Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
253results about How to "Adequate flow" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
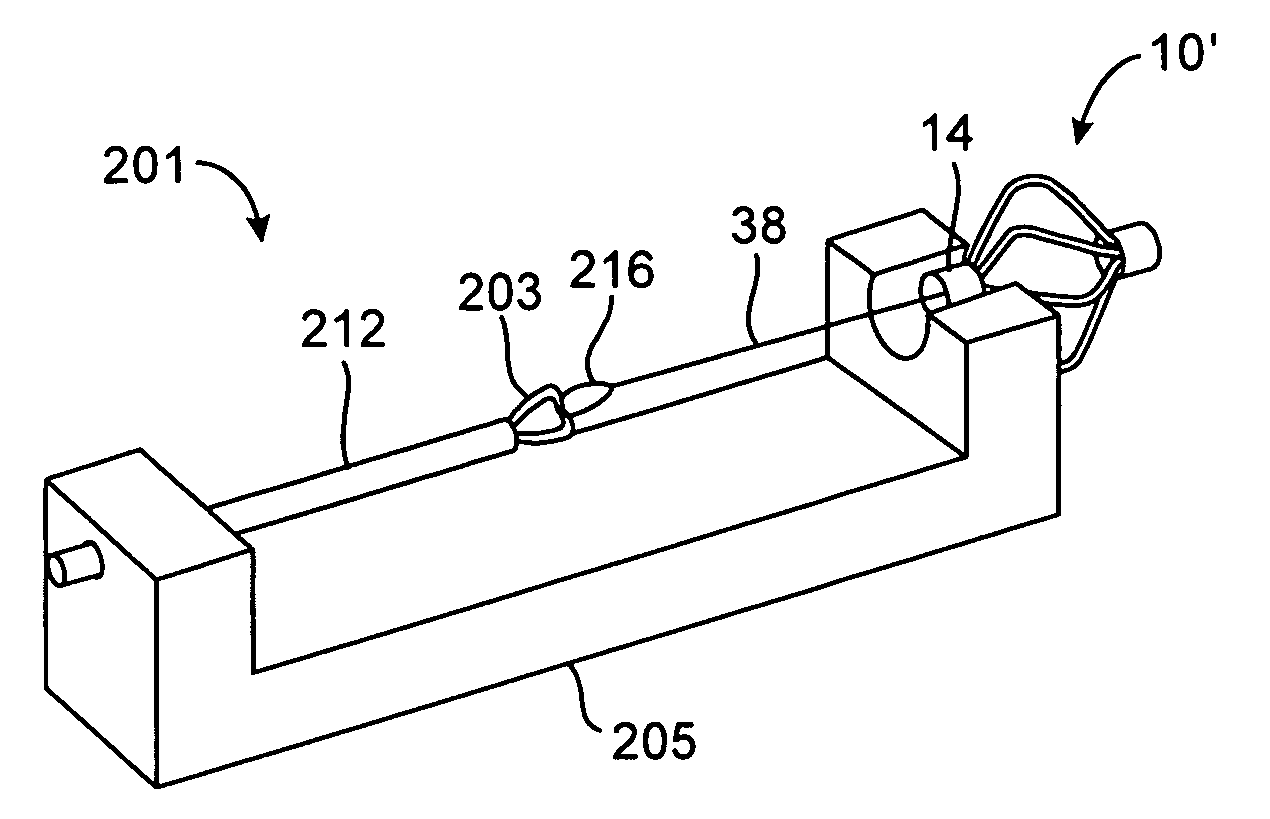
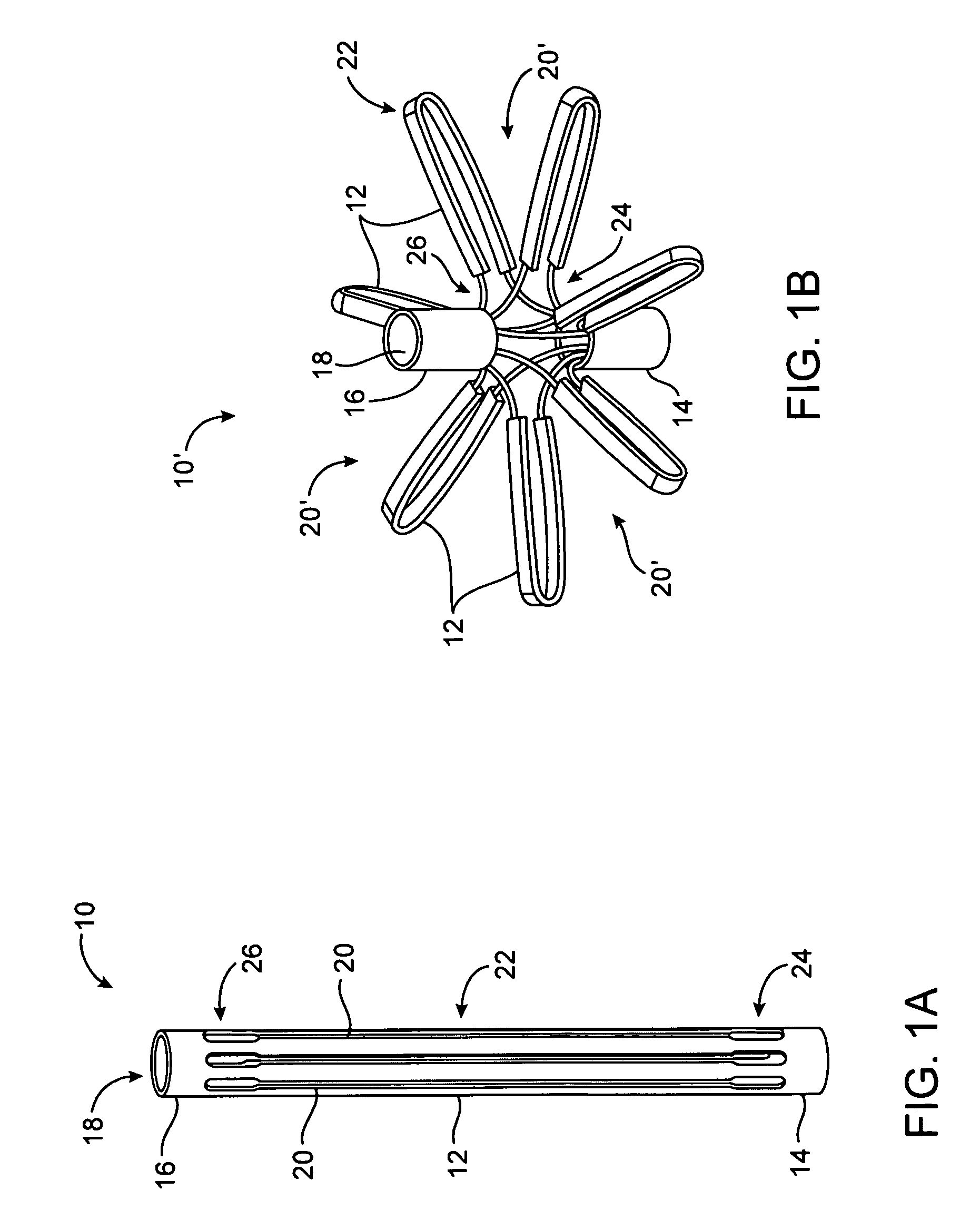
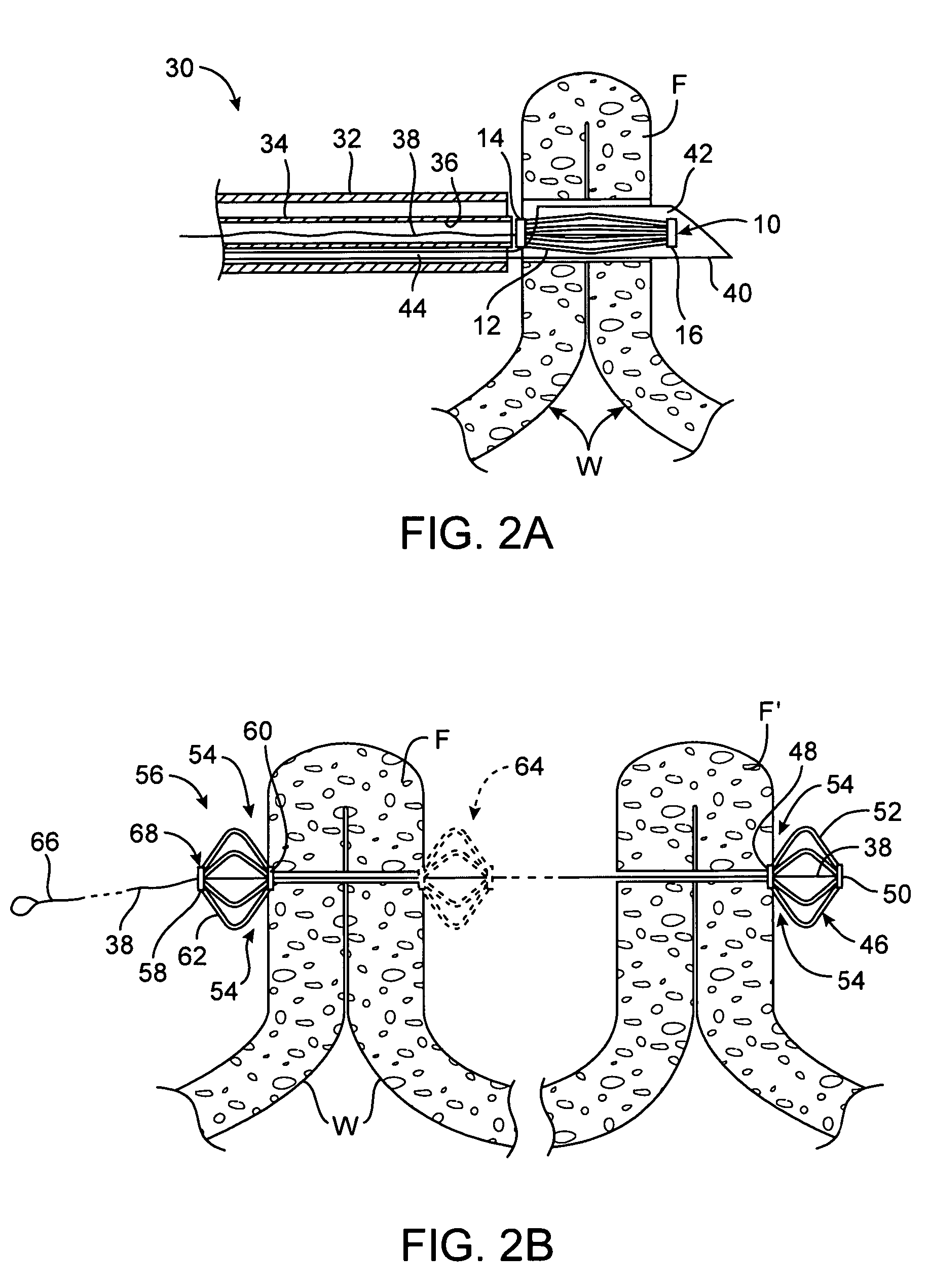
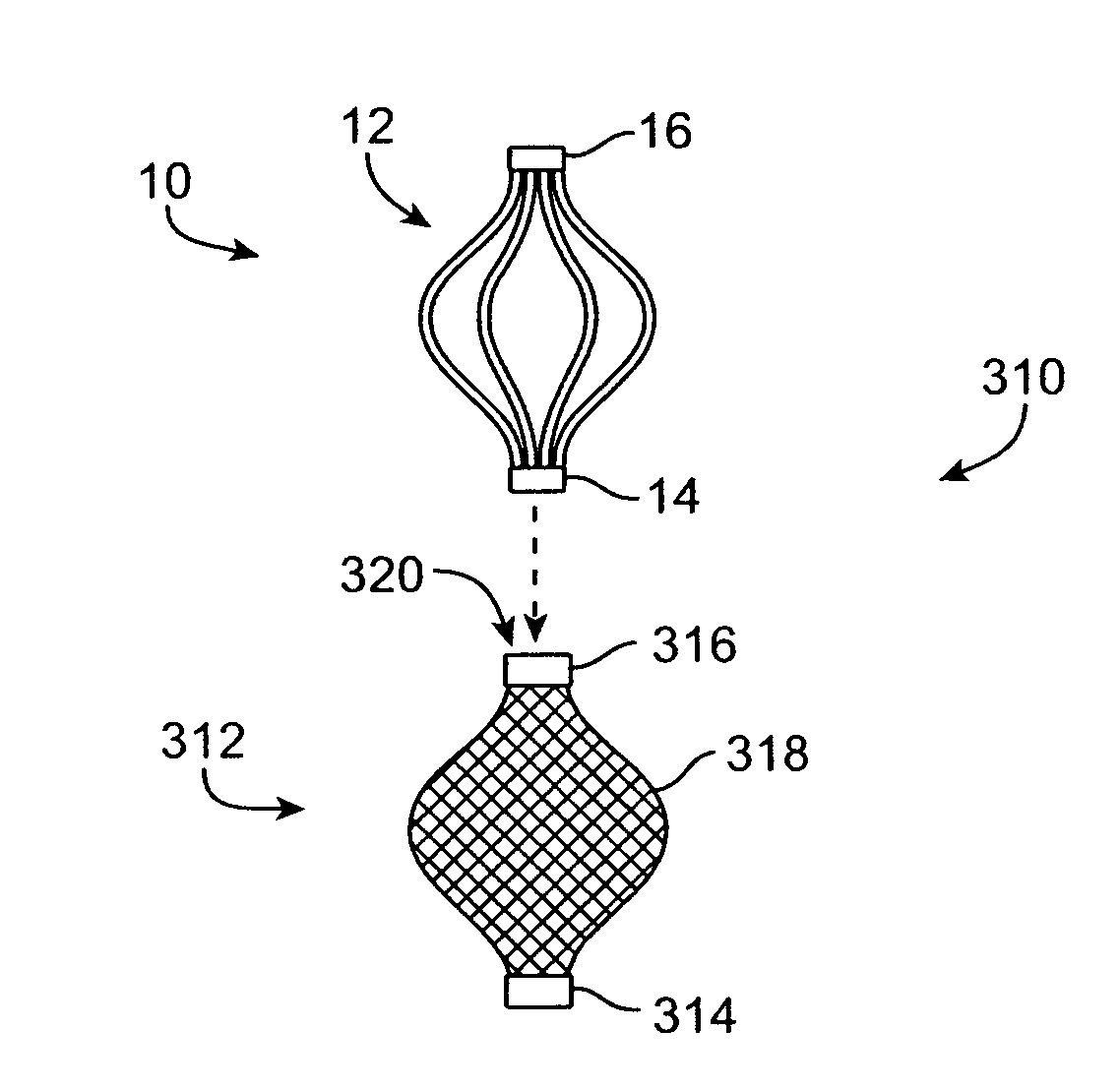
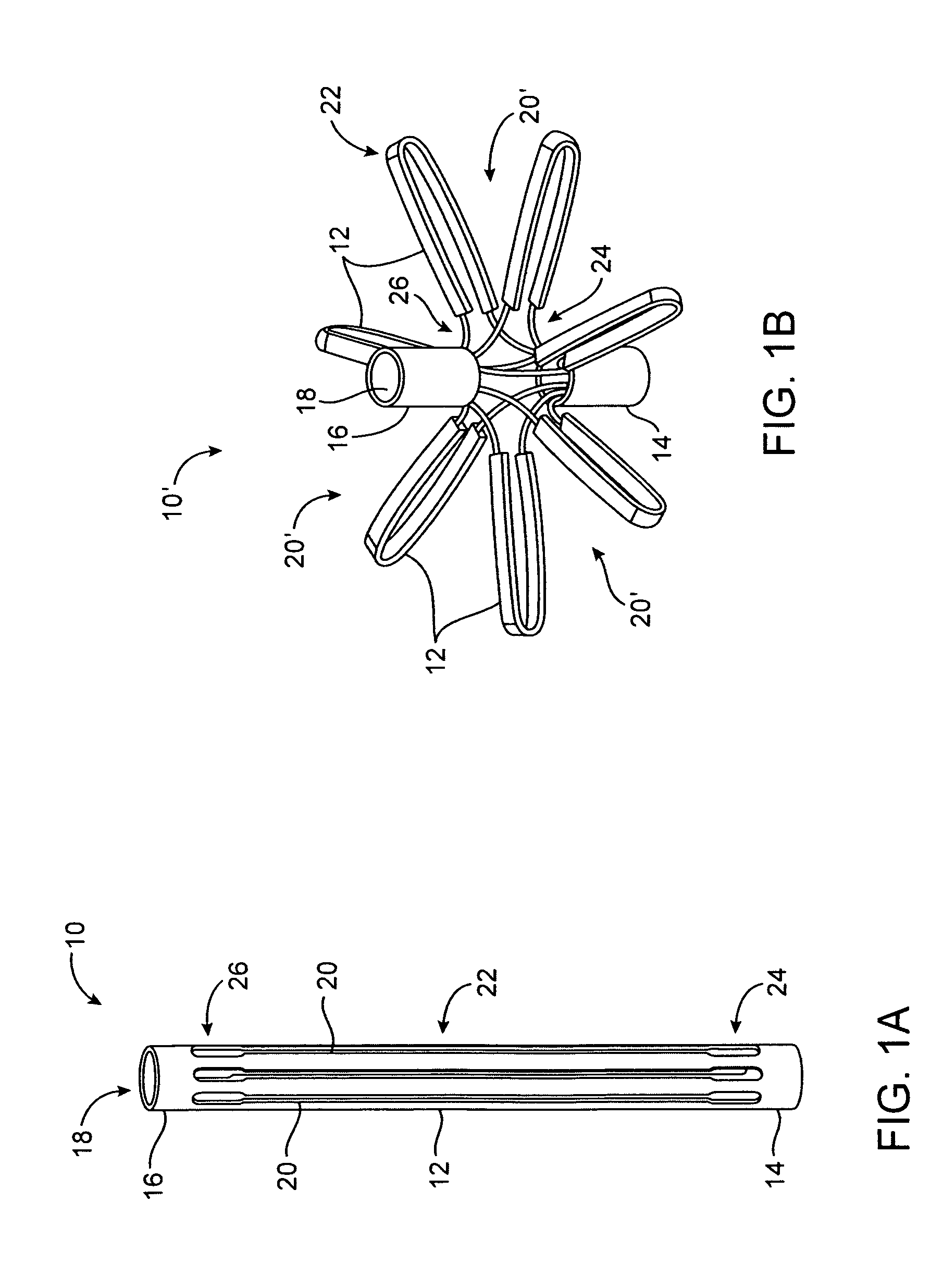
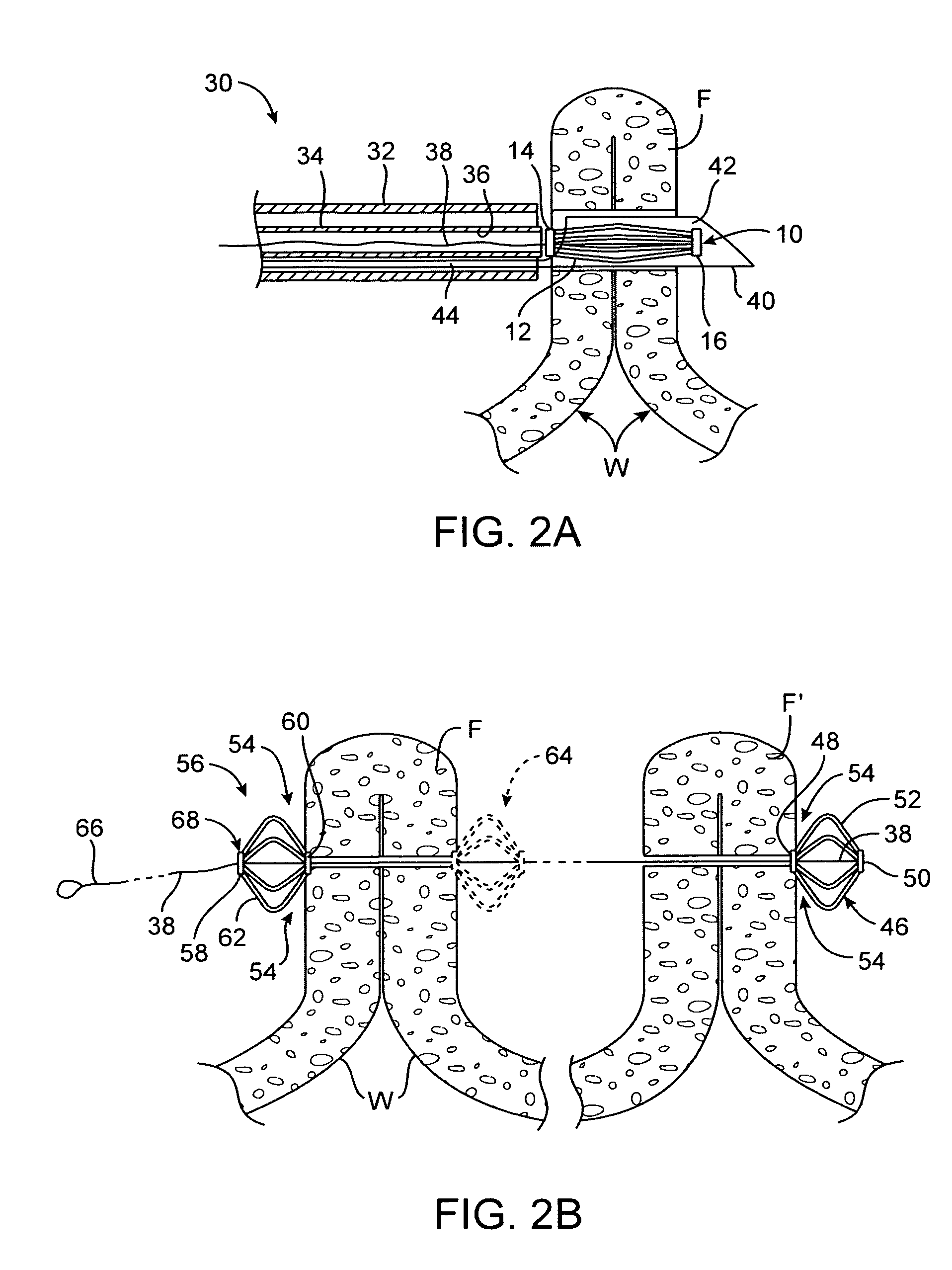
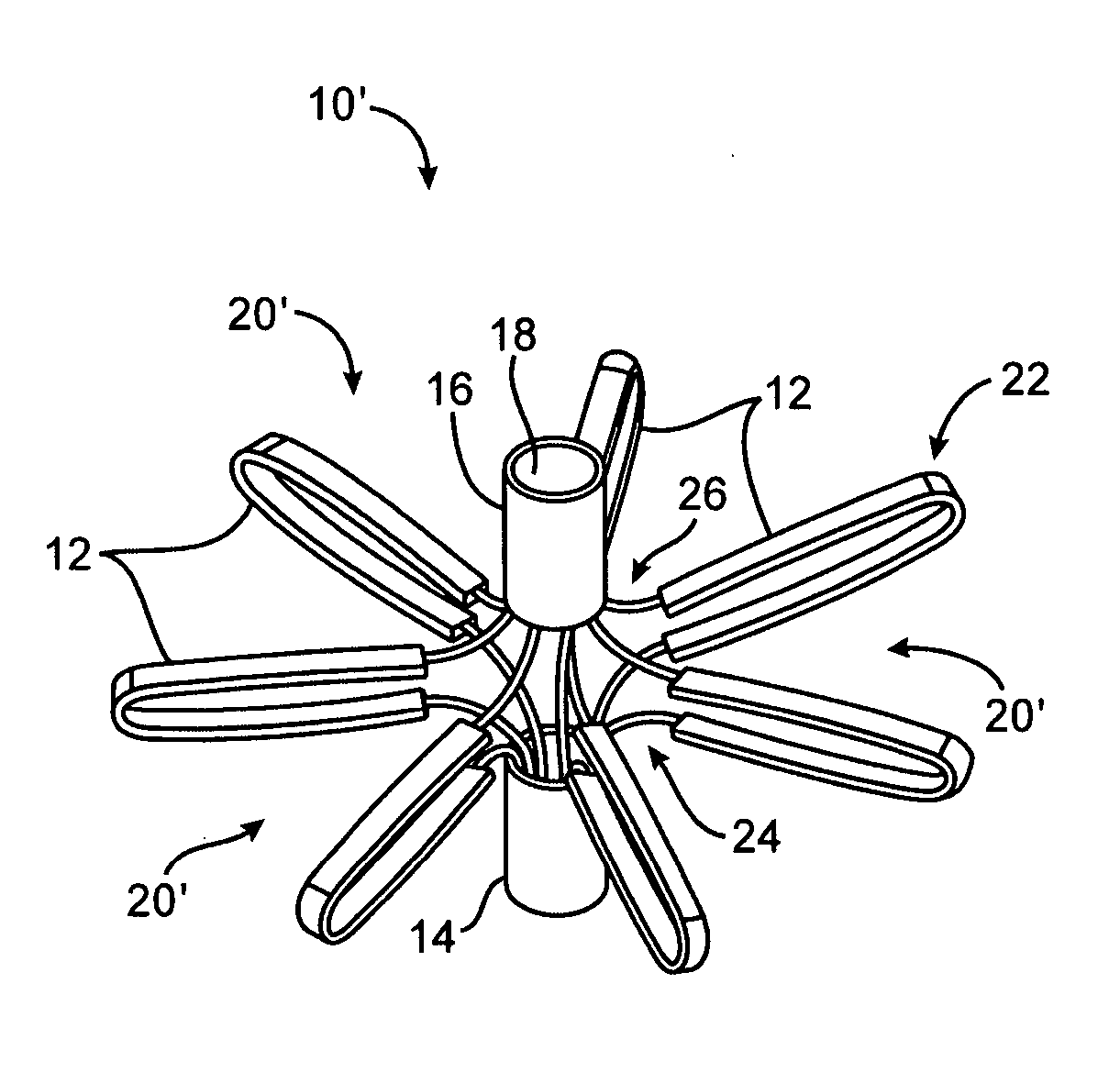
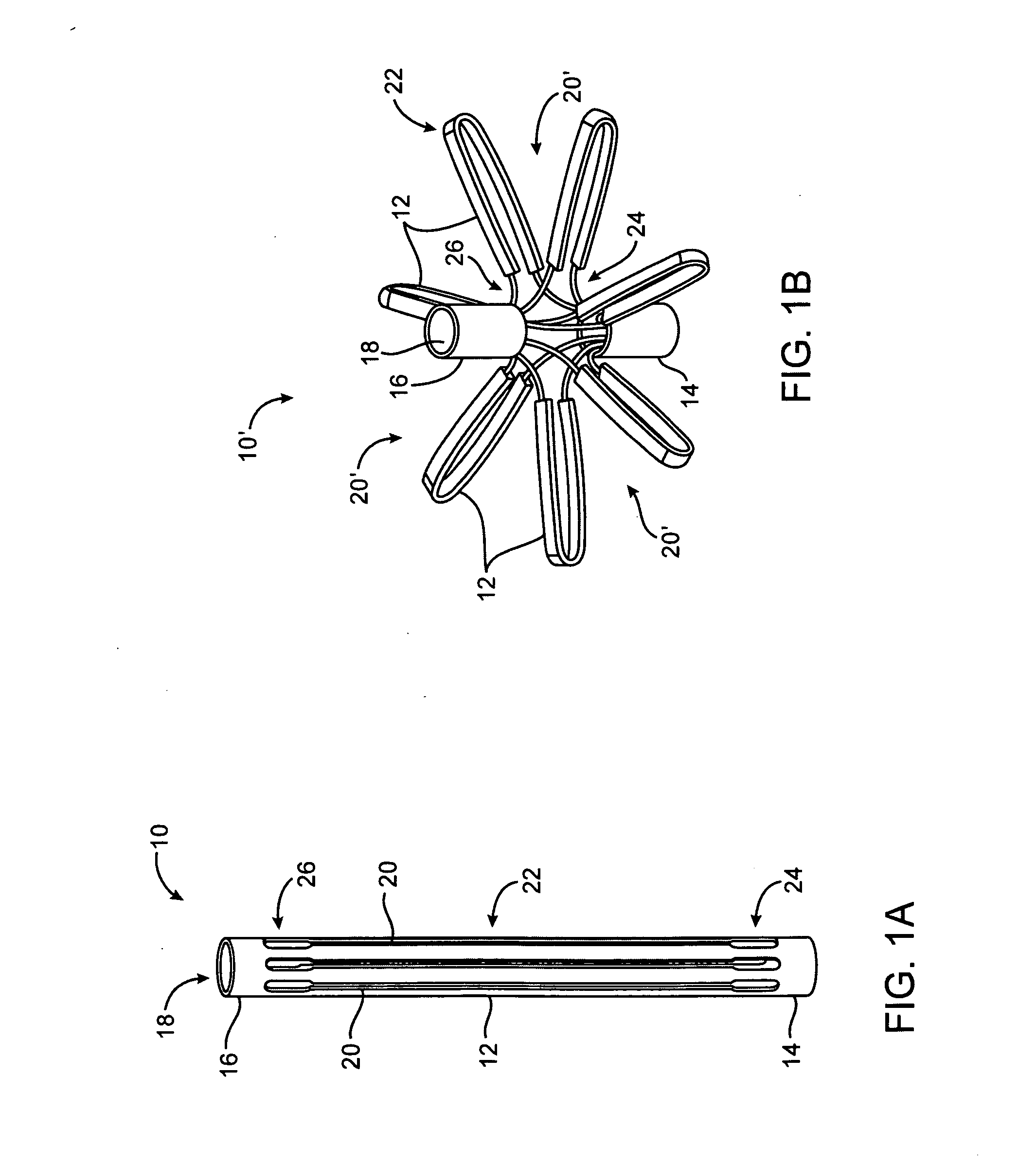
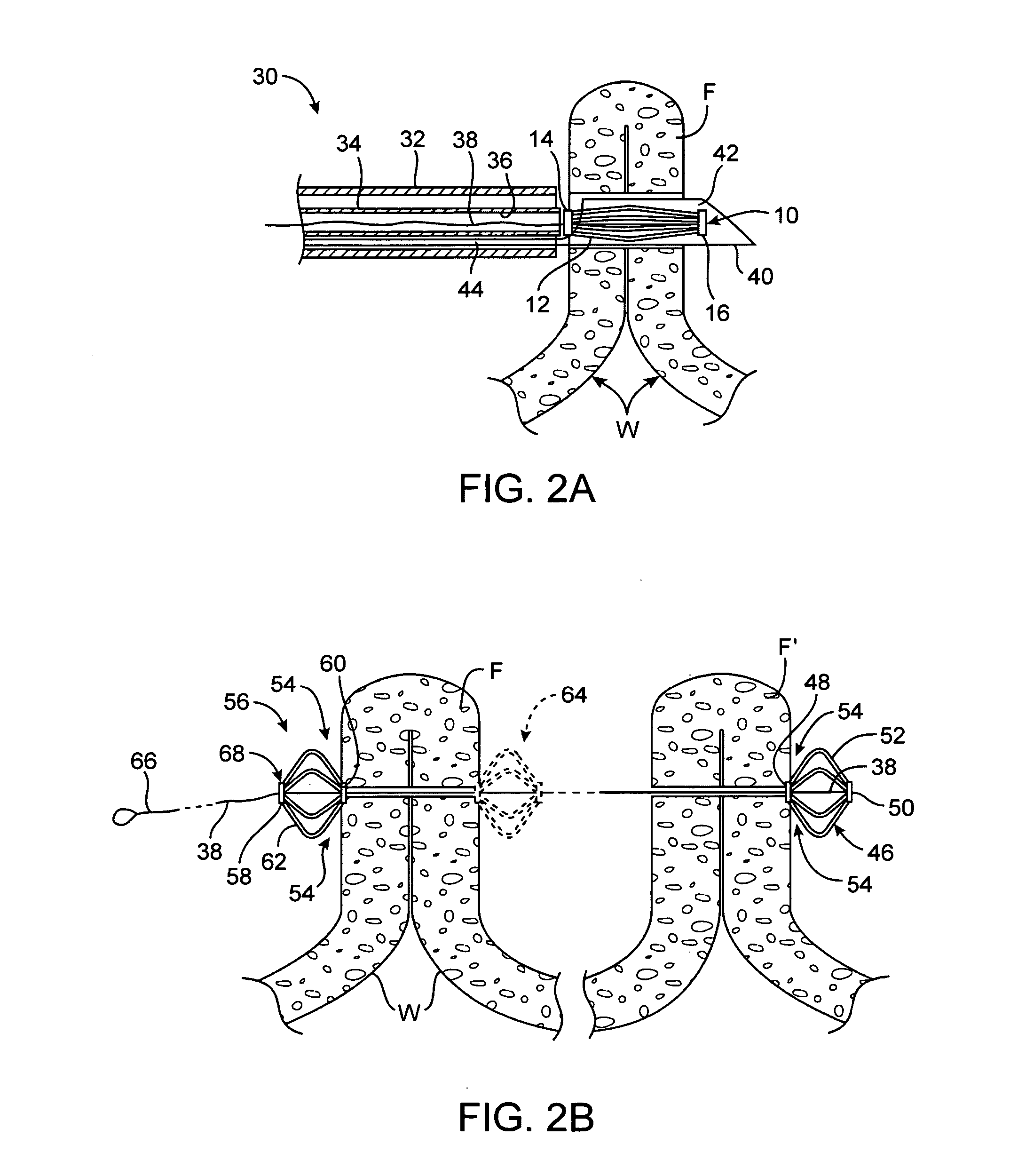
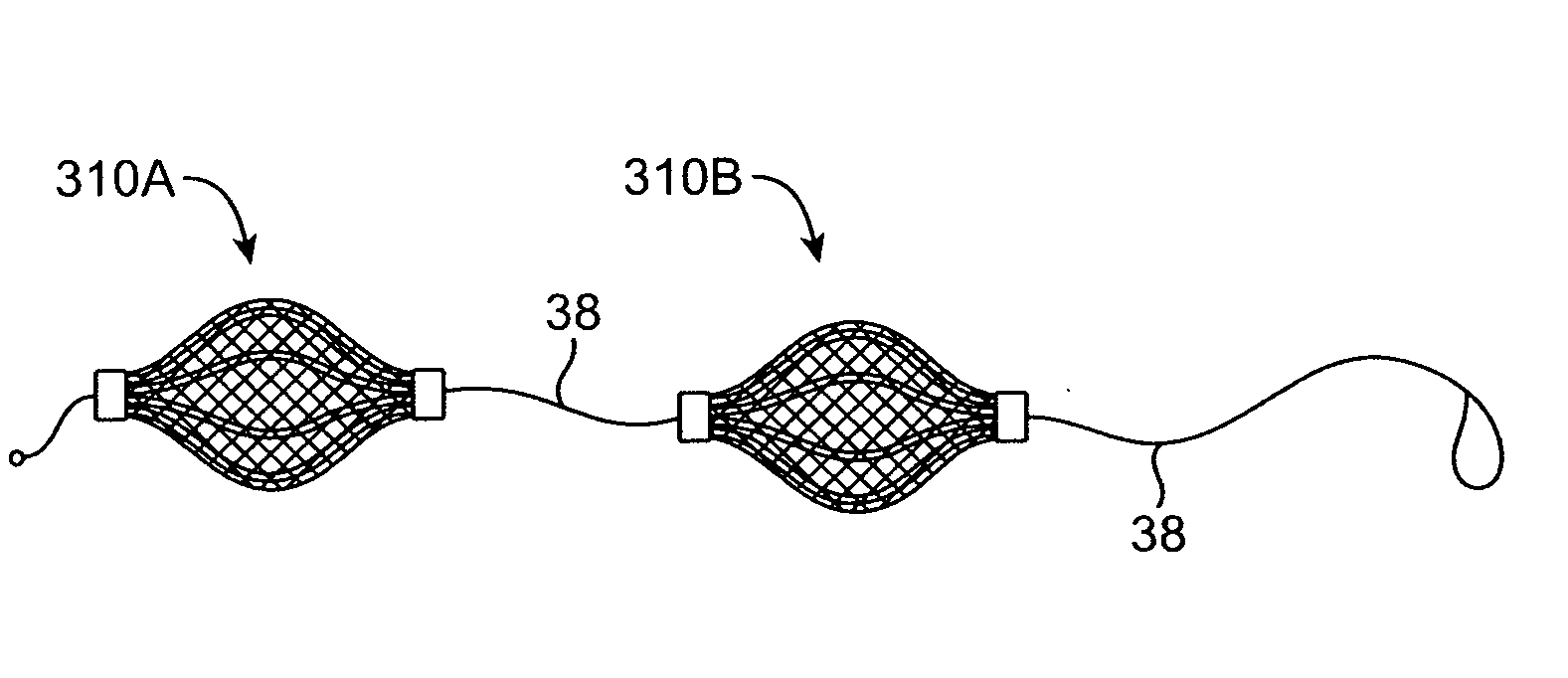
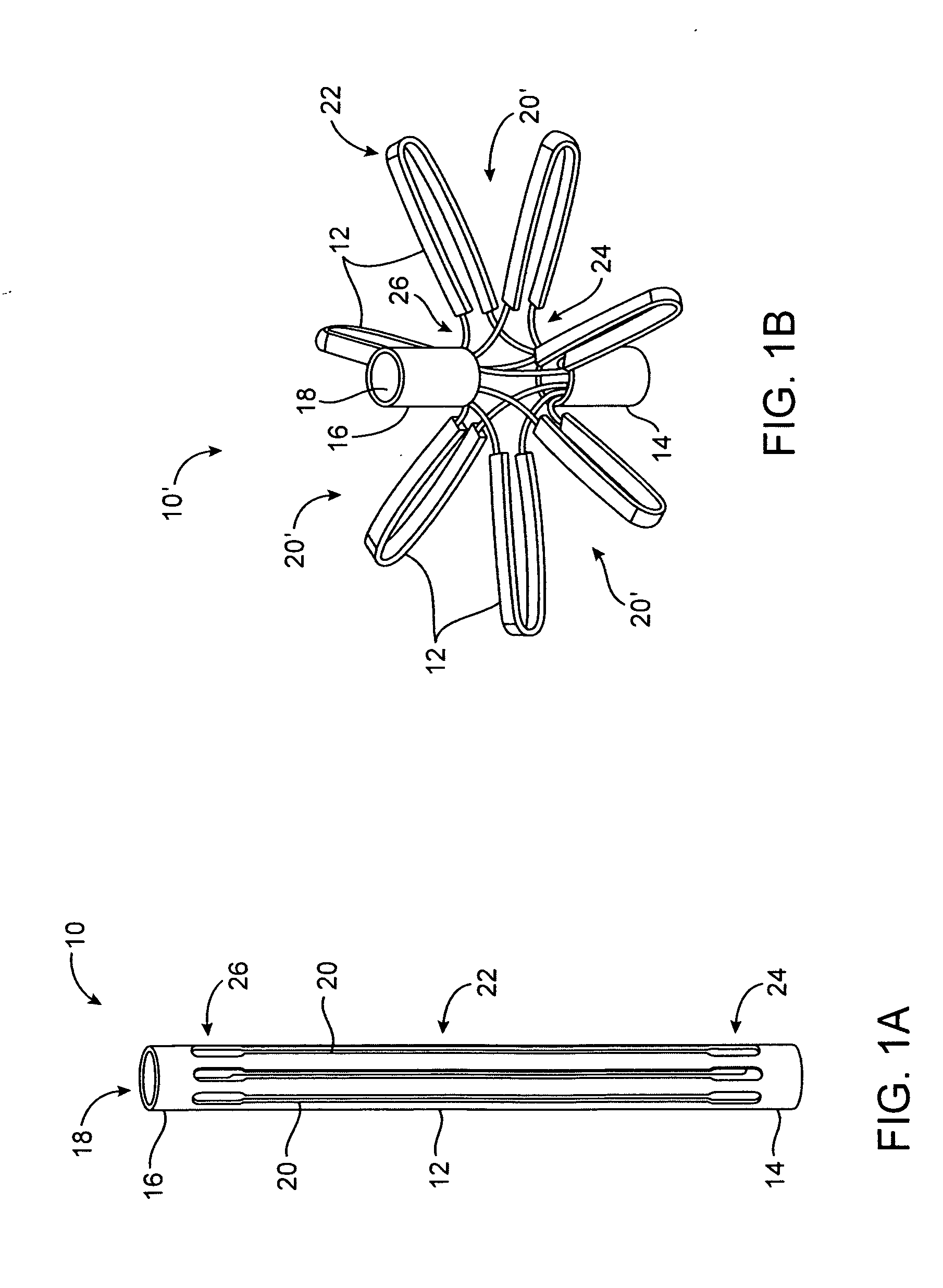
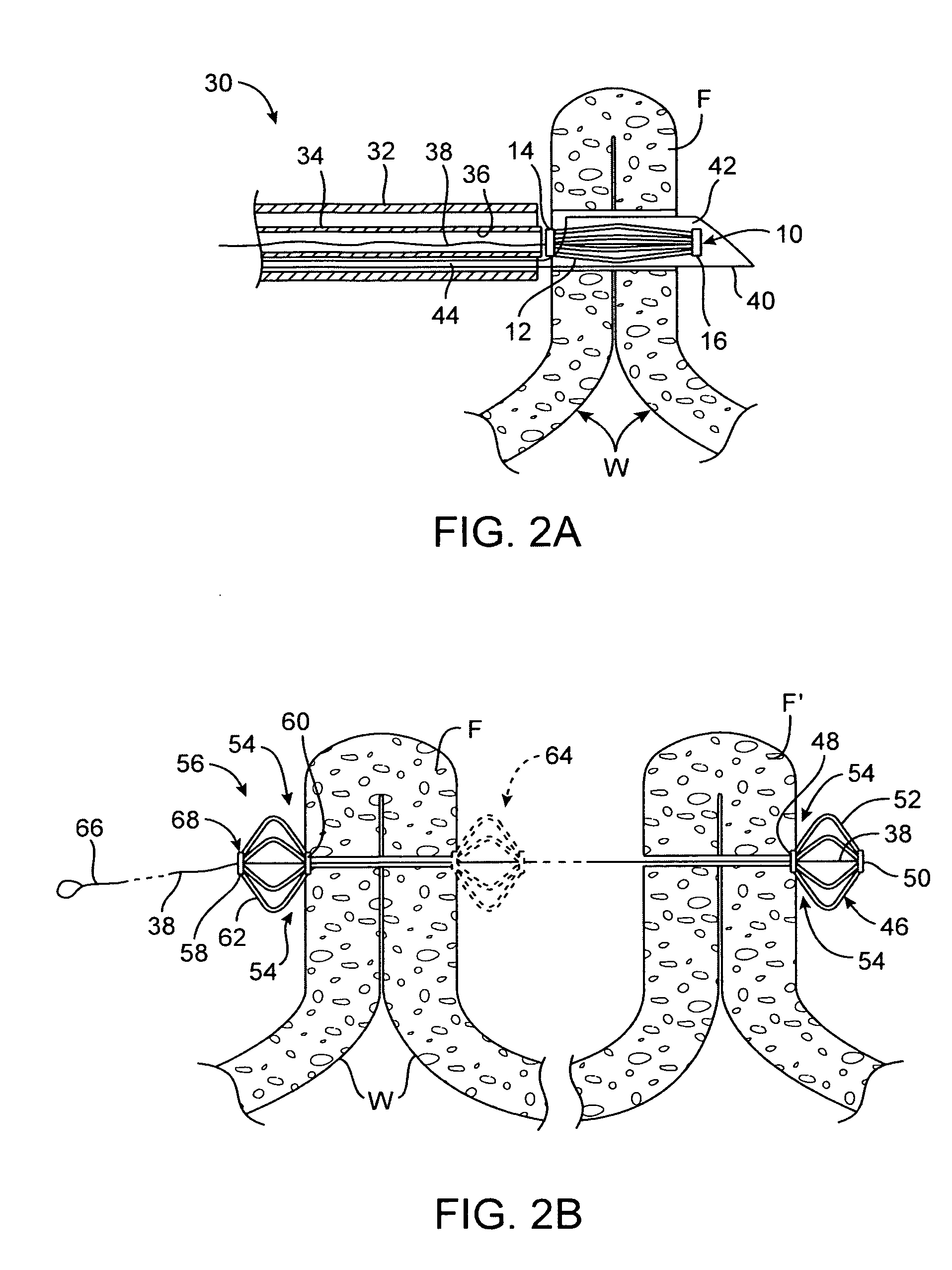
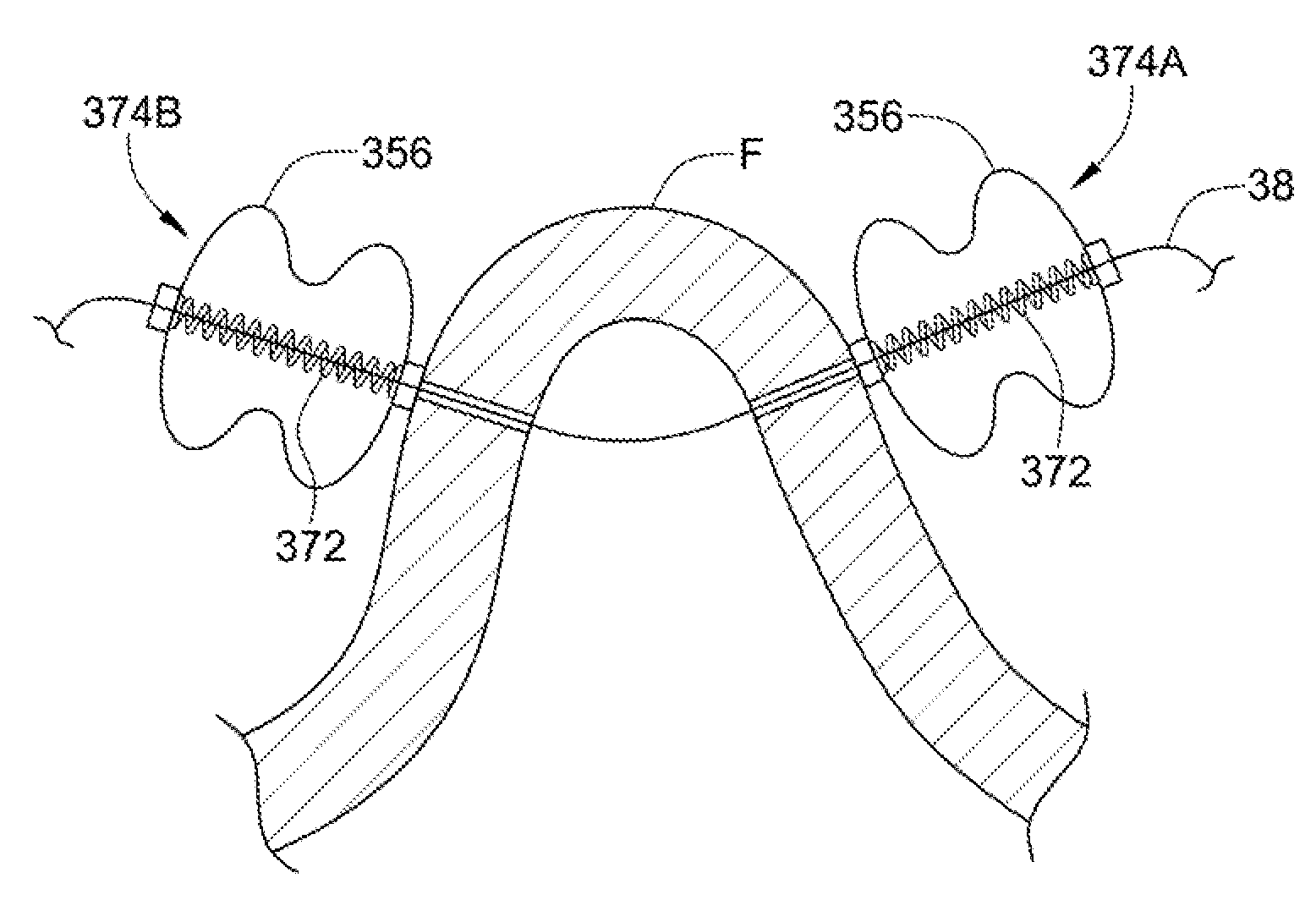
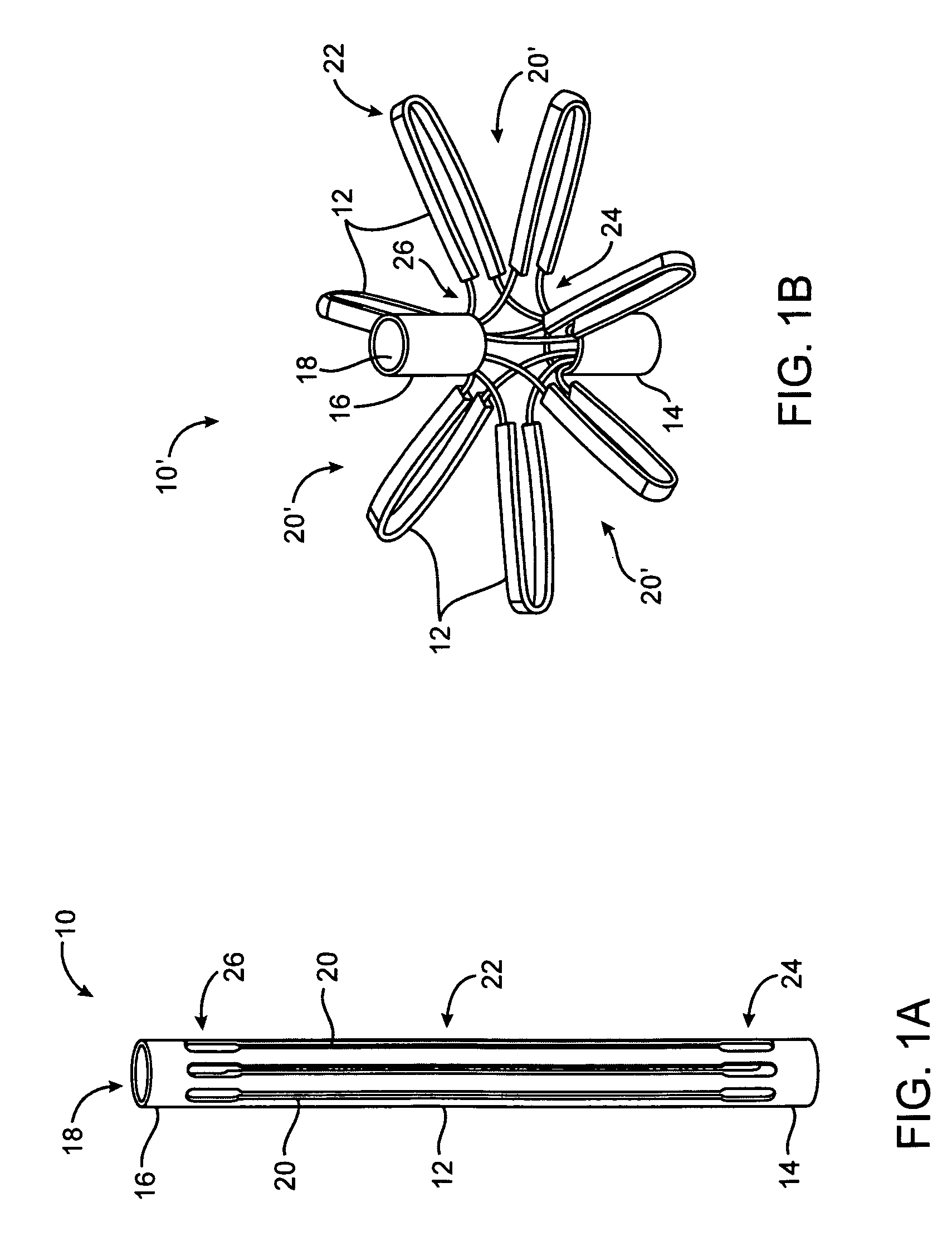
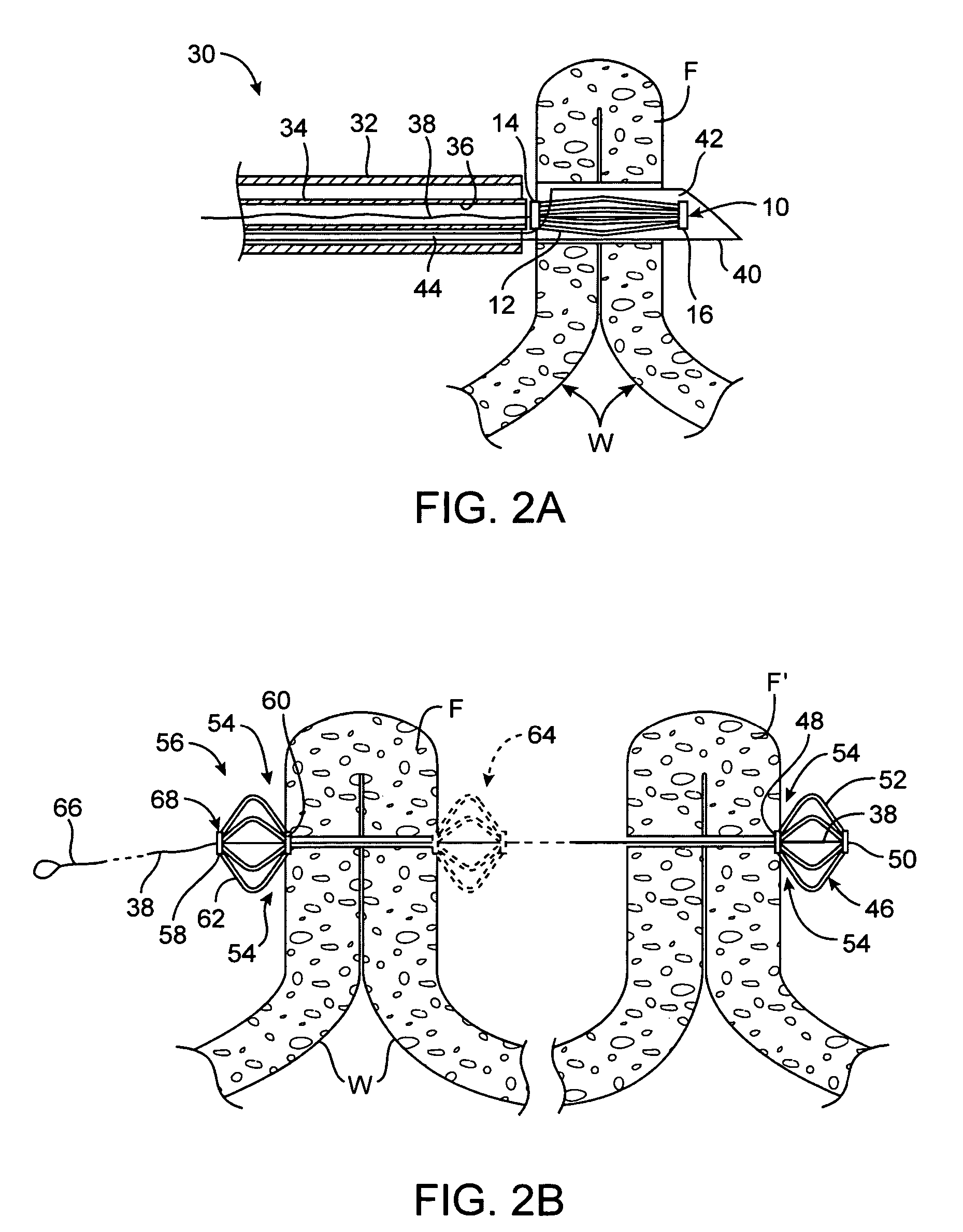
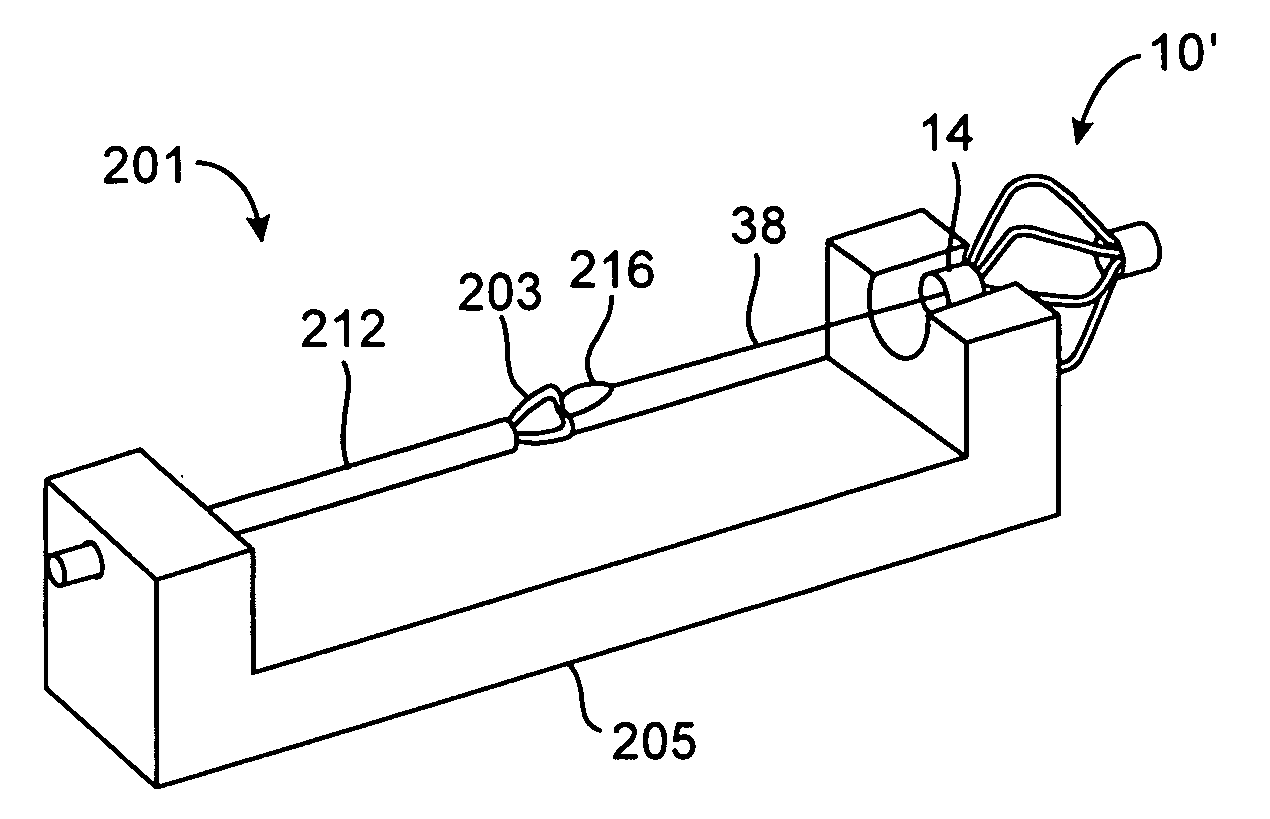
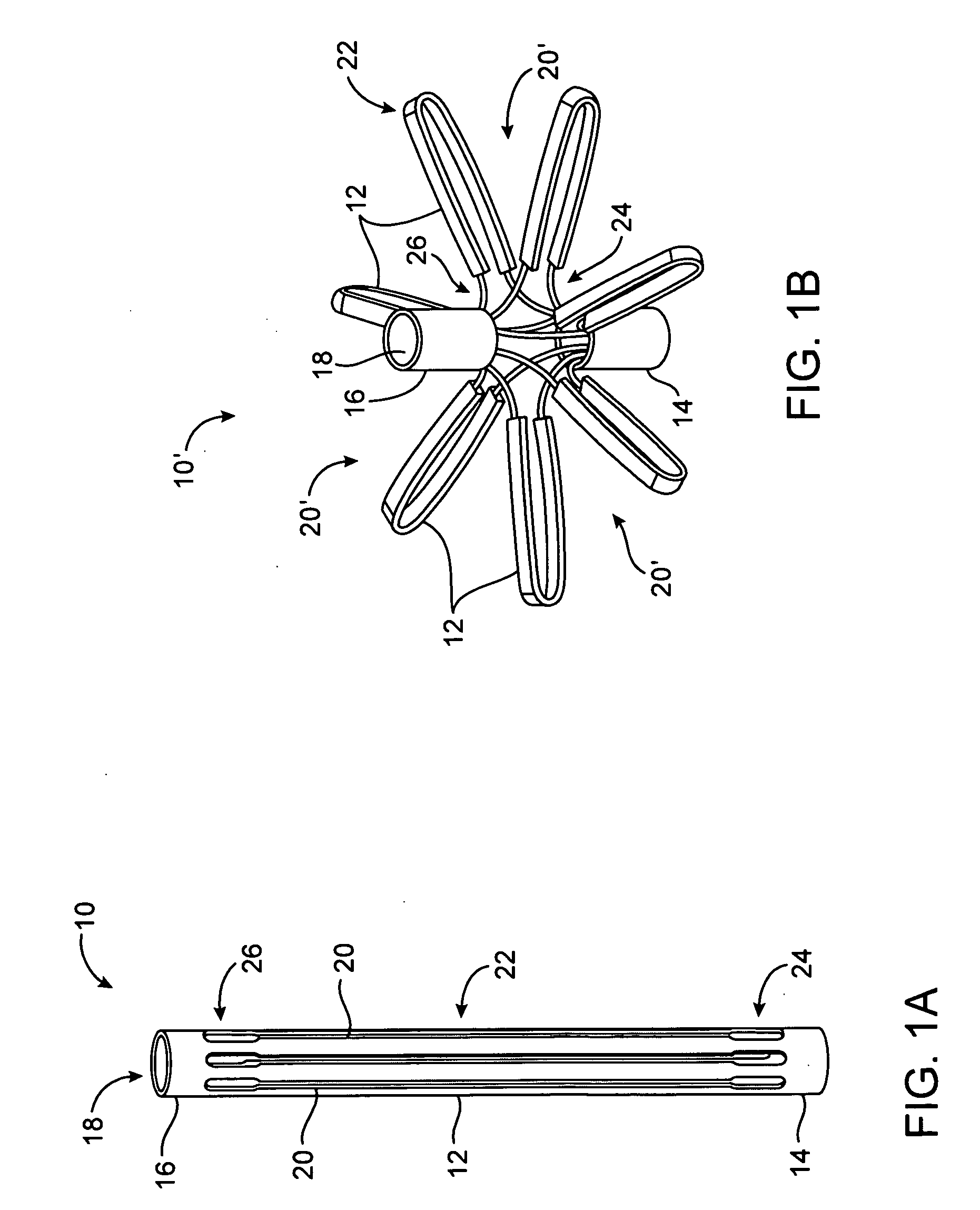
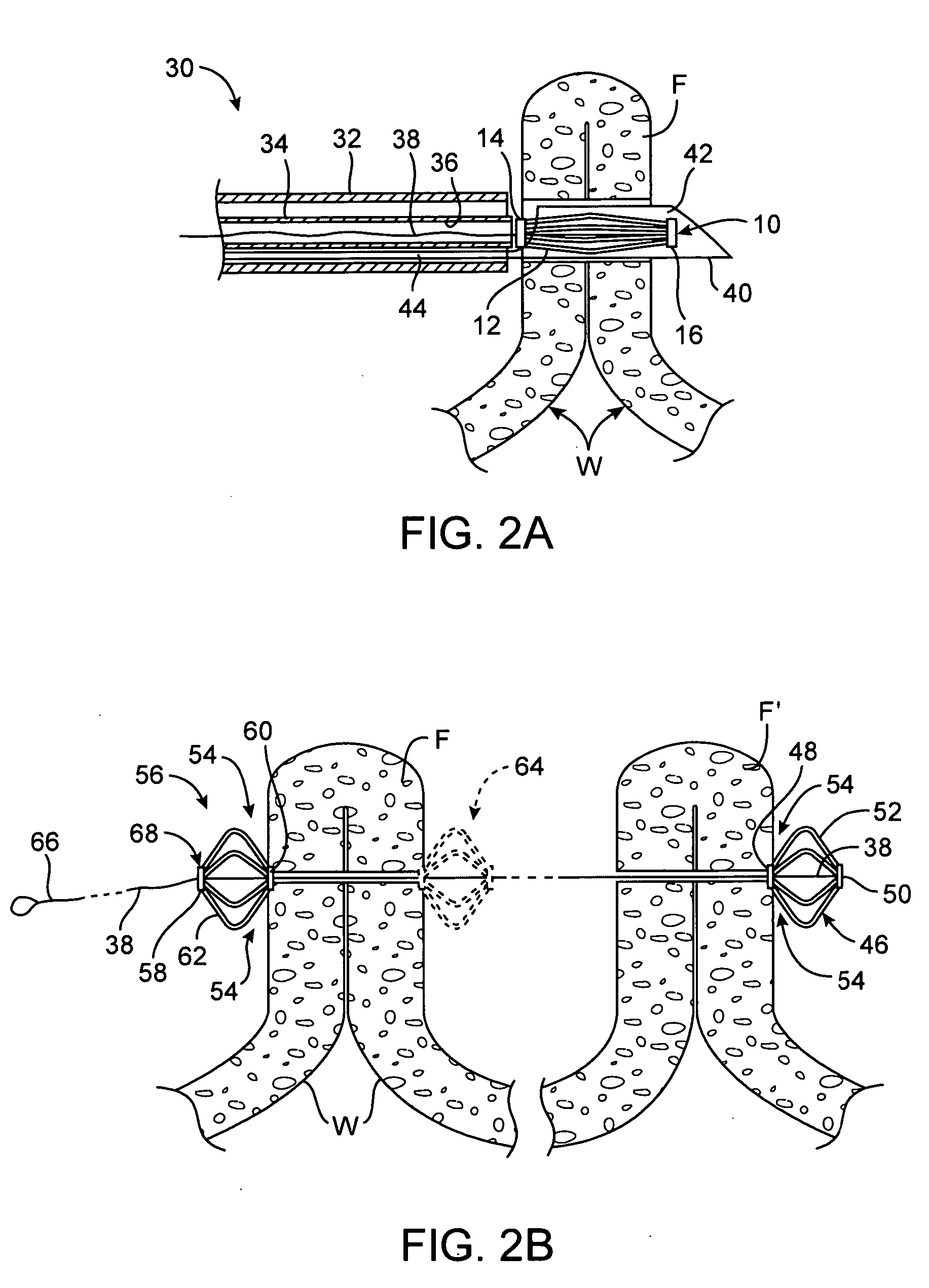
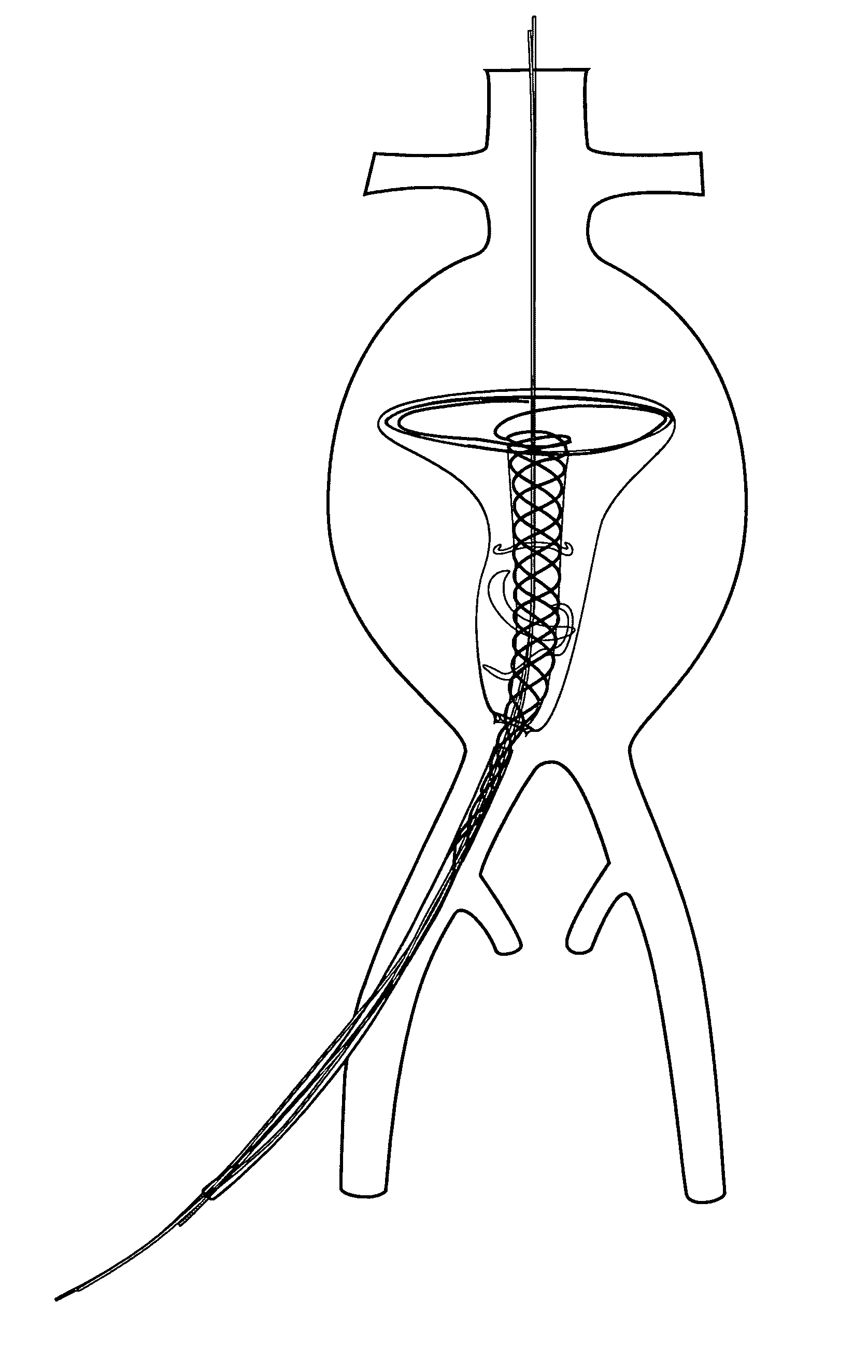
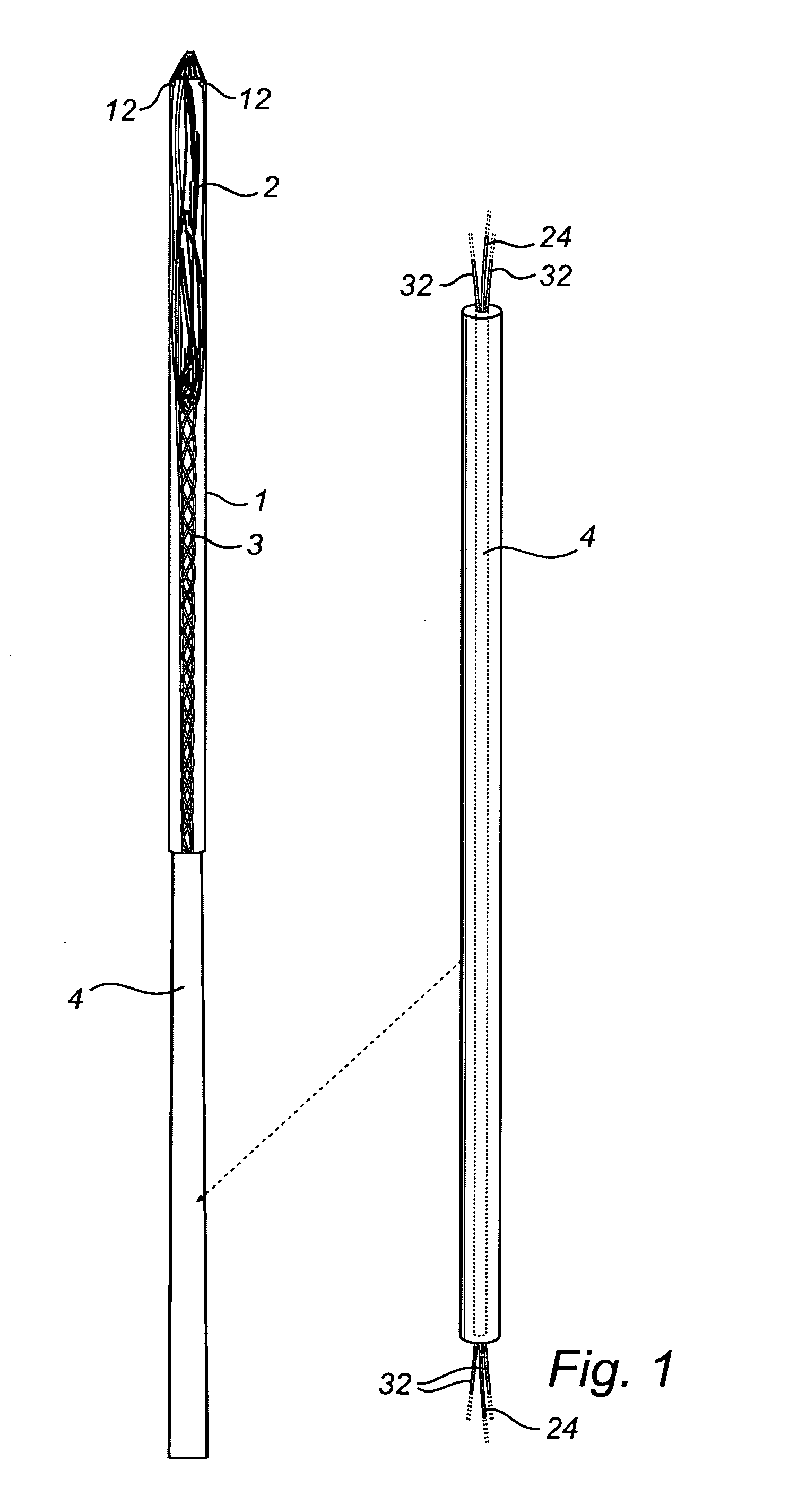
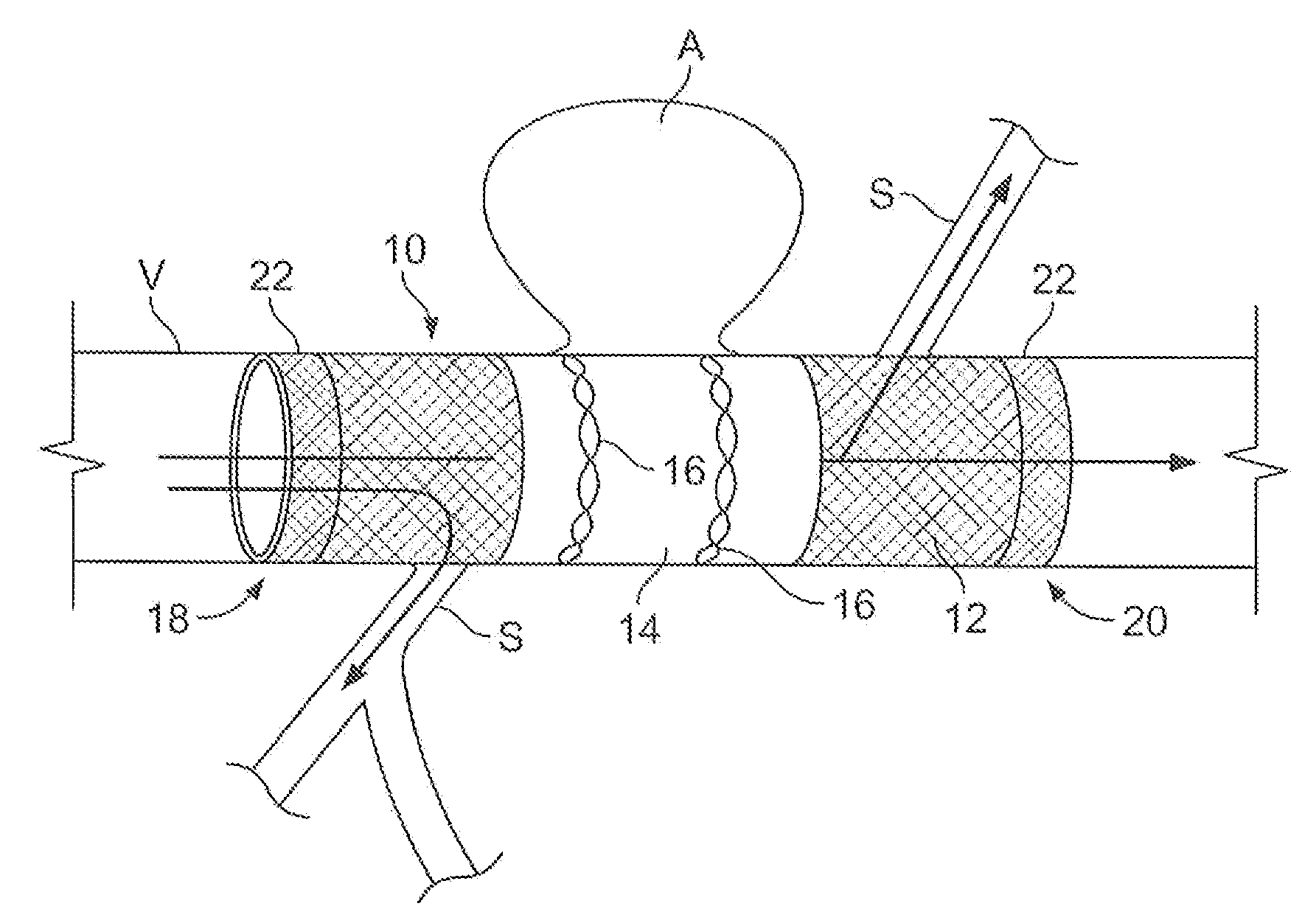
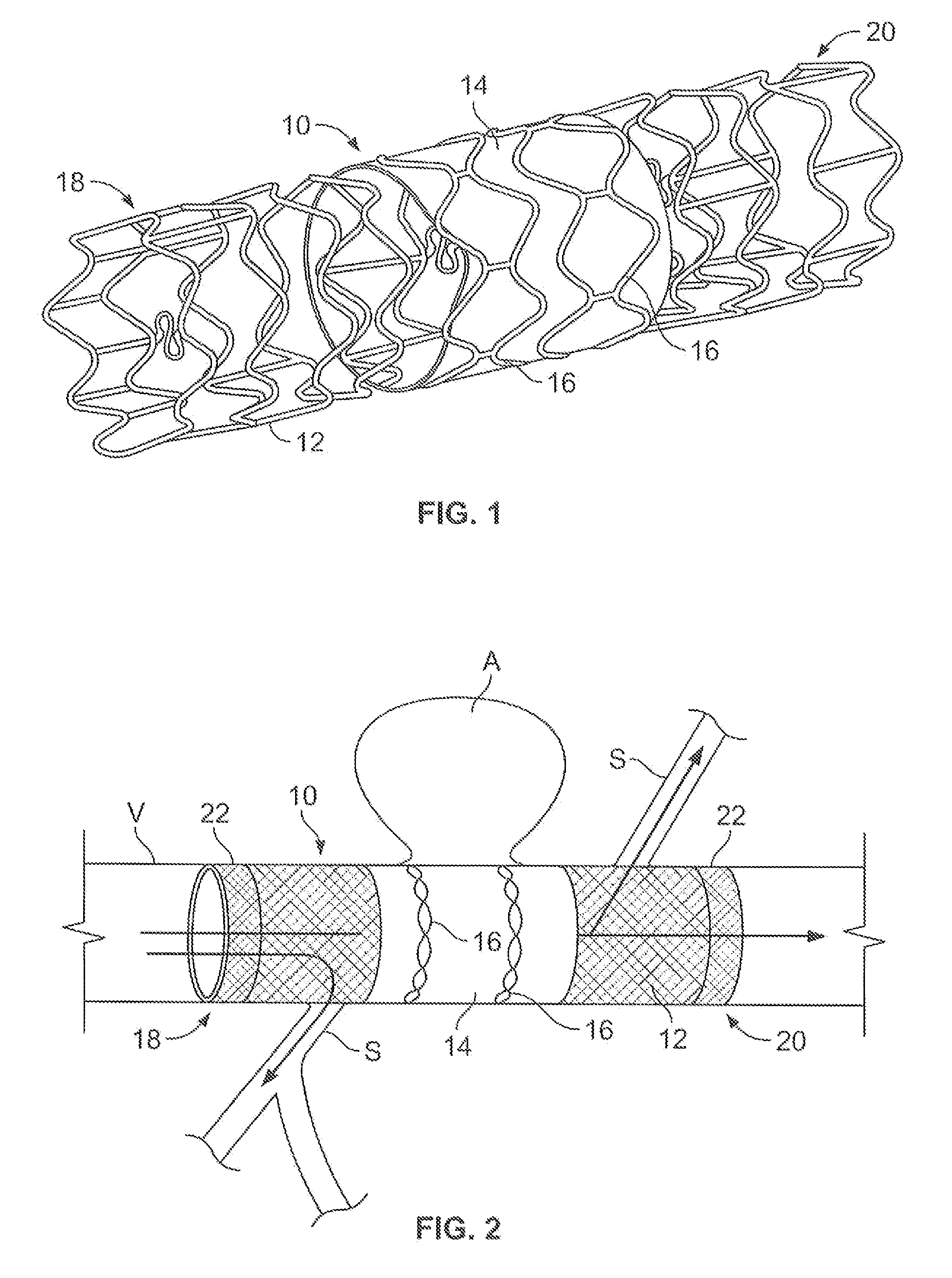
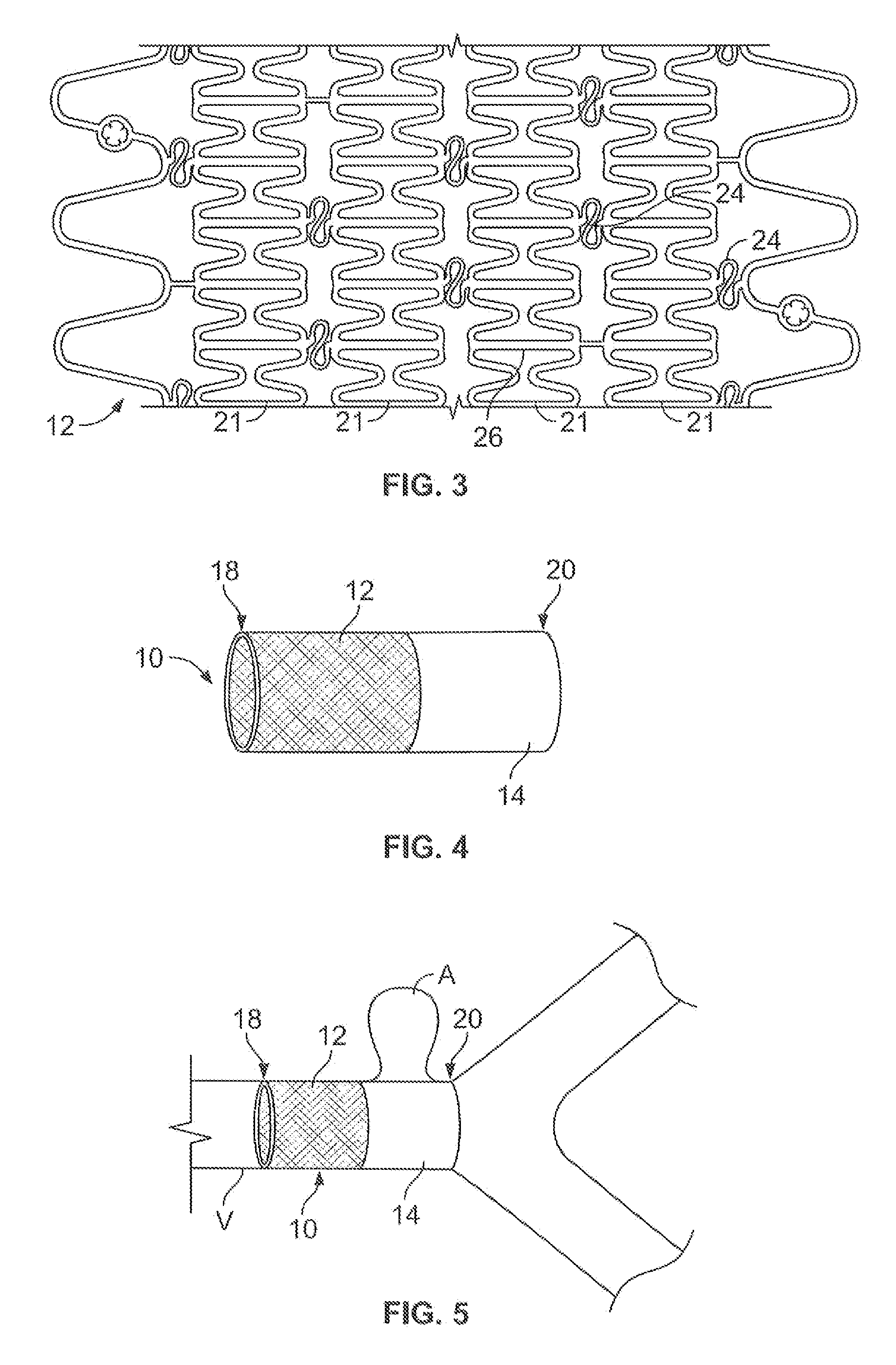
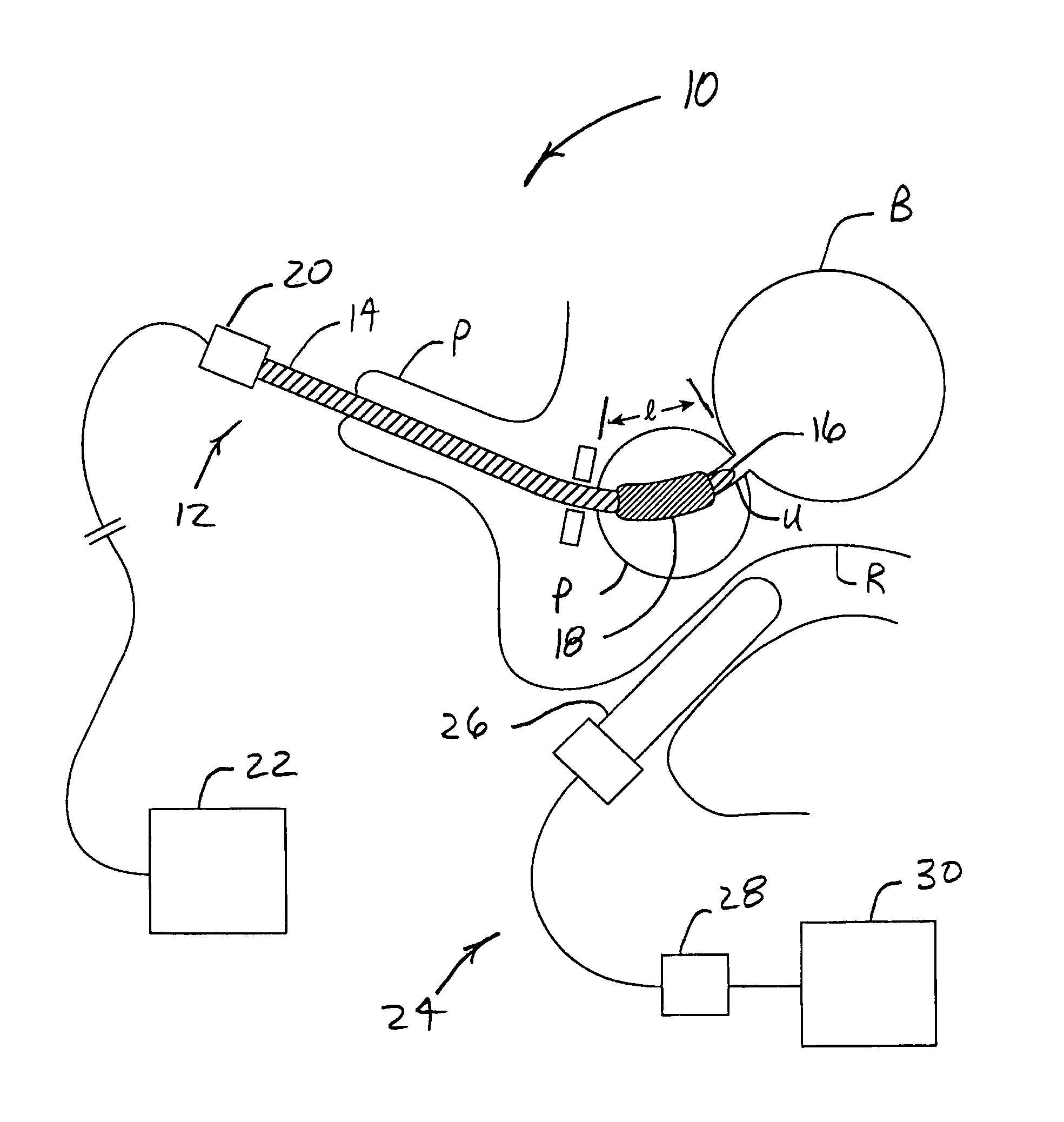
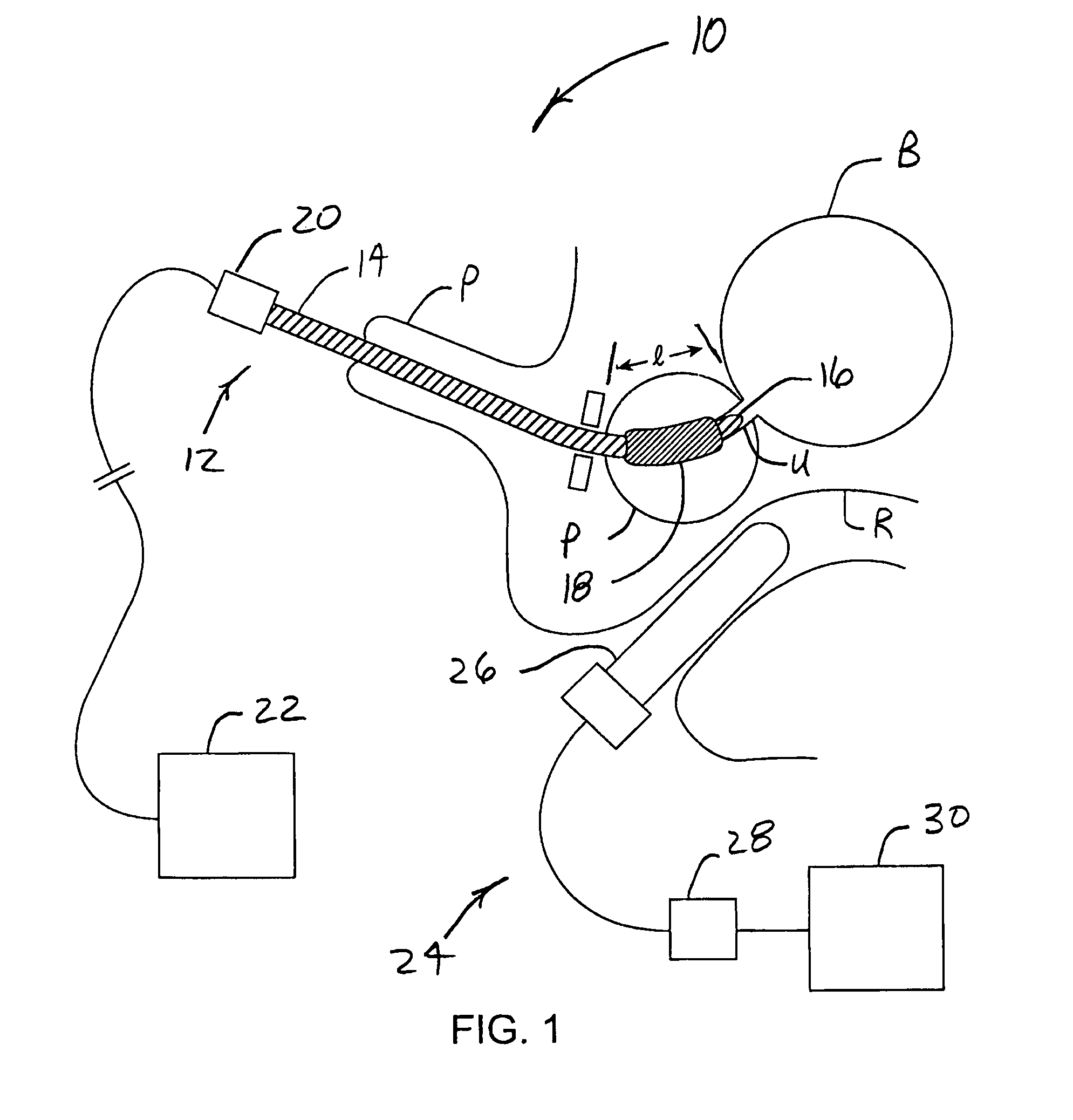
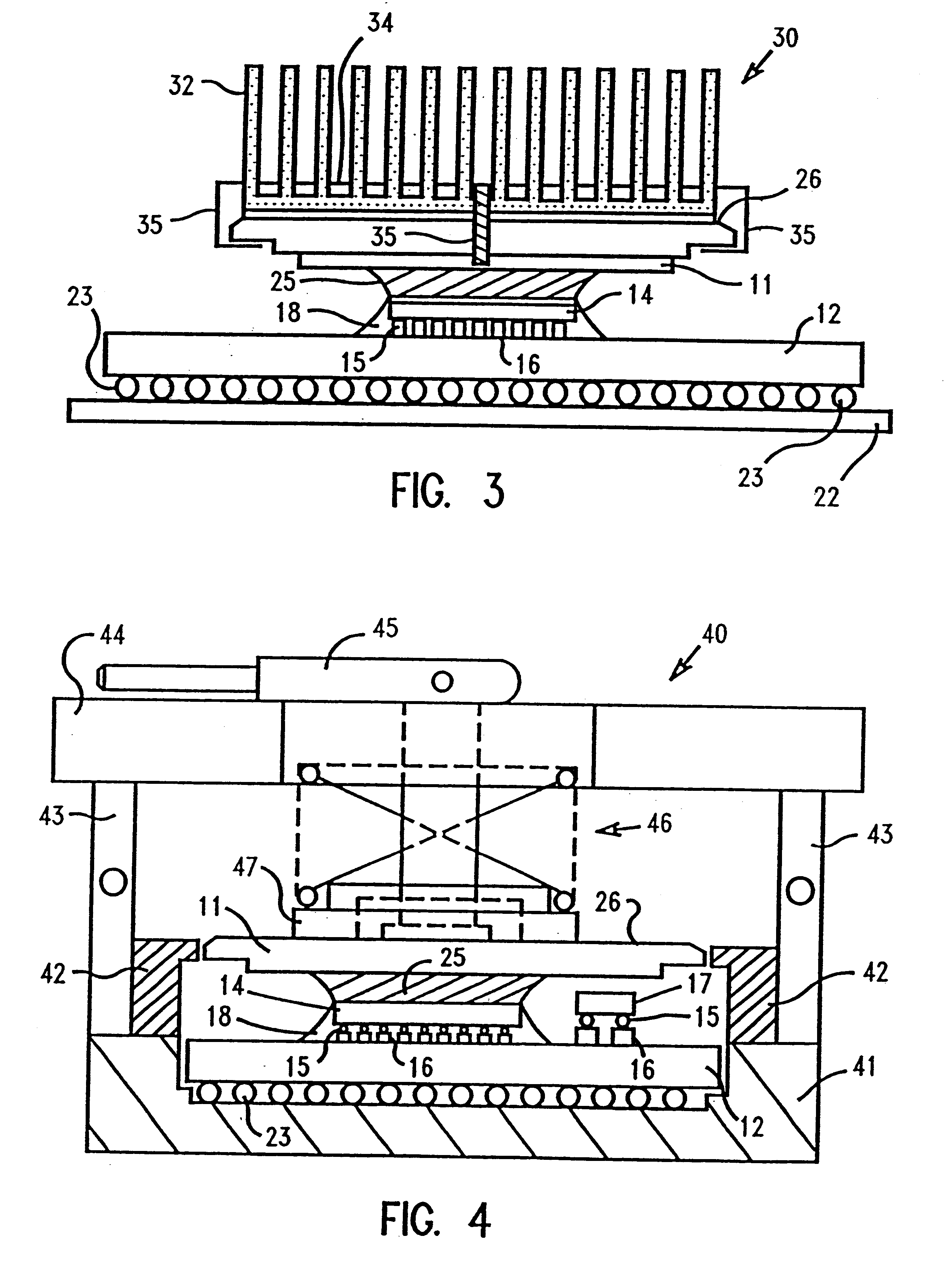
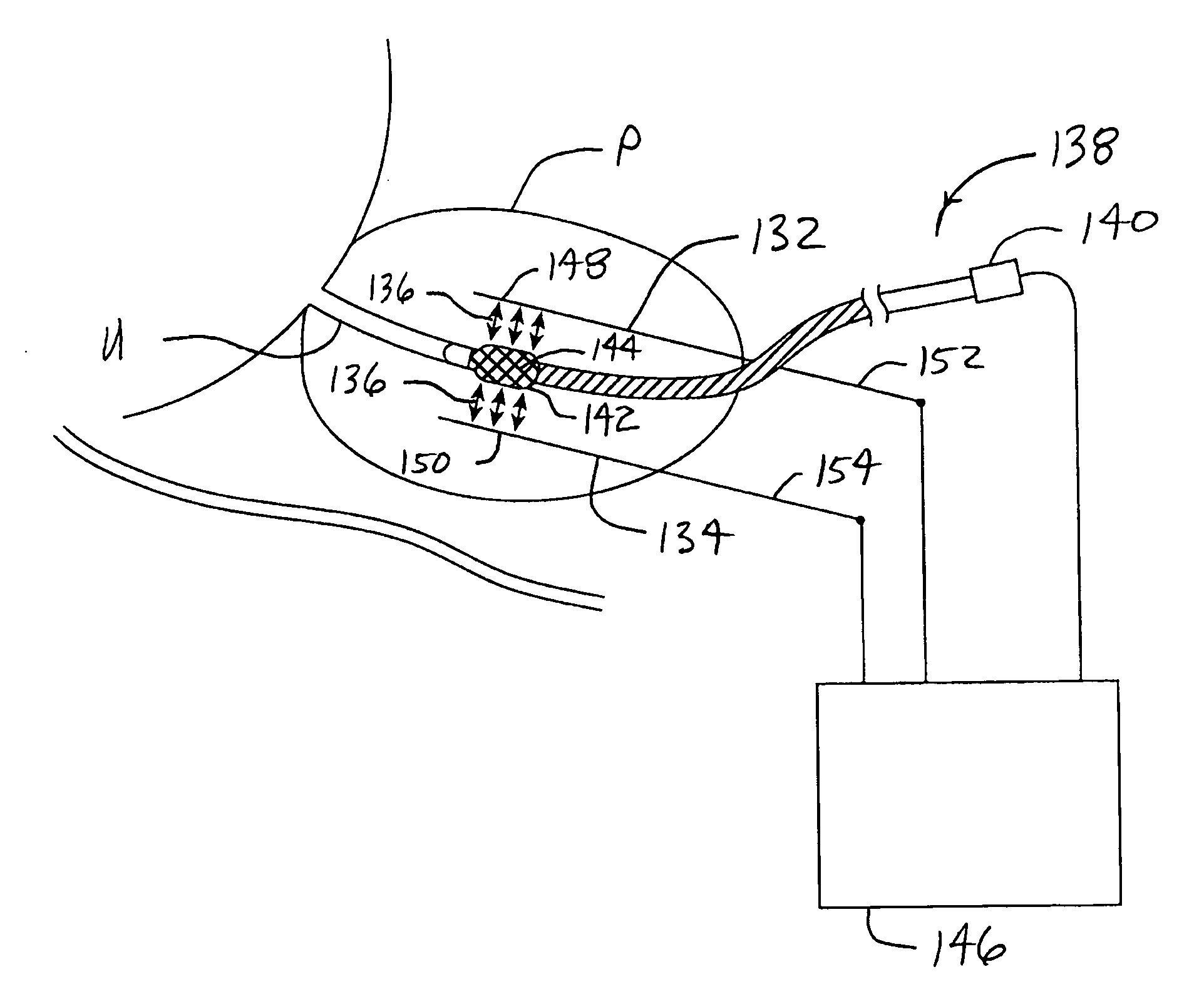
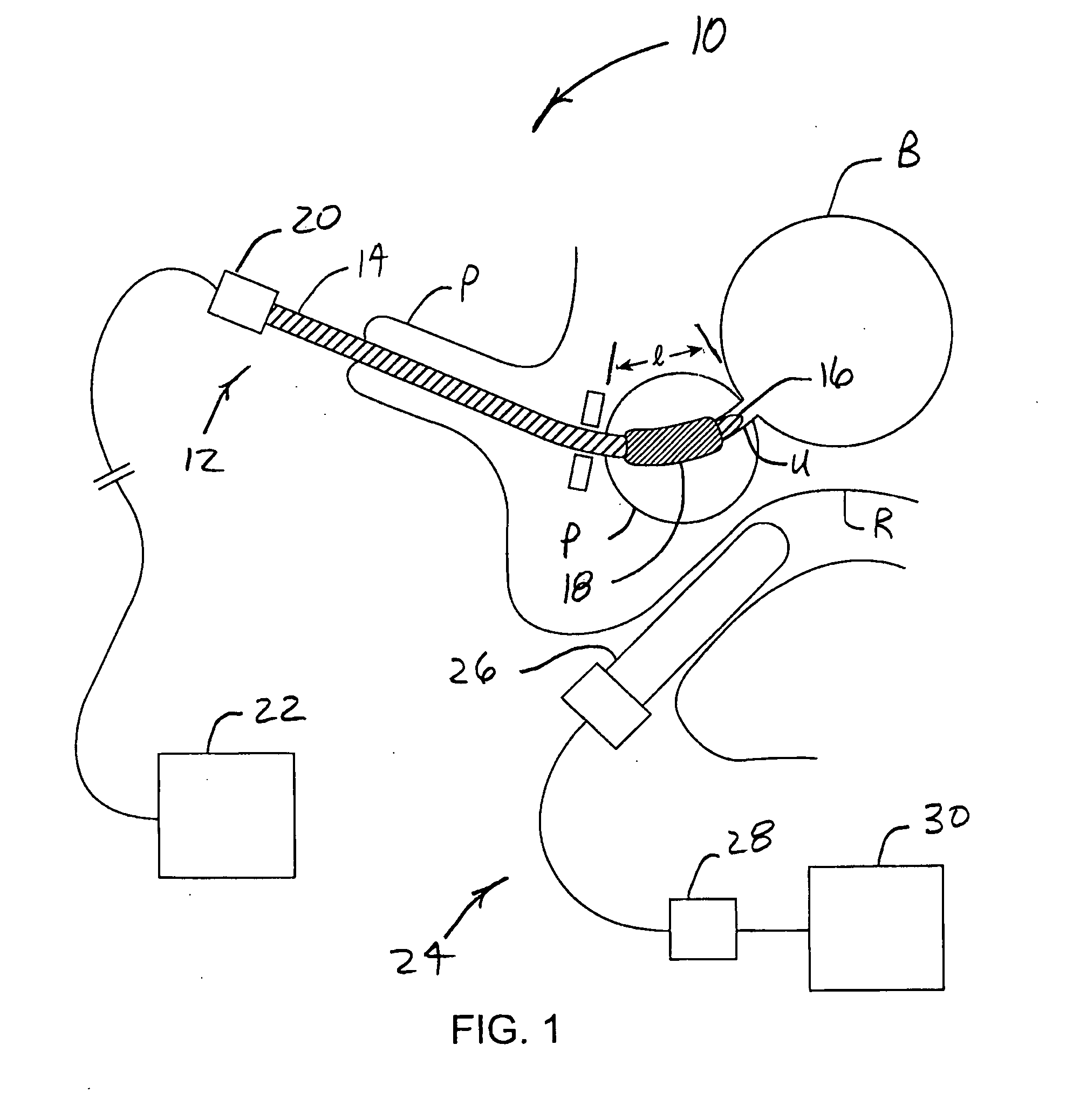
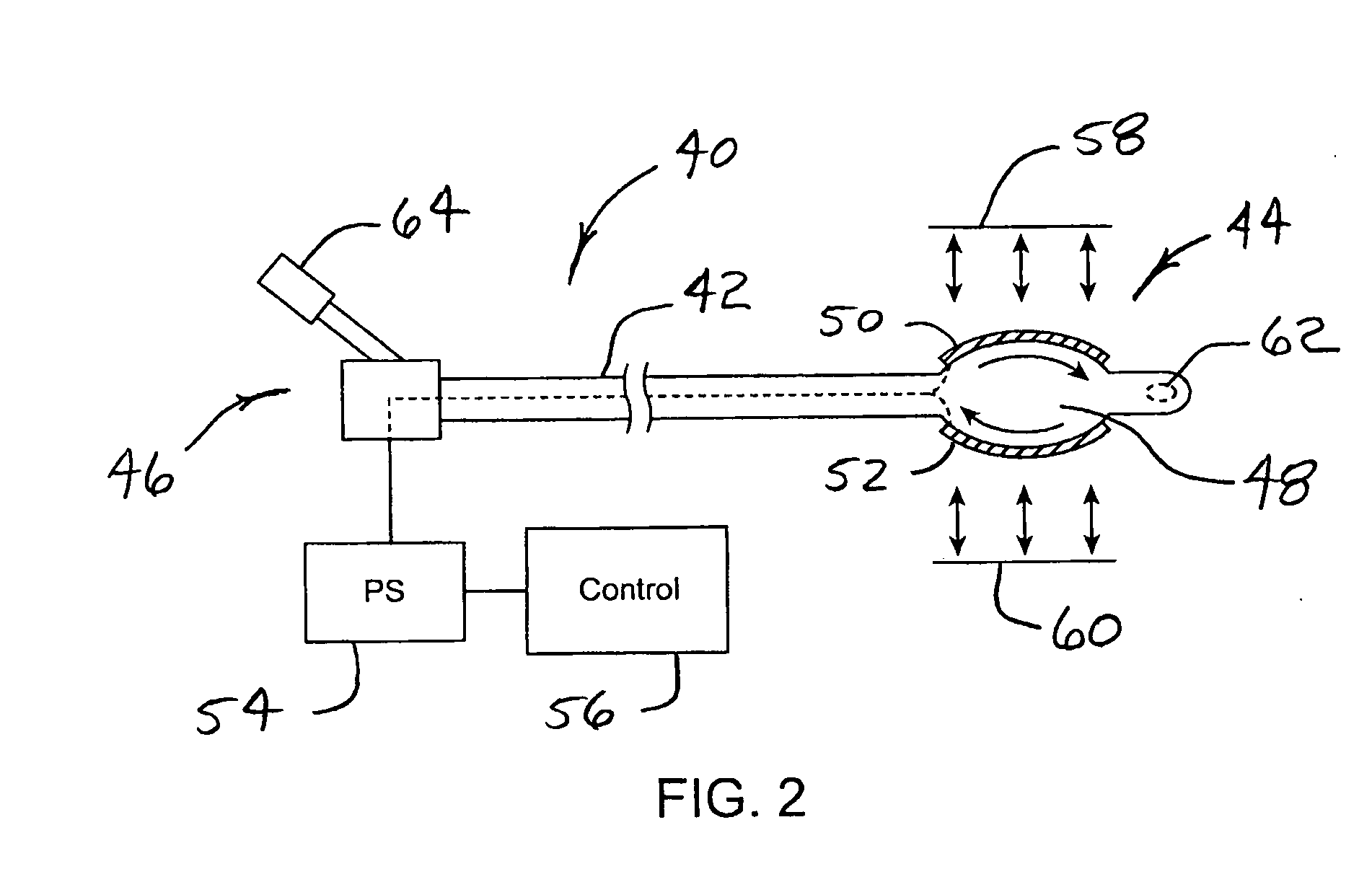
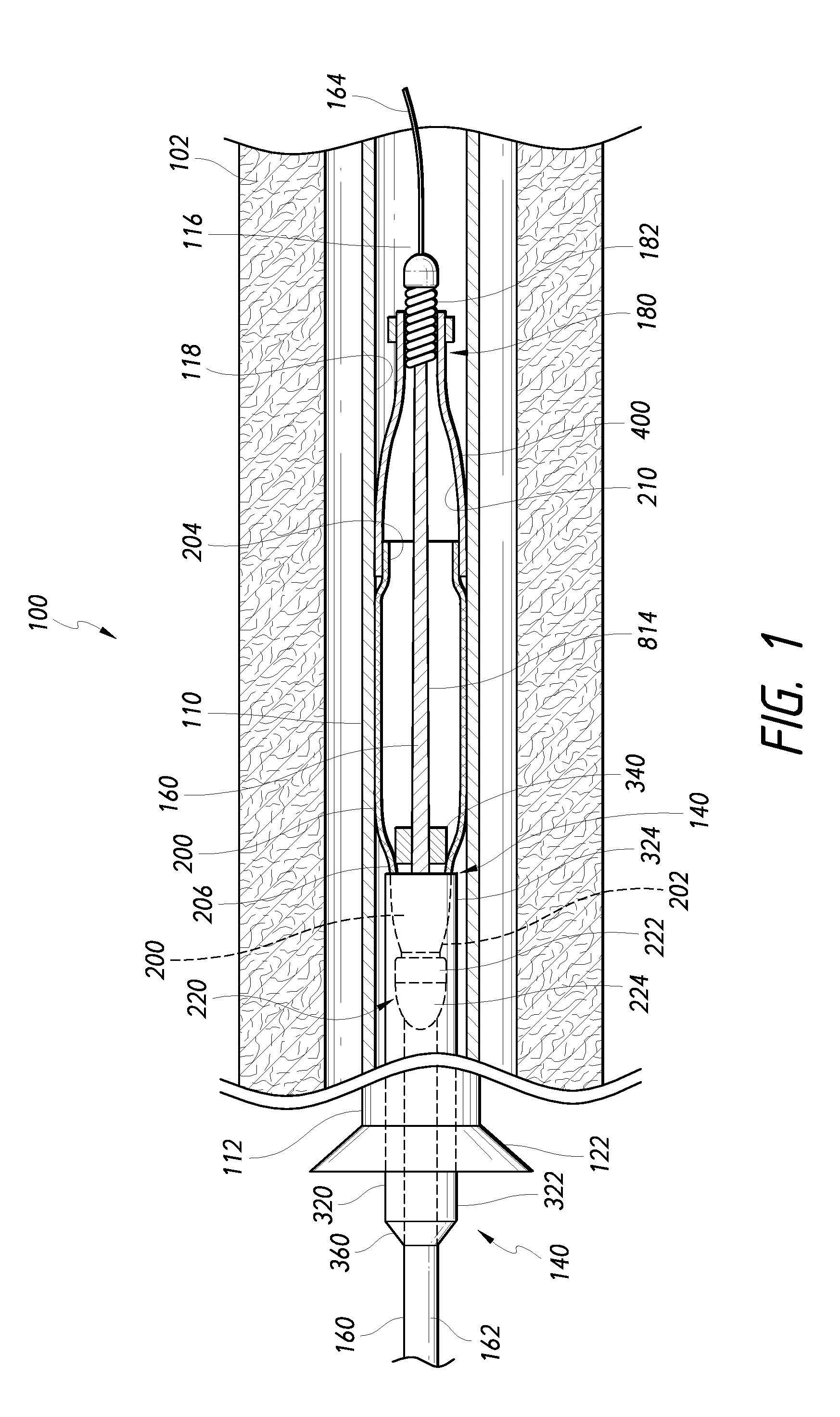
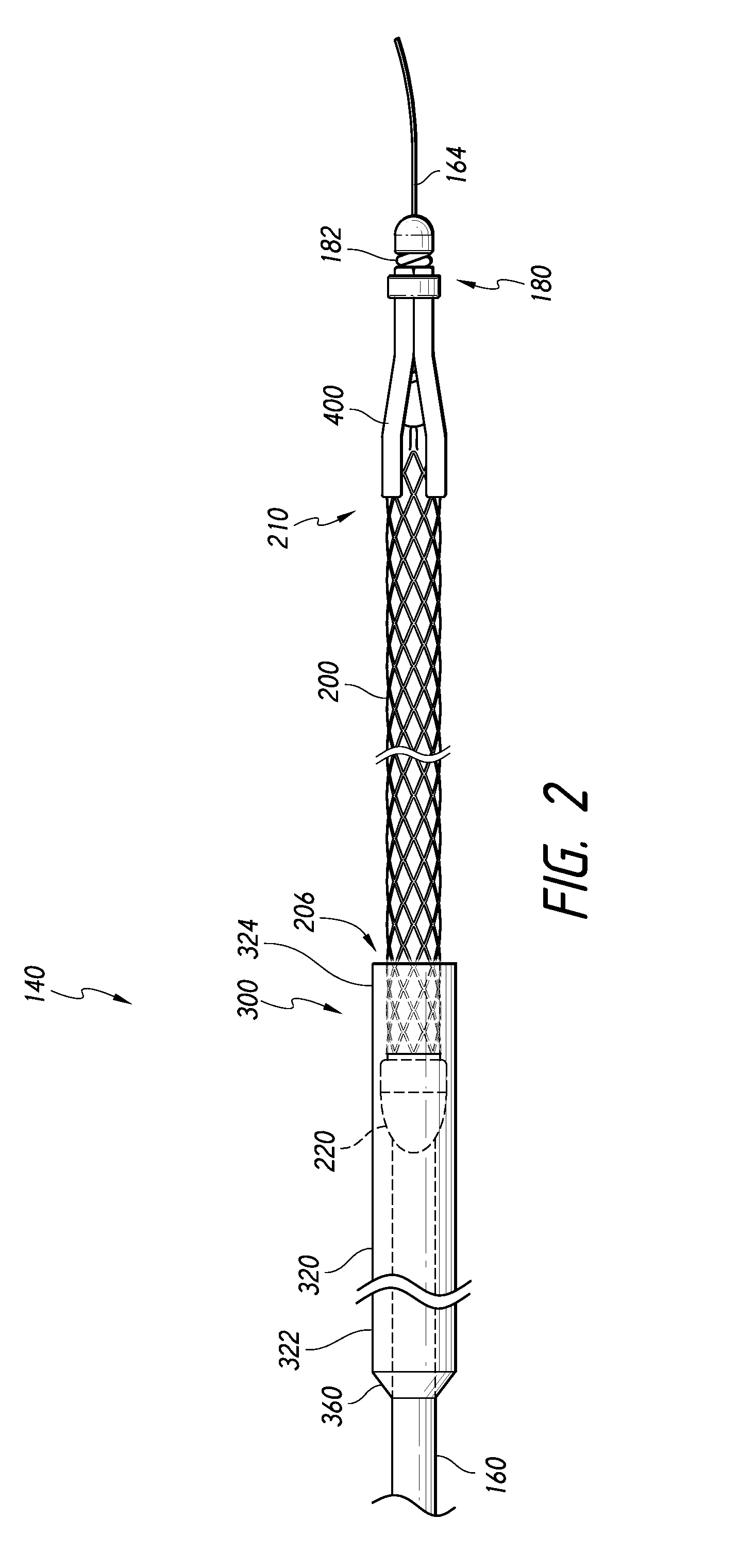
System for optimizing anchoring force
ActiveUS7695493B2Constant force against the tissuePrevent overcompressionSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsConstant forceStrain gauge
Systems for optimizing anchoring force are described herein. In securing tissue folds, over-compression of the tissue directly underlying the anchors is avoided by utilizing tissue anchors having expandable arms configured to minimize contact area between the anchor and tissue. When the anchor is in its expanded configuration, a load is applied to the anchor until it is optimally configured to accommodate a range of deflections while the anchor itself exerts a substantially constant force against the tissue. Various devices, e.g., stops, spring members, fuses, strain gauges, etc., can be used to indicate when the anchor has been deflected to a predetermined level within the optimal range. Moreover, other factors to affect the anchor characteristics include, e.g., varying the number of arms or struts of the anchor, positioning of the arms, configuration of the arms, the length of the collars, etc.
Owner:USGI MEDICAL
Compressible tissue anchor assemblies
ActiveUS7736379B2Constant force against the tissuePrevent overcompressionSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsConstant forceStrain gauge
Apparatus & methods for optimizing anchoring force are described herein. In securing tissue folds, over-compression of the tissue directly underlying the anchors is avoided by utilizing tissue anchors having expandable arms configured to minimize contact area between the anchor and tissue. When the anchor is in its expanded configuration, a load is applied to the anchor until it is optimally configured to accommodate a range of deflections while the anchor itself exerts a substantially constant force against the tissue. Various devices, e.g., stops, spring members, fuses, strain gauges, etc., can be used to indicate when the anchor has been deflected to a predetermined level within the optimal range. Moreover, other factors to affect the anchor characteristics include, e.g., varying the number of arms or struts of the anchor, positioning of the arms, configuration of the arms, the length of the collars, etc.
Owner:USGI MEDICAL
Compressible tissue anchor assemblies
ActiveUS20060217762A1Constant force against the tissuePrevent overcompressionSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsStrain gaugeBiomedical engineering
Apparatus & methods for optimizing anchoring force are described herein. In securing tissue folds, over-compression of the tissue directly underlying the anchors is avoided by utilizing tissue anchors having expandable arms configured to minimize contact area between the anchor and tissue. When the anchor is in its expanded configuration, a load is applied to the anchor until it is optimally configured to accommodate a range of deflections while the anchor itself exerts a substantially constant force against the tissue. Various devices, e.g., stops, spring members, fuses, strain gauges, etc., can be used to indicate when the anchor has been deflected to a predetermined level within the optimal range. Moreover, other factors to affect the anchor characteristics include, e.g., varying the number of arms or struts of the anchor, positioning of the arms, configuration of the arms, the length of the collars, etc.
Owner:USGI MEDICAL
Compressible tissue anchor assemblies
ActiveUS20050277966A1Constant force against the tissuePrevent overcompressionSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsConstant forceStrain gauge
Apparatus & methods for optimizing anchoring force are described herein. In securing tissue folds, over-compression of the tissue directly underlying the anchors is avoided by utilizing tissue anchors having expandable arms configured to minimize contact area between the anchor and tissue. When the anchor is in its expanded configuration, a load is applied to the anchor until it is optimally configured to accommodate a range of deflections while the anchor itself exerts a substantially constant force against the tissue. Various devices, e.g., stops, spring members, fuses, strain gauges, etc., can be used to indicate when the anchor has been deflected to a predetermined level within the optimal range. Moreover, other factors to affect the anchor characteristics include, e.g., varying the number of arms or struts of the anchor, positioning of the arms, configuration of the arms, the length of the collars, etc.
Owner:USGI MEDICAL
Compressible tissue anchor assemblies
ActiveUS7678135B2Constant force against the tissuePrevent overcompressionSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsConstant forceStrain gauge
Owner:USGI MEDICAL
System for optimizing anchoring force
ActiveUS20050277983A1Avoid exposureConstant force against the tissueSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsConstant forceStrain gauge
Systems for optimizing anchoring force are described herein. In securing tissue folds, over-compression of the tissue directly underlying the anchors is avoided by utilizing tissue anchors having expandable arms configured to minimize contact area between the anchor and tissue. When the anchor is in its expanded configuration, a load is applied to the anchor until it is optimally configured to accommodate a range of deflections while the anchor itself exerts a substantially constant force against the tissue. Various devices, e.g., stops, spring members, fuses, strain gauges, etc., can be used to indicate when the anchor has been deflected to a predetermined level within the optimal range. Moreover, other factors to affect the anchor characteristics include, e.g., varying the number of arms or struts of the anchor, positioning of the arms, configuration of the arms, the length of the collars, etc.
Owner:USGI MEDICAL
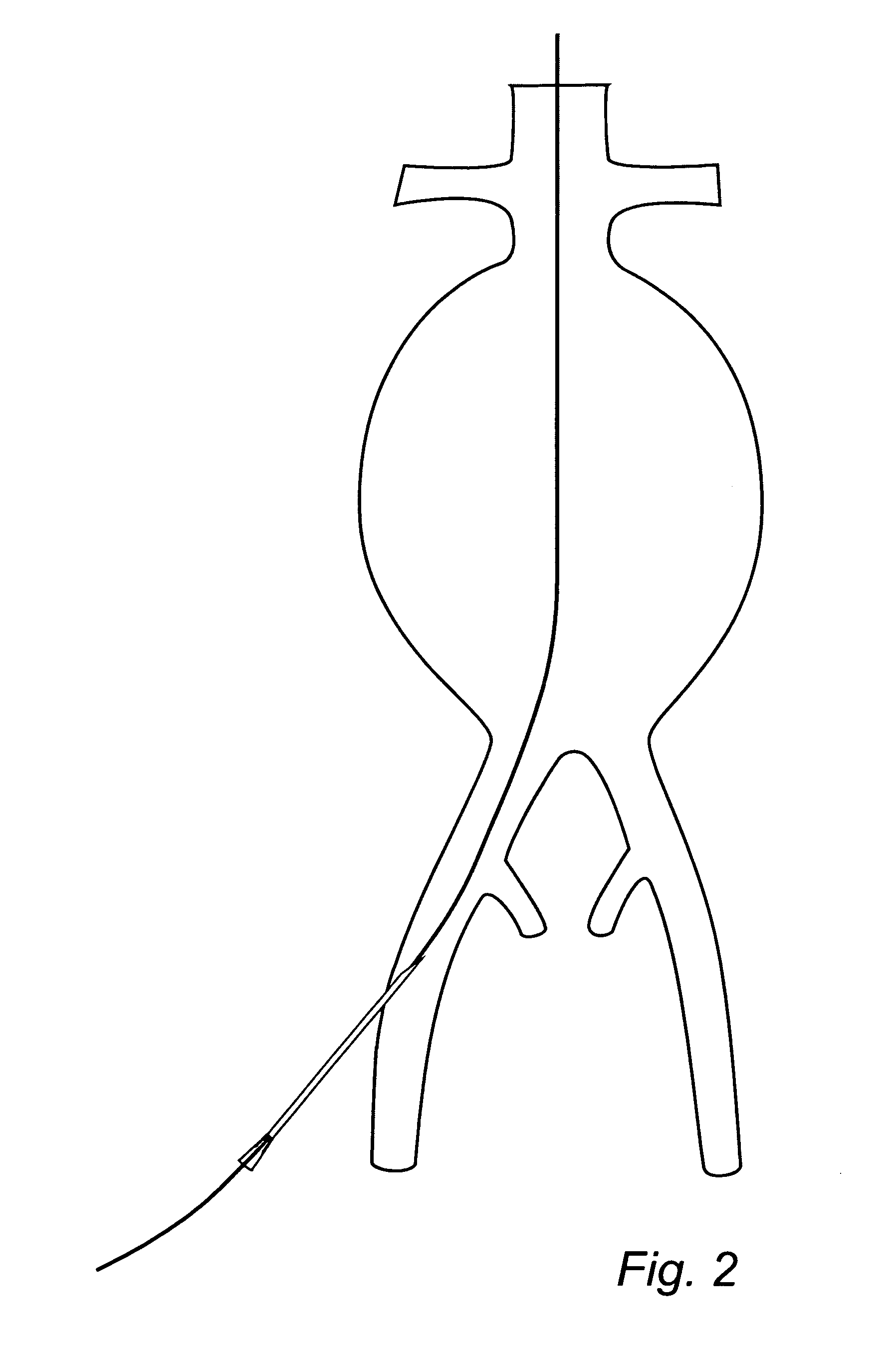
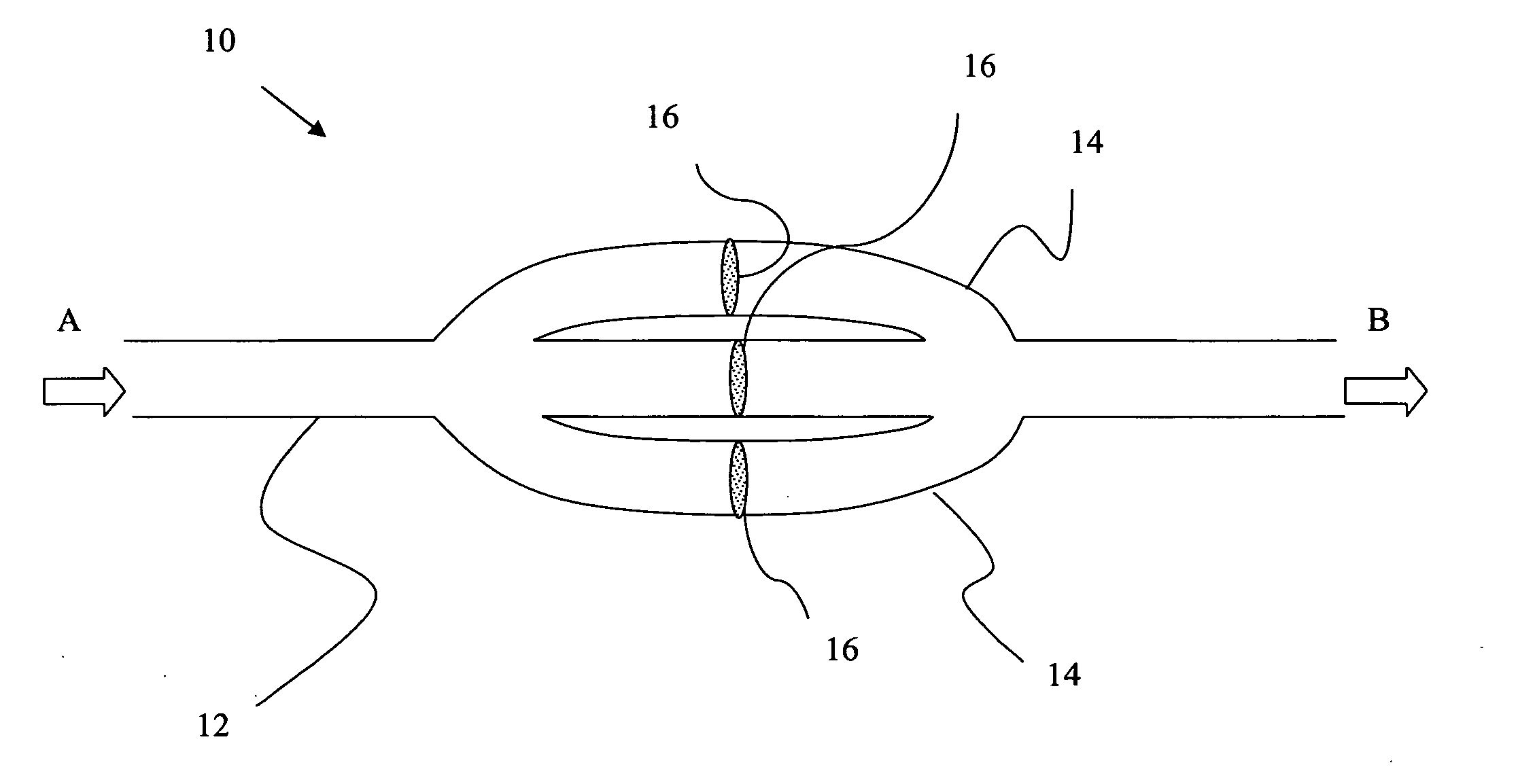
Device and method for treating ruptured aneurysms
InactiveUS20100324649A1Reduce the overall diameterNarrow diameterStentsBlood vesselsEndoscopic surgeryEndoscopic Procedure
A stent device for treating an aneurysm is disclosed. The stent device comprises an expandable balloon with a channel extending through said balloon from one side to another, and a supporting stent connected to said balloon. In an operative disposition, when the expandable balloon is expanded, the supporting stent is arranged at least partly within said channel of said expandable balloon. Further, the supporting stent has walls which are permeable to blood. The stent device may be introduced and removed by endoscopic procedures, with a relatively simple procedure. Thus, the stent device is highly useable for fast and temporary treatment of ruptured aneurysms.
Owner:GRAFTCRAFT I GOTEBORG
Partially covered stent devices and methods of use
InactiveUS20070219619A1Avoid flowMaintain blood flowStentsBlood vesselsFilling materialsCovered stent
Devices, systems and methods are provided for treating aneurysms, particularly cerebral aneurysms. Such treatment is achieved minimally invasively without the need for conventional filling materials and methods. Such treatments may be used for aneurysms located near blood vessel side-branches and bifurcations.
Owner:NFOCUS NEUROMEDICAL
High throughput separations based analysis systems
InactiveUS7169277B2Increase flow resistanceSufficient flow resistanceSludge treatmentFixed microstructural devicesElectrophoresisBulk samples
Devices, systems and methods for use in separating sample materials into different fractions that employ bulk fluid flow for loading of samples followed by electrophoretic separation of the sample material. Devices employ configurations that optionally allow bulk sample loading with some or no displacement of a separation matrix within a separation conduit. Methods of using these devices, and systems that incorporate these devices are also envisioned.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
Method And System For Fluid Flow Control In A Fluid Network System
ActiveUS20140094105A1Easy to identifyMinimize consumptionFlow control using electric meansPipeline systemsEngineeringStreamflow
A method of controlling fluid flow in a fluid network system by means of a plurality of fluid machines. The disclosure provides a simple empirical method of identifying network characteristics of the fluid network system used for providing the required fluid flow rate in the fluid network system utilizing minimal fluid machine power. The method includes the steps of determining a relation between a change in fluid machine speed and a corresponding change in fluid flow rate for each of the plurality of fluid machines empirically; determining a minimum total fluid machine power which provides a minimum required flow rate in the fluid network system based on a constraint involving the relation between the fluid flow rate and the corresponding fluid machine speed, and controlling a speed of the plurality of fluid machines such that the minimum total fluid machine power in the fluid network system is attained.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Methods and apparatus for luminal stenting
Described herein are flexible implantable devices or stents that can, for example, navigate tortuous vessels of the neurovasculature. The devices can also conform to the shape of tortuous vessels of the vasculature. In some embodiments, the devices can direct blood flow within a vessel away from an aneurysm or limit blood flow to the aneurysm. Methods and structures are provided for adjusting, along a length of the device, the porosity of the device while maintaining a cross-sectional dimension. In some embodiments, a distal stent cover covers the distal end of the device and reduces friction between the stent and an inner surface of a delivery device, such as a catheter.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
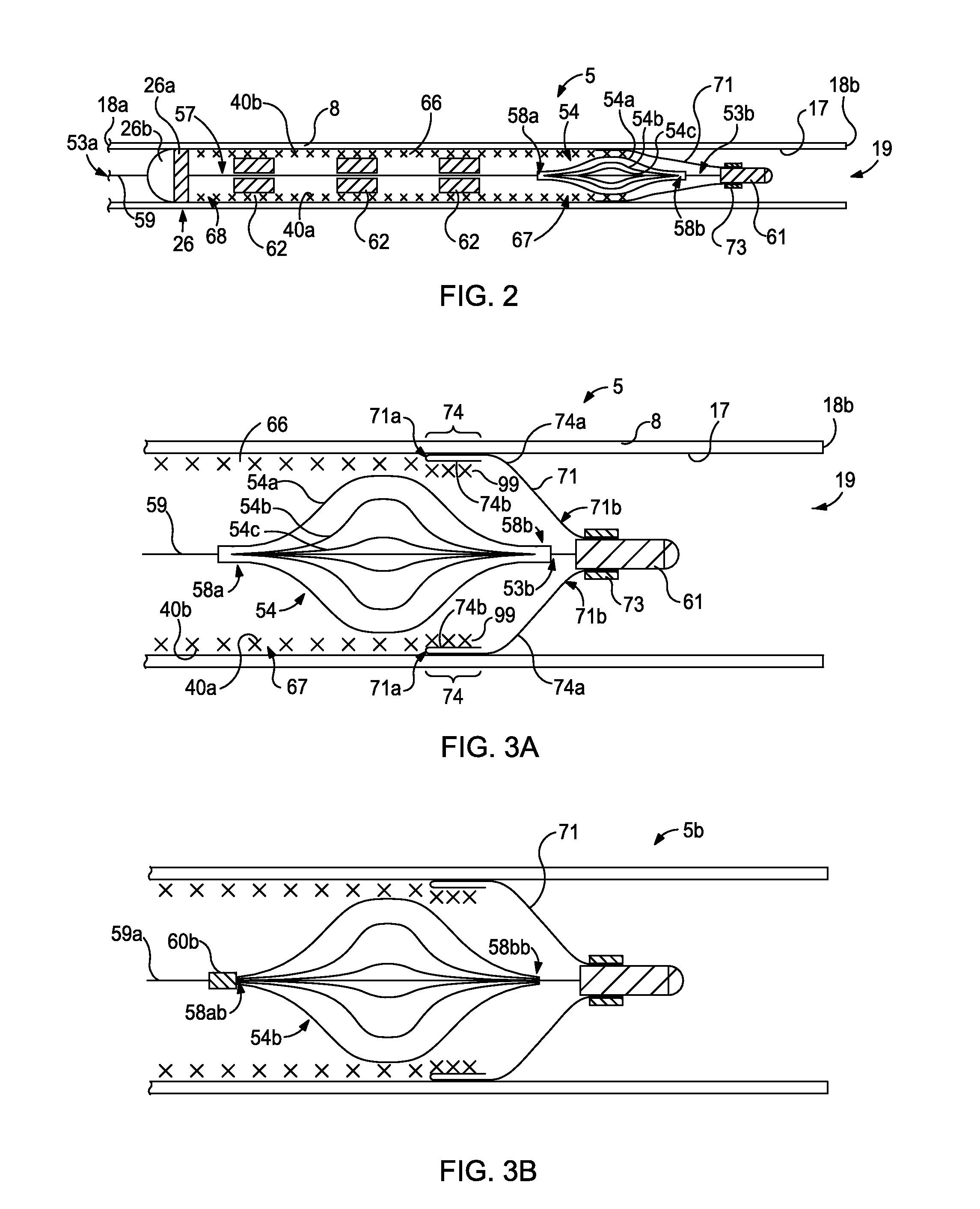
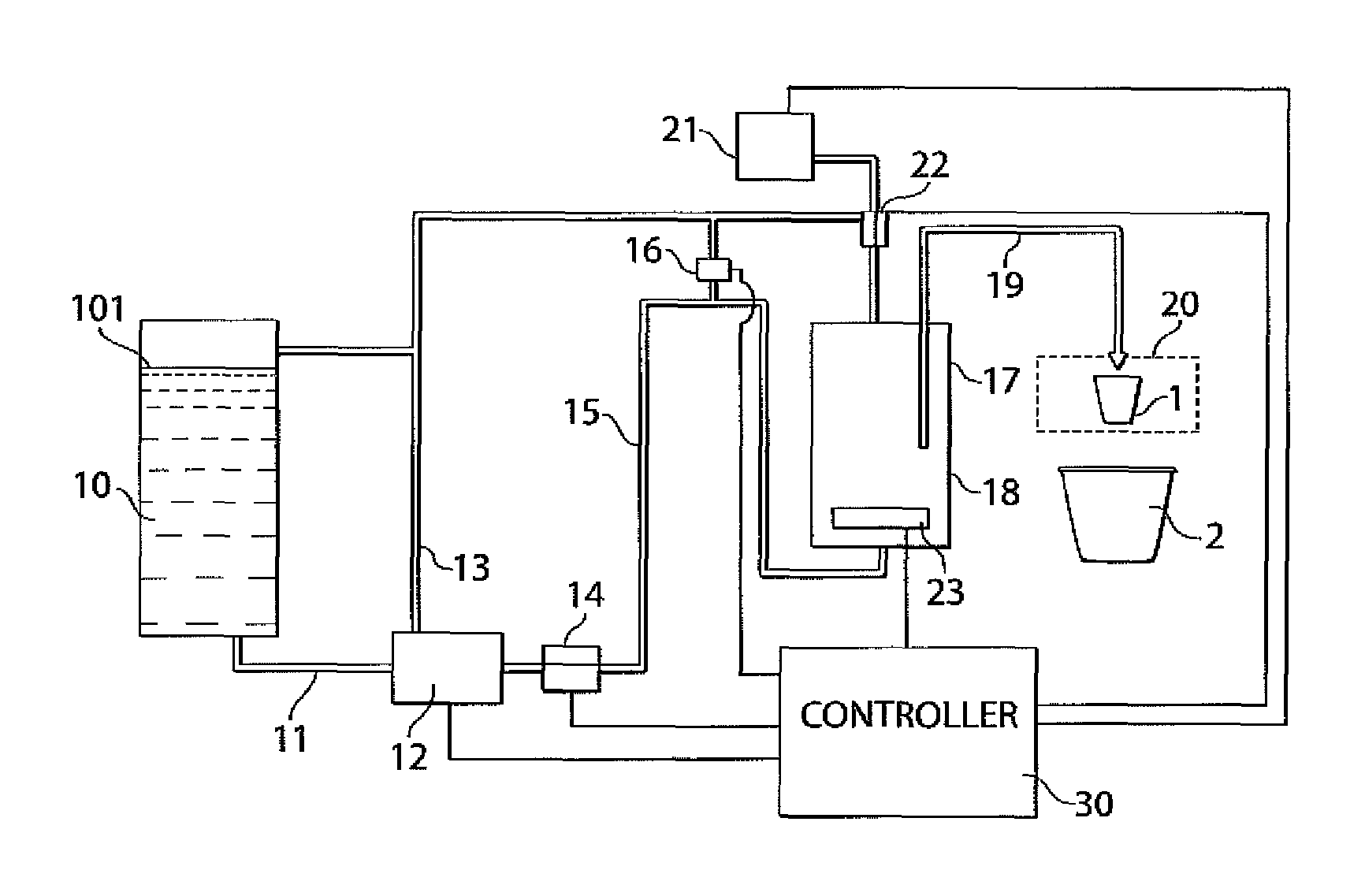
Beverage forming apparatus with centrifugal pump
ActiveUS8151694B2Adequate flowSufficient pressureBeverage vesselsFood preparationExhaust valveControl valves
Owner:KEURIG GREEN MOUNTAIN INC
Method for direct attachment of a chip to a cooling member
InactiveUS6413353B2High bonding strengthAdequate flowSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsAdhesive processes with surface pretreatmentHeat flowSilanes
A semiconductor chip module uses a silicone adhesive between the semiconductor chip and a cap, said adhesive having sufficient bond strength to secure said cap to said chip without additional mechanical constraint while providing a direct thermally conductive path and permitting sufficient heat flow from said chip to said cap to maintain steady state operation of said semiconductor chip. The preferred silicone adhesive comprises a primerless, two-part polysiloxane-based adhesive made by reacting polydimethyl siloxane, an organosilicon compound, a polysiloxane, and a silane, in the presence of a catalyst.
Owner:IBM CORP
Implantable prosthetic device for connection to a fluid flow pathway of a patient
An implantable prosthetic for connection to a fluid flow pathway of a patient. The prosthetic is comprised of a primary tube structure which is in communication with a plurality of secondary tube structures each of which contains filters for trapping embolic particles, such as blood clots, air bubbles, thrombus. etc. within a fluid flow pathway within a patient. The prosthetic also contains a monitoring device to non-invasively the flow of fluids through a patient's fluid flow pathway.
Owner:TECH ADVANCEMENT GROUP
Transurethral systems and methods for ablation treatment of prostate tissue
Transurethral systems and methods for delivering electrical energy and controlled, mild heating to a prostate tissue of a patient for destruction of cancerous and / or hyperplastic tissue. A method includes positioning an elongate urethral probe having an expandable member with electrode elements at a target location in the patient's urethra, and inflating or expanding at the target location. Secondary electrodes are positioned within or adjacent to the prostate tissue and spaced from the electrode elements of the expandable member, and an alternating electrical current flow is established between the electrode elements of the expandable member and the one or more secondary electrodes. Current delivery can be selected so as to destroy or ablate cancerous cells of the prostate tissue.
Owner:LAZURE SCI
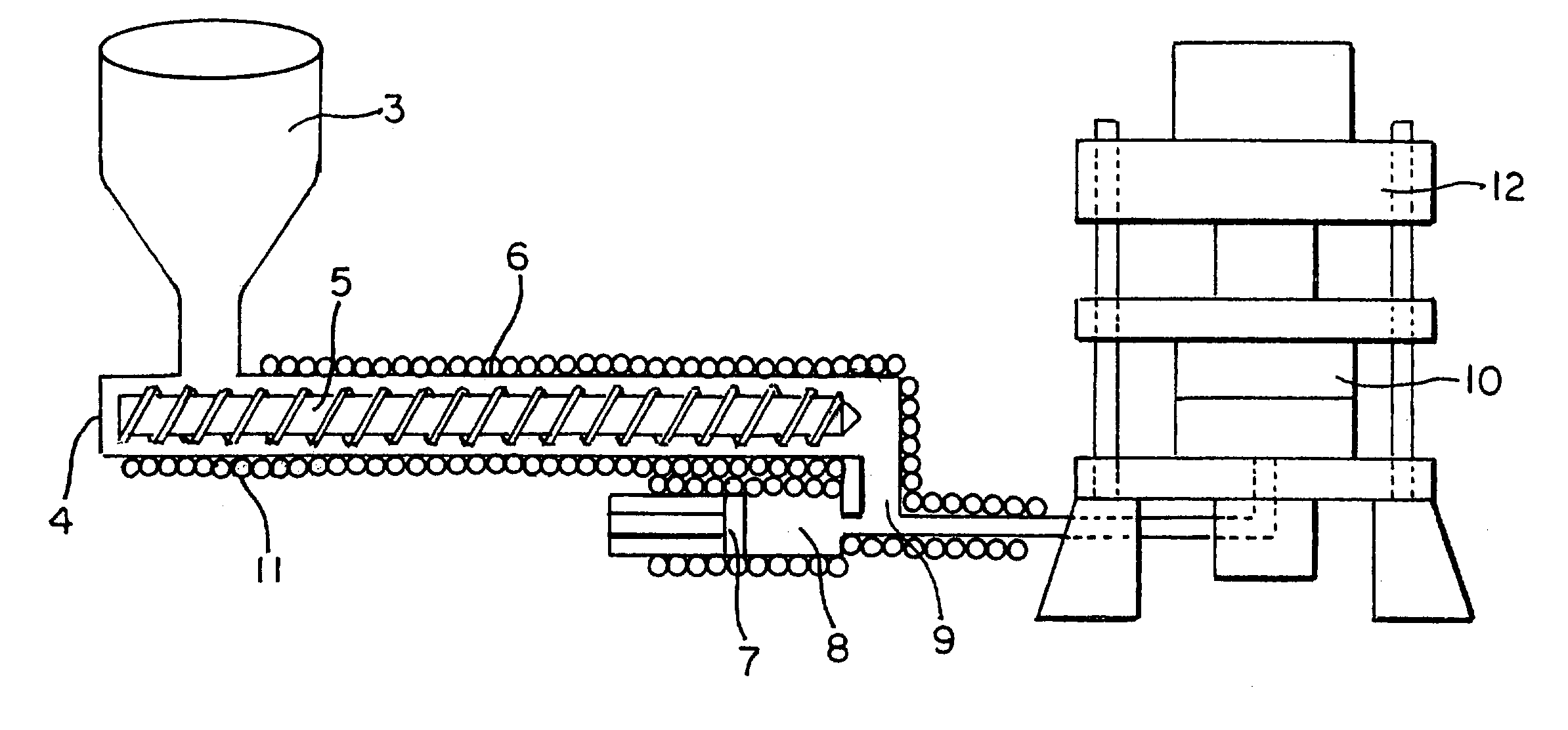
Rapid densification of porous bodies (preforms) with high viscosity resins or pitches using a resin transfer molding process
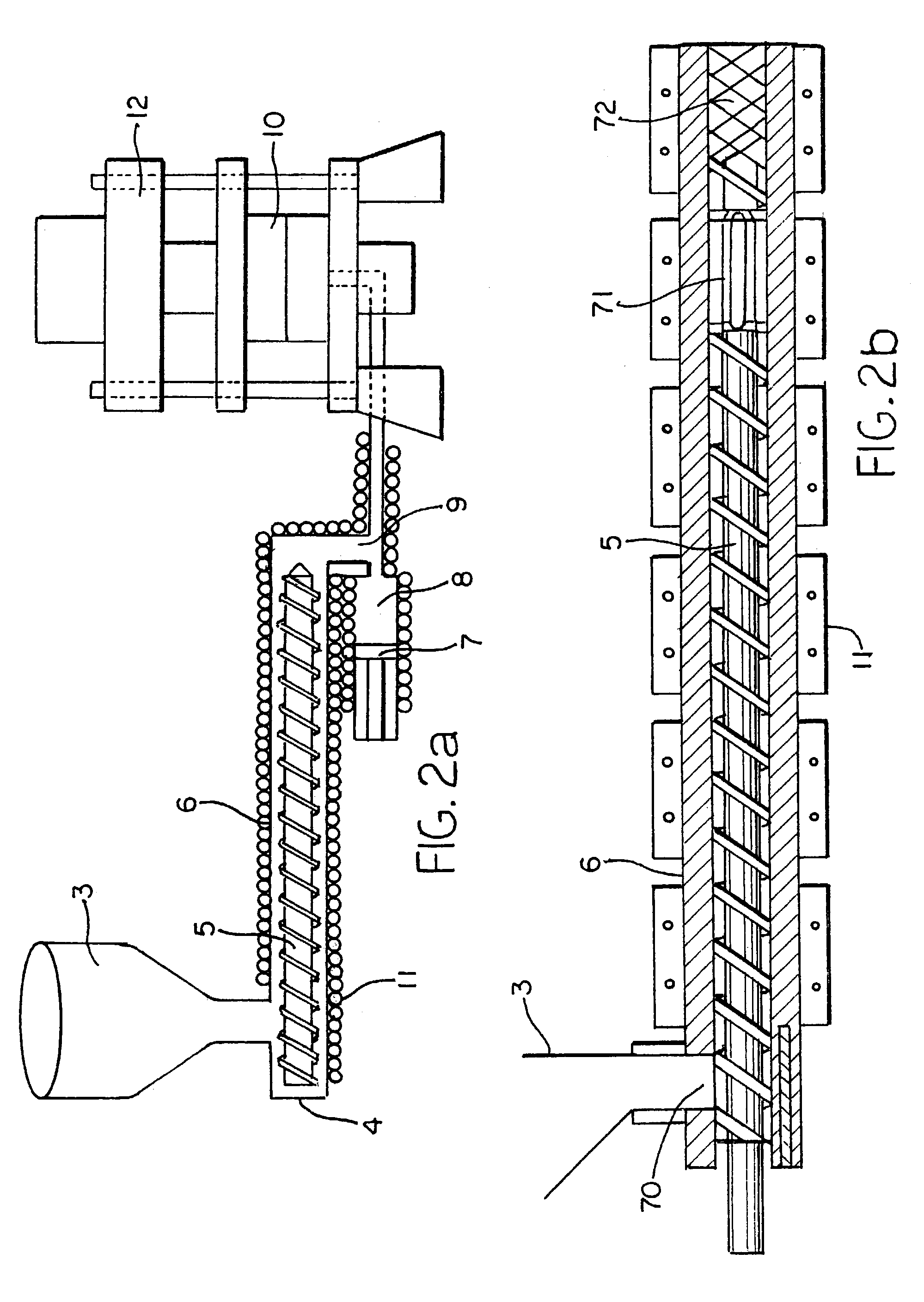
InactiveUS7172408B2Efficiently distributePromote adequate molten resin flowConfectioneryWood working apparatusFiberNozzle
A resin transfer molding (RTM) process is disclosed for rapidly filling a fibrous preform and / or a rigid, porous body with high viscosity resin or pitch. The process is suitable for impregnated multiple porous bodies stacked in a single mold. The process uses a fibrous preform or rigid porous body which is placed into a mold matching the desired part geometry. A resin is injected into the mold at temperature and pressure. After cooling, the infiltrated component is removed from the mold. The mold is constructed from two halves fitted to form at least one mold cavity. A gate fitted with a nozzle is set into one of the mold halves, and a valve admits resin or pitch into the gate area. Venting or vacuum can be applied to the mold. The mold is held in a hydraulic press and an extruder, optionally fitted with an accumulator, supplies molten resin or pitch to the mold.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
IC module, method of manufacturing the same and IC card provided with IC module
InactiveUS6308894B1Improve protectionSpeed up the flowOther printing matterSolid-state devicesEngineeringRing doughnut
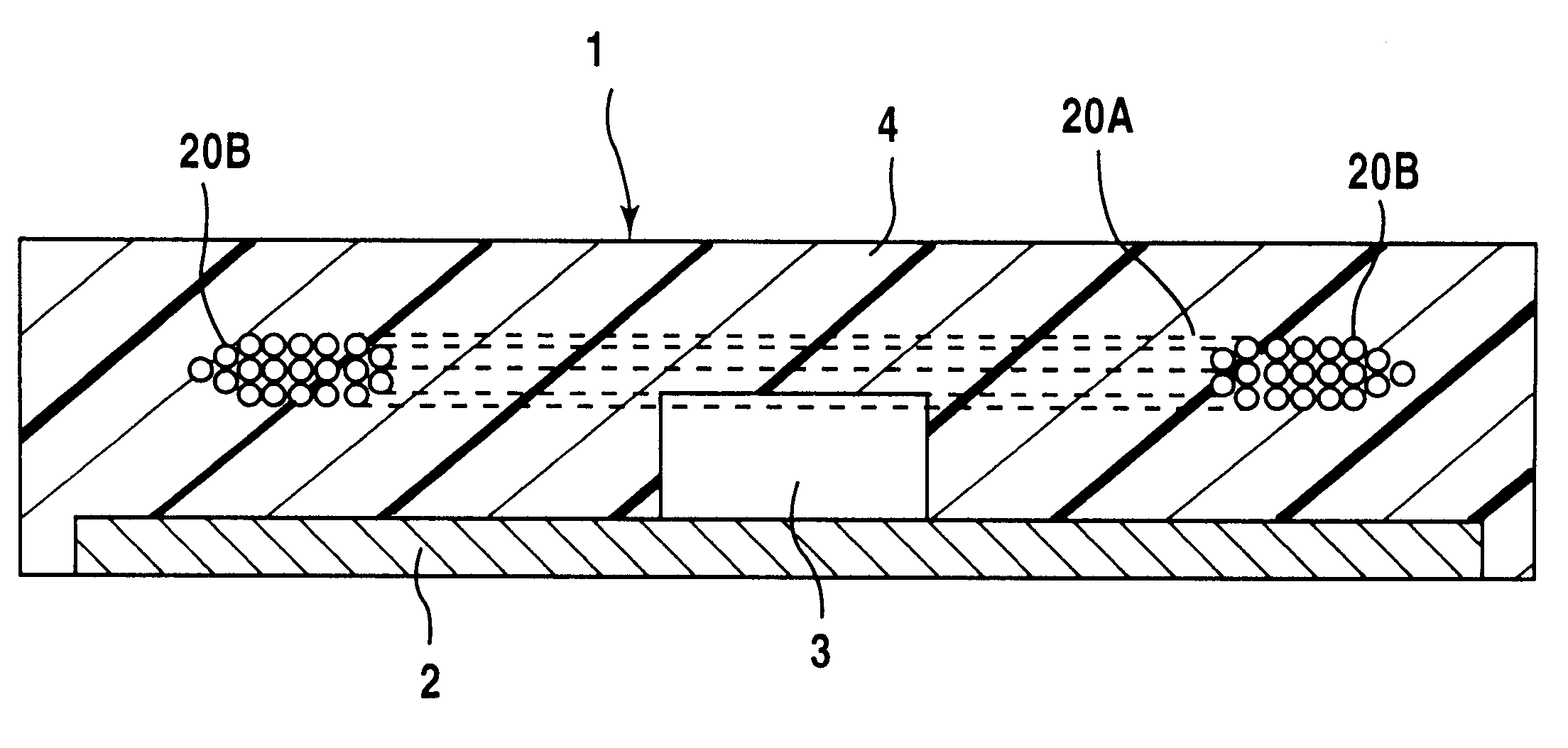
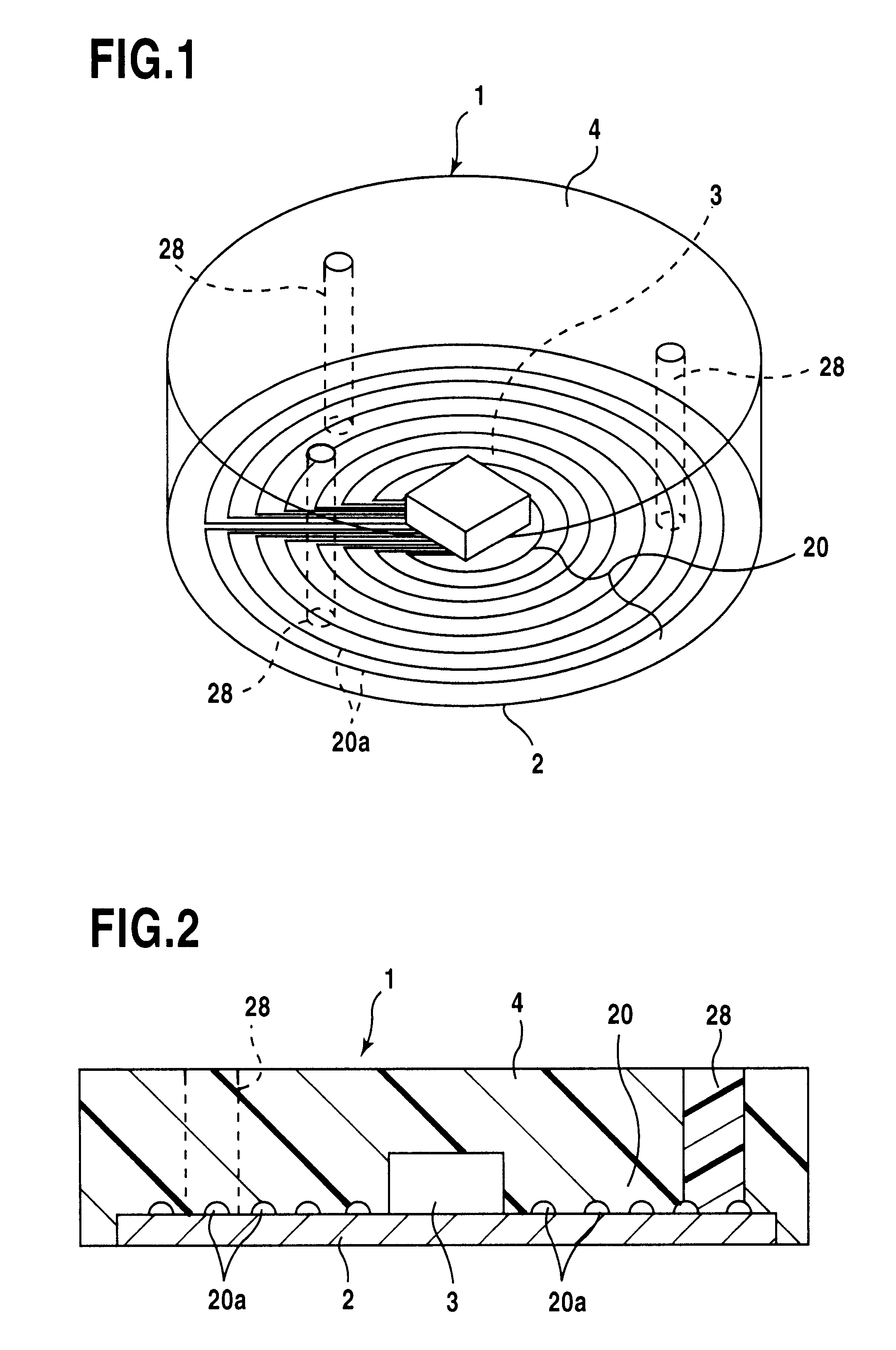
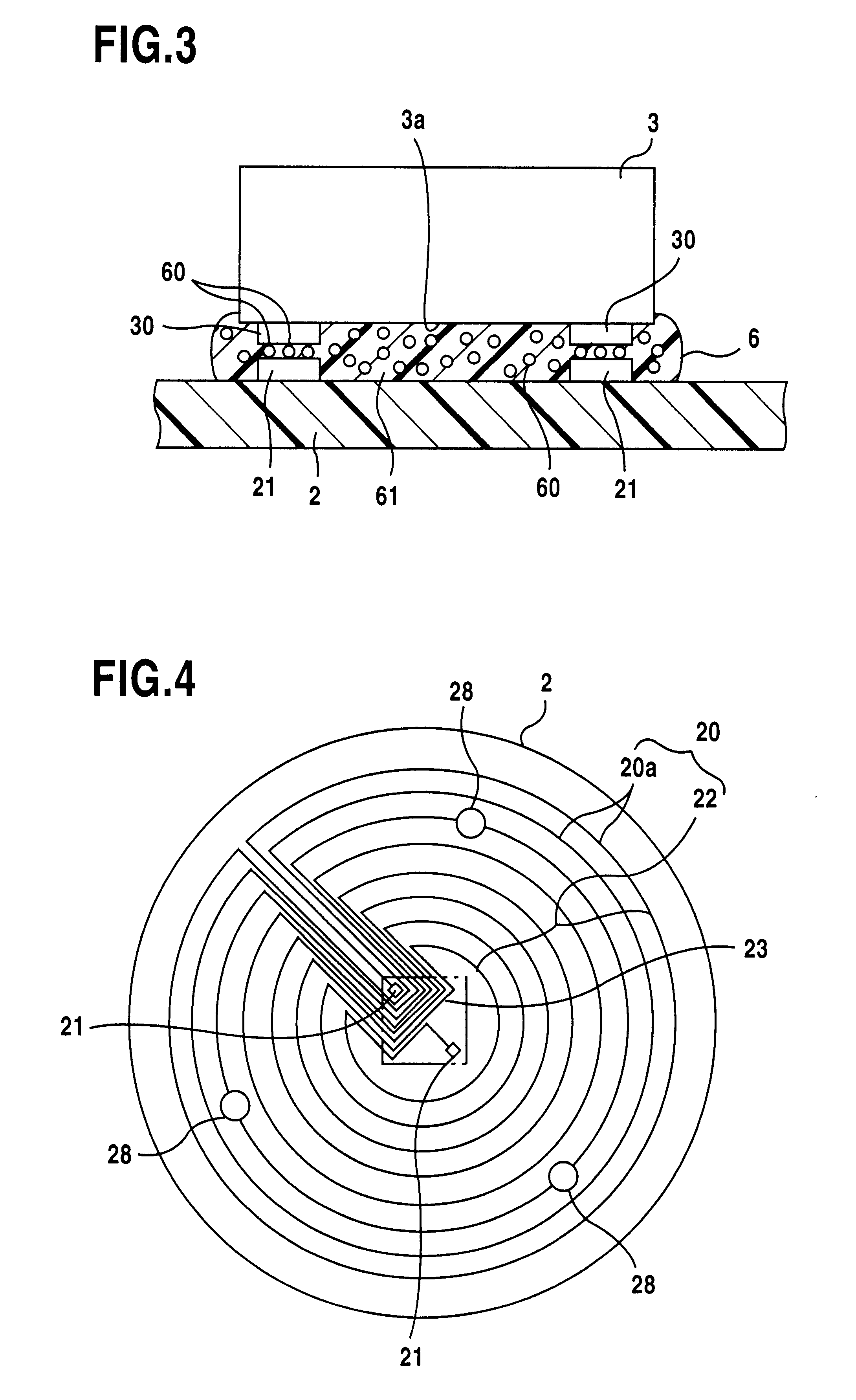
In the method of manufacturing an IC module (1) including a resin packaging process using upper and lower dies (5) for forming a cavity (50) while the dies are clamped, the resin packaging process is carried out by introducing a melted resin while a substrate (2) on which an IC chip (3) is placed and a coil (20A) which has a doughnut shape when observed from above and is flattened as a whole are housed in the cavity (50). When a substrate (2) on which an antenna coil (20) is patterned is to be packaged with a resin, the resin packaging process is carried out by forming a spacer (28) having an equal and almost equal height to the height of the cavity (50) on the substrate (2), housing it in the cavity (50), and introducing a melted resin. Instead of forming the spacer (28) on the substrate (2), a substrate (2) housed in a cavity (50) may be sucked. The manufacturing method can provide good protection of an IC chip and an antenna coil.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Selective apparatus and method for removing an undesirable cut from drilling fluid
A skid mounted first and second stage centrifuges, each being provided with an input pump. Drilling mud is delivered to the first pump, the first stage and then into a tank for storing temporarily the liquids separated from the mud. The heavier weight components are segregated, stored and later added back to the liquid discharge of the second stage to provide an output stream of drilling mud having a specified weight for use in drilling. The lighter weight components are removed at the second stage and are discarded to clean the mud. A control system provides for operation and control without overloading.
Owner:HUTCHISON HAYES PROCESS MANAGEMENT
Device and method for positioning and controlling railway vehicles with ultra-large bandwidth
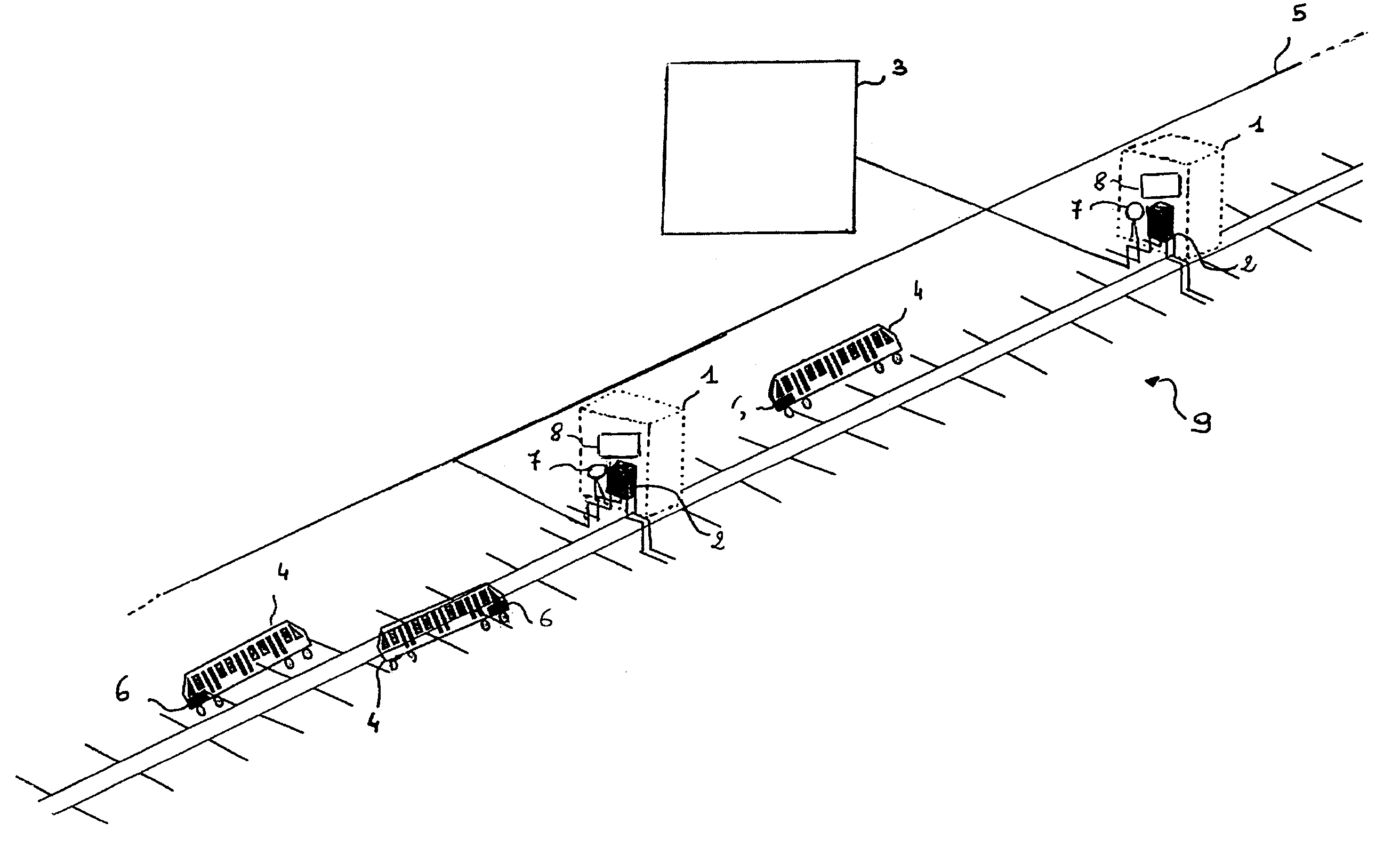
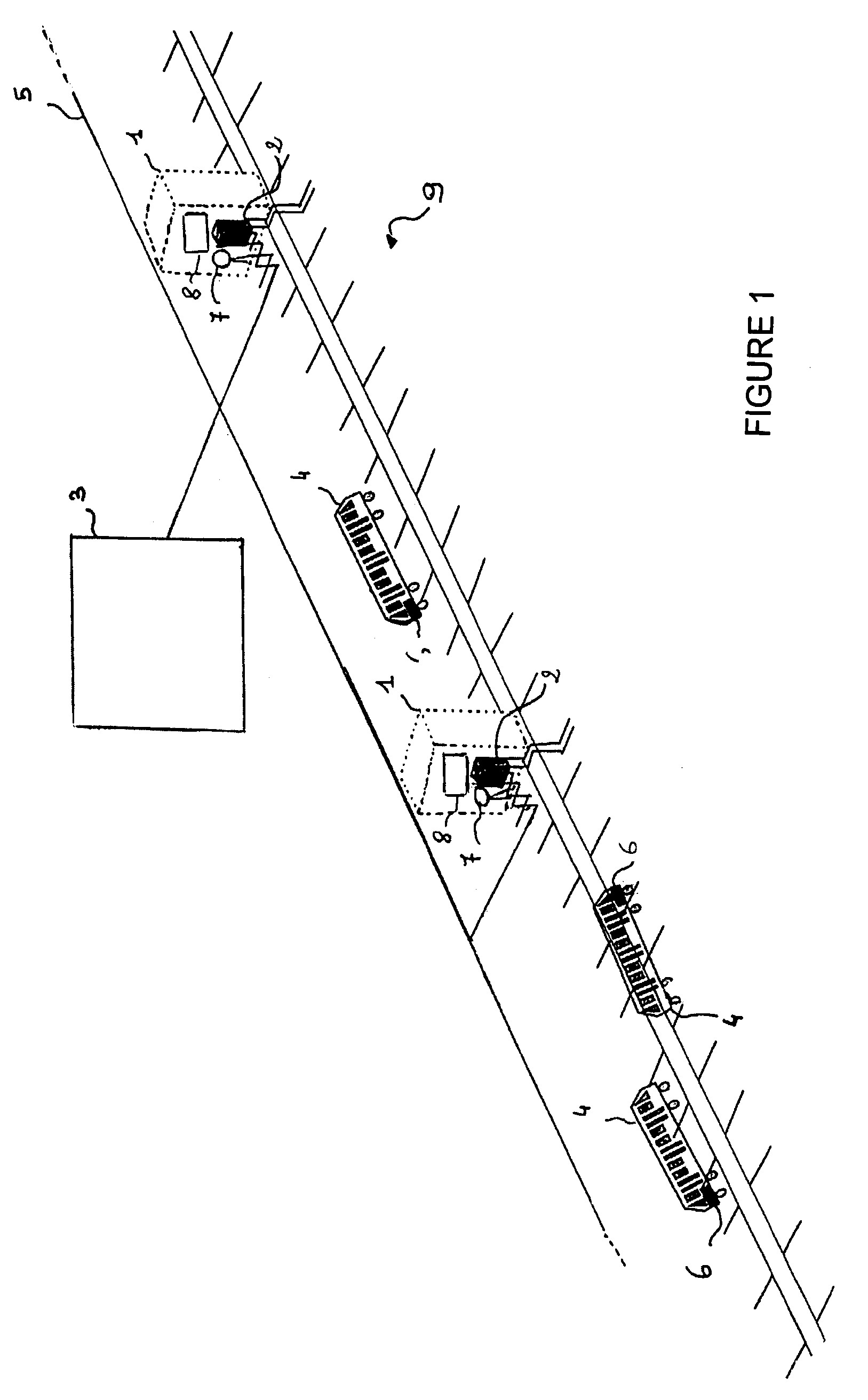
InactiveUS7725252B2Improve transfer rateControlling the riskDigital data processing detailsPosition fixationFrequency spectrumProcessing element
A device and method for positioning and controlling railway vehicles. The device includes fixed stations (1) including first elements for transmitting / receiving (2) signals and a central control station (3) to which the fixed stations (1) are connected. Each railway vehicle (4) includes second elements for transmitting / receiving (6) signals. The signals transmitted by the first and second transmitting / receiving elements (2, 6) including an identifier specific to the transmitter and at least one message and consist in non-sinusoidal radio signals with very large bandwidth whose spectrum ranges between 1 and 10 GHz. Each railway vehicle (4) and each fixed station (1) include processing elements (8) for determining the identifier and the at least one message of each received signal. The central control station (3) sends command control instructions.
Owner:INSTITUT NAT DE RES & DEV SUR LES TRANSPORTS & LEUR SECURITE INRETAB +1
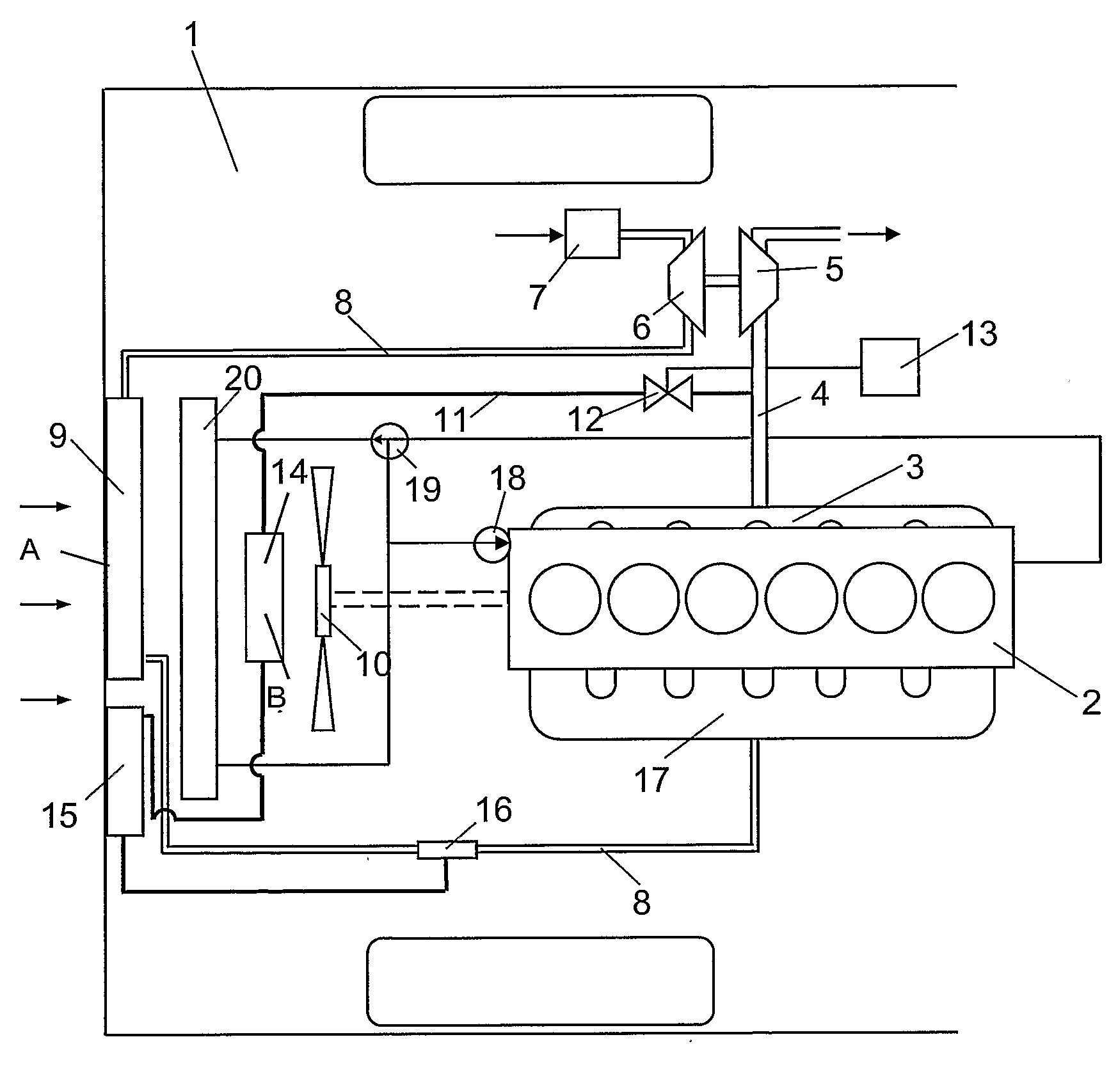
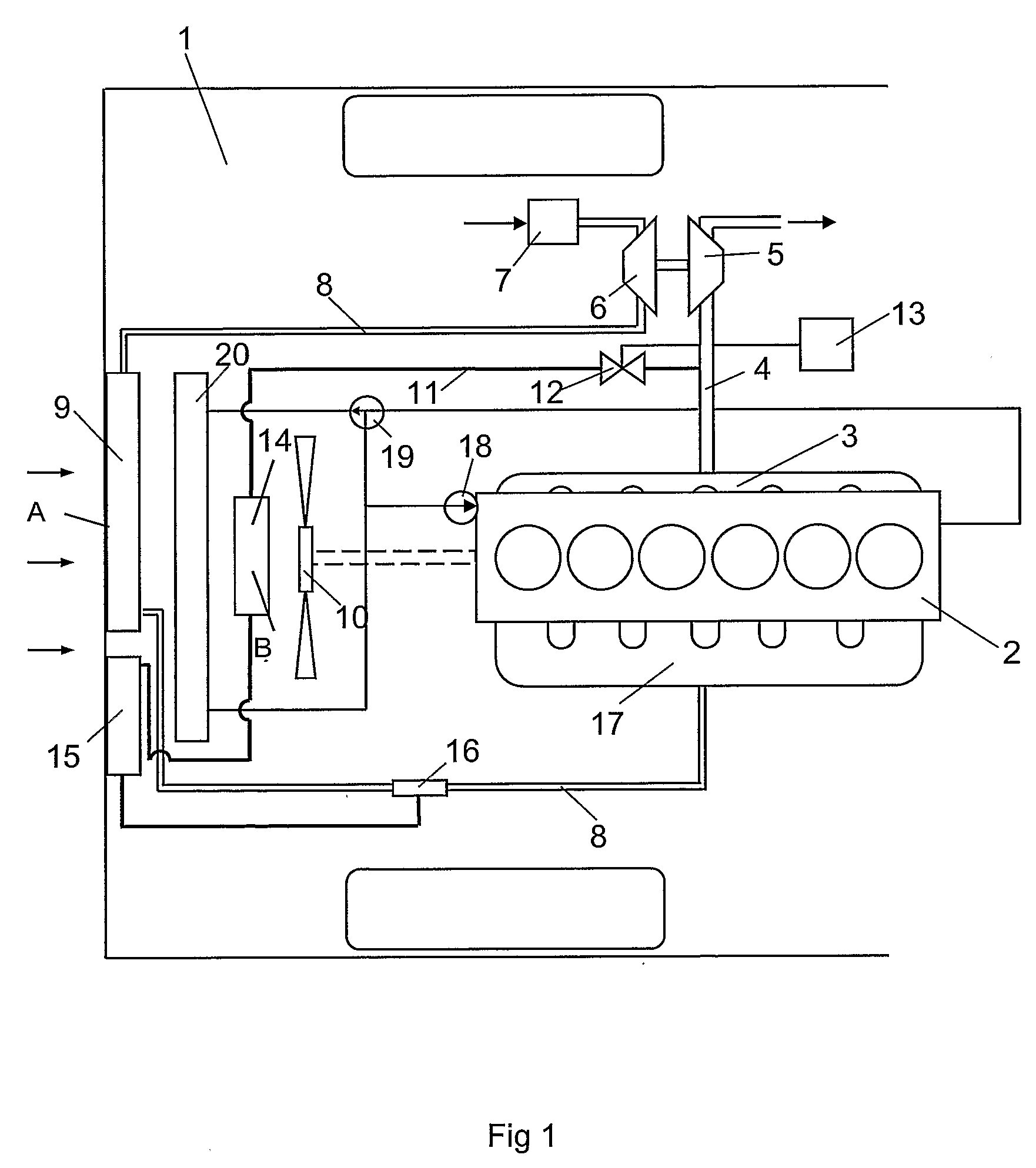
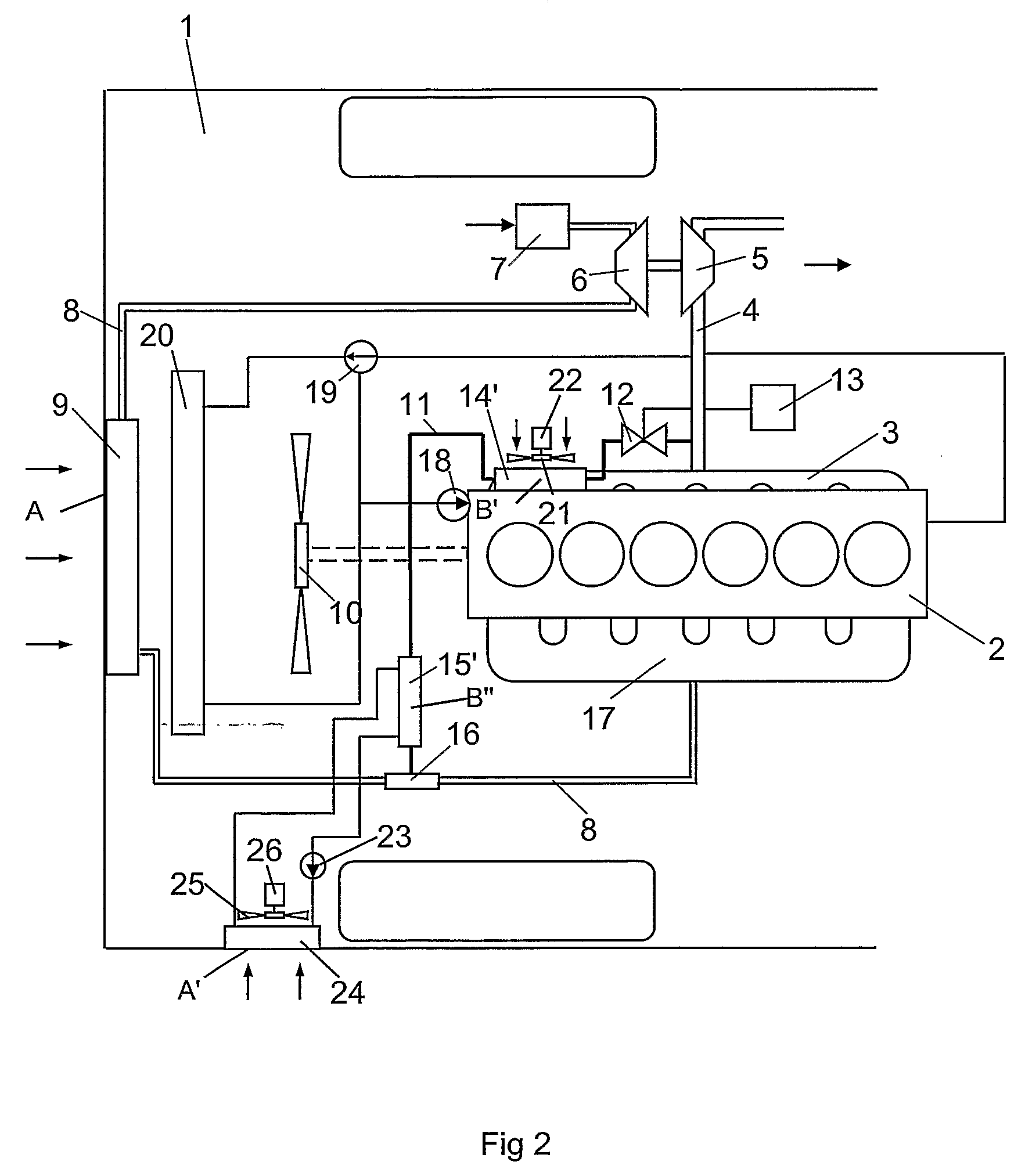
Method and Device for Generating Compressed Air and for Blowing it into an Internal Combustion Engine
ActiveUS20110041496A1Reduce riskImproving the engine dynamicsNon-fuel substance addition to fuelExhaust gas recirculationCombustionTurbocharger
The invention relates to a method for producing compressed air and for injecting the same in an internal combustion engine, in particular a diesel motor, comprising an exhaust turbocharger. The method has the following steps: determination of operating parameters of the internal combustion engine to identify operating states of the internal combustion engine; production of compressed air by the internal combustion engine using the determined operating parameter in an operating state without combustion and storage of the produced compressed air; and injection of the stored compressed air into the combustion engine using the determined operating parameter in an operating state with combustion of the internal combustion engine in order to increase the pressure in an induction cycle. The invention also relates to a corresponding device.
Owner:KNORR-BREMSE SYST FUER NUTZFAHRZEUGE GMBH
Dynamically compliant catheter
InactiveUS20020095117A1Minimizes wound sizeLow production costInfusion syringesCatheterGuide tubeBlood vessel
A catheter enabling a reduced puncture hole size into the skin and blood vessel is disclosed. In one embodiment, the catheter has an elongate body having an expandable sheath extending at least a portion of its length. A pressure constraining sheath is positioned to surround the expandable sheath, at a selected region to prevent expansion of the inner sheath at the region of the constraining sheath. In one preferred use, the constraining sheath is positioned at the puncture hole. During use, the catheter increases in cross-section by an expandable sheath expanding from a first diameter to a second diameter. However, the outer sheath does not expand, maintaining a small diameter at the puncture site.
Owner:WILSON ROBERT F +1
Myoelectrically activated respiratory leak sealing
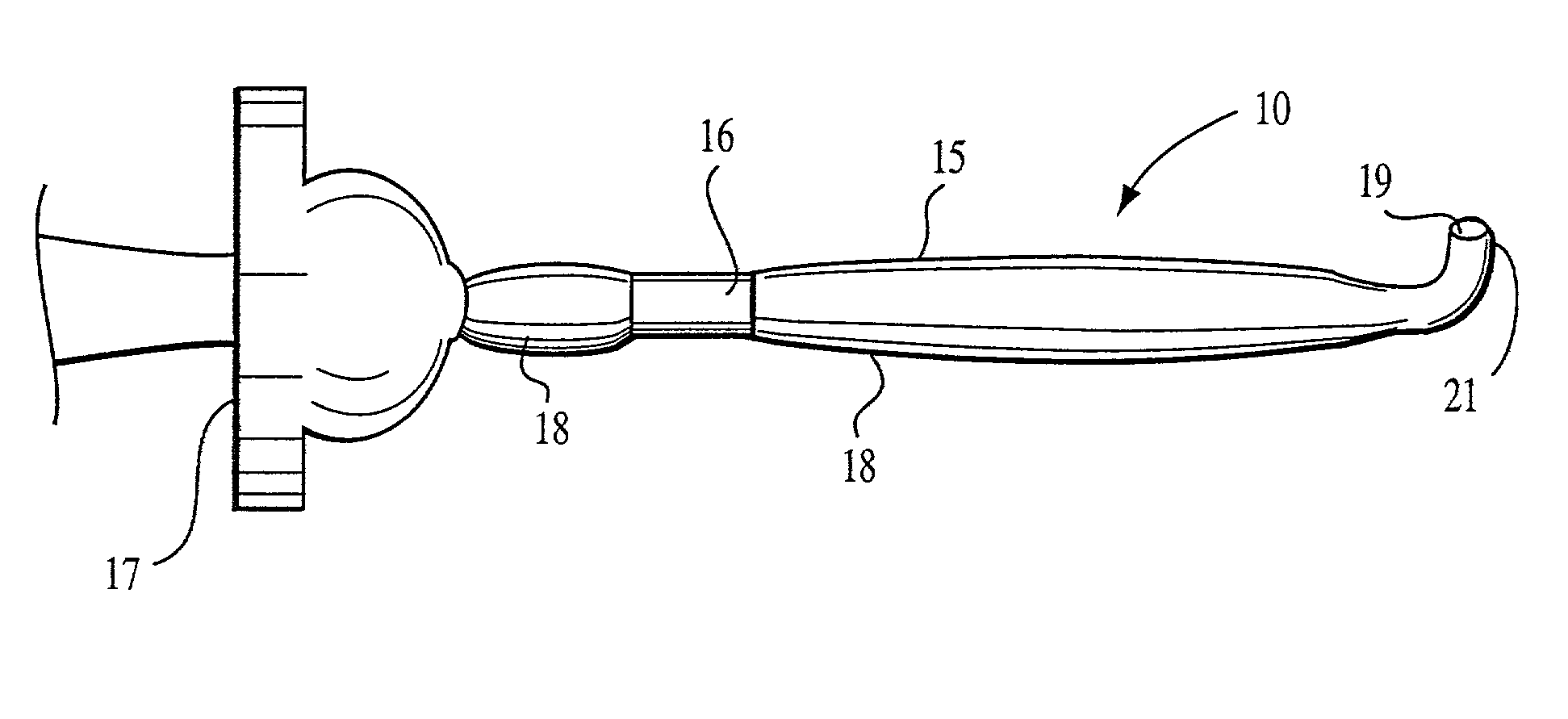
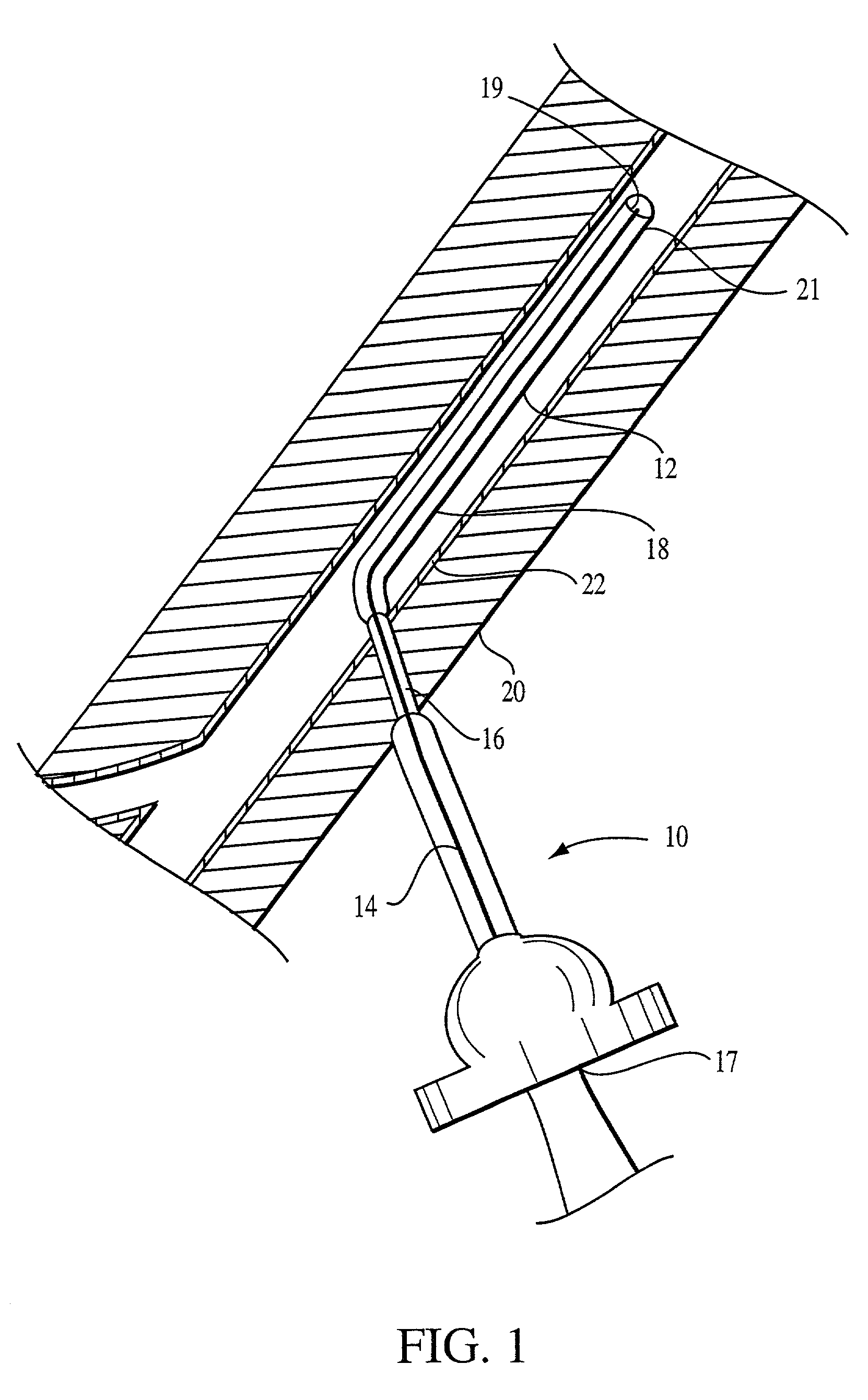
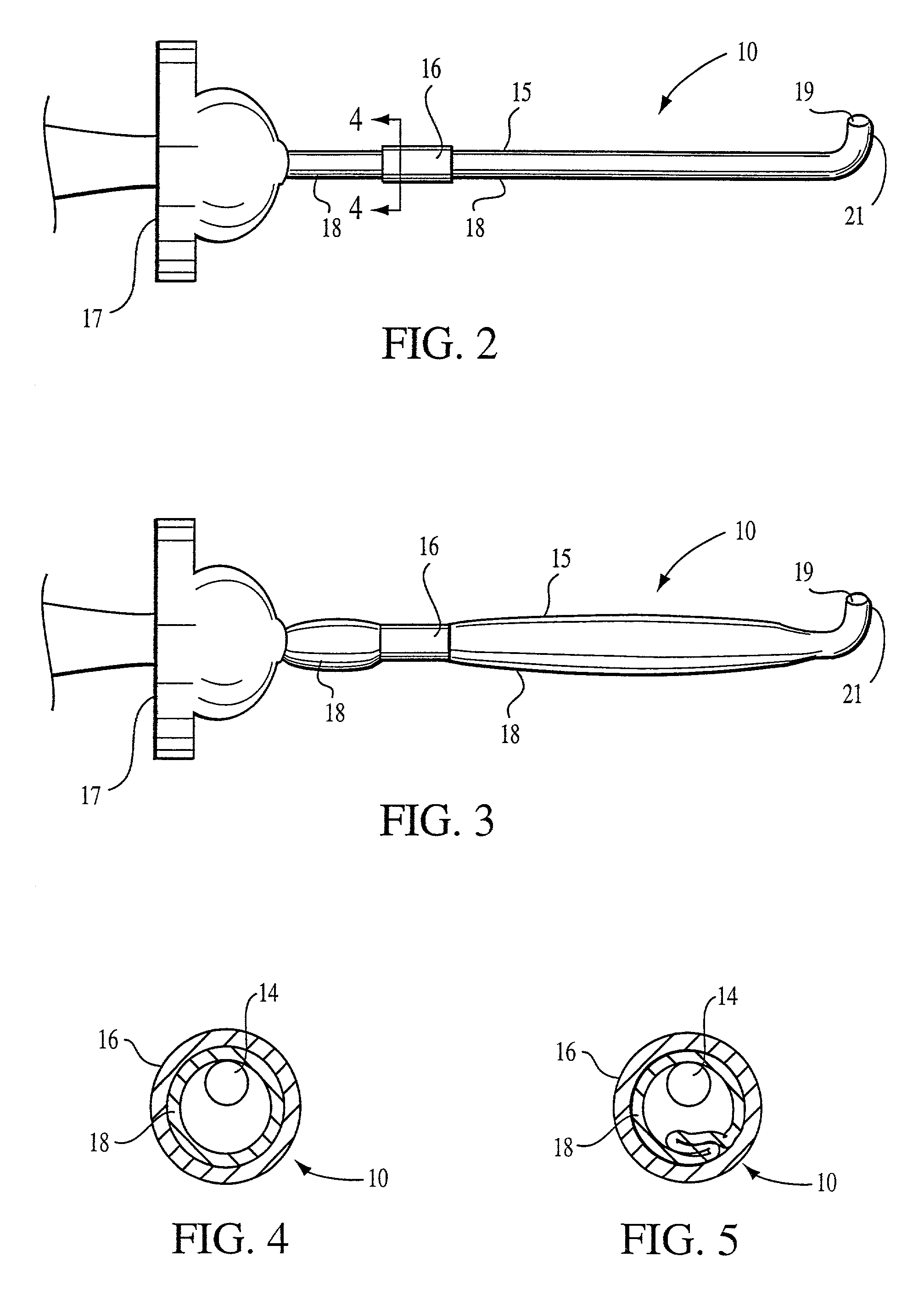
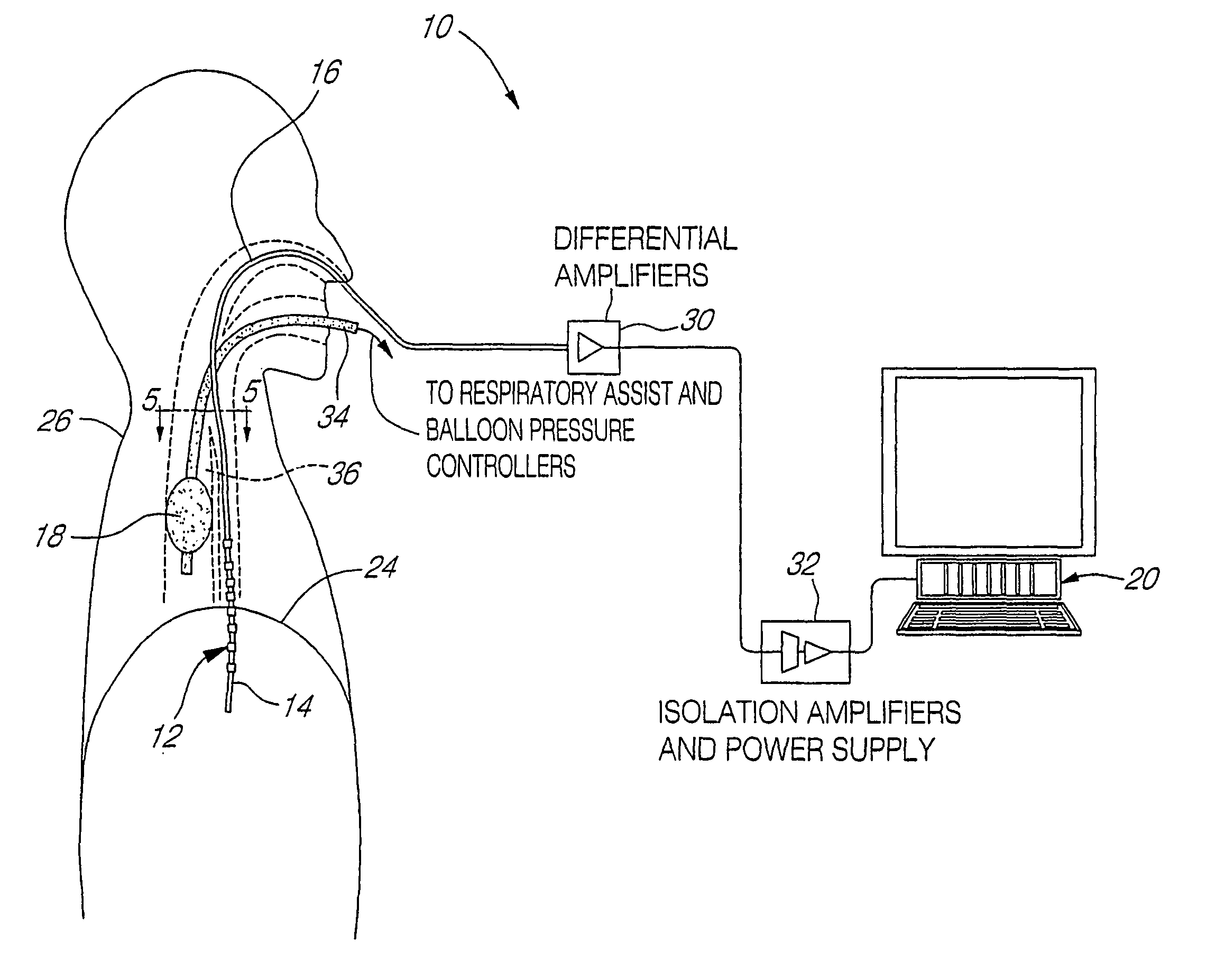
InactiveUS7963283B2Reduce decreaseAdequate flowTracheal tubesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory flowRespiratory pressure
Owner:MONTREAL UNIV DE
Separator device
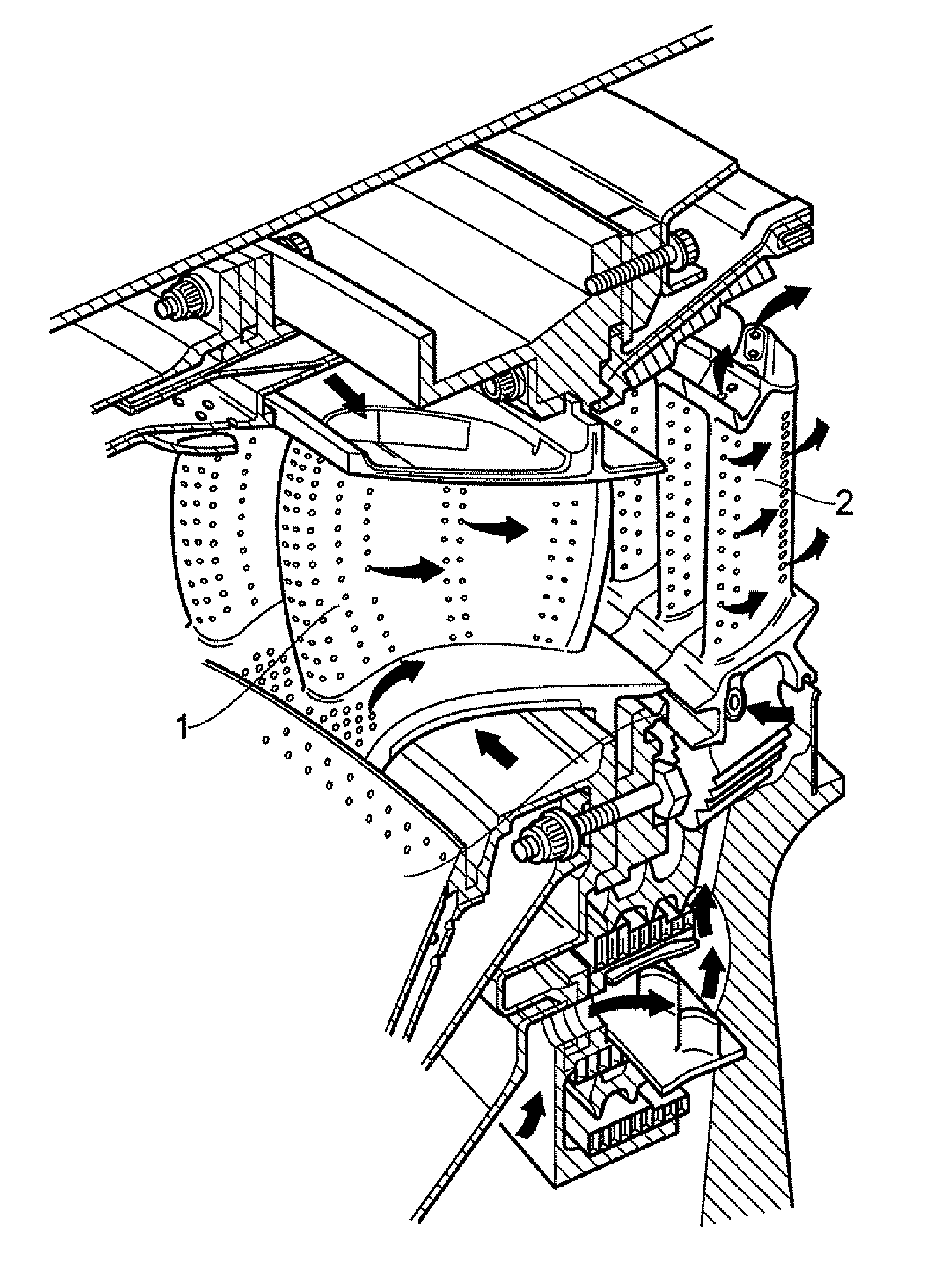
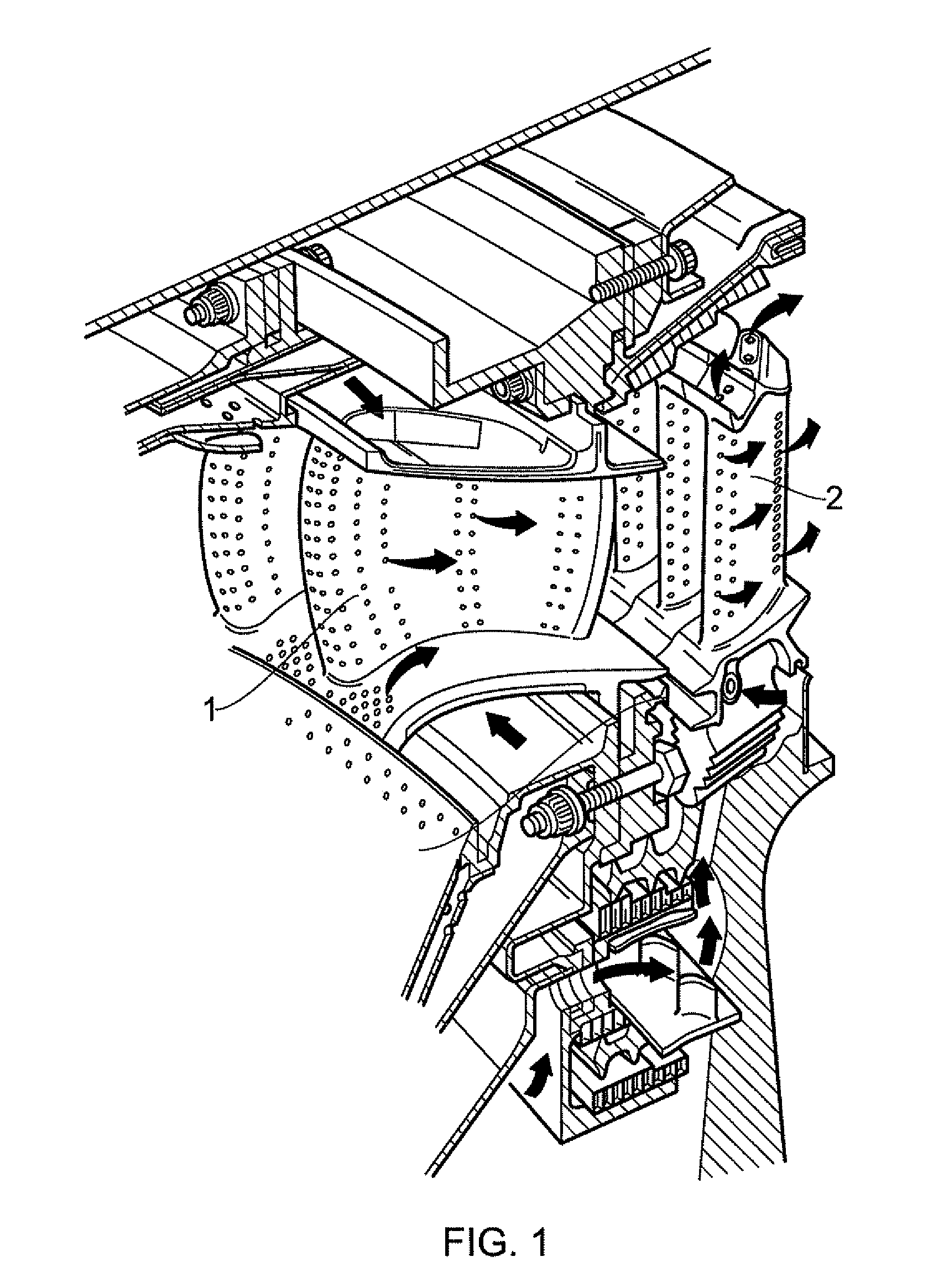
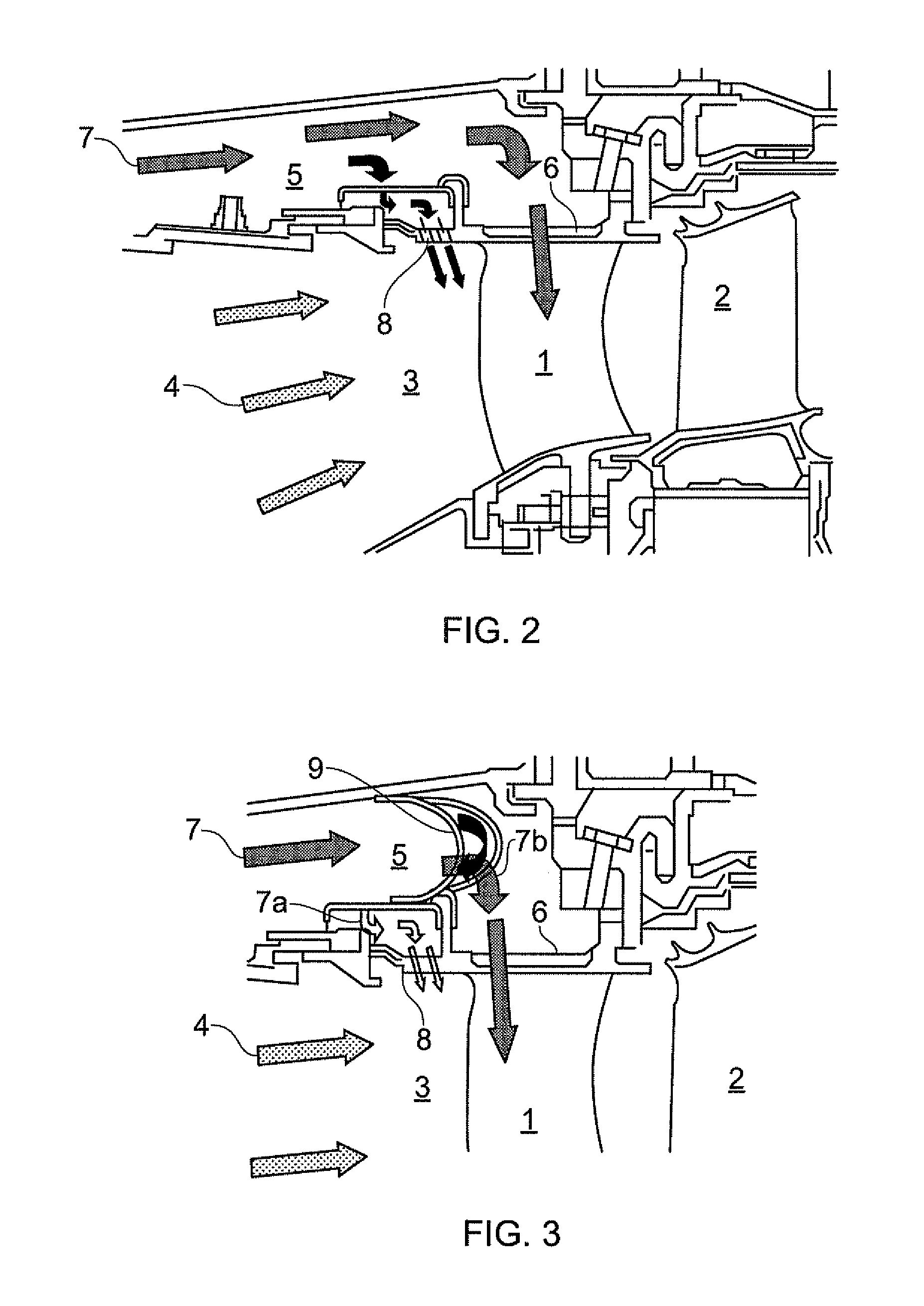
InactiveUS20110067378A1Adequate flowNarrow widthCombination devicesEngine manufactureGas turbinesHigh concentration
A separator device is provided for separating dirt particles from a flow of cooling air fed to airfoils of the turbine section of a gas turbine engine. In use the separator device extends across a conduit which bypasses the combustor of the engine to convey pressurised cooling air carrying dirt particles from the compressor section of the engine to openings which direct the air into the airfoils. The separator device is configured to direct a first portion of the impinging cooling air flow away from the openings and to allow a second portion of the impinging cooling air to continue to the openings. The first portion of cooling air has a higher concentration of the coarsest dirt particles carried by the cooling air than the second portion of cooling air.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Endoscope and endoscopic instrument system having reduced backlash when moving the endoscopic instrument within a working channel of the endoscope
An endoscopic instrument has a portion having an outer surface with a non-circular cross-sectional shape. The non-circular cross-sectional shape may be provided to the instrument by providing peripheral projections or fins along the length of the portion or by providing the periphery of the portion with a polygonal shape. Where fins are used, the fins are preferably quite small and only have a minimal effect on the fluid flow cross sectional area between the interior of the working channel and the endoscopic instrument. The resulting instrument has significantly reduced backlash while maintaining adequate fluid flow in the working channel. According to a second embodiment of the invention, a portion of the interior of the working channel of the endoscope has an interior surface having a non-circular cross sectional shape by the inclusion of a plurality of radially spaced and inwardly directed ribs or by being polygonally shaped. The resulting endoscope reduces the backlash of an endoscopic instrument inserted therein while maintaining adequate fluid flow in the working channel.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
Fuel cell power pack
InactiveUS20070087241A1High outputIncrease productionReactant parameters controlFuel cells groupingElectricityElectrical ballast
A fuel cell power pack comprises a base module, a ballast module, a fuel supply module, a generator module and an enclosure consisting in part of panels, that is shaped to fit within the battery bay of an electric vehicle. The base and ballast modules are configured to provide ballast for the electric vehicle, to hold the fuel supply module, and to form part of the power pack enclosure. The fuel supply module comprises a fuel storage cylinder and a length-minimized fuel supply assembly to provide a maximized fuel supply to the generator module. The generator module comprises a fuel cell stack and balance of plant components operable to generate electricity. An explosion dissipation structure is provided on at least one enclosure panel.
Owner:GENERAL HYDROGEN CORP
Methods and apparatus for luminal stenting
A stent delivery assembly and methods of use are provided. The assembly can comprise a catheter, a cover member, a core member, a stent, and a stent retention mechanism. The stent can extend within the cover member lumen and have a section extending at least partially between an inner layer of the cover member and the core member. The stent retention mechanism can be coupled to the core member and comprise an outer surface that is configured to exert a radially outward force against the stent for axially restraining the stent relative to the core member when the stent is in contact with the inner layer of the cover member.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Arrangement for Recirculation of Exhaust Gases of a Supercharged Internal Combustion Engine
InactiveUS20080256949A1More compact designAdequate flowNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust fumesEngineering
An arrangement for recirculation of exhaust gases of a supercharged combustion engine in a vehicle. A first EGR cooler effects a first step of cooling the recirculating exhaust gases in the return line by means of a cooling medium in the form of a cooling air flow, and a second EGR cooler effects a second step of cooling the recirculating exhaust gases in the return line by means of a cooling medium which is at substantially the temperature of the surroundings. The first EGR cooler is fitted in an internal region of the vehicle which is adapted to have the cooling air flow passing through it during operation of the combustion engine.
Owner:SCANIA CV AB
Porous and durable ceramic filter monolith coated with a rare earth for removing contaminants from water
InactiveUS20100230359A1Reduce arsenic levelsReduce pollutantsOther chemical processesSolid sorbent liquid separationMulti pollutantRare earth
The invention is directed generally to a porous and durable ceramic filter monolith coated with one or more rare earth-containing compositions for removing contaminants from a fluid, particularly for removing one or more contaminants from water.
Owner:MOLYCORP MINERALS
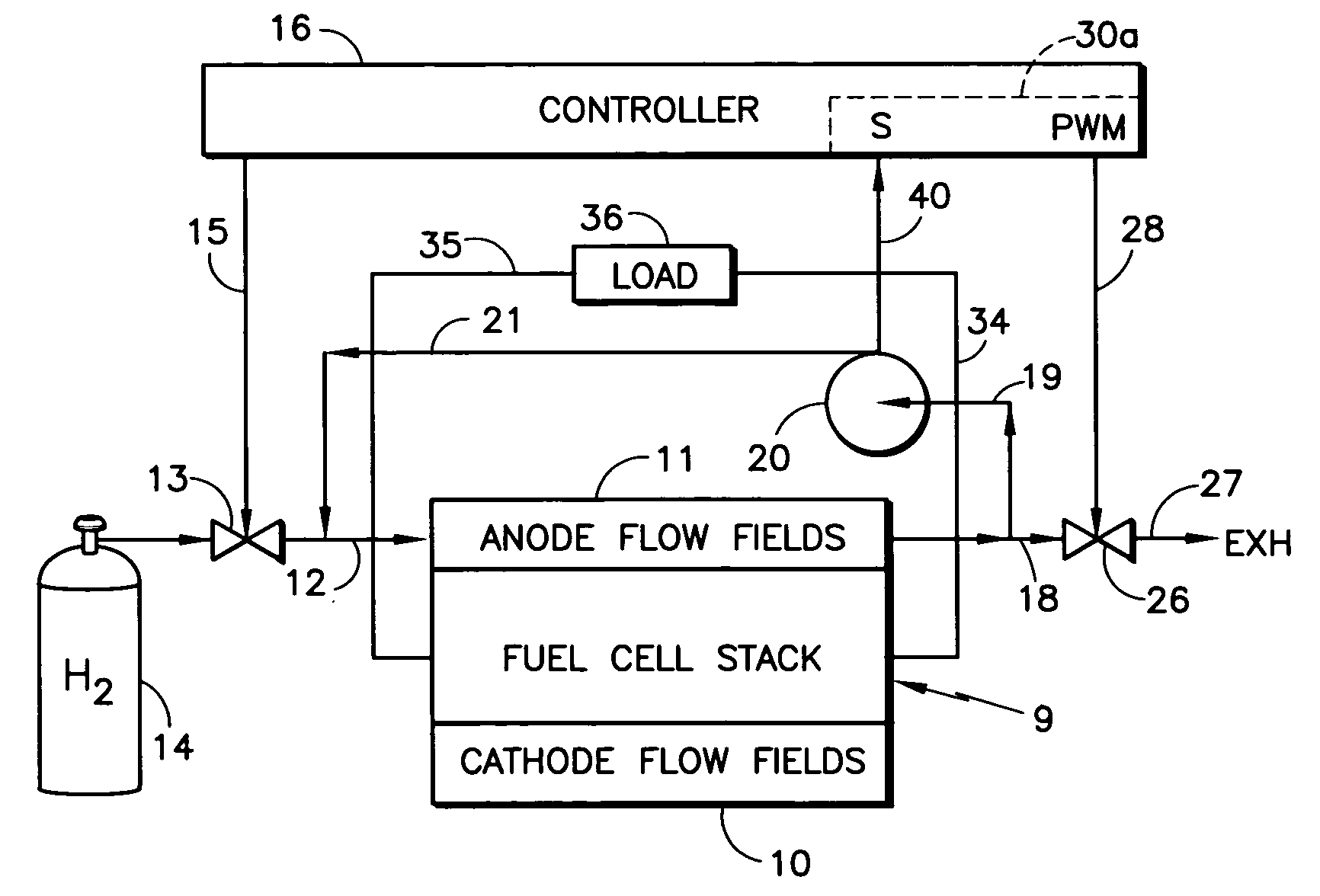
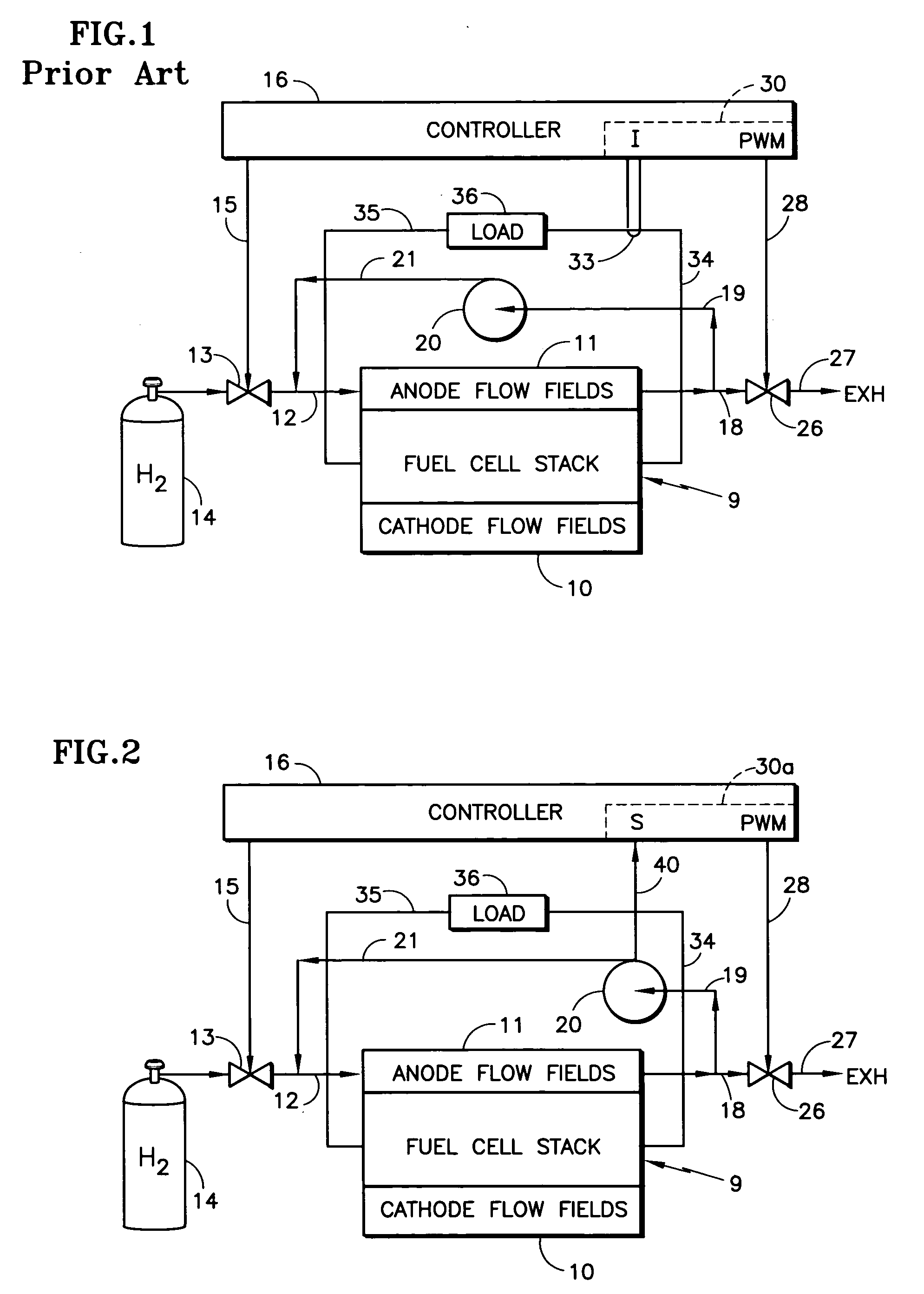
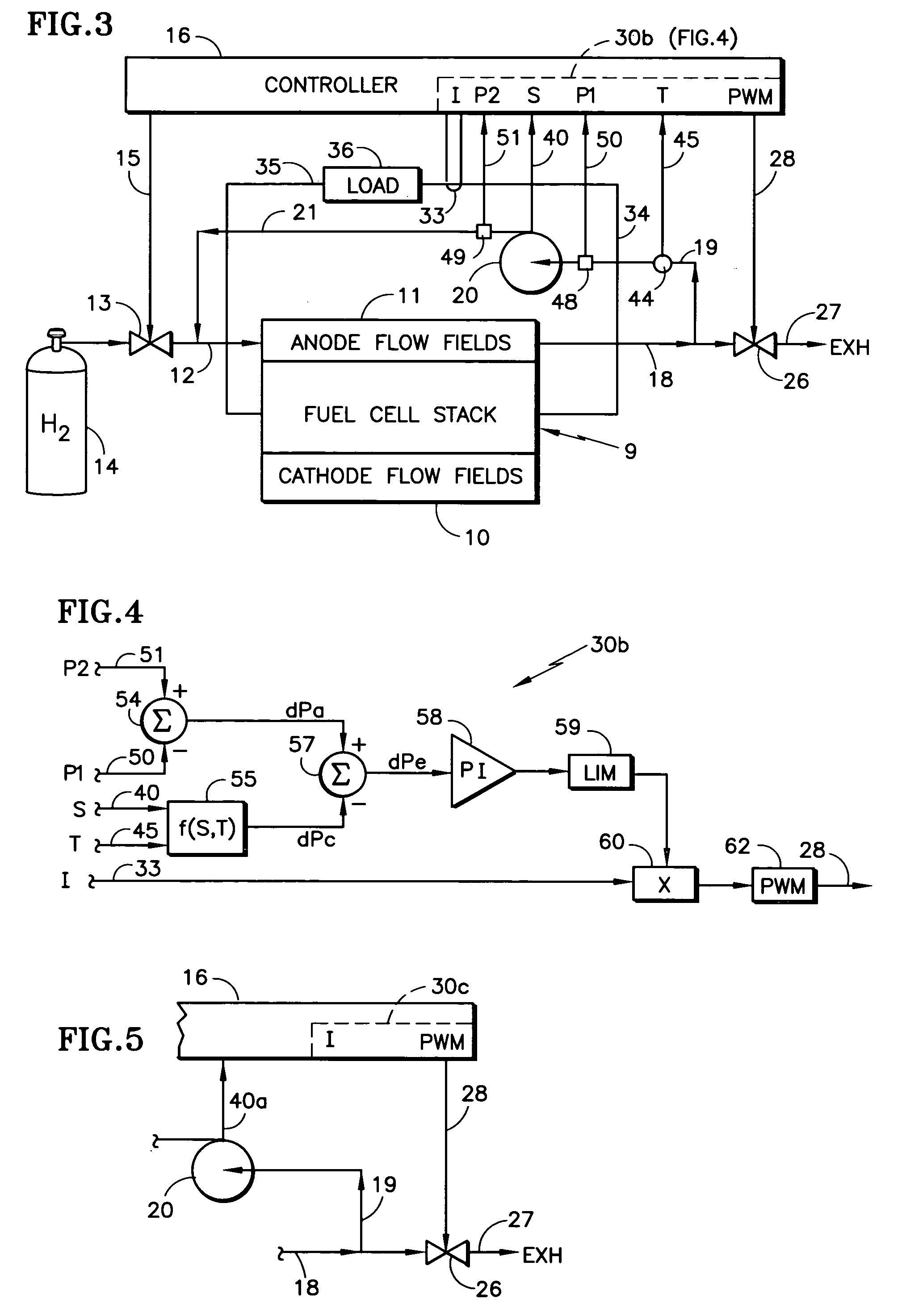
Controlling fuel cell fuel purge in response to recycle fuel blower operating conditions
InactiveUS20060003204A1Easy to controlImproved startup and shutdownFuel cell heat exchangeFuel cells groupingPressure riseFuel cells
A fuel cell power plant fuel purge valve (26) is controlled in response to a parameter (40, 40a) of a fuel recycle blower which is indicative (20) of the recycle fuel impelled thereby, either alone or together with load current (33), pressure rise of the blower (50, 51), and temperature of the fuel recycle gas (44), to provide a pulse width modulation-control signal (28) controlling the purge valve.
Owner:INT FUEL CELLS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com