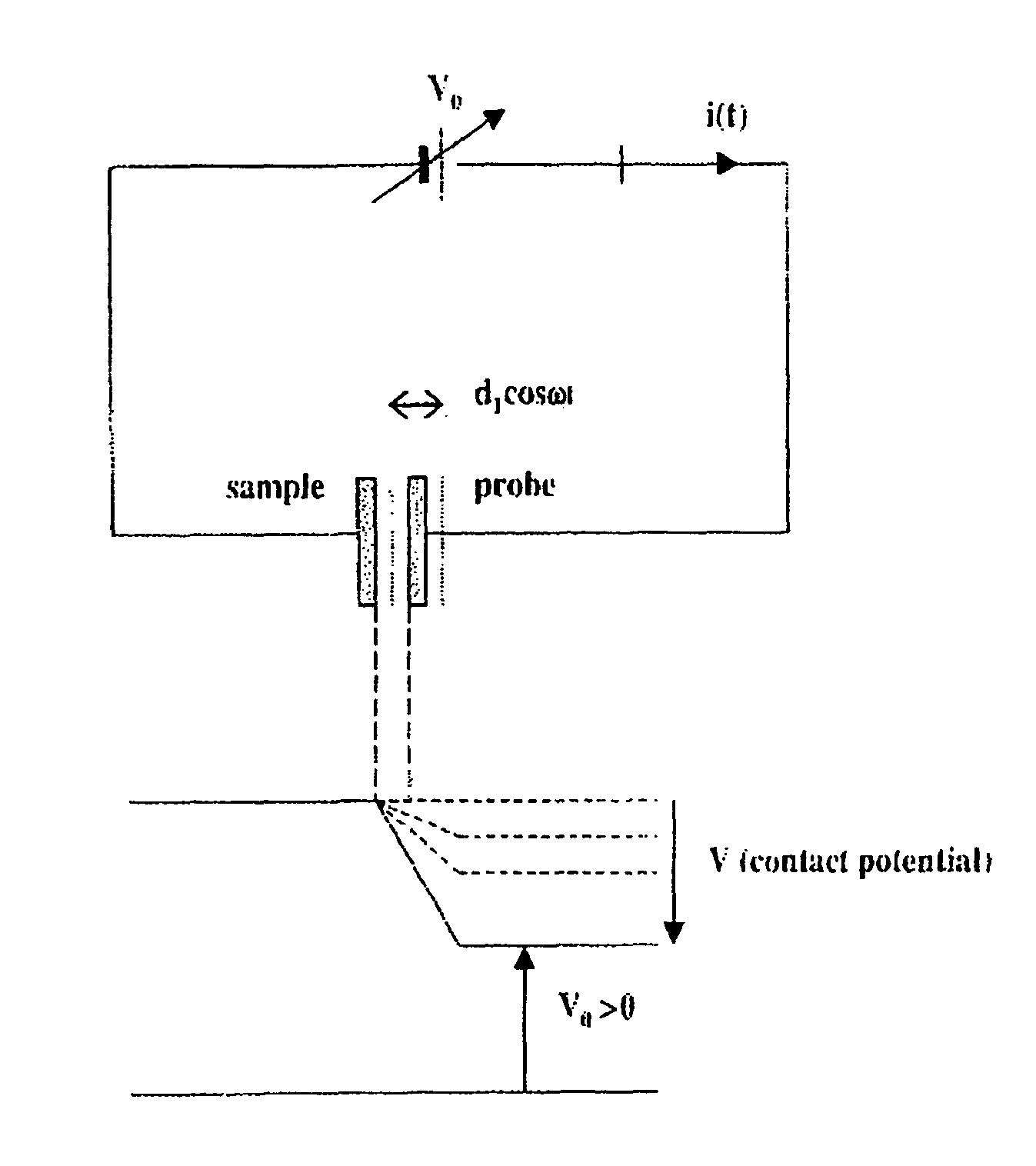
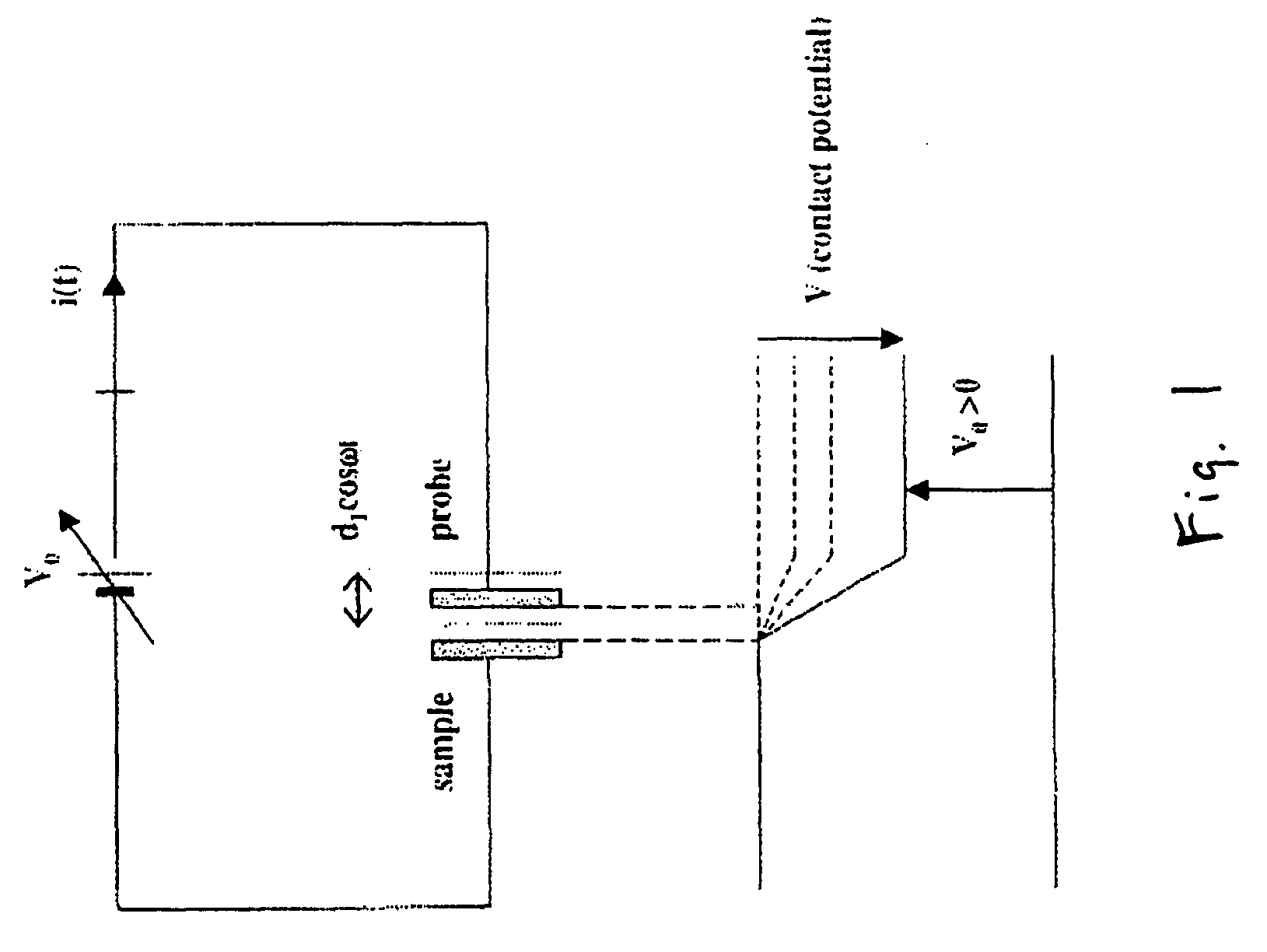
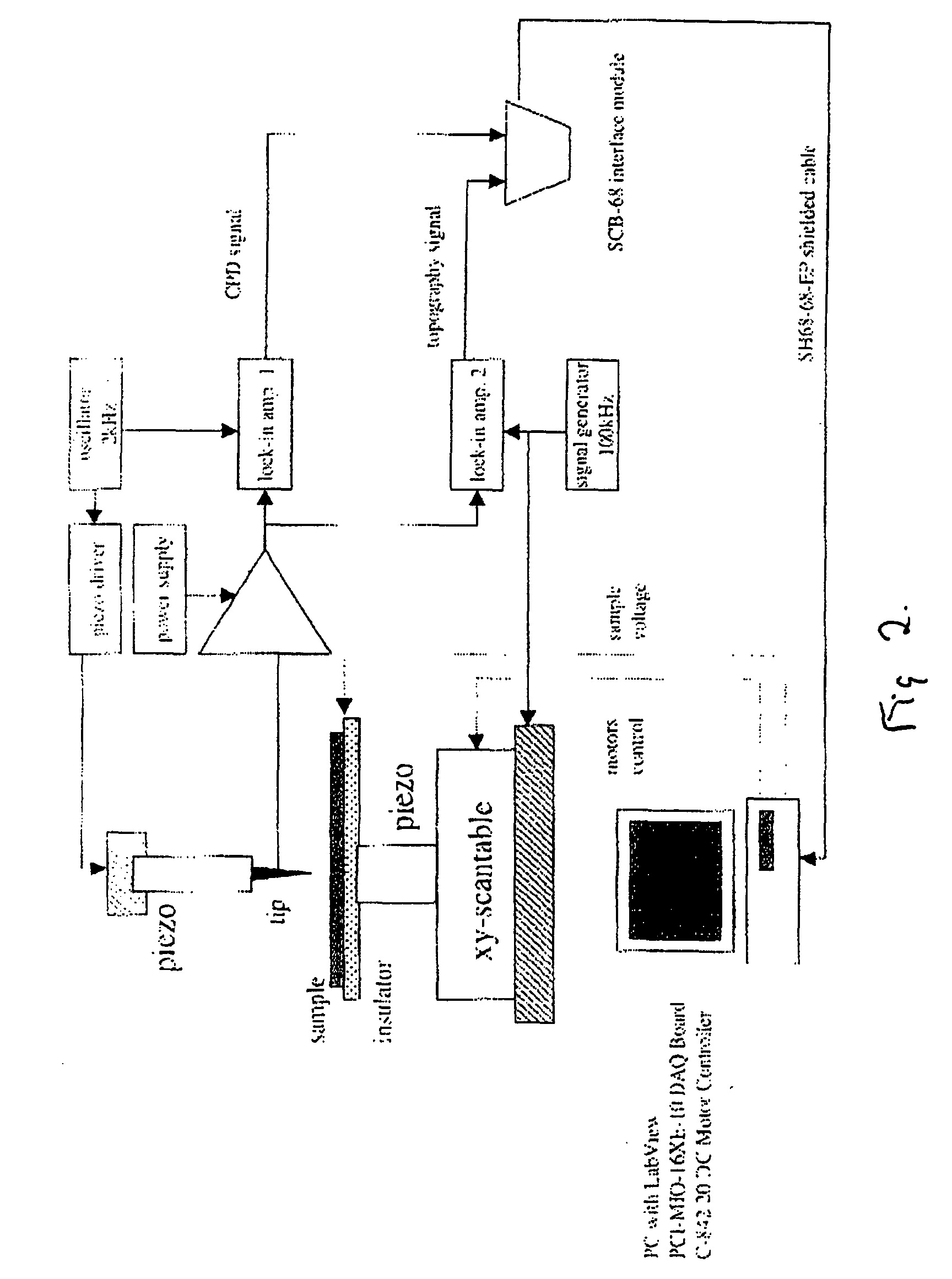
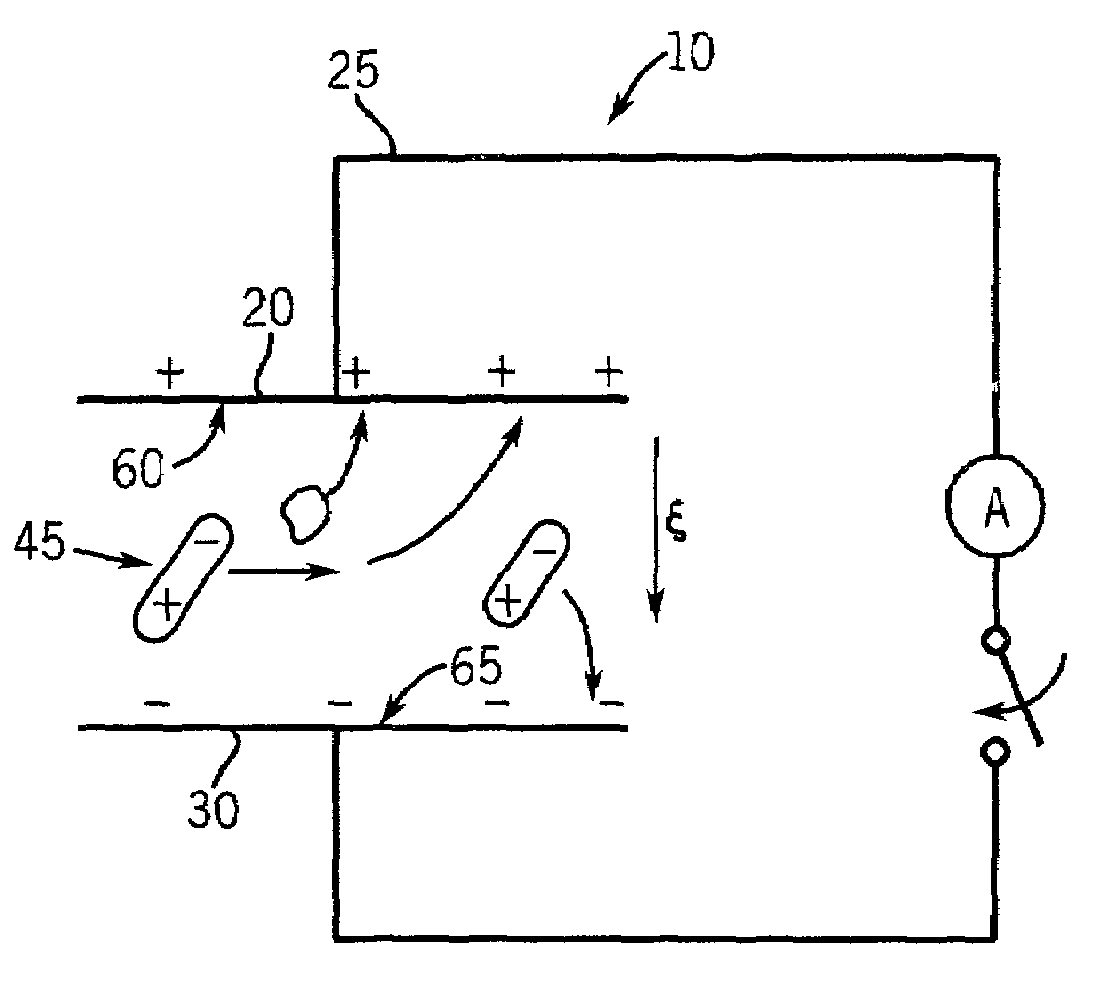
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
72results about "Material work function voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
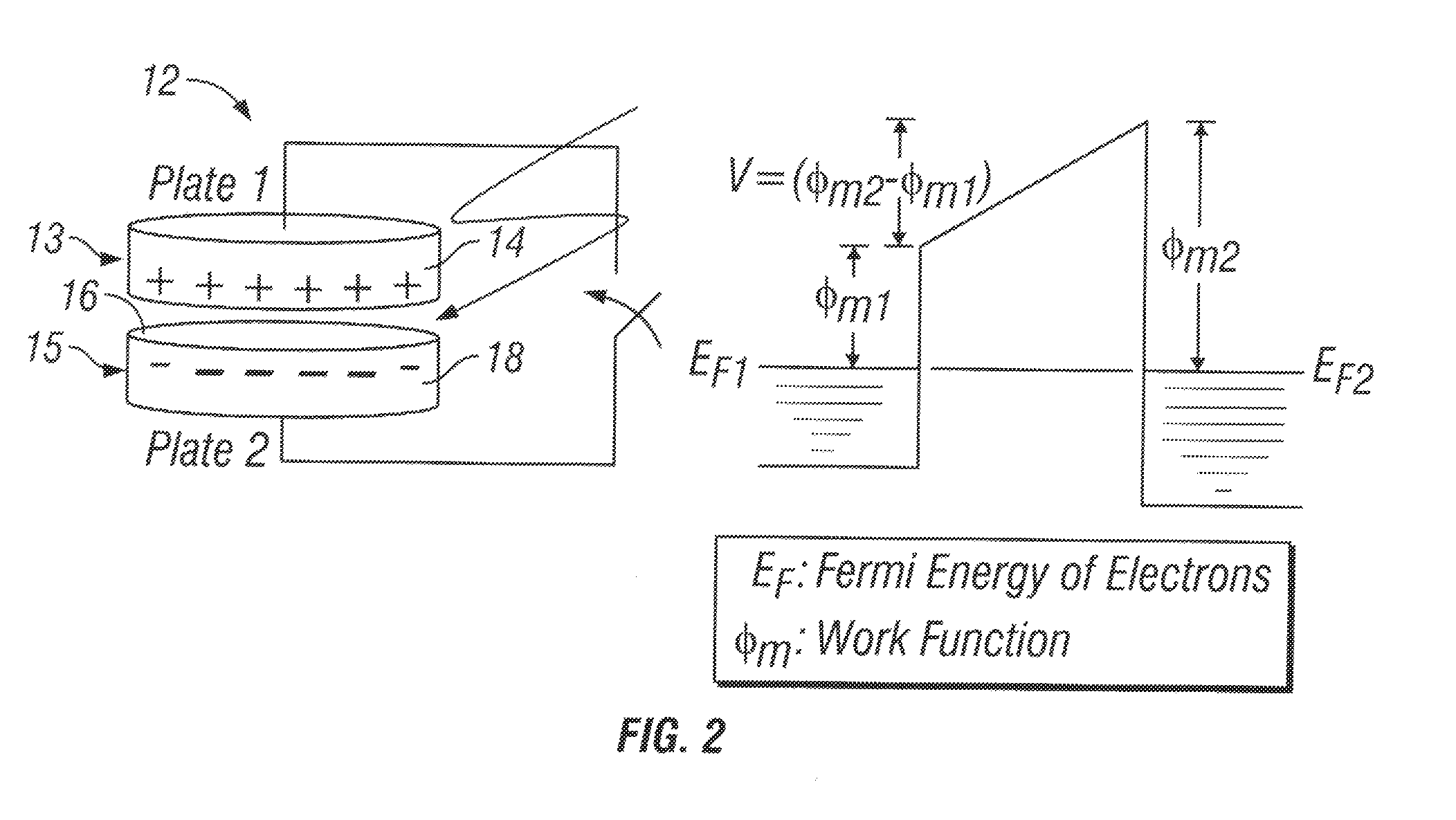
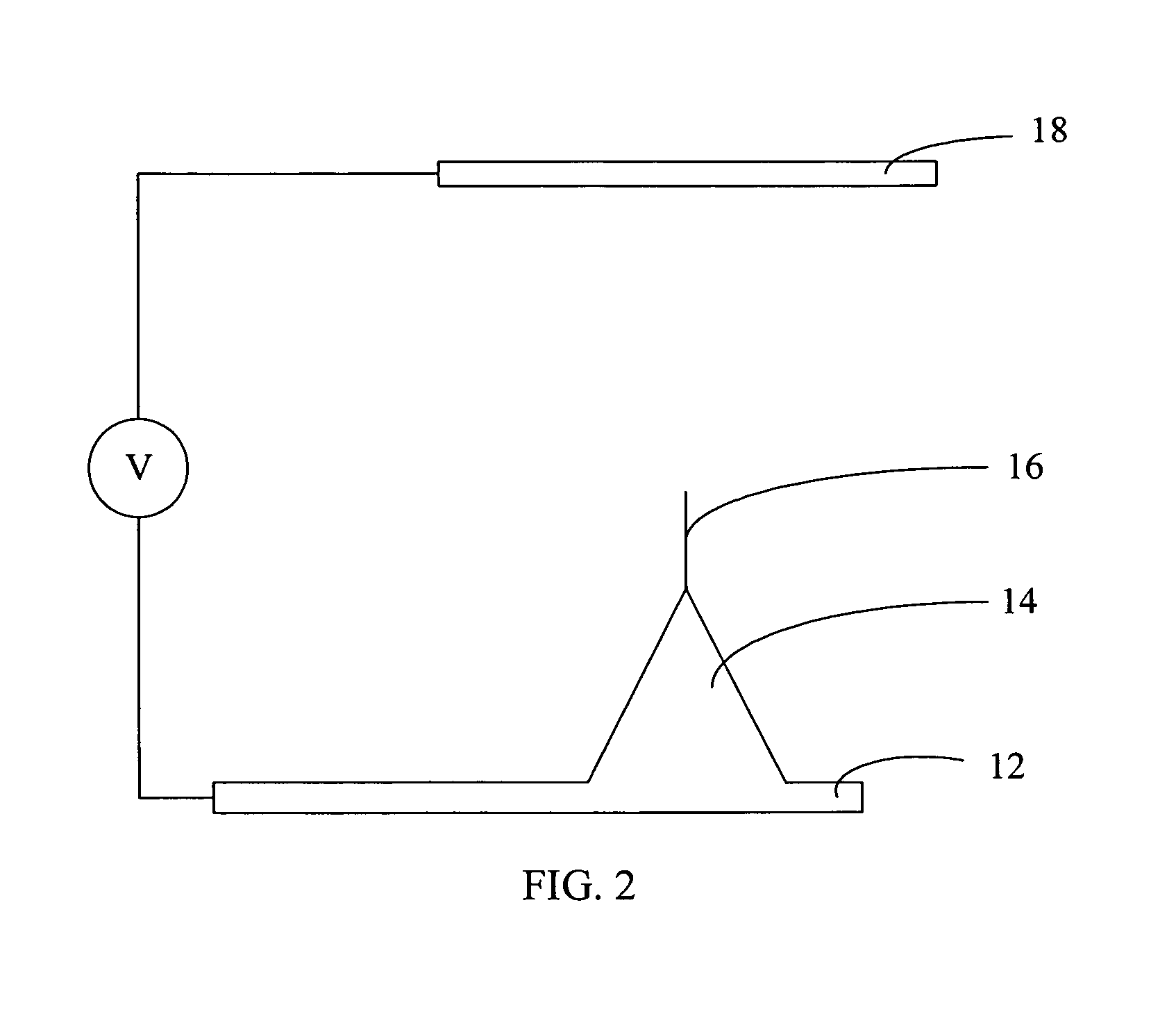
Method and system for detecting metal contamination on a semiconductor wafer
InactiveUS20020090746A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesElectricityWork function
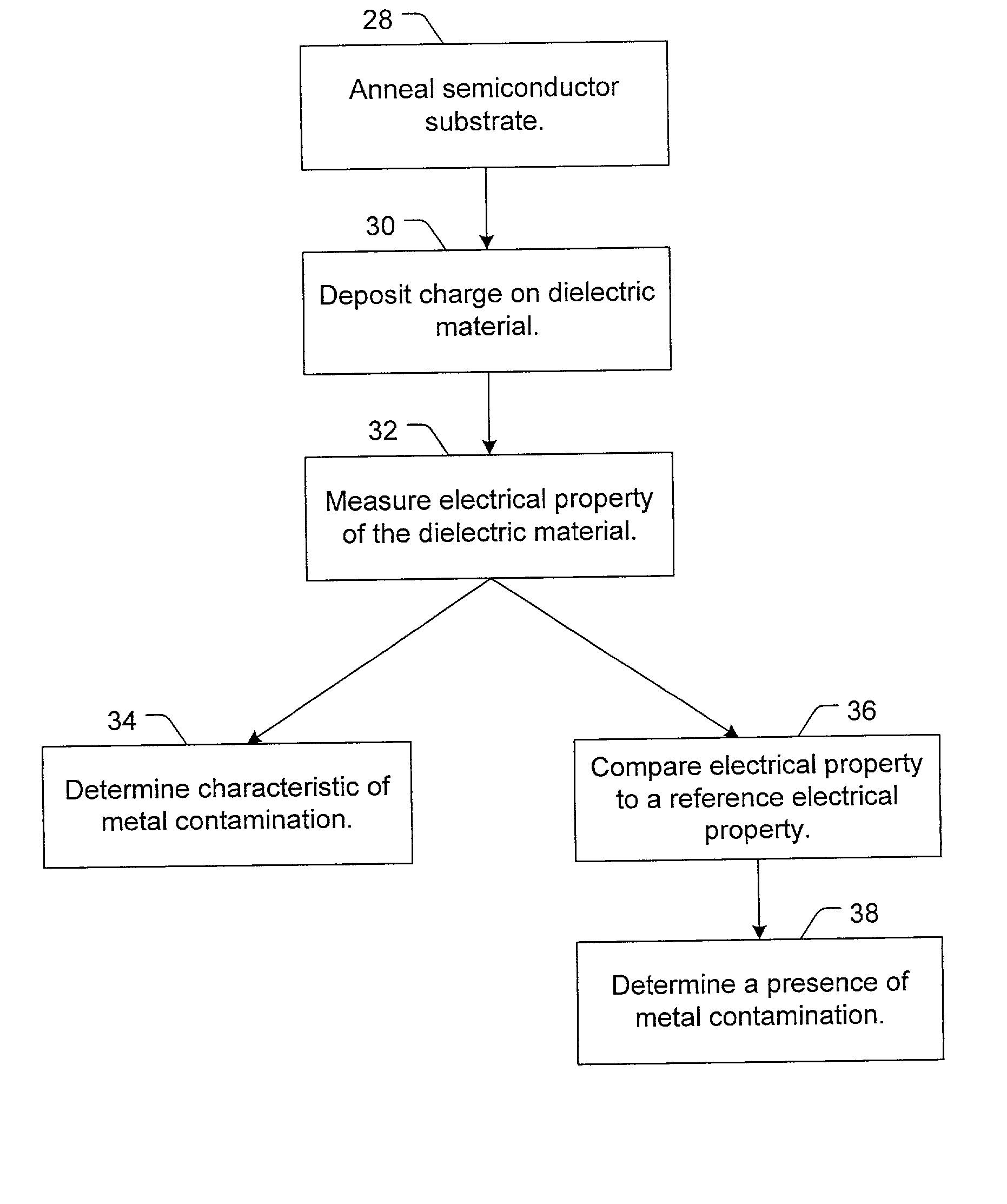
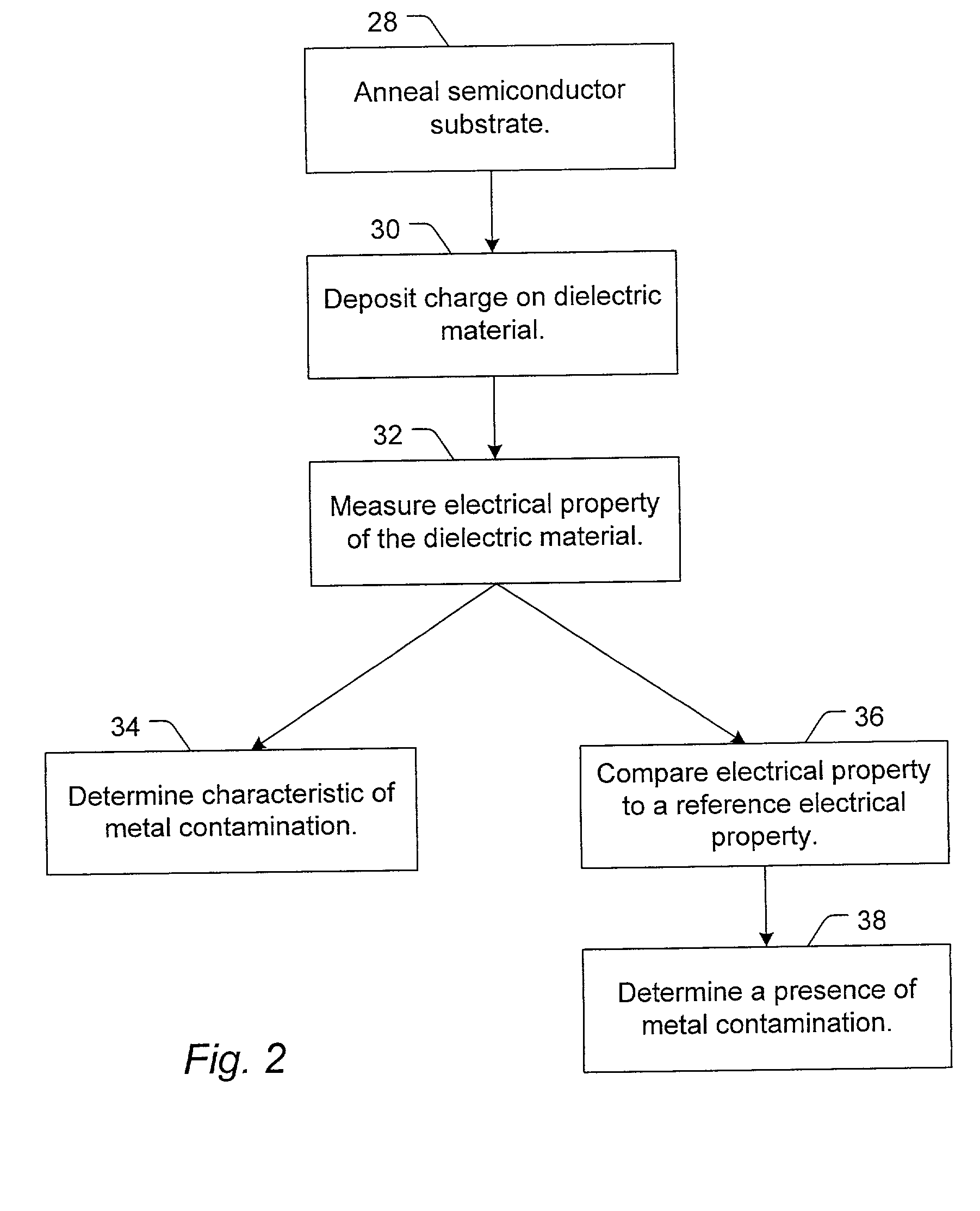
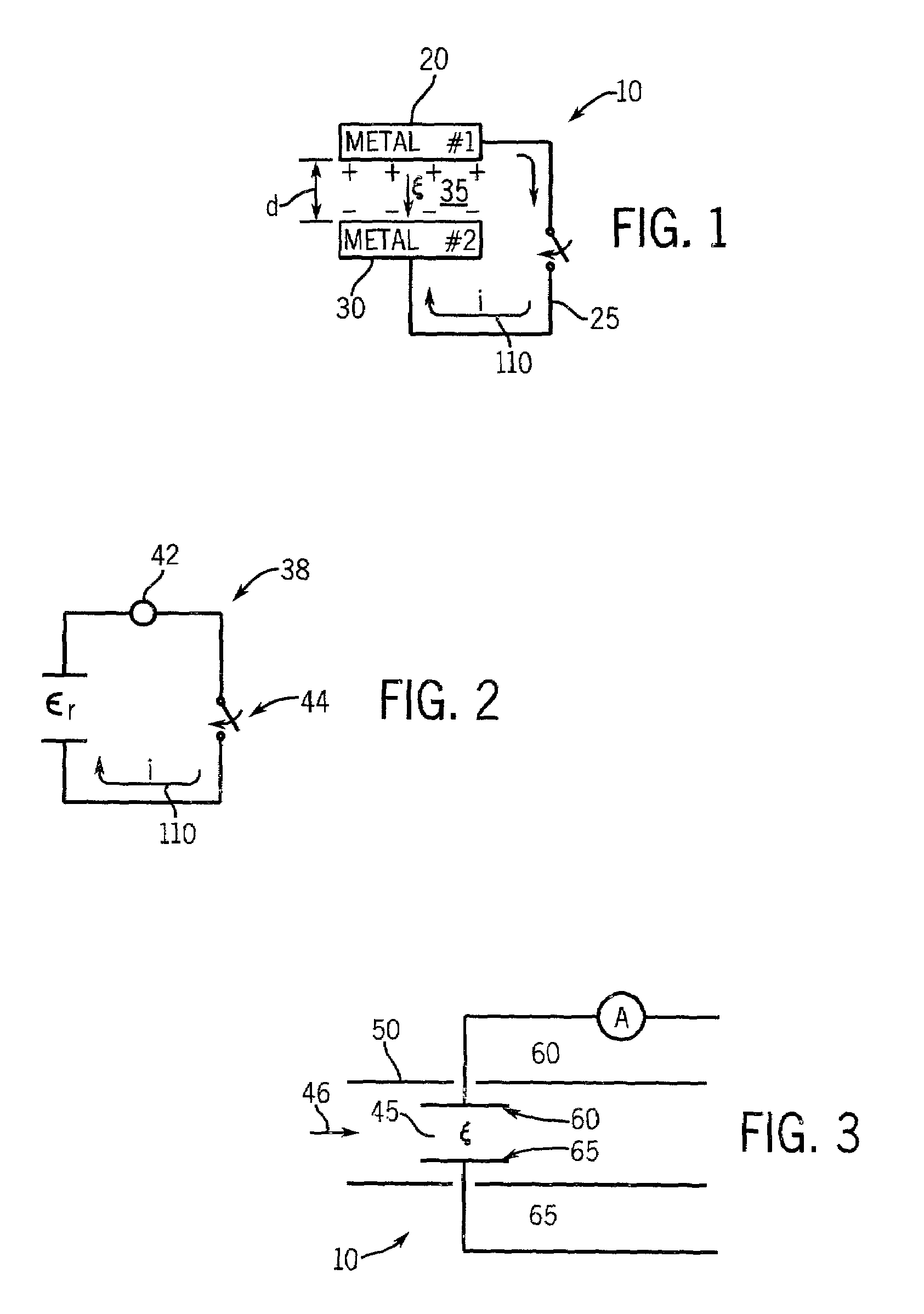
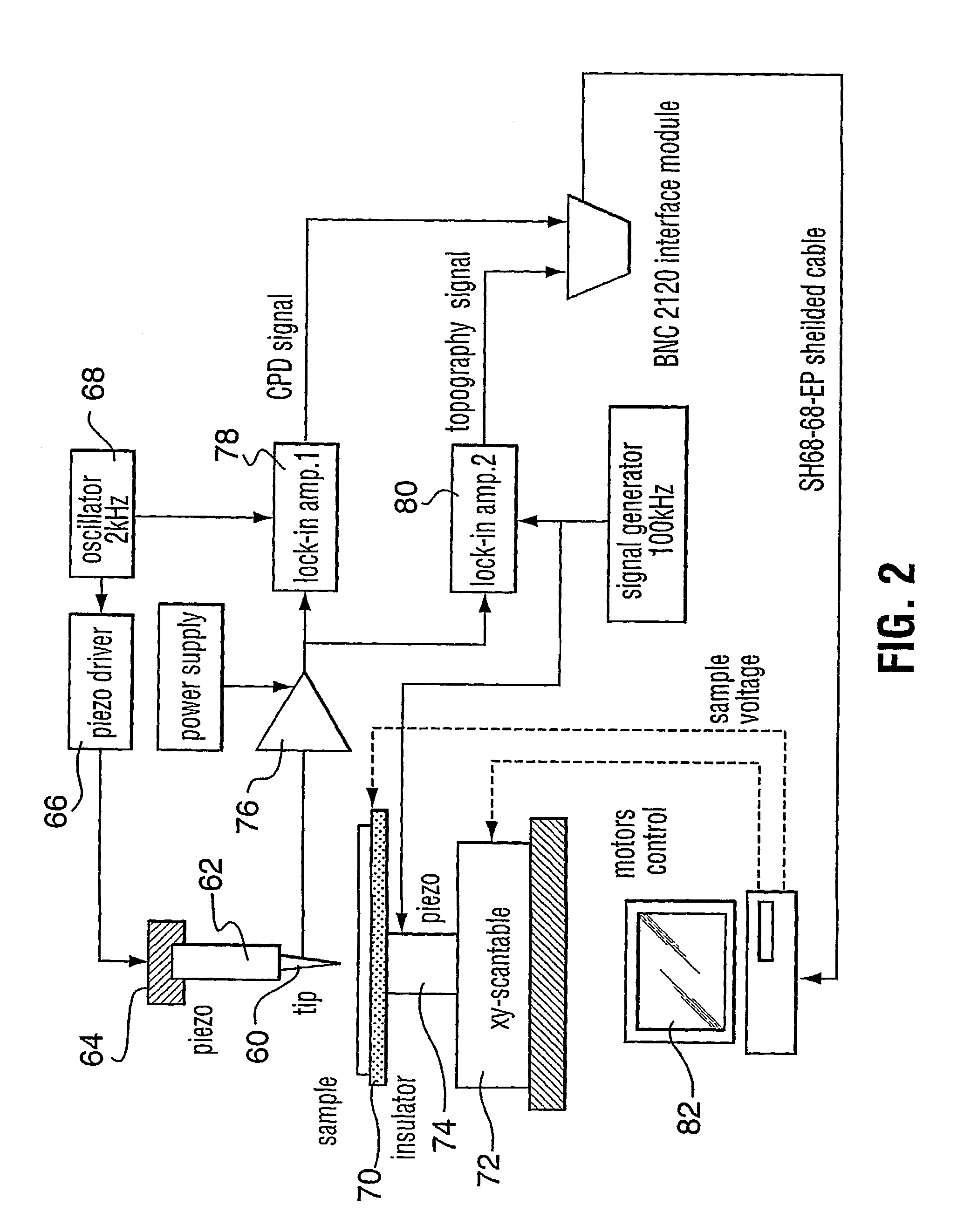
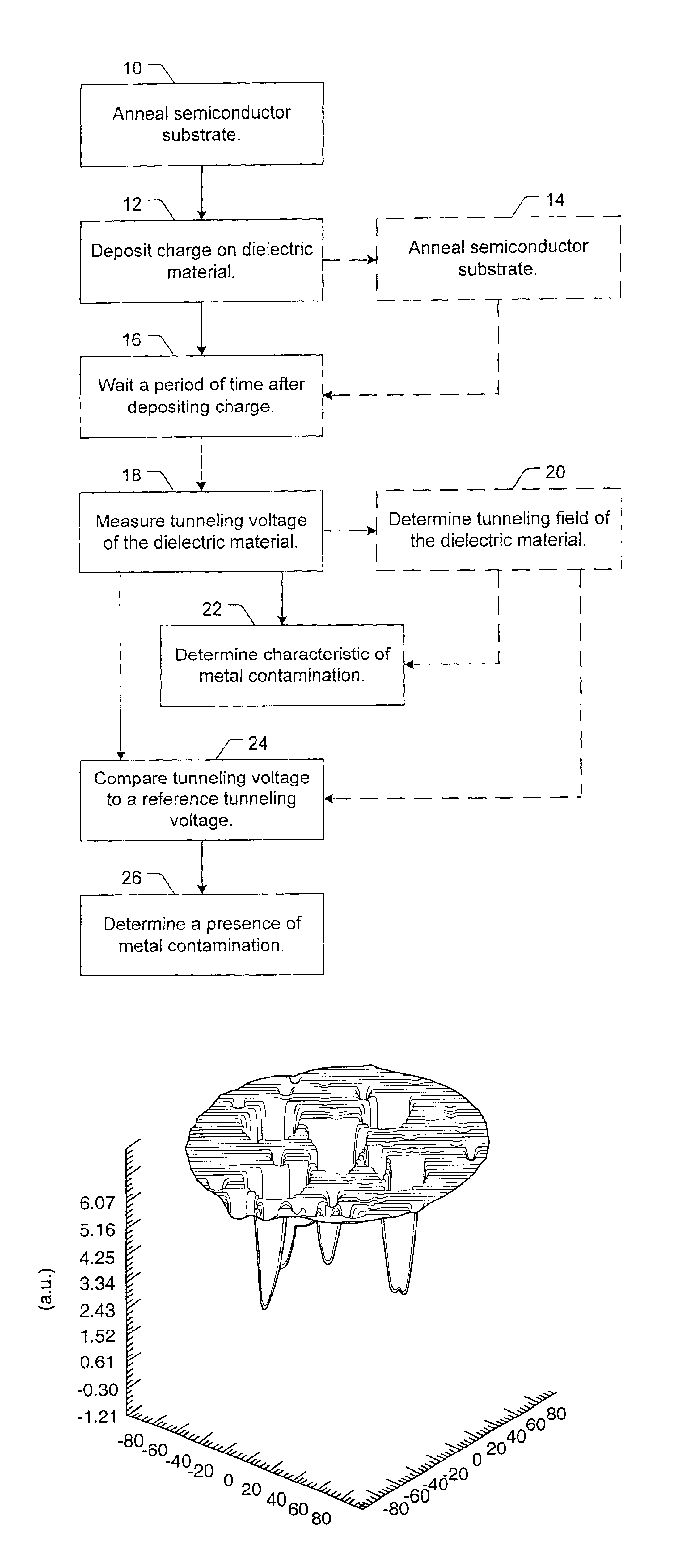
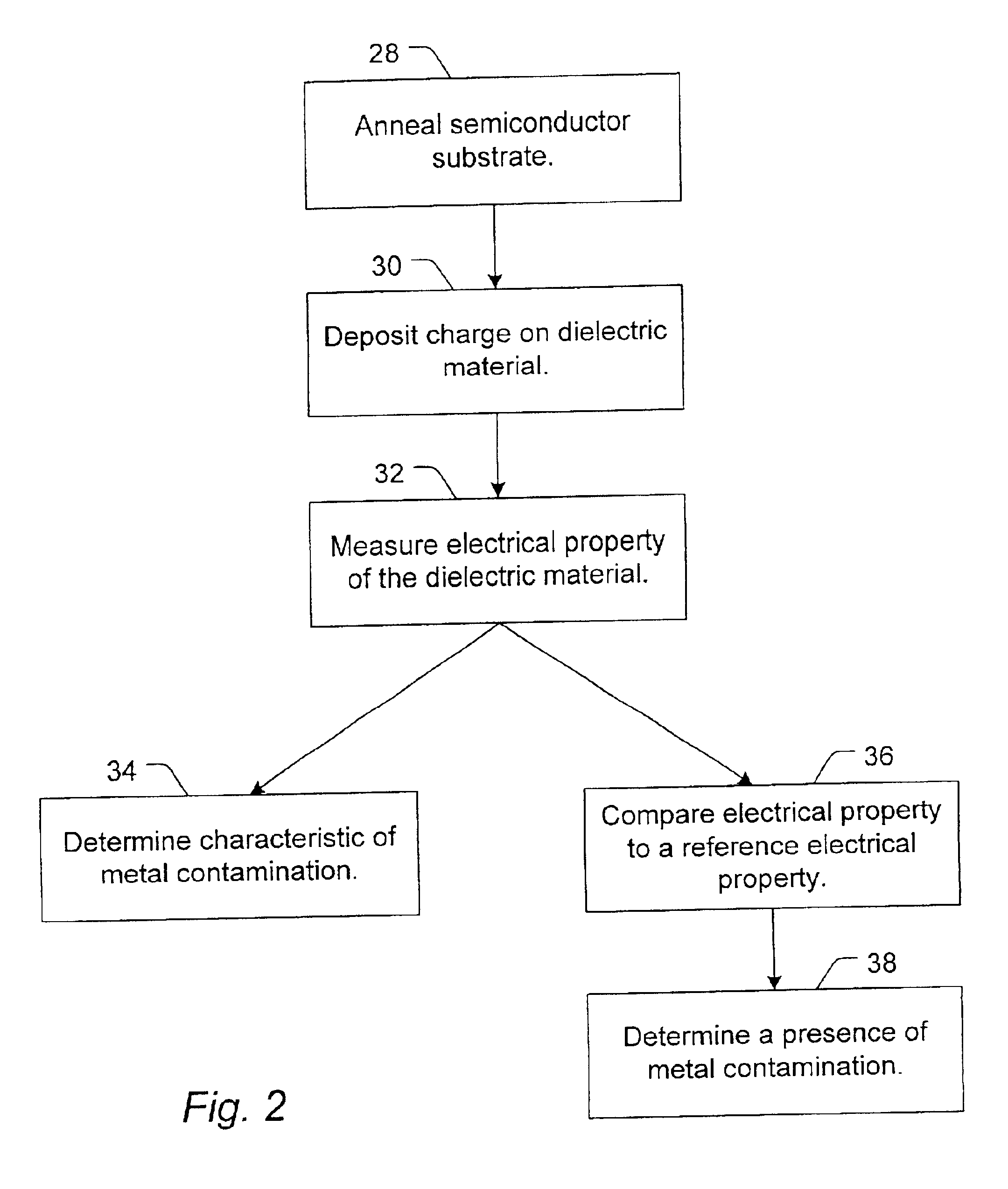
A method to detect metal contamination on a semiconductor topography is provided. The semiconductor topography may include a semiconductor substrate or a dielectric material disposed upon a semiconductor substrate. The metal contamination may be driven into the semiconductor substrate by an annealing process. Alternatively, the annealing process may drive the metal contamination into the dielectric material. Subsequent to the annealing process, a charge may be deposited upon an upper surface of the semiconductor topography. An electrical property of the semiconductor topography may be measured. A characteristic of at least one type of metal contamination may be determined as a function of the electrical property of the semiconductor topography. The method may be used to determine a characteristic of one or more types of metal contamination on a portion of the semiconductor topography or the entire semiconductor topography. A system configured to detect metal contamination on a semiconductor topography is also provided. An oven may be incorporated into the system and may be used to anneal the semiconductor topography. The system may also include a device that may be configured to deposit a charge on an upper surface of the semiconductor topography. A sensor may also be included in the system. The sensor may use a non-contact work function technique to measure an electrical property of the semiconductor topography.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
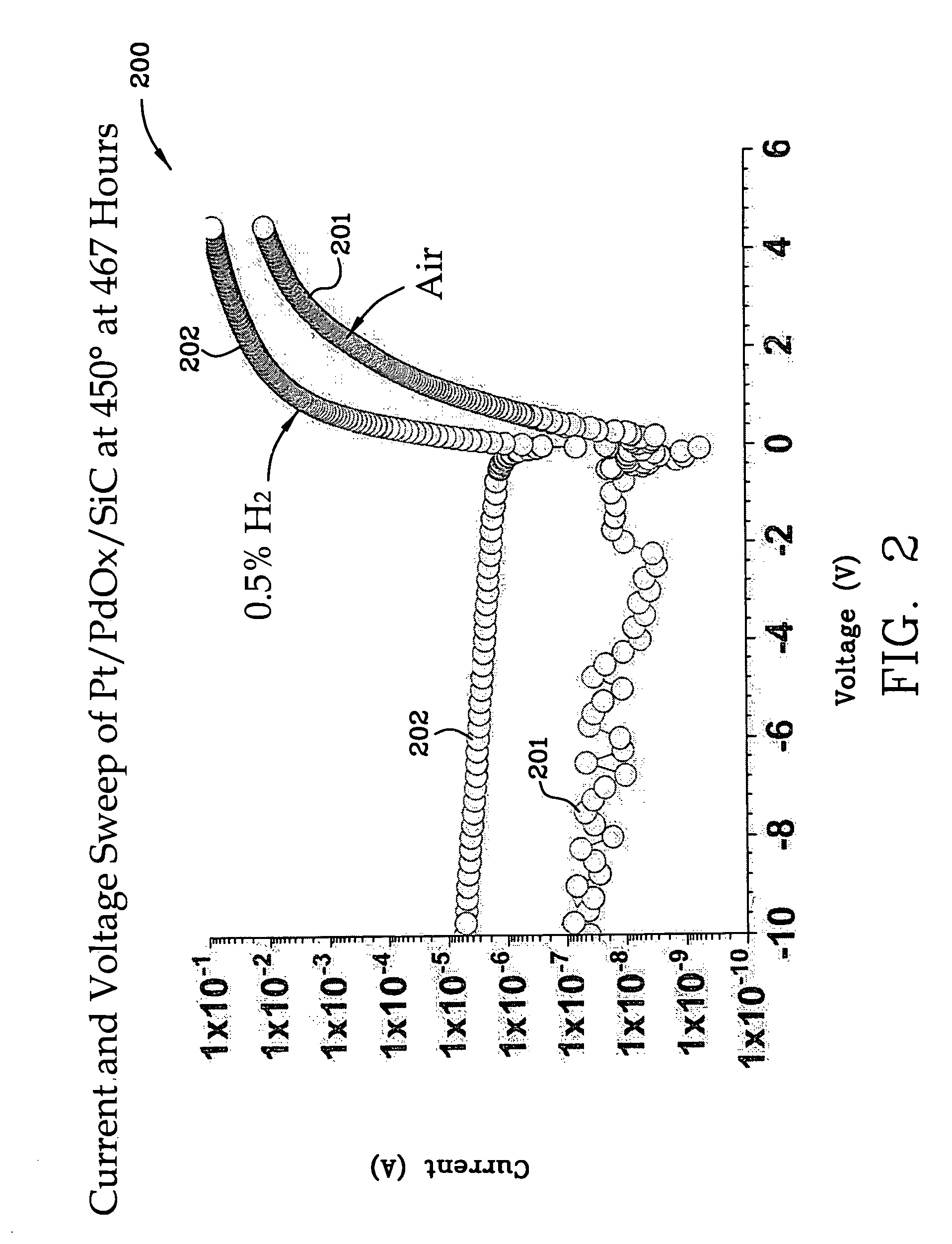
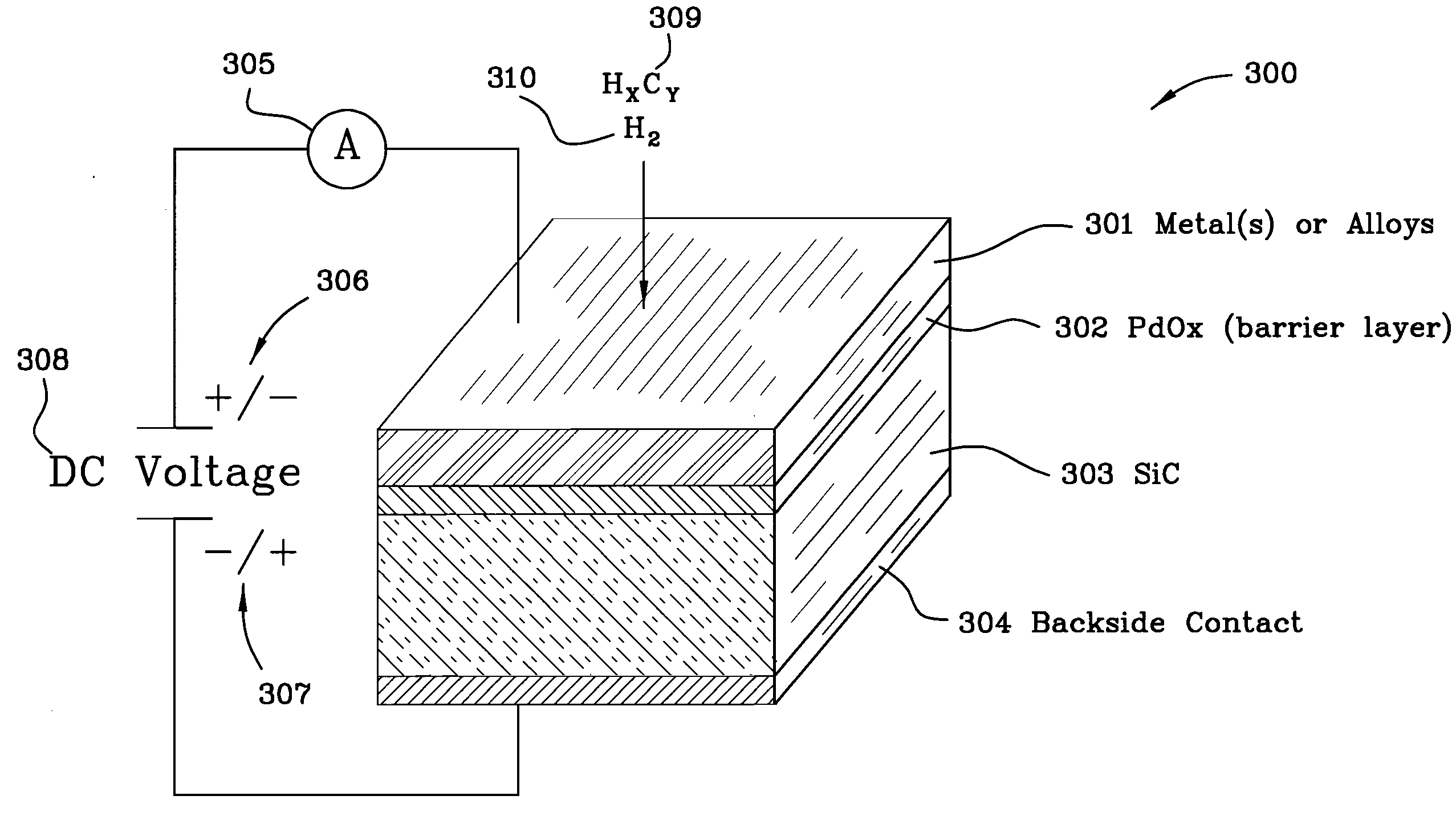
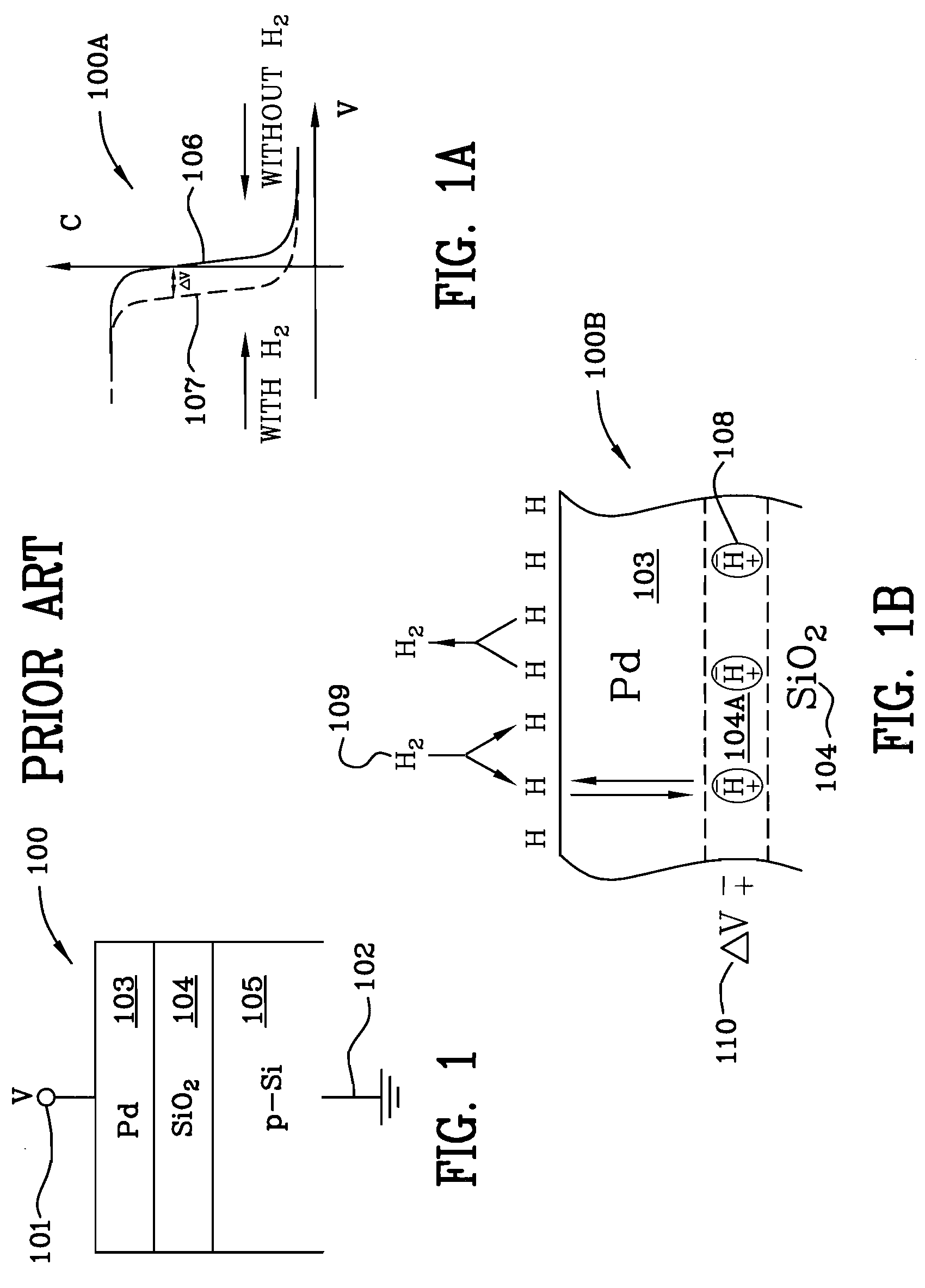
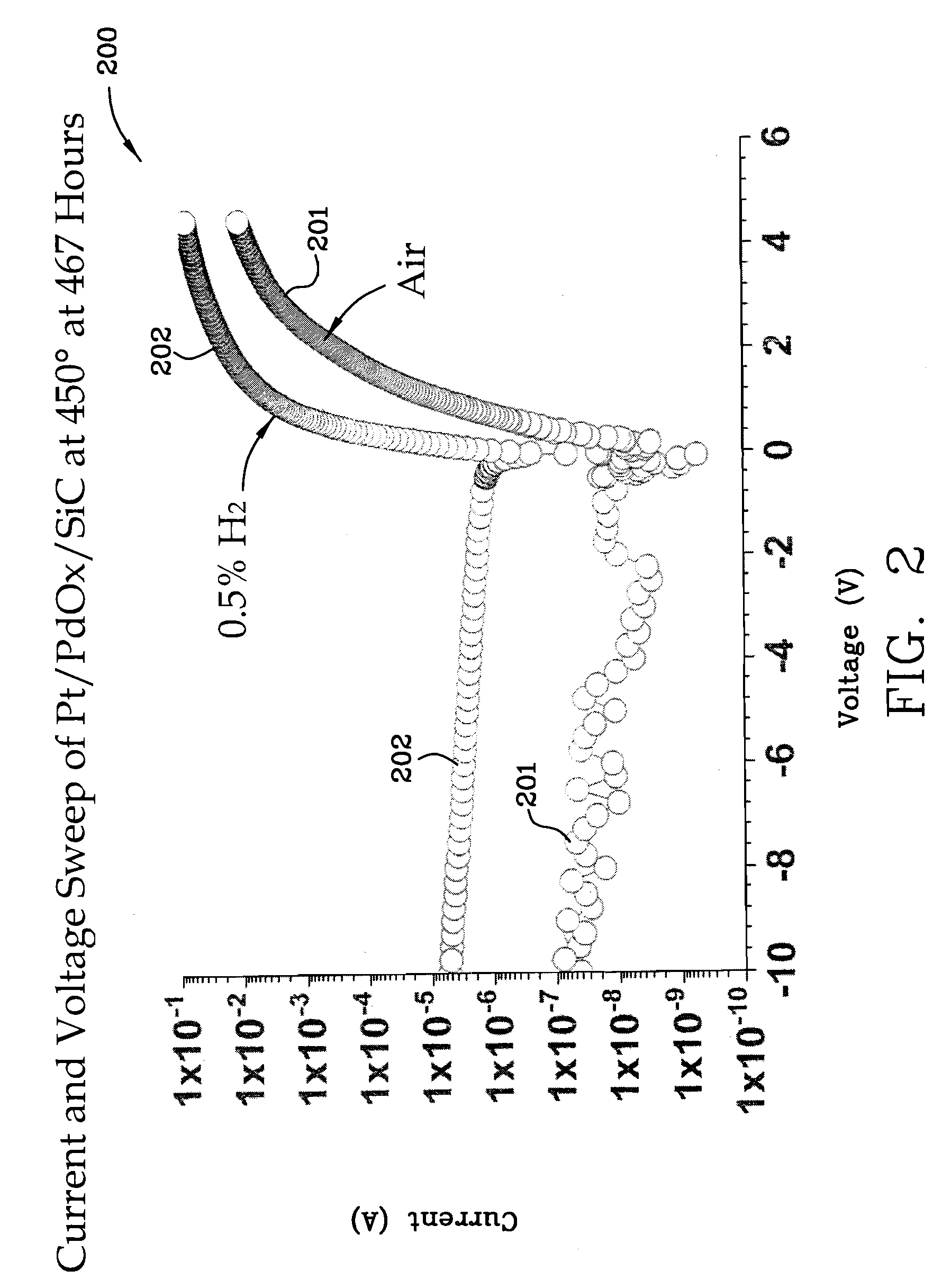
Miniaturized metal (metal alloy)/ PdOx/SiC hydrogen and hydrocarbon gas sensors
InactiveUS7389675B1Improve high temperature performanceMaterial work function voltageSemiconductor devicesHydrogenSemiconductor structure
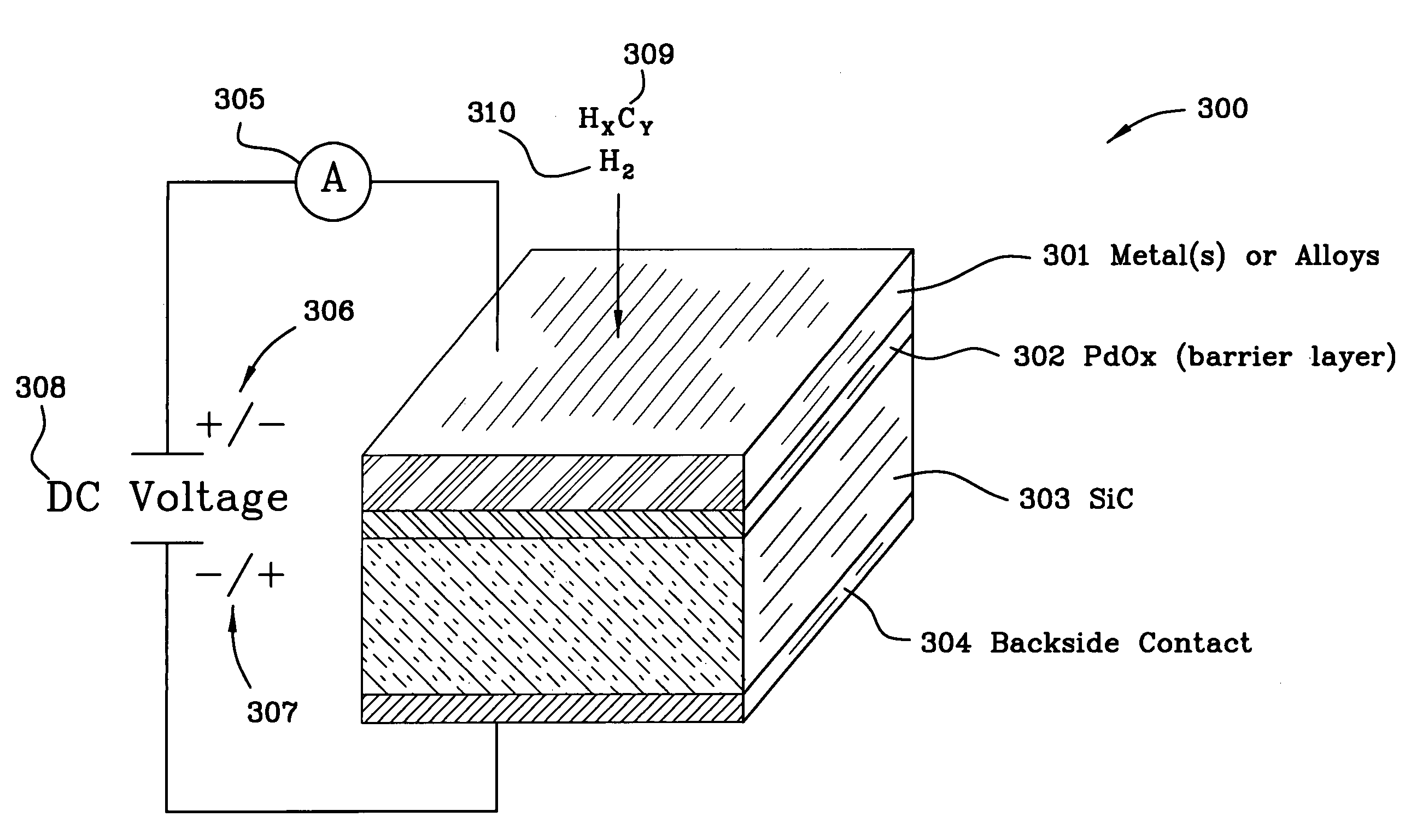
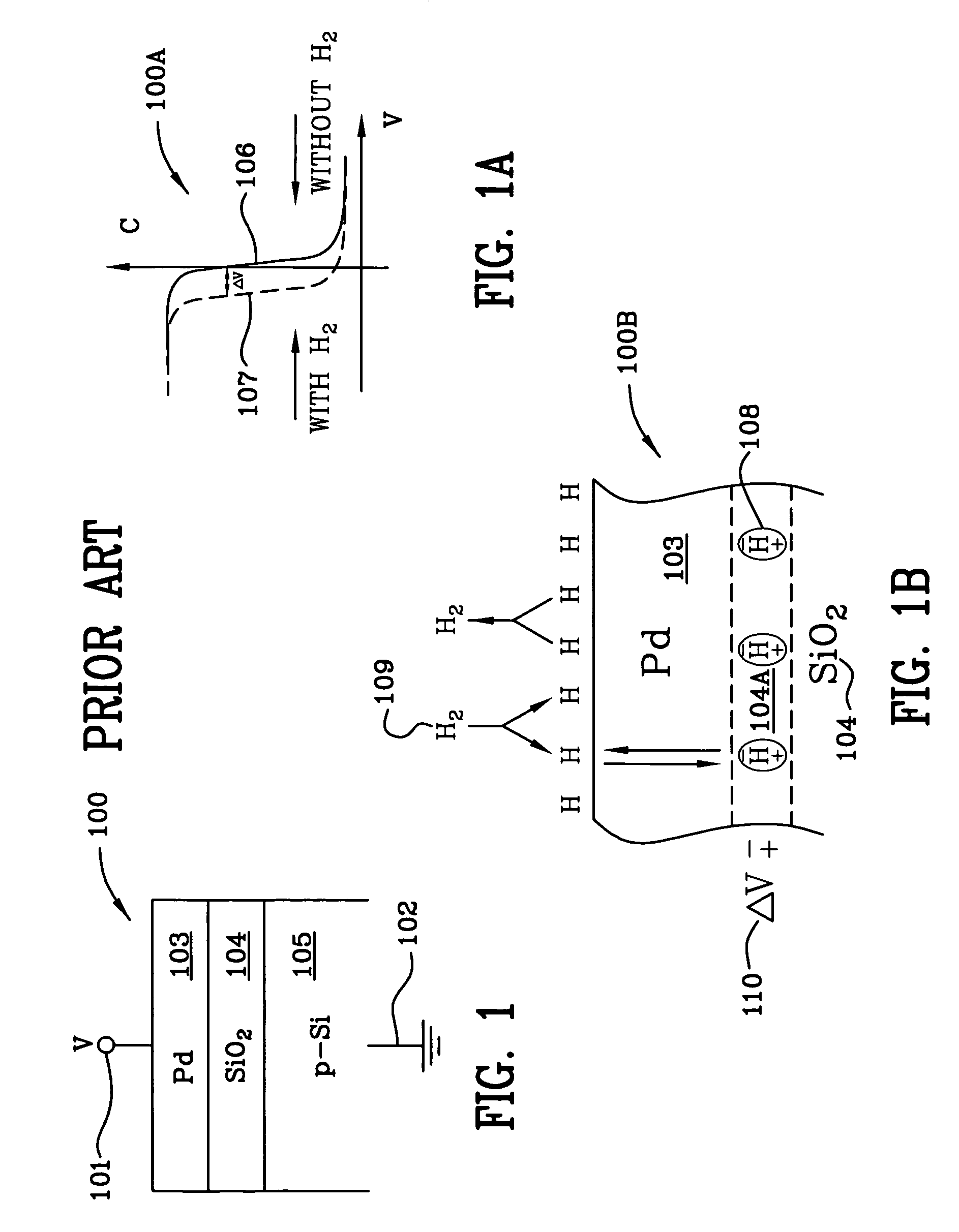
A miniaturized Schottky diode hydrogen and hydrocarbon sensor and the method of making same is disclosed and claimed. The sensor comprises a catalytic metal layer, such as palladium, a silicon carbide substrate layer and a thin barrier layer in between the catalytic and substrate layers made of palladium oxide (PdOx). This highly stable device provides sensitive gas detection at temperatures ranging from at least 450 to 600° C. The barrier layer prevents reactions between the catalytic metal layer and the substrate layer. Conventional semiconductor fabrication techniques are used to fabricate the small-sized sensors. The use of a thicker palladium oxide barrier layer for other semiconductor structures such as a capacitor and transistor structures is also disclosed.
Owner:NASA
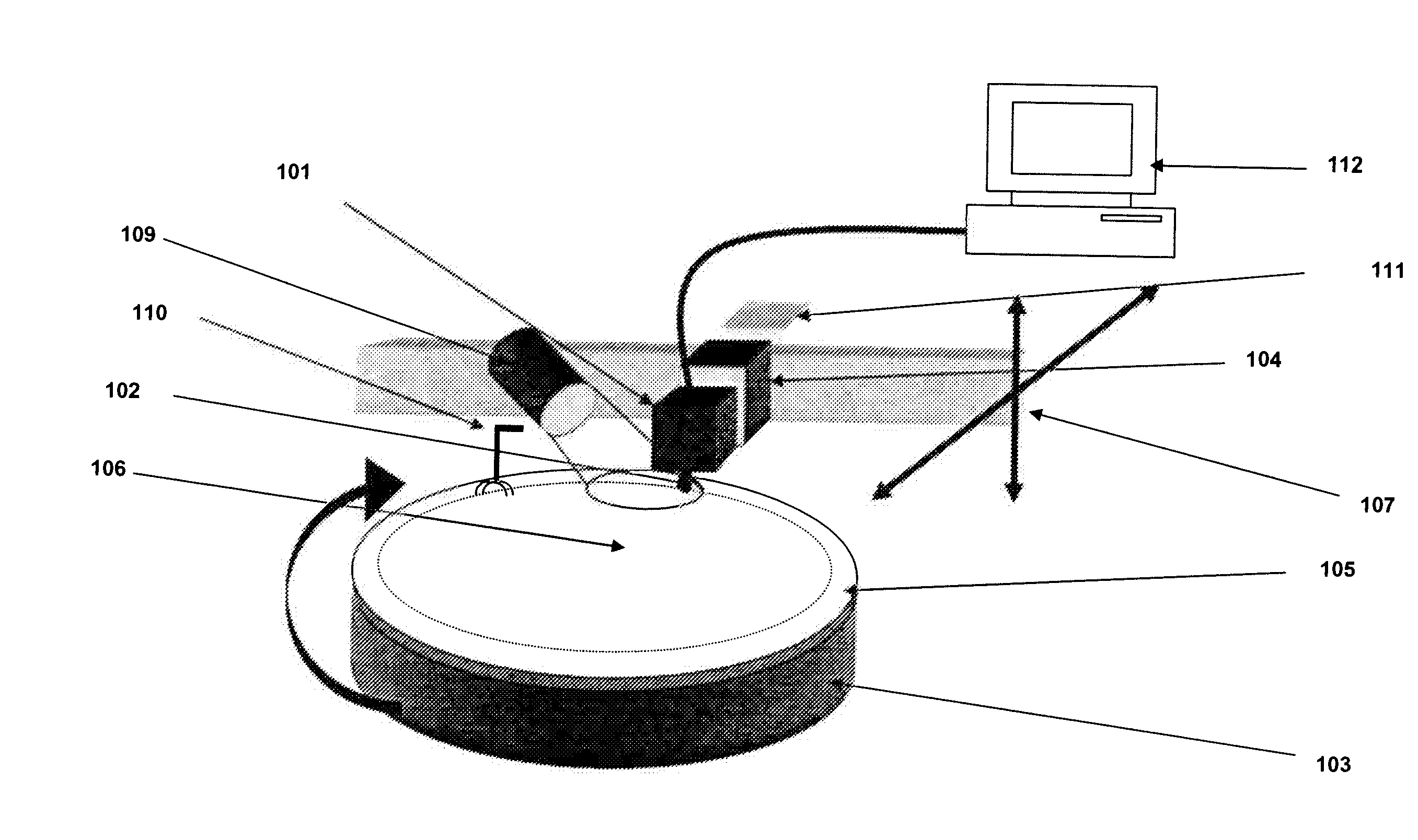
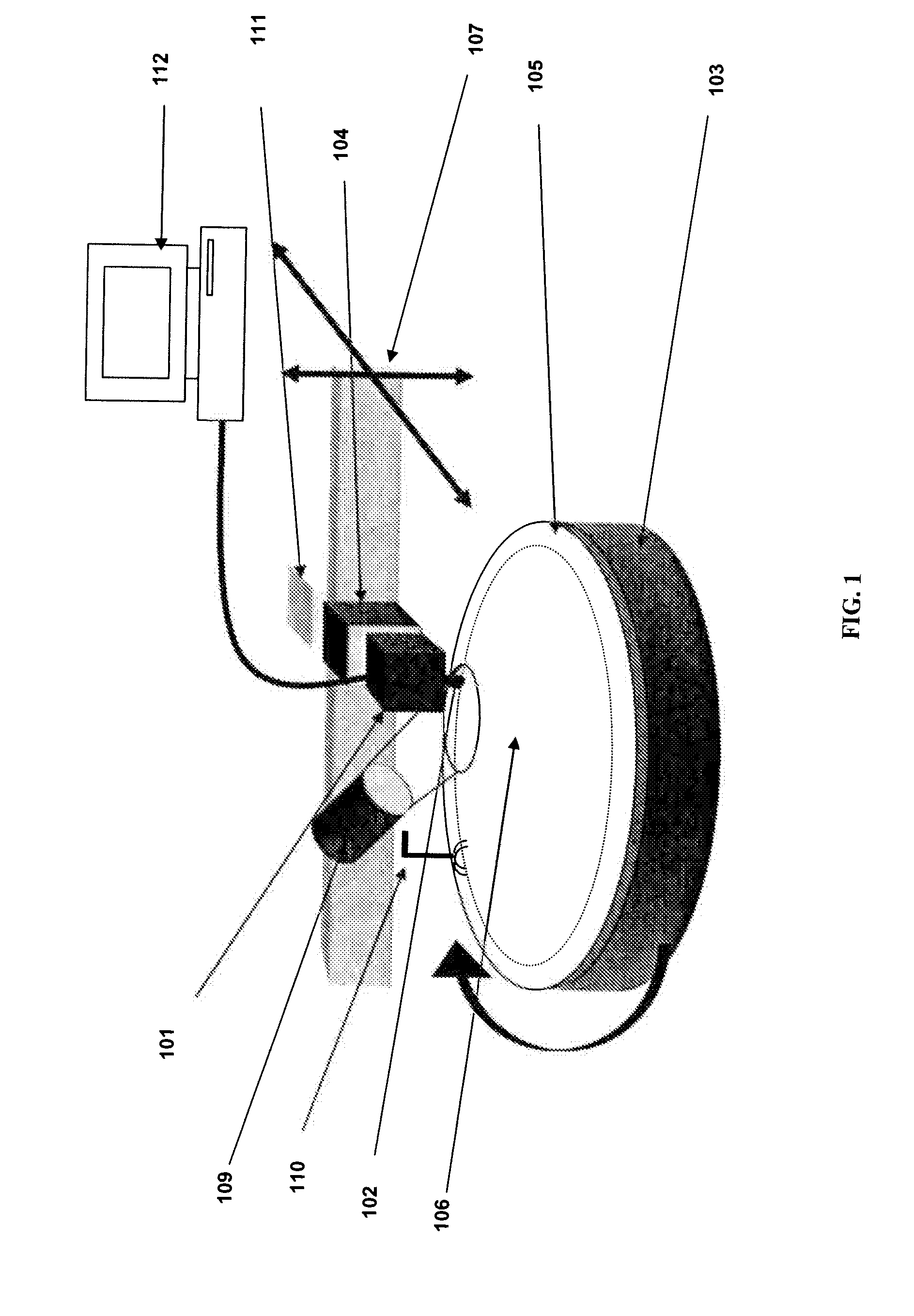
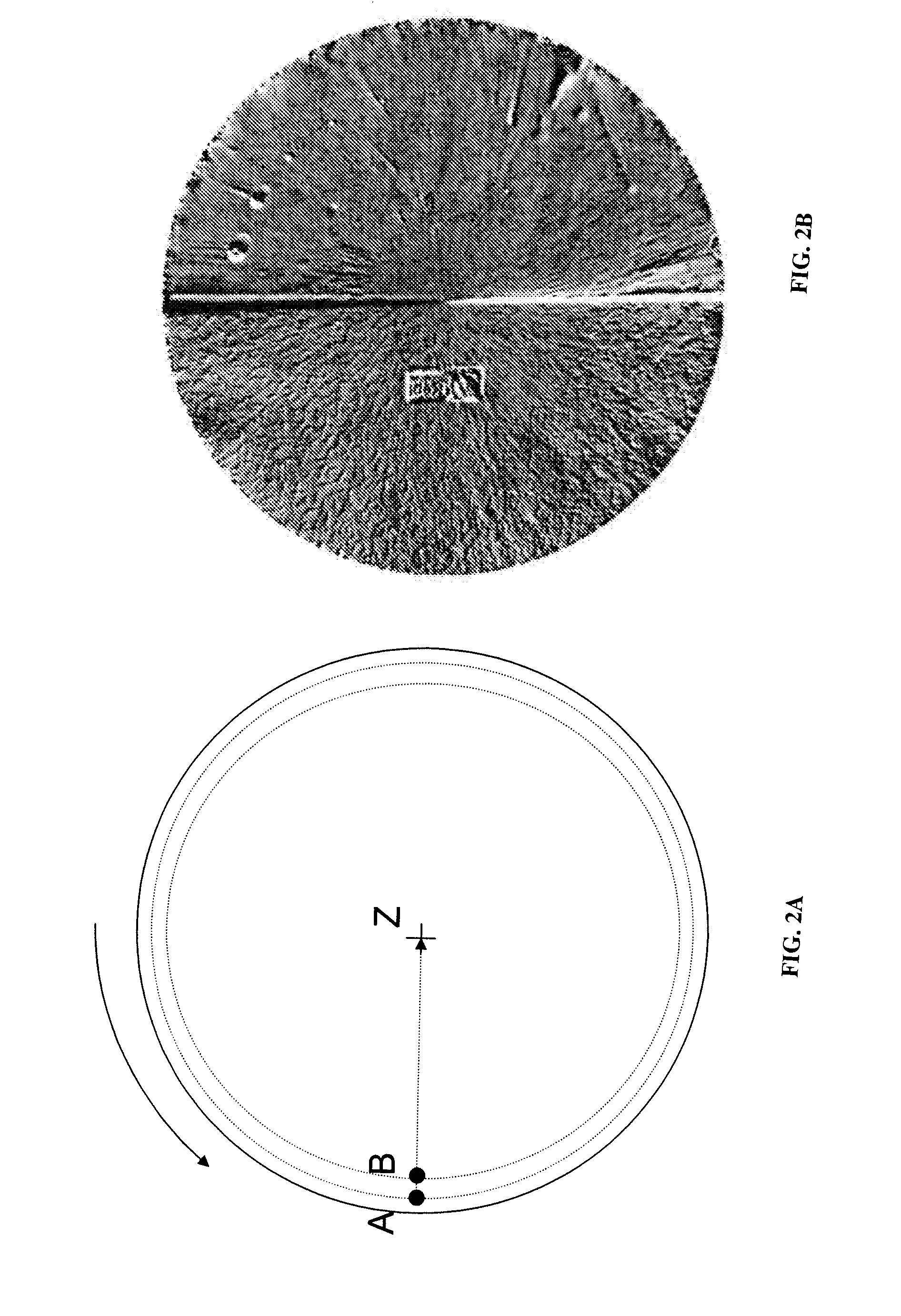
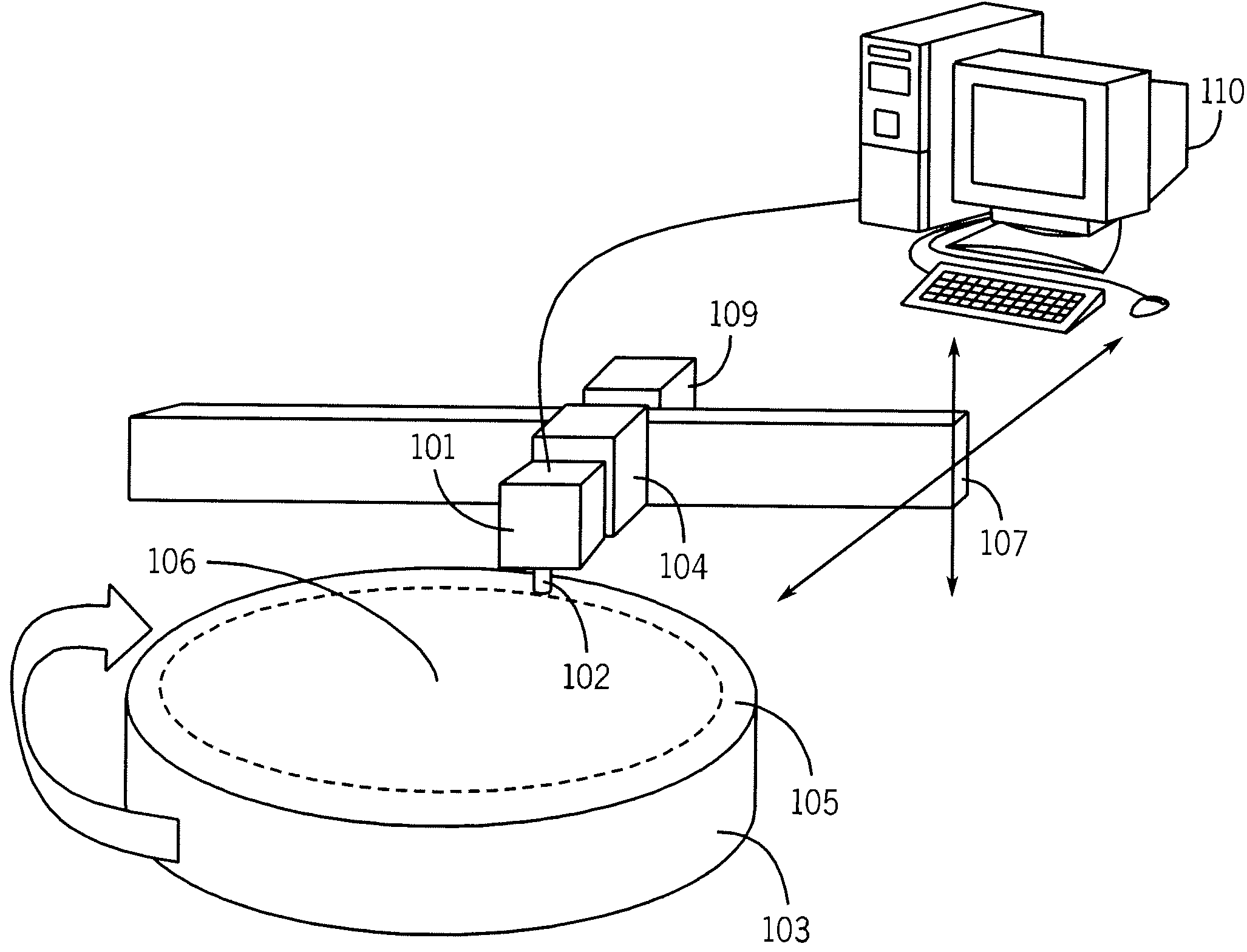
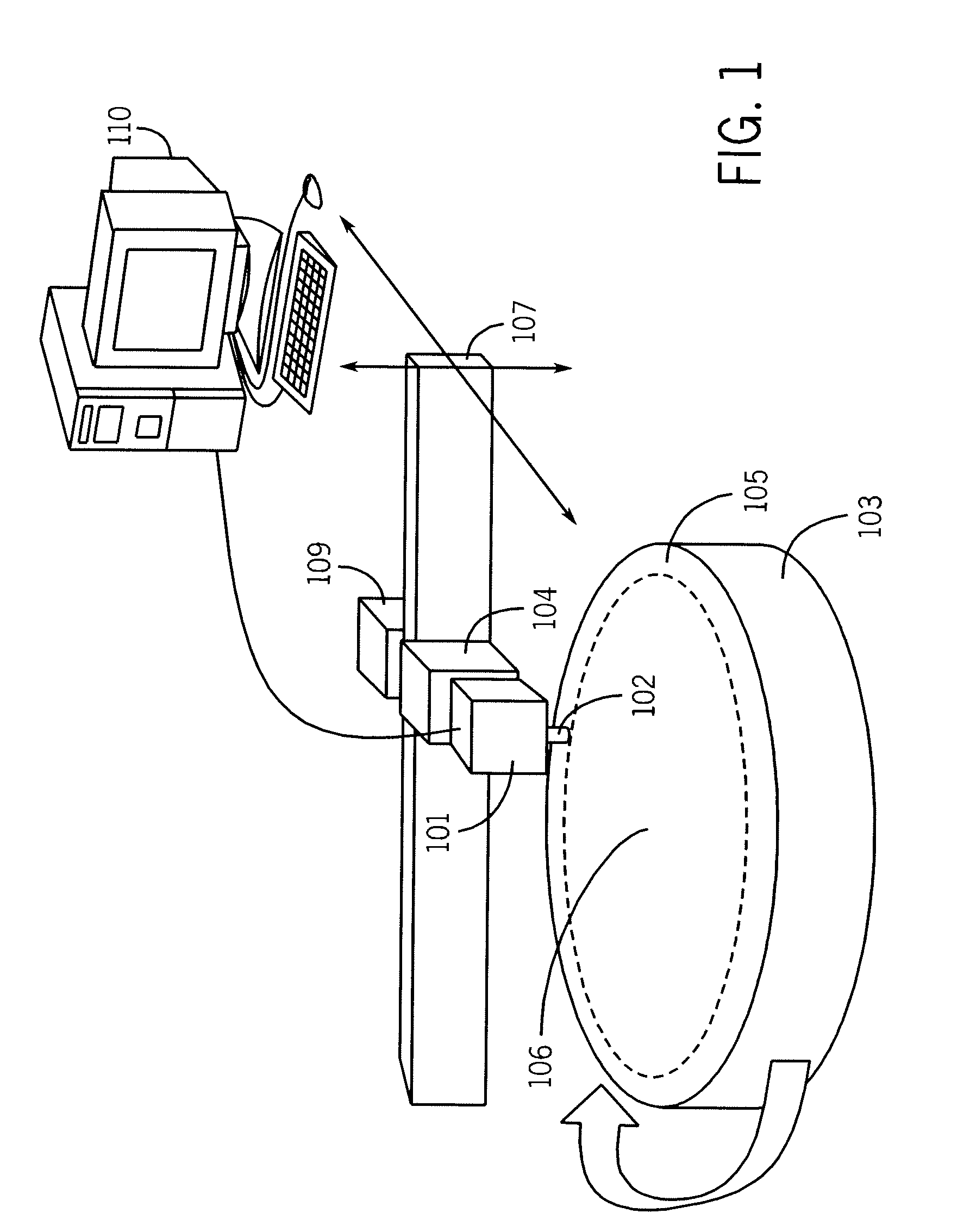
Inspection system and apparatus
InactiveUS20050162178A1Minimize complexitySimple signal processingSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRapid imagingPotential difference
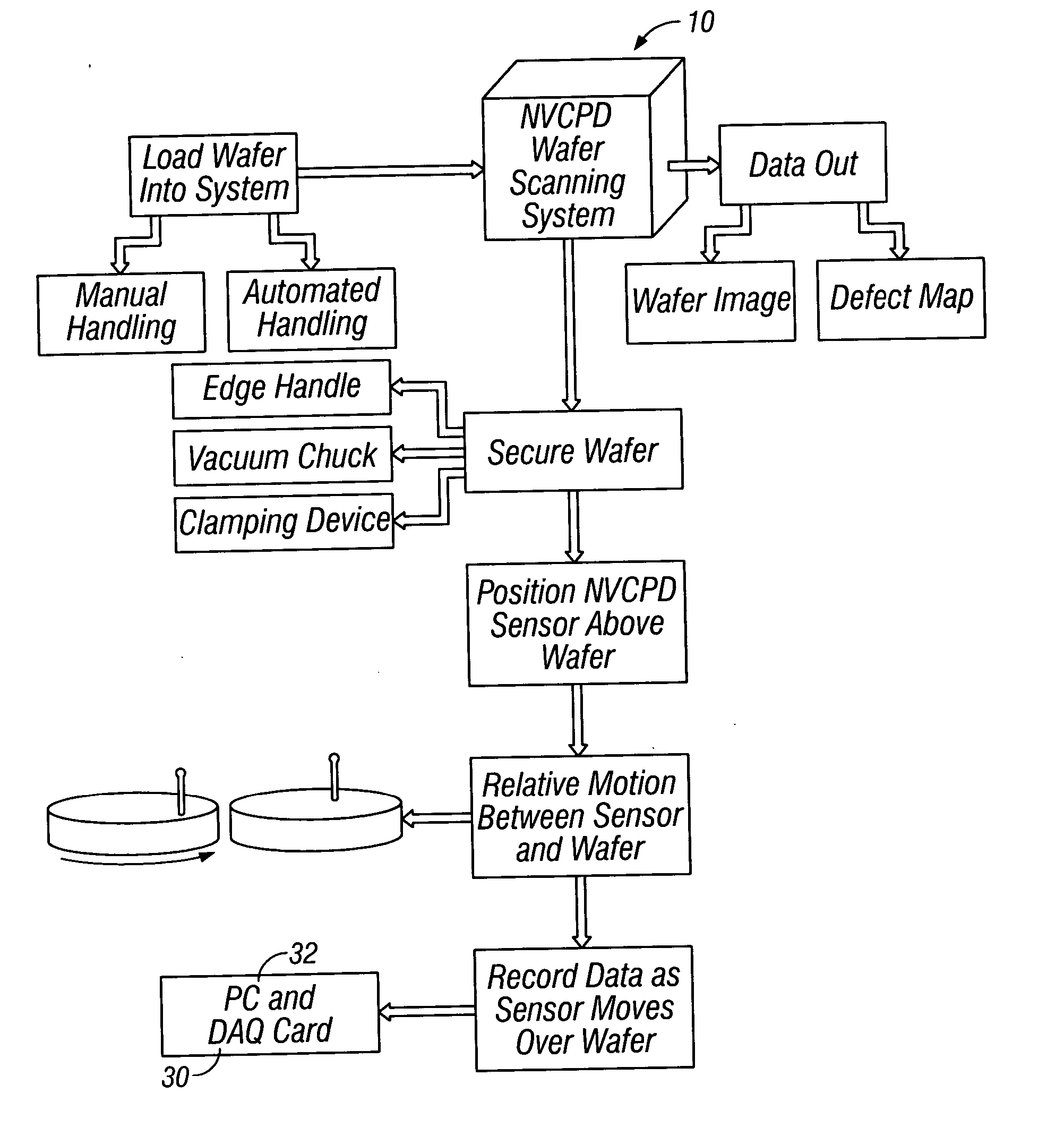
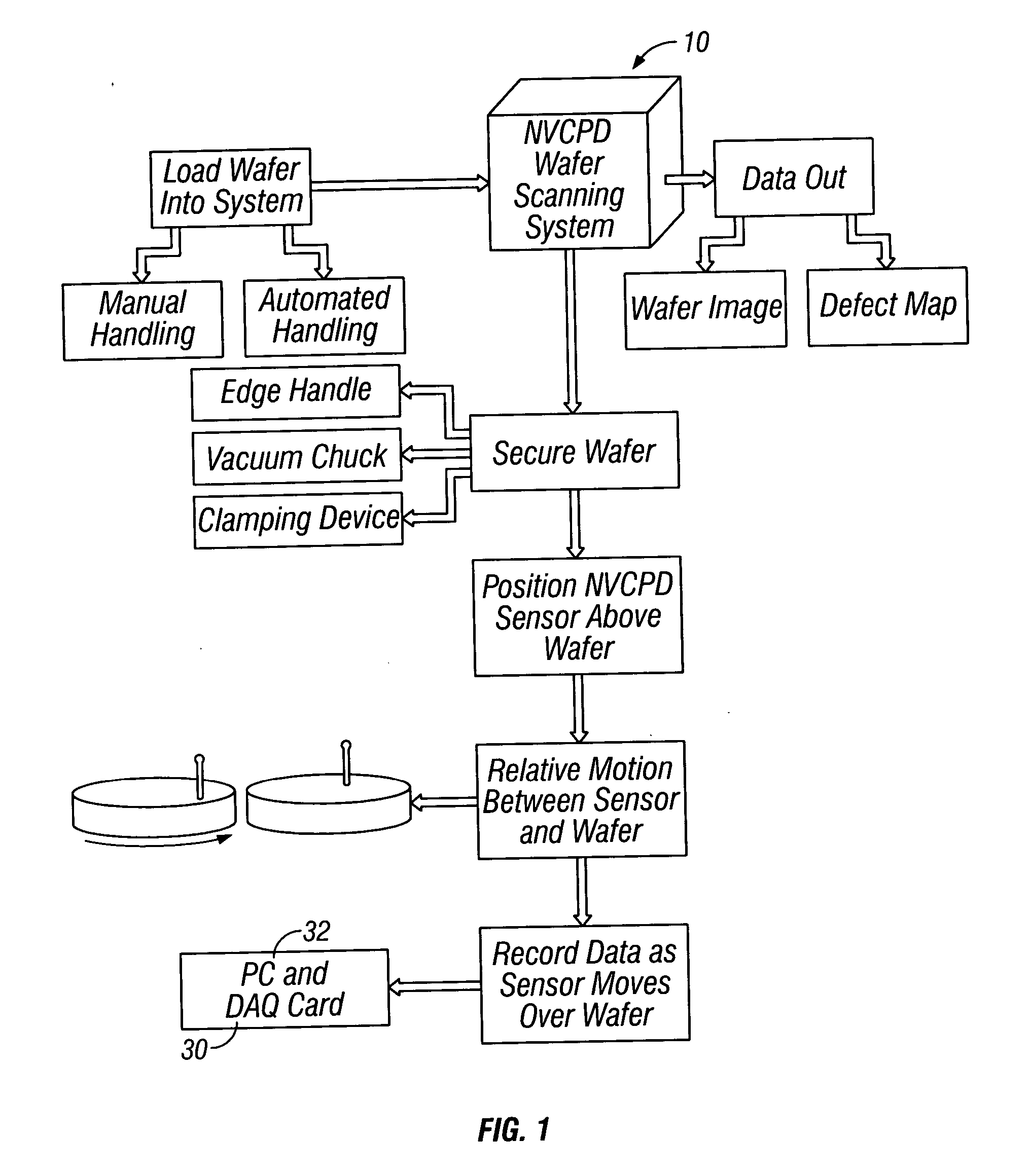
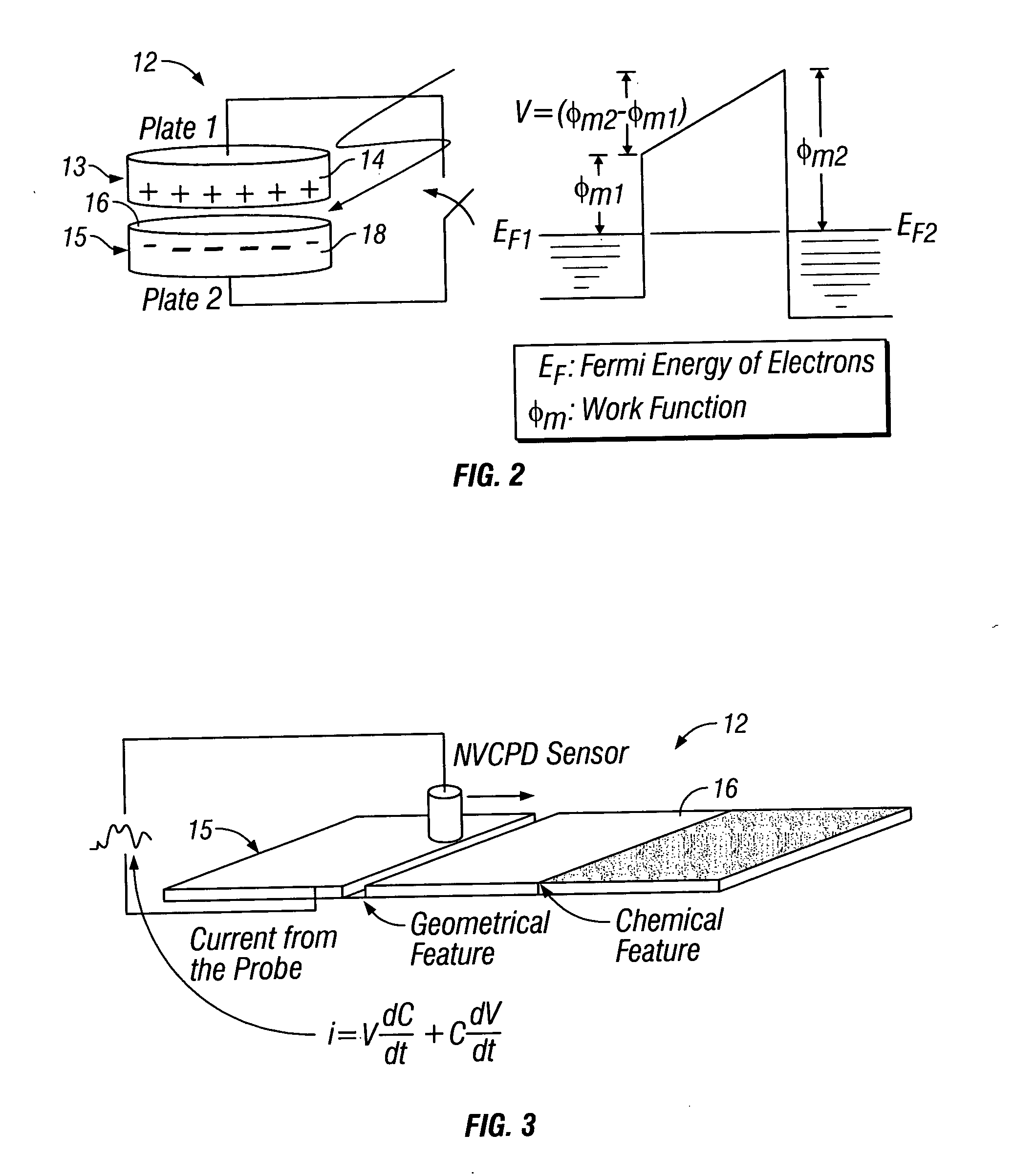
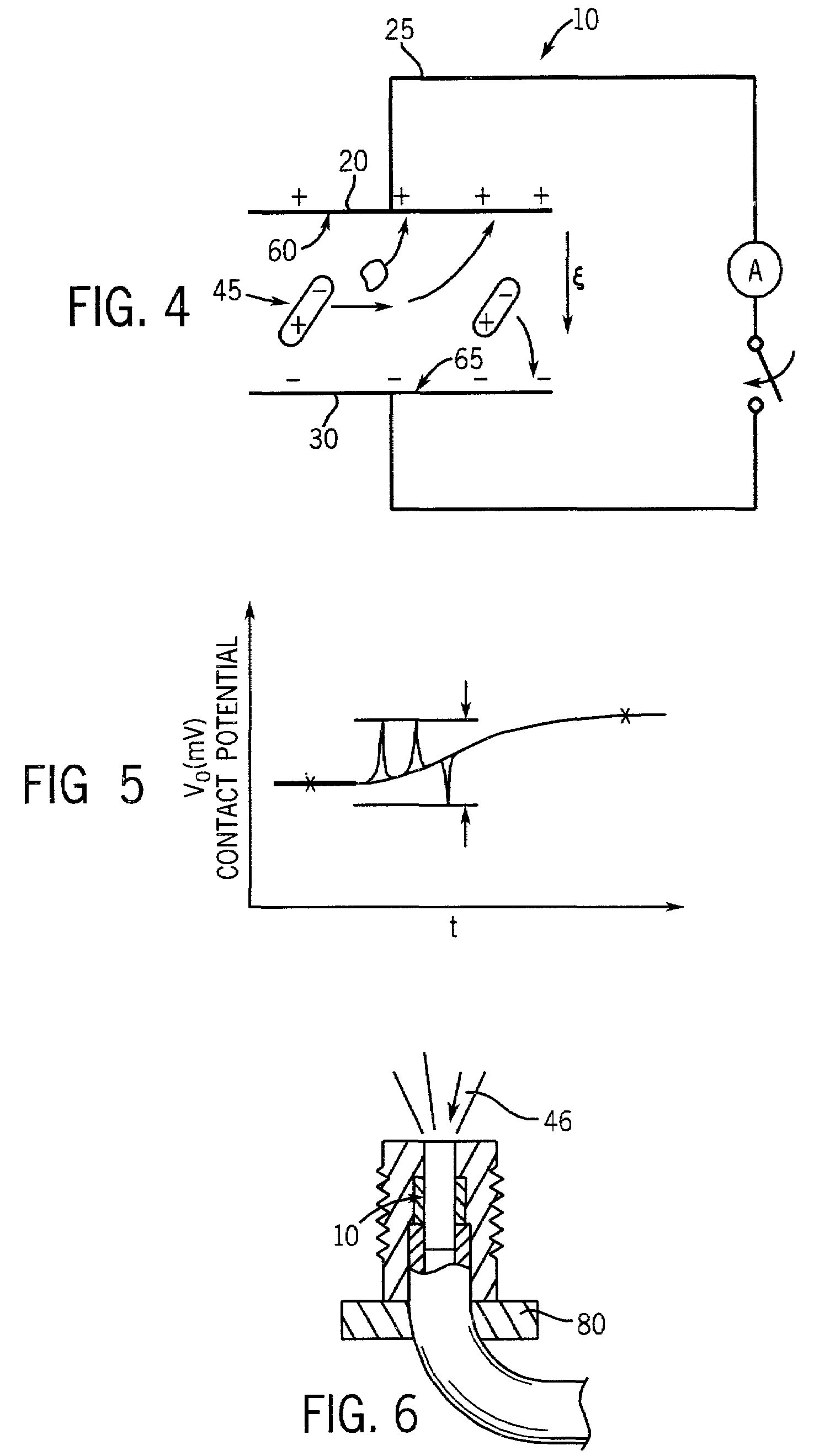
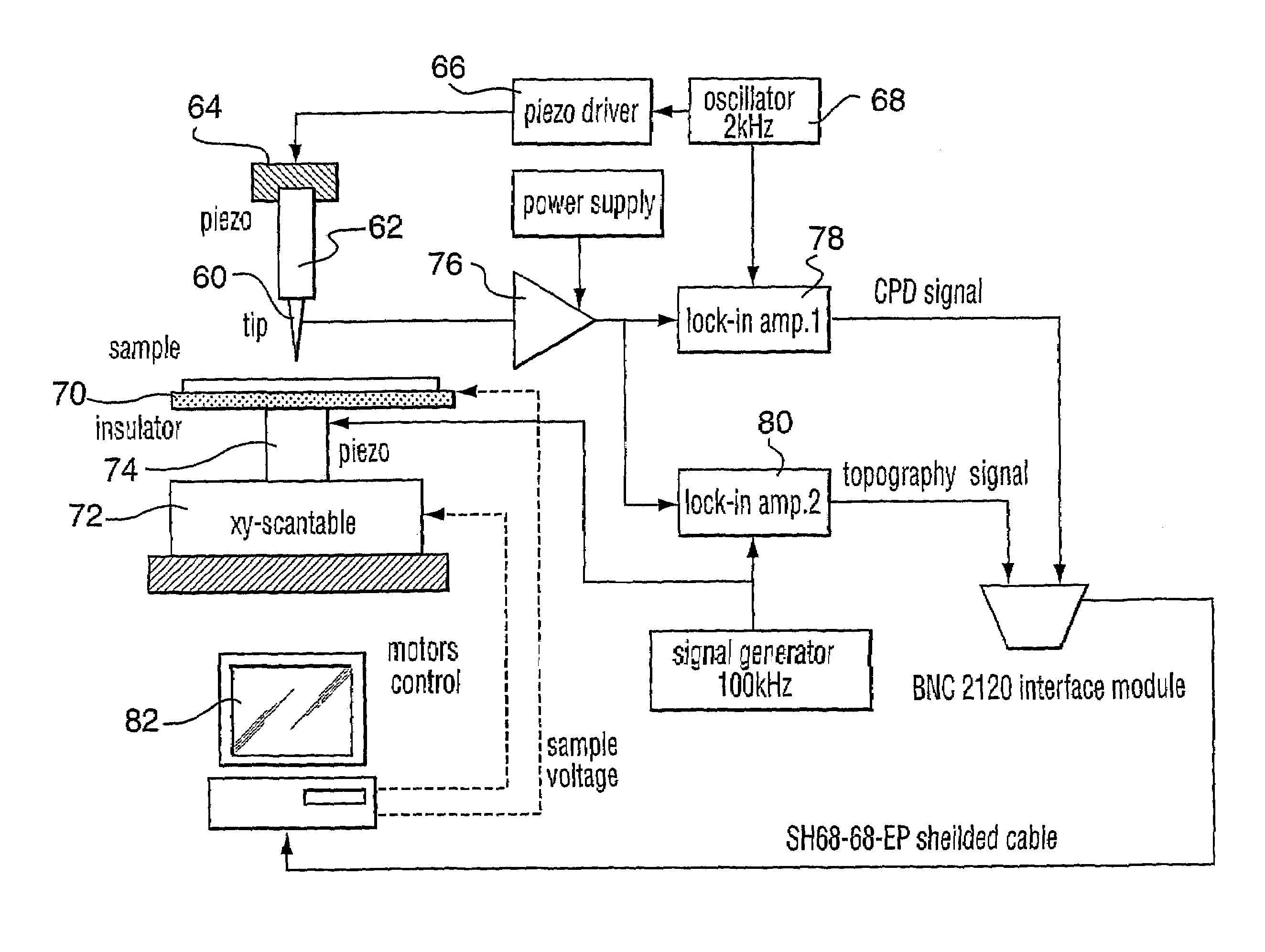
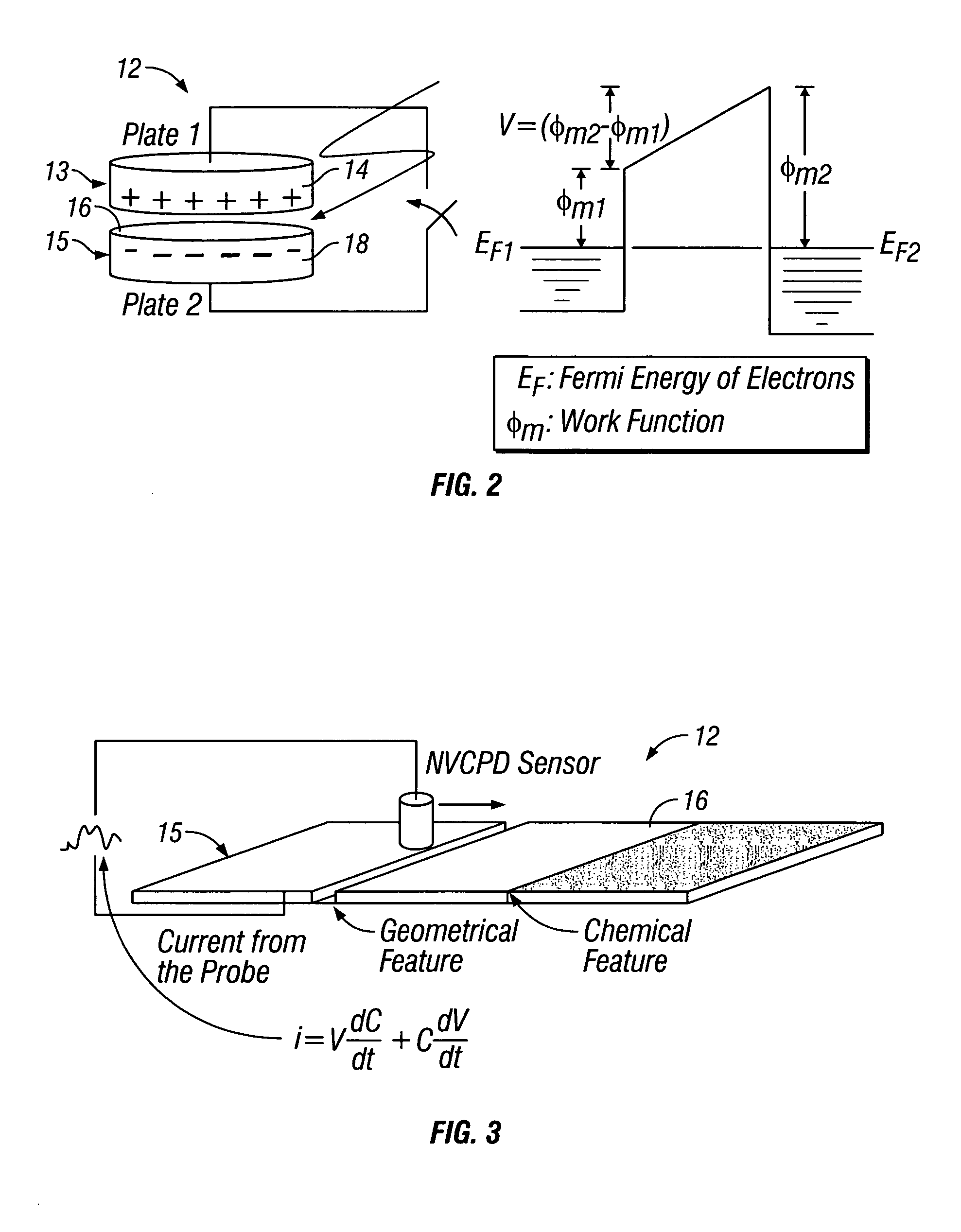
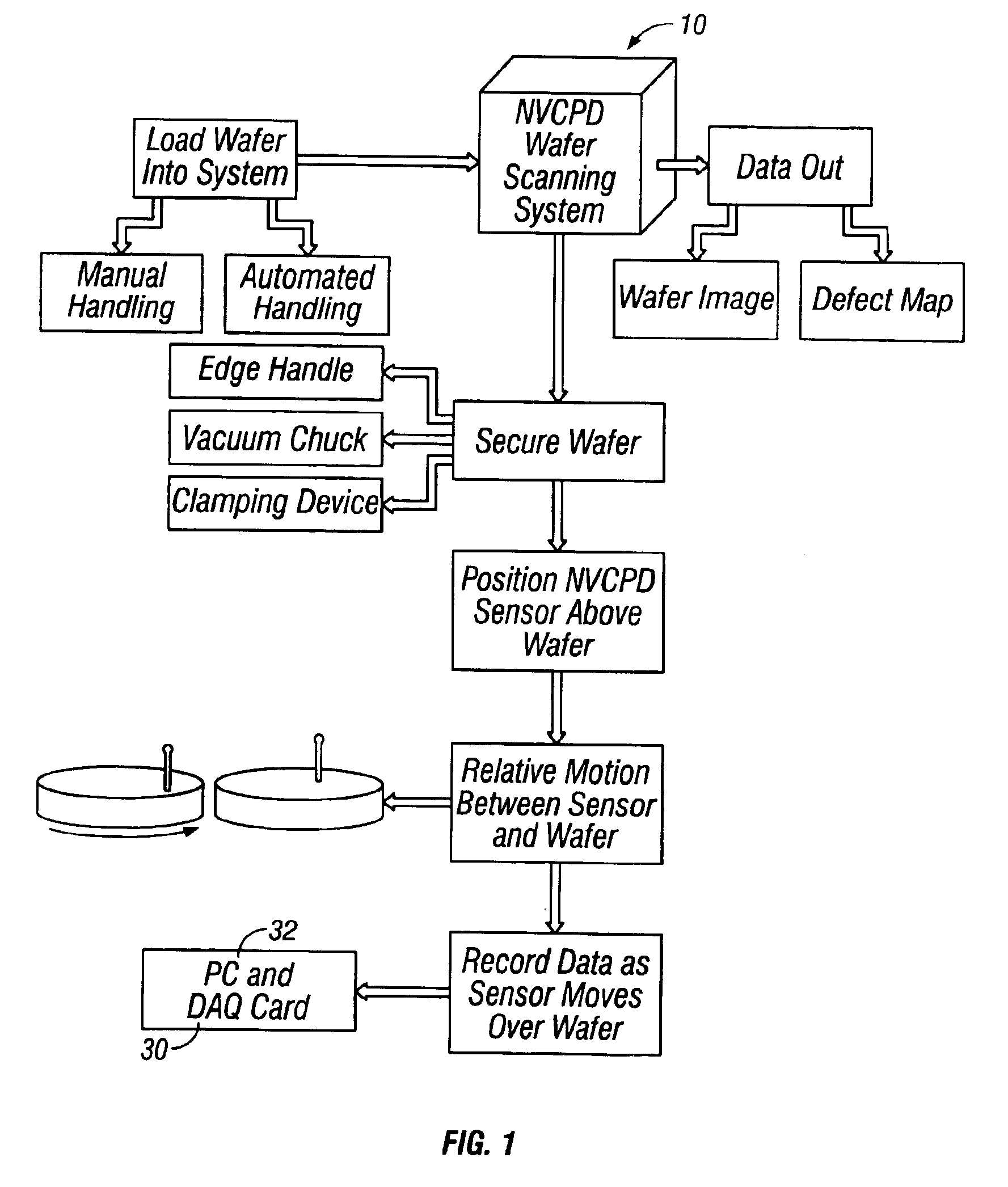
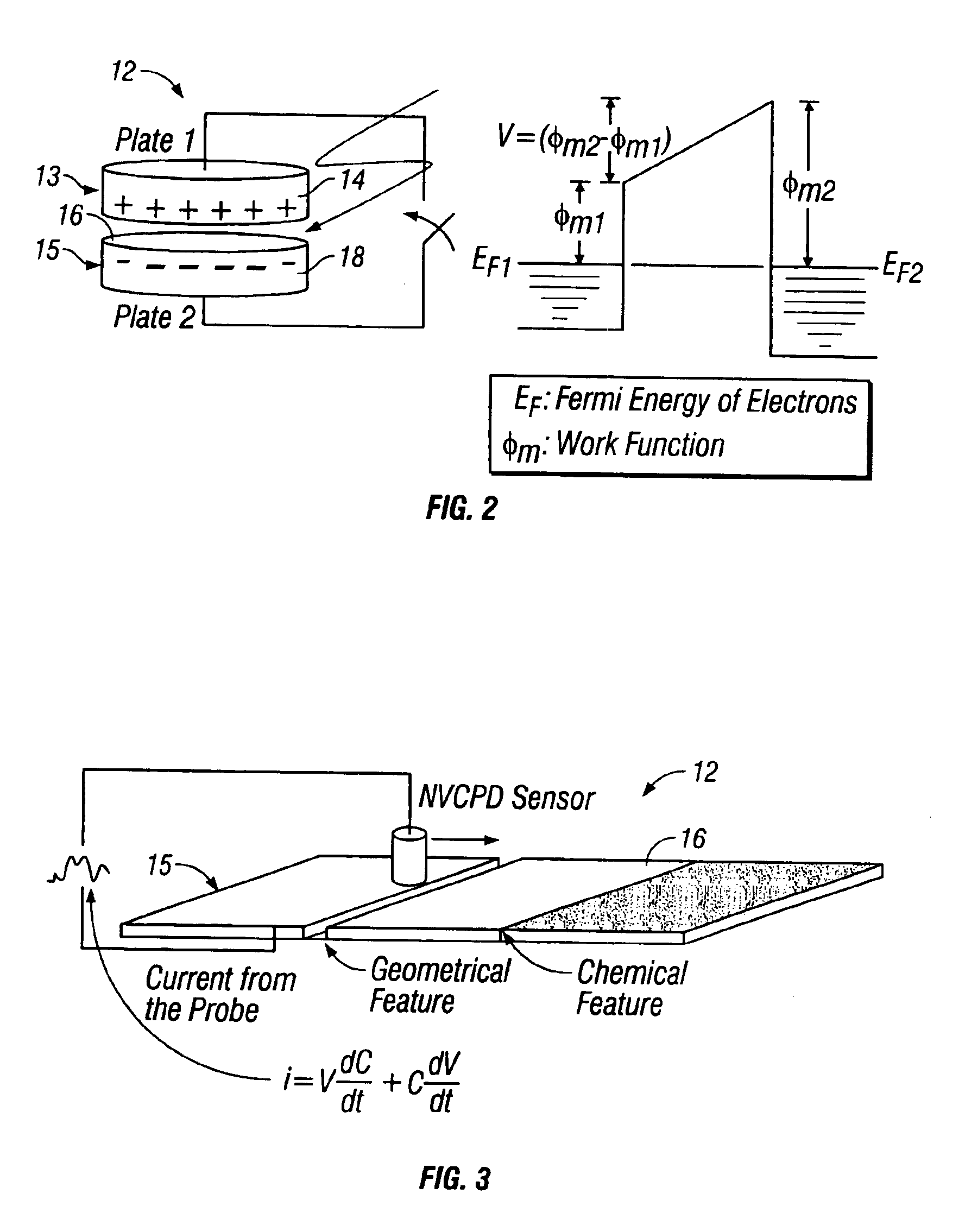
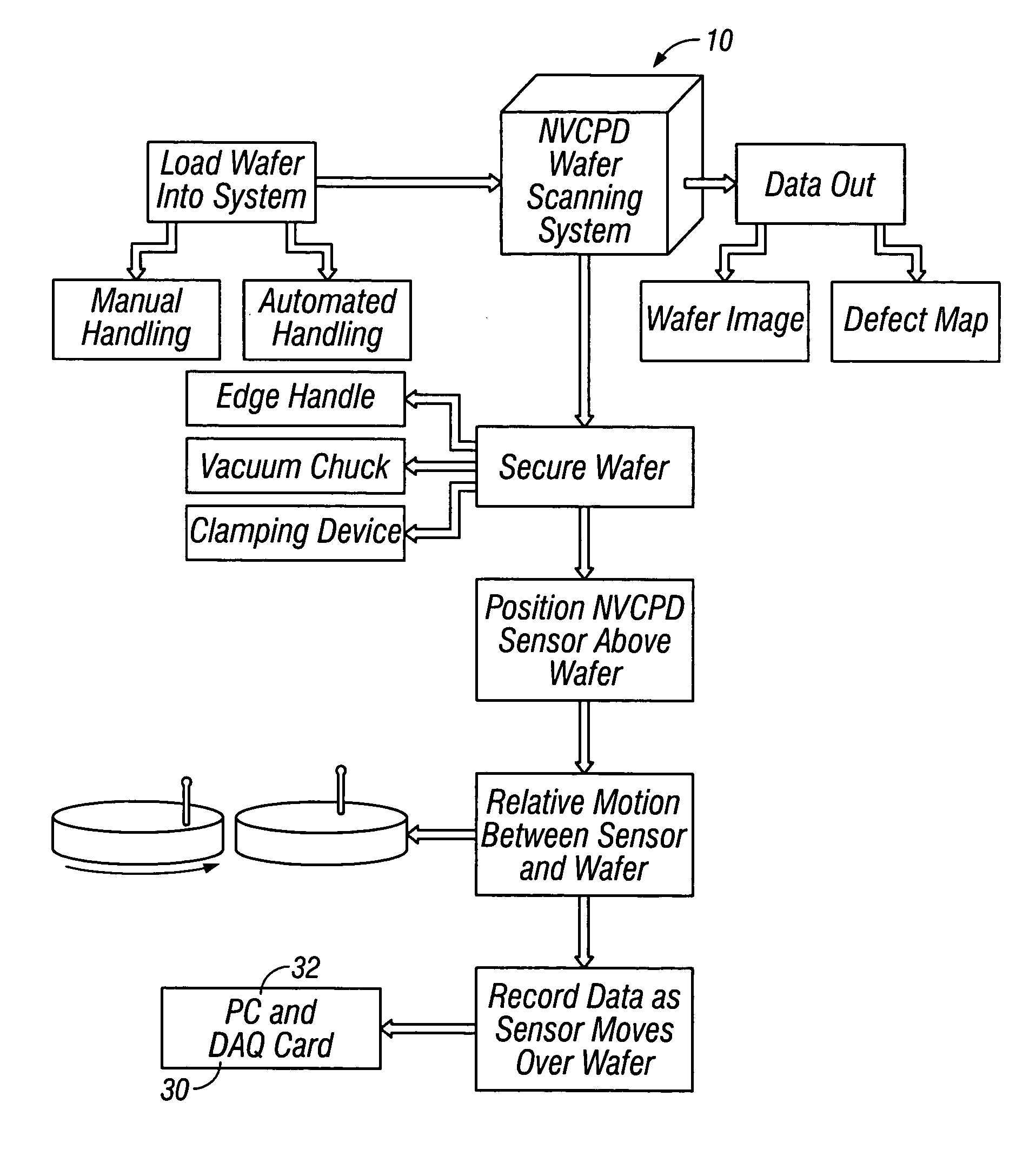
A method and system for identifying a defect or contamination on a surface of a sample. The system operates by detecting changes in work function across a surface via both vCPD and nvCPD. It utilizes a non-vibrating contact potential difference (nvCPD) sensor for imaging work function variations over an entire sample. The data is differential in that it represents changes in the work function (or geometry or surface voltage) across the surface of a sample. A vCPD probe is used to determine absolute CPD data for specific points on the surface of the sample. The combination of vibrating and non-vibrating CPD measurement modes allows the rapid imaging of whole-sample uniformity, and the ability to detect the absolute work function at one or more points.
Owner:QCEPT INVESTMENTS LLC
Scanning kelvinmicroprobe system and process for biomolecule microassay
InactiveUS20040029131A1Improve spatial resolutionHigh resolutionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPotential differenceAntibody antigen
There is provided a system and process for detecting biomolecular interaction on a substrate having a biomolecule immobilized on a surface of the substrate. The system and process incorporate a scanning Kelvin microprobe (SKM) capable of analyzing surface topography as well as a contact potential difference image signal. Also provided is the use of SKM in measuring and analyzing biochemical molecular interactions between a probe bound to the surface of the substrate, and a target suspected to be present in a liquid sample. One of the probe and target combination is a biomolecule such as a nucleic acid, a polypeptide, or a small molecule, and an antibody antigen combination may be used.
Owner:SENSORCHEM INT
Contact potential difference sensor to monitor oil properties
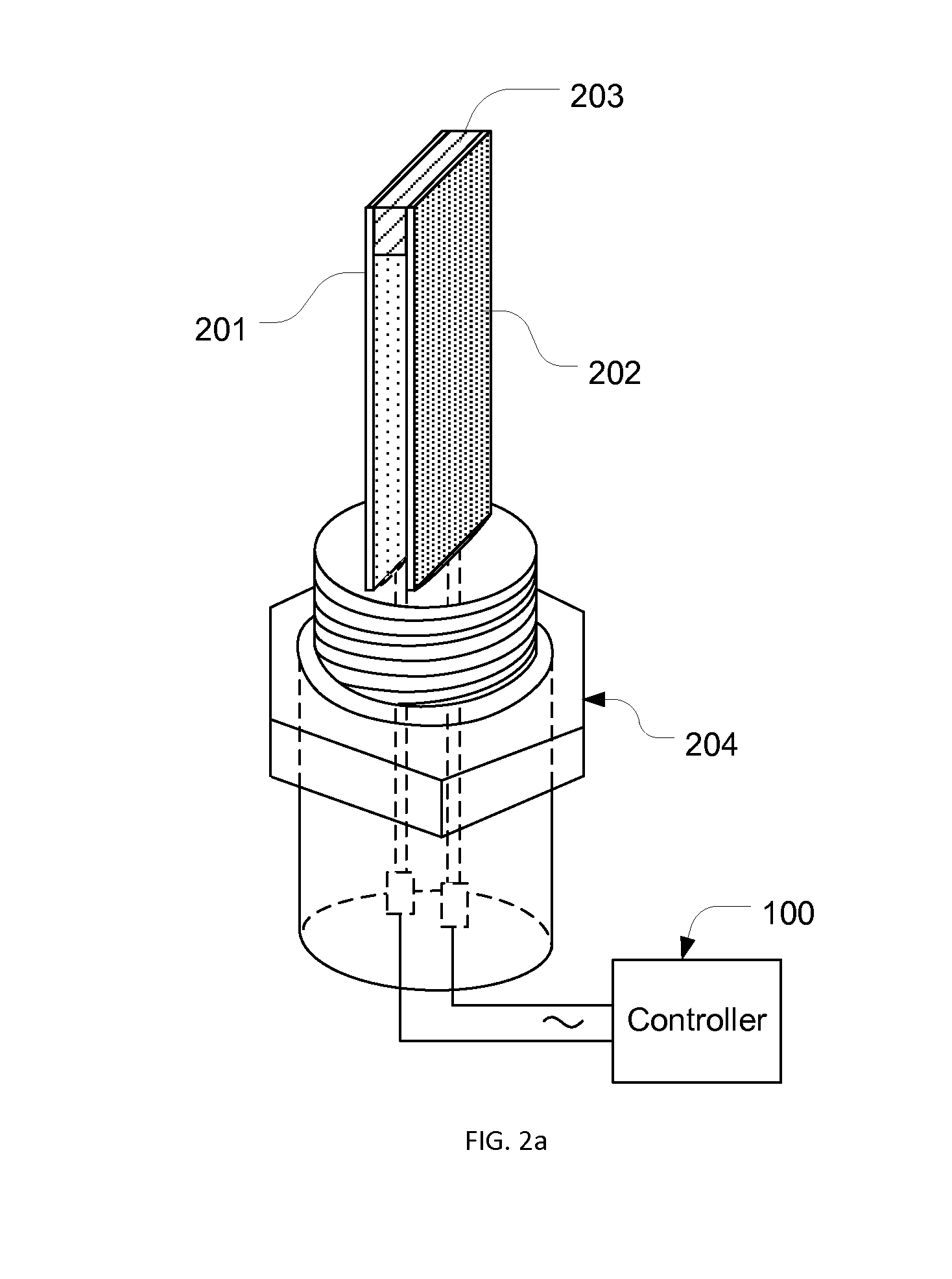
A method and system for contact potential sensing of dielectric properties of a fluid. The method and system include a contact potential sensor, an open or closed loop for passing a fluid past the sensor, measuring a contact potential to characterize dielectric properties of the fluid and outputting the dielectric property information for analysis and response thereto.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Scanning kelvin microprobe system and process for analyzing a surface
InactiveUS7084661B2Superior lateral resolutionThe process is stable and reliableBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSelf-assembled monolayerNano devices
A scanning Kelvin microprobe (SKM) system capable of measuring and analyzing surface characteristics of samples is provided. Also provided is a process of measuring and analyzing surface characteristics of samples. Further, there are provided uses of the SKM system in measuring and analyzing surface characteristics of conductors, semiconductors, insulators, chemicals, biochemicals, photochemicals, chemical sensors, biosensors, biochemical microarrays, microelectronic devices, electronic imaged devices, micromachined devices, nano-devices, corroded materials, stressed materials, coatings, adsorbed materials, contaminated materials, oxides, thin films, and self assembling monolayers.
Owner:SENSORCHEM INT
Method and system for detecting metal contamination on a semiconductor wafer
InactiveUS6759255B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesElectricityWork function
A method to detect metal contamination on a semiconductor topography is provided. The semiconductor topography may include a semiconductor substrate or a dielectric material disposed upon a semiconductor substrate. The metal contamination may be driven into the semiconductor substrate by an annealing process. Alternatively, the annealing process may drive the metal contamination into the dielectric material. Subsequent to the annealing process, a charge may be deposited upon an upper surface of the semiconductor topography. An electrical property of the semiconductor topography may be measured. A characteristic of at least one type of metal contamination may be determined as a function of the electrical property of the semiconductor topography. The method may be used to determine a characteristic of one or more types of metal contamination on a portion of the semiconductor topography or the entire semiconductor topography. A system configured to detect metal contamination on a semiconductor topography is also provided. An oven may be incorporated into the system and may be used to anneal the semiconductor topography. The system may also include a device that may be configured to deposit a charge on an upper surface of the semiconductor topography. A sensor may also be included in the system. The sensor may use a non-contact work function technique to measure an electrical property of the semiconductor topography.
Owner:KLA CORP
Gas-sensitive field-effect transistor with air gap
Owner:MICRONAS
Inspection system and apparatus
InactiveUS7107158B2Minimize complexityFast and inexpensive and effective meanSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectrostatic cleaningRapid imagingPotential difference
Owner:QCEPT INVESTMENTS LLC
Fluid Quality Sensing Means with Reference Sensor
ActiveUS20150075268A1Internal-combustion engine testingMaterial work function voltageEngineeringOil quality
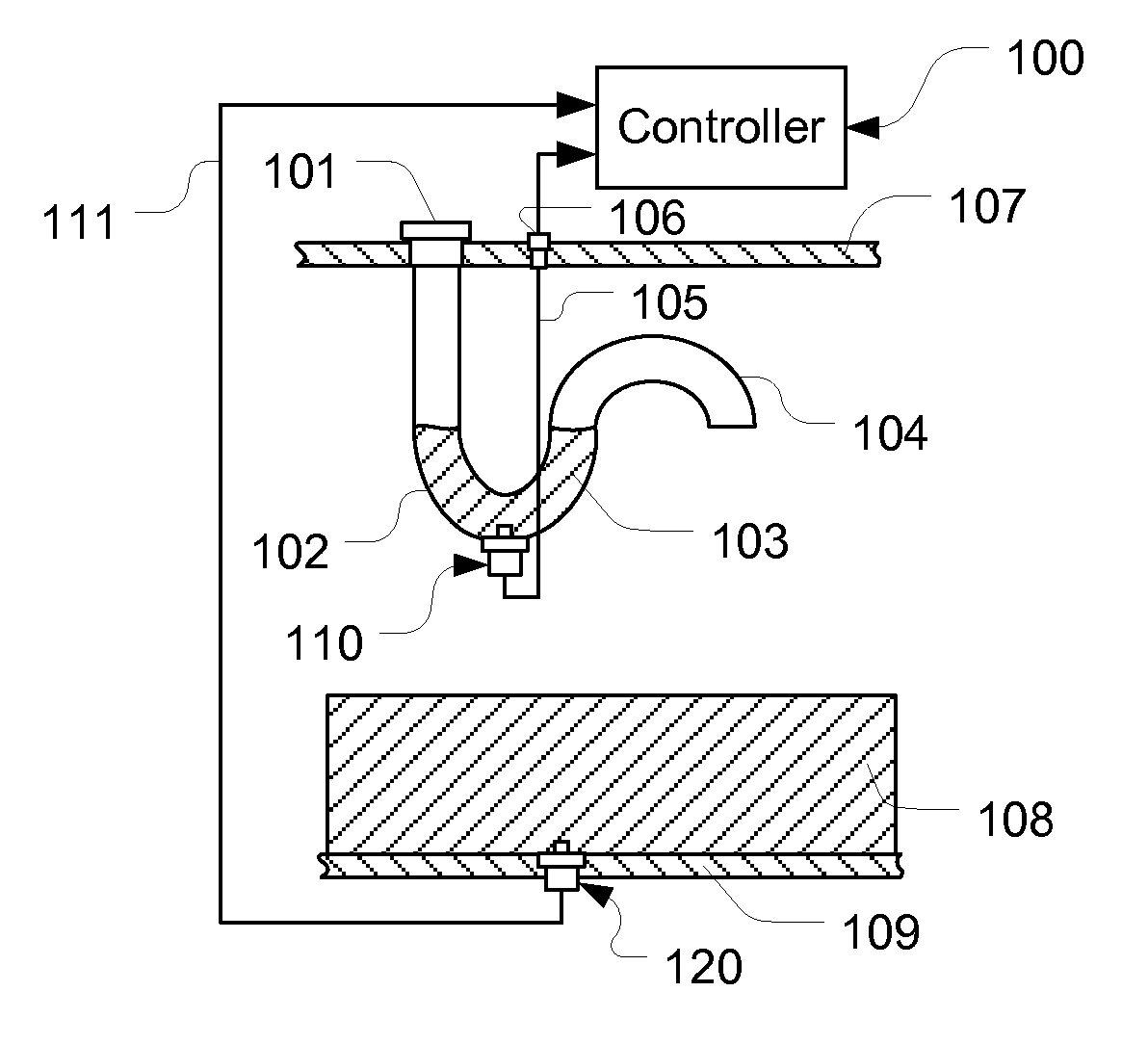
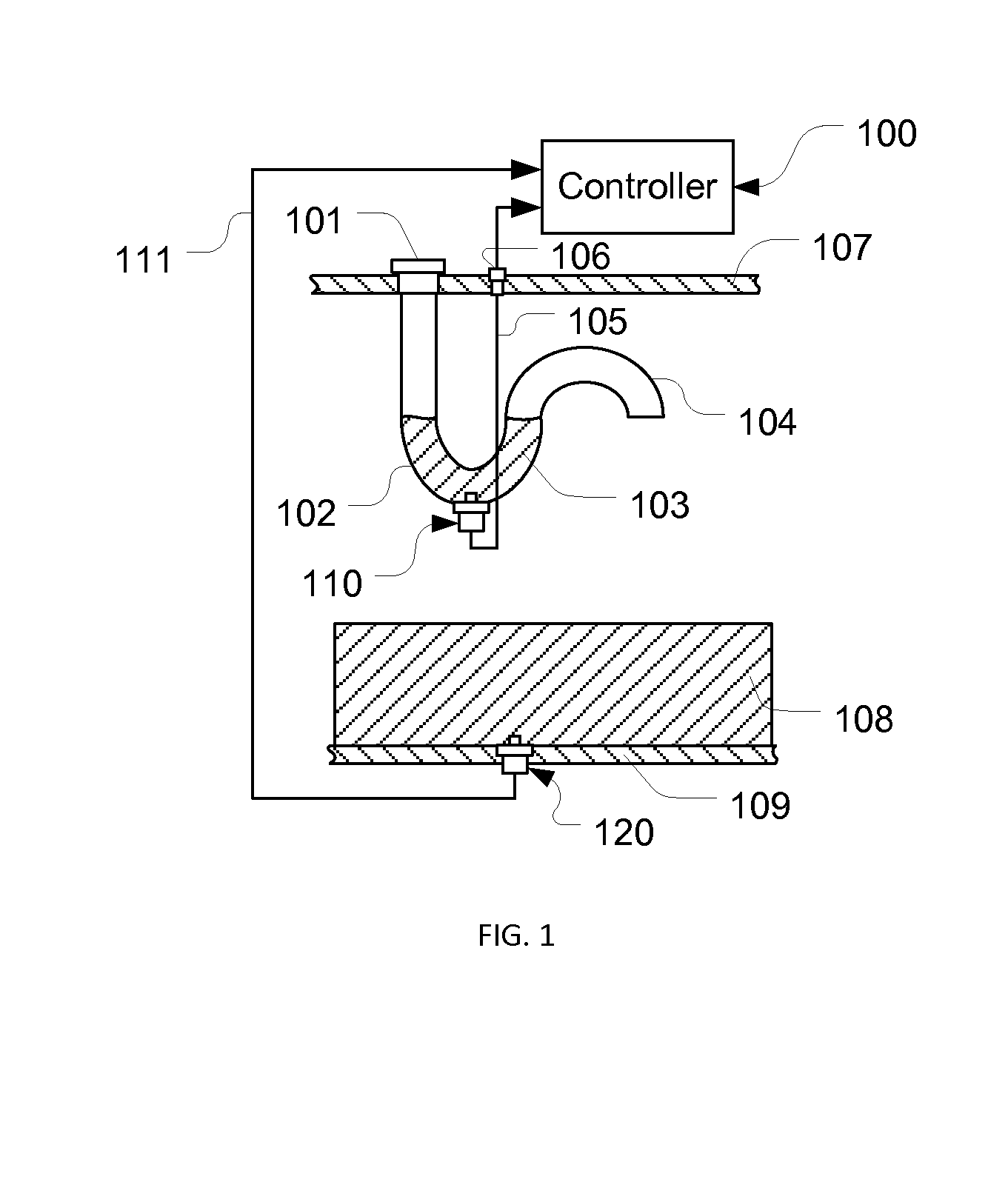
A sensing apparatus for detecting fluid quality change using signals obtained from a fluid quality sensor for exposure to a fluid and a reference sensor positioned in a reference sensing means having a fluid trap section holding a part of the fluid. Sensing values obtained from the fluid quality sensor and the reference sensor are compared in determining an aging factor. An application of the sensing apparatus is an apparatus for detecting engine oil quality change in an engine system. With the sensing apparatus, a first aging factor can be calculated after an engine cold soak and a second one can be obtained during engine operation. With these two aging factors, in addition to oil quality change, failures in the engine system and sensors, and oil change events can also be detected. Additionally, since reference sensing values are provided by the reference sensor, power disconnections have least effects.
Owner:QI BAOHUA
Semiconductor wafer inspection system
InactiveUS6957154B2Avoid timeAvoid expensesSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPotential differenceBiomedical engineering
A method and system for identifying a defect or contamination on a surface of a material. The method and system involves providing a material, such as a semiconductor wafer, using a non-vibrating contact potential difference sensor to scan the wafer, generate contact potential difference data and processing that data to identify a pattern characteristic of the defect or contamination.
Owner:QCEPT INVESTMENTS LLC
Method and apparatus for measuring dopant profile of a semiconductor
InactiveUS6893884B2NanotechSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementTemperature differenceCondensed matter physics
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method and apparatus for measuring dopant profile of a semiconductor
InactiveUS20030186471A1NanotechSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementTemperature differenceCondensed matter physics
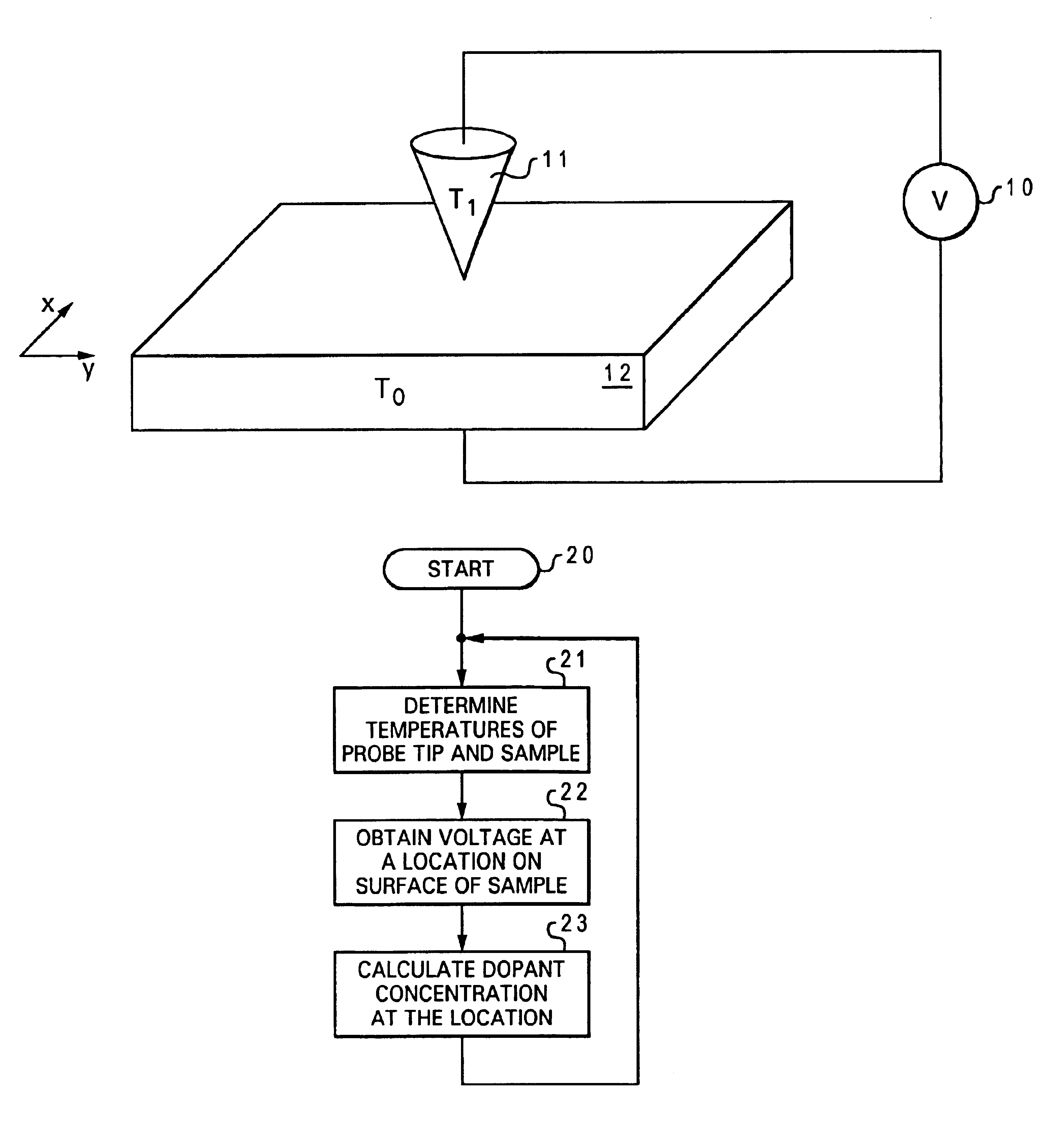
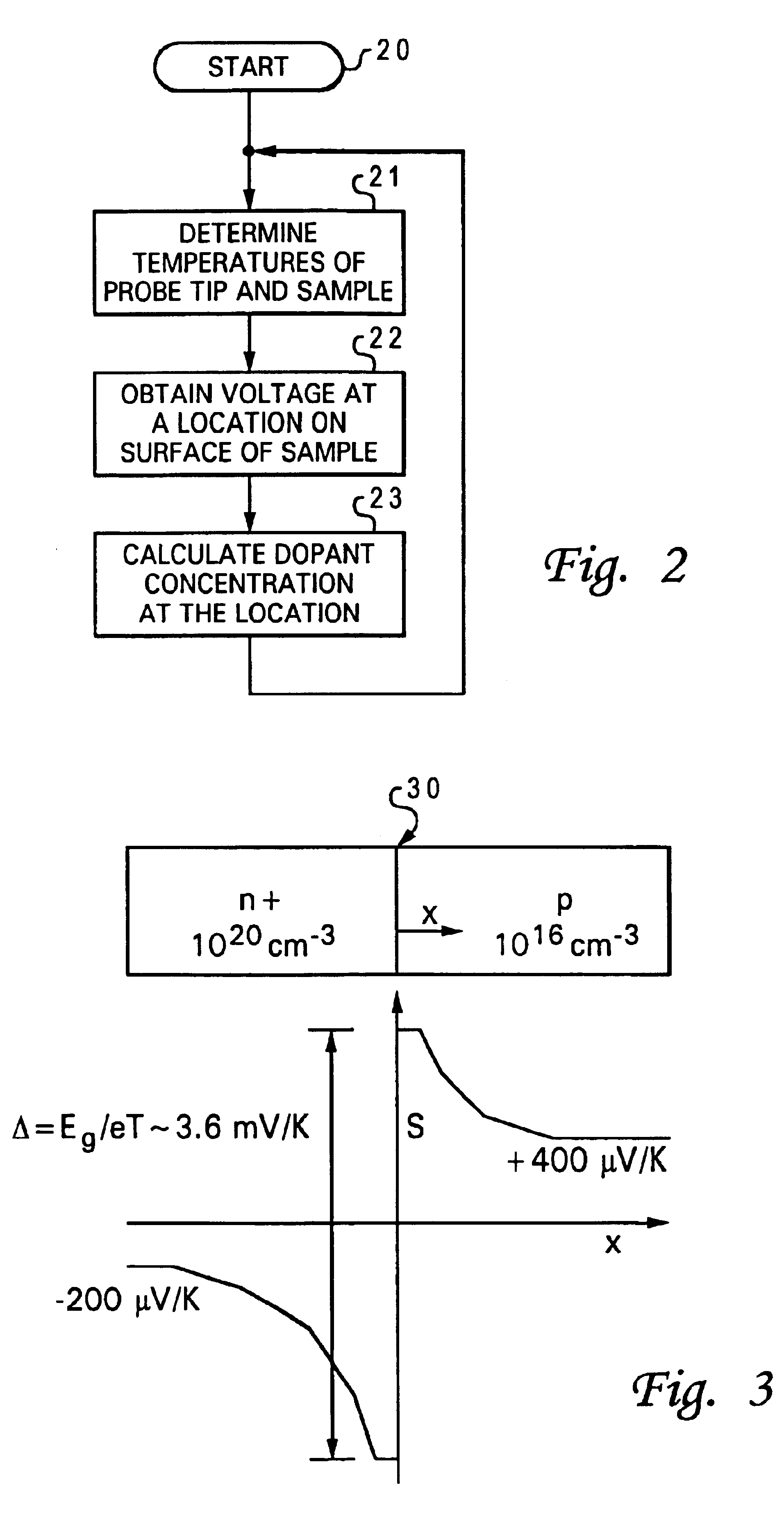
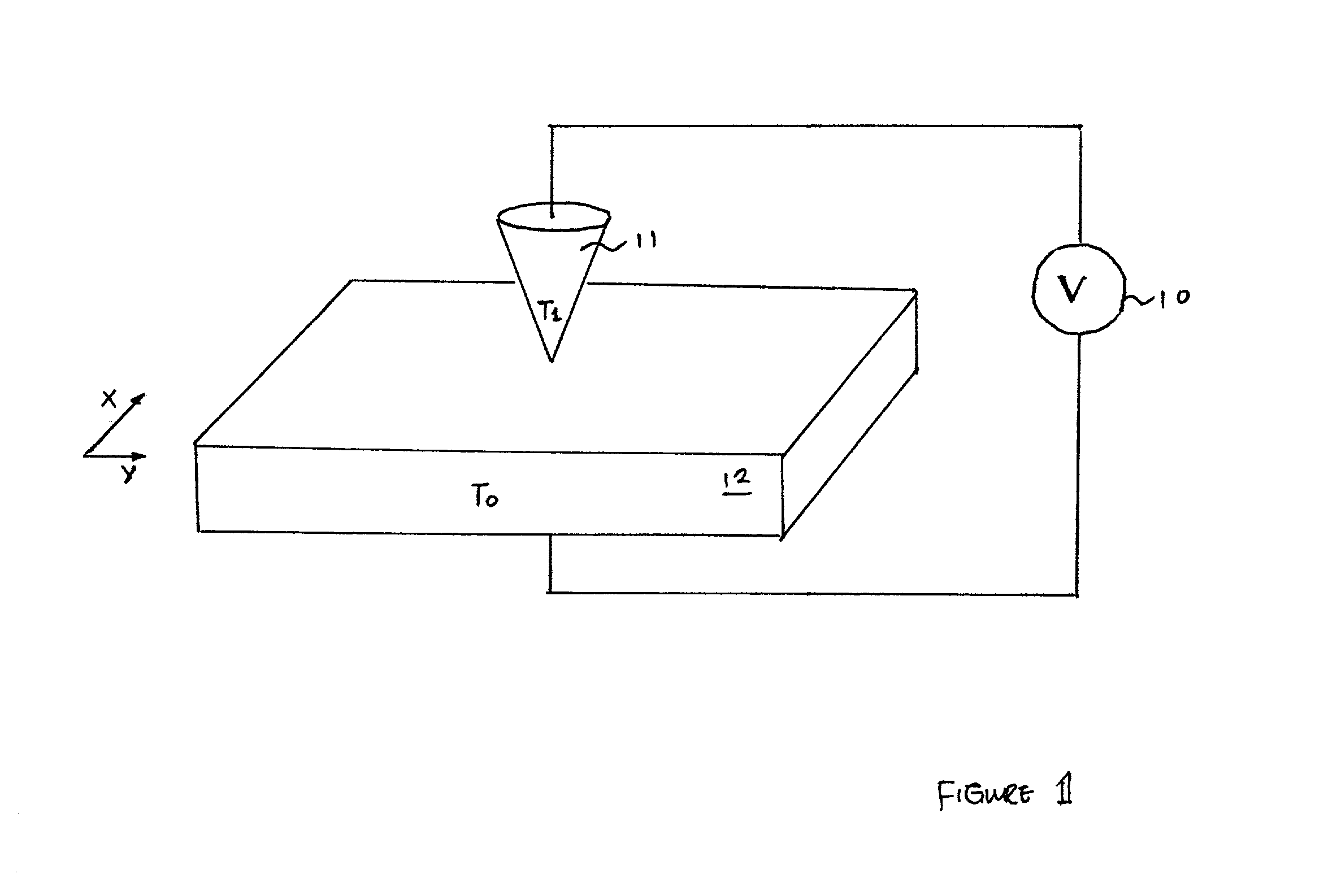
A method and apparatus for measuring dopant profile of a semiconductor is disclosed. Initially, the temperature of a tip of a probe and the temperature of a semiconductor sample are ascertained. Then, a voltage at a location on a surface of the semiconductor sample is obtained via the tip of the probe. The dopant concentration at the location of the surface of the semiconductor sample is subsequently determined by combining the obtained voltage and the temperature difference between the probe tip and the semiconductor sample. The above-mentioned steps can be repeated in order to generate a dopant profile of the semiconductor.
Owner:IBM CORP
Miniaturized Metal (Metal Alloy)/ PdOx/SiC Hydrogen And Hydrocarbon Gas Sensors
ActiveUS20090113992A1Improve high temperature performanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingHydrogenSemiconductor structure
Owner:NASA
Systems and methods for using non-contact voltage sensors and corona discharge guns
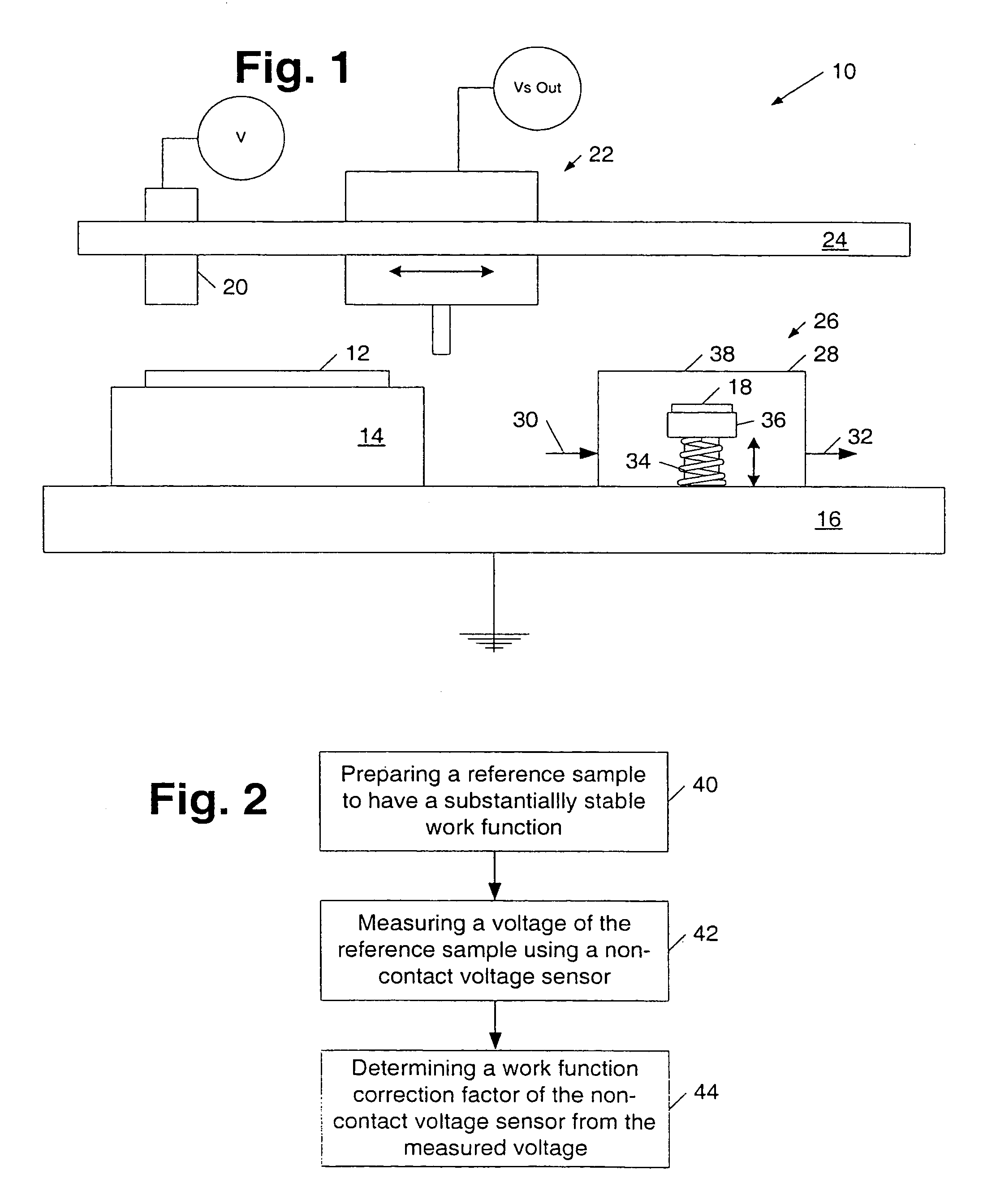
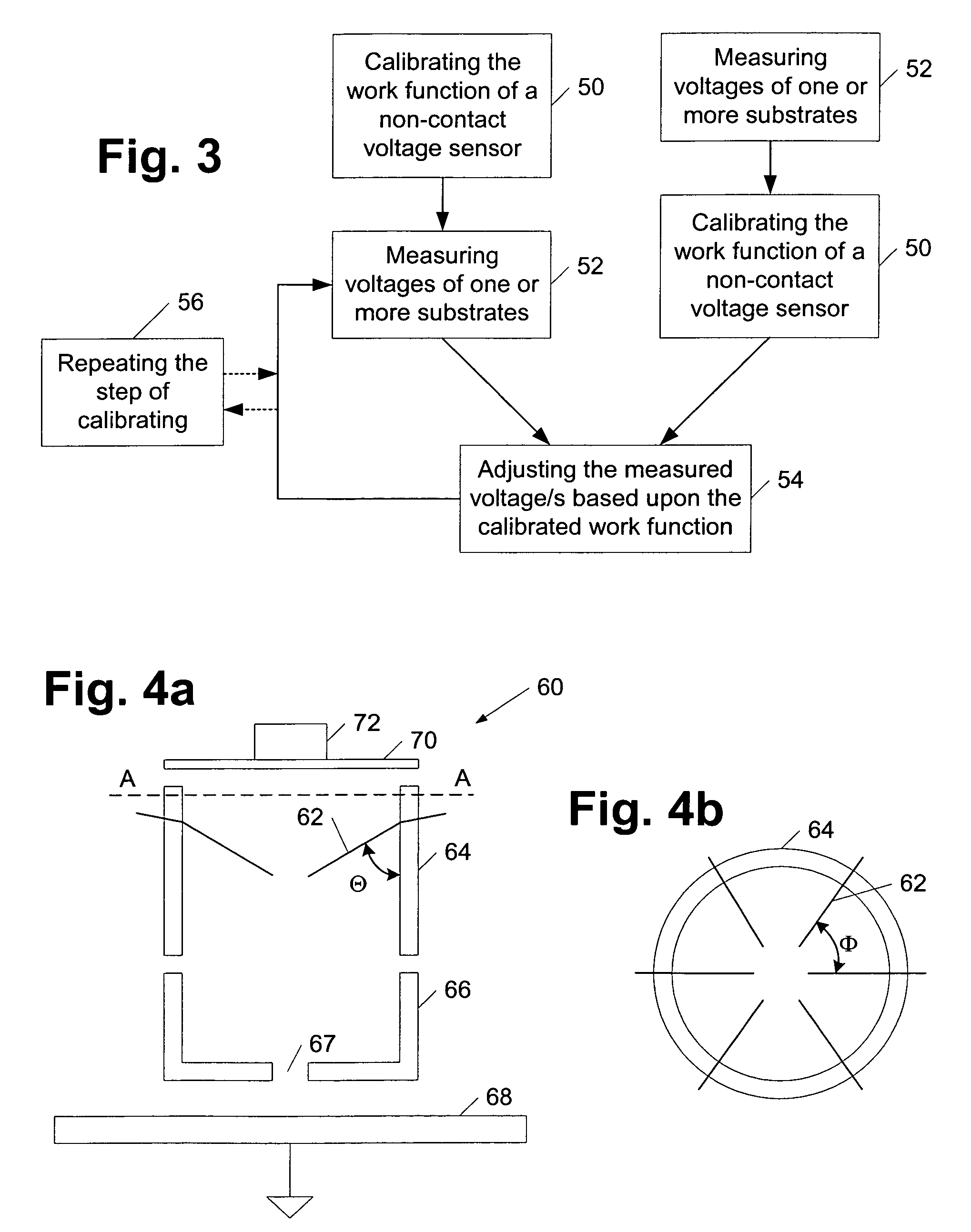
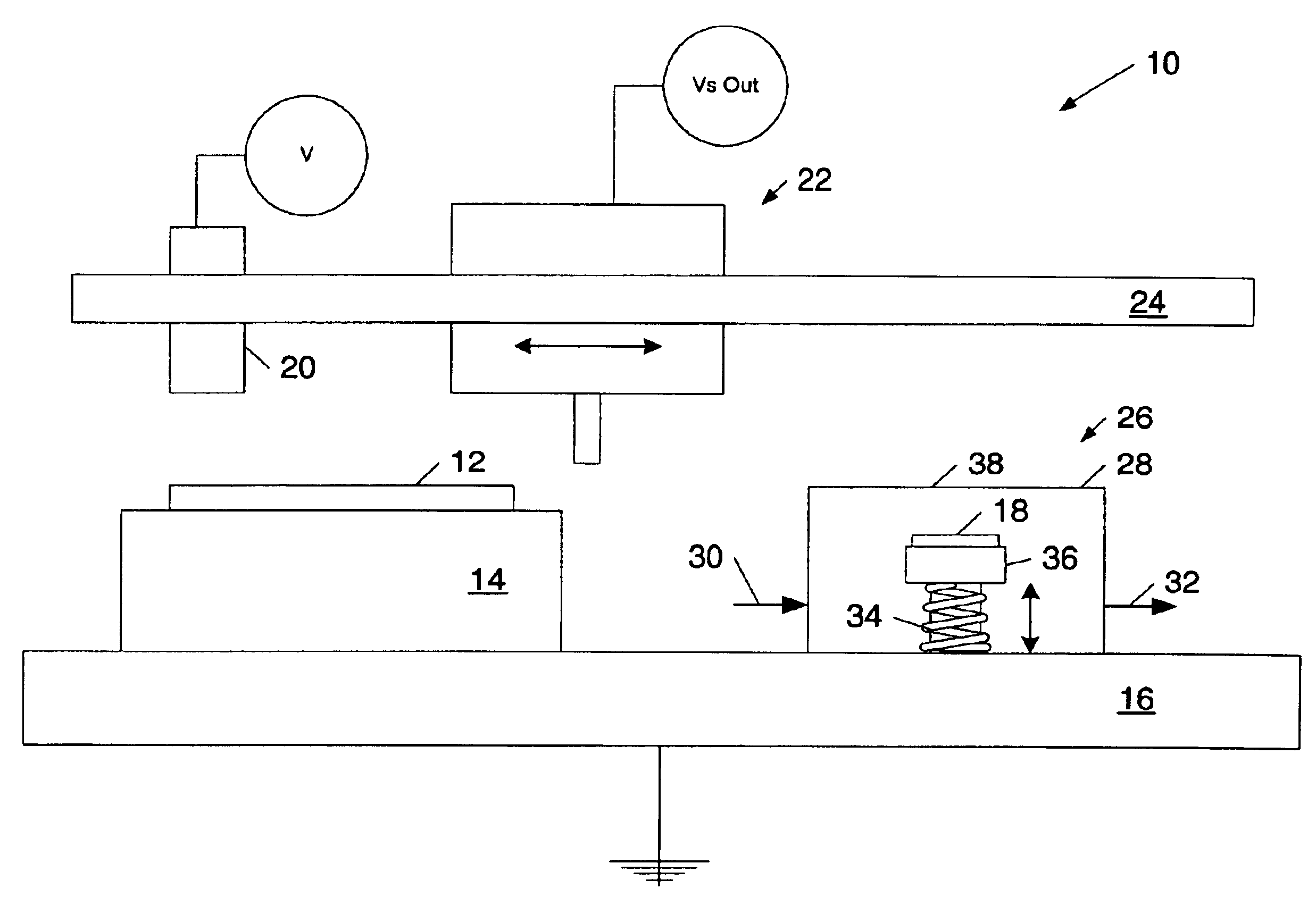
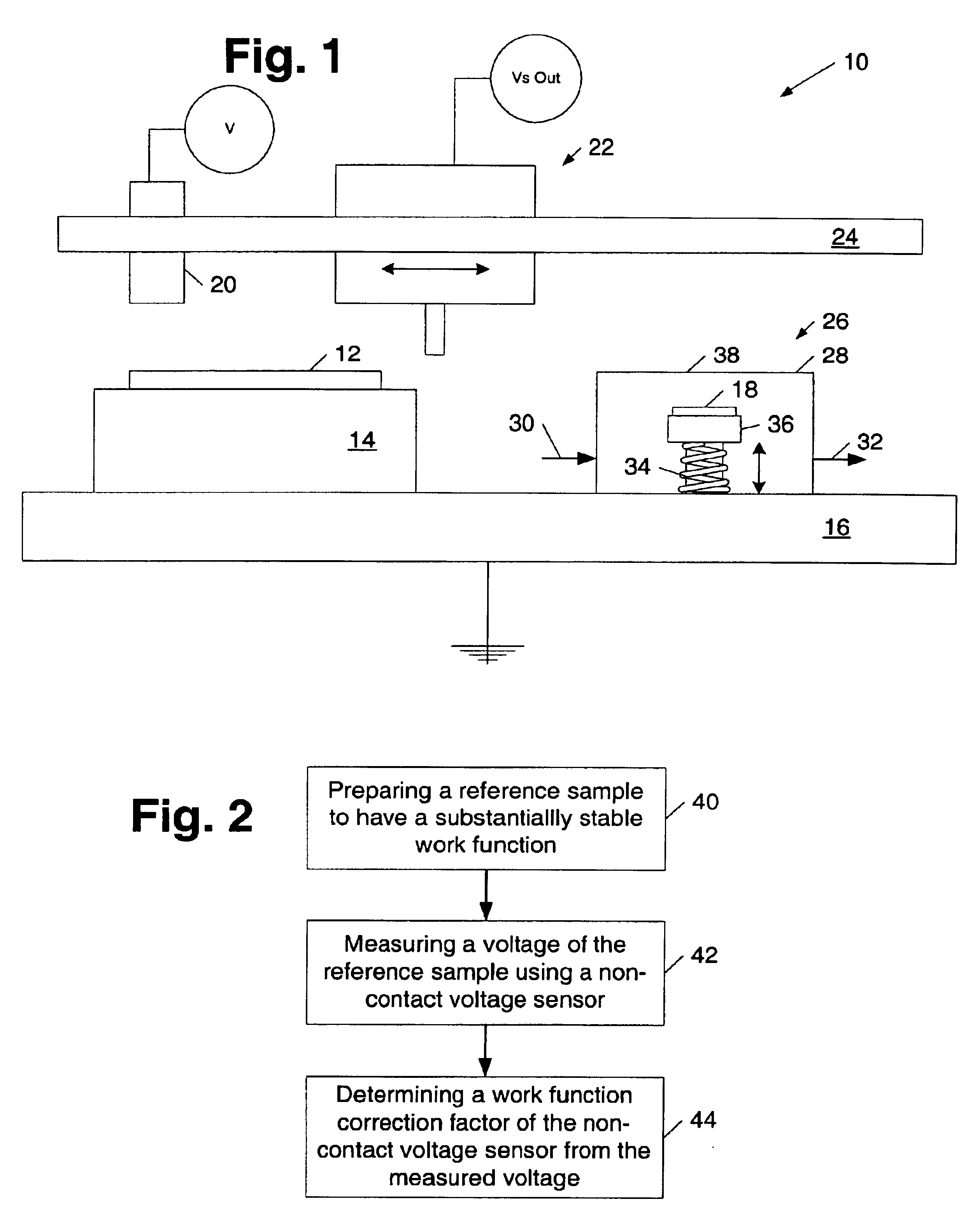
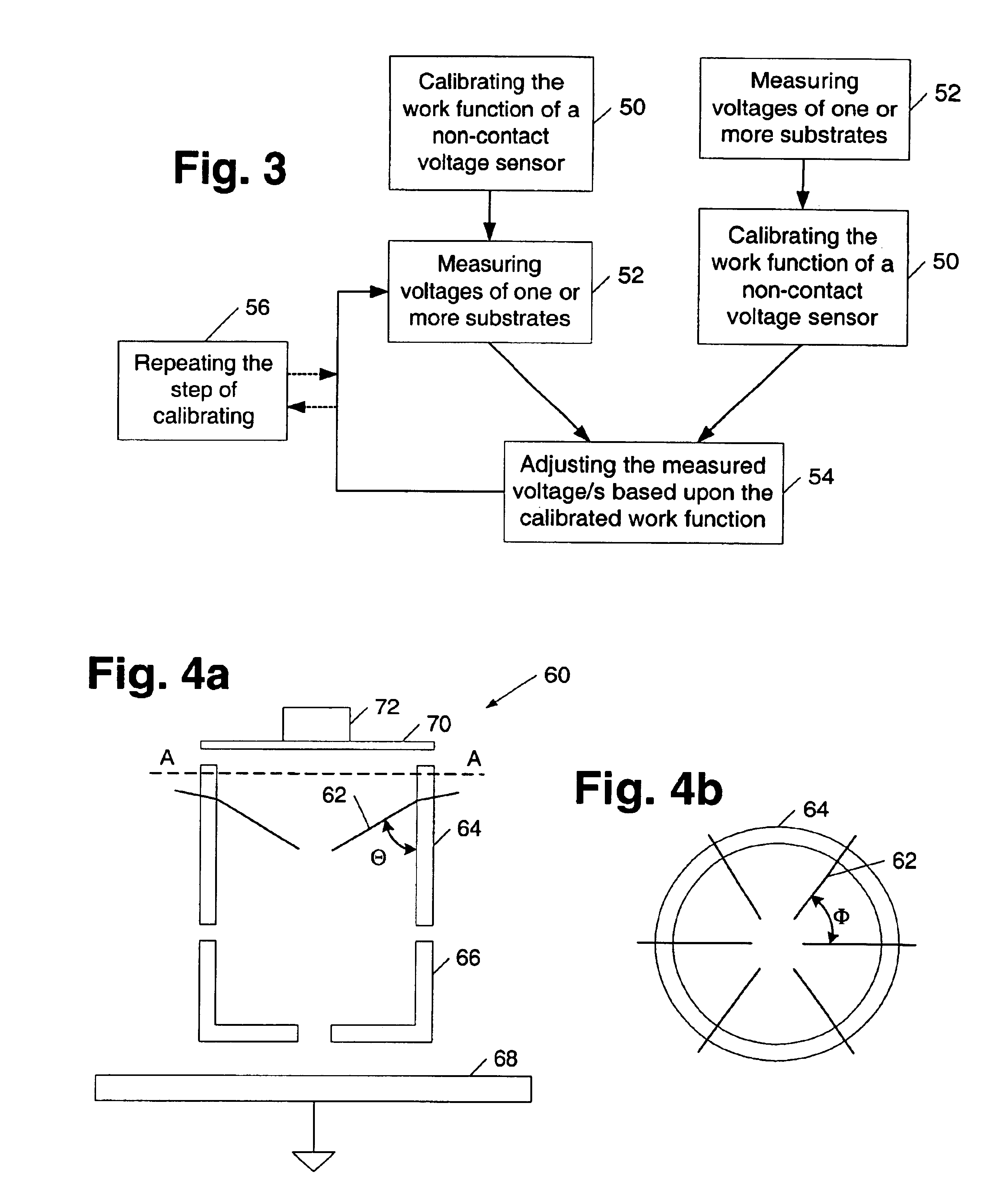
InactiveUS7110238B1Accurate measurementAccurate valueMaterial work function voltageRelaysReference sampleWork function
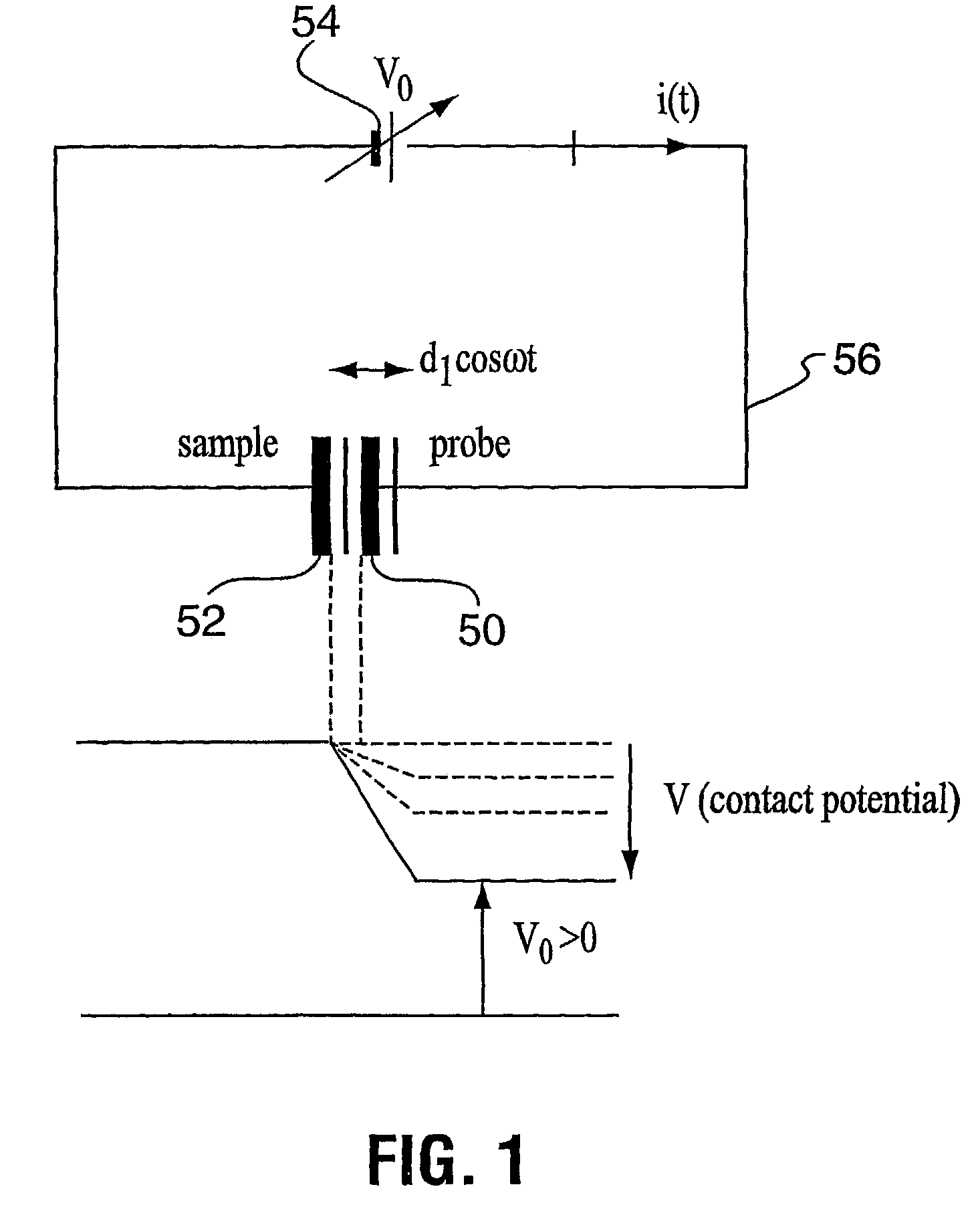
A method and a system for calibrating the work function of a non-contact voltage sensor are provided. The method includes preparing a reference sample to have a stable work function, measuring a voltage of the sample using a non-contact voltage sensor, and determining a work function correction factor of the sensor from the measured voltage. In turn, the calibrated work function may be used to adjust voltages of substrates measured by the sensor. A corona gun which includes a first electrode and one or more conductive rods is provided. In some embodiments, the conductive rods may be angled between 0 and 90 degrees with respect to a first electrode sidewall and / or be concentrically arranged less than 90 degrees from each other. In addition or alternatively, the corona gun may be adapted to alter its length and / or include a second electrode partially inset within a space surrounded by the first electrode.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Inspection system and apparatus
InactiveUS7103482B2Minimize complexityFast and inexpensive and effective meanSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectrostatic cleaningPotential differenceContamination
A method and system for identifying a defect or contamination on a surface of a material. The method and system involves providing a material, such as a semiconductor wafer, using a non-vibrating contact potential difference sensor to scan the wafer, generate contact potential difference data and processing that data to identify a pattern characteristic of the defect or contamination.
Owner:QCEPT INVESTMENTS LLC
Defect classification utilizing data from a non-vibrating contact potential difference sensor
InactiveUS20090139312A1Minimize the differenceDistance minimizationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementNanotechnologyPotential differenceEngineering
A method and system for identifying and classifying non-uniformities on the surface of a semiconductor or in a semiconductor. The method and system involves scanning the wafer surface with a non-vibrating contact potential difference sensor to detect the locations of non-uniformities, extracting features characteristic of the non-uniformities, and applying a set of rules to these features to classify the type of each non-uniformity.
Owner:QCEPT INVESTMENTS LLC
Systems and methods for using non-contact voltage sensors and corona discharge guns
InactiveUS6909291B1Accurate measurementAccurate valueElectrical testingMaterial work function voltageReference sampleWork function
A method and a system for calibrating the work function of a non-contact voltage sensor are provided. The method includes preparing a reference sample to have a stable work function, measuring a voltage of the sample using a non-contact voltage sensor, and determining a work function correction factor of the sensor from the measured voltage. In turn, the calibrated work function may be used to adjust voltages of substrates measured by the sensor. A corona gun which includes a first electrode and one or more conductive rods is provided. In some embodiments, the conductive rods may be angled between 0 and 90 degrees with respect to a first electrode sidewall and / or be concentrically arranged less than 90 degrees from each other. In addition or alternatively, the corona gun may be adapted to alter its length and / or include a second electrode partially inset within a space surrounded by the first electrode.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Thermoelectric conductivity measurement instrument of thermoelectric device and measuring method of the same
InactiveUS20150130472A1Material thermal conductivityCurrent/voltage measurementAcousticsThermoelectric effect
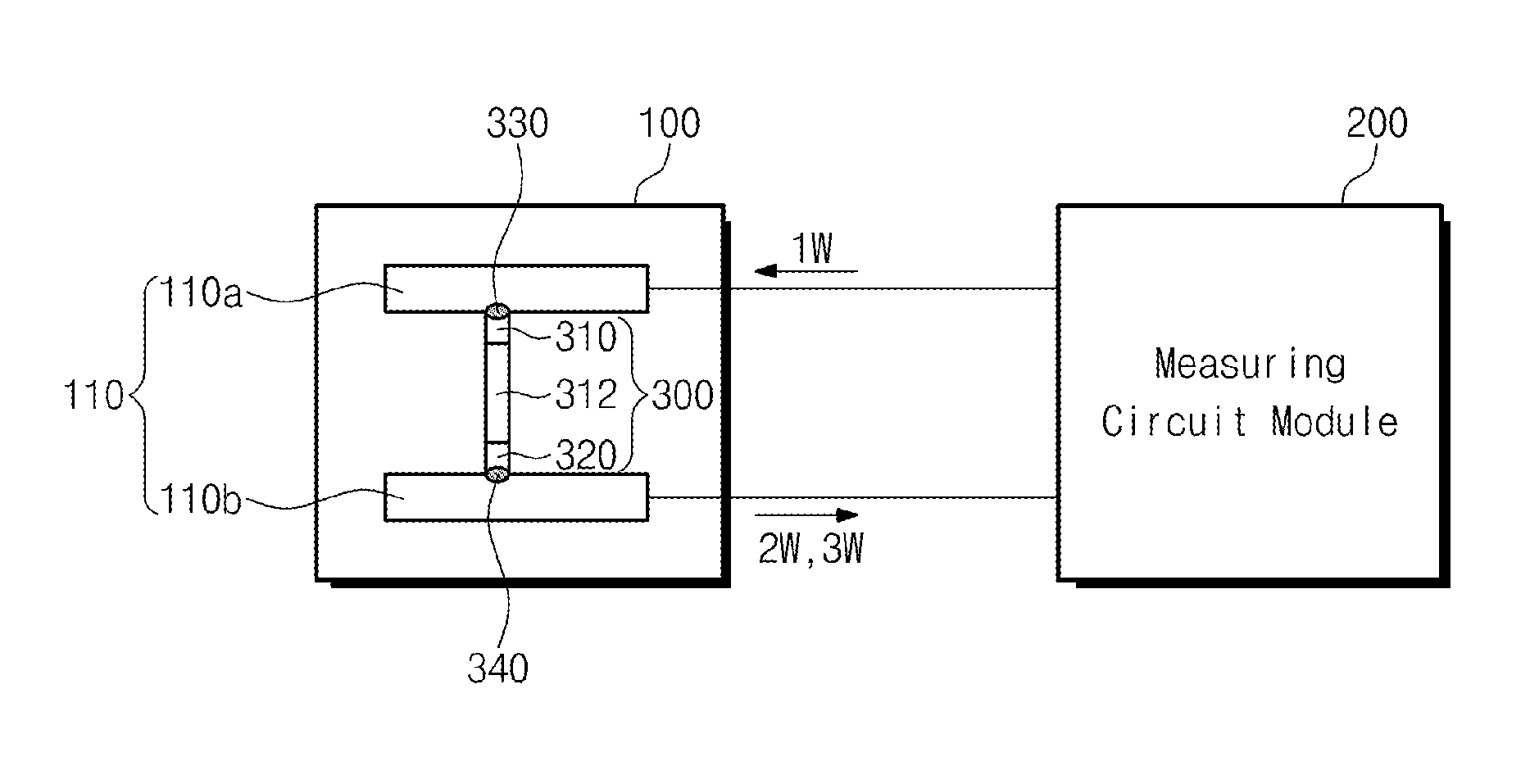
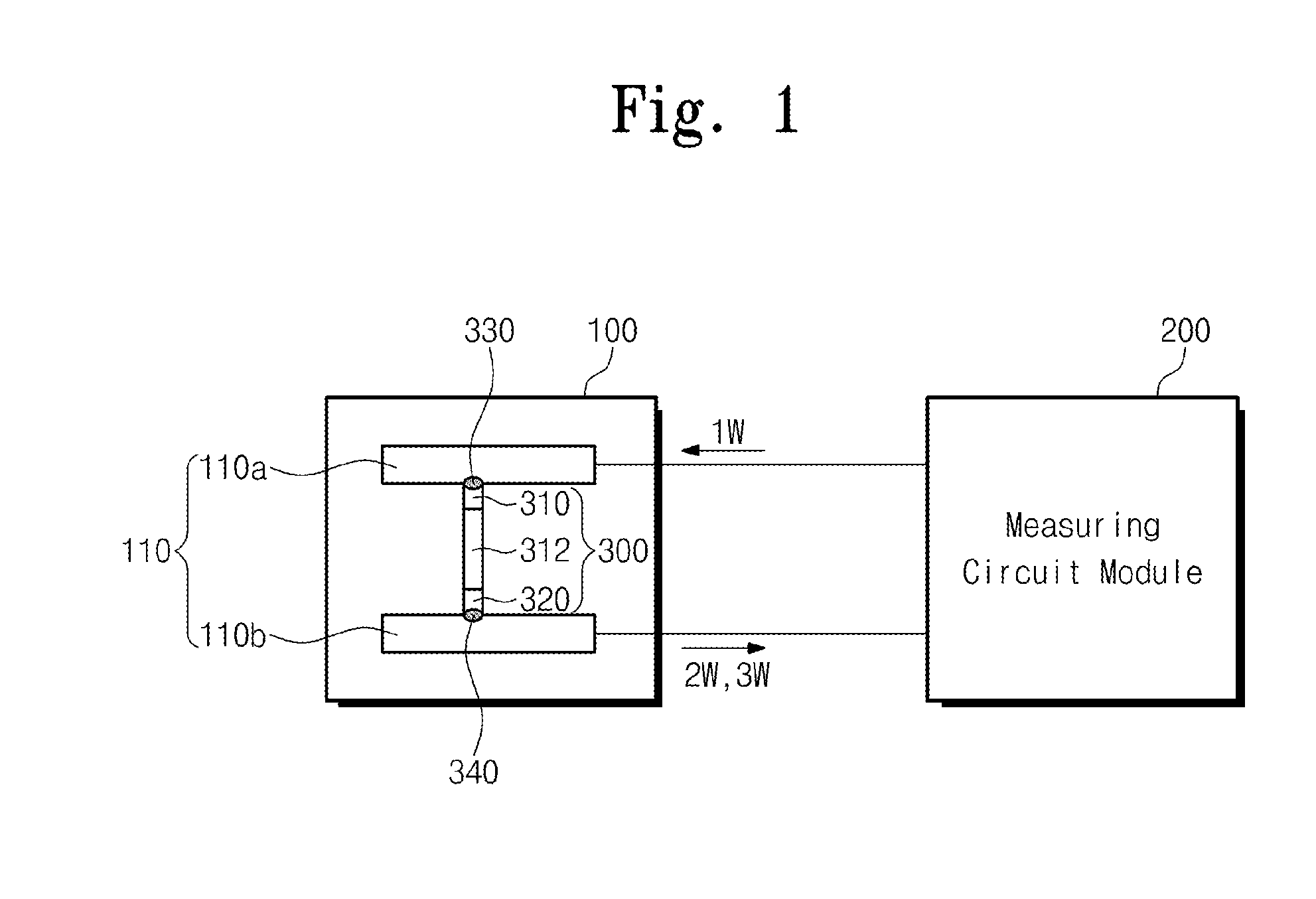
Provided are a thermoelectric conductivity measurement instrument of a thermoelectric device and a measuring method of the same. The thermoelectric conductivity measurement instrument of the thermoelectric device includes a sample piece fixing module configured to provide an environment for measuring physical properties of the thermoelectric device as a sample piece and comprising an electrode part configured to provide contact points which are respectively in contact with both ends of the sample piece, and a measuring circuit module configured to provide a source AC voltage of a first frequency heating the sample piece to the electrode part, detect a first thermoelectric AC voltage of a second frequency greater than the first frequency and a second thermoelectric AC voltage of a third frequency greater than the second frequency, which are generated by a temperature change occurring at the contact points, and then obtain the thermoelectric conductivity.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
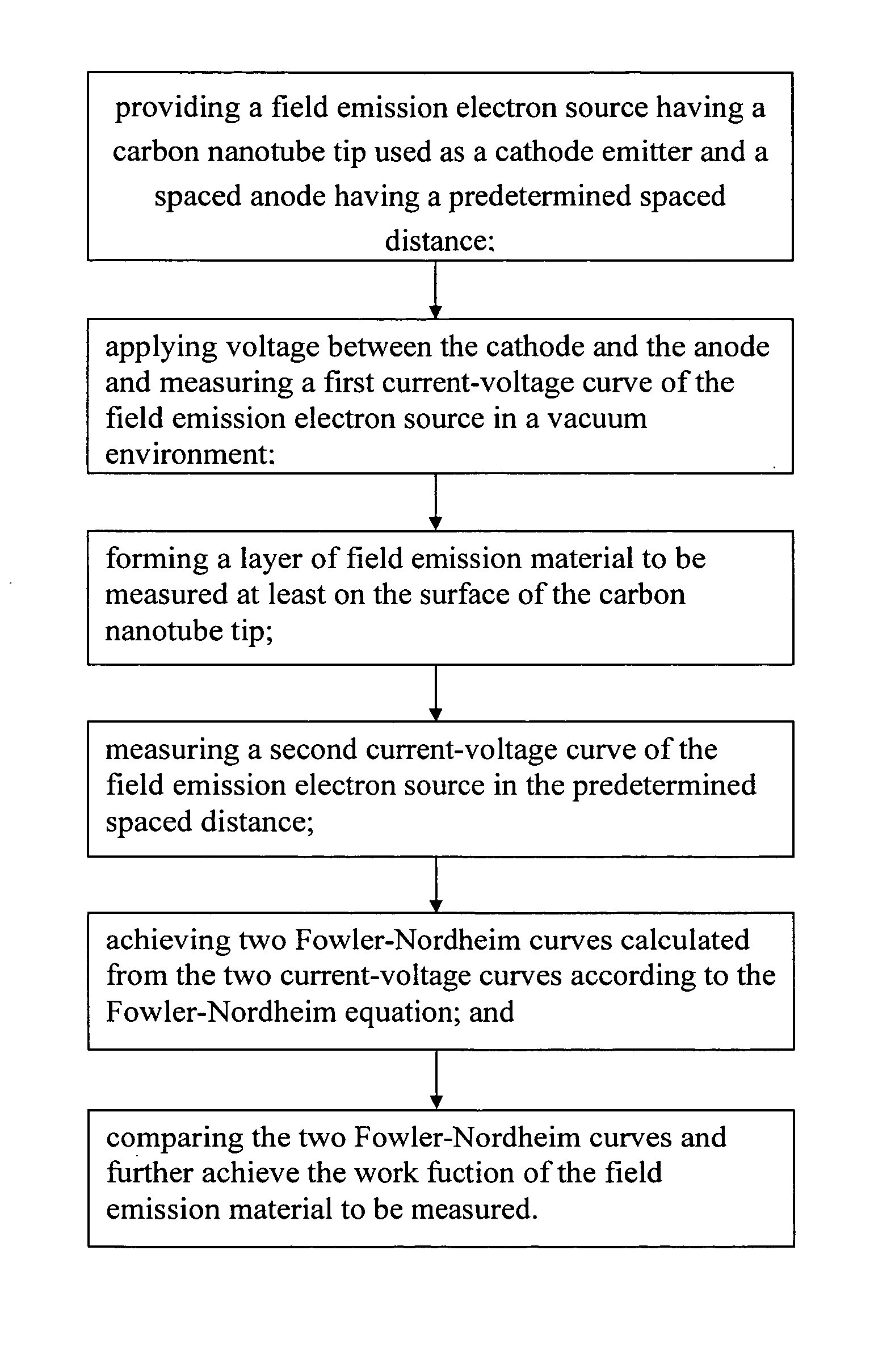
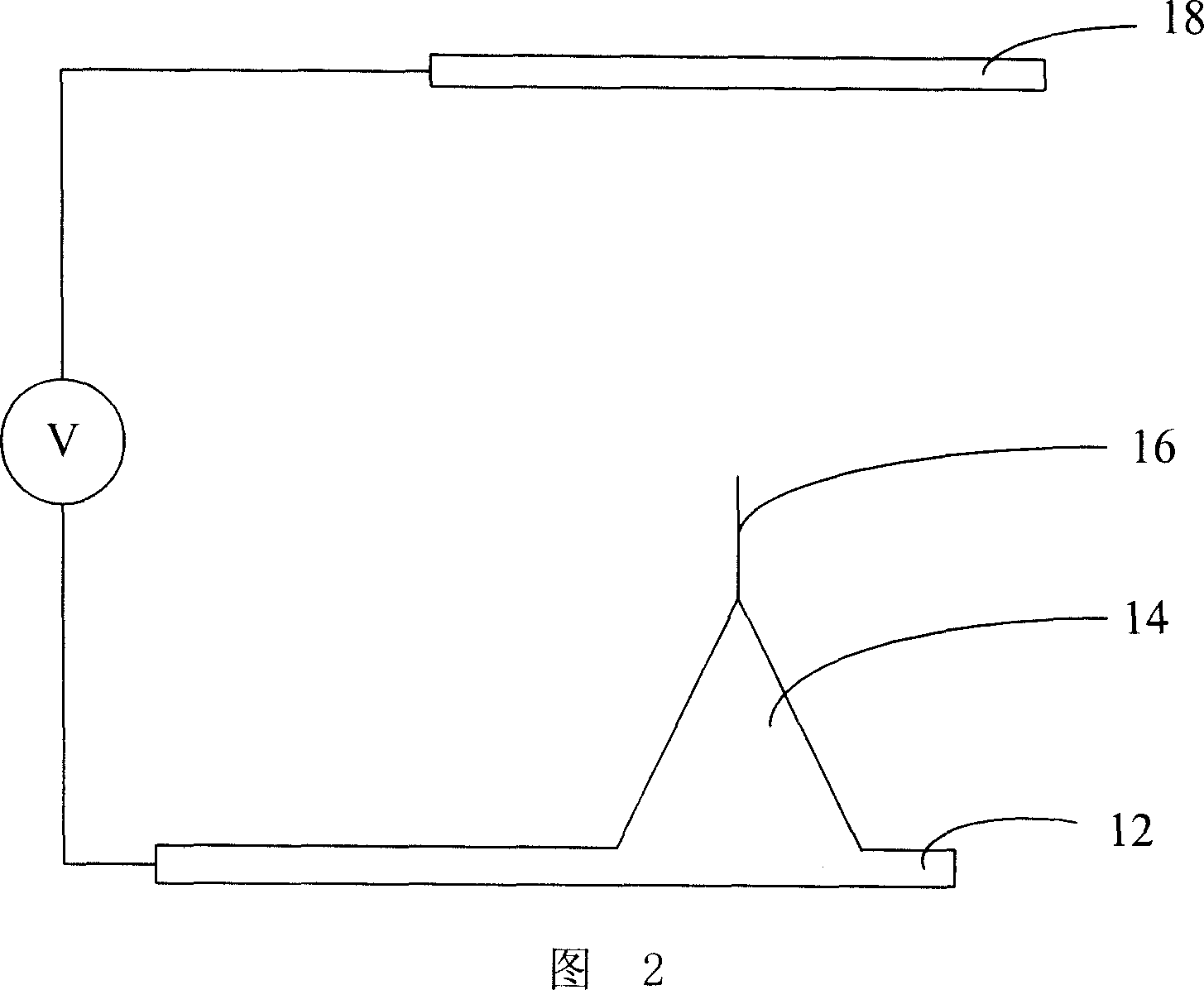
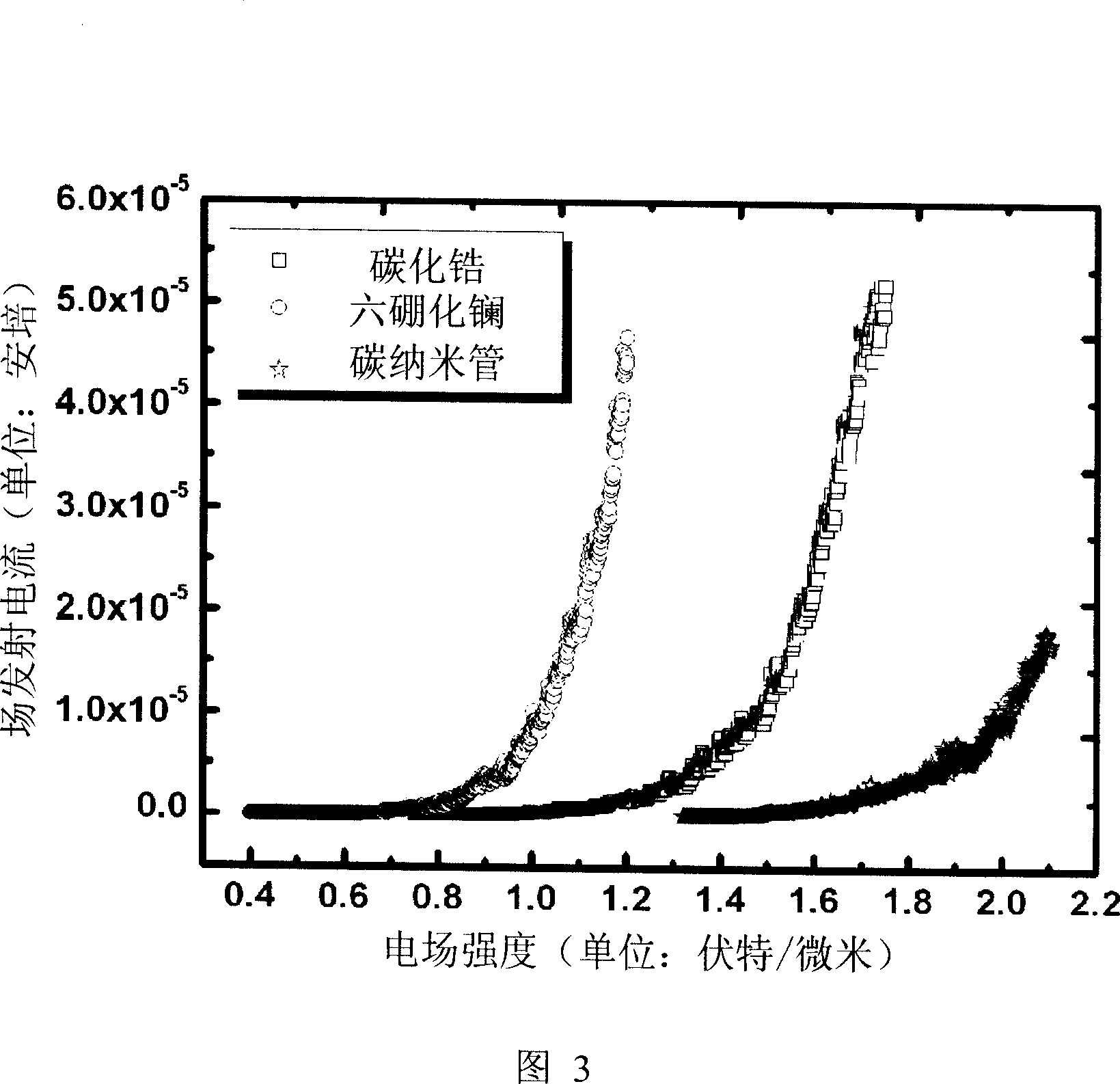
Method for measuring work function
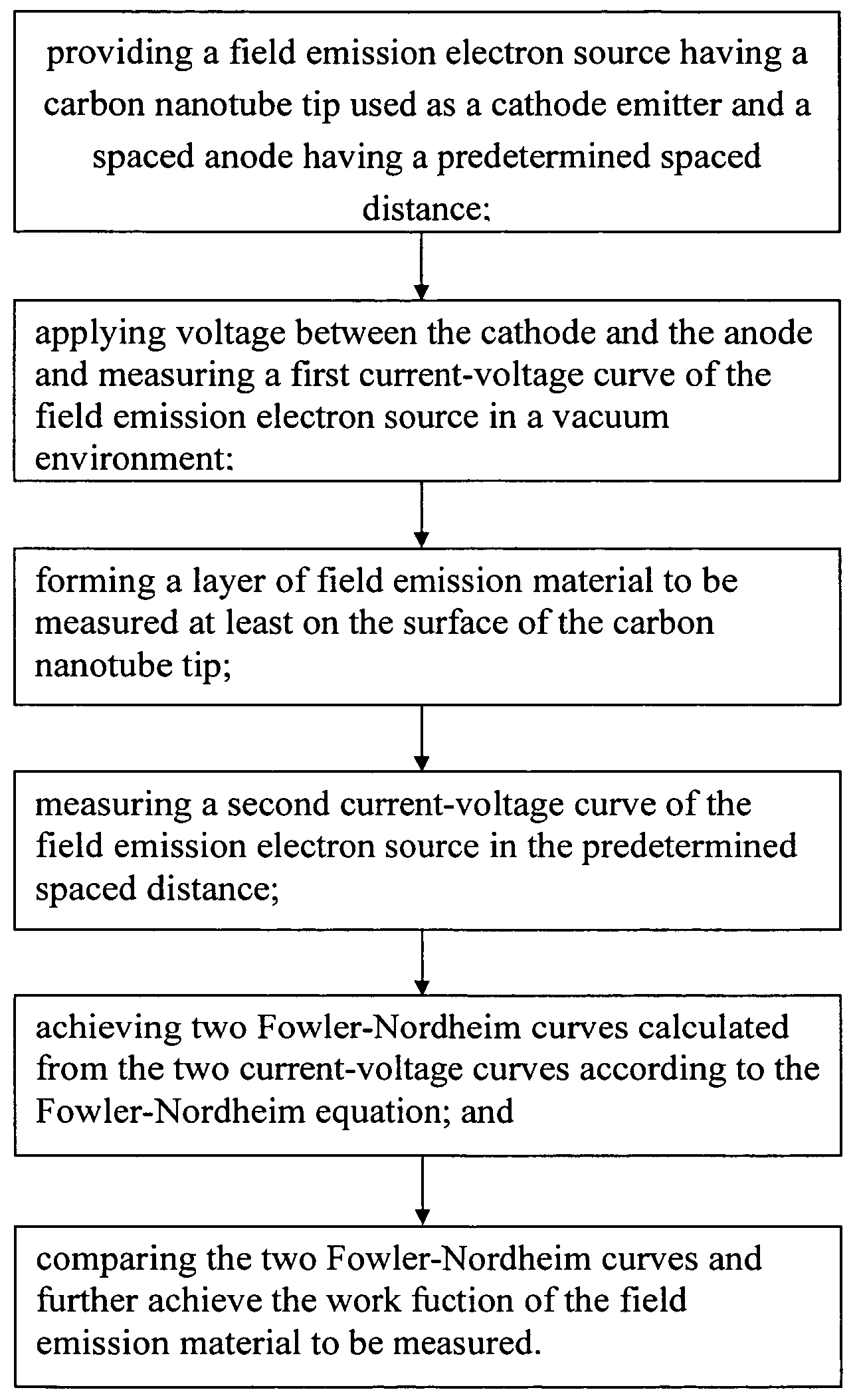
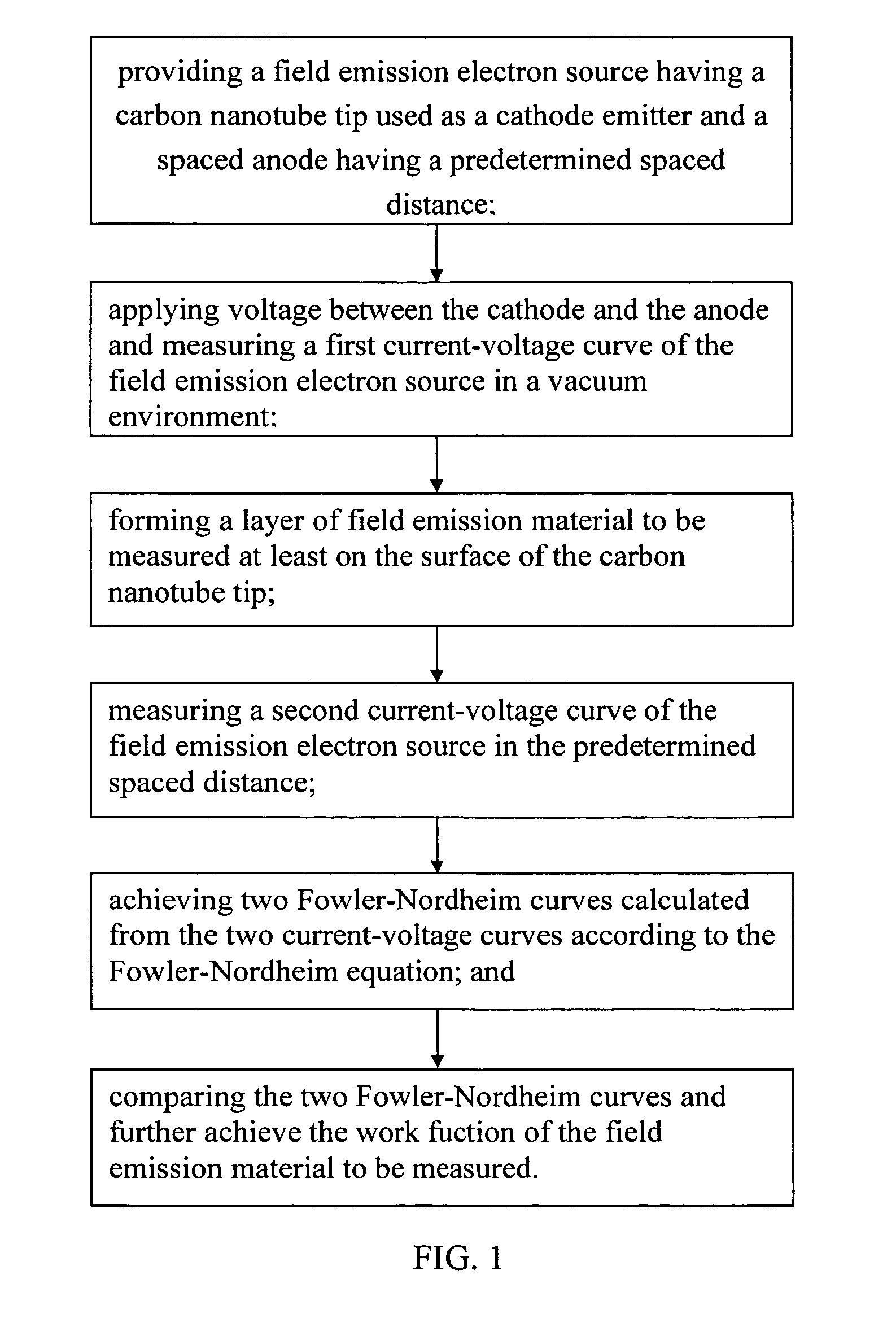
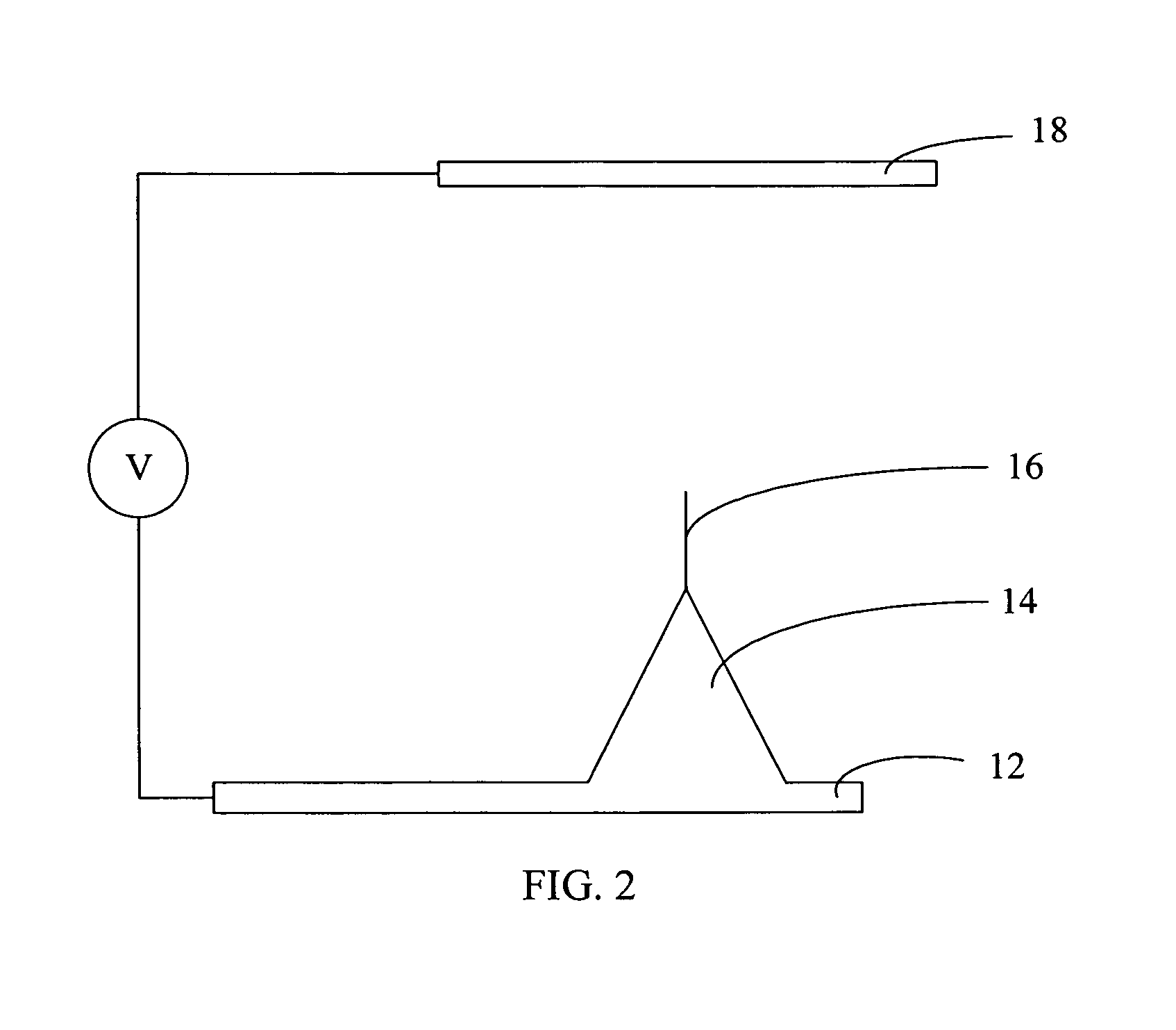
A method for measuring work function includes the steps of: (a) providing a field emission electron source having a carbon nanotube tip as a cathode electrode and a spaced anode electrode, having a predetermined spaced distance therebetween; (b) applying a voltage between the cathode electrode and the anode electrode and measuring a first current-voltage curve of the field emission electron source in a vacuum environment; (c) forming a layer of field emission material at least on the surface of the carbon nanotube tip; (d) measuring a second current-voltage curve of the now-treated field emission electron source in the same conditions as that in the step (b); (e) achieving two Fowler-Nordheim curves calculated from the two current-voltage curves according to the Fowler-Nordheim equation; and (f) comparing the two Fowler-Nordheim curves and calculating the work function of the field emission material therefrom.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
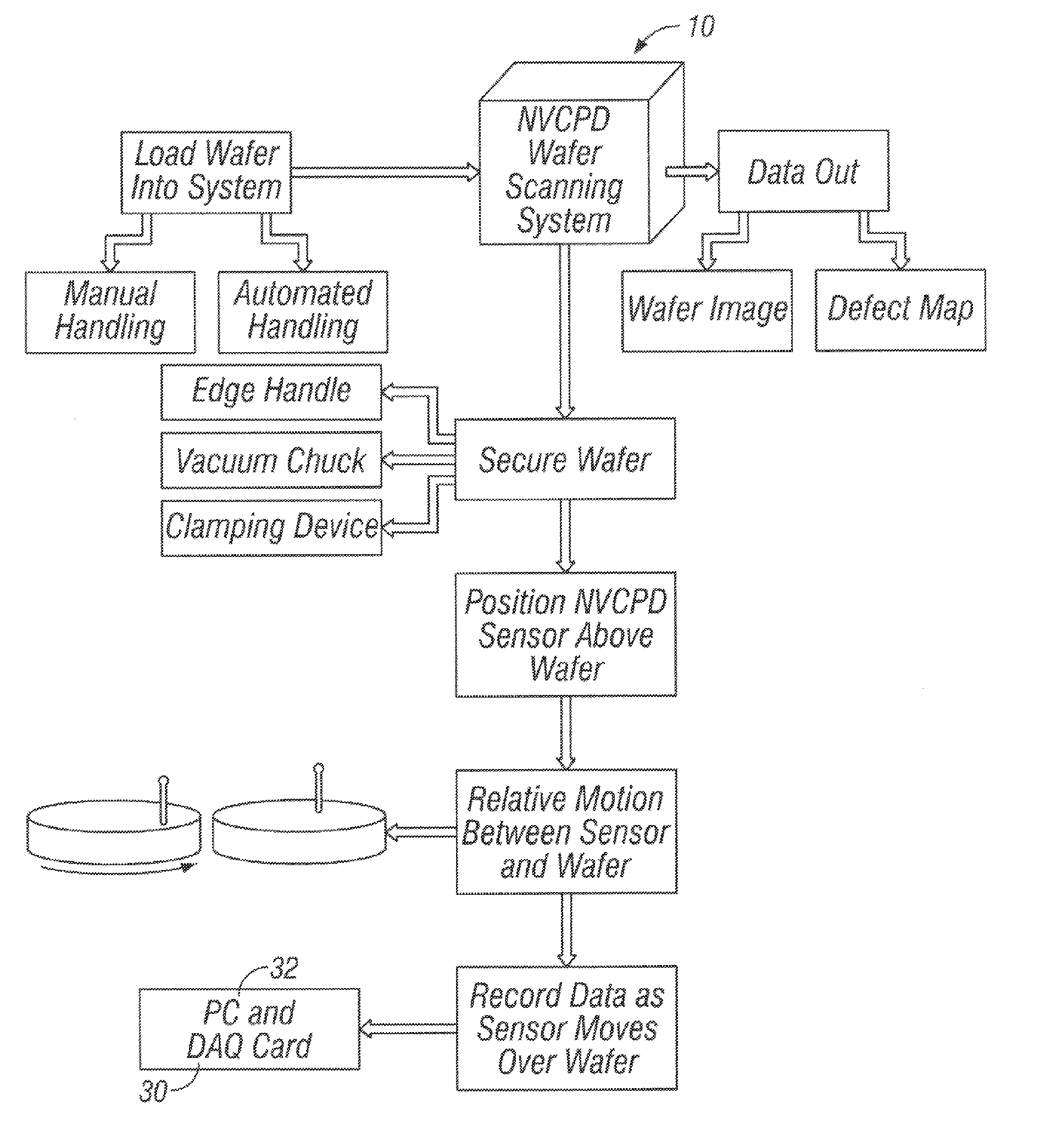
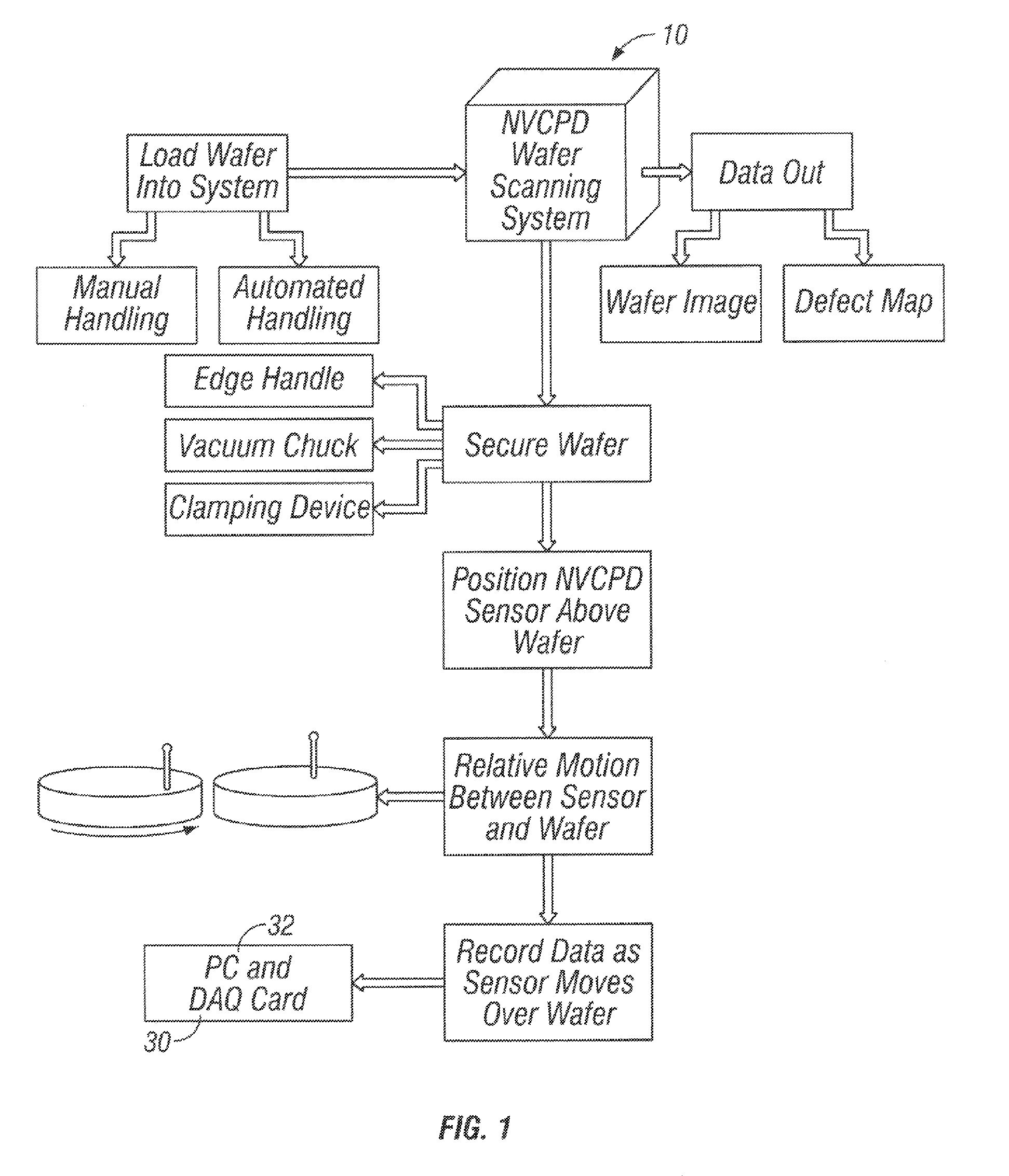
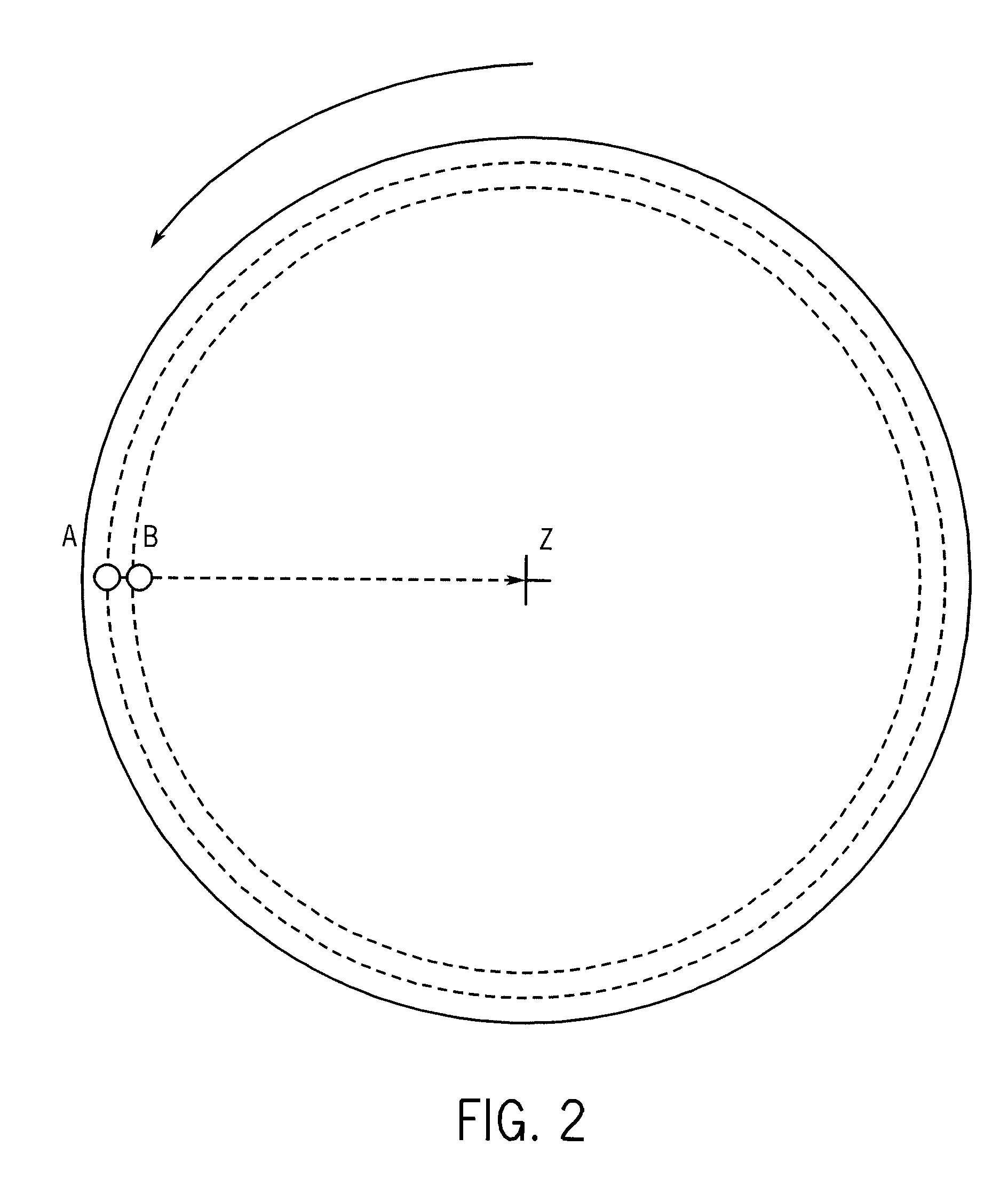
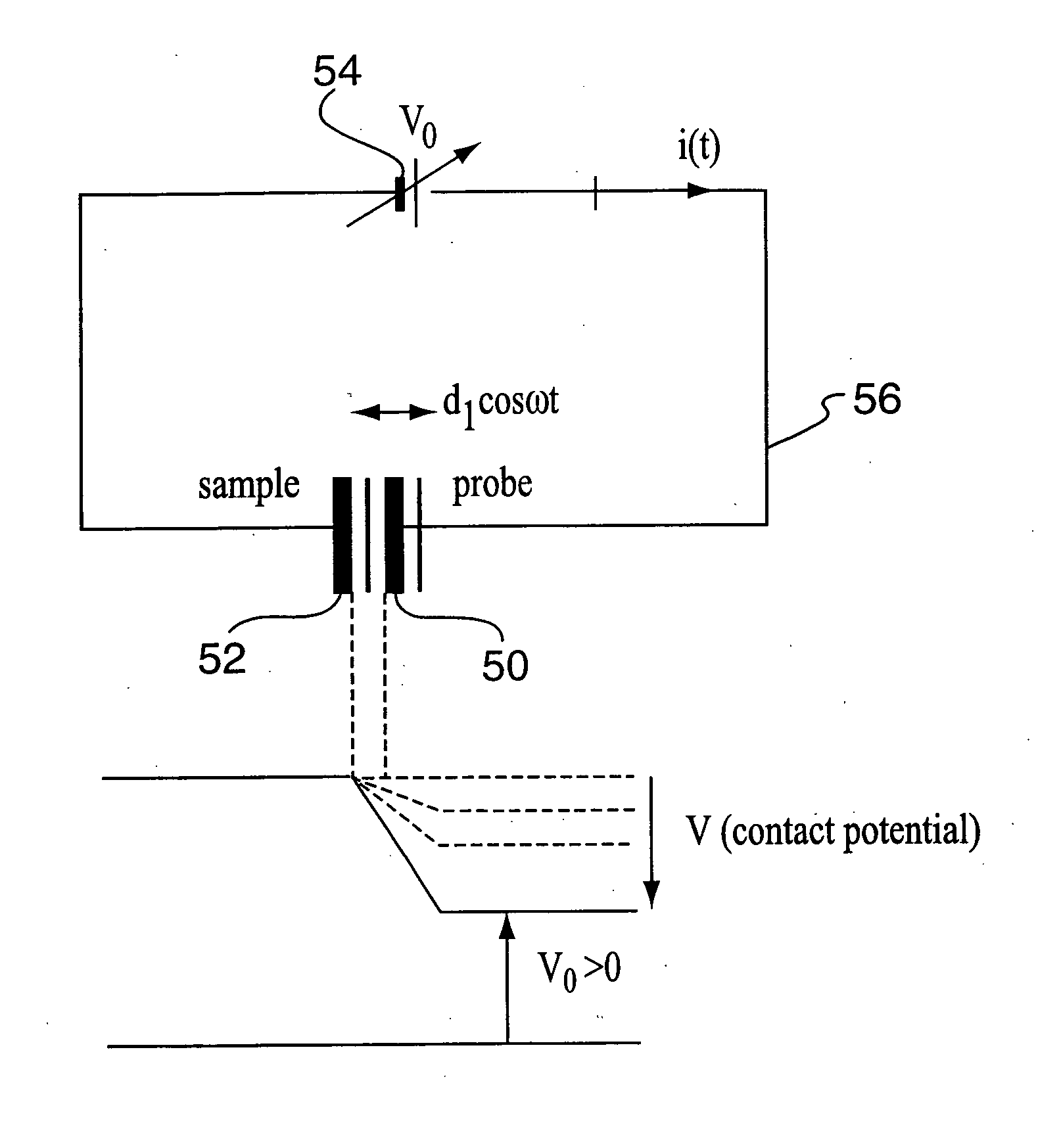
Calibration of non-vibrating contact potential difference measurements to detect surface variations that are perpendicular to the direction of sensor motion
InactiveUS7752000B2Fast imagingFast dataSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectrical testingPotential differenceSurface change
A method and system for determining the contact potential difference of a wafer surface using a non-vibrating contact potential difference probe and a vibrating contact potential difference probe. The method and system involves scanning the wafer surface with a non-vibrating contact potential difference sensor, integrating and scaling the resulting data, and applying offsets to individual tracks of data to match the integrated scaled data to measurements made using a vibrating contact potential difference sensor.
Owner:QCEPT INVESTMENTS LLC
Work function measuring method
ActiveCN101105488AImprove conductivityAccurate measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial work function voltageElectron sourceField emission current
The invention relates to a measuring method of work function which comprises the following steps: a carbon nanometer tube field eradiation electron source is a cathode, and an anode is provided in the preset distance to the cathode; voltage is exerted in the field eradiation electron source in the vacuum environment, and the field eradiation current-voltage curve is measured; one layer of field eradiation material of measured working function is formed on the surface of the carbon nanometer tube of the carbon nanometer tube field eradiation electron source; under the same condition of the same distance, the current-voltage curve of the carbon nanometer tube field eradiation electron source of the measured field eradiation material is measured; according to the Fowler-Nordheim equation and the current-voltage curve diagram which is measured, the Fowler-Nordheim curve sketch diagram of electron eradiated from the field eradiation electron source can be measured; furthermore, the working function of the measured eradiation material can be measured.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Fluid quality sensing means with reference sensor
A sensing apparatus for detecting fluid quality change using signals obtained from a fluid quality sensor for exposure to a fluid and a reference sensor positioned in a reference sensing means having a fluid trap section holding a part of the fluid. Sensing values obtained from the fluid quality sensor and the reference sensor are compared in determining an aging factor. An application of the sensing apparatus is an apparatus for detecting engine oil quality change in an engine system. With the sensing apparatus, a first aging factor can be calculated after an engine cold soak and a second one can be obtained during engine operation. With these two aging factors, in addition to oil quality change, failures in the engine system and sensors, and oil change events can also be detected. Additionally, since reference sensing values are provided by the reference sensor, power disconnections have least effects.
Owner:QI BAOHUA
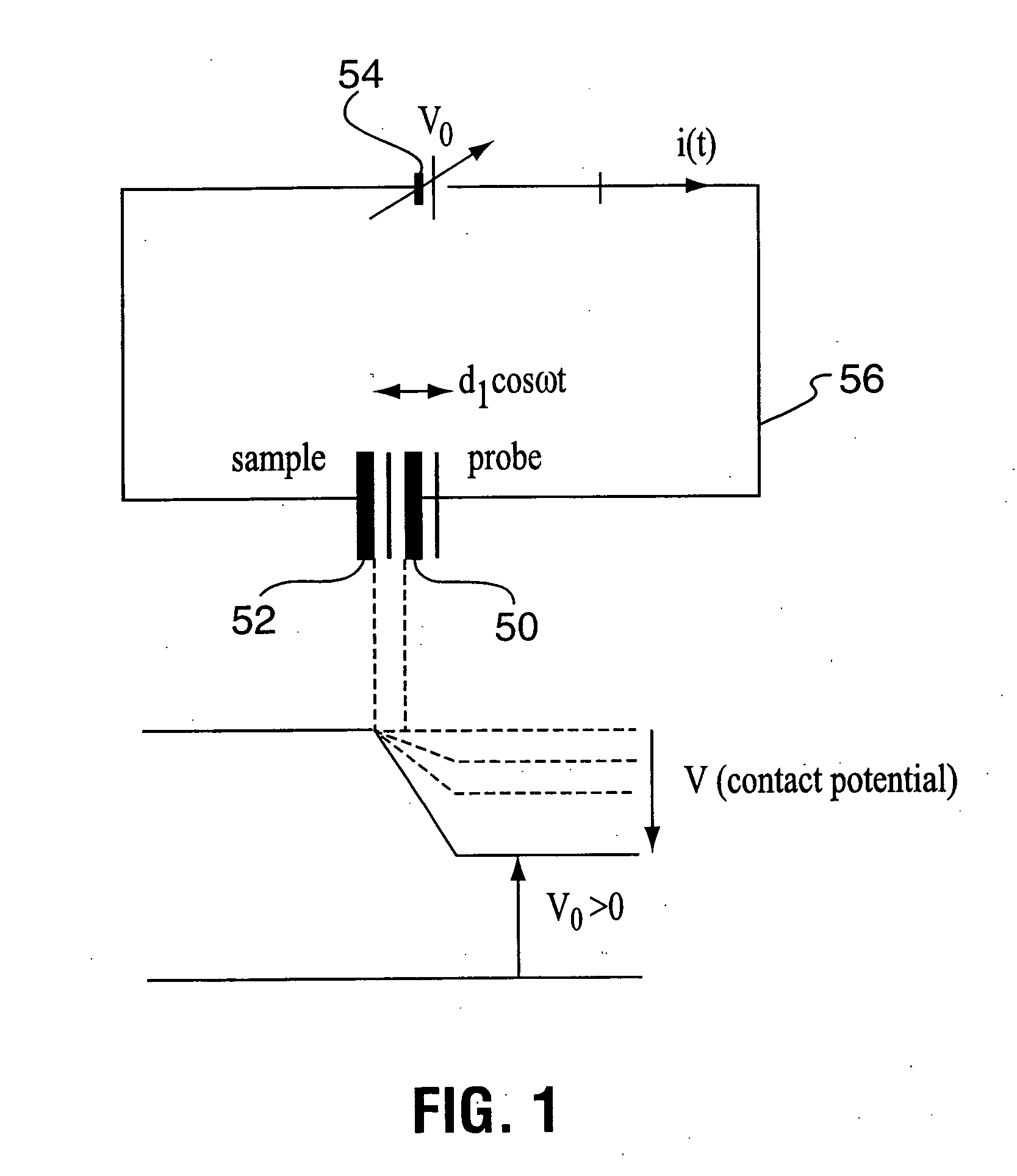
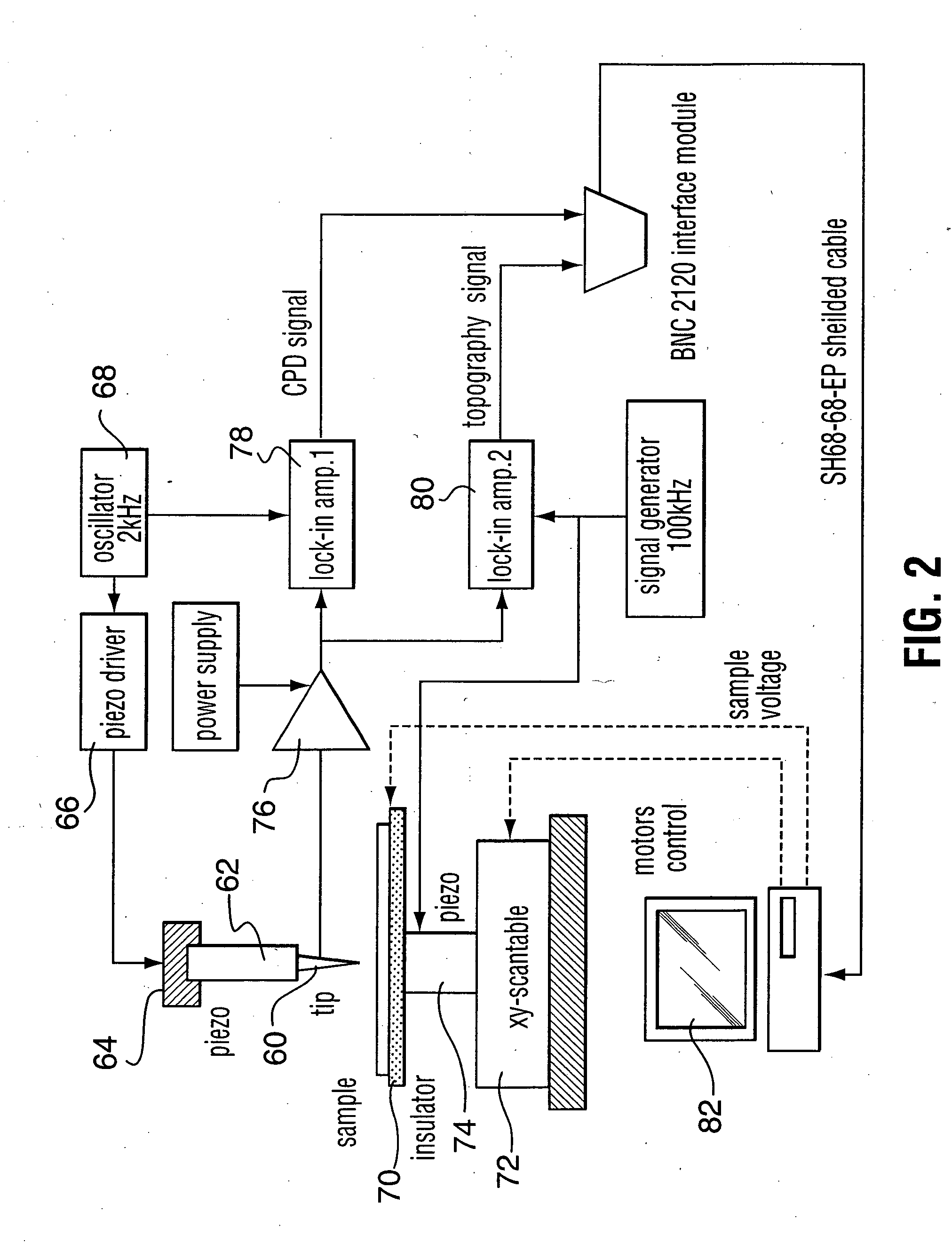
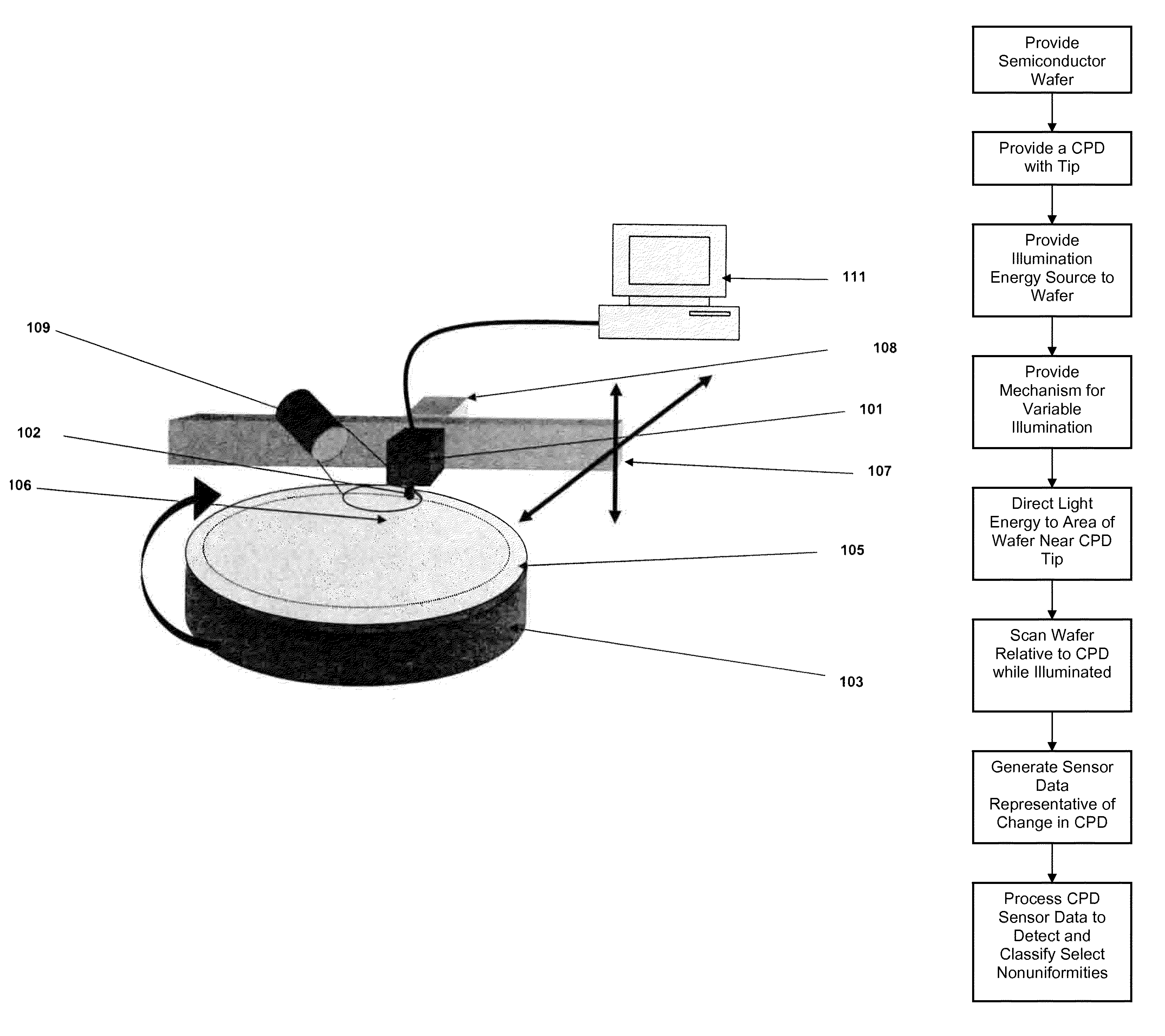
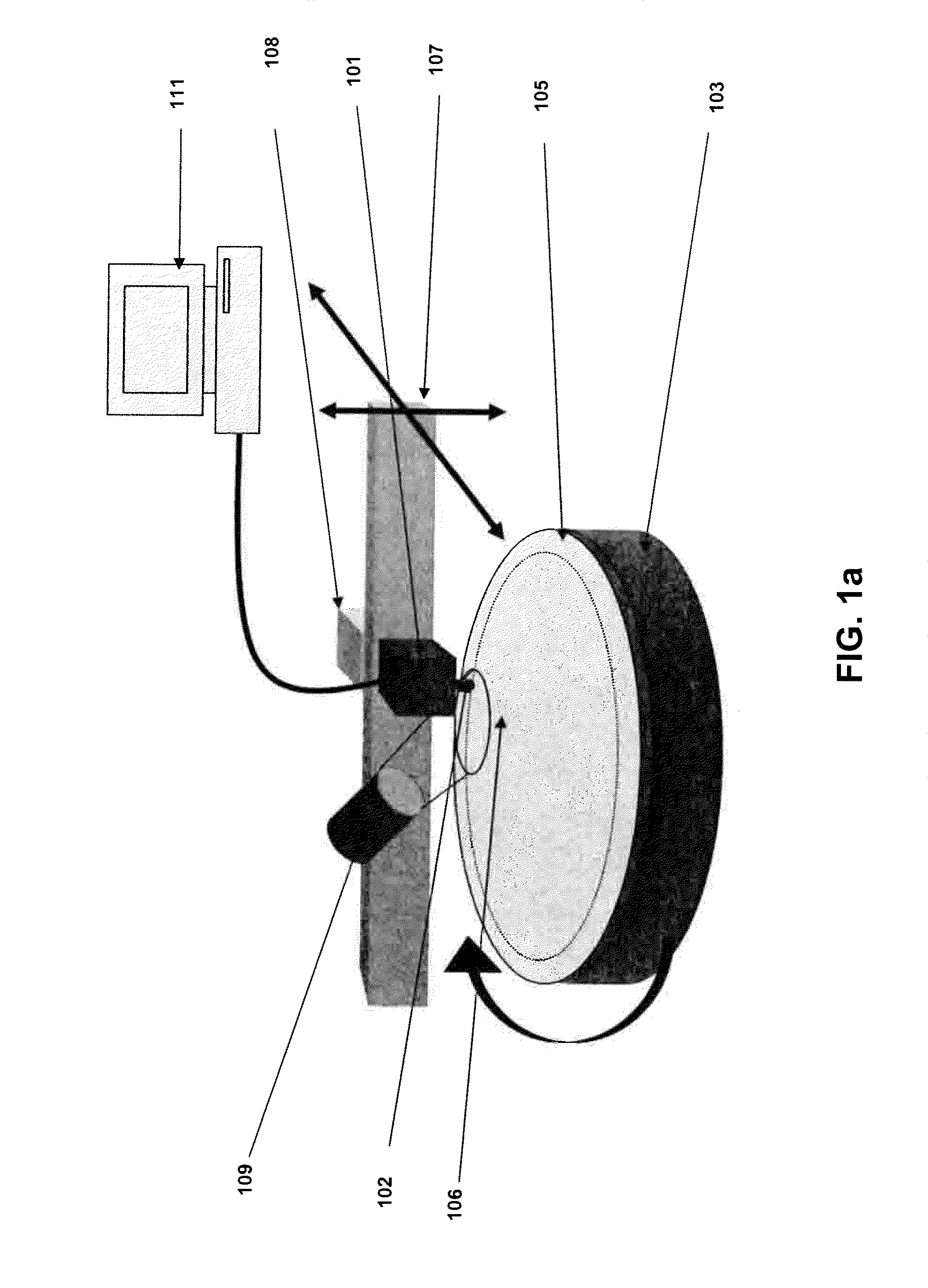
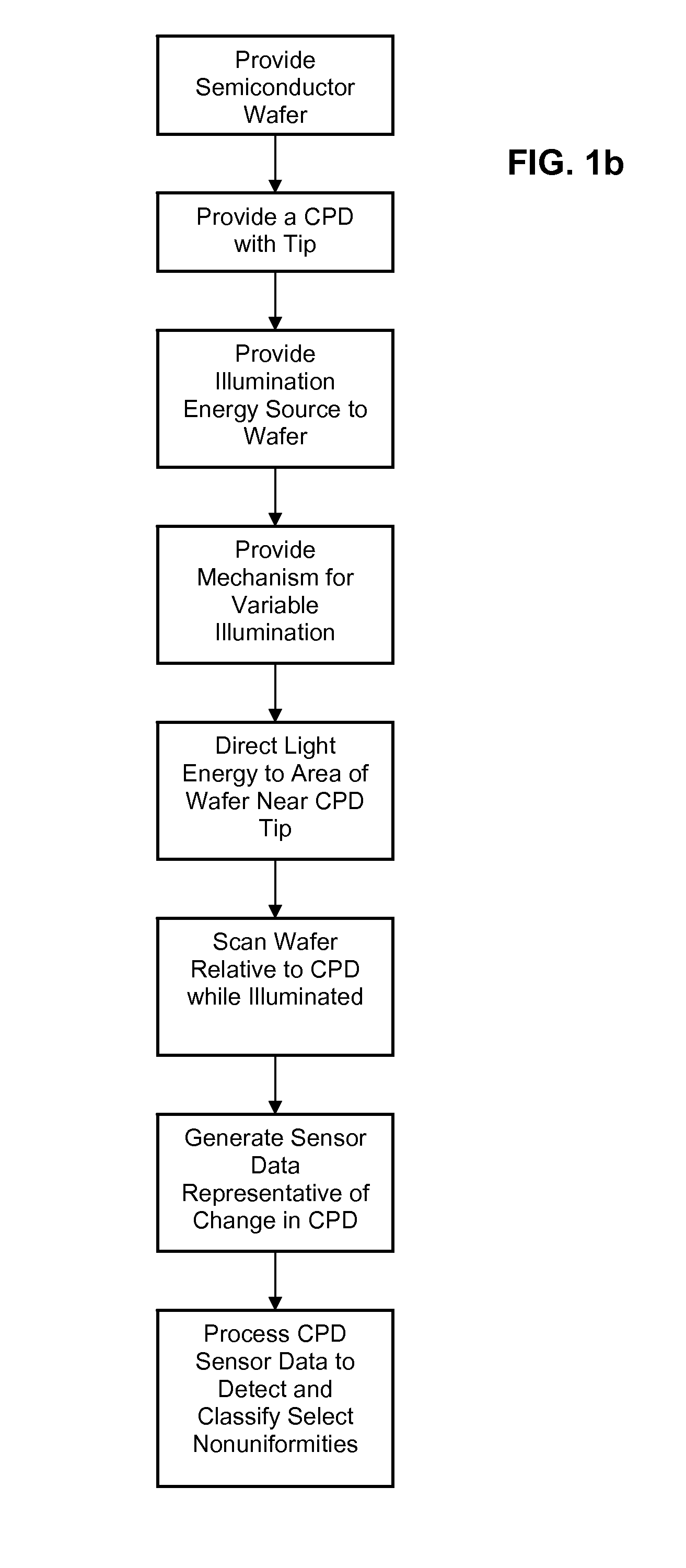
Semiconductor inspection system and apparatus utilizing a non-vibrating contact potential difference sensor and controlled illumination
InactiveUS20080217530A1Easy to detectEasy to classifyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPotential differenceLength wave
A method and system for identifying a defect or contamination on the surface of a semiconductor or in a semiconductor. The method and system involves providing a semiconductor with a surface, such as a semiconductor wafer, providing a non-vibrating contact potential difference sensor, providing a source of illumination with controllable intensity or distribution of wavelengths, using the illumination source to provide controlled illumination of the surface of the wafer under or near the non-vibrating contact potential sensor probe tip, using the non-vibrating contact potential difference sensor to scan the wafer surface during controlled illumination, generating data representative of changes in contact potential difference across the wafer surface, and processing that data to identify a pattern characteristic of a defect or contamination.
Owner:QCEPT INVESTMENTS LLC
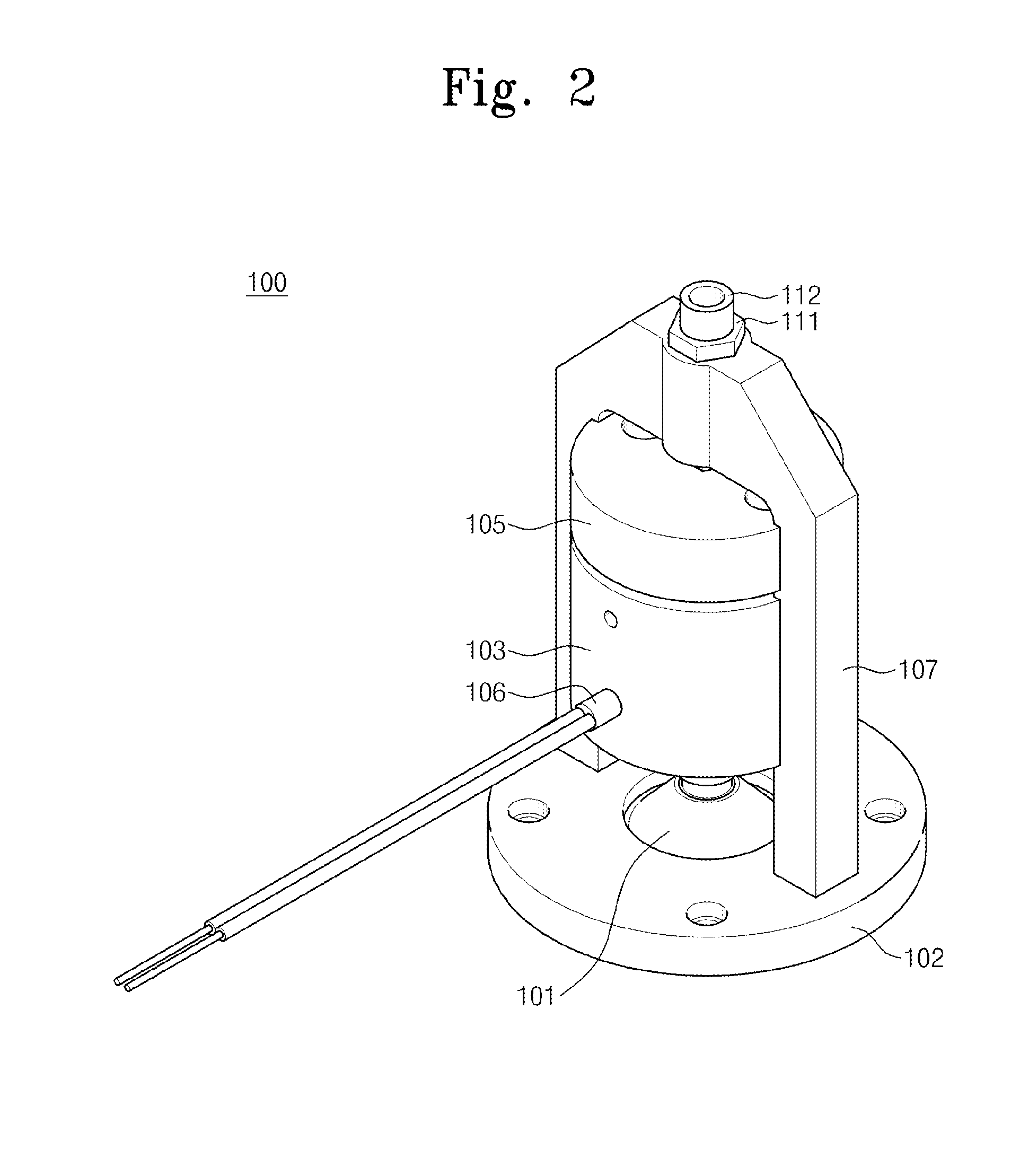
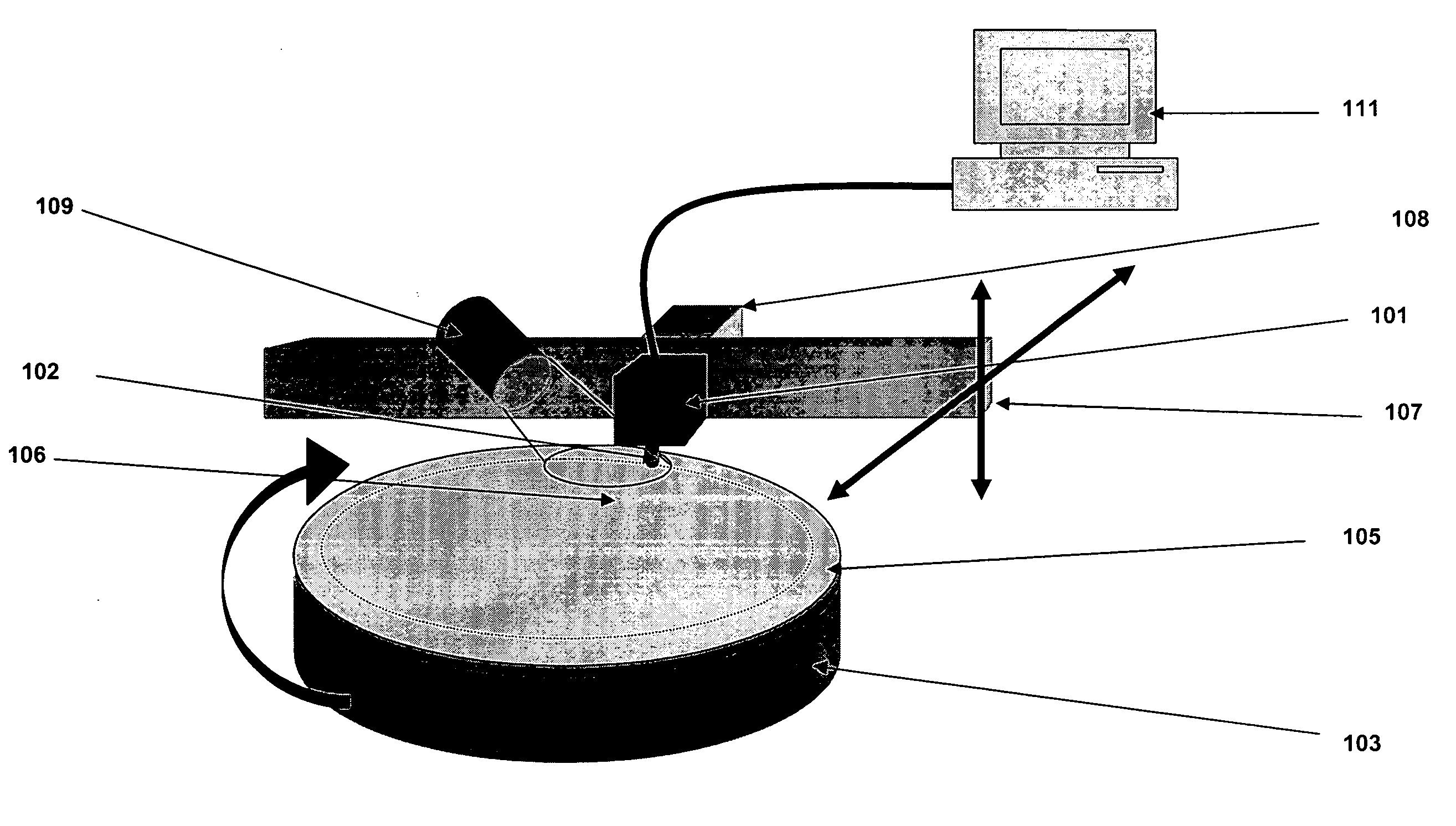
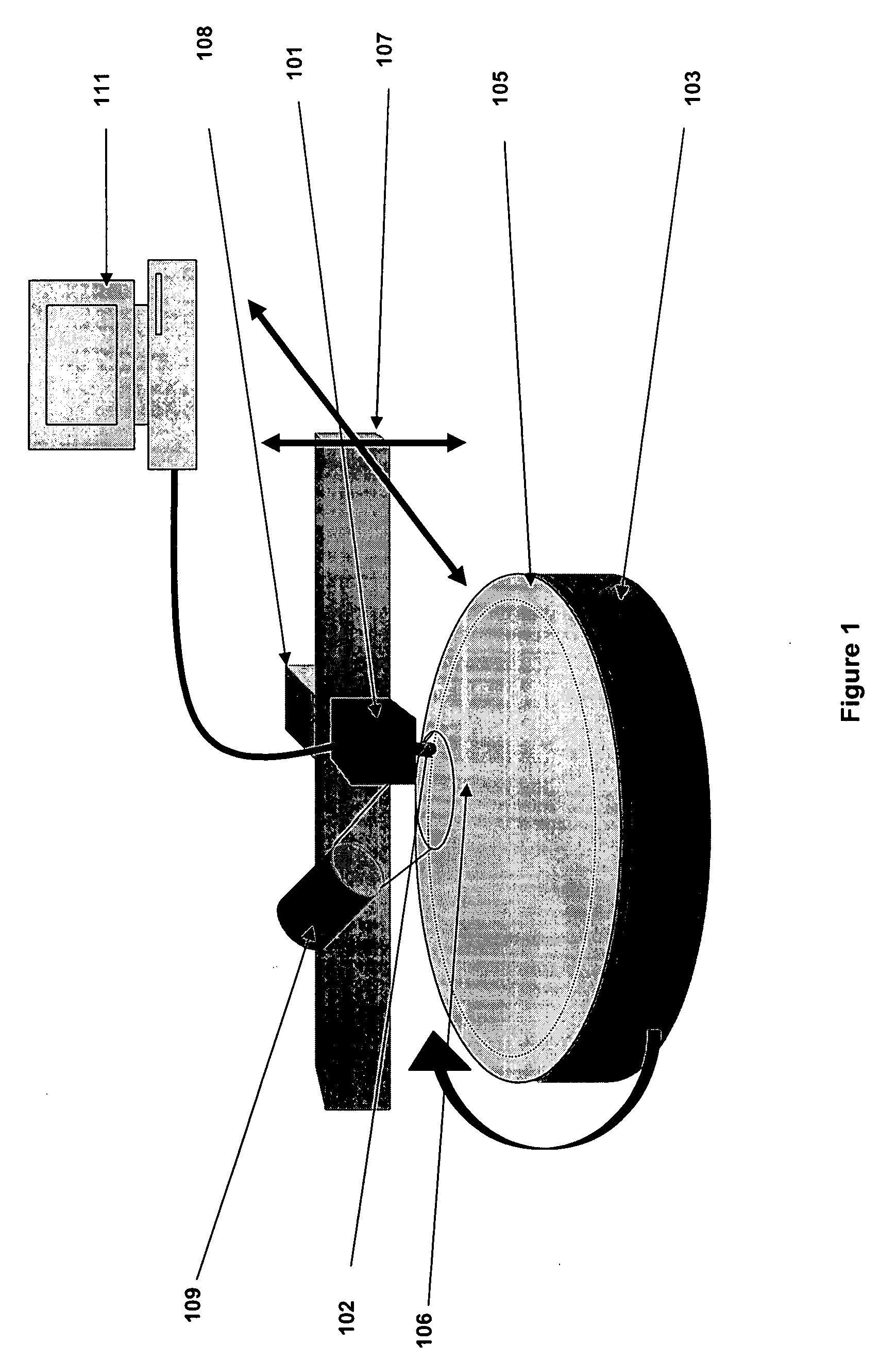
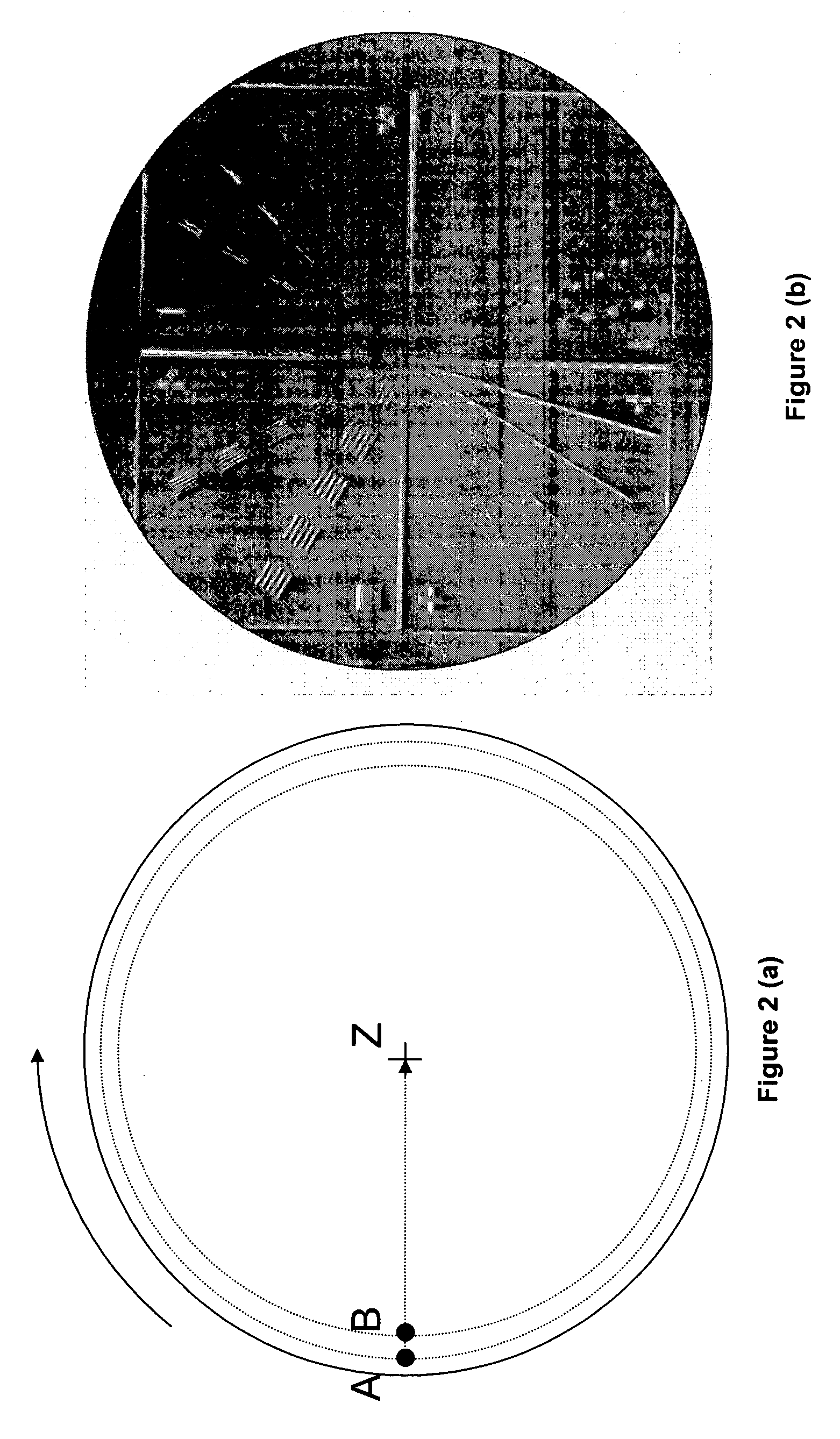
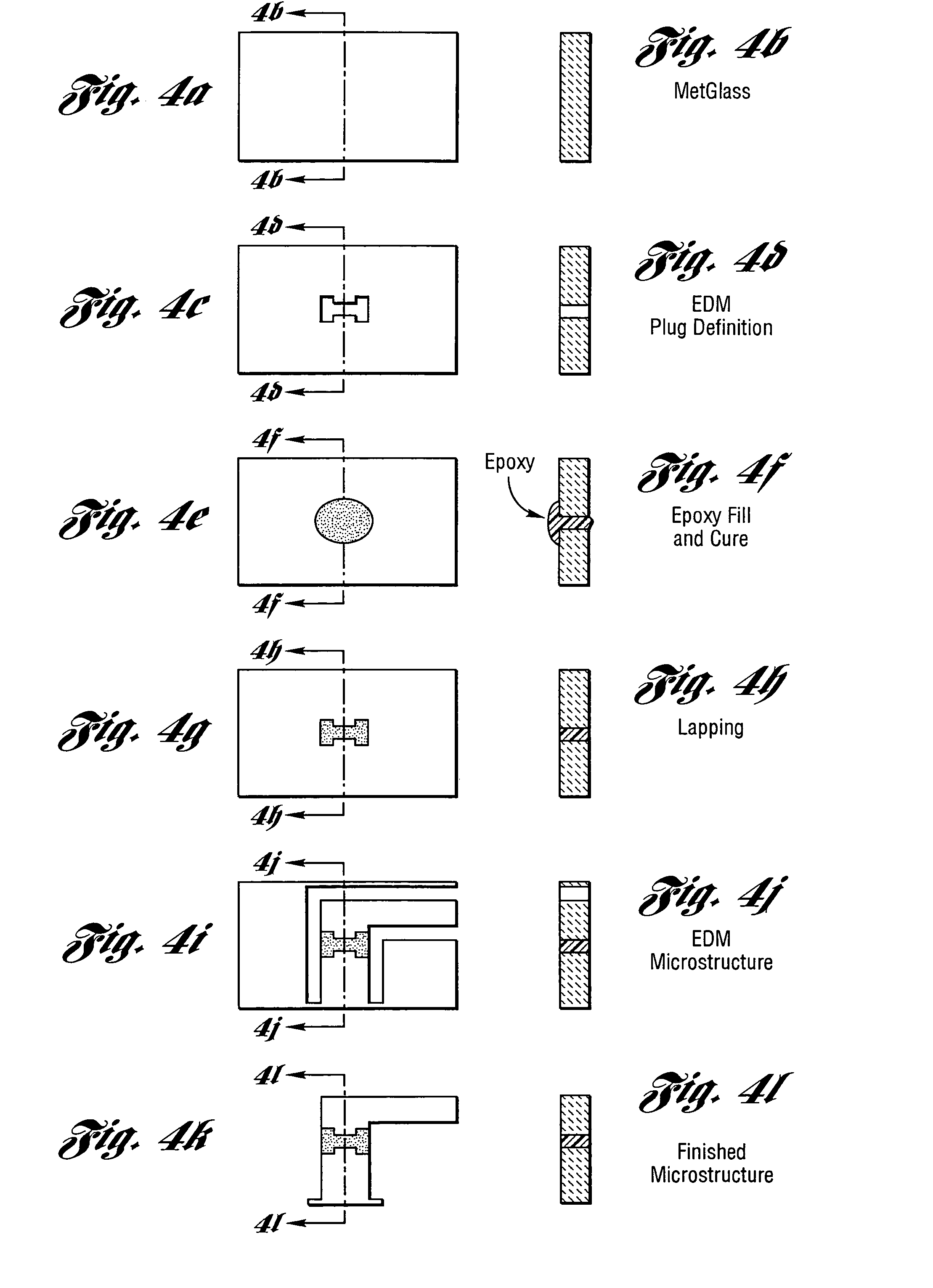
Micromachined probe apparatus and methods for making and using same to characterize liquid in a fluidic channel and map embedded charge in a sample on a substrate
ActiveUS7116115B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationResistance/reactance/impedenceEpoxyElectrothermal actuator
A micromachined probe apparatus and methods for making and using same to characterize liquid in a fluidic channel and map embedded charge in a sample on a substrate are provided. The probe apparatus includes an integrated scanning tip and a dither actuation mechanism. The actuation is achieved using a bent-beam electrothermal actuator, and the probe tip is insulated from the actuator with a wide isolation gap. The device is fabricated by a modified micro electro-discharge machining process which allows electrical isolation within the micromachined structure using an epoxy plug. The apparatus may be used to measure changes in the external surface potential of a microfluidic channel as a function of varying pH of liquid inside the channel. The apparatus also may be used to map embedded charge in a thin layer on a substrate, showing it to be suitable for monitoring microelectronics manufacturing processes.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND +1
Wafer inspection system
InactiveUS7308367B2Minimize complexityFast and inexpensive and effective meanSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementInstrumental componentsPotential differenceContamination
A method and system for identifying a defect or contamination on a surface of a material. The method and system involves providing a material, such as a semiconductor wafer, using a non-vibrating contact potential difference sensor to scan the wafer, generate contact potential difference data and processing that data to identify a pattern characteristic of the defect or contamination.
Owner:QCEPT INVESTMENTS LLC
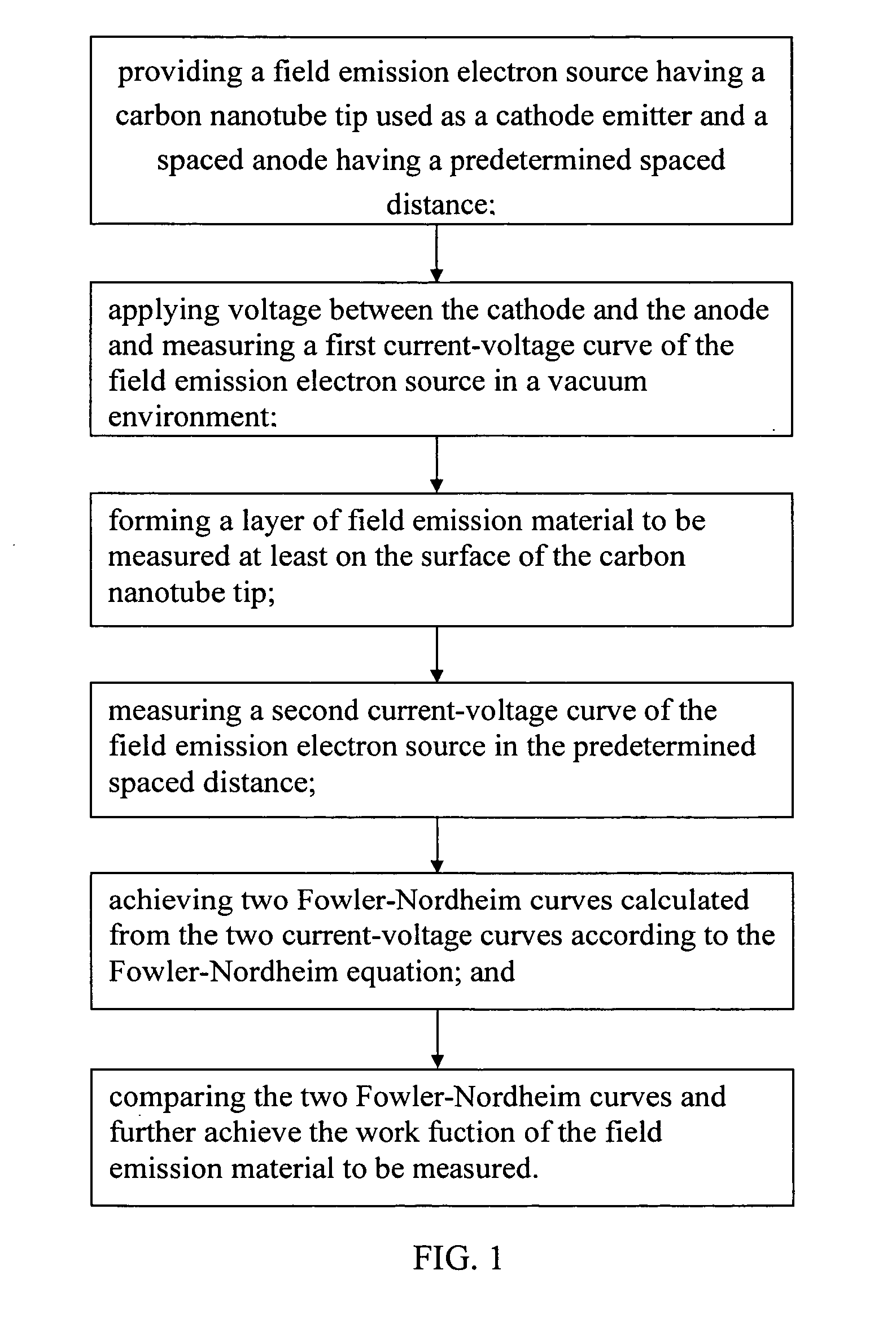
Method for measuring work function
A method for measuring work function includes the steps of: (a) providing a field emission electron source having a carbon nanotube tip as a cathode electrode and a spaced anode electrode, having a predetermined spaced distance therebetween; (b) applying a voltage between the cathode electrode and the anode electrode and measuring a first current-voltage curve of the field emission electron source in a vacuum environment; (c) forming a layer of field emission material at least on the surface of the carbon nanotube tip; (d) measuring a second current-voltage curve of the now-treated field emission electron source in the same conditions as that in the step (b); (e) achieving two Fowler-Nordheim curves calculated from the two current-voltage curves according to the Fowler-Nordheim equation; and (f) comparing the two Fowler-Nordheim curves and calculating the work function of the field emission material therefrom.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Method for detecting gas with the use of photocurrent amplification and the like and gas sensor
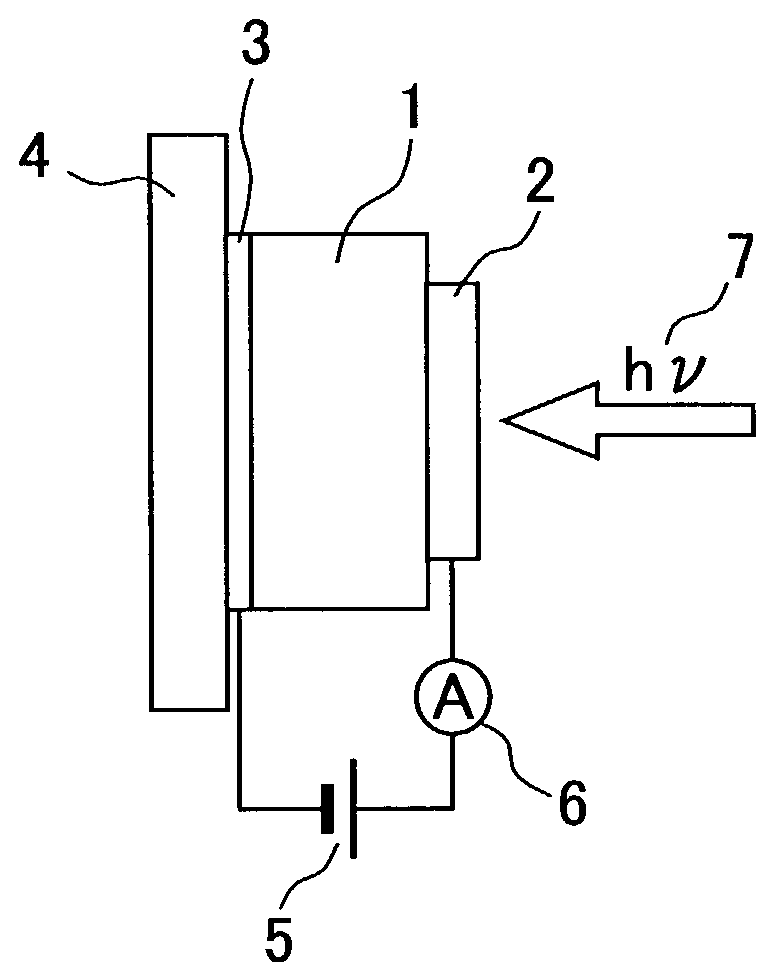
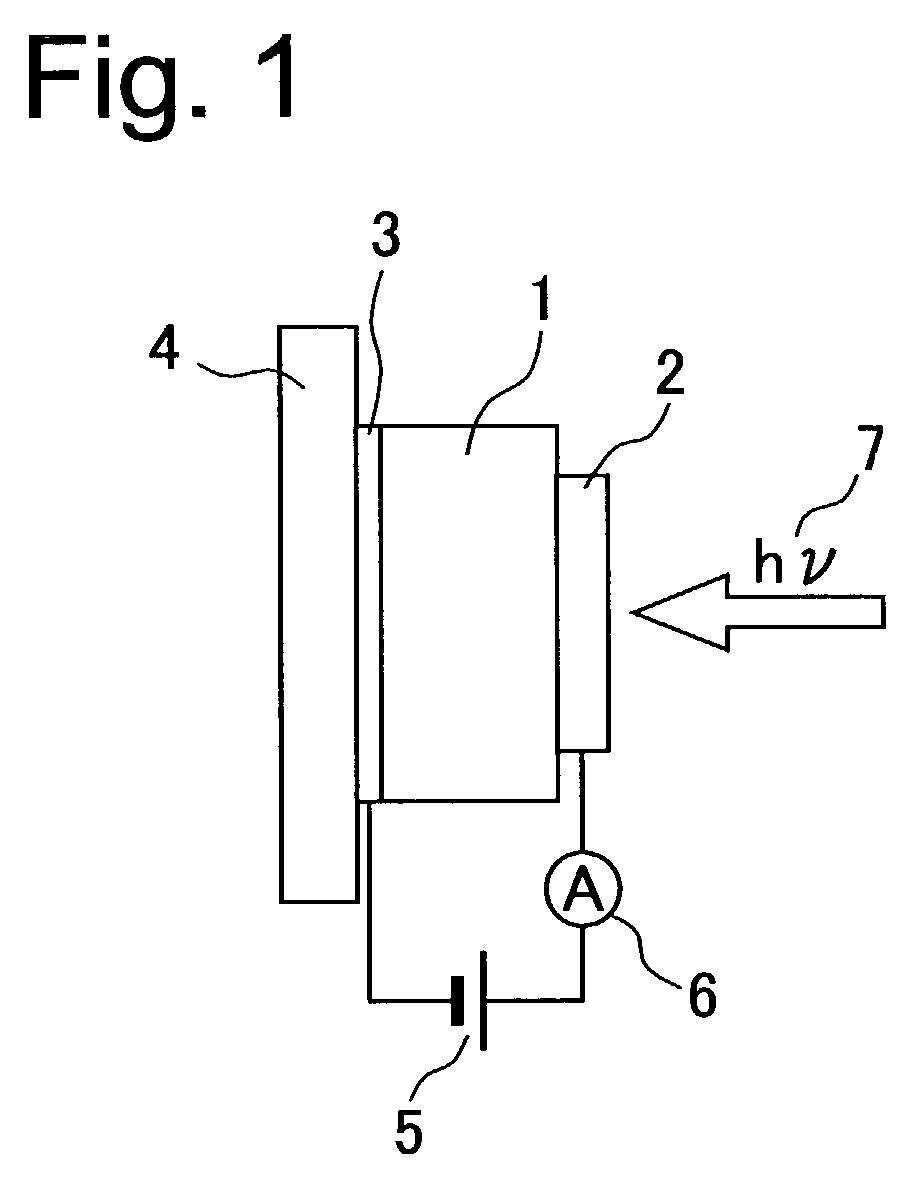
InactiveUS7081368B2High sensitivityImprove response speedSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesIndiumPhthalocyanine
An indium electrode film (2) is formed closely adhering to one face of an organic semiconductor film (1) made of copper phthalocyanine while a gold electrode film (3) is formed on the other face. A voltage is applied to the organic semiconductor film (1) so that the indium electrode (2) side is biased positively. By applying a voltage so that the electrode (2) side is charged positively and irradiating with a light having a wavelength absorbable by the organic semiconductor film (1) the phenomenon of photocurrent multiplication arises at the interface of the organic semiconductor film (1) and the electrode (2). When put under an oxygen or moisture atmosphere in the above state, this gas sensor can detect oxygen or moisture depending on a change in photocurrent due to the multiplication.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Scanning kelvin microprobe system and process for biomolecule microassay
InactiveUS20060089825A1Improve spatial resolutionHigh resolutionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPotential differenceAntibody antigen
There is provided a system and process for detecting biomolecular interaction on a substrate having a biomolecule immobilized on a surface of the substrate. The system and process incorporate a scanning Kelvin microprobe (SKM) capable of analyzing surface topography as well as a contact potential difference image signal. Also provided is the use of SKM in measuring and analyzing biochemical molecular interactions between a probe bound to the surface of the substrate, and a target suspected to be present in a liquid sample. One of the probe and target combination is a biomolecule such as a nucleic acid, a polypeptide, or a small molecule, and an antibody antigen combination may be used.
Owner:THOMPSON MICHAEL +2
Semiconductor inspection system and apparatus utilizing a non-vibrating contact potential difference sensor and controlled illumination
InactiveUS7659734B2Easily detect and classifySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor characterisationPotential differenceLength wave
A method and system for identifying a defect or contamination on the surface of a semiconductor or in a semiconductor. The method and system involves providing a semiconductor with a surface, such as a semiconductor wafer, providing a non-vibrating contact potential difference sensor, providing a source of illumination with controllable intensity or distribution of wavelengths, using the illumination source to provide controlled illumination of the surface of the wafer under or near the non-vibrating contact potential sensor probe tip, using the non-vibrating contact potential difference sensor to scan the wafer surface during controlled illumination, generating data representative of changes in contact potential difference across the wafer surface, and processing that data to identify a pattern characteristic of a defect or contamination.
Owner:QCEPT INVESTMENTS LLC
Popular searches
Individual semiconductor device testing Contactless circuit testing Specific gravity measurement Testing semiconductor materials Special data processing applications Mechanical roughness/irregularity measurements Mechanical solid deformation measurements Biochemistry cleaning apparatus Material analysis by optical means Biomass after-treatment
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com