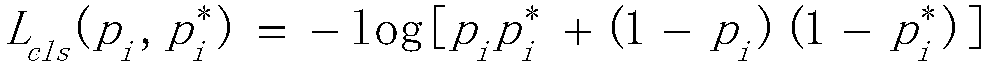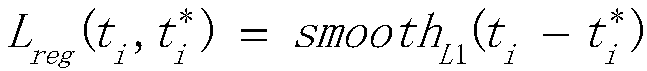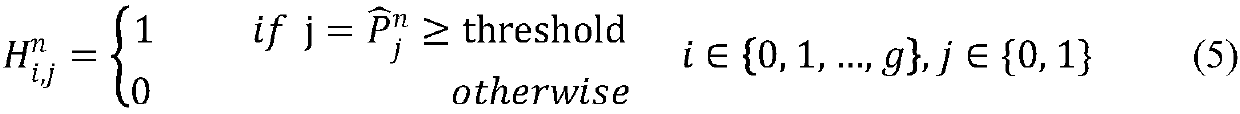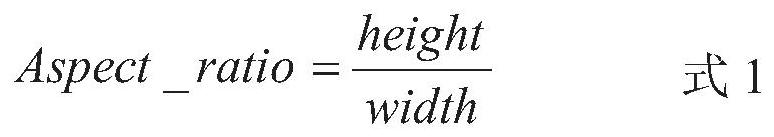Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
191 results about "Abnormal thyroid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
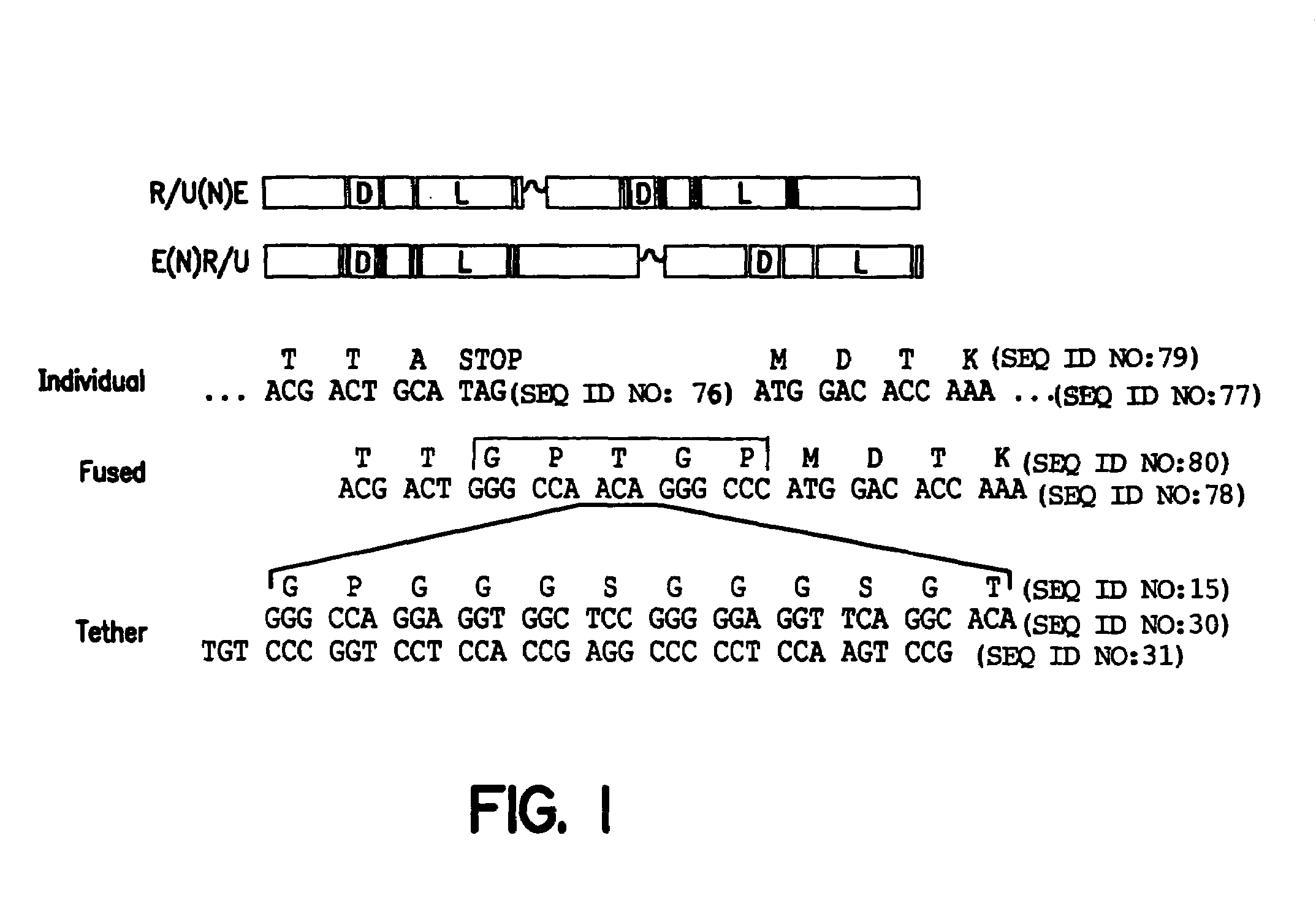
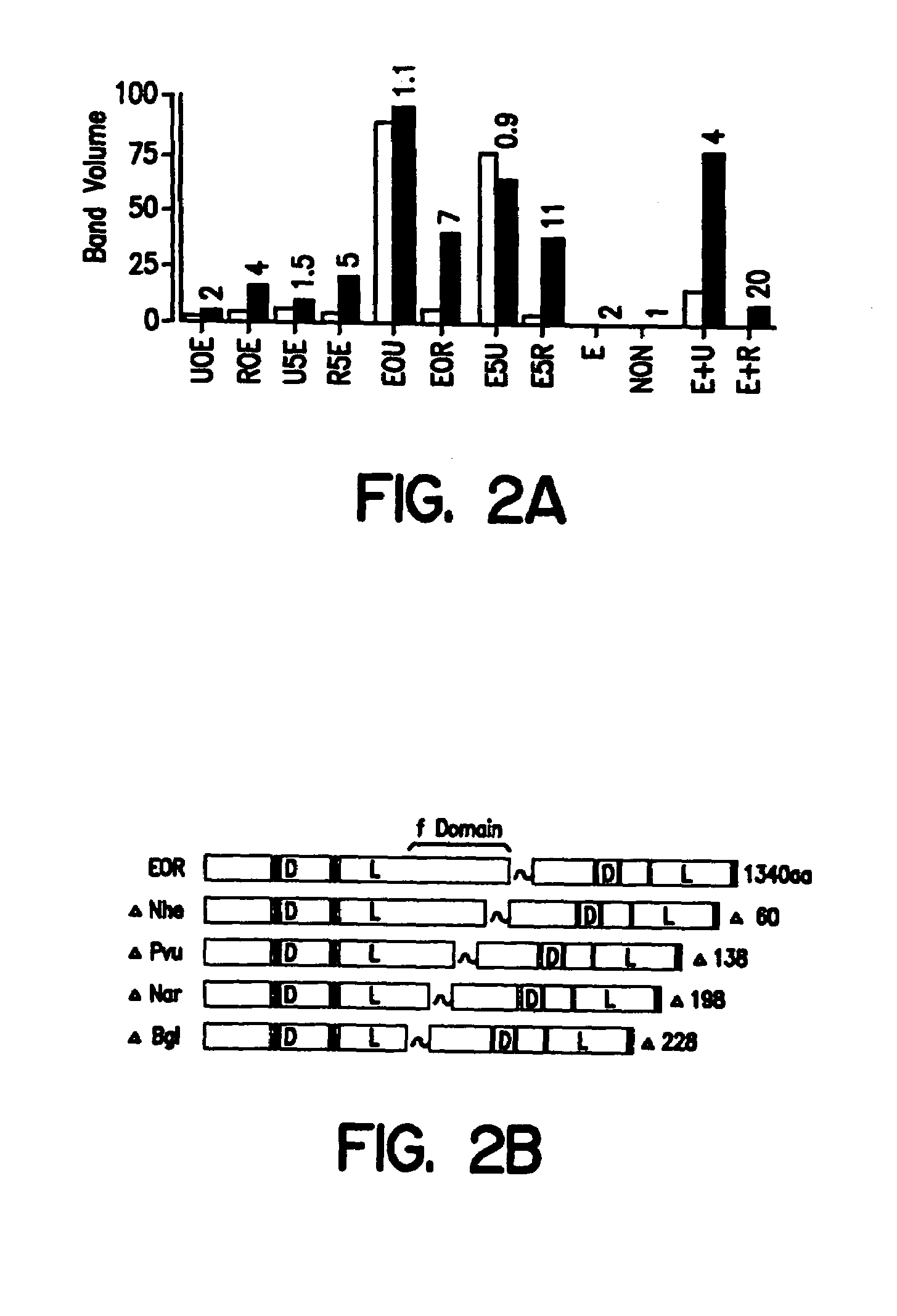
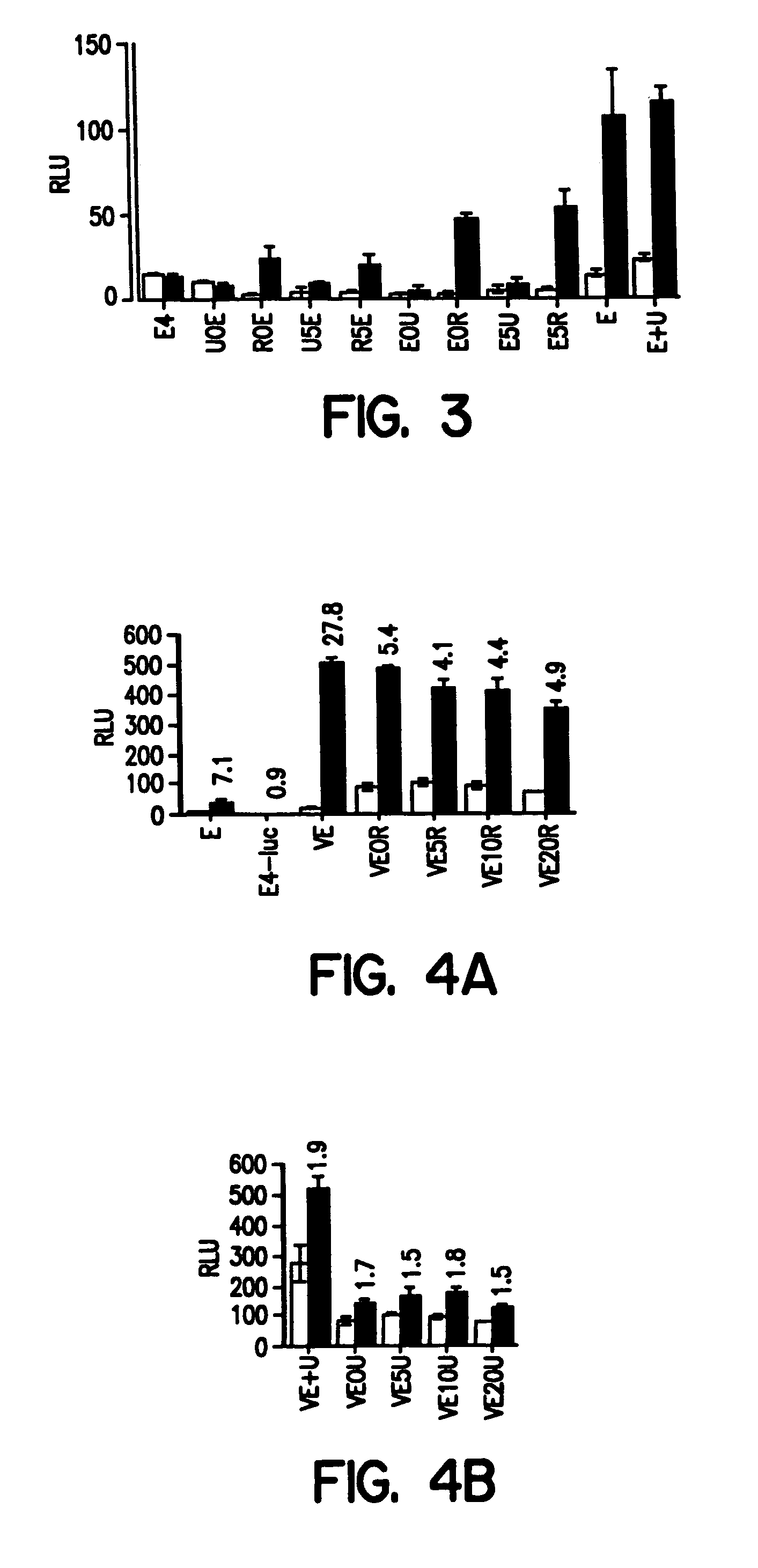
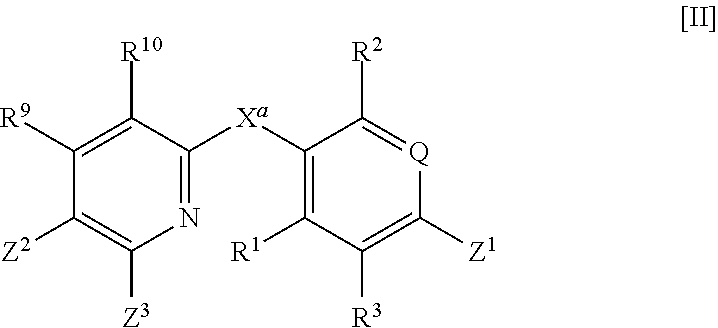
Hormone receptor functional dimers and methods of their use
InactiveUS7057015B1Enhance possibility of producingIncrease flexibilityFusion with DNA-binding domainSugar derivativesADAMTS ProteinsProtein Unit
The invention provides chimeric proteins having at least two functional protein units, each containing the dimerization domain of a member of the steroid / thyroid hormone nuclear receptor superfamily. The chimeric proteins can fold under crystallization conditions to form functional entities. The functional entities optionally contain a novel flexible peptide linker of variable lengths between at least two of the protein units. In a preferred embodiment, the linker is designed to be increased in increments of 12 amino acids each to aid in preparation of variant chimeric proteins. The DNA binding characteristics of the invention functional entities differ from those of wild-type complexes formed between “monomeric” receptors and their binding partners. Some functional entities, e.g. dimers expressed as fusion proteins, transactivate responsive promoters in a manner similar to wild-type complexes, while others do not promote transactivation and function instead essentially as constitutive repressors. The invention further provides nucleotide sequences encoding the invention chimeric proteins, cells containing such nucleotide sequences, and methods for using the invention chimeric proteins to modulate expression of one or more exogenous genes in a subject organism. In addition, isolated protein crystals suitable for x-ray diffraction analysis and methods for obtaining putative ligands for the invention chimeric proteins are provided.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
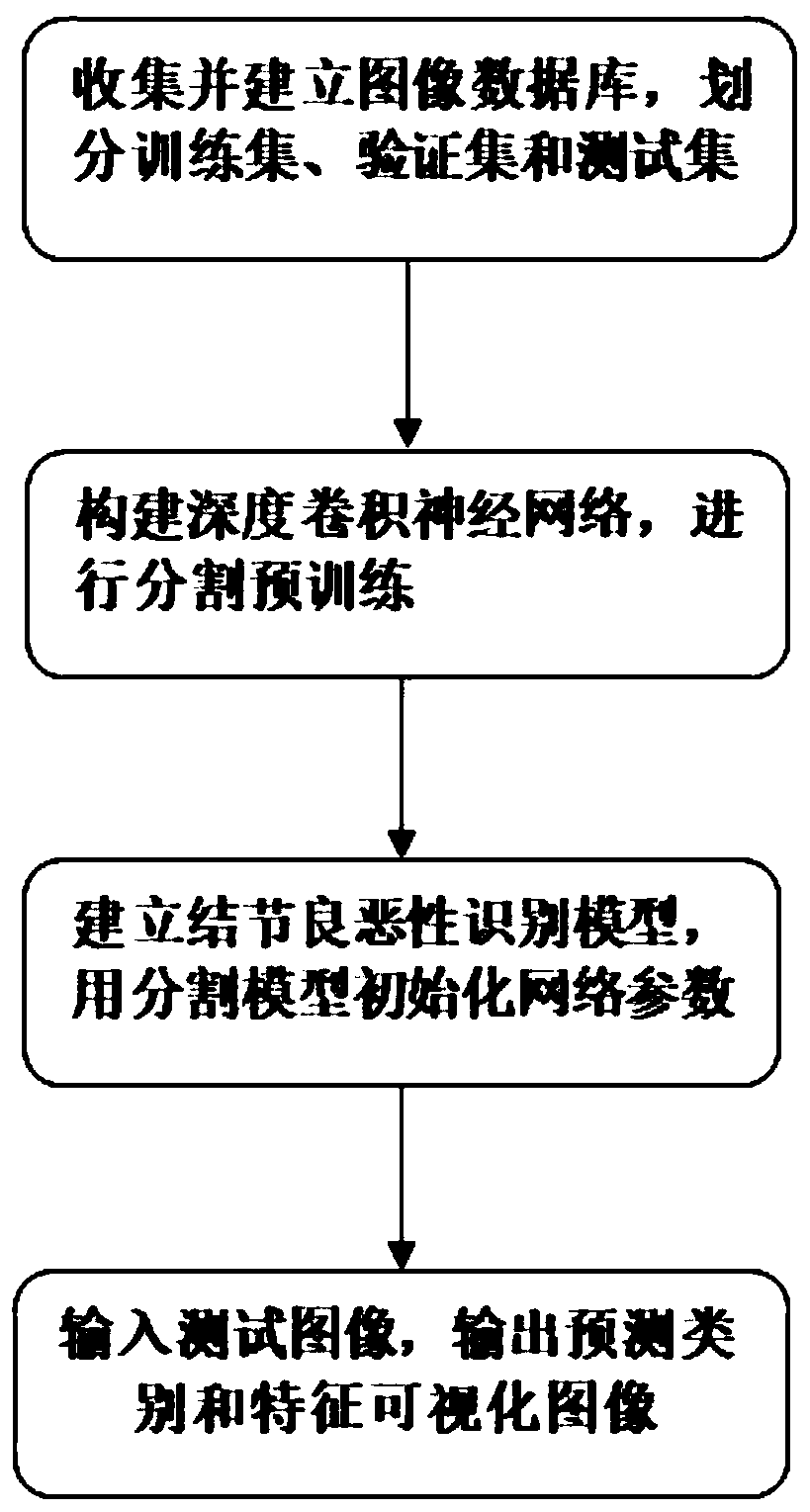
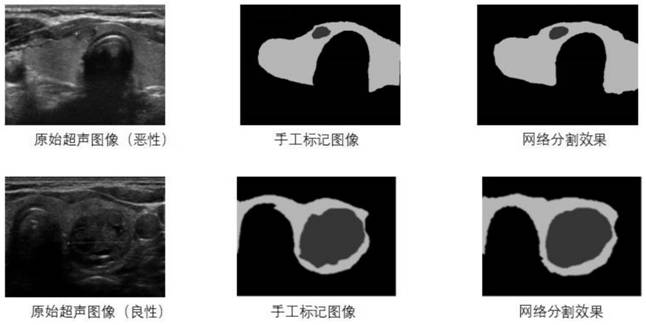
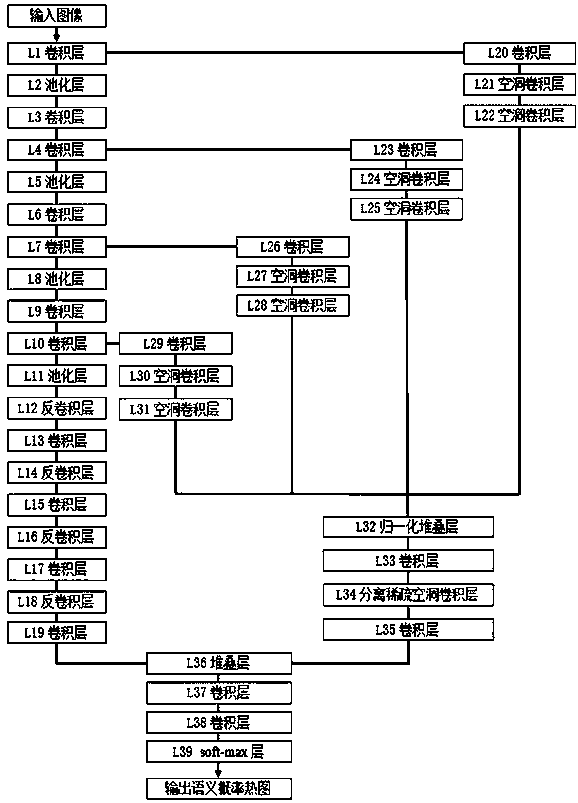
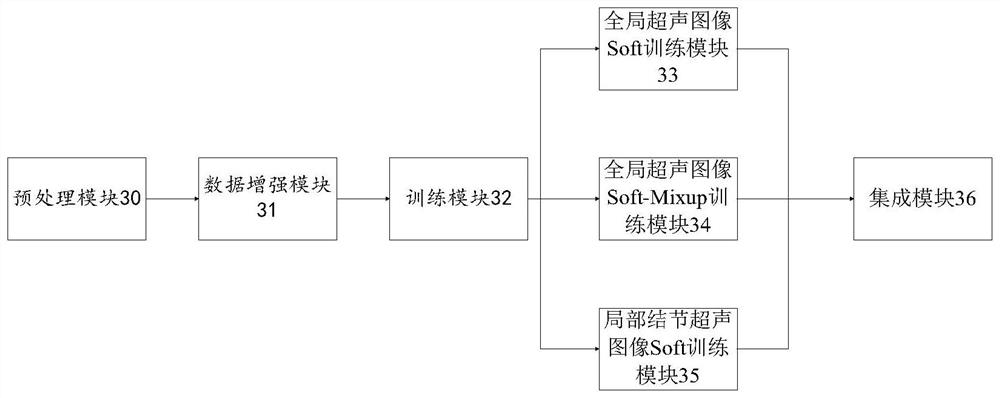
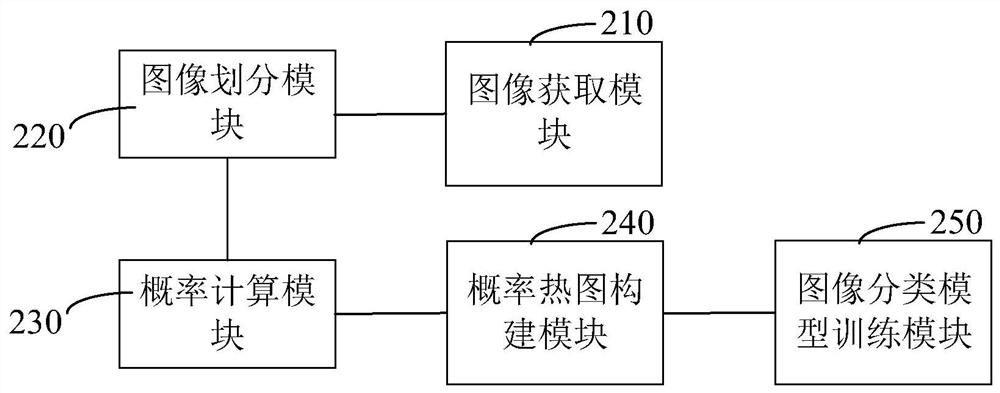
Ultrasonic thyroid nodule benign and malignant feature visualization method based on deep learning
PendingCN111243042AEasy to analyzeIncrease success rateImage enhancementImage analysisNodular thyroidNerve network
The invention relates to a medical image processing technology, and aims to provide an ultrasonic thyroid nodule benign and malignant feature visualization method based on deep learning. The method comprises the following steps: collecting case data with both a thyroid nodule ultrasonic image and a clinical operation pathological result, distinguishing benign and malignant conditions, and markinga nodule region to generate a mask image; selecting a basic structure of a deep convolutional neural network, and performing segmentation pre-training on the mask image data of all thyroid nodules; initializing a basic network by using the model parameters, and constructing a deep convolutional neural network for identification; training and verifying in a folding intersection mode to obtain a benign and malignant recognition model; and inputting a test image, predicting an identification result by using the benign and malignant identification model, and generating a malignant feature visualization image. According to the invention, the relation between the benign and malignant probability of the nodule and the image area can be visually observed. A user can better analyze the image characteristics of the ultrasonic thyroid nodule, clinical puncture examination is further guided, and the success rate of a puncture operation is increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG DE IMAGE SOLUTIONS CO LTD
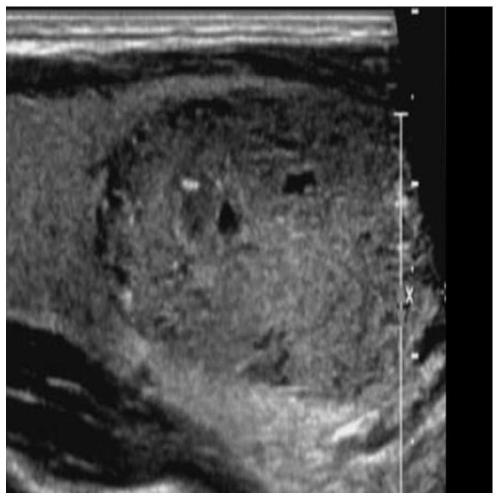
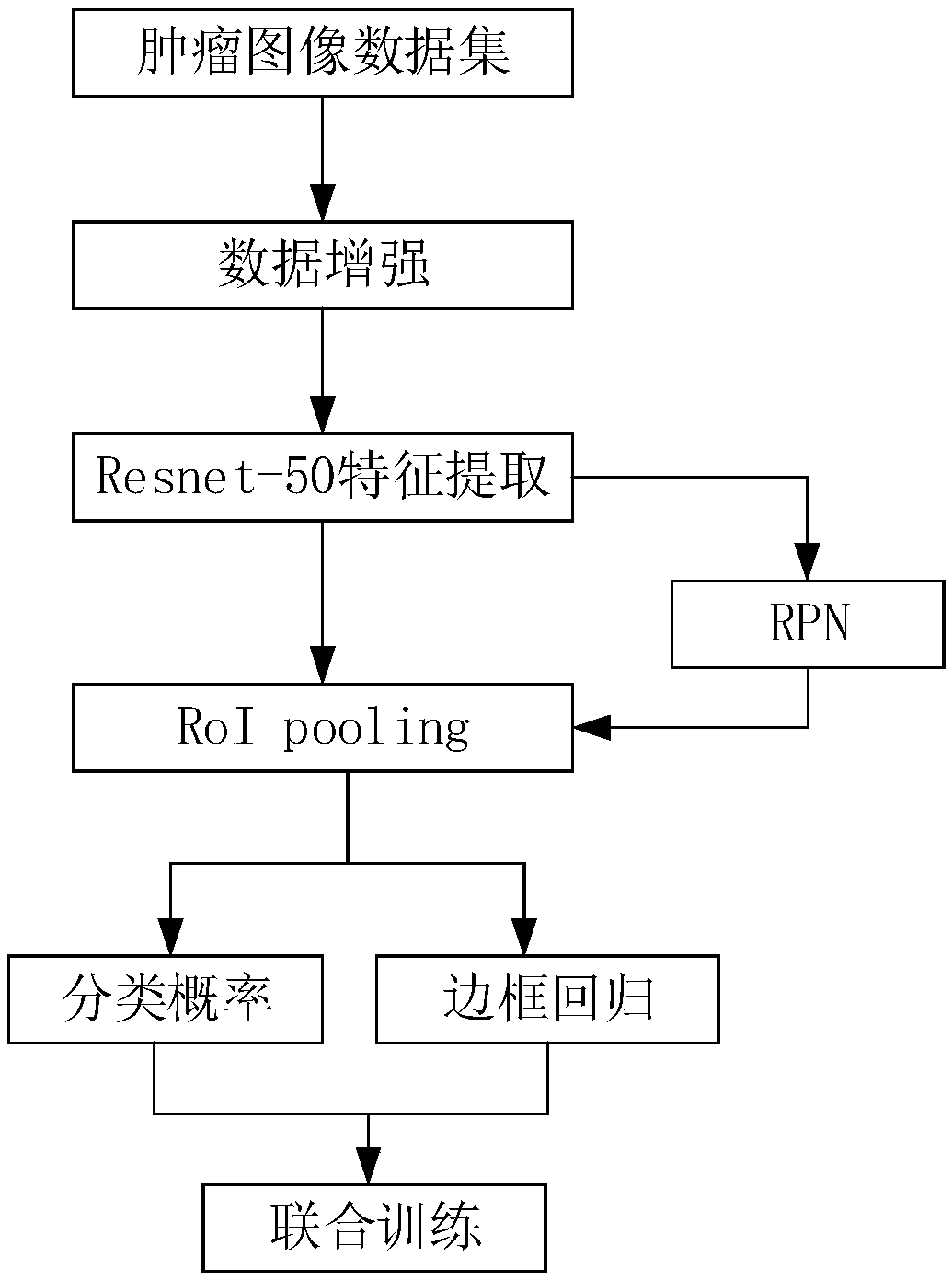
Automatic identification method of thyroid tumor ultrasound image based on faster r-cnn
InactiveCN108734694AEffective trainingIncrease the number ofImage enhancementImage analysisData setSonification
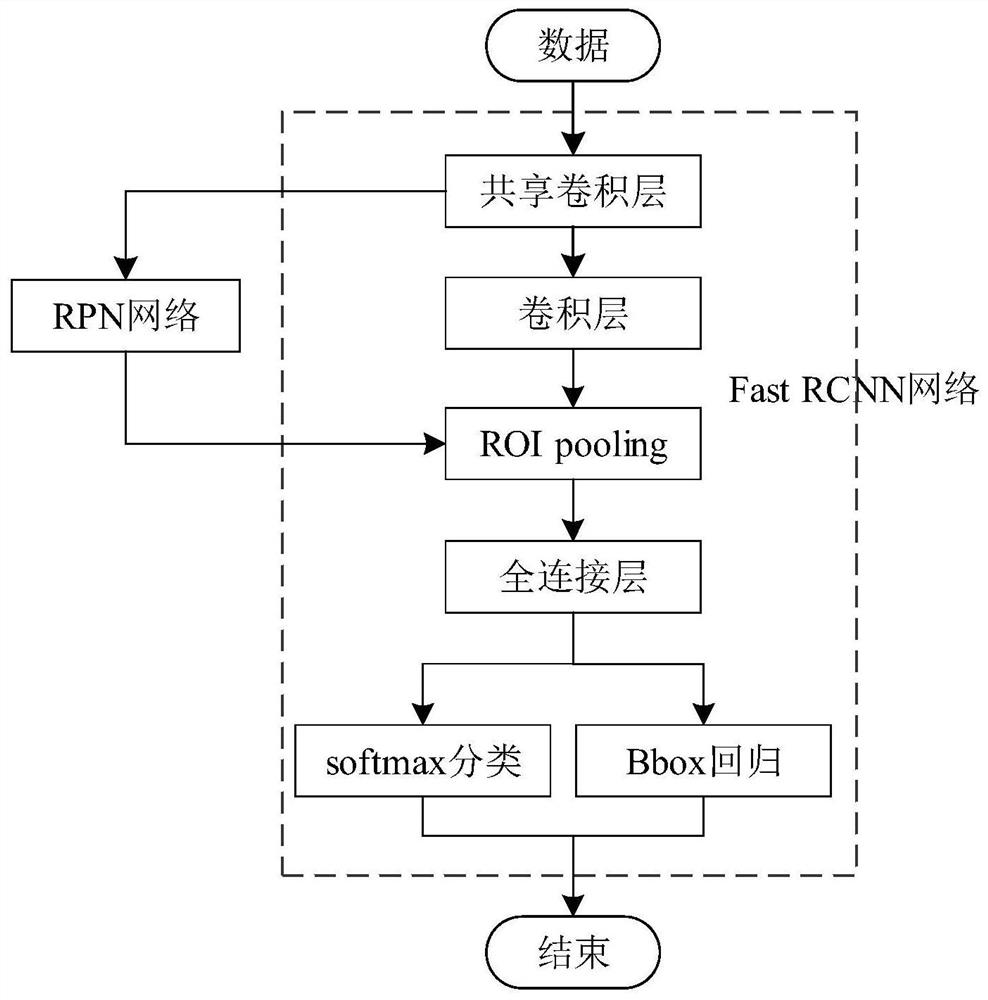
The invention discloses an automatic identification method of a thyroid tumor ultrasound image based on faster r-cnn. The method comprises the following steps: performing data enhancement on a markedthyroid tumor ultrasound image, and increasing the number and scale of training samples; performing feature extraction on an image data set by using a resnet-50 network model; generating a proposal window (proposals) by using a region proposal network RPN, and mapping the proposal window onto a feature map to generate a region proposal box; then causing each RoI to generate a feature map with a fixed size through RoI pooling; and finally performing joint training on a classification probability and border regression by using softmax Loss and softmax L1 Loss. By adoption of the method disclosedby the invention, the tumor ultrasound image does not need to be manually segmented, end-to-end network training can be achieved, and the identification rate is improved by data enhancement.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Auxiliary analysis method and system for pathological image of thyroid cancer cells based on deep learning
InactiveCN110335668AEasy to storeEasy to manageStill image data indexingCharacter and pattern recognitionImage analysisData transmission
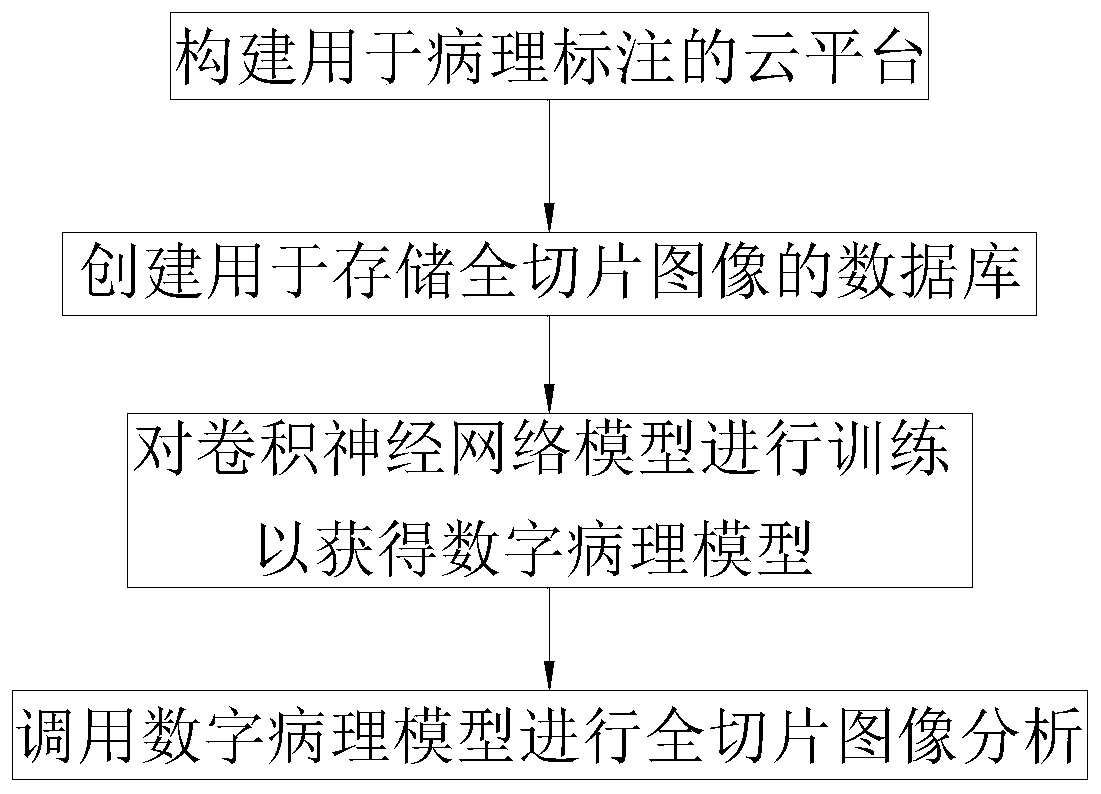
The invention provides an auxiliary analysis method and system for a pathological image of thyroid cancer cells based on deep learning. The method comprises the following steps: S1, constructing a cloud platform for digital pathological labeling to obtain a labeled training set, a labeled verification set and a labeled test set; S2, creating a database for storing a pathological digital full-sliceimage; S3, training a convolutional neural network model by using the training set, the verification set and the test set to obtain a digital pathological model; S4, calling a digital pathological model to carry out digital pathological image analysis on the pathological digital full-slice image. The invention provides the cloud platform for data labeling, the data transmission and labeling are carried out on line, and there is no special equipment requirement, thereby improving the labeling and data transmission efficiency; the database used for storing the full-slice image is constructed, the corresponding pathological digital full-slice images are obtained from the database in the labeling process, the training process and the subsequent analysis and detection process, thereby achieving the full-slice digital pathology analysis with a very large auxiliary data flow.
Owner:台州市中心医院
Method for efficiently inducing reprogramming of human body cells into pluripotent stem cells
ActiveCN102093981AImprove the efficiency of inducing iPSCsShort induction periodVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsNuclear reprogrammingExpression gene
The invention provides a method for efficiently inducing reprogramming of human body cells into pluripotent stem cells, belonging to the field of biomedicine. The method provided by the invention comprises the following step: before carrying out nuclear reprogramming on body cells, culturing the body cells for 2-4 days in a culture medium containing thyroid hormone T3. The method provided by the invention can increase the iPSC (induced pluripotent stem cell) induction efficiency by 20-100 times to about 1.2%, and shorten the induction cycle to 12-16 days; and meanwhile, different clones of the iPSC obtained by induction have uniform cellular morphology, multiplication capacity and pluripotent gene expression, and can be used for researching human diseases.
Owner:SHENZHEN BEIKE BIOTECH
Thyroid nodule diagnosis method based on deep learning network
ActiveCN112529894AEasy to set upConvenient treatmentImage enhancementImage analysisImage manipulationNetwork model
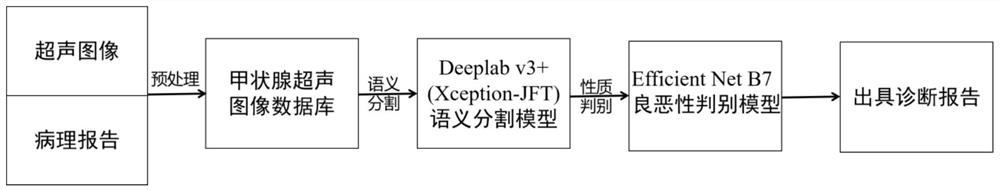
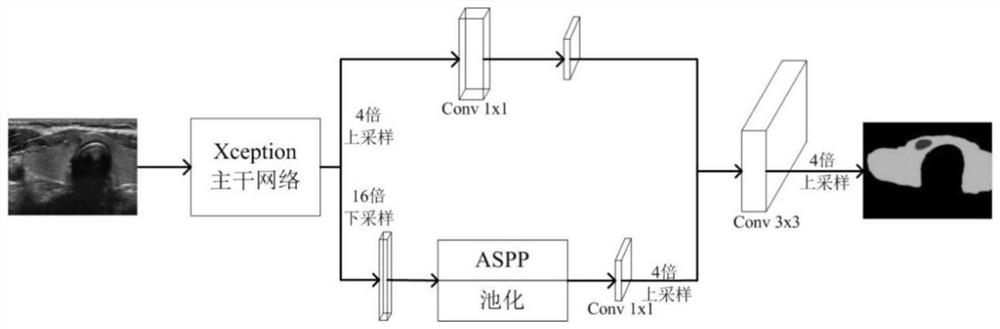
The invention discloses a thyroid nodule diagnosis method based on a deep learning network, and belongs to the field of image processing and artificial intelligence aided disease diagnosis. The methodcomprises the following steps: searching an ultrasonic original image and a pathological report of a thyroid nodule of a thyroid patient, and constructing a thyroid nodule database; preprocessing theultrasonic image; performing semantic segmentation on the ultrasonic image preprocessed in the step 2 through a Deeplab v3+ method based on Xception-JFT, and forming a semantic segmentation result graph; judging benign and malignant thyroid nodules based on a deep learning network; and forming a thyroid nodule diagnosis information report. According to the method, the Deeplab v3+ algorithm basedon Xeption-JFT is adopted to establish the thyroid ultrasound image segmentation network model, the optimal segmentation effect is achieved by continuously improving the backbone network Xception, nodule information can be automatically and rapidly recognized under high accuracy and high robustness, image features are automatically extracted for accurate segmentation to obtain a better diagnosis result, and an objective reference is provided for clinical diagnosis.
Owner:XUZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
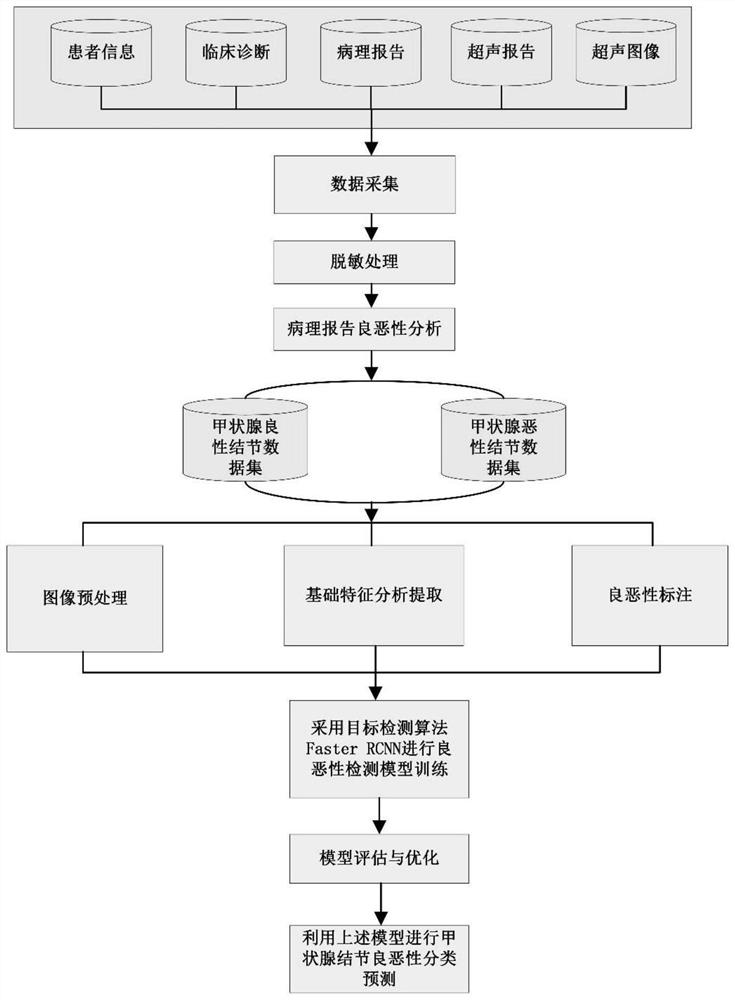
Ultrasonic image thyroid nodule intelligent detection system based on Fast-RCNN
PendingCN111612752ARealize automatic identification functionRapid automated detectionImage enhancementImage analysisMalignancyNeural network nn
The invention discloses an ultrasonic image thyroid nodule intelligent detection system based on a Faster-RCNN. When the adopted Faster-RCNN model is used for carrying out target detection, speed increases and storage space is optimized compared with a regional convolutional neural network RCNN so that rapid and automatic detection of benign and malignant nodules is realized. The features are optimized in the model construction. Key features in an ultrasonic diagnosis standard ACR TI-RADS are calculated before deep learning training, key image feature factors influencing clinical diagnosis aresearched and added to a convolutional neural network feature layer for improvement, a new identification model is constructed, and therefore the accuracy of a prediction result is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE HOSPITAL THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL WITH NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Multi-analyte diagnostic test for thyroid disorders
InactiveUS20070178604A1Reduce signalingIncrease ratingsDisease diagnosisBiological testingDiseaseDiagnostic test
Immunological assays for several biological markers for thyroid disorders in a biological sample are performed in a single test with a combination of sandwich-type, sequential competitive, and serological assays by the use of particles classified into groups that are distinguishable by flow cytometry, one group for the assay of each marker. Each group of particles is coated with a different immunological binding member, and coating densities, co-coating materials, and special buffer solutions are used to adjust for differences in the sensitivities and dynamic ranges of each of the markers in the typical sample.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
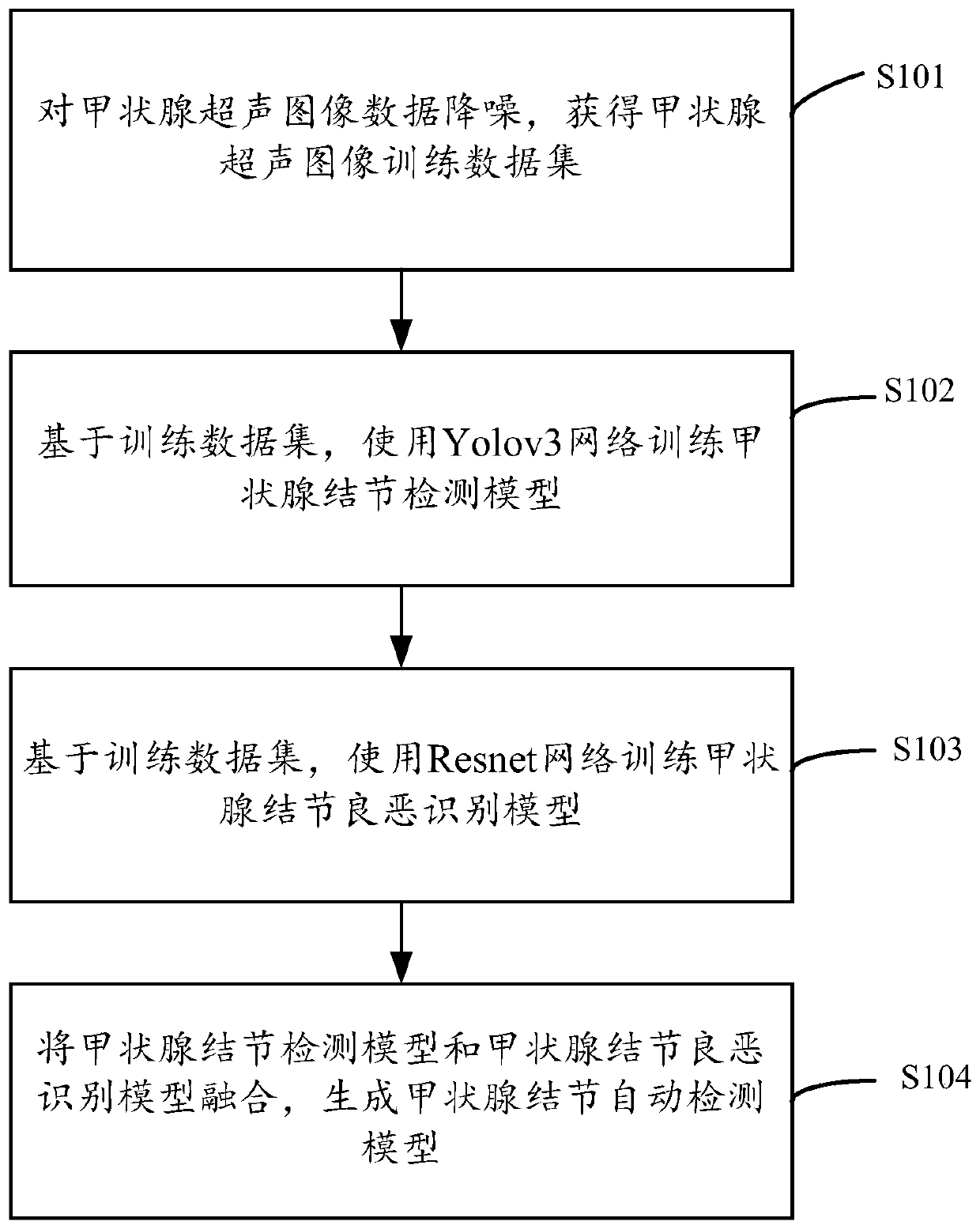
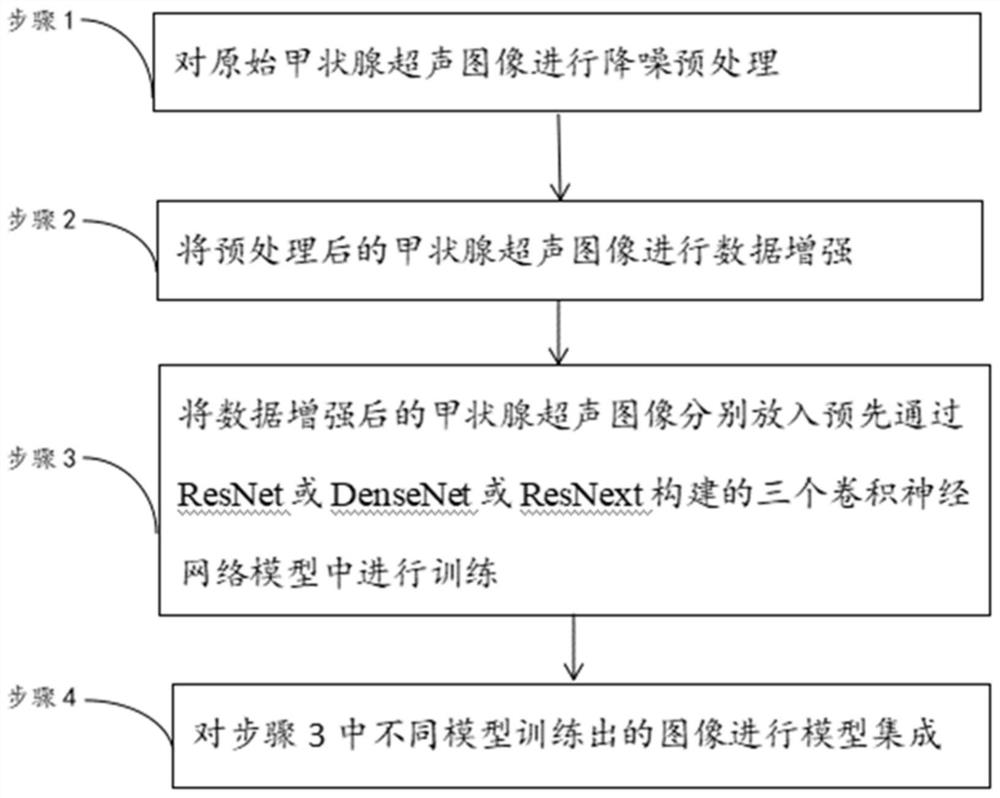
Thyroid nodule automatic detection model construction method, system and device
The invention discloses a thyroid nodule automatic detection model construction method, system and device based on a convolutional neural network, and the thyroid nodule automatic detection model construction method comprises the steps: carrying out the noise reduction of thyroid ultrasonic image data, and obtaining a thyroid ultrasonic image training data set; based on the training data set, using a Yolov3 network to train a thyroid nodule detection model; based on the training data set, using a Resnet network to train a thyroid nodule benign and malignant identification model; and fusing thethyroid nodule detection model and the thyroid nodule benign and bad recognition model to generate a thyroid nodule automatic detection model.
Owner:北京小白世纪网络科技有限公司
Thyroid cytology multi-type cell detection method based on deep learning
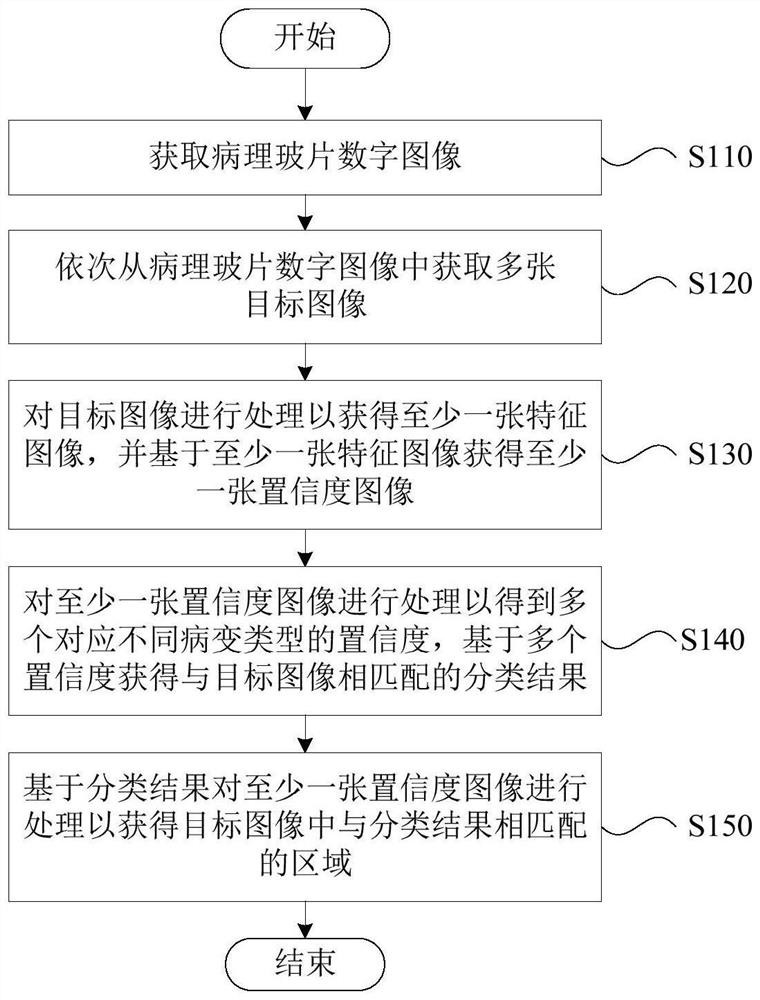
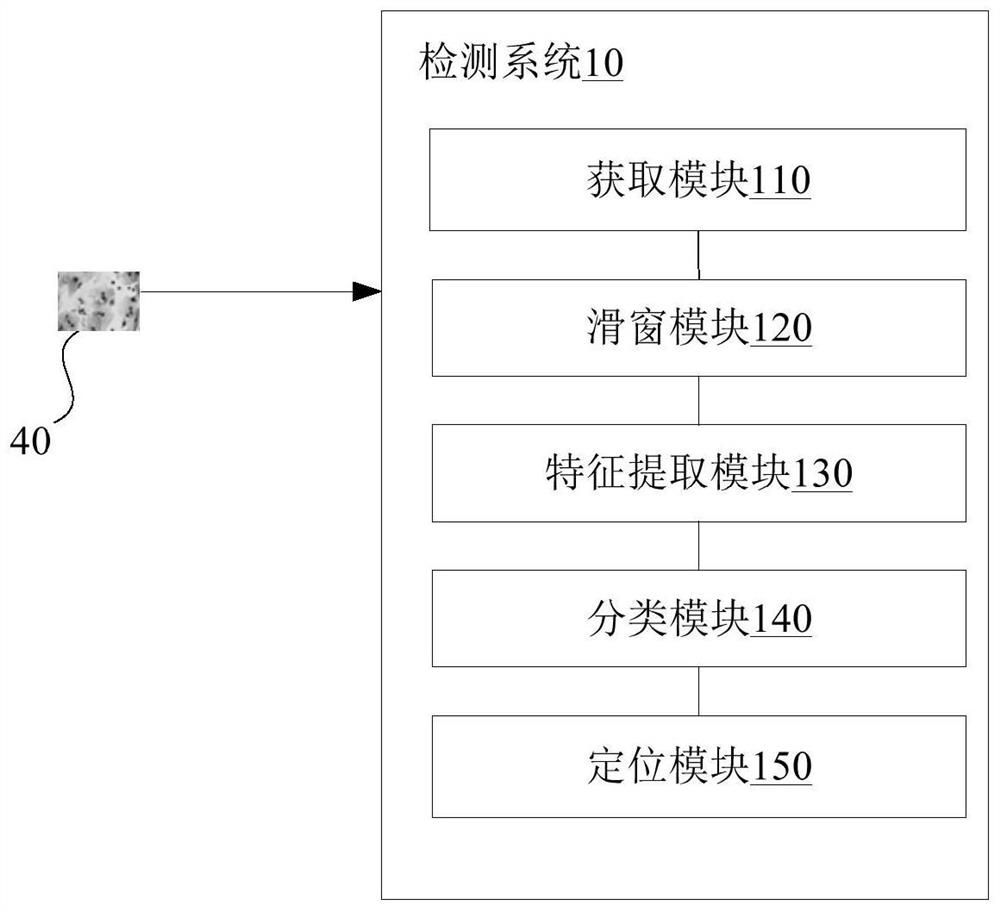
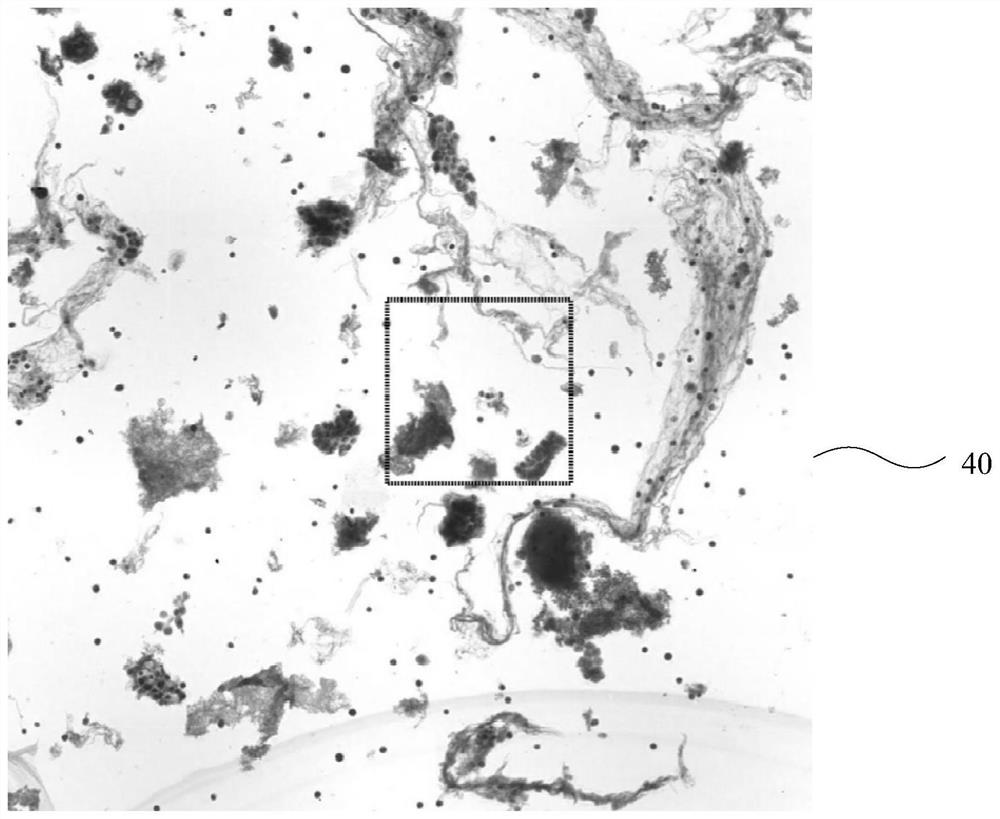
PendingCN114187277AImprove detection efficiencyReduce labeling costsImage enhancementImage analysisCytologyRadiology
The invention discloses a thyroid cytology multi-type cell detection method based on deep learning, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a cell pathology slide image of a thyroid cell, obtaining a plurality of target images from the cell pathology slide image through sliding window scanning with selectable step length, the adjacent target images have an overlapping area, the target images are processed to obtain at least one feature image and confidence images, and the number of the confidence images is the same as the number of lesion types of lesion cells of the thyroid; and processing the at least one confidence coefficient image to obtain a plurality of confidence coefficients corresponding to different lesion types, obtaining a classification result matched with the target image based on the plurality of confidence coefficients, and processing the at least one confidence coefficient image based on the classification result to obtain an area matched with the classification result in the target image. Therefore, the detection efficiency of the detection system can be improved, and the marking cost can be reduced when the detection system is trained.
Owner:赛维森(广州)医疗科技服务有限公司
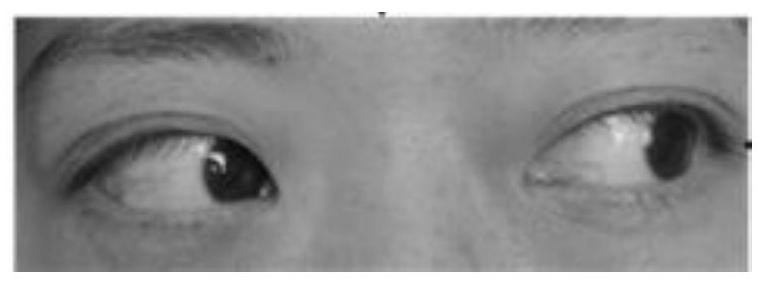
Eye sign recognition method and device for thyroid-related eye diseases
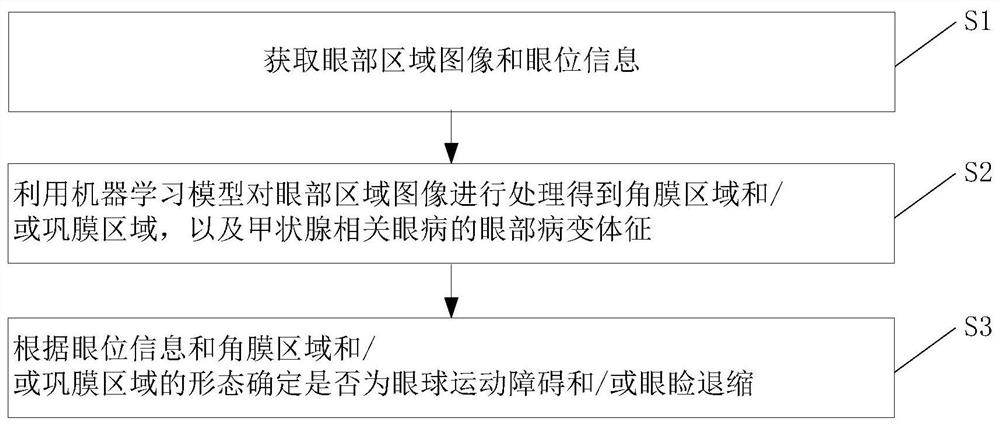
PendingCN111839455AImprove work efficiencyImprove objectivityImage enhancementImage analysisOcular diseaseEYELID RETRACTION
The invention provides an eye sign recognition method and device for thyroid-related eye diseases. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring an eye region image and eye position information; and processing the eye region image by using a machine learning model. The machine learning model comprises a segmentation model and a sign discrimination model, wherein the segmentation model isused for segmenting a cornea region and / or a sclera region from the eye region image. The sign discrimination model is used for extracting feature data from the eye region image and judging whether eye signs of thyroid-related eye diseases exist or not according to the feature data; and determining whether eyeball dyskinesia and / or eyelid retraction exists or not according to the eye position information and the form of the corneal region and / or sclera region.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGZHENG HOSPITAL +1
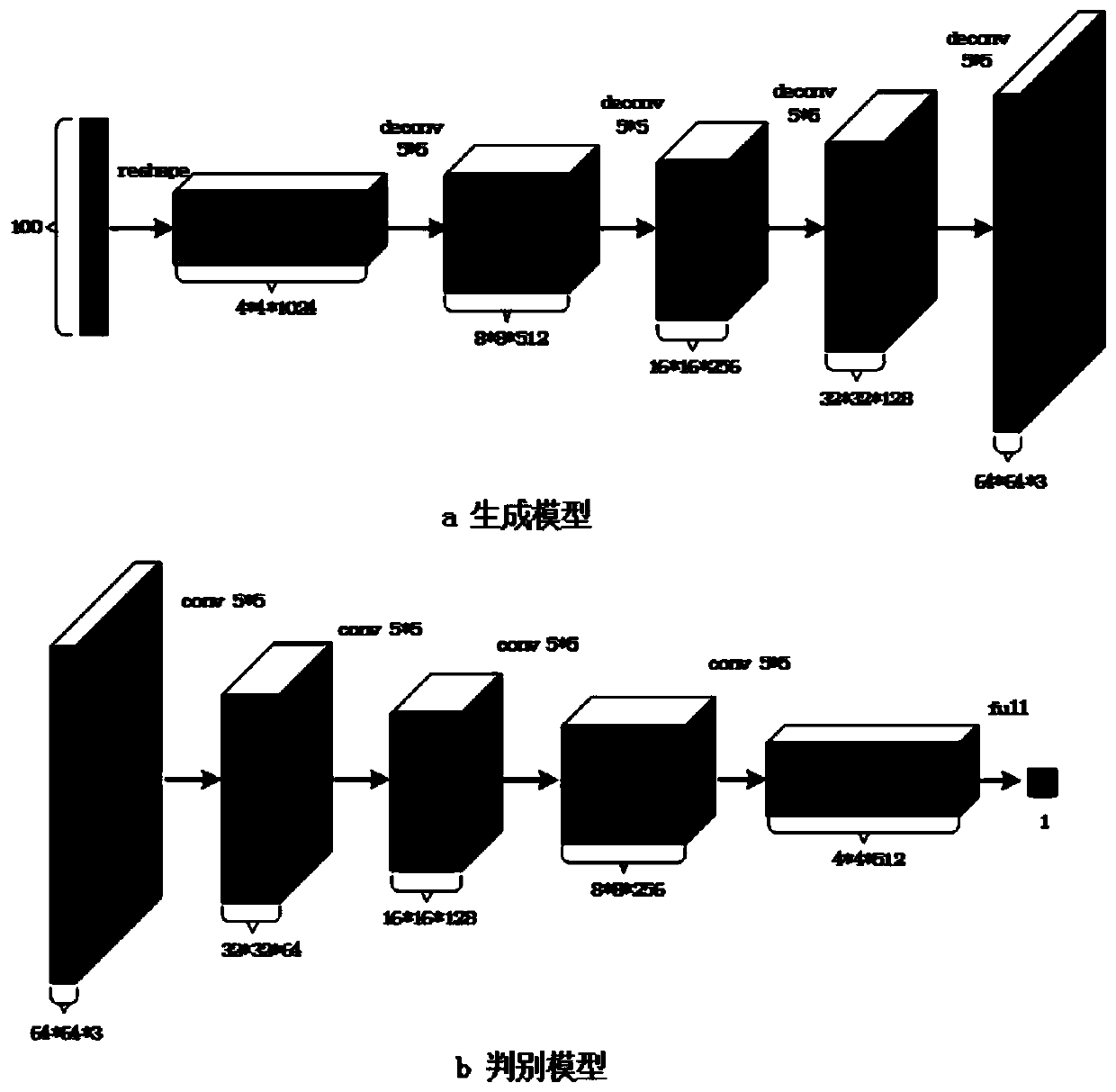
Thyroid nodule focus region generation data enhancement method based on a deep convolutional generative adversarial network
PendingCN109872296AAvoid unclear, abnormal physiological structure, etc.CredibleImage enhancementRadiologyMalignancy
The invention discloses a thyroid nodule focus region generation data enhancement method based on a deep convolutional generative adversarial network. According to the method, thyroid ultrasound images of a real patient are classified according to benign nodules and malignant nodules; a focus area image is generated by using a deep convolutional generative adversarial network; According to the method for generating image fusion in the lesion area, the image which is generated from the lesion area and is close to the real lesion is selected and fused with the thyroid image of a normal person toachieve the purpose of data enhancement, and the method for generating image fusion in the lesion area improves the quality and diversity of enhanced data, enables the generated image to be close tothe real image to the maximum extent and is more credible.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
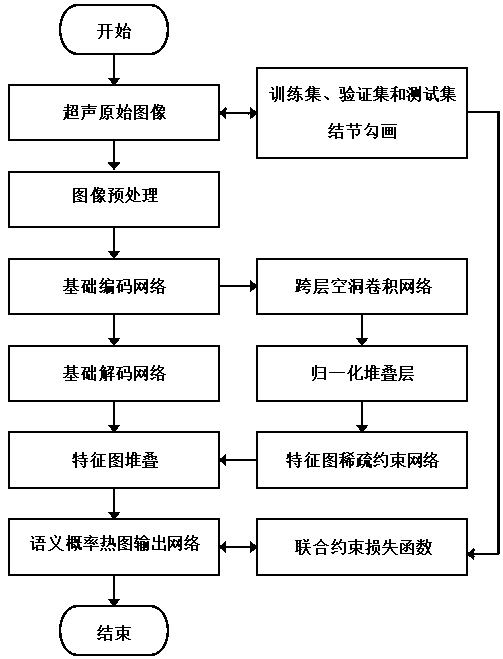
Thyroid nodule ultrasonic image processing method based on cross-layer sparse cavity convolution
ActiveCN111539959ASolve problems such as poor extraction effectImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingFeature extraction
The invention discloses a thyroid nodule ultrasonic image processing method based on cross-layer sparse cavity convolution. A novel cross-layer cavity convolution network structure, a sparse constraint network, a separation sparse cavity convolution layer, and a loss function with adaptive weight adjustment and sparse constraint are established, the method overcomes the defects that an existing method is poor in thyroid nodule ultrasonic image nodule region semantic resolution capability, and semantic feature extraction of the nodule region is susceptible to interference of similar backgrounds, and solves the problem of poor extraction effect of a thyroid nodule ultrasonic image semantic probability heat map caused by limited receptive field expansion ability of a deep learning network ina forward propagation step.
Owner:HANGZHOU CHUANGYING HEALTH MANAGEMENT CO LTD
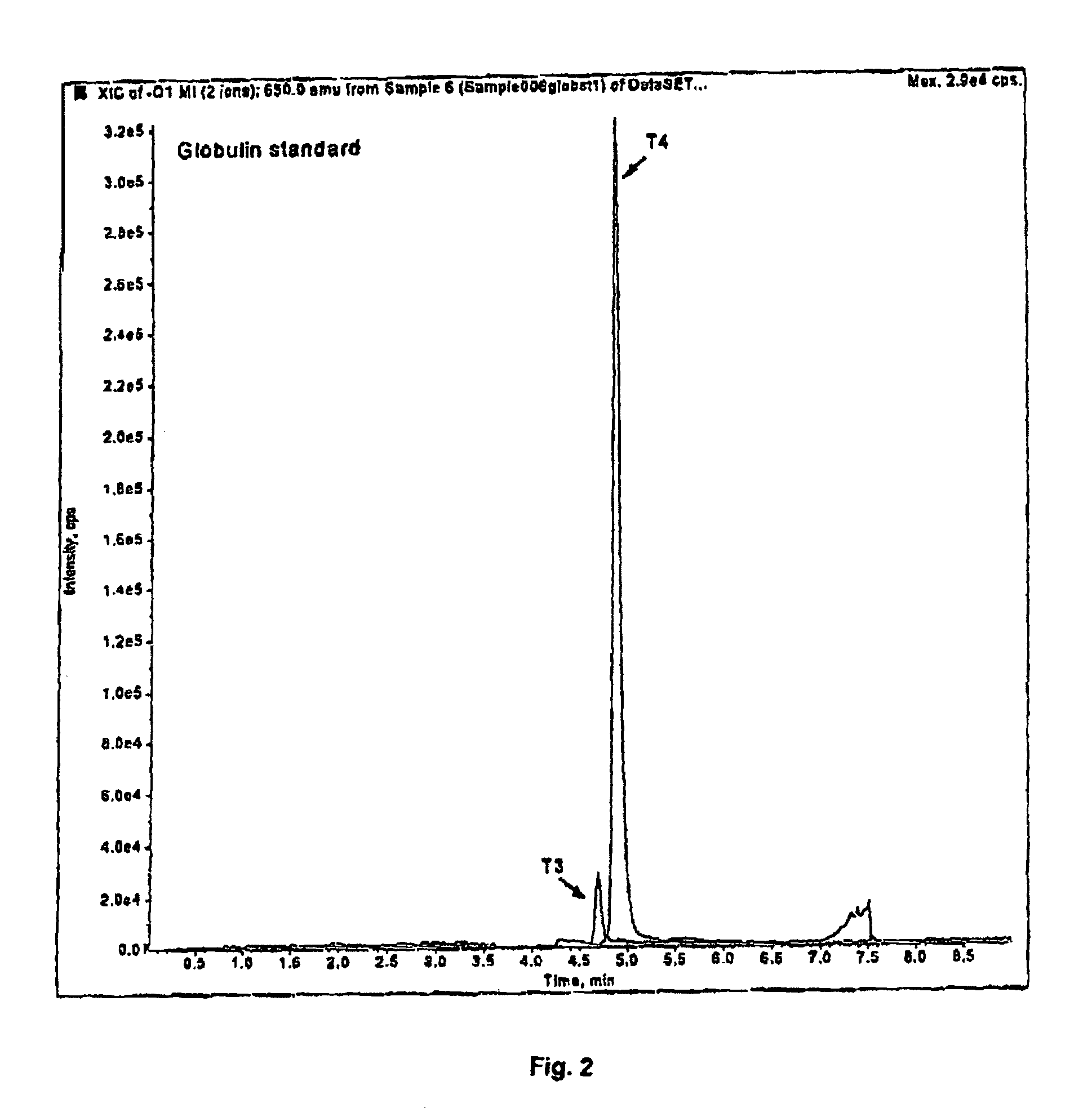
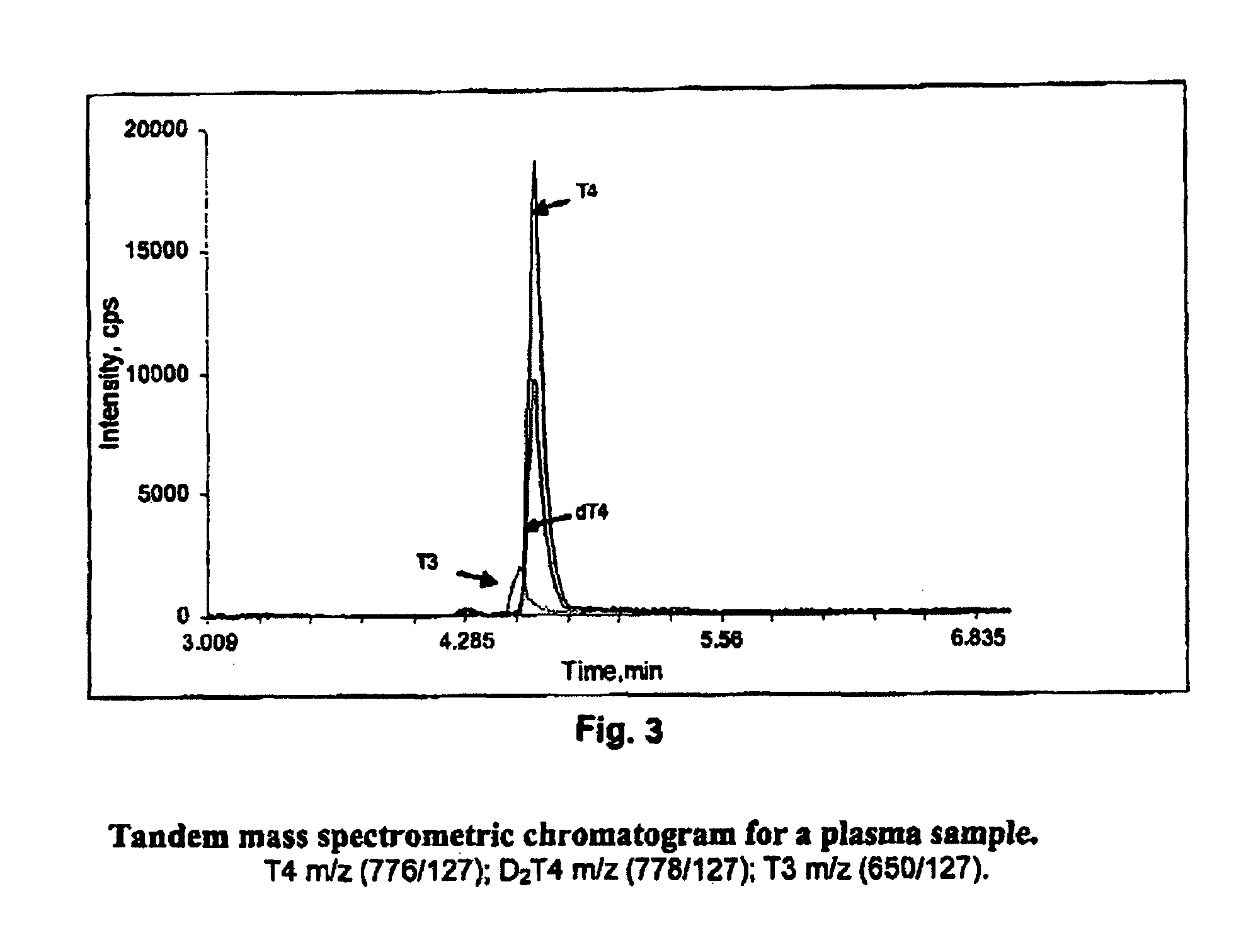
Thyroid hormone analysis by mass spectrometry
ActiveUSRE44401E1Fast and accurate methodFast and accurate of and quantificationAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurementThyroid hormonesMedicine
Methods, systems and kits for the simultaneous or sequential analysis of one or more hormones by mass spectrometry are disclosed. The methods require minimal sample size and minimal preparation time. The methods include ionizing the hormones and analyzing the hormones by mass spectrometry. In addition, methods, systems and kits for the simultaneous or sequential analysis of thyroid hormones are disclosed including ionization of the thyroid hormones in the negative mode using an electrospray source.
Owner:GEORGETOWN UNIV
Thyroid cell pathological section malignant region detection method based on deep learning
ActiveCN112508850AImprove work efficiencyReduce workloadImage enhancementImage analysisPrediction probabilityThyroid cell
The invention discloses a thyroid cell pathological section malignant region detection method based on deep learning. The method mainly comprises the following steps: performing pathological section on thyroid cells; carrying out digital processing on the image of the pathological section on a microscope, and smearing with different coloring agents to obtain a colored pathological section; cuttingthe complete pathological section into dices with proper sizes as the input of a deep neural network model; screening out invalid dices of the pathological sections; carrying out benign and malignantclassification on the pathological sections subjected to slicing and preliminary screening by adopting a weakly supervised learning method; constructing a random forest-based machine learning methodby utilizing a false positive removing scheme to remove false positive from a prediction result of benign and malignant classification; therefore, the detection accuracy can be further improved. A pathological section high-risk area display step includes normalizing the malignant prediction probability of each block and mapping the malignant prediction probability of each block into the original image to generate a thermodynamic diagram, and providing more intuitive visual display for pathologists.
Owner:PERCEPTION VISION MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
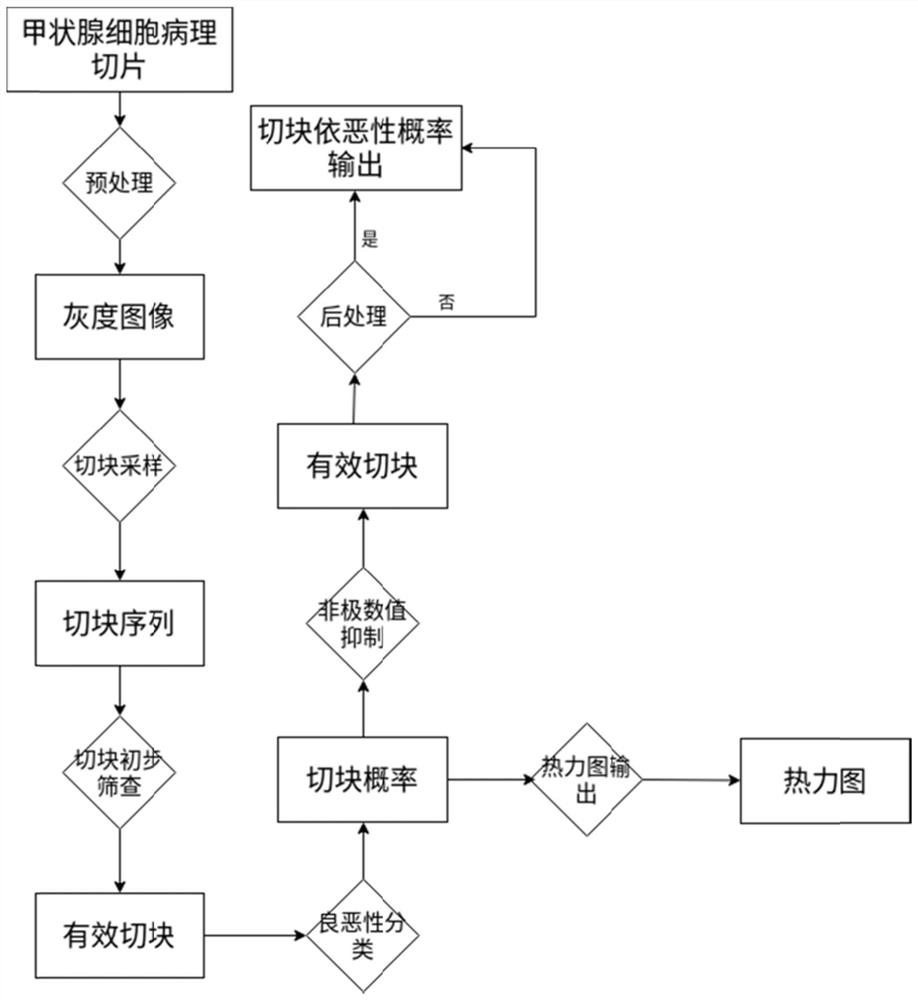
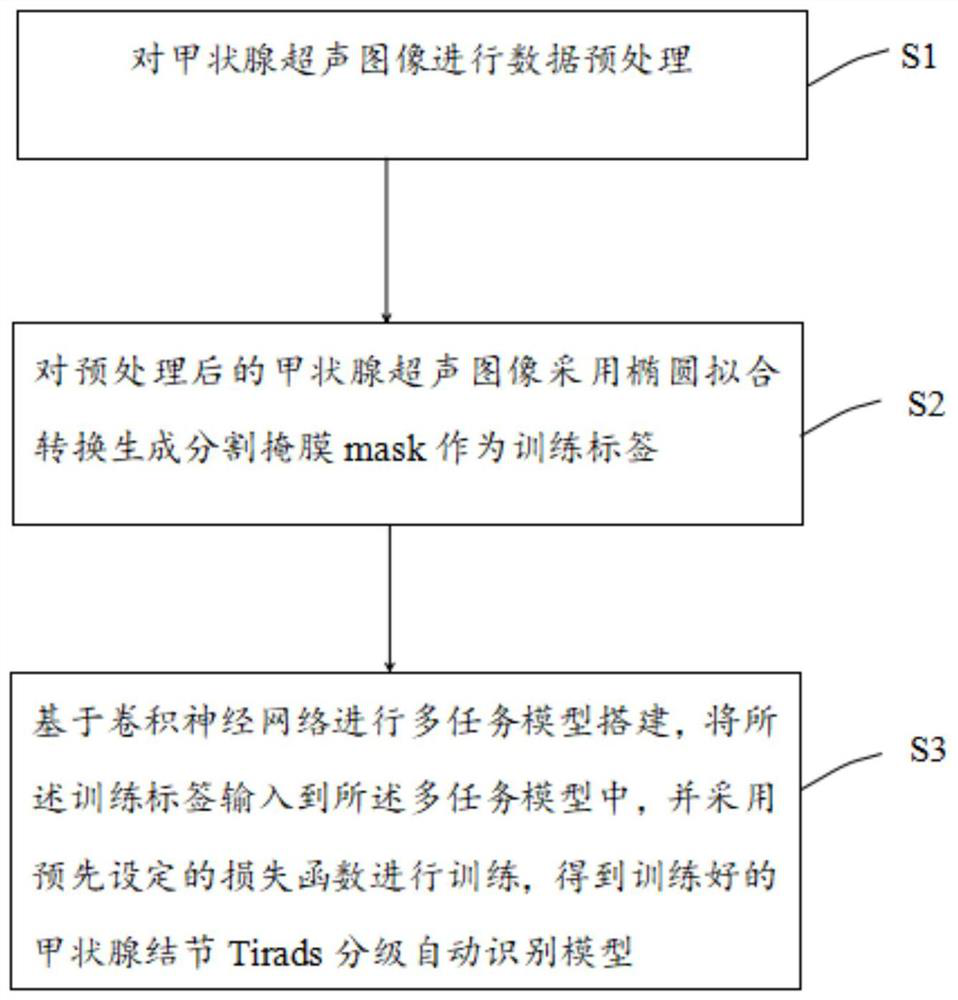
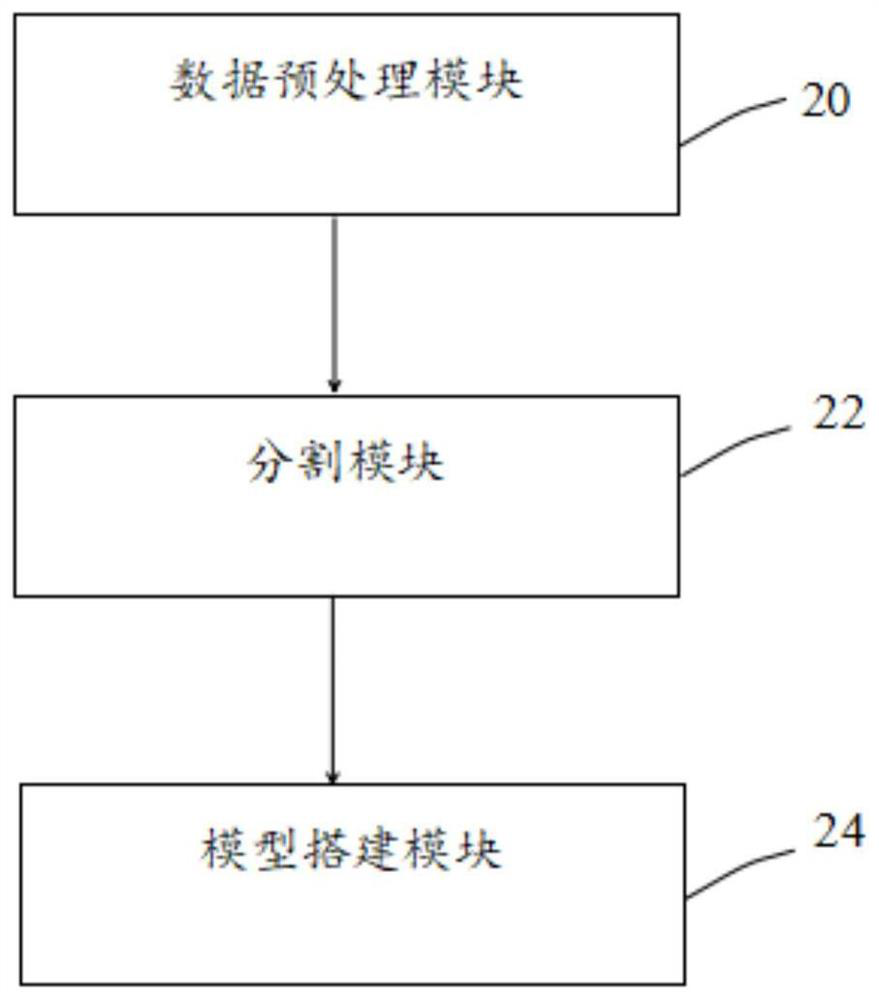
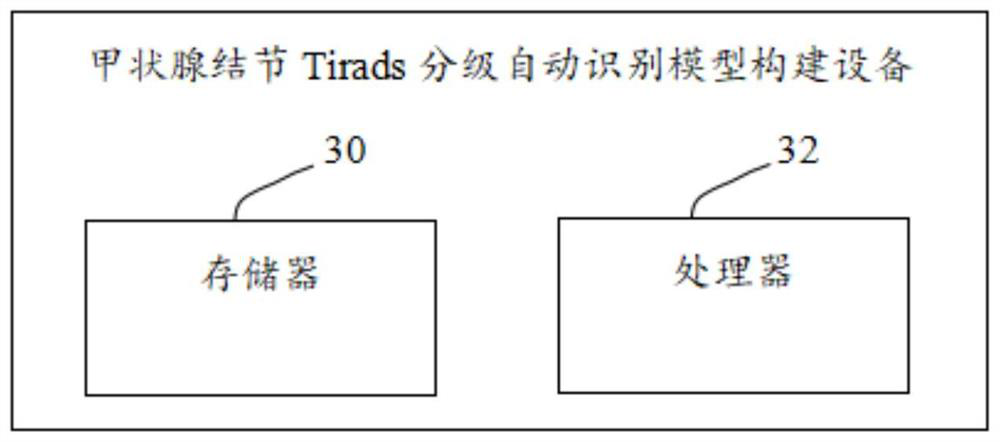
Thyroid nodule Tirads grading automatic identification model construction method and device
PendingCN112767355AImprove robustnessImprove generalization abilityImage enhancementImage analysisRadiologyComputer vision
The invention discloses a thyroid nodule Tirads grading automatic identification model construction method and device. The method comprises the following steps: S1, carrying out data preprocessing on a thyroid ultrasound image; s2, performing ellipse fitting conversion on the preprocessed thyroid ultrasound image to generate a segmentation mask as a training label; and S3, building a multi-task model based on a convolutional neural network, inputting the training label into the multi-task model, and performing training by adopting a preset loss function to obtain a trained thyroid nodule Tirads grading automatic identification model. According to the invention, in thyroid nodule TI-RADS grading automatic identification, the latest convolutional neural network framework is used for carrying out automatic identification tasks on thyroid ultrasound images in an end-to-end mode, TI-RADS grading is completed, detection work can be completed in the early stage of thyroid cancer, and therefore expensive work such as puncture does not need to be used; and a doctor is assisted to complete thyroid cancer screening.
Owner:北京小白世纪网络科技有限公司
Thyroid nodule invasiveness prediction method based on target detection
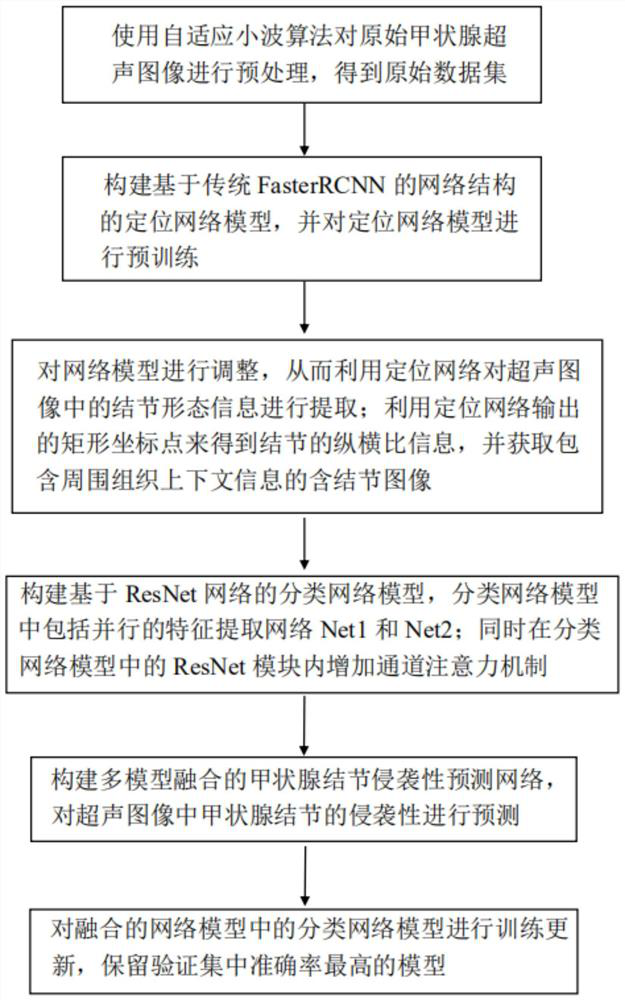
ActiveCN112927217AImprove reliabilityAchieve high-precision nodule diagnosis and predictionImage enhancementImage analysisOriginal dataNetwork model
The invention belongs to the technical field of image processing, and particularly relates to a thyroid nodule invasiveness prediction method based on target detection. The method comprises the following steps: S1, preprocessing a thyroid ultrasound image obtained clinically to obtain an original data set; S2, constructing a positioning network model of a network structure based on a traditional Faster RCNN, and pre-training the positioning network model; S3, extracting nodule form information in the ultrasonic image by using a positioning network, and obtaining aspect ratio information of the nodules and context information of gland tissues; S4, constructing a classification network model; S5, establishing a multi-model fusion thyroid nodule invasiveness prediction network, and predicting the thyroid nodule invasiveness in the ultrasonic image; and S6, training and updating the classification network model in the fused network model, and storing the model with the highest accuracy in the verification set. According to the method, end-to-end full-automatic auxiliary diagnosis can be achieved, and the defects that a traditional method is insufficient in accuracy and low in detection rate are overcome.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIVERSITY
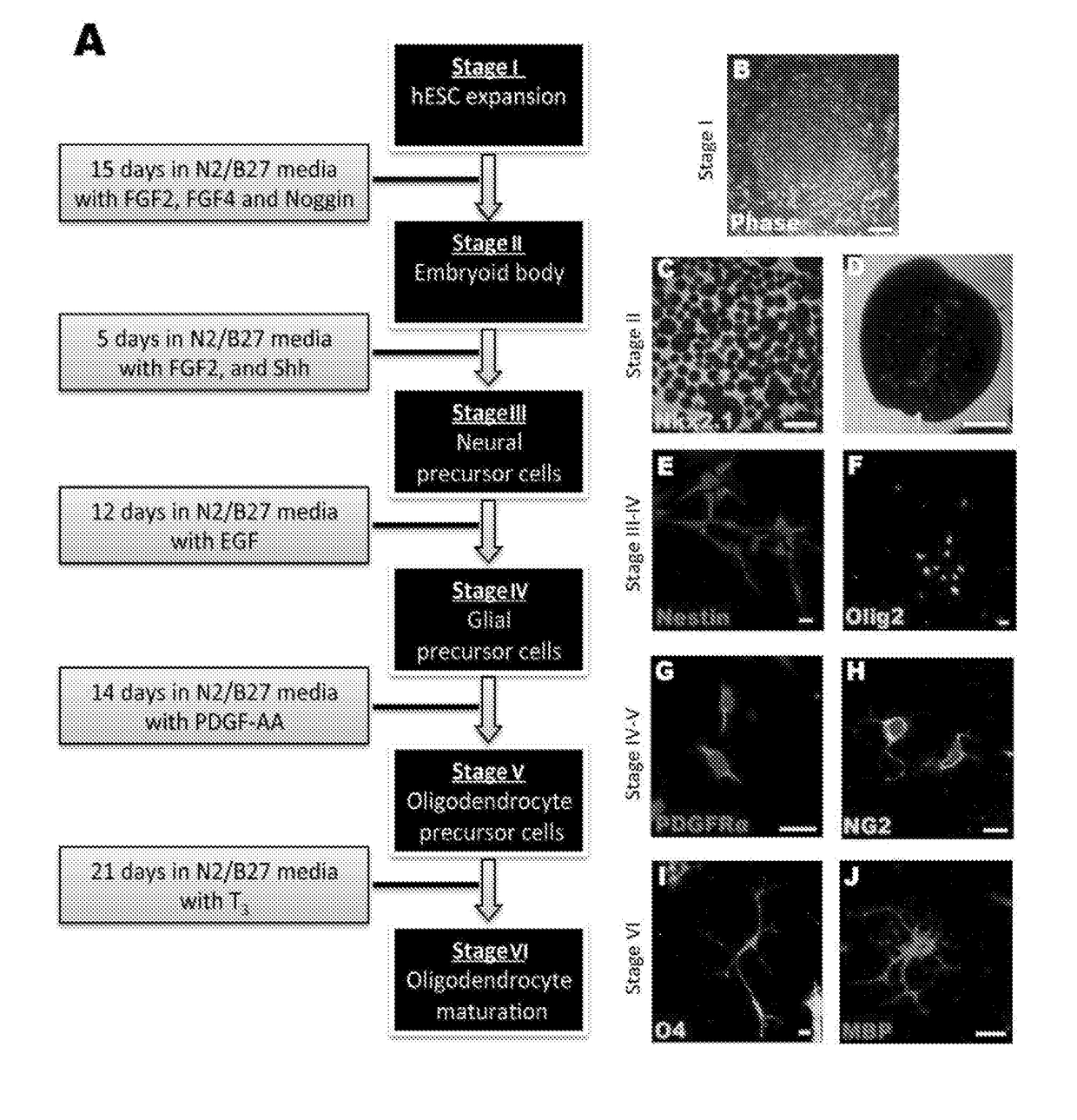
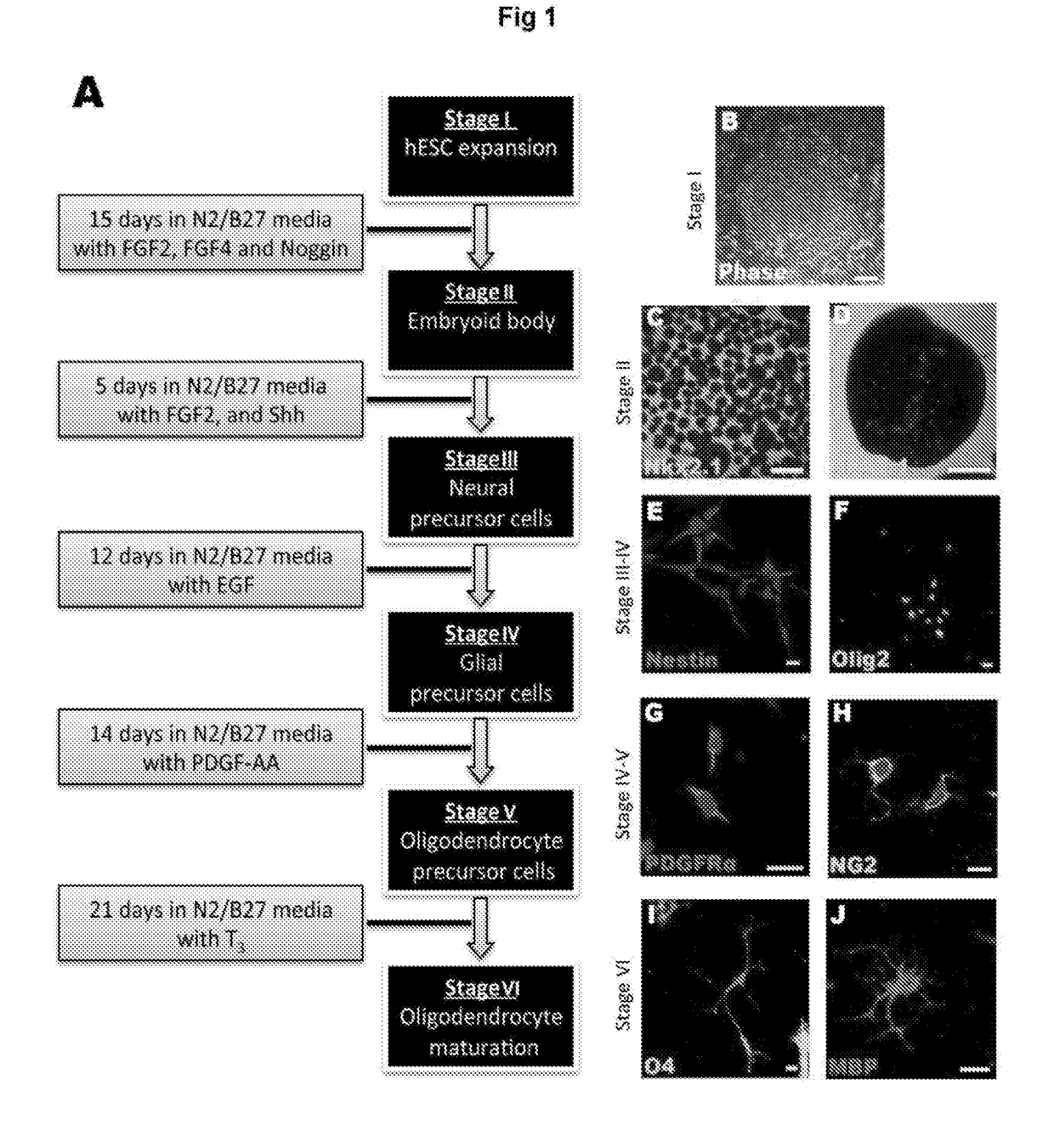
Improvements in Oligodendroglial Cell Culturing Methods and in Methods for Treating Neurodegenerative Disorders by Using Thyroid Hormones or Analogues
ActiveUS20170342380A1Easy to understandExtended shelf lifeNervous system cellsUnknown materialsDemyelinating DisorderThyroid hormones
The present invention relates to methods of treating or ameliorating certain neurodegenerative disorders (namely, dysmyelinating and demyelinating disorders) in patients in need of such treatment or amelioration. The invention provides methods of treating or ameliorating a patient in need of such treatment and includes the administration to the patient of: (a) thyroid hormones or thyroid hormone analogues; (b) cell replacement therapies involving the use of homogenous Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells derived from embryonic stem cells that have been treated with thyroid hormones or thyroid hormone analogues; (c) gene therapy to correct mutated genes in vivo; or (d) a combination of two or more of (a), (b) and (c). The invention also provides compositions and formulations of thyroid hormones and thyroid hormone analogues for use in treating or ameliorating such disorders.
Owner:NEUORPHAN PTY LTD
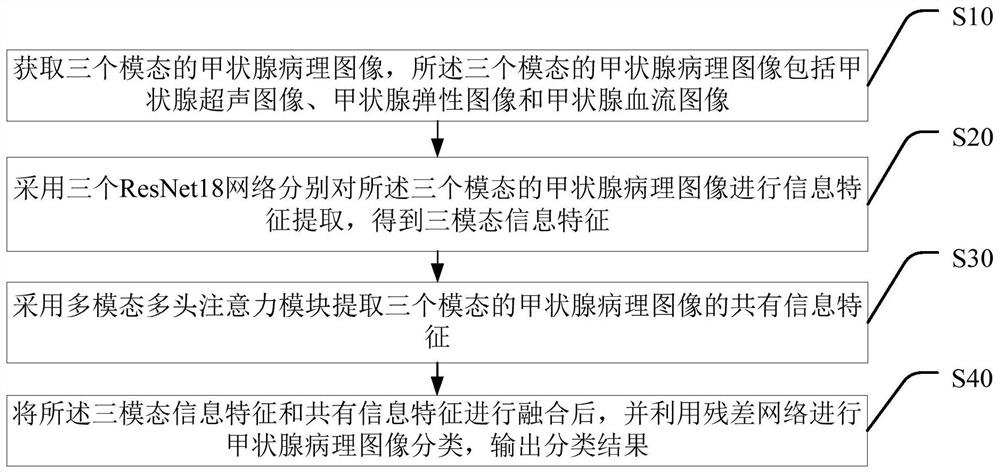
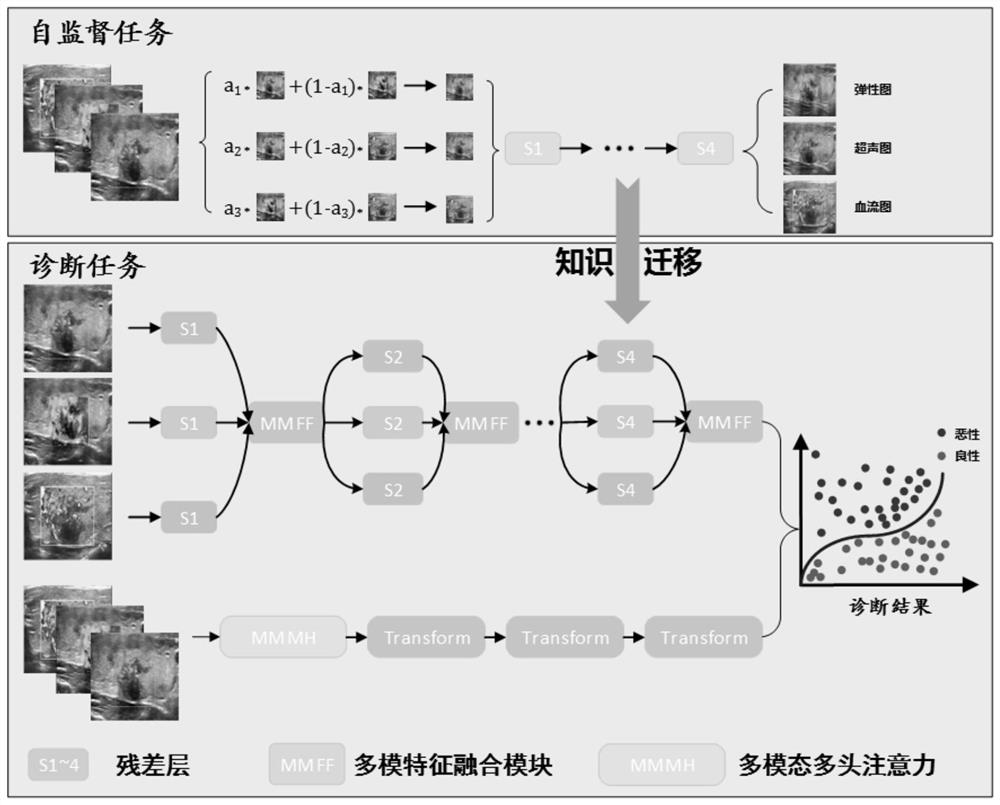
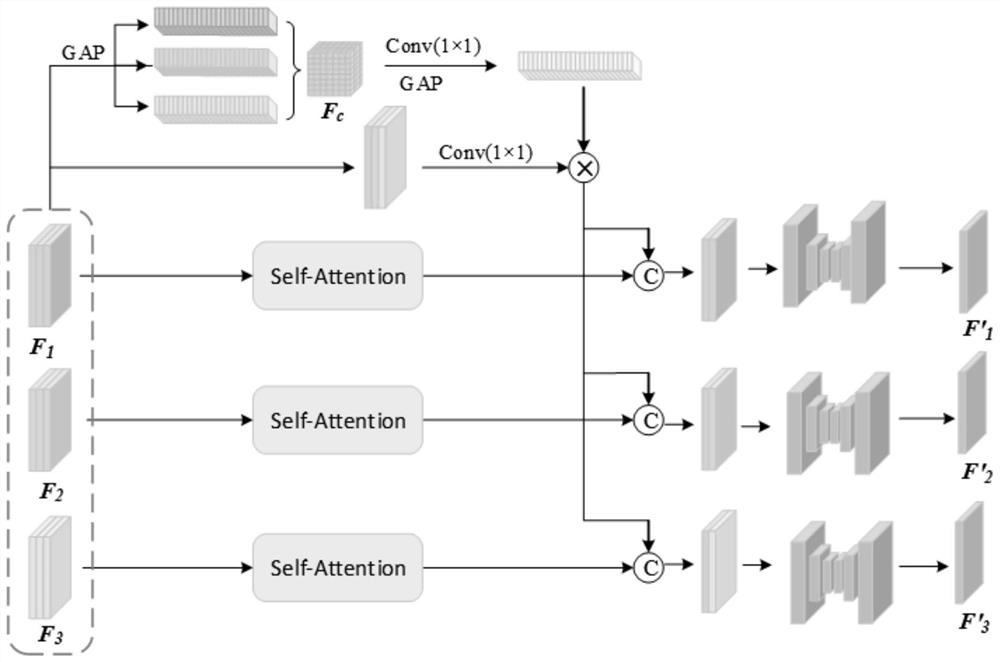
Thyroid tumor image classification method based on multiple modes and terminal equipment
PendingCN114332040AAccurate classificationReduce the differenceImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature extractionRadiology
The invention discloses a thyroid pathology image classification method and terminal equipment based on multiple modalities, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the information feature extraction of thyroid pathology images of three modalities through employing three ResNet18 networks, obtaining three-modal information features, and carrying out the classification of thyroid pathology images of three modalities; the thyroid pathology images in the three modes comprise a thyroid ultrasound image, a thyroid elasticity image and a thyroid blood flow image; adopting a multi-mode multi-head attention module to extract common information features of the thyroid pathology images of the three modes; and fusing the three-mode information features and the common information features, performing thyroid pathology image classification by using a residual network, and outputting a classification result. The designed multi-modal thyroid pathology image classification method is verified on a multi-modal thyroid ultrasound data set provided by a cooperative research unit, and a result proves that the thyroid pathology images can be accurately classified by the method, so that rapid and accurate assistance is provided for diagnosis of thyroid cancer by an ultrasound department doctor.
Owner:华中科技大学协和深圳医院
Thyroid nodule analysis system based on elastic ultrasonic imaging
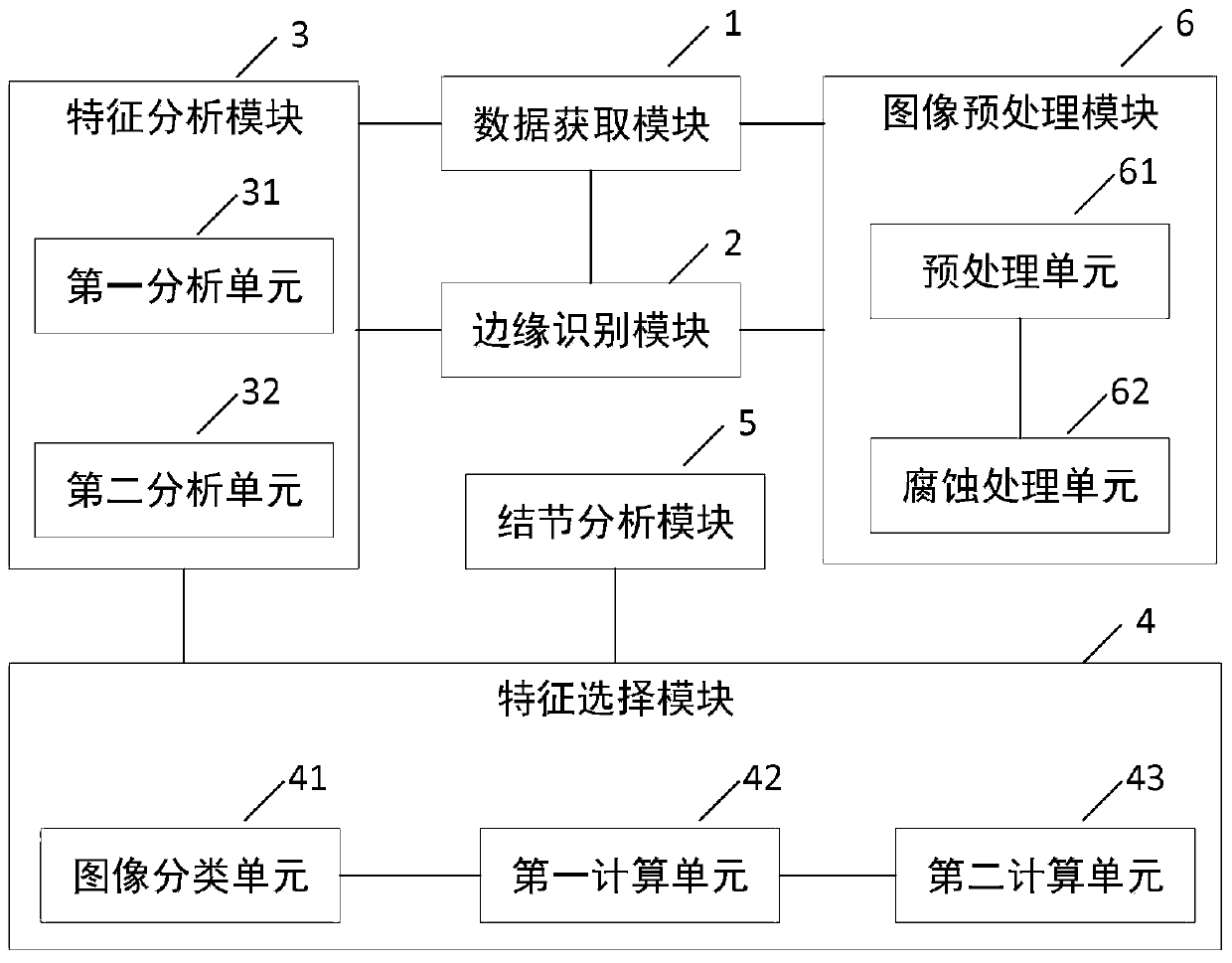
The invention provides a thyroid nodule analysis system based on elastic ultrasonic imaging, and relates to the technical field of computer-aided analysis. The system comprises: a data obtaining module which carries out thyroid nodule selection on an obtained elastic ultrasonic image, and obtains a thyroid nodule image; an edge recognition module used for carrying out edge recognition on the thyroid nodule image to obtain a nodule edge image; a feature analysis module used for respectively carrying out feature analysis on the thyroid nodule image and the nodule edge image to obtain a pluralityof image feature parameters; a feature selection module used for respectively calculating inter-class distances of the image feature parameters and adding the inter-class distances into a one-class interval sequence; and a nodule analysis module used for extracting the image feature parameters of the preset number of inter-class distances sorted in the front, and training to obtain a thyroid nodule state recognition model for subsequent thyroid nodule state recognition by taking the image characteristic parameters as input and the nodule state as output. The thyroid nodule analysis system hasthe advantage of effectively improving thyroid nodule state recognition accuracy.
Owner:上海深至信息科技有限公司
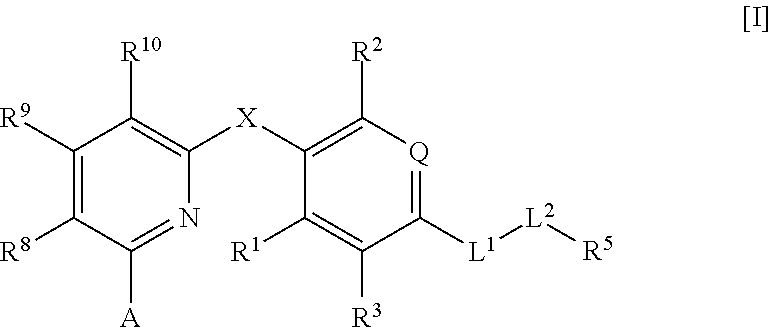
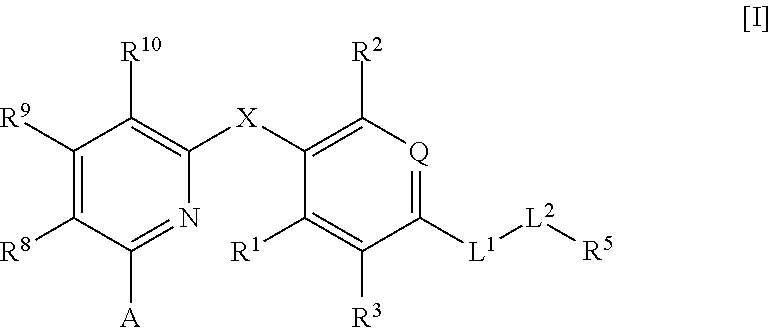
Thyroid hormone β receptor agonist
Owner:MITSUBISHI TANABE PHARMA CORP
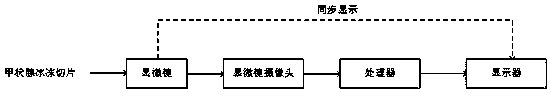
Thyroid frozen section diagnosis method and system
PendingCN110763677AShorten diagnostic timeImprove accuracyPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscope cameraRadiology
The invention relates to a thyroid frozen section diagnosis method, and the method is suitable for a thyroid frozen section diagnosis system. The method comprises the following steps that S10, a microscope camera acquires a pathological image of a thyroid frozen section under a microscope and sends the pathological image to a processor; S20, the processor preprocesses the pathological image, so that the HSV color space of the pathological image is consistent with a set threshold value; S30, the processor detects the preprocessed pathological image, determines the range of the tumor area, outputs the pathological image marked with the range of the tumor area, or judges the yin and yang of the tumor in the pathological image, and outputs the pathological image marked with the negative and positive of the tumor; S40, the display receives and displays the marked pathological image from the processor. According to the detection method provided by the invention, the expenditure of a high scanner is saved, the diagnosis time in thyroid surgery is shortened, the surgery time is shortened, and the convenience is brought to rapid and accurate treatment.
Owner:杭州迪英加科技有限公司
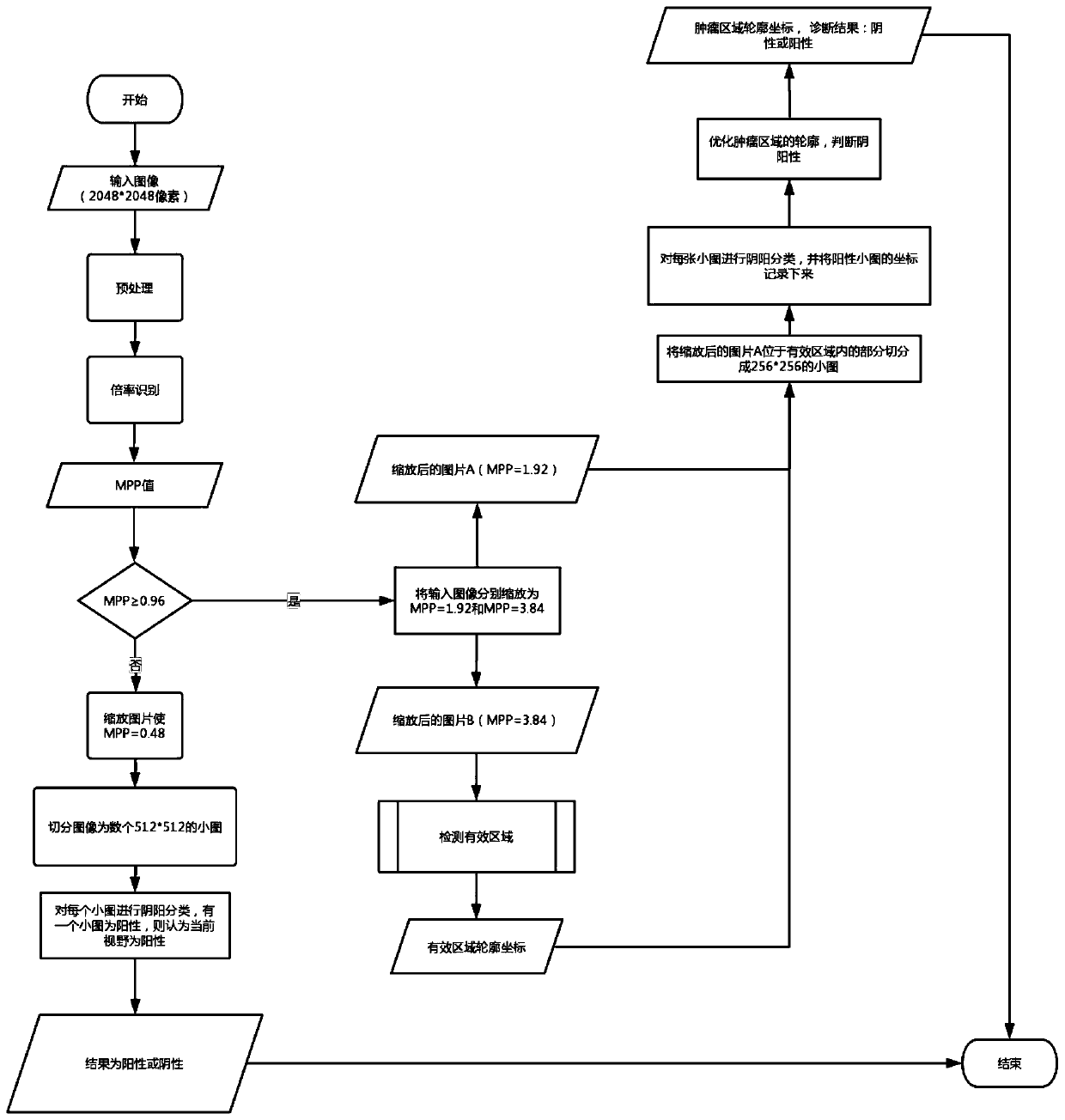
Method and device for automatically diagnosing benign and malignant thyroid nodules
PendingCN112820399AImprove the effect of automatic classificationImage enhancementImage analysisMalignancyNeural network nn
The invention discloses a method and a device for automatically diagnosing benign and malignant thyroid nodules. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, carrying out noise reduction preprocessing on an original thyroid ultrasound image; 2, performing data enhancement on the preprocessed thyroid ultrasound image; 3, the thyroid ultrasound image after data enhancement being respectively put into three convolutional neural network models which are constructed through ResNet, DenseNet or ResNext in advance for training; and 4, carrying out model integration on images trained by different models in the step 3. According to the method, the problem that the automatic classification effect of benign and malignant thyroid nodules is poor is solved, the deep learning image automatic recognition technology is applied, the latest framework is used for extracting image features, the automatic classification task of benign and malignant thyroid nodules is completed in an end-to-end mode, and meanwhile high accuracy is guaranteed.
Owner:北京小白世纪网络科技有限公司
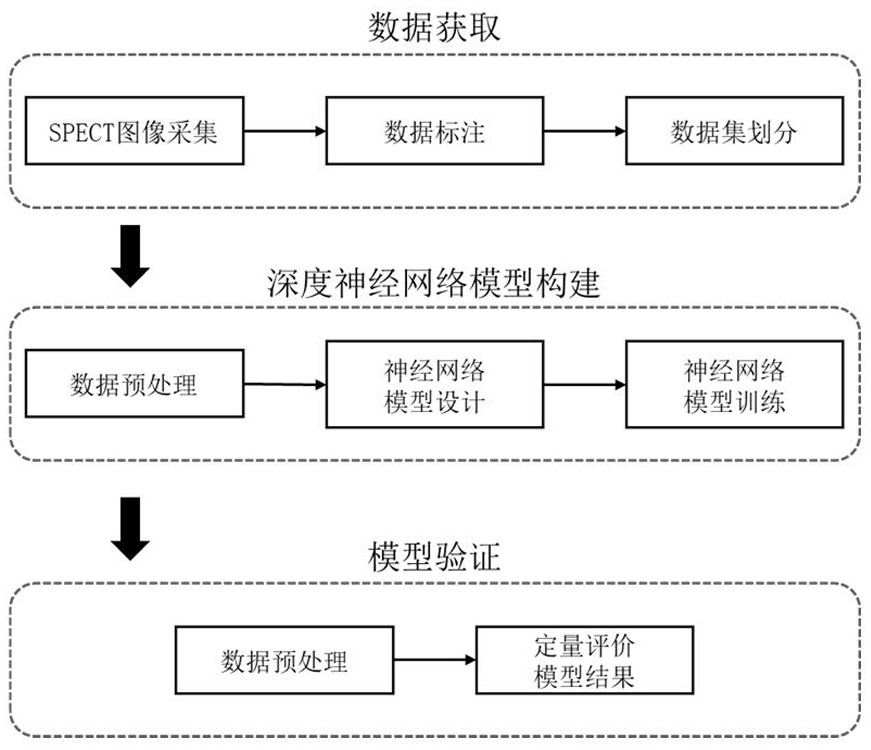
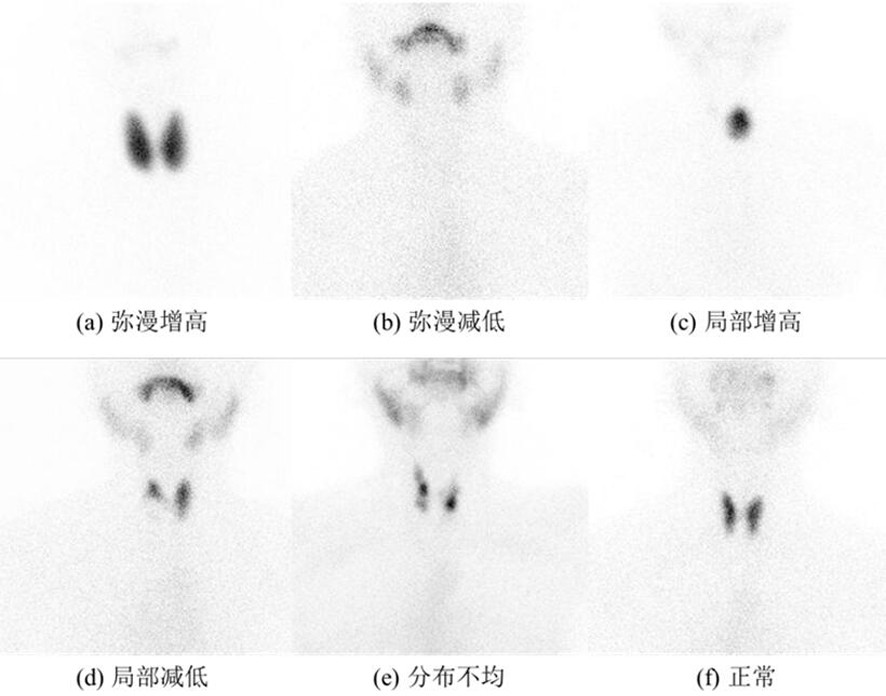
SPECT thyroid imaging intelligent recognition method based on deep neural network
ActiveCN112669320AReduce manual operationsConsistent resultsImage analysisNeural learning methodsData acquisitionNeural network nn
The invention discloses an SPECT thyroid imaging intelligent identification method based on a deep neural network, and relates to the technical field of image analysis and processing. The method comprises the following three steps: data acquisition, deep neural network model construction and model verification. According to the method, the SPECT thyroid image is processed by utilizing a computer technology, a doctor is replaced to complete identification of a thyroid shooting mode, manual operation can be reduced, a consistent processing result and considerable accuracy are achieved, and integration and large-scale application are facilitated.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
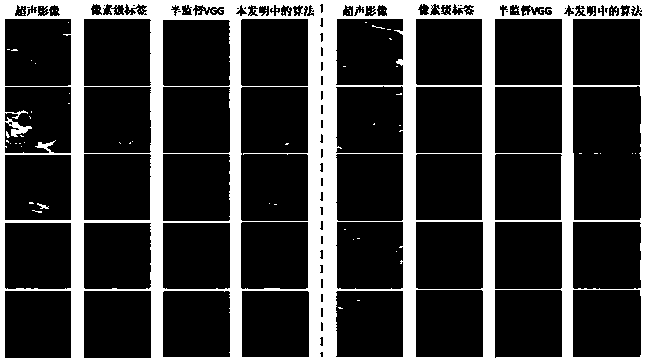
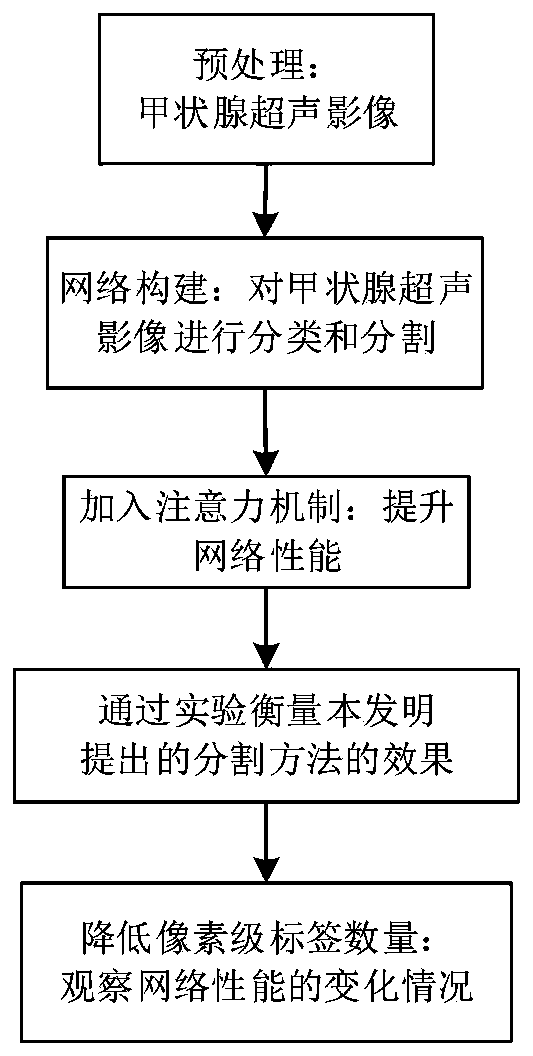
Thyroid nodule semi-supervised segmentation method based on attention mechanism
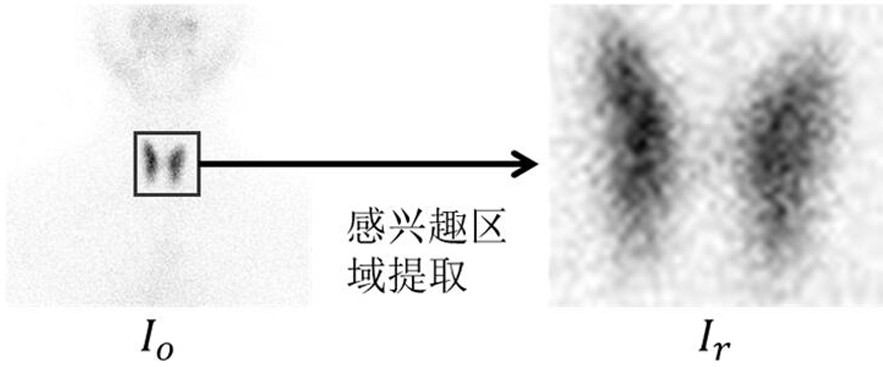
PendingCN110706793AAccurate predictionImprove classification performanceOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsPattern recognitionNodular thyroid
The invention discloses a thyroid nodule semi-supervised segmentation method based on an attention mechanism. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, carrying out preprocessing of a thyroid ultrasonic image, and removing an edge information region in the image; 2, constructing a semi-supervised segmentation neural network, performing classification and segmentation prediction tasks on theultrasonic image, and adjusting a network structure to adapt to a specific application scene; 3, adding an attention mechanism into the semi-supervised segmentation neural network to improve the network effect; 4, measuring the performances of a semi-supervised segmentation algorithm and an existing full-supervised segmentation algorithm in the field of thyroid nodule auxiliary diagnosis through an intersection-parallel ratio and a Dice coefficient; and 5, continuously reducing the number of the pixel-level labels, and observing the change condition of the network performance. According to theinvention, the thyroid nodule semi-supervised segmentation method based on an attention mechanism benefits from the semi-supervised effect of a small number of pixel-level labels while keeping the high segmentation performance of the semi-supervised segmentation model, learns the real benign and malignant characteristics of the nodules and improves the benign and malignant classification capacity.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
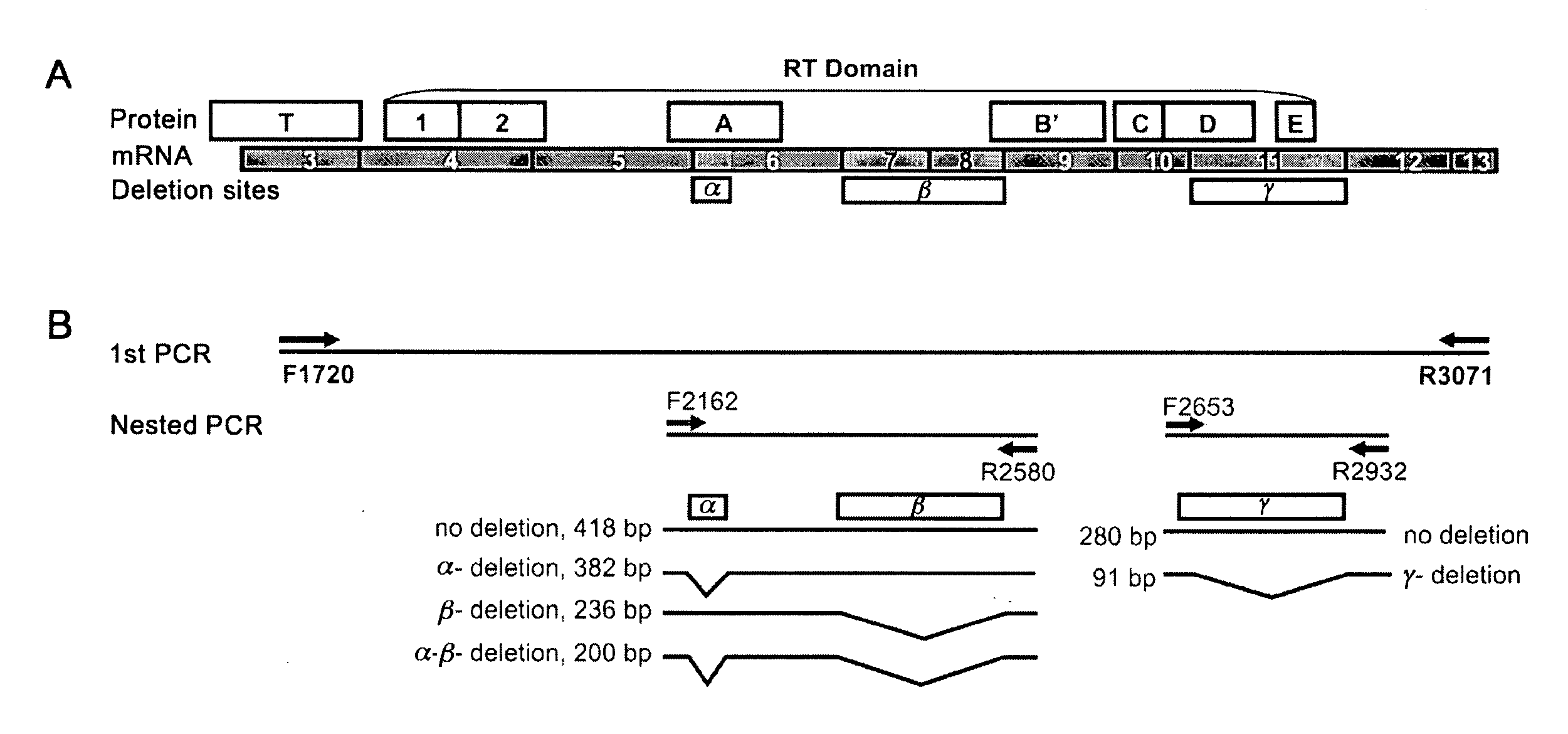
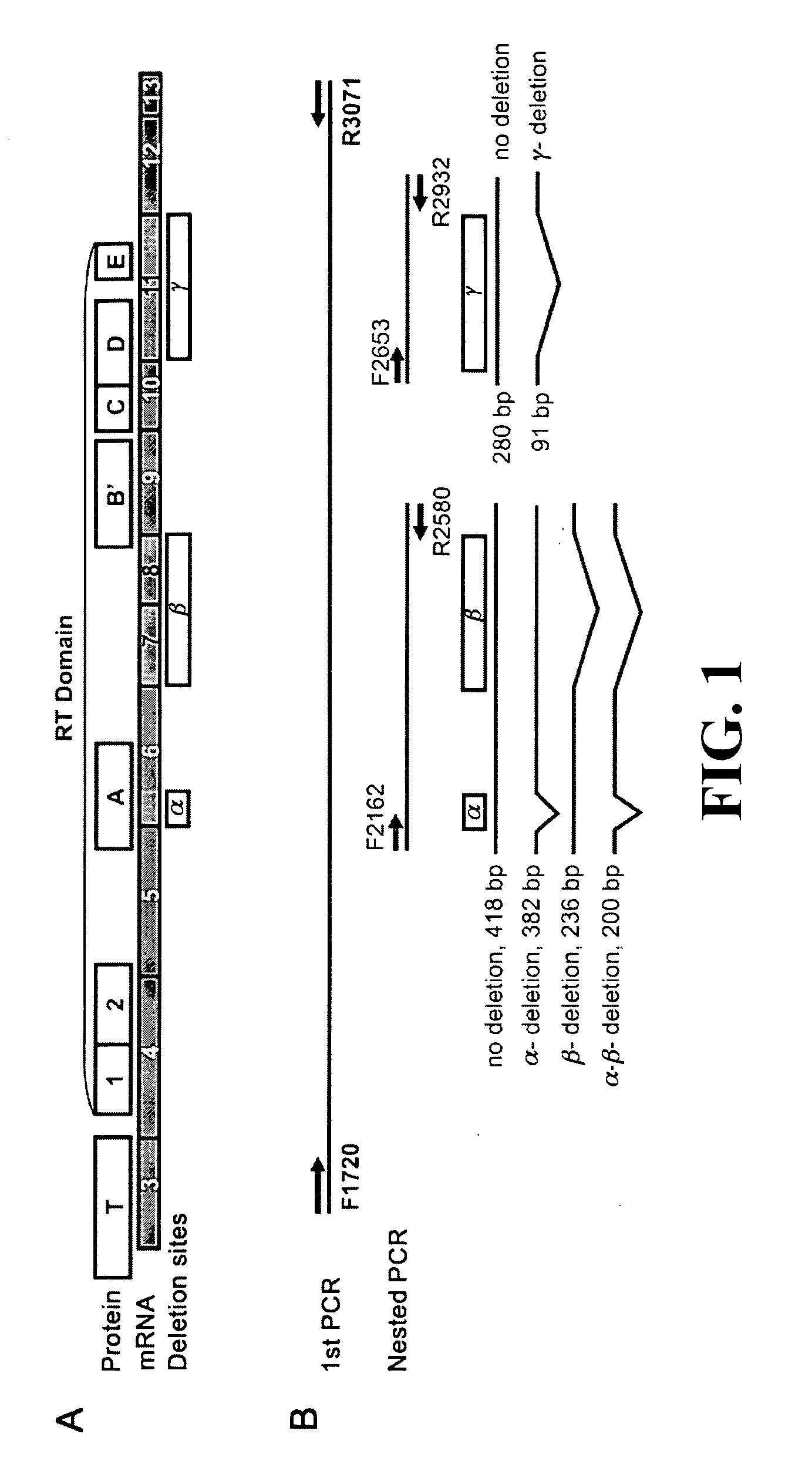
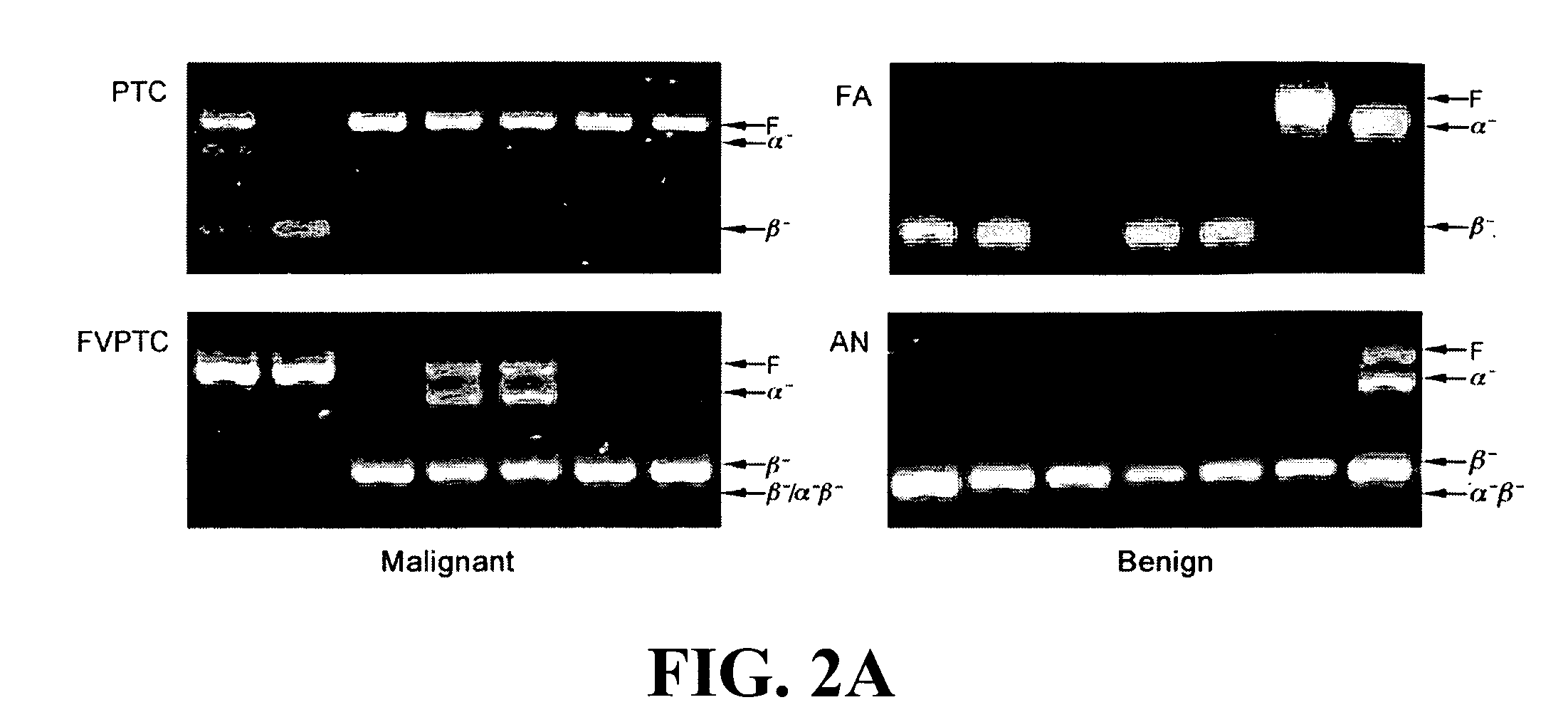
ALTERNATIVE SPLICE VARIANT PATTERNS OF HUMAN TELOMERASE REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE (hTERT) IN THYROID TUMORS TO DISTINGUISH BENIGN FROM MALIGNANT
This invention relates, e.g., to a method for determining if a thyroid tumor in a subject is malignant, comprising determining in a sample from the subject the amount of TERT (telomerase reverse transcriptase) mRNA which lacks the β sequence and the amount of TERT mRNA in the sample which comprises the β sequence, wherein a preponderance (e.g., at least about 55%) of TERT mRNA in the sample which comprises the β sequence indicates that the tumor is malignant, and wherein a preponderance of TERT mRNA which lacks the β sequence indicates that the tumor is not malignant.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
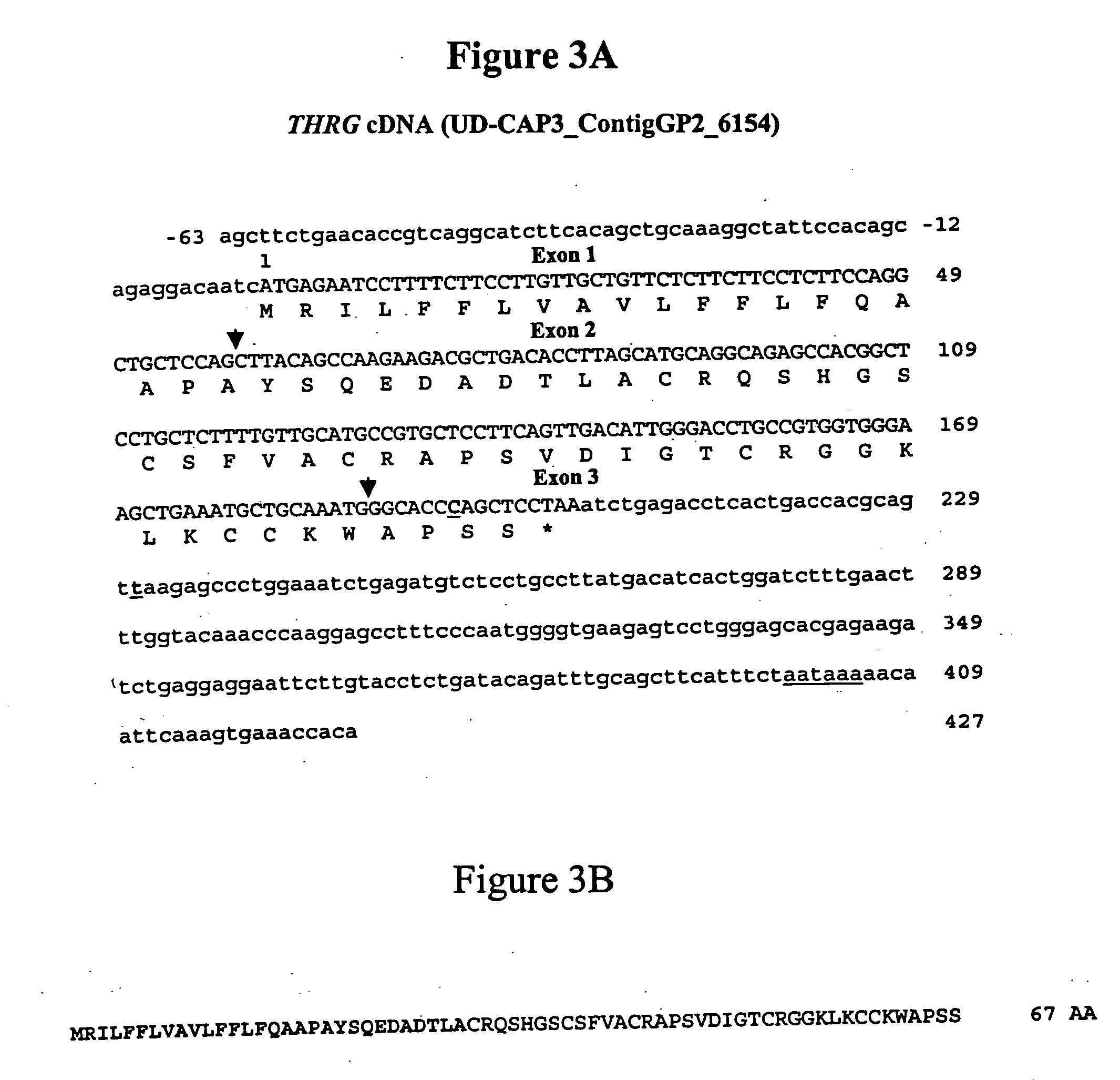
Molecular markers for identification of fat and lean phenotypes in chickens
InactiveUS20070092909A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementLean meatThyroid hormones
The invention provides molecular methods of screening chickens to determine those more likely to have a lean or fat phenotype by identifying the presence of at least one polymorphism in genetic material of a chicken in the thyroid hormone repressible gene (THRG) or its 3′ untranslated region (SEQ ID NO: 1) that is associated with a fat phenotype or a lean phenotype. The invention also provides methods of screening chickens to identify a polymorphism associated with a fat or lean phenotype. The invention further provides oligonucleotide probes and primers useful for detecting the polymorphisms associated with a fat or lean phenotype.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
Thyroid cancer pathological image classification method based on deep learning
ActiveCN112364920AEasy to classifySolve the problem of losing a large number of featuresCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesThyroid gland cancerThyroid pathology
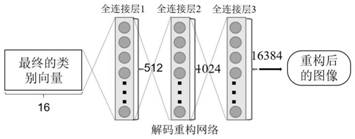
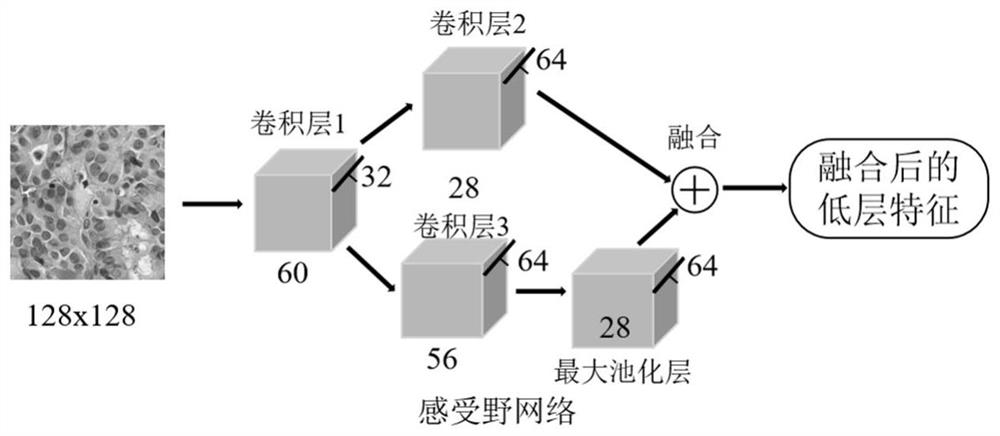
The invention discloses a thyroid cancer pathological image classification method based on deep learning, and mainly solves the problem of poor thyroid cancer pathological image classification effectof an existing method. According to the implementation scheme, the method comprises the following steps: reading a thyroid pathology image database, extracting low-level convolution and pooling features by a receptive field network, and fusing the features to obtain fused low-level features; extracting high-level features, namely predicted category vectors, from the fused low-level features through a capsule network; updating the category vector through a dynamic routing algorithm to obtain a final category vector, and calculating the modulus of the category vector through a compression activation function; carrying out image reconstruction on the vector with the maximum modulus value through a decoding reconstruction network; iteratively updating weights in the receptive field network andthe capsule network to complete model training; and finally, inputting a thyroid pathological image to be classified into the trained model to obtain a final classification result. The invention improves the classification accuracy of the thyroid cancer pathological images and can be used for computer-aided diagnosis.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Thyroid slice image classification model training method and device
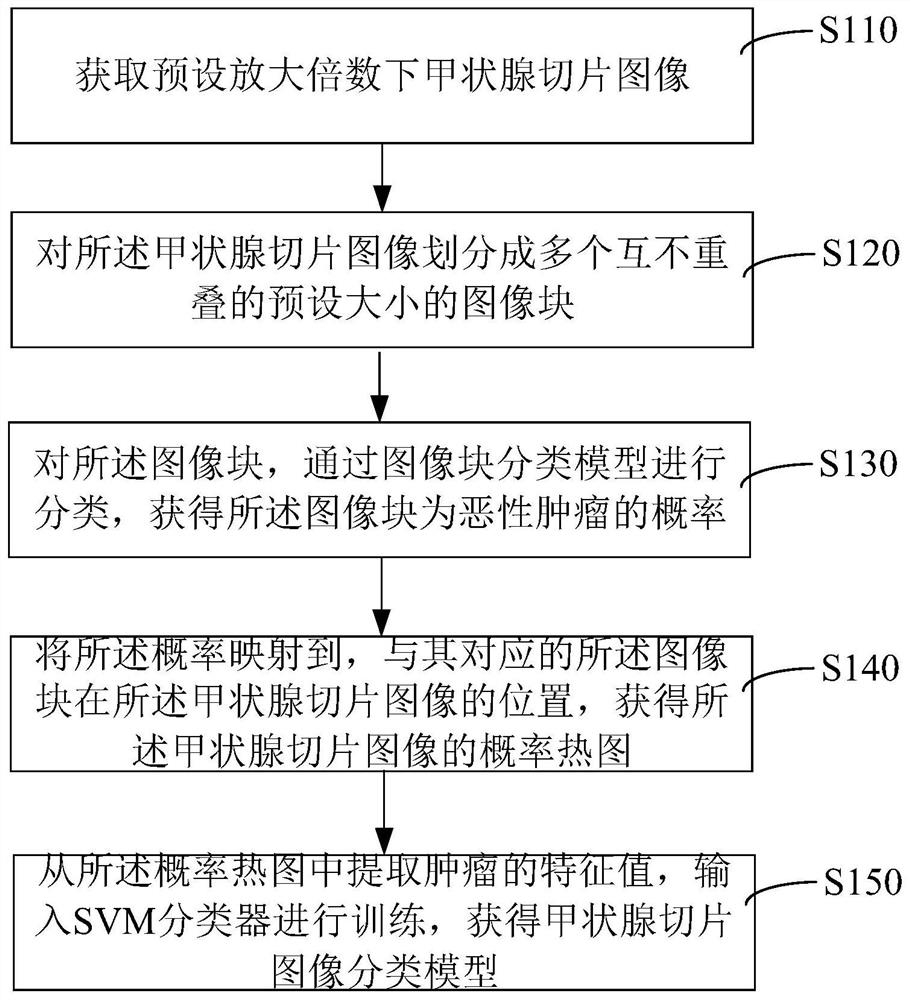
ActiveCN113139931AImprove accuracyImprove classification accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisHeat mapRadiology
The invention relates to a thyroid slice image classification model training method and device. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a thyroid slice image under a preset magnification; dividing the thyroid slice image into a plurality of image blocks which are not overlapped with each other and have a preset size; classifying the image blocks through an image block classification model to obtain the probability that the image blocks are malignant tumors; in the training process of the image block classification model, using an optimization loss function, and adjusting model parameters through a back propagation algorithm; mapping the probability to the position of the image block corresponding to the probability in the thyroid slice image to obtain a probability heat map of the thyroid slice image; and extracting a characteristic value of a tumor from the probability heat map, inputting the characteristic value into an SVM classifier for training, and obtaining a thyroid slice image classification model. By adopting the method, the model classification accuracy can be improved.
Owner:杭州迪英加科技有限公司
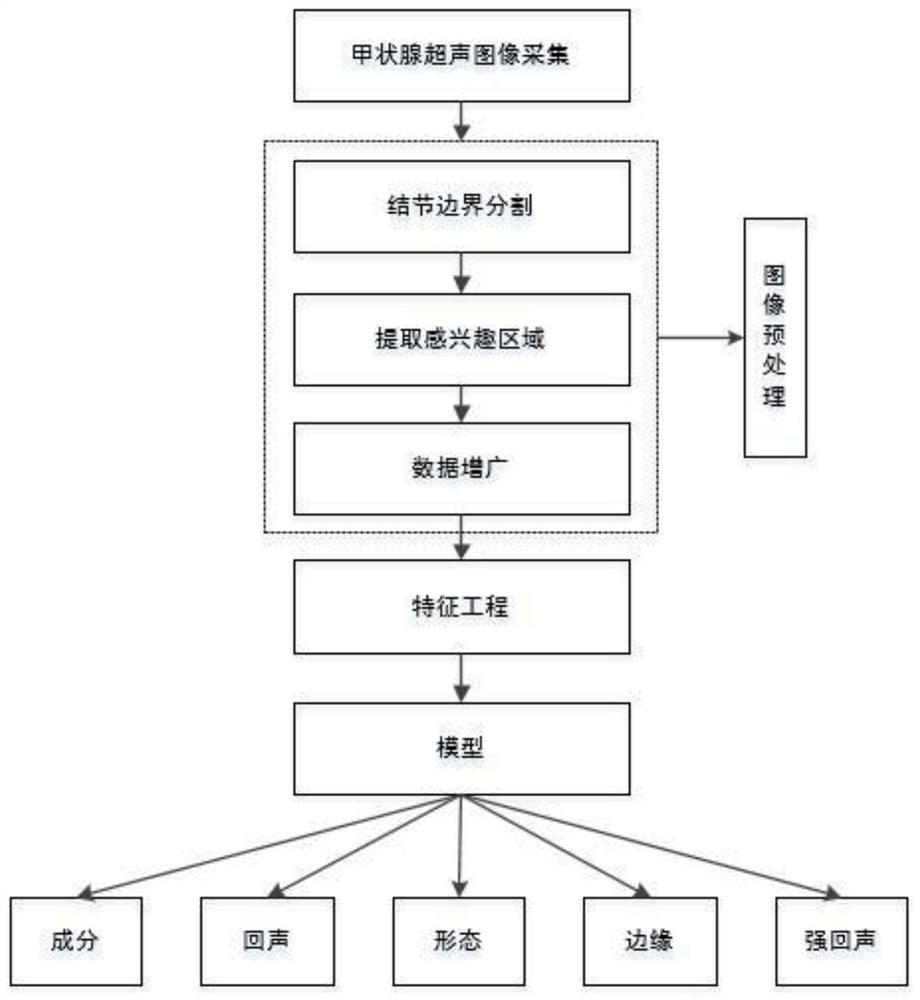
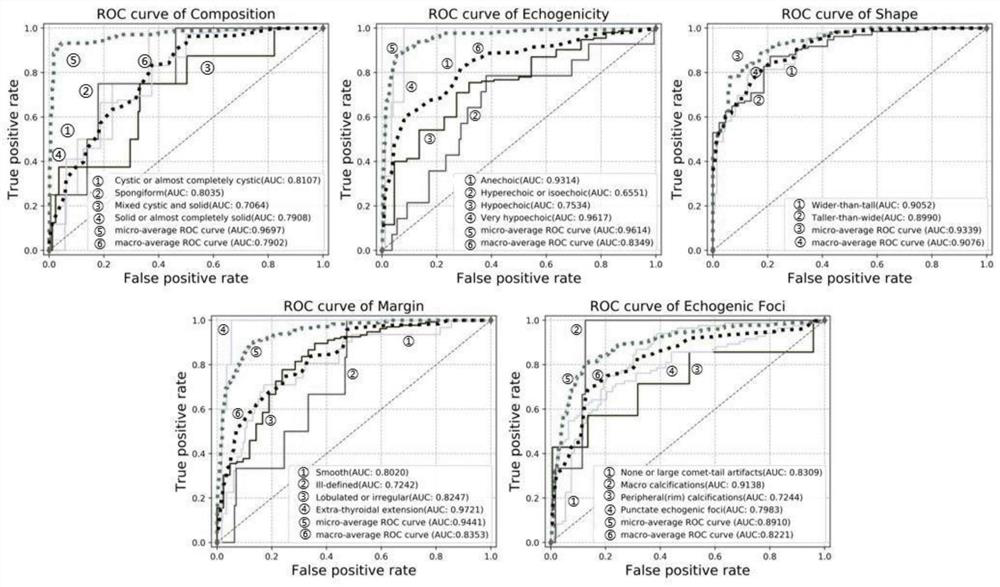
Integrated deep learning multi-label identification method based on TI-RADS
ActiveCN112270667AAccurate identificationAccurate identification of benign and malignantImage enhancementImage analysisMulti-label classificationRadiology
The invention relates to an integrated deep learning multi-label recognition method based on TI-RADS, and the method comprises the following steps: S1, preprocessing: carrying out the preprocessing ofa collected original thyroid ultrasound image, and the preprocessing comprises the segmentation of a nodule boundary of the original thyroid ultrasound image and the extraction of a nodule region ofinterest; S2, performing feature engineering, wherein the feature engineering is used for extracting geometrical features and texture features of the original thyroid ultrasonic image preprocessed inthe step S1; S3, building a model: performing feature fusion on the Effective Net model, the feature engineering and the FPN network model through a Concatenate function to obtain a deep learning model; and S4, inputting the original thyroid ultrasound image preprocessed in the step S1 and the geometrical characteristics and texture characteristics extracted in the step S2 into the deep learning model in the step S3, and outputting a multi-label classification result. The method has the advantages of being high in releasability and accurate in classification result.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com