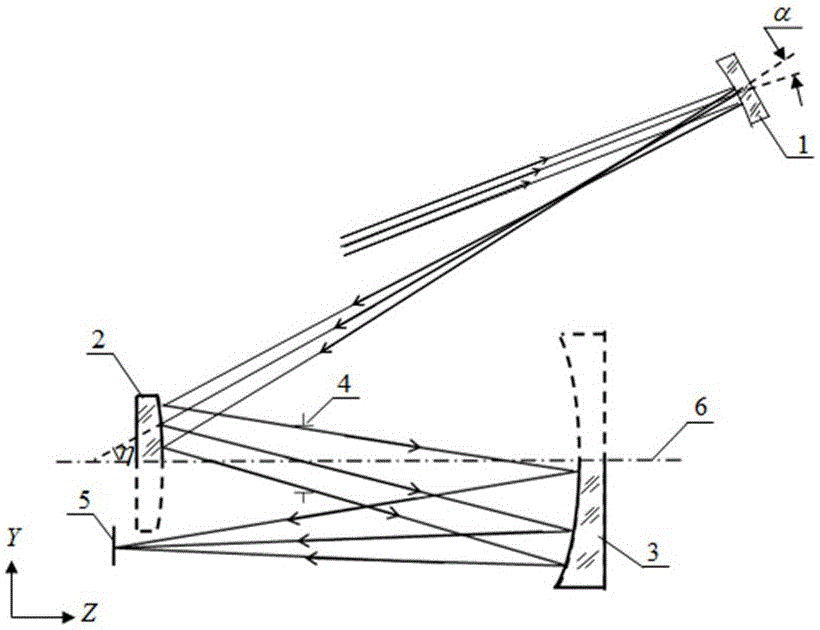
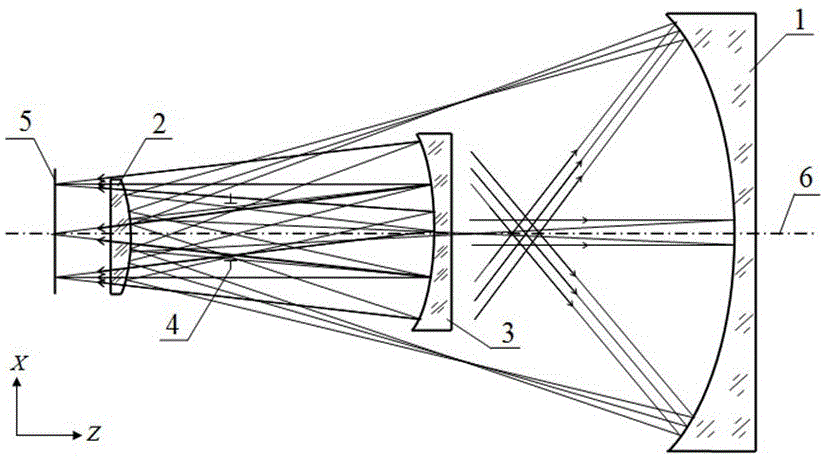
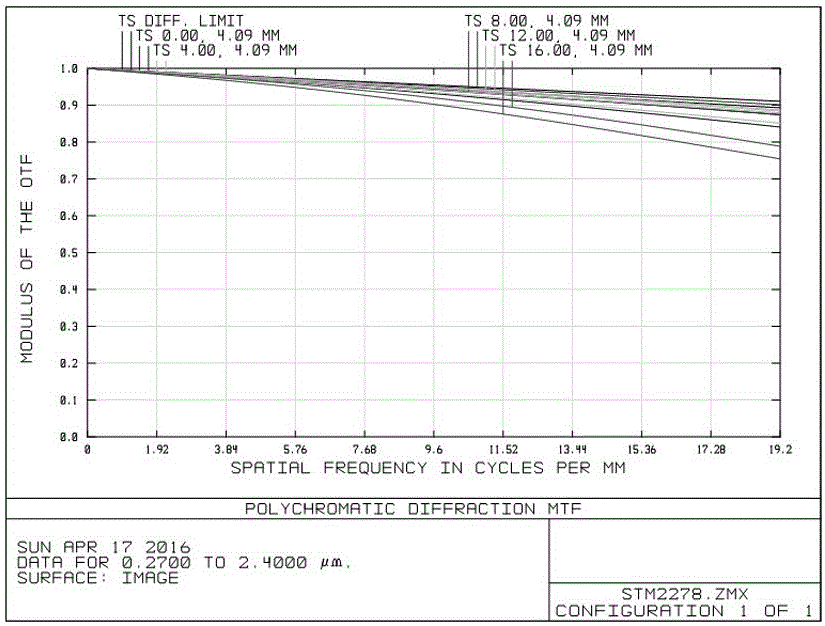
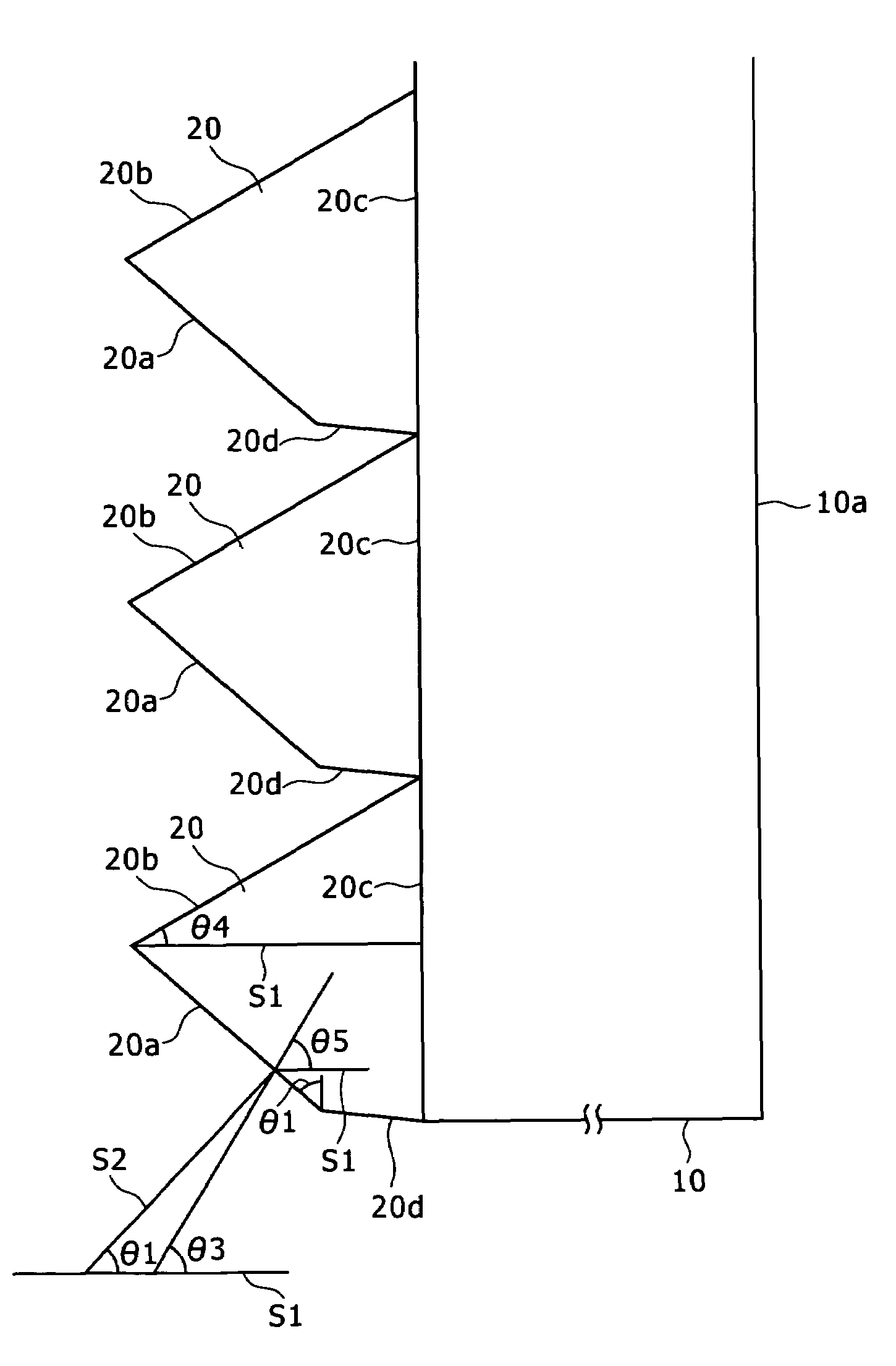
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
141results about How to "Suppress stray light" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
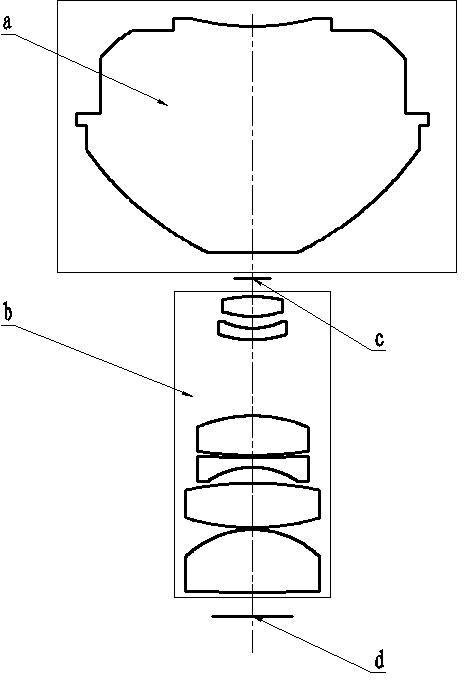
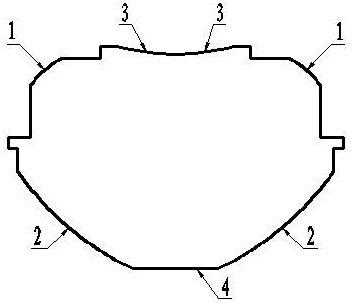
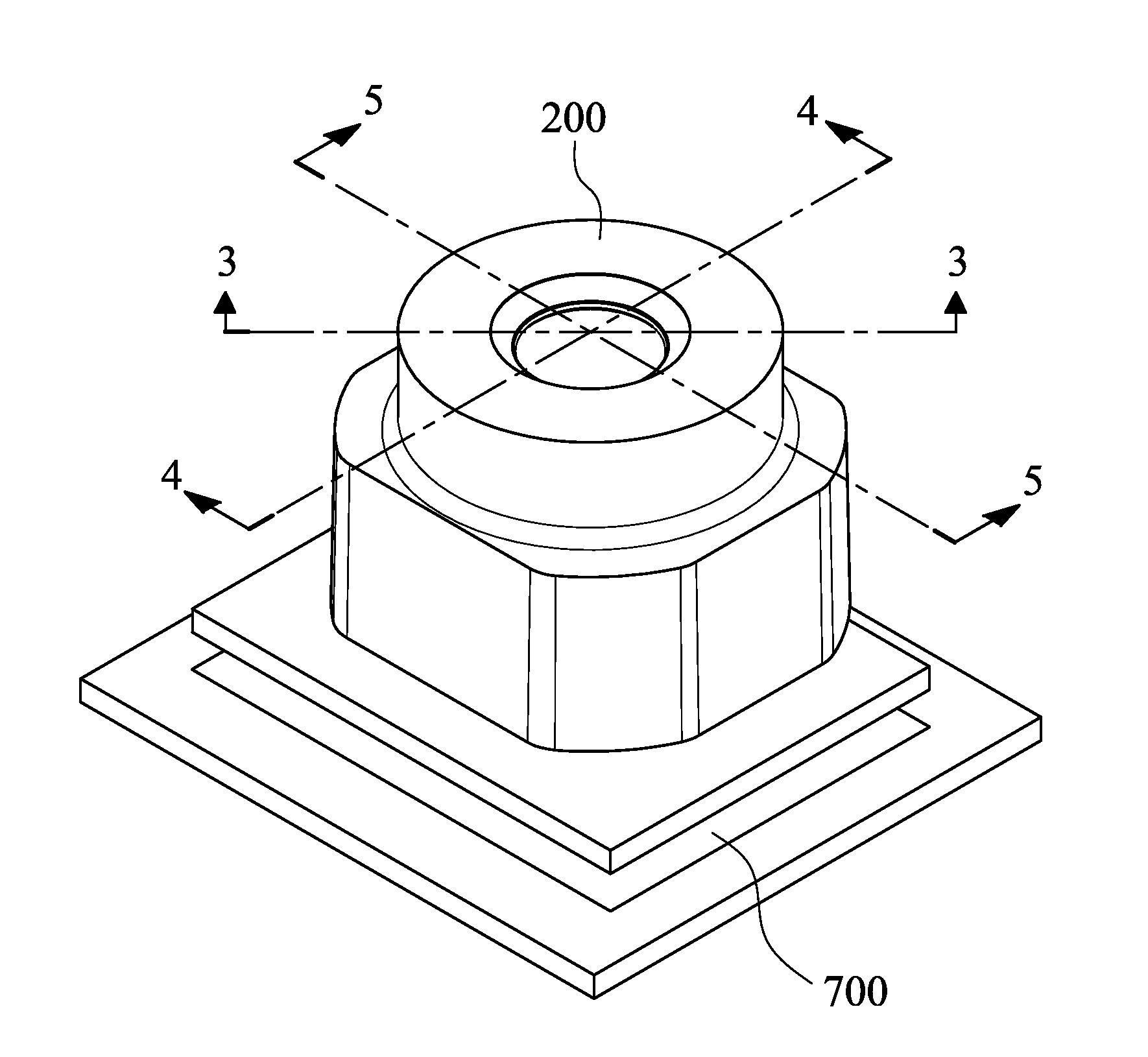
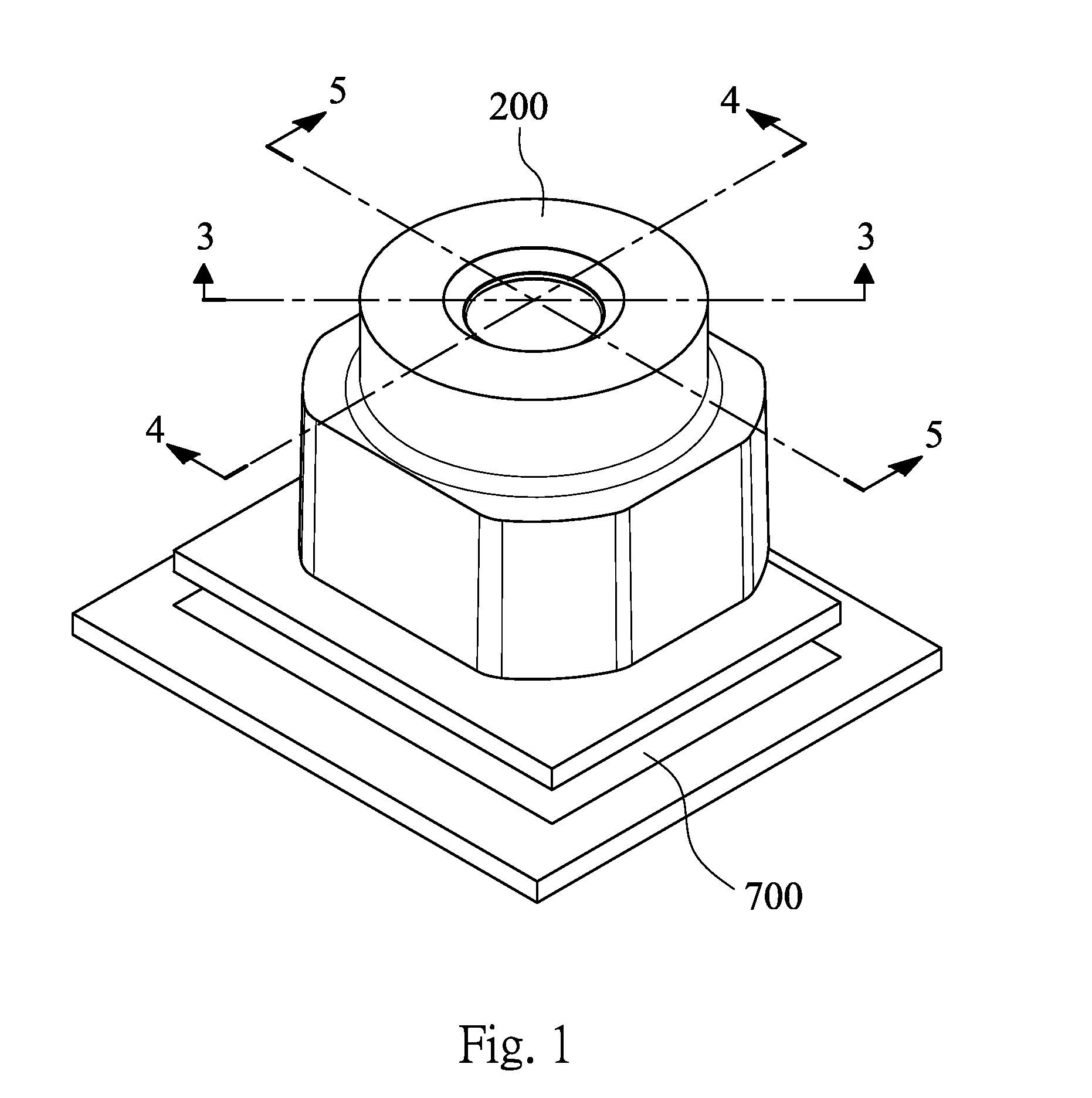
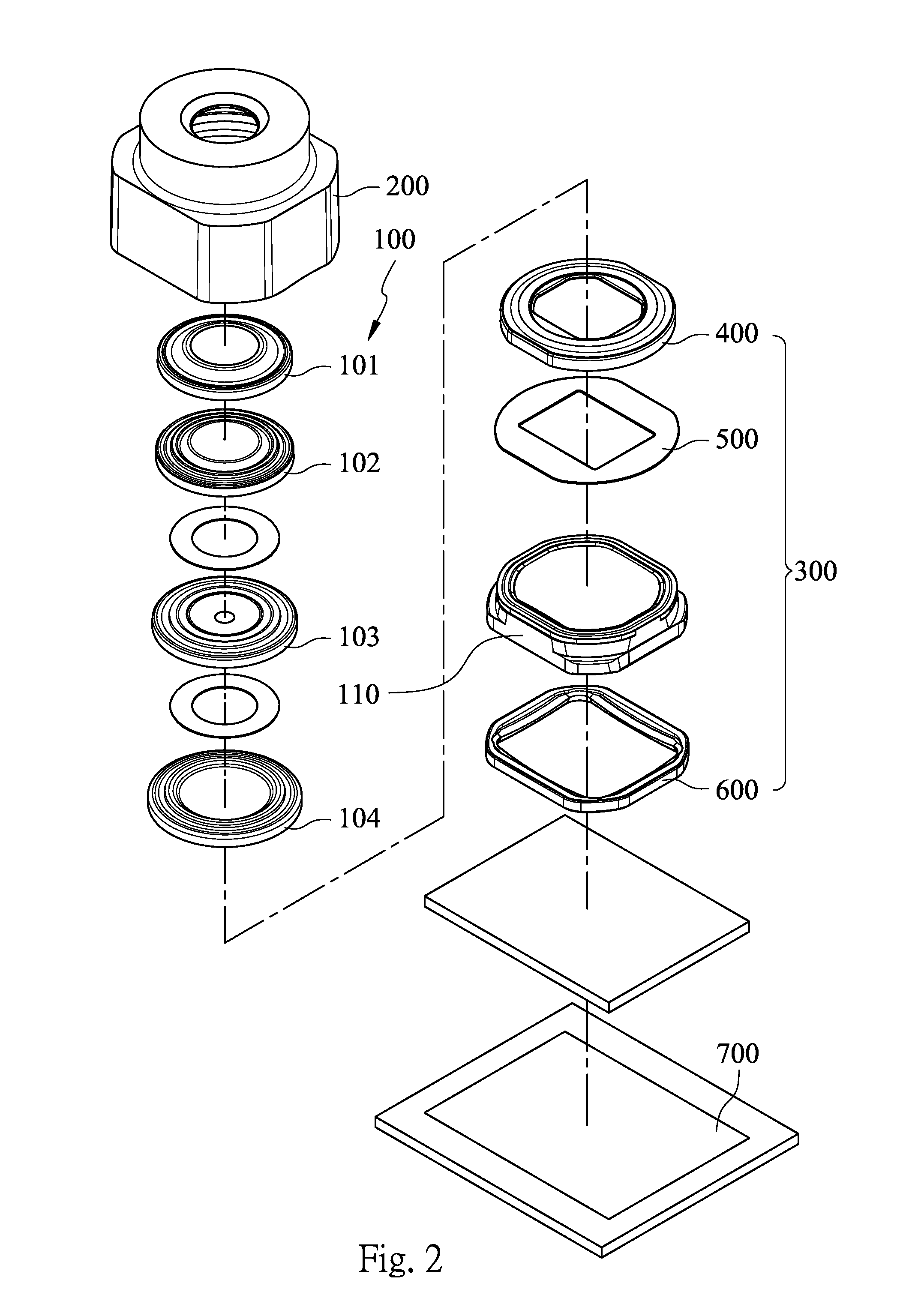
Image lens array
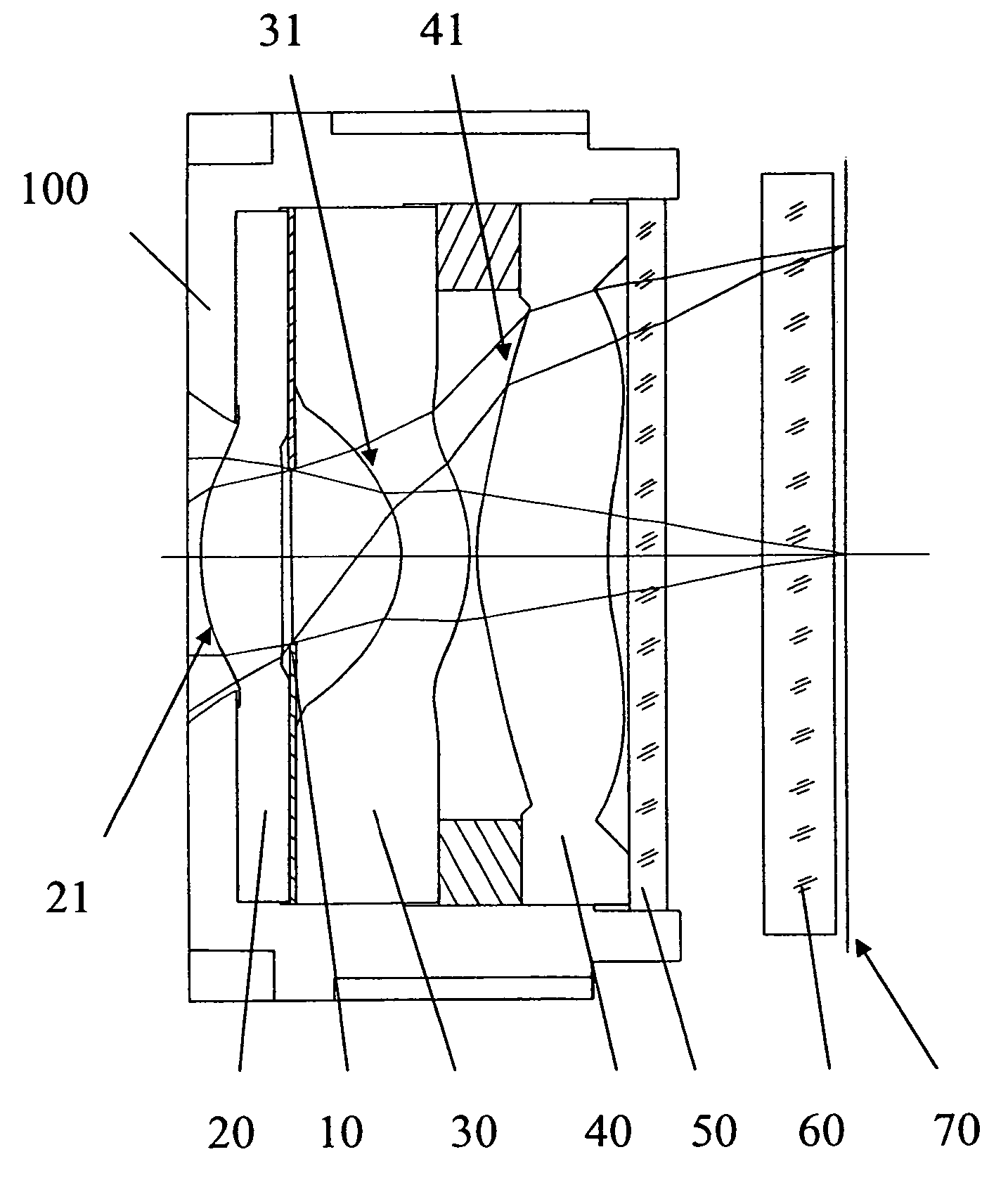
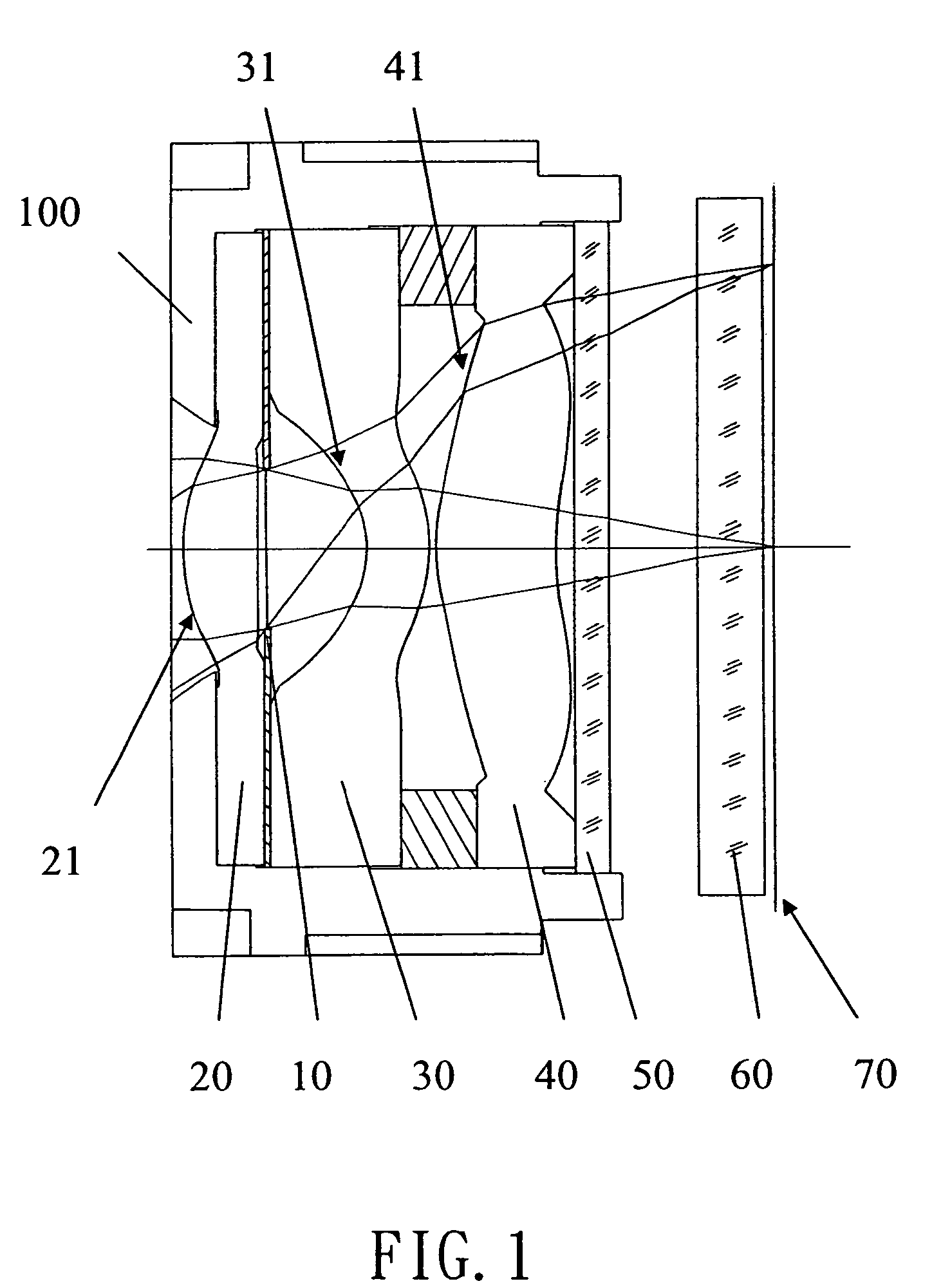
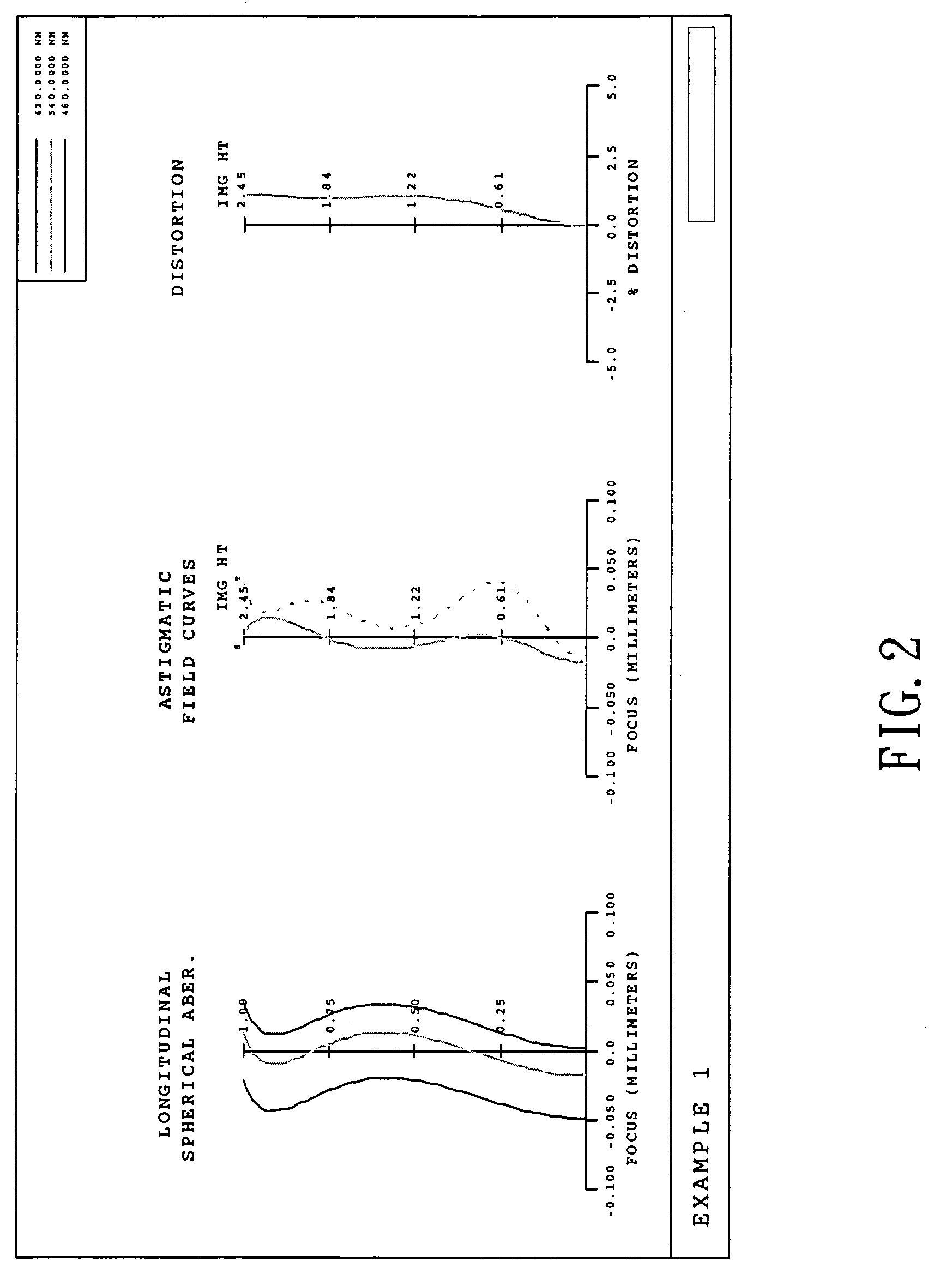
An image lens array, from object side, comprises: a first positive meniscus plastic lens with a convex surface facing forward, a second negative meniscus plastic lens with a concave surface facing forward, a third positive meniscus plastic lens with a convex surface facing forward, and an infrared filter disposed in the lens barrel of the image lens array, the central thickness of the first and second lenses are: CT 1 <1.0 mm, CT 2 <0.6 mm. The radius of curvature of the front and back surfaces of the first lens are L 1 R 1 and L 1 R 2 that satisfy the condition as: |L 1 R 1 / L 1 R 2 |<0.5. The radius of curvature of the front and back surfaces of the third lens are L 3 R 1 and L 3 R 2 that satisfy the condition: |L 3 R 1 / L 3 R 2 |>0.3.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
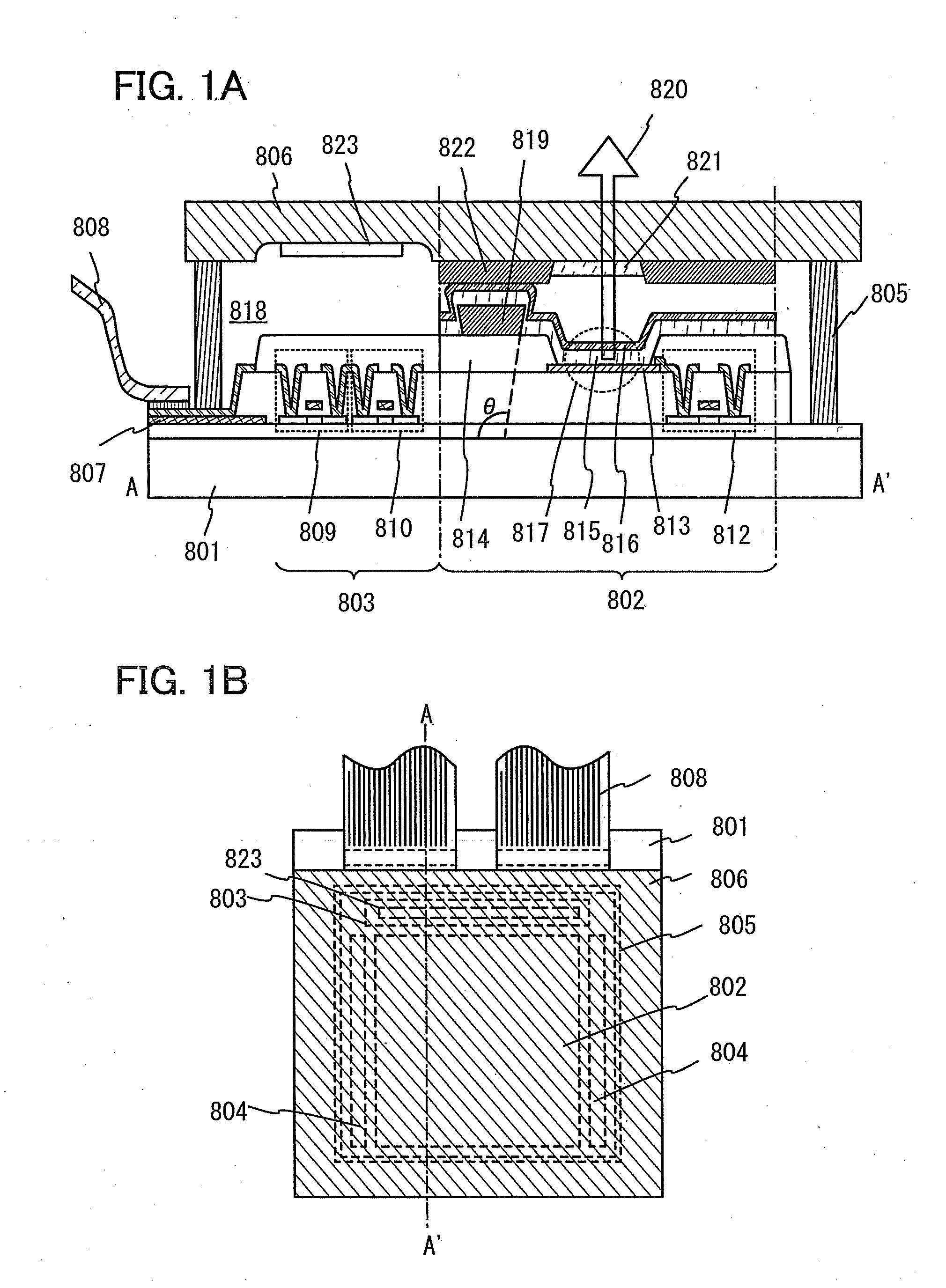
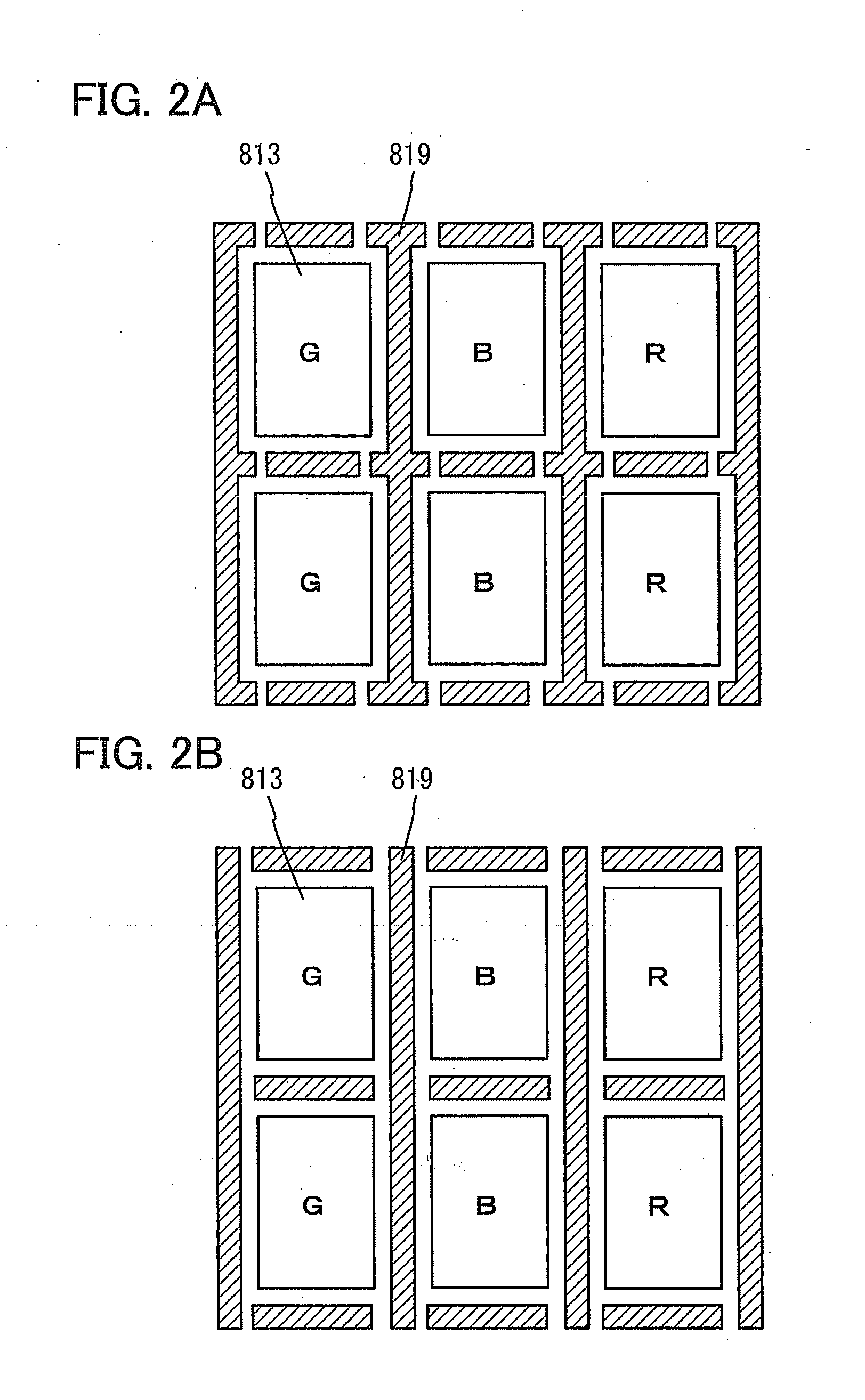
Light-Emitting Device and Manufacturing Method Thereof
ActiveUS20120273804A1Reduce light leakageUniform spacingSolid-state devicesPhotovoltaic energy generationEngineeringAdhesive
When a hollow structure in which a light-emitting element is provided between a pair of substrates is used in order to prevent oxygen or moisture from reaching the light-emitting element, light leakage to an adjacent pixel easily occurs as compared to a structure in which a space between a pair of substrates is filled with a resin such as an adhesive. In order to reduce light leakage to an adjacent pixel in the hollow structure, a light-blocking spacer is formed over a partition to keep the distance between the pair of substrates uniform. The cross-sectional shape of the light-blocking spacer is a trapezoid having a lower side shorter than an upper side.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
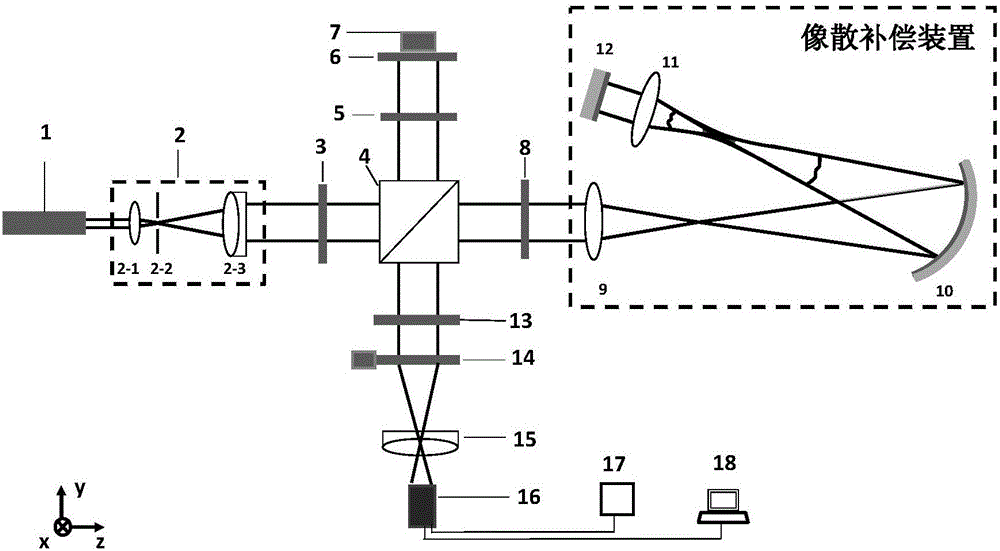
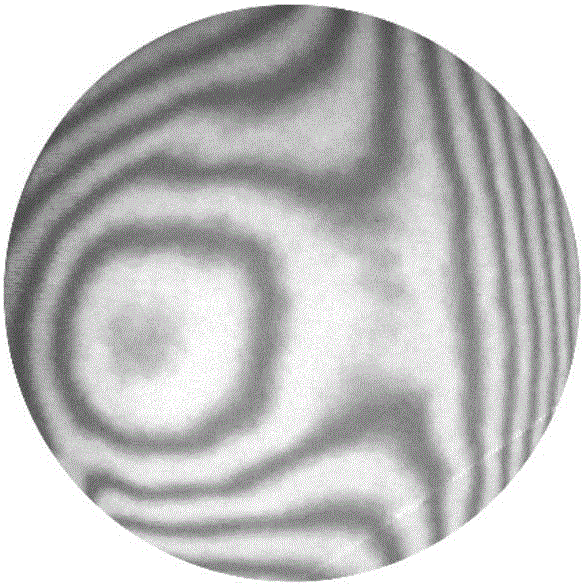
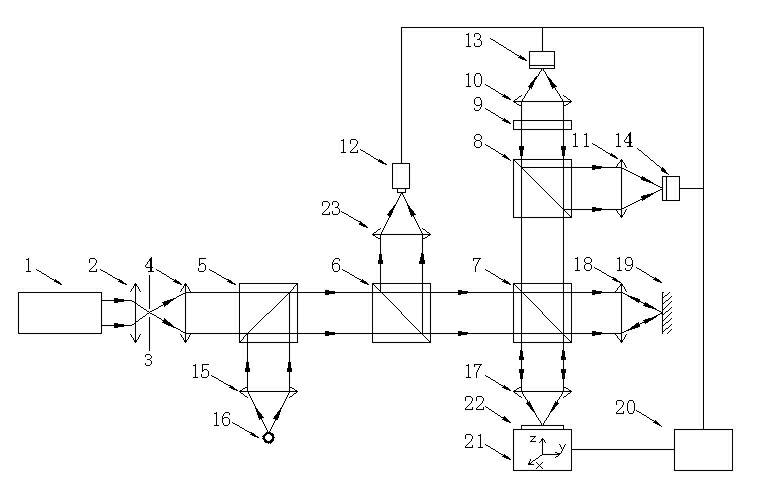
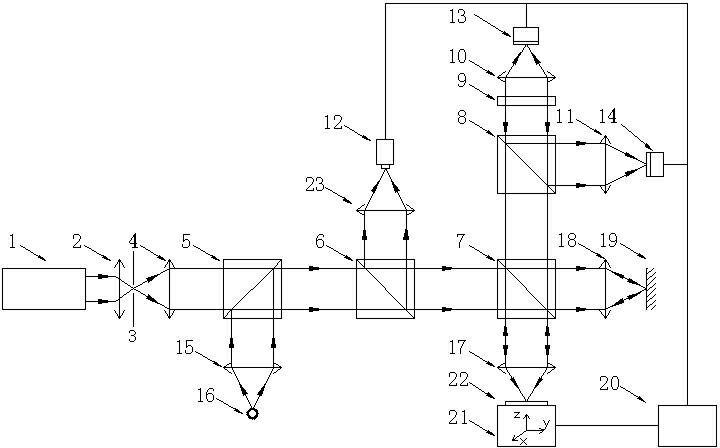
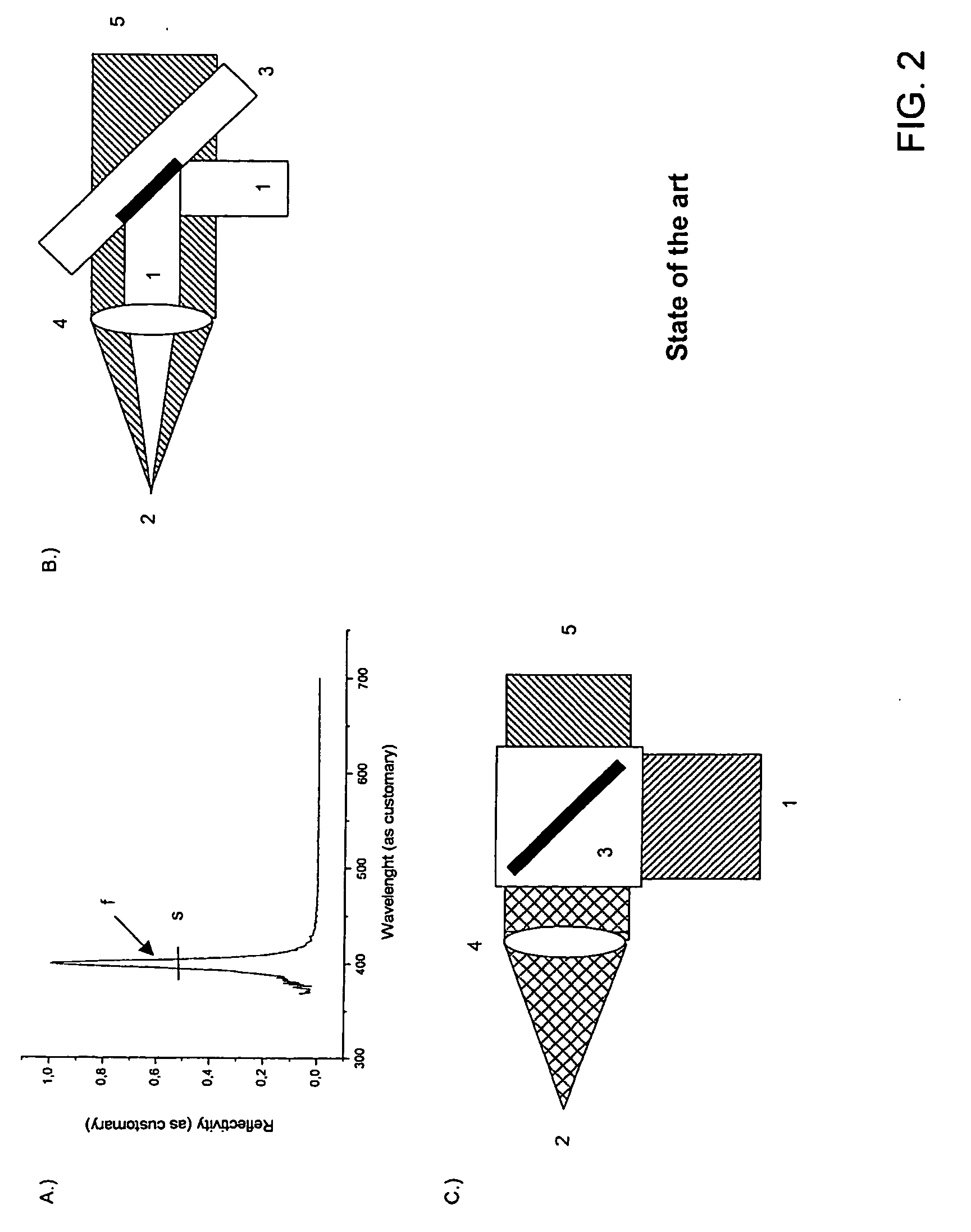
Astigmatic compensation type interference detecting device and method for optic free curved surfaces
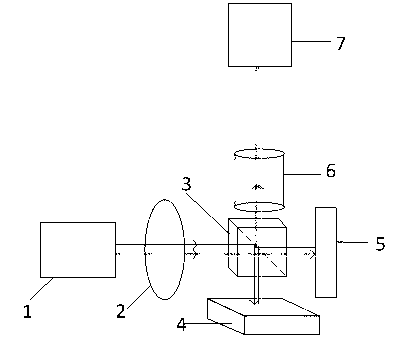
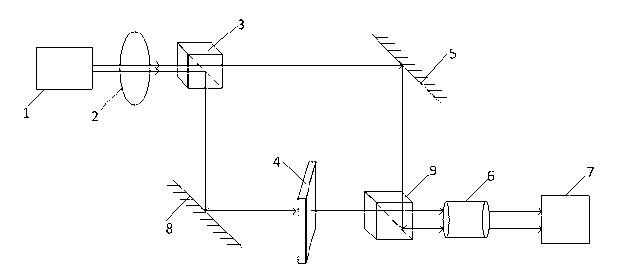
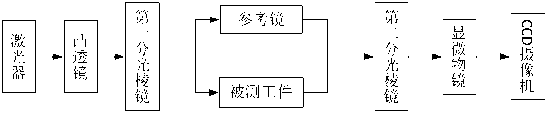
The invention discloses an astigmatic compensation type interference detecting device and method for optic free curved surfaces. The device comprises He-He lasers, a beam expander, a 1 / 2 wave plate, a polarized beam splitter, a first 1 / 4 wave plate, a second 1 / 4 wave plate, a standard plane reflector, a phase shifter, a first convergent lens, a to-be-tested free curved surface, a second convergent lens, a plane reflector, a polarizer, a rotating frosted glass screen, an imaging objective lens, a detector, a displayer and a computer. The method comprises the steps of placing the to-be-tested free curved surface in an inclined state to make test beams come in a specific angle in an inclined mode to compensate for main surface shape astigmatic error components of the to-be-tested free curved surface, therefore reducing the degree of divergence of the subsequent test beams, and making the stripes discernable on the detector. The detector collects a series of phase-shifting interferograms which are treated with a wave front reconstruction algorithm to obtain a surface shape of the to-be-tested free curved surface. According to the astigmatic compensation type interference detecting device and method for optic free curved surfaces, the astigmatic compensation method is used for testing optic free curved surfaces for which the main surface shape error components are astigmatism, the stability is high, and the cost is low.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Digital holographic detection device for subsurface defect of optical element
InactiveCN102519976AImprove signal-to-noise ratioSuppress stray lightPhase-affecting property measurementsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationHigh rateSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention relates to a digital holographic detection device for a subsurface defect of an optical element. A light beam in the device is divided into a measuring light beam and a reference light beam, so that a measuring light path is obliquely incident to an object to be measured and symmetrically receives reflected light, the reflected light interferes with reference light, scattered light information of the subsurface defect is acquired from an interference pattern, the direct reflected light on the surface and stray light in a system are inhibited, and the scattered light information of the subsurface defect of the optical element is acquired. The detection device has the characteristics that: (1) a light source is a short coherent light source, so that the stray light in the system can be inhibited; (2) the measuring light path in the device is obliquely incident and symmetrically receives the reflected light, so that the direct reflected light on the surface of the optical element can be inhibited, only scattered light from the subsurface defect is received, and the signal-to-noise ratio of a signal is improved; (3) an optical fiber probe in the device is used for receiving the scattered light information, so that the limitation that a high-rate microscope objective is used for receiving the subsurface defect is overcome; and (4) the acquired image is analyzed and processed according to a digital holographic calculation principle, so that the quantitative depth information of the subsurface defect is acquired.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
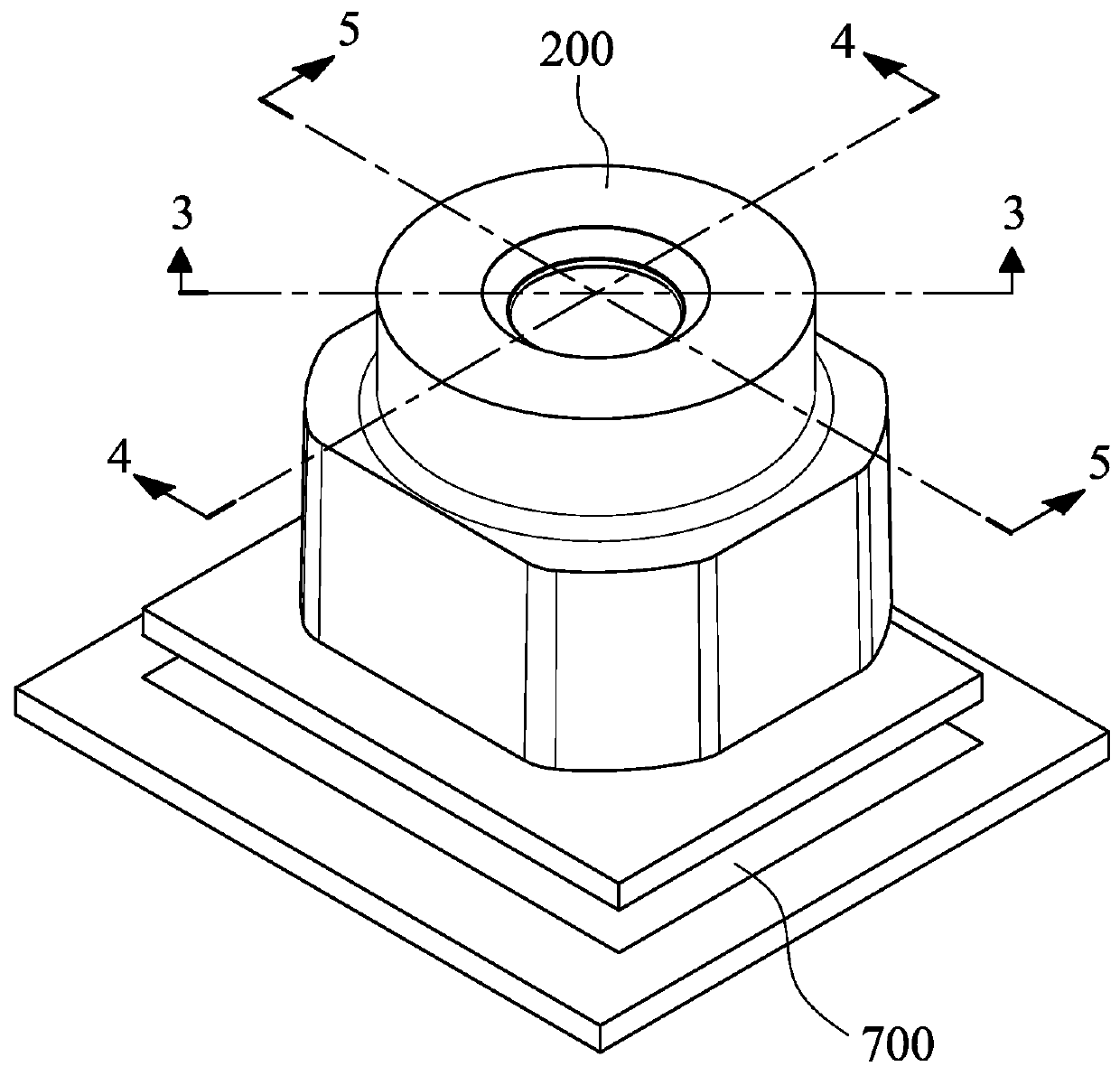
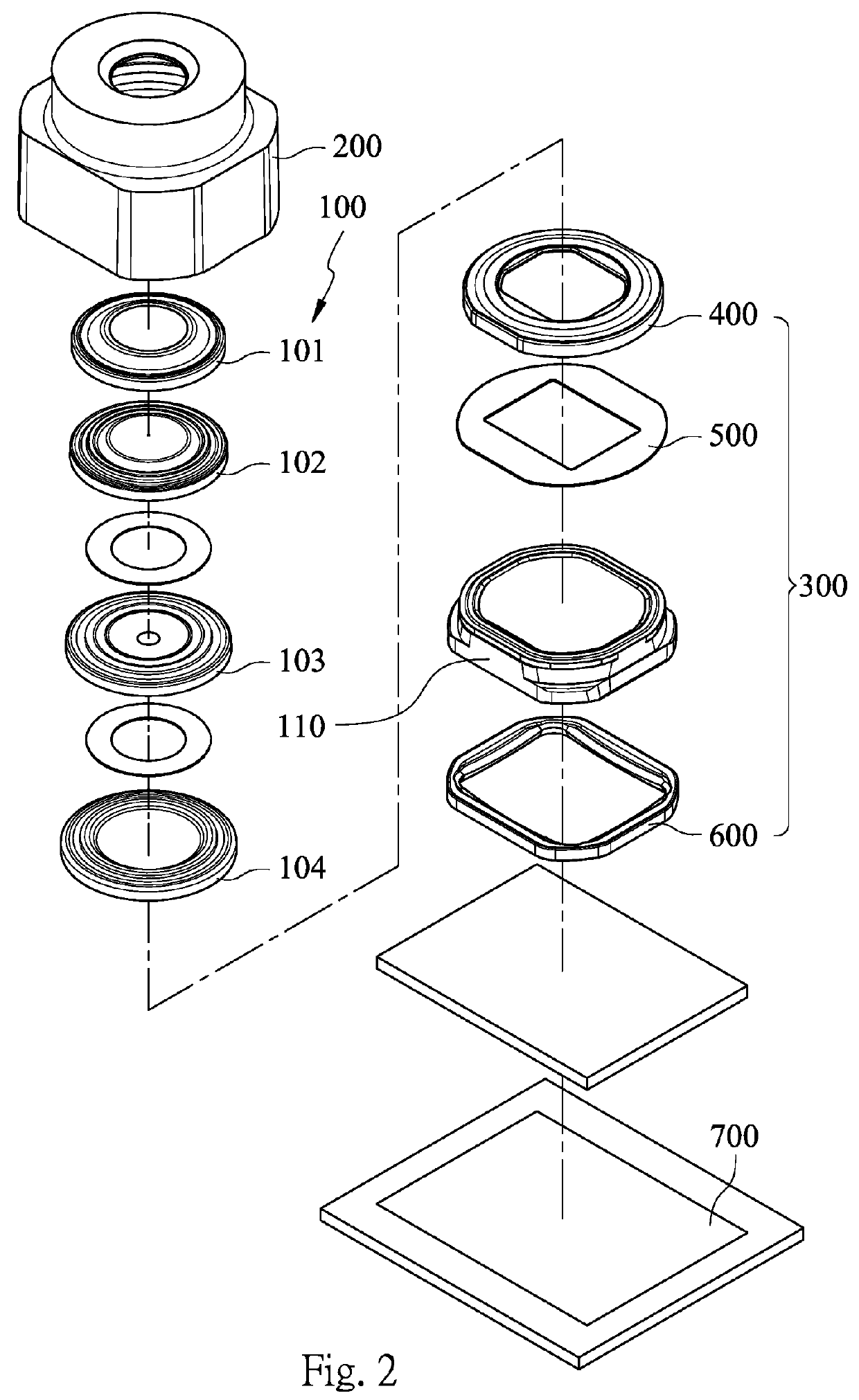
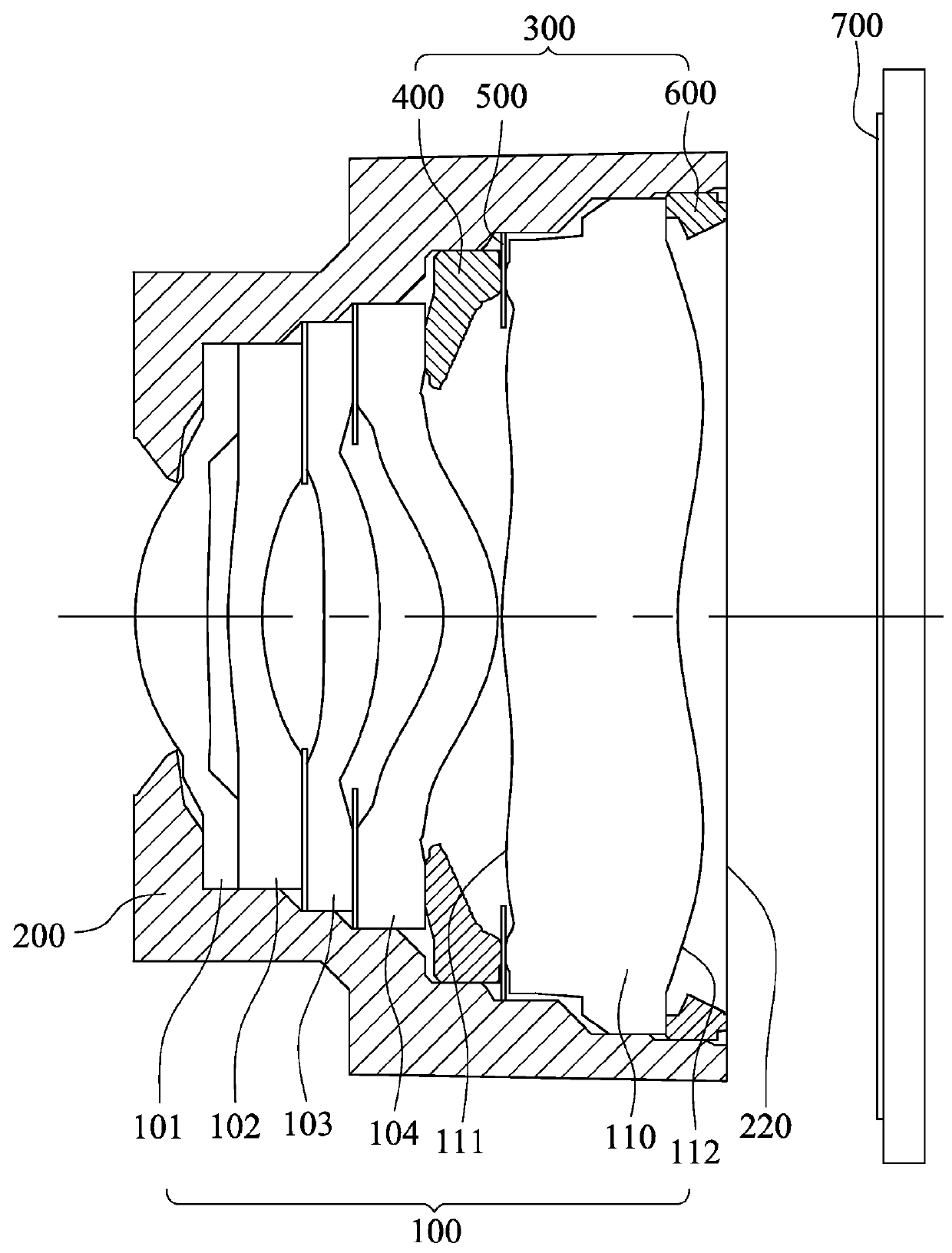
Imaging lens module and mobile terminal
An imaging lens module includes an imaging lens assembly and a first optical component. The imaging lens assembly has an optical axis and includes a lens element. The lens element includes an effective optical portion, which is non-circular and disposed on a center of the lens element. The first optical component has a non-circular opening hole. The effective optical portion of the lens element of the imaging lens assembly is corresponded to the non-circular opening hole of the first optical component.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
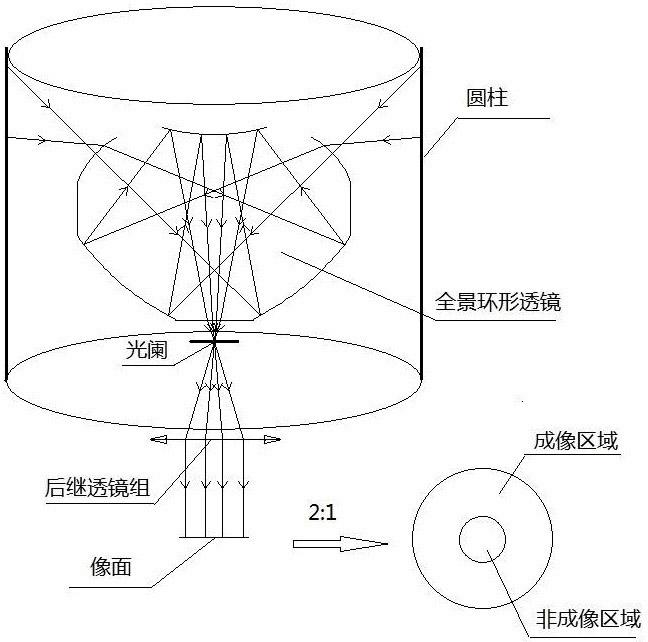
Panoramic imaging lens
InactiveCN102495460AImprove image qualitySuppress stray lightPanoramic photographyOptical elementsDistortionCamera lens
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical devices, and particularly discloses a panoramic imaging lens, comprising a panoramic annular lens, a subsequent lens system, a diaphragm and an image surface which are positioned on the same optical axis. The panoramic annular lens is made of a transparent medium in the shape of a convex polyhedron rotationally symmetric around the center optical axis, and the convex polyhedron consists of four refracting surfaces and two reflecting surfaces; the subsequent lens system consists of a series of spherical lenses made of different transparent media; the diaphragm is positioned between the panoramic annular lens and the subsequent lens system; and the image surface is positioned at the bottom end of a system. The panoramic imaging lens has the advantages of high resolution, low radial distortion, capability of avoiding distortion after an image is restored, and the like. In addition, the panoramic imaging lens is simple in structure, easy in processing and low in cost. The panoramic imaging lens is mounted at the front of a camera, and a simple panoramic image can be shot by the camera. Besides, the panoramic imaging lens can be applied to fields of pipeline detection, observation by the aid of a medical endoscope, video monitoring and the like.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
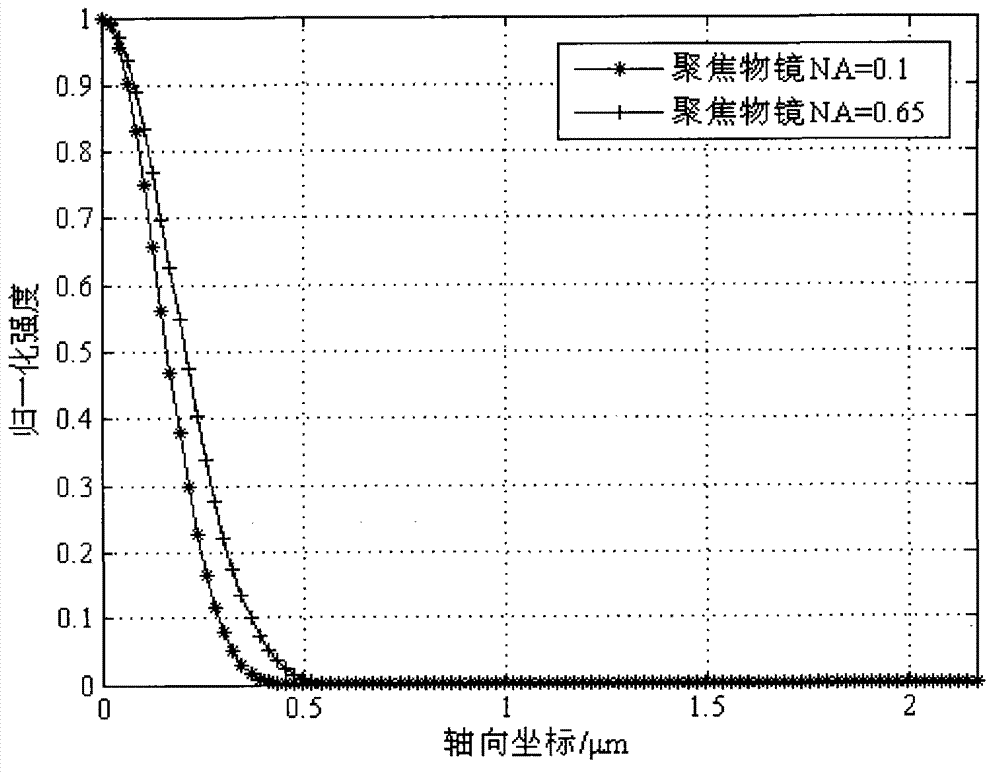
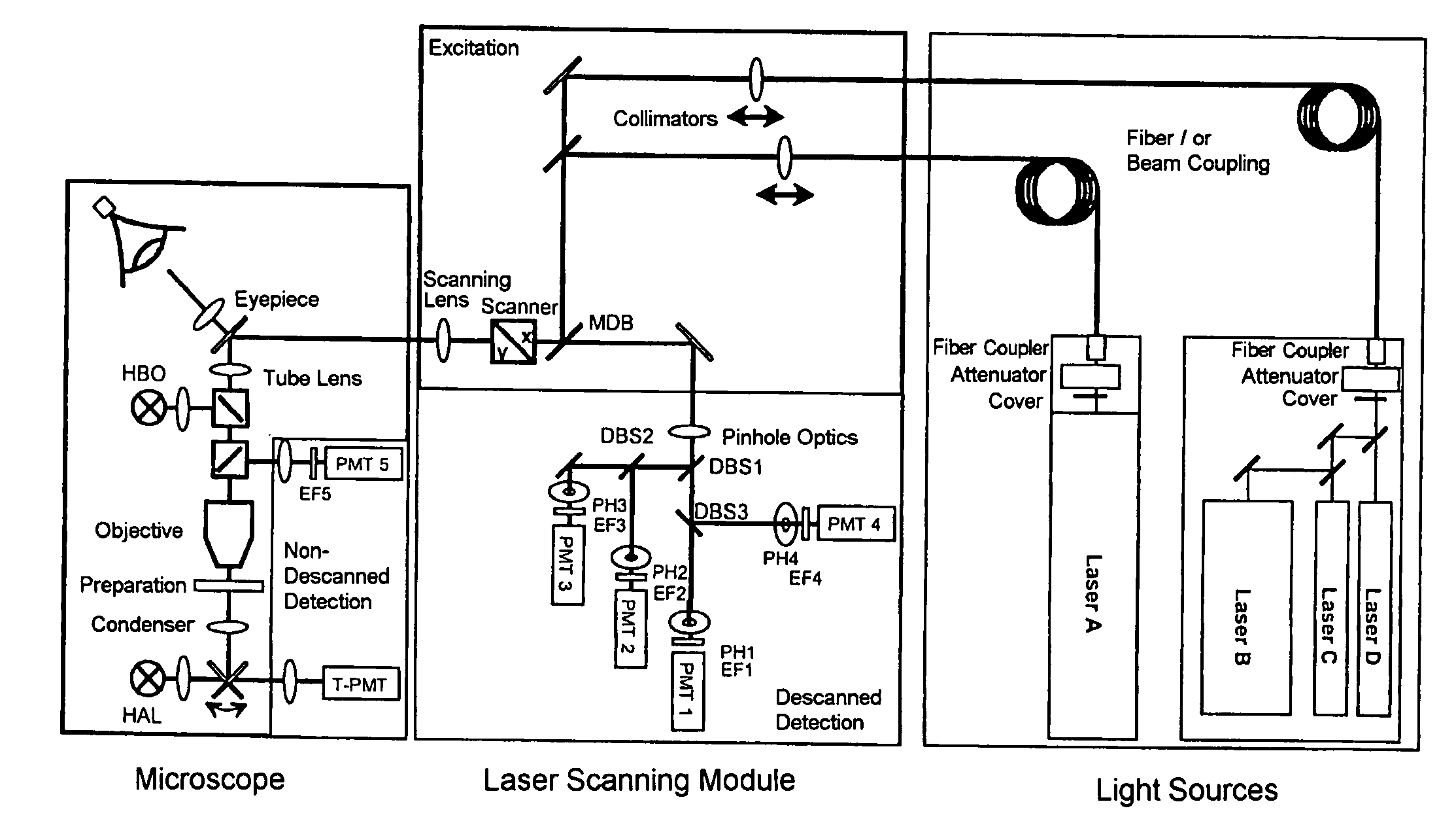
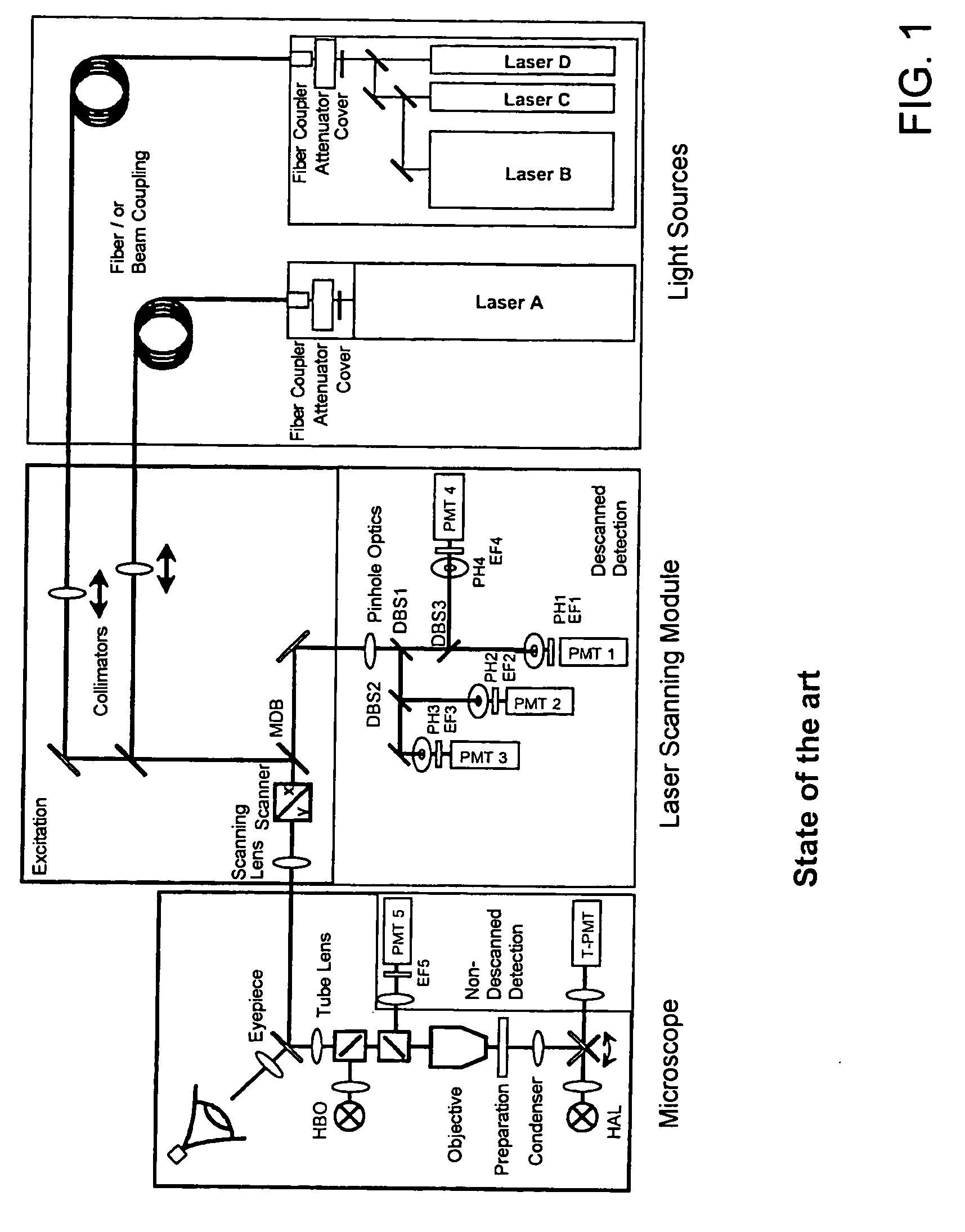
Conjugated bi-pass lighting confocal microscopic device of fluorescent reflecting mirror
ActiveCN102759331ASuppress stray lightOvercoming Interfering DisturbancesUsing optical meansPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A conjugated bi-pass lighting confocal microscopic device of a fluorescent reflecting mirror belongs to an optical micro measurement technology. A collimation beam expander and a beam splitter are sequentially arranged on a direct light path of a laser, a focusing object lens and a three-dimensional micromovement object stage are arranged on the reflected light path of the light splitter, a narrow-band filter and a converging object lens are arranged on the transmission light path of the beam splitter, transmission optical fibers transmit the converging light of the converging object lens to a photodetector, an ellipsoidal reflector is also arranged on the reflected light path of the beam splitter, the perifocus of the ellipsoidal reflector is positioned a sample surface which is put on the three-dimensional micromovement object stage, and the fluorescent reflecting mirror is arranged at the apofocus of the ellipsoidal reflector. The microscopic device prevents the interference which is generated by the mixed light-wave superposing which is caused by primary lighting and secondary lighting of bi-pass lighting, and has high signal-to-noise ratio and axial resolution.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Imaging lens module and mobile terminal
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Laser induced fluorescence detector
InactiveCN1400464AEfficient Imaging SystemSuppress stray lightComponent separationFluorescence/phosphorescenceCapillary electrochromatographyMicro hplc
The invention is a laser-inducing-fluorescence detector. It includes: a piece of inching equipment to plant and ajdust the position of sample holder; an aided light source to adjust the light path; an observation mirror for adjusting the light path; an exciting light source as its working light source made up of the laser, the reference photoelectric diode and light-reducing board and the dichroiscope; a group of optical lenses in imagine and focus the working light source, made up of the focus lens, the imagining lens, the light-filtering piece and the light diaphragm; and a photoelectric signal converter to receive and output the detecting signal. The invention is based on the common-focus mode to get the high-efficiency imagining system and it can be used in the separating-analysis technique such as Micro-HPLC, CE, CEC and so on.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
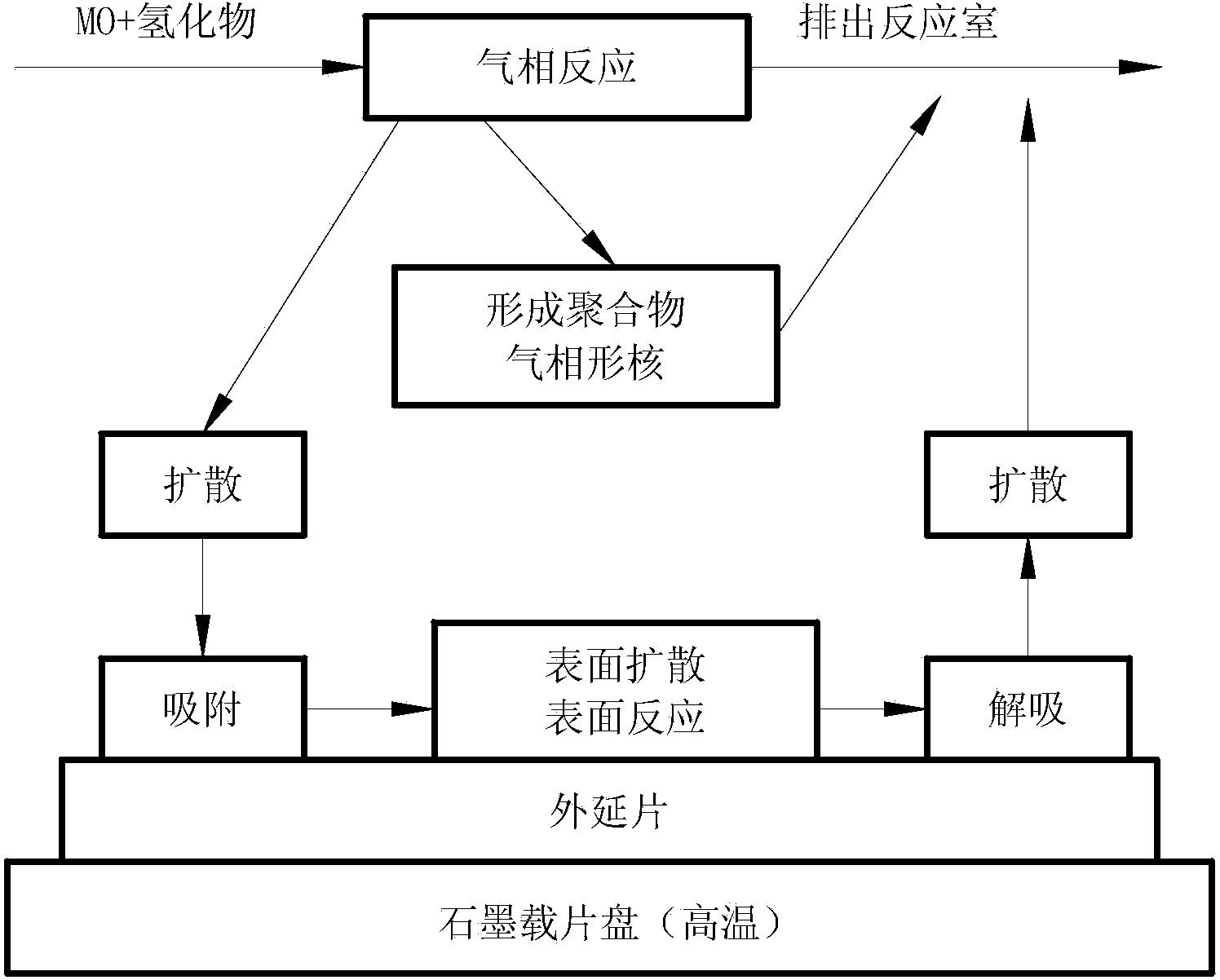
Online real-time representation device for film epitaxial growth
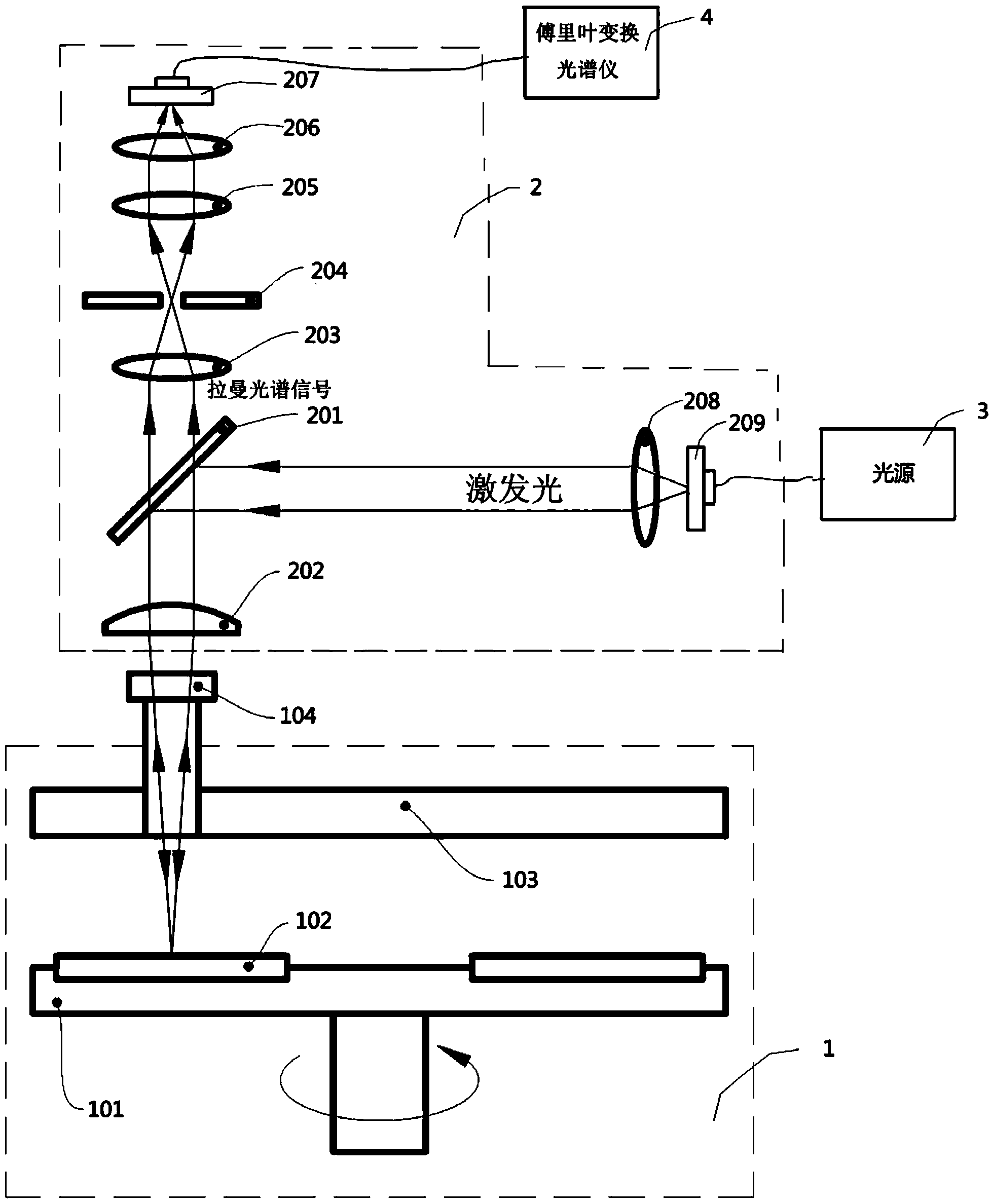
The invention discloses an online real-time representation device for film epitaxial growth. The online real-time representation device utilizes Raman spectroscopy signals to directly represent the microstructure of a nano material in MOCVD (Metal Organic Chemical Vapour Deposition) equipment in real time during a film epitaxial growth process. After reflected by a first spectroscope, excitation light is focused by a plane-convex lens, and the focus is radiated to an epitaxial wafer through an observing window in the top of the reaction cavity of the MOCVD equipment; since the Raman spectroscopy signals are excited in the radiation area of the focus of the plane-convex lens, most Raman spectroscopy signals are collected by the plane-convex lens; after passing through the first spectroscope, the Raman spectroscopy signals gather in the focus of the plane-convex lens, at the moment, a confocal pinhole is formed in the focus, and performs the function of space filtering and stray light resisting. The excitation light and the detection light (namely the Raman spectroscopy signals) share a light path front end unit, the size of a probe can be reduced as far as possible, and space limitation of the observing window of the reaction chamber is broken.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Constant resolution multi-spectral optical system applicable to large dynamic range and nearly-hemispherical view field
The invention provides a constant resolution multi-spectral optical system applicable to a large dynamic range and a nearly-hemispherical view field.The optical system sequentially comprises a homocentric sphere lens, multiple apertures and multiple imaging micro lenses which are in one-to-one correspondence with the apertures in the light incidence direction, and the apertures and the corresponding imaging micro lenses are distributed on the light-out position of the homocentric sphere lens in a fan-shaped mode and located on two different homocentric spherical surfaces of the homocentric sphere lens; each imaging micro lens and the corresponding aperture form a separate imaging channel; the imaging micro lenses comprise multiple short-focus correction lenses, multiple middle-focus correction lenses and multiple long-focus correction lenses, and correction lens sets with different focal lengths are adopted by the imaging micro lenses to correct aberrations in different view fields, so that the constant high resolution is guaranteed.According to the constant resolution multi-spectral optical system, interference of a local intense light source to all the view fields is avoided, and imaging detection within the large dynamic range can be achieved.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Full parameter detection apparatus of polished surface quality of optical element and detection method thereof
ActiveCN102425998ATrue and effective reflectionIncrease contrastPolarisation-affecting propertiesUsing optical meansControl cellEngineering
Owner:XIAN TECH UNIV
Radar/infrared two-waveband frequency selective surface
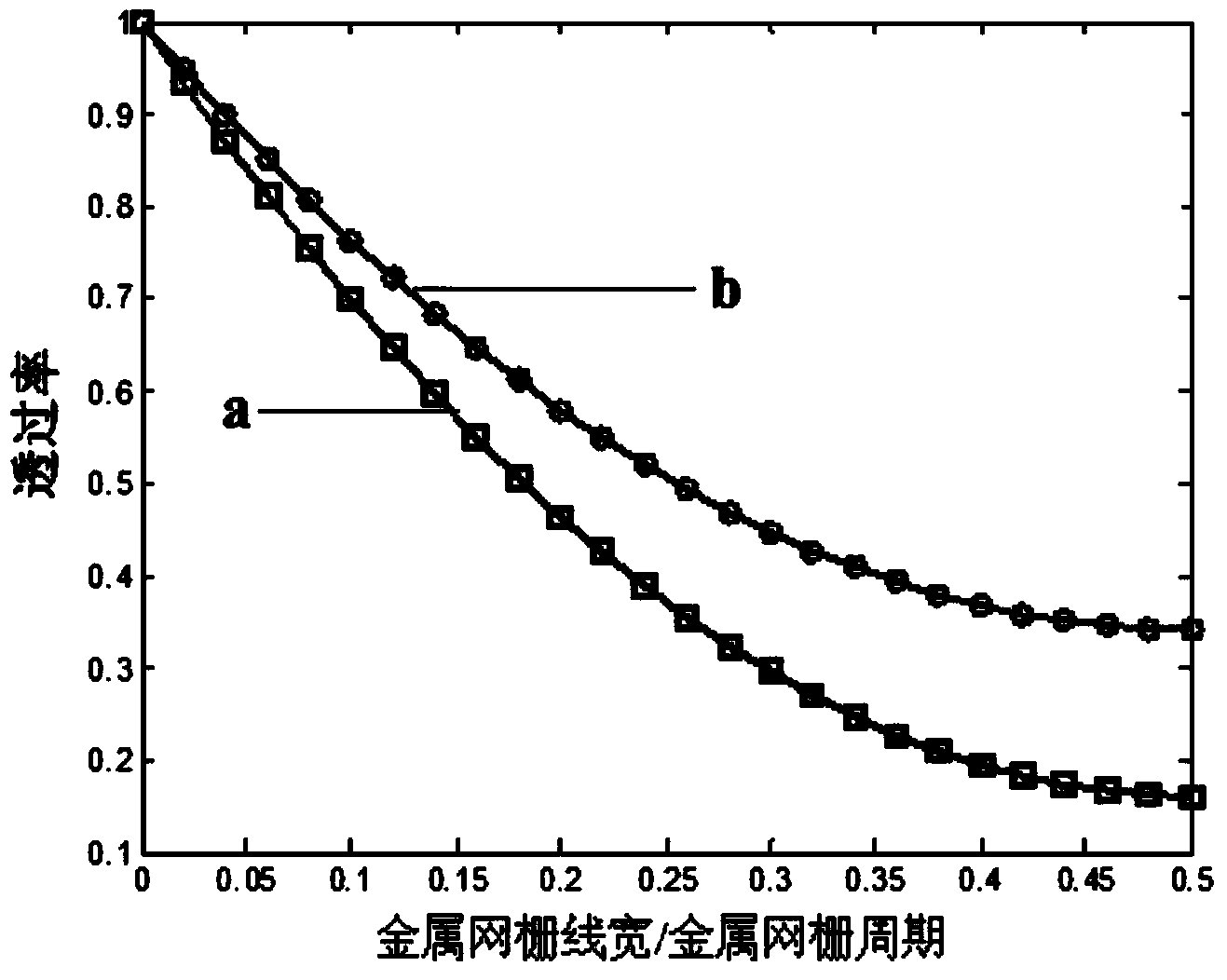
ActiveCN103487860AHigh optical transmittanceUniform distribution of diffracted light intensityDiffraction gratingsWaveguide type devicesWire widthRadar
The invention discloses a radar / infrared two-waveband frequency selective surface which solves the technical problems that a latticed metal mesh FSS in the prior art cannot further improve optical transmittance, the distribution of stray light is centralized, and the application in high-precision detection and imaging observation is not facilitated, and belongs to the technical field of electromagnetic shielding. The radar / infrared two-waveband FSS is a cross-hole-shaped periodic array on a metal mesh, the metal mesh is a round-hole-shaped metal mesh or a hexagonal metal mesh, the periods of cross hole shapes are the integer multiples of the period of the metal mesh, and each cross hole shape meets the two following constraint conditions that the slit width of the cross hole shapes is the integer multiples of the period of the metal mesh minus the wire width of the metal mesh; the difference between the slit length of the cross hole shapes and the slit width of the cross hole shapes is the even times of the period of the metal mesh. The radar / infrared two-waveband FSS is higher in optical transmittance, more even in diffraction light distribution and capable of effectively restraining the stray light.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Design method of multi-layer metal dielectric film capable of implementing imaging function
A design method for multi-layer metal dielectric film capable of realizing the imaging function is characterized by selecting incident wave; selecting two sets of metallic material and dielectric material with a certain thickness, alternatively arranging the metal and medium in two sets to form two kinds of multi-layer metal dielectric film structures, respectively computing the equivalent dielectric constant of the two kinds of multi-layer metal dielectric film structures based on equivalent dielectric constant of each material and the thickness of each film layer; realizing the variation of the value and plusminus of the dielectric constant in respective direction by designing the thickness of each film layer so as to make the optical wave diverge through the first set of multi-layer metal dielectric film structure and converge through the second set of multi-layer metal dielectric film structure; binding the divergent structure multilayer film and the convergent structure multilayer film together according to a specific thickness ratio to the multi-layer metal dielectric film structure device which can make the fine structure far less than the operating wavelength image so as to achieve the super resolution.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Daytime celestial body detecting device
InactiveCN101685162AImprove detection performanceSuppress stray lightMountingsElectromagnetic wave reradiationCcd cameraLight filter
The invention relates to a daytime celestial body detecting device, which is characterized by mainly comprising a light shield, a symmetrical turn-back type optical system, an eight-shift light filterturntable, a linear polaroid turntable, a CCD camera and a corresponding mechanical structure. The daytime celestial body detecting device adopts a spectral filtering method and a polarization methodto detect target celestial bodies under a daytime cloudless sky background while having novelties, and improves the performance of detecting the daytime celestial bodies.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
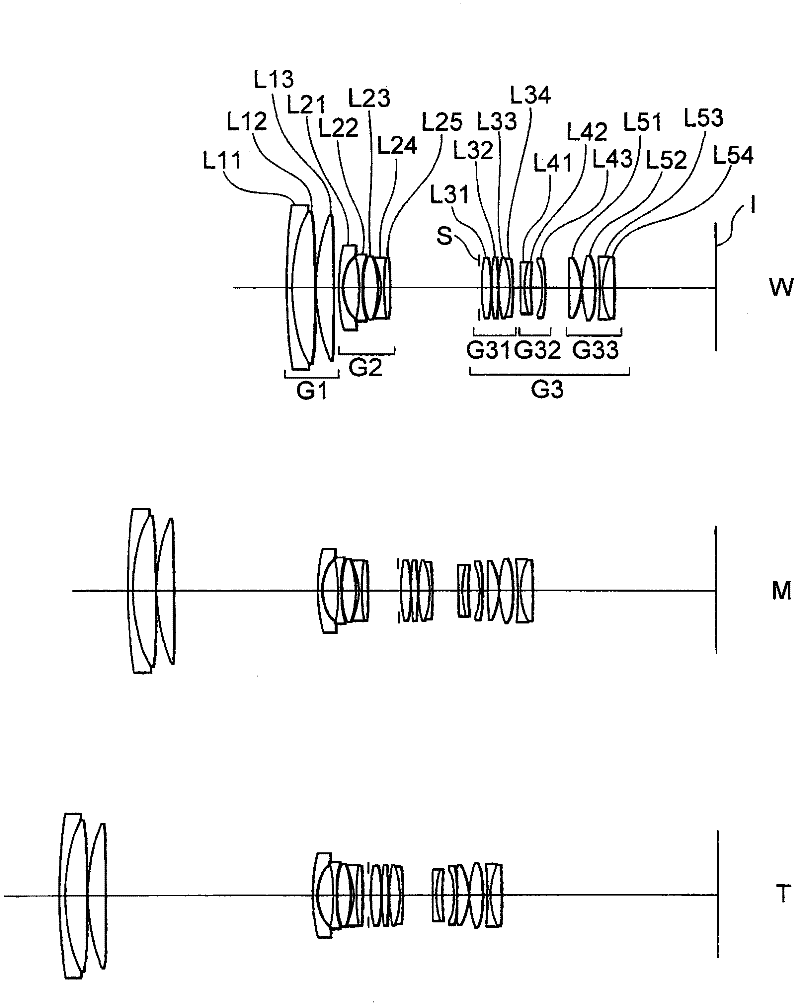
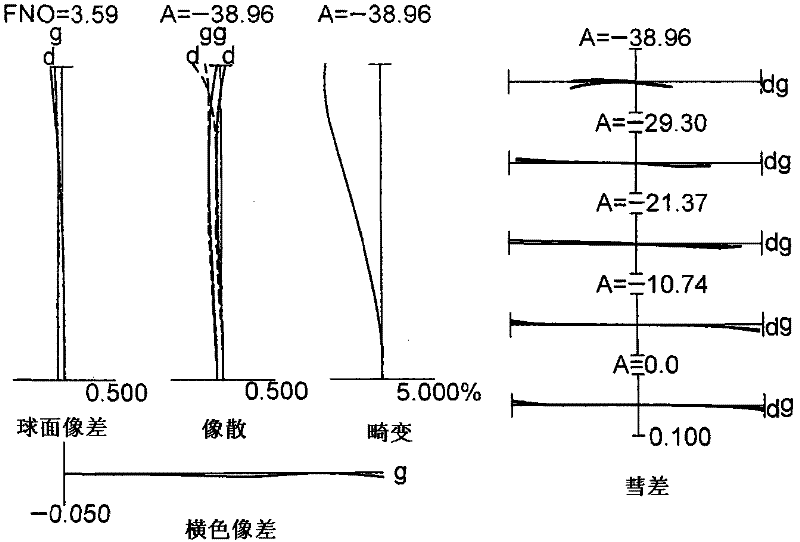
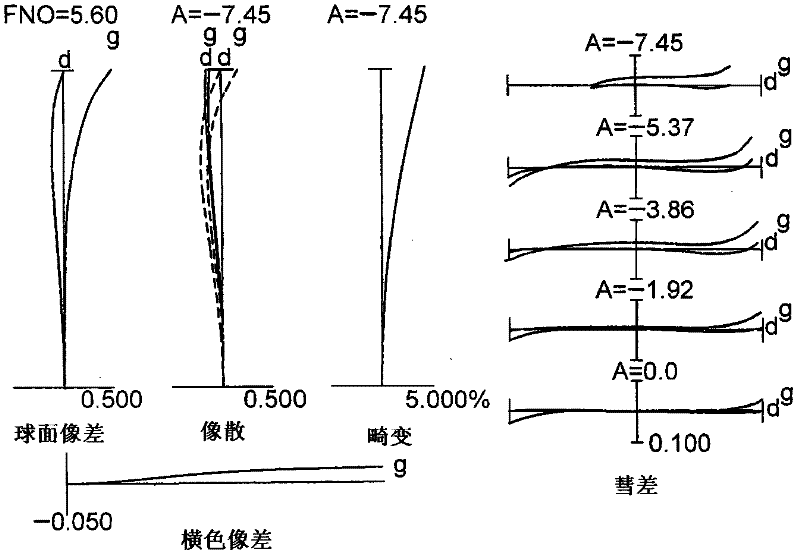
Zooming lens, optical apparatus and method of manufacturing zooming lens
The invention provides a zooming lens, which comprises a first lens group G1 having positive refractive power, a second lens group G2 having negative refractive power and a third lens group G3 having positive refractive power successively arranged along an optical axis. When zooming from a wide-angle end state W to a telephoto end state T, the distance between the first lens group G1 and the second lens group G2 is increased and the distance between the second lens group G2 and the third lens group G3 is reduced. Given conditions are satisfied. Therefore, the zooming lens is high in optical performance and can inhibit the aberration variation. The invention also provides an optical apparatus equipped with the zooming lens and a method for manufacturing the zooming lens.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Device for controlling light radiation
InactiveUS20060256426A1Suppress stray lightEasy to solveRaman/scattering spectroscopyPolarisation spectroscopyRefractive indexAcousto-optics
Device for controlling light radiation, which is excited in a specimen and / or which is backscattered and / or reflected and which contains one or more wavelengths, at a plurality of light outlets, wherein a separation of the light radiation into differently polarized components is carried out; and the components of the excitation radiation and / or detection radiation are affected in their polarization by means of a preferably birefringent, preferably acousto-optic or electro-optic medium, which changes the ordinary and extraordinary refractive index.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MIKROLMAGING
Follow-up light shield control system of space remote sensor
InactiveCN102566596ASuppress stray lightSuppressing Heat Flow ProblemsControl using feedbackHeat flowEngineering
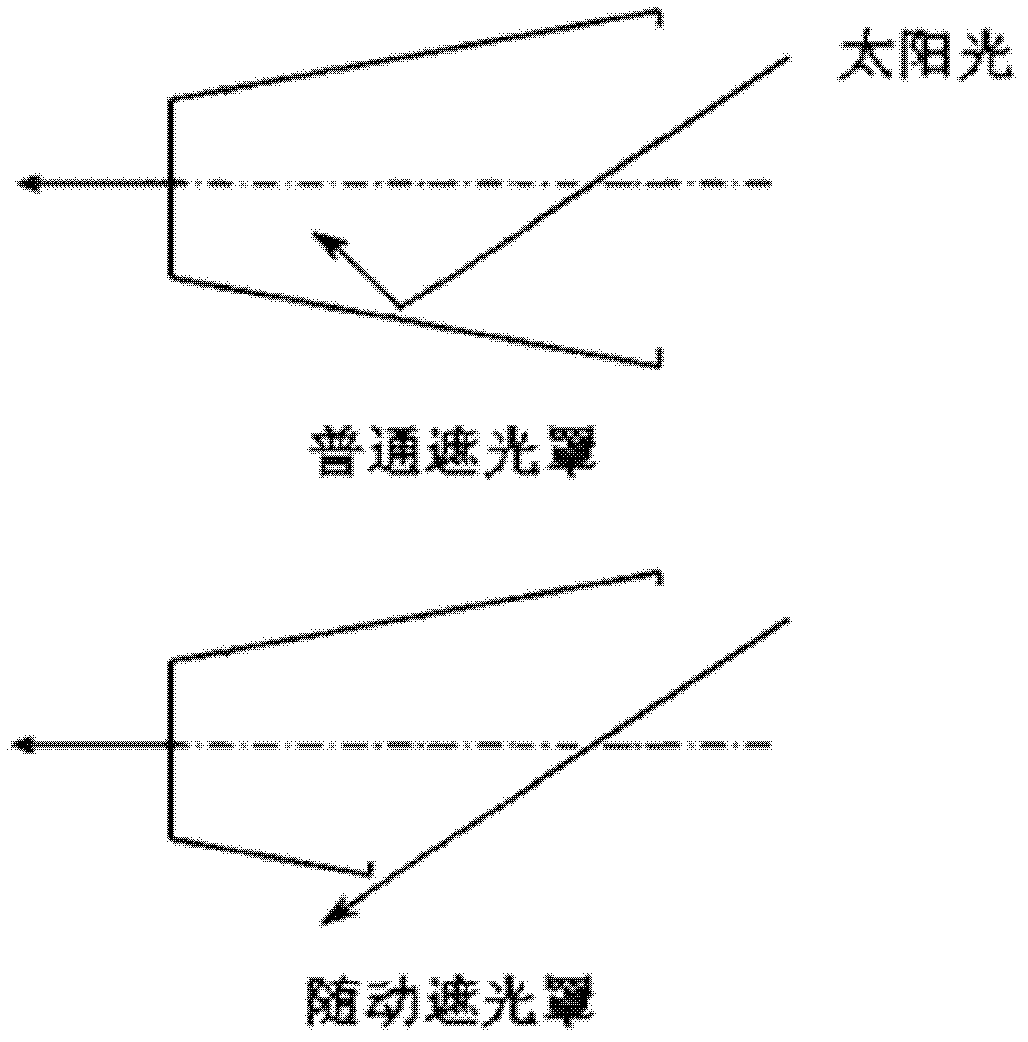
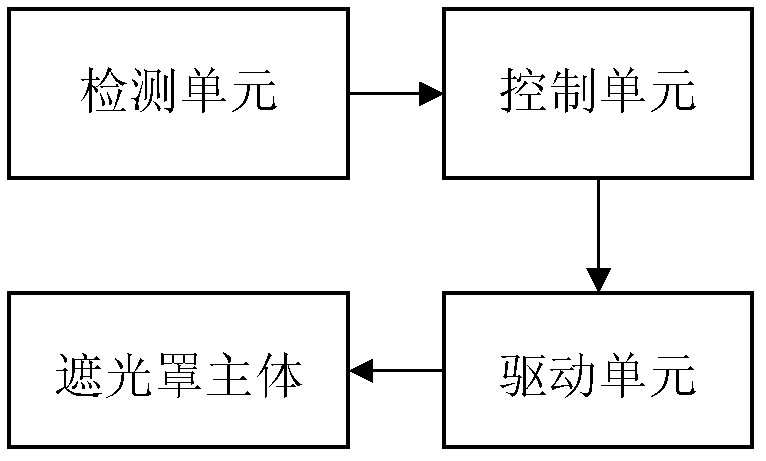
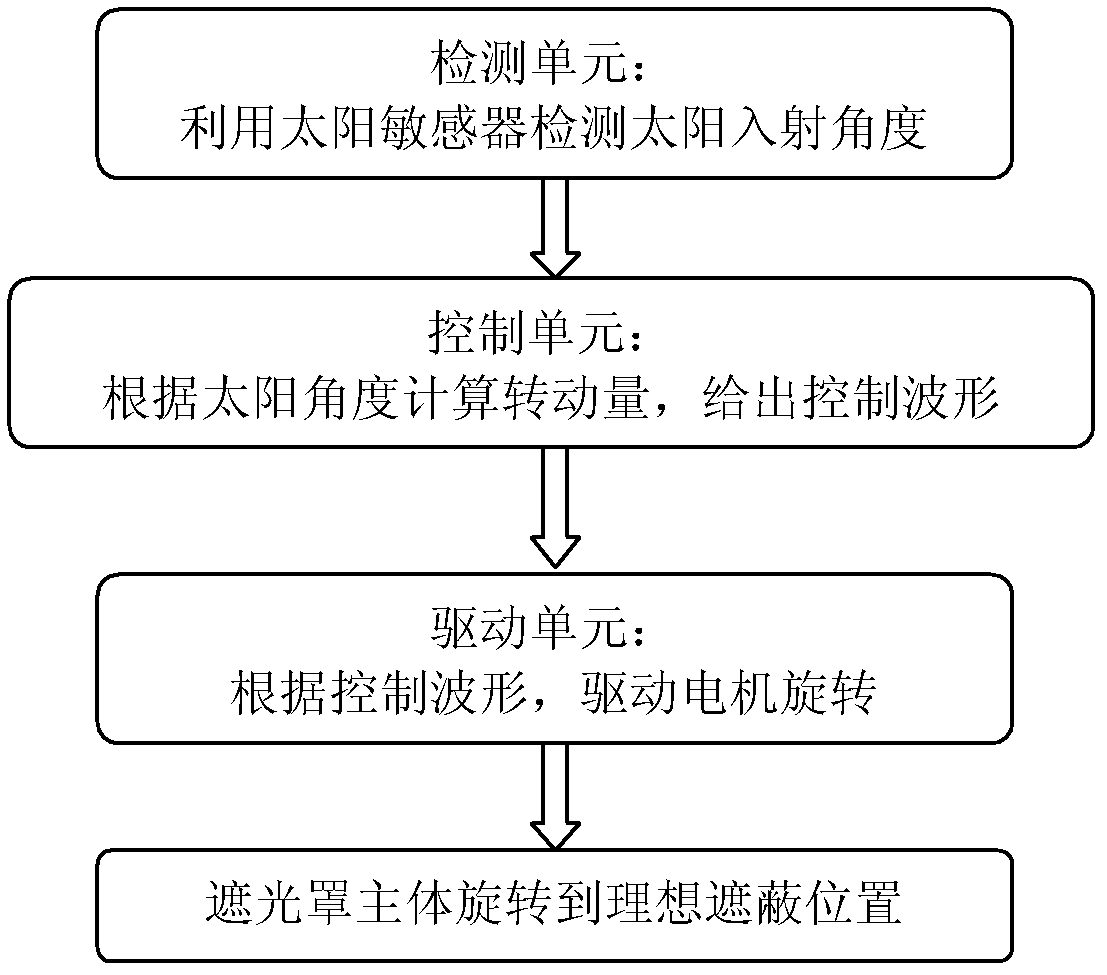
The present invention discloses a follow-up light shield control system of a space remote sensor. The opening of the light shield is a 45-DEG chamfer-shaped member. In operation of the system, a solar sensor is utilized for detecting an azimuth of the sun relative to the light shield, and the real-time azimuth information is transmitted to the control system; the control system calculates a required rotation angle of the light shield according to the obtained sun position information, and drives the light shield to rotate to an ideal shielding position through driving a stepping motor. At the ideal shielding position, the long edge of the light shield body faces the sun, and the short edge opposes the sun. The problems of stray light and heat flow caused by the sun can be settled fundamentally.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Thermally-assisted recording head and magnetic recording system
InactiveUS20120051195A1Avoid instabilityReduce lightRecord information storageMagnetic and optical recordingsWaveguideLaser beams
In a magnetic recording head including an optical waveguide for guiding a laser beam to a surface of a magnetic recording medium, a shield is provided in the vicinity of at least one portion changing discontinuously in structure of the optical waveguide to absorb or reflect non-propagating light leaking from the discontinuous portion to the outside of the optical waveguide.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20060029417A1Image quality of image can be can be prevented being deterioratedReduce noiseElectrographic process apparatusCarbon fibersImage formation
A second opening and closing door has a main body of the second opening and closing door, a sound absorbing member and a sound absorbing member cover. The sound absorbing member covers almost the entire surface of the main body of the second opening and closing door facing a guide member. The sound absorbing member cover is dyed black and made of an antistatic-treated cloth material which has air permeability, and is designed to cover almost the entire surface of the sound absorbing member facing the guide member. Further, the sound absorbing member cover is dyed with a dye which does not contain carbon, so that carbon-containing fibrous materials can be prevented from floating in an image forming apparatus while the light-shielding effect can be maintained.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Measuring device and measuring method for tiny surface defect through post-magnification digital holographic microscopy
InactiveCN103226001AImprove signal-to-noise ratioSuppress scattered lightOptically investigating flaws/contaminationUsing optical meansLight irradiationDigital holographic microscopy
The invention relates to a measuring device and a measuring method for a tiny surface defect through post-magnification digital holographic microscopy. The measuring method comprises the steps that a short coherent light source is adopted; scattered light information of the tiny surface defect of an optical element is obtained in an oblique incidence manner; scattered light interferes with a reference beam; interference image information is magnified in a post-magnification manner and received by a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) camera; and finally a pattern of the tiny surface defect and quantification information of depth distribution are computed and analyzed through a digital holographic principle. The device is mainly used for achieving detection of the tiny surface defect of the smooth optical element. The device can obtain depth and phase information of the surface defect by acquiring a single image and conducting related processing, can distinguish surface dust and indentation of the optical element, and can dynamically and rapidly measure. The device adopts a parallel light irradiation and off-axis holographic technique, and forms a post-magnification digital holographic recording system, so that the device is good in dynamic property and has the characteristics of non-destruction and information quantification.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method and device for simultaneous online detection of hidden damages and sugar content of yellow peaches by near infrared spectrum diffuse transmission technique
InactiveCN107621460ARealize simultaneous online detectionReduce the impact of uneven sugar contentMaterial analysis by optical meansSortingInfraredStray light
The invention discloses a method and device for simultaneous online detection of hidden damages and sugar content of yellow peaches by a near infrared spectrum diffuse transmission technique. The method and the device are characterized in that a) by light path arrangement in a manner of all-around irradiating and bottom receiving, influences caused by nonuniformity of sample sugar contents on model precision can be reduced; b) stray light can be effectively inhibited by a combination device under own gravity actions of samples; c) the method for simultaneous online detection of the hidden damages and the sugar content of the yellow peaches is provided.
Owner:EAST CHINA JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
High-resolution micro broad-spectrum reflective optical system for spectrograph
InactiveCN102141440AReduce volumeReduce weightRadiation pyrometryAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyGratingSpectrometer
The invention discloses a high-resolution micro broad-spectrum reflective optical system for a spectrograph, which relates to the field of optical analytical instruments and solves the problems of low spectral resolution capacity, low optical energy transfer efficiency and complex instrument processing, installation and debugging of the instrument having the conventional optical system. The system of the invention comprises an optical fiber interface, a slit, a collimator objective, an imaging objective, a detector image surface, a planar reflection grating and a rotating platform, wherein the planar reflection grating is arranged on the rotating platform, a sample light source is coupled to the optical fiber interface and projected into the collimator objective from the slit; the parallel light beam emitted by the light source and transmitted out from the collimator objective is projected to the planar reflection grating and reflected to the imaging objective; the light beam transmitted out from the imaging objective is imaged onto the detector image surface to form an image signal, and the spectral absorption components of the sample light source can be analyzed; and the collimator objective and the imaging objective are spherical reflector. The system can be widely used in portable spectrograph for field geological and hydrologic survey and military reconnaissance.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Lens capable of eliminating stray light and manufacturing method thereof
PendingCN107219580AQuality improvementEliminate stray lightOptical filtersAbrasive blastingOphthalmology
The invention discloses an aspherical lens of great stray light suppression effect and a manufacturing method thereof. The aspherical lens comprises a lens. The center of the lens is an aspherical curved surface. The aspherical lens is characterized in that the edges of the lens are provided with flange plates, the center and the edges of the lens are different in color and the edges of the lens are provided with clip ports. The aspherical lens is manufactured by a one-step formation method. The manufacturing method is simple so that the technical requirement for exquisite abrasive blasting for the edges of the lens can be reduced. According to the spherical lens, the center and the edges of the lens have two colors so that the stray light can be effectively suppressed and the frame photographing quality of the camera can be enhanced.
Owner:广州晶和光电科技有限公司
Fresnel lens sheet, transmission type screen and rear projection type display apparatus
InactiveUS20060109569A1Suppress stray lightBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsLensFresnel lensOptoelectronics
A rear projection type display apparatus is disclosed wherein image light reflected upon entrance thereof into a Fresnel lens sheet of the reflection type provided on a transmission type screen is suppressed from making stray light. A Fresnel lens sheet for converting incident light incoming at an incident angle within a predetermined angular range into parallel light includes a plurality of prisms arrayed on the light entrance face of a substrate. Each prism has a refracting face for refracting the incident light and a reflecting face for reflecting the refracted light from the refracting face toward the emergence face of the substrate. At least some of the prisms are configured such that the angle of a perpendicular to the refracting face with respect to a perpendicular to the emergence face is smaller than the incident angle at the position of the prism.
Owner:SONY CORP
Lobster eye lens for restricting generation of stray light by adopting light-absorbing coating
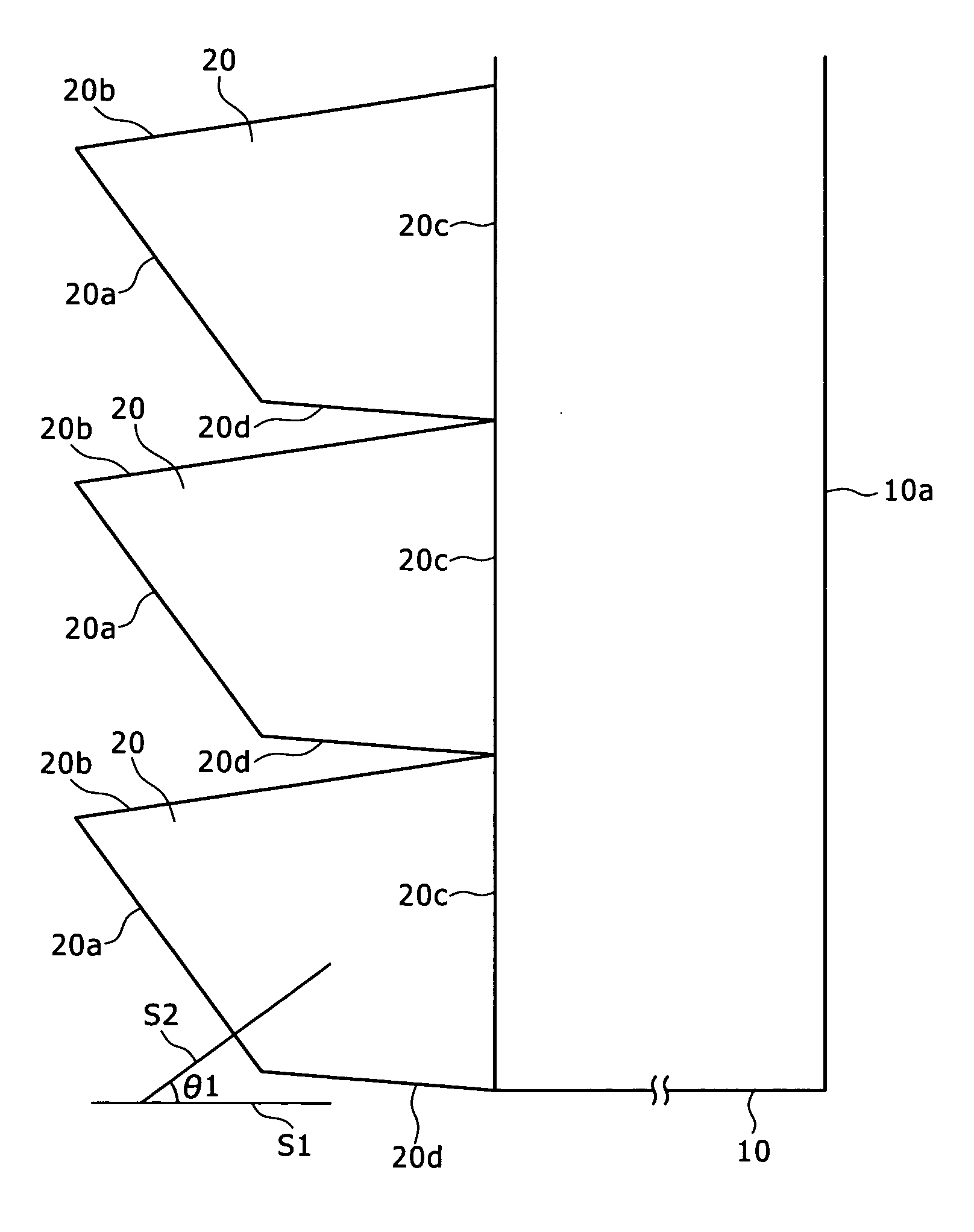
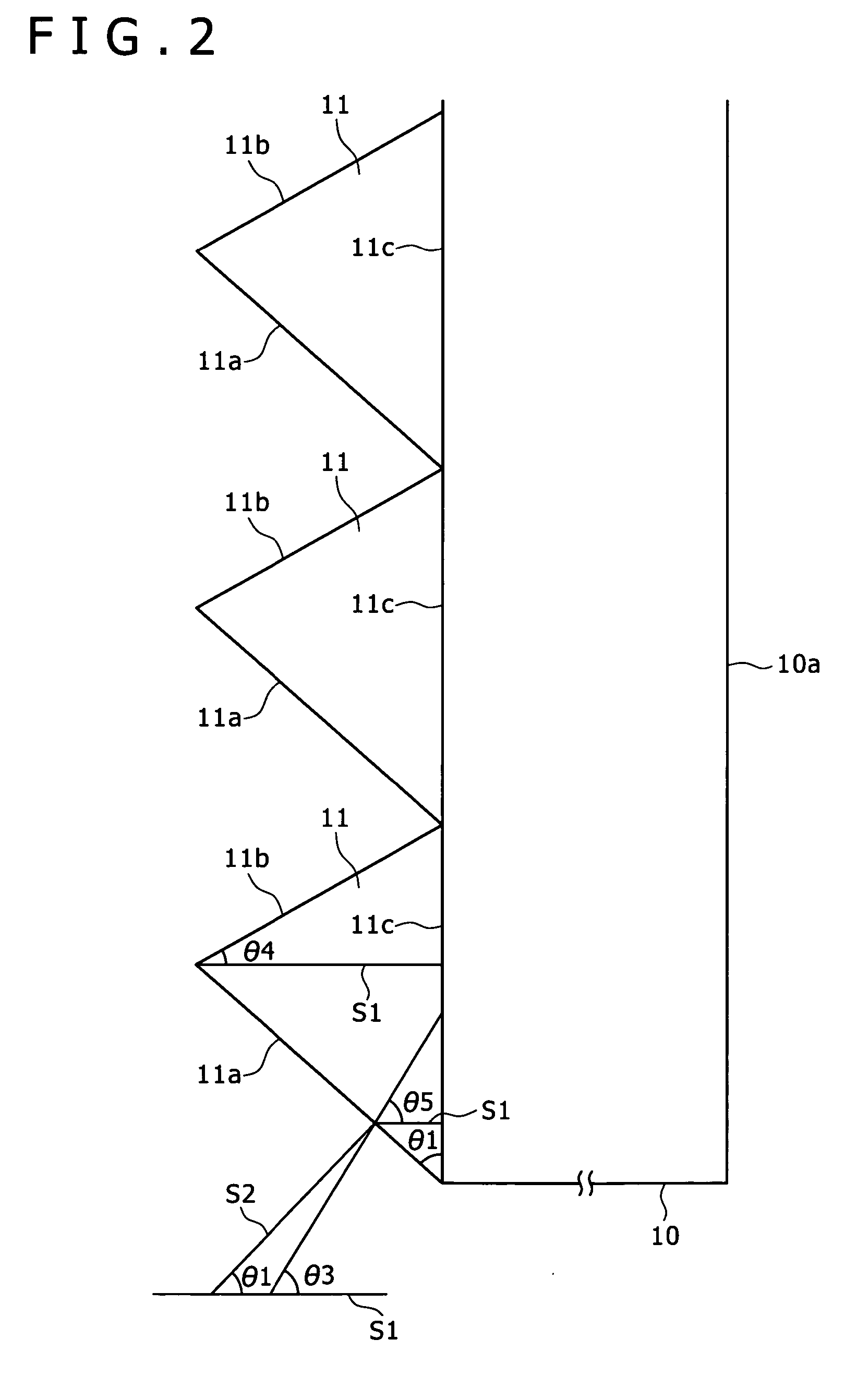
The invention relates to a lobster eye lens for restricting the generation of stray light by adopting a light-absorbing coating, belonging to the technical field of bionic optics. In the prior art, stray light is reflected to cause fuzzy images. The lobster eye lens comprises a plurality of micro-channel tubes in the shape of a regular square pyramid with a cone-apex angle alpha, inner walls of four isosceles trapezoidal sides of the regular square pyramid are used as reflecting walls, the outer margins of the micro-channel tubes are formed by four edges at the bottom surface of the regular square pyramid, the outer margin of each micro-channel tube is arranged on a sphere with a radius r1, the inner margins of the micro-channel tubes are formed by four edges at the top surface of the regular square pyramid, the inner margin of each micro-channel tube is arranged on sphere with a radius r2, the reflecting wall of each micro-channel tube is coated with an outer margin light-absorbing coating ring belt with a width s1 inwards from the outer margin, the reflecting wall of each micro-channel tube is coated with an inner margin light-absorbing coating ring belt with a width s2 inwards from the inner margin, and an included angel beta is formed between marginal rays of incident micro-channel tube parallel light e close to one side of an incident light optic axis and the reflecting walls below the micro-channel tubes.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Ultra-wide field-of-view off-axis three-reflector optical imaging system
The invention discloses an ultra-wide field-of-view off-axis three-reflector optical imaging system which comprises a main reflector with positive focal power, a second reflector with negative focal power, and a third reflector with positive focal power. The reflecting surface of the main reflector is a spherical surface. The reflecting surfaces of the secondary mirror and the third reflector are flat spherical secondary curved surfaces. The curvature radii of top points of the three reflectors approximately satisfy a flat image field condition. The main reflector generates a real image of a far scene between the main reflector and the second reflector. The second reflector and the third reflector perform relay imaging of the real image on an image plane. An aperture diaphragm is placed on the front focal plane of the third reflector, thereby realizing an image-side telecentric optical path. The main reflector inclines along an X-axis relative to incident main light of a central field-of-view. The second reflector is coaxial with the third reflector. After the main light of the central field-of-view in a meridian plane is reflected by the main reflector, an included angle is formed between the reflected main light and the common symmetric axis of the second reflector and the third reflector. The ultra-wide field-of-view off-axis three-reflector optical imaging system has advantages of ultra-wide field-of-view, intermediate relative aperture, wide working wave band, no image-side telecentric barrier, small object-side distortion, high imaging quality, etc. The ultra-wide field-of-view off-axis three-reflector optical imaging system is suitable for earth imaging observation field of a spatial camera, an imaging spectrometer, etc.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Fresnel lens sheet, transmission type screen and rear projection type display apparatus
InactiveUS7535637B2Suppress stray lightBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsLensFresnel lensOptoelectronics
A rear projection type display apparatus is disclosed wherein image light reflected upon entrance thereof into a Fresnel lens sheet of the reflection type provided on a transmission type screen is suppressed from making stray light. A Fresnel lens sheet for converting incident light incoming at an incident angle within a predetermined angular range into parallel light includes a plurality of prisms arrayed on the light entrance face of a substrate. Each prism has a refracting face for refracting the incident light and a reflecting face for reflecting the refracted light from the refracting face toward the emergence face of the substrate. At least some of the prisms are configured such that the angle of a perpendicular to the refracting face with respect to a perpendicular to the emergence face is smaller than the incident angle at the position of the prism.
Owner:SONY CORP
ND filter, method for manufacturing said filter, and multi-display device and image forming device using said filter
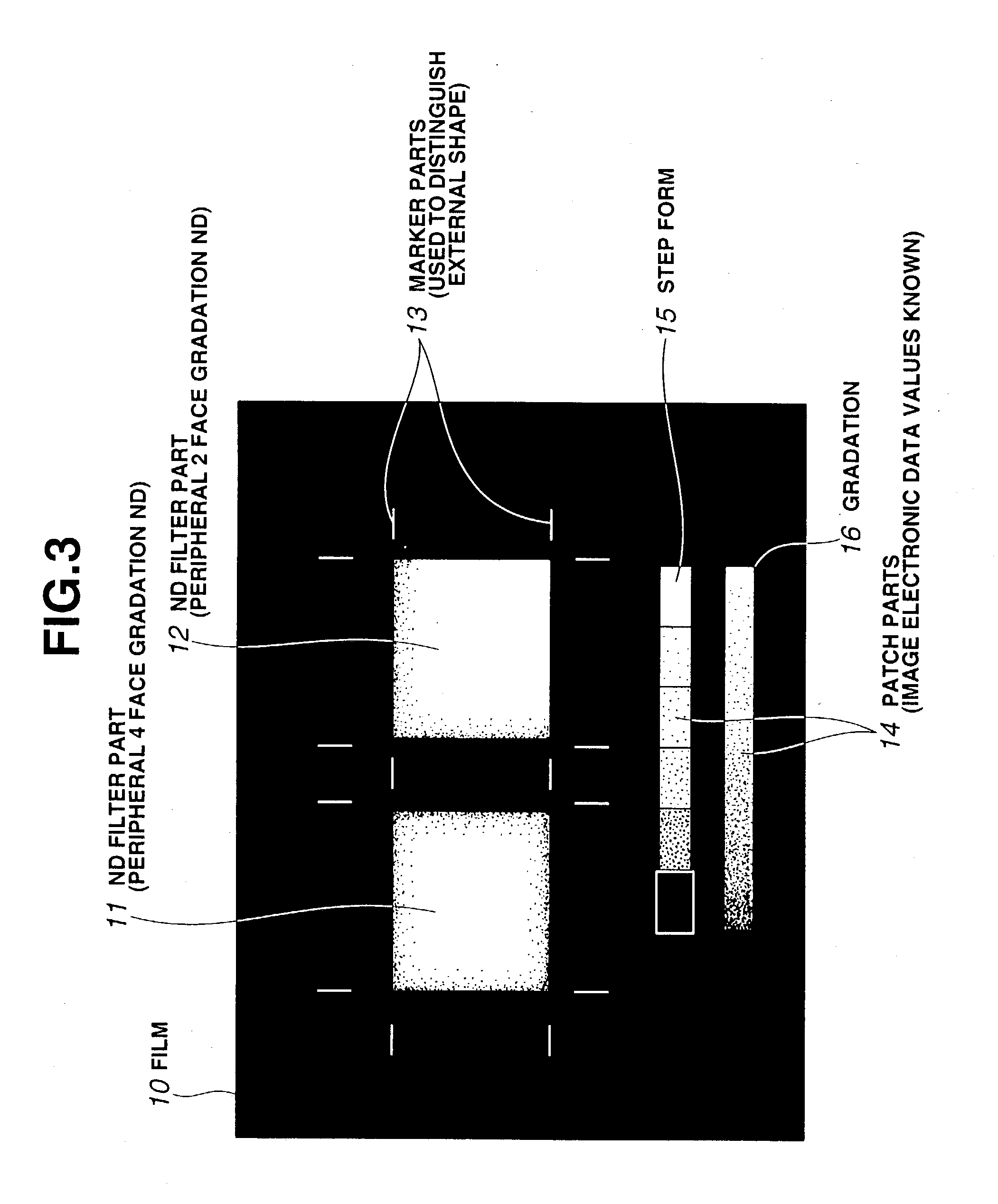
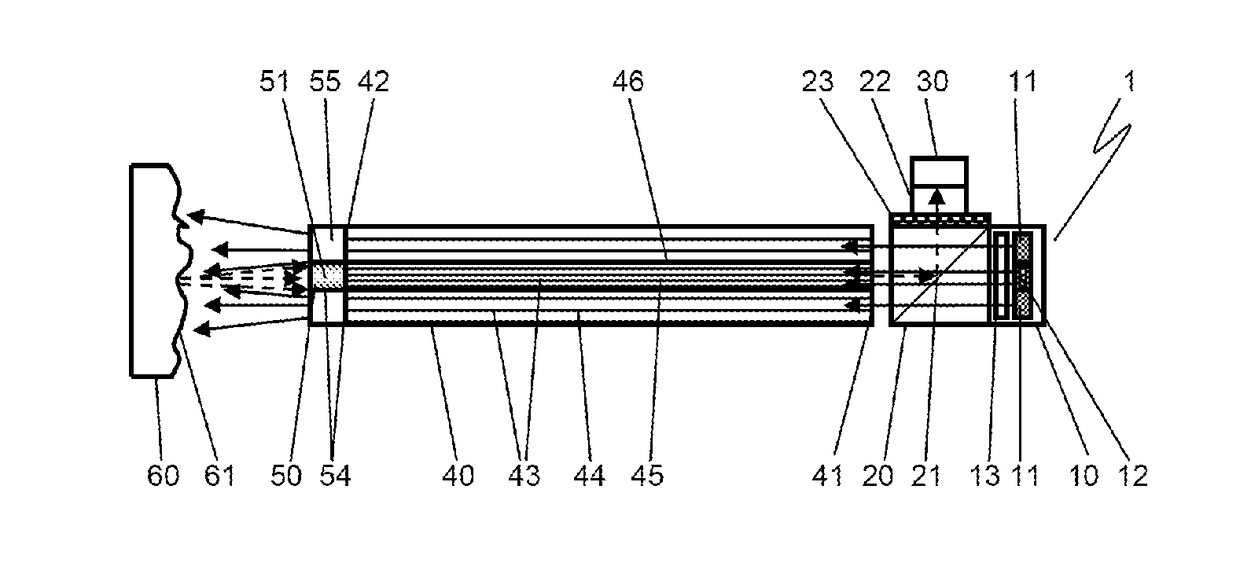
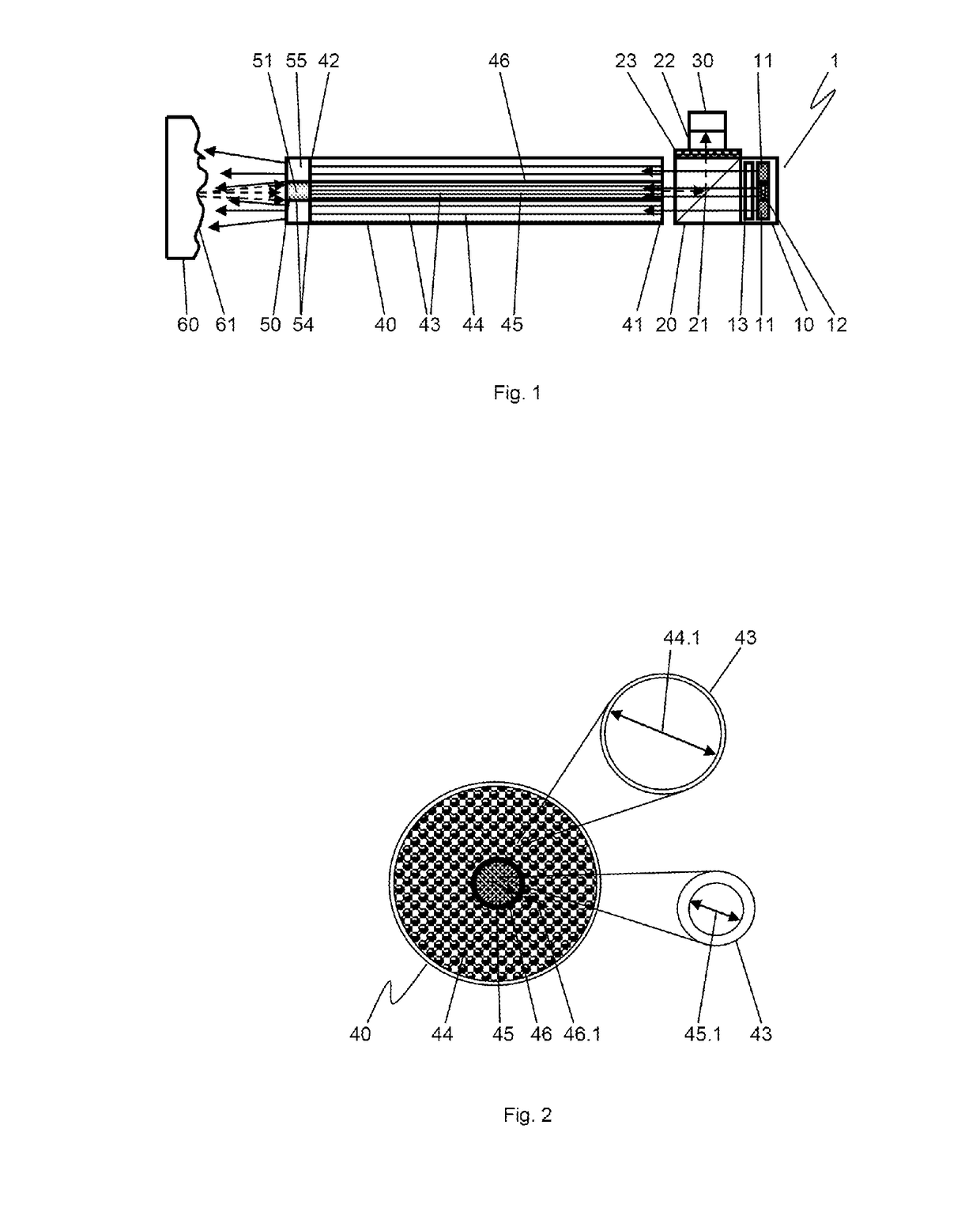
InactiveUS20030160946A1Suppress drop in transmittanceSuppress stray lightTelevision system detailsProjectorsOptical transmittanceDisplay device
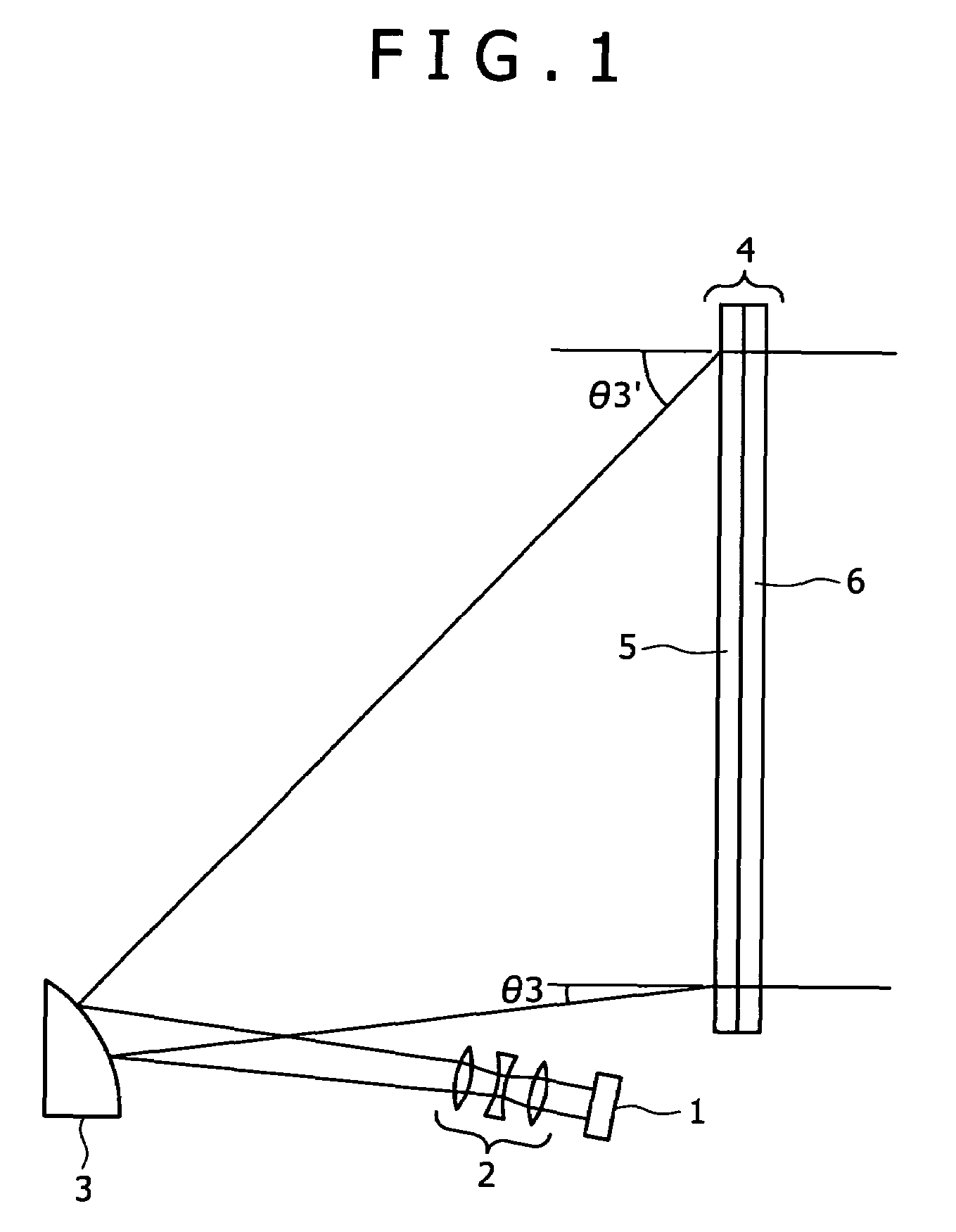
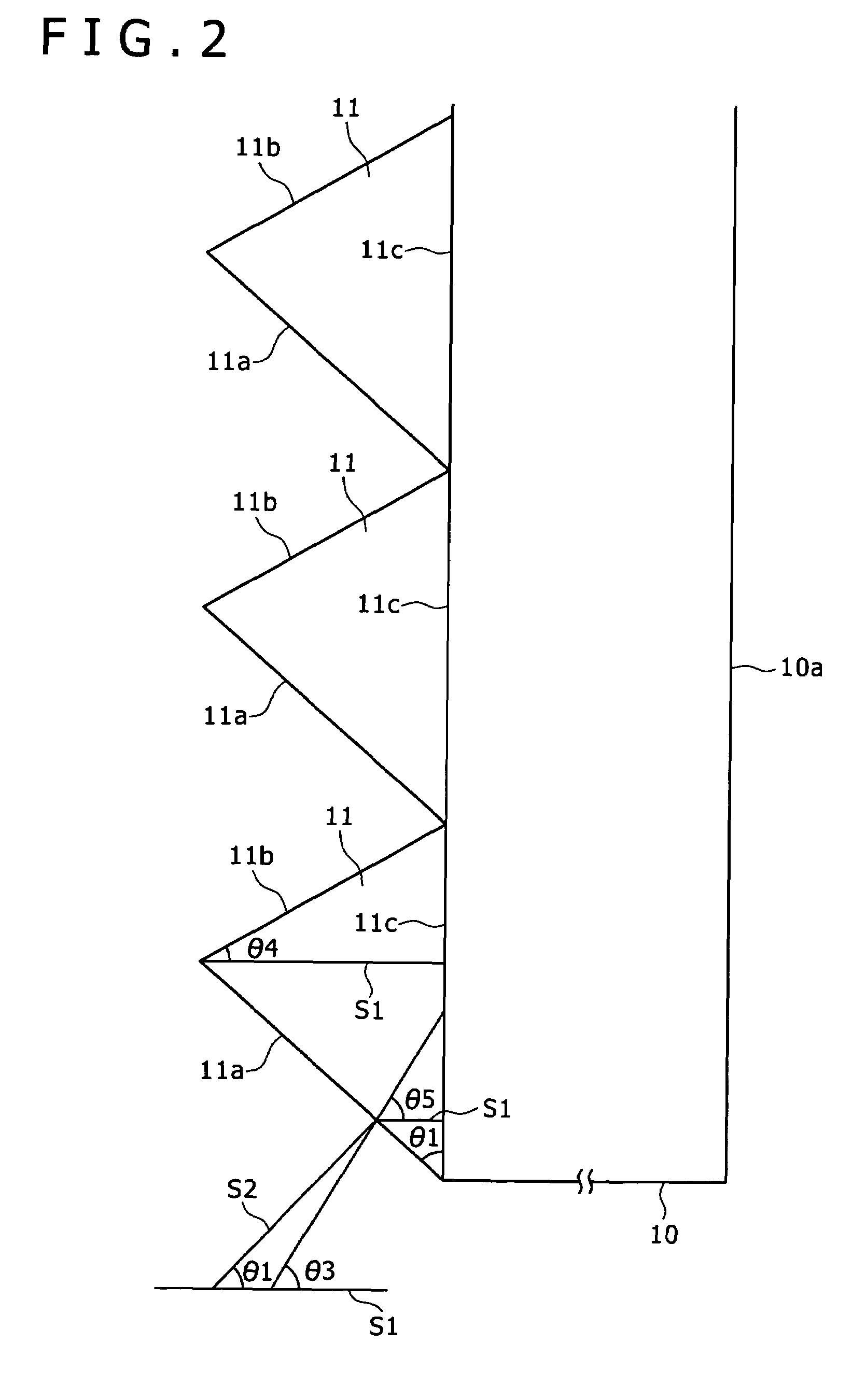
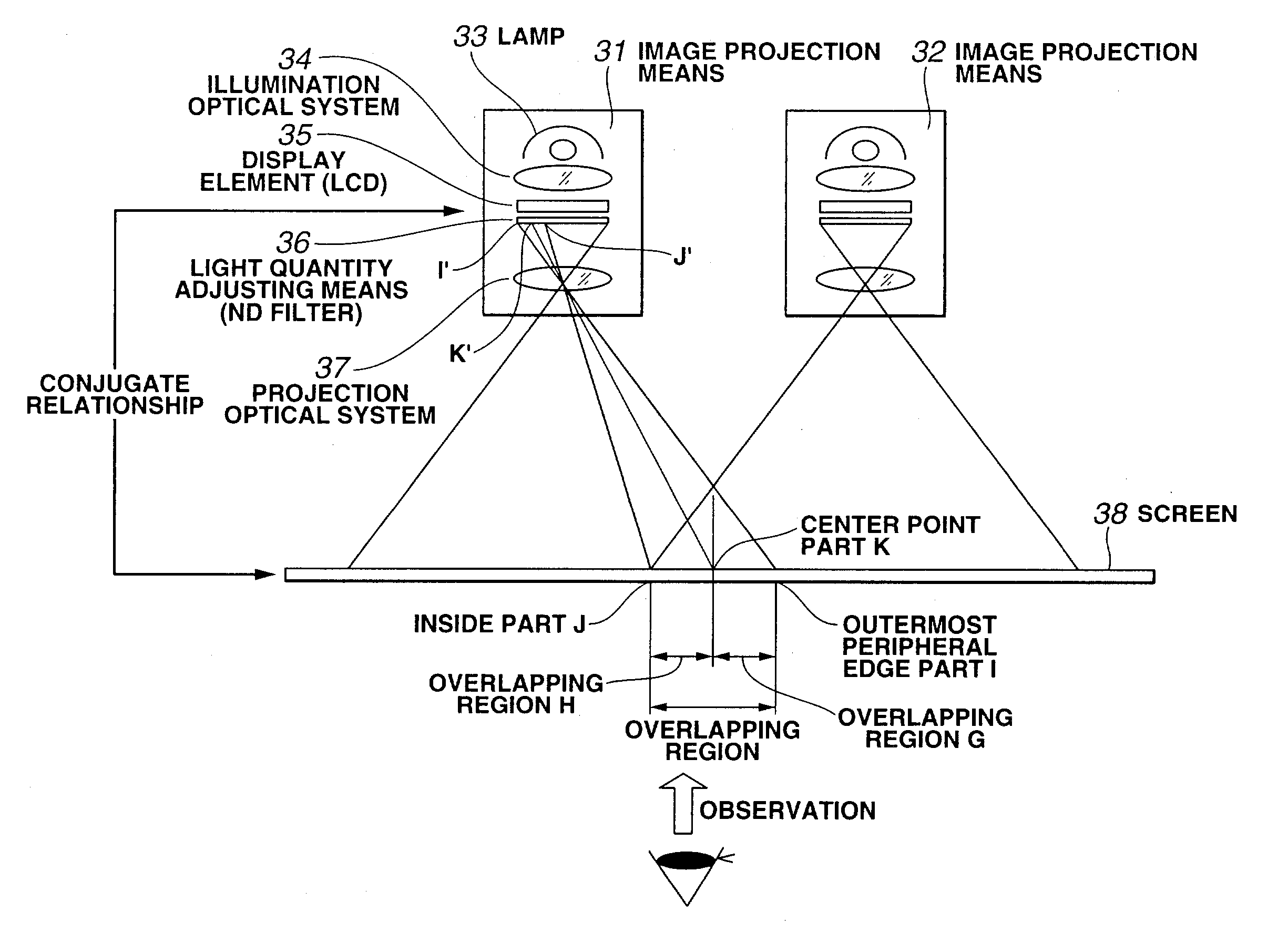
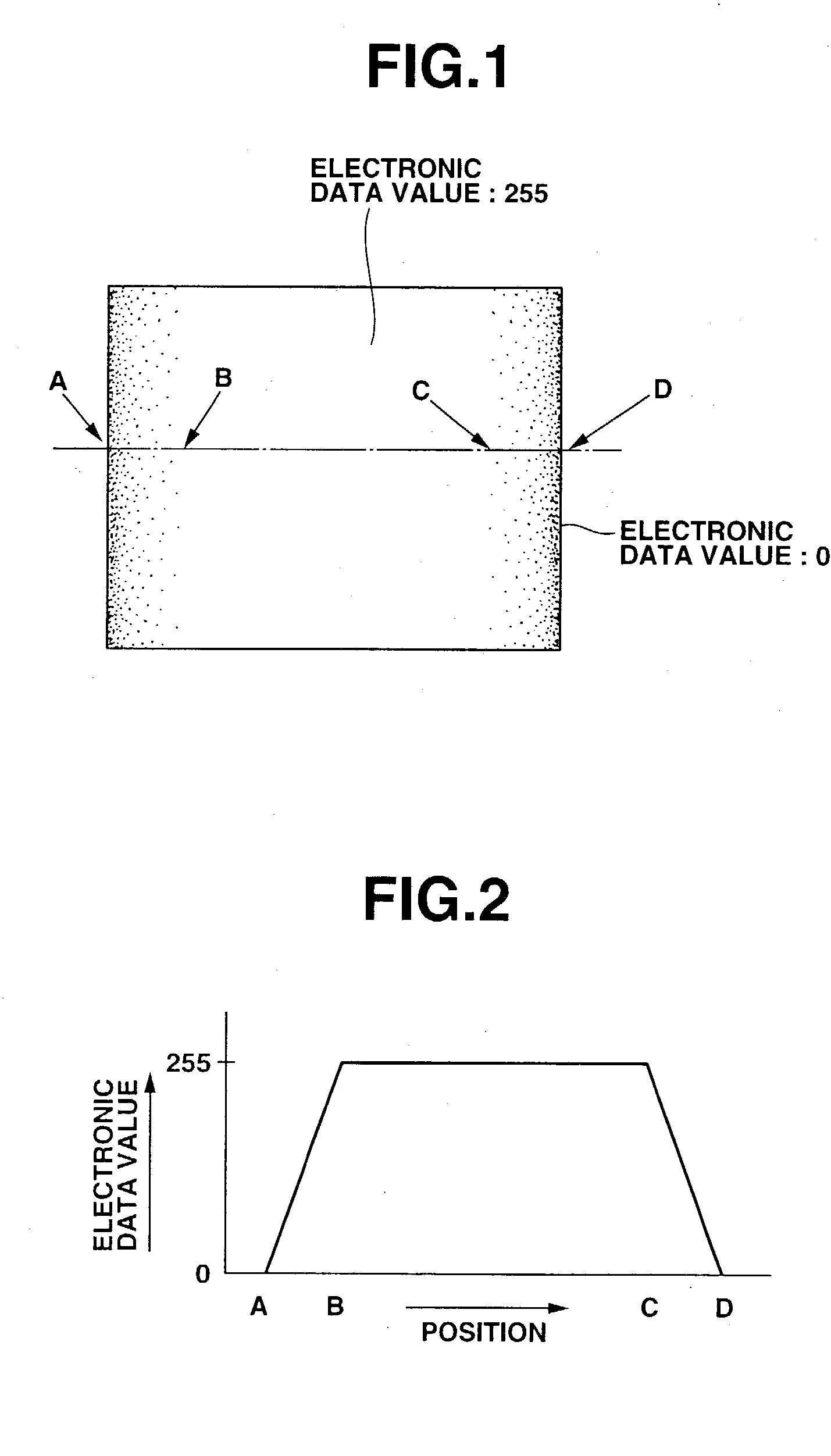
The present invention provides an ND filter manufacturing method which makes it possible to obtain an ND filter film that has light transmittance information in respective positions by exposing and imaging image electronic data that has light transmittance information for respective positions used to form an ND filter by employing an exposure imaging device that is capable of the direct exposure imaging of the image electronic data, and developing the film. Furthermore, the light transmittance distributions of ND filters disposed in positions corresponding to the overlapping regions in a multi-display device are constructed from curves, so that the overlapping regions are hard to distinguish from the non-overlapping regions.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Illumination system comprising heterogeneous fiber arrangement
ActiveUS20180081165A1Suppress stray lightImprove image qualityEndoscopesFibre light guidesFiberEngineering
An illumination system is provided that includes a spatial fiber arrangement with an optical element at the distal end of the fiber arrangement. The fiber arrangement has a first region including individual fibers with a significantly smaller active diameter in comparison with the individual fibers of a remaining region. The optical element at the distal end is assigned the remaining region. The fiber arrangement can be a rigid fiber rod that includes an intermediate region provided between the first region and the remaining region. The intermediate region suppresses stray light transfers between the first and remaining regions. The fiber arrangement can include an optical coupling element at a proximal end of the fiber rod.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com