Anti-IgE antibodies
a technology of anti-ige antibodies and antibodies, which is applied in the field of anti-ige antibodies, can solve the problems of conformational changes, reduction of binding affinity, and anaphylaxis of dangerous life-threatening conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
Preparation of Monoclonal Antibodies to IgE
[0382] Eight monoclonal antibodies (MAE10-MAE17) with the ability to block the binding of IgE to FcεR1 were prepared. Monoclonal antibodies to IgE were prepared from the supernatants of U266B1 cells (ATCC TIB 196) using affinity chromatography on an isolated anti-IgE antibody (Genentech MAE1). For MAE12, five BALB / c female mice, age six weeks, were immunized in their foot pads with 10 μg of purified IgE in Ribi's adjuvant. Subsequent injections were done in the same manner at one and three weeks after the initial immunizations. Three days after the final injection, the inguinal and popliteal lymph nodes were removed and pooled, and a single cell suspension was made by passing the tissue through steel gauze. The cells were fused at a 4:1 ratio with mouse myeloma P3X63-Ag8.653 (ATCC CRL 1580) in high glucose (DMEM) containing 50% w / v polyethylene glycol 4000. For MAE14, MAE15, and MAE13 the immunizations were done in a similar manner except...
example 2
Preparation of Humanized MaE11
Introduction:
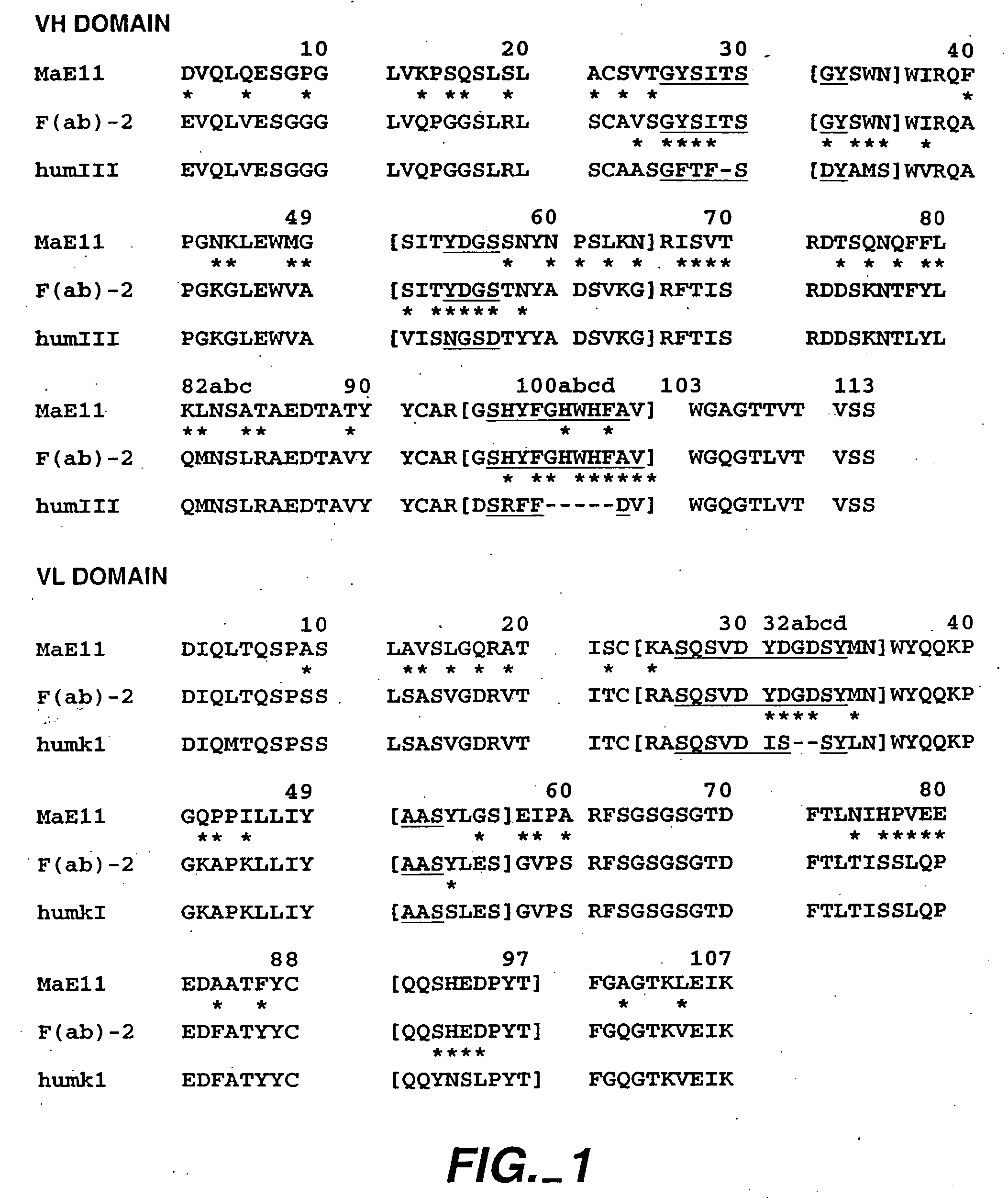
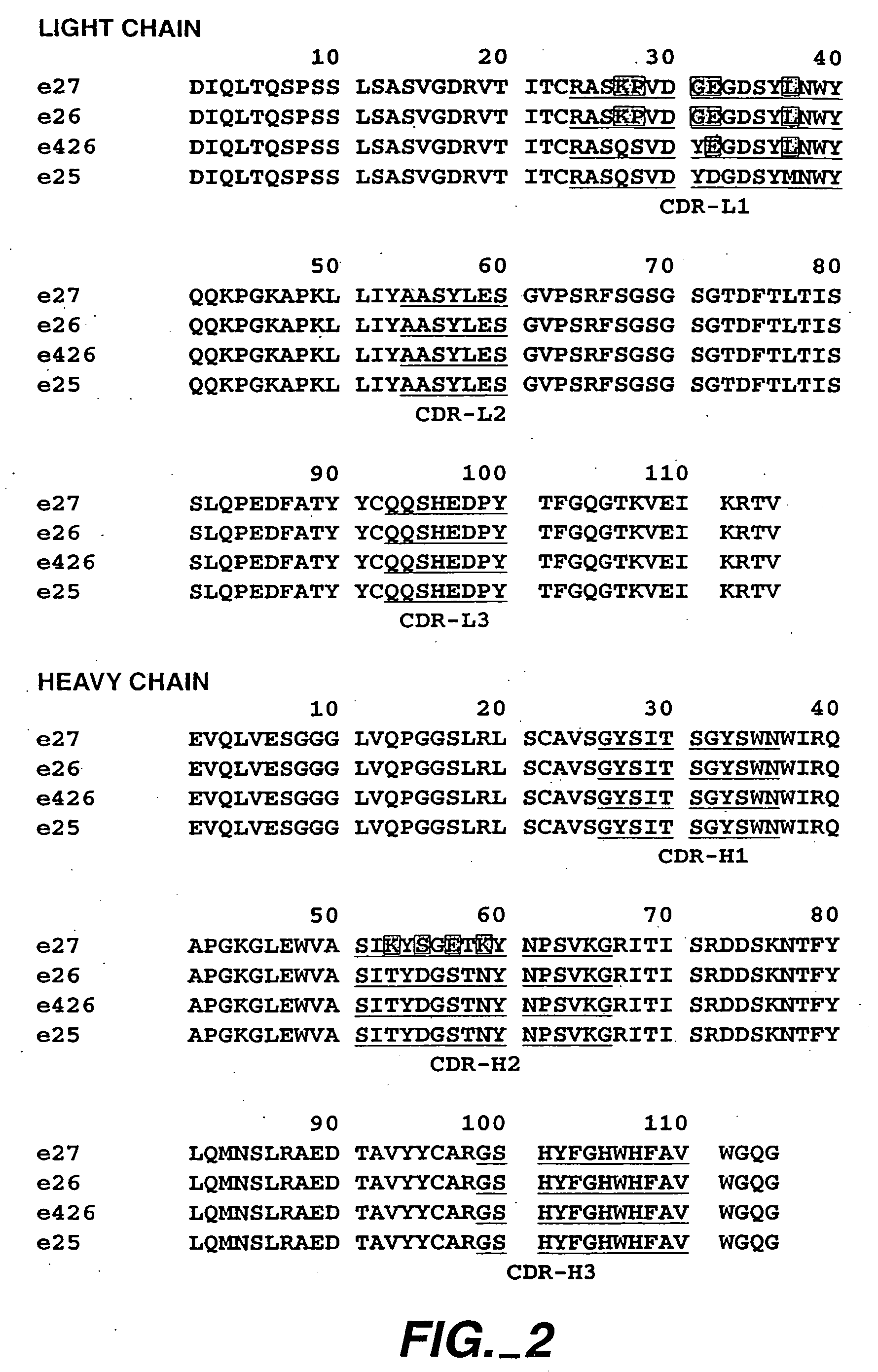
[0421] The following example describes various preparations of humanized MaE11 wherein residues were modified via site-directed mutagenesis to arrive at 12 anti-IgE MaE11 variants [F(ab)1-12]. The residues of F(ab)12 were used as the template to create rhuMaE25 or E25, a highly potent anti-IgE antibody described in Application PCT / US92 / 06860, filed Aug. 14, 1992.
Methods:
[0422] The murine anti-human IgE mAb MaE11, shown in FIG. 1, was modified by site-directed mutagenesis (Kunkel, T. A. (1985), Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82: 488) from a deoxyuridine-containing template containing a human k-subgroup I light chain and human subgroup III heavy chain (VH-CHI) in a pUC119-based plasmid, pAK2 (Carter et al. (1992), Proc. Natl. Aca. Sci. USA 89: 4285) to obtain the variant F(ab)-1. F(ab)-2 was constructed from the F(ab)-1 template and all other humanized F(ab) variants were constructed from a template of F(ab)-2. The plasmids were transformed...
example 3
[0452] Introduction:
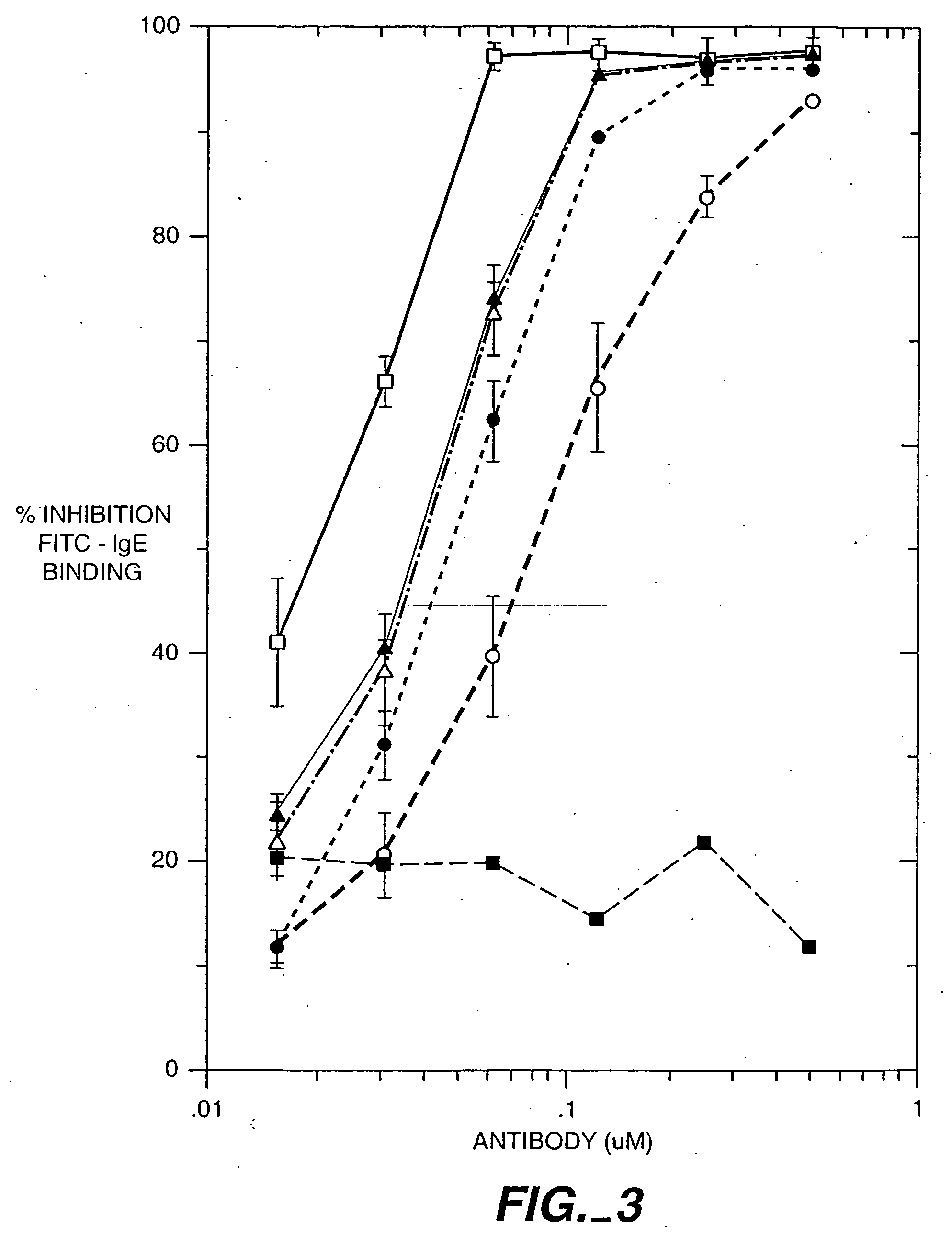
[0453] This is a rat mast cell histamine assay (RMCHA) which measures quantitatively the biological activity of a recombinant humanized, monoclonal anti-IgE antibody based on the ability of the antibody to block histamine release from allergen-sensitized RBL 48 cells. Furthermore, this determination is made under physiological conditions similar to those of the human body. The RBL 48 cell line was derived from the parental rat mast cell line RBL 2H3 which has been subsequently transfected with the α-subunit of the high affinity human IgE receptor (FcεRI). Gilfillan A. M. et al., J. Immunol. 149(7): 2445-2451 (1992).
[0454] Methods:
[0455] RBL 48 cells (Gilfillan et al., supra) are grown in sIMDM, Iscove's modified Dulbecco's media supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum, 2 mM glutamine, and 500μg / ml of active geneticin (Gibco, #860-1811) in a T175 tissue culture flask (Falcon #3028) at 37° C. in a humidified 5% CO2 incubator (Fischer, mode...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| flow rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com