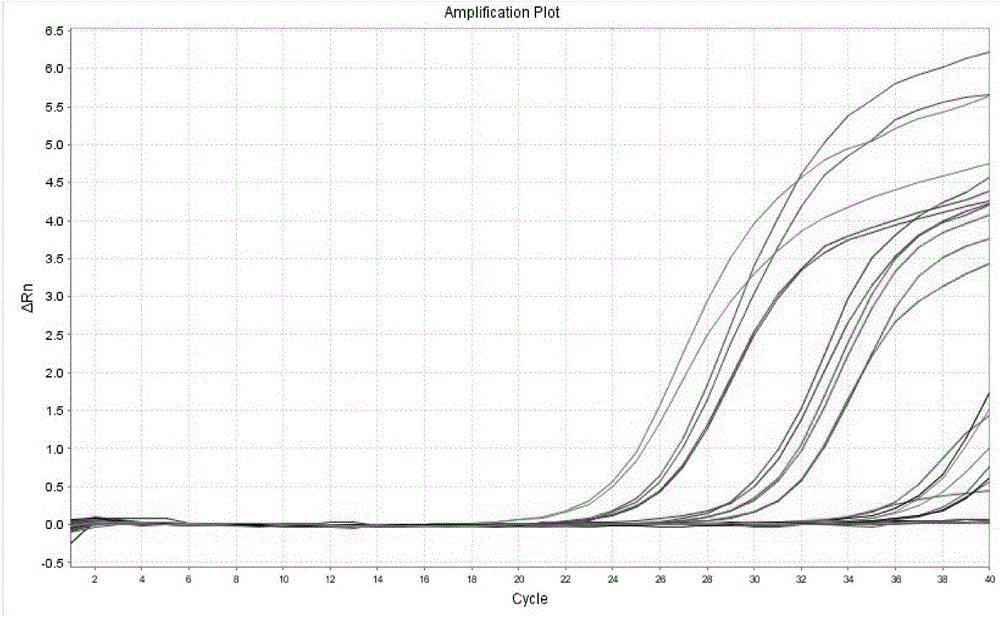
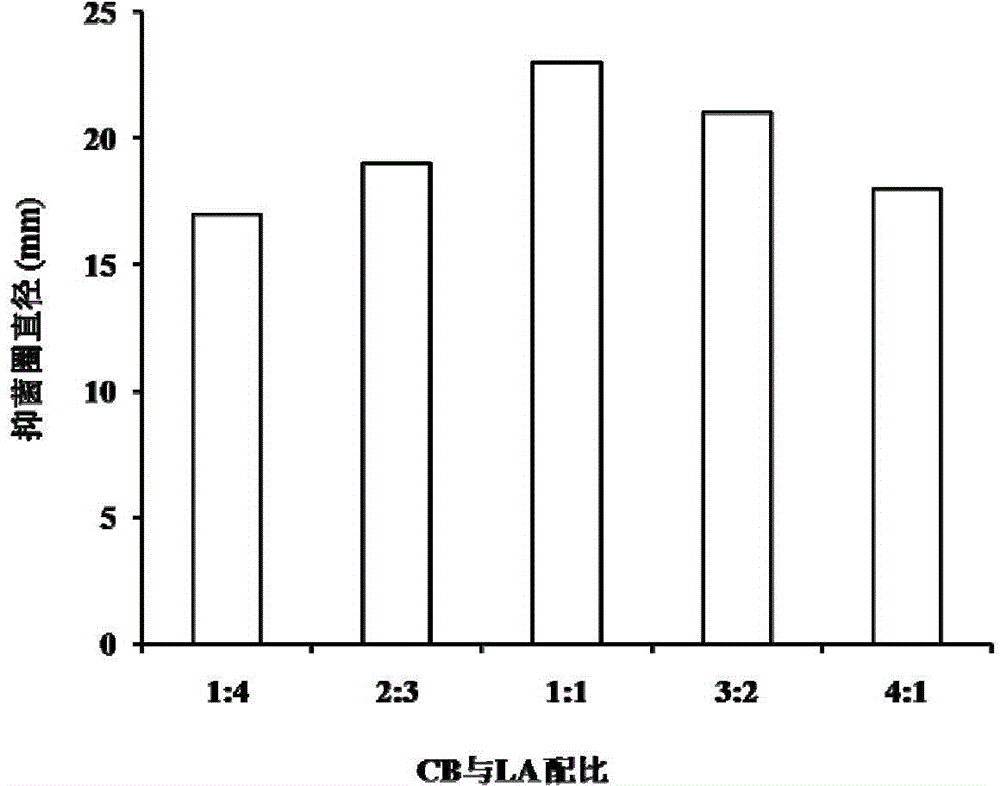
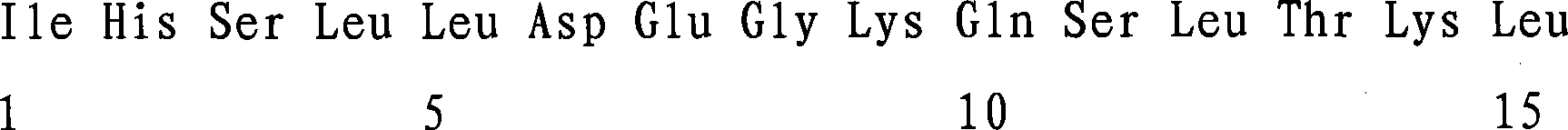Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
90 results about "Bacillus infections" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Probiotic lactic acid bacterium to treat bacterial infections associated with SIDS
Compositions including a non-pathogenic lactic acid-producing bacteria, such as a Bacillus species, spores or an extracellular product of B. coagulans, formulated for oral administration to the intestinal tract for inhibiting bacterial gastrointestinal infections are described. Methods and systems using the compositions for treating gastrointestinal infections, particularly sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) are also disclosed.
Owner:GANEDEN BIOTECH
Reduction in bacterial colonization by administering bacteriophage compositions
InactiveUS7459272B2Reduce and eliminate colonizationReduce riskAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesAcquired immunodeficiency
The present invention provides a method for reducing the risk of bacterial infection or sepsis in a susceptible patient by treating the susceptible patient with a pharmaceutical composition containing bacteriophage of one or more strains which produce lytic infections in pathogenic bacteria. Preferably, treatment of the patient reduces the level of colonization with pathogenic bacteria susceptible to the bacteriophage by at least one log. In a typical embodiment, the susceptible patient is an immunocompromised patient selected from the group consisting of leukemia patients, lymphoma patients, carcinoma patients, sarcoma patients, allogeneic transplant patients, congenital or acquired immunodeficiency patients, cystic fibrosis patients, and AIDS patients. In a preferred mode, the patients treated by this method are colonized with the pathogenic bacteria subject to infection by said bacteriophage.
Owner:INTRALYTIX
Reagent for detecting tubercle bacillus infection in vitro and method thereof
ActiveCN101446585AValid in vitro assayOvercome the disadvantages of unsatisfactory effectImmunoglobulins against bacteriaBiological testingBCG vaccineT cell
The invention discloses a reagent for detecting tubercle bacillus infection in vitro and a method thereof. The reagent comprises M233 polypeptide represented by SEQ ID No.1; and cytokine released from T cells is detected by contacting the M233 polypeptide or an analog thereof with the T cells of a tubercle bacillus host to determine whether the T cells identify the M233 polypeptide or the analog thereof. The reagent has the advantages of high sensitivity, good specificity, being free from interference of BCG vaccine and non-tuberculosis mycobacteria vaccine, being capable of detecting active pulmonary tuberculosis patients, the patients with dormant infection and healthy persons who contact with mycobacterium nontuberculosis. The reagent and the method are especially applicable to detecting tuberculosis and / or dormant infection thereof for Chinese people.
Owner:GUANGZHOU RHFAY BIOTECH CO LTD
Expression vectors for treating bacterial infections
The present invention is compositions and methods for producing anti-bacterial polypeptides, and for using those compositions and methods for treating diseases and conditions caused by a bacterial infection. More specifically, the compositions and methods include treating a gram-negative bacterium with a gram-positive host that produces a polypeptide effective against the gram-negative bacterium.
Owner:CANBIOCIN
Use of bacterial phage associated lysing enzymes for treating streptococcal infections of the upper respiratory tract-
A composition for treatment of bacterial infections of the eye is disclosed which comprises a lytic enzyme composition specific for the infecting bacteria, and a carrier for delivering said lytic enzyme.. The carrier for delivering at least one lytic enzyme to the eye may be but is not limited to the use of an isotonic solution..
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Hybridoma cell strain secreting tetanus exotoxin monoclonal antibody, monoclonal antibody prepared by same, Fab antibody and application
InactiveCN102690789AGood effectHas the effect of neutralizing tetanus exotoxinAntibacterial agentsFungiClostridium tetaniTotal rna
The invention relates to a mouse hybridoma cell strain secreting a clostridium tetani bacillus exotoxin monoclonal antibody, wherein the strain has a preservation number of CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection) NO. C201257. The invention further relates to a clostridium tetani bacillus exotoxin monoclonal antibody prepared by the mouse hybridoma cell strain; the invention further provides an Fab antibody, comprising a kappa chain and an Fd chain; the kappa chain and the Fd chain are obtained by amplifying from total RNA (ribonucleic acid) of the hybridoma cell strain. The invention further relates to a medicine for preventing or treating clostridium tetani bacillus infection, comprising the clostridium tetani bacillus exotoxin monoclonal antibody and / or the Fab antibody, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. According to the invention, a monoclonal antibody for effectively neutralizing tetanus exotoxin is screened with natural tetanus exotoxin, and an Fab gene engineering antibody which is produced by large scale in vitro and which has toxin neutralizing effect is prepared with a gene engineering antibody technology on the basis of the monoclonal antibody.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV +1
Colon bacillus outer membrane protein monoclonal antibody and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102584992AStrong specificityIncreased sensitivityAntibacterial agentsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaESCHERICHIA COLI ANTIGENBALB/c
The invention belongs to the technical field of veterinary biology, and particularly relates to a colon bacillus outer membrane protein monoclonal antibody and a preparation method and an application thereof. The antibody is prepared by taking cloned, expressed and purified taking avian pathogenic escherichia coli 78 (APECO78) outer membrane protein as an antigen immune BALB / c mouse with a hybrid tumor technology. The antibody has high specificity and high sensitivity, and an experimental basis is laid for future rapid and specific detection of colon bacillus infection with an immunology method. Meanwhile, as proved by an experiment, the monoclonal antibody disclosed by the invention has high neutralizing activity and protecting efficiency on colon bacillus infection of the same type, and can be used for preventing colibacillosis.
Owner:兆丰华生物科技(南京)有限公司 +1
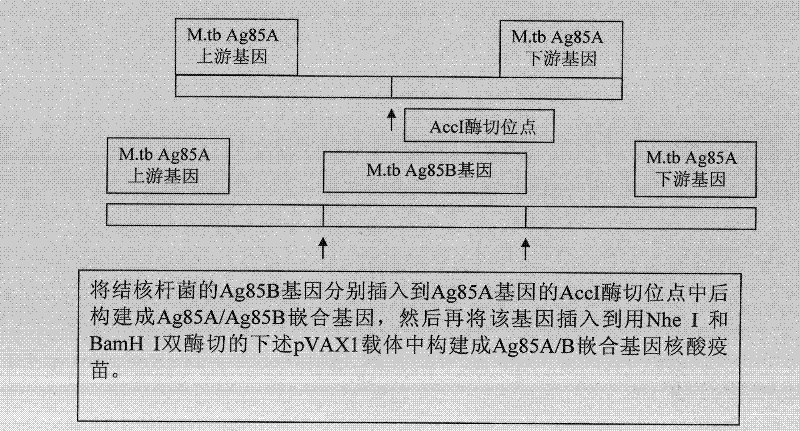
Mycobacterium tuberculosis ag85ab chimeric gene vaccine, its preparation method and application
ActiveCN102268446AStrong immune responseGood treatment effectAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAdjuvantLevamisole
The invention provides a mosaic gene, which comprises a gene for coding tubercle bacillus protein Ag85a and a gene which is mosaiced at a Kpn I recognition sequence at sites 245-250 and / or an Acc I recognition sequence at sites 430-435 of Ag85a gene for coding the tubercle bacillus protein Ag85b. The invention provides a mosaic gene-containing mosaic tubercle bacillus gene vaccine, wherein the Ag85a gene is connected to a eukaryotic expression vector. The invention also provides a preparation method of the mosaic tubercle bacillus gene vaccine. The method comprises the following steps of: performing PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification on an Ag85b gene segment; inserting the amplified Ag85b gene segment into the Ag85b gene-containing eukaryotic expression vector; and connecting by using ligase. The mosaic tubercle bacillus gene vaccine can be used for treating drug-resistant tubercle bacillus infection and can also be used in combination with levamisole serving as an adjuvantto induce stronger anti-tubercular cell immunological response.
Owner:GUAN DINGTAI HAIGUI BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Expression Vectors for Treating Bacterial Infections
The present invention is compositions and methods for producing anti-bacterial polypeptides, and for using those compositions and methods for treating diseases and conditions caused by a bacterial infection. More specifically, the compositions and methods include treating a gram-negative bacterium with a gram-positive host that produces a polypeptide effective against the gram-negative bacterium.
Owner:CANBIOCIN
Method of extracting mycobacterium tuberculosis DNA and kit for detecting multiple drug resistance of mycobacterium tuberculosis
InactiveCN103911365AAutomate processingEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationFluorescenceMycobacterium Infections
The invention discloses a method of extracting mycobacterium tuberculosis DNA and a kit for rapidly and accurately detecting multiple drug resistance (MDR) of mycobacterium tuberculosis. The method includes: extracting DNA to be detected from a clinical sample, determining mycobacterium tuberculosis infection by utilization of fluorescence real-time quantification PCR, indentifying whether the mycobacterium tuberculosis is drug-resistant or not and identifying the drug-resistant bacterial strain causing infection, and finally determining the pathogen infection quantity. The method can be used for detecting the whole drug-resistant genes with 29 sites that are determined to cause tubercle bacillus resistance to drugs (comprising rifampicin, isoniazide and ethambutol), and is the most comprehensive rapid molecular diagnosis system comprising tubercle bacillus drug-resistant genes so far. Through unique primers, probes and selection of fluorochrome marking designs, all the drug-resistant gene sites are detected by application of multiple qPCR. The application is simple, convenient and rapid. The results are accurate and reliable. The method and the kit have great practical value and wide application prospects for rapidly diagnosing tubercle bacillus infection and determining drug resistance, thus performing targeted treatment.
Owner:南京爱必梦生物材料有限公司
Antimicrobial therapy for bacterial infections
InactiveCN101460059AImprove treatment effectivenessAntibacterial agentsBiocideMicroorganismStaphylococcus cohnii
The disclosure provides compounds and methods to treat bacterial pathogenesis, and demonstrates that the S. aureus pigment is a virulence factor and potential novel target for antimicrobial therapy.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
1'-acetoxy chavicol acetic ester
InactiveCN101020638AAntibacterial agentsCarboxylic acid esters separation/purificationSilica gelRhizome
The present invention discloses a supercritical CO2 extraction and silica gel column chromatographic process for extracting, separating and refining 1'-acetoxy chavicol acetic ester with activity of resisting tubercle bacillus infection from dried galangal rhizome as one kind of Zingiberaceae plant.
Owner:HONGYI SCI & TECH CO LTD NANCHANG
Preparation and application of composite microecological feed additive
ActiveCN103602614AImprove conversion ratePromote growthAntibacterial agentsBacteriaBiotechnologyFreeze-drying
The invention relates to the field of microecological feed additives, and particularly relates to preparation and application of a composite microecological feed additive. The composite microecological feed additive provided by the invention is prepared from screened active compound probiotics. Diarrhea caused by domestic animal bacterial infections can be prevented and treated. Two probiotics used by the composite microecological feed additive have the abilities of inhibiting infection of common gastrointestinal pathogens of animals, including shigella dysenteriae, pathogenic escherichia coli and salmonella enteritidis, and also can reduce the toxicity caused by dysentery bacillus infection Caco-2 cells and inhibit adhesion of the shigella dysenteriae to the Caco-2 cells. Finally, the obvious effects of stimulating the animal immunity, improving the gastrointestinal digestion abilities of animals, and promoting animal growth are achieved. A production technology of a strain adopts a liquid fermental cultivation technology and a low-temperature freeze drying technology, so that the obtained inoculant is high in survival rate and purity. The composite microecological feed additive is a green environment-friendly feed additive.
Owner:南京曜动节能环保科技有限公司
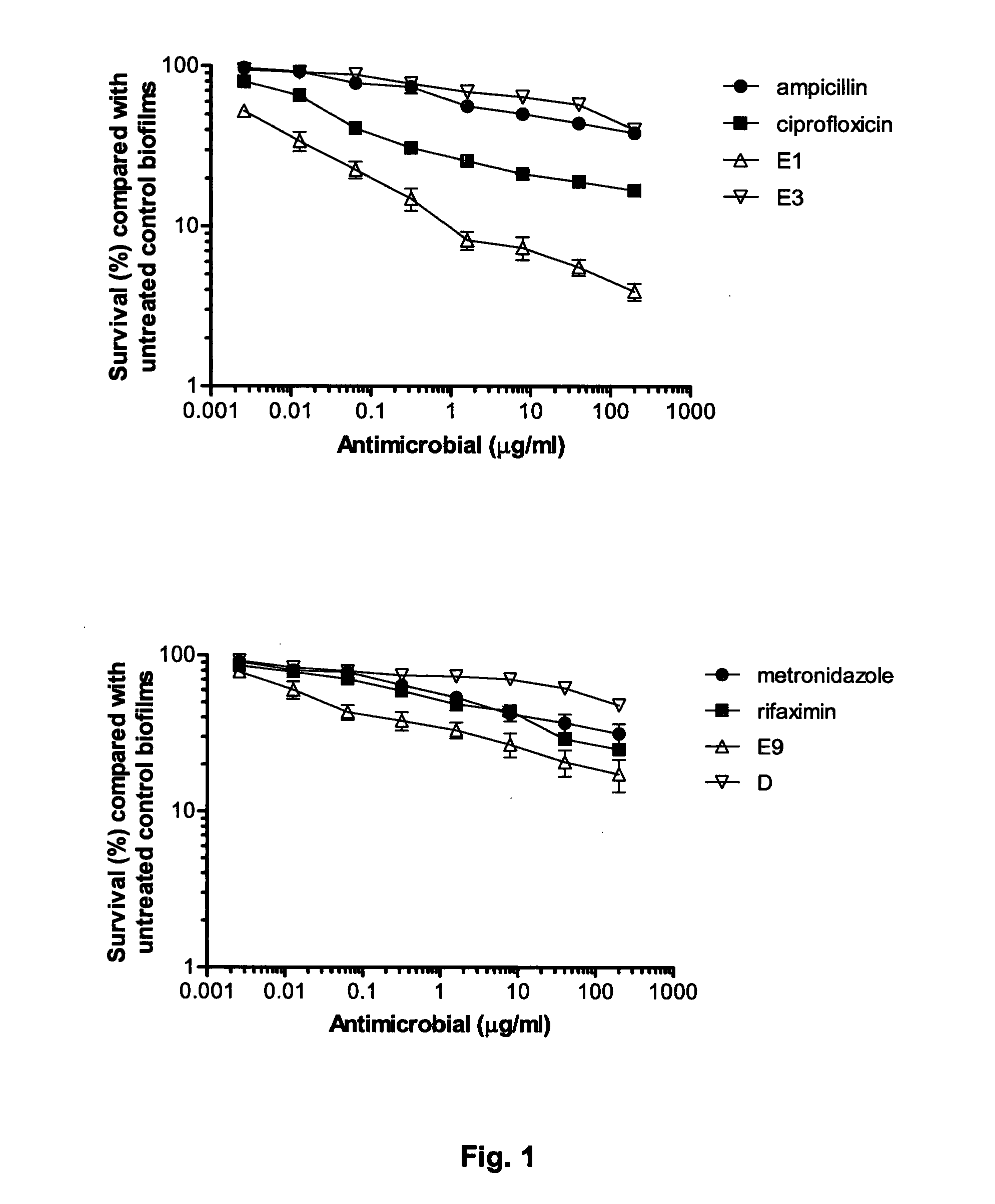
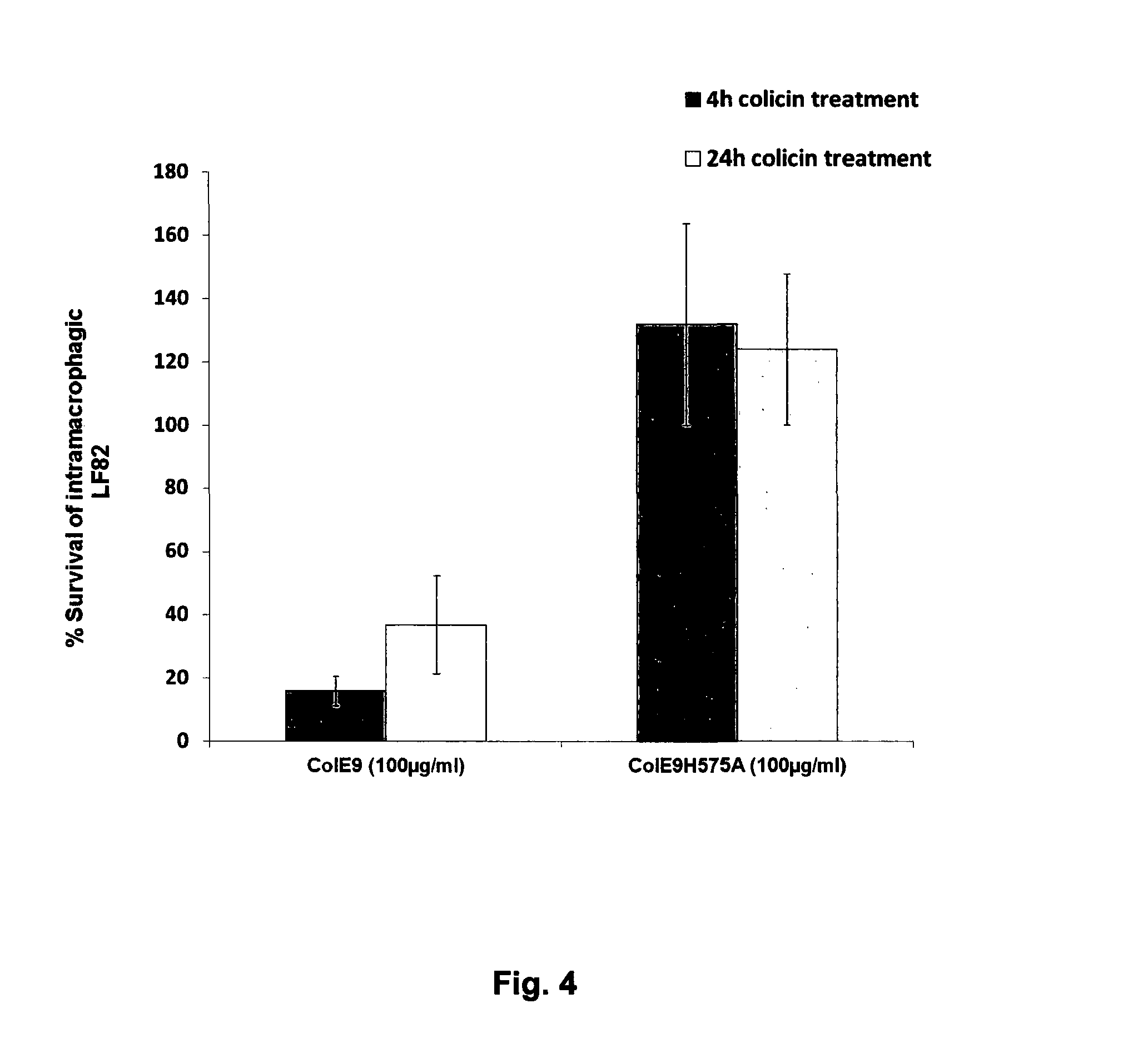
Colicins for Treating Bacterial Infections
InactiveUS20150164984A1Highly active andUsing treatment methodAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseEscherichia coli
The Invention relates to materials and methods for the treatment of conditions associated with bacterial biofilms, intracellular bacterial infections and / or adherent-invasive Escherichia coli infections, including Crohns' disease. In particular, the invention relates to the use of colicins and bacteria producing colicins, for the treatment of such conditions.
Owner:UNIV OF GLASGOW THE UNIV COURT OF
Bacterial endotoxin for the prevention of metabolic disorders and bacterial infections
InactiveUS20100113384A1Avoid developmentEffective preventionAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesGemella
The invention provides compositions and methods for preventing a metabolic disorder or bacterial infection in a subject, the composition comprising a bacterial endotoxin.
Owner:THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV OF ALBERTA
Preparation and application of synthetic polypeptide medicaments for treating tubercle bacillus infection contamination
InactiveCN101293925AAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntimicrobial peptidesComplete sequence
The invention provides a preparation method of a derivative of an antimicrobial peptide derived from Gekko sp. for treating Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection, belonging to the field of biomedicine. The antimicrobial peptide derivative is a single chain polypeptide synthesized from a natural polypeptide isolated from Chinese amphibian Gekko sp. The primary complete sequence of the polypeptide is: Val-Ser-Asn-Ala-Ala-Thr-His-Leu-Cys-Lys-His-Ala-His-Cysteine-His-Phe-Arg-Asp-Val-Cys-His-Asn-Trp-Met-Arg-His-Phe-Thr-Cys-Arg (NH2-VSNAATH LCKH AHC HF RDVCHNW MRHFTCR-COOH). The inventive antimicrobial peptide derivative can remarkably inhibit the growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis including multi-drug resistant strains, and can be used in preparing drugs for treating infection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis including multi-drug resistant strains.
Owner:王鹤尧 +1
Treatment of intracellular bacterial infection
An intracellular bacterial infection in a plant or animal is treated by administration to a plant cell or animal cell of a particle to which an infectious bacteriophage is covalently attached, wherein the particle is internalised by the cell. Particles with phage attached and compositions comprising the particles are provided. A formulation, for treatment of a bacterial infection, comprises bacteriophage, liquid carrier and adhesive, which dries so that the adhesive adheres the bacteriophage to a surface, one such formulation comprising liquid carrier: 85%-99.98% by weight; bacteriophage: 0.01%-5% by weight; and adhesive: 0.01%-10% by weight.
Owner:FIXED PHAGE
Mycobacterium tuberculosis EEC fusion protein, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110684116AEffectively differentiate infectionEffectively distinguish dead bacteria sensitizedAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsPolynucleotideTGE VACCINE
The invention discloses a mycobacterium tuberculosis EEC fusion protein. The amino acid sequence of the fusion protein is SEQ ID NO.8 in a sequence table; polynucleotide for encoding the polypeptide is shown as SEQ ID NO.7 in the sequence table; and the fusion protein contains a carrier of the polynucleotide and host cells. The invention further relates to preparation of the fusion protein, and effects of the fusion protein in tuberculosis auxiliary diagnosis, tubercle bacillus infection screening and tuberculosis vaccine development.
Owner:成都可恩生物科技有限公司 +1
Polypeptide for specificity detection of tubercle bacillus infection contamination, method and reagent kit thereof
InactiveCN101367867AReduce false positive rateNo change in false positive ratePeptidesMaterial analysisOrganismVaccine Immunogenicity
The present invention discloses a polypeptide with tubercle bacillus immunogenicity, which contains a sequence shown by Seq ID No.2 in the sequence table. The present invention also discloses an ELISPOT method, which utilizes the polypeptide to detect if a biological sample is infected with tubercle bacillus, and an agent box containing the polypeptide. When the polypeptide, the method and the agent box are adopted to detect the infectivity of tubercle bacillus, the false positive rate is greatly decreased, while the true positive rate can be kept unchanged.
Owner:SHENZHEN DAKEWE BIOENG
Treatment of intracellular bacterial infection
An intracellular bacterial infection in a plant or animal is treated by administration to a plant cell or animal cell of a particle to which an infectious bacteriophage is covalently attached, wherein the particle is internalized by the cell. Particles with phage attached and compositions comprising the particles are provided. A formulation, for treatment of a bacterial infection, comprises bacteriophage, liquid carrier and adhesive, which dries so that the adhesive adheres the bacteriophage to a surface, one such formulation comprising liquid carrier: 85%-99.98% by weight; bacteriophage: 0.01%-5% by weight; and adhesive: 0.01%-10% by weight.
Owner:FIXED PHAGE
Herbal Nutraceutical Formulation to Reduce Oxidative Stress, Viral and Microbial Infections, and Inflammation
ActiveUS20190209634A1Potent antioxidantPotent anti-inflammatory propertyOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderTherapeutic effectBacillus infections
The main objective of the present invention is to develop an herbal formulation with high polyphenol concentrations. A therapeutic effect of ingredients in herbal composition with Antioxidants, Anti-inflammatories, Anti Viral & Anti Microbial properties to reduce Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Viral and Microbial Infections. The herbal composition promotes management of diabetes, regulation of cholesterol, also immune system processes that helps to fight against viral and bacterial infections, colds, or the flu, skin ailments such as Psoriasis & eczema. Herbal Composition comprises synergistic combination of Moringa Oleifera Leaf Powder, Spirulina & Aqueous extracts of Oregano Vulgare Leaf Extract, Shilajit extract, Rosemary Leaf extract, Pomegranate Fruit Preel extract, Amla fruit extract, Fenugreek Seed Extract, Curcumin Extract, Piperine extract. Therefore, the chosen herbal blend provides the body with all of the vitamins, minerals, and nutrients it needs to continuously boost health.
Owner:MORINGO ORGANICS INC
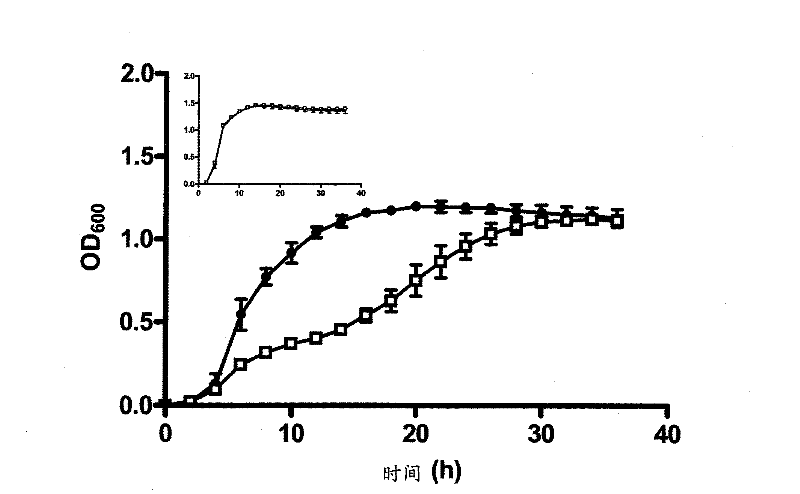
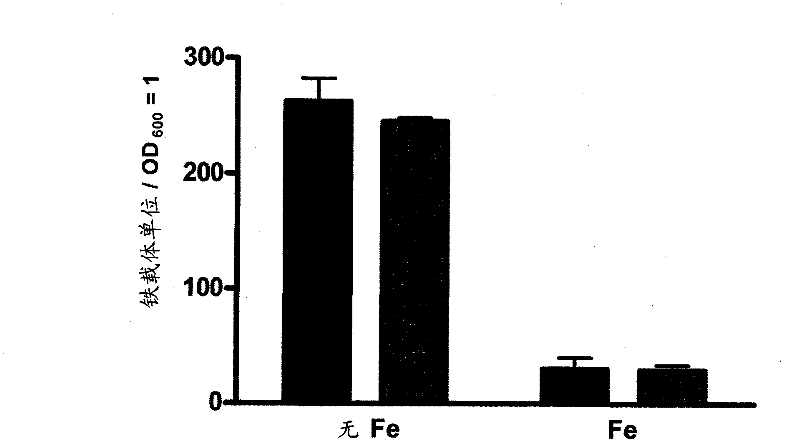
Siderophore-mediated iron uptake in bacterial infection
The present invention relates to methods of inhibiting S. aureus comprising inhibiting siderophore-mediated iron uptake, for example, staphyloferrm-mediated iron uptake Such methods of inhibiting S. aureus include the inhibition of staphyloferrm A- and staphyloferrm B- mediated uptake either by inhibiting expression or activity of staphyloferrm A and B or by inhibiting transport of staphyloferrm A and B The methods as provided would be useful for treating S. aureus infection.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
Gene chip detection method for detecting tubercle bacillus infection from clinical specimen
InactiveCN103571940AEasy to getSimple detection operationMicrobiological testing/measurementTotal rnaComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
The invention relates to a gene chip detection method for detecting tubercle bacillus infection from a clinical specimen. The gene chip detection method is used for detecting small RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) of tubercle bacillus in the clinical specimen. The method comprises the following steps: 1, extracting total RNA in the clinical specimen; 2, performing reverse transcription by taking the total RNA extracted in the step 1 to synthesize cDNA (complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid) and marking; 3, detecting the marked cDNA synthesized in the step 2 by using a gene chip.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation and application of antimicrobial peptide medicaments for treating tubercle bacillus infection contamination
InactiveCN101293926AAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntimicrobial peptidesComplete sequence
The invention provides a preparation method of a derivative of an antimicrobial peptide derived from Gekko sp. for treating Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection, belonging to the field of biomedicine. The antimicrobial peptide derivative is a single chain polypeptide synthesized from a natural polypeptide isolated from Chinese amphibian Gekko sp. The primary complete sequence of the polypeptide is: Val-Asn-Asn-Gly-Gly-Ser-Cys-Leu-Cys-Glu-His-Ile-His-Leu-Ile-Arg-Gly-Val-Cys-His-His-Leu-Met-Arg-Cys-Tyr-Ile-Lys-Arg (NH2-VNNGGS CLCEHIHLIRGVCHHLMRCYIKR-COOH). The inventive antimicrobial peptide derivative can remarkably inhibit the growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis including multi-drug resistant strains, and can be used in preparing drugs for treating infection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis including multi-drug resistant strains.
Owner:王鹤尧 +1
Hybridoma cell strain secreting tetanus exotoxin monoclonal antibody, monoclonal antibody prepared by same, Fab antibody and application
InactiveCN102690789BGood effectHas the effect of neutralizing tetanus exotoxinAntibacterial agentsFungiGenetic engineeringBacillus infections
The invention relates to a mouse hybridoma cell strain secreting a clostridium tetani bacillus exotoxin monoclonal antibody, wherein the strain has a preservation number of CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection) NO. C201257. The invention further relates to a clostridium tetani bacillus exotoxin monoclonal antibody prepared by the mouse hybridoma cell strain; the invention further provides an Fab antibody, comprising a kappa chain and an Fd chain; the kappa chain and the Fd chain are obtained by amplifying from total RNA (ribonucleic acid) of the hybridoma cell strain. The invention further relates to a medicine for preventing or treating clostridium tetani bacillus infection, comprising the clostridium tetani bacillus exotoxin monoclonal antibody and / or the Fab antibody, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. According to the invention, a monoclonal antibody for effectively neutralizing tetanus exotoxin is screened with natural tetanus exotoxin, and an Fab gene engineering antibody which is produced by large scale in vitro and which has toxin neutralizing effect is prepared with a gene engineering antibody technology on the basis of the monoclonal antibody.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV +1
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method for detecting tubercle bacillus infection from clinical specimen
ActiveCN103571938AEasy to getResistance to degradationMicrobiological testing/measurementTotal rnaComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
The invention relates to a reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method for detecting tubercle bacillus infection from a clinical specimen. The PCR detection method is used for detecting small RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) of tubercle bacillus in the clinical specimen. The method comprises the following steps: 1, extracting total RNA in the clinical specimen; 2, performing reverse transcription by taking the total RNA extracted in the step 1 to synthesize cDNA (complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid); 3, performing PCR detection aiming at a tubercle bacillus small RNA detection primer and cDNA synthesized in the step 2.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Polypeptide for specificity detection of tubercle bacillus infection contamination and reagent kit thereof
InactiveCN101367867BReduce false positive rateNo change in false positive ratePeptidesMaterial analysisTrue positive rateImmunogenicity
The present invention discloses a polypeptide with tubercle bacillus immunogenicity, which contains a sequence shown by Seq ID No.2 in the sequence table. The present invention also discloses a kit containing the polypetide as above. When the polypeptide and the kit are adopted to detect the infectivity of tubercle bacillus, the false positive rate is greatly decreased, while the true positive rate can be kept unchanged.
Owner:SHENZHEN DAKEWE BIOENG
Application of Myriberine A in preparing antituberculous medicines
InactiveCN103356629AIncrease varietyTuberculosis resistantAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMedicineMortality rate
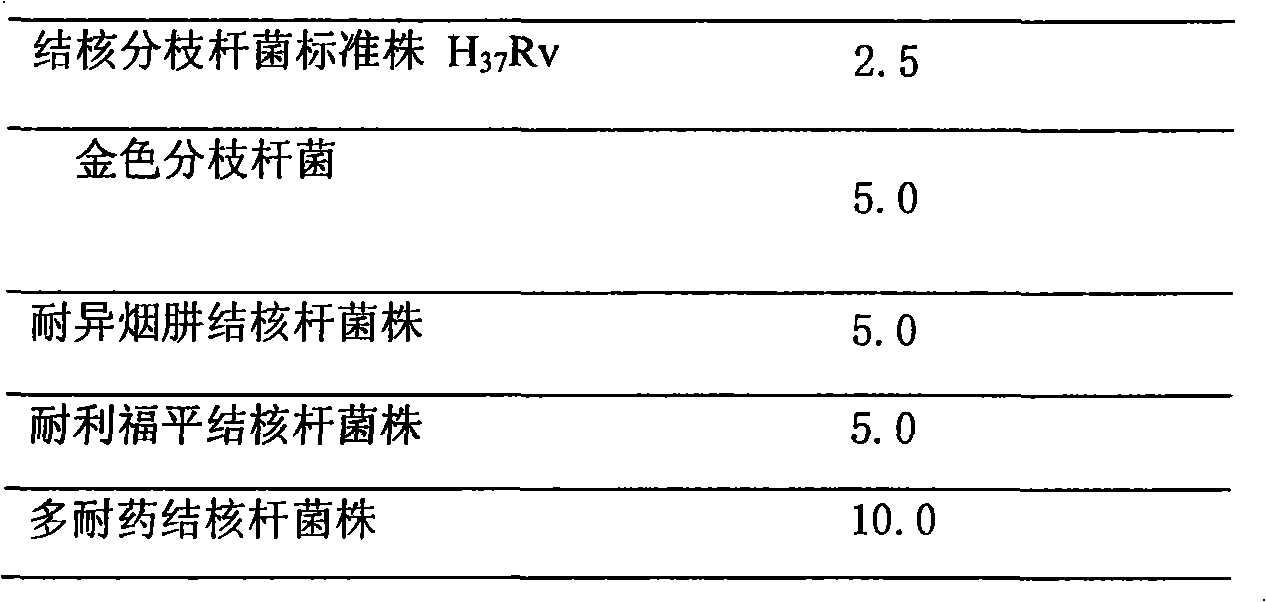
The invention discloses an application of Myriberine A in preparing antituberculous medicines. The application of the Myriberine A aims at current situations that high tuberculosis incidence and appearance of multi-drug resistant strains of tubercle bacillus result in the rising tendency in the incidence and mortality rate of the tuberculosis, and the Myriberine A is found to have remarkable tubercle bacillus inhibitory activity and a good application prospect. The application of the Myriberine A in preparing the antituberculous medicines is disclosed for the first time. The framework type is a brand-new framework type, and therefore the Myriberine A has unexpected tubercle bacillus inhibitory activity. The Myriberine A has prominent substantive features and is impossibly revealed by other compounds, and has remarkable progresses when used for preventing and treating tubercle bacillus infection.
Owner:ZIBO DINGLI PATENT INFORMATION CONSULTING CO LTD
Application of gypensapogenin A to anti-tubercle bacillus drugs
ActiveCN102872049AIncrease varietyTuberculosis resistantAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMortality rateResistant strain
The invention discloses application of gypensapogenin A to preparation of anti-tubercle bacillus drugs. According to the high tubercle bacillus morbidity and the emergence of mycobacterium tuberculosis multiple-resistant strain, the tubercle bacillus morbidity and mortality are one the rise; and gypensapogenin A has remarkable tubercle bacillus suppression activity and good application prospect. The application of gypensapogenin A to the preparation of the anti-tubercle bacillus drugs is firstly publicized, the skeleton type is brand-new, the tubercle bacillus suppression activity is unexpectedly strong and the possibility of giving any revelation by other compounds does not exist, so that prominent substantive features are provided and a remarkable progress in the prevention and treatment of the tubercle bacillus infection is made at the same time.
Owner:南通三聚知识产权服务有限公司
Method for attenuating a bacterium of the mycobacterium tuberculosis complex for producing a tuberculosis vaccine
InactiveCN104271732AShort lifeAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteroidesMycobacterium smegmatis
The present invention relates to the use of a strain of a mycobacterium of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex, into which an mspA gene capable of expressing a Mycobacterium smegmatis porin A has been inserted, for producing a vaccine for the prevention of an infection by a bacterium of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in a host comprising eukaryotic cells, preferably macrophages, wherein said mycobacterial strain thus transformed exhibits reduced growth in said eukaryotic cells.
Owner:FOND MEDITERRANEE INFECTION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com