Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
52results about How to "Reduce torque variation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
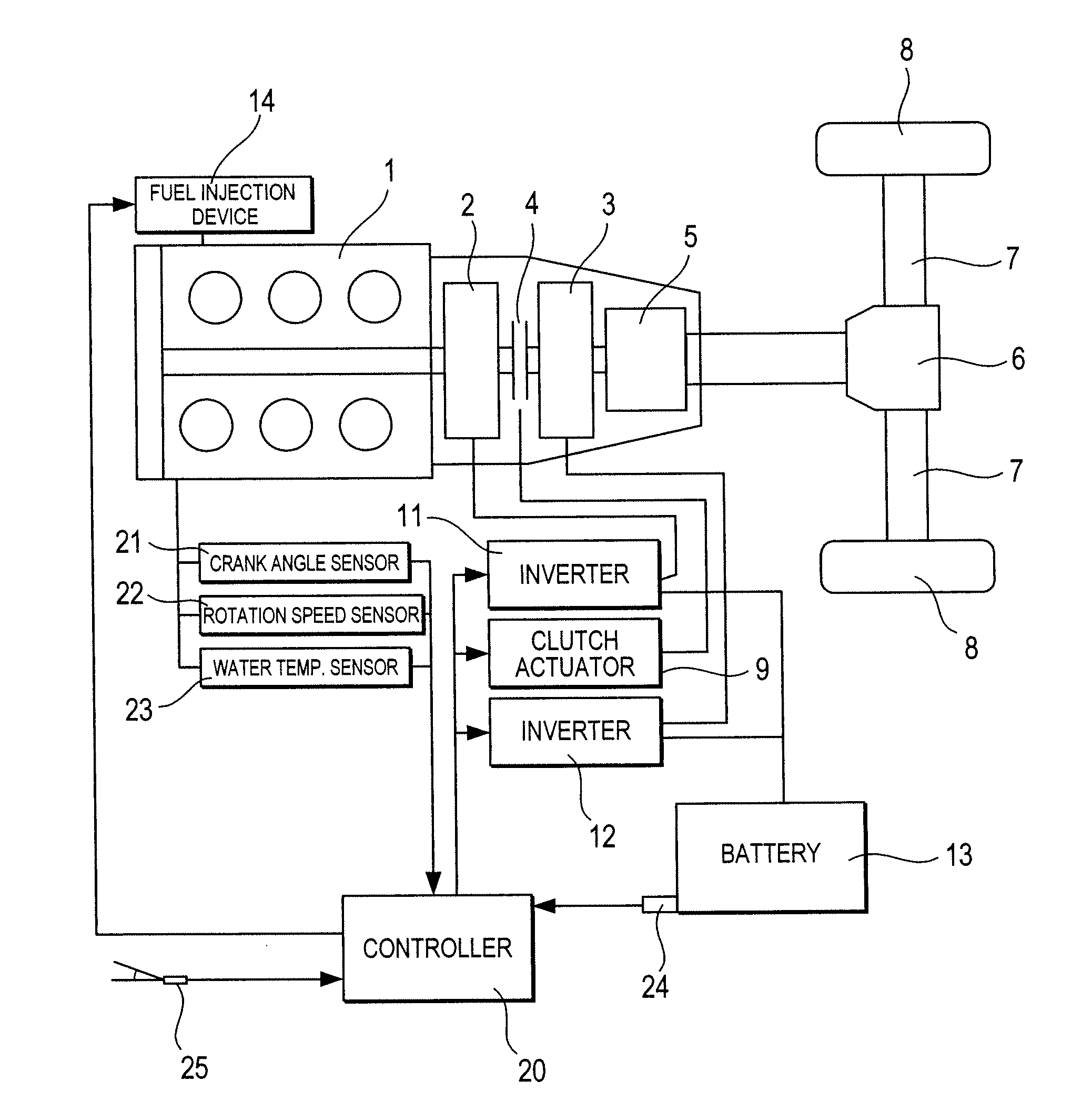
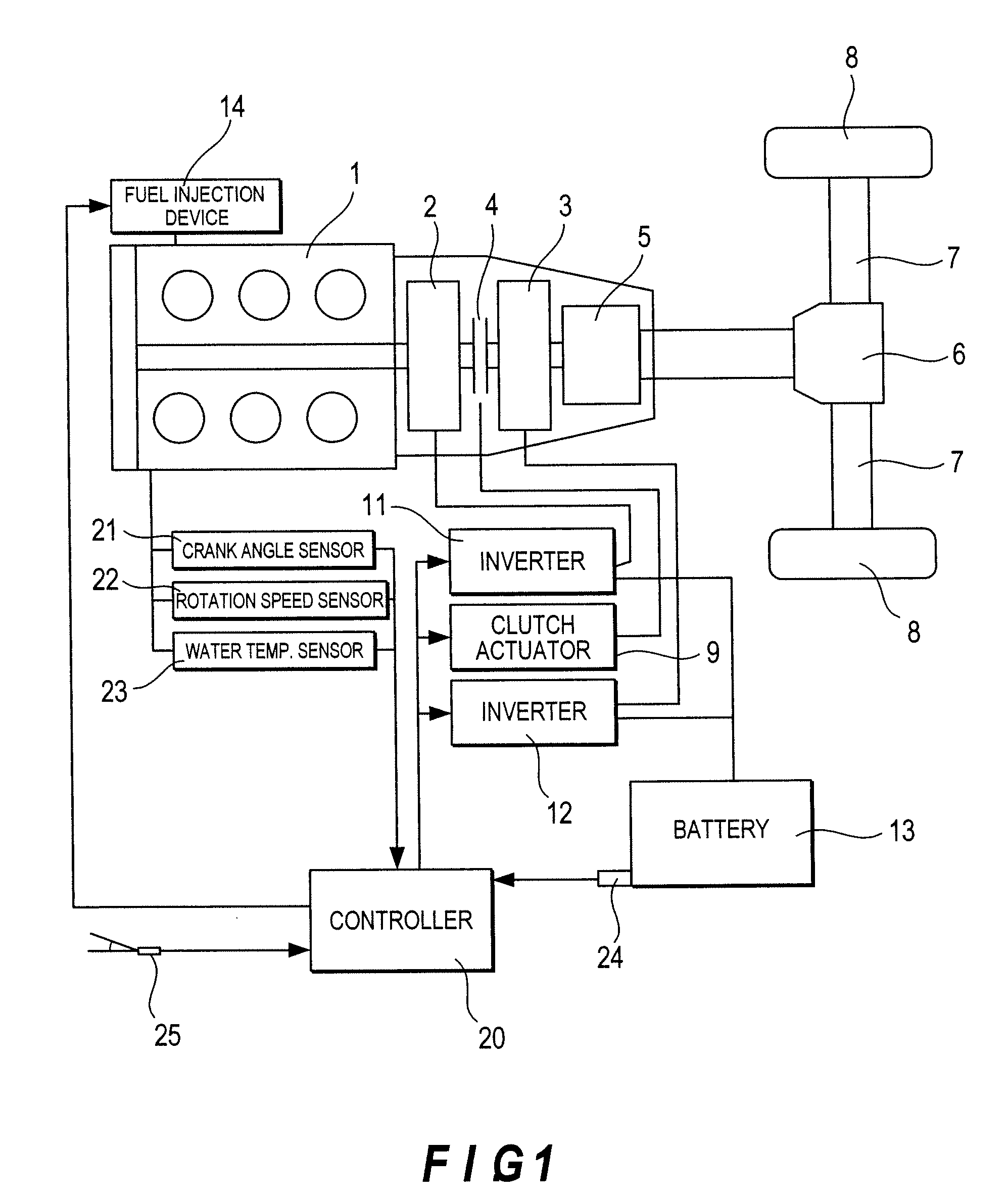
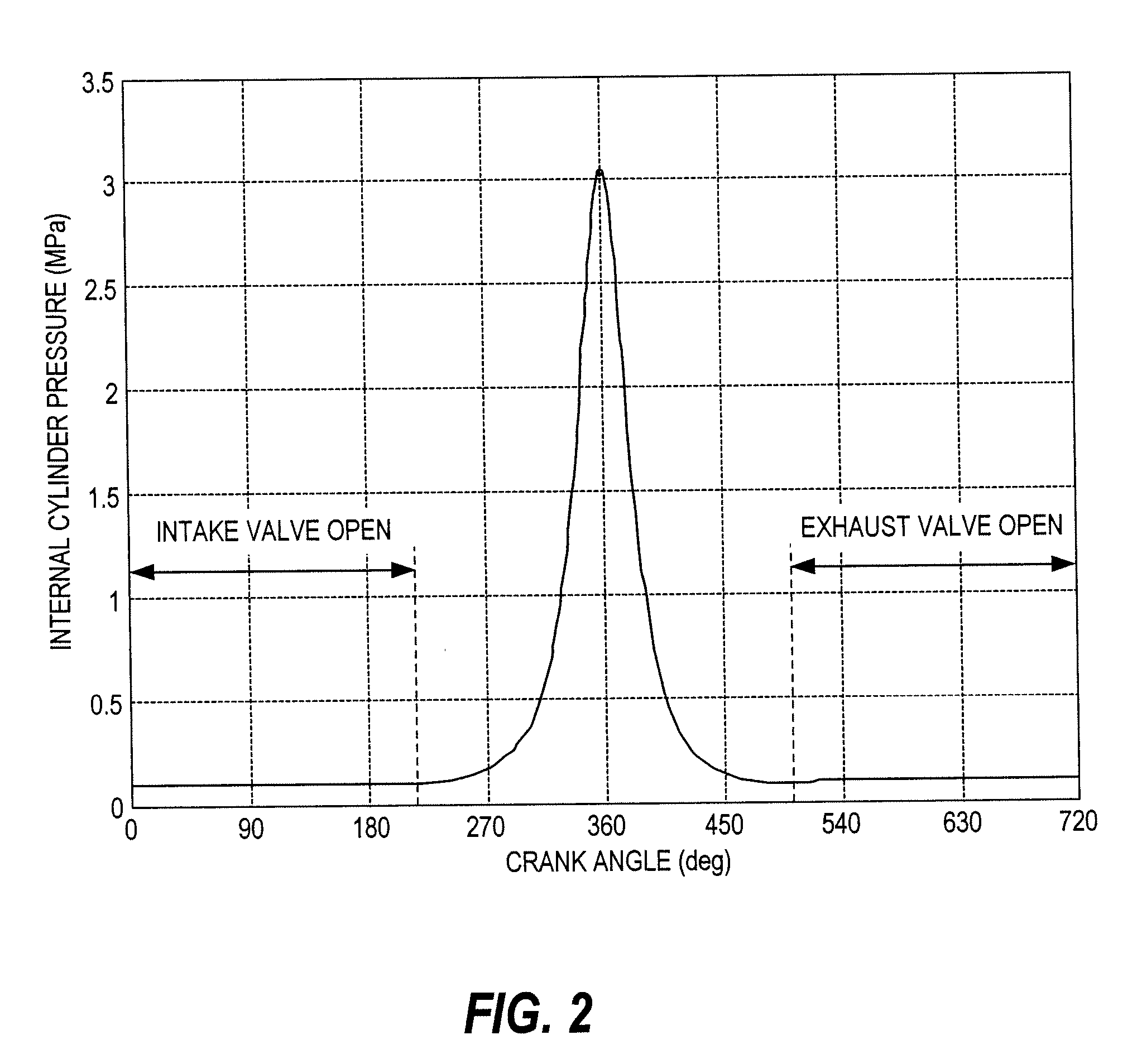
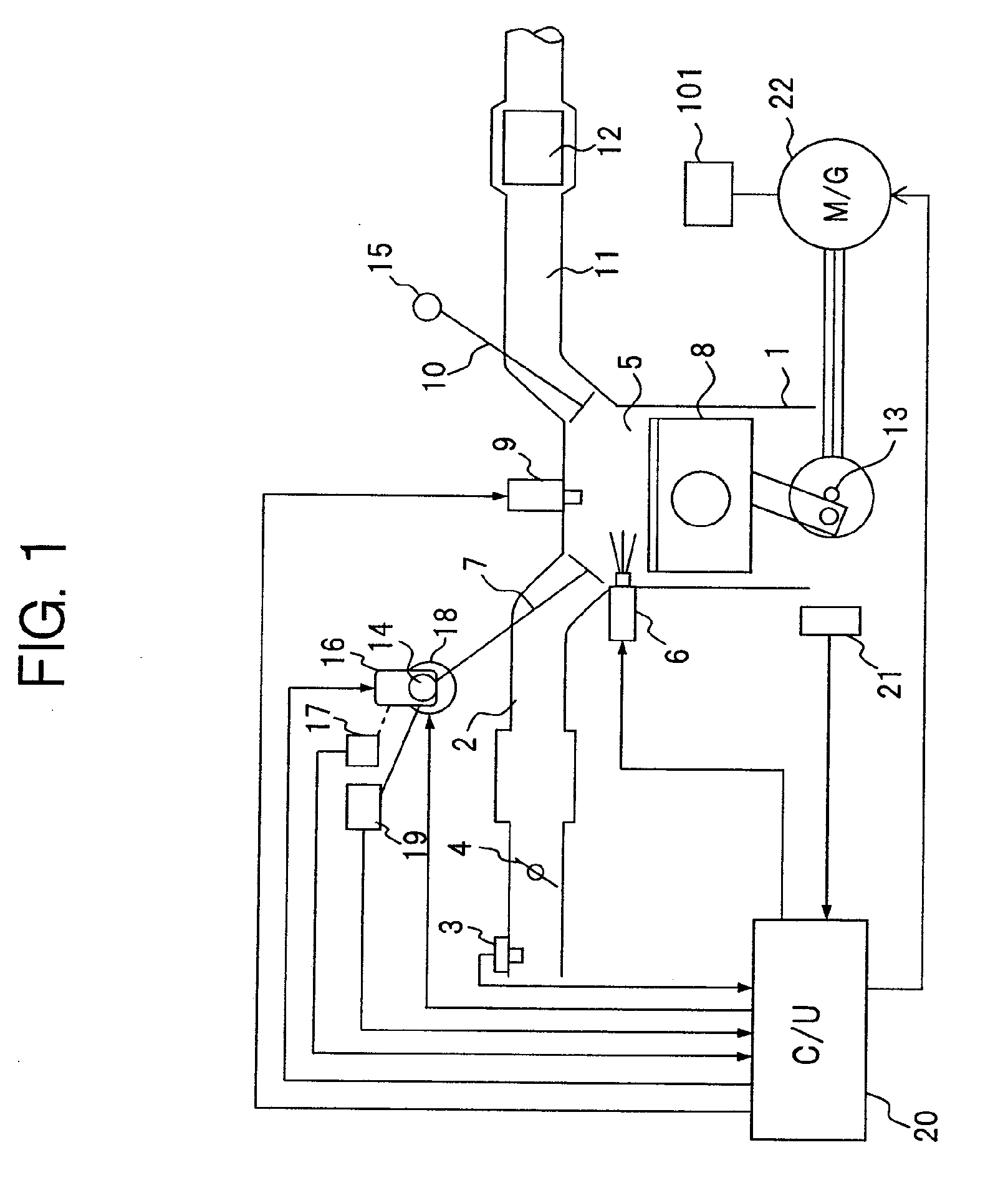
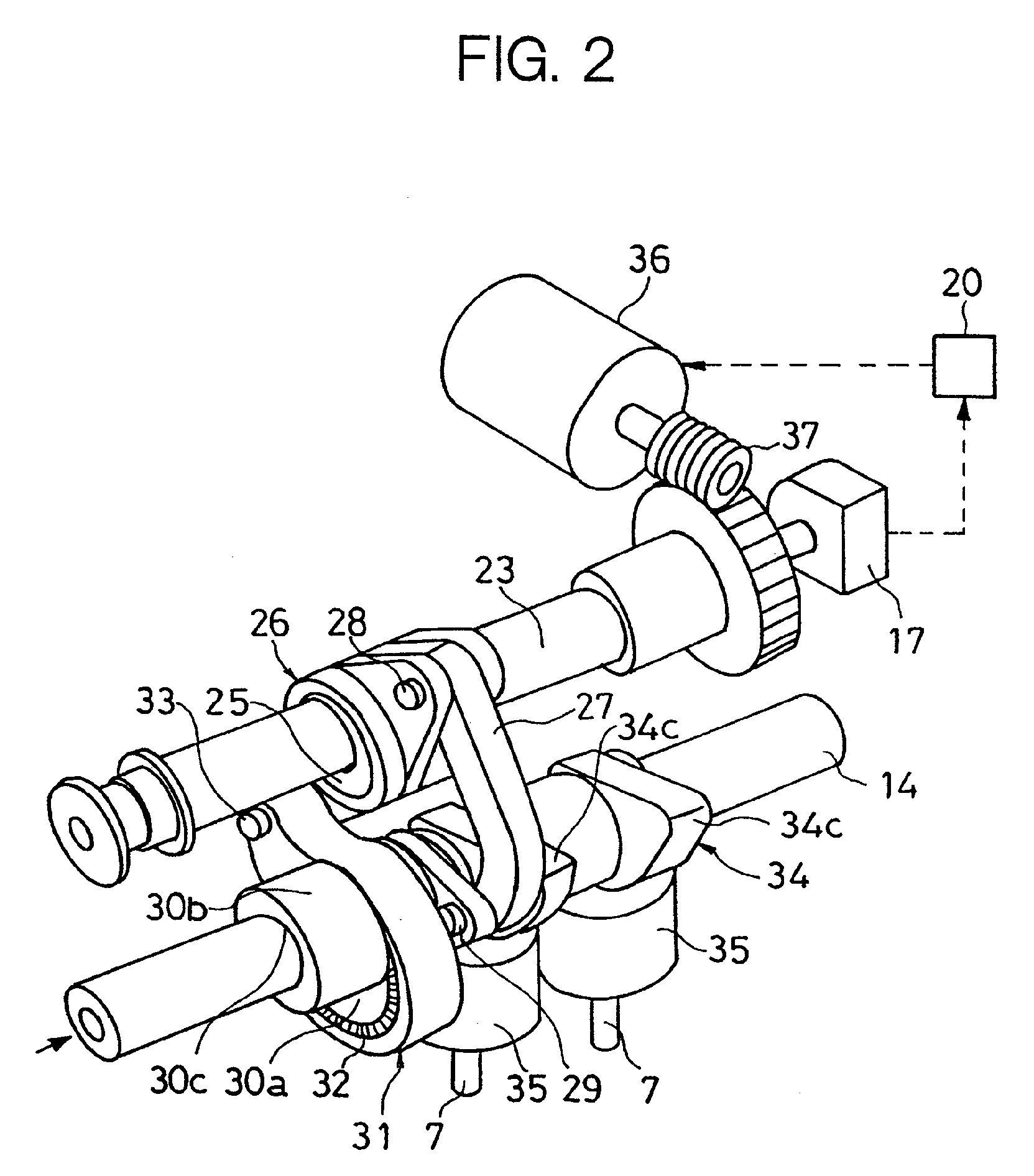
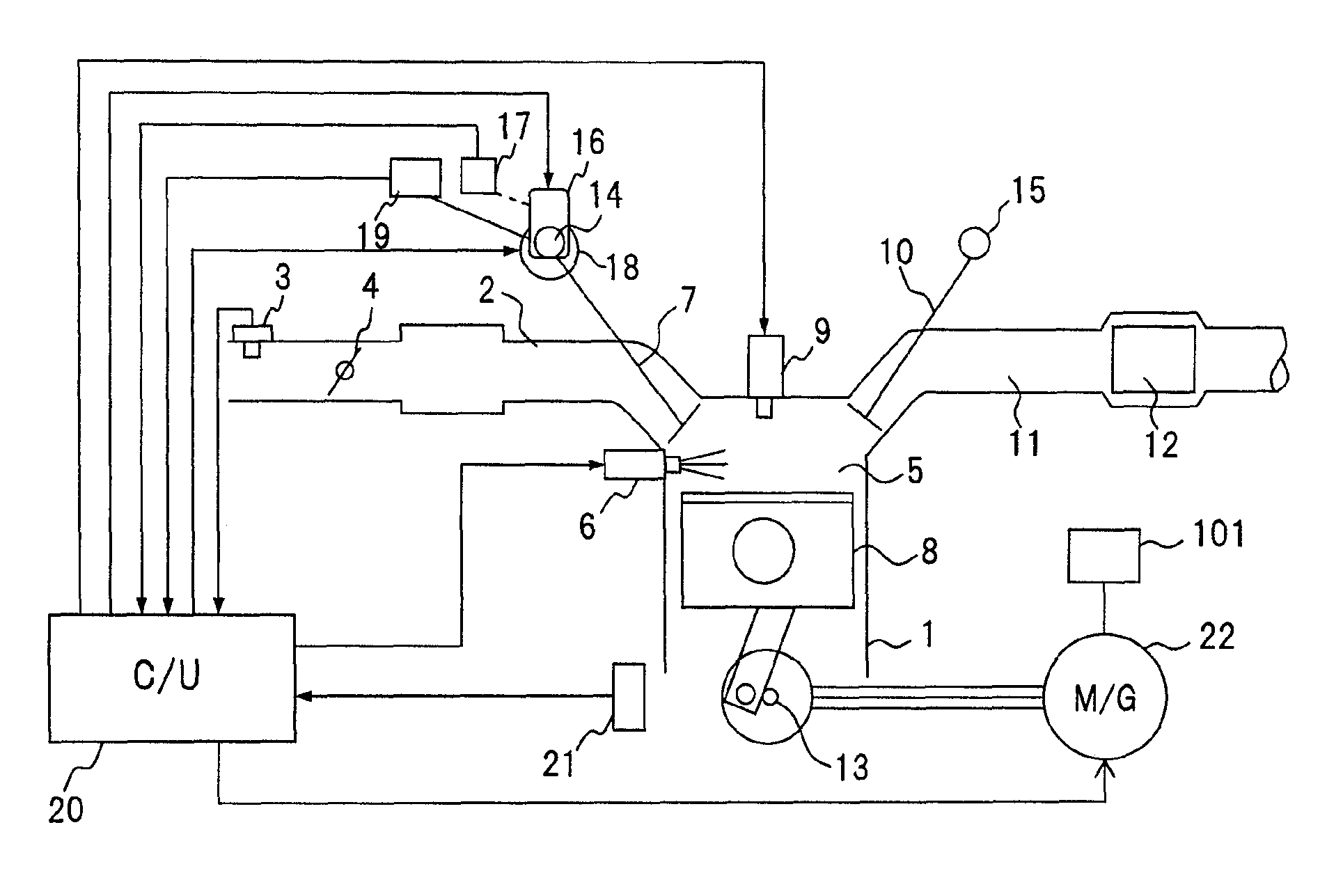
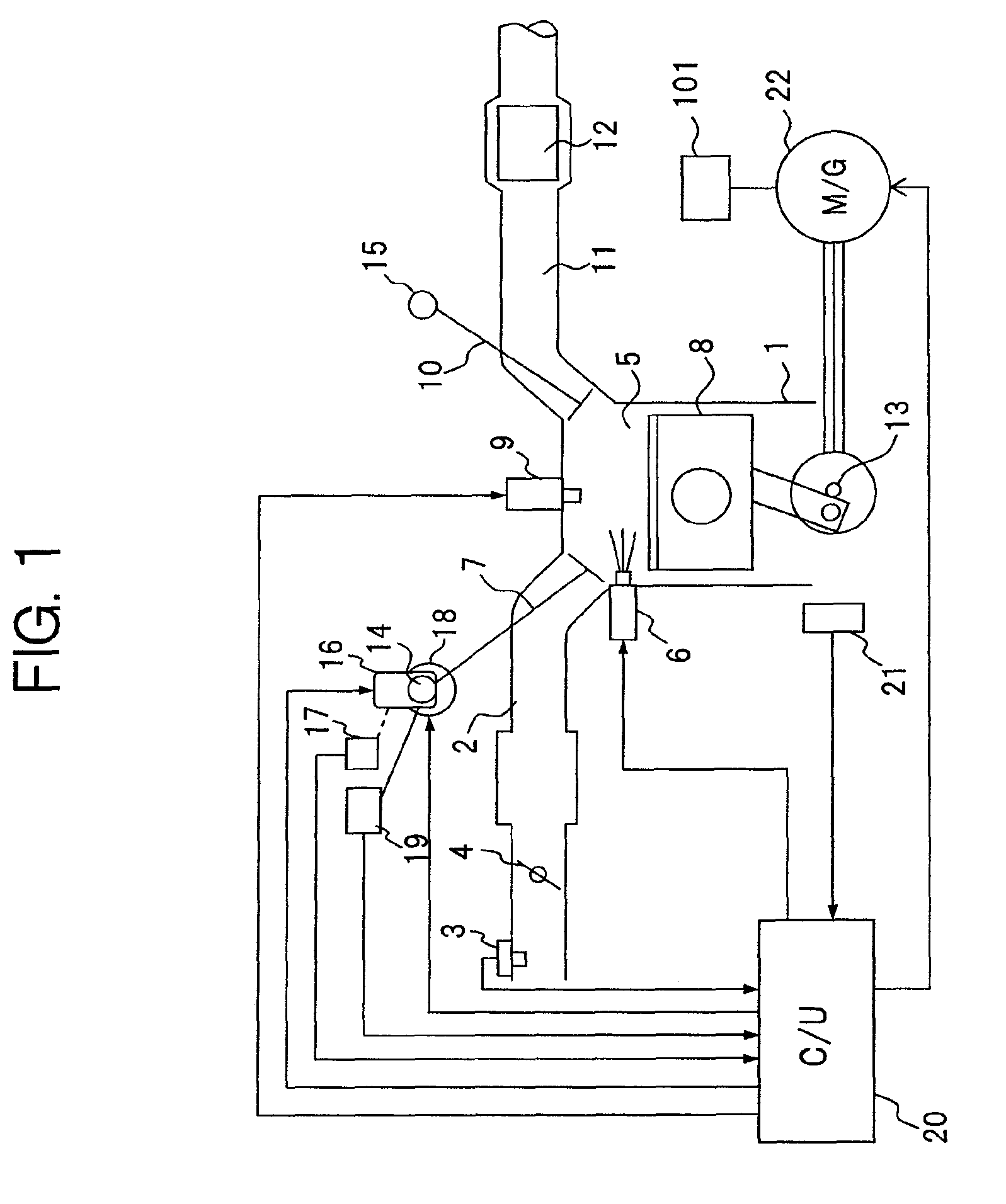
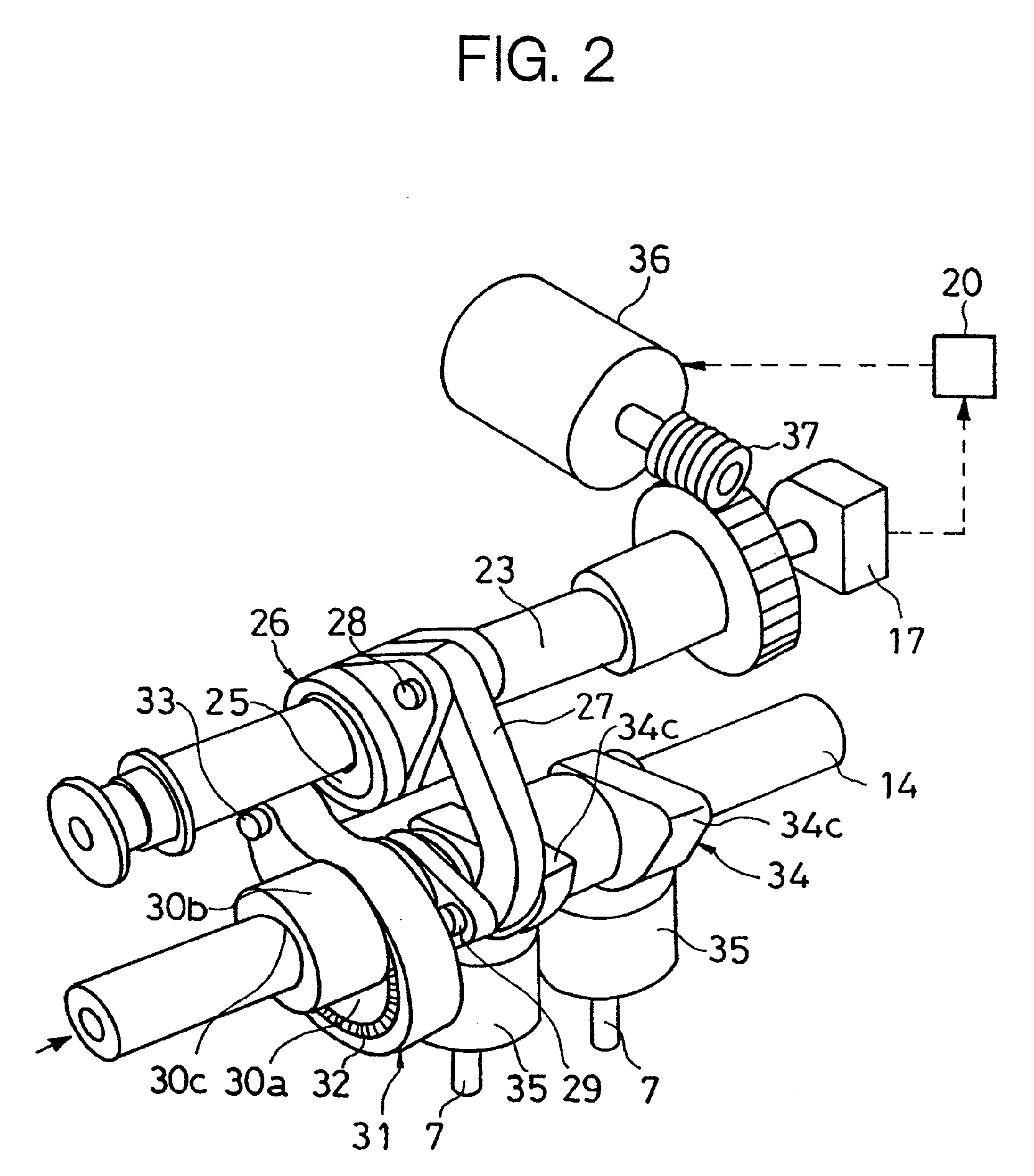
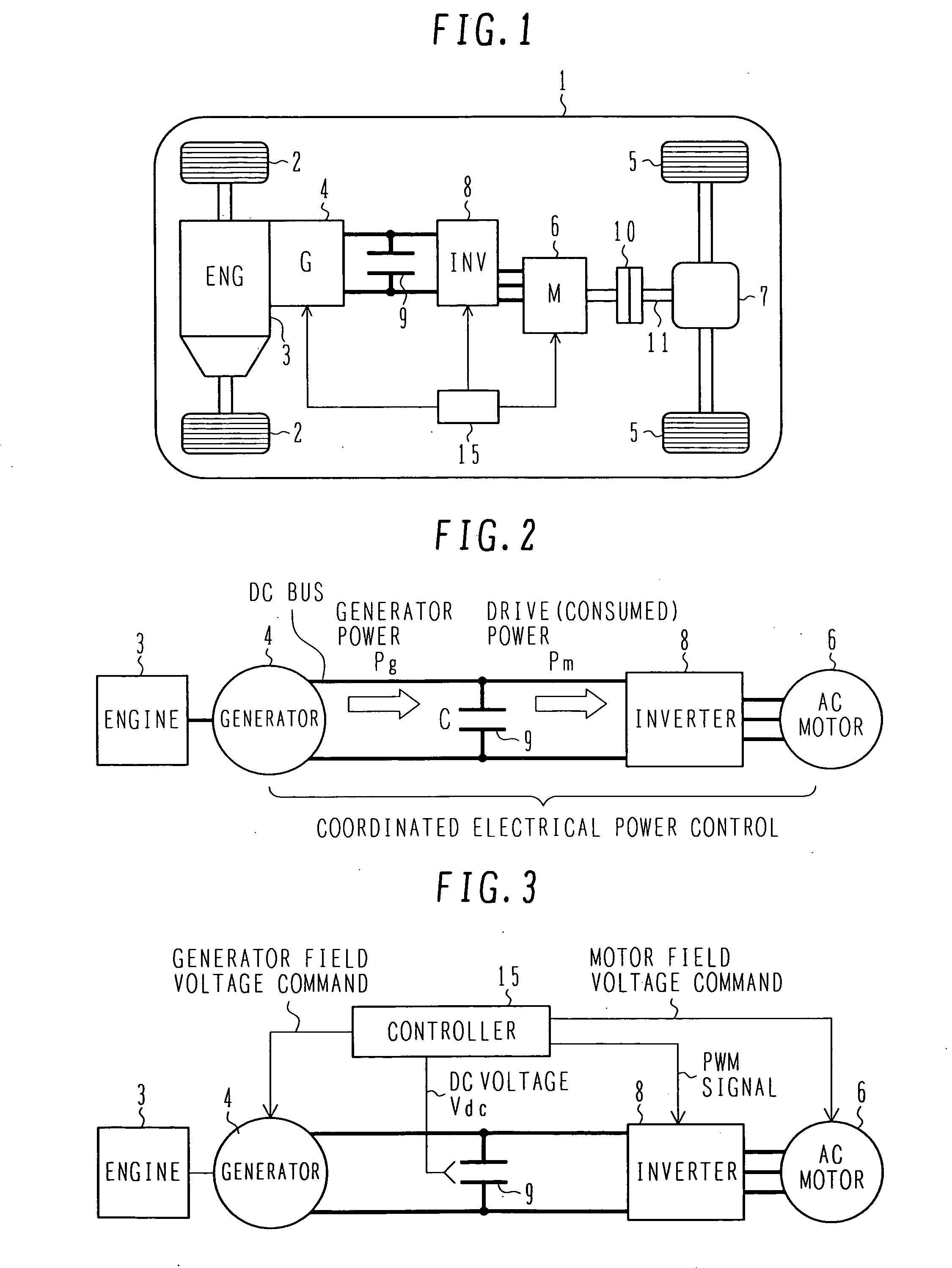
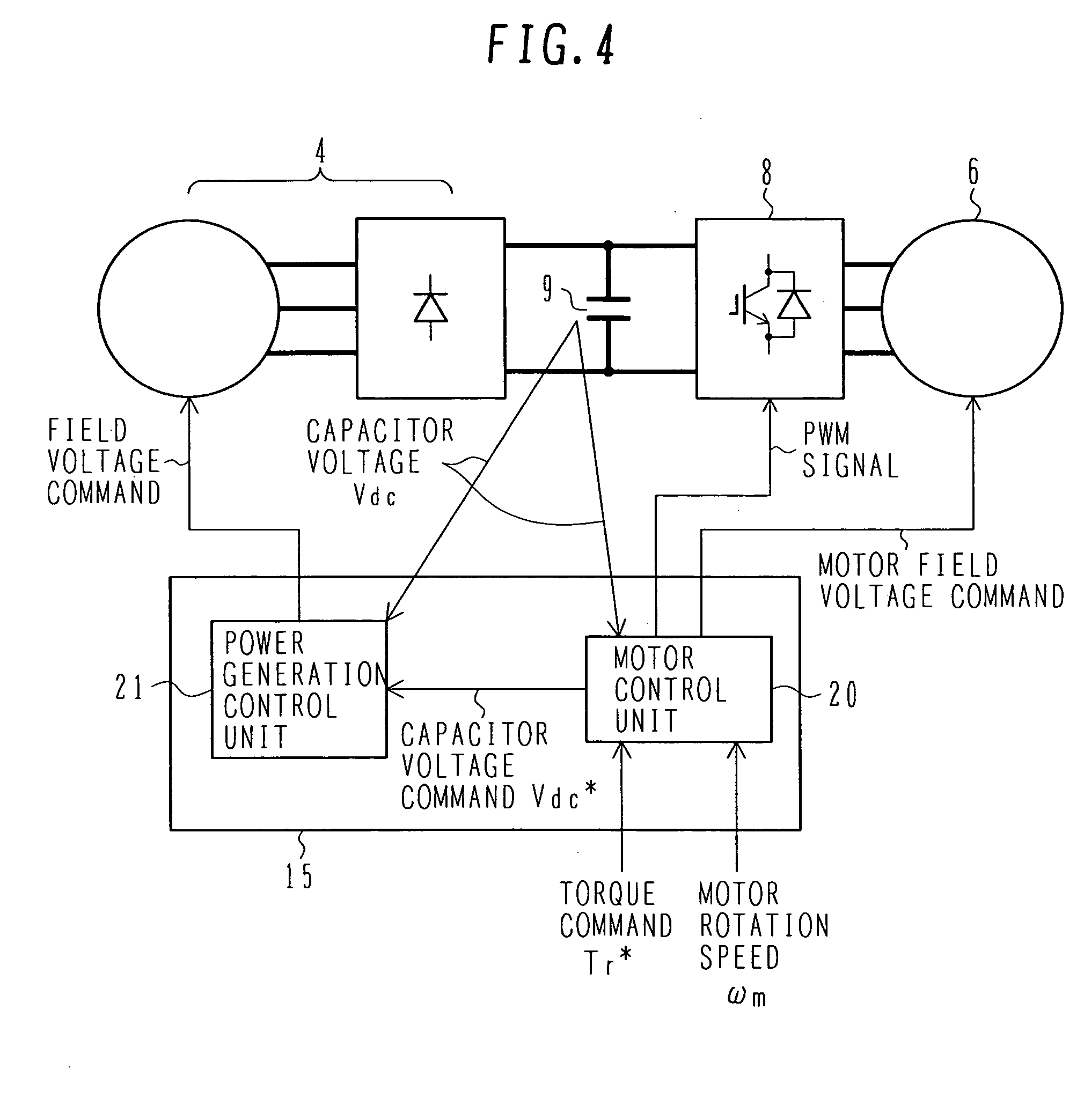
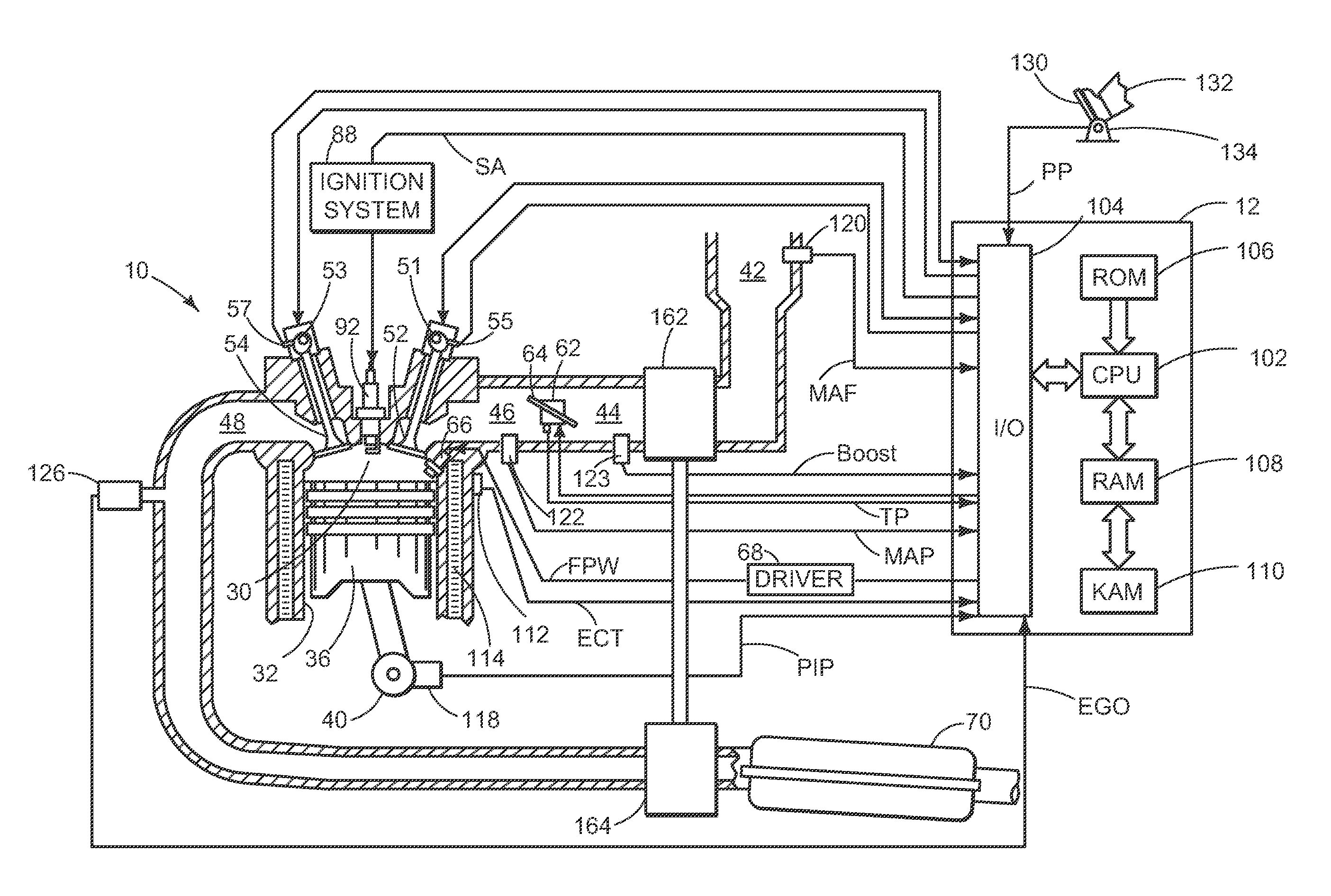
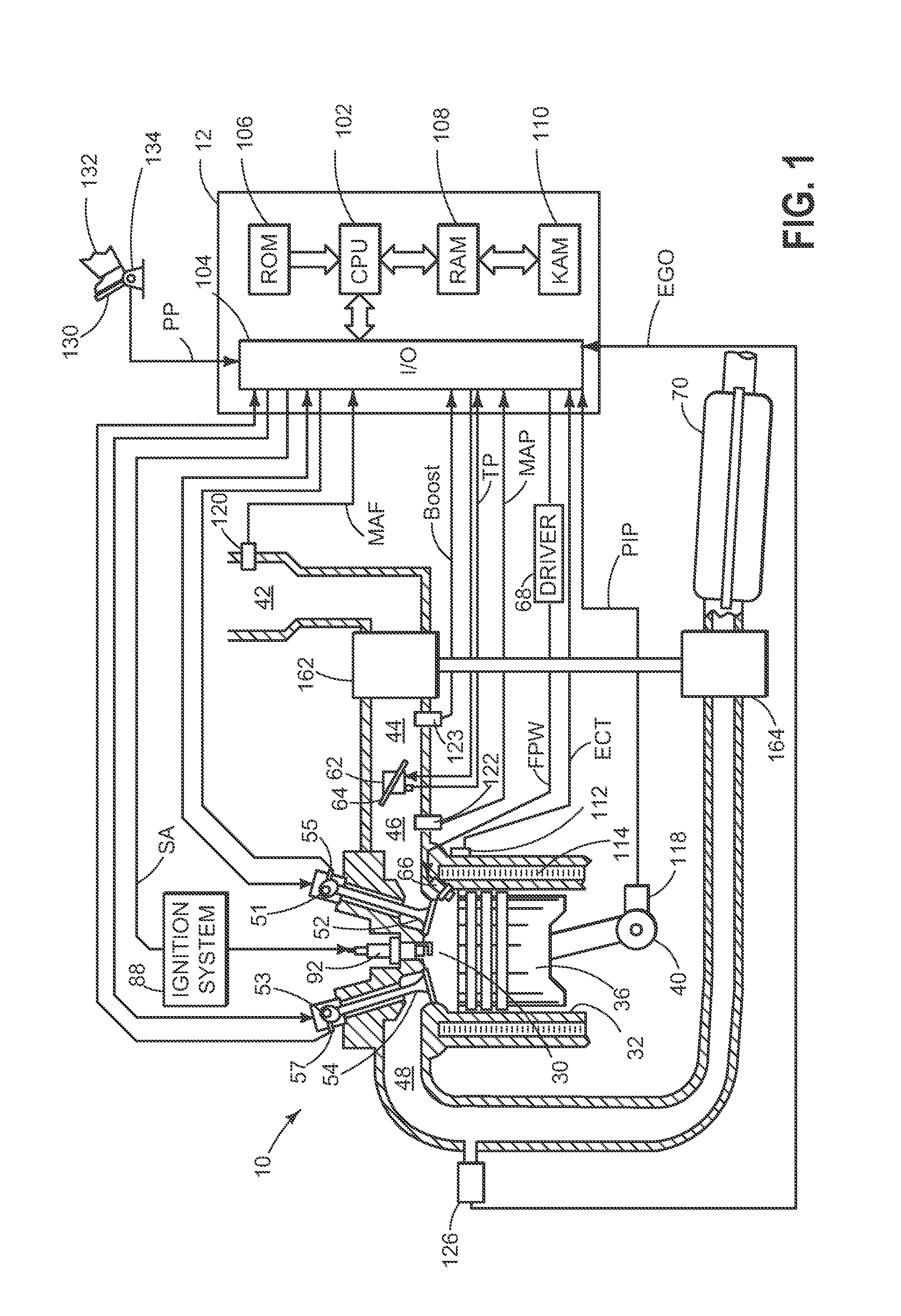
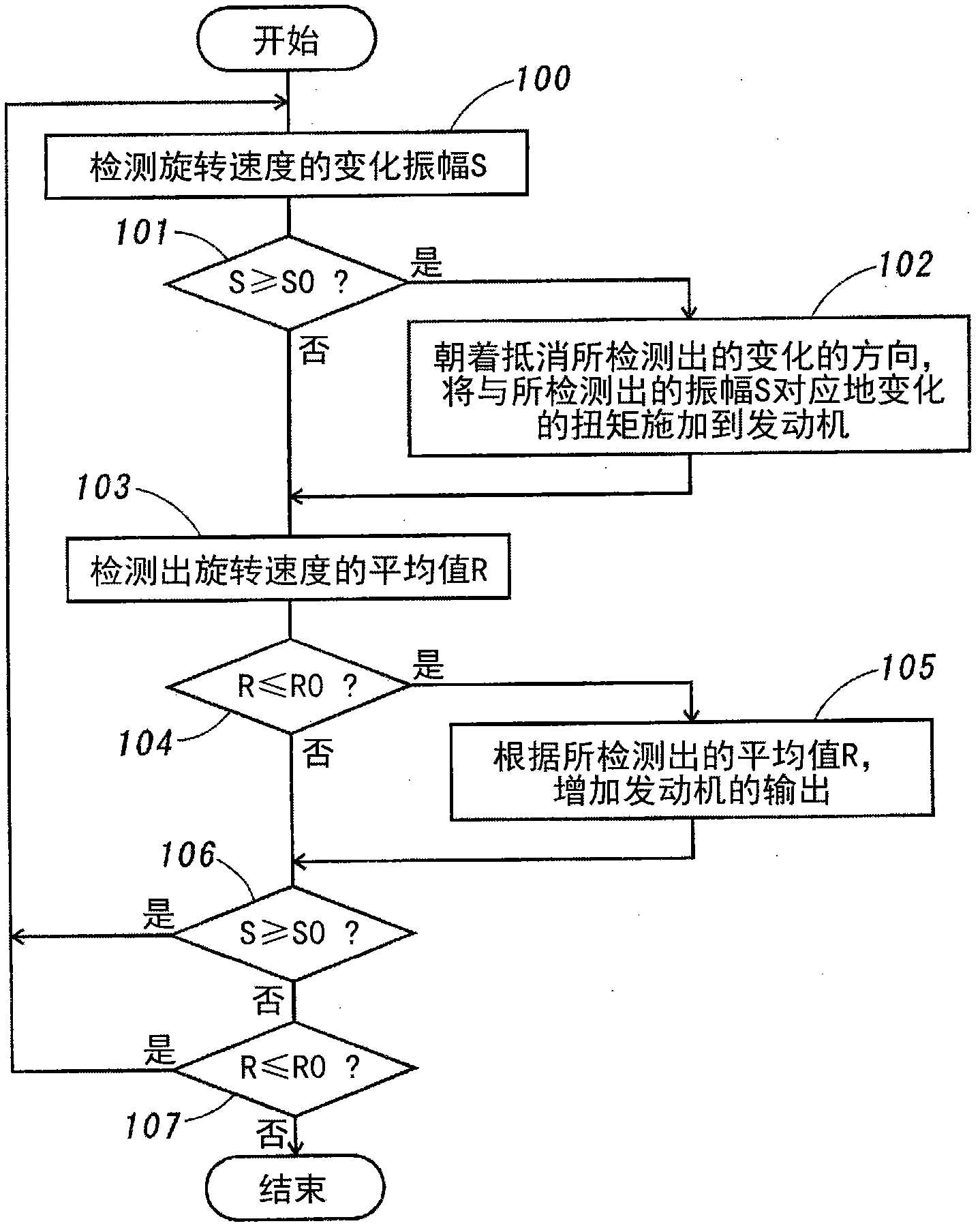
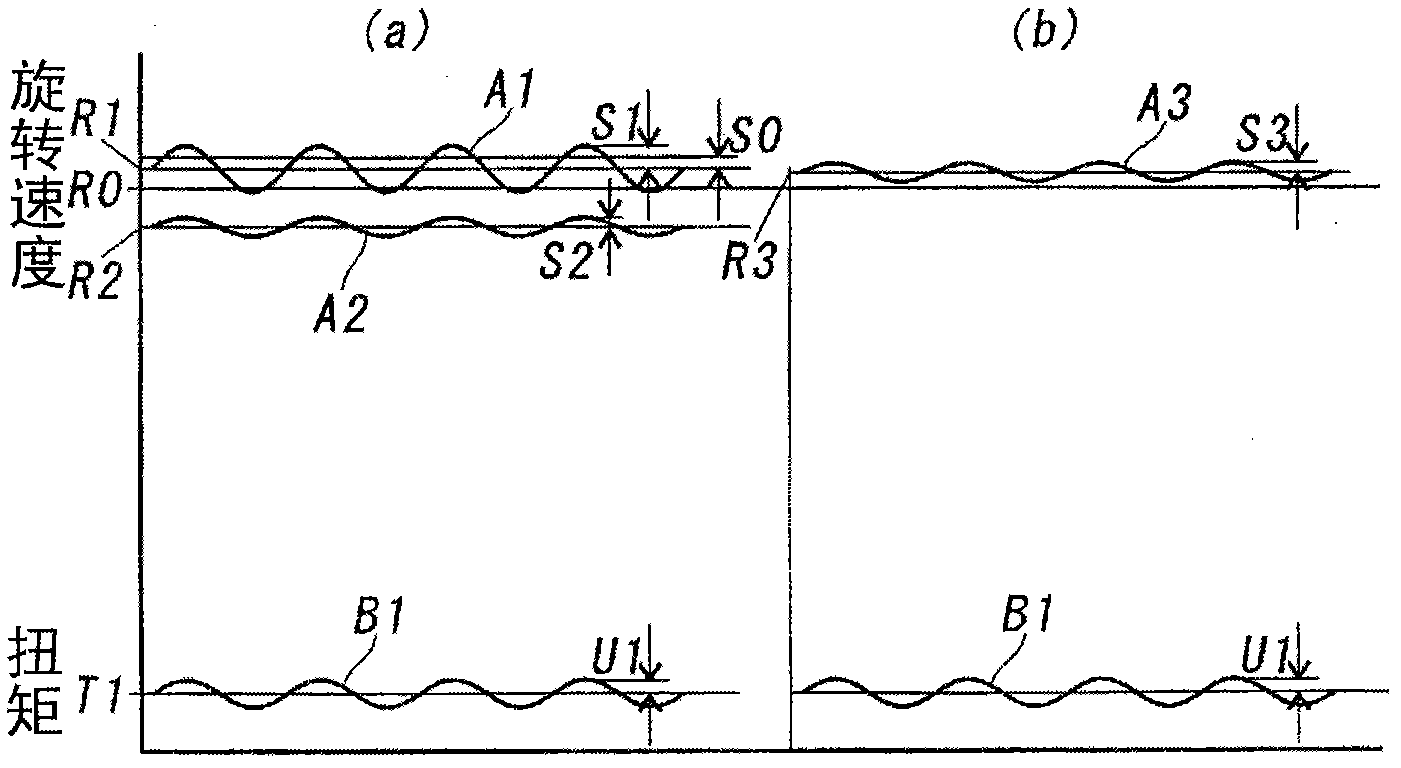
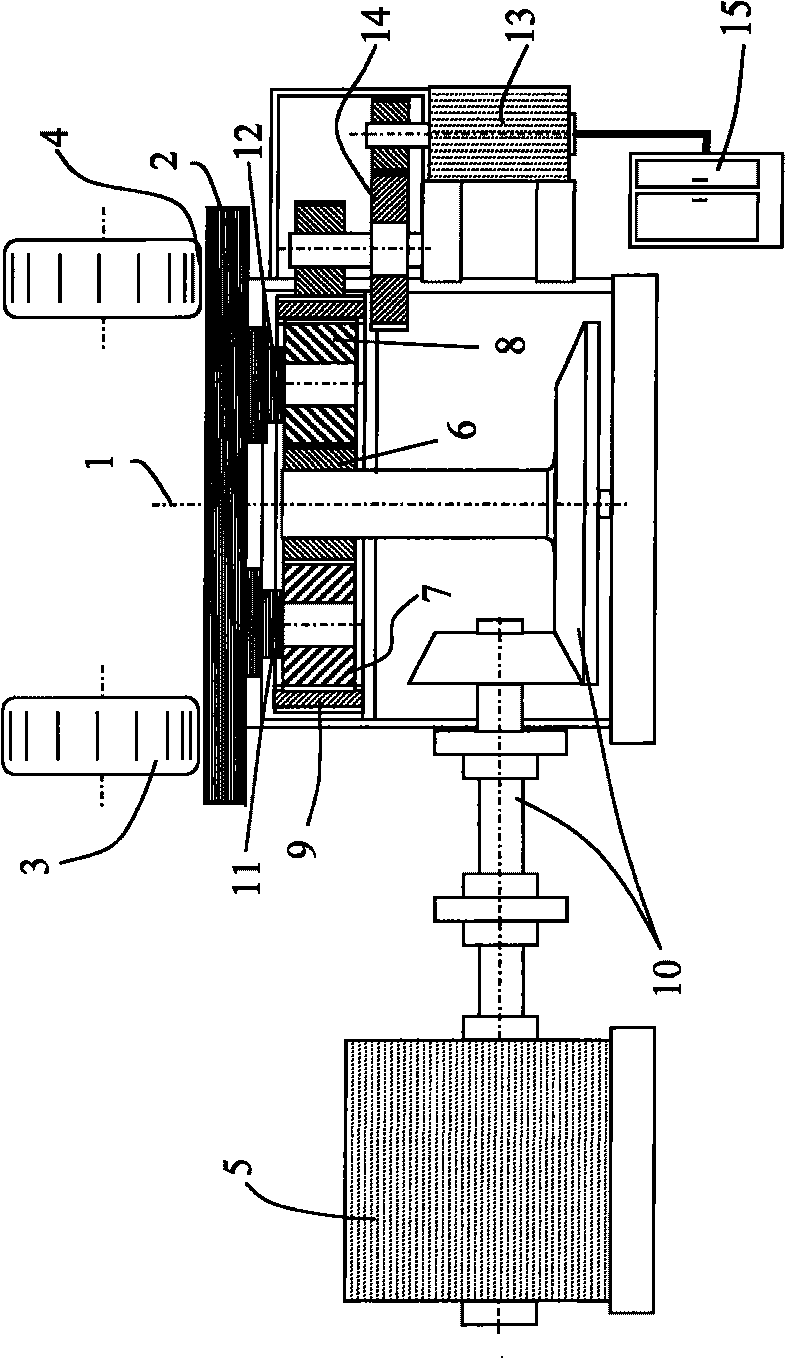
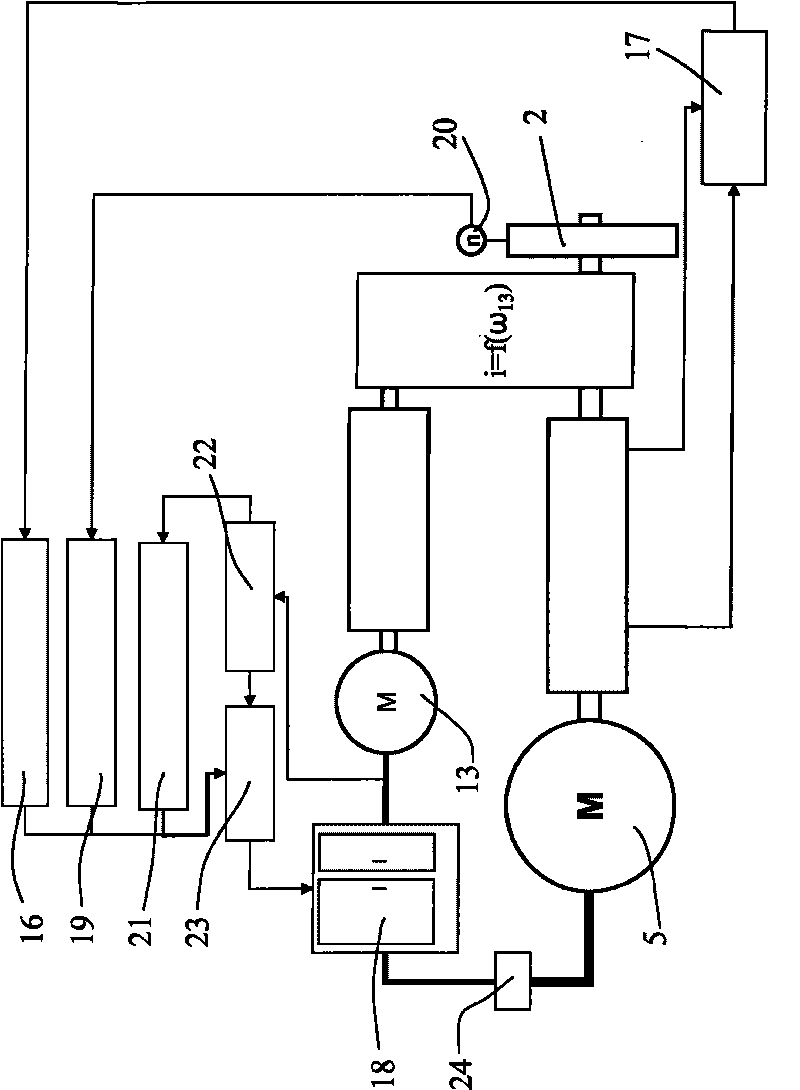
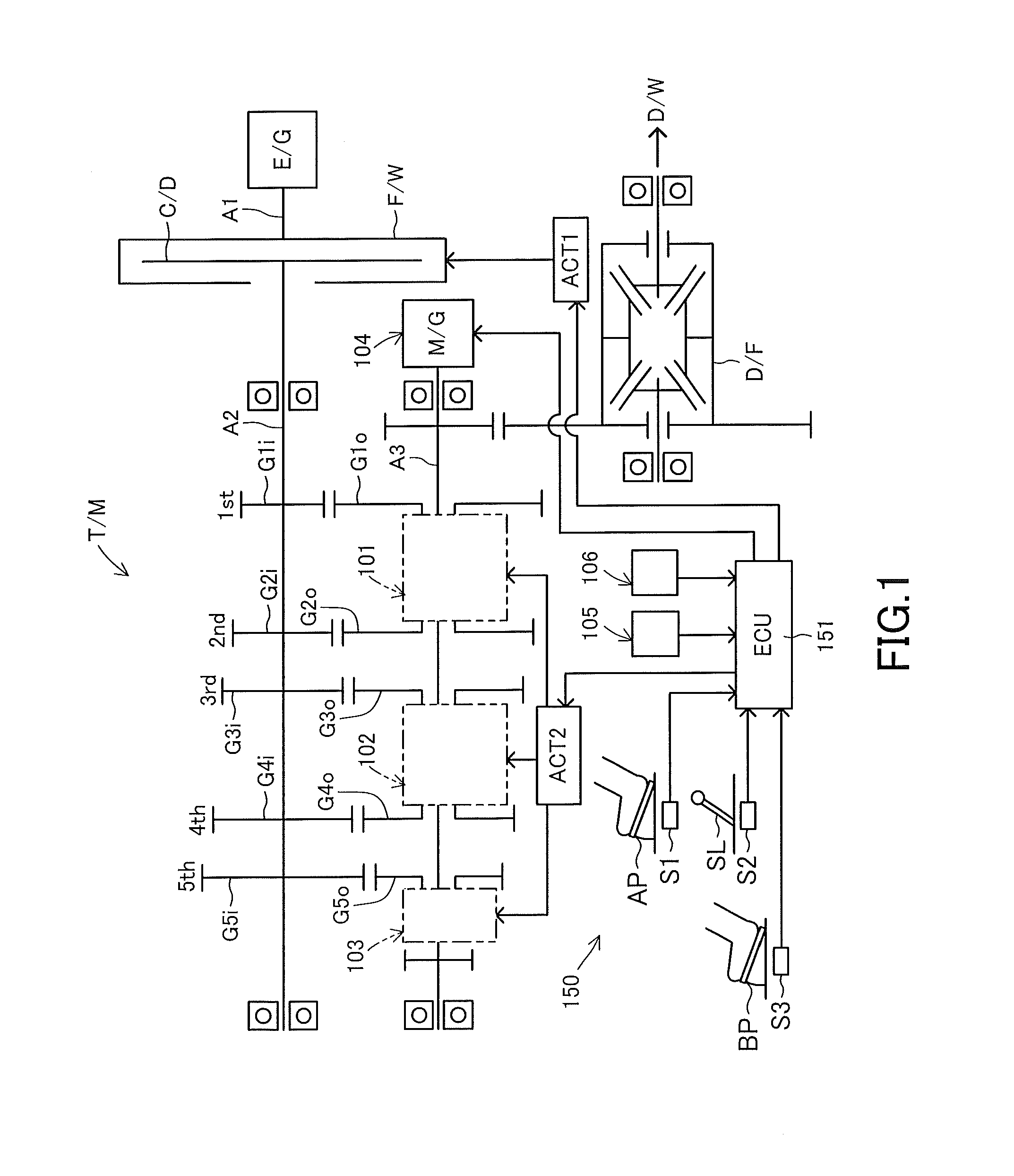
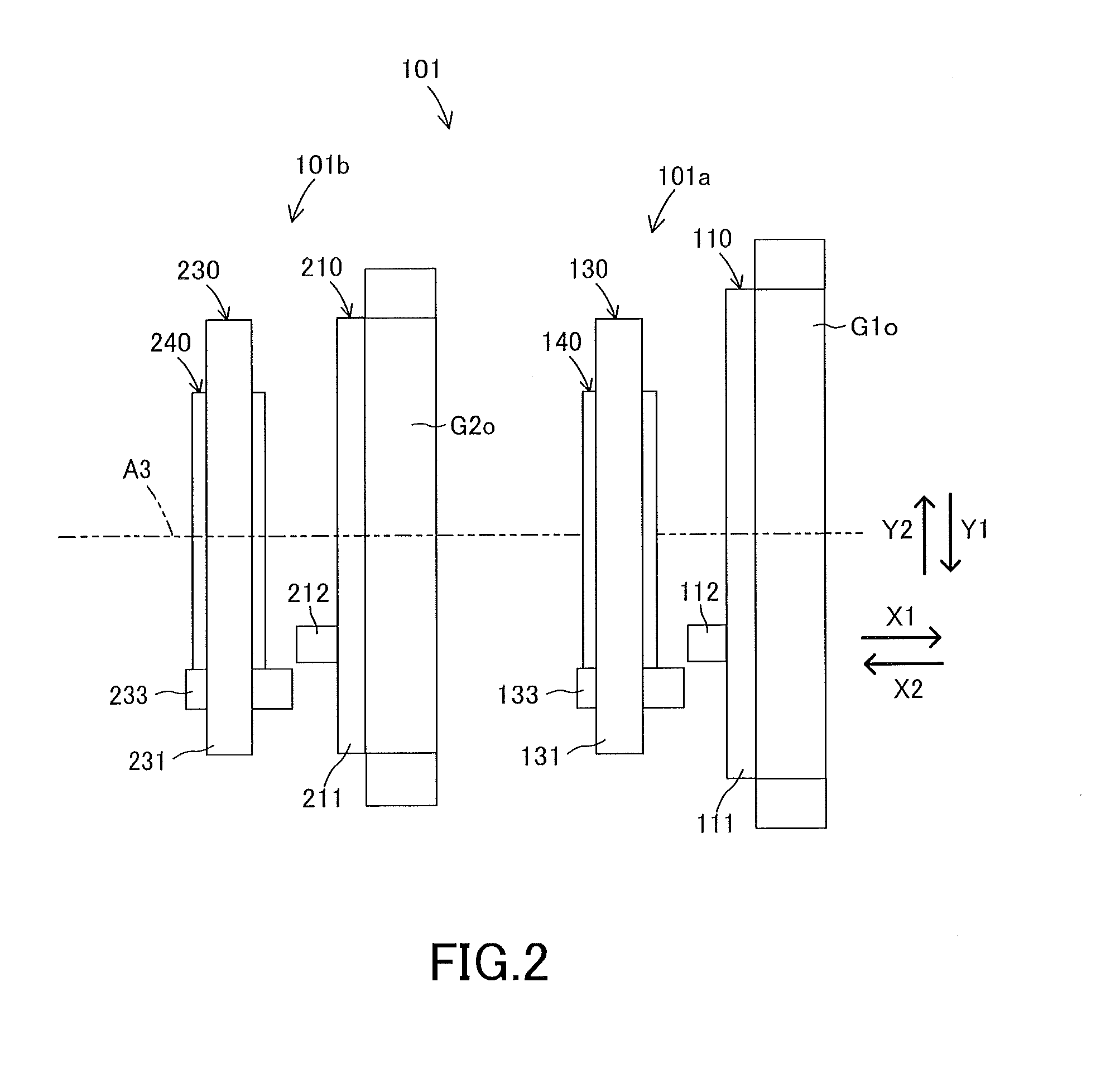
Engine vibration suppression device and suppression method thereof
InactiveUS20070101965A1Reduce the ratioReduce torque variationHybrid vehiclesSpeed controllerControl theoryMotor–generator
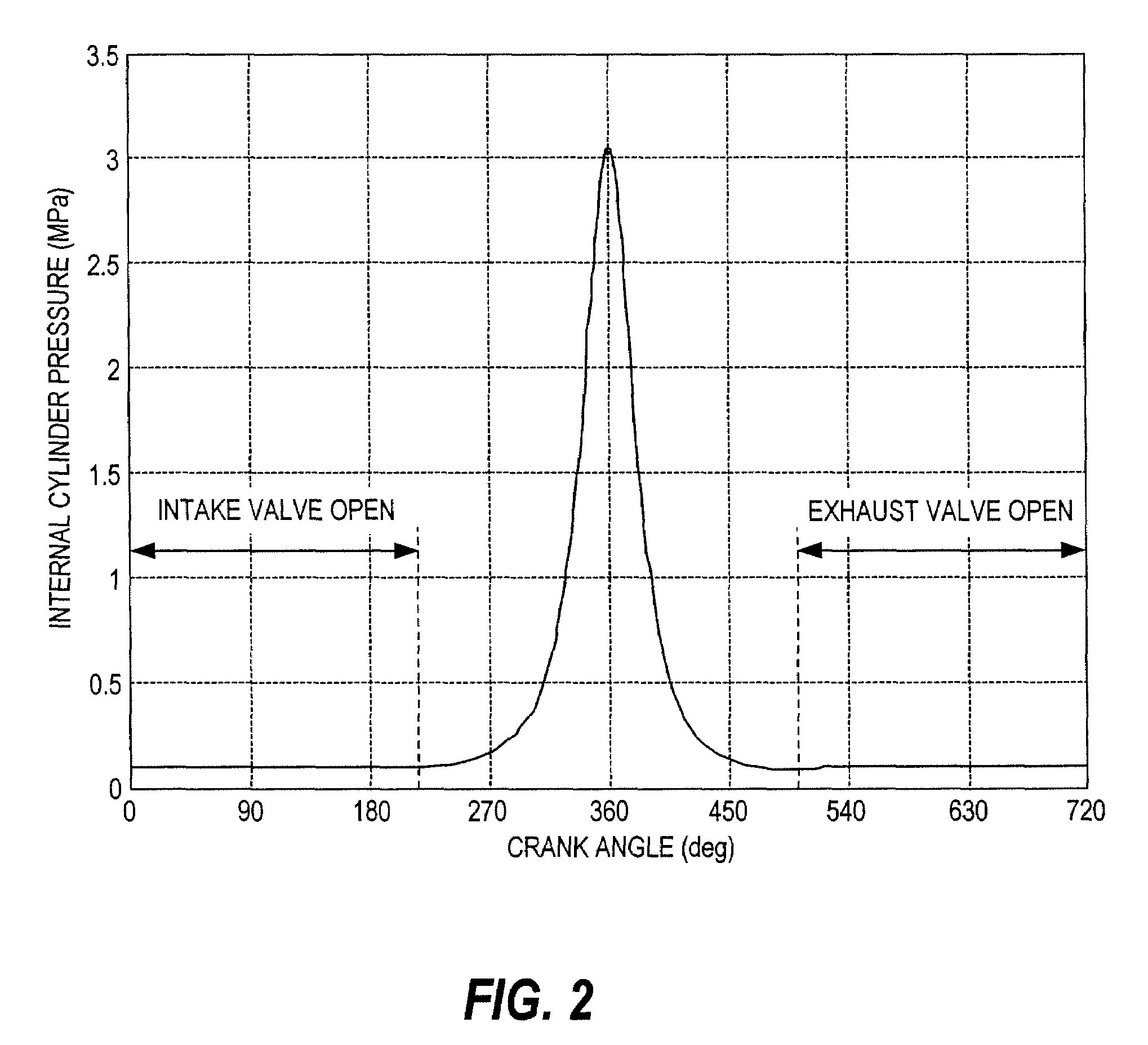
A controller (20) estimates an internal cylinder pressure of an engine (1) on the basis of the operating conditions of the engine (1), torque variation in the engine (1) is calculated on the basis of the estimated internal cylinder pressure, and an opposite phase torque of the torque variation in the engine (1) is calculated as a torque correction amount. The controller (20) then calculates a torque command value for a motor generator (2) by adding the torque correction amount to a basic torque value for driving the motor generator (2) to rotate, and performs torque control such that the torque of the motor generator (2) equals the torque command value.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Vibration-Damping Control Apparatus and Vibration-Damping Control Method for Internal Combustion Engine
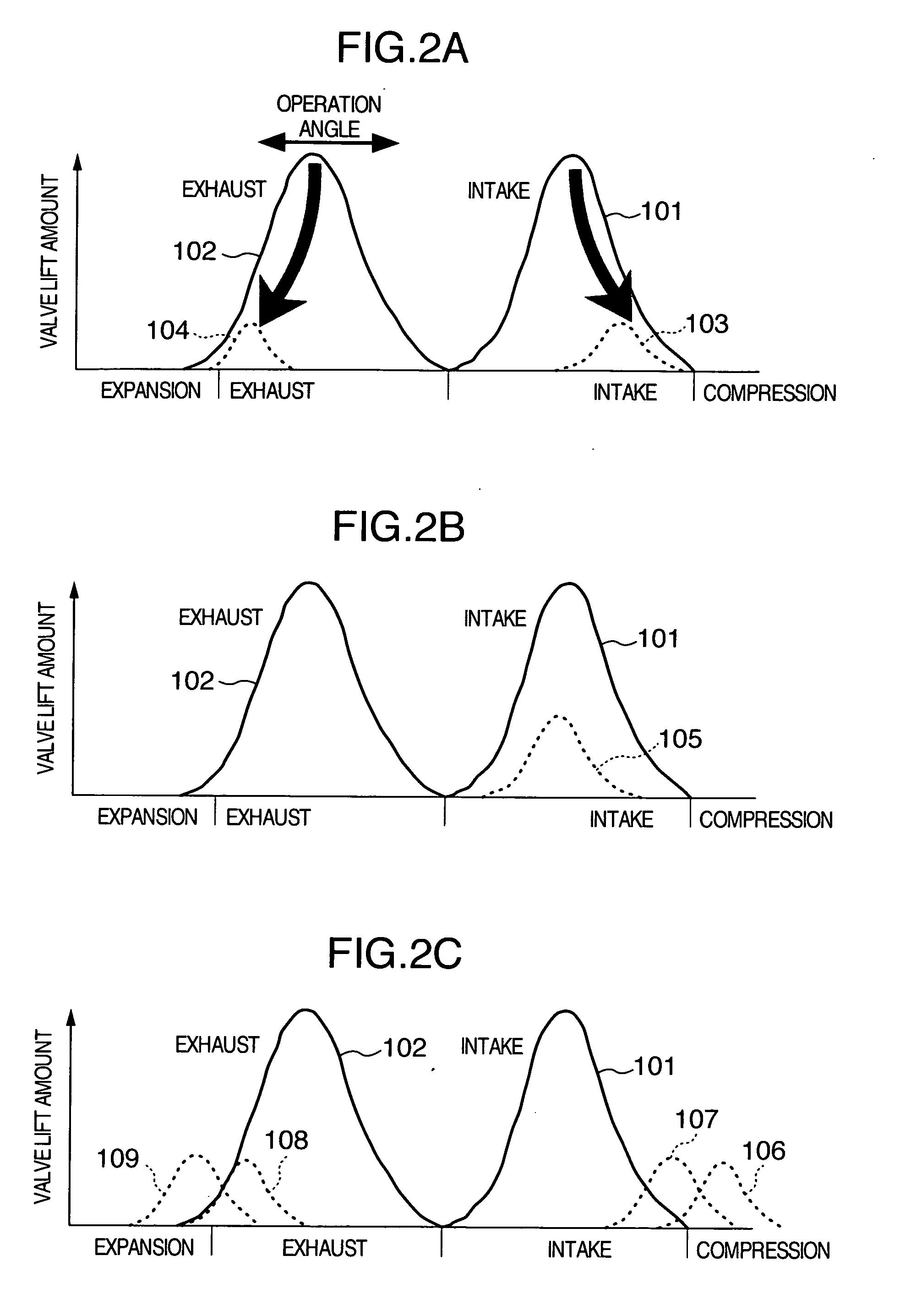
InactiveUS20090145381A1Reduce torque variationReduce the amount requiredValve arrangementsElectrical controlCombustionExhaust valve
An apparatus and method of controlling vibration-damping for a vehicular internal combustion engine. The combustion is temporarily stopped in some cylinders among a plurality of cylinders, and the engine is operated by the remaining cylinders. Then, a variable valve mechanism which varies a valve lift amount of at least one of intake and exhaust valves of each cylinder is controlled, to decrease the valve lift amount of at least one of the intake and exhaust valves of each cylinder in which the combustion is temporarily stopped. Further, a rotating electric machine having at least one of functions of an electric motor and a generator is controlled, to apply torque to an output shaft of the engine thereby suppressing torque variation in the output shaft at the time when the combustion is temporarily stopped in some cylinders, so that the torque variation due to uneven explosion intervals is reduced.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Vibration-damping control apparatus and method for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS8015960B2Reduce torque variationReduce the amount requiredValve arrangementsElectrical controlExhaust valveCombustion
An apparatus and method of controlling vibration-damping for a vehicular internal combustion engine. The combustion is temporarily stopped in some cylinders among a plurality of cylinders, and the engine is operated by the remaining cylinders. Then, a variable valve mechanism which varies a valve lift amount of at least one of intake and exhaust valves of each cylinder is controlled, to decrease the valve lift amount of at least one of the intake and exhaust valves of each cylinder in which the combustion is temporarily stopped. Further, a rotating electric machine having at least one of functions of an electric motor and a generator is controlled, to apply torque to an output shaft of the engine thereby suppressing torque variation in the output shaft at the time when the combustion is temporarily stopped in some cylinders, so that the torque variation due to uneven explosion intervals is reduced.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
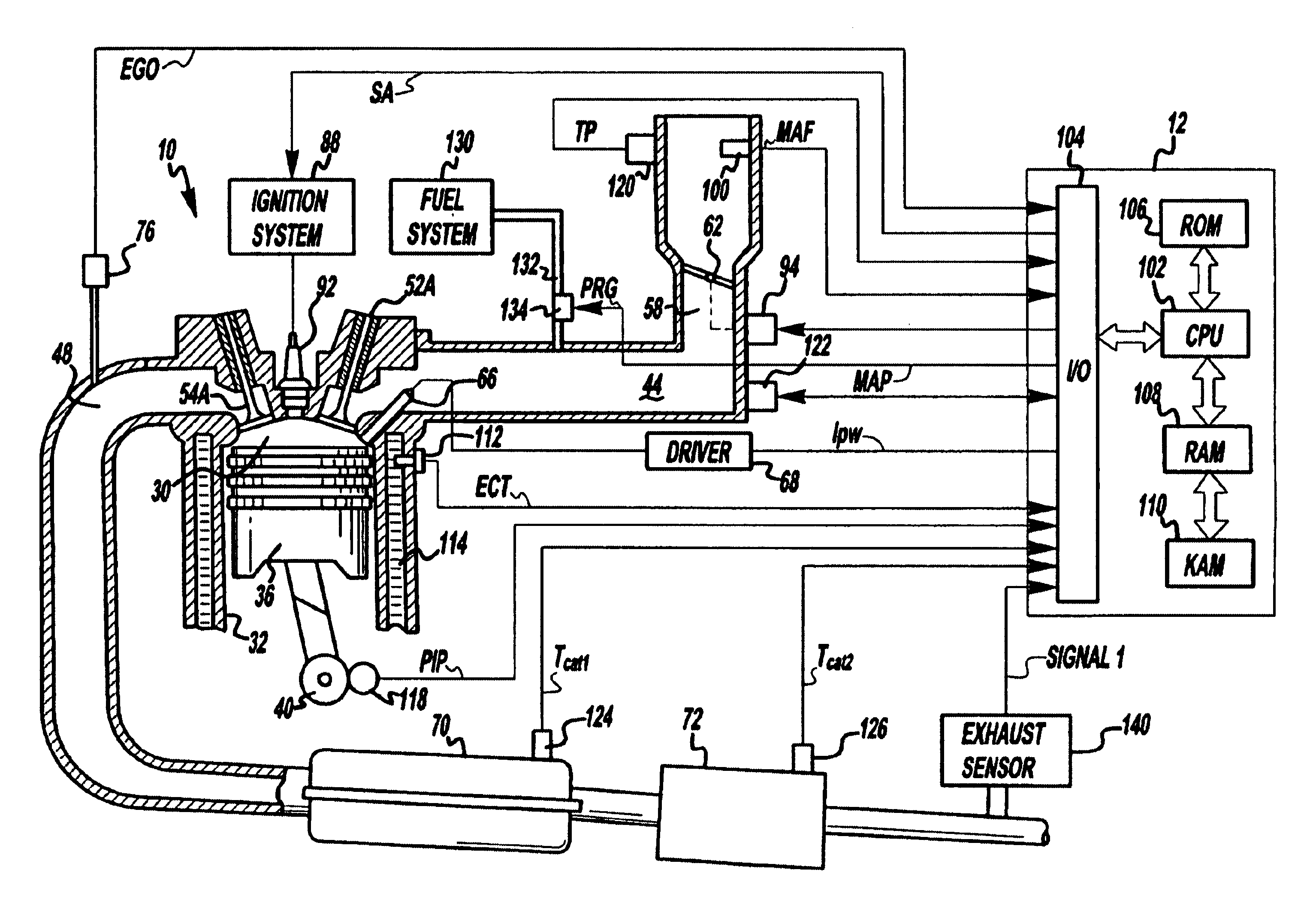
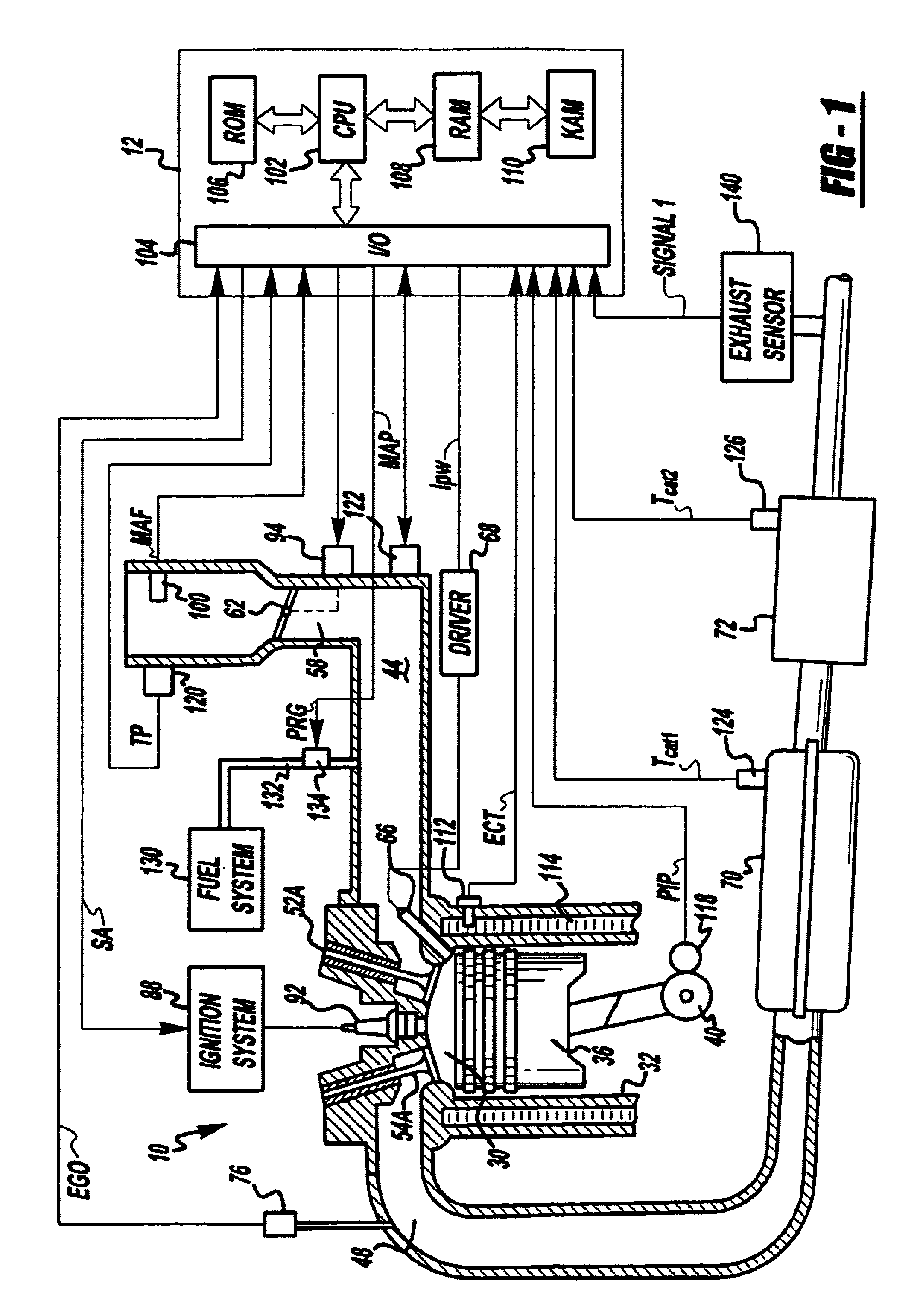
Computer controlled engine adjustment based on an exhaust flow
InactiveUS6854264B2Precise temperature controlDelay transitionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesTemperature controlControl theory
A microprocessor-based controller is provided for generated heat in at various locations in an exhaust system of an engine by changing the heat generation technique utilized. In one case, some cylinder air-fuel ratios are modulated between stoichiometry and rich, while others are modulated between stoichiometry and lean. Another approach operates some cylinder lean, while others are modulated between a first rich, and a second, less rich, value. Further, compensation based on engine airflow is also provided. Finally, various methods are described for temperature control and for controlling modulation of air-fuel ratio.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Controller for an electric four-wheel-drive vehicle
InactiveUS7495411B2Average power consumptionMinimize changesAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlPower flowMotor control
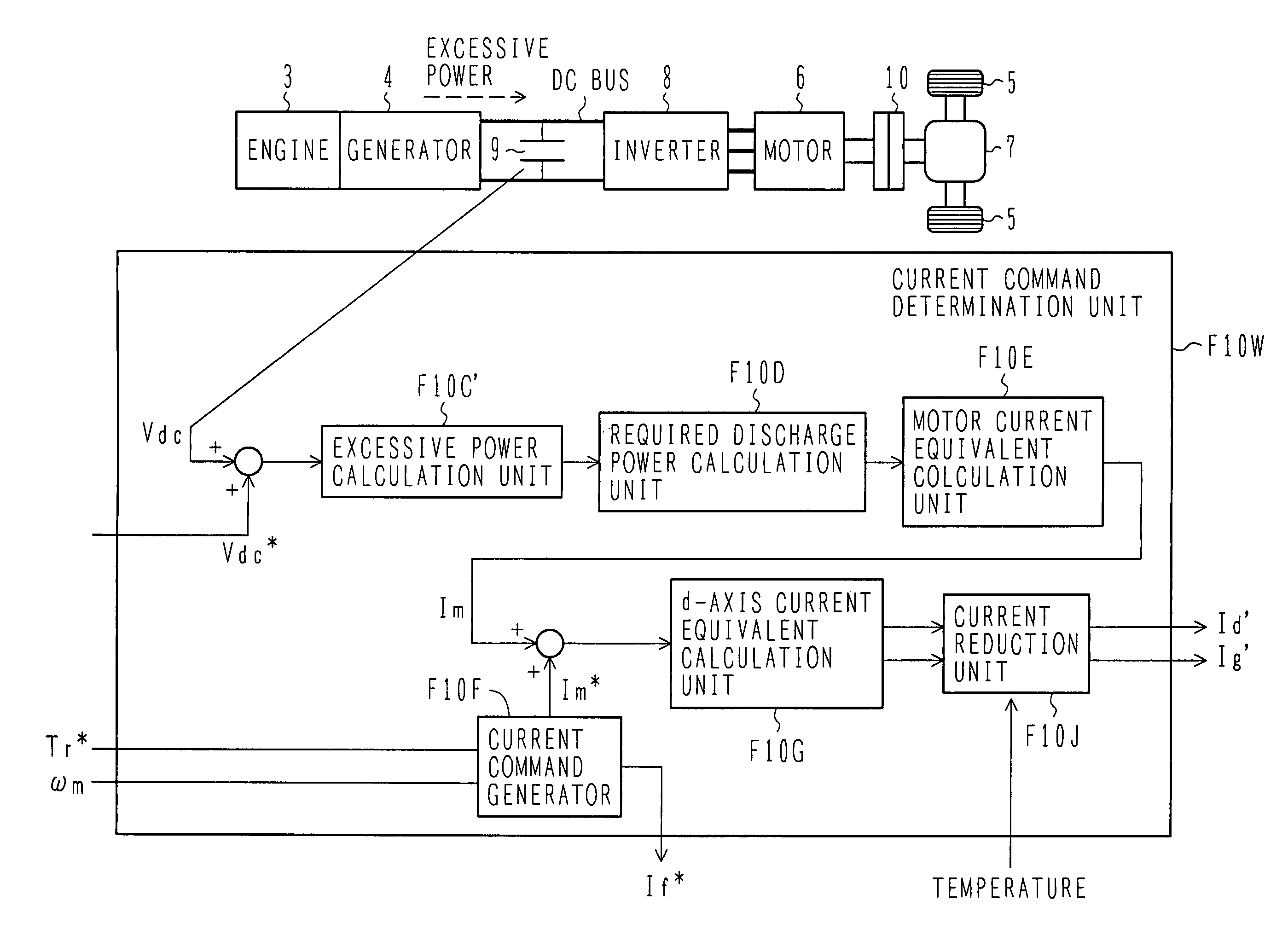
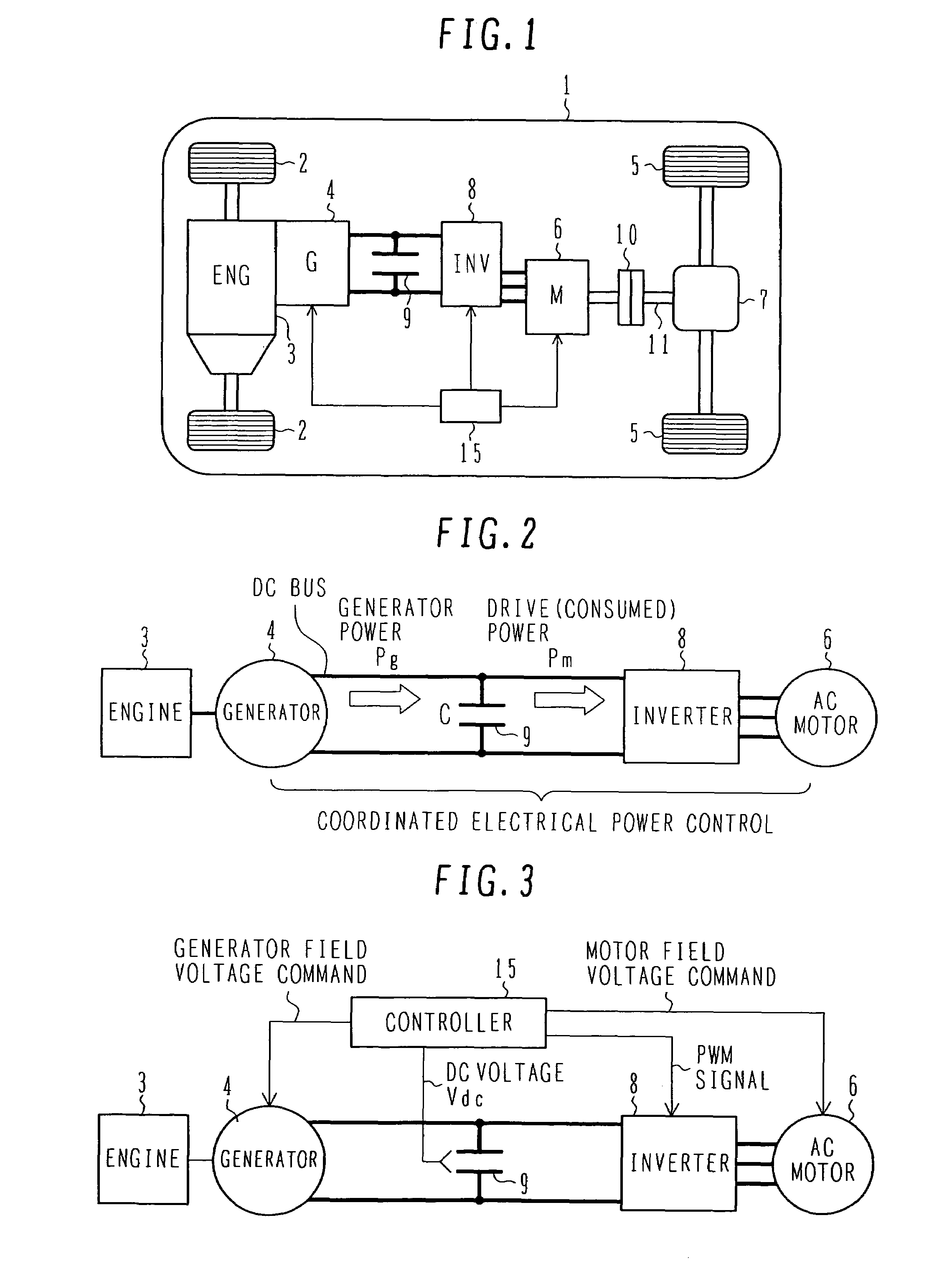
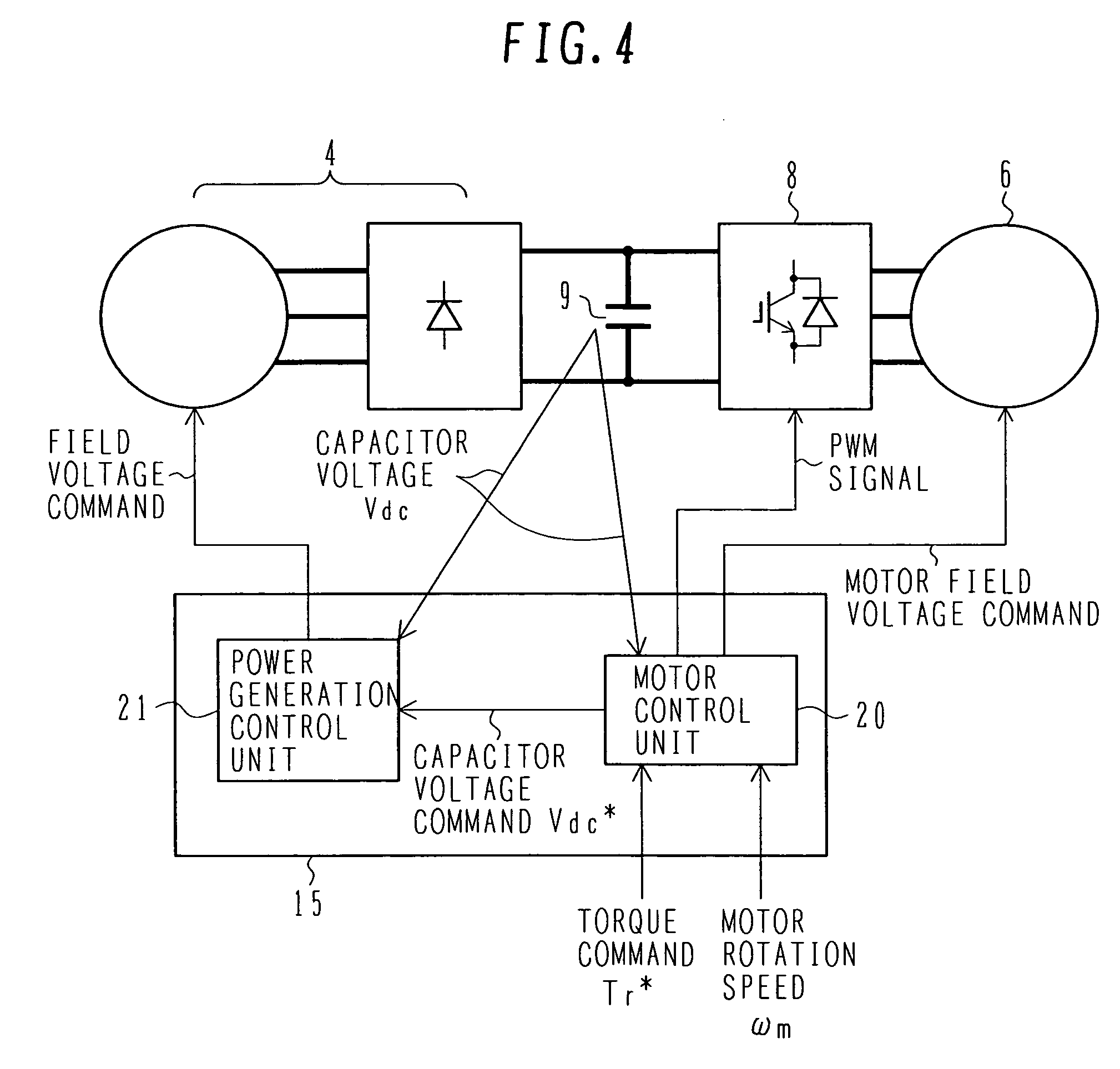
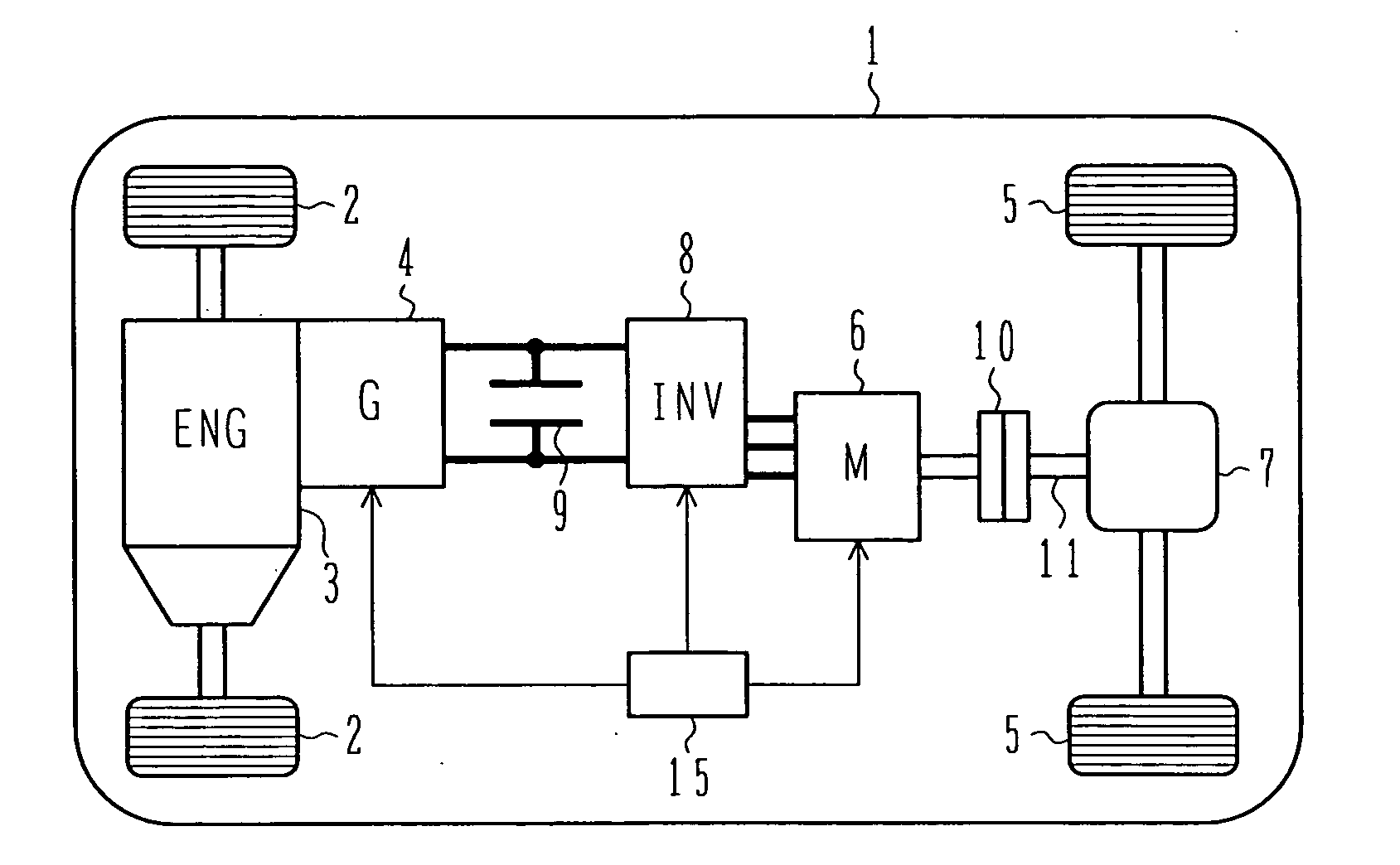
An object of the present invention is to provide a controller for an electric four-wheel-drive vehicle, which is capable of minimizing torque changes and consuming excessive power even when the excessive power is generated by a generator. A motor control unit causes an AC motor to generate desired torque by controlling an inverter. When the power generated by the generator exceeds the power consumed by the inverter and AC motor to generate excessive power, a current command determination unit in the motor control unit consumes the excessive power by increasing a loss in the AC motor.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
Controller for an electric four-wheel-drive vehicle
InactiveUS20070200529A1Reduce torque changeConsume excessive powerDC motor speed/torque controlAC motor controlFour-wheel driveDynamo
An object of the present invention is to provide a controller for an electric four-wheel-drive vehicle, which is capable of minimizing torque changes and consuming excessive power even when the excessive power is generated by a generator. A motor control unit causes an AC motor to generate desired torque by controlling an inverter. When the power generated by the generator exceeds the power consumed by the inverter and AC motor to generate excessive power, a current command determination unit in the motor control unit consumes the excessive power by increasing a loss in the AC motor.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
Engine vibration suppression device and suppression method thereof
InactiveUS7406939B2Reduce the ratioReduce torque variationHybrid vehiclesSpeed controllerEngineeringControl theory
A controller (20) estimates an internal cylinder pressure of an engine (1) on the basis of the operating conditions of the engine (1), torque variation in the engine (1) is calculated on the basis of the estimated internal cylinder pressure, and an opposite phase torque of the torque variation in the engine (1) is calculated as a torque correction amount. The controller (20) then calculates a torque command value for a motor generator (2) by adding the torque correction amount to a basic torque value for driving the motor generator (2) to rotate, and performs torque control such that the torque of the motor generator (2) equals the torque command value.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Gear screw adjuster
InactiveUS7052164B2Easy to installCost-effectiveCoupling device connectionsLighting support devicesGear wheelRadial compression
A headlamp assembly including a simplified adjusting mechanism for adjusting the aim of the headlamp. The mechanism includes a gear screw that is snap fit into the headlamp housing with or without an adjuster housing. The gear screw has an O-ring in radial compression so as to ensure a good seal.
Owner:BURTON TECH
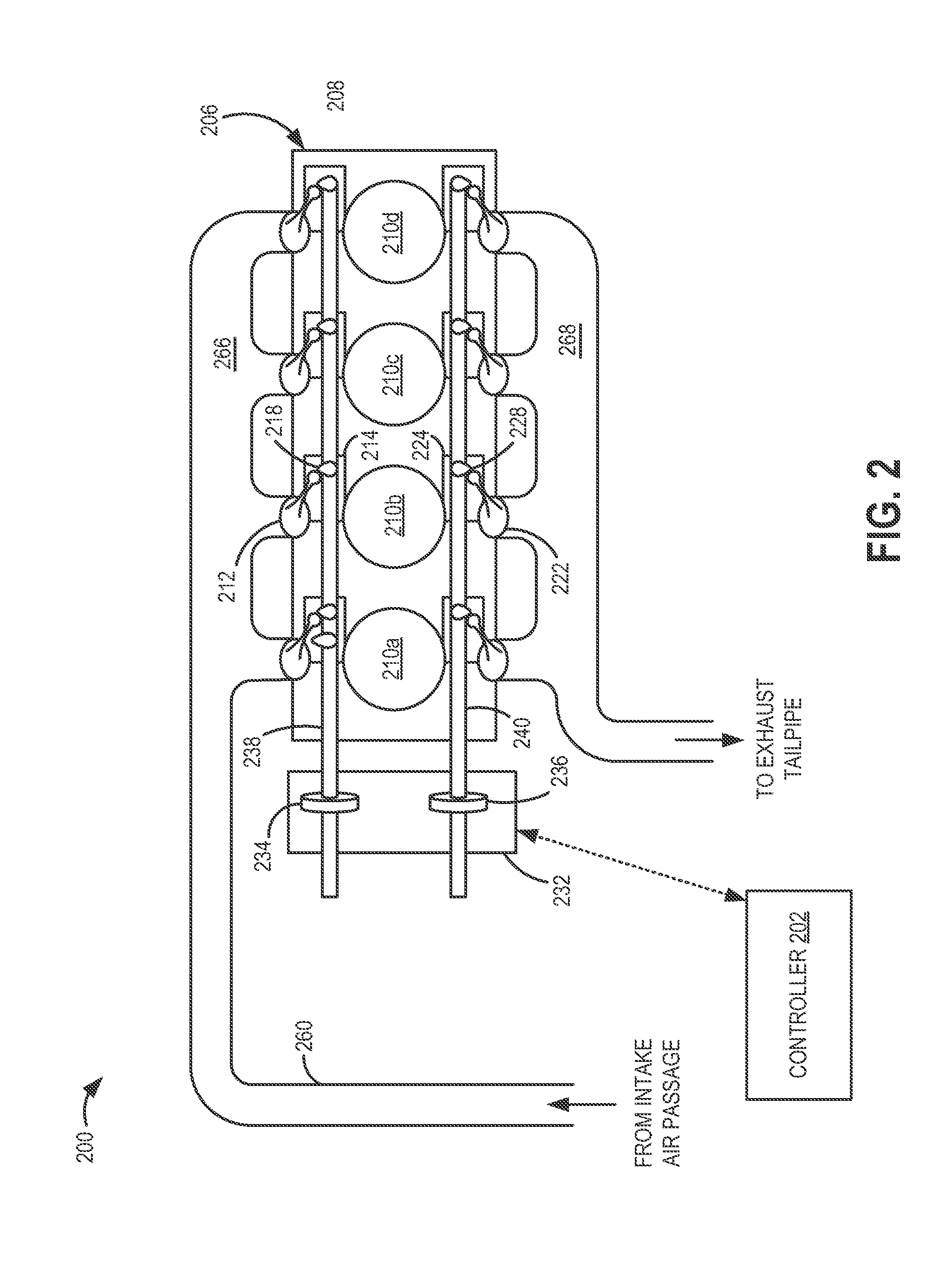
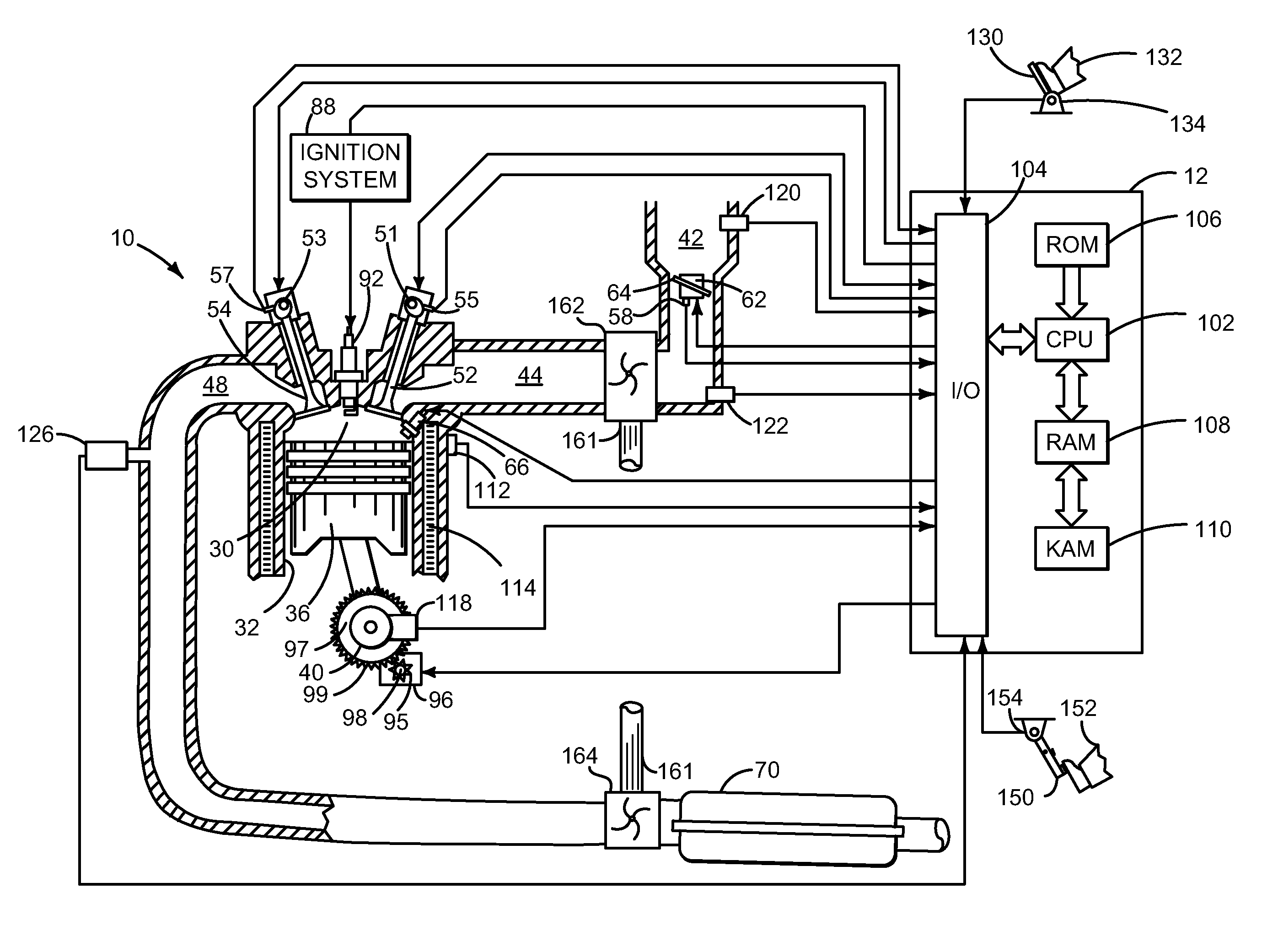
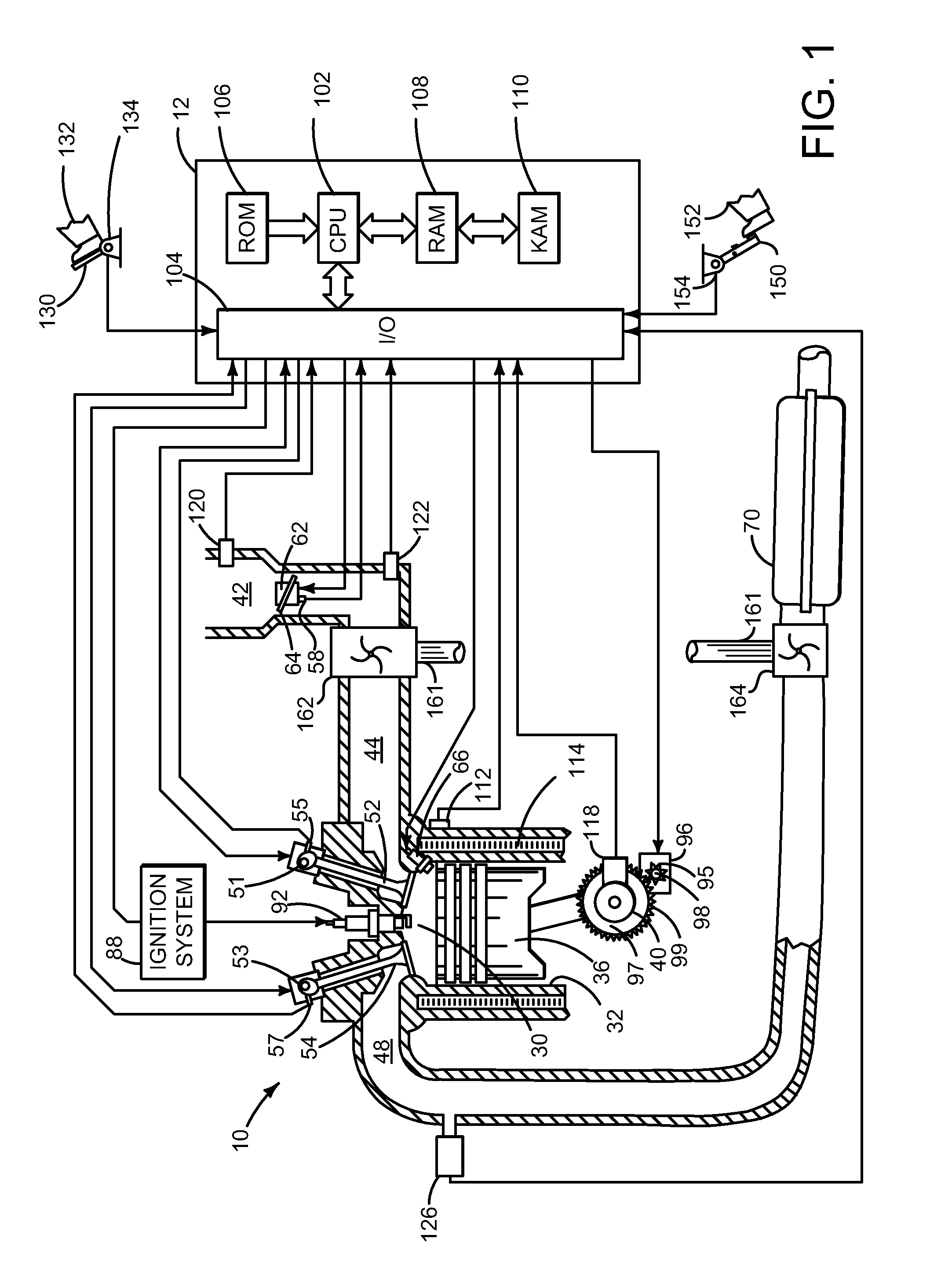
Method and system for engine air control
ActiveUS20130245921A1Increase in torque variationAggravate torque variationElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustionControl theory
Methods and systems are provided for reducing idling torque imbalances between cylinders by actuating a common camshaft to which the cylinders are coupled. The camshaft may be adjusted within camshaft limits during each combustion event of each cylinder. In this way, idling NVH issues may be addressed.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Hybrid power unit control system
InactiveCN102007029ASuppression of torsional vibrationReduce torque variationRailway vehiclesToothed gearingsEngineeringTorsional vibration
Disclosed is a means to attenuate torsional vibration in a power unit transmission system generated by torque fluctuations in the engine in an automotive hybrid power unit, and thereby eliminate noise, such as chattering from the power transmission gears and muffled body noise, etc. Disclosed is a hybrid power unit control system for a hybrid power unit that is equipped with a first drive train, which is configured with a gear transmission mechanism linked to a first input shaft that transmits engine drive power via a first friction clutch; a second drive train, which is configured with a gear transmission mechanism linked to a second input shaft that transmits engine drive power via a second friction clutch; a motor generator, which is connected to said first input shaft or second input shaft; and a driven apparatus, which is driven by the drive power transmitted from the output shaft of the gear transmission mechanism of said first drive train or the output shaft of the gear transmission mechanism of said second drive train. Said motor generator is started as an electric power generator when fluctuation in the rotational speed of said engine, which is detected by a rotational speed sensor, exceeds a predetermined upper limit amplitude value, so that torque of opposite phase to said rotational speed fluctuation is applied to said engine with the same periodicity as said rotational speed fluctuation.
Owner:AISIN AI CO LTD +2
Roll mill
InactiveCN101754815AReduce torque variationShorten speedGearingGrain treatmentsEngineeringRolling mill
Owner:KRUPP POLYSIUS AG
Converter for an electrical machine, controller and method for operating a converter
InactiveCN102882467AReduce deliverySave spaceAC motor controlElectric motor controlElectric machineElectrical connection
Owner:MAGNA POWERTRAIN GMBH & CO AG
Control device and control method for vehicle
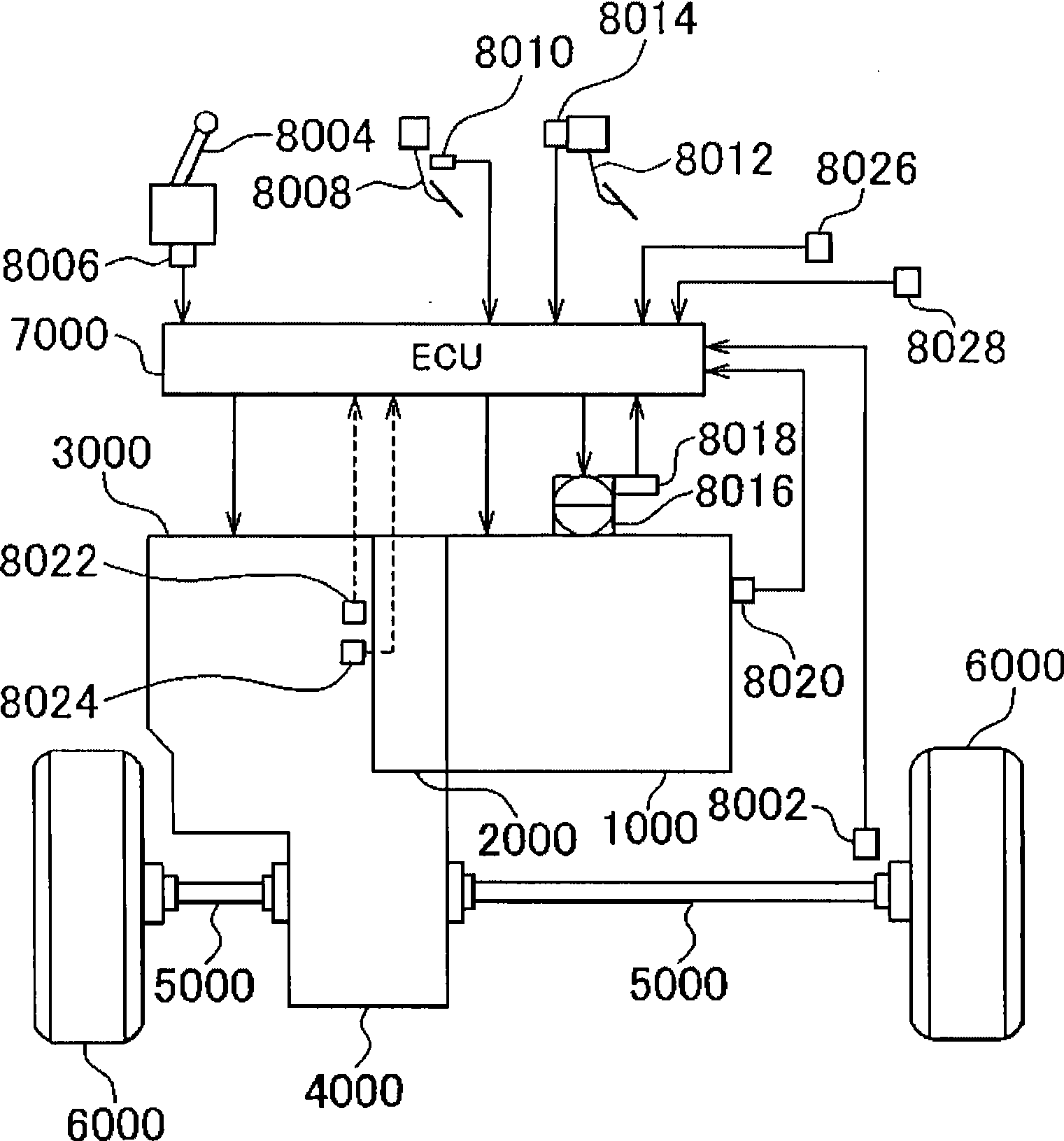
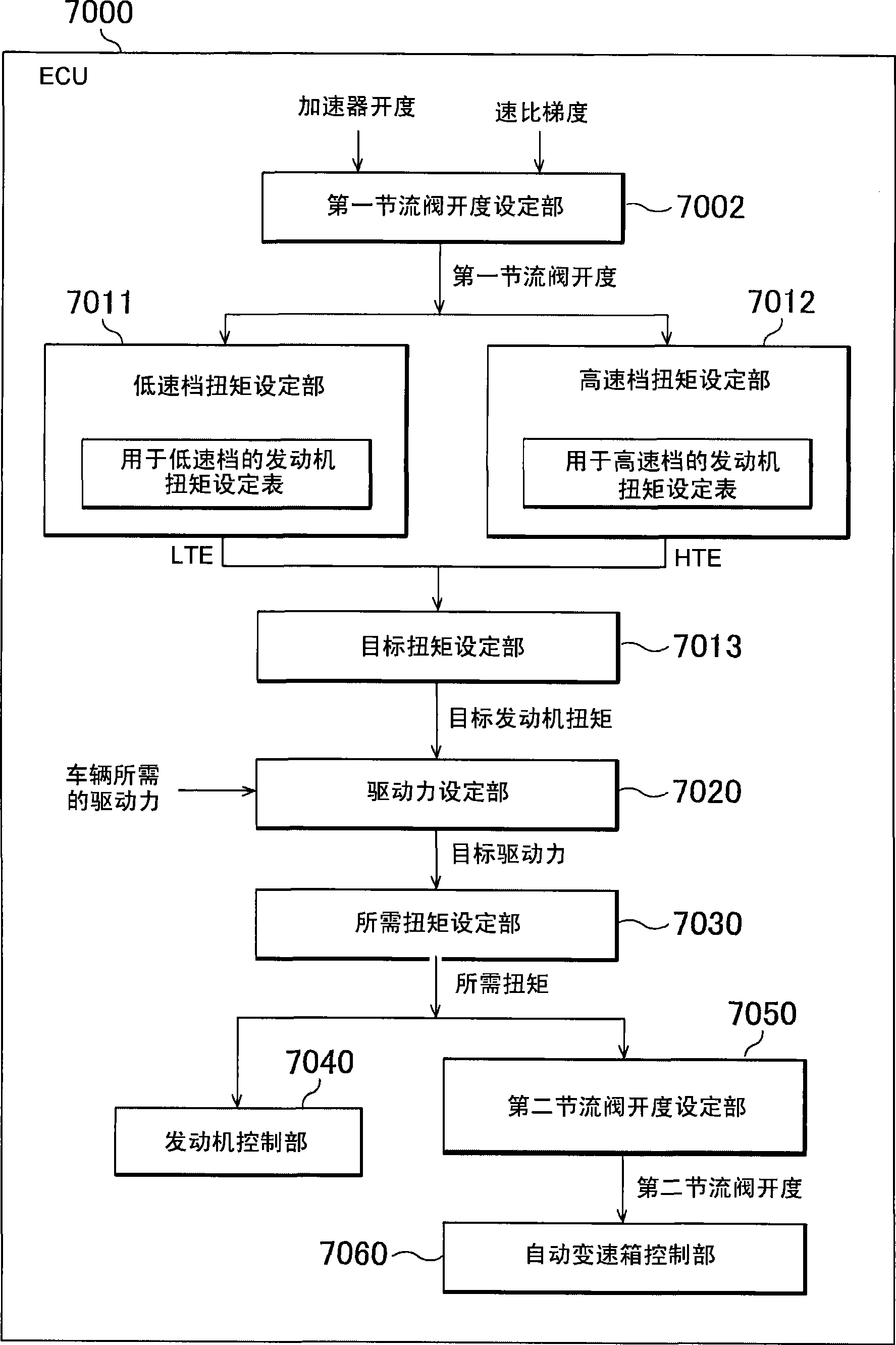
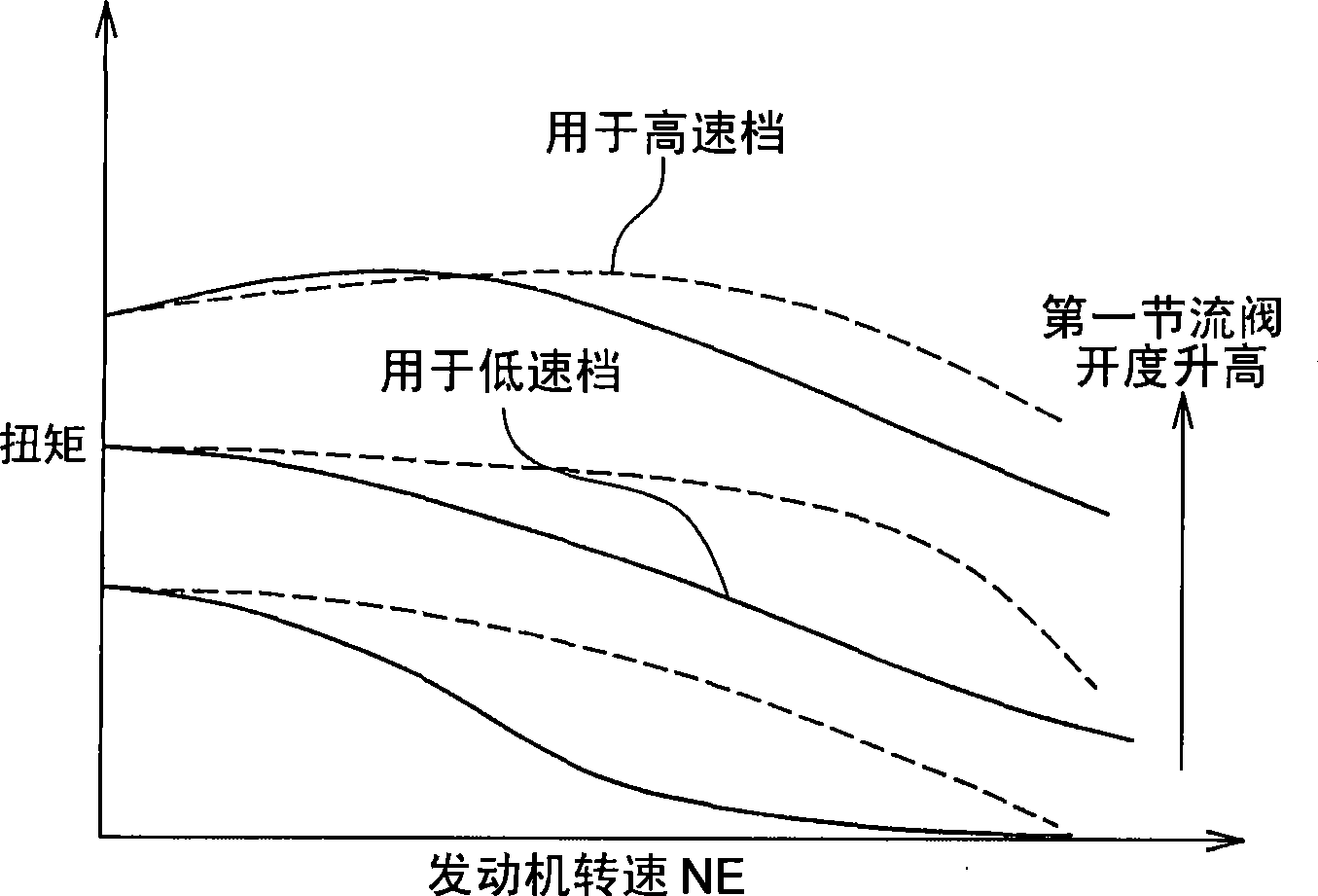
ActiveCN101432516AReduce torque variationLittle changeElectrical controlMachines/enginesControl theoryThrottle opening
An ECU executes a program including the steps of: setting a first throttle opening degree (SlOO), setting a low gear torque LTE based on an engine torque map for low gear having the first throttle opening degree and an engine speed (rpm) as parameters (S200), setting a high gear torque HTE based on an engine torque map for high gear having the first throttle opening degree and the engine speed as parameters (S300), setting a target engine torque TTE by combining the low gear torque LTE and the high gear torque HTE by using a correction ratio KGR determined by a gear step (S400), and controlling the engine to produce a required torque set by using the target engine torque TTE (S700). In this way a torque can be obtained in accordance with the engine speed.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
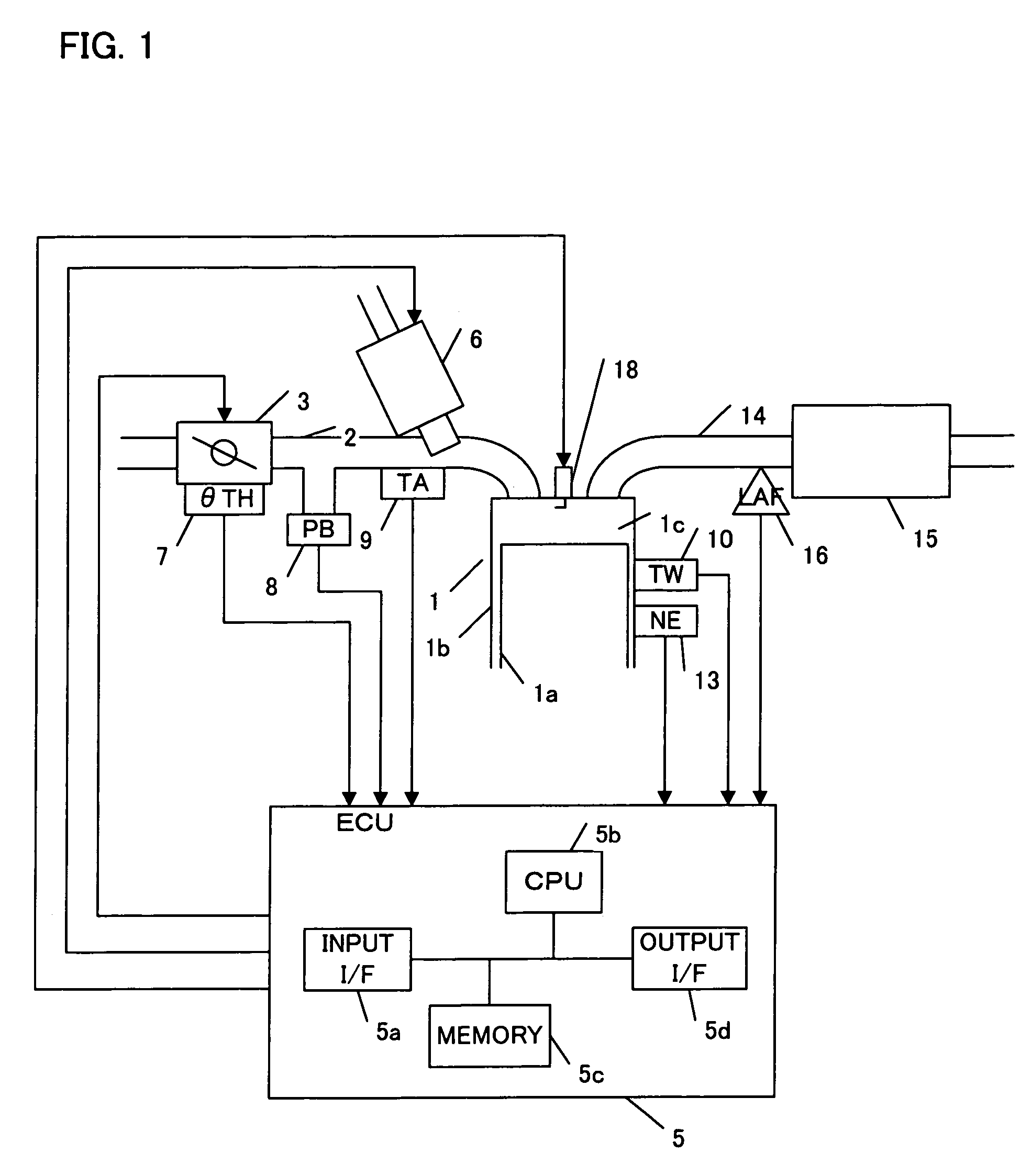
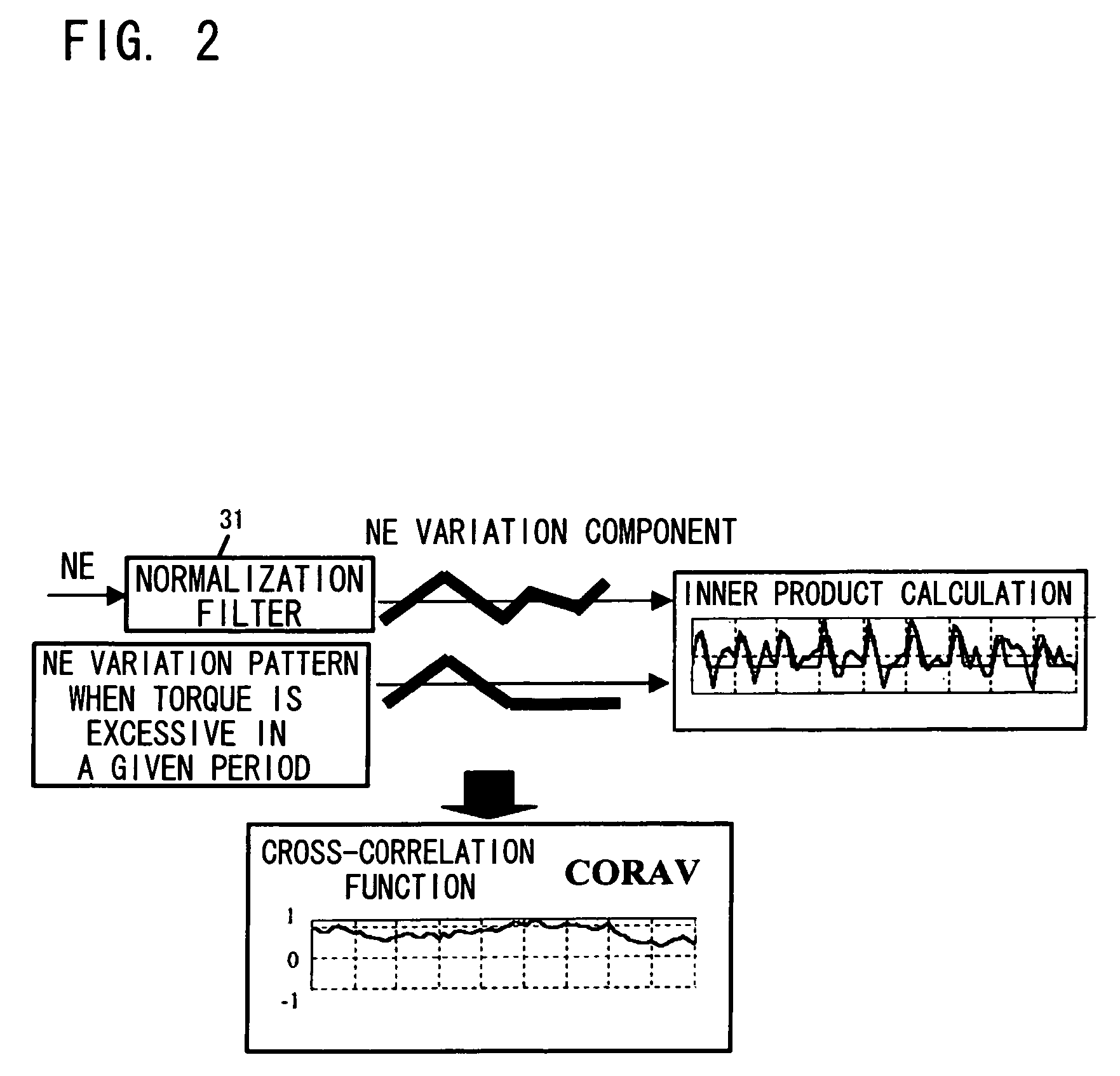
Control system for correcting a torque variation of an engine
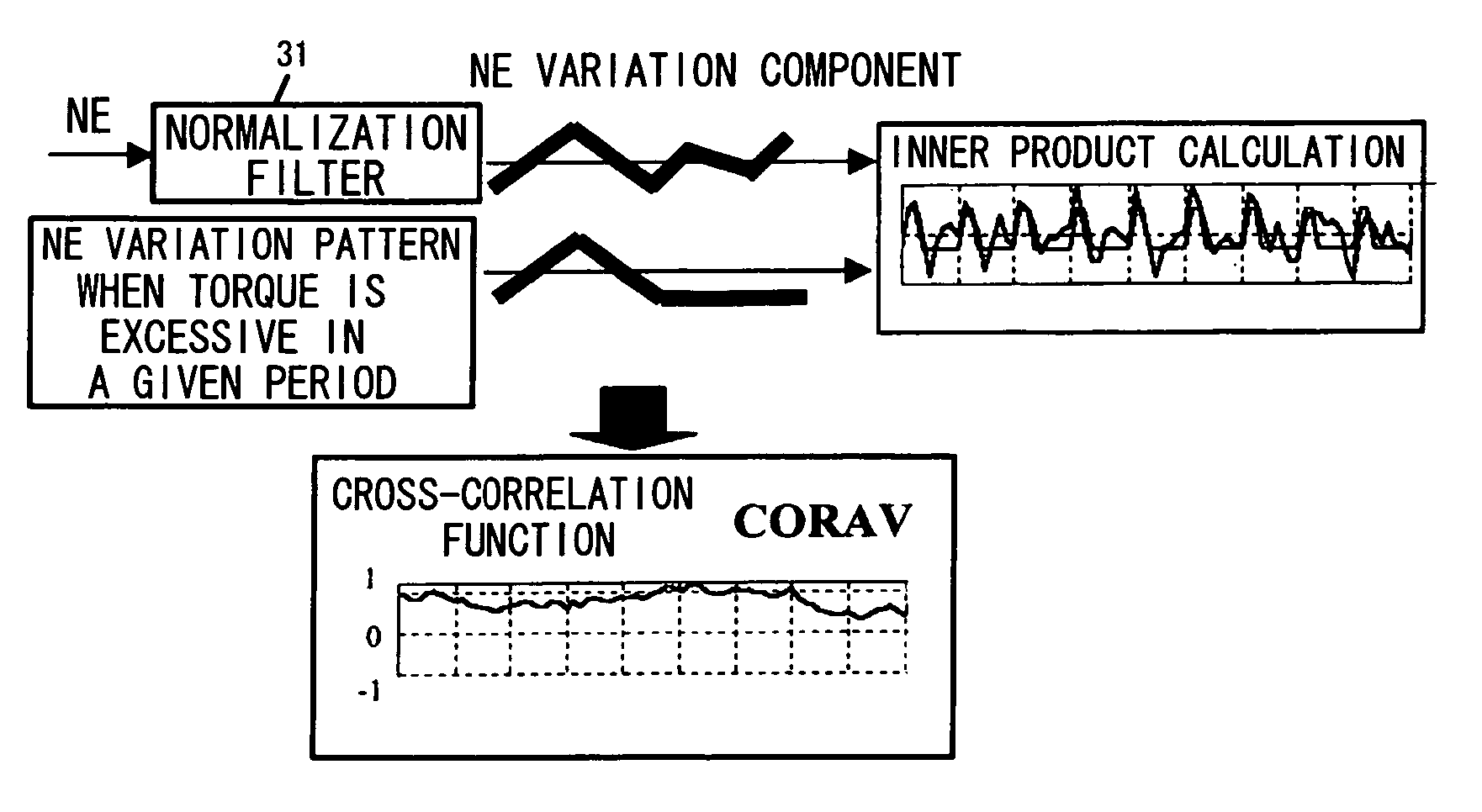
InactiveUS6975934B2Magnitude of can readilyReduce detected torque variationAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlControl systemInternal combustion engine
The present invention provides a control system for an internal combustion engine for detecting a torque variation based on a rotational speed of the engine and suppress the torque variation. The system includes a detector for detecting a rotational speed of the engine, a memory for storing a variation pattern of the rotational speed of the engine when a torque of the internal combustion engine is excessive and a controller for calculating a variation component of the rotational speed based on the detected rotational speed, The controller calculates the correlation between the variation component and the variation pattern that is read out from the memory and then determines a torque variation state of the engine based on the correlation.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
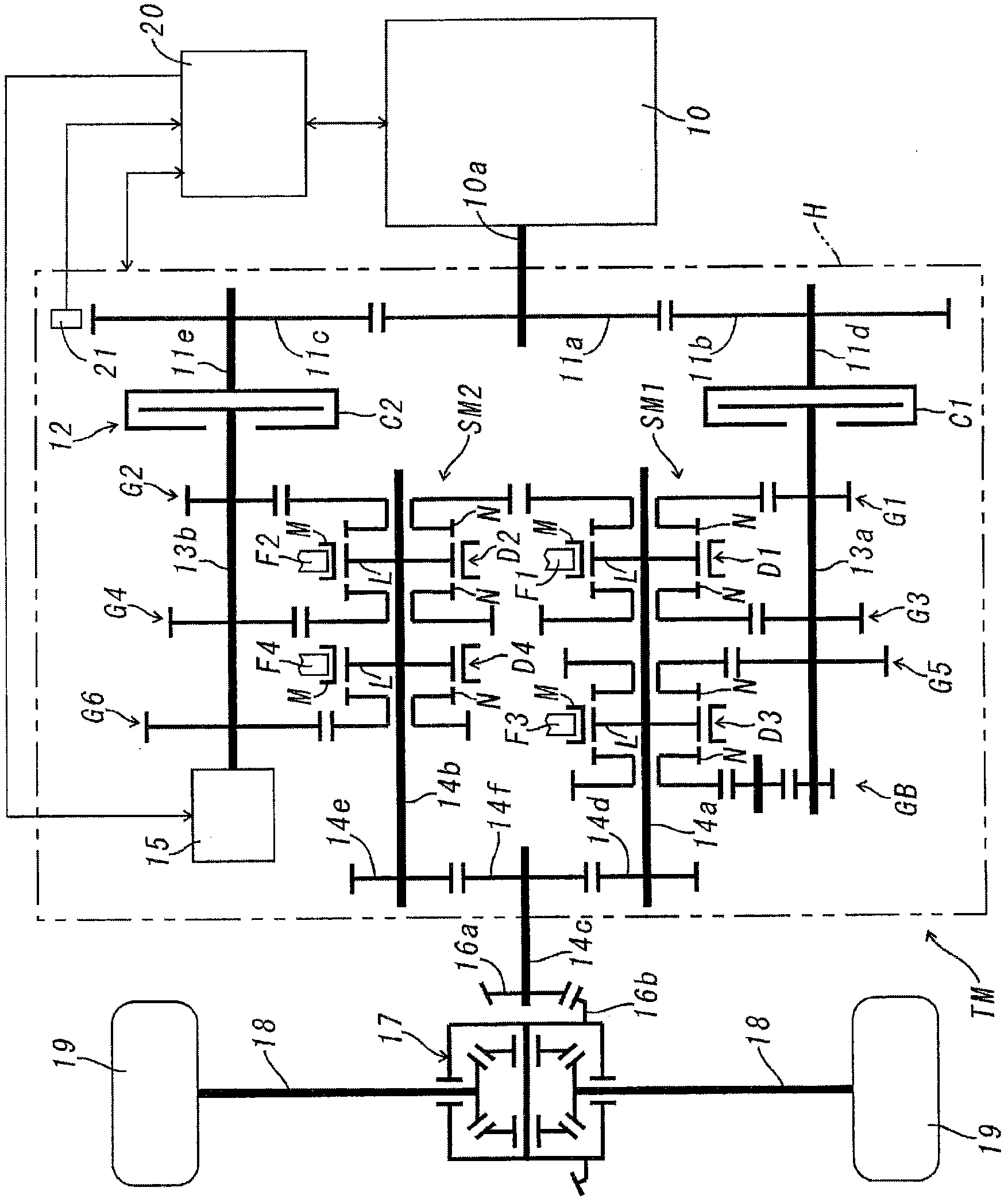
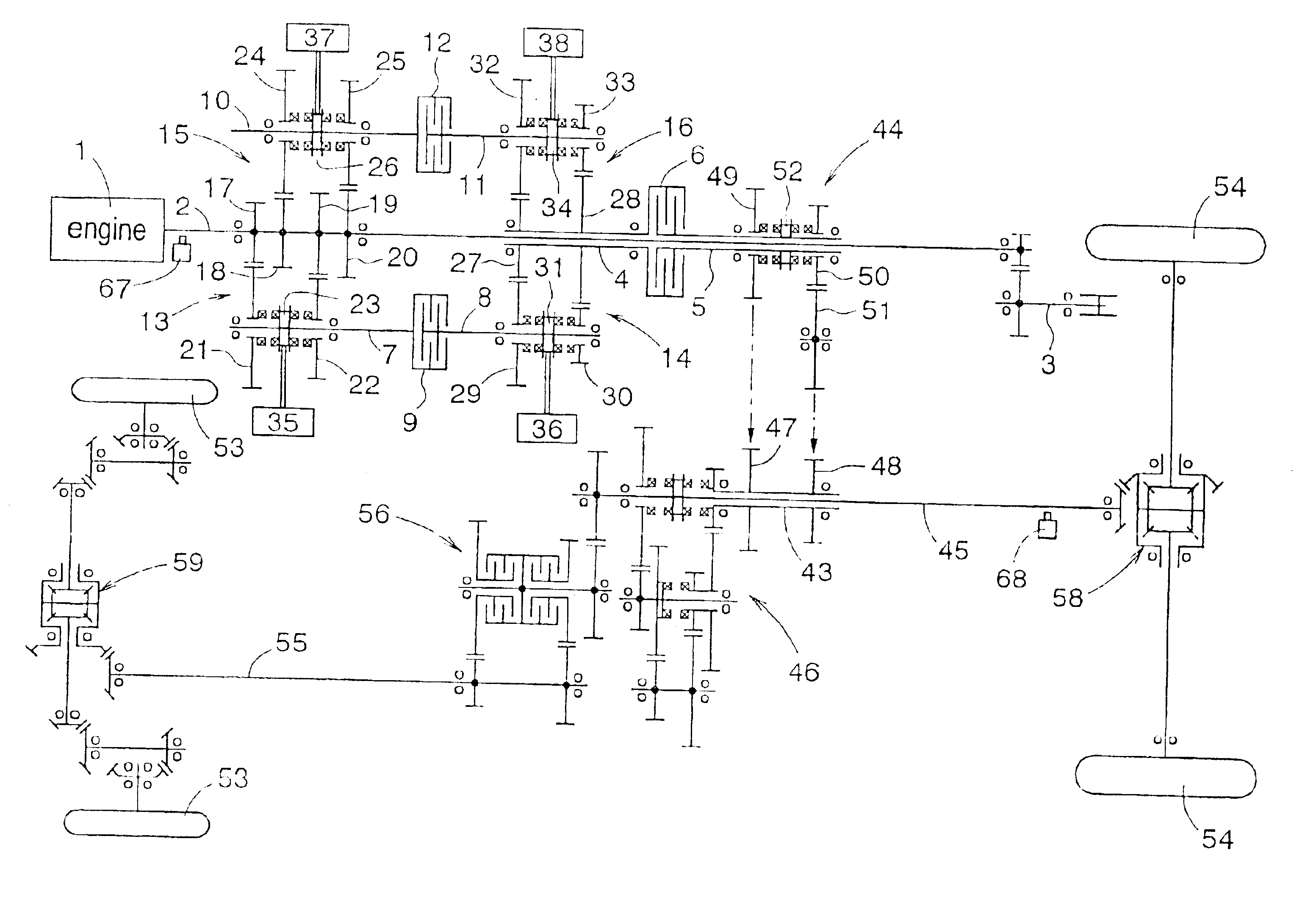
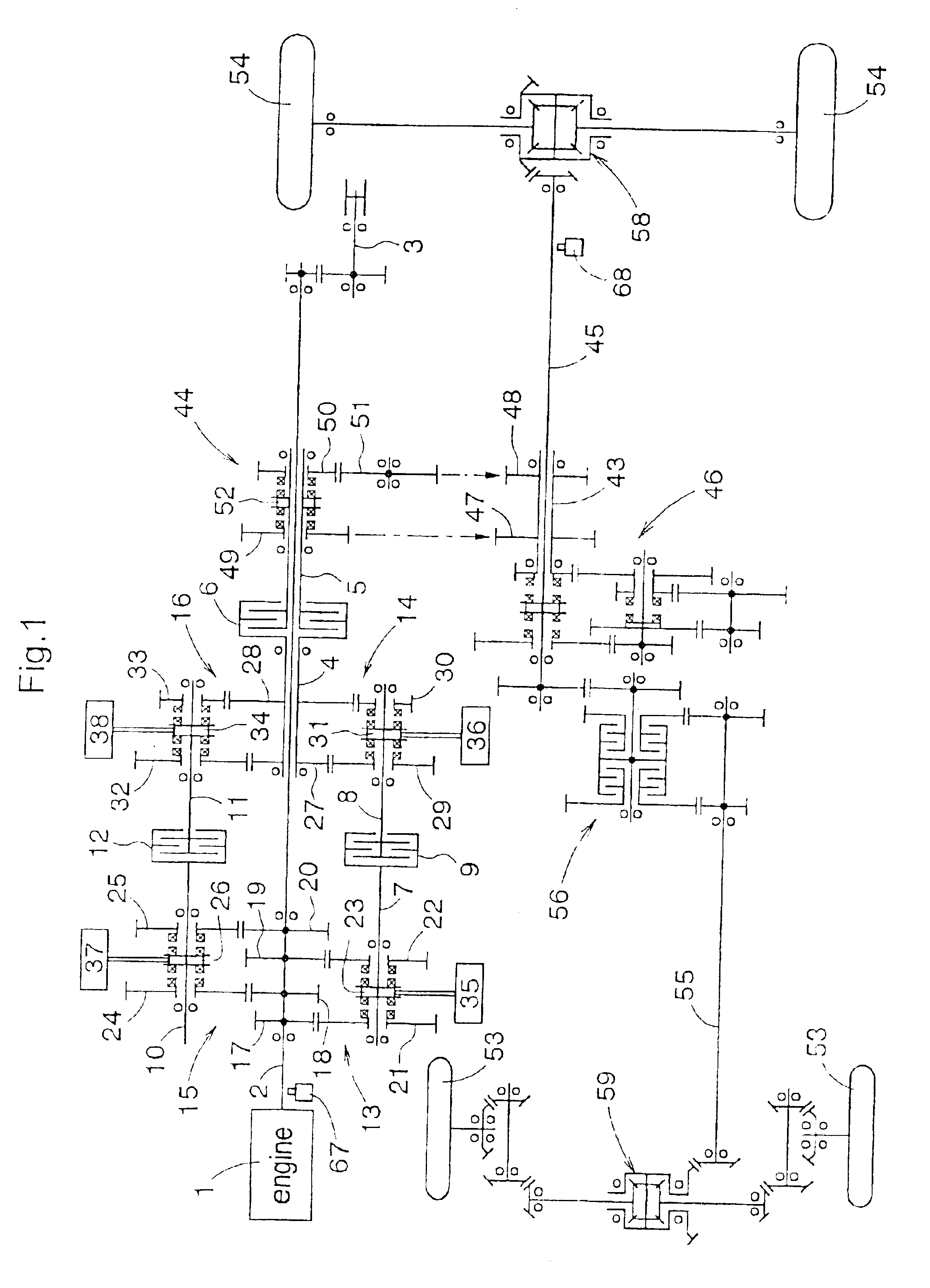
Control apparatus for transmission
InactiveUS6851328B2Reducing a change-speed shockTorque variation can be minimizedHybrid vehiclesToothed gearingsDrive shaftEngineering
A transmission control apparatus includes transmission lines disposed between a pair of transmission shafts and a hydraulic multiple disc transmission clutch disposed on one side of the transmission lines. Power from an engine is transmitted via one of the transmission lines to a traveling unit. Each of the transmission lines has a friction clutch. A first gear mechanism operated by a first actuator is disposed between one of the transmission shafts and the first transmission line. A second gear mechanism operated by a second actuator is disposed between one of the transmission shafts and the second transmission line. When the first transmission line is powered, a first system operates the second gear mechanism into a speed position; the first clutch to a non-transmitting state and the second clutch to a transmitting state, thereby providing a progressive shifting of the transmission clutch from a transmitting state to a semi-transmitting state.
Owner:KUBOTA LTD
Powered brake device
ActiveUS20180194334A1Quiet operationSmall variationAC motor controlBraking action transmissionEngineeringHigh torque
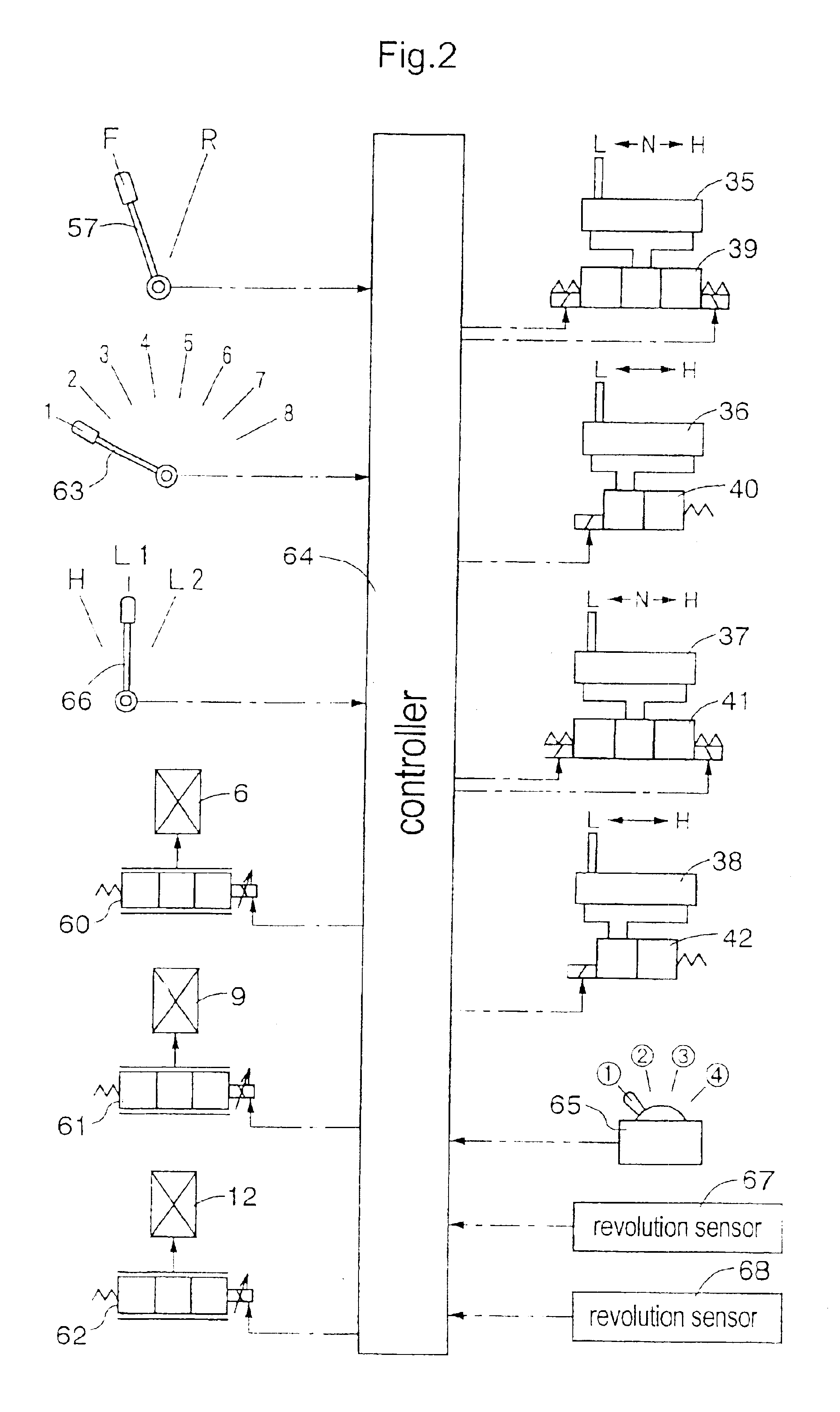
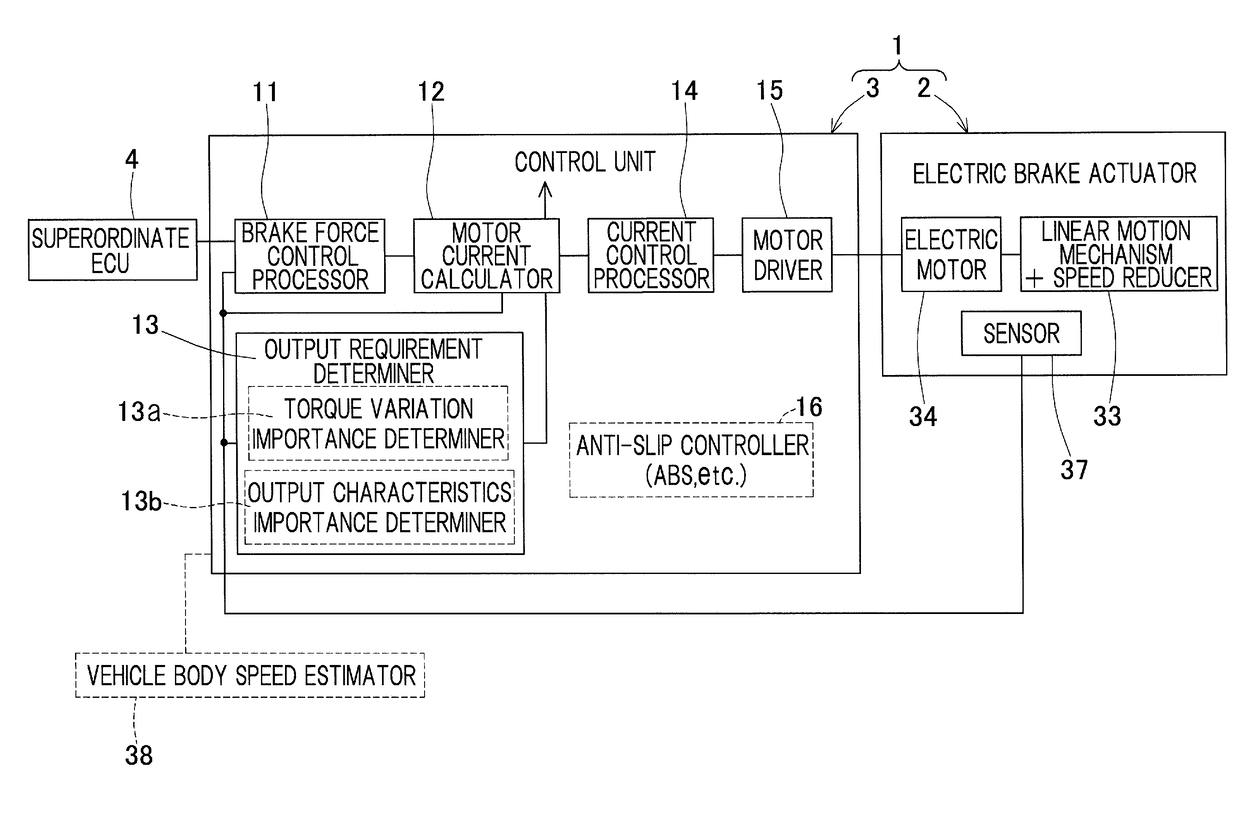
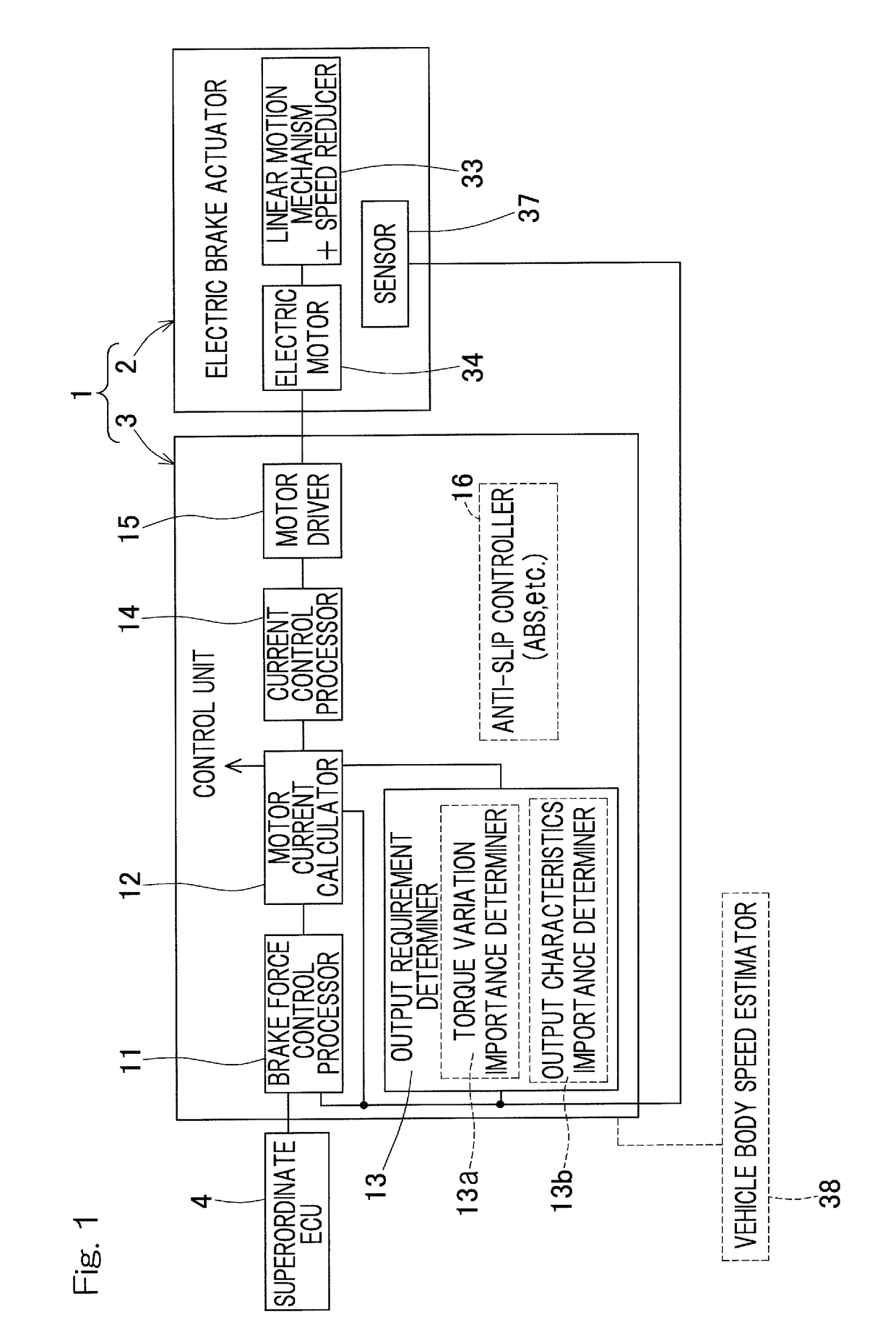
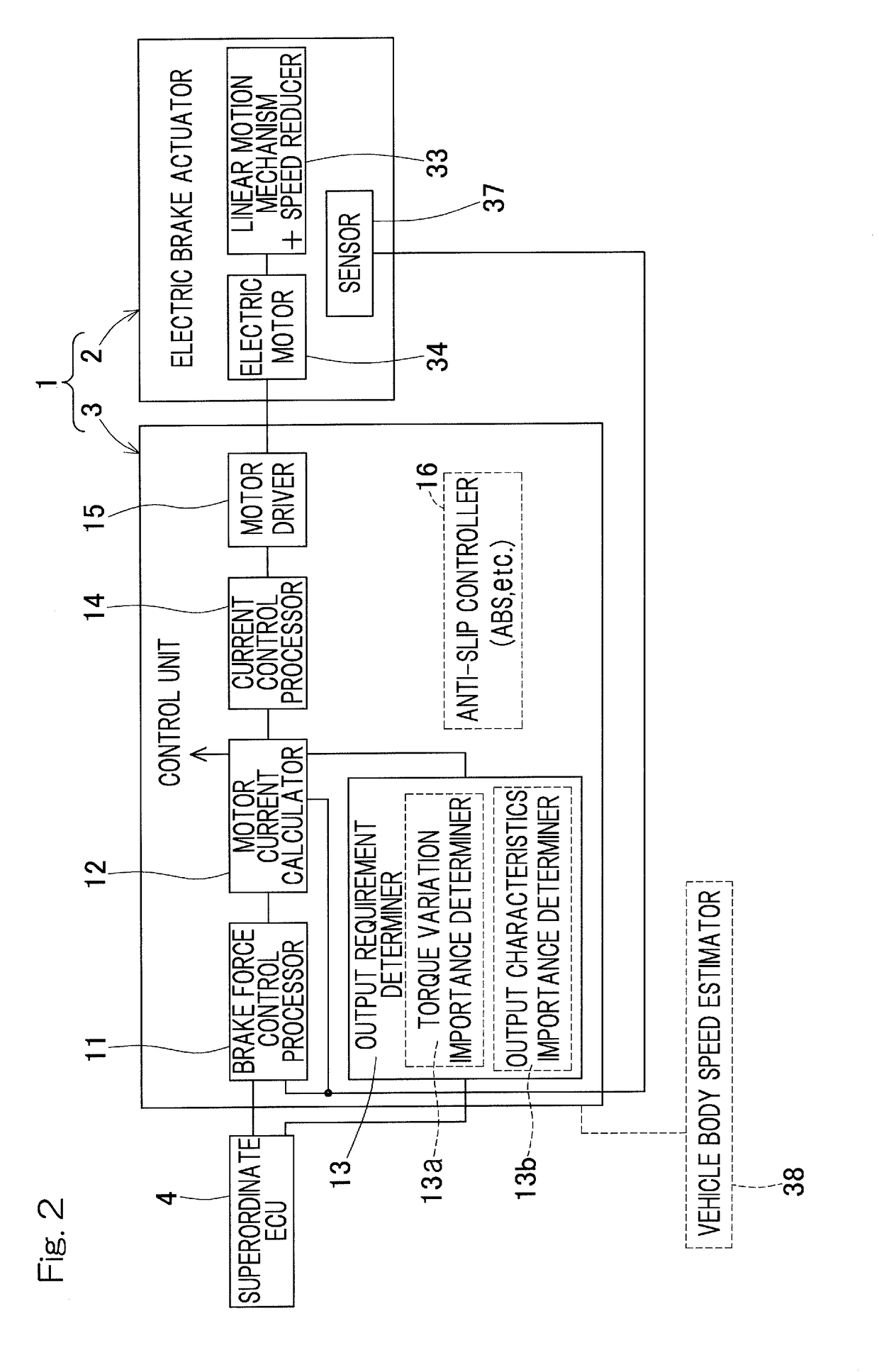
Both of a quiet operation with smaller torque variation for prioritizing NVH and a high torque operation or high output operation for prioritizing torque or output may be provided by selectively using, based on requests, a control scheme that reduces torque variation and a control scheme that maximizes a torque. A motor current calculator may be capable of selectively using an output prioritizing control scheme that prioritizes a torque output and a torque variation suppressing control scheme that prioritizes smaller torque variation. An output requirement determiner may be provided to calculate a degree of importance of suppressing torque variation of an electric motor, based on one or both of a braking request and a travel condition of a vehicle. In accordance with this determination result, the motor current calculator may selectively use the output prioritizing control scheme and the torque variation suppressing control scheme.
Owner:NTN CORP
Shift control apparatus of automatic transmission of motor vehicle
InactiveUS7074158B2Improve robustnessShift shocks are sufficiently reducedGearingRoad transportMobile vehicleFluid coupling
A shift control apparatus of an automatic transmission of a motor vehicle to which torque is transmitted from an engine via a fluid coupling device is provided. In the automatic transmission including a plurality of hydraulically operated friction elements, a clutch-to-clutch downshift is carried out during coasting of the vehicle by releasing one of the friction elements and engaging another friction element. A controller of the shift control apparatus detects a difference between input and output rotation speeds of the fluid coupling device, and increases an engine speed by a controlled amount based on the difference between the input and output rotation speeds when the clutch-to-clutch downshift is carried out during coasting of the vehicle, so that the vehicle is brought into a minimal driving state in which the engine speed is slightly higher than the output rotation speed of the fluid coupling device.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Vortex compressor and refrigerator using ammonia-like as refrigrant
InactiveCN1405951AJet easyImprove efficiencyRotary/oscillating piston combinations for elastic fluidsWindings insulation materialEngineeringRefrigerant
The scroll compressor includes a scroll compression mechanism portion in combination of an orbiting scroll and a fixed scroll, a frame for supporting the compression portion, a rotary shaft fitted in the orbiting scroll, a motor portion coupled to the rotary shaft, and a hermetic chamber incorporating the above-mentioned components. Windings of a stator of a motor in the motor portion are formed of aluminum wires which are coated with fluororesin compound, that is, the aluminum wires are coated with fluororesin and is molded with a resin material. Ammonia group refrigerant is used in the scroll compressor. Further, a refrigerating system using the above-mentioned scroll compressor, is incorporated therein with a circuit for injecting ammonia group refrigerant into a compression room in the compression mechanism portion.
Owner:HITACHI JOHNSON CONTROLS AIR CONDITIONING INC
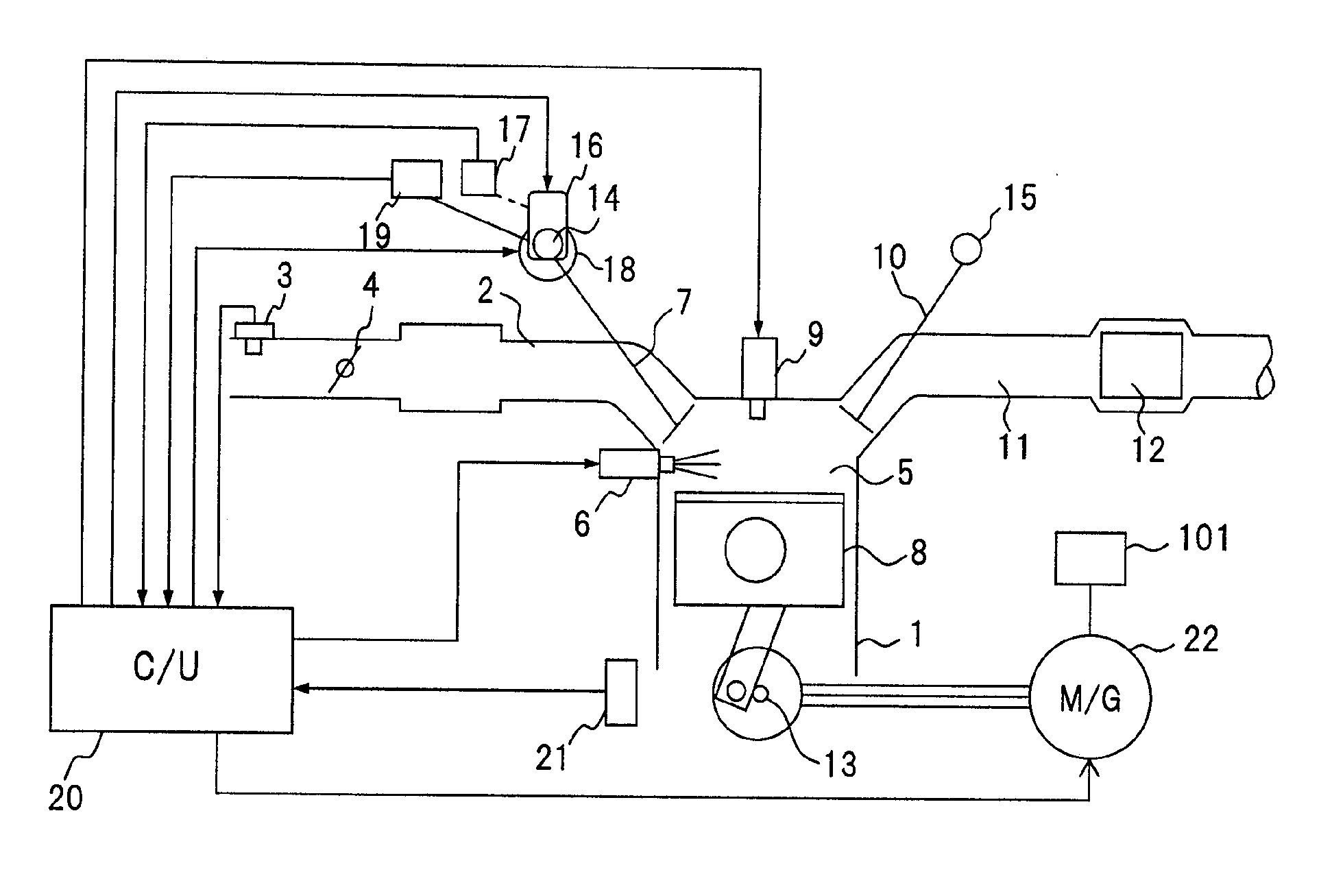
Apparatus and method for controlling internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20070062485A1Deterioration of exhaust emission is also suppressedReduce torque variationElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustionMode control
A control apparatus of an engine having a compression ignition combustion mode and a spark ignition combustion mode selects the spark ignition combustion mode when operation conditions fall within a spark ignition operation area set in a spark ignition operation area / compression ignition operation area setting map memory part and selects the compression ignition combustion mode when the operation conditions fall within a switching stable area set in the memory part upon operation by the spark ignition combustion mode. The control apparatus controls to continue the compression ignition combustion mode as long as the operation conditions fall within a compression ignition operation area set in the memory part upon operation by the compression ignition combustion mode.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
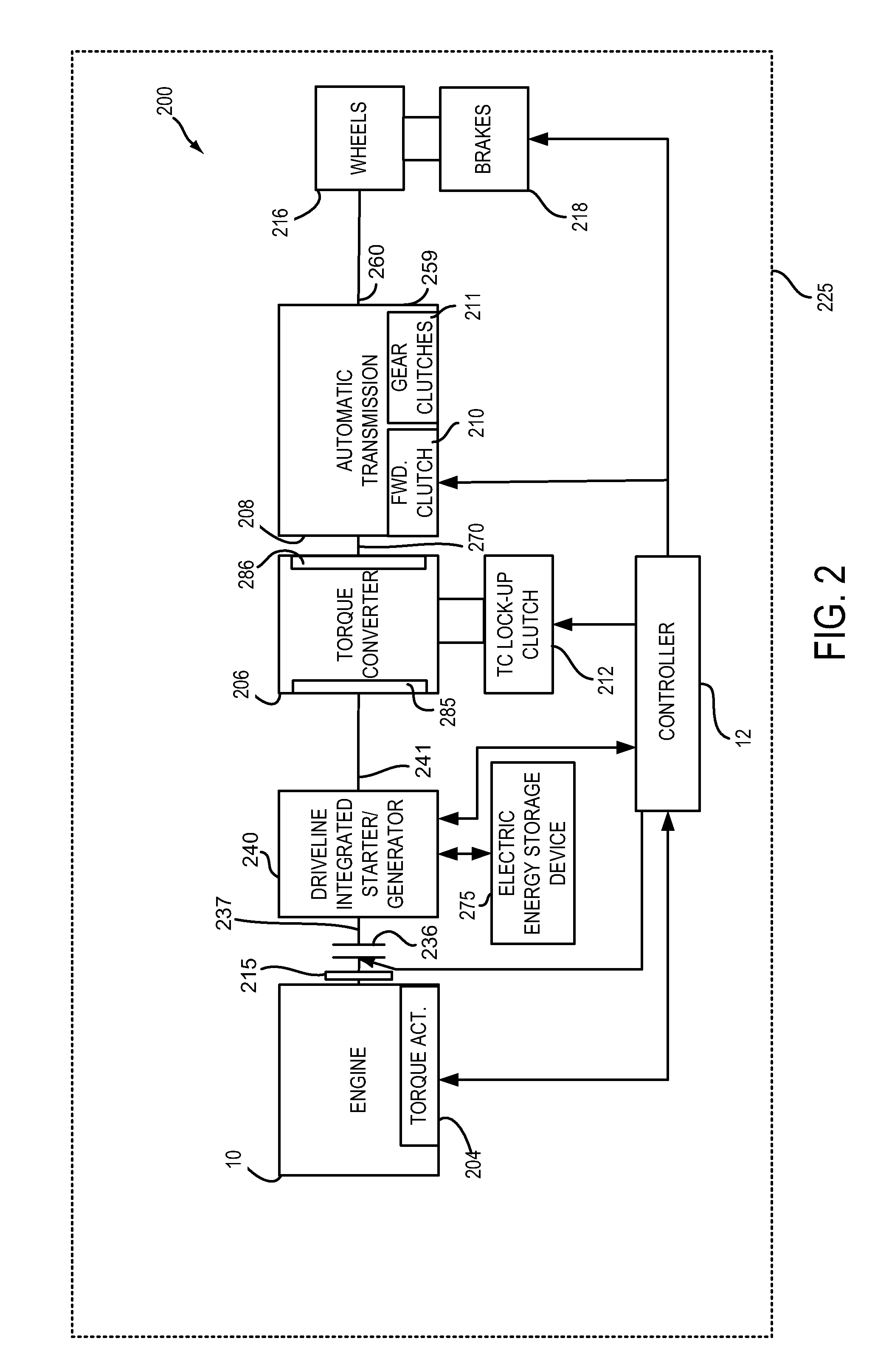
Methods and system for improving hybrid transmission gear shifting
ActiveUS20160069318A1Reducing engine torqueLow engine torqueHybrid vehiclesPower operated startersEngineeringControl theory
Systems and methods for improving transmission gear shifting of a hybrid vehicle are presented. The systems and methods may allow transmission input shaft torque to be lowered to levels where driveline torque disturbances may be reduced even though the driveline has a larger inertia. In one example, driveline torque may be reduced via retarding spark timing.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Friction compensation logic of motor driven power steering and method thereof
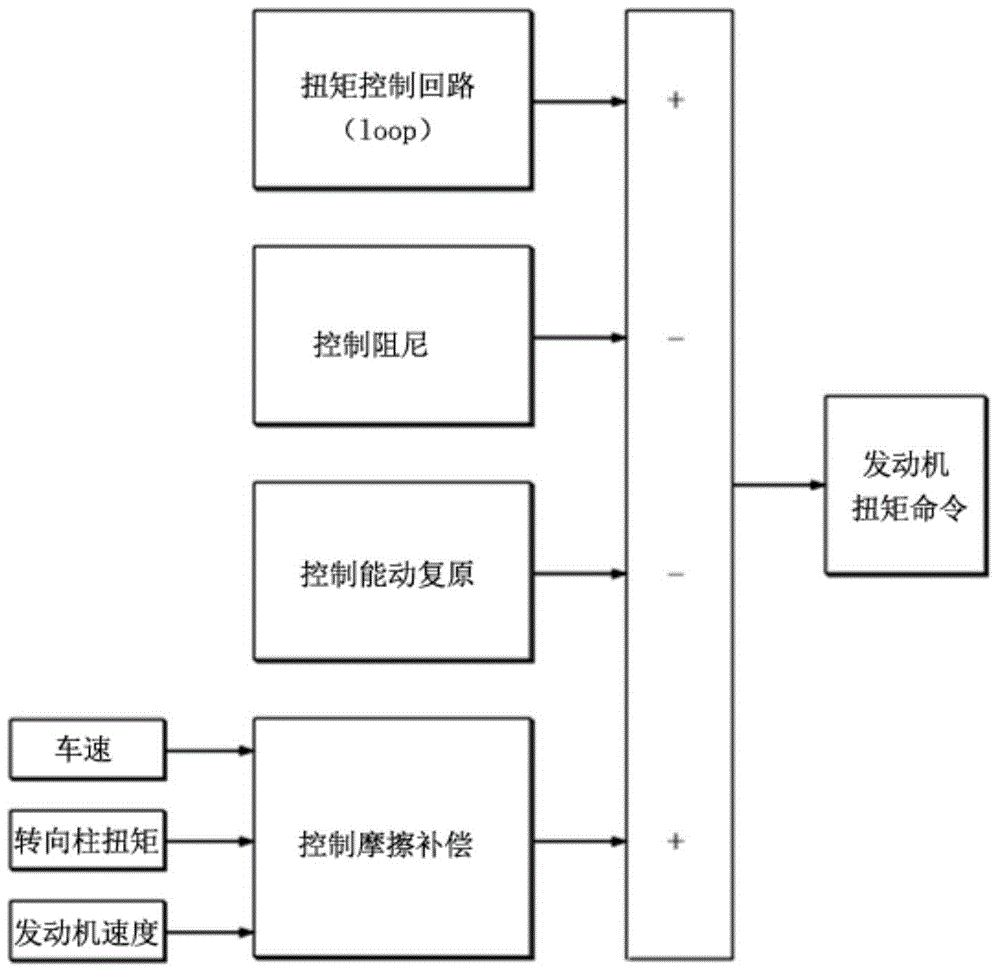
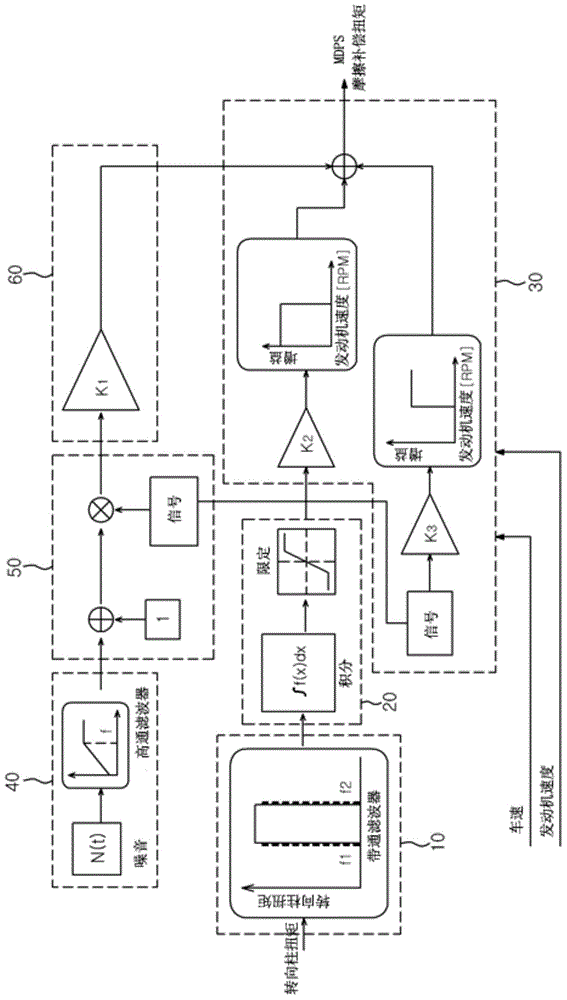
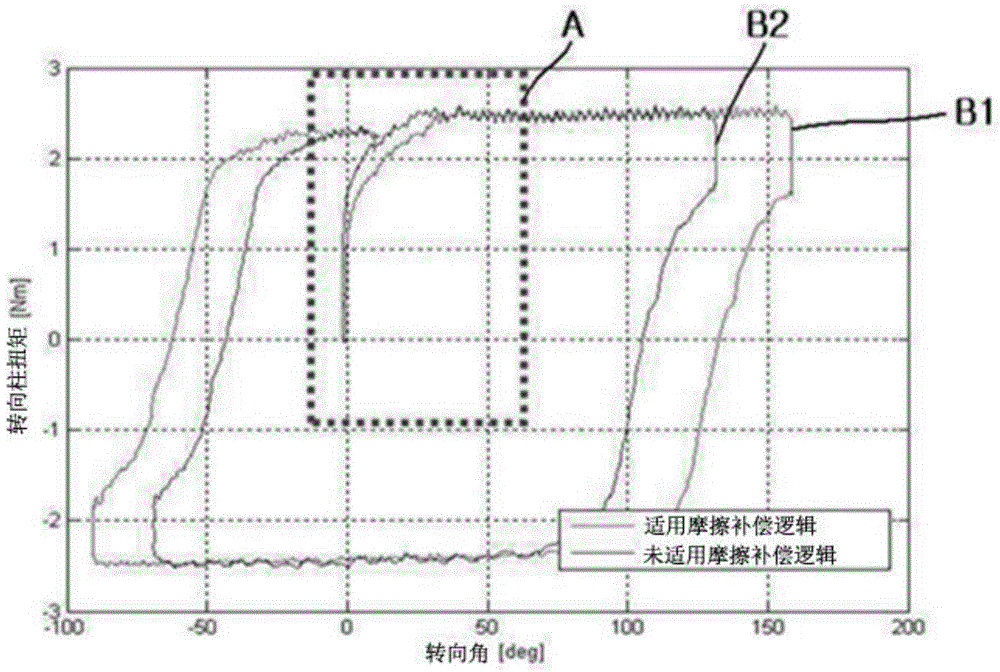
ActiveCN104554423AReduce torque variationPromote recoveryElectric motor controlSteering linkagesMotor driveSteering column
Exemplary embodiments of the present invention relate to a friction compensation logic of MDPS and a friction compensation method using the same. The friction compensation logic of MDPS in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention includes: a signal processor configured to extract only a signal having a limited range from column torque signals input from a column torque; a friction compensation sign calculator configured to determine a friction compensation sign by integrating the column torque signal extracted by the signal processor and calculating the friction compensation sign by limiting the integrated value to a set value; and a friction compensation torque calculator configured to calculate a friction compensation torque by reflecting a friction compensation amount to a value calculated by the friction compensation sign calculator.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOBIS CO LTD
Electric power steering apparatus
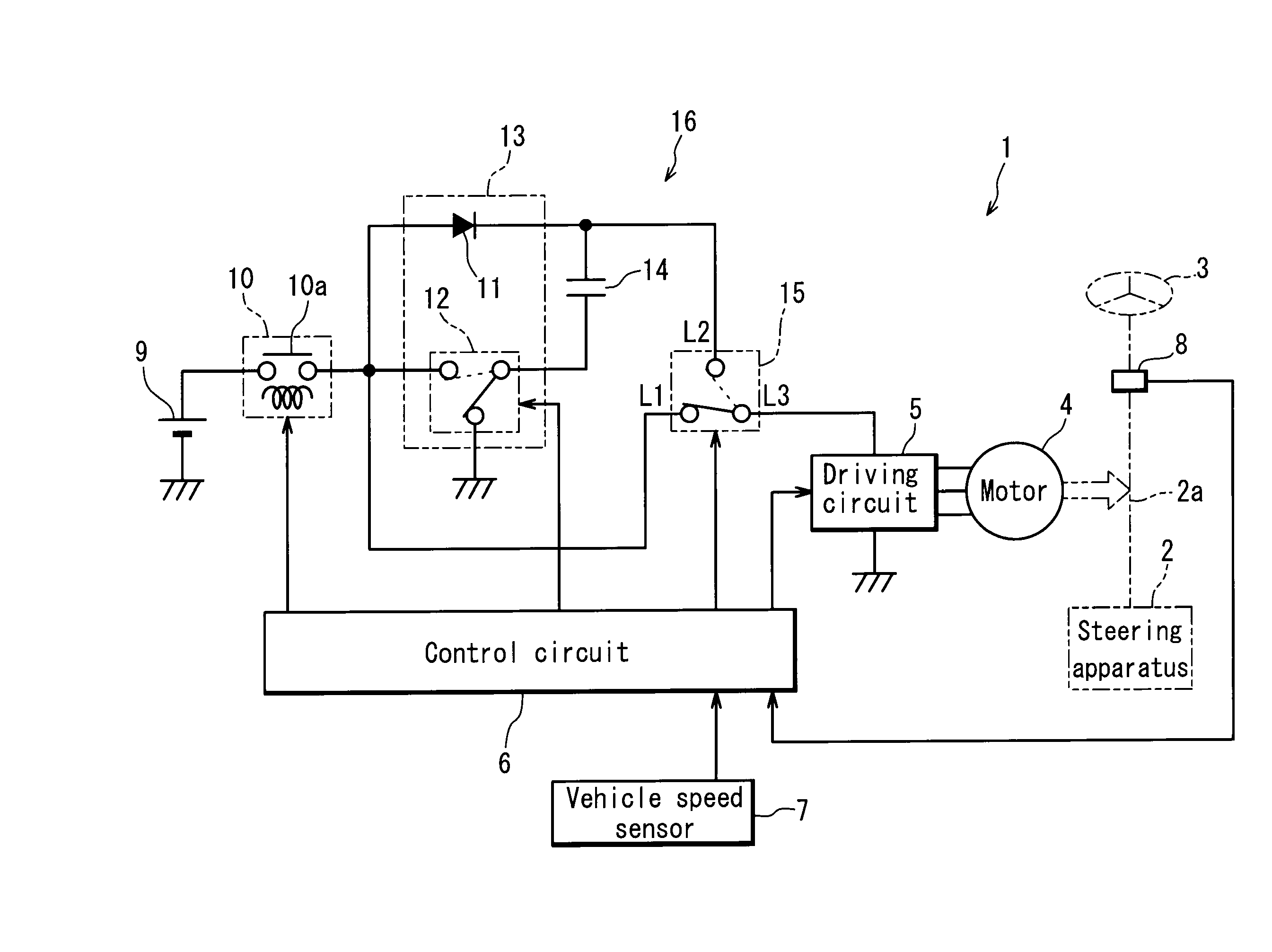
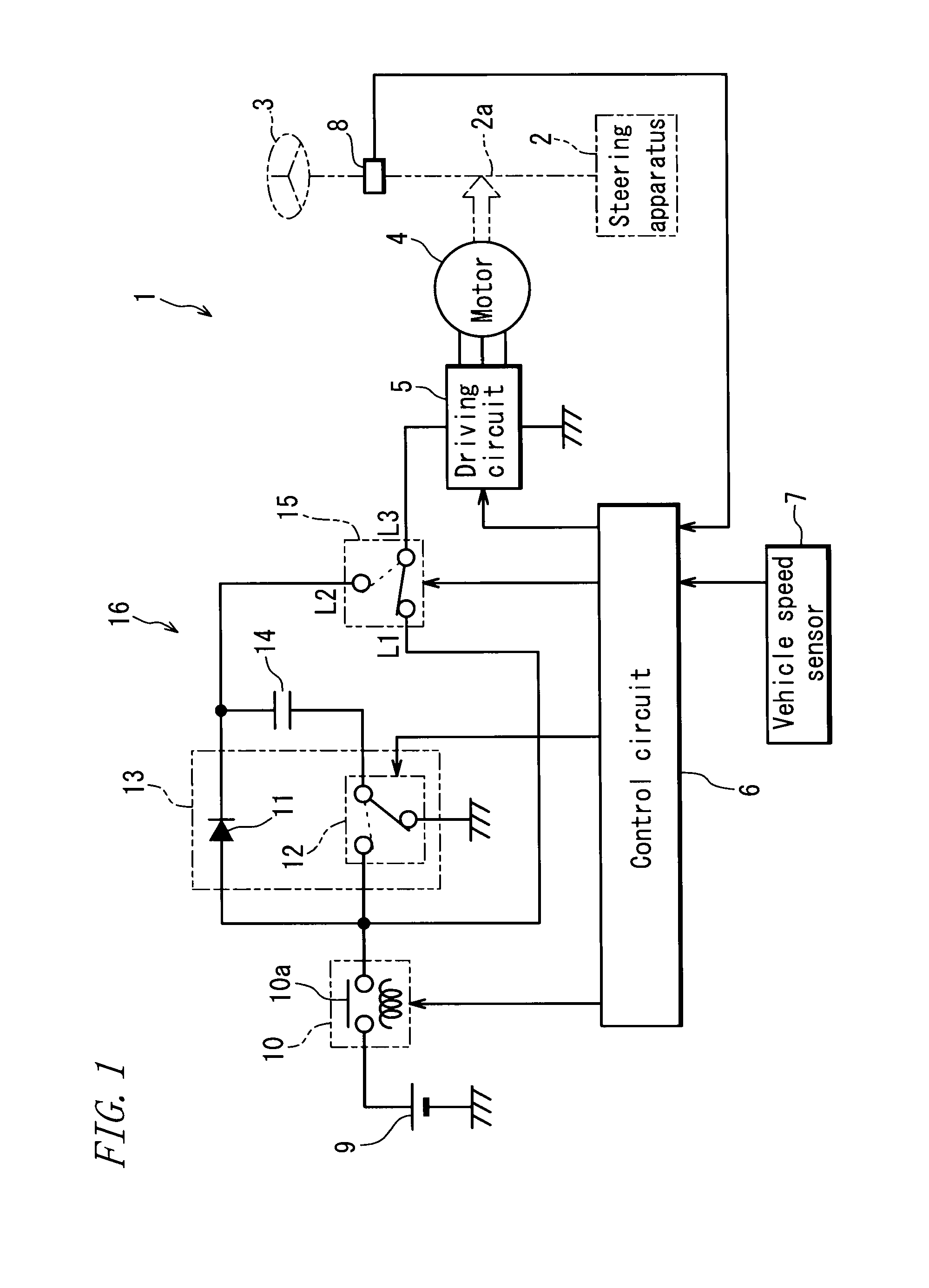
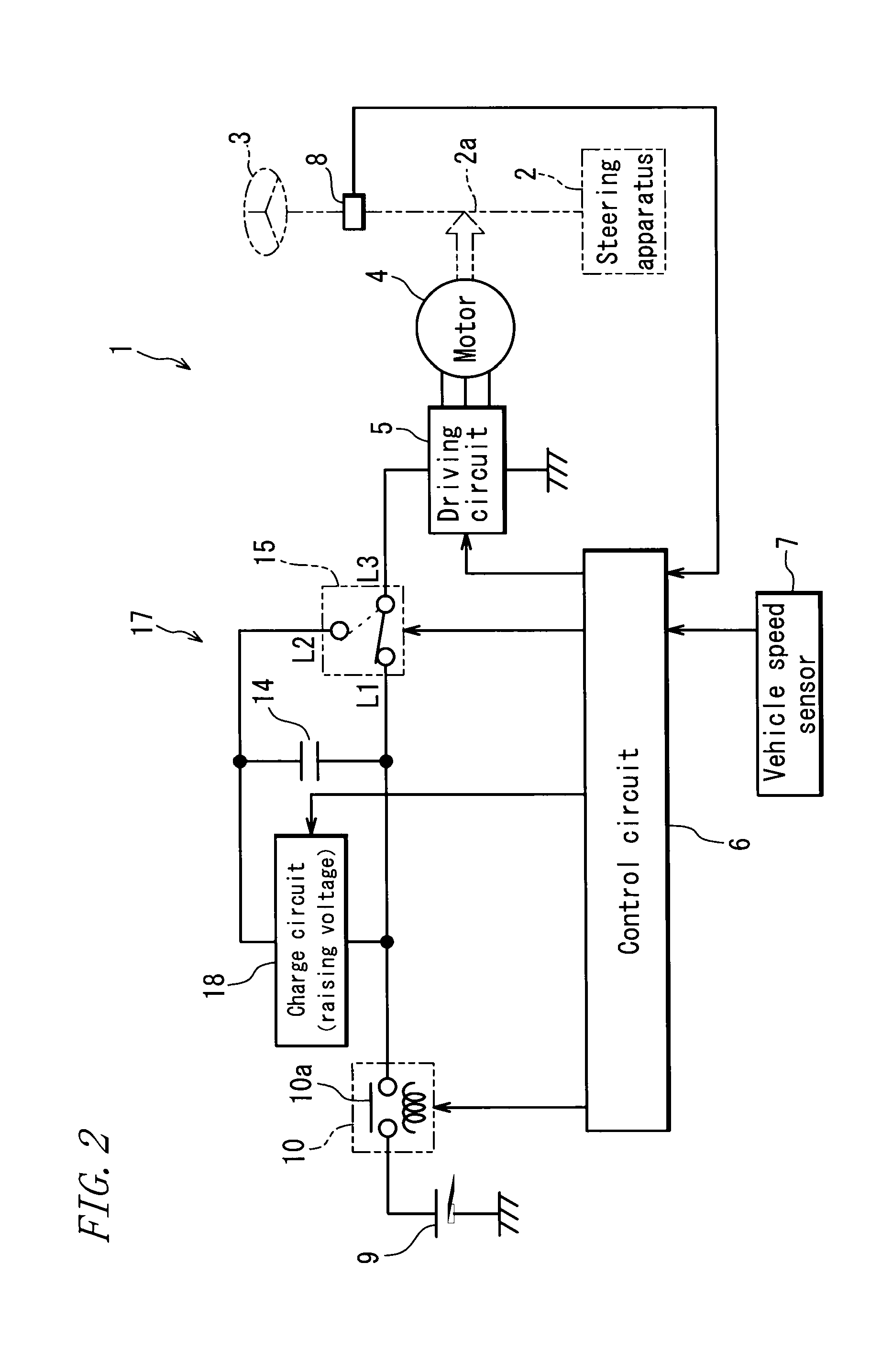
ActiveUS20100211266A1Reduce torque variationPrevent huntingBatteries circuit arrangementsSteering initiationsElectric power steeringElectric power system
In an electric power steering apparatus including a charge-discharge circuit 16 that selectively configures a first output mode in which only a main power supply including a battery 9 is used to supply an electric power to a motor 4 or a second output mode in which the main power supply and an auxiliary power supply 14 are used to supply the electric power to the motor 4, and a control circuit 6 that selects the output mode of the charge-discharge circuit 16 according to the electric power required for steering assist, the control circuit 6 selects the second output mode when the electric power required for steering assist in the first output mode becomes equal to or higher than an upward threshold value P1 or selects the first output mode when the electric power required for steering assist in the second output mode becomes equal to or lower than a downward threshold value P2 that is lower than the upward threshold value P1.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Permanent magnet type motor and method of producing permanent magnetic type motor
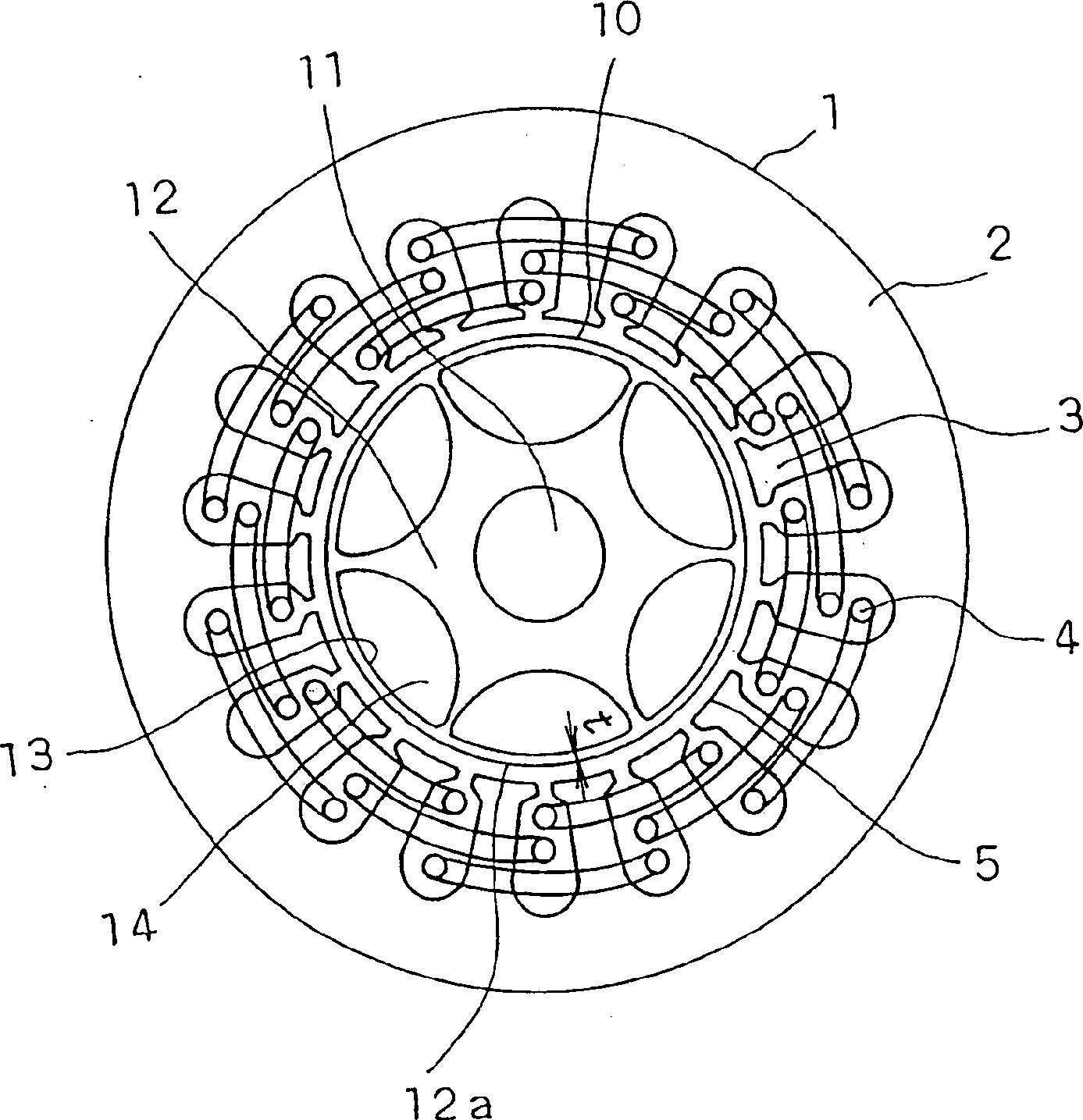
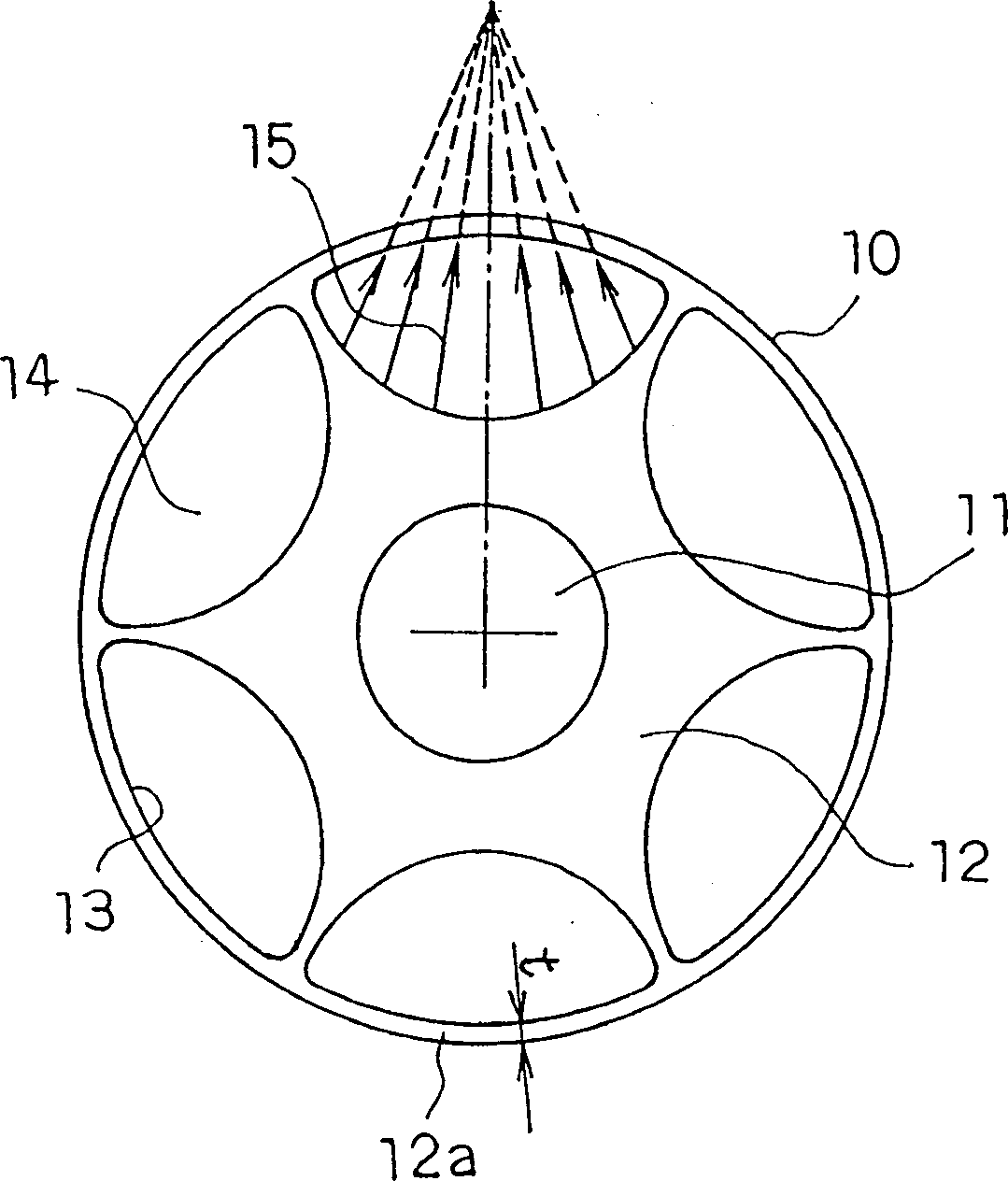
InactiveCN1251382CTorque variation does not increaseLow elimination efficiencyMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic polesMulti phase
A permanent magnet type motor with a permanent magnet, capable of reducing vibration and noise without lowering the motor efficiency, which comprises a stator (1) having multi-phase stator windings, and a rotor (10) disposed inside the stator in opposed relation through air gaps, and having a stator core (12) and permanent magnets (14) installed in the stator core, wherein the permanent magnets (14) are so shaped that their section at right angles with the axis of rotation is convexed on both inner and outer diameter sides and that the focus of magnetism orientation in each magnet pole of the permanent magnet (14) is disposed outside the rotor (10).
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
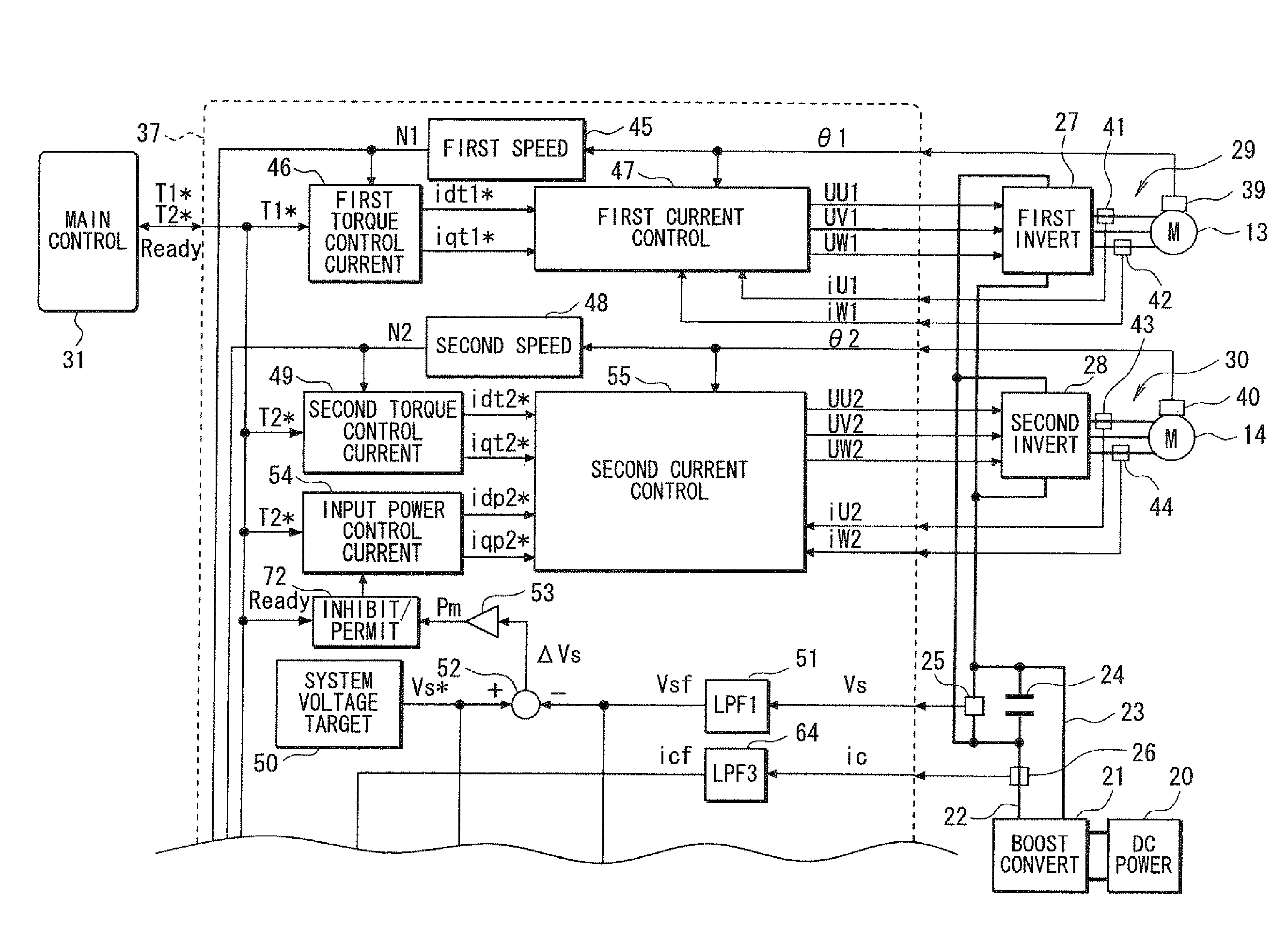
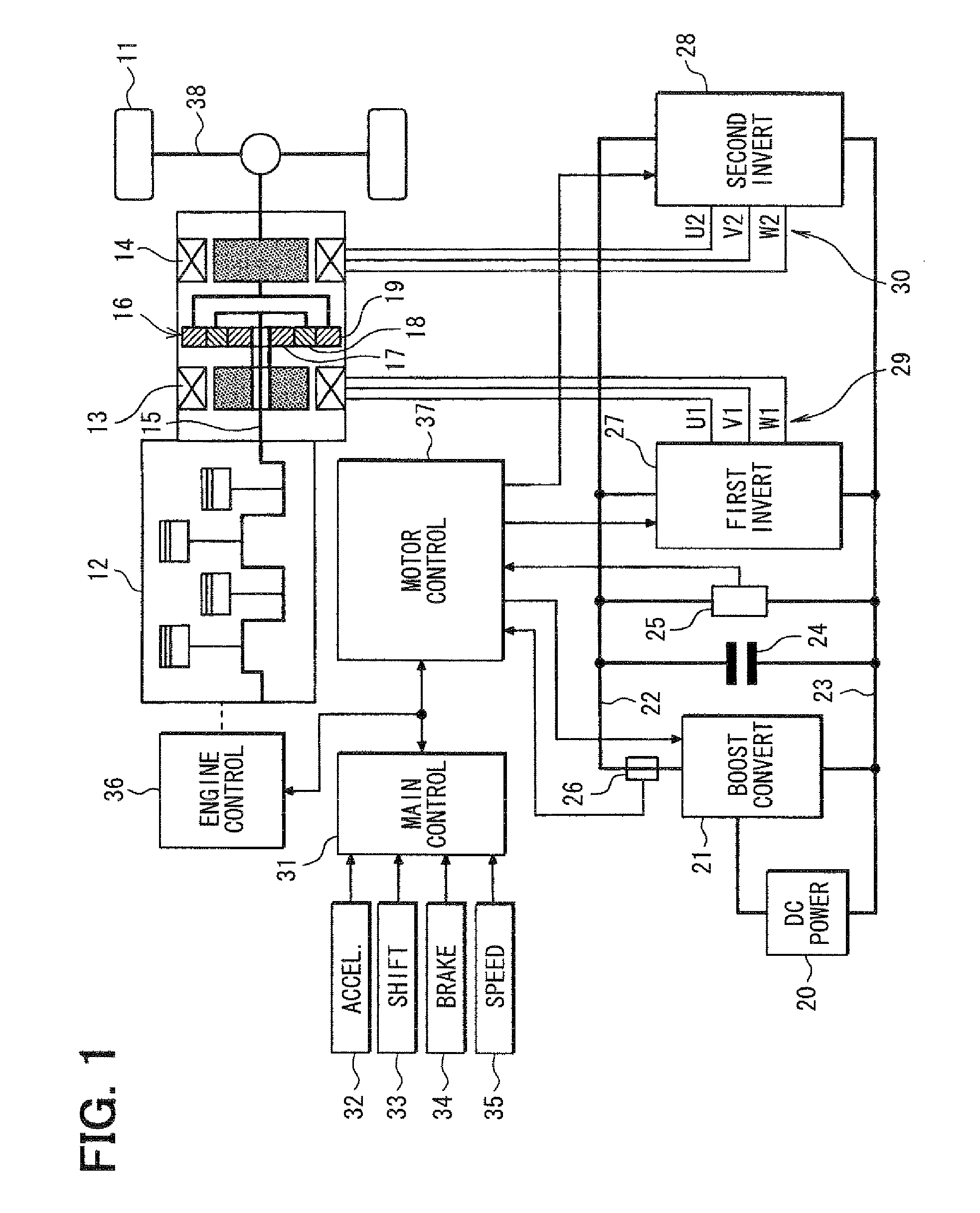
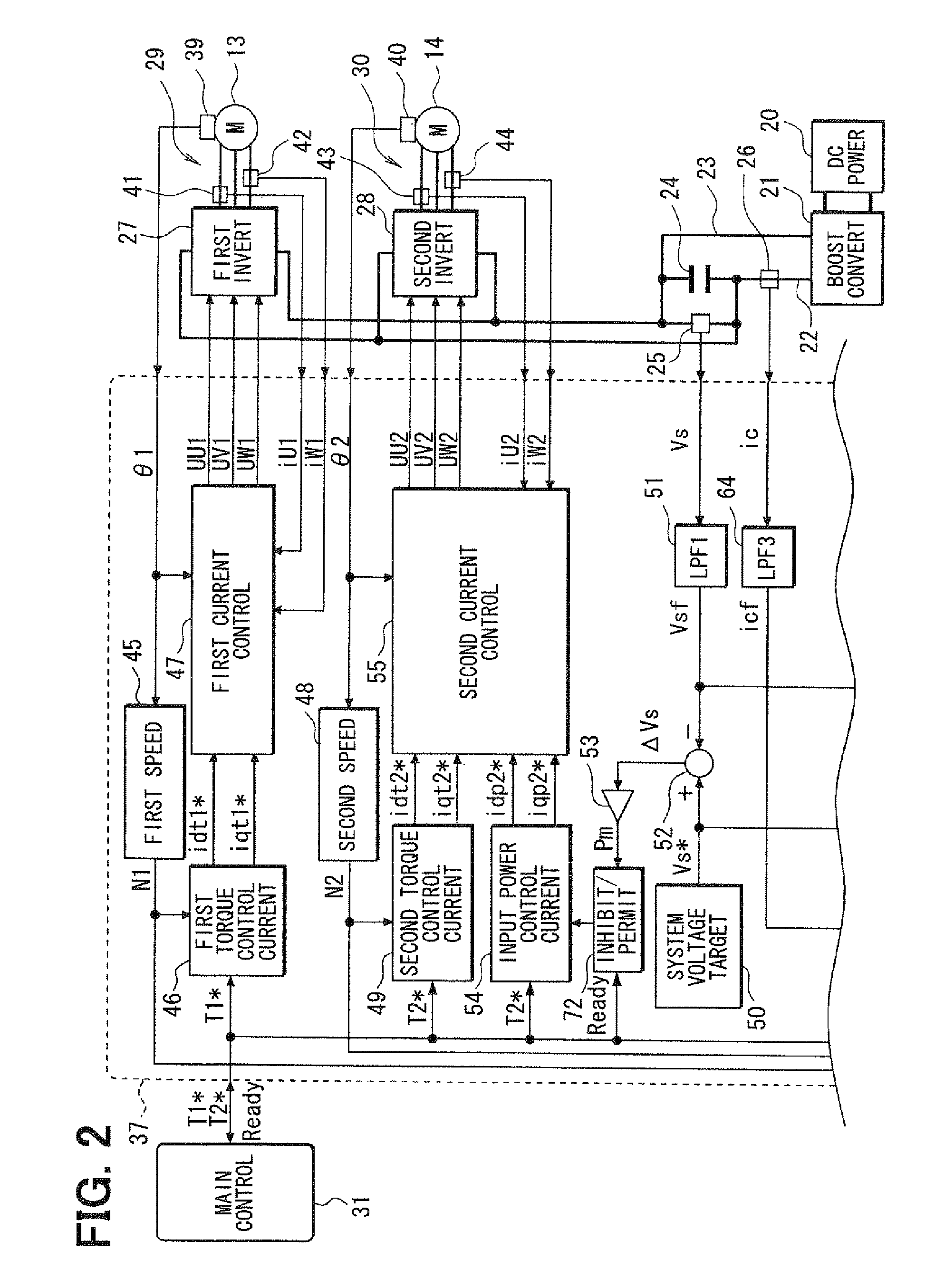
Control apparatus for electric vehicles
ActiveUS8082072B2Small sizeLow costAuxillary drivesDigital data processing detailsElectric machineMotor control
A motor control unit controls the input electric power of a MG unit to thereby suppress variations of a system voltage and stabilize the system voltage. The torque control of an AC motor and the input electric power control of the MG unit are executed independently from each other, so that the torque control and the input electric power control are stabilized. Further, torque variation zeroing control for correcting a phase of a pulse waveform voltage is executed so that a difference between a first estimated torque computed based on a torque control detection current vector of the AC motor and a second estimated torque computed based on a detection motor current vector is reduced to zero. Thus, uncomfortable torque variation is suppressed in a transient condition of the input electric power control of the MG unit.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Control apparatus for electric vehicles
ActiveUS7808194B2Small sizeLow costPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingVehicular energy storageInput controlElectric vehicle
In a hybrid vehicle control apparatus, a motor control unit executes the input power control on a MG unit independently from a torque control on an AC motor so that the input power control and the torque control are stabilized. The motor control unit further executes a torque difference reduction control, which controls current vector of the AC motor, to reduce a torque difference to zero substantially thereby preventing uncomfortable torque variation in a transient condition of input power control of the MG unit. The torque difference is calculated based on a first estimated torque calculated from a detected motor torque of the AC motor and a second estimated torque calculated from a command current vector for torque control of the AC motor.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Lock-up device and torque converter
ActiveUS20160290462A1Avoid it happening againImprove the attenuation effectFluid actuated clutchesFluid gearingsImpellerControl theory
A torque converter includes a lock-up device that directly connects a torque converter cover that rotates together with a pump impeller to a turbine runner connected to an output axis. The lock-up device includes a damper spring in a clutch piston that contacts with or moves away from the torque converter cover. In addition, an intermediate member is provided inside the damper spring. A center part of the damper spring is projected toward the inner side of the clutch piston in the radial direction by damper pressing portions and fixed to both ends of the damper spring and a connecting member and pushed onto the projecting part of the intermediate member.
Owner:FCC KK
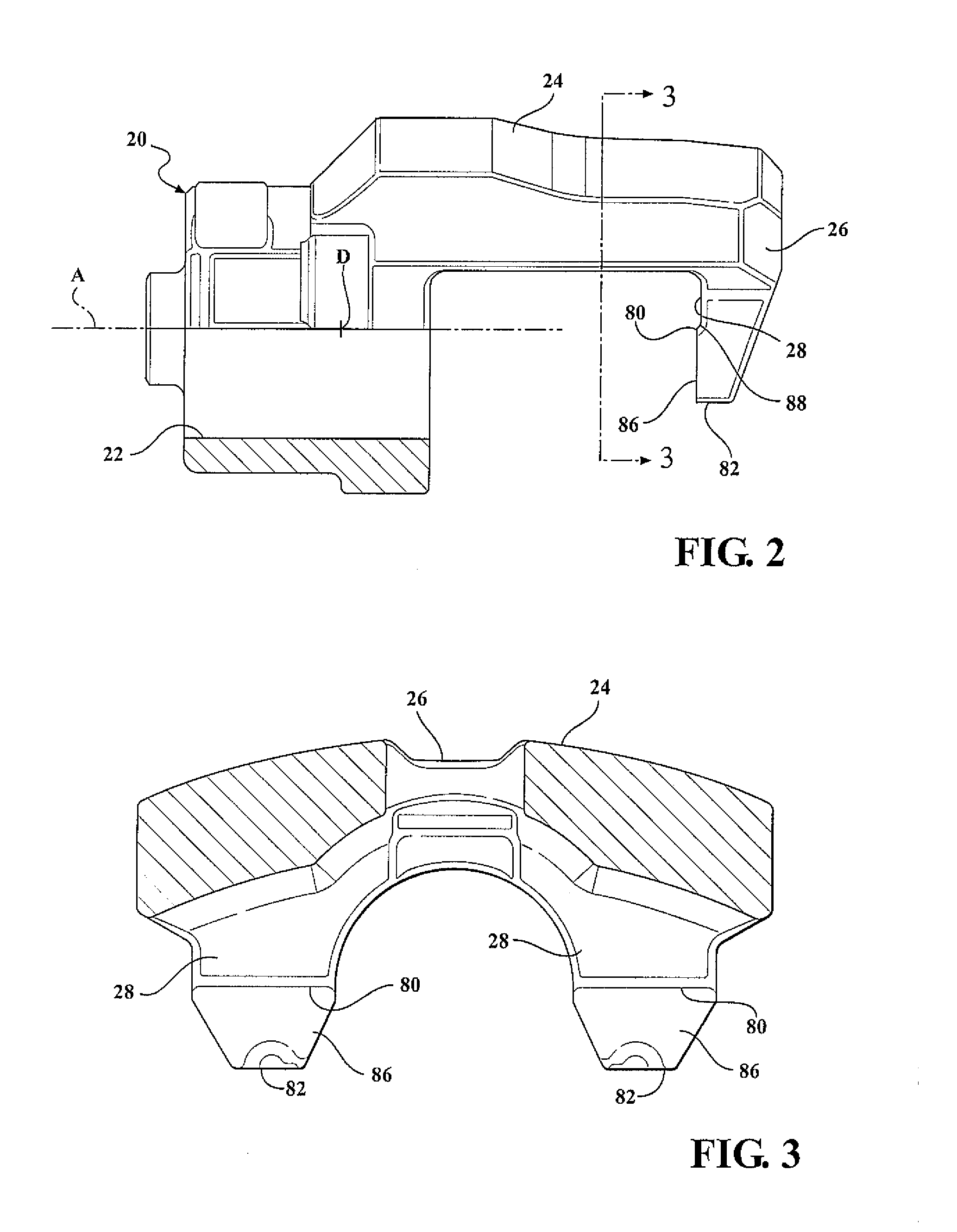
Pivot pad brake caliper
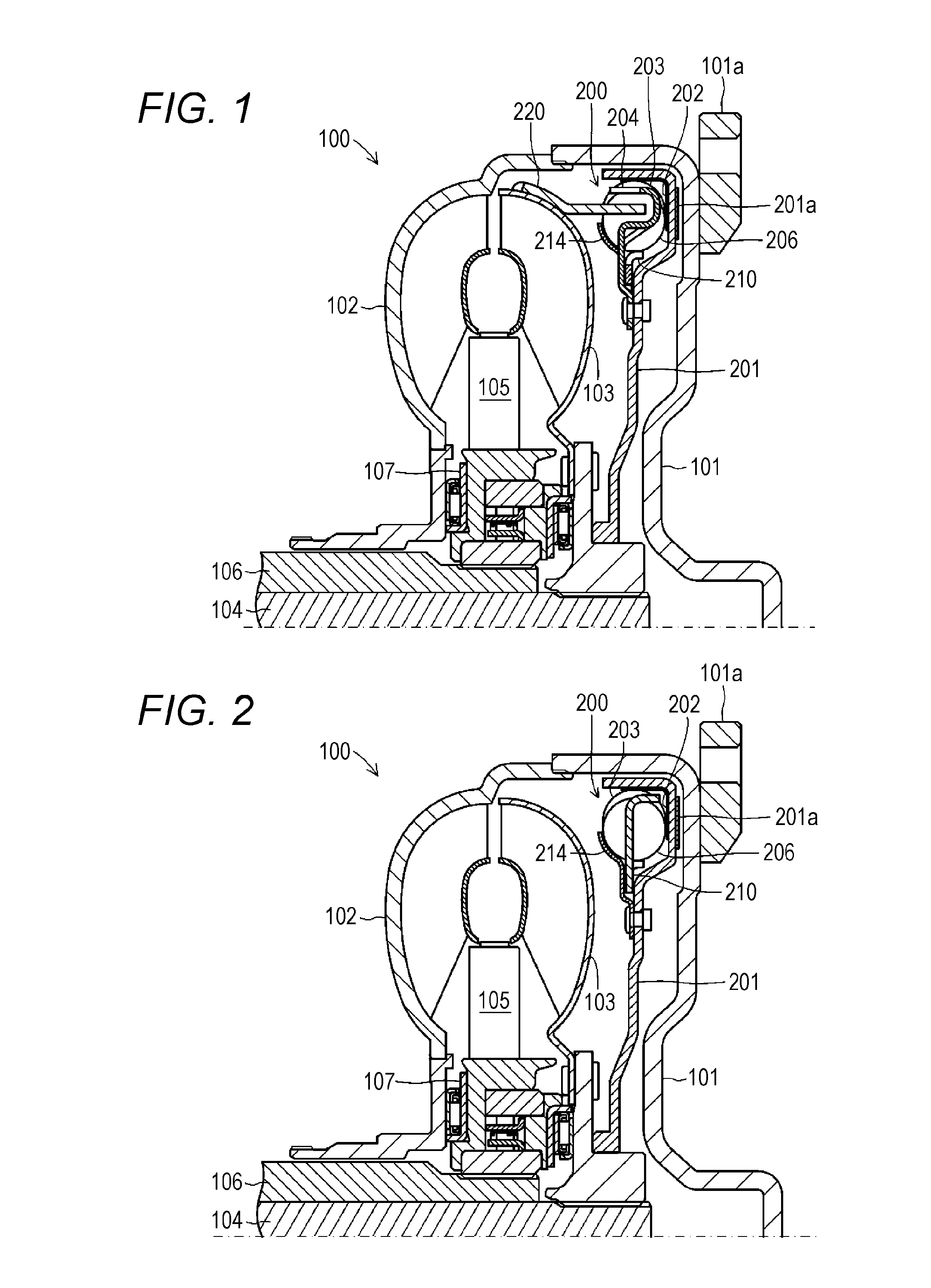
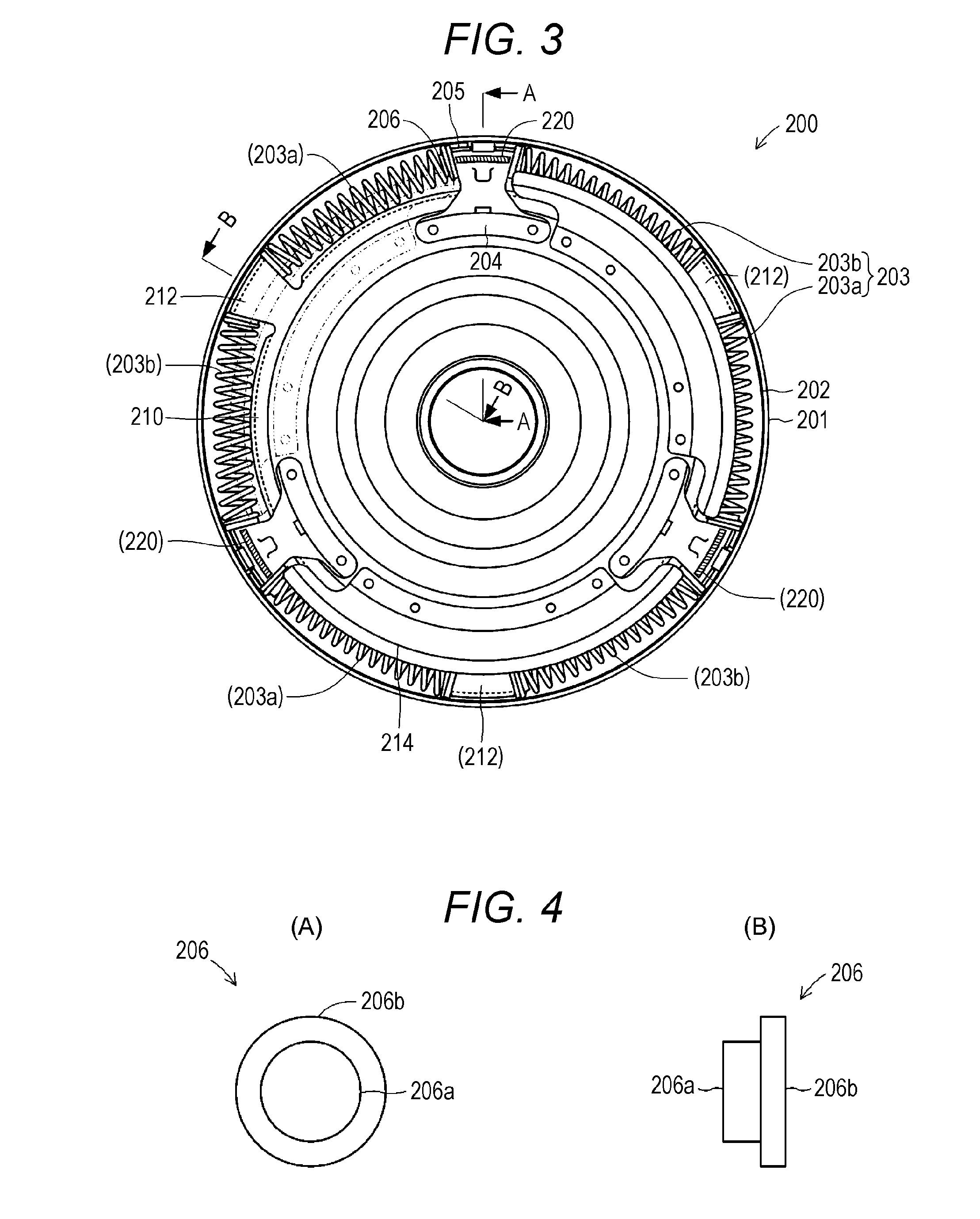
ActiveUS20140124303A1Reduce torque variationReduction of judder sensationFluid actuated brakesBraking element arrangementsPistonEngineering
A caliper housing including a piston bore and a bridge extending between the piston bore and a pair of caliper fingers interconnecting the caliper fingers and the piston bore. The caliper fingers of the caliper housing extend downwardly from the bridge to define a flat surface. A rotor having a disc shape defines a first side and a second side and disposed adjacent to the caliper fingers. An outer brake pad defining a first centroid is disposed adjacent to the first side of the rotor abutting the caliper fingers allowing the caliper fingers to urge the outer brake pad into engagement with the first side of the rotor. Each of the caliper fingers defines a pivot edge extending between the outer brake pad and the flat surface of the caliper fingers allowing the outer brake pad to pivot about the pivot edge.
Owner:BEIJINGWEST INDUSTRIES
Methods and system for improving hybrid transmission gear shifting
ActiveUS9523341B2Reducing engine torqueLow engine torqueHybrid vehiclesPower operated startersControl theoryHybrid vehicle
Systems and methods for improving transmission gear shifting of a hybrid vehicle are presented. The systems and methods may allow transmission input shaft torque to be lowered to levels where driveline torque disturbances may be reduced even though the driveline has a larger inertia. In one example, driveline torque may be reduced via retarding spark timing.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Lock-up device and torque converter
ActiveUS10876611B2Avoid it happening againImprove the attenuation effectFluid actuated clutchesFluid gearingsImpellerEngineering
A torque converter includes a lock-up device that directly connects a torque converter cover that rotates together with a pump impeller to a turbine runner connected to an output axis. The lock-up device includes a damper spring in a clutch piston that contacts with or moves away from the torque converter cover. In addition, an intermediate member is provided inside the damper spring. A center part of the damper spring is projected toward the inner side of the clutch piston in the radial direction by damper pressing portions and fixed to both ends of the damper spring and a connecting member and pushed onto the projecting part of the intermediate member.
Owner:FCC KK
Transmission for a vehicle
InactiveUS20160010726A1Reduce torque changed shockReduce shift shockToothed gearingsGearing controlControl modePower transmission
A power transmission mechanism transmits torque of the input shaft to the output shaft, and includes gear mechanisms corresponding to each of gear stages respectively. A control device controls the power transmission mechanism to realize one of a first control mode, a second control mode and a third control mode selectively. In the first control mode, a first gear stage is selected and the power transmission mechanism transmits torque via only a first gear mechanism. In the second control mode, a second gear stage is selected and the power transmission mechanism transmits torque via only a second gear mechanism. In the third control mode, at gear-shift from the first gear stage to the second gear stage, the power transmission mechanism circulates torque having a prescribed amount to the input shaft from the output shaft via the first gear mechanism while transmitting torque of the input shaft to the output shaft.
Owner:AISIN AI CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com