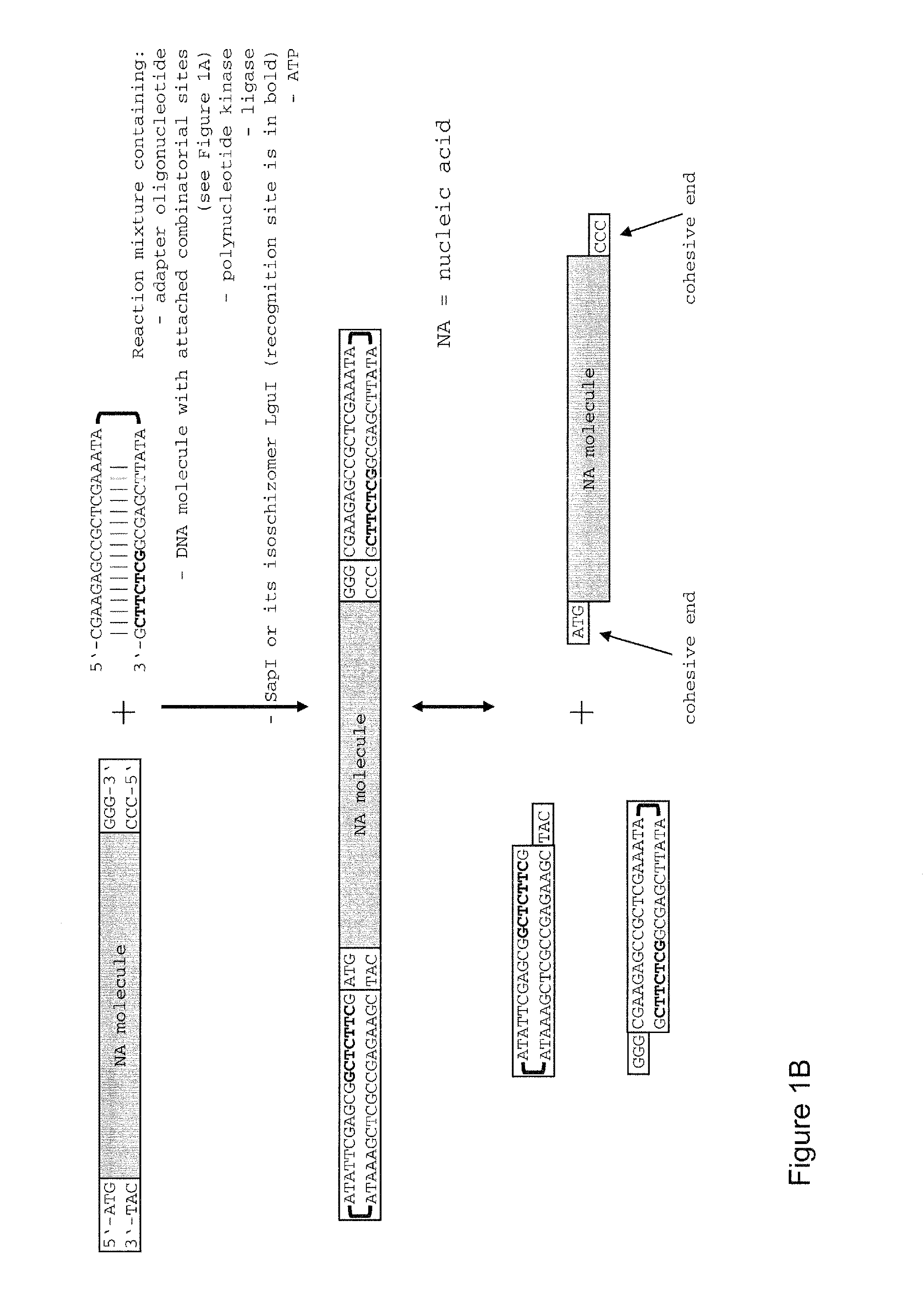
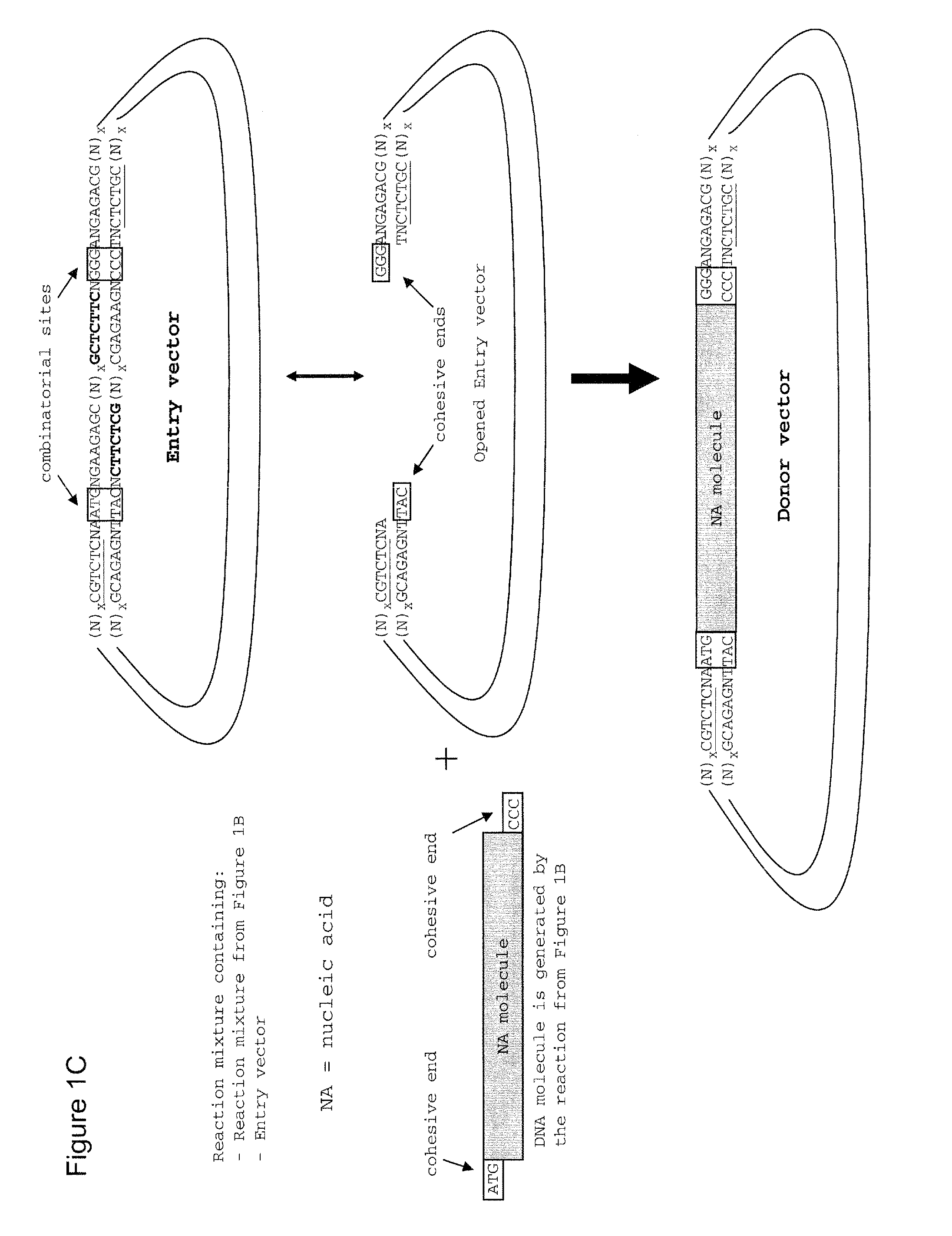
Method of cloning at least one nucleic acid molecule of interest using type iis restriction endonucleases, and corresponding cloning vectors, kits and system using type iis restriction endonucleases
The present invention refers to methods of (sub)cloning at least one nucleic acid molecule of interest. One embodiment relates to a method of (sub)cloning at least one nucleic acid molecule of interest comprising a) providing at least one (replicable) Entry vector into which the at least one nucleic acid molecule of interest is to be inserted, wherein the at least one Entry vector carries two recognition sites for at least one first type IIS and / or type IIS like restriction endonuclease and wherein said at least one nucleic acid molecule of interest can be excised from the at least one Entry vector at two combinatorial sites with one (same) or more (different) cohesive ends that are formed by the at least one first type IIS or type IIS like restriction endonuclease, and b) providing an Acceptor vector, into which the at least one nucleic acid molecule of interest is transferred from the at least one Entry vector carrying the at least one nucleic acid molecule of interest, wherein said Acceptor vector comprises at least one recognition site for at least one second type IIS restriction endonuclease and / or at least one recognition sites for at least one type IIS like restriction endonuclease, and wherein said Acceptor vector provides two combinatorial sites identical to the two combinatorial sites present in the Entry vector. The inventions also relates respective cloning vector and kits.
Owner:PHILIPPS UNIV MARBURG
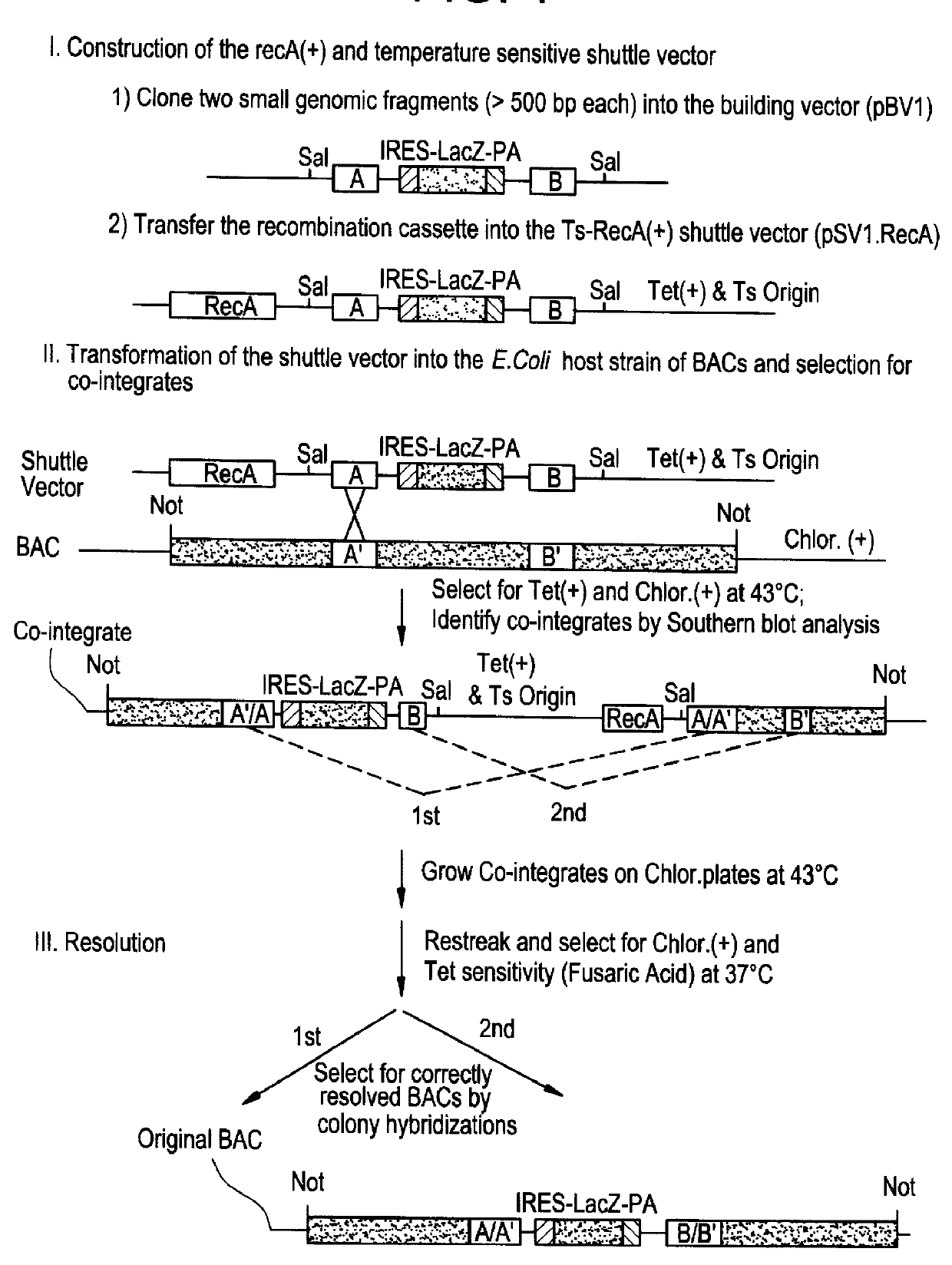
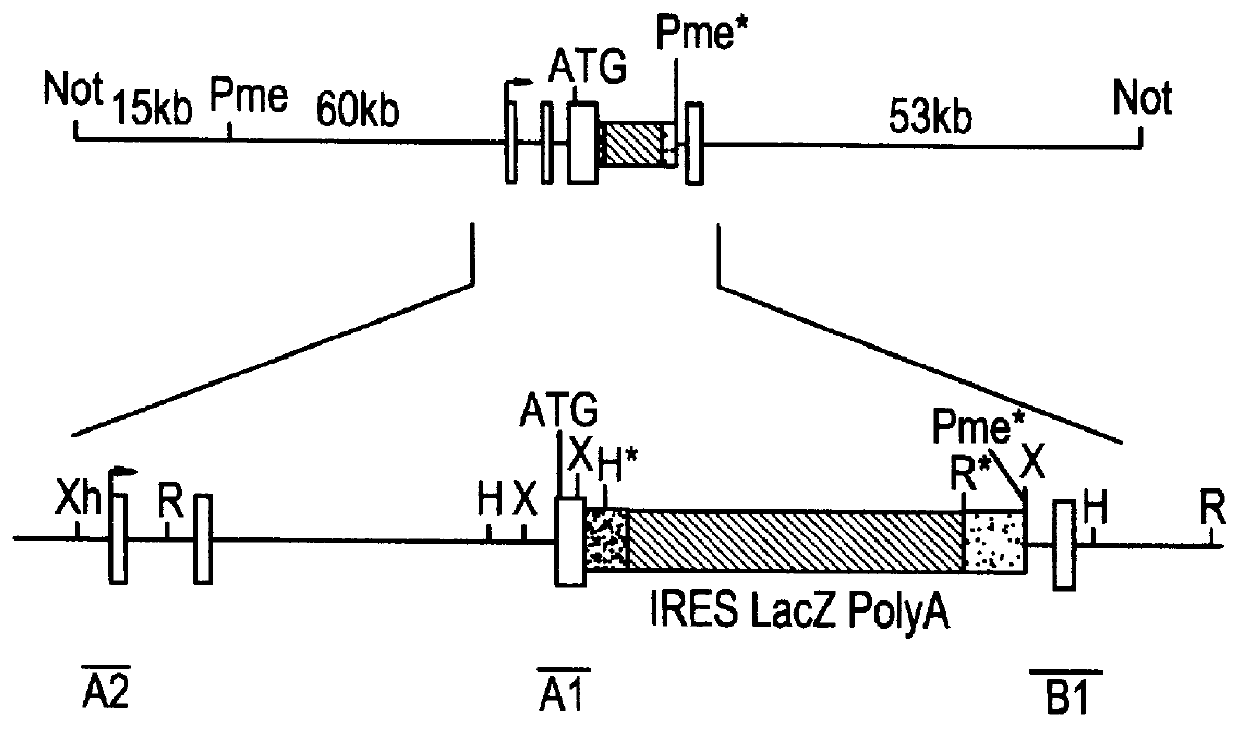
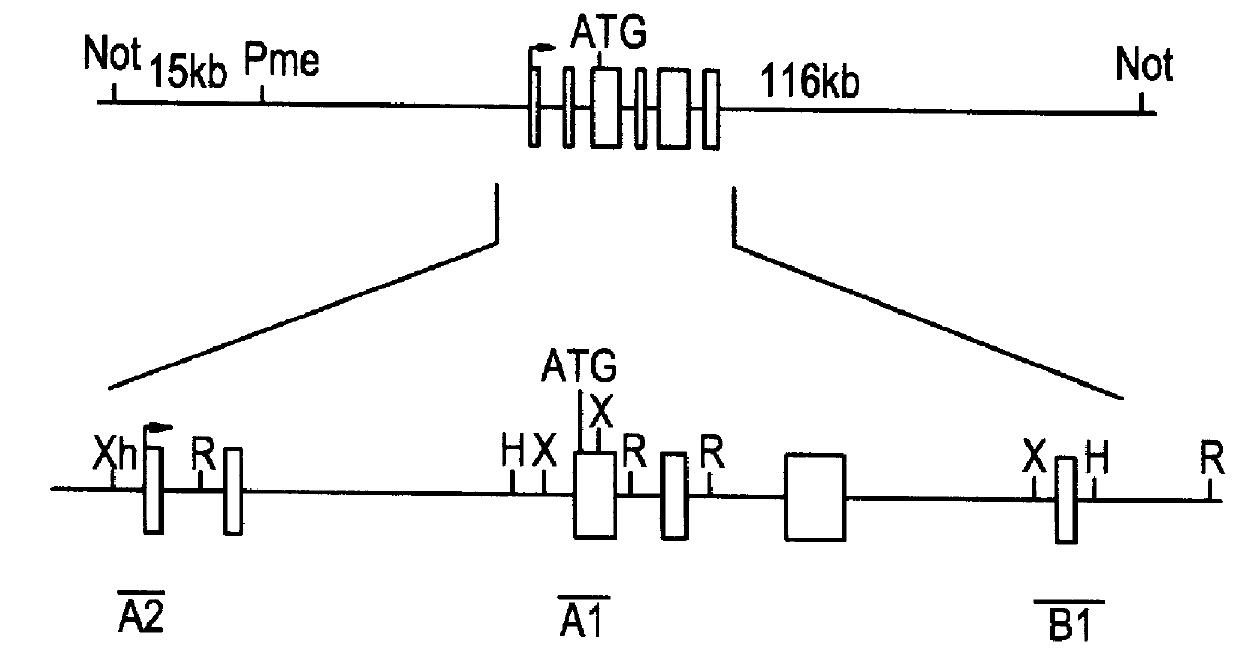
Methods of performing homologous recombination based modification of nucleic acids in recombination deficient cells and use of the modified nucleic acid products thereof
A simple method for modifying genes in a recombination deficient host cell is disclosed. Such modifications include generating insertion, deletions, substitutions, and / or point mutations at any chosen site in the independent origin based cloning vector. The modified gene can be contained in an independent origin based cloning vector that is used to introduce a modified heterologous gene into a cell. Such a modified vector may be used in the production of a germline transmitted transgenic animal, or in gene targeting protocols in eukaryotic cells.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
POLYMERIC IMMUNOGLOBULIN FUSION PROTEINS THAT TARGET LOW AFFINITY FCyRECEPTORS
InactiveUS20090117133A1Small size range and conformationPromote generationSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsLow affinityNACHT domain
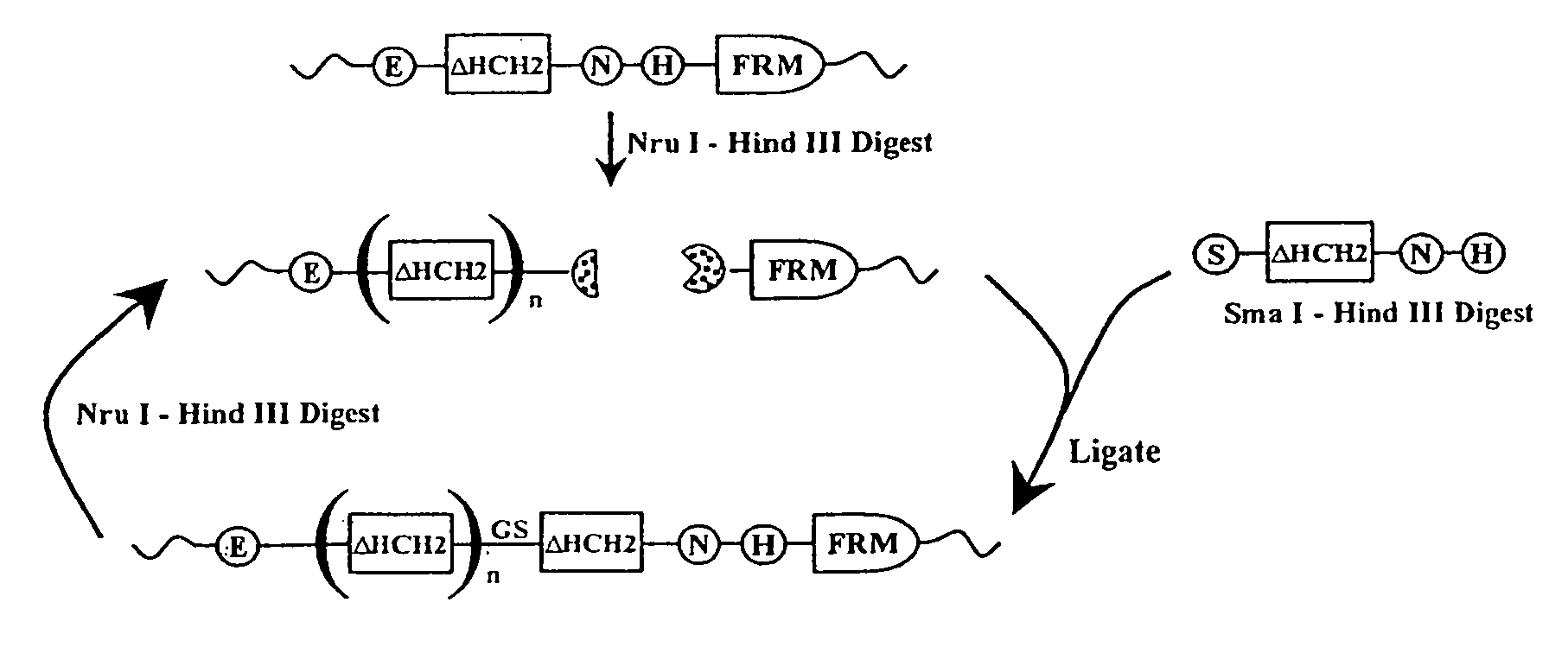
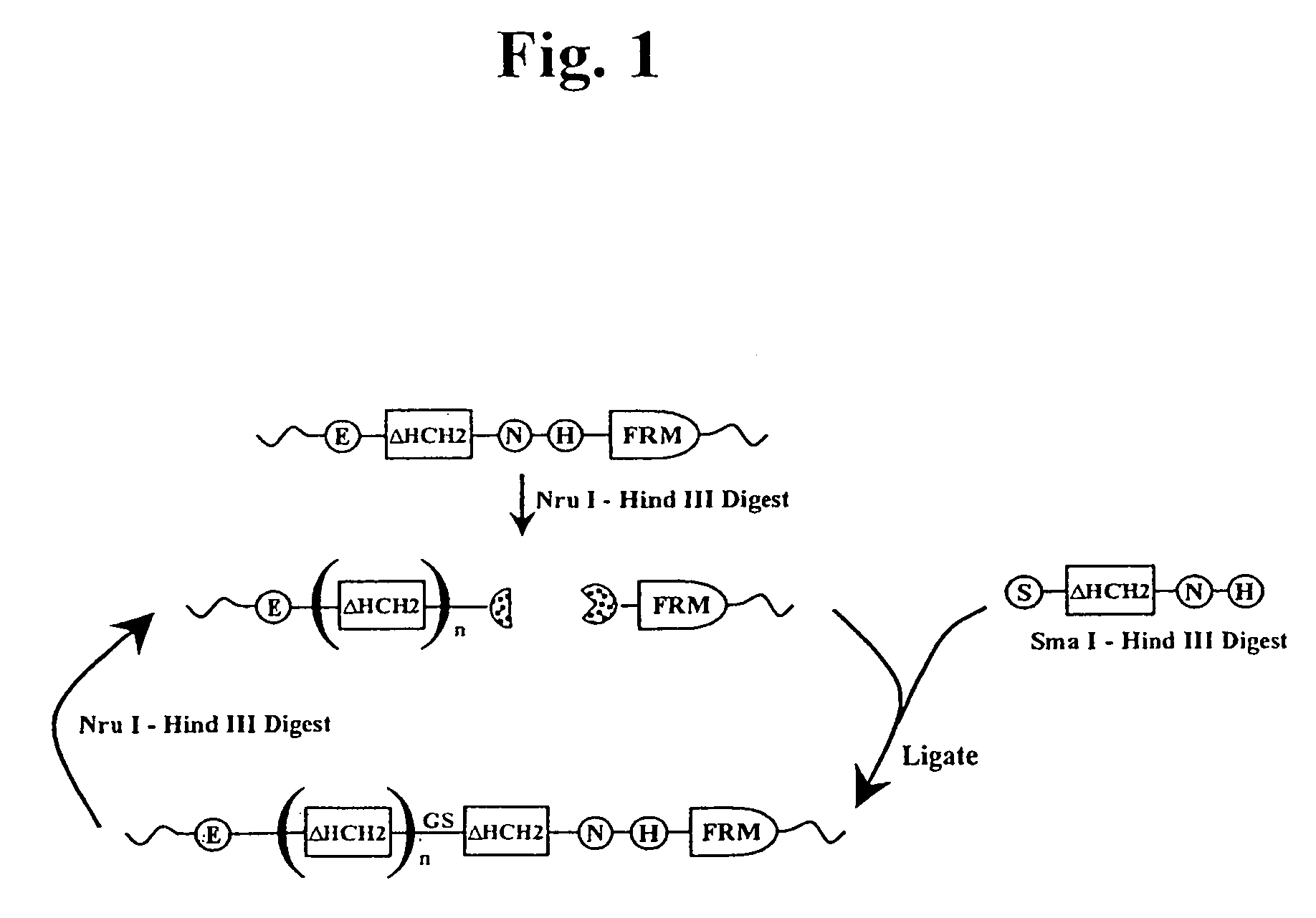
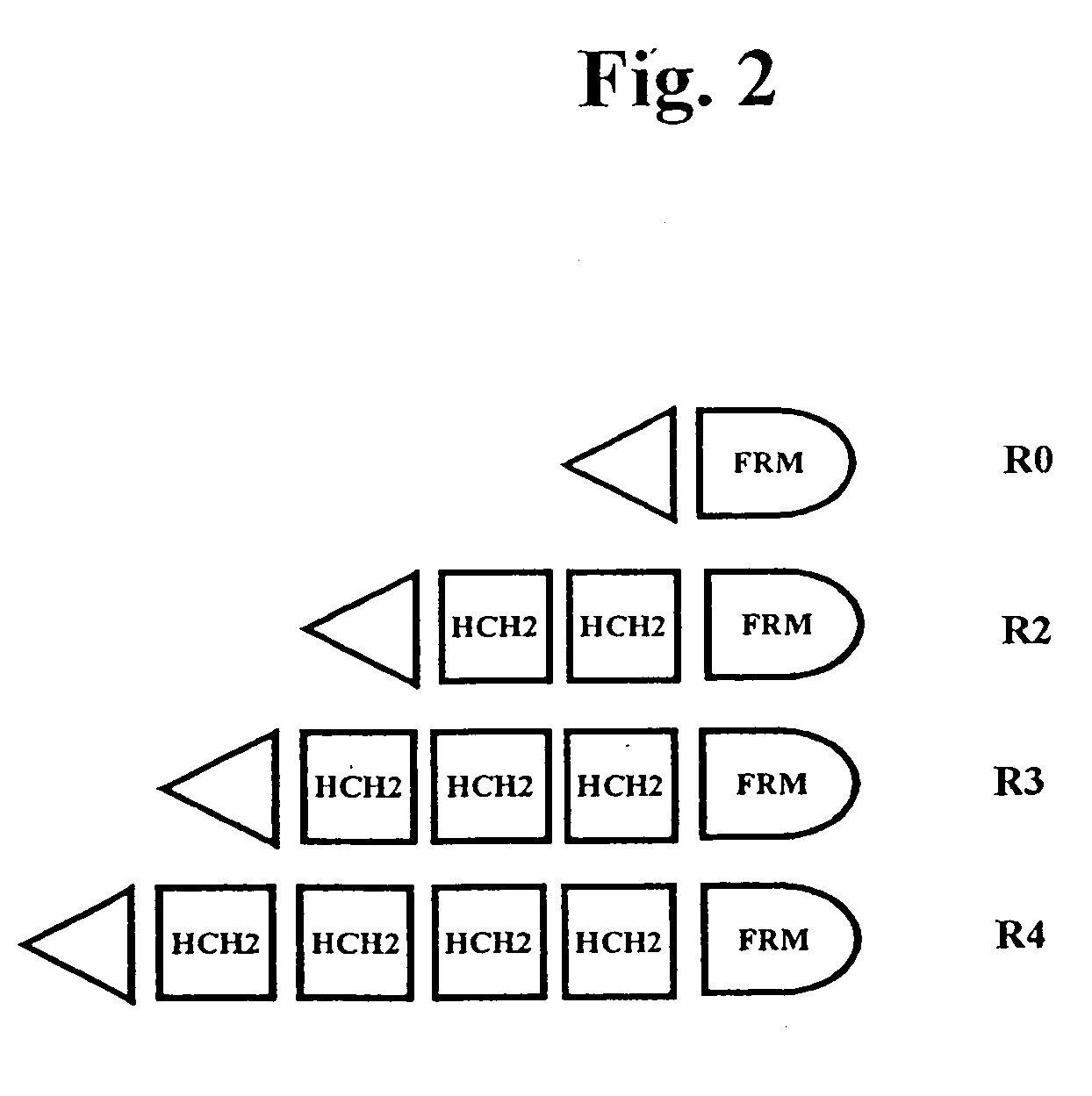
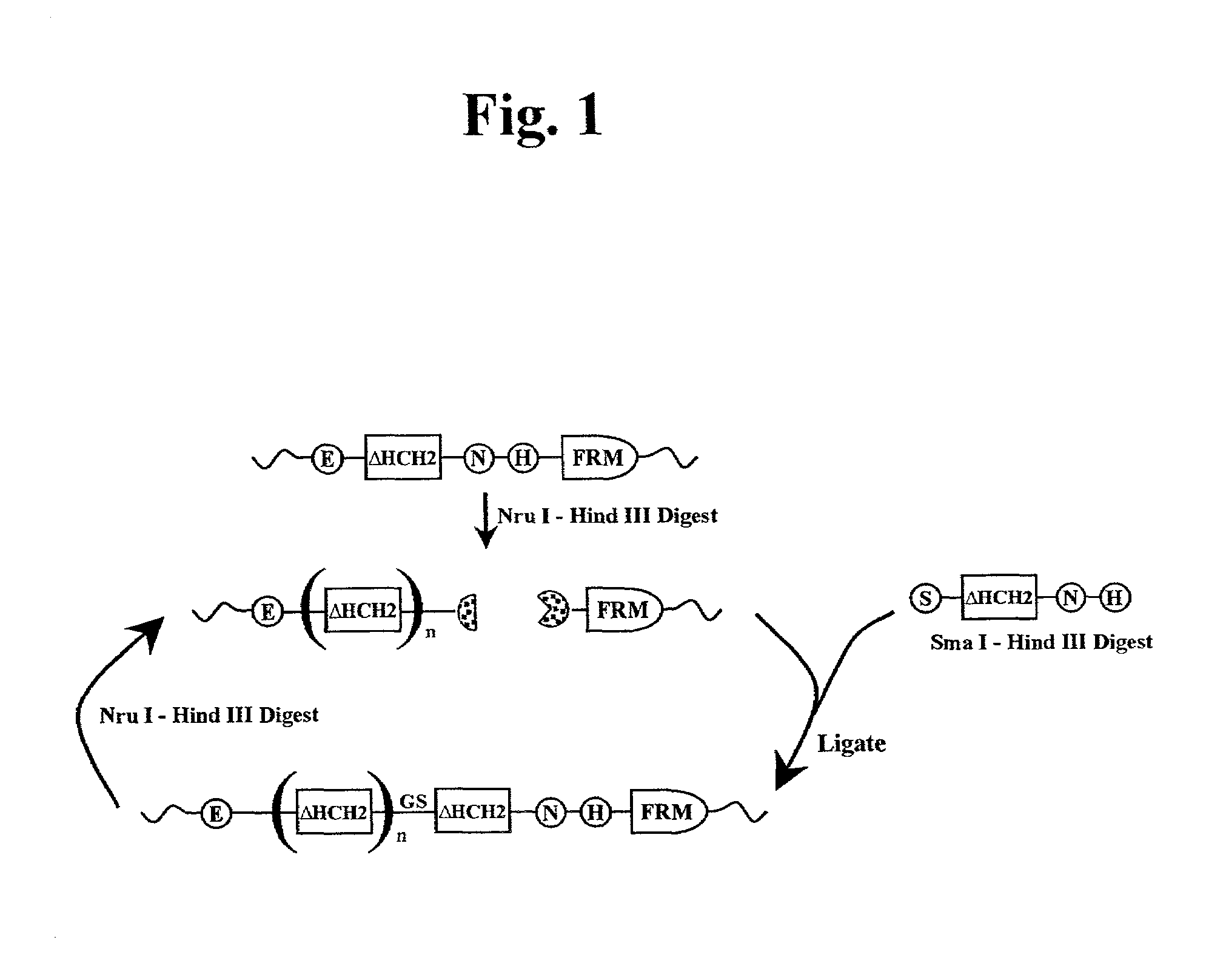
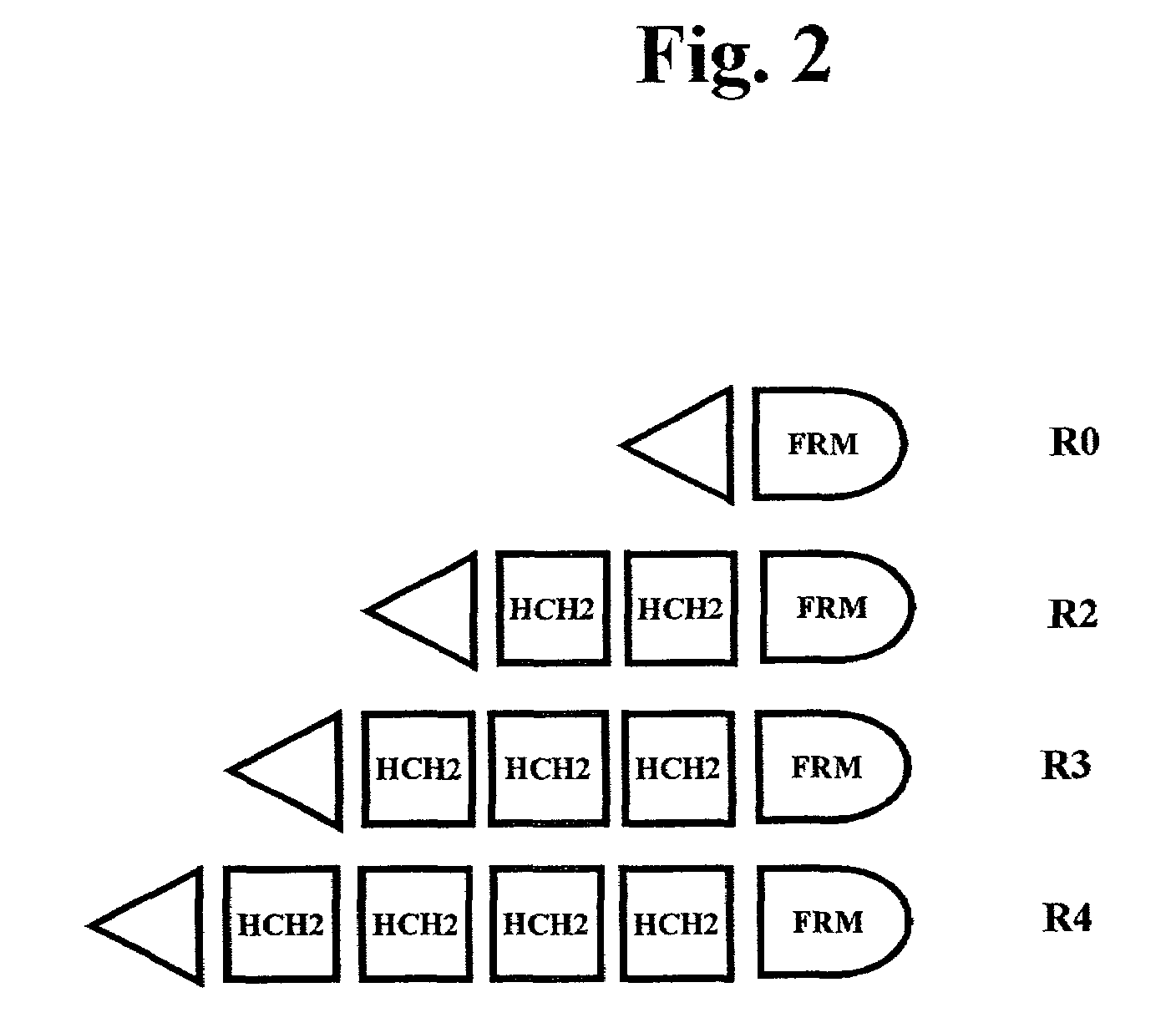
The present invention concerns a family of nucleic acids, polypeptides and cloning vectors which direct expression of fusion proteins that can mimic aggregated IgG (AIG) and immune complex function with respect to their interactions with FcγR and which allow for the inclusion and targeting of a second protein domain to cells expressing FcγR. This was accomplished by expressing multiple linear copies of the hinge and CH2 domains (HCH2) of human IgG1 fused to the framework region of human IgG1. Convenient restriction sites allow for the facile introduction of additional amino-terminal domains. Methods for treating patients using fission proteins are also disclosed. The HCH2 polymers described here represent a new strategy in the design of recombinant proteins for the therapeutic targeting of FcγR in autoimmune disorders.
Owner:ITERATIVE THERAPEUTICS
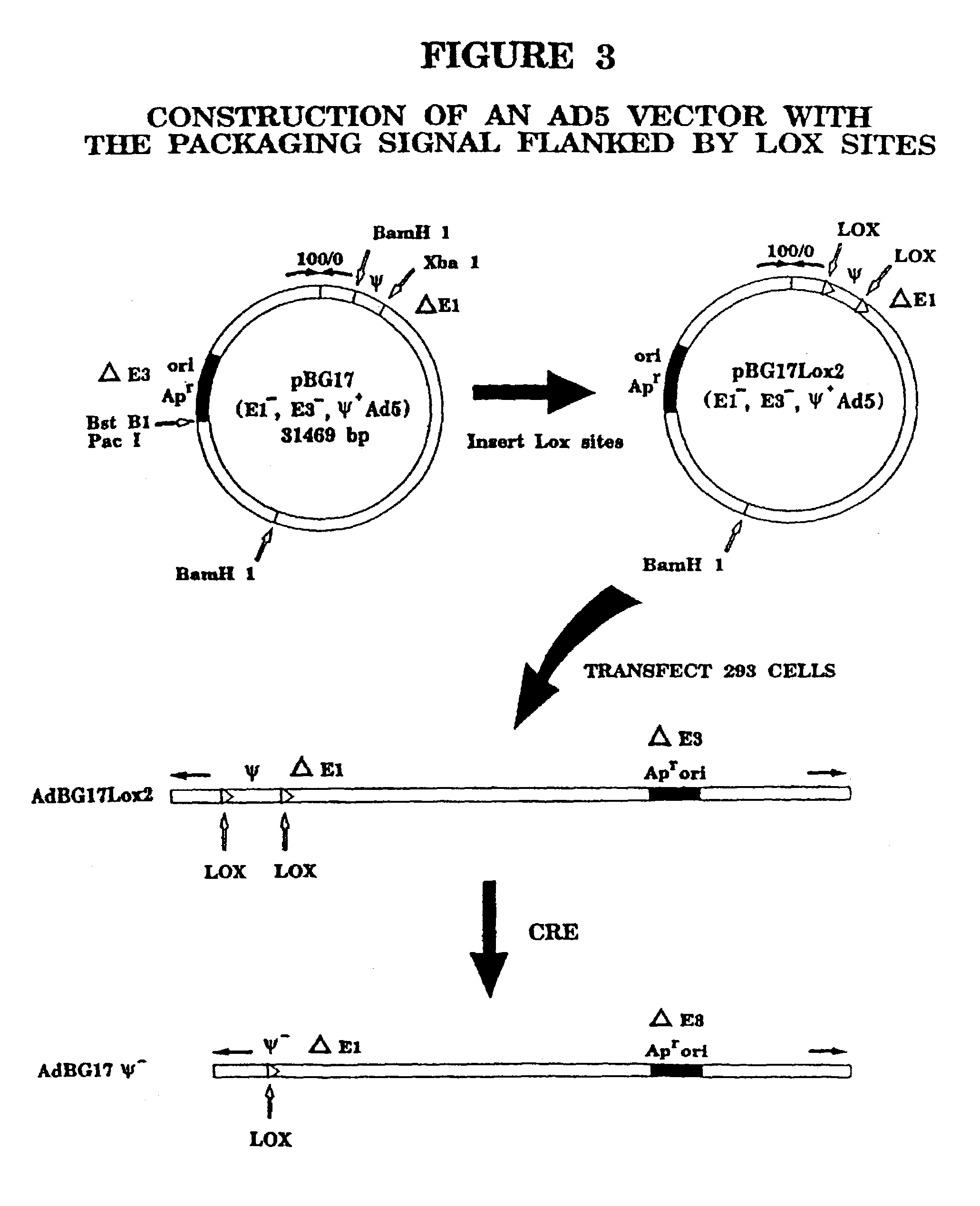
Adenovirus vectors generated from helper viruses and helper-dependent vectors
InactiveUS6080569ALarge capacityReduce in quantityMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic material ingredientsVector systemHelper virus
The present invention provides an improved helper-dependent vector system for production of high capacity adenoviral cloning vectors. The invention makes use of the DNA size packaging constraints imposed on a pIX-defective Ad virion that prevent such virions from packaging DNA larger than approximately 35 kb. This constraint can be used to develop helper viruses that do not package their DNA. In one embodiment, the invention combines this methodology with the Cre-loxP helper-dependent system to decrease the quantity of contaminating helper virus in vector preparations. In another embodiment the invention is used for vector growth.
Owner:ADVEC
Polymeric immunoglobulin fusion proteins that target low-affinity Fcγreceptors
ActiveUS7511121B2Improve effectivenessModerating disease severitySenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsFusion Protein ExpressionLow affinity
The present invention concerns a family of nucleic acids, polypeptides and cloning vectors which direct expression of fusion proteins that can mimic aggregated IgG (AIG) and immune complex function with respect to their interactions with FcγR and which allow for the inclusion and targeting of a second protein domain to cells expressing FcγR. This was accomplished by expressing multiple linear copies of the hinge and CH2 domains (HCH2) of human IgG1 fused to the framework region of human IgG1. Convenient restriction sites allow for the facile introduction of additional amino-terminal domains. Methods for treating patients using fusion proteins are also disclosed. The HCH2 polymers described here represent a new strategy in the design of recombinant proteins for the therapeutic targeting of FcγR in autoimmune disorders.
Owner:ITERATIVE THERAPEUTICS
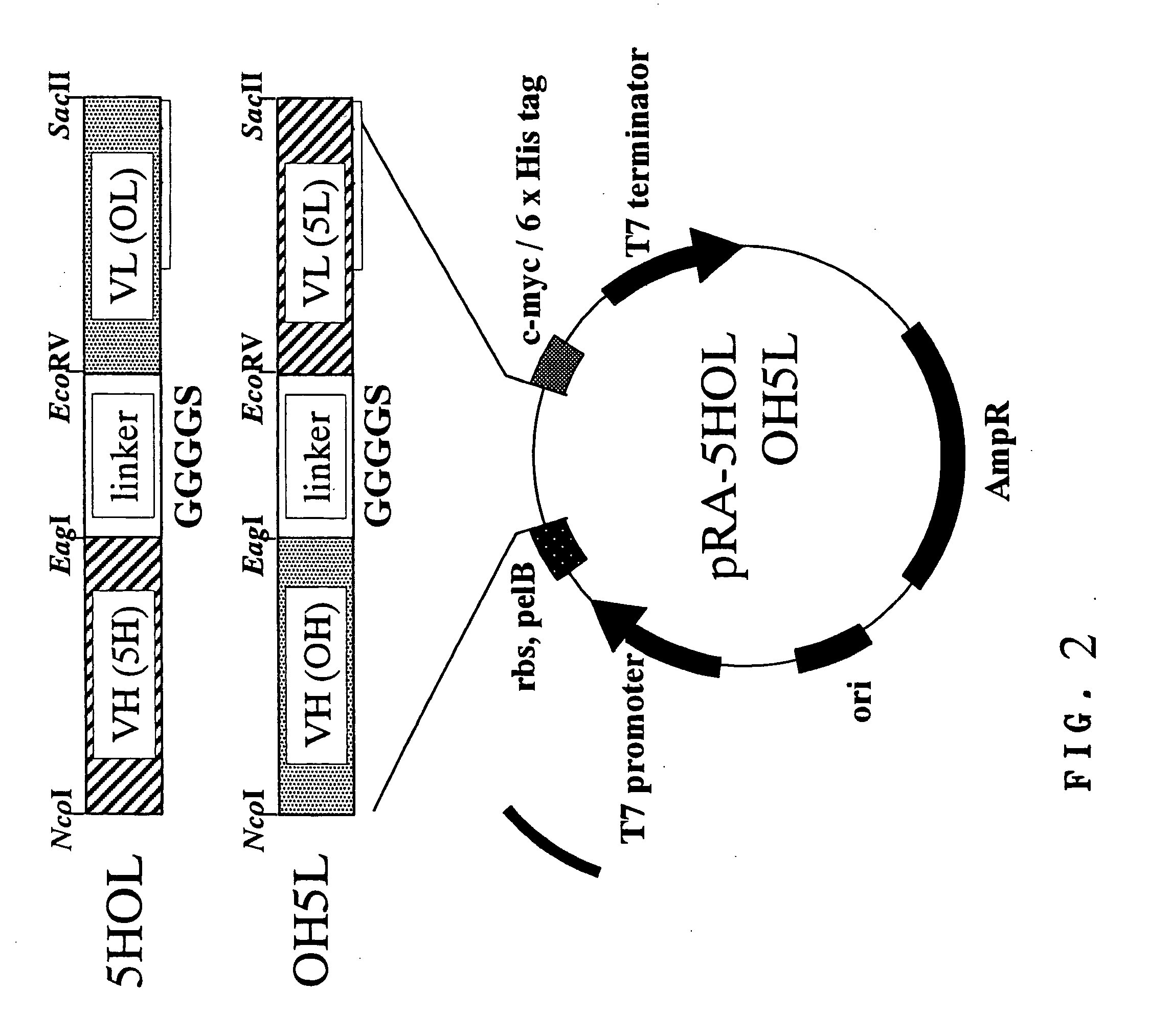
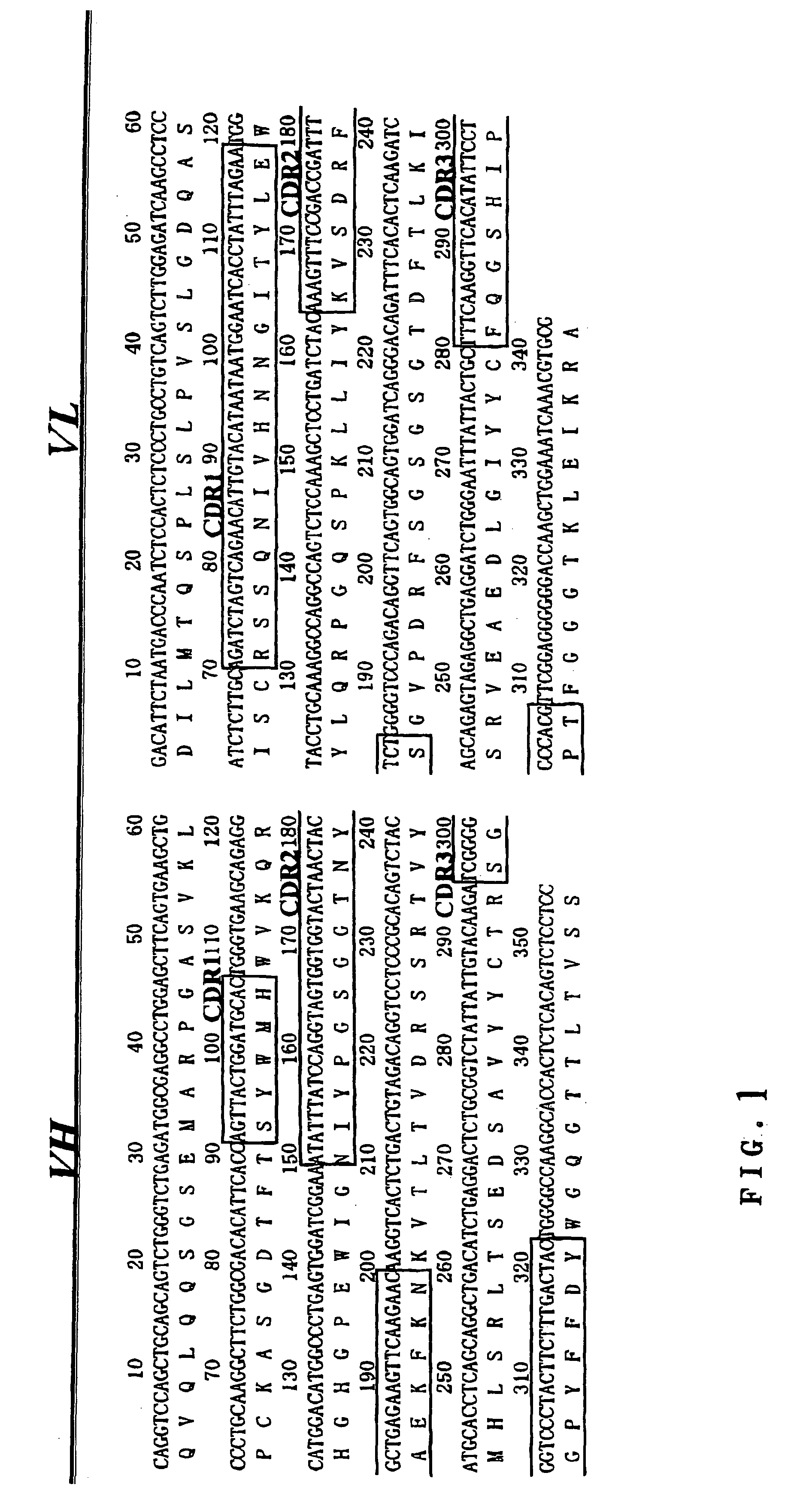
Novel diabody-type bispecific antibody
InactiveUS20060210564A1Increase productionBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsChemical synthesisGenetic engineering
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a diabody-type bispecific antibody, which is characterized by having low immunogenicity and high infiltrating activity into tumor tissues, and by being easily mass-produced at a low cost with use of microorganisms, and by being easily altered in function by means of genetic engineering. The diabody-type bispecific antibody shows a more remarkable effect than the conventional diabody-type bispecific antibodies and chemically synthesized bispecific antibodies even in a very low concentration and in the absence of the super antigen. The present invention is related to a diabody-type bispecific antibody, having a first specificity to a human epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor and a second specificity to a surface antigen expressed by a cell having phagocytosis or cytotoxic activity, a single-chain polypeptide constituting the antibody or each region contained therein, a nucleic acid encoding the polypeptide, a replicable cloning vector or expression vector comprising the nucleic acid, a host cell transformed with the vector, and a pharmaceutical preparation comprising thereof.
Owner:TOHOKU TECHNO ARCH CO LTD
Cloning vectors and their preparation and use for mRNA expression pattern analysis
InactiveUS6303308B1Cost-effective and high throughput analysisAvoid disadvantagesSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCloning SiteCloning vector
Disclosed herein are cloning vectors which include: (a) a cloning site which permits the cloning of a nucleic acid in defined orientation; (b) at least one cleavage site adjacent to the cloning site, the cleavage site being rarely-occurring in nucleic acids; and (c) a long region which is located on the side of the cloning site opposite to the cleavage site (b), wherein the long region and the region between the cloning site and the cleavage site (b) contain neither the cloning site nor at least two frequently-occurring cleavage sites.
Owner:SWITCH BIOTECH
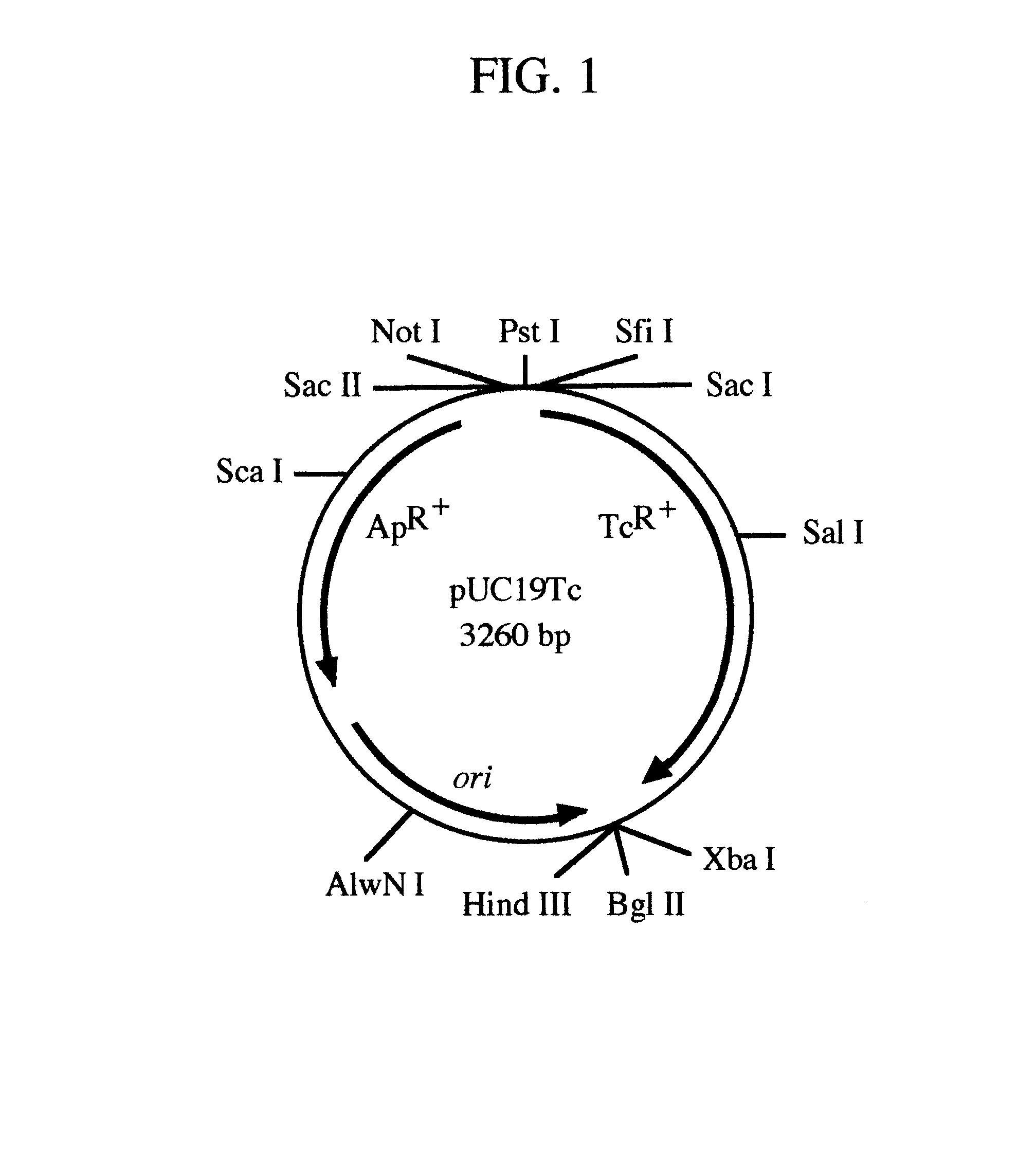
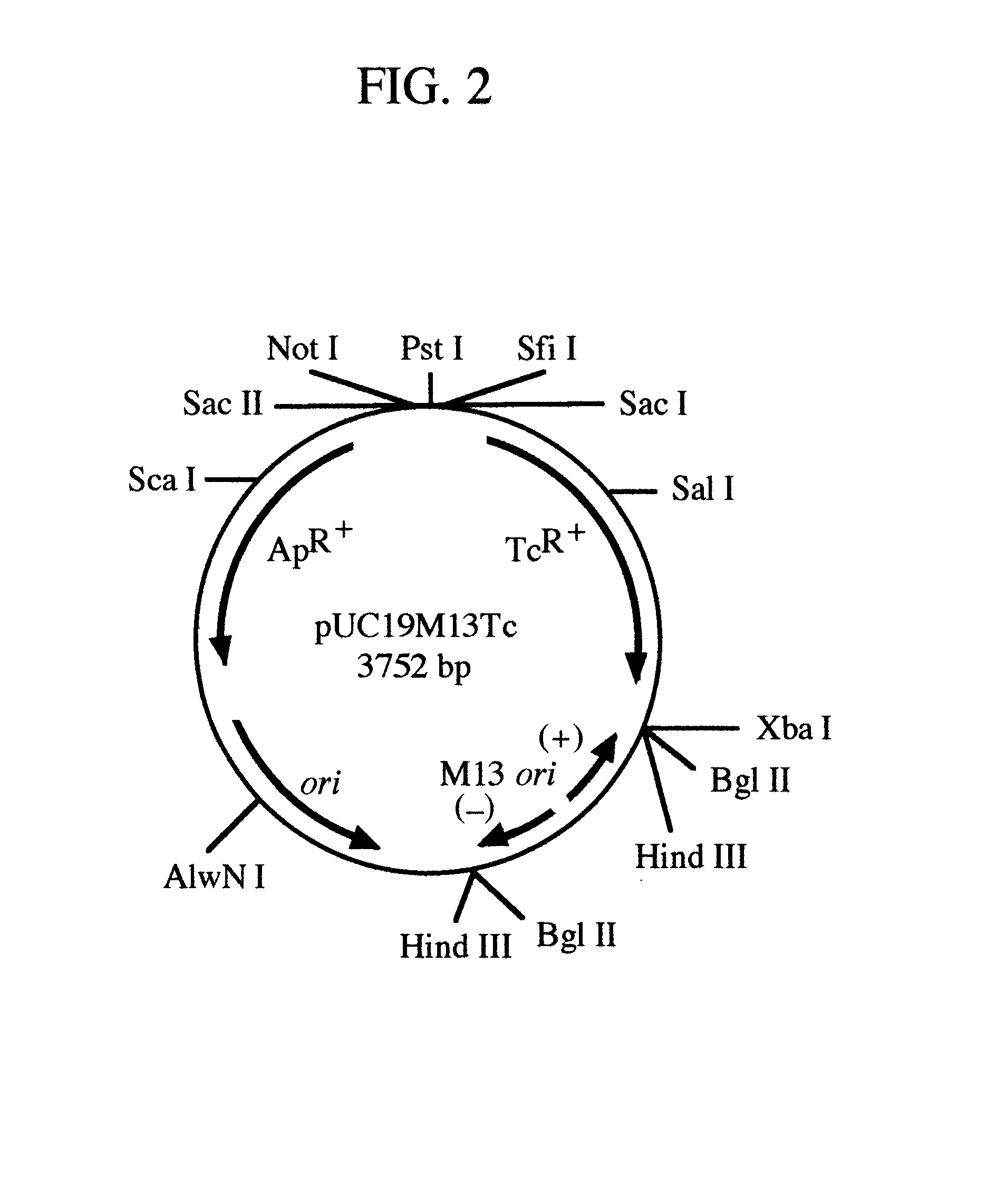
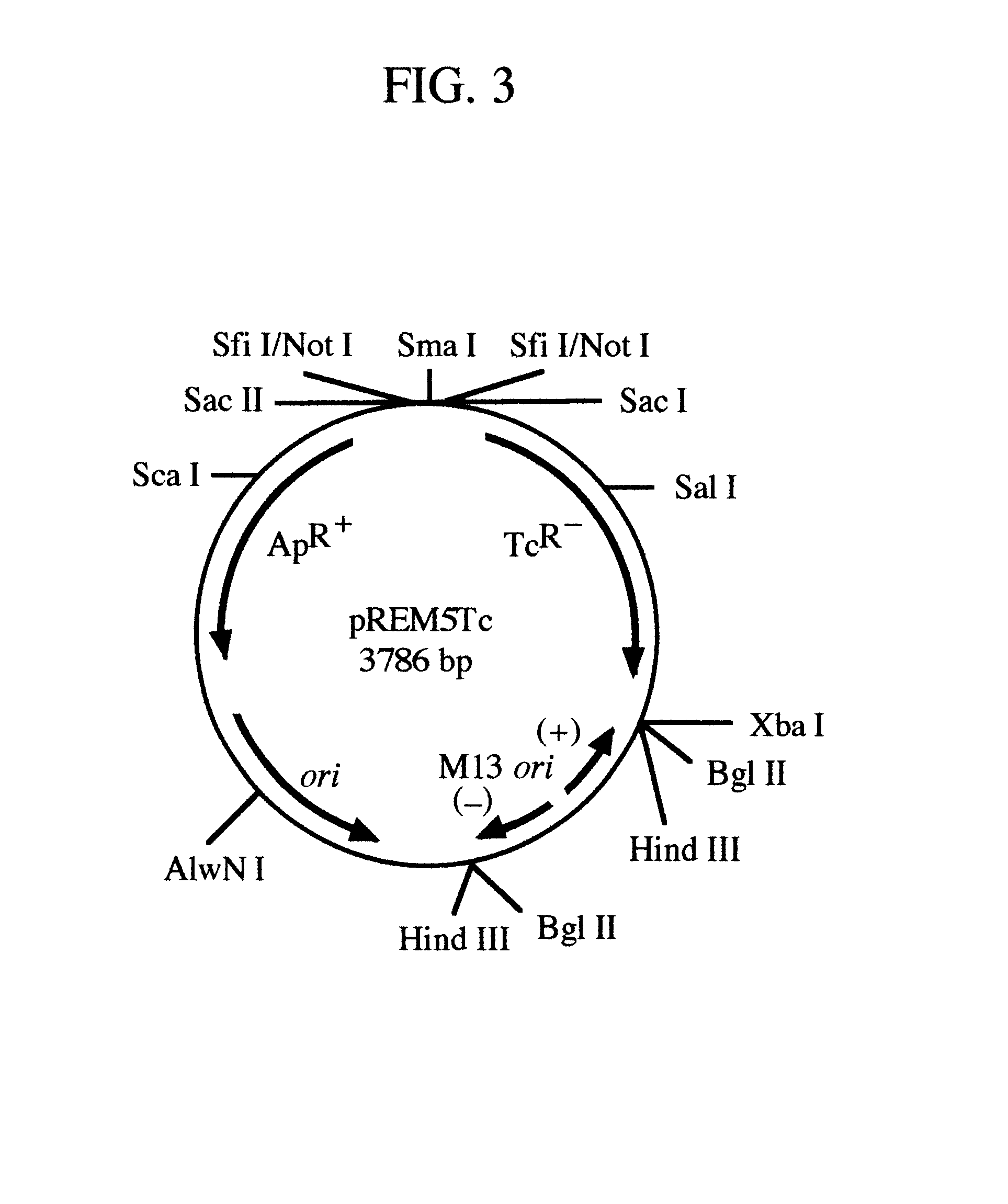
pREM: a positive selection vector system for direct PCR cloning
InactiveUS6544782B1Eliminate and greatly reduce false positive cloneSimple cloningSugar derivativesFermentationEscherichia coliBiology
The present invention describes the development of a positive selection vector based on regulatory element modulation, wherein such modulation is achieved via insertional reconstruction or destruction of a regulatory element controlling transcription, translation, DNA replication and termination. A positive selection cloning vector pREM5Tc has been developed based on insertional reconstruction of a regulatory element of a reporter gene. The vector pREM5Tc carries the tetracycline resistance reporter gene with no functional -35 region of its promoter, a regulatory element, thus resulting in no expression of the tetracycline resistance gene. Hence a host cell carrying the vector pREM5Tc is unable to produce the tetracycline resistance gene protein resulting in inhibition of its growth in presence of tetracycline. An E. coli consensus -35 region is recognized as 5'-TTGACA-3' and a primer used in polymerase chain reaction (PCR) carries at its 5' end the sequence 5'-TGTCAA-3', which is the complementary sequence of 5'-TTGACA-3'. The PCR-amplified DNA fragment is ligated to pREM5Tc thus reconstructing the functional promoter of the tetracycline resistance reporter gene. Subsequent transformation of a host cell with the recombinant vector (carrying an insert DNA) results in production of the tetracycline resistance reporter gene protein that confers resistance to tetracycline thus allowing only the recombinants to grow in presence of tetracycline. The positive selection vector pREM5Tc greatly reduces, if not eliminates, the number of exonuclease-generated false positive clones.
Owner:SYNTHEGEN SYST
Diabody-type bispecific antibody
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a diabody-type bispecific antibody, which is characterized by having low immunogenicity and high infiltrating activity into tumor tissues, and by being easily mass-produced at a low cost with use of microorganisms, and by being easily altered in function by means of genetic engineering. The diabody-type bispecific antibody shows a more remarkable effect than the conventional diabody-type bispecific antibodies and chemically synthesized bispecific antibodies even in a very low concentration and in the absence of the super antigen. The present invention is related to a diabody-type bispecific antibody, having a first specificity to a human epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor and a second specificity to a surface antigen expressed by a cell having phagocytosis or cytotoxic activity, a single-chain polypeptide constituting the antibody or each region contained therein, a nucleic acid encoding the polypeptide, a replicable cloning vector or expression vector comprising the nucleic acid, a host cell transformed with the vector, and a pharmaceutical preparation comprising thereof.
Owner:TOHOKU TECHNO ARCH CO LTD
High fidelity PCR cloning
InactiveUS6566067B2Minimizes number of doublingImprove fidelitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliPolymerase L
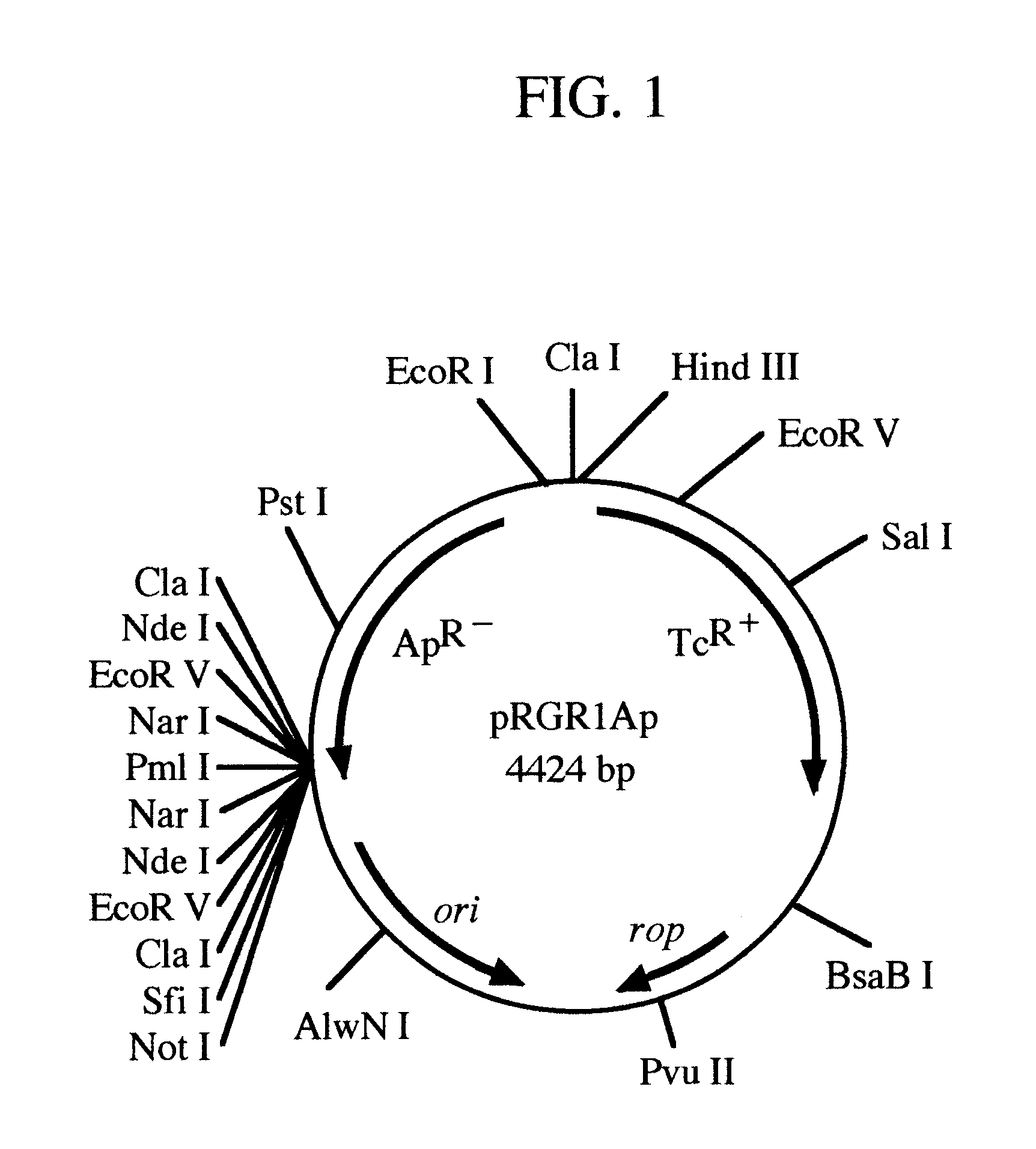
The present invention describes a methodology for generating high fidelity PCR products, and also cloning of such high fidelity PCR products in a suitable vector. Generation of polymerase-induced mutant fraction of target sequences during PCR amplification is linearly proportional to the number of doublings of the target sequences. Thus the high fidelity PCR products are generated by minimizing the number of doublings of the target nucleic acid sequences during PCR amplification. Minimization of number of doublings of the target sequences is achieved by reducing the number of cycles of PCR amplification of the target sequences. The high fidelity PCR products thus obtained are then cloned into a suitable vector. As an example, a 960 bp target sequence from E. coli DNA was PCR-amplified only for 3 cycles, and it was then directly cloned into a positive selection cloning vector pRGR2Ap. The functional analysis of the inserts in all clones showed that the clones carried functionally wild-type DNA fragments, and hence the inserts most probably carry no mutation. Cloning of PCR products obtained from 3 cycles of amplification, instead of 30 cycles of amplification, theoretically achieves 10-fold reduction of mutations in the cloned fragments. The invention also contemplates cloning of a target cDNA obtained by primer extension.
Owner:SYNTHEGEN SYST
DNA modular cloning vector plasmids and methods for their use
A group of modular cloning vector plasmids for the synthesis of a transgene or other complicated DNA construct, by providing a backbone having docking points therein, for the purpose of gene expression or analysis of gene expression. The invention is useful for assembling a variety of DNA fragments into a de novo DNA construct or transgene by using cloning vectors optimized to reduce the amount of manipulation frequently needed. The module vector contains at least one multiple cloning site (MCS) and multiple sets of rare restriction and / or unique homing endonuclease (“HE”) sites, arranged in a linear pattern. This arrangement defines a modular architecture that allows the user to place domain modules or inserts into a PE3 transgene vector construct without disturbing the integrity of DNA elements already incorporated into the PE3 vector in previous cloning steps. The PE3 transgenes produced using the invention may be used in a single organism, or in a variety of organisms including bacteria, yeast, mice, and other eukaryotes with little or no further modification.
Owner:REED THOMAS D +1
Method for acquiring rhodotorula glutinis phenylalanine deaminase gene sequence
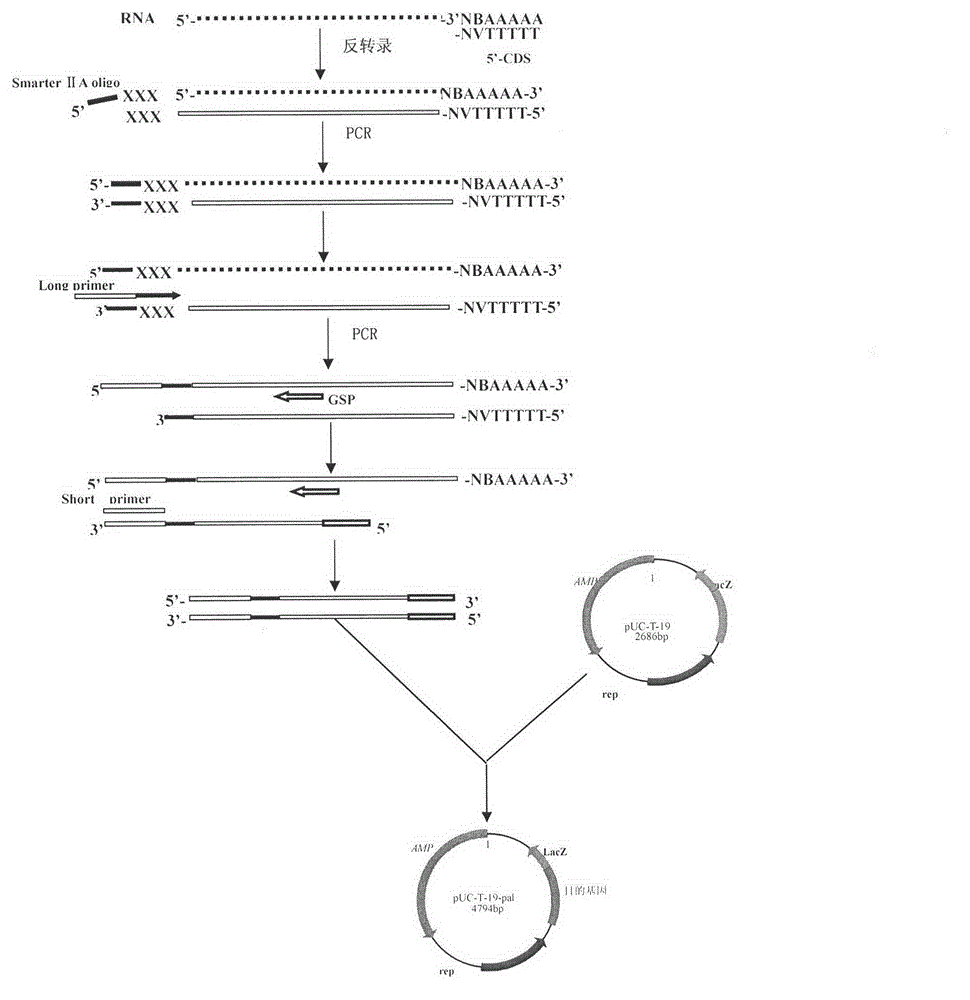
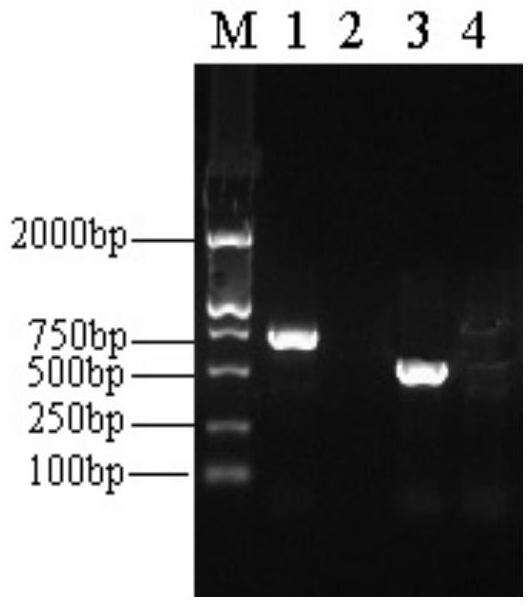
The invention discloses a method for acquiring a rhodotorula glutinis phenylalanine deaminase gene. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting RNA (Ribose Nucleic Acid); carrying out inverse transcription; carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification; establishing a cloning vector pUCm-T-pal; and measuring a sequence to obtain a full-length phenylalanine deaminase gene sequence. The invention belongs to the technical field of gene clone. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of easiness for operation and higher efficiency and success rate.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
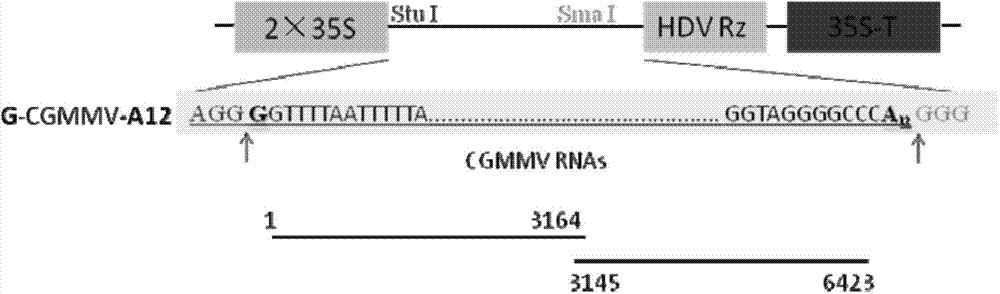
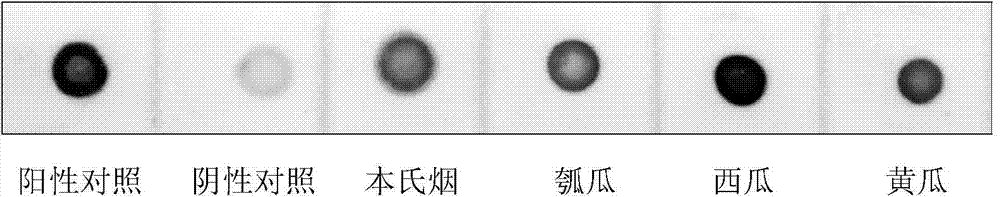
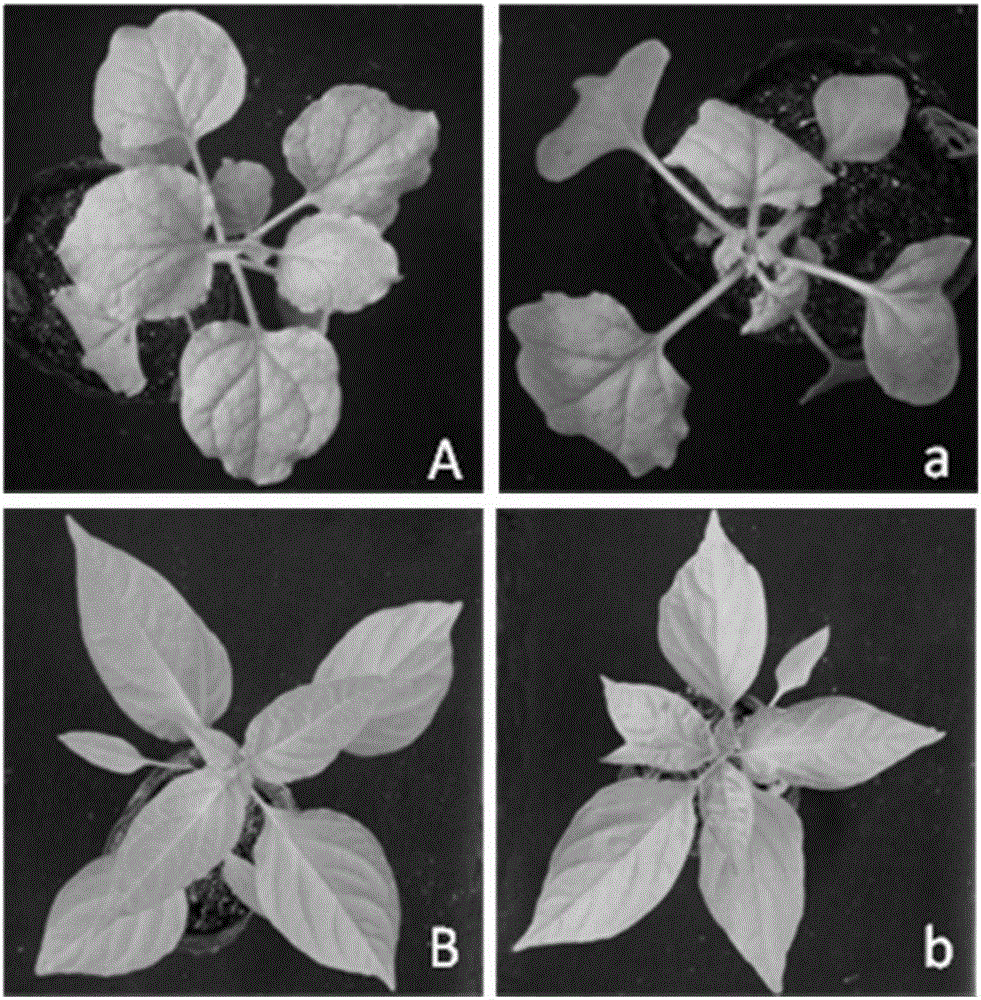
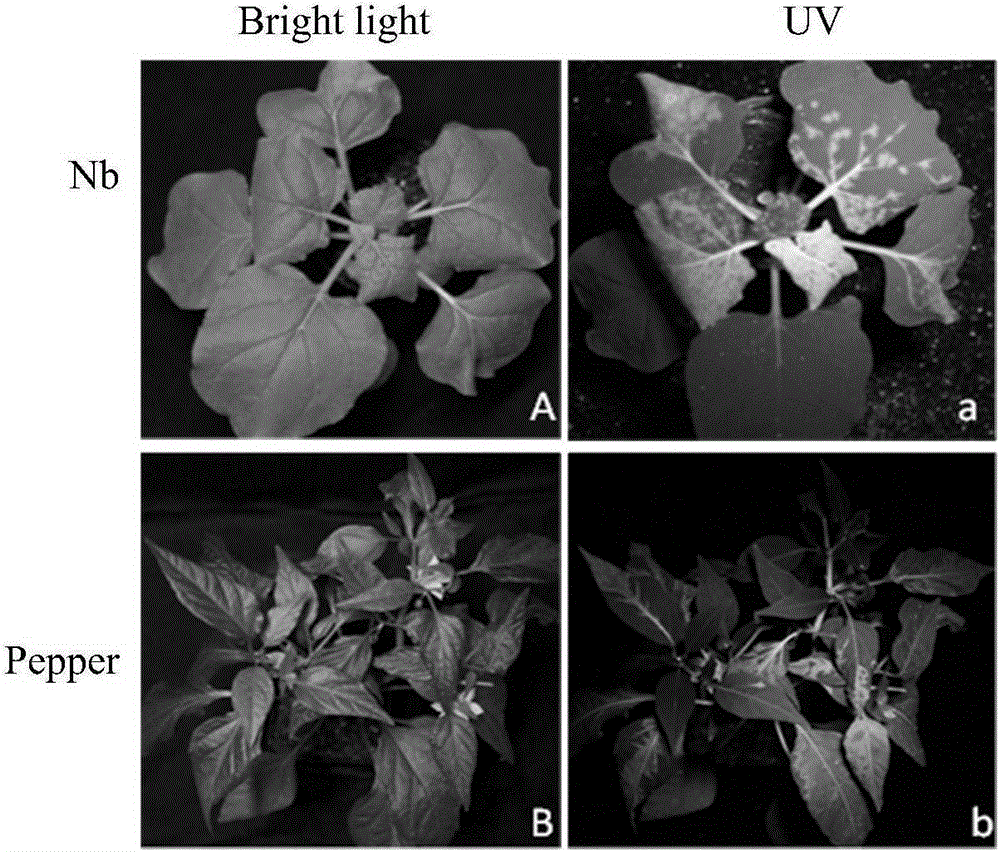
Infectious clone vector of cucumber green mottle mosaic virus (CGMMV), agrobacterium strain and preparation method and application of infectious clone vector of cucumber green mottle mosaic virus (CGMMV)
InactiveCN104498521AInvasive cloneInfestation notBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBacilliCloning vector
The invention relates to preparation of an infectious clone vector of cucumber green mottle mosaic virus (CGMMV) of RNA plant virus, namely, and tobamovirus and analysis of pathogenicity of agrobacterium strain carrying infectious clone of CGMMV. An infectious clone vector of the CGMMV is prepared by fusing the CGMMV with complete sequence into a vector pCB301-CH carrying 35S promoters and ribozyme Rz; the complete sequence of the CGMMV is shown as Seq ID No: 12. The agrobacterium strain can generate massive infectious clones of the CGMMV; the infectious clones only infect plants, rather than insects or animal and human, so that the safety can be ensured.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Transgenic animal model of bone mass modulation
InactiveUS20090023905A1Optimization orderEasy to identifySugar derivativesBone-inducing factorOligonucleotide primersOsteopoikilosis
The present invention relates to methods and materials used to express the HBM protein in animal cells and transgenic animals. The present invention also relates to transgenic animals expressing the high bone mass gene, the corresponding wild-type gene, and mutants thereof. The invention provides nucleic acids, including coding sequences, oligonucleotide primers and probes, proteins, cloning vectors, expression vectors, transformed hosts, methods of developing pharmaceutical compositions, methods of identifying molecules involved in bone development, and methods of diagnosing and treating diseases involved in bone development. In preferred embodiments, the present invention is directed to methods for treating, diagnosing and preventing osteoporosis.
Owner:WYETH LLC
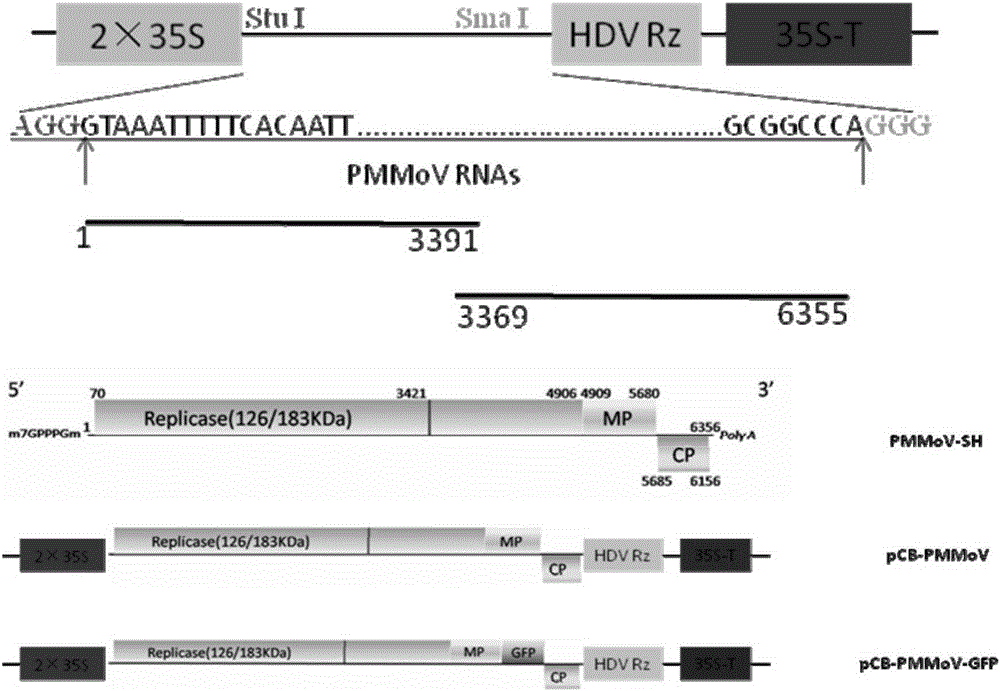
Infectious clone vector of pepper mild mottle virus, agrobacterium tumefaciens strain, method for preparing same and application of infectious clone vector
InactiveCN105219800AInvasive cloneEfficient infectionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPlant virusTobacco mosaic virus
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering, in particular to preparation of an infectious clone vector of a Pepper mild mottle virus (PMMoV) of RNA (ribonucleic acid) plant viruses and tobacco mosaic viruses, pathogenesis analysis on an infectiously cloned agrobacterium tumefaciens strain with the pepper mild mottle virus and exogenous proteins infectiously cloned and expressed by the aid of the PMMoV. The preparation, the pathogenesis analysis and exogenous proteins have the advantages that genomes of Shanghai bay isolate of the pepper mild mottle virus are constructed onto efficient plant expression vectors pCB301-CH by the aid of a genetic recombination process, the recombinant vectors are transferred into the agrobacterium tumefaciens strain by means of electroporation, and accordingly the virus vector with infection ability can be obtained; the plant expression vectors can be constructed by means of infectious cloning, and the exogenous proteins can be efficiently and stably expressed in host plants; mature systems can be provided for studying structures and functions of the virus genomes and studying interaction between the virus and hosts.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Porcine circovirus type 3 genetic engineering subunit vaccine and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a porcine circovirus type 3 (PCV3) genetic engineering subunit vaccine and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: S1, constructing a PCV3cap protein gene cloning vector; S2, carrying out splicing and expression screening on a PCV3cap protein gene cloned by S1, and determining a splicing manner; S3, optimizing a codon for expressing the PCV3cap protein gene screened by S2; S4, fusing and connecting a specific gene segment with the upstream of a PCV3cap protein gene N-end gene optimized by S3; S5, constructing expression engineering bacteria by utilizing the gene recombined by S4, and expressing soluble PCV3cap protein by adopting the expression engineering bacteria, wherein the subunit molecular weight is about 25 kDa; purifying the soluble PCV3cap protein; S6, obtaining purified protein which is circovirus sample particles with the diameter of 17.74 nm to 18.20 nm under an electron microscope, and adding an immunoenhancer into thepurified expression protein to prepare the vaccine. After experiment pigs are immunized by utilizing the vaccine, an antibody, which resists the PCV3cap protein, can be detected, and the PCV3 virus loading amount in blood serum of the experiment pigs can be remarkably reduced in a anti-virus protection experiment; the vaccine has a remarkable protection effect on the experiment pigs.
Owner:荣俊
Method for producing D(-)-tartaric acid or salt thereof by using gene engineering bacteria
The invention relates to a nucleotide sequence from microorganism for coding cis-epoxy succinate hydrase, a cloning vector containing the nucleotide sequence, a recombined host bacterium obtained by transforming the nucleotide sequence and a cis-epoxy succinate hydrase amino acid sequence coded by the recombined host bacterium, and further relates to a method of using the cis-epoxy succinate hydrase to hydrolyze cis-epoxy succinate or salts thereof to prepare D(-)-tartaric acid or salts thereof.
Owner:HANGZHOU BIOKING BIOCHEM ENG
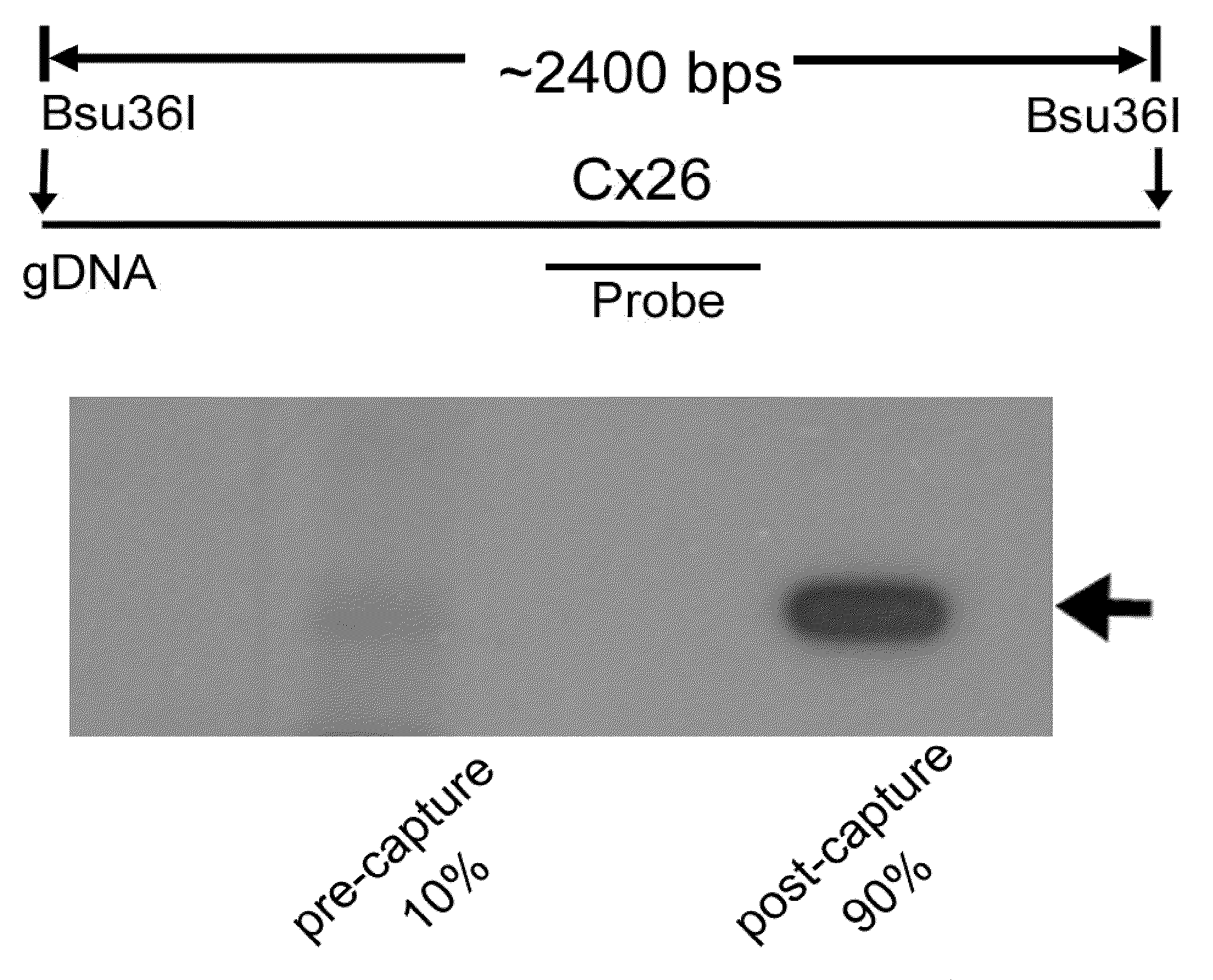
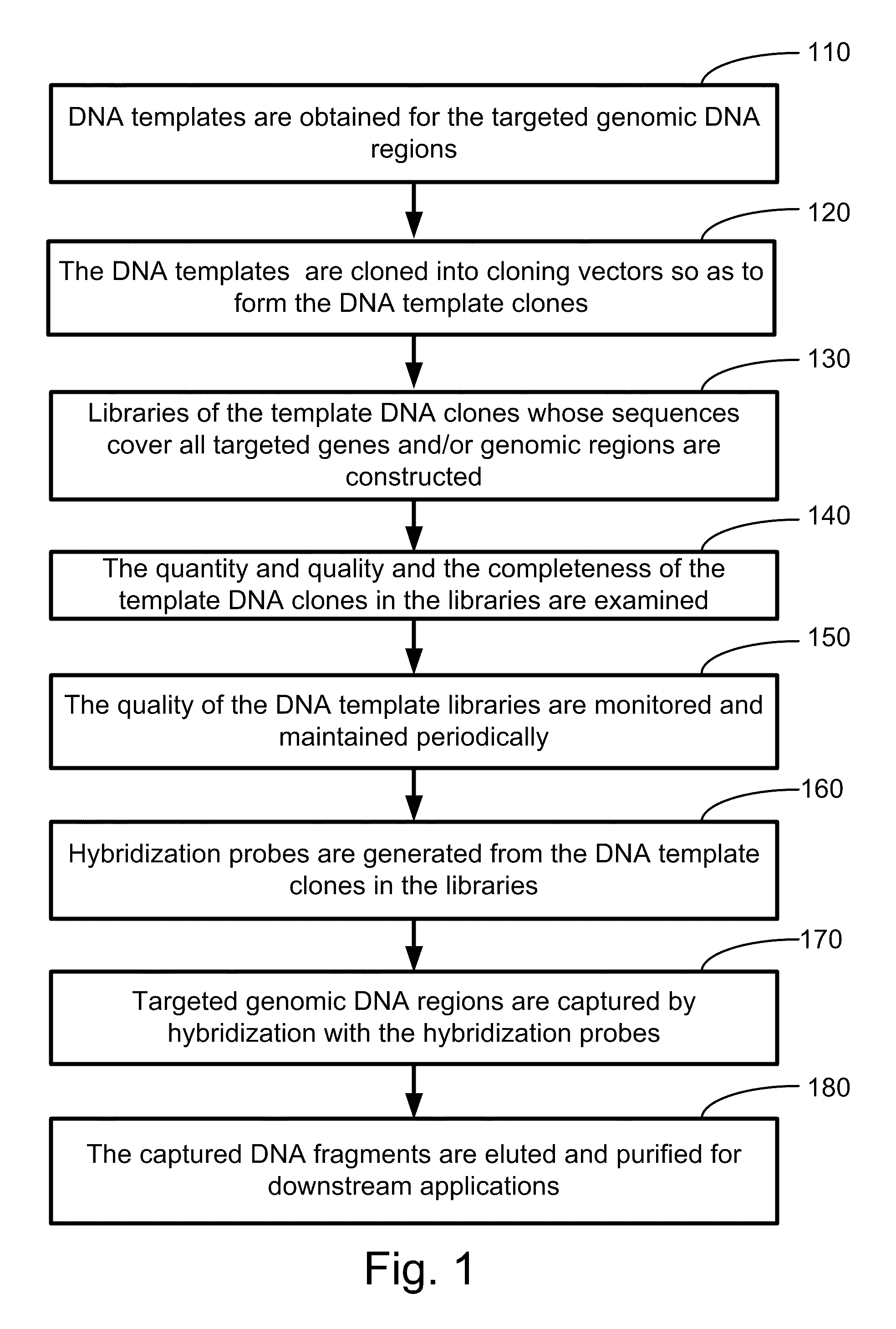
Methods for selectively capturing and amplifying exons or targeted genomic regions from biological samples
InactiveUS20090318305A1Easy to storeEasy amplificationLibrary screeningDNA preparationGenomic SegmentHybridization probe
In one aspect, the present invention relates to a method for selectively capturing and / or amplifying exons or targeted genomic regions from biological samples. In one embodiment, the method includes the steps of obtaining DNA templates for the targeted genomic region, cloning the DNA templates into cloning vectors to form template DNA clones, constructing libraries of the template DNA clones that cover at least the targeted genomic regions, generating hybridization probes from the DNA template clones in the libraries, capturing the targeted genomic DNA regions by hybridizing the targeted genomic DNA samples (fragmented either mechanically or enzymatically) with the generated hybridization probes, and eluting the captured genomic fragments by using conditions for releasing and separating the bound DNA from the hybridization probes.
Owner:LIN XI ERICK +1
Cloning vector and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN105400809ANucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliMultiple cloning site
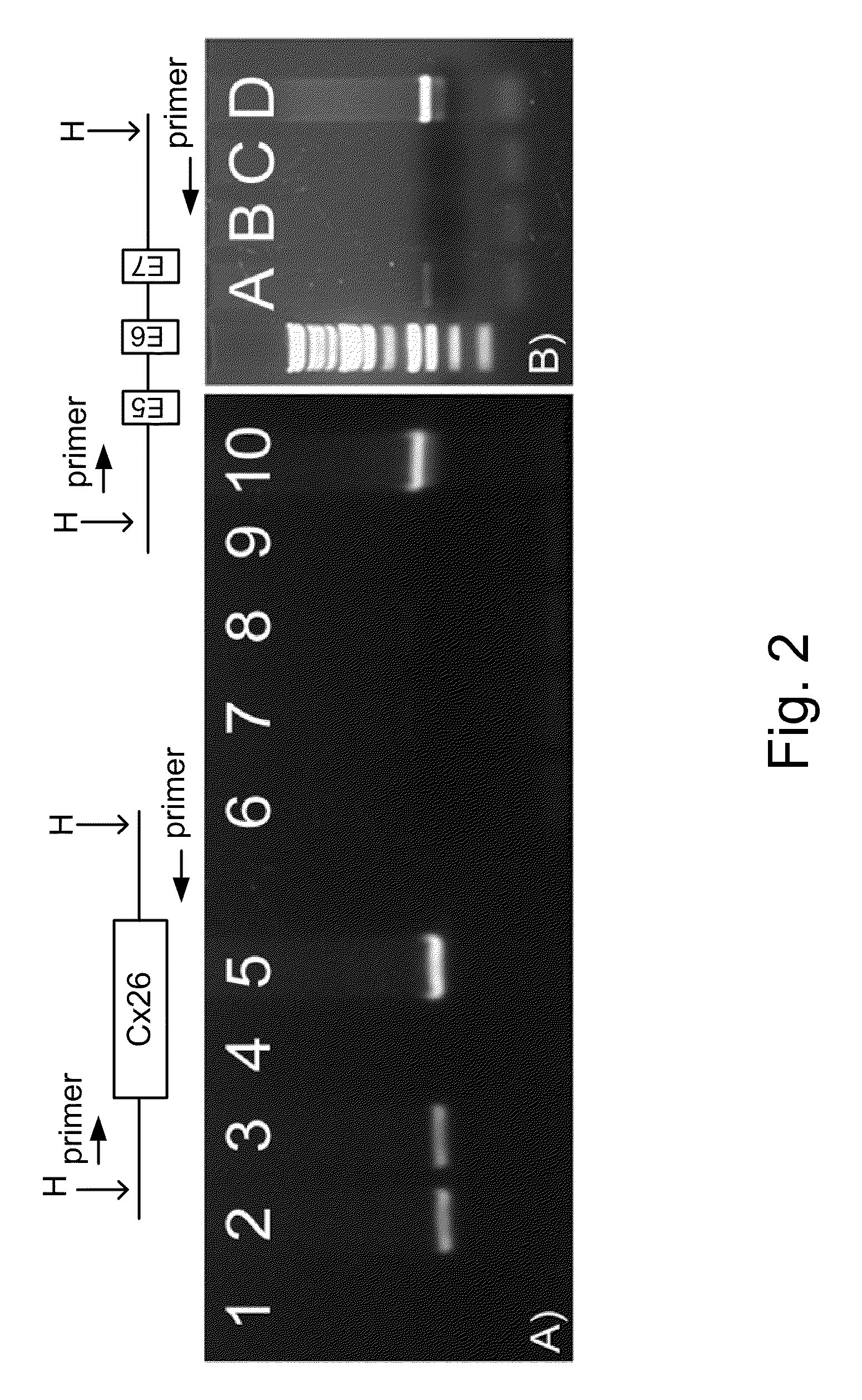
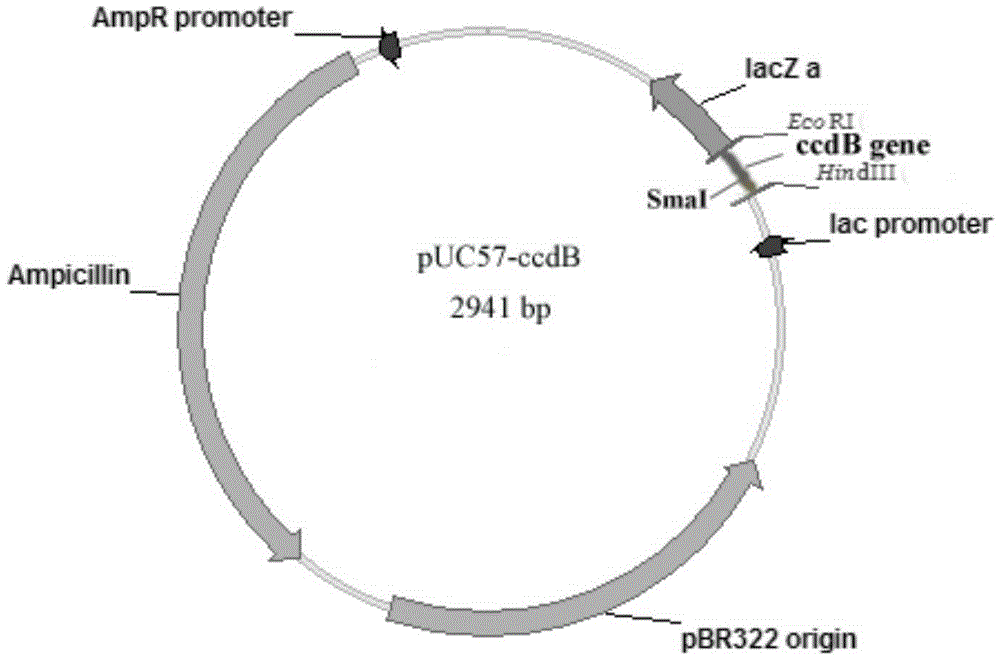
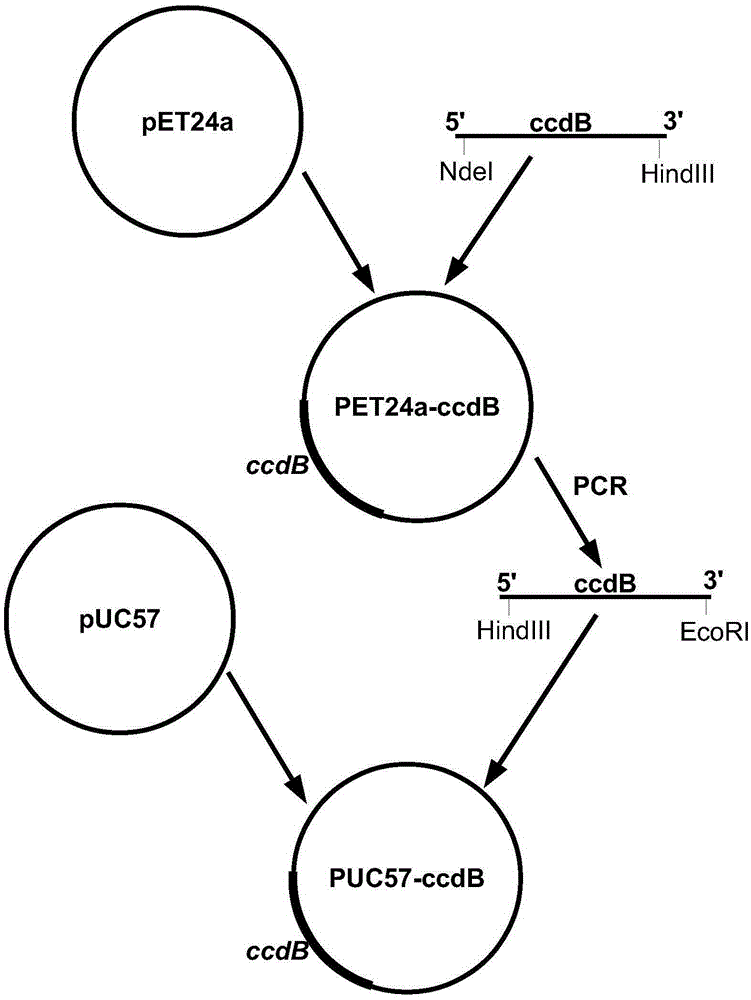
The invention relates to a cloning vector and preparation and application thereof and discloses a cloning vector pUC57-ccdB which is a modified vector with ccdB genes inserted at multiple cloning sites of a pUC57 vector, wherein the ccdB genes have blunt-end restriction enzyme digested recognition sites. By means of the lethal effect of CcdB protein on escherichia coli not containing F plasmids, the ccdB genes having the restriction enzyme Sma I digested sites are inserted on the pUC57 plasmids through the molecular biological technology to obtain the vector pUC57-ccdB. Blunt ends are generated through Sma I digestion and are connected with the genes needing to be cloned so that insertion of the genes needing to be cloned can be achieved. Meanwhile, bacterial colonies with empty vectors are avoided. The cloning vector plays an important role in the fields of molecular biology and genetic engineering.
Owner:生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司
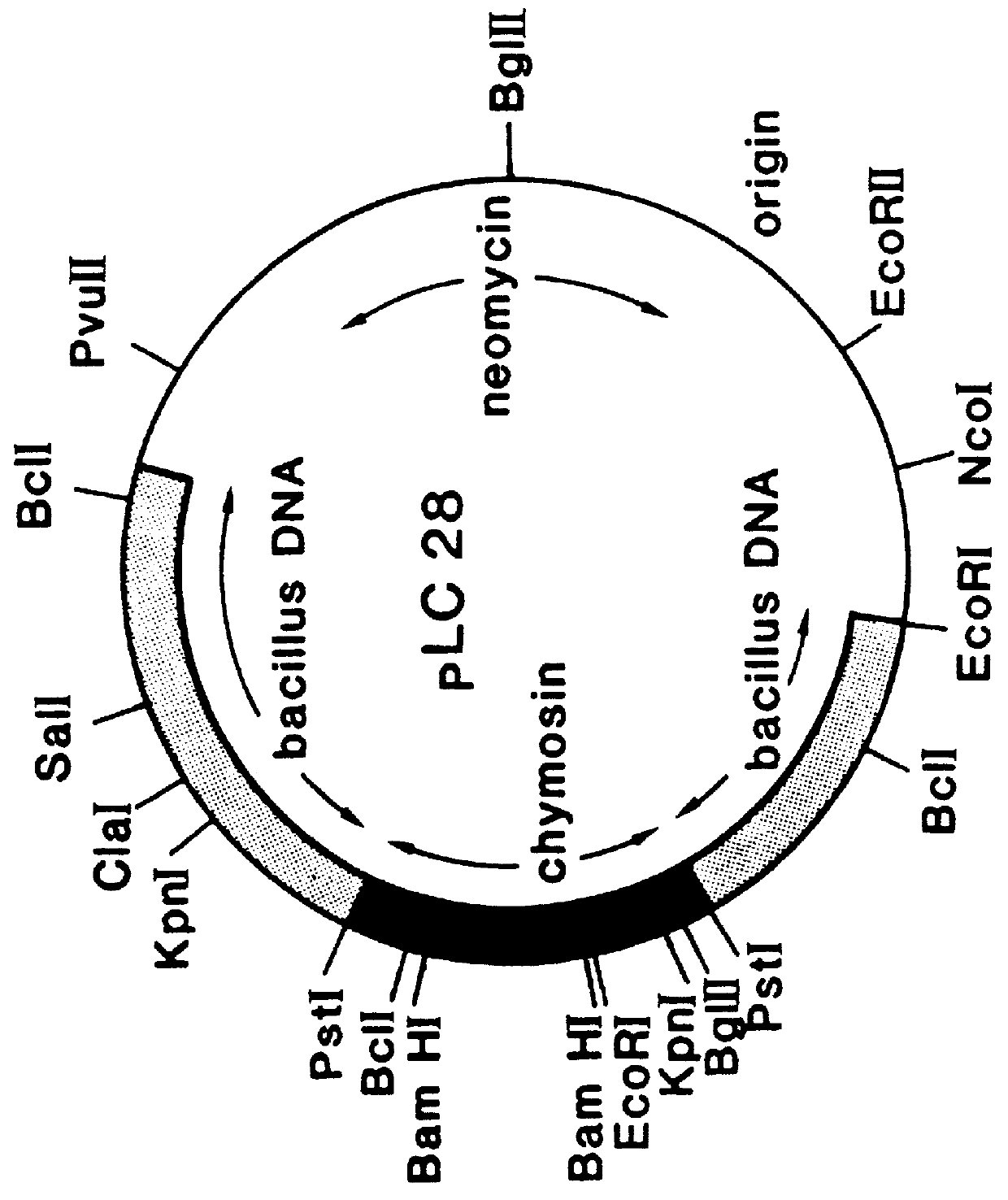
Transformed industrial bacillus strains and methods for making and using them
Novel methods and novel industrial unicellular microorganism strains, particularly industrial Bacillus strains, are provided for enhanced production of endogenous and exogenous polypeptides. Cloning vehicles containing the gene expressing the polypeptide of interest are introduced into a compatible host. Transformed hosts harboring the introduced vehicle in a stable way by integration of the vehicle into the host cells chromosome are selected. Efficient transfer of the vehicle containing the gene of interest is achieved, with the resulting industrial strain transformants being effective, stable producers of the desired polypeptide product.
Owner:GIST BROCADES NV
Traceless cloning and reorganizing method by means of activity of exonuclease
InactiveCN102604982AAvoid introducingBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnzyme digestionDNA fragmentation
The invention provides a traceless cloning and reorganizing method by means of activity of exonuclease, which includes: adding DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sections with the length of 10-30bp identical with that of sequence at two ends of an insertion site of a cloning carrier to two ends of a target gene respectively, then reorganizing with the carrier DNA under the action of the exonuclease, manly during preparing sections of the target gene, adding the DNA sections with the length of 10-30bp identical with the sequence of the two ends of the insertion site of the cloning carrier respectively to the 5' ends of an amplimer. The traceless cloning and reorganizing method has the advantages that (1) enzyme digestion for the target gene or the DNA sections is omitted, enzyme digestion sites inside the target gene or the DNA sections can be ignored, and the target gene or the DNA sections are free of limits by limit incision enzyme identification sites on the carrier; and (2) unnecessary sequence is avoided introducing when the target genes and the DNA sections are connected to the carrier, namely the traceless cloning.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Condon optimized African swine fever virus P54 gene, nucleic acid vaccine and application thereof
InactiveCN103805615ATo solve the immune prevention and controlSame immune effectViral antigen ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsImmune effectsAfrican swine fever
The invention relates to a condon optimized African swine fever virus P54 gene and a nucleic acid vaccine based on the gene, wherein the nucleic acid vaccine consists of an eukaryotic expression vector and the condon optimized African swine fever virus P54 gene. The nucleic acid vaccine is constructed through the following steps of optimizing the condon of P54protein, designing a specific primer, transferring sequence of the artificially synthesized African swine fever virus P54 gene into a cloning vector and recombining the purified P54 gene into the eukaryotic expression vector. The nucleic acid vaccine can be used for preventing the occurrence of African swine fever and is a powerful tool for solving the immune prevention and control of the African swine fever. Compared with the traditional vaccines, the nucleic acid vaccine has the advantages of small quantity, security, long-term effect, stability and convenience in operation when reaching same immune effect.
Owner:孙洁
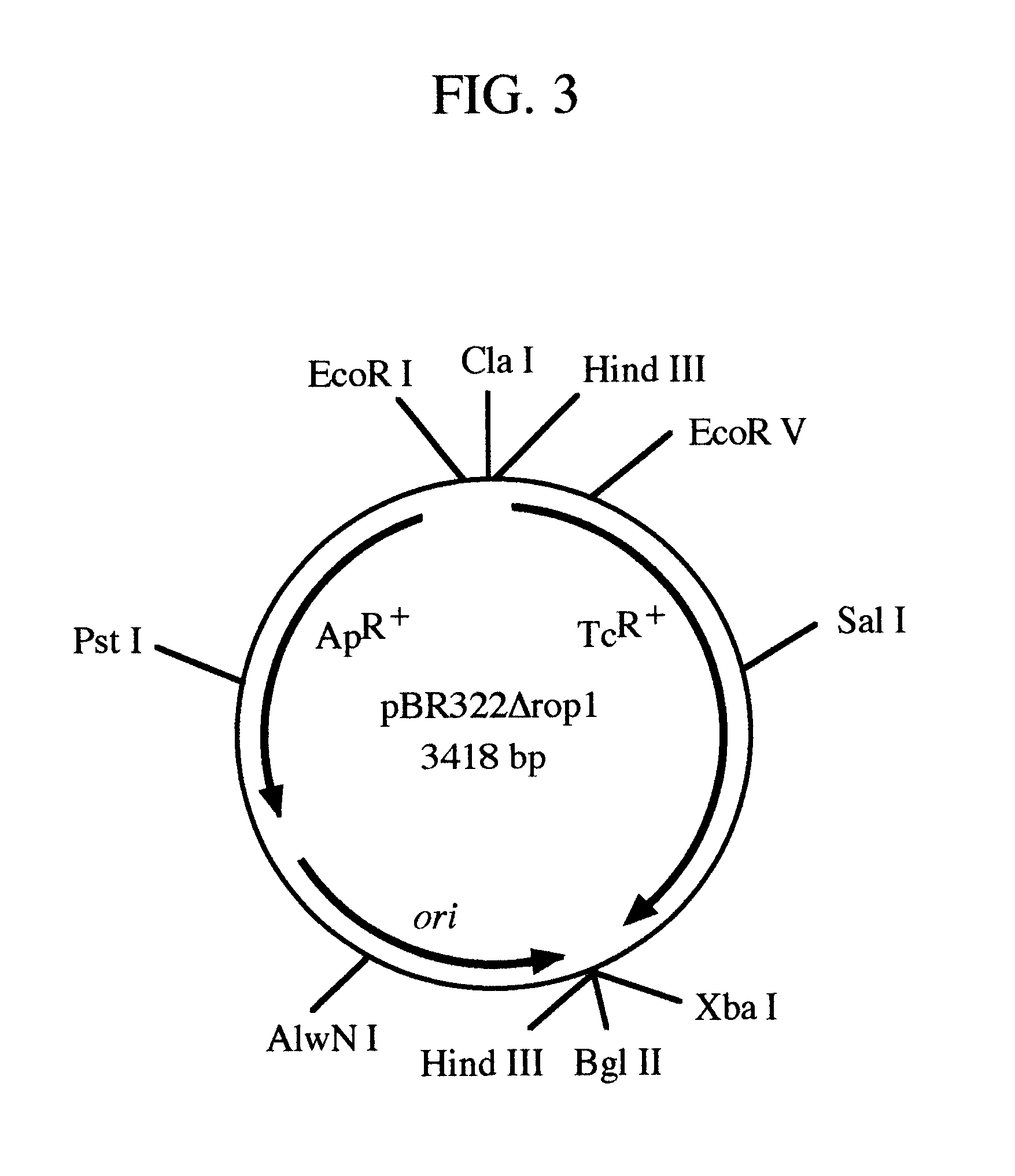
pRGR: a positive selection vector system for direct cloning of PCR amplified DNA fragments
InactiveUS6569678B1Easy extractionEliminate and greatly reduce generationFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionWild typeGene control
The present invention relates to the development of a positive selection vector based on insertional reconstruction of a reporter gene or of a regulatory gene controlling the expression of a reporter gene. The cloning vector carries a reporter gene or a regulatory gene with a mutation rendering the reporter or the regulatory gene protein functionally inactive. A primer carrying a nucleic acid sequence that corrects the mutation is used during PCR amplification of a targeted nucleic acid sequence, and the amplified DNA fragment is then ligated to the said vector thus reconstructing the wild-type reporter or regulatory gene.
Owner:SYNTHEGEN SYST
Methods for dynamic vector assembly of DNA cloning vector plasmids
A method for using cloning vector plasmids to produce DNA molecules, such as transgenes, in a single cloning step. The transgenes can be used for the purpose of gene expression or analysis of gene expression. The plasmid cloning vectors are engineered to minimize the amount of manipulation of DNA fragment components by the end user of the vectors and the methods for their use. Transgenes produced using the invention may be used in a single organism, or in a variety of organisms including bacteria, yeast, mice, and other eukaryotes with little or no further modification.
Owner:REED THOMAS D
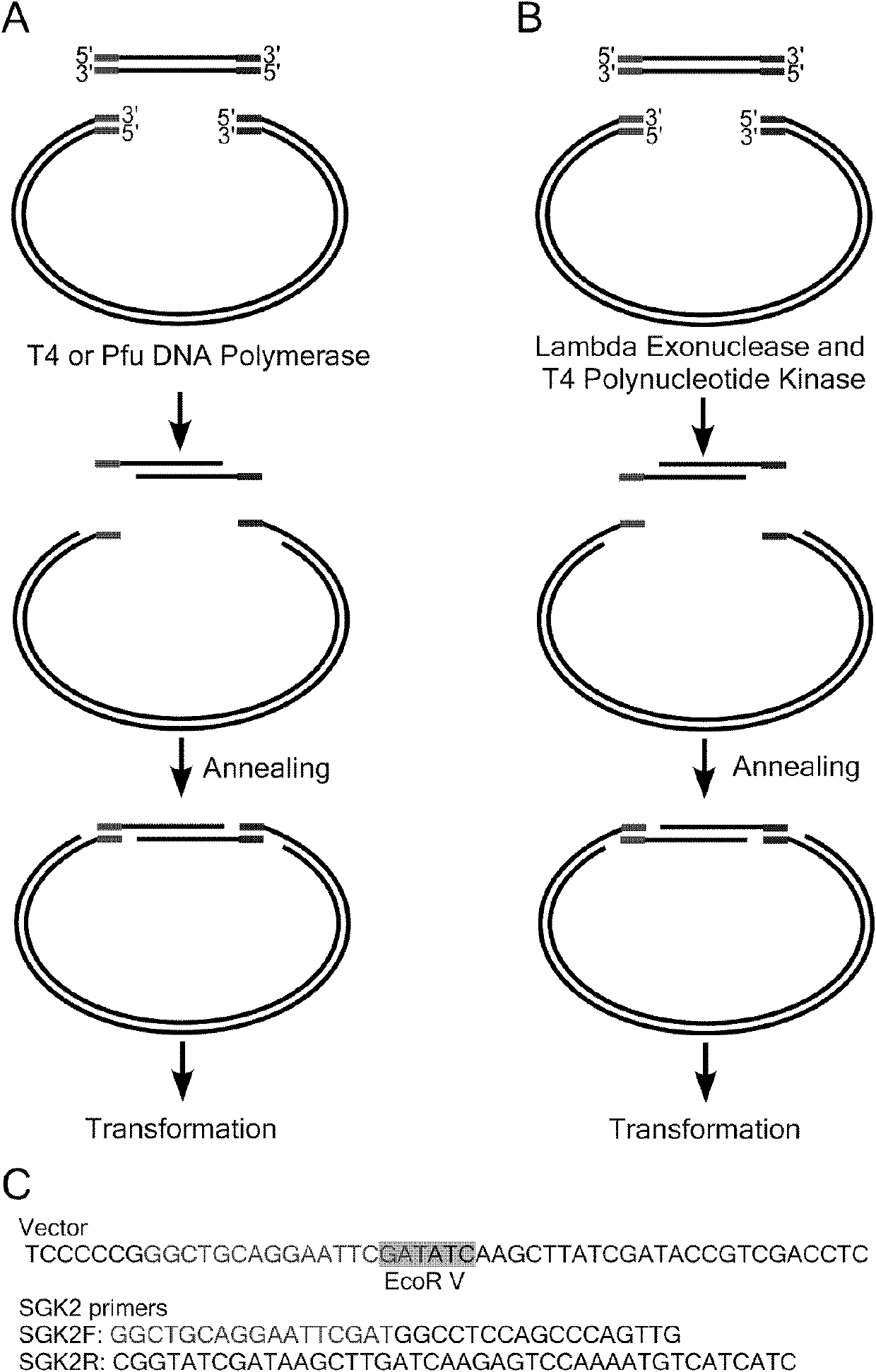
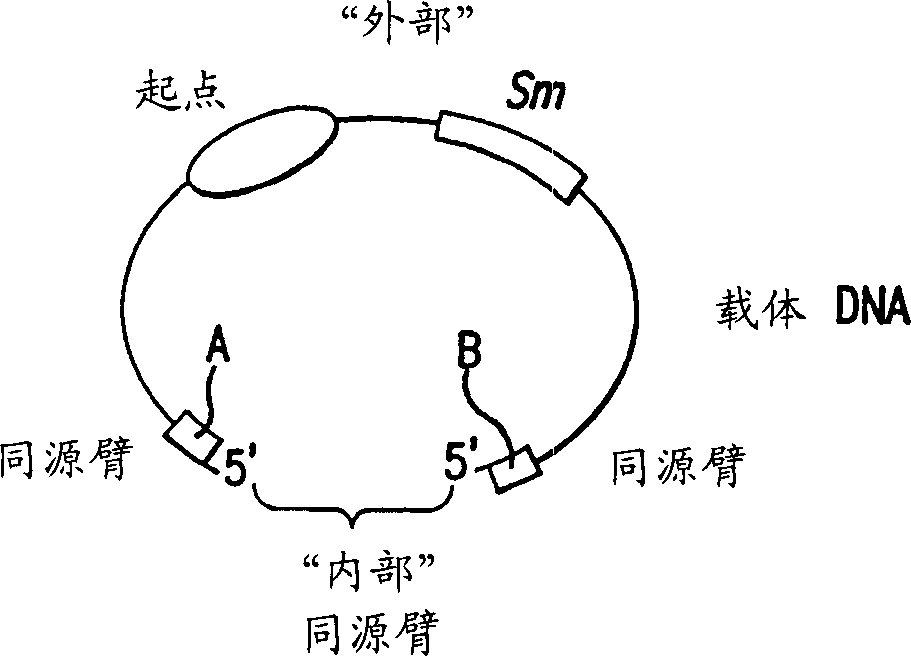
Method and compositions for directed clonning and subclonning using homologous recombination
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for DNA subcloning using bacterial recombinase-mediated homologous recombination technology. The present invention relates to methods of cloning, compositions containing polynucleotides used as cloning vectors, cells containing the polynucleotide compositions, and cloning kits mediated by bacterial recombinases such as RecE / T and Redα / β.
Owner:EURO LAB FUER MOLEKULARBIOLOGIE EMBL
Helper dependent adenovirus vectors based on integrase family site-specific recombinases
InactiveUS7045347B2Practical and convenientLarge capacityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideIntegrasesSite-specific recombination
This invention provides helper-dependent adenovirus cloning vectors and helper adenoviruses, and methods for making and Using such preparations, wherein the helper adenoviruses contain recombinase target sites that are useful in reducing the level of contamination of helper virus in helper-dependent adenovirus vector preparations.
Owner:ADVEC
Preparation method of water-soluble human collagen VI polypeptide
InactiveCN102061296AGood water solubilityProtect from UV raysConnective tissue peptidesPeptide preparation methodsEscherichia coliSolubility
The invention provides a preparation method of a water-soluble human collagen VI polypeptide, which comprises the following steps: linking coding genes of the human collagen VI polypeptide into a cloning vector, transforming Escherichia coli, constructing engineering bacteria, inducing the engineering bacteria to express the human collagen VI polypeptide, and respectively establishing an engineering bacteria fermentation process and a target protein purification process. The protein electrophoretic analysis and activity verification indicate that the molecular weight of the human collagen VI polypeptide is 46kDa, and the human collagen VI polypeptide is soluble in supernatant, has favorable water solubility and exists in the form of a monomer or polymer. The human collagen VI polypeptide in vitro can protect cells from ultraviolet injury, and has the functions of diminishing inflammation and moistening. The invention realizes a large-scale gene engineering preparation method of a water-soluble human collagen VI polypeptide.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Gene encoding beta-glucosidase
InactiveCN101363026AAvoid pollutionSolve the world energy crisisEnzymesGenetic engineeringBeta-glucosidaseNucleotide
The invention provides a gene of coded beta-glucosaccharase, which is called Unbgl1B and is obtained by constructing Metagenome DNA library of uncultured microorganisms of alkality contaminated soil and by the detecting and screening method of the activity of the beta-glucosaccharase of clone library, so as to be one of the following nucleotide sequences: 1) DNA sequences and partial sequence thereof in sequence 1 of a sequence table; 2) DNA sequences having more than 80% of homoeology compared with the DNA sequences defined by the sequence 1 of the sequence table. The DNA in the sequence 1 of a sequence table is DNA sequences of a pGEM-3Zf(+) part of a cloning vector and DNA of exogenetic uncultured microorganisms cloned on the vector, and the exogenetic DNA segment consists of 838 basic groups; the GC content of the gene is 54.3%. The gene is used for producing the beta-glucosaccharase, so as to dissociate cellobiose into single glucose molecule.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Primer group, kit and method for identifying tachysurus fulvidraco and leiocassis longirostris hybrid species
InactiveCN105695590AEfficient managementMonitor negative impactsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAquaculture industryA-DNA
The invention provides a primer group for identifying a male parent and a female parent of tachysurus fulvidraco and leiocassis longirostris hybrid species. The primer group comprises a primer pair for amplifying COI genes and a primer pair for amplifying an ITS sequence, wherein the primer pair for amplifying COI genes consists of a primer COIF and a primer COIR; the primer pair for amplifying an ITS sequence consists of a primer ITSF and a primer ITSR. The invention also provides a kit which is for identifying the male parent and the female parent of tachysurus fulvidraco and leiocassis longirostris hybrid species and comprises the primer group. The kit also comprises any one or more of the following reagents: a buffer solution for PCR, dNTP, heat-resistant DNA polymerase, a cloning vector, a DNA ligase, and a buffer solution for ligation. The invention also provides a method for identifying the male parent and the female parent of tachysurus fulvidraco and leiocassis longirostris hybrid species. The primer group, the kit or the method can be used for accurately identifying the male parent and the female parent of the tachysurus fulvidraco and leiocassis longirostris hybrid species, thus effectively managing a breeding plan and monitoring negative influence thereof, and has great significance in sustainable development of aquaculture industry.
Owner:YANGTZE RIVER FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com