Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
44results about How to "Loss of resolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
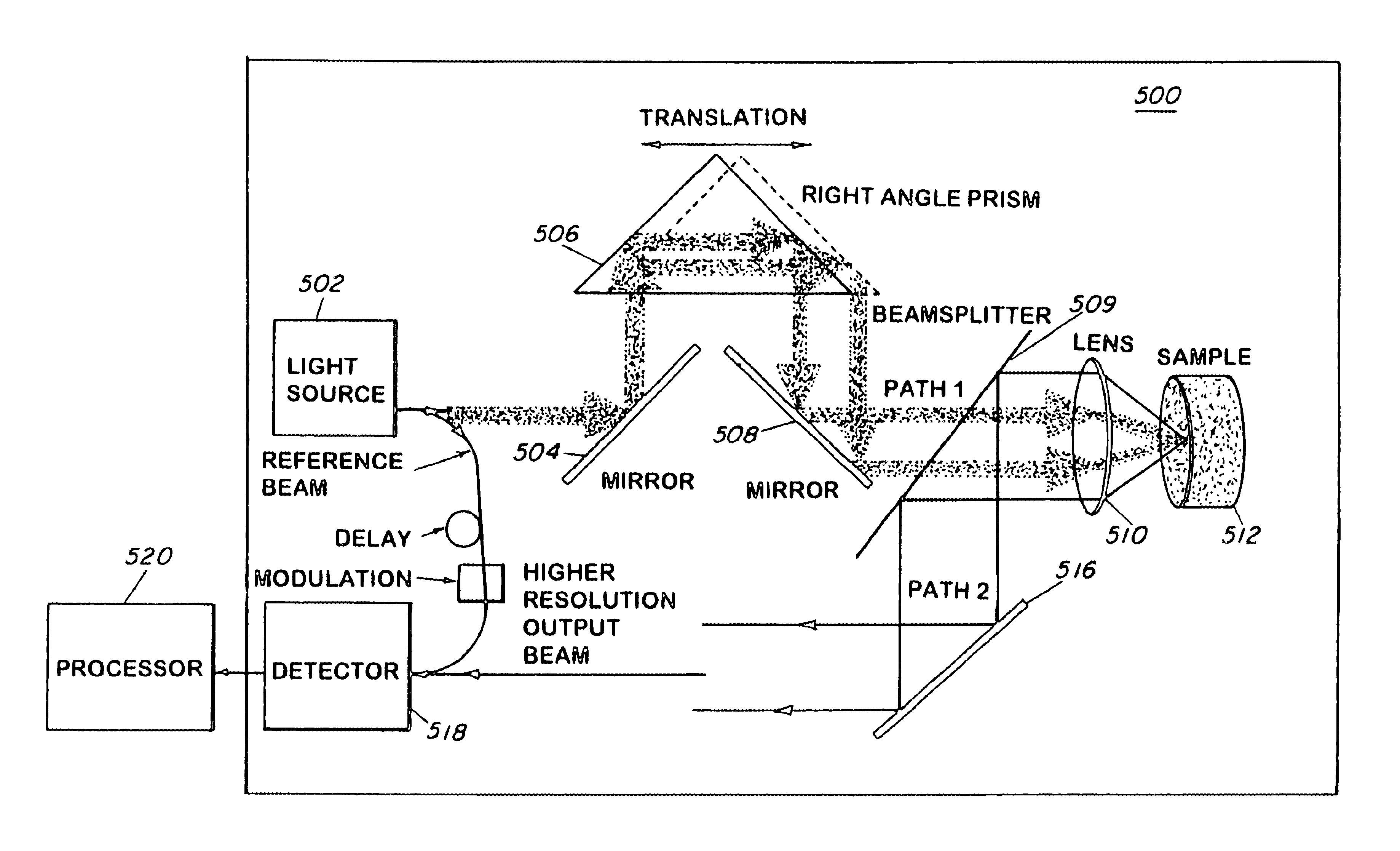
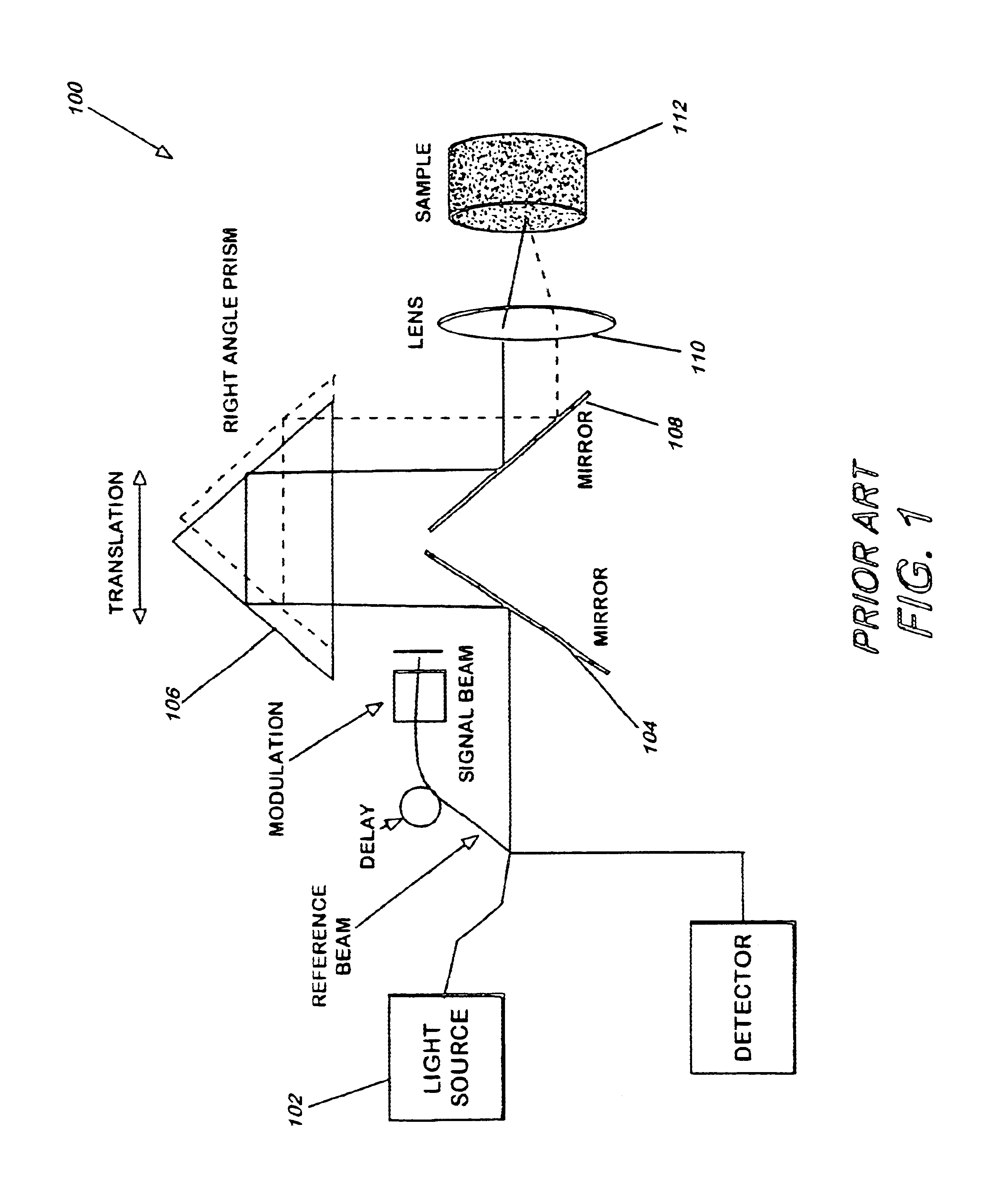
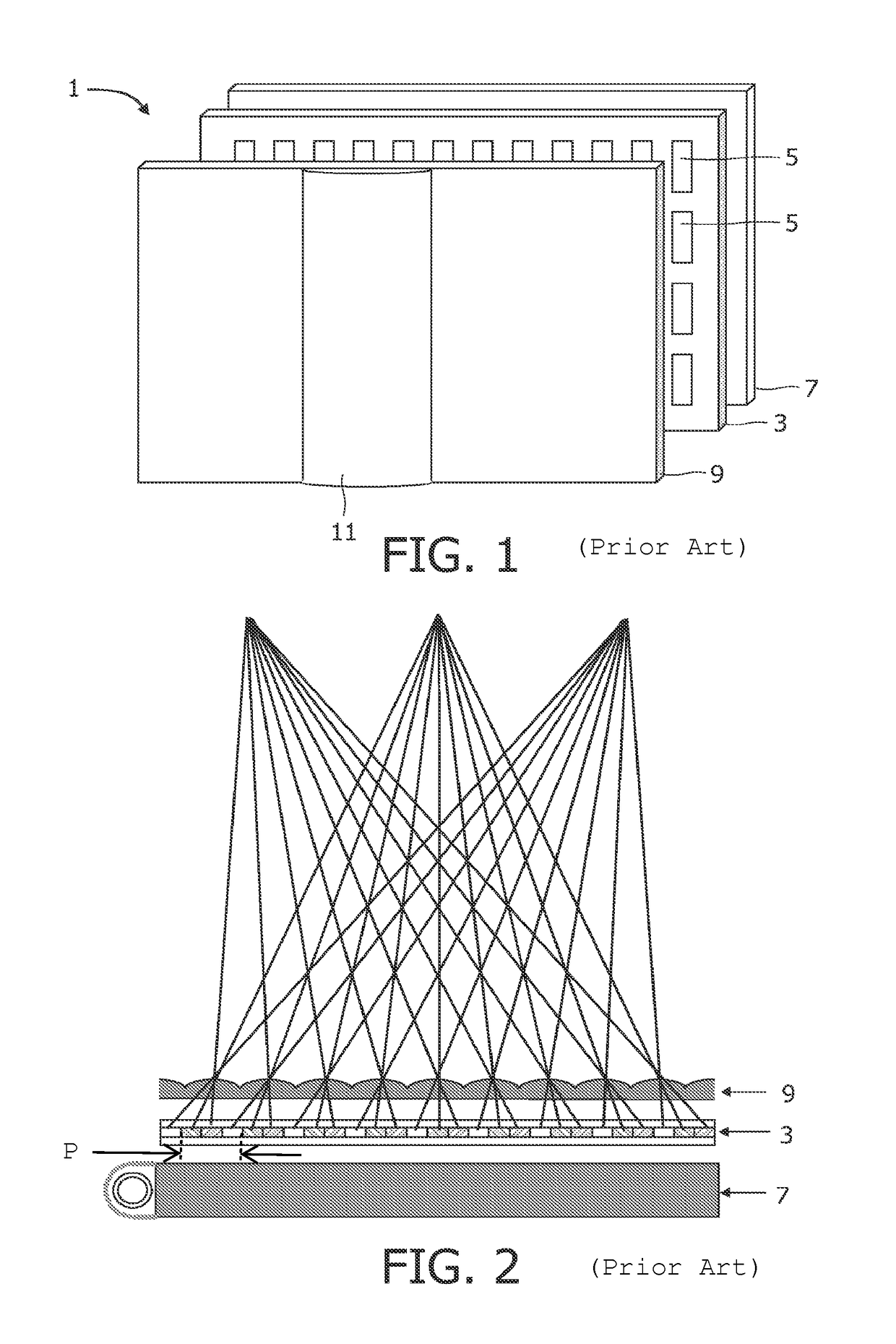
Method and apparatus for reducing speckle in optical coherence tomography images
InactiveUS6847449B2Simple and inexpensive methodImprove resolutionScattering properties measurementsLight polarisation measurementImage resolutionLow input
A method and apparatus for reducing speckle due to MSL, without any loss of resolution, by averaging over different angles of the incident light at low input resolution, while collecting the backscattered light at a full resolution of a lens is described. The present invention allows discrimination against the speckle due to coherent MSL.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
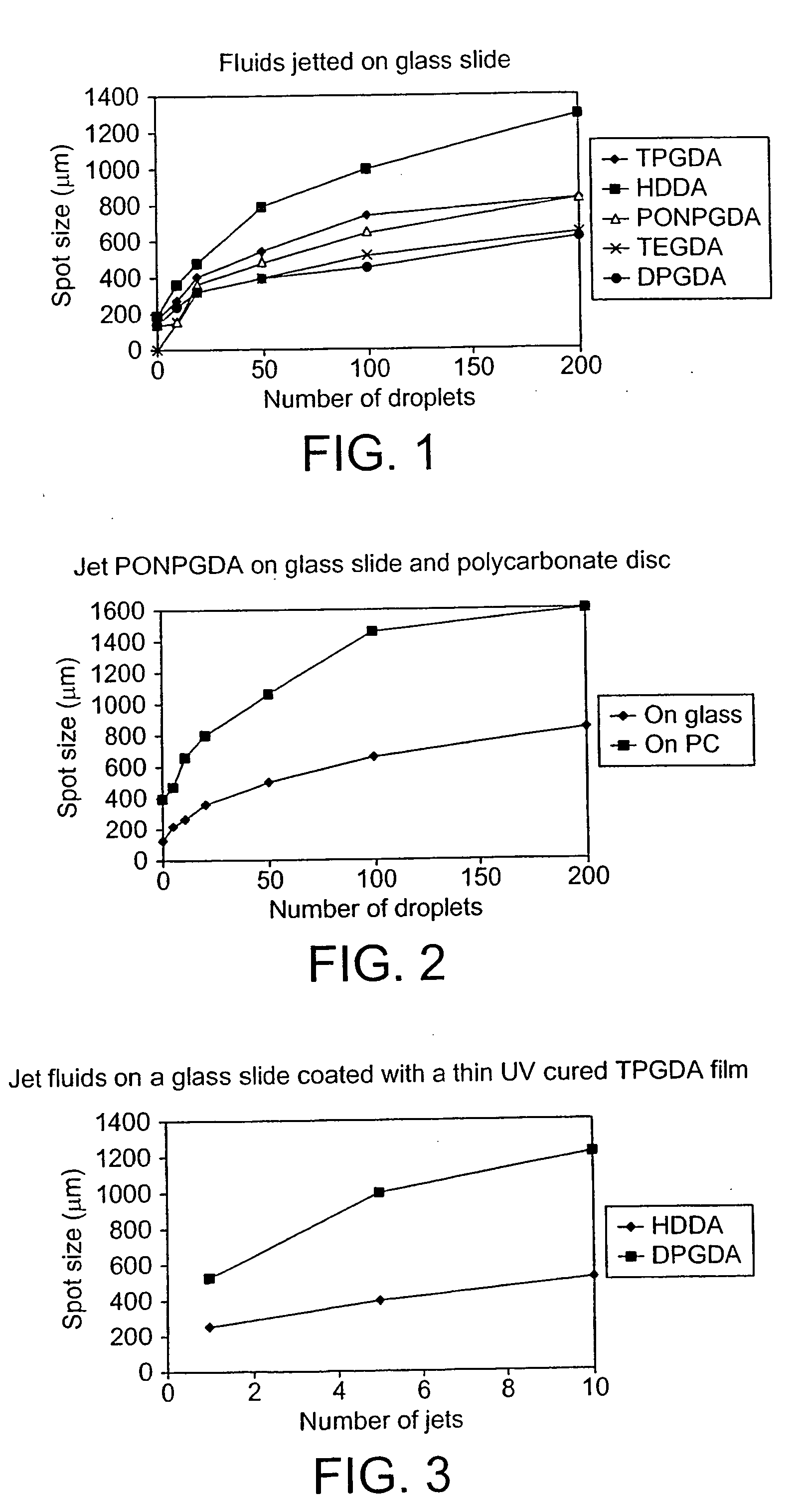
Production of composites articles composed of thin layers
InactiveUS20060035034A1Large spreadLow viscosityAdditive manufacturing apparatusLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingThin layerViscosity
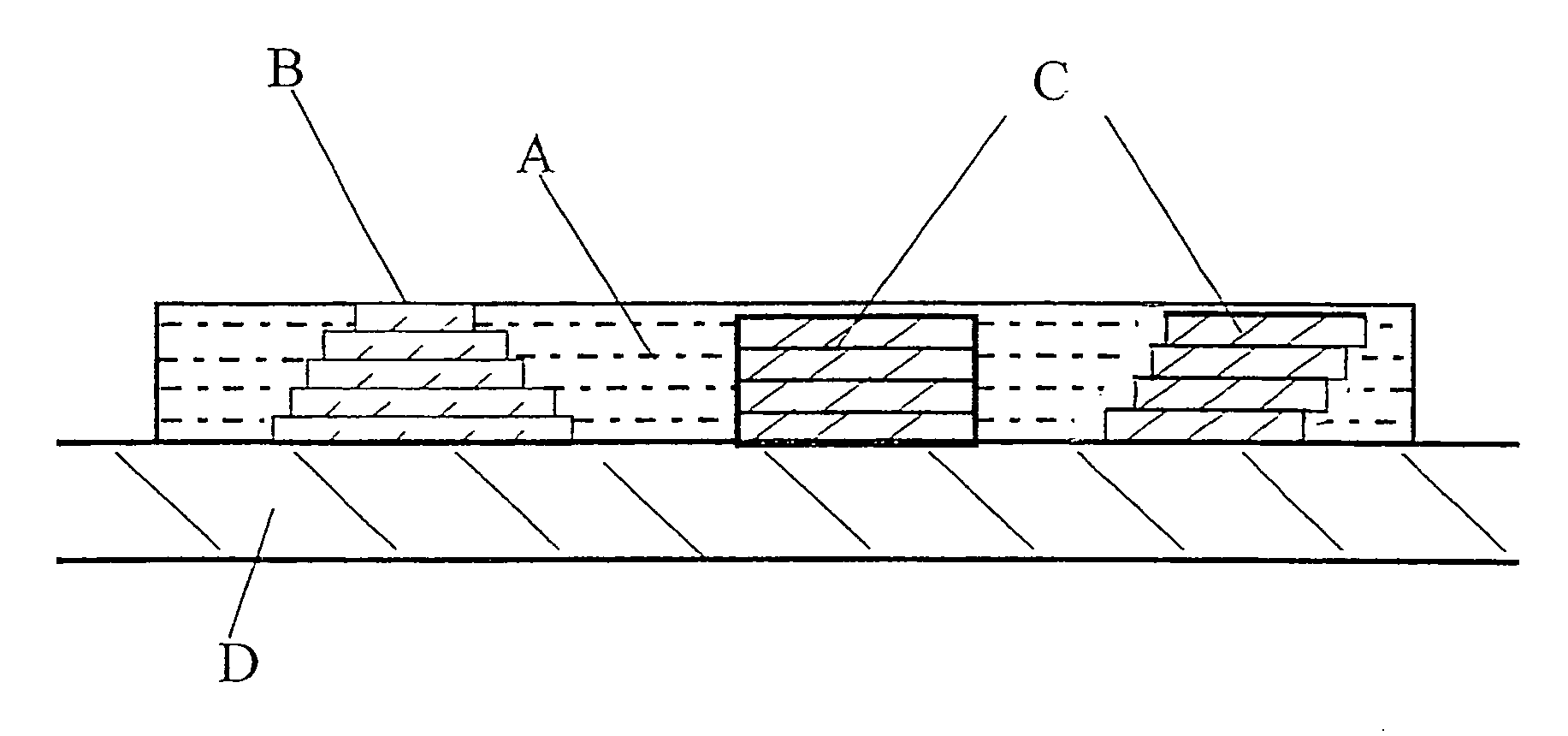
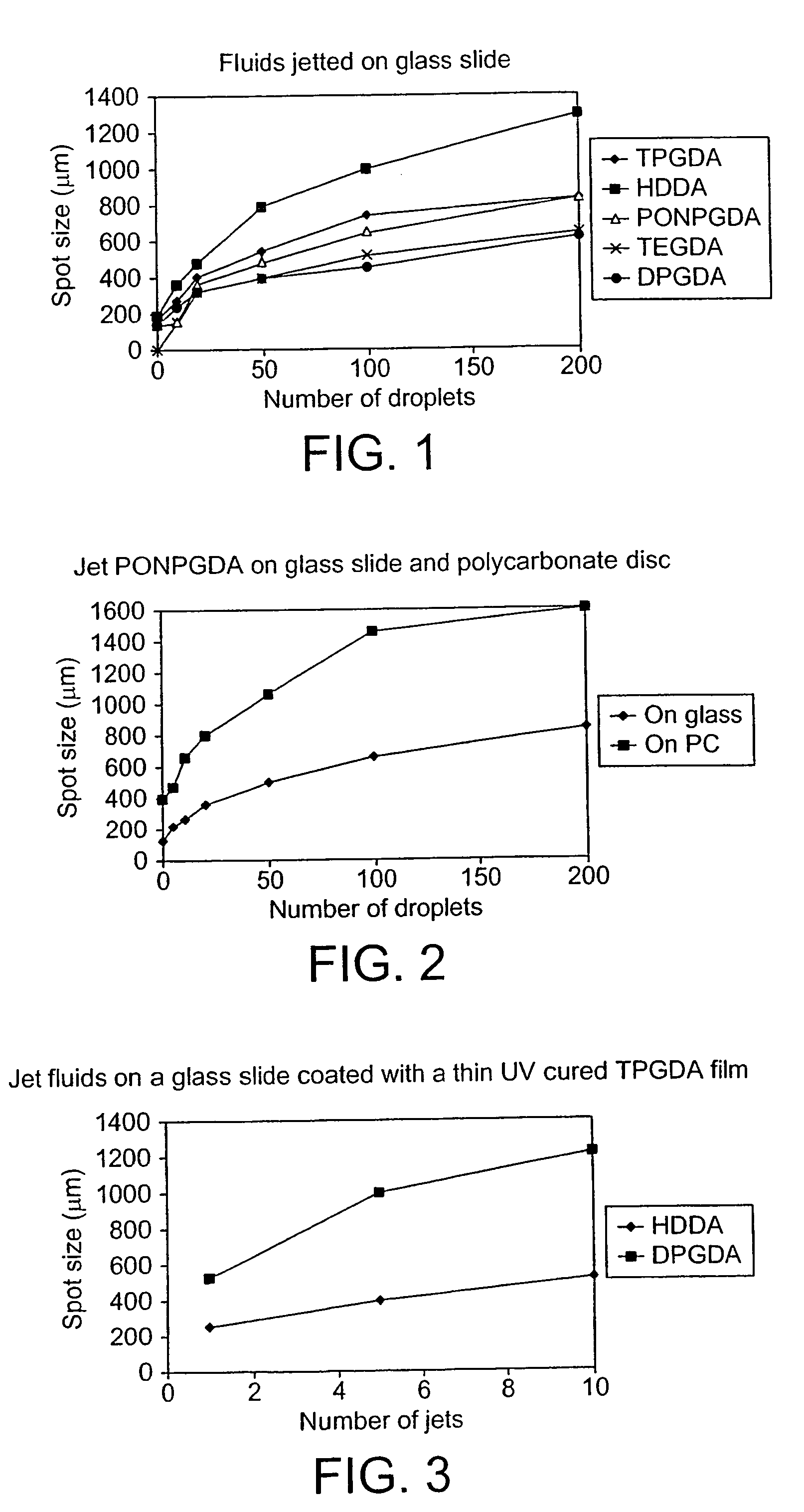
A method is described of producing thin layers (below 10 μm in thickness) by directing droplets (preferably by inkjet printing techniques) onto precise locations on a substrate, the liquid of the droplets having a viscosity such that the droplets, on impact with the substrate, spread out to form relics on the substrate that are at least 1.4 times the diameter of the droplets in flight, adjacent droplets merging to form a continuous layer on the substrate. The droplets may have different compositions to form images within the layer. Successive layers may be added to built up a three dimensional structure whose properties can be tailored by the compositions used to build up a composite.
Owner:HUNTSMAN ADVANCED MATERIALS AMERICAS INC +1
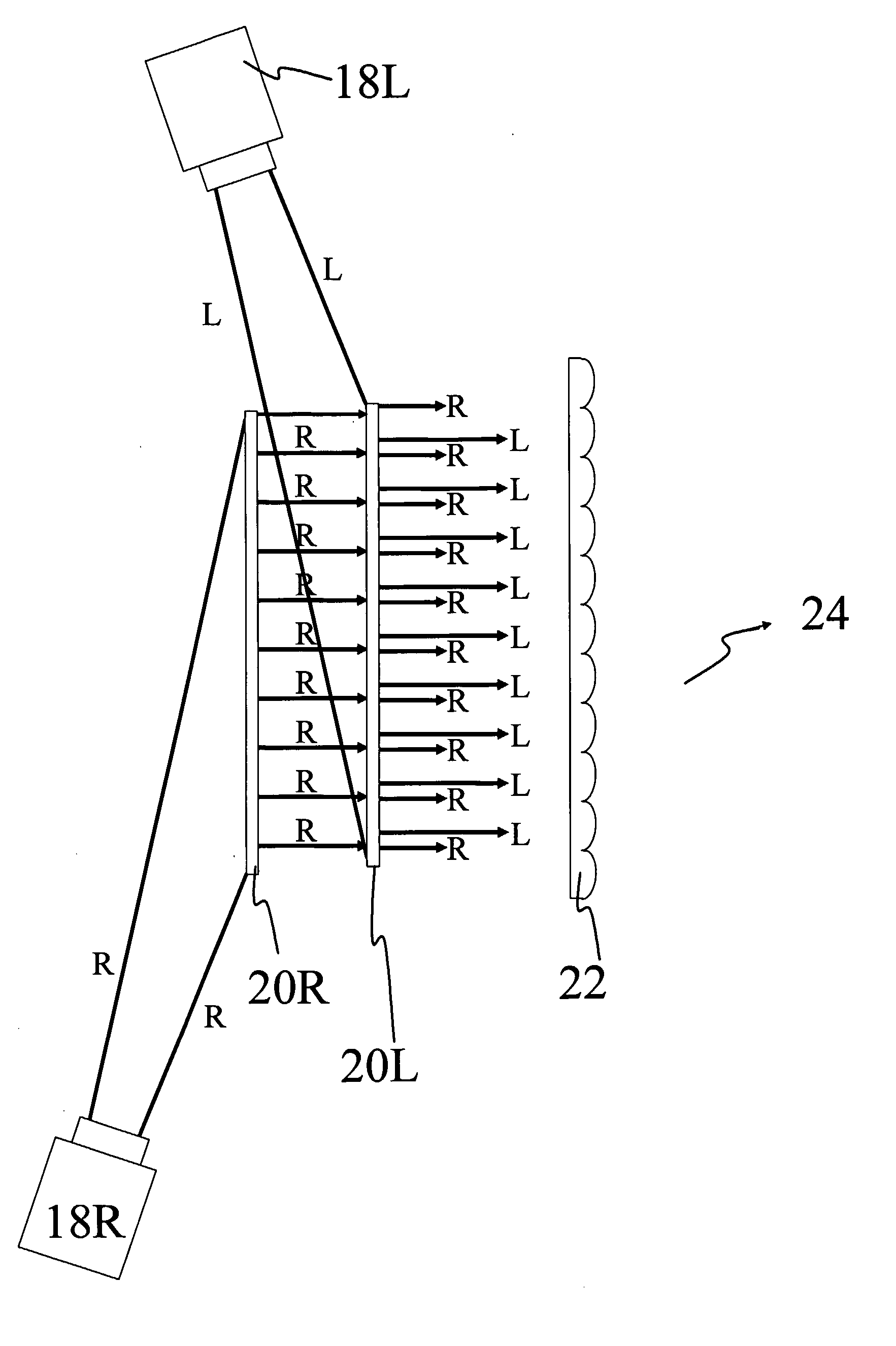
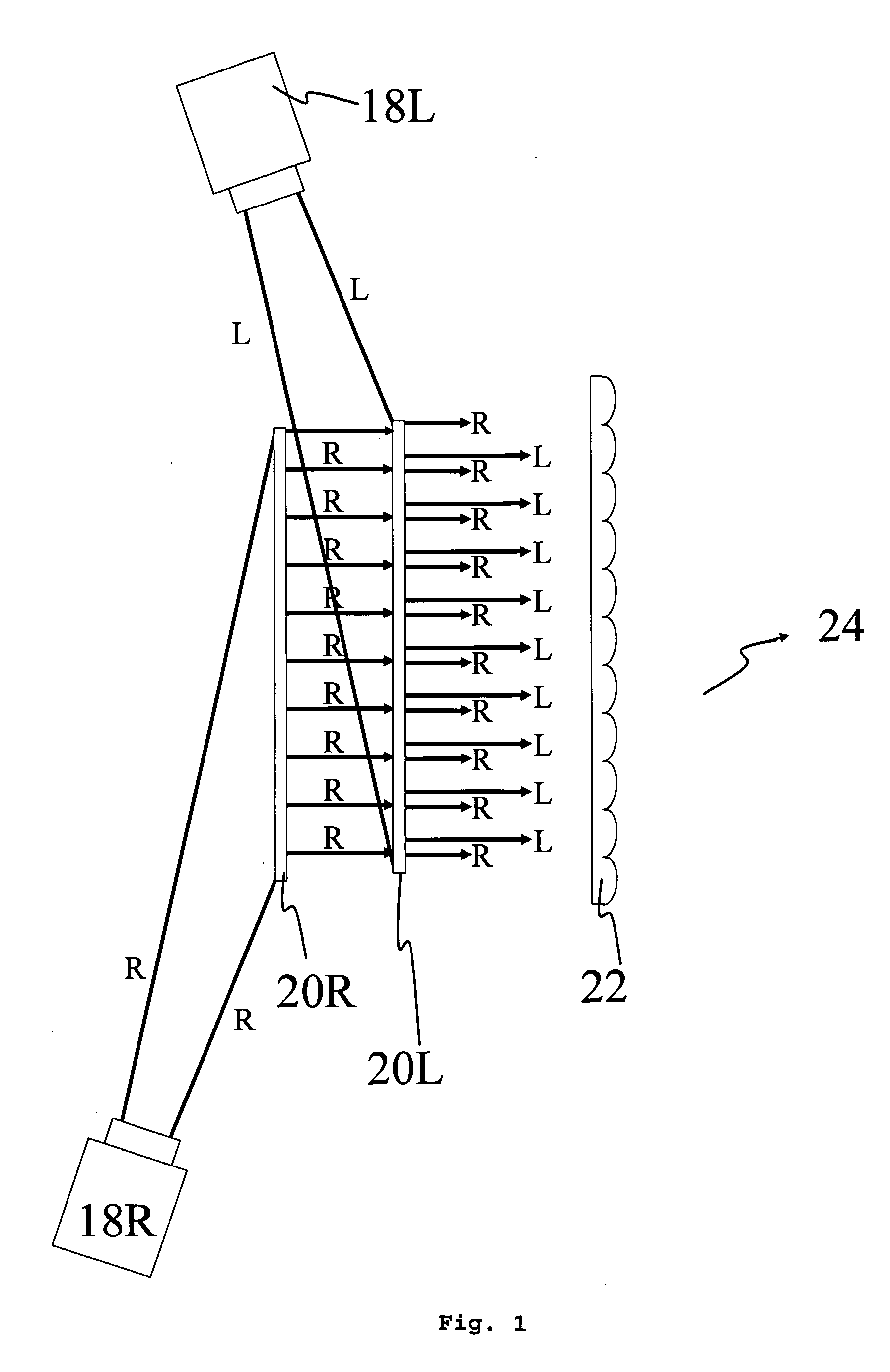
Rear Projection Screen and Associated Display System
InactiveUS20070296920A1Improve scalabilityHigh resolutionProjectorsSteroscopic systemsParallax3d image
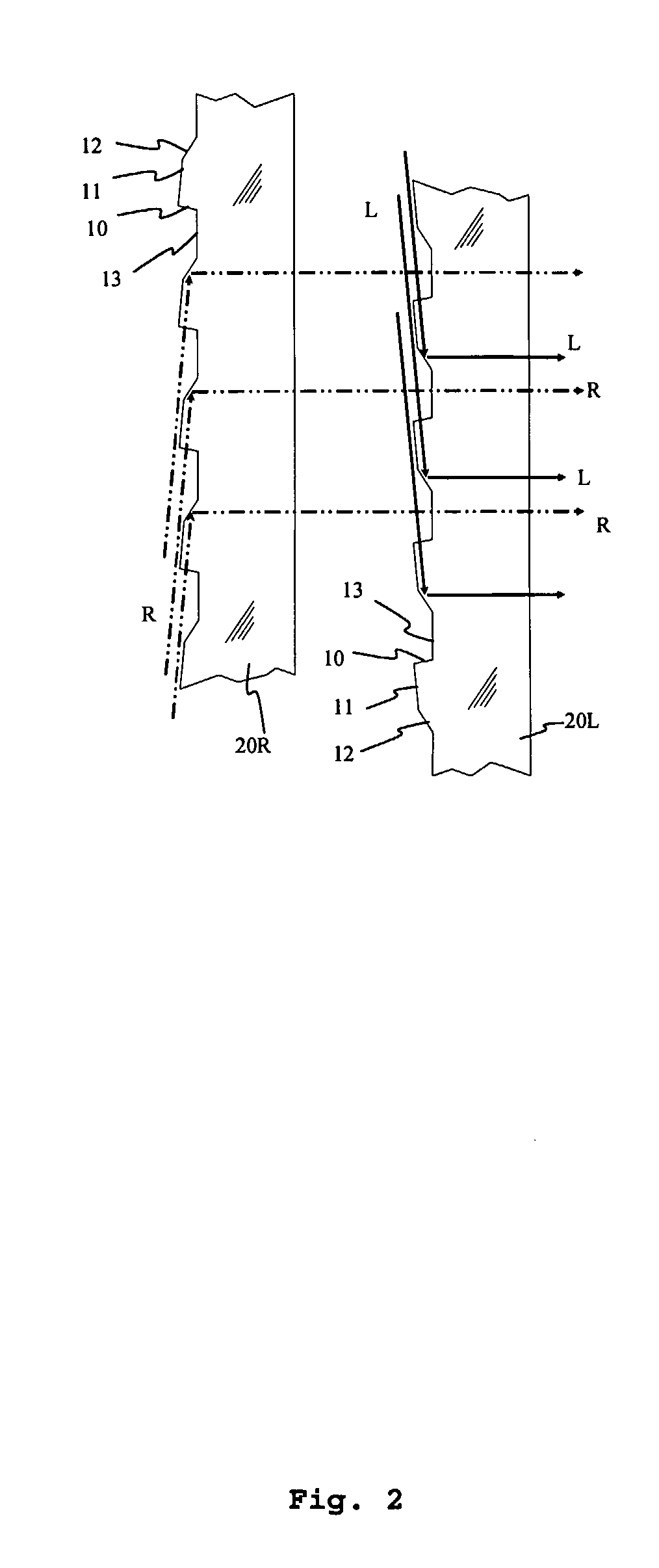
A rear projection display method and system, for displaying an image. The system comprises projection means ( 18 L, 18 R) to project first and second stereoscopic image components; a first light-redirecting panel ( 20 R) and a second downstream light-redirecting panel ( 20 L) to receive light representative of the first and second image components, respectively, from the projection means and to redirect that light substantially in a downstream direction, the first and second panels arranged to spatially multiplex the first and second image components; and a parallax optic element ( 22 ) located downstream of the second panel to provide at a downstream viewing zone ( 24 ) the first and second image components for autostereoscopic viewing of the image. The projection means may be switchable between 2D and 3D viewing modes. A 3D image may be produced by simultaneously or sequentially projecting a series of 2D image sections, using diffuser elements ( 45 ). A method of displaying a 3D image is also disclosed.
Owner:MICROSHARP CORP LTD
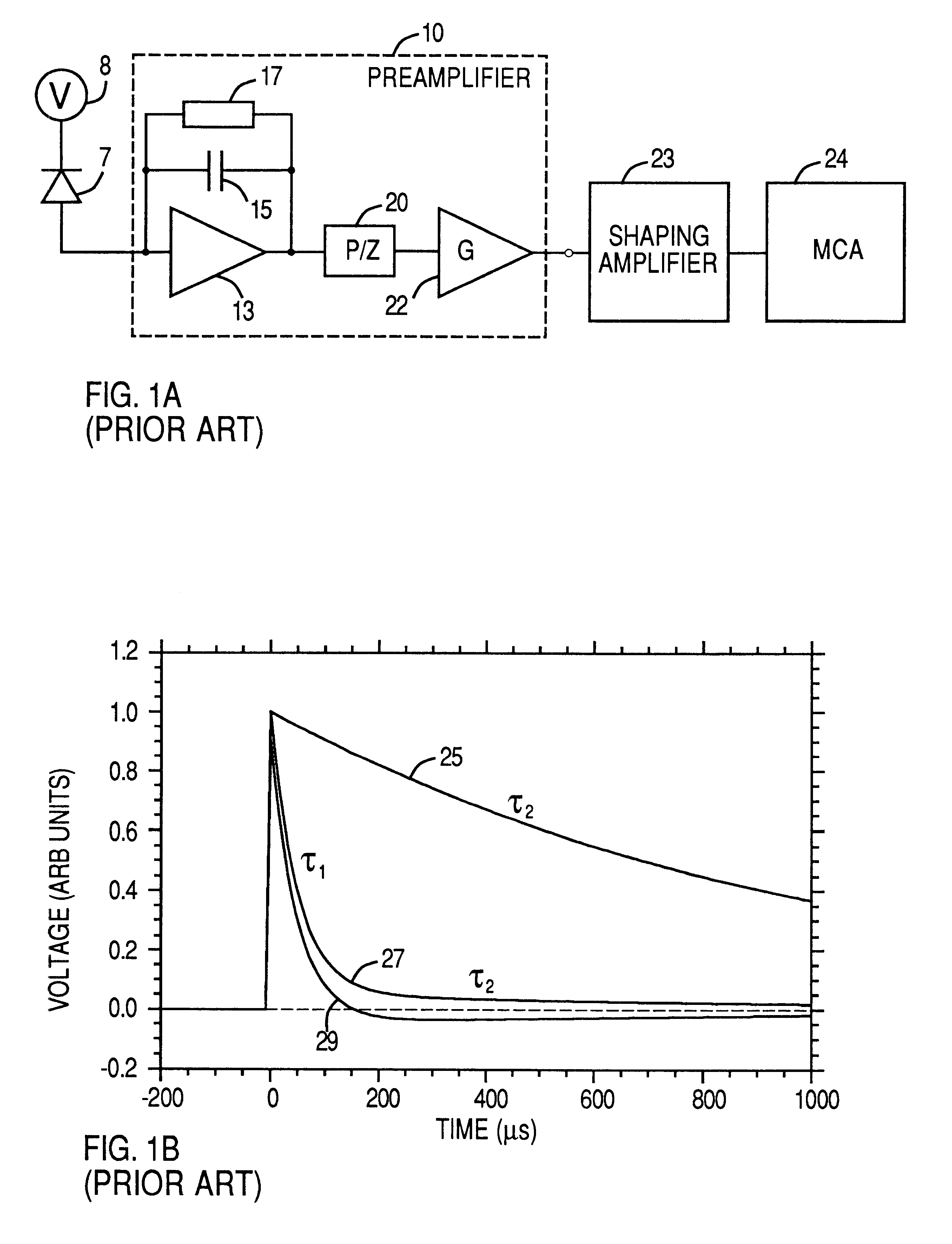
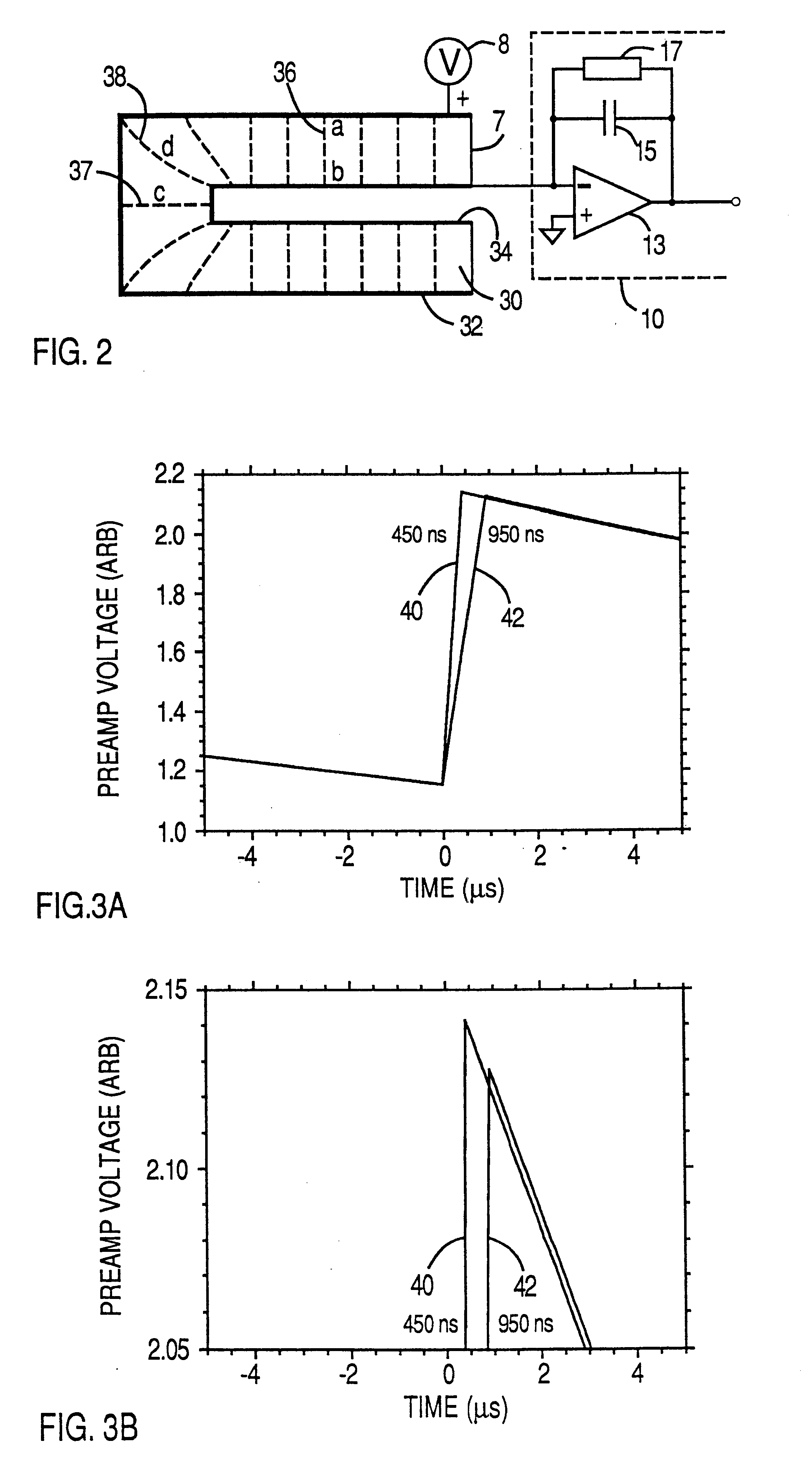
Method and apparatus for improving resolution in spectrometers processing output steps from non-ideal signal sources
InactiveUS20040158440A1Increase rangeAccurate valueAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsTime correlationImage resolution
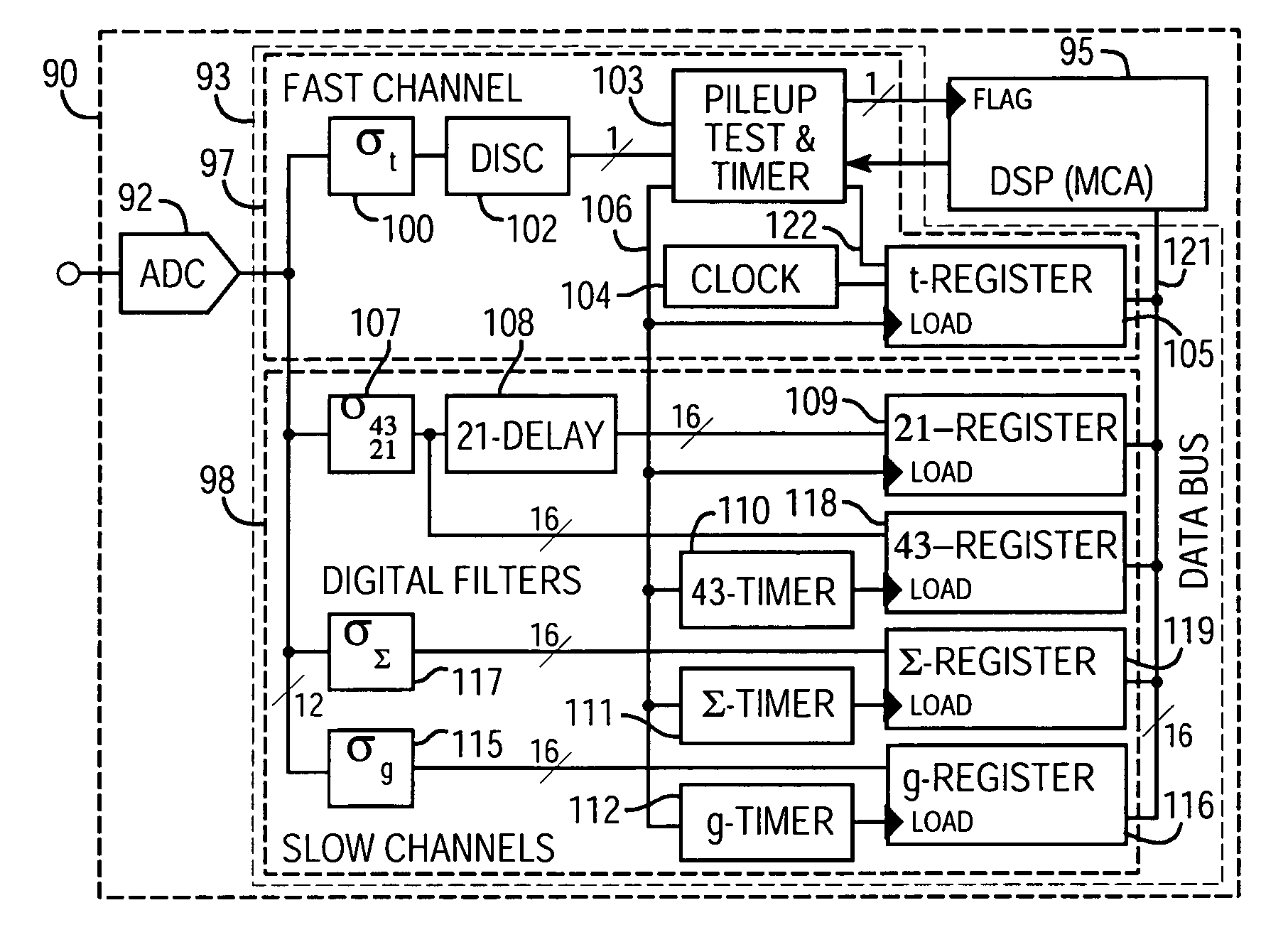
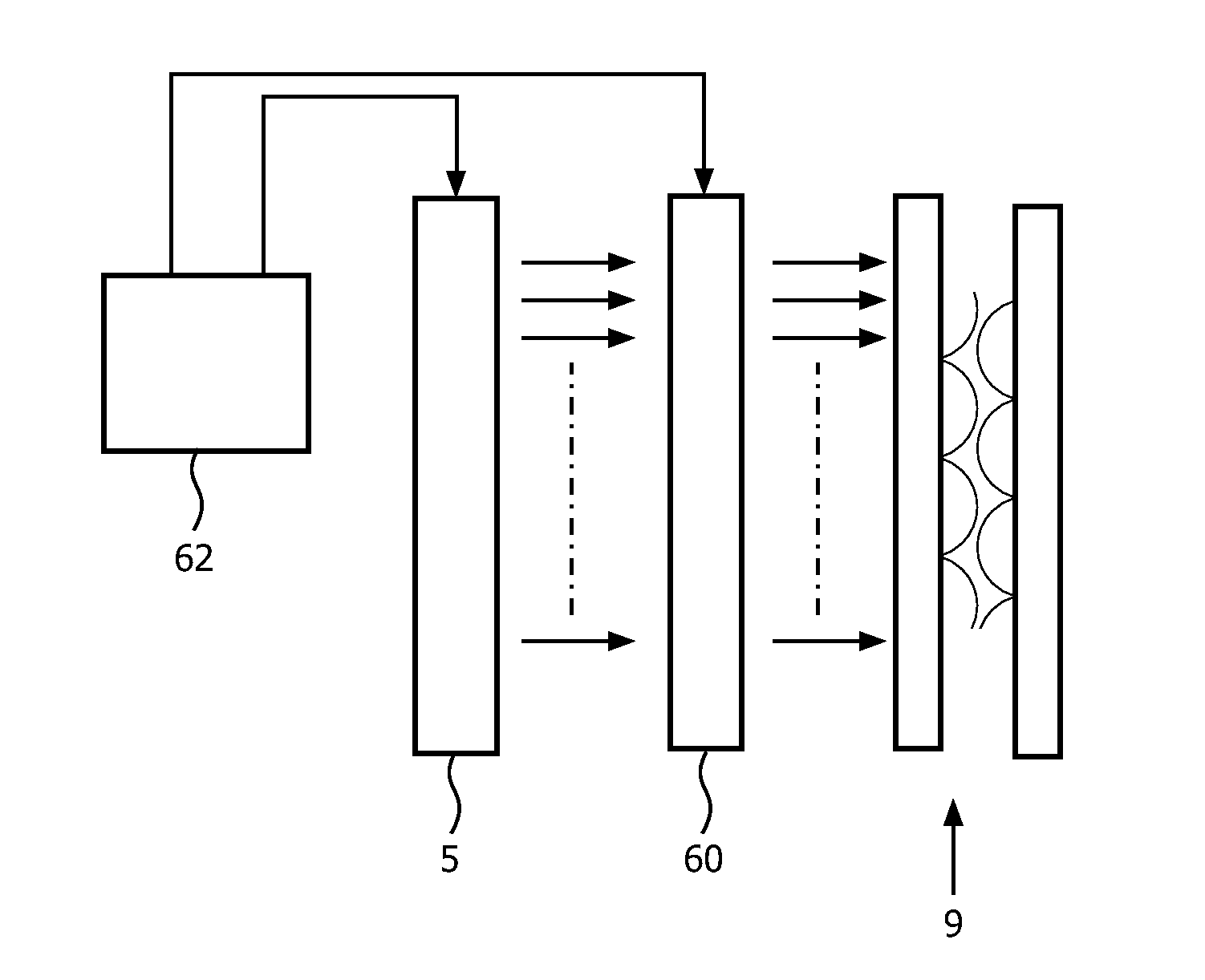
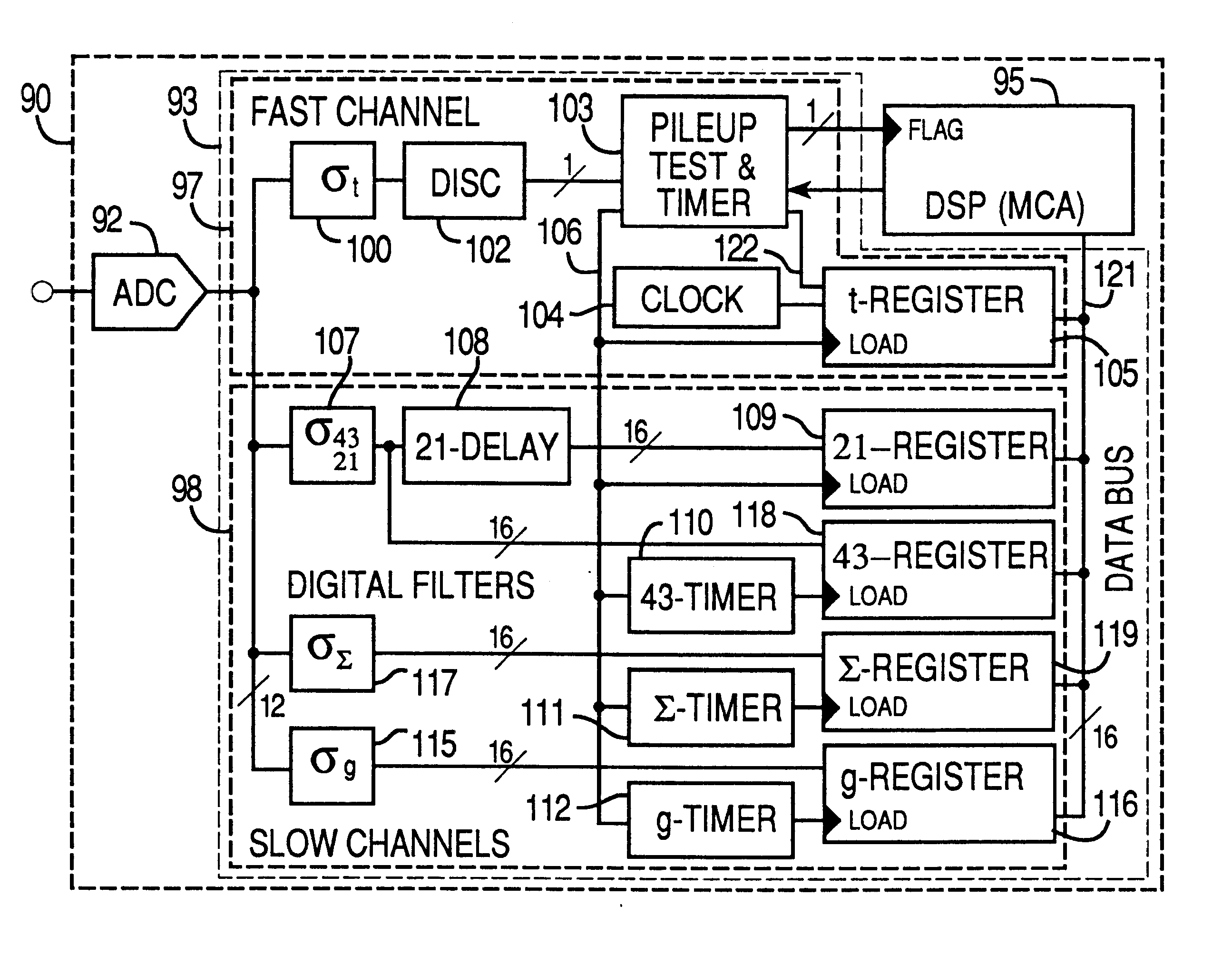
A method and apparatus for processing step-like output signals (primary signals) generated by non-ideal, for example, nominally single-pole ("N-1P ") devices. An exemplary method includes creating a set of secondary signals by directing the primary signal along a plurality of signal paths to a signal summation point, summing the secondary signals reaching the signal summation point after propagating along the signal paths to provide a summed signal, performing a filtering or delaying operation in at least one of said signal paths so that the secondary signals reaching said summing point have a defined time correlation with respect to one another, applying a set of weighting coefficients to the secondary signals propagating along said signal paths, and performing a capturing operation after any filtering or delaying operations so as to provide a weighted signal sum value as a measure of the integrated area QgT of the input signal.
Owner:WARBURTON WILLIAM K
Method of making flexographic printing members
InactiveUS20120048135A1Minimal of edge definitionHigh printing densityAddressographsPrinting press partsElastomerEngineering
An imaging method provides a flexographic printing member used to transfer ink from an image area to a receiver element. This flexographic printing member has a relief image including an image area that is composed of an elastomeric composition that has an elastomeric topmost surface and a relief image floor. The relief image has a plurality of dots within a sub-area of the elastomeric topmost surface wherein each dot has a minimum receiver element contact area. A fraction less than 1 of the plurality of dots, known as (b) dots, have a topmost surface that is undercut below the elastomeric topmost surface. The (b) dots are undercut below the elastomeric topmost surface in a predetermined number and arrangement so that the (b) dots are still able to transfer ink to the receiver element. Each of the remainder of the plurality of dots in the sub-area, known as (a) dots, has a topmost surface that is essentially coincident with the elastomeric topmost surface.
Owner:MIRACLON CORP
Method and Apparatus for Parameter Free Regularized Partially Parallel Imaging Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging
InactiveUS20080298661A1Reduce exerciseImprove signal-to-noise ratioMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionPrior informationImage resolution
Embodiments of the invention are directed to a method and apparatus for parameter free regularized partially parallel imaging (PPI). Specific embodiments relate to a method and apparatus for high pass GRAPPA (hp-GRAPPA), doubly calibrated GRAPPA (db-GRAPPA), and / or image ratio constrained reconstruction (IRCR). The subject techniques can be applied individually or in combination. In a specific application of an embodiment of the subject method, hp-GRAPPA is used to reconstruct high frequency information, and db-GRAPPA is used reconstruct low frequency information regularized with prior information. In another specific application of an embodiment of the subject method, the result of IRCR a regularization term for db-GRAPPA. Experiments demonstrate that the results obtained by implementing embodiments of the subject method have significantly higher SNR than results obtained utilizing un-regularized techniques and have higher spatial resolution and / or lower error than results obtained using regularized SENSE. The subject double calibration technique lessens the motion problem of the pre-scan even when significant structure change occurs. High quality images generated by a specific embodiment of the subject double calibration technique are demonstrated with a net reduction factor as high as 4.8.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Arrangement for the optoelectronic recording of large-area fingerprints
InactiveUS20060169159A1Increase expenditurePrevent movementScattering properties measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionImage resolutionImage recording
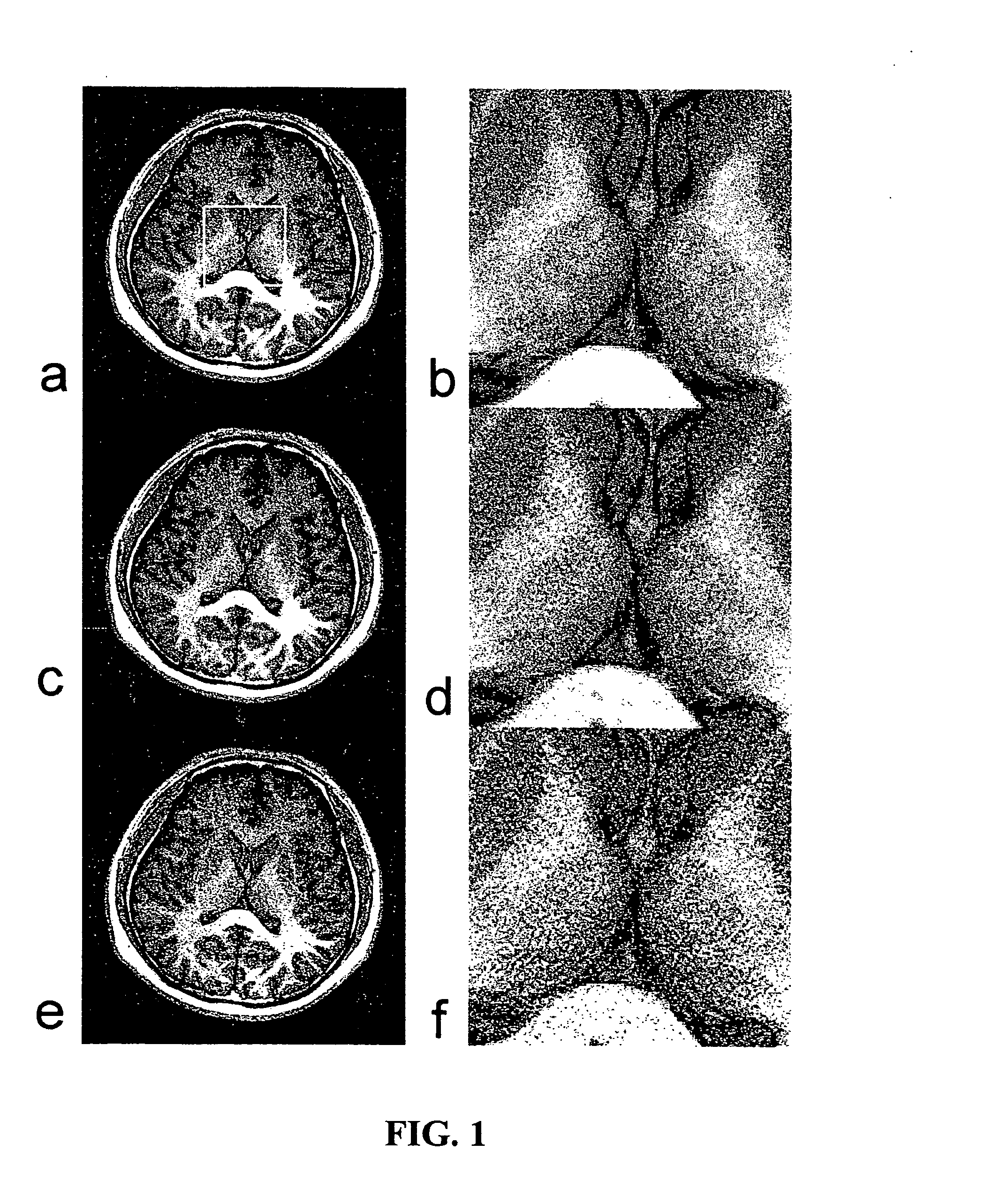
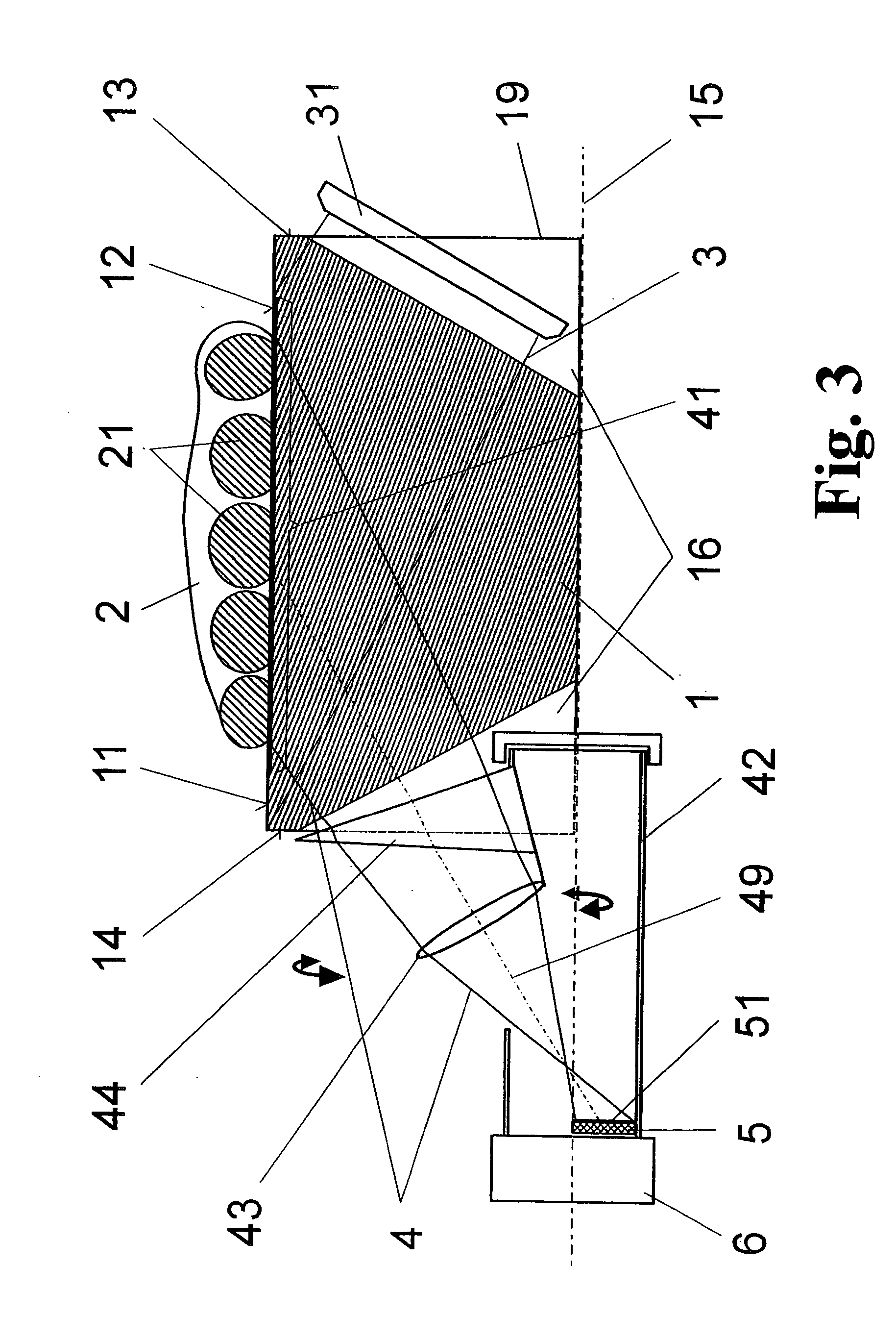
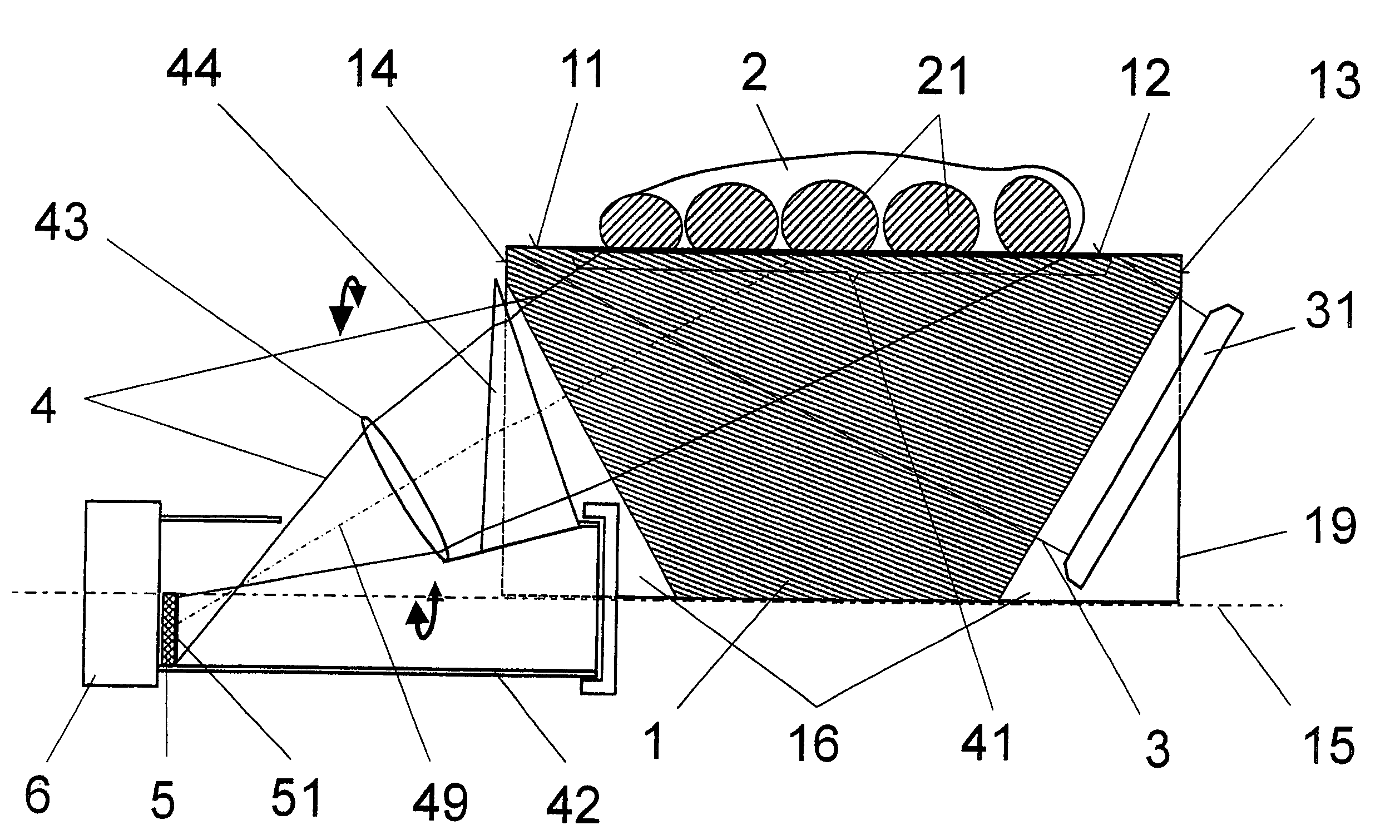
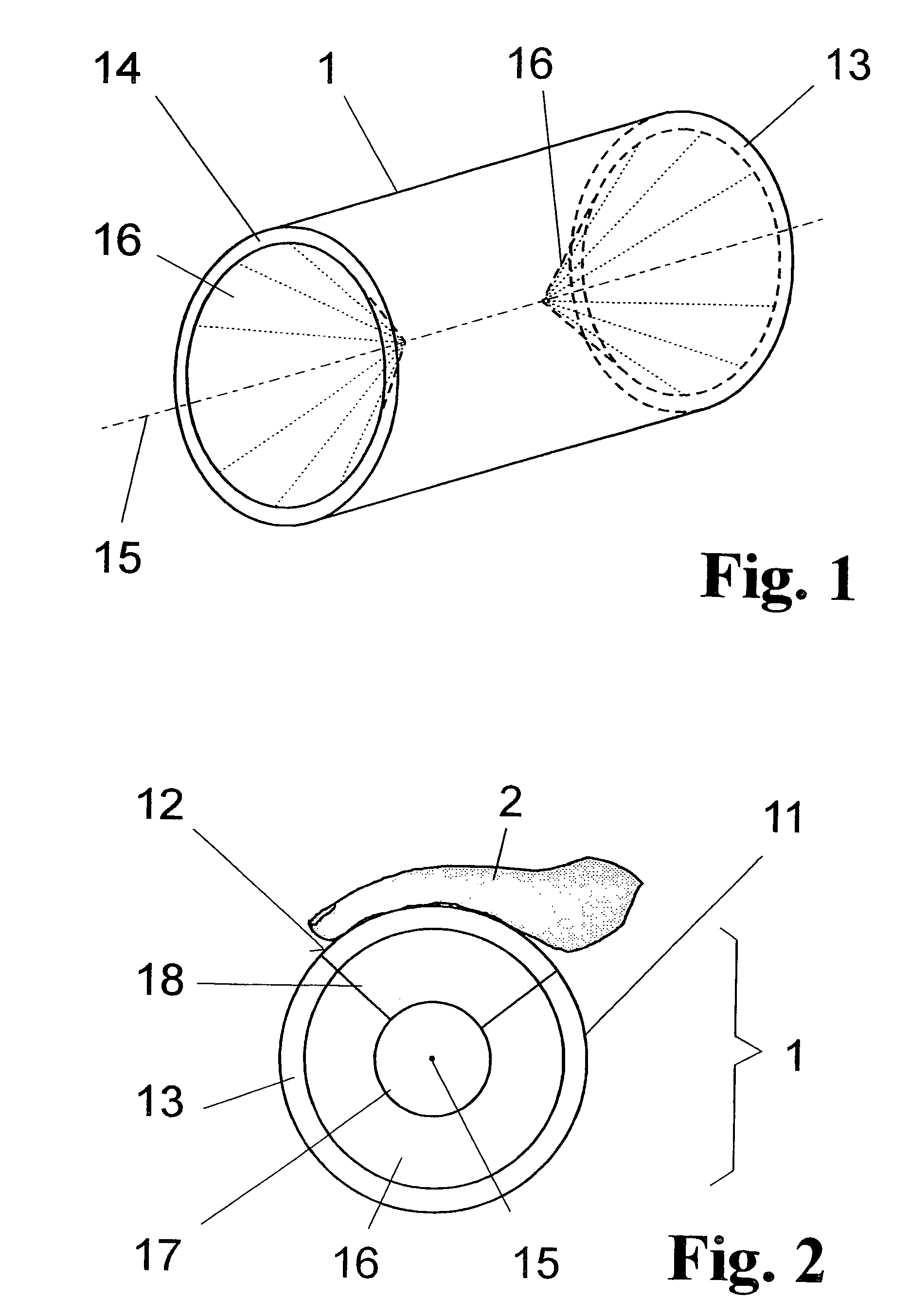
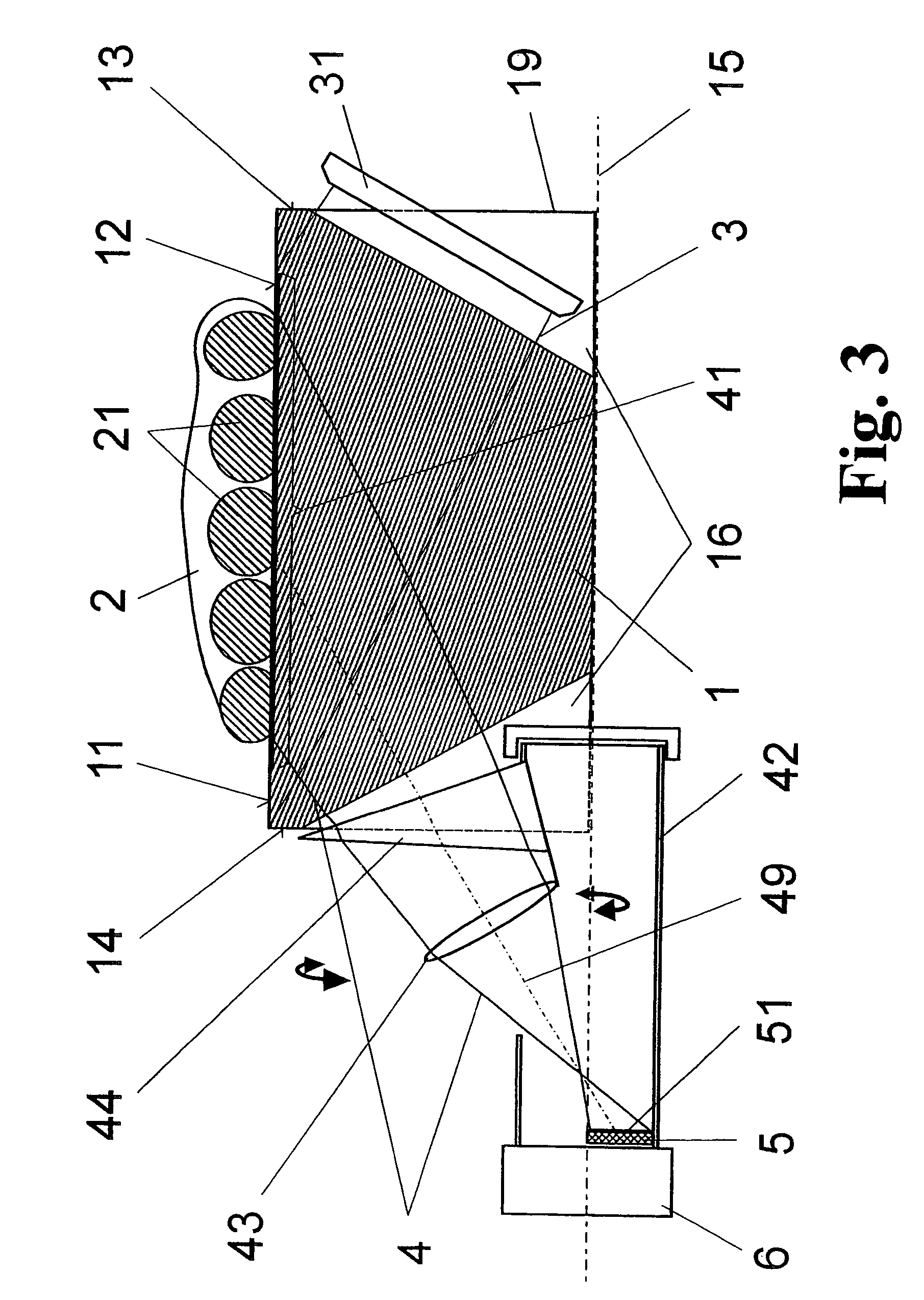
The invention is directed to an arrangement for the optoelectronic recording of large-area fingerprints, particularly for acquiring prints of the entire palm of the hand. The object of the invention is to find a novel possibility for recording the papillary ridge pattern of a hand which permits a complete optoelectronic image recording with one-time placement of large-area concave skin parts without the use of optical beam paths that are subject to contamination and without having to accept a loss of resolution. This object is met, according to the invention, in that the support body for supporting the skin parts has the basic shape of a cylinder providing a portion of the outer surface with a sufficient radian measure and radius as support surface, the end faces of the support body are each provided with a conical recess which is arranged coaxially around the cylinder axis in order to couple in an illumination beam path and an imaging beam path through the surface lines of the conical recesses, and the imaging beam path and a linearly extending image sensor are rotatable synchronously around the cylinder axis in order to record successive line-shaped strips of the frustrated total reflection at the illuminated outer surface of the support body with the supported skin part.
Owner:CROSS MATCH TECH
Auto-stereoscopic display device
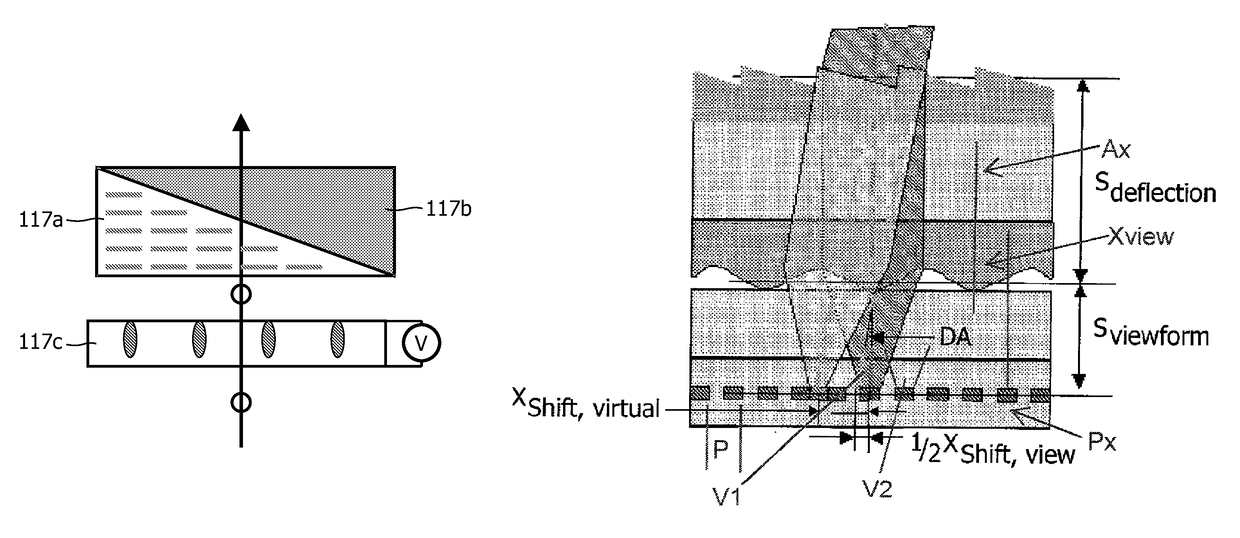
InactiveUS20100259819A1Increase the number ofResolution is sacrificedSteroscopic systemsNon-linear opticsComputer graphics (images)Image resolution
An auto-stereoscopic display device which addresses the problem of how to provide an improved three dimensional effect without degrading the resolution of the views. The auto-stereoscopic display device comprises: image forming means having an array of display pixels for producing a display; view forming means positioned in registration with the image forming means and having an array of view forming elements, the view forming elements each being configurable to focus the outputs of groups of the display pixels into a plurality of views projected towards a user in different directions; and view deflecting means positioned in registration with the view forming means, the view deflecting means being arranged to selectably change the directions in which the plurality of views are projected towards the user. The view deflecting means comprise at least one birefringent prism having a first refractive index for light having a first polarization direction and a second refractive index for light having a second polarization direction. The view deflecting means further comprise a polarization switch in registration with the birefringent prism for providing the birefringent prism with display light having the first or second polarization direction. Specific arrangements of the image forming means, the view forming means and the view deflection means provide an even distribution of pixels and virtual pixels associated with the deflected views
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Multi-view autostereoscopic display device
InactiveUS20120092339A1Increase output resolutionReduce bandingSteroscopic systems3D-image renderingImage resolutionComputer graphics (images)
An autostereoscopic display device comprises a display panel (3) having an array of display pixel elements (5) for producing a display, the display pixel elements being arranged in rows and columns. An imaging arrangement (9) directs the output from different pixel elements to different spatial positions to enable a stereoscopic image to be viewed. The imaging arrangement comprises first and second polarization-sensitive lenticular arrays (50,52), wherein the light incident on the imaging arrangement is controllable to have one of two possible polarizations, and wherein each of the two possible polarizations gives a different 3D mode. These multiple modes can be used to increase the resolution, or increasing the number of views, or provide additional functionality to the display device.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and apparatus for improving resolution in spectrometers processing output steps from non-ideal signal sources
InactiveUS6587814B1Low electronic noise levelImprove noiseRecording apparatusX-ray spectral distribution measurementHigh rateGamma ray
A method and apparatus for processing step-like output signals generated by non-ideal, nominally single-pole ("N-1P") devices responding to possibly time-varying, pulse-like input signals of finite duration, wherein the goal is to recover the integrated areas of the input signals. Particular applications include processing step-like signals generated by detector systems in response to absorbed radiation or particles and, more particularly, to digitally processing such step-like signals in high resolution, high rate gamma ray (gamma-ray) spectrometers with resistive feedback preamplifiers connected to large volume germanium detectors. Superconducting bolometers can be similarly treated. The method comprises attaching a set of one or more filters to the device's (e.g., preamplifier's) output, capturing a correlated multiple output sample from the filter set in response to a detected event, and forming a weighted sum of the sample values to accurately recover the total area (e.g., charge) of the detected event.
Owner:WARBURTON WILLIAM K
Flexographic printing members
InactiveUS20120048133A1Minimal of edge definitionHigh printing densityPlate printingFoil printingElastomerEngineering
The present invention provides a flexographic printing member used to transfer ink from an image area to a receiver element. This flexographic printing member has a relief image including an image area that is composed of an elastomeric composition that has an elastomeric topmost surface and a relief image floor. The relief image has a plurality of dots within a sub-area of the elastomeric topmost surface wherein each dot has a minimum receiver element contact area. A fraction less than 1 of the plurality of dots, known as (b) dots, have a topmost surface that is undercut below the elastomeric topmost surface. The (b) dots are undercut below the elastomeric topmost surface in a predetermined number and arrangement so that the (b) dots are still able to transfer ink to the receiver element. Each of the remainder of the plurality of dots in the sub-area, known as (a) dots, has a topmost surface that is essentially coincident with the elastomeric topmost surface.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
NMR methods for measuring fluid flow rates
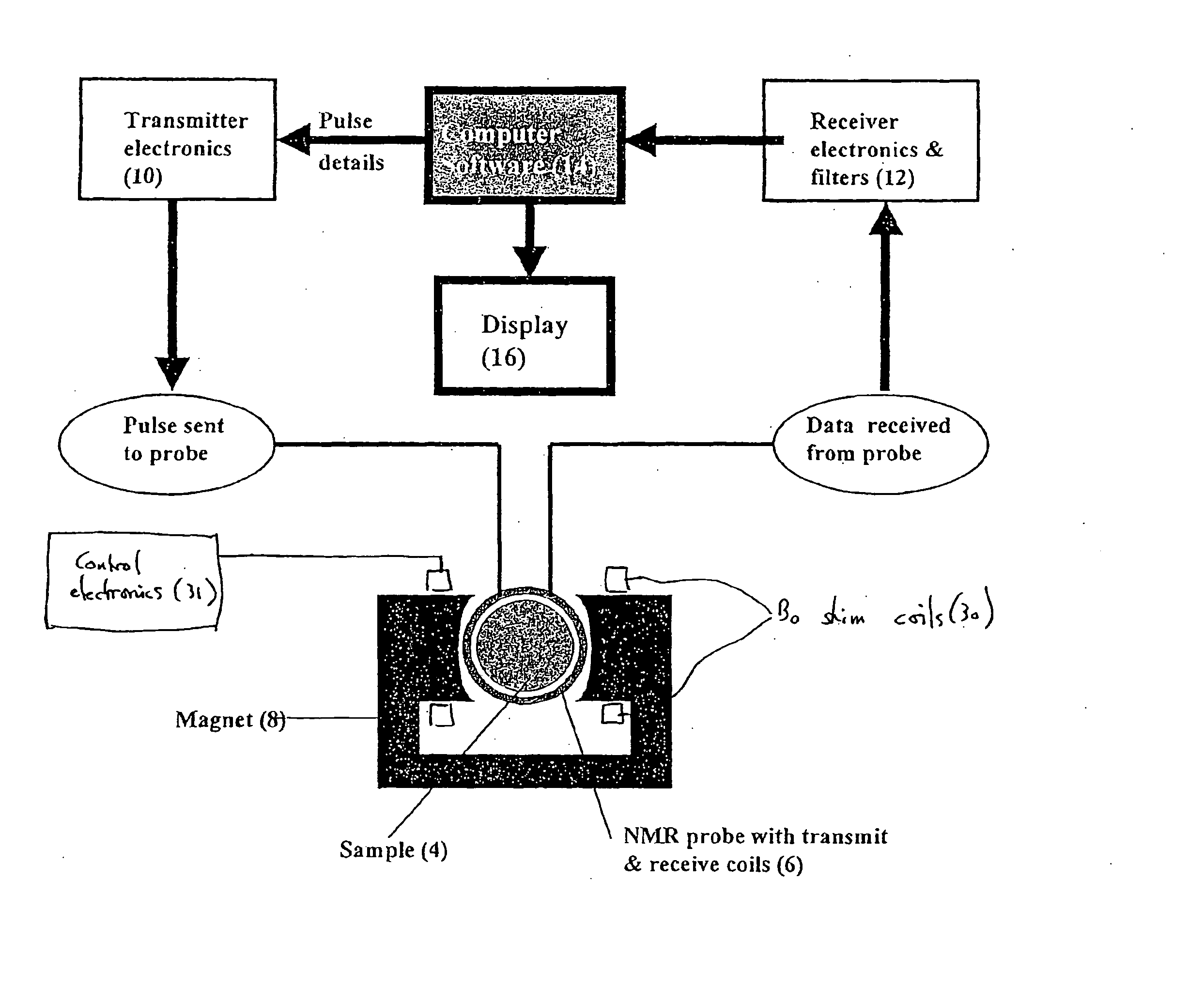
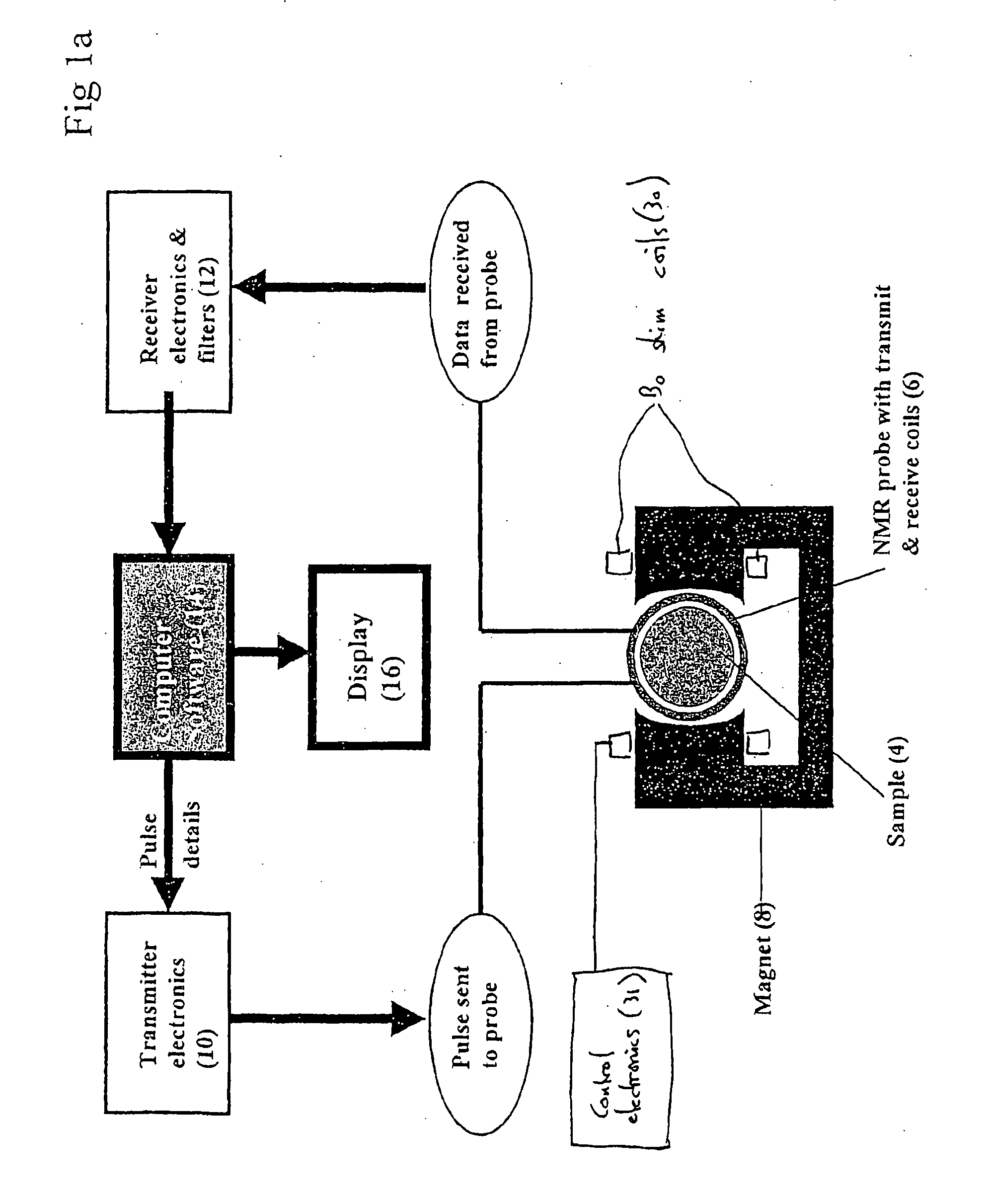
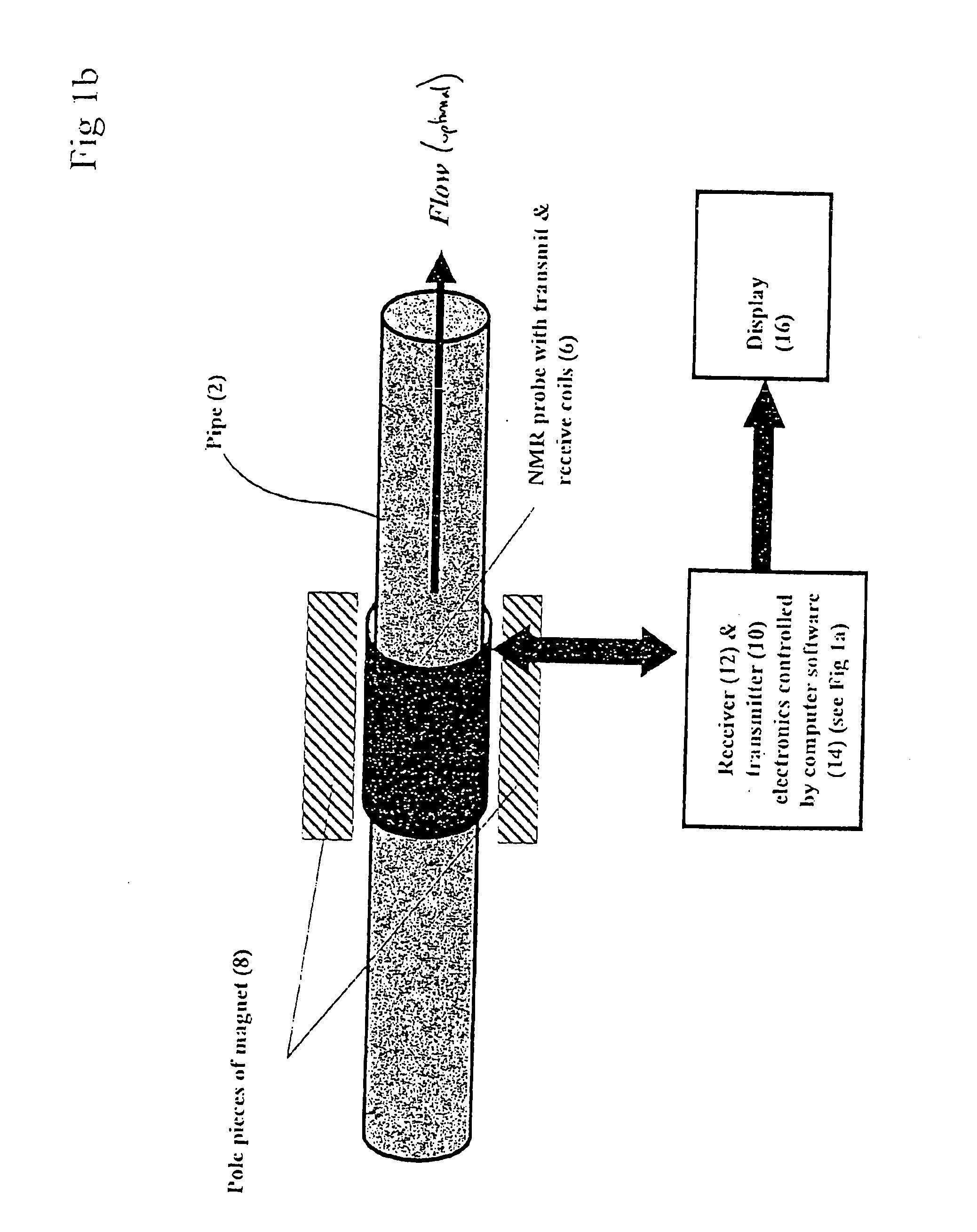
InactiveUS20060213283A1Loss of resolutionReduce resolutionVolume/mass flow by electromagnetic flowmetersElectric/magnetic detectionUltimate tensile strengthFree induction decay
A method for measuring fluid flow rates comprises the steps of: (a) creating a non-oscillating magnetic field of a predetermined strength across a flowing fluid; (b) performing the sub-steps of: (i) exposing the flowing fluid to an oscillating magnetic field pulse orthogonal to the non-oscillating magnetic field to generate an NMR signal, and (ii) detecting the NMR signal from the flowing fluid in the form of a free induction decay; and (c) determining the fluid flow rate from the initial magnitude of the free induction decay.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Arrangement for the optoelectronic recording of large-area fingerprints
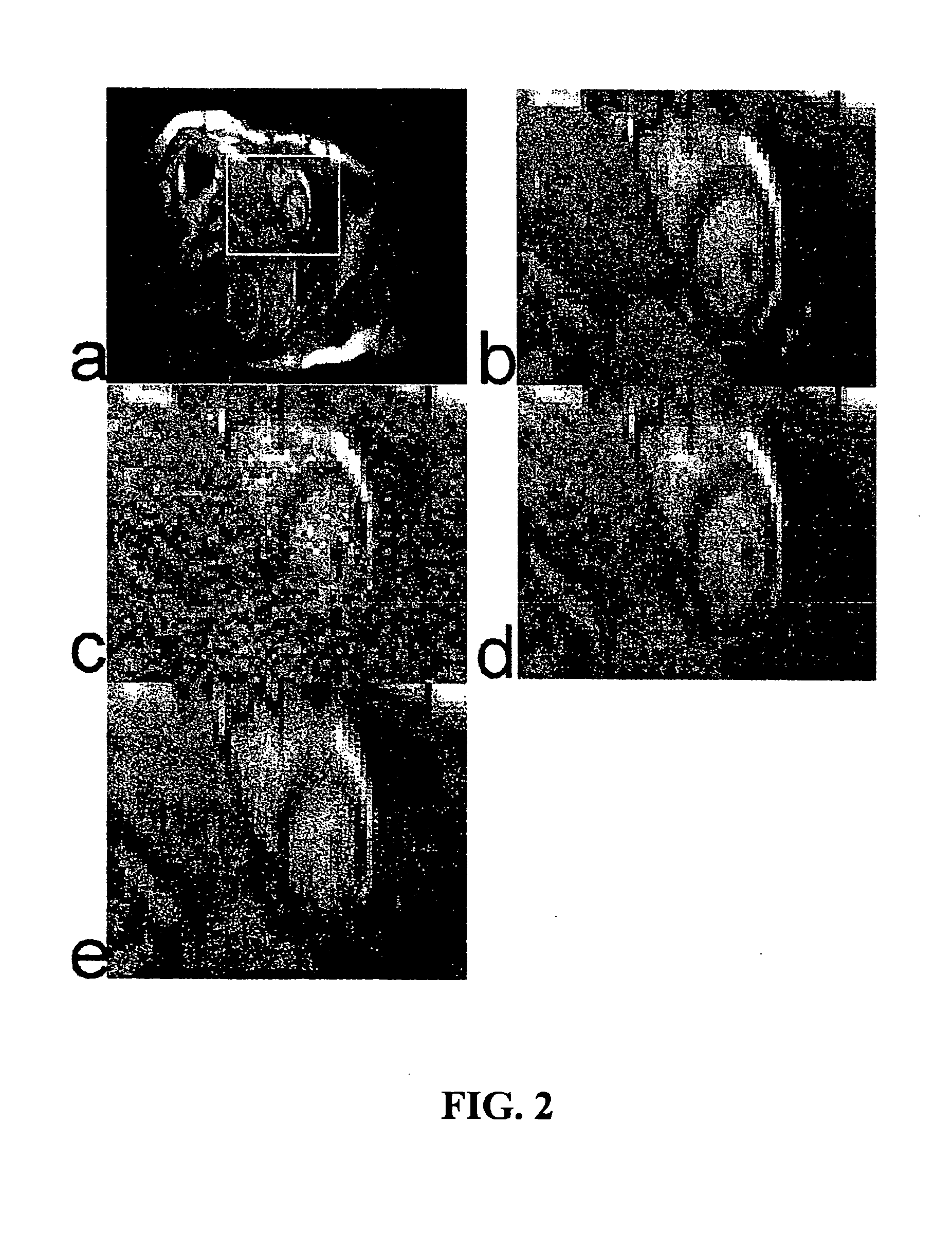
InactiveUS7567342B2Prevent movementImprove robustnessScattering properties measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionImage recordingEngineering
The invention is directed to an arrangement for the optoelectronic recording of large-area fingerprints, particularly for acquiring prints of the entire palm of the hand. The object of the invention is to find a novel possibility for recording the papillary ridge pattern of a hand which permits a complete optoelectronic image recording with one-time placement of large-area concave skin parts without the use of optical beam paths that are subject to contamination and without having to accept a loss of resolution. This object is met, according to the invention, in that the support body for supporting the skin parts has the basic shape of a cylinder providing a portion of the outer surface with a sufficient radian measure and radius as support surface, the end faces of the support body are each provided with a conical recess which is arranged coaxially around the cylinder axis in order to couple in an illumination beam path and an imaging beam path through the surface lines of the conical recesses, and the imaging beam path and a linearly extending image sensor are rotatable synchronously around the cylinder axis in order to record successive line-shaped strips of the frustrated total reflection at the illuminated outer surface of the support body with the supported skin part.
Owner:CROSS MATCH TECH
PRML based magnetic servo position demodulator
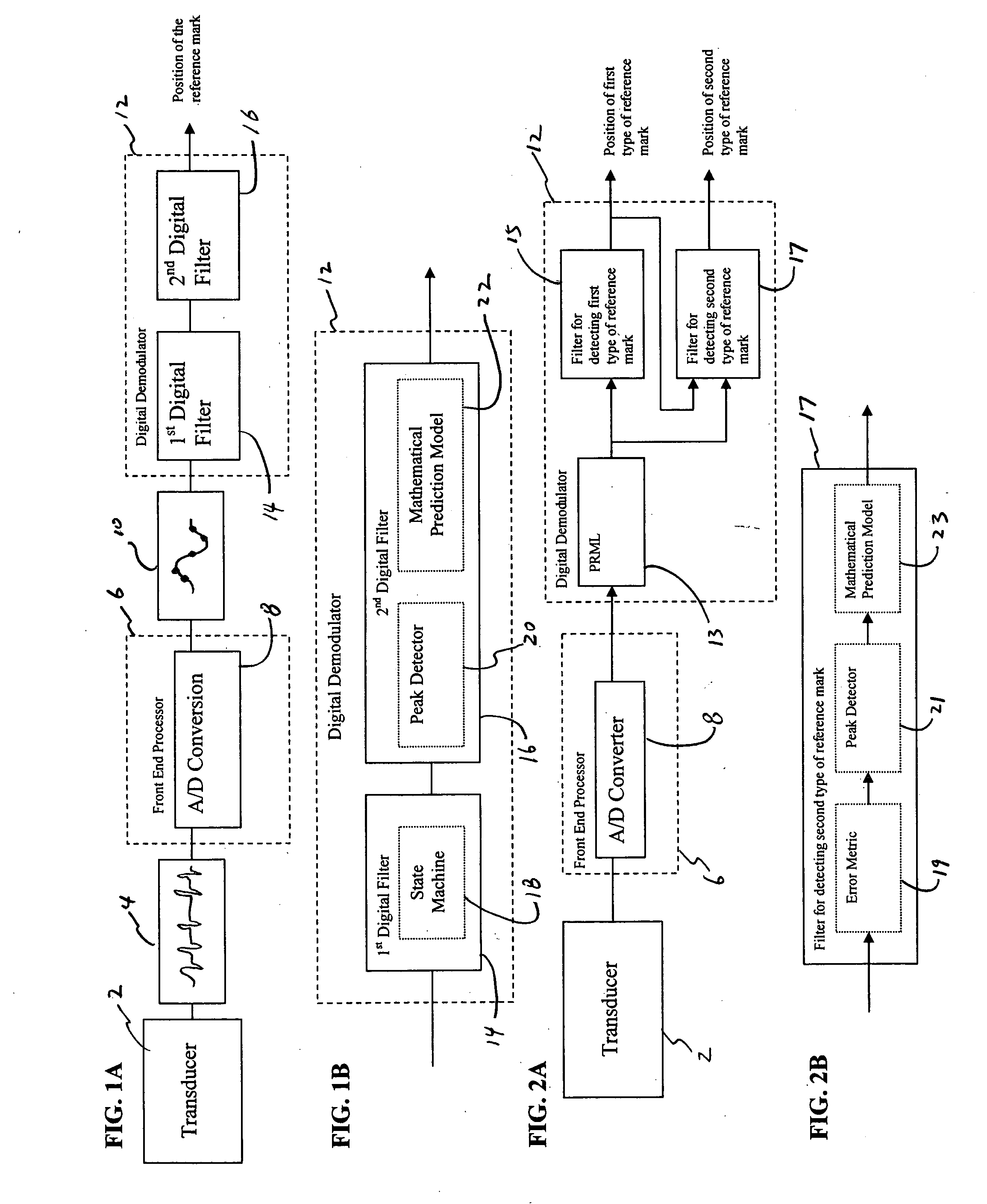
InactiveUS20070019316A1Loss of resolutionNot easy to detectModification of read/write signalsAlignment for track following on tapesDigital filterComputer science
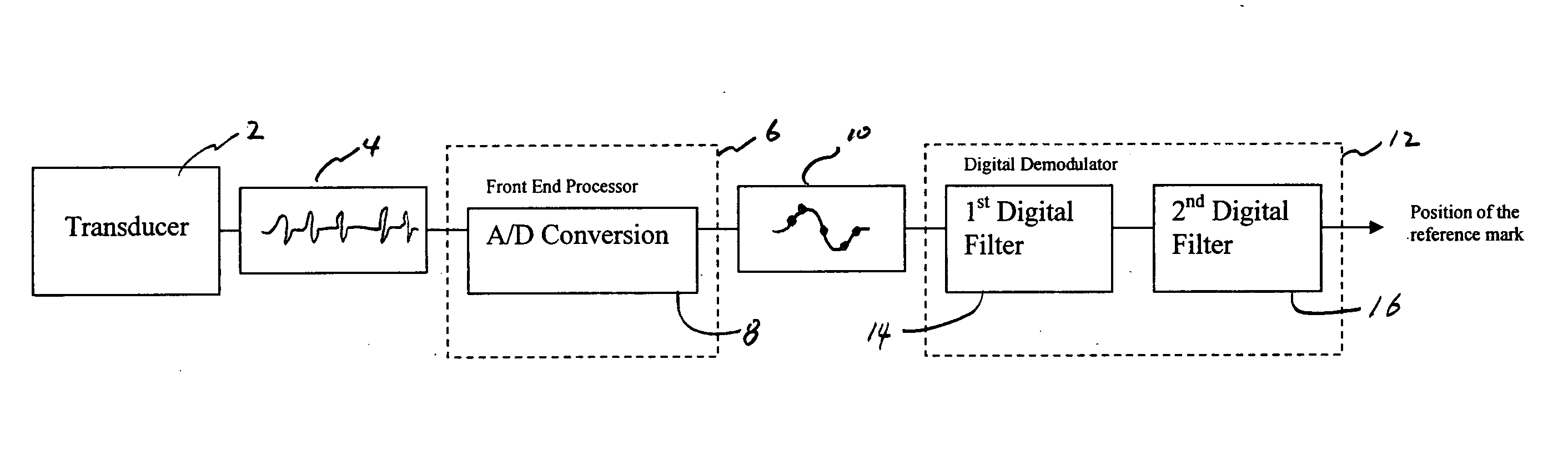
Apparatuses and methods for detecting reference marks on magnetic data storage mediums are described herein. In one variation, the apparatus comprises a magnetic servo position demodulator operable to extract information from the magnetic data storage medium utilizing Partial Response / Maximum Likelihood (PRML) technique. Synchronization marks stored within the PRML channel is then detected utilizing a digital filter. For each of the detected synchronization mark, a further refined position of the synchronization mark can be determined utilizing a mathematical prediction model.
Owner:QUANTUM CORP
Autostereoscopic reproduction system for 3-D displays
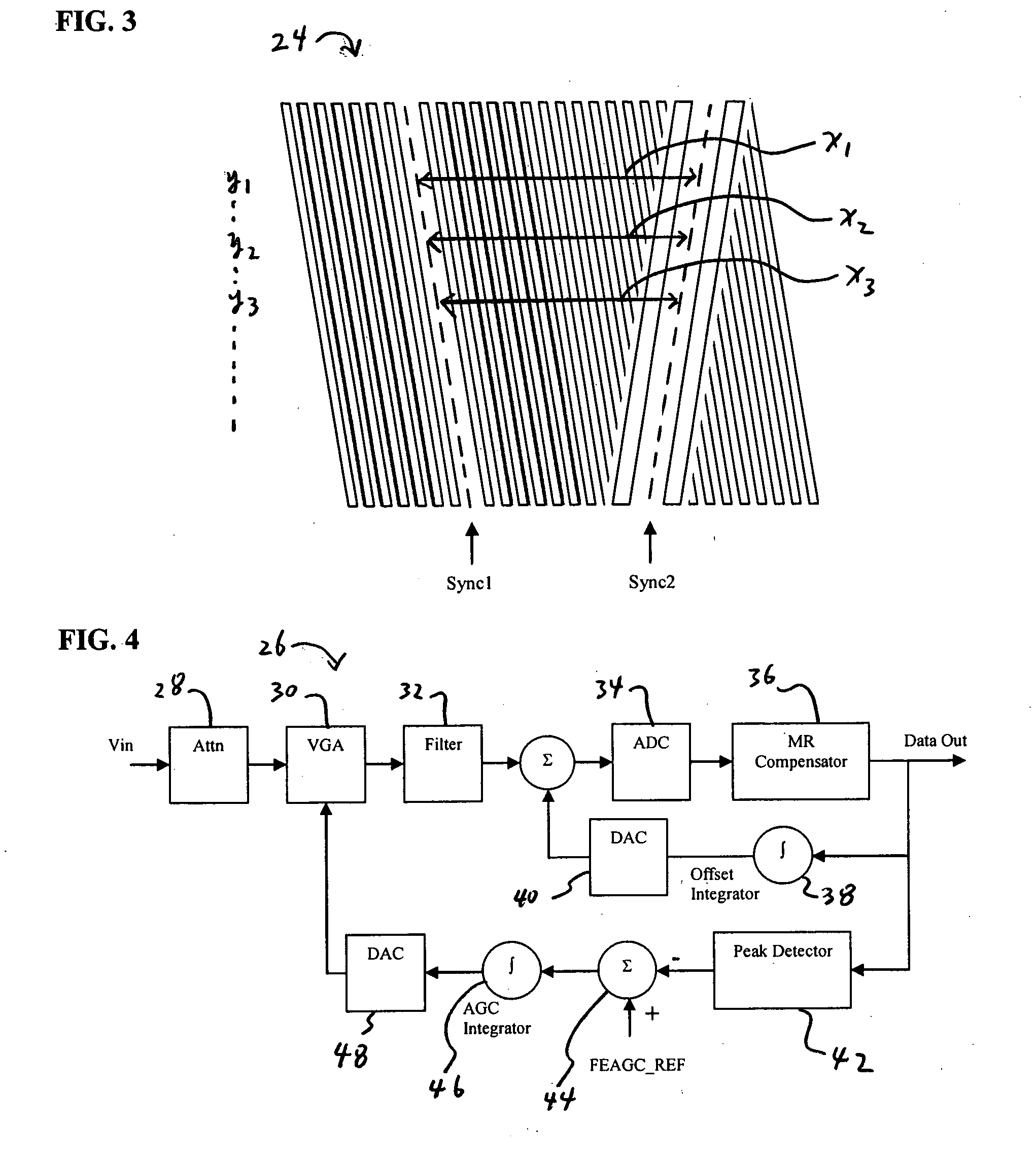
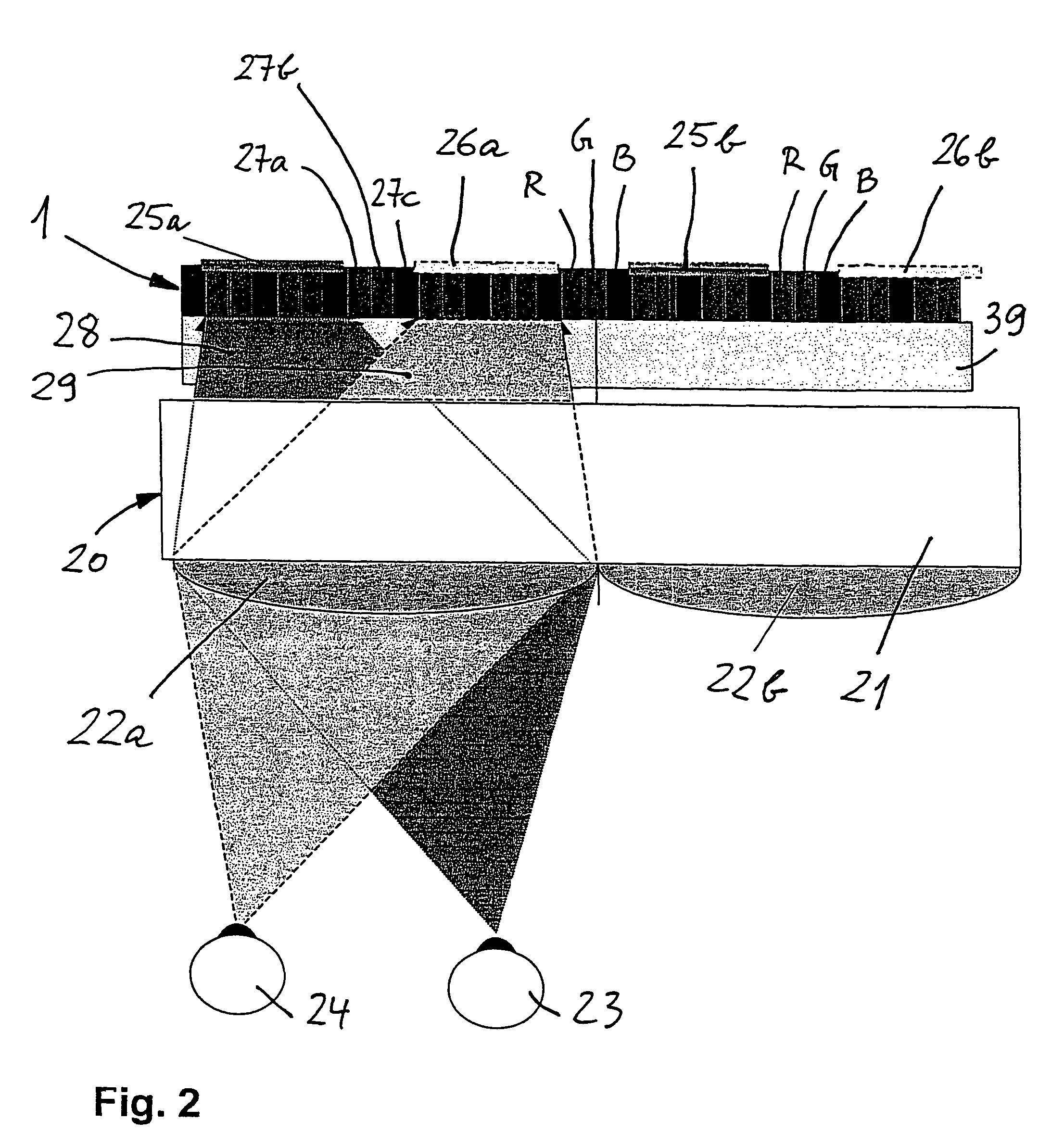
InactiveUS7839430B2Loss of resolutionColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsGratingDisplay device
What is described is a position-adaptive autostereoscopic 3-D reproduction system for generating 3-D images or scenes, having a flat image screen (1) with colour subpixels (R, G, B) lying side by side, a raster screen (2), a coding unit (6, 9) and a processor unit (3) for generating perspective images. According to the invention, the coding unit (6, 9) is controllable and the raster screen (2) is dimensioned and arranged such that first and second mutually interlaced subpixel strips appear on the image screen (1) and from these, first and second image strips are generated, which appear to the two eyes of an observer to be disjoint for a defined viewing region in front of the image screen (1), whereby a constant sequence of colours of the subpixels is maintained in the first (second) subpixel strips.
Owner:HENTSCHKE SIEGBERT
Image recording apparatus
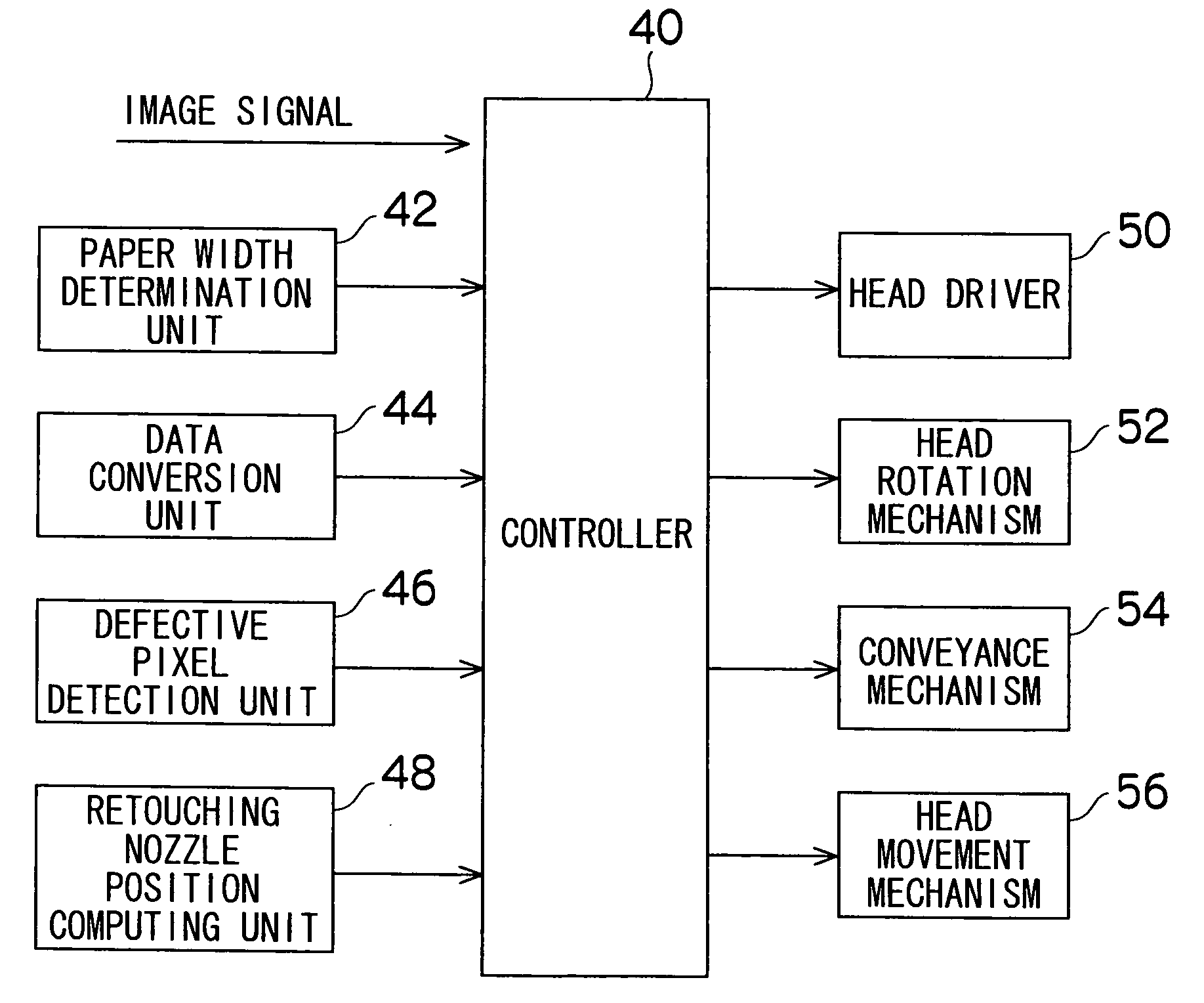
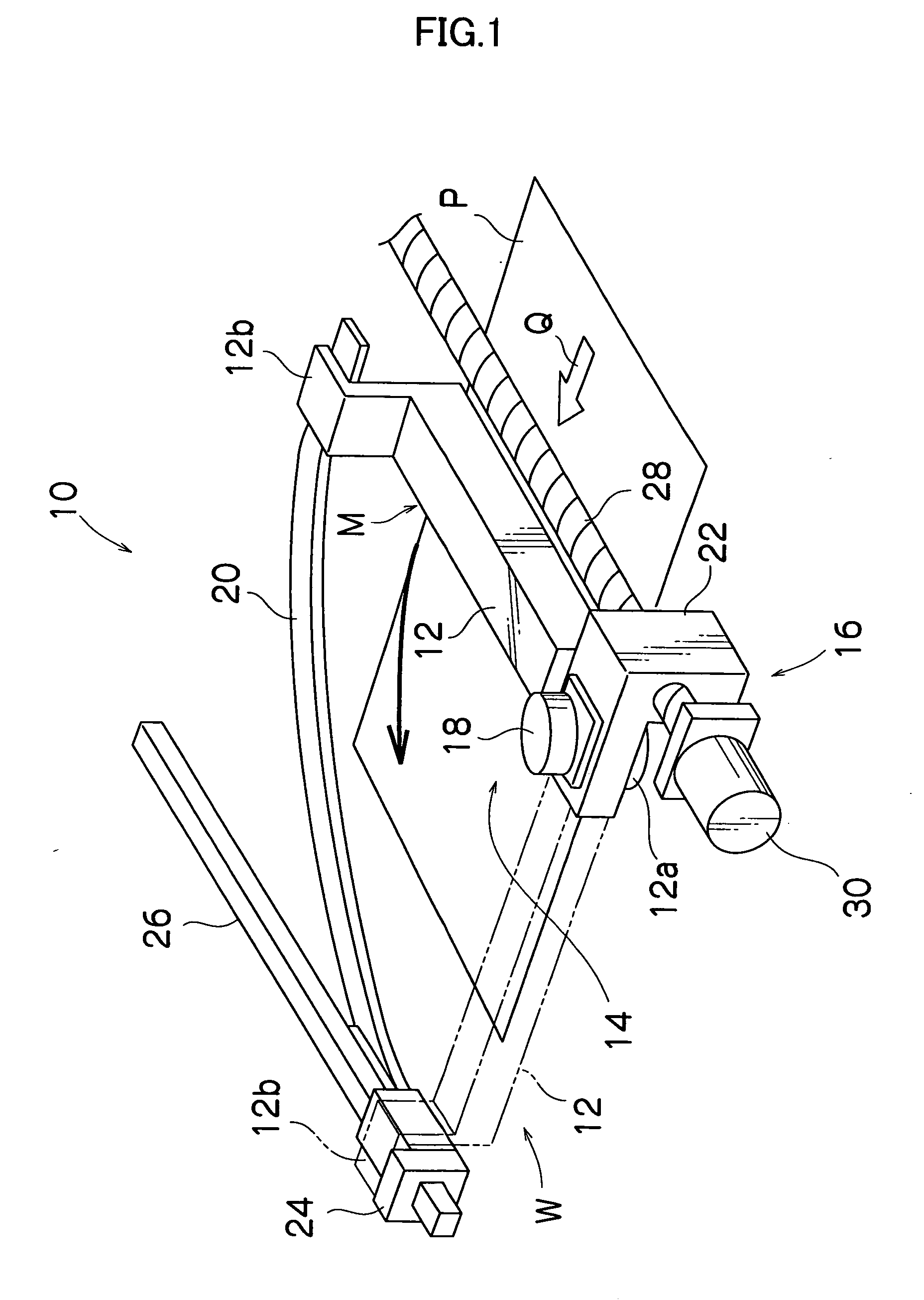
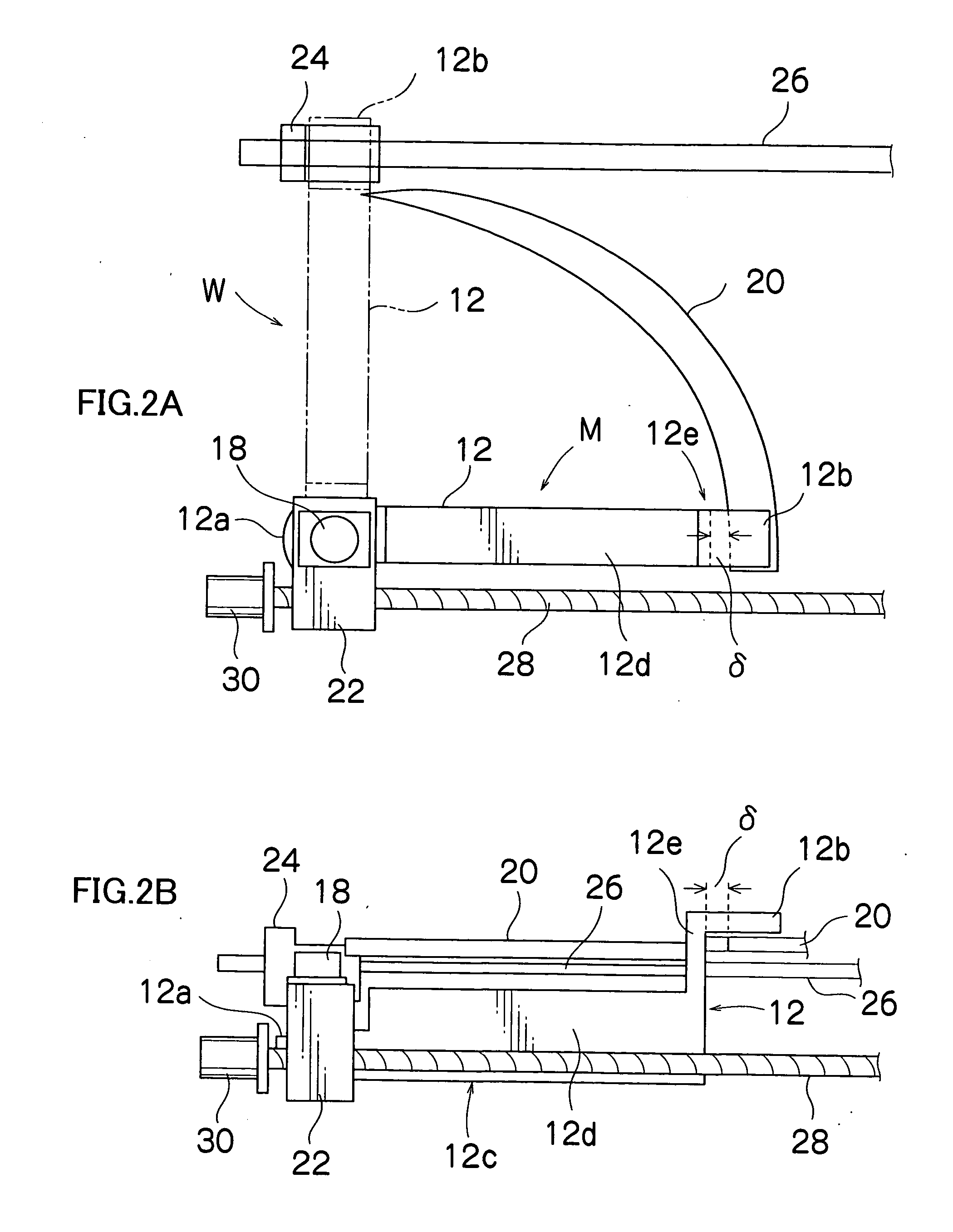
InactiveUS20050063666A1Easy to retouchDefective pixelTelevision system detailsSpacing mechanismsImage recordingComputer science
The image recording apparatus for recording images to a recording medium comprises a recording head arrangement device for arranging the line recording head so that at least the lengthwise direction of the line recording head is in an orthogonal position substantially orthogonal to the conveyance direction of the recording medium, or the lengthwise direction of the line recording head is in a parallel position substantially parallel to the conveyance direction of the recording medium; and a shuttle scan mechanism for causing the line recording head to shuttle-scan in the direction substantially orthogonal to the conveyance direction while the parallel position is maintained, wherein the line recording head records images as a line head when arranged in the orthogonal position, and records images by shuttle scanning when arranged in the parallel position.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Production of composites articles composed of thin layers
InactiveUS7416764B2Fast jettingHigh resolutionAdditive manufacturing apparatusPretreated surfacesThin layerViscosity
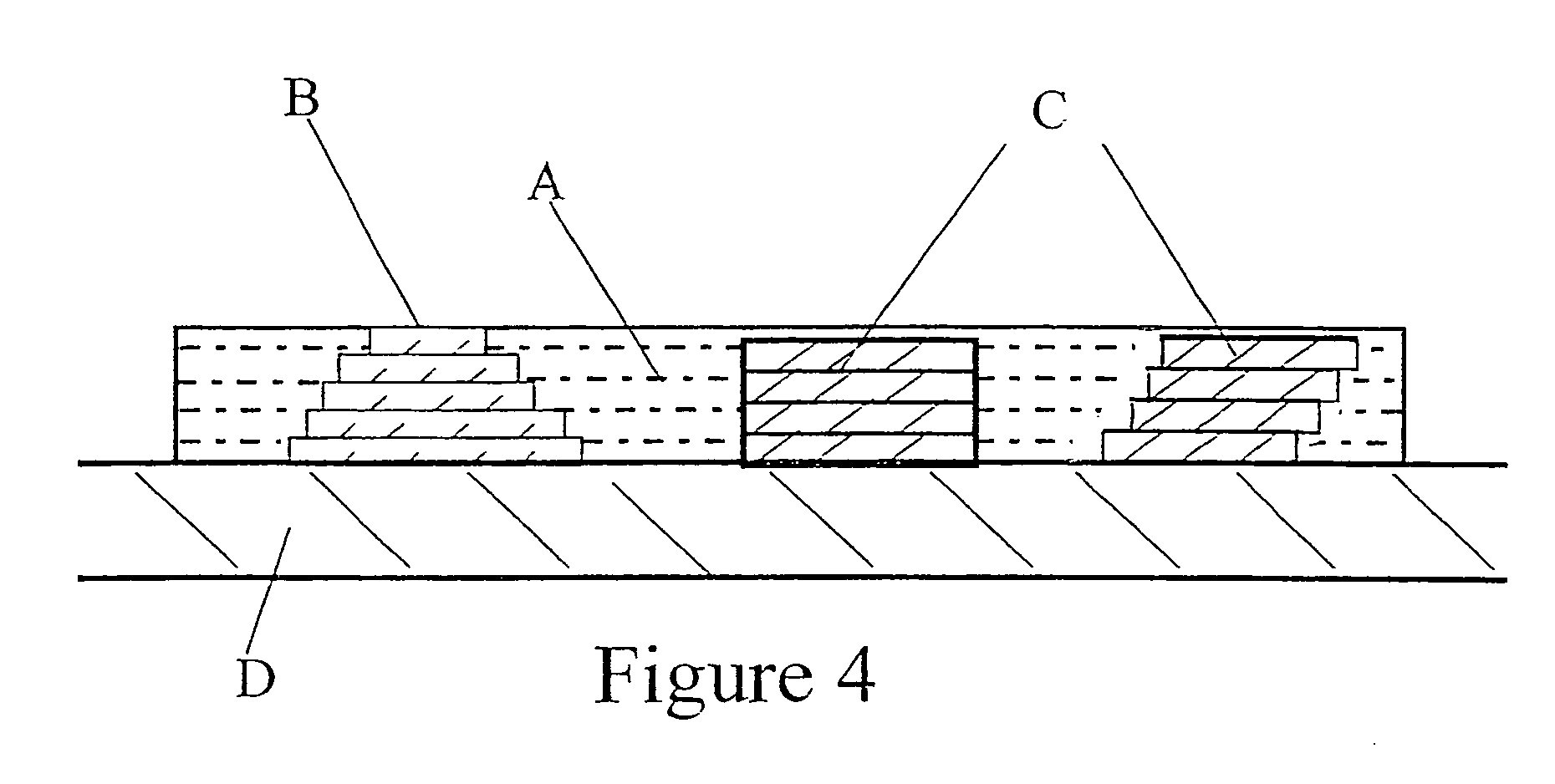
A method is described of producing thin layers (below 10 μm in thickness) by directing droplets (preferably by inkjet printing techniques) onto precise locations on a substrate, the liquid of the droplets having a viscosity such that the droplets, on impact with the substrate, spread out to form relics on the substrate that are at least 1.4 times the diameter of the droplets in flight, adjacent droplets merging to form a continuous layer on the substrate. The droplets may have different compositions to form images within the layer. Successive layers may be added to built up a three dimensional structure whose properties can be tailored by the compositions used to build up a composite.
Owner:HUNTSMAN ADVANCED MATERIALS AMERICAS INC +1
High-performing electrophoresis gels with extended shelf lives
ActiveUS20100187114A1Short runtimeLoss of resolutionElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementElectrophoresisHydroxymethyl
Polyacrylamide gels that offer high resolution as electrophoretic media for protein separations and an improved resistance to hydrolysis upon storage are made by including either taurine, asparagine, or both as an ampholyte, in combination with either tris(hydroxymethyl)-aminomethane or bis(2-hydroxyethyl)amino-tris(hydroxymethyl)methane as a buffer, plus other conventional components.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Spatial phase filter for light beams, system and corresponding method
InactiveUS20050259917A1Small sizeEasy to decoupleOptical filtersCoupling light guidesRegular distributionPhase filter
The invention relates to a spatial phase filter capable of receiving an incident light beam so as to transmit it to a single mode output fibre comprising a spatially variable phase profile and being adapted to excite the evanescent modes of the output fibre. The profile has: an adjustable pattern with a phase distribution substantially corresponding to a combination of at least one quantile of normal distribution on at least one dimension (301); and a phase shifting zone support (320) limited in relation to the incident beam according to the dimension(s). The invention also relates to a system implementing several filters and a method for filter calculating.
Owner:OPTOGONE
Developer compositions and processes
InactiveUS6348292B1Increase charge levelLoss of resolutionDevelopersElectrographic process apparatusPhysical chemistryColoring agents
Owner:XEROX CORP
High-performing electrophoresis gels with extended shelf lives
ActiveUS8945360B2Short runtimeLoss of resolutionElectrolysis componentsElectrolytic capacitorsElectrophoresisPolyacrylamide
Polyacrylamide gels that offer high resolution as electrophoretic media for protein separations and an improved resistance to hydrolysis upon storage are made by including either taurine, asparagine, or both as an ampholyte, in combination with either tris(hydroxymethyl)-aminomethane or bis(2-hydroxyethyl)amino-tris(hydroxymethyl)methane as a buffer, plus other conventional components.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
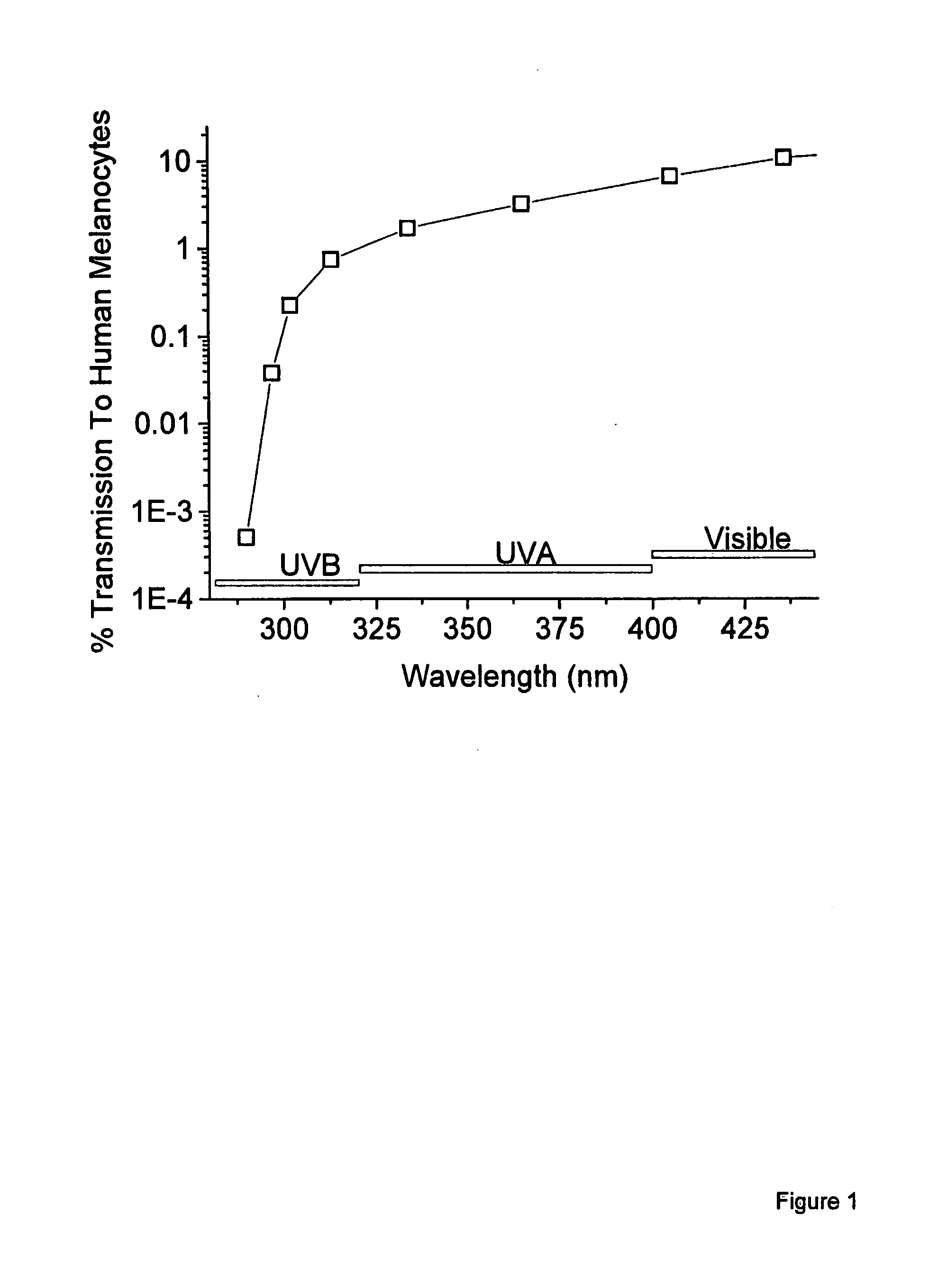
System and methods for measuring a skin protection factor
InactiveUS20080056995A1Eliminate loss of resolutionEliminates loss of resolutionCompounds screening/testingBiocideMelanocyteDNA damage
The present invention is a system and methods of establishing a Melanocyte Protection Factor (MPF), which indicates the level of protection against DNA damage to a target cell, such as the level of protection a particular sunscreen offers against UVA rays when compared to the unprotected case, i.e., no sunscreen. The present invention determines and records levels of stable melanin radicals (SMR) in a target cell. Light is applied to the target cell forming light-induced melanin radicals (LIR). The levels of SMR and intensity of LIR are measured to determine the amount of incident light reaching the target cell. Since LIR is proportional to the square root of light intensity reaching the target cell, the ratio of light reaching the target cell is defined as the MPF: MPF=UV reaching melanocytewithout sunscreenUV reaching melanocytewith sunscreen=[SMR+screenLIR+UV+screen]2[SMRcontrolLIR+UV control]2
Owner:STC UNM
Developer compositions and processes
A liquid developer contains, for example, a nonpolar liquid, thermoplastic resin, optional colorant, and an inorganic filler
Owner:XEROX CORP
3D image display device
ActiveUS20160125814A1Image degradationLoss of resolutionStatic indicating devicesSteroscopic systems3d imageDisplay device
A 3D image display device includes a backlight unit for generating an original light, a display panel, a light modulating unit, and a controller connected to the display panel and the light modulating unit. According to a first signal, the original light passes through the display panel generates a first light, the first light passes through the light modulating unit, and has a first position on an objective plane parallel to the display panel. According to a second signal, the original light passes through the display panel to generate a second light, the second light passes through the light modulating unit and has a second position on the objective plane, wherein the first position is different from the second position.
Owner:INNOLUX CORP
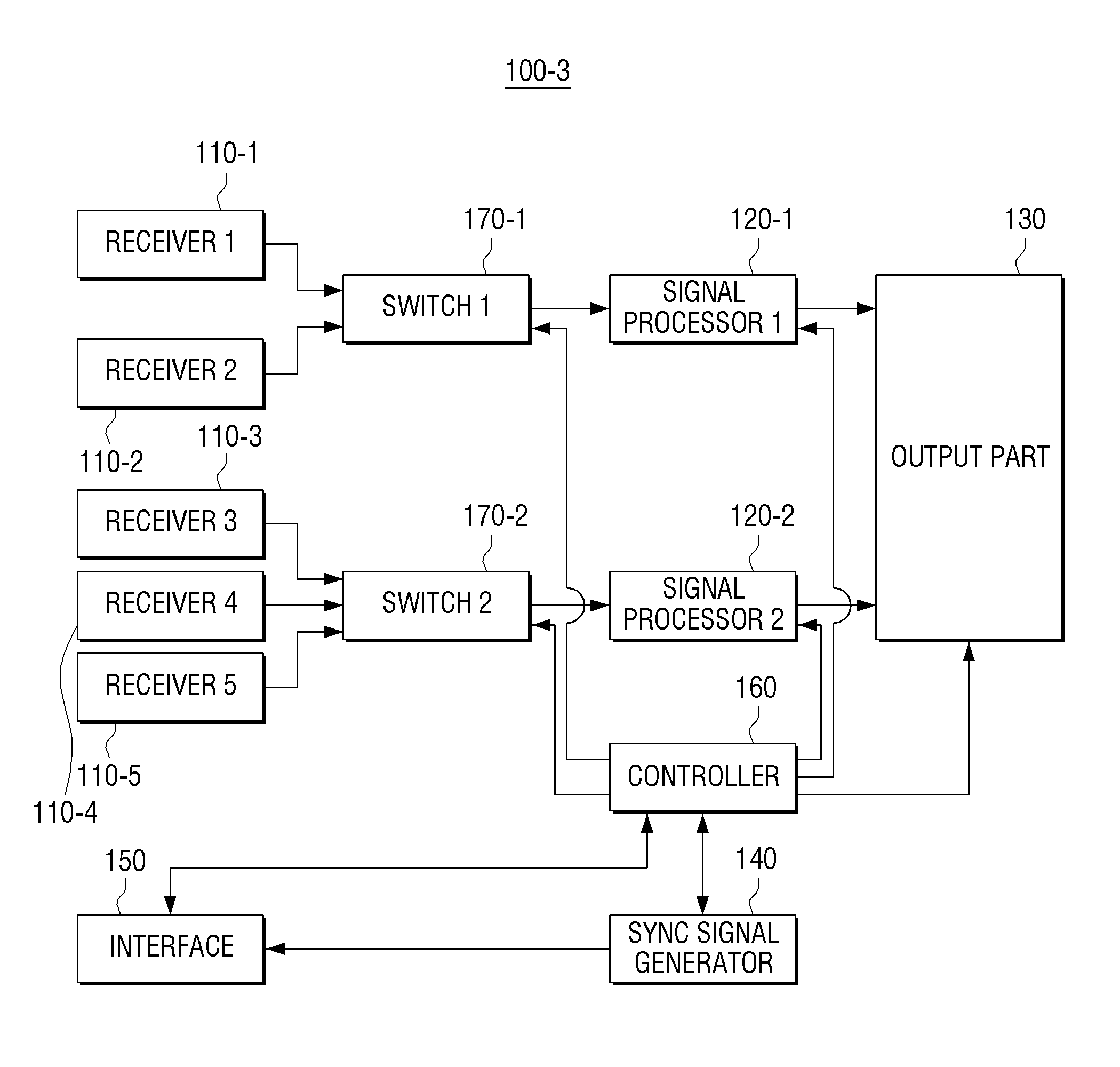
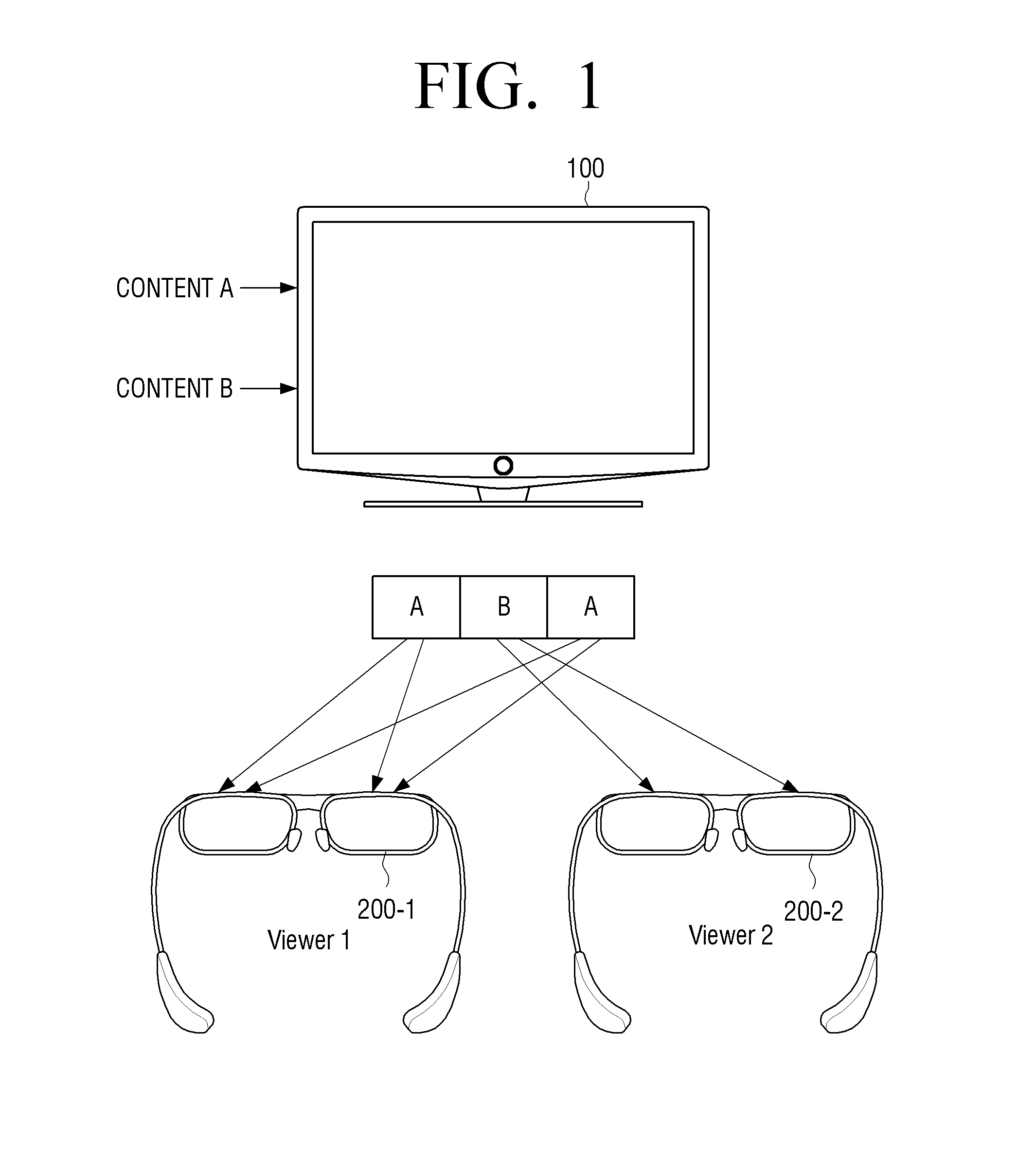
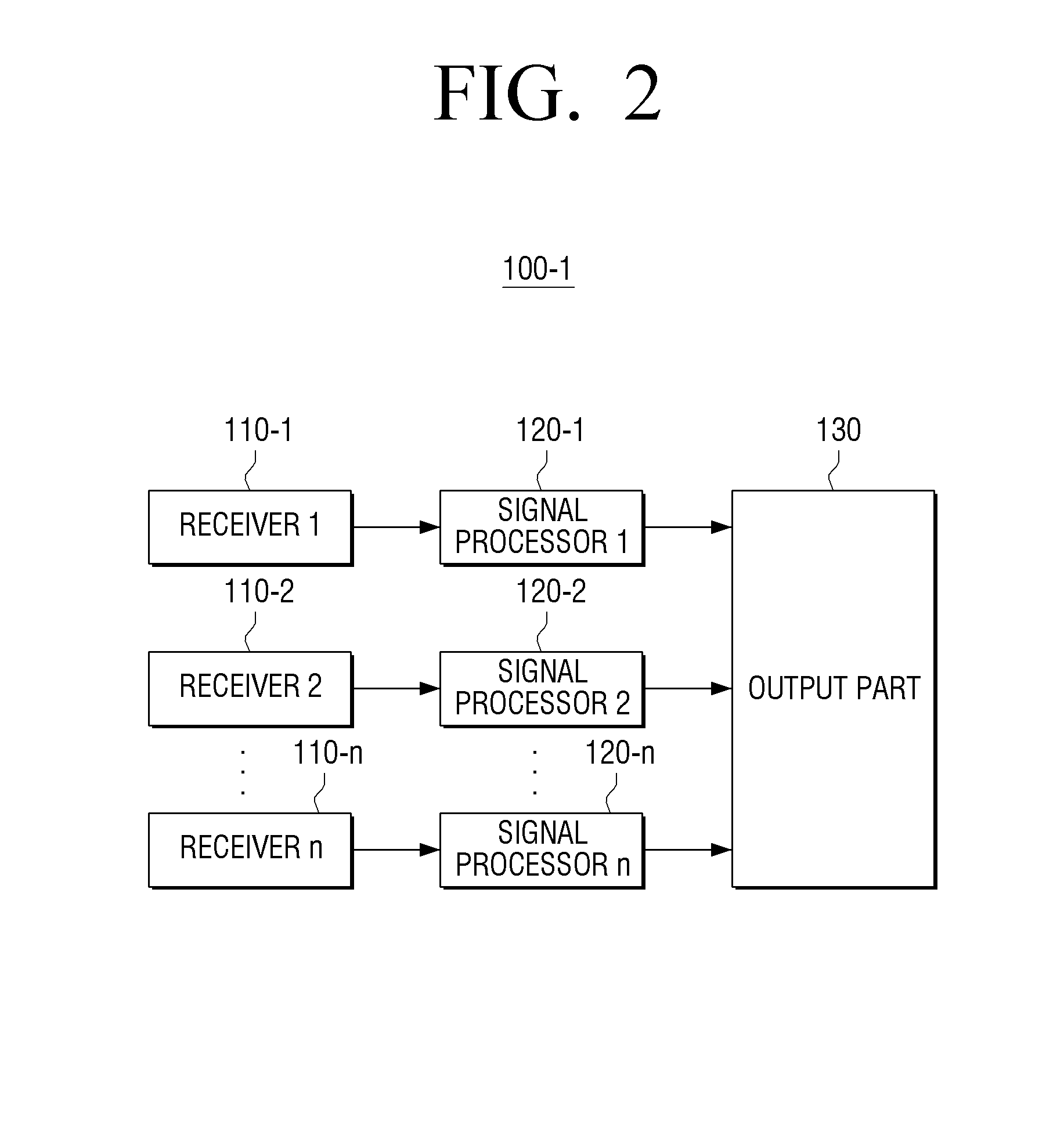
Display apparatus and display method
InactiveUS20140160354A1Loss of resolutionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSignal processingFrame rate
A display apparatus and a display method are provided. The display apparatus includes a plurality of receivers which are configured to receive a plurality of contents of a multi-view content, a plurality of signal processors which are configured to independently convert frame rates of the plurality of contents, and an output part which is configured to alternately output the plurality of contents according to the converted frame rates.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for processing of images
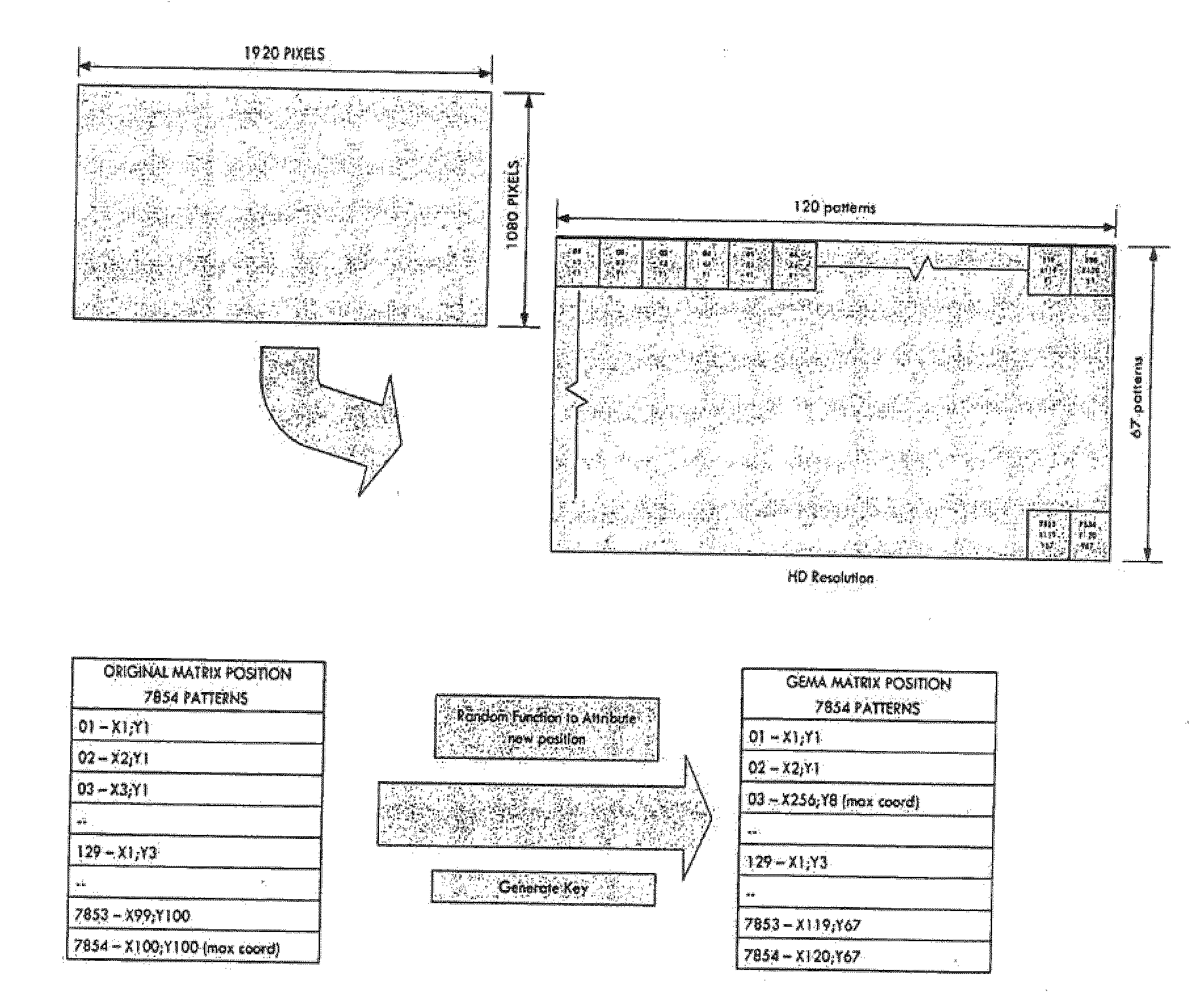
InactiveUS20100189252A1Easy to reorganizeMaintain resolutionGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)Fish eye lens
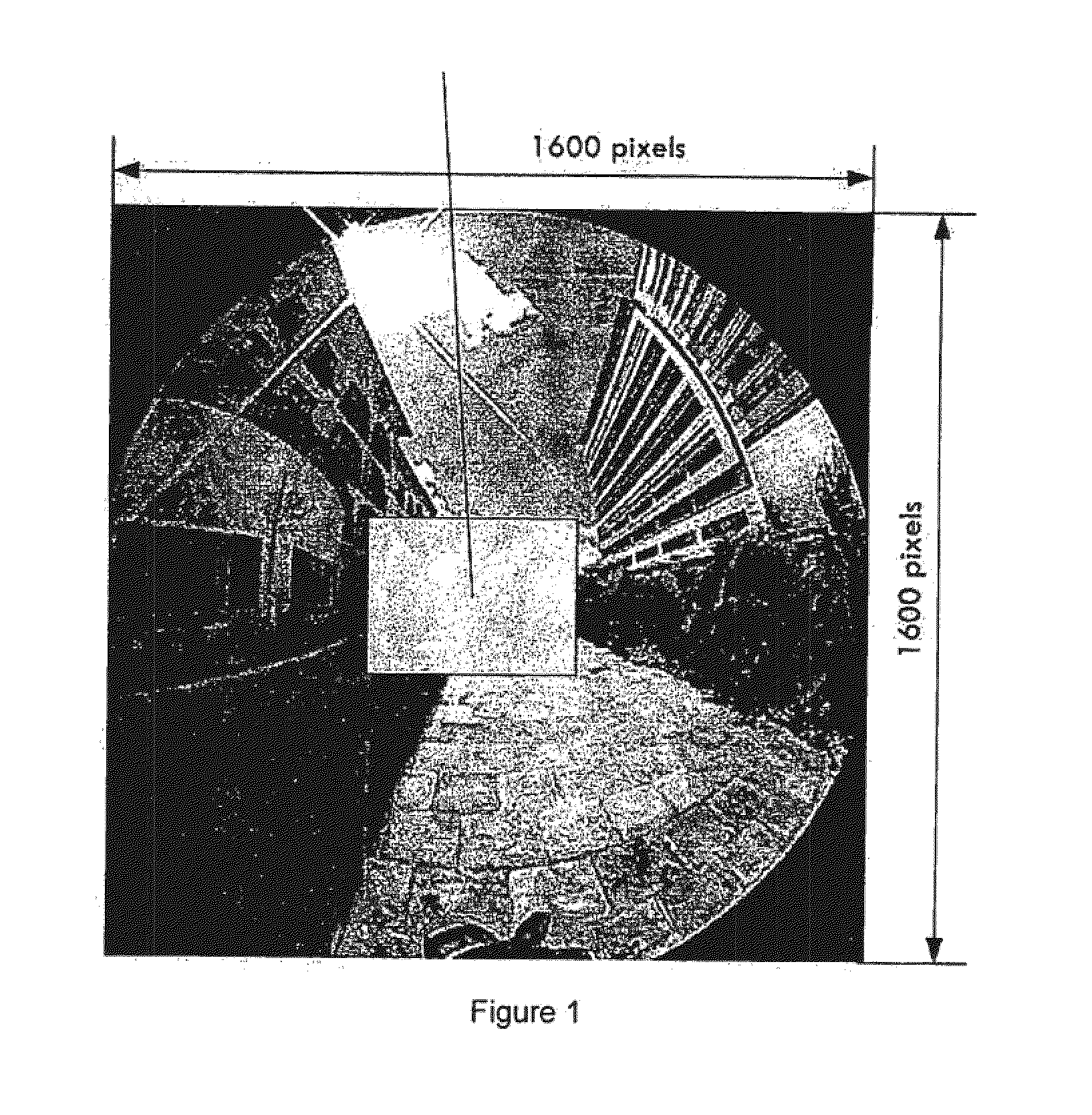
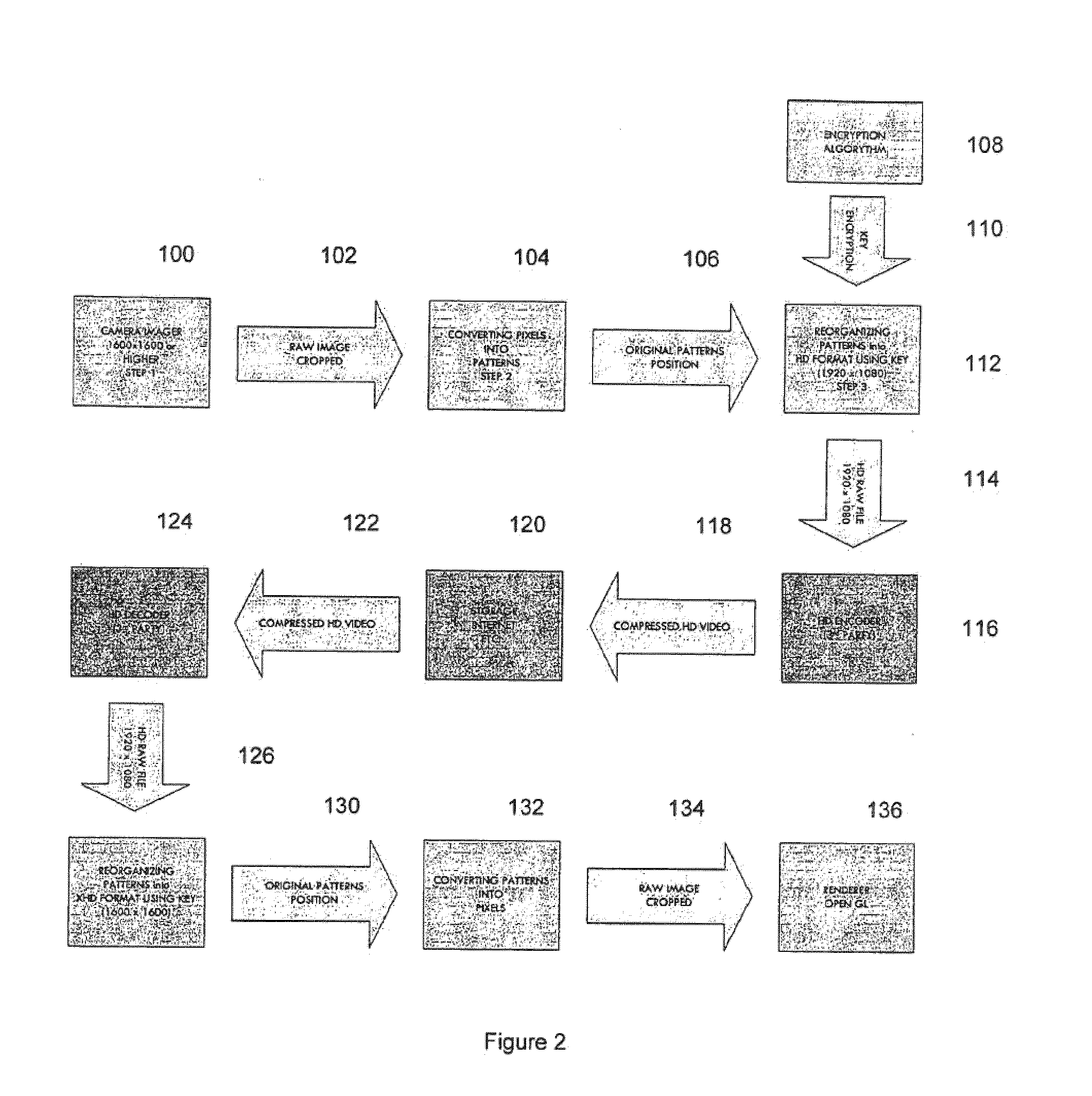
XHD video is acquired from a camera fitted with an ultra-wide field-of-view lens such as a fish eye lens. The active picture portion of the images are divided into patterns each having a plurality of pixels. The patterns are assigned coordinate values and then reformatted into HD format using an encryption key which reorders the patterns. The images are processed in the HD format and then returned to XHD formation by applying the reverse reordering process under the control of the key.
Owner:DOO TECH FZCO
Developer compositions and processes
A liquid developer comprised of a nonpolar liquid, thermoplastic resin, optional colorant, and an alumina charge acceptance additive.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method of making flexographic printing members
InactiveUS8408130B2Improved flexographic printing membersAdd highlightsAddressographsPrinting press partsElastomerEngineering
An imaging method provides a flexographic printing member used to transfer ink from an image area to a receiver element. This flexographic printing member has a relief image including an image area that is composed of an elastomeric composition that has an elastomeric topmost surface and a relief image floor. The relief image has a plurality of dots within a sub-area of the elastomeric topmost surface wherein each dot has a minimum receiver element contact area. A fraction less than 1 of the plurality of dots, known as (b) dots, have a topmost surface that is undercut below the elastomeric topmost surface. The (b) dots are undercut below the elastomeric topmost surface in a predetermined number and arrangement so that the (b) dots are still able to transfer ink to the receiver element. Each of the remainder of the plurality of dots in the sub-area, known as (a) dots, has a topmost surface that is essentially coincident with the elastomeric topmost surface.
Owner:MIRACLON CORP
System and method for expansion of field of view in a vision system
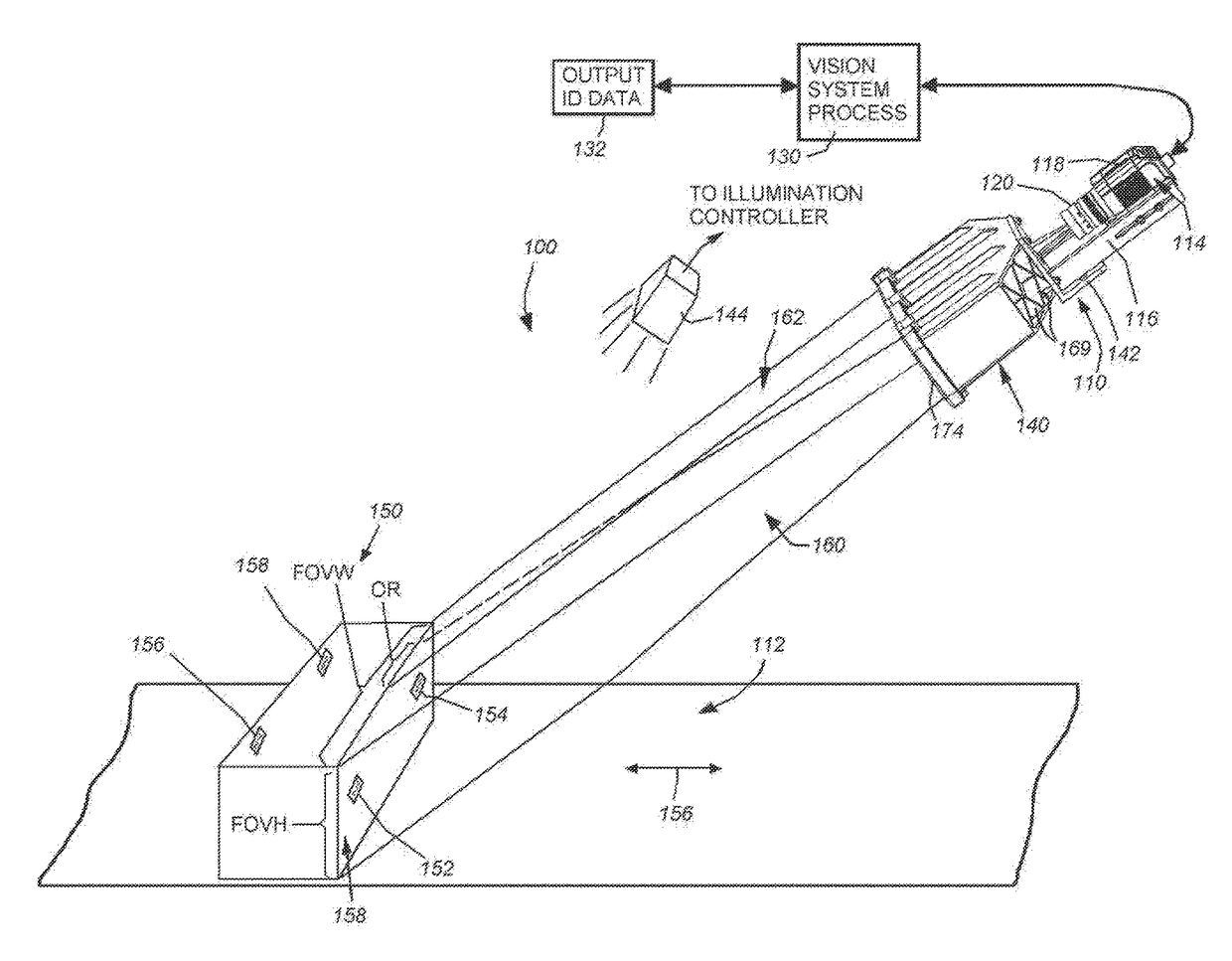
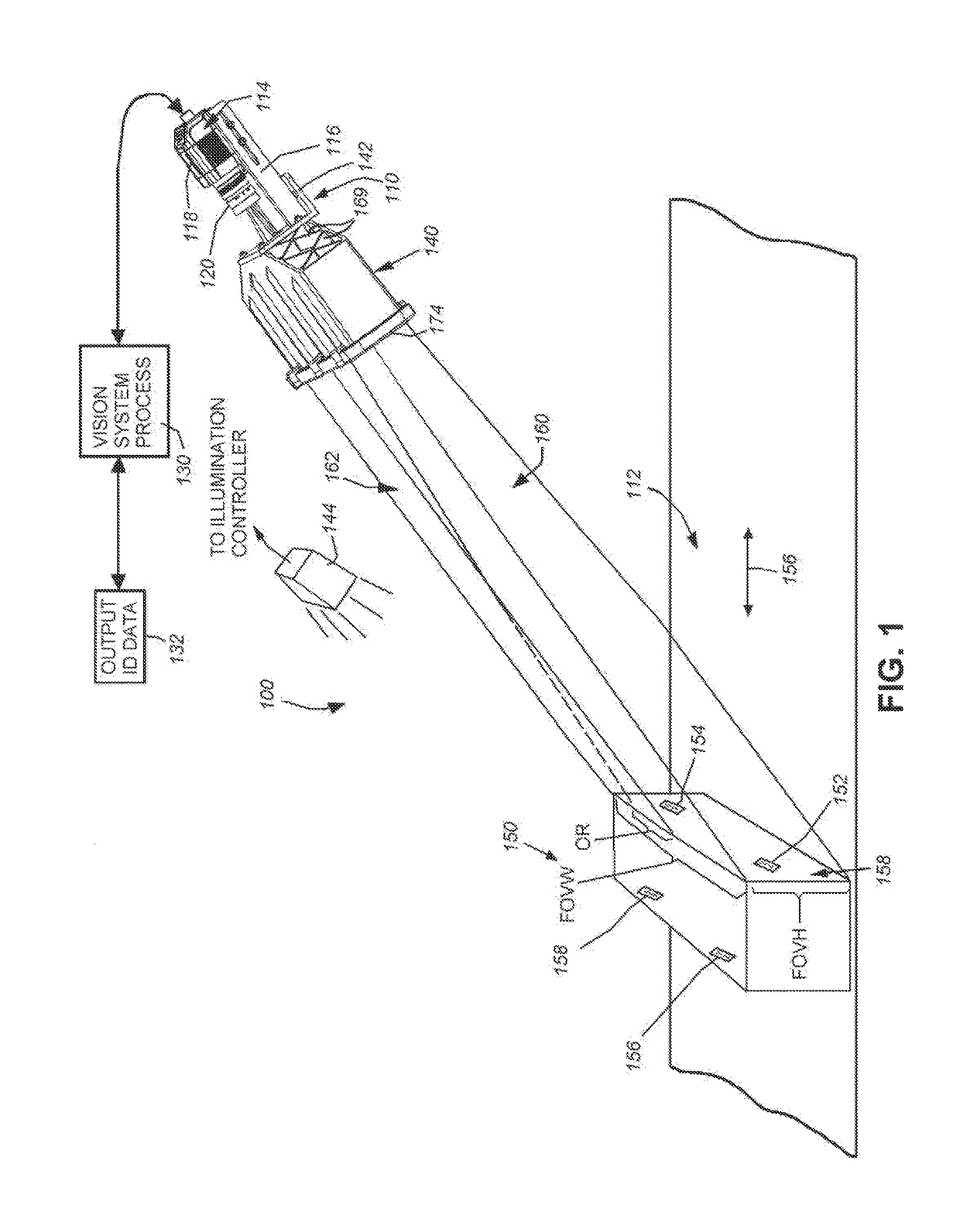
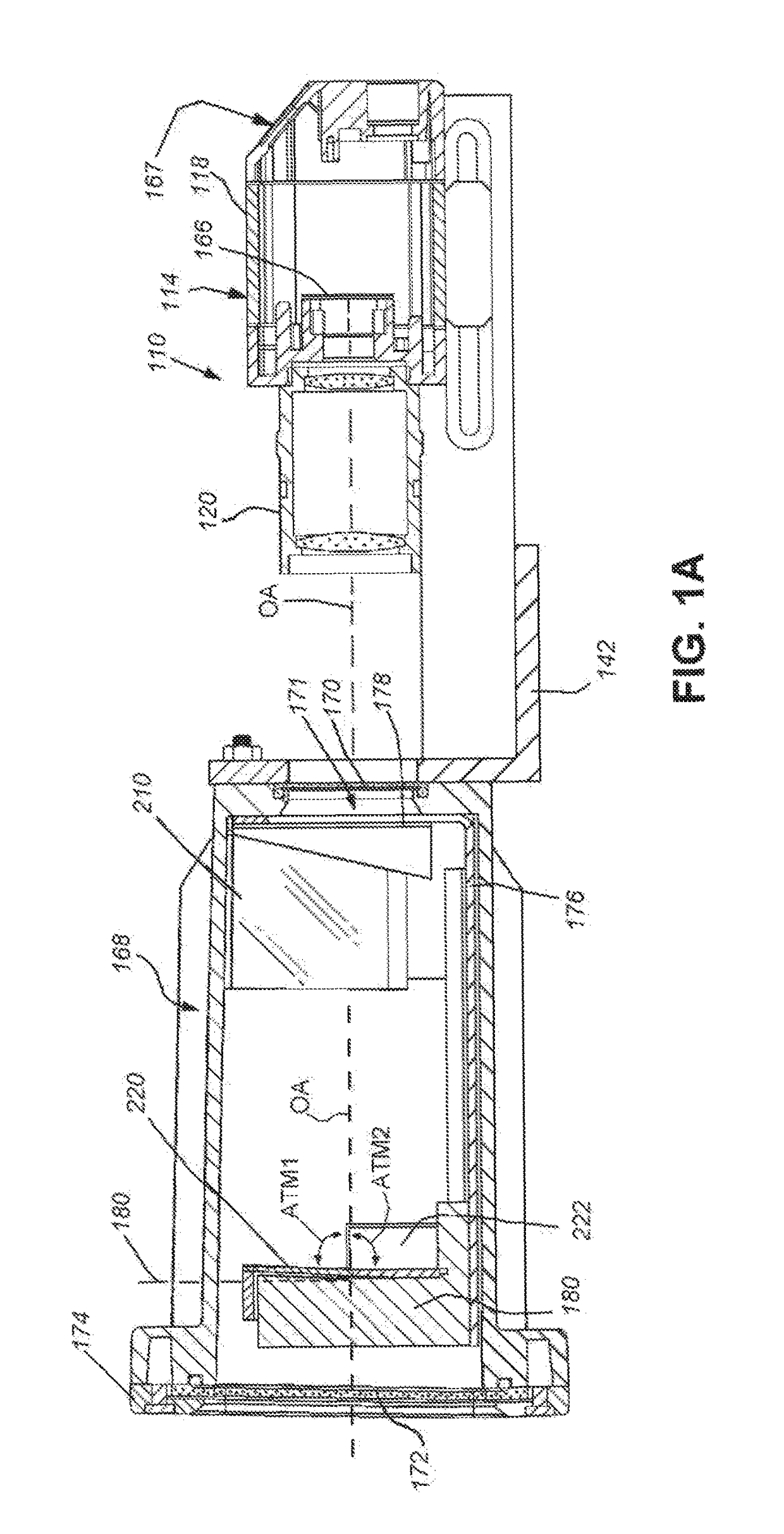
ActiveUS9892298B2Reduce resolutionStraightforward to installTelevision system detailsColor television detailsVisual field lossOptical axis
This invention provides a field of view expander (FOVE) removably attached to a vision system camera having an image sensor defining an image plane. In an embodiment the FOVE includes first and second mirrors that transmit light from a scene in respective first and second partial fields of view along first and second optical axes. Third and fourth mirrors respectively receive reflected light from the first and second mirrors. The third and fourth mirrors reflect the received light onto the image plane in a first strip and a second strip adjacent to the first strip. The first and second optical axes are approximately parallel and a first focused optical path length between the scene and the image plane and a second focused optical path between the image plane and the scene are approximately equal in length. The optical path can be rotated at a right angle in embodiments.
Owner:COGNEX CORP
Auto-stereoscopic display device
InactiveUS9807377B2Add depthWide viewing angleSteroscopic systemsNon-linear opticsRefractive indexDisplay device
An auto-stereoscopic display device includes a display panel having an array of display pixels for producing a display; and a view forming unit having an array of view forming elements. Each view forming elements is configurable to focus the outputs of groups of the display pixels into views projected towards a user in different directions. The display device further includes a view deflecting unit to selectably change the directions in which the plurality of views is projected towards the user. The view deflecting unit includes at least one birefringent prism having a first refractive index for light having a first polarization direction and a second refractive index for light having a second polarization direction. The view deflecting unit further includes a polarization switch in registration with the birefringent prism for providing the birefringent prism with display light having the first or second polarization direction.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com