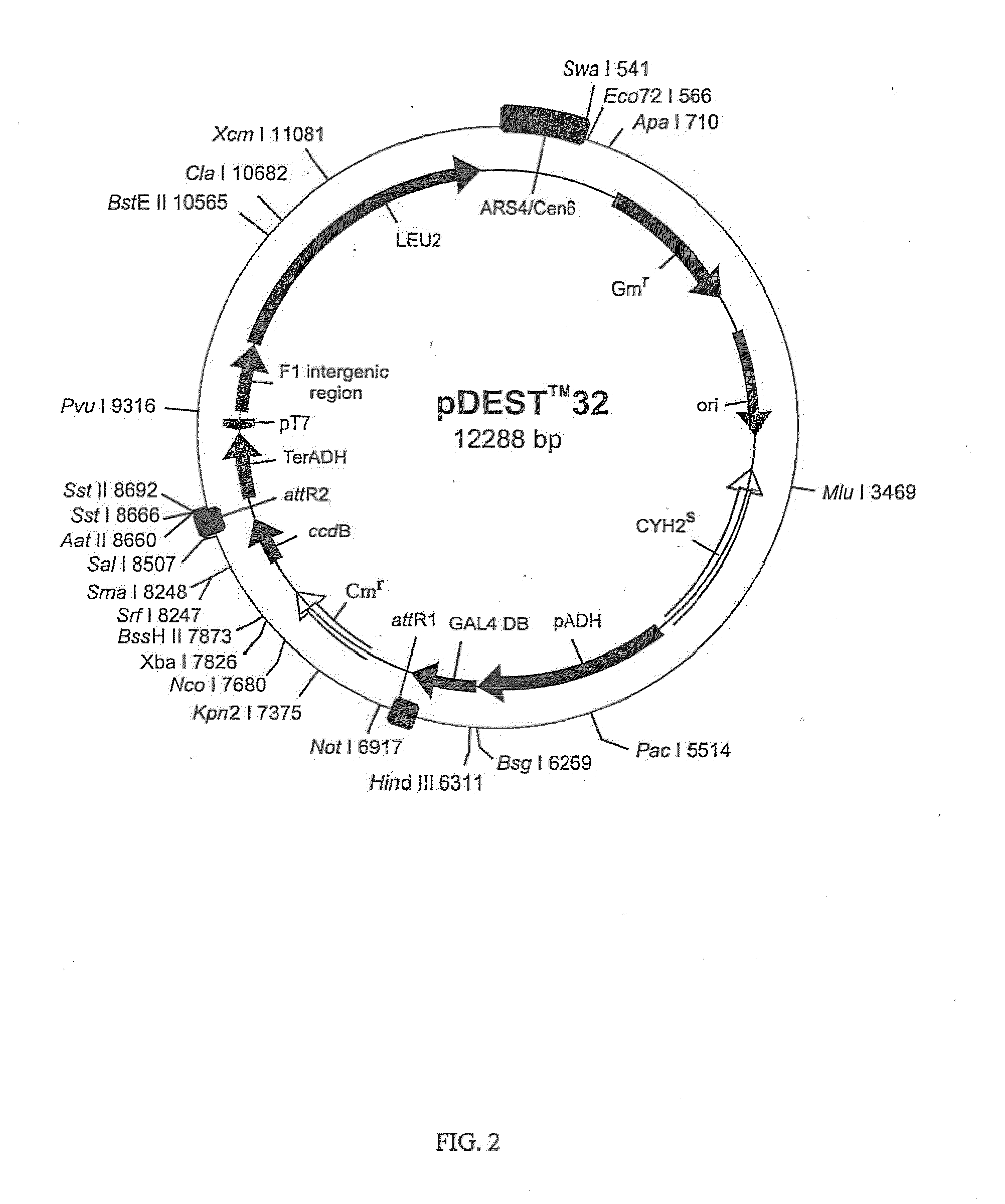
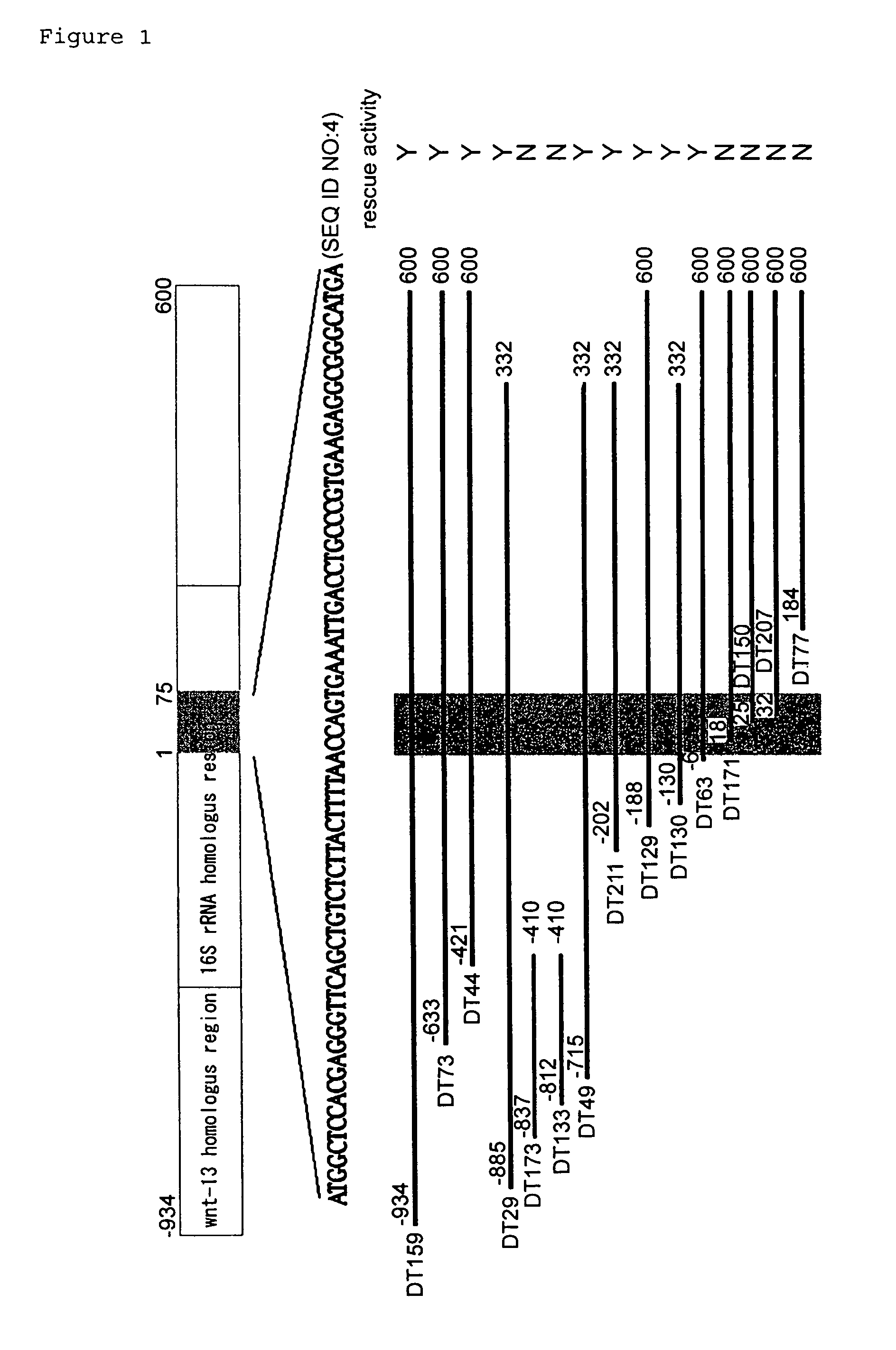
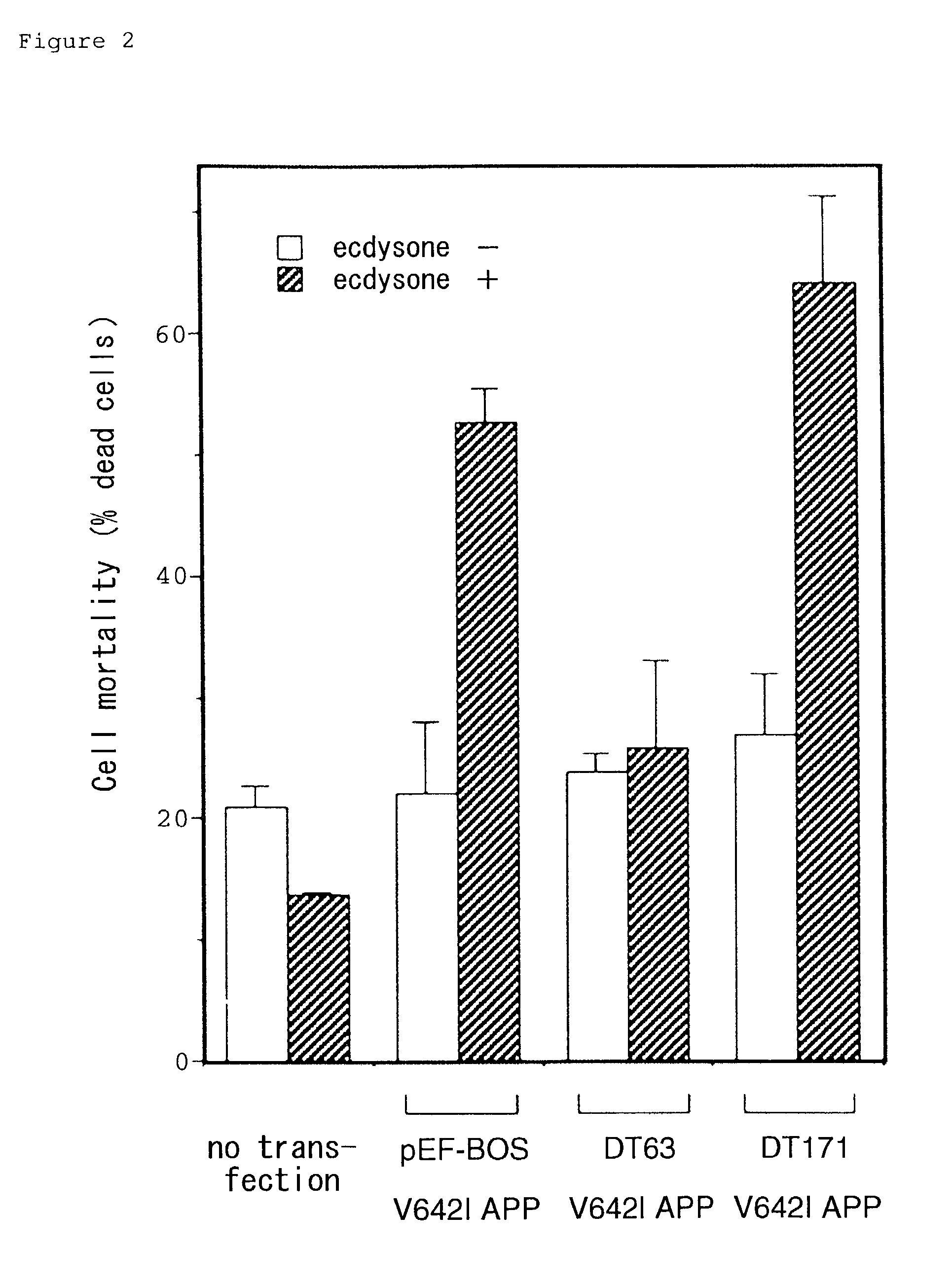
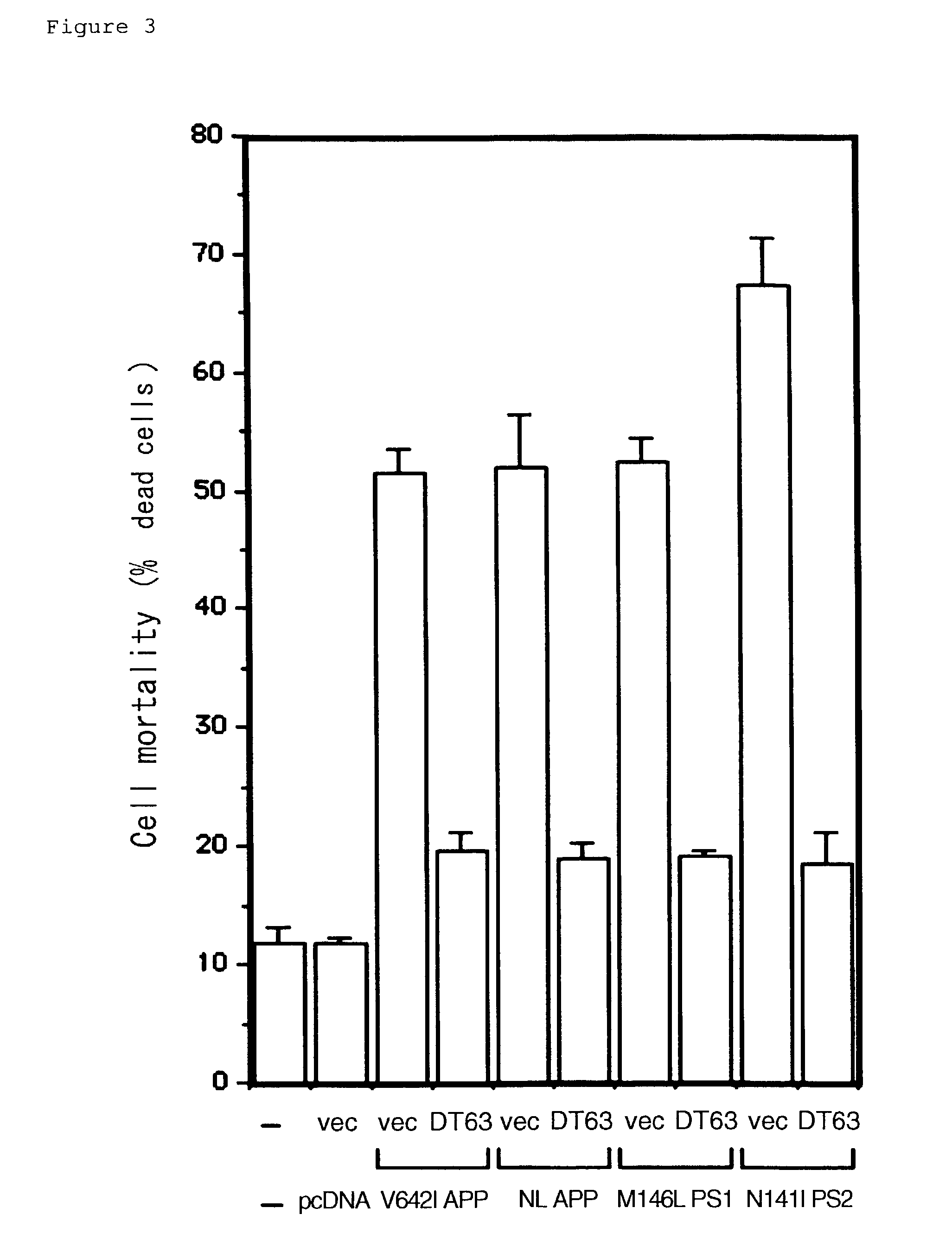
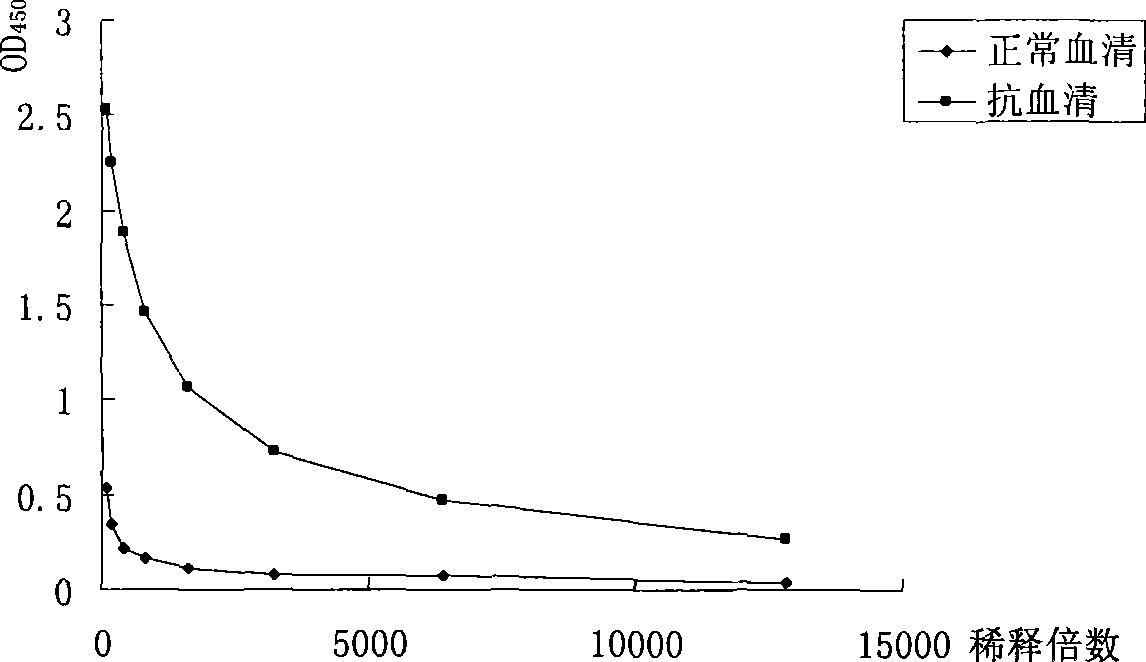
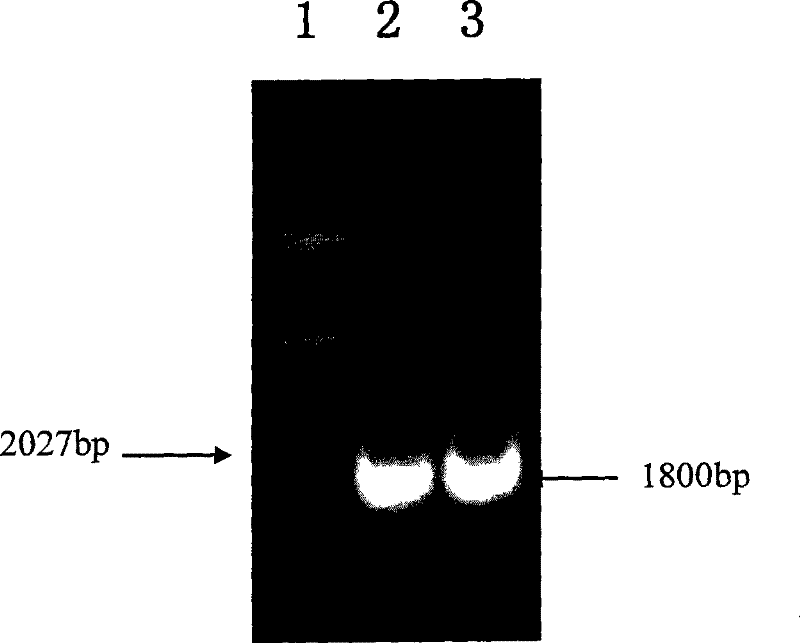
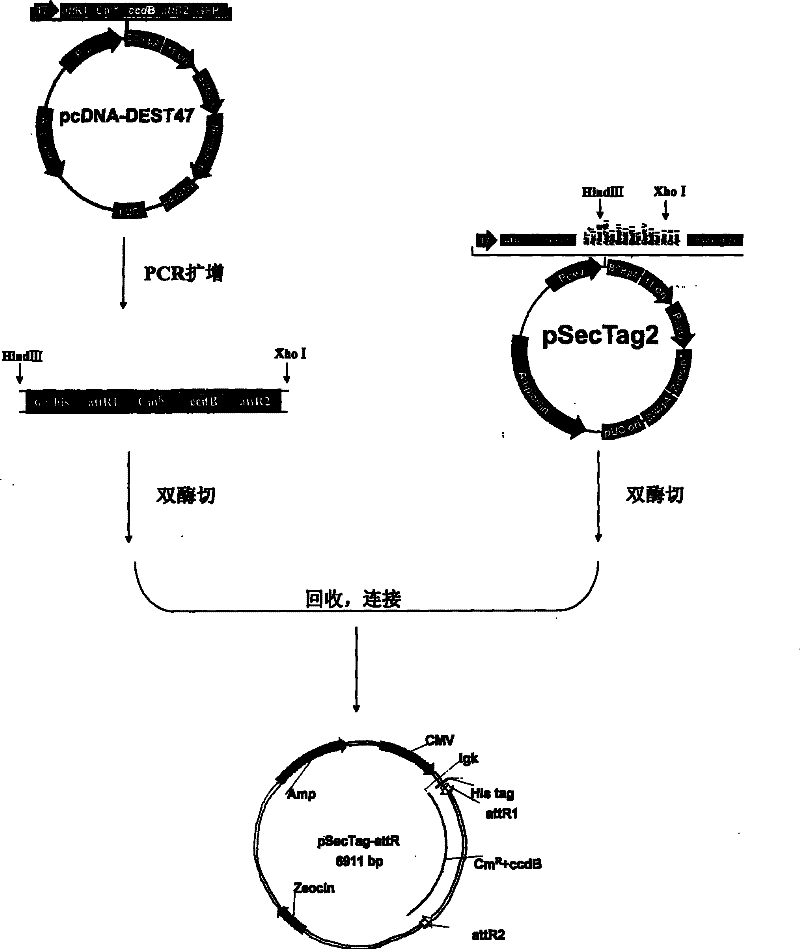
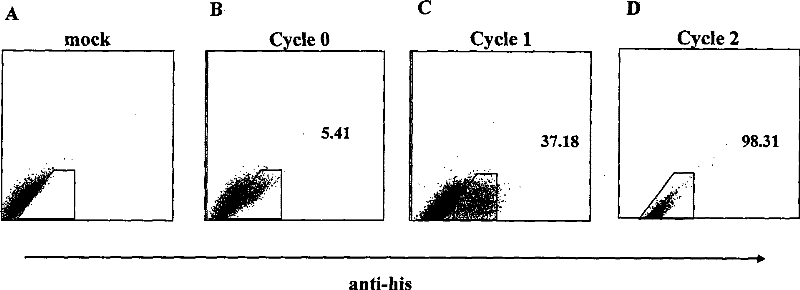
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31 results about "Cdna expression" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
DNA microarrays can be used to detect DNA (as in comparative genomic hybridization), or detect RNA (most commonly as cDNA after reverse transcription) that may or may not be translated into proteins. The process of measuring gene expression via cDNA is called expression analysis or expression profiling.
Methods and reagents to detect and characterize norwalk and related viruses
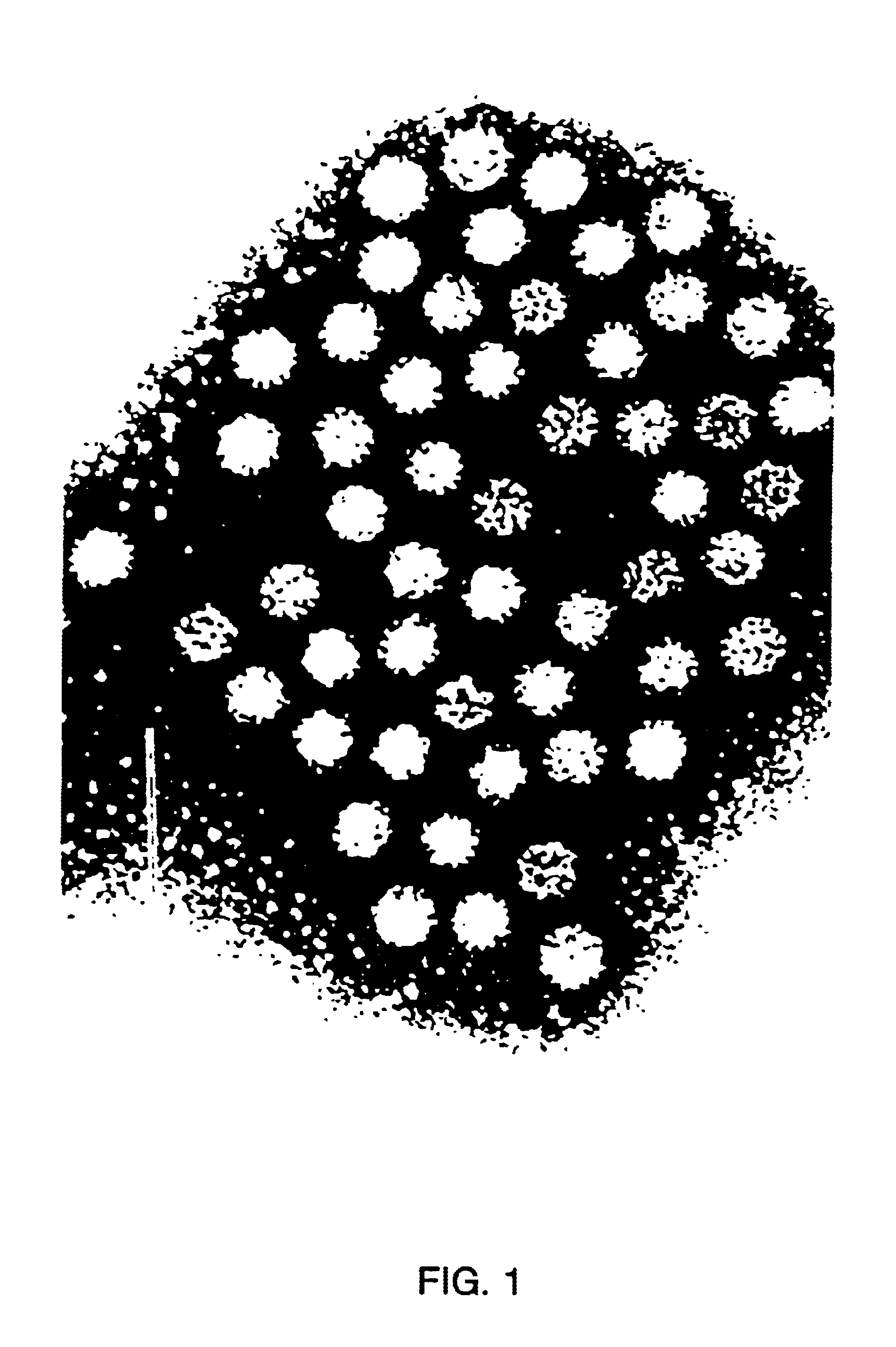
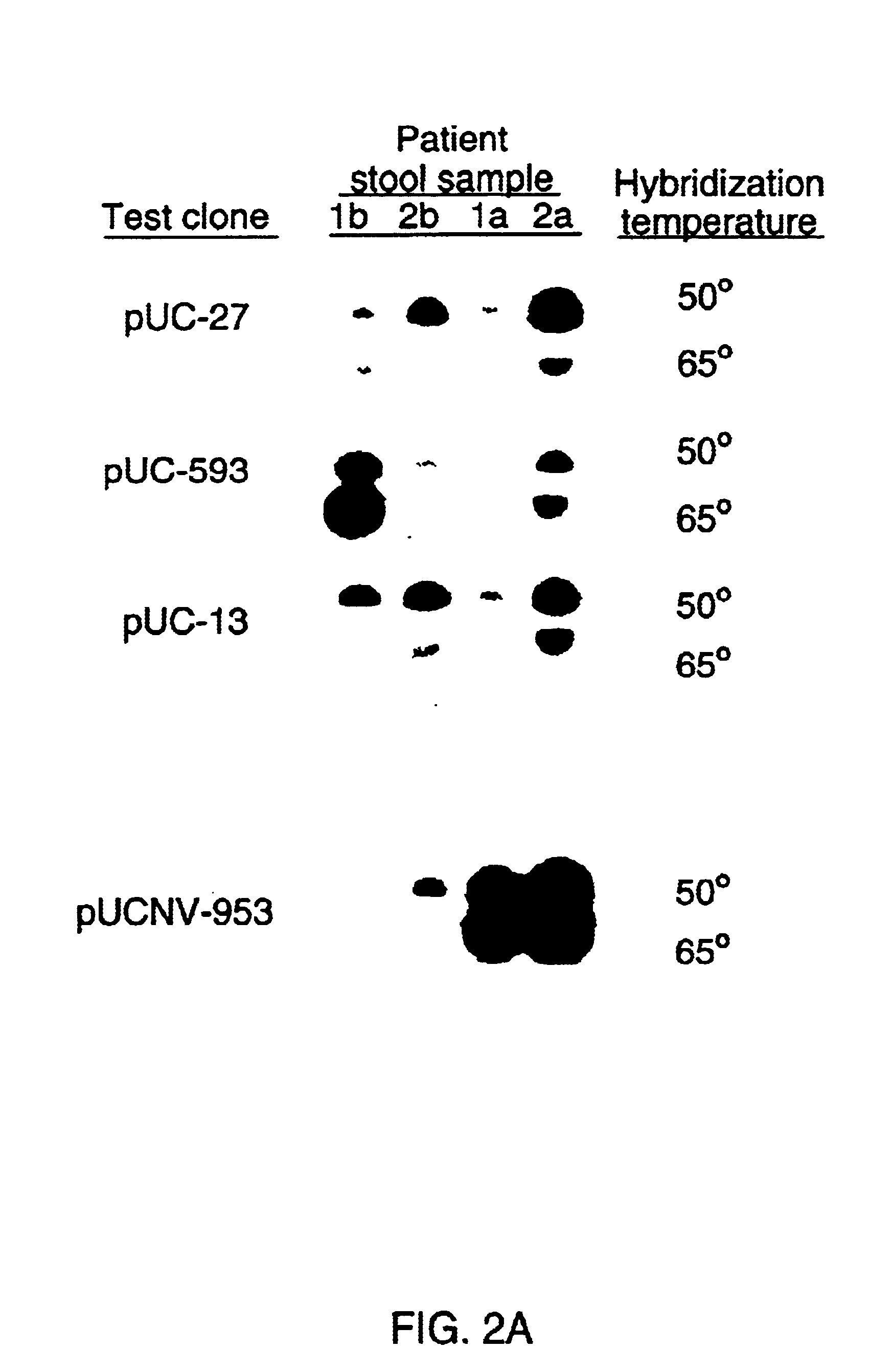
Double-stranded cDNA was synthesized from nucleic acid extracted from Norwalk virus purified from stool specimens of volunteers. One clone was isolated from a cDNA library constructed in a pUC-13 vector after amplification of the cDNA. The specificity of this cDNA (pUCNV-953) was shown by hybridization assays. The cDNA reacted with post (but not pre-) infection stool samples from Norwalk volunteers and with highly purified Norwalk virus, but not with other common enteric viruses such as hepatitis A virus and rotavirus. Finally, the probe detected virus in the same fractions of CsCl gradients in which viral antigen was detected using a specific Norwalk virus radioimmunoassay, and particles were detected by immune electron microscopy. Single-stranded RNA probes derived from the DNA clone after subcloning into an in vitro transcription vector were also used to show that the Norwalk virus contains a ssRNA genome of about 8 kb in size. The original clone was also used to detect additional cDNAs which represent at least 7 kb of nucleic acid of the Norwalk genome. The availability of a Norwalk-specific cDNA and the first partial genome sequence information allow rapid cloning of the entire genome and of establishment of sensitive diagnostic assays. Such assays can be based on detection of Norwalk virus nucleic acid or Norwalk viral antigen using polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies to proteins expressed from the cDNA or to synthetic peptides made based on the knowledge of the genome sequence. Assays using proteins deduced from the Norwlk virus genome and produced in expression systmes can measure antibody responses. Vaccines made by recombinant DNA technology are now feasible.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
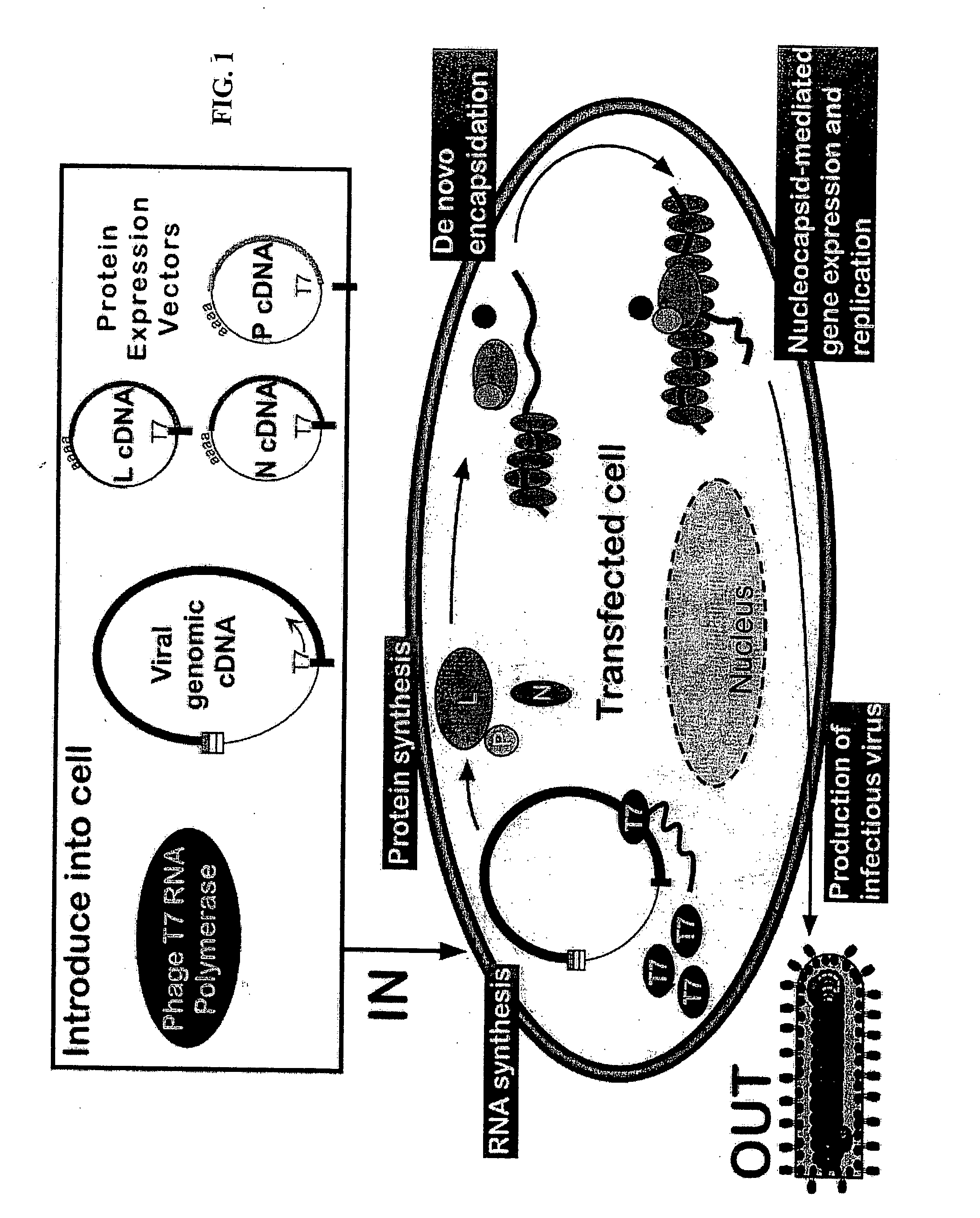
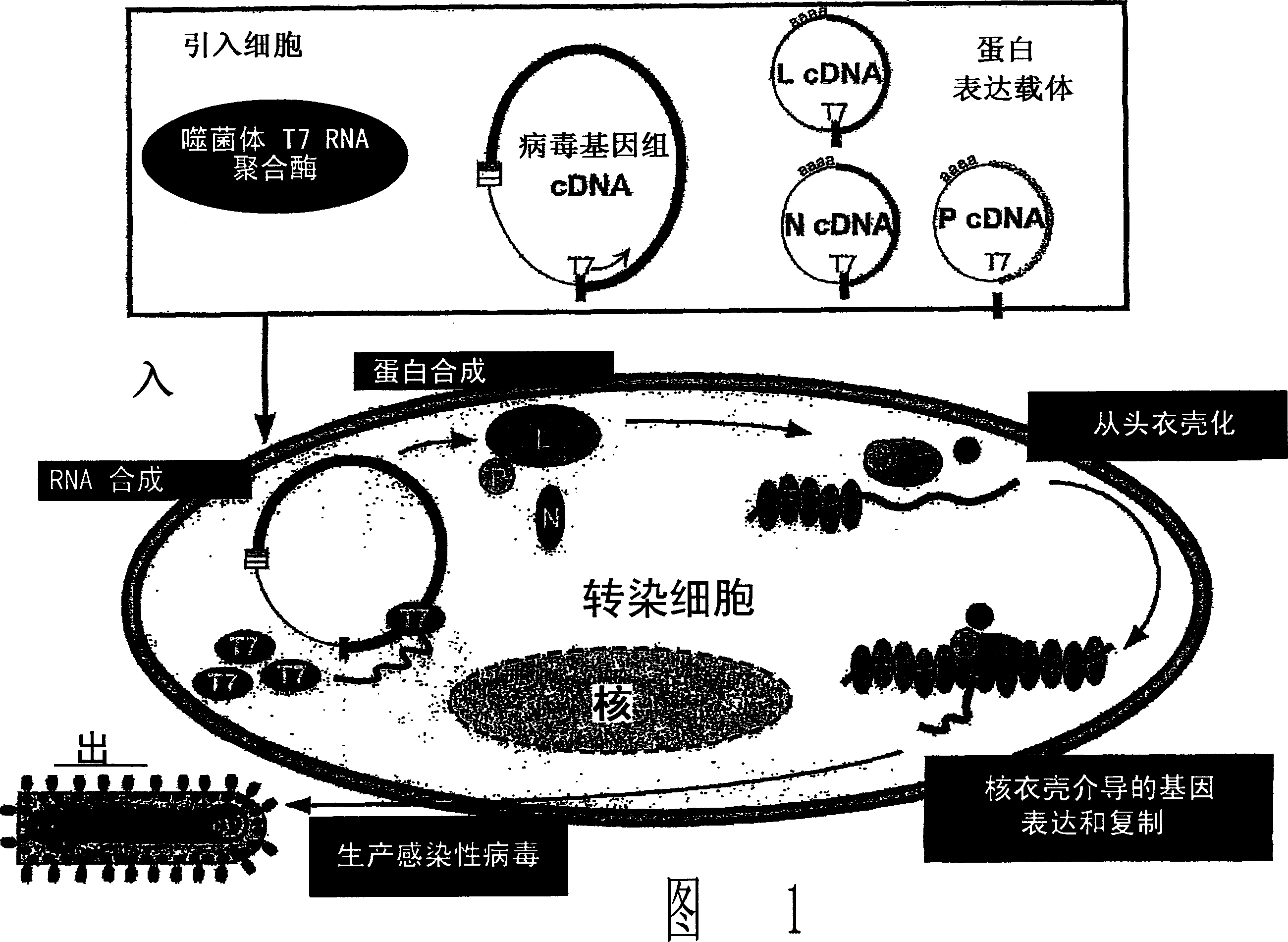
Method for the recovery of non-segmented, nagative-stranded RNA viruses from cDNA
InactiveUS20060153870A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseGenetic material ingredientsNegative strandSubviral particle
Methods for producing infectious, non-segmented, negative-stranded RNA viruses of the Order Mononegavirales are provided that involve coexpression of a viral cDNA along with essential viral proteins, N, P, and L in a host cell transiently transfected with an expression vector encoding an RNA polymerase. In alternate methods, after the host cell is transfected with a viral cDNA expression vector and one or more vectors encoding the RNA polymerase, N protein, P protein, and L protein, the host cell is exposed to an effective heat shock under conditions sufficient to increase recovery of the recombinant virus. In other alternate embodiments, the host cells are transferred after viral rescue begins into co-culture with a plaque expansion cell, typically a monolayer of expansion cells, and the assembled infectious, non-segmented, negative-stranded RNA virus is recovered from the co-culture. Also provided within the invention are compositions for producing infectious, non-segmented, negative-stranded RNA virus of the Order Mononegavirales, recombinant viruses produced using the foregoing methods and compositions, and immunogenic compositions and methods employing the recombinant viruses. In additional embodiments, the methods and compositions of the invention are employed to produce growth- or replication-defective non-segmented negative-stranded RNA viruses and subviral particles.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Chimeric antigen receptor targeting of tumor endothelium
InactiveUS20160228547A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyCell membraneAntigen binding
Disclosed are methods, protocols, and compositions of matter related to utilization of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) expressing cells for the targeting of tumor endothelium utilizing chimeric antigen receptor expressing stem cells. In one embodiment tumor endothelium specific antigens are utilized as targets of the antigen binding domain of a CAR, which is attached to an extracellular hinge domain, a domain that transverses the T cell membrane and an intracellular domain associated with T cell signaling. Suitable antigens for the practice of the invention include TEM-1, ROBO-4, surviving, and FasL. In other aspects of the invention antigens are identified through serological analysis of recombinant cDNA expression libraries (SEREX) using plasma from a patient immunized with placental endothelial cells.
Owner:BATU BIOLOGICS
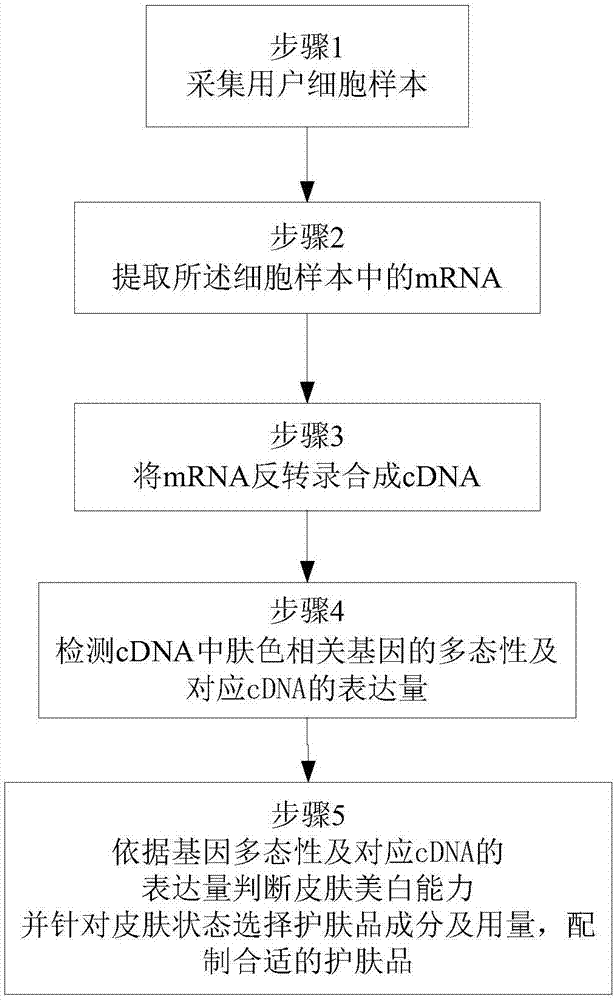
Whitening skin care product customizing method
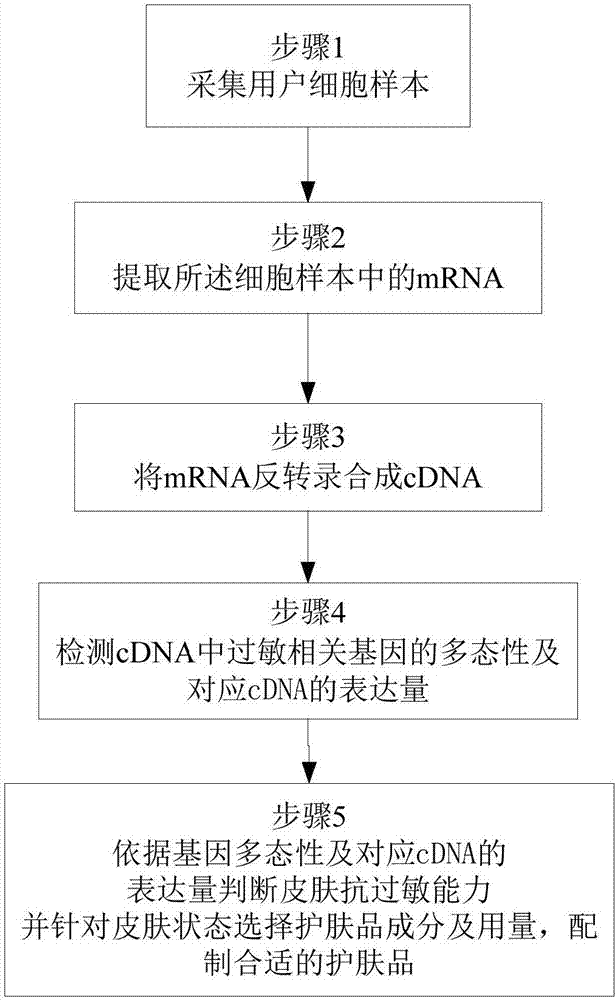
InactiveCN108004328AThe test result is accurateFree from external stimuliCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsSkin colorCdna expression
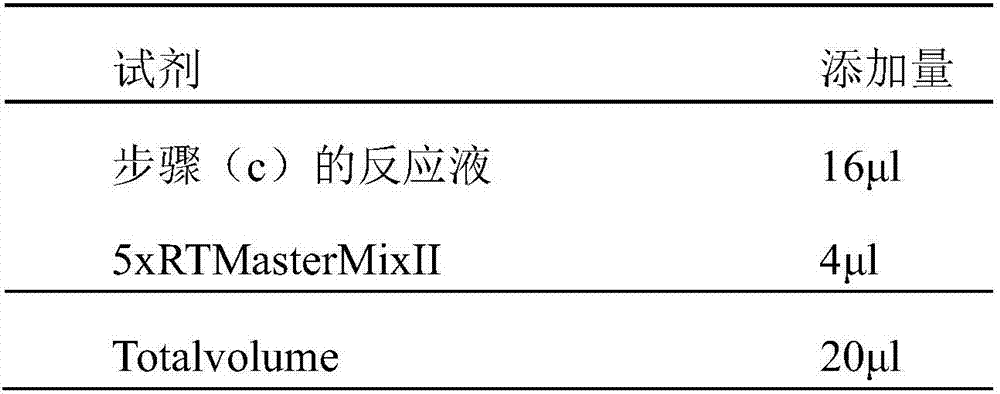
The invention discloses a whitening skin care product customizing method. The whitening skin care product customizing method comprises the following steps of 1, acquiring a cell sample of a user; 2, extracting mRNA in the cell sample; 3, conducting reverse transcription on mRNA to be synthesized into cDNA; 4, detecting the polymorphism of a skin color related relevant gene in cDNA and the expression quantity of a corresponding cDNA, wherein the skin color related relevant gene comprises at least one of MC1R, GSTP1 and SLC24A5; 5, judging the whitening capability according to the polymorphism of the gene and the expression quantity of the corresponding cDNA, and aiming at the whitening capability, selecting components and dose of the whitening skin care product to prepare an appropriate whitening skin care product. By means of the method, by measuring the expression quantity of the skin color related relevant gene, the whitening capabilities of different users are obtained, and according to the specific whitening capabilities of the users, the appropriate whitening skin care product is prepared.
Owner:杜立波
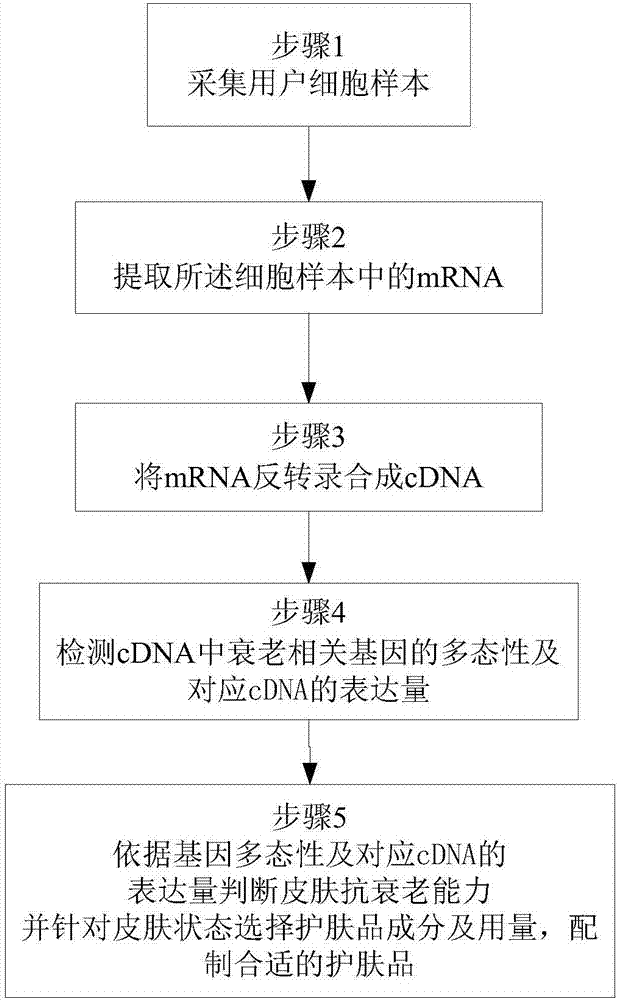
Custom customization method of anti-aging skincare product
PendingCN107881216AThe test result is accurateFree from external stimuliMicrobiological testing/measurementSenescence associated genesSOD1
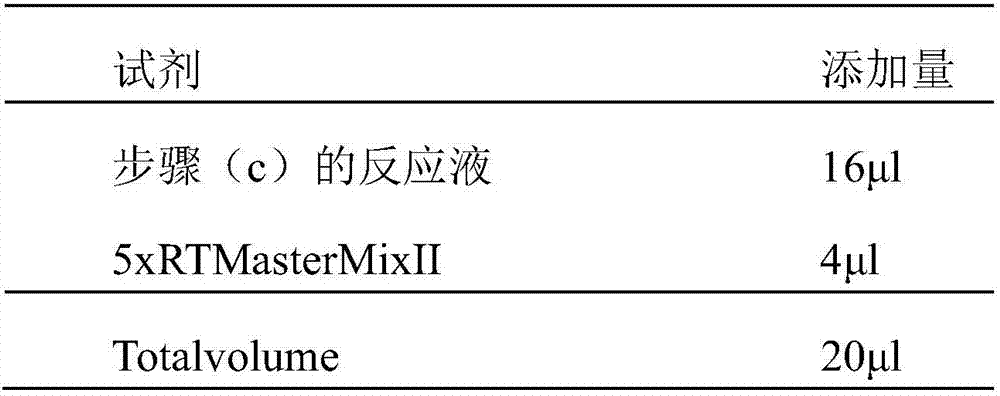
The invention discloses a custom customization method of an anti-aging skincare product. The custom customization method comprises the following steps: step 1, collecting user cell samples; step 2, extracting mRNA in the cell samples; step 3, performing reverse transcription for the mRNA to synthesize cDNA; step 4, detecting polymorphism of aging-related genes in cDNA and expression of corresponding cDNA, wherein the aging-related gene contains at least one of MMP9, NQ01, SOD1 and FOXO4; and step 5, judging the anti-aging capacity according to the gene polymorphism and the corresponding cDNA expression, selecting anti-aging skincare product components and use amount according to the anti-aging capacity, and preparing the appropriate anti-aging skincare product. The anti-aging capacity of different users is acquired by measuring the expression of the aging-related gene, and the appropriate anti-aging skincare product is prepared according to the specific anti-aging capacity of the user.
Owner:杜立波
Method for the recovery of non-segmented, nagative-stranded rna viruses from cdna
InactiveCN1871355AEliminate Contamination ConcernsEliminate bad effectsSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsNegative strandVirus Protein
Methods for producing infectious, non-segmented, negative-stranded RNA viruses of the Order Mononegavirales are provided that involve coexpression of a viral cDNA along with essential viral proteins, N, P, and L in a host cell transiently transfected with an expression vector encoding an RNA polymerase. In alternate methods, after the host cell is transfected with a viral cDNA expression vector and one or more vectors encoding the RNA polymerase, N protein, P protein, and L protein, the host cell is exposed to an effective heat shock under conditions sufficient to increase recovery of the recombinant virus. In other alternate embodiments, the host cells are transferred after viral rescue begins into co-culture with a plaque expansion cell, typically a monolayer of expansion cells, and the assembled infectious, non-segmented, negative-stranded RNA virus is recovered from the co-culture. Also provided within the invention are compositions for producing infectious, non-segmented, negative-stranded RNA virus of the Order Mononegavirales, recombinant viruses produced using the foregoing methods and compositions, and immunogenic compositions and methods employing the recombinant viruses. In additional embodiments, the methods and compositions of the invention are employed to produce growth- or replication-defective non-segmented negative-stranded RNA viruses and subviral particles.
Owner:WYETH LLC
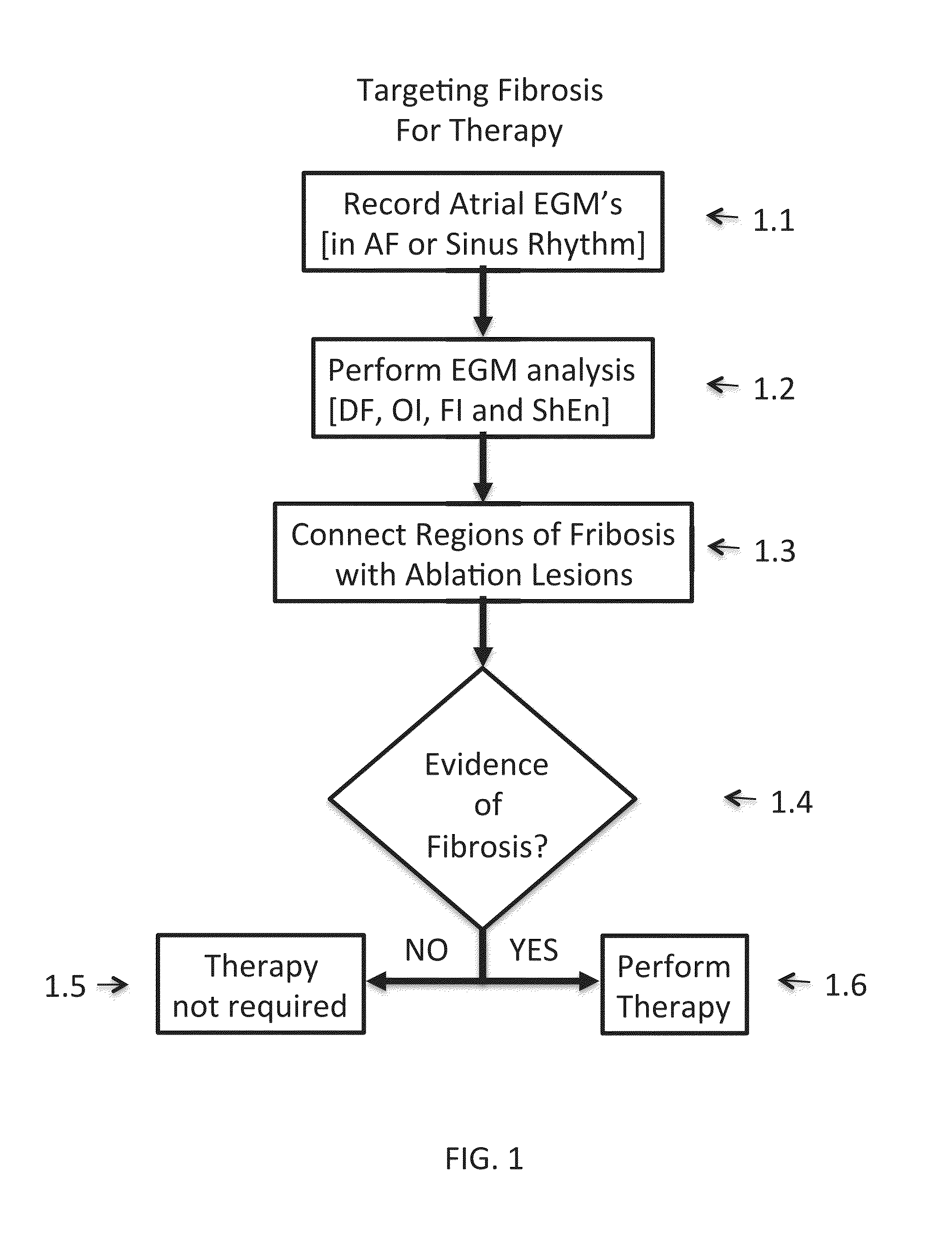
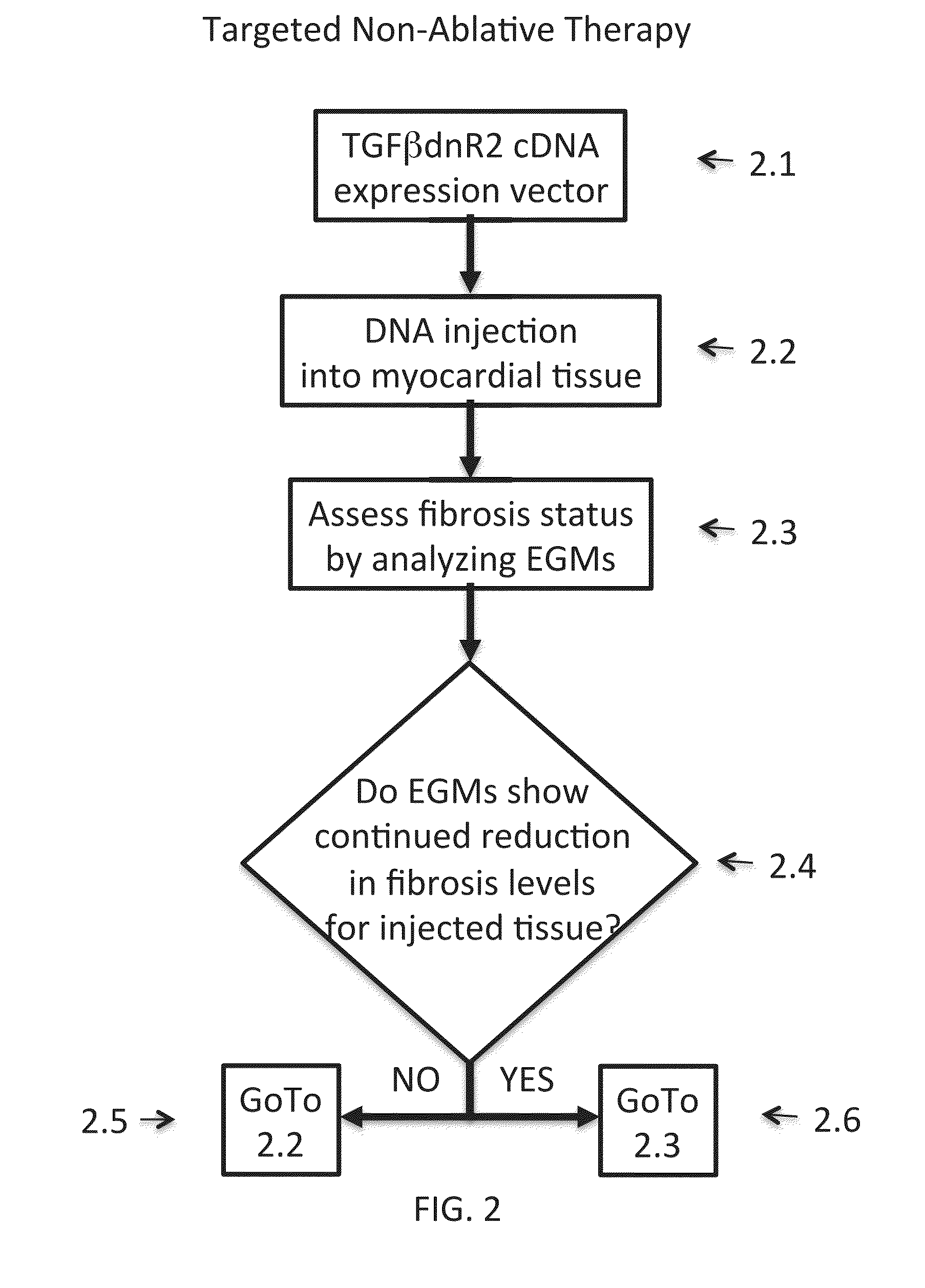
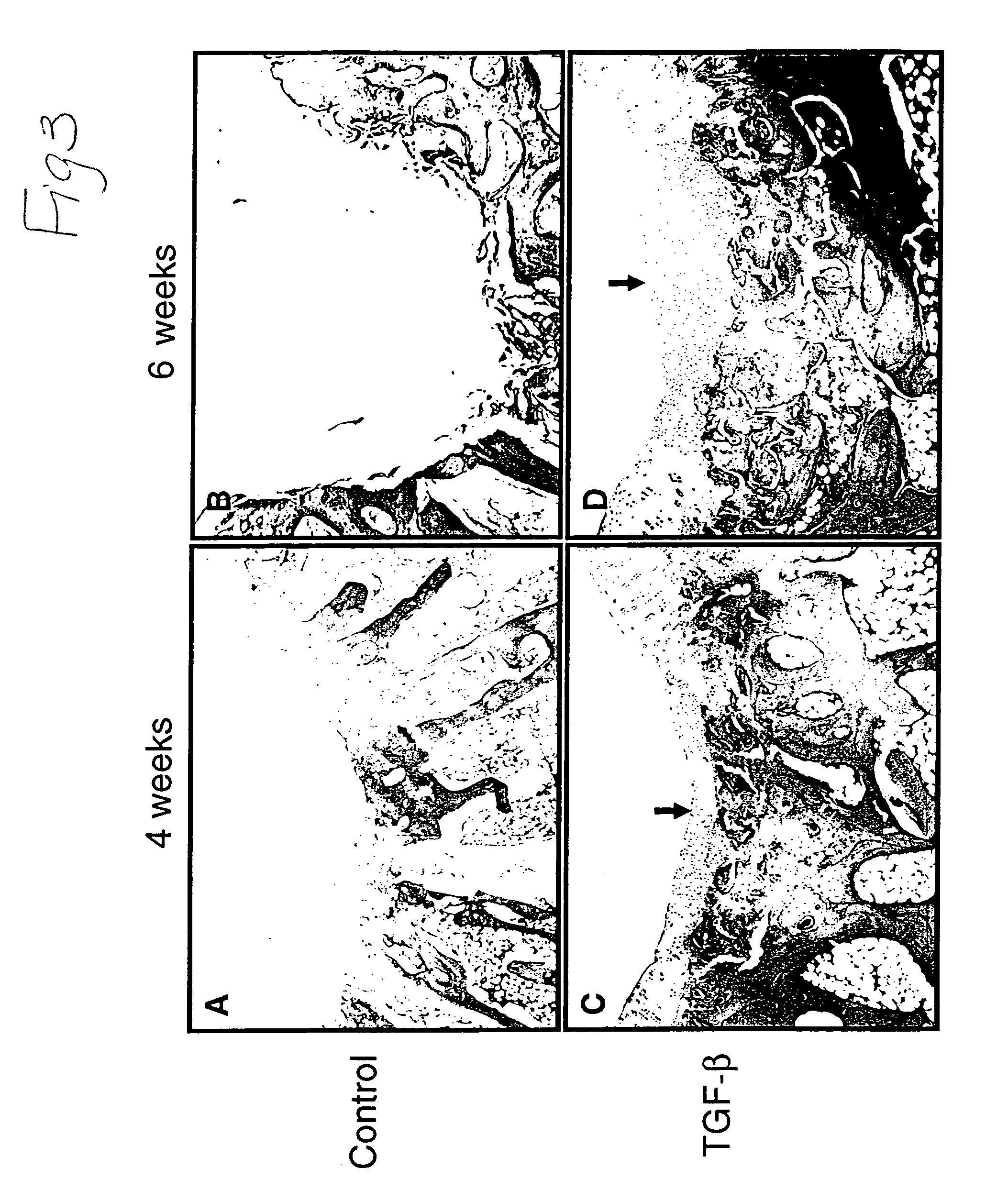
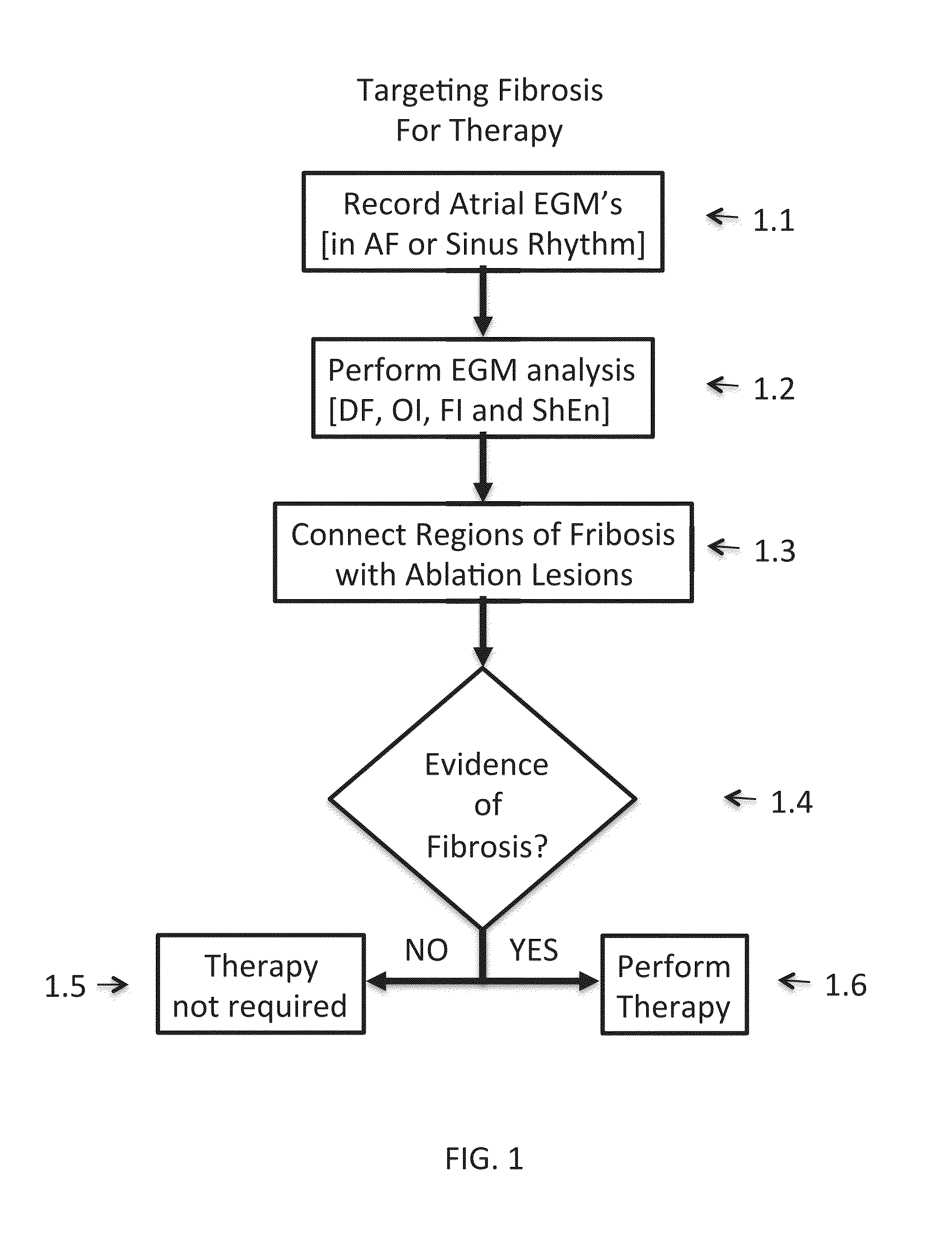
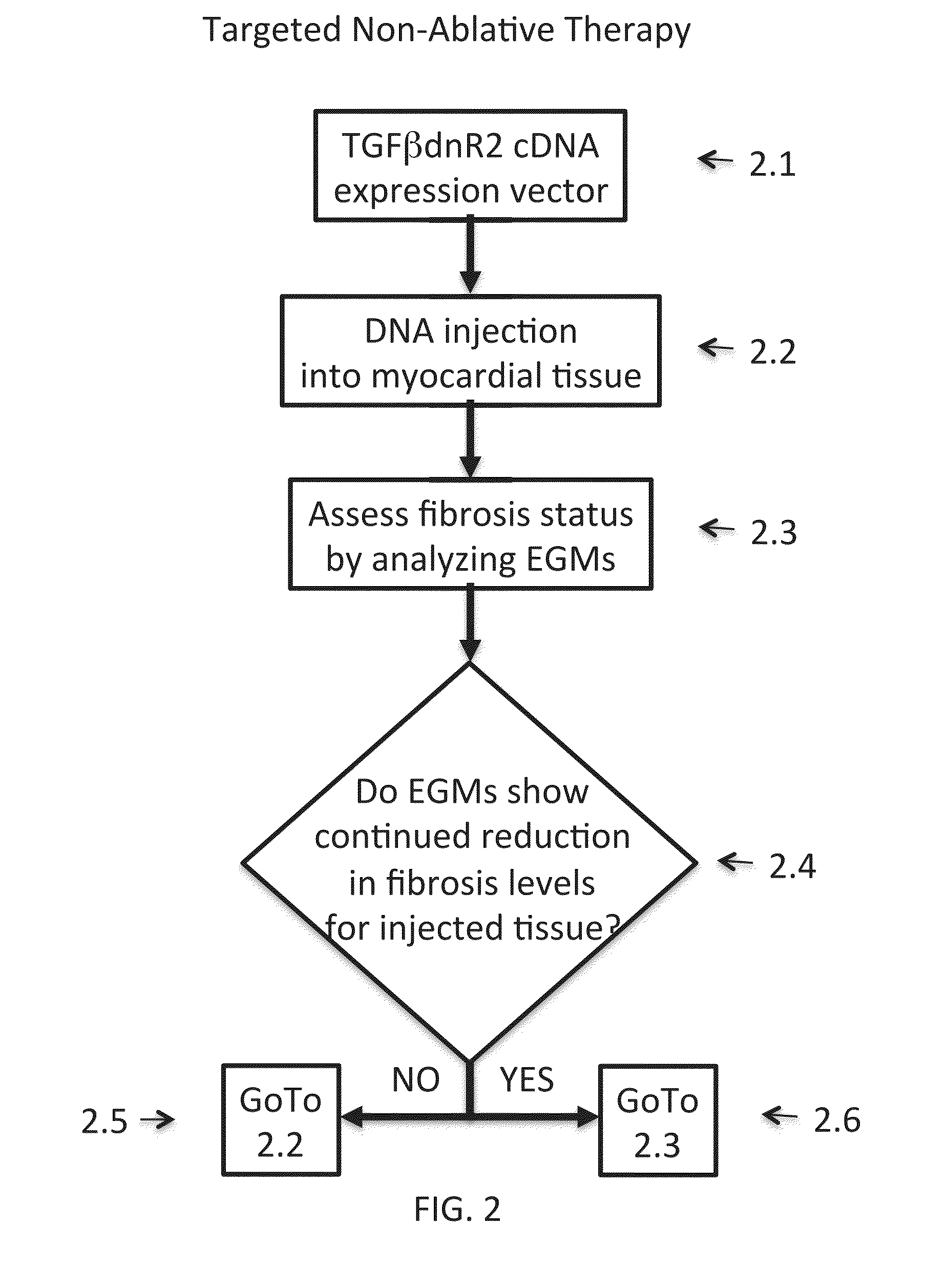
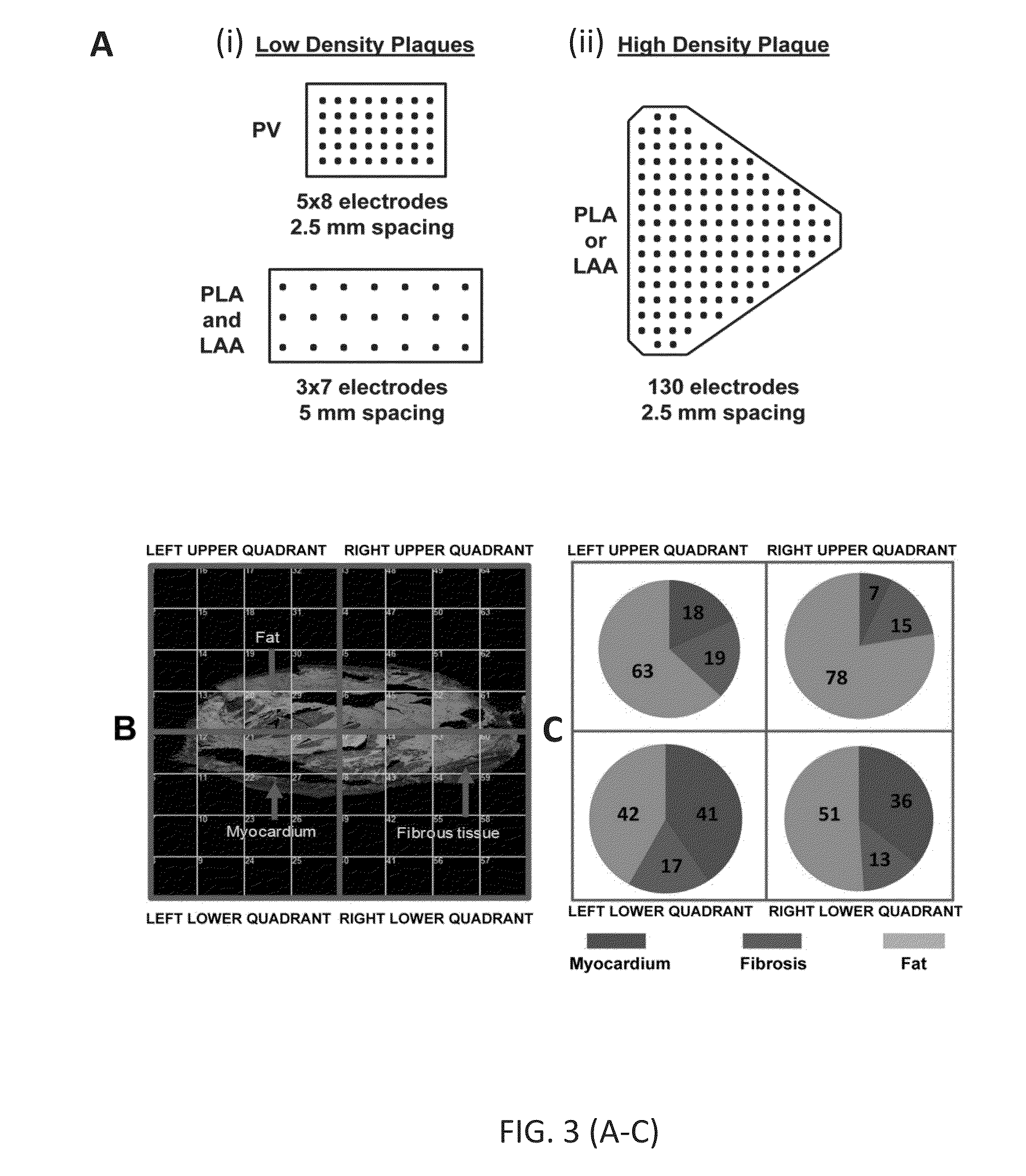
Inhibition of fibrosis and af by tgf-beta inhibition in the posterior left atrium (PLA)
ActiveUS20140037545A1Reducing AF fibrosisElectrocardiographyPeptide/protein ingredientsFibrosisProviding material
The disclosed methods pertain to diagnosing whether a non-ablative, gene therapy is needed for reducing AF fibrosis in a subject, and if so, methods of reducing AF fibrosis in a subject using gene therapy with a dominant negative TGF-β R2 cDNA expression vector. Kits and computer program products are also described, wherein the kits provide materials for diagnosing and treating AF fibrosis, and the computer program products include a computer readable medium having computer readable program code for monitoring the efficacy of therapeutic ablation of fibrosis in a subject using a gene therapy method.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Gene therapy using TGF-beta
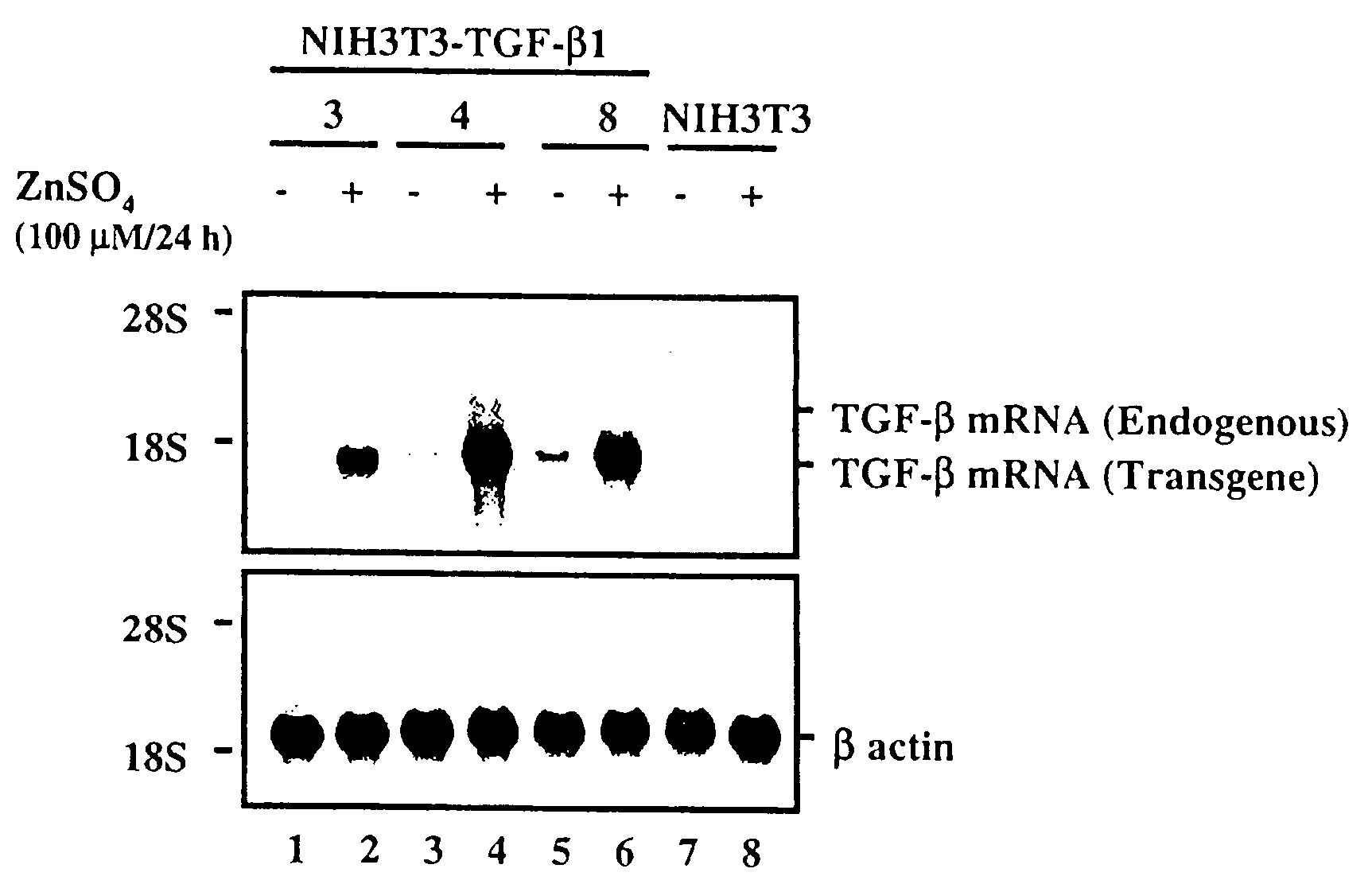
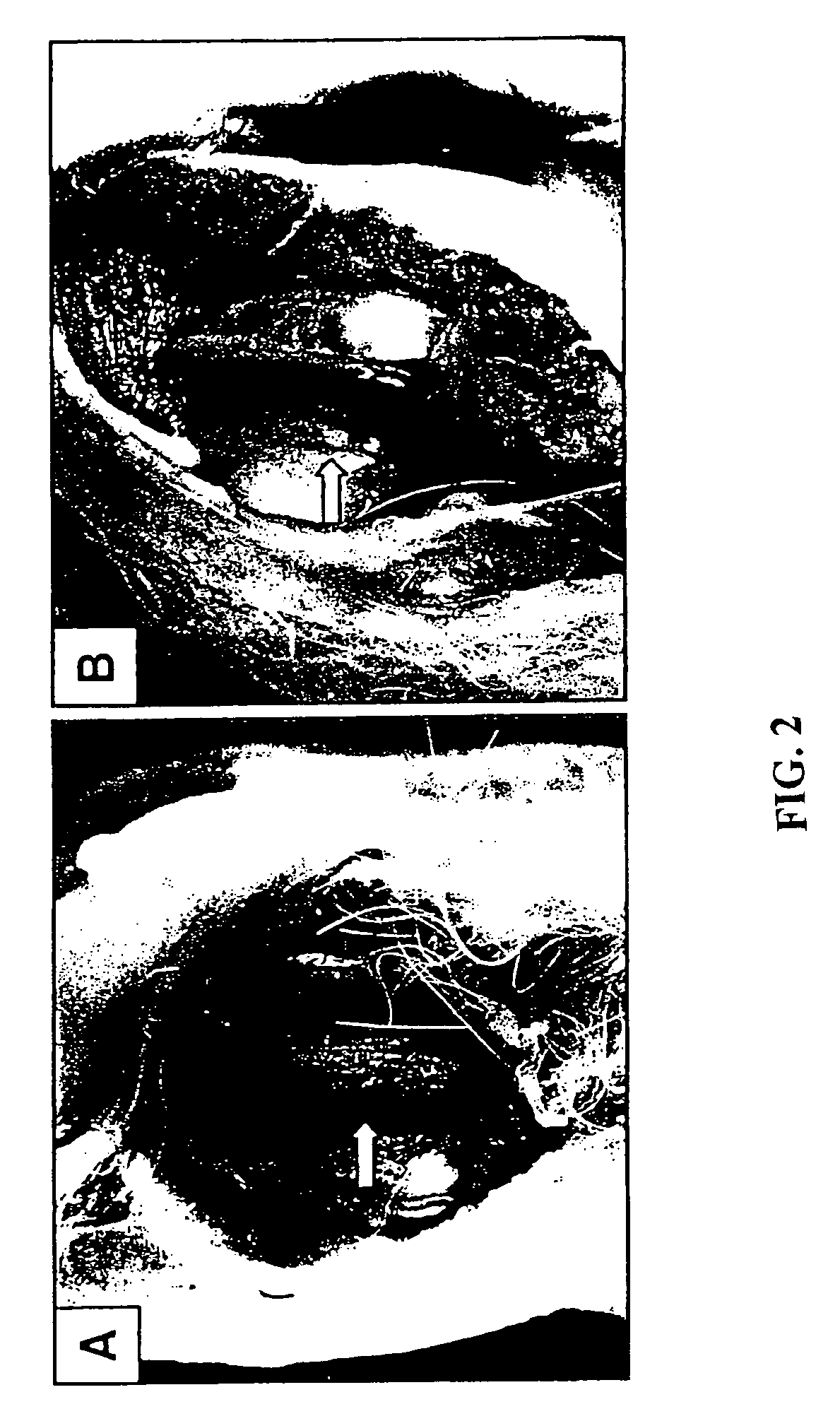
The subject invention is related to a cell-mediated gene therapy treatment for orthopedic disease using a member belonging to the transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) superfamily. TGF-β gene therapy as a new treatment method for degenerative arthritis is demonstrated. After transfection of TGF-β cDNA expression vectors into fibroblasts (NIH 3T3-TGF-β1), the cells were injected into rabbit achilles tendon and knee joints with artificially-made cartilage defects. Intratendinous injections were performed to determine the optimal concentration for in vivo expression. Partially defected cartilage model was made to simulate degenerative arthritis of the knee joint. The partial cartilage defect treated with the cell-mediated gene therapy procedure was covered by newly formed hyaline cartilage which indicates that the cells survived and stimulated matrix formation in this area. Completely denuded cartilage areas were covered by fibrous collagen.
Owner:KOLON TISSUEGENE INC
Inhibition of fibrosis and AF by TGF-beta inhibition in the posterior left atrium (PLA)
The disclosed methods pertain to diagnosing whether a non-ablative, gene therapy is needed for reducing AF fibrosis in a subject, and if so, methods of reducing AF fibrosis in a subject using gene therapy with a dominant negative TGF-β R2 cDNA expression vector. Kits and computer program products are also described, wherein the kits provide materials for diagnosing and treating AF fibrosis, and the computer program products include a computer readable medium having computer readable program code for monitoring the efficacy of therapeutic ablation of fibrosis in a subject using a gene therapy method.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Echinococcus granulosus developmental-stage secretory protein expression gene chip
ActiveCN102943308AShort screening cycleLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein nucleotide librariesProtective antigenDevelopmental stage
The invention discloses an echinococcus granulosus developmental-stage secretory protein expression gene chip. The echinococcus granulosus developmental-stage secretory protein expression gene chip is characterized in that sequences of isolated cDNA expression sequence labels of echinococcus granulosus protoscolex, vesicle, oncosphere and adult developmental stage secretory proteins are combined with vectors; and the cDNA expression sequence labels are shown in the formulas of SEQ ID No.1 to SEQ ID No.30. The echinococcus granulosus developmental-stage secretory protein expression gene chip has commercial values and scientific research values. Through the novel cDNA expression sequence labels, a genetic map is drawn. The echinococcus granulosus developmental-stage secretory protein expression gene chip has an important effect of research of secretory protein gene expression. The expression sequence labels can realize screening of targets of a cystic echinococcosis-resistant drug and through the expression sequence labels, the optimal echinococcosis-resistant drug molecules are selected out. The echinococcus granulosus developmental-stage secretory protein expression gene chip can be used for screening of a cystic echinococcosis diagnostic marker and can be used for research and development of an echinococcosis diagnostic kit having high specificity. The echinococcus granulosus developmental-stage secretory protein expression gene chip can be used for screening of cystic echinococcosis protective antigens and can be used for research and development of echinococcosis vaccines suitable for the animal husbandry and pet dogs.
Owner:THE FIRST TEACHING HOSPITAL OF XINJIANG MEDICAL UNIVERCITY
Method for constructing membrane protein cDNA library and use thereof
ActiveCN101338454AStrong specificityEliminate distractionsBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceCDNA libraryFluorescence
The invention relates to a construction method of a Membrane protein cDNA library and an application thereof. The method constructs a eukaryotic expression vector used for the specificity selection of the membrane protein. The expression vector can perform clone recombination with any cDNA clone library provided with the recombination site attL of Lambada bacteriophage so as to acquire a cDNA expression library. After the transfection of COS-1 cell, expression membrane protein clone is further selected by immunofluorescence so as to acquire the membrane protein cDNA expression library. As the application of the method, the liver lymphocyte membrane protein cDNA library of a C57BL / 6 rat is built up. The method is proved to be an effective proposal of the high flux specificity selection membrane protein through the identification and analysis of the library, and the method provides a powerful method to describe the map of the membrane protein of the cell surface of certain issue and to research the unknown membrane protein.
Owner:IMMUNOPHARMACEUTIC INST OF HEFEI RUIDA CO LTD
Gene Therapy Using TGF-beta
The subject invention is related to a cell-mediated gene therapy treatment for orthopedic disease using a member belonging to the transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) superfamily. TGF-β gene therapy as a new treatment method for degenerative arthritis is demonstrated. After transfection of TGF-β cDNA expression vectors into fibroblasts (NIH 3T3-TGF-β1), the cells were injected into rabbit achilles tendon and knee joints with artificially-made cartilage defects. Intratendinous injections were performed to determine the optimal concentration for in vivo expression. Partially defected cartilage model was made to simulate degenerative arthritis of the knee joint. The partial cartilage defect treated with the cell-mediated gene therapy procedure was covered by newly formed hyaline cartilage which indicates that the cells survived and stimulated matrix formation in this area. Completely denuded cartilage areas were covered by fibrous collagen.
Owner:TISSUEGENE INC
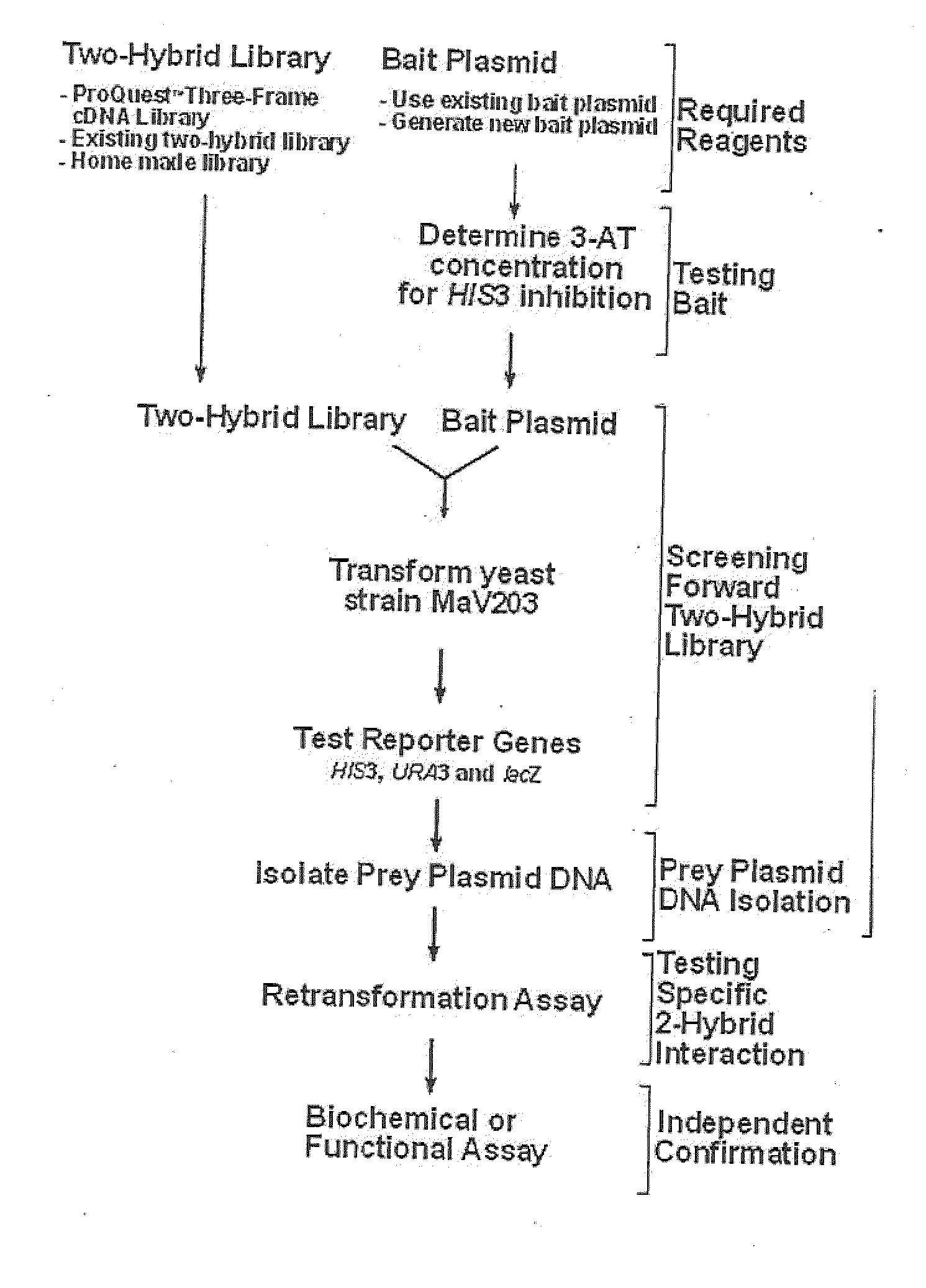
Three Frame cDNA Expression Libraries for Functional Screening of Proteins
InactiveUS20100105576A1High frequencyImprove efficiencySugar derivativesLibrary creationProtein compositionProtein insertion
Compositions and methods are provided for generating three frame cDNA expression libraries for functional screening of proteins. The invention includes sets of 5′ adapters for cloning cDNA molecules in which the sets include three adapters that can be used to clone a particular cDNA in all three reading frames. The libraries so generated have greater complexity of expressed open reading frames, and thus can improve the success of functional protein screens, such as two hybrid screens. The adapters also have recombination sites for efficient cloning and transfer between systems.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Method of screening disease depressant gene
The present invention provides methods for screening and testing disorder suppressor genes and disorder suppressor polypeptides. By screening the cDNA expression library incorporated with nucleic acids derived from an organism suffering from a disorder that accompanies cell death, genes having suppressive effects on the disorder symptoms were successfully cloned. Furthermore, suppressive effects of the nucleic acid and polypeptide encoded by the nucleic acid on the disorder have been also examined. Screening of nucleic acids or polypeptides derived from an organism suffering from a disorder that accompanies cell death enables the efficient isolation and selection of suppressor genes of the disorder.
Owner:KEIO UNIV
Protease-activated receptor 3 and uses thereof
Disclosed are cDNAs and genomic DNAs encoding protease-activated receptor 3 (PAR3) from mouse and human, and the recombinant polypeptides expressed from such cDNAs. The recombinant receptor polypeptides, receptor fragments and analogs expressed on the surface of cells are used in methods of screening candidate compounds for their ability to act as agonists or antagonists to the effects of interaction between thrombin and PAR3. Agonists are used as therapeutics to treat wounds, thrombosis, atherosclerosis, restenosis, inflammation, and other thrombin-activated disorders. Antagonists are used as therapeutics to control blood coagulation and thereby treating heart attack and stroke. Antagonists mediate inflammatory and proliferative responses to injury as occur in normal wound healing and variety of diseases including atherosclerosis, restenosis, pulmonary inflammation (ARDS) and glomerulosclerosis. Antibodies specific for a protease-activated receptor 3 (or receptor fragment or analog) and their use as a therapeutic are also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
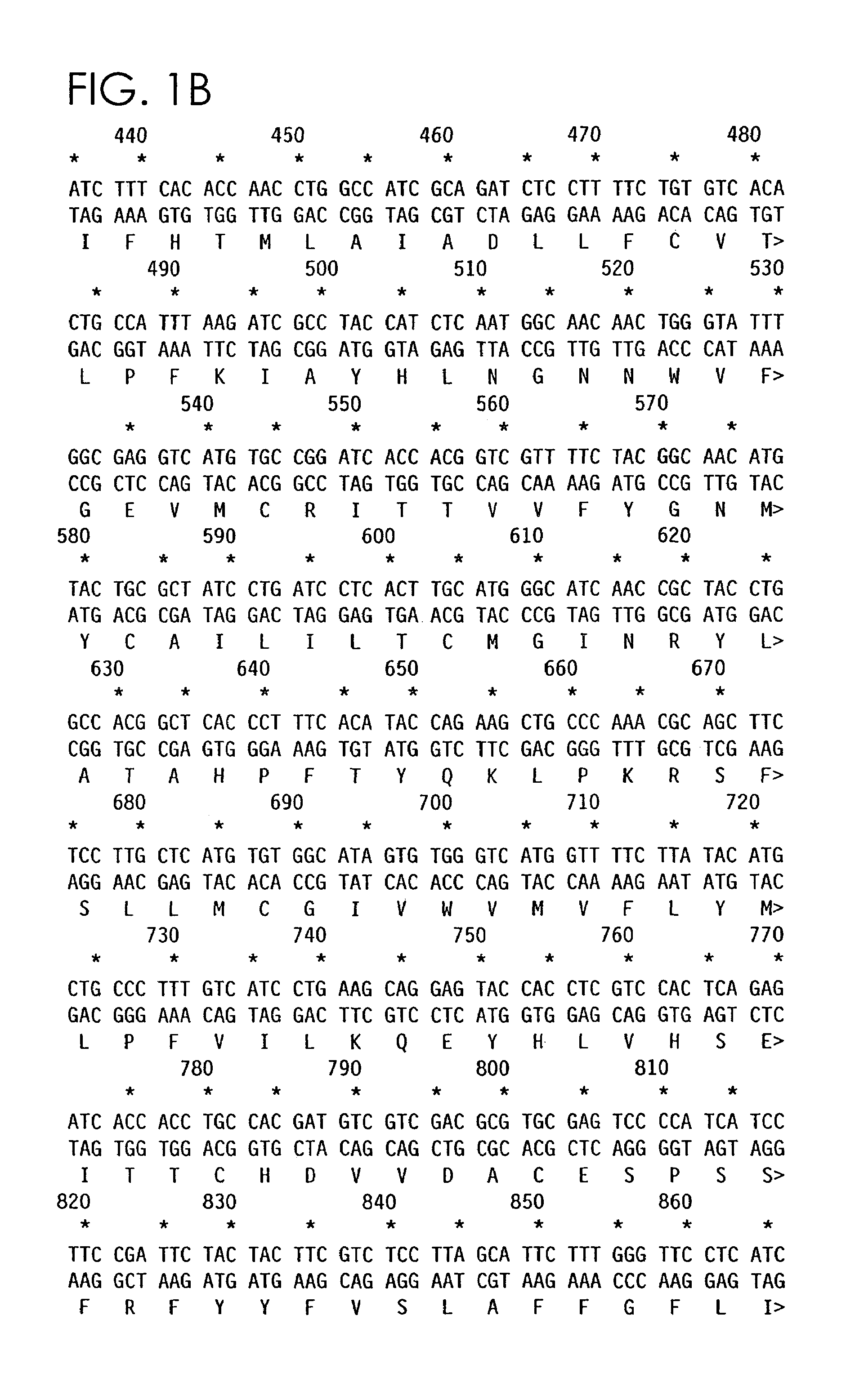
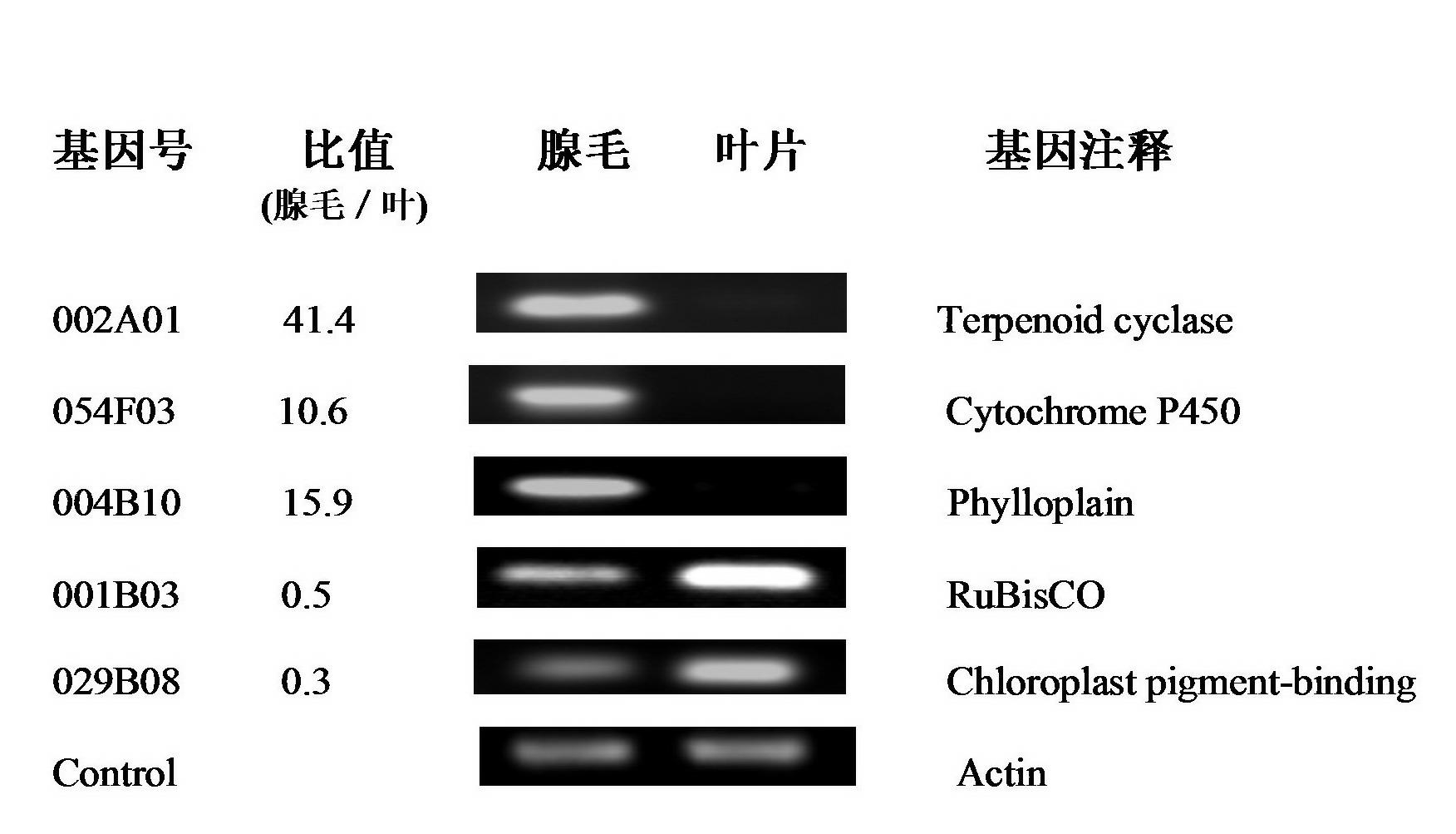
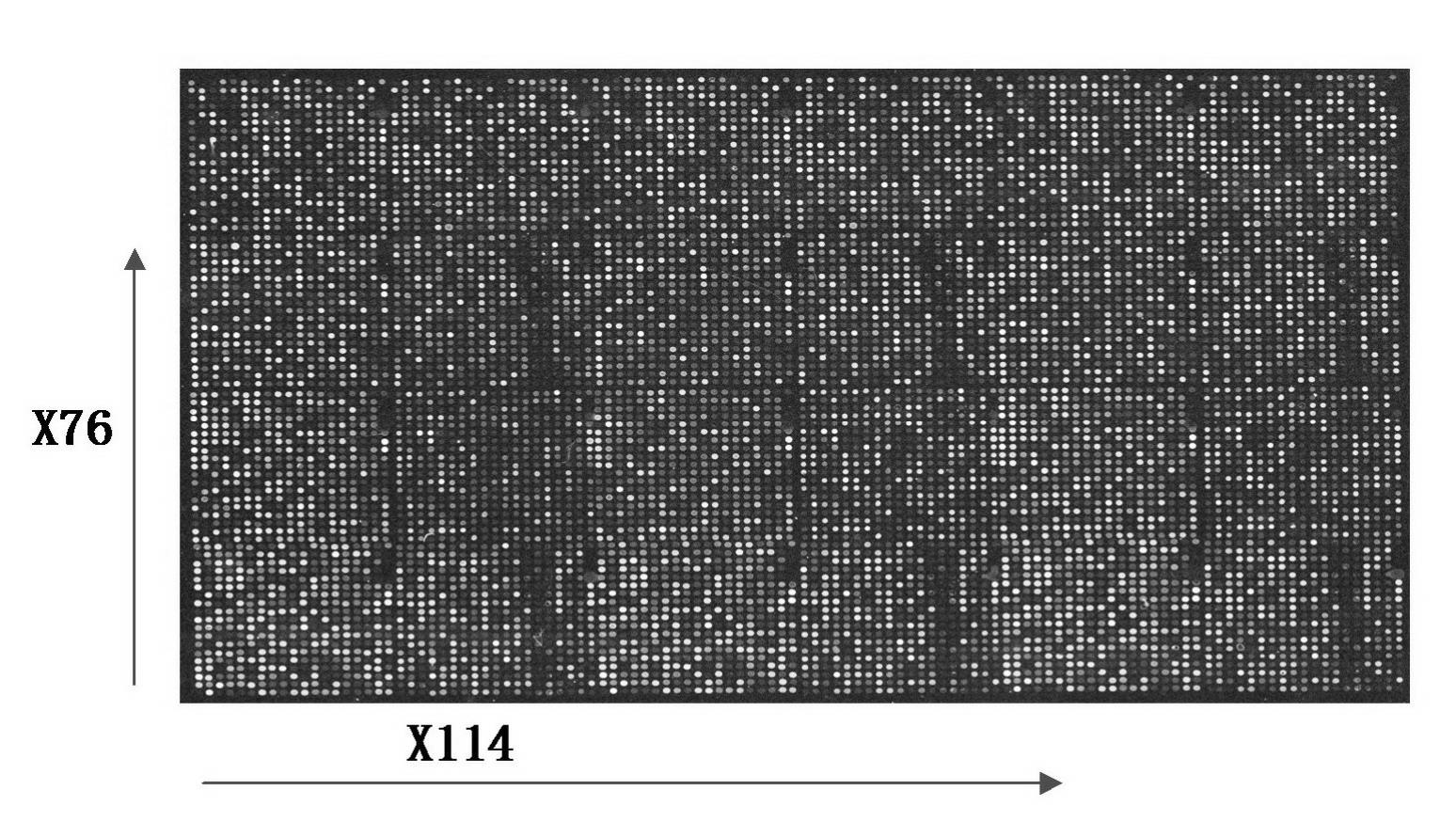
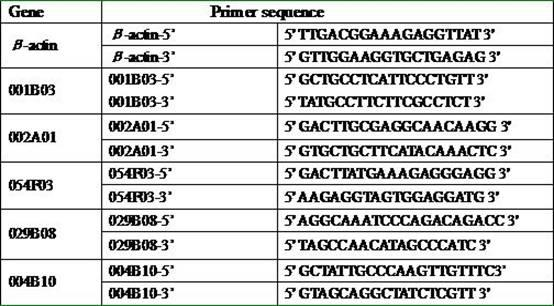
Tobacco glandular hair cDNA (complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid) microarray for expression profile and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN102154484AImprove throughputHigh precisionMicrobiological testing/measurementCDNA libraryNicotiana tabacum
The invention relates to a tobacco glandular hair cDNA (complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid) microarray for an expression profile and preparation and application thereof. A preparation method of the microarray comprises the following steps of: separating tobacco leaf glandular hairs, extracting total RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) and constructing a tobacco glandular hair cDNA library; randomly sequencing the cDNA library to obtain a tobacco glandular hair EST (Expressed Sequence Tag) database and amplifying an EST sequence by undergoing a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) to obtain the tobacco glandular hair cDNA microarray for the expression profile; and analyzing tobacco glandular hairs and glandular hair removed leaf gene expression by using the microarray to obtain up-regulated expression ESTs in glandular hairs and screen a specific expression gene. The microarray obtained by the invention has the advantages of high efficiency, sensitivity, high flux, high accuracy and high specificity, and is suitable for researching tobacco glandular hairs, cultivating measures, environmental stress and the like. By adopting the microarray, the expression modes of a large number of genes can be detected at one time, and the gene expression change rules of a plurality of samples are comprehensively analyzed under the same testing condition.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Hepatitis B virus vaccine synergistic protein and its gene
InactiveCN1948493AImproving immunogenicityImprove immunityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsSequence analysisHepatitis B immunization
This invention relates to a hepatitis B virus vaccine synergic protein and its genes, and utilizes gene engineering principle to express the method and application of the protein. CDNA of the protein is gained by screening from human liver CDNA expression bank, after sequence analysis ,using the way of gene engineering to clone to prokaryotic cell, eukaryotic cell(animals, plants) to express protein by coding of the CDNA ,for instance ,cloning CDNA to prokaryotic expression vector and gaining recombination protein by expression depuration in Bacterium coli. Combination of the protein and hepatitis B virus vaccine can improve vaccine immune effectiveness, reinforcing the immunity of hepatitis B virus infectors, increasing antibody titer. Protein of this invention can be used as adjuvant to hepatitis B vaccine.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
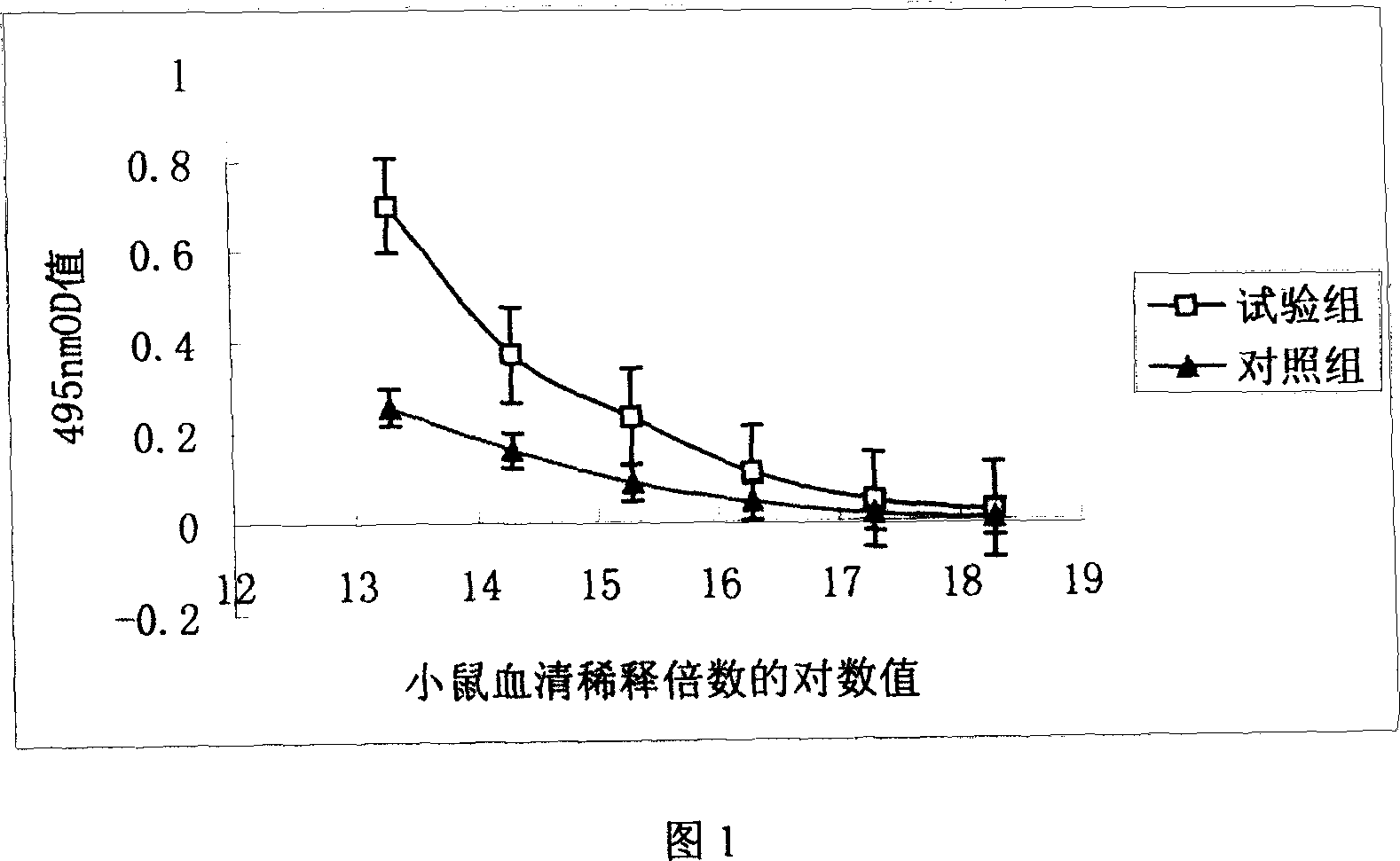
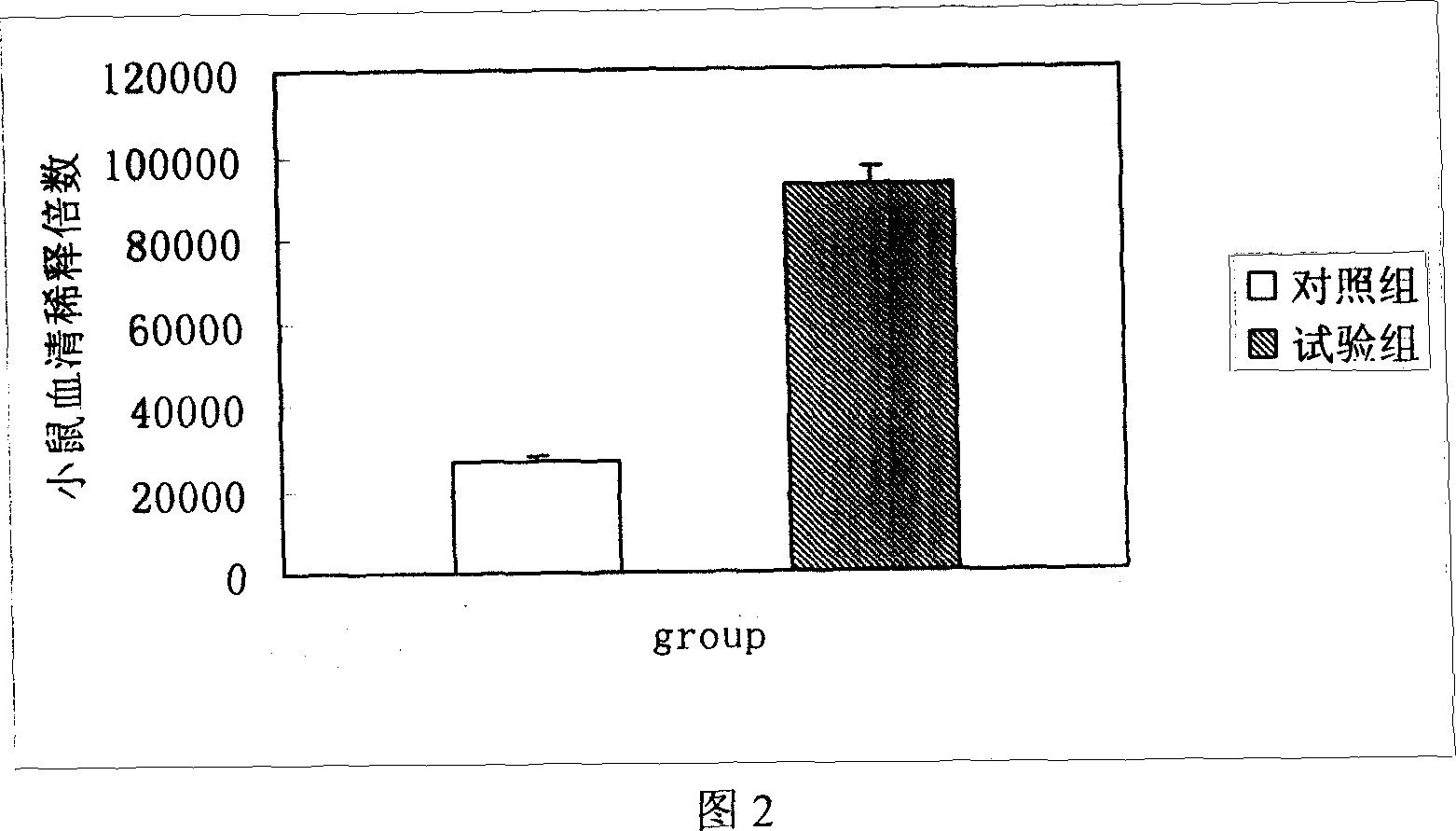
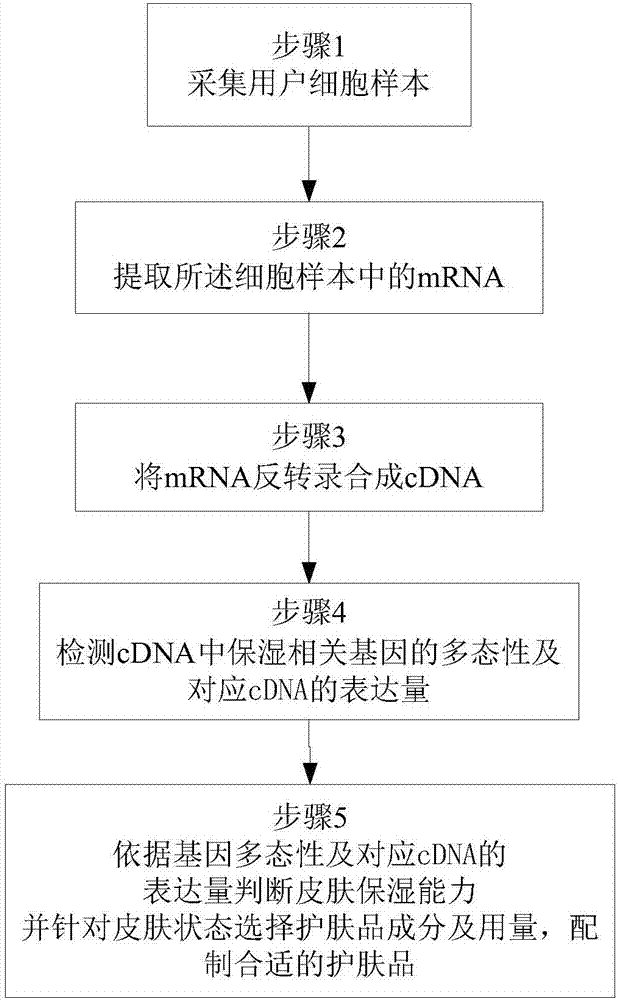
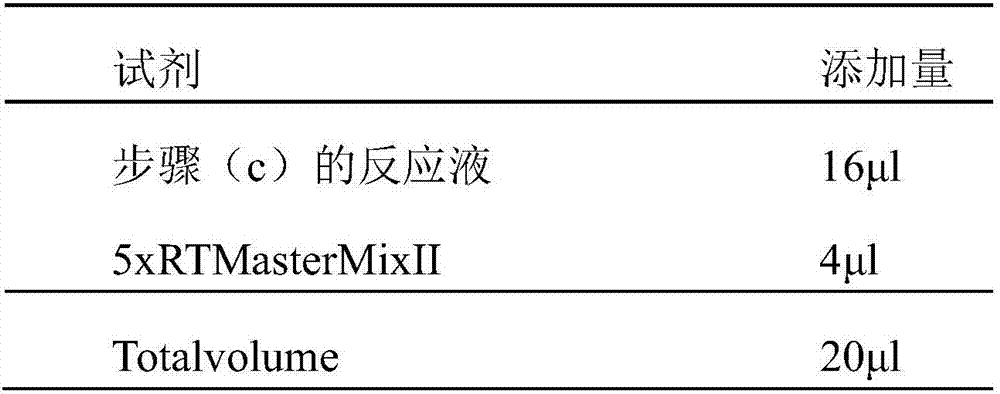
Moisturizing skin care product customization method
InactiveCN107881217AThe test result is accurateFree from external stimuliMicrobiological testing/measurementAdditive ingredientCdna expression
The invention discloses a moisturizing skin care product customization method, which comprises the following steps: (1) collecting a user cell sample; (2) extracting mRNA in the cell sample; (3) carrying out reverse transcription on the mRNA to synthesize cDNA; (4) detecting polymorphism of a moisturizing related gene in the cDNA and expression quantity corresponding to the cDNA, wherein the moisturizing related gene contains at least one of AQP3, CLDN1 and JAM1; (5) judging a moisturizing capacity according to the gene polymorphism and the expression quantity corresponding to the cDNA, selecting ingredients and dosages of a moisturizing skin care product for the moisturizing capacity, and preparing the appropriate moisturizing skin care product. According to the method, the moisturizing capacities of different users are obtained through measuring the expression quantities of the moisturizing related genes, and the appropriate moisturizing skin care product is prepared according to theconcrete moisturizing capacity of one user.
Owner:杜立波
Skin nursing product customization method for improving allergic skin
PendingCN108004329AImprove allergic skin qualityAccurately Characterize SensitivityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsAllergyCdna expression
The invention discloses a skin nursing product customization method for improving allergic skin. The method includes the following steps of collecting cell samples of users; extracting mRNAs of the cell samples; conducting inverse transcription on the mRNAs to synthesize cDNAs; detecting the polymorphism of correlative allergy genes in the cDNAs and the corresponding expression quantity of the cDNAs, wherein the correlative allergy genes comprise at least one of FLG, DDB2 and NLRP3; according to the polymorphism of the genes and the corresponding expression quantity of the cDNAs, judging the sensitivity, selecting skin nursing components and dosage for improving the allergic skin according to the sensitivity, and preparing appropriate skin nursing products for improving the allergic skin.According to the method, by measuring the expression quantity of the correlative allergy genes, the sensitivity of different users is obtained, and the appropriate skin nursing products for improvingthe allergic skin are prepared according to the specific sensitivity of the users.
Owner:杜立波
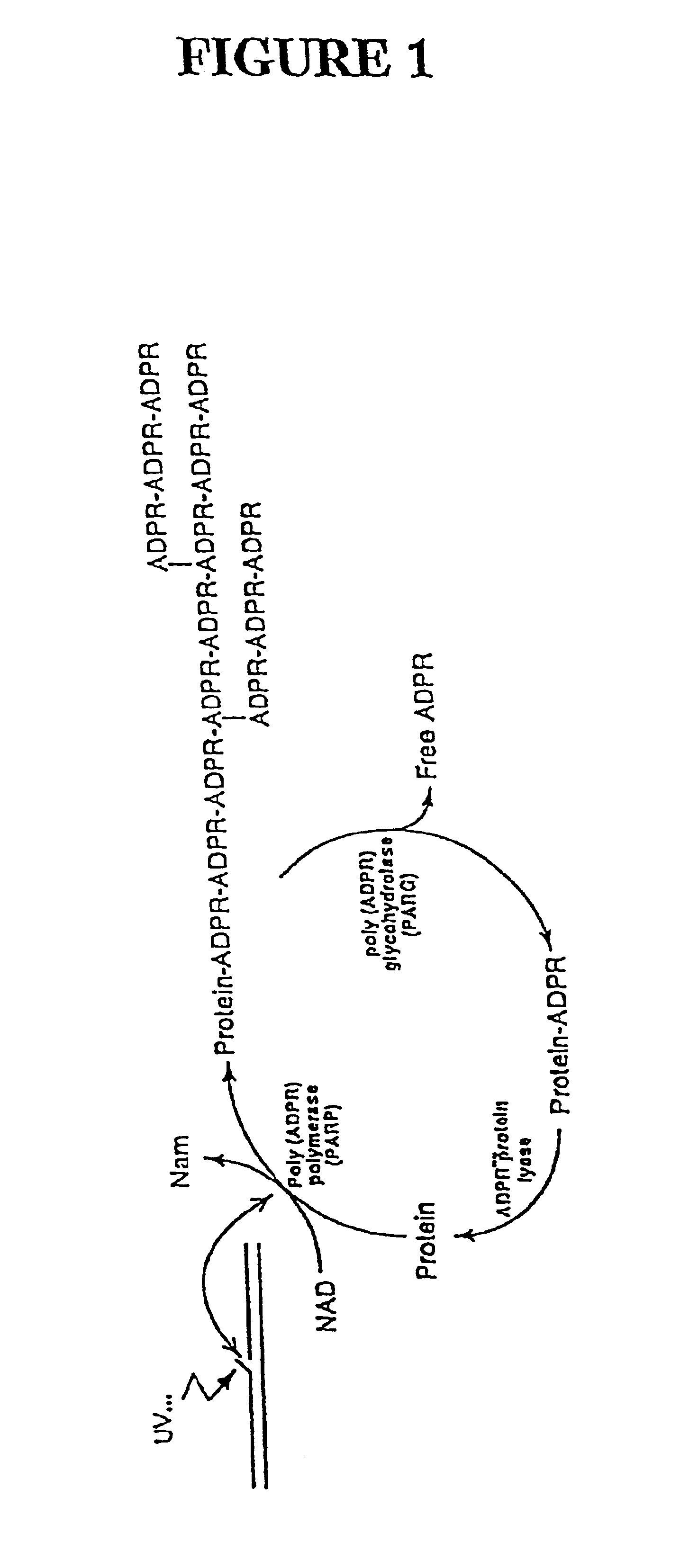
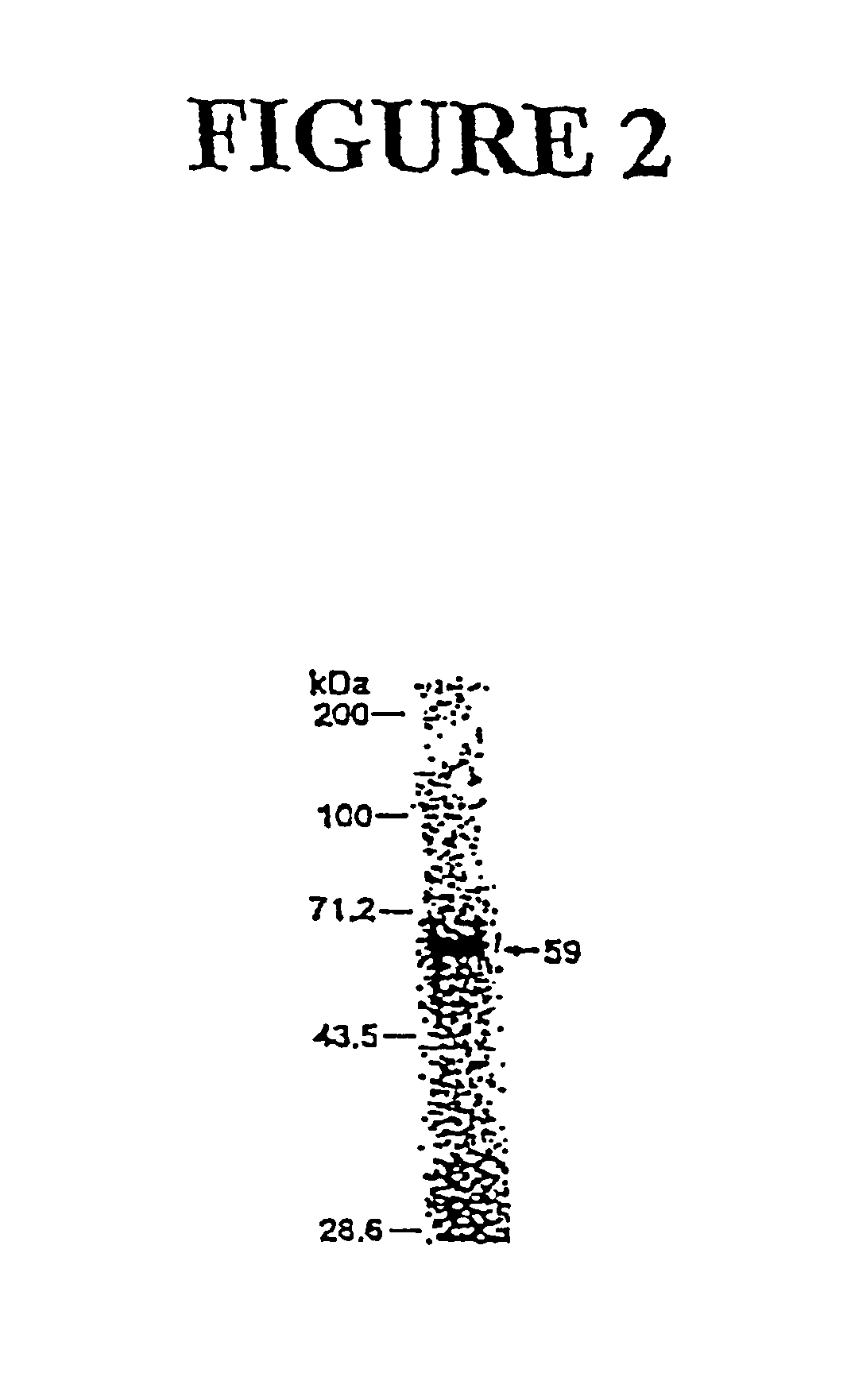
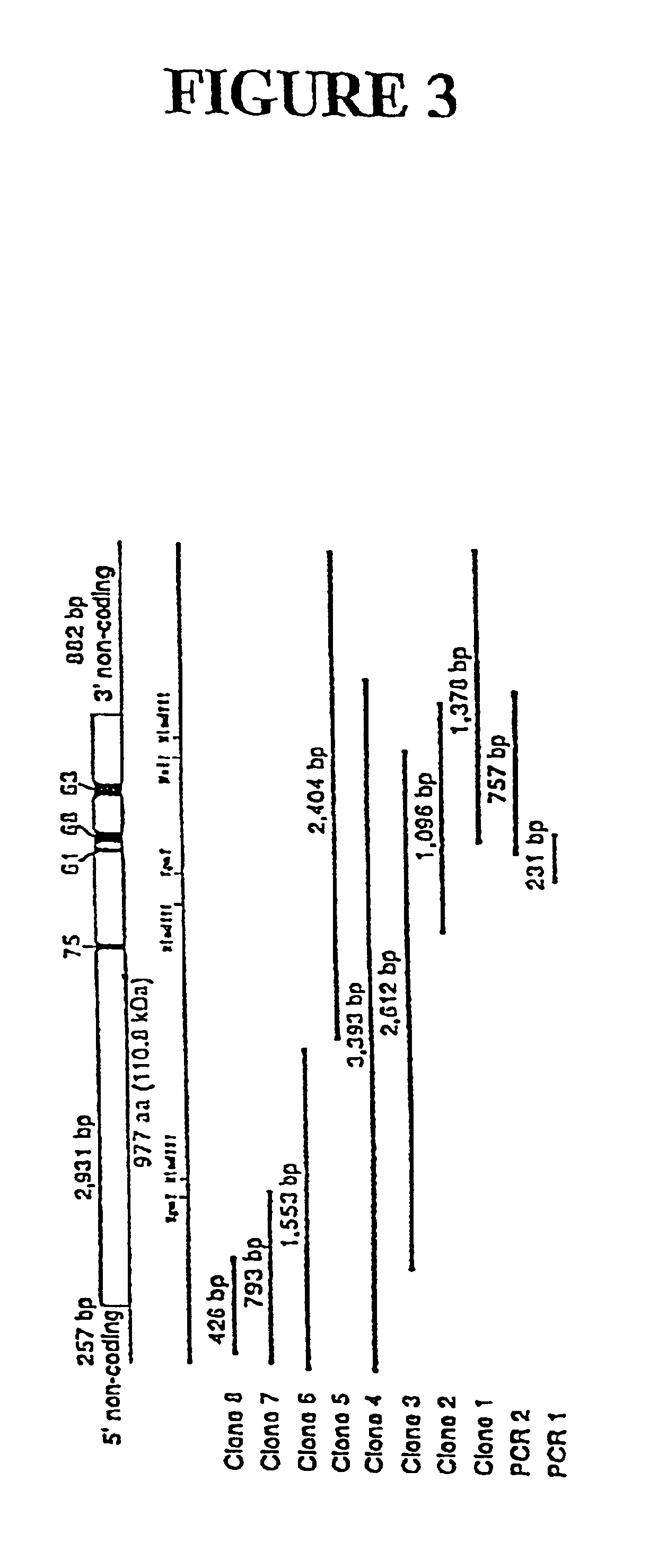
Genes encoding several poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase (PARG) enzymes, the proteins and fragments thereof, and antibodies immunoreactive therewith
InactiveUS6906180B2Modulate activitySugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEscherichia coliADAMTS Proteins
The isolation and characterization of cDNAs encoding poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase (PARG) enzymes and the amino acid sequences of PARGs from several species are described. PARG is involved in the cellular response to DNA damage and its proper function is associated with the body's response to neoplastic disorder inducing agents and oxidative stress. Expression vectors containing the cDNAs and cells transformed with the vectors are described. Probes and primers that hybridize with the cDNAs are described. Expression of the cDNA in E. coli results in an enzymatically active protein of about 111 kDa and an active fragment of about 59 kDa. Methods for inhibiting PARG expression or overexpressing PARG in a subject for therapeutic benefit are described. Exemplary of PARG inhibitors are anti-sense oligonucleotides. The invention has implications for treatment of neoplastic disorder, heart attack, stroke, and neurodegenerative diseases. Methods for detecting a mutant PARG allele are also described. Antibodies immunoreactive with PARGs and fragments thereof are described.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Chimeric antigen receptor targeting of tumor endothelium
InactiveUS20180008670A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntigen receptorsCell membrane
Disclosed are methods, protocols, and compositions of matter related to utilization of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) expressing cells for the targeting of tumor endothelium utilizing chimeric antigen receptor expressing stem cells. In one embodiment tumor endothelium specific antigens are utilized as targets of the antigen binding domain of a CAR, which is attached to an extracellular hinge domain, a domain that transverses the T cell membrane and an intracellular domain associated with T cell signaling. Suitable antigens for the practice of the invention include TEM-1, ROBO-4, surviving, and FasL. In other aspects of the invention antigens are identified through serological analysis of recombinant cDNA expression libraries (SEREX) using plasma from a patient immunized with placental endothelial cells.
Owner:BATU BIOLOGICS
Biologically phenotypic RNA array of high-flux detection of mRNA expression abundance
InactiveCN1390956AAccurate evaluationQuantitatively accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementConcentration gradientCdna expression
A biologically phenotypic RNA array for high-flux detection of mRNA expression abundance features that different biological pheno typic RNAs are applied onto an array carrier, and each RNA has a particular concentration gradient, so said array has different concentration gradients for different samples, resulting in precisely quantitating particular mRNA. Said array can be used for disease diagnosis, gene detection and therapy, agricultural purpose, etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
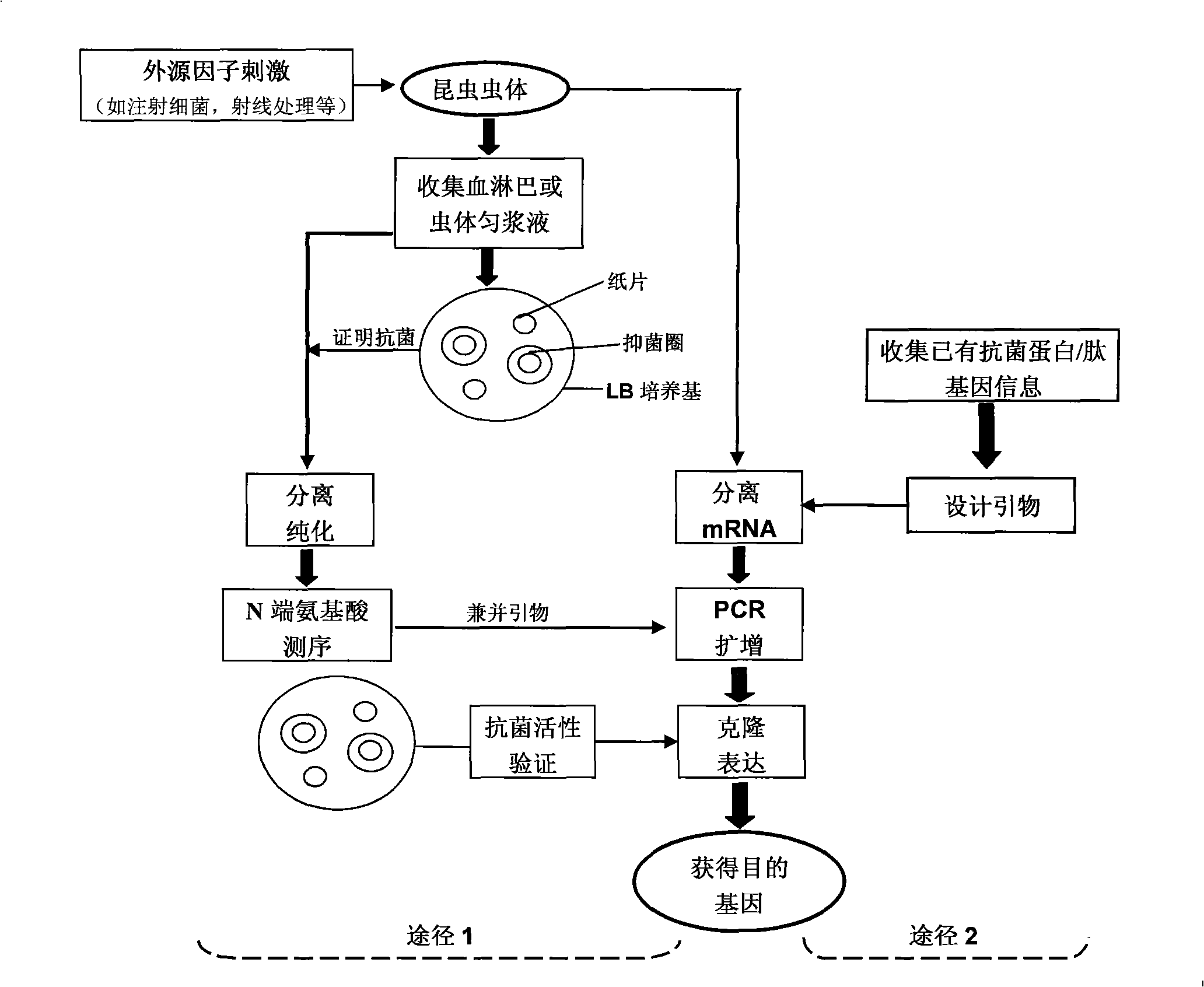
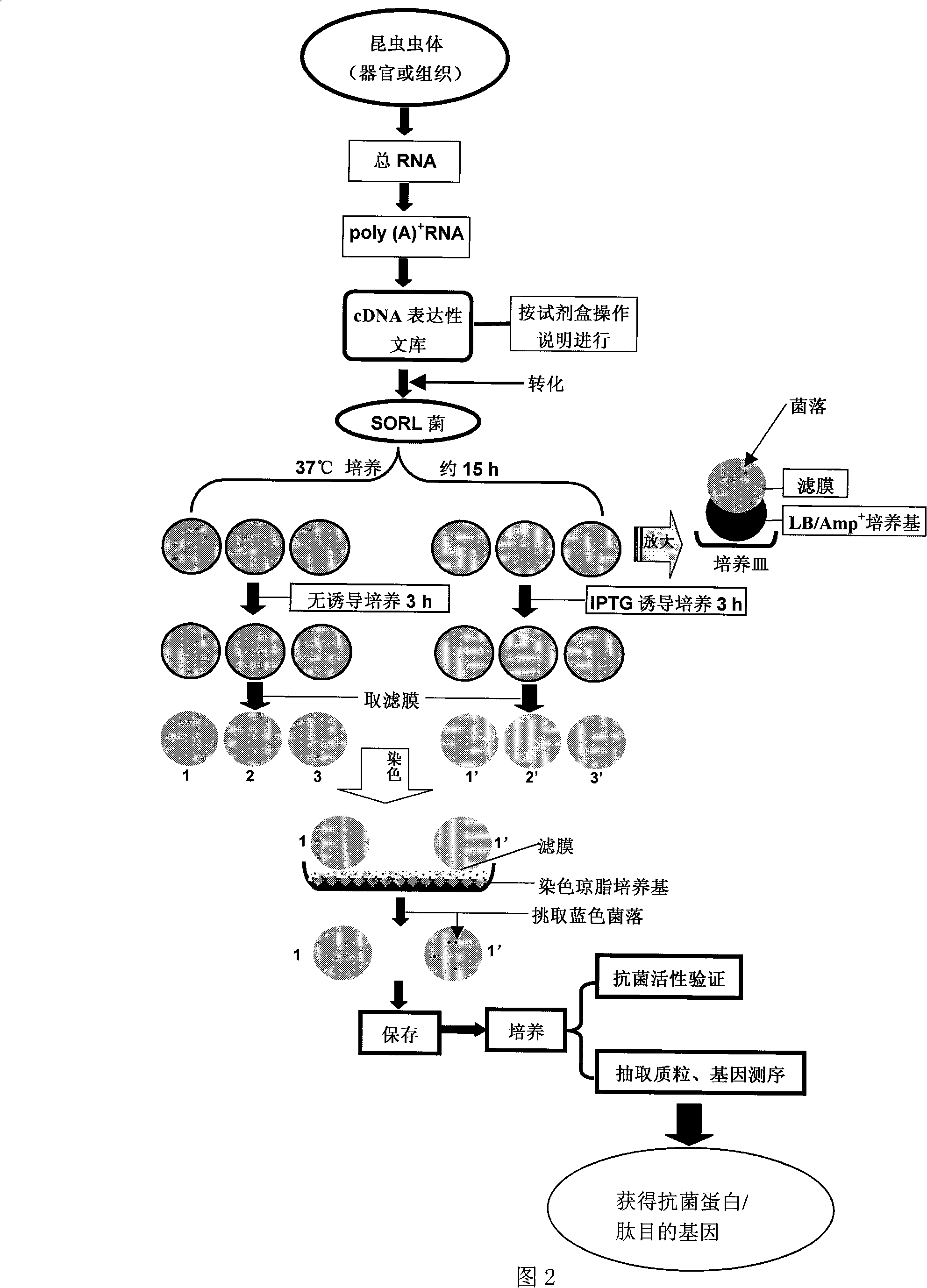
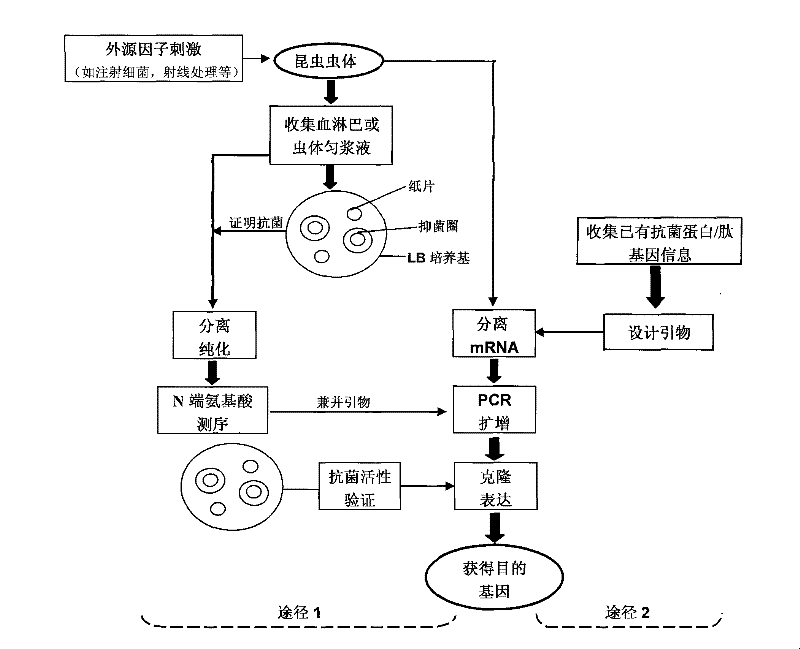
Construction of insect source antibiotic protein/peptide gene and screening method thereof
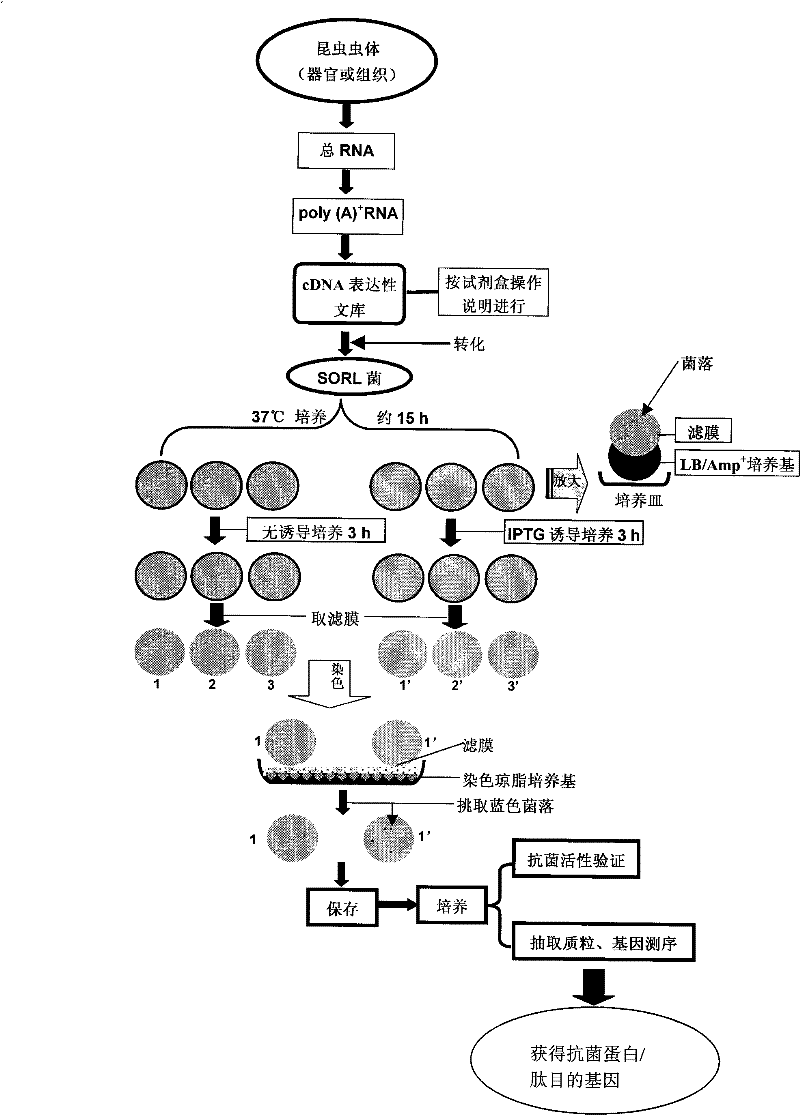
InactiveCN101328616ADirect screeningQuick filterMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningFiltration membraneScreening method
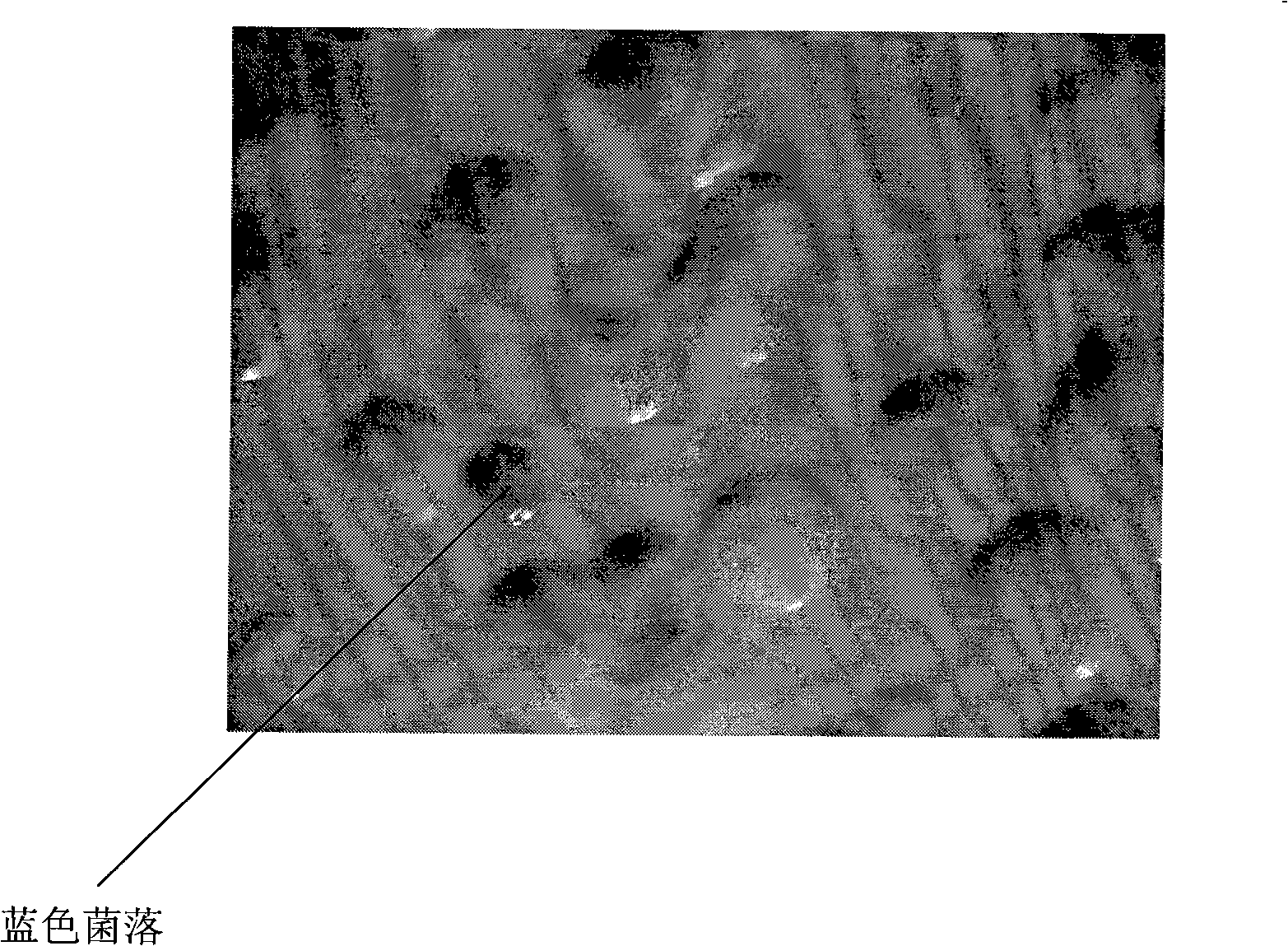
The invention relates to a method for establishing and screening an insect source antibacterial protein / peptide gene library, comprising the following steps: firstly, a cDNA expression library of an insect source antibacterial protein / peptide gene is established; and secondly, the cDNA expression library is screened, which comprises the following steps: a. an SOLR bacterium liquid is prepared; b. a prophage library is transferred into the prepared SOLR bacterium liquid for titer measurement; c. a LB / Amp<+> filtration membrane flat plate is prepared; and d. the transferred SOLR bacterium liquid is taken for being applied to the plate, and cultivation is performed until colonies are grown up to between 0.9 and 1.1 millimeters, the colonies are transferred into a dyeing agar culture medium for dyeing; simultaneously the colonies are compared with colonies which do not undergo IPTG induction culture; blue colonies are selected and stored in 100 milliliters of LB / Amp<+> culture media which contain 20 percent of glycerol at a temperature of 70 DEG C below zero, and then the insect source antibacterial protein / peptide gene library is obtained. By adoption of the method to establish and screen the insect source antibacterial protein / peptide gene library, the pertinence and the efficiency of the screening can be greatly improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Construction of insect source antibiotic protein/peptide gene and screening method thereof
InactiveCN101328616BDirect screeningQuick filterMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningFiltration membraneScreening method
The invention relates to a method for establishing and screening an insect source antibacterial protein / peptide gene library, comprising the following steps: firstly, a cDNA expression library of an insect source antibacterial protein / peptide gene is established; and secondly, the cDNA expression library is screened, which comprises the following steps: a. an SOLR bacterium liquid is prepared; b.a prophage library is transferred into the prepared SOLR bacterium liquid for titer measurement; c. a LB / Amp<+> filtration membrane flat plate is prepared; and d. the transferred SOLR bacterium liquid is taken for being applied to the plate, and cultivation is performed until colonies are grown up to between 0.9 and 1.1 millimeters, the colonies are transferred into a dyeing agar culture medium for dyeing; simultaneously the colonies are compared with colonies which do not undergo IPTG induction culture; blue colonies are selected and stored in 100 milliliters of LB / Amp<+> culture media which contain 20 percent of glycerol at a temperature of 70 DEG C below zero, and then the insect source antibacterial protein / peptide gene library is obtained. By adoption of the method to establish and screen the insect source antibacterial protein / peptide gene library, the pertinence and the efficiency of the screening can be greatly improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
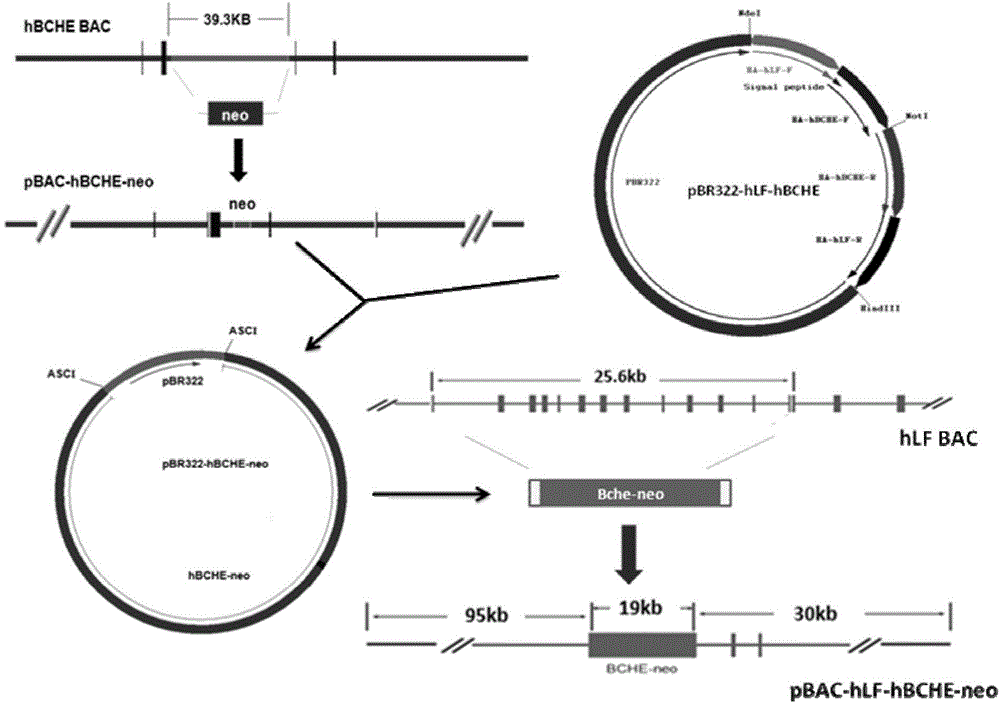
Method for utilizing human butyrylcholinesterase minigene to express recombinant human butyrylcholinesterase in mammary gland
The present invention provides a method for utilizing human butyrylcholinesterase minigene to express recombinant human butyrylcholinesterase in mammary gland. According to the method, the human butyrylcholinesterase minigene is adopted to completely replace the target gene on the artificial chromosome of the mammal mammary gland specific expression protein by using the recombinant technology, such that the exogenous gene acquires the complete regulation sequence highly expressing the target gene in the mammary gland; under the premise of no influence on transcription and translation of the butyrylcholinesterase gene, the size of the human butyrylcholinesterase gene is reduced through the modification on the artificial chromosome so as to obtain the human butyrylcholinesterase minigene; and the obtained recombinant artificial chromosome is transformed into the mammal so as to express the recombinant human butyrylcholinesterase in the animal mammary gland. According to the present invention, the disadvantages that the position effect of the exogenous gene expression and easy silencing of the cDNA expression exogenous gene are overcome, the in vitro recombination operation is easy to perform, the vector construction is convenient, and the new strategy is provided for the expression of the large structure gene protein.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Methods for detection and treatment of neural cancers
InactiveUS7192704B2Prevent proliferationCompound screeningApoptosis detectionNervous systemNeural cell
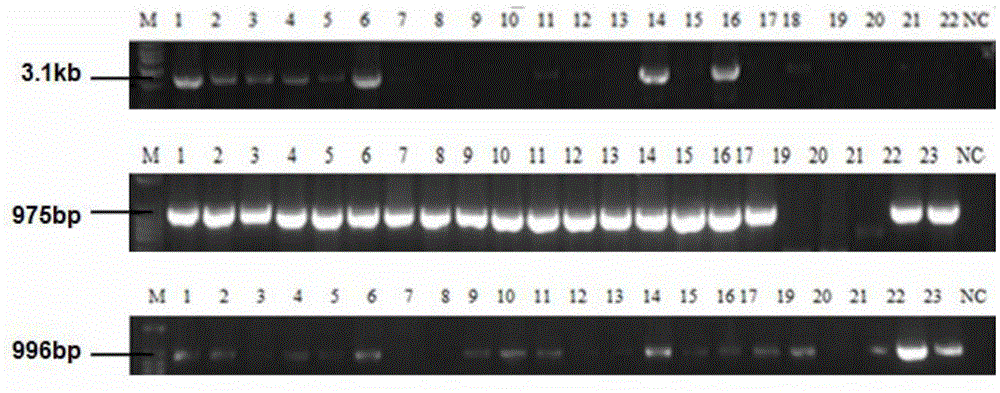
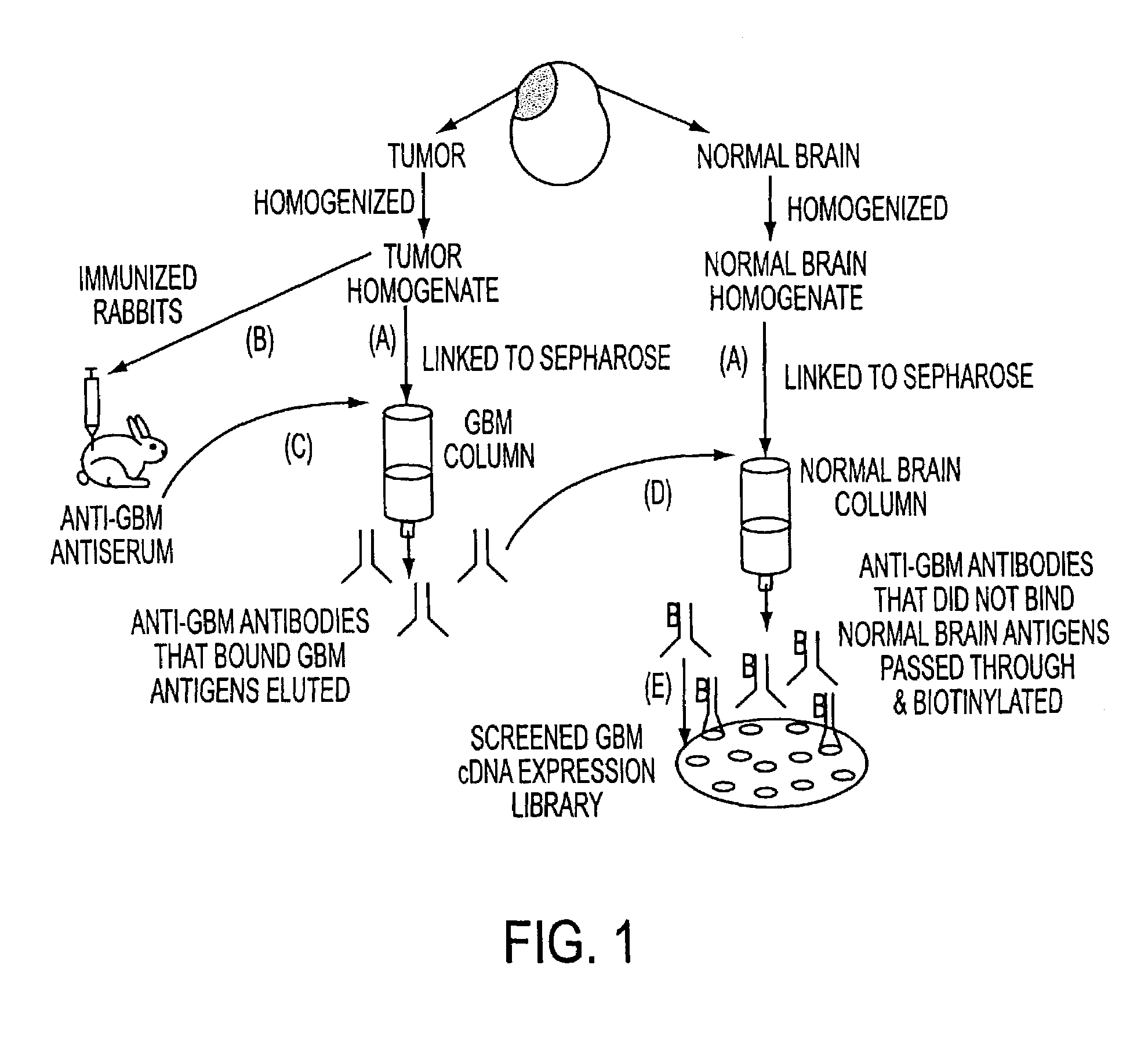
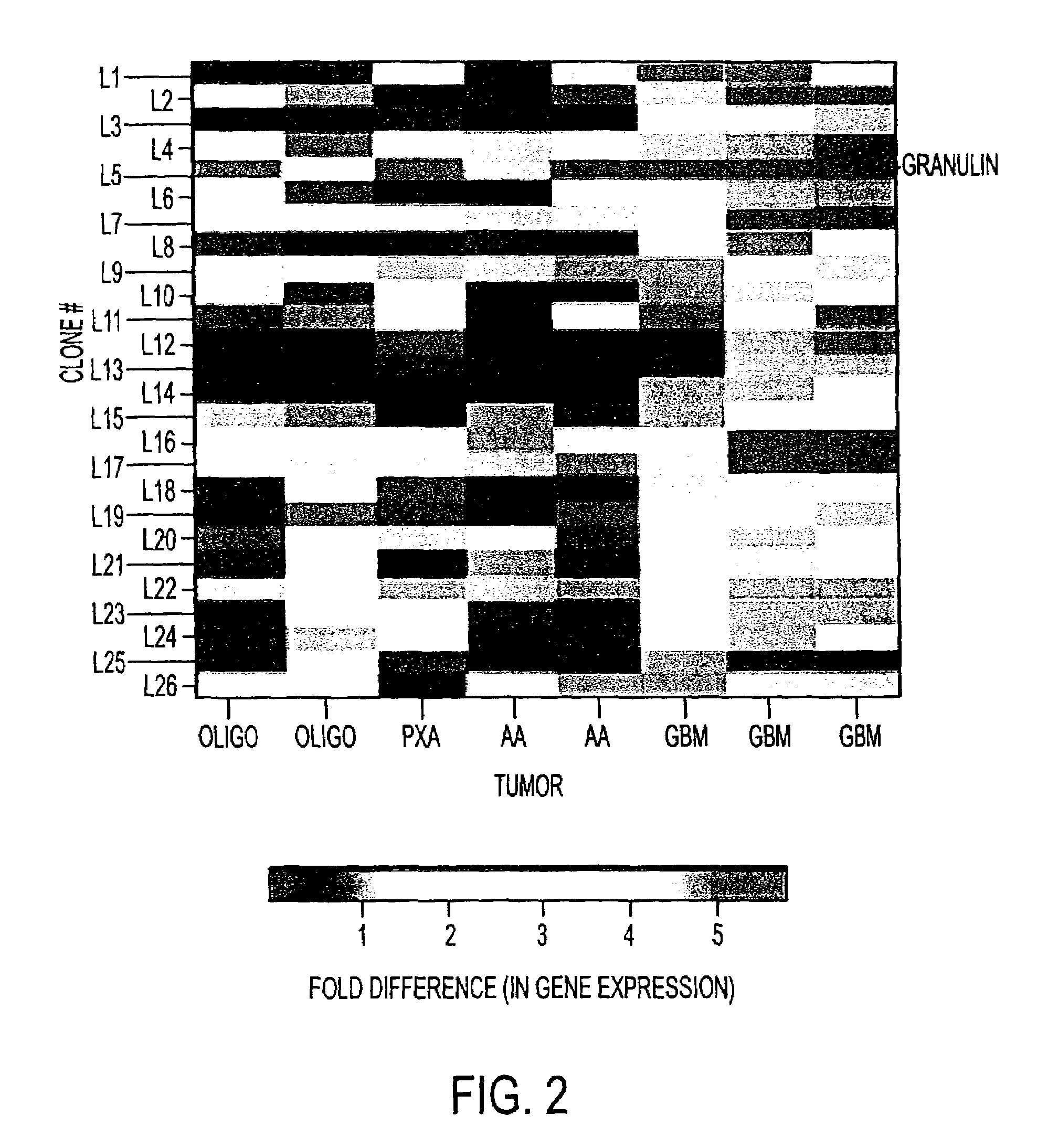
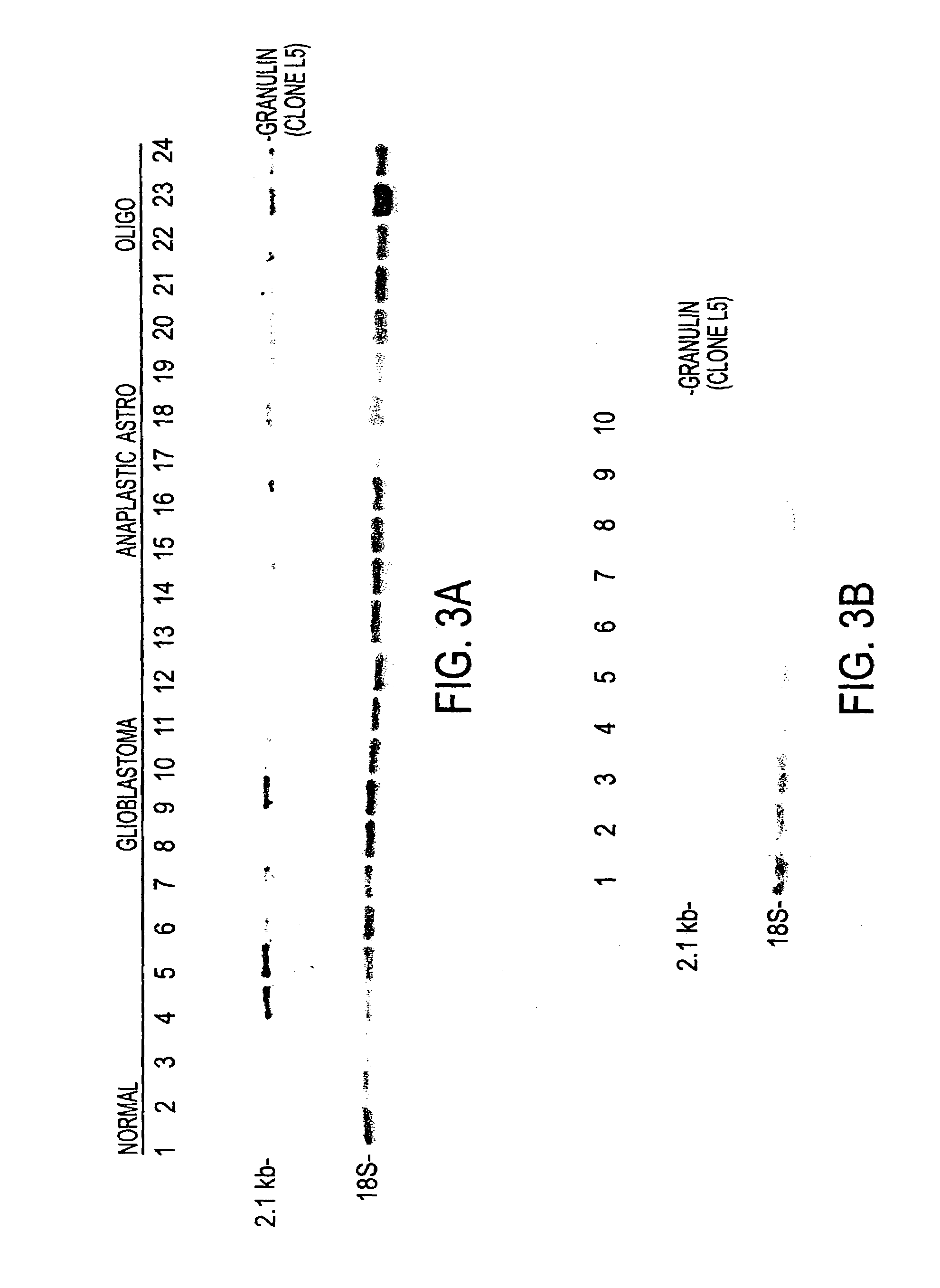
The invention provides a method for inhibiting proliferation of neural cells. The neural cells can be tumor cells, glial cells, neuronal cells, and cells of the central or peripheral nervous systems. The method comprises contacting a neural cell with a molecule that disrupts the biological activity of a granulin molecule. In one embodiment, the molecule is an antibody directed against a granulin peptide. In other embodiments, the molecule is an antisense nucleotide directed against a granulin nucleic acid molecule, or a vaccine comprising a granulin peptide or a polynucleotide encoding a granulin peptide. The invention additionally provides methods for detecting and treating cancer in a neural tissue using granulin-related molecules. Also provided is a method for indenting differentially expressed gene products that are translated from mRNA species, using antibody-based screening of a cDNA expression library. This method, termed differential immuno-absorption (DIA), can be coupled to cDNA microarray hybridization and used in the identification of genes that play a role in the malignant progression of cancer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Application of human heparinase cDNA expression vector in preparing anti human heparinase immune antibody
InactiveCN101457232AAids in clinical diagnosisAids in prognosisSerum immunoglobulinsVector-based foreign material introductionTumour tissueSerum ige
The invention discloses a novel use of a human heparanase cDNA expression vector that is the application in preparation of the human heparanase immune antibody. The human heparanase cDNA expression vector is a recombinant vector containing a human heparanase complete coding cDNA. The detection results show that the immune serum obtained by the human heparanase cDNA expression vector in the invention has an immunological characteristics aiming at the heparanase, the purified anti-human heparanase immune antibody can be used in the scientific research and clinic such as the human blood serum, the qualitative and quantitative detection of the heparanase in a tumour tissue and is useful for the clinic diagnosis and prognosis judgement of the relative disease. The human heparanase cDNA expression vector plays important roll in the preparation of the anti-human heparanase immune antibody and the medicine field and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:FIELD OPERATION BLOOD TRANSFUSION INST OF PLA SCI ACAD OF MILITARY
Method for constructing membrane protein cDNA library and use thereof
ActiveCN101338454BStrong specificityEliminate distractionsBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceCDNA libraryFluorescence
The invention relates to a construction method of a Membrane protein cDNA library and an application thereof. The method constructs a eukaryotic expression vector used for the specificity selection of the membrane protein. The expression vector can perform clone recombination with any cDNA clone library provided with the recombination site attL of Lambada bacteriophage so as to acquire a cDNA expression library. After the transfection of COS-1 cell, expression membrane protein clone is further selected by immunofluorescence so as to acquire the membrane protein cDNA expression library. As theapplication of the method, the liver lymphocyte membrane protein cDNA library of a C57BL / 6 rat is built up. The method is proved to be an effective proposal of the high flux specificity selection membrane protein through the identification and analysis of the library, and the method provides a powerful method to describe the map of the membrane protein of the cell surface of certain issue and to research the unknown membrane protein.
Owner:IMMUNOPHARMACEUTIC INST OF HEFEI RUIDA CO LTD
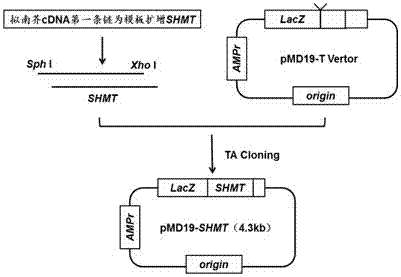
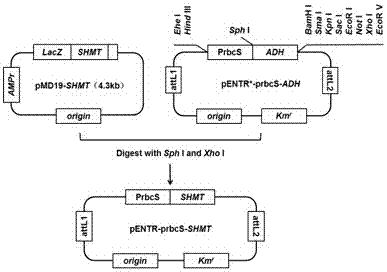
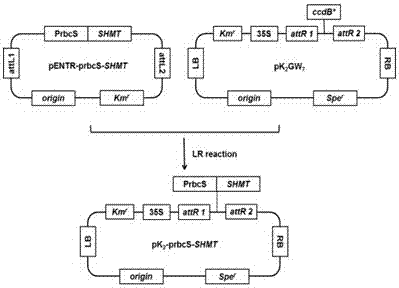
Application of Dual Expression of Serine Hydroxymethyltransferase Gene and Formate Dehydrogenase Gene in Arabidopsis
ActiveCN104774866BIncrease absorption rateIncrease resistanceFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHigh concentrationNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses the dual expression application of Arabidopsis thaliana serine hydroxymethyltransferase gene and formate dehydrogenase gene. The invention uses Arabidopsis thaliana serine hydroxymethyltransferase SHMT gene cDNA to construct a plant expression vector, and mediates it through Agrobacterium Transform into tobacco, after the detection is correct, the plant expression vector constructed by Arabidopsis formate dehydrogenase FDH gene cDNA is transferred into it through Agrobacterium-mediated, and the double-expression transgenic tobacco with two exogenous genes SHMT / FDH inserted can be obtained. Improve the plant's ability to absorb and tolerate formaldehyde; the experimental results show that double-expression transgenic tobacco can effectively reduce the toxicity of HCHO to plants by changing the content of tobacco chlorophyll and soluble sugar, so that the transgenic tobacco leaves can maintain better under the stress of higher concentration of HCHO HCHO absorption energy; double-expression transgenic tobacco can effectively reduce the occurrence of oxidative stress, and this effect is more significant than single-expression transgenic tobacco.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Three Frame cDNA Expression Libraries for Functional Screening of Proteins
InactiveUS20070231906A1High frequencyImprove efficiencySugar derivativesFermentationProtein compositionCdna expression
Compositions and methods are provided for generating three frame cDNA expression libraries for functional screening of proteins. The invention includes sets of 5′ adapters for cloning cDNA molecules in which the sets include three adapters that can be used to clone a particular cDNA in all three reading frames. The libraries so generated have greater complexity of expressed open reading frames, and thus can improve the success of functional protein screens, such as two hybrid screens. The adapters also have recombination sites for efficient cloning and transfer between systems.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com