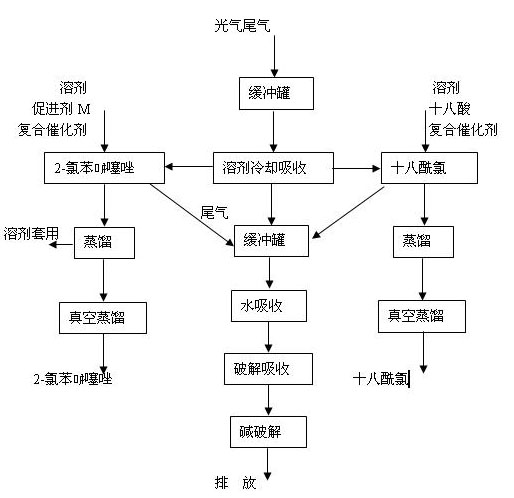
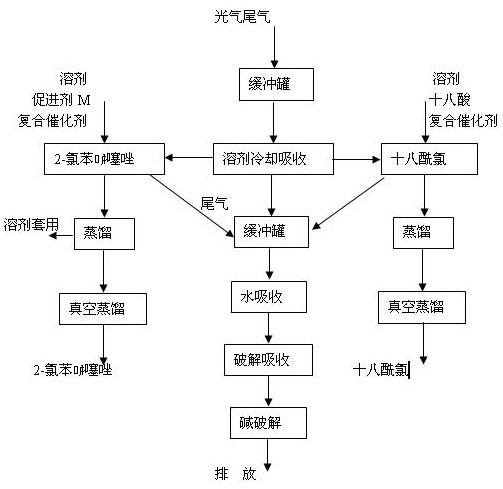
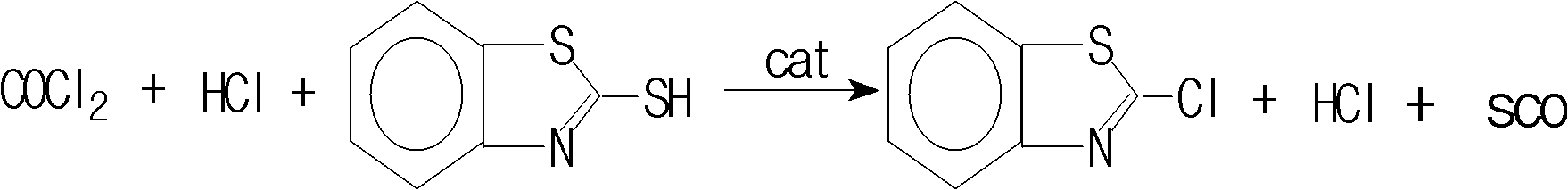
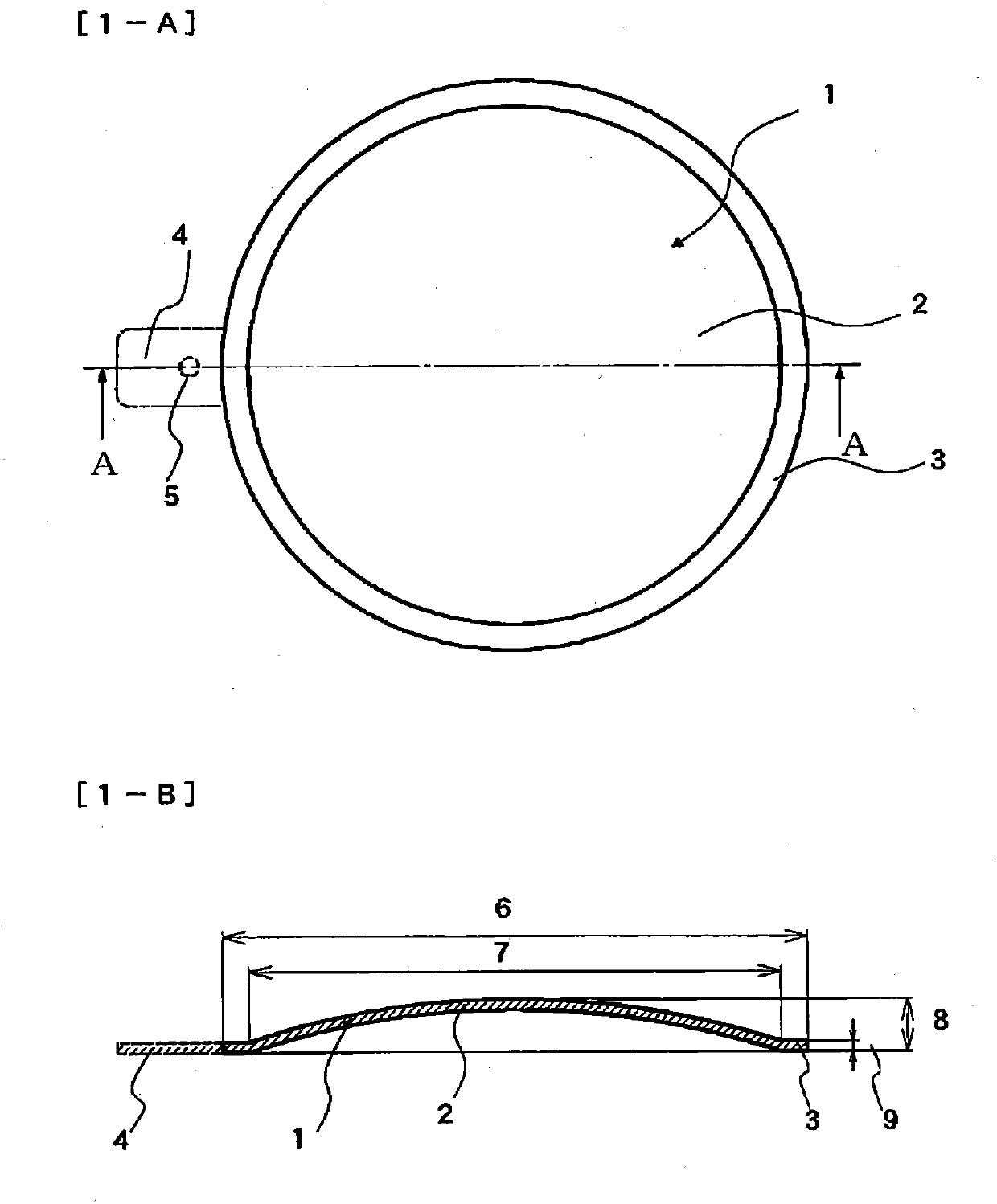
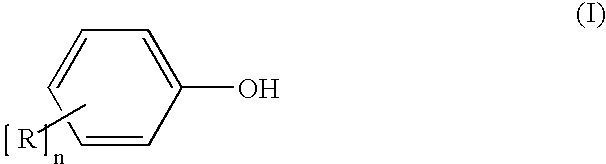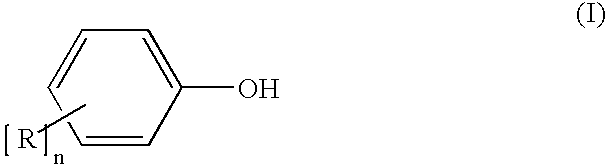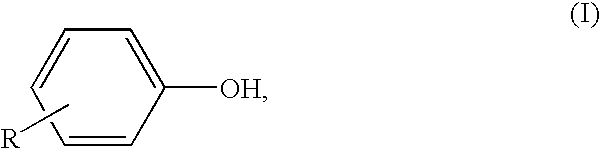Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
141results about "Phosgene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
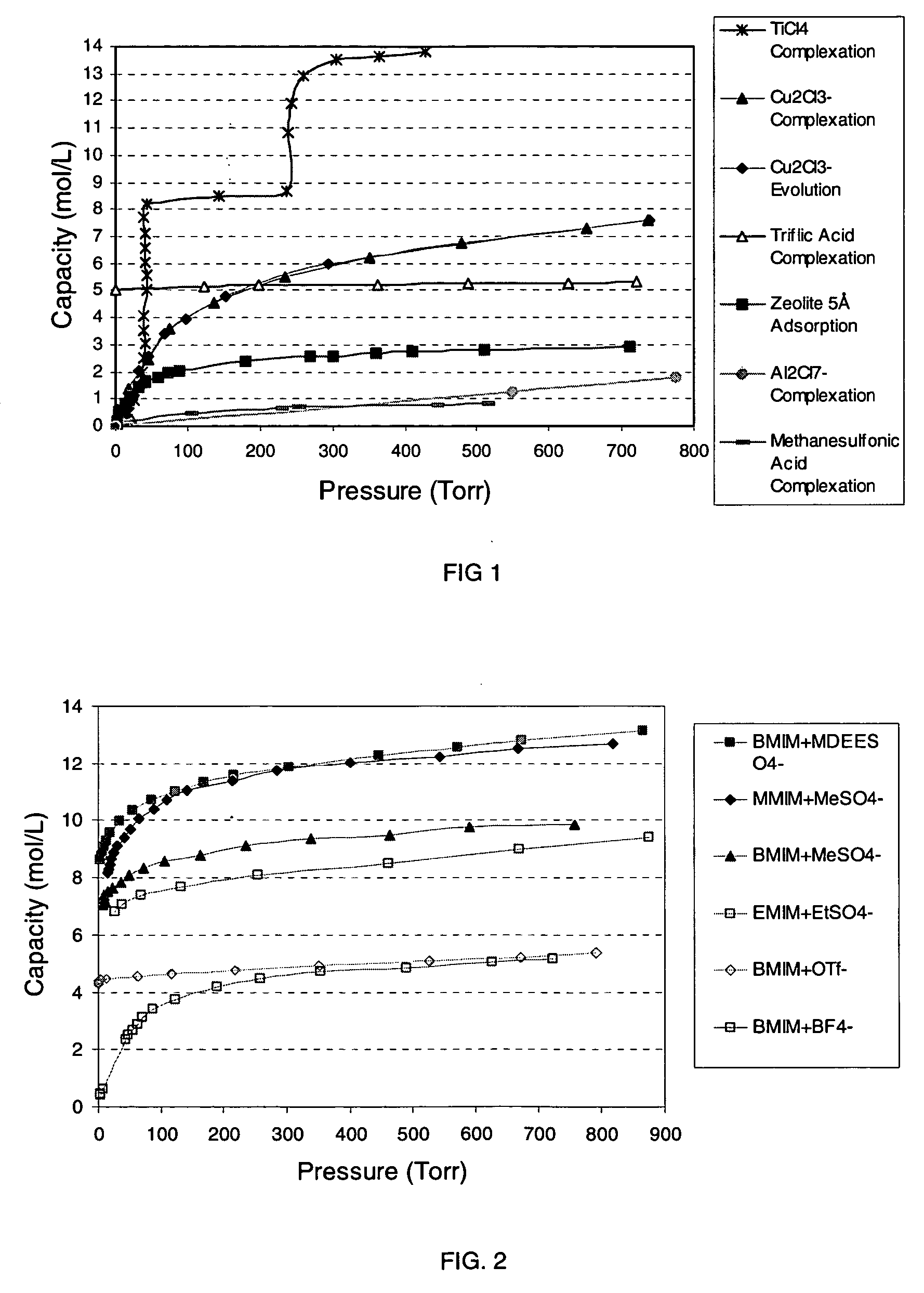
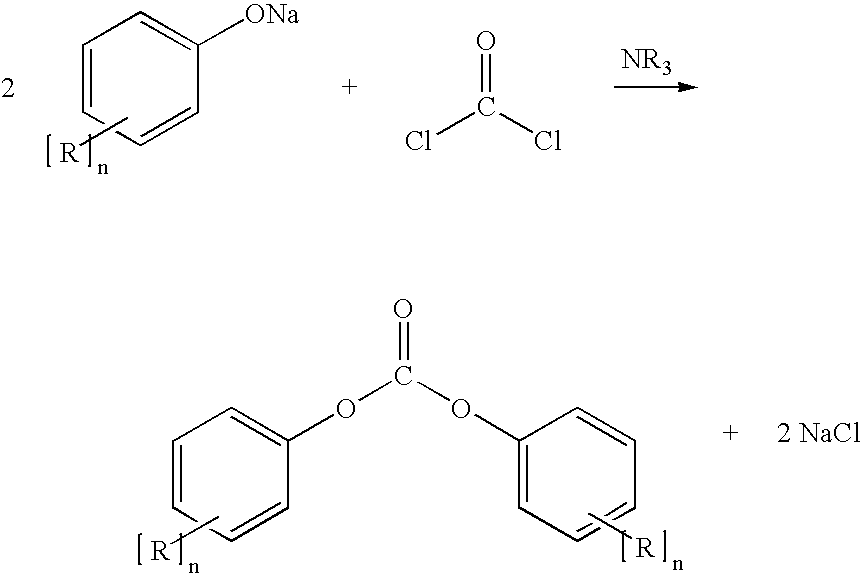
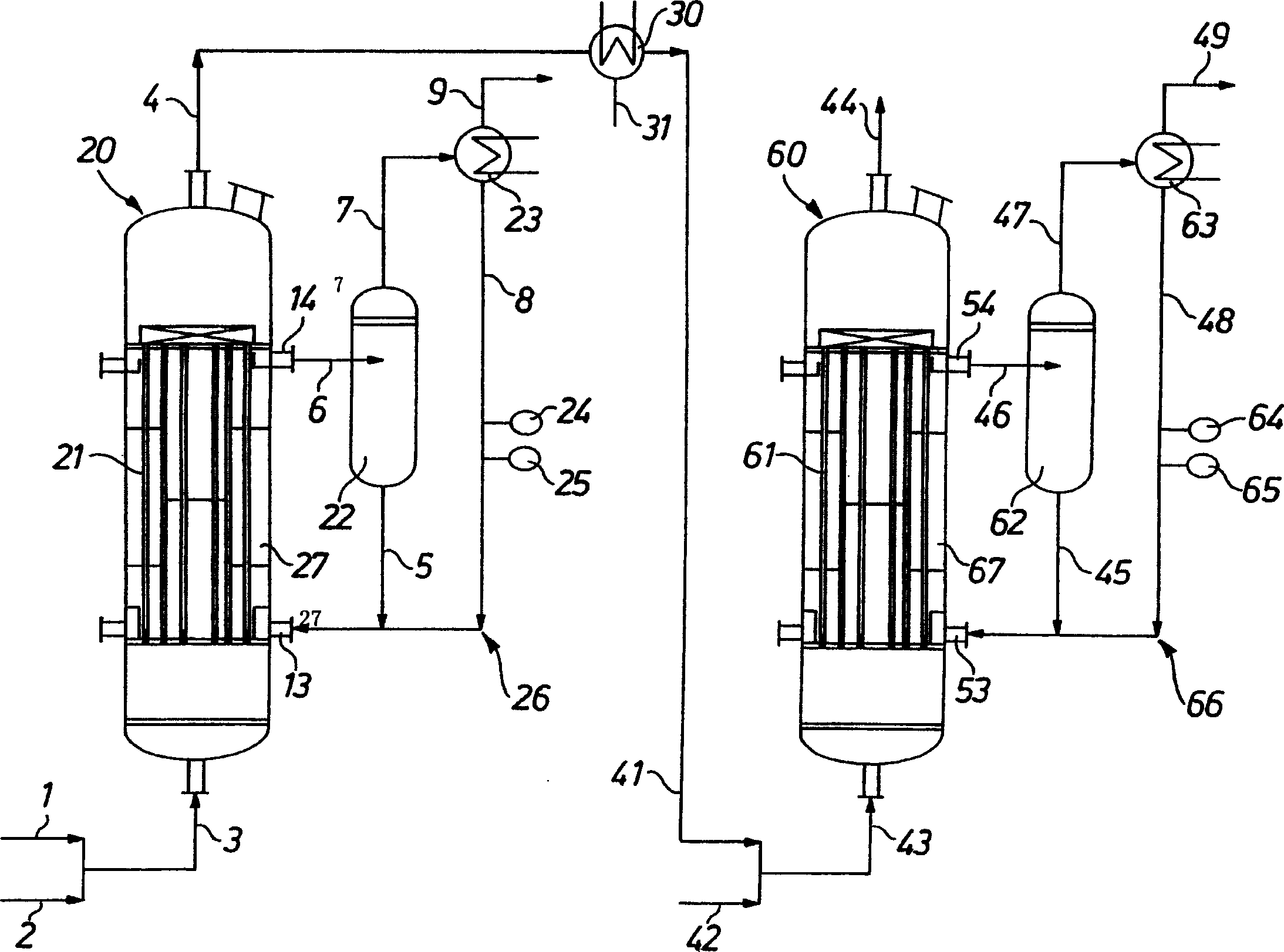
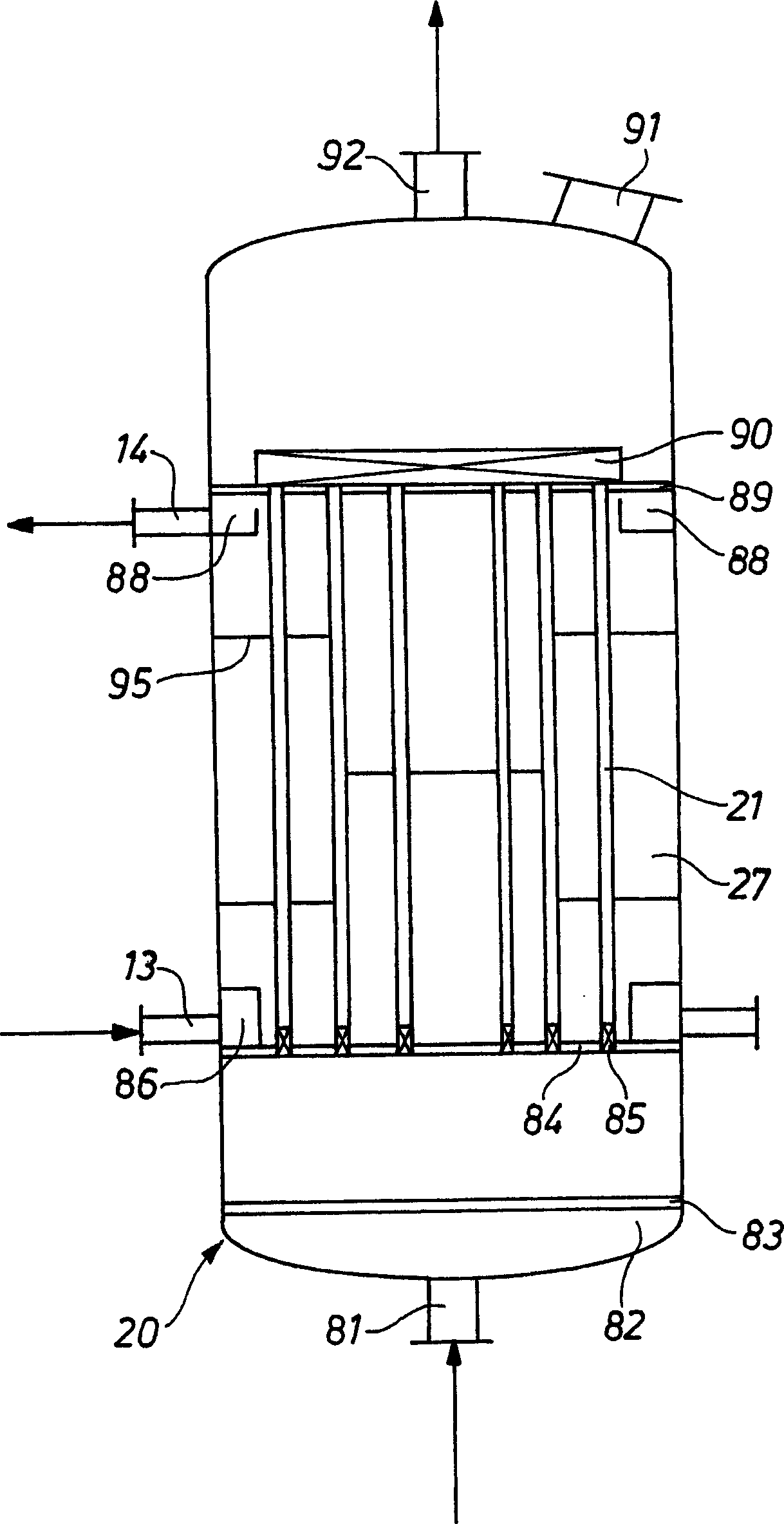
Ionic liquid based mixtures for gas storage and delivery
InactiveUS20060060817A1Oxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideLiquid degasificationChemical reactionIonic liquid
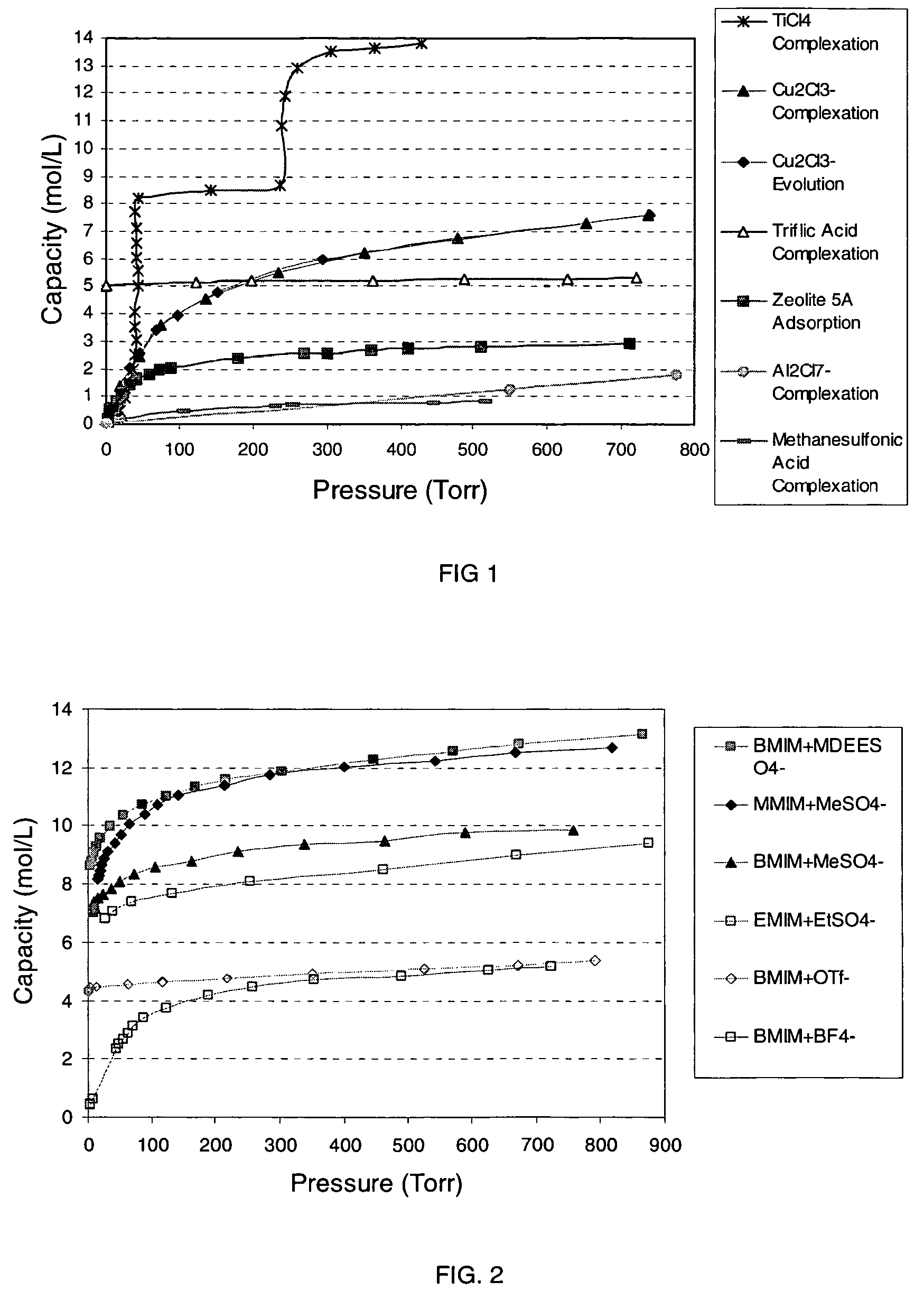
A mixture and method for the storage and delivery of at least one gas are disclosed herein. In one aspect, there is provided a mixture for the storage and delivery of at least one gas comprising: an ionic liquid comprising an anion and a cation; and at least one gas that is disposed within and is reversibly chemically reacted with the ionic liquid. In another aspect, there is provided a method for delivering at least one gas from a mixture comprising an ionic liquid and at least one gas comprising: reacting the at least one gas and the ionic liquid to provide the mixture and separating the at least one gas from the mixture wherein the at least one gas after the separating step is substantially the same as the at least one gas prior to the reacting step.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
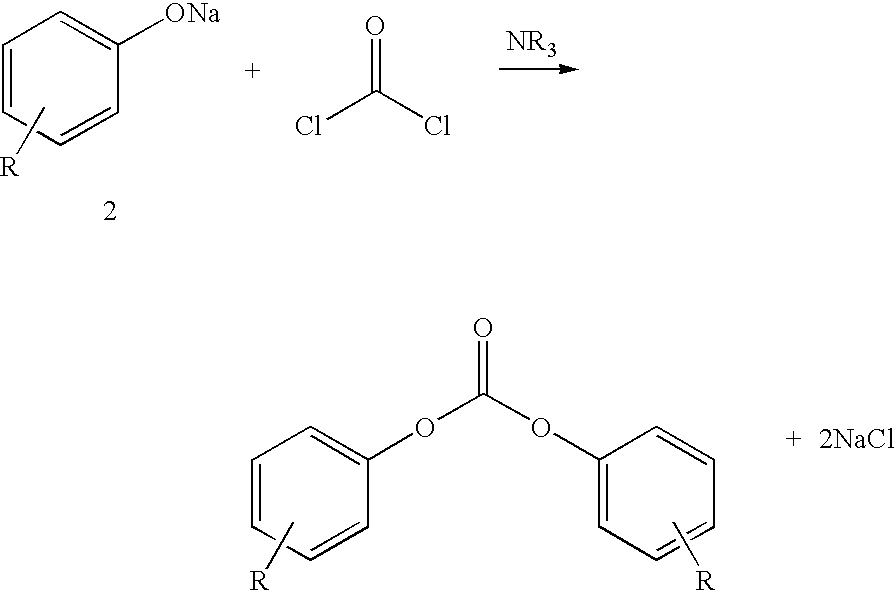
Process for the production of diaryl carbonates and treatment of alkalichloride solutions resulting therefrom
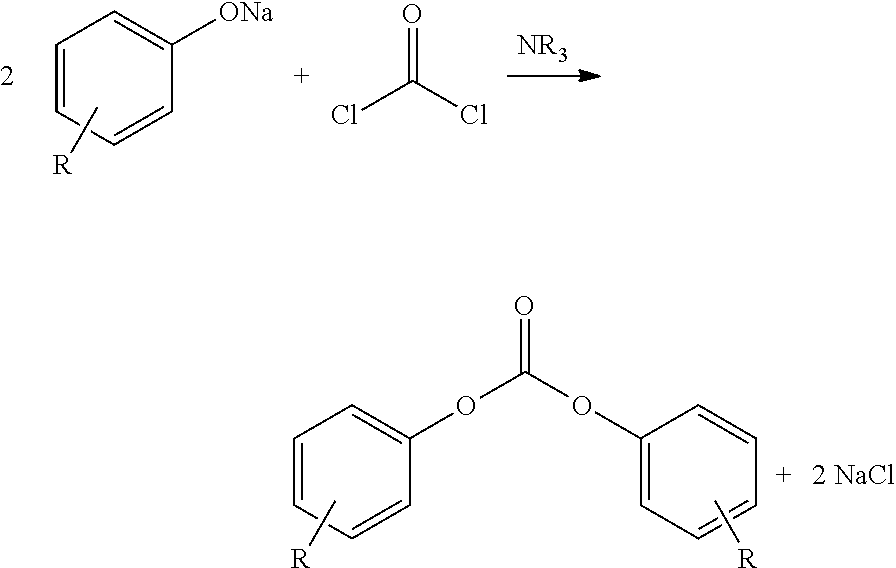
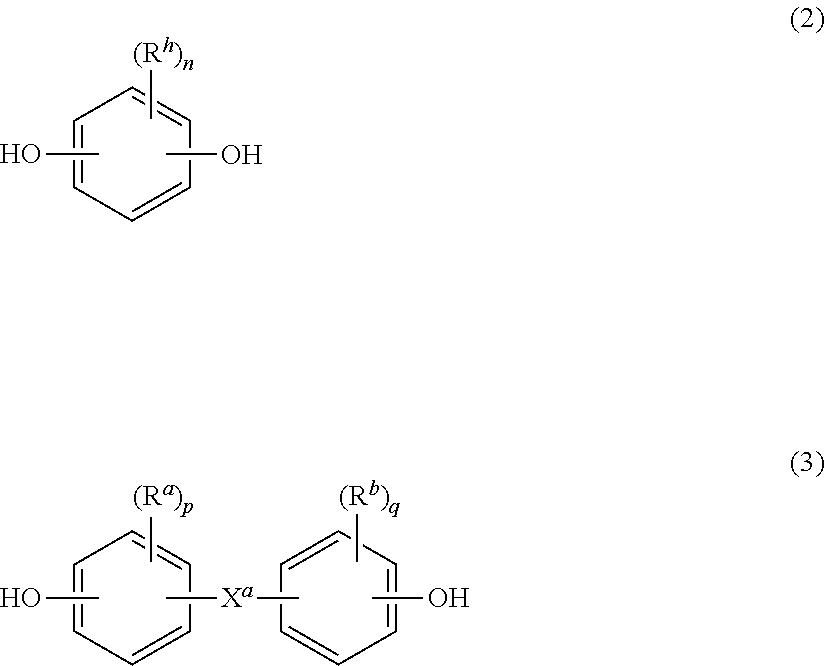
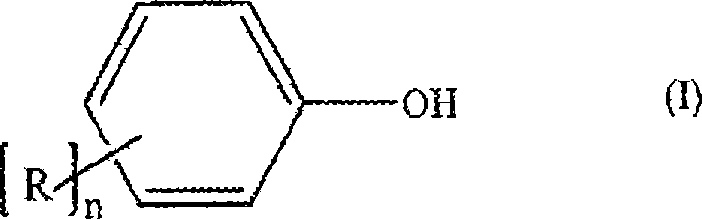
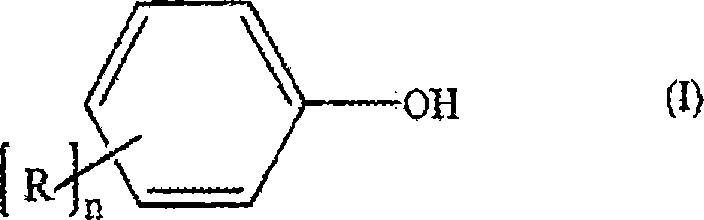
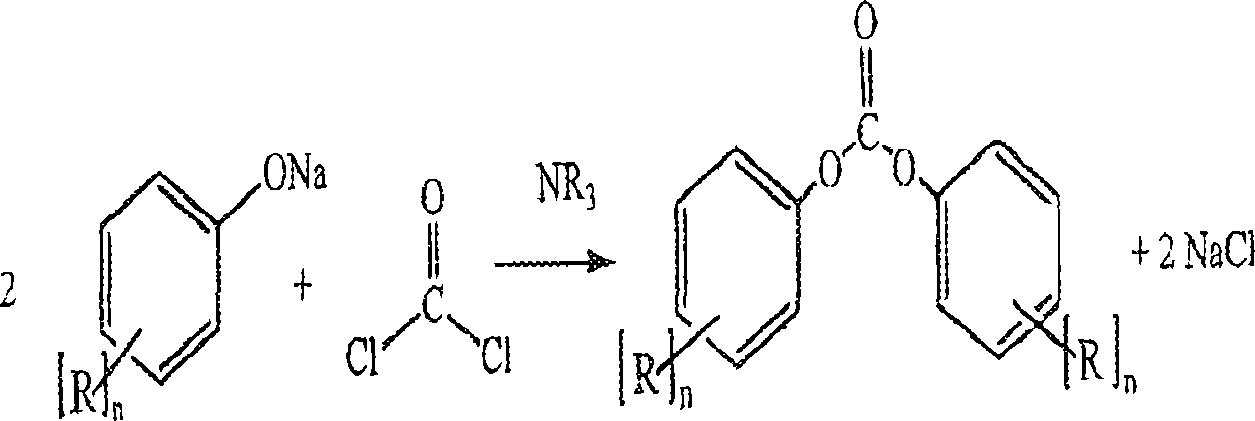
Processes comprising: (a) reacting phosgene and a monohydroxyl aryl compound in the presence of a suitable catalyst to form a diaryl carbonate and a solution comprising an alkali chloride; (b) separating the diaryl carbonate from the solution; (c) adjusting the pH of the solution to a value of less than or equal to 8 to form a pH-adjusted solution; (d) treating the pH-adjusted solution with an adsorbent to form a treated solution; (e) subjecting at least a portion of the treated solution to electrochemical oxidation to form chlorine and an alkali hydroxide solution; and (f) recycling at least a portion of one or both of the chlorine and the alkali hydroxide solution.
Owner:BAYER MATERIALSCIENCE AG
Process for production of diaryl carbonate
The invention relates to a process for production of diaryl carbonate combined with the electrolysis of the resultant alkali metal chloride-containing process wastewater. The process according to the invention makes possible, inter alia, improved utilization in electrolysis of the alkali metal chloride-containing solution obtained in the production of diaryl carbonate.
Owner:BAYER MATERIALSCIENCE AG
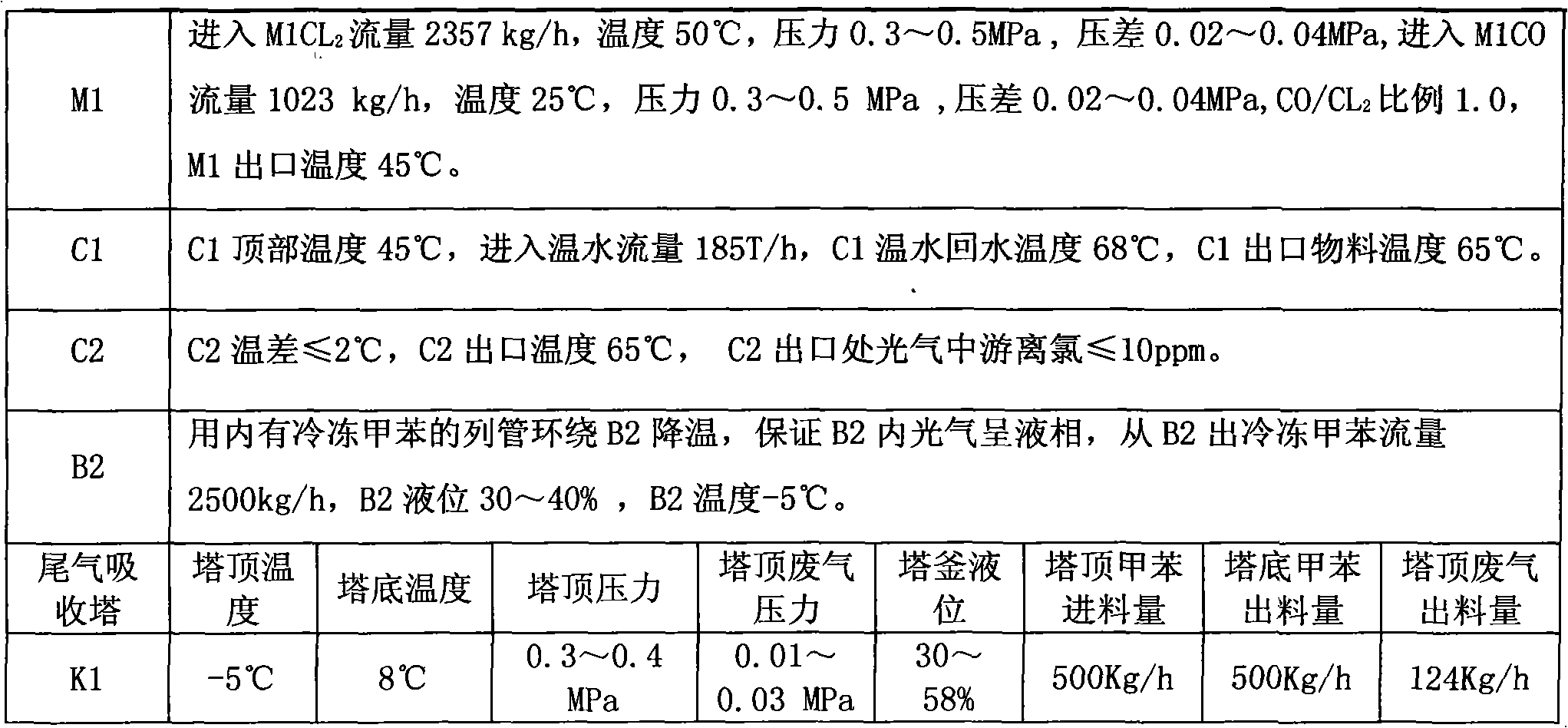
Method for continuously preparing phosgene
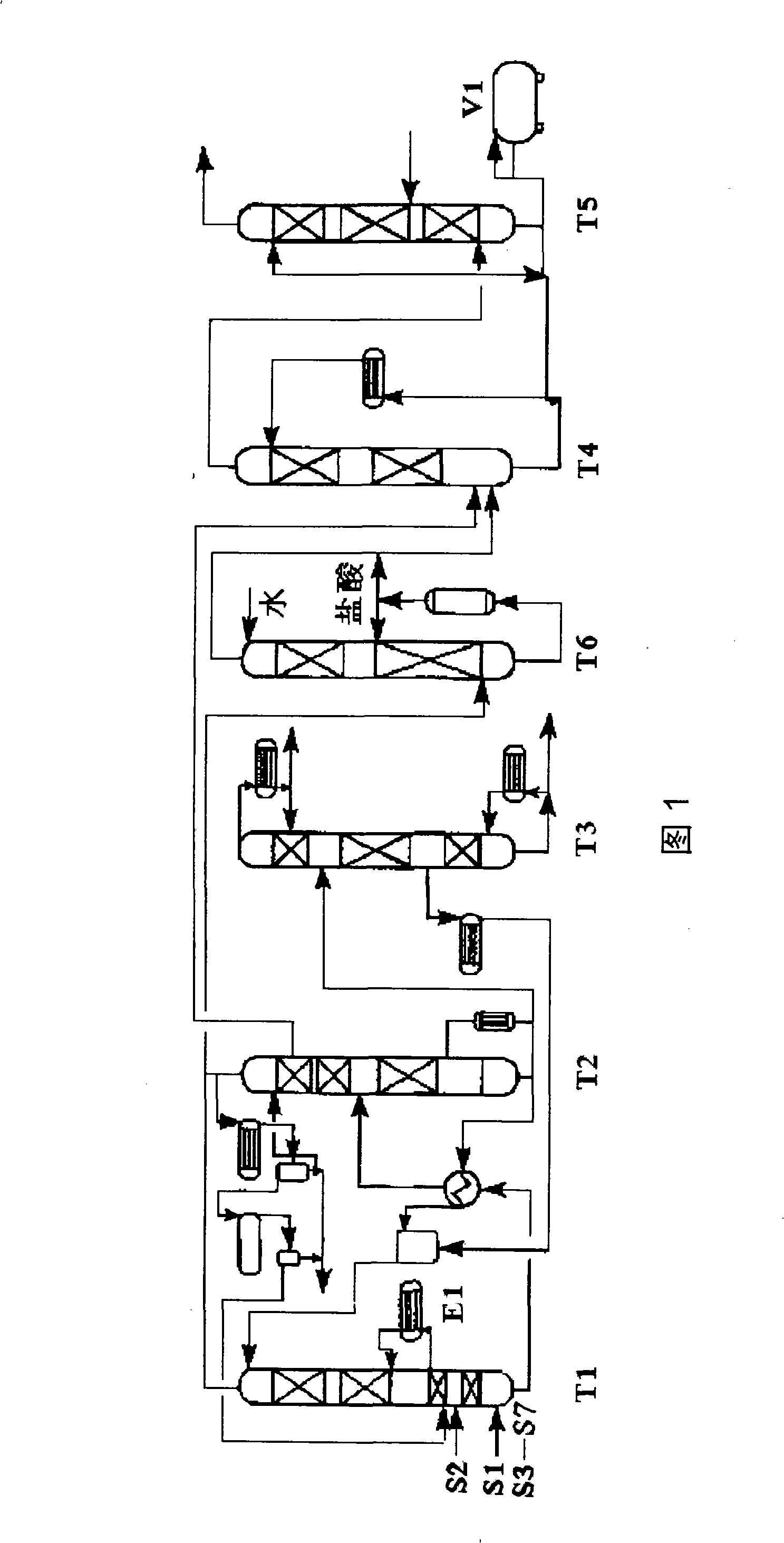
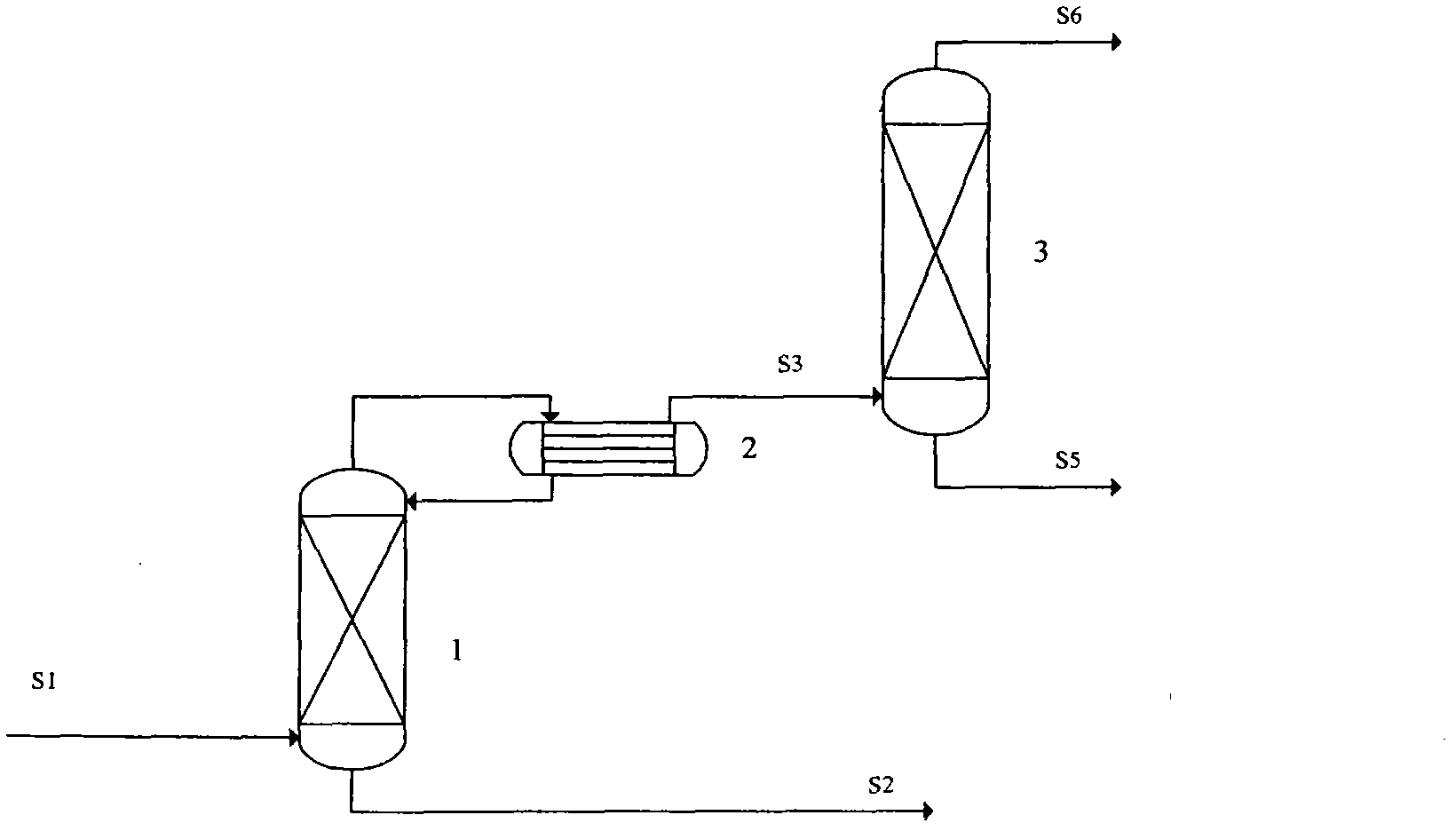
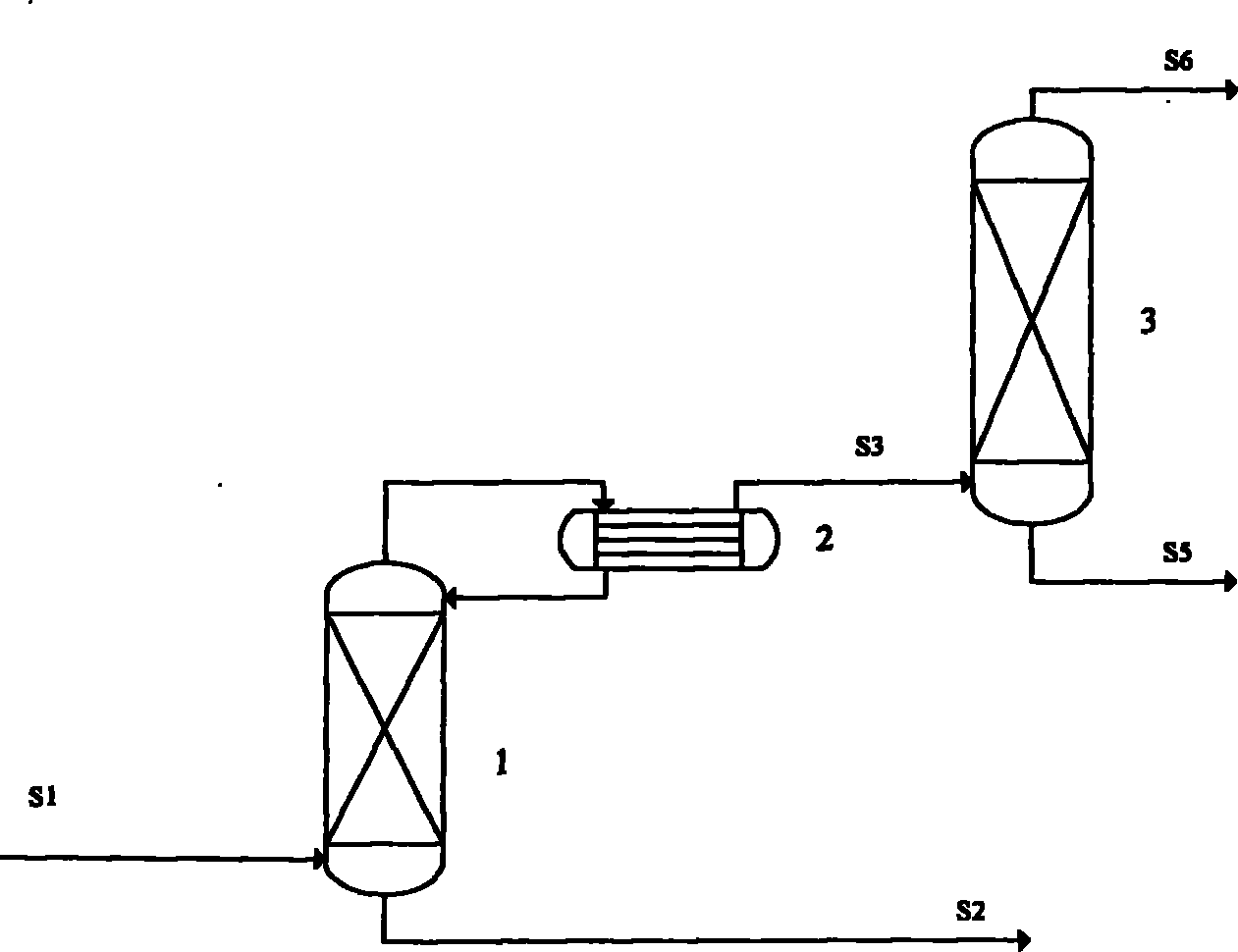
The invention relates to a method for producing phosgene through the reaction of chlorine and carbon monoxide, and in particular to a method that chlorine and carbon monoxide are used to perform an exothermic reaction in a tube reactor in the presence of an activated carbon catalyst and generate phosgene. In the method provided by the invention, after chlorine is mixed with excess carbon monoxidein a mixer M1, then the mixture enters a tubular reactor C1 to react under the action of the activated carbon catalyst and generate phosgene and then passes through a protection reactor C2 to ensure that chlorine reacts completely; and the heat generated by the reaction is led out by a 60 DEG C cooling water system in closed cycle, the generated gaseous phosgene is cooled through W1 condensation and W2 condensation and enters a phosgene gas-liquid separation tank B2, the un-condensed gas enters an exhaust gas absorber K1, and -5 DEG C toluene is used to absorb and recycle phosgene in tail gas.
Owner:甘肃银光聚银化工有限公司 +1
Phosgene producing method and equipment
ActiveCN1765740AEasy to manufactureImprove reliabilityProcess control/regulationChemical industryActivated carbonPtru catalyst
In the production of phosgene by reacting chlorine and carbon monoxide in the presence of an activated charcoal catalyst in a tube aggregate reactor with several reaction tubes surrounded by a coolant chamber, (a) the reaction tubes are cooled externally by evaporation cooling with water in the coolant chamber and (b) the reaction tubes operate at a pressure higher than that in the coolant chamber. An independent claim is also included for the plant used.
Owner:COVESTRO DEUTSCHLAND AG
Ionic liquid based mixtures for gas storage and delivery
A mixture and method for the storage and delivery of at least one gas are disclosed herein. In one aspect, there is provided a mixture for the storage and delivery of at least one gas comprising: an ionic liquid comprising an anion and a cation; and at least one gas that is disposed within and is reversibly chemically reacted with the ionic liquid. In another aspect, there is provided a method for delivering at least one gas from a mixture comprising an ionic liquid and at least one gas comprising: reacting the at least one gas and the ionic liquid to provide the mixture and separating the at least one gas from the mixture wherein the at least one gas after the separating step is substantially the same as the at least one gas prior to the reacting step.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
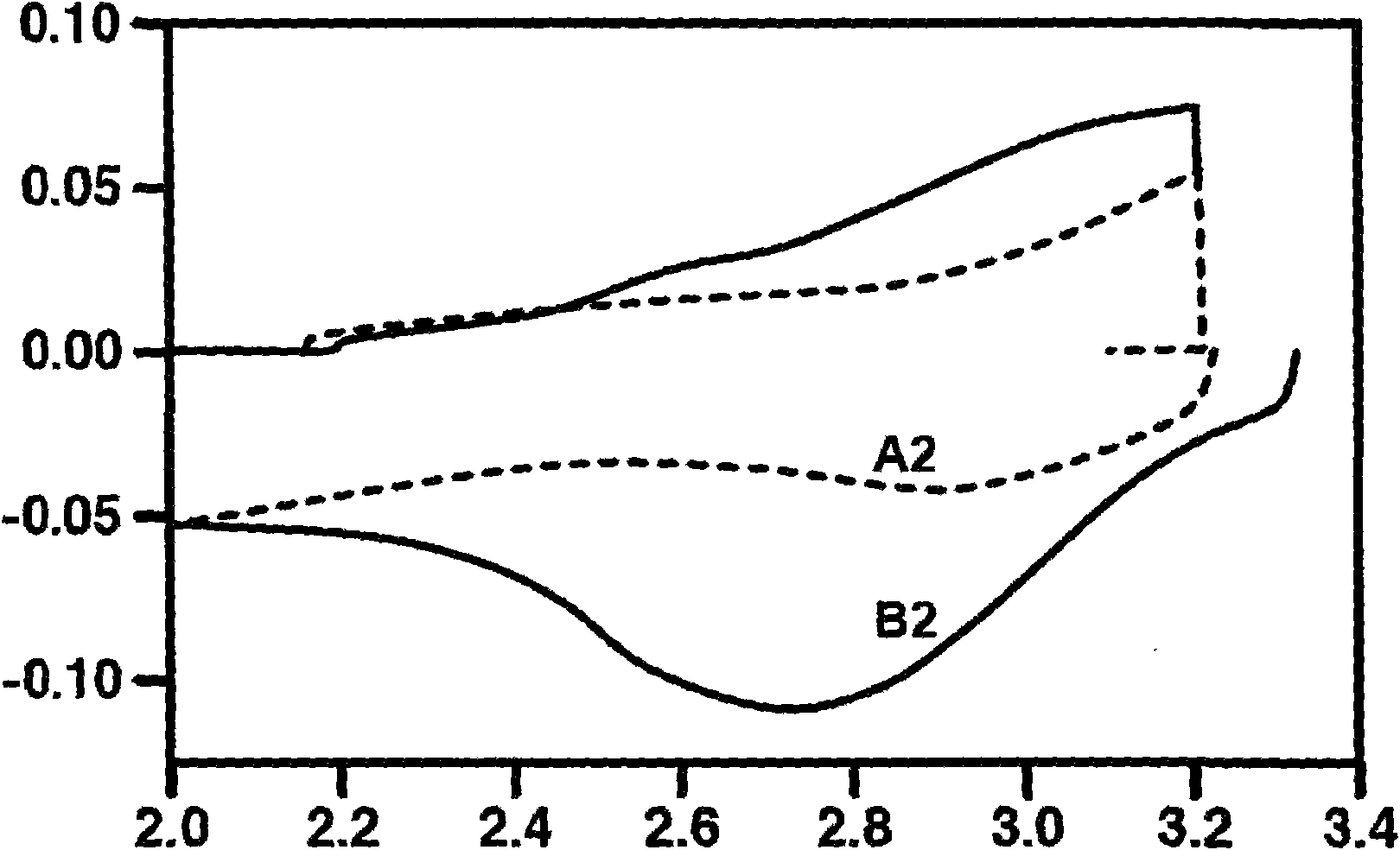
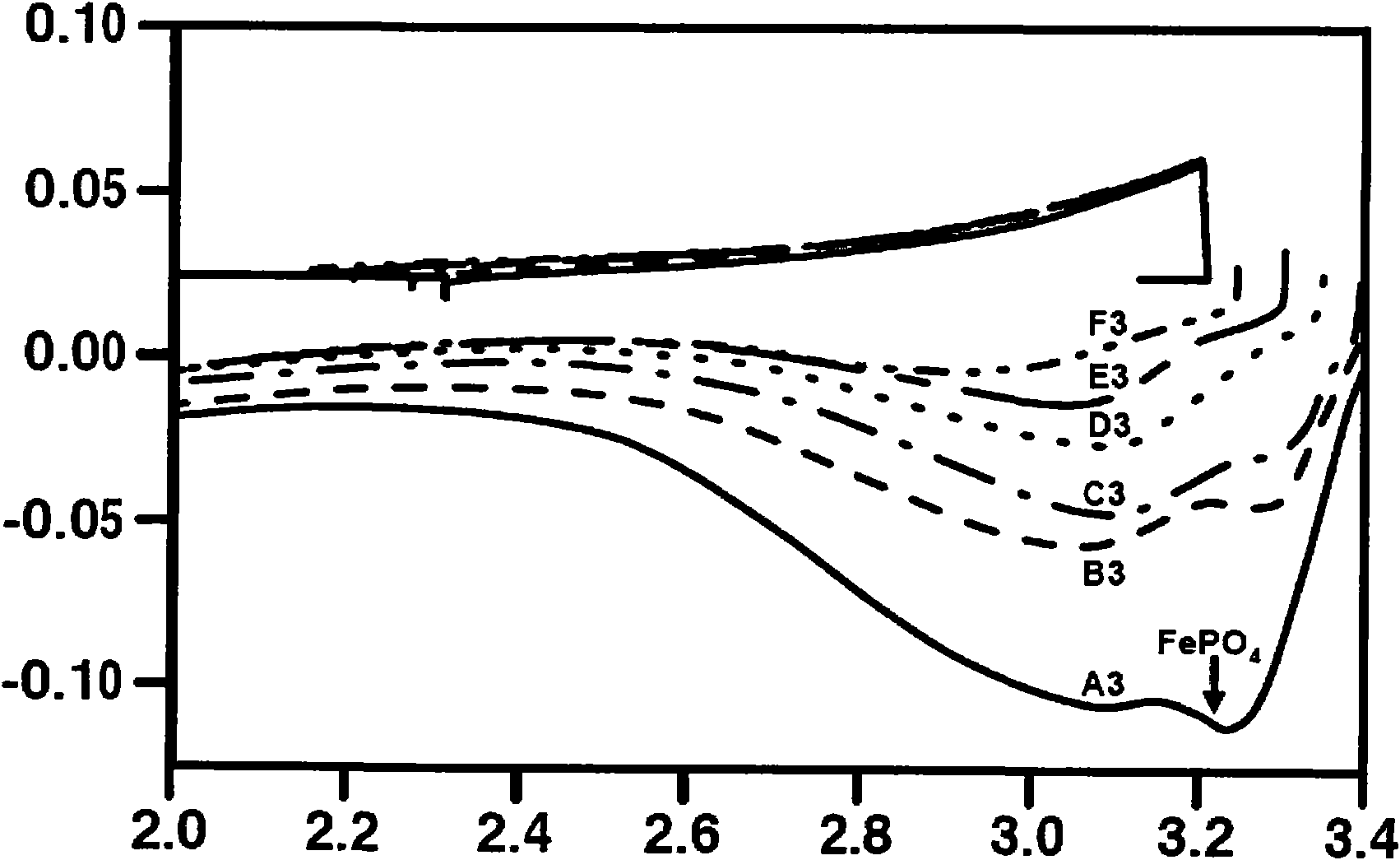
Carbonated complex oxides and method for making the same
The invention relates to a method for preparing a carbonated complex oxide having a very low water content, and to the use thereof as a cathode material. The carbonated complex oxide is made of particles of an olivine-structure AMXO4 compound bearing on a portion at least of their surface a carbon film deposited by pyrolysis. A is Li alone or partially replaced with at most 10 at % of Na or K. M is FeII alone or partially replaced with at most 50 at % of one or more other metals selected from Mn, Ni and Co and / or with at most 10 at % of one or more aliovalent or isovalent metals other than Mn, Ni or Co and / or with at most 5 at % of FeIII. XO4 is PO4 alone or partially replaced with at most 10 molar % of SO4 and SiO4. The material has a water content lower than 1000 ppm.
Owner:福斯泰克锂公司 +1
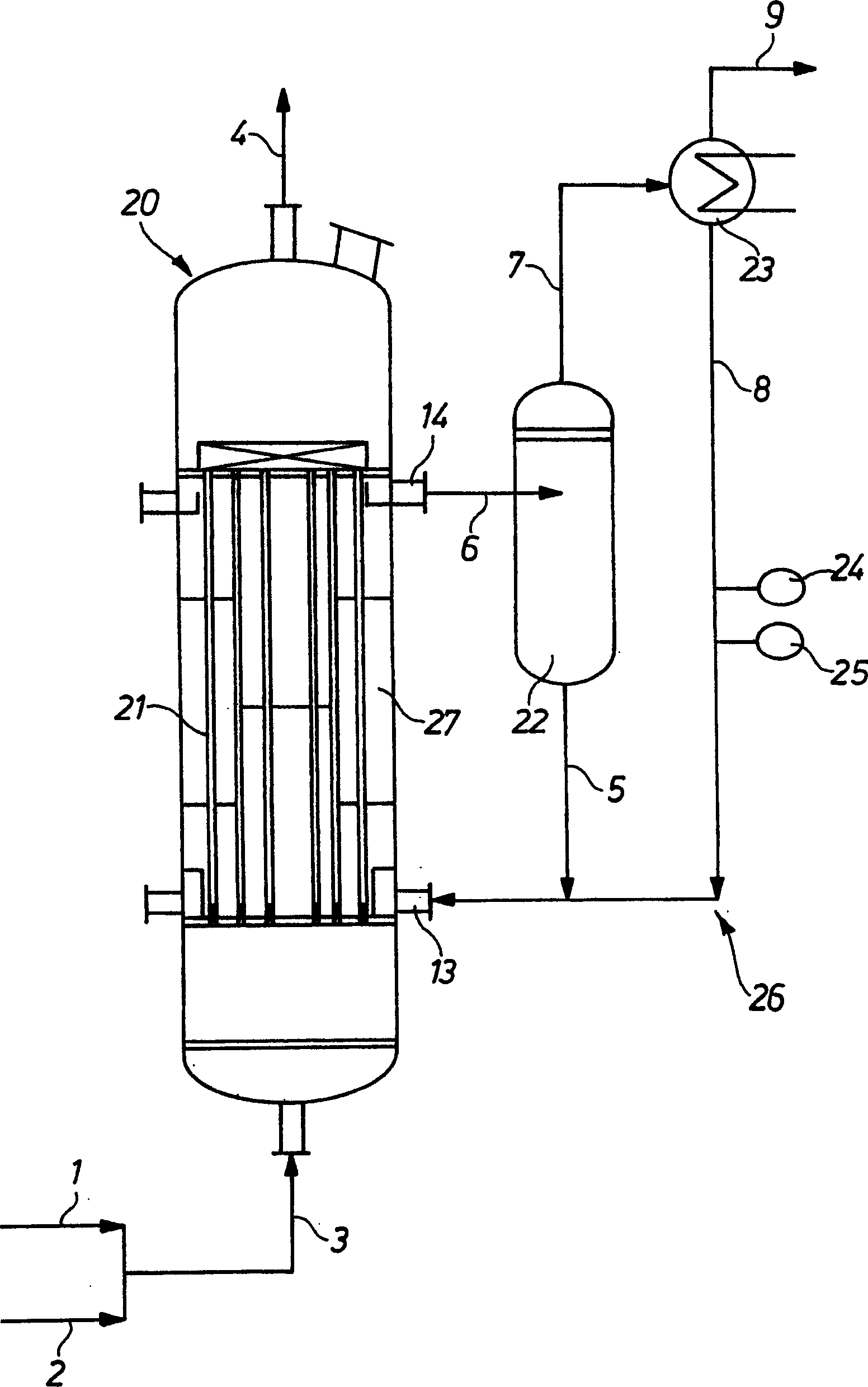
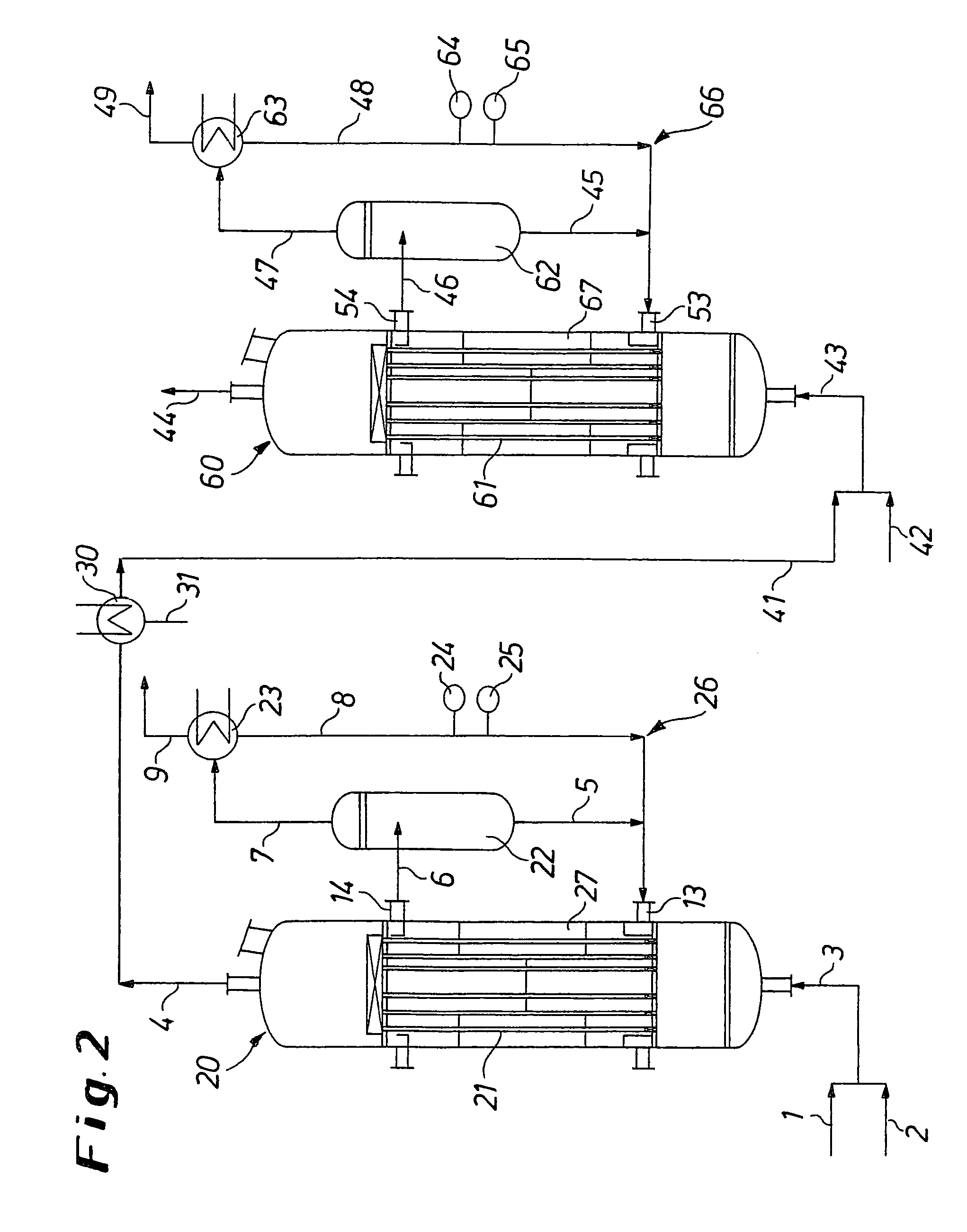
Process and apparatus for the production of phosgene
The invention relates to a process for the production of phosgene, in which chlorine and carbon monoxide are reacted in the presence of an activated charcoal catalyst in a shell-and-tube reactor which contains a plurality of reaction tubes and a coolant space surrounding the reaction tubes, in whicha) cooling of the reaction tubes is from the outside through the coolant space with water by evaporative cooling, andb) operation of the reaction tubes is at a pressure above the pressure in the coolant space.
Owner:COVESTRO DEUTSCHLAND AG
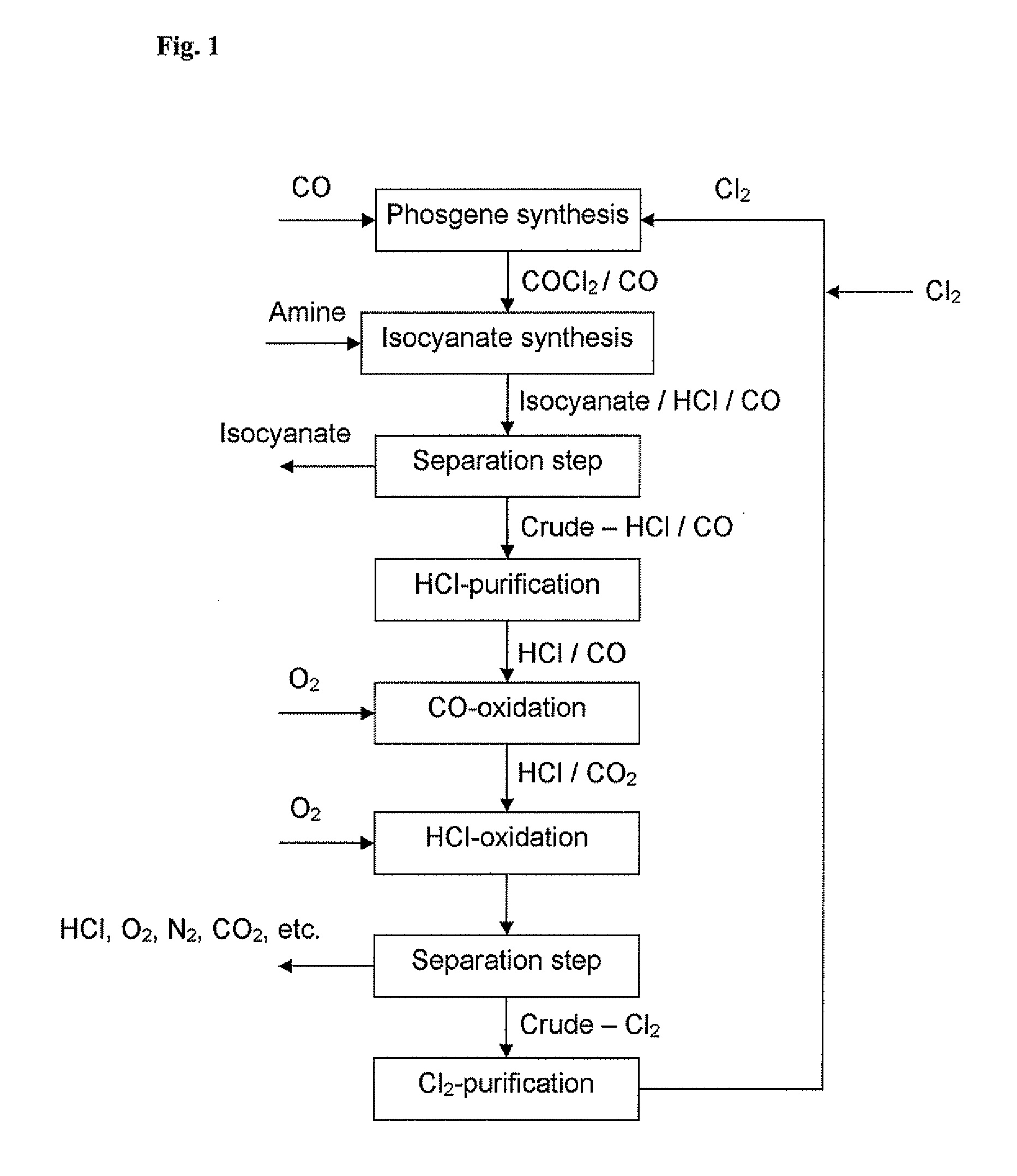
Processes for the production of organic isocyanates
InactiveUS20070276154A1Reduce needReduce riskIsocyanic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationPhosgeneChlorine
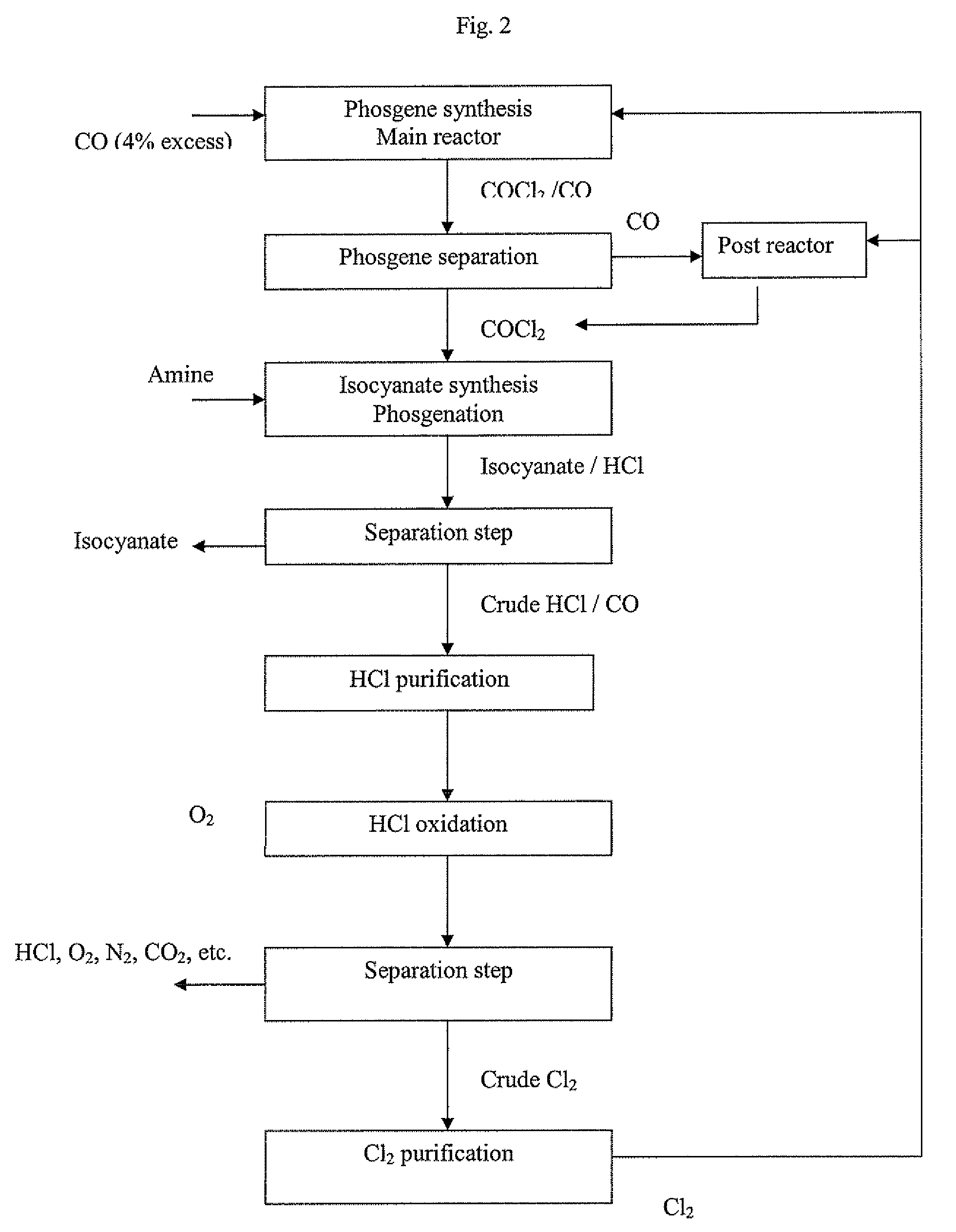
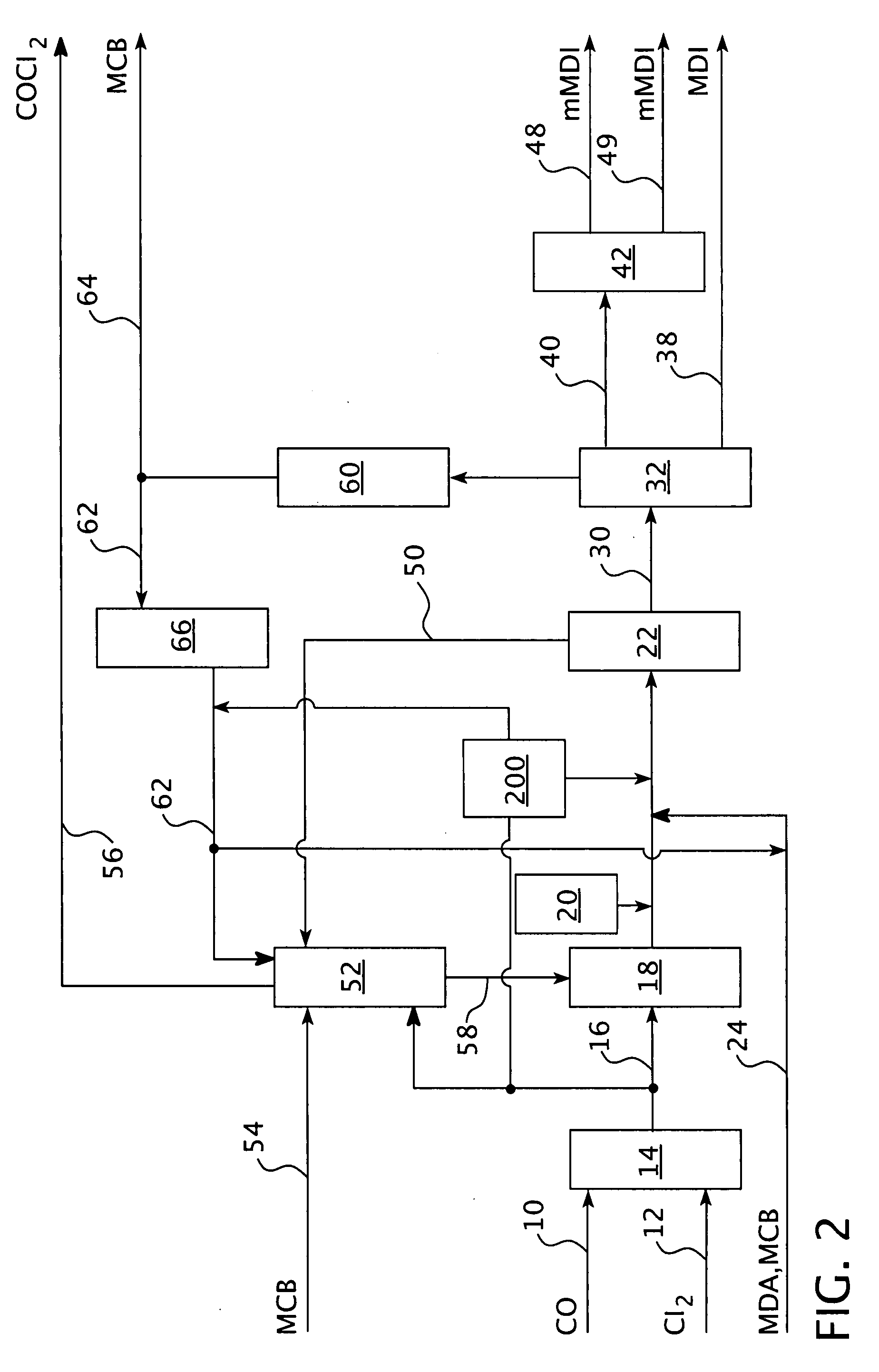
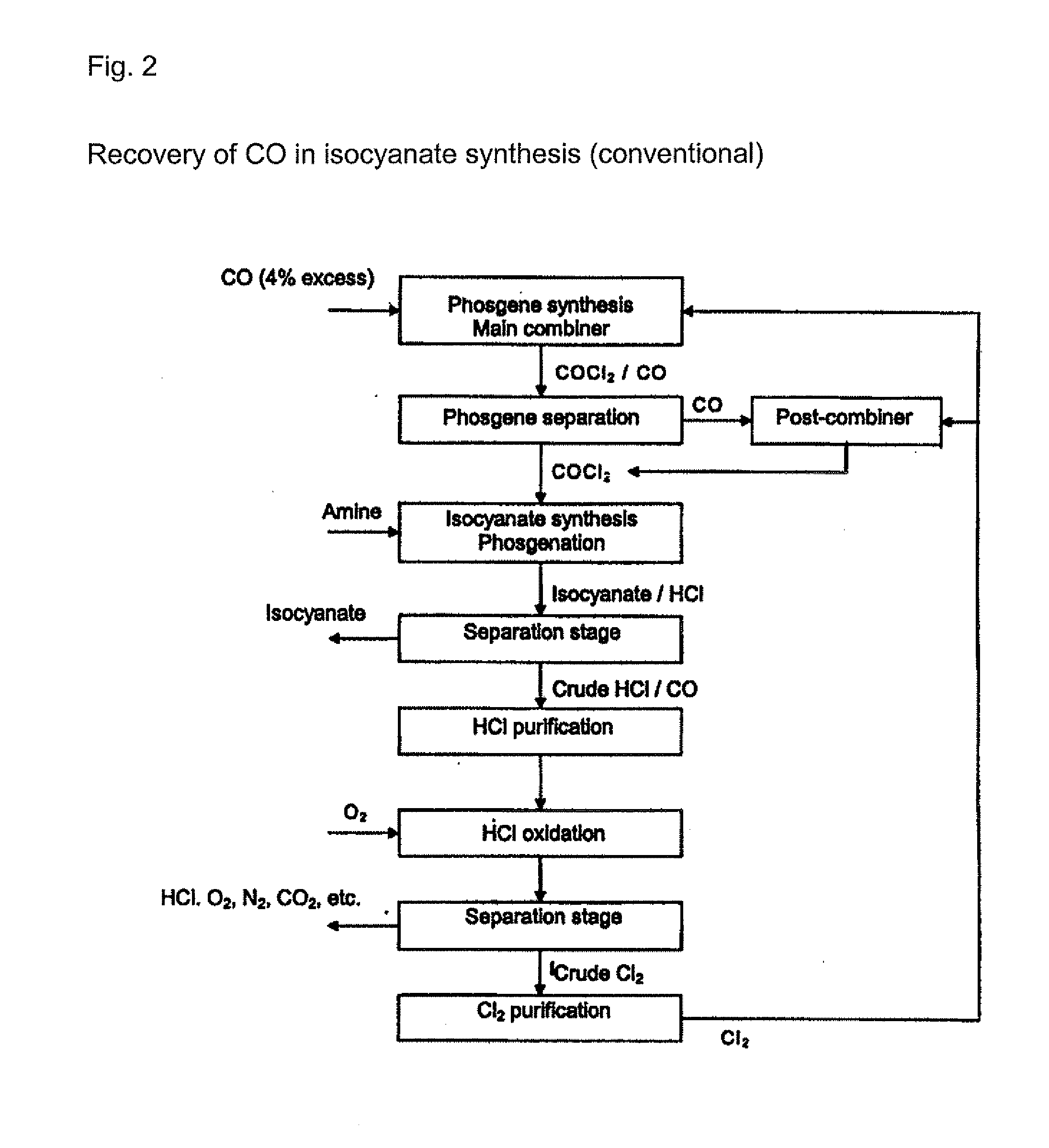
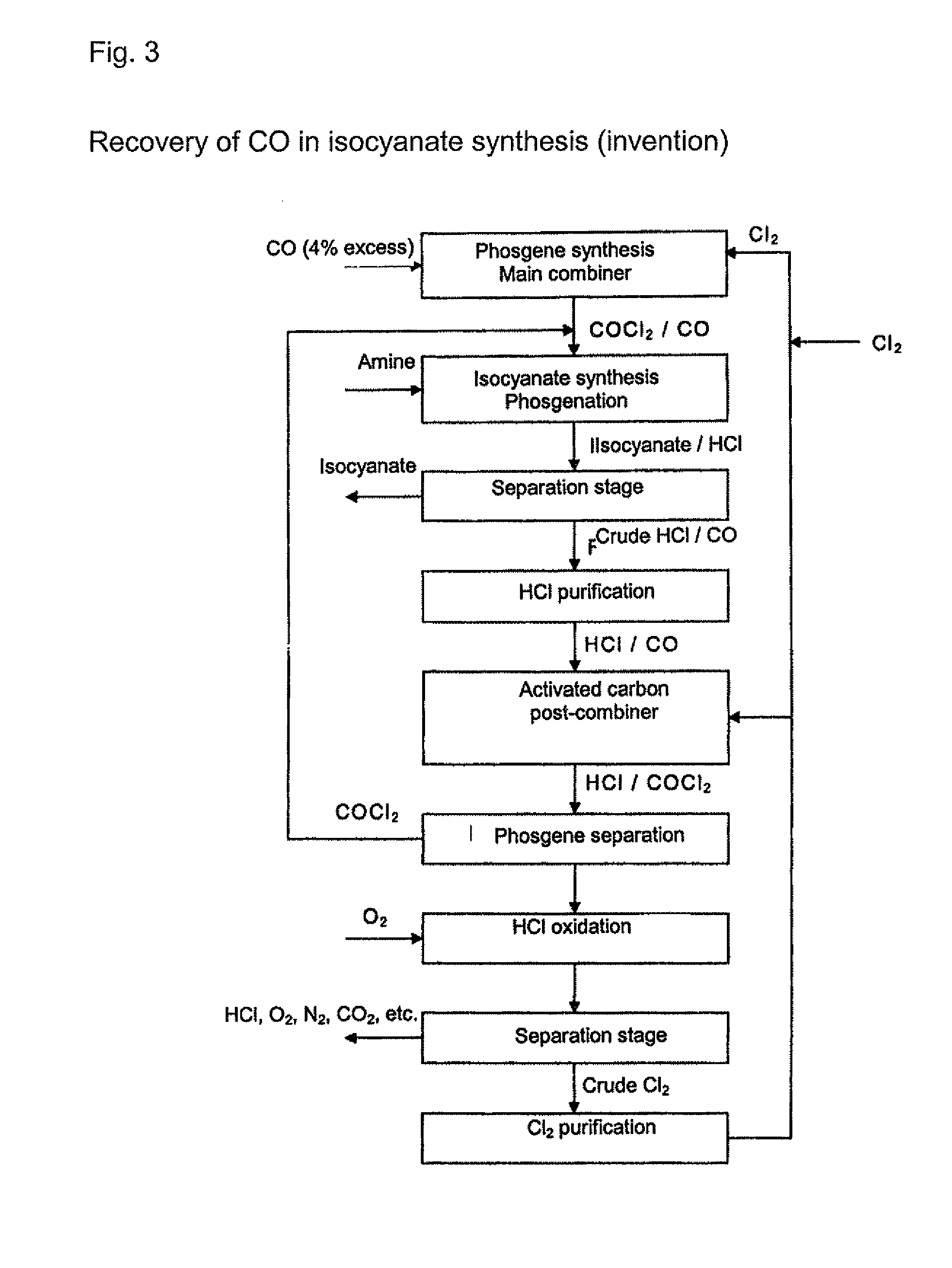
Processes for the production of organic isocyanates, comprising the production of phosgene by reaction of CO with Cl2, the reaction of the phosgene with organic amines to form the organic isocyanates, and the separation of the organic isocyanates, which is characterised in that the carbon monoxide is removed from the HCl-containing waste gas from the isocyanate synthesis by reaction with chlorine to form phosgene. The phosgene can be separated off and can optionally be fed back into an isocyanate synthesis The HCl-containing, CO-depleted gas is preferably subjected to HCl oxidation (Deacon). A closed chlorine cycle can be used in the isocyanate synthesis.
Owner:BAYER MATERIALSCIENCE AG
Method for purifying a chlorine supply
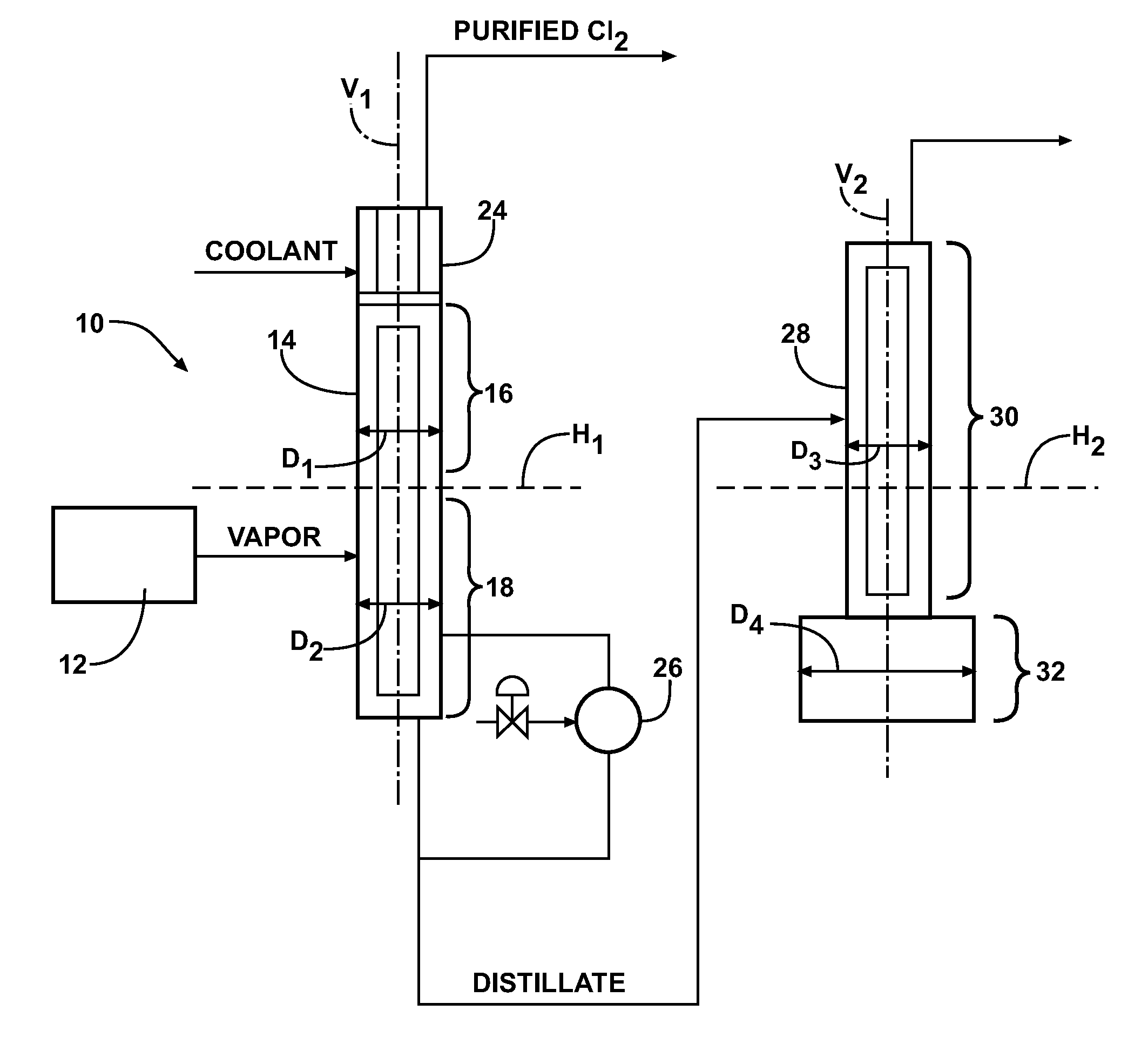
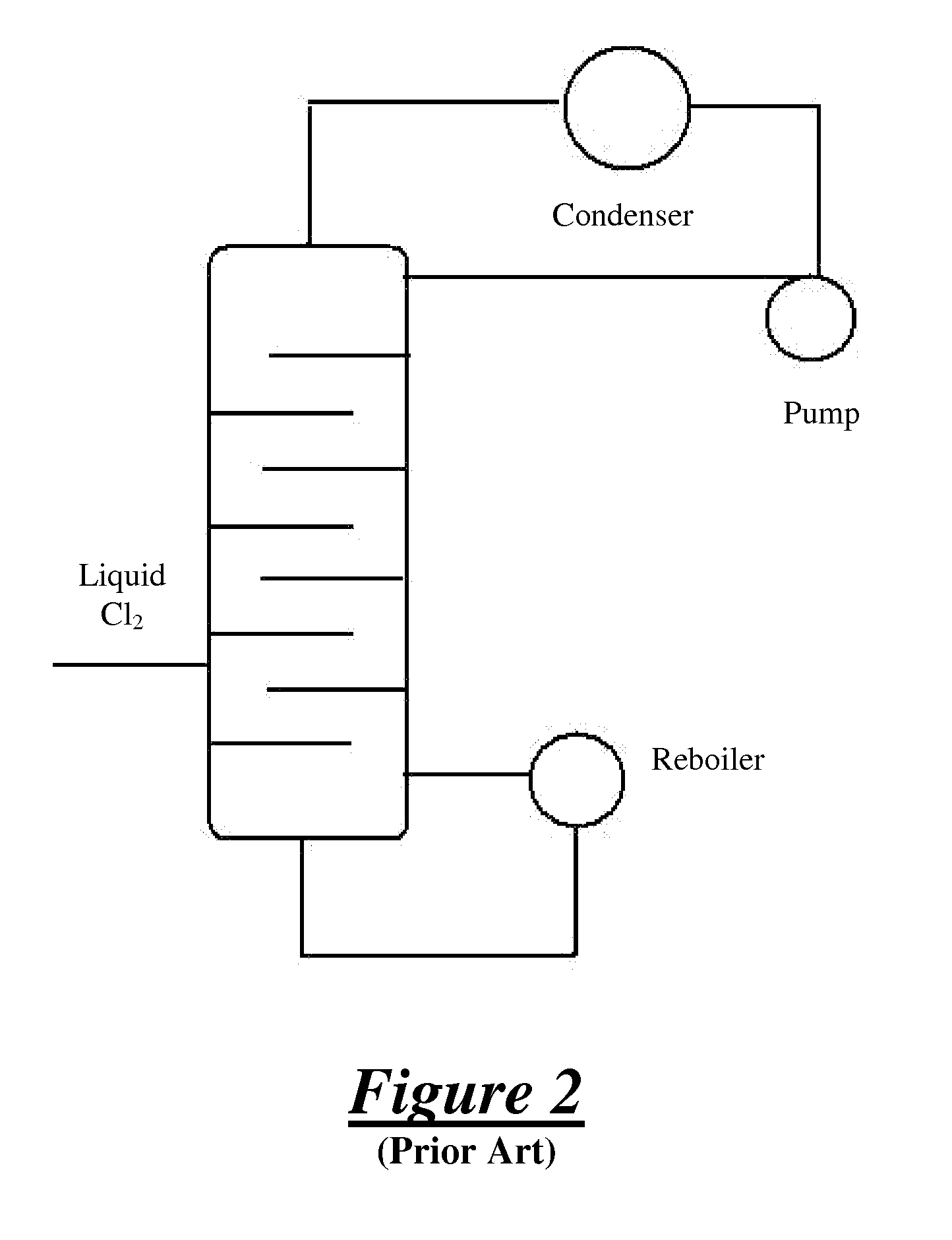
ActiveUS20110144381A1Improve energy efficiencyReduce environmental problemsIsocyanic acid derivatives preparationLiquid degasificationRefluxReboiler
This invention provides a method for purifying a chlorine supply that includes a chlorine component, a bromine component, and nitrogen trichloride. The method includes the steps of introducing the chlorine supply into a vaporizer, heating the chlorine supply in the vaporizer to form a vapor, and introducing the vapor into a distillation system to provide purified chlorine gas, a distillate that includes liquid chlorine and the bromine component, and a bottoms component including the nitrogen trichloride. The method also includes the steps of condensing the vapor in a reflux condenser, heating the condensate in a reboiler, removing the purified chlorine gas from the distillation system, and removing the distillate from the distillation system.
Owner:BASF AG
Process for production of diaryl carbonate
The invention relates to a process for production of diaryl carbonate combined with the electrolysis of the resultant alkali metal chloride-containing process wastewater. The process according to the invention makes possible, inter alia, improved utilization in electrolysis of the alkali metal chloride-containing solution obtained in the production of diaryl carbonate.
Owner:COVESTRO DEUTSCHLAND AG
Processes for removing organic components from gases containing hydrogen chloride
ActiveUS20080264253A1Reduce lossesSolidificationChlorine/hydrogen-chloride purificationHydrogen chlorideImpurity
Processes comprising: providing a crude gas stream having a temperature not exceeding 40° C., the crude gas stream comprising hydrogen chloride and at least one organic impurity; condensing at least a portion of the at least one organic impurity from the crude gas stream at a temperature not exceeding 0° C. to form a prepurified gas stream and a condensate comprising condensed organic impurity; subjecting at least a portion of the prepurified gas stream to adsorption on an adsorption medium to provide a purified gas stream; and separating the condensate into at least a head gas stream comprising residual hydrogen chloride and a sump stream comprising at least a portion of the condensed organic impurity.
Owner:COVESTRO DEUTSCHLAND AG
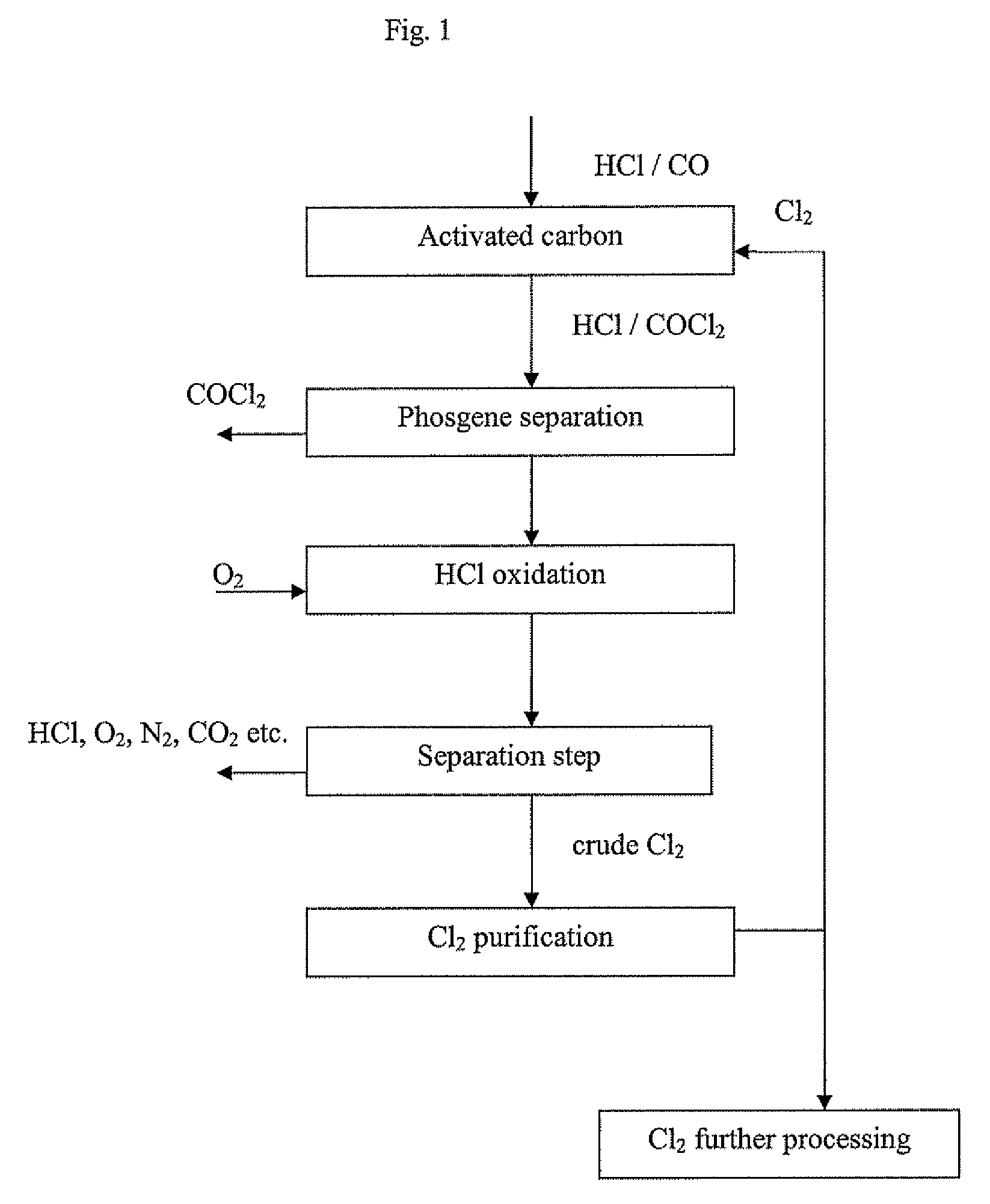
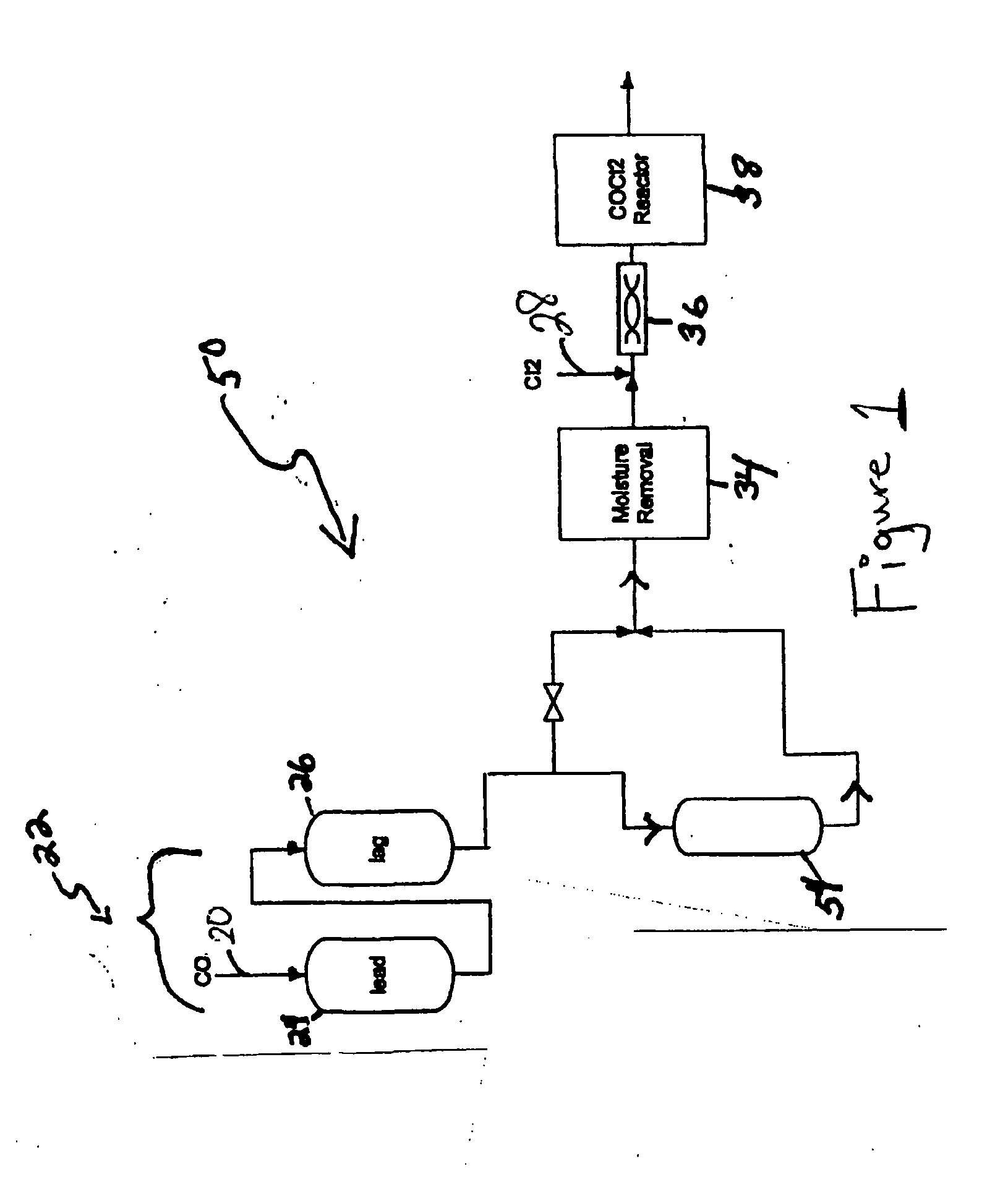
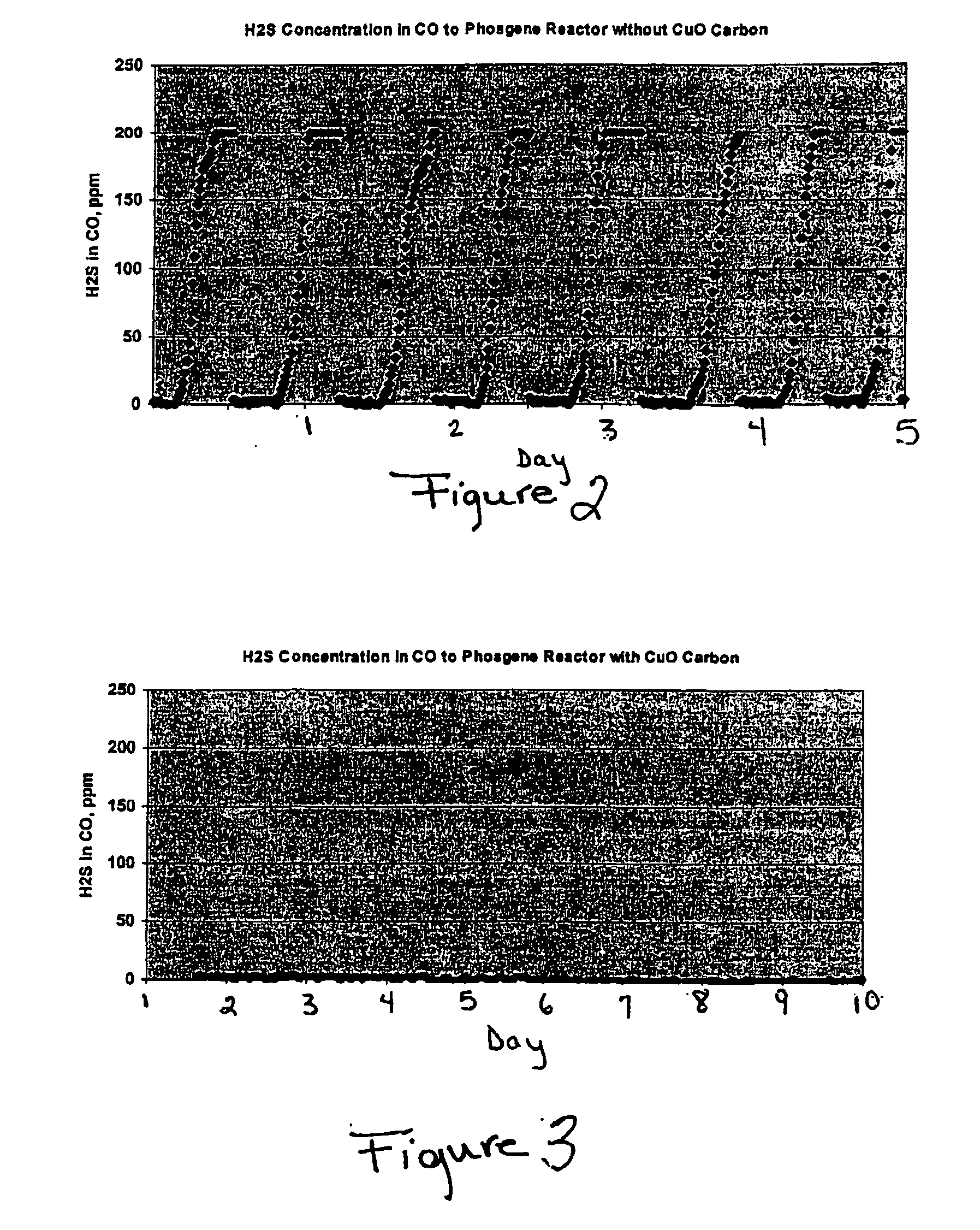
Processes and systems for making phosgene
InactiveUS20050025693A1Reduce the concentration of hydrogen sulfideOrganic compound preparationDispersed particle separationActivated carbonPhosgene
One process for producing phosgene comprises: introducing a carbon monoxide stream to a metal oxide impregnated activated carbon, reducing a hydrogen sulfide concentration in the carbon monoxide stream to produce a cleaned stream, wherein a cleaned stream hydrogen sulfide concentration is less than or equal to about 20 ppm, and reacting carbon monoxide in the cleaned stream with chlorine to produce phosgene.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
Processes for the oxidation of carbon monoxide in a gas stream containing hcl
InactiveUS20080267849A1Easy to operateSolution to short lifeIsocyanic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationTin dioxideProduct gas
Processes comprising: providing a gas stream comprising hydrogen chloride and carbon monoxide; and oxidizing at least a portion of the carbon monoxide in the gas stream in the presence of a catalyst to form a product gas comprising hydrogen chloride and carbon dioxide; wherein the catalyst comprises tin dioxide and a ruthenium compound comprising at least one element selected from the group consisting of oxygen and chlorine.
Owner:BAYER MATERIALSCIENCE AG
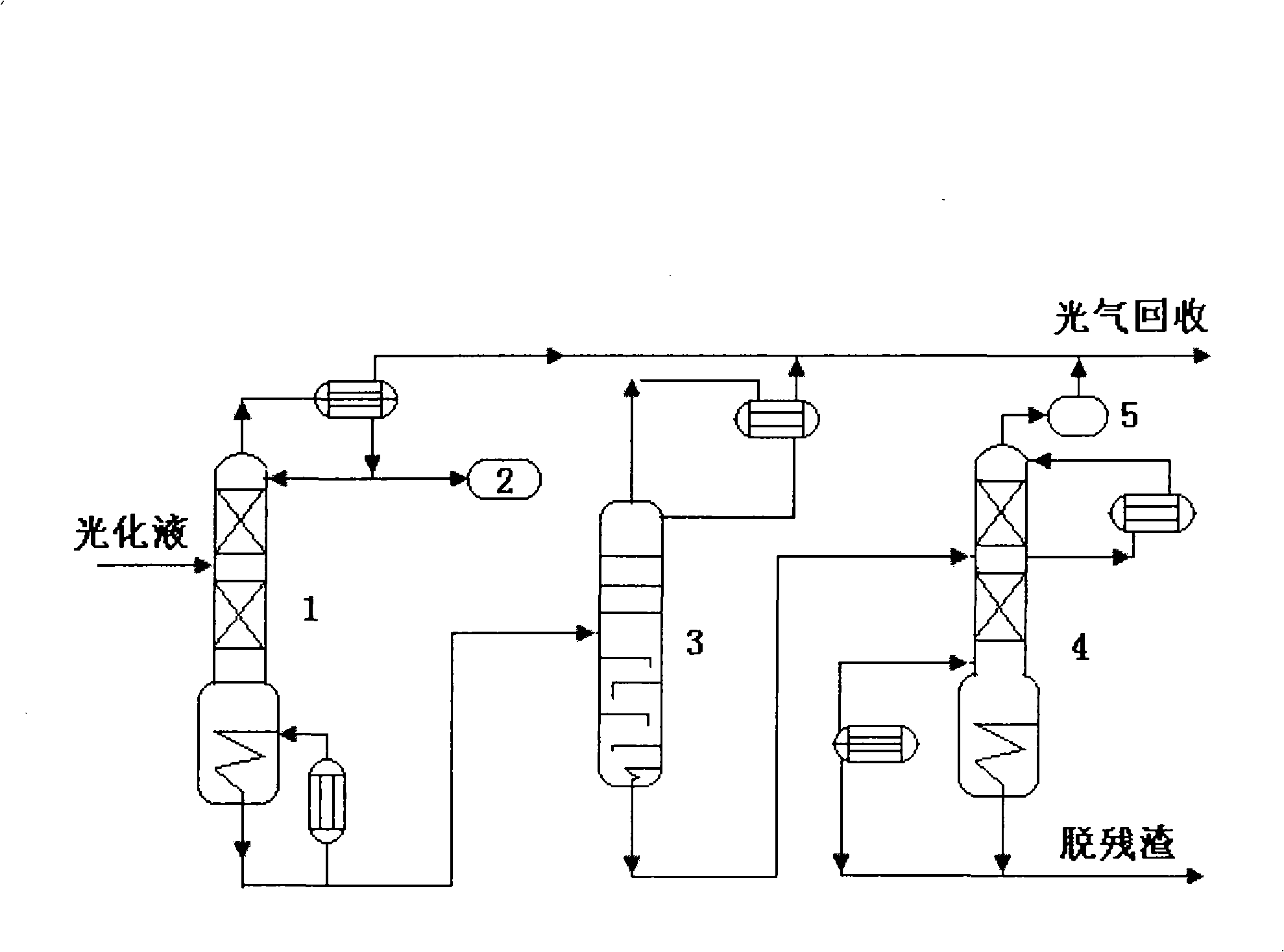
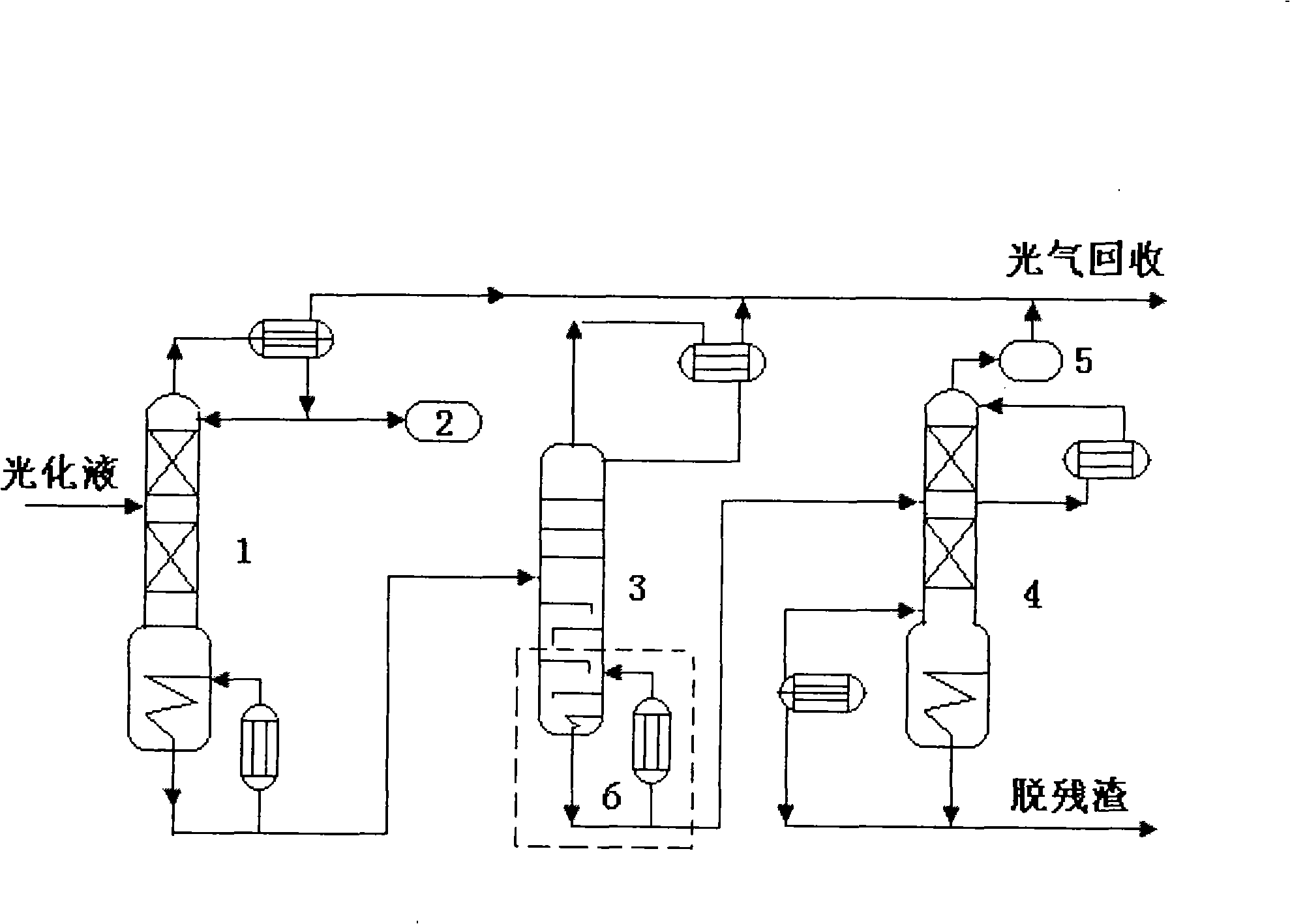
Phosgene recovery method for toluene diisocyanate production process
The invention provides a method for recovering phosgene in toluene diisocynate preparation process. In the method, materials containing HCl, ethyl chloride and phosgene are firstly absorbed by solvents containing benzene, cooled by toluene absorption system and has HCl fixed gases absorbed by alkaline liquors, toluene absorption liquids absorbing ethyl chloride and phosgene are subjected to separation, and the toluene obtained after separation is recovered; the phosgene materials containing ethyl chloride obtained after separation are subjected to phosgene destruction, ethyl chloride separated is neutralized by alkaline liquors, and the phosgene separated is recovered and returned back to a phosgene room.
Owner:GANSU YINGUANG CHEM IND GRP CO LTD
Ionic liquid based mixtures for gas storage and delivery
InactiveUS7563308B2Reduce solubilityIncrease temperatureOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideLiquid degasificationChemical reactionCompound (substance)
A mixture and method for the storage and delivery of a gas are disclosed herein. In one aspect, there is provided a mixture comprising: an ionic liquid comprising an anion and a cation, at least a portion of the gas that is disposed within and reversibly chemically reacted with the ionic liquid, and optionally an unreacted gas. In another aspect, there is provided a method for delivering a gas from a mixture comprising an ionic liquid and one or more gases comprising: reacting at least a portion of the gas with the ionic liquid to provide the mixture comprising a chemically reacted gas and an ionic liquid and separating the chemically reacted gas from the mixture wherein the chemically reacted gas after the separating step has substantially the same chemical identity as the chemically reacted gas prior to the reacting step.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
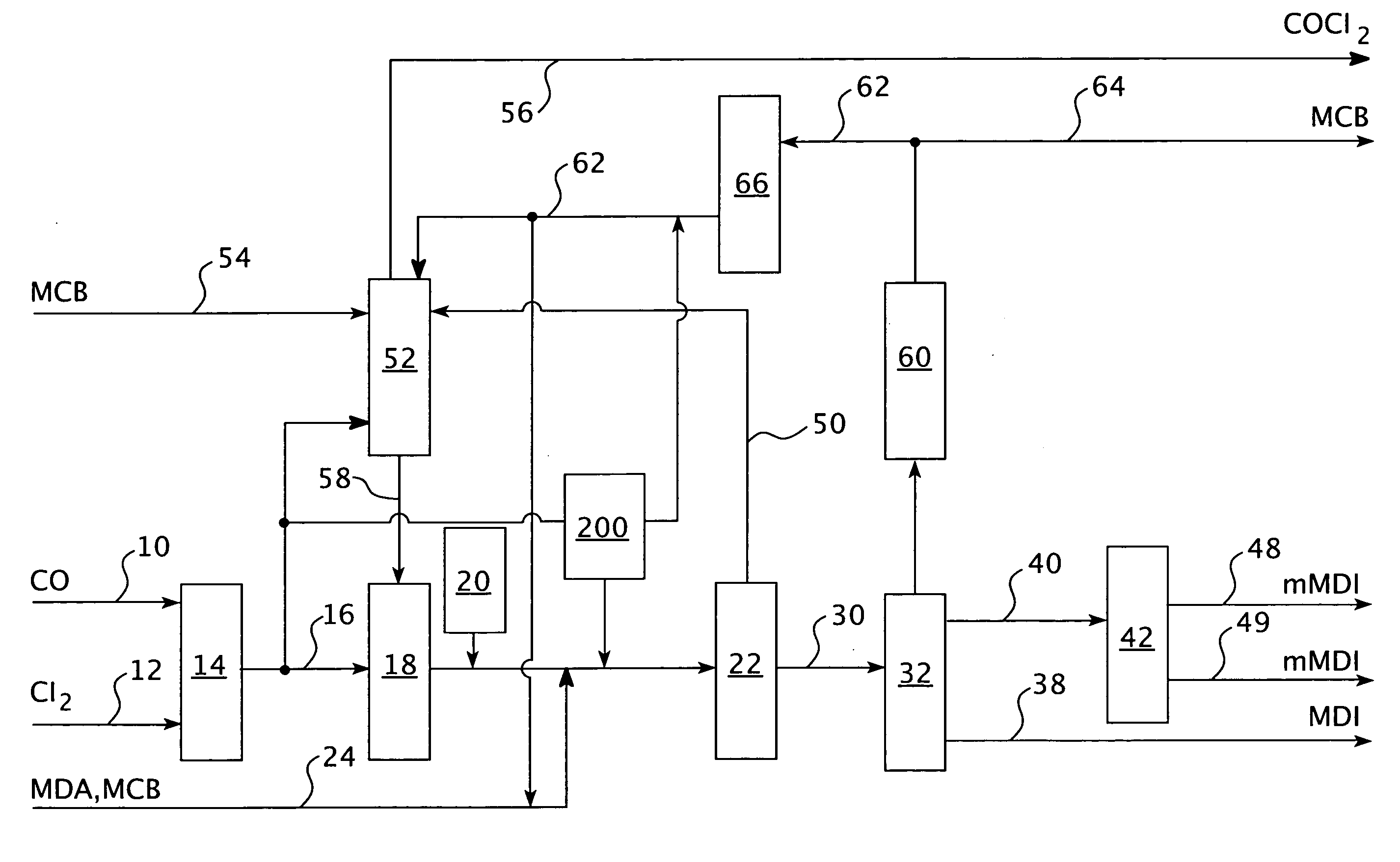
Method for producing carbonates
ActiveUS20170001943A1Heat exhanger conduitsChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsPhosgeneCarbon tetrachloride
In an embodiment, a method of producing a carbonate comprises reacting carbon monoxide and chlorine in a phosgene reactor in the presence of a catalyst to produce a first product comprising phosgene; wherein carbon tetrachloride is present in the first product in an amount of 0 to 10 ppm by volume based on the total volume of phosgene; and reacting a monohydroxy compound with the phosgene to produce the carbonate; wherein the phosgene reactor comprises a tube, a shell, and a space located between the tube and the shell; wherein the tube comprises one or more of a mini-tube section and a second tube section; a first concentric tube concentrically located in the shell; a twisted tube; an internal scaffold; and an external scaffold.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
Production technology of high purity phosgene with low hydrogen chloride content
The invention relates to a production technology of high purity phosgene with low hydrogen chloride content. The production technology comprises the following operation steps: the mixed gas with rich phosgene, unreacted excessive carbon monoxide and other impurities enters at least one rectifying tower, the top of each rectifying tower is provided with a fractional condenser, the liquid phase is used for refluxing, most of hydrogen chloride is discharged from the top of the rectifying tower along with CO and high purity phosgene is obtained at the bottom of the rectifying tower; and the gas discharged from the top of the rectifying tower passes through at least one absorption tower to wash away and recycle phosgene. The production technology in the invention has simple process flow and low production cost and is convenient to operate; and the hydrogen chloride content of the obtained phosgene product is greatly reduced, the purity of phosgene is more than 99.90% and the obtained phosgene can be used for the products using phosgene as a raw material such as isocyanate and polycarbonate and the like.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Method for absorbing and utilizing phosgene tail gas
ActiveCN102160956ALess investmentReduce energy consumptionOrganic compound preparationDispersed particle separationHalohydrocarbonRare earth
The invention discloses a method for absorbing and utilizing phosgene tail gas. The method comprises the following steps: the phosgene tail gas generated in a phosgenation process (especially the phosgene tail gas generated in the phosgenation process with content of between 10 and 50 percent (V / V), such as the phosgene tail gas generated in the phosgenation process of diuron, chlortoluron and other products) is directly cooled and absorbed through a halohydrocarbon solvent, phosgene and partial hydrogen chloride in the phosgene tail gas are recovered to obtain a phosgene tail gas solution; the phosgene tail gas solution is used as a phosgene raw material for synthesizing pesticide intermediate or acyl chloride chemical products in the action of a composite catalyst; and the composite catalyst contains at least one pyridine or bipyridyl and Lewis acid salt of at least one rare-earth metal. Compared with other methods, the solvent cooling direct absorption method has the advantages of less investment, low energy consumption, convenience in operation and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU KUAIDA AGROCHEM
Method for preparing isocyanate via reaction distillation method
InactiveCN104892458ALower side discharge temperatureIncrease operating loadChlorine/hydrogen-chloride purificationOrganic compound preparationReactive distillationPhysical chemistry
The invention belongs to the technical field of isocyanate preparation and relates to a method for preparing isocyanate via a reaction distillation method. The method includes that amine reacts with liquid phosgene to prepare the isocyanate, the amine and the liquid phosgene are in cold reaction in a jet reactor firstly prior to entering a reactive distillation column to be subjected to thermal reaction for preparing crude isocyanate, meanwhile excessive phosgene and a by-product HCL (hydrogen chloride) gas are separated by distillation, and the phosgene and the HCL gas are refined prior to recycling. The method is simple in technique, convenient to operate, capable of separating the by-product in time, energy saving, low in cost, high in efficiency and environment friendly.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Method for producing carbonyl chloride
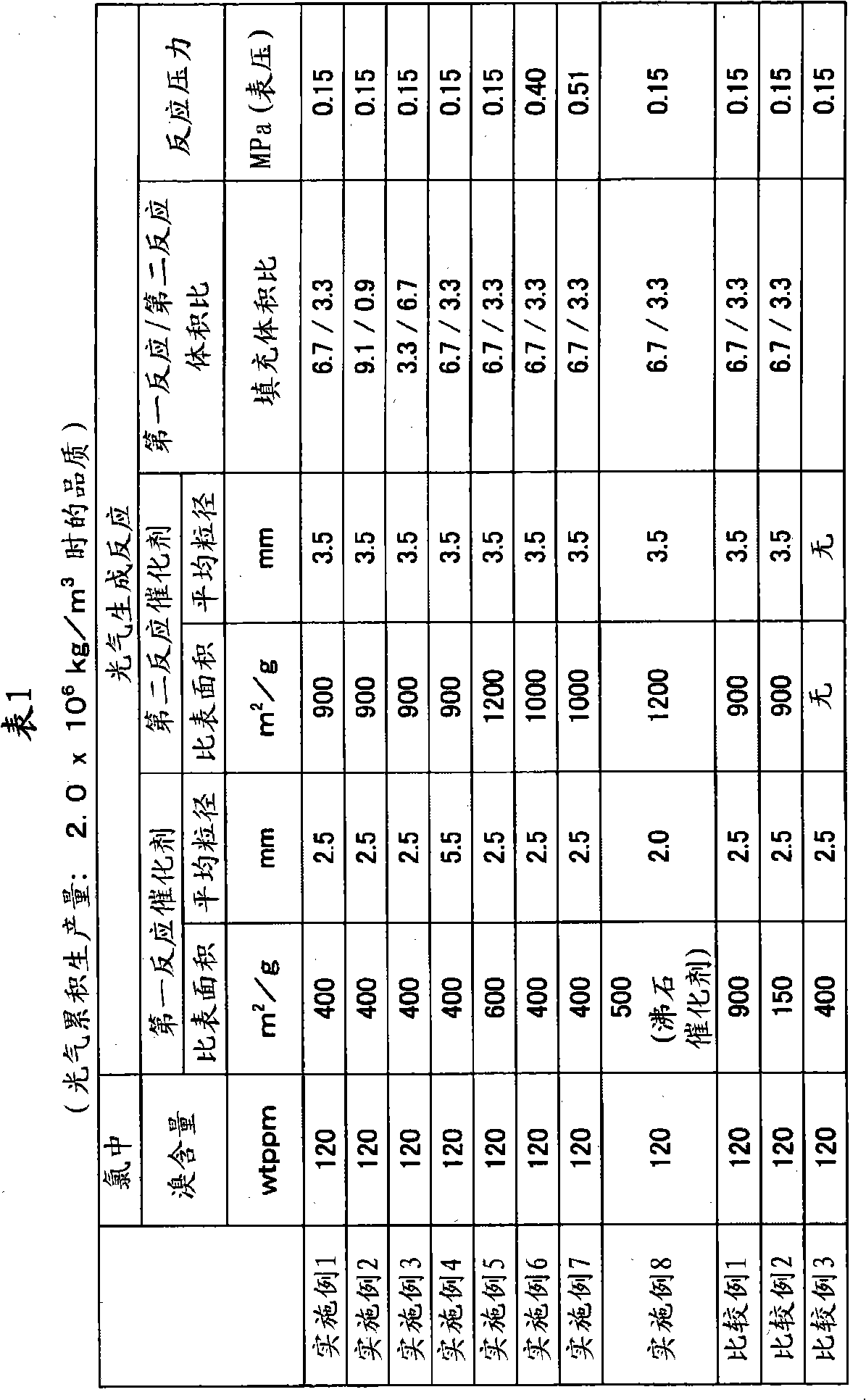
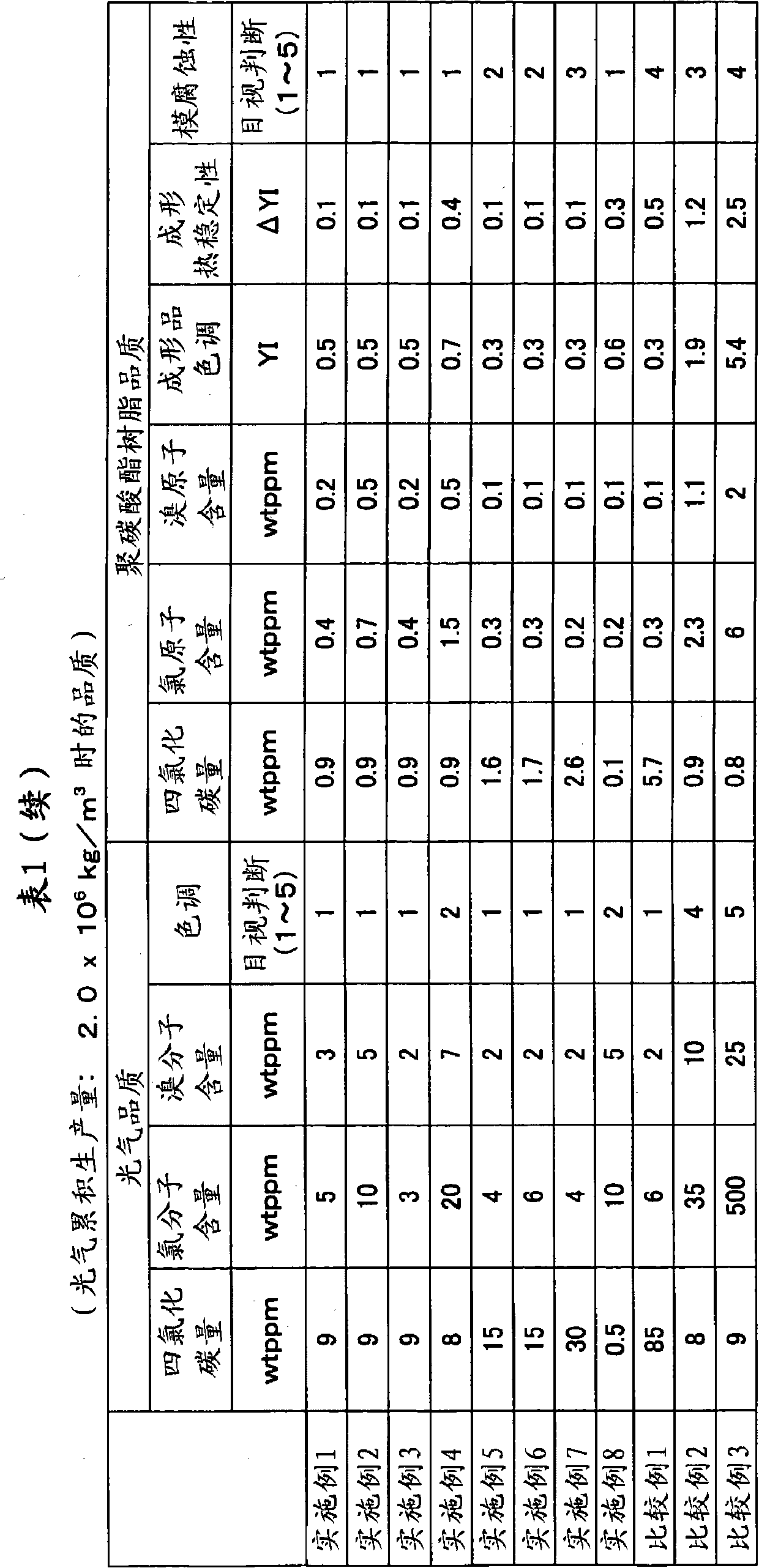
Provided are a method for producing carbonyl chloride which has few impurities and a good hue, and a method for producing polycarbonate resins which contain little metal-corroding material, have an excellent hue, and have excellent thermal stability when moulded. The method for producing carbonyl chloride containing small amounts of carbon tetrachloride, molecular chlorine and molecular bromine includes a process (i) wherein chlorine and carbon monoxide are brought into contact with a first catalyst having a specific surface area of 200 to 800 m2 / g and a second process (ii) wherein the product obtained in (i) is brought into contact with a second catalyst having a specific surface area of 800 to 1,500 m2 / g. A method for producing polycarbonate resin using the carbonyl chloride obtained is also included.
Owner:TEIJIN KASEK KK
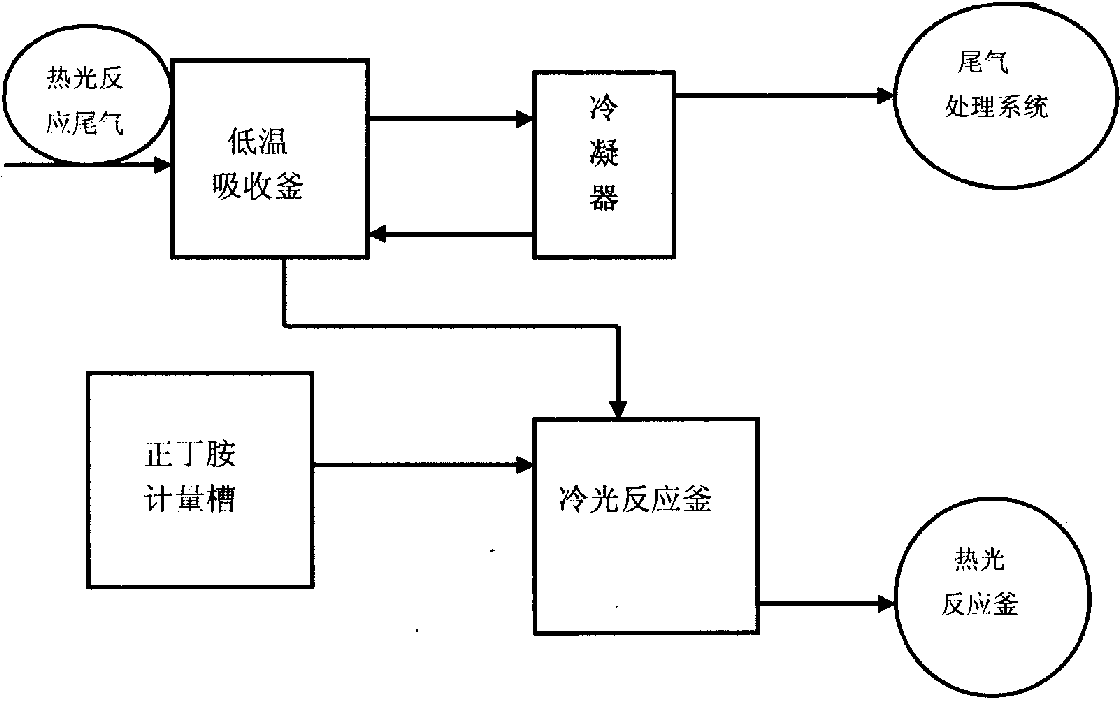
Recycling method for phosgene in tail gas generated in calorescence reaction for synthesizing normal-butyl isocyanate
ActiveCN103638688ATake advantage ofMaximize utilizationDispersed particle separationVapor condensationCalorescenceN-butylisocyanide
The invention relates to a recycling method for phosgene in tail gas generated in calorescence reaction for synthesizing normal-butyl isocyanate. The recycling method comprises the steps of continuously cooling and absorbing the tail gas generated in the calorescence reaction for synthesizing the normal-butyl isocyanate through a low temperature solvent, and condensing the tail gas through a condenser, wherein the non-condensing gas directly enters a tail gas processing system; preparing normal-butyl acyl chloride from the solvent containing the phosgene with certain quality concentration through cold light reaction, metering the phosgene-containing solvent, shifting the solvent into a cold light kettle, dropwise adding n-butylamine at -8 DEG C to -2 DEG C, after the dropwise adding, keeping the temperature for 1 hour so as to obtain the n-butylamine acyl chloride; and resolving the n-butylamine acyl chloride in a calorescence reaction kettle to obtain the normal-butyl isocyanate. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the phosgene is utilized to the greatest extent, the load of the tail gas generated in the normal-butyl isocyanate calorescence reaction in a tail gas processing system and the alkali charge during tail gas processing are reduced, the production cost of the product is reduced, and the purpose of saving and recycling resources is achieved.
Owner:HUNAN GOFAR FINE CHEM IND TECH CO LDT
Carbonyl fluoride purifying method
ActiveCN103303894AHigh purityEfficient separationPhosgeneFractional distillationCarbonyl fluorideChemical industry
The invention relates to a carbonyl fluoride purifying method and belongs to the technical field of fluorine chemical industry and electronic industry gases. The purifying method comprises the following steps of: firstly, performing light component removal and heavy component removal treatment on the crude product gas of COF2, wherein during the light component removal treatment, the temperature at the bottom of a purifying device ranges from -112 to 48 DEG C, the pressure at the bottom ranges from 0.01 to 0.6 MPa, and the temperature of the top is 0.5-30 DEG C lower than that of the bottom, during the heavy component removal treatment, the temperature at the bottom of the purifying device ranges from minus 81 to 80 DEG C, the pressure at the bottom ranges from 0.01 to 0.6 MPa, and the temperature of the top is 0.5-30 DEG C lower than that of the bottom; then obtaining an initial refined mixed gas; performing secondary refining purification, wherein the temperature at the bottom of the purifying device ranges from minus 123 to 36 DEG C, the pressure at the bottom ranges from 0.01 to 1.03 MPa, and the temperature of the top is 0.2-45 DEG C lower than that of the bottom; then obtaining the purified gas. The purifying method is especially suitable for the crude product gas of COF2 high in CO2 content; the COF2 purity in the purified gas is greater than or equal to 99%, and the CO2 content therein is less than 1000 ppm.
Owner:PERIC SPECIAL GASES CO LTD
Phosgene removing method for TDI production
InactiveCN101348446AReduce loadReduced amount of phosgeneIsocyanic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationHigh pressureTower
A phosgene removal method used for manufacturing TDI relates to a method for removing poisonous gas from a gas-liquid mixture. The method comprises the following steps that a reaction liquid which contains TDI, a solvent isophthalic acid diethylester and superfluous phosgene and is discharged from a phosgenation reactor undergoes high-pressure phosgene removal treatment at first and then undergoes low-pressure phosgene removal treatment; moreover, the reaction liquid is reheated during low-pressure phosgene removal treatment so as to reboil the phosgene; then, the reaction liquid enters a negative-pressure phosgene removal stage so as to remove the phosgene in the material through negative-pressure phosgene removal treatment; and finally, final product TDI can be obtained after the reaction liquid is treated by a residue removal tower and a solvent removal tower.
Owner:GANSU YINGUANG CHEM IND GRP CO LTD
Process for controlling a production process
InactiveUS20080147208A1Process control/regulationSampled-variable control systemsProcess engineeringIsocyanate
A production process such as an isocyanate production process, conducted with a production facility having (a) at least two incoming streams, b) at least one exit stream and c) at least one inner recycling stream is controlled by adjusting at least one incoming stream amount by means of regulating controls to control the exit stream concentration and / or amount.
Owner:BAYER MATERIALSCIENCE AG
Processes for preparing low-chlorine isocyanates
ActiveUS20090054684A1Lower Level RequirementsIsocyanic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationReaction zonePhosgene
Processes comprising providing an amine reactant, and reacting the amine reactant with a stream of phosgene in a reaction zone to form a product comprising a corresponding isocyanate, wherein the phosgene stream has a CO content of 0.5% by weight or more.
Owner:COVESTRO DEUTSCHLAND AG
Processes for separating carbon monoxide from a hydrogen chloride-containing gas
InactiveUS20070276158A1Reduce needReduce riskChlorine/hydrogen-chloride purificationGas treatmentHydrogen chloridePhosgene
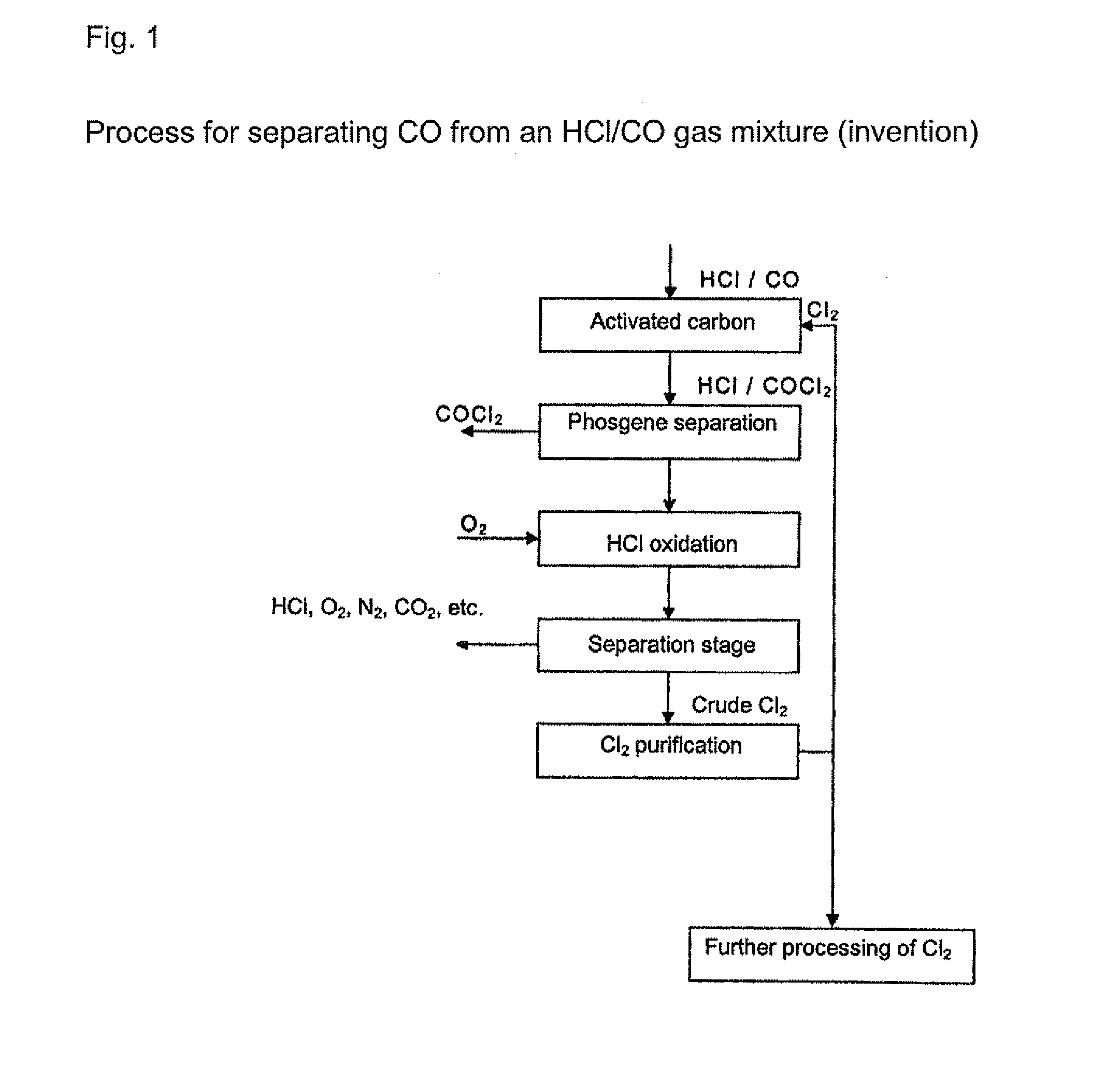
Processes for separating carbon monoxide from a hydrogen chloride-containing gas, which comprise reacting the carbon monoxide with chlorine to form phosgene and then optionally separating the phosgene from the hydrogen chloride-containing gas. The hydrogen chloride-containing gas that is used preferably derives from a phosgenation or isocyanate forming reaction.
Owner:BAYER MATERIALSCIENCE AG
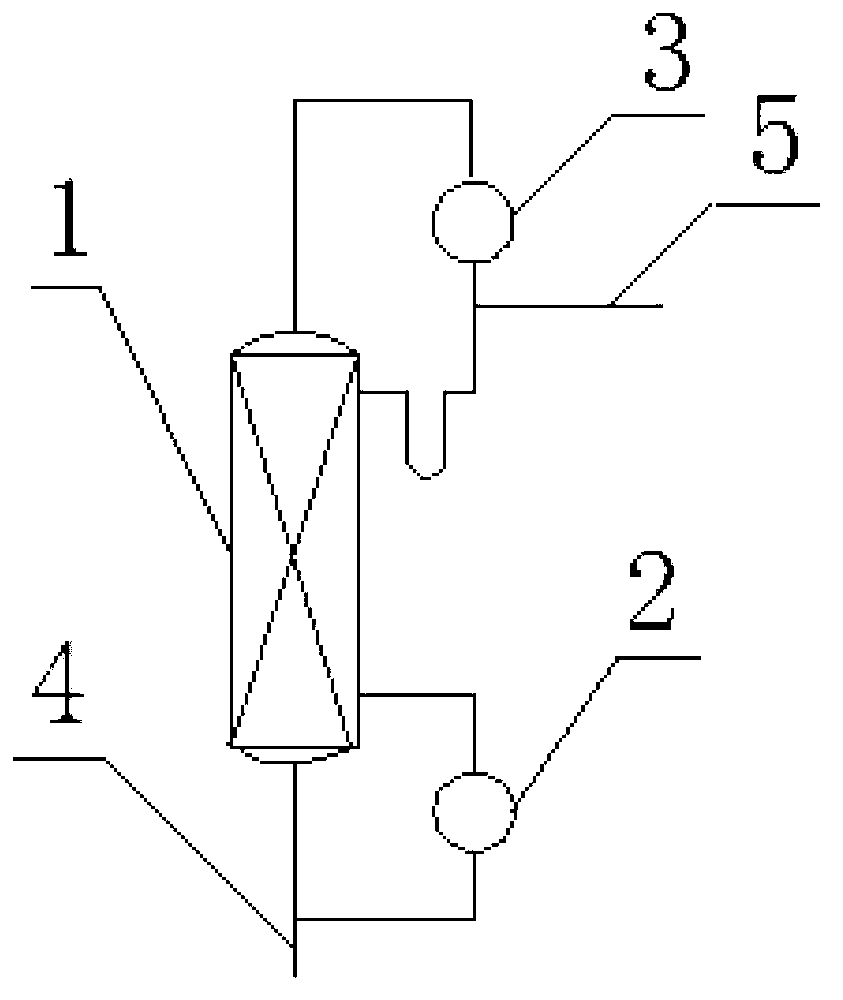
Method and apparatus for producing high purity phosgene
InactiveUS20160207779A1Organic compound preparationIndirect heat exchangersParticulatesConductive materials
In an embodiment, a method of producing phosgene in a tube reactor comprises introducing a feed comprising carbon monoxide and chlorine to a tube of the reactor, the tube having a particulate catalyst disposed therein, wherein a thermally conductive material separate from the tube contacts at least a portion of the particulate catalyst; to produce a product composition comprising phosgene, and carbon tetrachloride in an amount of 0 to 10 ppm by volume based on the volume of the phosgene.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
Process for the production of diaryl carbonates and treatment of alkalichloride solutions resulting therefrom
Processes comprising: (a) reacting phosgene and a monohydroxyl aryl compound in the presence of a suitable catalyst to form a diaryl carbonate and a solution comprising an alkali chloride; (b) separating the diaryl carbonate from the solution; (c) adjusting the pH of the solution to a value of less than or equal to 8 to form a pH-adjusted solution; (d) treating the pH-adjusted solution with an adsorbent to form a treated solution; (e) subjecting at least a portion of the treated solution to electrochemical oxidation to form chlorine and an alkali hydroxide solution; and (f) recycling at leasta portion of one or both of the chlorine and the alkali hydroxide solution.
Owner:BAYER MATERIALSCIENCE AG
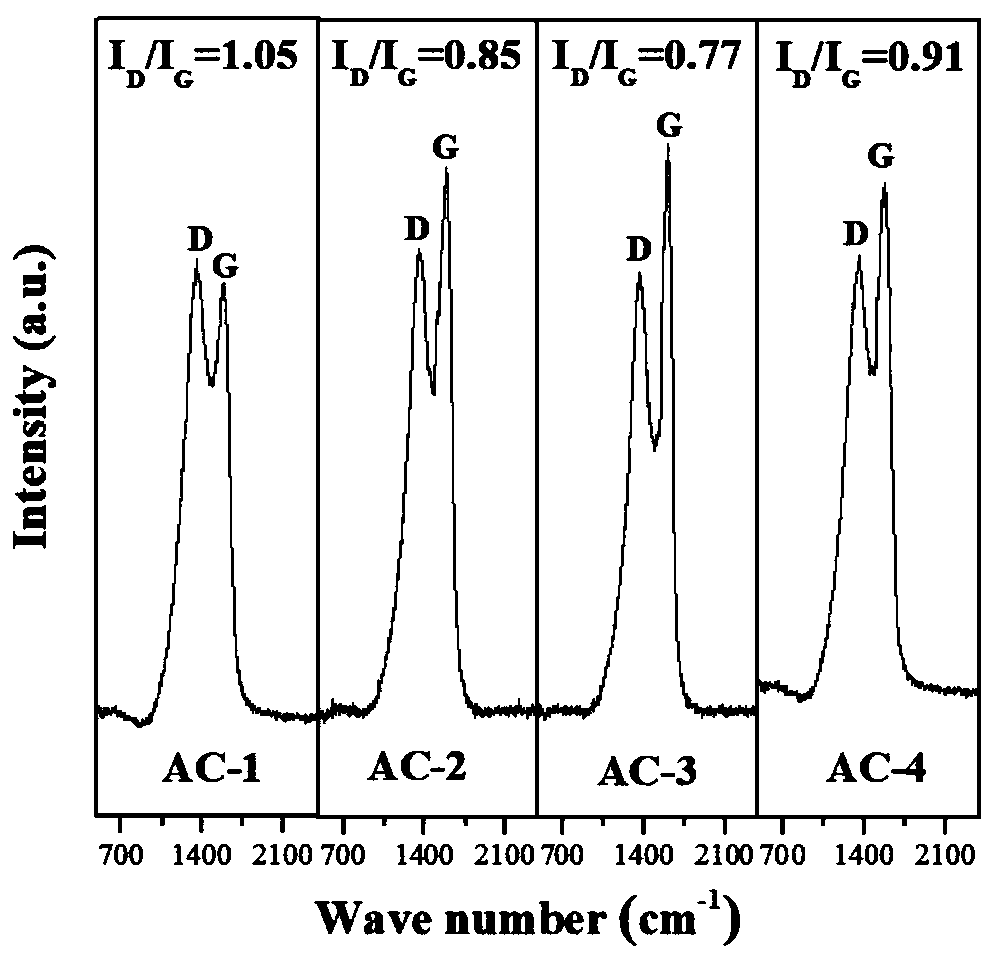
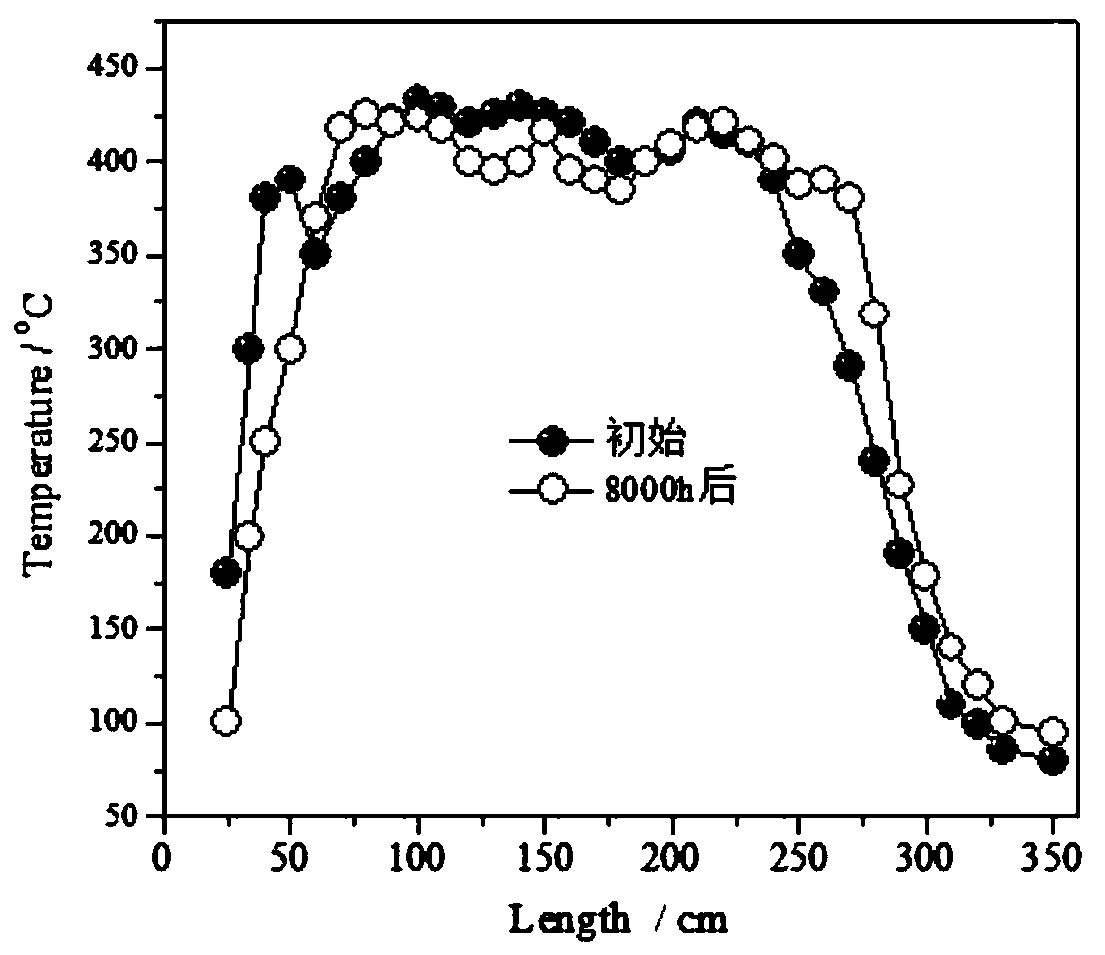
Catalyst for phosgene synthesis, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110449147AHigh activityImprove thermal conductivityPhosgeneMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsSynthesis methodsCarbon nanotube
The invention relates to a catalyst for phosgene synthesis, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The active components of the catalyst include activated carbon and carbon nanotubes, the intensity ratio of the graphitization degree of the activated carbon in the D band to the G band in Raman spectroscopy is 0.6-1.0, and the specific surface area is greater than 800 m<2> / g; and the thermal conduction coefficient of the catalyst is greater than 1 W.m<-1>.K<-1>. The preparation method of the catalyst is simple. The activated carbon and carbon nanotubes are treated by using a nitricacid solution of bismuth nitrate to obtain carbon nanotubes and activated carbon which are connected by chemical bonds, and the catalyst has the advantages of high activity, high thermal conductivityand long service life. advantage. A phosgene synthesis method adopting the catalyst of the present invention makes the temperature distribution of a reactor bed uniform, so heat release in the phosgene synthesis reaction can be easily used to obtain high-quality phosgene, and the also method can effectively extend the safe and stable running cycle of a device and reduce the running and maintaining cost.
Owner:万华化学(福建)有限公司 +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com