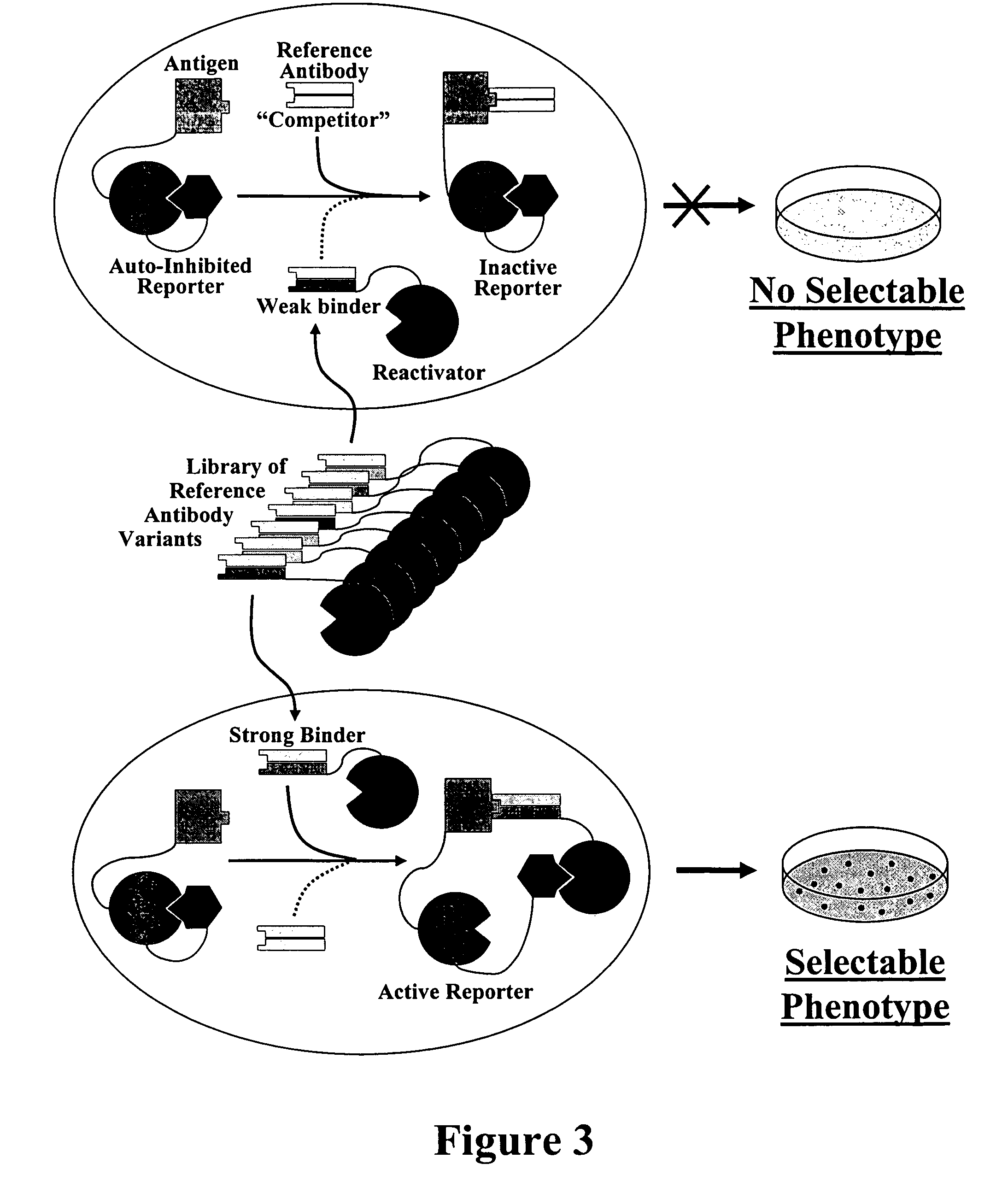
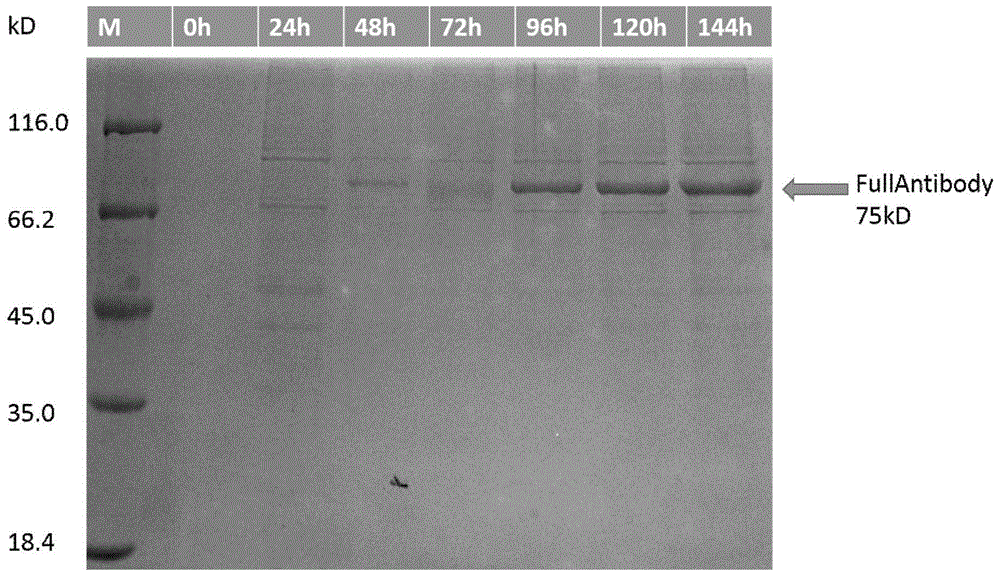
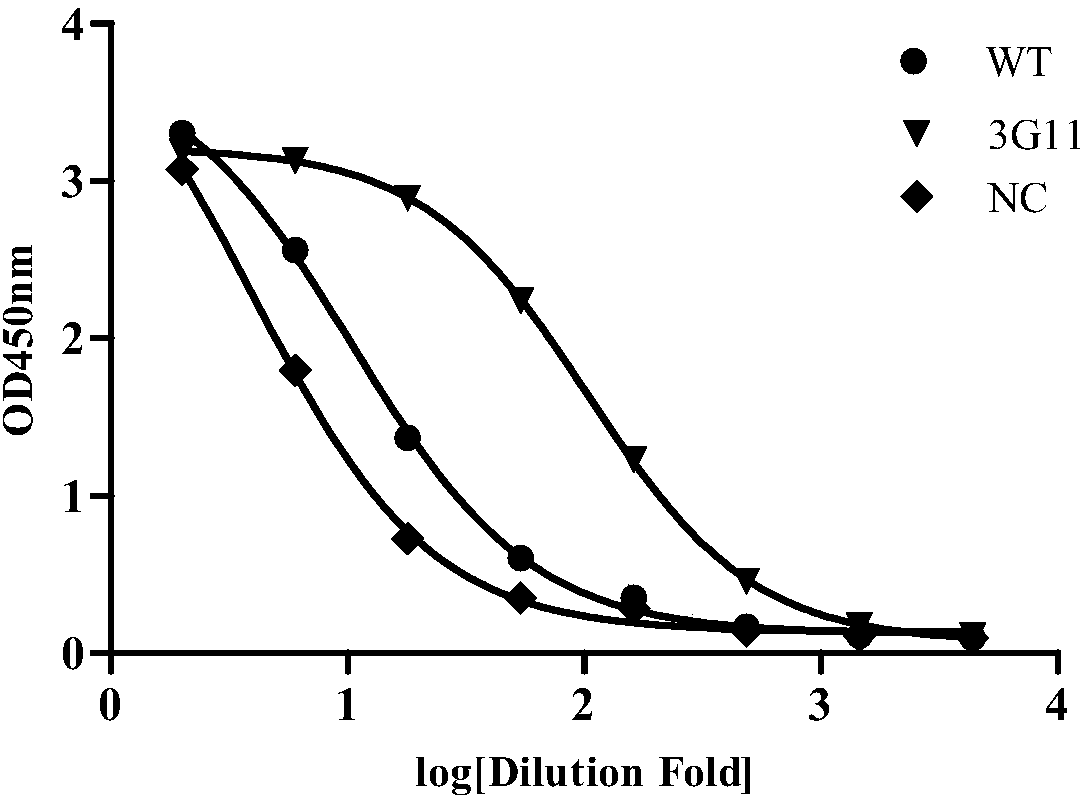
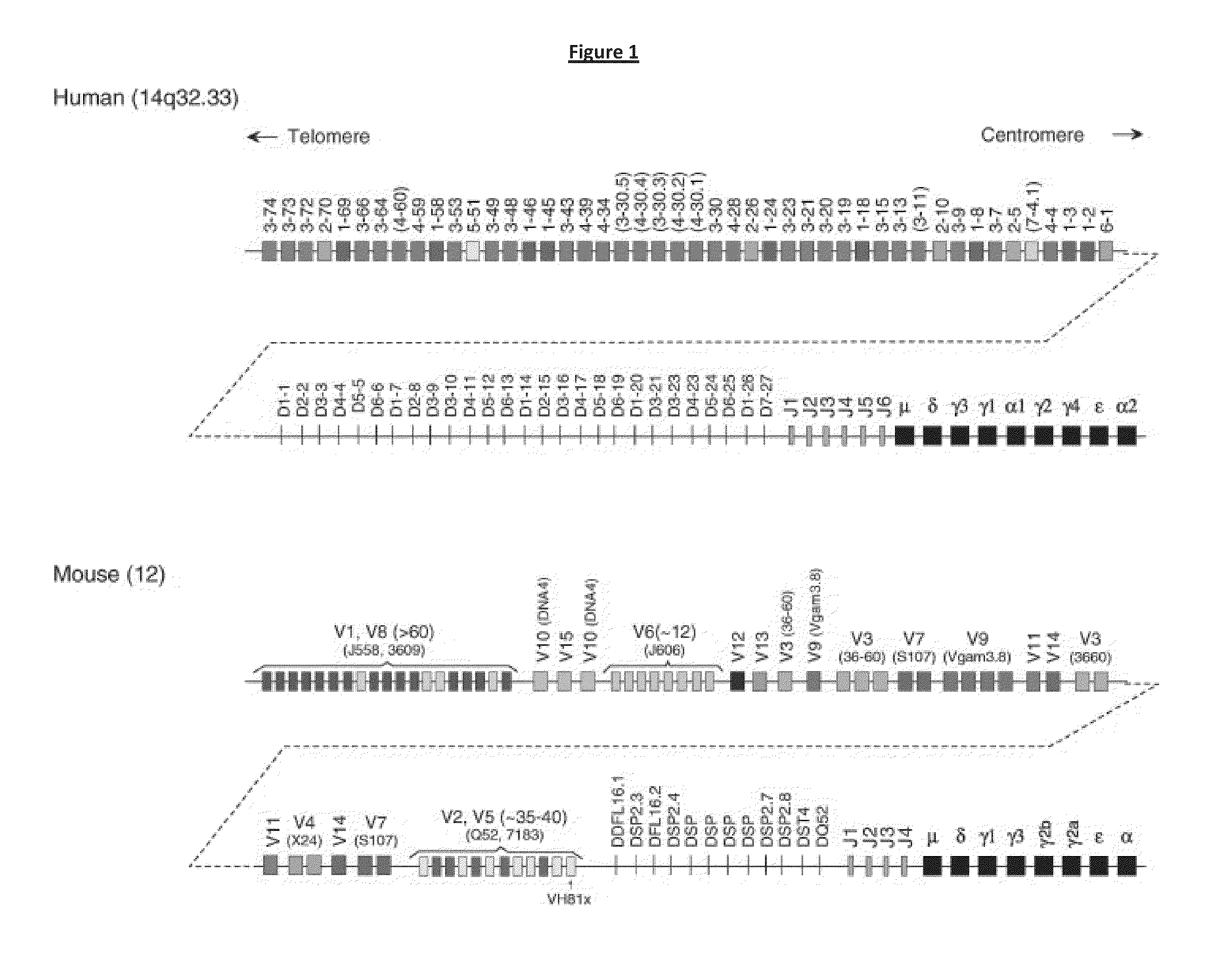
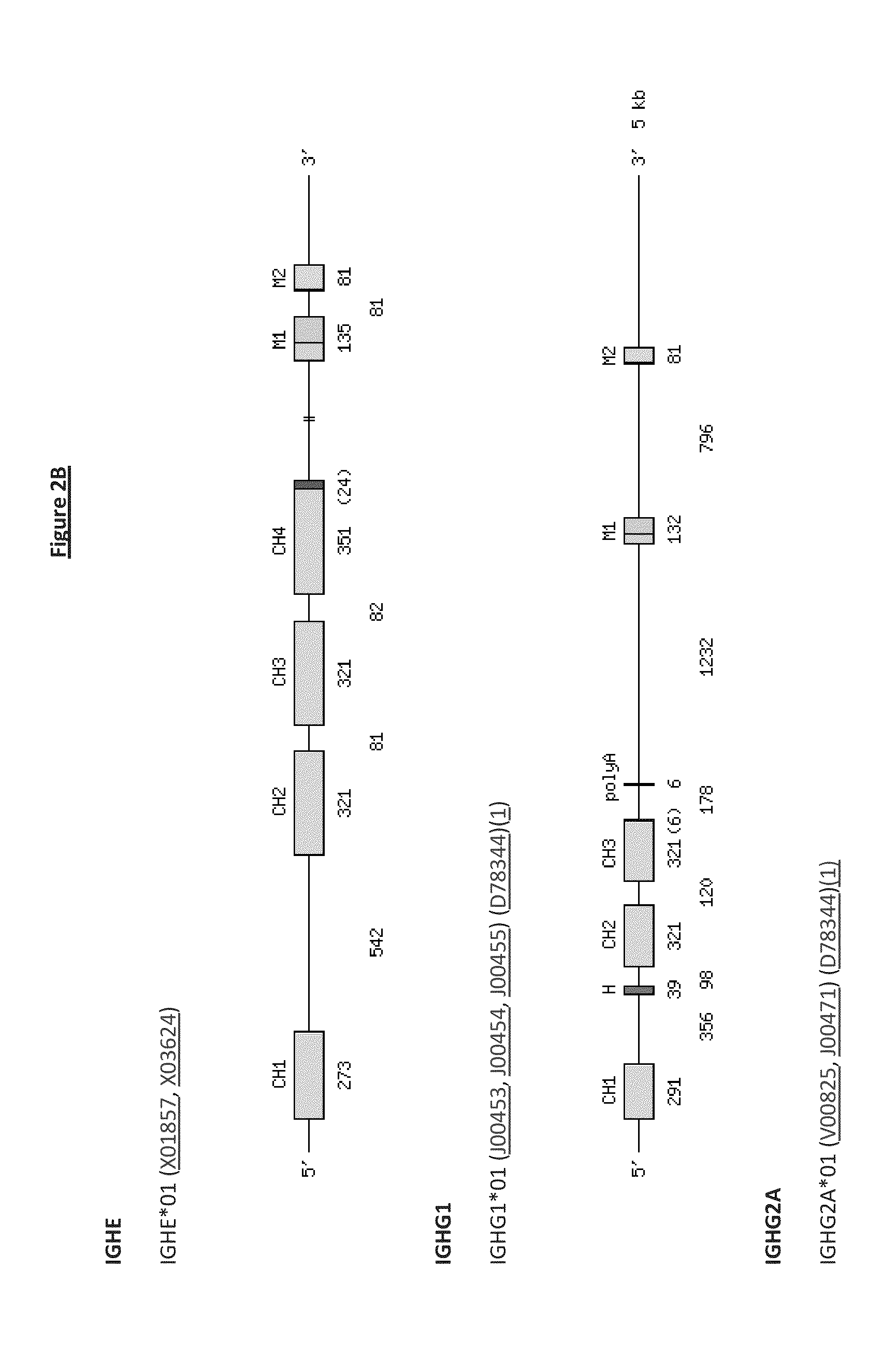
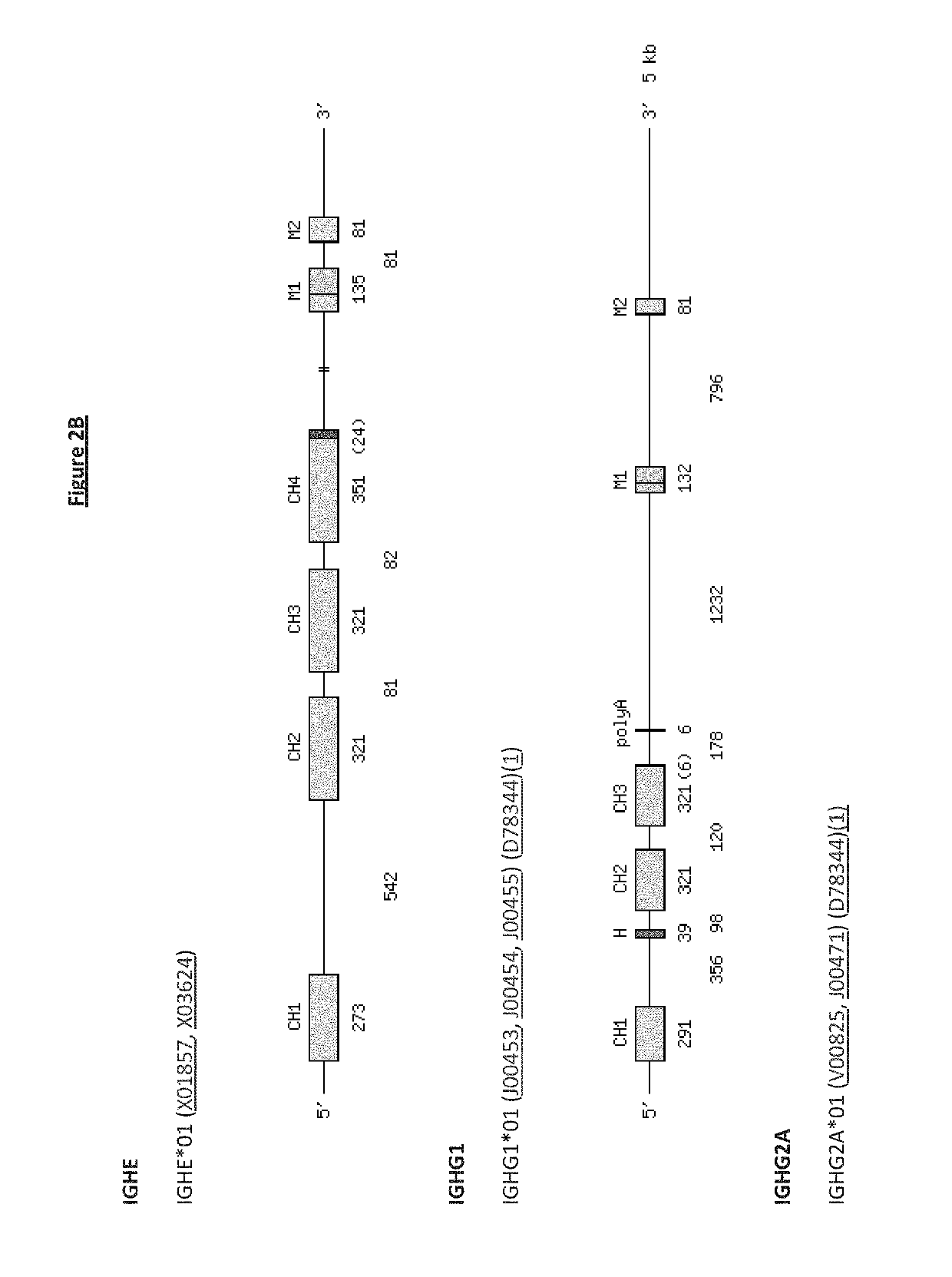
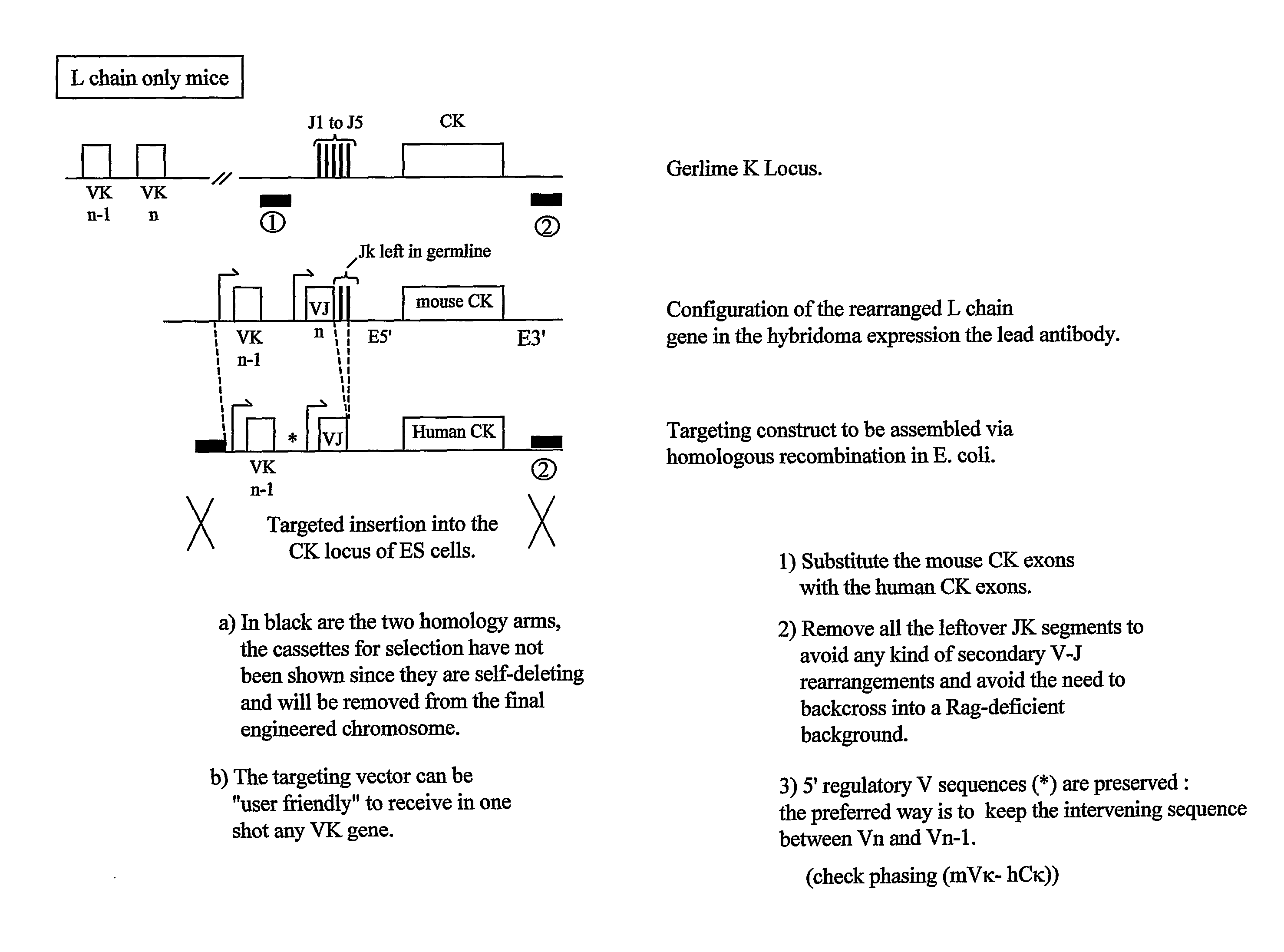
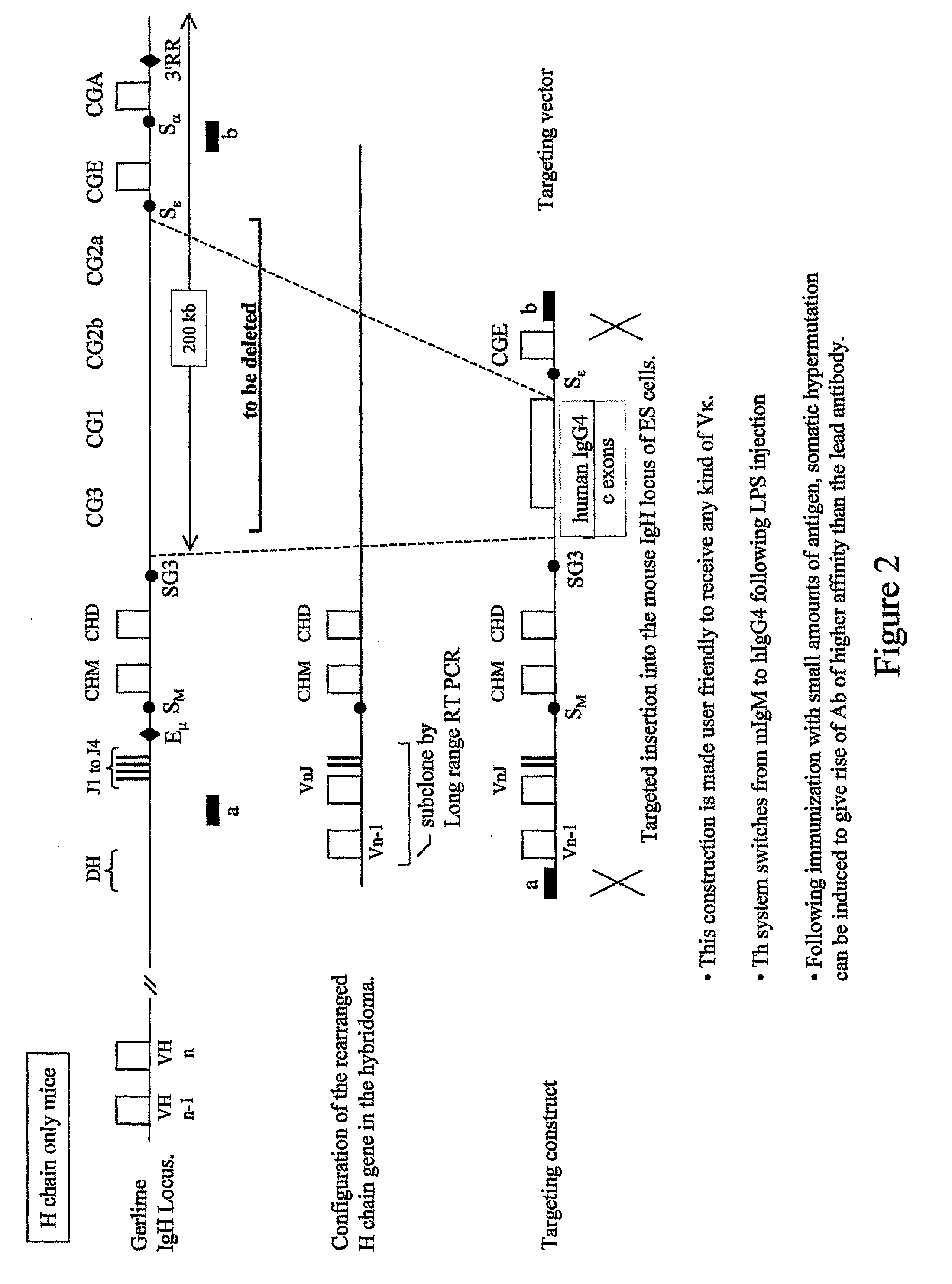
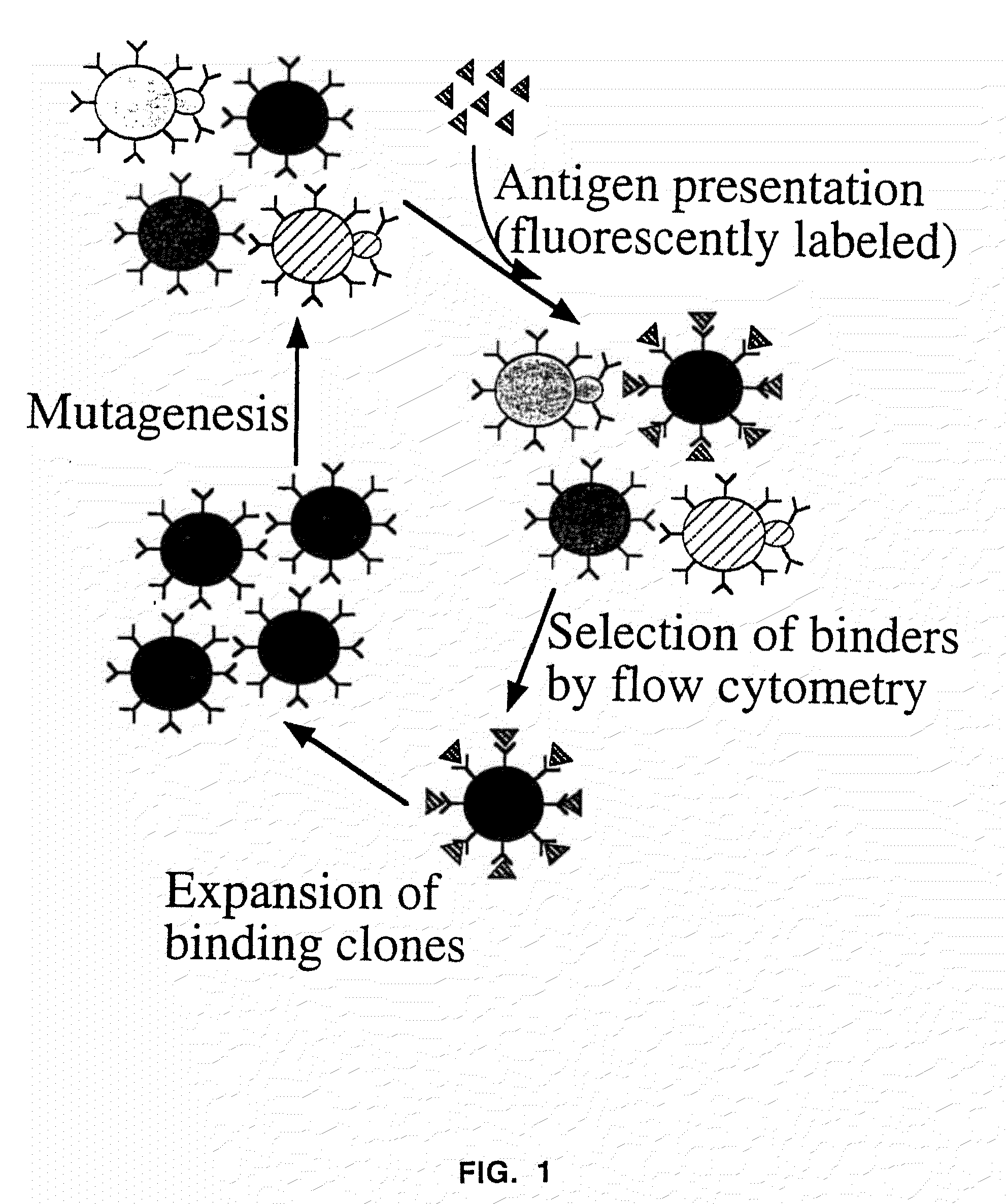
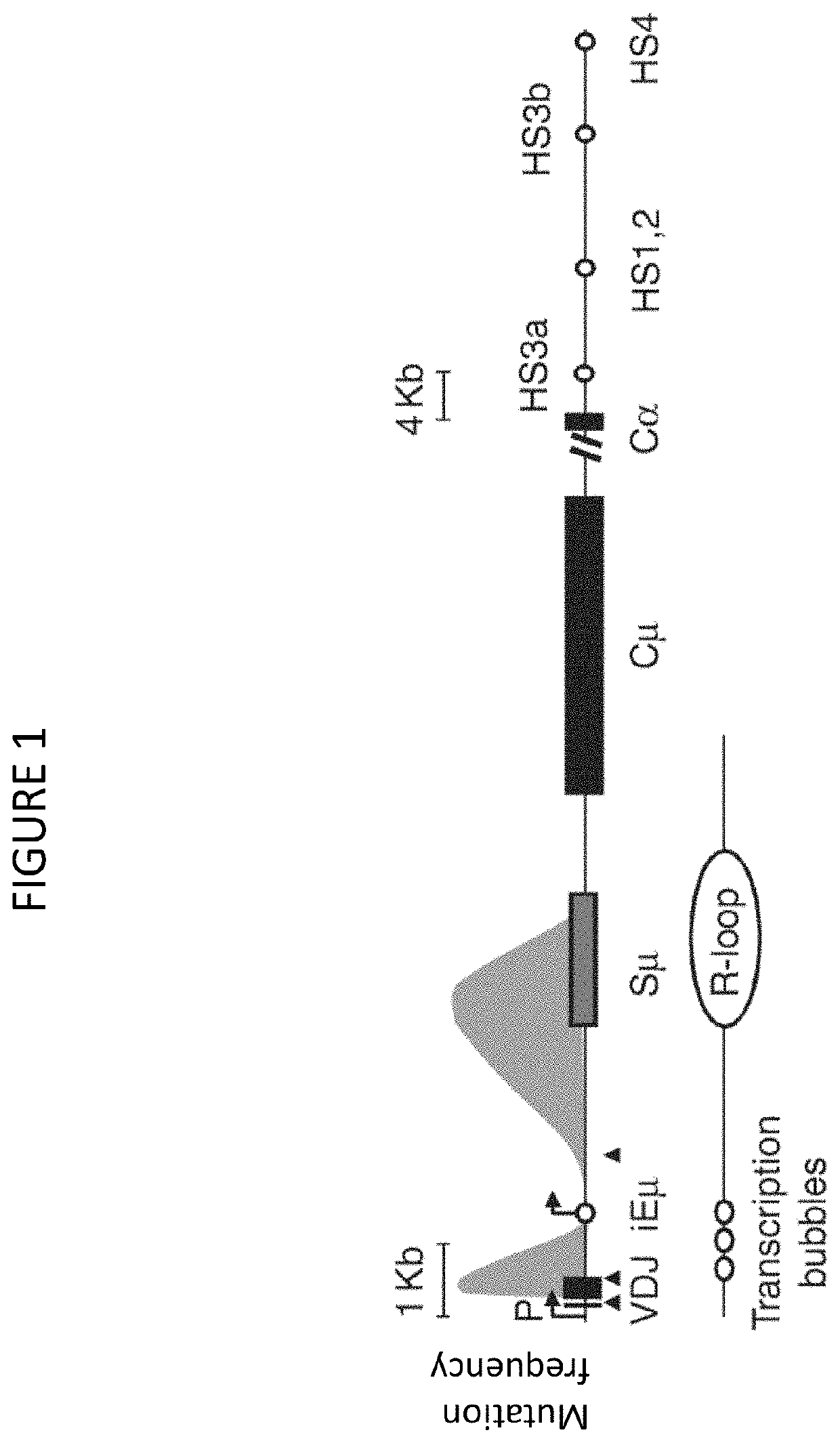
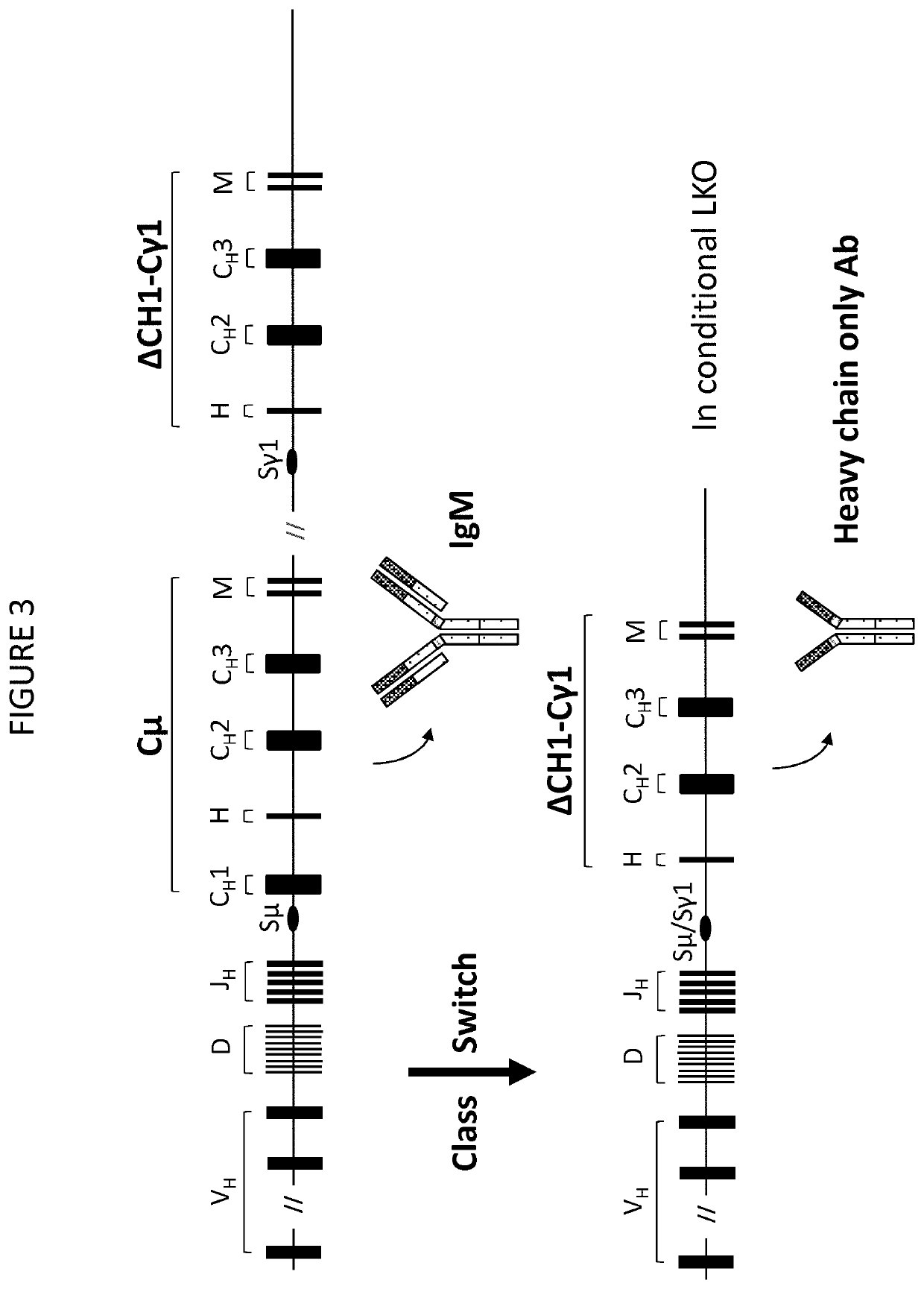
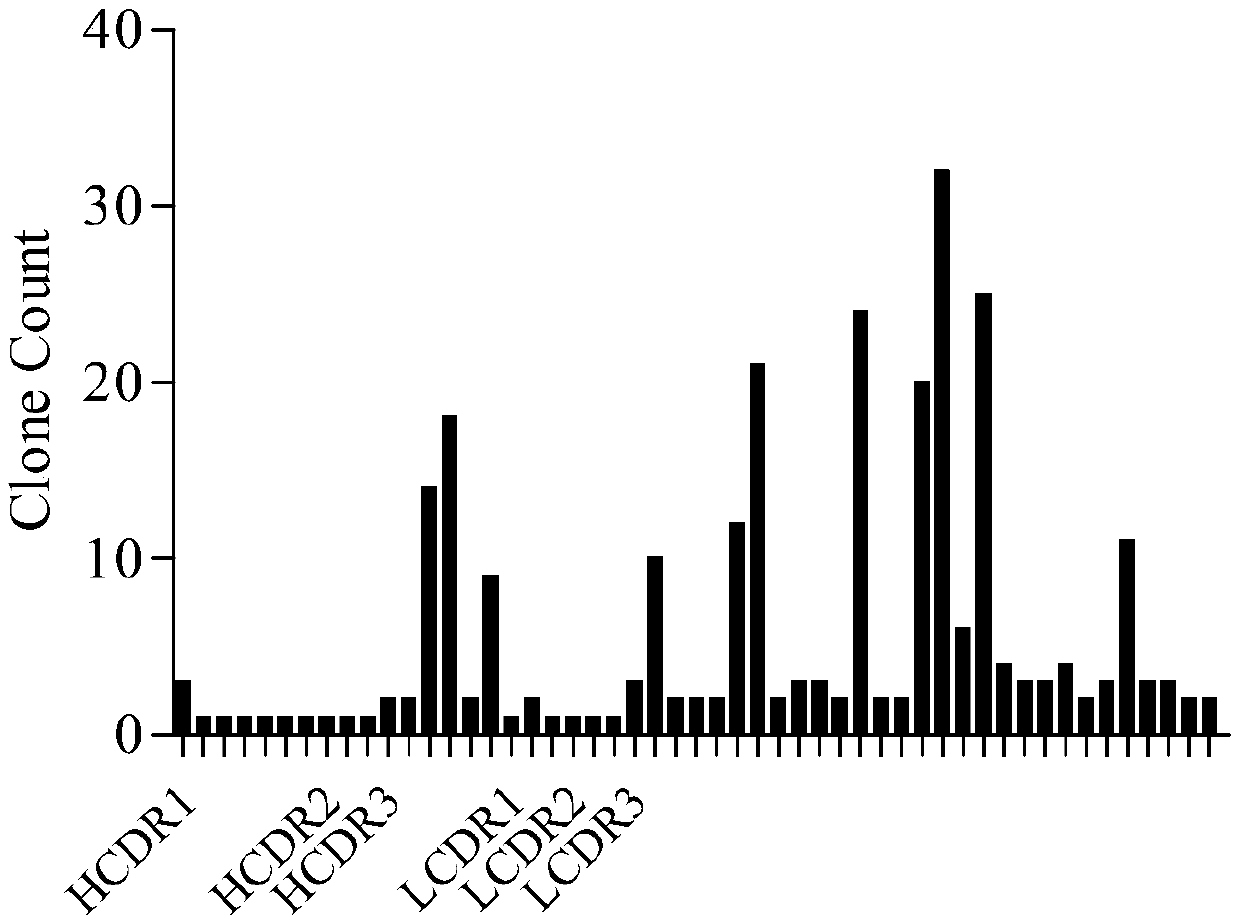
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
79 results about "B-cell affinity maturation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
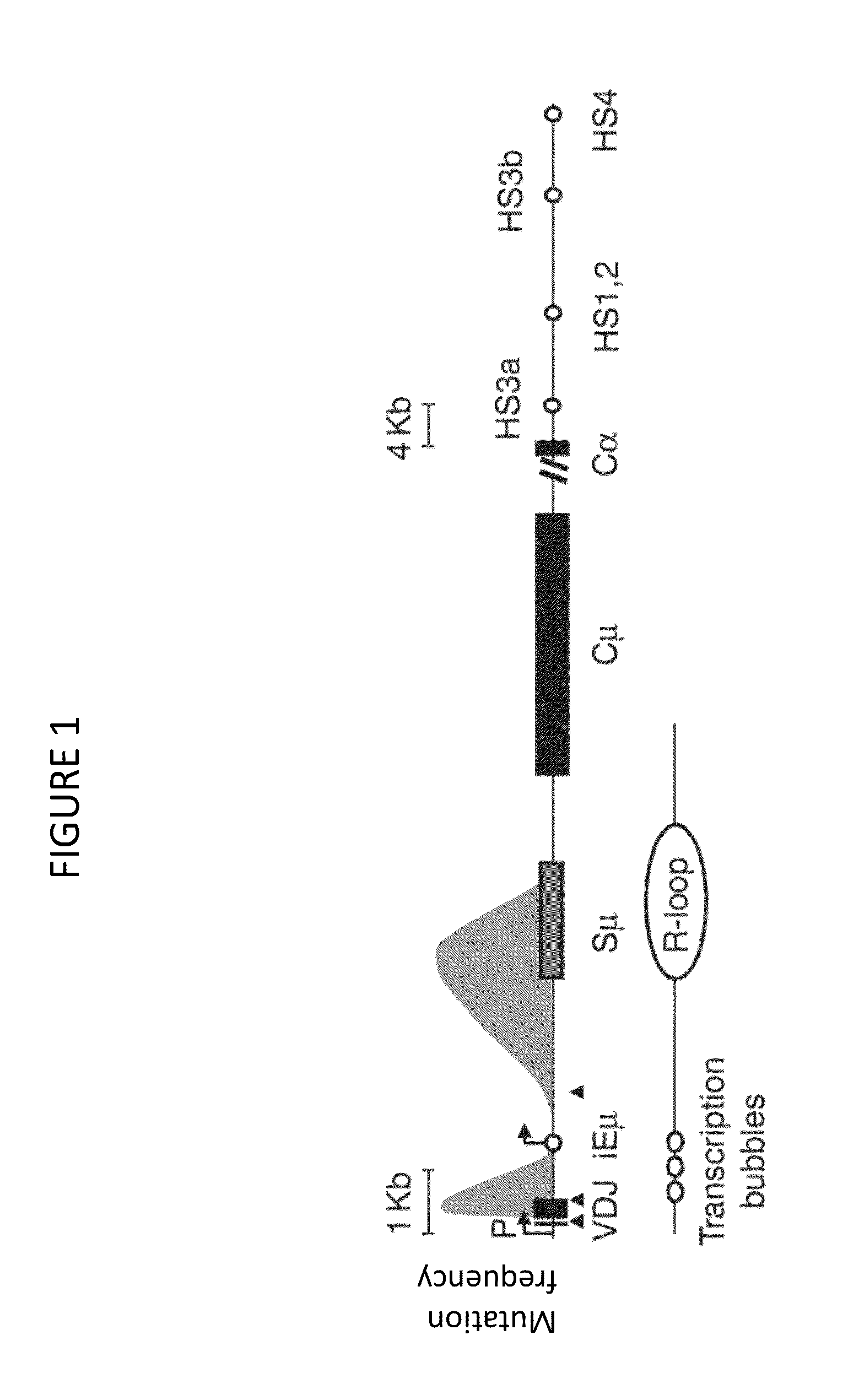
In immunology, affinity maturation is the process by which Tfh cell-activated B cells produce antibodies with increased affinity for antigen during the course of an immune response. With repeated exposures to the same antigen, a host will produce antibodies of successively greater affinities.
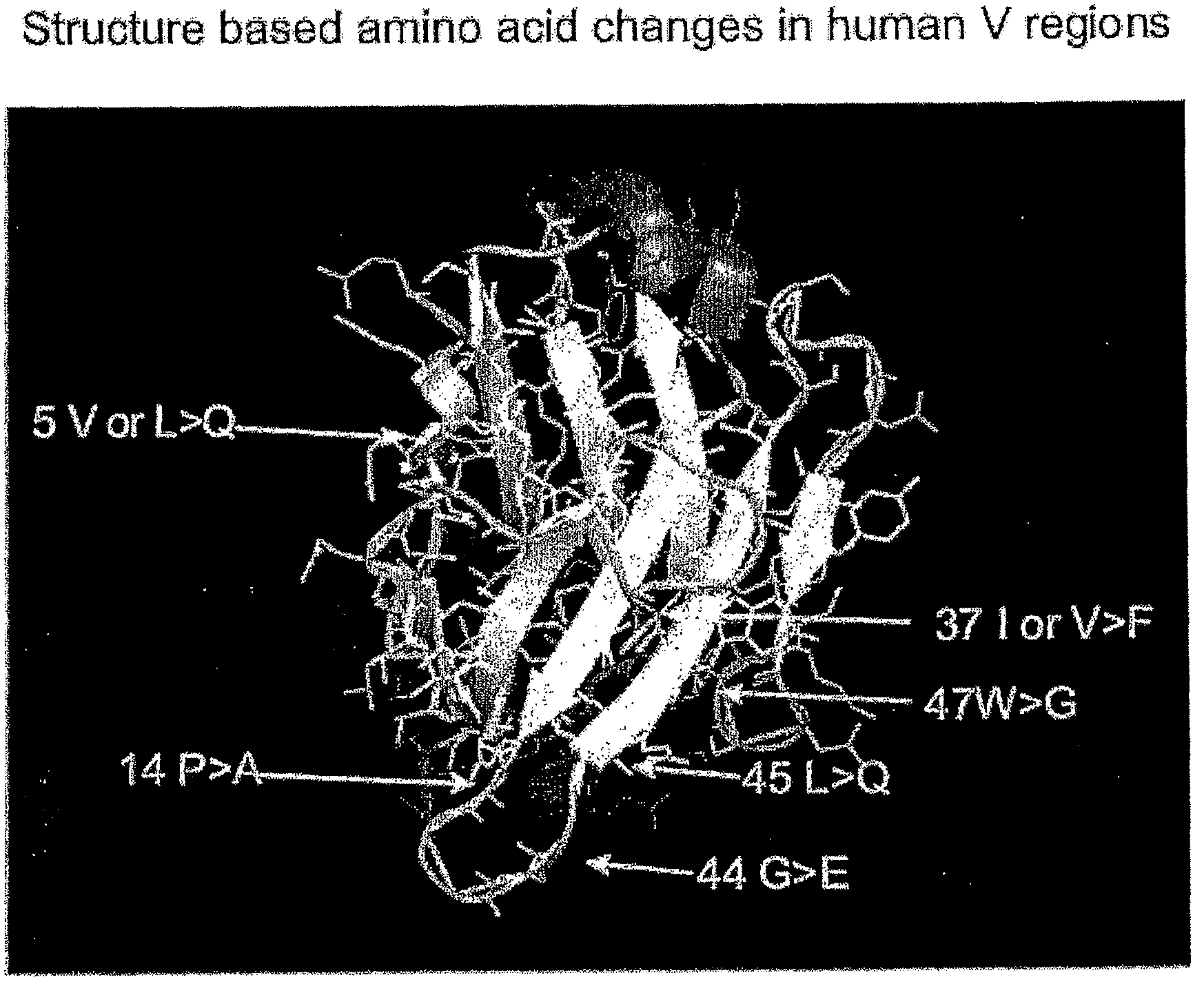
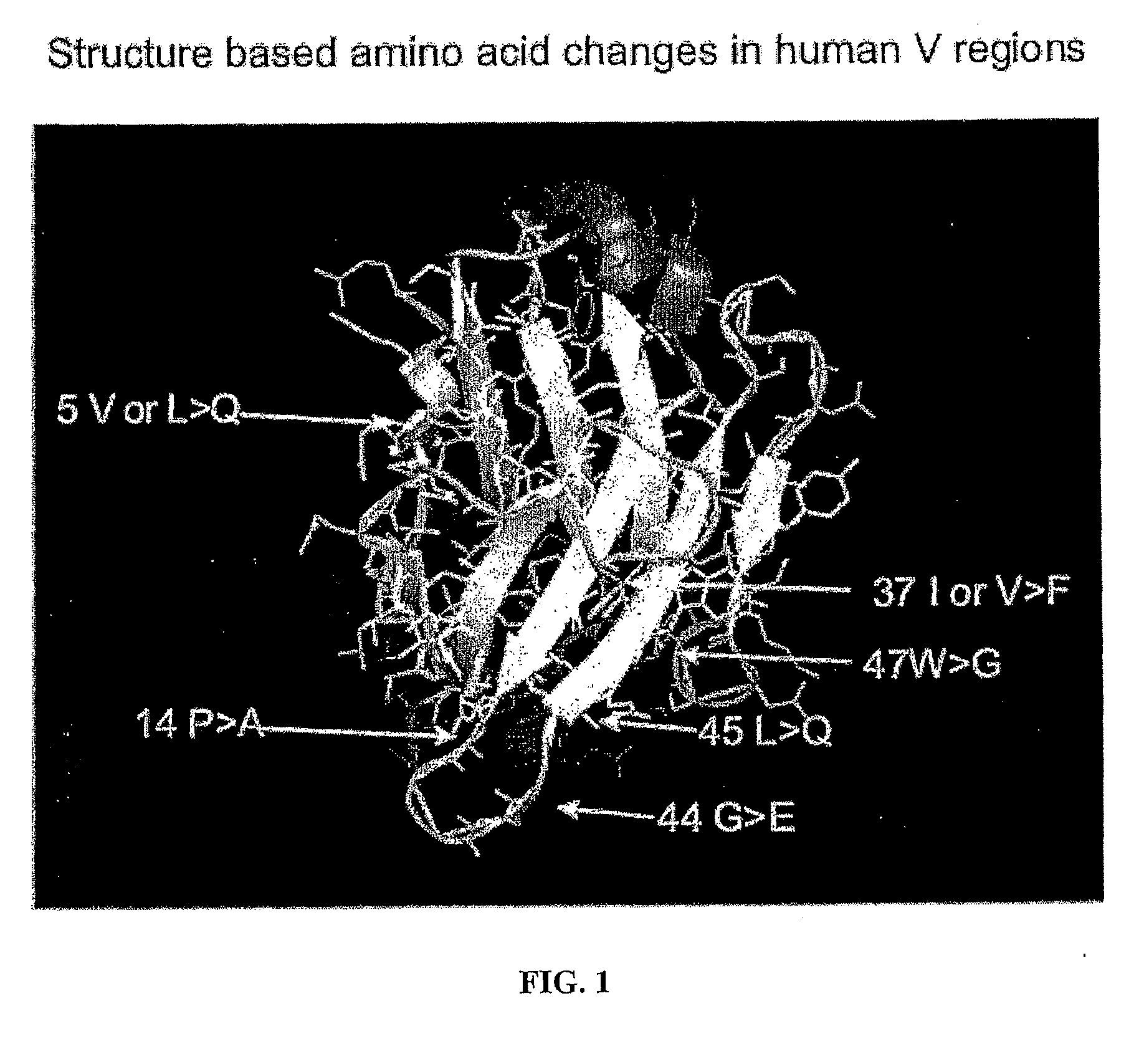
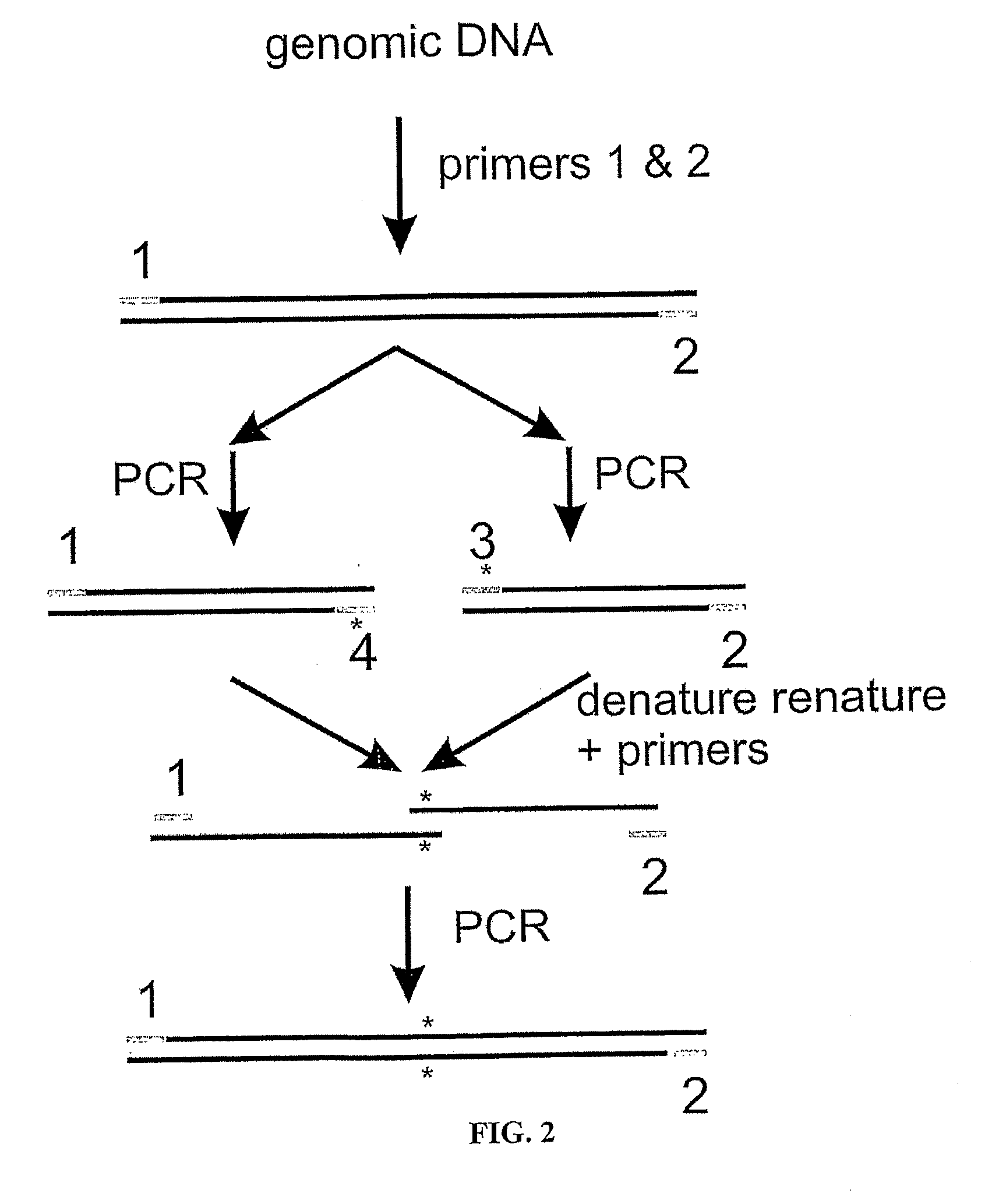
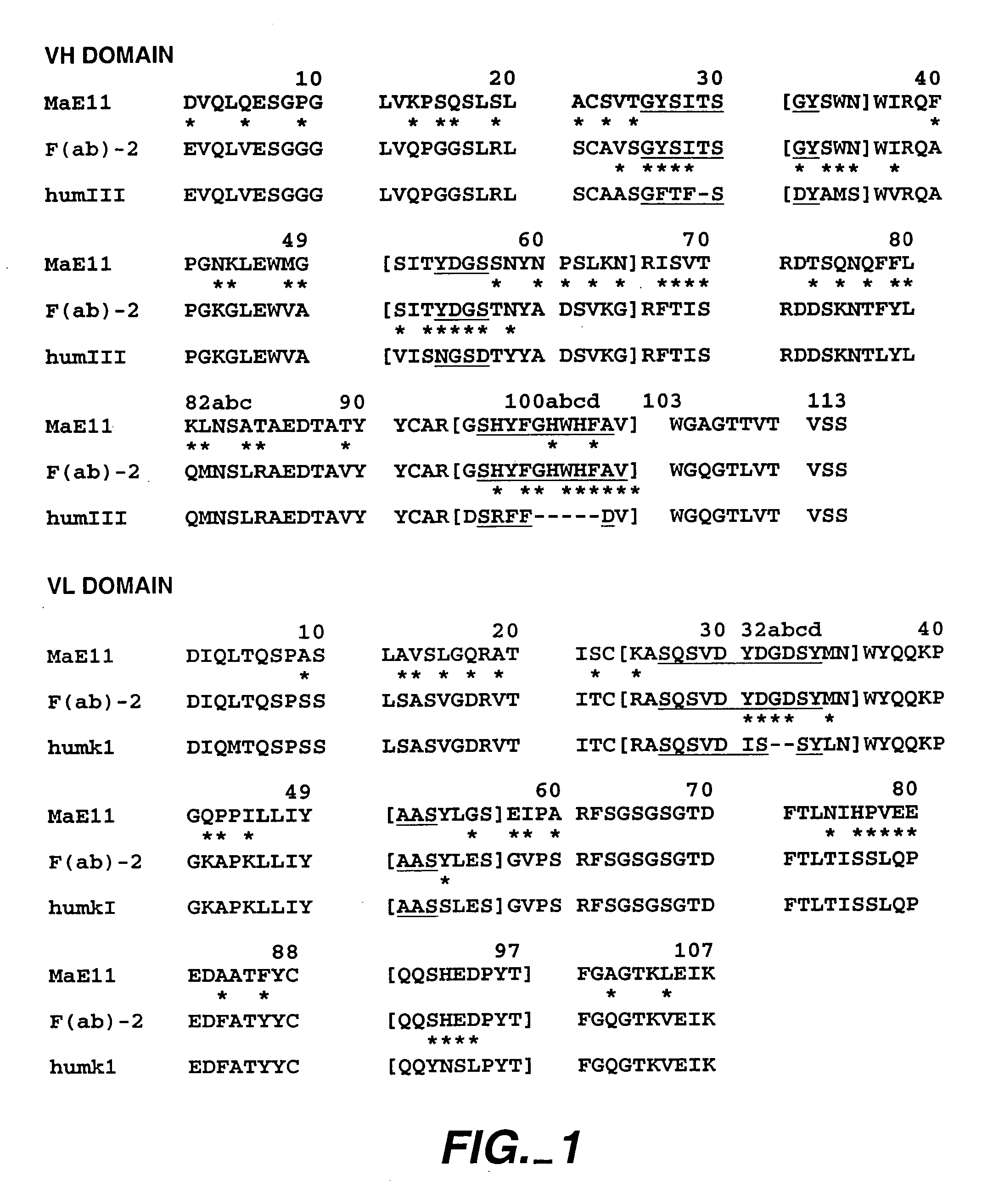
Structure-based selection and affinity maturation of antibody library
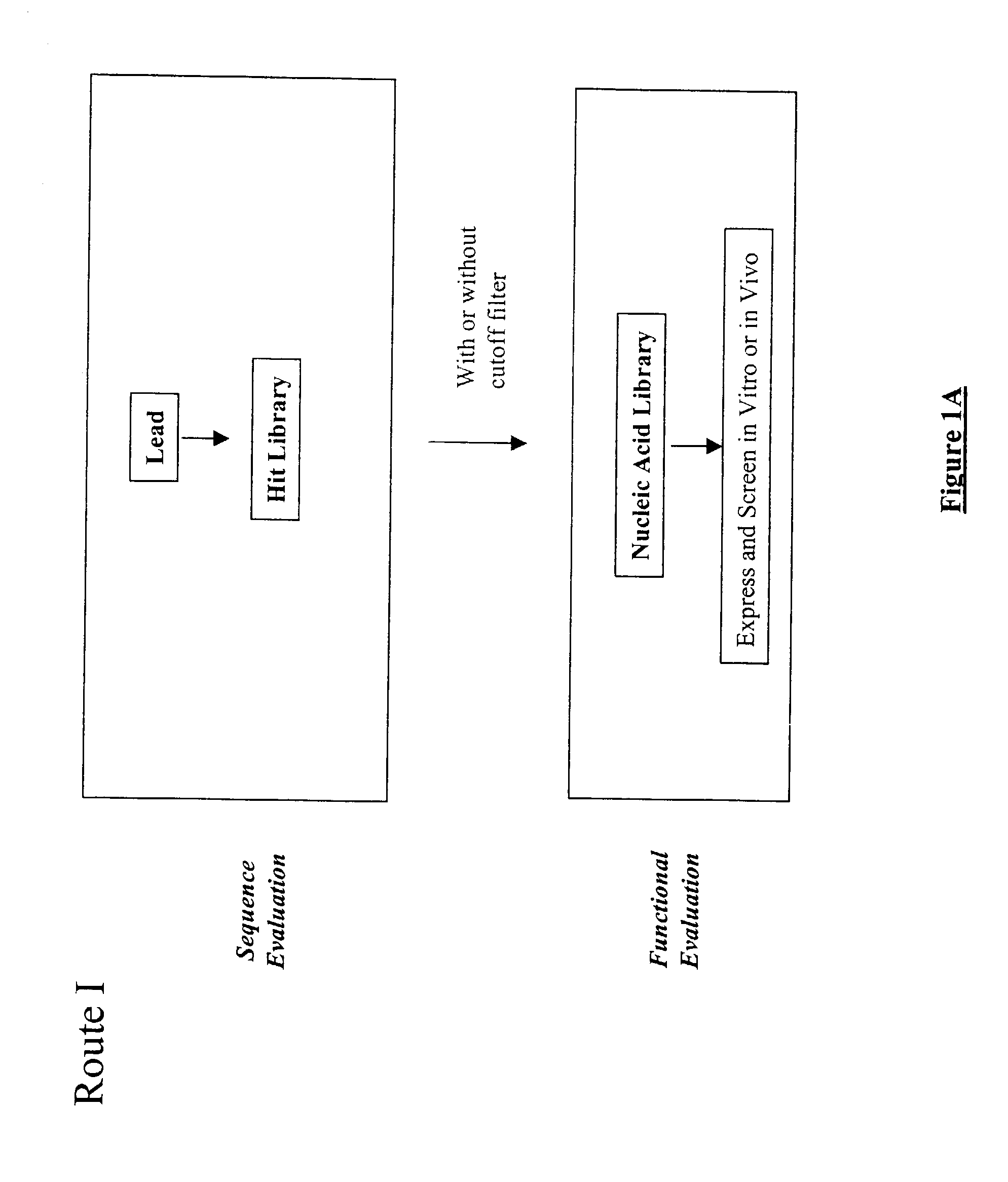
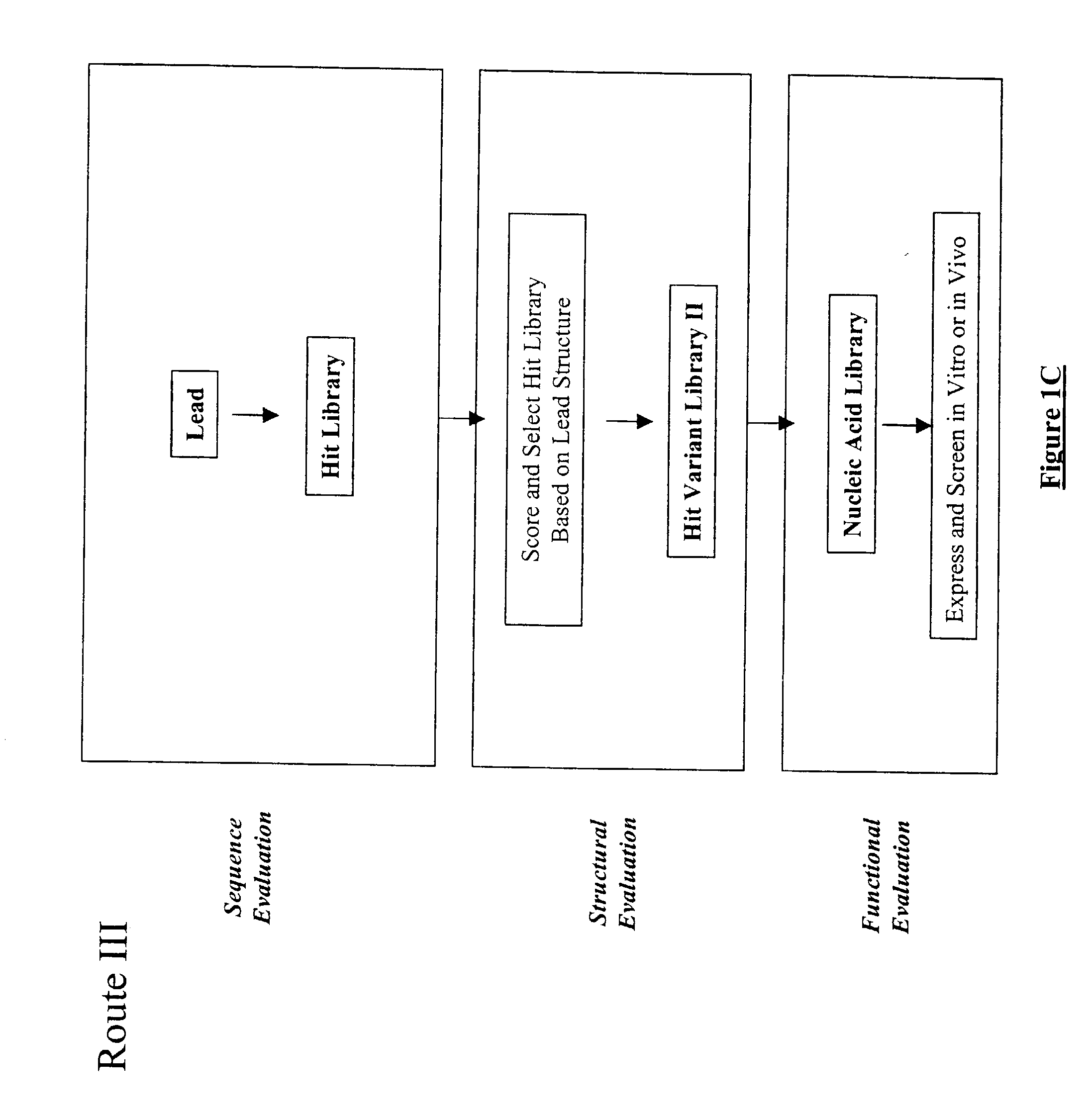
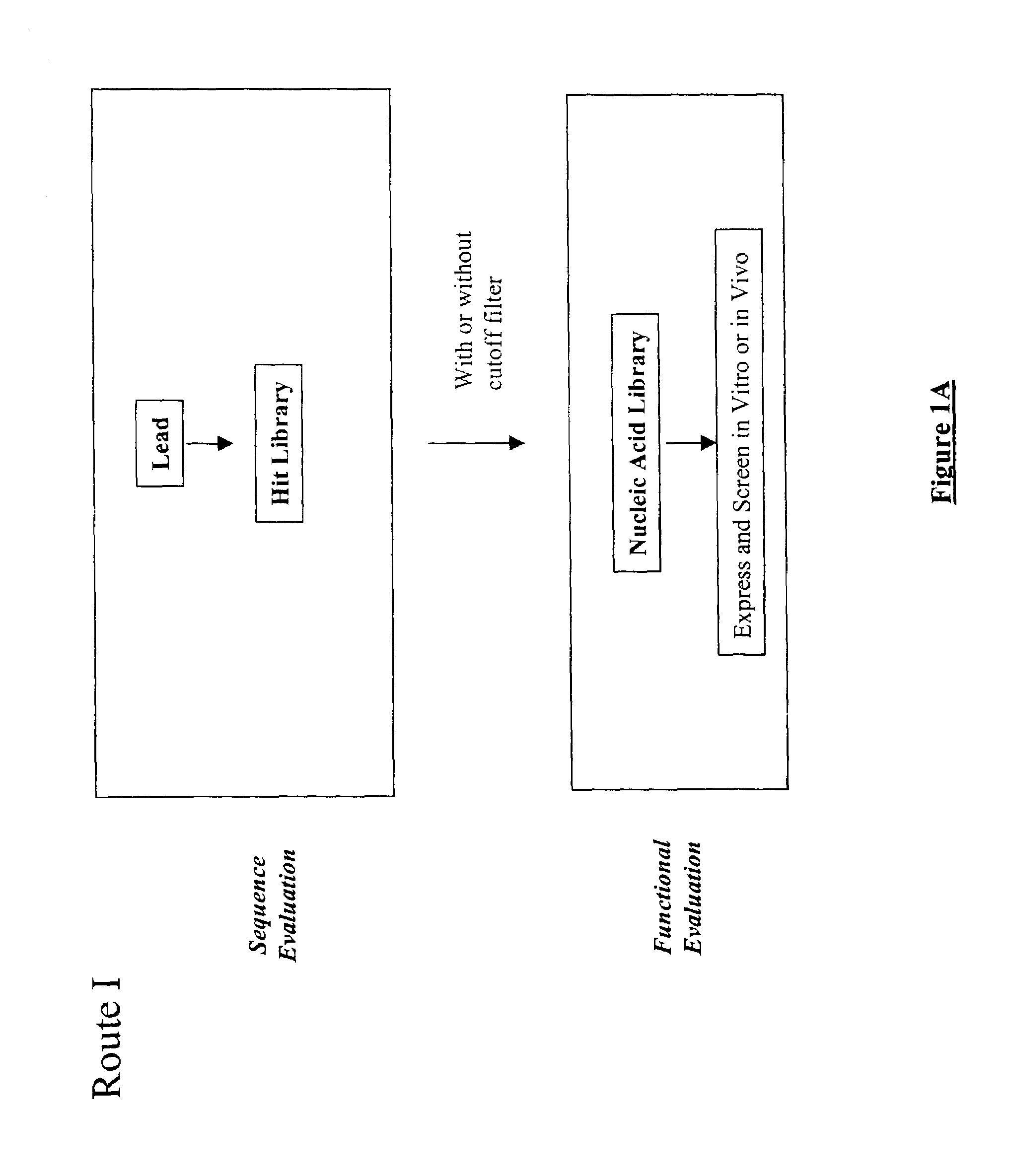
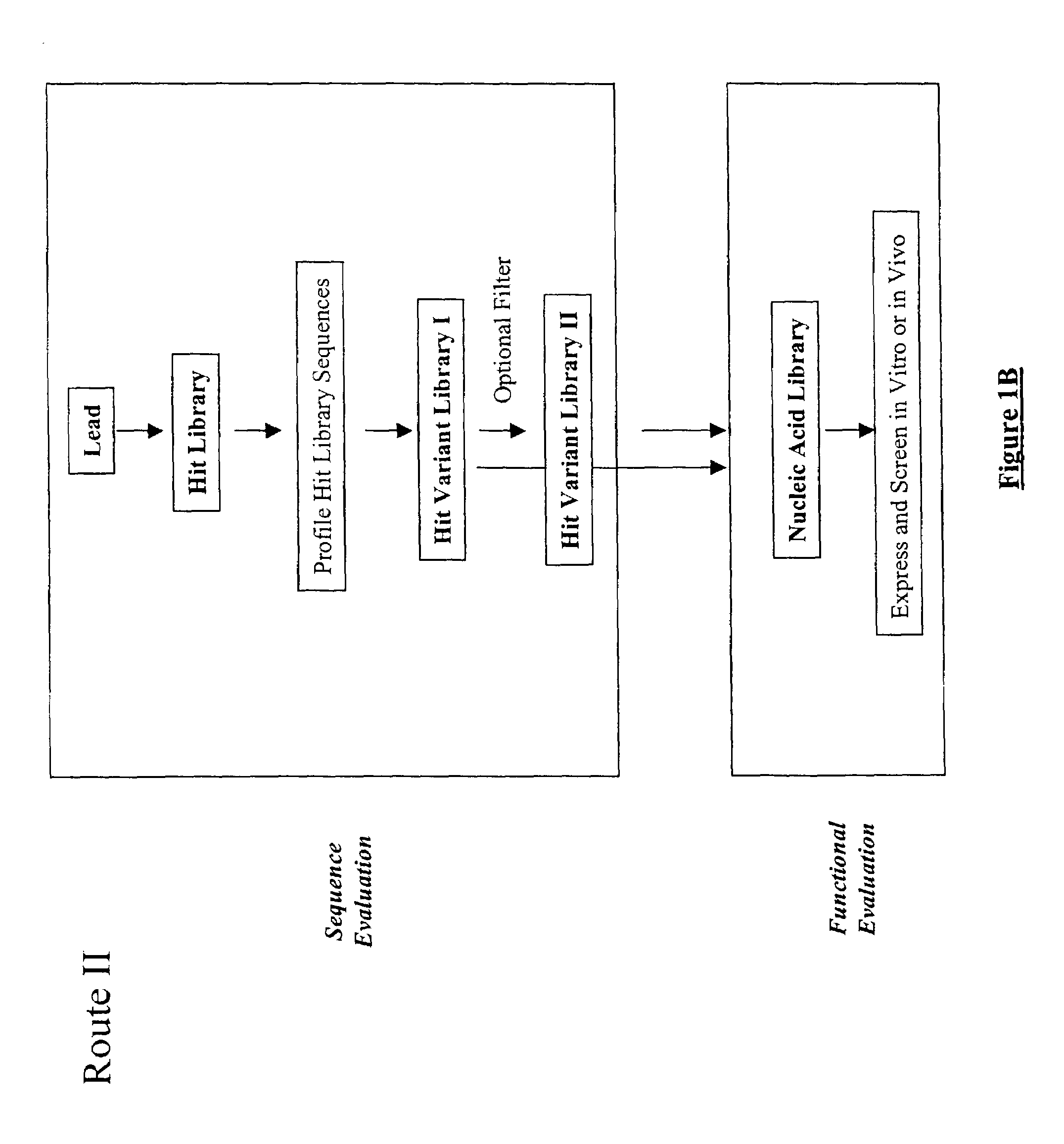
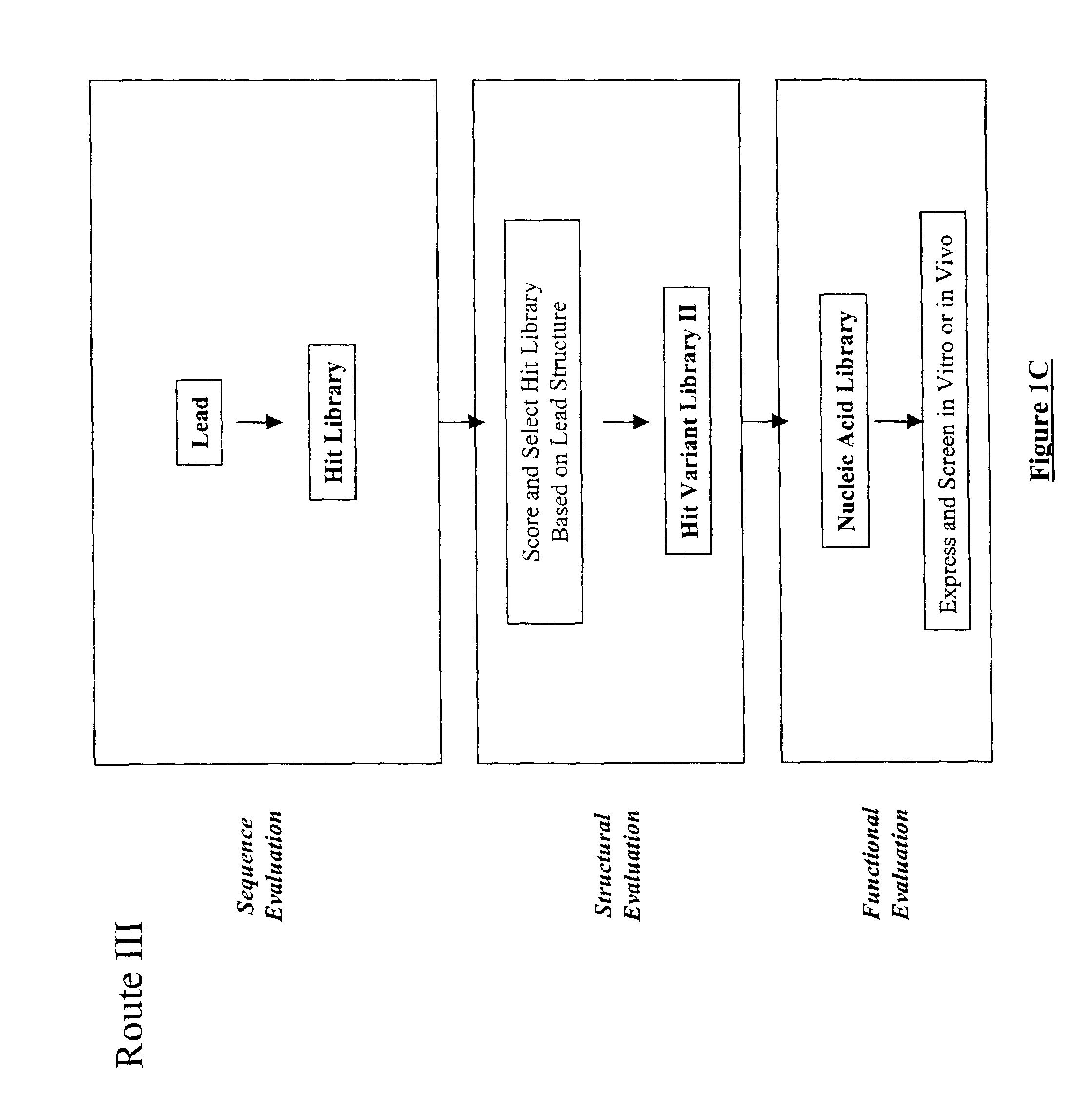
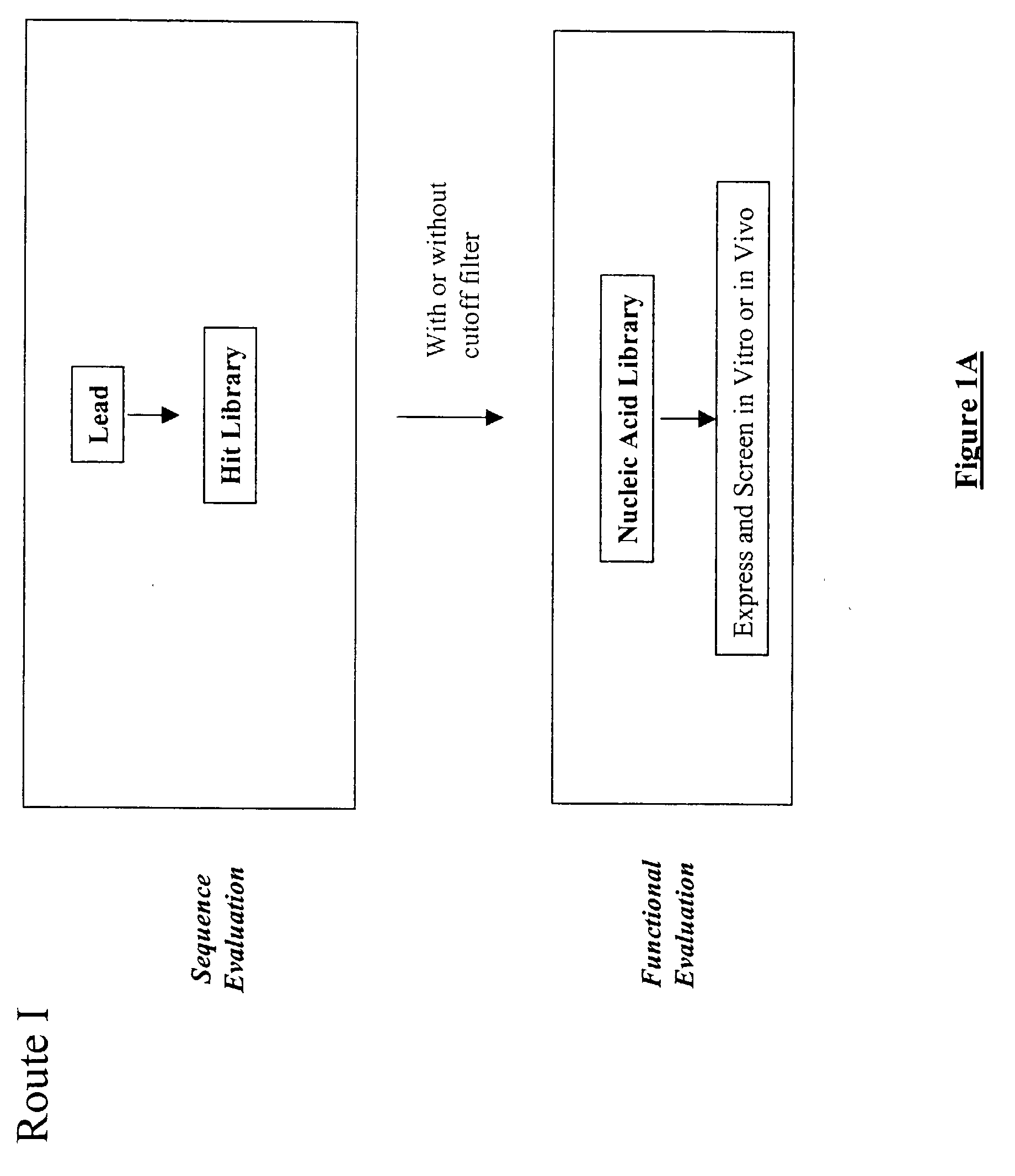
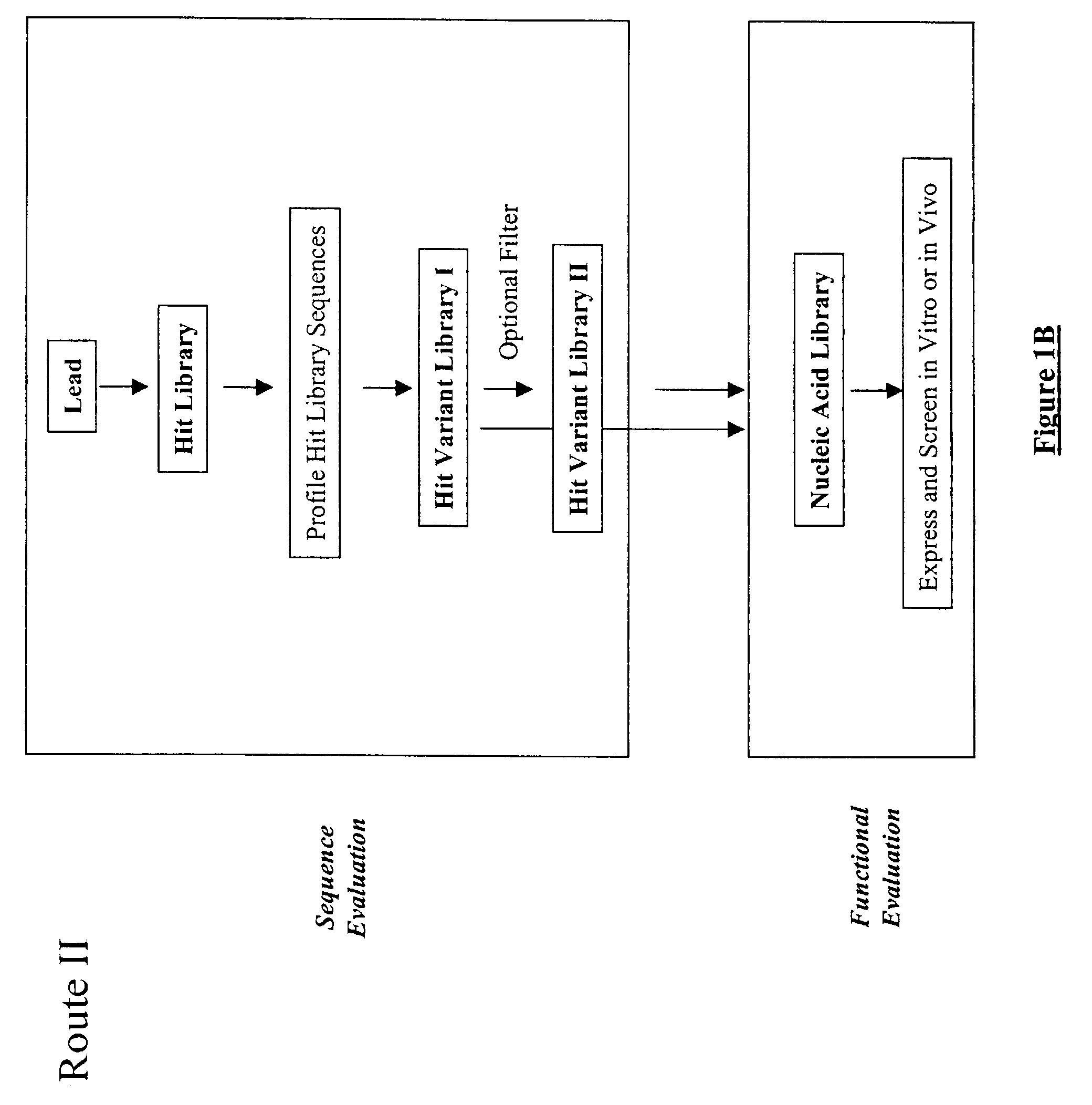
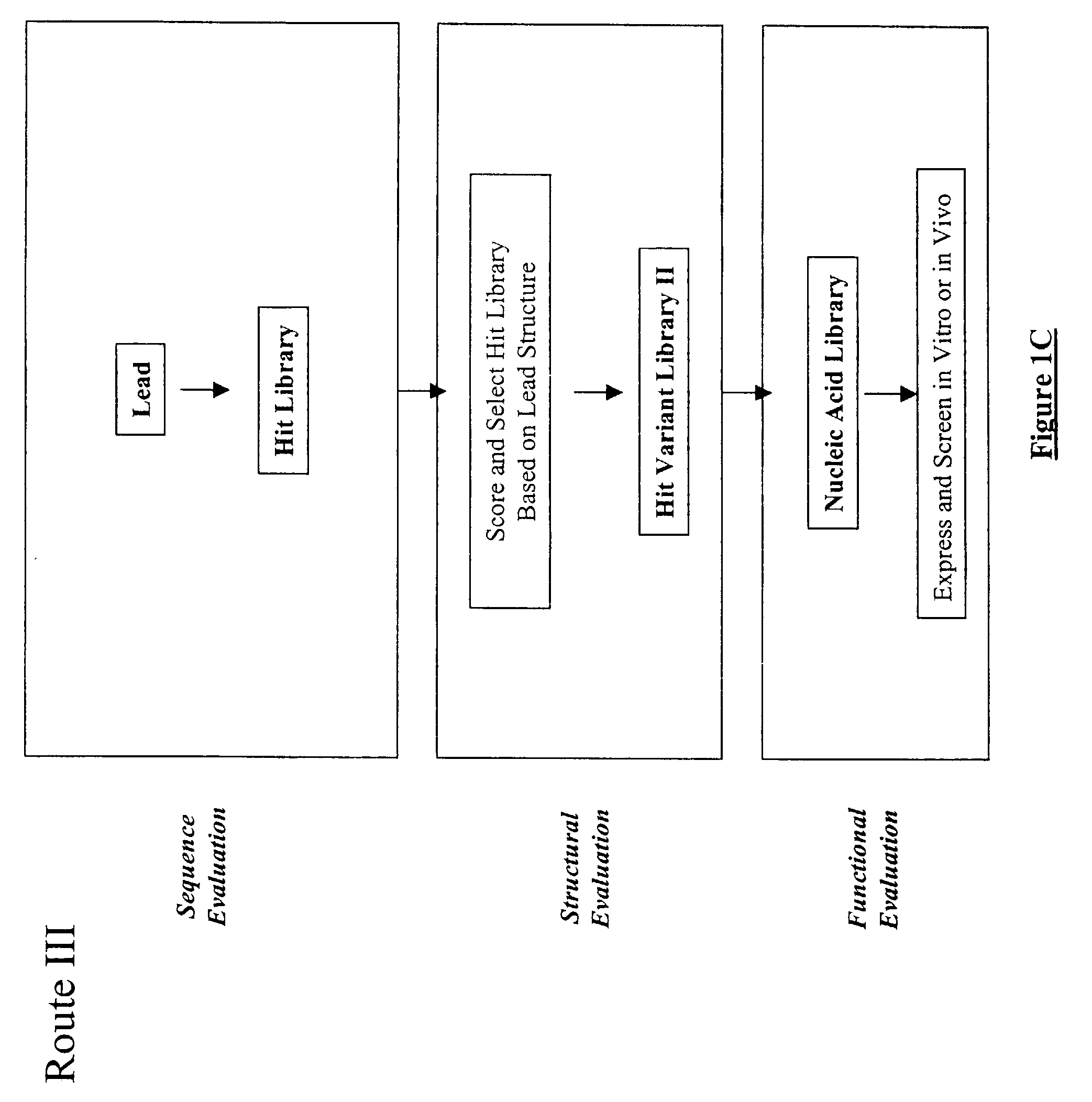
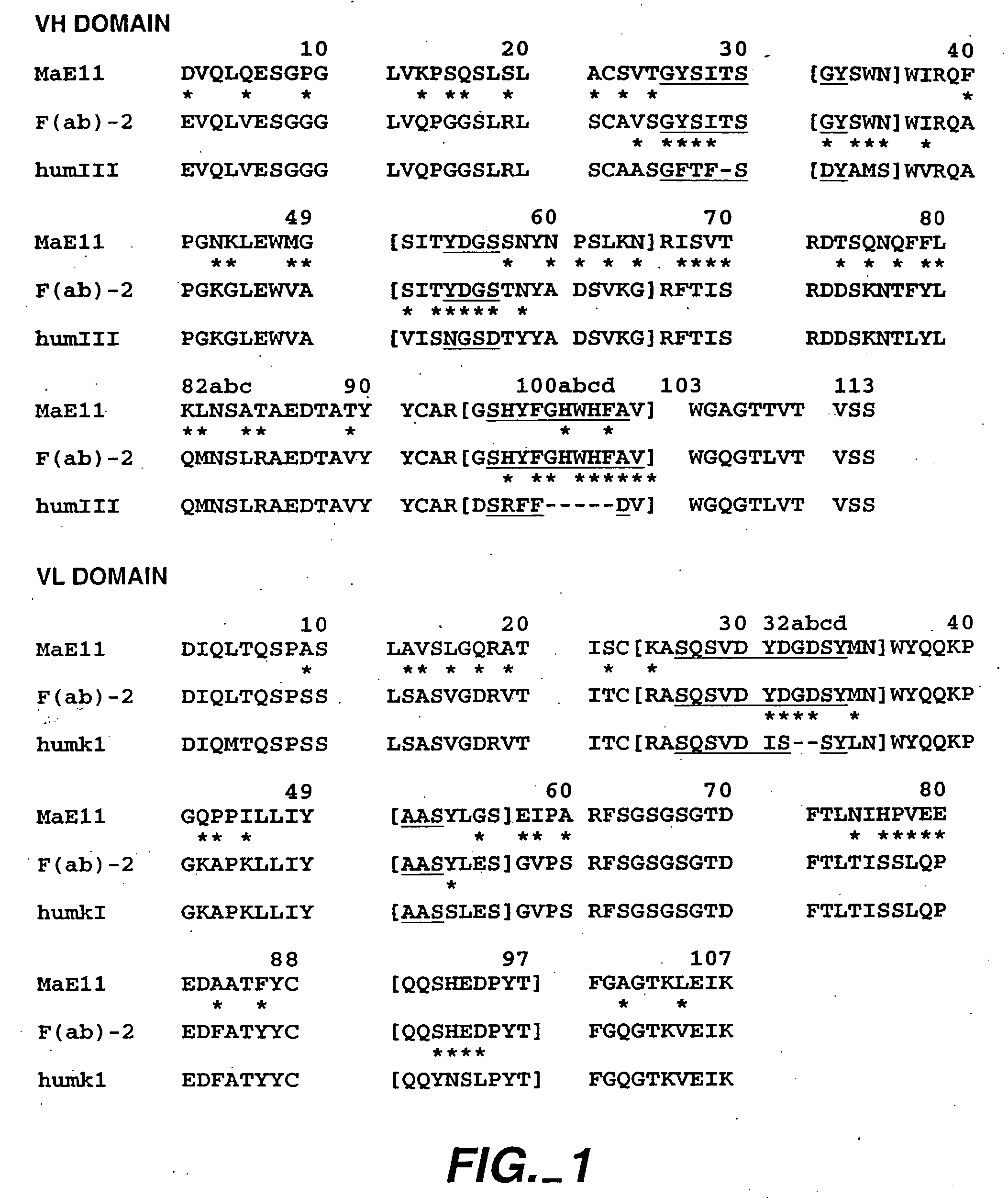
The present invention provides a structure-based methodology for efficiently generating and screening protein libraries for optimized proteins with desirable biological functions, such as antibodies with high binding affinity and low immunogenicity in humans. In one embodiment, a method is provided for constructing a library of antibody sequences based on a three dimensional structure of a lead antibody. The method comprises: providing an amino acid sequence of the variable region of the heavy chain (VH) or light chain (VL) of a lead antibody, the lead antibody having a known three dimensional structure which is defined as a lead structural template; identifying the amino acid sequences in the CDRs of the lead antibody; selecting one of the CDRs in the VH or VL region of the lead antibody; providing an amino acid sequence that comprises at least 3 consecutive amino acid residues in the selected CDR, the selected amino acid sequence being a lead sequence; comparing the lead sequence profile with a plurality of tester protein sequences; selecting from the plurality of tester protein sequences at least two peptide segments that have at least 10% sequence identity with lead sequence, the selected peptide segments forming a hit library; determining if a member of the hit library is structurally compatible with the lead structural template using a scoring function; and selecting the members of the hit library that score equal to or better than or equal to the lead sequence. The selected members of the hit library can be expressed in vitro or in vivo to produce a library of recombinant antibodies that can be screened for novel or improved function(s) over the lead antibody.
Owner:ABMAXIS
Structure-based selection and affinity maturation of antibody library
InactiveUS7117096B2High affinityImprove throughputPeptide librariesPeptide/protein ingredientsProtein insertionIn vivo
The present invention provides a structure-based methodology for efficiently generating and screening protein libraries for optimized proteins with desirable biological functions, such as antibodies with high binding affinity and low immunogenicity in humans. In one embodiment, a method is provided for constructing a library of antibody sequences based on a three dimensional structure of a lead antibody. The method comprises: providing an amino acid sequence of the variable region of the heavy chain (VH) or light chain (VL) of a lead antibody, the lead antibody having a known three dimensional structure which is defined as a lead structural template; identifying the amino acid sequences in the CDRs of the lead antibody; selecting one of the CDRs in the VH or VL region of the lead antibody; providing an amino acid sequence that comprises at least 3 consecutive amino acid residues in the selected CDR, the selected amino acid sequence being a lead sequence; comparing the lead sequence profile with a plurality of tester protein sequences; selecting from the plurality of tester protein sequences at least two peptide segments that have at least 10% sequence identity with lead sequence, the selected peptide segments forming a hit library; determining if a member of the hit library is structurally compatible with the lead structural template using a scoring function; and selecting the members of the hit library that score equal to or better than or equal to the lead sequence. The selected members of the hit library can be expressed in vitro or in vivo to produce a library of recombinant antibodies that can be screened for novel or improved function(s) over the lead antibody.
Owner:ABMAXIS
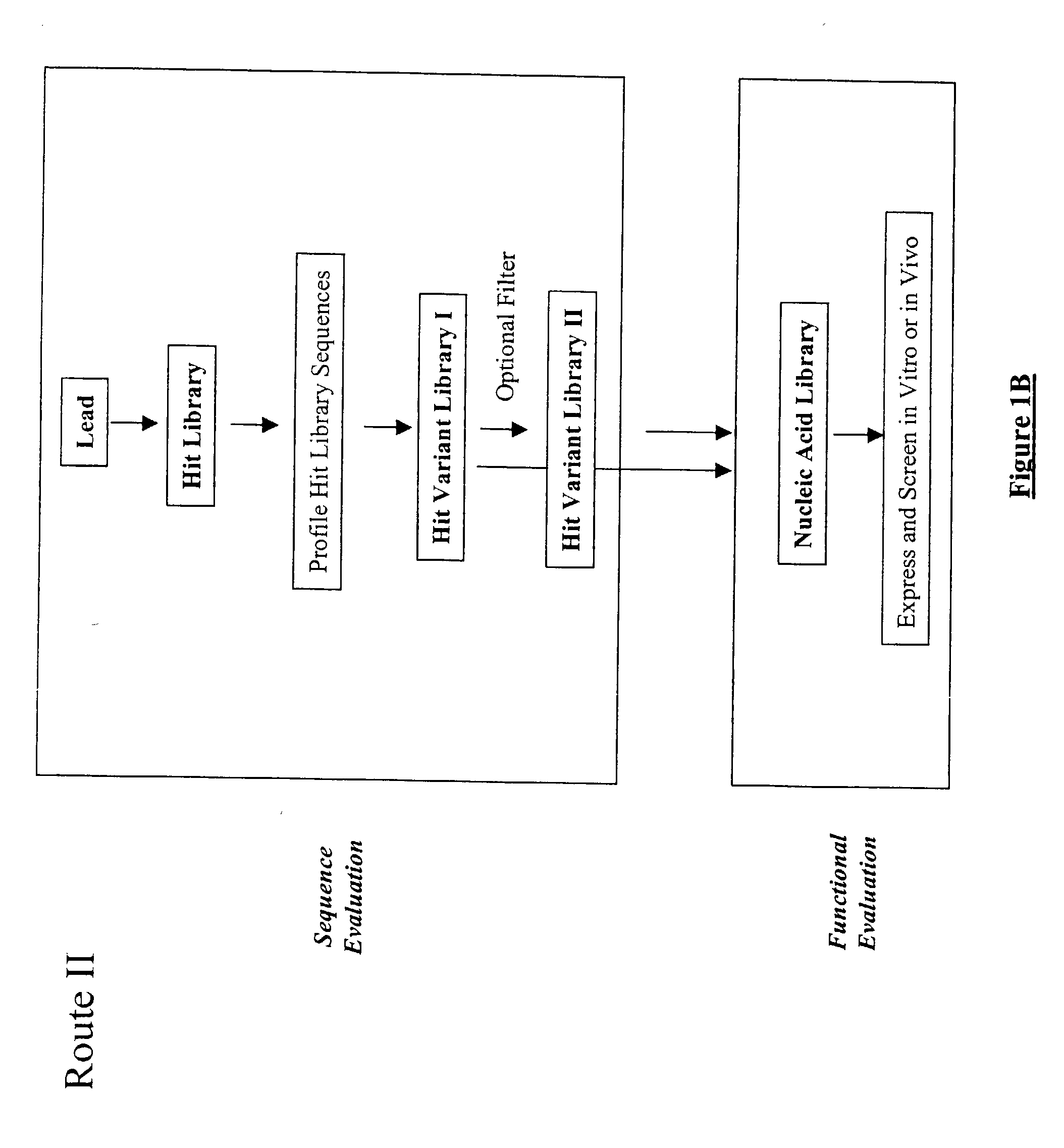
Generation and affinity maturation of antibody library in silico
The present invention provides a methodology for efficiently generating and screening protein libraries for optimized proteins with desirable biological functions, such as improved binding affinity towards biologically and / or therapeutically important target molecules. The process is carried out computationally in a high throughput manner by mining the ever-expanding databases of protein sequences of all organisms, especially human. In one embodiment, a method is provided for constructing a library of antibody sequences based on the amino acid sequence of a lead antibody. The method comprises: providing an amino acid sequence of the variable region of the heavy chain (VH) or light chain (VL) of a lead antibody; identifying the amino acid sequences in the CDRs of the lead antibody; selecting one of the CDRs in the VH or VL region of the lead antibody; providing an amino acid sequence that comprises at least 3 consecutive amino acid residues in the selected CDR, the selected amino acid sequence being a lead sequence; comparing the lead sequence with a plurality of tester protein sequences; and selecting from the plurality of tester protein sequences at least two peptide segments that have at least 15% sequence identity with the lead sequence, the selected peptide segments forming a hit library. The hit library of antibody sequences can be expressed in vitro or in vivo to produce a library of recombinant antibodies that can be screened for novel or improved function(s) over the lead antibody.
Owner:ABMAXIS
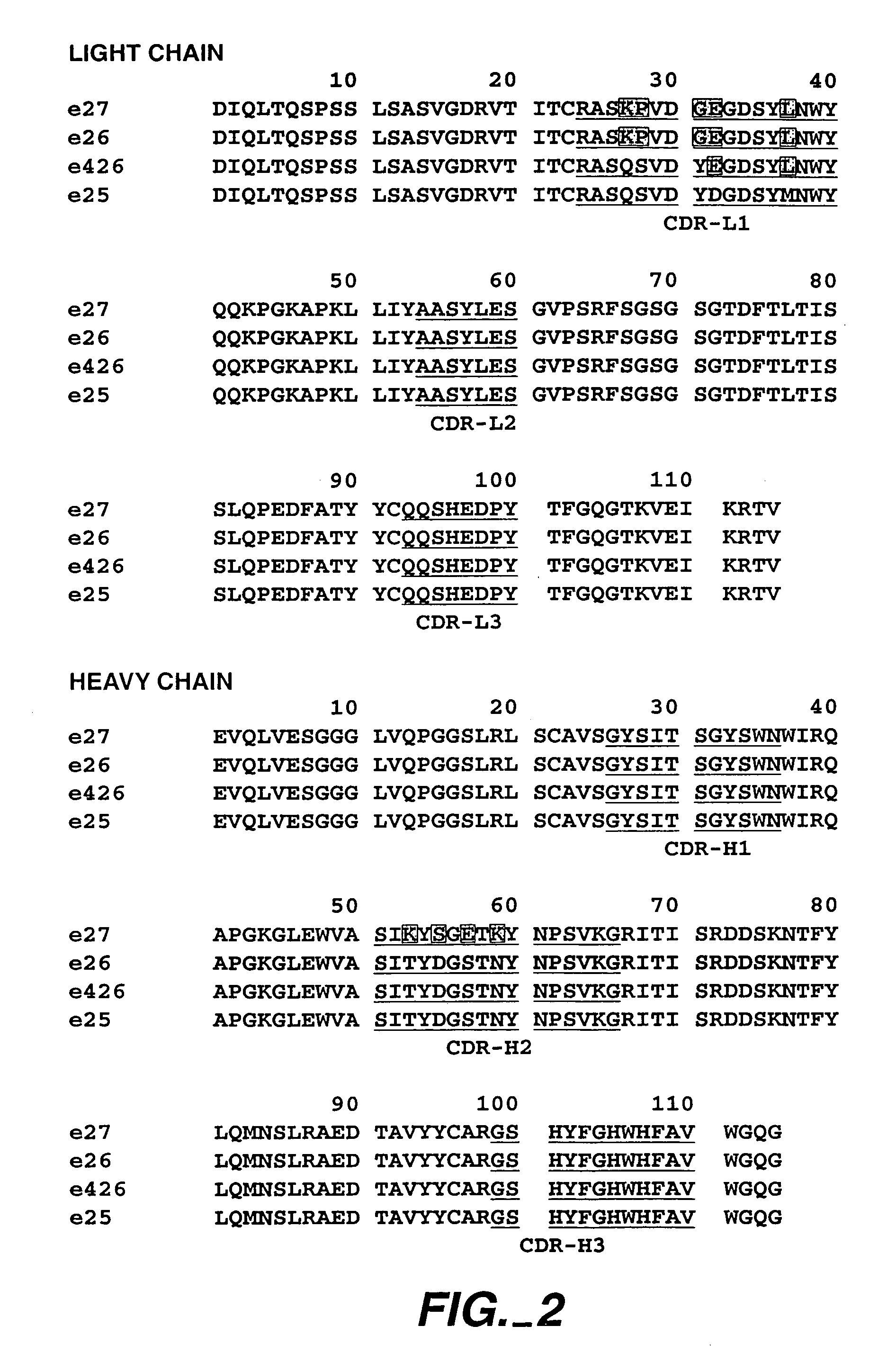
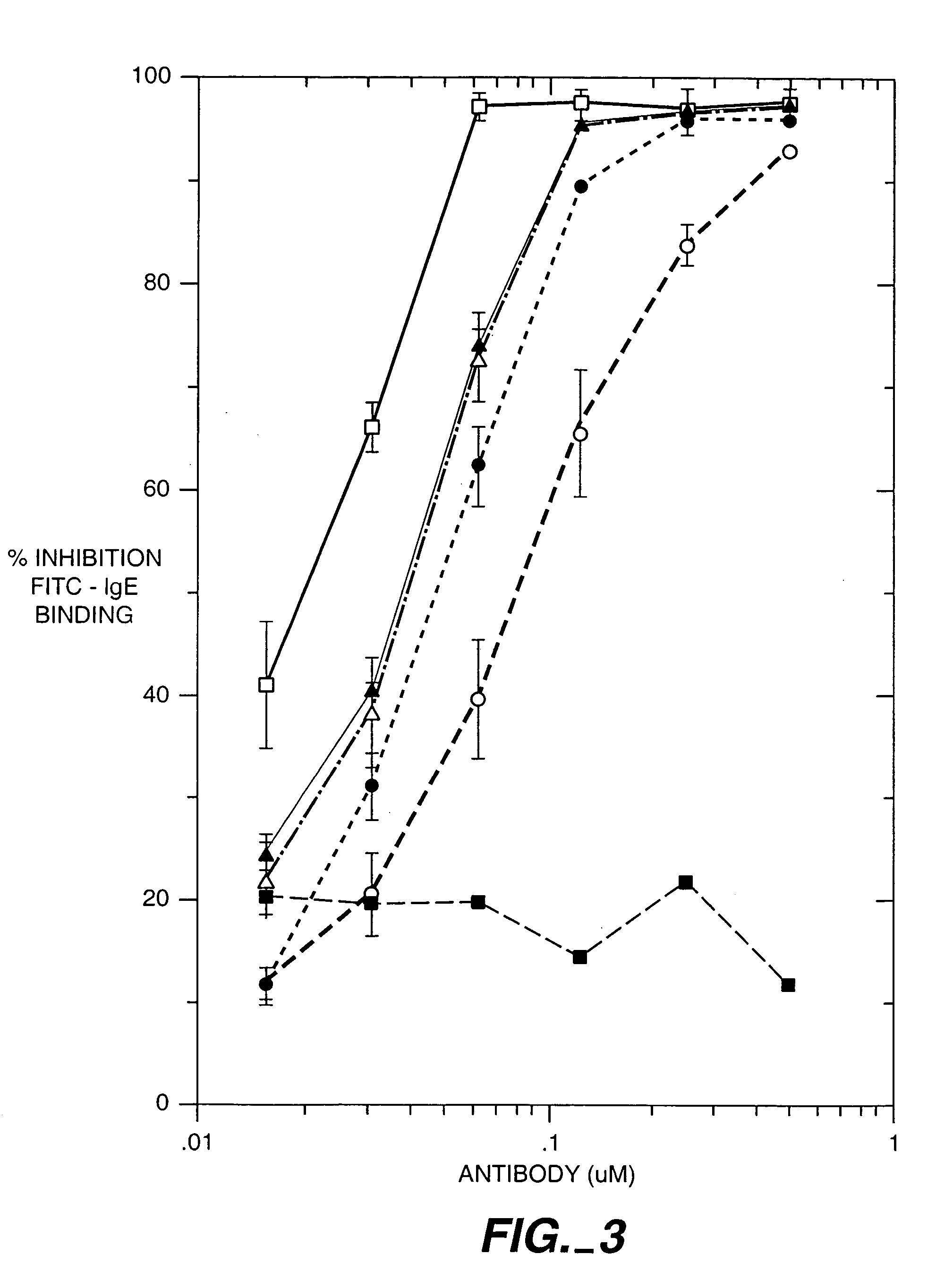
Anti-IgE antibodies
InactiveUS20080003218A1Reducing and inhibiting IgE-mediated productionAnimal cellsSugar derivativesIsomerizationBacteriophage
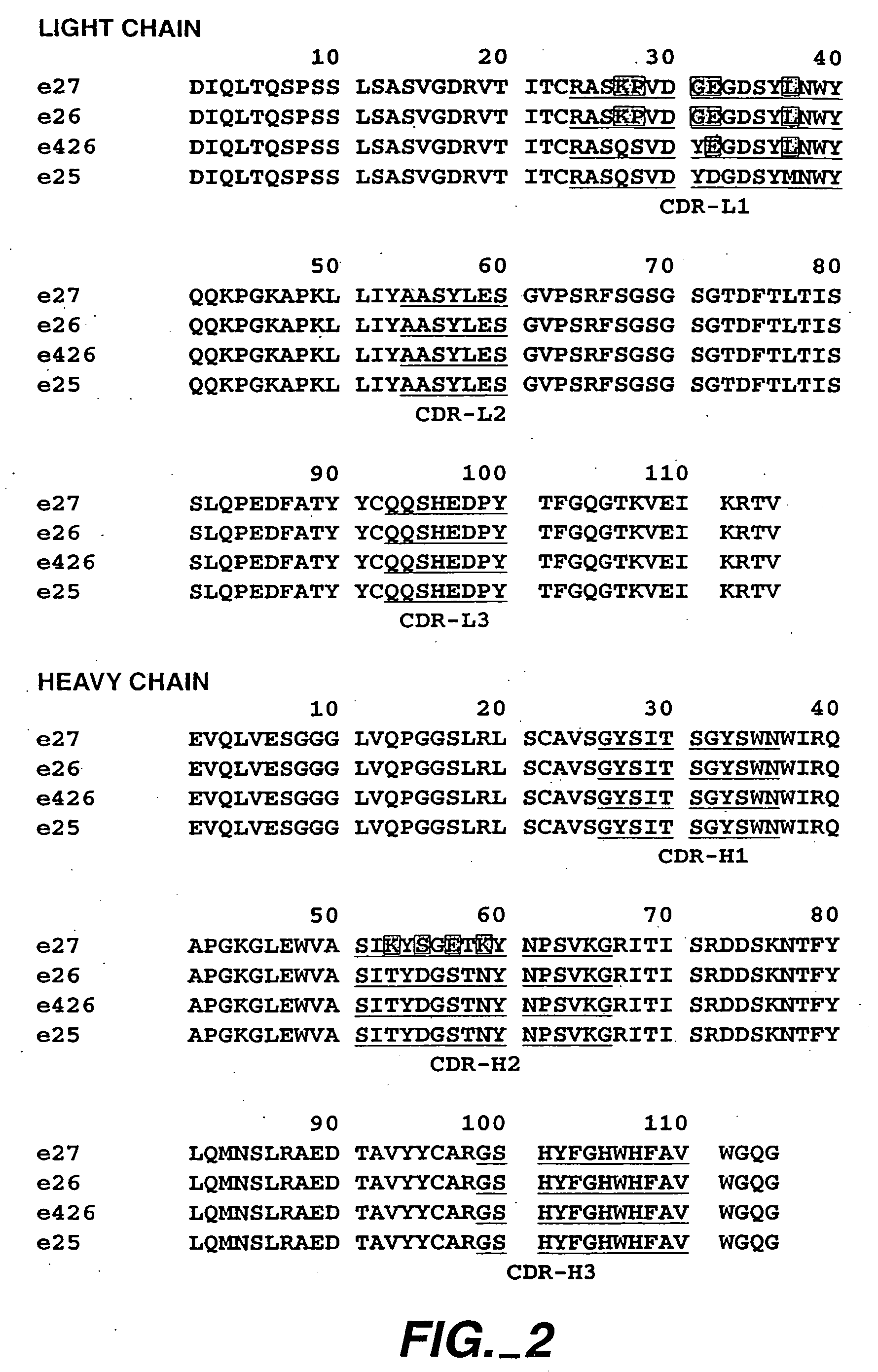
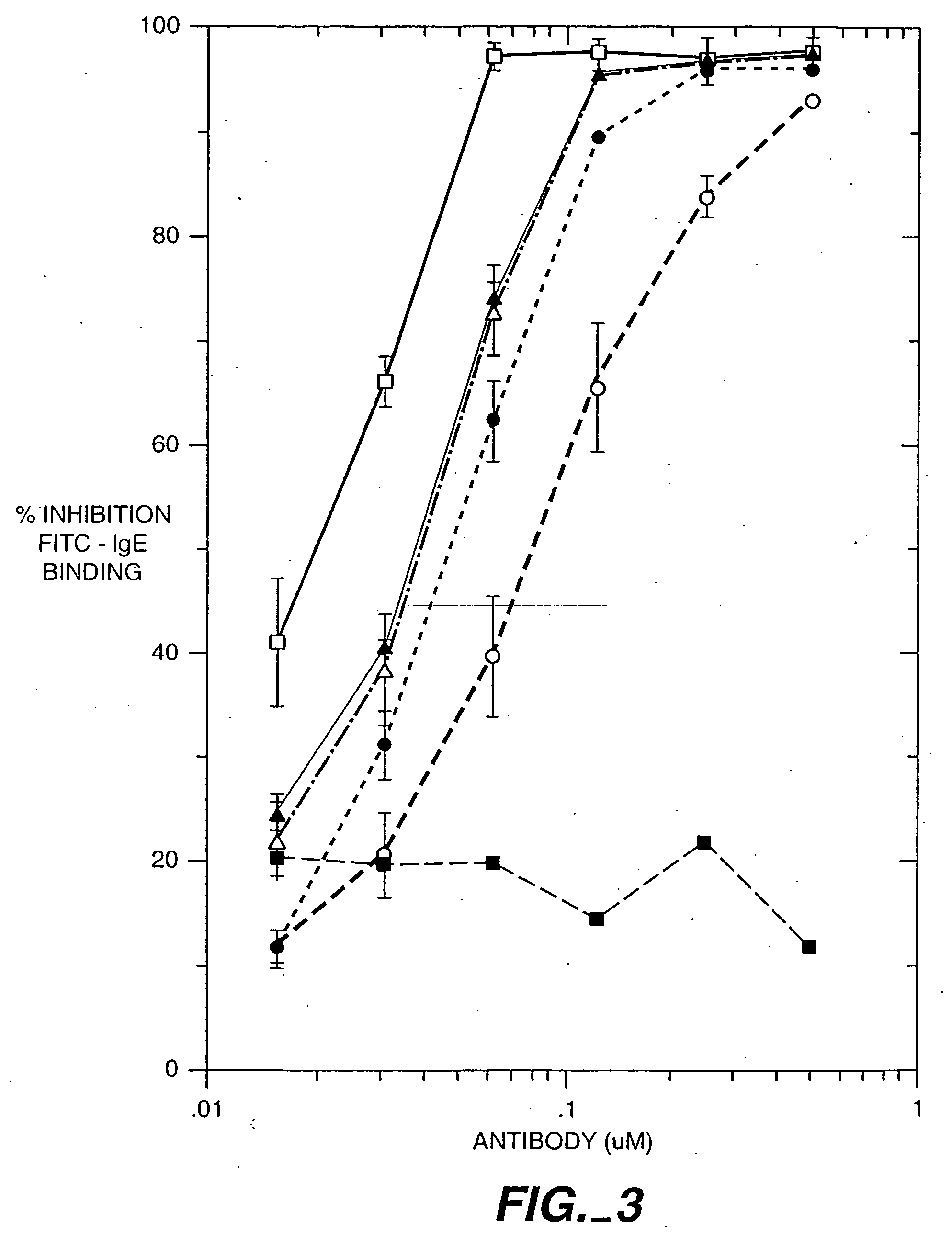
The present invention relates to a method for adjusting the affinity of a polypeptide to a target molecule by a combination of steps, including: (1) the identification of aspartyl residues which are prone to isomerization; (2) the substitution of alternative residues and screening the resulting mutants for affinity against the target molecule. In a preferred embodiment, the method of subtituting residues is affinity maturation with phage display (AMPD). In a further preferred embodiment the polypeptide is an antibody and the target molecule is an antigen. In a further preferred embodiment, the antibody is anti-IgE and the target molecule is IgE. In another embodiment, the invention relates to an anti-IgE antibody having improved affinity to IgE.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Antikine antibodies that bind to multiple cc chemokines
ActiveUS20110059107A1Inhibition of chemotaxisAvoid interactionAntipyreticAnalgesicsCCL3Hybridoma cell
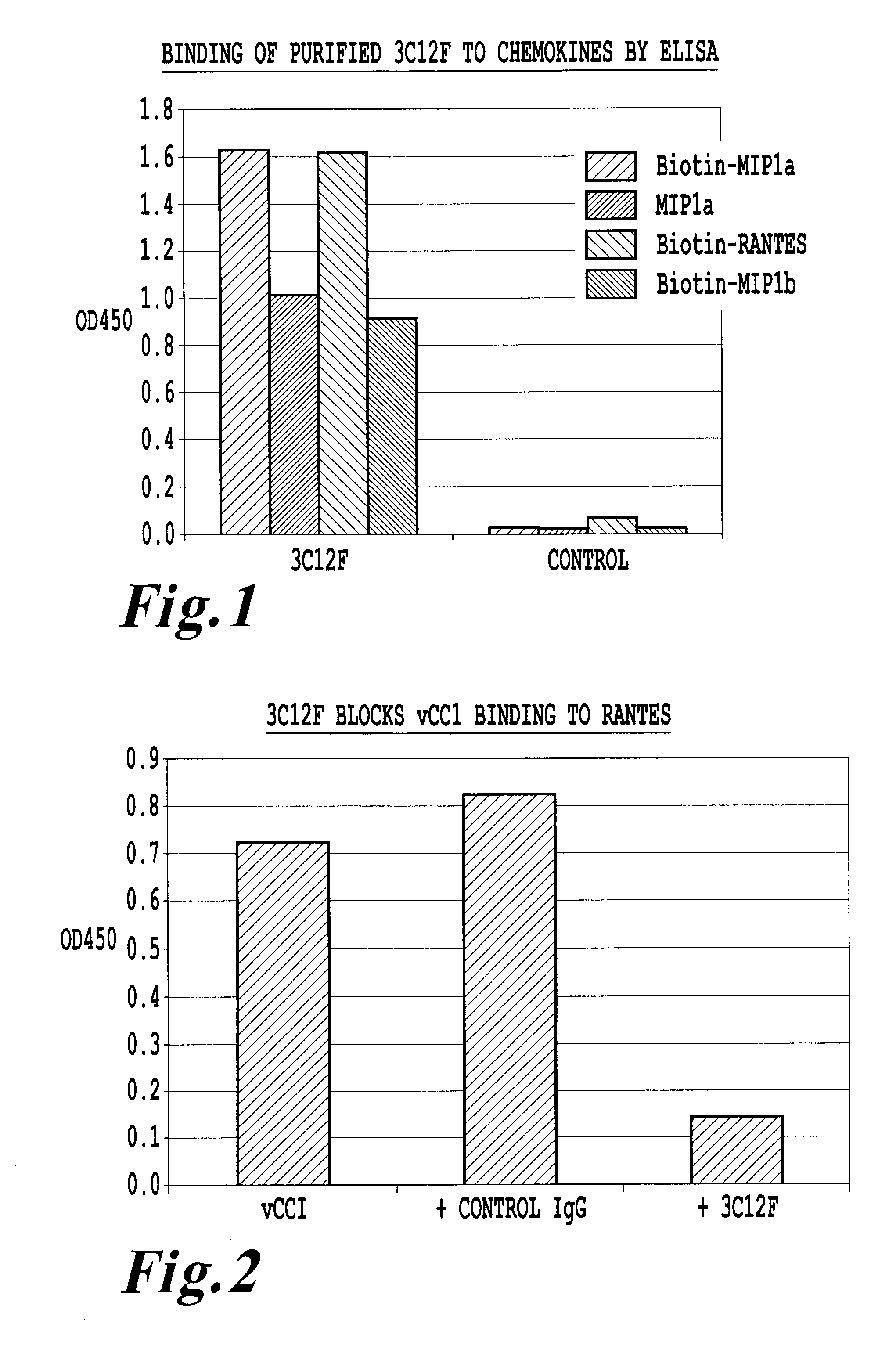
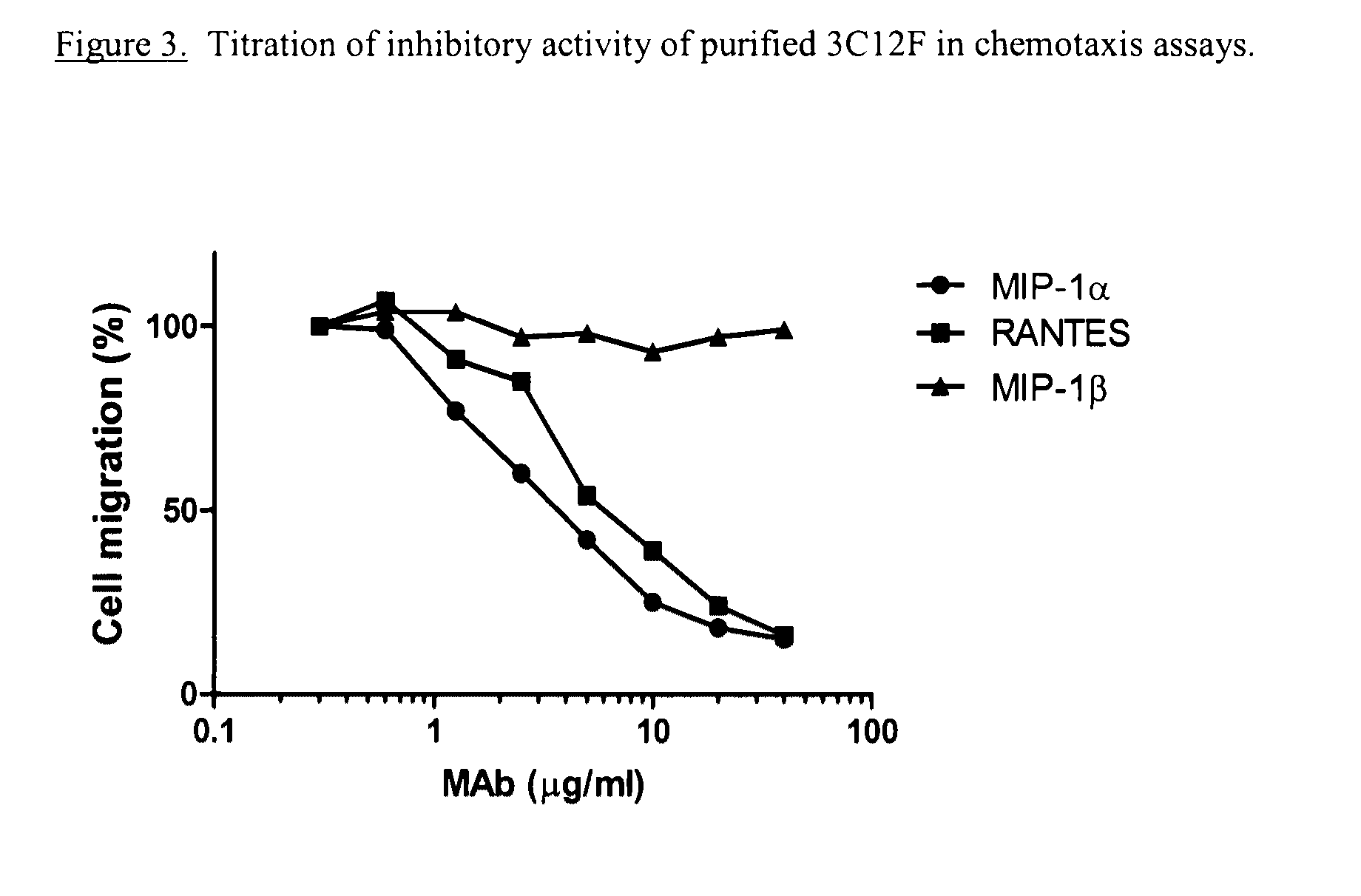
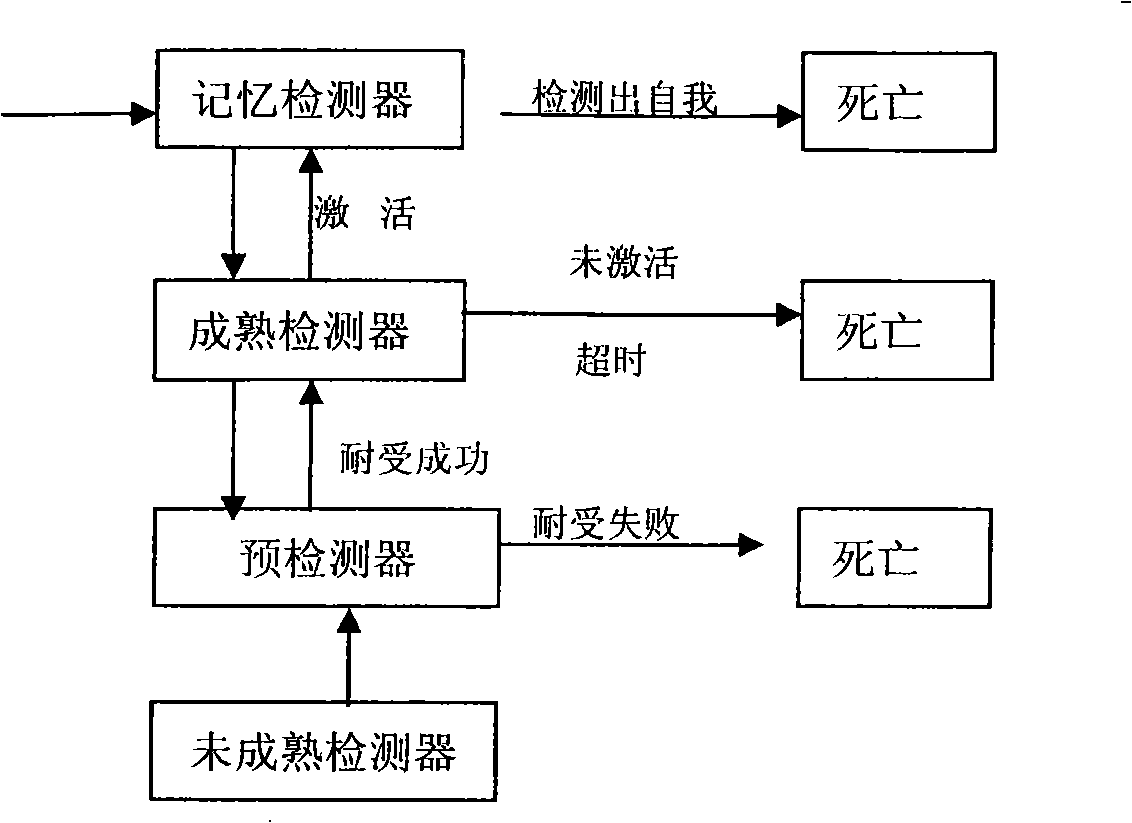
An antikine antibody binds to two, three, four, five or more CC chemokines, such as RANTES / CCL5, MIP-1α / CCL3, MIP-1β / CCL4, or MCP-1 / CCL2. Methods for affinity maturation and humanization of antikine antibodies as well as the production of hybridoma cell lines producing antikine antibodies by sequential immunization are also disclosed.
Owner:VLST +1
Method for detecting dynamic gridding instruction based on artificial immunity
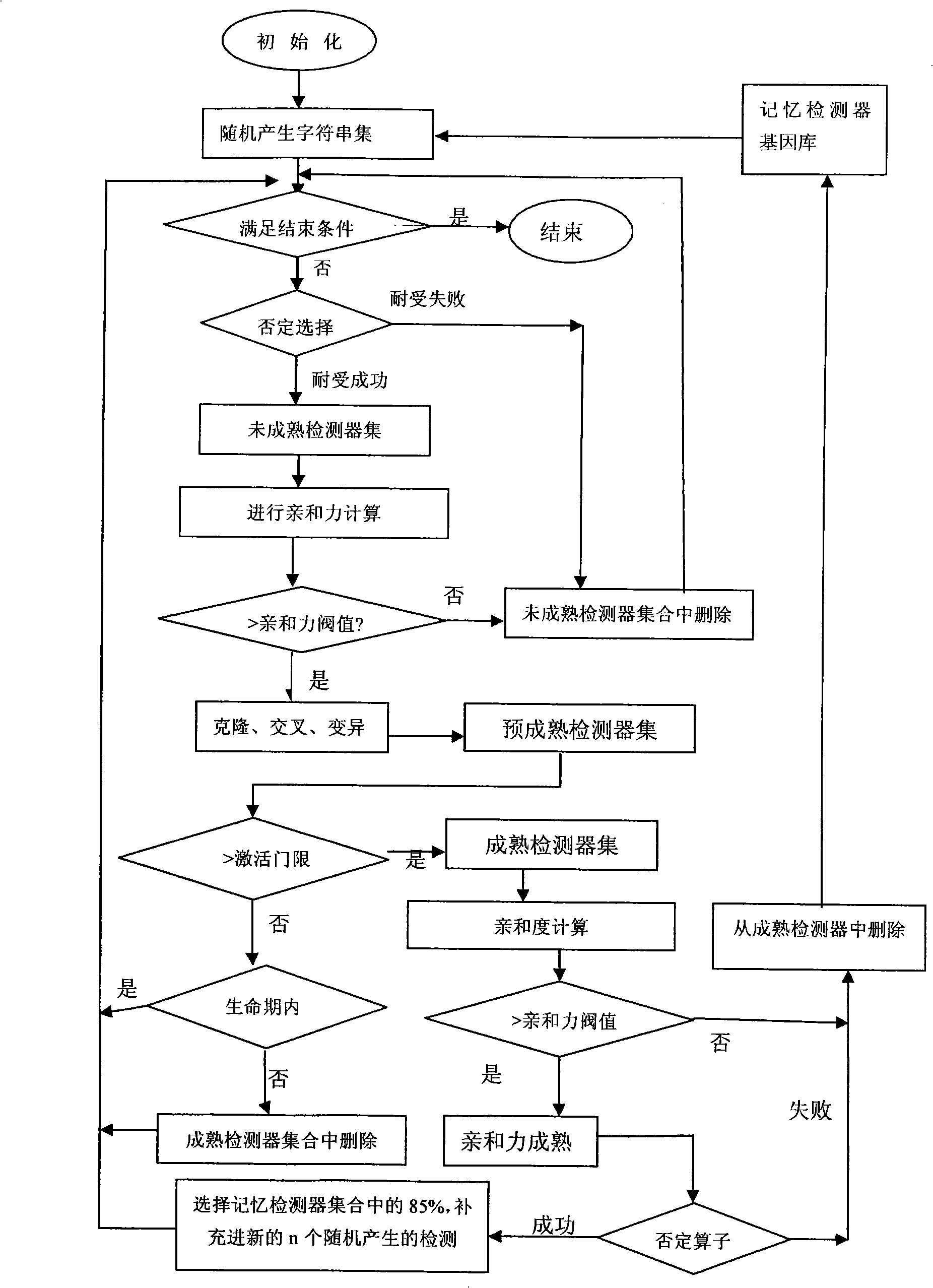
InactiveCN101299691AEasy to coverHigh-precision detectionGenetic modelsData switching networksClonal selectionClonal selection algorithm
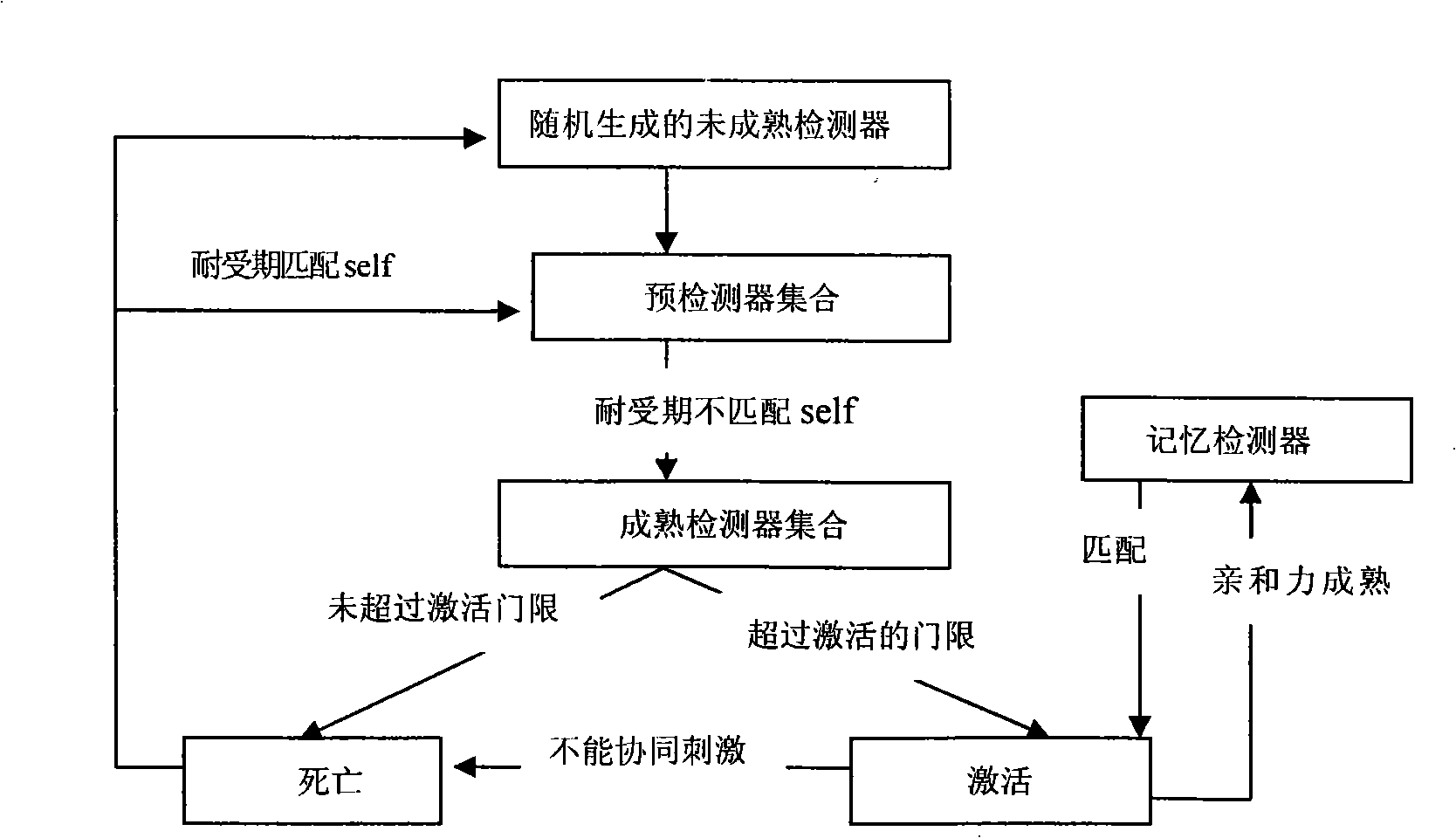
A method for detecting dynamic gridding instruction based on artificial immunity, is a method for detecting instruction facing to gridding which takes use the artificial immunity technique for reference. According to the dynamic and real time requirement of the instruction detection under gridding surroundings, the method takes the prior clonal selection algorithm as main body, combines negative selection, clonal selection, affinity maturation and memory detector gene bank method, so at to dynamic handle the instruction detection under gridding surroundings. The method includes a dynamic detector evolvement process and a gridding instruction detection process which are based on artificial immunity, which is characterized in by using the artificial immunity technique for reference, and combining the negative selection, clonal selection, affinity maturation and memory detector gene bank method; firstly obtaining an evolvement matured detector; and then dynamically handling the instruction detection problem in the gridding surroundings under the coordination of the artificial immunity mechanism, to complete the entire process of dynamic gridding instruction detection.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Binding molecules
InactiveUS20090271880A1MaximiseReduce hydrophobicityImmunoglobulins against animals/humansFermentationSolubilityHeavy chain
The present invention relates to methods for engineering VH domains to improve their solubility and stability. The invention provides for the incorporation of defined amino acid substitutions based on 3-D structural information into the V segments of a heavy chain locus, expressing the locus in a non-human mammal and selecting soluble VH domains. Further stabilising or solubilising mutations maybe introduced as a result affinity maturation during B-cell maturation in vivo.
Owner:ERASMUS UNIV MEDICAL CENT ROTTERDAM ERASMUS MC
Antigenic mimics of discontinuous epitopes of pathogen recognized by broadly neutralizing antibodies
InactiveUS20130039927A1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPeptide sequenceDiscontinuous epitope
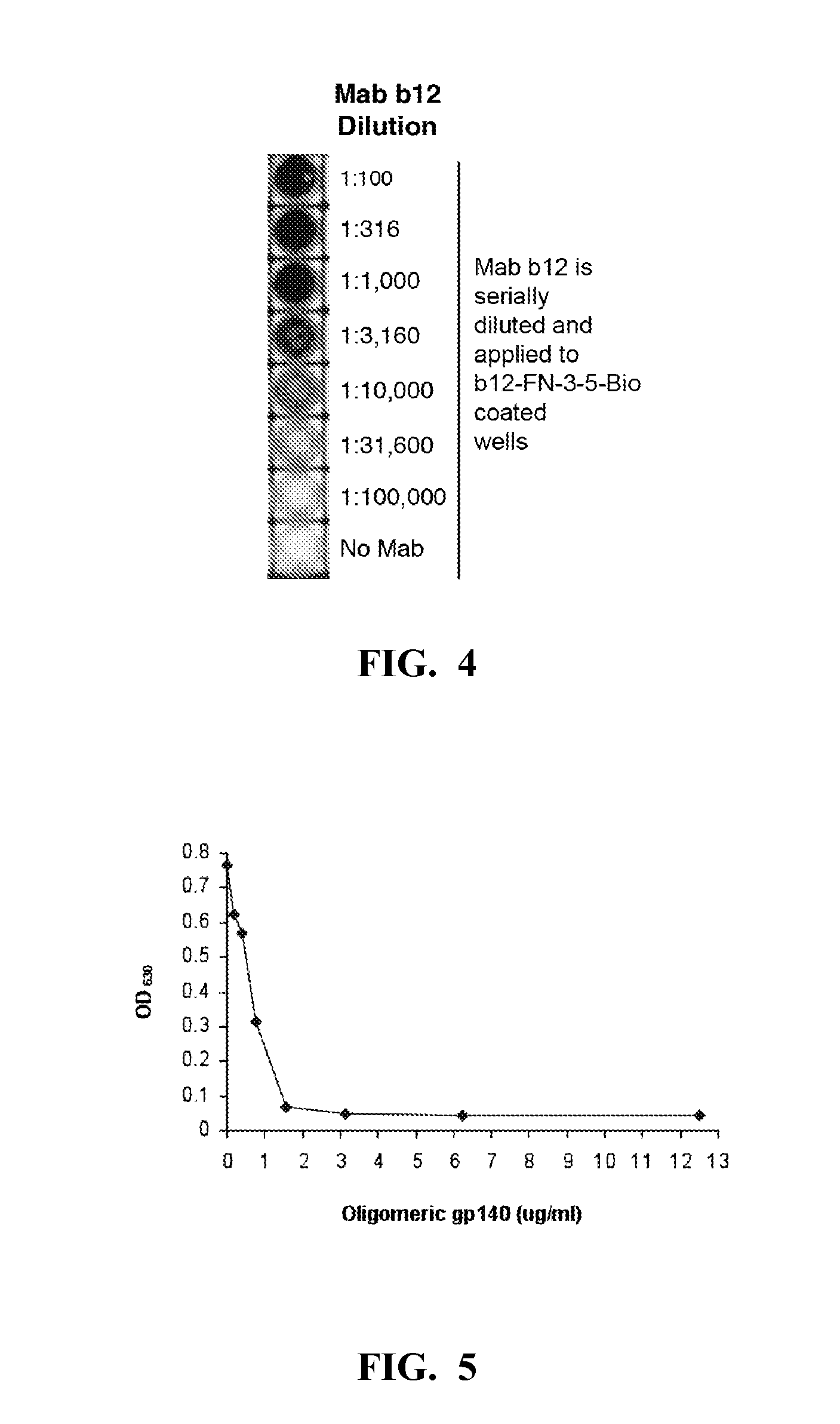
The present invention relates to an anti-idiotypic polypeptide scaffold that includes two or more peptide sequences that mimic a discontinuous epitope of a pathogen that is recognized by or induces formation of a broadly neutralizing antibody. Using a fibronectin FNfn10 scaffold bearing two or more modified discontinuous loops, scaffolds that recognize broadly neutralizing antibodies in vitro and from patient serum have been identified. These scaffolds should induce an immune response or mobilize germline specificities to initiate their affinity maturation.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Method for the production of a single heavy chain antibody
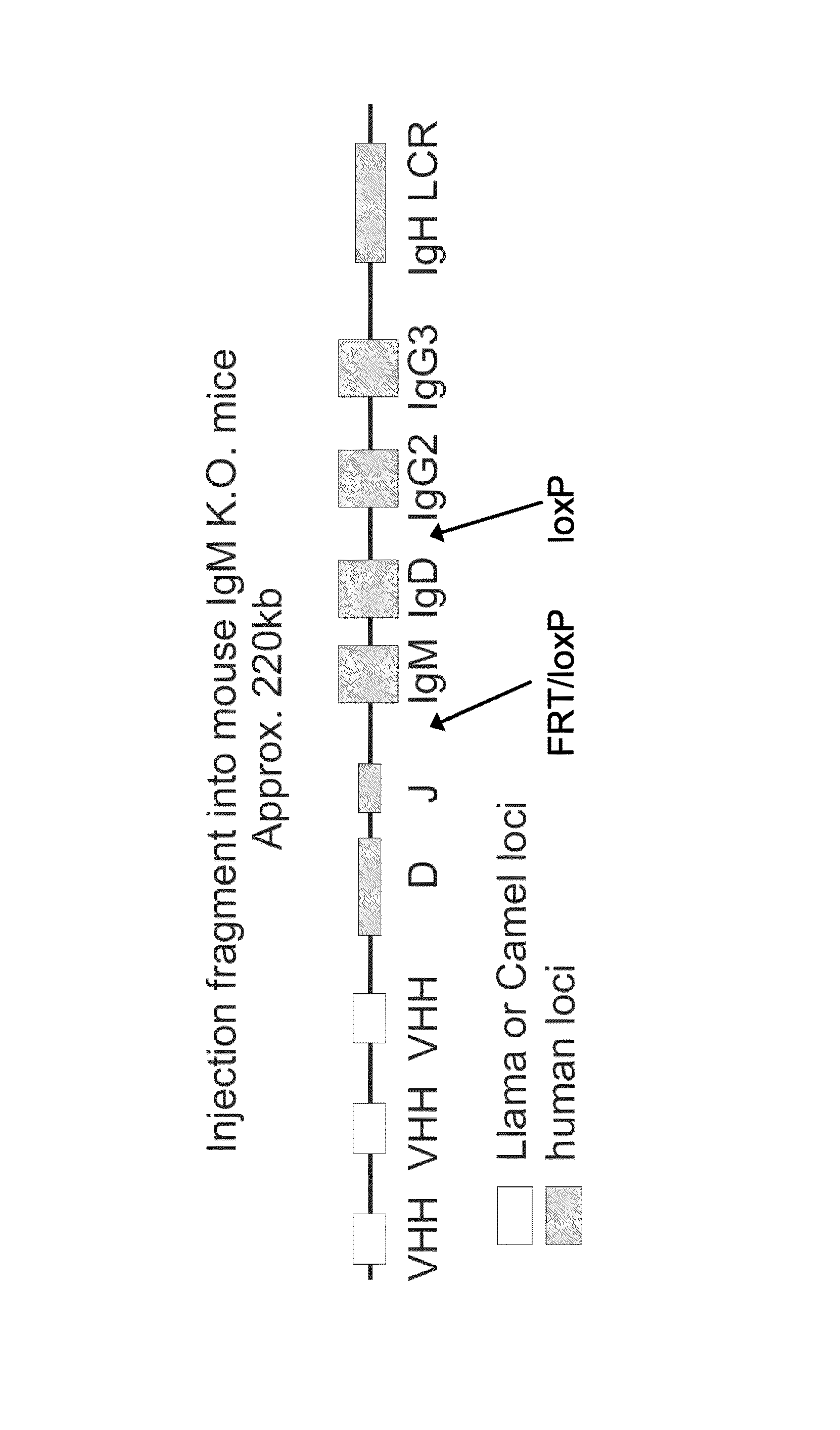
The present invention relates to a method for the generation of single chain immunoglobulins in a mammal. In particular, the present invention relates to a method for the generation of single chain camelid VHH antibodies in a mammal which undergo the process of class-switching and affinity maturation found within antibody producing B cells. Single chain antibodies generated using the method of the present invention and the uses thereof are also described.
Owner:ERASMUS UNIV MEDICAL CENT ROTTERDAM ERASMUS MC
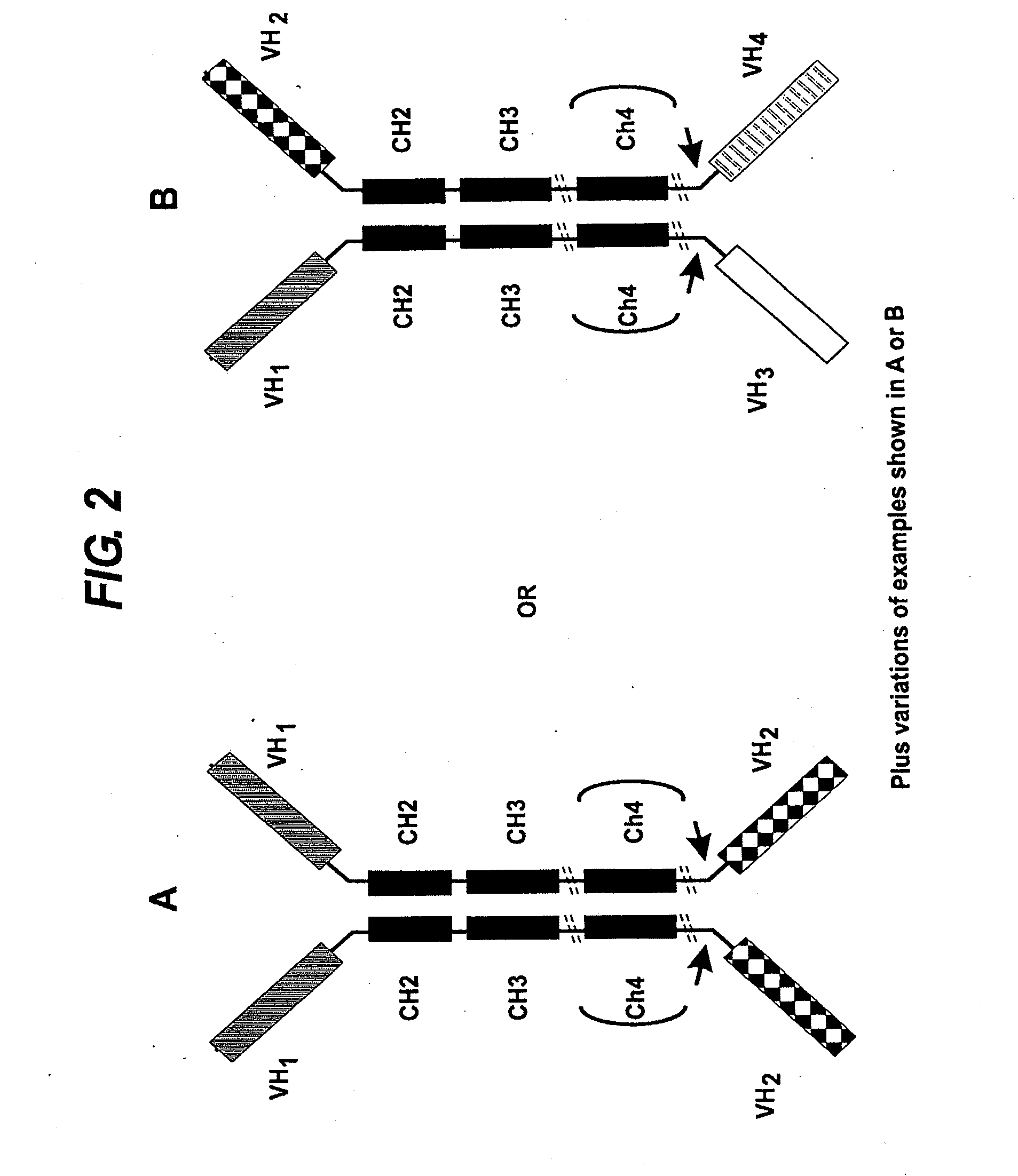
Transgenic non-human vertebrate for the in vivo production of dual specificity immunoglobulins or hypermutated heavy chain only immunoglobulins
ActiveUS20150133641A1Avoid problemsHeavy productionAnimal cellsHybrid immunoglobulinsVariable domainIn vivo
The invention relates, in one aspect, generally to novel concept of guided selection of antibody variable domains, combination and expression entirely in vivo. An application is to produce multivalent polypeptides. The present invention relates to multivalent (eg, multispecific) antibodies, antibody chains and polypeptides, as well as heavy chain-only antibodies (H2 antibodies) that are devoid of light chains. The invention further relates to the selection, maturation and production of these in vivo in non-human vertebrates and non-human vertebrate cells. To this end the invention also relates to such non-human vertebrates and cells. The invention also relates to the provision of means to produce and select heavy chain-only antibodies and heavy chains comprising variable domains that have undergone affinity maturation.
Owner:KIMAB LTD
Method for treating IgE-mediated disorders
InactiveUS7157085B2Reducing and inhibiting IgE-mediated productionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseIsomerization
The present invention relates to a method for adjusting the affinity of a polypeptide to a target molecule by a combination of steps, including: (1) the identification of aspartyl residues which are prone to isomerization; (2) the substitution of alternative residues and screening the resulting mutants for affinity against the target molecule. In a preferred embodiment, the method of subtituting residues is affinity maturation with phage display (AMPD). In a further preferred embodiment the polypeptide is an antibody and the target molecule is an antigen. In a further preferred embodiment, the antibody is anti-IgE and the target molecule is IgE. In another embodiment, the invention relates to an anti-IgE antibody having improved affinity to IgE.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
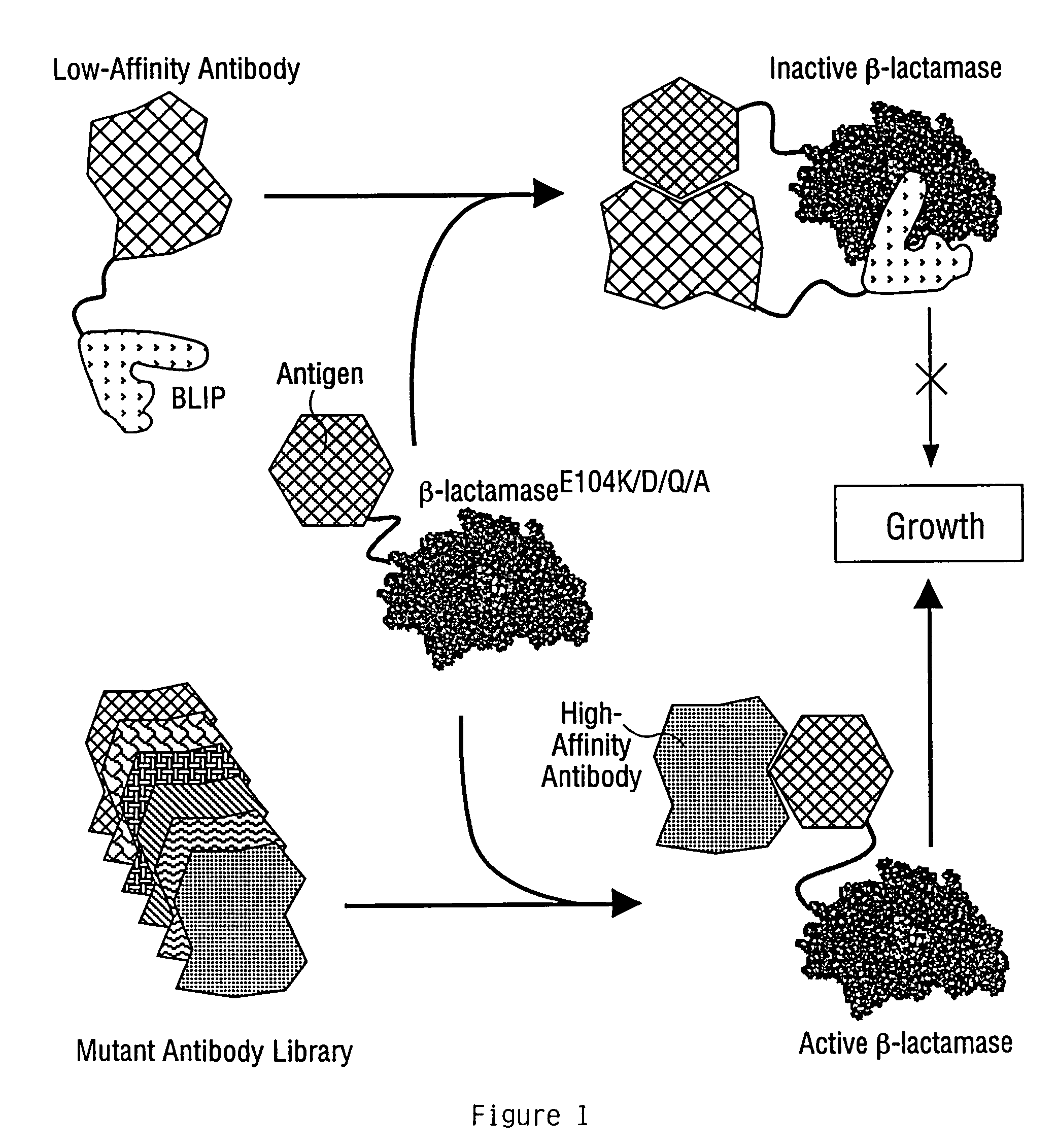
Methods for affinity maturation
InactiveUS7432063B2High affinitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementStereochemistryAvidity
This invention provides methods of obtaining a binding molecule, e.g., an antibody, that has enhanced affinity for a binding partner relative to a reference binding molecule.
Owner:KALOBIOS PHARMA
Humanized anti-PD-1 and c-MET bispecific antibody, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105085680ALow immunogenicityEasy to manufactureImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsSequence signalSequence analysis
The invention belongs to the biotechnical field, and concretely relates to a recombinant humanized anti-PD-1 and c-MET bispecific antibody, and a preparation method and an application thereof. Humanized antibody database comparison, computer molecular structure simulation, molecular docking simulation and sequence analysis are carried out, and recombinant humanized anti-PD-1 and c-MET bispecific antibody molecule designing comprising affinity maturation, structure optimization, humanization and codon optimization is carried out, and an expression plasmid of the recombinant humanized anti-PD-1 and c-MET bispecific antibody is constructed on the basis of an optimized signal peptide sequence and a plasmid expression vector replicon. The bispecific antibody has the characteristics of low immunogenicity, simple and safe preparation process, high yield, high purity and high activity, and can be used to further prepare new specific drugs for treating non-small cell lung cancer.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
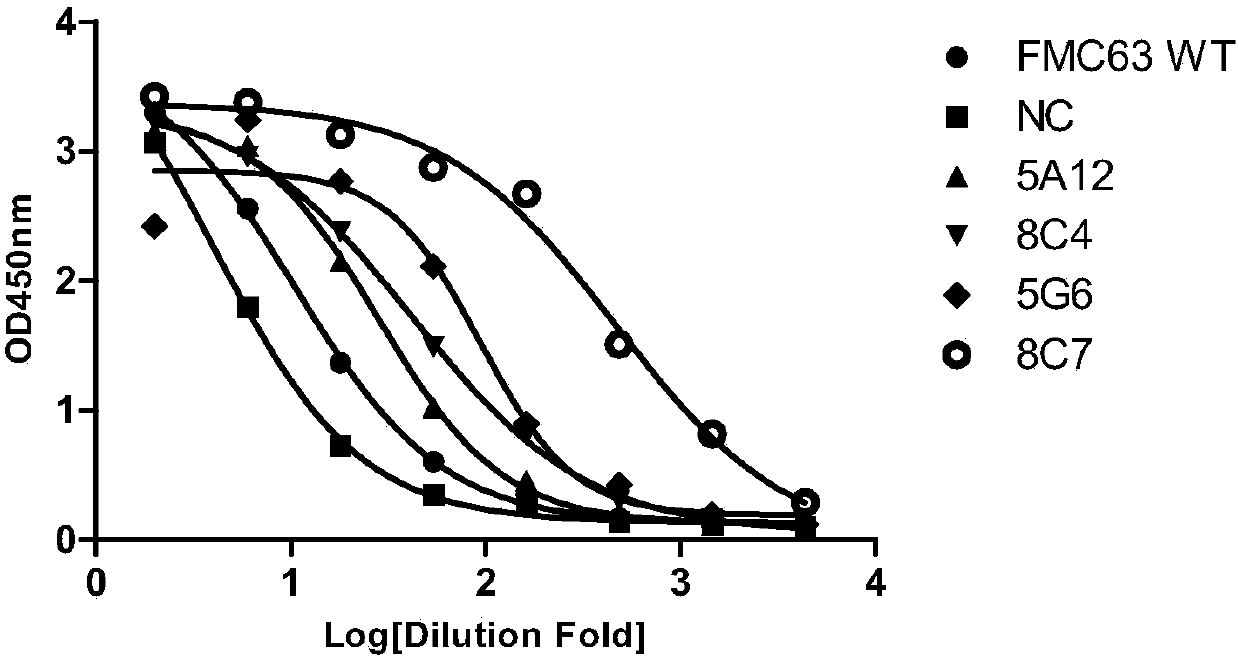
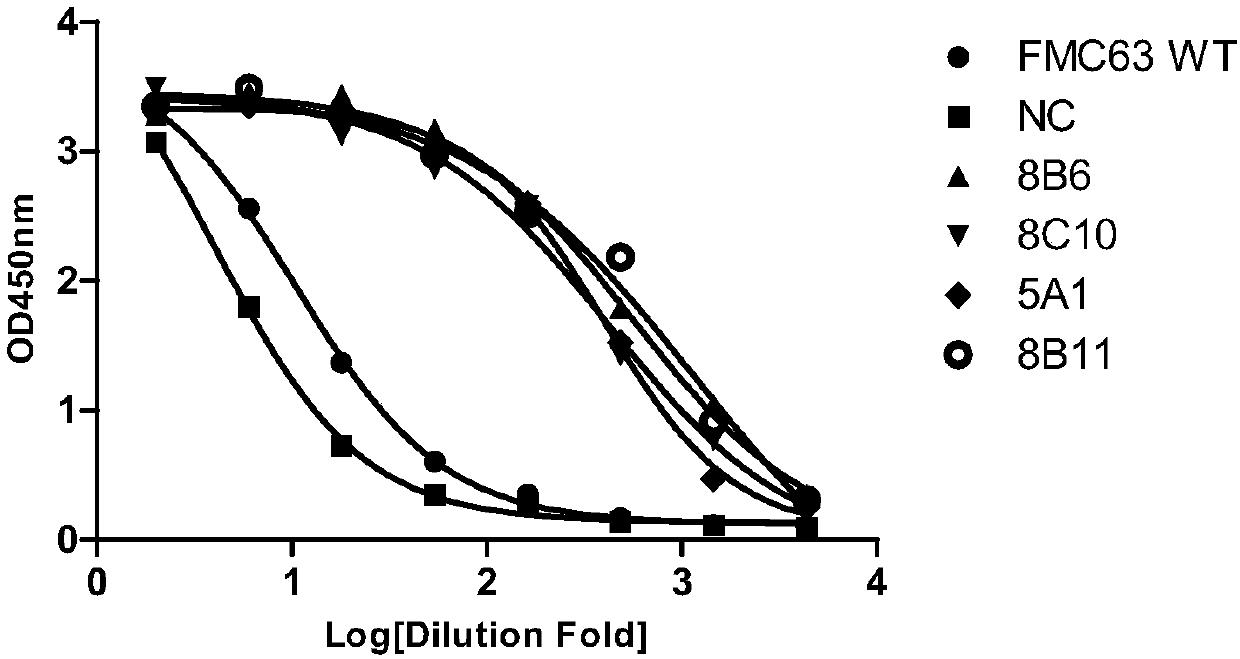
Anti-CD19 antibody and preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN107793478AHigh affinityIncrease lethalityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetically modified cellsHeavy chainSingle-Chain Antibodies
The invention relates to the technical field of biotechnology and particularly relates to an anti-CD19 antibody and a preparation method and use thereof. CDR in a heavy chain variable region of the anti-CD19 antibody comprises CDR-H1 with an amino acid sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID No. 1, CDR-H2 with an amino acid sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID No. 2 and CDR-H3 with an amino acid sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID No. 3. The CDR of a light chain variable region of the anti-CD19 antibody comprises CDR-L1 with an amino acid sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID No. 4, CDR-L2 with an amino acid sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID No. 5 and CDR-L3 with an amino acid sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID No. 6. The FMC63 scFv is screened in affinity maturation through a phage display technology so that a high affinity single chain antibody against CD19 is obtained.
Owner:HUADAO SHANGHAI BIOPHARMA CO LTD
Transgenic Non-Human Vertebrate for the Expression of Class-Switched, Fully Human, Antibodies
ActiveUS20150082466A1Avoid problemsProduct can be usedAnimal cellsHybrid immunoglobulinsBiophysical profileIn vivo
The present invention relates to humanisation of antibodies in vivo. The invention provides non-human vertebrates, cells, populations and methods useful for humanising chimaeric antibodies in vivo. Using the present invention it is possible straightforwardly and rapidly to obtain antigen-specific antibodies that are fully human (ie, comprising human variable and constant regions) and have undergone recombination, junctional diversification, affinity maturation and isotype switching in vivo in a non-human vertebrate system. Furthermore, such antibodies are humanised (eg, totally human)—and selected—totally in vivo, and as such the present invention harnesses in vivo filtering for expressibility, affinity and biophysical characteristics in the context of the desired human variable and constant region pairings. This is avoids problems of down-grading antibody characteristics when humanising the constant region of chimaeric antibodies in vitro.
Owner:KIMAB LTD
Transgenic non-human vertebrate for the expression of class-switched, fully human, antibodies
ActiveUS10251377B2Avoid problemsProduct can be usedHybrid immunoglobulinsSugar derivativesBiophysical profileIn vivo
The present invention relates to humanisation of antibodies in vivo. The invention provides non-human vertebrates, cells, populations and methods useful for humanising chimaeric antibodies in vivo. Using the present invention it is possible straightforwardly and rapidly to obtain antigen-specific antibodies that are fully human (ie, comprising human variable and constant regions) and have undergone recombination, junctional diversification, affinity maturation and isotype switching in vivo in a non-human vertebrate system. Furthermore, such antibodies are humanised (eg, totally human)—and selected—totally in vivo, and as such the present invention harnesses in vivo filtering for expressibility, affinity and biophysical characteristics in the context of the desired human variable and constant region pairings. This is avoids problems of down-grading antibody characteristics when humanising the constant region of chimaeric antibodies in vitro.
Owner:KIMAB LTD
Transgenic Animals and Methods of Making Recombinant Antibodies
InactiveUS20080196112A1Weak affinityIncrease contentMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid vectorChimeric antibodyAntibody production
The present invention concerns a means for obtaining cells which produce human, humanized or chimeric antibodies in commercially useful quantities. The invention permits high antibody producer cells to be selected and isolated from animals for use in culture to produce antibodies. The invention also provides methods for the affinity maturation of human, humanized or chimeric immunoglobulins.
Owner:INNATE PHARMA SA +1
Yeast cell surface display of proteins and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090280560A1Effectively mimickedHigh affinityFungiSaccharide peptide ingredientsSurface displayAgglutinin-B
The present invention provides a genetic method for tethering polypeptides to the yeast cell wall in a form accessible for binding to macromolecules. Combining this method with fluorescence-activated cell sorting provides a means of selecting proteins with increased or decreased affinity for another molecule, altered specificity, or conditional binding. Also provided is a method for genetic fusion of the N terminus of a polypeptide of interest to the C-terminus of the yeast Aga2p cell wall protein. The outer wall of each yeast cell can display approximately 104 protein agglutinins. The native agglutinins serve as specific adhesion contacts to fuse yeast cells of opposite mating type during mating. In effect, yeast has evolved a platform for protein-protein binding without steric hindrance from cell wall components. As one embodiment, attaching an scFv antibody fragment to the Aga2p agglutinin effectively mimics the cell surface display of antibodies by B cells in the immune system for affinity maturation in vivo. As another embodiment, T cell receptor mutants can be isolated by this method that are efficiently displayed on the yeast cell surface, providing a means of altering T cell receptor binding affinity and specificity by library screening.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
High throughput generation and affinity maturation of humanized antibody
Compositions, methods, and kits are provided for efficiently generating and screening humanized antibody with high affinity against a specific antigen. The library of humanized antibody is generated by mutagenizing a chimeric antibody template that combines human antibody framework and antigen binding sites of a non-human antibody. Alternatively, the library of humanized antibody is generated by grafting essential antigen-recognition segment(s) such as CDRs of the non-human antibody into the corresponding position(s) of each member of a human antibody library. This library of humanized antibody is then screened for high affinity binding toward a specific antigen in vivo in organism such as yeast or in vitro using techniques such as ribosome display or mRNA display. The overall process can be efficiently performed in a high throughput and automated manner, thus mimicking the natural process of antibody affinity maturation.
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
Transgenic non-human vertebrate for the in vivo production of dual specificity immunoglobulins or hypermutated heavy chain only immunoglobulins
ActiveUS10667501B2Avoid problemsHeavy productionHybrid immunoglobulinsNucleic acid vectorVertebrate AnimalsIn vivo
Owner:KIMAB LTD
Anti-CD19 antibody and preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN107793480AIncrease lethalityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMammal material medical ingredientsSingle-Chain AntibodiesComplementarity determining region
The invention relates to the technical field of biotechnology and particularly relates to an anti-CD19 antibody and a preparation method and use thereof. The anti-CD19 antibody comprises a heavy chainvariable region and a light chain variable region. The complementarity determining region of the heavy chain variable region comprises CDR-H1 with an amino acid sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID No. 1, CDR-H2 with an amino acid sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID No. 2 or 3 and CDR-H3 with an amino acid sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID No. 4. The complementarity determining region of the light chain variable region comprises CDR-L1 with an amino acid sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID No. 5, CDR-L2 with an amino acid sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID No. 6 and CDR-L3 with an amino acid sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID No. 7. The FMC63 scFv is screened in affinity maturation through a phage display technology so that a high affinity single chain antibodyagainst CD19 is obtained.
Owner:SHANGHAI GENBASE BIOTECH CO LTD
Binding molecules
ActiveUS20100197897A1Antibacterial agentsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigen challengeAntigen binding
The present invention relates to the manufacture of a diverse repertoire of functional heavy chain-only antibodies that undergo affinity maturation, and uses thereof. The invention also relates to the manufacture and use of a diverse repertoire of class-specific heavy chain-only antibodies and to the manufacture and use of multivalent polypeptide complexes with antibody heavy chain functionality, preferably antibody heavy chain binding functionality, constant region effector activity and, optionally, additional effector functions.The present invention also relates to a method of generation of fully functional heavy chain-only antibodies in transgenic mice in response to antigen challenge. In particular, the present invention relates to a method for the generation of human antigen-specific, high affinity, heavy chain-only antibodies of any class, or mixture of classes and the isolation and expression of fully functional VH antigen-binding domains.
Owner:HARBOUR ANTIBODIES BV +1
High throughput generation and affinity maturation of humanized antibody
InactiveUS9464286B2Generate efficientlyEfficient screeningMicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementAntigen bindingHumanized antibody
Compositions, methods, and kits are provided for efficiently generating and screening humanized antibody with high affinity against a specific antigen. The library of humanized antibody is generated by mutagenizing a chimeric antibody template that combines human antibody framework and antigen binding sites of a non-human antibody. Alternatively, the library of humanized antibody is generated by grafting essential antigen-recognition segment(s) such as CDRs of the non-human antibody into the corresponding position(s) of each member of a human antibody library. This library of humanized antibody is then screened for high affinity binding toward a specific antigen in vivo in organism such as yeast or in vitro using techniques such as ribosome display or mRNA display. The overall process can be efficiently performed in a high throughput and automated manner, thus mimicking the natural process of antibody affinity maturation.
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
Binding molecules
ActiveUS20100216974A1Antibacterial agentsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntiendomysial antibodiesAntigen challenge
The present invention relates to the manufacture of a diverse repertoire of functional heavy chain-only antibodies that undergo affinity maturation, and uses thereof. The invention also relates to the manufacture and use of a diverse repertoire of class-specific heavy chain-only antibodies and to the manufacture and use of multivalent polypeptide complexes with antibody heavy chain functionality, preferably antibody heavy chain binding functionality, constant region effector activity and, optionally, additional effector functions.The present invention also relates to a method of generation of fully functional heavy chain-only antibodies in transgenic mice in response to antigen challenge. In particular, the present invention relates to a method for the generation of human antigen-specific, high affinity, heavy chain-only antibodies of any class, or mixture of classes and the isolation and expression of fully functional VH antigen-binding domains.
Owner:HARBOUR ANTIBODIES BV +1
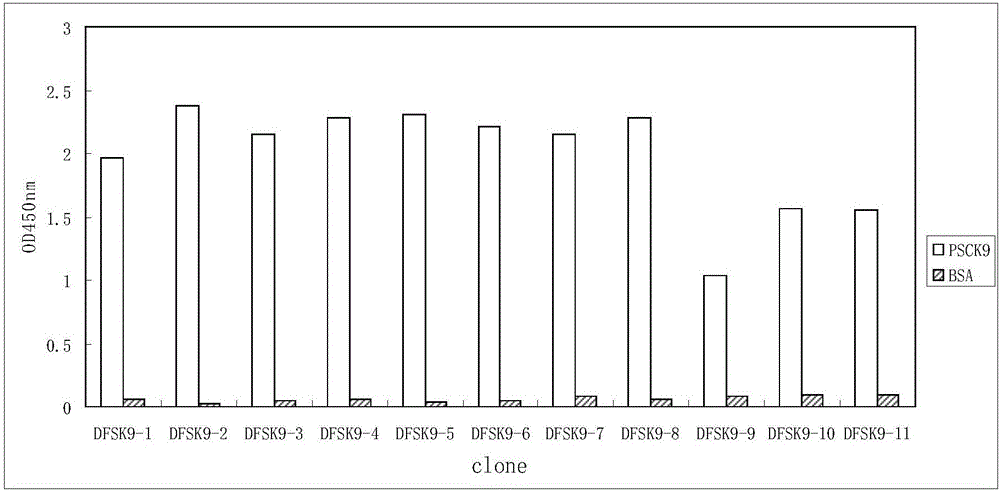
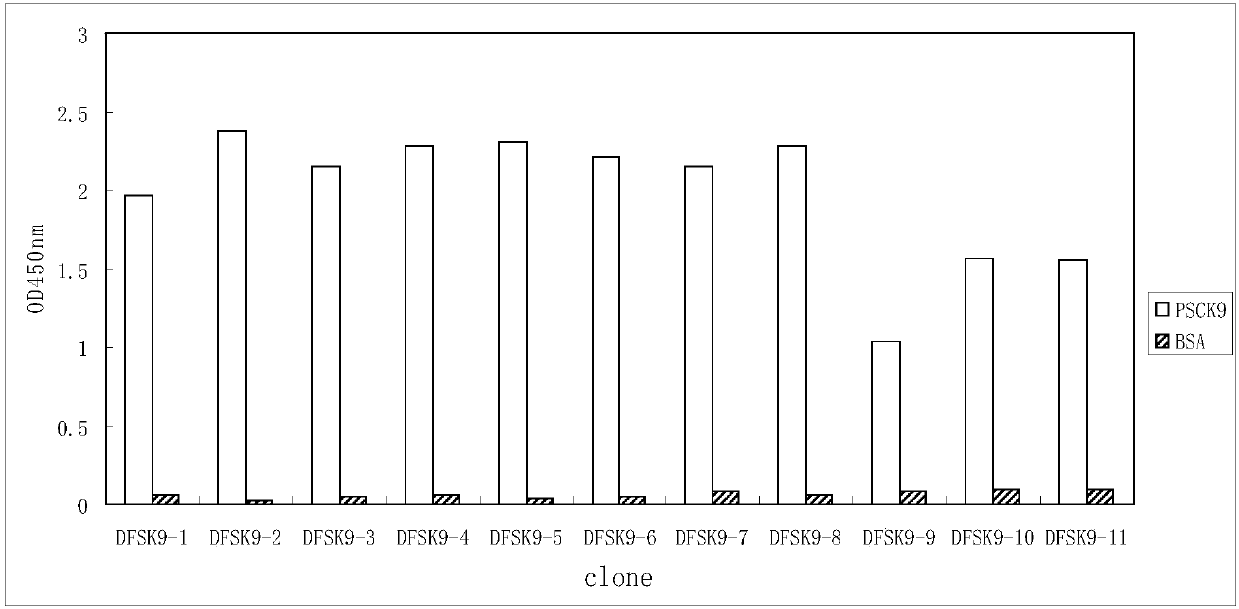
Anti-PCSK9 monoclonal antibody
ActiveCN106749670ABinding blockIncrease intakeMetabolism disorderMammal material medical ingredientsDyslipidemiaAmino acid
The invention relates to the technical field of antibody engineering and specifically discloses an anti-PCSK9 monoclonal antibody. The invention comprises an amino acid sequence coding an antibody variable region and a CDR region as well as an acquisition method and an application of the monoclonal antibody. The monoclonal antibody disclosed by the invention is prepared by the following steps: screening out anti-PCSK9 monoclonal antibodies from a phage library; performing affinity maturation by a method of establishing phage library through strand displacement; screening the mutant libraries of light-chain CDR1, 2, and 3 regions of the monoclonal antibody obtained by primary screening, and selecting the monoclonal antibodies with relatively high affinity; and screening the mutant libraries of heavy-chain CDR1, 2, and 3 to finally obtain the anti-PCSK9 monoclonal antibody with high affinity. In the invention, the obtained PCSK9 antibody has good affinity on PCSK9 and can inhibit combination of the PCSK9 with ligand thereof and can be used for treating dyslipidemia, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and thrombosis-obstructive diseases.
Owner:BEIJING DONGFANG BIOTECH
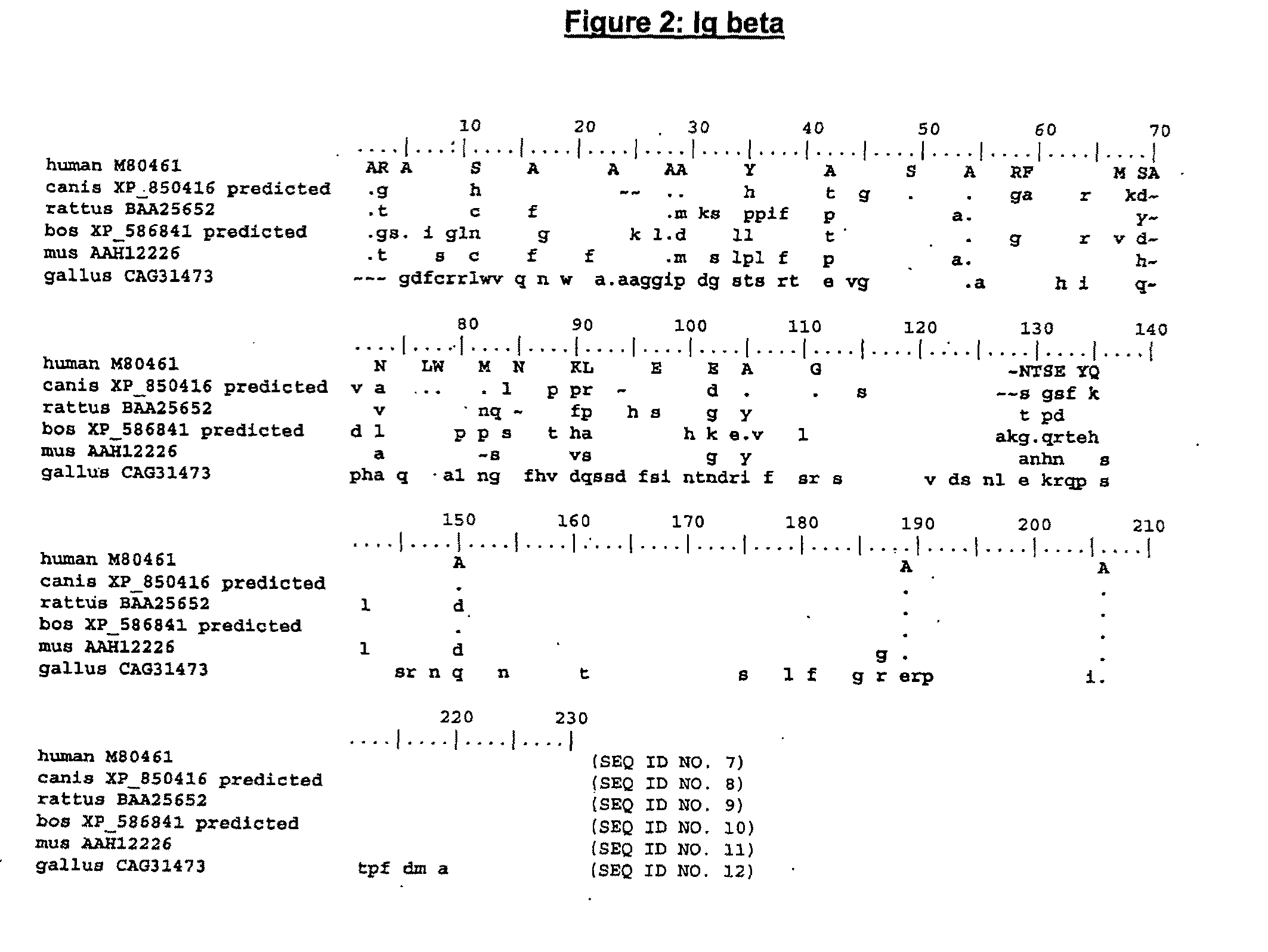
Enhanced expression of human or humanized immunoglobulin in non-human transgenic animals
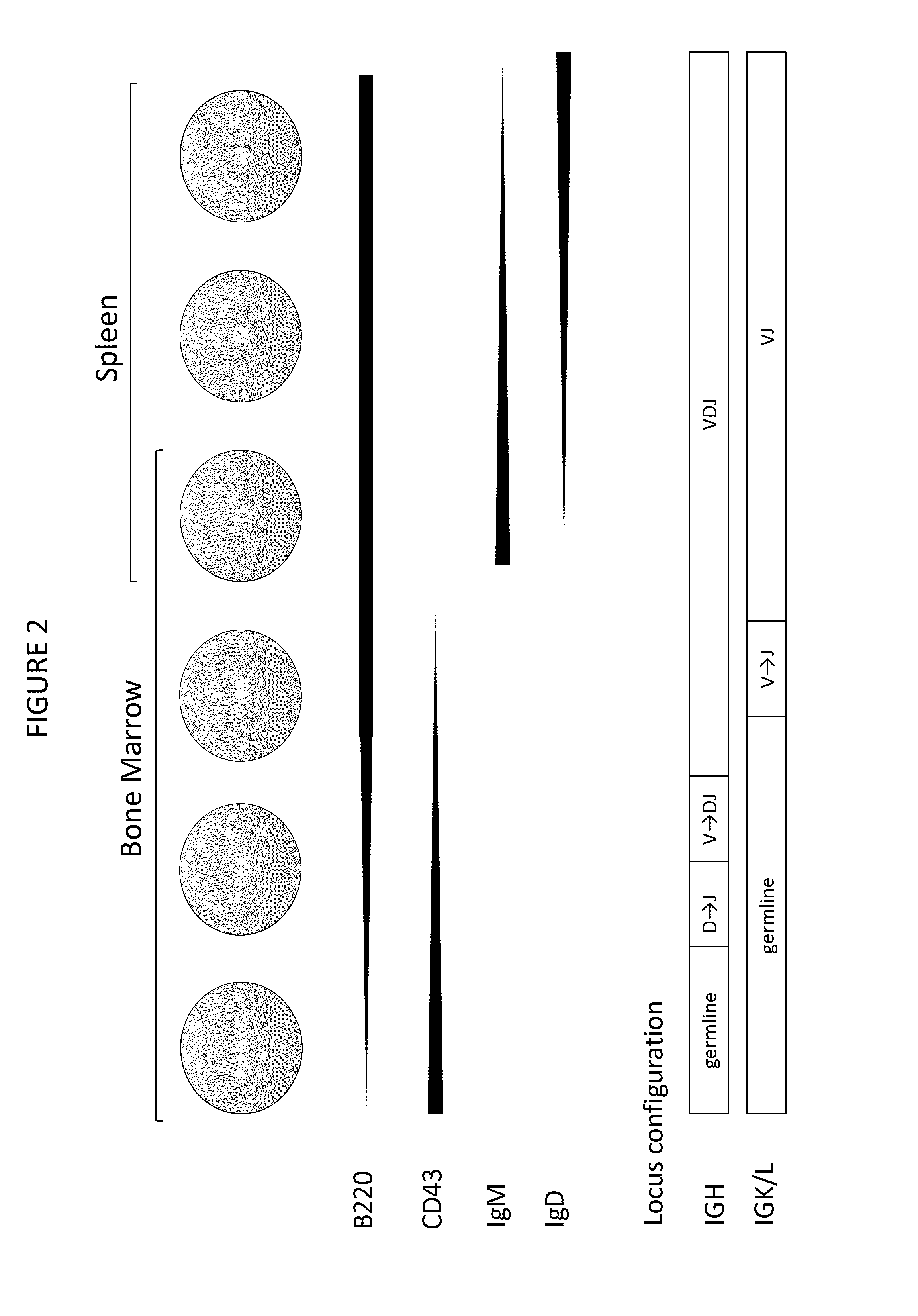
The present invention describes transgenic animals with human(ized) immunoglobulin loci and transgenes encoding human(ized) Igα and / or Igβ sequences. Of particular interest are animals with transgenic heavy and light chain immunoglobulin loci capable of producing a diversified human(ized) antibody repertoire that have their endogenous production of Ig and / or endogenous Igα and / or Igβ sequences suppressed. Simultaneous expression of human(ized) immunoglobulin and human(ized) Igα and / or Igβ results in normal B-cell development, affinity maturation and efficient expression of human(ized) antibodies.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
Enhanced Expression of Human or Humanized Immunoglobulin in Non-Human Transgenic Animals
The present invention describes transgenic animals with human(ized) immunoglobulin loci and transgenes encoding human(ized) Igα and / or Igβ sequences. Of particular interest are animals with transgenic heavy and light chain immunoglobulin loci capable of producing a diversified human(ized) antibody repertoire that have their endogenous production of Ig and / or endogenous Igα and / or Igβ sequences suppressed. Simultaneous expression of human(ized) immunoglobulin and human(ized) Igα and / or Igβ results in normal B-cell development, affinity maturation and efficient expression of human(ized) antibodies.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
Humanized monoclonal antibody against hIL-33 and application of monoclonal antibody
ActiveCN111378037AAffinity ensuresLow heterogeneityNervous disorderAntipyreticAntiendomysial antibodiesDrug biological activity
In order to provide a antibody against hIL-33 with clinical application prospect, the invention provides a high-affinity mouse anti-human IL-33 antibody by adopting a panning technology of immunizingmouse B cells, based on the action mechanism of IL-33 in inflammation and tumors in the prior art, the function of IL-33 in regulating cytokine secretion, and cytokines involved in inflammation and tumors. After recombinant expression of mouse-derived antibodies, preliminary screening of biological activity, humanization transformation, affinity maturation and biological activity rescreening, a humanized monoclonal antibody against hIL-33 is obtained, and the monoclonal antibody has the characteristics of high stability, high affinity, good biological activity, broad clinical application prospects, etc.
Owner:NANJING NOVOACINE BIO-TECH CO LTD
Anti-CD19 antibody and preparation method and use thereof
PendingCN107793479AHigh affinityIncrease lethalityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsMammal material medical ingredientsSingle-Chain AntibodiesComplementarity determining region
The invention relates to the technical field of biotechnology and particularly relates to an anti-CD19 antibody and a preparation method and use thereof. The anti-CD19 antibody comprises a heavy chainvariable region and a light chain variable region. The complementarity determining region of the heavy chain variable region comprises CDR-H1 with an amino acid sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID No. 1, CDR-H2 with an amino acid sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID No. 2 and CDR-H3 with an amino acid sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID No. 3. The complementarity determining region ofthe light chain variable region comprises CDR-L1 with an amino acid sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID No. 4, CDR-L2 with an amino acid sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID No. 5, No. 6 or No.7 and CDR-L3 with an amino acid sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID No. 8. The FMC63 scFv is screened in affinity maturation through a phage display technology so that a high affinity single chain antibody against CD19 is obtained.
Owner:SHANGHAI GENBASE BIOTECH CO LTD
PCSK9 (Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin Kexin Type 9) resistant monoclonal antibody
ActiveCN107698680ABinding blockIncrease intakeMetabolism disorderMammal material medical ingredientsKexinPhage antibodies
The invention relates to the technical field of antibody engineering and in particular discloses a PCSK9 (Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin Kexin Type 9) resistant monoclonal antibody. The monoclonal antibody disclosed by the invention comprises an amino acid sequence coding an antibody variable region and a CDR region. The invention further discloses an acquiring method and application of the monoclonal antibody. The method comprises the following steps: screening a PCSK9 resistant monoclonal antibody from a phage antibody library, performing affinity maturation through a method for constructing the phage antibody library by virtue of strand displacement, performing mutant library-construction screening on light-chain CDR1, 2 and 3 regions of the monoclonal antibody obtained by preliminaryscreening, selecting a monoclonal antibody with high affinity, performing mutant library-construction screening on heavy-chain CDR1, 2 and 3 regions of the monoclonal antibody, and finally screeningthe PCSK9 resistant monoclonal antibody with high affinity. The PCSK9 resistant monoclonal antibody obtained in the invention has excellent affinity to PCSK9, is capable of inhibiting binding betweenthe PCSK9 and ligands thereof, and can be used for treating dyslipidemia, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and thrombosis-obstructive diseases.
Owner:BEIJING DONGFANG BIOTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com