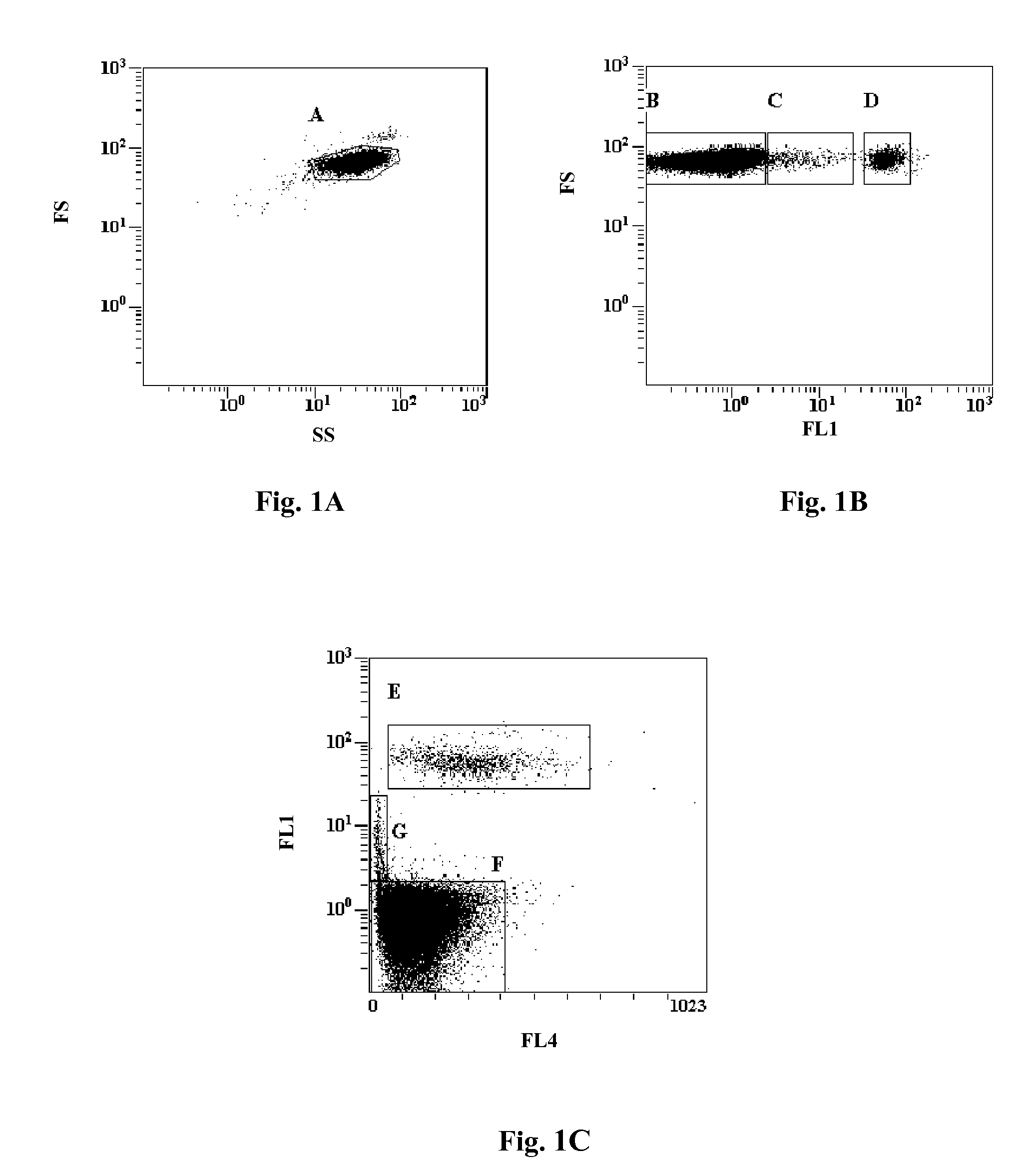
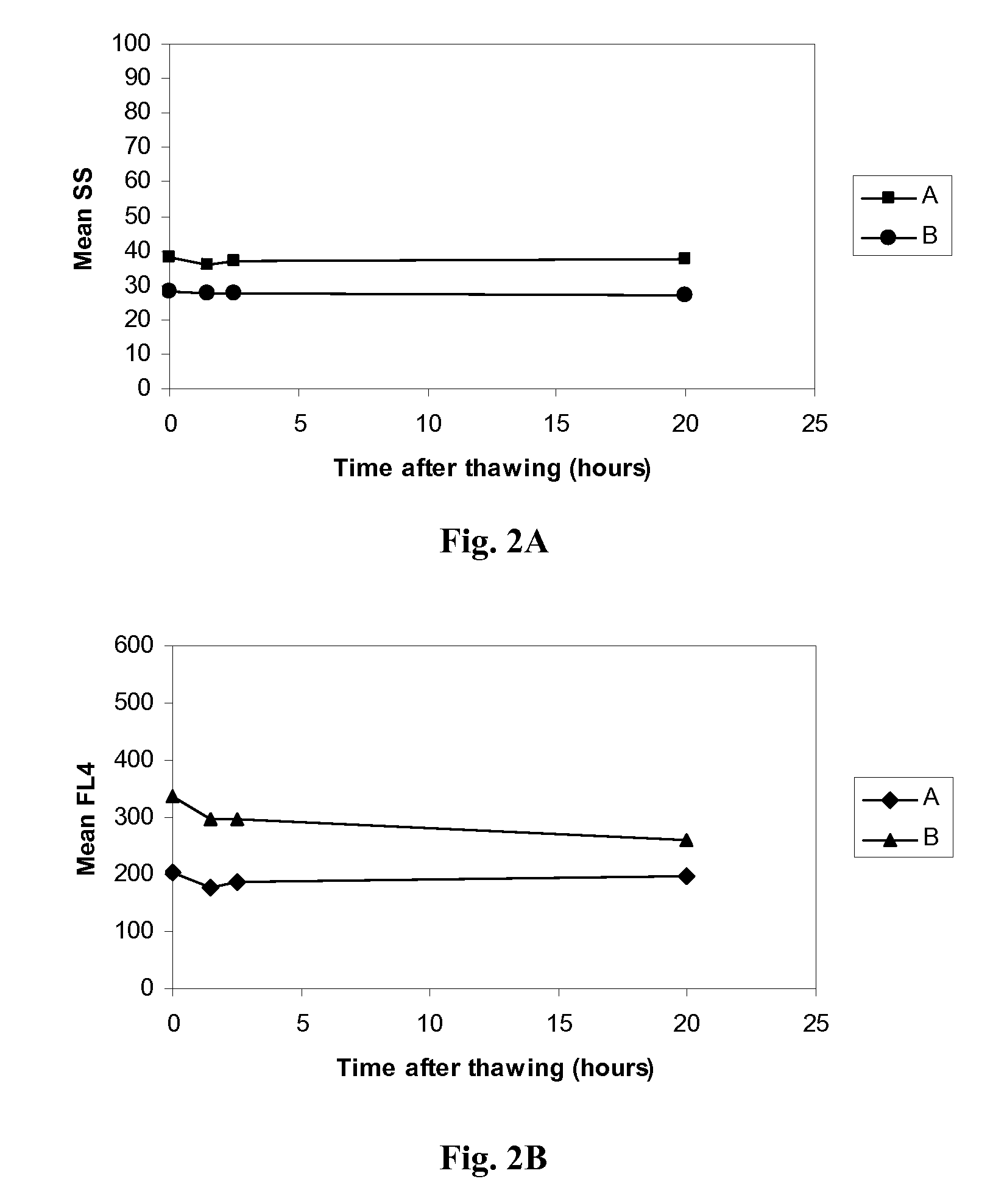
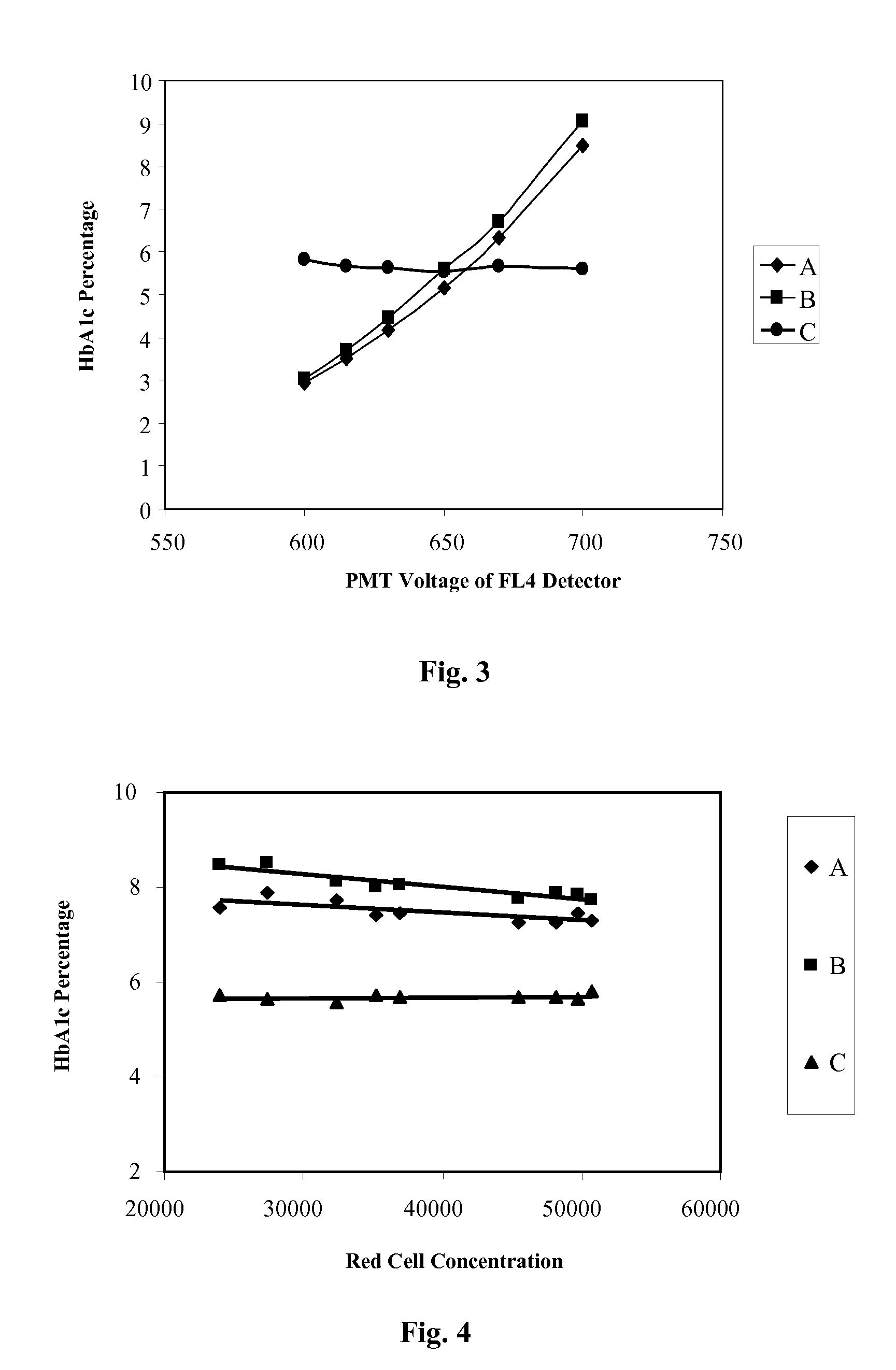
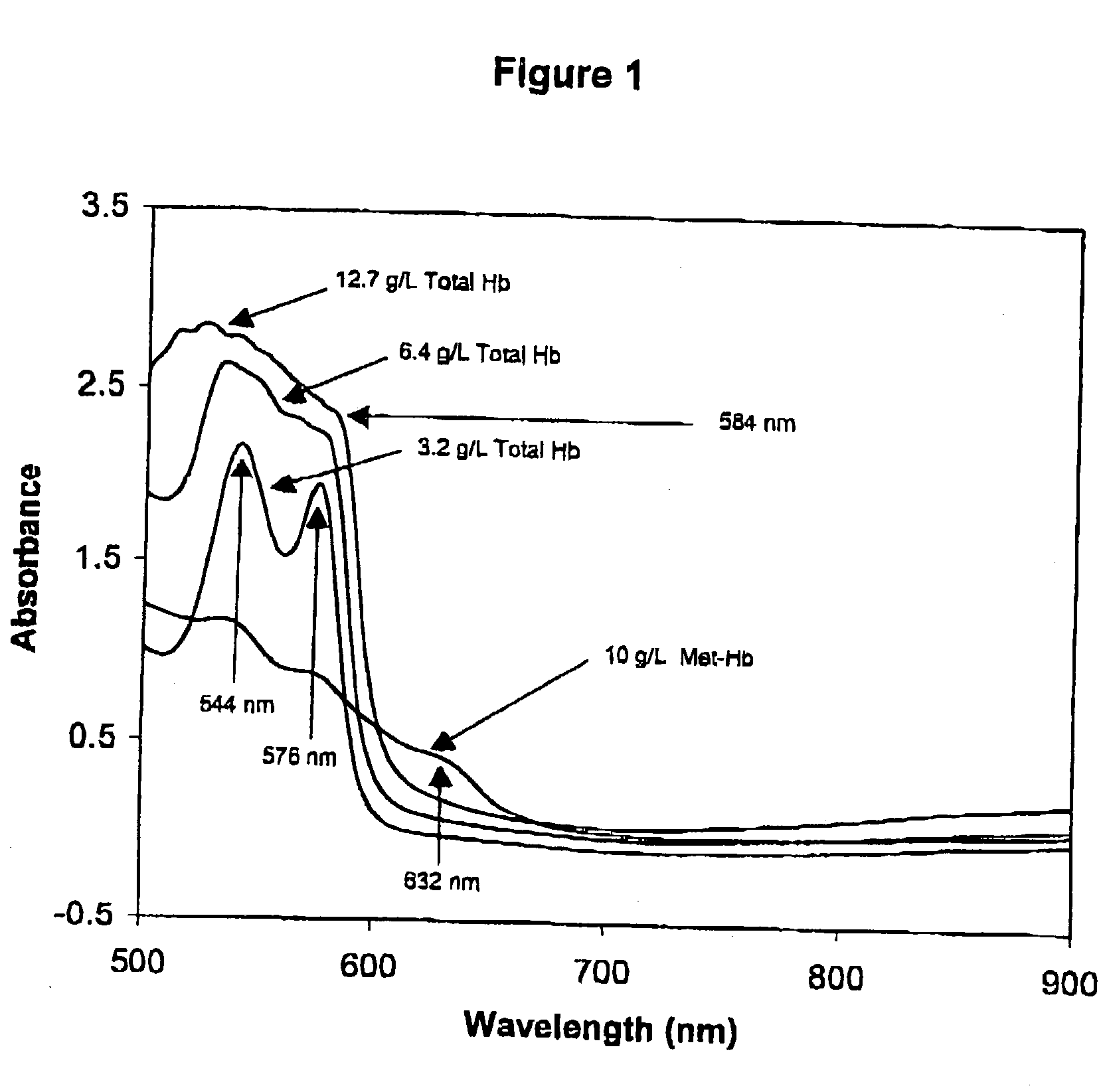
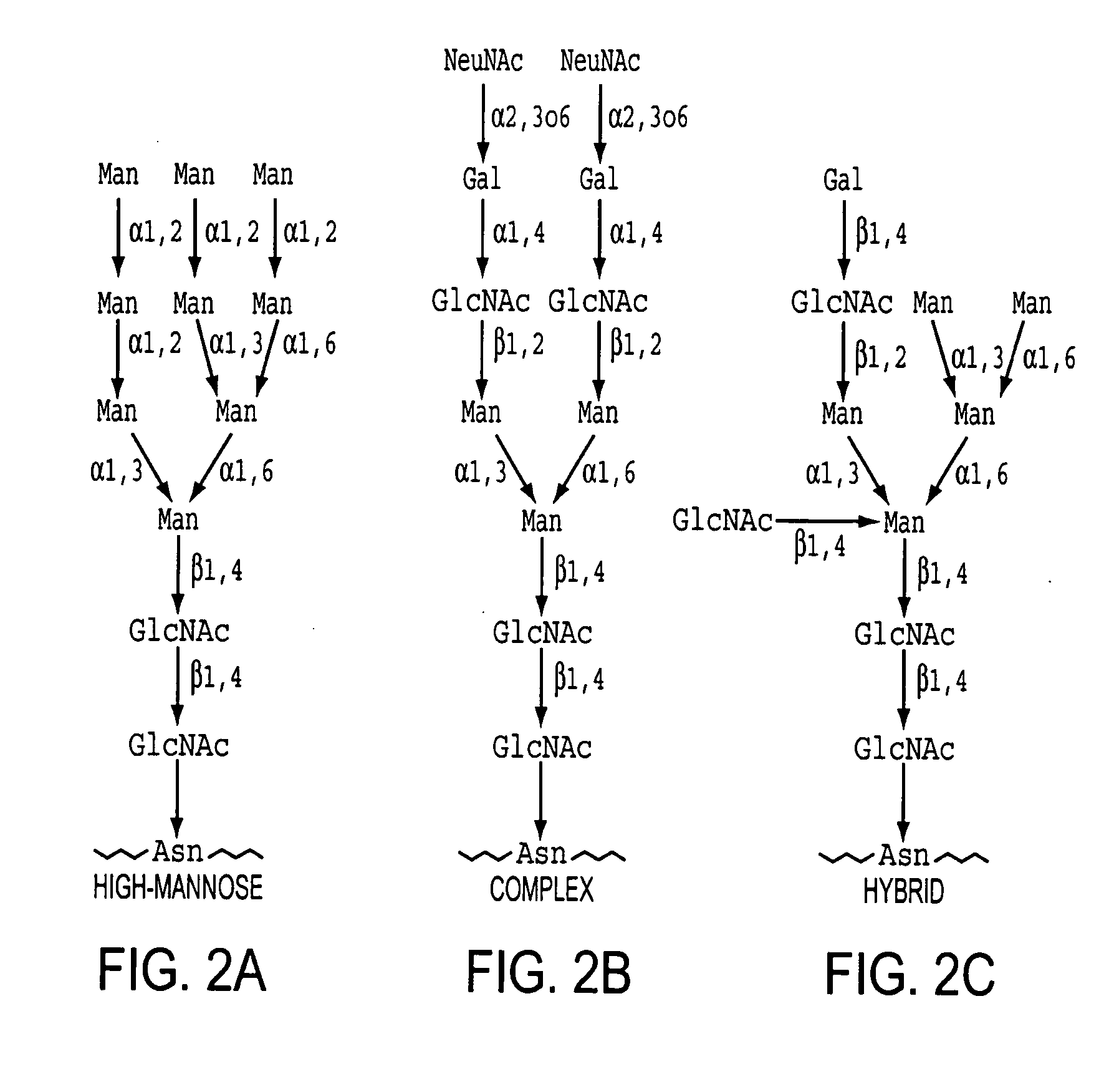
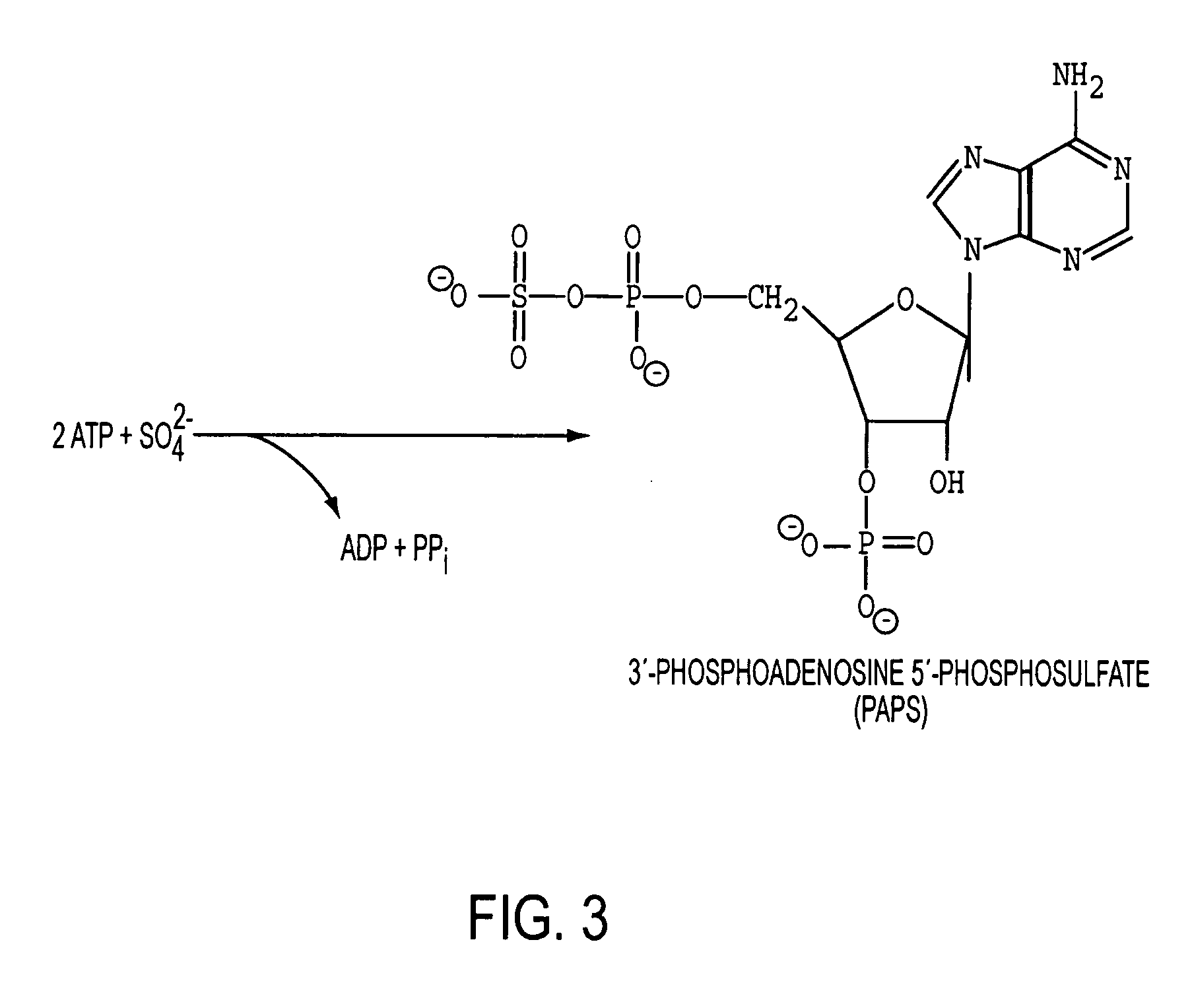
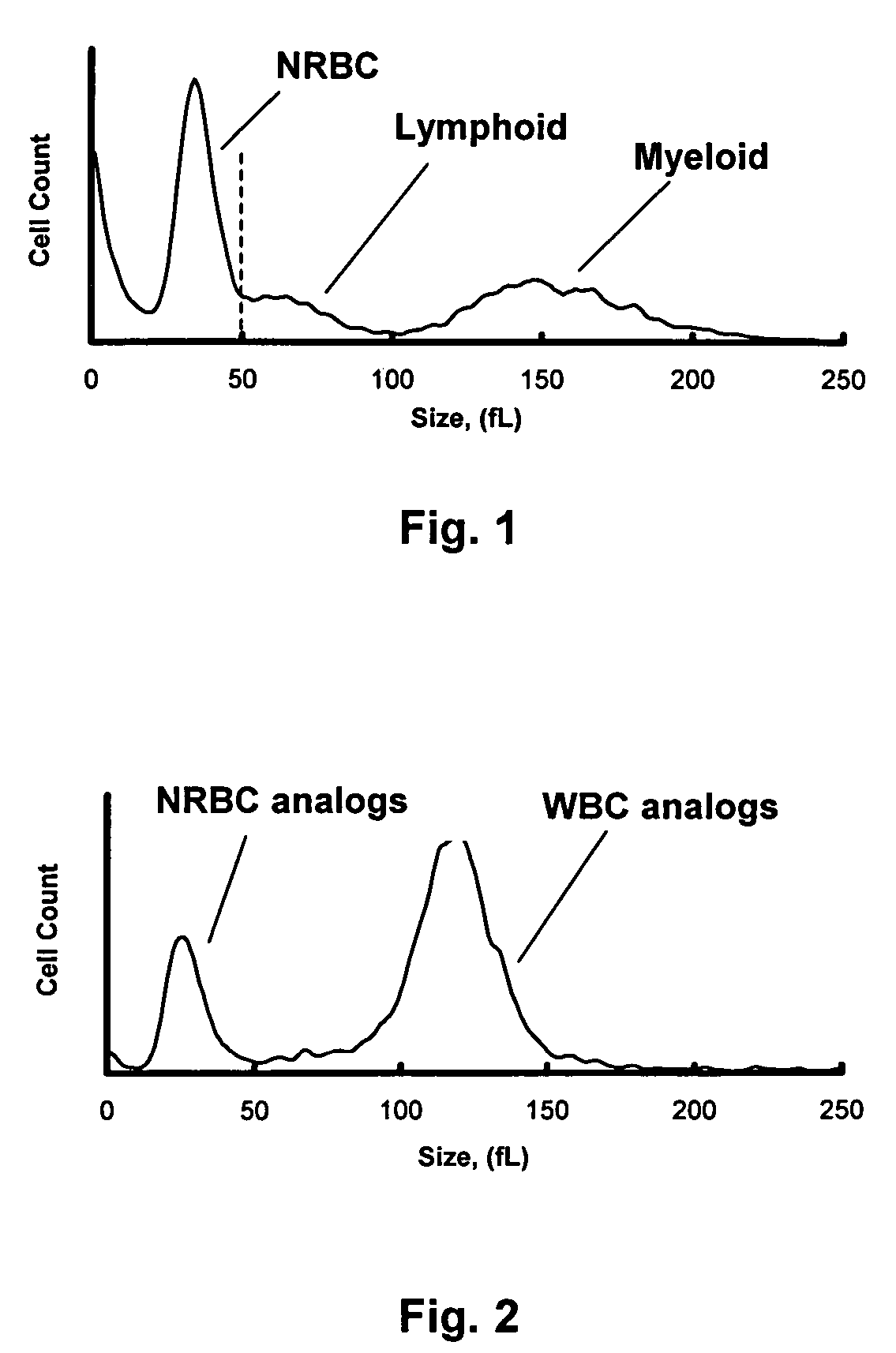
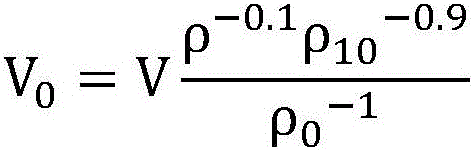Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
213results about "Reference solutions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
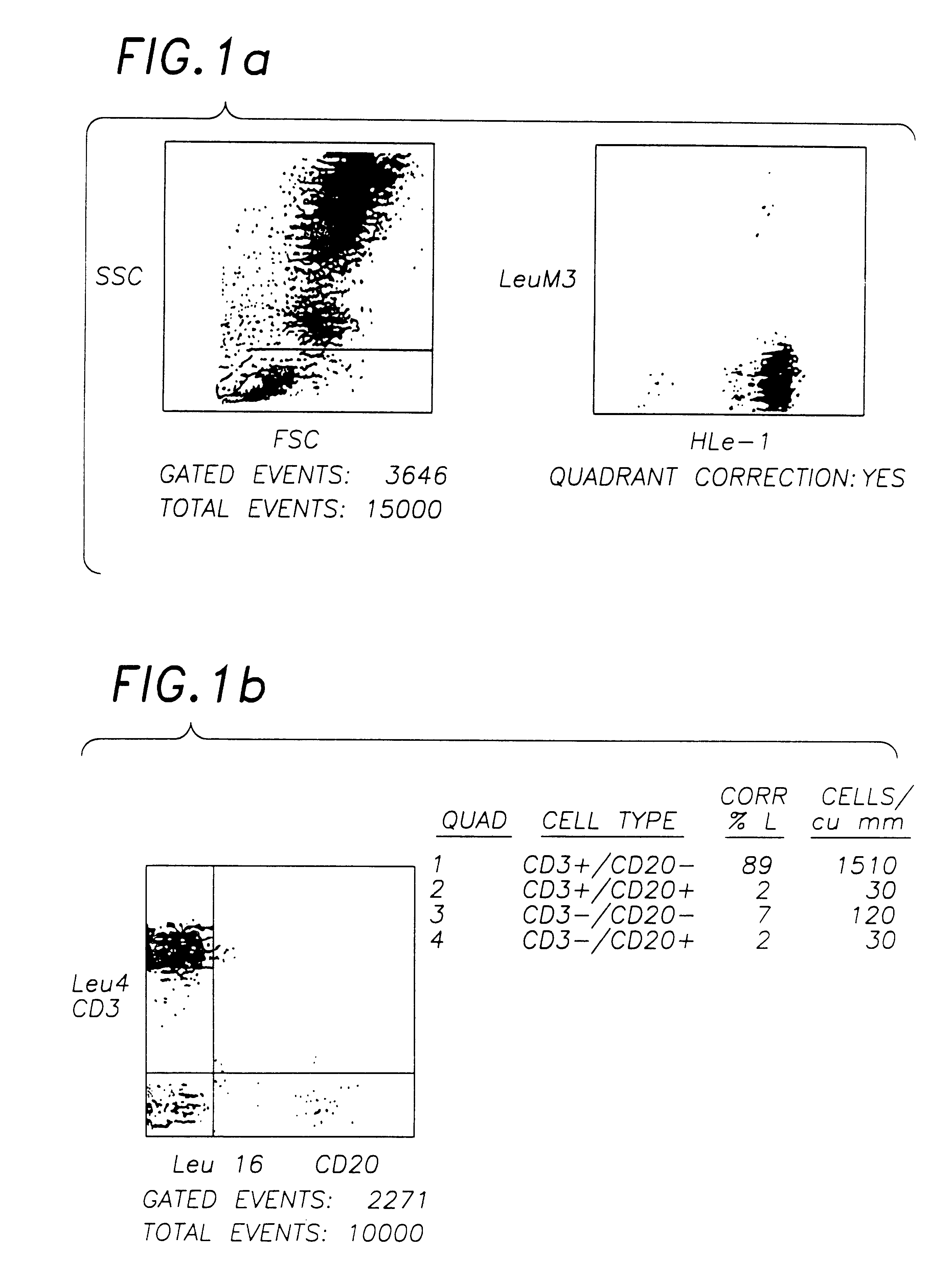
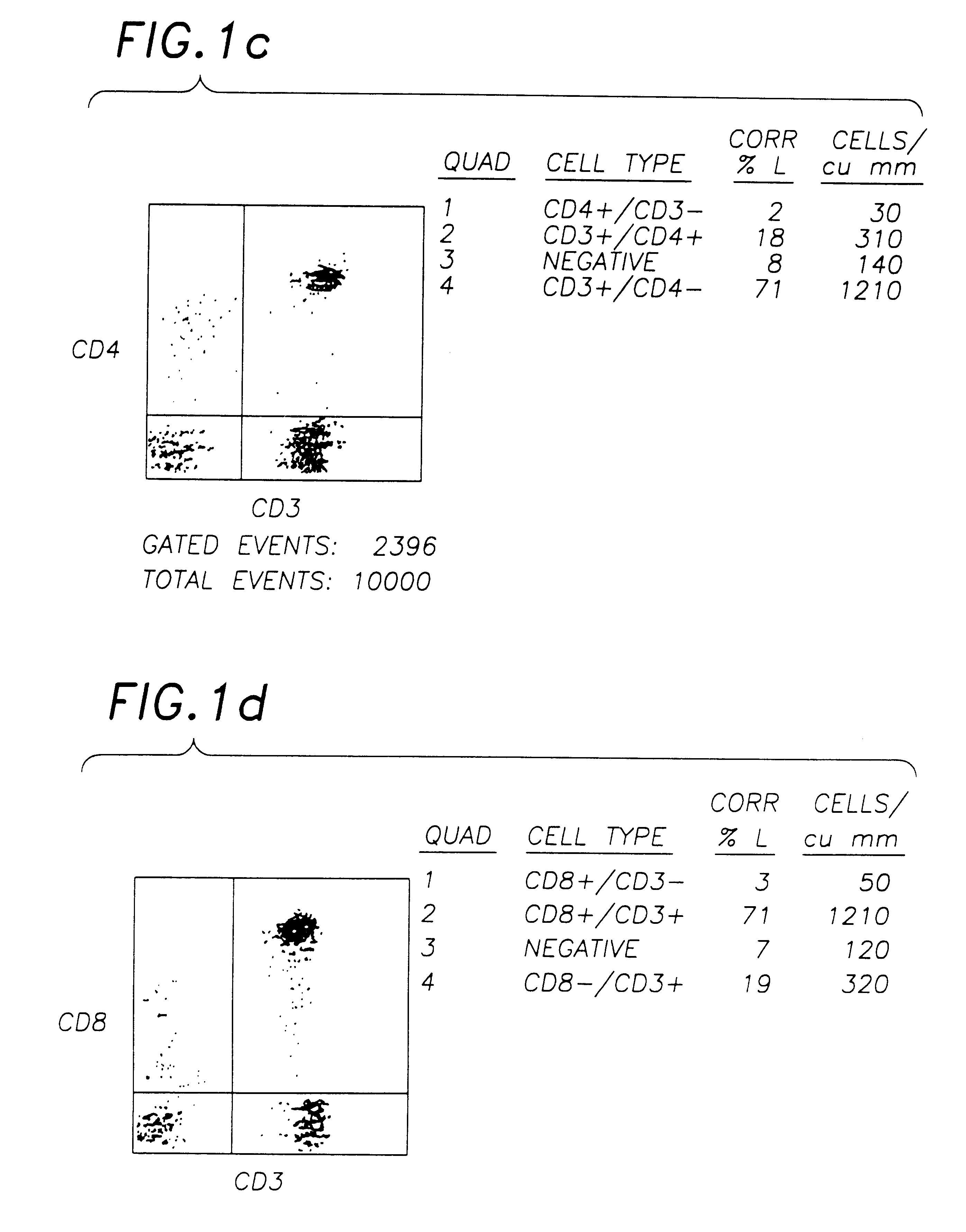
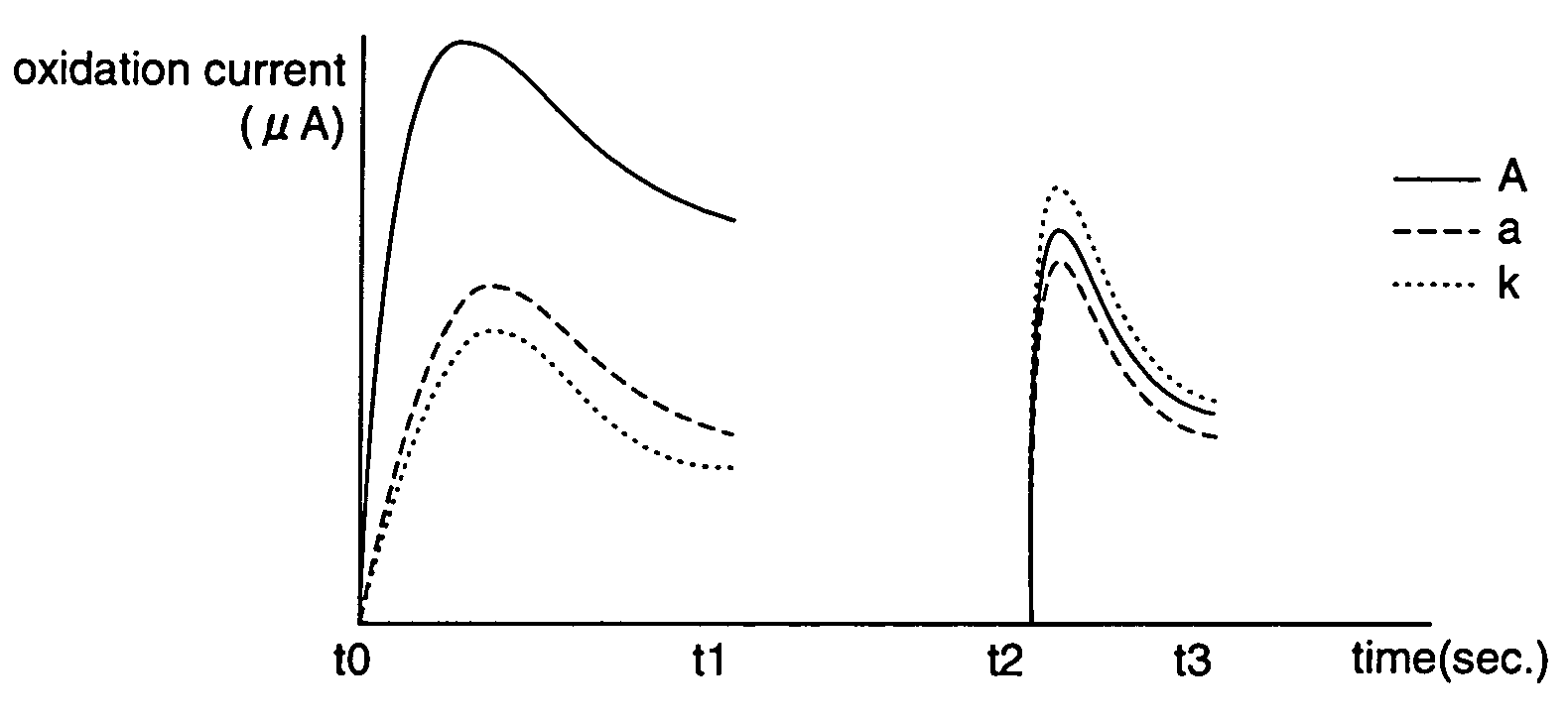
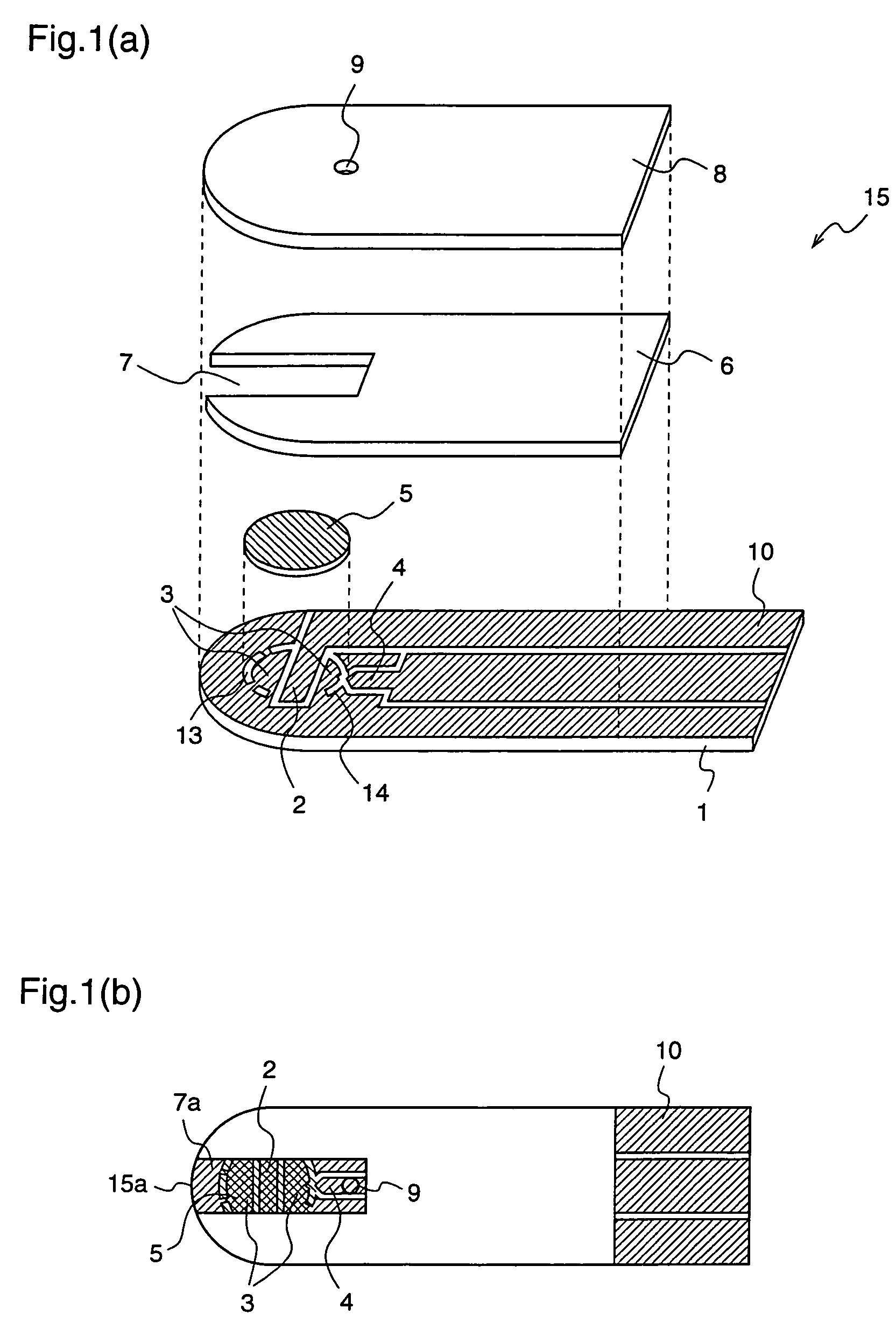
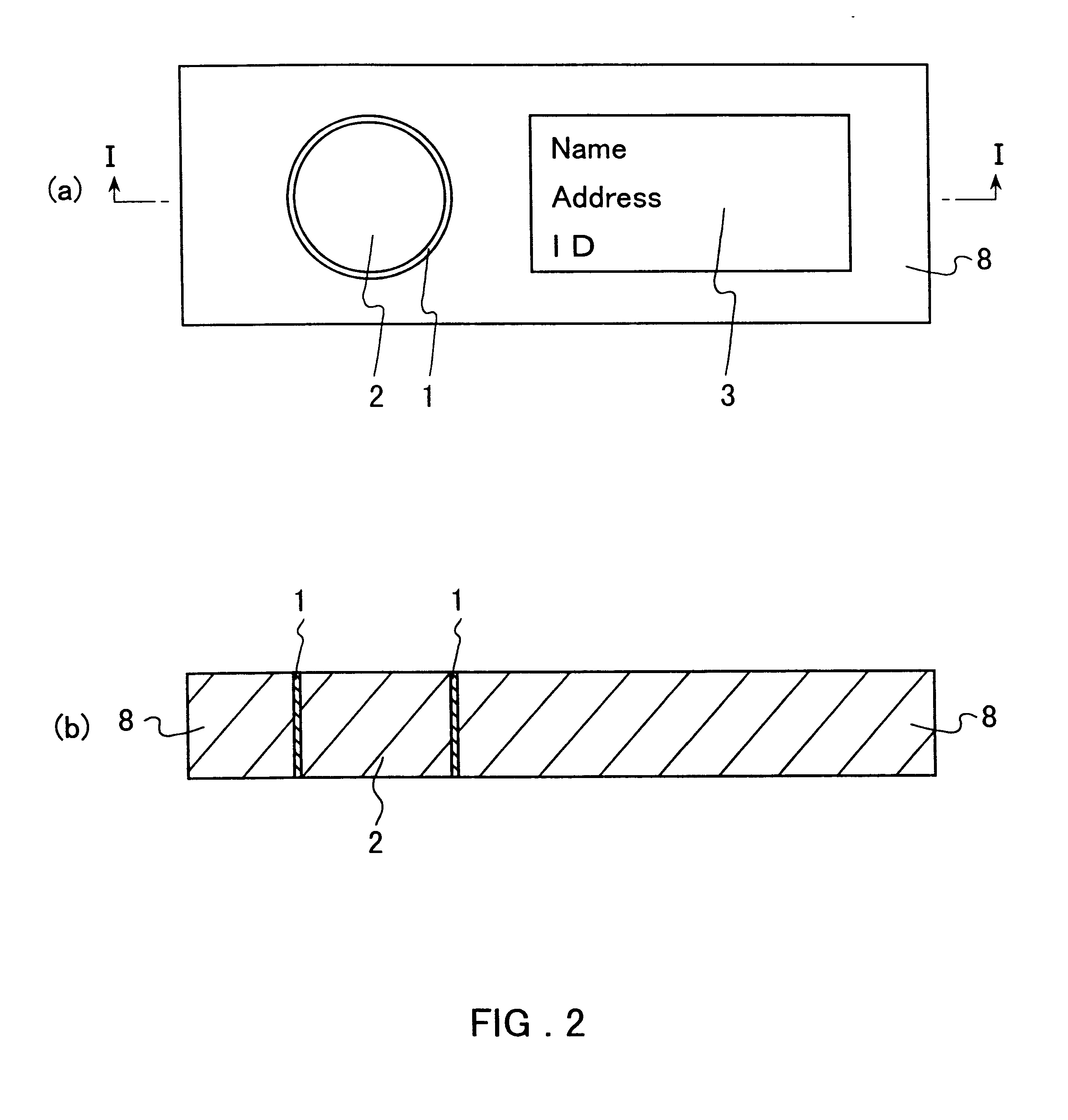
Determination method for automatically identifying analyte liquid and standard solution for biosensor
ActiveUS20050247562A1Improve accuracyHigh-precision identificationElectrolysis componentsWeather/light/corrosion resistanceAnalyteMeasuring instrument
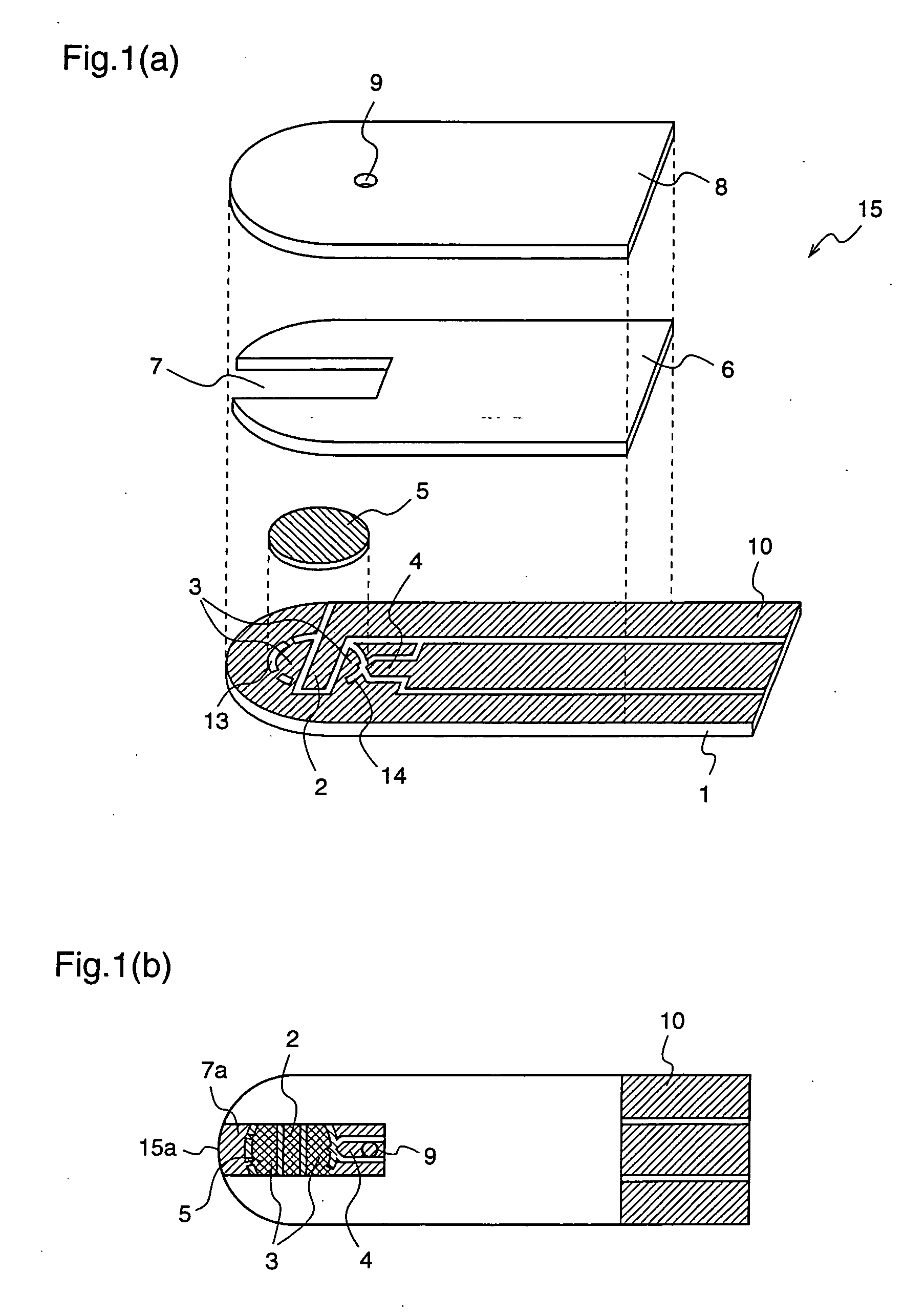
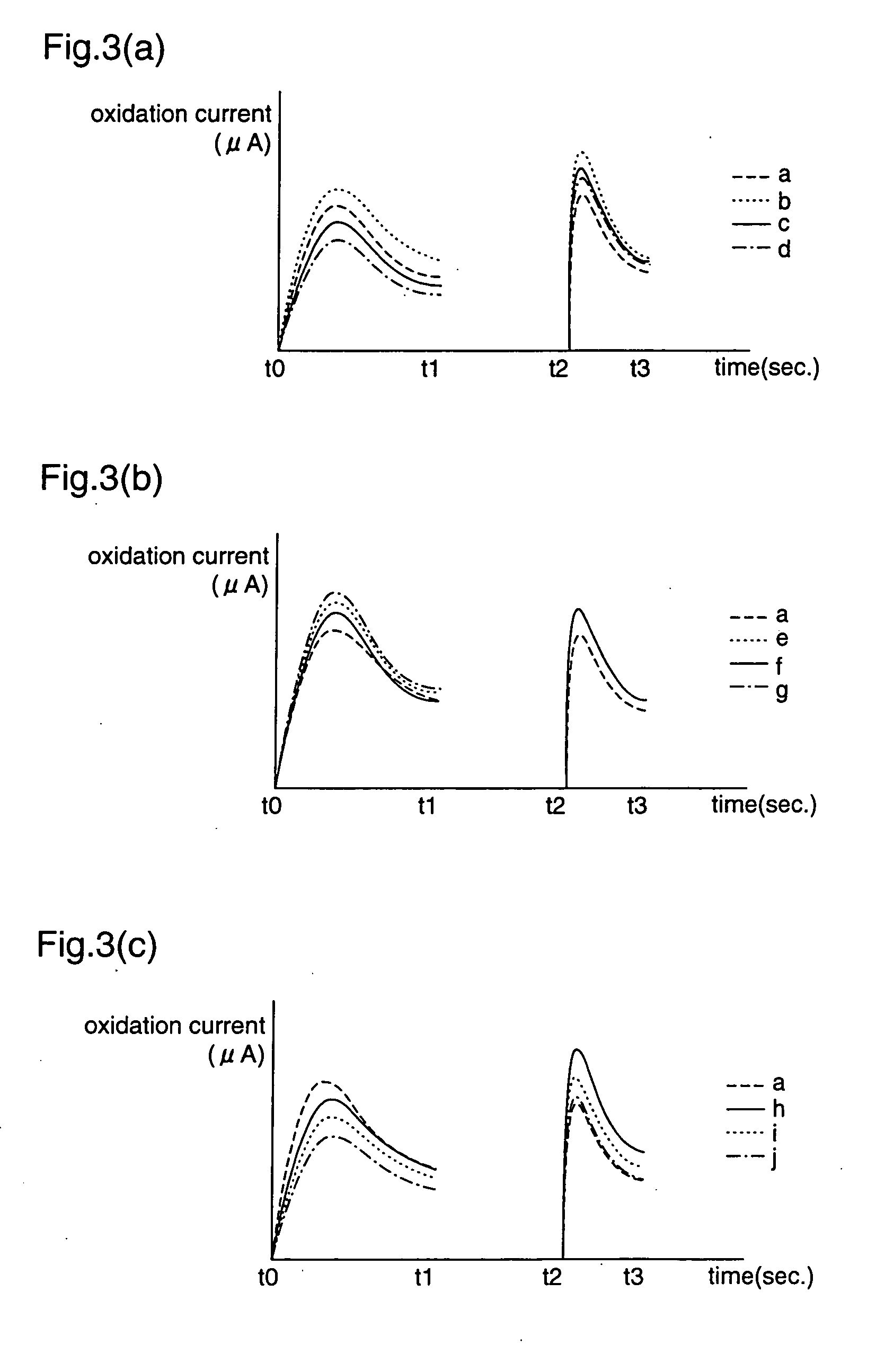
According to the standard solution and the determination method of the present invention, in a case where a voltage is applied by a drive voltage of a measurement apparatus to an electrode portion of a biosensor comprising an electrode portion including a counter electrode and a measuring electrode formed on an insulating substrate, and a reagent layer which reacts with a sample solution supplied to the electrode portion, and a current value which flows at the application is measured, thereby determining a substrate contained in the sample solution, a reducing substance is contained in the standard solution used for controlling a precision of measurement of the measurement apparatus. Therefore, when the standard solution is measured, a large change occurs in a current waveform between time t0 and t1 shown in FIG. 6 due to the reducing substance, thereby discriminating whether the analyte liquid being measured is the standard solution or the sample solution and easily identifying the kind of analyte liquid.
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
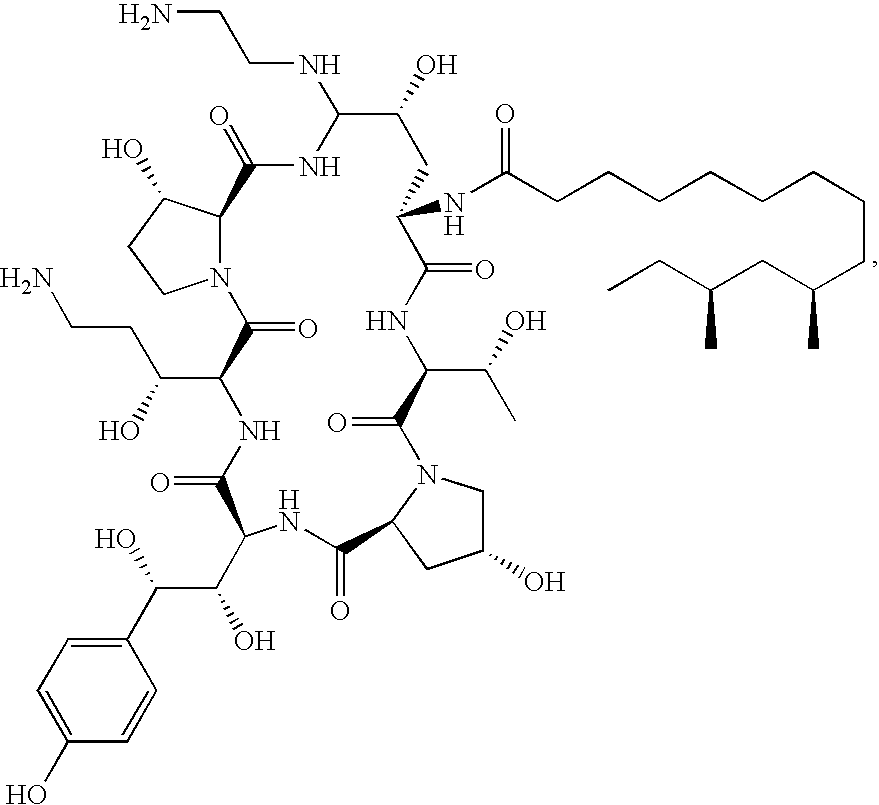
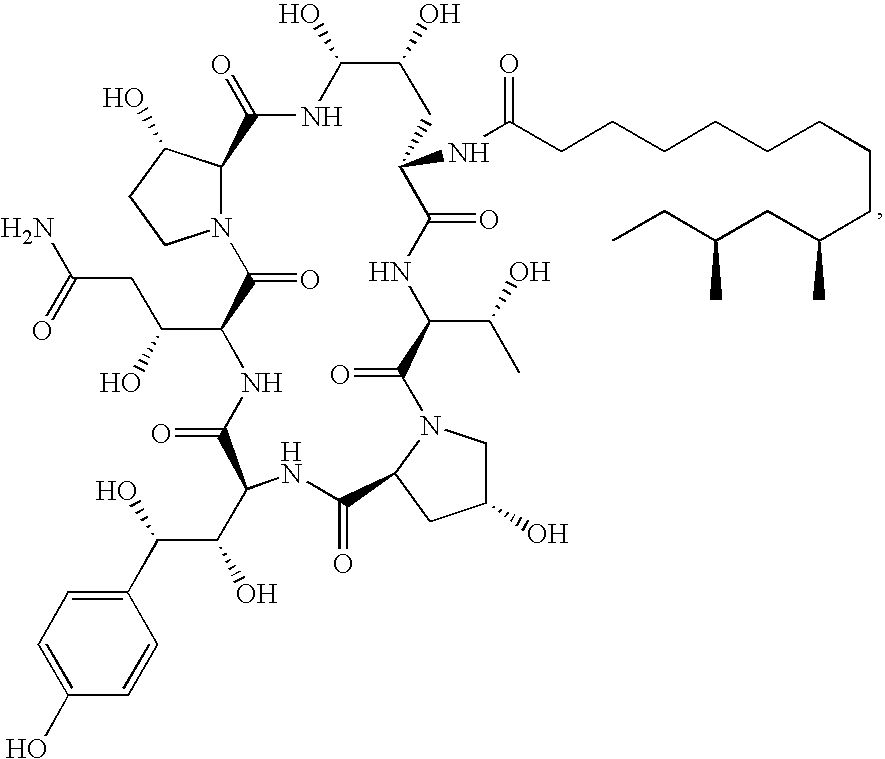
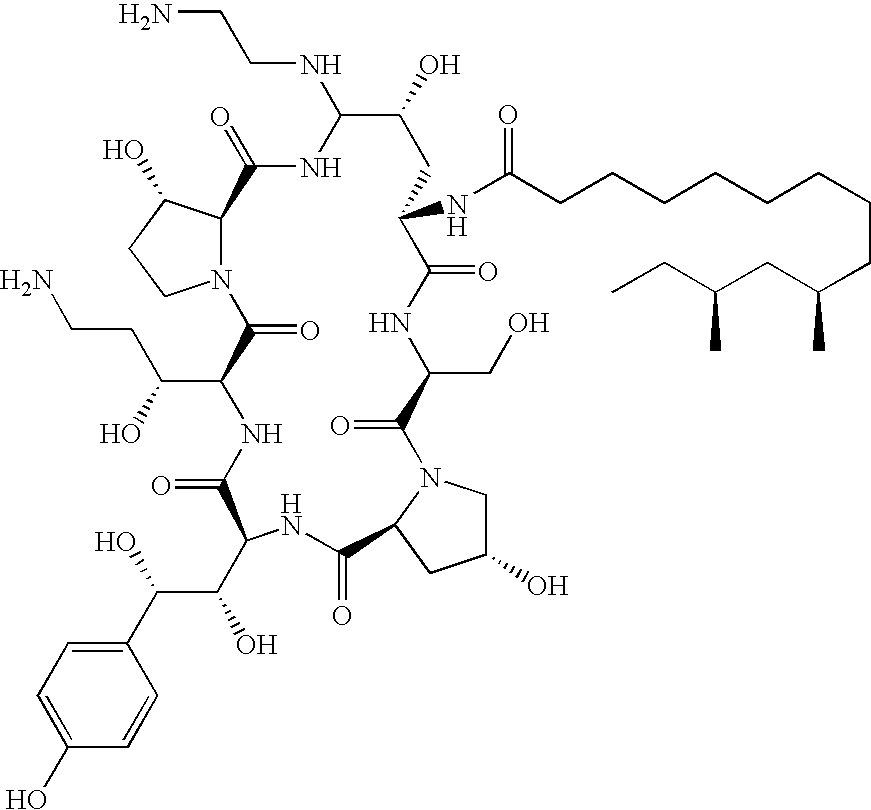
Caspofungin free of caspofungin impurity A
Provided is caspofungin free of caspofungin impurity A, methods for preparation thereof and isolation of caspofungin impurity A.
Owner:TEVA PHARM USA INC
Method for preparing a stabilized blood cell preparation using aged transition metal ion solution
InactiveUS6197539B1Preparing sample for investigationPharmaceutical delivery mechanismBlood componentWhite blood cell
The invention is directed to novel methods of stabilizing blood compositions for use in the quality control of analytical techniques. The novel method comprises removing leucocytes from a blood composition to yield a depleted blood composition, stabilizing the leucocytes by treatment with an effective amount of a stabilizing agent comprising an aged transition metal solution, and then adding the resultant stabilized leucocytes to the depleted blood composition or a second blood component composition.
Owner:SHEFFIELD TEACHING HOSPITALS NAT HEALTH SERVICE TRUST +1
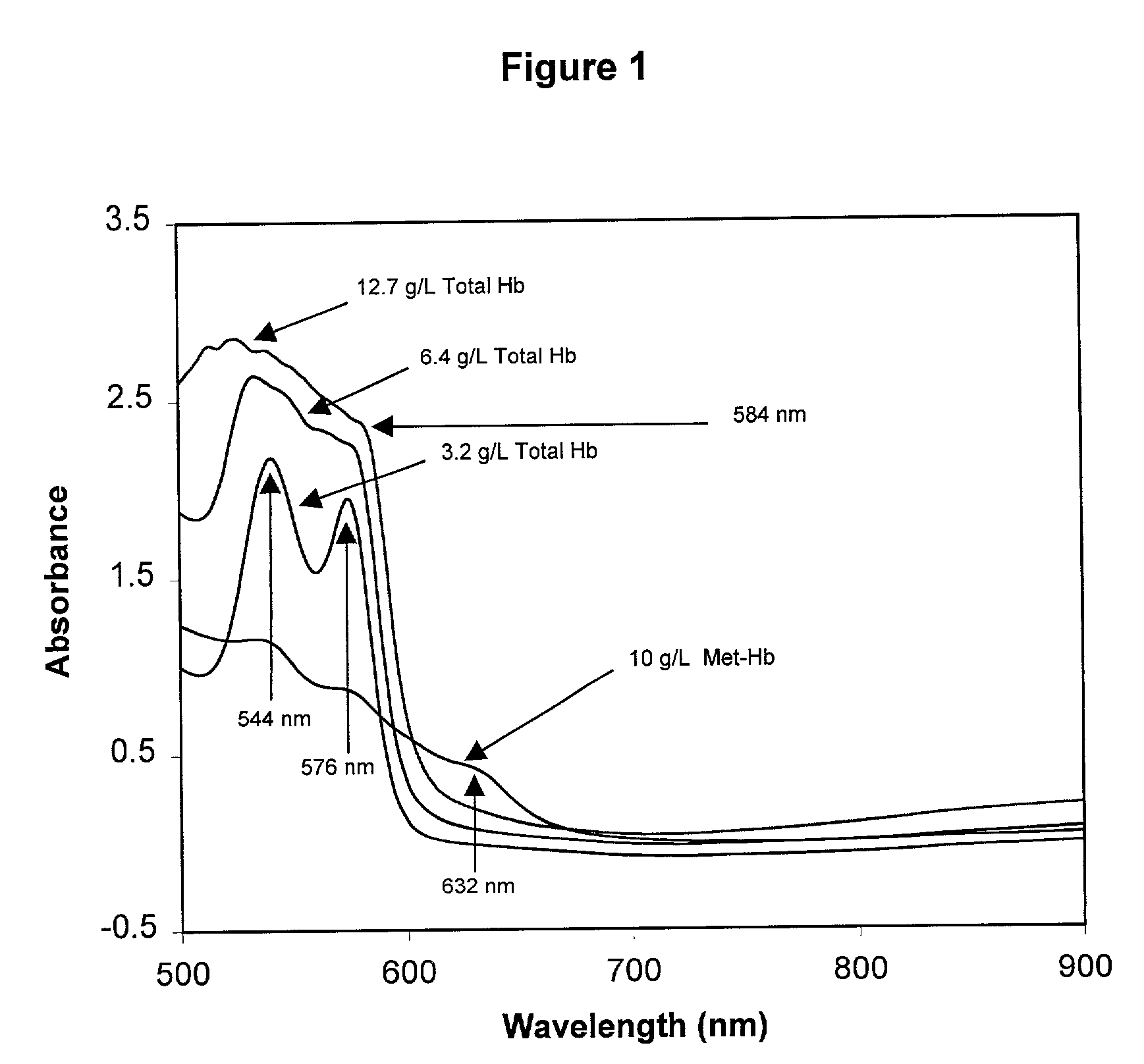
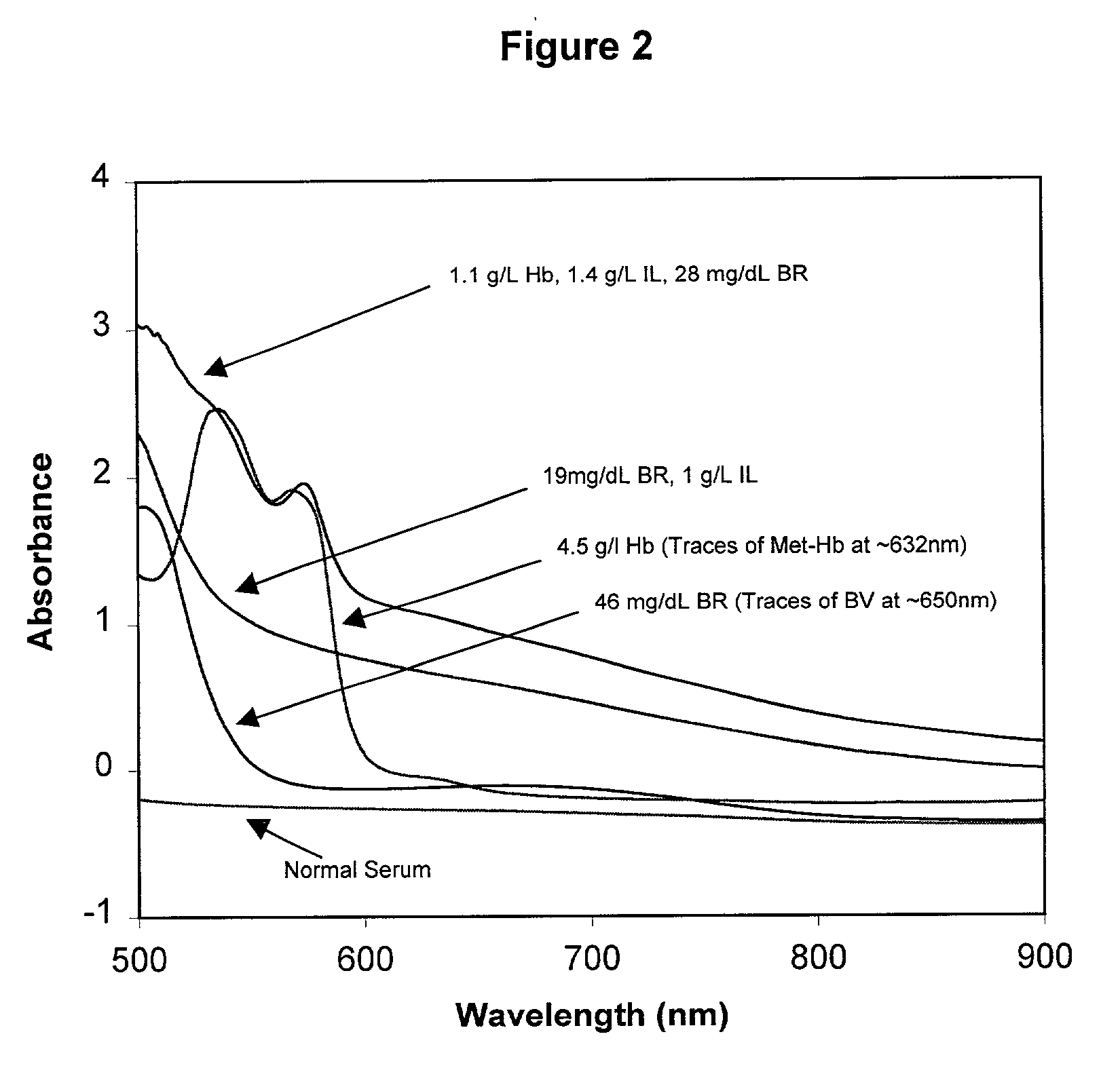
Calibrator material for instruments which measure interferents in serum and plasma specimens
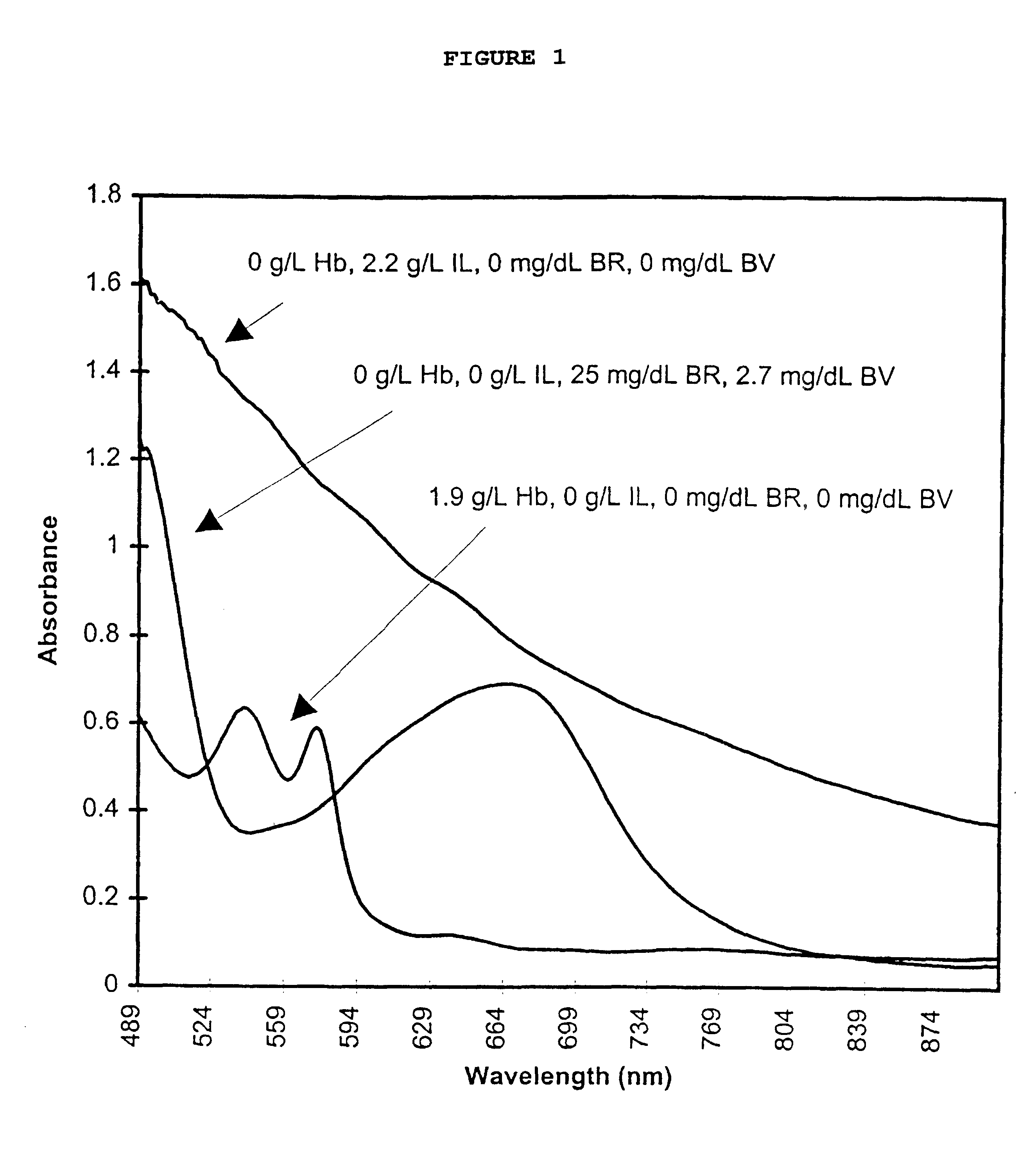
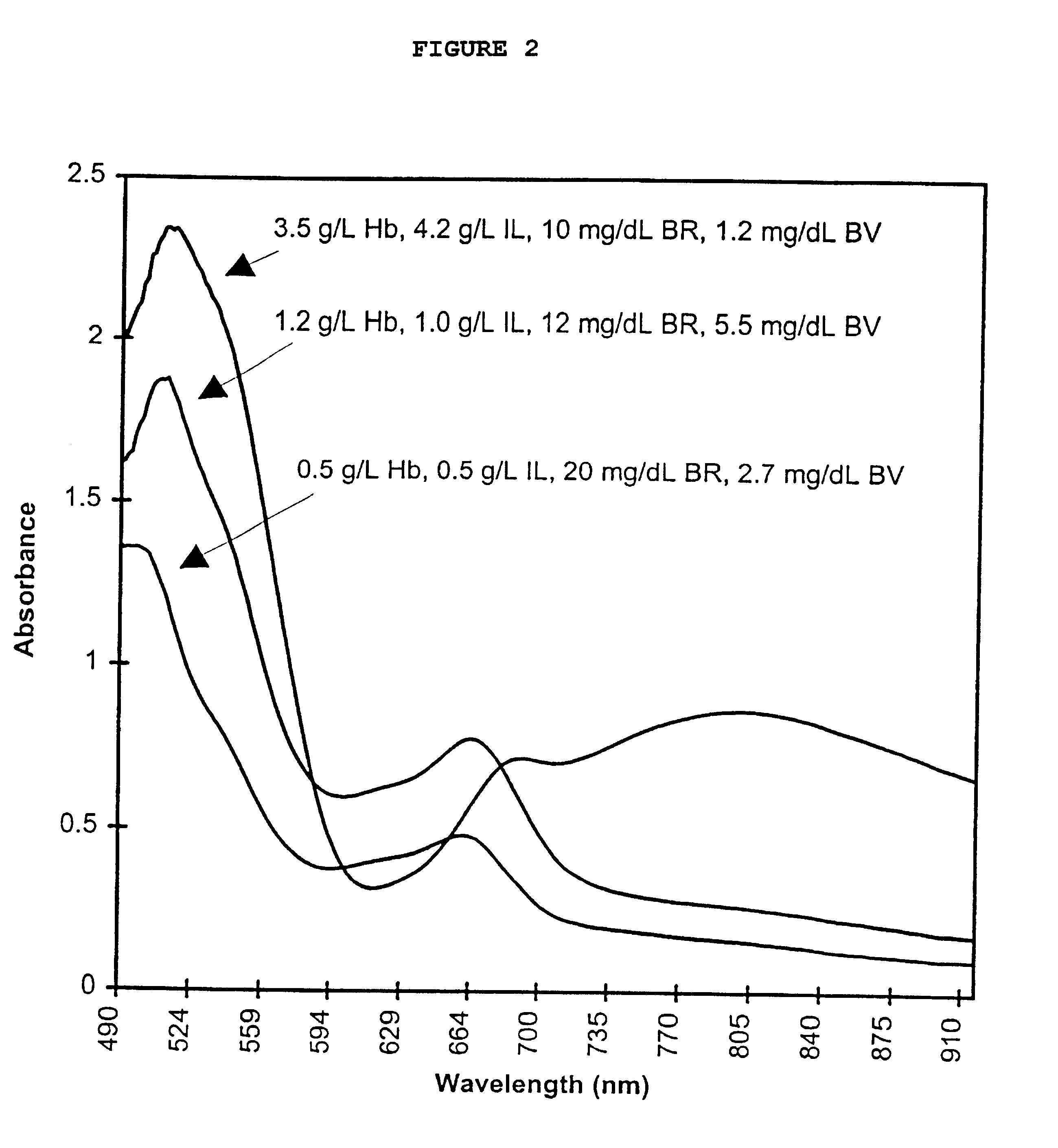
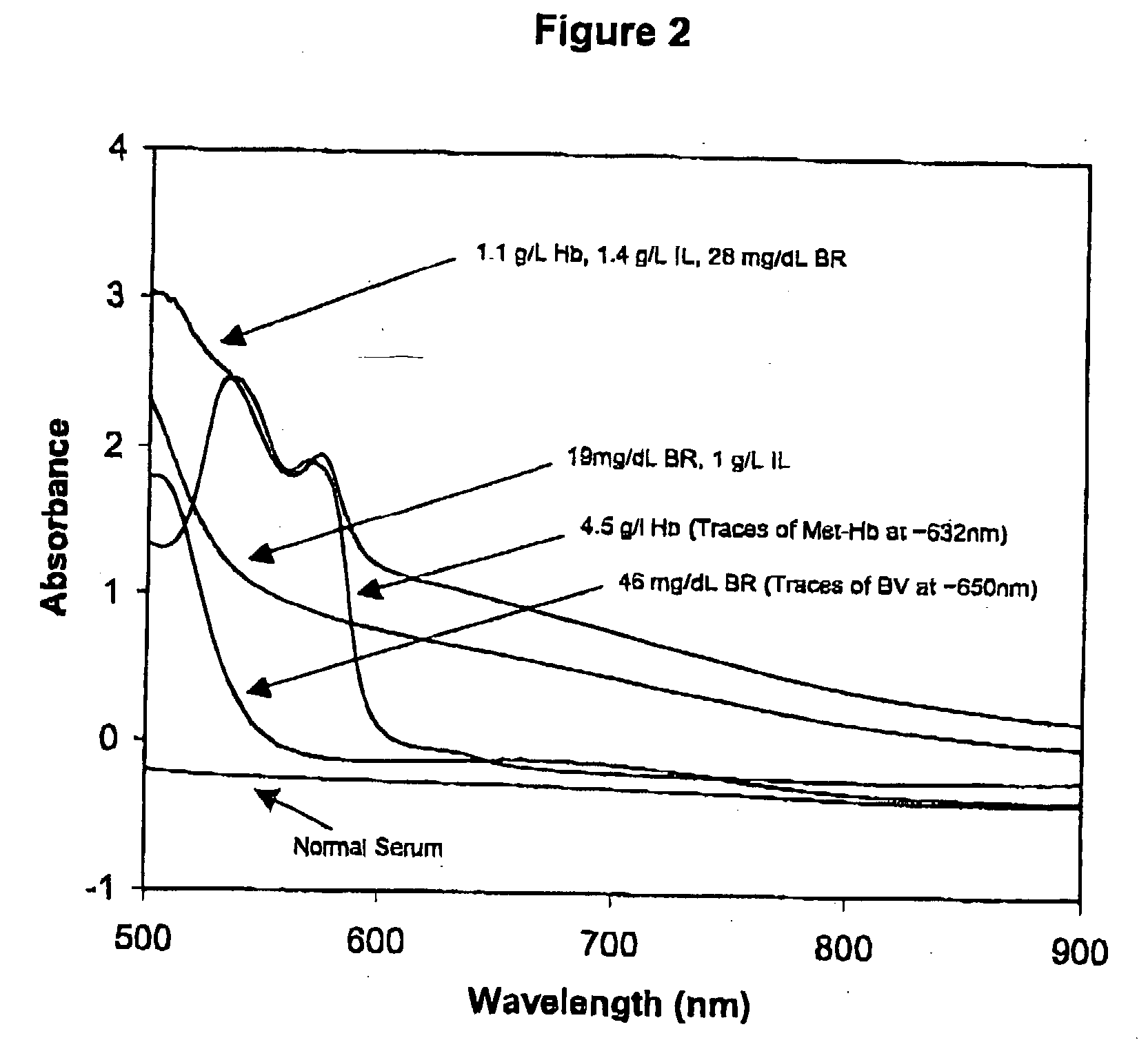
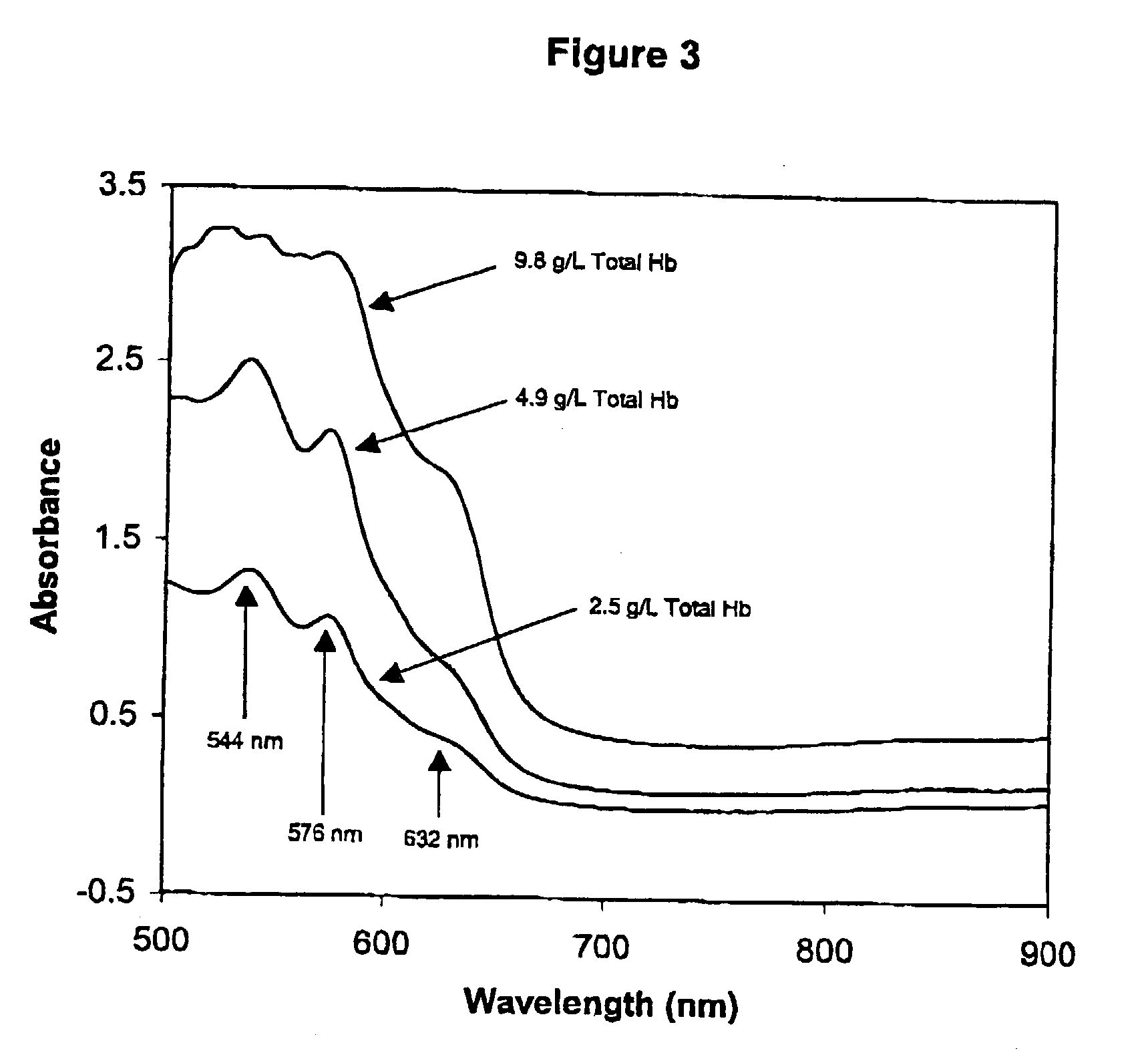
InactiveUS6372503B1Increase absorbanceLeft outBiological testingSpecial data processing applicationsBILIRUBINAEMIAHemolysis
A quality control material is disclosed which is used to monitor the calibration or used for recalibration of instruments used to screen for interferents in serum or plasma specimens. In particular, the quality control material disclosed is used to monitor instrument calibrations or used for recalibration for instruments which assess the amount of hemolysis, turbidity, bilirubinemia and biliverdinemia, either separately, or any two, or any three, or all four simultaneously, in plasma or serum samples. The quality control material does not contain any blood products such as plasma lipids, bile pigments, or hemoglobin, is stable at room temperature, and is ready for use with up to four constituents.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Quality control method
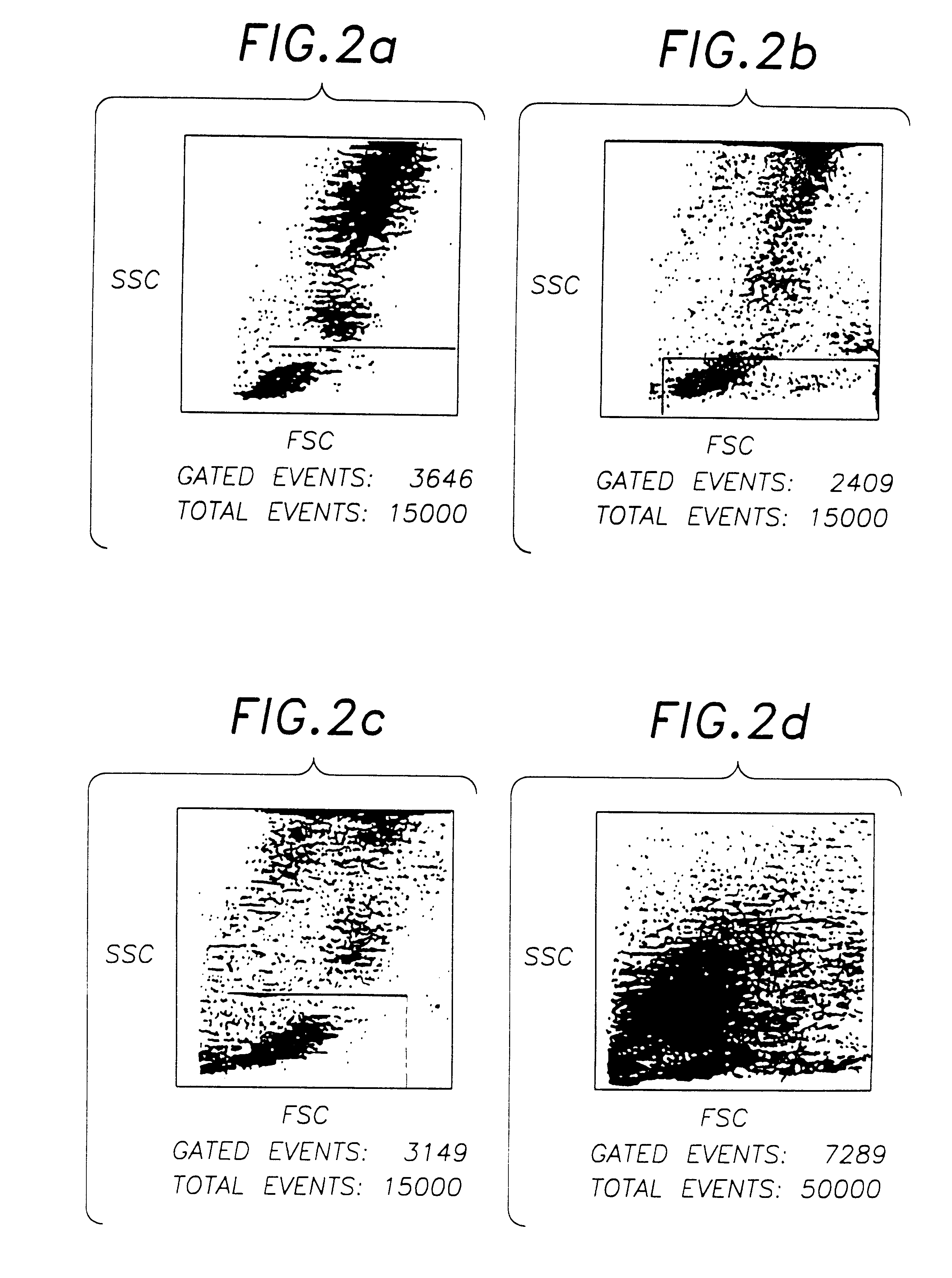
InactiveUS6509192B1Reduce probabilityIncreasing mean corpuscular volumeIndividual particle analysisBiological testingLysisRed Cell
A method of quality control to diagnose the cause of a malfunction of an instrument. The method uses measurements of the physical property of a sample to diagnose the cause of a malfunction of an instrument. The spatial position of a control product sample is analyzed. Alternatively, the spatial position of a statistically significant number of patient blood samples can be used. The method enables the monitoring of an instrument for problems associated with debris and noise caused by red cell lysis inefficiency; instrument reagents pump volume settings; instrument laser alignments; instrument gain settings; and flow noise caused by partial plugs, residual plugs or other flow problems. The method provides a more specific indication of the type and cause of an instrument malfunctioning than non specific flagging provided by prior art methods.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Normalisation of microarray data based on hybridisation with an internal reference
InactiveUS20050153290A1Large intensityMinimal levelBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteQuantitative determination
The invention relates to methods and corresponding arrays especially suited to correct for signal errors due to variations in sample preparation. Methods and compositions for performing quantitative array-based assays are provided. In the subject methods, both a reporter and an analyte is employed, where the reporter is characterized by binding selectively to an internal reference present on the array, i.e. at least a subset of, if not all of, the spots present on the array employed in the method contain an internal reference which can be bound by reporter.
Owner:PAMGENE
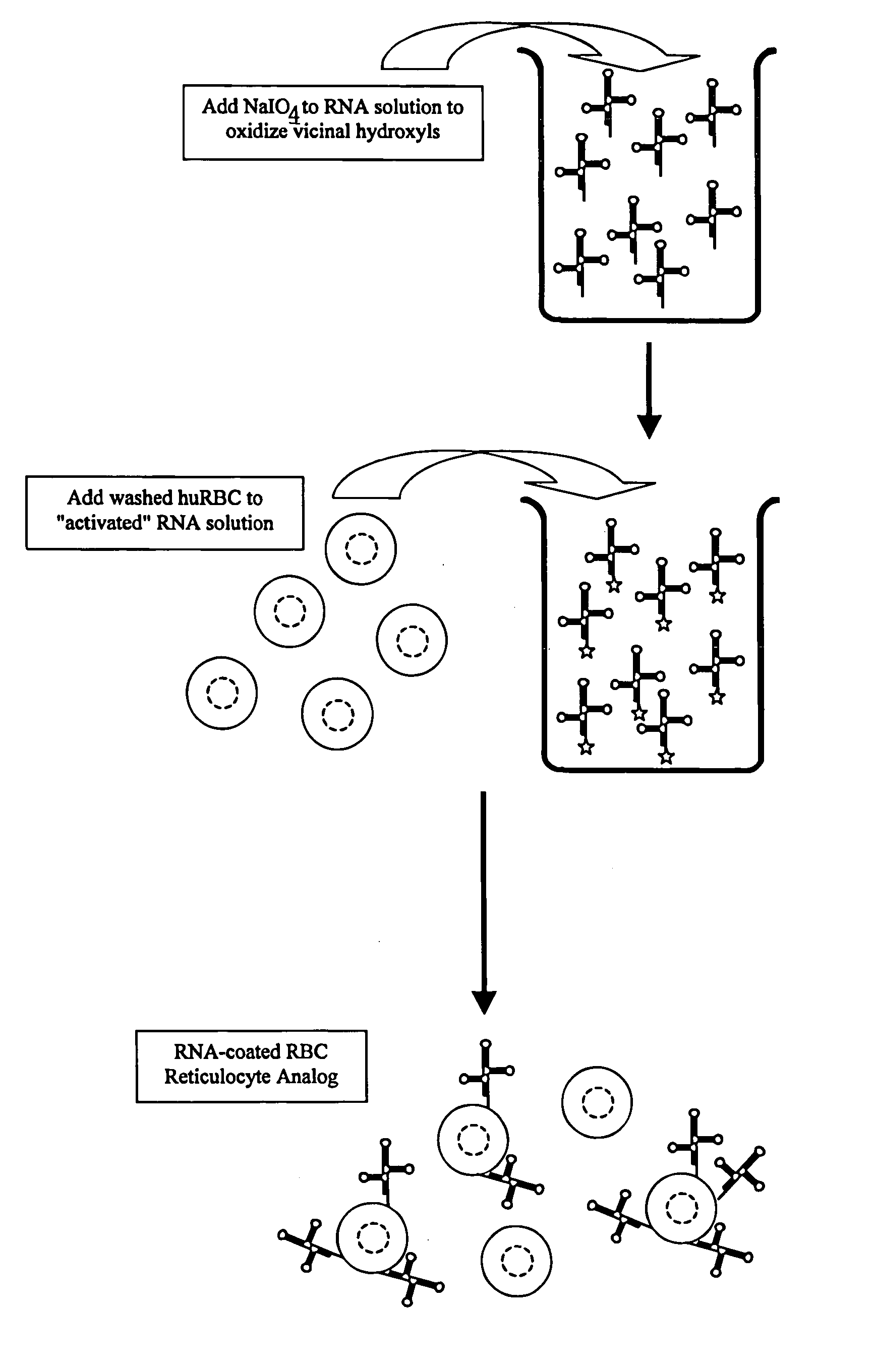
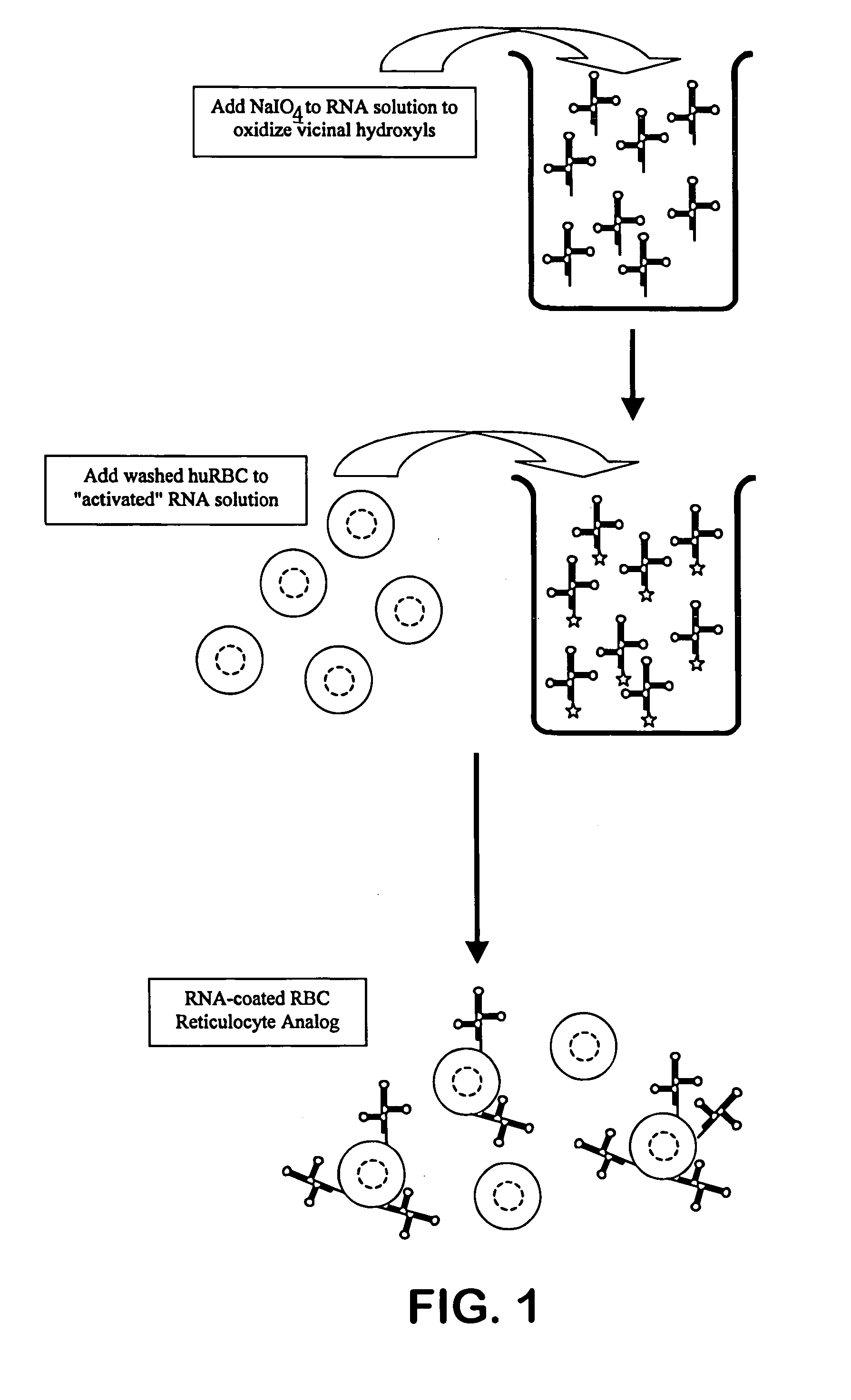
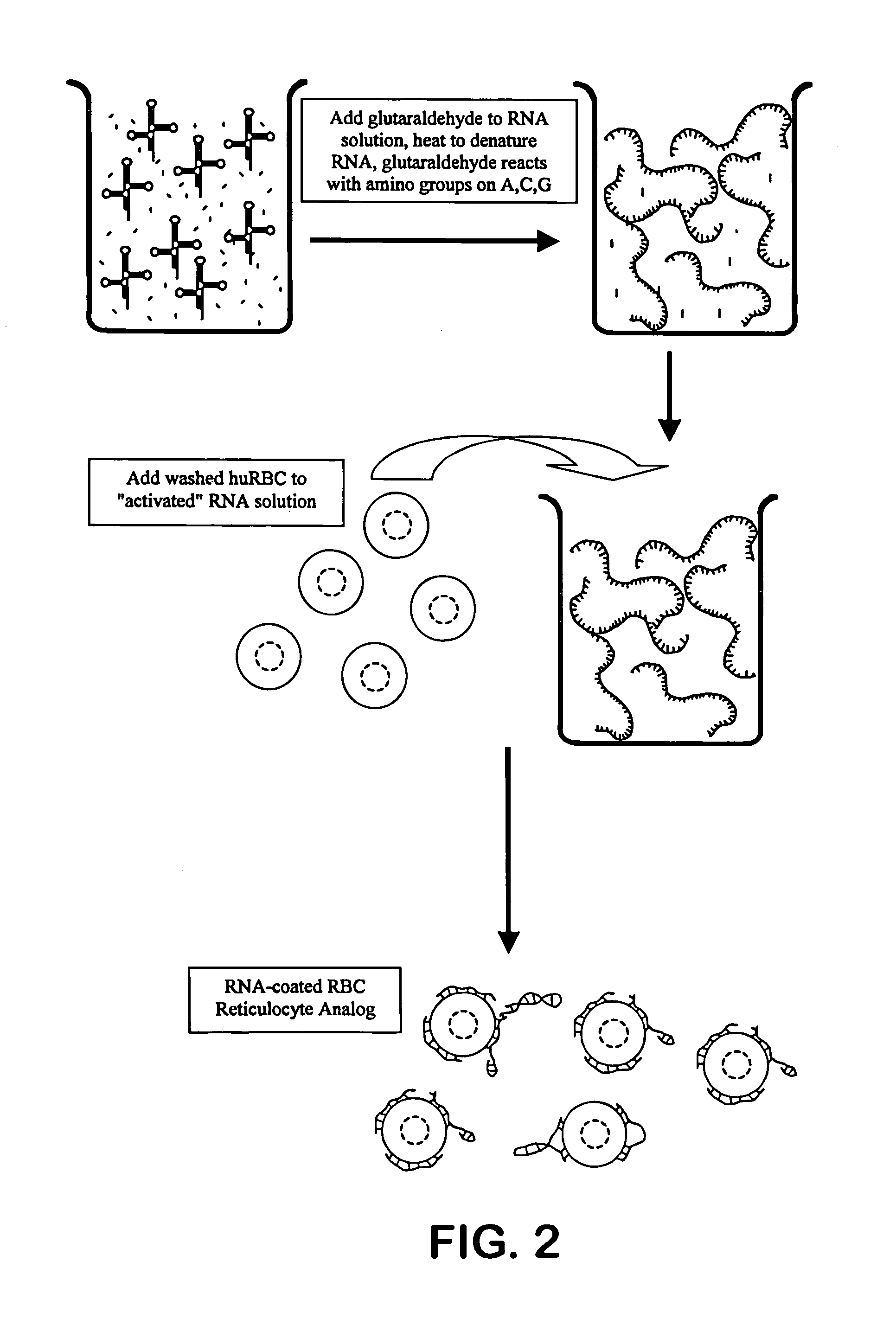
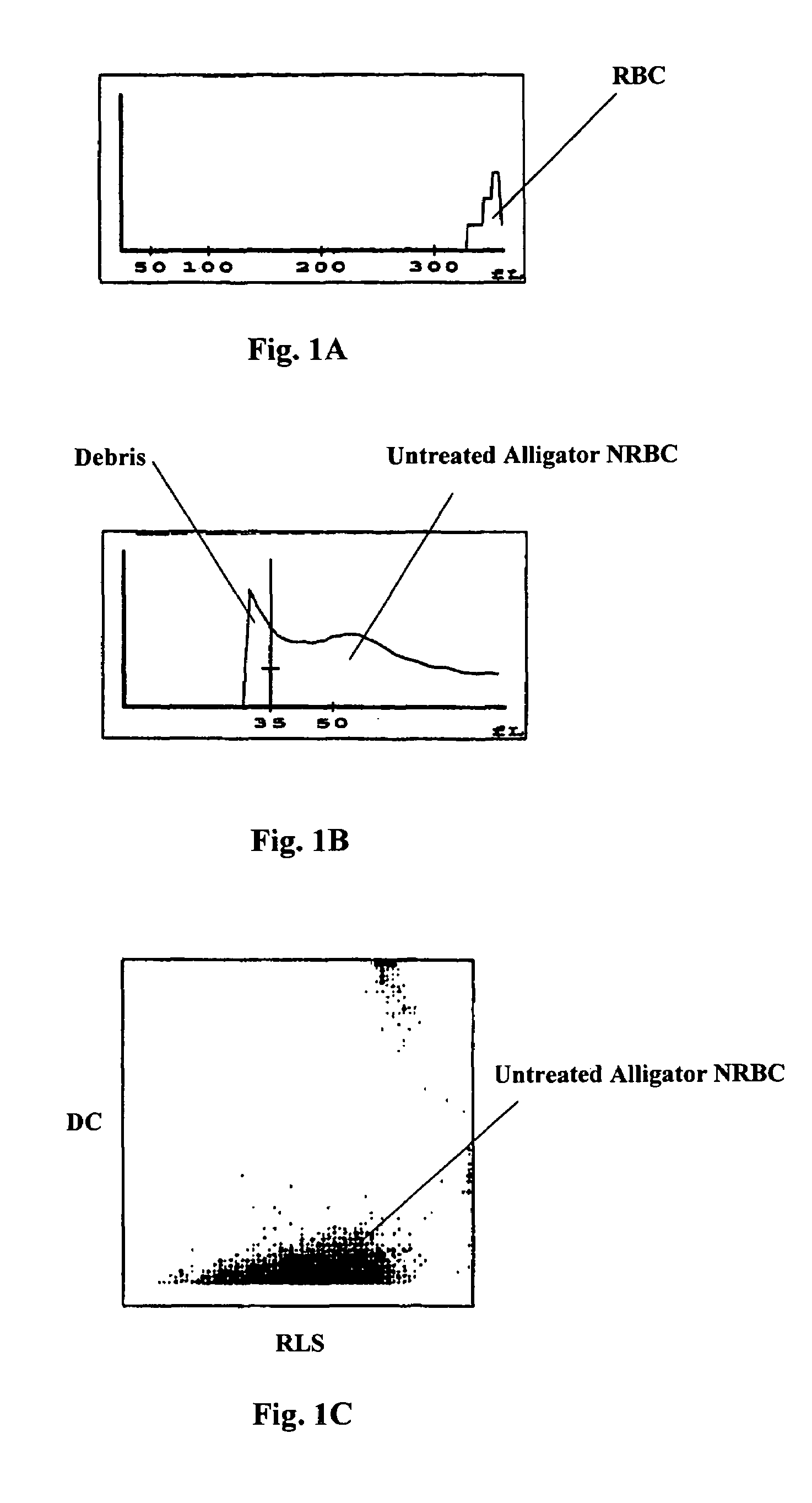
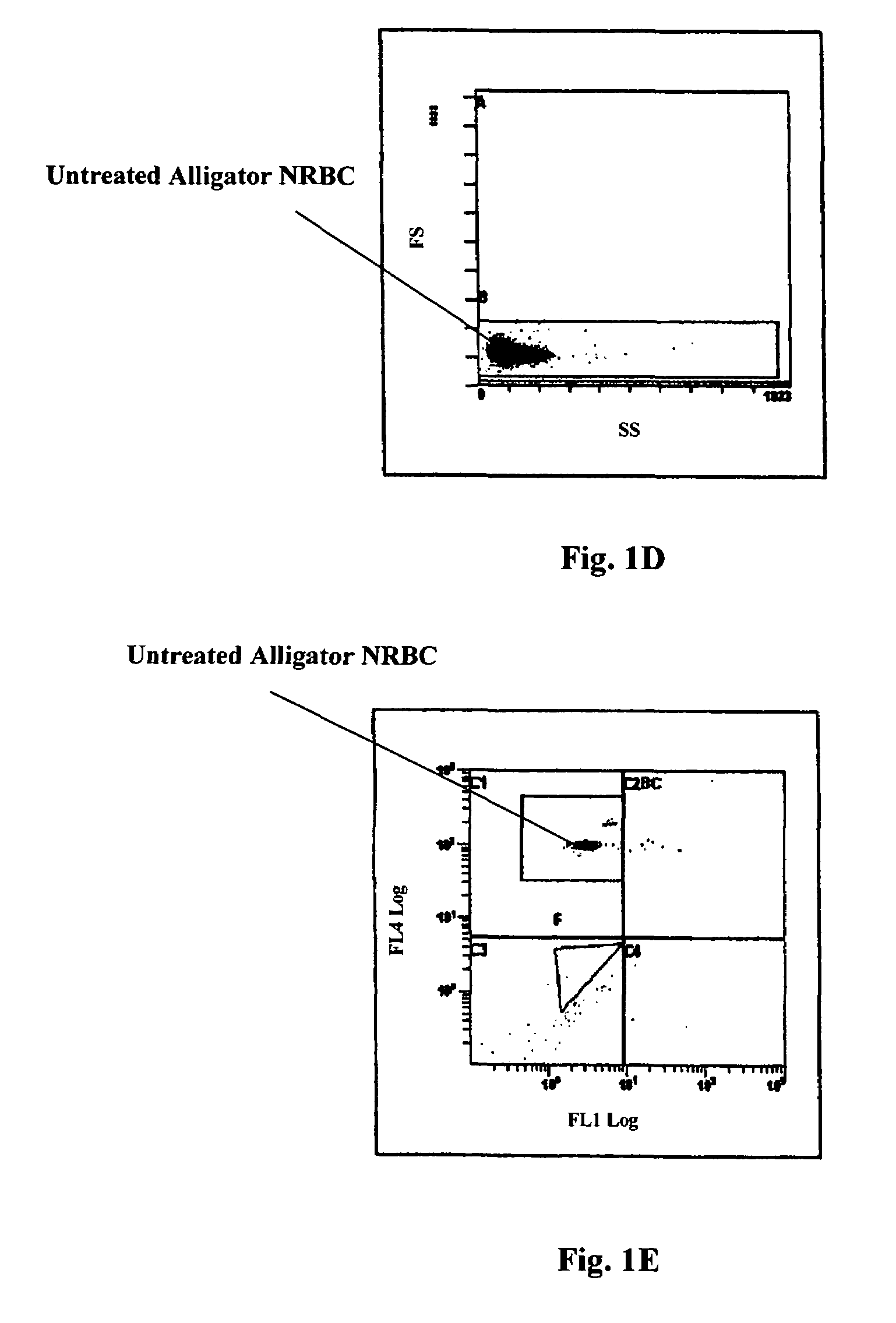
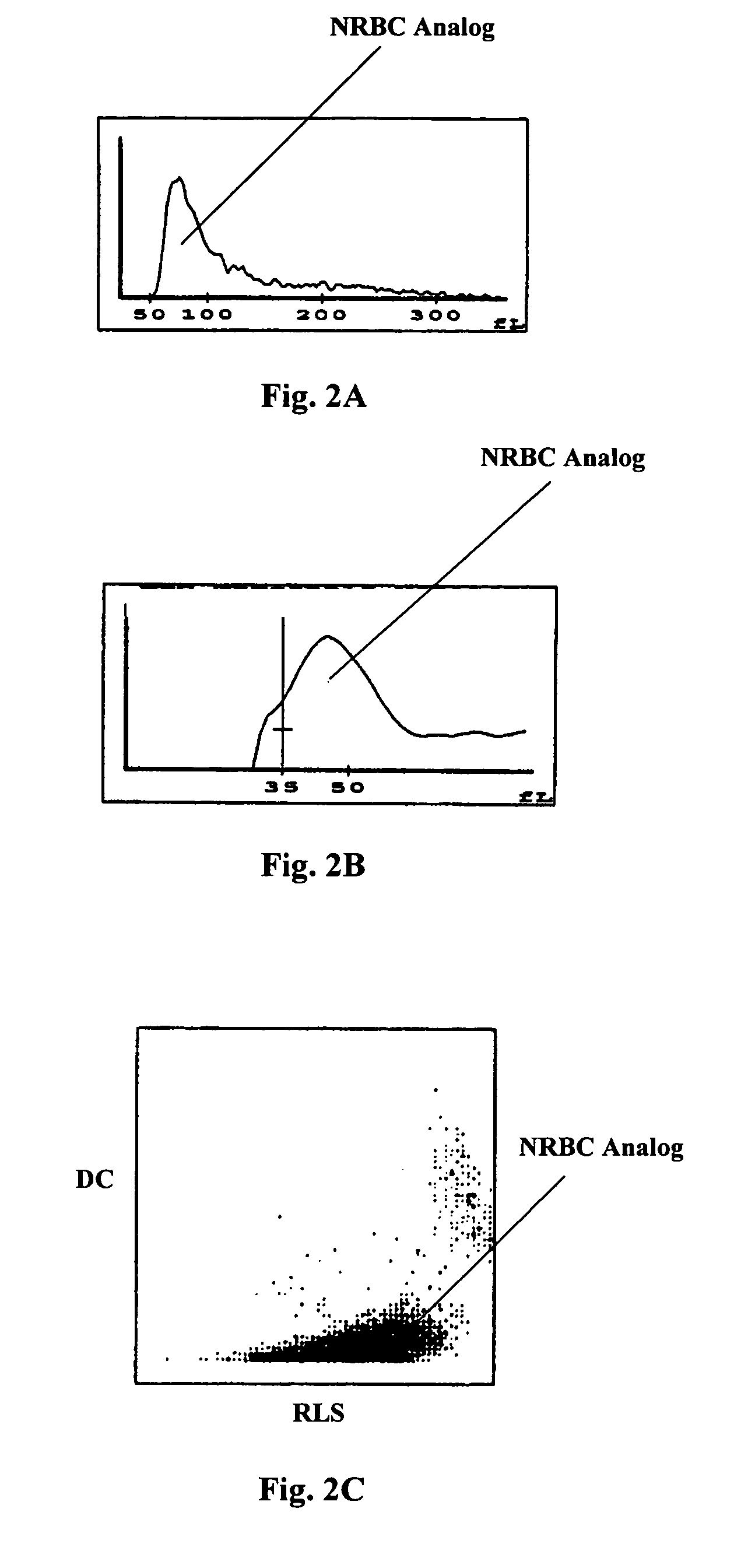
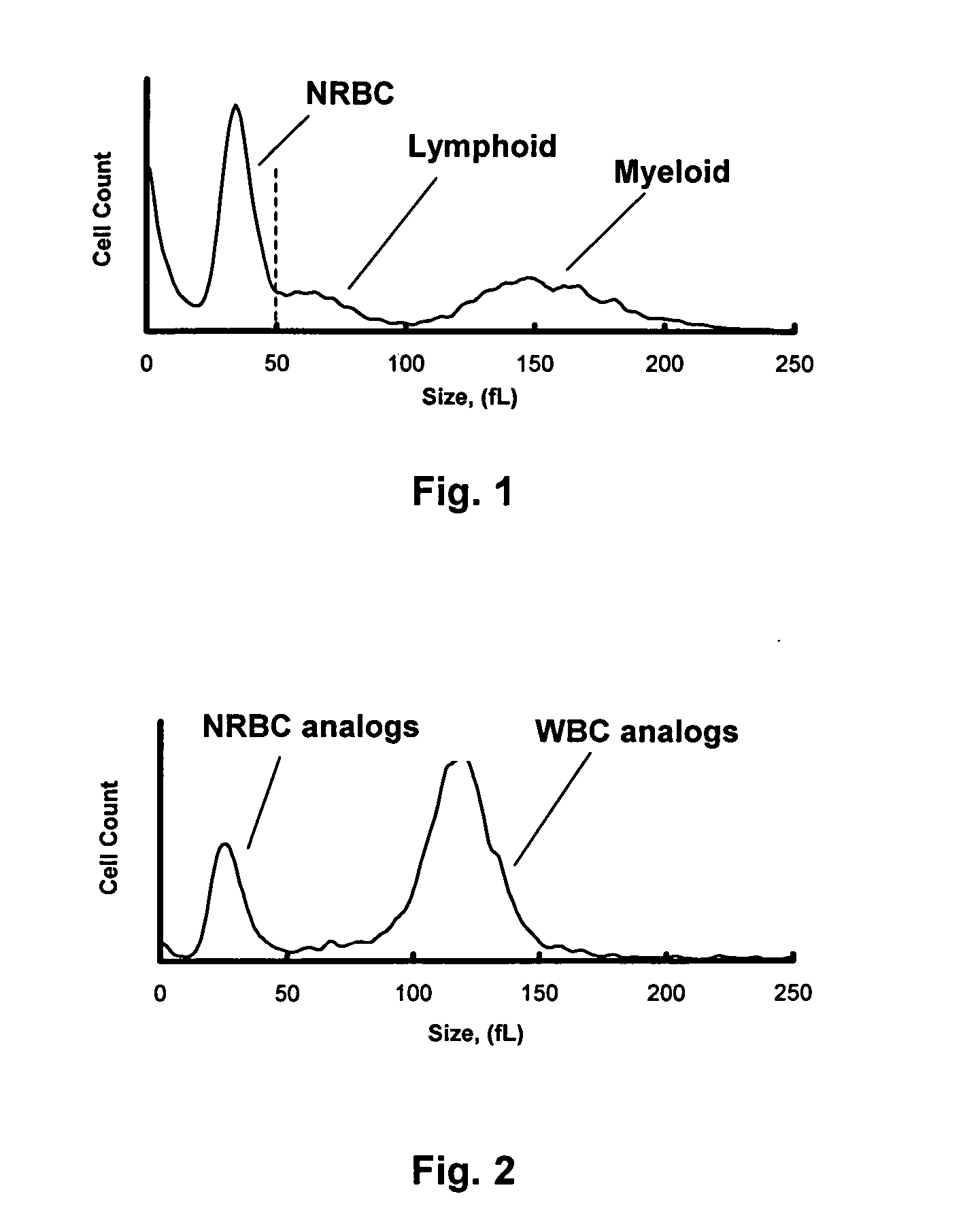
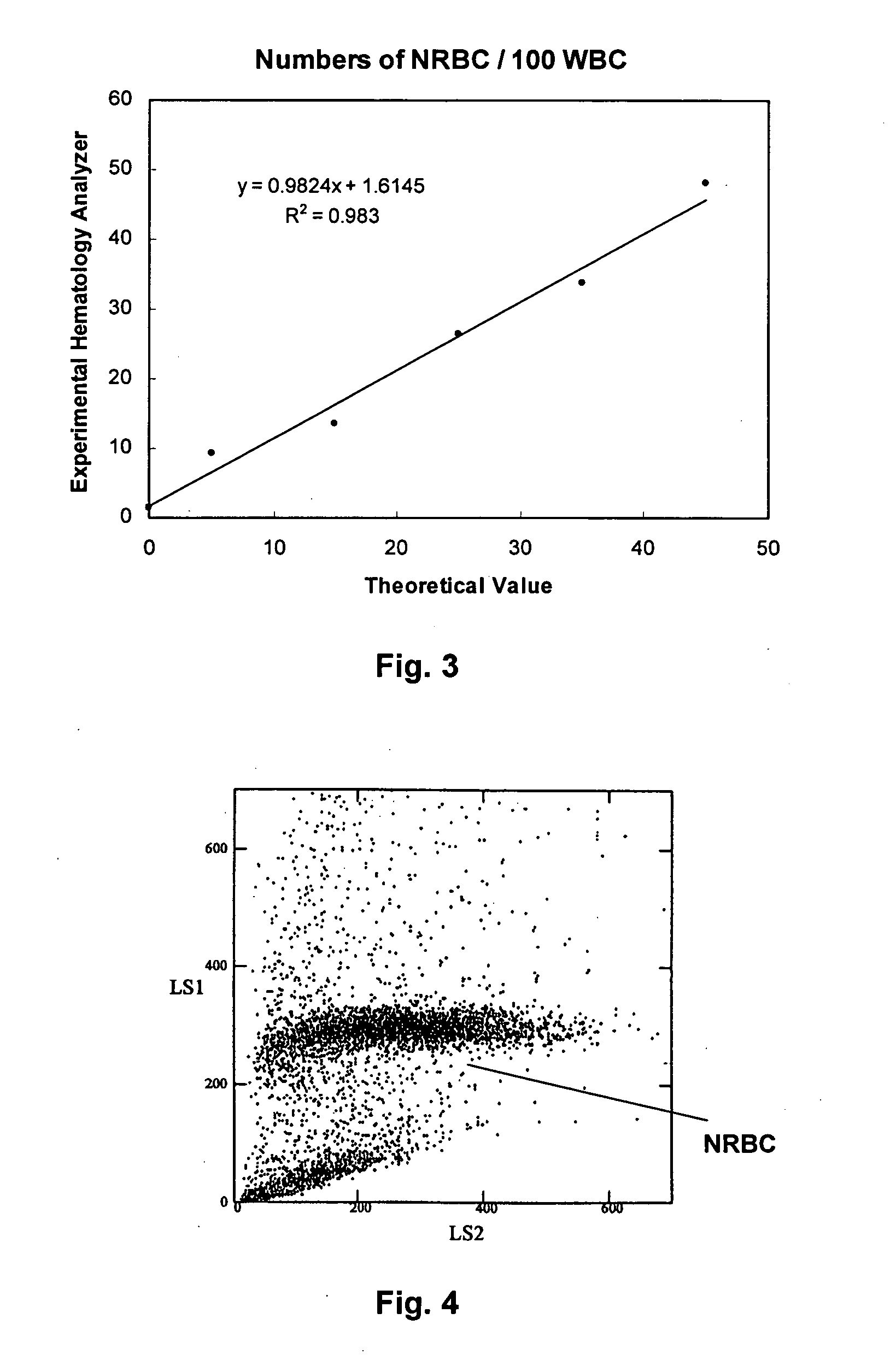
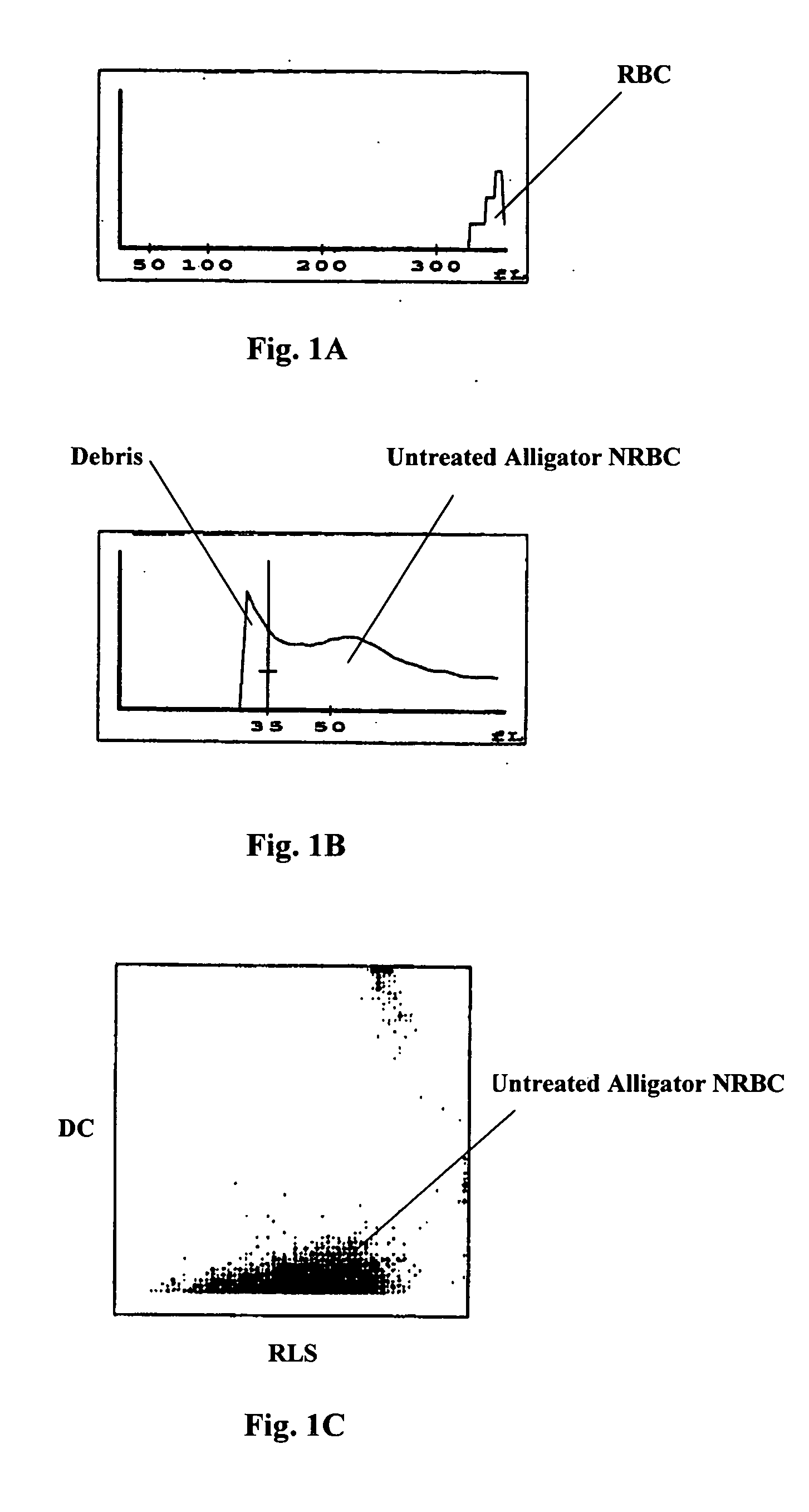
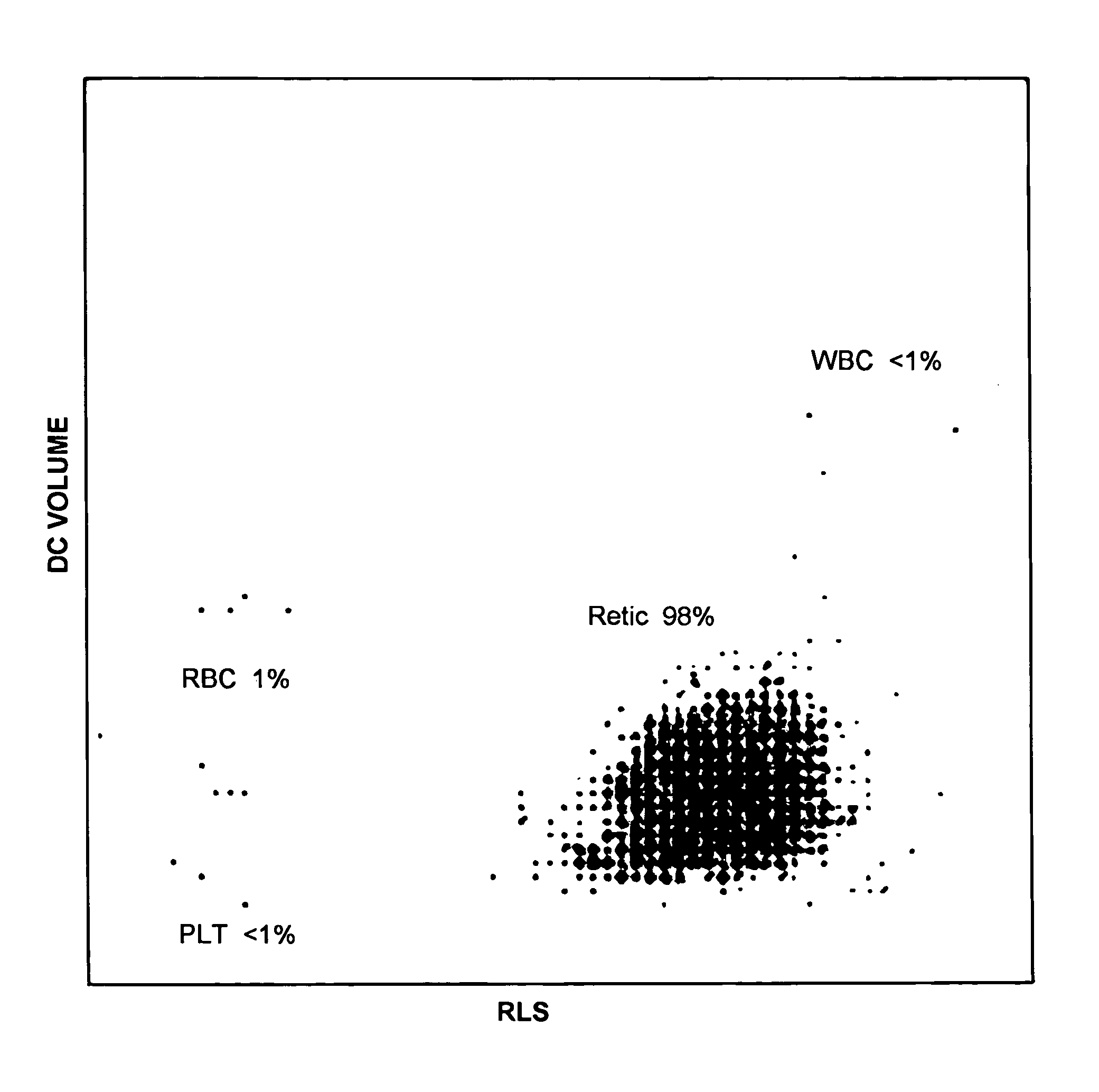
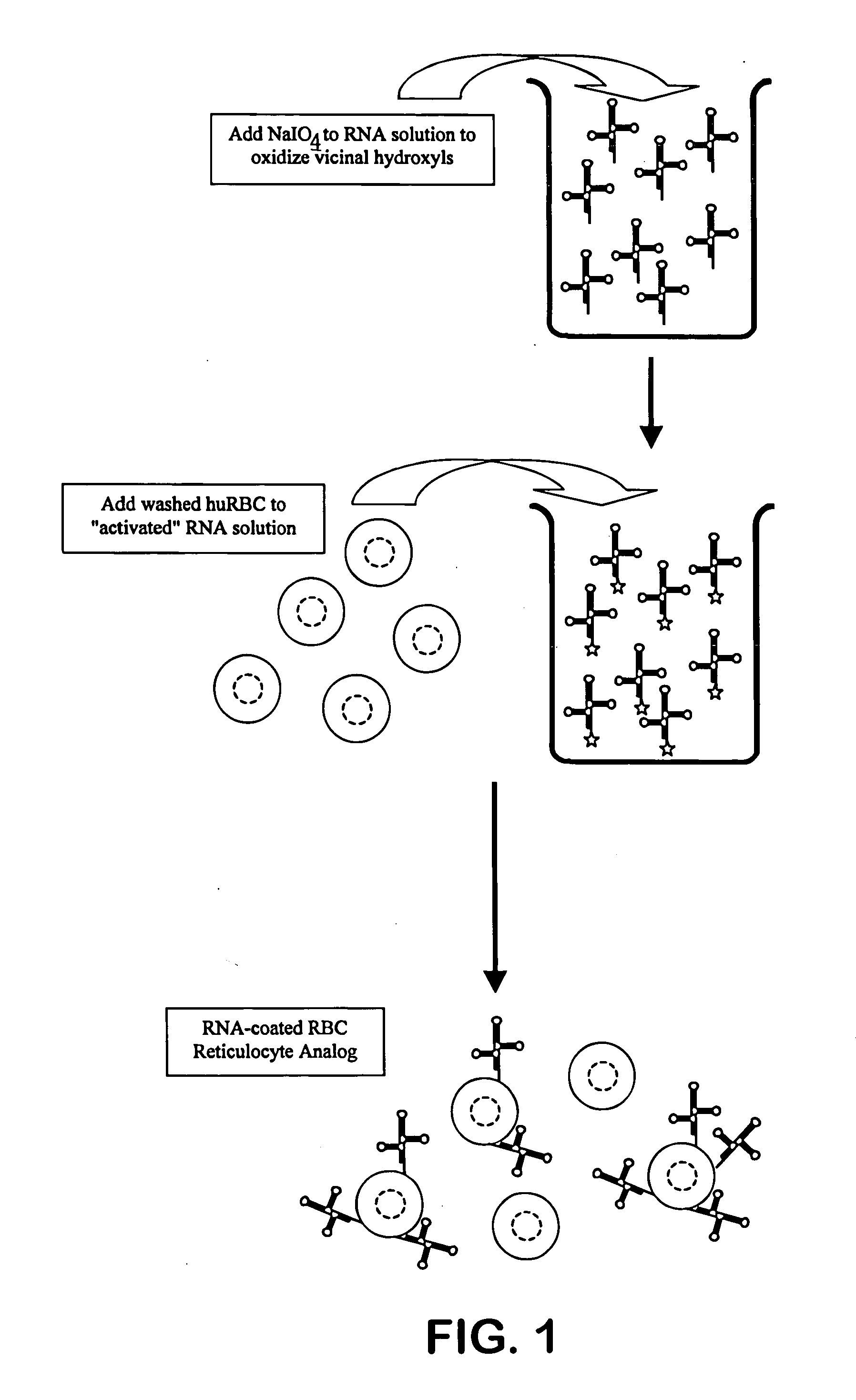
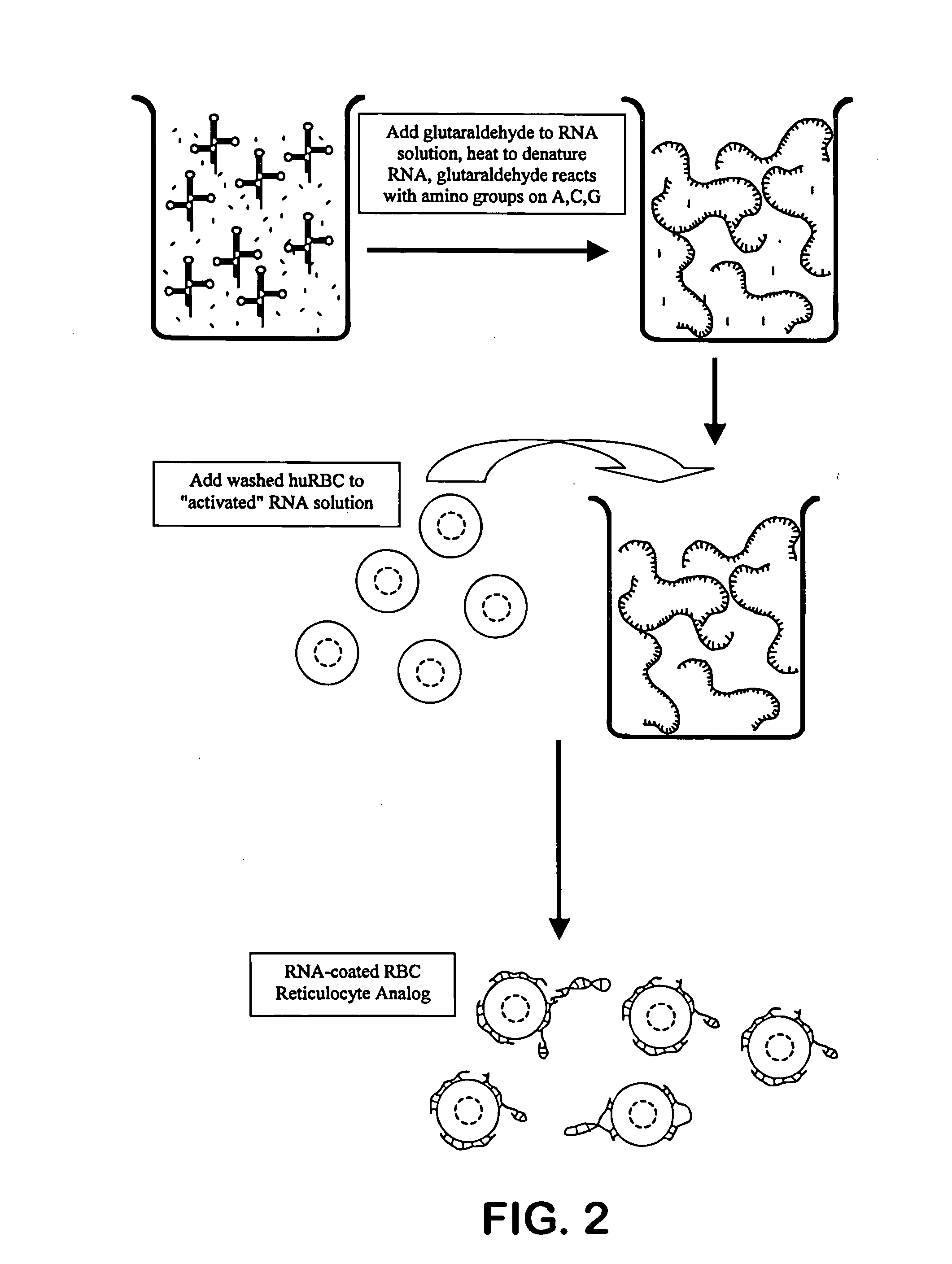
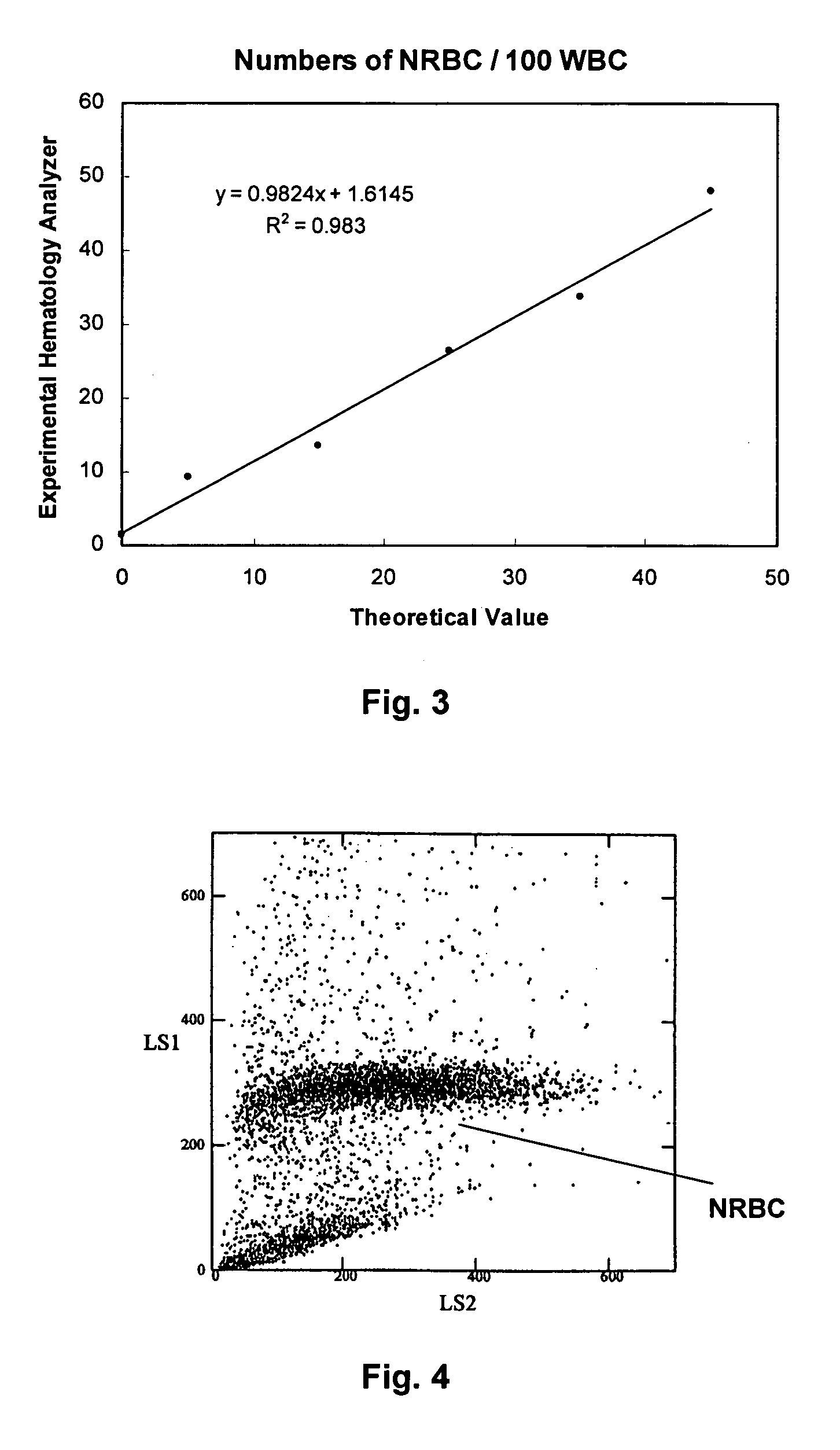
Hematology controls for reticulocytes and nucleated red blood cells
ActiveUS7195919B2Microbiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsMedicine.hematologyBiopolymer
The present invention is drawn to a hematology control made from particles a particle having a biopolymer attached to a surface of the particle. The particle simulates a component of a blood sample, such as a reticulocyte or nucleated red blood cell component of a blood cell sample in a flow cytometer or hematology analysis instrument. The present invention is further drawn to methods of making and using the hematology control.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Determination method for automatically identifying analyte liquid and standard solution for biosensor
ActiveUS7504020B2Easy to identifyImprove accuracyImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMeasurement deviceAnalyte
Owner:PHC HLDG CORP
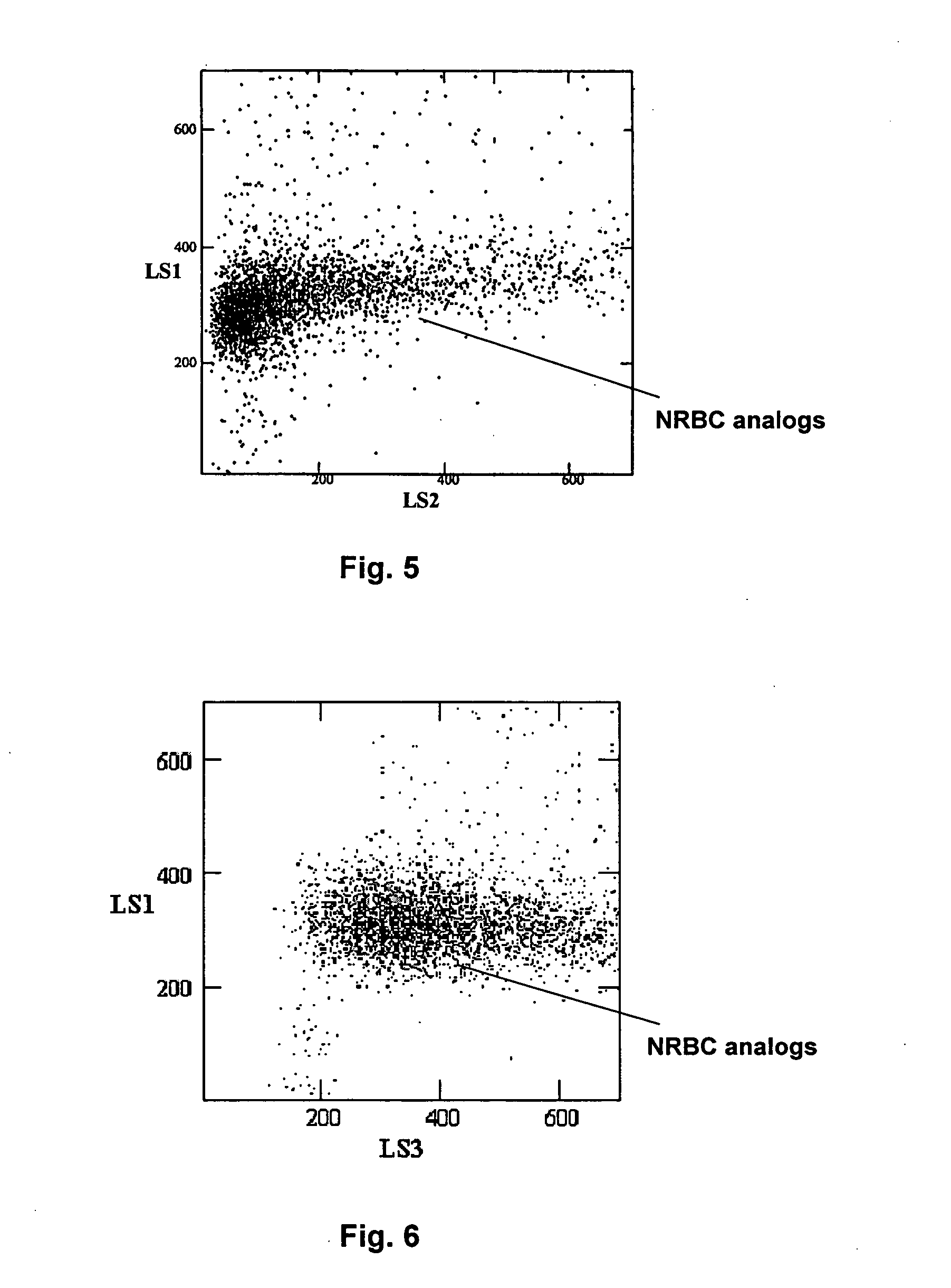
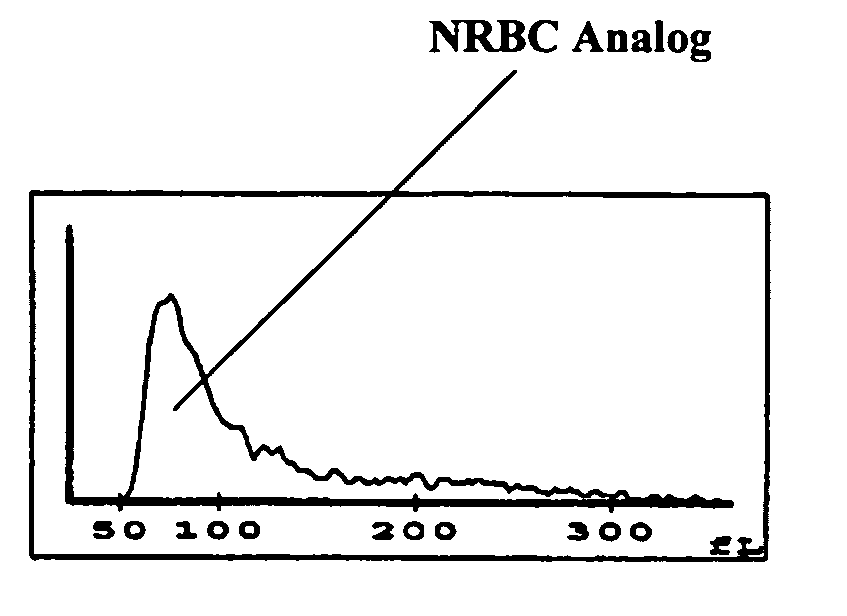
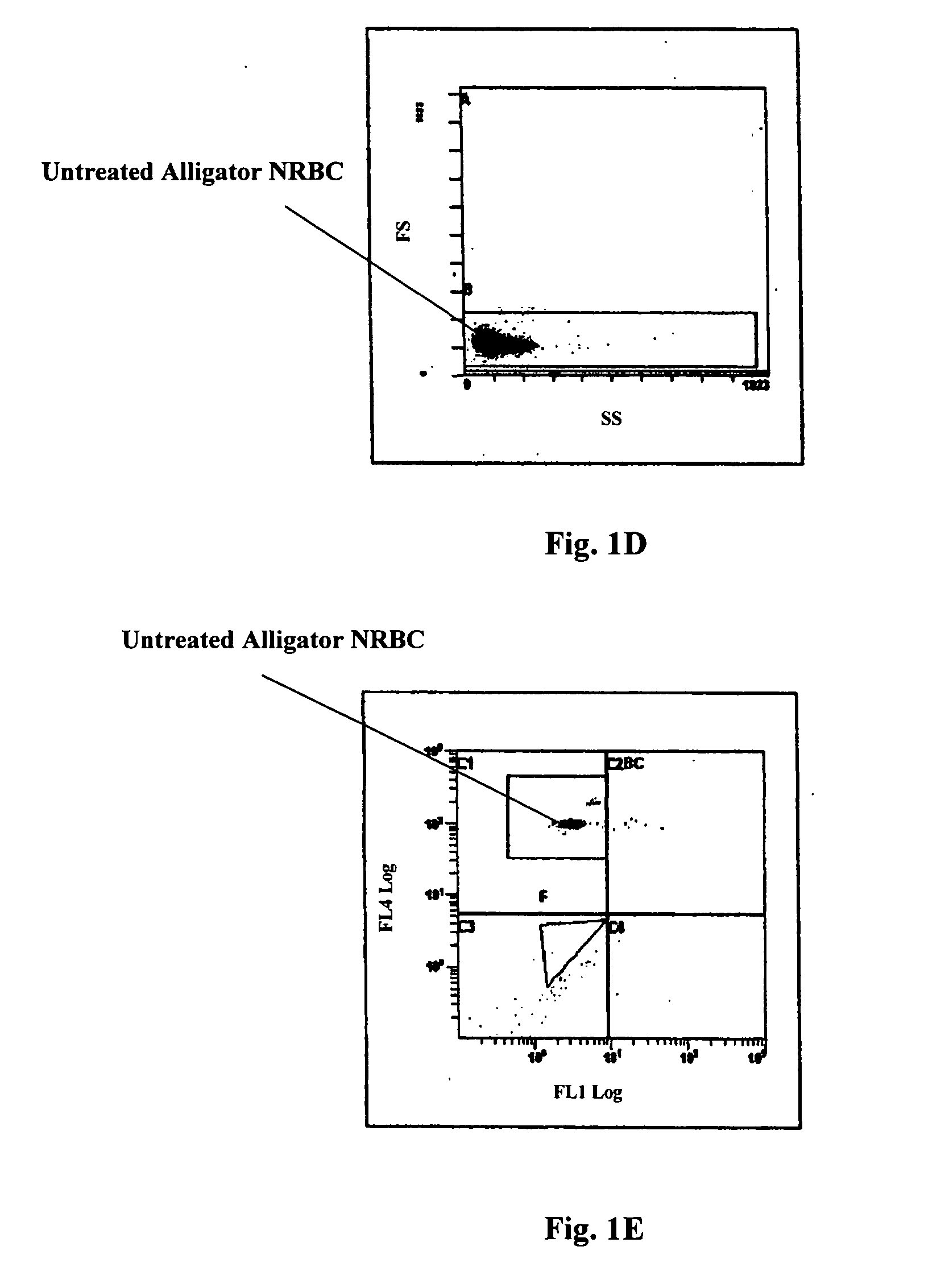
Reference control containing a nucleated red blood cell component
A method of making a reference control containing a nucleated red blood cell component includes providing a blood cell containing a nucleus; treating the blood cell with a treatment solution to alter a nucleus property from a natural value to a target value suitable for simulating nucleated red blood cells on a blood analyzer; and suspending treated blood cell in a suspension medium to form a reference control. The method also includes integrating the nucleated red blood cell component with white blood cell, red blood cell, platelet and reticulocyte components. Further disclosed is a cell treatment composition for altering a nucleus property, which includes a conditioning component, a lytic component for permeating cell membrane, and a fixing component for preserving the cell nucleus. Also disclosed is a method of using the reference control for measurement of nucleated red blood cells on a blood analyzer.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Hematological reference control composition containing leukocyte analogs, methods of making, and uses thereof
InactiveUS6362003B1Reduce probabilityIncreasing mean corpuscular volumeMammal material medical ingredientsIndividual particle analysisLysisWhite blood cell
A method of quality control to diagnose the cause of a malfunction of an instrument. The method uses measurements of the physical property of a sample to diagnose the cause of a malfunction of an instrument. The spatial position of a control product sample is analyzed. Alternatively, the spatial position of a statistically significant number of patient blood samples can be used. The method enables the monitoring of an instrument for problems associated with debris and noise caused by red cell lysis inefficiency; instrument reagents pump volume settings; instrument laser alignments; instrument gain settings; and flow noise caused by partial plugs, residual plugs or other flow problems. The method provides a more specific indication of the type and cause of an instrument malfunctioning than non specific flagging provided by prior art methods.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Method of using a reference control composition for measurement of nucleated red blood cells
ActiveUS20050079623A1Analysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionBiological testingRed blood cellOptical measurements
Methods of using a reference control composition containing a nucleated red blood cell component for measurement of nucleated red blood cells are disclosed. The nucleated red blood cell component is made of stabilized or processed nucleated blood cells which have impedance and optical properties simulating the impedance and optical properties of human nucleated red blood cells under a blood lysing condition as measured by a specific measurement. The methods include mixing the reference control composition with a lytic reagent, and analyzing the control sample mixture on a flow cytometric instrument by impedance, impedance and optical measurement, or DC impedance and a multi-dimensional measurement of light scatter, radio frequency and a second DC impedance; and reporting the simulated nucleated red blood cells in the reference control composition.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Reference control containing a nucleated red blood cell component
A method of making a reference control containing a nucleated red blood cell component includes providing a blood cell containing a nucleus; treating the blood cell with a treatment solution to alter a nucleus property from a natural value to a target value suitable for simulating nucleated red blood cells on a blood analyzer; and suspending treated blood cell in a suspension medium to form a reference control. The method also includes integrating the nucleated red blood cell component with white blood cell, red blood cell, platelet and reticulocyte components. Further disclosed is a cell treatment composition for altering a nucleus property, which includes a conditioning component, a lytic component for permeating cell membrane, and a fixing component for preserving the cell nucleus. Also disclosed is a method of using the reference control for measurement of nucleated red blood cells on a blood analyzer.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
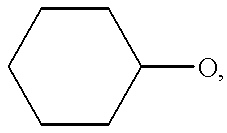
Method for preventing blood denaturation and blood test tool to be used therein
InactiveUS6379318B1Easy to operateAvoid it happening againDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBlood testSucrose
A blood test tool with which blood in a dried state can be held without denaturation. In the blood test tool wherein a card made of filter paper is impregnated with the blood and then the blood is held in a dried state, a carboxylic acid such as citric acid is added to the part for holding blood. Thus, the carboxylic acid exerts an effect of preventing the blood in the dried state from denaturation. It is preferable to add a non-reducing sugar (sucrose, etc.), an anticoagulant (EDTA, etc.) and an antioxidant (glutathione, etc.) together with the carboxylic acid. This blood test tool can be produced by impregnating a filter paper card with a solution containing citric acid, etc. dissolved therein and then air-drying.
Owner:ARKRAY INC
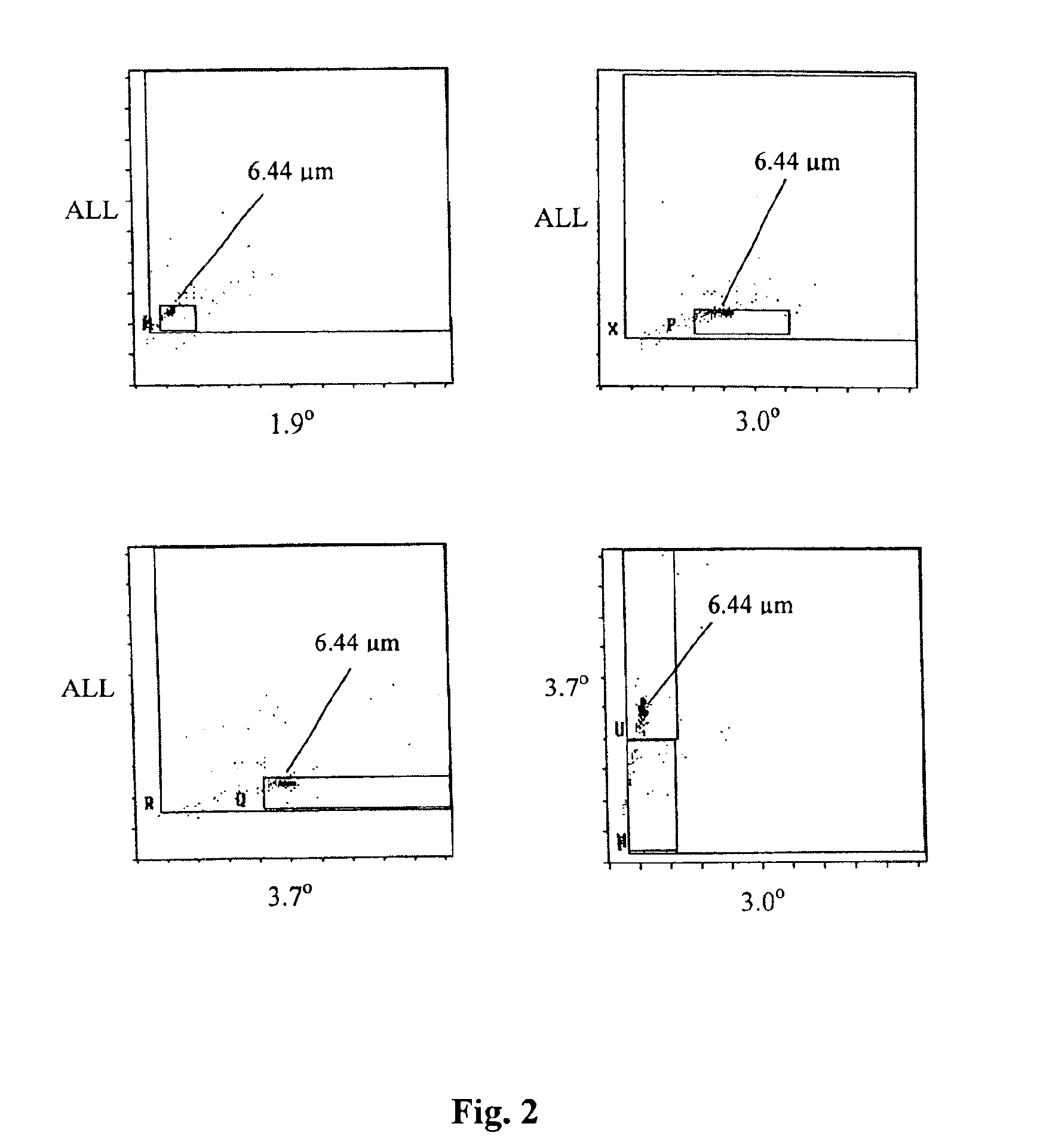
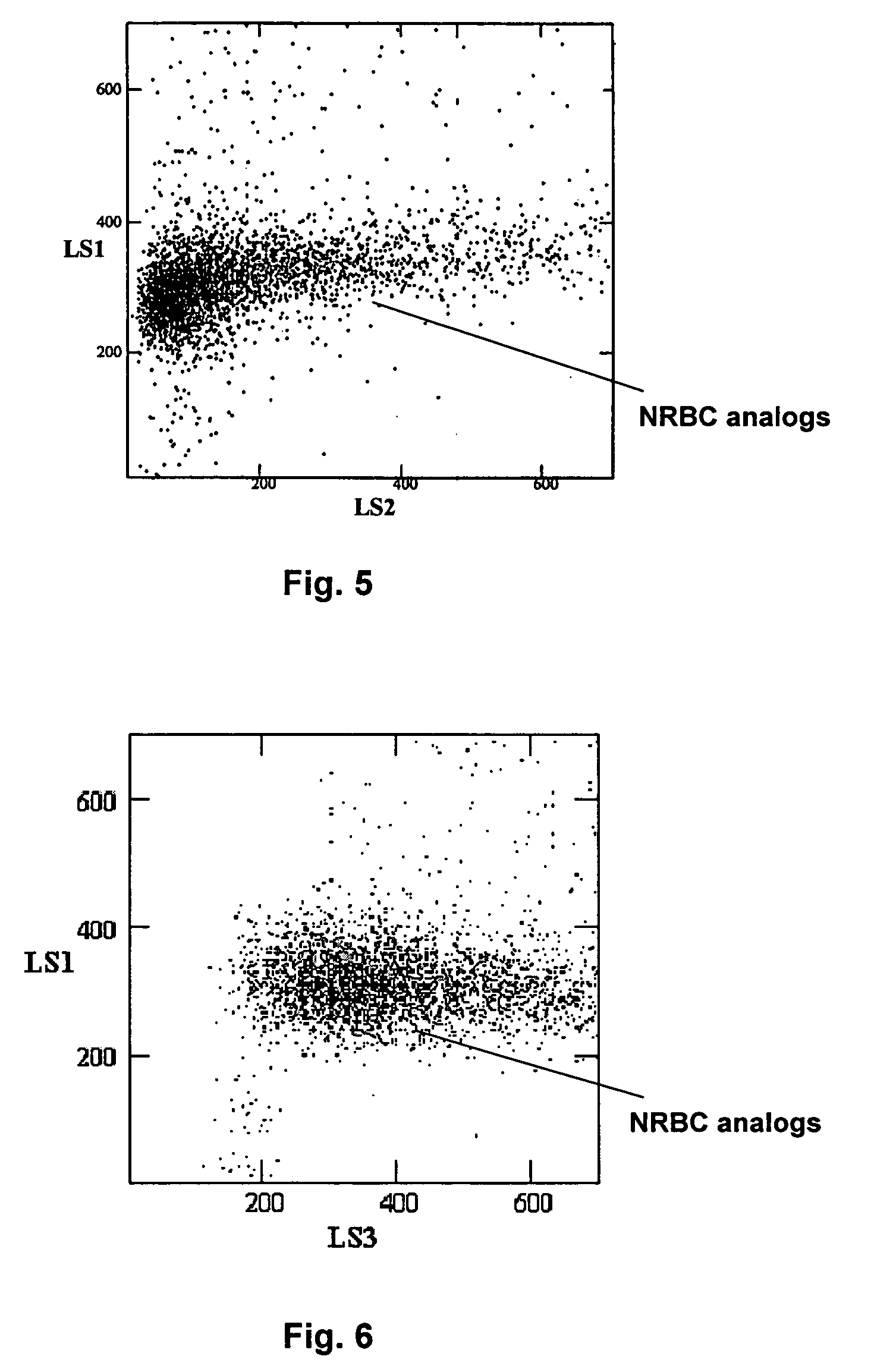
Reference control for optical measurement of nucleated red blood cells of a blood sample
ActiveUS6962817B2Dead animal preservationAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionSpherical granuleOptical property
Reference control compositions and the method of use are disclosed for measurement of nucleated red blood cells, which includes one set of synthetic spherical particles having a mean particle diameter ranging from 6.2 μm to 6.8 μm and a refractive index from 1.58 to 1.62 monodispersed in an aqueous suspension medium. The synthetic spherical particles have optical properties simulating optical properties of nucleated red blood cells as measured by optical measurements. The reference control composition can further include a second set of the synthetic spherical particles having optical properties simulating optical properties of white blood cells. Further disclosed is a reference control system which includes a series of reference control compositions, each having an amount of one type of synthetic spherical particles which have optical properties simulating the optical properties of nucleated red blood cells having a specific cell maturity.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Novel standard reference solutions
Owner:BIONOSTICS
Hematology controls for reticulocytes and nucleated red blood cells
ActiveUS20050136409A1Microbiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsMedicine.hematologyBiopolymer
The present invention is drawn to a hematology control made from particles a particle having a biopolymer attached to a surface of the particle. The particle simulates a component of a blood sample, such as a reticulocyte or nucleated red blood cell component of a blood cell sample in a flow cytometer or hematology analysis instrument. The present invention is further drawn to methods of making and using the hematology control.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Calibrator For Immunoassays
Owner:ONCIMMUNE
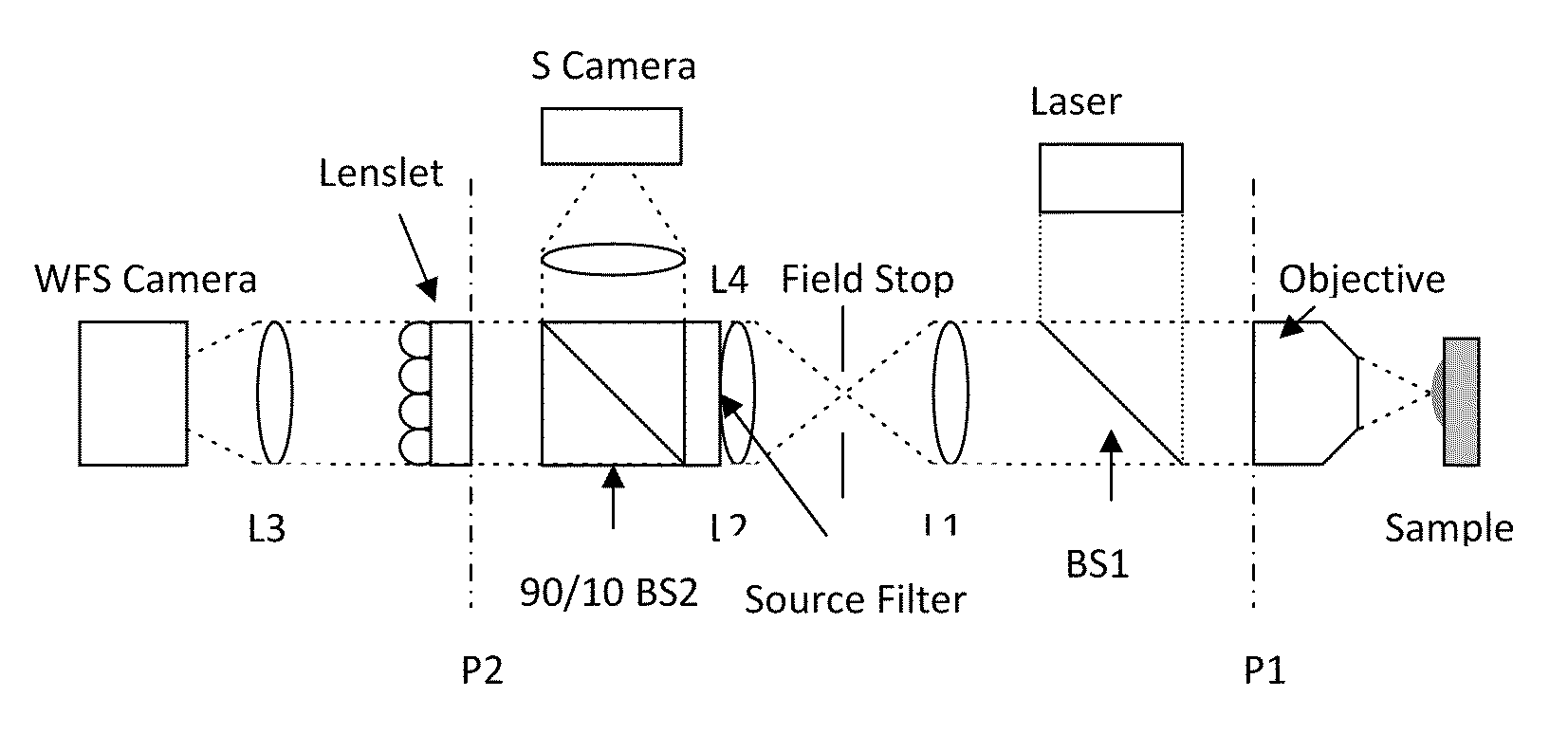
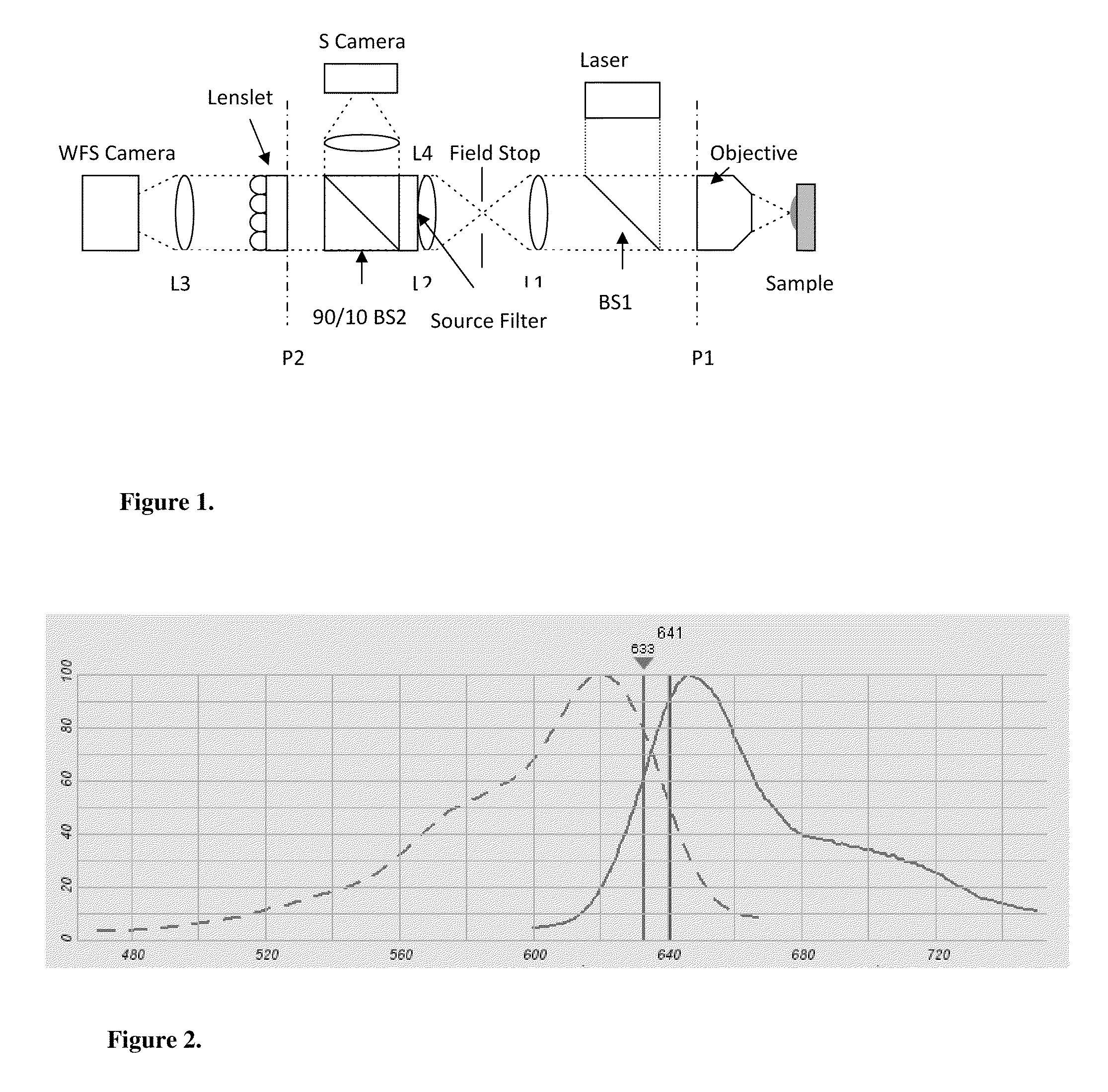
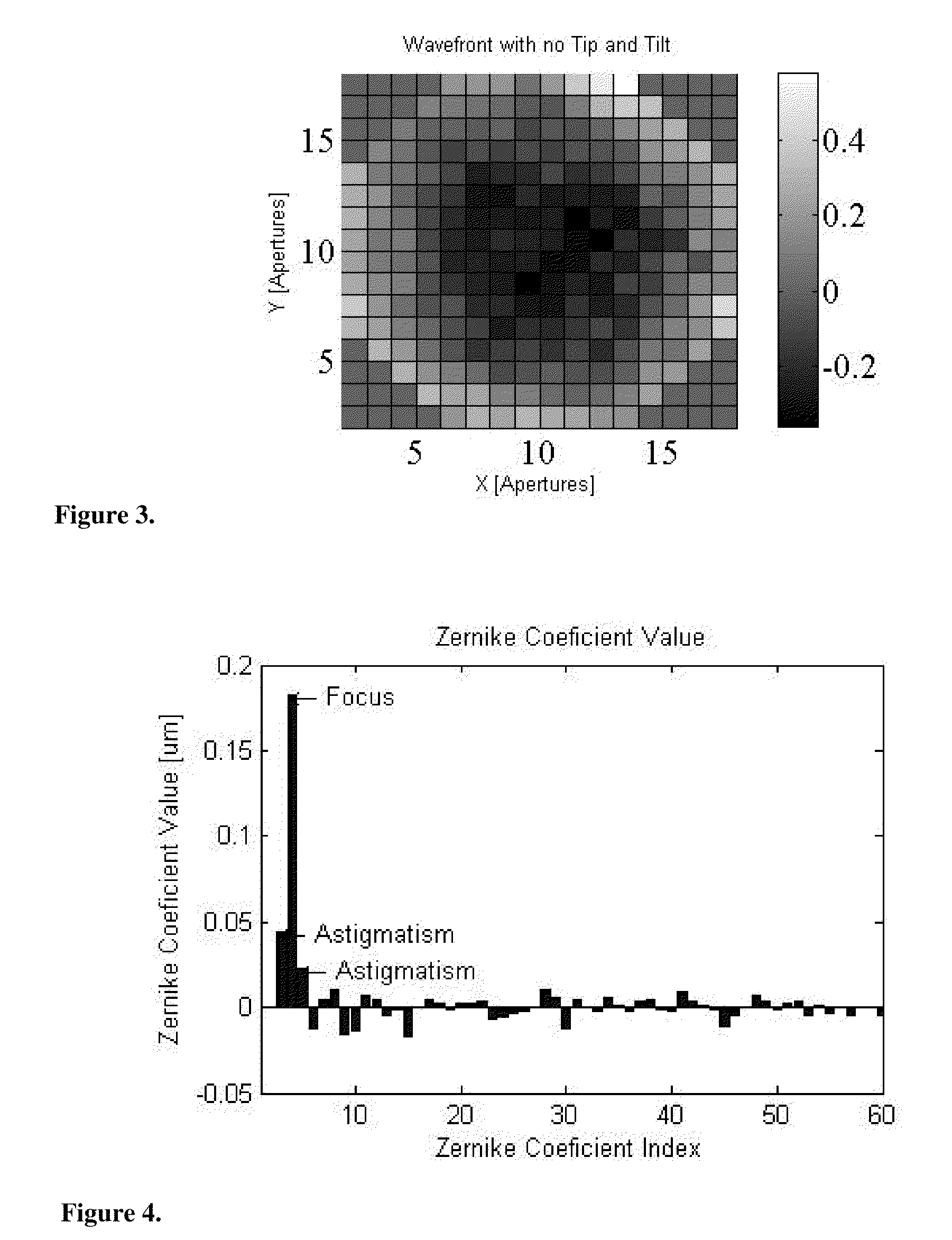
Use of a reference source with adaptive optics in biological microscopy
ActiveUS20100105105A1Raise the ratioMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationMicro imagingStrehl ratio
Methods of microscopic imaging of biological tissue using adaptive optics technology to improve the image focus and sharpness. Wavefront measurements are taken by using a novel method of seeding biological tissue by using a fluorescent microsphere as a “guide star” as a natural point-source reference. The current methods are capable of improving the Strehl ratio of modern biological microscopes as much as 15 times.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
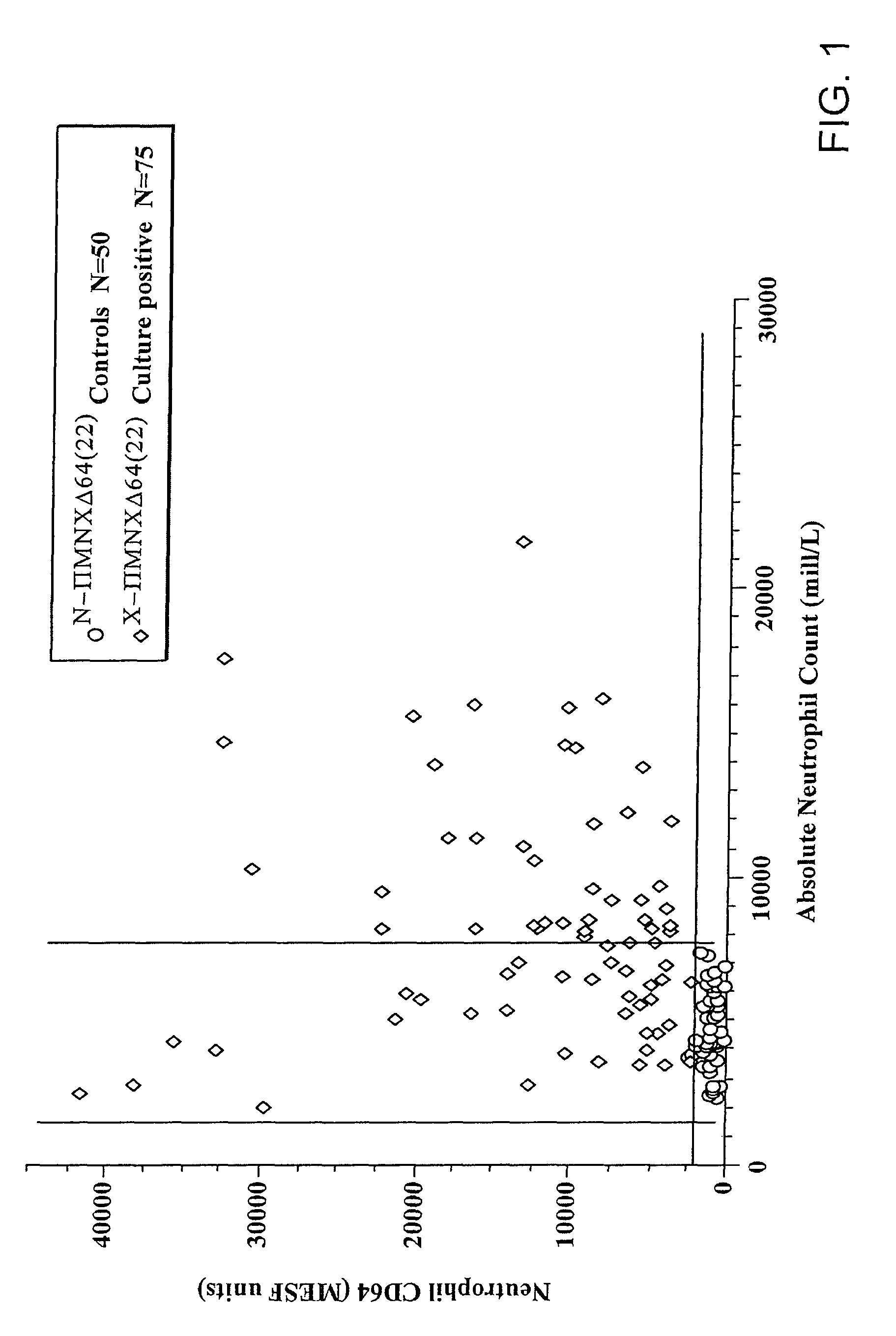
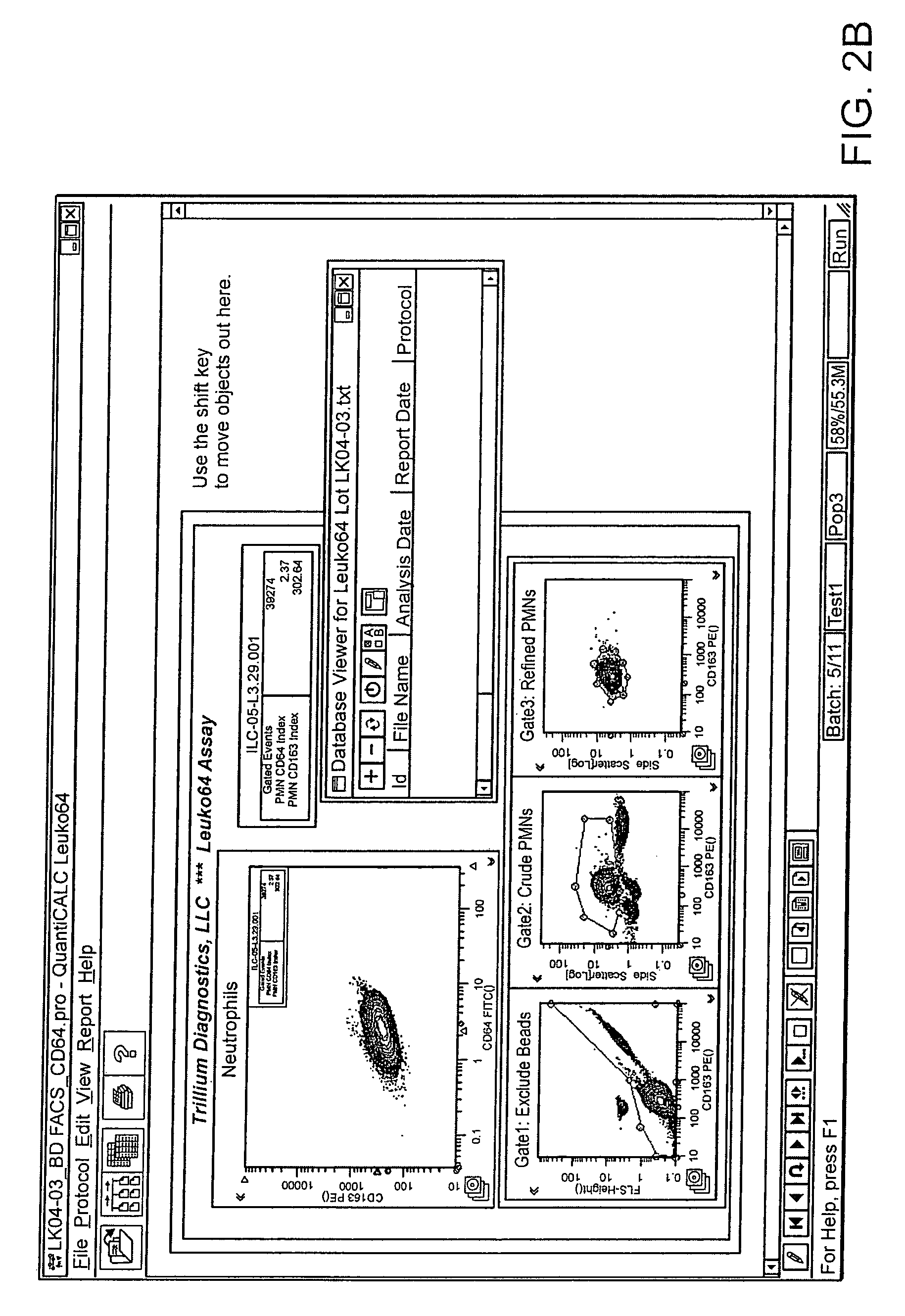
Software integrated cytometric assay for quantification of the human polymorphonuclear leukocyte FcγRI receptor (CD64)
ActiveUS8116984B2High sensitivityEasy to measureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalysis dataFluorescence
Owner:TRILLIUM DIAGNOSTICS
Reference Control for Cell by Cell Analysis
ActiveUS20100041011A1Avoid reactionMicrobiological testing/measurementDead animal preservationFluorescenceCell membrane
A reference control for cell by cell analysis on flow cytometric analyzers contains cellular analogs made of permeated blood cells containing therein aggregated intracellular proteins and preserved antigenic sites thereof, having cellular membrane permeable to antibodies and a suspension medium. The reference control is frozen after being prepared and thawed prior to use. The cellular analogs further contain a fluorescence marker therein. Further disclosed are a method of making the reference control and a method using the reference control, as an internal or stand-alone control, for measurements of cellular hemoglobin and cellular hemoglobin variant of a blood sample.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Quality control material for reagentless measurement of analytes
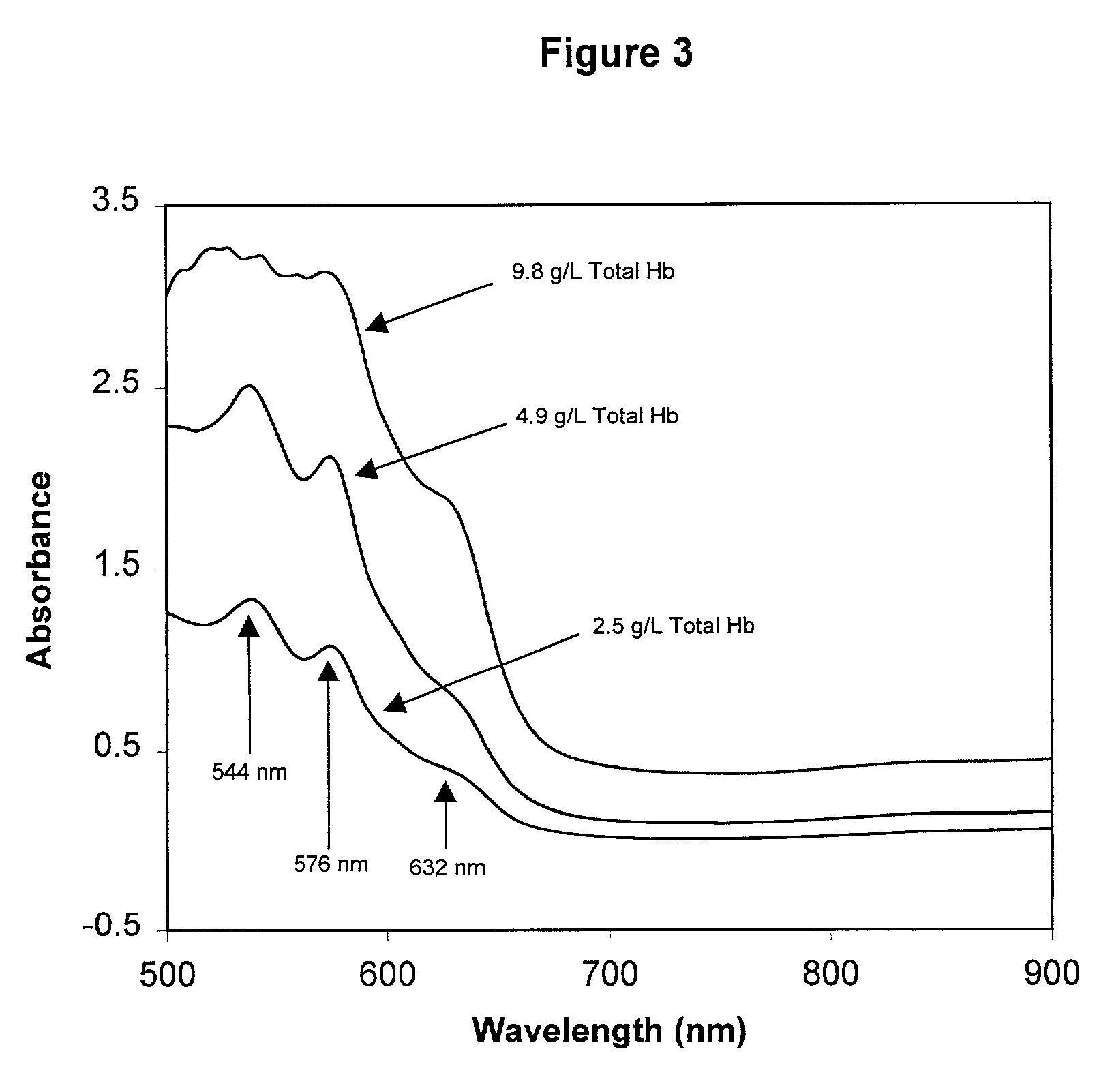
The present invention provides a method of monitoring calibration of a spectrophotometric apparatus that comprises one or more than one calibration algorithm for one or more than one analyte. This method comprises measuring absorbance of a quality control material with the apparatus to obtain a measurement, where the quality control material exhibits an absorbance spectra characterized as having a negative slope for a continuous spectral segment from about 5 nm to about 400 nm in length, or a wavelength there between, and where the spectral segment includes a principal calibration wavelength for the one or more than one analyte. The method then involves calculating one or more than one concentration values from the measurement using the one or more than one calibration algorithms, followed by comparing the one or more than one concentration values with an assigned value given to the quality control material for each of the one or more than one analytes. In this way one or more than one calibration algorithm of the apparatus may be monitored. A reagentless method for determining the concentration of one or more than one analyte in a sample in a spectrophotometric apparatus comprising one or more than one primary calibration algorithm is also disclosed. The present invention also provides to a method for selecting one or more than one substance as a quality control material for monitoring one or more than one primary calibration algorithm on a spectrophotometric apparatus. The present invention includes a quality control material for mimicking two or more than two analytes comprising, one or more than one substances having a combined absorption spectrum exhibiting a negative slope for a continuous spectral segment of from about 5 nm to 400 nm in length, or a wavelength there between, in a portion of an absorption spectrum, including one or more than one principal calibration wavelengths, for the two or more than two analytes.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Method for the direct detection and/or quantification of at least one compound with a molecular weight of at least 200
ActiveUS9612250B2Enhanced advantageGood reproducibilitySugar derivativesMass spectrometric analysisCulture cellRetention time
Owner:SANIFIT THERAPEUTICS SA
Hematology control composition including lymphocyte analogs and method for preparation and use
A control composition, and method of preparing a control composition, that includes stabilized, mammalian granulocytes having altered physical properties so that the granulocytes function as a human lymphocyte analogs when used on an automated blood cell analyzer.
Owner:BIO TECHNE
Homogeneous populations of molecules
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
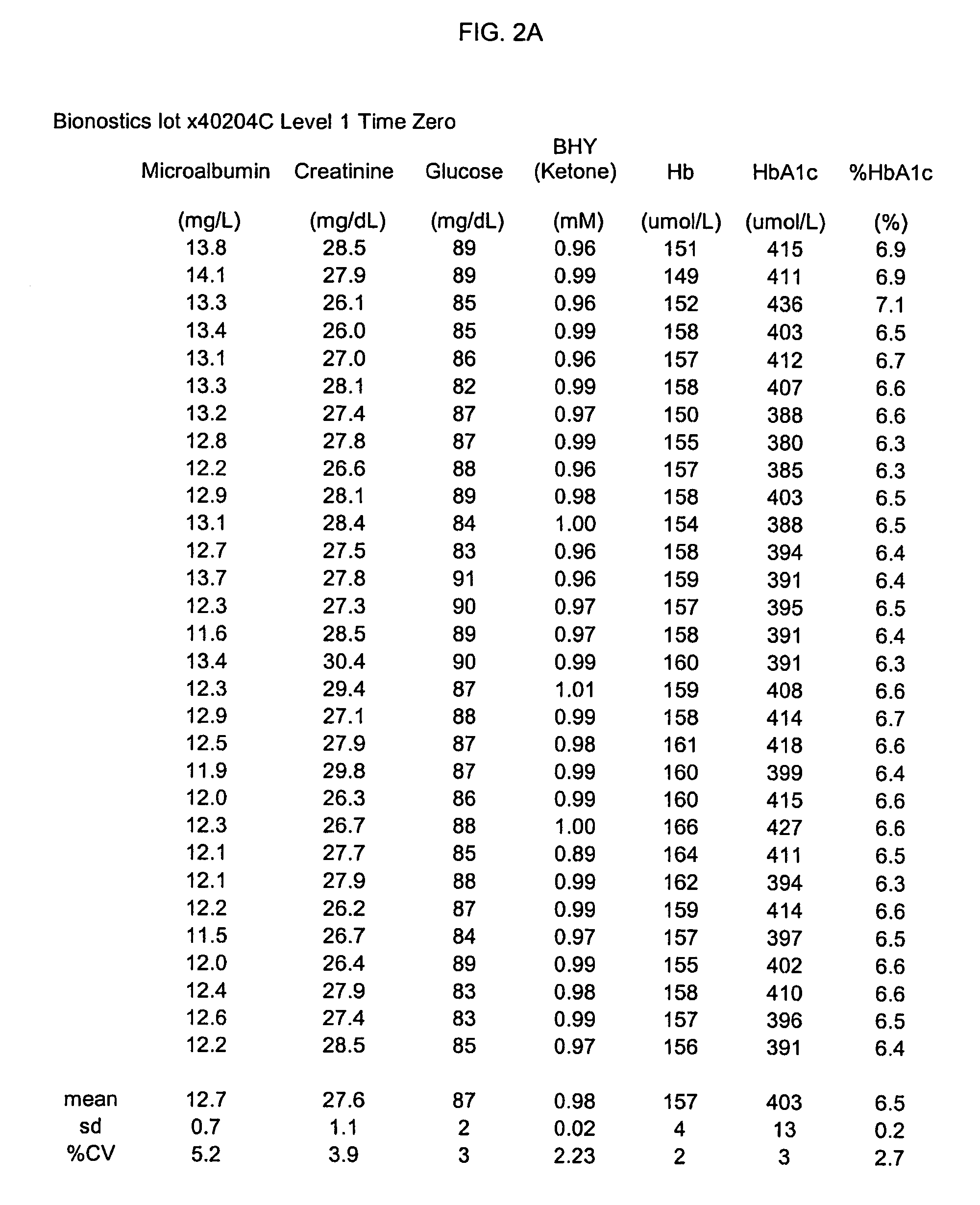
Preparation method of quality control material of glycosylated hemoglobin and quality control material thereof
ActiveCN106771261ASimple methodHigh measurement accuracyBiological testingReference solutionsDiabetes mellitusCentrifugation
The invention provides a preparation method of a quality control material of glycosylated hemoglobin, comprising the following steps: collecting a blood sample of a nondiabetic patient, performing centrifugation and plasmapheresis to obtain red blood cells; adding red blood cell preserving fluid to the red blood cells to obtain a red blood cell sample; adding the red blood cell sample slowly into separating fluid and centrifuging to obtain separated red blood cells, wherein red blood cells adaptive to the cell separation fluid are dispersed in the cell separation fluid of each density; separately charging the separated red blood cells into different test tubes, adding physiological saline to each test tube to obtain a red blood cell suspension, regulating the hemoglobin concentration of the red blood cell suspensions to 120g / L, and screening out red blood cell suspensions with the HbA1c value of 3-5% to obtain the quality control material of glycosylated hemoglobin. The invention also provides the quality control material. The preparation method provided by the invention can perform mass production of low-value quality control materials of glycosylated hemoglobin.
Owner:深圳市雷诺华科技实业有限公司
Software integrated cytometric assay for quantification of the human polymorphonuclear leukocyte fctri receptor (CD64)
ActiveUS20090117605A1Easy diagnosisImprovement in therapeutic monitoringBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAssayFluorescence
The invention relates a method of quantifying CD64 and CD163 expression in leukocytes and, specifically to a kit for use with a flow cytometer including a suspension of quantitative fluorescent microbead standards, fluorescent labeled antibodies directed to CD64 and CD163, and analytical software. The software is used to take information on the microbead suspension and fluorescent labeled antibodies from a flow cytometer and analyse data, smooth curves, calculate new parameters, provide quality control measures and notify of expiration of the assay system.
Owner:TRILLIUM DIAGNOSTICS
Method of using a reference control composition for measurement of nucleated red blood cells
ActiveUS7198953B2Analysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionBiological testingRed blood cellOptical measurements
Methods of using a reference control composition containing a nucleated red blood cell component for measurement of nucleated red blood cells are disclosed. The nucleated red blood cell component is made of stabilized or processed nucleated blood cells which have impedance and optical properties simulating the impedance and optical properties of human nucleated red blood cells under a blood lysing condition as measured by a specific measurement. The methods include mixing the reference control composition with a lytic reagent, and analyzing the control sample mixture on a flow cytometric instrument by impedance, impedance and optical measurement, or DC impedance and a multi-dimensional measurement of light scatter, radio frequency and a second DC impedance; and reporting the simulated nucleated red blood cells in the reference control composition.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Quality control material for reagentless measurement of analytes
Owner:NELLCOR PURITAN BENNETT LLC
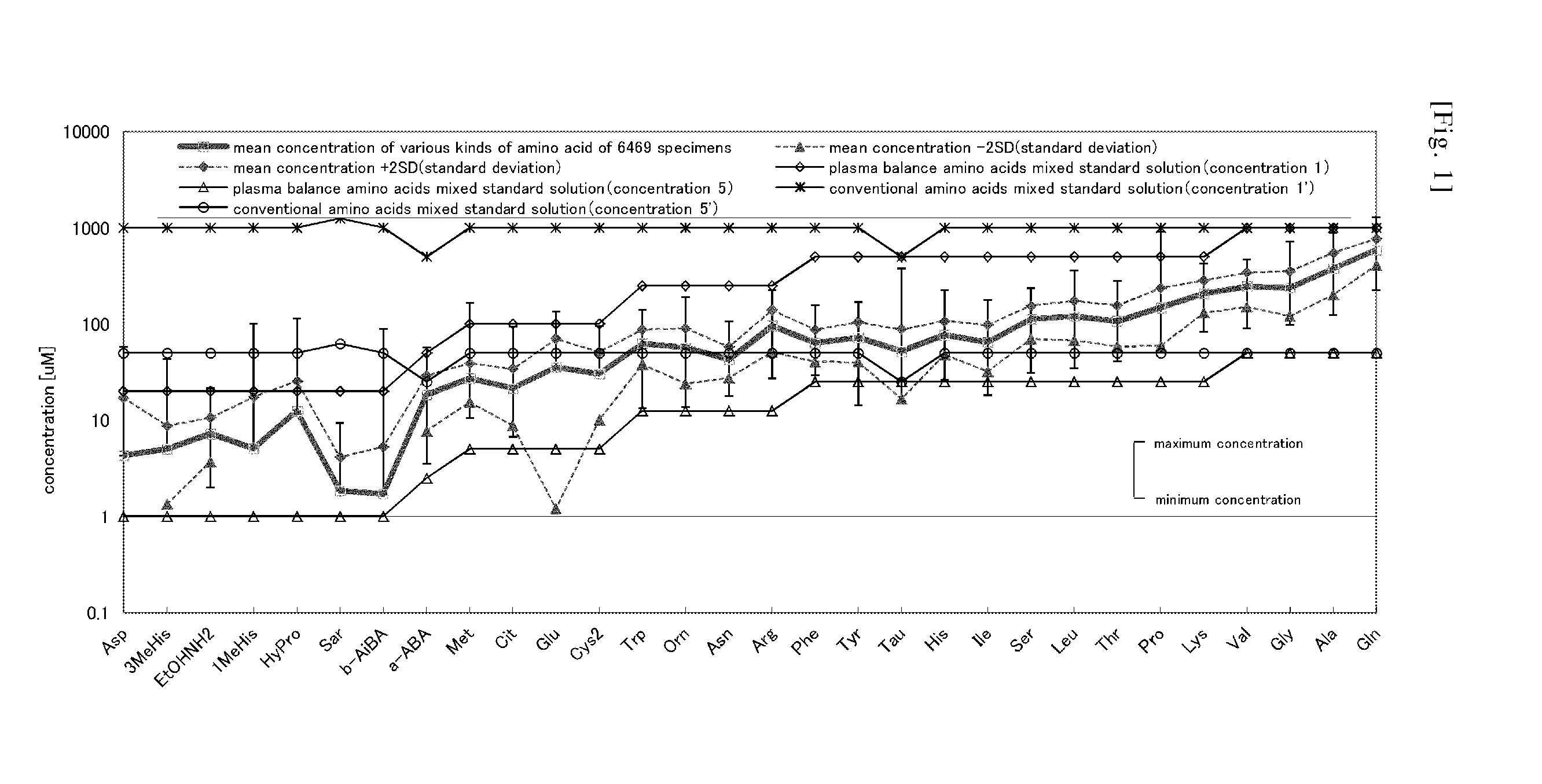
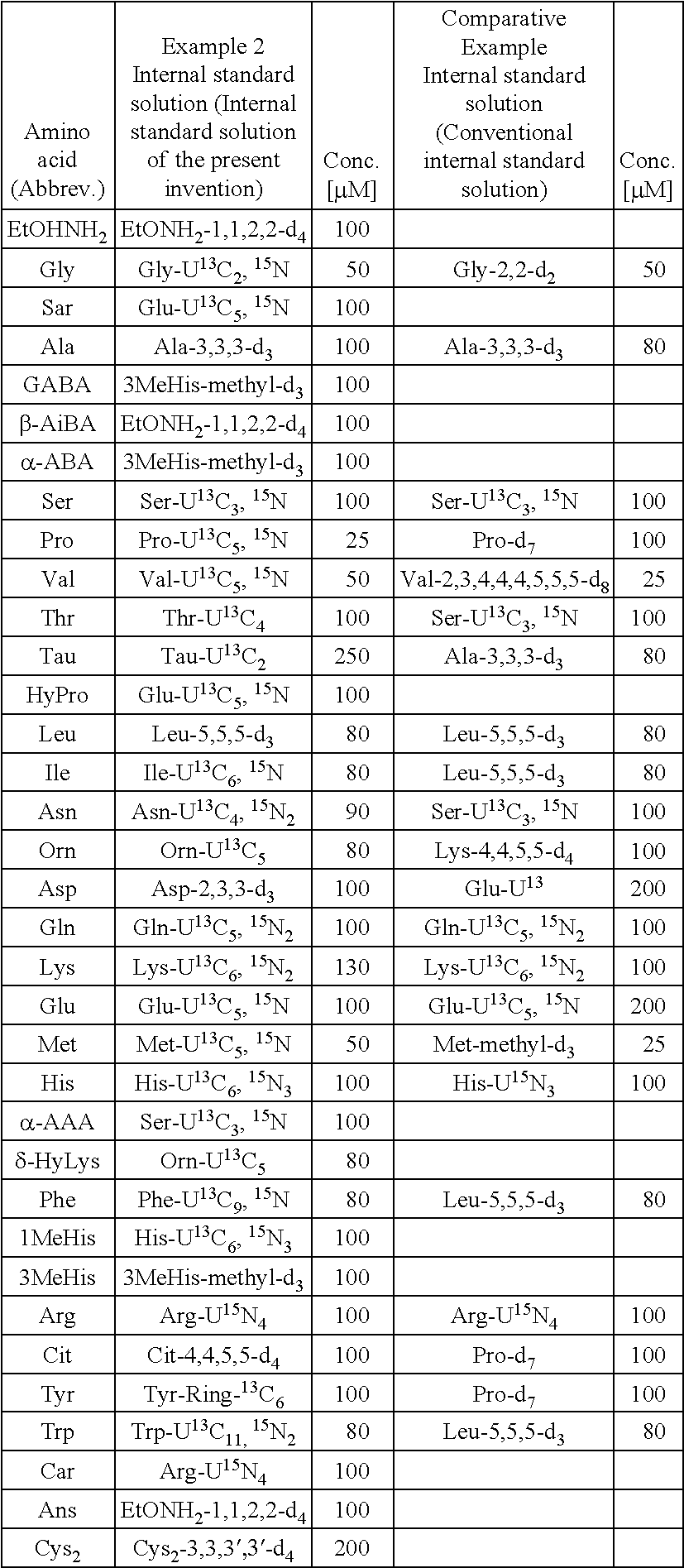
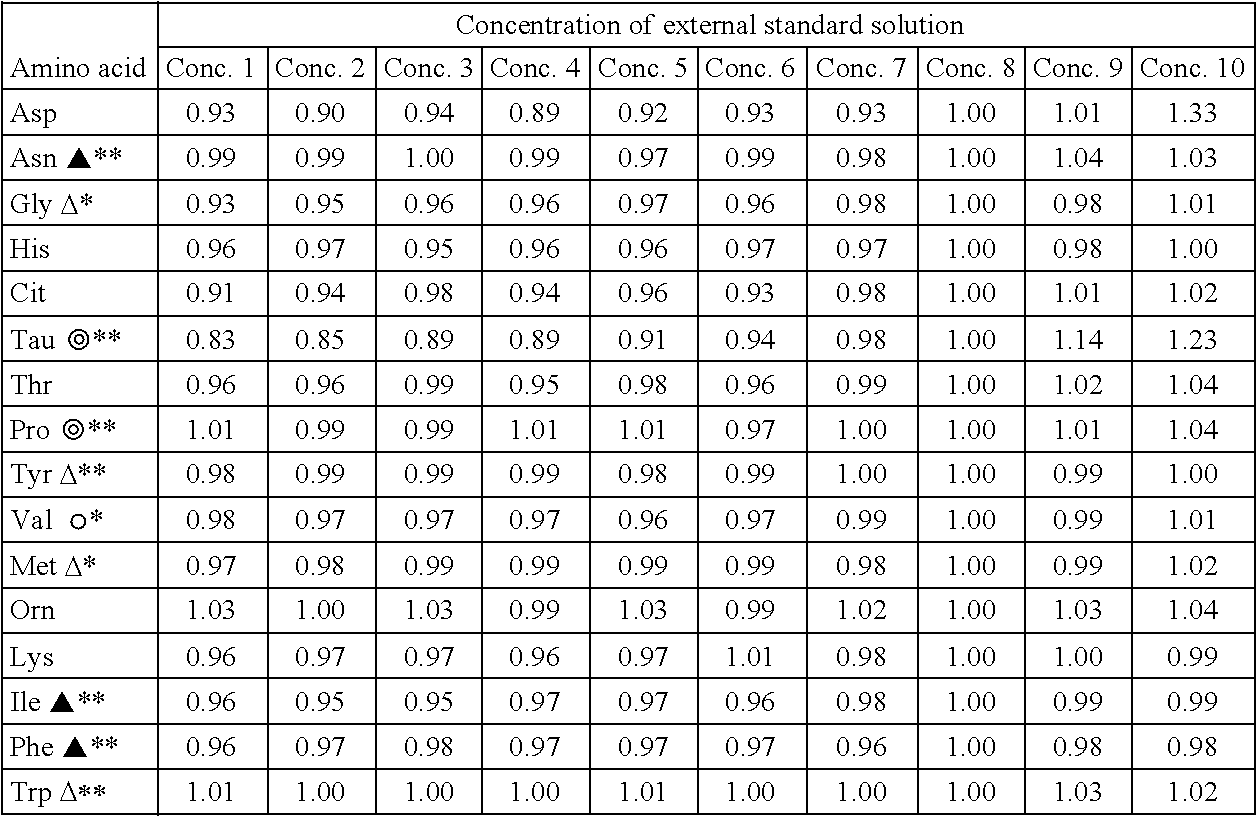
Standard solution for use in analysis of amino acid in plasma
ActiveUS20150064792A1Reduce mistakesAccurate measurementComponent separationBiological testingCitrullineTyrosine
An external standard solution for use in the analysis of amino acid in plasma, containing,(1) at least one amino acid selected from the following components A, at a concentration of 0.0007 M to 0.49 M, and (2) (i) at least one amino acid selected from the following components B, at a concentration of 0.2 to 0.9 times of the lowest-concentration amino acid among the amino acids selected from components A, (ii) at least one amino acid selected from the following components C, at a concentration of 0.1 to 0.4 times of the lowest-concentration amino acid among amino acids selected from the components A, or (iii) at least one amino acid selected from the following components D, at a concentration of 0.05 to 0.2 times of the lowest-concentration amino acid among amino acids selected from the components A,[Components A] valine, glycine, alanine and glutamine[Components B] serine, proline, threonine, taurine, leucine, isoleucine, lysine, histidine, phenylalanine and tyrosine[Components C] asparagine, ornithine, arginine and tryptophan[Components D] glutamic acid, methionine, citrulline and cystine.
Owner:FUJIFILM WAKO PURE CHEM CORP +1
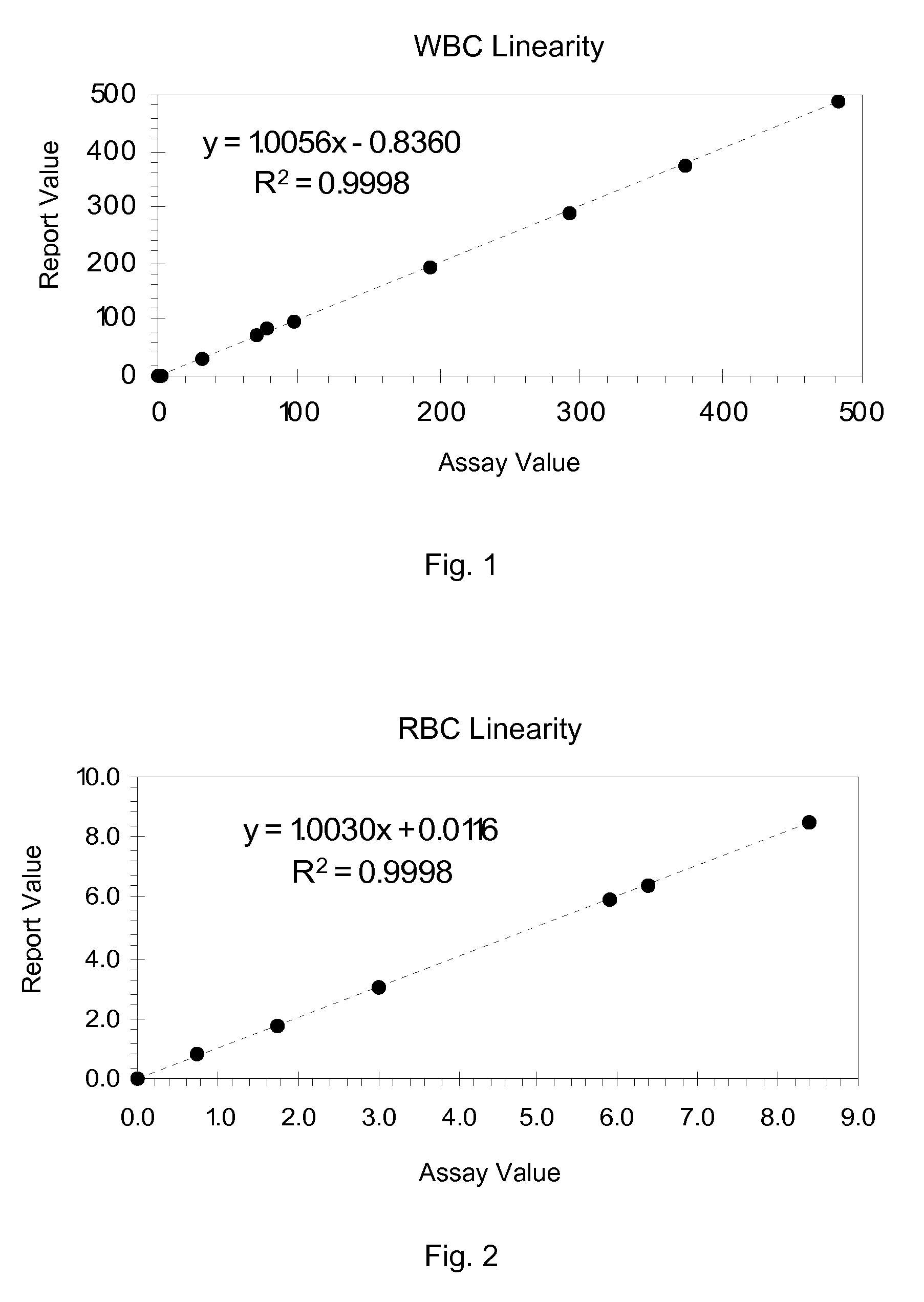
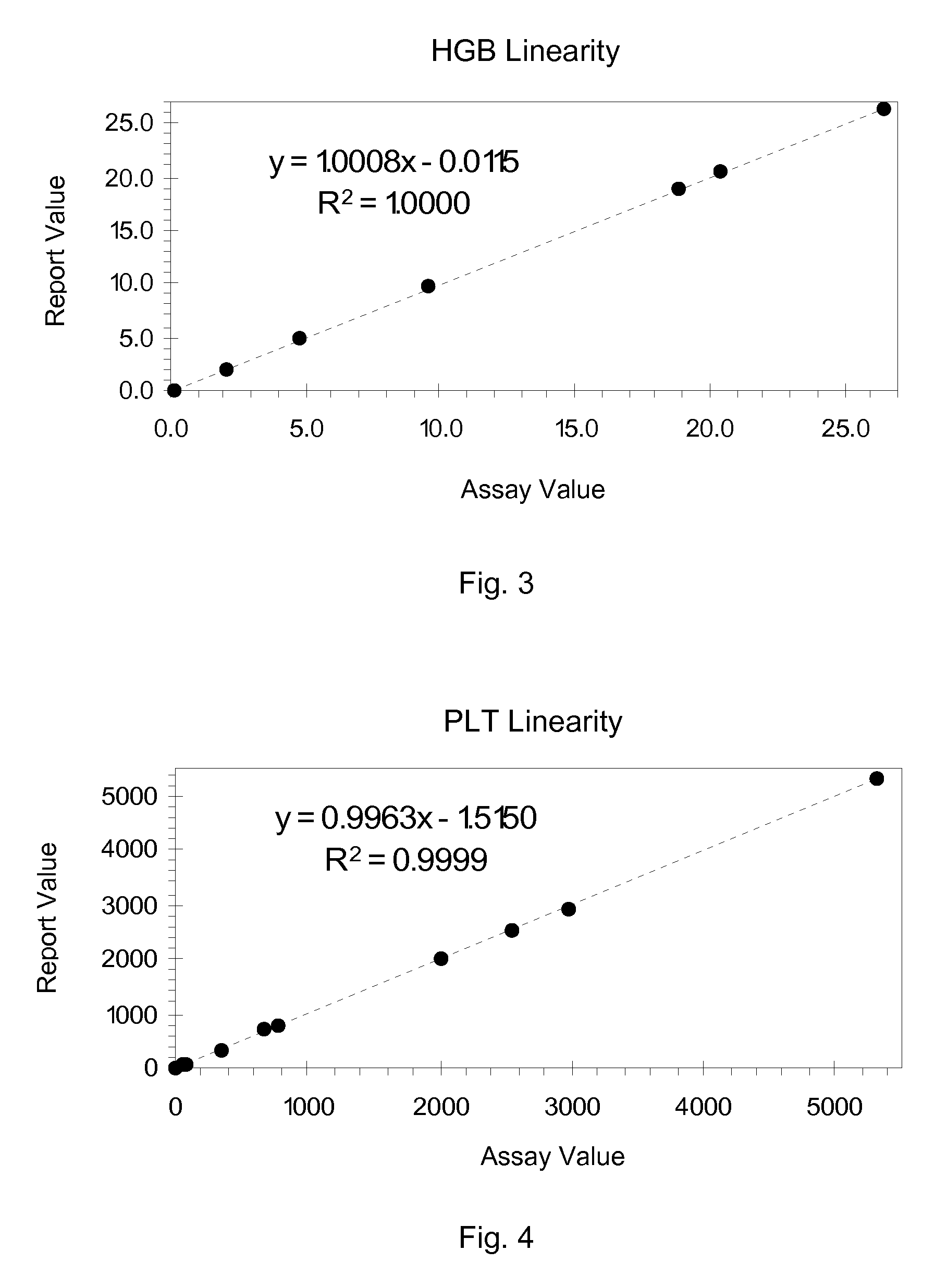
Hematology Linearity Control Composition, System and Method of Use
ActiveUS20080113438A1Affect measurementReduce concentrationDead animal preservationIndividual particle analysisMedicine.hematologyWhite blood cell
A linearity control system includes a series of linearity control compositions, each thereof includes white blood cell analogs and stabilized red blood cells in a suspension medium. The concentration of the white blood cell analogs in the series of control compositions increases from 0.2×103 to 800×103 analogs per microliter, and the concentration of the white blood cell analogs in at least one control composition is greater than 120×103 analogs per microliter. The stabilized red blood cells facilitate mono-dispersion of the white blood cell analogs in the suspension medium by gently mixing. The control compositions further include platelet analogs, or additionally include reticulocyte and / or nucleated red blood cell analogs. The linearity control system allows the verification of the reportable measurement range and linearity of the measurements of hematology analyzers for white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets in extended concentration ranges.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com