Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
81results about How to "Reduced signaling process" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
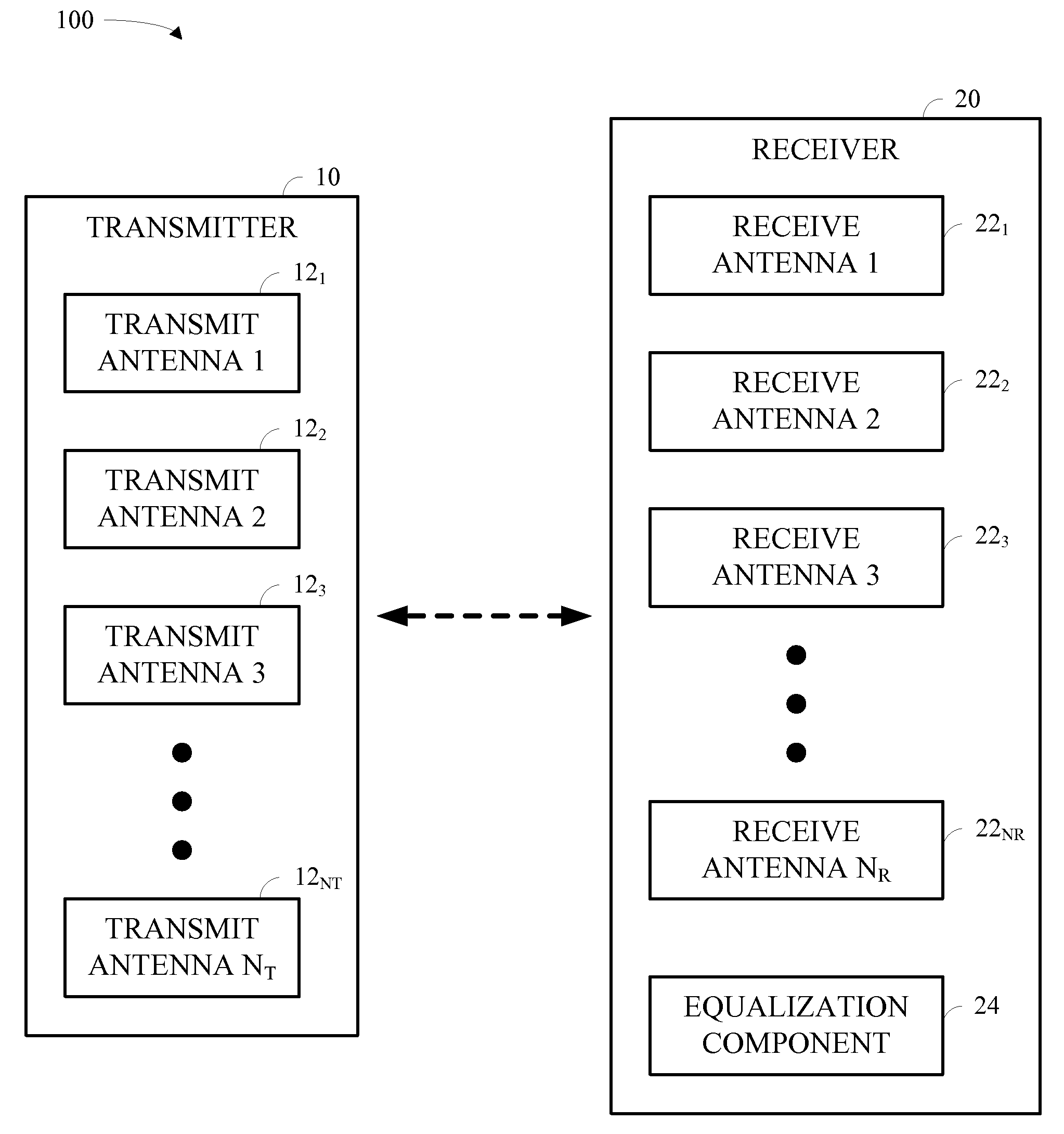
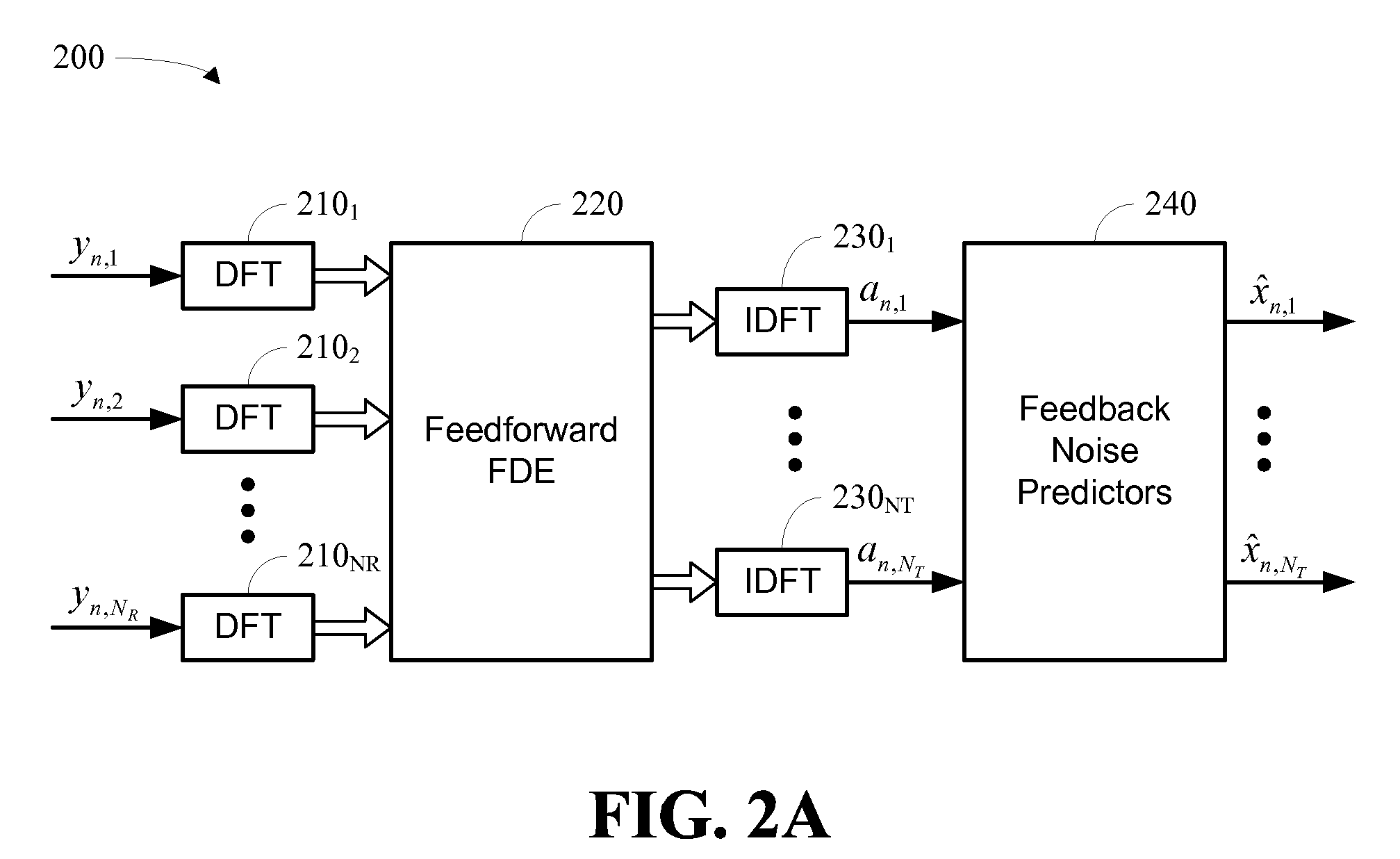
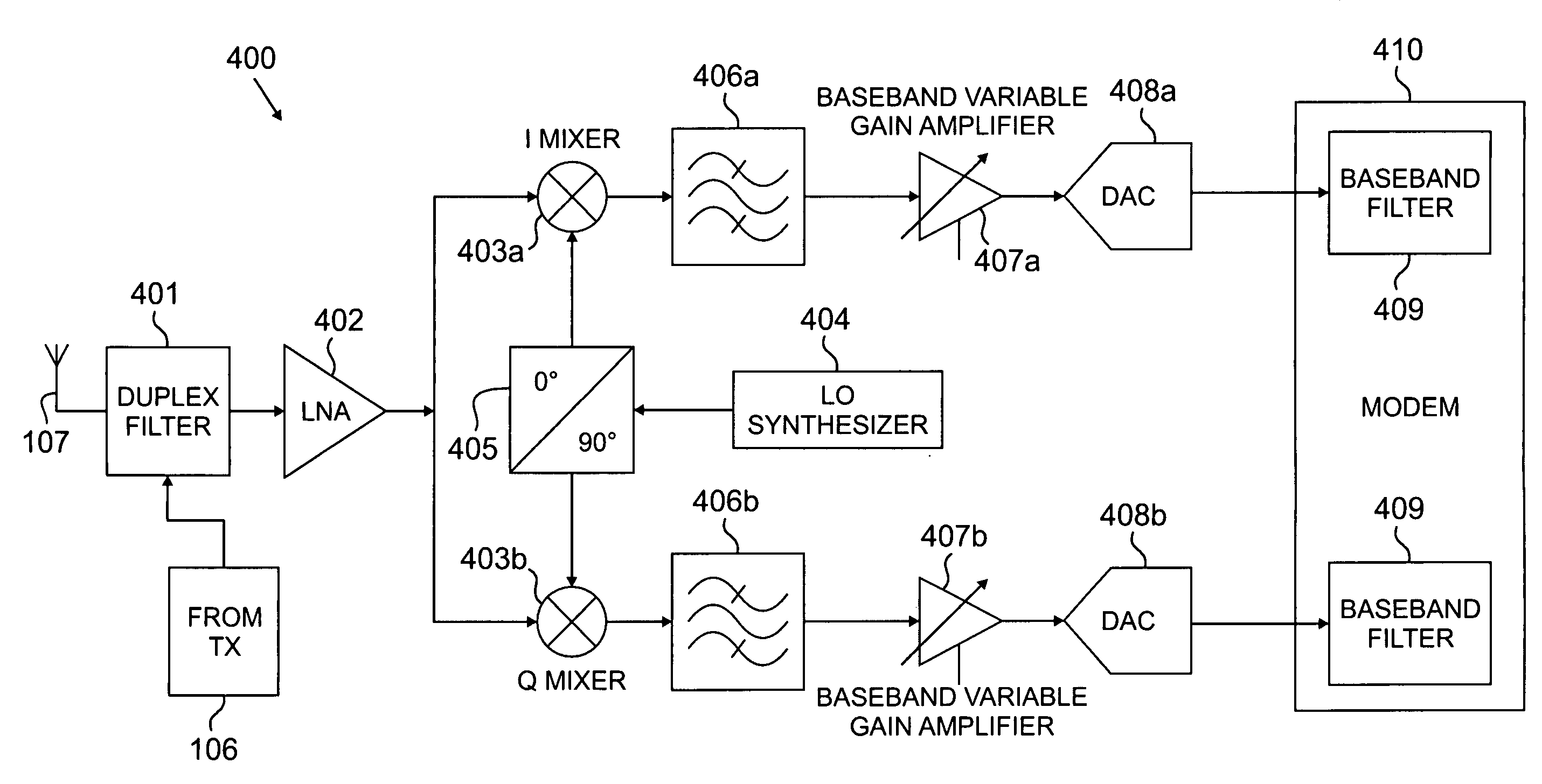
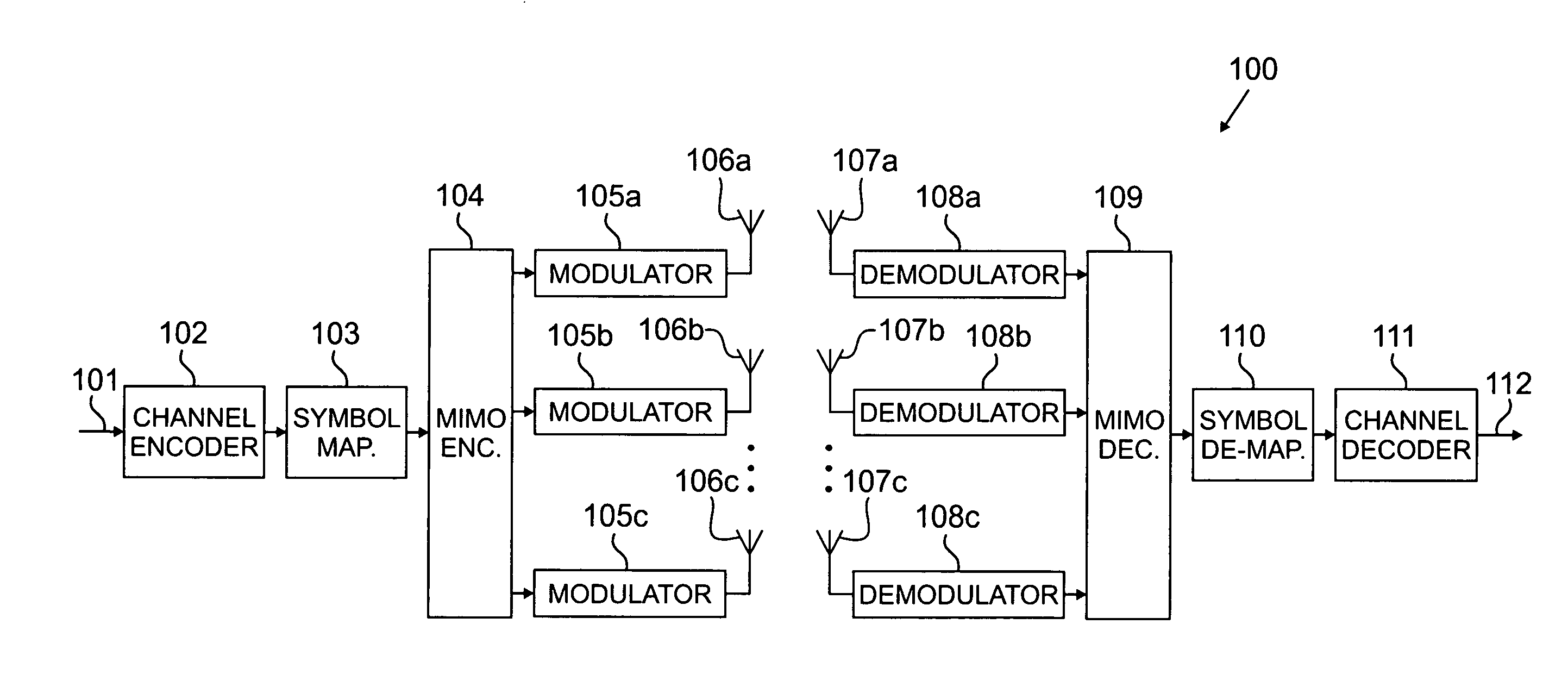
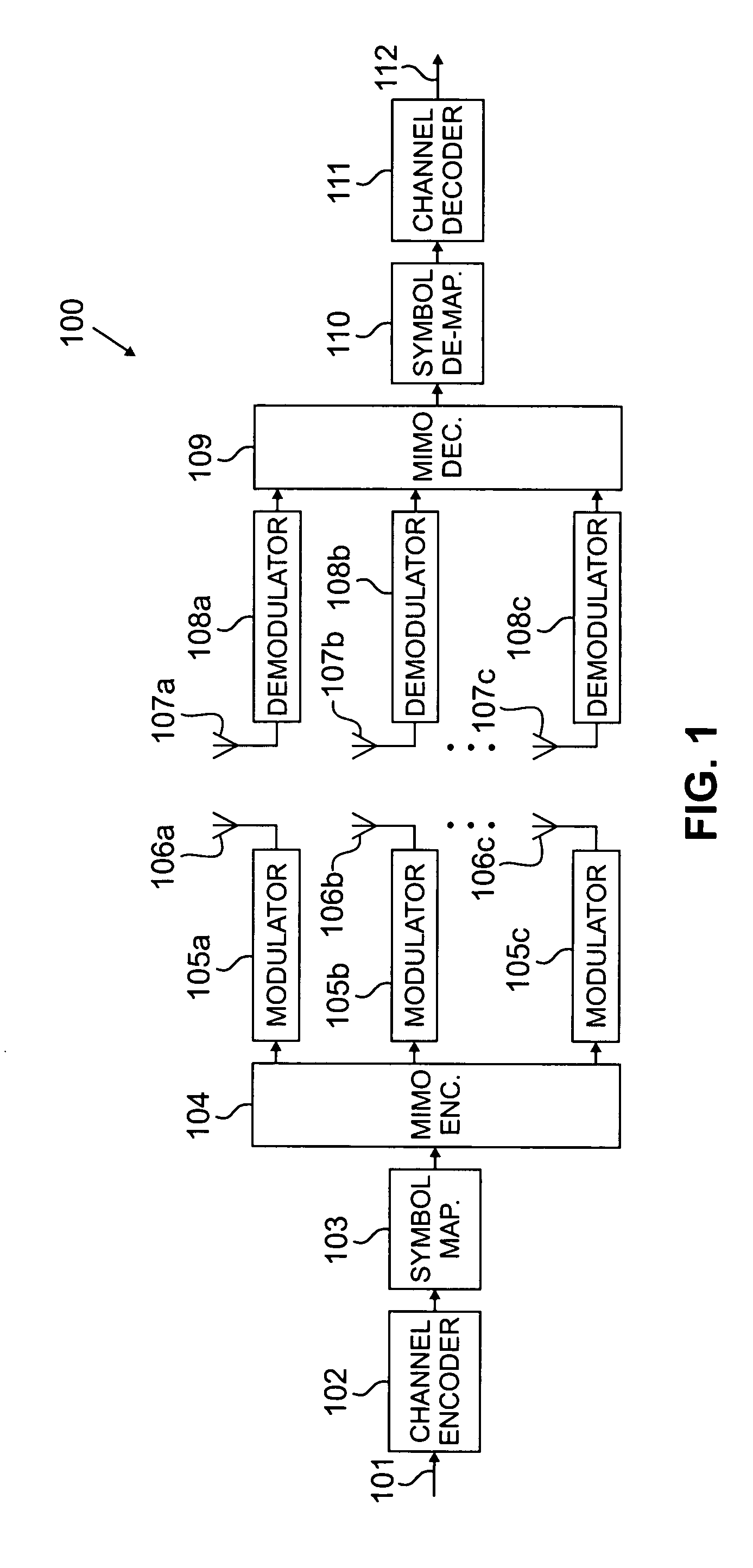
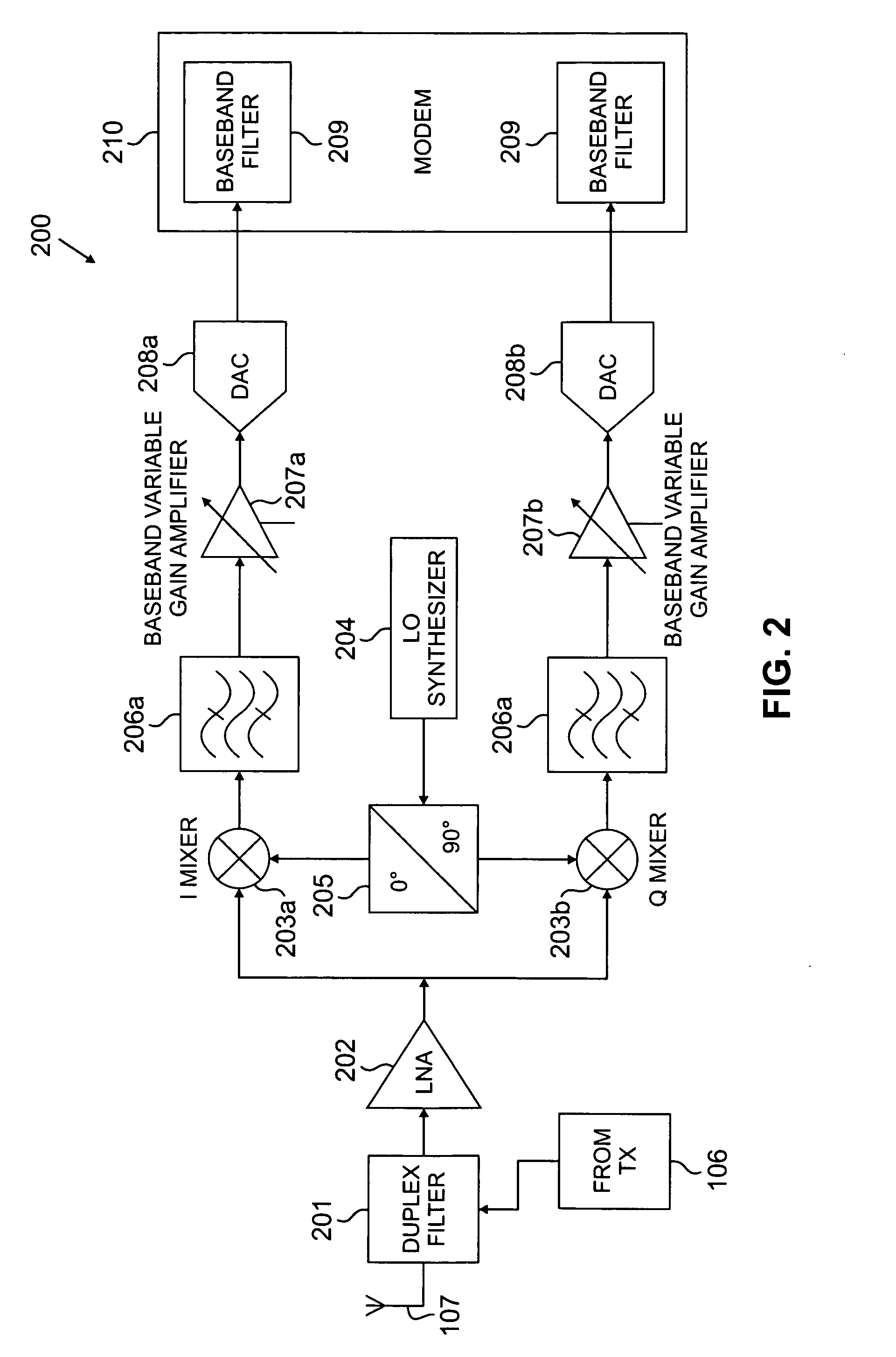
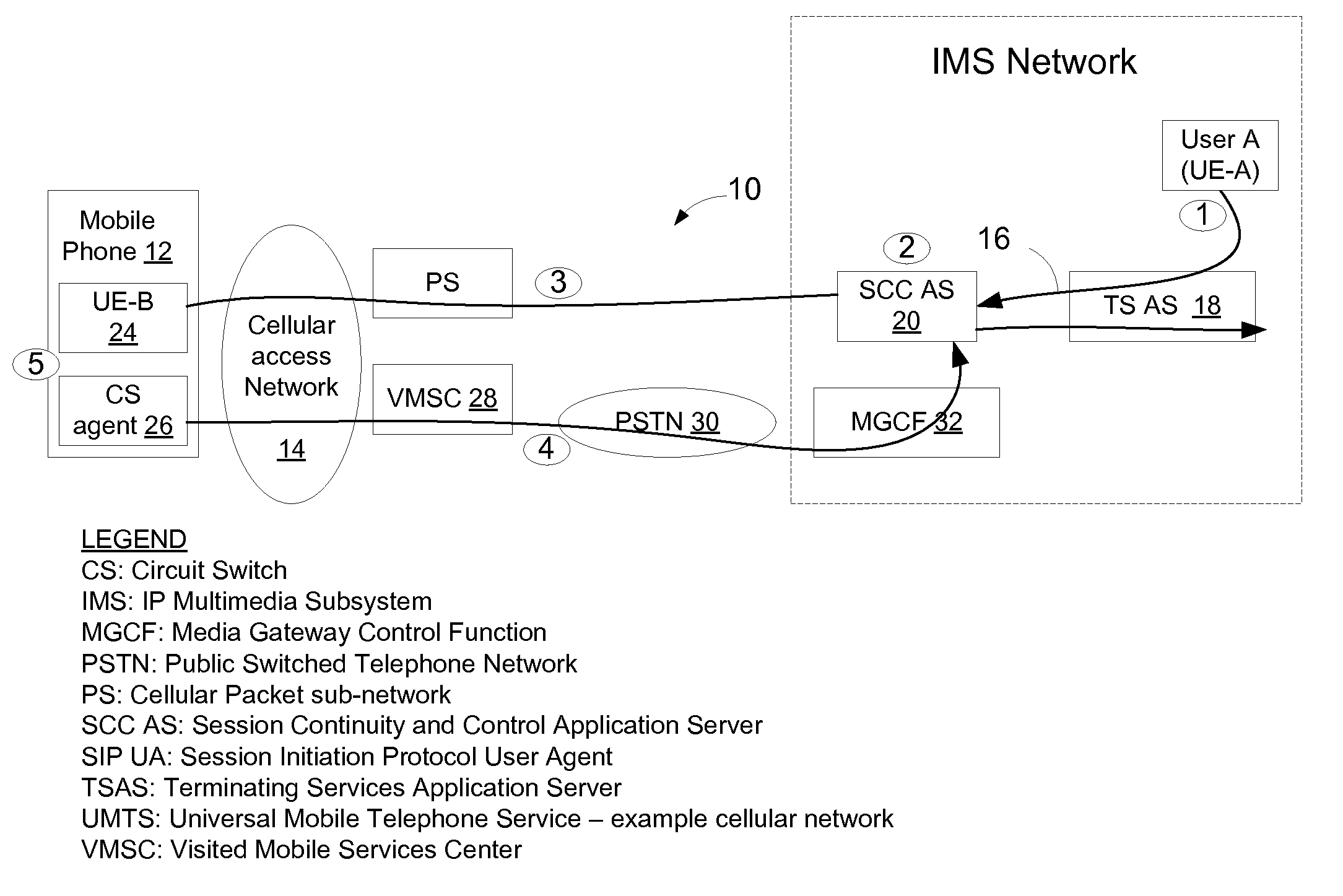
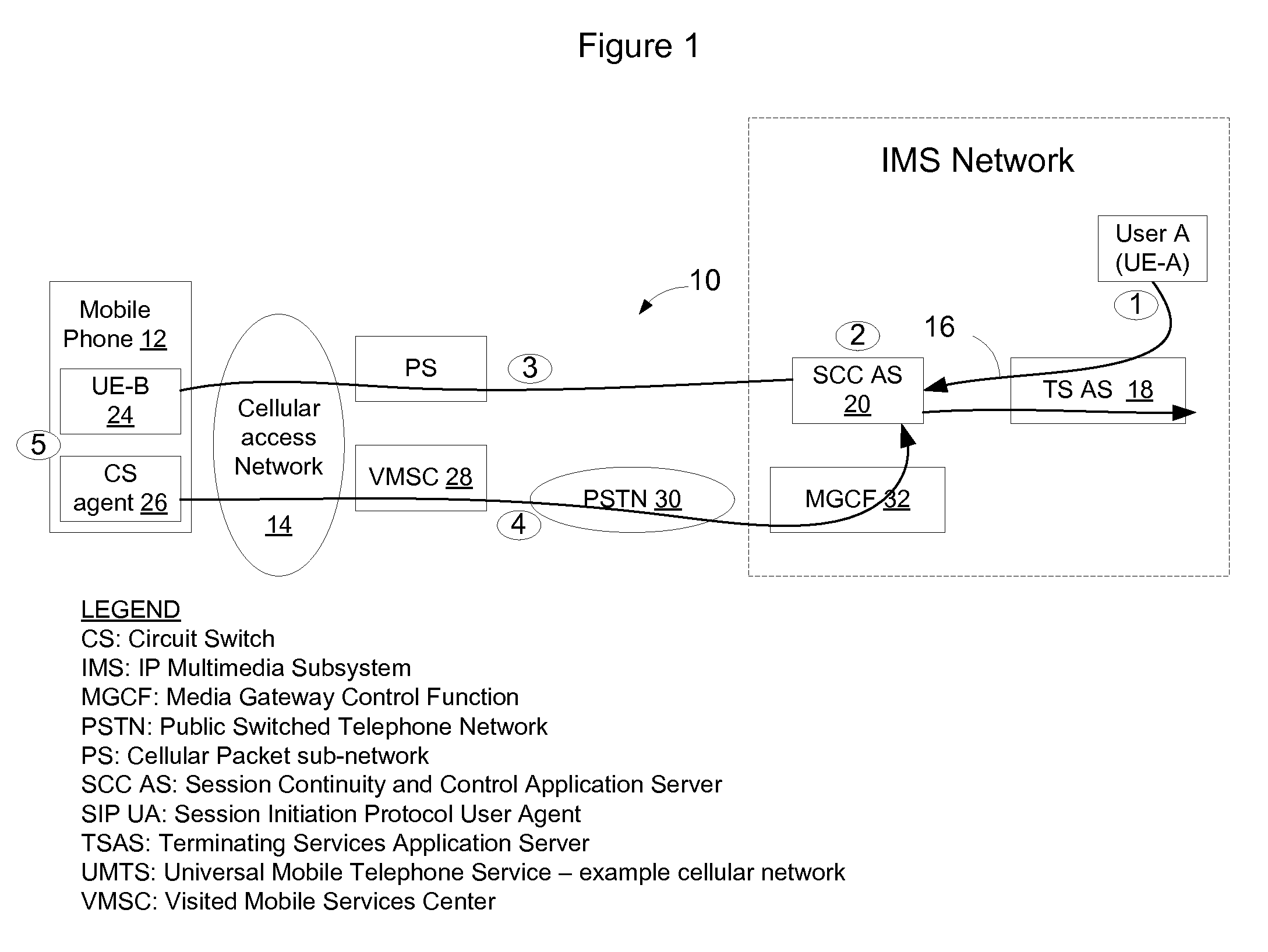
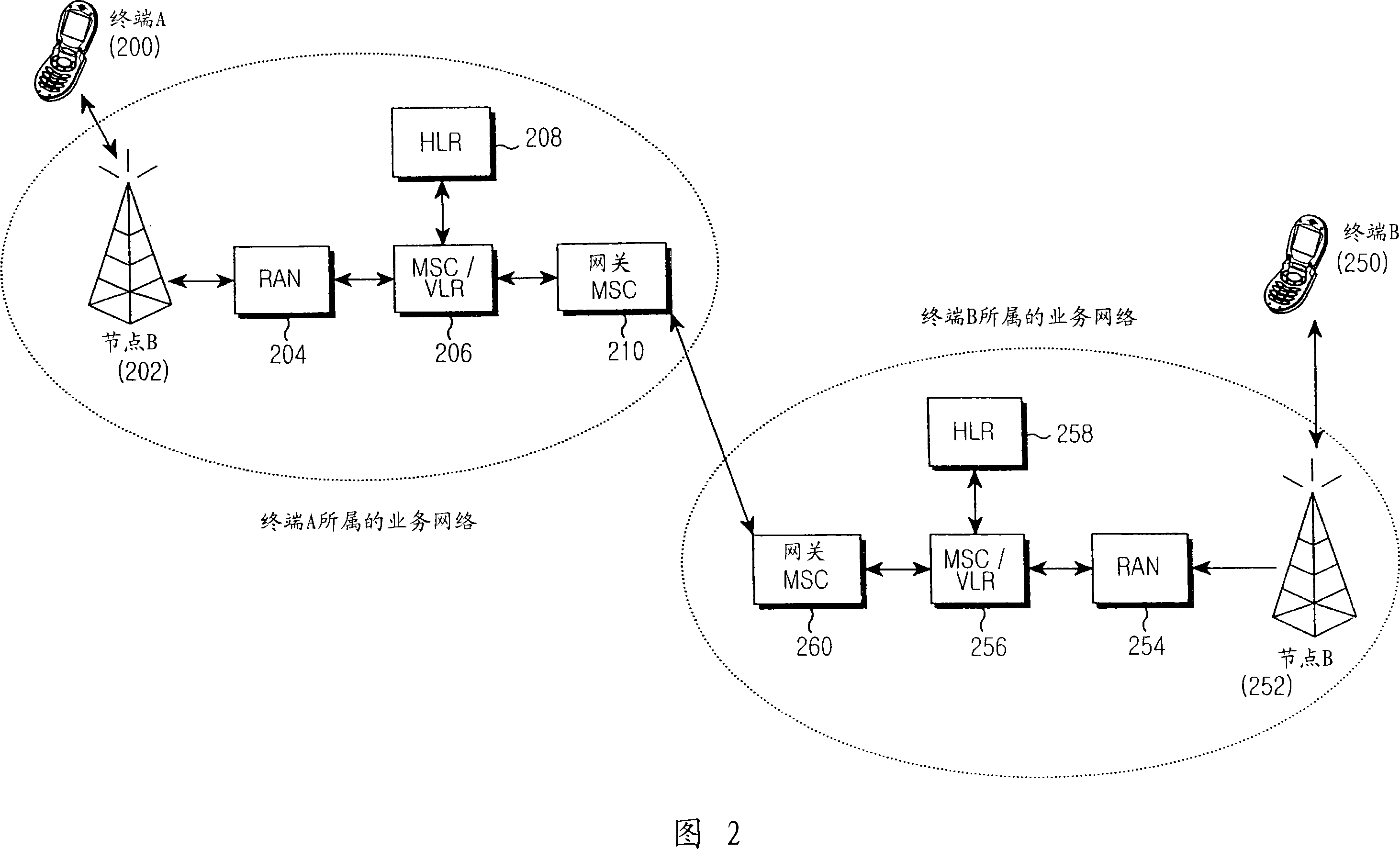
Hybrid time-frequency domain equalization over broadband multi-input multi-output channels
InactiveUS20080304558A1Good flexibilityMore reliabilityMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsMulti inputData stream
A system and methodology for channel equalization are provided. According to one aspect, a receiver structure for a MIMO system is provided that employs frequency domain equalization (FDE) with noise prediction (FDE-NP). The FDE-NP structure may include a feedforward linear frequency domain equalizer and a group of time domain noise predictors (NPs), which may operate by predicting a distortion corresponding to a given linearly equalized data stream based on previous distortions of all linearly equalized data streams. According to another aspect, a receiver structure for a MIMO system is provided that employs FDE-NP with successive interference cancellation (FDE-NP-SIC), which can extend the functionality of FDE-NP by ordering all linearly equalized data streams according to their minimum mean square errors (MMSEs) and detecting those streams which have a low MMSE first, thereby allowing current decisions of lower-indexed streams to be considered along with previous decisions for all data streams for noise prediction. According to a third aspect, a method for analyzing the performance of a MIMO system with equalization is provided. Pursuant to the method, a general expression of MMSE may first be derived. The MMSE expression may then be related to an error bound by applying the modified Chernoff bounding methodology in a general MIMO system. The parameters in the result may then be varied for applicability to single-input single-output (SISO), multiple-input single-output (MISO), and single-input multiple-output (SIMO) systems with receiver equalization technology.
Owner:YIM TU INVESTMENTS
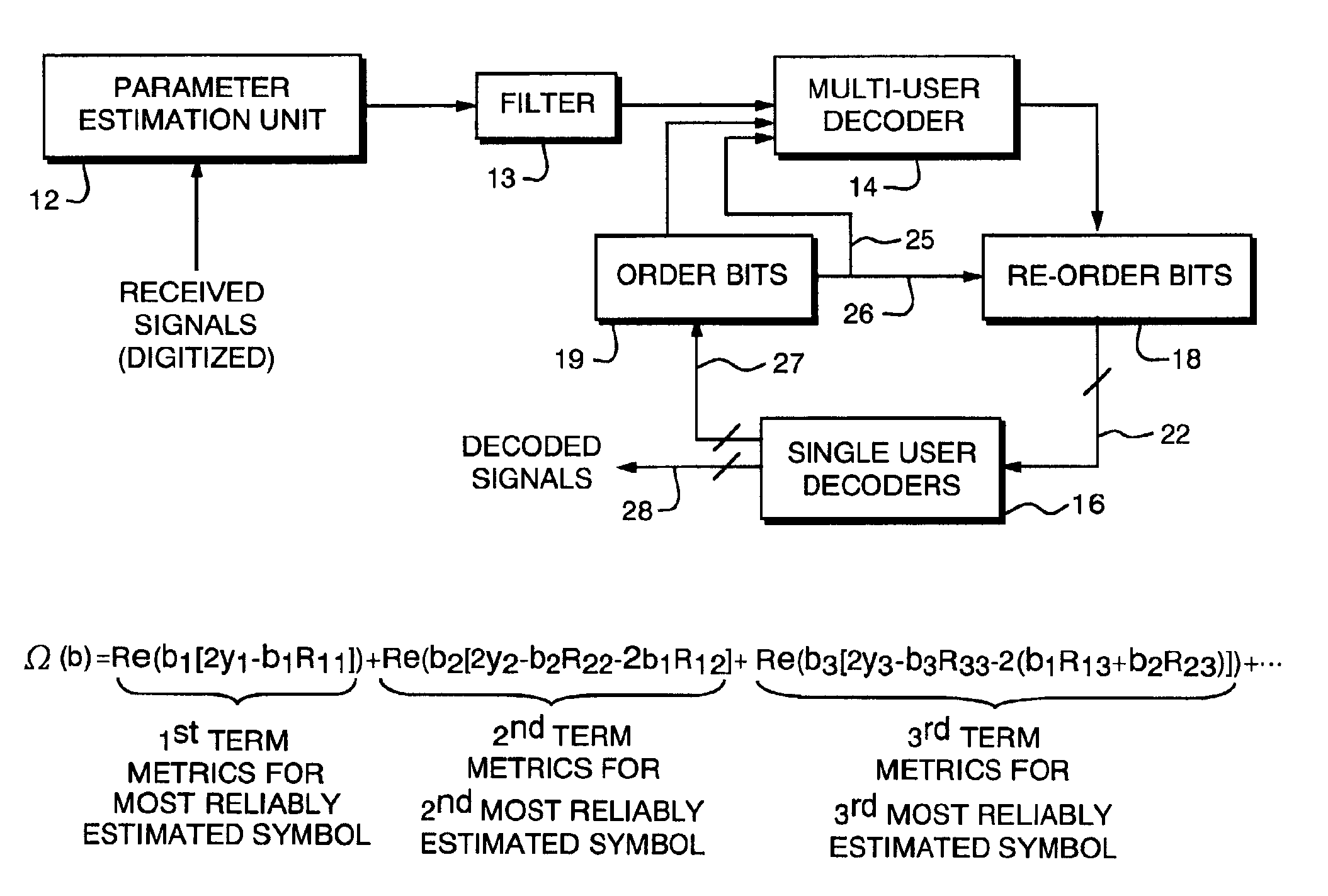
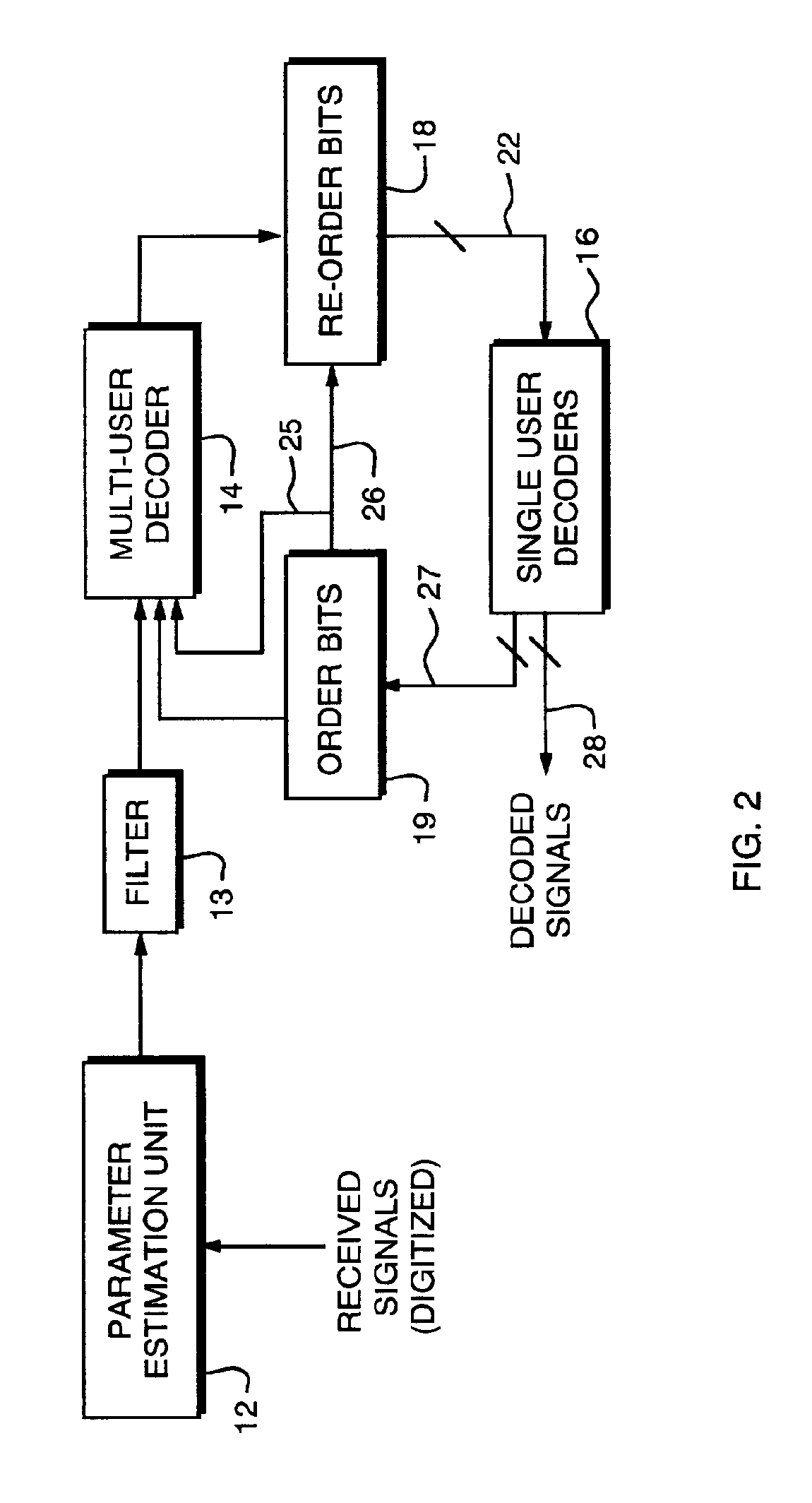
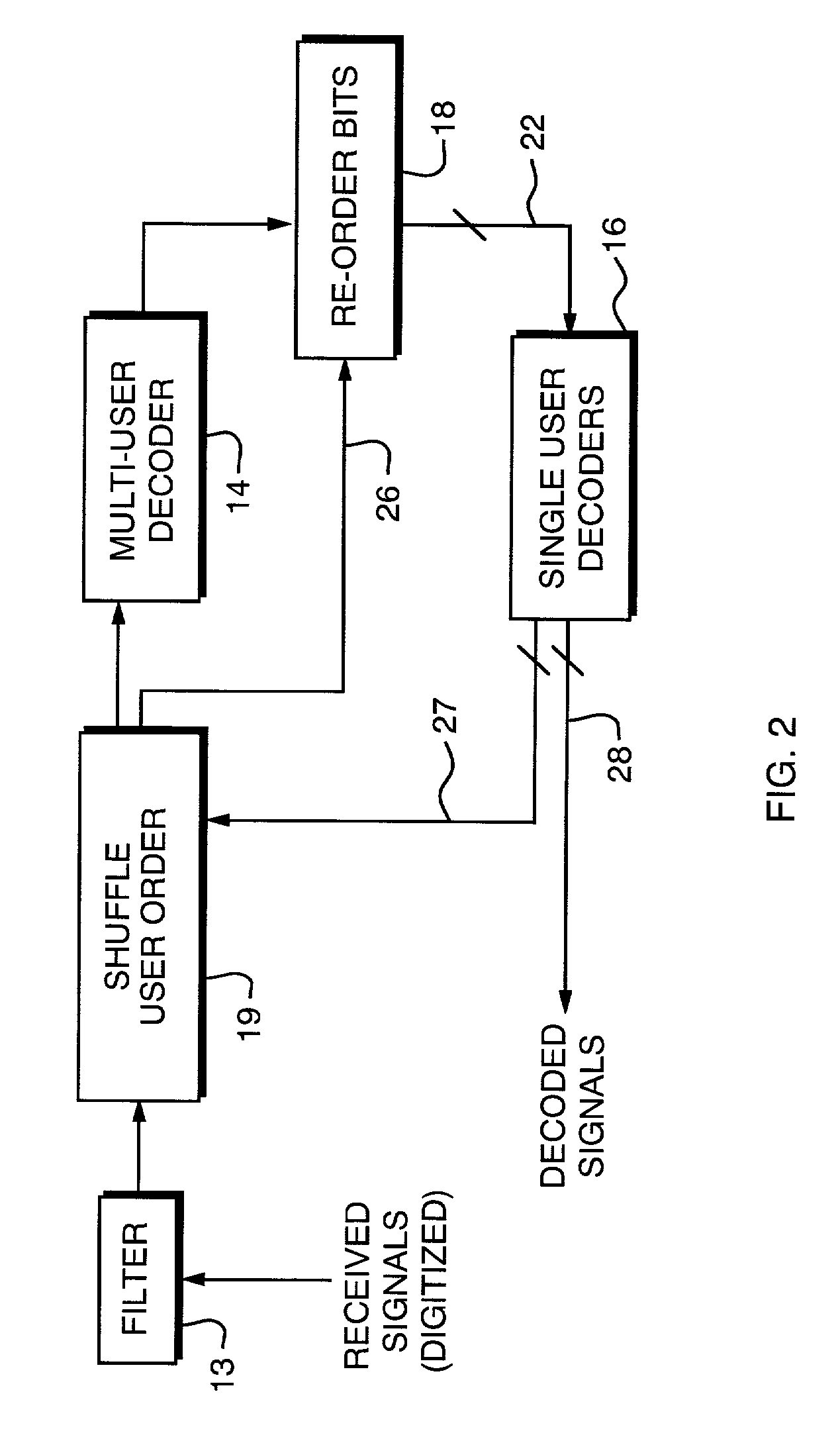
Method and apparatus for improved turbo multiuser detector
InactiveUS6947506B2Reduce signal processing timeReduced signaling processTime-division multiplexLine-faulsts/interference reductionComputational probabilityRound complexity
A multi-user turbo decoder combining multi-user detection and forward error correction decoding is disclosed that utilizes iterative decoding of received, interfering signals, and the construction of a decoding tree of the decoder is changed for each iteration of the decoding based on the previous conditional probability estimates of the value of the data bits of each signal making up the received, interfering signals. Before each iteration of multi-user decoding, a probability estimate is calculated that the value of the bit in a signal has a certain value for all of the data bits. Using the probability estimate a new decoding tree is constructed before each iteration of decoding such that the signal bit having the most reliable estimate is assigned to the lowest or root level of the tree. Using the probability estimate for the other signal bits, the signal bit having the next most reliable estimate is assigned to the second level of the tree, and so forth, with the signal bit having the least reliable estimate being assigned to the highest level of the tree adjacent the terminating nodes or leaves of the tree. By building the decoding tree in this manner for each iteration of symbol decoding, a reduced complexity search is more likely to include paths (and nodes) in the tree containing the correct value for the channel symbols.
Owner:COLLISION COMM INC
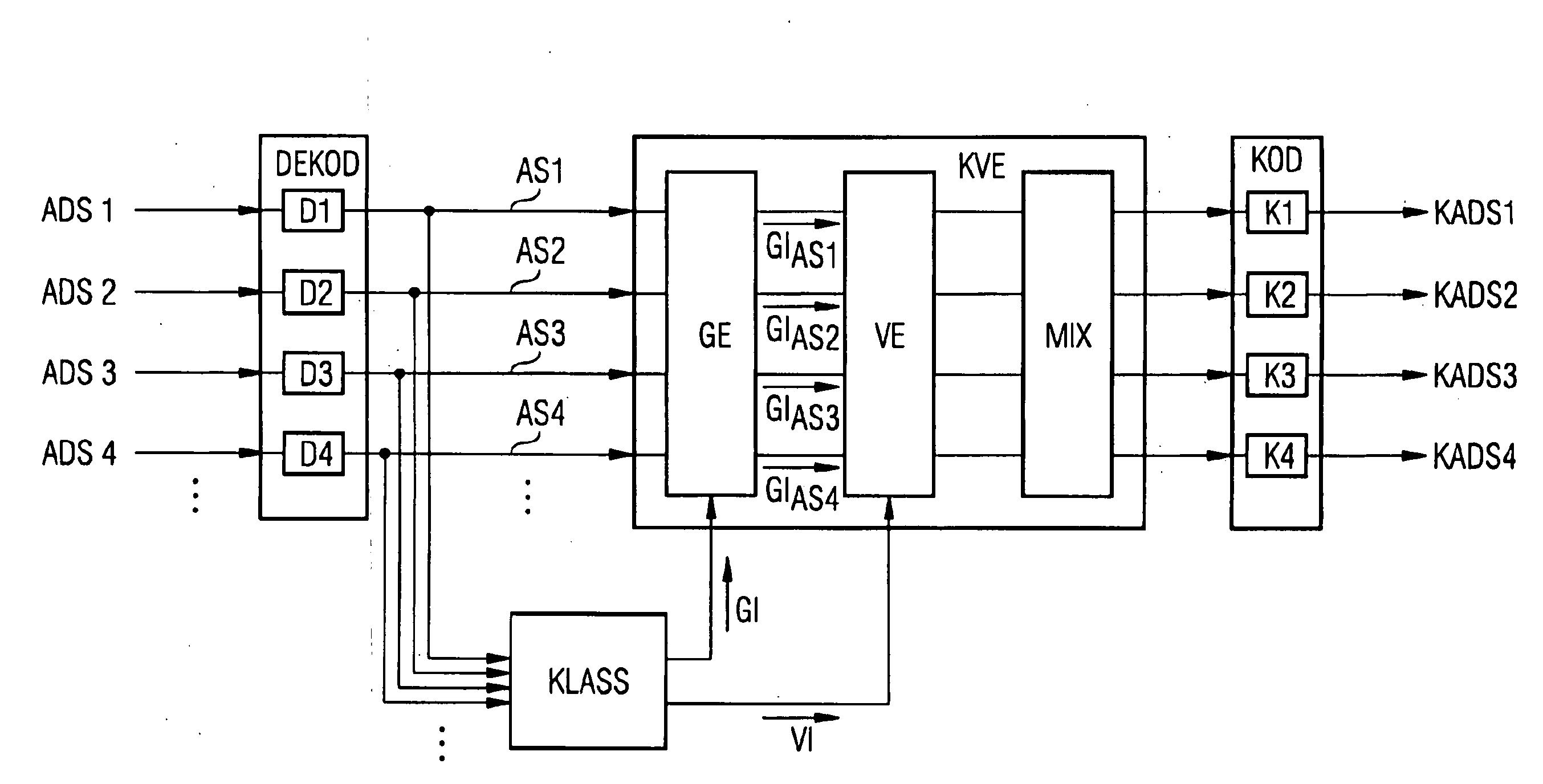
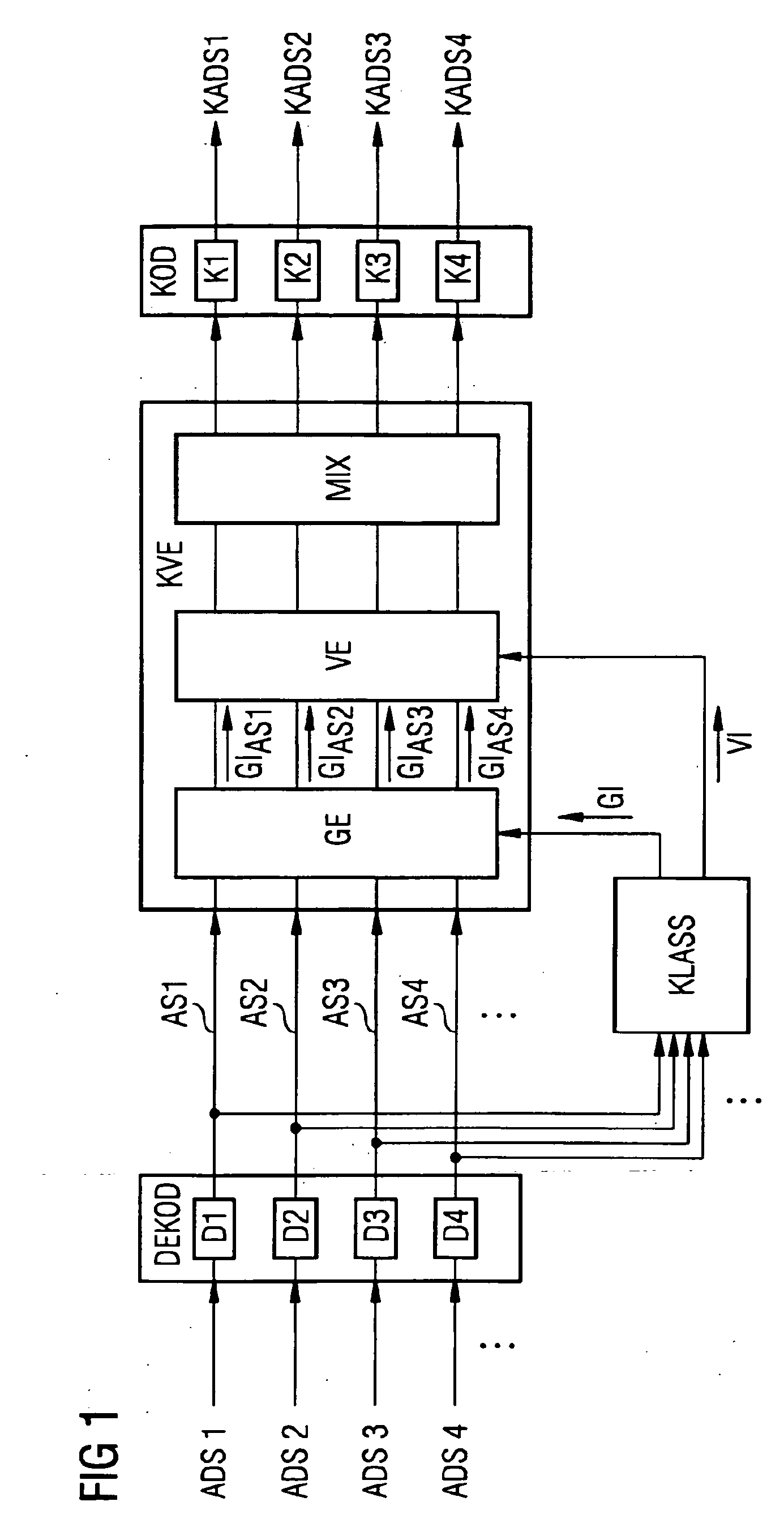
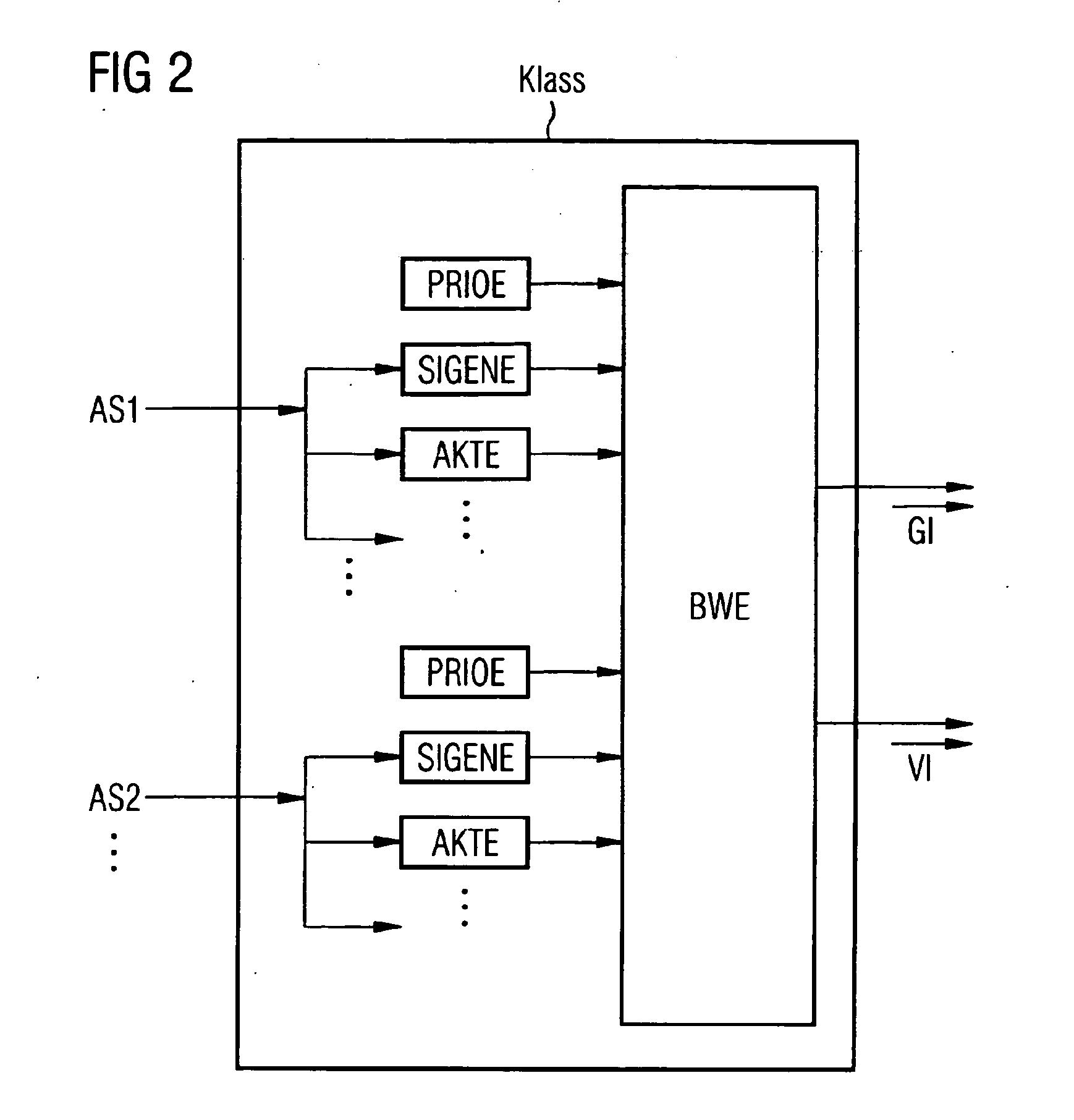
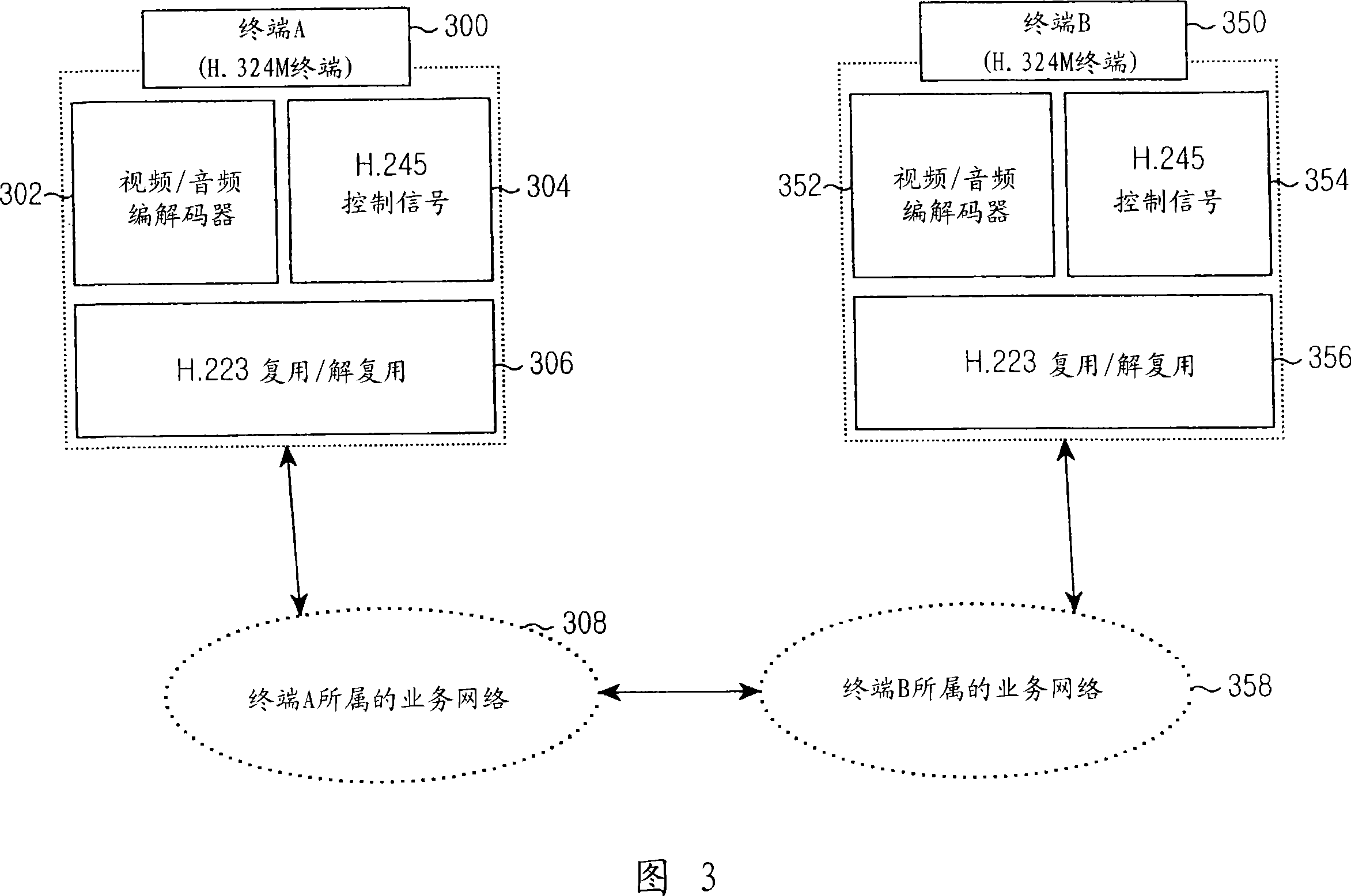
Method for carrying out an audio conference, audio conference device, and method for switching between encoders
ActiveUS20100020954A1Reduce quality lossAvoid mistakesSpeech analysisSpecial service for subscribersData connectionData stream
A method and an audio conference device for carrying out an audio conference are disclosed, whereby classification information associated with a respective audio date flow is recorded for supplied audio data flows. According to a result of an evaluation of the classification information, the audio data flows are associated with at least three groups which are homogeneous with regard to the results. The individual audio data flows are processed uniformly in each group in terms of the signals thereof, and said audio data flows processed in this way are superimposed in order to form audio conference data flows to be transmitted to the communication terminals. Further, an audio conference device and a method for switching between a first encoder and a second encoder for an audio data connection are disclosed, wherein the encoders use, inter alia, encoding parameters influenced by an audio data history, for the encoding process. The audio data connection from the first encoder to the second encoder is switched in such a way that, during the switching process, the encoding parameters of the second encoder are matched with the encoding parameters of the first encoder, and when the encoding parameters are matched, the audio connection is switched to the second encoder.
Owner:RINGCENTRAL INC
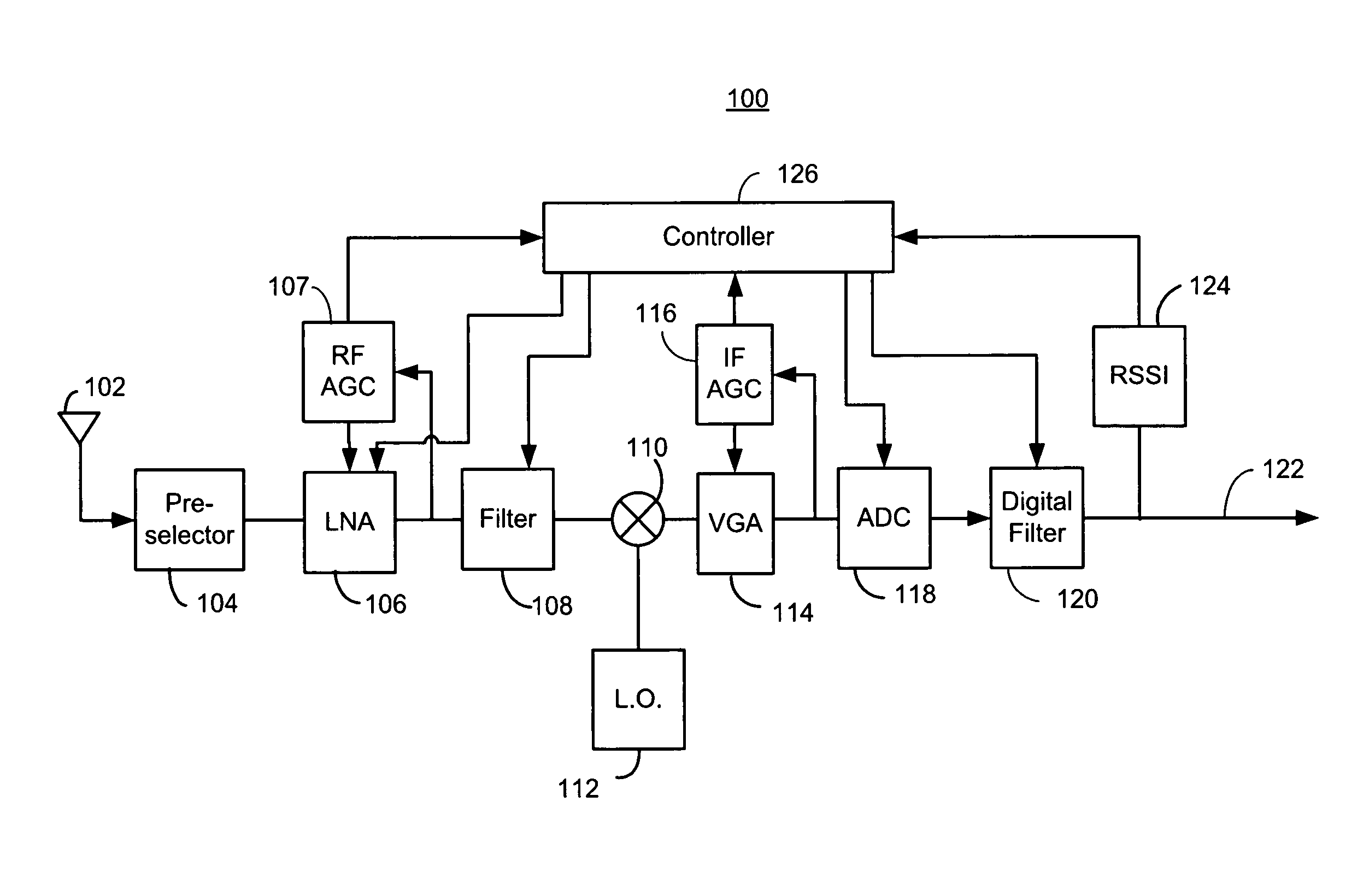
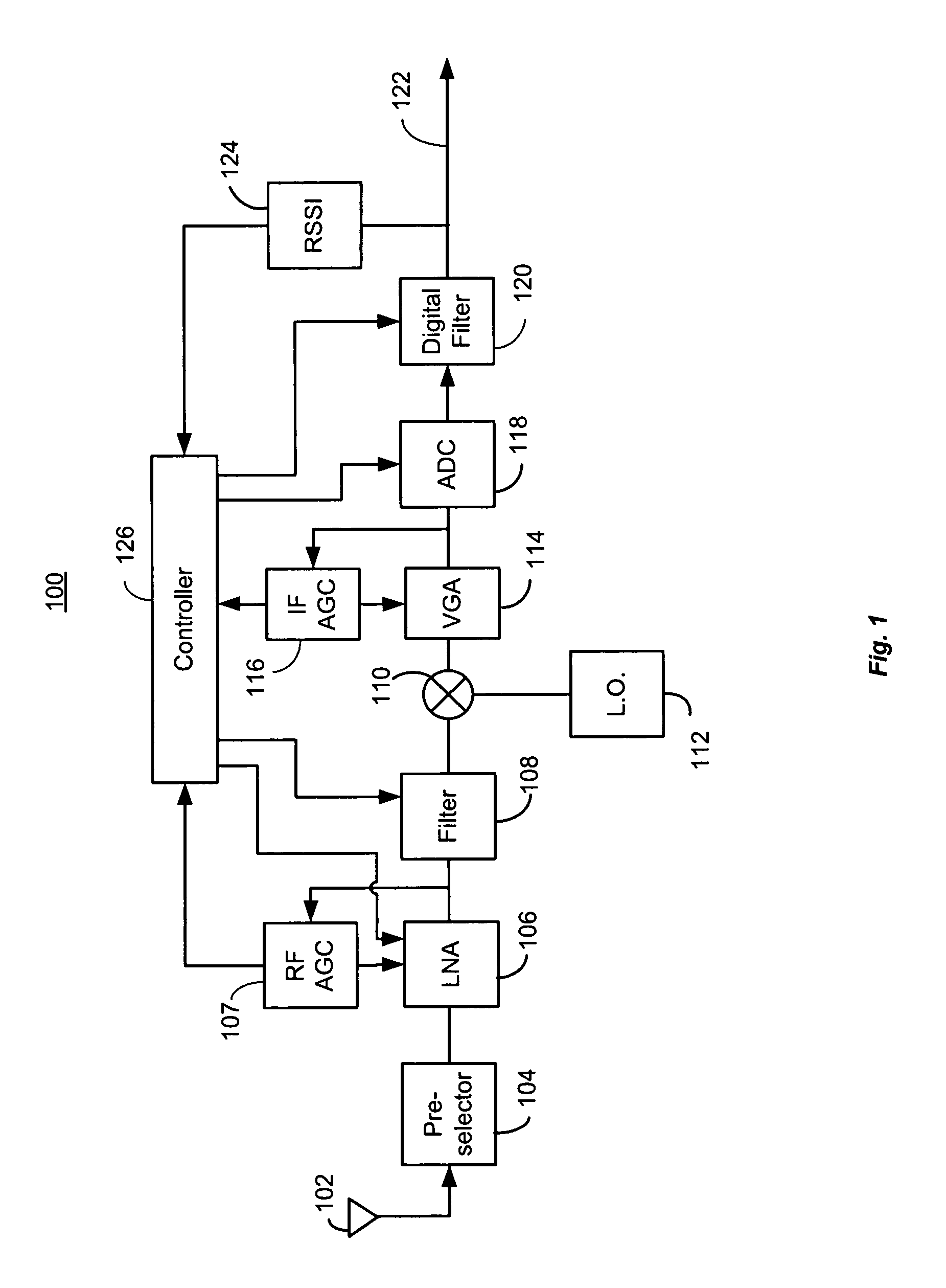
Receiver dynamic power management
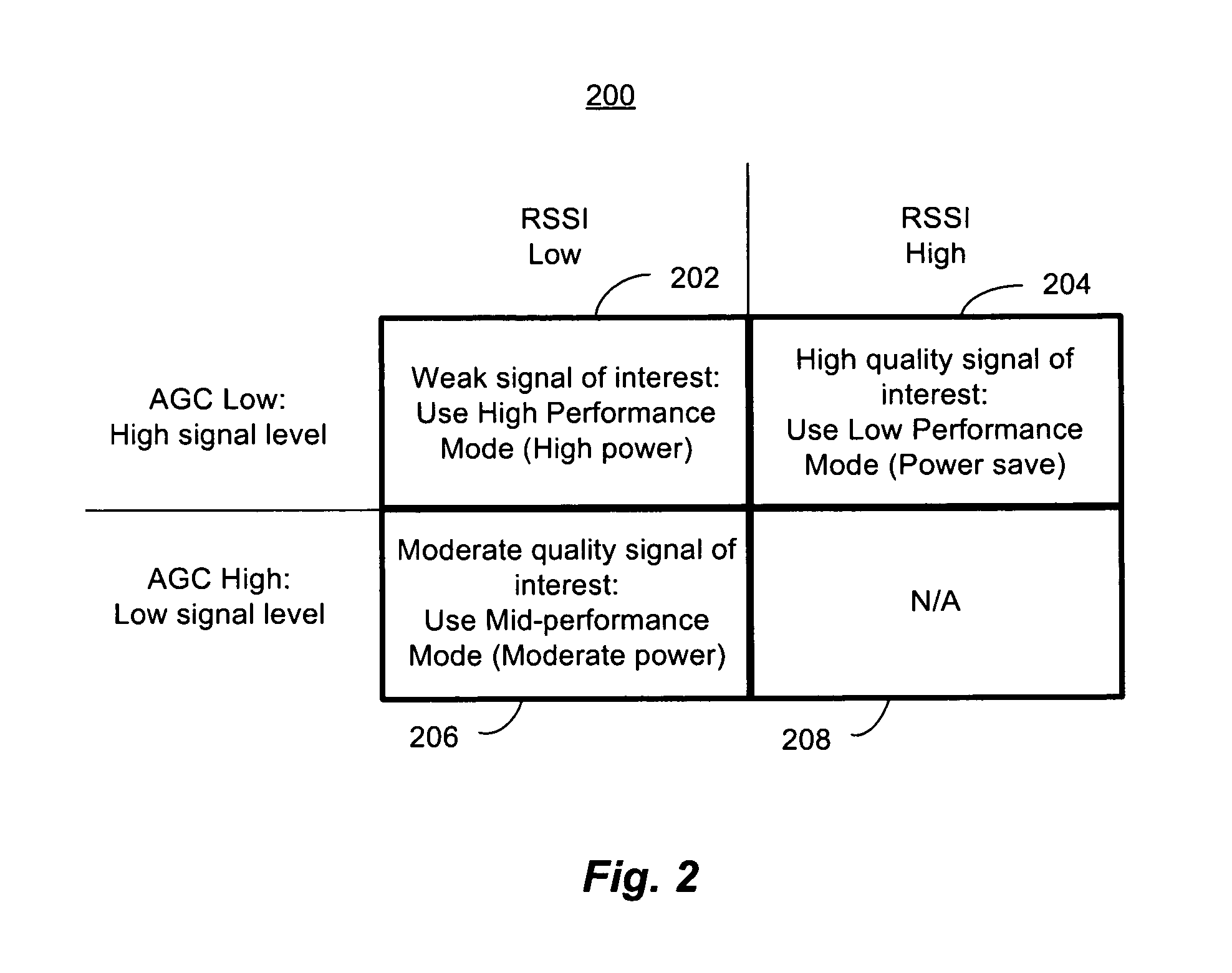
ActiveUS8428535B1Improve performanceReduce the noise floorGain controlTransmission monitoringLow noiseAdaptive filter
A controller in a receiver monitors RSSI and AGC gain levels to determine signal conditions and adjust filter performance accordingly to optimize power consumption while providing acceptable signal quality. When RSSI level is high and AGC gain is low, a strong signal-of-interest is present. In this case, adaptive filter bias currents may be reduced raise the noise floor and degrade intermodulation to reduce power consumption because the strong signal-of-interest can tolerate the higher noise and distortion. When the RSSI level is low and AGC gain is high, a weak signal is present a low noise mode may be effected by increasing bias current to filters used to lower the noise floor, but intermodulation effects may still be tolerated so those filters may be cut back. Other cases are supported. RSSI and AGC gain level thresholds may be dynamically altered based on relative RSSI and AGC levels.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
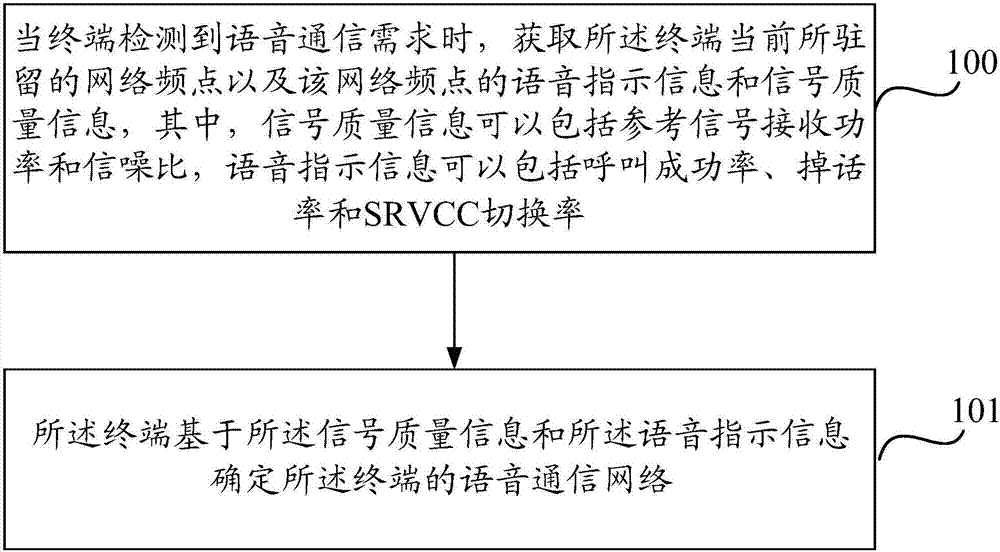
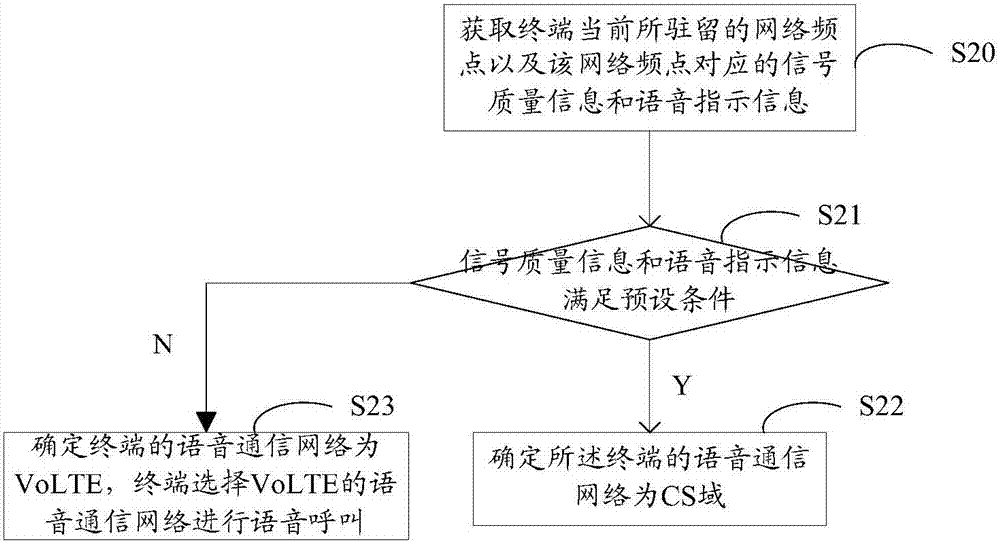
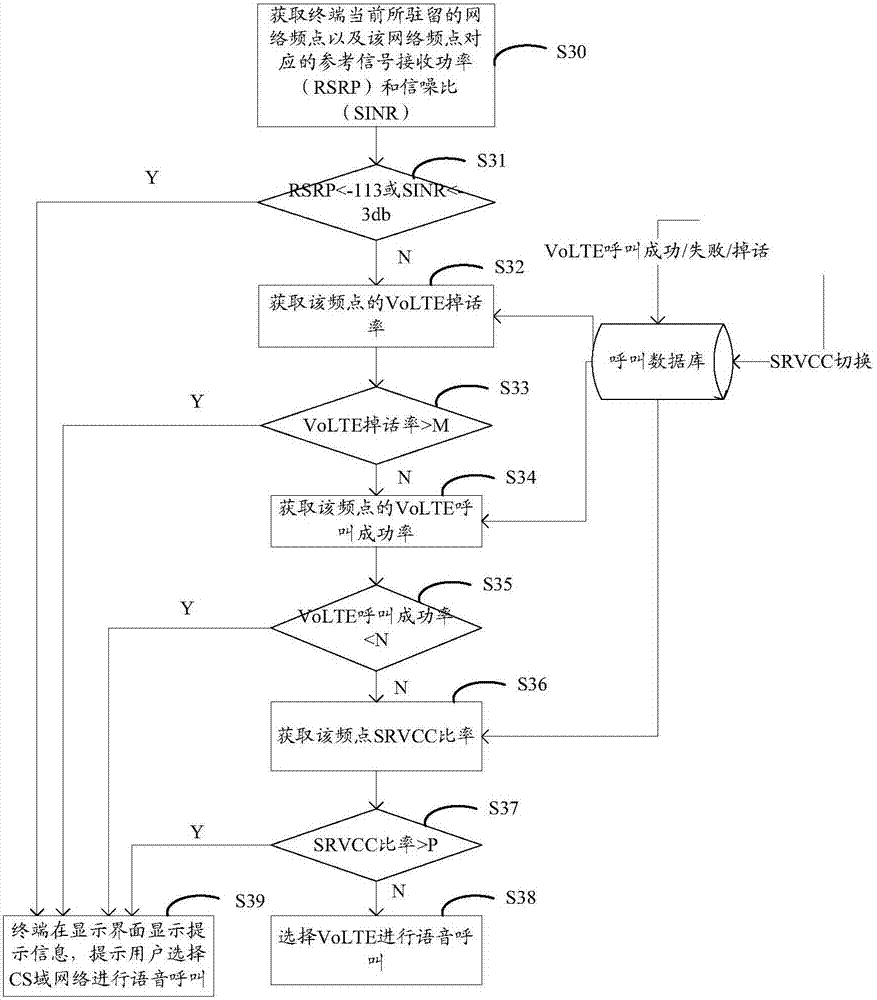
Determination method and device for voice communication network
ActiveCN107454633AReduced signaling processReduce loadWireless communicationSignal qualitySignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses a determination method and device for a voice communication network. The method comprises the steps that a terminal in support of a VoLTE (Voice over Long Term Evolution) obtains a network frequency point at which the terminal currently resides, and the voice indicator information and signal quality information of the network frequency point, when a voice communication demand is detected, wherein the signal quality information may comprise reference signal receiving power and a signal to noise ratio, and the voice indicator information may comprise a call success rate, a call drop rate and an SRVCC (Single Radio Voice Call Continuity) switching rate; and the terminal determines the voice communication network of the terminal based on the voice indicator information and the signal quality information. In this way, the terminal can carry out comprehensive judgment according to the voice indicator information and signal quality information corresponding to the frequency point of a service cell of the terminal, the suitable voice communication network is selected, the voice call quality of the terminal is improved, moreover, SRVCC switching signal processes are reduced, and network loads are reduced.
Owner:HUAWEI DEVICE CO LTD
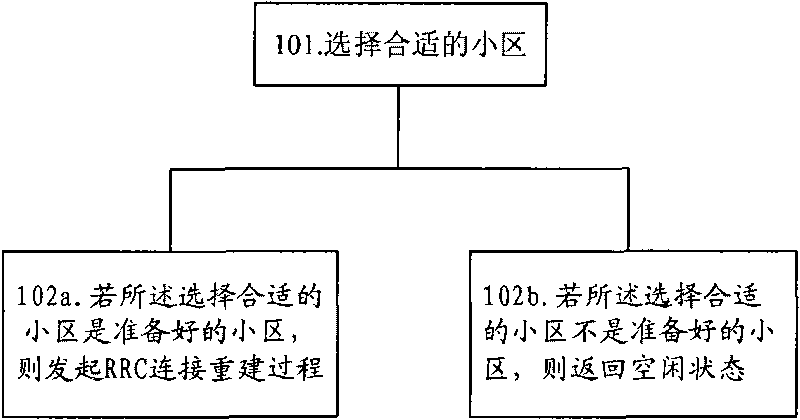
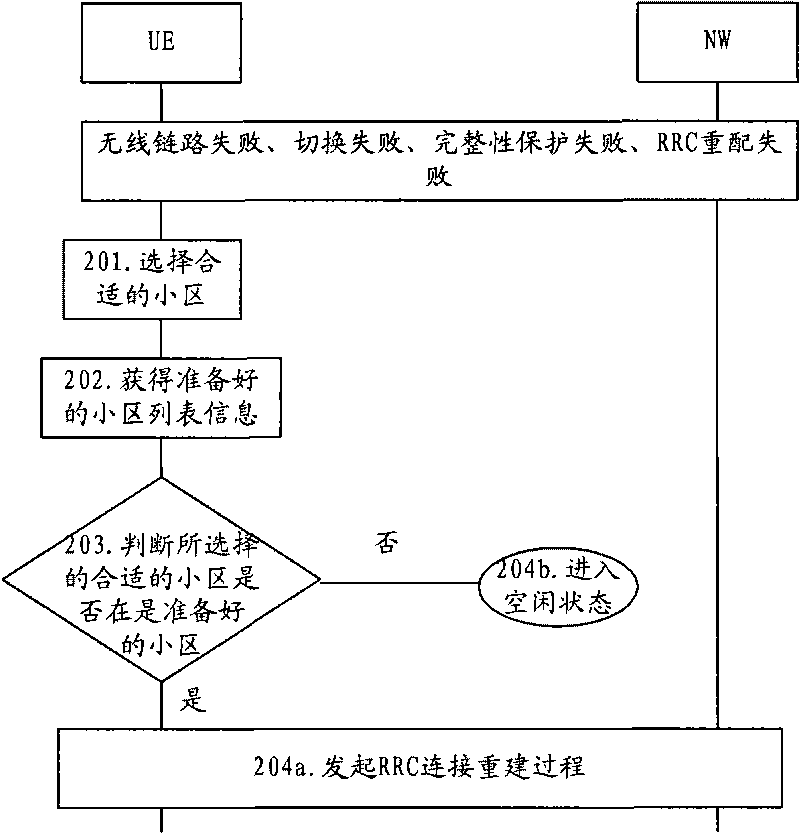
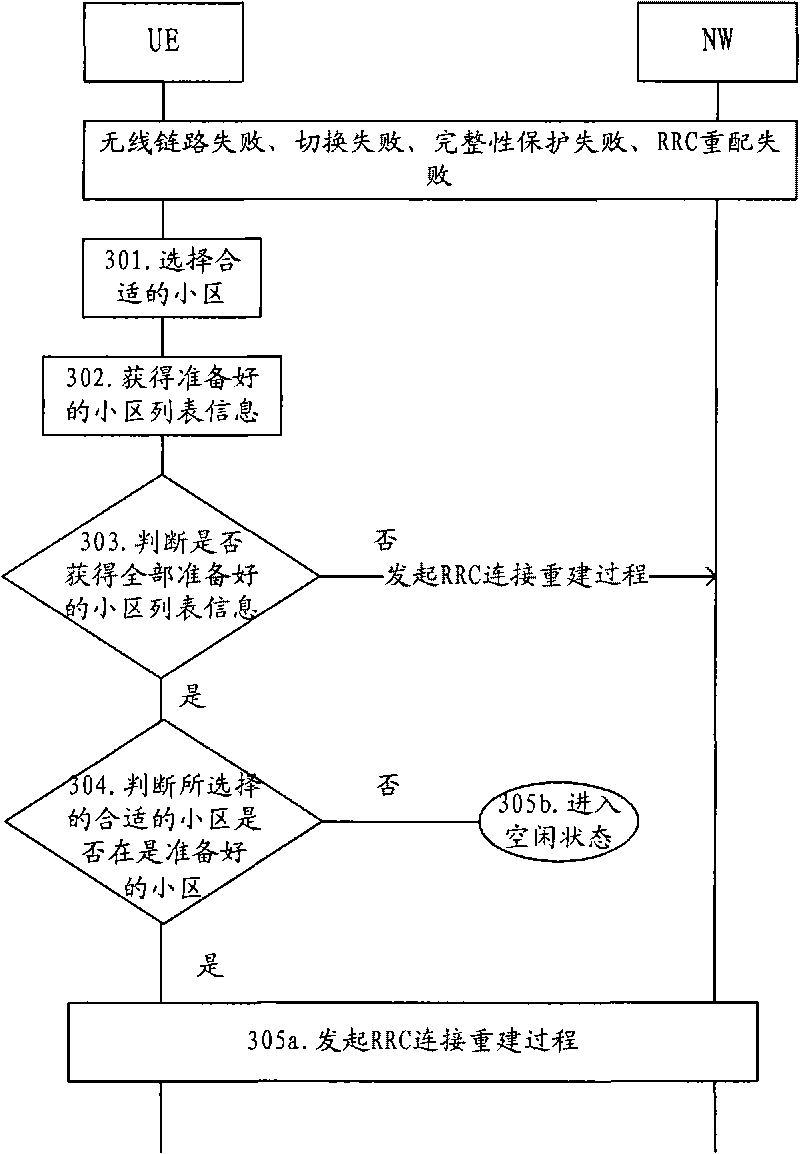
Method and device for RRC connection reestablishment
ActiveCN101754414AAvoid sendingReduced signaling processAssess restrictionConnection managementComputer networkWireless resources
The invention provides a method and a device for RRC connection reestablishment. The method is that a proper community is selected; the RRC connection reestablishment is initiated if the selected proper community is viewed as a prepared community; and idle state is returned if the selected proper community is viewed as an unprepared community. By adopting the method and the device for controlling the RRC connection reestablishment through wireless resources, the signaling flow is saved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
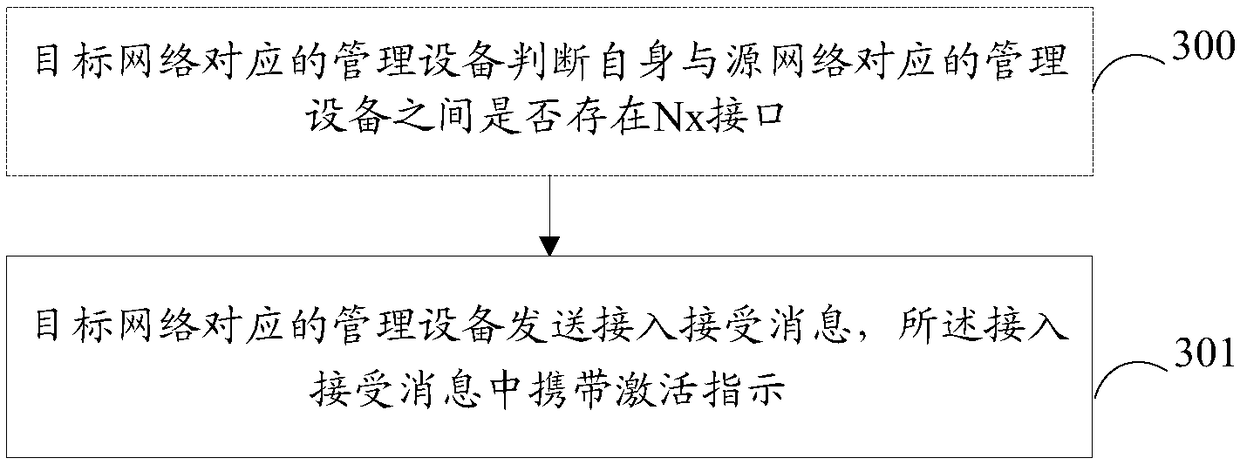
Method, device and equipment for terminal changing between 4G and 5G networks
ActiveCN108632915AReduce signalingReduce energy consumptionAssess restrictionConnection managementProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access5G
The invention provides a method, device and equipment for a terminal changing between 4G and 5G networks. The method comprises that management equipment corresponding to the target network sends an access acceptance message with an activation indication; and the activation indication indicates the terminal to reactivate public data network (PDN) connection or a protocol data unit (PDU) of the source network in the target network, or indicates the terminal that the public data network (PDN) connection or a protocol data unit (PDU) has been activated in the target network.
Owner:ZTE CORP
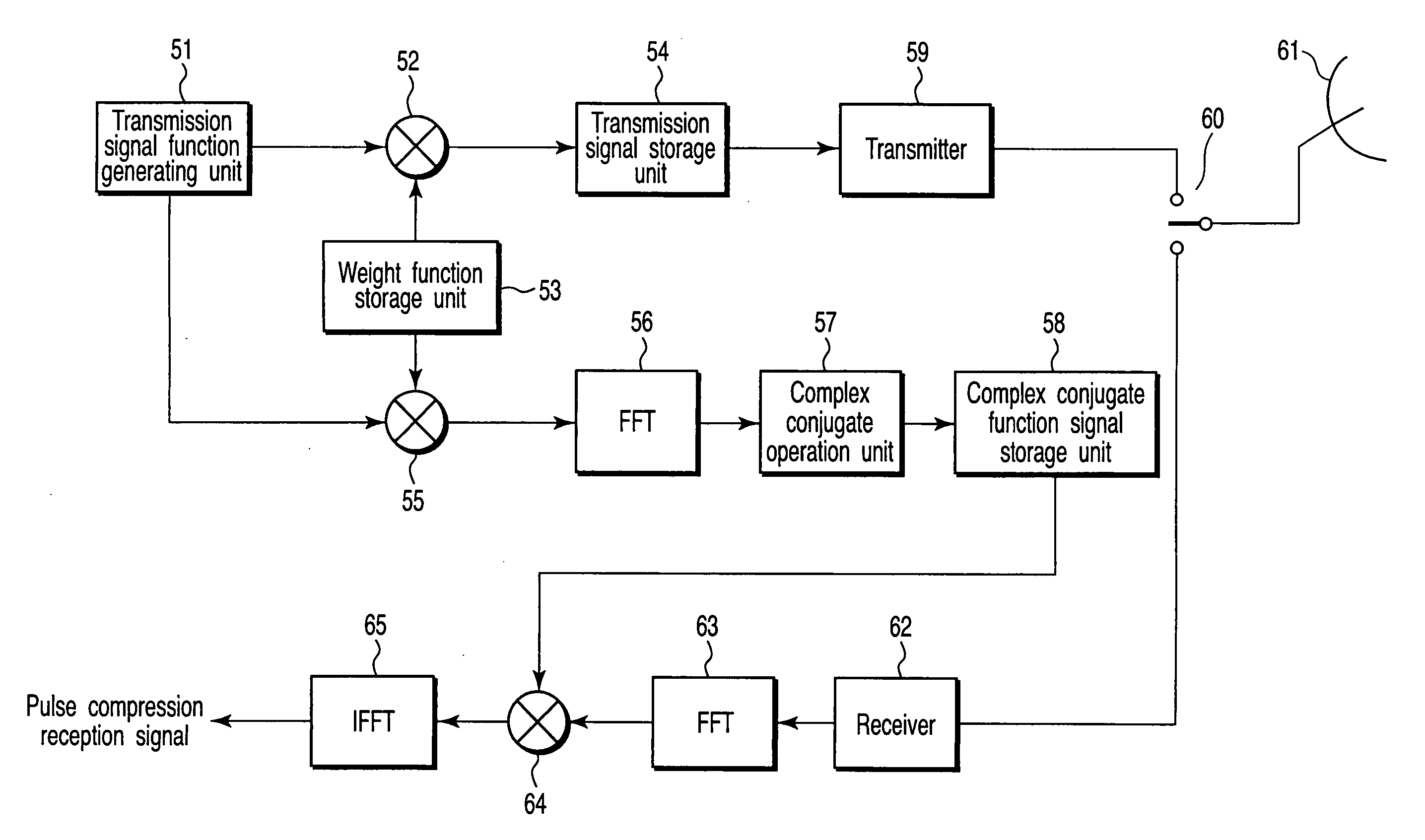
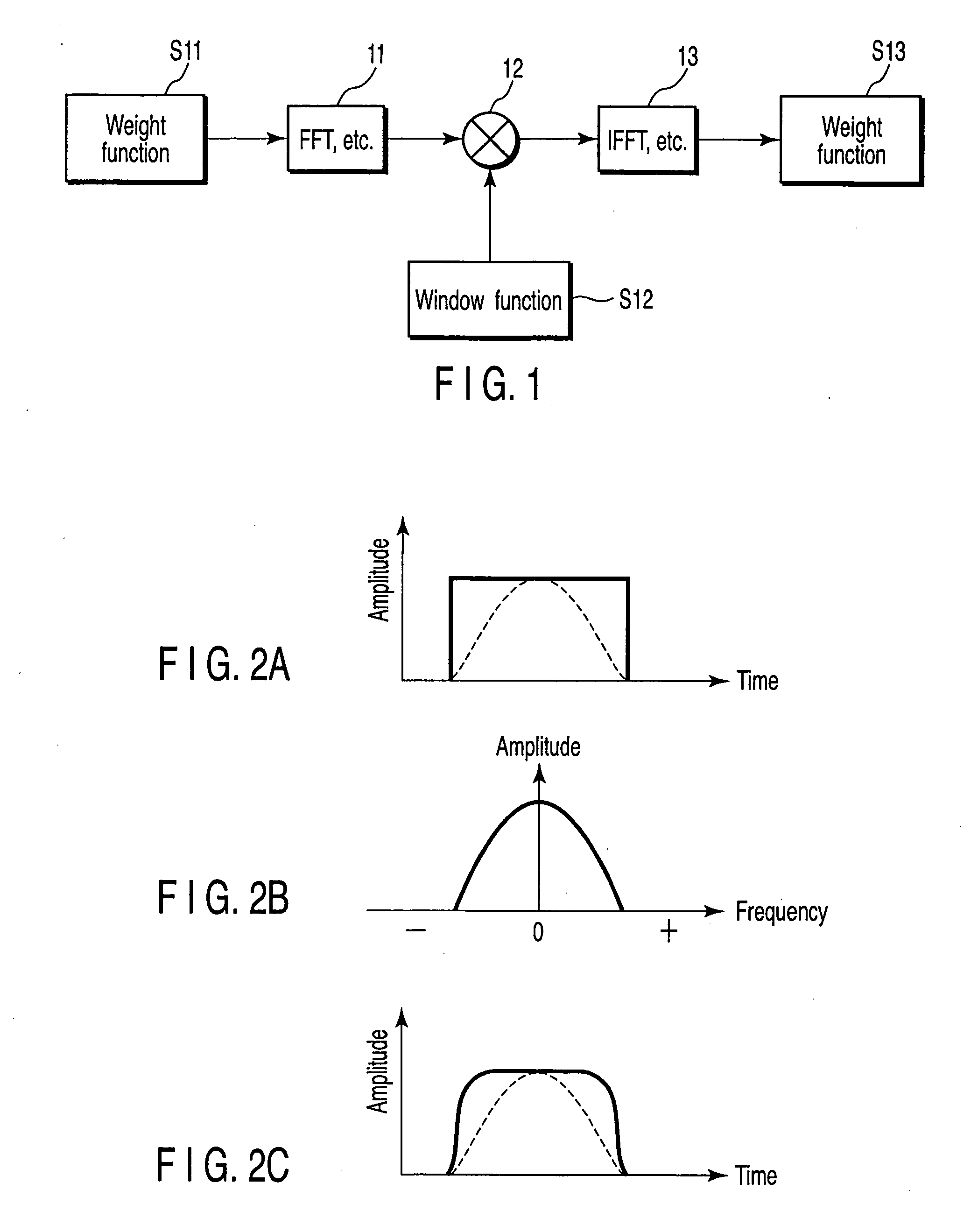
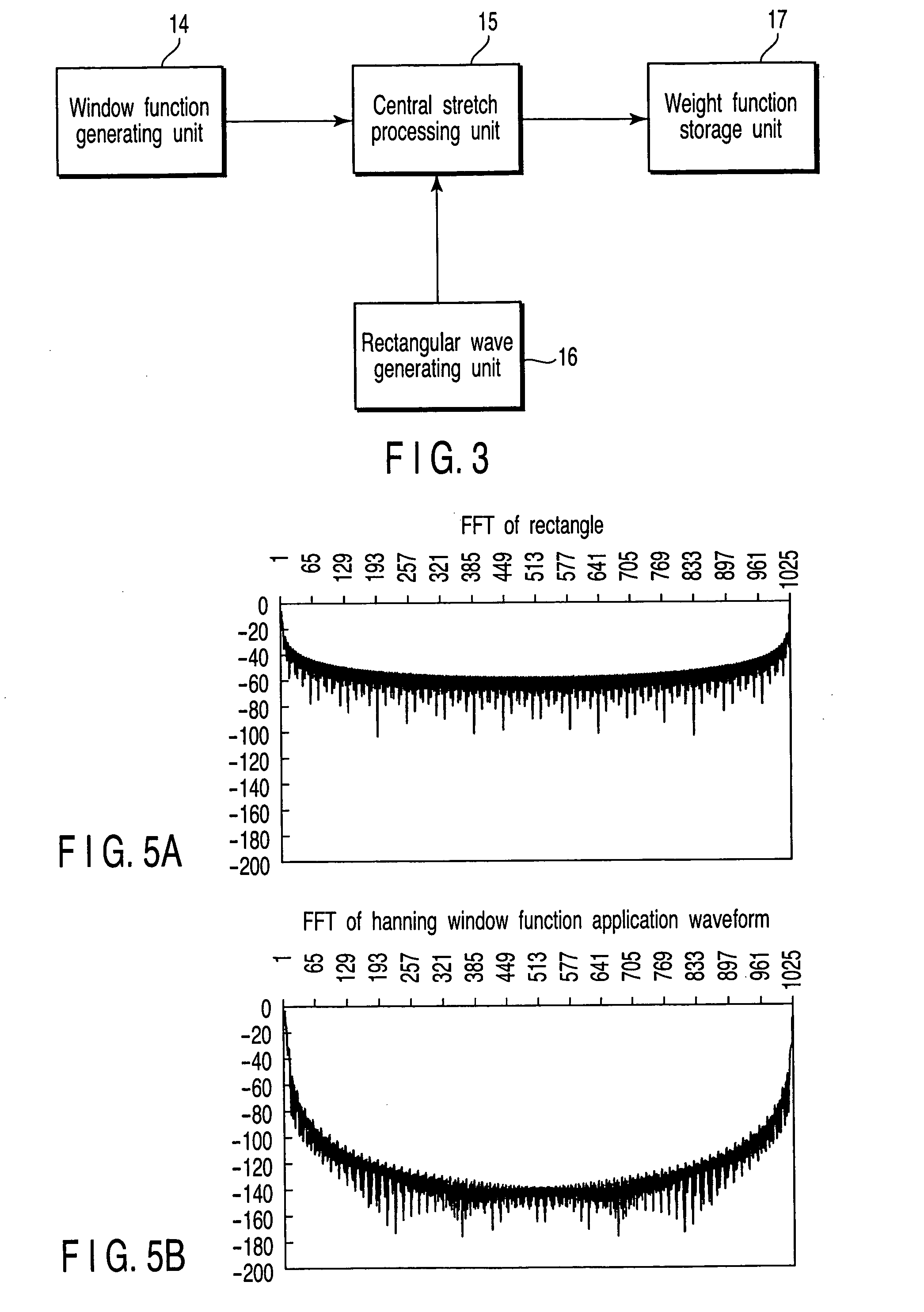
Weight function generating method, reference signal generating method, transmission signal generating apparatus, signal processing apparatus and antenna
ActiveUS20050203730A1Improve featuresReduce signal processing lossDigital technique networkSpeech analysisTime domainComputational physics
A rectangular wave for determining a range of a weight function is transformed to frequency domain by an FFT or the like, and after being multiplied by a window function (BlackmanHarris window function, for example) generated on a frequency axis by a multiplier, the frequency domain is transformed again to the time domain by an IFFT or the like thereby to generate a weight function.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method and apparatus for random shuffled turbo multiuser detector
InactiveUS6981203B2Reduce signal processing timeReduced signaling processJoint error correctionData representation error detection/correctionMulti user detectionRound complexity
A multi-user turbo decoder combining multi-user detection and forward error correction decoding is disclosed in which randomly ordered indices are assigned to interfering users before a decoding tree is constructed in the multi-user decoder for each symbol interval for every iteration and for each new block of data. By building the decoding tree in this manner for each symbol interval, a reduced complexity search is more likely to include paths (and nodes) in the tree containing the correct value for the channel symbols. All users thus share in the benefit of root level placement in the decoding tree. In an alternative embodiment of the invention only one decoding pass is accomplished and there is no re-construction of the decoding tree based on further random index ordering for iterative decoding. No modification to the transmitted signaling method is needed.
Owner:COLLISION COMM
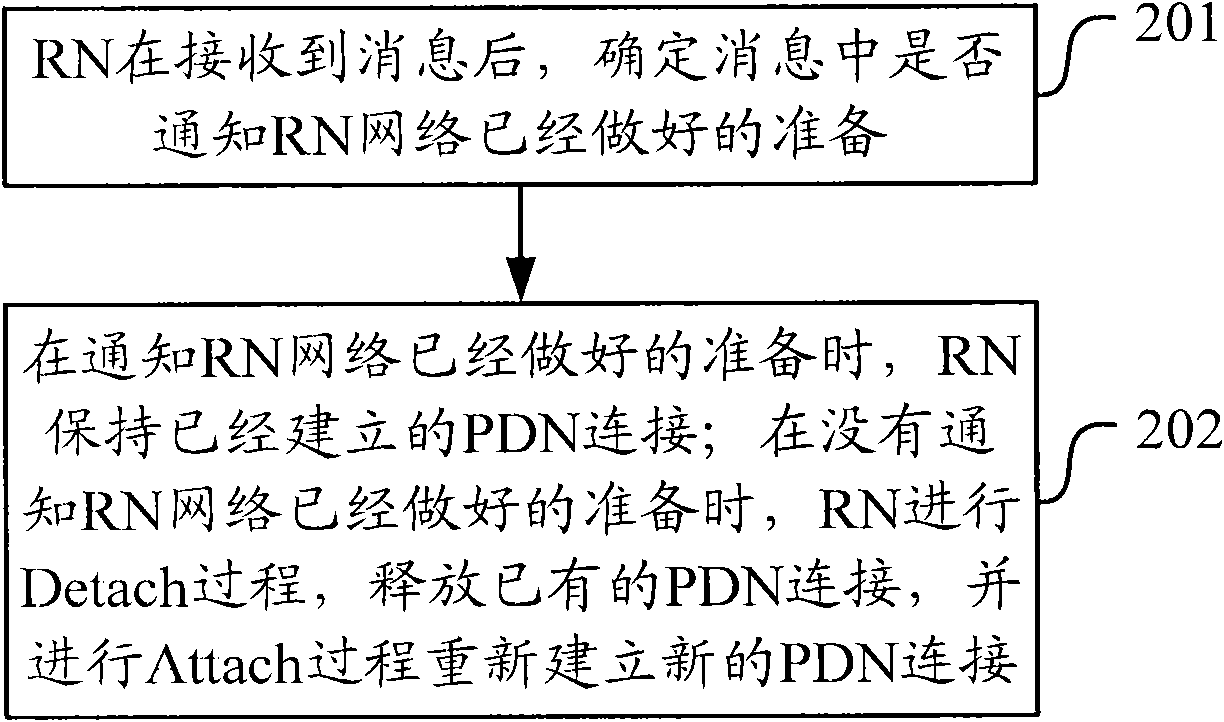
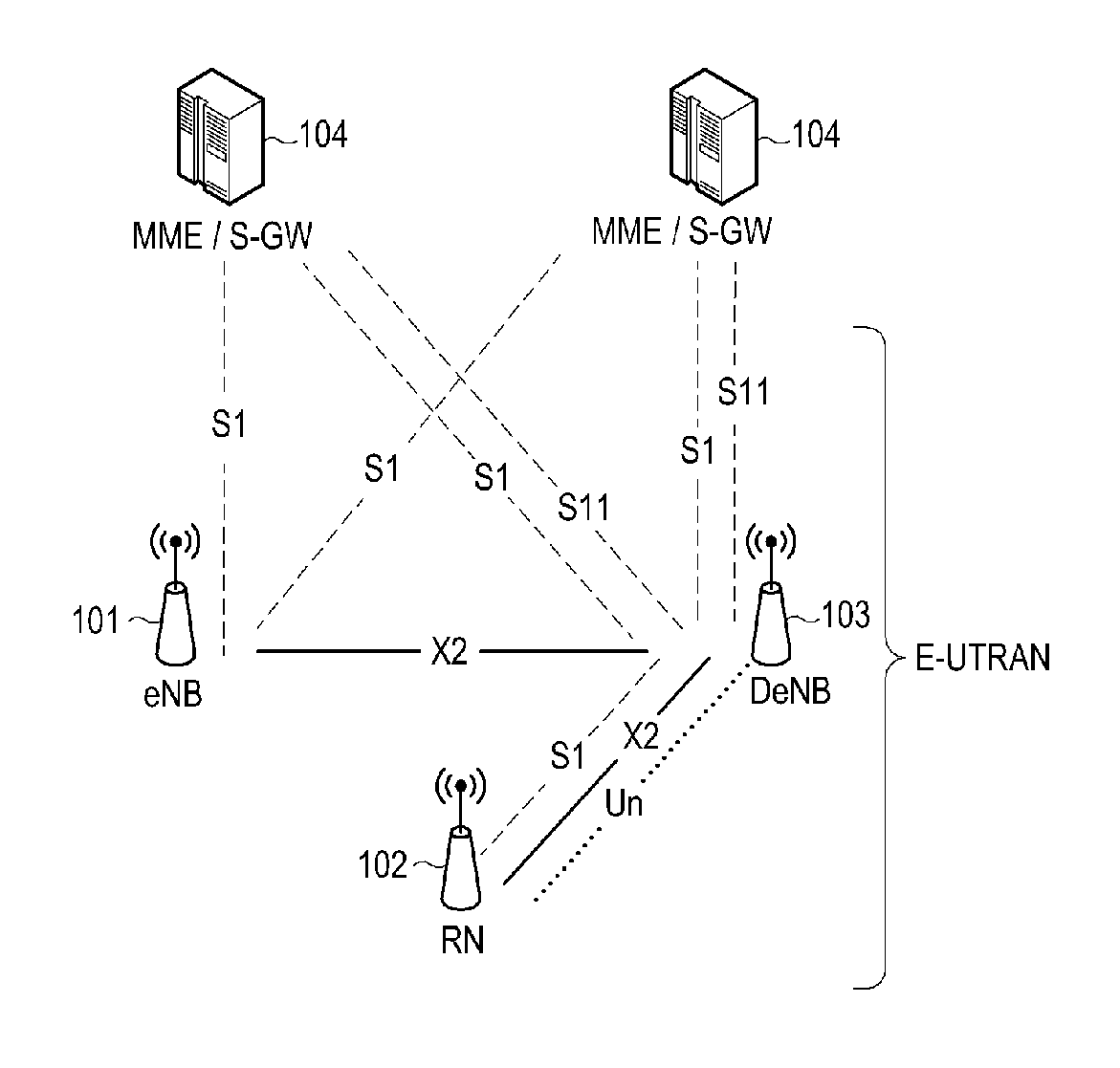
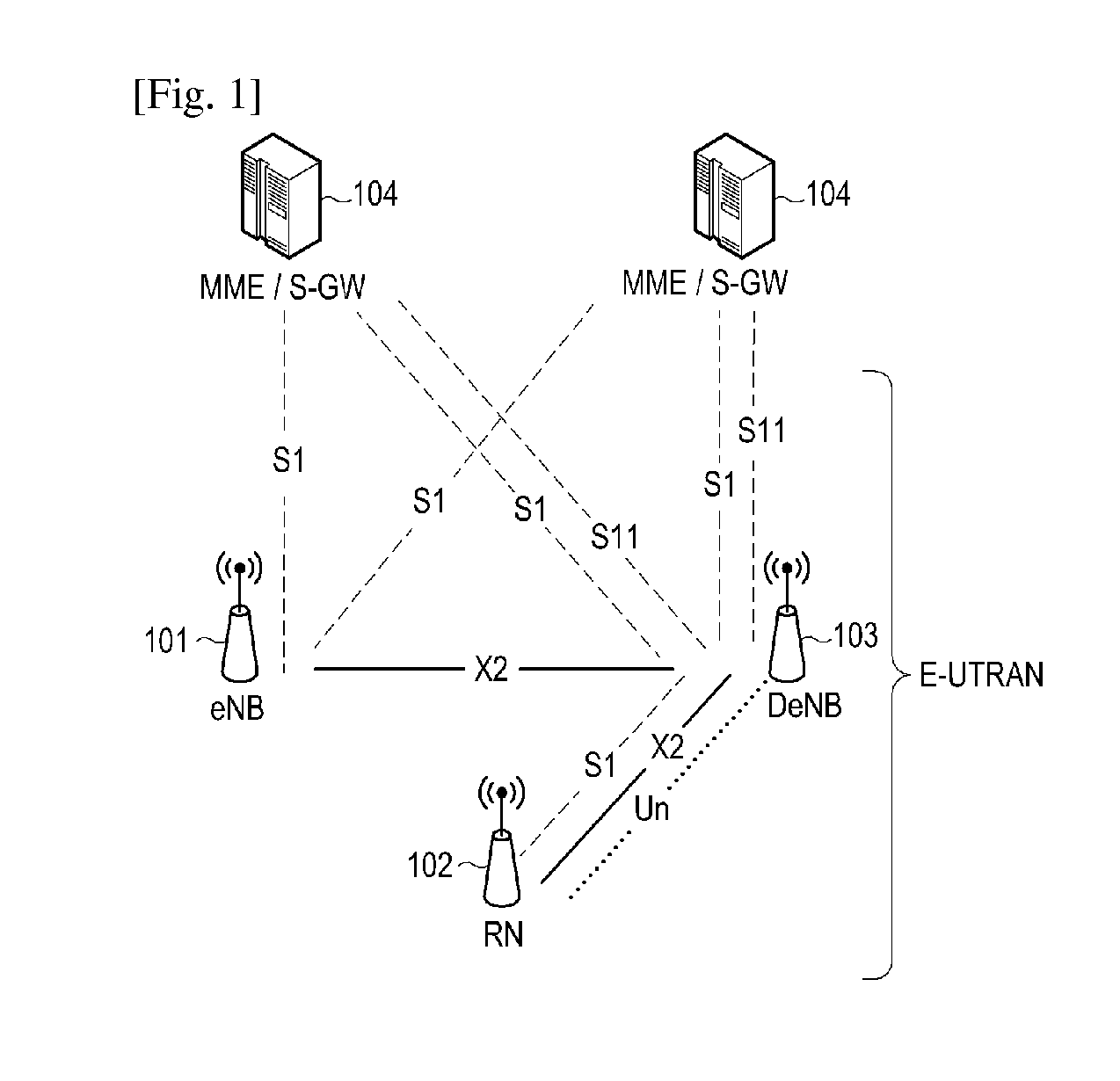
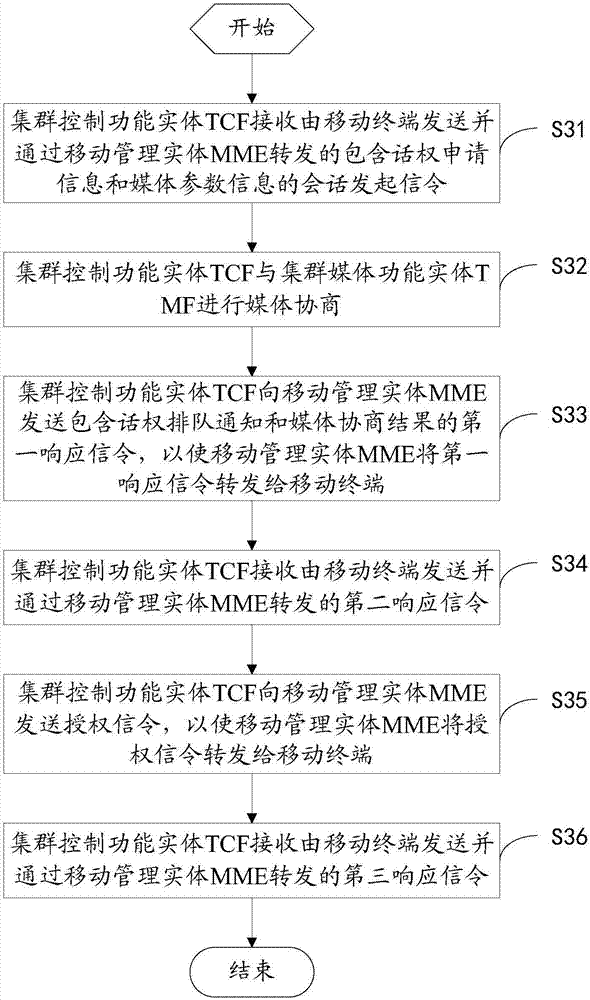
Relay node non-access stratum processing method and equipment
ActiveCN102378393ASimplify the startup processReduce startup timeConnection managementStart timeMobility management
The invention discloses a relay node non-access stratum processing method and equipment. The method comprises the steps that after access equipment is determined to be a relay node by a mobility management entity, when the access cell of the mobility management entity and the relay node on an evolved node B supports the relay node, the evolved node B is informed about that a network has been already prepared; after the evolved node B is determined to be selected as a serving gateway / packet data network gateway for the relay node, an indication that the network has been already prepared is transmitted to the relay node; when the relay node is informed about that the network has been already prepared, the relay node keeps the built connection with a packet data network; and when the relay node is not informed about that the network has been already prepared, the relay node conducts a detaching process to release the existing connection with the packet data network and conducts an attaching process to rebuild new connection with the packet data network. The relay node non-access stratum processing method and the equipment have the advantages that the starting process of the relay node can be simplified, the starting time of the relay node is shortened and the unnecessary signaling process and bearer management are reduced.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
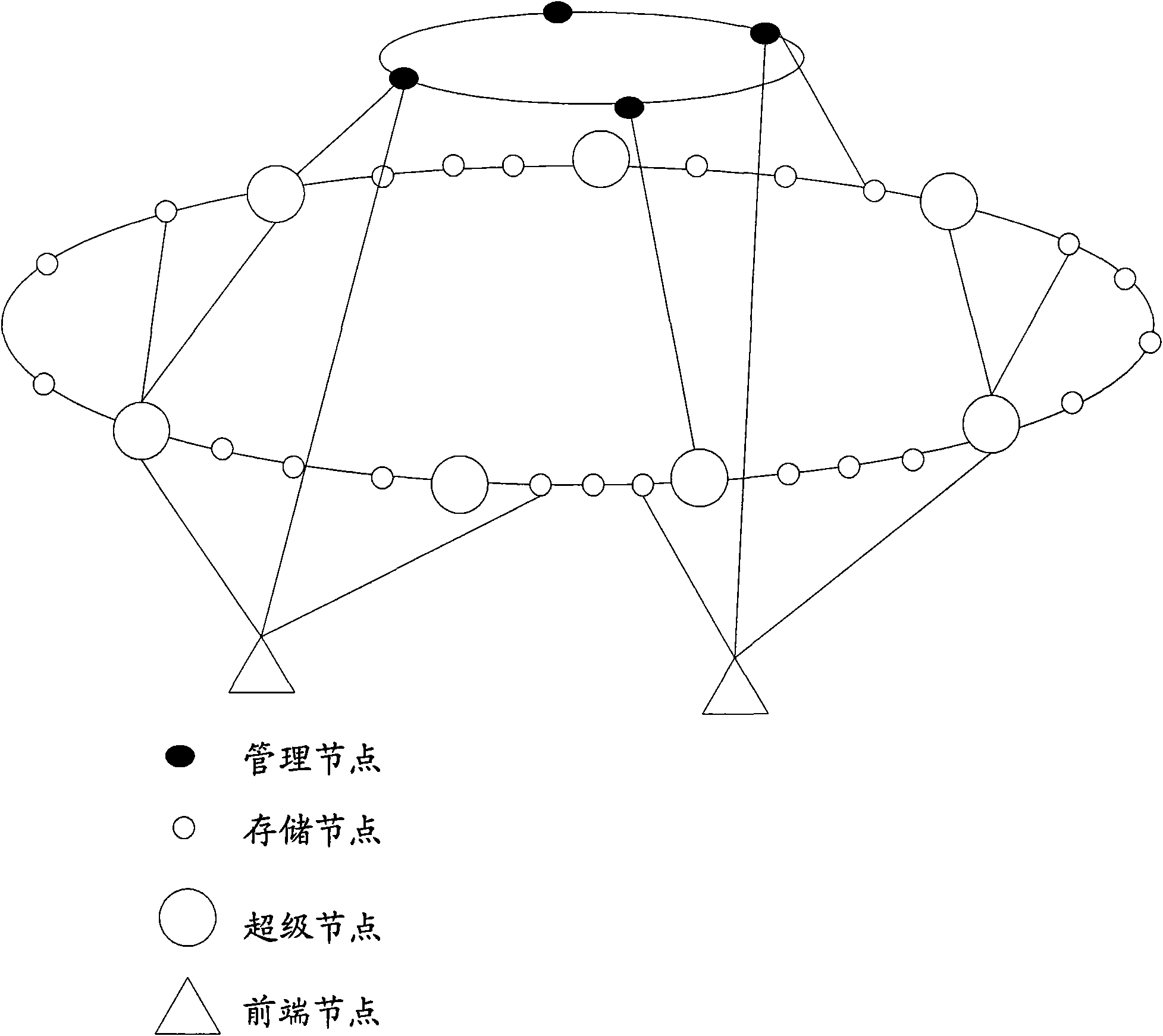
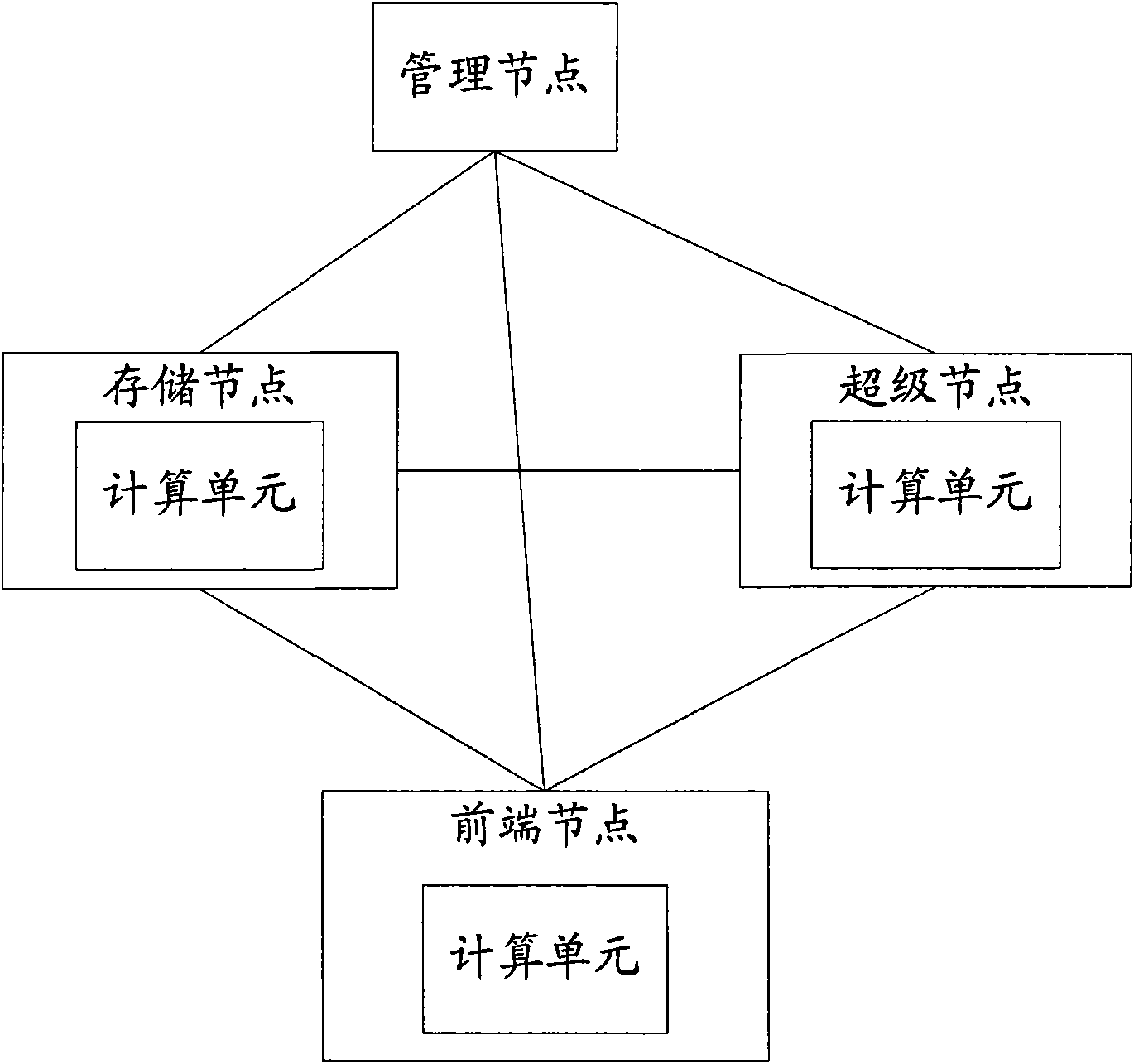
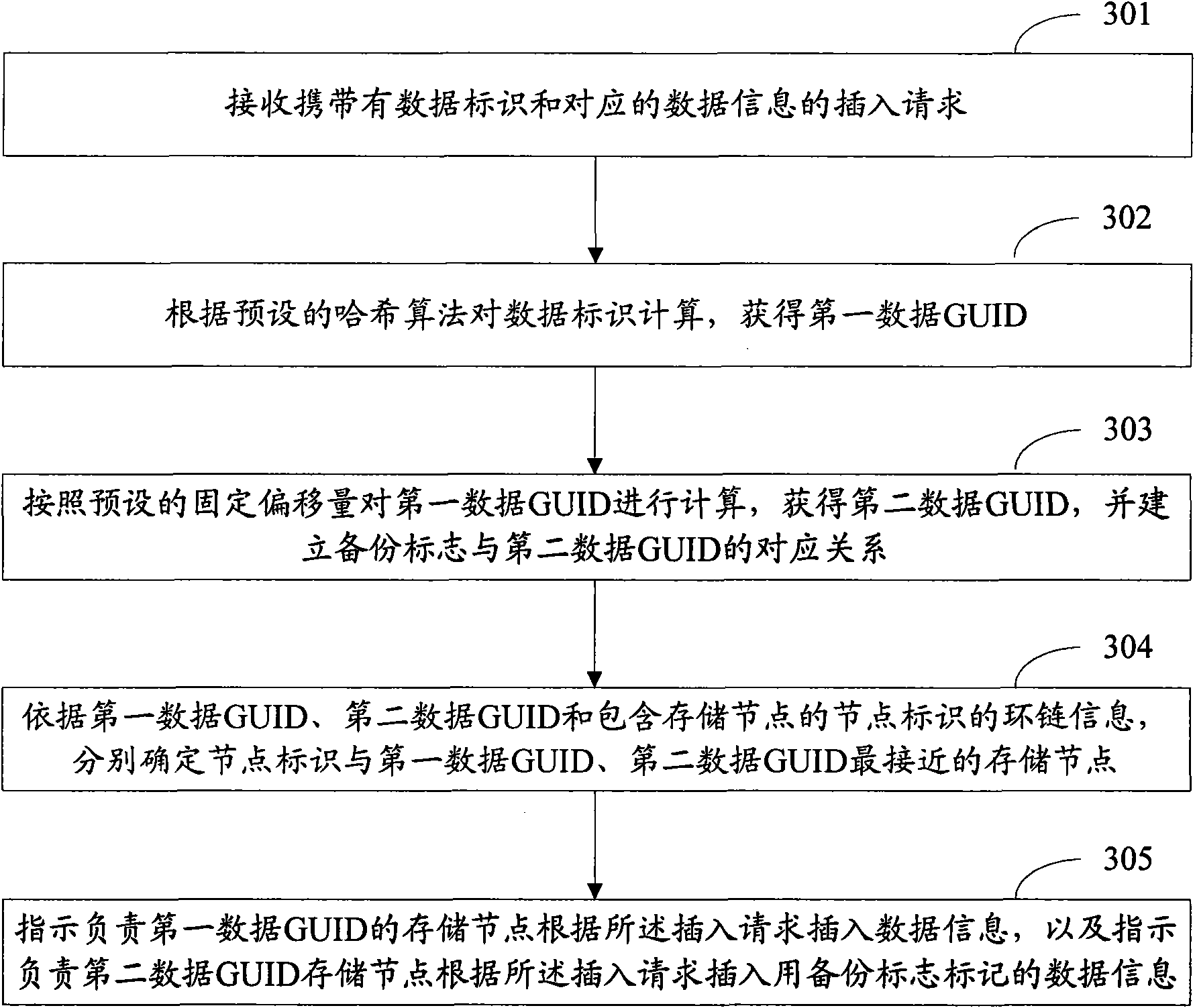
Data storage system in communication network and information processing method
ActiveCN101626563ARealize distributed storageSave the registration processTransmissionNetwork data managementInformation processingData information
The invention discloses a data storage system in a communication network used for realizing distributed storage of data. The system comprises front-end nodes, storage nodes, super nodes, management nodes, and calculating units which are positioned in the front-end nodes, the super nodes or the storage nodes, and are used for calculating first data GUID according to preset fixed offset to obtain second data GUID, determining a super node of which the node identification is most close to the second data GUID according to link chain information acquired on the management nodes and the second data GUID, and forwarding an insertion request carrying the second data GUID, the data information and a backup flag to the determined super node. The invention also discloses a method for processing information by the system.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
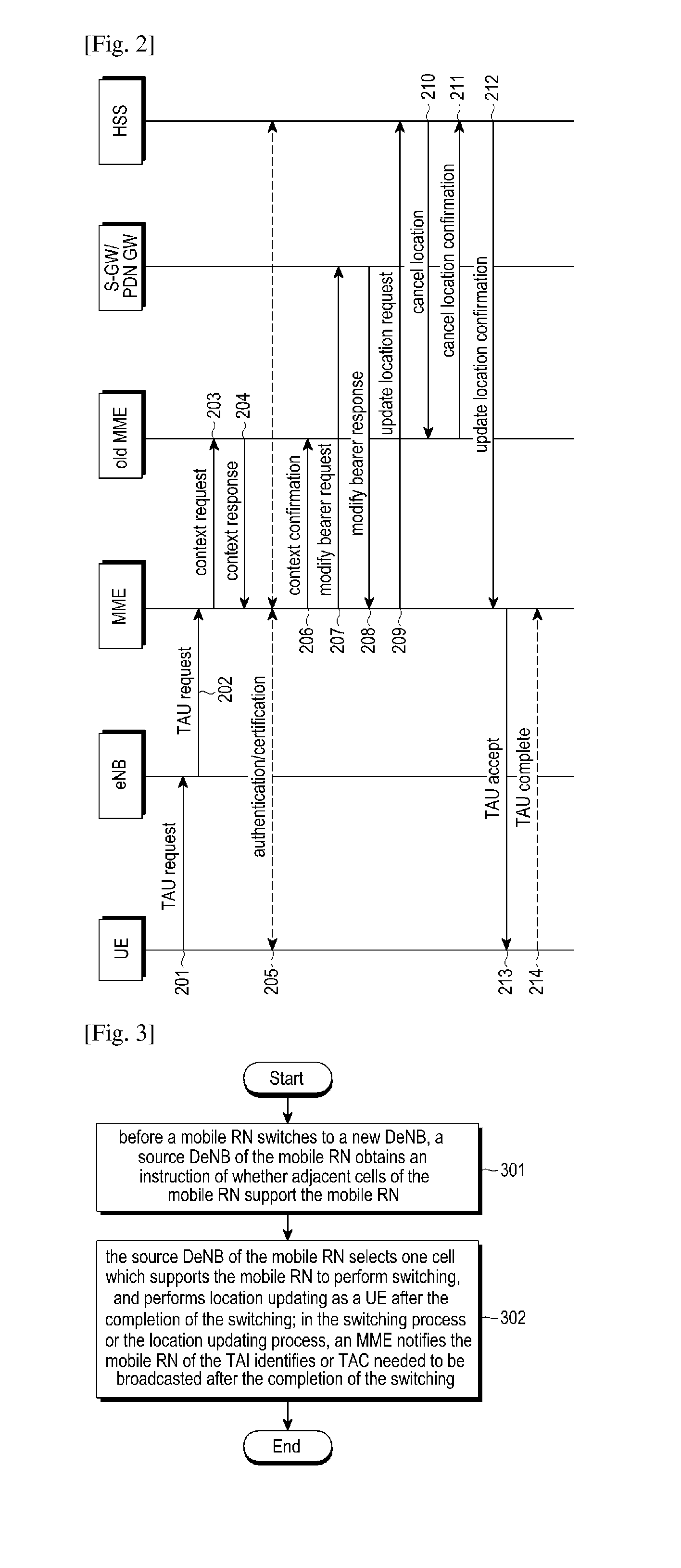
Method for mobile relay node obtaining ta information, method for mobile relay node switching, method for updating location of user location and method for paging user
InactiveUS20150063199A1Reduced signaling processAvoid network congestionFrequency-division multiplex detailsAssess restrictionMobile relayComputer science
The present invention provides a method for RN switching and location updating, a method for updating location of UE and a method for paging UE. Application of the methods of the present invention, can present each UE under the relay from initiating a tracking area update process, reduce network congestion, and save system sources.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
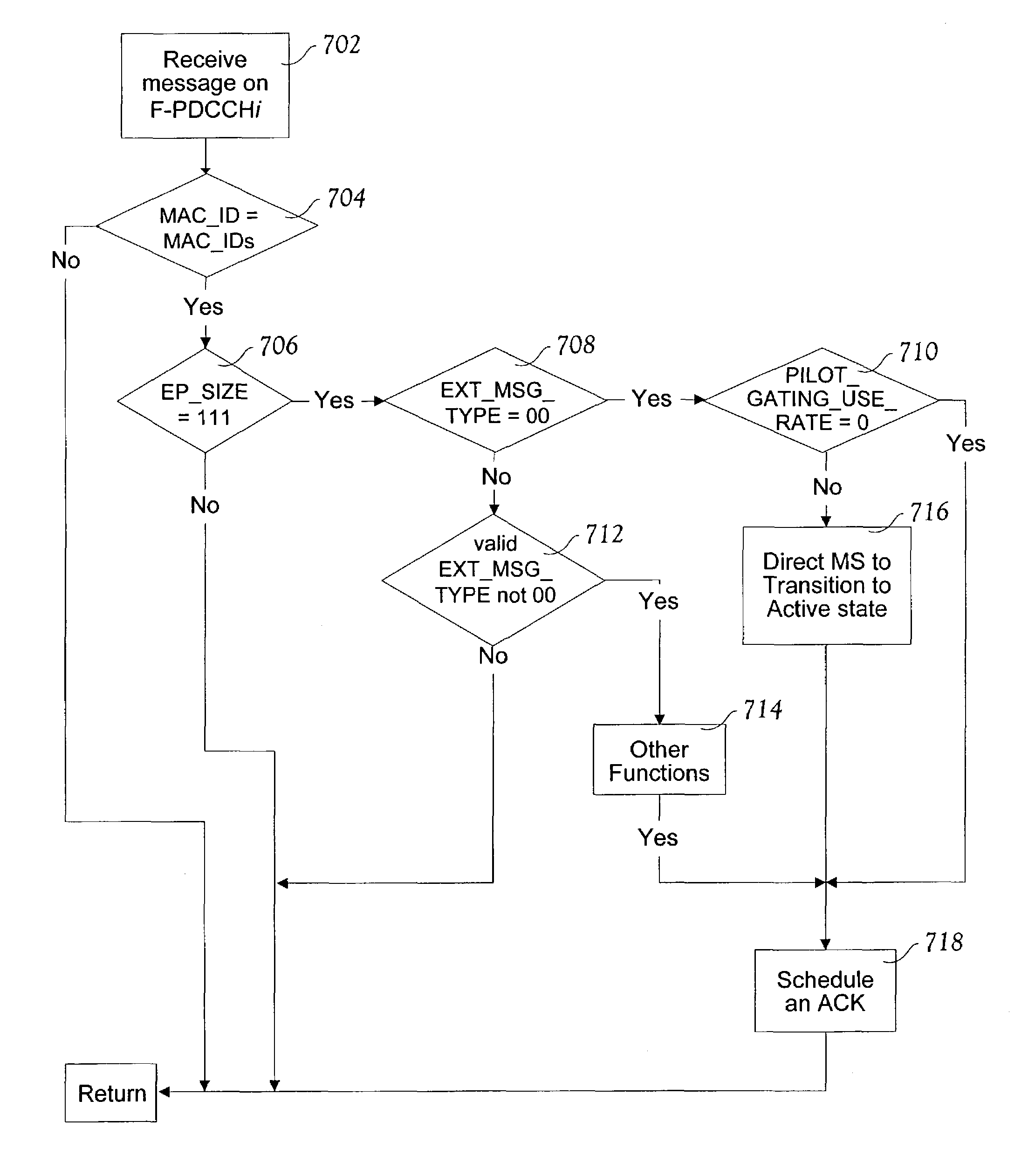
Method and apparatus for reducing power of a CDMA mobile station by controlled transition from control hold to active state
ActiveUS7203527B2Reduce power consumptionReduced signaling processPower managementEnergy efficient ICTData contentMobile station
A method and apparatus for reducing power dissipation in mobile stations that are configured to provide concurrent voice and high-speed packet data communication capability in a cellular telecommunications system. A state is defined during which data directed to a mobile station (MS) is not fully receive processed by the MS. Such a reduced receive processing state may be co-extensive with a Control Hold state. A notification mechanism is presented by which a serving base station directs a mobile station to return from reduced to full receive processing in advance of transmitting data on a packet data channel. The notification may take several forms, such as a message presenting the MS MAC address and one or more other bits of predetermined data content. Return to active (full receive) status may be required to be completed within a predetermined time, such as one ACK delay, after notification.
Owner:APPLE INC
Cell switching method and device
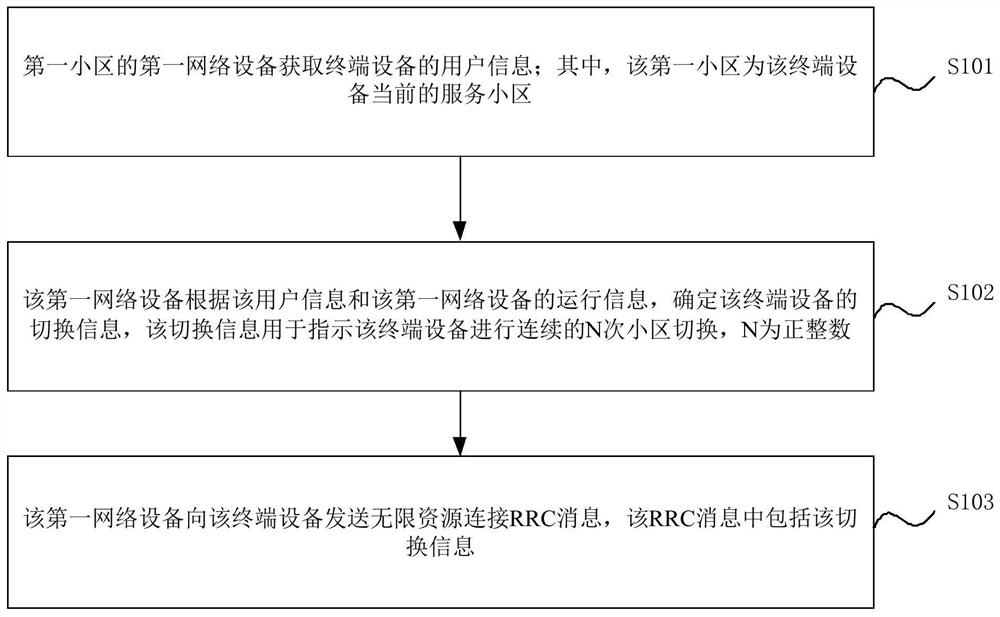
ActiveCN112020108AReduced signaling processReduce overheadNetwork topologiesTerminal equipmentEngineering
The embodiment of the invention provides a cell switching method and device. A first network device of a first cell acquires user information of a terminal device, so the first network equipment can determine the switching information according to the user information and the operation information of the first network equipment, after the first network device sends an RRC message containing the switching information to the terminal device, the terminal equipment can carry out continuous N times of cell switching according to the switching information; in the N times of cell switching, the first network device can configure the switching conditions of subsequent N times of switching in advance at one time only by acquiring the user information once, so that the signaling flow and overhead of the network can be reduced, the response time of switching can be reduced, and the method and the device are suitable for network switching in a satellite scene.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Call routing method and related network element
InactiveCN105828307AShorten connection timeReduced signaling processCommmunication supplementary servicesNetwork data managementApplication serverContinuation
The embodiment of the present invention provides a call routing method and related network elements. The MSC receives the call from the calling user in the CS domain to the called user; and determines that the called user has registered VoLTE according to the information of the called user found. service, and the address of the VoLTE AS anchored when the called user registers for the VoLTE service; the VoLTE AS sends an IDP message to the VoLTE AS, and the VoLTE AS queries the HSS for the called user's resident address based on the called number of the called user carried in the IDP message. Network: Based on the query result that the network where the called user resides is a 2 / 3G network, the VoLTE AS sends a continue message to the MSC, so that the MSC completes the connection to the called user in the CS domain. The connection time of the called user is shortened. The invention relates to the field of mobile communication.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GRP BEIJING
Dynamic channel configuration method based on source rate estimation
InactiveCN1404248AImprove resource utilization efficiencyAccurate Rate EstimationCode division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsDynamic channelCommunication quality
There has the features of burst in grouping service and large range of dynamic change in speed rate among the CDMA cellular mobile communication system. If you want to raise the utilization efficiency of the system resources, the reasonable and dynamic channel disposal should be carried out, otherwise the utilization efficiency and the communication quality will be low. The dynamic channel disposal can be realized by measuring service volume and to report the measured service volume. The present patent has provided a dynamic channel disposal method base on the estimation to the service source speed, which can estimate the instant speed of service source quickly and accurately and to dispose the new channel resources according to it for effectively raising the utilization rate of system resources and reducing the unnecessary frequency of channel redisposing.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
MIMO transceiver with pooled adaptive digital filtering
InactiveUS20080112470A1Reduced signaling processMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsTransceiverInstructions per second
MIMO transceiver with a reconfigurable pooled digital filter is disclosed. A processor sets parameters of the filter to minimize the number of instructions per second and the amount of power required by the filter to perform, while matching the filter to at least one of: a transmitter filter and a receiver filter. The processor uses an algorithm or a lookup table stored in memory to select the combination of filter parameters. The parameters may be selected from at least one of: a number of taps, a filter length, a word length, a coefficient quantization, a sampling rate, bits per sample, a sampling bit, a tap delay and a coefficient length. After selecting a combination of filter parameters, the processor sends a control signal to the adaptive filter. The pooled adaptive filter reconfigures itself in accordance with the selected filter parameters.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
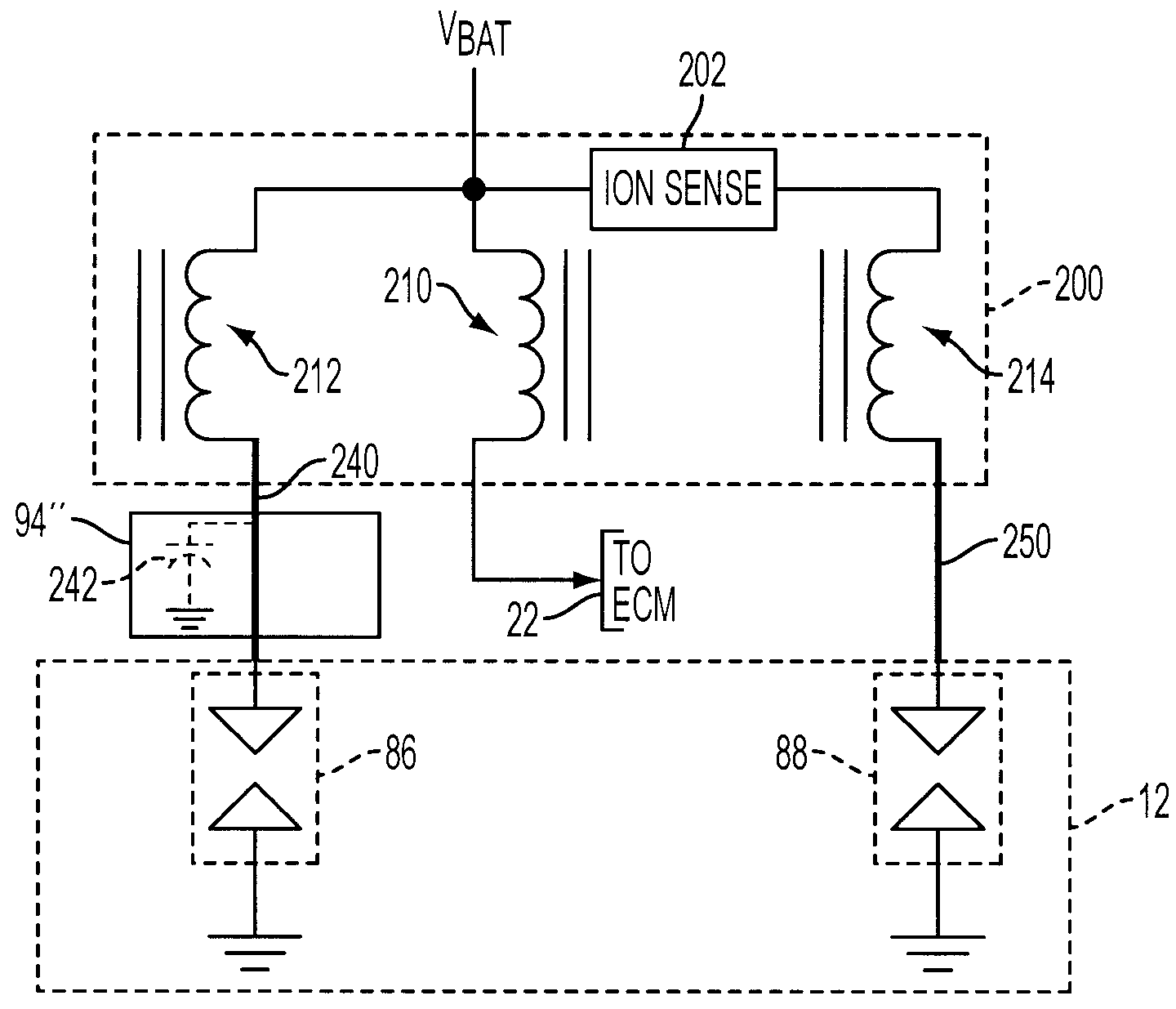
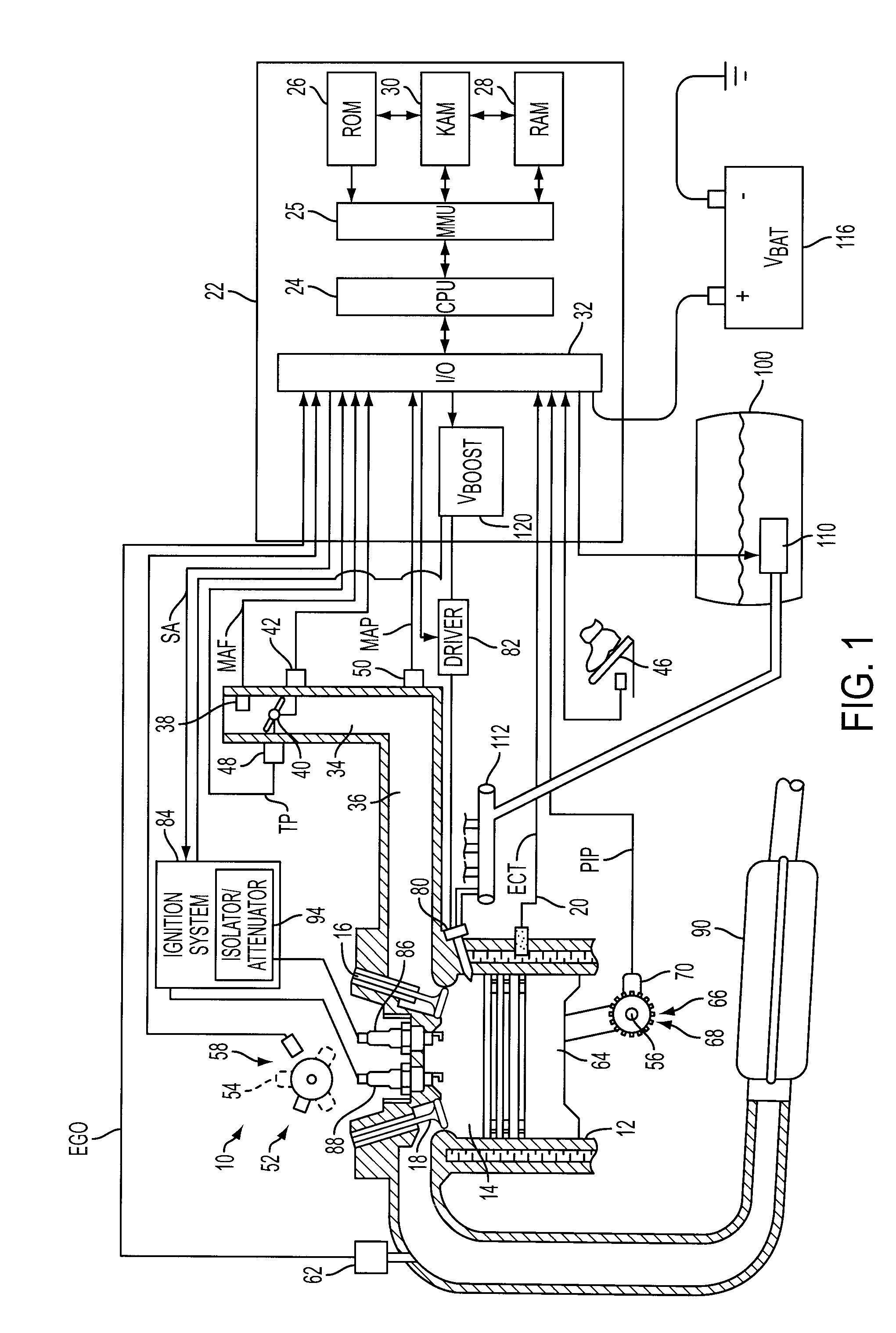
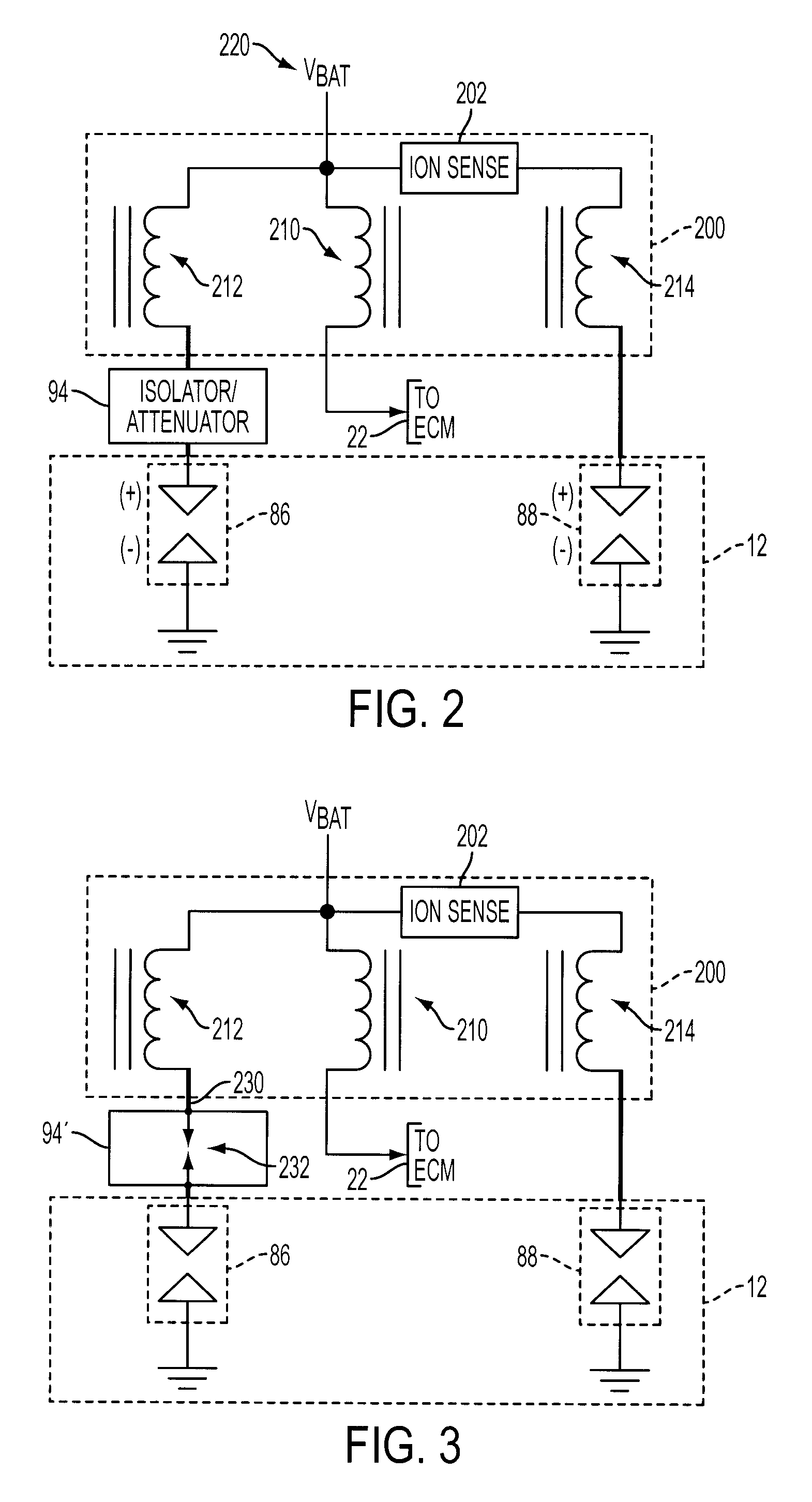
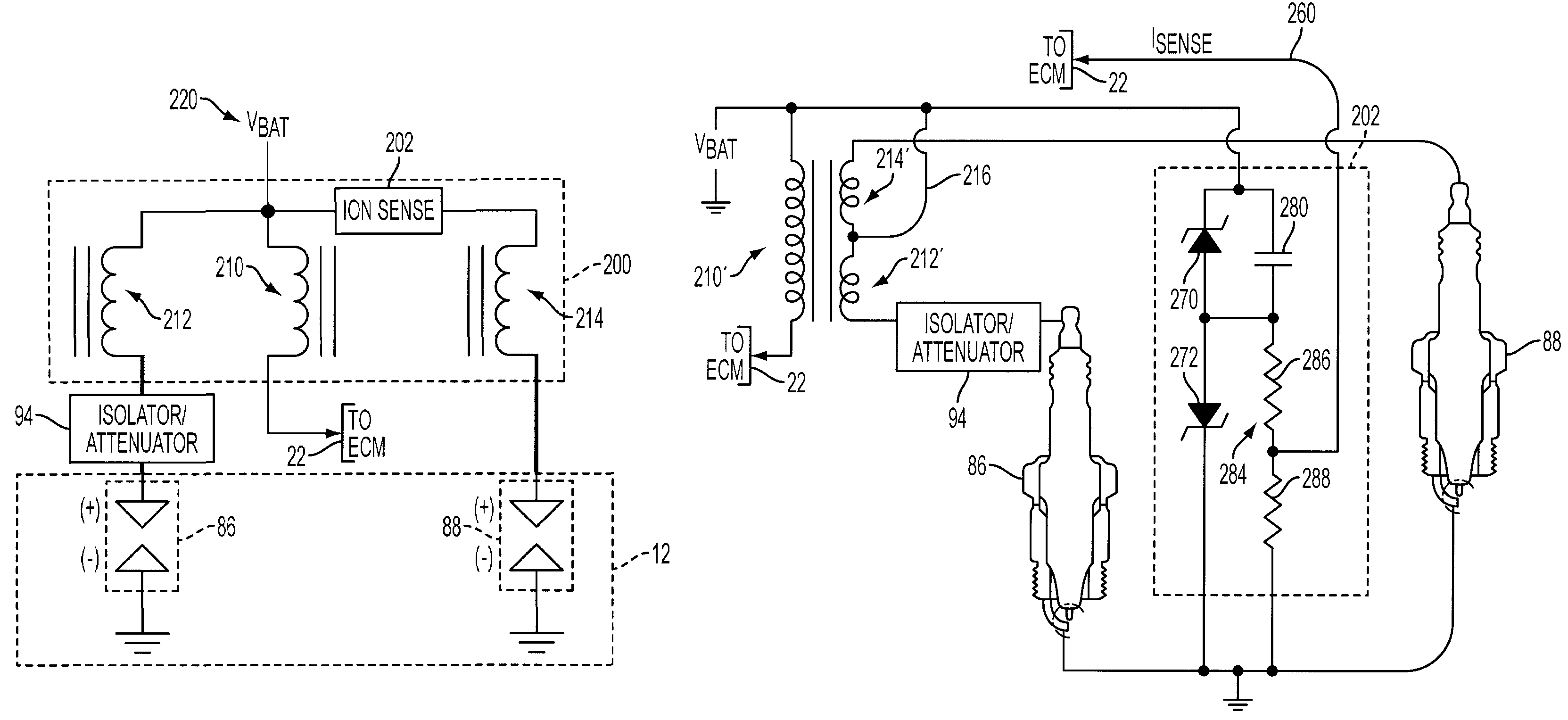
Internal combustion engine with multiple spark plugs per cylinder and ion current sensing
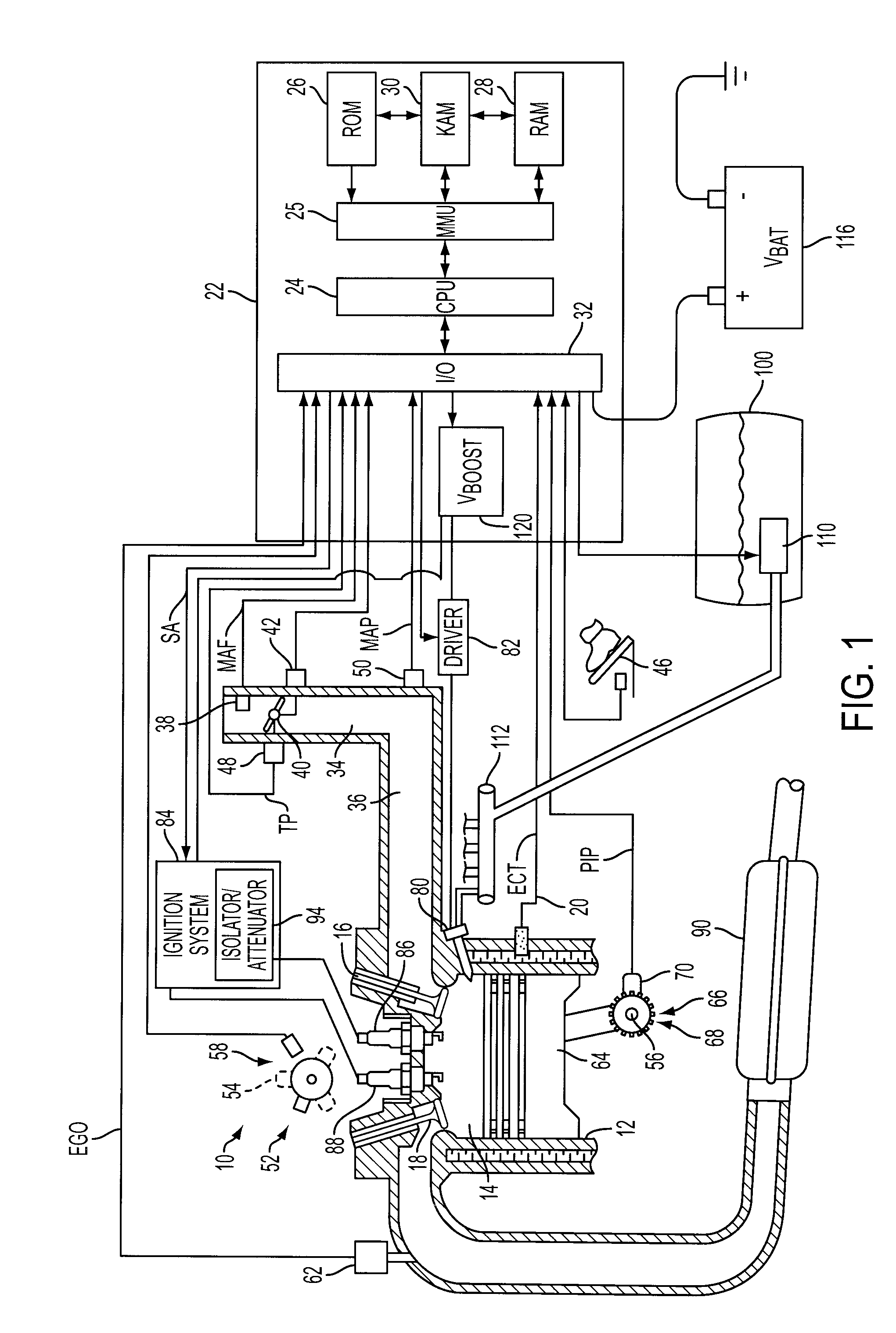
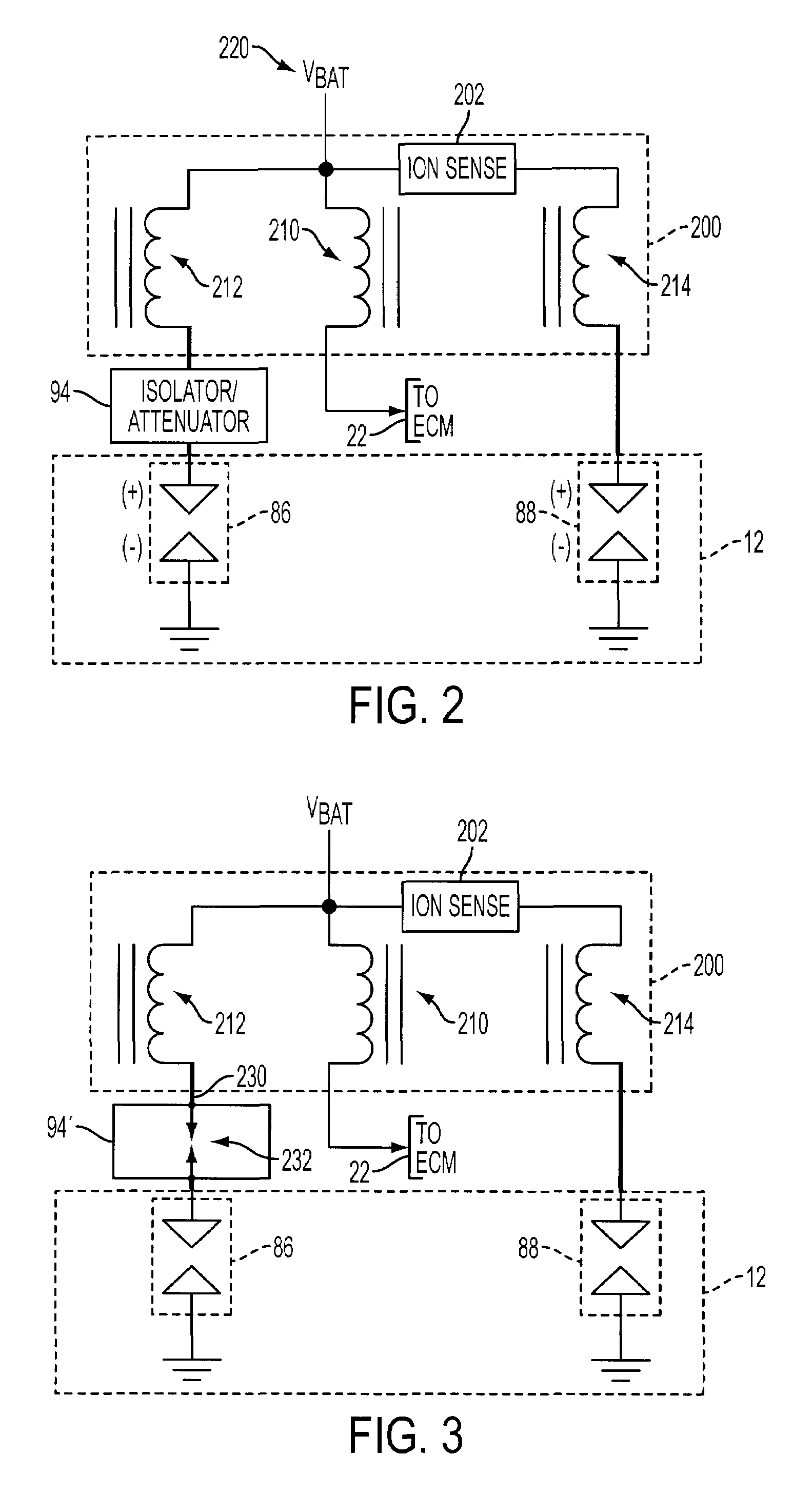
InactiveUS20090107457A1Low costReduce Signal Processing ComplexitySparking plugsMachines/enginesIonization currentIon current
A system and method for operating a multiple cylinder internal combustion engine having at least two spark plugs per cylinder include selectively isolating all but one spark plug associated with the cylinder at least during an ionization current sensing period to reduce or eliminate interference among ionization current signals flowing through more than one spark plug.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Service request method and service request device
ActiveCN104703220AReduced signaling processImprove business request efficiencyNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionResource informationThe Internet
The invention relates to the technical field of mobile communication, and particularly relates to a service request method and a service request device. In the prior art, as interactive processes of internets of different types are complicated, user equipment spends a lot of time on service request. The service request method and device aim to shorten the time for service request. The method of the embodiment mainly comprises the steps that a synergic network element receives the service request of the user equipment (UE), wherein the synergic network element is set for unified management of cells of different network types; if the synergic network element confirms that a source cell cannot support the service request of the UE according to the service request of the UE and network resource information reported by cell management equipment of the source cell, according to network resource information reported by cell management equipment of the adjacent cell of the source cell, the synergic network element determines at least one of the adjacent cells of the source cell, which supports the service request of the UE, and then informs the UE, so that the UE can select one from at least one adjacent cell as a target cell and sends the service request to the target cell.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
Internal combustion engine with multiple spark plugs per cylinder and ion current sensing
InactiveUS7677230B2Reduce and eliminate interferenceLow costMachines/enginesInstallations with induction energy storageIonization currentIon current
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
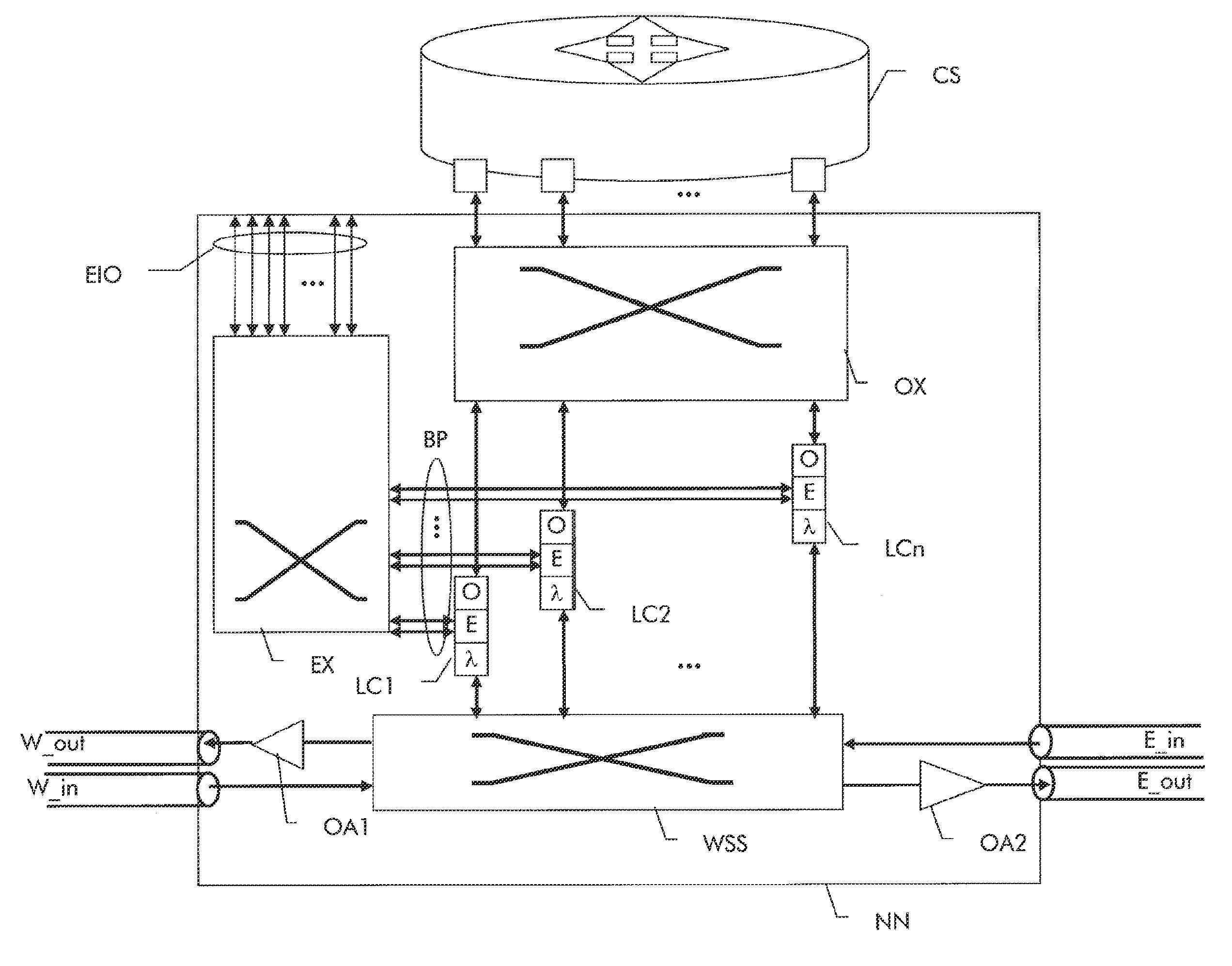
Transponder and related network node for an optical transmission network
ActiveUS20130243431A1Reduce power consumptionReduced signaling processMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsLine cardEngineering
In order to reduce power consumption in network equipment for optical transmission networks, it is proposed by reducing E / O conversion and signal processing in optical networks when not needed. A network node has two or more line cards. Each line card contains a receive side transponder section with a network side optical receiver, a first electrical section, and a client side optical transmitter and a transmit side transponder section with a network side optical transmitter, a second electrical section, and a client side optical receiver. The first electrical section has at least one intermediate electrical output the second electrical section has at least one intermediate electrical input. The intermediate electrical outputs and inputs lead to an electrical switch matrix, which controllably interconnects the intermediate electrical outputs and inputs. Preferably, the transponders can additionally contain second intermediate electrical outputs and inputs additionally bypassing a Forward-Error-Correction processing function in the line cards
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
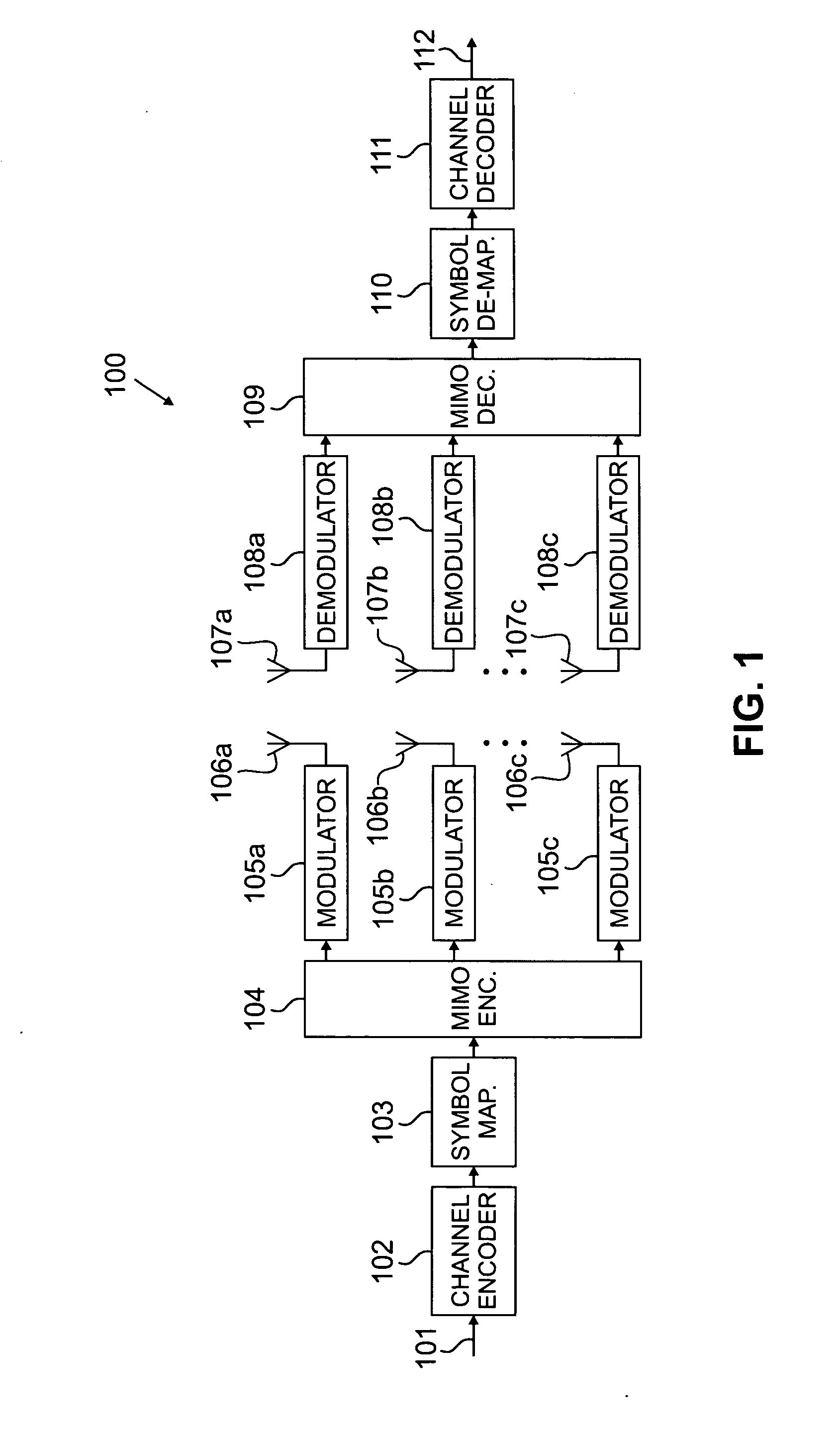
Method for transmitting data in a MIMO communication system
ActiveUS20070009058A1Improve system performanceAvoid it happening againDiversity/multi-antenna systemsSecret communicationCommunications systemData transmission
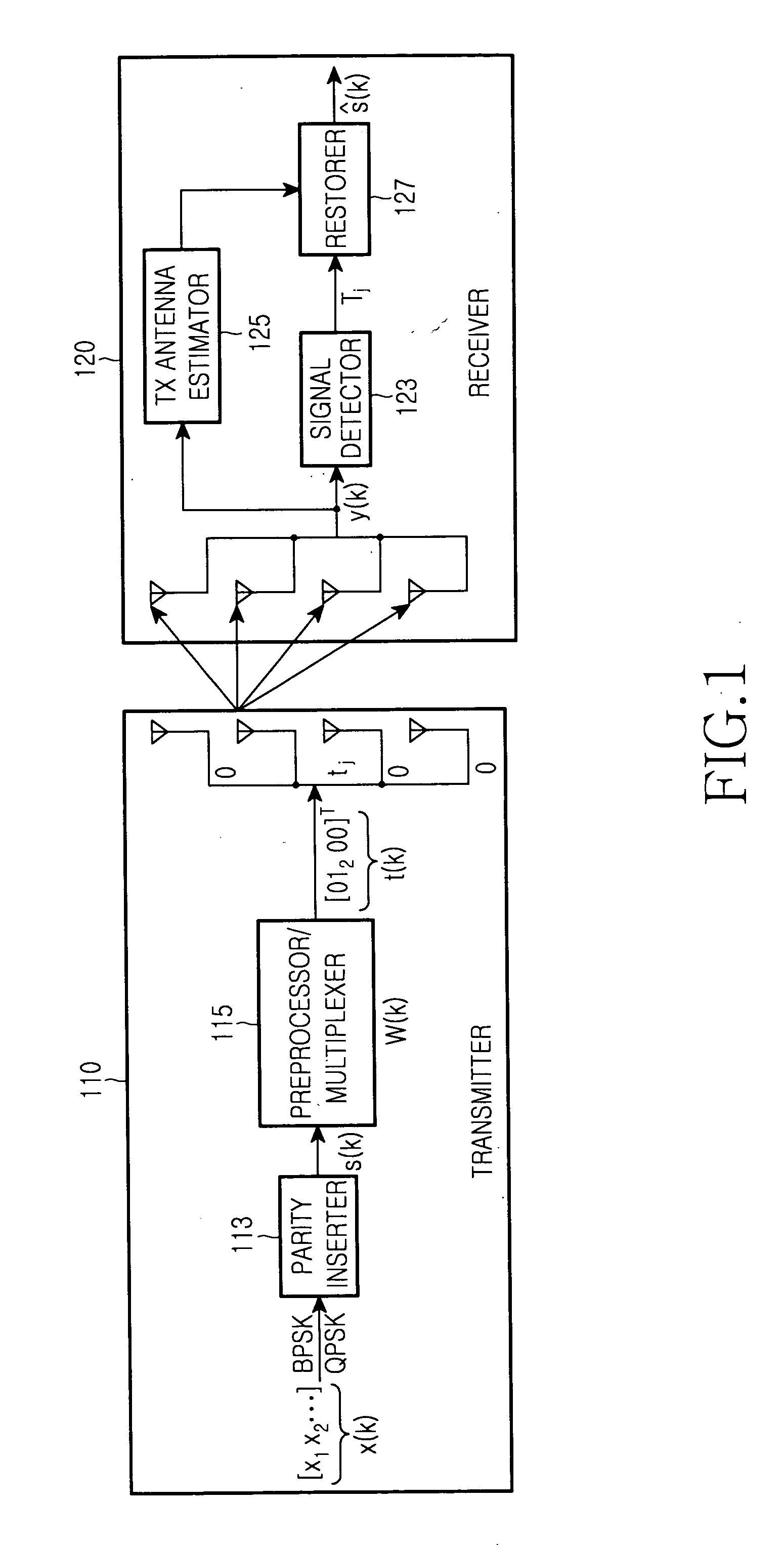
Provided is a multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) data transmission method. A transmitter generates a transmission symbol by adding a parity symbol to a predetermined number of data symbols, generates a preprocessed symbol by multiplying the predetermined number of transmission symbols by a preprocessing matrix in units of blocks, selects a transmission antenna associated with a non-zero transmission symbol among preprocessed transmission symbols constituting the preprocessed symbol, and transmits the preprocessed symbol via the selected transmission antenna. A receiver receives a signal transmitted from the transmitter, estimates a preprocessed symbol and a transmission antenna index from the received signal, and restores the transmission symbols using the estimated preprocessed symbol and transmission antenna index.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
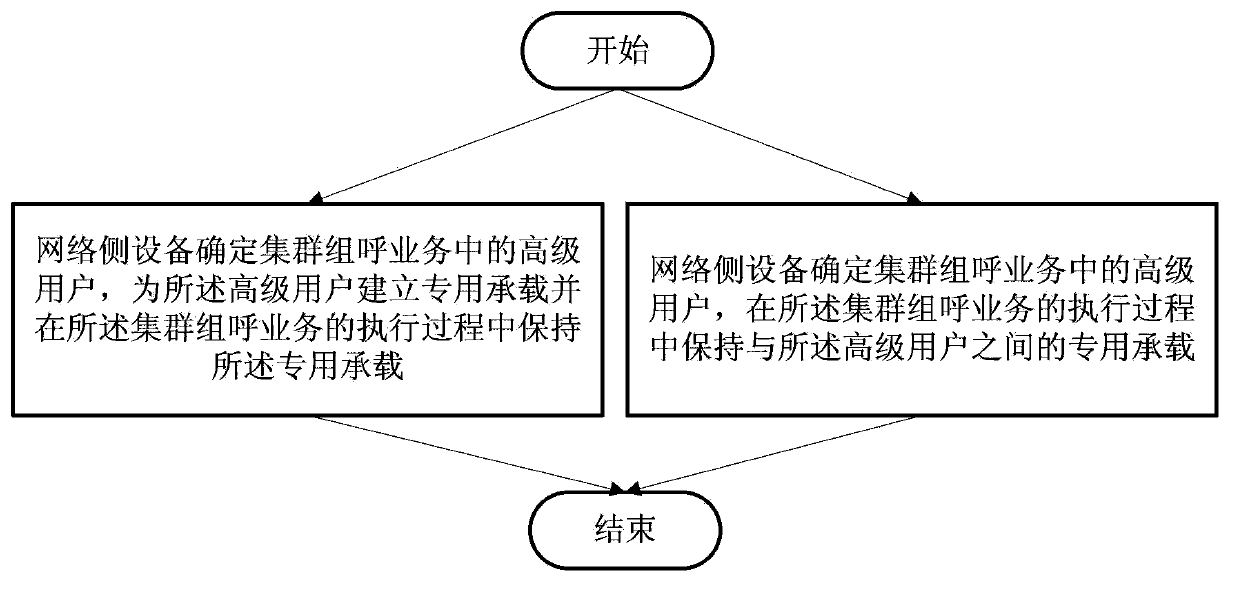
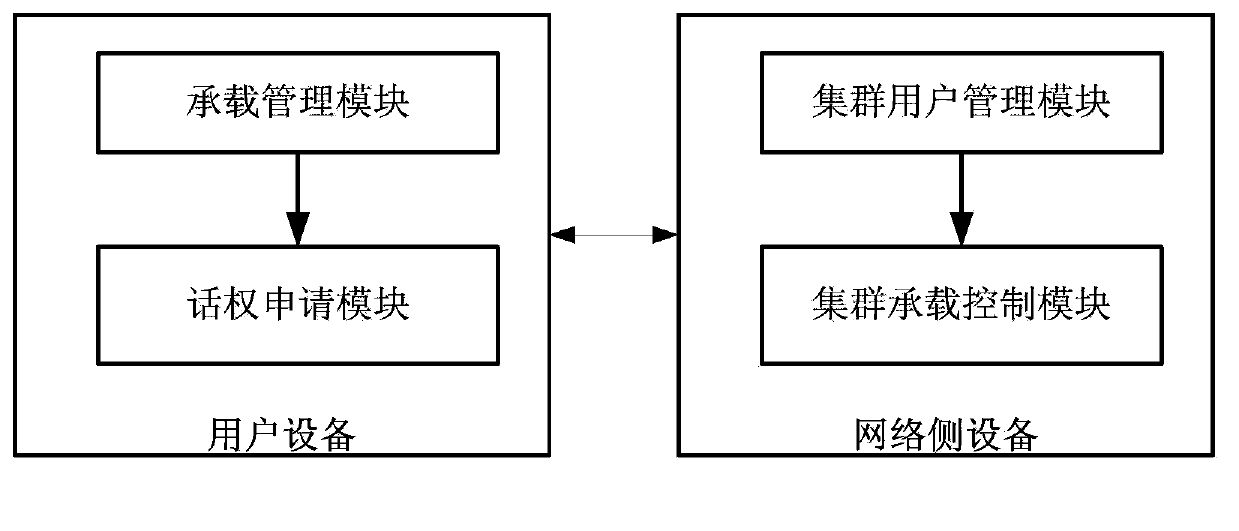
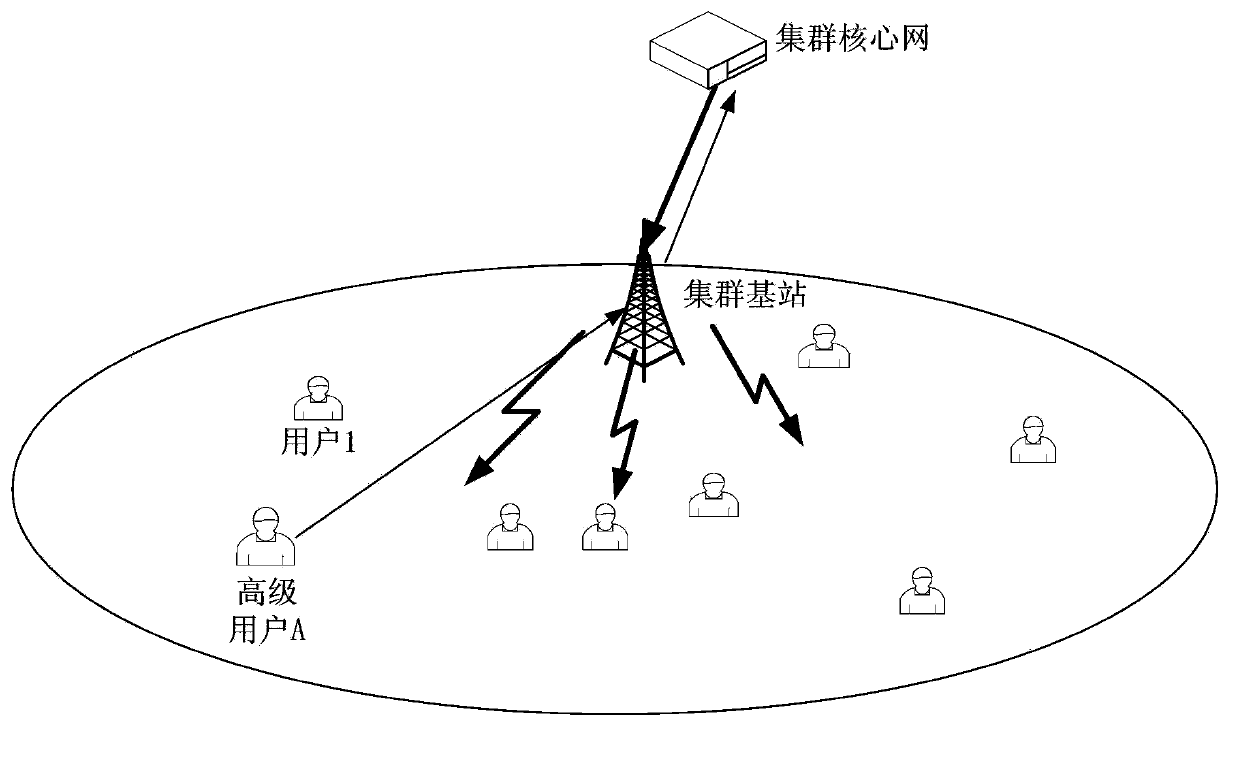
Cluster business control method, network-side equipment and user equipment
InactiveCN103974205AConvenient business executionImprove experienceBroadcast service distributionTelecommunicationsDifferentiated service
A method, a network side device and a user equipment for controlling cluster service, wherein the method includes: the network side equipment determines senior users in a cluster group call service, and maintains a dedicated bearer established with the senior users during an implementation process of the cluster group call service; or the network side device determines senior users in a cluster group call service, establishes a dedicated bearer for the senior users and maintains the dedicated bearer during an implementation process of the cluster group call service.
Owner:ZTE CORP
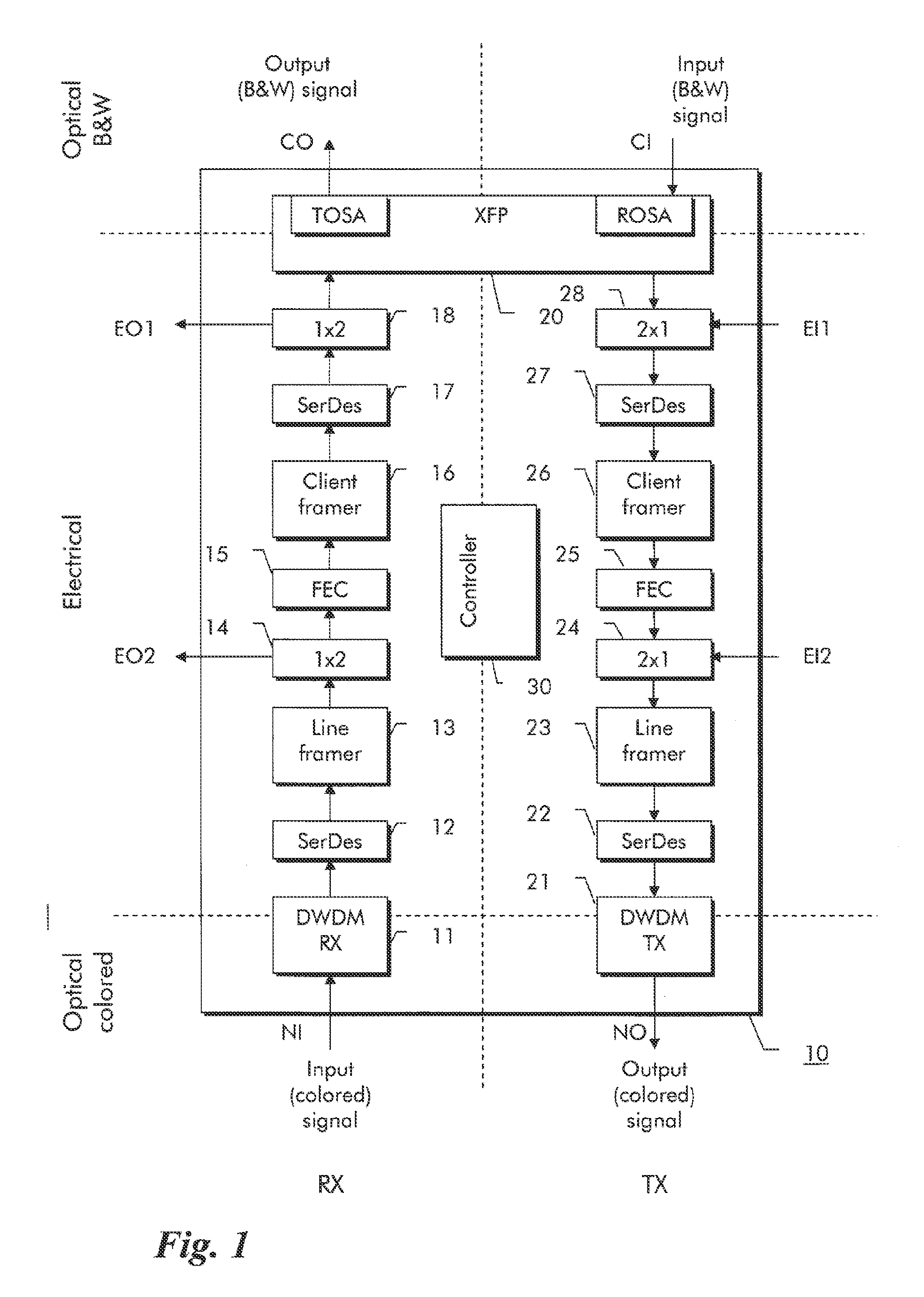
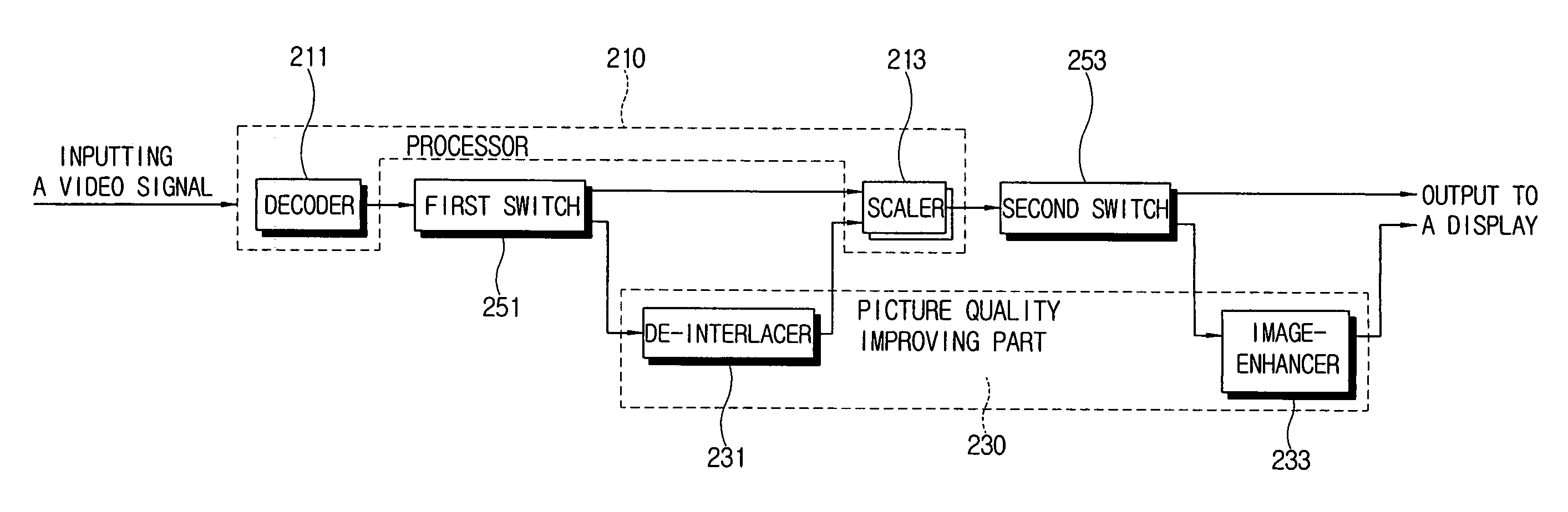
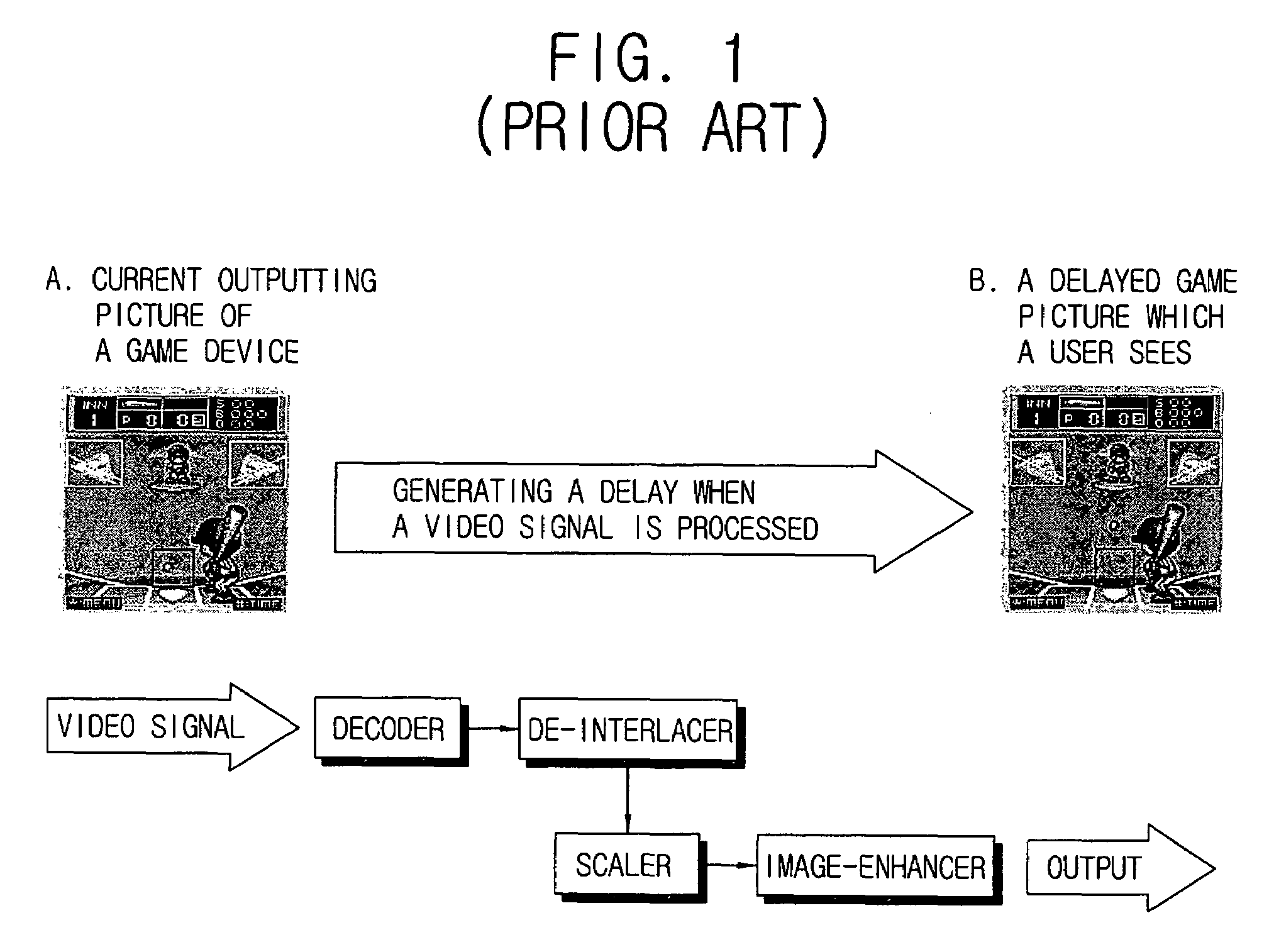
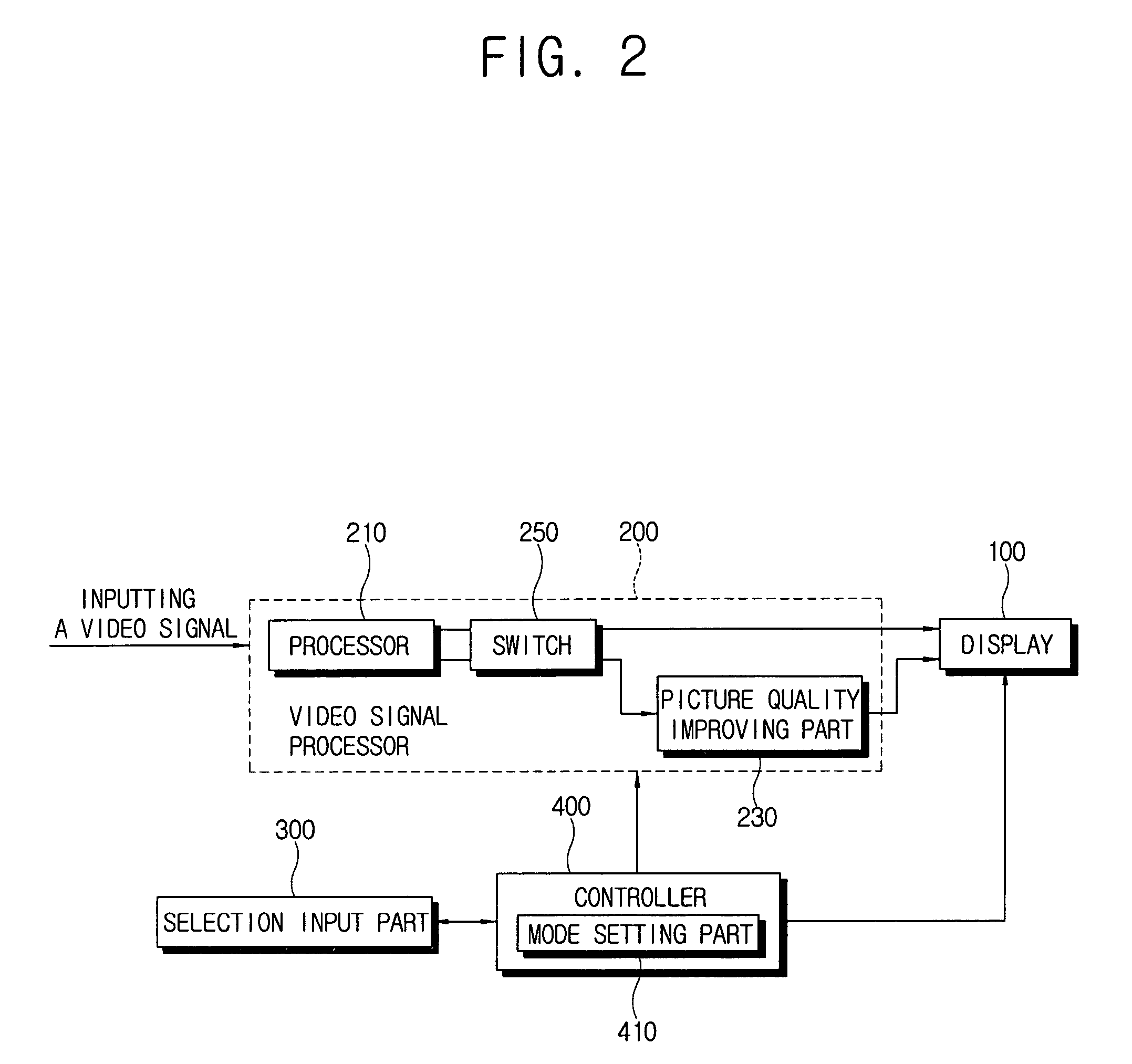
Video signal processing circuit having a bypass mode and display apparatus comprising the same
ActiveUS7586546B2Reduced signaling processSelectively bypassTelevision system detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsSignal processing circuitsDisplay device
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
MIMO receiver with pooled adaptive digital filtering
InactiveUS20070258600A1Reduced signaling processSpatial transmit diversityReceivers monitoringInstructions per secondControl signal
MIMO receiver with a reconfigurable pooled digital filter is disclosed. A processor sets parameters of the filter to minimize the number of instructions per second and the amount of power required by the filter to perform, while matching the filter to a transmitter filter. The processor uses an algorithm or a lookup table stored in memory to select the combination of filter parameters. The parameters may be selected from at least one of: a number of taps, a filter length, a word length, a coefficient quantization, a sampling rate, bits per sample, a sampling bit, a tap delay and a coefficient length. After selecting a combination of filter parameters, the processor sends a control signal to the adaptive filter. The pooled adaptive filter reconfigures itself in accordance with the selected filter parameters.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
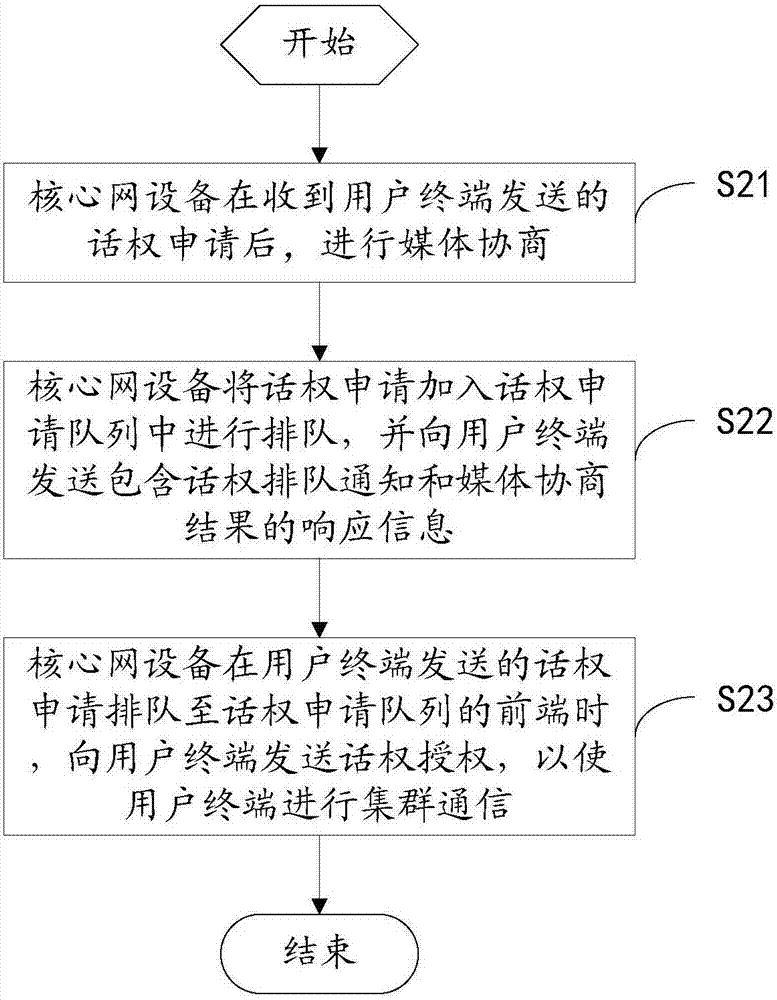
Core network equipment and trunking communication method thereof
ActiveCN107222846ASpeed up the processReduced signaling processConnection managementBroadcast service distributionTrunkingAuthorization
The invention discloses core network equipment and a trunking communication method thereof. The trunking communication method comprises the steps that after the core network equipment conducts media negotiation after receiving a speaking right request sent by a user terminal; the core network equipment adds the speaking right application into a speaking right application queue to queue and sends a response message containing a speaking right queueing notification and a media negotiation result to the user terminal; and when the speaking right application sent by the user terminal queues to the front end of the speaking right application queue, the core network equipment sends speaking right authorization to the user terminal to enable the user terminal to conduct trunking communication. In this way, the trunking communication method has the advantages that when the speaking right application queues to the front end of the queue, speaking right authorization can be achieved immediately, the signaling procedures are decreased, time is saved, and the trunking communication process is accelerated.
Owner:HYTERA COMM CORP
Mobile Fast Alerting
InactiveUS20100331055A1Reduce timeFaster feedbackInterconnection arrangementsConnection managementReceiptHandset
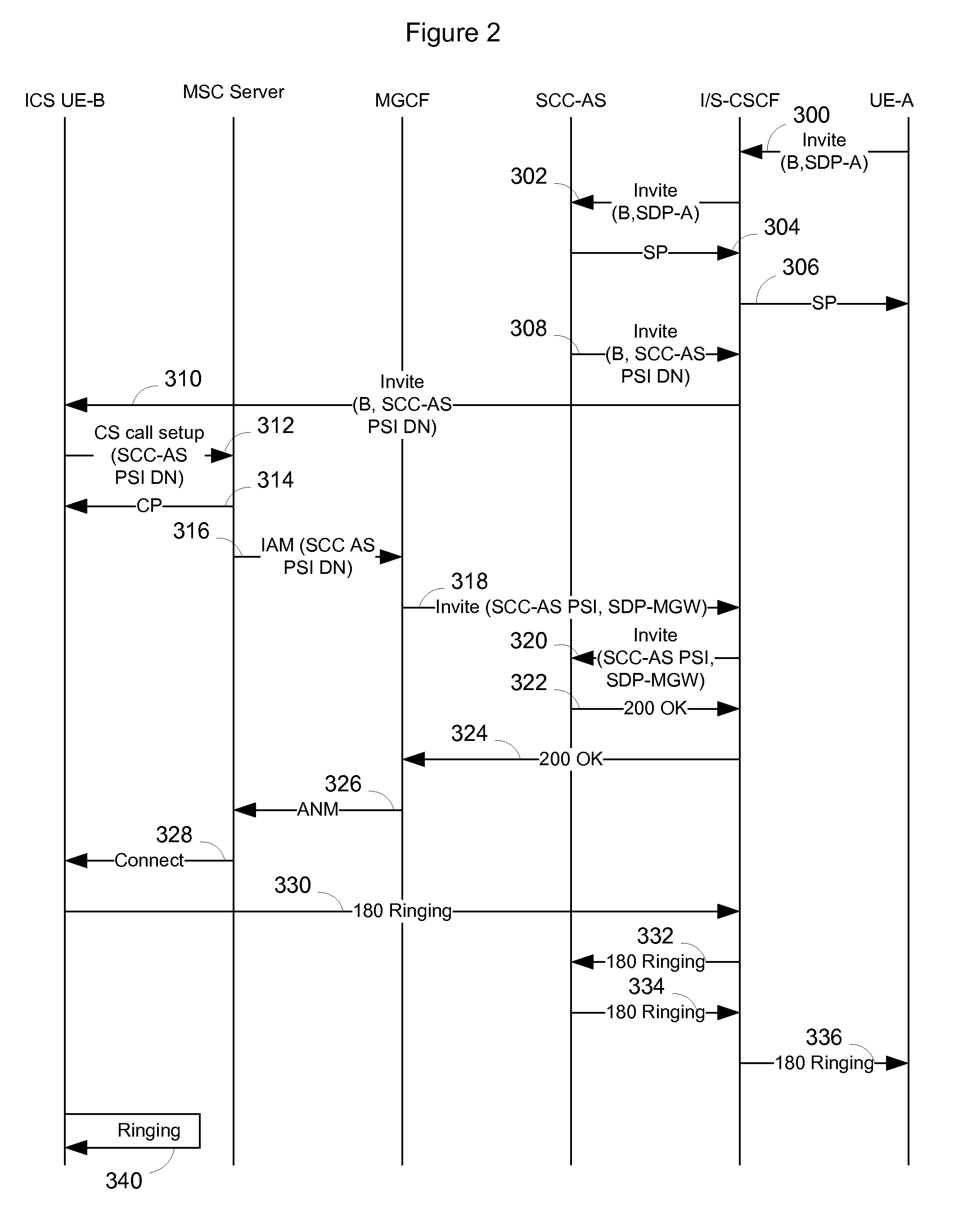
Where a separate bearer channel is required to be set up in a mobile network to complete a hybrid VoIP call on the mobile network as specified in 3GPP ICS standard TR 23.892, an alerting process may be started after a provisionable delay rather than upon completion of the network call setup. This allows the mobile network user to start responding to the impending call before signaling of the call has been completed, so that the person can answer closer in time to completion of call signaling. Additionally, the person who placed the call may be provided with ringing feedback to make it sound like the call has been completed. The amount of delay between receipt of a SIP invite and the onset of an alerting process may be specified in the mobile handset or may be specified as a header in the SIP invite. The amount of delay may be fixed or adjusted based on feedback.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
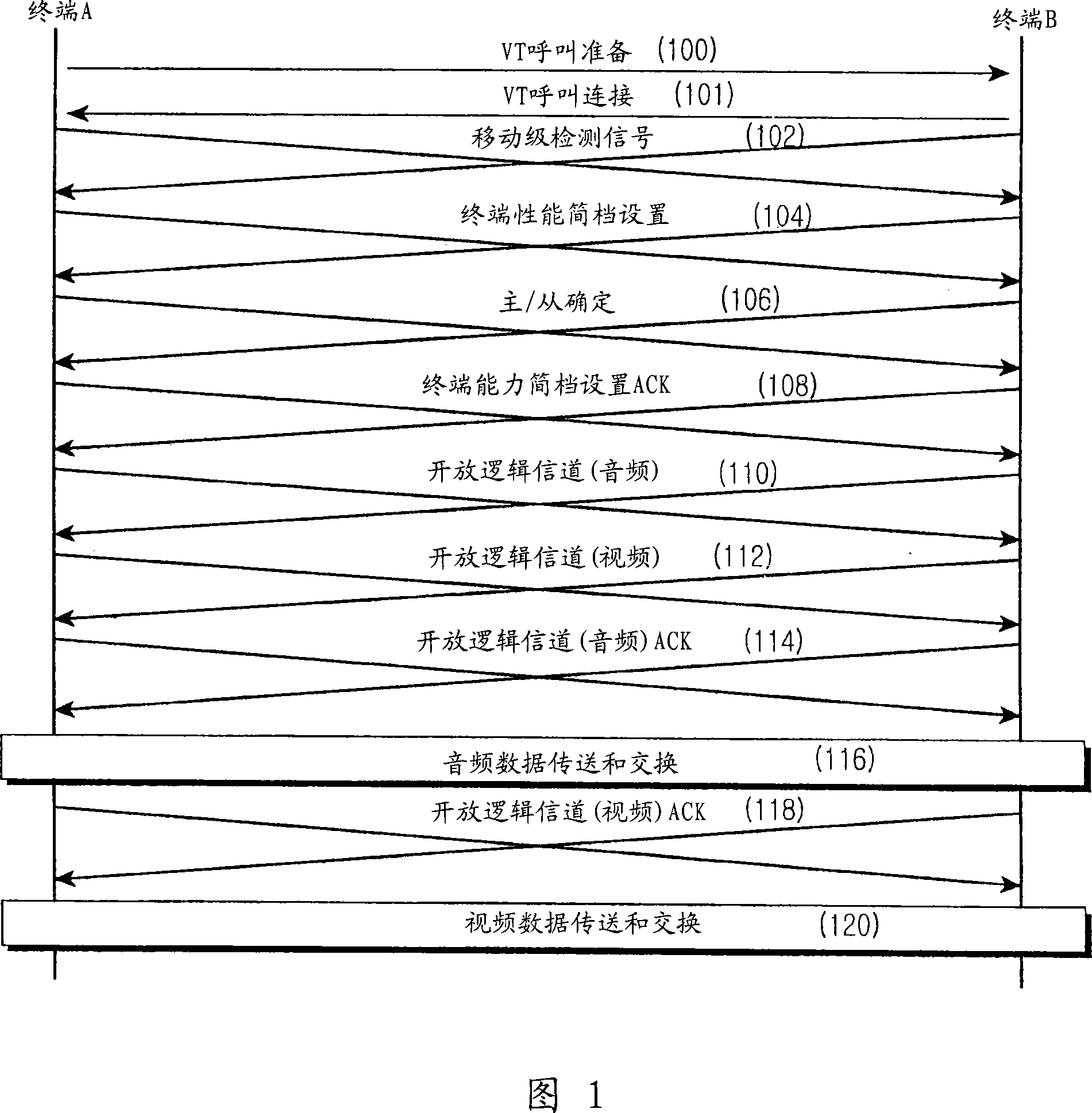
Method and apparatus for video telephony in mobile communication terminal
InactiveCN101137245AReduced signaling processRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTwo-way working systemsTelephonyTelephone call
Provided are a method and an apparatus for video telephony in a mobile communication terminal. According to the method, when a calling mobile communication terminal attempts video telephony, call connection between the calling mobile communication terminal and a called mobile communication terminal is made. The calling mobile communication terminal checks whether video telephony profile data of the called mobile communication terminal has been registered. When the video telephony profile data of the called mobile communication terminal has been registered, the calling mobile communication terminal selects the video telephony profile data and transmits the profile data to the called mobile communication terminal to form a video telephony channel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
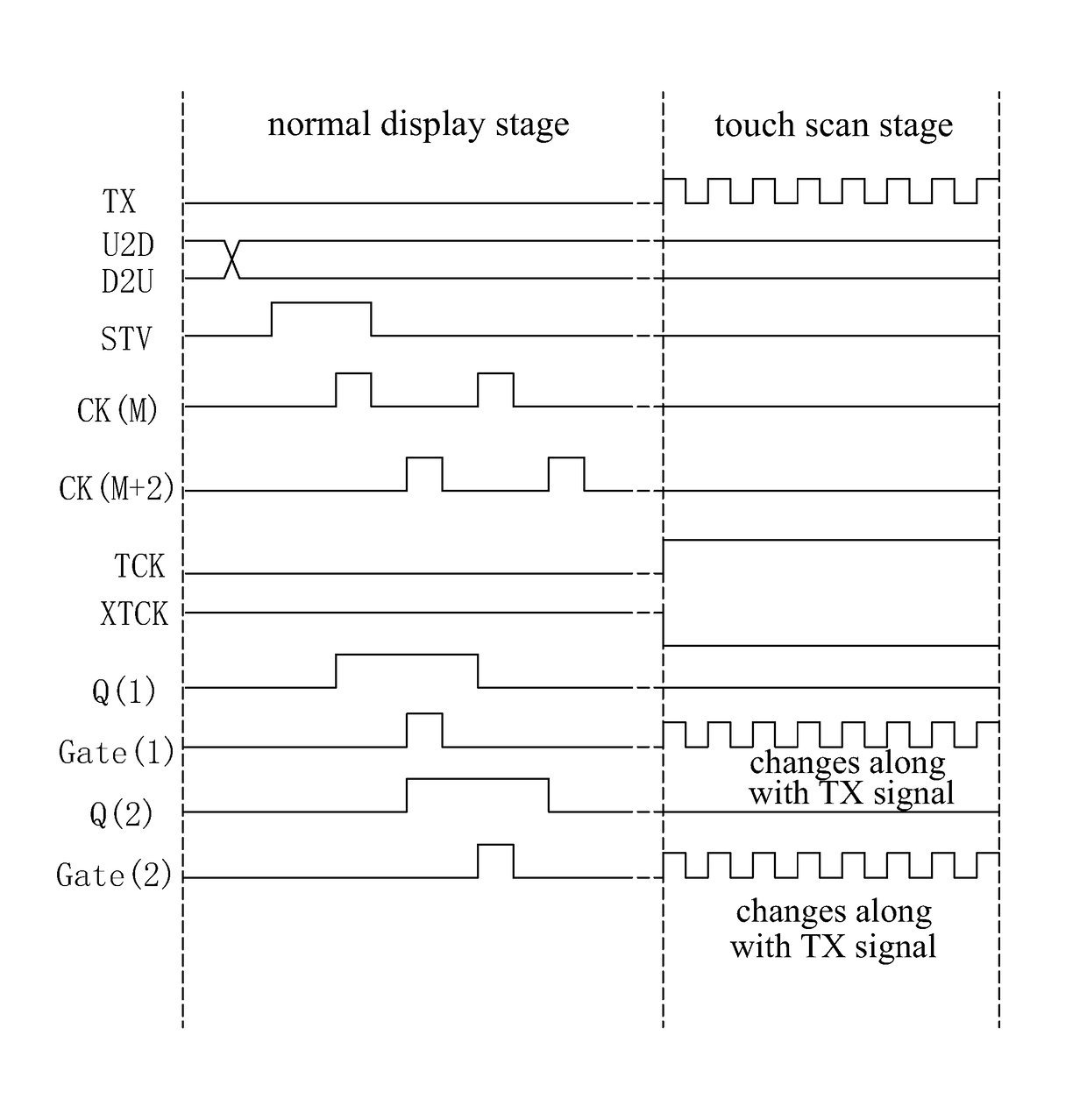
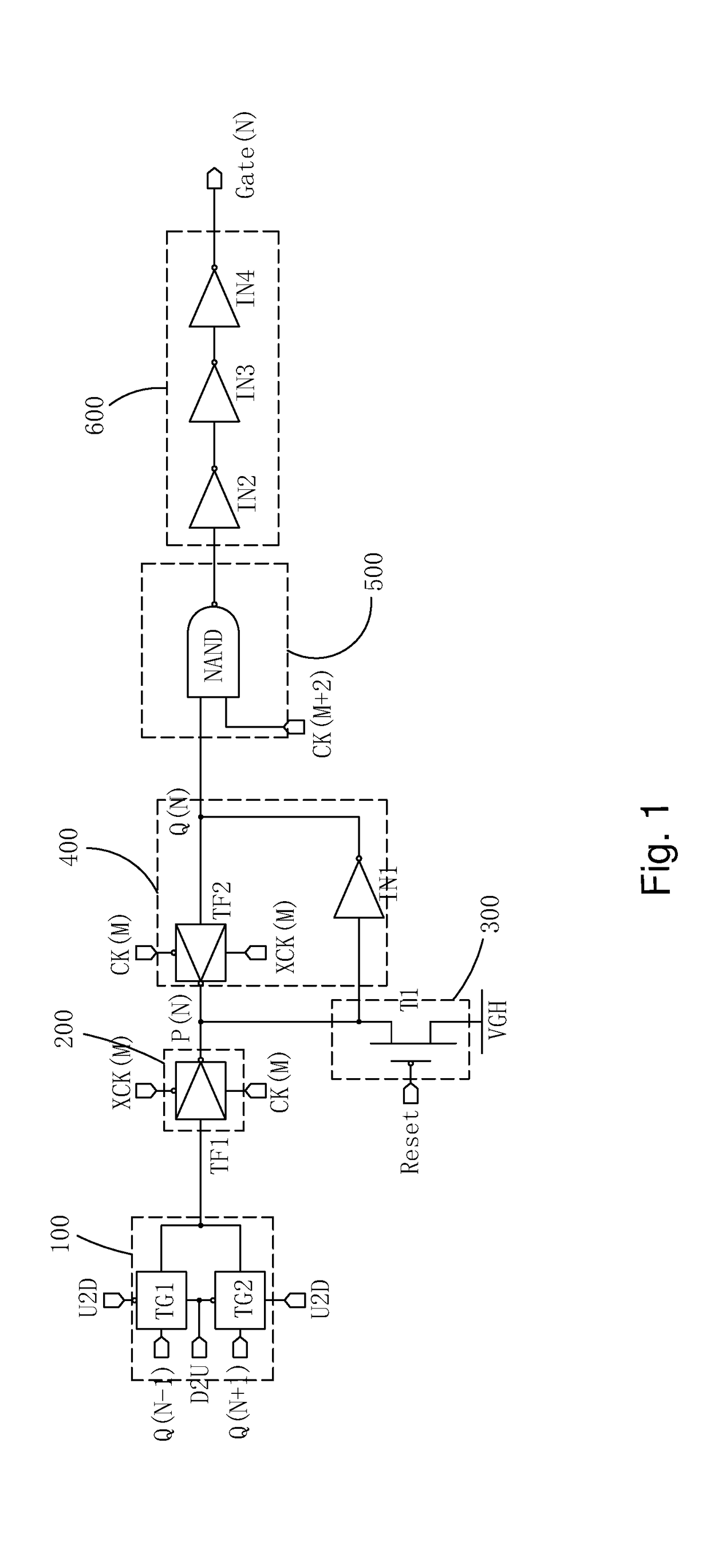
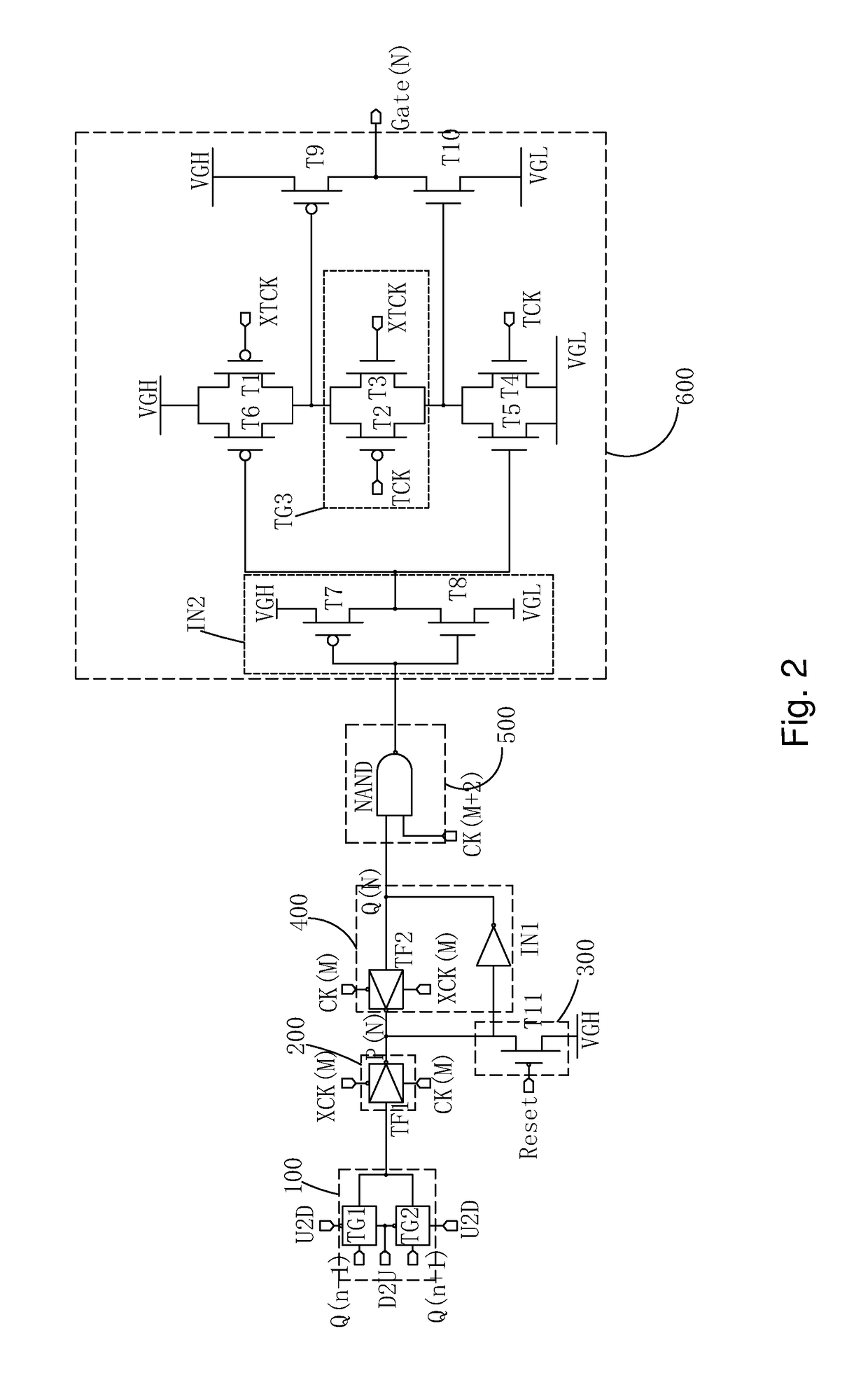
Goa circuit applied for in cell type touch display panel
ActiveUS20180059829A1Help work efficiencyReduced signaling processStatic indicating devicesDigital storageTransmission gateLow voltage
The present invention provides a GOA circuit applied for the In Cell type touch display panel. The third transmission gate (TG3) comprising the second P-type thin film transistor (T2) and the third N-type thin film transistor (T3), the first P-type thin film transistor (T1) and the fourth N-type thin film transistor (T4) are added in the output buffer module (600), and the touch control signal (TCK) and the inverted touch control signal (XTCK) are introduced to control the working status of the output buffer module (600). Thus, in the touch scan stage, the third transmission gate (TG3) is deactivated, and the first, the fourth thin film transistors (T1, T4) are activated, and the gate scan driving signal output end (Gate(N)) is floating, and similarly jumps between high, low voltage levels along with that the touch scan driving signal jumps between high, low voltage levels.
Owner:WUHAN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
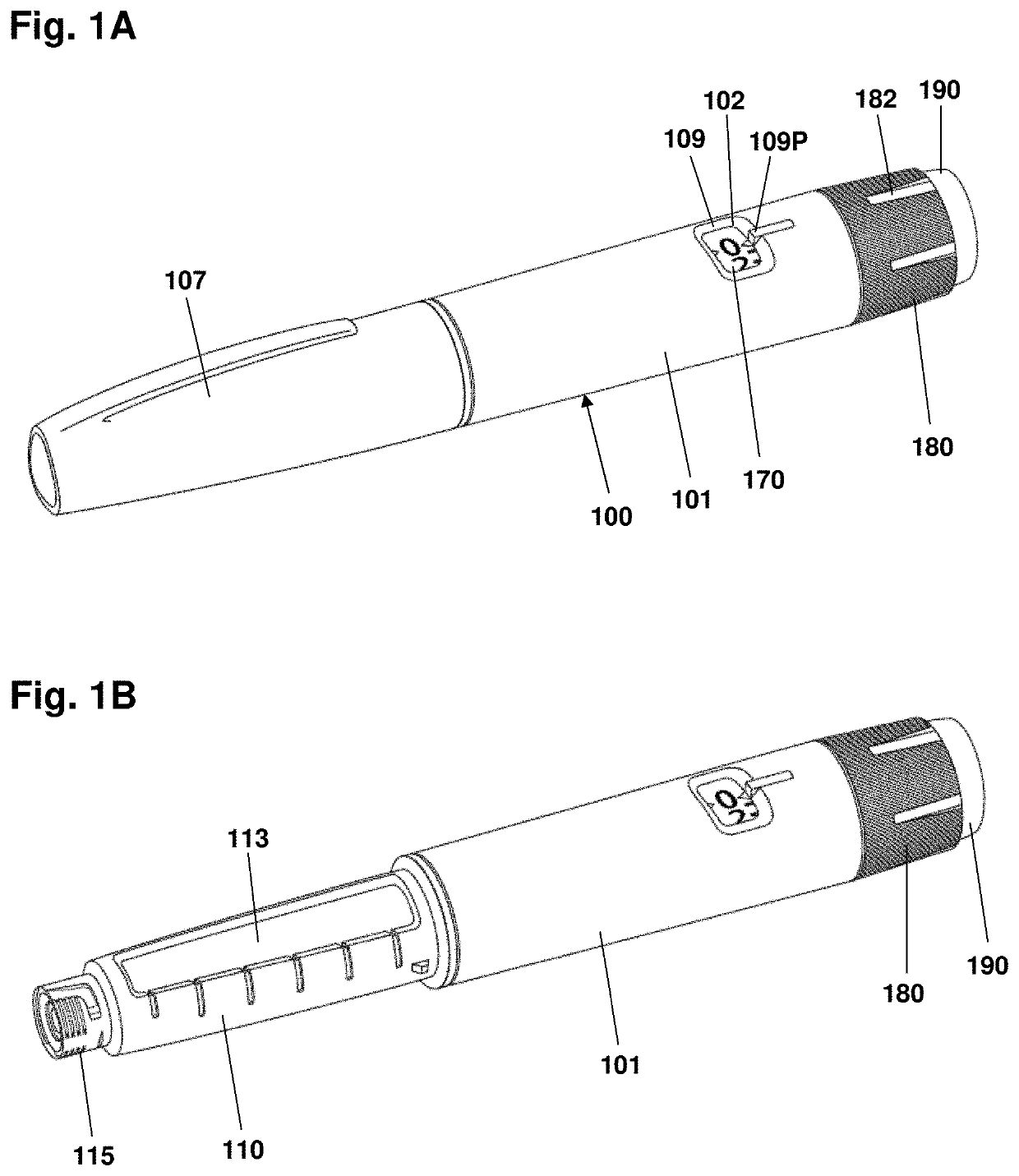
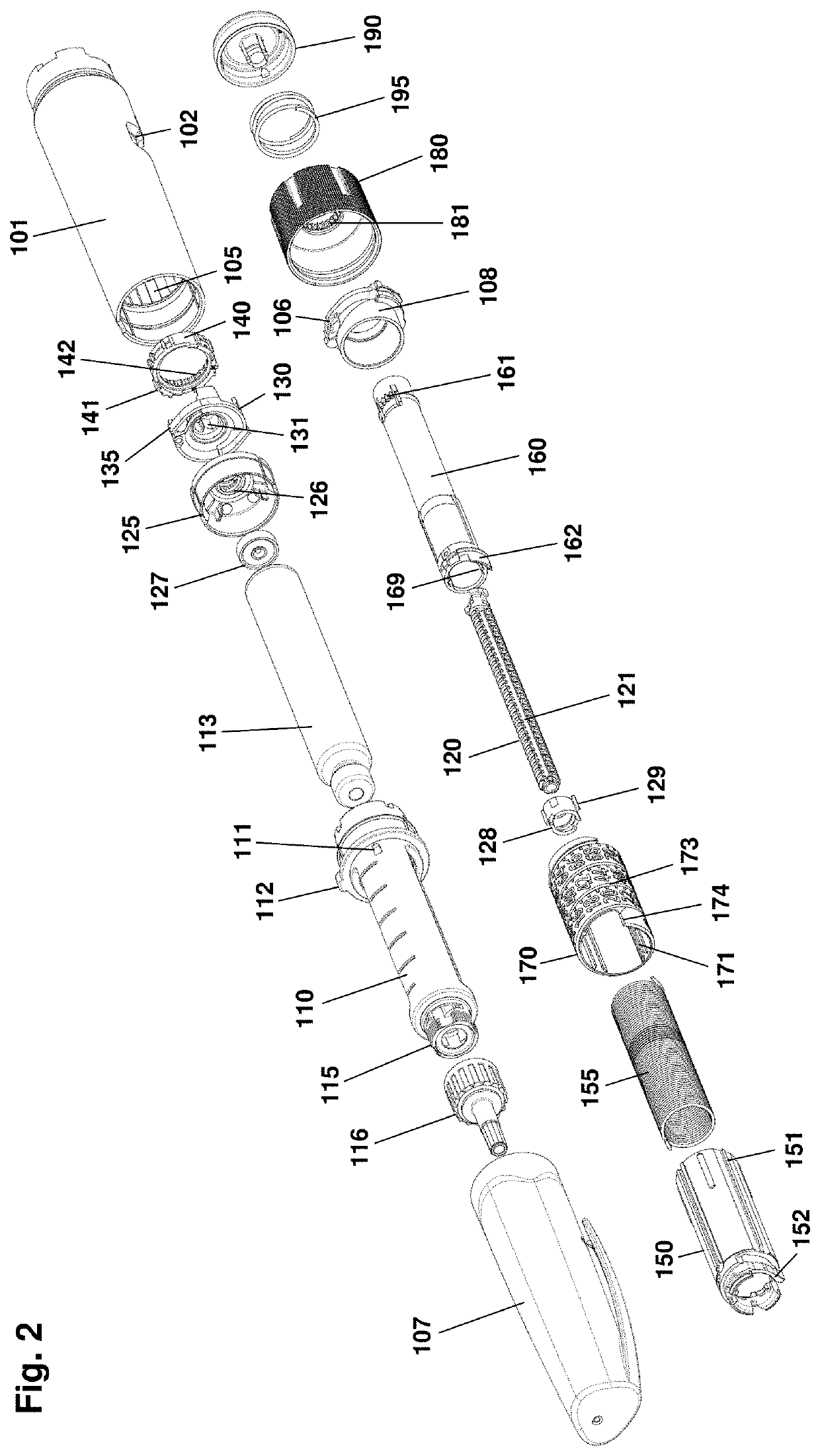
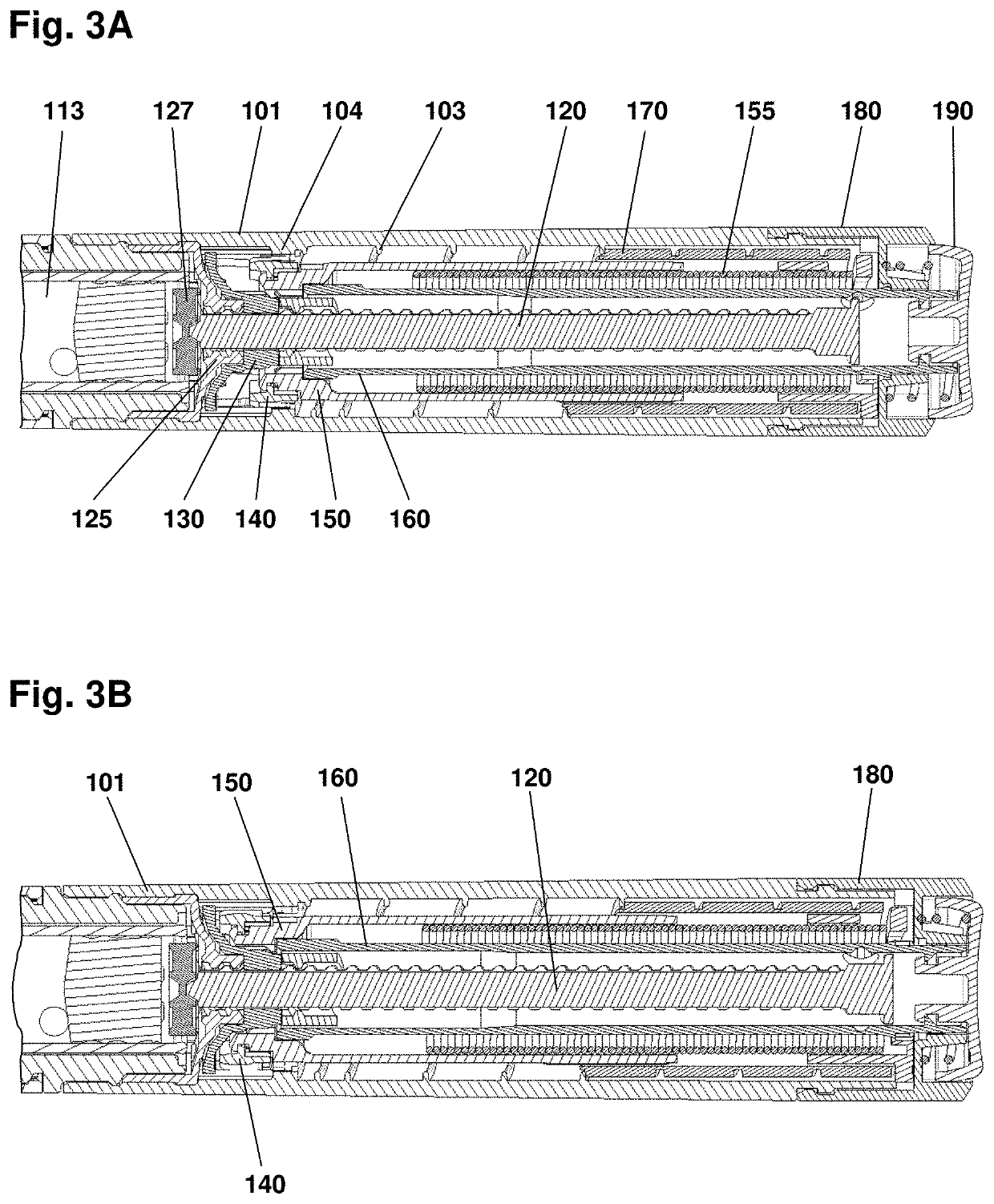
Drug delivery system with magnetic ring and sensors arranged in a ring pattern
ActiveUS10682469B2Cost-effectiveReduce energy consumptionInfusion syringesMedical devicesPharmaceutical drugRing pattern
A drug delivery system comprises an indicator element and a sensor system. The indicator element is arranged to rotate relative to a reference component and corresponding to a reference axis and comprises a magnetic ring. The sensor system comprises a plurality of magnetometers arranged non-rotational relative to the reference component and adapted to determine continuous magnetic field values from the plurality of dipole magnets, as well as processor means configured to determine on the basis of measured values from the plurality of magnetometers a rotational position and / or a rotational movement of the indicator element.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com