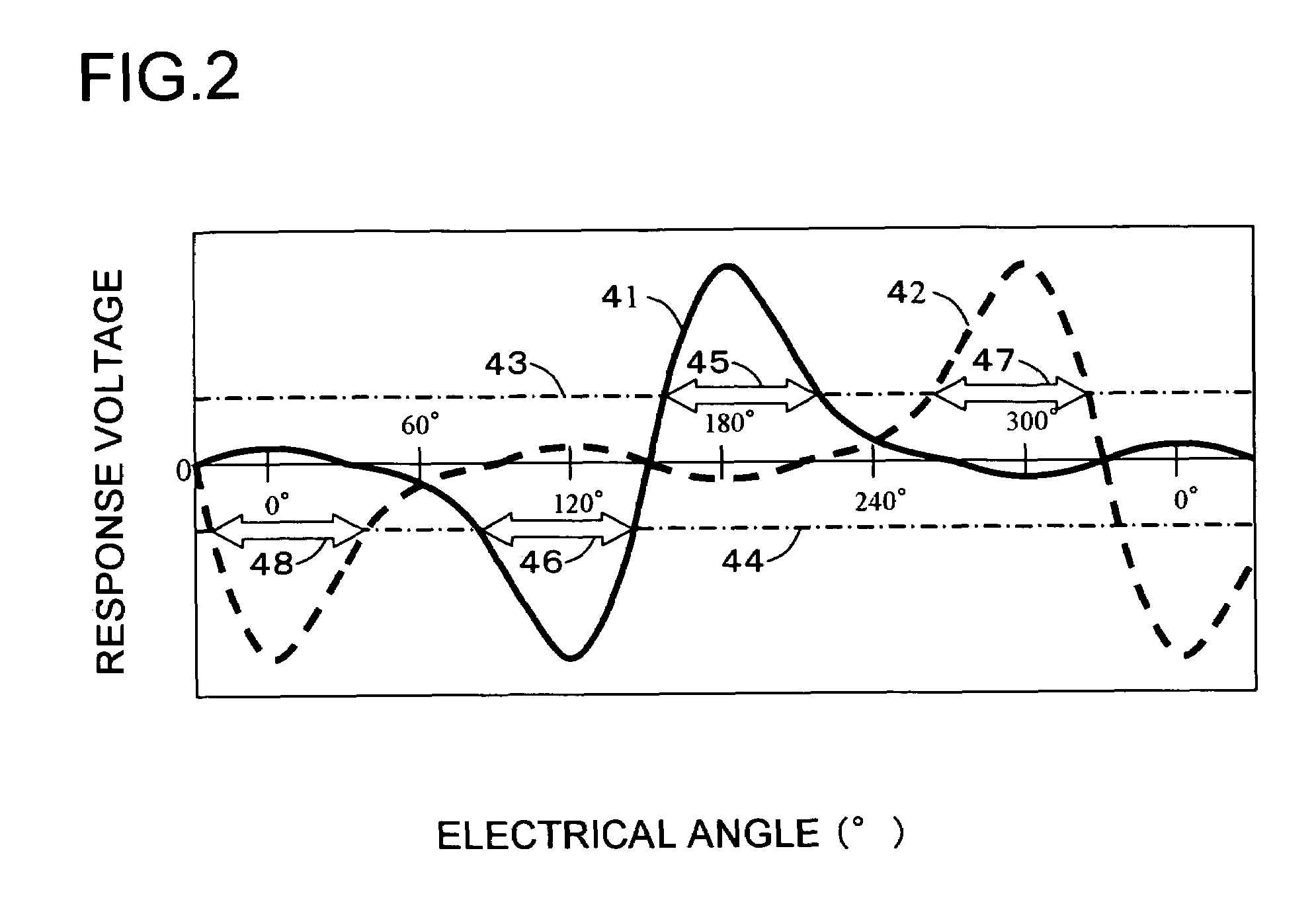
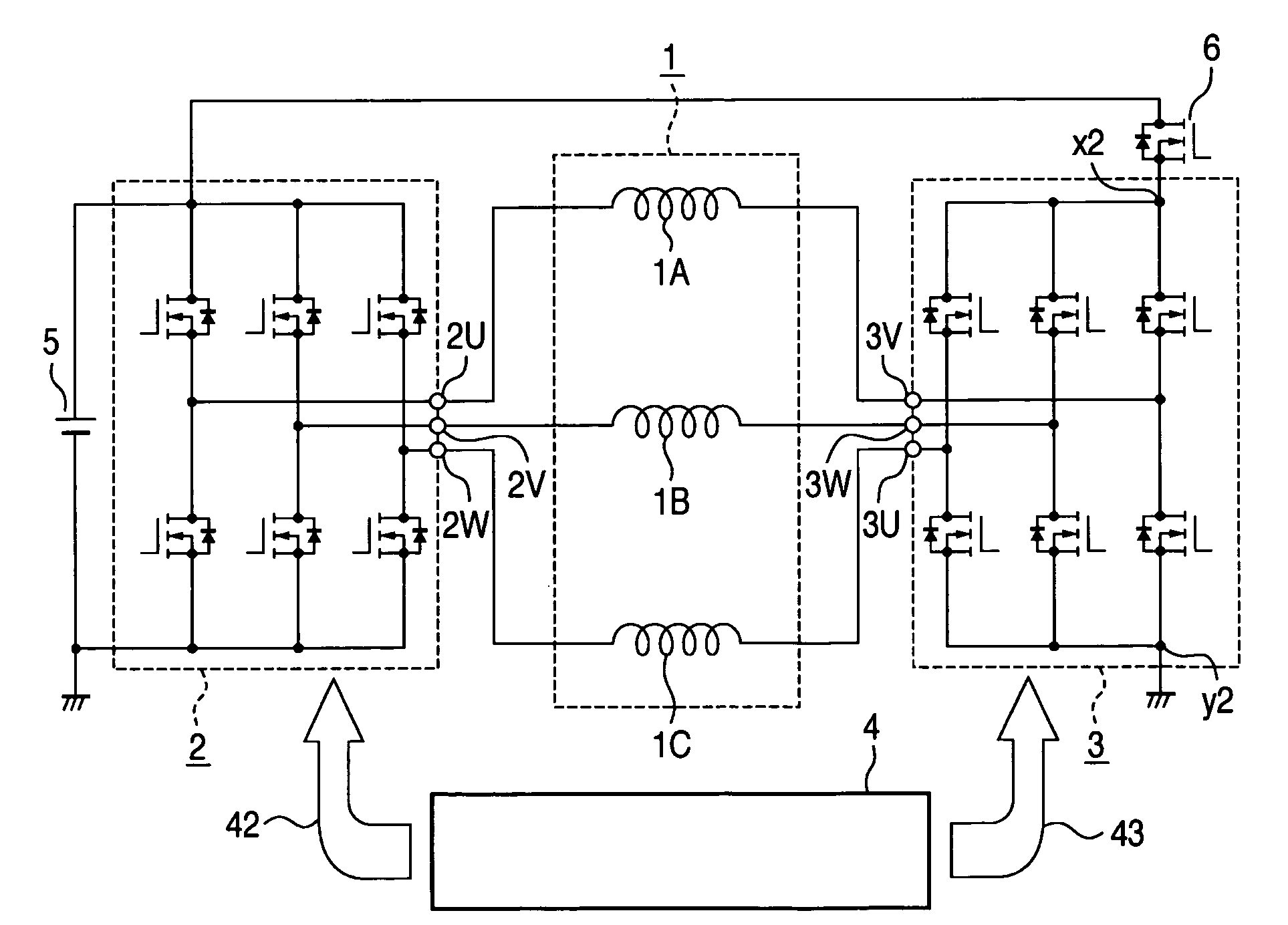
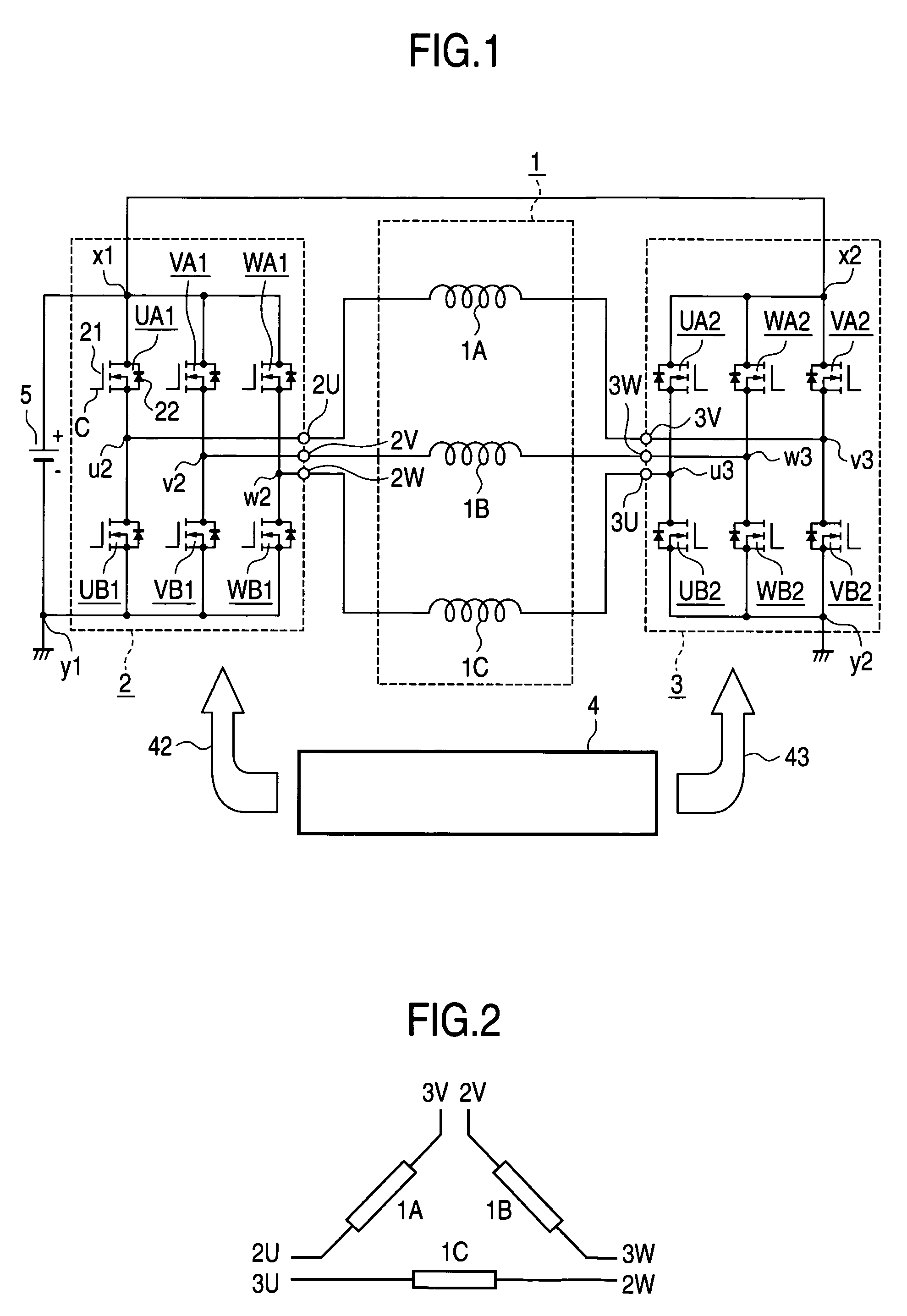
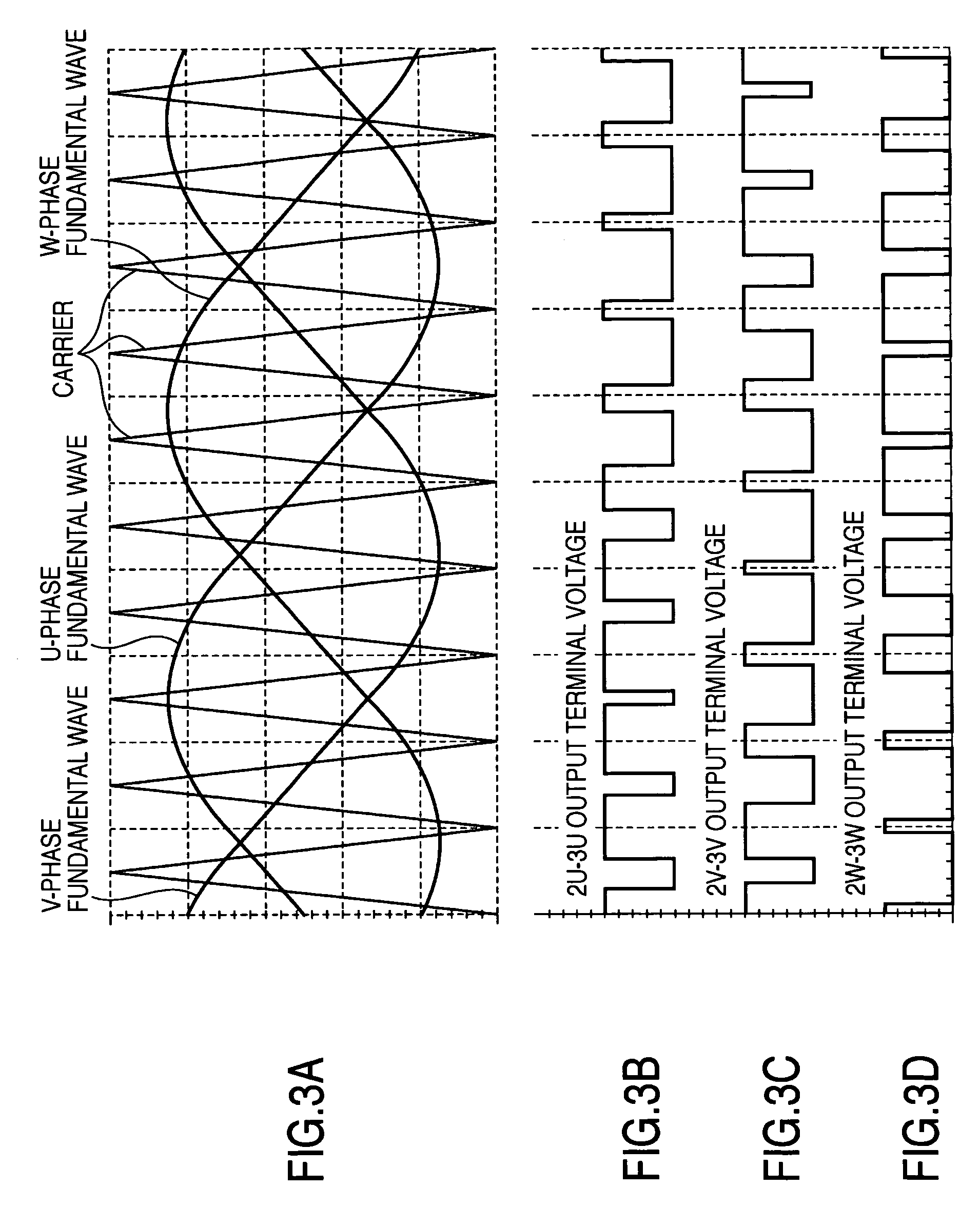
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
178results about "Motor control for very low speeds" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
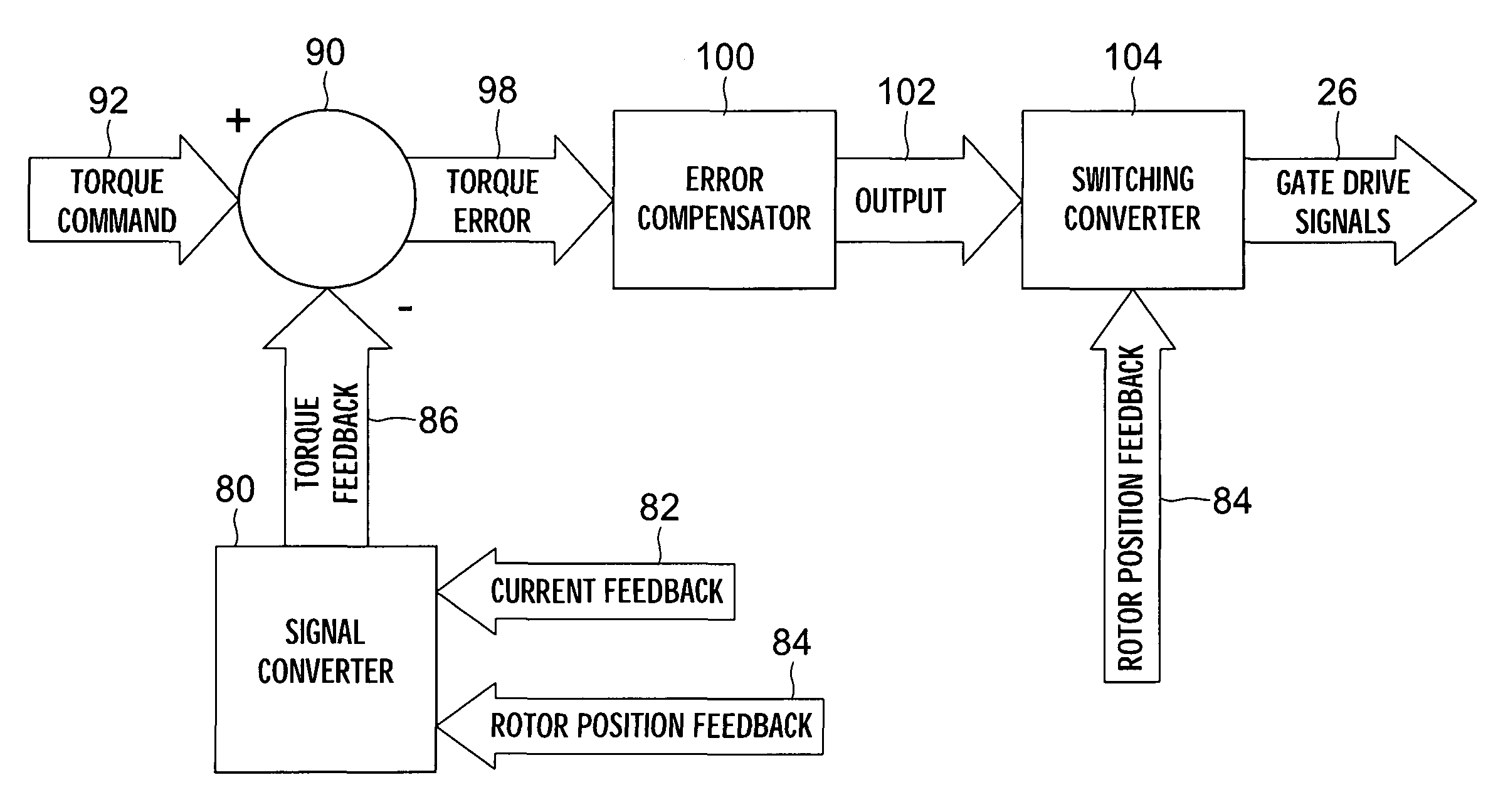
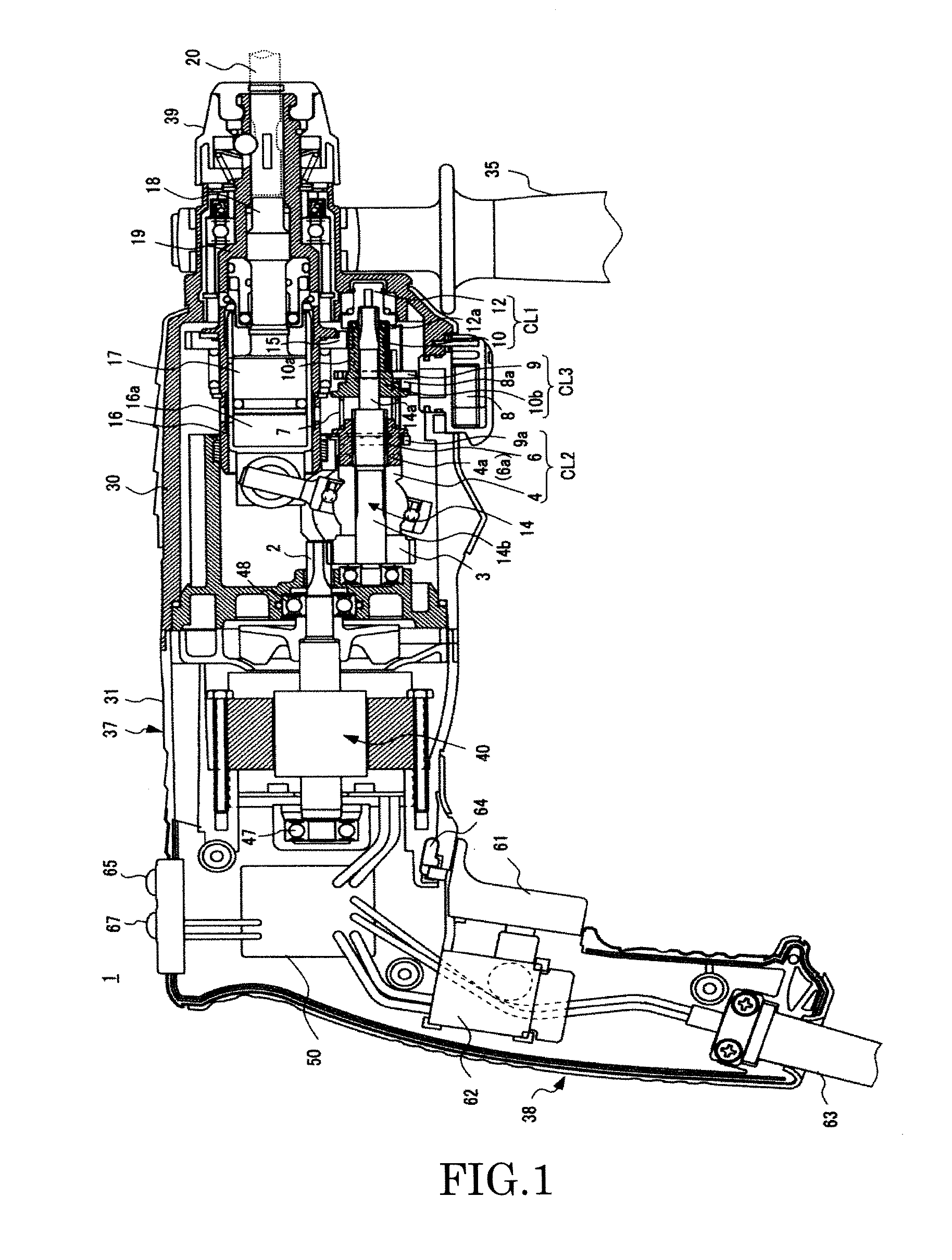
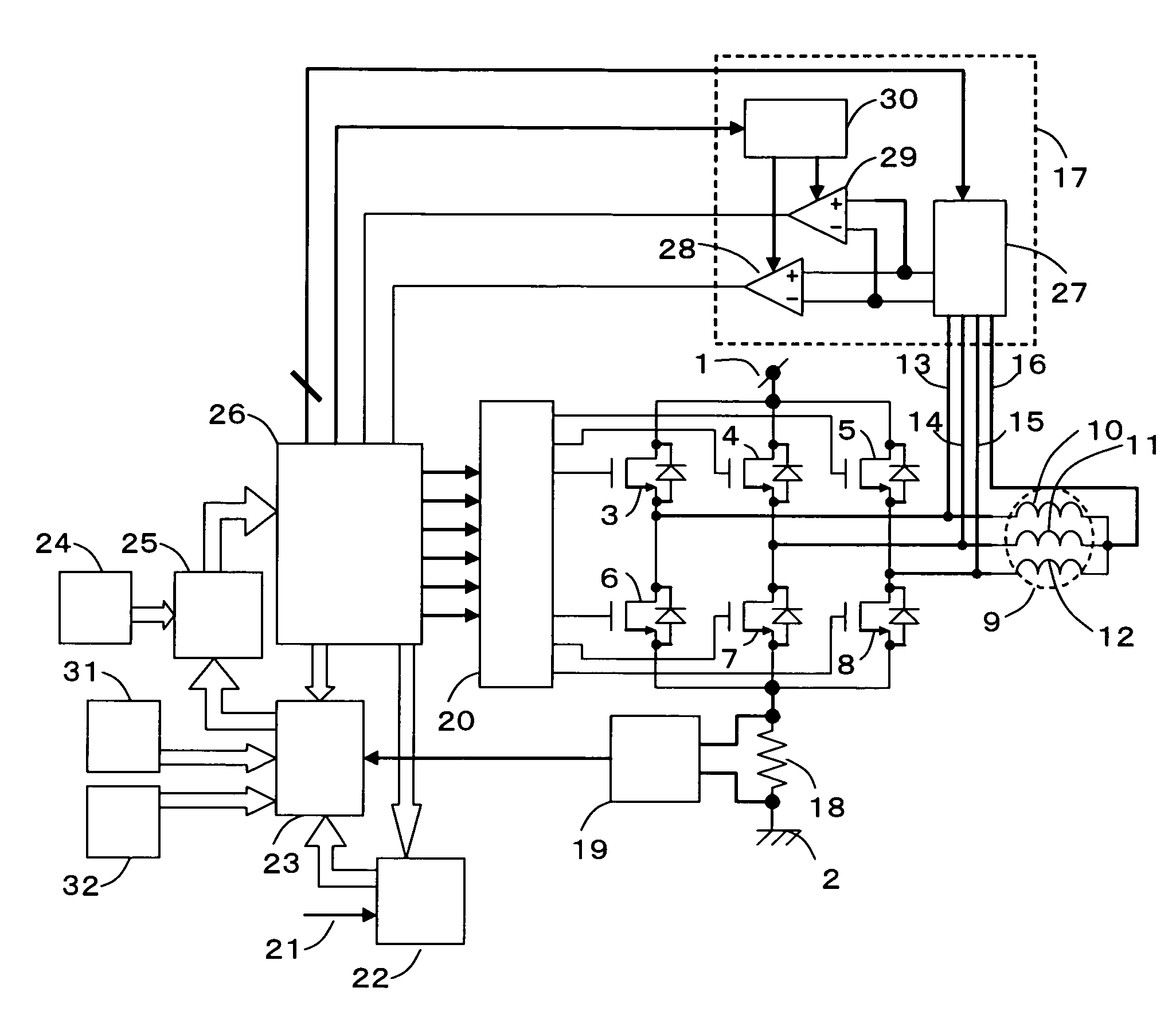
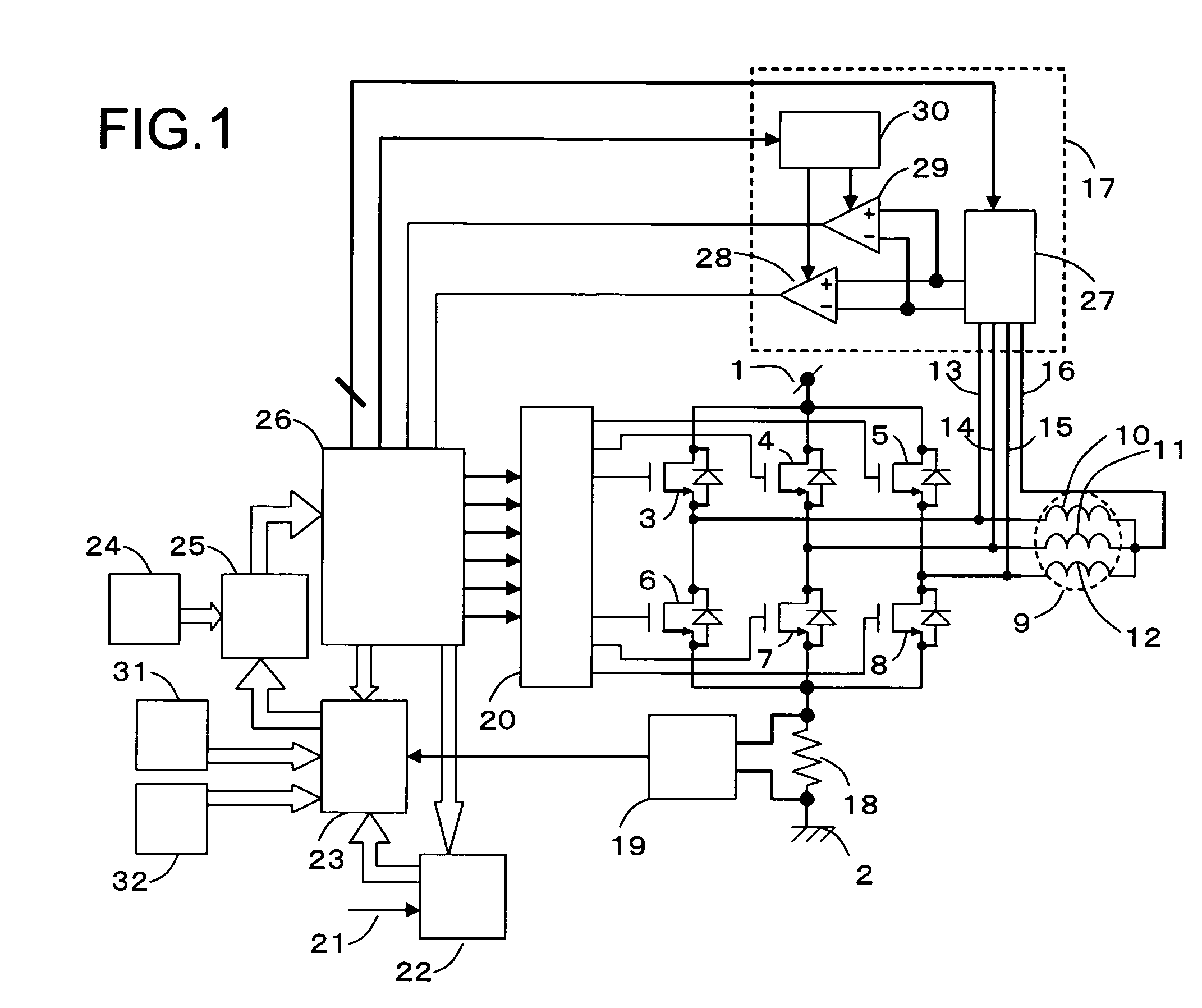
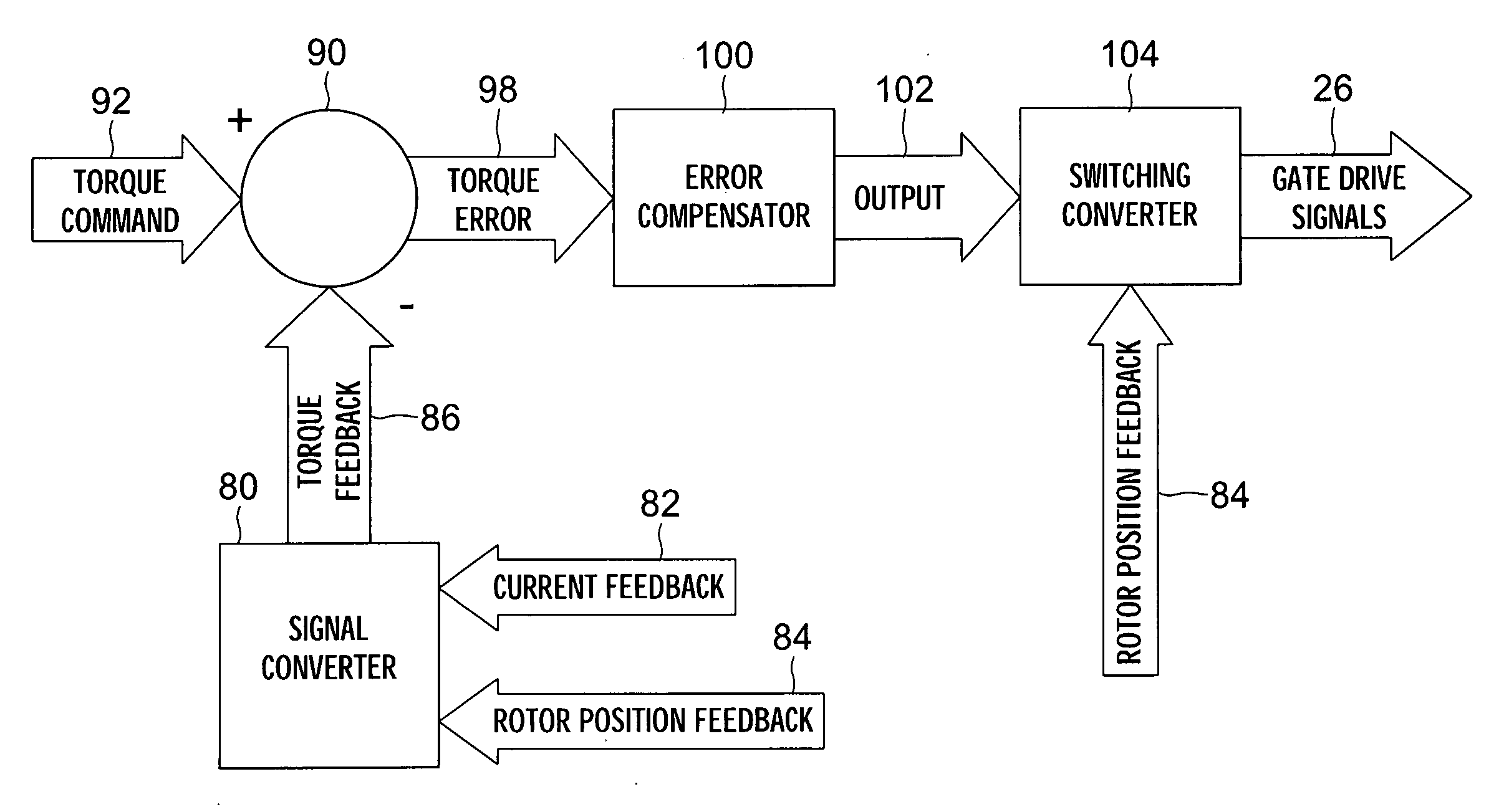
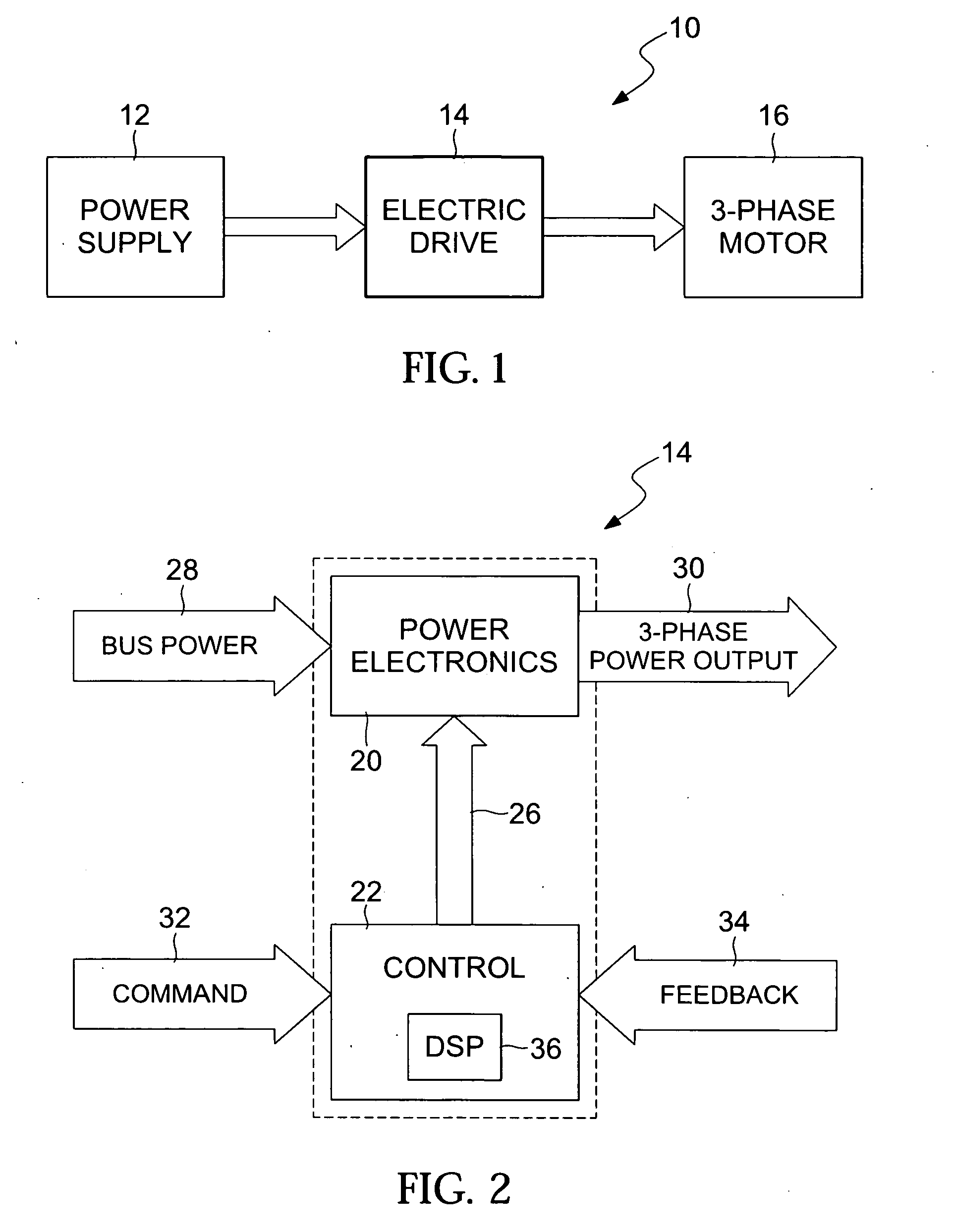
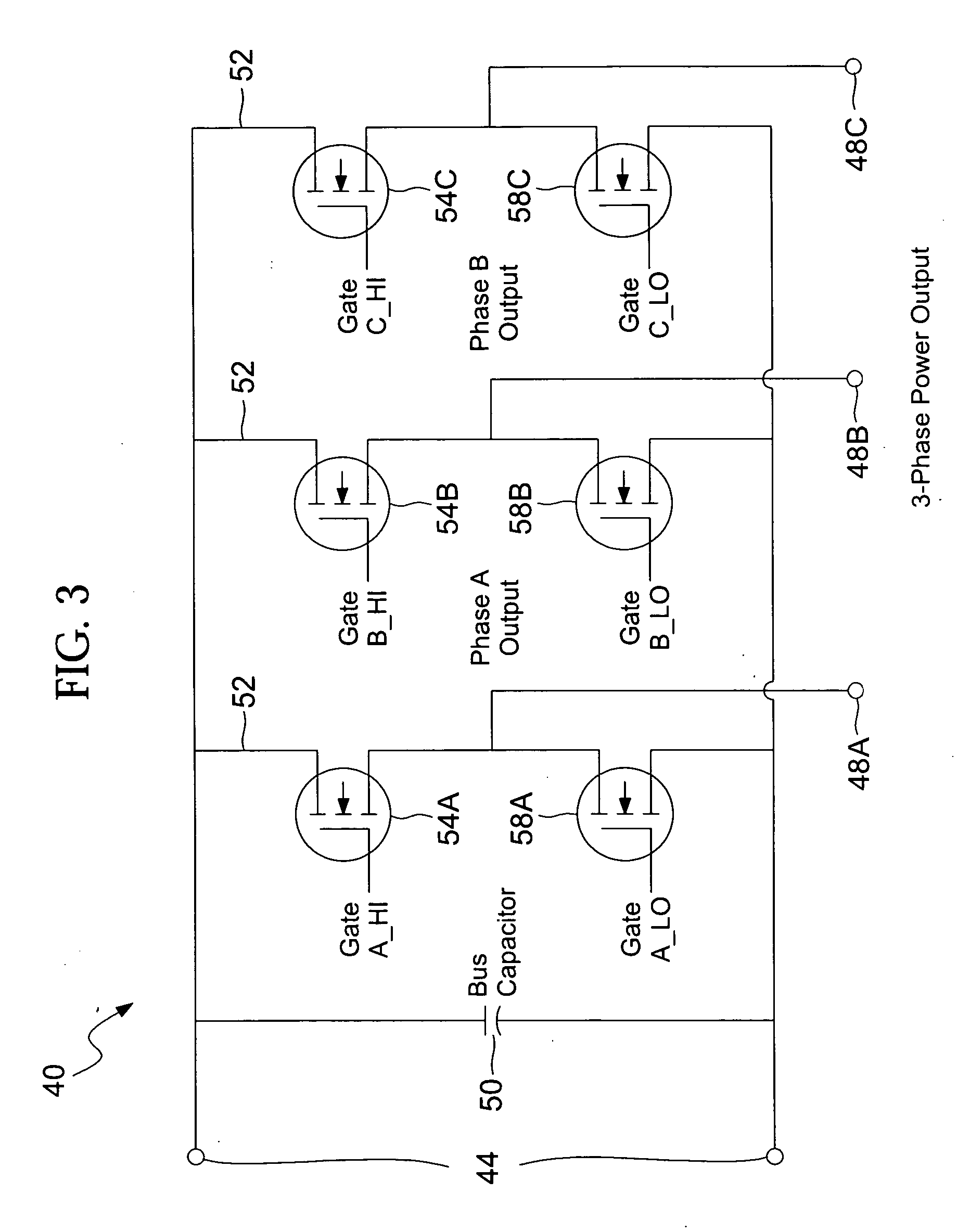
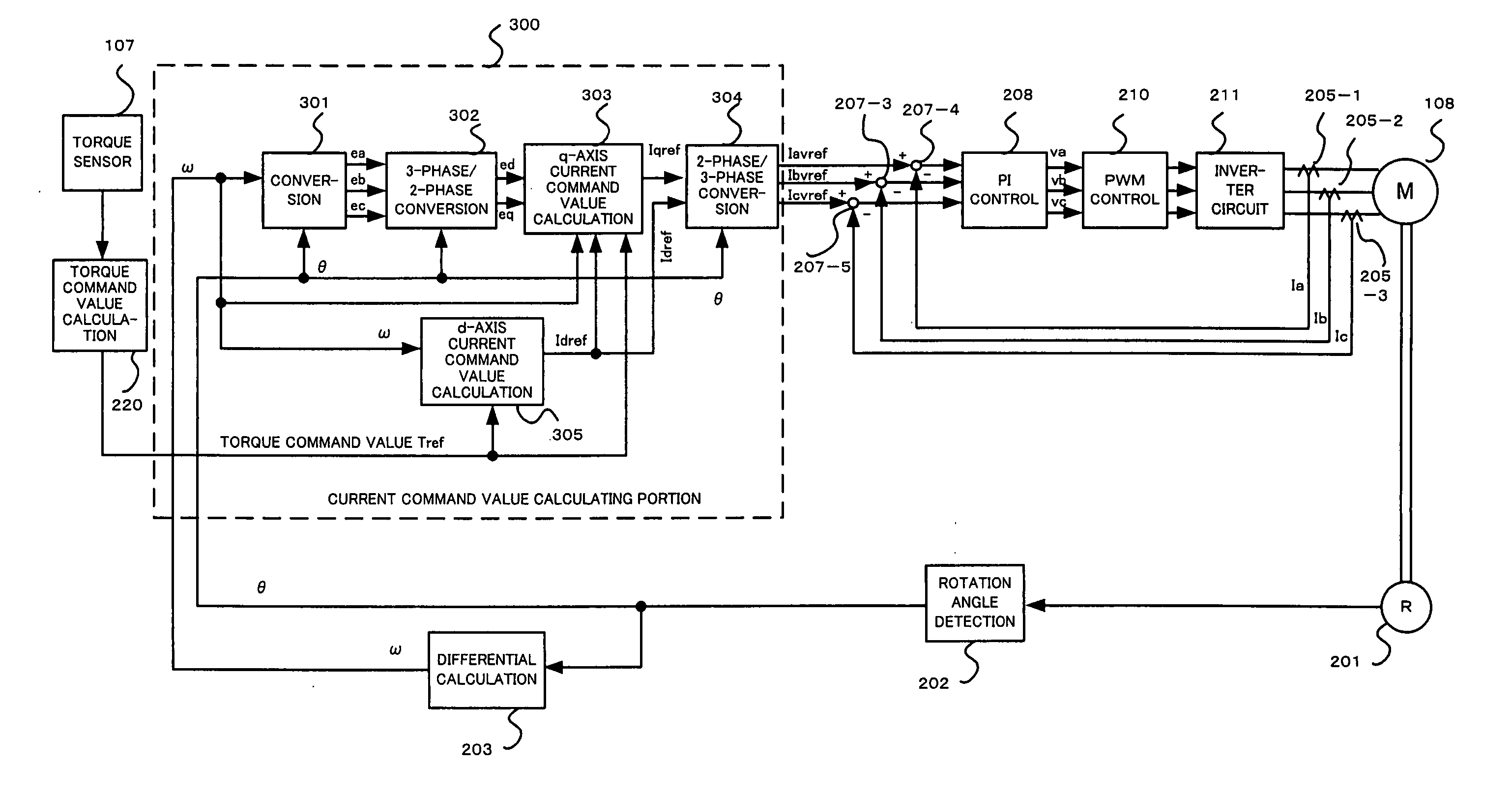
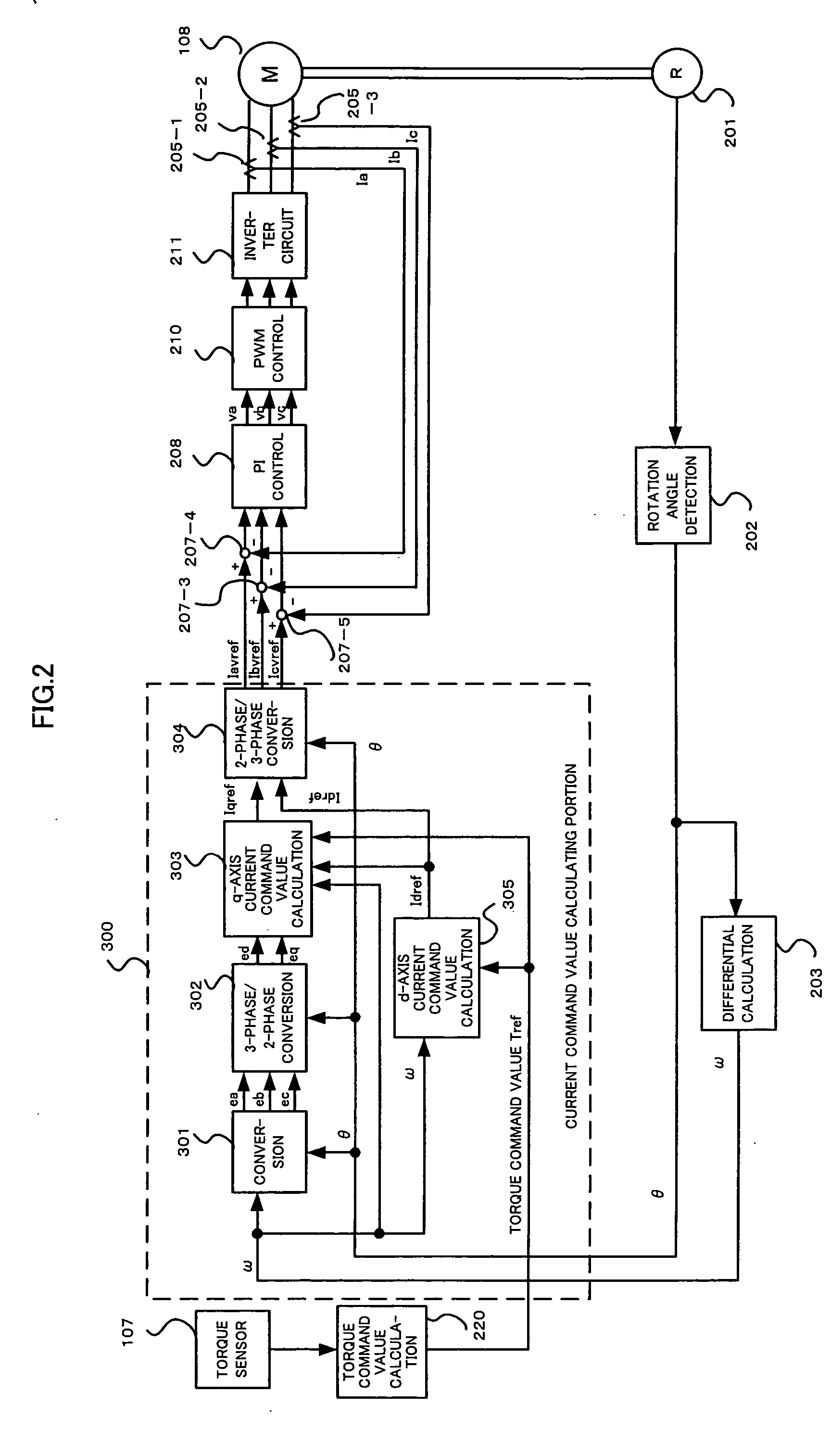
Torque controller in an electric motor
ActiveUS7898198B2Motor control for very low speedsDC motor speed/torque controlMaximum torqueSlow rotation
The torque of a motor operated by an inverter circuit is controlled to allow maximum torque in the motor when the motor is stalled or at low rotation speeds. Control is accomplished by providing a switching frequency to the motor at a first switching frequency, detecting a rotation speed of the motor, and switching the current to the motor to a second switching frequency when the rotation speed of the motor drops to a predetermined slow rotation speed. The second switching frequency is less than the first switching frequency.
Owner:DRS NETWORK & IMAGING SYST
Sensorless controller of AC motor and control method
InactiveUS7045988B2Improve efficiencyMagnetic saliency at the high frequency is reducedVector control systemsSingle motor speed/torque controlLow speedSignal on
Owner:YASKAWA DENKI KK
High-Efficiency Wheel-Motor Utilizing Molded Magnetic Flux Channels with Transverse-Flux Stator
InactiveUS20090322165A1Reducing hysteresis lossIncrease torqueMotor/generator/converter stoppersMotor control for very low speedsTransverse fluxEngineering
A motor including an outside rotor having a rotor disc with plural magnets alternating polarities flush mounted in the disc, an inside stator assembly with a ring of pole pieces forming a channel to house a transversely wound stator windings, and a controller coupled with feedback electronics for monitoring a timing, speed and direction and coupling a signal to a processing unit for adjusting the drive electronics driving the phase windings. A u-shaped gap above the channel to receive the rotor disc and focus the captured magnetic flux in the pole pieces toward the magnets. In an embodiment the molded magnetic flux channel pole pieces of the inside stator are sets of molded magnetic flux channel pole pieces, each set forming a channel and corresponding to one phase of the motor; and a section of each one of the transverse windings passing through one channel, the remaining section folding back outside the set in close proximity to the outer base of the set of molded magnetic flux channel pole pieces.
Owner:RITTENHOUSE NORMAN P
Synchronous motor driving system
InactiveUS20030052640A1DC motor speed/torque controlSynchronous motors startersSynchronous motorMagnetic poles
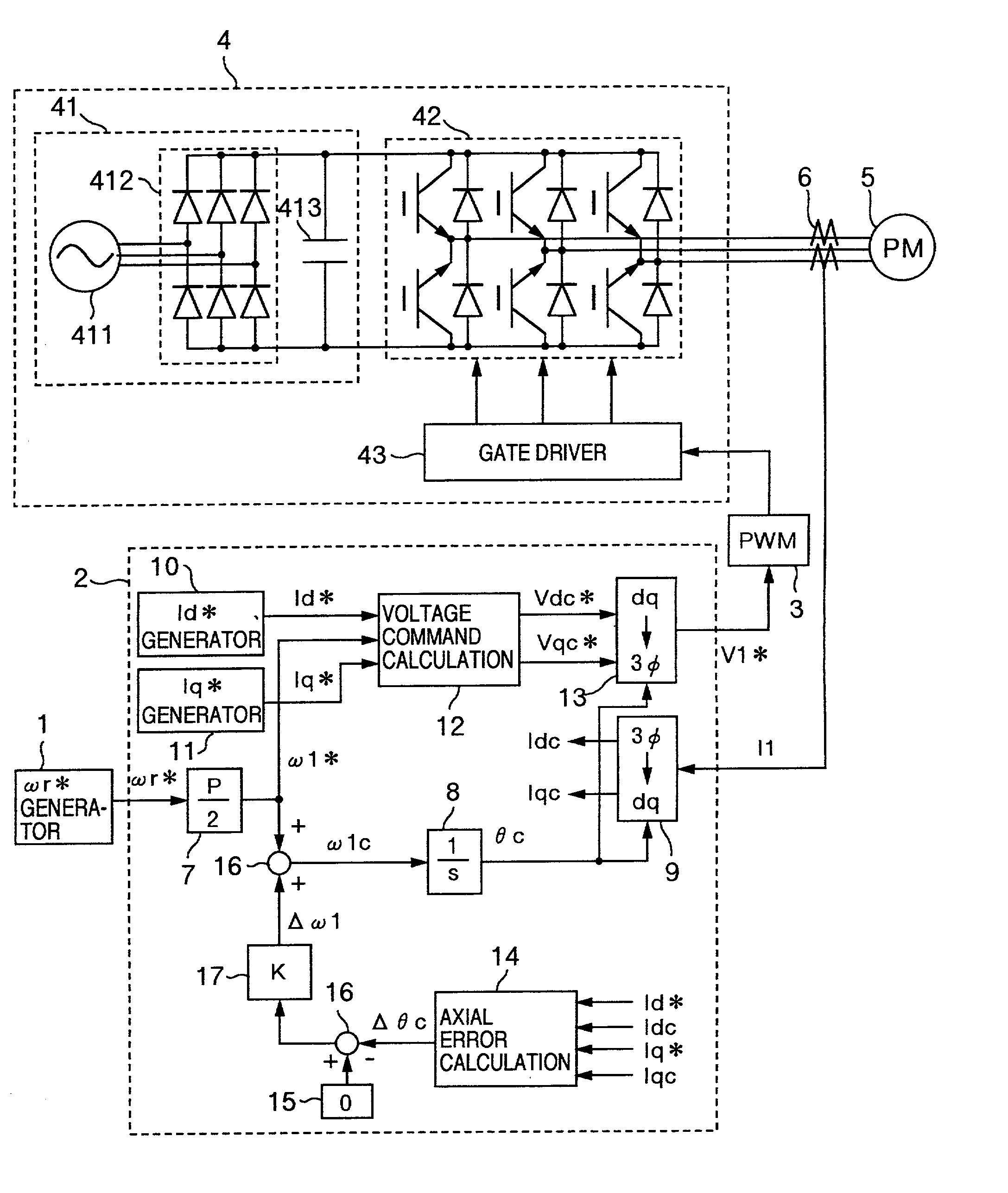
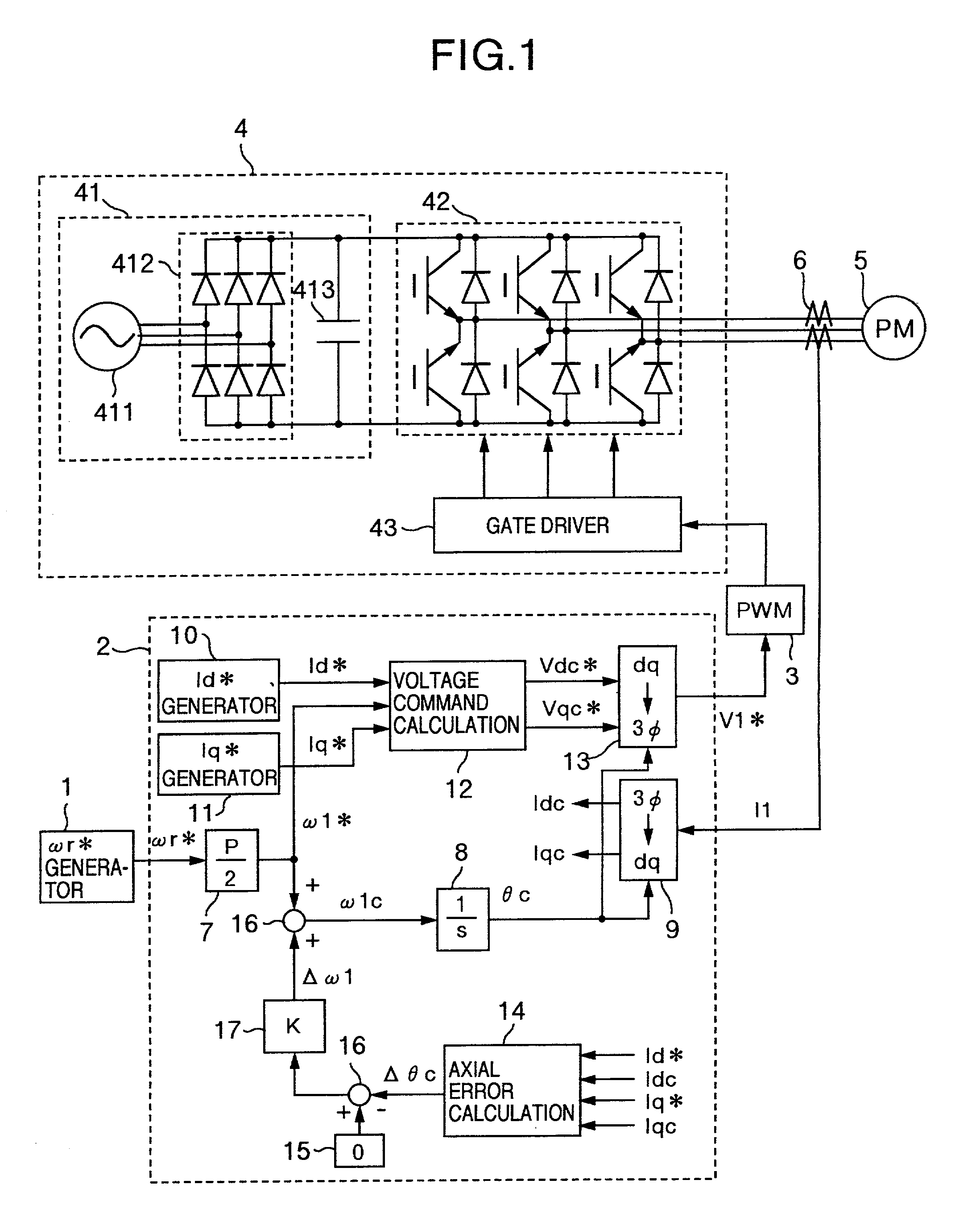
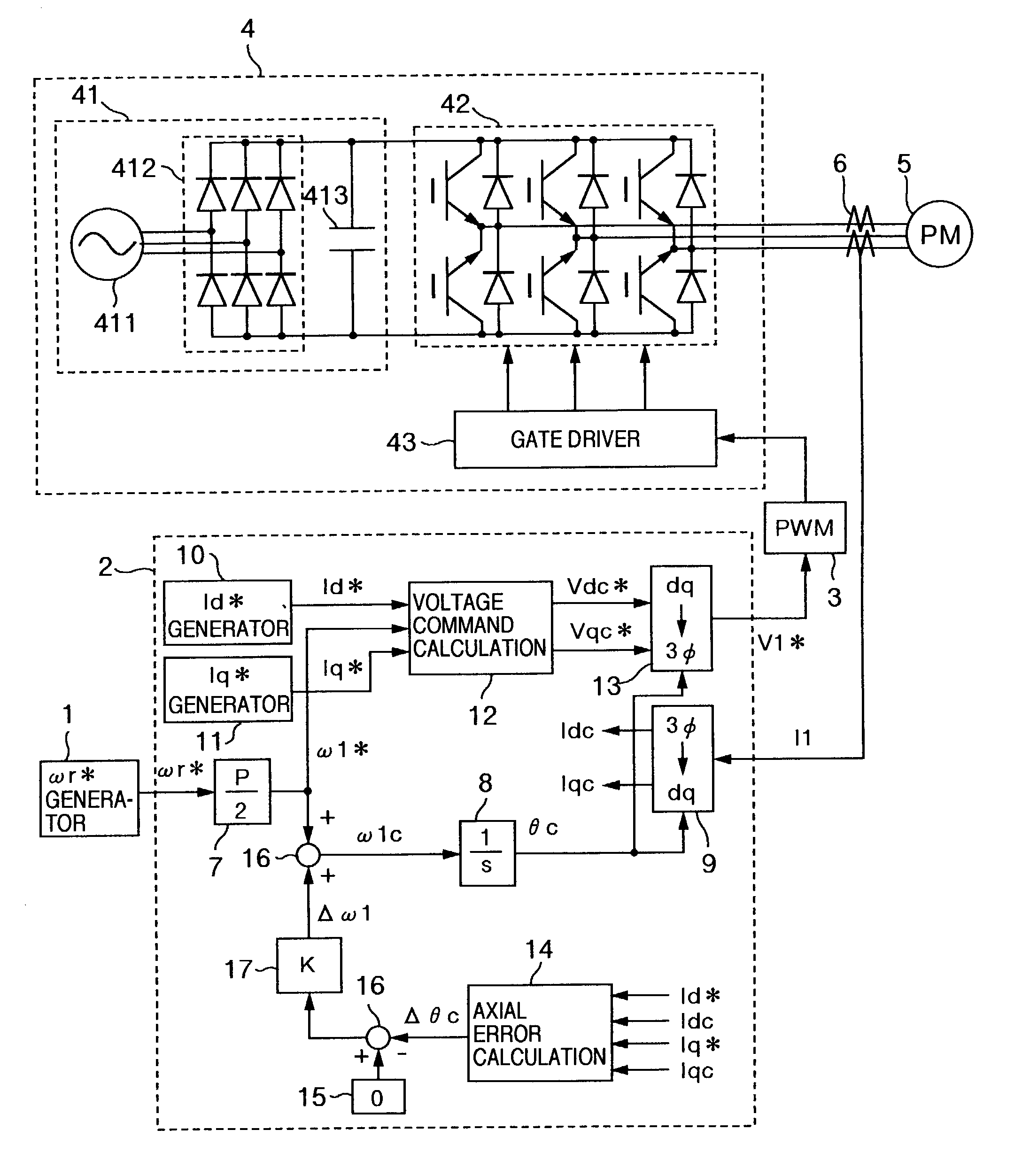
Axial error calculation unit is provided for estimating an axial error DELTAtheta between a d-q axis and a dc-qc axis by using Ld, Lq, Ke, Id*, Iq*, Idc and Iqc in a range of all rotational speeds except zero of a rotational speed command of a synchronous motor, Ld denoting an inductance on a magnetic pole axis d of the synchronous motor, Lq an inductance on a q axis orthogonal to the magnetic pole axis d, Ke a generated power constant of the motor, Id* a current command of the d axis, Iq* a current command on a q axis, Idc a detected current value on an assumed dc axis on control, and Iqc a detected current value on an assumed qc axis orthogonal to the assumed dc axis. Irrespective of presence of saliency, position sensorless control can be achieved in a wide range a low to high speed zone.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Synchronous motor driving system and sensorless control method for a synchronous motor
InactiveUS20030057912A1Synchronous motors startersDC motor speed/torque controlSynchronous motorMagnetic poles
Axial error calculation unit is provided for estimating an axial error DELTAtheta between a d-q axis and a dc-qc axis by using Ld, Lq, Ke, Id*, Iq*, Idc and Iqc in a range of all rotational speeds except zero of a rotational speed command of a synchronous motor, Ld denoting an inductance on a magnetic pole axis d of the synchronous motor, Lq an inductance on a q axis orthogonal to the magnetic pole axis d, Ke a generated power constant of the motor, Id* a current command of the d axis, Iq* a current command on a q axis, Idc a detected current value on an assumed dc axis on control, and Iqc a detected current value on an assumed qc axis orthogonal to the assumed dc axis. Irrespective of presence of saliency, position sensorless control can be achieved in a wide range a low to high speed zone.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Electric boring tool
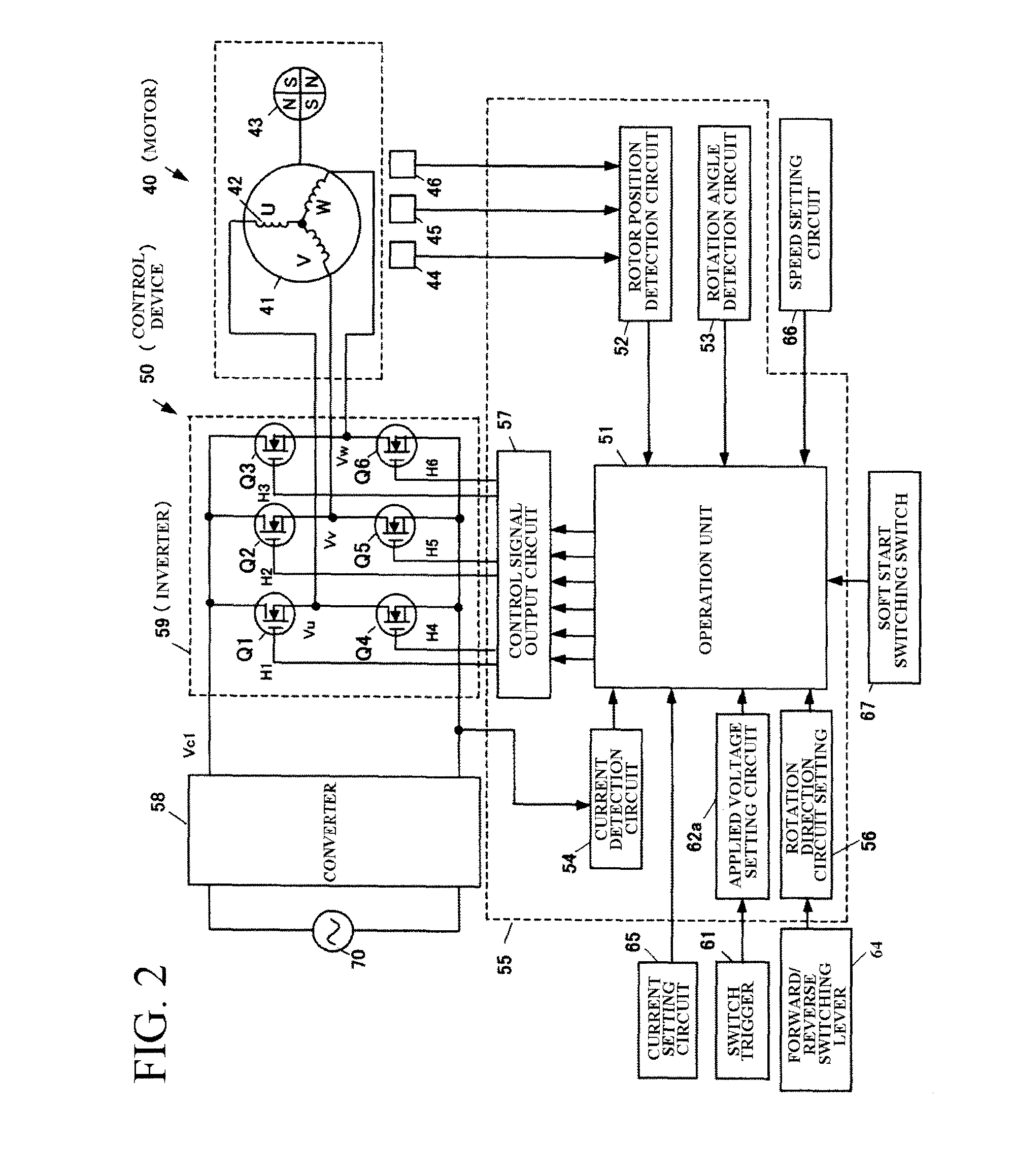
InactiveUS9314855B2Prevent and ease damageMotor control for very low speedsDC motor speed/torque controlPower flowMotor control
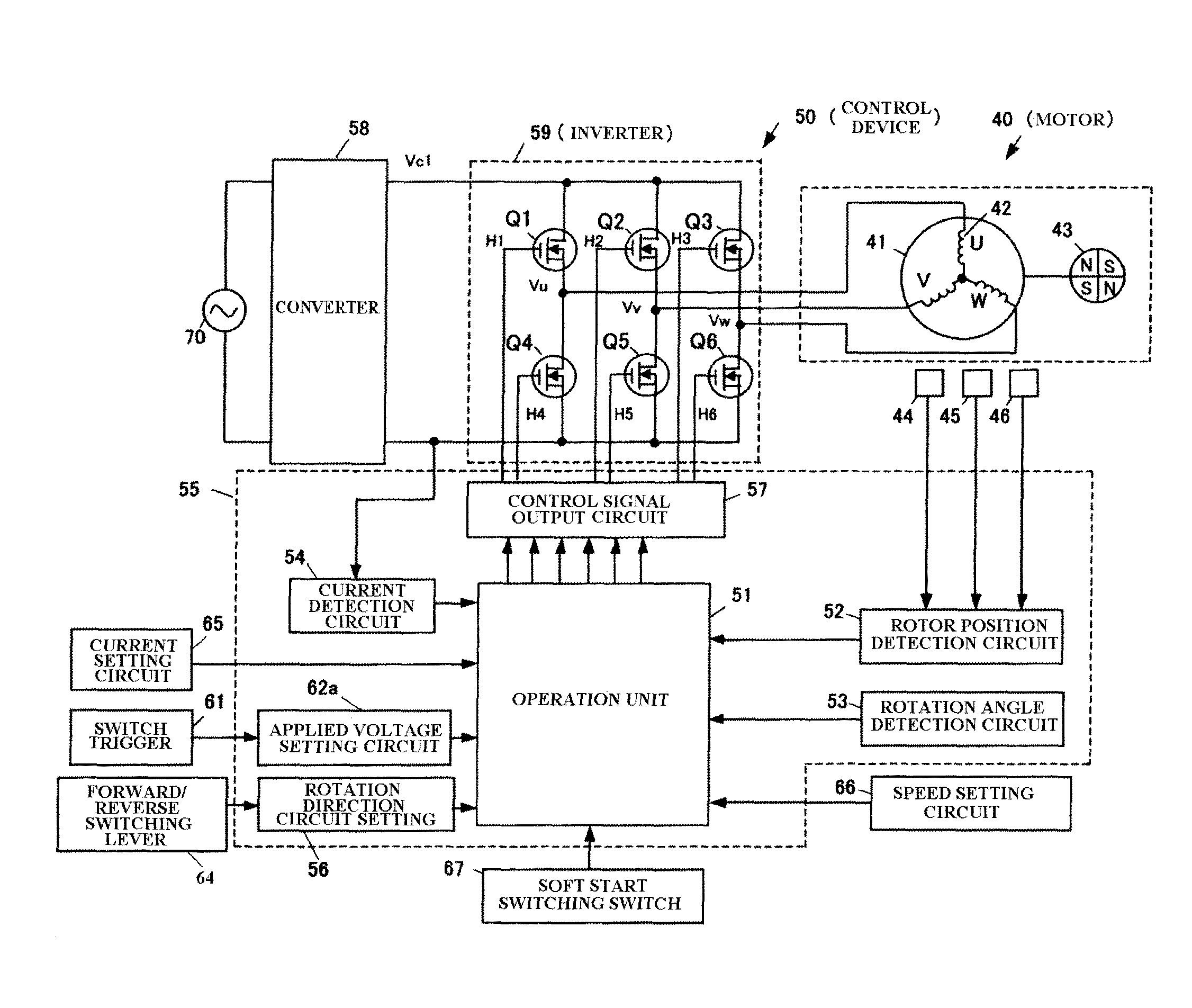
An electric boring tool comprises an electric motor, a switch trigger, a tip tool driven by driving force of the electric motor, a power transmission mechanism for transmitting the driving force of the electric motor to the tip tool as rotational force and / or hammer force, and a motor control unit for controlling speed of the electric motor in response to an extent of pulling of the switch trigger. The motor control unit subjects the electric motor to low speed control after the electric motor is started up, and controls the speed of the electric motor in response to the extent of pulling of the switch trigger when the load current of the electric motor is set value or greater during the low speed control.
Owner:KOKI HLDG CO LTD
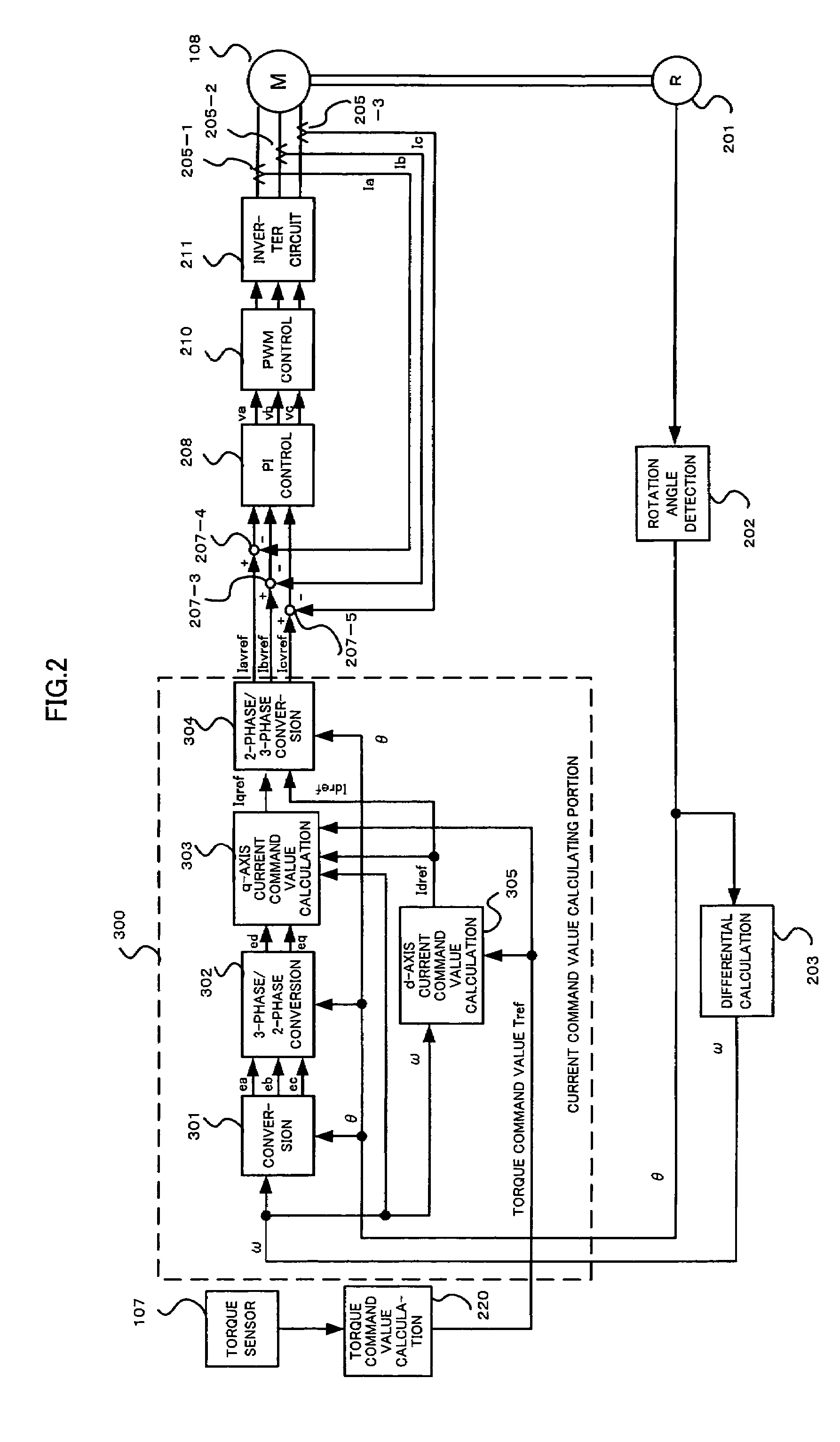
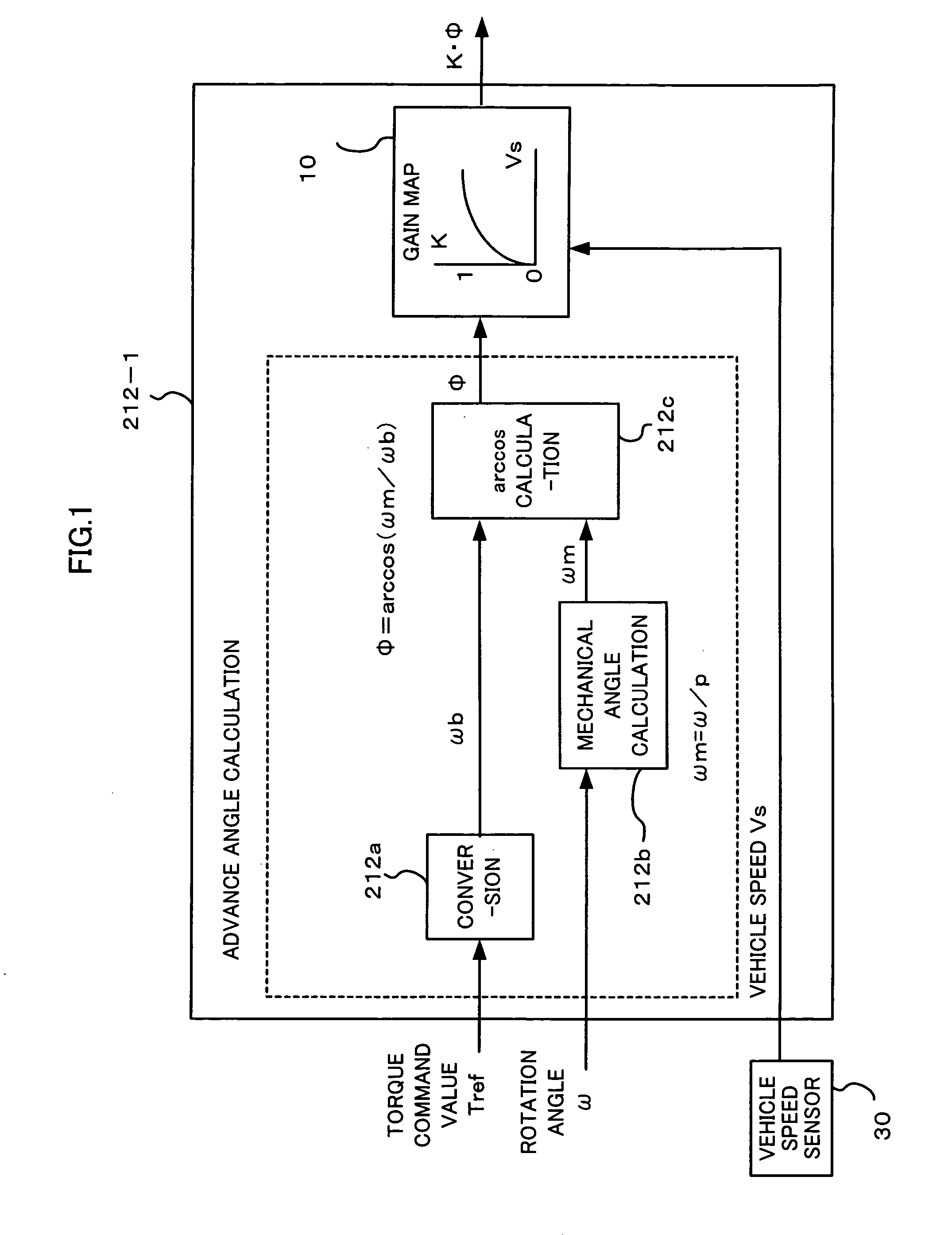
Control unit for electric power steering apparatus
ActiveUS7394214B2Reduce motor noiseImproving a wheel steering feelDC motor speed/torque controlVector control systemsElectric power steeringRoad surface
In order to solve a problem that a motor generates a noise so as to deteriorate an environment in a vehicle if a field weakening control is executed to the motor of a electric power steering apparatus, in the case that a vehicle speed is high, the same field weakening control as the conventional one is applied to the motor because a noise generated due to a friction between a tire and a road surface and a wind noise of a vehicle body are large, and in the case that the vehicle speed is low, the field weakening control is weakly applied in comparison with the conventional one because the noise generated by the motor is felt relatively largely. Accordingly, the field weakening control can be executed in response to the vehicle speed in such a manner as to make the motor noise smaller.
Owner:NSK LTD +1
Variable speed motor
ActiveUS20060181238A1Expand the variable rangeLow production costSingle-phase induction motor startersVector control systemsMotor speedLow speed
A variable speed motor is disclosed. The variable speed motor includes: a main winding including first and second main windings, and an auxiliary winding including first and second auxiliary windings, wherein the main winding and the auxiliary winding are wound on a stator to form a plurality of poles; and a plurality of relays for performing a switching operation between serial / parallel connections of the first and second main windings or the first and second auxiliary windings. The variable speed motor includes: a stator on which a 4-pole winding and a 12-pole winding are wound; a plurality of tap windings connected in series to a 4-pole main winding forming 4 poles, for extending a variable range of rotation speed of the motor during a 4-pole operation mode; and a phase control circuit for varying rotation speed of the motor by controlling a phase of an input power-supply signal during a 12-pole operation mode. Therefore, the variable speed motor greatly extends the range of a variable speed of the motor, and does not require an additional drive unit for varying the motor speed, such that production costs are greatly reduced, and electromagnetic vibration noise caused by a low-speed control mode of the motor is also greatly reduced. Rotation speed of the motor is controlled by a phase control operation and a winding switching operation, such that the variable speed motor effectively controls the motor speed, and greatly reduces power consumption.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
High-efficiency wheel-motor utilizing molded magnetic flux channels with transverse-flux stator
InactiveUS7868510B2Improve efficiencyImprove magnetismMotor control for very low speedsMagnetic circuit rotating partsTransverse fluxElectric machine
A motor including an outside rotor having a rotor disc with plural magnets alternating polarities flush mounted in the disc, an inside stator assembly with a ring of pole pieces forming a channel to house a transversely wound stator windings, and a controller coupled with feedback electronics for monitoring a timing, speed and direction and coupling a signal to a processing unit for adjusting the drive electronics driving the phase windings. A u-shaped gap above the channel to receive the rotor disc and focus the captured magnetic flux in the pole pieces toward the magnets. In an embodiment the molded magnetic flux channel pole pieces of the inside stator are sets of molded magnetic flux channel pole pieces, each set forming a channel and corresponding to one phase of the motor; and a section of each one of the transverse windings passing through one channel, the remaining section folding back outside the set in close proximity to the outer base of the set of molded magnetic flux channel pole pieces.
Owner:RITTENHOUSE NORMAN P
Motor driving device and motor driving method
InactiveUS20070018599A1Improve startup speedImprove response qualitySynchronous motors startersVector control systemsMotor driveEngineering
A rotor position sensorless multiphase motor driving device includes a rotor; a plurality of phase windings; a common terminal to which one terminal of terminals at both ends of each winding is star connected; an upper-side drive transistor and a lower-side drive transistor connected to the other terminal of the winding; a commutation control unit operable to select two terminals other than the common terminal of the windings, and to turn on the corresponding pair of upper-side drive transistor and the lower-side drive transistor; a rotor position search pulse applying unit operable to apply a search pulse to the selected two terminals; and a comparing unit operable to detect a rotor position based on a response signal generated between the terminal which was unselected and the common terminal according to the search pulse application.
Owner:COLLABO INNOVATIONS INC
Harmonic torque ripple reduction at low motor speeds
ActiveCN101567661AMotor control for very low speedsElectric motor controlMotor speedUltrasound attenuation
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
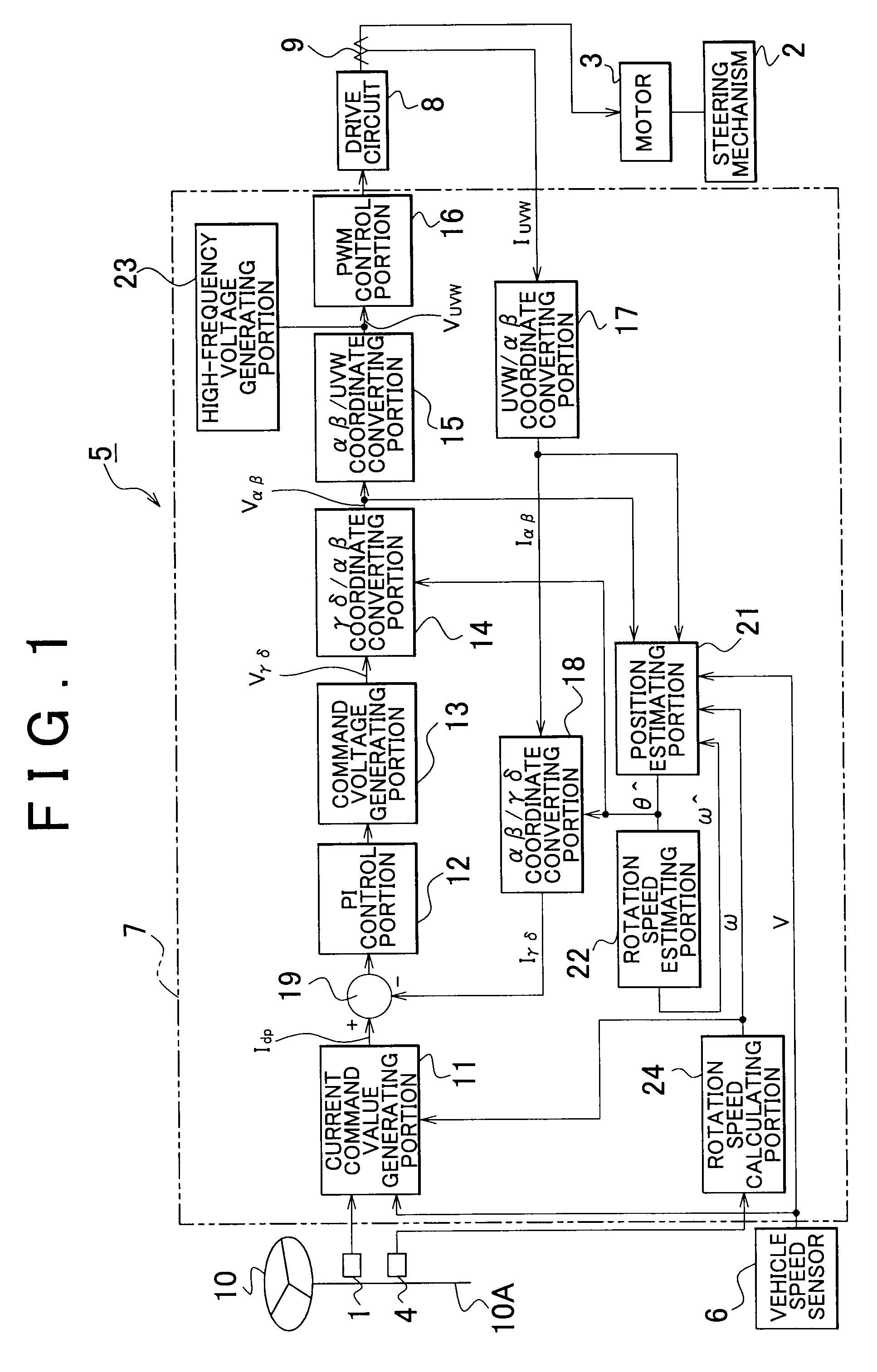
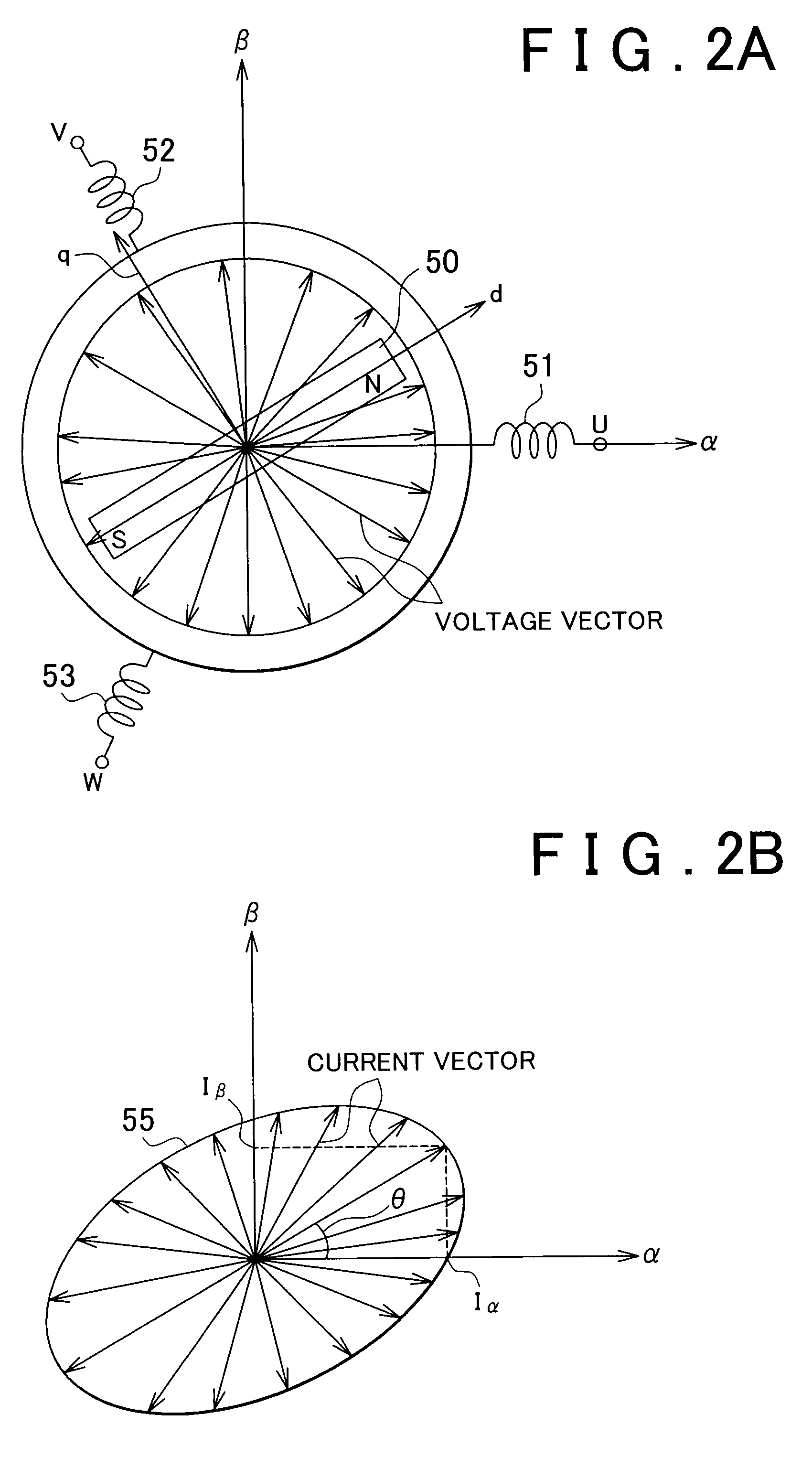
Motor controller and vehicular steering system using said motor controller
InactiveUS20090190903A1Accurate calculationImprove accuracySynchronous motors startersVector control systemsLow speedElectric machinery
A low speed region position estimating portion is designed to be suitable for when the motor is operating in a low speed region, and estimates a low speed estimated rotational position θ̂L. A high speed region position estimating portion is designed to be suitable for when the motor is operating in a high speed region, and estimates a high speed estimated rotational position θ̂H. A dividing portion obtains a divided estimated rotational position θ̂M by internally dividing the low speed estimated rotational position θ̂L and the high speed estimated rotational position θ̂H. A rotation speed calculating portion obtains a rotation speed ω of a rotor based on an output signal from a steering sensor. The rotational position of the rotor is then obtained by selecting one of i) the low speed estimated rotational position θ̂L, the high speed estimated rotational position θ̂H, or the divided estimated rotational position θ̂M, based on that rotation speed ω.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Motor driving device and motor driving method
InactiveUS7298106B2Low costImprove startup speedSynchronous motors startersVector control systemsMotor driveConductor Coil
A rotor position sensorless multiphase motor driving device includes a rotor; a plurality of phase windings; a common terminal to which one terminal of terminals at both ends of each winding is star connected; an upper-side drive transistor and a lower-side drive transistor connected to the other terminal of the winding; a commutation control unit operable to select two terminals other than the common terminal of the windings, and to turn on the corresponding pair of upper-side drive transistor and the lower-side drive transistor; a rotor position search pulse applying unit operable to apply a search pulse to the selected two terminals; and a comparing unit operable to detect a rotor position based on a response signal generated between the terminal which was unselected and the common terminal according to the search pulse application.
Owner:COLLABO INNOVATIONS INC
Motor controller
ActiveUS7294984B2Reduce in quantityLow costMotor/generator/converter stoppersMotor control for very low speedsPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
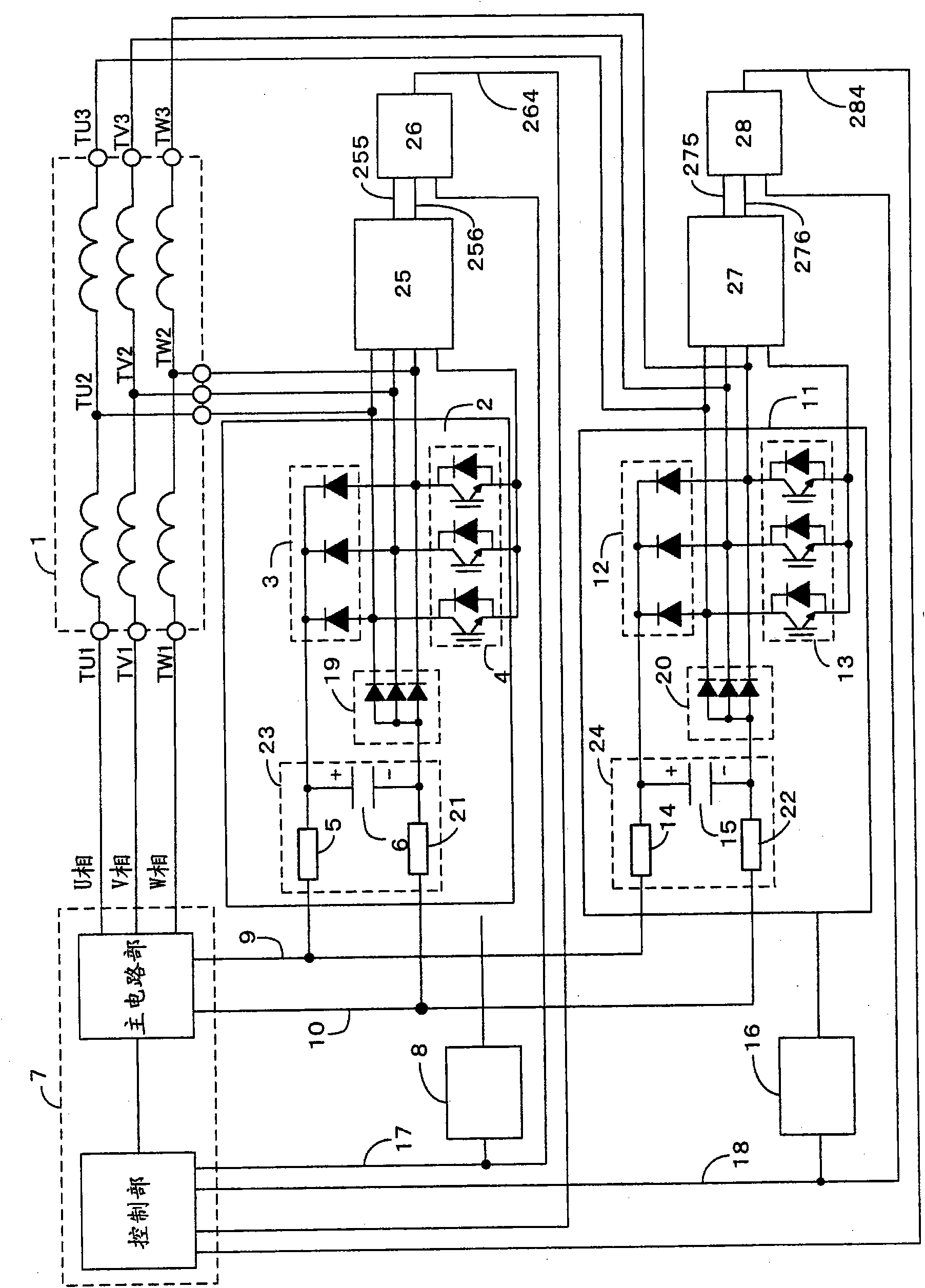
A motor controller is provided which can be reduced in the number of the wirings and power semiconductor devices required while maintaining the function equivalent to or higher than that of the motor controller adopting the existing winding changeover scheme, thereby realizing cost and size reduction and life increase. The motor is made in a structure having motor windings opened at both ends. The one end terminals of phase windings are respectively connected to the output terminals of a first inverter circuit while the other end terminals are respectively connected to the output terminals of a second inverter circuit. During power generation, any one of the inverter circuits is driven on all the phases by means of a same control pulse.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Drive device for alternating current motor and electric motor vehicle
ActiveUS20110204831A1Electromagnetic noise and loss caused by the harmonic wave are minimizedGeneration amounts of the electromagnetic noise and the loss are dramatically reducedVector control systemsSingle motor speed/torque controlLow speedEngineering
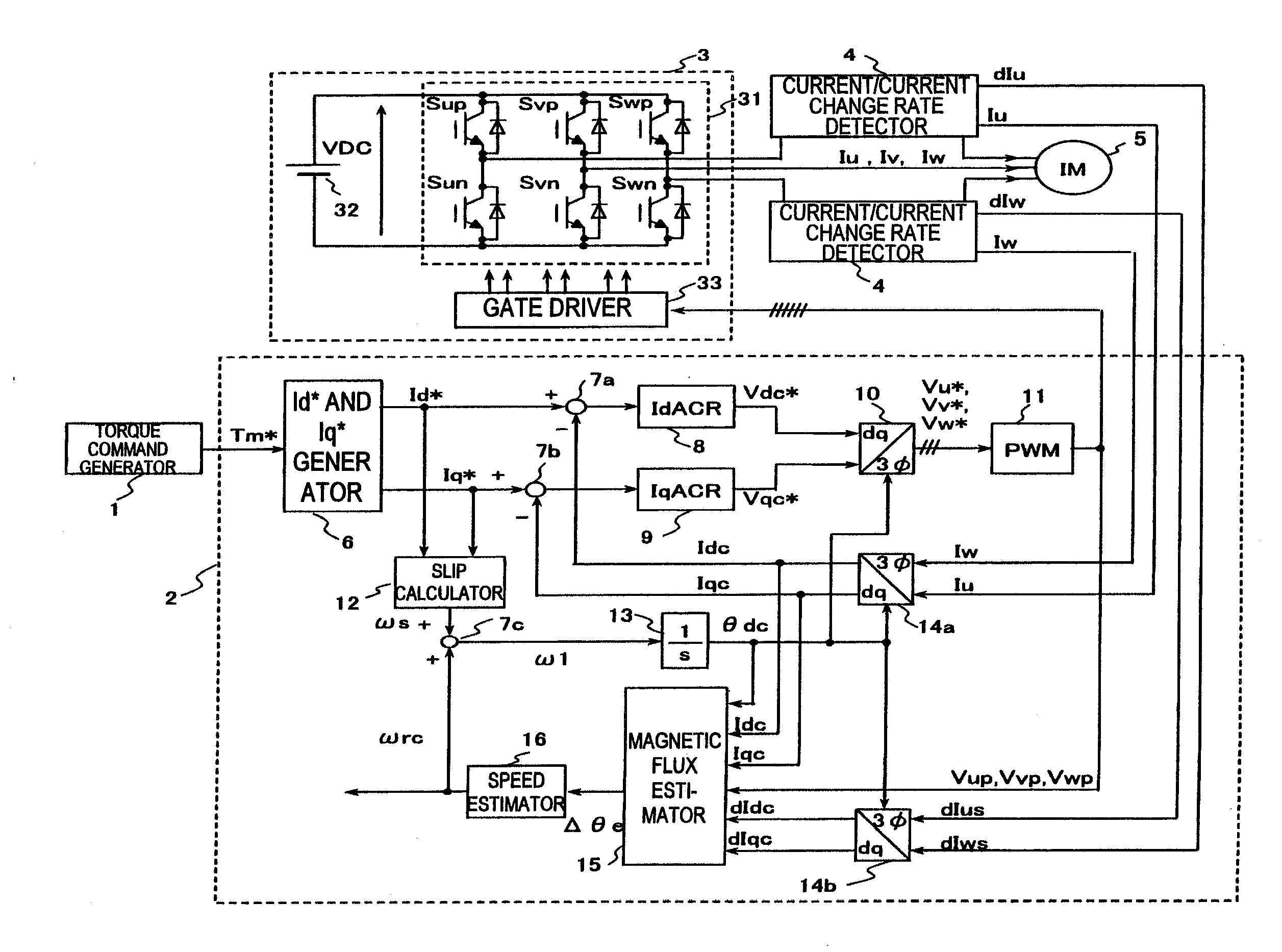
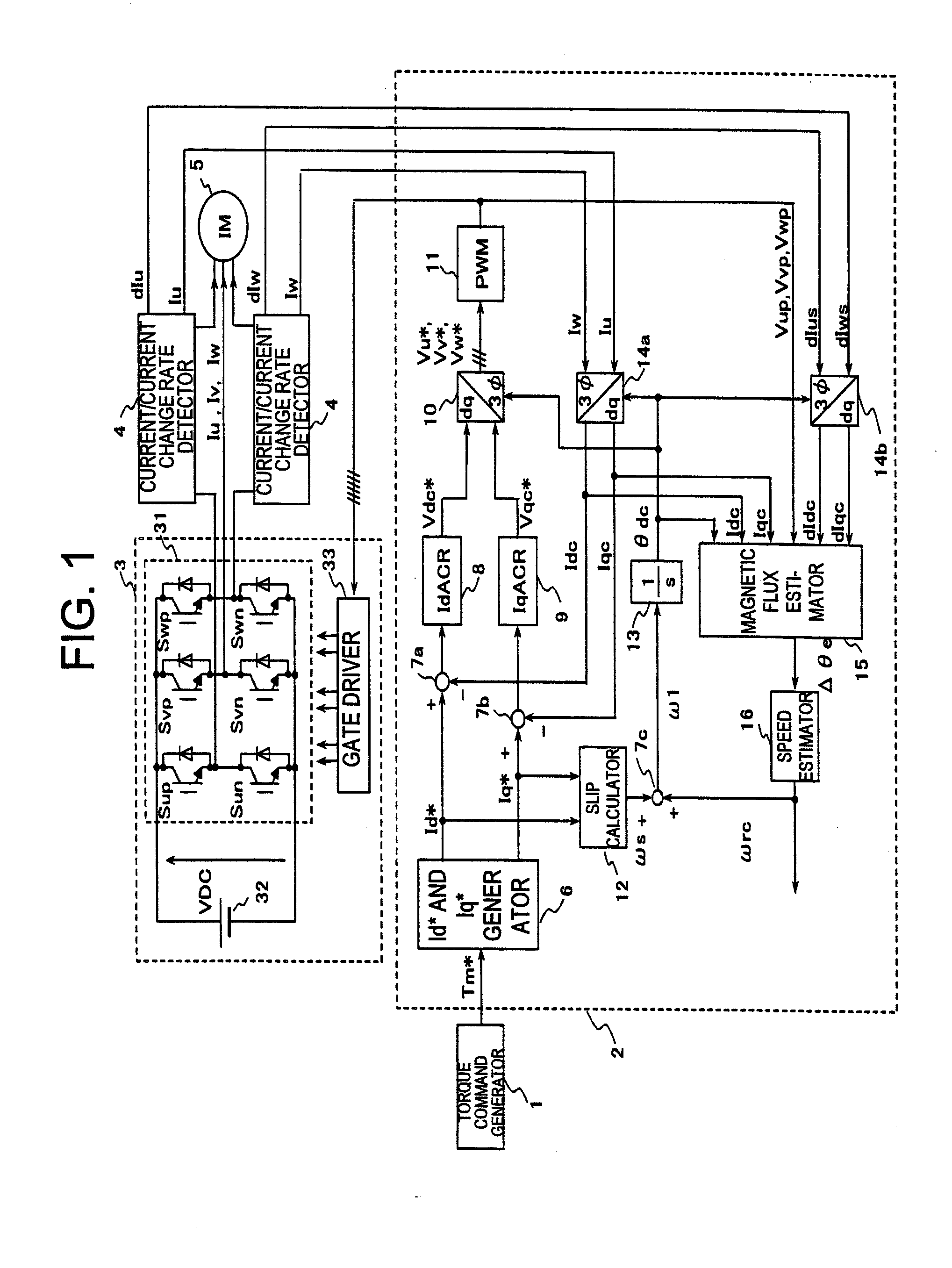
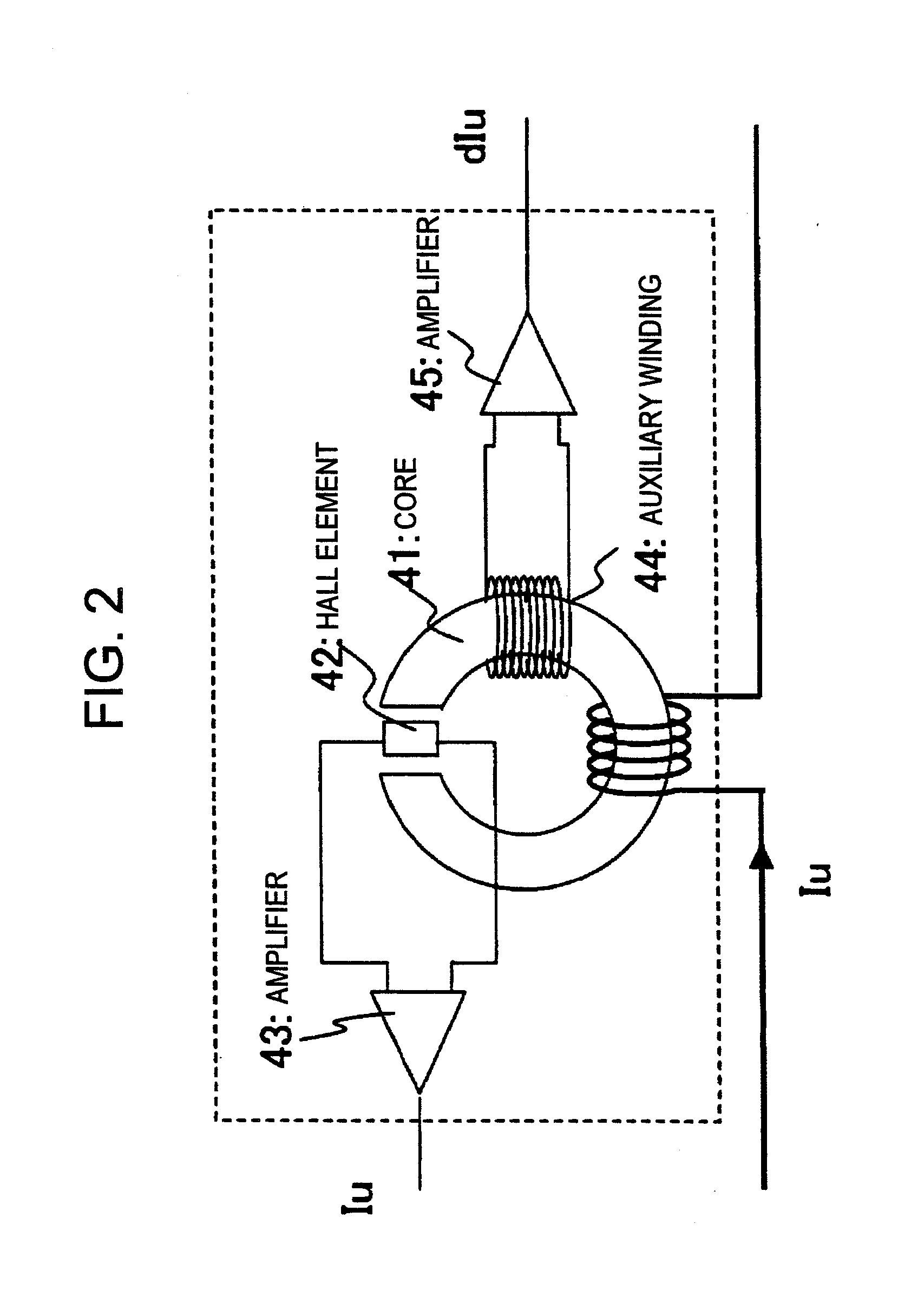
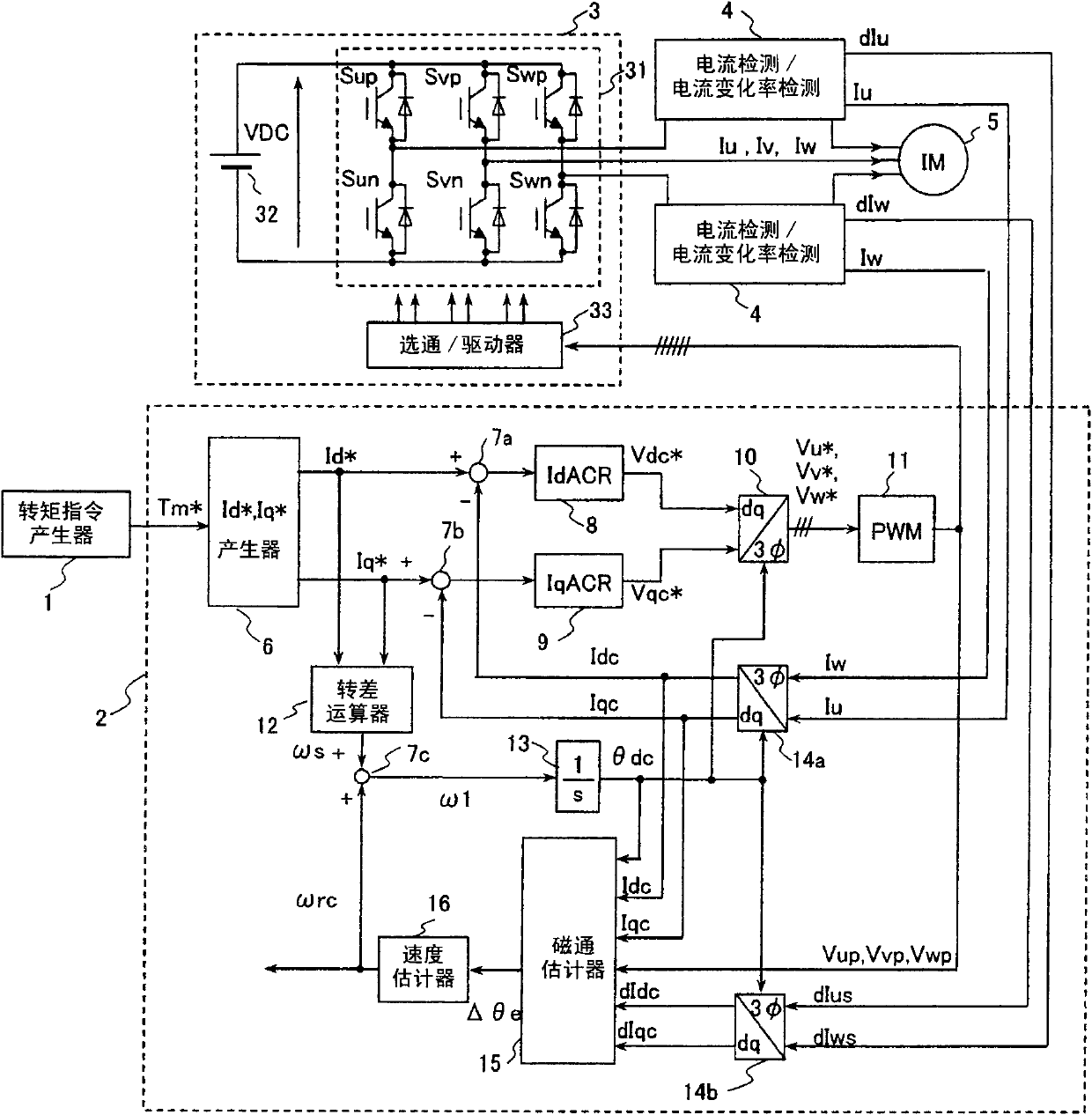
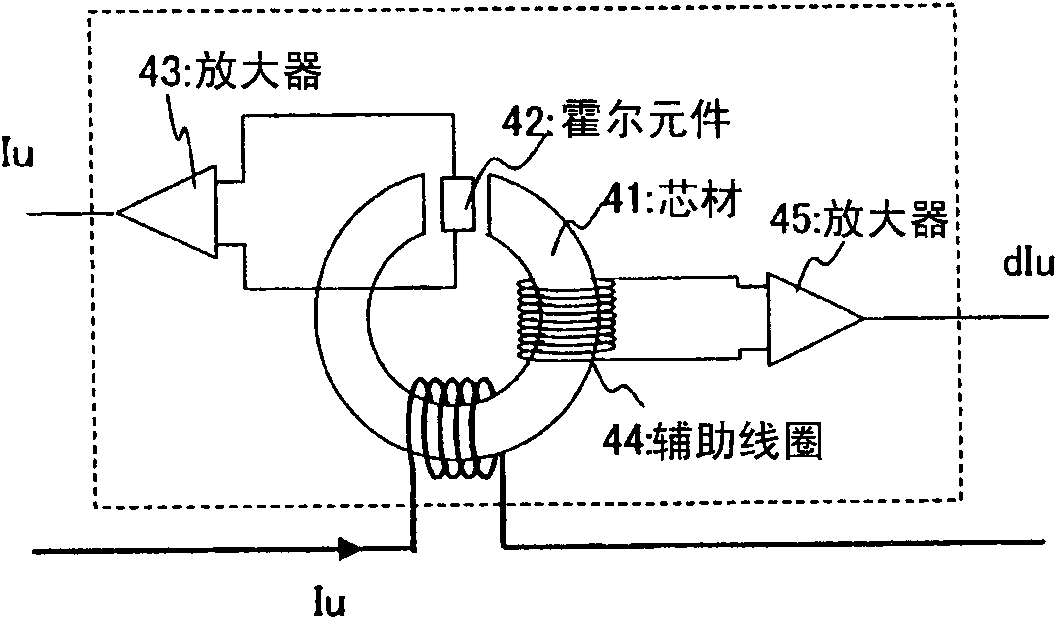
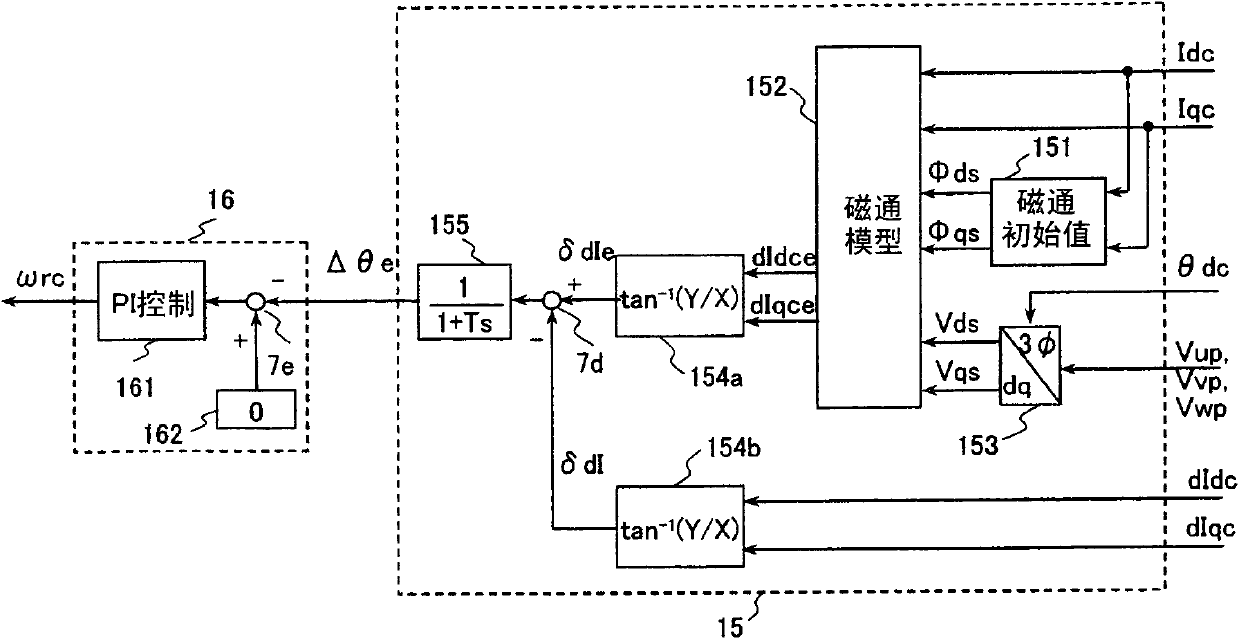
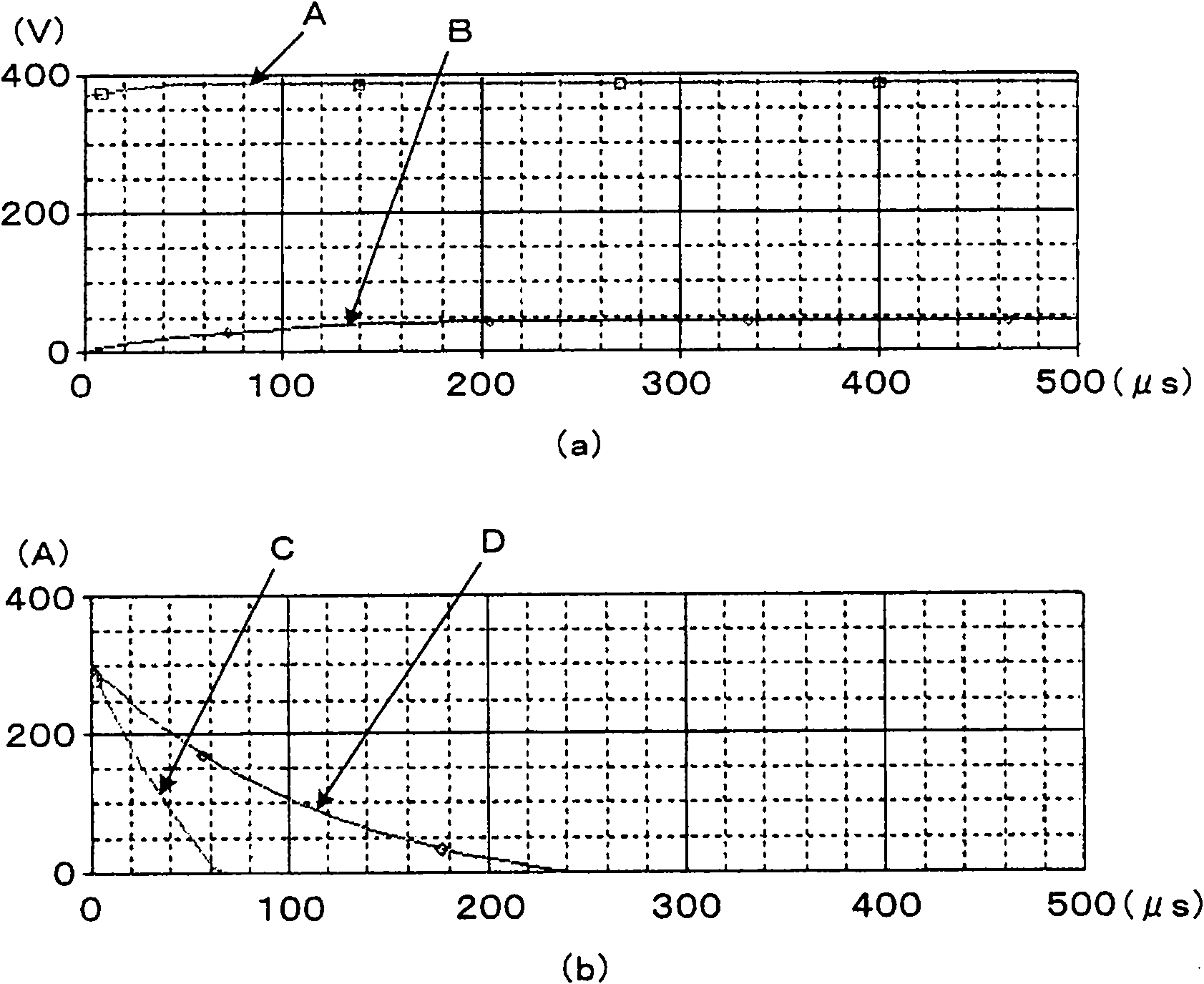
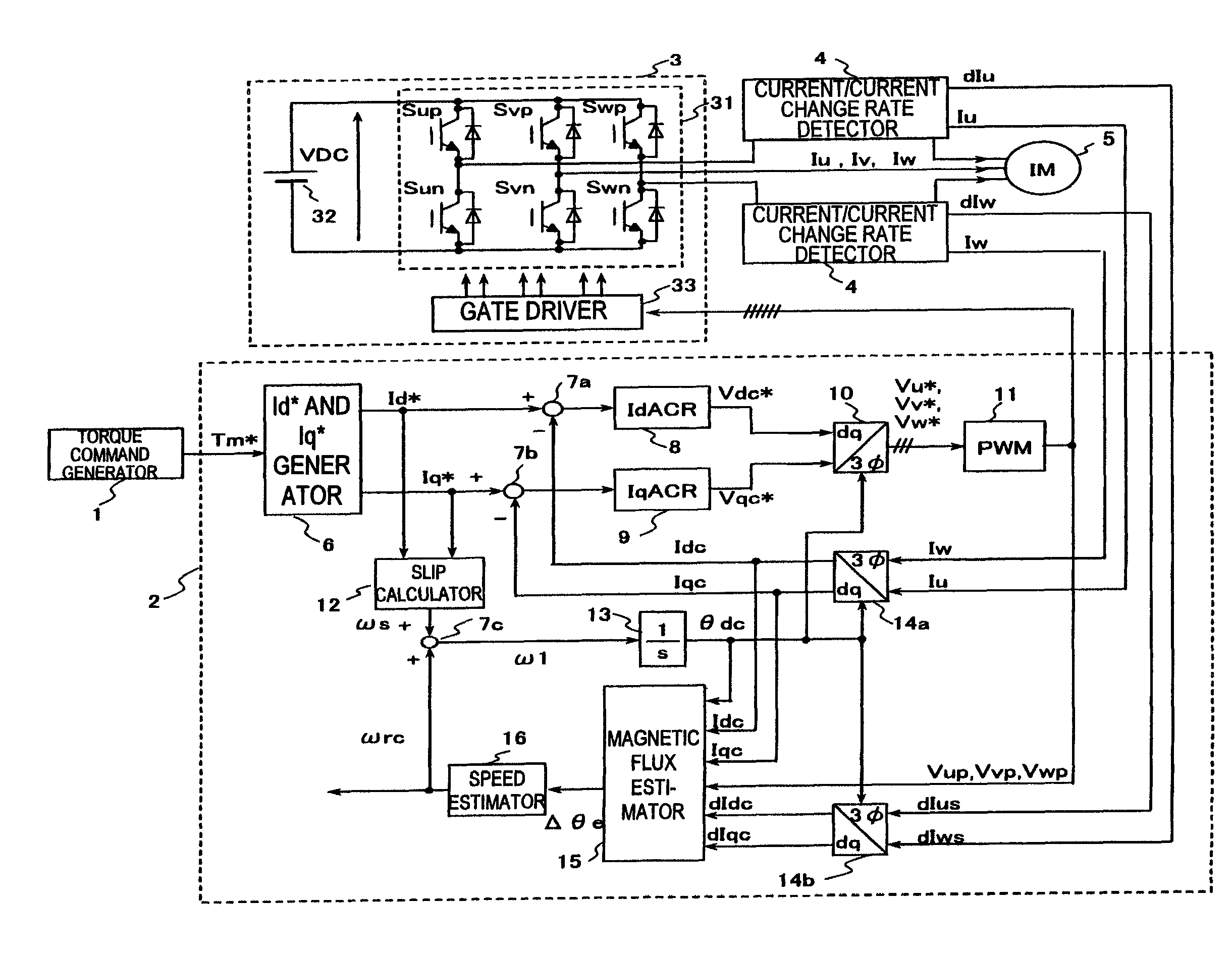
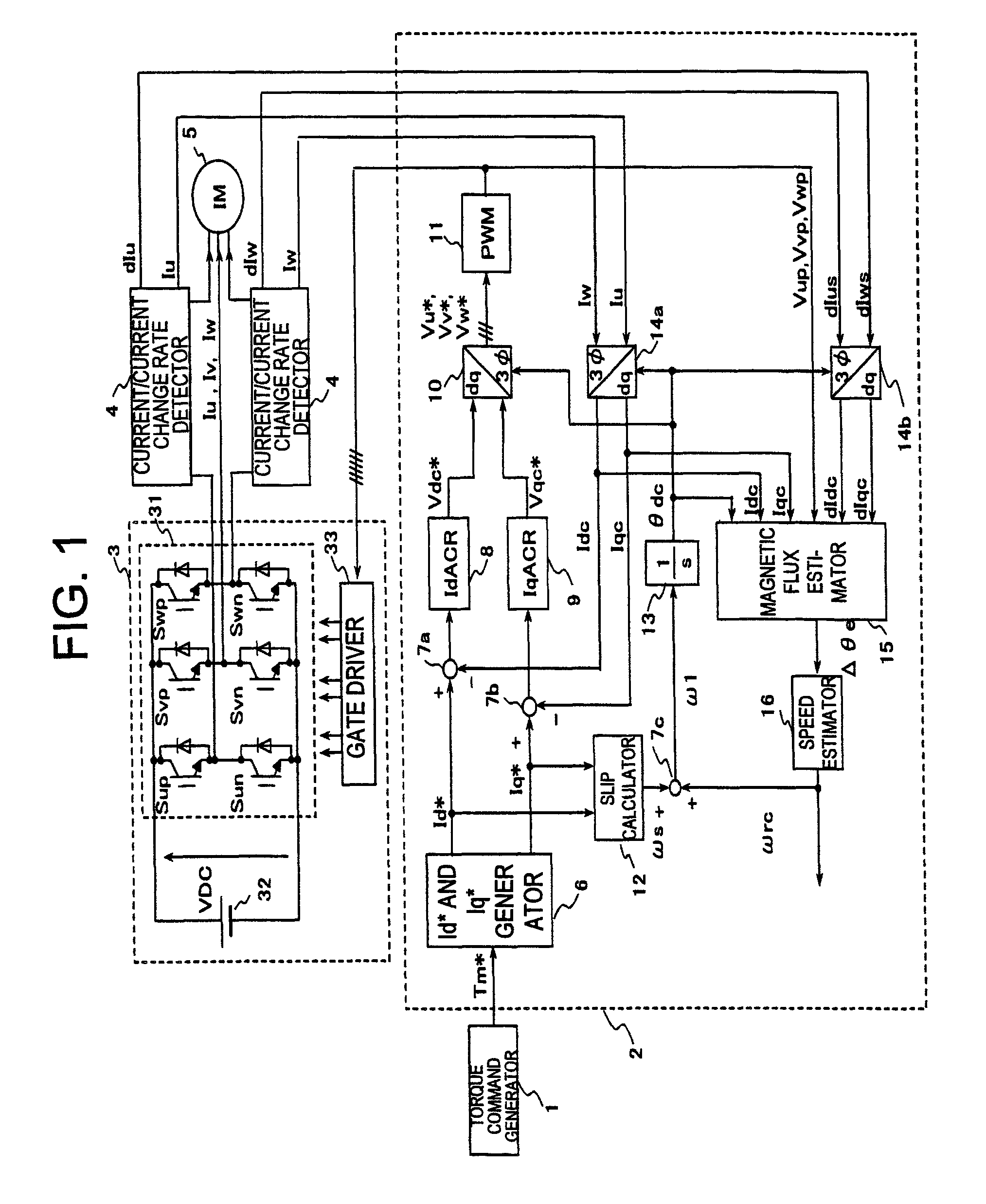
Provided is a drive device for an alternating current motor which performs vector control on sensorless driving of the alternating current motor in an extremely low speed region without applying a harmonic voltage intentionally while maintaining an ideal PWM waveform. A current and a current change rate of the alternating current motor are detected, and a magnetic flux position inside of the alternating current motor is estimated and calculated in consideration of an output voltage of an inverter which causes this current change. The current change rate is generated on the basis of a pulse waveform of the inverter, and hence the magnetic flux position inside of the alternating current motor can be estimated and calculated without applying a harmonic wave intentionally.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Vector Controller Of Induction Motor
InactiveUS20080048607A1Reduce unstable areaAvoid unstable areaVector control systemsLinear/angular speed measurementLow speedControl vector
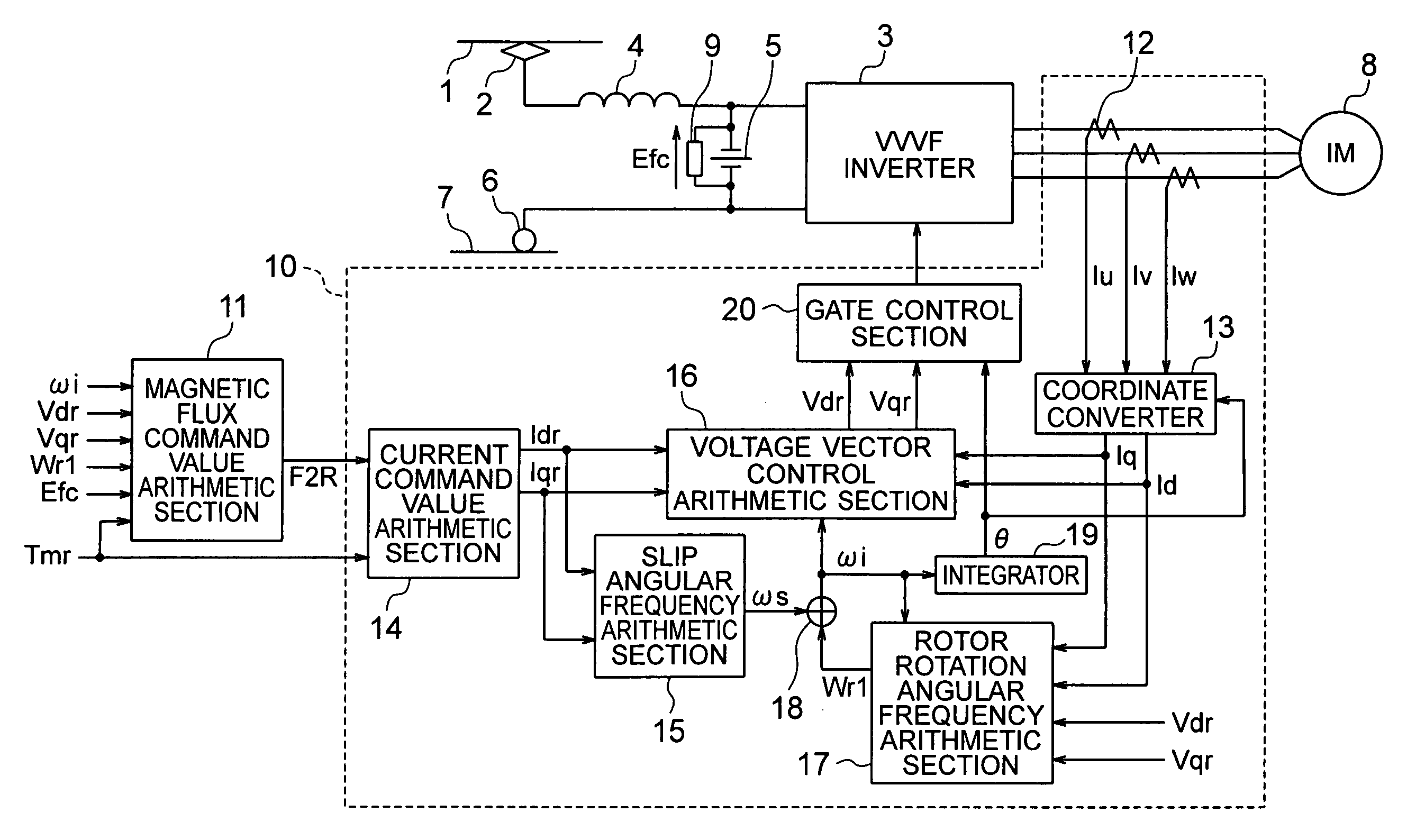
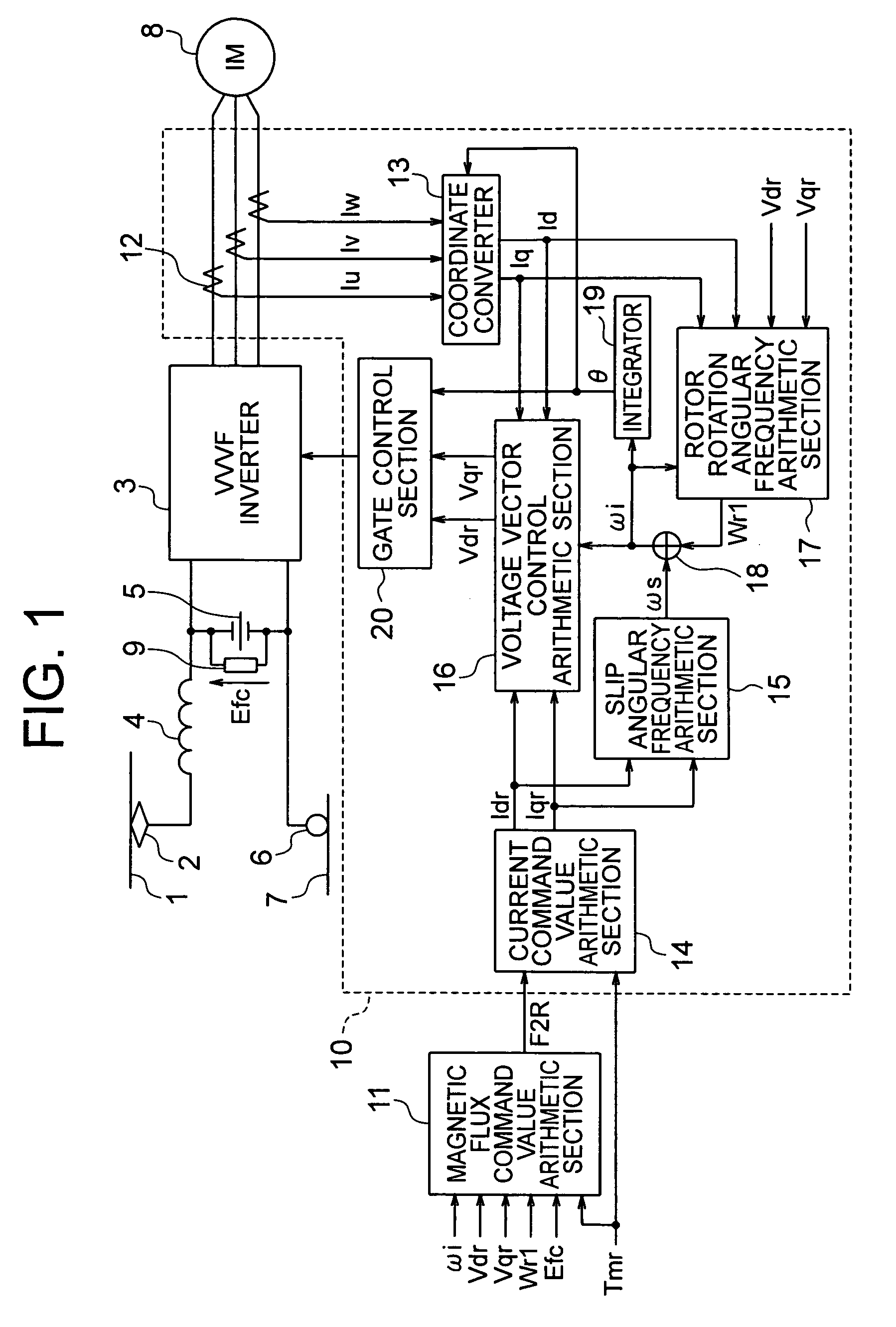
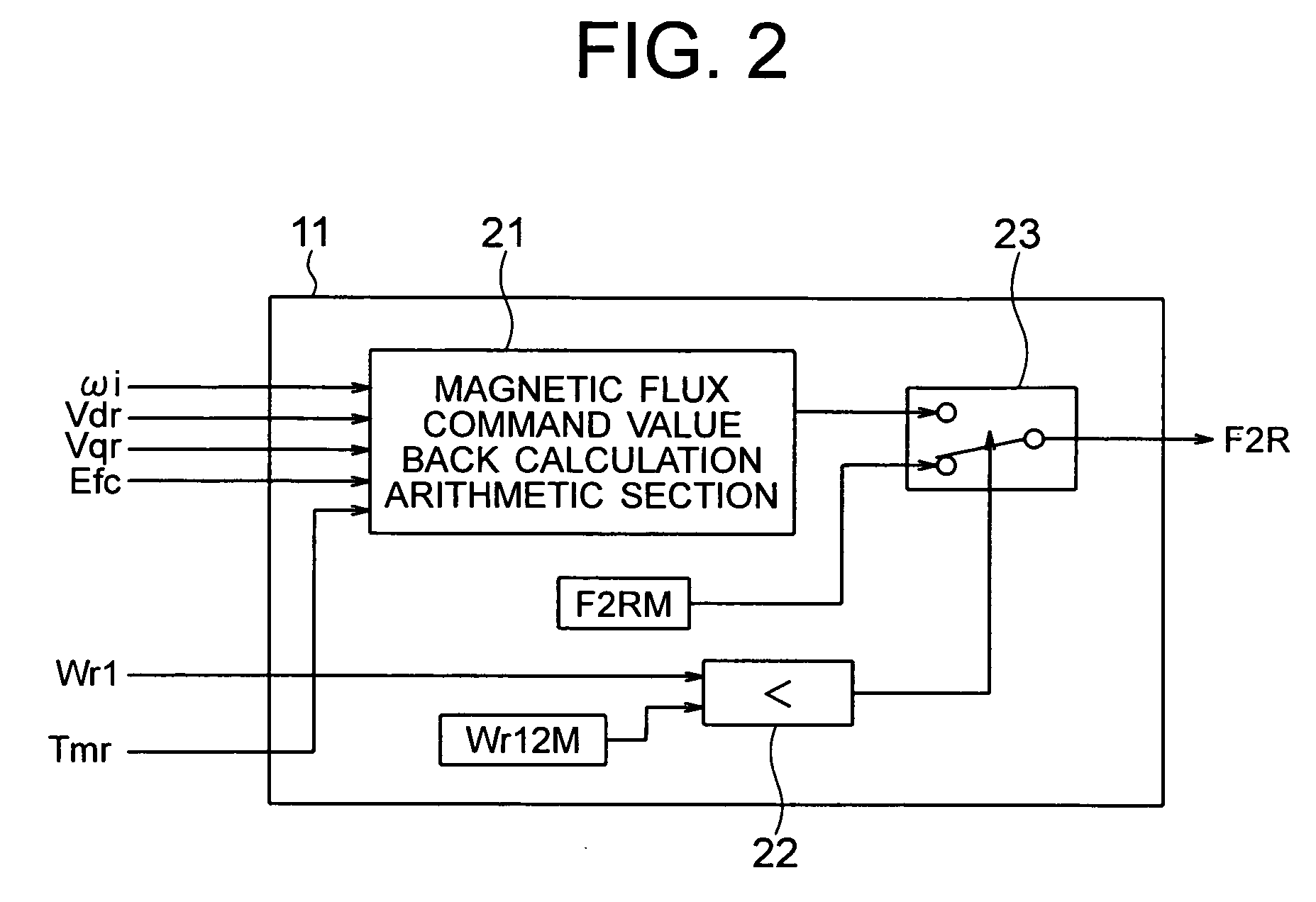
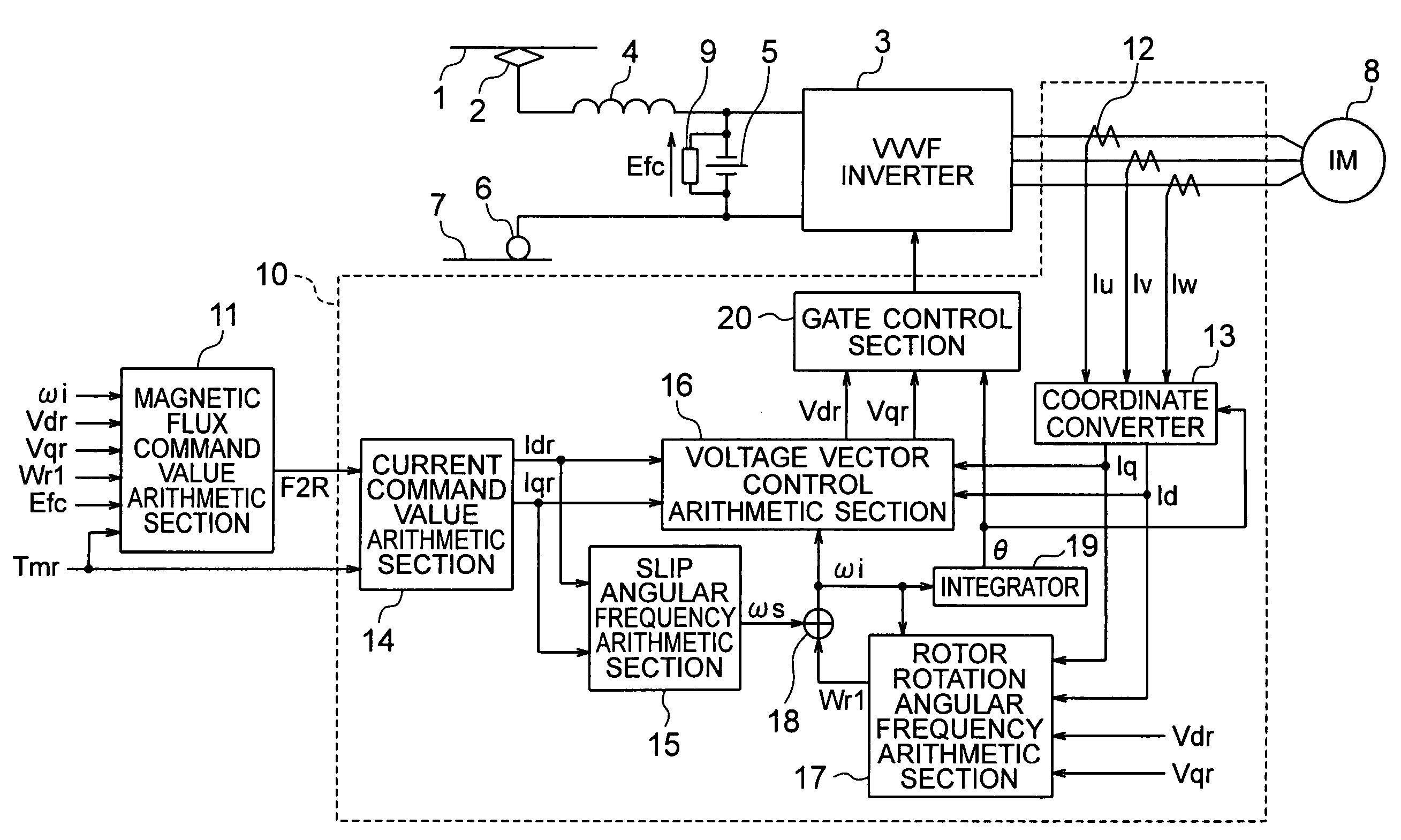
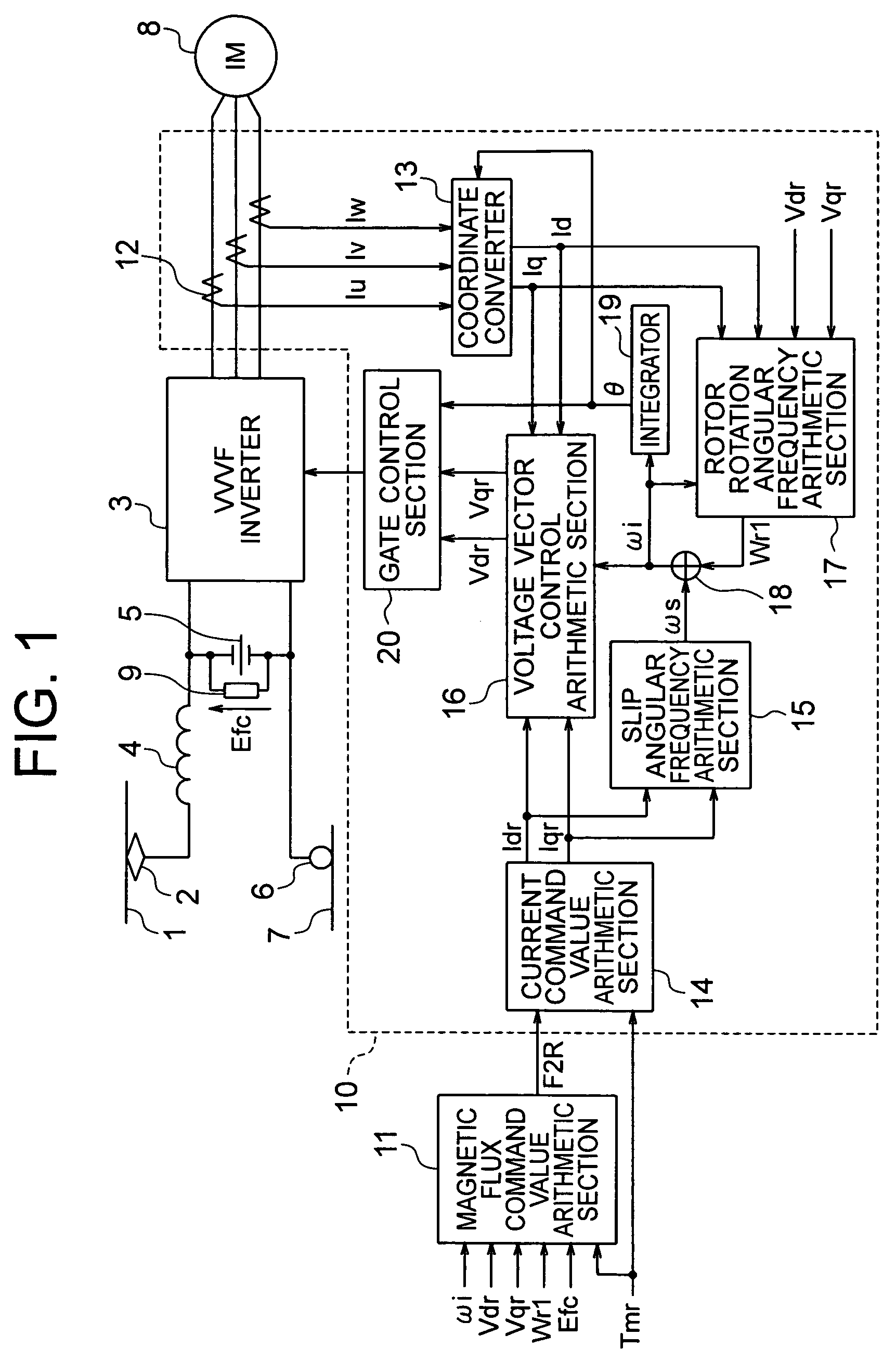
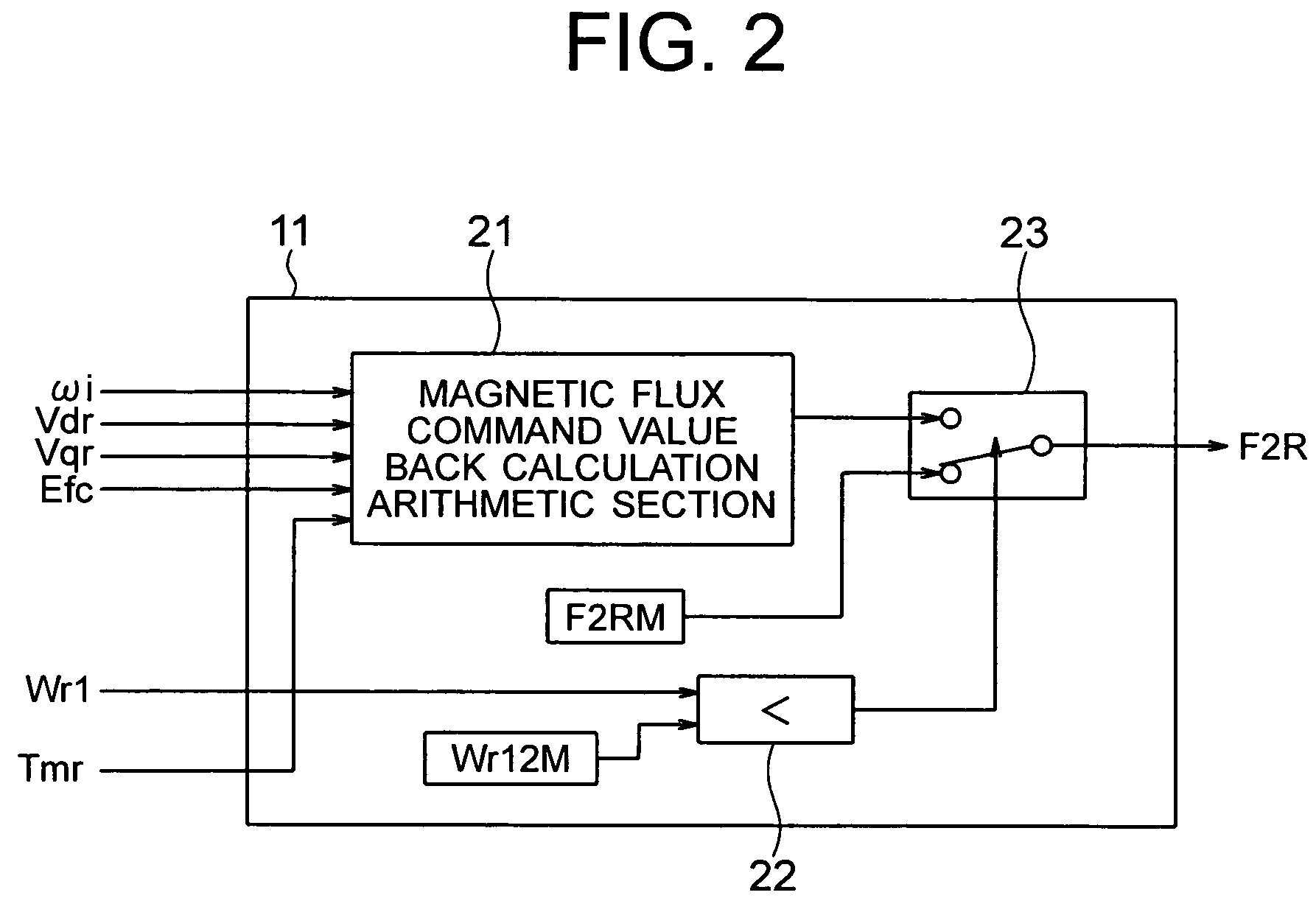
Provided is a vector control apparatus for an induction motor which is capable of obtaining stable rotation in a short period of time for adjustment even at the time of low-speed operation by increasing the SN ratio of an output voltage to suppress the arithmetic error in the primary angular frequency arithmetic value based on a magnetic flux command value calculated from a circuit constant and an actual measurement of the induction motor even in the case where the rotation velocity of the induction motor is lower. The vector control apparatus includes: magnetic flux command value arithmetic means (11) for selecting and outputting the magnetic flux command value on the basis of a torque command value Tmr that is input from the external, the circuit constant of the induction motor, and the actual measurement related to the induction motor; and vector control means (10) for controlling the inverter device (3) on the basis of the magnetic flux command value that is output from the magnetic flux command value arithmetic means (11) and the circuit constant of the induction motor (8). The magnetic flux command value arithmetic means (11) includes a magnetic flux command value back calculation arithmetic section (21) for calculating a magnetic flux command arithmetic value F2RB so that a voltage that is applied to the induction motor 8 becomes equal to or higher than a setting value corresponding to an unstable area.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Vector controller of induction motor
InactiveUS7411370B2Increase output ratioReduce areaVector control systemsLinear/angular speed measurementLow speedControl vector
Provided is a vector control apparatus for an induction motor which is capable of obtaining stable rotation in a short period of time for adjustment even at the time of low-speed operation by increasing the SN ratio of an output voltage to suppress the arithmetic error in the primary angular frequency arithmetic value based on a magnetic flux command value calculated from a circuit constant and an actual measurement of the induction motor even in the case where the rotation velocity of the induction motor is lower. The vector control apparatus includes a magnetic flux command value arithmetic section for selecting and outputting the magnetic flux command value on the basis of a torque command value that is externally input, the circuit constant of the induction motor, and the actual measurement related to the induction motor; and a vector controller for controlling an inverter device on the basis of the magnetic flux command value that is output from the magnetic flux command value arithmetic section and the circuit constant of the induction motor. The magnetic flux command value arithmetic section includes a magnetic flux command value back calculation arithmetic section for calculating a magnetic flux command arithmetic value so that a voltage that is applied to the induction motor becomes equal to or higher than a setting value corresponding to an unstable area.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Drive device for an alternating current motor and an electric motor vehicle
InactiveCN102170261ANo problem drivingElectromagnetic noise minimizationVector control systemsSingle motor speed/torque controlLow speedEngineering
Provided is a drive device for an alternating current motor which performs vector control on sensorless driving of the alternating current motor in an extremely low speed region without applying a harmonic voltage intentionally while maintaining an ideal PWM waveform. A current and a current change rate of the alternating current motor are detected, and a magnetic flux position inside of the alternating current motor is estimated and calculated in consideration of an output voltage of an inverter which causes this current change. The current change rate is generated on the basis of a pulse waveform of the inverter, and hence the magnetic flux position inside of the alternating current motor can be estimated and calculated without applying a harmonic wave intentionally.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Driver of electric compressor
ActiveUS7084598B2Sufficient torqueDecrease advancementSynchronous motors startersDC motor speed/torque controlControl theoryVoltage
A compressor driver for a compressor is provided, wherein at the start of the compressor, a phase of the current flowing in the motor is controlled to be ahead of an induction voltage, then the advancement of the phase is controlled to decrease. Under an unstable condition to detect a position, such as at the start under pressure-difference, the foregoing control allows the phase to advance up to the current-phase where the max. torque can be produced, thereby drawing the instantaneous max. torque of the motor for starting the compressor. Then the control reduces the advancement for obtaining a stable operation.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Winding change-over switch of three-phase AC motor
ActiveCN101911473AQuick switchAvoid abnormal operationElectronic commutation motor controlMotor control for very low speedsLow speedThree-phase
A winding change-over switch of a three-phase AC motor which can switch the motor current quickly while minimizing disturbance of a sine wave current and can prevent an abnormal operation or the destruction of an apparatus by detecting wrong wiring or abnormality of a component. A winding change-over section ((2(11)) connects a positive-side charging resistor (5(14)), a negative-side charging resistor (21(22)) and a capacitor (6(15)) in series between the DC positive-side bus (9) and the DC negative-side bus (10) of an inverter (7), connects the positive side of the capacitor with the cathode of a diode portion (3(12)) and then changes over a high-speed winding to from a low-speed winding under such a state that the potential of the capacitor is equalized to the DC bus voltage of the inverter. In addition, wrong wiring or abnormality of a component is detected by means of a state detector (25(27)) and a comparator (26(28)).
Owner:YASKAWA DENKI KK
Drive device for alternating current motor and electric motor vehicle
ActiveUS8674647B2Electromagnetic noise and loss caused by the harmonic wave are minimizedGeneration amounts of the electromagnetic noise and the loss are dramatically reducedAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcLow speedEngineering
Provided is a drive device for an alternating current motor which performs vector control on sensorless driving of the alternating current motor in an extremely low speed region without applying a harmonic voltage intentionally while maintaining an ideal PWM waveform. A current and a current change rate of the alternating current motor are detected, and a magnetic flux position inside of the alternating current motor is estimated and calculated in consideration of an output voltage of an inverter which causes this current change. The current change rate is generated on the basis of a pulse waveform of the inverter, and hence the magnetic flux position inside of the alternating current motor can be estimated and calculated without applying a harmonic wave intentionally.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
System and method for low speed control of polyphase ac machine
ActiveUS20130155731A1Material nanotechnologyHeavy metal active ingredientsDroop speed controlElectrical conductor
A method of starting a wind turbine generator of any type of polyphase AC machine, including, but not limited to, brushless DC or permanent magnet machines is disclosed. The machine starts from a dead stop or from low speed operation and is accelerated to the cut in speed for power production. The start-up is realized utilizing the common set of electrical conductors and the power converter also used for capturing the generated power. Under initial operation, the power converter executes a PWM modulation technique to drive the machine. Periodically, the PWM modulation is stopped to read the electrical position of the generator.
Owner:FAITH TECH INC
Method and device for testing speed of servo motor during low-speed running
InactiveCN102590544AReduce the impactEasy to analyze and judgeMotor control for very low speedsLinear/angular speed measurementProgrammable logic controllerThird party
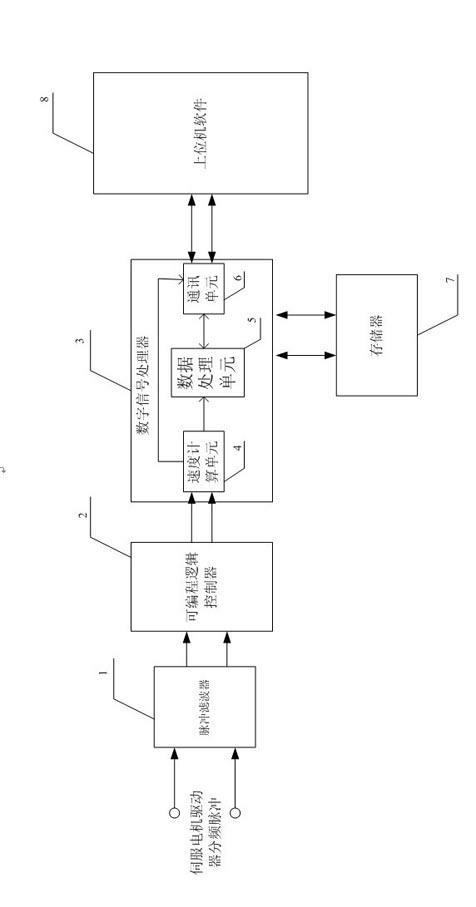
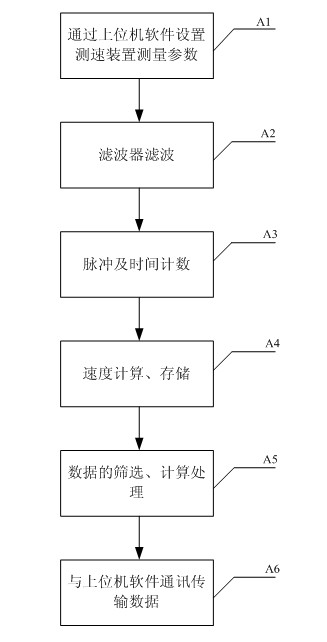
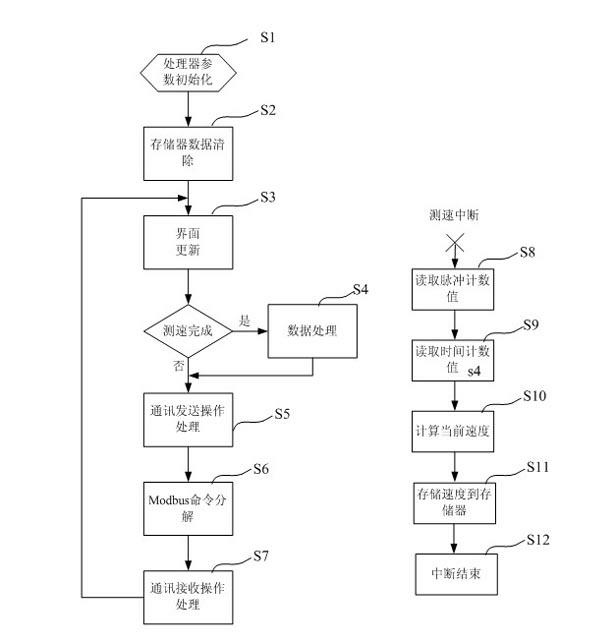
The invention discloses a method and a device for testing the speed of a servo motor during low-speed running. The device for testing the speed of the servo motor during low-speed running comprises a pulsed filter, a programmable logic controller, a digital signal processor and a storage. The method for testing the speed of the servo motor during low-speed running comprises the following steps of: setting parameters of the device by using upper computer software, performing frequency or period method (M / T method) speed testing on a pulse generator (PG) fractional frequency pulse of a servo driver by using a testing device, and processing multiple batches of data, and after data is screened, displaying by using the upper computer software for analysis. By using the method and the device, the low speed of the motor can be detected independently and accurately; and through visual display of an upper computer, the low-speed running condition of the motor can be analyzed conveniently, and the device for testing the speed of the servo motor can be used as a third-party testing device to meet the servo low-speed performance test requirements.
Owner:ESTUN AUTOMATION TECH +1
Torque controller in an electric motor
ActiveUS20070001636A1DC motor speed/torque controlMotor control for very low speedsMaximum torqueSlow rotation
The torque of a motor operated by an inverter circuit is controlled to allow maximum torque in the motor when the motor is stalled or at low rotation speeds. Control is accomplished by providing a switching frequency to the motor at a first switching frequency, detecting a rotation speed of the motor, and switching the current to the motor to a second switching frequency when the rotation speed of the motor drops to a predetermined slow rotation speed. The second switching frequency is less than the first switching frequency.
Owner:DRS NETWORK & IMAGING SYST
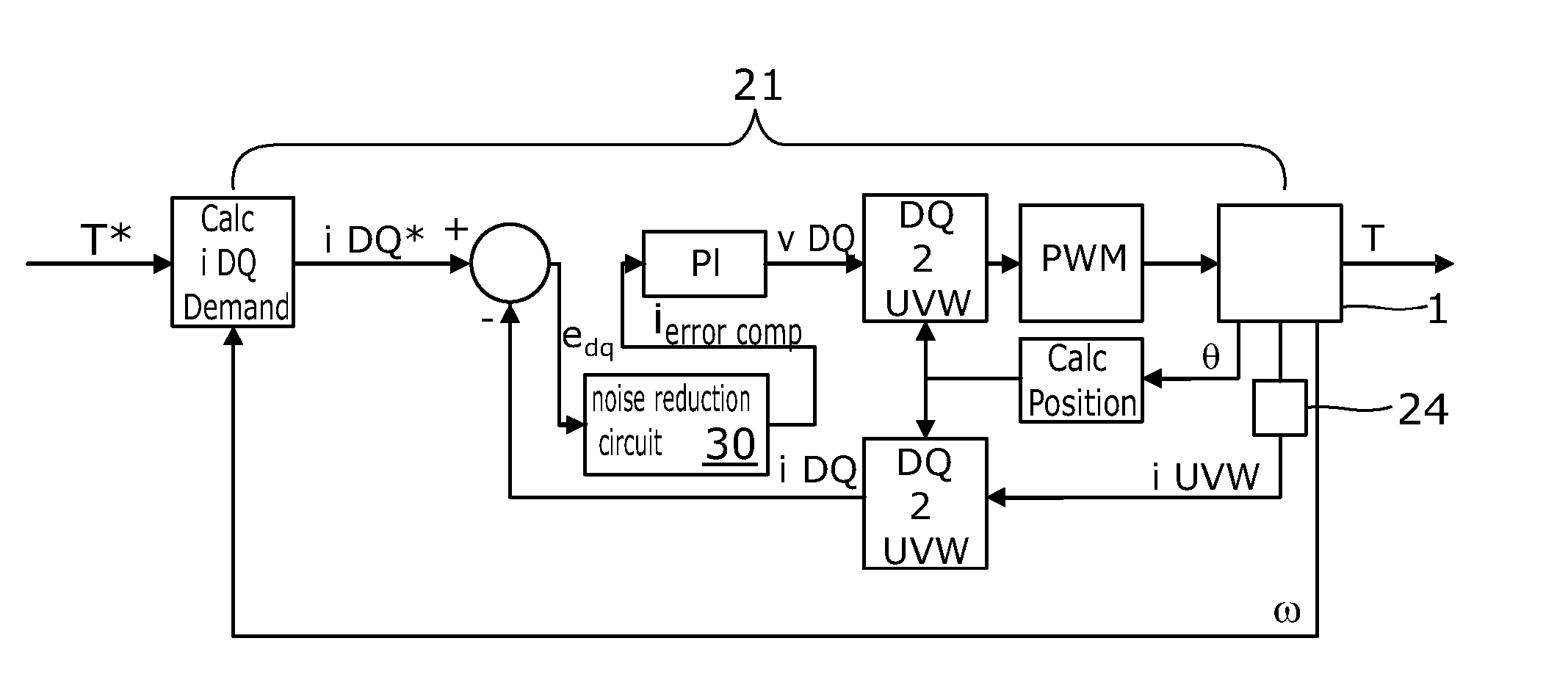
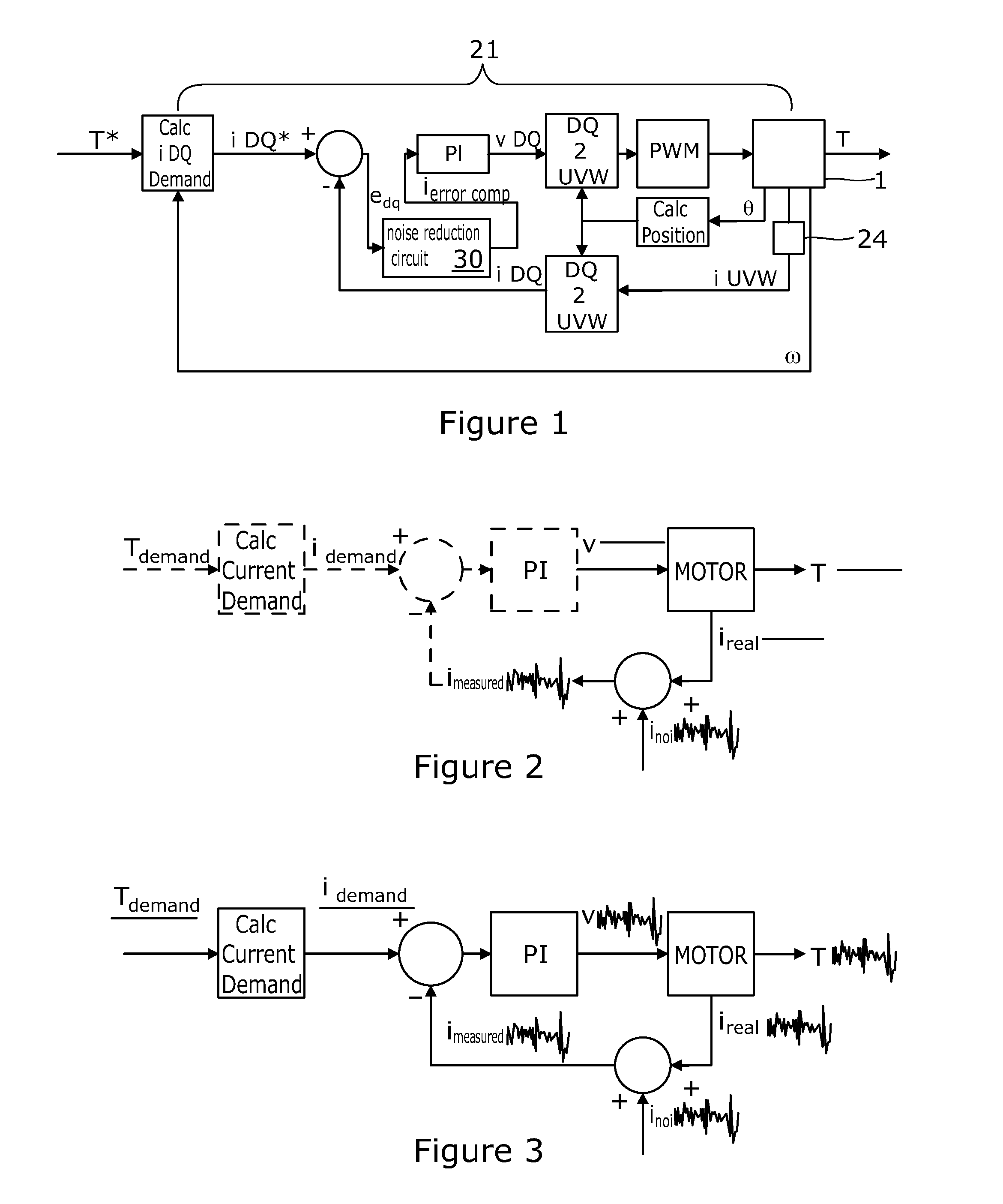
Motor Control
ActiveUS20160028335A1Reduced responseGain of the controller is effectively reducedTorque ripple controlDC motor speed/torque controlElectric power steeringLow speed
A motor control circuit for an electric motor of an electric power assisted steering system of the kind in which a measurement of torque carried by a part of the steering system is used to produce a torque demand signal indicative of a torque to be applied to the steering system by the motor, the control circuit comprising a switching circuit comprising a plurality of electrical switches, and a motor current controller that generates voltage demand signals to be passed to a drive circuit for the switches that in turn generates pulse width modulated switching signals for the switching circuit that cause the switches to selectively connect the phases to a power supply so as to cause current to flow through the phases of the motor. The current controller is responsive to an error signal that represents the difference between a current demand signal and an actual current signal, and a noise reduction circuit adapted to identify an operating condition of the system in which the motor is stationary or rotating at a very low speed, and in the event that the operating condition is identified the noise reduction circuit is adapted to reduce the response of the controller to variations in the error signal.
Owner:TRW LIMITED
Sensorless-Brushless Motor Control Device and Electric Fluid Pump Using the Same
InactiveUS20100244754A1Low costIncrease speedSynchronous motors startersMultiple motor speed/torque controlBrushless motorsPower flow
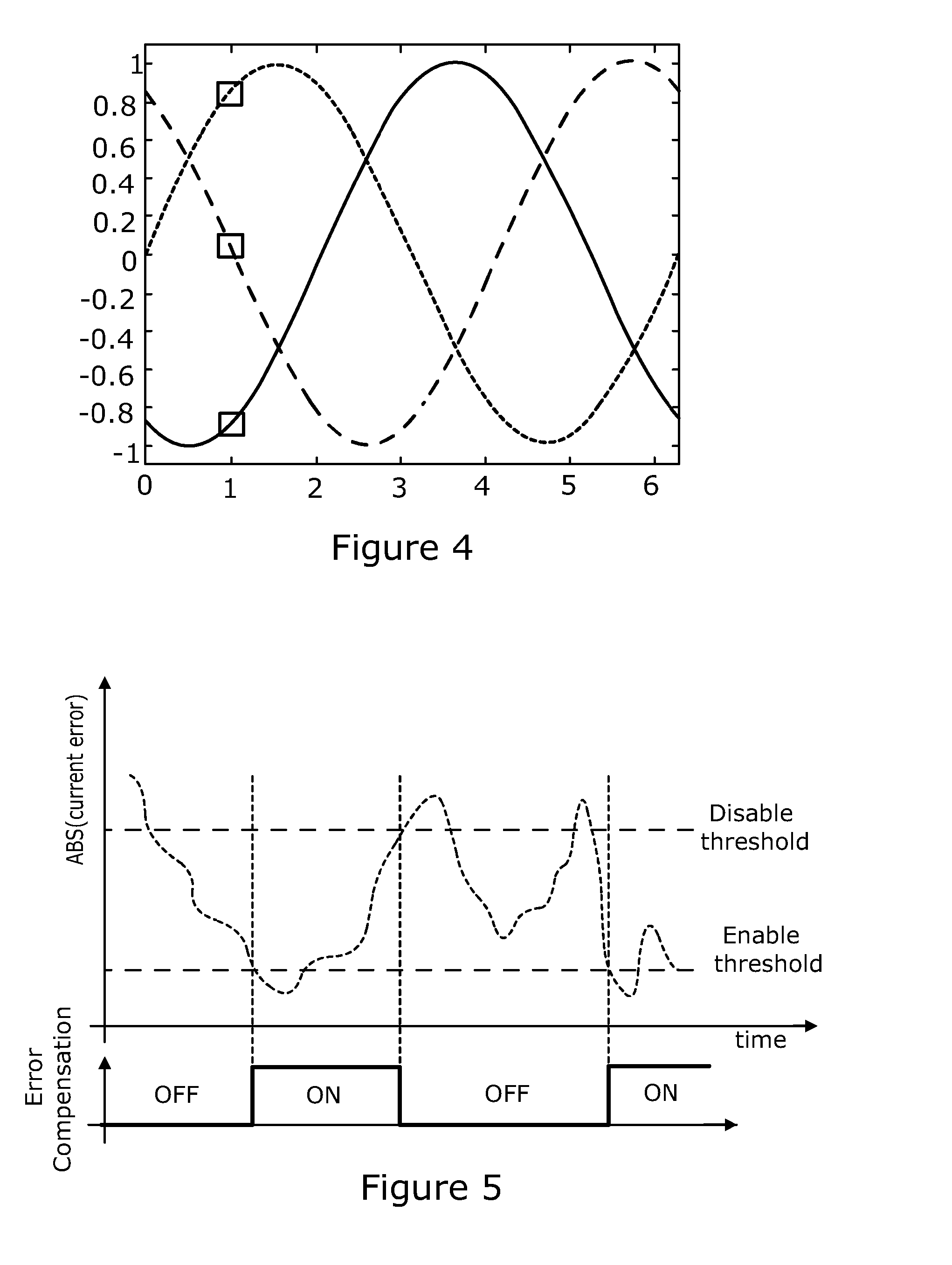
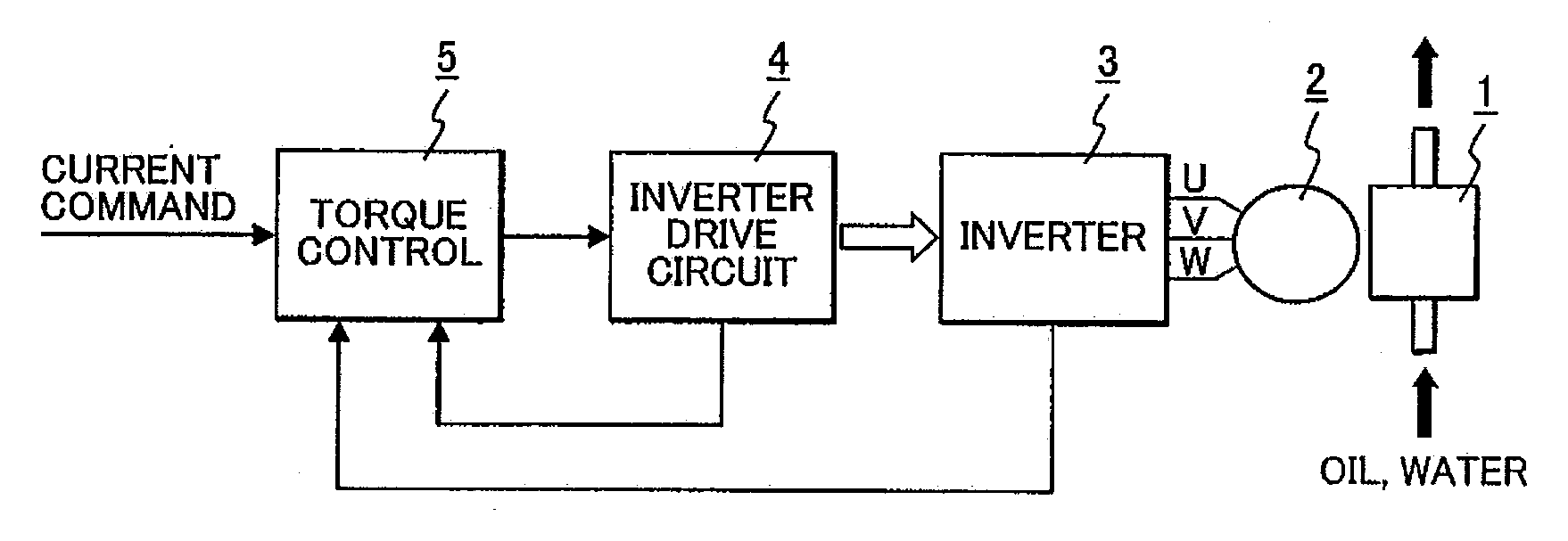
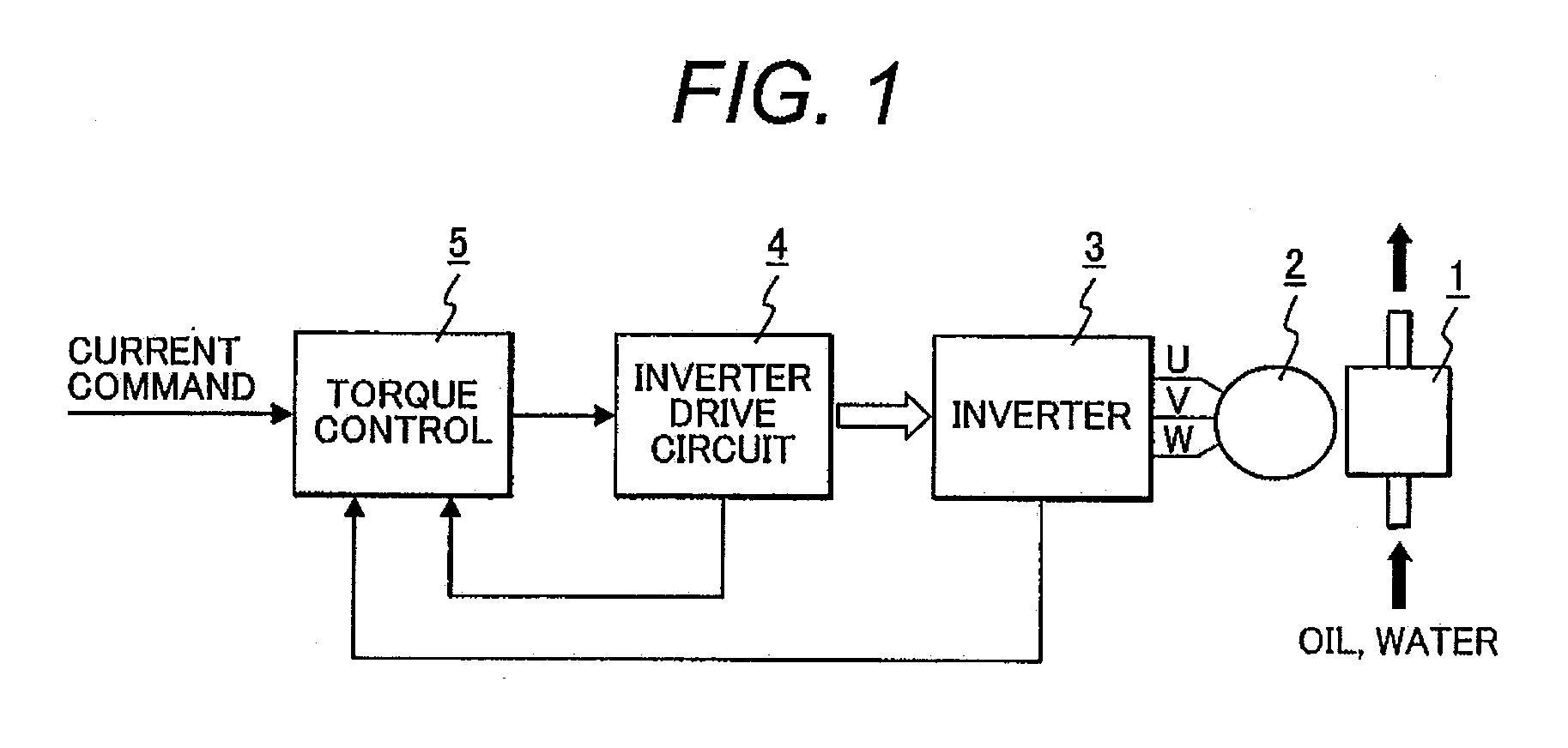
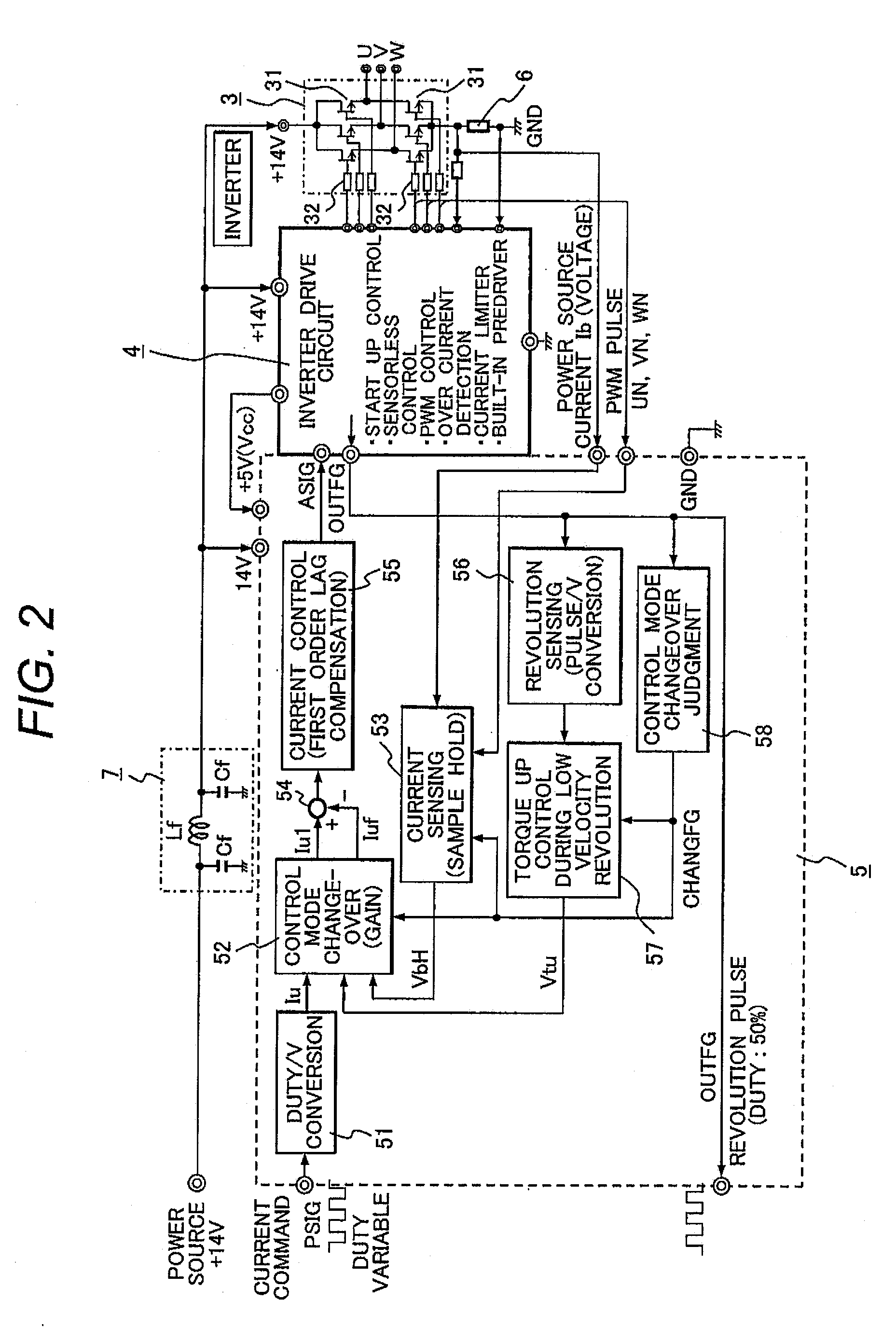
A sensorless-brushless motor control device comprises an inverter, an inverter drive circuit that drives the inverter and a current control part that controls the inverter drive circuit according to a current command from a superior control part and includes a first order lag compensating part. The device is characterized by further comprising a control mode changeover judging part that judges changeover of a control gain of the current control part after startup of the sensorless-brushless motor in response to a motor revolution sensing signal from the inverter drive circuit and a control mode changeover part that changes over the control gain of the current control part in response to an output of the control mode changeover judging part.
Owner:HITACHI CAR ENG CO LTD
Rotor position detection device
ActiveCN102025252AAccurately getVector control systemsSingle motor speed/torque controlLocation detectionMagnetic tension force
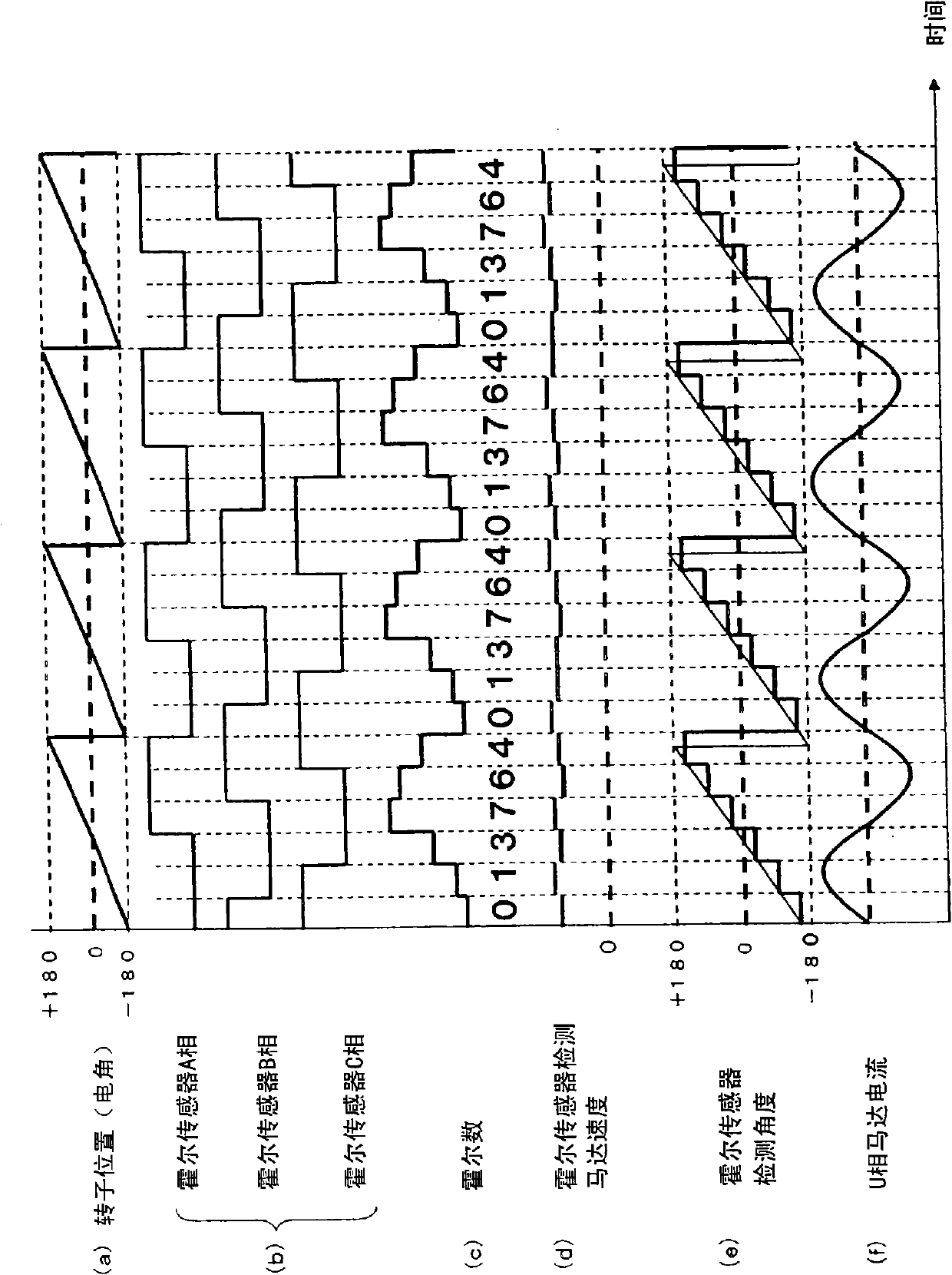
The invention relates to a rotor position detection device. A magnetic detection sensor with low costs can be used to detect the position of a rotor correctly, when a permanent magnet motor disposed in the rotor is provided with a plurality of permanent magnets, parts of which have different magnetic forces. The permanent magnet motor (1) disposed in the rotor (3) is provided with two magnets, one is a neodymium magnet (9a) and the other is an alnico magnet (9b). 3 Hall sensors (68) (A,B,C) can be used by a speed. position detection part (55) to detect the rotation speed of the permanent magnet motor (1), and the position of the rotor (3) can be detected based on the rotation speed. The rotation speed or the position of the rotor, which are detected by the speed. position detection part (55), can be corrected, when the speed. position detection part (55) detects the boundary between the neodymium magnet (9a) and the alnico magnet (9b) according to the changing state of the sensor signal output by the Hall sensors (68).
Owner:TOSHIBA LIFESTYLE PROD & SERVICES CORP +1
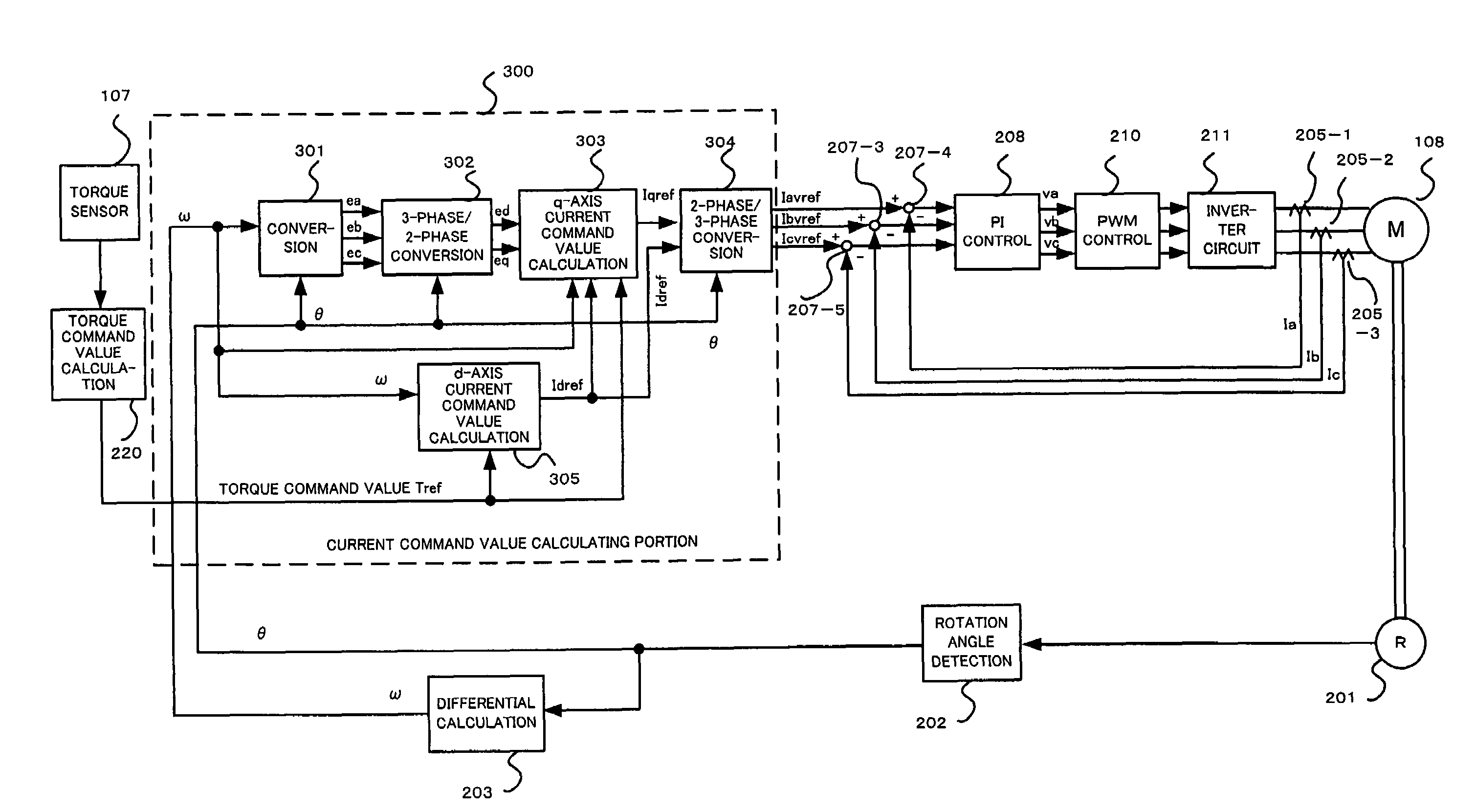
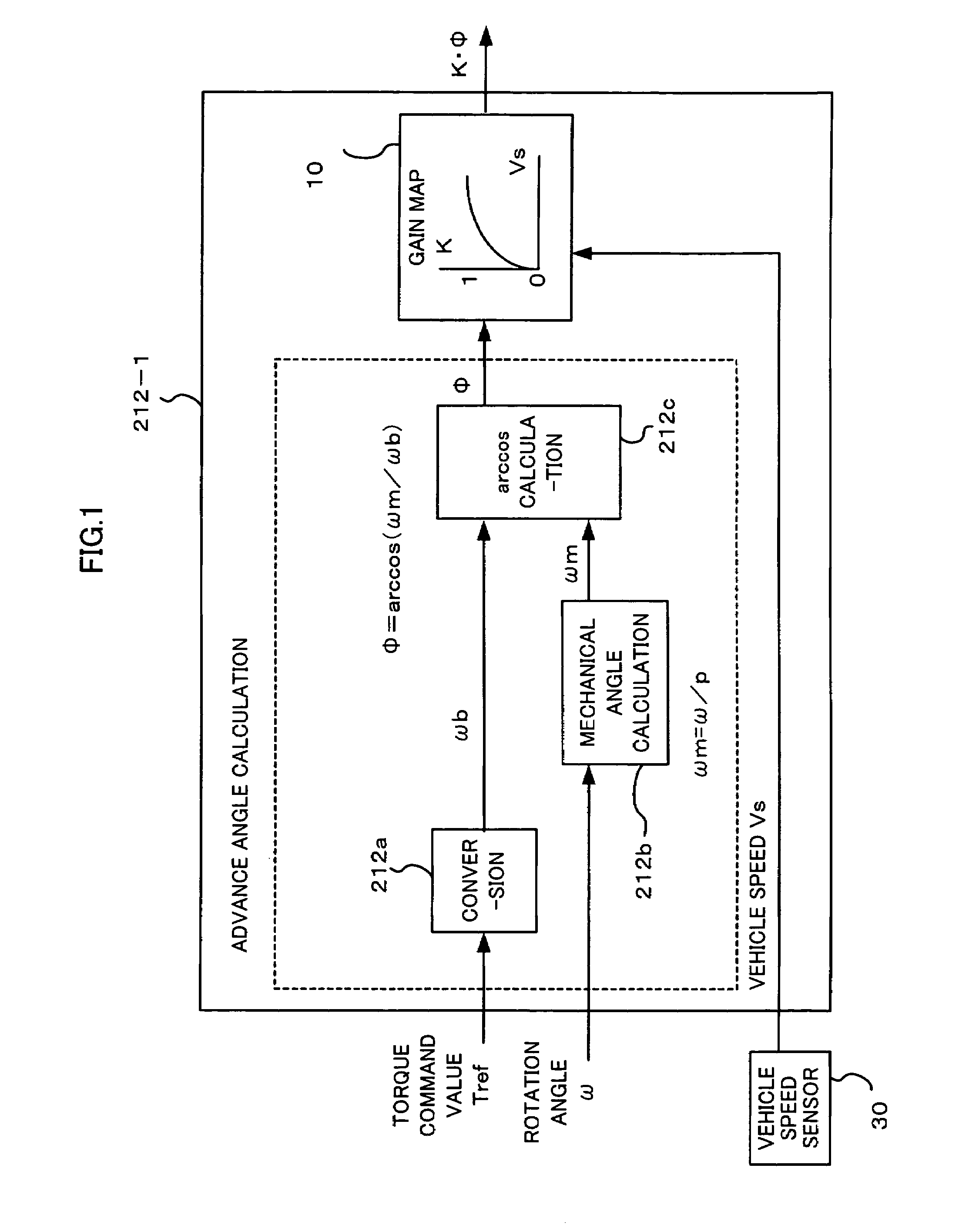
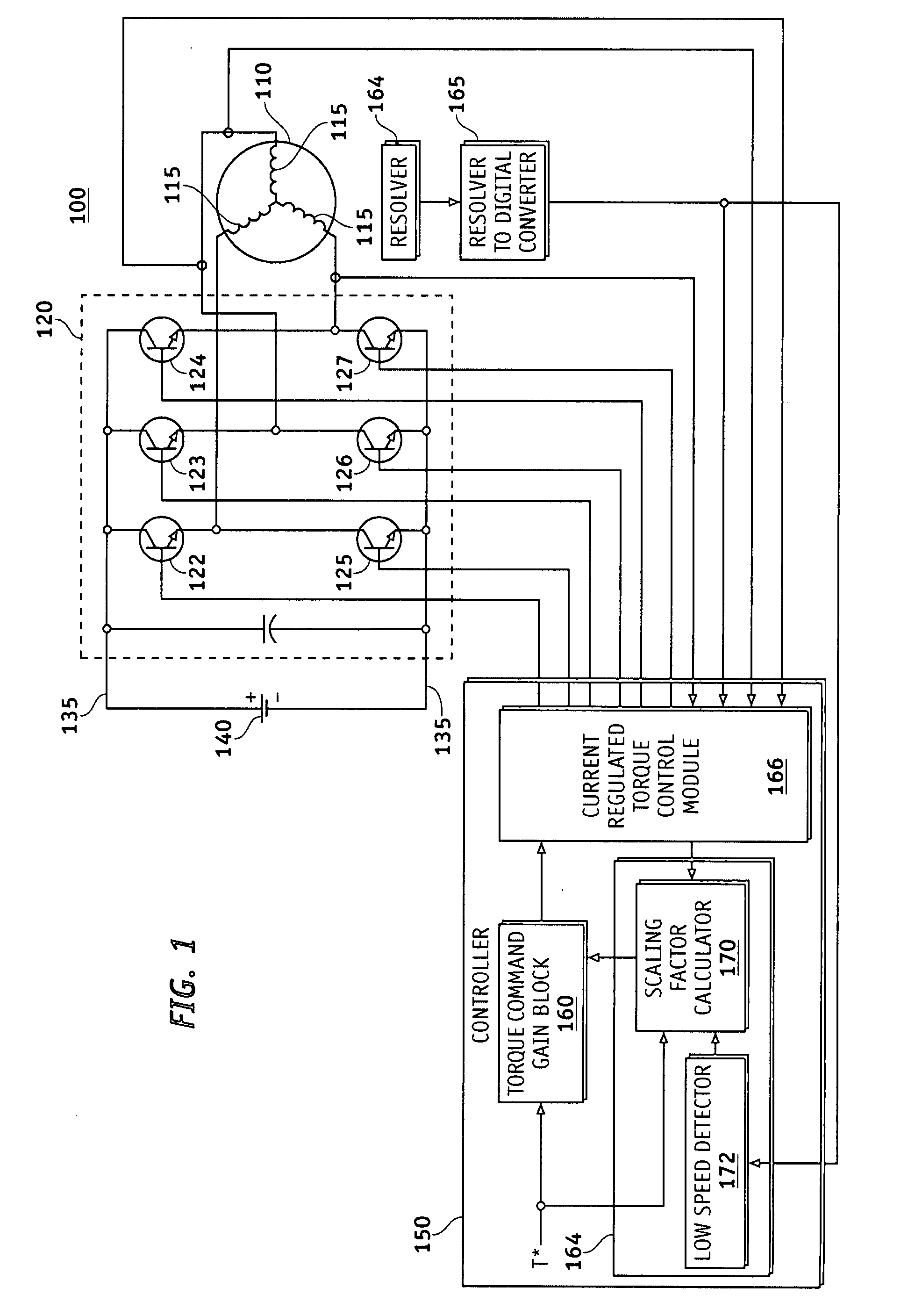
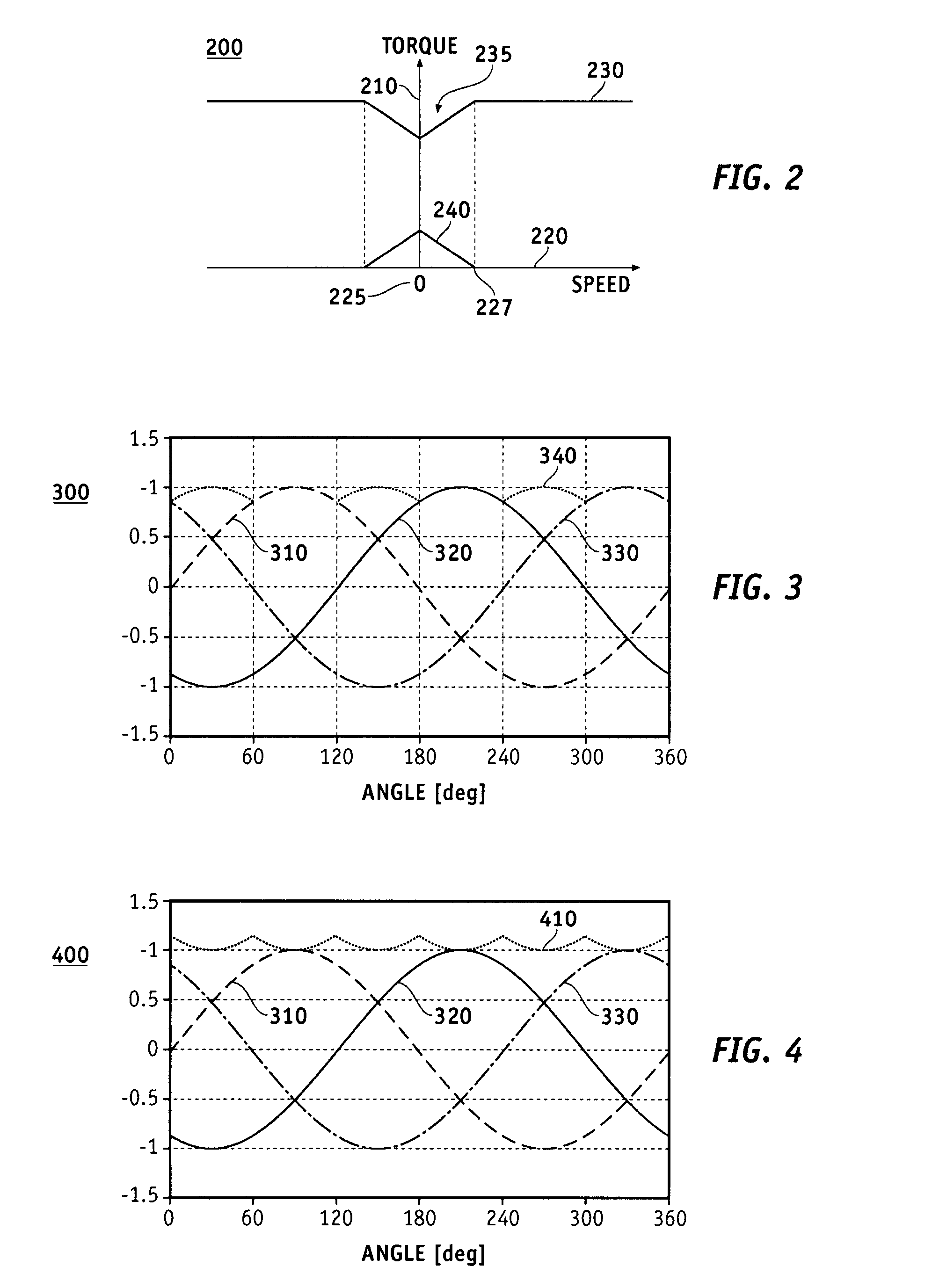
Low speed synchronous motor drive operation
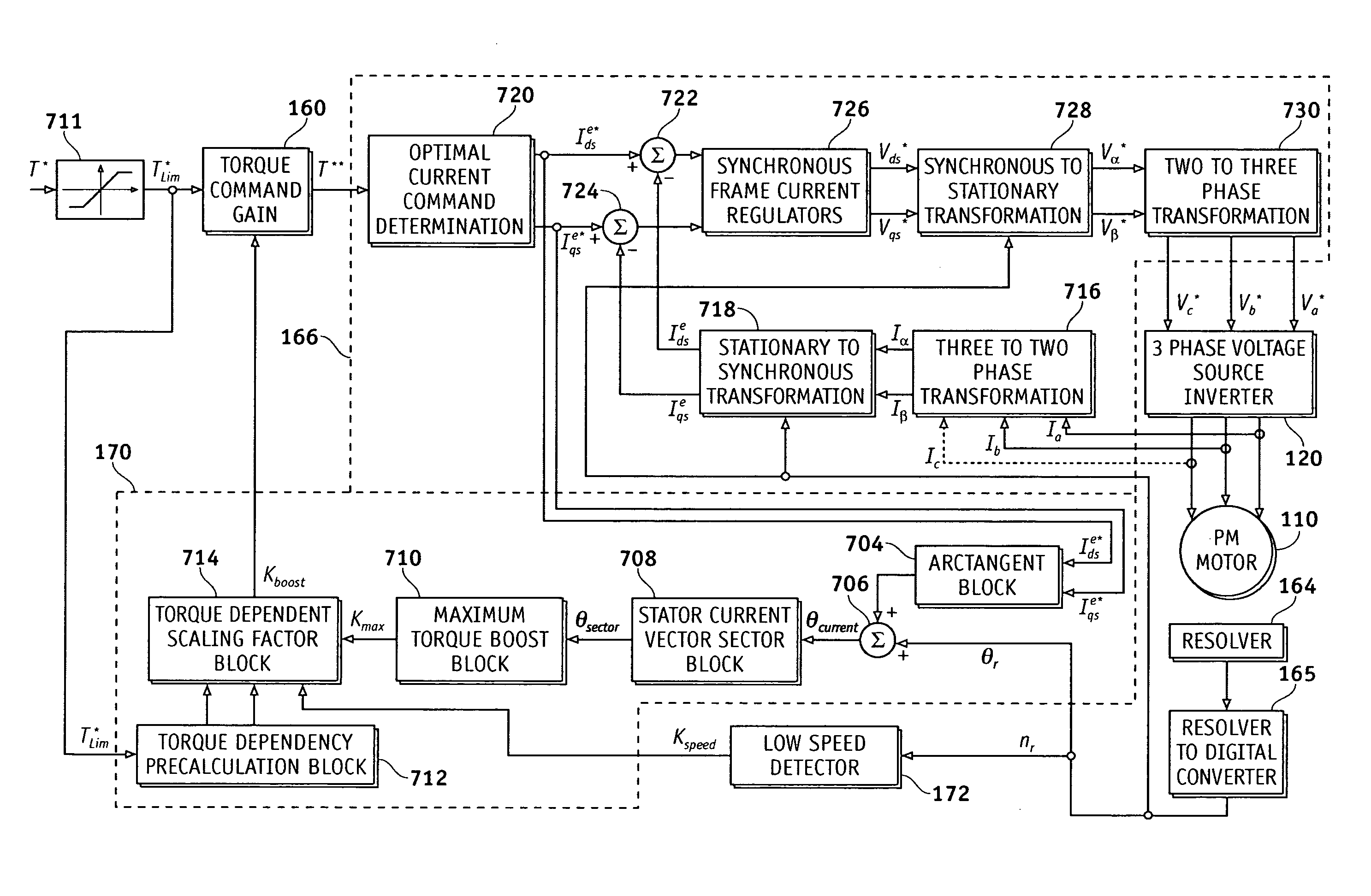
Methods and apparatus are provided for providing a torque boost in an electric motor system at low speeds. The electric motor system comprises an alternating current (AC) synchronous electric motor, an inverter and a controller. The inverter is coupled to the AC synchronous electric motor and provides electric control therefore. The controller is coupled to the inverter and provides operational control signals thereto for operation of the electric motor. The controller includes a torque command gain block which modifies a torque command to generate a boosted torque signal in response to a detected speed of the electric motor, the torque command modified to define the boosted torque signal defined in accordance with a torque dependent scaling factor calculated in response to the torque command.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Double fed synchronous generator motor
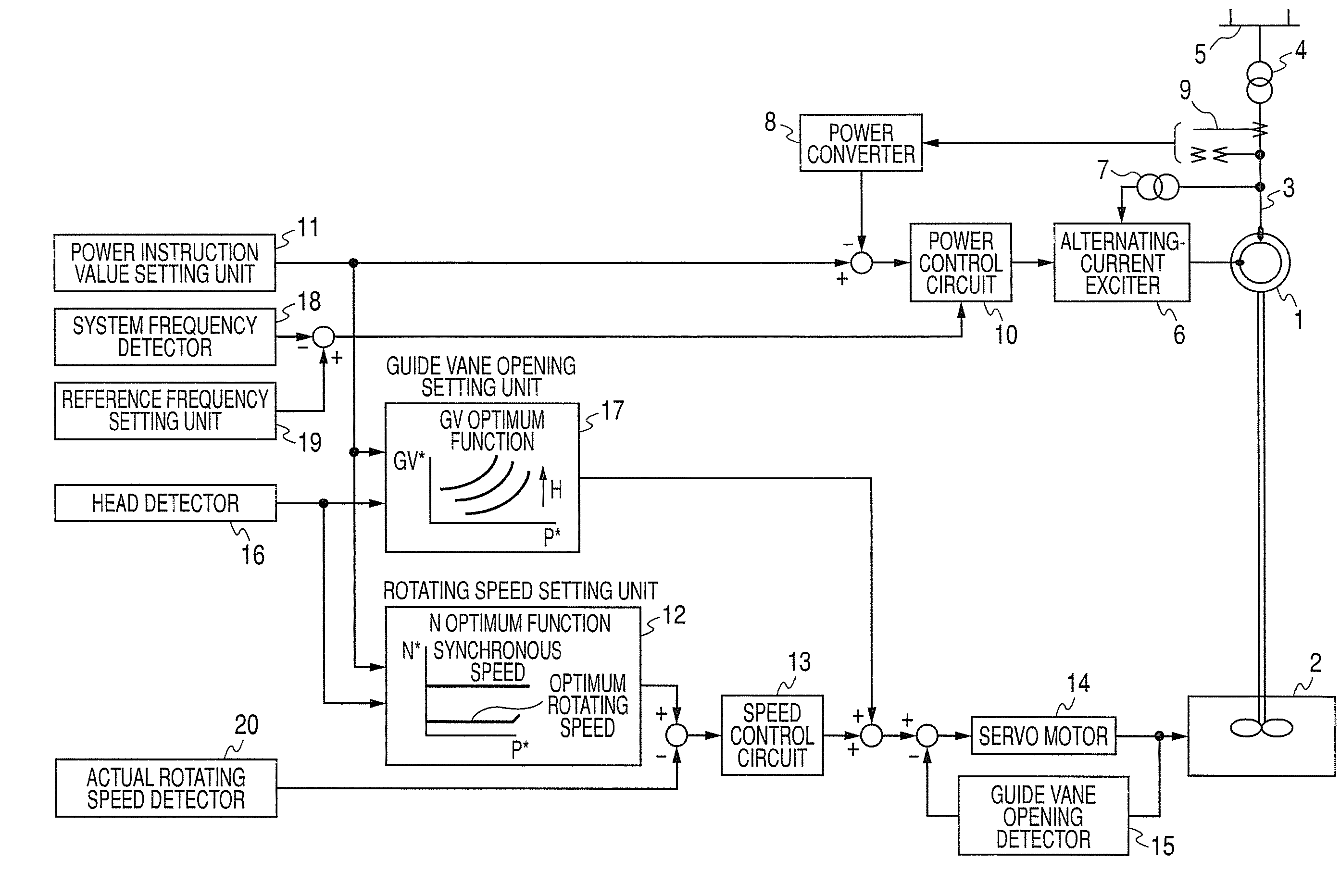
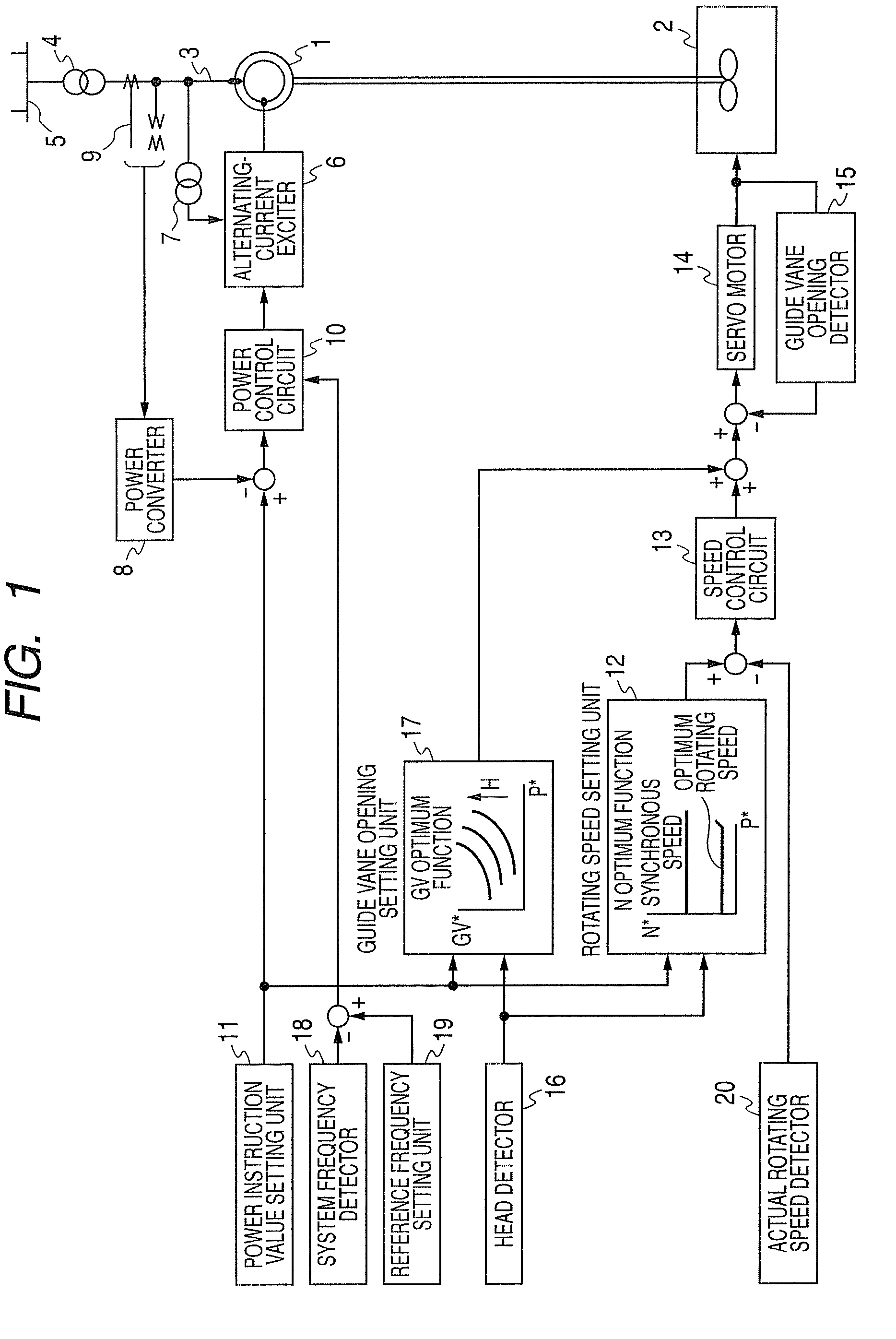
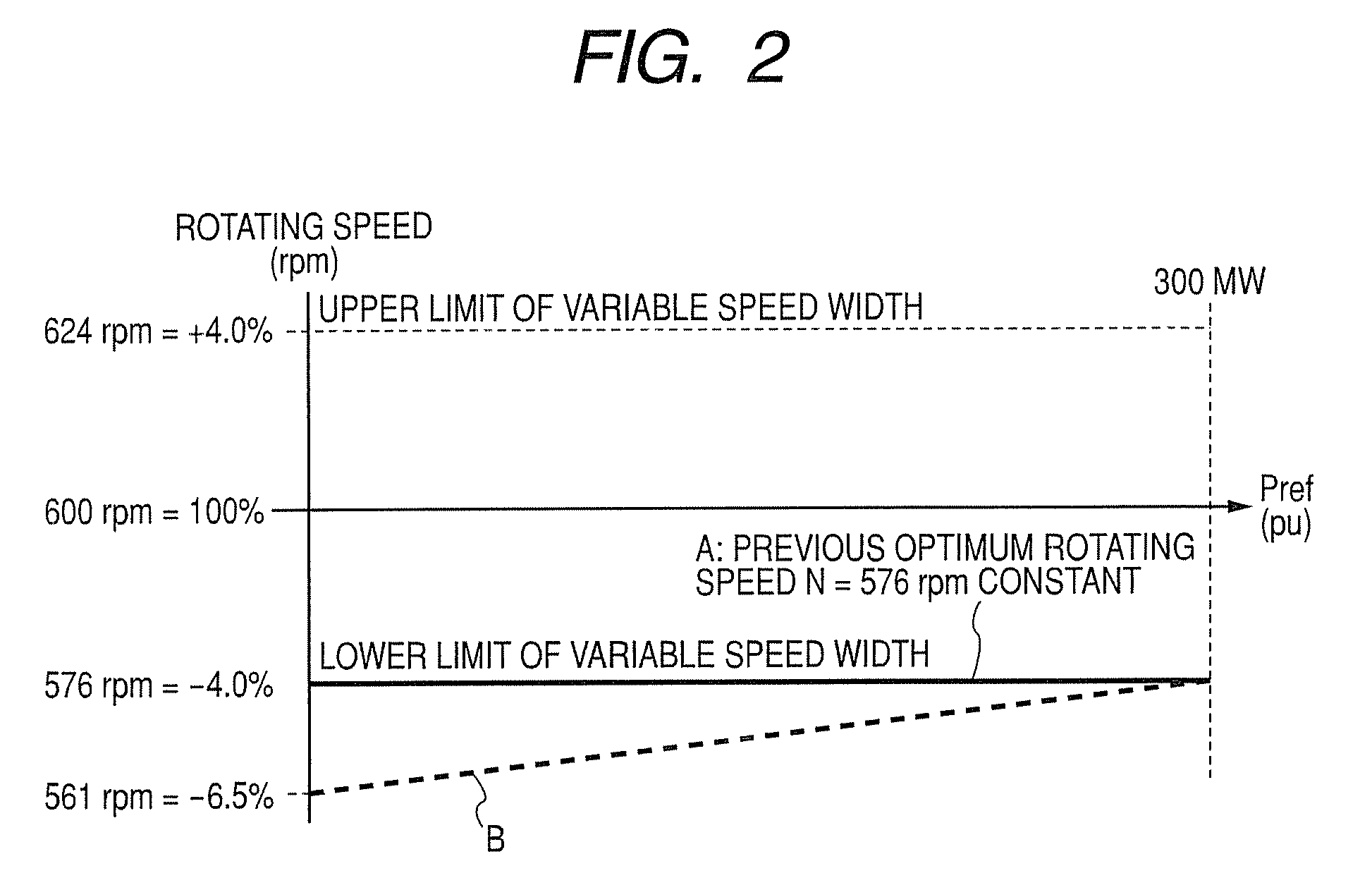
ActiveUS20090302607A1Improve efficiencyGenerator control circuitsMotor control for very low speedsLower limitOperation mode
A double fed synchronous generator motor which is coupled to a reversible pump-turbine and operated while switched to a power generating operation mode or a pumping operation mode, is equipped with a controller for controlling the double fed synchronous generator motor so that power output from the double fed synchronous generator motor is coincident with an instruction value and the rotating speed is set between upper and lower limit values of the rotating speed by changing exciting current. In the power generating operation mode, the lower limit value of the rotating speed is varied by active power output from the double fed synchronous generator motor, and when the active power is small, the lower limit value of the rotating speed is set to a smaller value than that when the active power is large.
Owner:HITACHI MITSUBISHI HYDRO
Control unit for elctric power steering apparatus
ActiveUS20070103105A1Reduce motor noiseImproving a wheel steering feelDC motor speed/torque controlVector control systemsElectric power steeringEngineering
In order to solve a problem that a motor generates a noise so as to deteriorate an environment in a vehicle if a field weakening control is executed to the motor of a electric power steering apparatus, in the case that a vehicle speed is high, the same field weakening control as the conventional one is applied to the motor because a noise generated due to a friction between a tire and a road surface and a wind noise of a vehicle body are large, and in the case that the vehicle speed is low, the field weakening control is weakly applied in comparison with the conventional one because the noise generated by the motor is felt relatively largely. Accordingly, the field weakening control can be executed in response to the vehicle speed in such a manner as to make the motor noise smaller.
Owner:NSK LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com