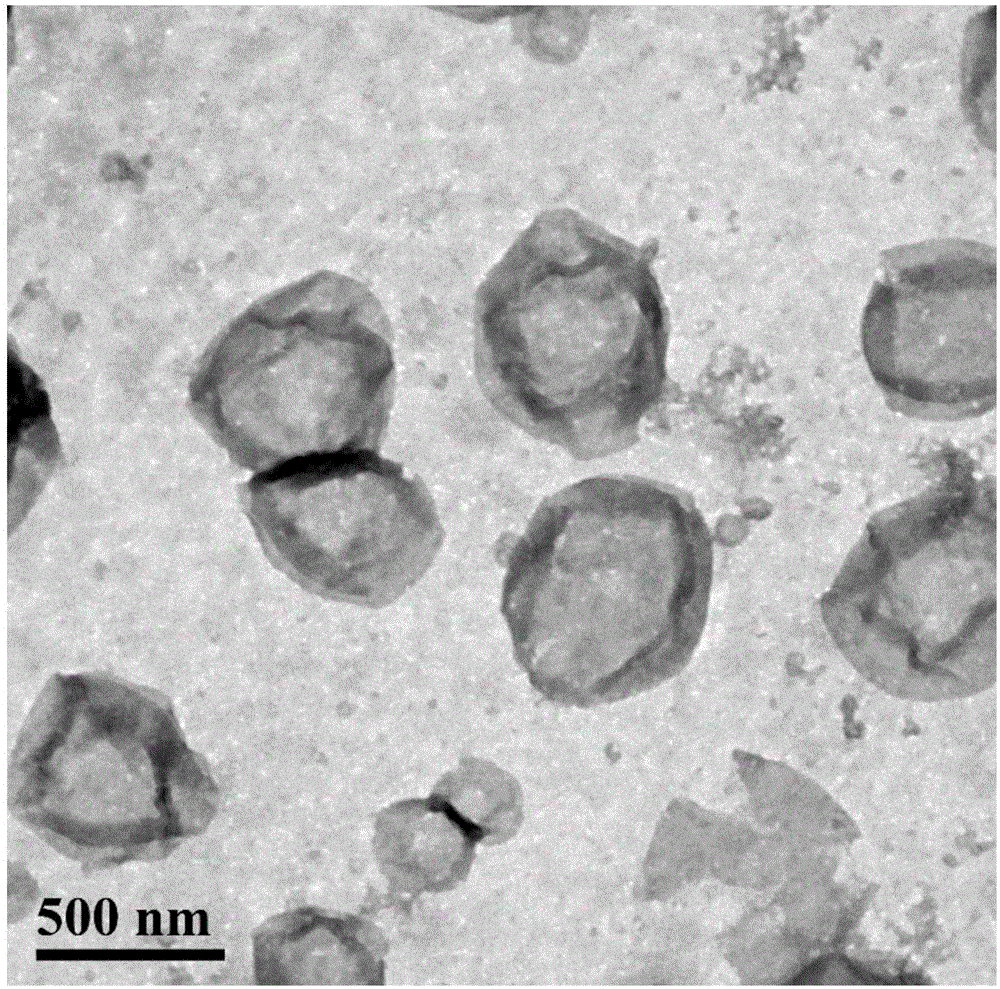
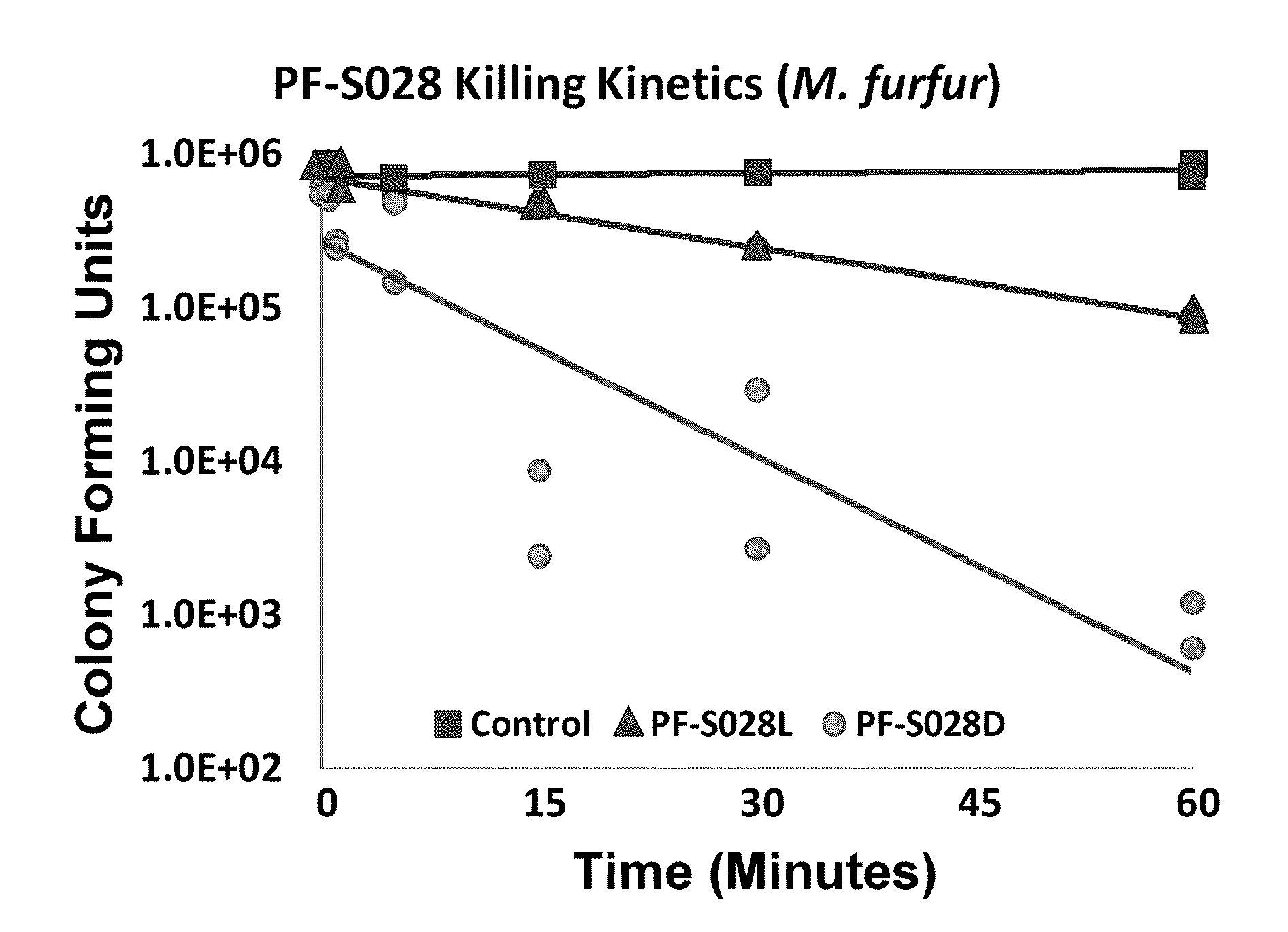
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
159 results about "Anti microbial peptide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
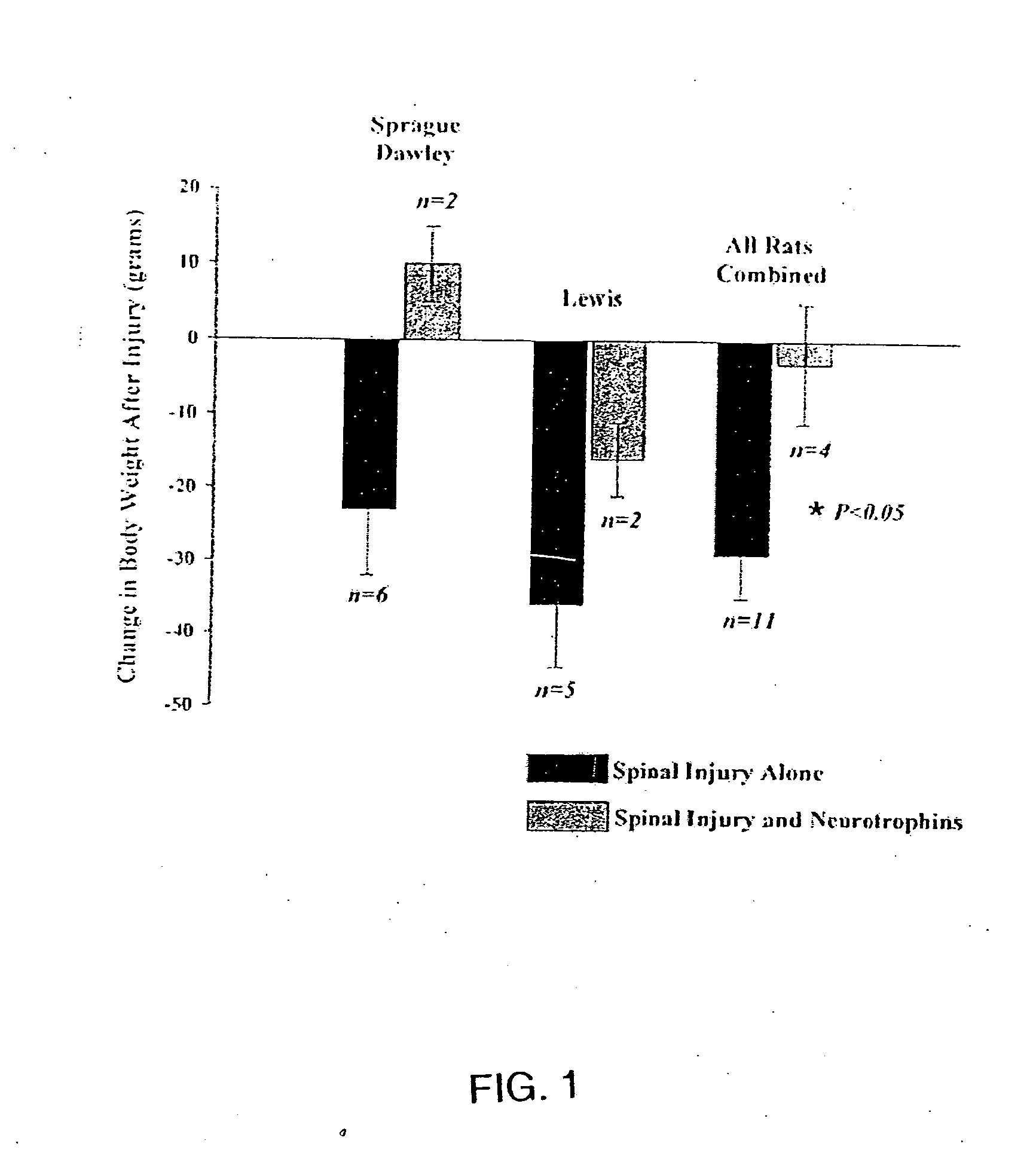
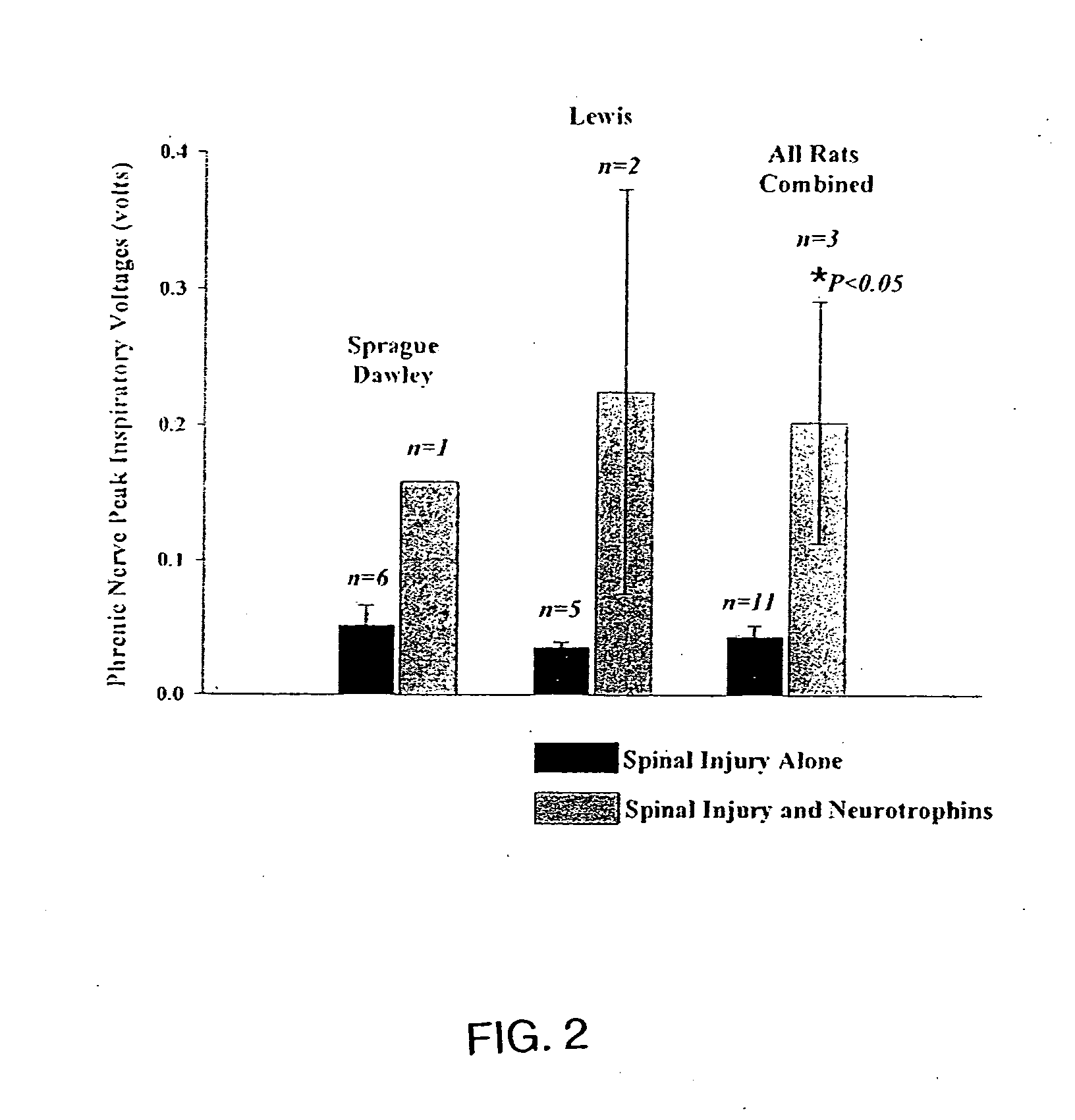
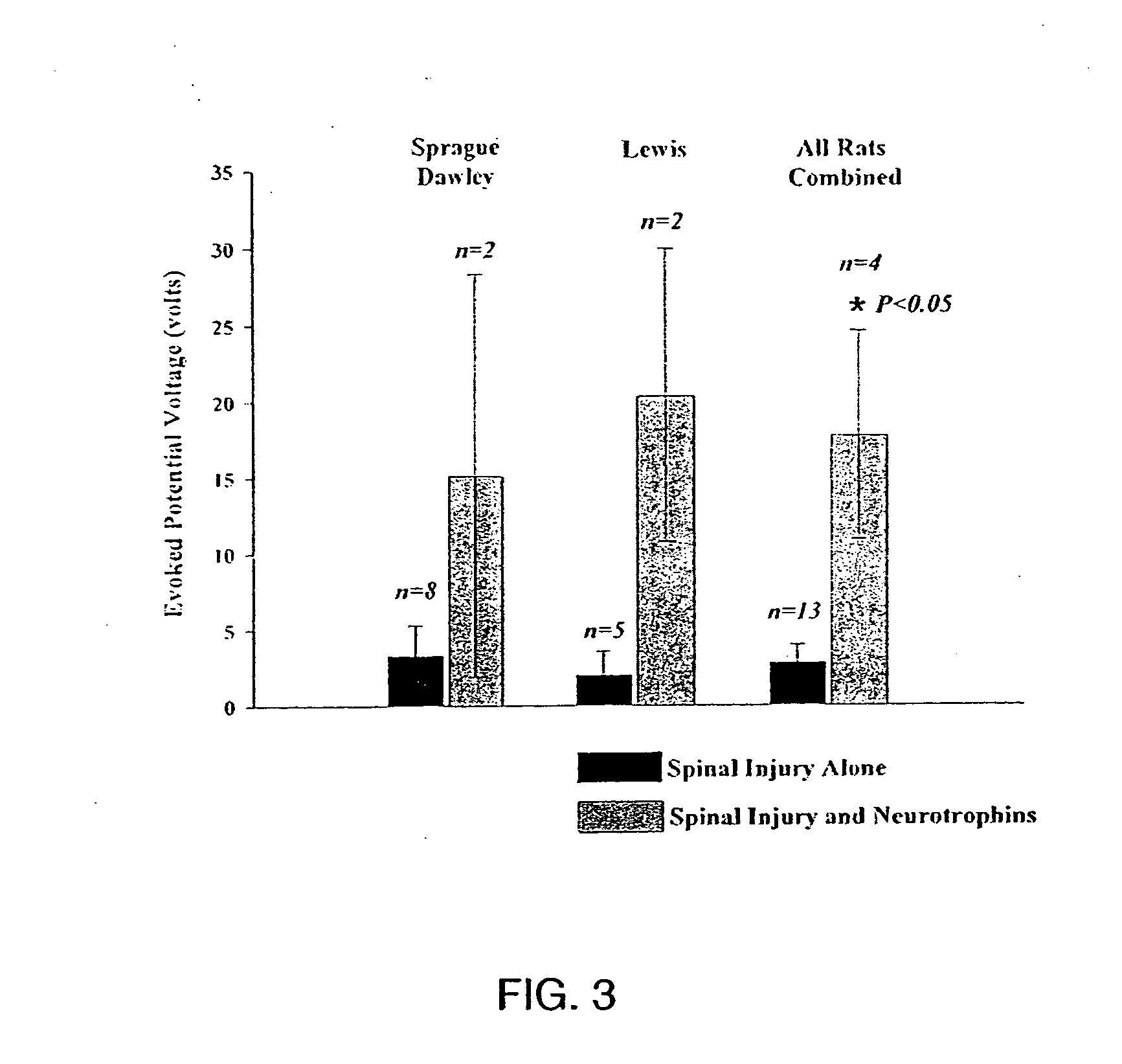
Trophic factor combinations for nervous system treatment
The present invention relates to a composition including an effective amount of at least one of an antimicrobial peptide and a substance having an antimicrobial peptide effect and an effective amount of a neurotrophin. The composition can also include an effective amount of at least one of a growth factor and a neuropeptide. The present invention also relates a method of treating an injury to a nervous system of an animal that includes the steps of identifying the injury to the nervous system and applying to the injury an effective amount of at least one of antimicrobial peptide and a substance having an antimicrobial peptide effect. The method can also include applying an effective amount of one or more trophic factors selected from the group consisting of a growth factor, a neurotrophin, and a neuropeptide to the injury.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
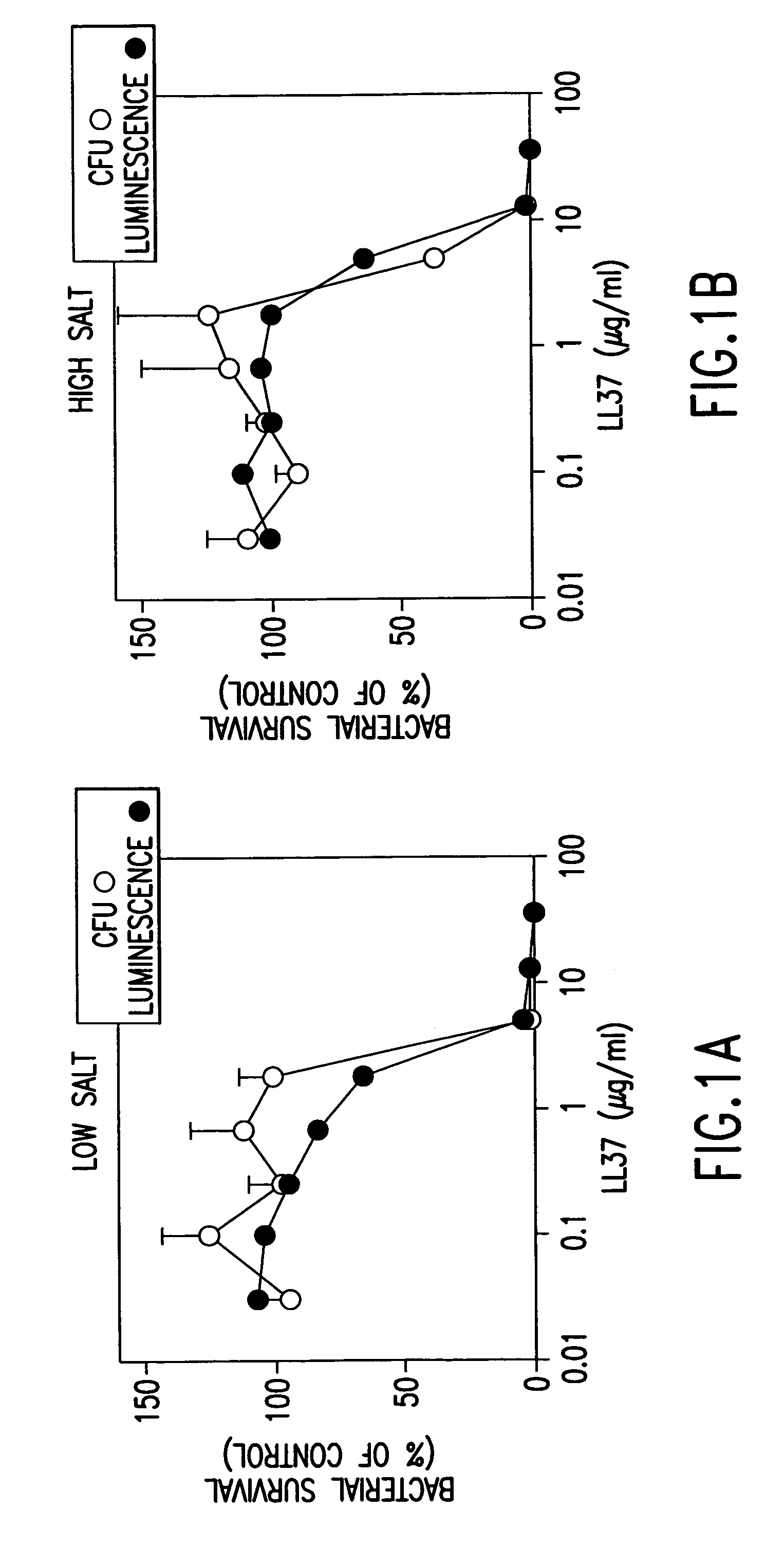
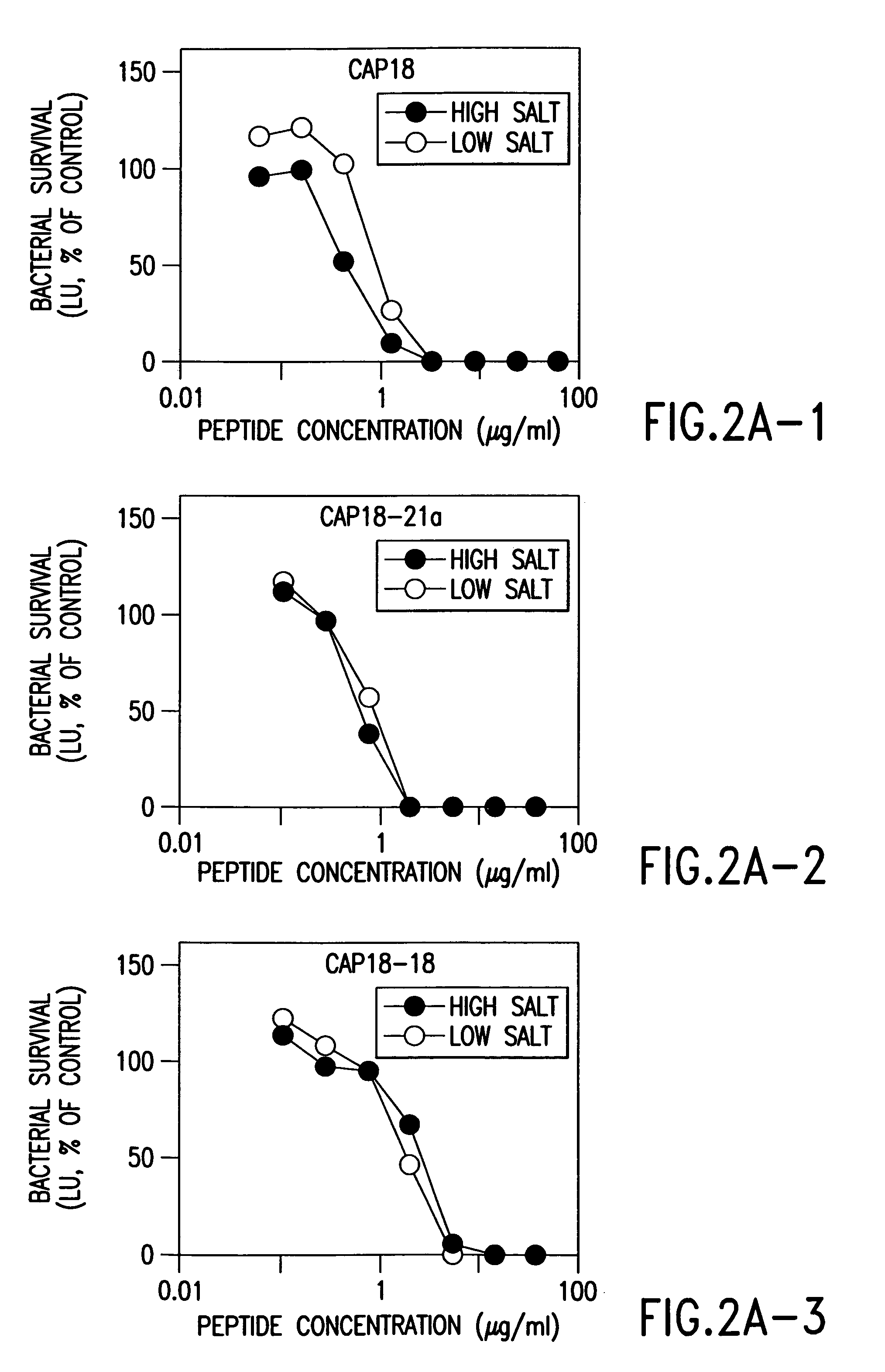
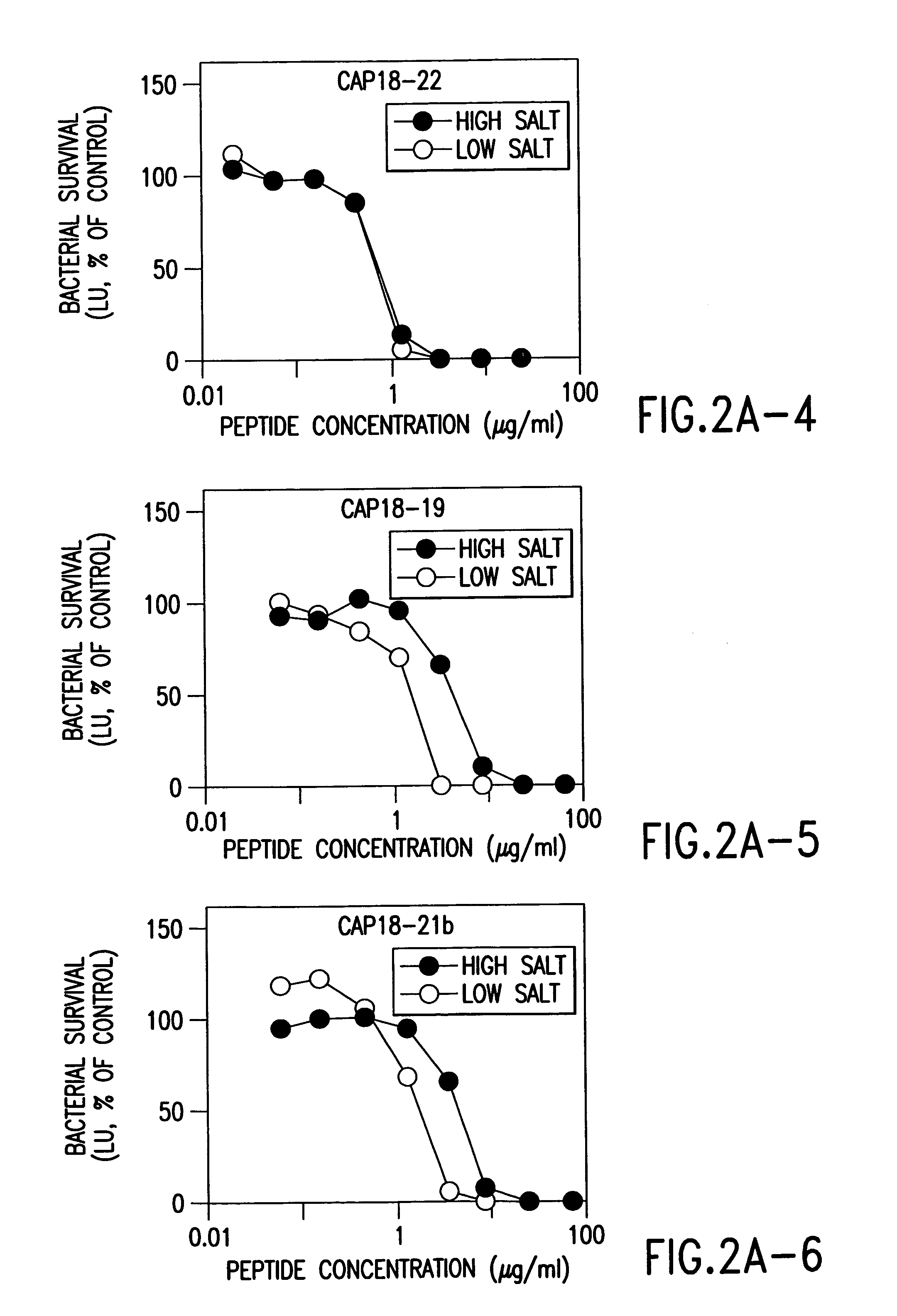
Alpha helical peptides with broad spectrum antimicrobial activity that are insensitive to salt
InactiveUS7071293B1Enhanced microbialEnhanced bacterial killingPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide sourcesMicroorganismAntimicrobial peptides
The present invention relates to the use of antimicrobial peptides in the inhibition of microbial growth and proliferation. Novel antimicrobial truncated peptides are disclosed which are based upon SMAP 29 and RCAP 18, but which contain a lesser number of amino acid residues yet still retain bactericidal activity. In addition, synthetic peptides based upon the SMAP 29 protein are disclosed which have fewer amino acid residues and include substitutions yet retain substantial activity. The invention also relates to a method of inhibiting microbial growth by administering an effective amount of a peptide in accordance with the invention, or by combining the peptides with other antimicrobial agents or antibiotics.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND +1
Process for recombinant expression and purification of antimicrobial peptides using periplasmic targeting signals as precipitable hydrophobic tags
A process was developed for expressing antimicrobial peptides in a recombinant host cell that eliminates host cell toxicity and antimicrobial peptide degradation, as well as providing a process for rapid purification. Fusion proteins comprising a periplasmic targeting signal, cleavage site, and antimicrobial peptides provide the basis for this process which produces antimicrobial peptides that may be used in antimicrobial compositions and articles.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Labeled antimicrobial peptides and method of using the same to detect microorganisms of interest
InactiveUS20070231833A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingMicroorganismAnti microbial peptide
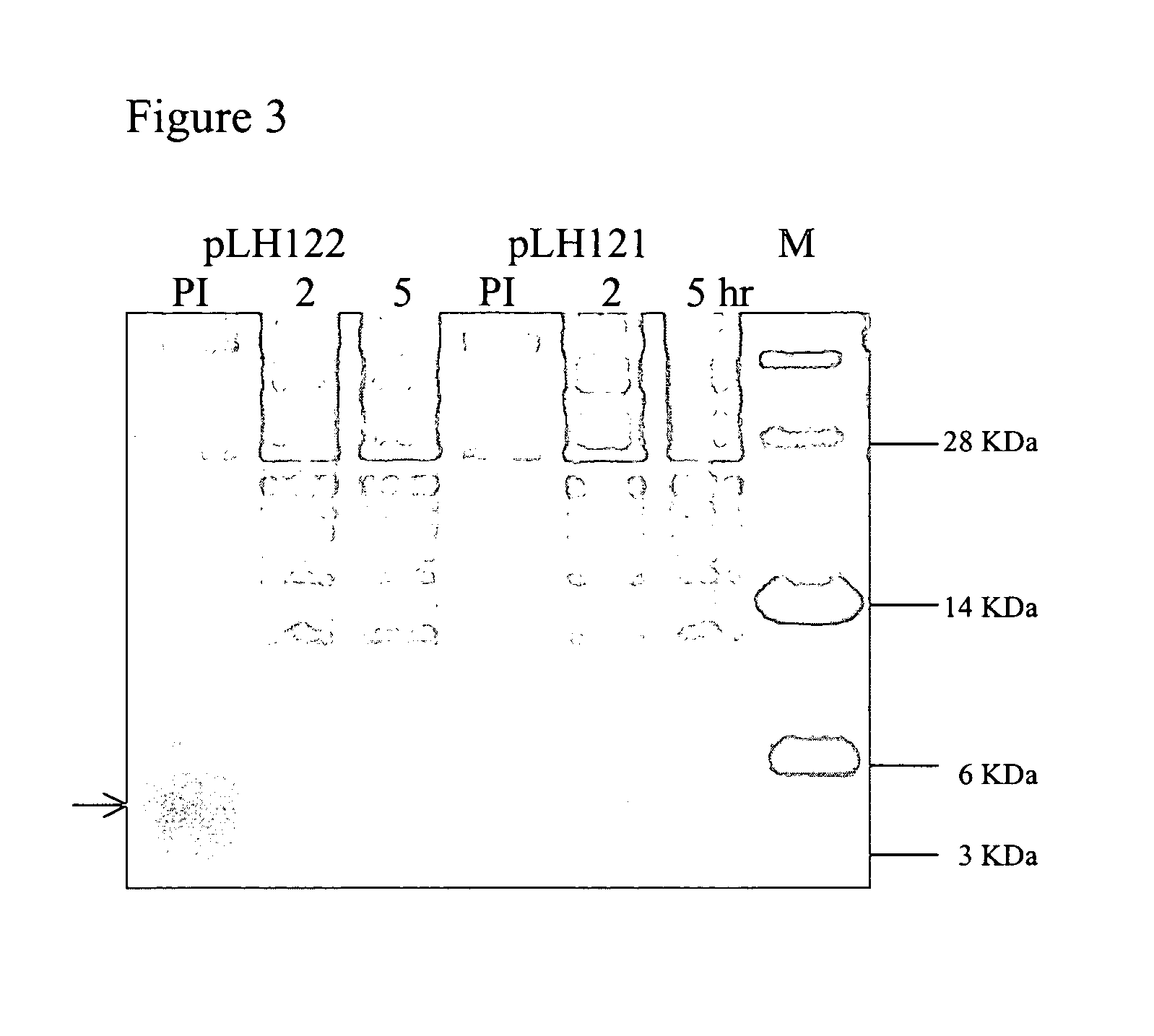
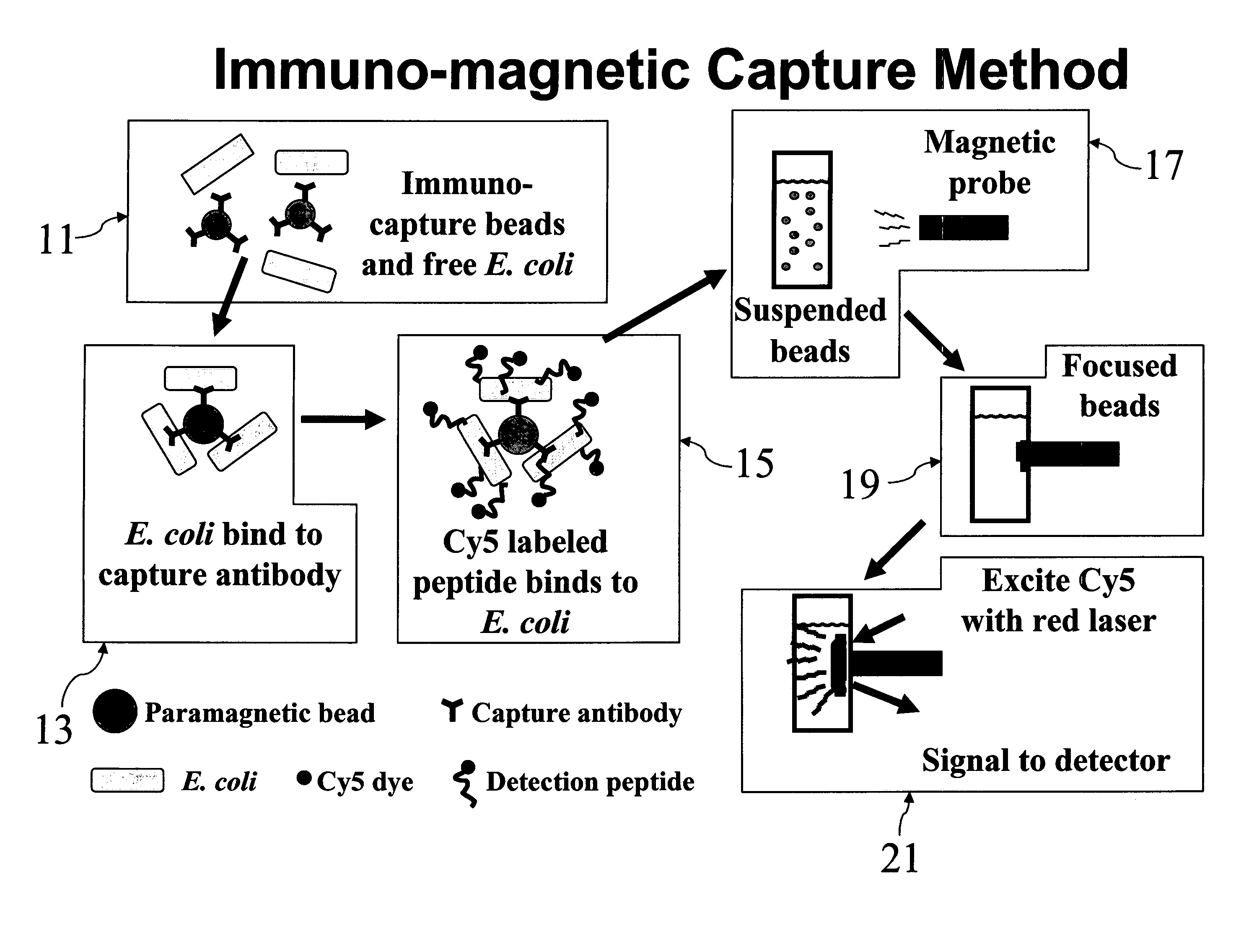
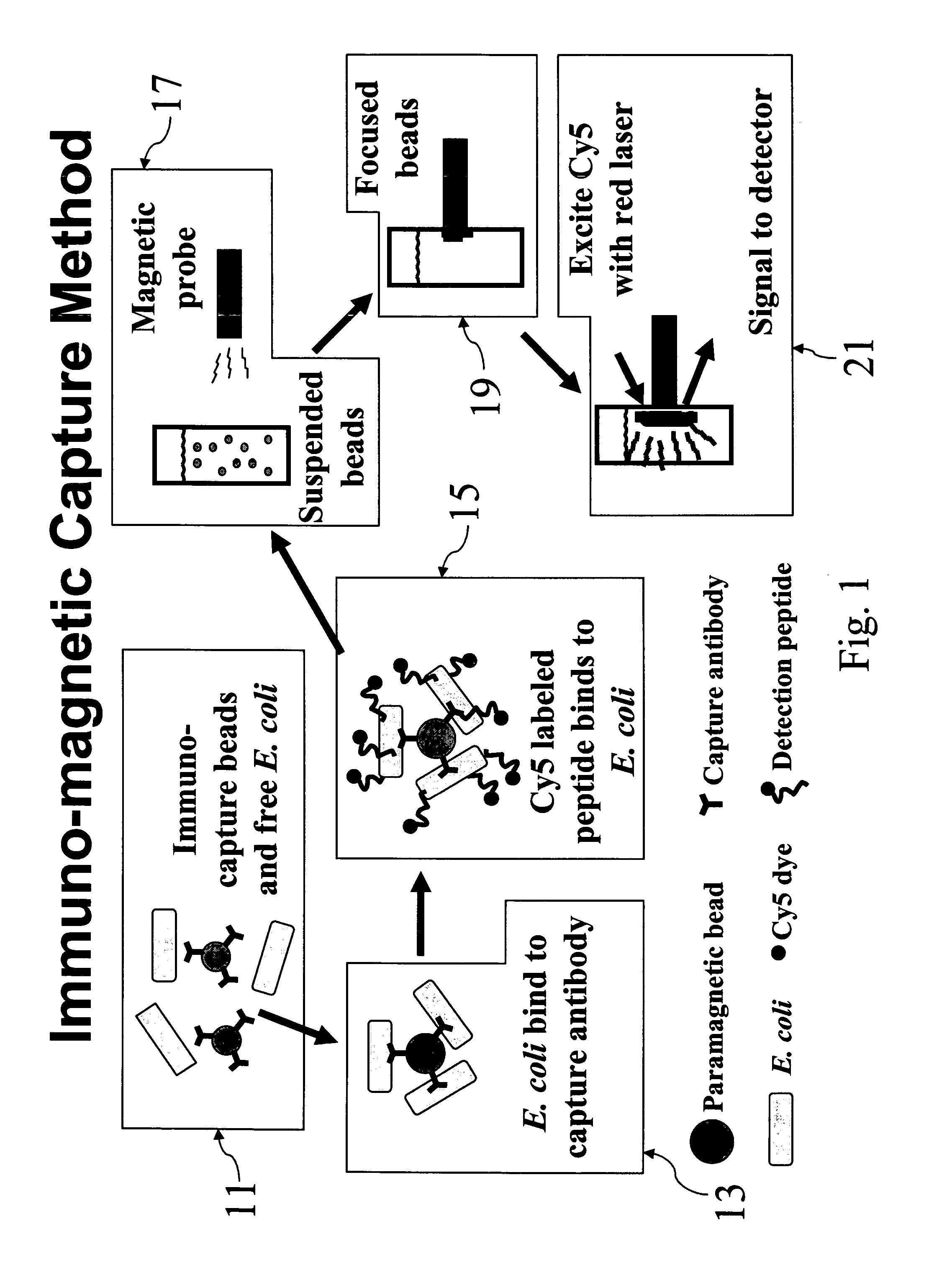
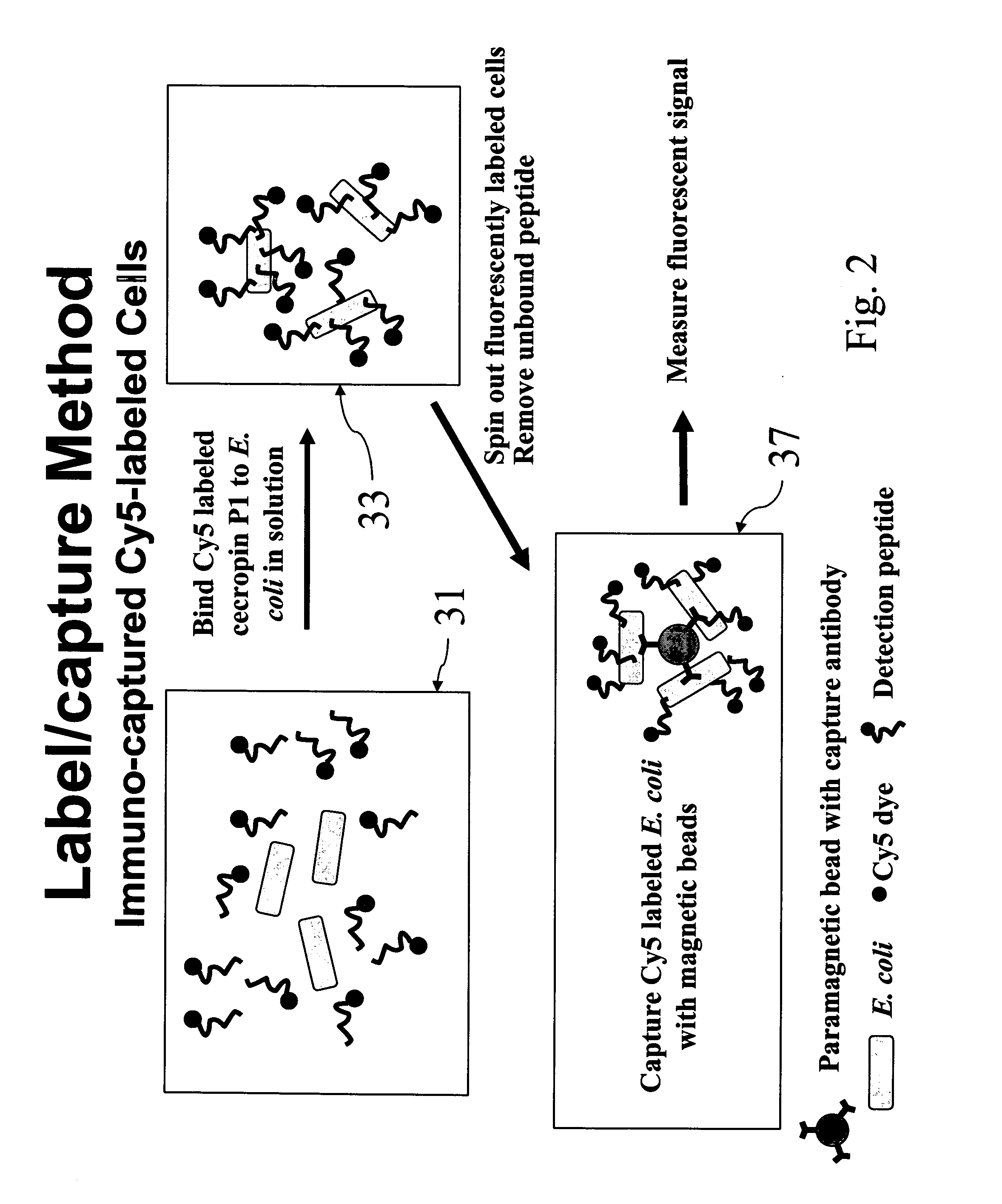
Labeled antimicrobial peptides and method of using the same to detect a microorganism of interest. In one embodiment, the method involves adding immuno-capture beads to a sample, the immuno-capture beads including capture antibodies coupled to a paramagnetic bead, the capture antibodies being specific for the type of microorganism of interest. After mixing, the target microorganism binds to the capture antibodies. Next, the beads are collected by positioning a magnet close to the sample, and the unbound material is removed from the sample. Then, a solution containing fluorescently-labeled antimicrobial peptide is added to the sample, the labeled peptide binding in great numbers to the immuno-captured microorganism. After removing unbound peptide, the beads are suspended in solution and a magnetic probe is used to collect the beads in a small volume. With the beads thus drawn together, the solution is excited with a laser. Such excitation causes the label to fluoresce, which fluorescence is then detected.
Owner:ARCIDIACONO STEVEN MICHAEL +3
Lipopolysaccharide fractions of vitreoscilla filiformis useful for stimulating the synthesis of Anti-microbial peptides of the skin
InactiveUS20090035294A1Prevent skinImprove the immunityAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsAnti microbial peptideMicroorganism
Specific fractions of Vitreoscilla filiformis comprising its Lipid A are useful for stimulating the synthesis of anti-microbial peptides of the skin.
Owner:LOREAL SA
Antimicrobial Peptides and Methods of Use
ActiveUS20090005300A1High activityStrong specificityAntibacterial agentsBiocideAntimicrobial peptidesAntibiotic Y
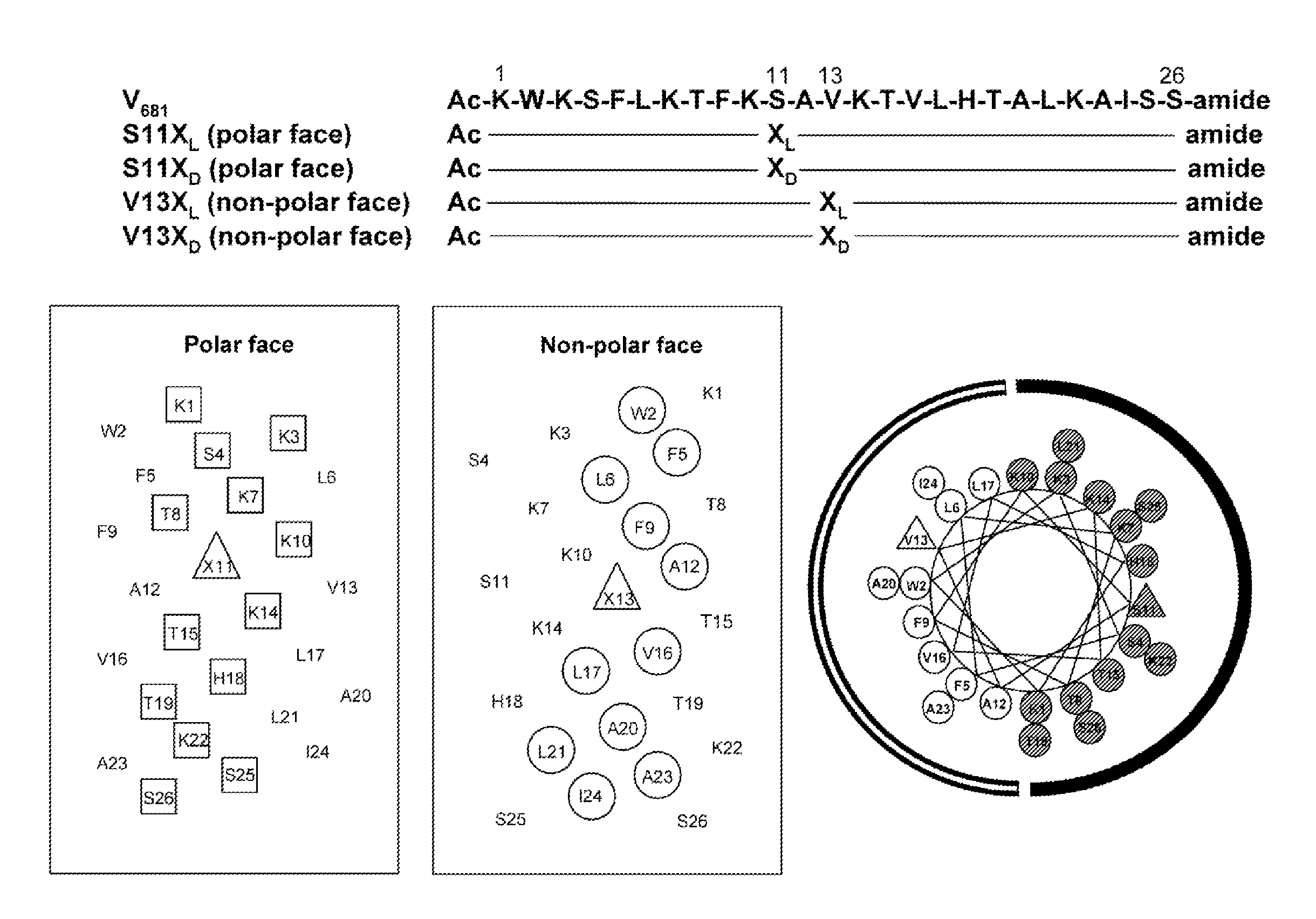
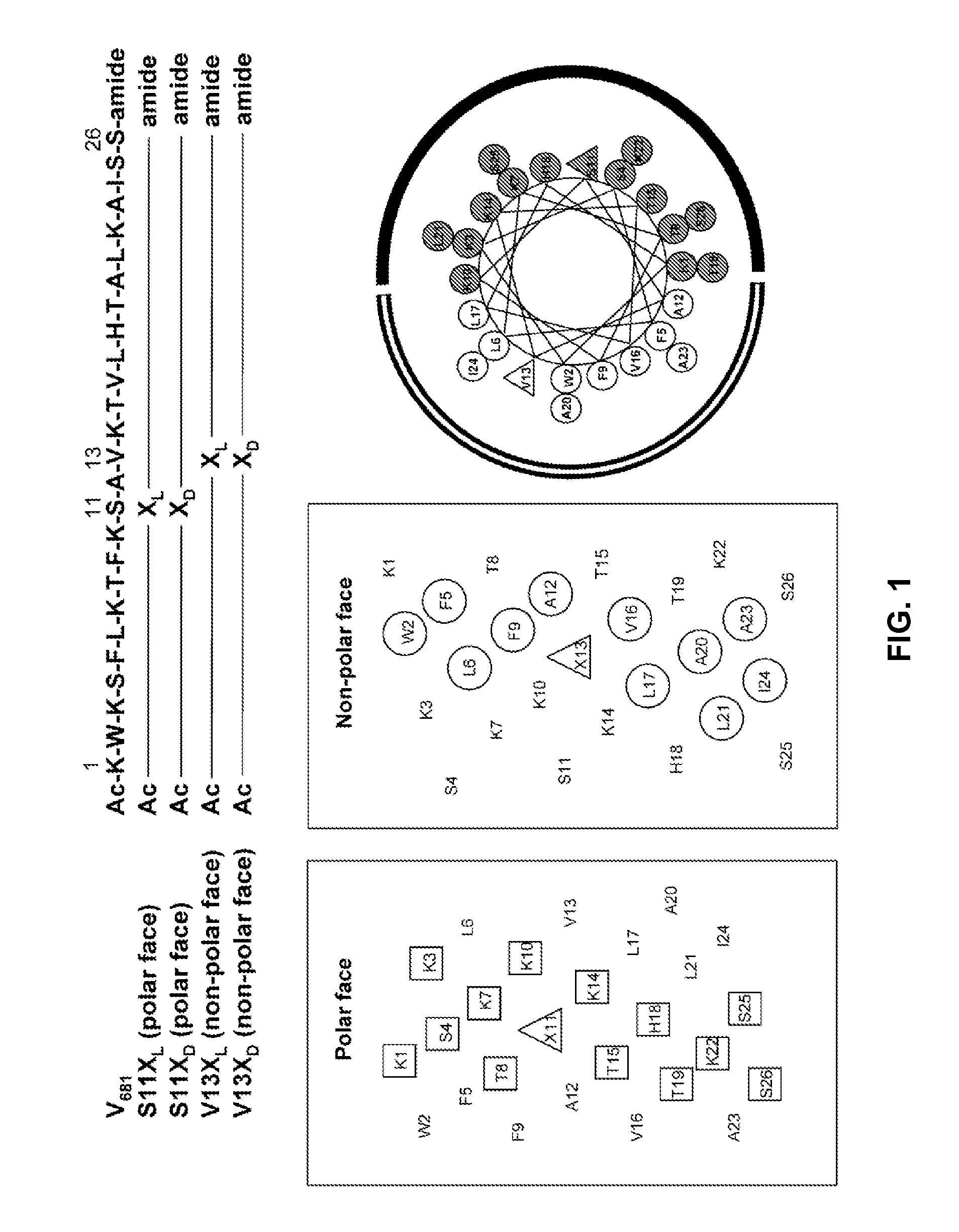
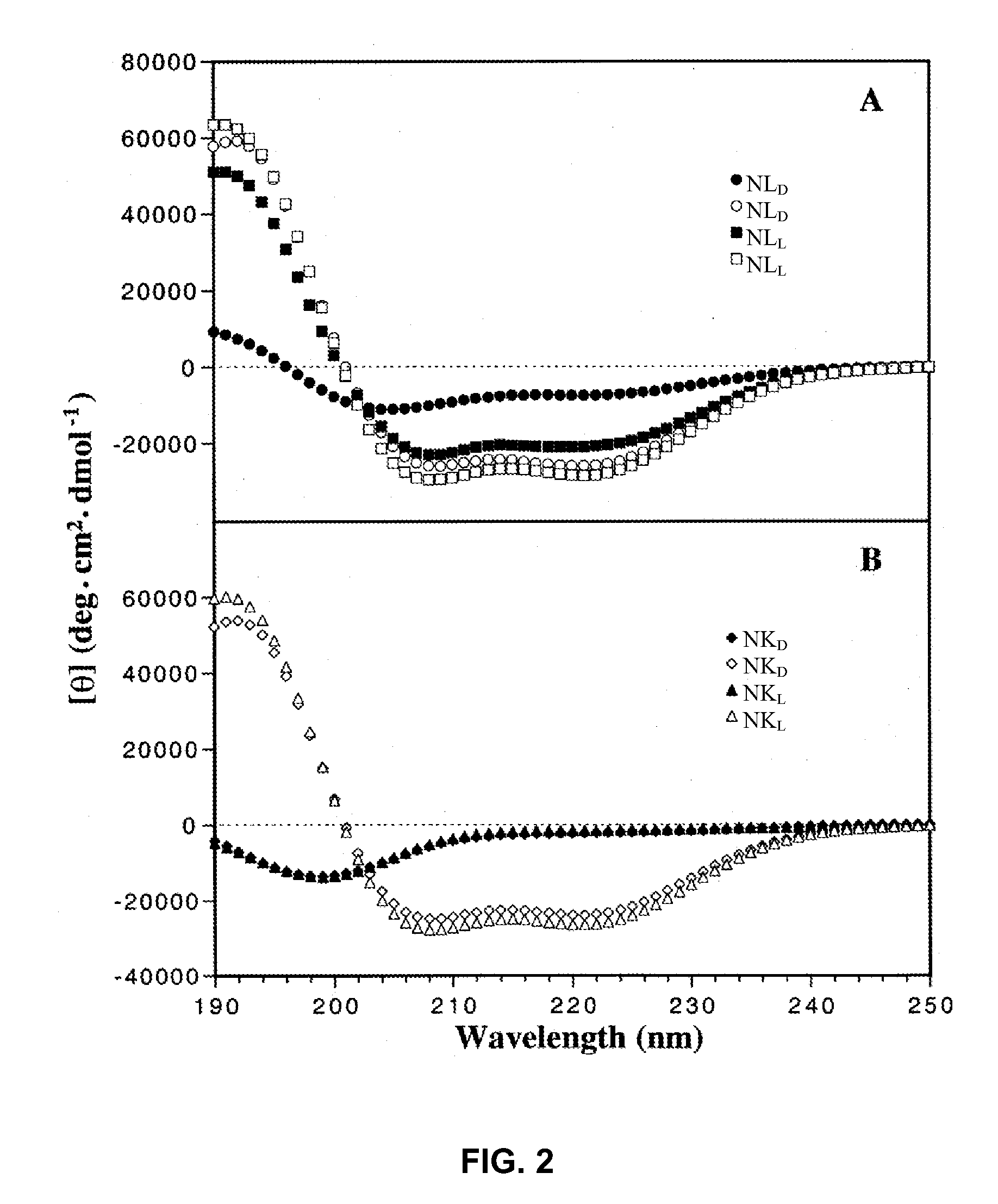
Disclosed herein are novel antimicrobial peptides with useful, improved, or superior properties such as antimicrobial activity, desirable levels of hemolytic activity, and therapeutic index against a broad range of microorganisms including gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria and other organisms having a cellular or structural component of a lipid bilayer membrane. Also provided are methods of making and using such peptides to control microbial growth and in pharmaceutical compositions for treatment or prevention of infections caused by such microorganisms. Certain peptides are disclosed utilizing a structure-based rational design relating to an antimicrobial peptide, V681, with single D- / L-amino acid substitutions or charged residue substitutions in or near the center of the peptide on the nonpolar or polar face. Also disclosed are peptides with one or more amino acids in the D configuration, including peptides with all amino acids in the D configuration. Modified peptide analogs herein can demonstrate one or more properties such as improved antimicrobial activity, specificity, and resistance to degradation. Compositions disclosed herein have useful clinical potential as antibiotics including broad spectrum antibiotics.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Process for providing antimicrobial surfaces
Processes for providing durable antimicrobial surfaces are disclosed that comprise treating a polymer substrate surface with formaldehyde followed by treatment with an antimicrobial peptide. Further embodiments include articles, including medical devices, characterized by a durable antimicrobial surface provided by the processes of the invention.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
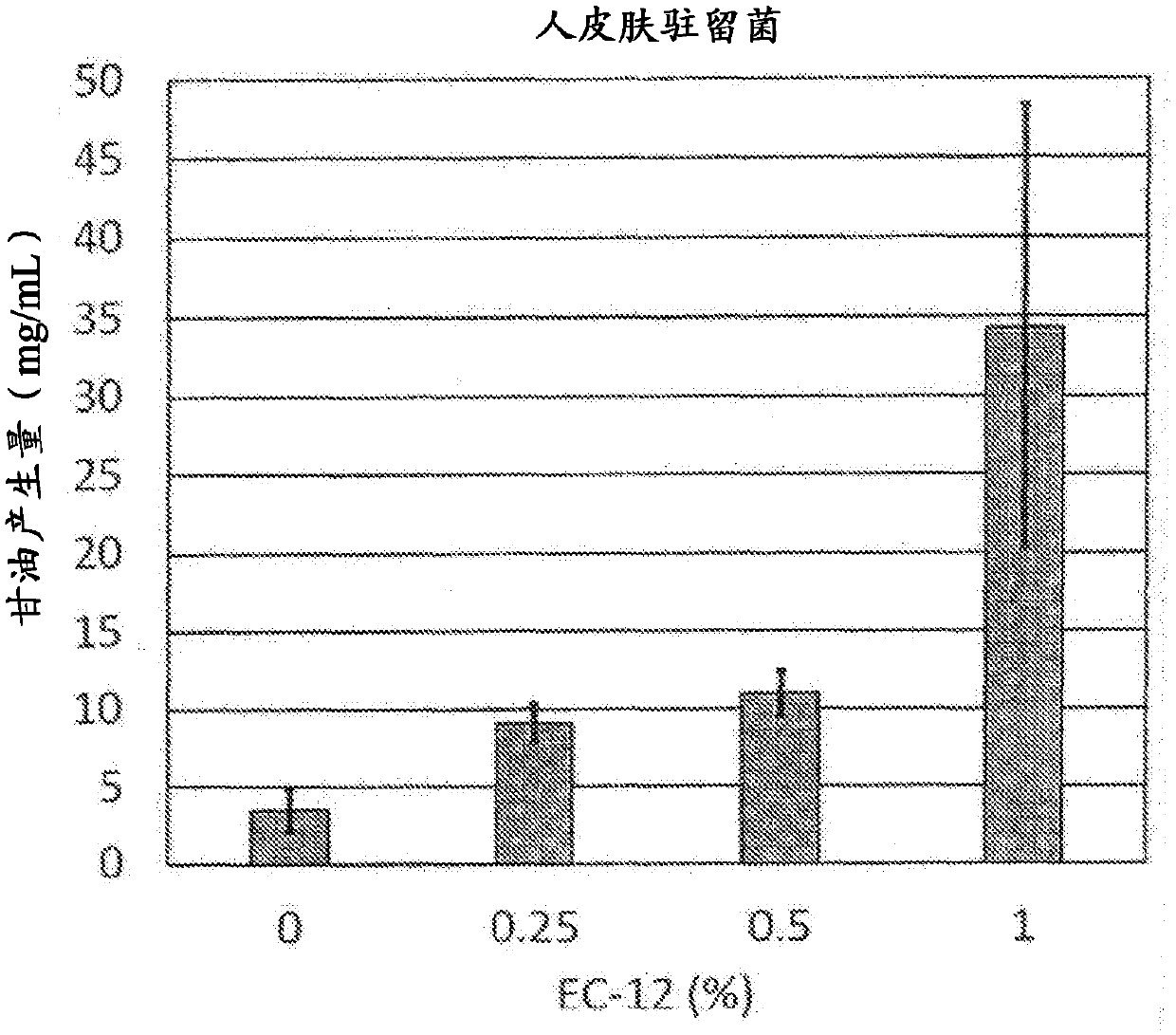
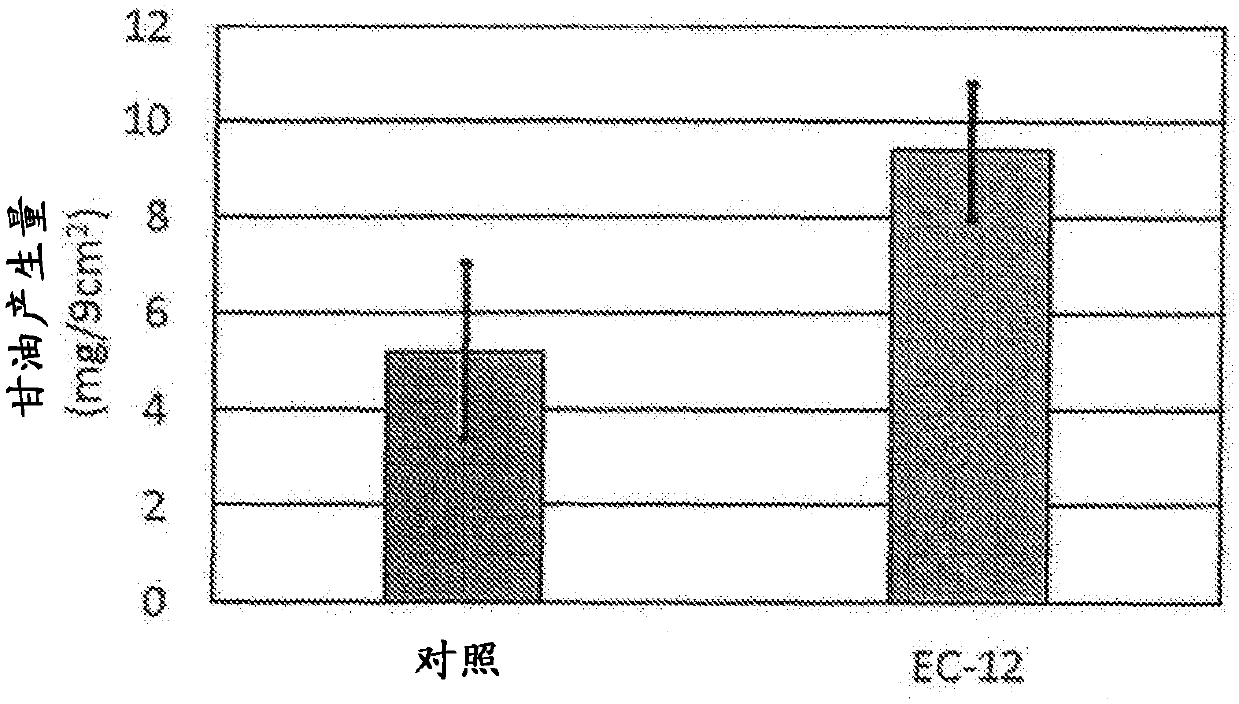
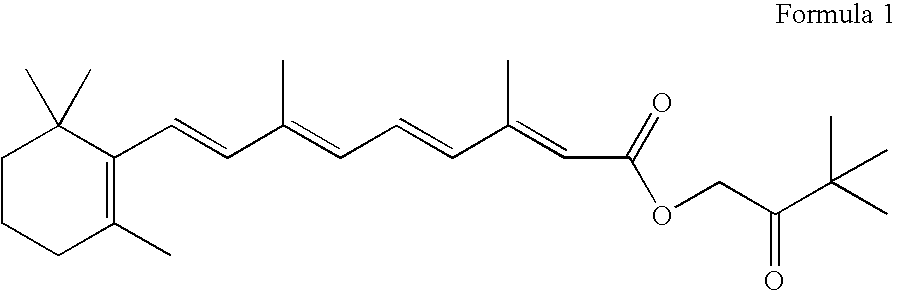
GLYCEROL PRODUCTION PROMOTER DERIVED FROM Staphylococcus Epidermidis, ANTIMICROBIAL PEPTIDE PRODUCTION PROMOTER DERIVED FROM SKIN EPIDERMAL KERATINOCYTES, AND UTILIZATION THEREOF IN EXTERNAL PREPARATION FOR SKIN PROTECTION
InactiveCN107922956APrevent drynessPerfect protection functionAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsCutinGenus Enterococcus
Provided are: a skin-protecting agent and an external preparation for skin protection, which not only synergistically work in combination with a plant polysaccharide but also has an effect of promoting the production of glycerol derived from Staphylococcus epidermidis, which is a skin resident bacterium useful on the skin, and the production of antimicrobial peptides derived from skin epidermal keratinocytes and exhibits excellent effect of improving the touch feeling when applied to the skin. More specifically, the present invention provides a skin protective agent and an external preparationfor skin protection, which comprise a lactic acid bacterium belonging to the genus enterococcus.
Owner:ICHIMARU PHARCOS CO LTD +1
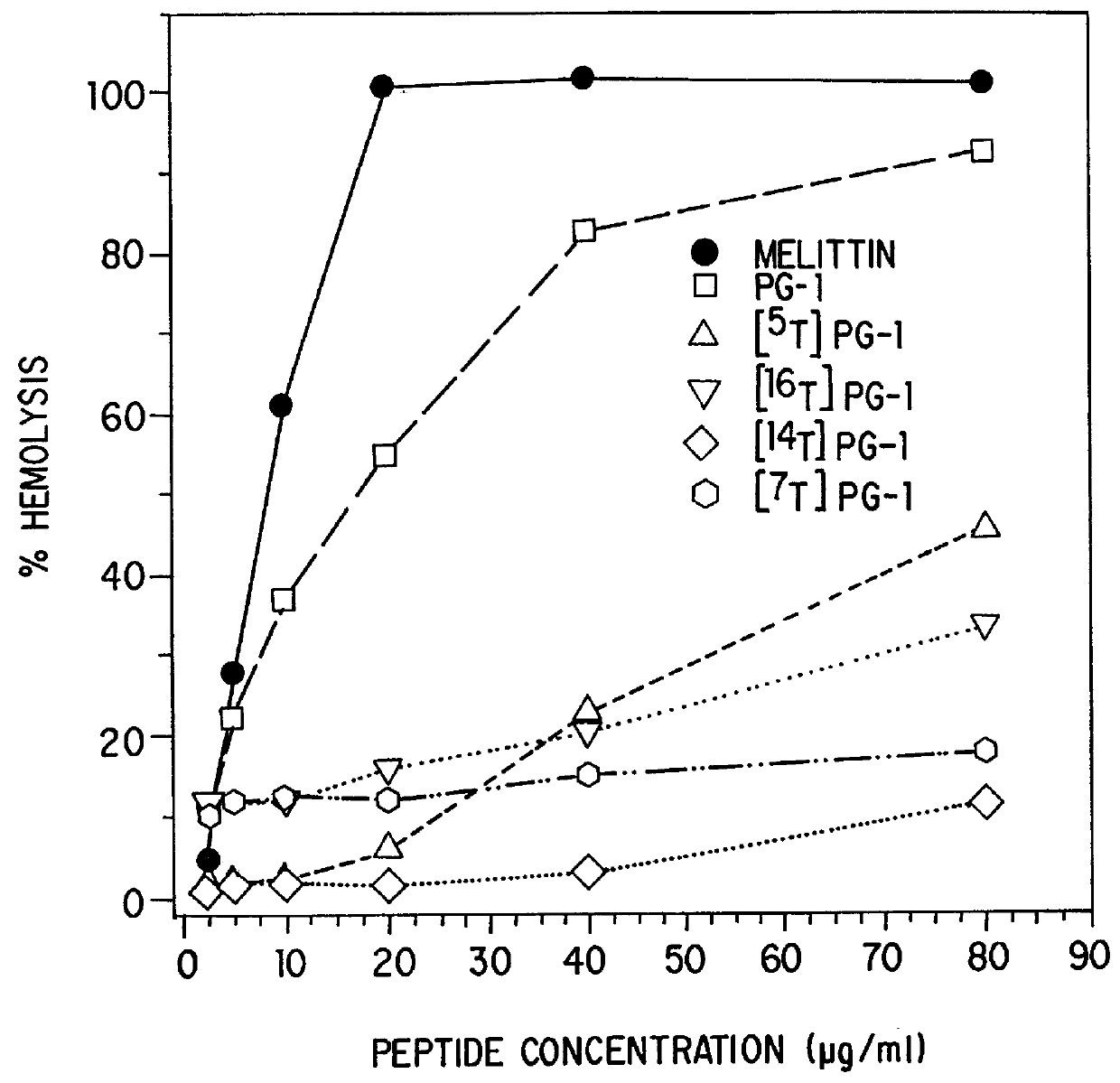
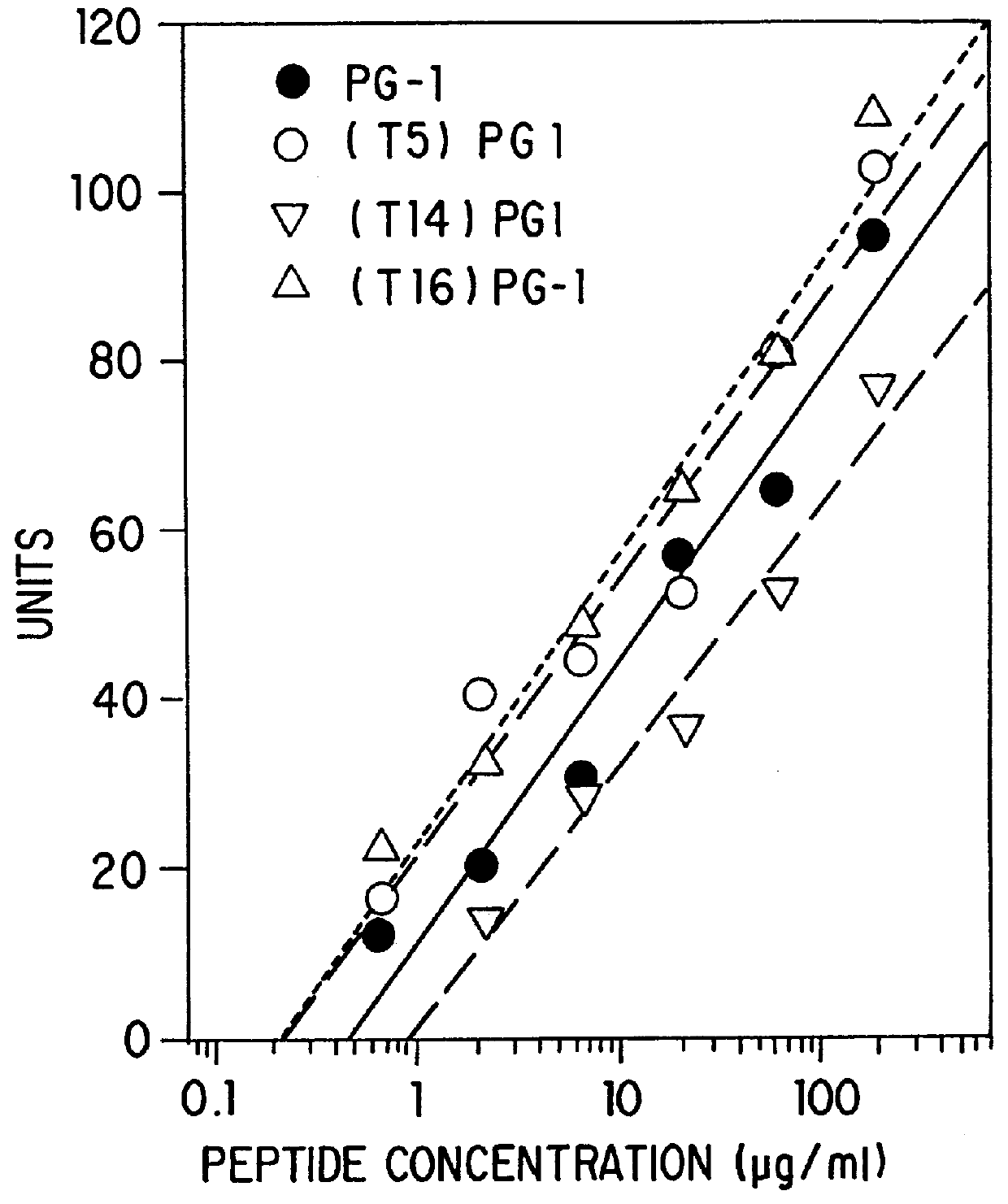
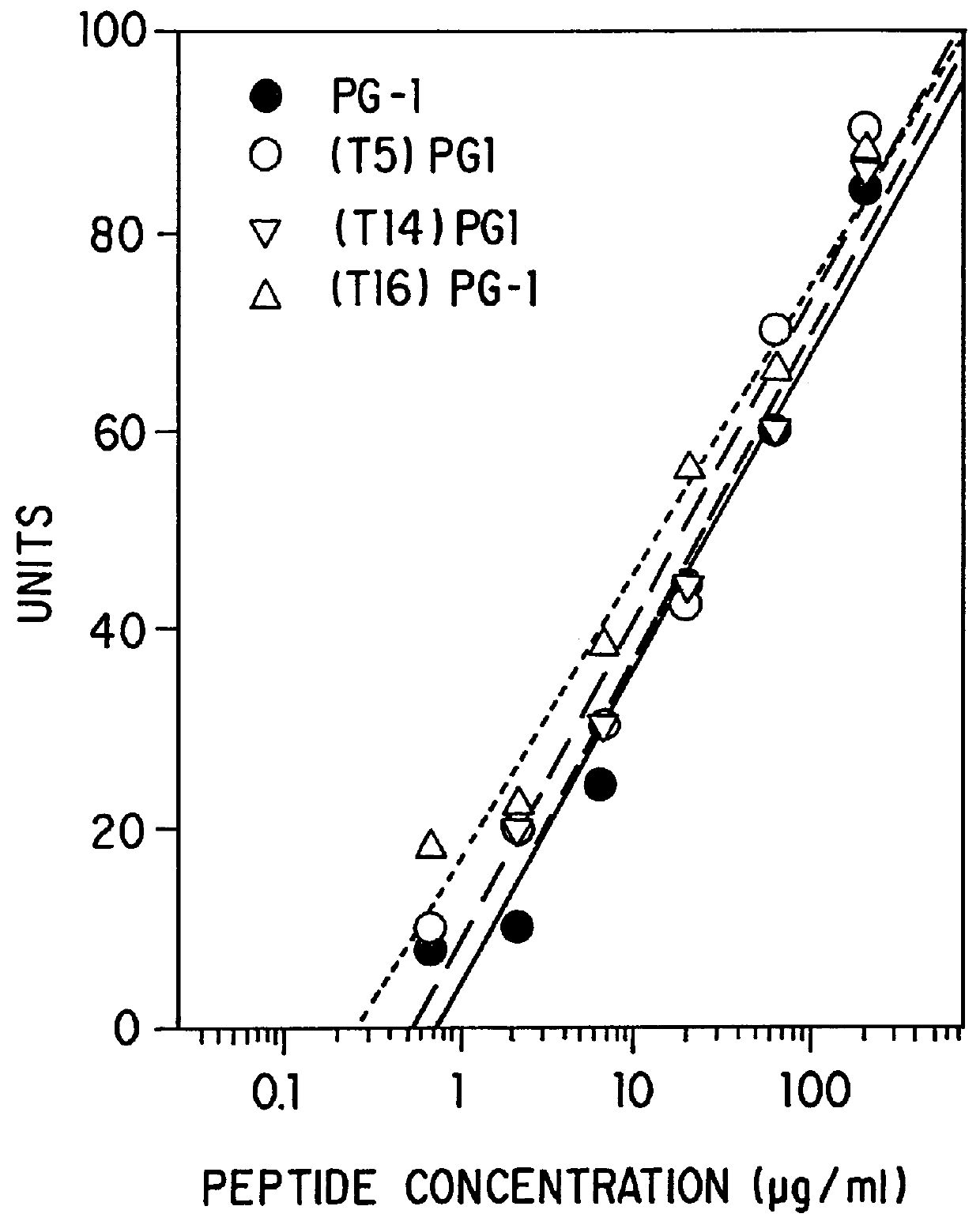
Threonine-containing protegrins
InactiveUS6043220AInhibit microbial growthGrowth of microbeAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseaseMedicine
The invention is directed to antimicrobial peptides related to naturally-occurring protegrin peptides, and methods of using the peptides in a variety of contexts, including the treatment or prevention of infections, and diseases related thereto.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Anti-acne composition
InactiveUS20070207112A1Lighten acne scarSimple compositionCosmetic preparationsBiocideAnti microbial peptideDelivery vehicle
The present invention relates to a composition for treating acne comprising an anti-microbial peptide made from the amino acids phenylalanine, alanine, leucine and lysine with said peptide admixed with salicylic acid and / or salicylate salts in a cosmetic delivery vehicle containing a rehydrating polymer. The invention further relates to a method for treating acne by topically administering one of the compositions in an amount therapeutically effective to reduce the redness and blemishes associated with acne.
Owner:GRANT INDS
Mass production method of antimicrobial peptide and DNA construct and expression system thereof
InactiveUS6699689B1Improve expression efficiencyBacteriaSugar derivativesAntimikrobielle peptideAnti microbial peptide
The present invention relates to DNA constructs that can produce antimicrobial materials efficiently from microorganisms and the preparation method thereof. The present invention also relates to the useful vector for the DNA construct. The DNA construct according to the present invention comprises a first gene coding for entire, a part of or a derivative of purF gene and a second gene coding for antimicrobial peptide. According to the present invention, antimicrobial peptides can be mass-produced by the following steps: preparing an expression vector containing a DNA construct comprising a first gene coding for an entire, a part of or a derivative of purF gene and a second gene coding for antimicrobial peptide; transforming the bacterial host cells with the above-mentioned vector, culturing the transformed cell to express the above-mentioned DNA construct; and recovering the above antimicrobial peptide.
Owner:SAMYANG BIOPHARMLS CORP
Polyvalent multimeric composition containing active polypeptides, pharmaceutical compositions and methods of using the same
InactiveUS20070053934A1Improve stabilityHigh activityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAntimicrobial peptidesDisease cause
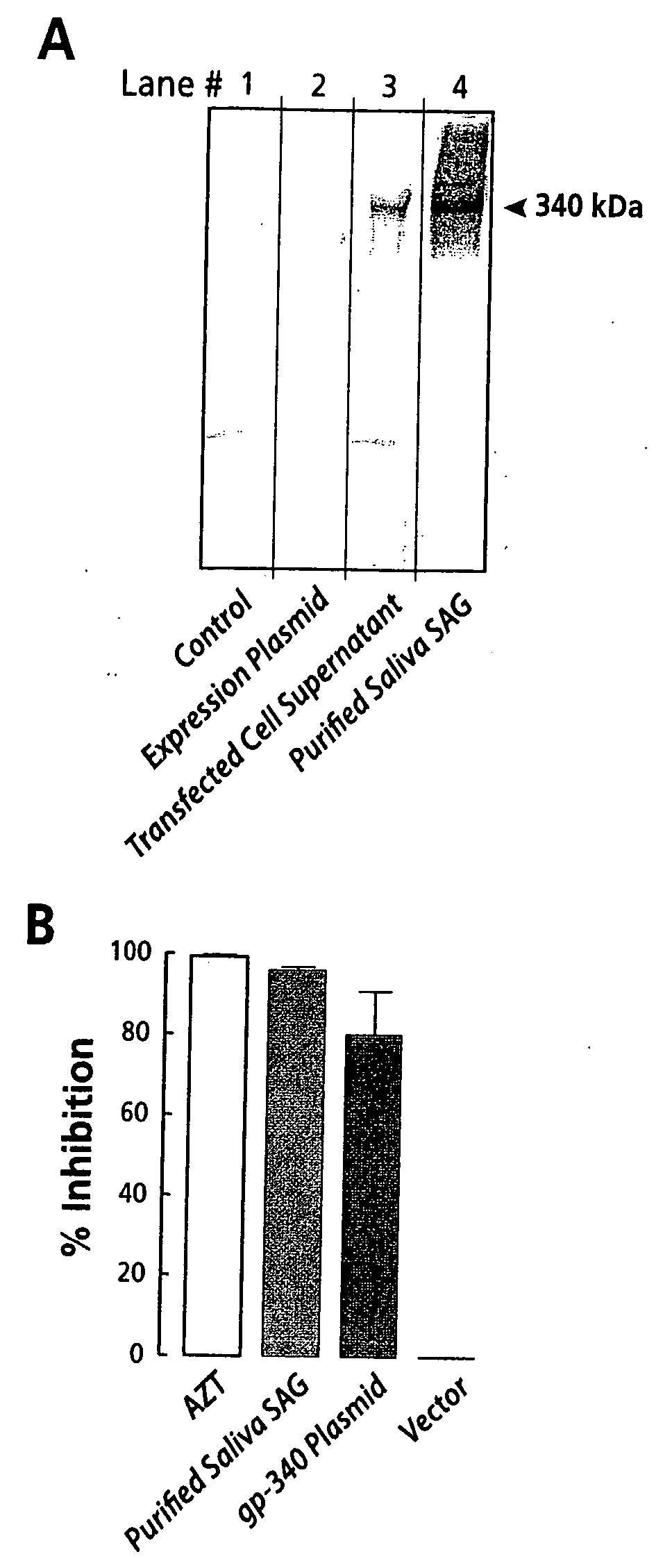
The invention is directed to compositions comprising polyvalent complexes containing a biocompatible polymer backbone to which is attached a plurality of monomeric anti-microbial peptides and to methods for using such complexes to stabilize anti-microbial peptides for treating or preventing a disease or condition resulting from infection with a microbe. Multivalent derivatives of existing antimicrobial peptides in which several peptides are covalently linked have been investigated. The resulting construct may contain up to 30 or more units, and exhibits a significant enhancement of anti-microbial effect relative to the free peptides: on the order of a ten fold improvement in effectiveness, suggesting that higher multimerization can indeed lead to more effective agents. The invention is also directed to the use of such complexes for delivery of anti-viral peptides, in particular, peptides and peptide fragments obtained from salivary agglutinin protein (gp-340) for use in treating or preventing infection with HIV.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Antimicrobial coating compositions
The invention relates to an antimicrobial coating composition for coating articles comprising: an antimicrobial peptide and a nanoparticle bound to said antimicrobial peptide, wherein the composition is suitable to be bonded to the surface of the article. The composition can comprise a coating composition of medical devices and laboratory surfaces.
Owner:BIOCANT CT DE INOVACAO EM BIOTECHA
Agonists for Antimicrobial Peptide Systems
InactiveUS20110118217A1Fine surfaceEnhanced barrier functionAntibacterial agentsBiocideAnti microbial peptideMicroorganism
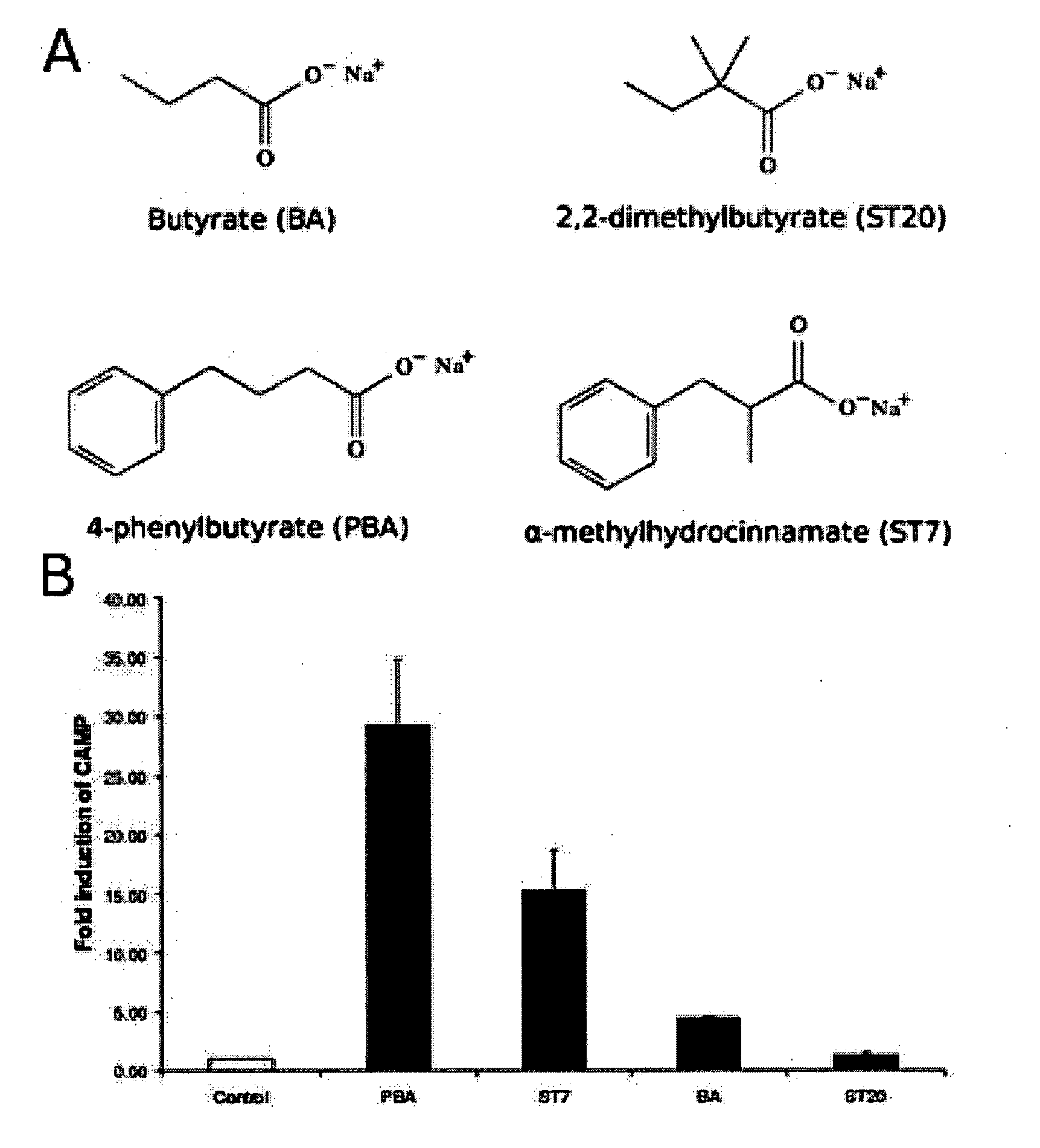
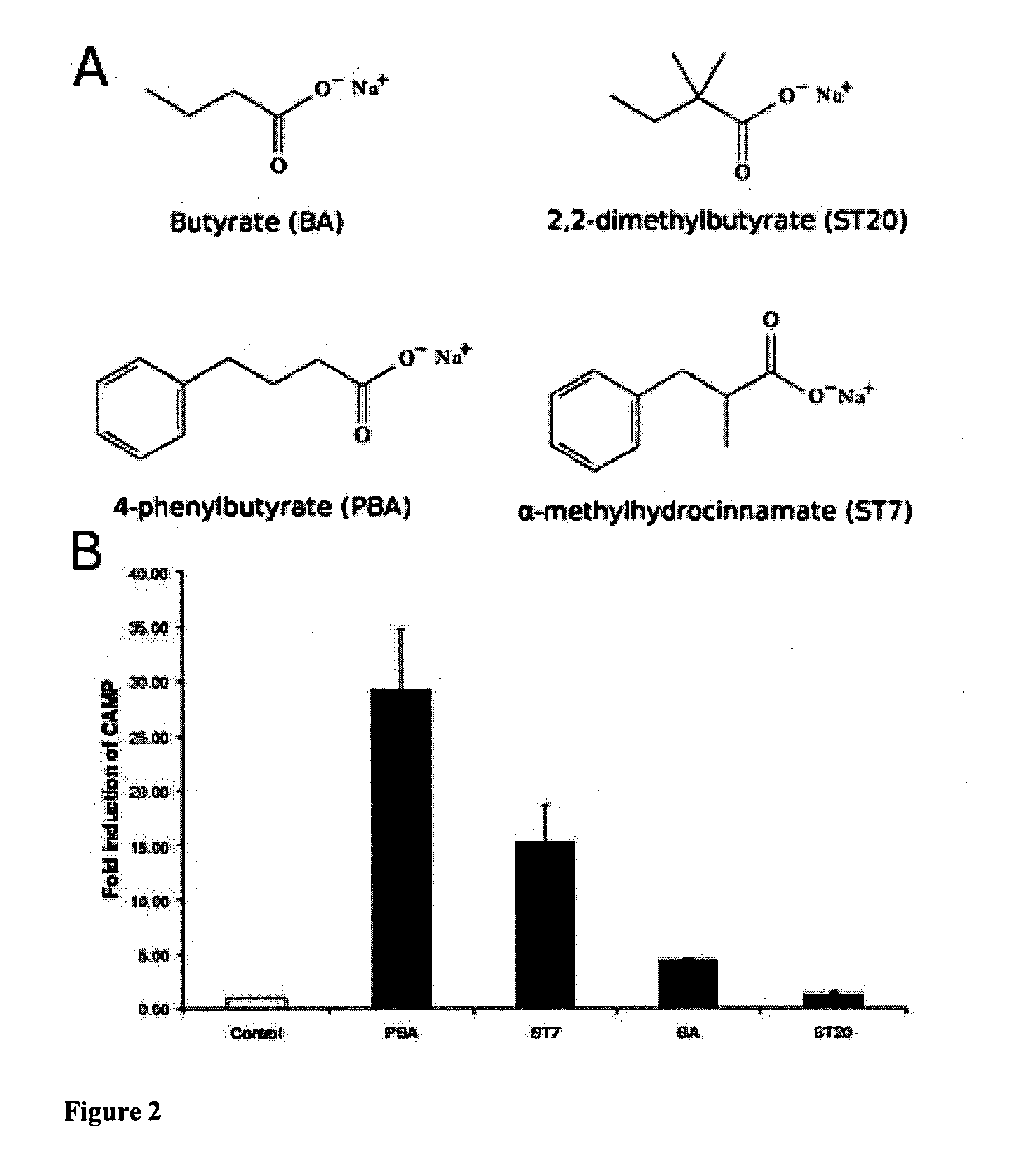
Short chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and glycerol esters of SCFAs not previously used for that purpose are provided for use as a medicament for treating, preventing or counteracting microbial infections in animals, including humans, by stimulating the innate antimicrobial peptide defense system. Preferred compounds include phenyl substituted short chain fatty acids (SCFAs) derivatives and. Also provided are methods and compositions for treating, preventing or counteracting microbial infections, including bacterial, viral, fungal, and parasitic infections, by administration of medicaments comprising a secretagogue-effective amount of the compounds of the invention.
Owner:AKTHELIA PHARMA
Anti-inflammatory/anti-microbial peptides for use in dialysis
InactiveUS20050074485A1Improve the protective effectBiocideAntipyreticHaemodialysis machineIncreased Diuresis
A composition and method of treatment are disclosed in which anti-microbial and anti-inflammatory peptides are used for hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis in dialysate and gel. An unexpected result of the invention has also been disclosed wherein the anti-microbial and anti-inflammatory peptides may be used in peritoneal dialysis to increase diuresis. Other embodiments of the invention include use of the anti-microbial and anti-inflammatory peptides in locking solutions used for catheters and other vascular access tubing or peritoneal access tubing.
Owner:ZENGEN
Fowlicidins and Methods of Their Use
InactiveUS20080119405A1Improve the bactericidal effectLow toxicityAntibacterial agentsBiocideAnti microbial peptideCathelicidin antimicrobial peptide
Antimicrobial peptides and methods for their use are provided. The peptides are optimized, truncated versions of chicken cathelicidins (“fowlicidins”).
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS FOR OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY
Production of Anti-microbial peptides
InactiveUS20100048480A1Decrease native antimicrobial activityImprove stabilityAntibacterial agentsBiocideMicroorganismAnti microbial peptide
The present application provides methods of producing antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) in a cell, for example by expression a fusion protein that includes small ubiquitin related modifier (SUMO) and an AMP in the cell. Also provided are nucleic acid and protein sequences of SUMO-AMP fusion proteins, and kits that include such molecules.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Bacillus subtilis culture medium for producing anti-microbial peptide and application thereof
PendingCN104878060AHigh potencyReduce manufacturing costMicroorganism based processesFermentationDipotassium phosphateAntimicrobial peptide production
The invention provides a bacillus subtilis culture medium for producing anti-microbial peptide and application thereof in producing the anti-microbial peptide. The fermentation medium is composed of, by weight, 0.5%-1.5% of soluble starch or corn starch, 0%-1.0% of polyvalent peptone or beef extract, 0%-0.5% of sodium chloride, 0%-0.3% of monopotassium phosphate, 0%-0.3% of dipotassium phosphate, 0.05%-0.15% of magnesium sulfate, 0.005-0.015% of calcium carbonate, 0.05%-0.15% of manganese sulfate and the balance being yellow serofluid, wherein the pH value is adjusted to 7.0-7.5. According to the method for producing the anti-microbial peptide, the cell number of bacillus subtilis in obtained fermentation broth is large, and the produced anti-microbial peptide is high in titer.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Antibacterial and antifungal peptides
This invention provides novel antimicrobial peptides and formulations thereof. The peptides and / or formulations are effective to kill or to inhibit the growth and / or proliferation of various bacteria, yeast, and fungi.
Owner:C3 JIAN LLC
Fowlicidins and methods of its use
InactiveUS20110143999A1Antibacterial agentsBiocideAnti microbial peptideCathelicidin antimicrobial peptide
Antimicrobial peptides and methods for their use are provided. The peptides are optimized, truncated versions of chicken cathelicidins (“fowlicidins”).
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS FOR OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY
Anti-microbial peptides and uses of same
A method of treating a bacterial infection in a subject is disclosed. The method comprises administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a peptide being between 3 and 5 amino acids, wherein at least one amino acid of said 3 and 5 amino acids is selected from the group consisting of tryptophan, cysteine, proline and methionine.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Modified alpha-MSH peptides and derivatives thereof
InactiveUS20060122121A1Enhanced anti-microbial activityReduce formationPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsAnti microbial peptideMicroorganism
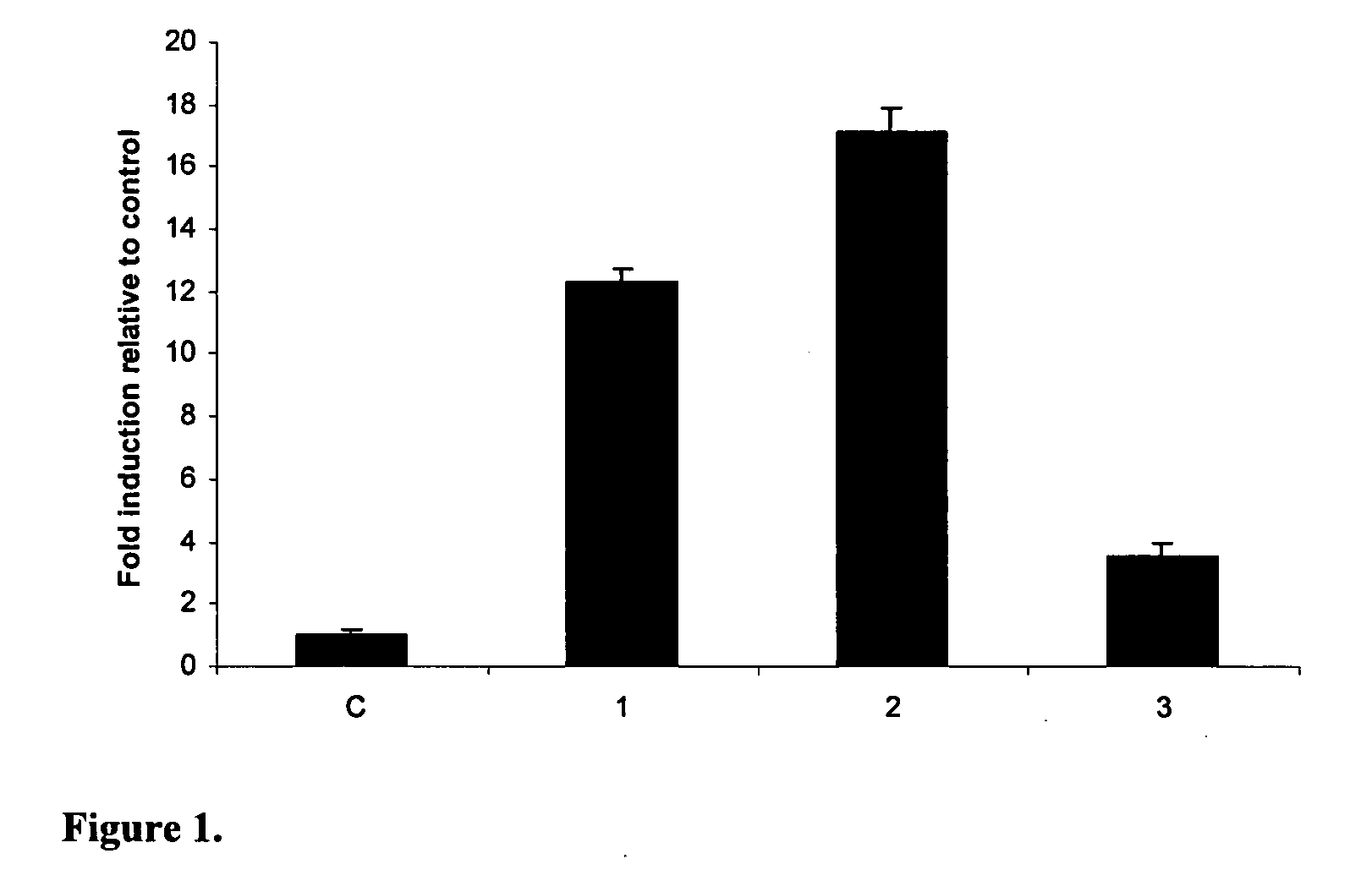
Novel peptides with antimicrobial activity are disclosed. The novel peptides are octomeric peptides modified from α-MSH. The modified α-MSH antimicrobial peptides disclosed herein may have enhanced activity against microbes over α-MSH due to modifications in peptide sequence and chirality of amino acids. Due an identified mechanism of action for antimicrobial activity in which cAMP accumulates in the microbial cell, it may be that microbes will not generate resistance to these modified α-MSH antimicrobial peptides.
Owner:ZENGEN
Methods and Systems for Generating and Evaluating Peptides
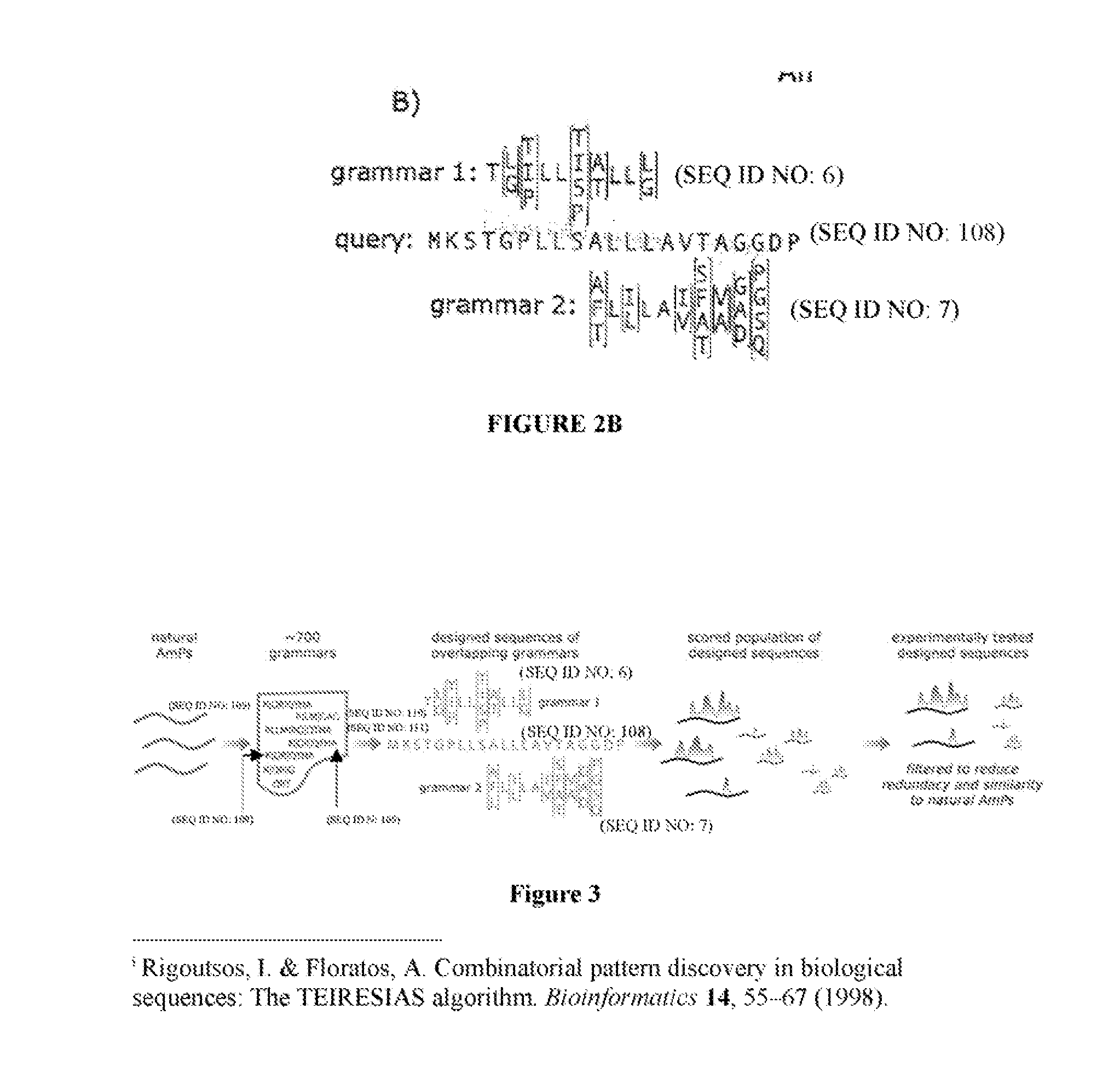
InactiveUS20070197773A1Peptide/protein ingredientsVirus peptidesAnti microbial peptideSequence database
A method has been developed to create databases of peptides having a desirable property, such as antimicrobial activity, based on analyzing a database of known peptides for a pattern statistically associated with an activity. One can determine a set of patterns that may be representative of a peptide having a desired characteristic or property, and evaluate a set of sequences against the set of patterns (grammars) to determine if the peptide sequence being evaluated has similar patterns to those of a peptide having the desired characteristic or property. The set of sequences being evaluated may include peptide sequences of a desired length comprising all or substantially all combinations of amino acids that conform to at least one of the set of patterns. Once the database is identified the database may be processed in a pattern recognition procedure that identifies a set of patterns that could be understood as representative of a peptide having the characteristic of interest. A set of newly generated peptides sequences may then be processed to score these new sequences against the identified patterns to correlate the patterns to the sequences and determine a degree of association or a similarity between a respective one of the new sequences and the set of identified patterns. The method is used to provide a database of sequences that are expected to have one or more desired activities, specific sequences within the database proven to have the desired activity, and the patterns or grammars used to create the database of sequences. Although described with reference to antimicrobial peptides, a database of peptides may be identified that contains peptides that have antiviral properties, wound response properties, or some other property of interest.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Inhibition of biofilm organisms
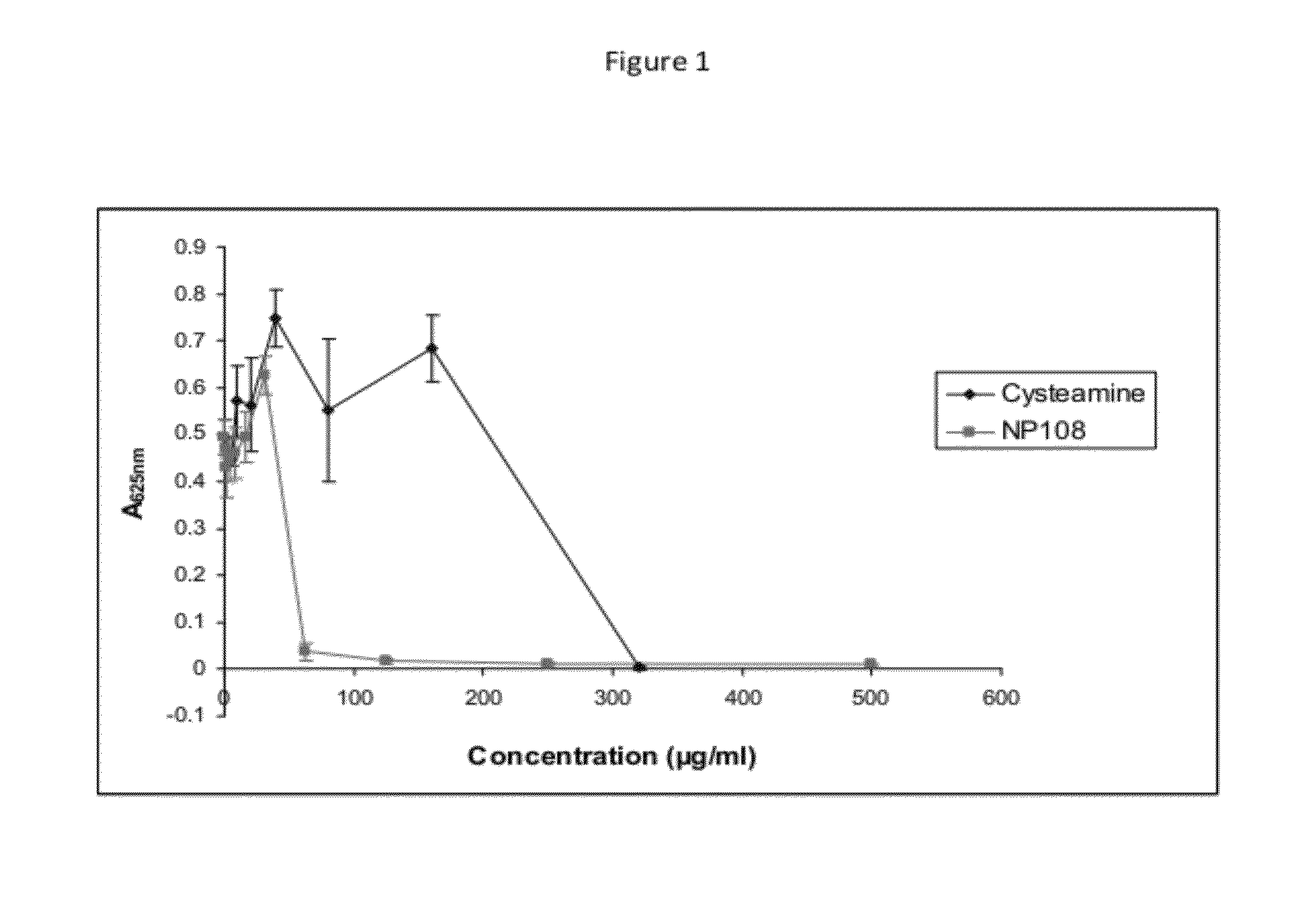
ActiveUS9339525B2Reducing MBEC valueHigh activityAntibacterial agentsBiocideAnti microbial peptideBiofilm
The present invention relates to a product comprising at least two antibiofilm agents wherein at least one of the antibiofilm agents is an antimicrobial peptide. The second antibiofilm agent is cysteamine. There is also provided the use of the product in the treatment of a microbial infection.
Owner:NOVABIOTICS LTD
Antibacterial peptoid and vesicle and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106279635AReduce the chance of occurrenceHas broad-spectrum antibacterial propertiesLiposomal deliveryDrug releaseAntibacterial property
The invention provides an antibacterial peptoid and a vesicle and a preparation method and application thereof. A hydrophilic part of the antibacterial peptoid is a lysine residue, and a hydrophobic part of the antibacterial peptoid is a diisocyanate unit, and the lysine residue links with the diisocyanate unit by means of a covalent bond. The antibacterial drug-loading vesicle is formed by self-assembling of the antibacterial peptoid and a drug in a mixture of an organic solvent and water. The antibacterial peptoid of the invention has a similar structure to that of a natural cationic anti-microbial peptide, and thus has a similar antibacterial mechanism; the antibacterial peptoid has broad-spectrum antibacterial properties, and cause the bacteria to be hard to produce drug resistance thereto; the antibacterial drug-loading vesicle has both antibacterial effect and dug-loading function, and can achieve sustained drug release.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Antimicrobial peptide Hainanenin-5 of Amolops hainanensis, gene of antimicrobial peptide Hainanenin-5 of Amolops hainanensis, separation and purification method and chemical synthesis method for antimicrobial peptide Hainanenin-5 of Amolops hainanensis and application of gene of antimicrobial peptide Hainanenin-5 of Amolops hainanensis
ActiveCN102516382ASmall molecular weightSimple structurePeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsChemical synthesisAmolops hainanensis
The invention discloses novel antimicrobial peptide Hainanenin-5 of Amolops hainanensis, a gene of the antimicrobial peptide Hainanenin-5 of Amolops hainanensis, a separation method and a chemical synthesis method for the antimicrobial peptide Hainanenin-5 of Amolops hainanensis and application of the gene of the antimicrobial peptide Hainanenin-5 of Amolops hainanensis, and belongs to the technical field of biomedicine. The Hainanenin-5 is small peptide which is obtained by the steps of electrically stimulating the Amolops hainanensis so as to collect a skin exudate, centrifuging, freeze-drying, performing gel filtration column chromatography and reverse phase-high performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) and purifying, and has a C terminal containing a seven-membered ring; the molecular weight is 2,337.91; and the isoelectric point is 10.11. A primary structure of the Hainanenin-5 is Phe<1>a<2>Leu<3>Gly<4>Ala<5>Val<6>Thr<7>Lys<8>Arg<9>Leu<10>Pro<11>Ser<12>Leu<13>Phe<14>Cys<15>Leu<16>Ile<17>Thr<18>Arg<19>Lys<20>Cys<21>. A gene for encoding a Hainanenin-5 precursor consists of 321 nucleotides, wherein a mature peptide part is encoded by 139th to 201st nucleotides. The Hainanenin-5 has low molecular weight and a simple structure, only contains one disulfide bond, and can be conveniently prepared through chemical synthesis and genetic engineering. The Hainanenin-5 is used for preparing a therapeutic medicine for pathogenic microorganism infectious diseases, has broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, has the activities on gram-positive bacteria, gram-negative bacteria and fungi (including clinically separated medicine-resistant strains), and also has the advantages of low hemolysis.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Novel antimicrobial peptide and use thereof
InactiveUS20050171335A1Prevent bacterial growthAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsNeutral Amino AcidsAnti microbial peptide
An object of the invention is to provide an antimicrobial peptide having an amino acid sequence which is different from a peptide existing and functioning as an antimicrobial peptide in the natural world and is not based on the conventional developmental approach for an antimicrobial peptide-containing antimicrobial agent, and a polynucleotide coding for said peptide. Another object is to provide an antimicrobial agent which contains such an antimicrobial peptide. Namely, an antimicrobial peptide represented by a general formula (1) (Xa)n-S (1) wherein Xa of the formula (1) is a hydrophilic amino acid residue, n is an integer of from 1 to 6, two or more of the Xa may be the same or different from one another, S is a peptide represented by hydrophobic amino acid part-basic amino acid part-bridge part-basic amino acid part-hydrophobic amino acid part, and amino acid residue of the bridge part is selected from the group consisting of hydrophobic amino acids and neutral amino acids.
Owner:TOAGOSEI CO LTD +1
Compositions and Methods for the Treatment of Huanglongbing (HLB) aka Citrus Greening in Citrus Plants
PendingUS20200102356A1Improve the bactericidal effectReduce sensitivityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPlant peptidesAnti microbial peptideAmphipathic helix
The invention may include engineered antimicrobial peptides to treat HLB disease, preferably in citrus plants. Specifically, the invention may include novel antimicrobial peptide derived from amphipathic helical peptides that may further be used to treat HLB disease in citrus plants. In one embodiment, the invention may include an engineered antimicrobial peptide formed by coupling two amphipathic helical peptides. Specifically, a generalized antimicrobial peptide of the invitation may include a first amphipathic helical peptide coupled with a second amphipathic helical peptide by a linker domain forming a helix-turn-helix scaffold formation. Such amphipathic helical peptides may be endogenous to a target host, preferably a citrus plant.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Antimicrobial peptide preparation for mucosal tissues
ActiveCN102363040AGood removal effectFast actingAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsAnti microbial peptideAntimicrobial peptides
The invention provides an antimicrobial peptide preparation for mucosal tissues. The antimicrobial peptide preparation comprises an effective amount of antibacterial peptide of which the sequence is SEQIDNO.1, preservative, humectant and isltonic buffer solution, and optionally comprises carbopol. Compared with the conventional antibiotics, the antimicrobial peptide preparation has the advantagesthat the preparation has quick response, residues are avoided, medicine resistance is hardly generated, and biological activity spectra are varied and the like.
Owner:RISE TECHNOLOGY CO LTD (BEIJING)
Cationic anti-microbial peptides and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20060240507A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisAnti microbial peptideMicroorganism
Described herein are methods of detecting a wound infection and for detecting the presence or absence of microorganisms, for example, wound pathogens in a sample, by contacting a sample with a cationic anti-microbial peptide that is degradable by an enzyme produced and / or secreted by a microorganism, and detecting degradation or the absence of degradation of the peptide, as an indicator of the presence or absence of the enzyme in the sample, and thus indicative of the presence or absence of a microorganism in the sample. The present invention also features a biosensor for detecting the presence or absence of a microorganism in a sample.
Owner:WOUNDCHEK LAB US
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com