Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
86results about How to "High power transmission" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Wireless Power Transmission System
InactiveUS20060266917A1Quick scanImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansData transmissionElectric power
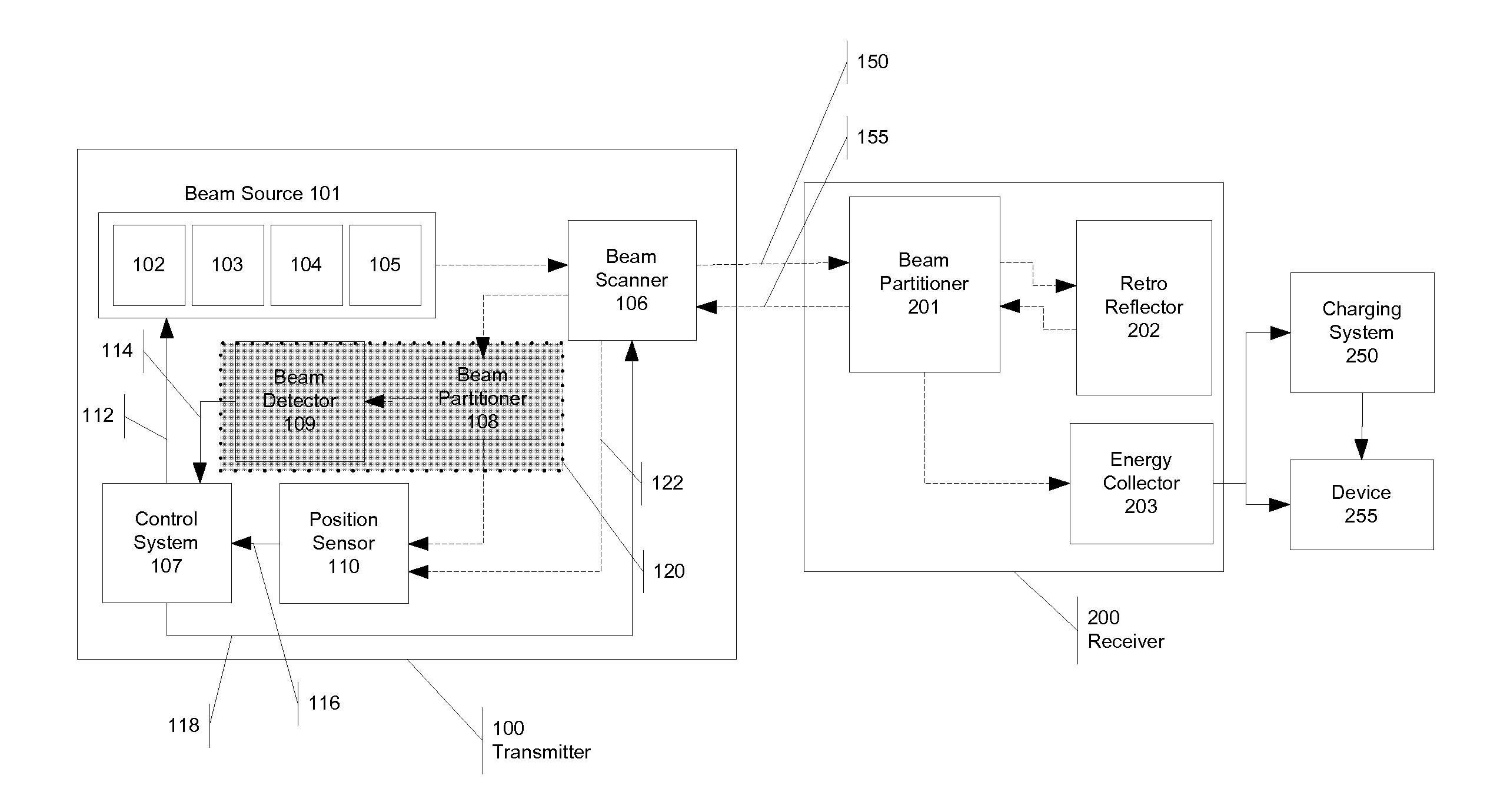
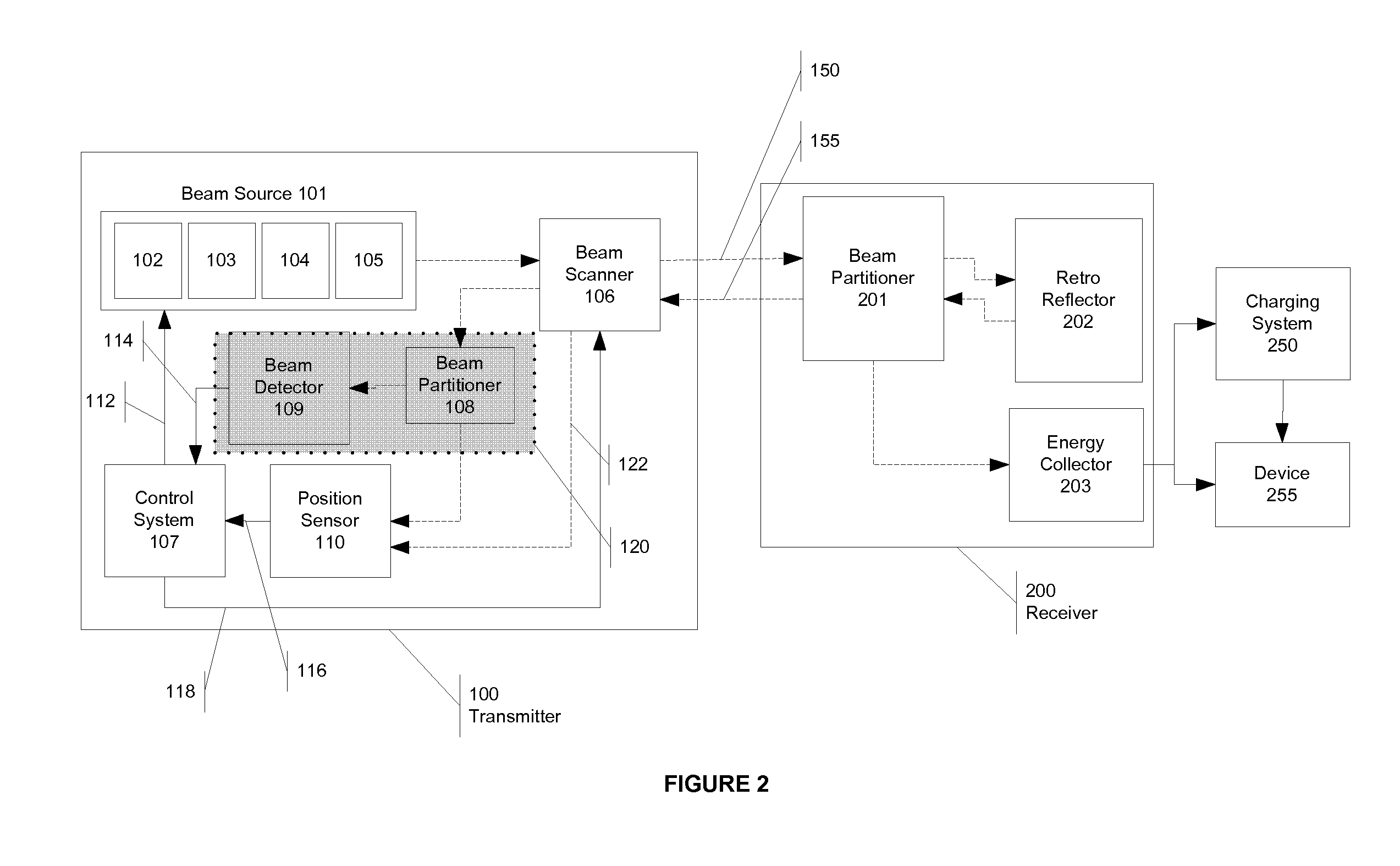
A novel method for wireless power transmission that comprises a transmitter and a receiver is disclosed. The receiver does not require an independent power source and is comprised of an optical feedback to the transmitter, and therefore does not require a separate communication channel to the transmitter. The transmitter uses the optical feedback to locate and track the receiver. The transmitter can optionally employ a macro adjusters and micro adjusters that direct the beam onto the receiver for optimal power transmission. The system also optionally has a tight loop beam detector to enhance safety of the system. Either the receiver and / or the transmitter may also encode data on the energy transmission, resulting in one-way or two-way data transmission.
Owner:BALDIS SISINIO F +2
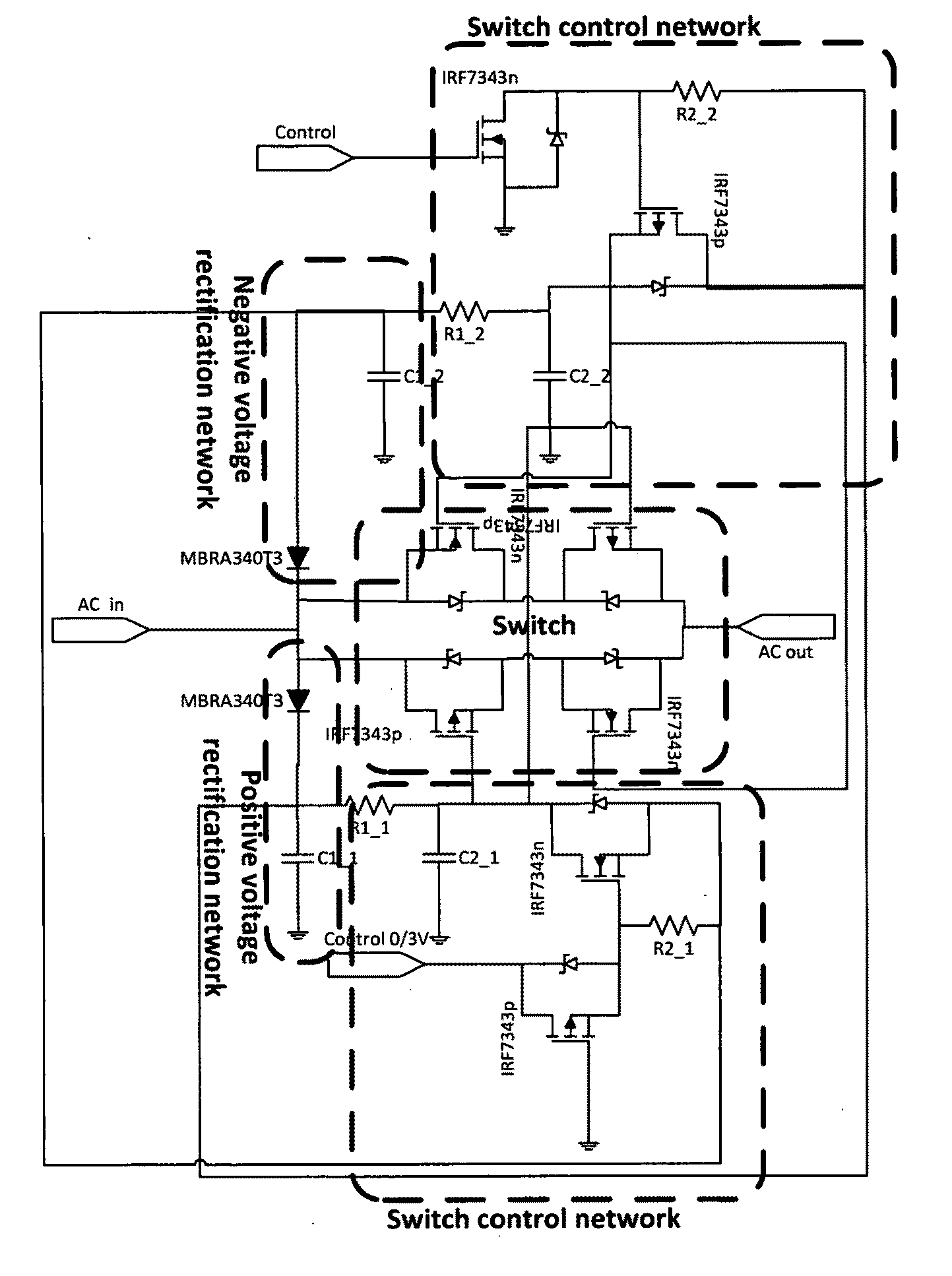
Miniature high voltage/current ac switch using low voltage single supply control
InactiveUS20100110741A1Improve efficiencyAvoid heatingAc-dc conversionSafety/protection circuitsElectric power transmissionHigh voltage igbt
Embodiments of the invention pertain to a method and apparatus for planar wireless power transfer where the receiver switches off and / or performs a duty cycle. In an embodiment, the switch can be used in a system that having a high voltage / current solid state switch, without having a high voltage control signal. An embodiment provides a switch that is capable of breaking, or greatly reducing, the connection of the receiver coil and the receiver circuitry in order to enable the receiver to decouple from the power transfer system. This embodiment can allow the transmitter to put out more power to other devices without providing power to the switched device. When the switch is used for a fully charged device, the switching can prevent or reduce damage to the fully charged device.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Resonant, contactless radio frequency power coupling
InactiveUS8212414B2Low costAvoid disadvantagesBatteries circuit arrangementsElectromagnetic wave systemDielectricElectricity
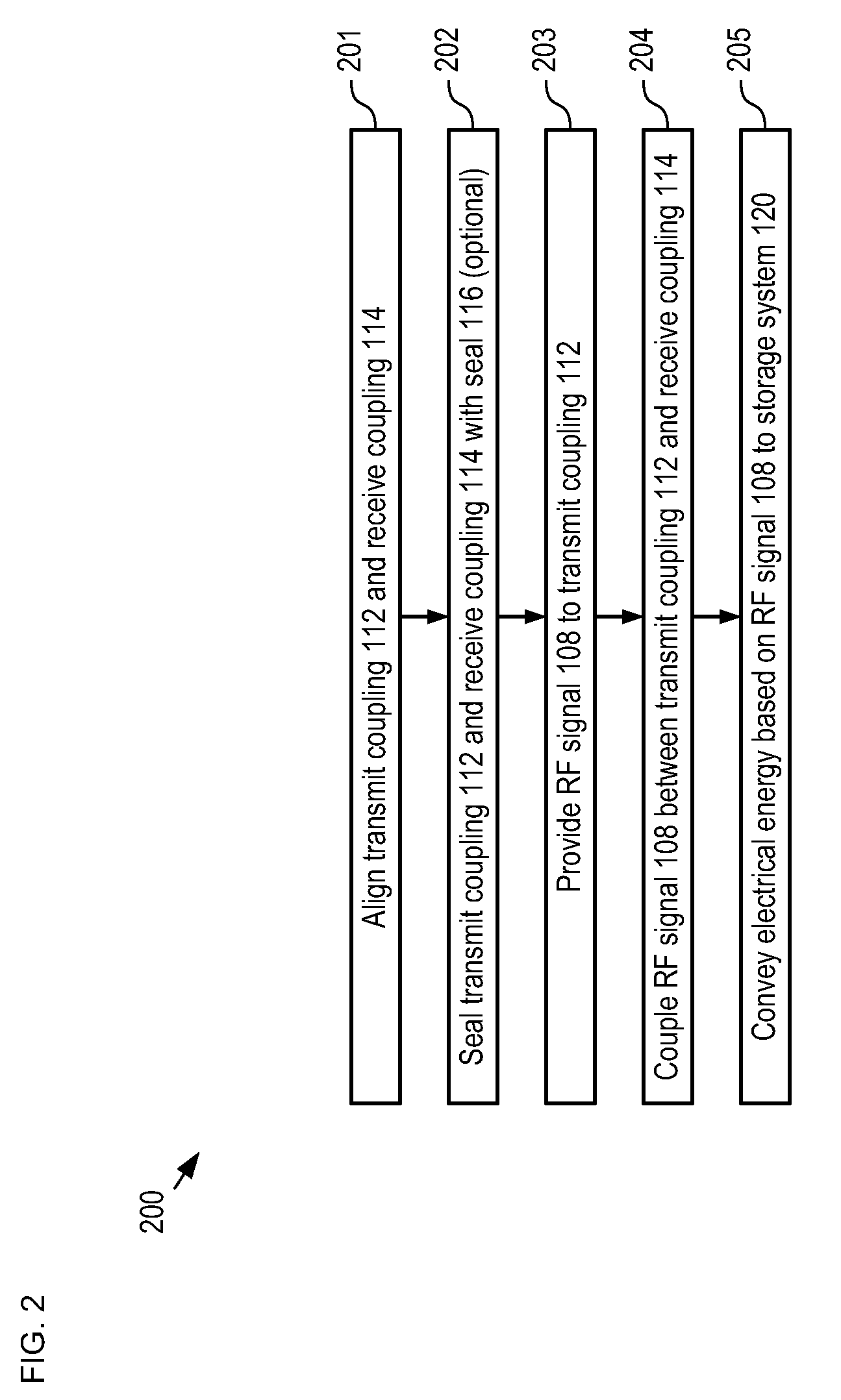
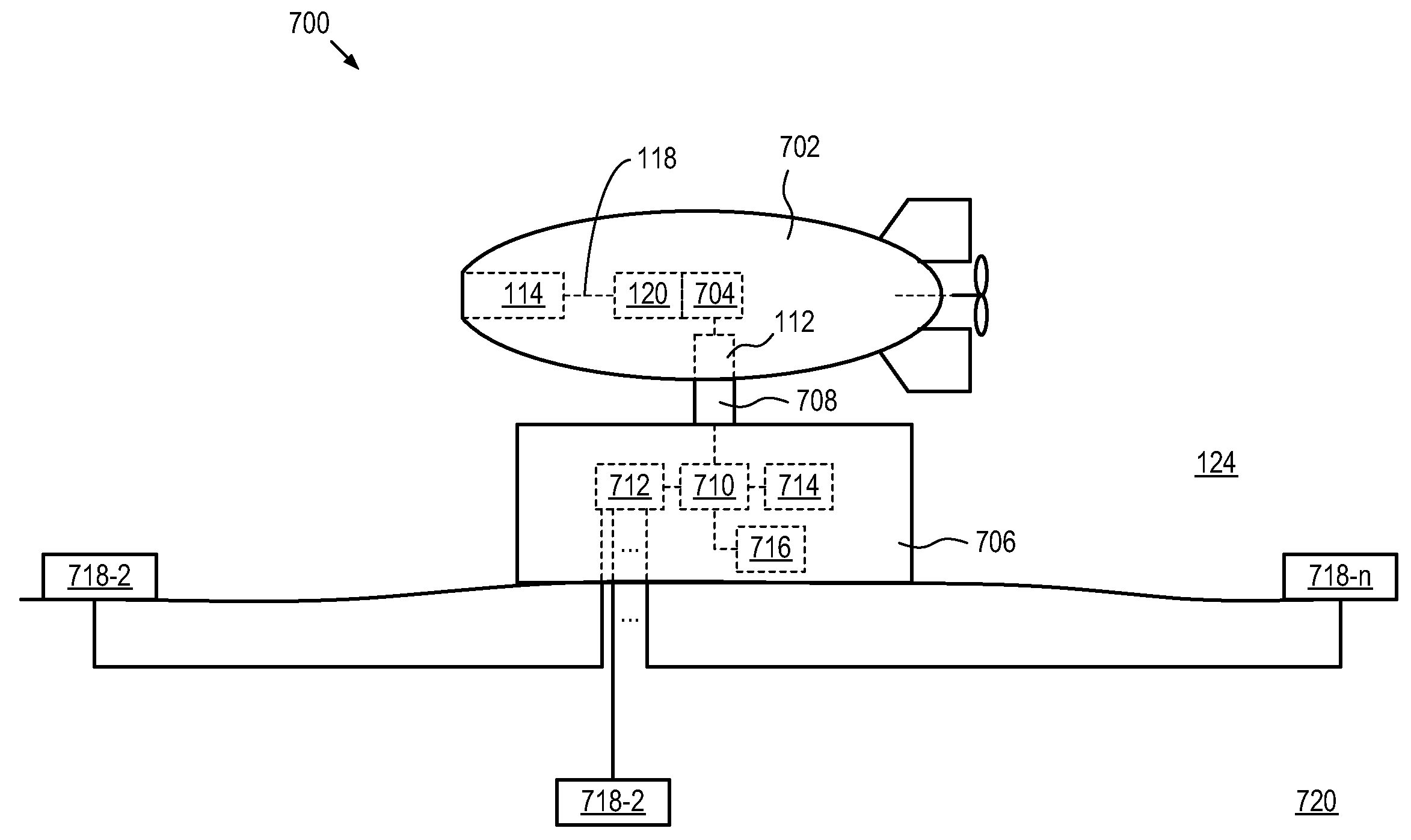
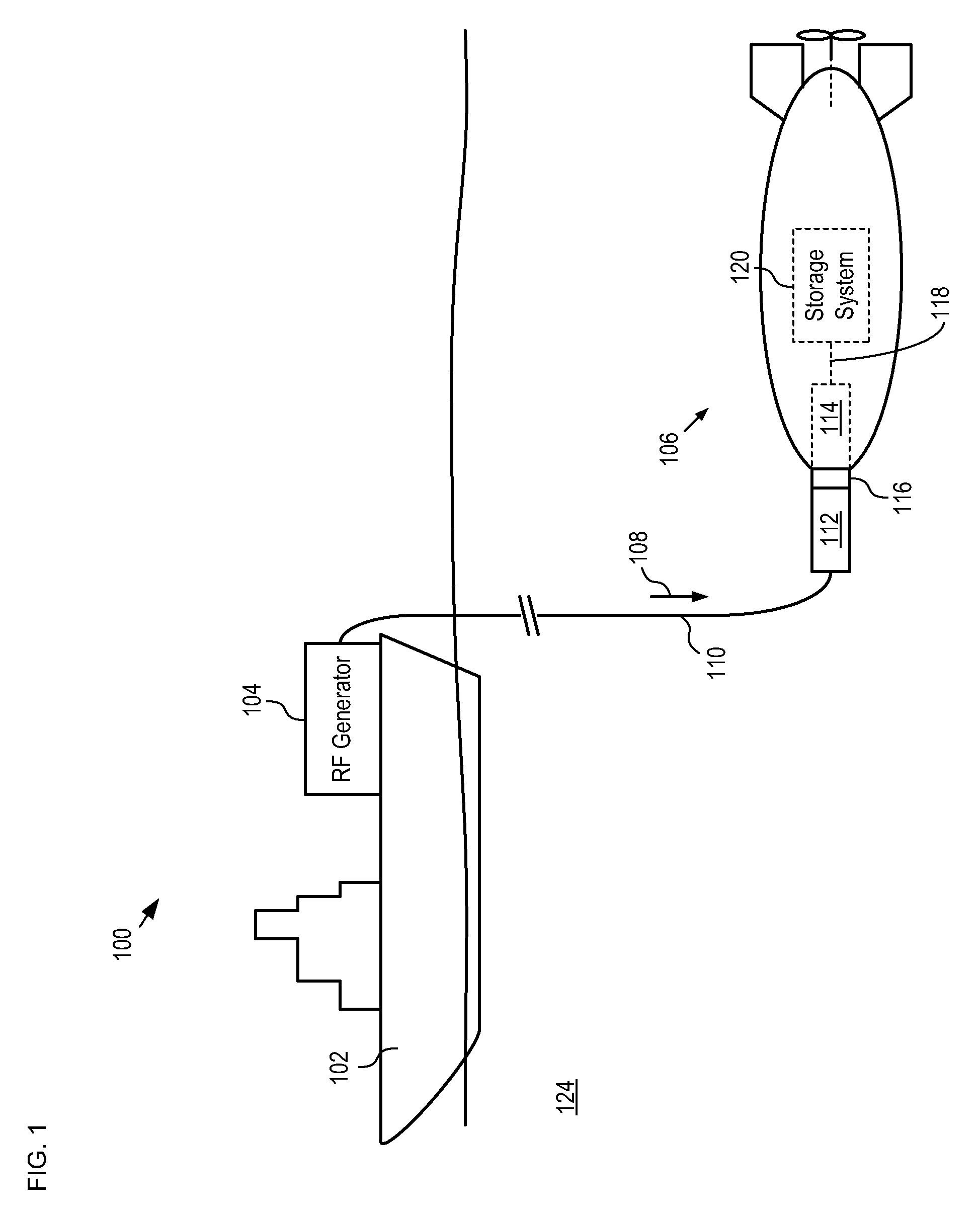
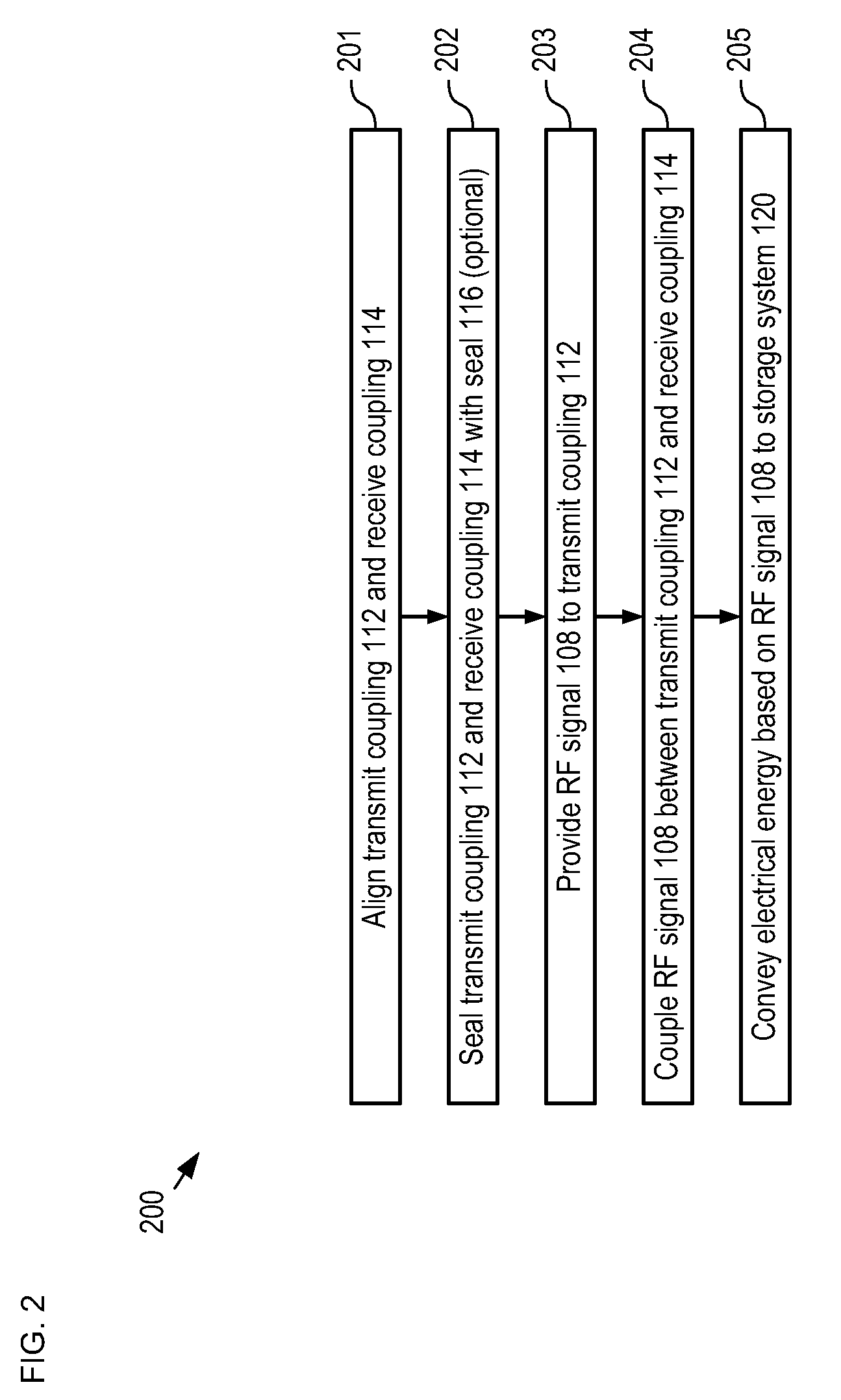
A resonant, contactless, RF power coupling suitable for high power-density applications and for use in an ocean environment is disclosed. In the illustrative embodiment, the power coupling includes a transmit coupling and a receive coupling, each of which include a resonant element. A high-powered RF generator is coupled to the transmit coupling and a rectifier circuit is coupled to the output coupling. Each of the resonant elements is disposed in its own electrically-conductive canister and advantageously potted in an appropriate insulating dielectric. Each canister has an open end to facilitate inductive coupling between the two resonant elements. In order to exclude seawater from the interface between the canisters, a seal of compliant material is disposed therebetween.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
System and method for locating objects and communicating with the same
ActiveUS7646330B2Level signalImprove signal-to-noise ratioRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsEngineeringTime of flight
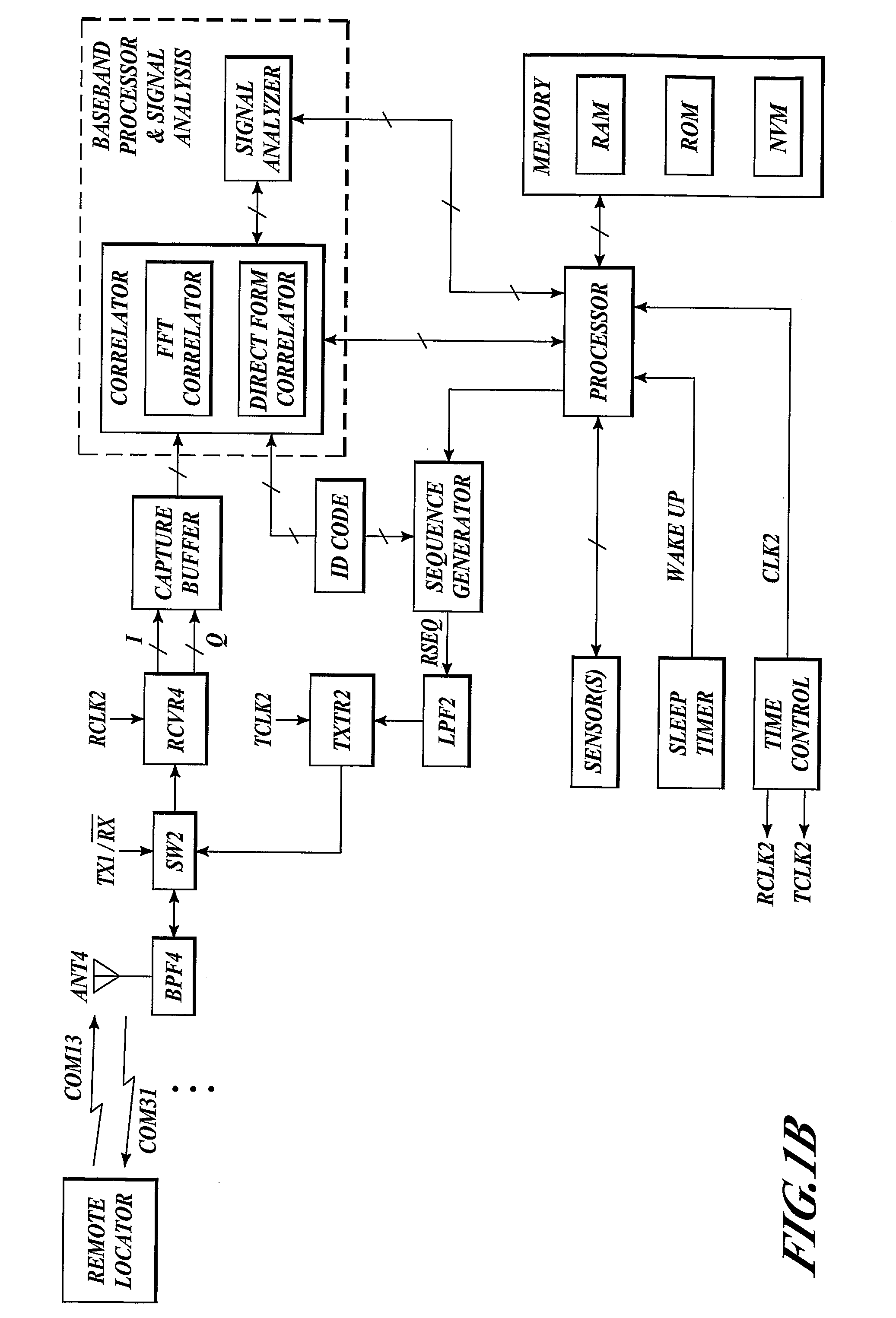
Communication between a remote locator and a transponder is used to determine the relative position of the transponder. The transponder and locator each include a transmitter and a receiver. The locator transmits an inquiry in the form of a relatively powerful cyclically encoded signal with repetitive elements, uniquely associated with a target transponder. Periodically, each transponder correlates its coded ID against a possible inquiry signal, determining frequency, phase and framing in the process. Upon a match, the transponder transmits a synthesized response coherent with the received signal. The locator integrates multiple cyclical response elements, allowing low-power transmissions from the transponder. The locator correlates the integrated response, determines round-trip Doppler shift, time-of-flight, and then computes the distance and angle to the transponder. The transponder can be wearable, bionically implanted, or attached to, or embedded in, some object.
Owner:SANTA MONICA SEMICON
Resonant, Contactless Radio Frequency Power Coupling
InactiveUS20100007214A1Low costAvoid disadvantagesBatteries circuit arrangementsCharging stationsDielectricElectricity
A resonant, contactless, RF power coupling suitable for high power-density applications and for use in an ocean environment is disclosed. In the illustrative embodiment, the power coupling includes a transmit coupling and a receive coupling, each of which include a resonant element. A high-powered RF generator is coupled to the transmit coupling and a rectifier circuit is coupled to the output coupling. Each of the resonant elements is disposed in its own electrically-conductive canister and advantageously potted in an appropriate insulating dielectric. Each canister has an open end to facilitate inductive coupling between the two resonant elements. In order to exclude seawater from the interface between the canisters, a seal of compliant material is disposed therebetween.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
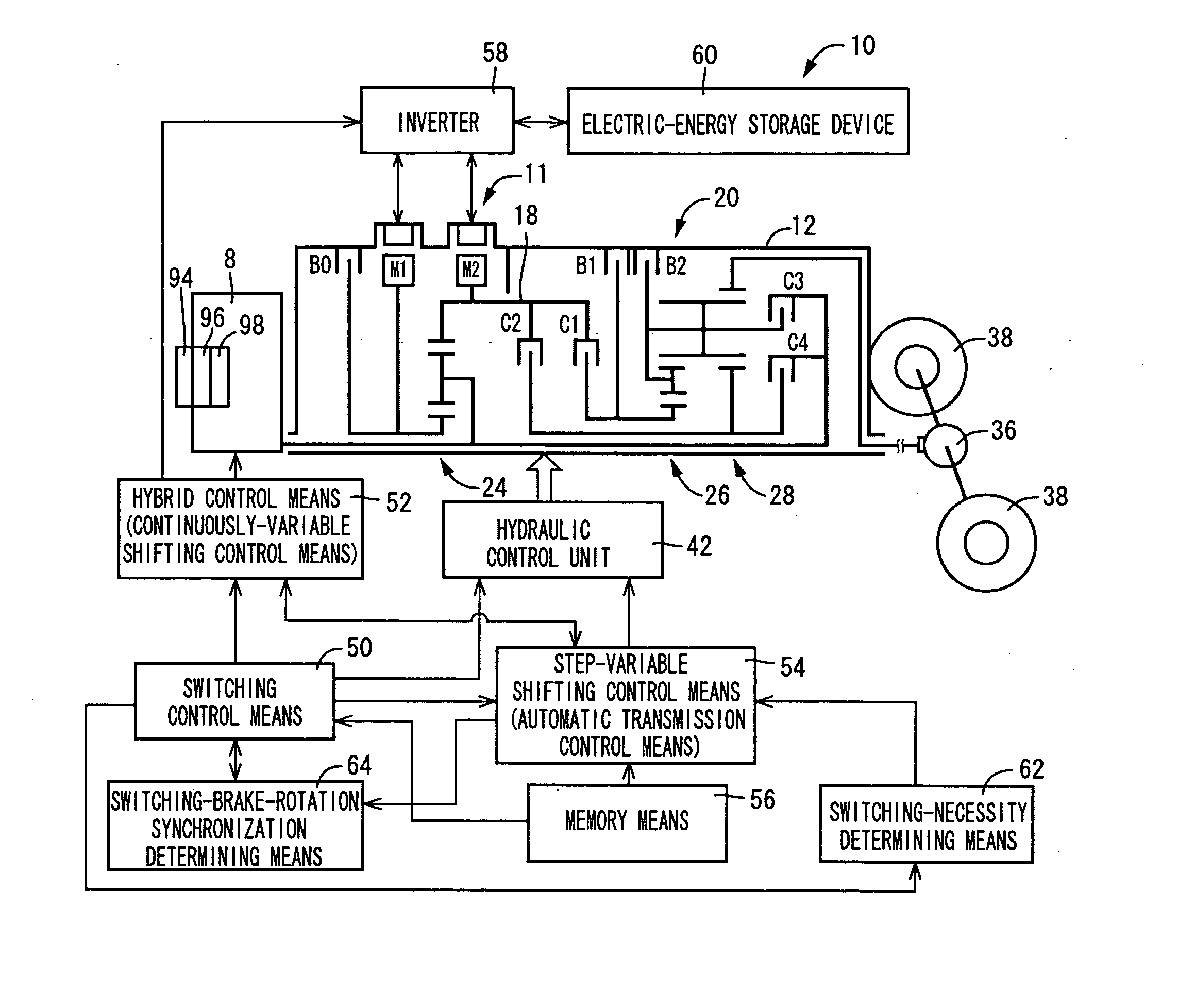
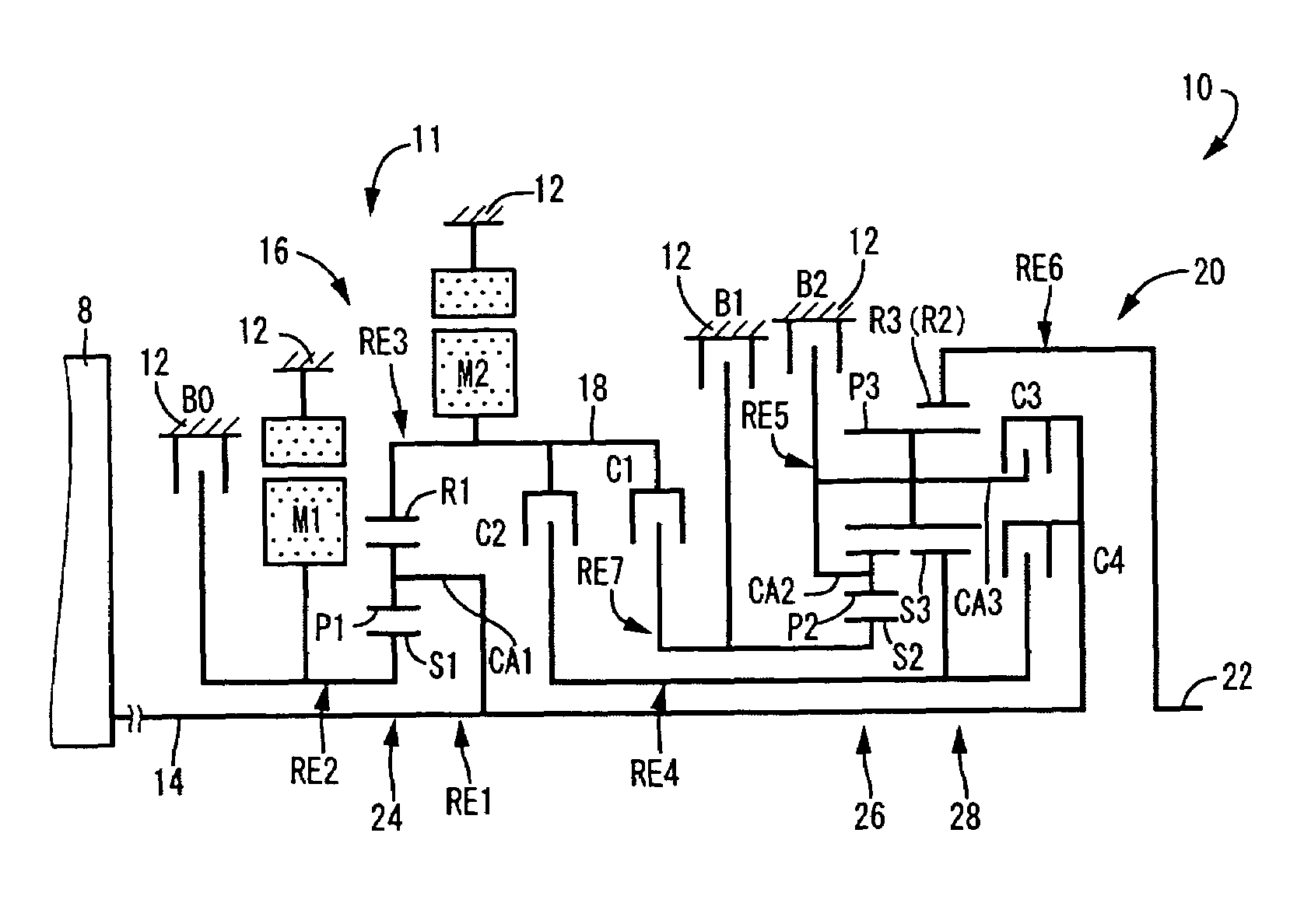
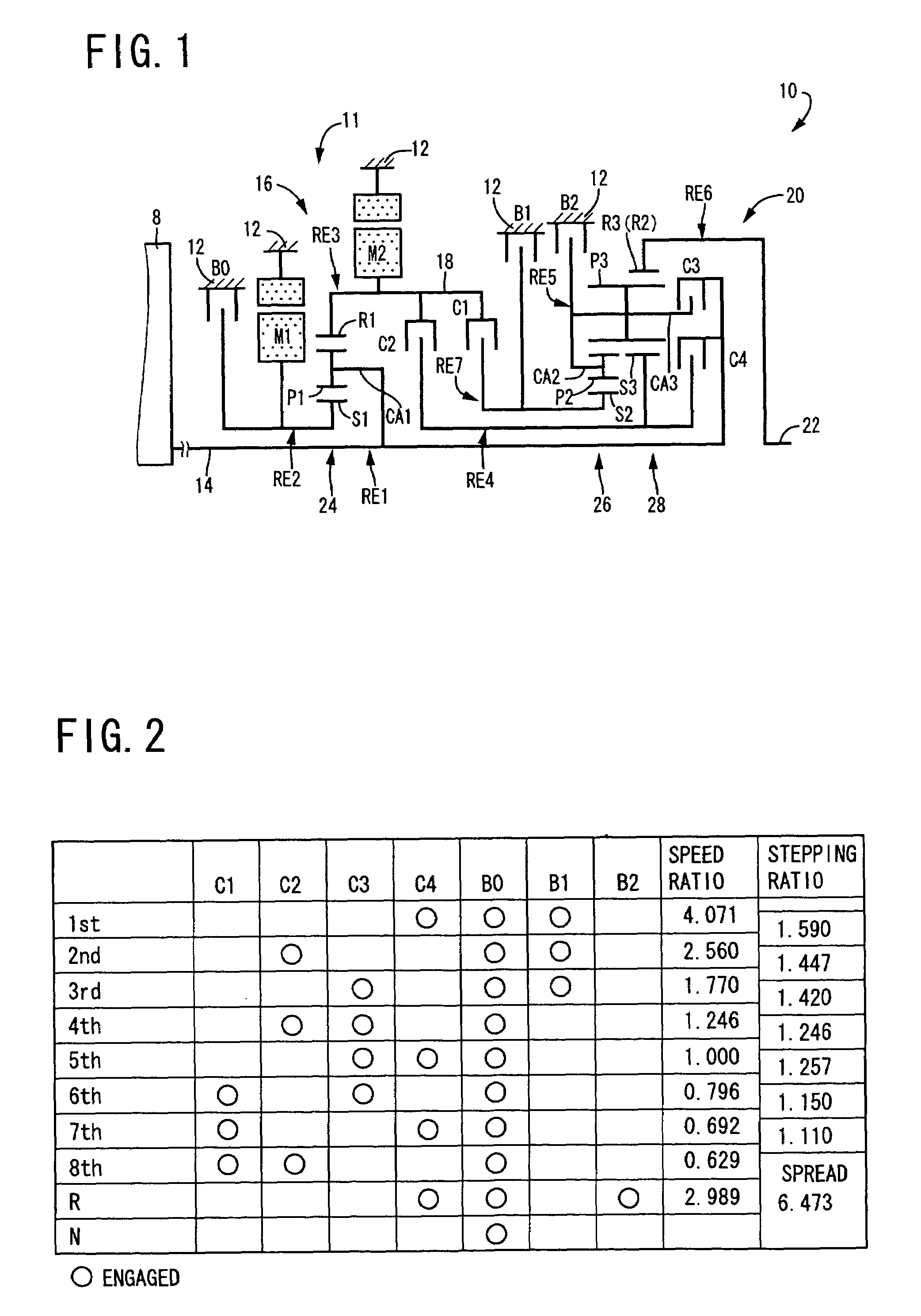
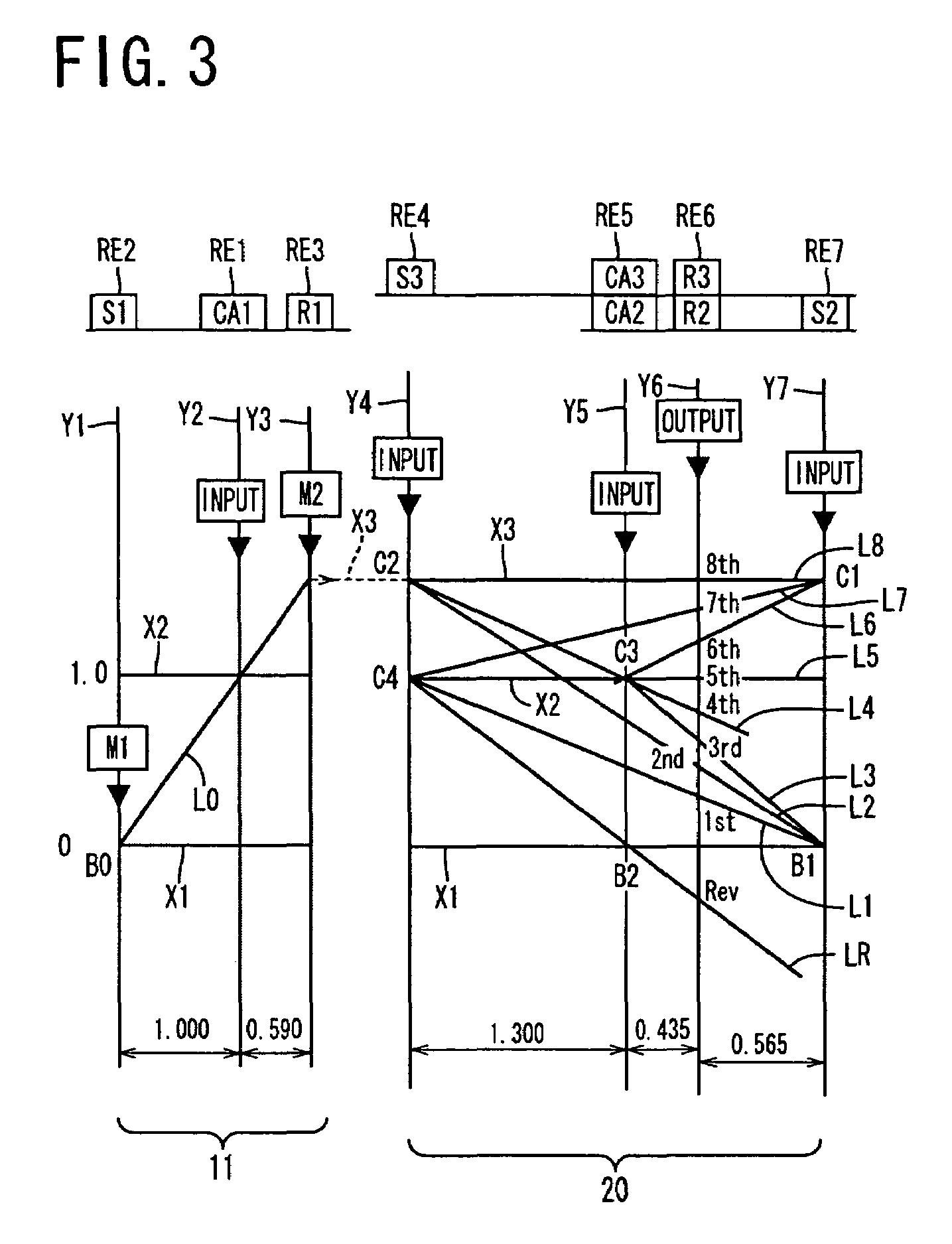
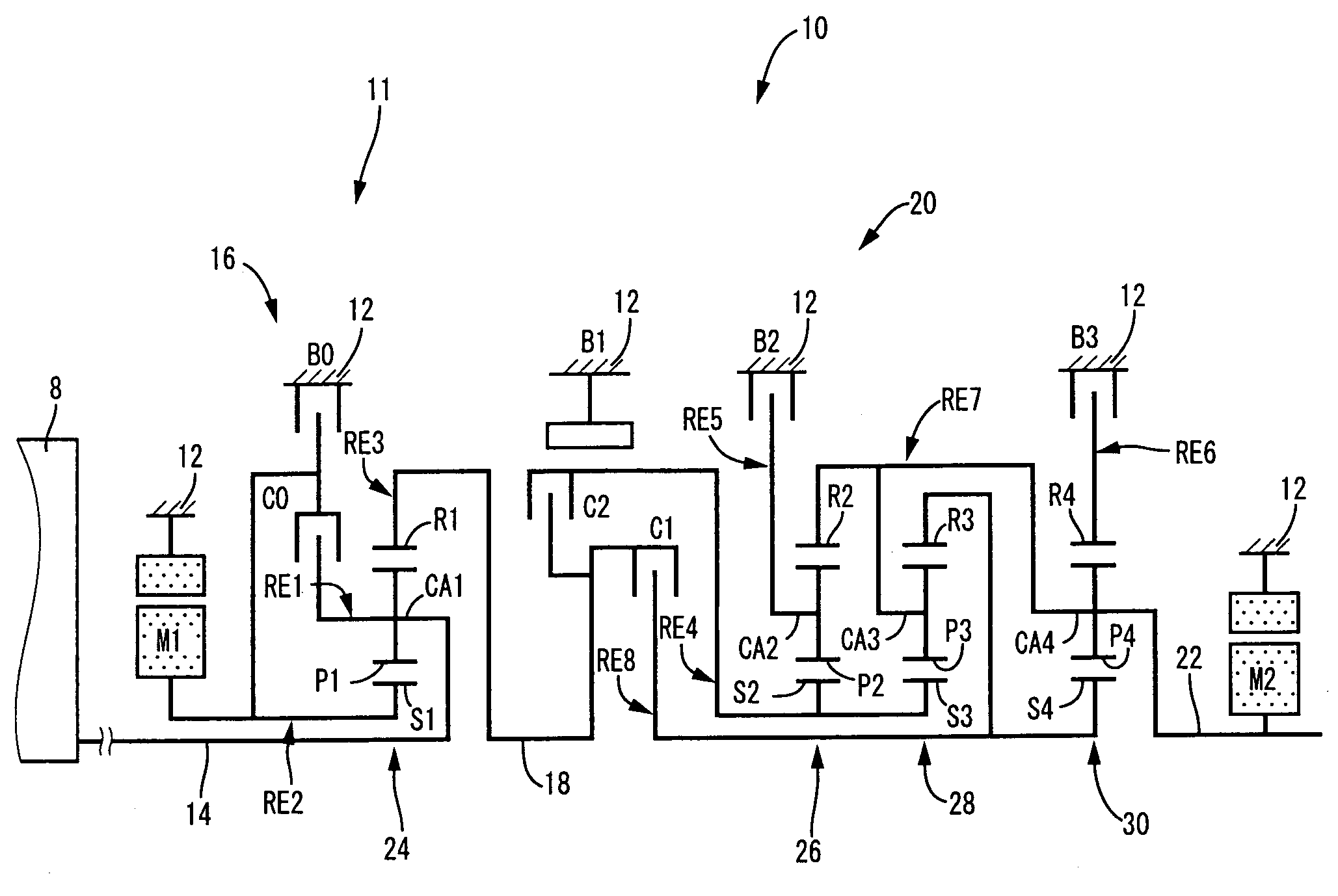
Control apparatus for vehicular drive system
InactiveUS20070105679A1Improve efficiencySmooth changeHybrid vehiclesElectric propulsion mountingDrive wheelDifferential function
A control apparatus for a vehicular drive system including a continuously-variable transmission portion operable as an electrically controlled continuously variable transmission, and a step-variable transmission portion, the continuously variable transmission portion having a differential mechanism operable to distribute an output of an engine to a first electric motor and a power transmitting member, and a second electric motor disposed in a power transmitting path between the power transmitting member and a drive wheel of a vehicle. The control apparatus including a differential-state limiting device provided in the differential mechanism, and operable to limit a differential function of the differential mechanism, for limiting an operation of the continuously-variable transmission portion as the electrically controlled continuously variable transmission, and an electric-motor control portion for controlling a drive-force assisting operation to generate an assisting drive force to drive the vehicle during a shifting action of the step-variable transmission portion, in different manners depending upon whether the continuously-variable transmission portion is placed in a continuously-variable shifting or a non-continuously-variable shifting state.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Powershift transmission in a motor vehicle
ActiveUS20130005525A1Increased power lossIncrease rangeToothed gearingsGearing controlMobile vehicleGear wheel
A powershift transmission in a motor vehicle is arranged between a prime mover and driven wheels of the motor vehicle for transmission of propulsive power and selection of different gear speed ratios. The powershift transmission includes at least two factional clutches for alternatively engaging at least two input shafts, a main transmission, a range section and an output shaft. A countershaft in the powershift transmission is rotationally connectable to the output shaft in order to establish a by-pass torque path, passing by the range section, and in which propulsive power can be transferred when the range section is gear shifted between different range speed ratios.
Owner:VOLVO LASTVAGNAR AB
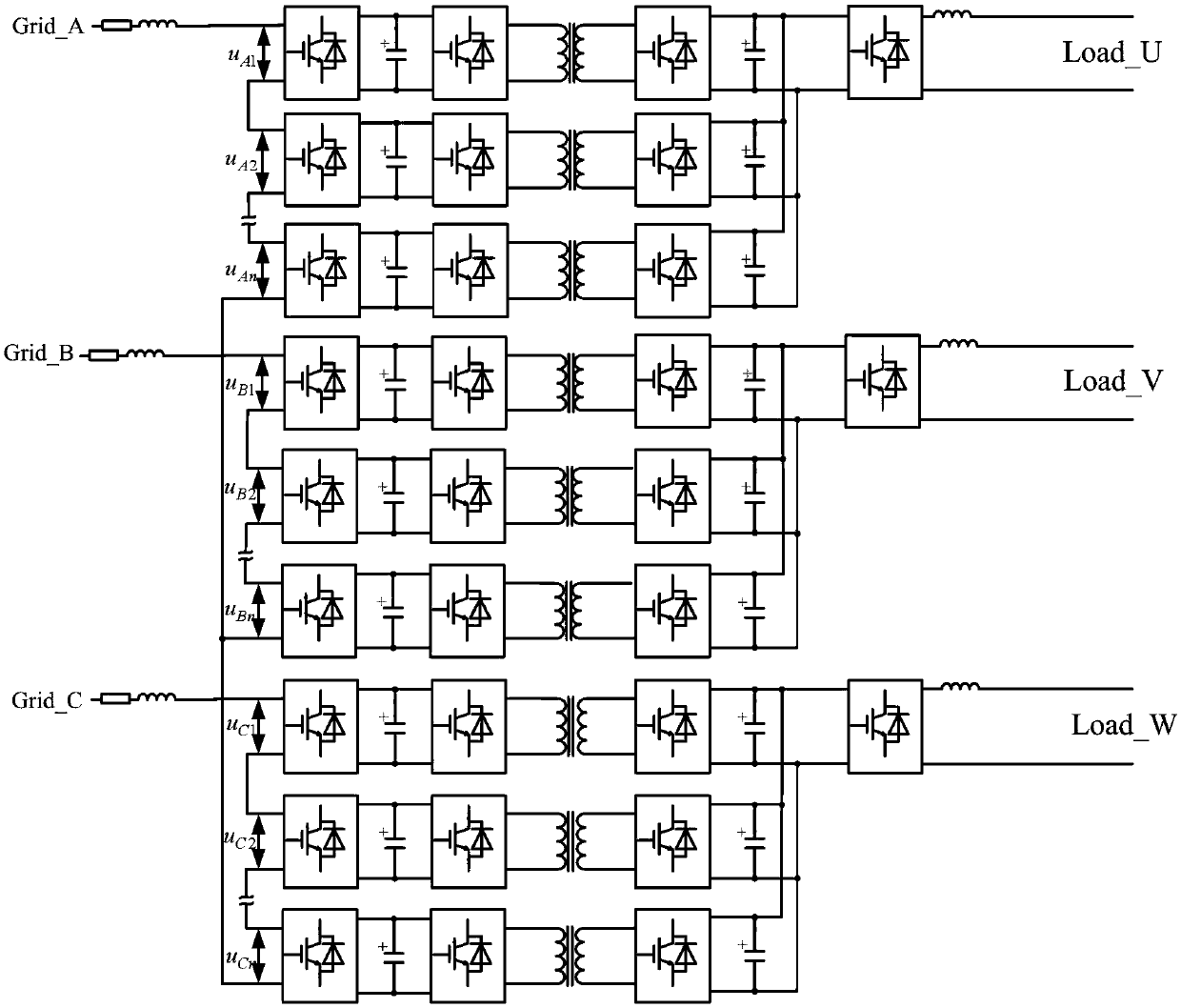
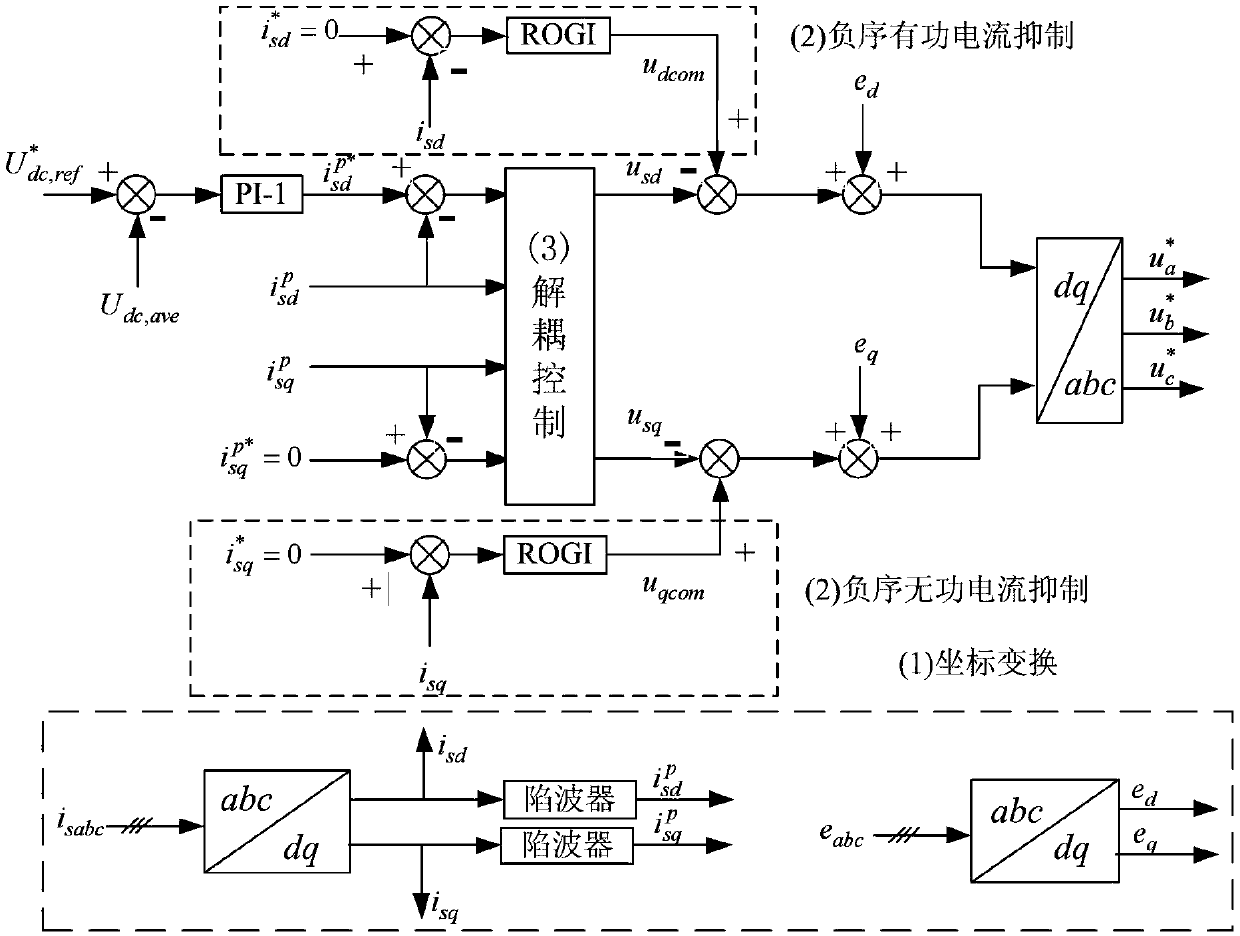
A cascaded power electronic transformer and an unbalance compensation control method thereof
ActiveCN109067193AImproved ability to deal with unbalanced conditionsHigh quality power transferPolyphase network asymmetry elimination/reductionAc-ac conversionLoop controlTransformer
The invention provides an unbalance compensation control method of a cascaded power electronic transformer, comprising a control component and a transformer, wherein the transformer is composed of aninput rectifier stage, an isolation stage and an output inverter stage. The input stage is a three-phase star-connected cascaded H-bridge rectifier, the isolation stage is a plurality of independent dual-active-bridge converters, and the output stage is a single-phase PWM inverter. The control method of the present invention includes an input rectifier stage stratification control unit, a voltageclosed loop control unit of an isolation stage and a constant voltage and current sharing control unit of an output inverter stage. The input rectifier stage stratification control unit, is further divided into an upper control unit and a lower control unit, wherein the upper control unit is composed of a coordinate transformation, a positive sequence decoupling control and a negative sequence current suppression, and the lower control unit is an in-phase voltage sharing control. The control method provided by the invention can simultaneously solve the negative sequence current compensation problem of the PET when the voltage at the network side and the three-phase load are unbalanced, thereby promoting the application of the power electronic transformer in the engineering practice.
Owner:南京雁展科技有限公司
Control apparatus for vehicular drive system
InactiveUS7566288B2Improve fuel economyHigh power transmissionHybrid vehiclesSpeed controllerDrive wheelDifferential function
A control apparatus for a vehicular drive system including a continuously-variable transmission portion operable as an electrically controlled continuously variable transmission having a differential mechanism operable to distribute an output of an engine to a first electric motor and a power transmitting member, and a second electric motor disposed in a power transmitting path between the power transmitting member and a drive wheel of a vehicle. The control apparatus includes: (a) a differential-state limiting device provided in the differential mechanism, and operable to limit a differential function of the differential mechanism, for limiting an operation of the continuously-variable transmission portion as the electrically controlled continuously variable transmission; and (b) a differential-state switching controller operable, when acceleration or deceleration of the vehicle is required, for removing the limitation imposed by the differential-state limiting device on the operation of the continuously-variable transmission portion as the electrically controlled continuously variable transmission.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
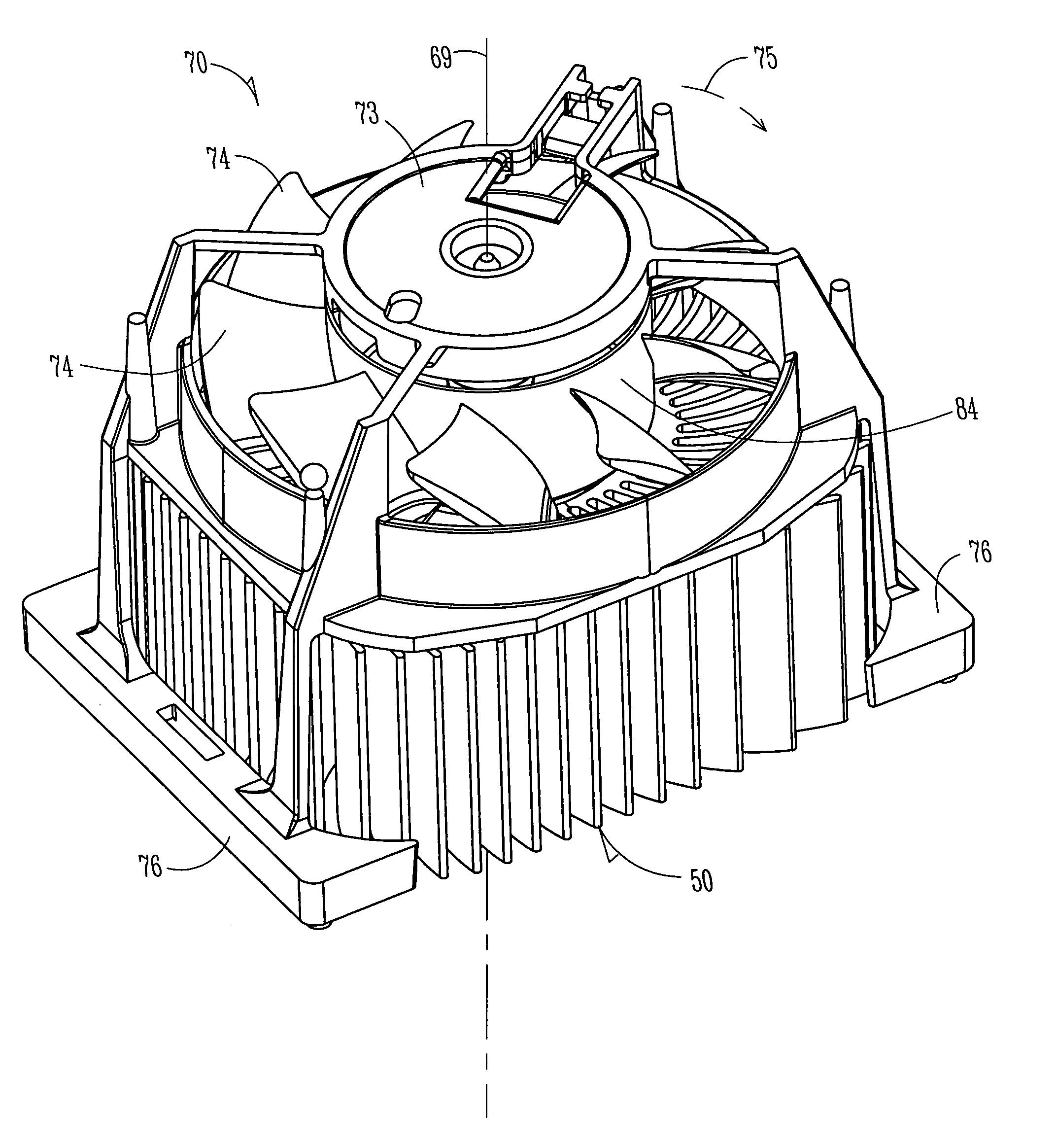
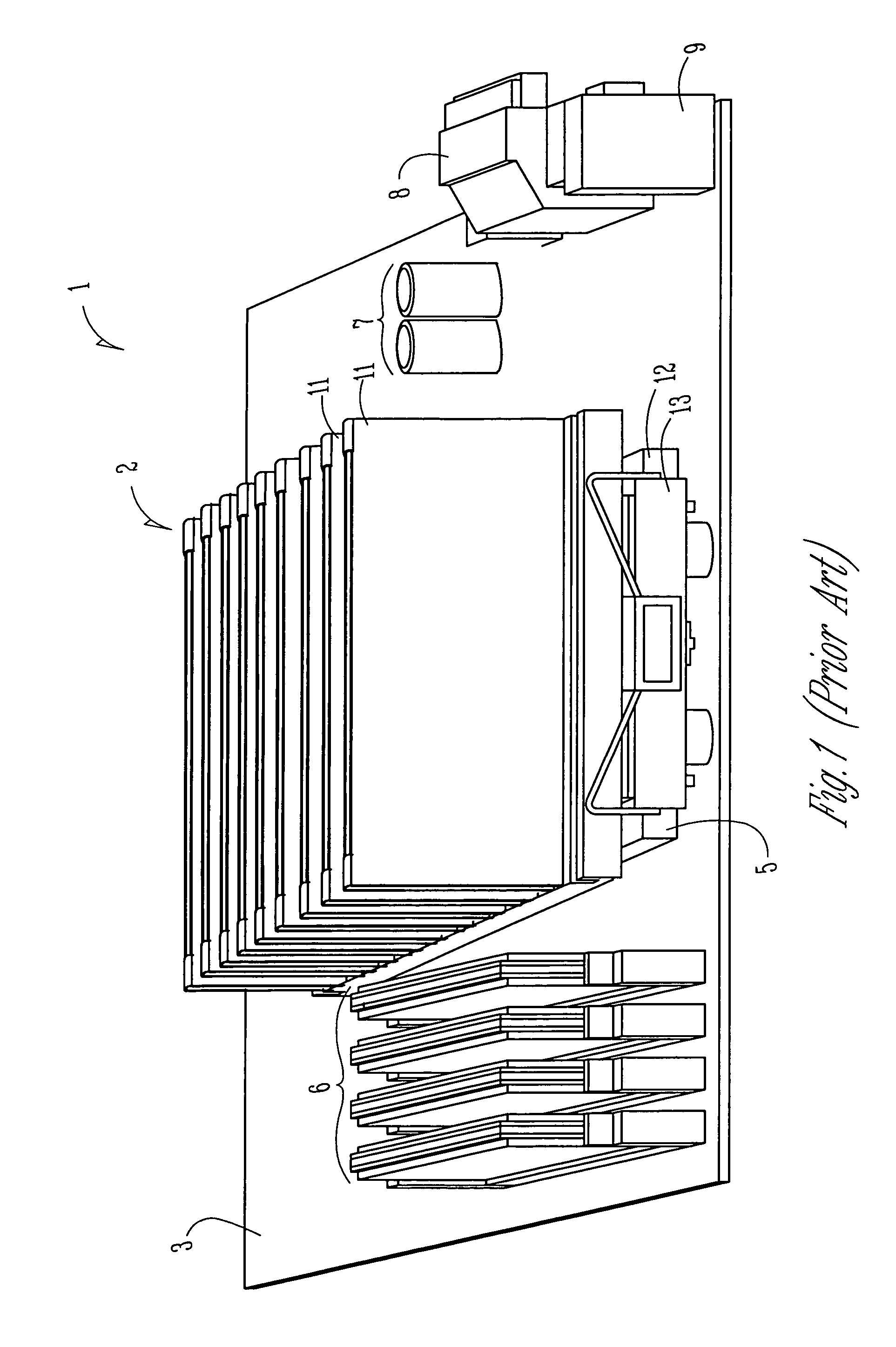
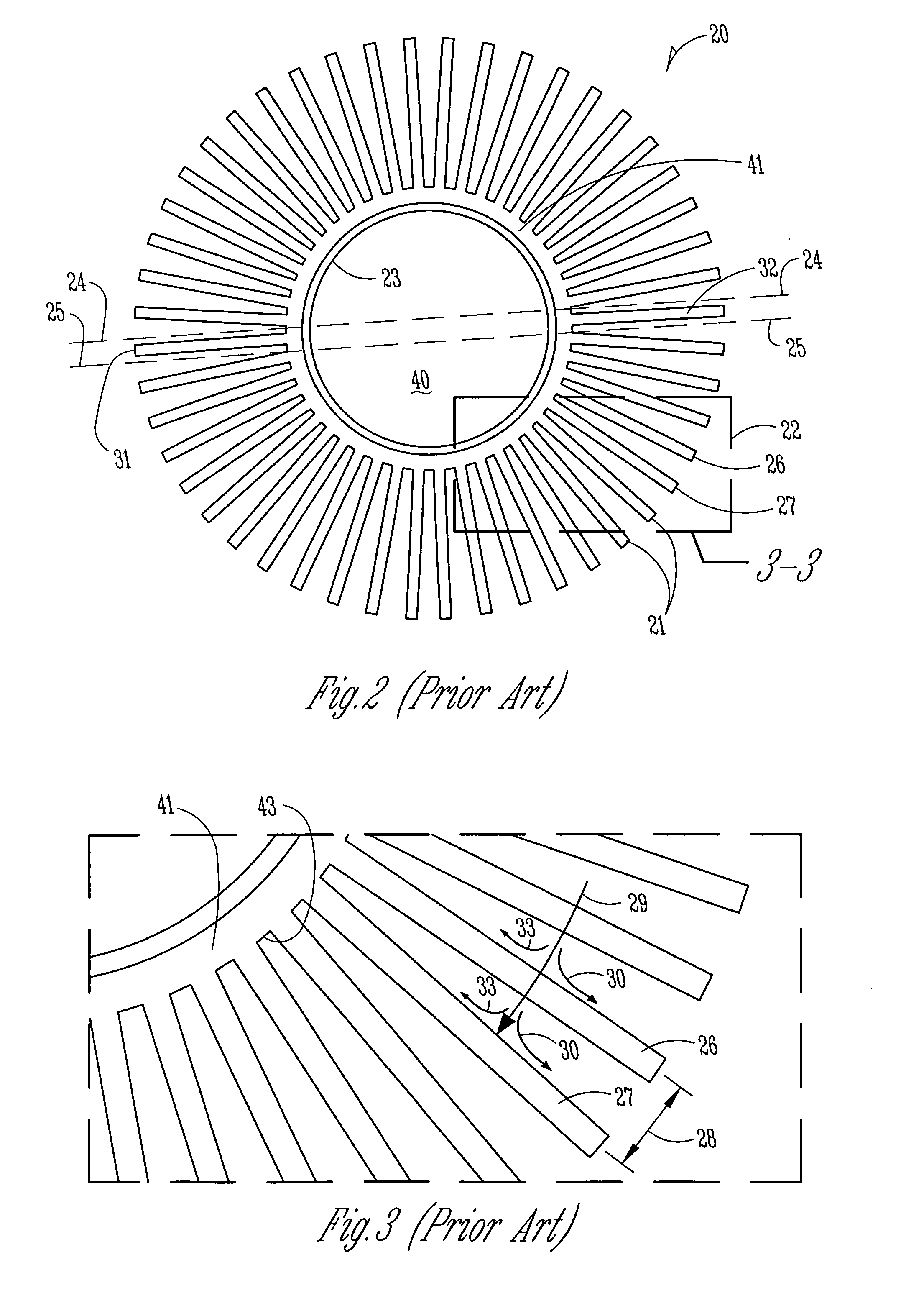
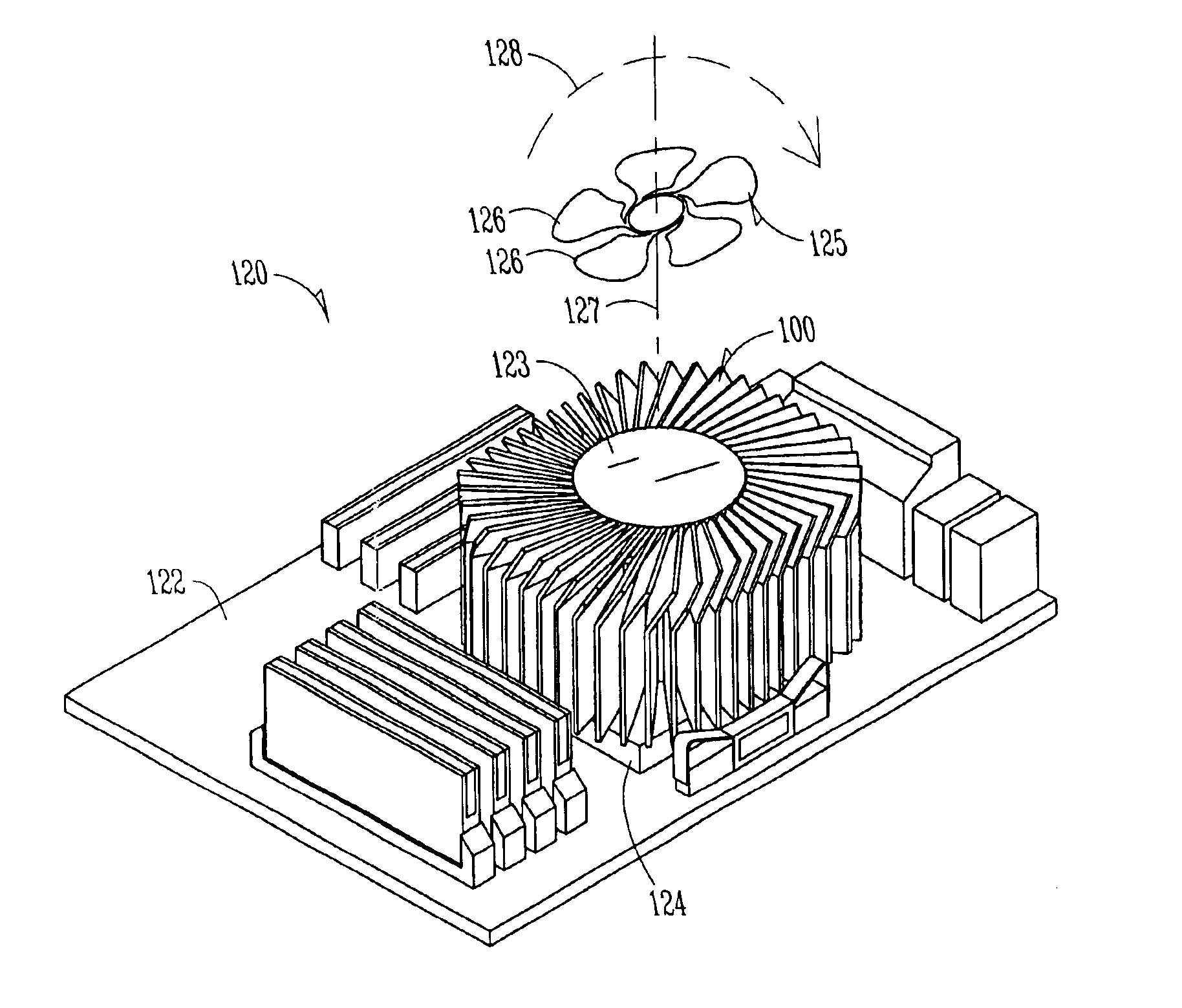
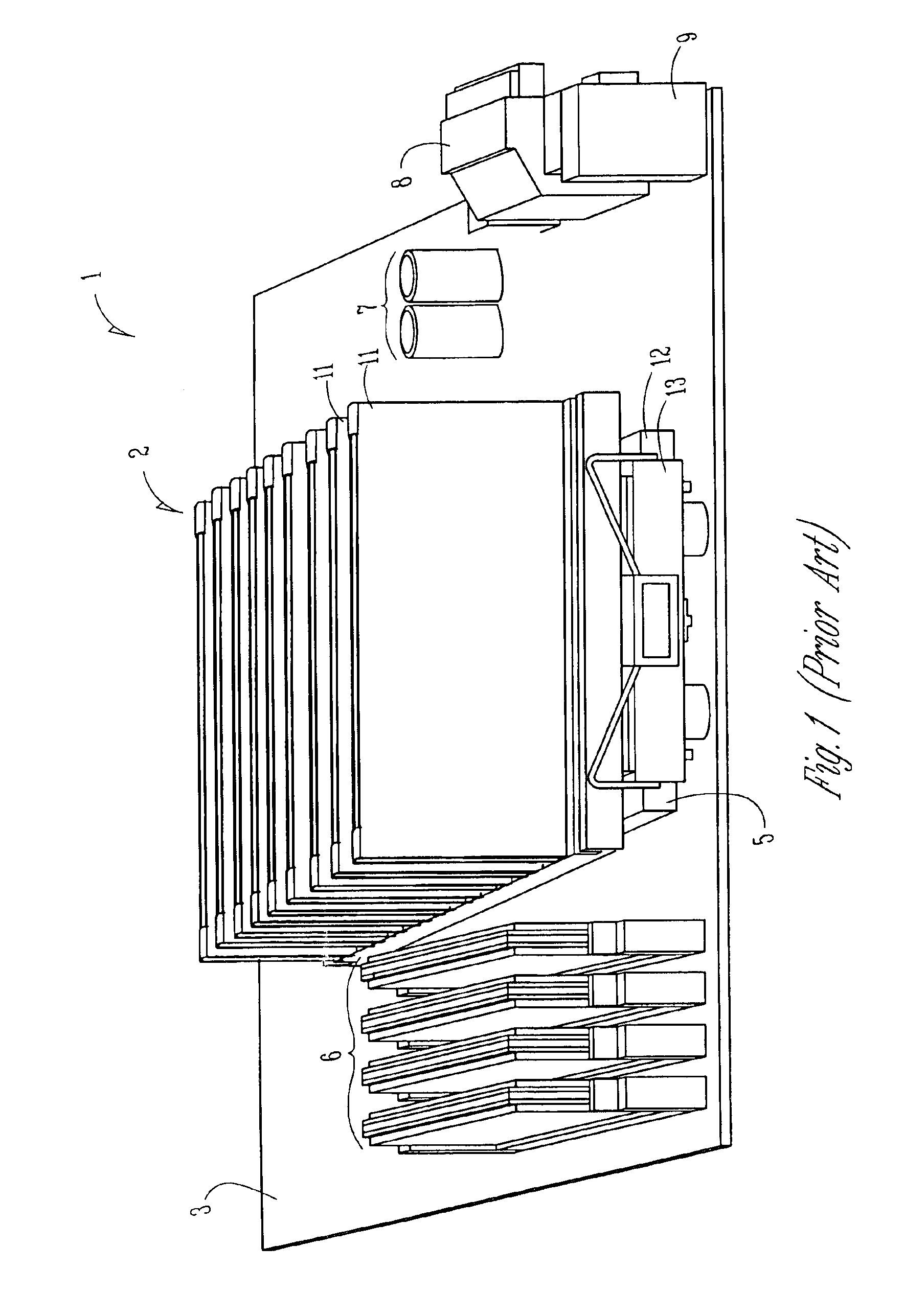
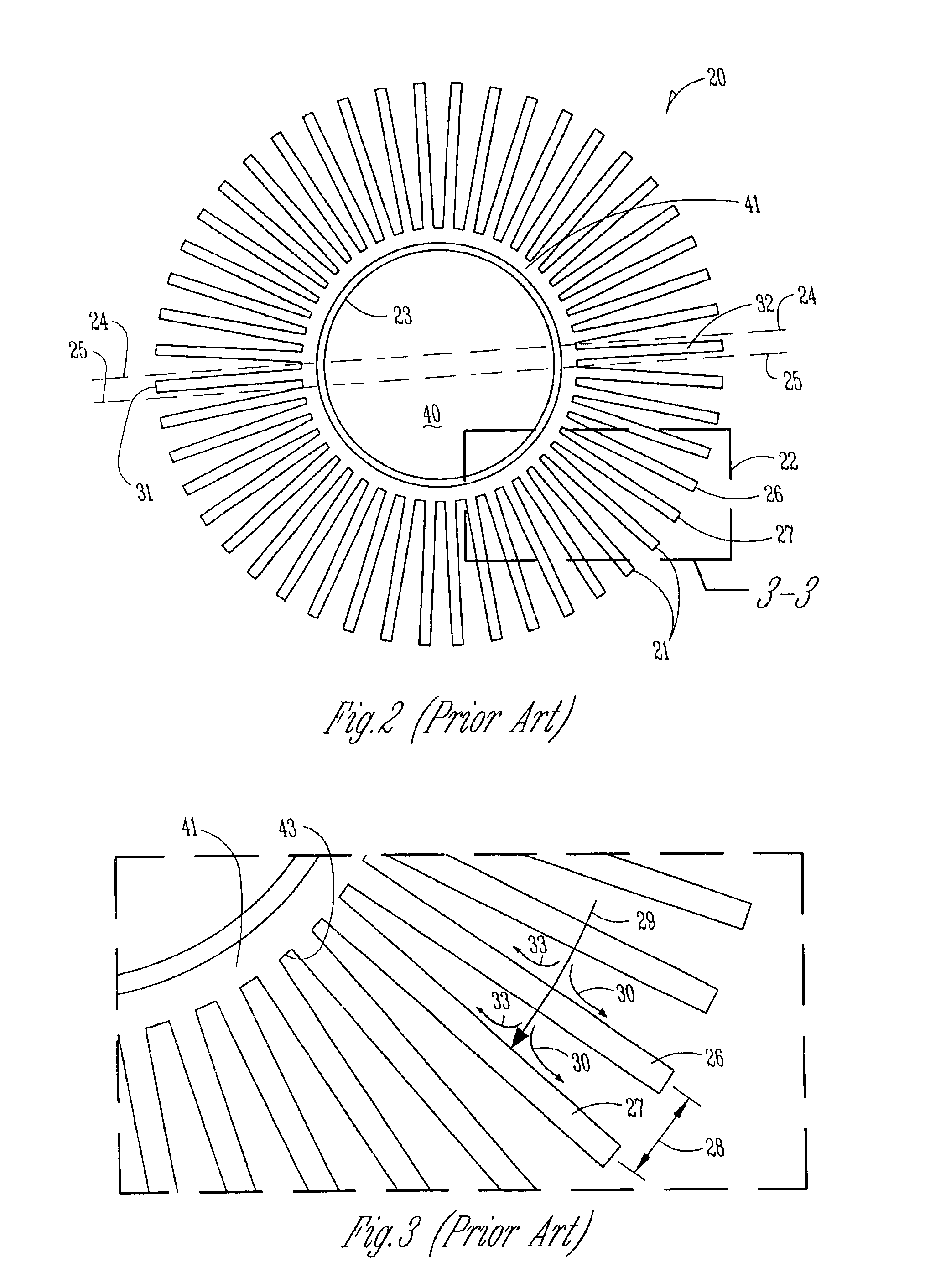
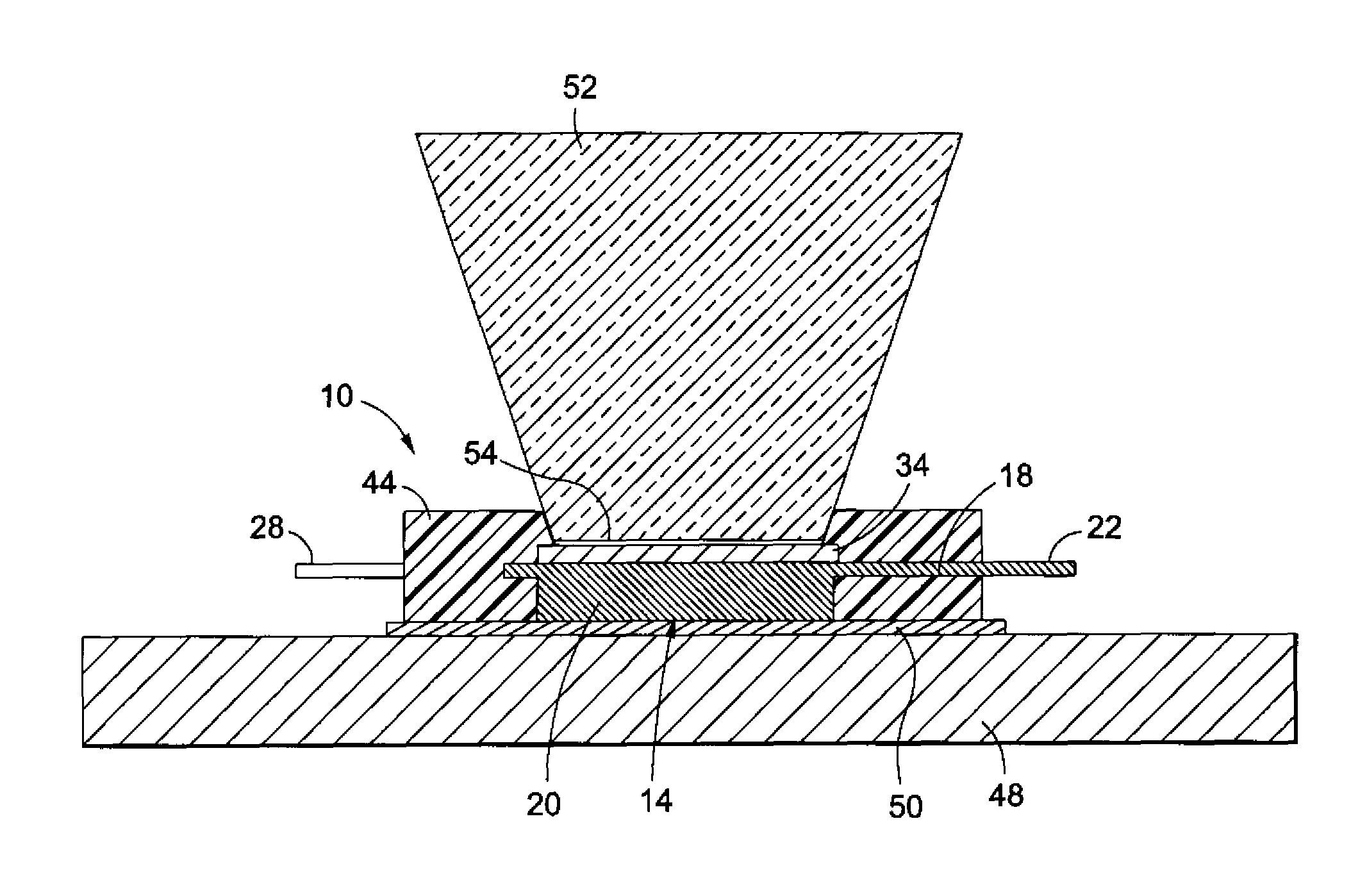
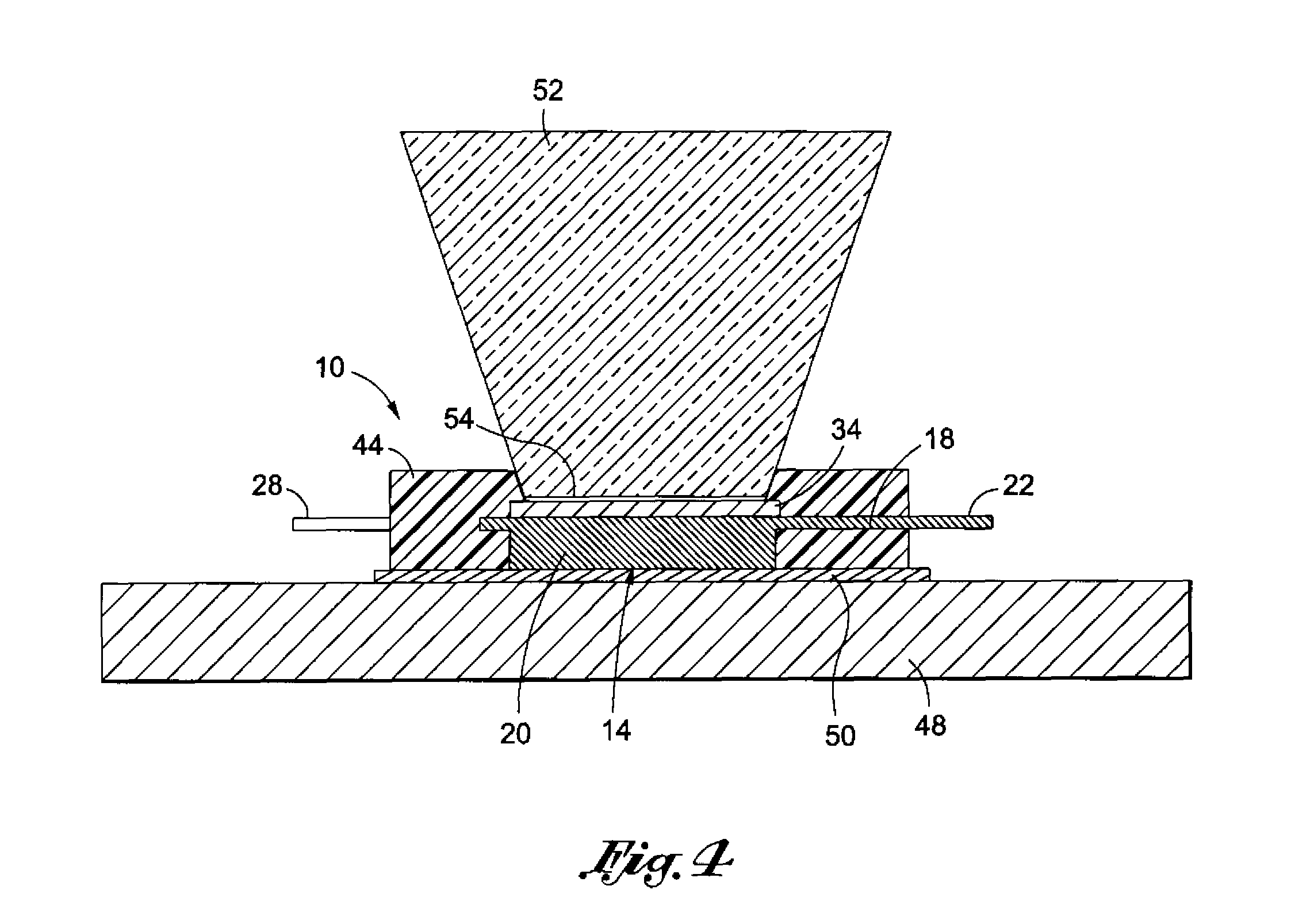
Electronic assemblies with high capacity curved and bent fin heat sinks and associated methods
InactiveUS20050280992A1Improve power densityMinimizes problemSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectronic systemsElectronic assemblies
An electronic assembly comprising one or more high performance integrated circuits includes at least one high capacity heat sink. The heat sink, which comprises a number of fins projecting substantially radially from a core, is structured to capture air from a fan and to direct the air to optimize heat transfer from the heat sink. The heat sink fins can be formed in different shapes. In one embodiment, the fins are curved. In another embodiment, the fins are bent. In yet another embodiment, the fins are curved and bent. Methods of fabricating heat sinks and electronic assemblies, as well as application of the heat sink to an electronic assembly and to an electronic system, are also described.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Electronic assemblies with high capacity bent fin heat sinks
InactiveUS7120020B2Improve power densityMinimizes problemSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectronic systemsElectronic assemblies
An electronic assembly comprising one or more high performance integrated circuits includes at least one high capacity heat sink. The heat sink, which comprises a number of fins projecting substantially radially from a core, is structured to capture air from a fan and to direct the air to optimize heat transfer from the heat sink. The heat sink fins can be formed in different shapes. In one embodiment, the fins are curved. In another embodiment, the fins are bent. In yet another embodiment, the fins are curved and bent. Methods of fabricating heat sinks and electronic assemblies, as well as application of the heat sink to an electronic assembly and to an electronic system, are also described.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Leadframe structure for concentrated photovoltaic receiver package
ActiveUS8680656B1Effective coolingImprove cooling effectSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLight guideComputer module
In accordance with the present invention, there is provided multiple embodiments of a concentrated photovoltaic receiver package or module. In each embodiment of the present invention, the module comprises a leadframe including a first section and a second section disposed in spaced relation to each other. Mounted to the first section of the leadframe is a receiver die. The receiver die is electrically connected to both the first and second sections of the leadframe. In one embodiment of the present invention, the receiver die is electrically connected to the second section of the leadframe by a plurality of conductive wires. In another embodiment of the present invention, the receiver die is electrically connected to the second section of the leadframe by a conductive bonding material. Portions of the leadframe may optionally be covered by a molded body which can be used to define an alignment feature for a light concentrating device such as a light guide or optical rod.
Owner:AMKOR TECH SINGAPORE HLDG PTE LTD
Line-replaceable transmit/receive unit for multi-band active arrays
InactiveUS20050253770A1Improve thermal performancePromote growthSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna arrays manufactureMulti bandEngineering
A line-replaceable unit for a phased array antenna including a thermally conductive housing having a front face and an opposed rear face, at least one open-ended waveguide extending through the housing from the front face to the rear face, at least one first radiating element including the waveguide and adapted to emit energy in a first frequency band; and at least one second radiating element positioned on the front face of the housing and adapted to emit energy in a second frequency band distinct from the first frequency band. The waveguide is dimensioned to pass energy in the first frequency band and is exposed to the environment outside the housing at the front and rear faces to define a cooling duct passing through the housing.
Owner:SAAB INC
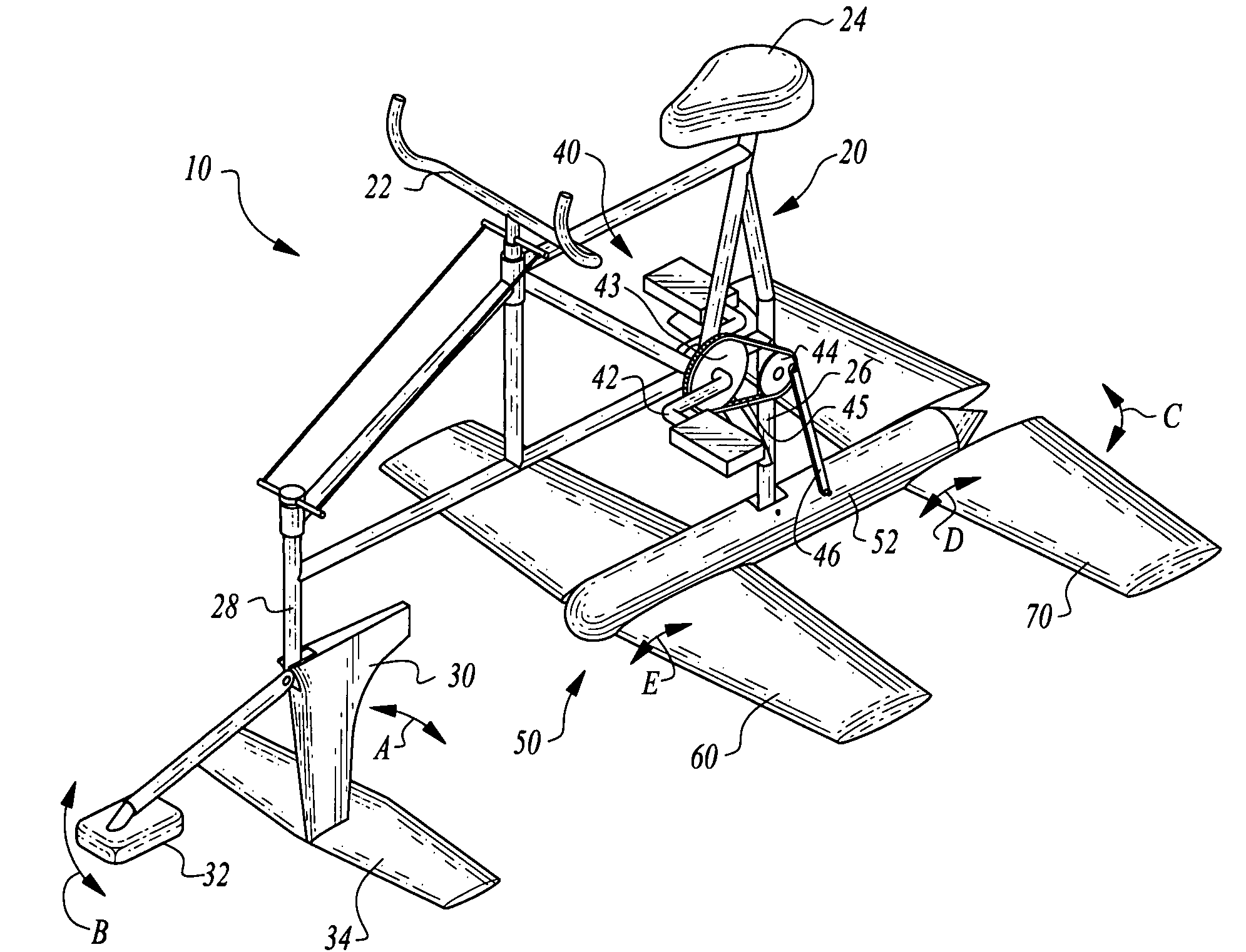
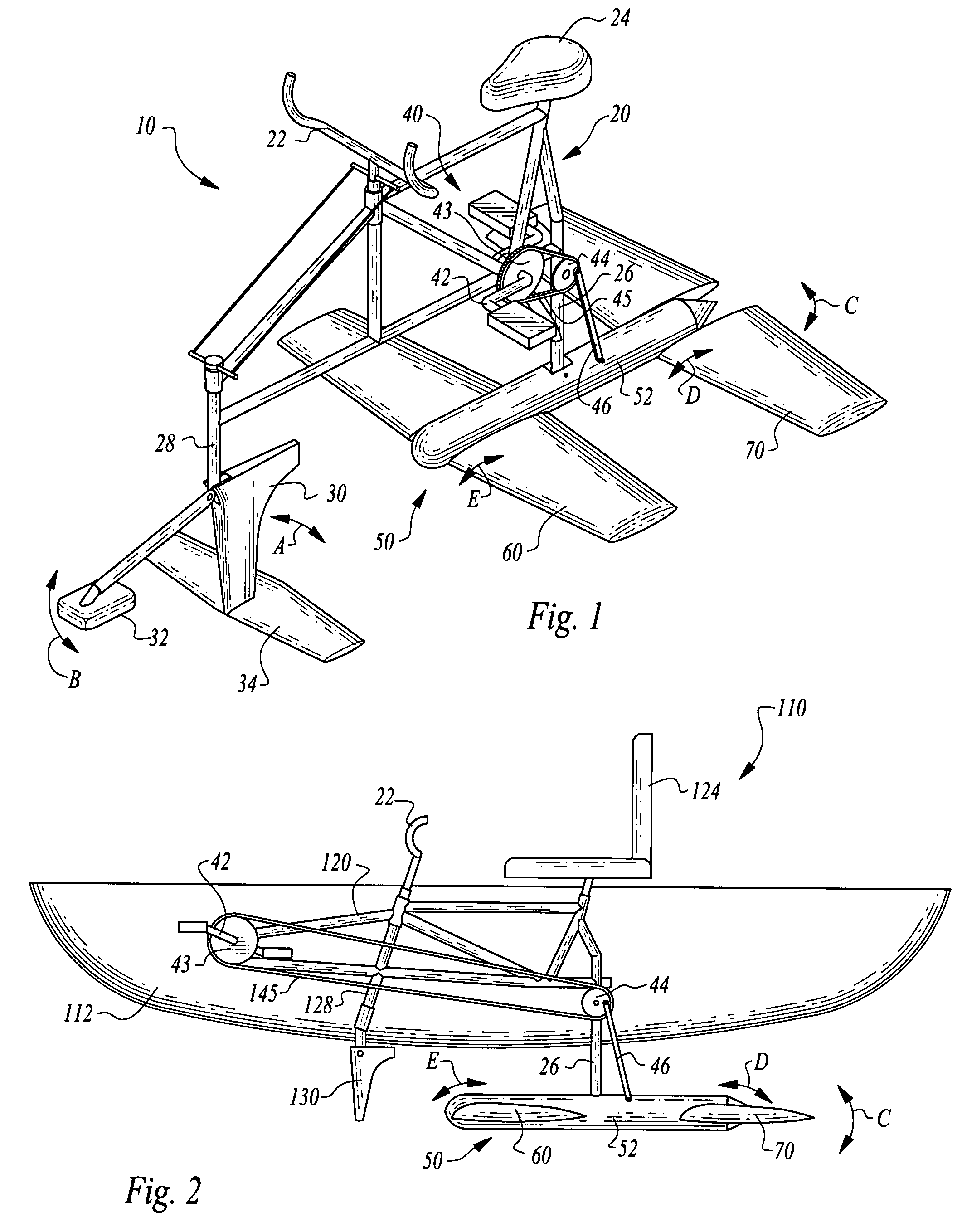
Human-powered flapping hydrofoil craft
InactiveUS7662004B1Easy to useHigh degreePropulsive elements of non-rotary typeMuscle power acting propulsive elementsNacelleClassical mechanics
A pair of foils are pivotably coupled to a nacelle. The nacelle is pivotably coupled to a mast extending down from to a frame and below a water surface. A push rod oscillates, causing the nacelle to experience a heaving motion, in turn causing the foils to flap up and down. The push rod is driven by a power plant such as a human rider. Angles of attack for the foils are actively controlled to optimize lift and propulsion forces provided by the foils to cause the water craft to move over the water. A steering fin is also provided for heading control of the water craft. A control system for separate angles of attack for the foil sends appropriate information to servo motors which cause the foils to rotate relative to the nacelle to achieve optimal angles of attack relative to the particular position of the nacelle at any given moment.
Owner:MARCH PHILIP A +3
Transmitting electric power into a bore hole
InactiveUS20110170320A1High voltageHigh power transmissionSurveyDrilling rodsVoltage converterElectric power transmission
A system for transmitting electric power into a bore hole, the system having an electric transmission line extending through the bore hole between an electric power source and a receiving station, wherein the receiving station includes frequency increasing means for increasing the frequency of the electric current supplied through the electric transmission line, voltage converter means for changing the voltage of the electric current supplied to it via the frequency increasing means, connecting means for supplying the frequency-increased electric current to the voltage converter means, and means for connecting an electric load to the receiving station.
Owner:ZEITECS
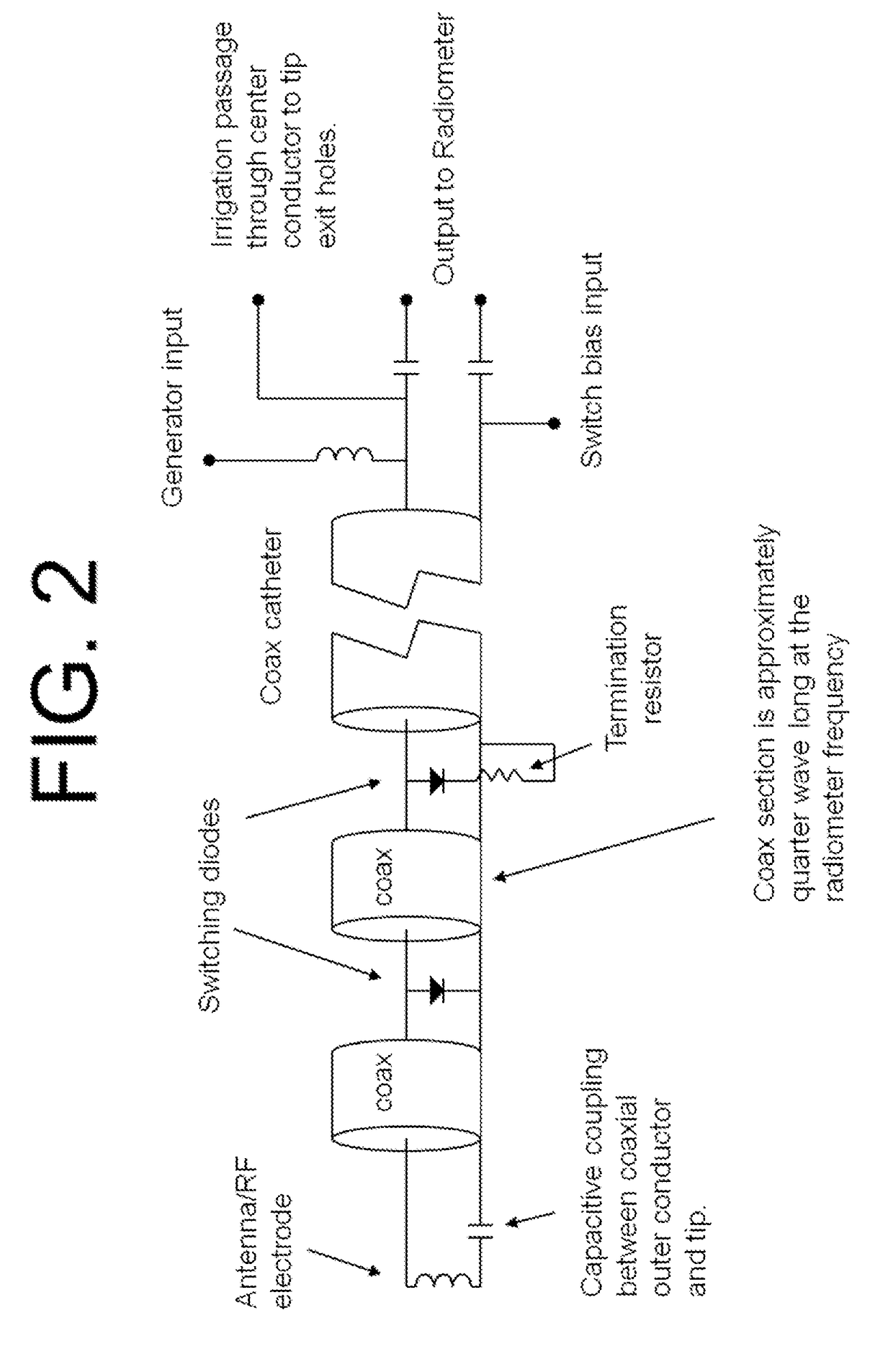
RF or microwave ablation catheter with remote dicke switch
ActiveUS20170105798A1Sufficient back biasEliminate the problemBody temperature measurementThermometers using physical/chemical changesRadiometerRadio frequency
The invention provides devices and systems, as well as associated methods of using them, that employ a remote Dicke switching element—i.e., distal to a radiometer. The devices, systems, and methods are suitable for both diagnostic and therapeutic applications in a wide variety of tissues.
Owner:CORAL SAND BEACH LLC
Manufacturing process for chalcogenide glasses
InactiveUS20100022378A1Minimize stressLow energy and stable statePot furnacesGlass furnace apparatusDistillationControl manner
The present invention is generally directed to a method of making chalcogenide glasses including holding the melt in a vertical furnace to promote homogenization and mixing; slow cooling the melt at less than 10° C. per minute; and sequentially quenching the melt from the top down in a controlled manner. Additionally, the present invention provides for the materials produced by such method. The present invention is also directed to a process for removing oxygen and hydrogen impurities from chalcogenide glass components using dynamic distillation.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Transmitting electric power into a bore hole
InactiveUS20060151211A1High frequencyHigh voltageEarth drilling toolsSurveyElectric power transmissionElectricity
A system for transmitting electric power into a bore hole, the system having an electric transmission line extending through the bore hole between an electric power source and a receiving station, wherein the receiving station includes frequency increasing means for increasing the frequency of the electric current supplied through the electric transmission line, voltage converter means for changing the voltage of the electric current supplied to it via the frequency increasing means, connecting means for supplying the frequency-increased electric current to the voltage converter means, and means for connecting an electric load to the receiving station.
Owner:A POWER
Magnetic resonance wireless power transmission device capable of adjusting resonance frequency
ActiveUS20170229921A1Highly reproducibleControl is possibleNear-field transmissionImpedence networksElectric power transmissionAudio power amplifier
A magnetic resonance wireless power transmission device capable of adjusting resonance frequency is disclosed. A wireless power transmission device according to an embodiment of the present invention comprises: a power amplifier for amplifying a wireless power signal using a driving frequency signal; a resonator for configuring a resonance tank and wirelessly transmitting, through magnetic resonance, the wireless power signal output from the power amplifier using a resonance frequency of the resonance tank; and a resonance control unit for controlling a duty ratio using a frequency applied to the resonator or a frequency signal generated by the resonator and adjusting the resonance frequency of the resonator.
Owner:MAPS
Antenna mandrel with multiple antennas
ActiveUS20170115511A1The process is convenient and fastReduce complexityNear-field transmissionAntenna supports/mountingsElectric power transmissionEngineering
Antennas and antenna mandrels or assemblies may be designed and configured to enable one of one- or two-way communication and / or power transfer with mechanical devices such as ophthalmic devices, including contact lenses. These antennas and antenna mandrels or assemblies may be utilized to transmit data from the mechanical devices to receive data from a transmitter, and / or inductively charge an electromechanical cell or the like incorporated into a mechanical device.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Control apparatus for vehicular drive system
InactiveUS20070111848A1Improve fuel economyHigh power transmissionHybrid vehiclesSpeed controllerDifferential functionDrive wheel
A control apparatus for a vehicular drive system including a continuously-variable transmission portion operable as an electrically controlled continuously variable transmission, the continuously-variable transmission portion having a differential mechanism operable to distribute an output of an engine to a first electric motor and a power transmitting member, and a second electric motor disposed in a power transmitting path between the power transmitting member and a drive wheel of a vehicle. The control apparatus includes: (a) a differential-state limiting device provided in the differential mechanism, and operable to limit a differential function of the differential mechanism, for limiting an operation of the continuously-variable transmission portion as the electrically controlled continuously variable transmission; and (b) a differential-state switching controller operable, when acceleration or deceleration of the vehicle is required, for removing the limitation imposed by the differential-state limiting device on the operation of the continuously-variable transmission portion as the electrically controlled continuously variable transmission.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Control device for vehicular drive system, vehicle having the control device, and method for controlling vehicular drive system
InactiveUS20070087893A1Small sizeImprove efficiencyHybrid vehiclesElectric propulsion mountingDrive wheelEngineering
A control apparatus for a vehicular drive system including a first transmission portion having a differential mechanism operable to distribute an engine output to a first electric motor and a power transmitting member, and a second electric motor disposed in a power transmitting path between the power transmitting member and a drive wheel; and a second transmission portion constituting a part of the power transmitting path. The control apparatus includes a switching device provided in the differential mechanism and operable to selectively place the first transmission portion in a continuously-variable shifting state and in a non-continuously-variable shifting state, rendering the first transmission portion respectively capable or not capable of operating as an electrically controlled continuously variable transmission; and a transmission controller operable to change a speed ratio of the second transmission portion, concurrently with switching of the first transmission portion between the continuously-variable shifting state and the non-continuously-variable shifting state.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Atomizing, dust removing and haze removing vehicle controlled by PLC and provided with vector spraying port
InactiveCN105728225AIncrease speedHigh power transmissionSpraying vehiclesClosed circuit television systemsCycloneHydraulic motor
The invention discloses a PLC-controlled spray dust removal and haze removal vehicle with a vector nozzle, which comprises a six-wheeled vehicle chassis, a front vector cyclone sprayer, a first worm wheel, a first worm, a first plunger hydraulic motor and the like. The front vector cyclone sprayer is fixedly installed on the upper part of the first worm wheel through a bracket. The first worm gear rotates vertically and is installed on the boss on the lifting platform. The first worm is installed on the support of the lifting platform for lateral rotation, and cooperates with the first worm wheel. The invention can achieve large power transmission in a small space, so that the high-speed fan can easily reach a very high speed and is stable and noiseless. By setting the vector nozzle, the front vector cyclone sprayer and the rear vector cyclone sprayer can be sprayed The direction and angle can be adjusted more precisely, so as to achieve better dust removal effect.
Owner:徐明
Non-contact power transmission device
InactiveUS7782633B2Improve transmission efficiencyReduce device sizeTransformersEfficient power electronics conversionHarmonicEngineering
A non-contact power transmission device, which is capable of efficiently reducing the device size and reducing unnecessary radiation of a harmonic component from a primary side coil, is provided. The non-contact power transmission device which includes a primary side unit and a secondary side unit which house a primary side and a secondary side of a coupling transformer individually and can be separated from each other, a capacitor C1 which resonates with a primary side coil L1 is connected to the primary side coil L1 in series so that a primary side series resonance circuit is formed, an L-shaped resonance circuit which has a coil L3 and a capacitor C7 resonating with the coil L3 is inserted between the primary side series resonance circuit and a driving circuit, and the L-shaped resonance circuit is connected to the primary side series resonance circuit in series.
Owner:HOKUSHIN ELECTRIC
Control apparatus for vehicular drive system, vehicle provided with the control apparatus, and method of controlling vehicular drive system
InactiveUS7481737B2Improve fuel economyHigh power transmissionHybrid vehiclesElectric propulsion mountingDrive wheelEngineering
A control apparatus for a vehicular drive system including a first transmission portion having a differential mechanism operable to distribute an engine output to a first electric motor and a power transmitting member, and a second electric motor disposed in a power transmitting path between the power transmitting member and a drive wheel; and a second transmission portion constituting a part of the power transmitting path. The control apparatus includes a switching device provided in the differential mechanism and operable to selectively place the first transmission portion in a continuously-variable shifting state and in a non-continuously-variable shifting state, rendering the first transmission portion respectively capable or not capable of operating as an electrically controlled continuously variable transmission; and a transmission controller operable to change a speed ratio of the second transmission portion, concurrently with switching of the first transmission portion between the continuously-variable shifting state and the non-continuously-variable shifting state.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Control apparatus for vehicular drive system
InactiveUS7503870B2Improve fuel economyHigh power transmissionHybrid vehiclesElectric propulsion mountingDrive wheelEngineering
A control apparatus for a vehicular drive system including a continuously-variable transmission portion, and a step-variable transmission portion, the continuously variable transmission portion having a differential mechanism operable to distribute an output of an engine to a first electric motor and a power transmitting member, and a second electric motor disposed in a power transmitting path between the power transmitting member and a drive wheel of a vehicle, the step-variable transmission portion constituting a part of the power transmitting path, the control apparatus includes a differential-state limiting device provided in the differential mechanism for limiting an operation of the continuously-variable transmission portion, and an electric-motor control device to control a drive-force assisting operation to drive the vehicle during a shifting action of the step-variable transmission portion, differently depending upon whether the continuously-variable transmission portion is placed in a continuously-variable shifting state or a non-continuously-variable shifting state.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
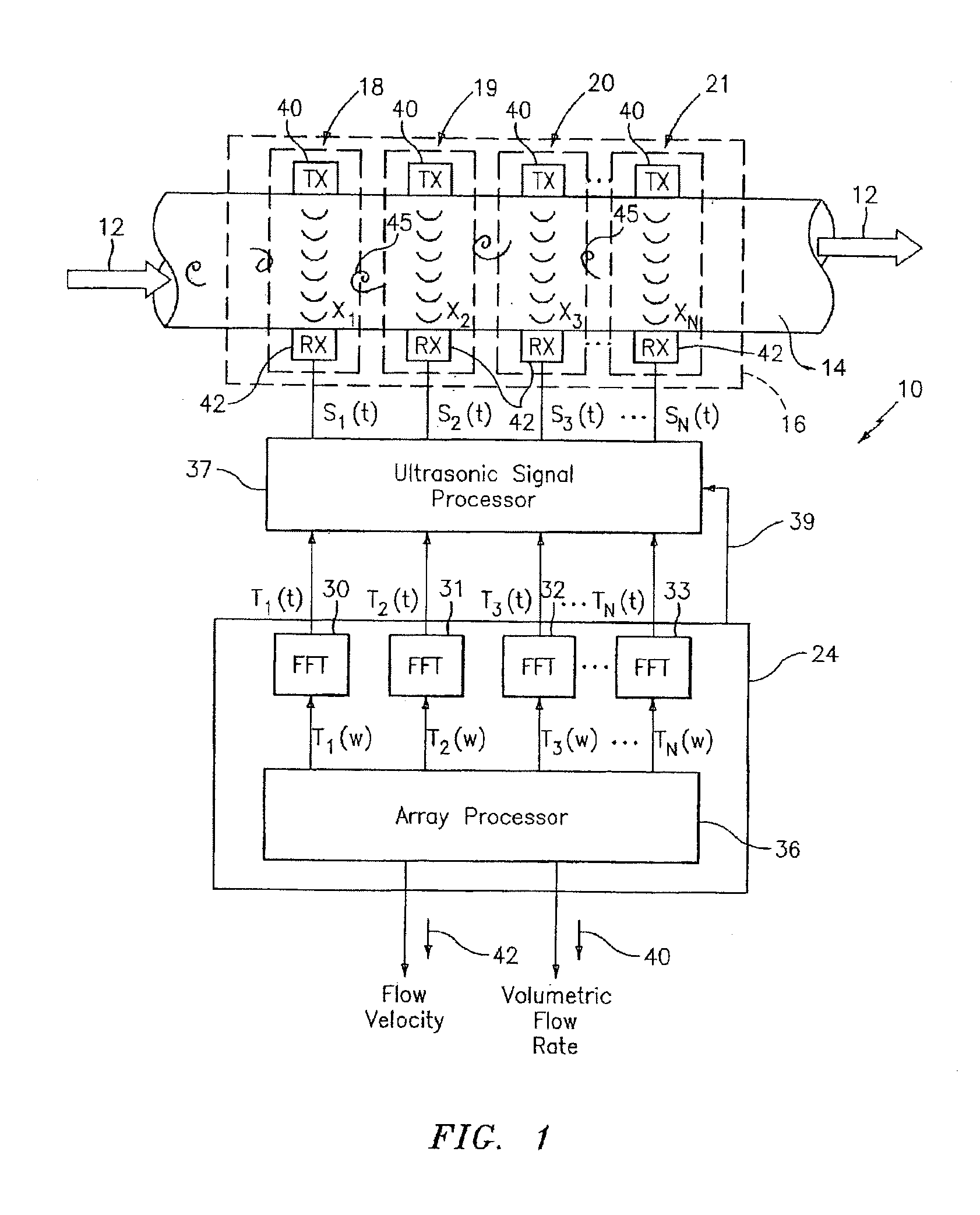
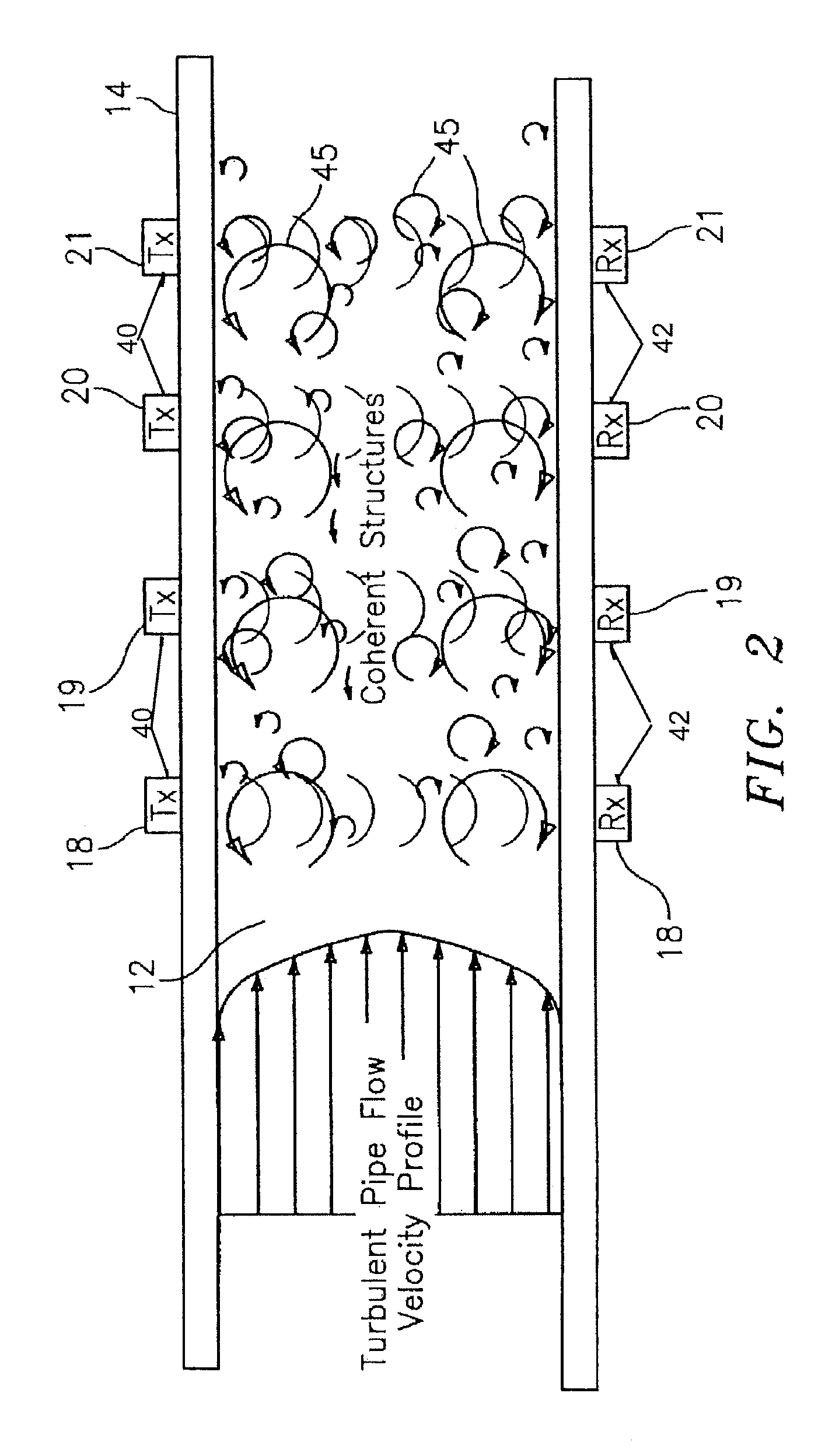
Apparatus and method of lensing an ultrasonic beam for an ultrasonic flow meter
ActiveUS7673526B2Accurate inductionOptimize signal characteristic of signalVolume/mass flow measurementUltrasonic beamLight beam
A method for sensing flow within a pipe having an internal passage disposed between a first wall portion and a second wall portion is provided, comprising the steps of: 1) providing a flow meter having at least one ultrasonic sensor unit that includes an ultrasonic transmitter attached to the first wall portion and an ultrasonic receiver attached to the second wall portion and aligned to receive ultrasonic signals transmitted from the transmitter; 2) selectively operating the ultrasonic transmitter to transmit a beam of ultrasonic signal, which beam has a focal point such that within the pipe, the beam is either colliminated, divergent or convergent; and 3) receiving the ultrasonic signals within the beam using the ultrasonic receiver. An apparatus operable to perform the aforesaid method is also provided.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
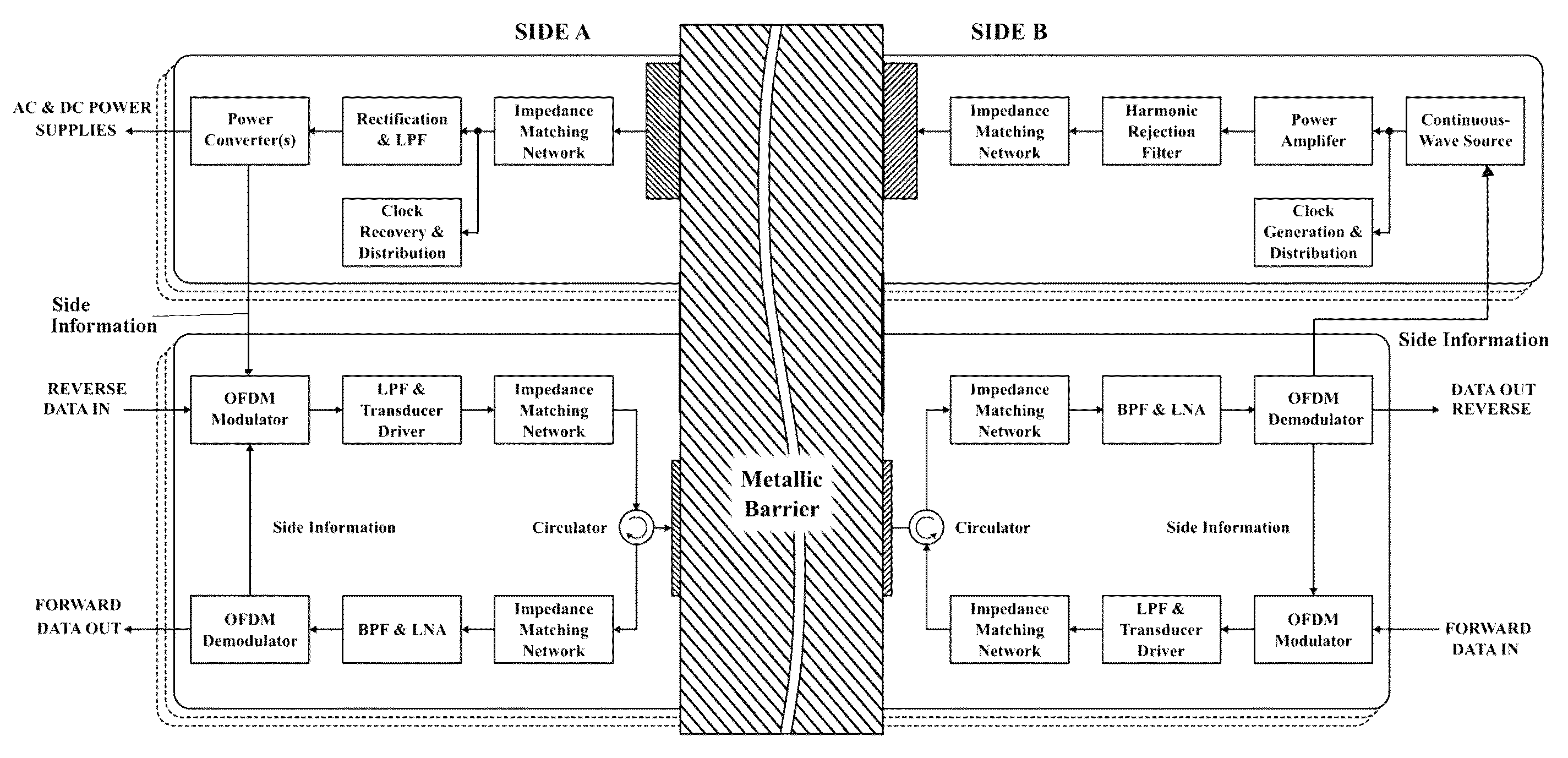
Adaptive system for efficient transmission of power and data through acoustic media
ActiveUS9054826B2Reduce dataReduce total powerSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionMulti-frequency code systemsSonificationAcoustic medium
An apparatus and method for transmitting data and power through a metal barrier using ultrasonic waves, having ultrasonic transmission channels through the barrier formed by coupling ultrasonic transducers on opposite sides of the barrier. A power transmitter sends power over a channel and forward and reverse data transmitters send forward and reverse data signals by orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing OFDM over a separate channel. The data signals are made up of plural sub-carriers at plural different sub-carrier frequencies with none of the sub-carriers of the forward transmission signal being at a power harmonic frequency.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
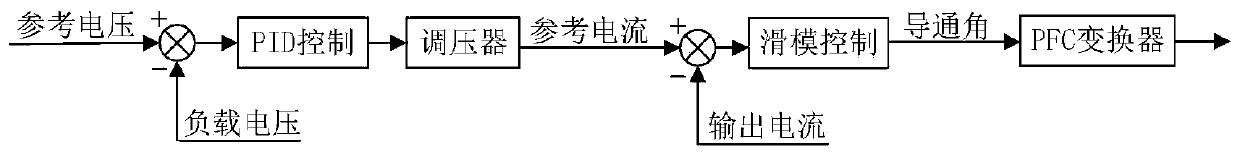
Method for controlling electric vehicle wireless dynamic charging system
ActiveCN110103740AReasonable distributionReduce grid harmonicsCharging stationsElectric vehicle charging technologyPower qualityElectric energy
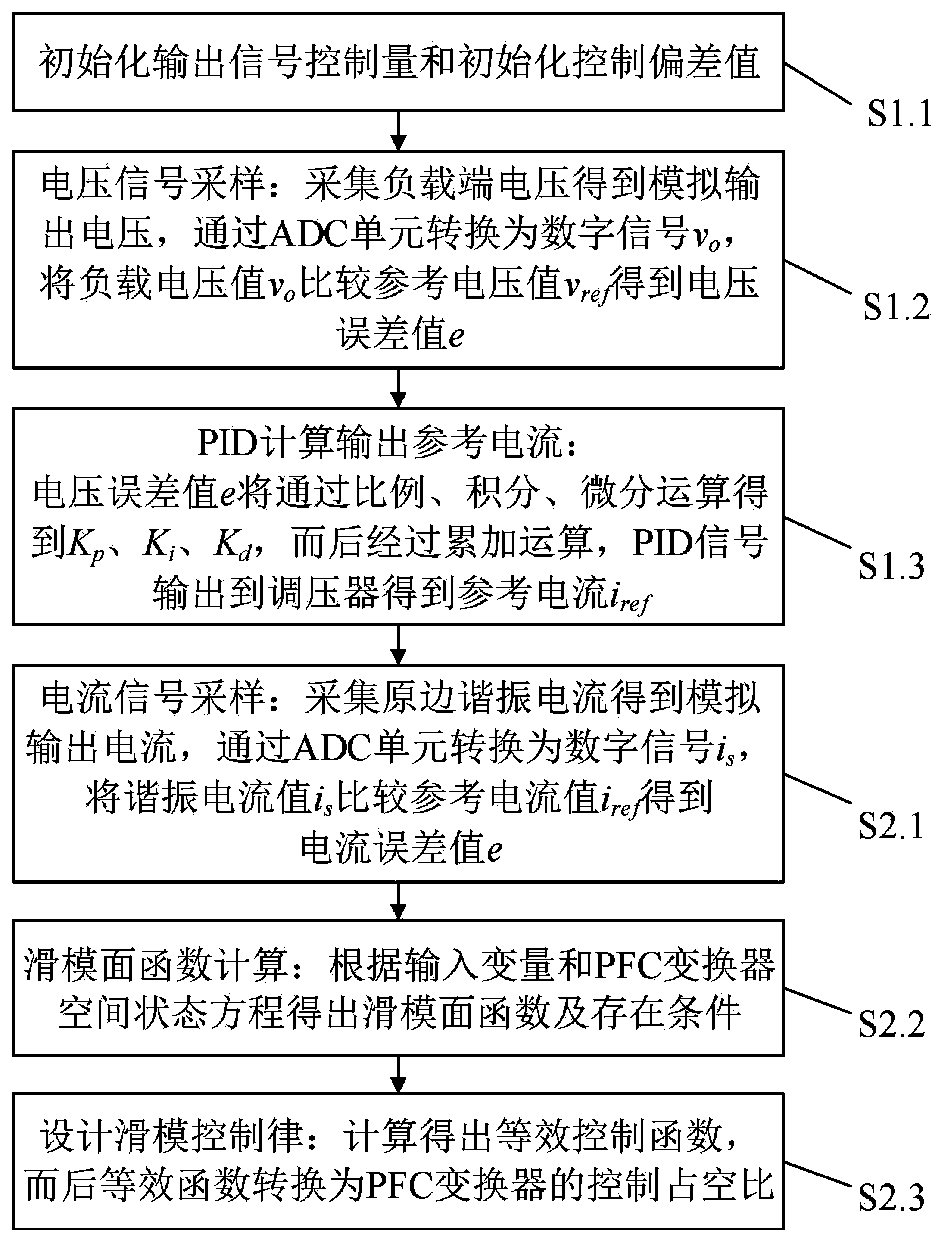
The invention discloses a method for controlling electric vehicle wireless dynamic charging system, and belongs to the technical field of electric vehicle wireless charging. The method includes the steps that a transmitter end and a receiver end are controlled simultaneously, sliding mode PID control is adopted to a PFC converter at the transmitter end, and fuzzy algorithm control is conducted over a DC-DC converter at the receiver end, and information exchange is realized through a wireless communication module. According to the method for controlling electric vehicle wireless dynamic charging system, the rational allocation of system resources can be realized, harmonic waves of a power grid is reduced, the power quality is improved, the power loss in the power transmission process is saved, magnetic leakage is reduced, the system transmission efficiency is improved, the stability of electric vehicle dynamic charging is ensured, and safety and reliability are improved.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Auxiliary circuits for selection and enhancement of multi-frequency wireless power transfer to multiple loads
ActiveCN106464033AEnhanced couplingHigh power transmissionCircuit arrangementsReed receiverPower flow
This invention is related to a novel method and apparatus that provides selective and enhanced power flow in wireless power transfer systems with multiple receivers. Auxiliary circuits are introduced in the receiver circuits (and relay circuits if applicable) so as to ensure proper frequency-selective wireless power flow to the appropriate targeted receivers, with the pickup power by the non-targeted receivers substantially reduced even if the chosen tuned frequencies for different receivers are not widely apart.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com