Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34results about How to "Excessive emission" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
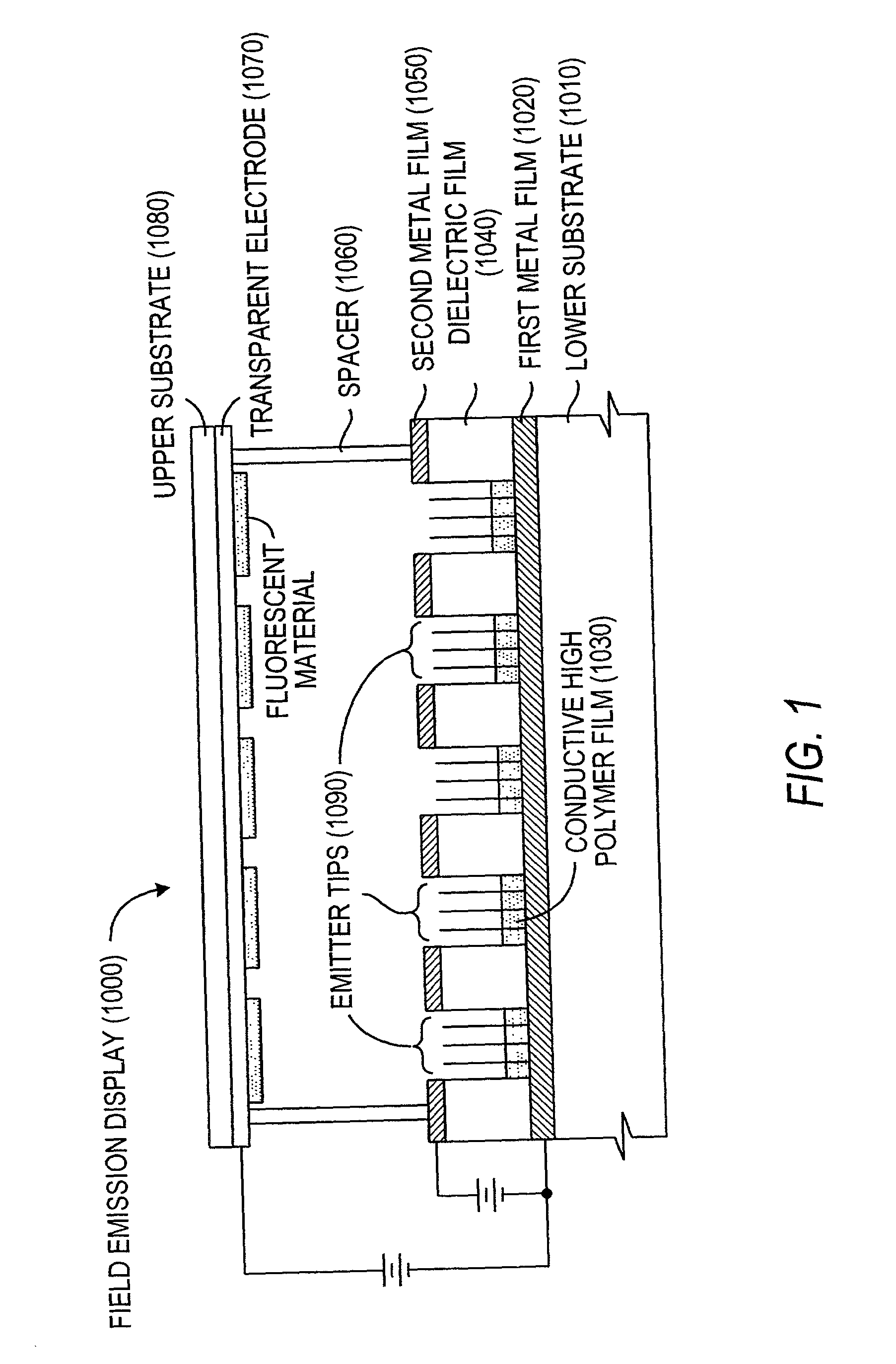
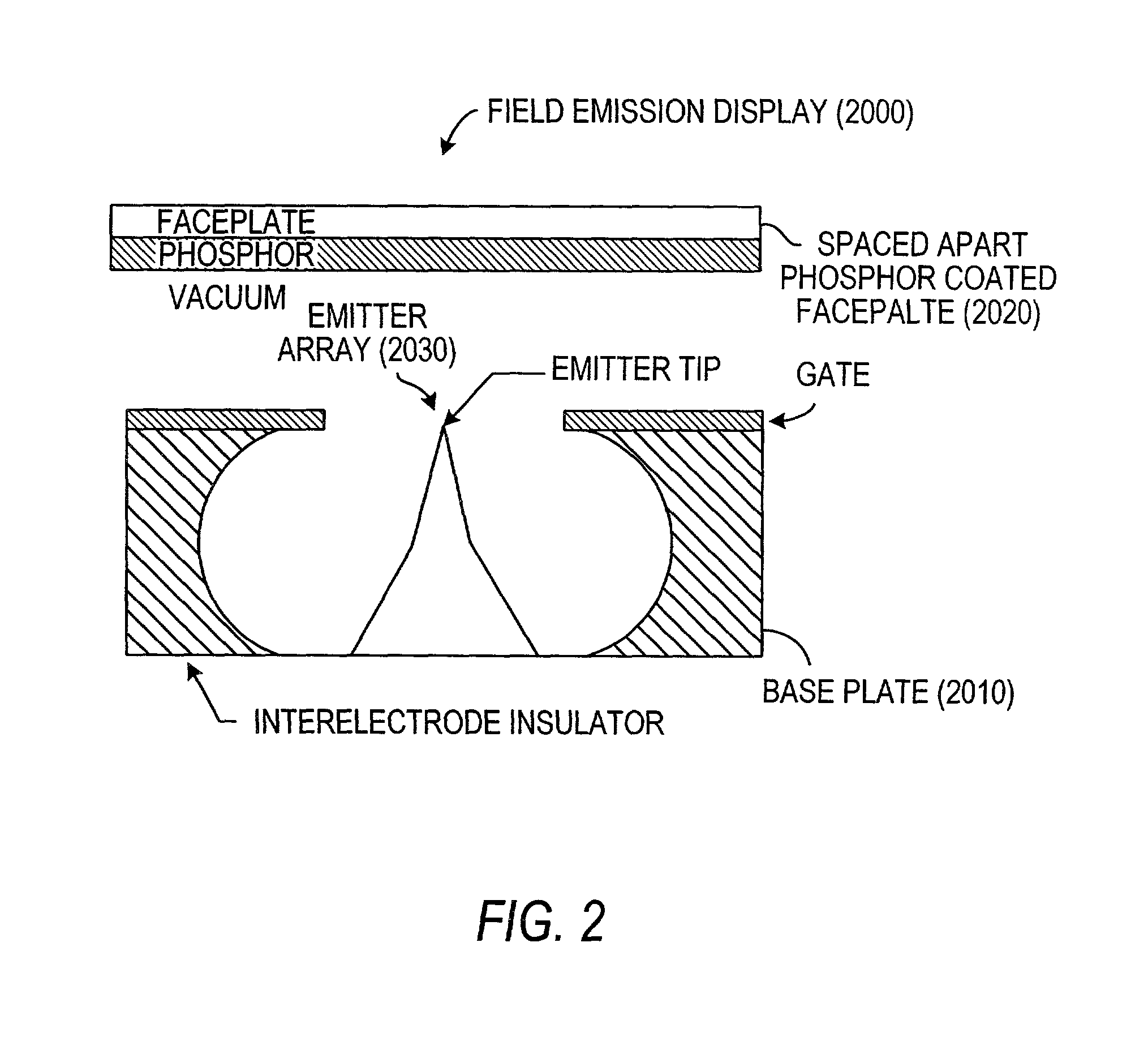
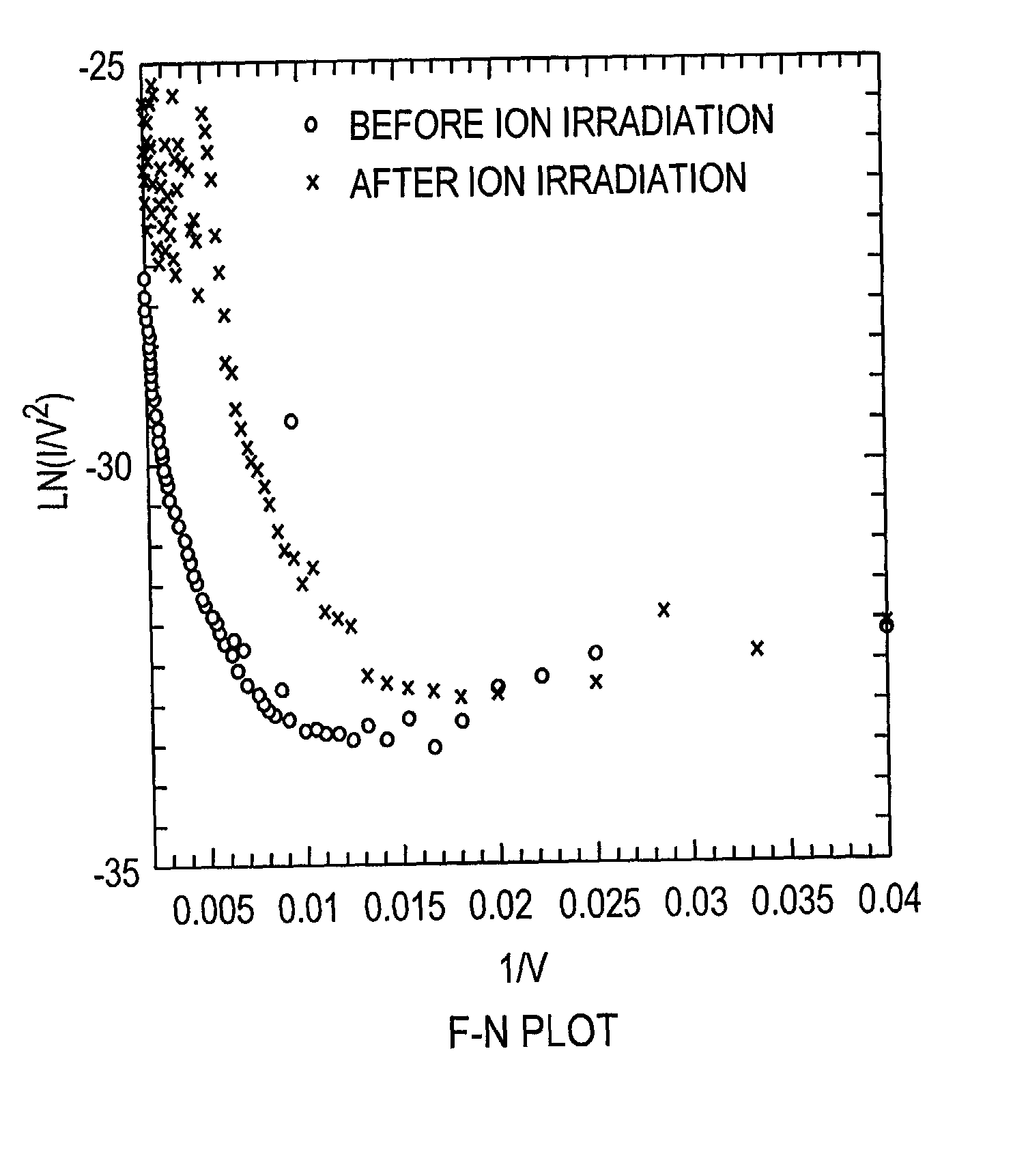
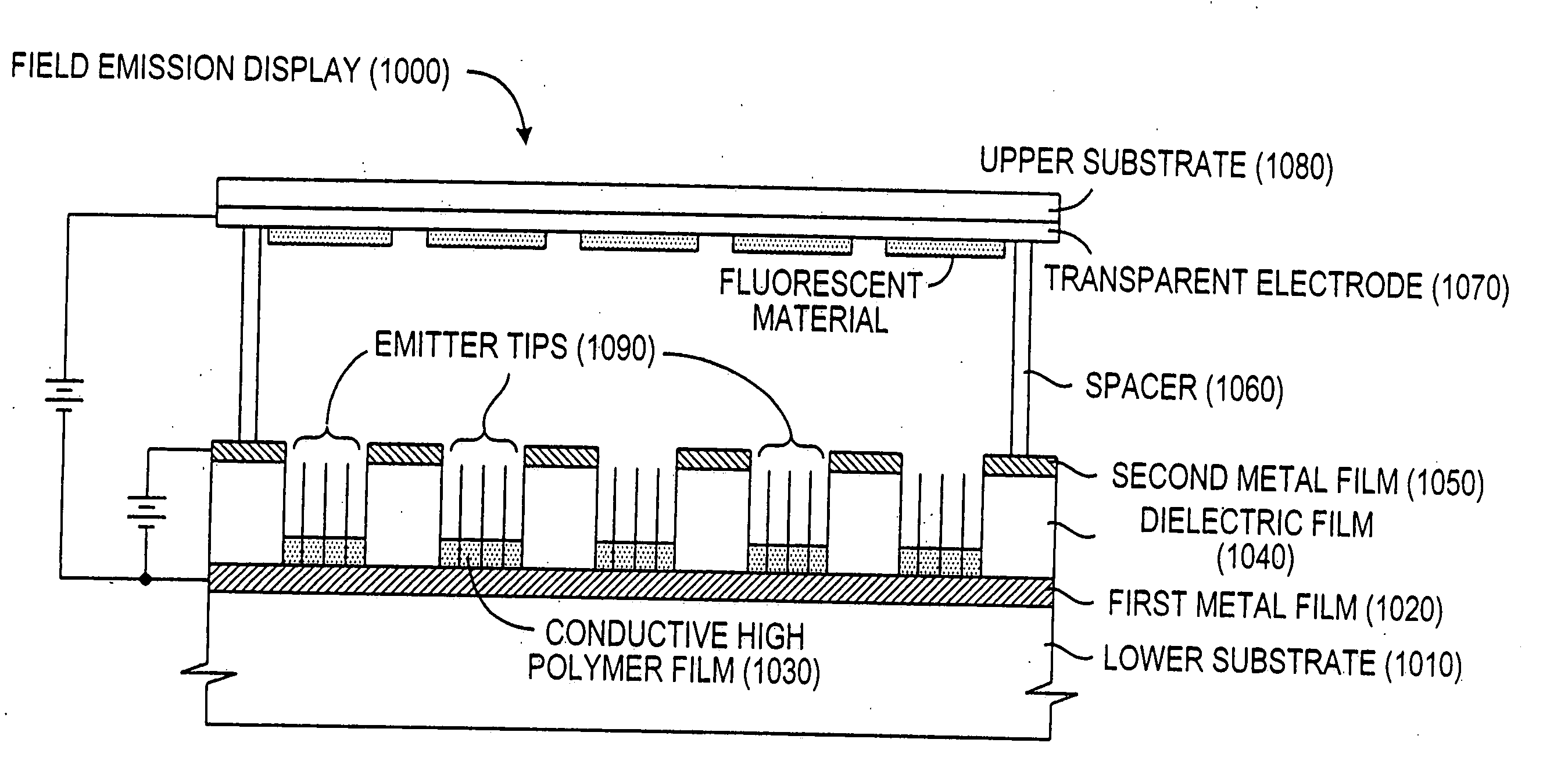
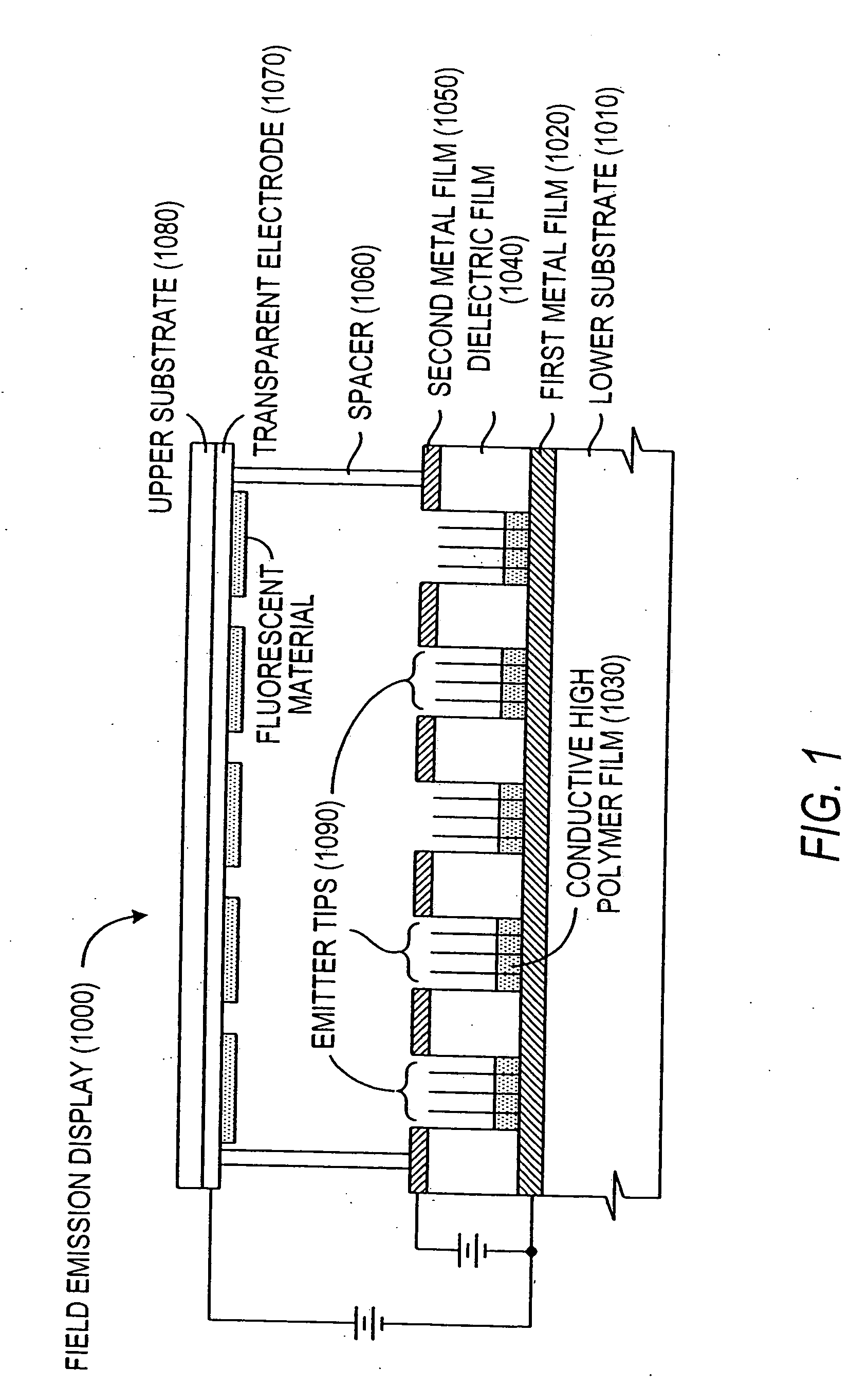
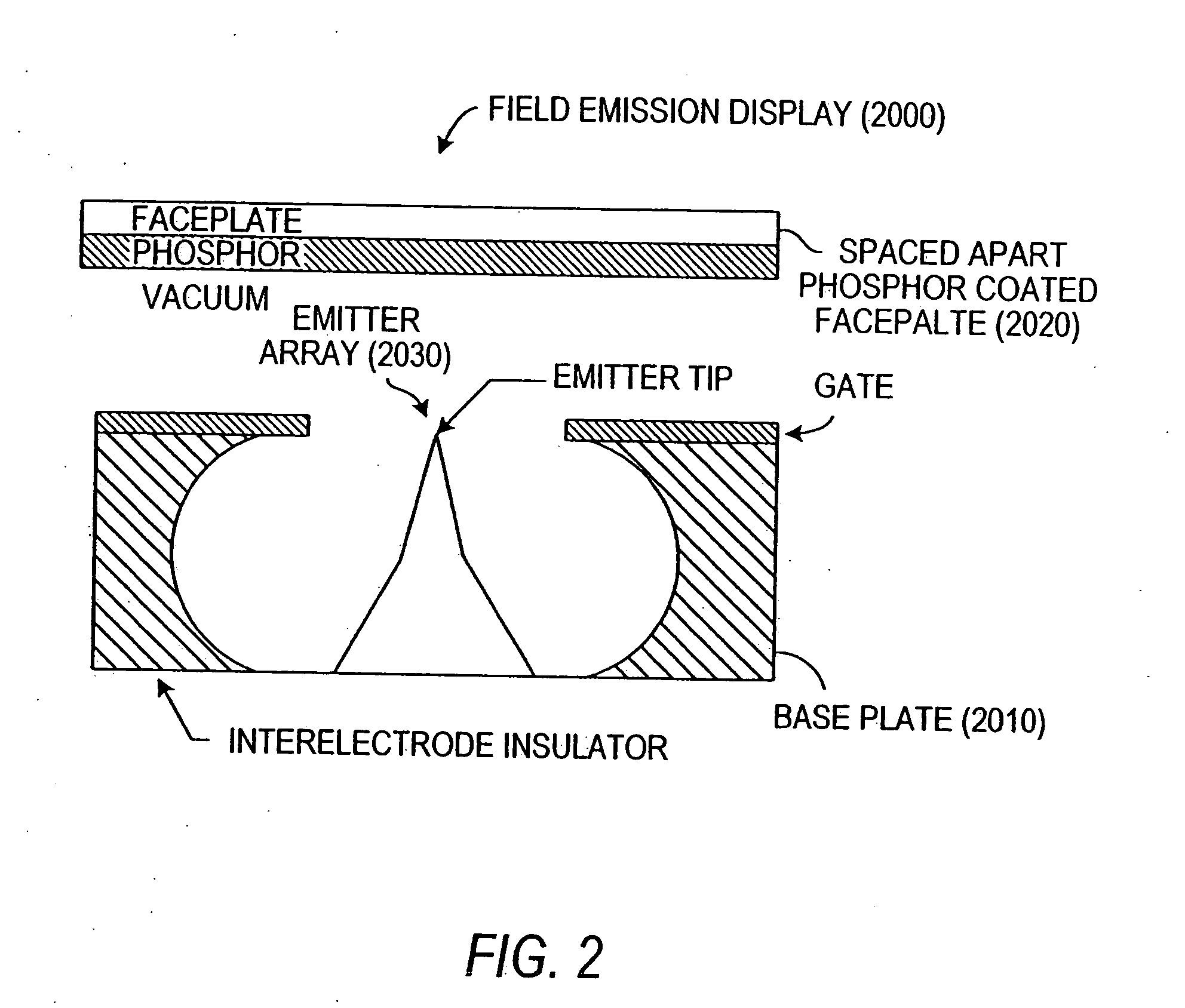
Field emission devices using modified carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS20030090190A1Accelerate emissionsReduce voltageNanostructure manufactureNanoinformaticsField emission deviceModified carbon
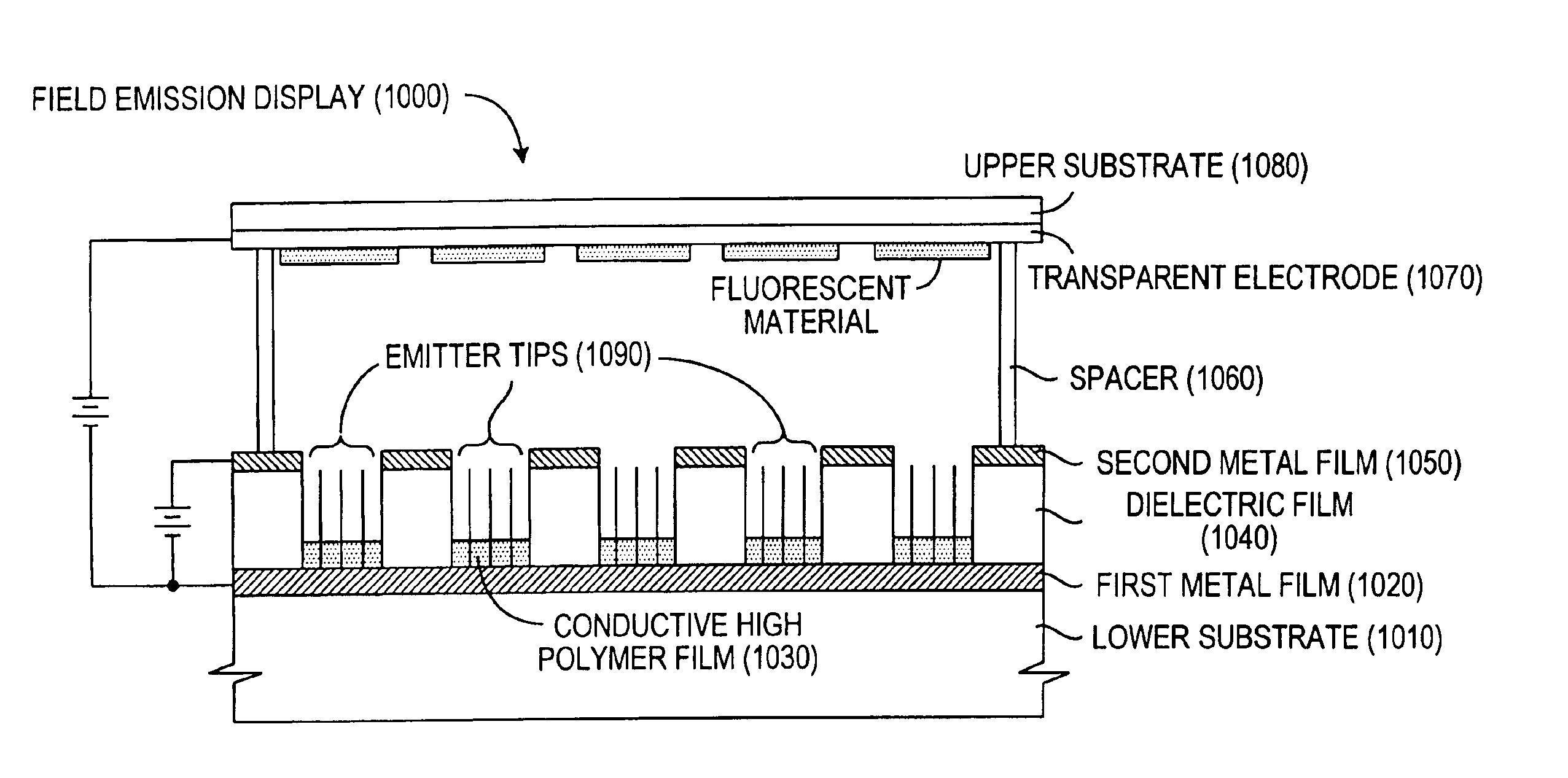
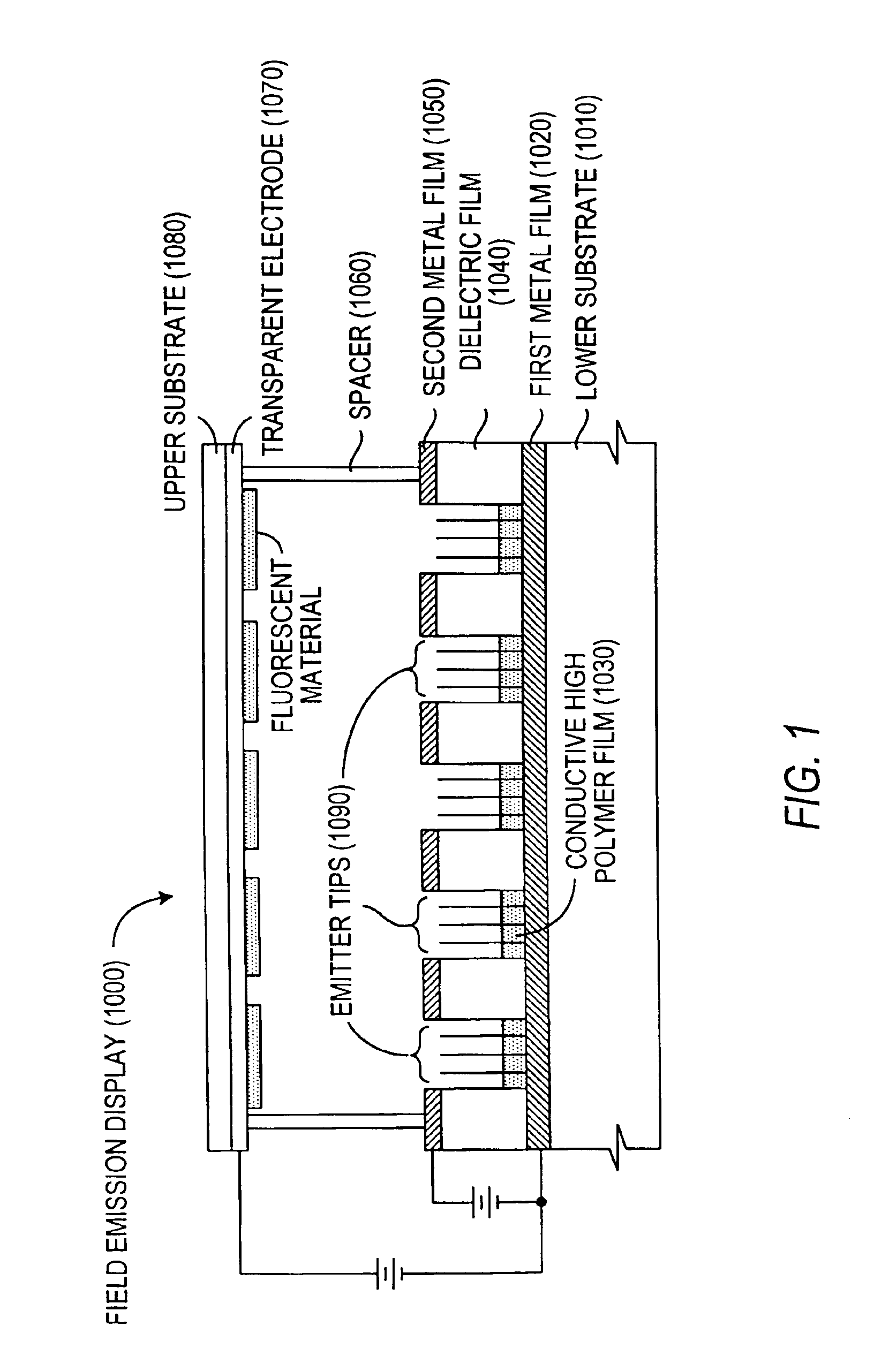
The present invention relates to a field emission device comprising an anode and a cathode, wherein said cathode includes carbon nanotubes nanotubes which have been subjected to energy, plasma, chemical, or mechanical treatment. The present invention also relates to a field emission cathode comprising carbon nanotubes which have been subject to such treatment. A method for treating the carbon nanotubes and for creating a field emission cathode is also disclosed. A field emission display device containing carbon nanotube which have been subject to such treatment is further disclosed.
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
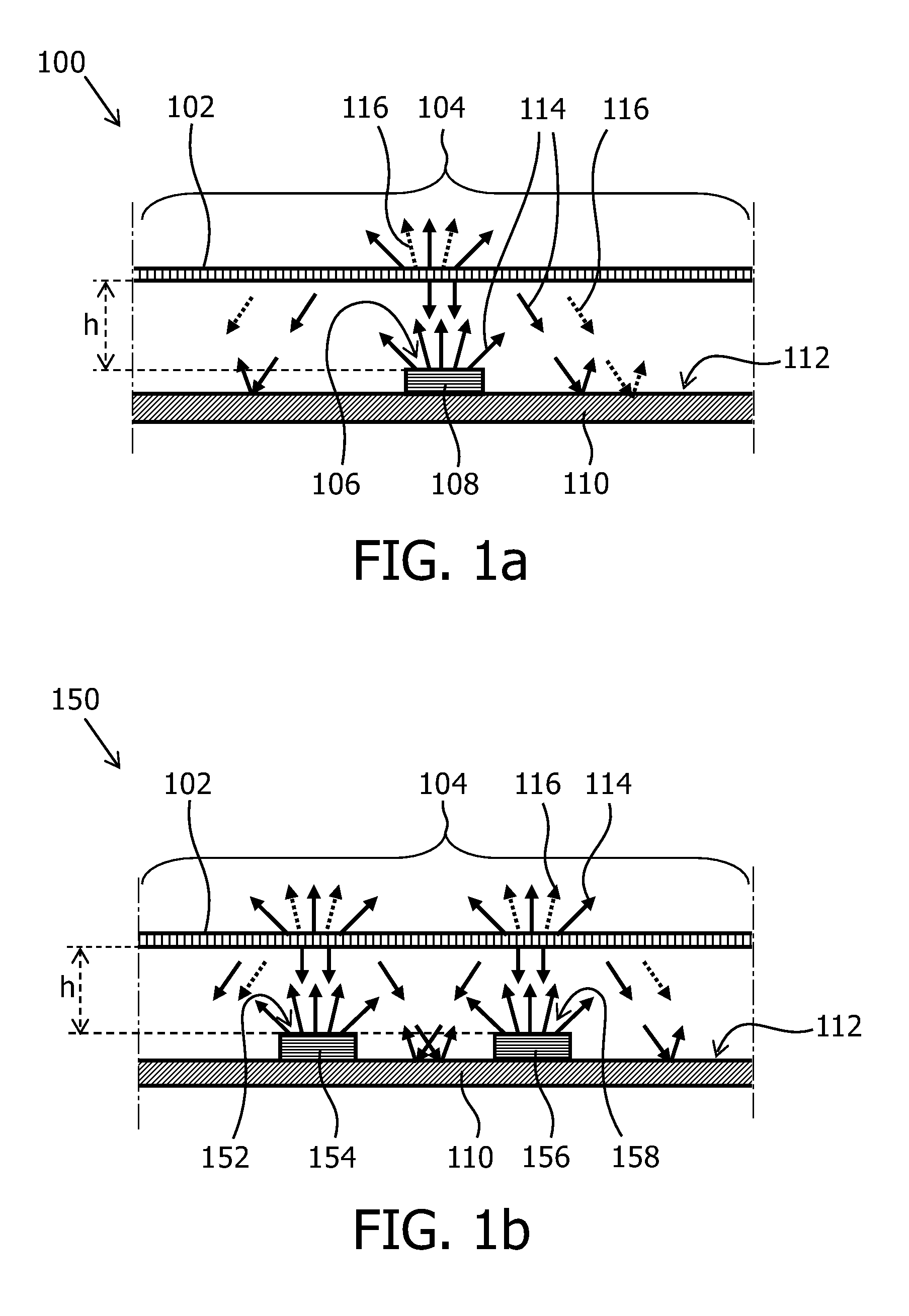
Light emitting module, a lamp, a luminaire and a display device
ActiveUS20130334559A1Cost reductionLess lightSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesReflection coefficientSolid-state
A light emitting module 150 emits light through a light exit window 104 and comprises a base 110, a solid state light emitter 154, 156 and a partially diffusive reflective layer 102. The base 110 has a light reflective surface 112 which faces towards the light exit window 104. The light reflective surface 112 has a base reflection coefficient Rbase which i defined by a ratio between the amount of light that is reflected by the light reflective surface and the amount of light that impinges on the light reflective surface. The solid state light emitter 154, 156 emits light of a first color range 114, comprises a top surface 152, 158 and has a solid state light emitter reflection coefficient R_SSL which is defined by a ratio between the amount of light that is reflected by the solid state emitter 154, 156 and the amount of light that impinges on the top surface 152, 158 of the solid state light emitter 154, 156. The light exit window 104 comprises at least a part of the partially diffusive reflective layer 102. A solid state light emitter area ratio ρSSL is defined as the ratio between the area of the top surface of the at least one solid state light emitter and the area of the light reflective surface of the base. A relatively efficient light emitting module is obtained if Rbase>R_SSL+c*(1−R_SSL) and the factor c is 0.2≦c≦1 for 0<ρSSL<0.1, 0.3≦c≦1 for 0.1≦ρSSL≦0.25, and 0.4≦c≦1 for ρSSL>0.25.
Owner:LUMILEDS
Field emission devices using ion bombarded carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS6911767B2Reduce voltageAccelerate emissionsCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesNanoinformaticsField emission deviceOxygen
The present invention relates to a field emission device comprising an anode and a cathode, wherein said cathode includes carbon nanotubes which have been treated with an ion beam. The ion beam may be any ions, including gallium, hydrogen, helium, argon, carbon, oxygen, and xenon ions. The present invention also relates to a field emission cathode comprising carbon nanotubes, wherein the nanotubes have been treated with an ion beam. A method for treating the carbon nanotubes and for creating a field emission cathode is also disclosed. A field emission display device containing carbon nanotube which have been treated with an ion beam is further disclosed.
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
Field emission devices using ion bombarded carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS20030044519A1Easy to disassembleReduce voltageCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesNanoinformaticsField emission deviceOxygen
The present invention relates to a field emission device comprising an anode and a cathode, wherein said cathode includes carbon nanotubes which have been treated with an ion beam. The ion beam may be any ions, including gallium, hydrogen, helium, argon, carbon, oxygen, and xenon ions. The present invention also relates to a field emission cathode comprising carbon nanotubes, wherein the nanotubes have been treated with an ion beam. A method for treating the carbon nanotubes and for creating a field emission cathode is also disclosed. A field emission display device containing carbon nanotube which have been treated with an ion beam is further disclosed.
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
Composition and method for oxidizing mercury in combustion processes
InactiveUS7413719B2Emission reductionExcessive emissionUsing liquid separation agentEmission preventionCombustion chamberCombustor
The invention can be summarized as follows. There is provided a method for oxidizing elemental mercury in a combustion process comprising, adding a composition comprising an aluminum silicate to a combustion chamber, boiler or kiln downstream from the burner region combustion zone. There is further provided a method for reducing the emission of one or more heavy metals in a combustion process by adding a composition comprising an aluminum silicate to a combustion chamber downstream from the burner region combustion zone. There is also provided a composition comprising an aluminum silicate that may be employed to oxidize elemental mercury generated in a combustion process. The composition also may be employed to reduce the emission of one or more heavy metals generated in a combustion process.
Owner:DIGDON WILLIAM TROY
Method and device for keeping coke furnace chambers hot when a waste heat boiler is stopped
InactiveUS9057023B2Avoid emissionsReduce processing stepsCombustible gas coke oven heatingVertical chamber coke ovensCombustorFlue gas
A process for keeping coke oven chambers hot during the stoppage of a waste heat boiler. The coke oven chambers are kept hot after emptying using externally heated burners, in which a flue gas low in pollutants is obtained from the burners. The waste heat boilers which, during normal operation, cool the flue gases can be shut off and overhauled, and a flue gas low in pollutants which can be dissipated directly into the atmosphere is obtained by the burner operation. Also disclosed is an apparatus for keeping coke oven chambers hot, the apparatus has a coke oven chamber bench, a flue gas collection line, a flue gas chimney, a waste heat boiler, a waste gas collection line and a waste gas purification system, wherein the flue gas chimney and the waste heat boiler can be shut off on the flue gas side and on the waste gas side.
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP IND SOLUTIONS AG
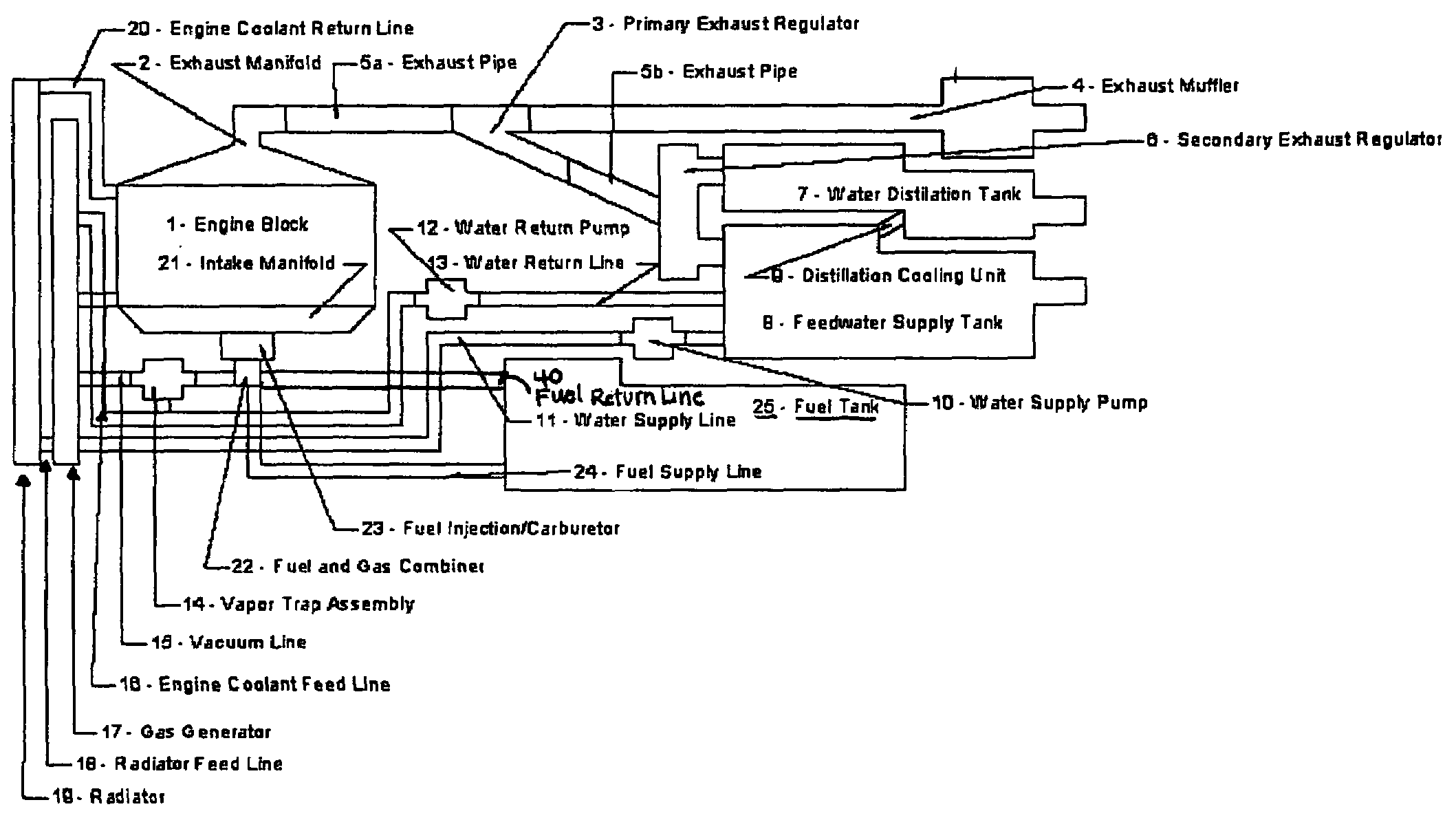
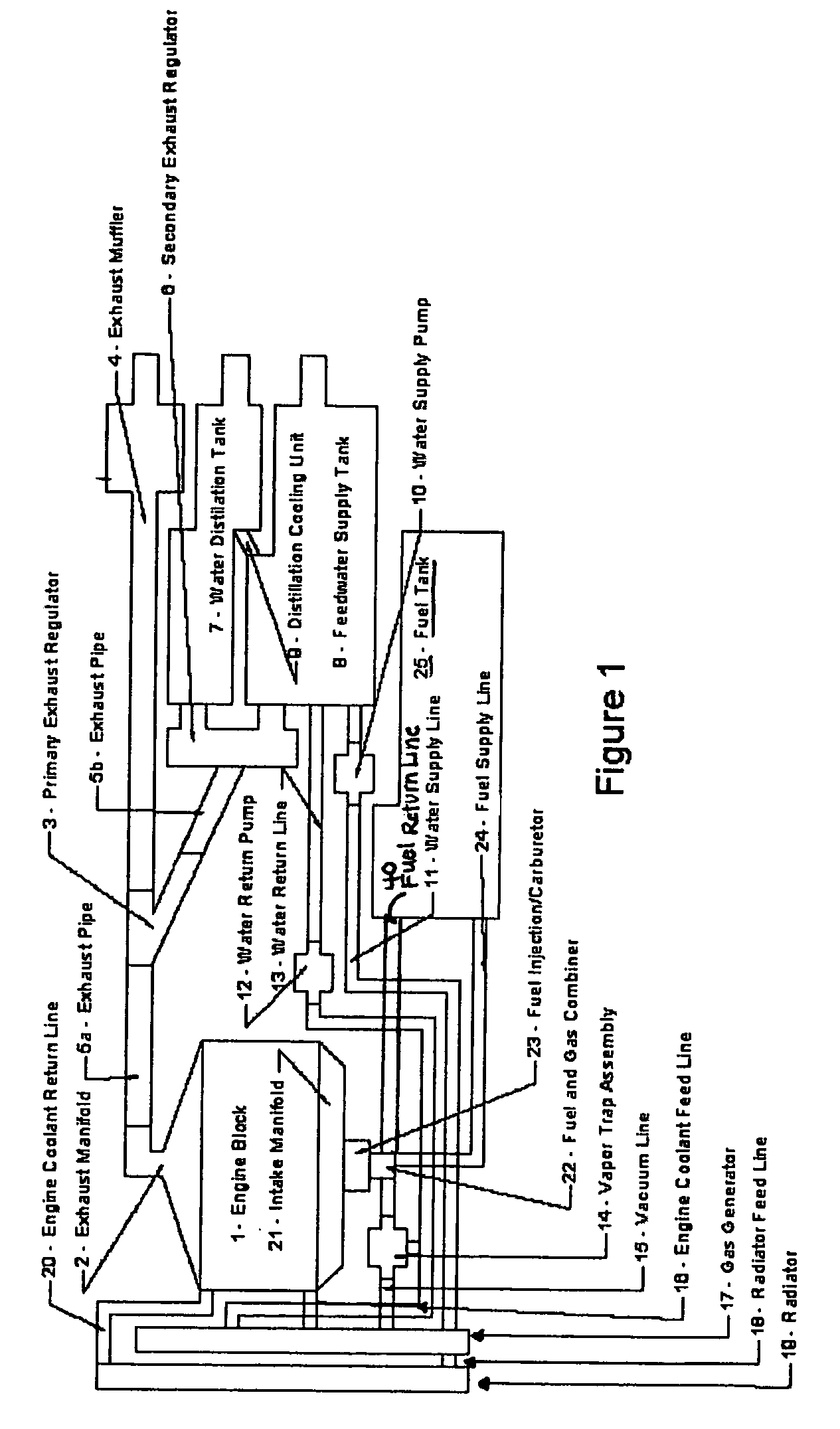
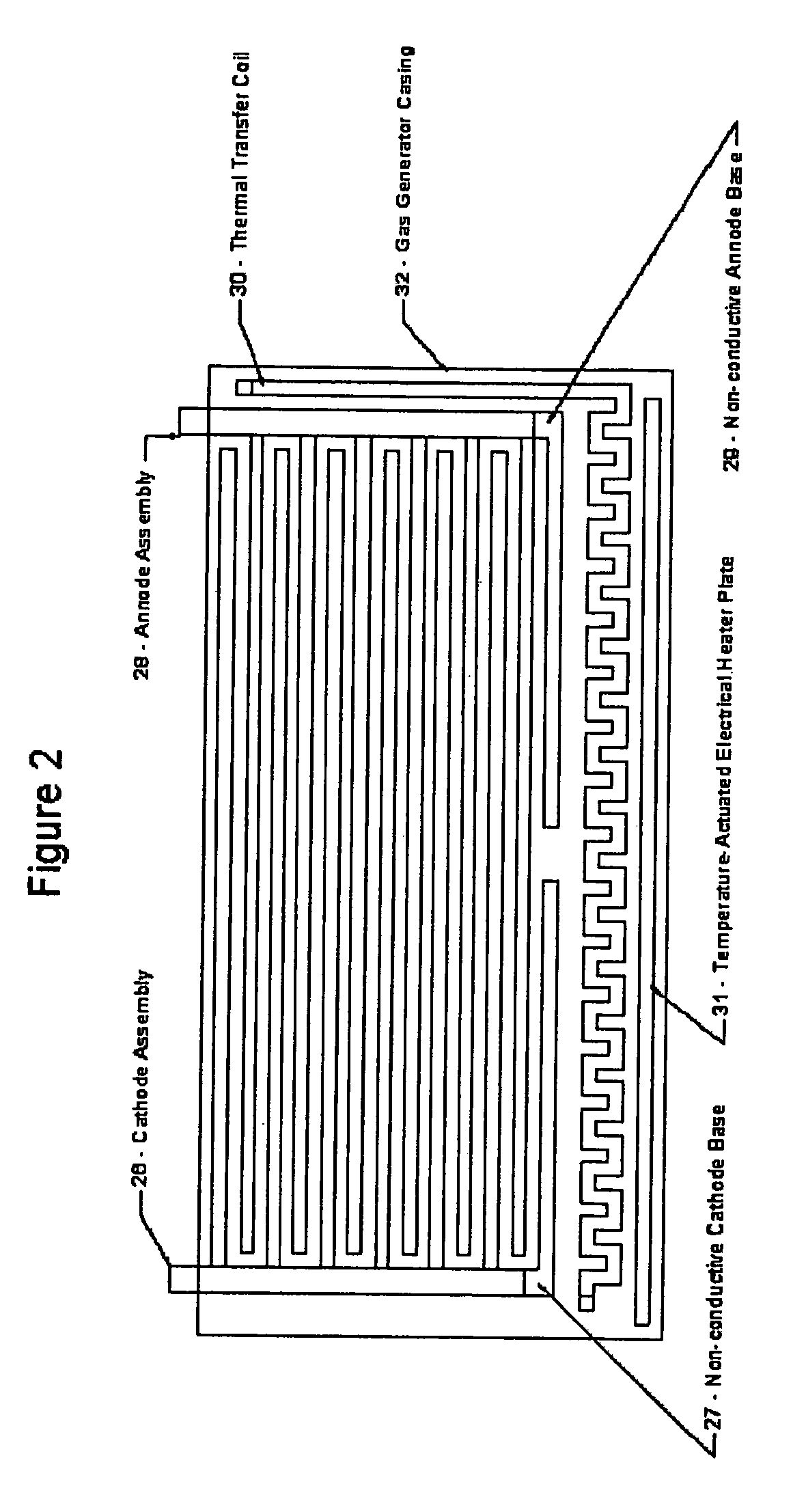
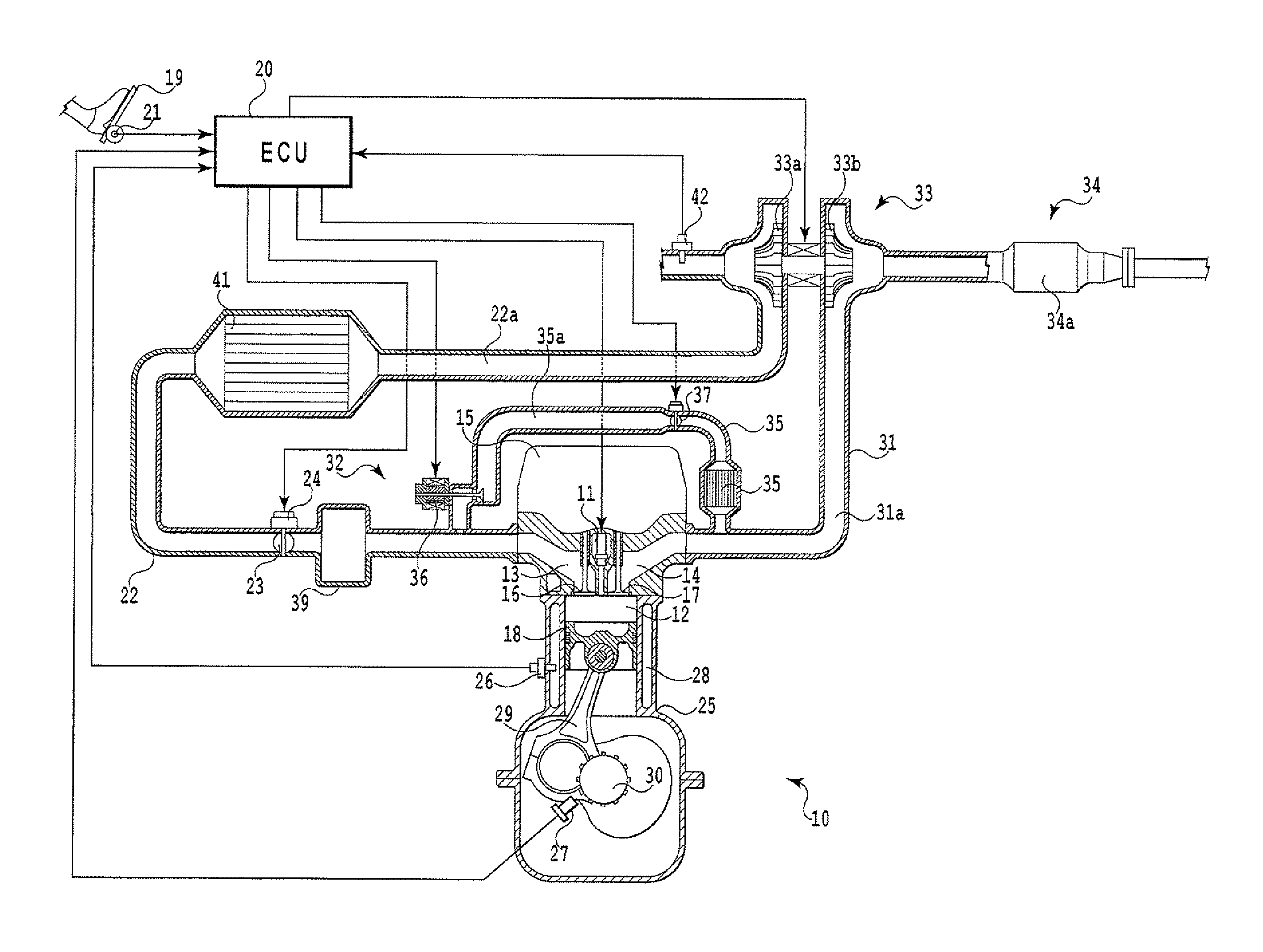
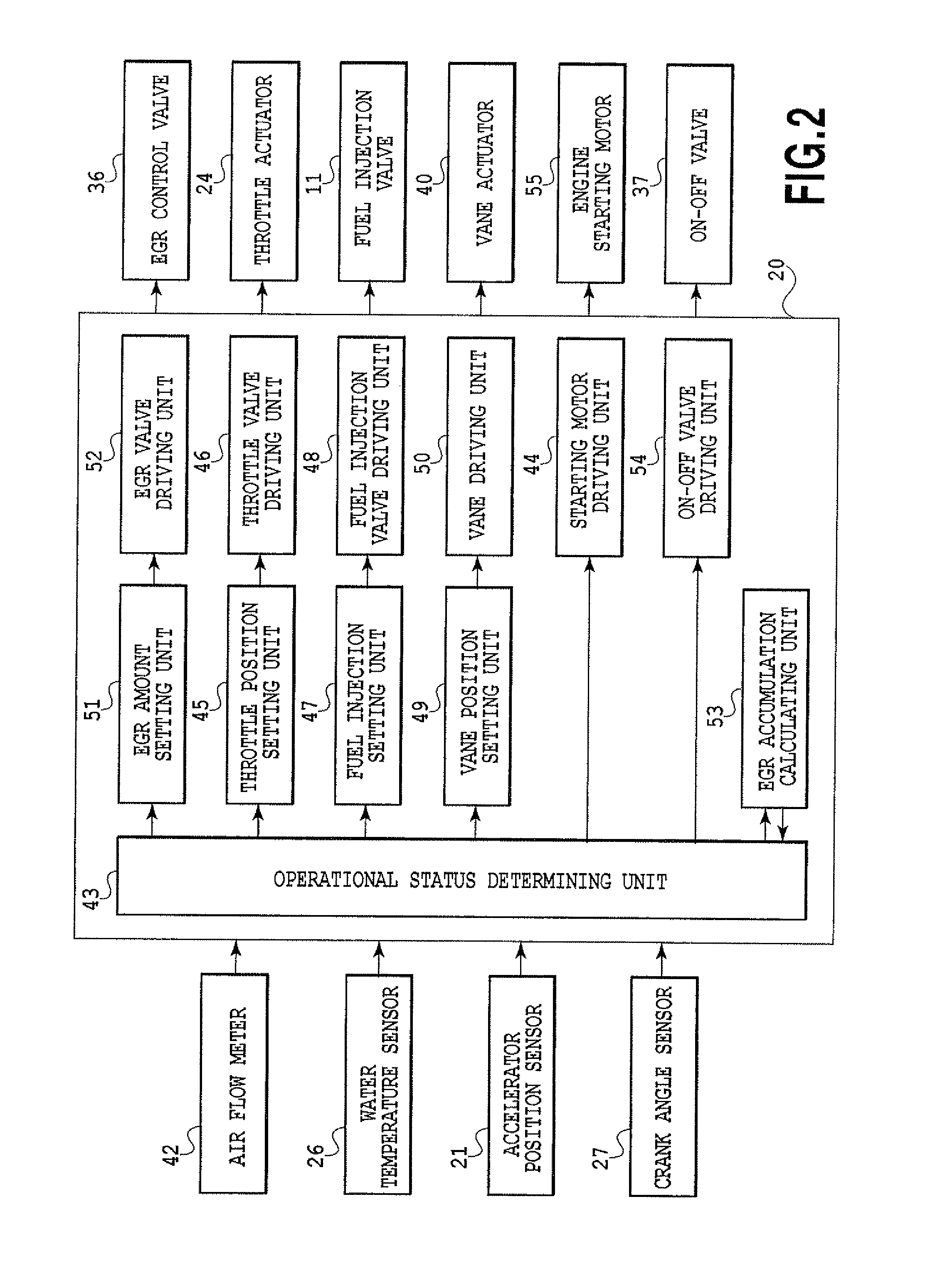
Hydrogen oxygen generation system for an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20060090712A1Improve fuel efficiencyExcessive emissionInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelDistillationInternal combustion engine
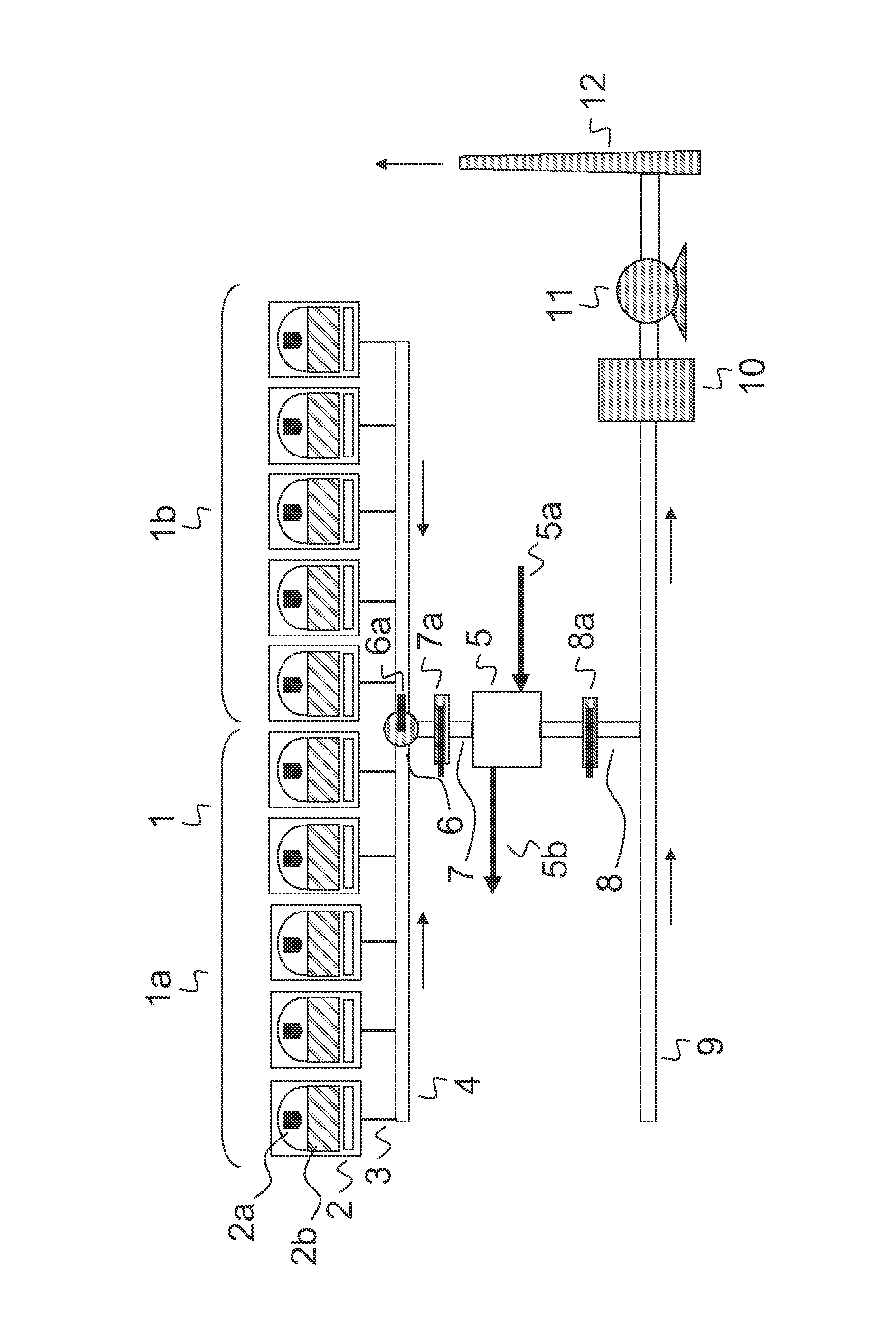
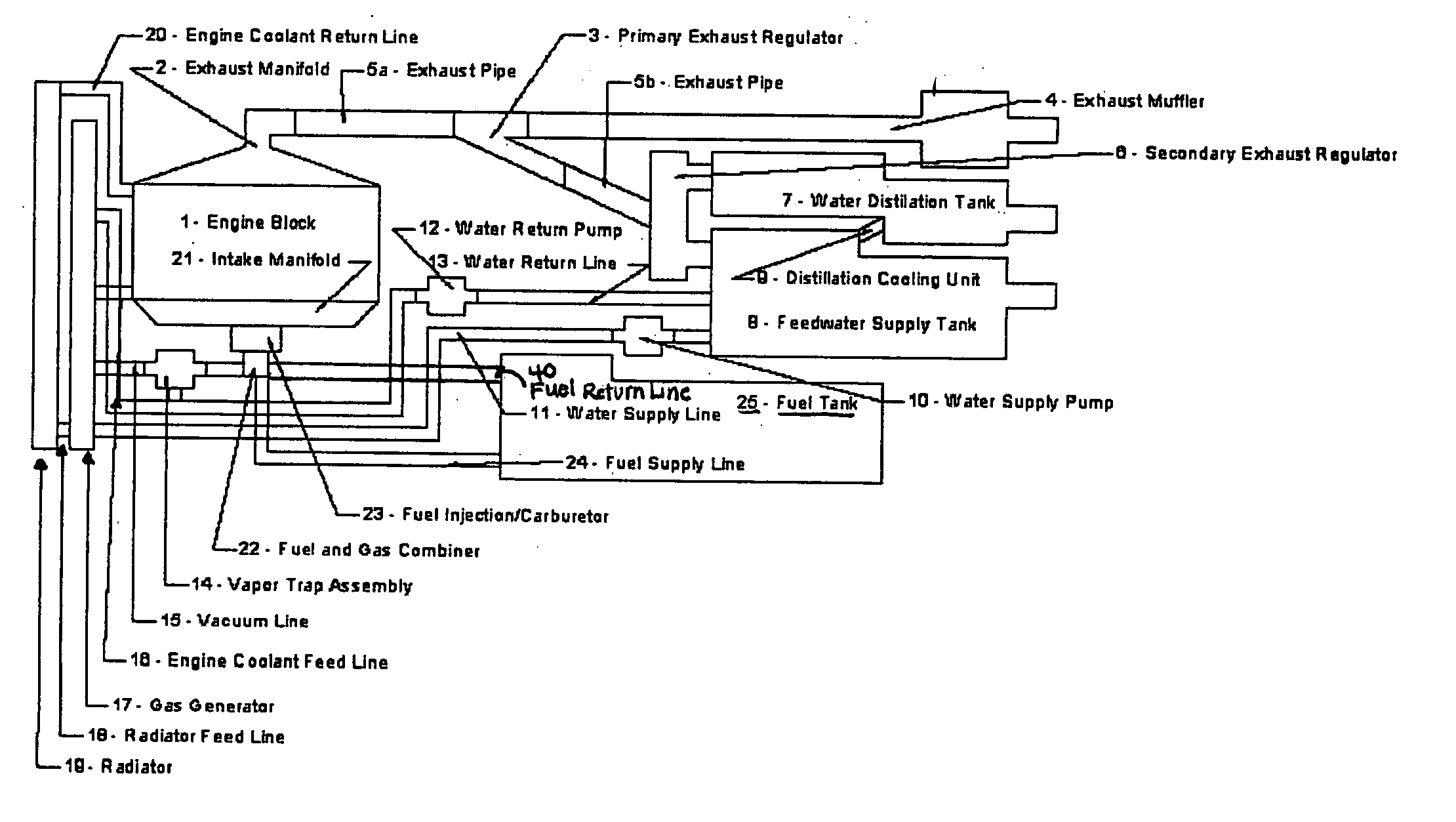
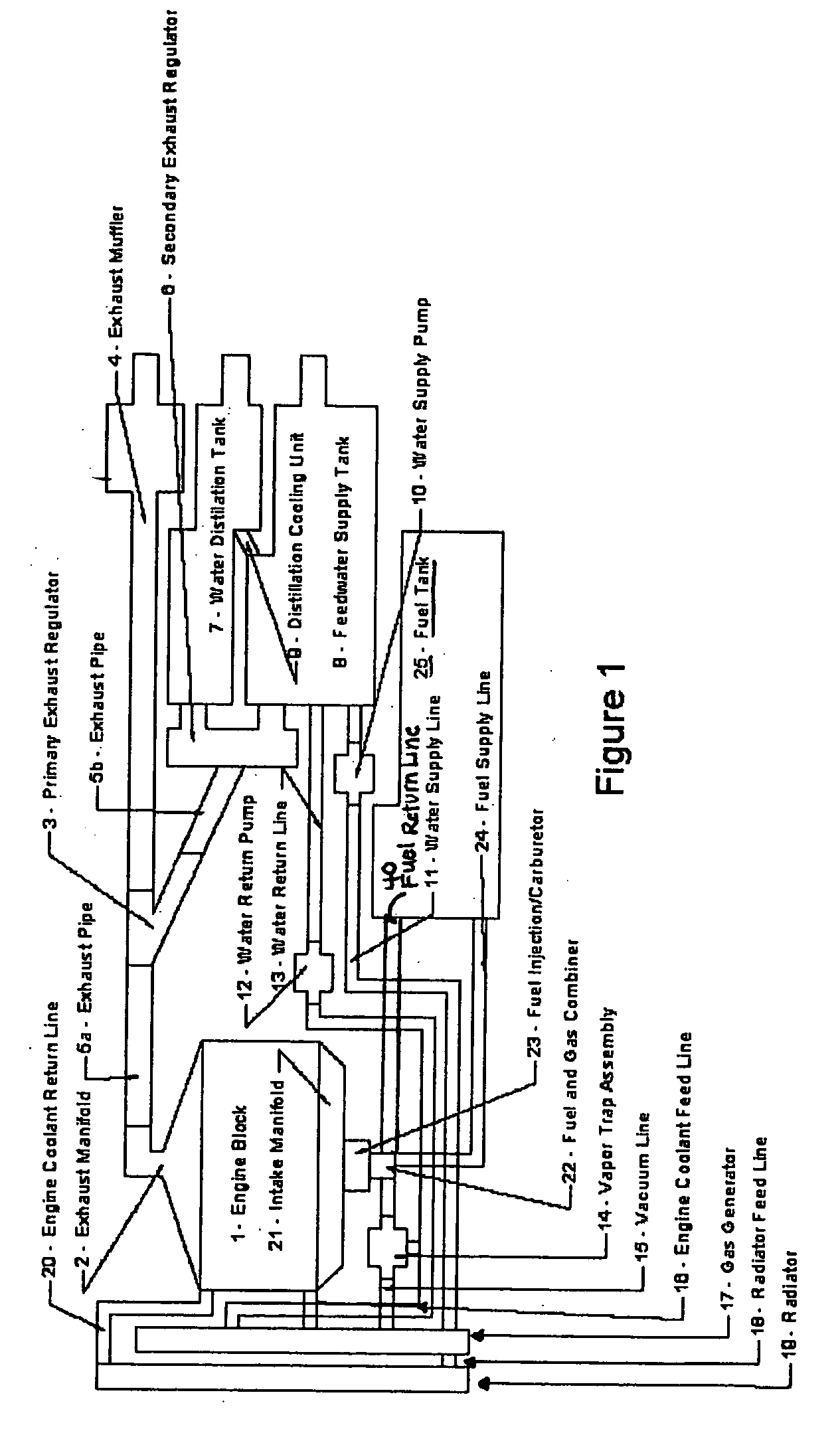
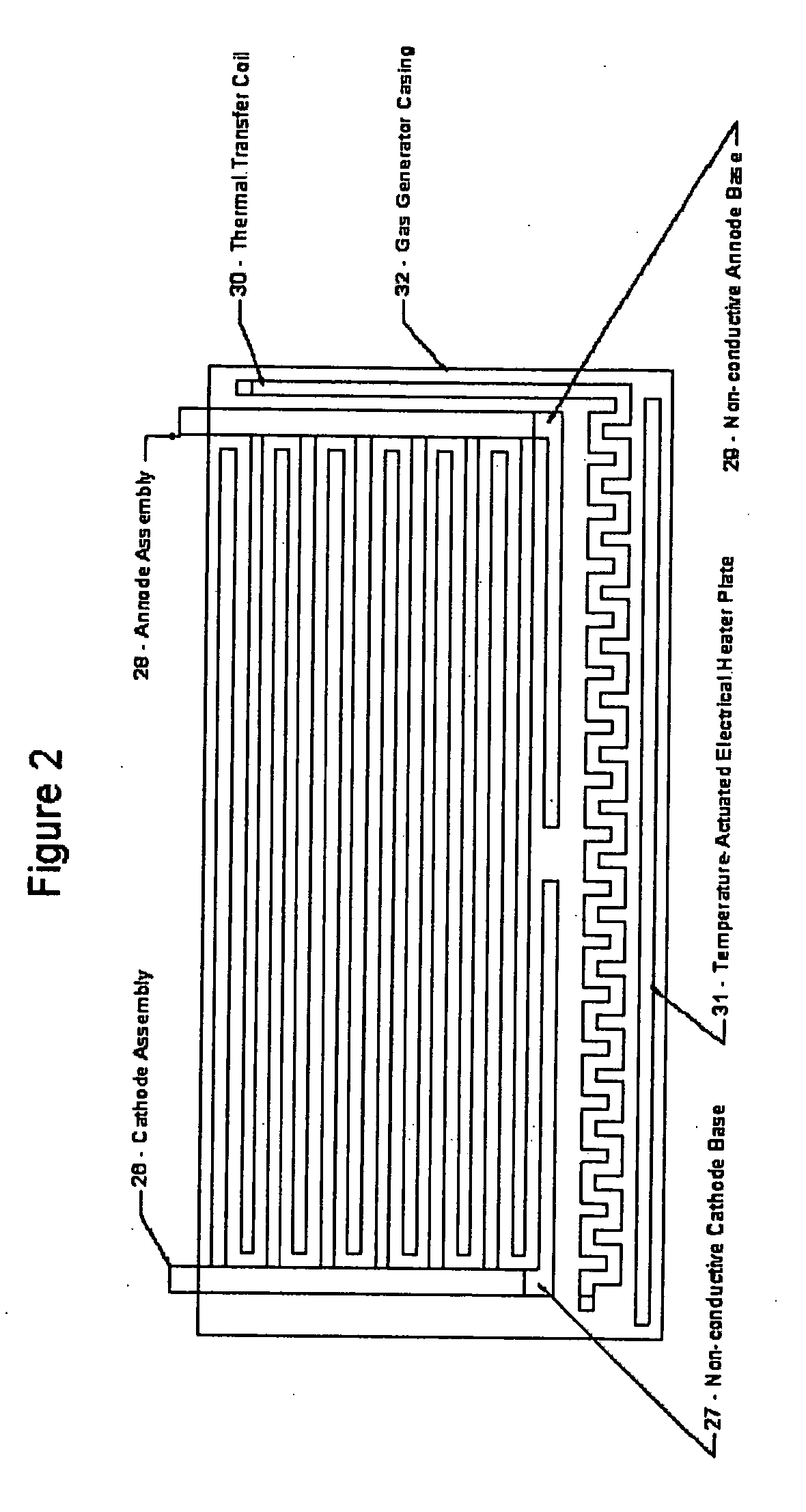
A system is provided which, when integrated with an internal combustion engine, generates hydrogen and oxygen gases to enrich an internal combustion engine's petroleum fuel source. The system's primary components are a gas generation unit, heated water supply tanks, and a gas combiner for mixing generated hydrogen and oxygen gas with petroleum fuel to create hydrogenated and oxygenated petroleum fuel. The gas generation unit includes at least one cathode, at least one anode, vacuum regulatory units, a thermal transfer system, an electrical heating element, a feedwater management system, a gas collection and supply system, and water traps. The heated water tanks include a thermal transfer system, pressure and regulatory units as well as a distillation apparatus for producing distilled water. Electrical power is supplied to the system's power amplifier from the internal combustion engine's alternator or associated electrical system.
Owner:EHRETEK
Hydrogen oxygen generation system for an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7100542B2Improve fuel efficiencyExcessive emissionNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineDistillation
Owner:EHRETEK
Field emission devices using modified carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS20050275331A1Reduce voltageAccelerate emissionsNanostructure manufactureNanoinformaticsField emission deviceModified carbon
The present invention relates to a field emission device comprising an anode and a cathode, wherein said cathode includes carbon nanotubes nanotubes which have been subjected to energy, plasma, chemical, or mechanical treatment. The present invention also relates to a field emission cathode comprising carbon nanotubes which have been subject to such treatment. A method for treating the carbon nanotubes and for creating a field emission cathode is also disclosed. A field emission display device containing carbon nanotube which have been subject to such treatment is further disclosed.
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
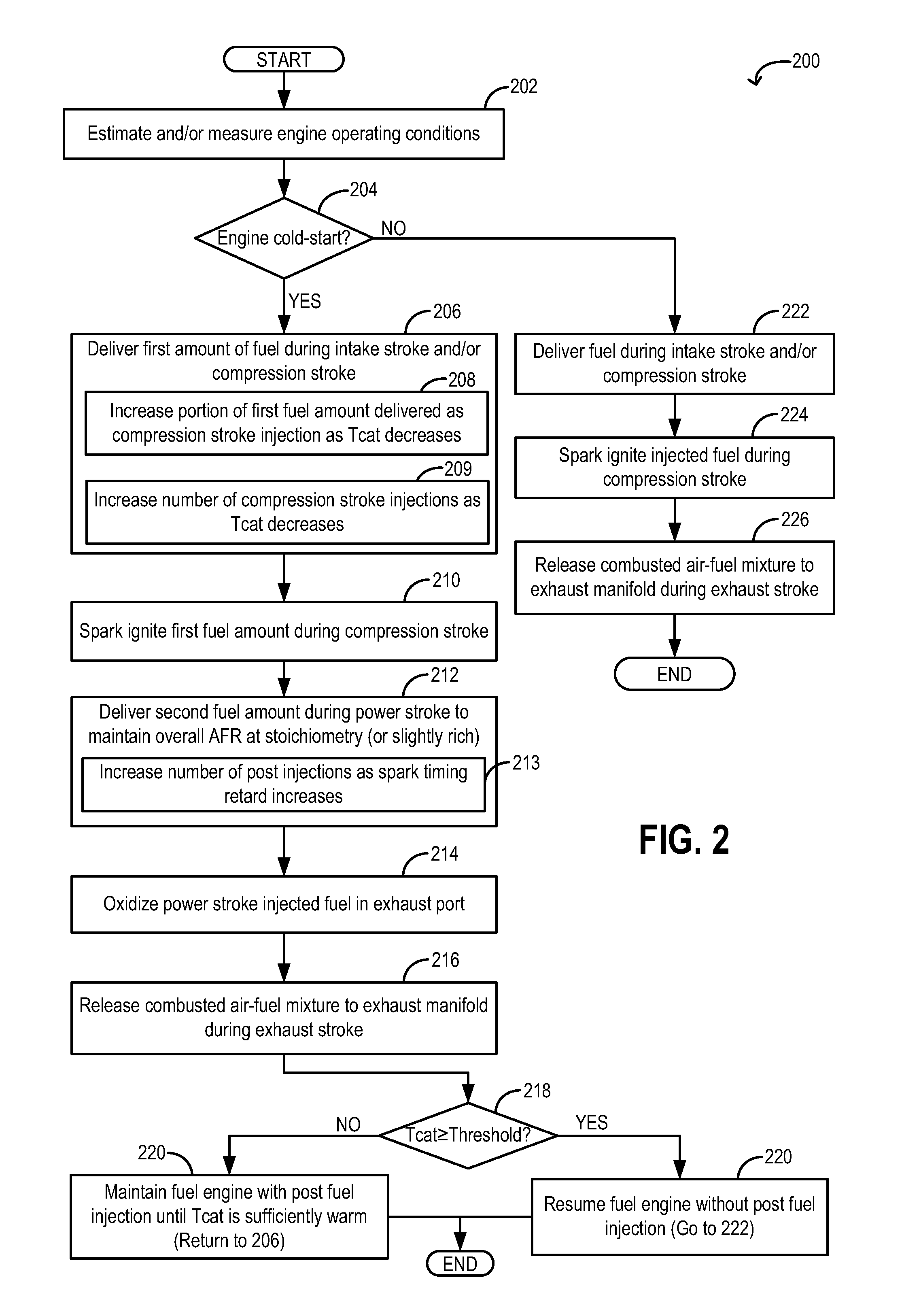
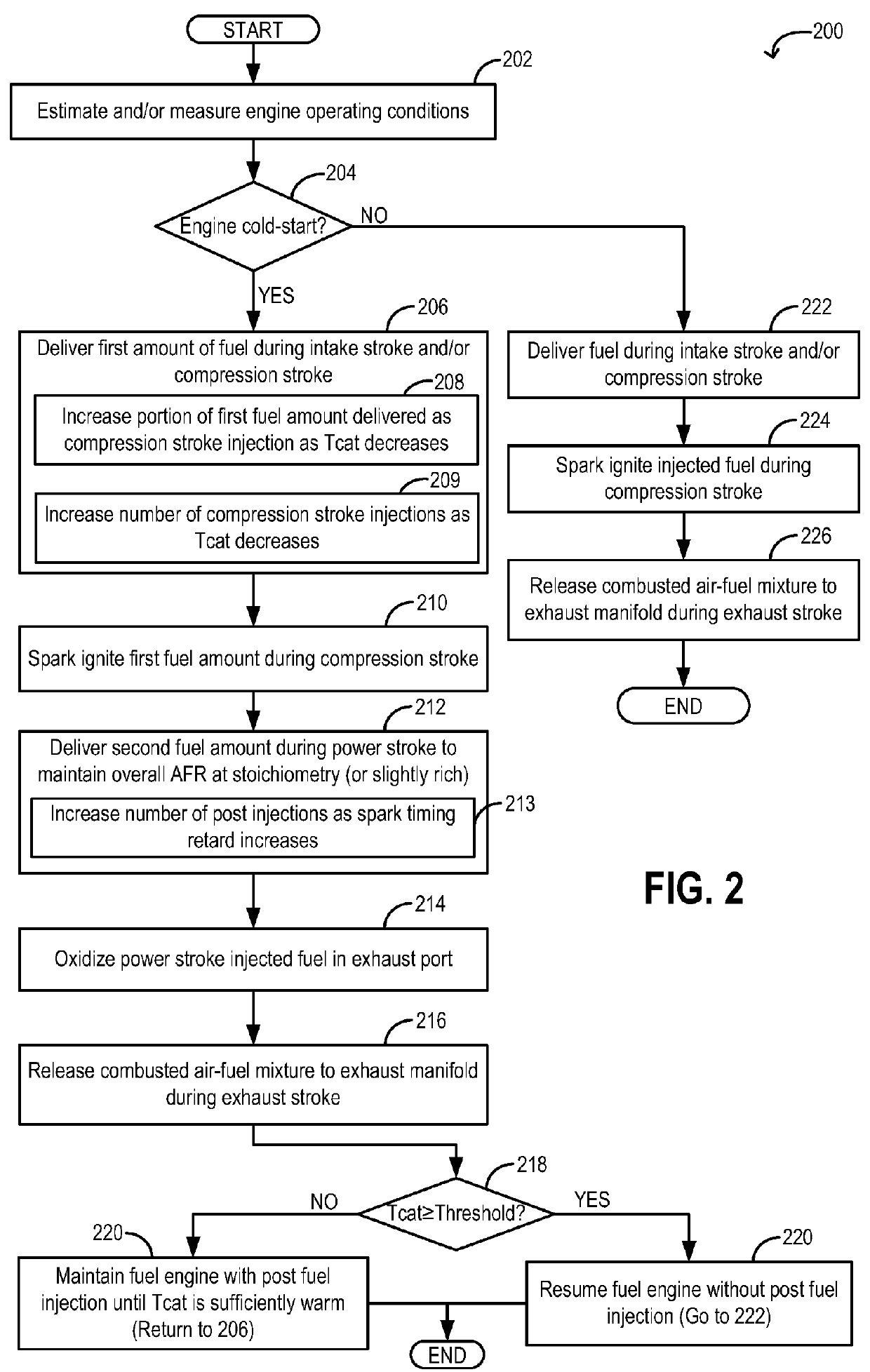
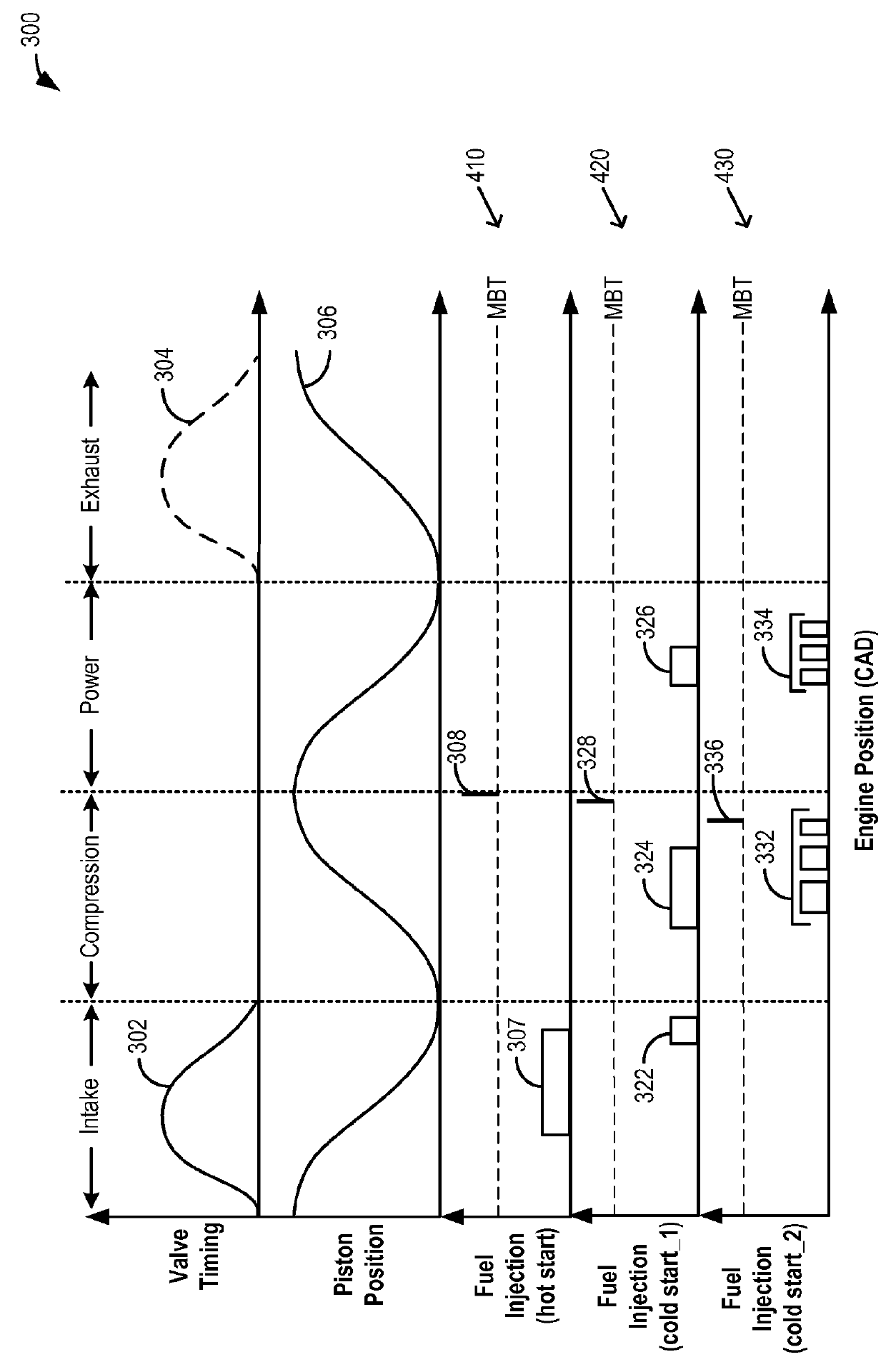
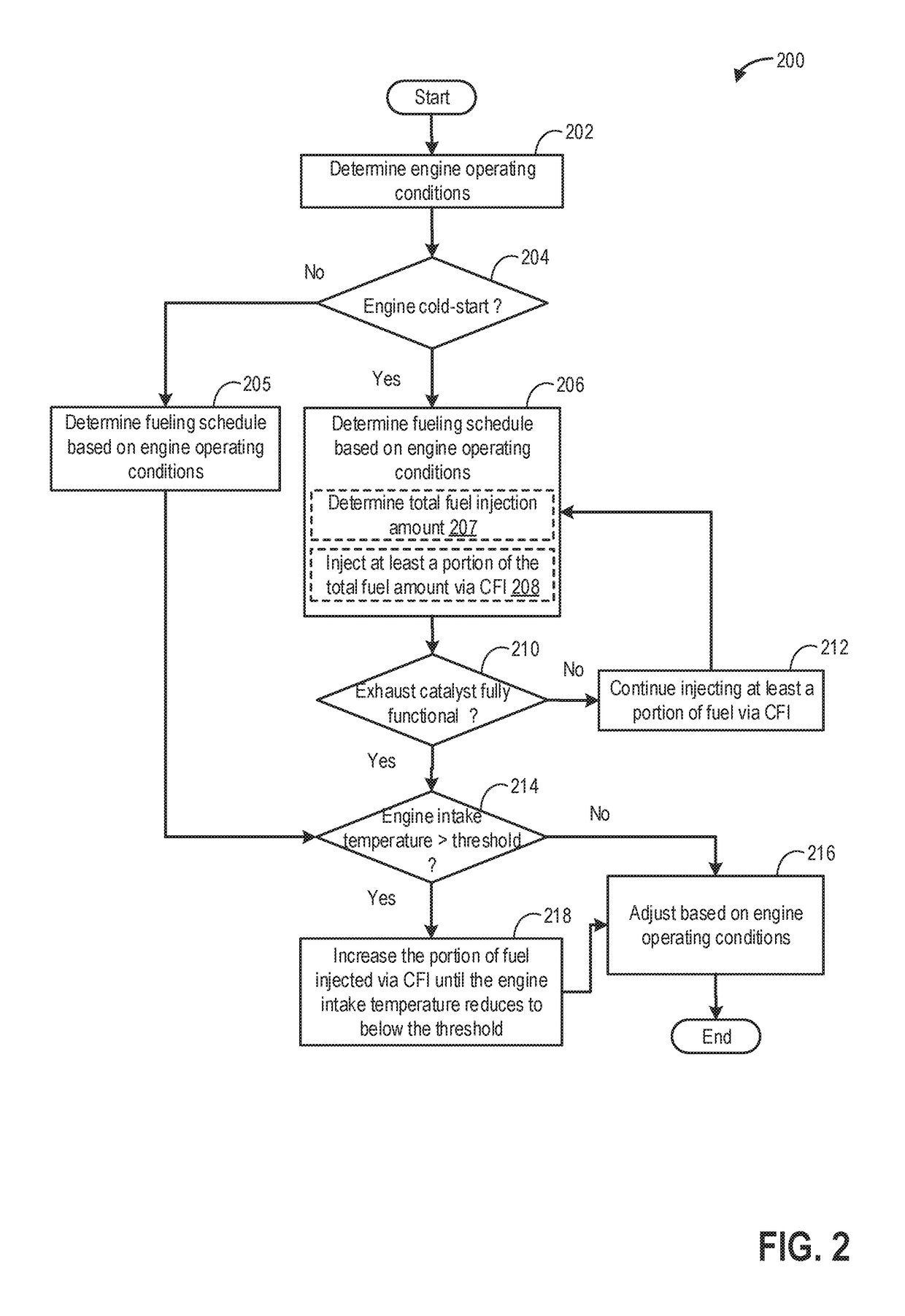
Post fuel injection of gaseous fuel to reduce exhaust emissions
InactiveUS20150167576A1Improve fuel efficiencyImprove cooling effectElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust fumesFuel injection
Methods and systems are provided for delivering gaseous fuel as multiple fuel injections split between an intake stroke, a compression stroke, and / or a power stroke to expedite exhaust catalyst heating during an engine cold-start. Fuel injected in the intake and compression stroke is ignited and combusted. The power stroke fuel injections are combusted in the exhaust port to increase exhaust temperature and pressure for faster catalyst light-off.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
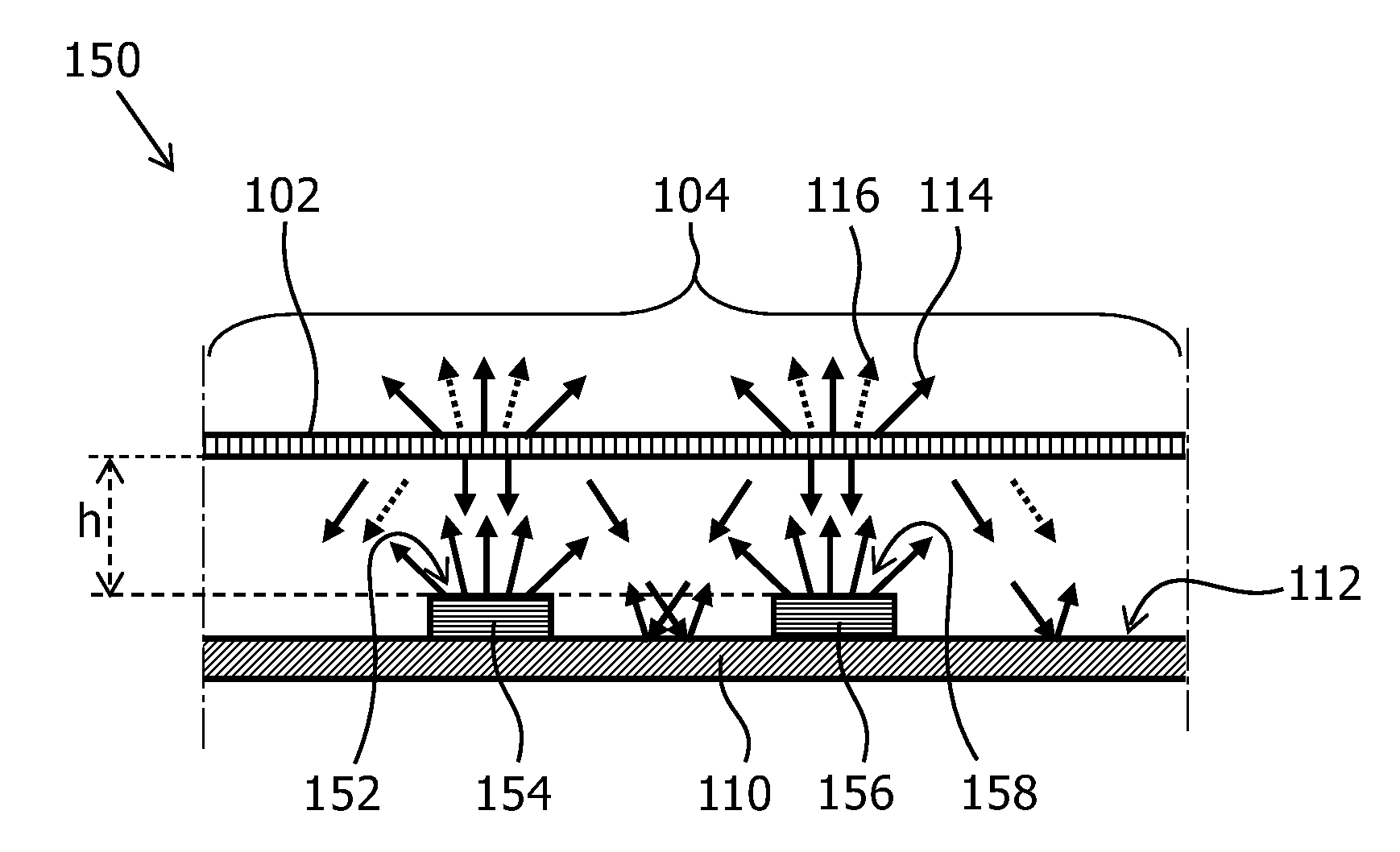
Light emiting module, a lamp, a luminaire and a display device
ActiveUS20150009649A1Low costLess lightNon-electric lightingLight source combinationsDisplay deviceReflective layer
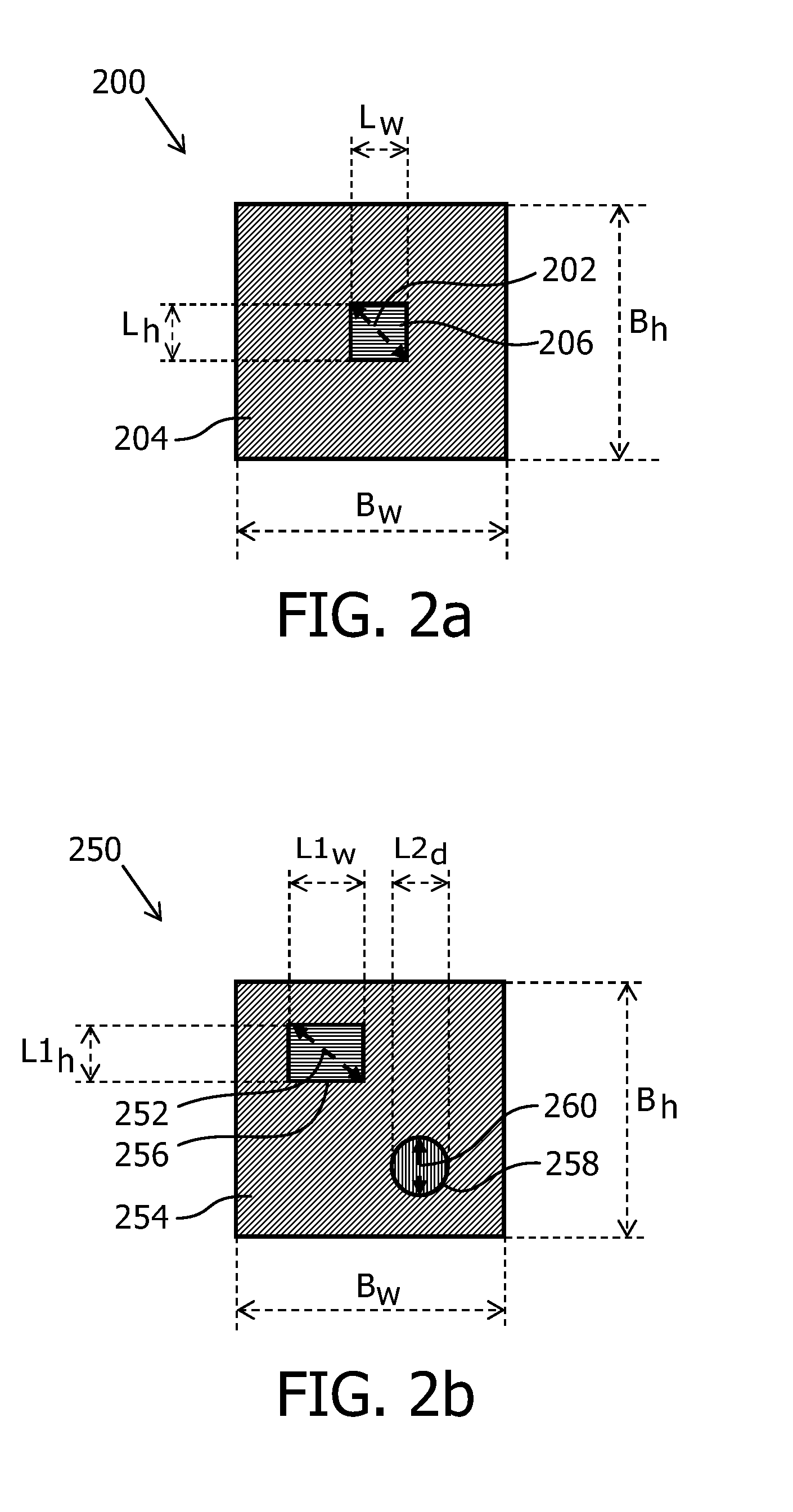
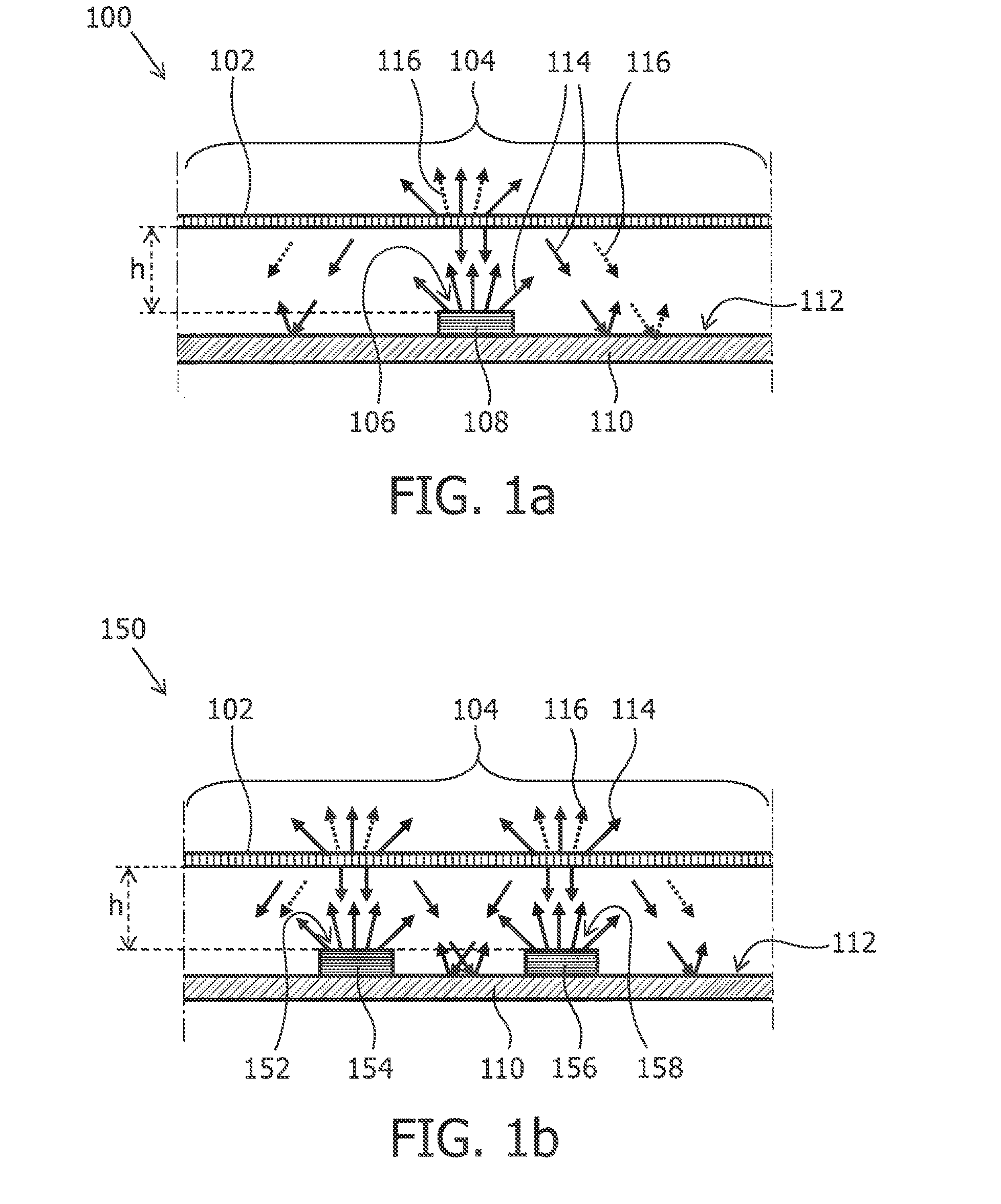
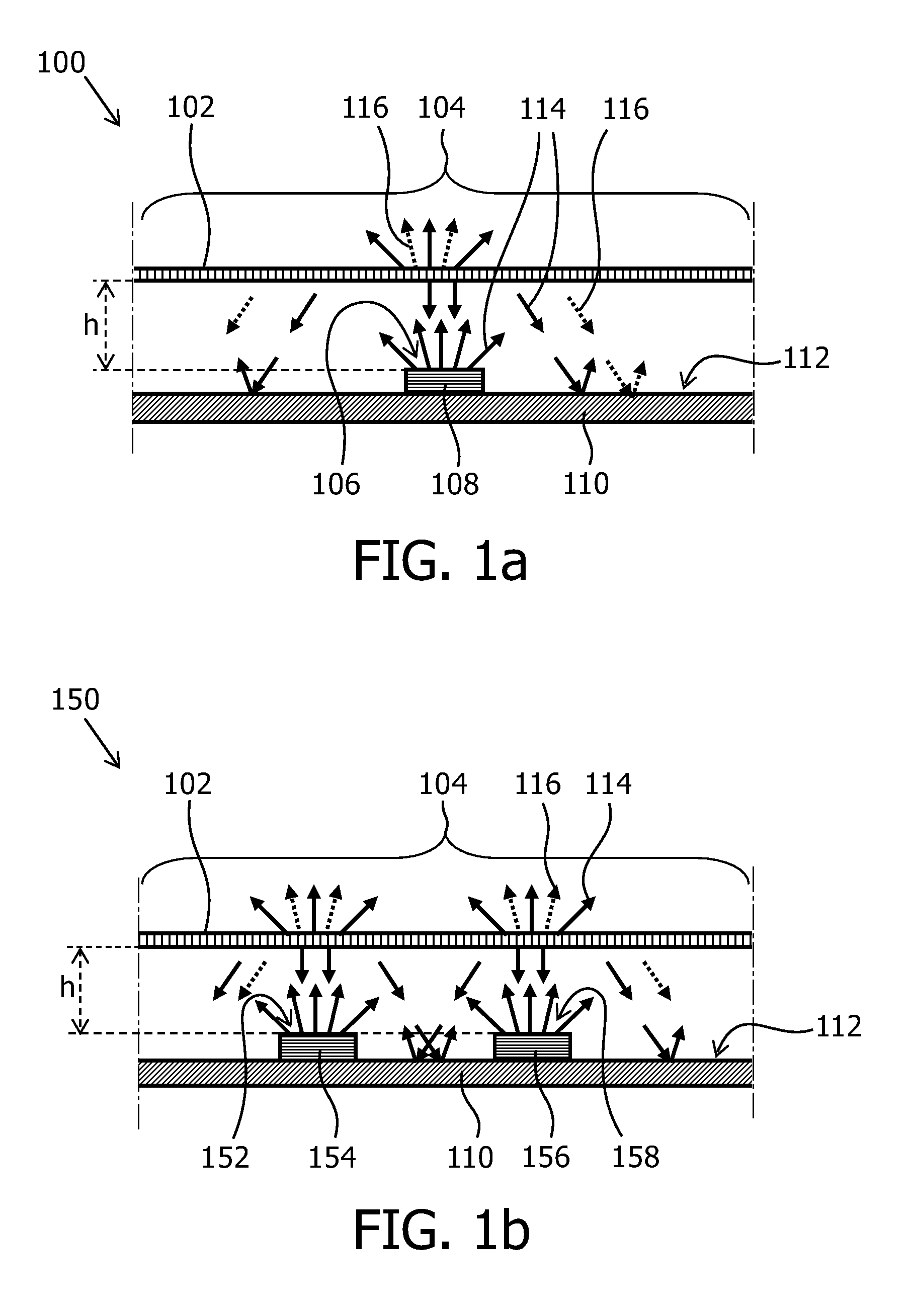
A light emitting module (150) emits light through a light exit window (104) and comprises a base (110), a solid state light emitter (154, 158) and a partially diffusive reflective layer (102). The base (110) has a light reflective surface (112) which faces towards the light exit window (104). The light reflective surface (112) has a base reflection coefficient Rbase which is defined by a ratio between the amount of light that is reflected by the light reflective surface and the amount of light that impinges on the light reflective surface. The solid state light emitter (154, 158) emits light of a first color range (114), comprises a top surface (152, 158) and has a solid state light emitter reflection coefficient R_SSL which is defined by a ratio between the amount of light that is reflected by the solid state emitter (154,156) and the amount of light that impinges on the top surface (152, 158) of the solid state light emitter (1154, 156). A largest linear size dssL of the top surface (106) of the at least one solid state light emitter is defined as the longest distance from a point on the top surface (152, 158) of the at least one solid state light emitter to another point on the top surface (152, 158) of the at least one solid state light emitter along a straight line. The light exit window (104) comprises at least a part of the partially diffusive reflective layer (102). A solid state light emitter area ratio ρSSL is defined as the ratio between the area of the top surface of the at least one solid state light emitter and the area of the light reflective surface of the base. A gap with a distance h is present between the top surface (152, 158) of the at least one solid state light emitter
Owner:LUMILEDS
Lightweight composite materials produced from carbonatable calcium silicate and methods thereof
ActiveUS20160340261A1Avoid problemsSuitable for useSolid waste managementCeramic shaping apparatusCalcium silicateCompressive strength
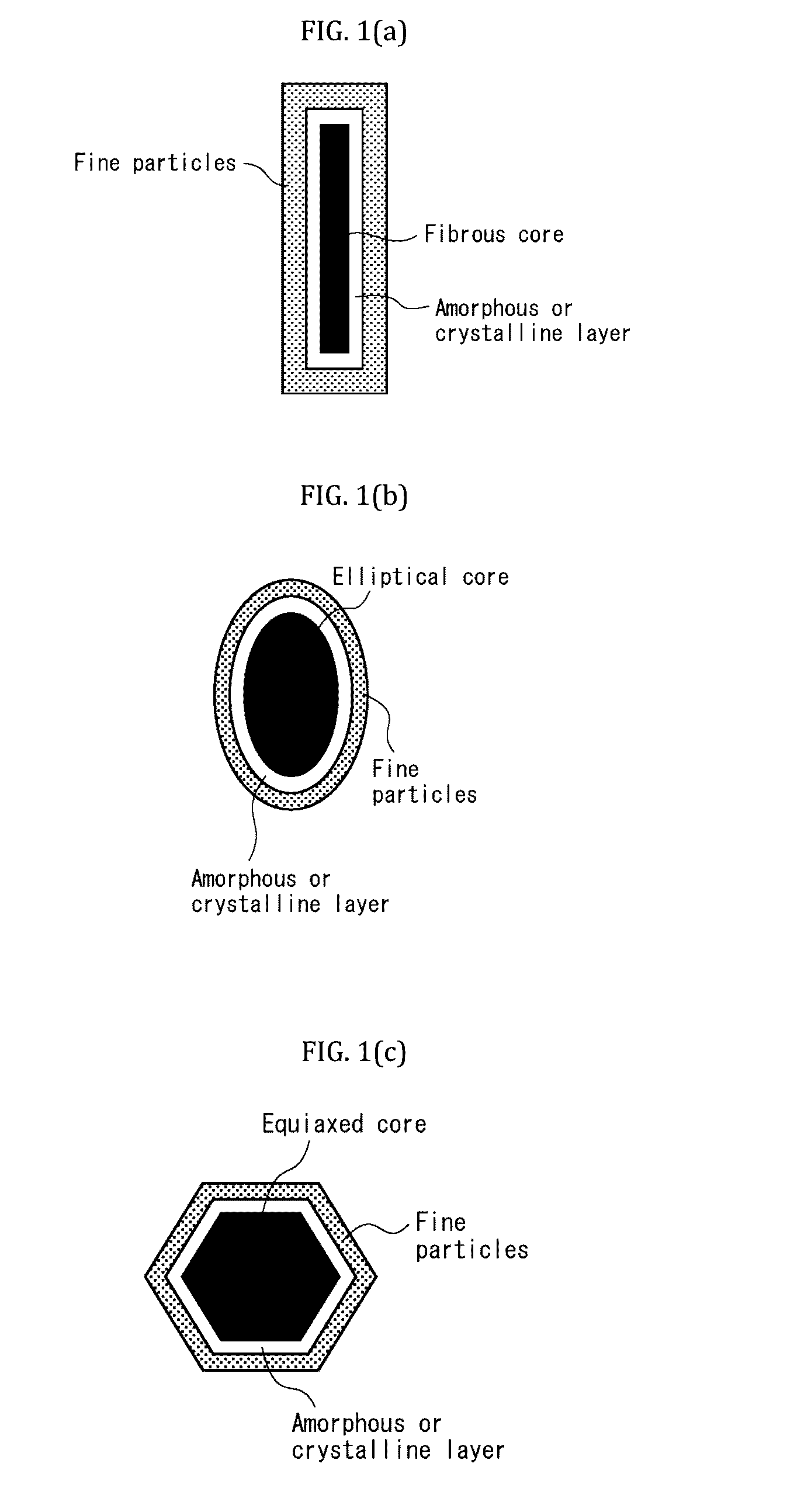
An aerated composite material produced from carbonatable calcium silicate compositions (carbonation cured AAC) that has a compressive strength equivalent to autoclaved aerated concrete (ordinary AAC) at substantially the same density and a process of production of the same are provided. The composite material of the present invention comprises: a plurality of bonding elements, each including a core comprising calcium silicate, a first layer which partially or fully surrounds the core and is rich in SiO2, and a second layer which partially or fully surrounds the first layer and is rich in CaCO3; a plurality of filler particles having their particle sizes ranging from 0.1 μm to 1000 μm; and a plurality of voids; wherein the plurality of bonding elements and plurality of filler particles together form a bonding matrix and are substantially evenly dispersed in the matrix and bonded together, the plurality of voids are bubble-shaped and / or interconnected channels, a pore volume with a radius of 0.004 μm to 10.0 μm in the plurality of voids is 0.30 ml / composite material 1 g or less, and a estimated compressive strength expressed by the following formula (1): estimated compressive strength (absolute dry density=0.50)=compressive strength×(0.50÷absolute dry density)2 is 2.0 N / mm2 or greater.
Owner:SOLIDIA TECH +1
Post fuel injection of gaseous fuel to reduce exhaust emissions
InactiveUS9382857B2Improve cooling effectImprove fuel efficiencyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesTemperature and pressureFuel injection
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Light emitting module, a lamp, a luminaire and a display device
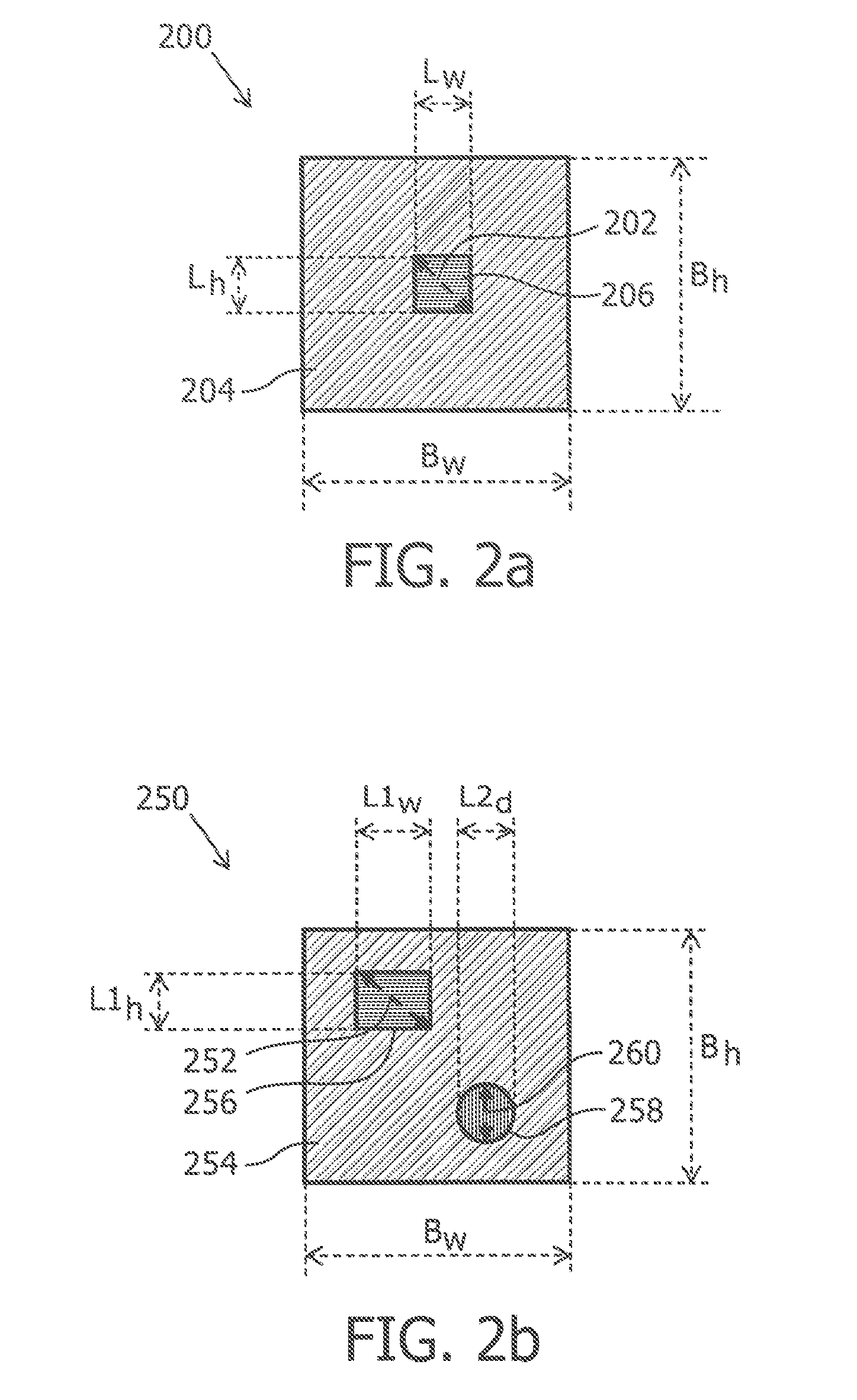
ActiveUS9599292B2Less lightImprove lighting efficiencyLight source combinationsSolid-state devicesPhosphorDisplay device
A light emitting module includes at least one LED mounted on a reflective base and surrounded by reflective walls to form a cavity. A partially diffusive layer containing a phosphor is mounted above the LED with a gap therebetween. Some of the light emitted by the phosphor is backscattered toward the LED, base, and walls. The LED absorbs a significant amount of the light, while the reflective base and walls efficiently reflect over 90% of the light back toward the phosphor layer for exiting the module. Various equations are provided that allow the designer to select an optimal gap between the LED and the partially diffusive layer to maximize light extraction efficiency out of the diffusive layer. The optimal gap range for maximizing light extraction efficiency is a product of LED largest linear length, LED surface area, base area, wall area, and reflective coefficients of the various elements.
Owner:LUMILEDS
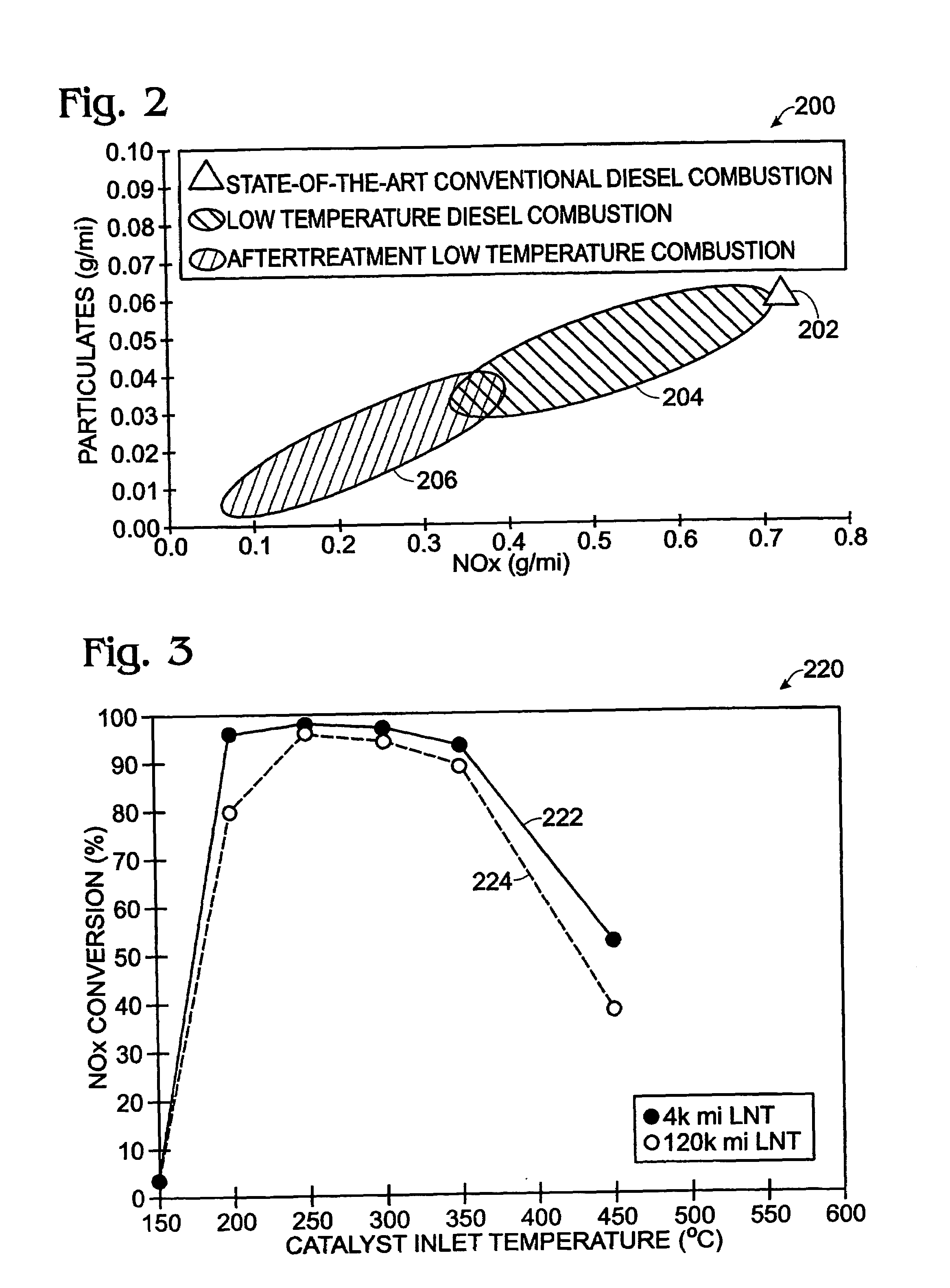
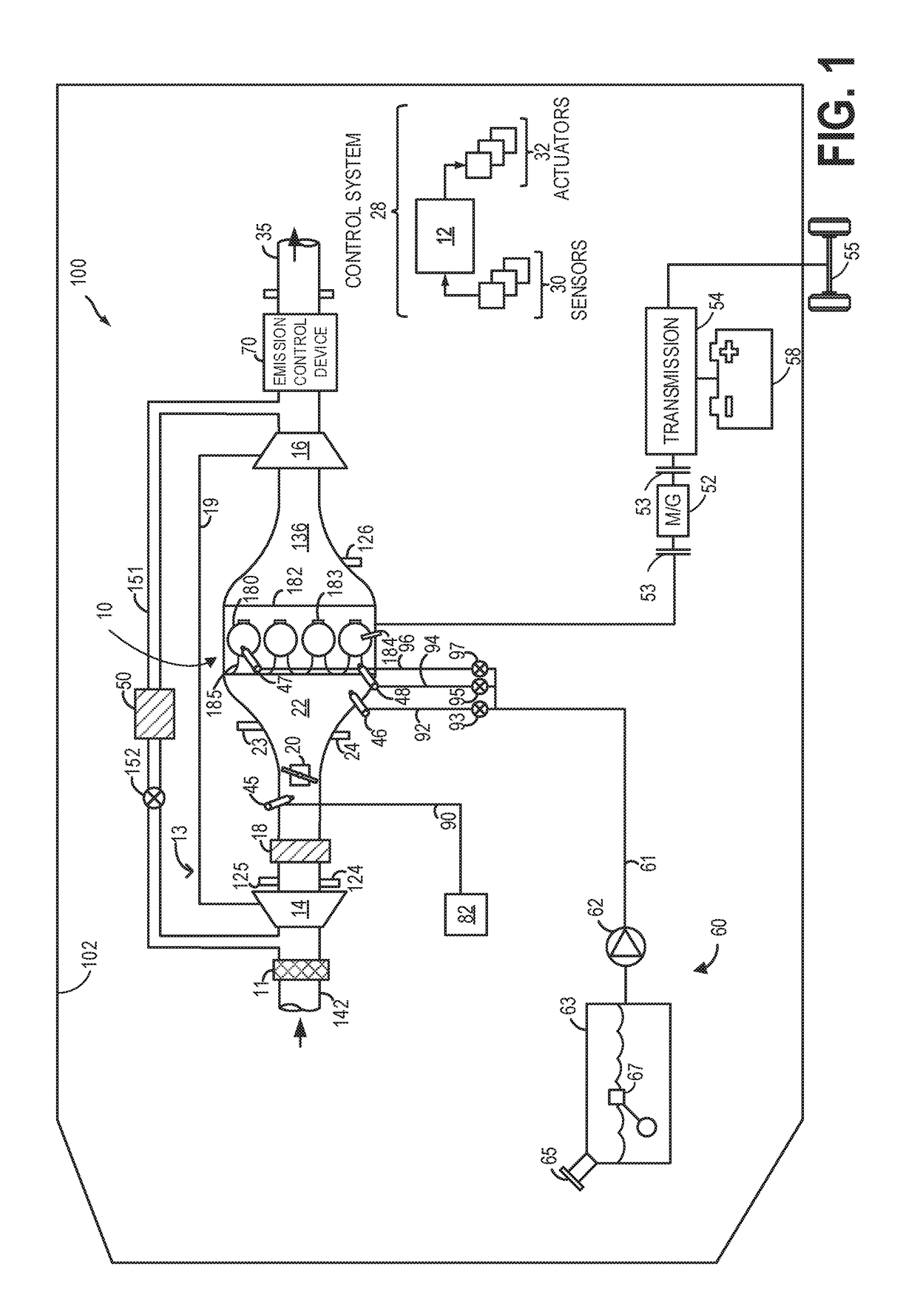
System and method for reducing NOx emissions in an apparatus having a diesel engine
ActiveUS7398644B2Reduce the concentration of nitrogen oxidesNegatively impact performanceValve arrangementsElectrical controlCombustion chamberExhaust fumes
In a mechanical apparatus having a diesel engine including a combustion chamber, the mechanical apparatus also having an aftertreatment device configured to treat emissions from the diesel engine and an intake valve for passing air into the combustion chamber, a method of operating the engine is disclosed, wherein the method includes performing at least one combustion in the combustion chamber at a first intake valve closure timing, determining a temperature of the aftertreatment device, and if the temperature of the aftertreatment device is equal to or below a preselected temperature threshold, then performing at least one combustion in the combustion chamber at a second intake valve closure timing to thereby increase the temperature of exhaust emitted by the diesel engine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
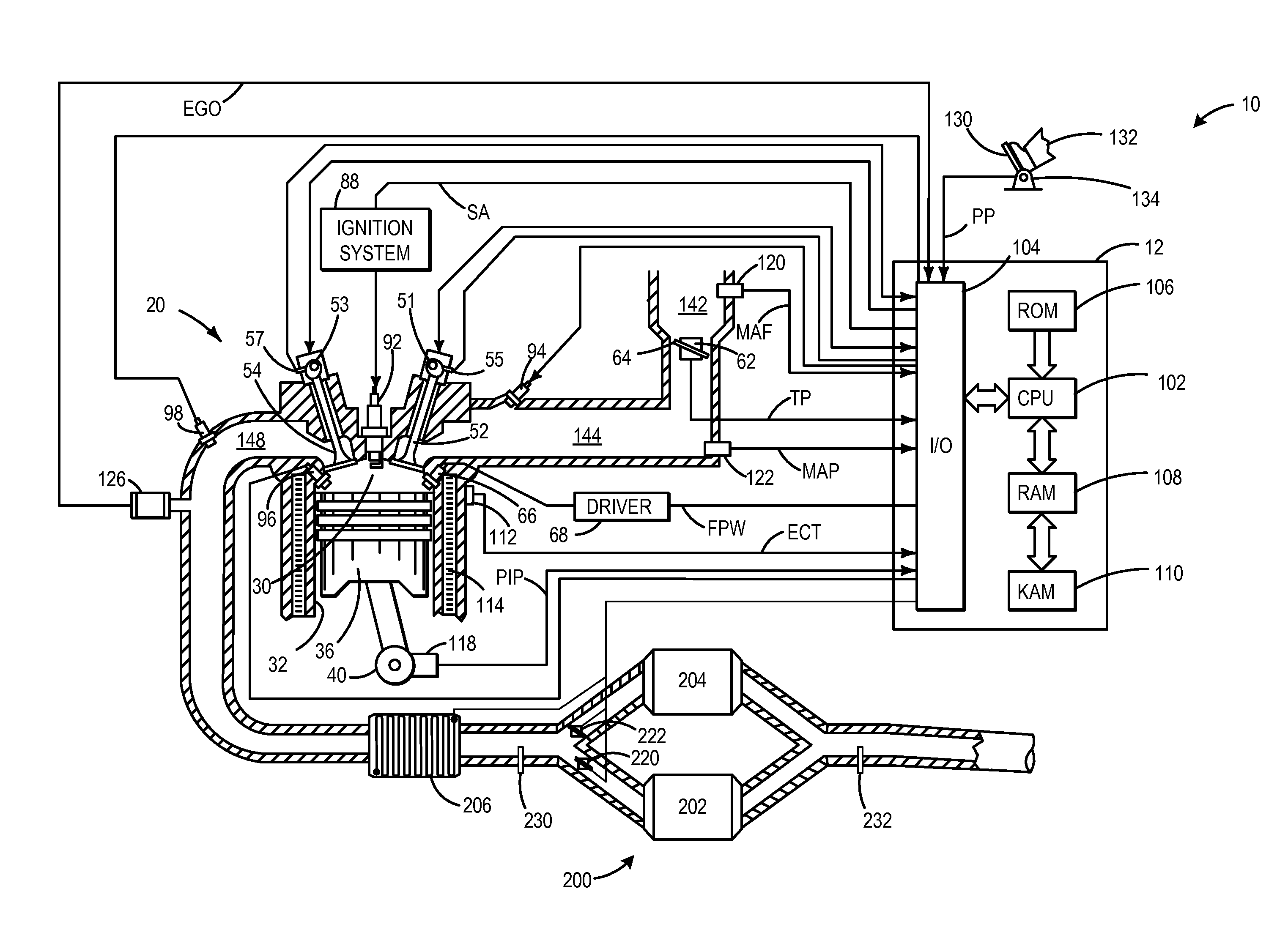
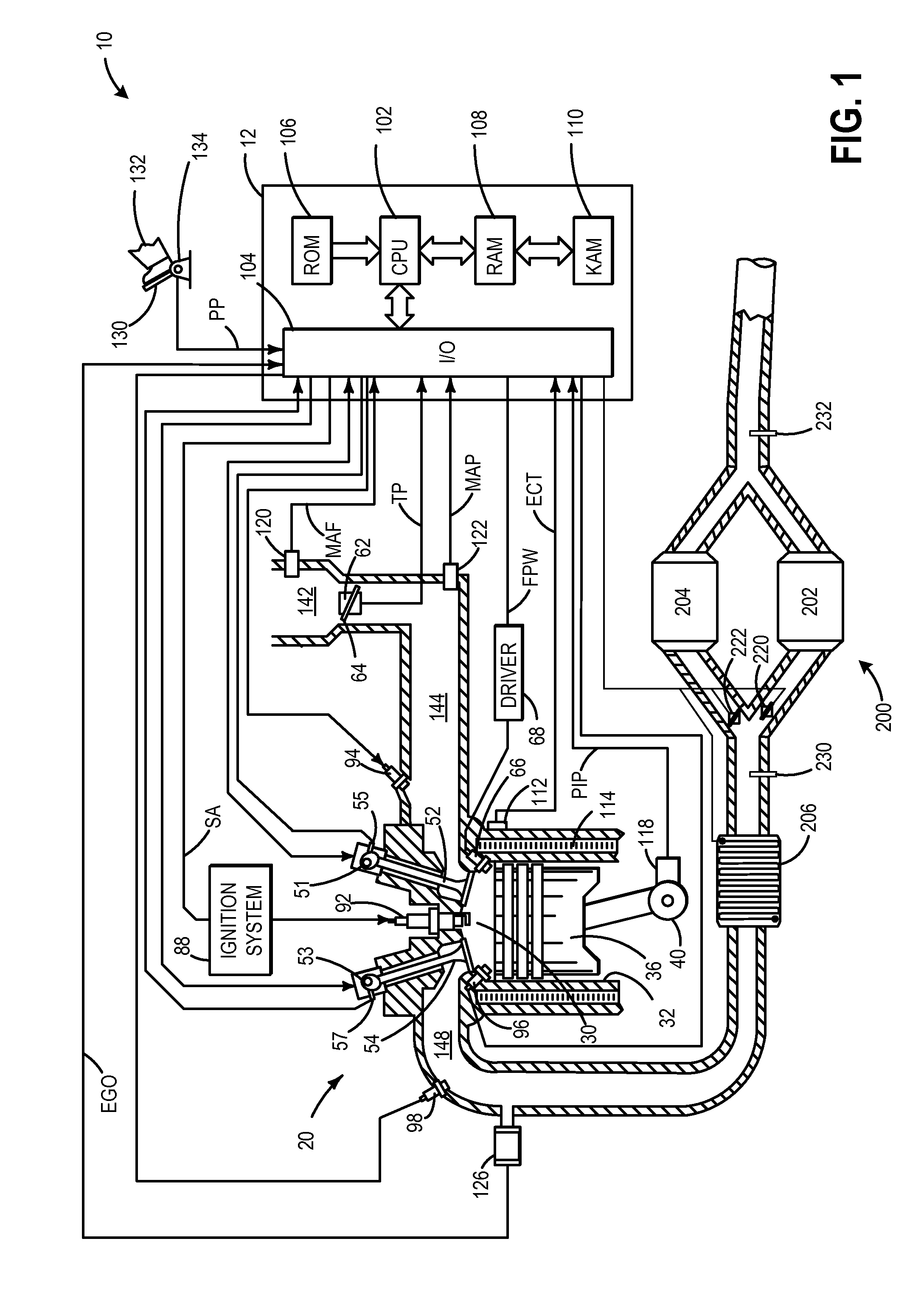
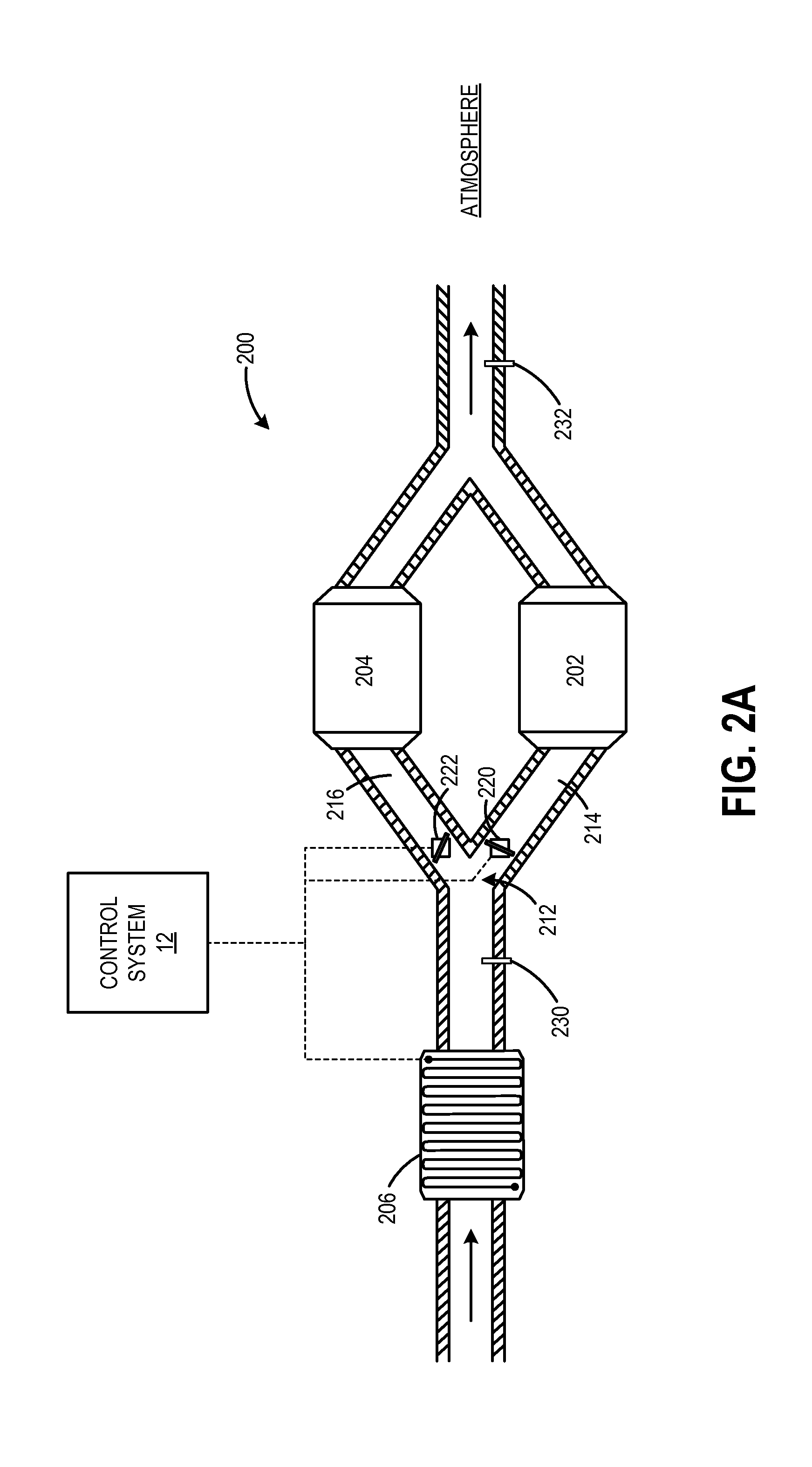
Systems and methods for differential heating of exhaust catalysts
ActiveUS20160251989A1Improve device performanceIncreasing heater thermal outputInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusOperating temperatureExhaust gas
Exhaust aftertreatment systems and methods are described for reducing emissions output therefrom. In one example, an exhaust gas aftertreatment system comprises a first catalyst downstream of a branchpoint in a first exhaust pathway, a second catalyst downstream of the branchpoint in a second exhaust pathway, an electrical heater positioned upstream of the branchpoint for heating the exhaust flow, a control unit for adjusting an exhaust heating current of the electrical heater, and a valve for adjusting a distribution of exhaust flow to the first and second catalyst, the control unit including instructions to adjust the valve responsive to a substrate temperature within one or more of the first and second catalysts. In this way, an exhaust system with increased efficiency across a range of operating temperatures is realized that reduces emissions and energy expended during usage.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Light emitting module, a lamp, a luminaire and a display device
ActiveUS9082946B2Less lightImprove lighting efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesLight reflectionDisplay device
A light emitting module 150 emits light through a light exit window 104 and comprises a base 110, a solid state light emitter 154, 156 and a partially diffusive reflective layer 102. The base 110 has a light reflective surface 112 which faces towards the light exit window 104. The light reflective surface 112 has a base reflection coefficient Rbase which i defined by a ratio between the amount of light that is reflected by the light reflective surface and the amount of light that impinges on the light reflective surface. The solid state light emitter 154, 156 emits light of a first color range 114, comprises a top surface 152, 158 and has a solid state light emitter reflection coefficient R_SSL which is defined by a ratio between the amount of light that is reflected by the solid state emitter 154, 156 and the amount of light that impinges on the top surface 152, 158 of the solid state light emitter 154, 156. The light exit window 104 comprises at least a part of the partially diffusive reflective layer 102. A solid state light emitter area ratio ρSSL is defined as the ratio between the area of the top surface of the at least one solid state light emitter and the area of the light reflective surface of the base. A relatively efficient light emitting module is obtained if Rbase>R_SSL+c*(1−R_SSL) and the factor c is 0.2≦c≦1 for 0<ρSSL<0.1, 0.3≦c≦1 for 0.1≦ρSSL≦0.25, and 0.4≦c≦1 for ρSSL>0.25.
Owner:LUMILEDS
Electron emitter comprising emitter section made of dielectric material
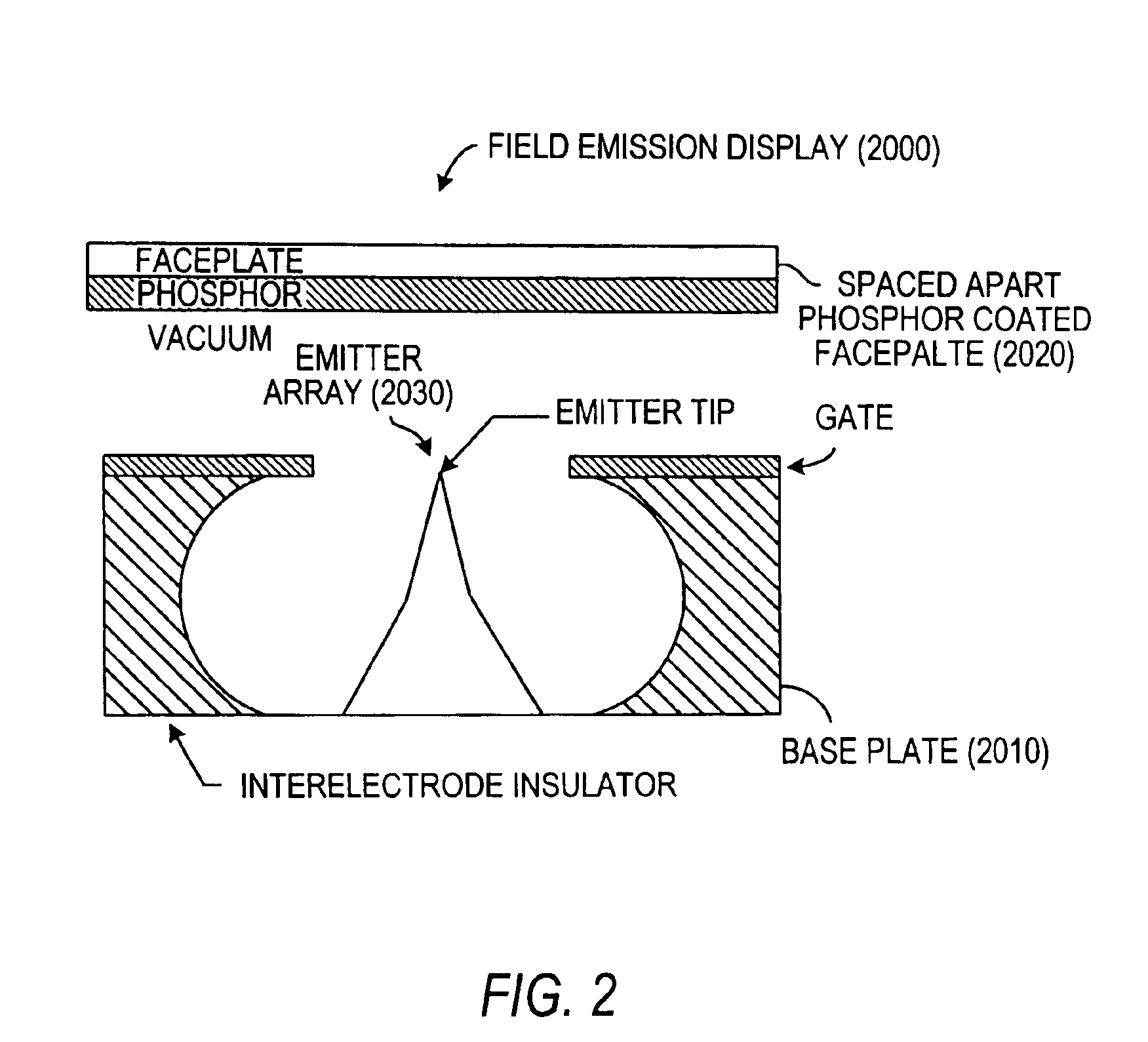
InactiveUS6975074B2Long service lifeHigh reliabilityControl electrodesStatic indicating devicesOptoelectronicsCathode electrode
An electron emitter has an emitter section having a plate shape, a cathode electrode formed on a front surface of the emitter section, and an anode electrode formed on a back surface of the emitter section. A drive voltage from a pulse generation source is applied between the cathode electrode and the anode electrode through a resistor. The anode electrode is connected to GND (ground) through another resistor. A collector electrode is provided above the cathode electrode, and the collector electrode is coated with a fluorescent layer. A bias voltage is applied to the collector electrode through another resistor.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Backlight, display device and method for controlling backlighting thereof
ActiveUS20150378212A1Uniform brightnessExcessive emissionIlluminated signsNon-linear opticsBackplaneLight source
The present disclosure provides a backlight, a display device and a method for controlling backlighting thereof. The present disclosure relates to the field of display technology, and enables a display panel with uniform brightness. The backlight comprises a backplate and a light emitting unit which is arranged on a surface of the backplate. The light emitting unit comprises a substrate and a plurality of light sources which are fixed onto the substrate. The substrate comprises an attached part which is fixed to a central area of the surface of the backplate and a bendable part which forms a preset angle with a non-central area of the surface of the backplate.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
System and method for reducing NOx emissions in an apparatus having a diesel engine
ActiveUS20060283174A1Improve engine efficiencyReduce the concentration of nitrogen oxidesValve arrangementsElectrical controlCombustion chamberDiesel engine
In a mechanical apparatus having a diesel engine including a combustion chamber, the mechanical apparatus also having an aftertreatment device configured to treat emissions from the diesel engine and an intake valve for passing air into the combustion chamber, a method of operating the engine is disclosed, wherein the method includes performing at least one combustion in the combustion chamber at a first intake valve closure timing, determining a temperature of the aftertreatment device, and if the temperature of the aftertreatment device is equal to or below a preselected temperature threshold, then performing at least one combustion in the combustion chamber at a second intake valve closure timing to thereby increase the temperature of exhaust emitted by the diesel engine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Rotary engine
ActiveUS20170184016A1Avoid flowReduce the amount requiredInternal combustion piston enginesPump componentsCombustion chamberEngine efficiency
The present invention provides a rotary engine including a housing having therein N rob accommodating portions (N is a natural number equal to or greater than 3), and combustion chambers communicating with the rob accommodating portions, respectively, a rotor having N−1 robs eccentrically rotating centering on a center of the rob accommodating portions, and consecutively accommodated in the respective rob accommodating portions during the eccentric rotation, and combustion controllers provided at both sides of each combustion chamber, and configured to limit a combustion range of mixed gas, whereby an excessive emission of unburned gas caused in an existing rotary engine can be overcome, efficiency of the engine can be improved, and a rotary engine with an optimized design condition can be provided.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
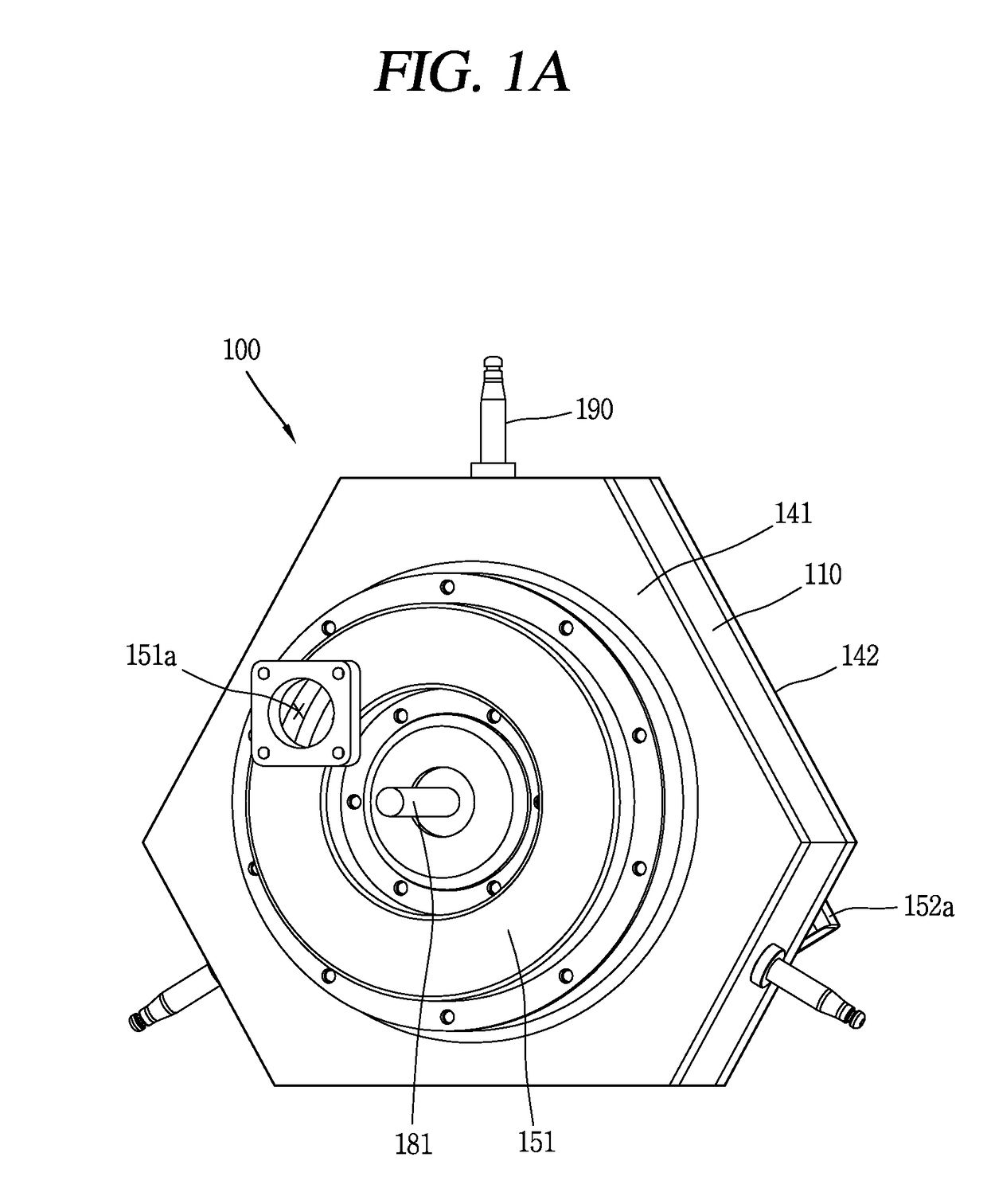
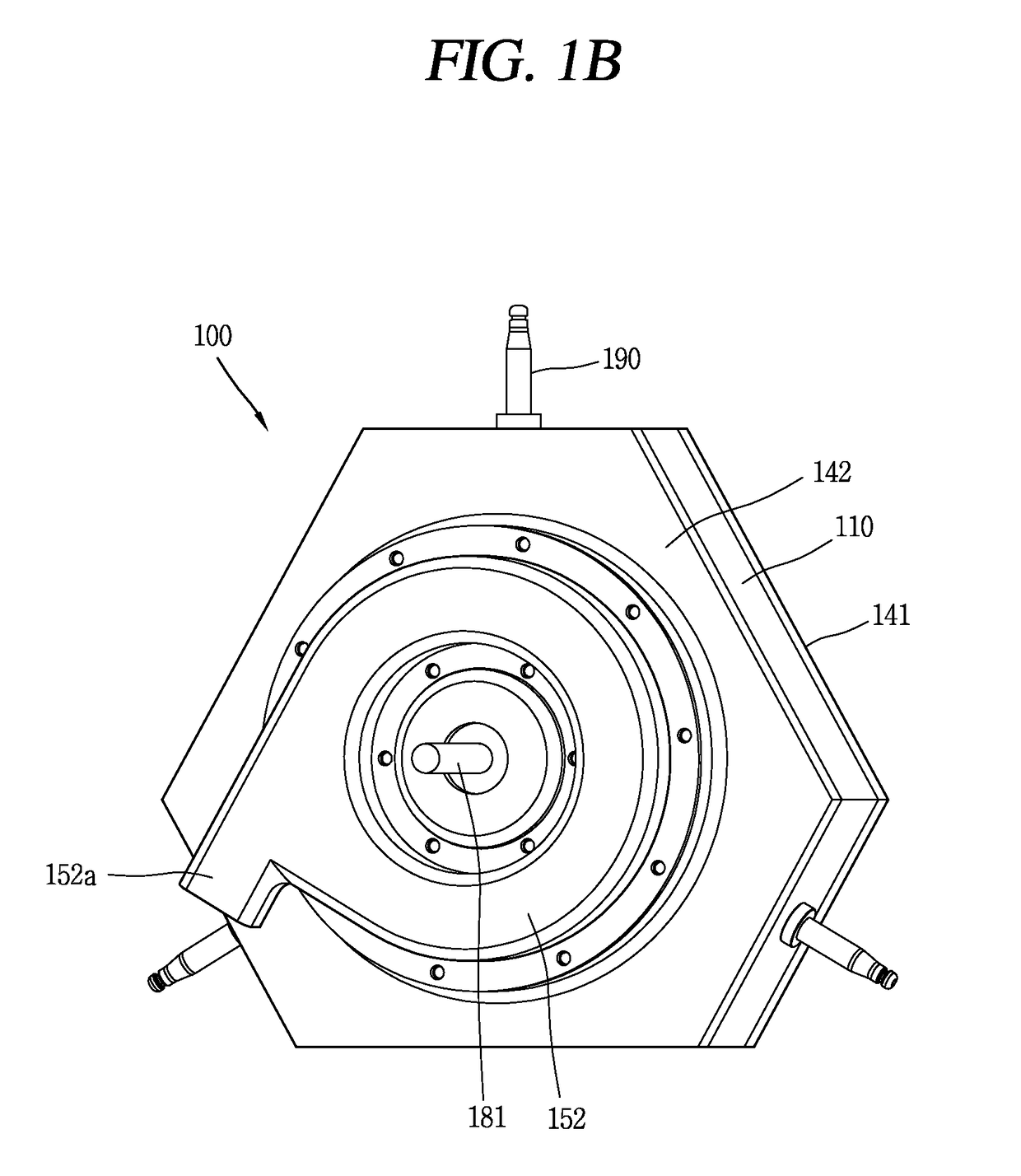
Exhaust gas recirculation device
InactiveUS8955499B2Suppress corrosion of heat exchangerSuppress emissionElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelExhaust fumesEngineering
An exhaust gas recirculation system according to the present invention includes an EGR passage for introducing a part of exhaust gas emitted from an engine to an intake passage, the EGR passage communicating at one end thereof with the intake passage whereas at the other end thereof with an exhaust passage, an EGR control valve for controlling the flow rate of the exhaust gas flowing therein, the EGR control valve being disposed at one end of the EGR passage, an on-off valve for opening or closing the EGR passage, the on-off valve being disposed at the other end of the EGR passage, and a heat exchanger for cooling the exhaust gas introduced to the EGR passage, the heat exchanger) being disposed nearer the other end of the EGR passage than the on-off valve.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method and device for operating a dual-fuel internal combustion engine
InactiveUS10287997B2Avoiding excessive emissionAvoiding jump in torqueElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineLiquid fuel
A method for operating a dual-fuel internal combustion engine, having an intake path and an engine having a number of cylinders. In the method the engine is operated in a first operating state in diesel operation with diesel or another liquid fuel, and in a second operating state in gas operation with gas as fuel in a charge mixture, and switching between diesel operation and gas operation takes place in a switchover range determined, in particular predetermined, by switchover operating parameters.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE SOLUTIONS GMBH
Composition and method for oxidizing mercury in combustion processes
InactiveUS20070212296A1Reduce emissionEmission reductionUsing liquid separation agentEmission preventionChemistryCombustion chamber
The invention can be summarized as follows. There is provided a method for oxidizing elemental mercury in a combustion process comprising, adding a composition comprising an aluminum silicate to a combustion chamber, boiler or kiln downstream from the burner region combustion zone. There is further provided a method for reducing the emission of one or more heavy metals in a combustion process by adding a composition comprising an aluminum silicate to a combustion chamber downstream from the burner region combustion zone. There is also provided a composition comprising an aluminum silicate that may be employed to oxidize elemental mercury generated in a combustion process. The composition also may be employed to reduce the emission of one or more heavy metals generated in a combustion process.
Owner:DIGDON WILLIAM TROY
Indirect luminaire
ActiveUS20190170927A1Sufficient lightingSatisfactory homogeneityMechanical apparatusLight guides for lighting systemsTotal internal reflectionEdge surface
A luminaire (1) is disclosed comprising at least one optical chamber (10) delimited by a light exit window (11) and a curved reflective surface (15) extending from the light exit window to a mounting surface (17) extending from the curved reflective surface towards the light exit window. Each optical chamber comprises a light source (20) mounted on the mounting surface; and a light guide (30) extending across part of the optical chamber. The light guide comprises a total internal reflection major surface (40) facing the light exit window; a further major surface (50) facing the curved reflective surface, said further major surface comprising a light outcoupling portion (51) comprising a plurality of light outcoupling structures (53); a first edge surface (60) optically coupled to the light source; and a further edge surface (70) opposite the first edge surface arranged to direct light towards the curved reflective surface.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Black layer coated heat exchanger
InactiveUS6959757B2High emissivityEmit more heatEnergy efficient heating/coolingAir heatersEmissivityPlate heat exchanger
Hot combustion products exchange heat with air in a heat exchanger of a condensing furnace. The hot combustion products flow on one side of the heat exchanger, and the air flows on the opposing side of the heat exchanger. The heat exchanger is electrochemically coated with a coating of copper metal. The copper coating is oxidized with an aqueous oxidizing alkaline solution to form a matte black layer of cupric oxide. As the layer of cupric oxide is black, the layer has a high emissivity and emits more heat, increasing the efficiency of the primary heat exchanger. Alternatively, iron can be electrochemically coated on the primary heat exchanger and oxidized to black magnetite to increase emissivity.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
Backlight, display device and method for controlling backlighting thereof
The present disclosure provides a backlight, a display device and a method for controlling backlighting thereof. The present disclosure relates to the field of display technology, and enables a display panel with uniform brightness. The backlight comprises a backplate and a light emitting unit which is arranged on a surface of the backplate. The light emitting unit comprises a substrate and a plurality of light sources which are fixed onto the substrate. The substrate comprises an attached part which is fixed to a central area of the surface of the backplate and a bendable part which forms a preset angle with a non-central area of the surface of the backplate.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Systems and methods for differential heating of exhaust catalysts
ActiveUS9657621B2Improve device performanceImproved heat outputInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusElectricityPower flow
Exhaust aftertreatment systems and methods are described for reducing emissions output therefrom. In one example, an exhaust gas aftertreatment system comprises a first catalyst downstream of a branchpoint in a first exhaust pathway, a second catalyst downstream of the branchpoint in a second exhaust pathway, an electrical heater positioned upstream of the branchpoint for heating the exhaust flow, a control unit for adjusting an exhaust heating current of the electrical heater, and a valve for adjusting a distribution of exhaust flow to the first and second catalyst, the control unit including instructions to adjust the valve responsive to a substrate temperature within one or more of the first and second catalysts. In this way, an exhaust system with increased efficiency across a range of operating temperatures is realized that reduces emissions and energy expended during usage.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
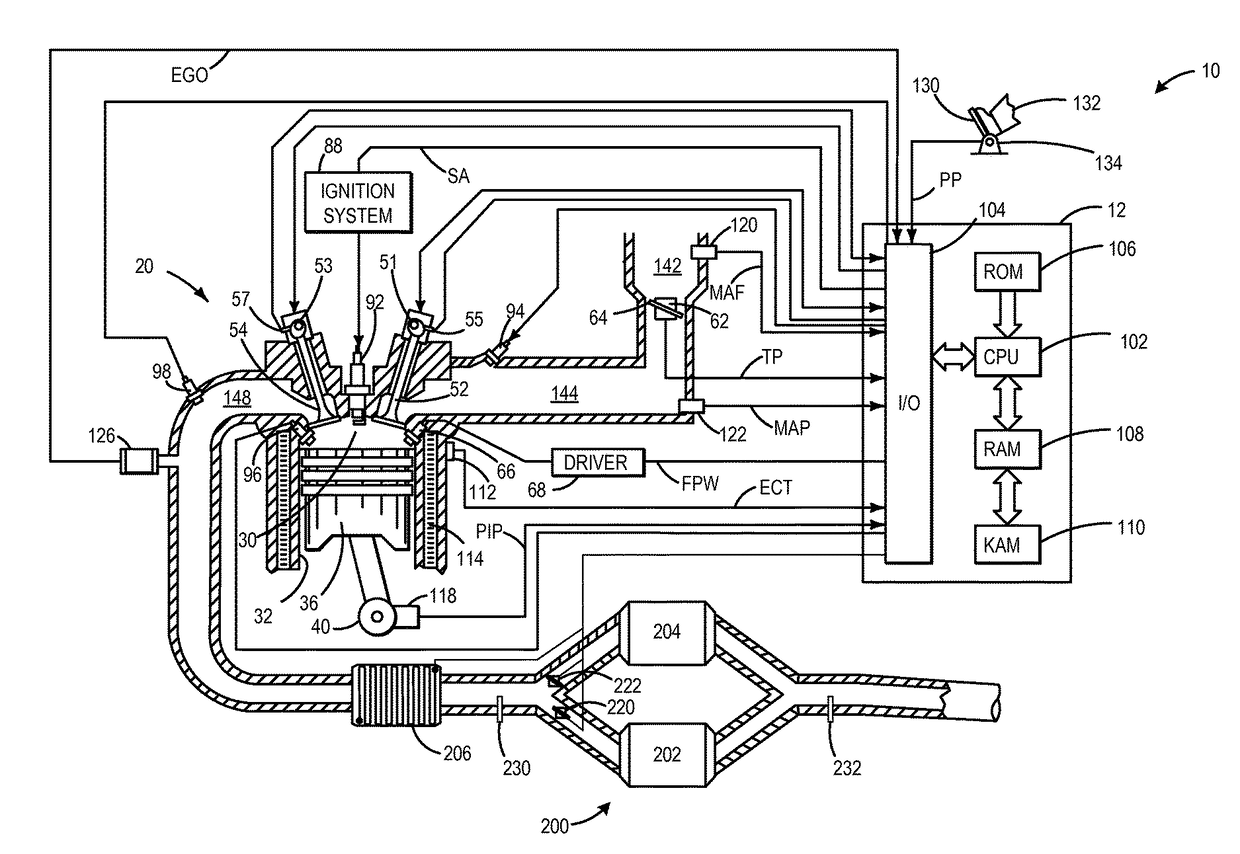
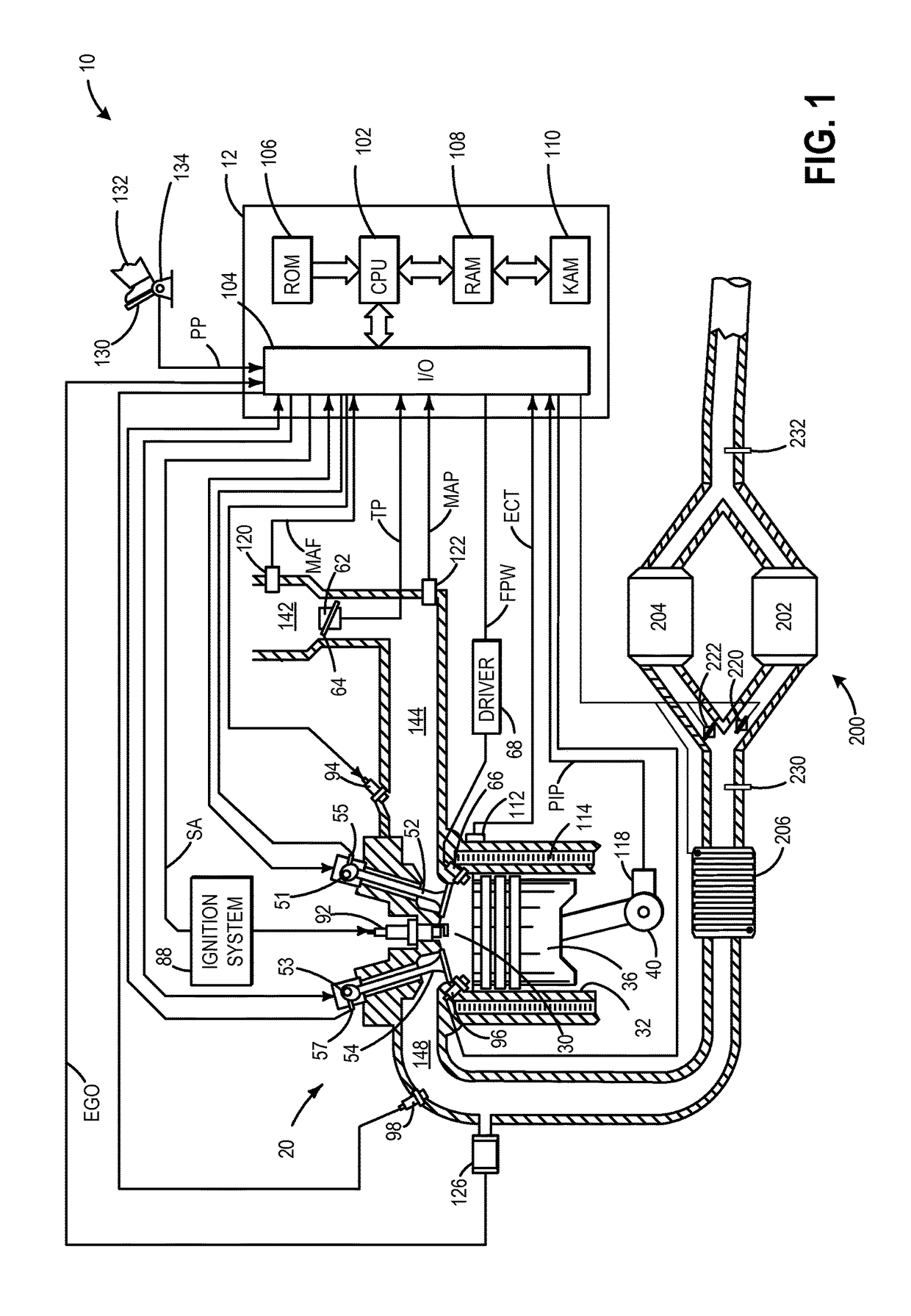
Methods and systems for central fuel injection
ActiveUS10119490B1Less turbulenceGood reliefInternal-combustion engine testingElectrical controlOperant conditioningChemical measurement
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and device for operating an internal combustion engine including an electrically supported exhaust gas-driven supercharging device
ActiveUS11391228B2Less fuel consumptionModerate rangeElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust fumesInternal combustion engine
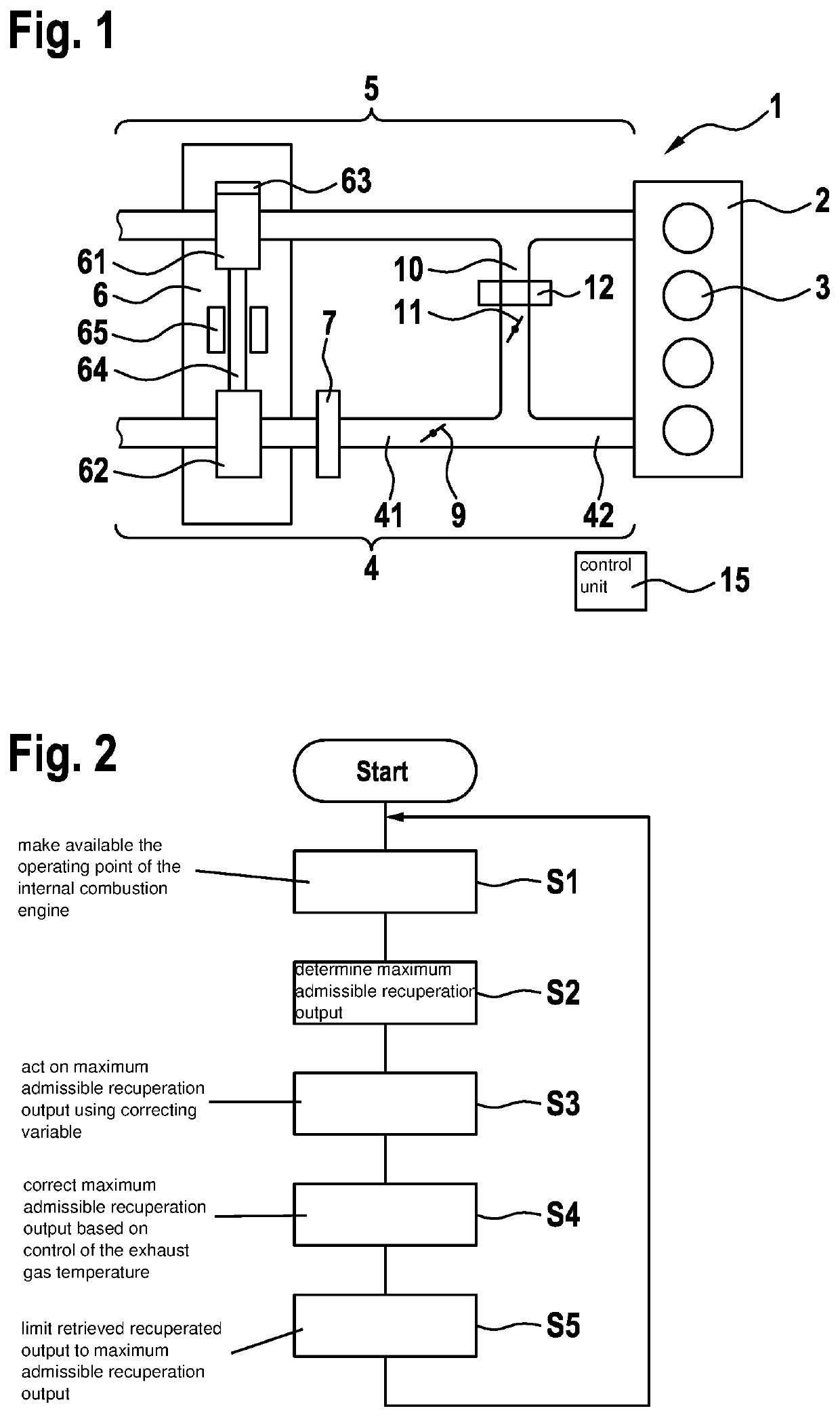
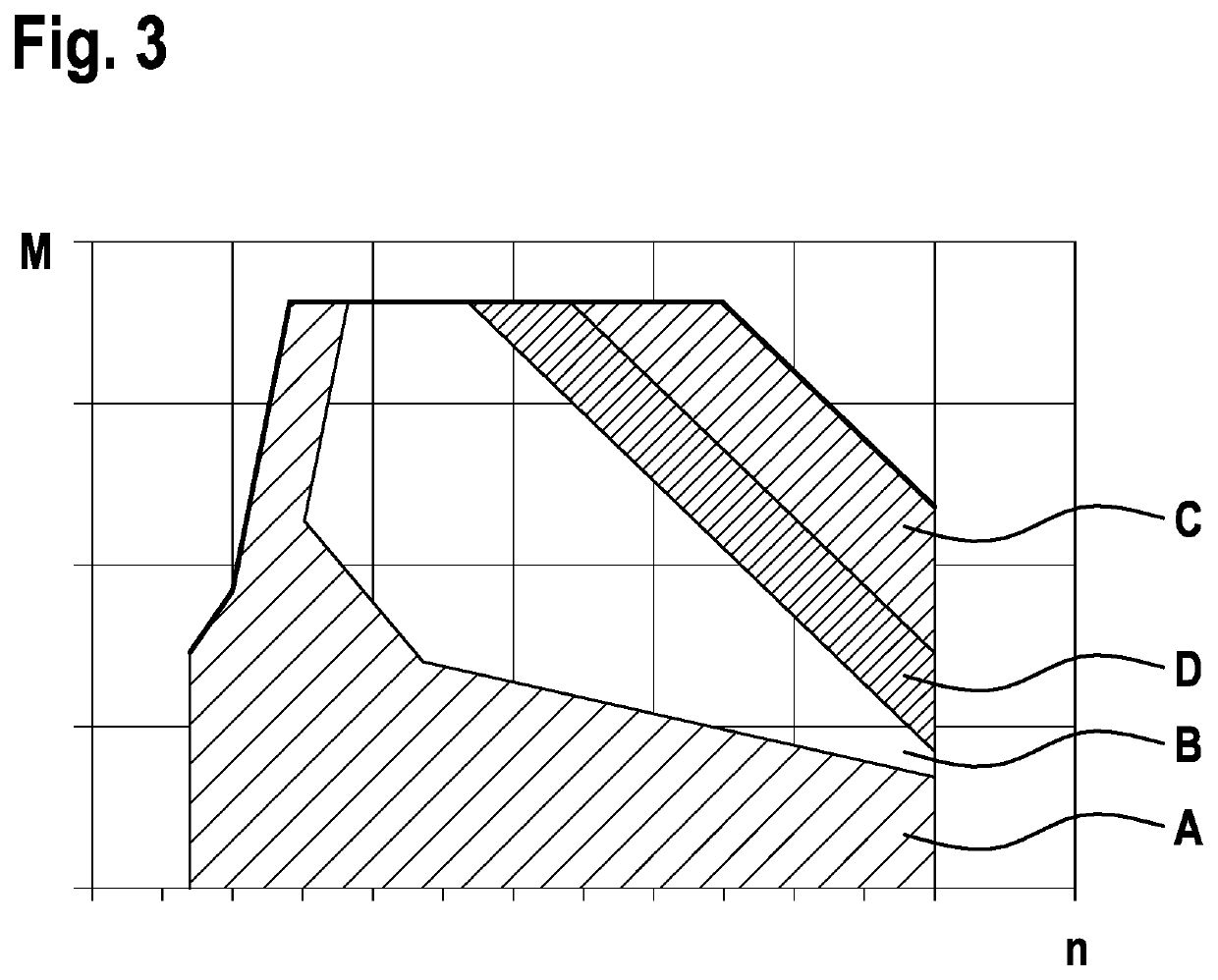
A method for operating an internal combustion engine including an exhaust gas-driven supercharging device having an electric support drive. The method includes providing an operating point specification of the internal combustion engine, ascertaining a maximum admissible recuperation output in a recuperation mode of the electric support drive as a function of the operating point specification, and limiting the recuperation output to the maximum admissible recuperation output in the recuperation mode.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com