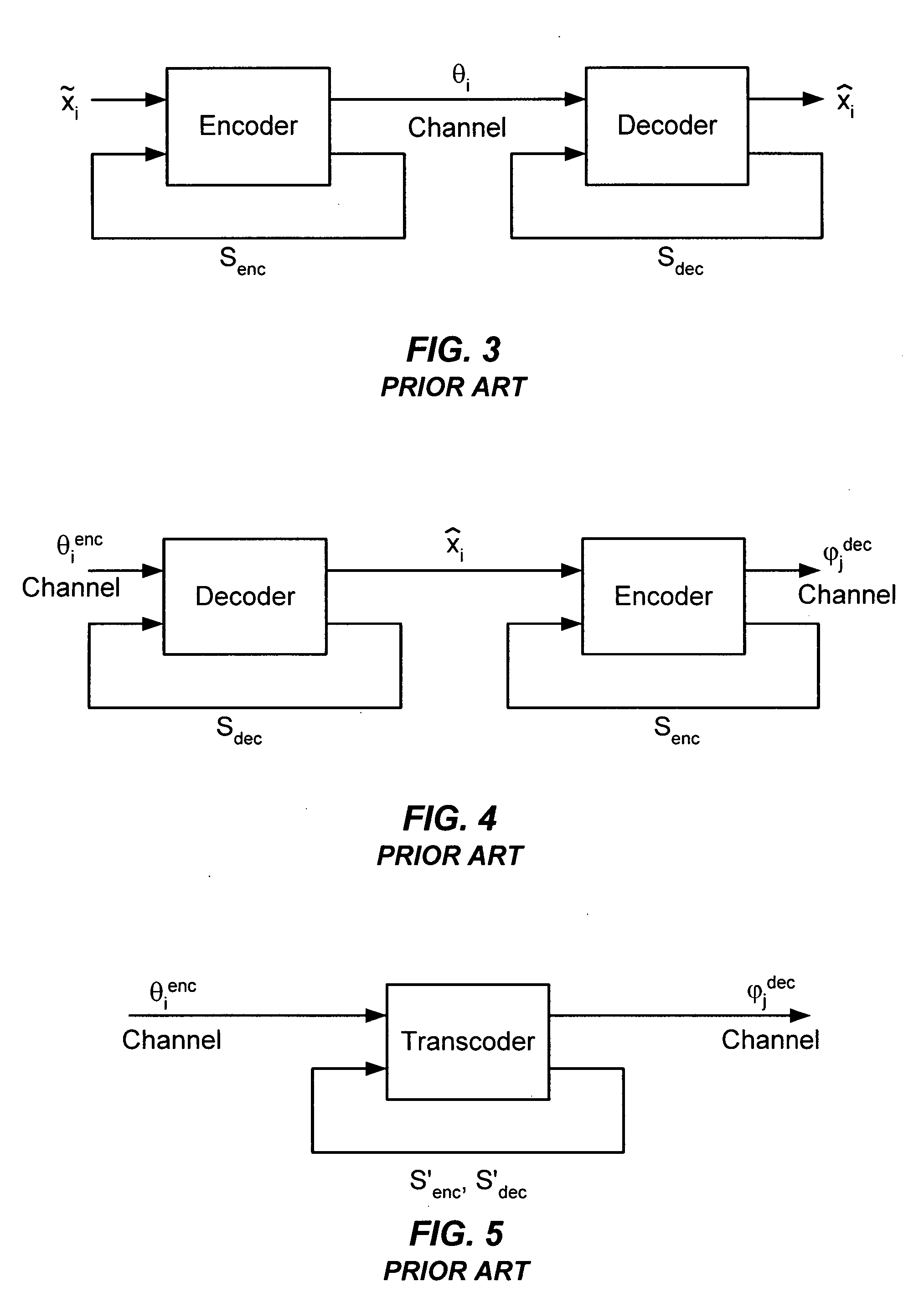
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
162results about How to "Computational complexity is reduced" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
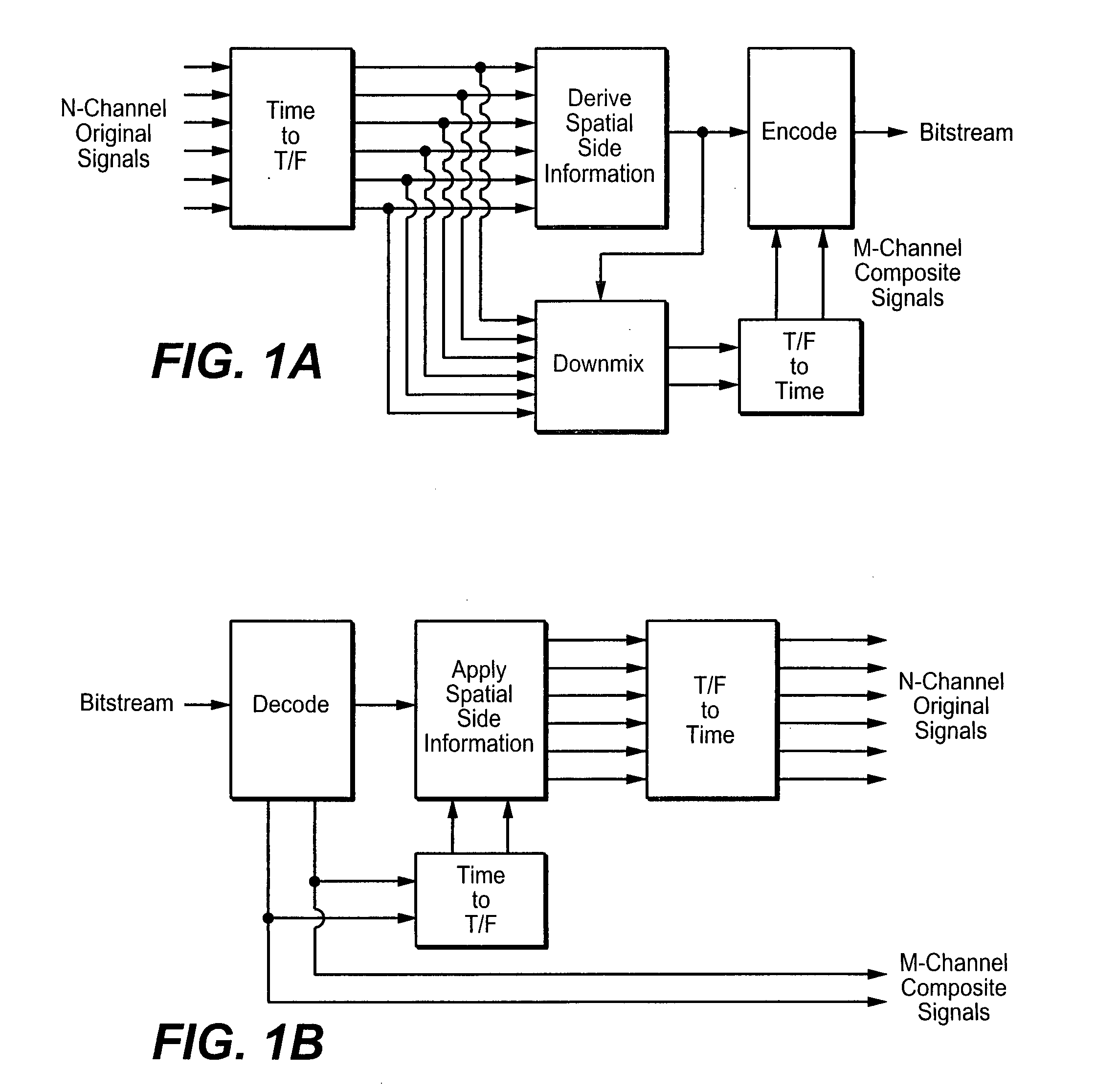
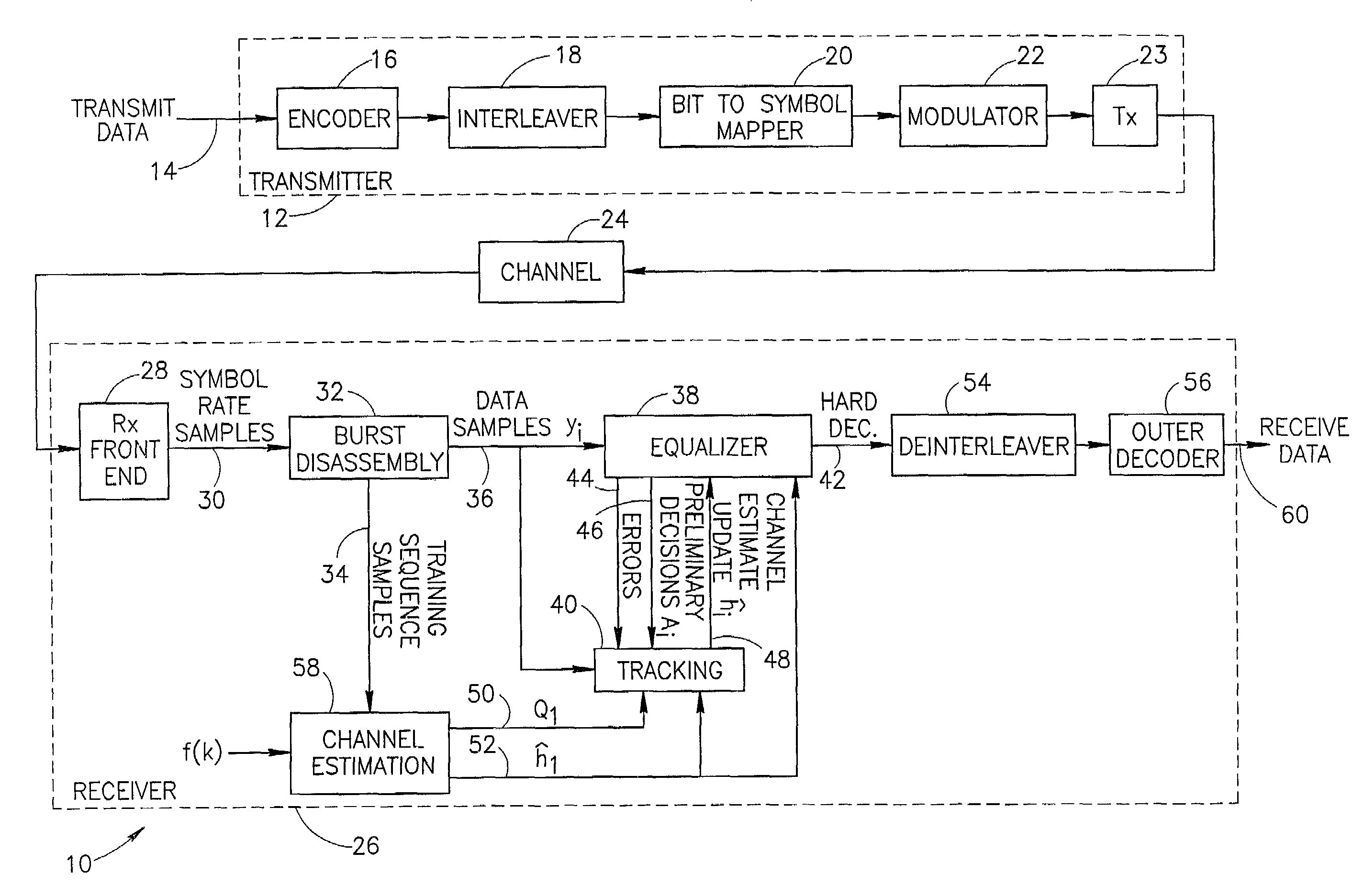
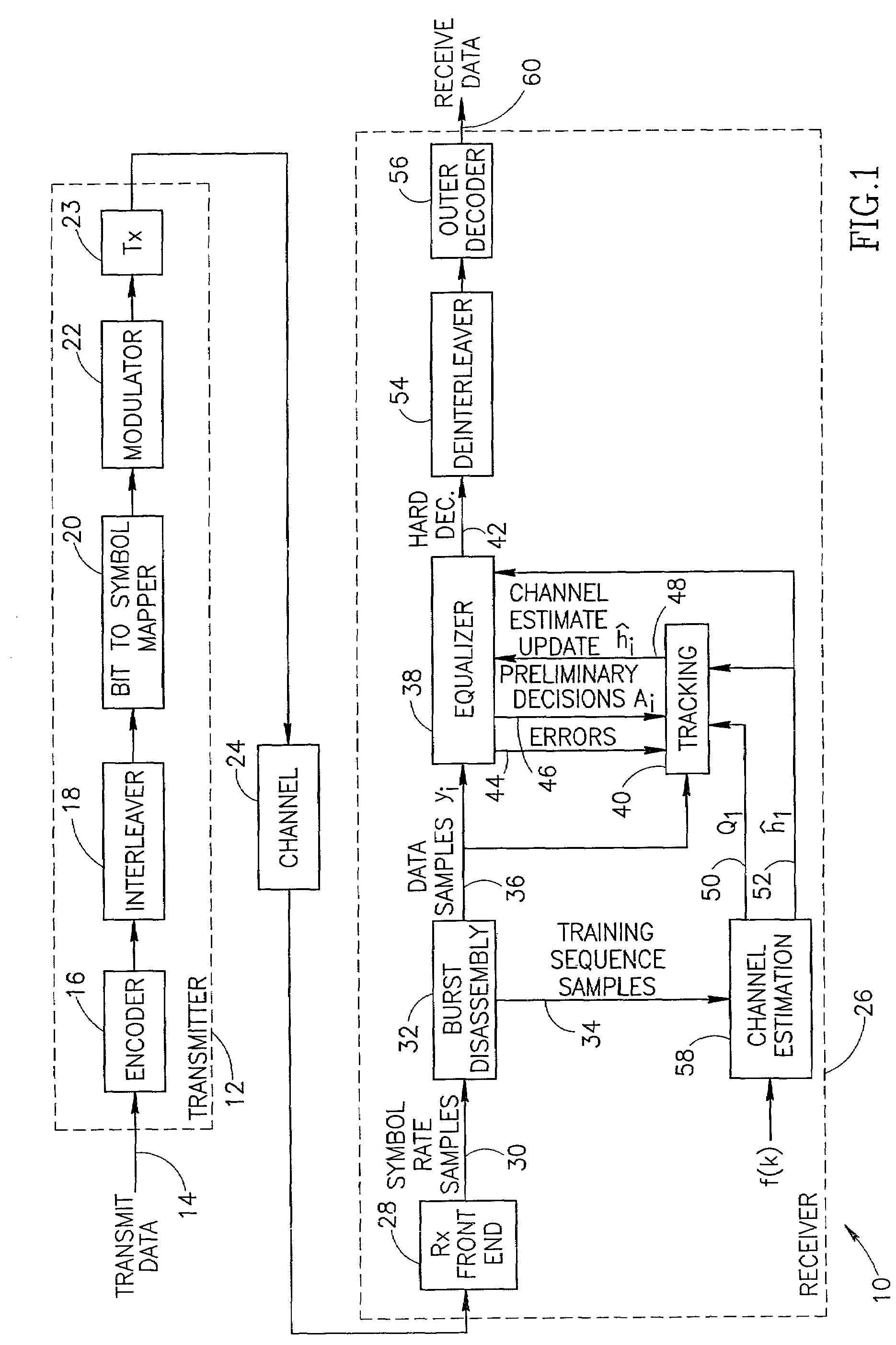
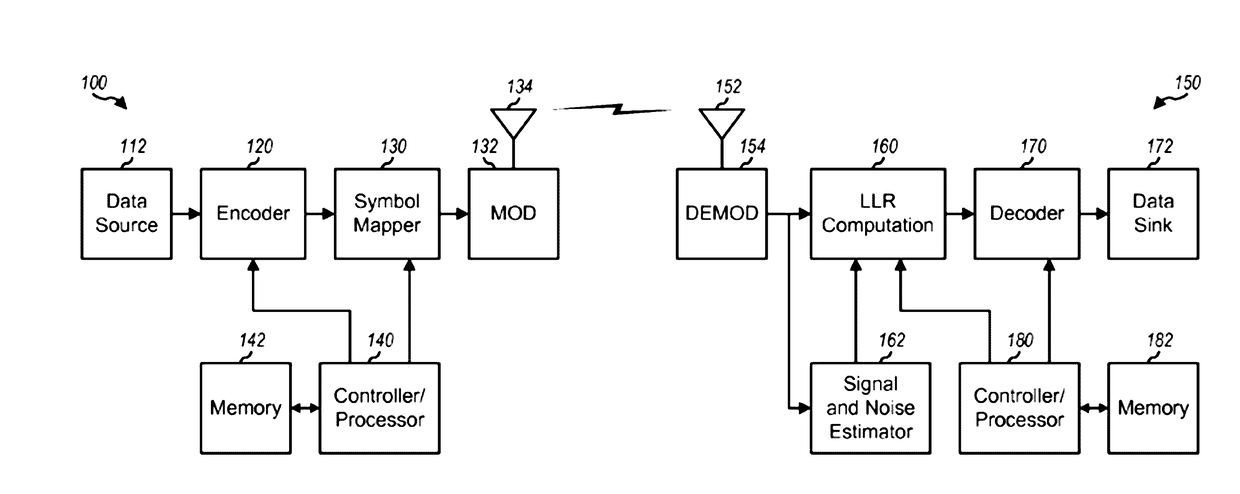
Inter-layer prediction for extended spatial scalability in video coding
ActiveUS20080165855A1Improving inter-layer predictionReduce computational complexityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionInter layerMotion vector
An improved system and method for providing improved inter-layer prediction for extended spatial scalability in video coding, as well as improving inter-layer prediction for motion vectors in the case of extended spatial scalability. In various embodiments, for the prediction of macroblock mode, the actual reference frame index and motion vectors from the base layer are used in determining if two blocks should be merged. Additionally, multiple representative pixels in a 4×4 block can be used to represent each 4×4 block in a virtual base layer macroblock. The partition and motion vector information for the relevant block in the virtual base layer macroblock can be derived from all of the partition information and motion vectors of those 4×4 blocks.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
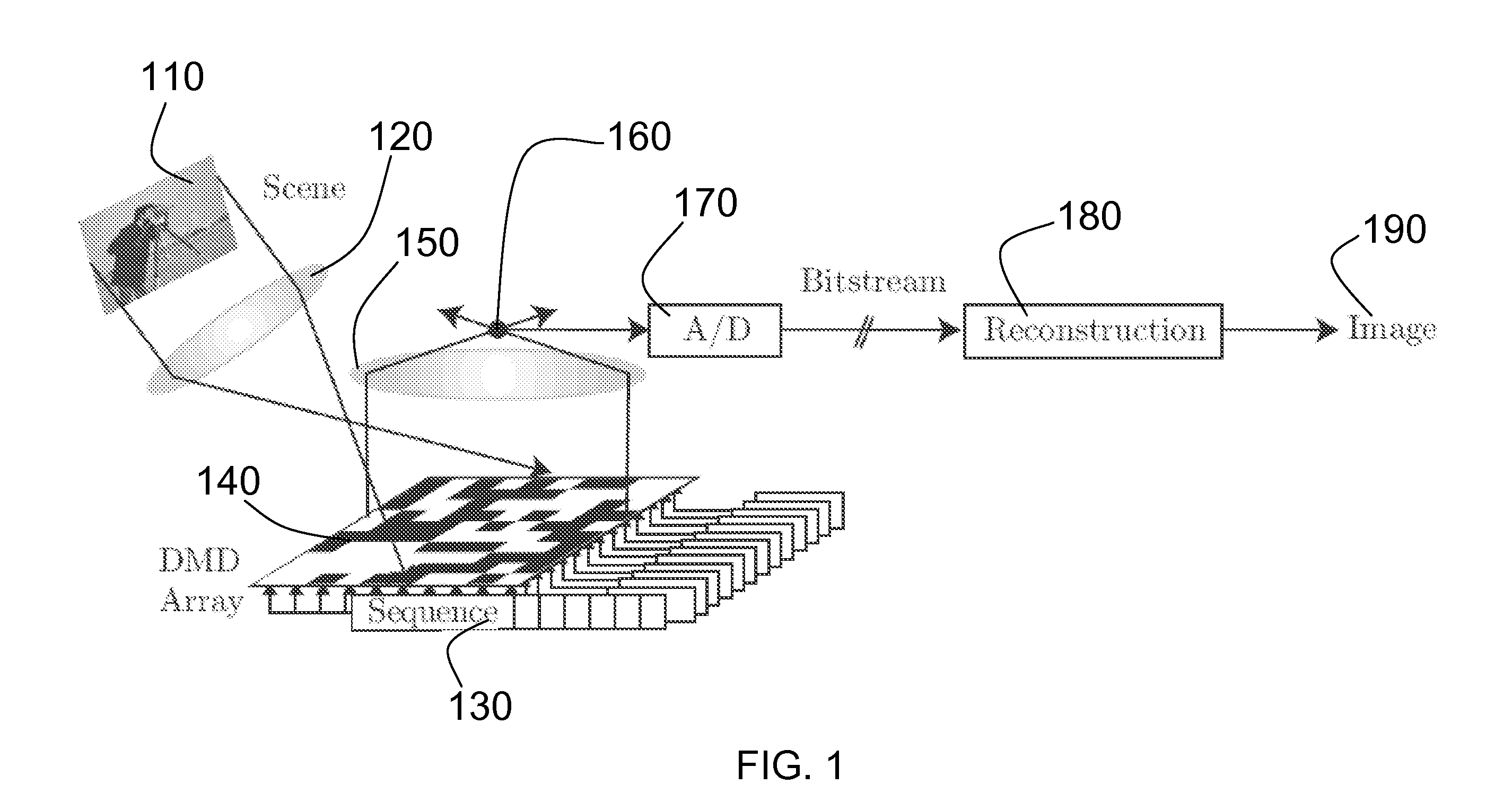
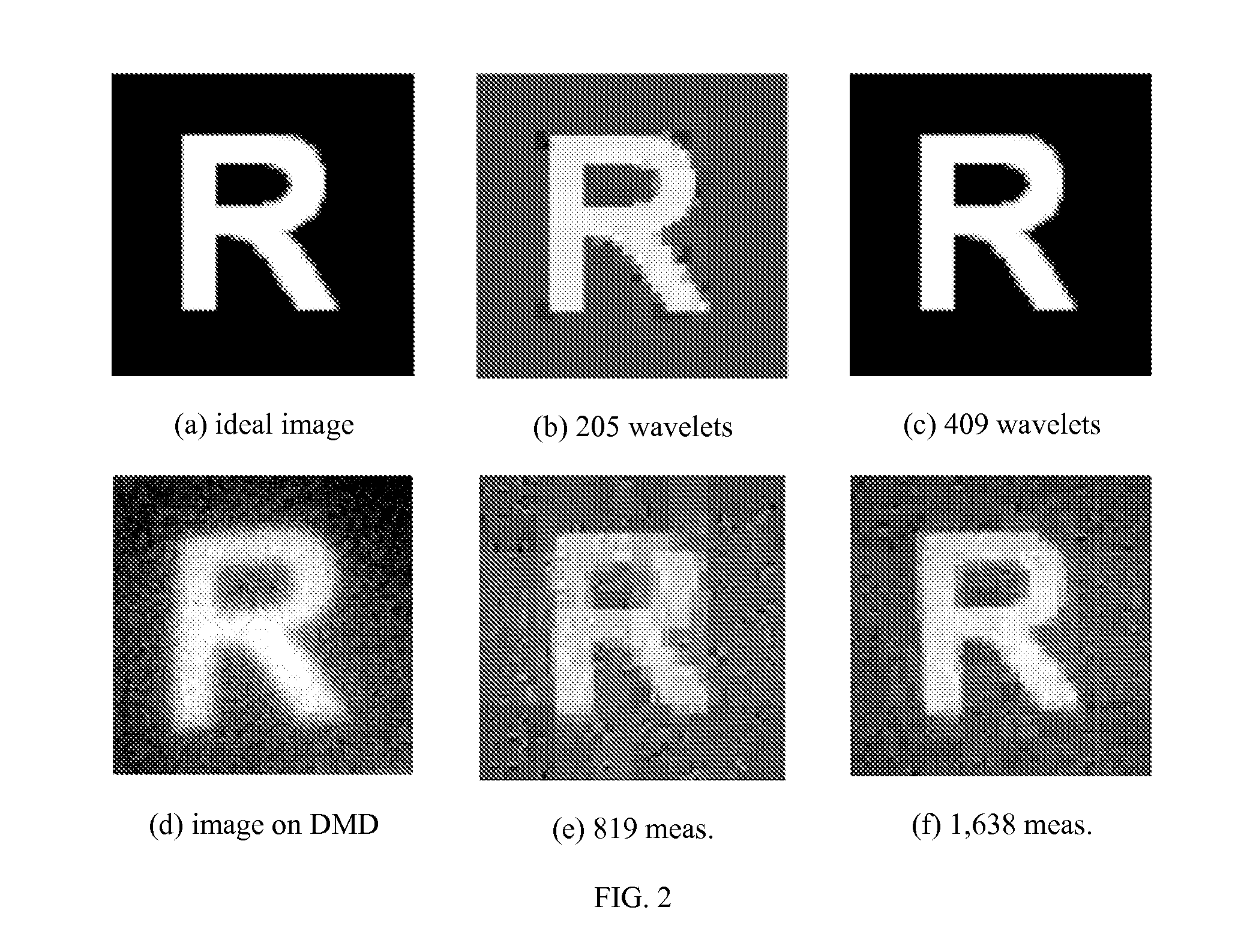
Method and Apparatus for Compressive Imaging Device
InactiveUS20060239336A1Computational complexity be reduceComputational complexity is reducedTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOSVoxel
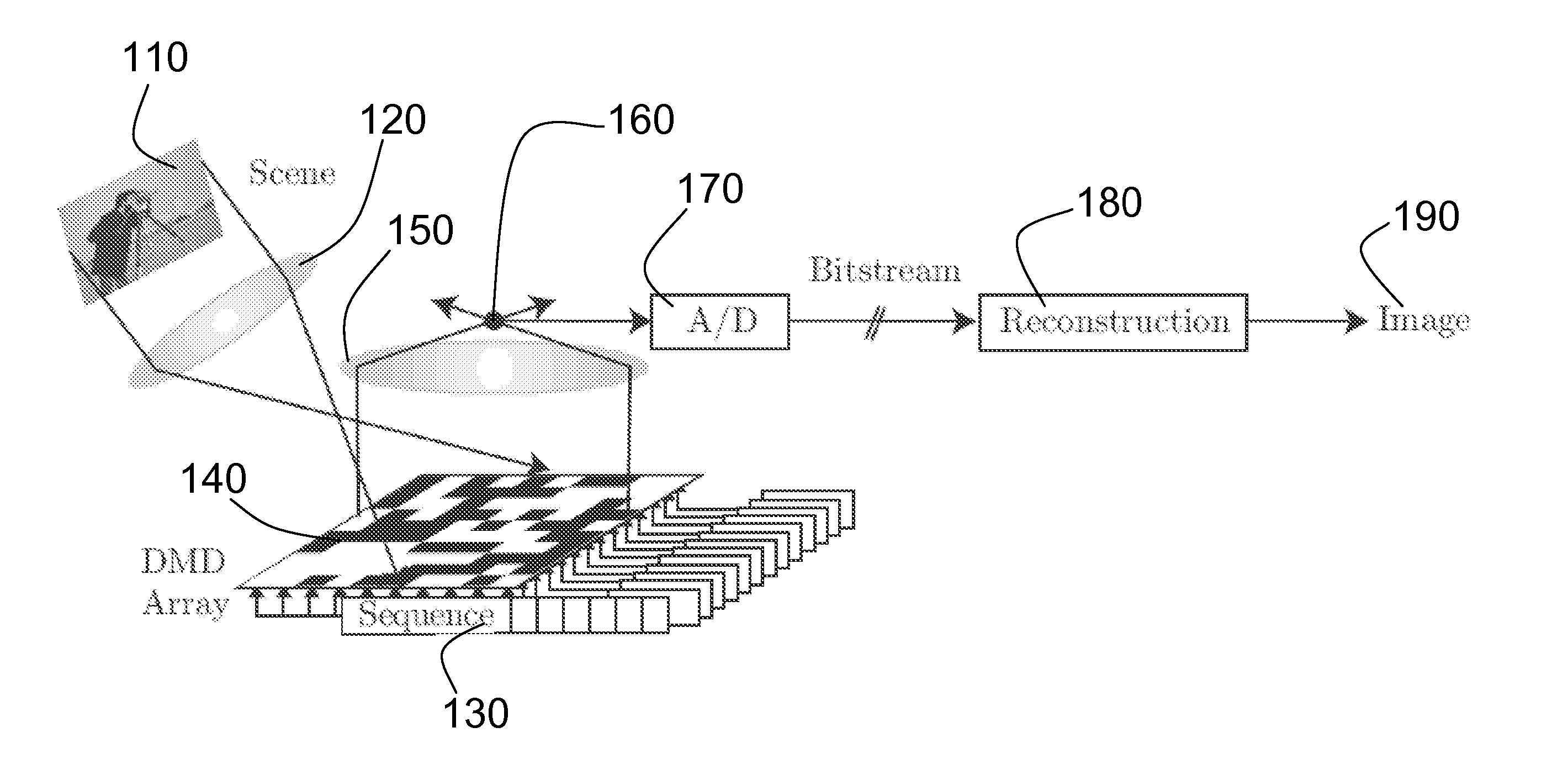
A new digital image / video camera that directly acquires random projections of the incident light field without first collecting the pixels / voxels. In one preferred embodiment, the camera employs a digital micromirror array to perform optical calculations of linear projections of an image onto pseudorandom binary patterns. Its hallmarks include the ability to obtain an image with only a single detection element while measuring the image / video fewer times than the number of pixels or voxels—this can significantly reduce the computation required for image / video acquisition / encoding. Since the system features a single photon detector, it can also be adapted to image at wavelengths that are currently impossible with conventional CCD and CMOS imagers.
Owner:RICE UNIV
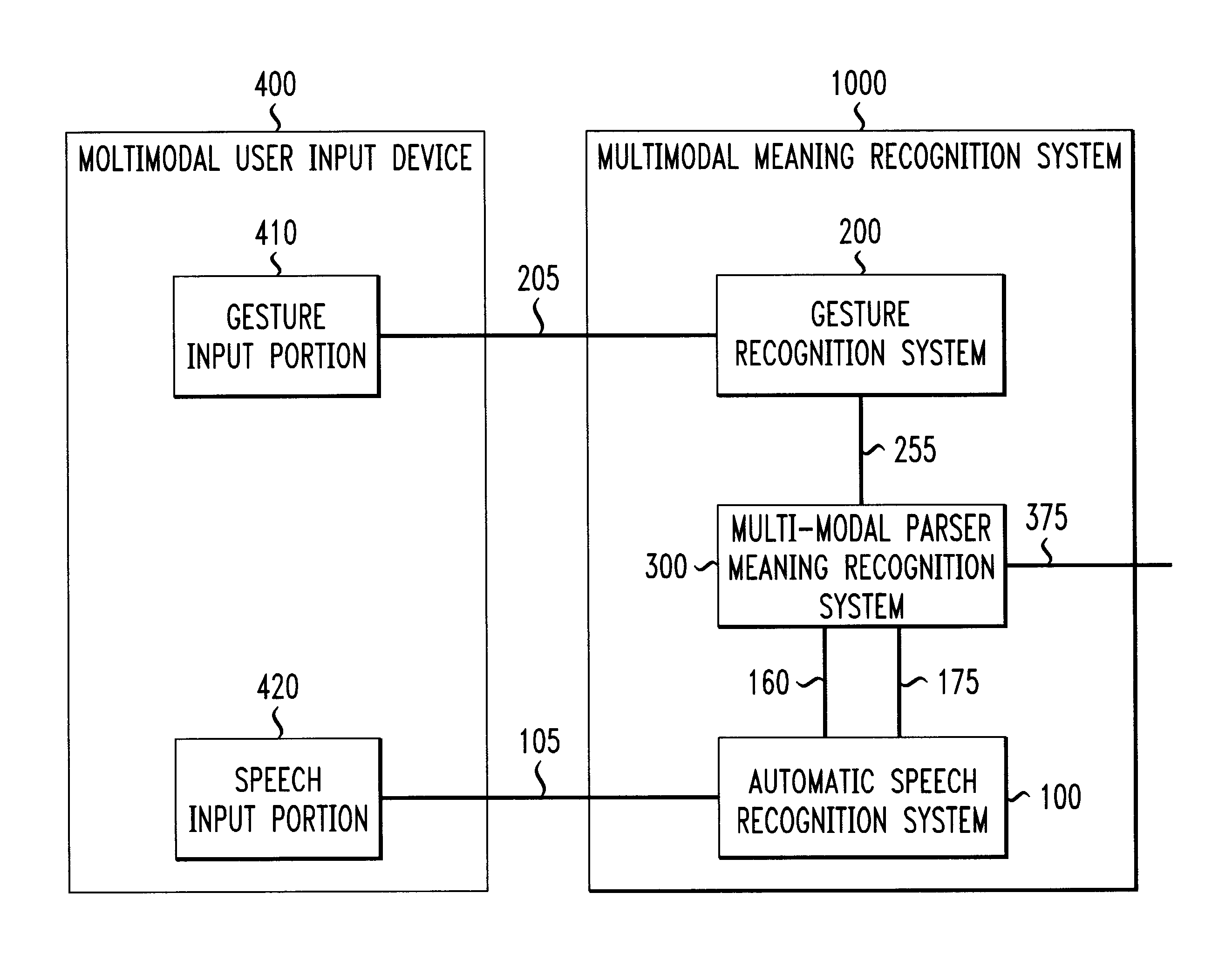
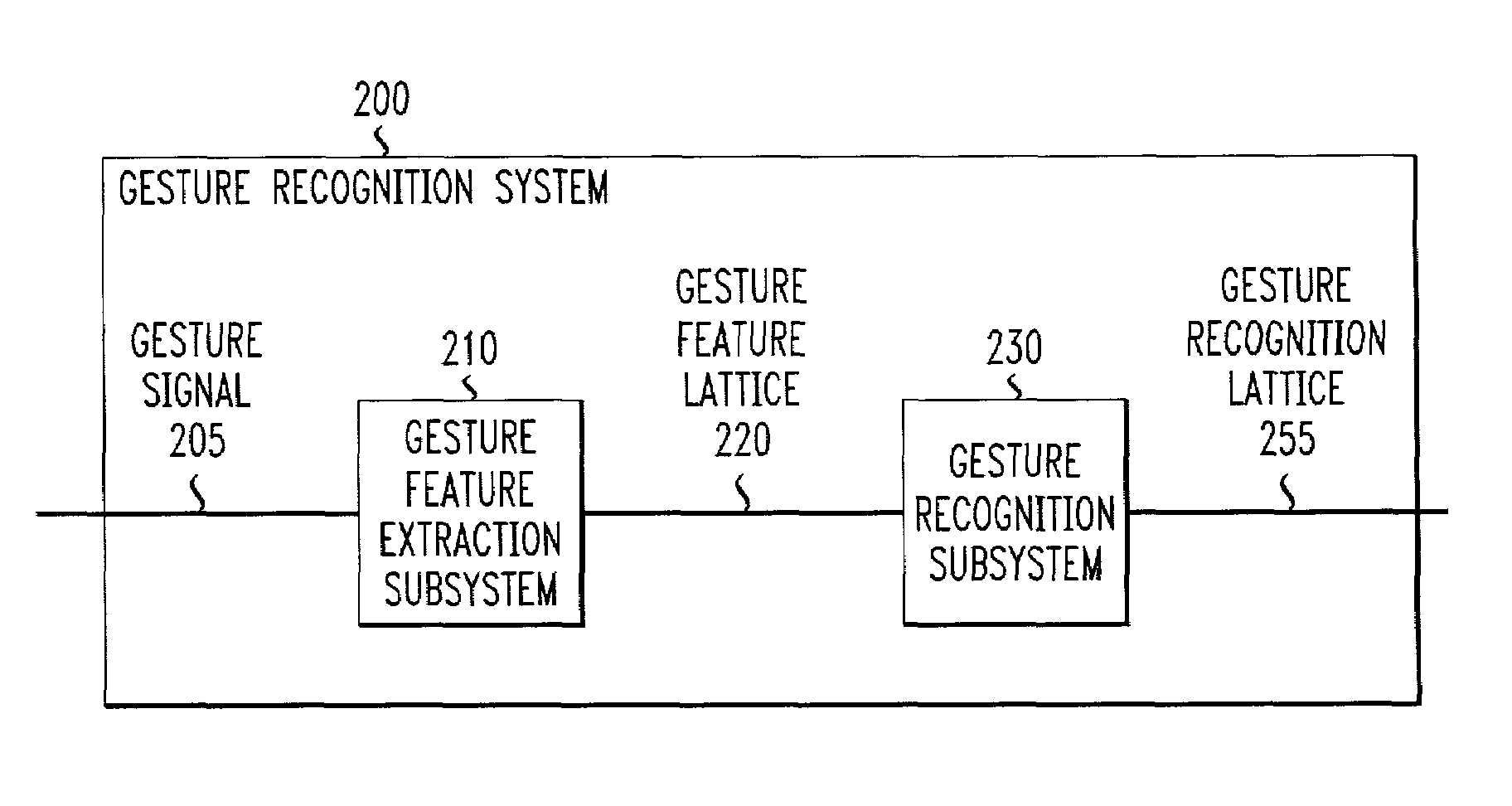
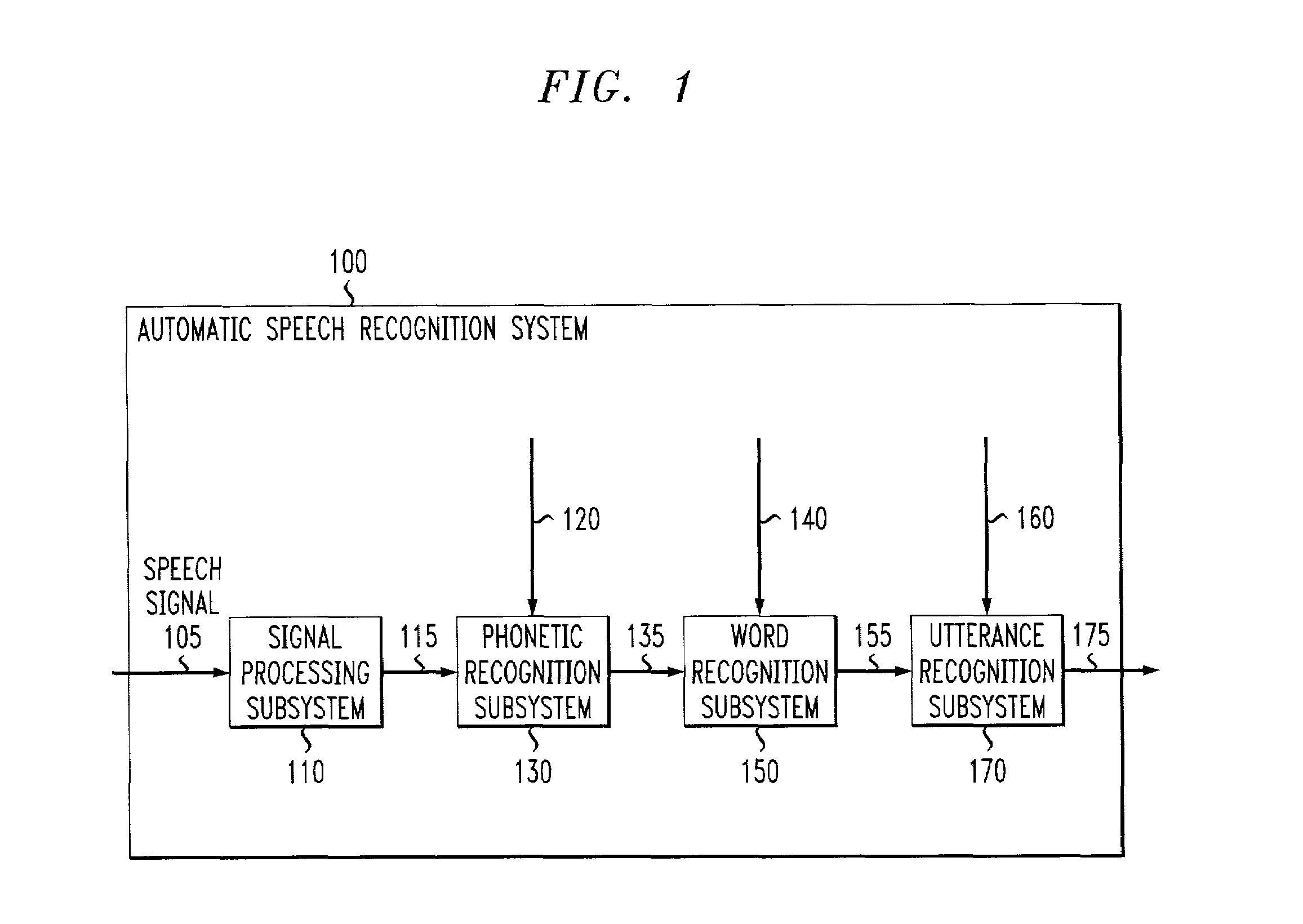
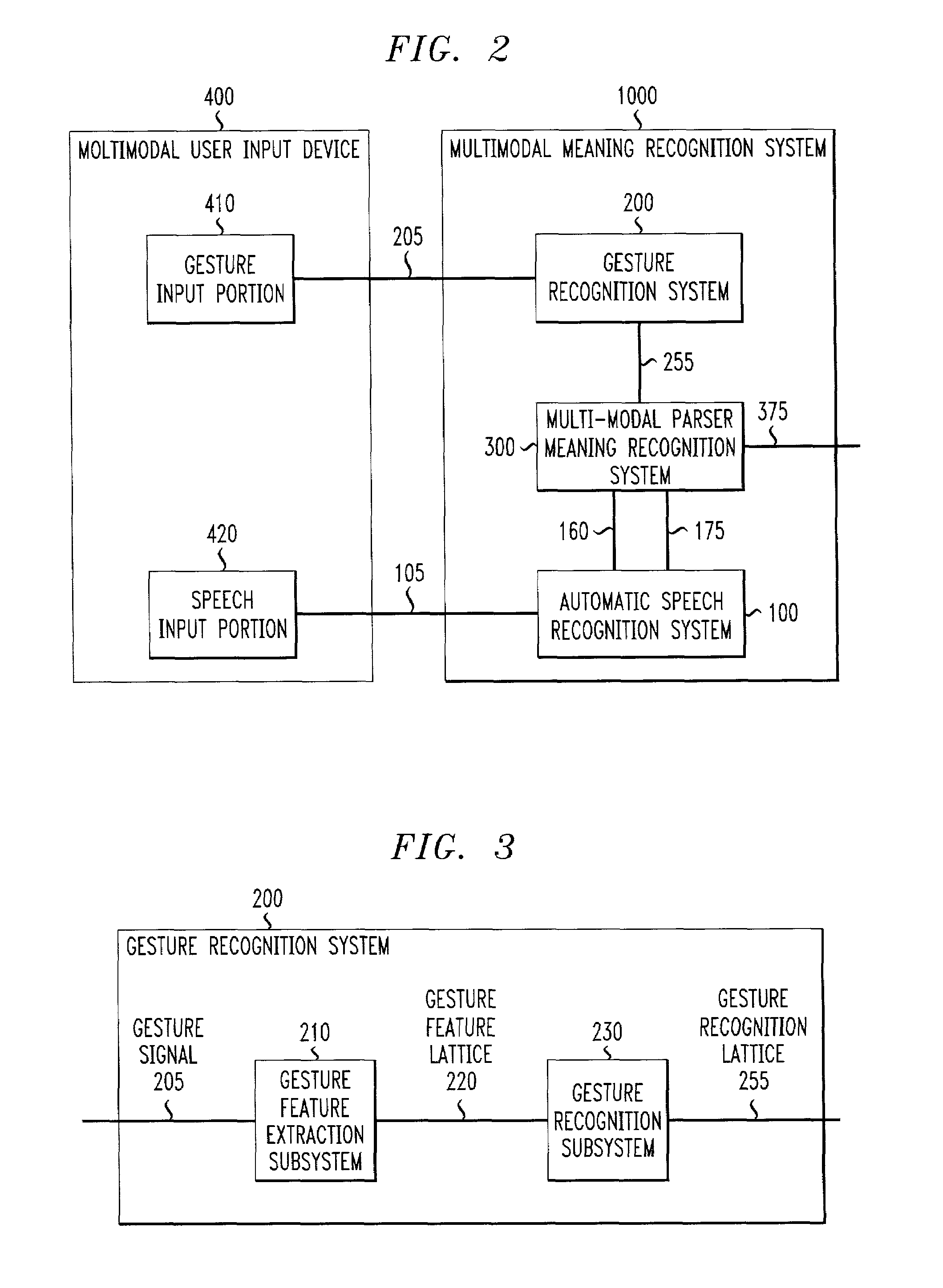
Systems and methods for extracting meaning from multimodal inputs using finite-state devices
InactiveUS6868383B1Computational complexity is reducedCharacter and pattern recognitionSpeech recognitionSpeech inputAutomatic speech
Multimodal utterances contain a number of different modes. These modes can include speech, gestures, and pen, haptic, and gaze inputs, and the like. This invention use recognition results from one or more of these modes to provide compensation to the recognition process of one or more other ones of these modes. In various exemplary embodiments, a multimodal recognition system inputs one or more recognition lattices from one or more of these modes, and generates one or more models to be used by one or more mode recognizers to recognize the one or more other modes. In one exemplary embodiment, a gesture recognizer inputs a gesture input and outputs a gesture recognition lattice to a multimodal parser. The multimodal parser generates a language model and outputs it to an automatic speech recognition system, which uses the received language model to recognize the speech input that corresponds to the recognized gesture input.
Owner:INTERACTIONS LLC (US)
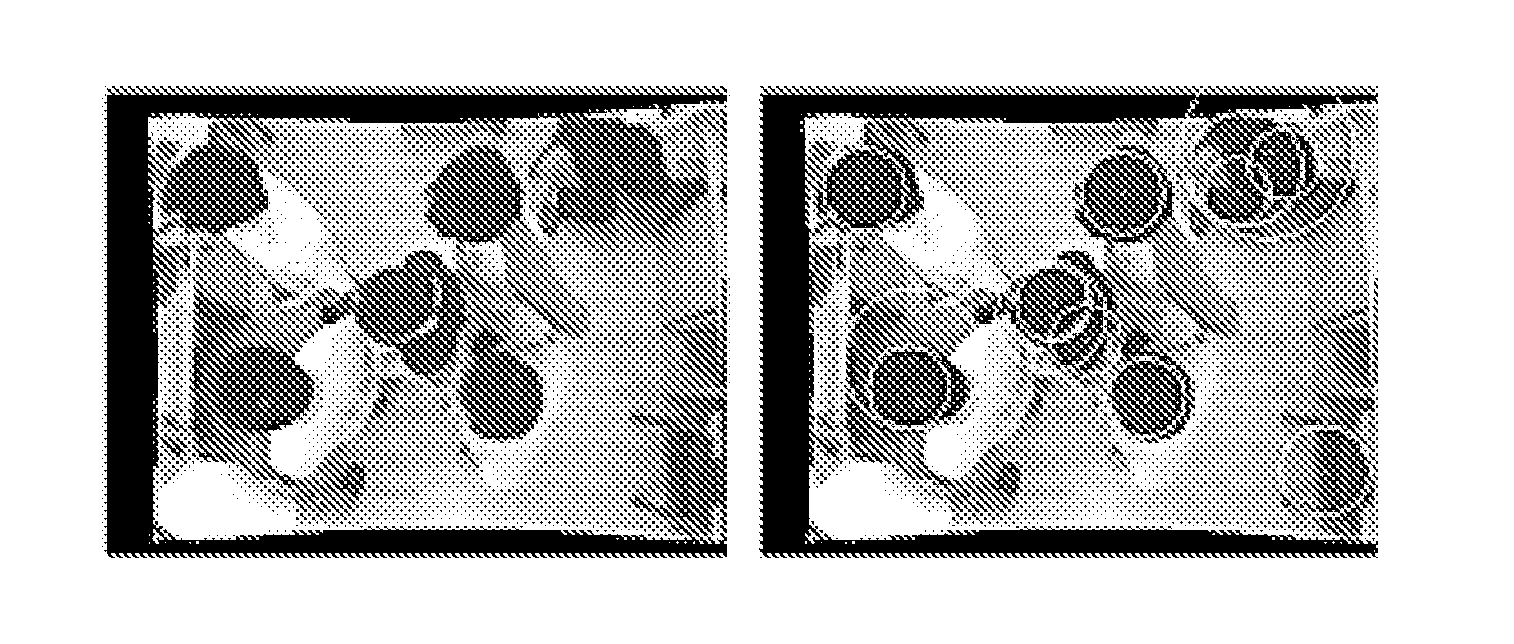
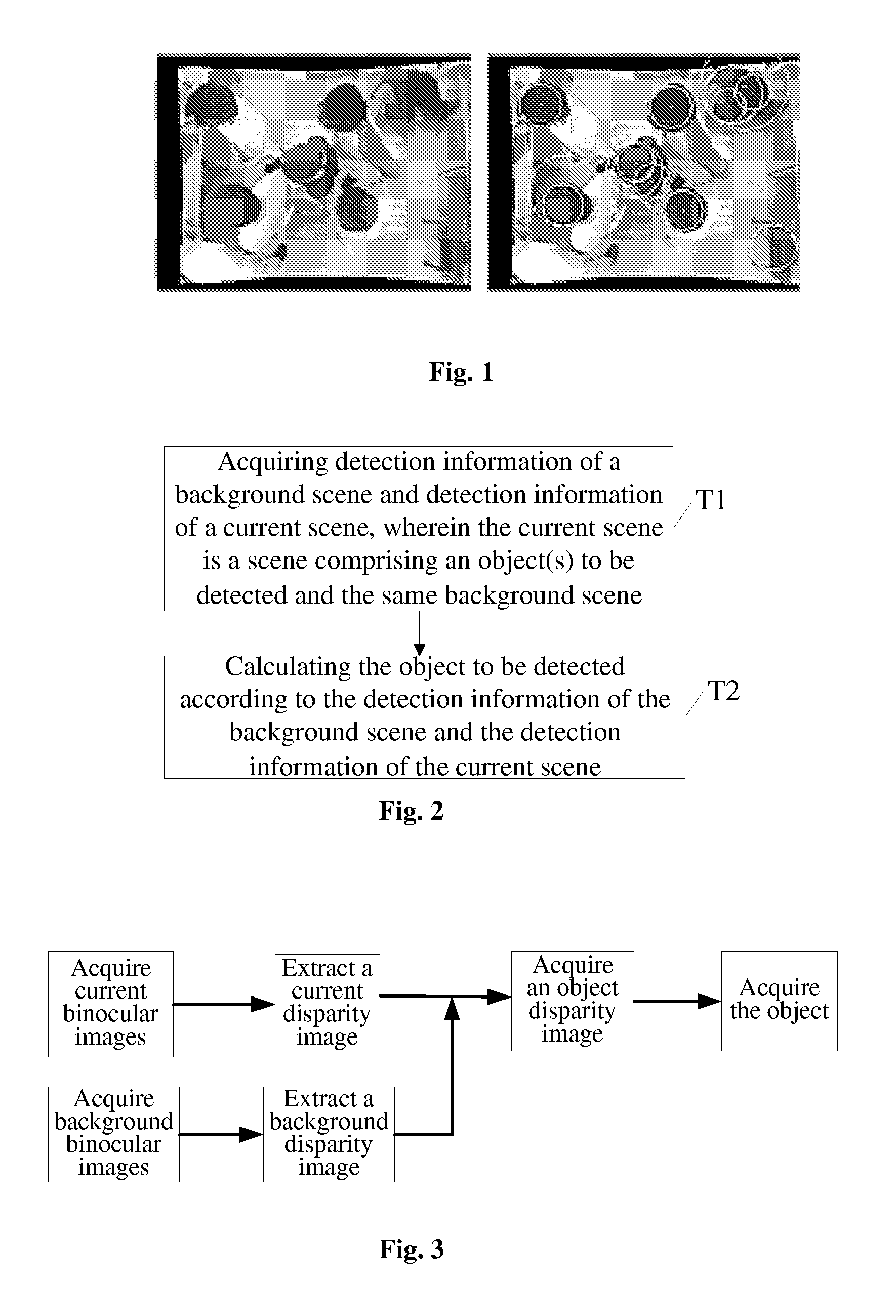
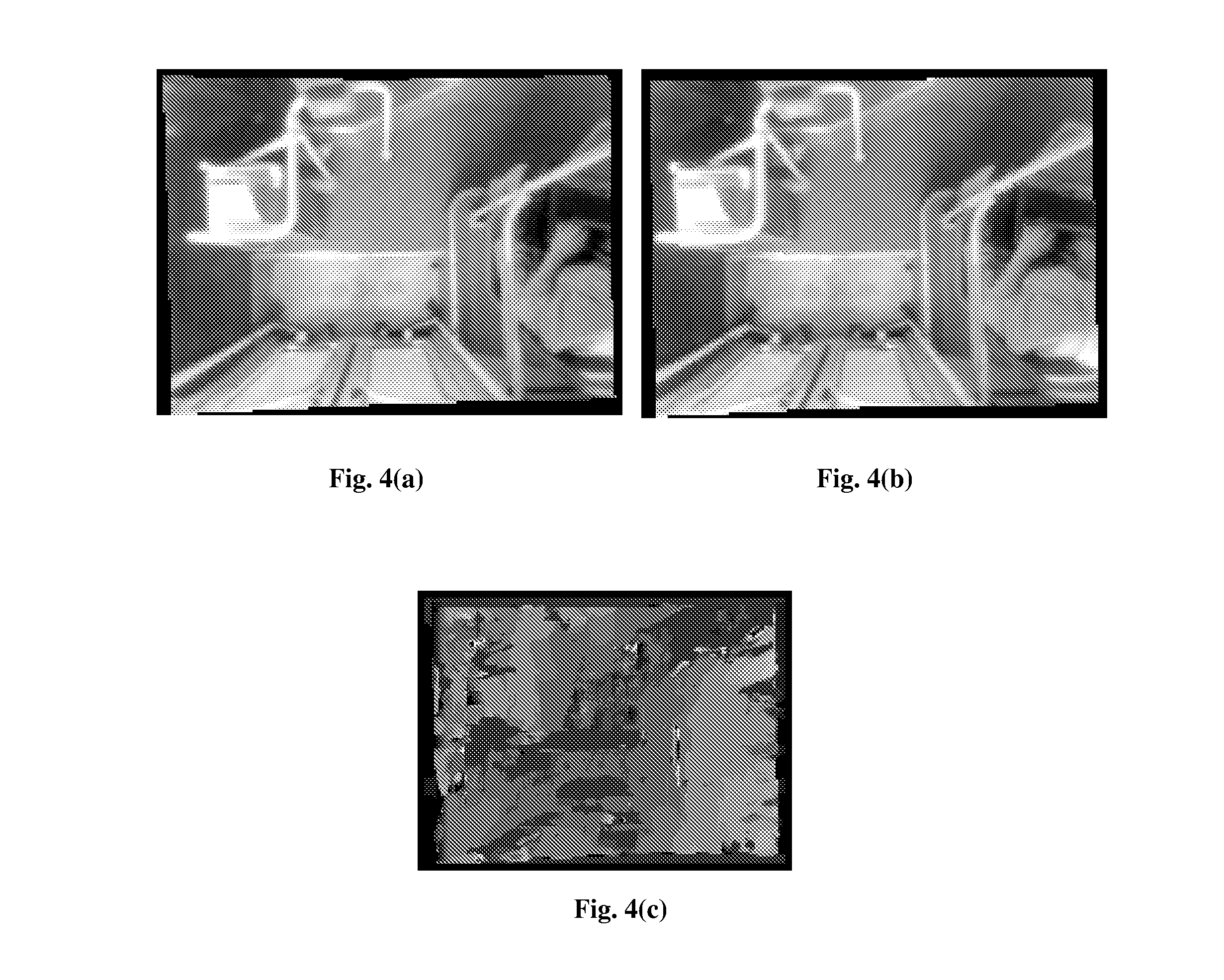
Motion detection method, apparatus and system
ActiveUS20110044502A1Reduce computational complexityImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisVideo imageLightness
A motion detection method, apparatus and system are disclosed in the present invention, which relates to the video image processing field. The present invention can effectively overcome the influence of the background on motion detection and the problem of object “conglutination” to avoid false detection, thereby accomplishing object detection in complex scenes with a high precision. The motion detection method disclosed in embodiments of the present invention comprises: acquiring detection information of the background scene and detection information of the current scene, wherein the current scene is a scene comprising an object(s) to be detected and the same background scene; and calculating the object(s) to be detected according to the detection information of the background scene and the detection information of the current scene. The present invention is applicable to any scenes where moving objects need to be detected, e.g., automatic passenger flow statistical systems in railway, metro and bus sectors, and is particularly applicable to detection and calibration of objects in places where brightness varies greatly.
Owner:HISENSE
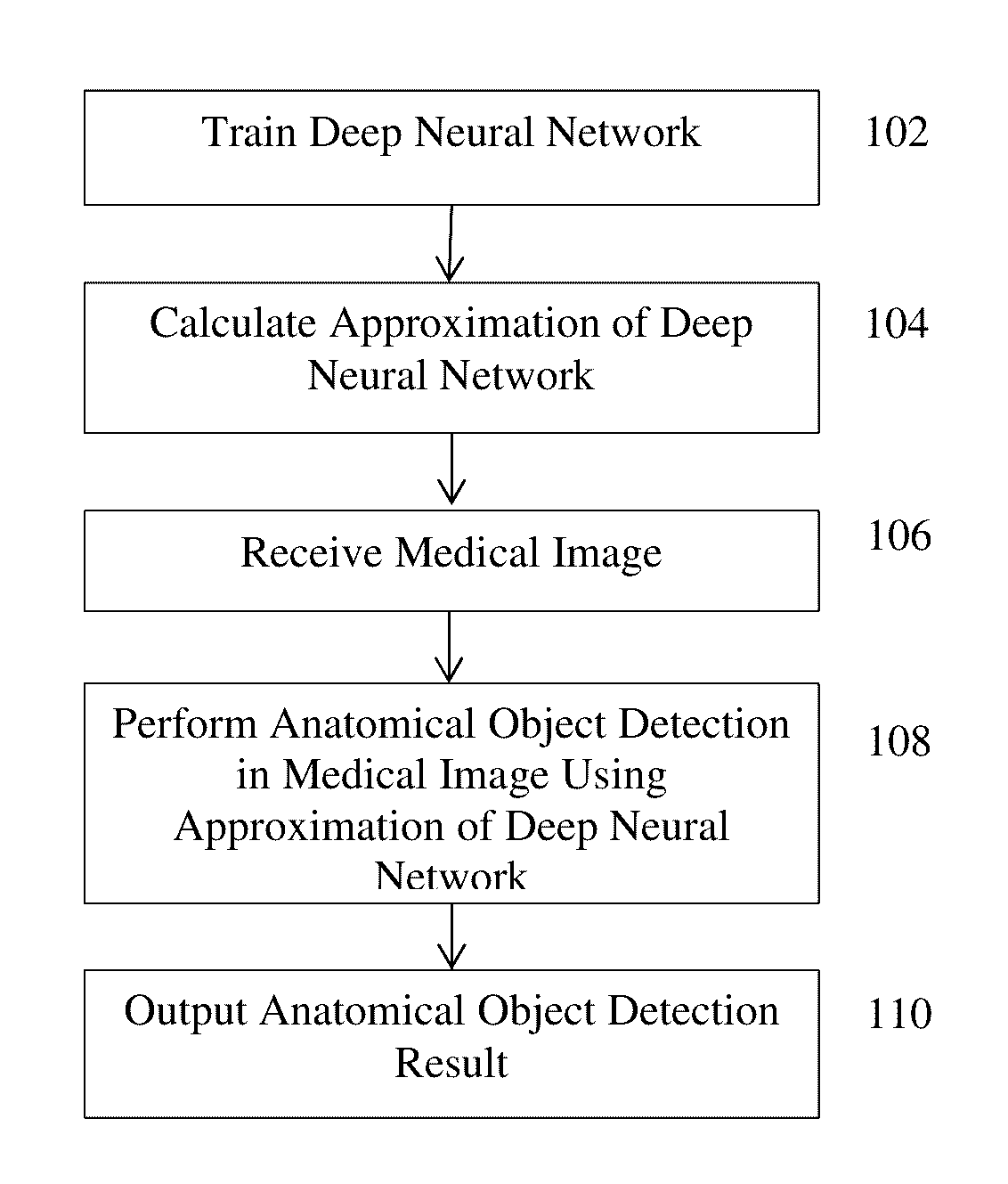
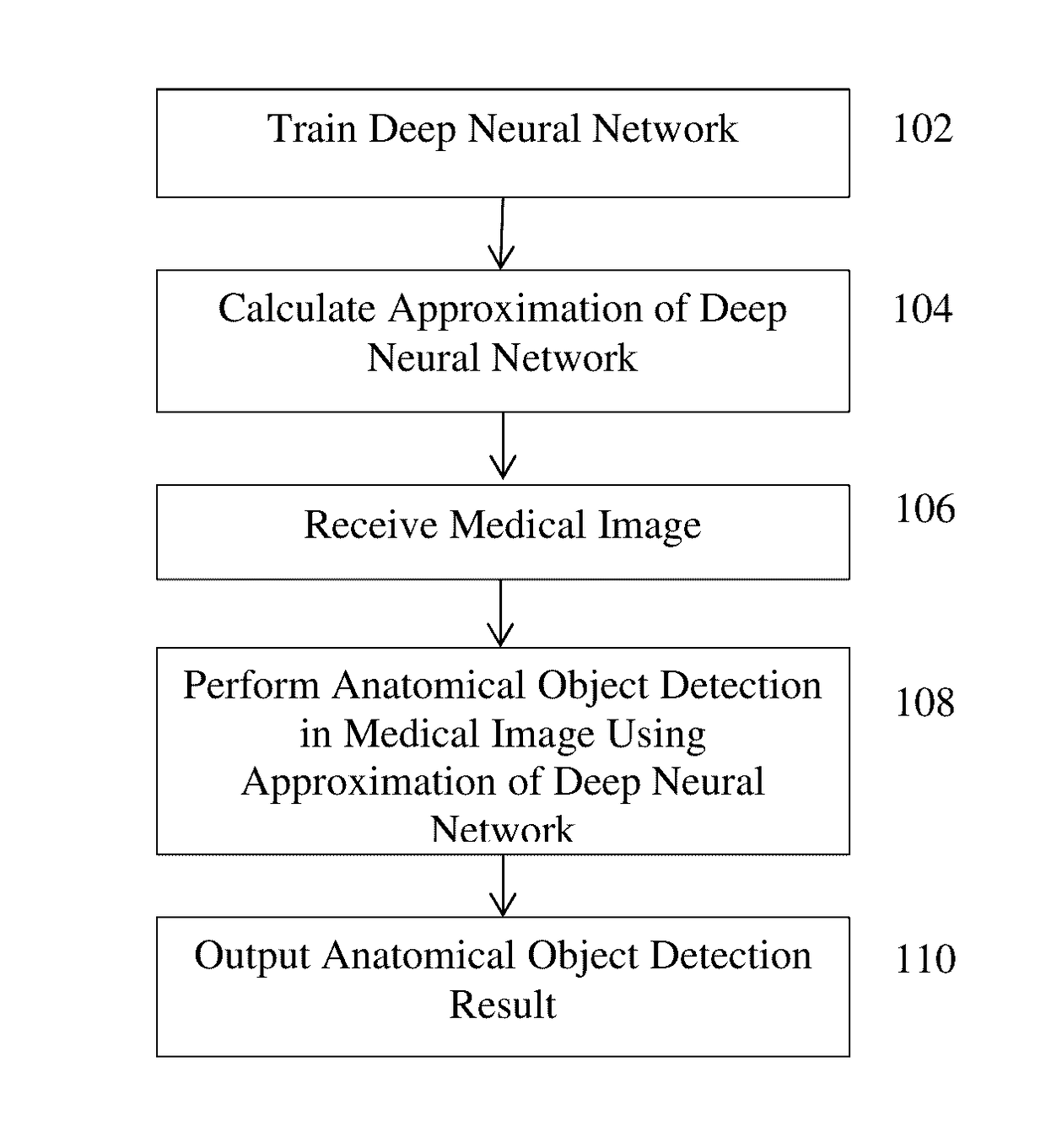
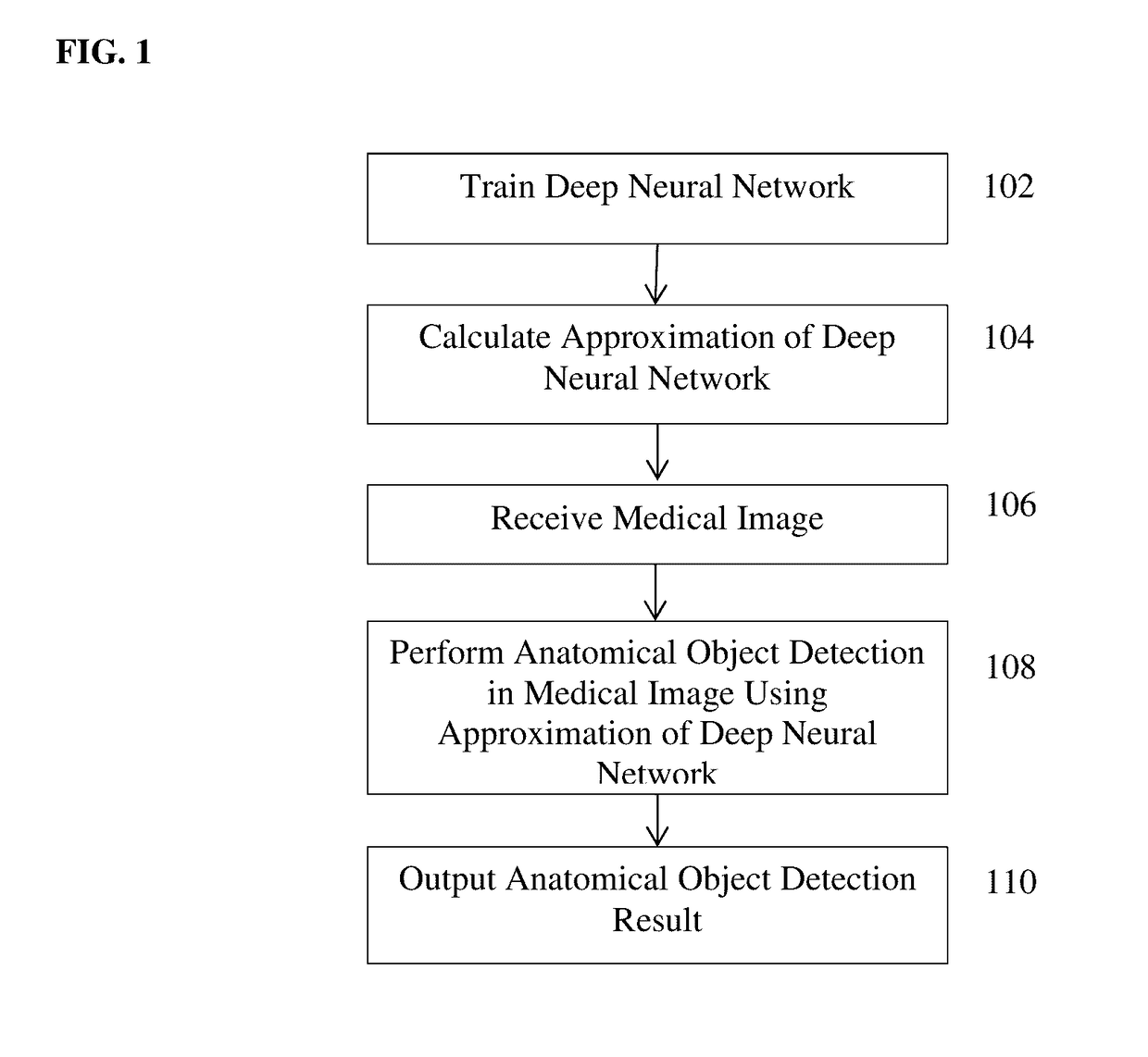
Method and System for Approximating Deep Neural Networks for Anatomical Object Detection
ActiveUS20160328643A1Reduce complexityComputationally efficientImage enhancementImage analysisComputation complexityMachine learning
A method and system for approximating a deep neural network for anatomical object detection is discloses. A deep neural network is trained to detect an anatomical object in medical images. An approximation of the trained deep neural network is calculated that reduces the computational complexity of the trained deep neural network. The anatomical object is detected in an input medical image of a patient using the approximation of the trained deep neural network.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
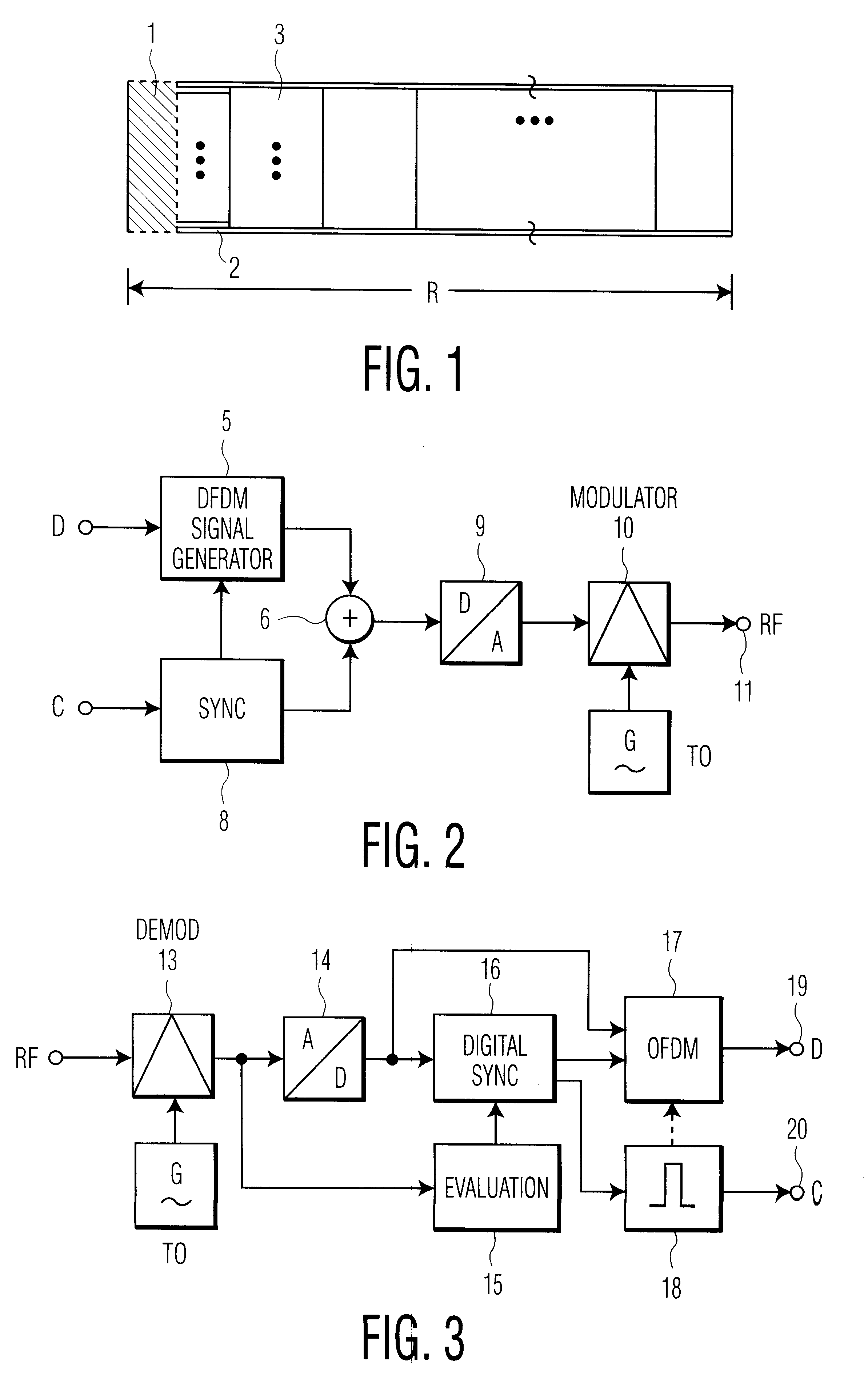
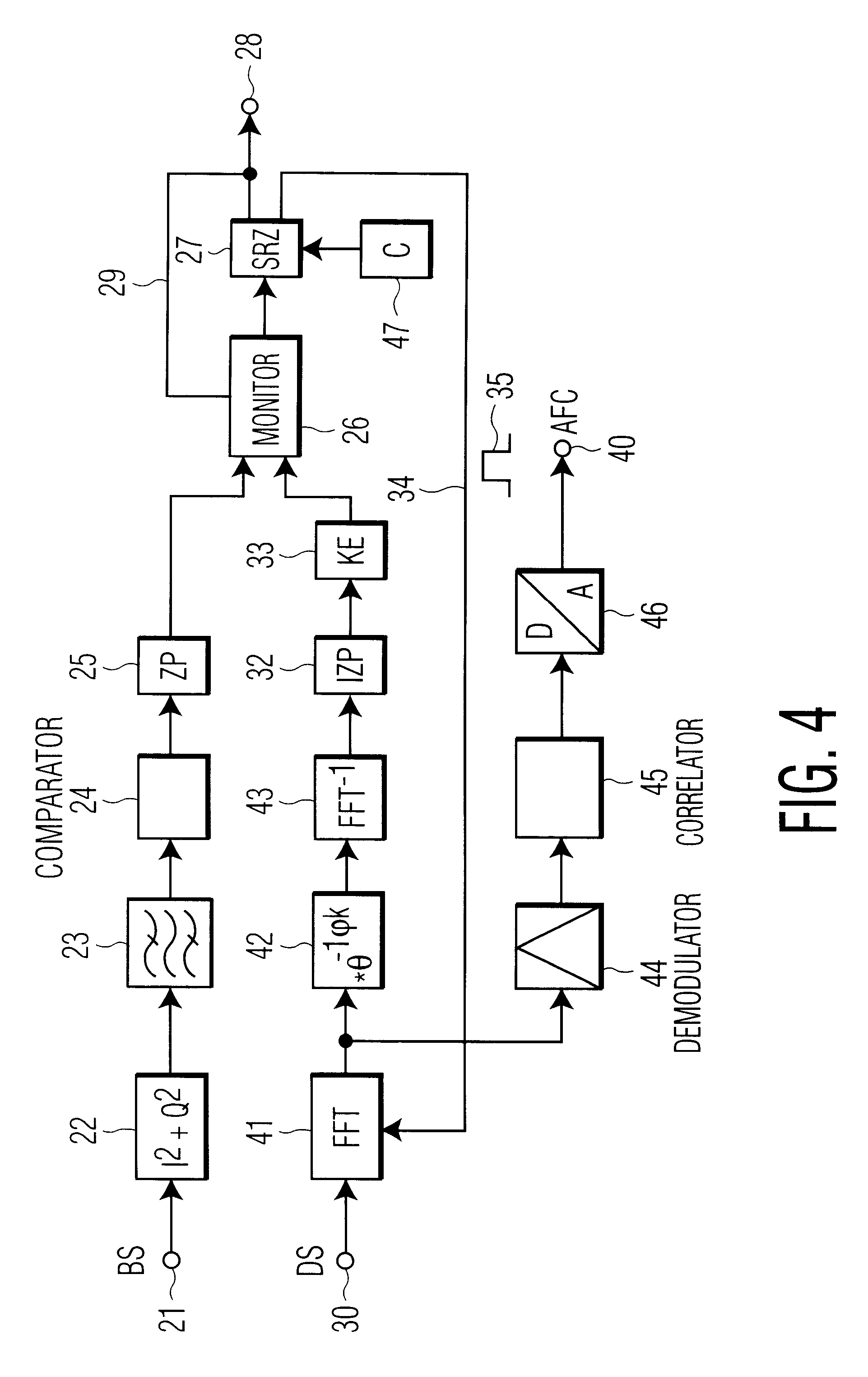
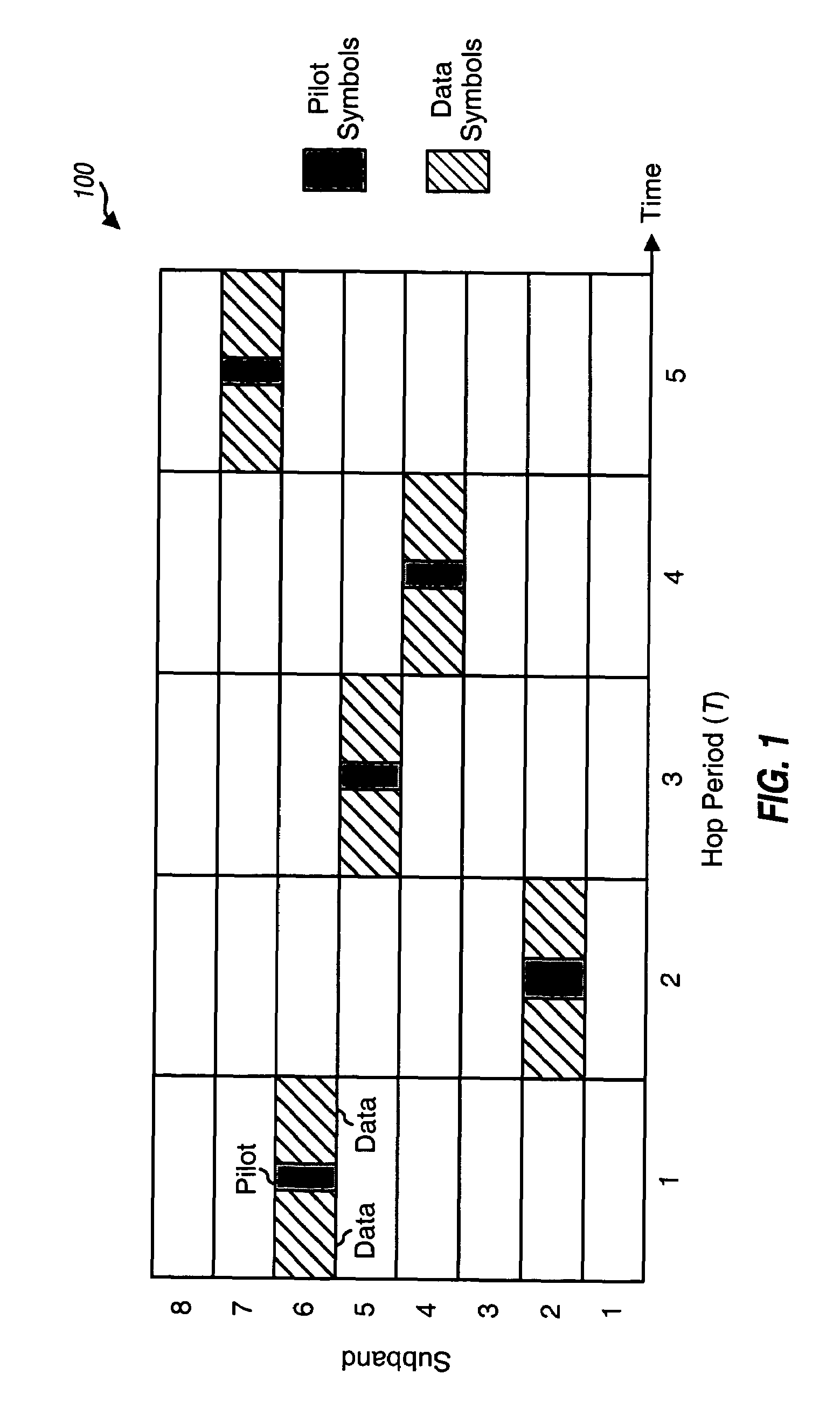
Method for the transmission of reference signals in an OFDM system
InactiveUS6226337B1Comparable and even slightly improved protectionGood choiceTransmission path divisionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsCarrier signalEngineering
A method and device in which only a single symbol is required for synchronization, and which permits the detection of appreciable deviations from the normal receiver oscillator frequency or of a deviation of the transmitter frequency from the given frequency pattern, and the correction of the oscillator frequency. The invention further includes an evaluation method for the signal which contains a multiplicity of modulated carriers. In a decoder, additional sequences are evaluated after demodulation and differential reconversion by means of a correlation.
Owner:DEUTSCHE THOMSON-BRANDT GMBH
Object recognition using incremental feature extraction
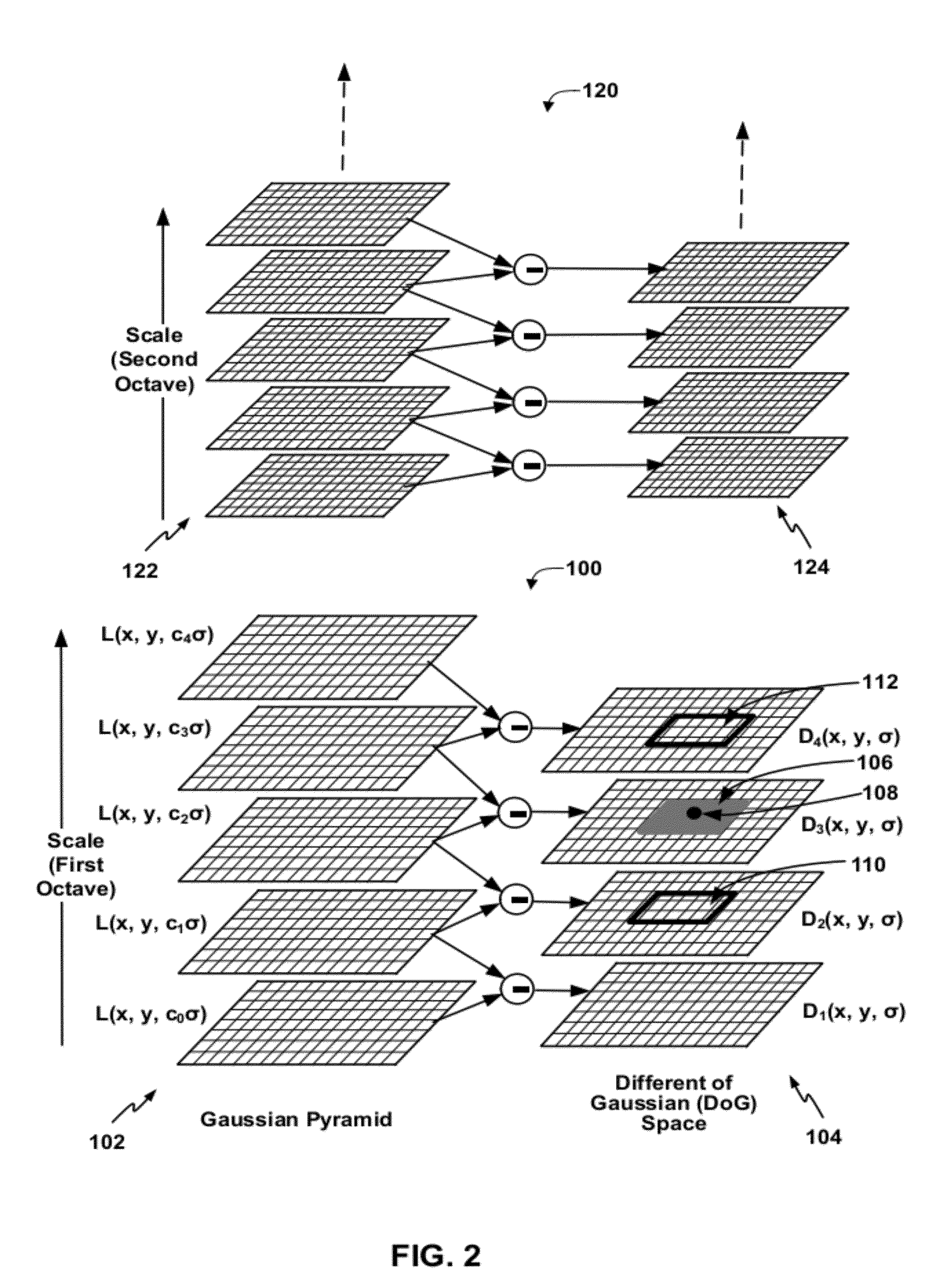
ActiveUS20120027290A1Computational complexity is reducedCharacter and pattern recognitionOctaveDigital image
In one example, an apparatus includes a processor configured to extract a first set of one or more keypoints from a first set of blurred images of a first octave of a received image, calculate a first set of one or more descriptors for the first set of keypoints, receive a confidence value for a result produced by querying a feature descriptor database with the first set of descriptors, wherein the result comprises information describing an identity of an object in the received image, and extract a second set of one or more keypoints from a second set of blurred images of a second octave of the received image when the confidence value does not exceed a confidence threshold. In this manner, the processor may perform incremental feature descriptor extraction, which may improve computational efficiency of object recognition in digital images.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
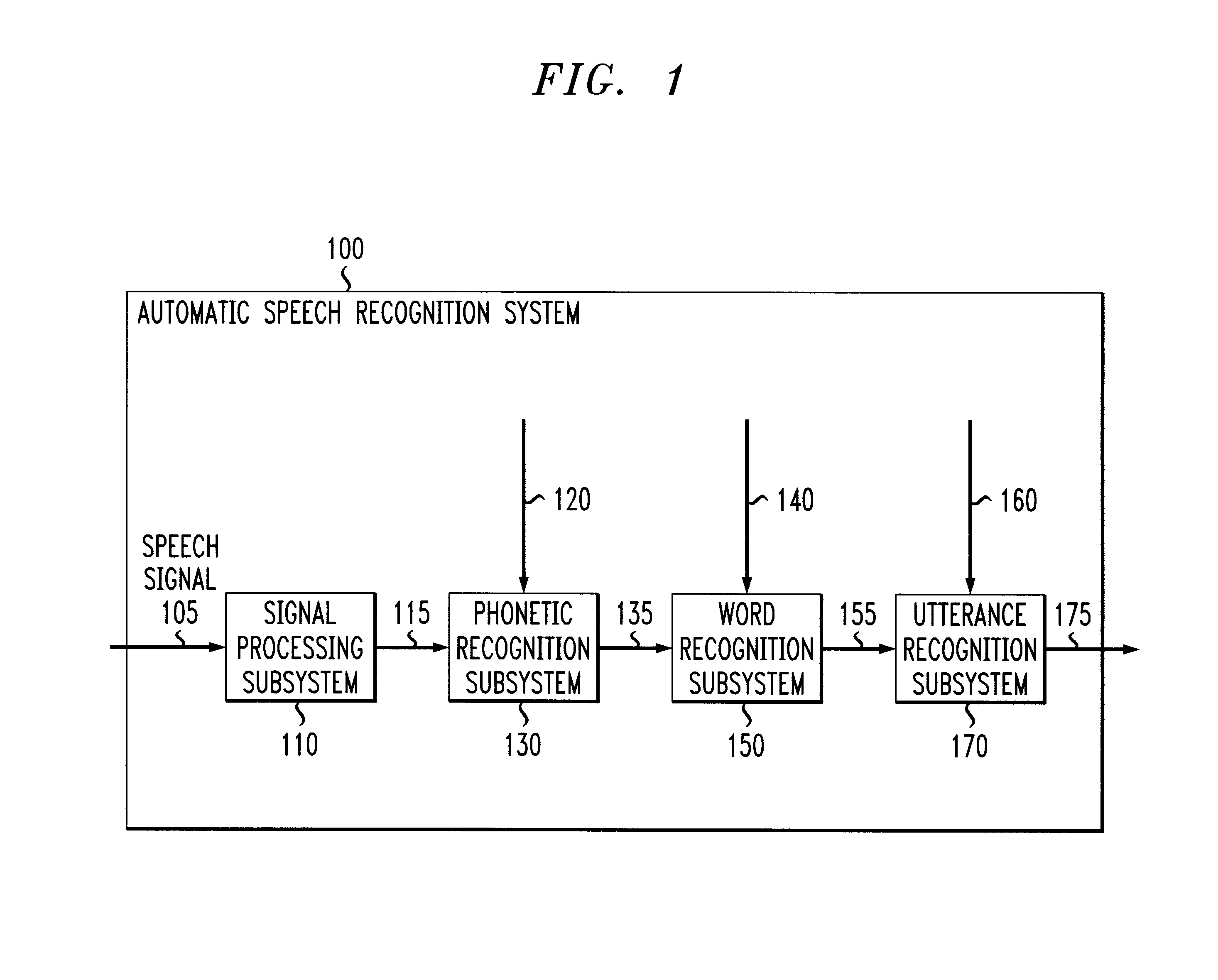
Systems and methods for extracting meaning from multimodal inputs using finite-state devices
ActiveUS7069215B1Reduce computational complexityComputational complexity is reducedCharacter and pattern recognitionSpeech recognitionComputation complexitySemantic representation
Finite-state systems and methods allow multiple input streams to be parsed and integrated by a single finite-state device. These systems and methods not only address multimodal recognition, but are also able to encode semantics and syntax into a single finite-state device. The finite-state device provides models for recognizing multimodal inputs, such as speech and gesture, and composes the meaning content from the various input streams into a single semantic representation. Compared to conventional multimodal recognition systems, finite-state systems and methods allow for compensation among the various input streams. Finite-state systems and methods allow one input stream to dynamically alter a recognition model used for another input stream, and can reduce the computational complexity of multidimensional multimodal parsing. Finite-state devices provide a well-understood probabilistic framework for combining the probability distributions associated with the various input streams and for selecting among competing multimodal interpretations.
Owner:INTERACTIONS LLC (US)
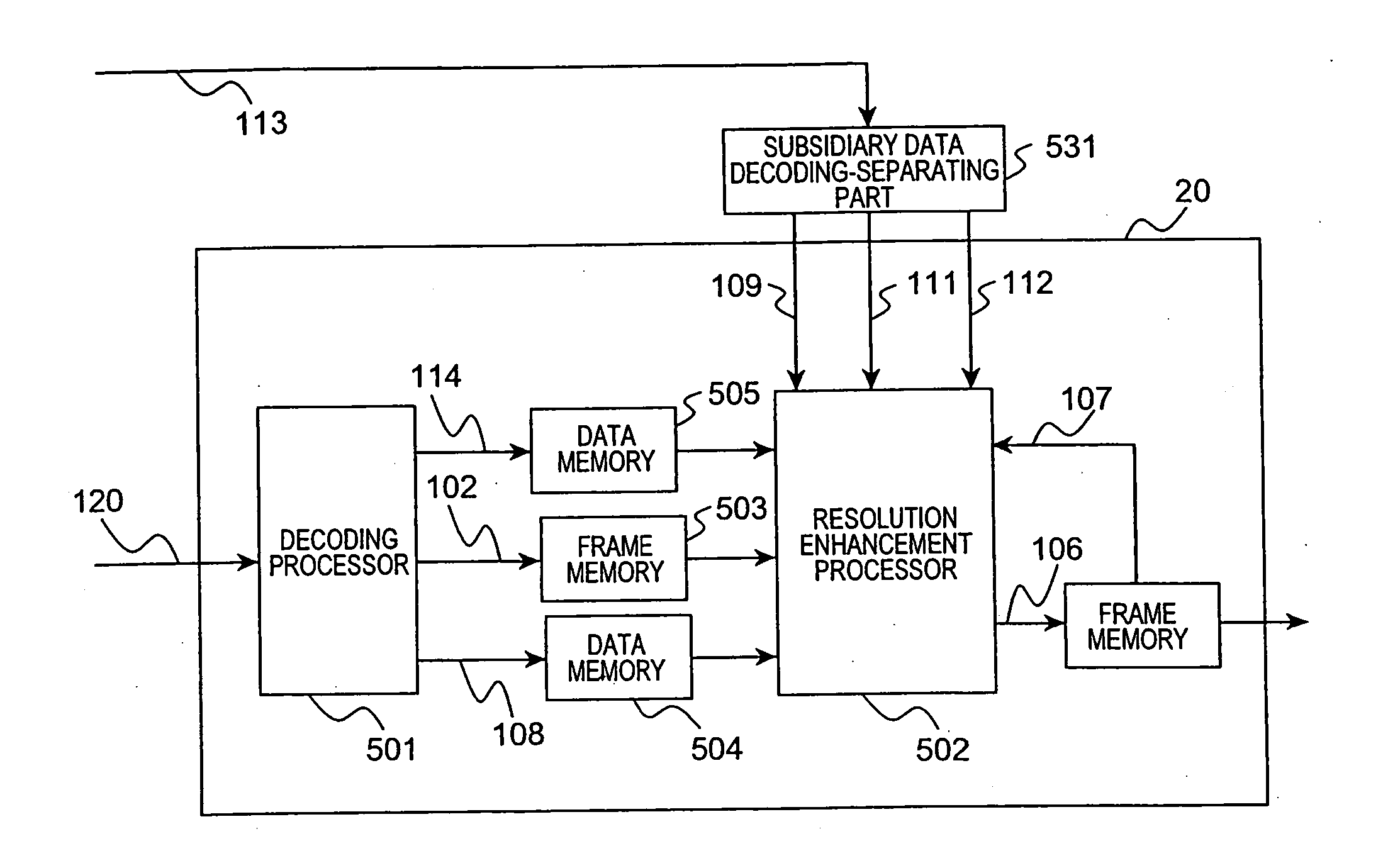
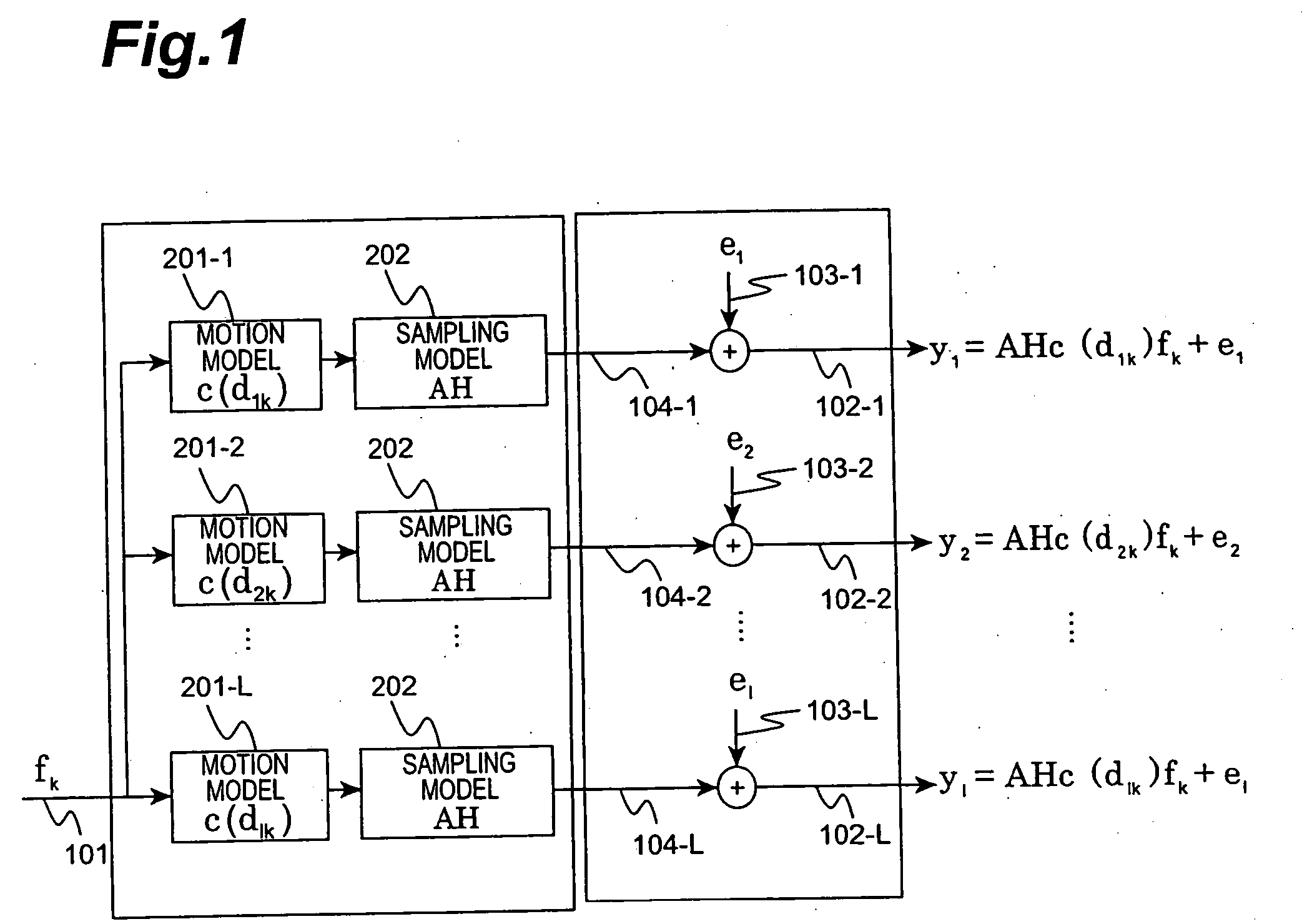
Image decoding apparatus, image decoding program, image decoding method, image encoding apparatus, image encoding program, and image encoding method
InactiveUS20060126952A1Improve accuracyComputational complexity is reducedImage enhancementImage analysisMotion vectorImage resolution
An image decoding apparatus has a video data decoder for receiving and decoding encoded video data to acquire a plurality of reconstructed images; a subsidiary data decoder for receiving and decoding subsidiary data to acquire subsidiary motion information; and a resolution enhancer for generating motion vectors representing time-space correspondences between the plurality of reconstructed images, based on the subsidiary motion information acquired by the subsidiary data decoder, and for generating a high-resolution image with a spatial resolution higher than that of the plurality of reconstructed images, using the generated motion vectors and the plurality of reconstructed images acquired by the video data decoder.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
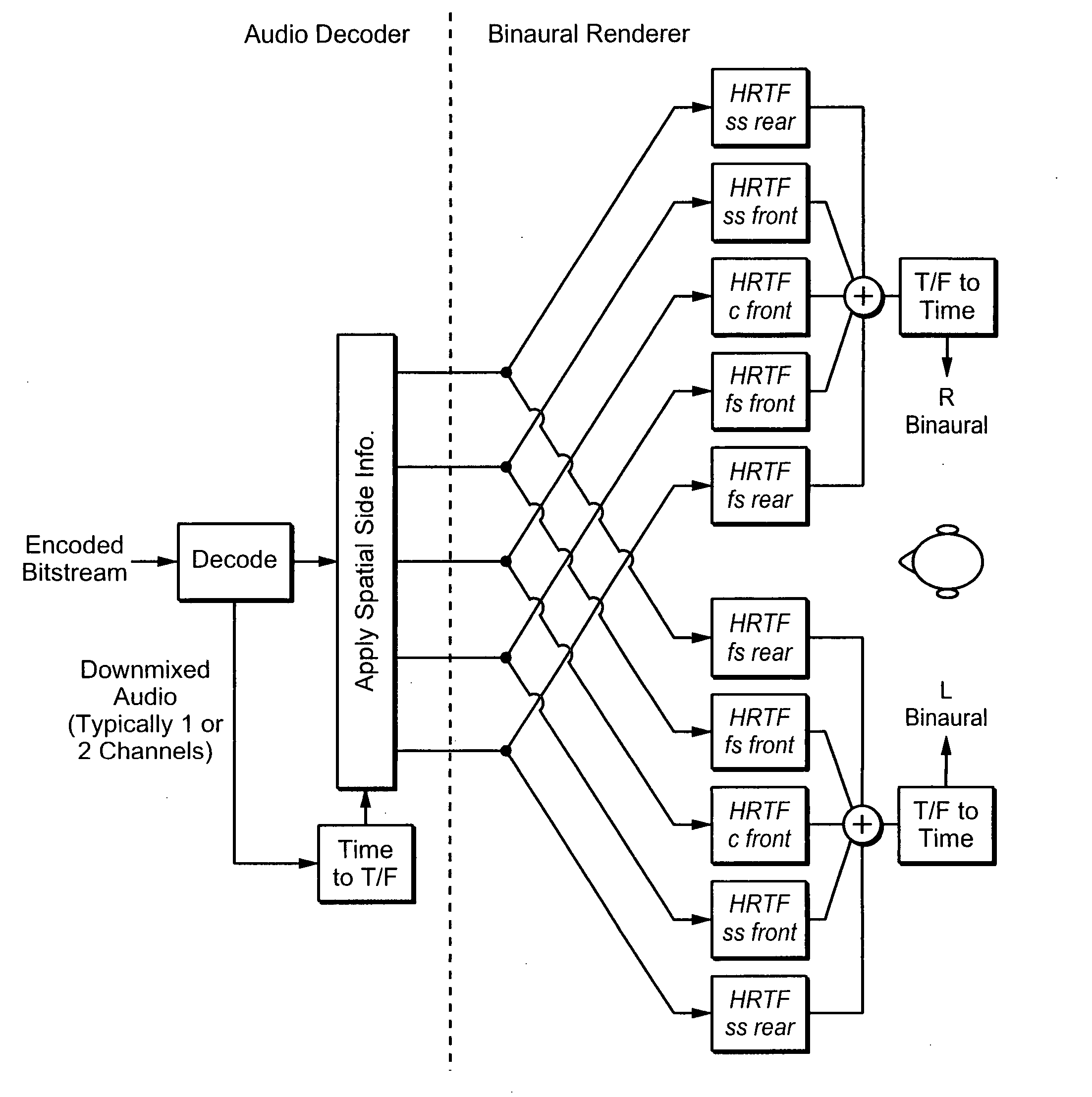
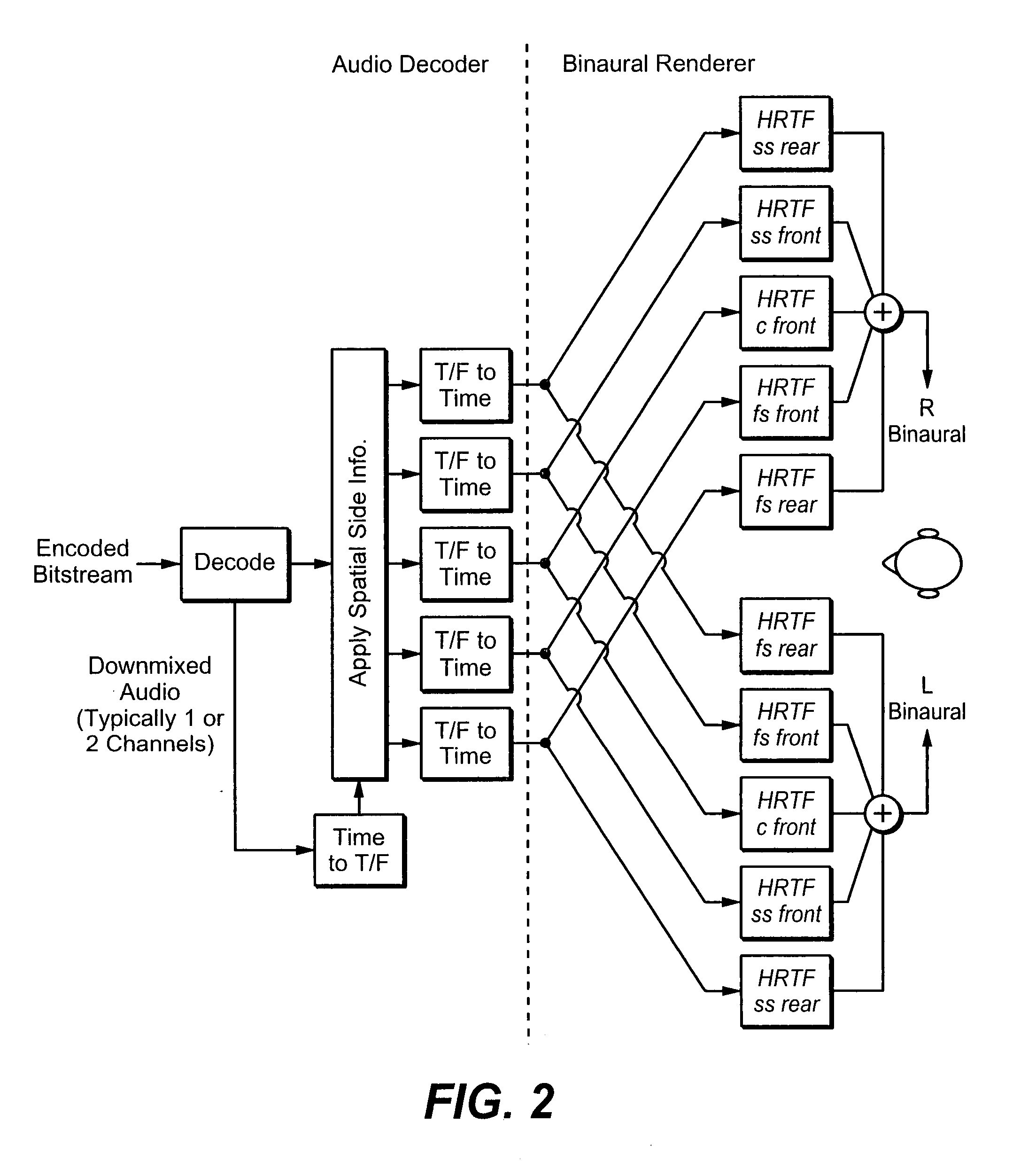
Binaural rendering using subband filters
InactiveUS20080025519A1Efficient implementationComputational complexity is reducedSpeech analysisStereophonic systemsPhase correctionFrequency spectrum
Transfer functions like Head Related Transfer Functions (HRTF) needed for binaural rendering are implemented efficiently by a subband-domain filter structure. In one implementation, amplitude, fractional-sample delay and phase-correction filters are arranged in cascade with one another and applied to subband signals that represent spectral content of an audio signal in frequency subbands. Other filter structures are also disclosed. These filter structures may be used advantageously in a variety of signal processing applications. A few examples of audio applications include signal bandwidth compression, loudness equalization, room acoustics correction and assisted listening for individuals with hearing impairments.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
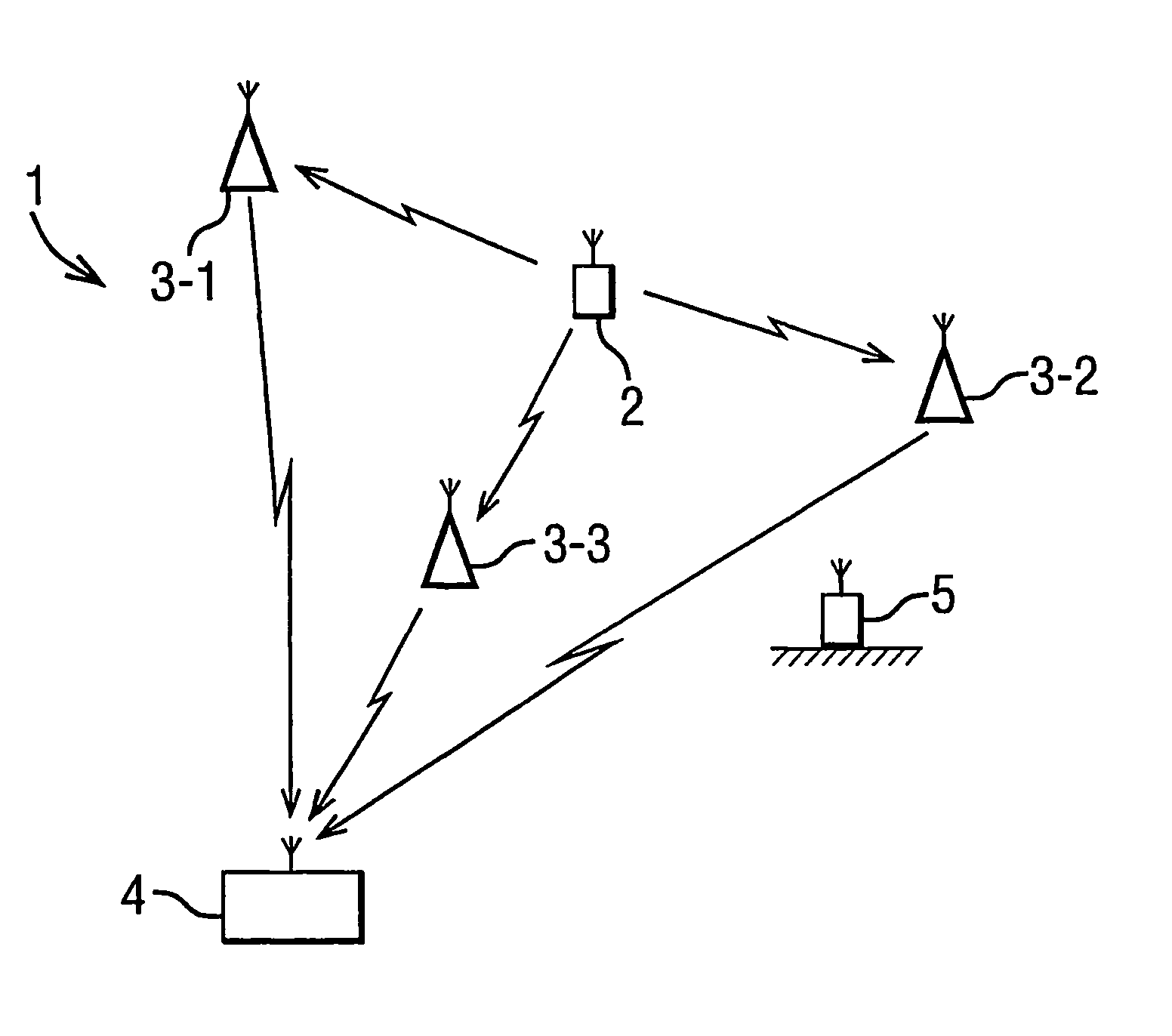
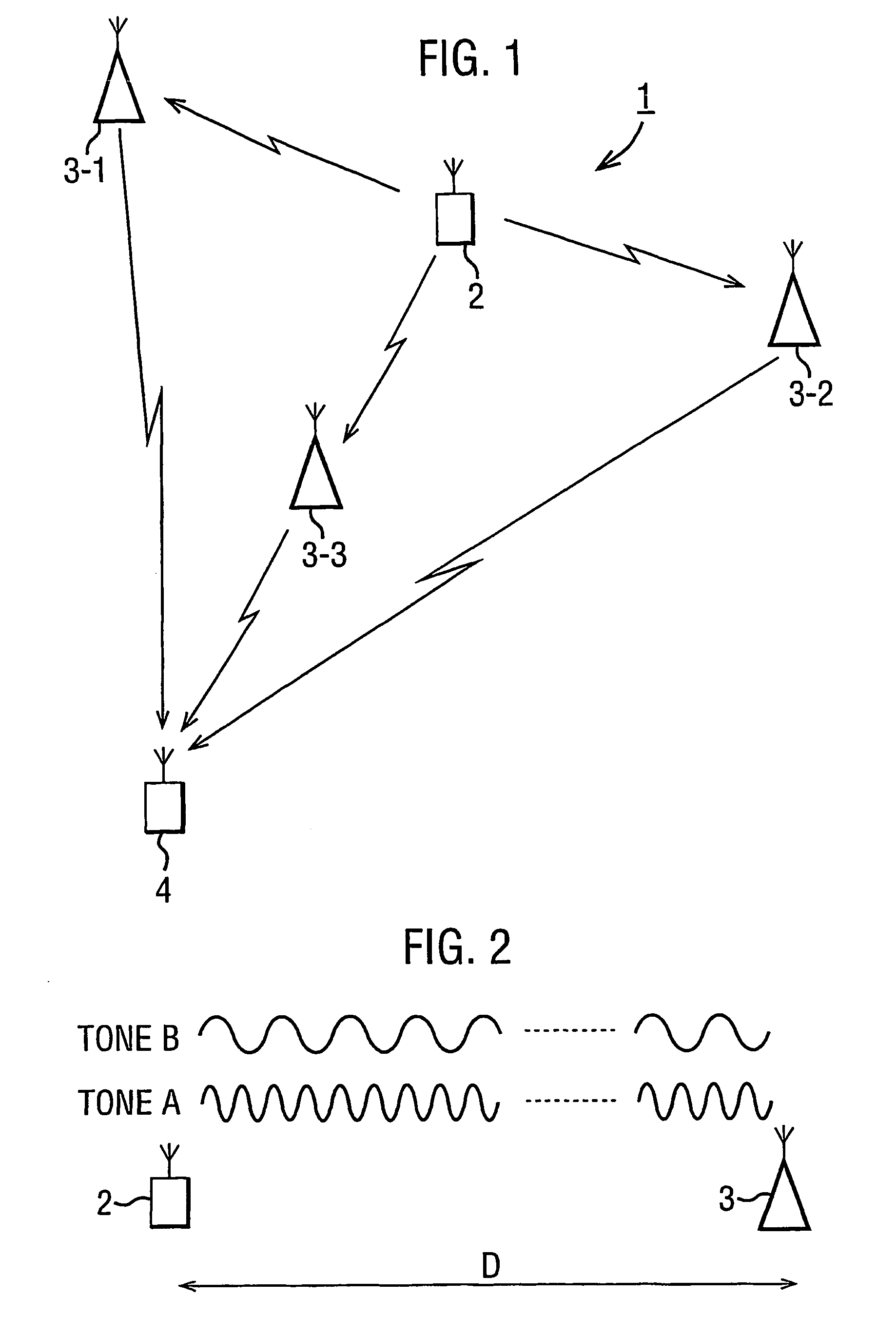
Tag tracking
InactiveUS7228228B2Simple designSimplifies tagBeacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationSignal onFinite range
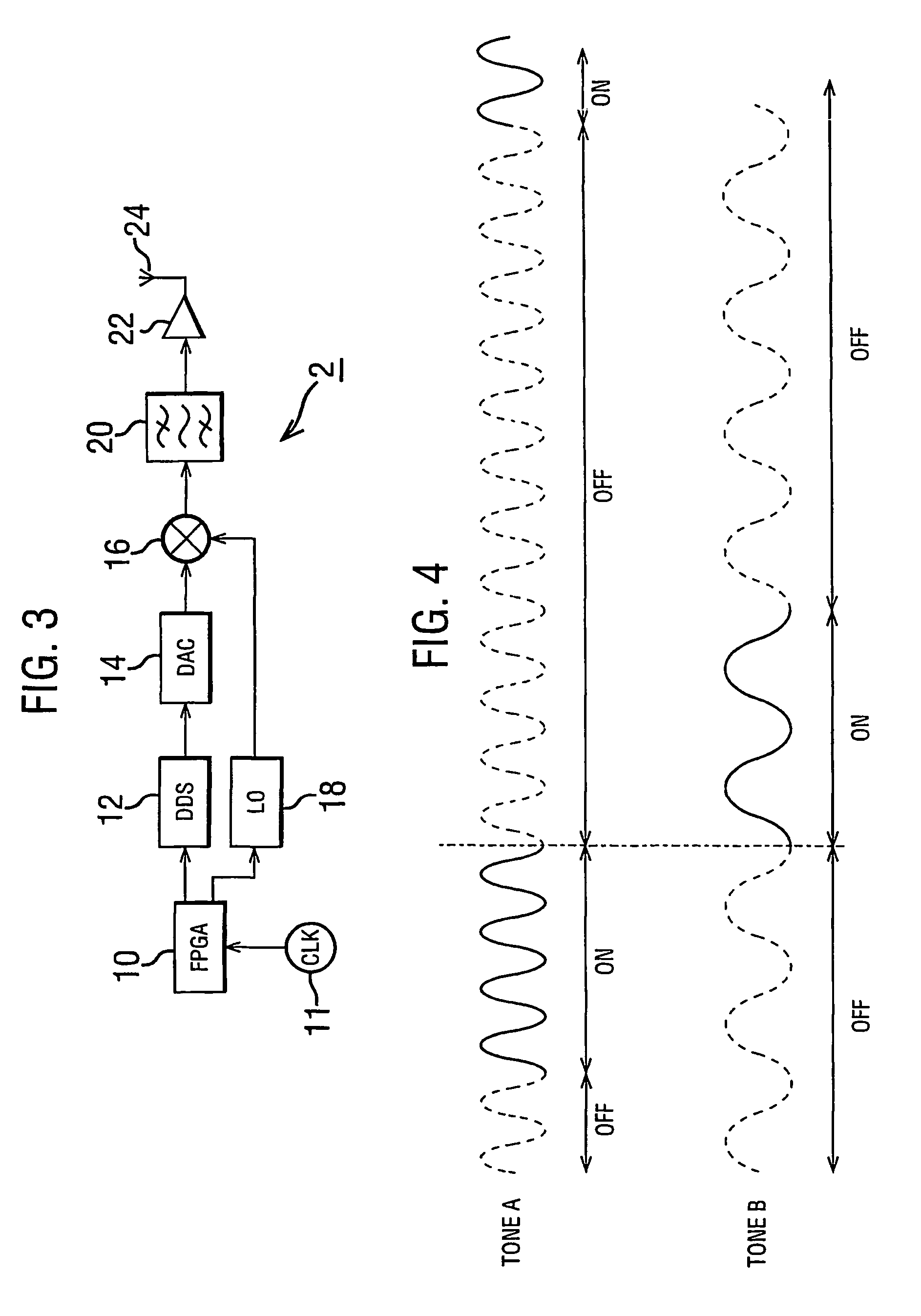
The present invention provides a tracking system in which a mobile tag having an unknown position, which tag is to be tracked in space over time, transmits a signal comprising a pair of tones at different frequencies. The transmitted signal is received at each of three receivers, each having a known location, where the phase of each of the tones within the signal is measured. The measured phases are passed to a processing unit which determines the position of the tag at the time of transmission of the signal on the basis of the difference between the measured phases of the two tones. The tracking system operates over a defined finite range to track the position of the mobile tag uniquely in space.
Owner:TURFTRAX GROUP
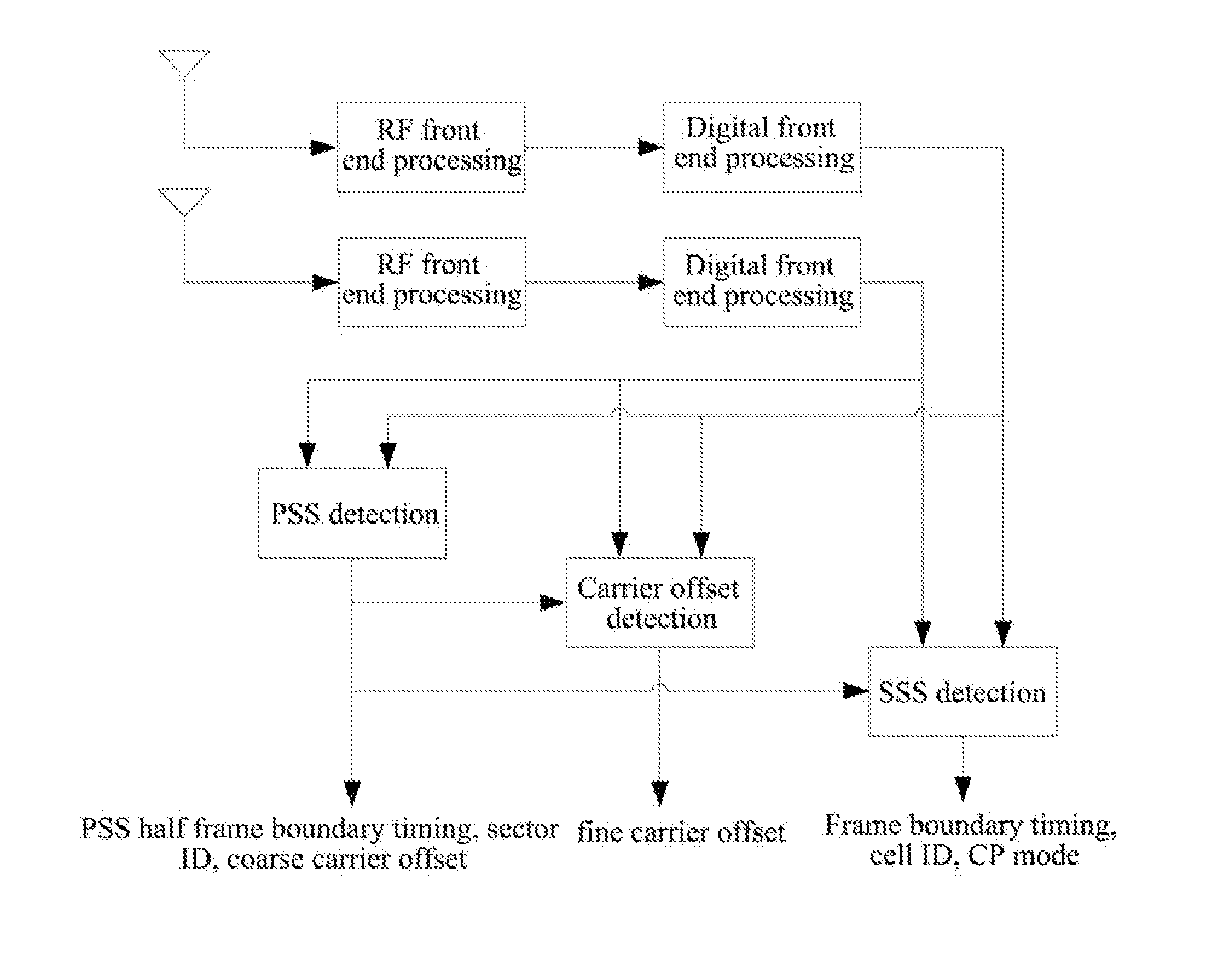
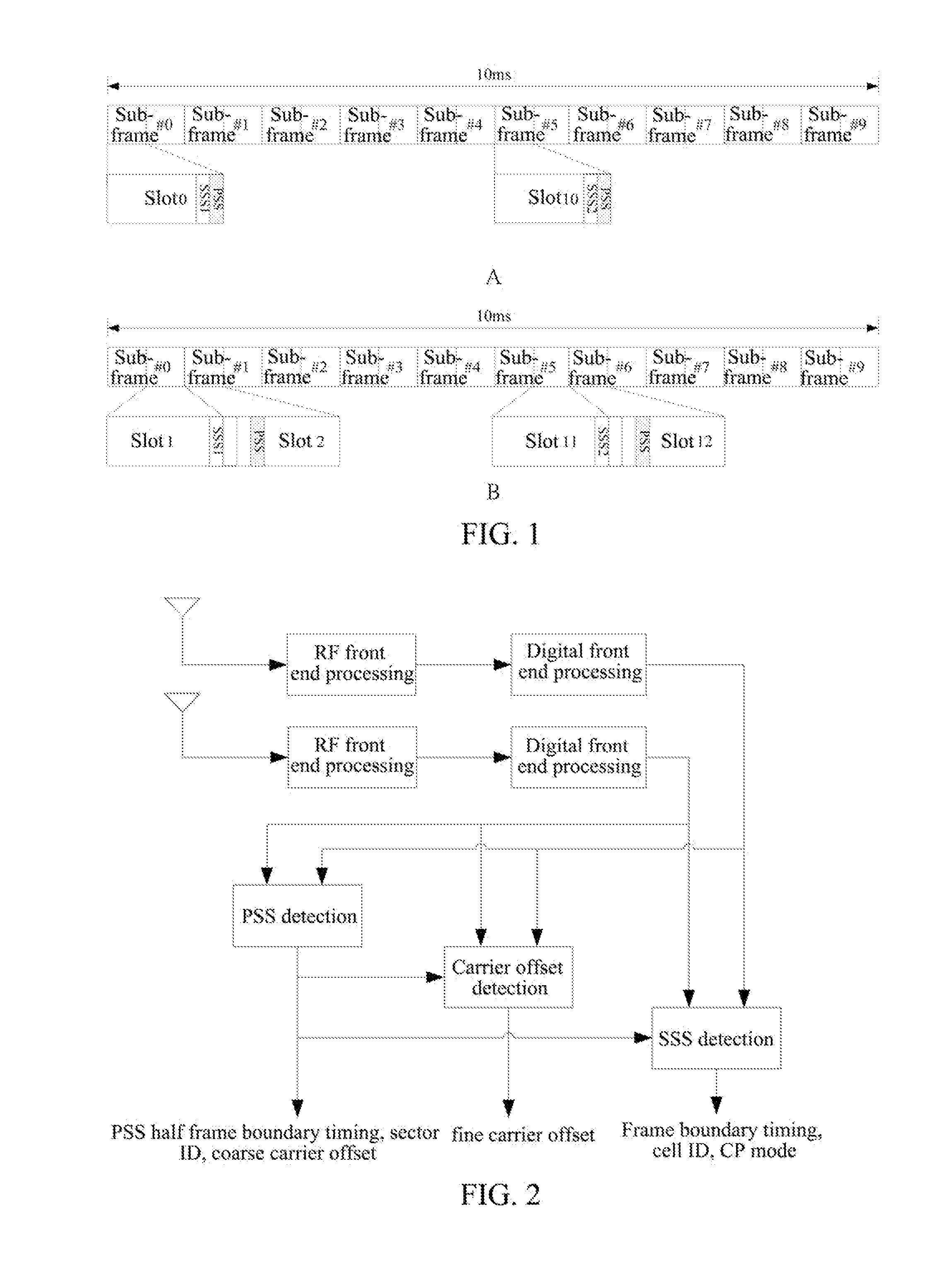
Apparatus and method for secondary synchronization channel detection in a 3GPP WCDMA receiver
ActiveUS7095811B1Computational complexity be reduceReduce numberError preventionError coding/decoding sychronisationFrame timeCell search
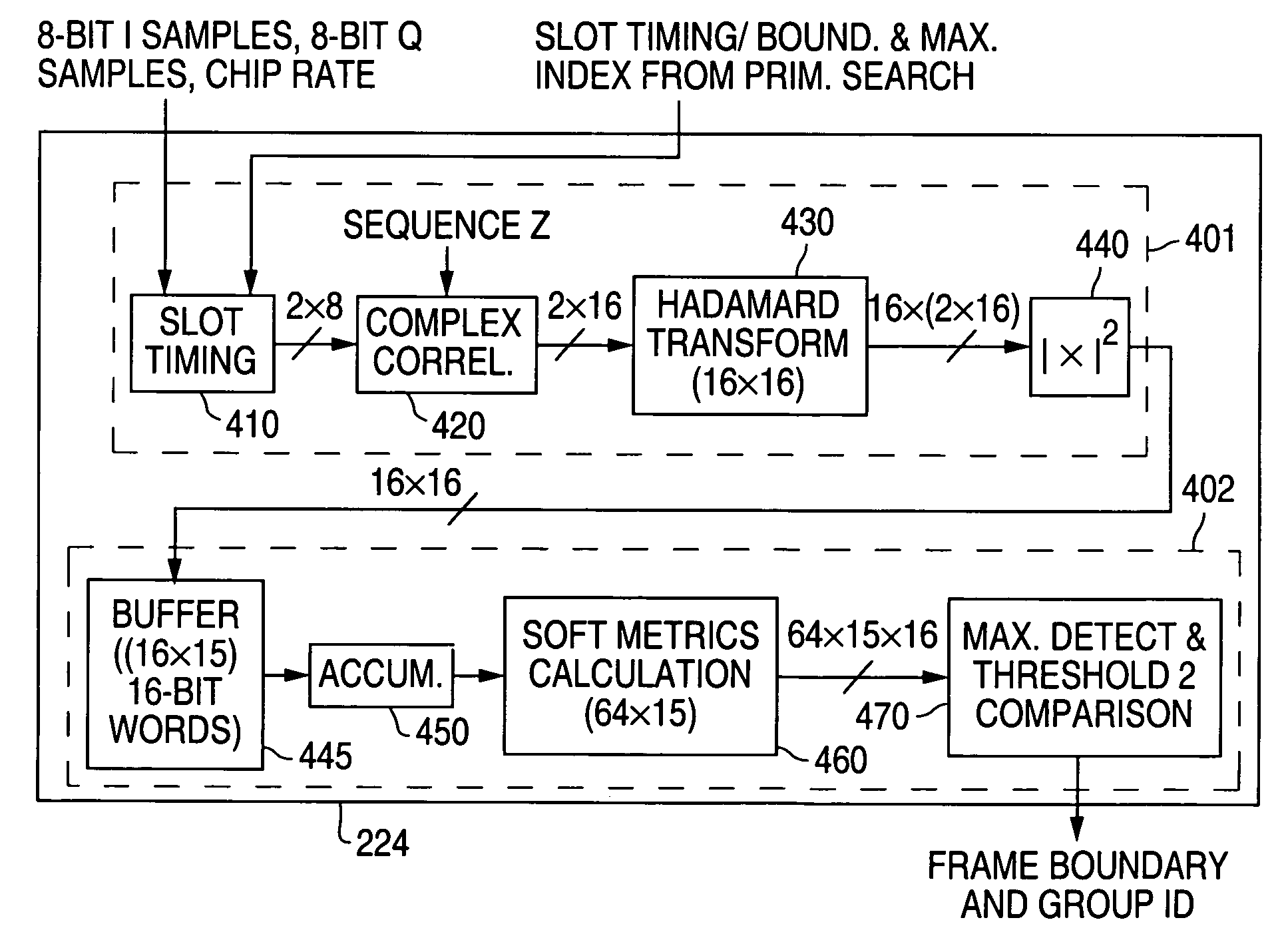
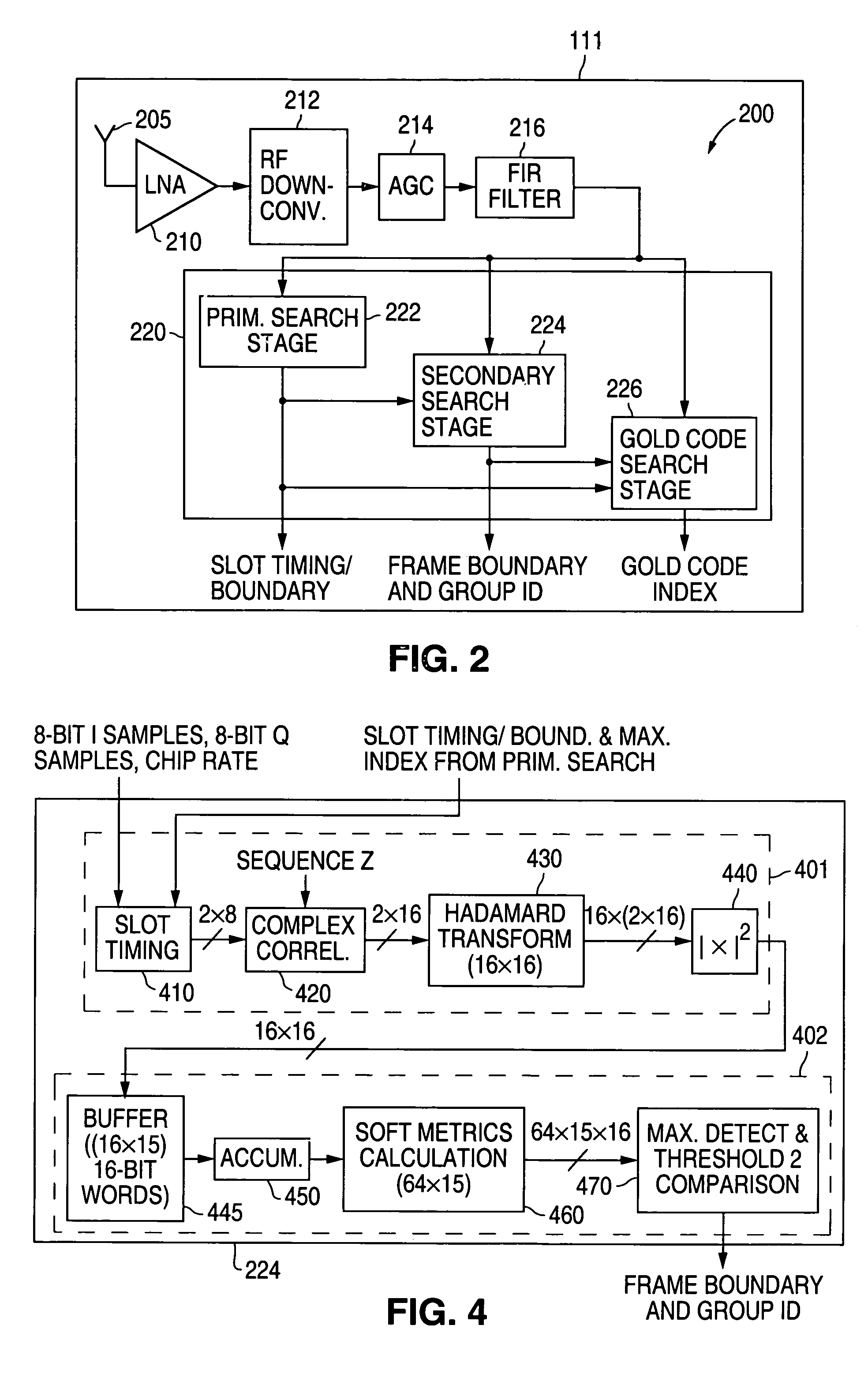
A pipelined cell search apparatus comprises a secondary search stage that receives a secondary synchronization channel (S-SCH) signal. The secondary search stage comprises: 1) a correlation block for i) correlating the S-SCH signal with a 256-bit sequence z to produce a first correlated output sequence and ii) correlating the first correlated output sequence with sixteen Hadamard sequences to produce a vector output sequence, each vector comprising sixteen Hadamard-correlated values, one for each of the sixteen Hadamard sequences; 2) a maximum detection block for detecting a maximum Hadamard-correlated value in the each vector and generating an index sequence, each index identifying a vector position of the maximum Hadamard-correlated value; 3) a Reed-Solomon (R-S) decoding correction block for decoding and correcting 15 consecutive indexes in the index sequence and determining therefrom a codeword of length 3; and 4) a frame-time detector for determining from the codeword of length 3 a frame boundary of the S-SCH signal based on syndrome properties of an R-S code associated with the S-SCH code.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Block based channel tracking using weighted recursive least squares
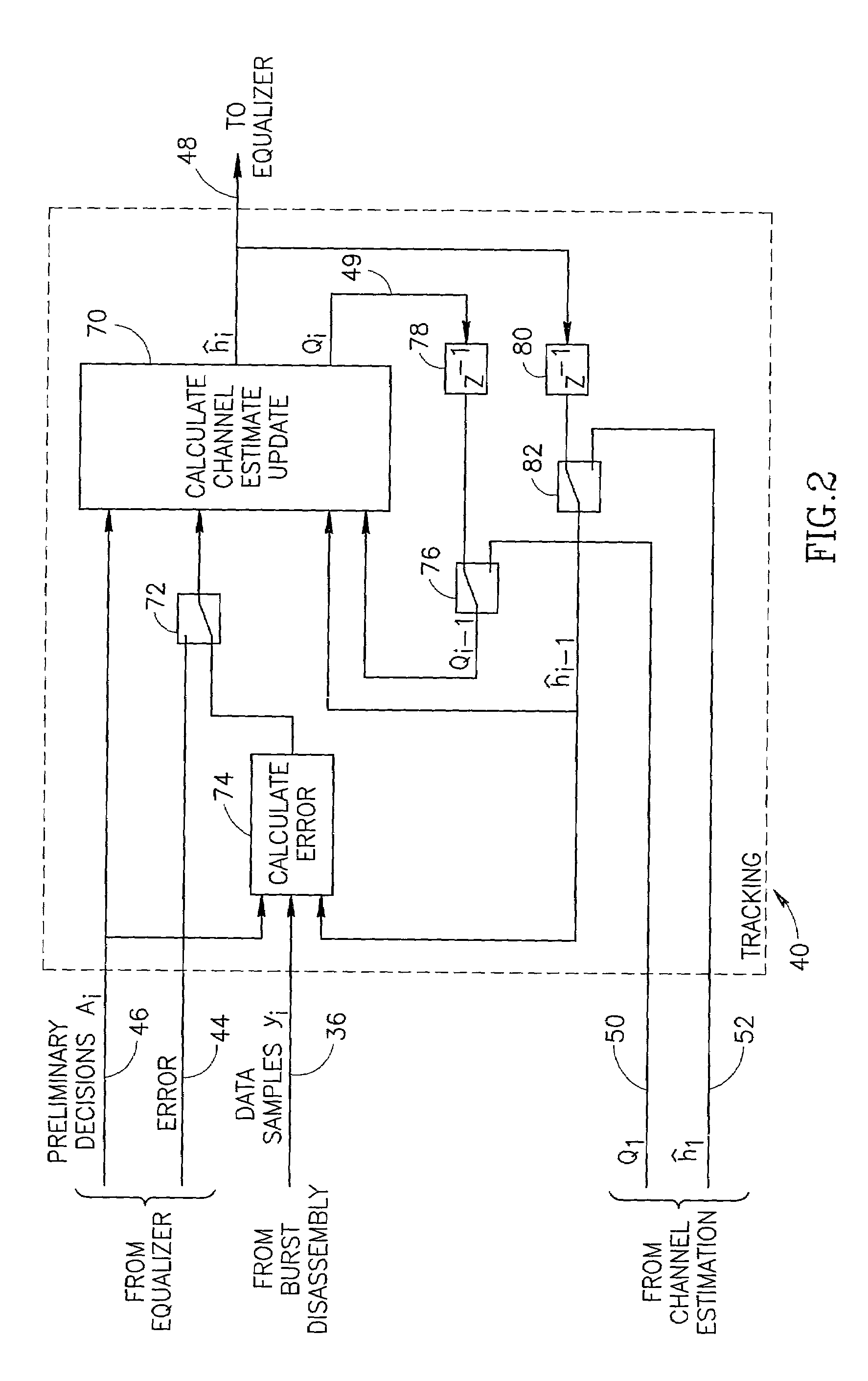
InactiveUS7050513B1Improve performanceOvercome disadvantagesMultiple-port networksModulation transferenceModel parametersDecision taking
A novel and useful channel tracking mechanism operative to generate channel estimate updates on blocks of samples during reception of a message. The tracking mechanism is based on the weighted recursive least squares algorithm and implements the estimation process by recursively updating channel model parameters upon the arrival of new sample data. The mechanism is operative to update channel estimate information once per sample block. An interblock exponential weighting factor is also applied. The block length is chosen short enough to enable good tracking performance while being sufficiently long enough to minimize the overhead of generating preliminary decisions and of updating precalculated tables in the equalizer. The method of the invention can be performed in either hardware or software. A computer comprising a processor, memory, etc. is operative to execute software adapted to perform the channel tracking method of the present invention.
Owner:COMSYS COMM & SIGNAL PROC
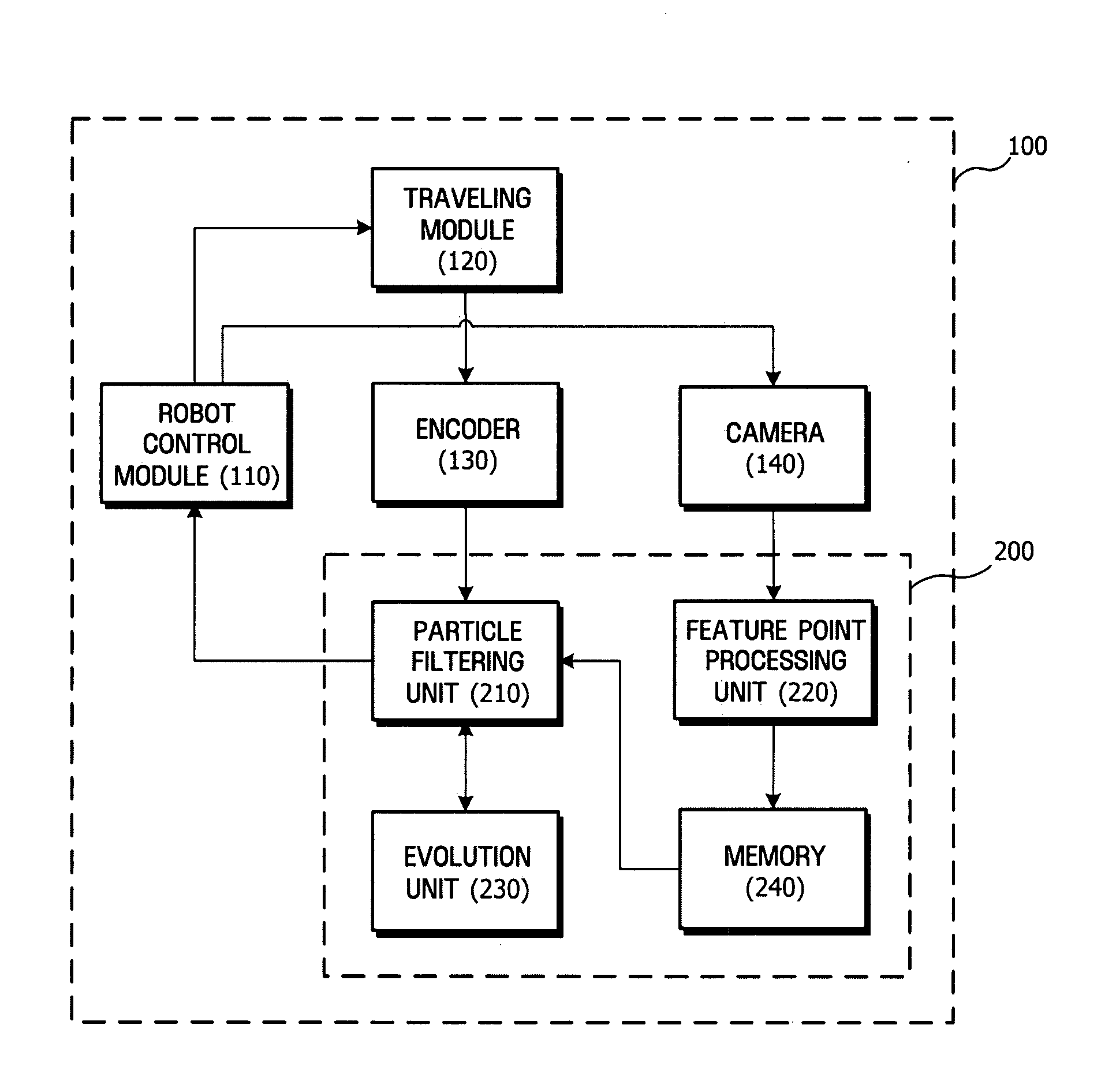
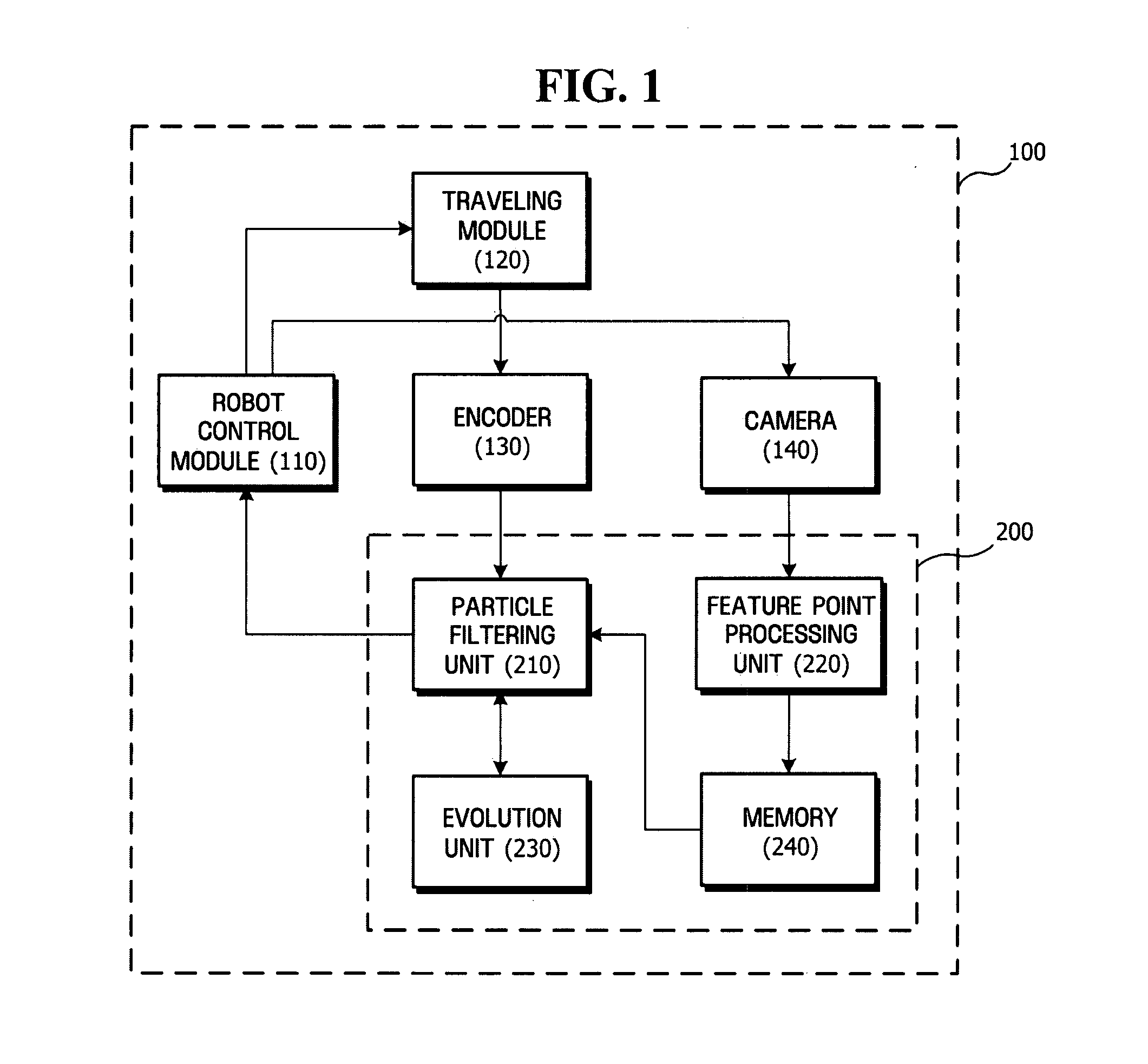
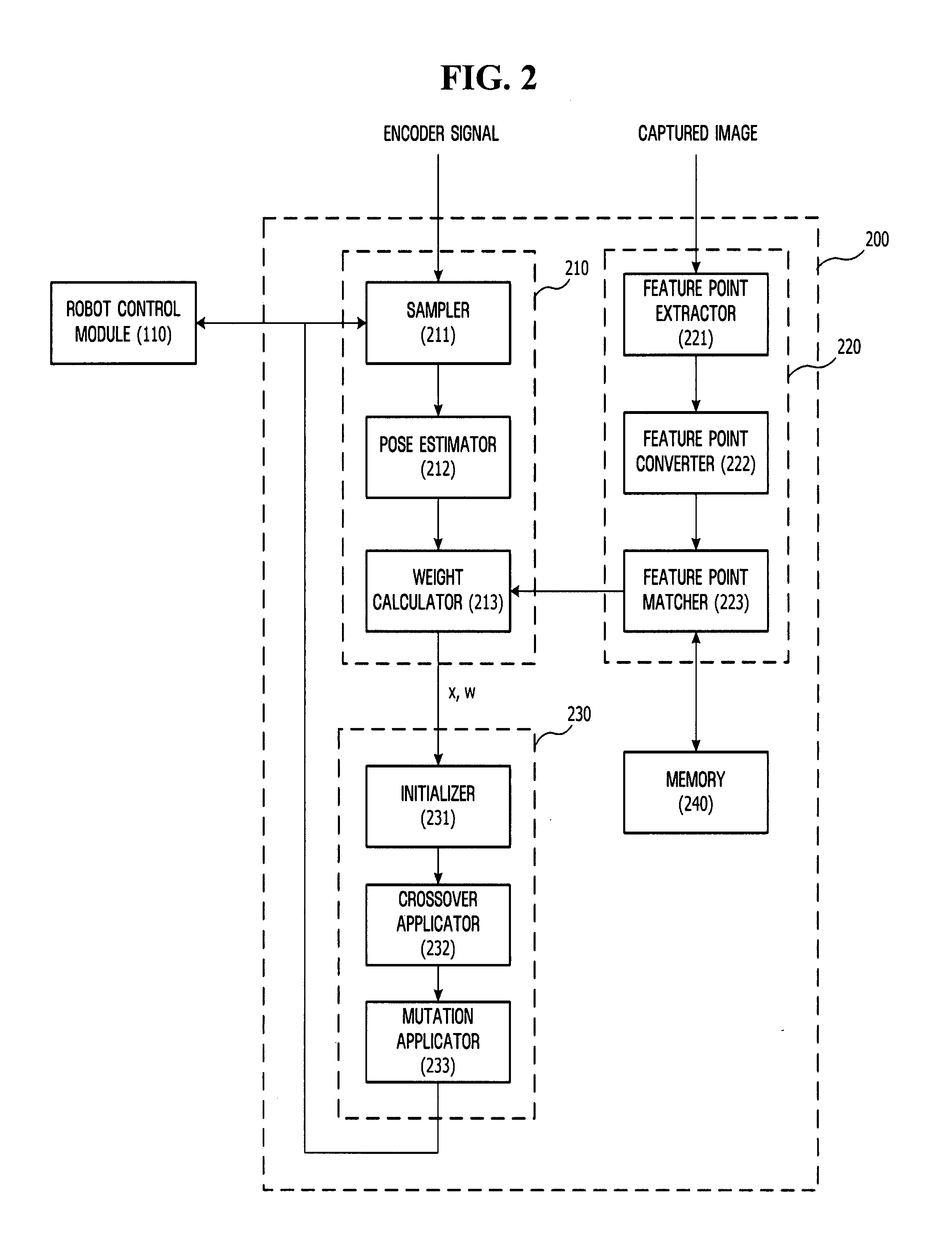
Method, medium, and system estimating pose of mobile robots
ActiveUS20080065267A1Reduce computational complexityComputational complexity is reducedProgramme-controlled manipulatorClosed circuit television systemsComputation complexitySimultaneous localisation and mapping
A method, medium, and system reducing the computational complexity of a Simultaneous Localization And Mapping (SLAM) algorithm that can be applied to mobile robots. A system estimating the pose of a mobile robot with the aid of a particle filter using a plurality of particles includes a sensor which detects a variation in the pose of a mobile robot, a particle filter unit which determines the poses and weights of current particles by applying the detected pose variation to previous particles, and an evolution unit which updates the poses and weights of the current particles by applying an evolution algorithm to the poses and weights of the current particles.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH +1
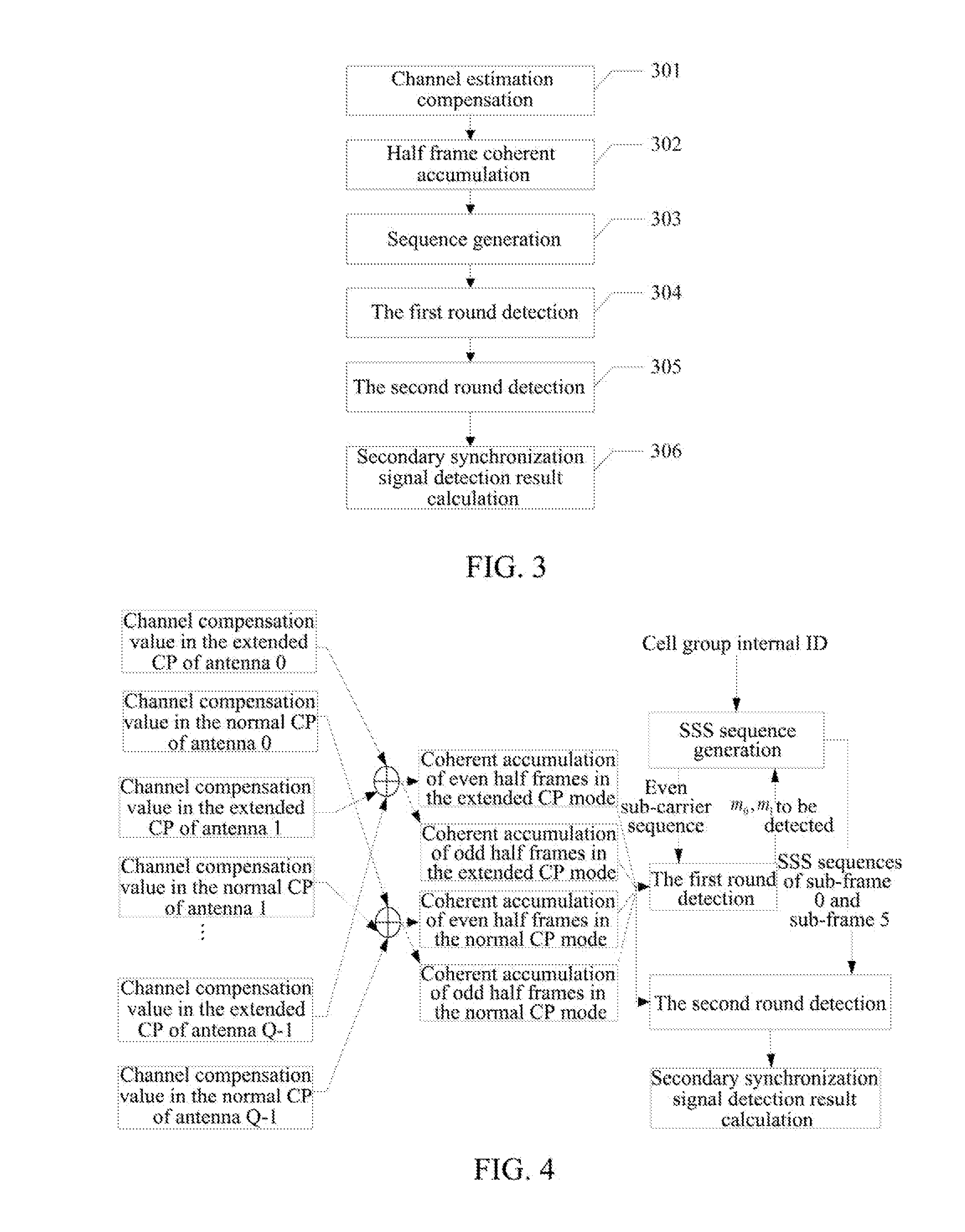
Method and Apparatus for Detecting Secondary Synchronization Signal
ActiveUS20130176991A1Reduce the amount of calculationIncrease resource consumptionSynchronisation arrangementModulated-carrier systemsTelecommunicationsCell ID
a method and apparatus for detecting a secondary synchronization signal, the method including: calculating a channel estimation compensation value of each sub-carrier of a Secondary Synchronization Signal (SSS) symbol in different Cyclic Prefix (CP) modes; obtaining coherent accumulative results of even half frames and odd half frames of each sub-carrier according to the channel estimation compensation value of each sub-carrier of said SSS symbol; generating a SSS sequence; obtaining an index of the SSS sequence corresponding to an over-threshold value of a first round detection, determining indexes composed of the SSS sequence used in a second round detection according to said index, using coherent accumulative results of all the sub-carriers in the even and odd half frames and SSS sequences of all the sub-carriers to obtain an over-threshold value of the second round detection; and obtaining a CP mode, and calculating a cell ID and a radio frame boundary.
Owner:SANECHIPS TECH CO LTD
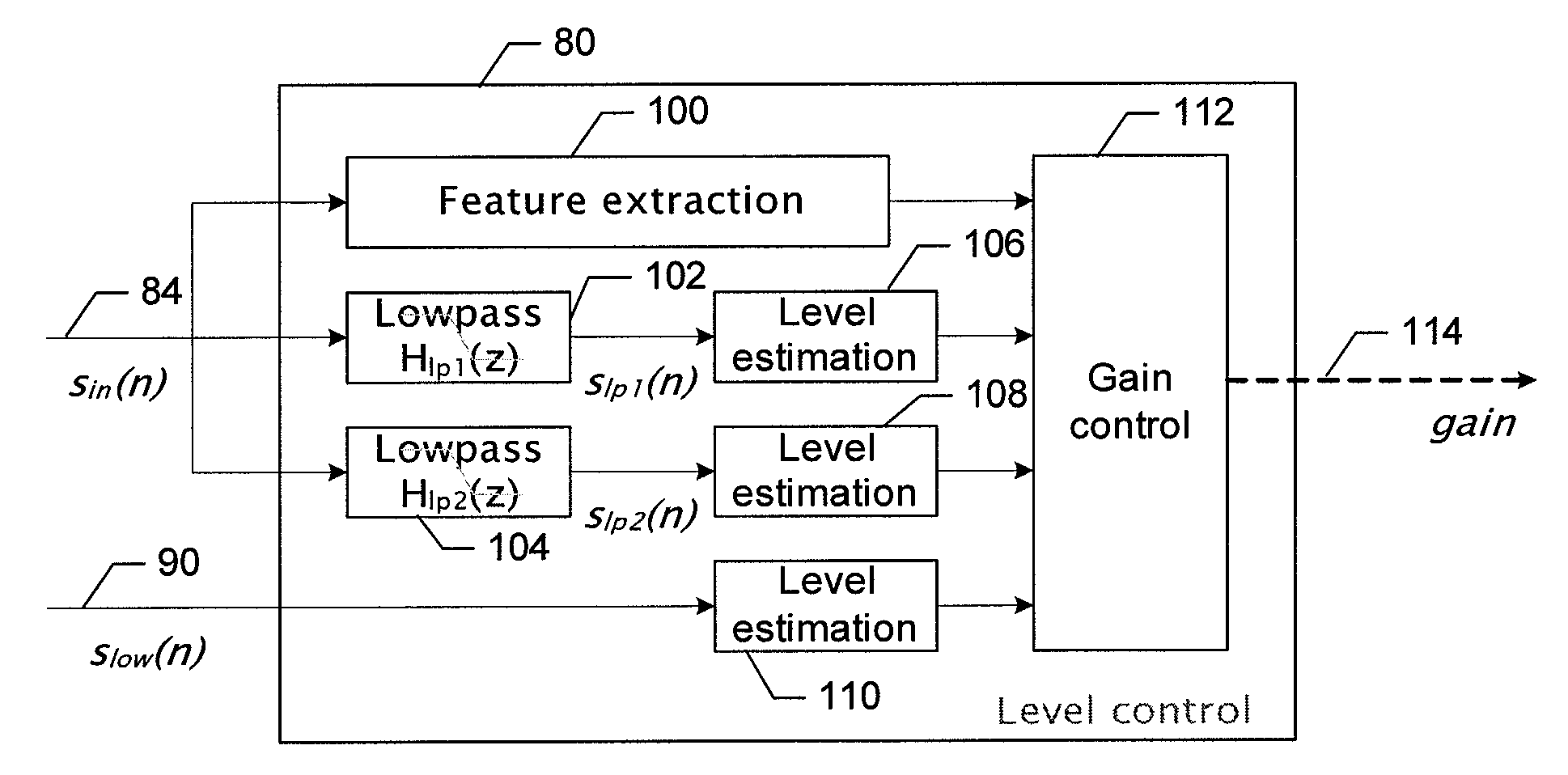
Method, Apparatus and Computer Program Product for Providing Low Frequency Expansion of Speech
InactiveUS20070299655A1Quality improvementComputational complexity is reducedSpeech analysisFeature vectorHarmonic
An apparatus for providing low frequency expansion of speech includes a nonlinear function element, a band-pass filter element and a level control element. The non-linear function element is configured to receive a signal including at least two harmonic components and to produce a signal including at least one lower frequency harmonic component having a lower frequency than a highest frequency component of the at least two harmonic components responsive to the signal including at least two harmonic components. The band-pass filter element is in communication with the non-linear function element and configured to filter the signal including the at least one lower frequency harmonic component. The level control element is configured to apply a level control to alter the filtered signal based on a feature vector associated with an input speech signal.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
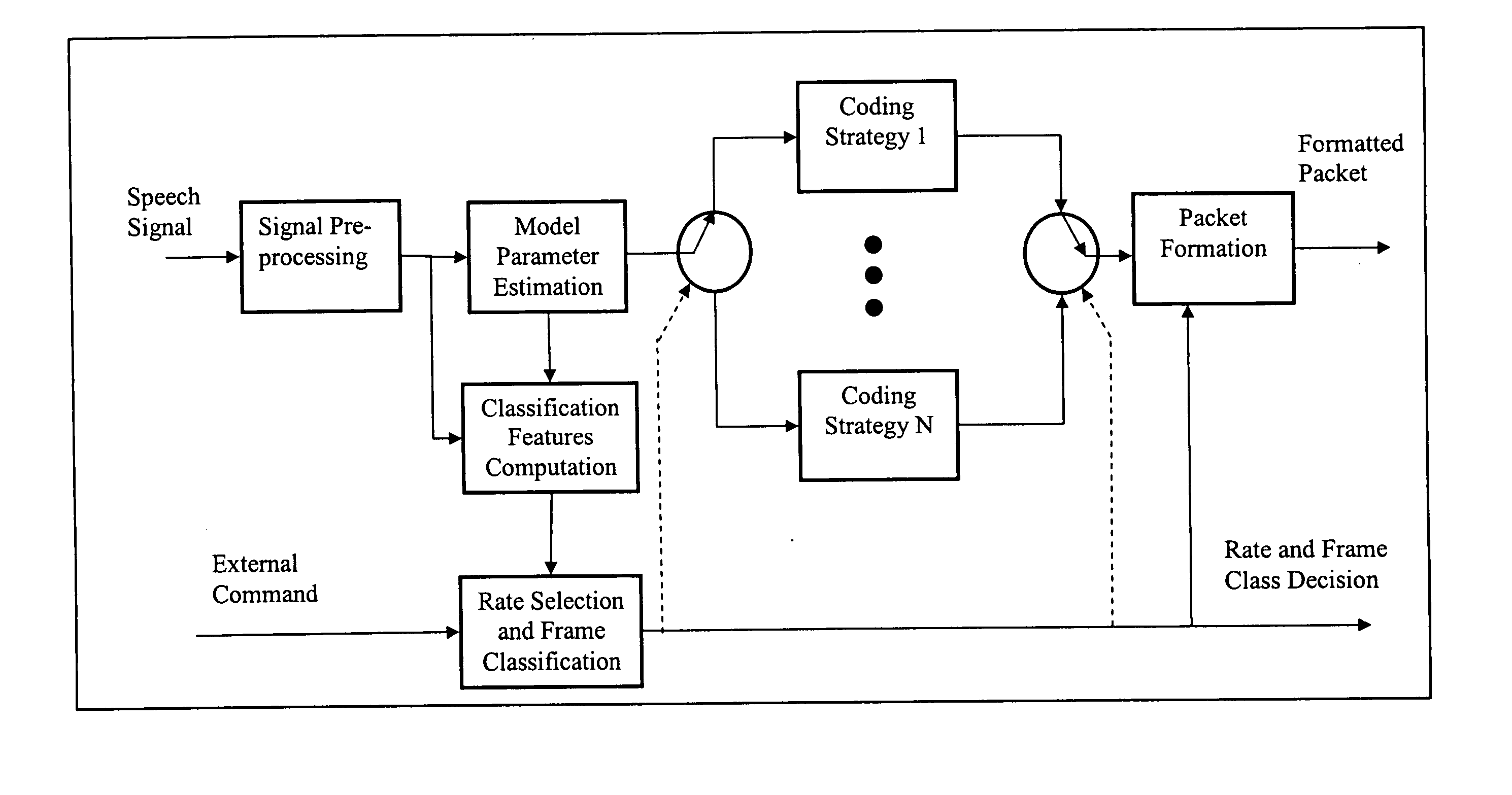
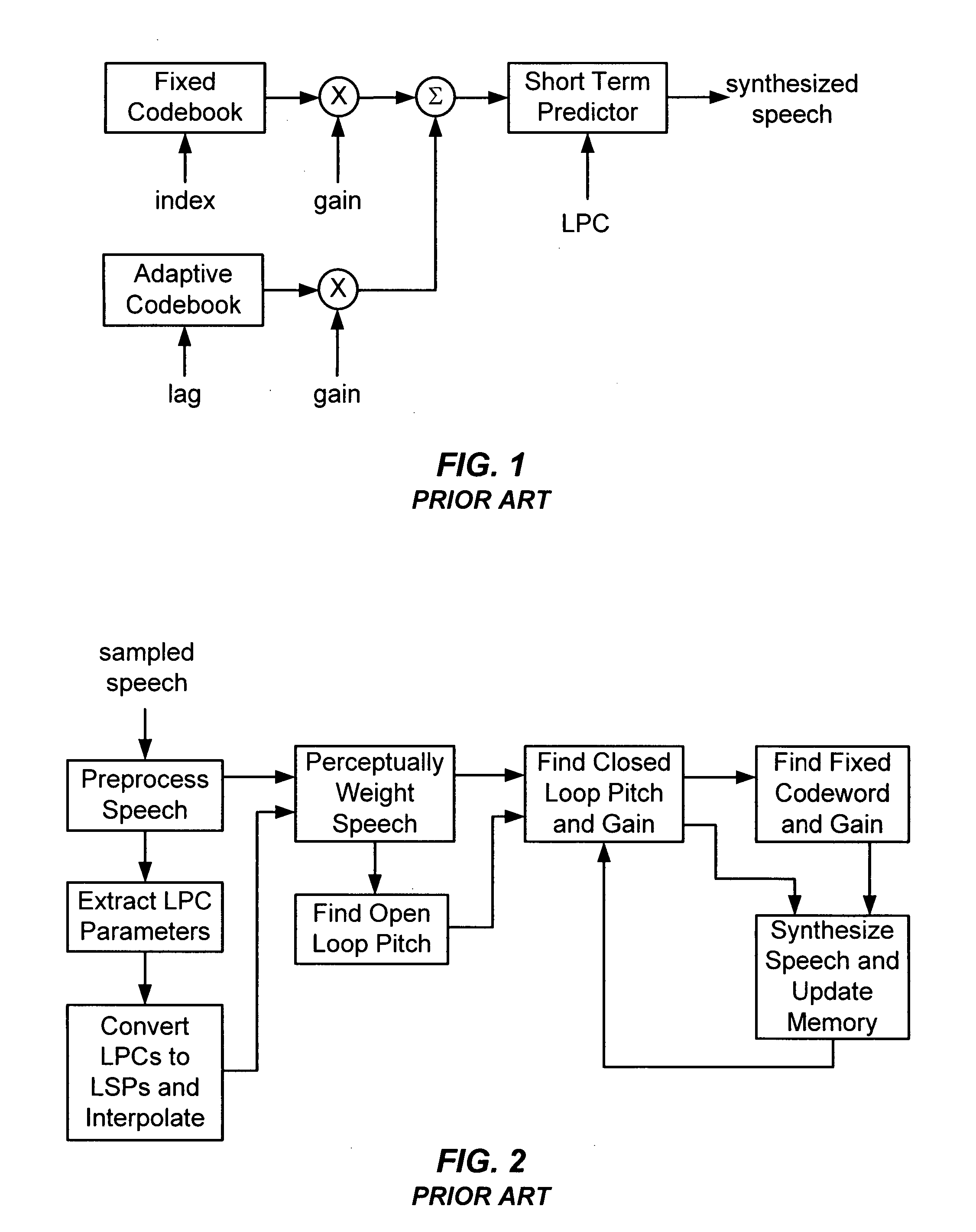
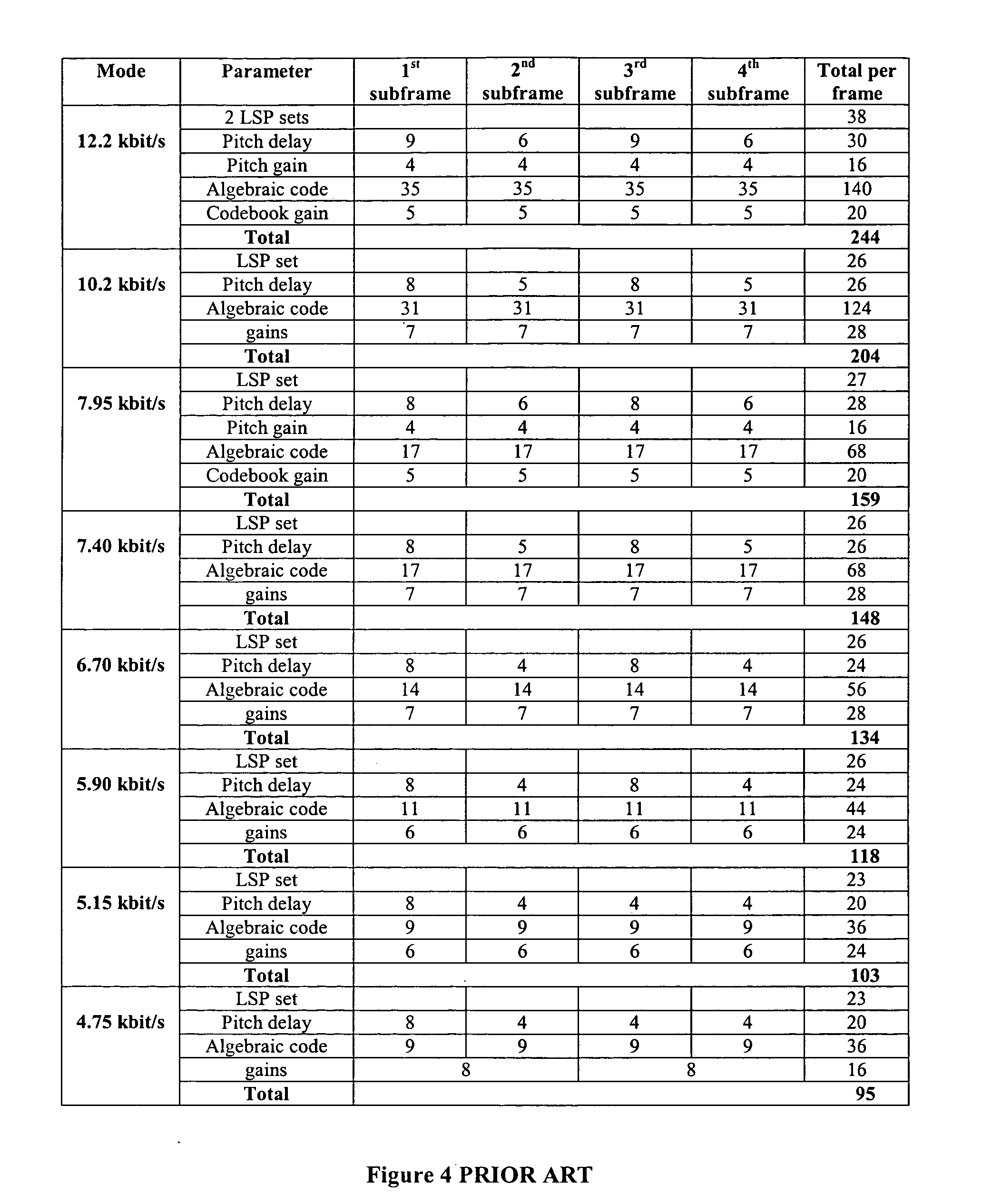
Method and apparatus for frame classification and rate determination in voice transcoders for telecommunications
InactiveUS20050049855A1Reduce computational complexityComputational complexity is reducedSpeech analysisTime-division multiplexLagFeature parameter
A method and apparatus for frame classification and rate determination in voice transcoders. The apparatus includes a classifier input parameter preparation module that unpacks the bitstream from the source codec and selects the codec parameters to be used for classification, parameter buffers that store previous input and output parameters of previous frames, and a frame classification and rate decision module that uses the source codec parameters from the current frame and zero or more frames to determine the frame class, rate, and classification feature parameters for the destination codec. The classifier input parameter preparation module separates the bitstream code and unquantizes the sub-codes into the codec parameters. These codec parameters may include line spectral frequencies, pitch lag, pitch gains, fixed codebook gains, fixed codebook vectors, rate and frame energy. The frame classification and rate decision module comprises M sub-classifiers and a final decision module. The characteristics of the sub-classifiers are obtained by a classifier construction module, which comprises a training set generation module, a learning module and an evaluation module. The method includes preparing the classifier input parameters, constructing the frame and rate classifier and determining the frame class, rate decision and classification feature parameters for the destination codec using the intermediate parameters and bit rate of the source codec. Constructing the frame and rate classifier includes generating the training and test data and training and / or building the classifier.
Owner:ONMOBILE GLOBAL LTD
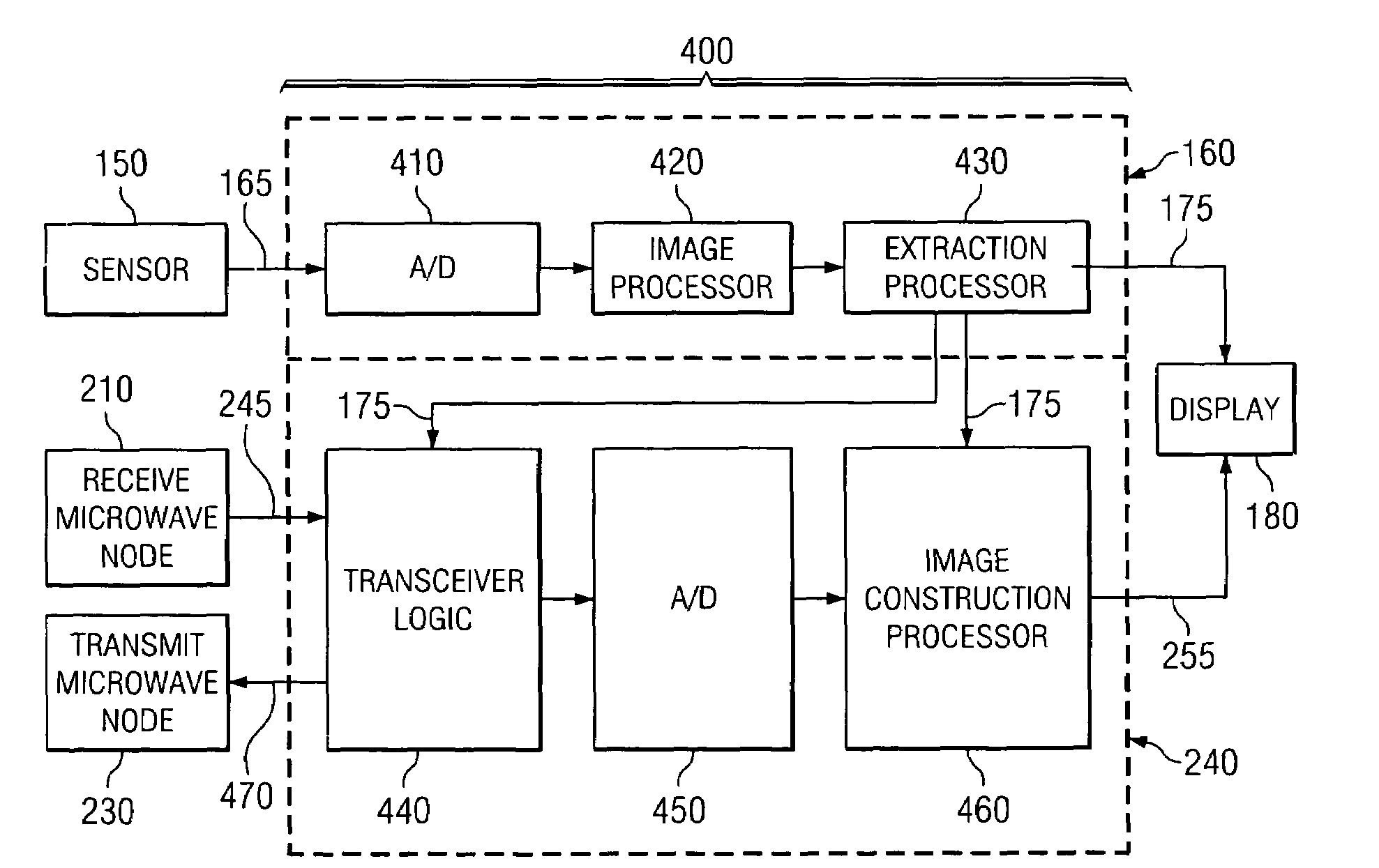
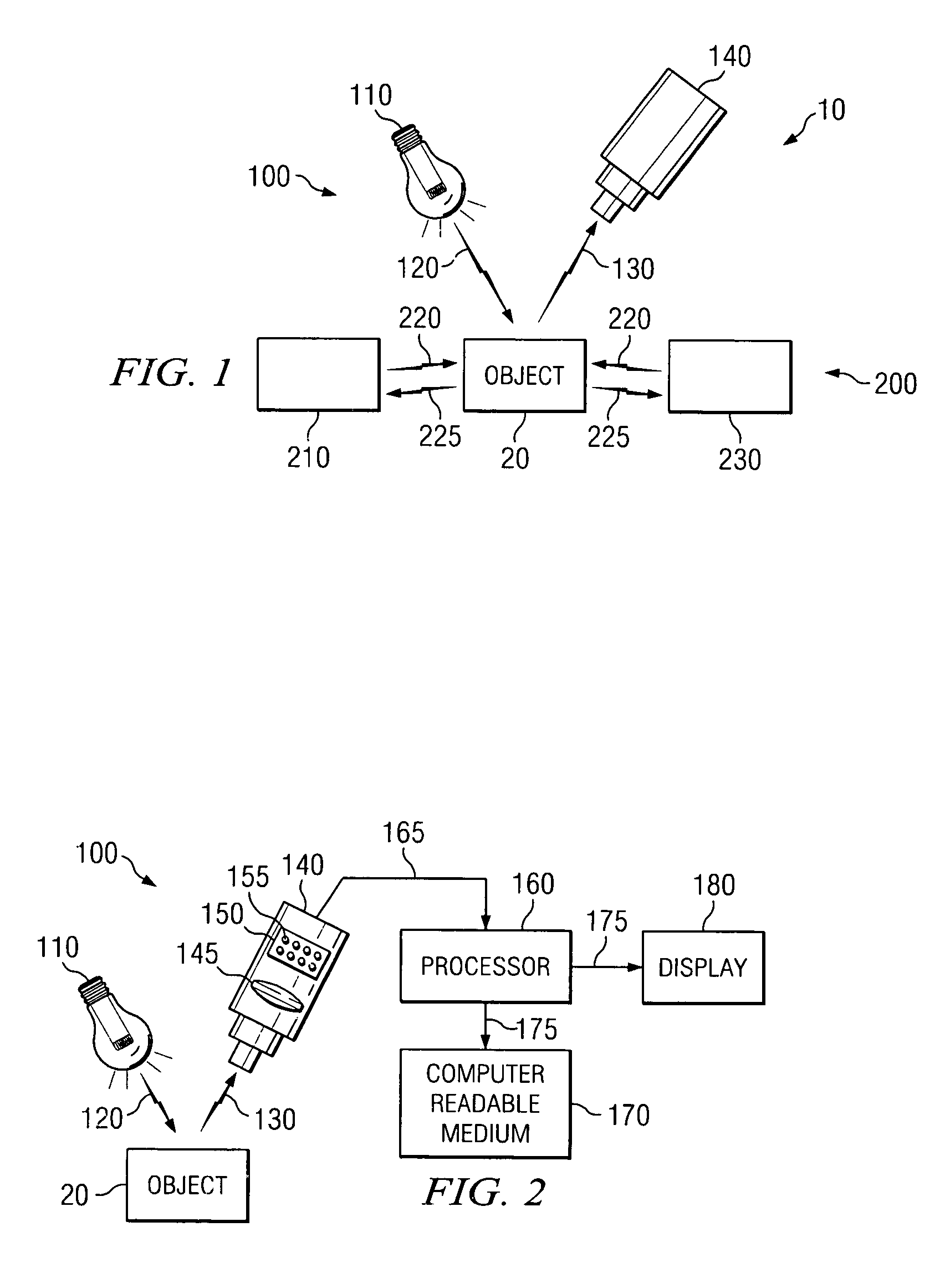
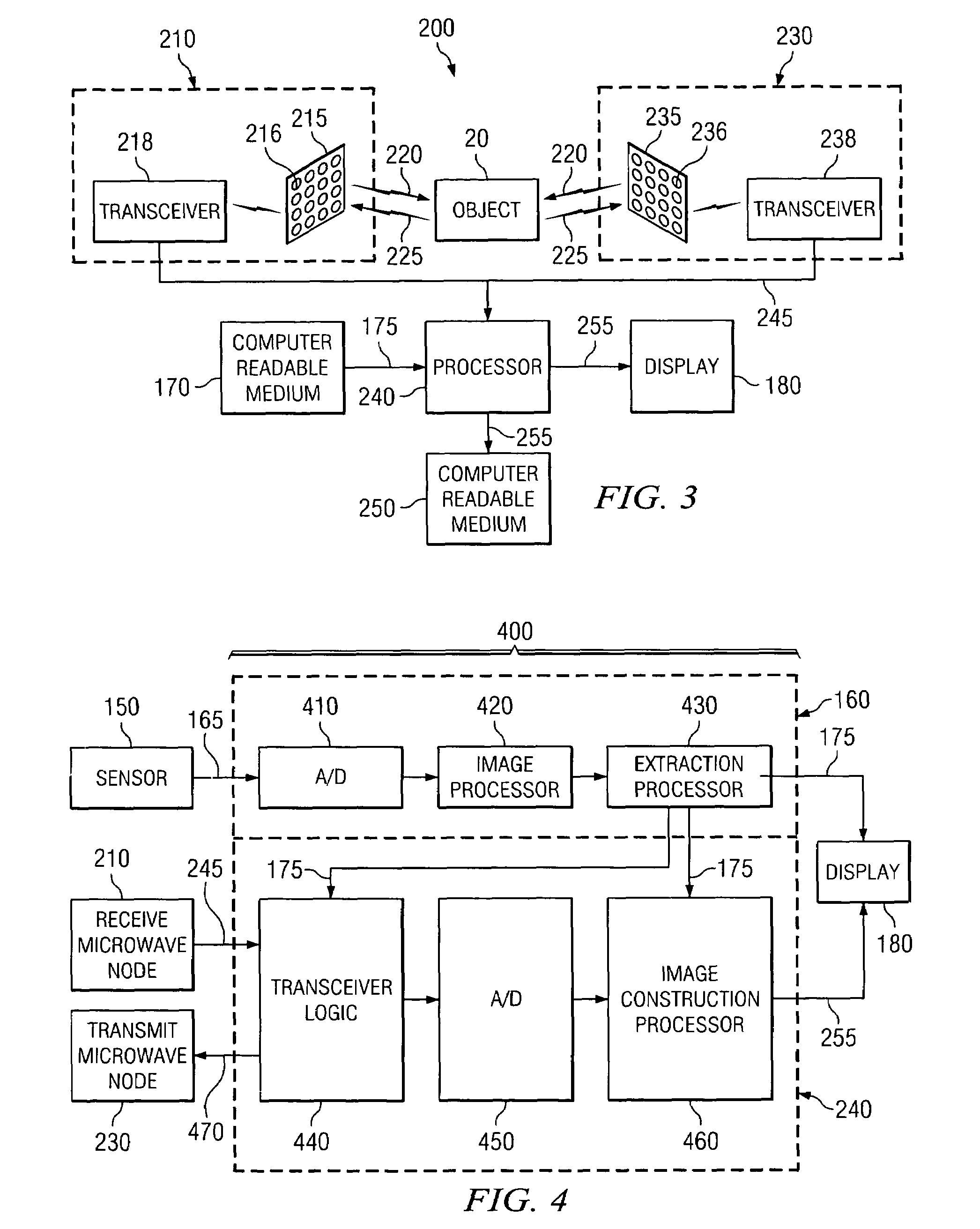
Optically-augmented microwave imaging system and method
ActiveUS6972714B1Fast and simple algorithmReduce computational complexityMaterial analysis using microwave meansElectromagnetic wave reradiationComputer scienceMicrowave imaging
An imaging system includes an optical (visible-light or near IR) imaging system and a microwave imaging system. The optical imaging system captures an optical image of the object, produces optical image data representing the optical image and extracts optical image information from the optical image data. The microwave imaging system produces microwave image data representing a microwave image of the object in response to the optical image information.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
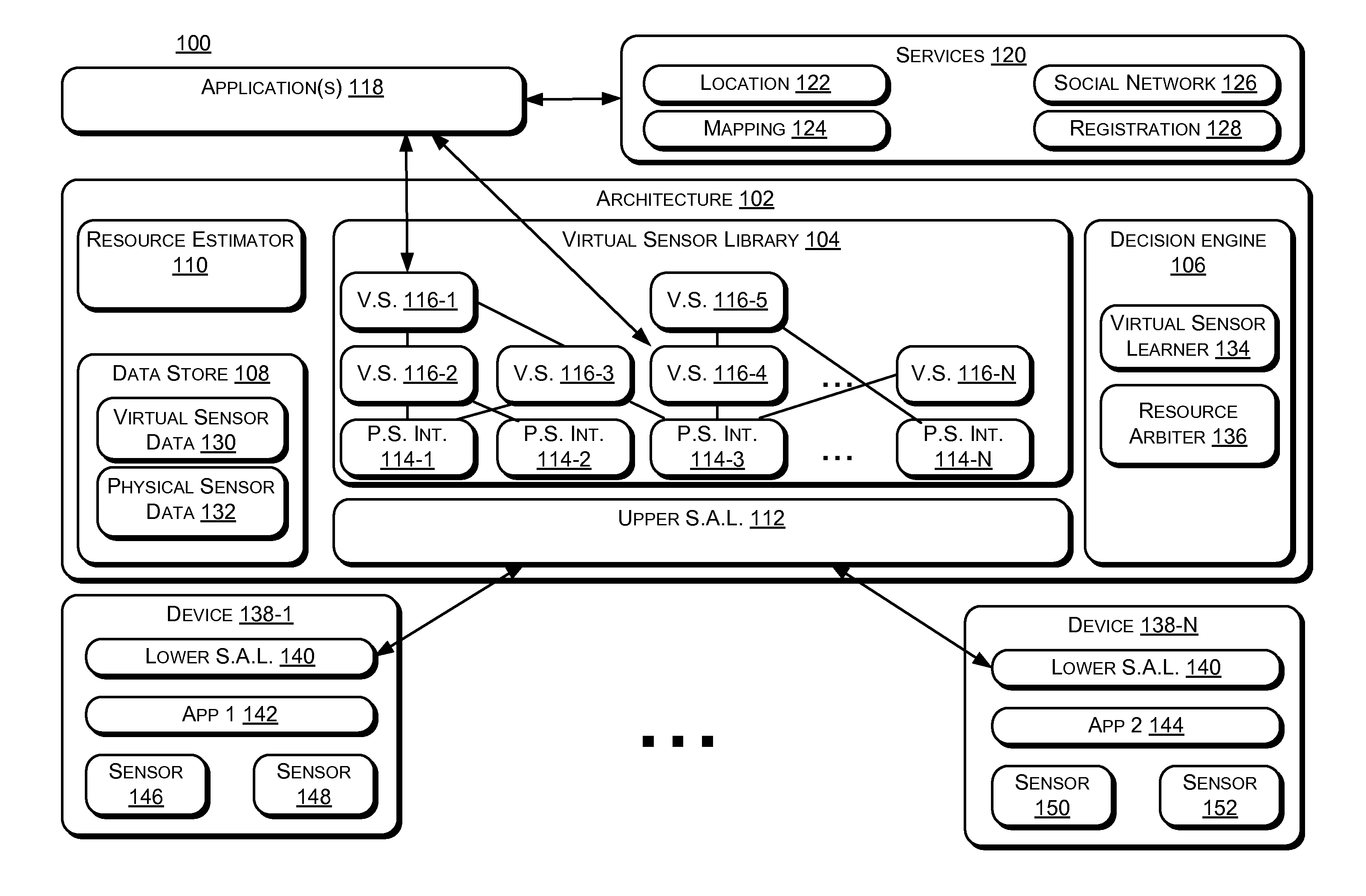
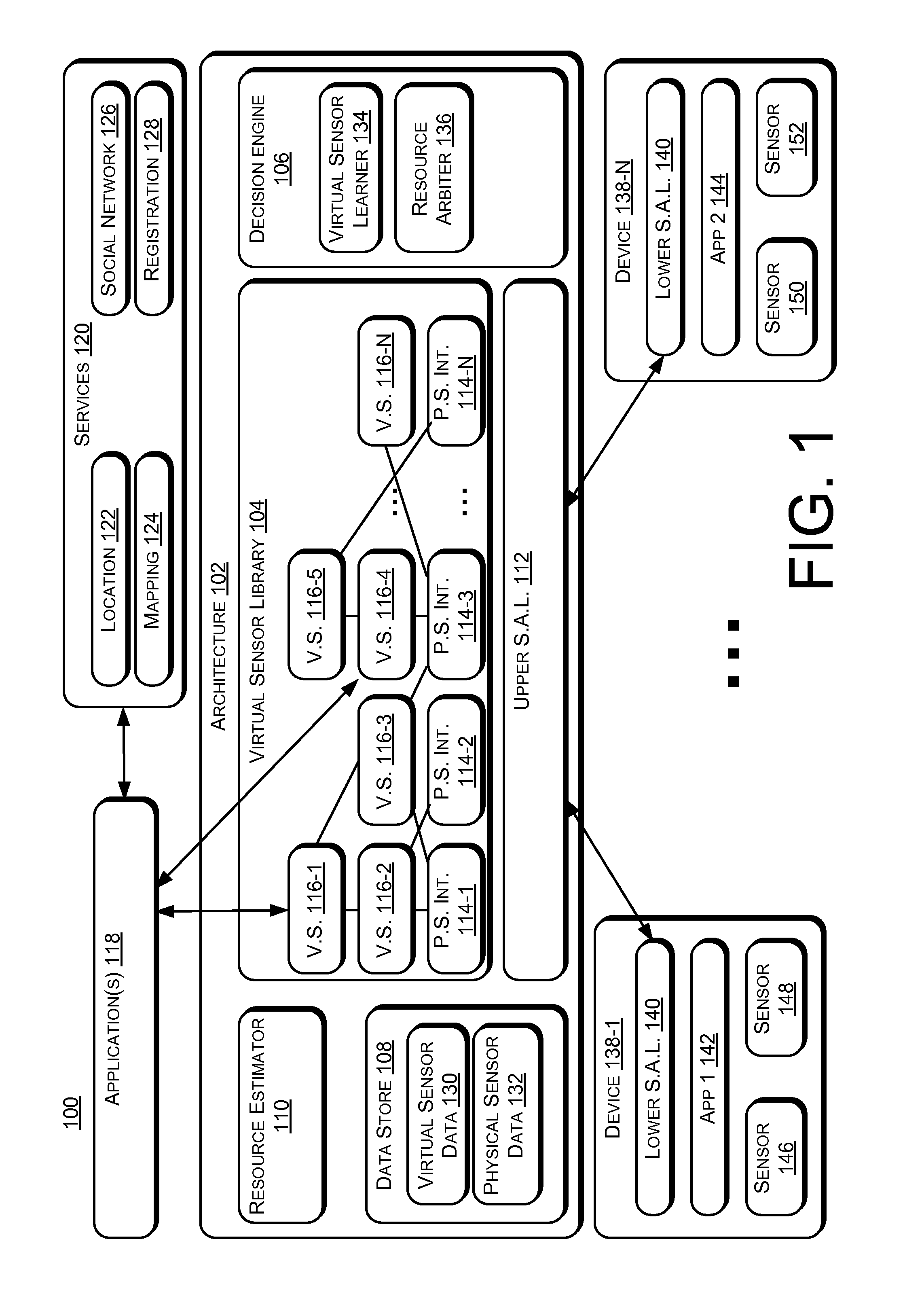
Virtual Sensor Development
ActiveUS20130159223A1More energyMore resource efficientDigital computer detailsMeasurement arrangements for variableVirtual sensorsMobile device
Embodiments include processes, systems, and devices for developing a virtual sensor. The virtual sensor includes one or more inference models. A decision engine utilizes an inference model associated with a mobile device to determine another inference model that is configured to accept physical sensor data from another mobile device. In this way, the virtual sensor can be developed for use with many mobile devices using initial inference models developed for a small number of mobile devices or a single mobile device. Embodiments also include methods to select mobile devices from which to request physical sensor data for virtual sensor input. Embodiments also include architectures that provide a library of virtual sensors.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and system for approximating deep neural networks for anatomical object detection
ActiveUS9633306B2Reduce complexityComputationally efficientImage enhancementImage analysisComputation complexityMachine learning
A method and system for approximating a deep neural network for anatomical object detection is discloses. A deep neural network is trained to detect an anatomical object in medical images. An approximation of the trained deep neural network is calculated that reduces the computational complexity of the trained deep neural network. The anatomical object is detected in an input medical image of a patient using the approximation of the trained deep neural network.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
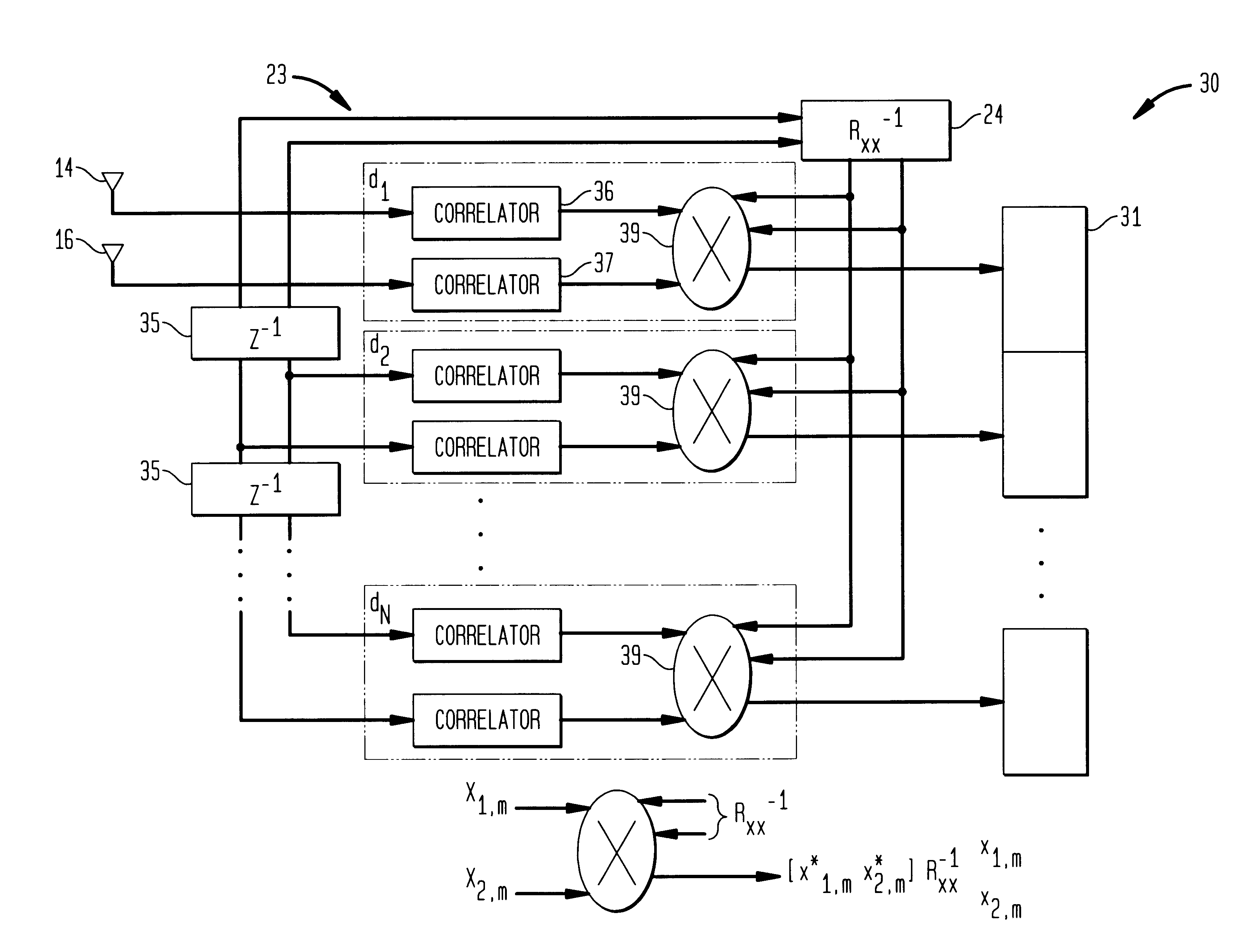
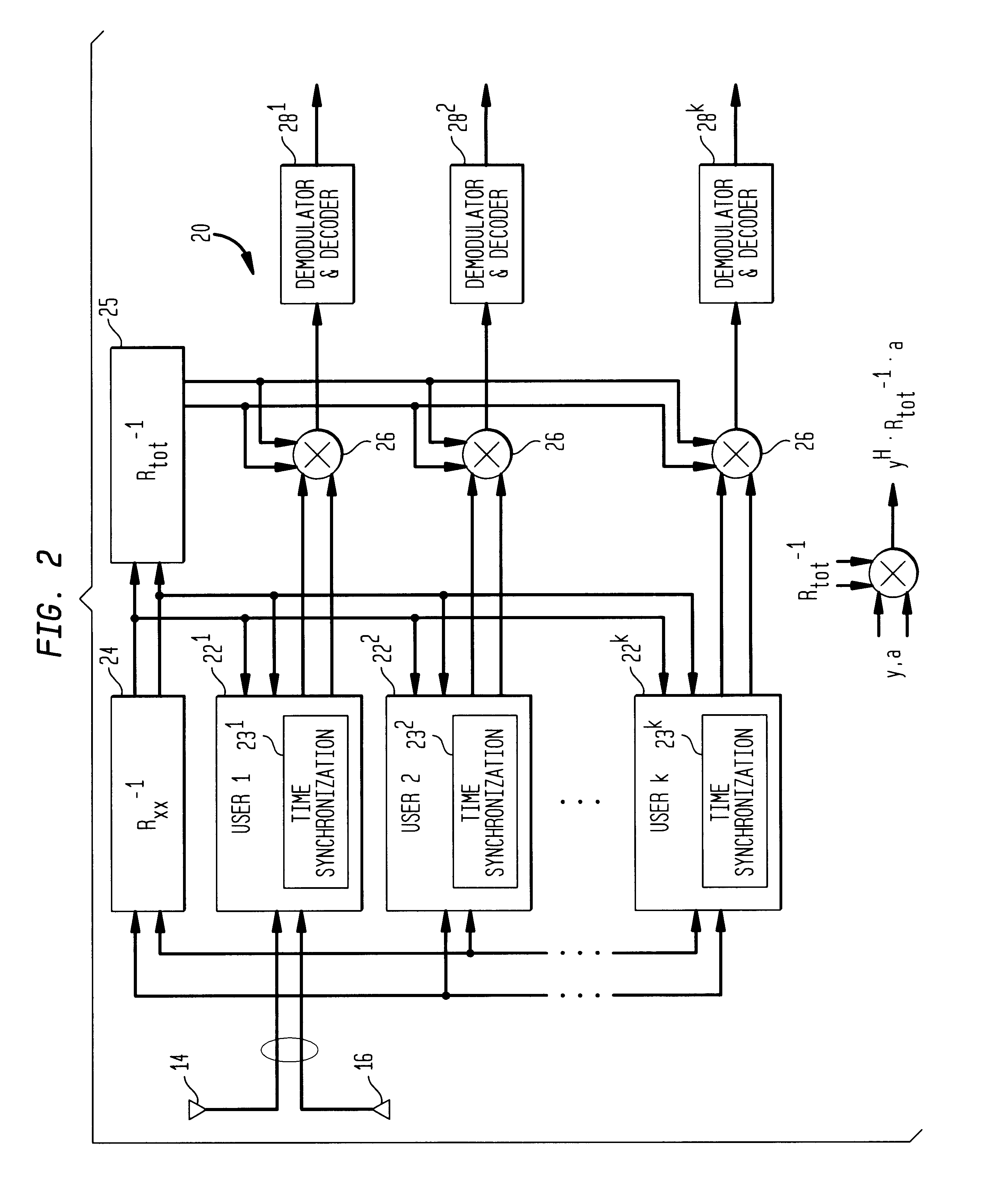
Code division multiple access system and method of operation with improved signal acquisition and processing
InactiveUS6549565B1Computational complexity is reducedGood synchronizationSpatial transmit diversityCode division multiplexSignal qualitySignal processing circuits
A Code Division Multiple Access system and method of operation provides reduced interference for received signals and improved signal acquisition and processing with reduced computational complexity. The system includes a base station coupled to an antenna array of at least two or more antennas and serving a plurality of users. A receiver in the base station includes a universal inverse cross-correlation matrix coupled to the antenna array, a signal acquisition and a signal processing circuit serving each user. Each signal acquisition circuit comprises a series of delay stages in which the incoming antenna signals in each stage are correlated with a spreading code and combined in a multiplier coupled to the universal inverse cross-correlation matrix which facilitates improved time delay estimation for signal acquisition. Each multiplier combines the correlated signals of the stage with the output of the universal inverse cross-correlation matrix to provide a signal amplitude representative of the signal energy in an antenna path for a given time period, with individual delays separated by a half of chip period. The amplitudes for each of the delay stages are captured in buffers which contain threshold information for selection of the strongest received signal. The signal processing circuit combines the strongest received signal with a channel estimate and the universal inverse matrix output in a multiplier to provide an output signal for demodulation and decoding with improved signal quality due to (a) reduced interference, (b) improved synchronization for signal acquisition and processing, and (c) the universal inverse cross-correlation matrix reducing computational complexity in signal acquisition and signal processing.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
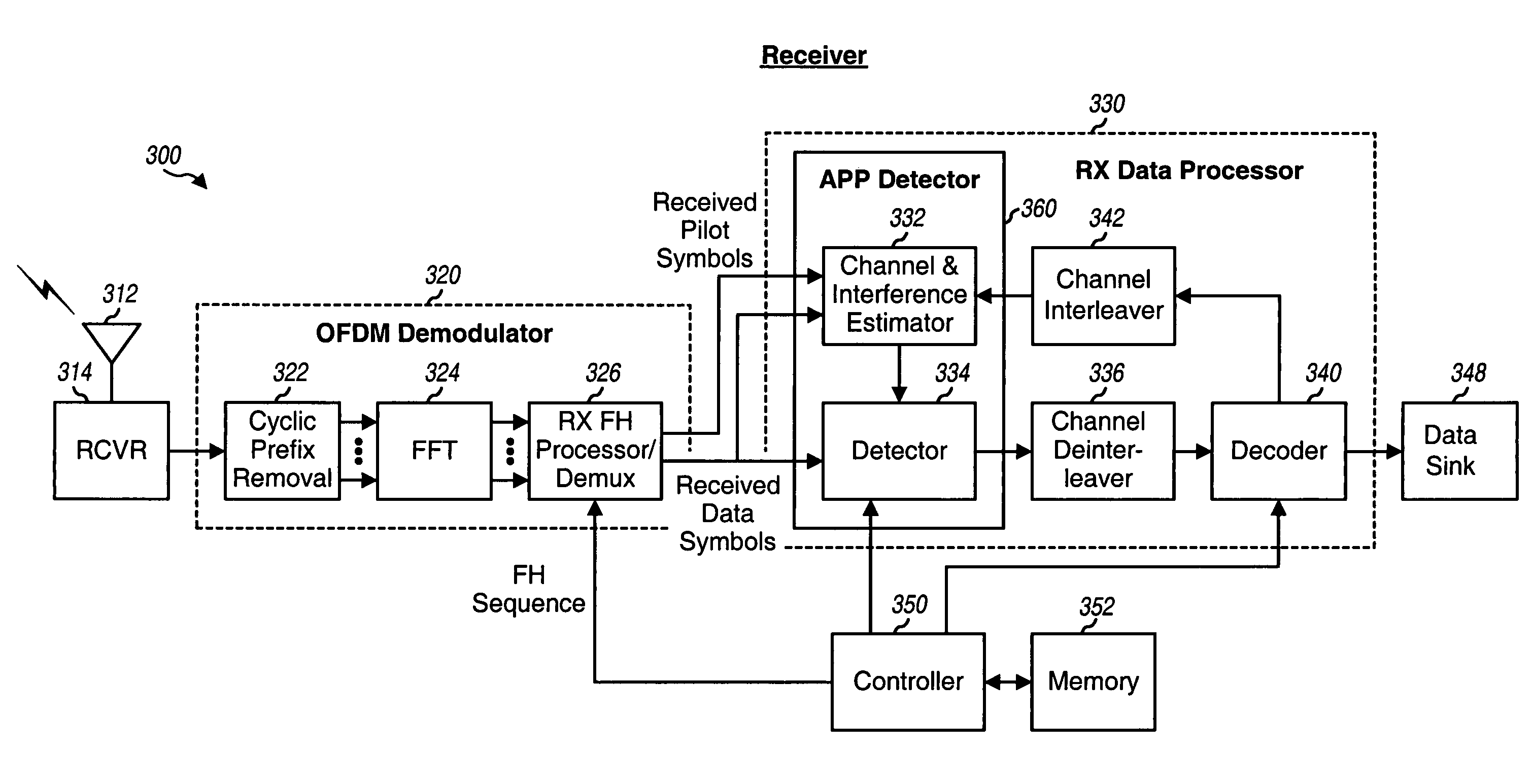
Iterative channel and interference estimation and decoding
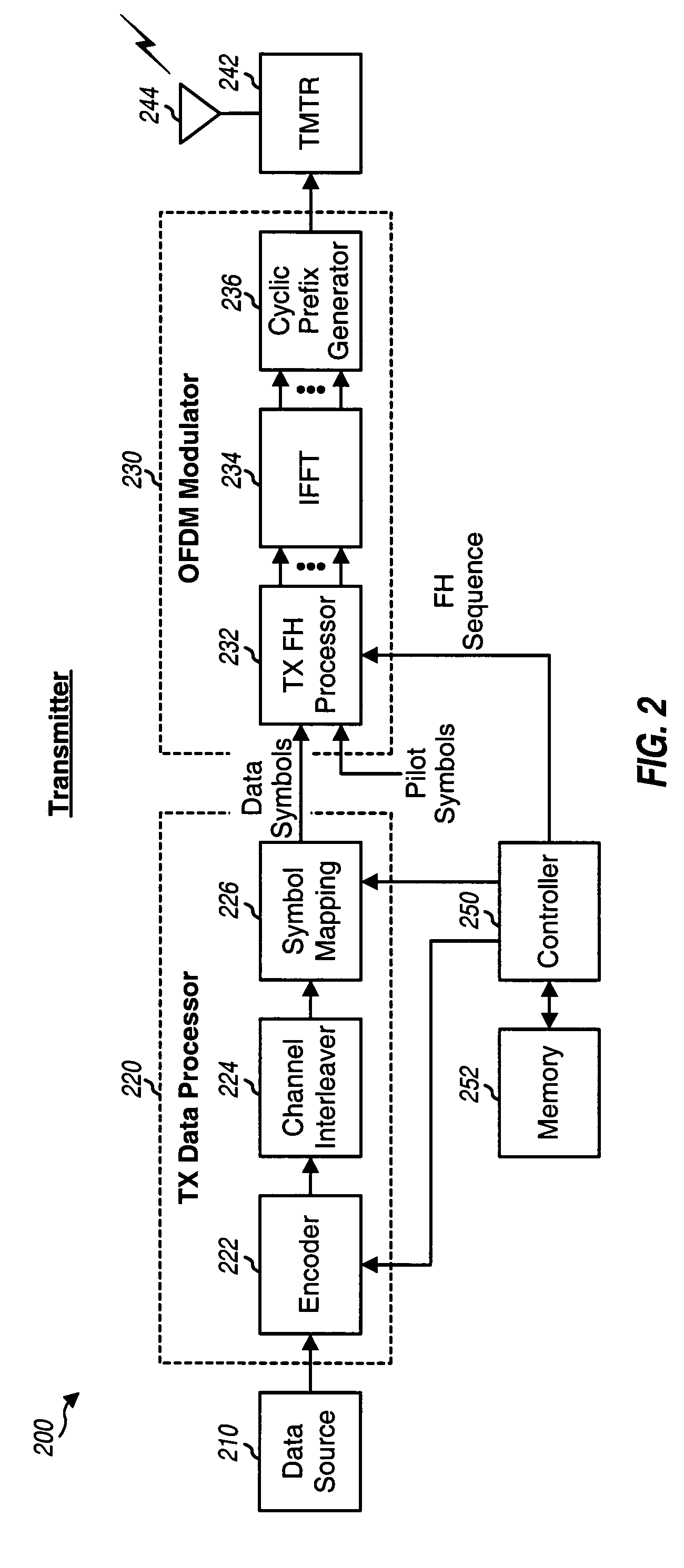
ActiveUS7421041B2Improve performanceComputational complexity is reducedError prevention/detection by using return channelAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsPrior informationLog likelihood
For an iterative channel and interference estimation and decoding scheme, prior information for channel gain and interference is initially obtained based on received pilot symbols. Forward information for code bits corresponding to received data symbols is derived based on the received data symbols and the prior information and then decoded to obtain feedback information for the code bits corresponding to the received data symbols. A posteriori information for channel gain and interference for each received data symbol is derived based on the feedback information for that received data symbol. The a posteriori information for the received data symbols and the prior information are combined to obtain updated information for channel gain and interference for each received data symbol. The process can be repeated for any number of iterations. The prior, a posteriori, and updated information may be represented by joint probability distributions on channel gain and interference. The forward and feedback information may be represented by log-likelihood ratios.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
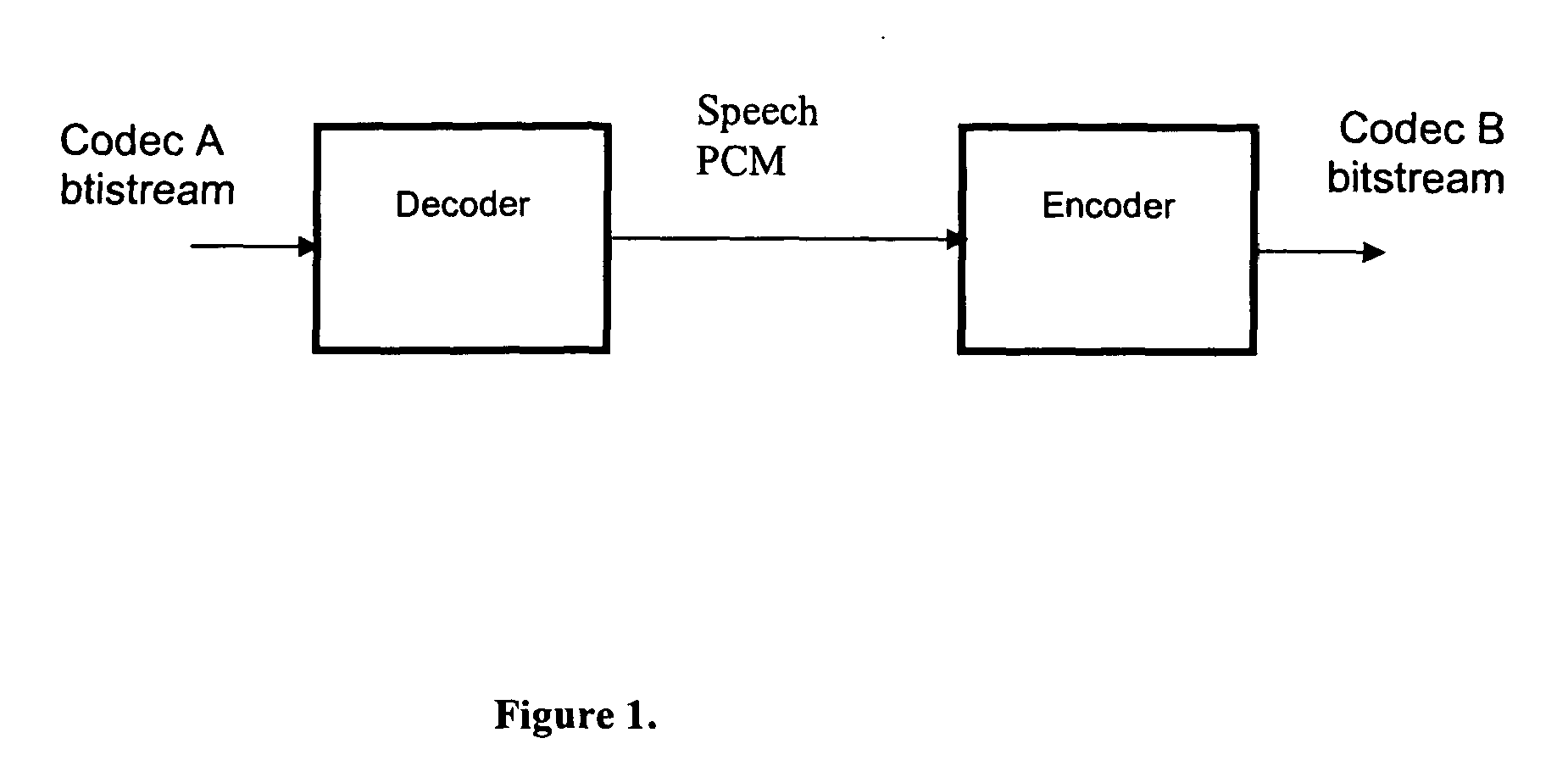
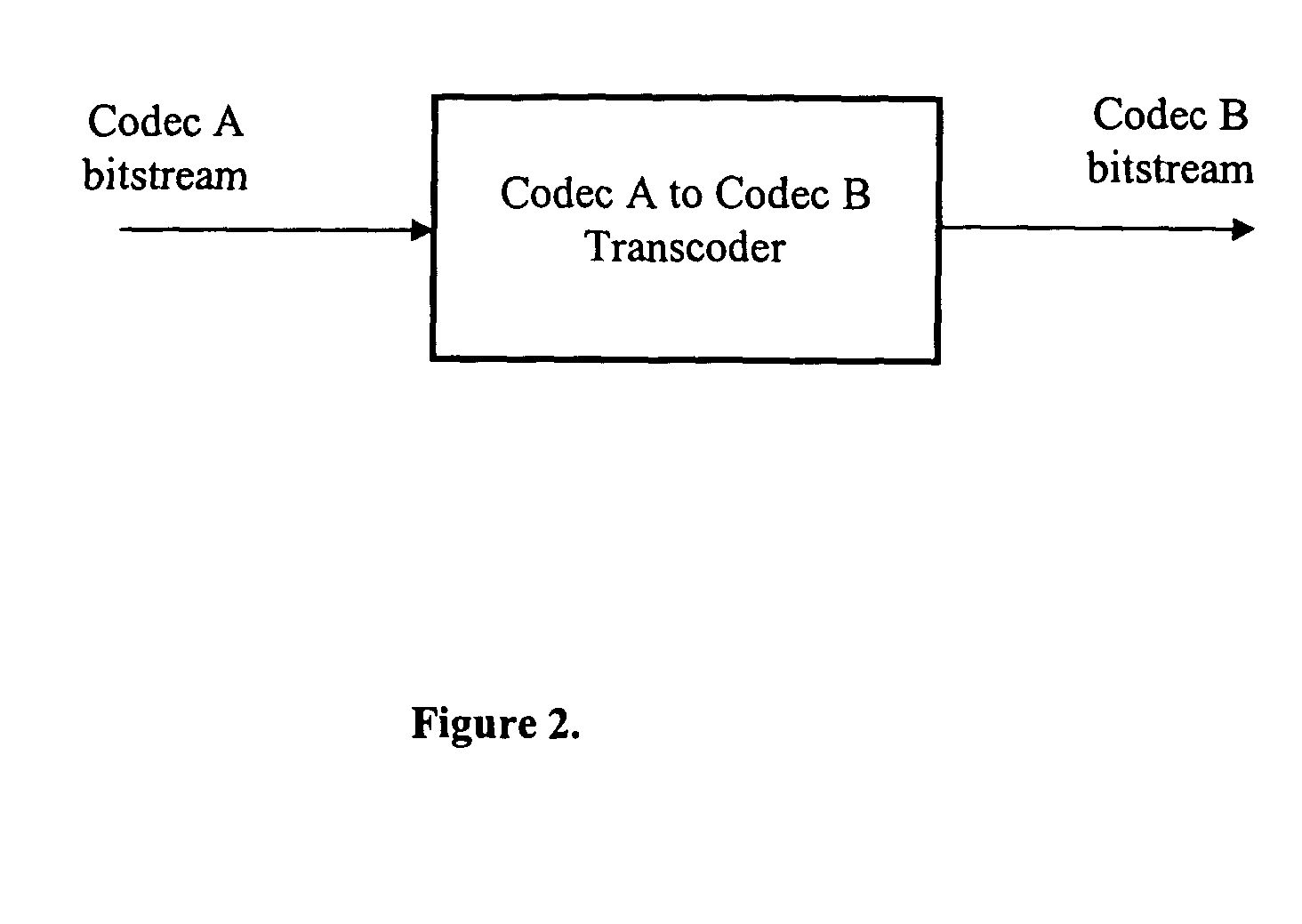
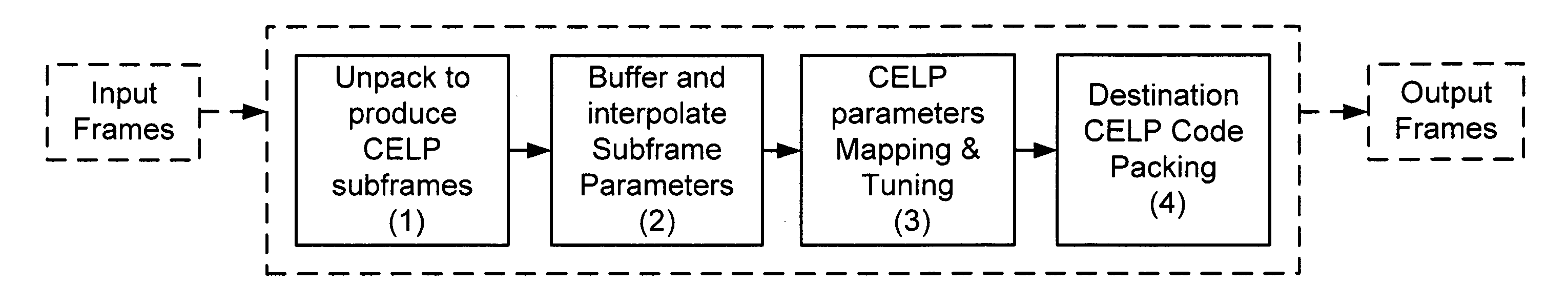
Transcoding method and system between CELP-based speech codes with externally provided status
InactiveUS20080077401A1Computational complexity is reducedReduce the amount requiredSpeech analysisSpeech codeComputer science
A method for transcoding a CELP based compressed voice bitstream from source codec to destination codec. The method includes processing a source codec input CELP bitstream to unpack at least one or more CELP parameters from the input CELP bitstream and interpolating one or more of the plurality of unpacked CELP parameters from a source codec format to a destination codec format if a difference of one or more of a plurality of destination codec parameters including a frame size, a subframe size, and / or sampling rate of the destination codec format and one or more of a plurality of source codec parameters including a frame size, a subframe size, or sampling rate of the source codec format exist. The method includes encoding the one or more CELP parameters for the destination codec and processing a destination CELP bitstream by at least packing the one or more CELP parameters for the destination codec.
Owner:DILITHIUM NETWORKS PTY LTD
Resource allocation method in a multicarrier communication system
InactiveUS20050288030A1Reduce computational complexityEfficient resource managementTransmission path divisionCriteria allocationCommunications systemMobile station
A resource allocation method in a multicarrier communication system where a base station allocates resources to a plurality of mobile stations according to feedback channel information from the mobile stations. The base station receives a resource request message from each mobile station and selects a set of mobile stations offering a maximum system gain without overlapped resources at a specific point in time based on the resource request messages from all mobile stations in the system. The requested resources and then allocated to the selected mobile stations.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Method and apparatus for suppressing communication signal interference
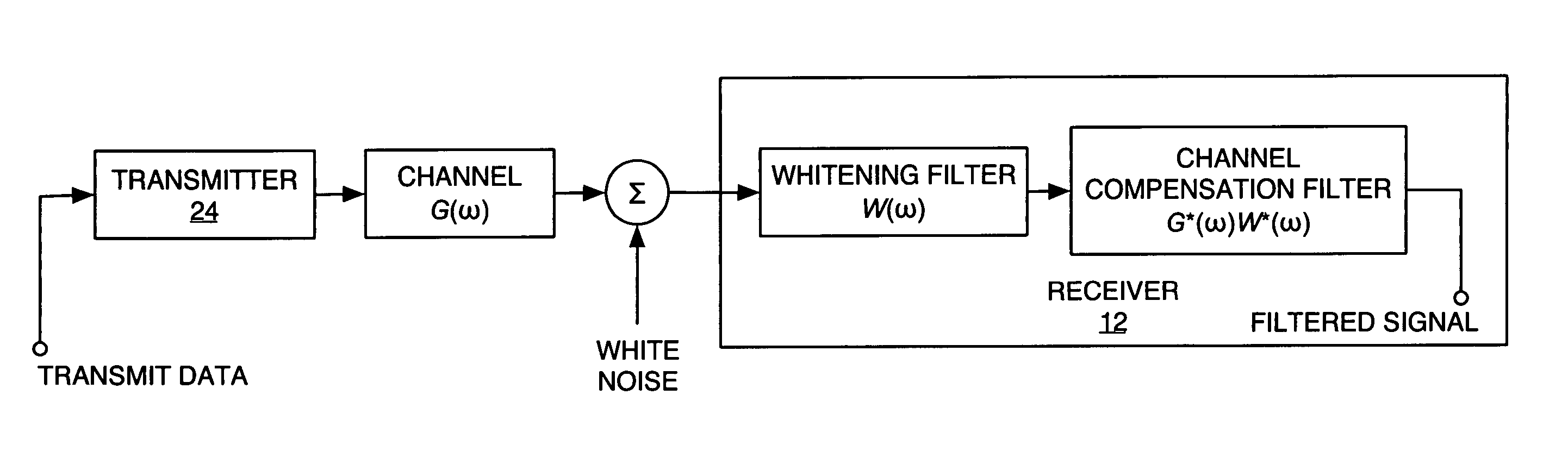
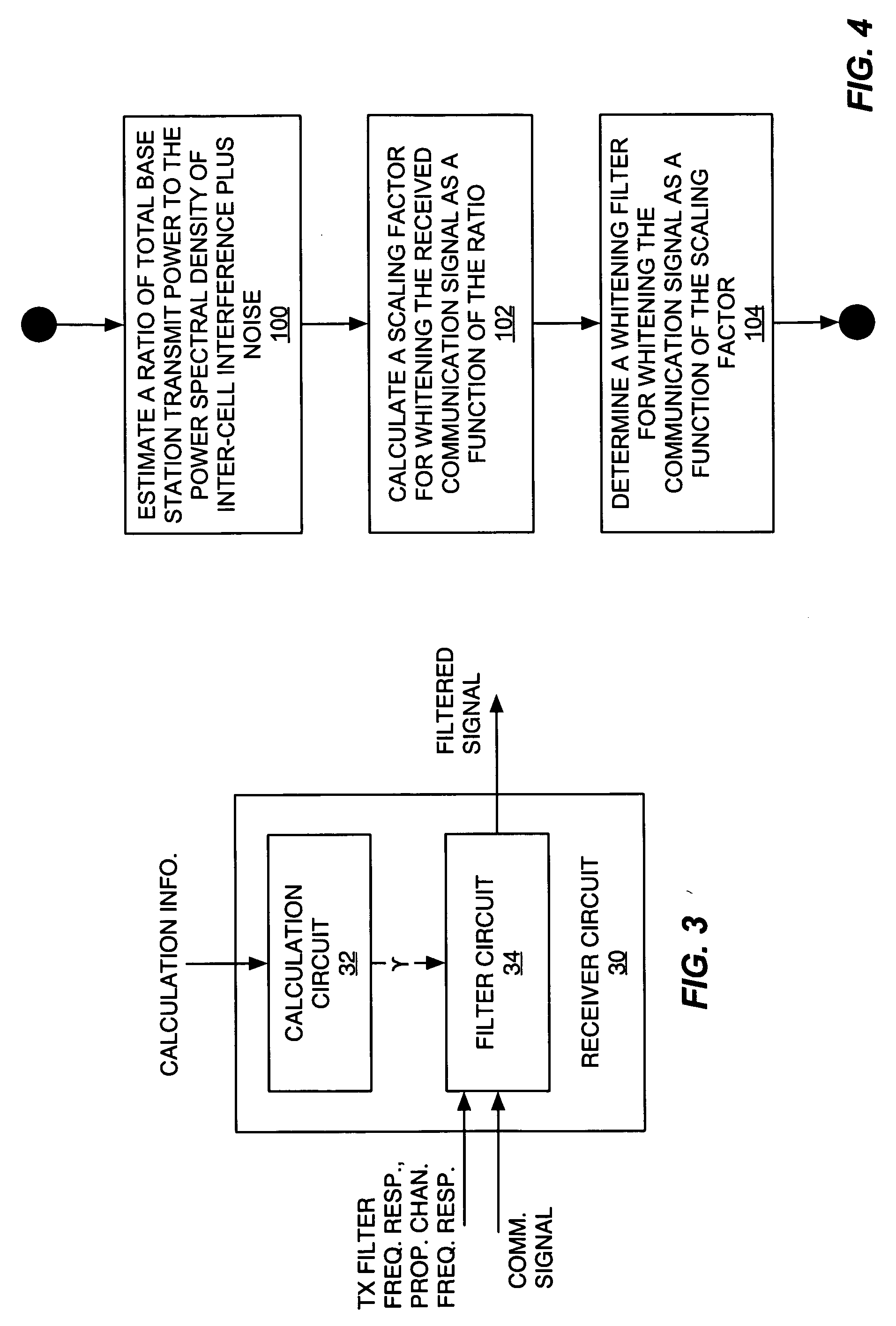
InactiveUS20060072485A1Reduce computational complexityEasy constructionError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionTransmitted powerEngineering
A frequency domain representation of a whitening filter is made to depend on essentially one unknown, namely, a scaling factor that is based on an estimated ratio of total base station power to the power spectral density (PSD) of inter-cell interference plus noise. In turn, that scaling factor can be computed based on the modeling terms used in a parametric model of the impairment correlations for a received communication signal. Preferably, the model comprises an interference impairment term scaled by a first model fitting parameter, and a noise impairment term scaled by a second model fitting parameter. Further, the scaling factor can be computed by directly estimating total base station transmit power and the PSD of inter-cell interference plus noise. In any case, the whitening filter can be used in whitening a received communication signal in conjunction with channel equalization processing or RAKE receiver processing, for example.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
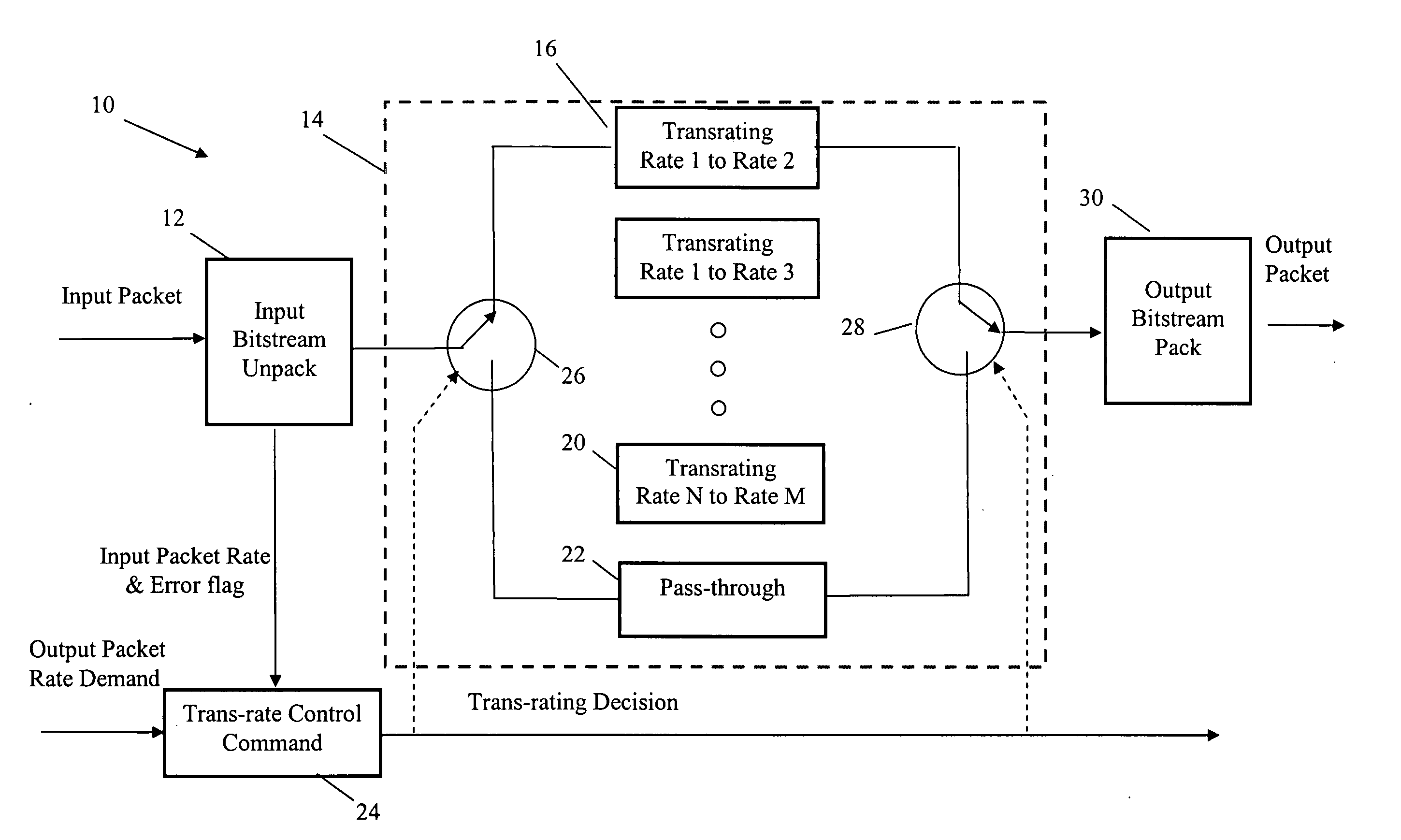
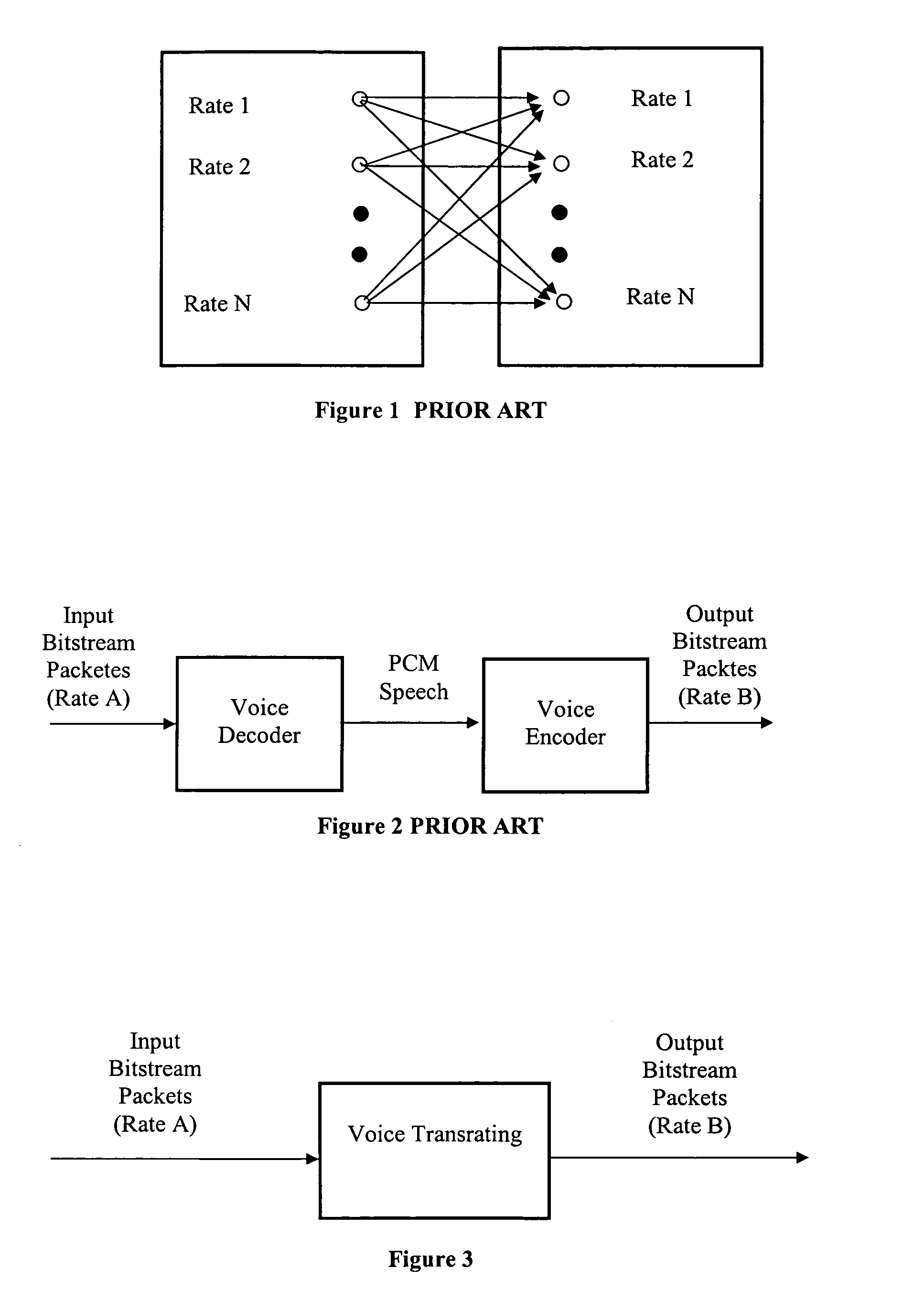
Method and apparatus for voice trans-rating in multi-rate voice coders for telecommunications
InactiveUS20050258983A1Improve voice qualityComputational complexity is reducedSpeech analysisCode conversionCompression methodSpeech sound
Method and apparatus for trans-rating a bitstream of data through multi-rate voice coders converting a bitstream representing frames of data encoded according to a first voice compression method of a first rate to a second voice compression method according to a second rate. A trans-rating pair includes voice compression parameters mapping modules. The method of trans-rating includes either bit-unpacking or unquantization on an encoded packet at input site to obtain rate information and voice compression parameters according to the first rate voice compression method. The information of the first rate and the required output rate, namely a second rate type, in addition to external control commands, are then used to determine the converting strategy of the trans-rating pair. Next, at least some of the compression parameters of the first rate are passed through, or mapped, into compression parameters of the second rate compatible with the second rate voice compression method.
Owner:DILITHIUM NETWORKS PTY LTD
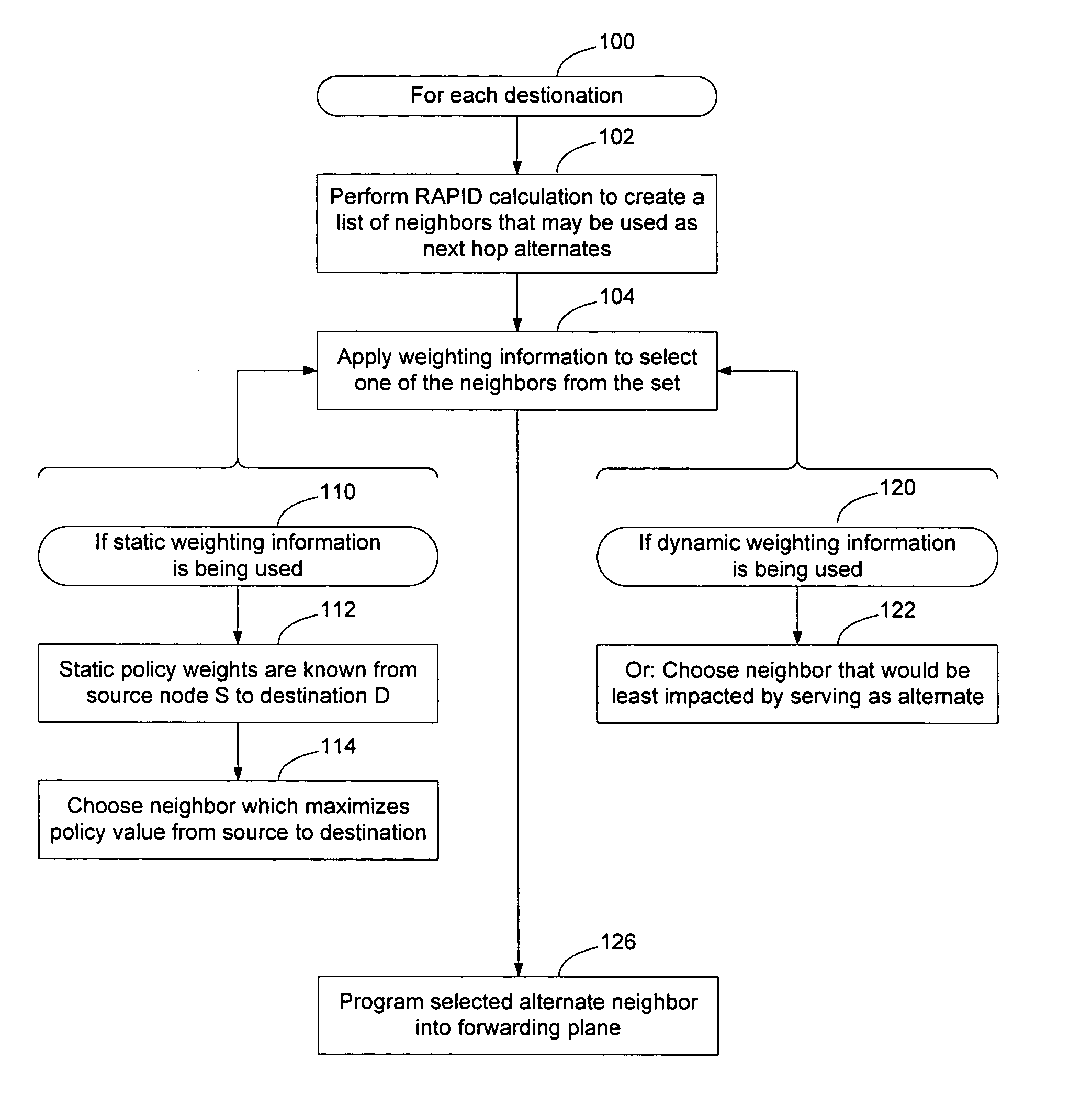
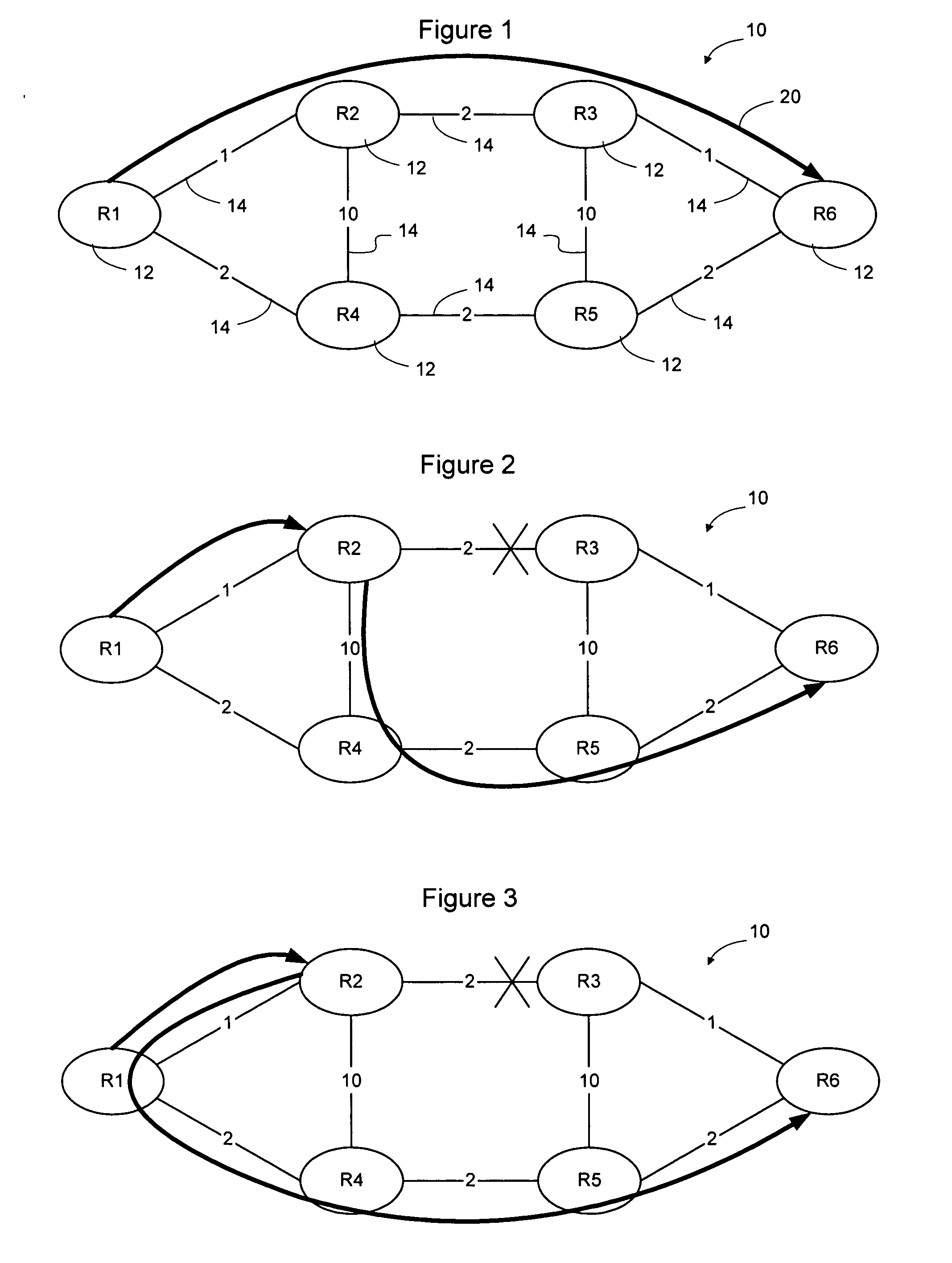
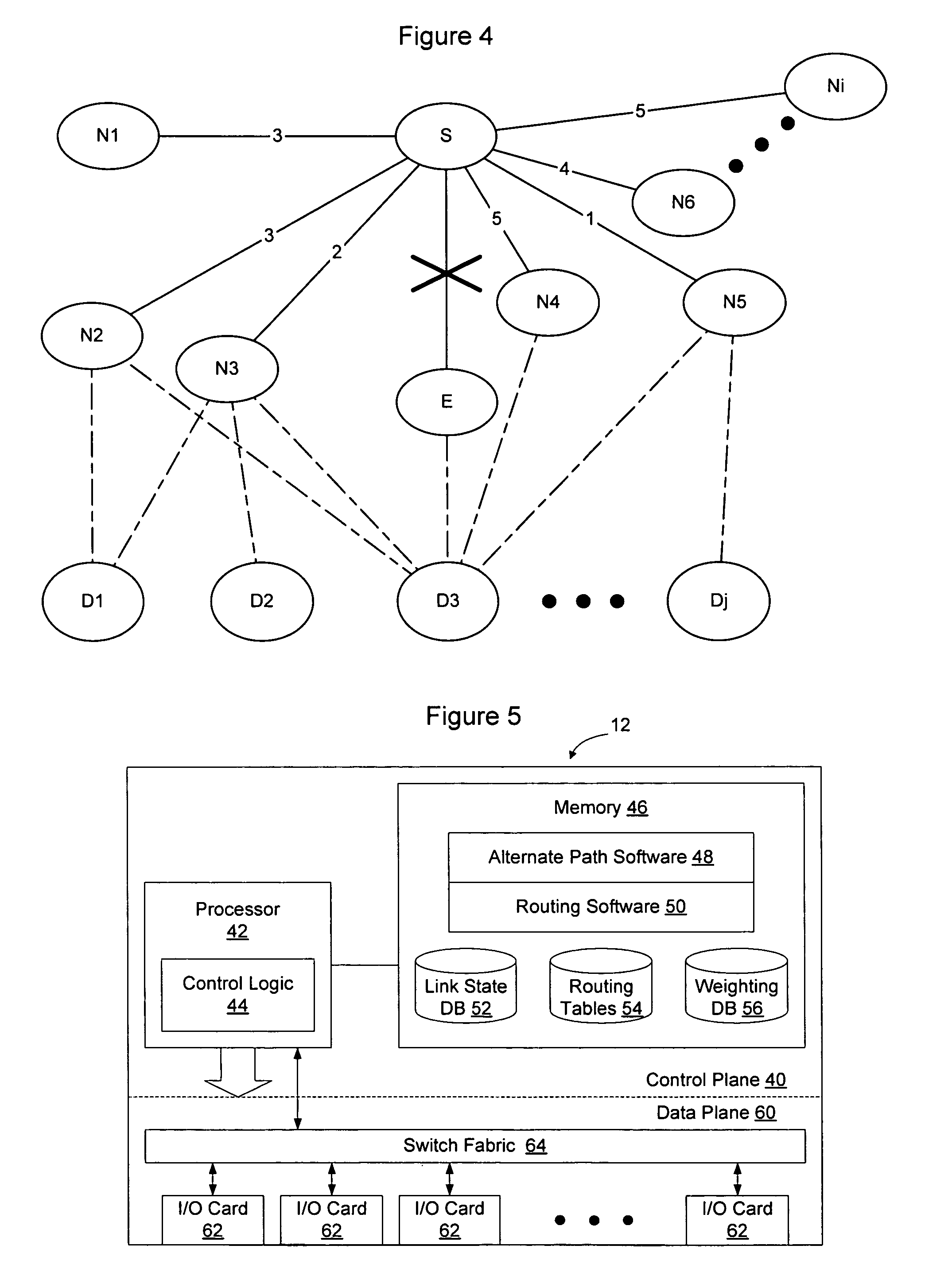
Method and apparatus for selecting between available neighbors in a rapid alternate path calculation
InactiveUS20080056137A1Reduce computational complexityComputational complexity is reducedError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityRapid processing
A weighting process may be used to select between alternate neighbors in a RAPID calculation to enable policy and / or traffic engineering considerations to affect the selection of an alternate path through the network. The information used to weight the neighbors may static administratively assigned weighting information or dynamic weighting information such as local statistical traffic condition information. The process may take into account the amount of traffic being handled by the current primary next hop for the destination, the available capacity of the available alternate neighbors, the ability of the alternate neighbors to handle the additional traffic, and other considerations. Weighting may occur after a set of available loop free alternate neighbors has been determined. Alternatively, weighting may occur before the RAPID calculation has been performed to cause the neighbors to be ordered prior to RAPID processing. This may enable RAPID calculation to stop without considering all available neighbors.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
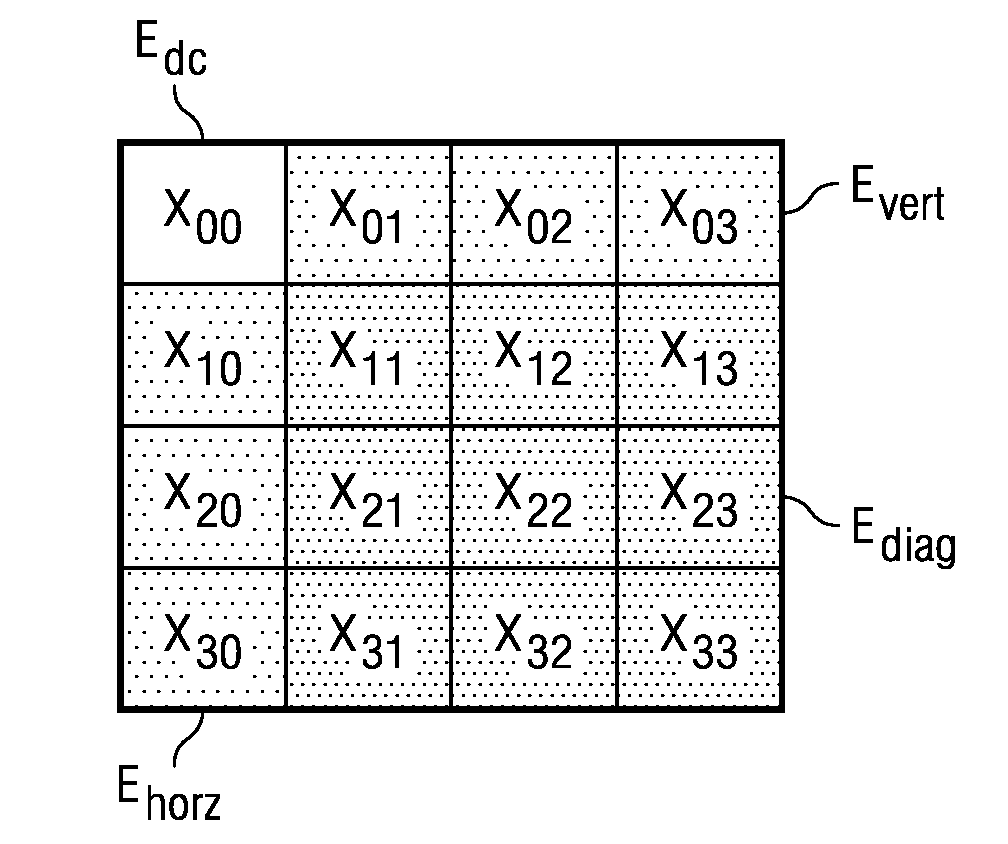
Transform Domain Fast Mode Search for Spatial Prediction in Advanced Video Coding
ActiveUS20080304763A1Reduce complexityMaintaining same qualityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionFrequency domainFast mode
This invention is method for determining direction mode for an image block in intra prediction of video frames. The method calculates a plurality of energy terms from the spatial frequency domain image block, then determines a coarse classification from these energy terms. For at least some coarse classifications the method searches from among a subset of less than all possible direction modes. The method also searches a most likely direction mode determined from neighbor blocks when available.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Fast Log-Likelihood Ratio (LLR) Computation for Decoding High-Order and High-Dimensional Modulation Schemes
ActiveUS20170126360A1Reduce in quantityReduce computational complexityError preventionMultiple carrier systemsHigh dimensionalityLog likelihood
A method receives the symbol transmitted over a channel, selects, from a constellation of codewords, a first codeword neighboring the received symbol and a set of second codewords neighboring the first codeword, and determines a relative likelihood of each second codeword being the transmitted symbol with respect to a likelihood of the first codeword being the transmitted symbol. Next, the method determines an approximation of a log-likelihood ratio (LLR) of each data bit in the received symbol as a log of a ratio of a sum of the relative likelihoods of at least some of the second codewords having the same value of the data bit to a sum of the relative likelihoods of at least some of the second codewords having different value of the data bit and decodes the received symbol using the LLR of each data bit.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
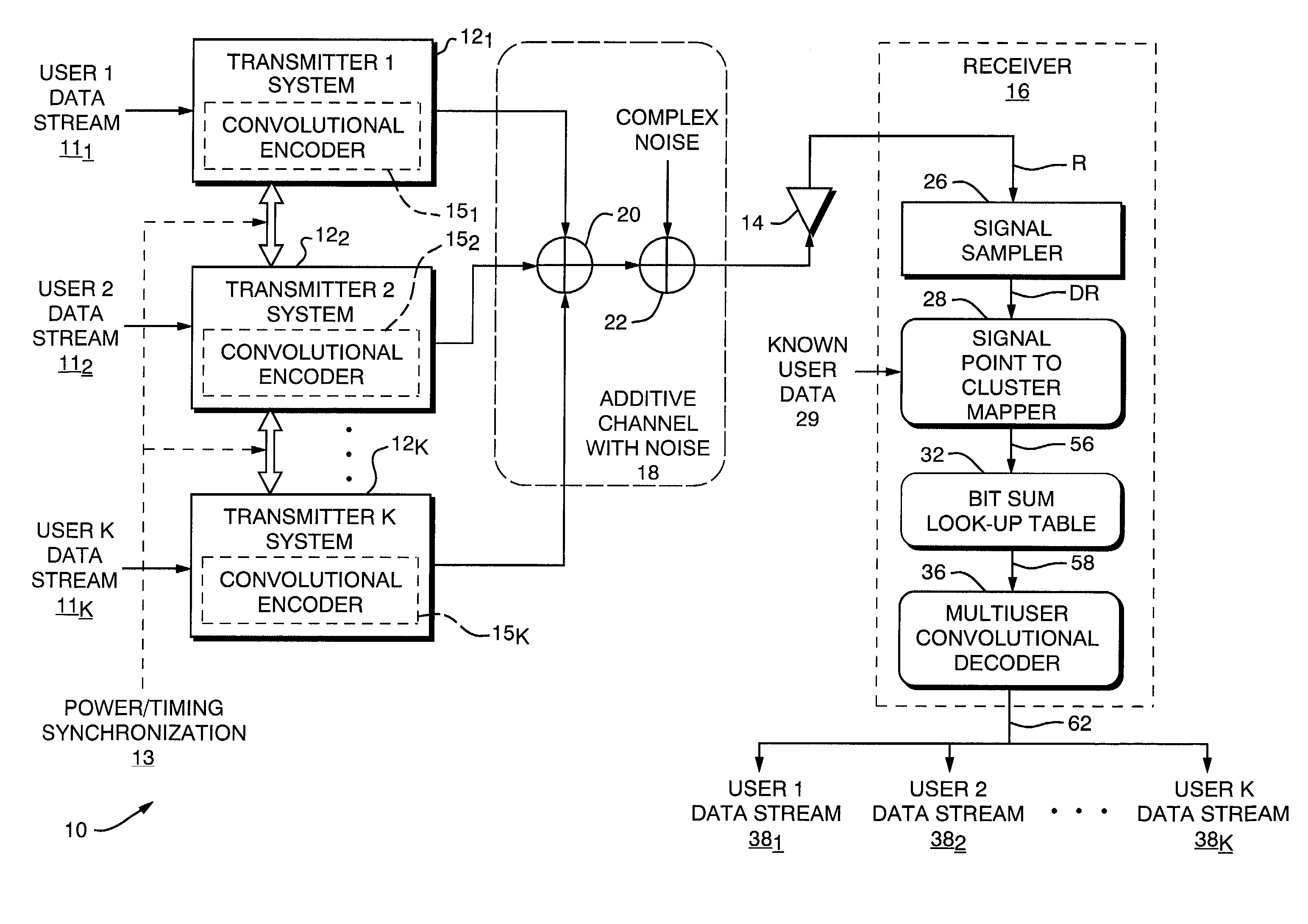
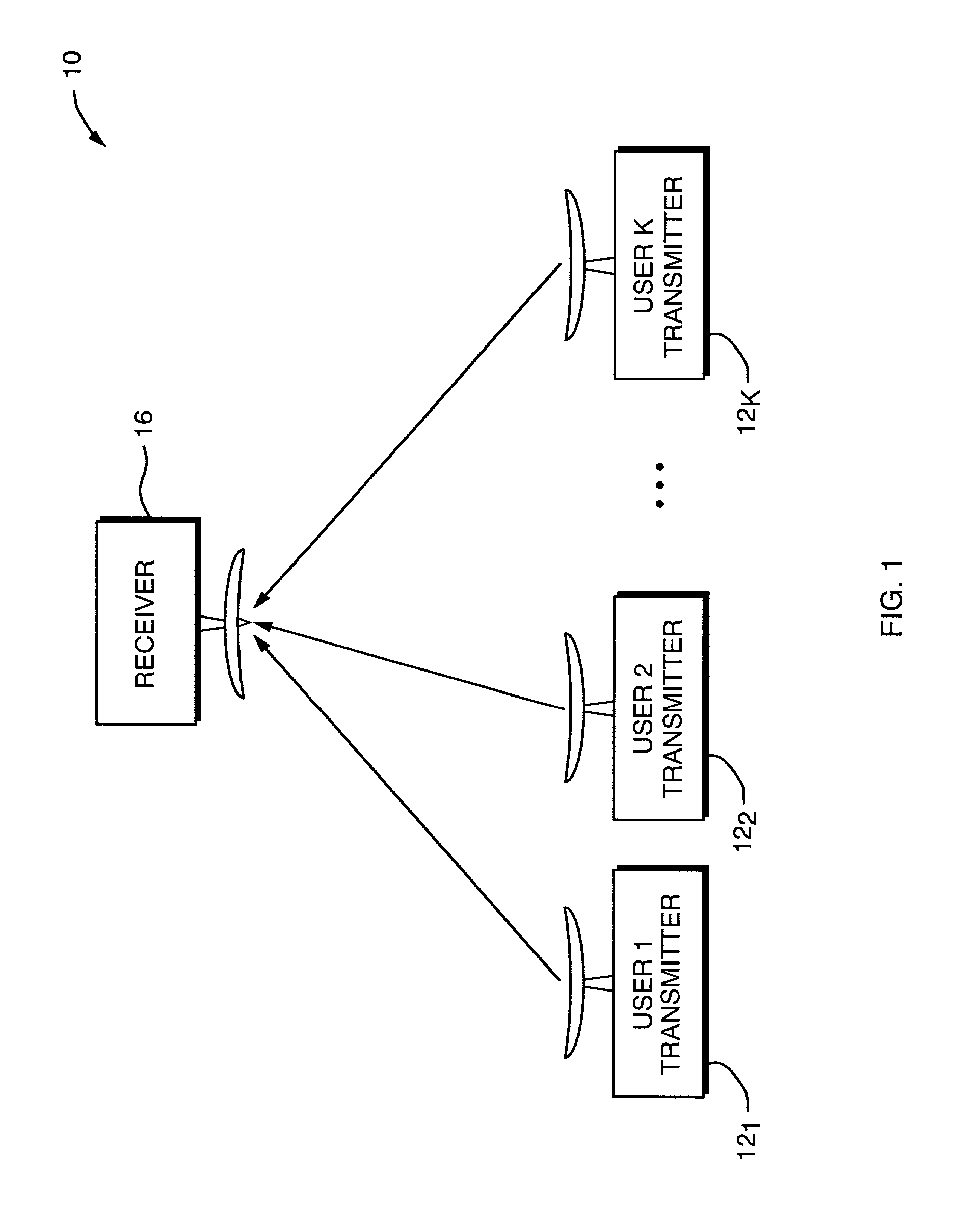
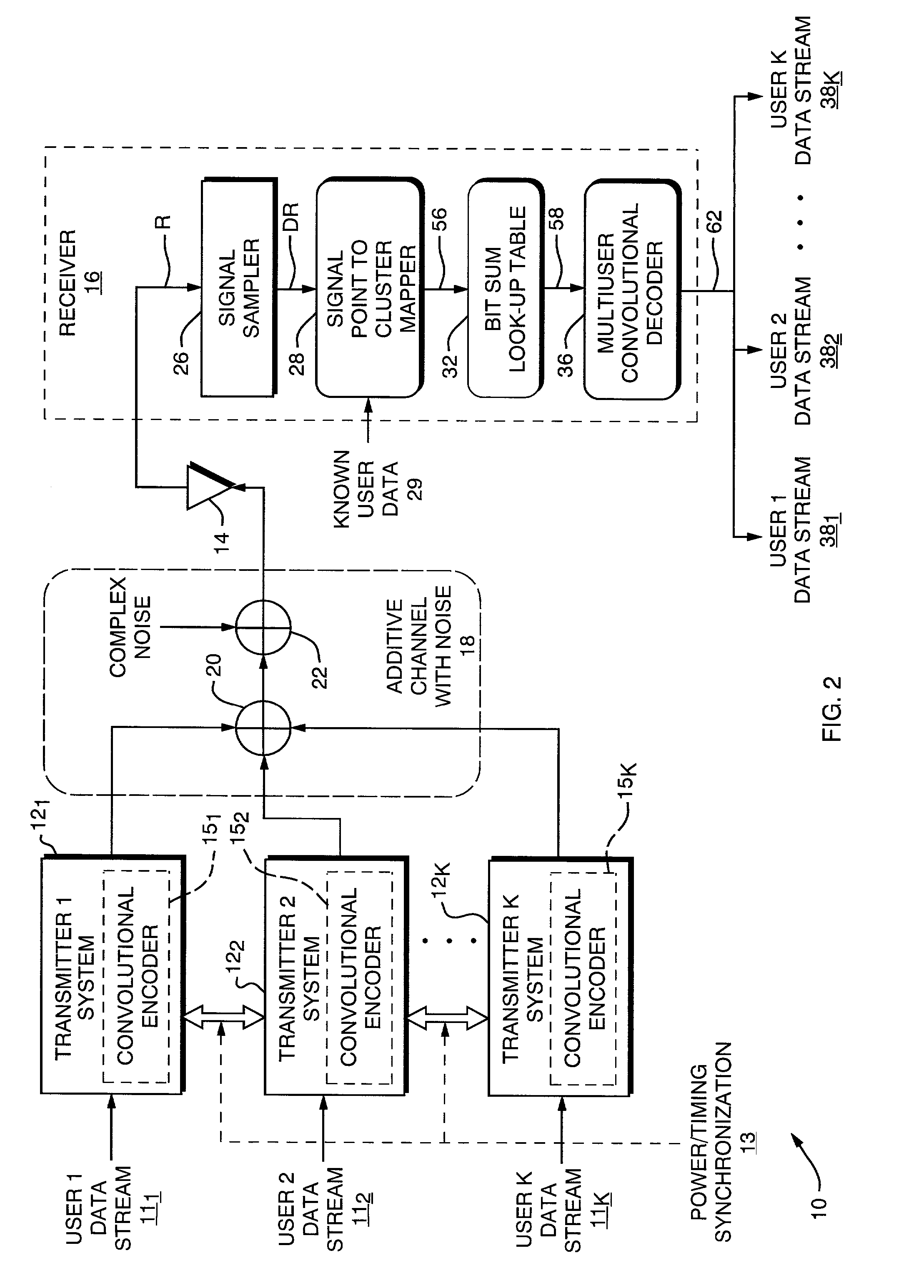
Cooperative code-enhanced multi-user communications system
ActiveUS20030026357A1High data rateComputational complexity is reducedError preventionCombined modulated pulse demodulationDigital dataData stream
A cooperative code-enhanced multiuser communications system having a receiver for resolving user ambiguity in a received composite signal by using convolutional encoder state machine properties to analyze strings of bit sums and separate out individual user data. The receiver comprises a signal sampler which converts a received composite signal to a digital data. A single point cluster mapper determines a closest pseudo-constellation point, and the pseudo-constellation point is formed with the aid of power and timing control in the transmitters. A bit sum look-up table maps symbol points to bit sums. A deterministic loop tests for bit sum cases where symbols can be determined immediately. A guess loop tests the bit sum after the deterministic loop test and performs guesses until all bits are decided. The bit sum is provided to a multiuser convolutional decoder to decide all user data streams.
Owner:COLLISION COMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com