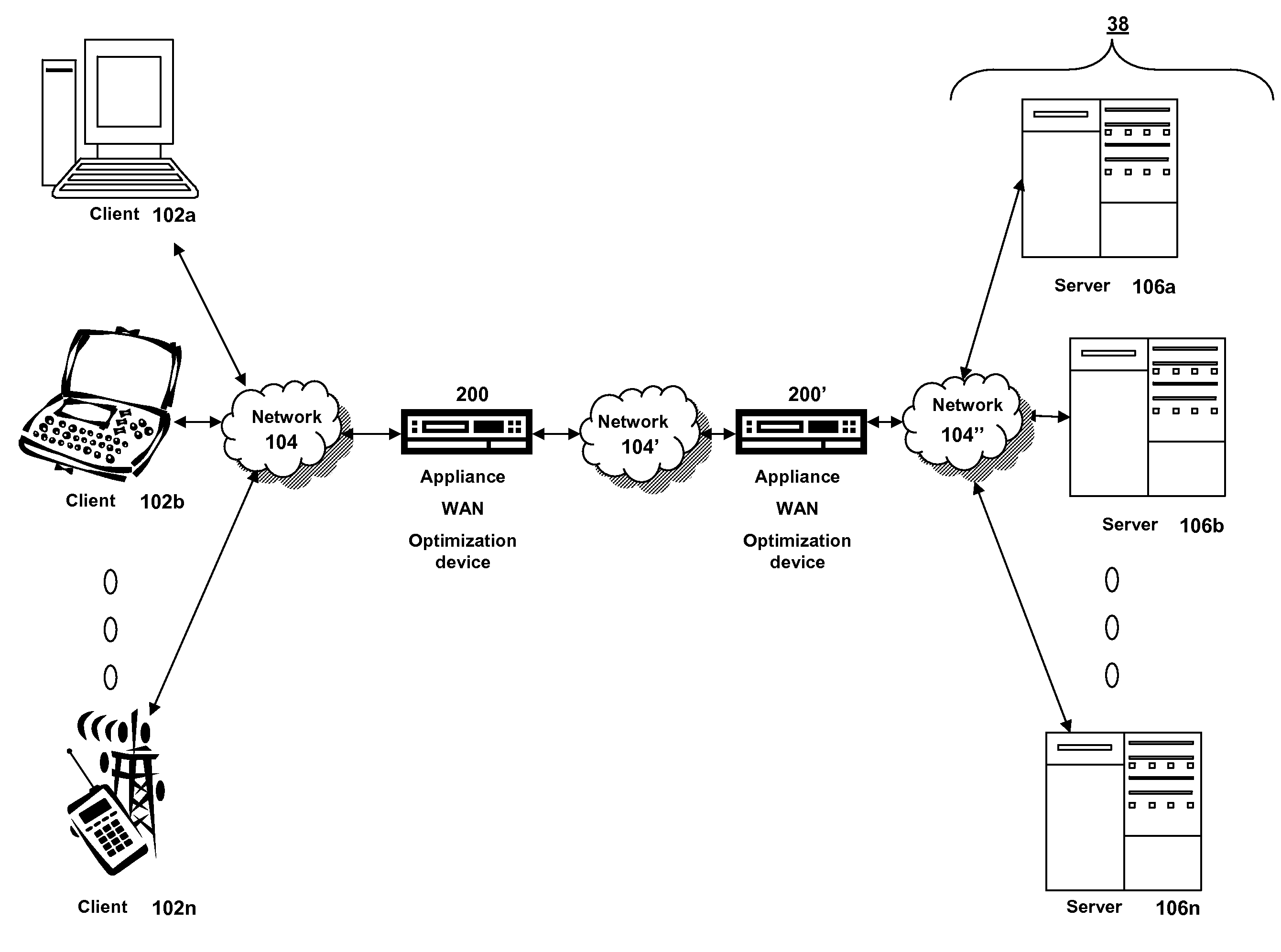
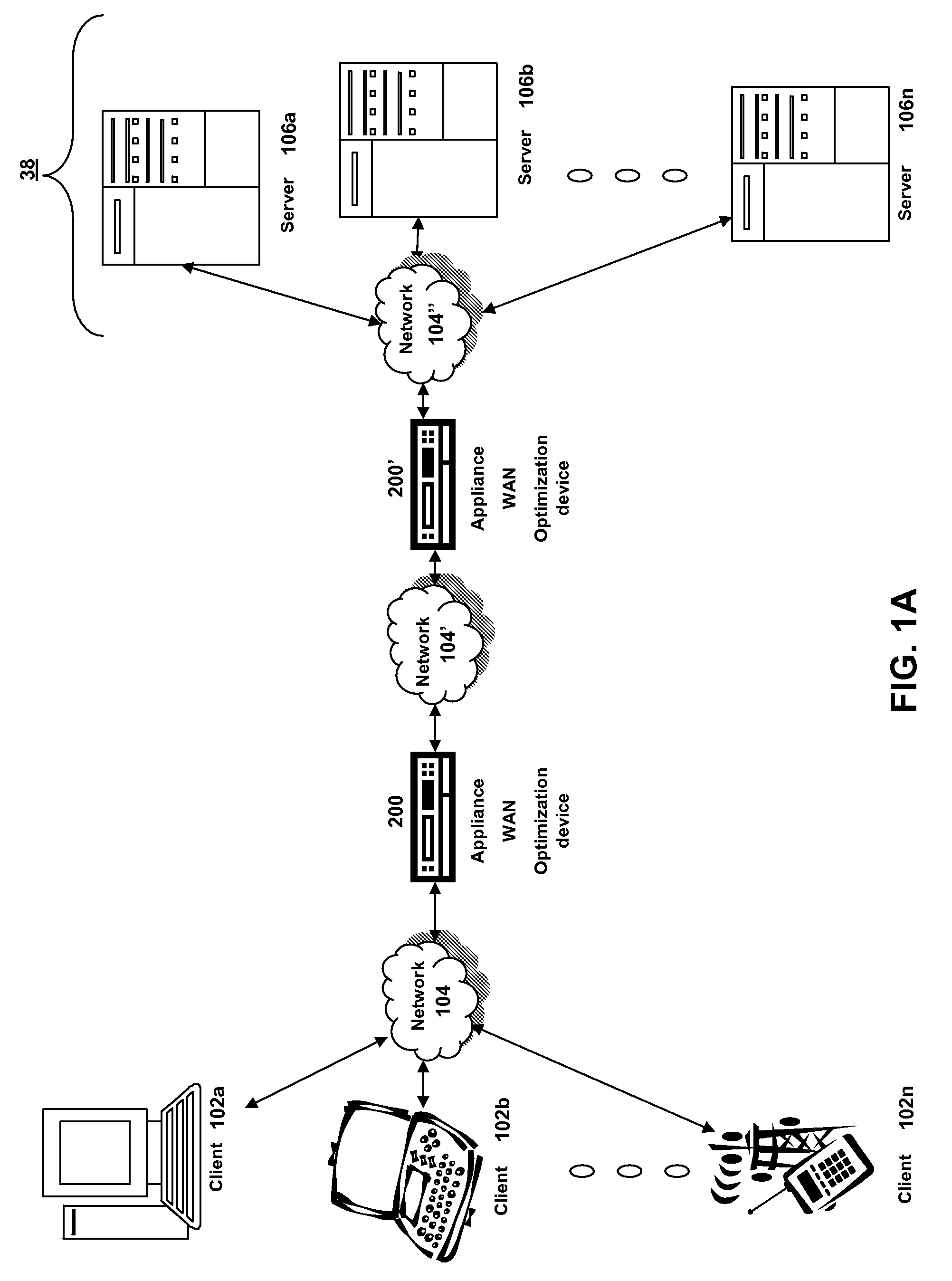
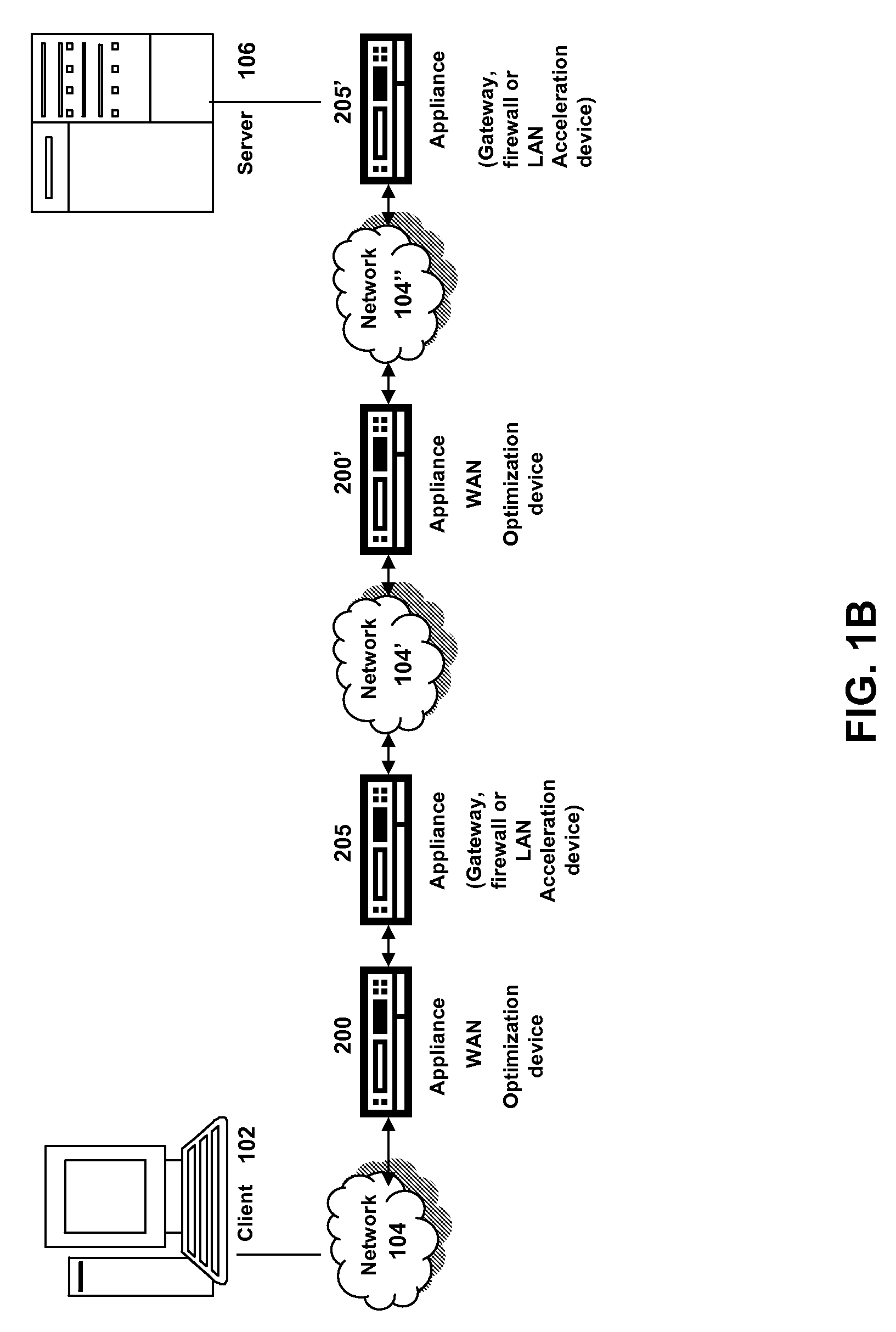
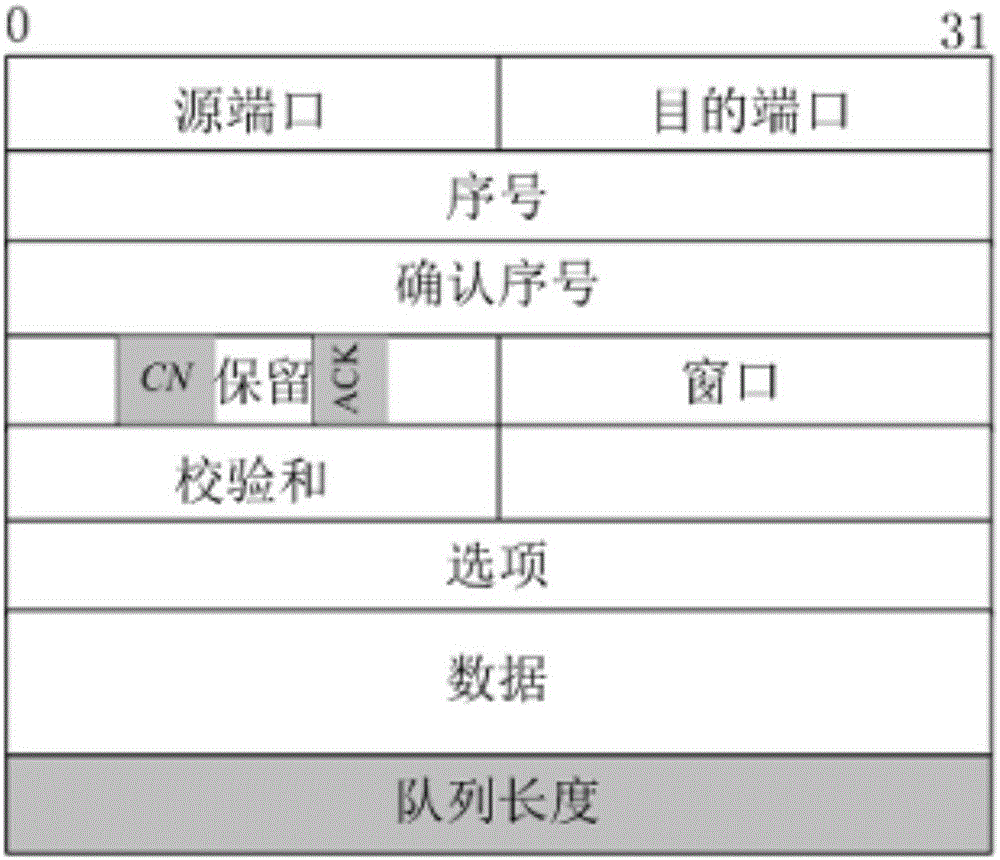
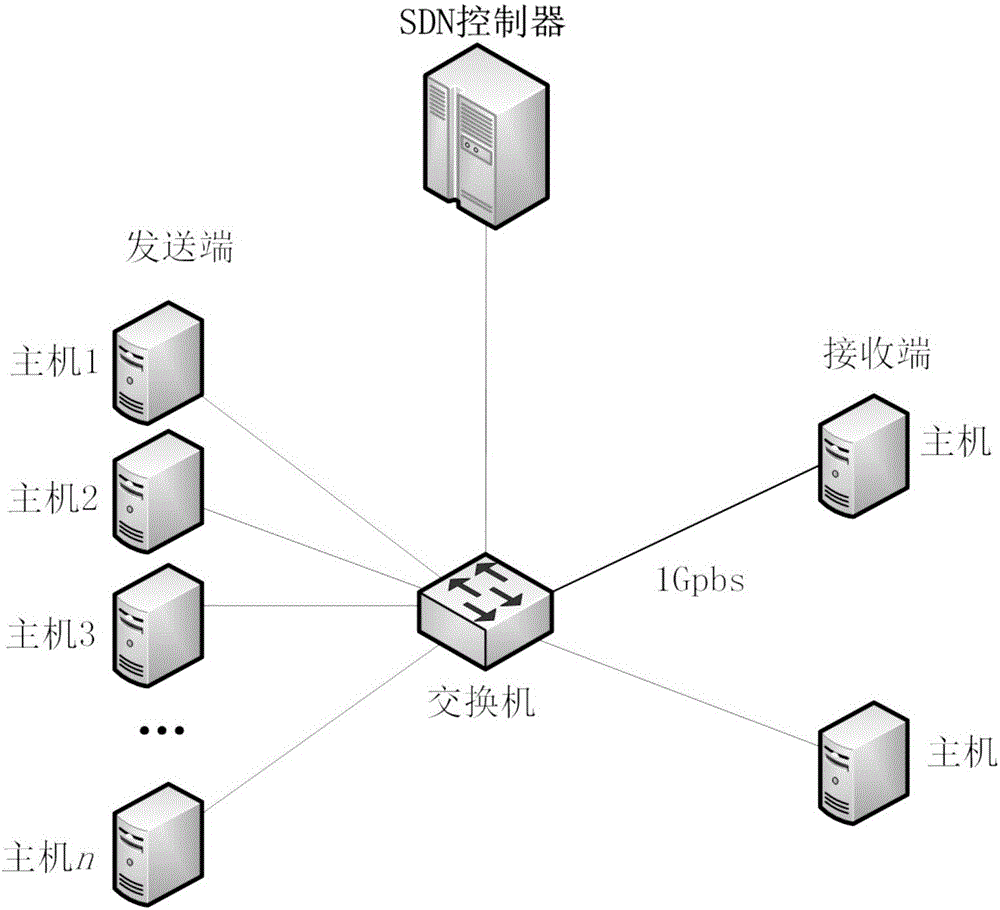
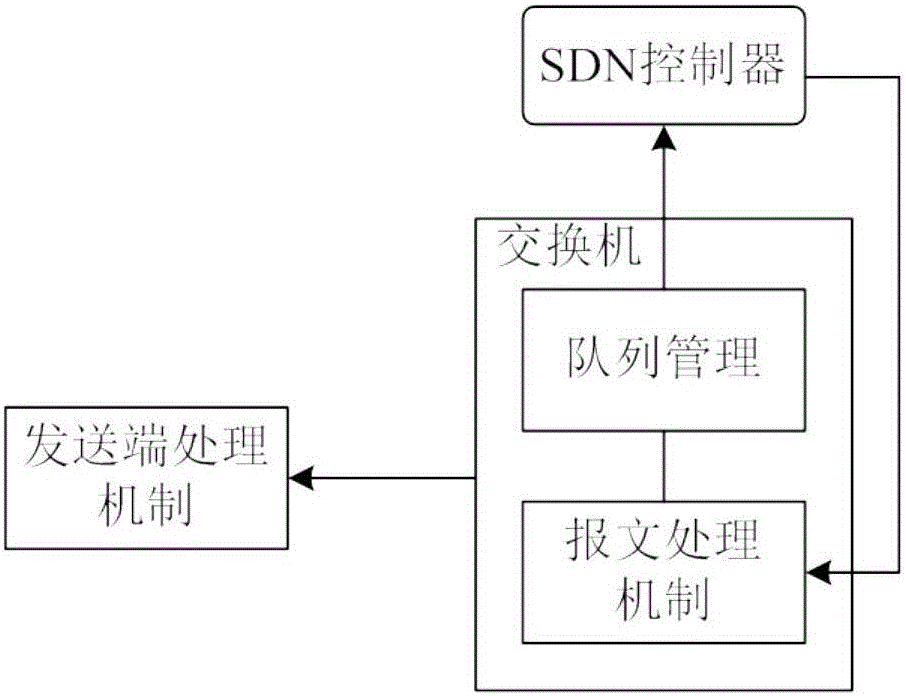
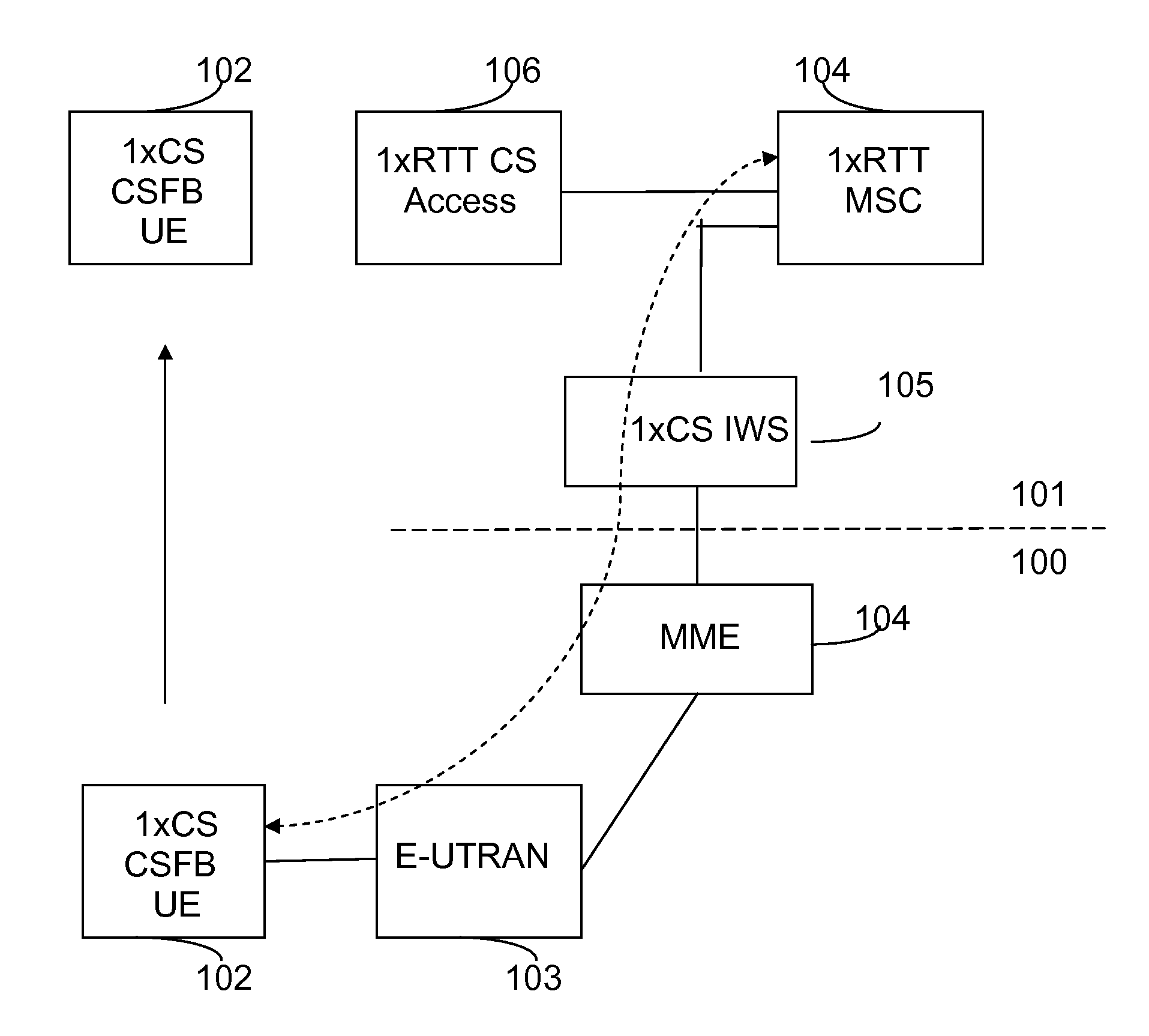
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
135 results about "TCP congestion-avoidance algorithm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
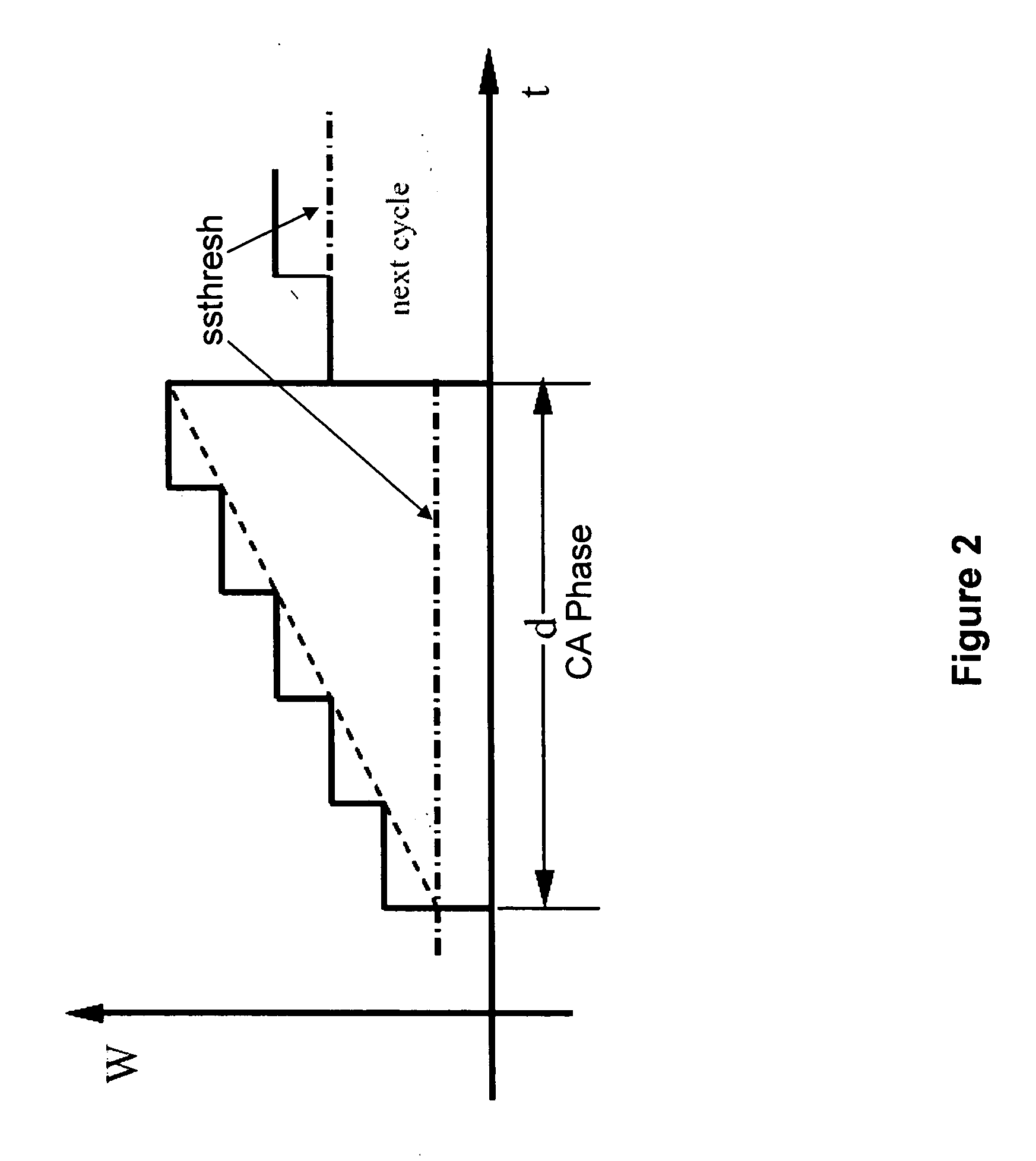
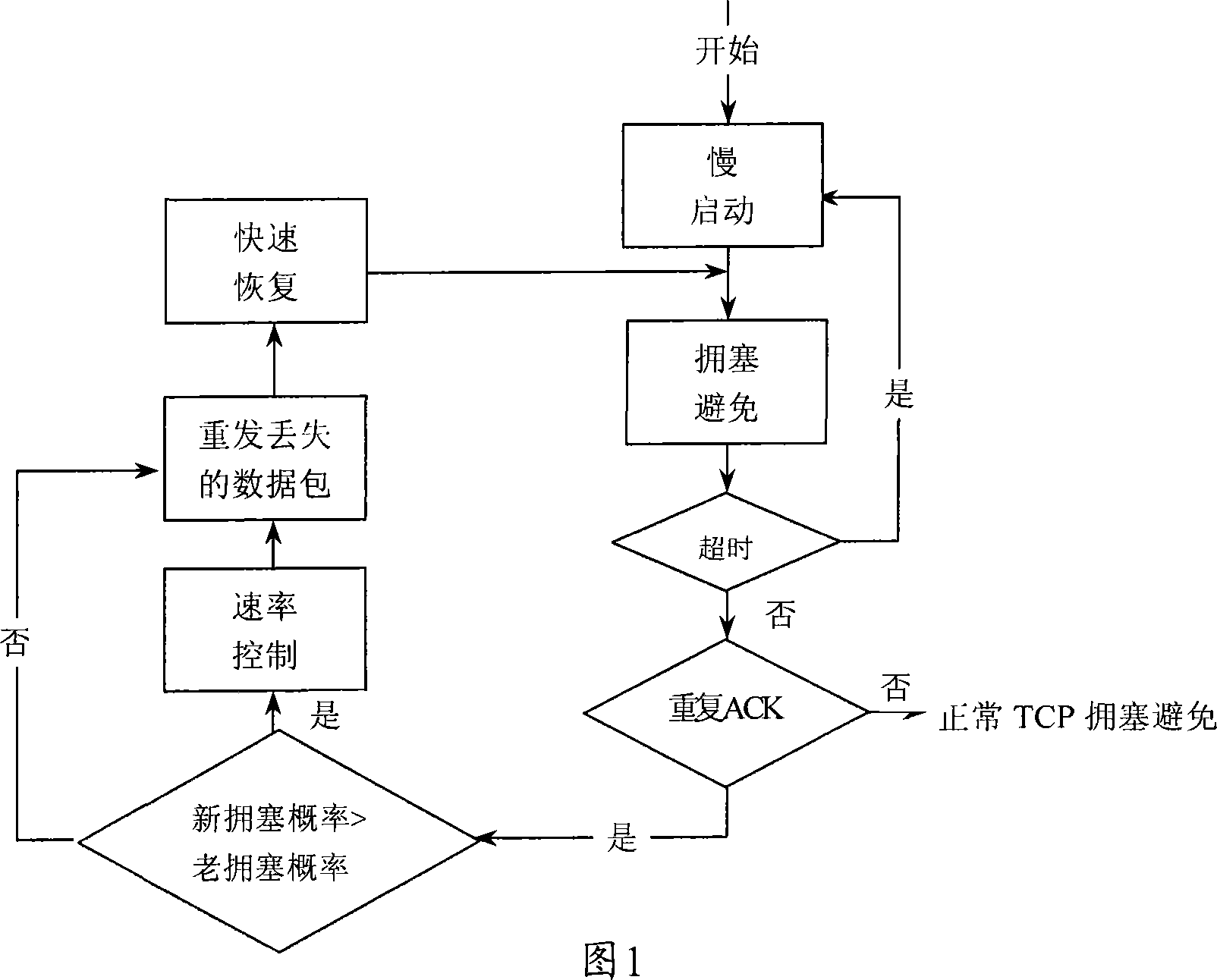
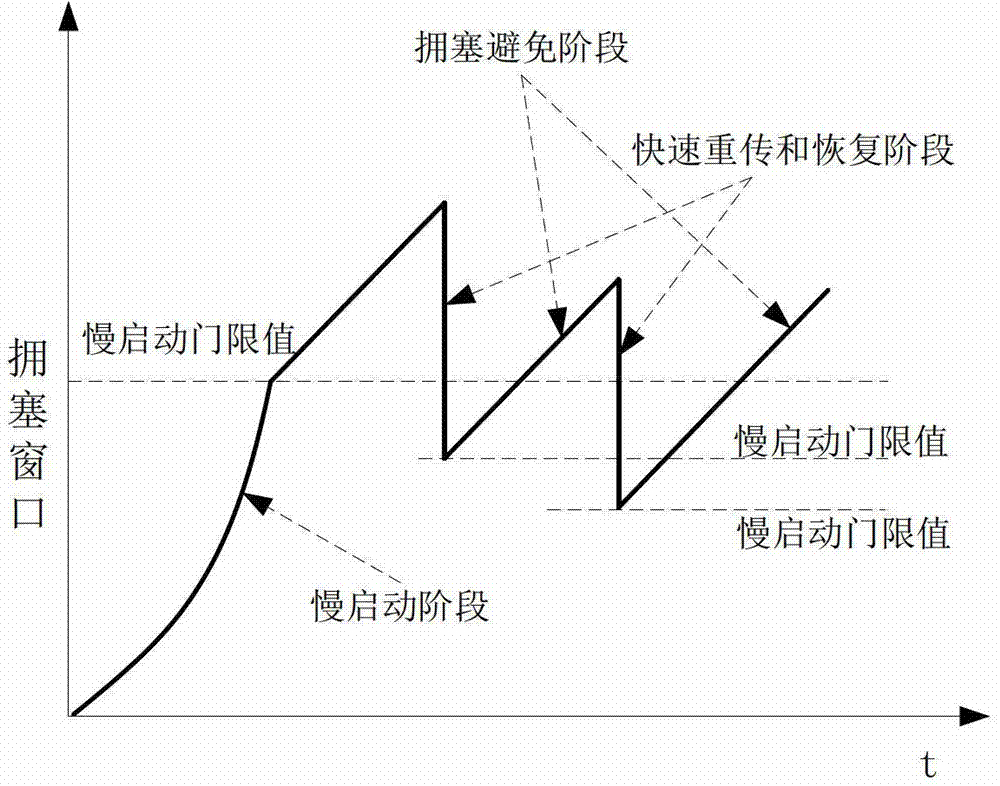
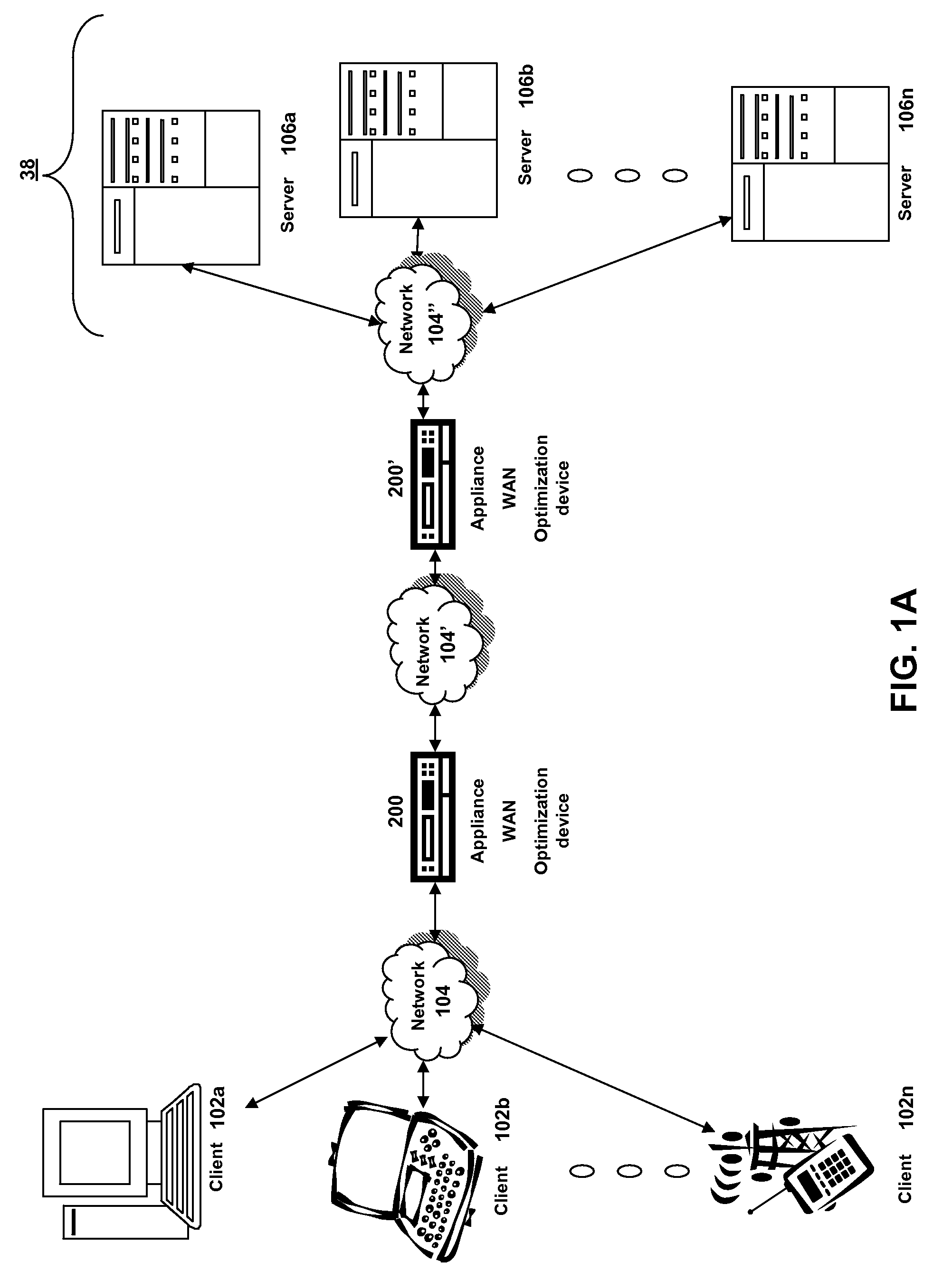
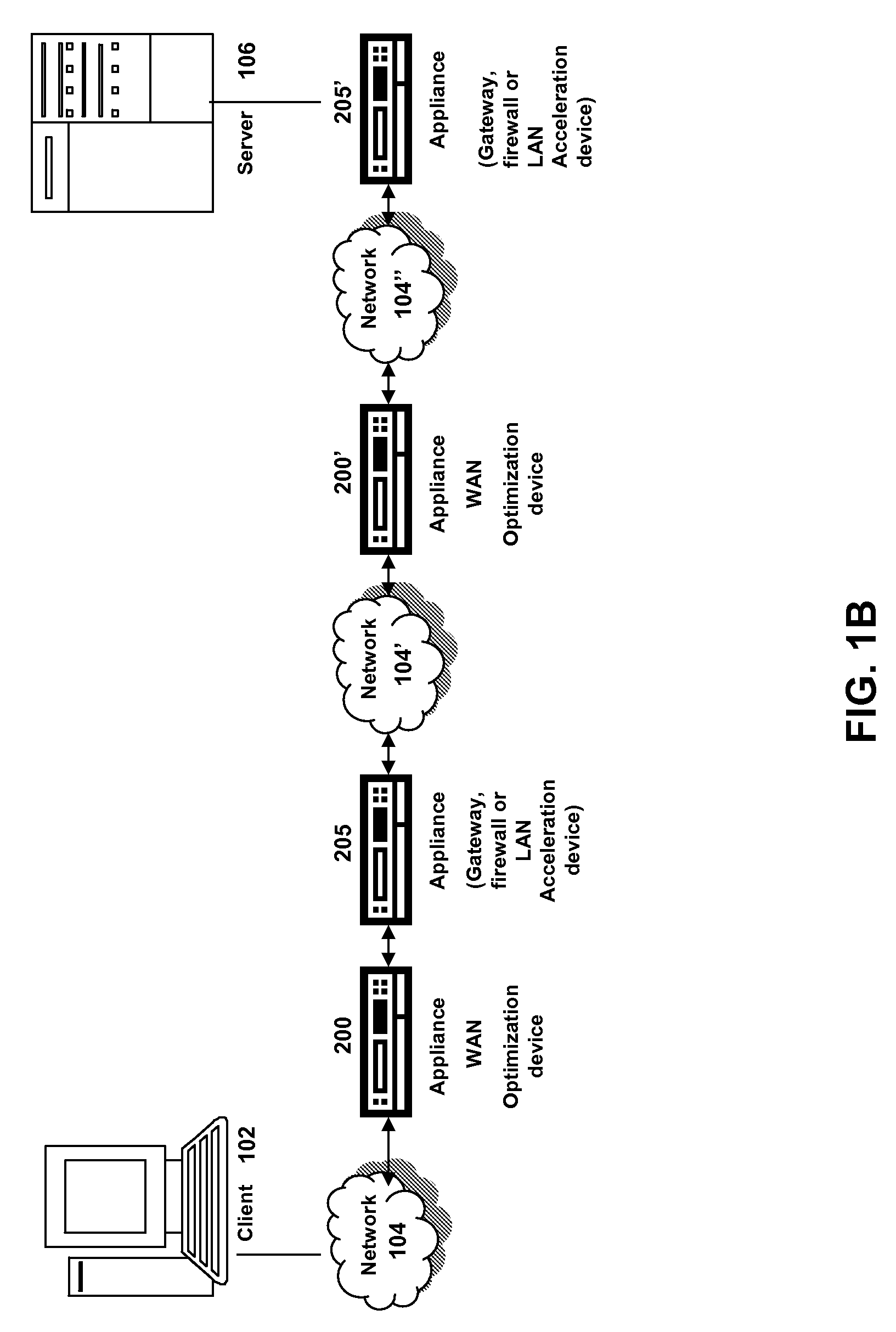
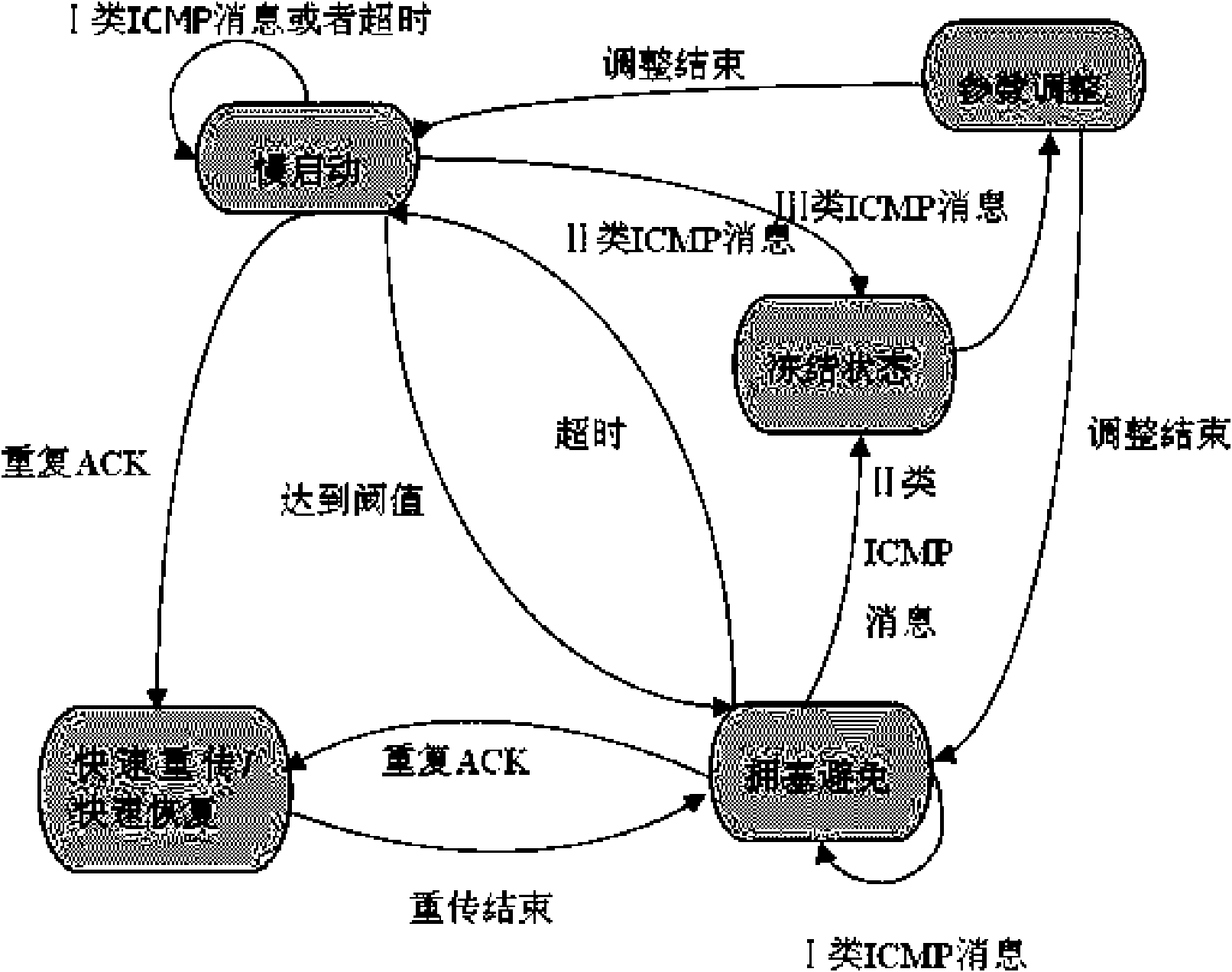
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) uses a network congestion-avoidance algorithm that includes various aspects of an additive increase/multiplicative decrease (AIMD) scheme, along with other schemes including slow start and congestion window, to achieve congestion avoidance. The TCP congestion-avoidance algorithm is the primary basis for congestion control in the Internet. Per the end-to-end principle, congestion control is largely a function of internet hosts, not the network itself. There are several variations and versions of the algorithm implemented in protocol stacks of operating systems of computers that connect to the Internet.
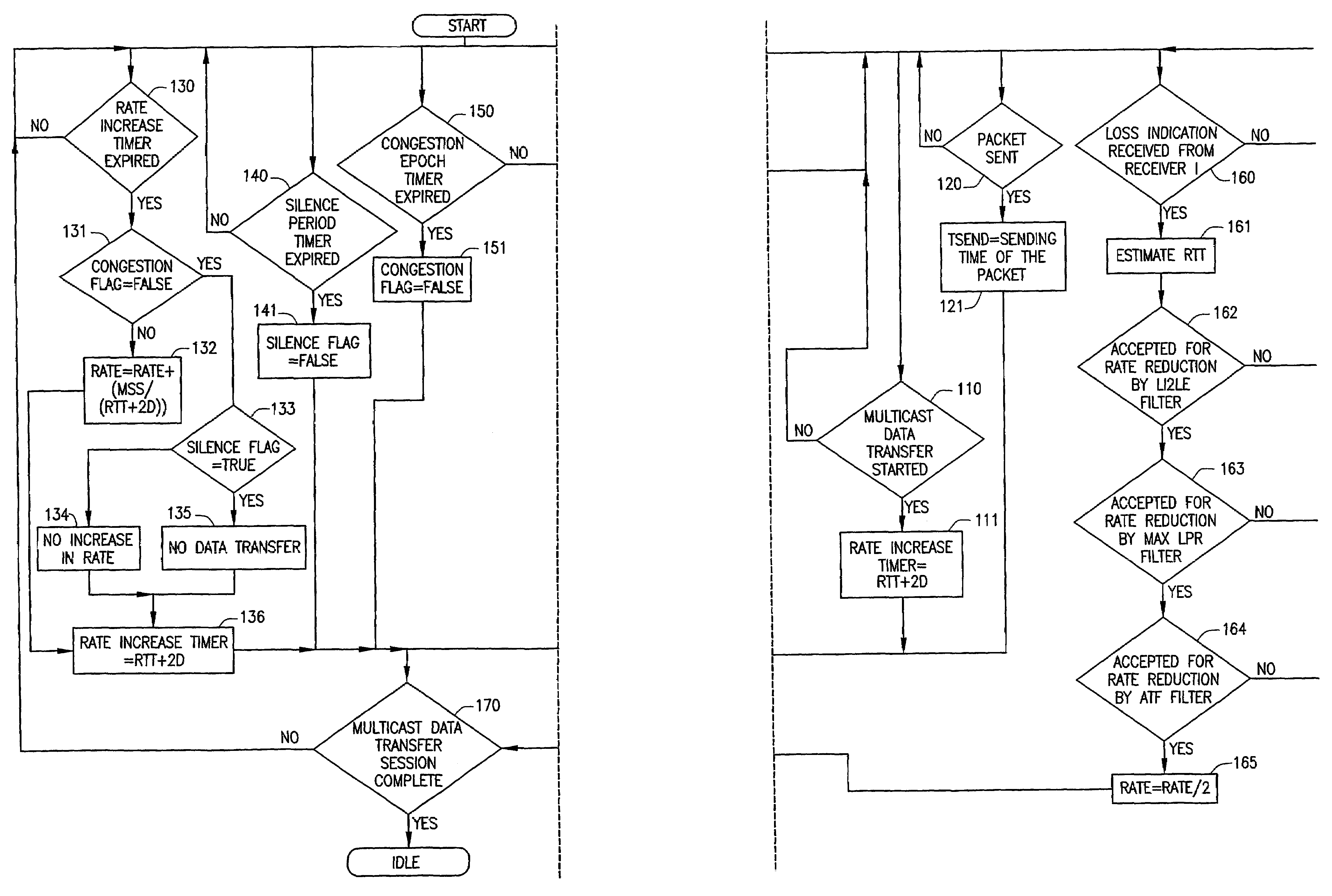
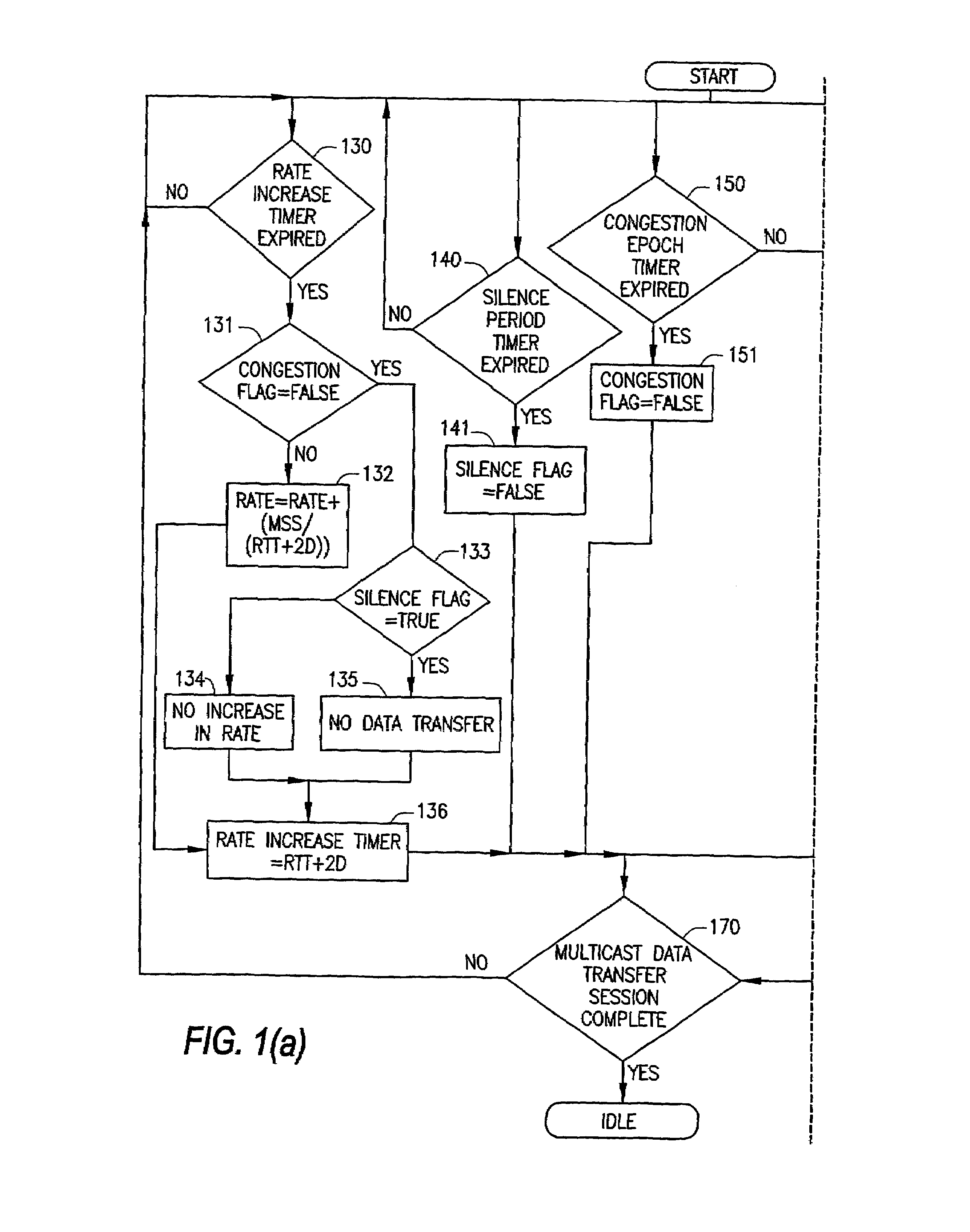
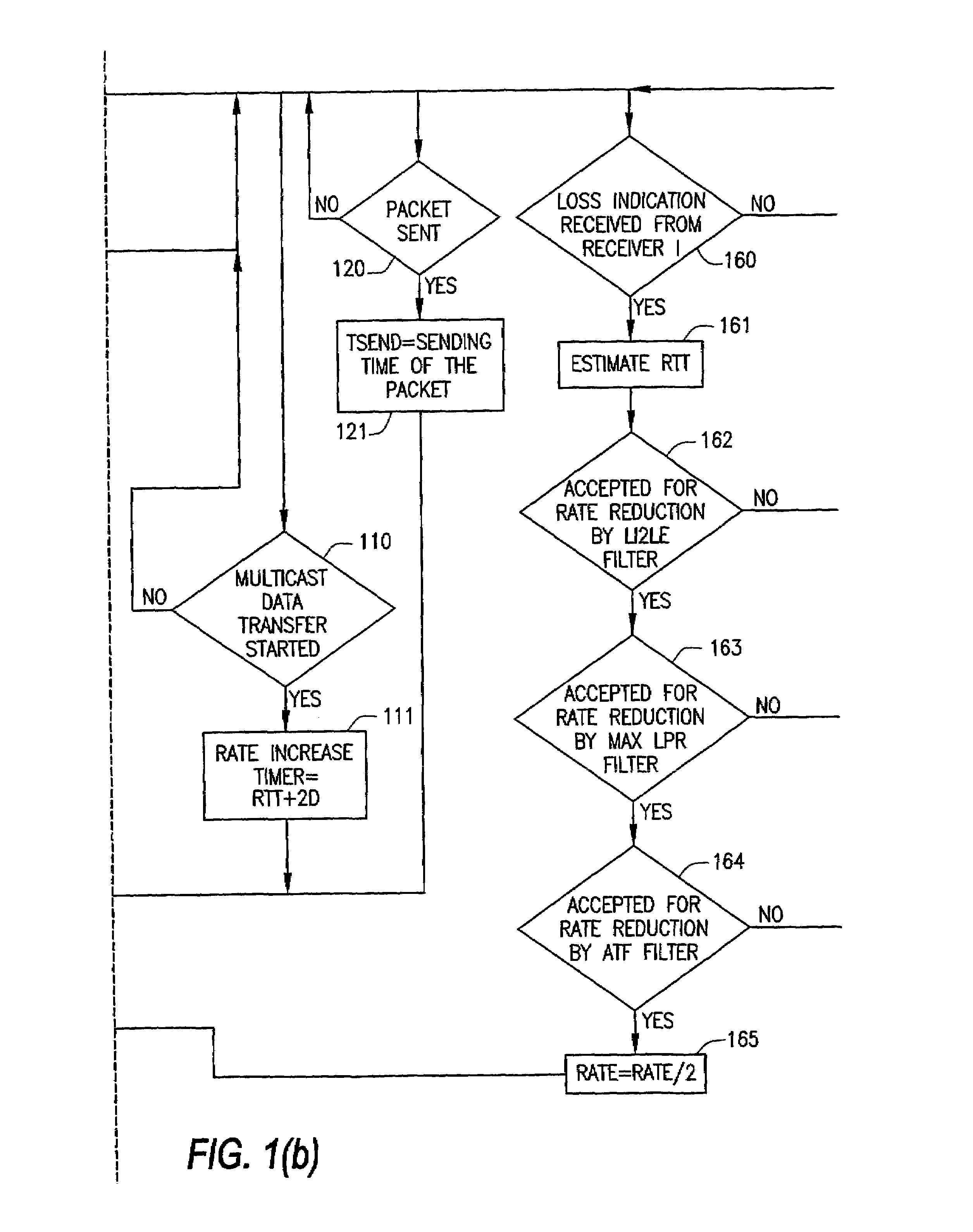
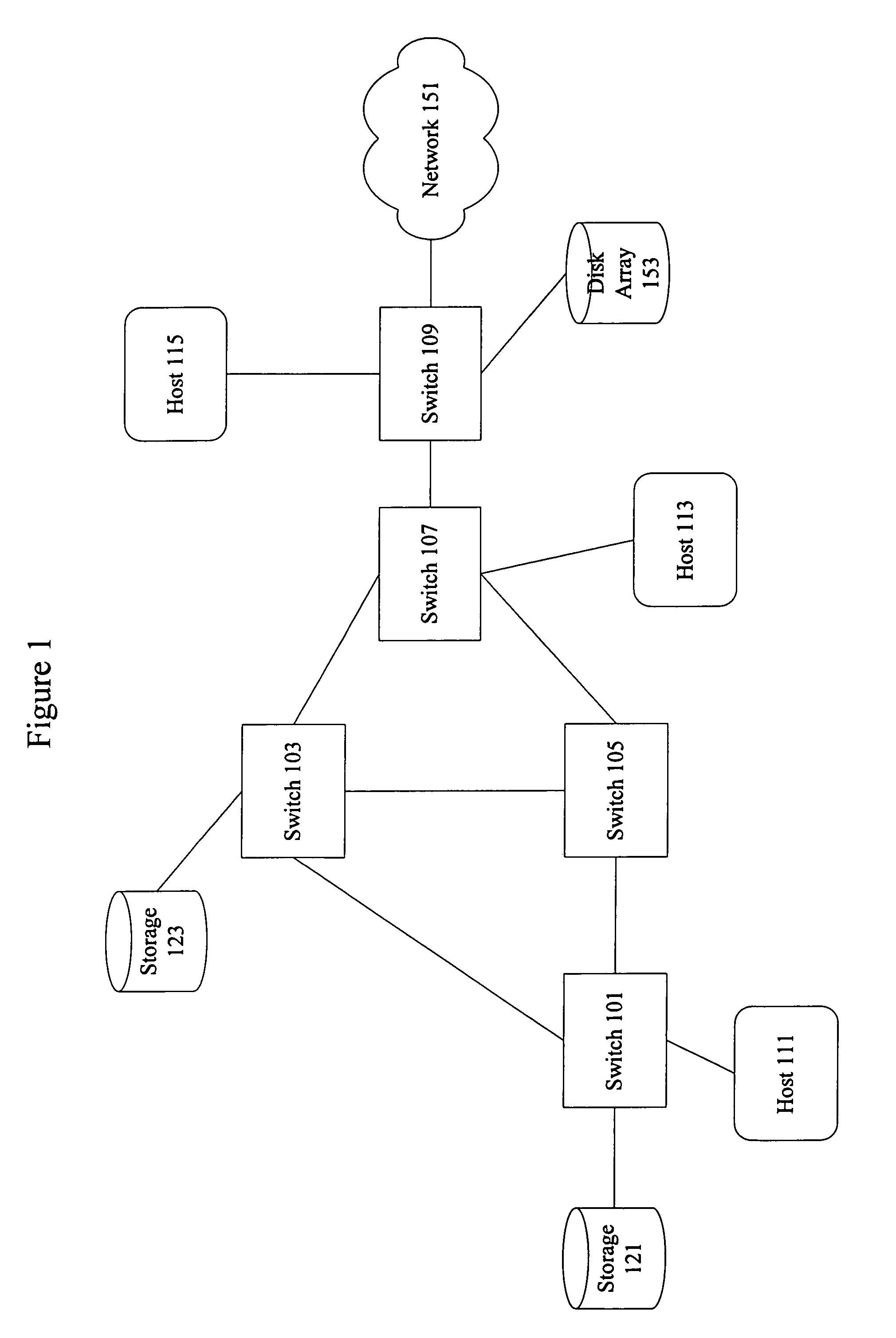
System and method of source based multicast congestion control
InactiveUS7020714B2Control congestionIncrease multiplicative decrease moduleSpecial service provision for substationEnergy efficient ICTComputer networkMulticast congestion control
The present invention provides for a method of congestion control for multicast transmission that is entirely managed at the source of the transmission. The various types of filters as well as round trip time estimators (130) that are used in the invention to determine when the rate of the multicast transmission should be reduced to alleviate congestion. The source of the transmission adjusts the rate of transmission based on loss indications that the receivers would otherwise transmit.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Adaptive application sensitive rate control system for packetized networks
InactiveUS20070115848A1Limited bandwidthError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsControl systemSelf adaptive
A method operates a limited-bandwidth network in a differential service (DiffServ) mode with DCCP congestion control to provide high throughput with good QoS.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
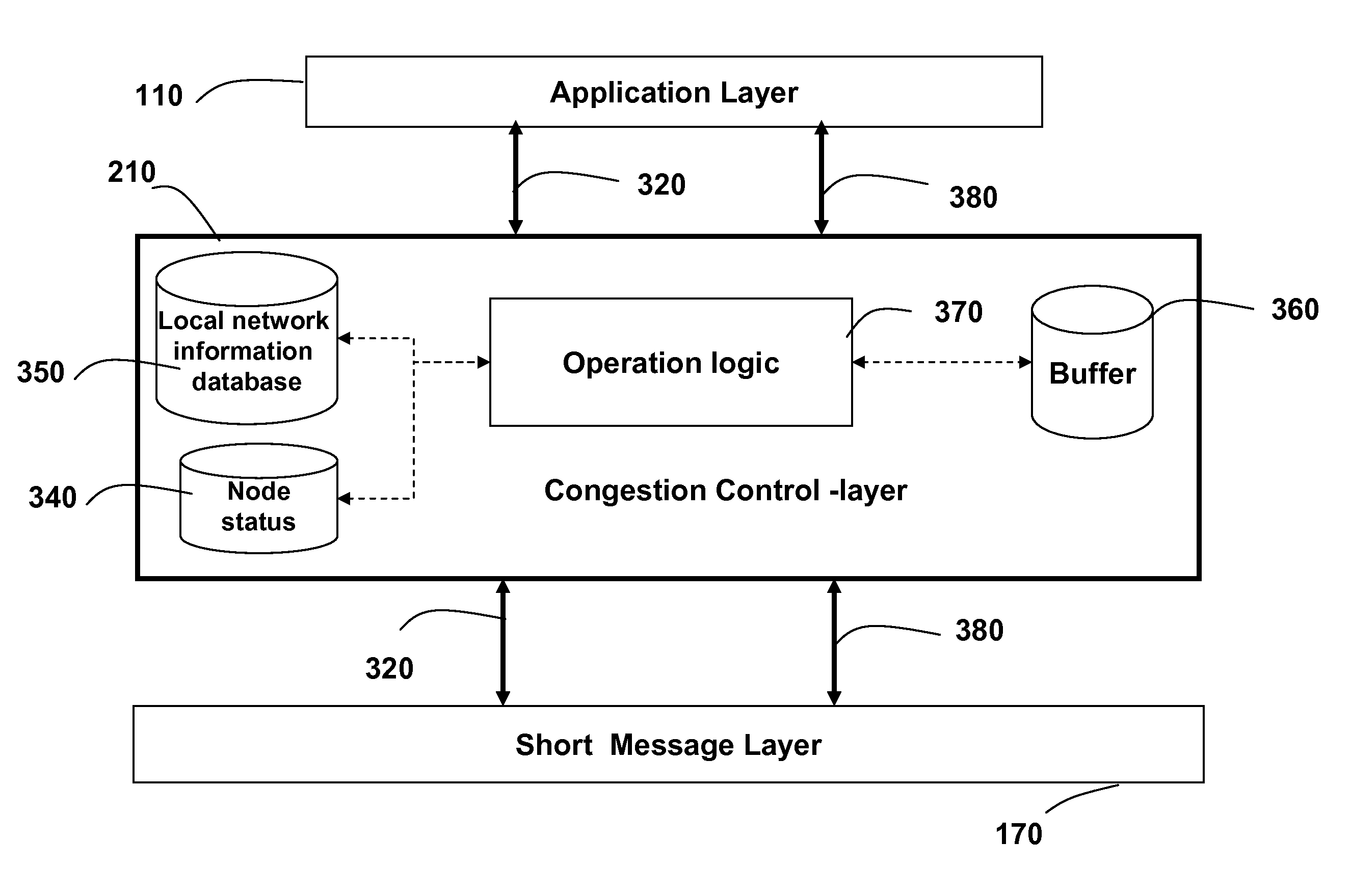
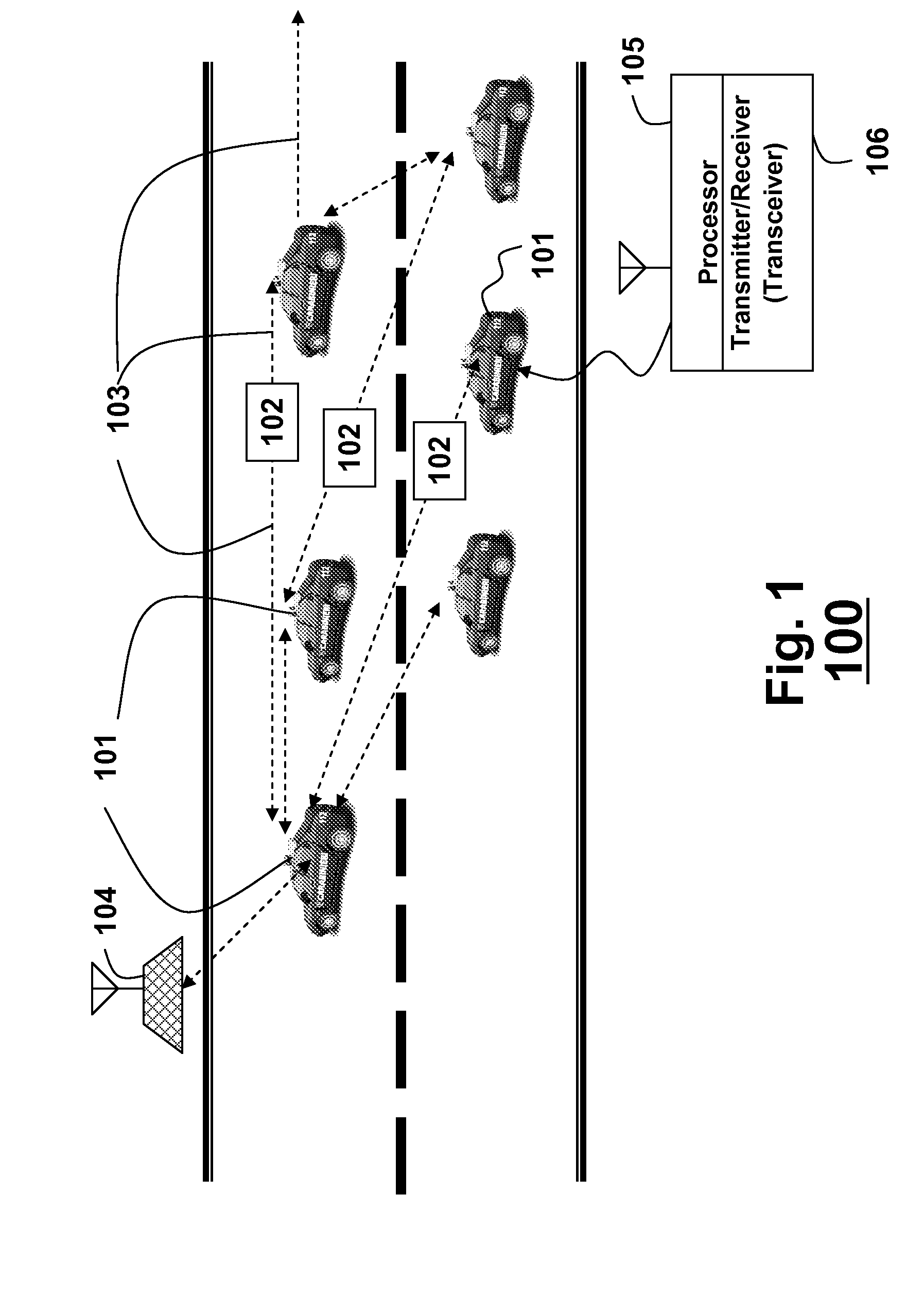
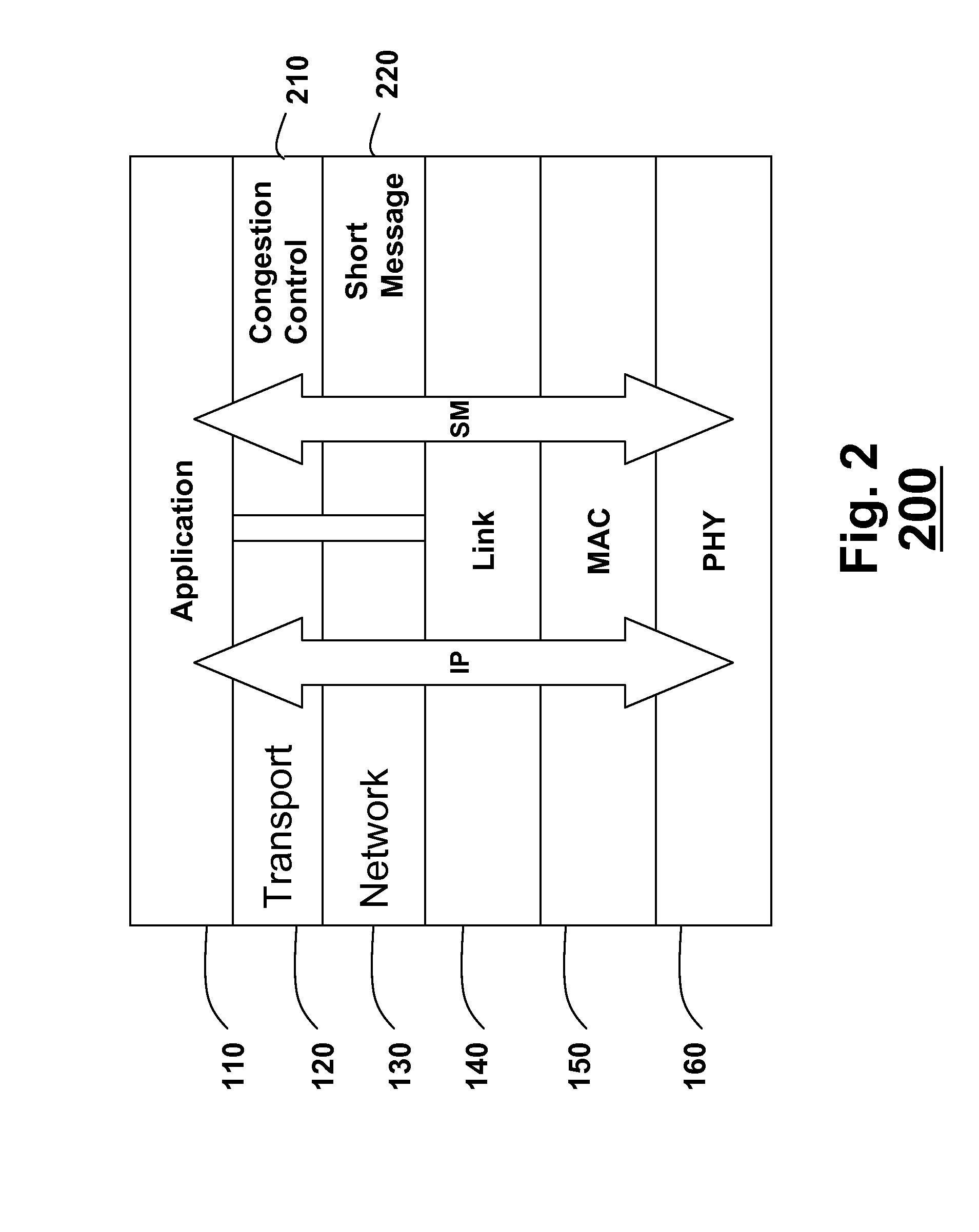
Method and protocol for congestion control in a vehicular network
In a vehicle ad-hoc network (VANET), a transceiver node is arranged in a vehicle. The node includes a protocol stack, which includes an application layer, a link layer; and a congestion control layer arranged between the application layer and the link layer. The congestion layer transfers short messages between the application layer and the link layer. The short messages are defined according to a standard for the VANET, and the congestion layer optimizes a network-wide rate allocation for the short messages.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Method and communication system for optimizing the throughput of a TCP flow in a wireless network
ActiveUS20080025216A1Optimize uplink throughputIncrease uplink speedError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransport layerCommunications system
A method and a system is provided for optimizing the throughput of a TCP flow from a TCP source to a TCP destination in a wireless network with the path of the flow encompassing a wireless link between a wireless transmitter and a wireless receiver. The throughput is optimized by using link-layer mechanisms at the wireless transmitter which are adaptive to the instantaneous TCP dynamics of the TCP flow. In particular, a cross-layer approach is disclosed which serves to tunnel information of TCP congestion control dynamics directly from the TCP based transport layer to the data link-layer which selects in response to these information modulation and / or coding schemas to transmit TCP segments via data link-layer blocks with improved TCP throughput.
Owner:DEUTSCHE TELEKOM AG
Content compression in networks
ActiveUS7975071B2Well formedTime-division multiplexMultiple digital computer combinationsData packRecipient side
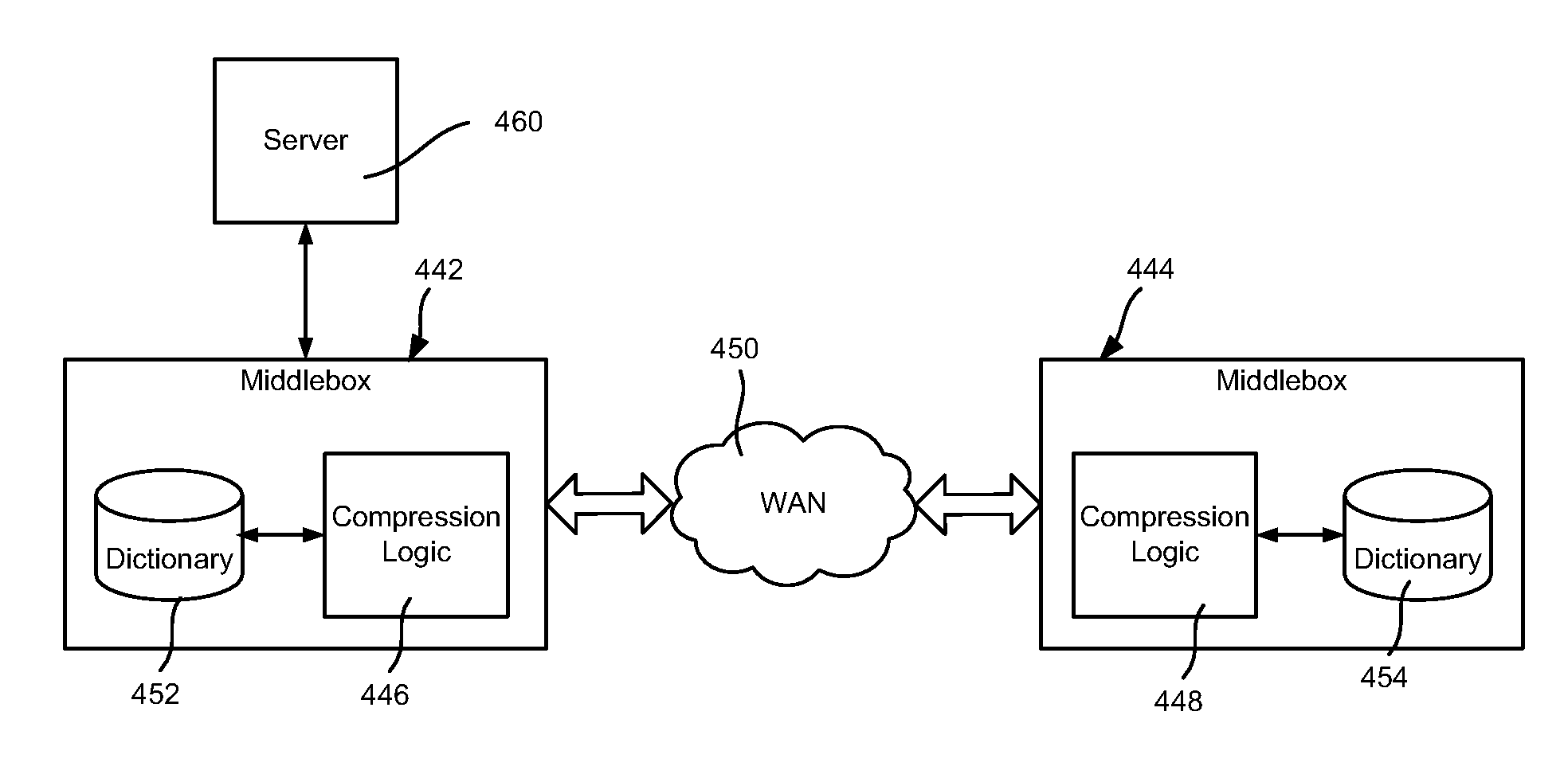
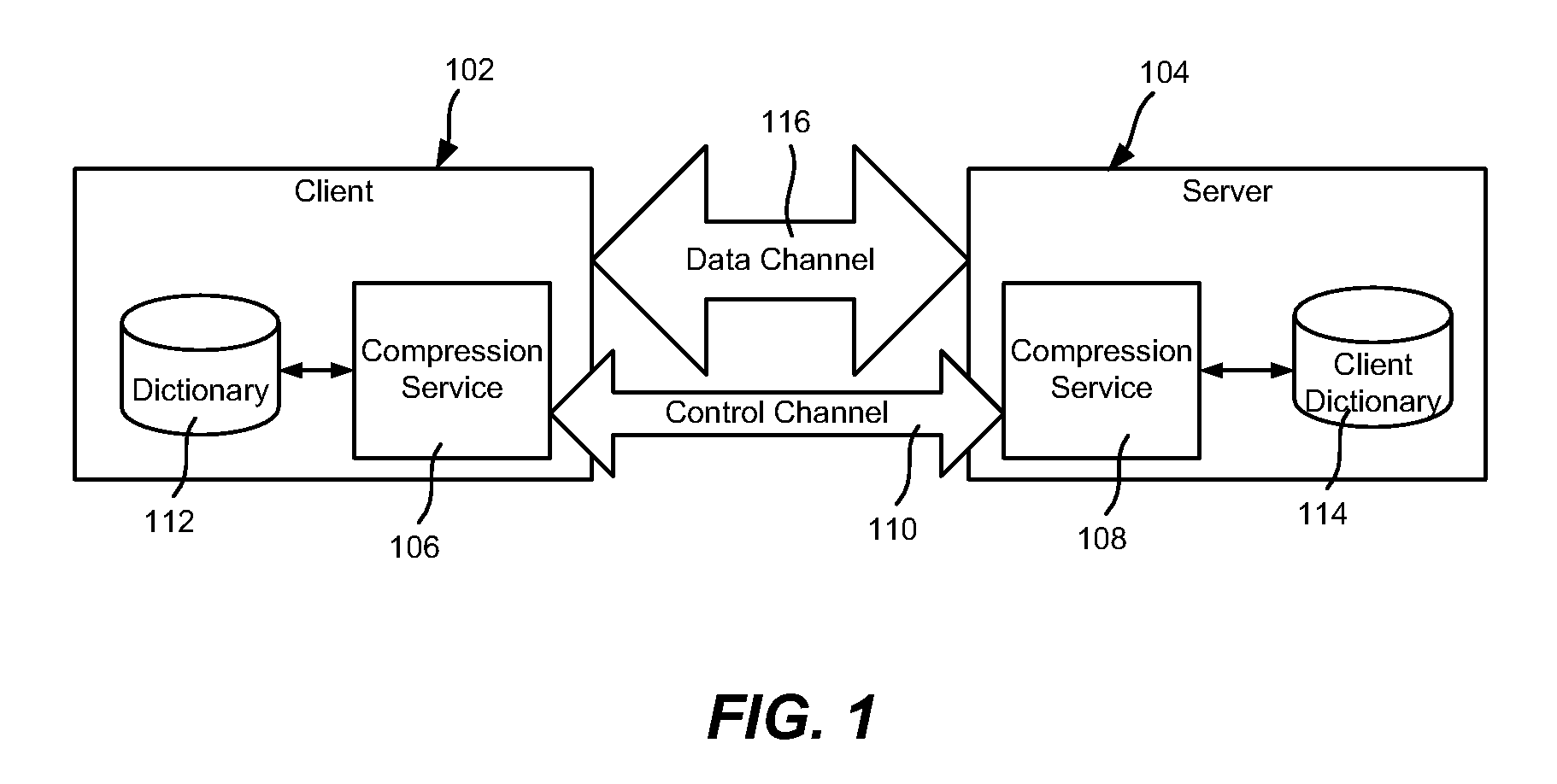
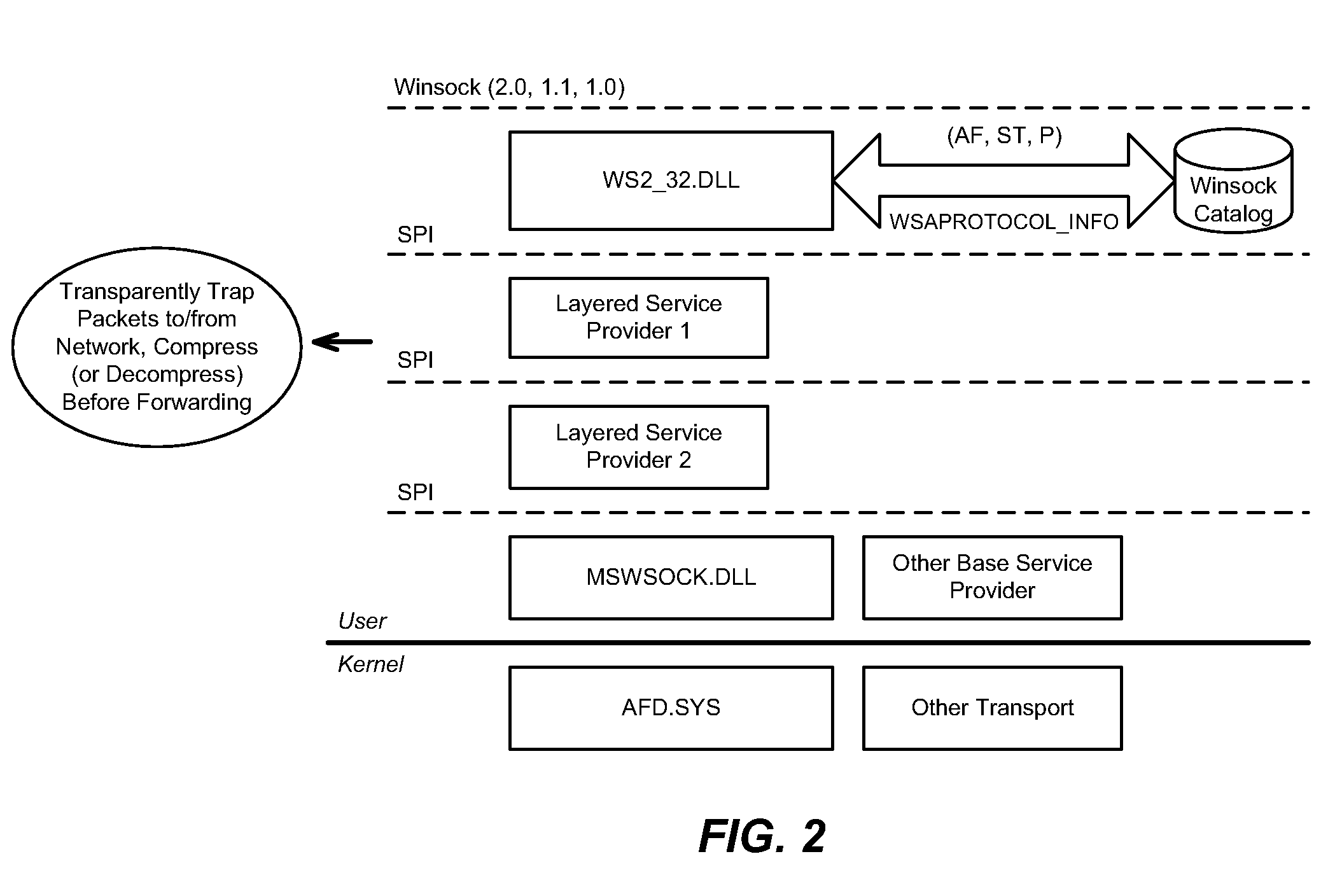
Described is transparently compressing content for network transmission, including end-to-end compression. An end host or middlebox device sender sends compressed packets to an end host or middlebox device receiver, which decompresses the packets to recover the original packet. The sender constructs compressed packets including references to information maintained at the receiver, which the receiver uses to access the information to recreate actual original packet content. The receiver may include a dictionary corresponding to the sender, e.g., synchronized with the sender's dictionary. Alternatively, in speculative compression, the sender does not maintain a dictionary, and instead sends a fingerprint (hash value) by which the receiver looks up corresponding content in its dictionary; if not found, the receiver requests actual content. Scheduling to maintain fairness and smoothing bursts to coexist with TCP congestion control are also described, as are techniques for routing compressed data over networked end hosts and / or compression-enabled middlebox devices.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Systems and methods for providing quality of service precedence in TCP congestion control
ActiveUS20080225721A1Low transfer rateError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of serviceTransport layer
Systems and methods for dynamically controlling bandwidth of connections are described. In some embodiments, a proxy for one or more connections may allocate, distribute, or generate indications of network congestion via one or more connections in order to induce the senders of the connections to reduce their rates of transmission. The proxy may allocate, distribute, or generate these indications in such a way as to provide quality of service to one or more connections, or to ensure that a number of connections transmit within an accepted bandwidth limit. In other embodiments, a sender of a transport layer connection may have a method for determining a response to congestion indications which accounts for a priority of the connection. In these embodiments, a sender may reduce or increase parameters related to transmission rate at different rates according to a priority of the connection.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
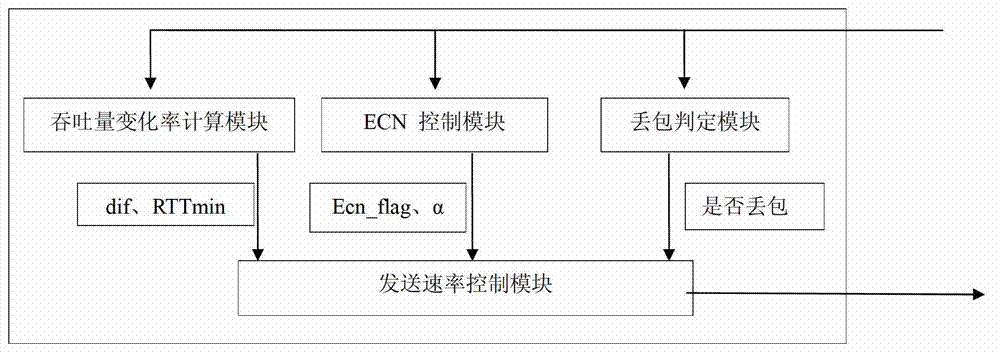
TCP (transmission control protocol) congestion control method based on throughout change rate and ECN (Explicit Congestion Notification) mechanism
ActiveCN103051554AAvoiding the TCP Incast phenomenonAvoid halvingData switching networksPacket lossData center
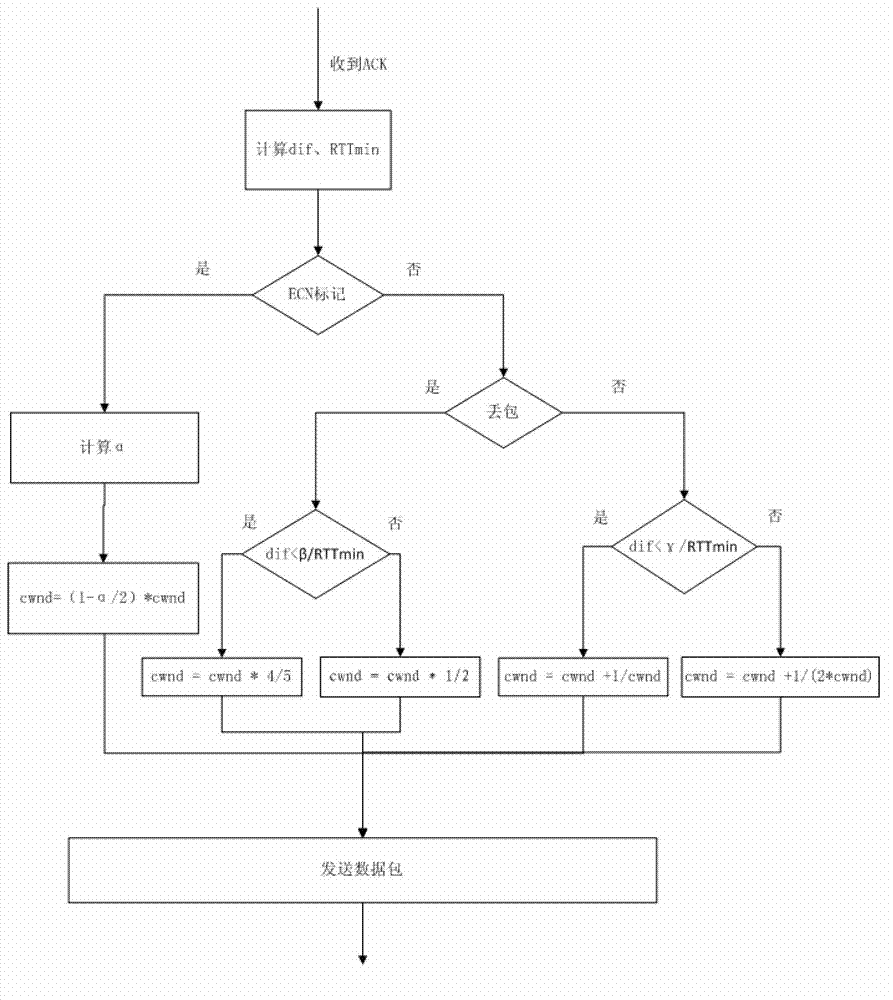
The invention provides a TCP (transmission control protocol) congestion control method based on throughout change rate and an ECN (Explicit Congestion Notification) mechanism. The method uses an ECN mechanism to prevent congestion, and comprises the following steps of when no ECN marks exist, if a packet is lost, judging the reason of packet loss according to the change rate of throughout, further adjusting a transmitting velocity instead of halving blindly, thereby avoiding severe performance problems caused by wireless random packet loss; and meanwhile, when no packet is lost, adjusting the increasing of windows according to the change rate of the throughout, further preventing congestion. By combining the ECN technology and the control method based on the throughout change rate, ECN can perform controlling in mild congestion of a network, thereby avoiding TCP Incast phenomenon in a wired data center; the control method based on the throughout change rate can be used for adjusting the sending windows according to the throughout change rate of the current network, when the packet is lost, the reason of the packet loss can be judged, so that the halving of the sending windows caused by wireless random packet loss can be avoided.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
ECN mechanism-based congestion control method in the mixed network
InactiveCN101056260AAvoid blindnessImprove throughputData switching networksError prevention/detection by diversity receptionPacket lossTCP congestion-avoidance algorithm
The invention discloses a congestion control method based on ECN mechanism in the mixed network, including the following steps: extract final section of ECN feedback information of the router, computer the congestion probability according to the distribution of the congestion mask, the sender can predict the congestion via the change trend of the congestion probability and adjust the congestion control mechanism according to the prediction result. The invention deduces the congestion according to the change rule of the congestion probability, namely only when the congestion probability value shows the increase trend, the congestion can be identified, so it can avoid the instantaneous and blind determination of the network status when the independent ECN feedback is used. The prediction results of the feedback are used to control the response behavior of the TCP packet loss and can accurately eliminate the influences of the non-congestion packet loss on the TCP congestion control in the mixed network.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
TCP congestion control method for bandwidth reservation network
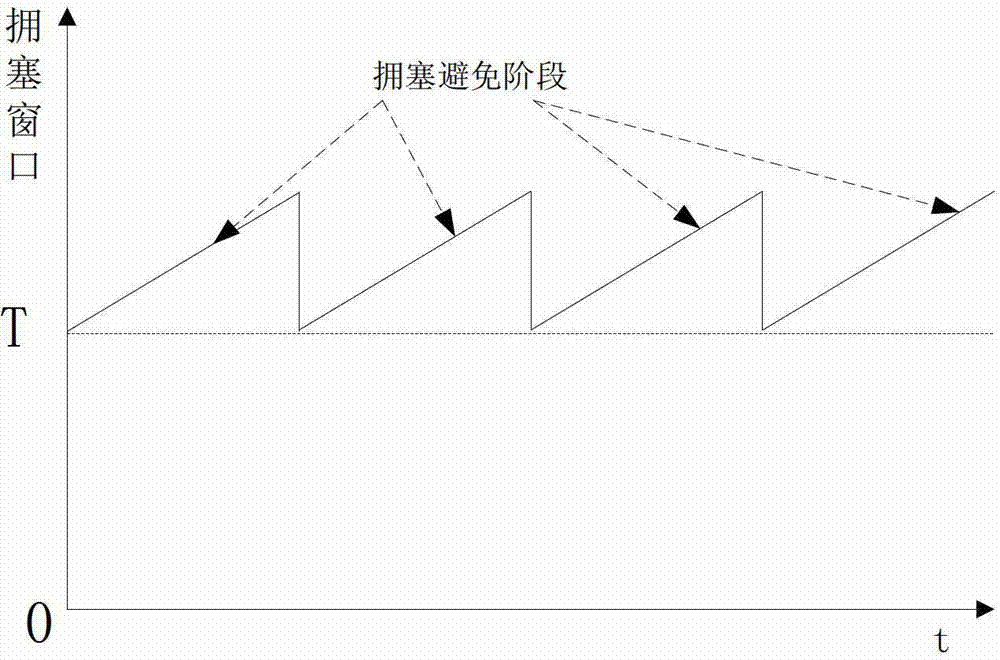
The invention relates to a TCP congestion control method for a bandwidth reservation network. The method comprises the steps of detecting the current usable bandwidth in a network link, the minimum round-trip delay for TCP connection, and the average data packet size for TCP connection; calculating the starting threshold T of a TCP sliding window according to the usable bandwidth, the minimum round-trip delay and the average data packet size; setting the initial size of the TCP sliding window as the starting threshold T and directly entering the congestion avoiding stage; reducing the size of the current congestion window to be T and reentering the congestion avoiding stage once packet loss or timeout occurs during data packet transmission.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
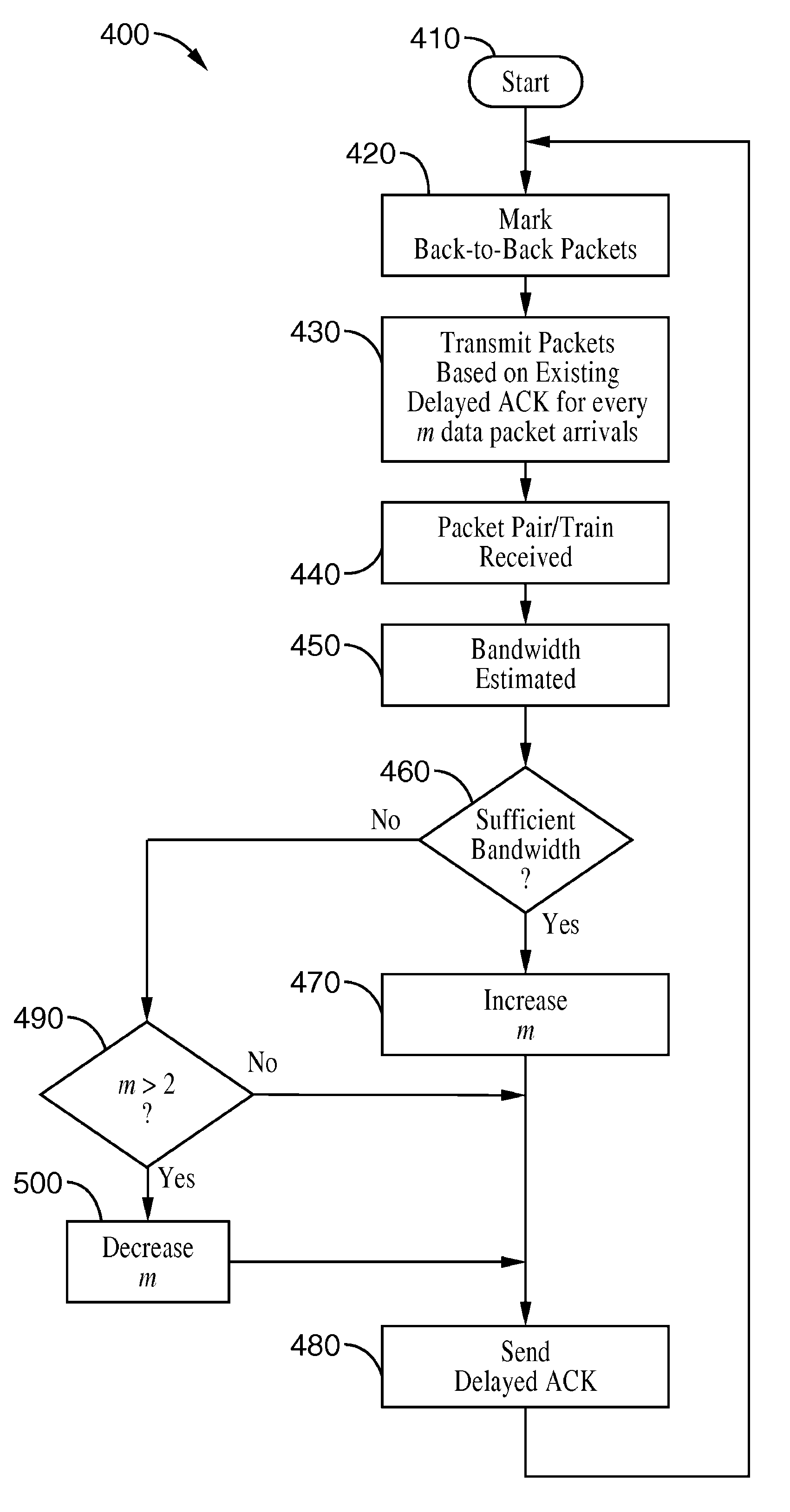
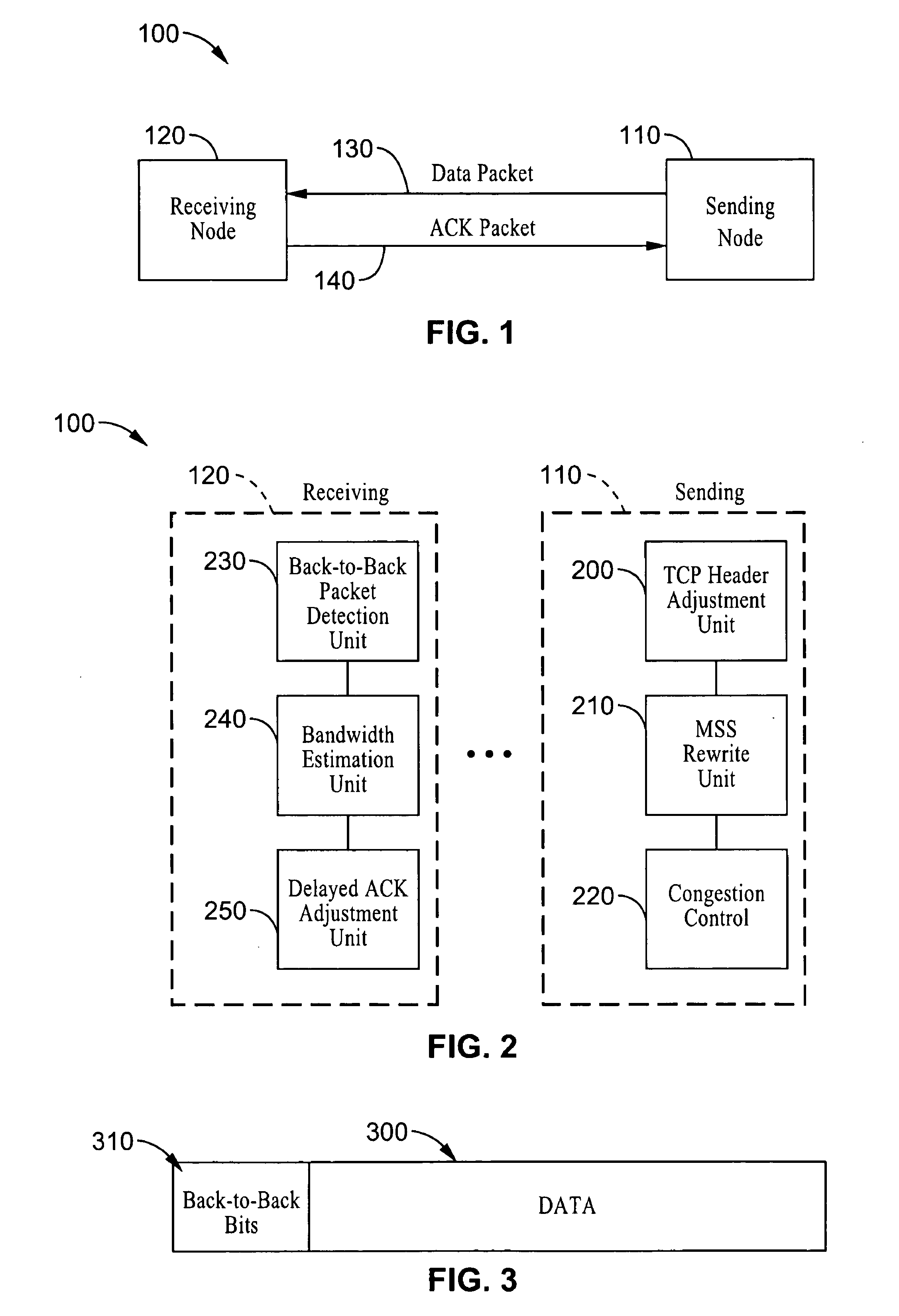
TCP congestion control based on bandwidth estimation techniques
InactiveUS20050228896A1Reduce loss rateControl congestionError prevention/detection by using return channelMultiple digital computer combinationsTraffic capacityTransport control protocol
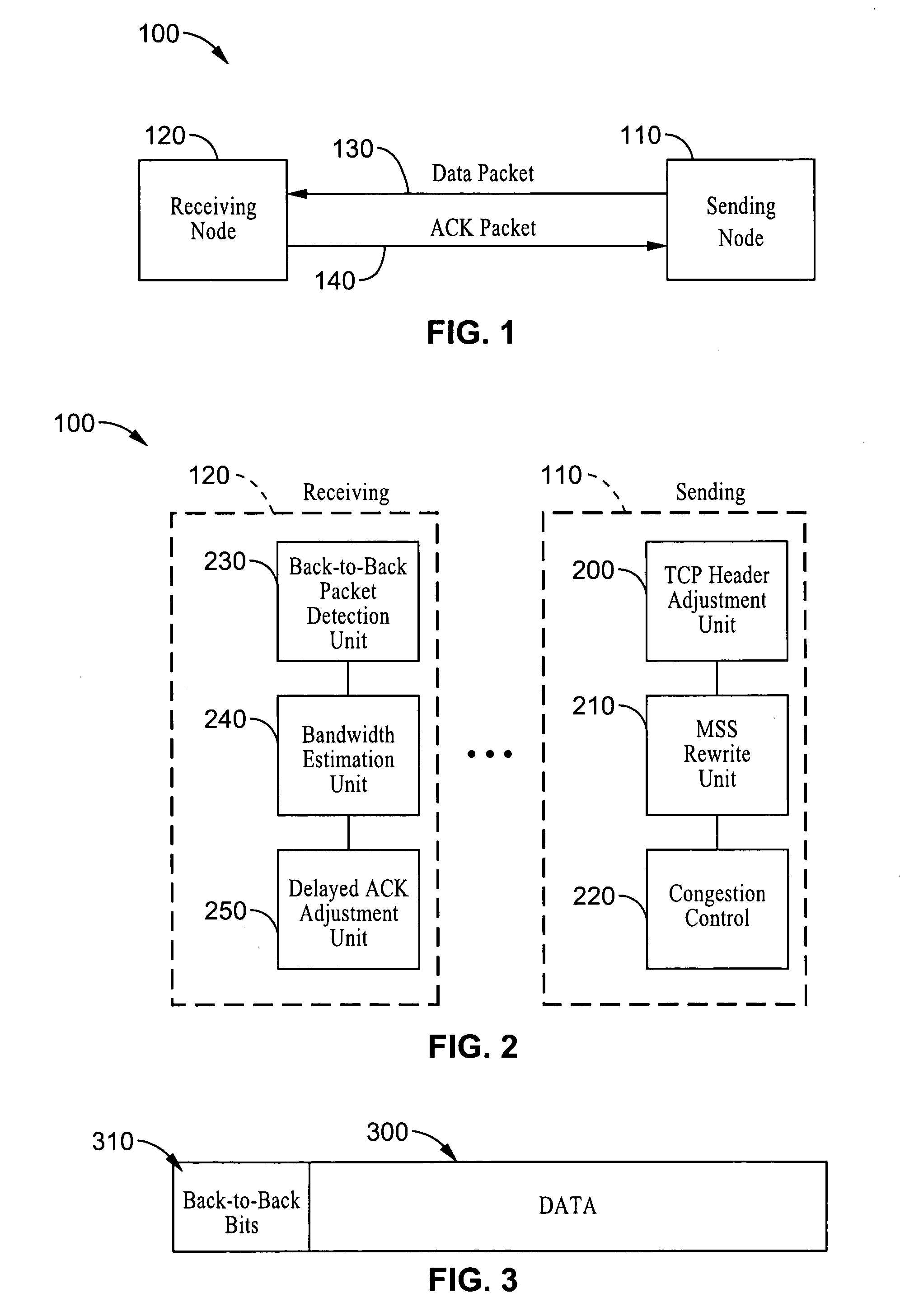
Systems and methods are described for controlling congestion, such as within the transport control protocol (TCP) based on bandwidth estimation techniques which provide explicit indications of back-to-back packet traffic. In response to registered back-to-back traffic, receiver-side bandwidth estimation techniques are exploited to enhance the congestion control behavior of TCP based networks. By way of example, a sender marks packets in the header or by changing segment size within a packet to indicate whether the packet is being sent back-to-back. A receiver utilizes the explicit back-to-back information, optionally in conjunction with other back-to-back packet estimation techniques, when estimating available bandwidth and setting congestion parameters. In addition a mechanism for controlling the length of packet trains is described which is based on modulating the transmission of delayed acknowledgements, such as sending acknowledgements upon receipt of a selected number of packets.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
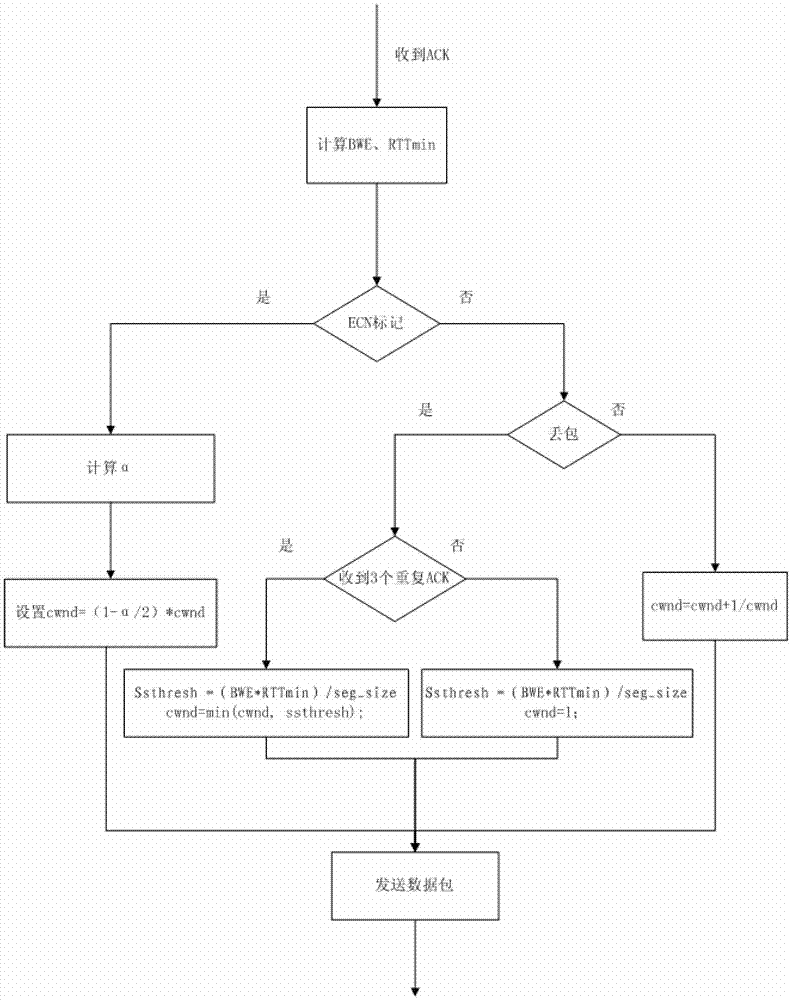
TCP (transmission control protocol) congestion control method based on network effective bandwidth and ECN (Explicit Congestion Notification) mechanism
InactiveCN103051555AAvoiding the TCP Incast phenomenonAvoid halvingData switching networksPacket lossTransport control protocol
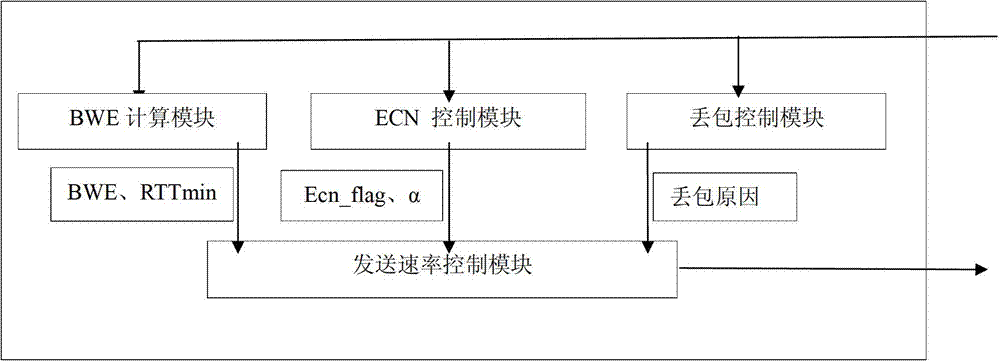
The invention provides a TCP (transmission control protocol) congestion control method based on network effective bandwidth and an ECN (Explicit Congestion Notification) mechanism. The method comprises the following steps of step 1, performing ECN marking on a switch; step 2, setting ECN-echo by a receiver; step 3, dynamically adjusting a sending window by a transmitter, when a transmitting end receives an ACK (acknowledgement character), firstly calculating effective bandwidth BWE and minimum round-trip time delay RTTmin of a current network by a BWE calculation module; and then looking over whether the ACK sets an ECN-echo bit by an ECN control module, if so, setting ecn_flag showing that the sending velocity is needed to be adjusted according to the ECN, and calculating the ratio alpha of the received ACK with the ECN-echo marks to the total number of data packets sent by the previous sending window. By adopting the ECN technology and the control method based on the network effective bandwidth, the ECN can perform controlling in mild congestion of the network, thereby avoiding TCP Incast phenomenon in a wired data center; the control method based on BWE can be used for adjusting the sending window according to the effective bandwidth of the current network when the packet is lost, so that the halving of the sending windows caused by wireless random packet loss can be avoided.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
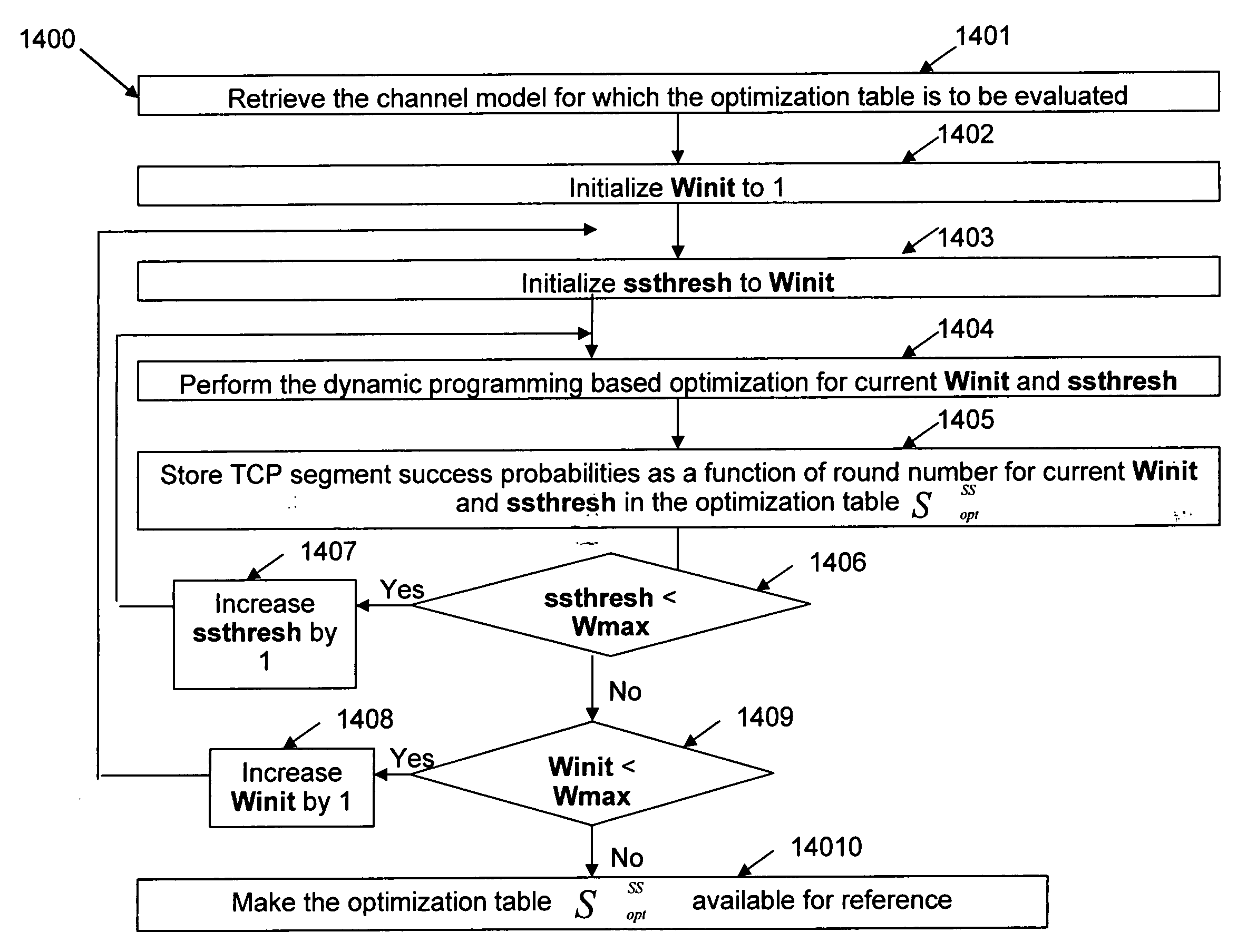
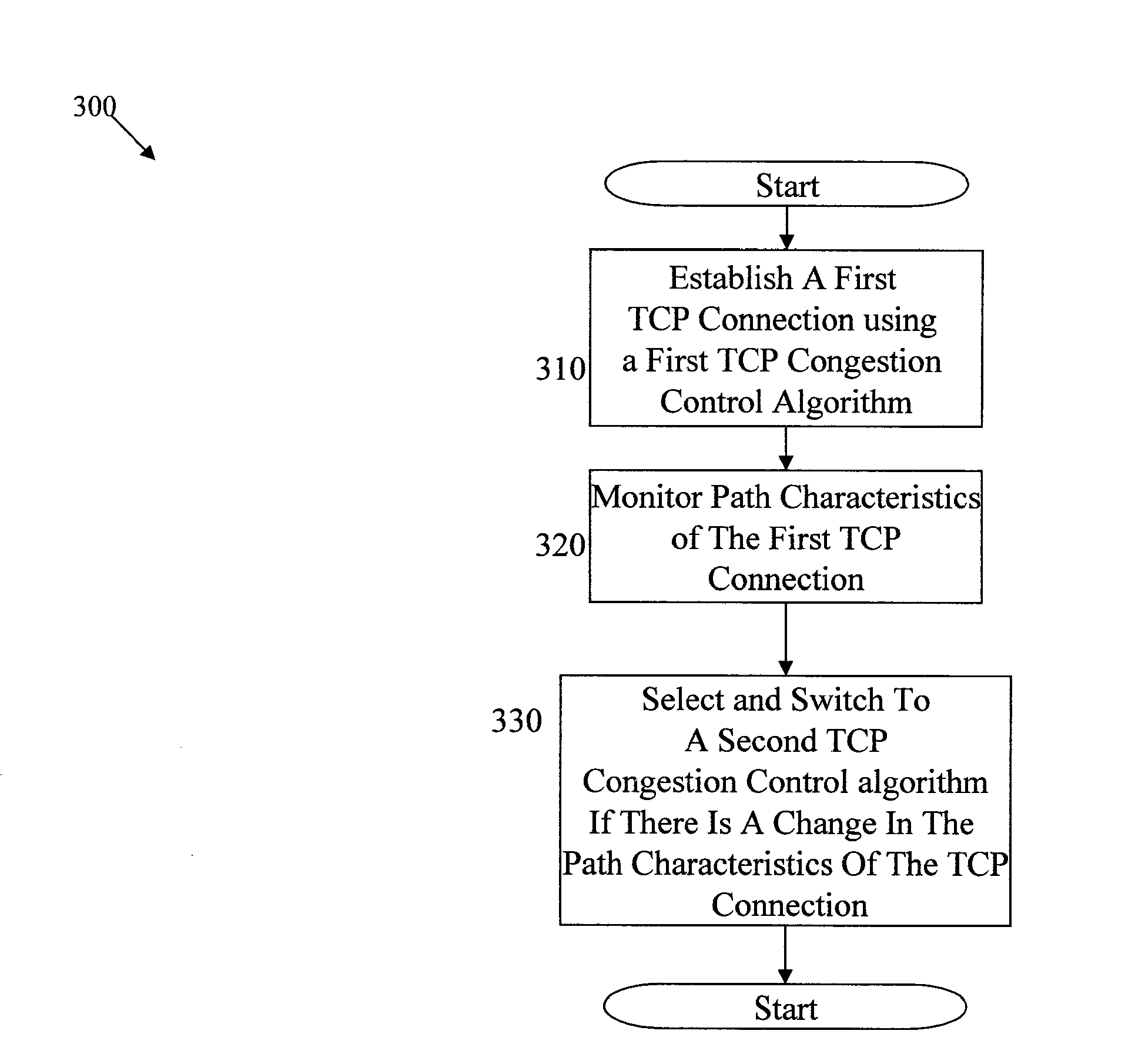
Methods, Systems and Computer Program Products for Dynamic Selection and Switching of TCP Congestion Control Algorithms Over a TCP Connection
InactiveUS20090316581A1Error preventionTransmission systemsComputer programTCP congestion-avoidance algorithm
Methods, systems and computer program products for dynamic selection and switching of TCP congestion control algorithms over a TCP connection. Exemplary embodiments include a TCP congestion control algorithm management method, including establishing a first TCP connection on a first network having an end point, wherein the TCP connection includes a first TCP congestion control algorithm, monitoring path characteristics of the TCP connection and dynamically selecting and switching to a second TCP congestion control algorithm in a response to a change in the path characteristics of the TCP connection.
Owner:IBM CORP
Systems and methods for providing quality of service precedence in TCP congestion control
ActiveUS7760642B2Low transfer rateError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of serviceTransport layer
Systems and methods for dynamically controlling bandwidth of connections are described. In some embodiments, a proxy for one or more connections may allocate, distribute, or generate indications of network congestion via one or more connections in order to induce the senders of the connections to reduce their rates of transmission. The proxy may allocate, distribute, or generate these indications in such a way as to provide quality of service to one or more connections, or to ensure that a number of connections transmit within an accepted bandwidth limit. In other embodiments, a sender of a transport layer connection may have a method for determining a response to congestion indications which accounts for a priority of the connection. In these embodiments, a sender may reduce or increase parameters related to transmission rate at different rates according to a priority of the connection.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
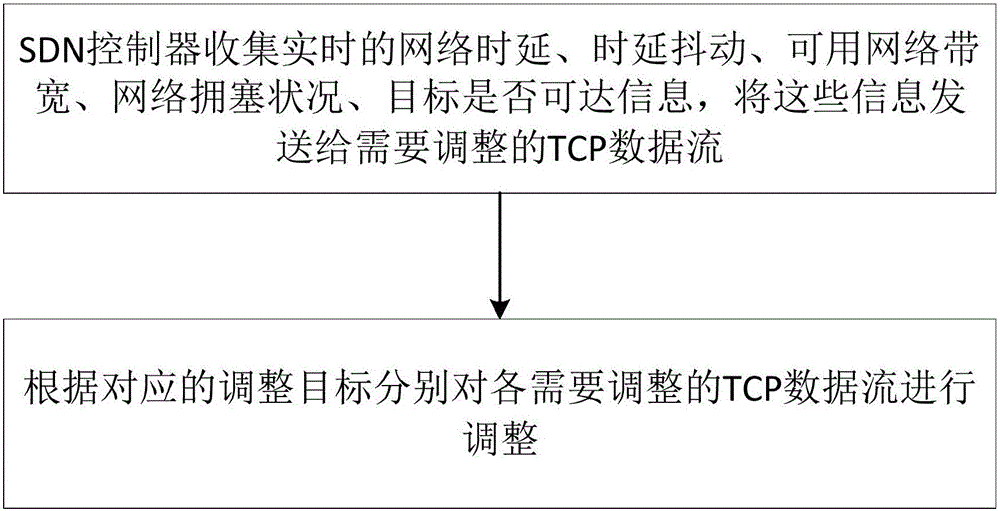
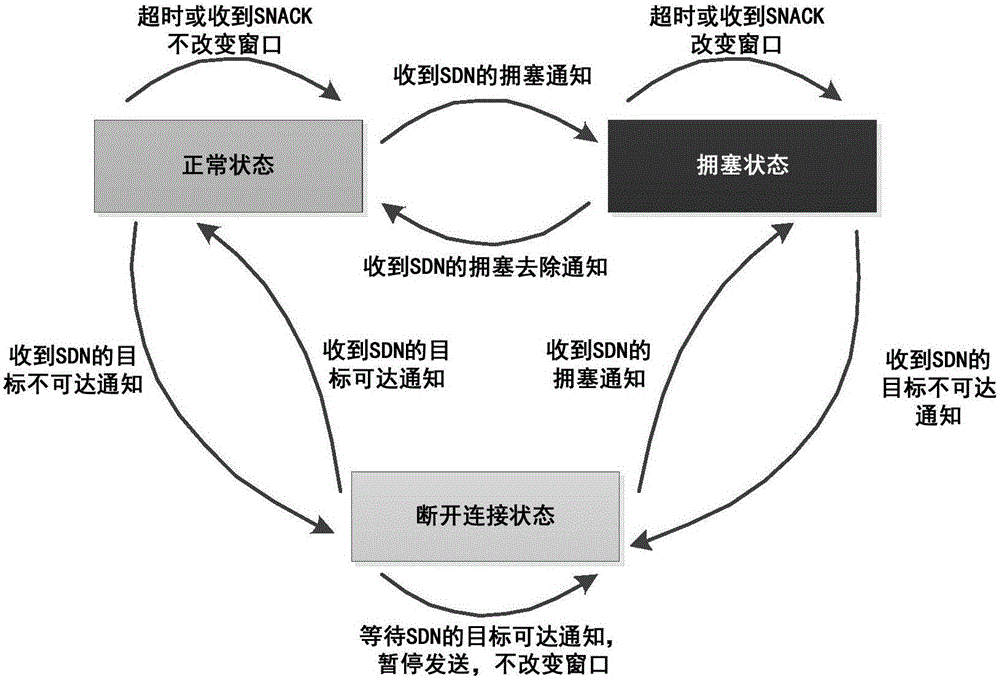
TCP congestion control method based on SDN network
ActiveCN106102094AFast retransmissionImprove transmission efficiencyNetwork traffic/resource managementWireless network protocolsAir interfaceNetwork conditions
The invention discloses a TCP congestion control method based on an SDN network. The method comprises the steps: enabling an SDN controller to collect real-time network time delay, time delay jitter, usable network bandwidth, network congestion conditions and information whether a target is reachable or not, and transmitting the above information to to-be-adjusted TCP data flows; and respectively adjusting the to-be-adjusted TCP data flows according to the corresponding adjustment targets. The method can quickly sense the network time delay, congestion condition, bandwidth and error codes through interaction with the SDN controller. Especially for a high-time-delay and high-error-rate wireless network environment, the method can discriminate air interface package loss and network congestion package loss quickly and accurately, enables a TCP protocol to be able to quickly sense the network condition, and quickly adjusts the congestion control mechanism of the TCP protocol, thereby improving the transmission efficiency of the TCP protocol.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HAIGE COMM GRP INC
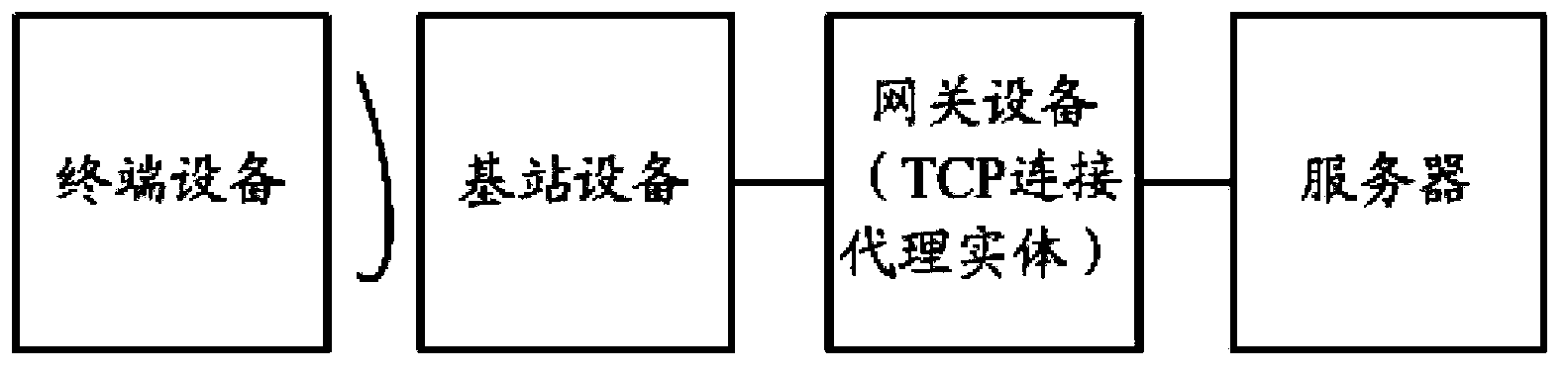
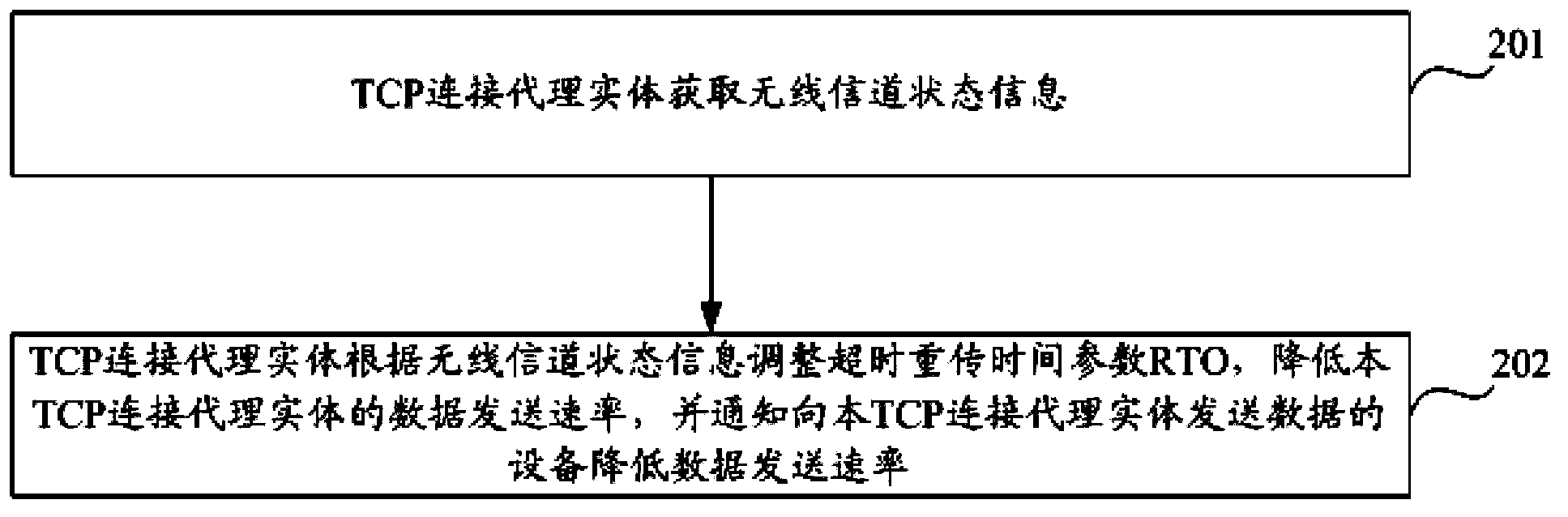
Sending rate adjustment method and device based on wireless channel feedback
ActiveCN104243090AEfficient use ofAvoid wastingError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementChannel state informationRetransmission time out
The invention discloses a sending rate adjustment method and device based on wireless channel feedback. The sending rate adjustment method comprises the steps that a TCP connection agent entity acquires wireless channel state information; the TCP connection agent entity adjusts retransmission time out (RTO) parameters according to the wireless channel state information, the data sending rate of the TCP connection agent entity is reduced, and a device sending data to the TCP connection agent entity is notified to reduce the data sending rate. According to the sending rate adjustment method and device based on wireless channel feedback, the TCP connection agent entity can reasonably adjust the sending rate according to the wireless channel state information, channel resources obtained after modulation modes are switched can be efficiently utilized in time, and waste of radio resources can be avoided. Furthermore, blind search jitter of TCP congestion control caused by unstable wireless channels can be avoided, RTO, queue congestion and the like are avoided, and therefore wireless data service user experience is improved.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) congestion control method based on congestion queue length
InactiveCN106027412AImprove accuracyIncrease flexibilityData switching networksDirect feedbackData center
The invention discloses a TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) congestion control method based on a congestion queue length for use in a data center SDN (Software Defined Networking) environment. The method comprises the following steps that: a queue management module monitors a queue length of a switch port; when the queue length exceeds a certain threshold, a current network is considered to be in a congestion state, and congestion announcement information is transmitted to a controller through an SDN / OpenFlow protocol; after the controller receives the information, a flow table is issued to a switch, and an ACK (Acknowledgement) message reversely flowing through the port is modified in order that the ACK message carries queue length information of a network congestion point; and after a transmitting end receives the ACK message, the transmission rate of the transmitting end is lowered according to the queue length information in the ACK message in order to relieve network congestion. According to the method, a congestion degree is represented by direct feedback at the network congestion point, so that the problem of data center network congestion can be solved effectively, and the network throughput is increased. Meanwhile, an SDN / OpenFlow technology is utilized in the method, so that the method is more flexible and efficient.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
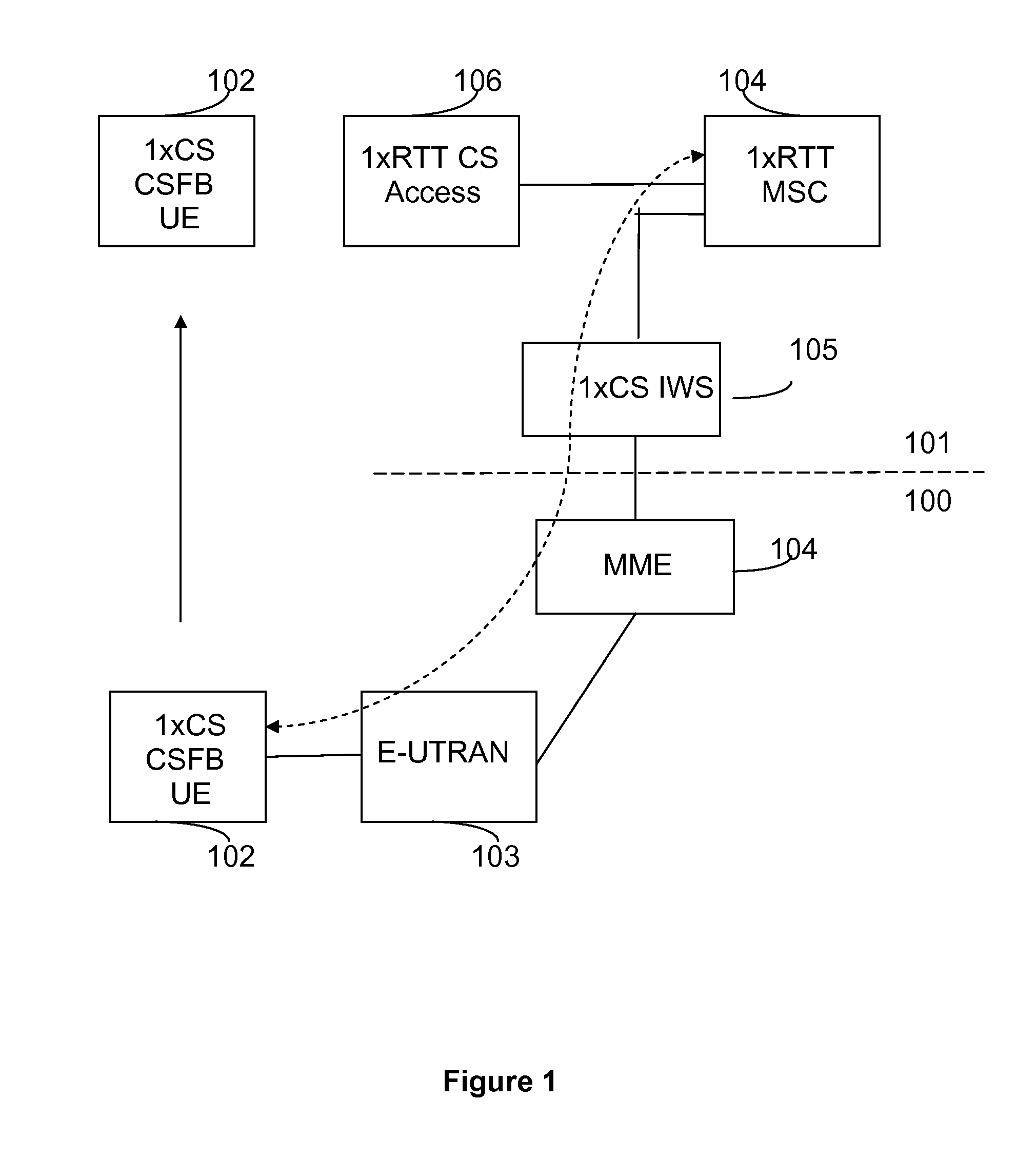
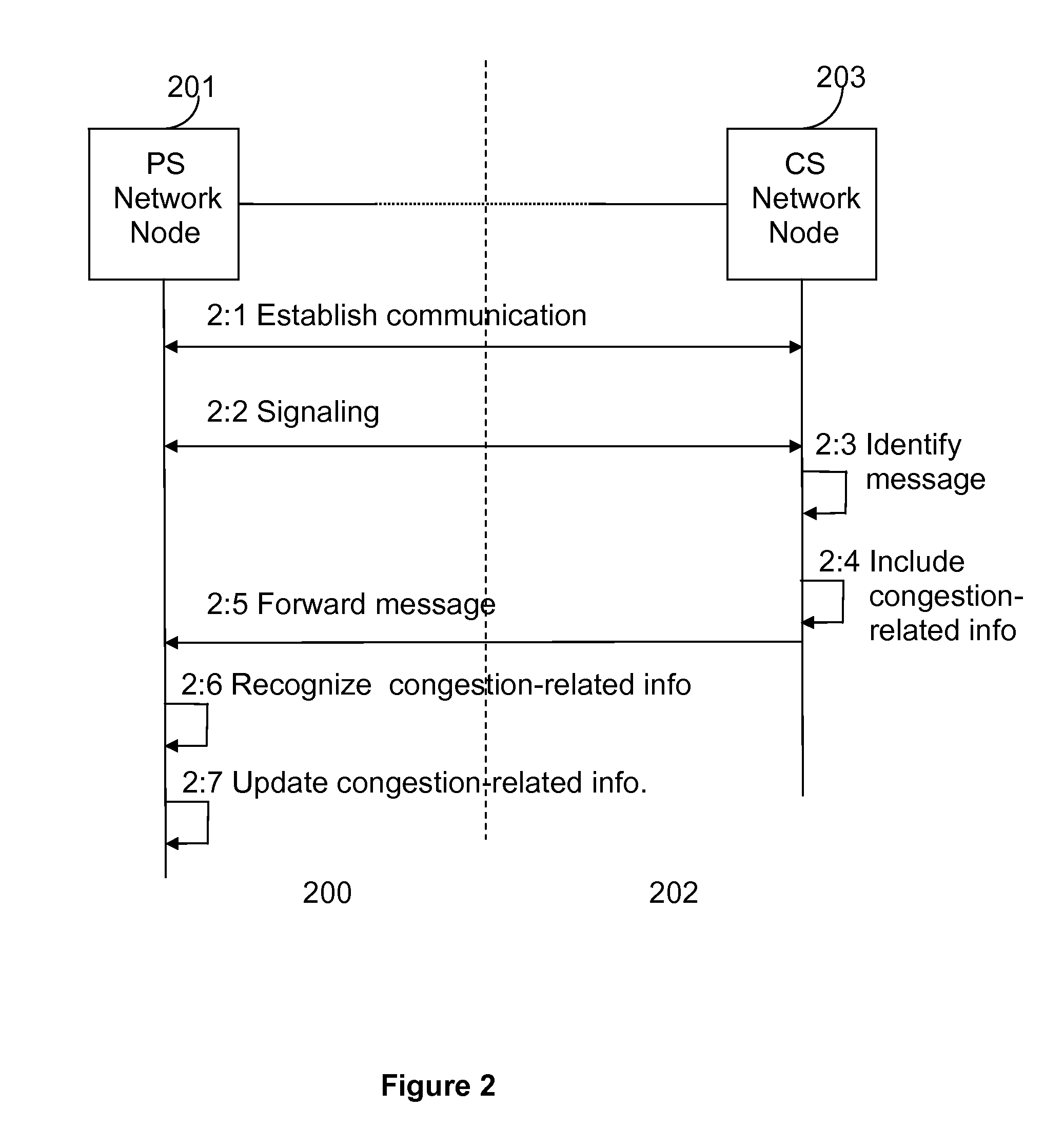
Method and Apparatus for Congestion Control for Inter-Working Communication Networks
InactiveUS20110110228A1Access latencyExcessive signaling is avoidedError preventionTransmission systemsCommunications systemCellular communication systems
A method for allowing distribution of congestion-related information between a cellular communication system supporting circuit-switched services and a cellular communication system supporting packet-switched services. A message destined for the packet-switched communication system is identified at the circuit-switched communication system, and congestion-related information, indicating the present congestion status of the circuit-switched communication network is included into the message. The message is then forwarded to a network node of the packet-switched communication system, where either a user equipment or the network node of the first cellular communication system can control Circuit-switched Fallback (CSFB) attempts towards the second communication system on the basis of the congestion-related information prior to having to initiate any access signaling associated with the CSFB attempts.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
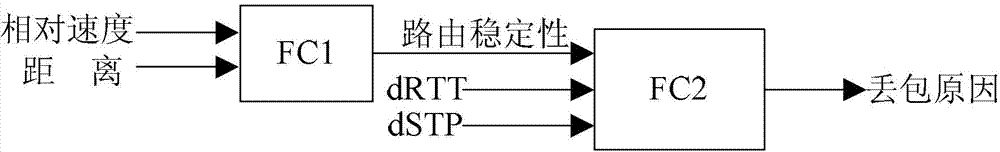
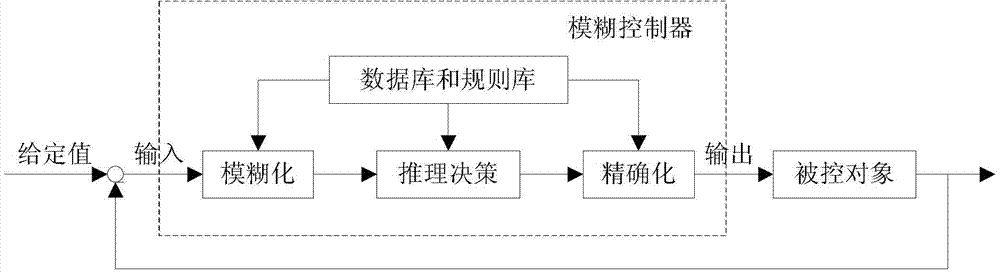
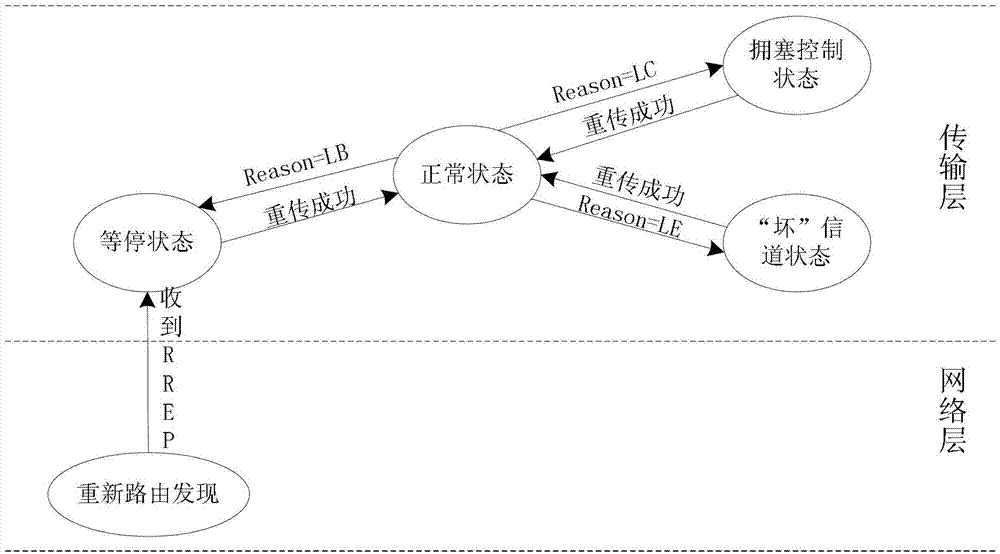
Fuzzy-control-based TCP (transmission control protocol) congestion control method in vehicle-mounted communication network
InactiveCN103209434ATroubleshoot slow transfer performanceImprove transmission performanceNetwork traffic/resource managementPacket lossShort terms
The invention discloses a fuzzy-control-based TCP congestion control method in a vehicle-mounted communication network and relates to the field of wireless communication. The method includes utilizing fuzzy control and introducing relative speed of neighboring nodes, distance between neighboring nodes, relative round-trip-delay change rate, short-term throughout change rate as the input parameters of fuzzy inference to establish a fuzzy control rule library; and determining a packet loss reason through the fuzzy inference, and improving TCP congestion control strategies and route switching strategies in combination with cross-layer schemes to take different processing countermeasures for different packet loss reasons, so that the route stability can be enhanced, the transmission interruptions caused by route switching can be reduced, and the system throughput and the average delay can be improved. The fuzzy-control-based TCP congestion control method in the vehicle-mounted communication network is used for improving the TCP transmission performance in the vehicle-mounted communication network, and is particularly applicable to conditions of high-speed node motion, frequent topological change and poor channel quality.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
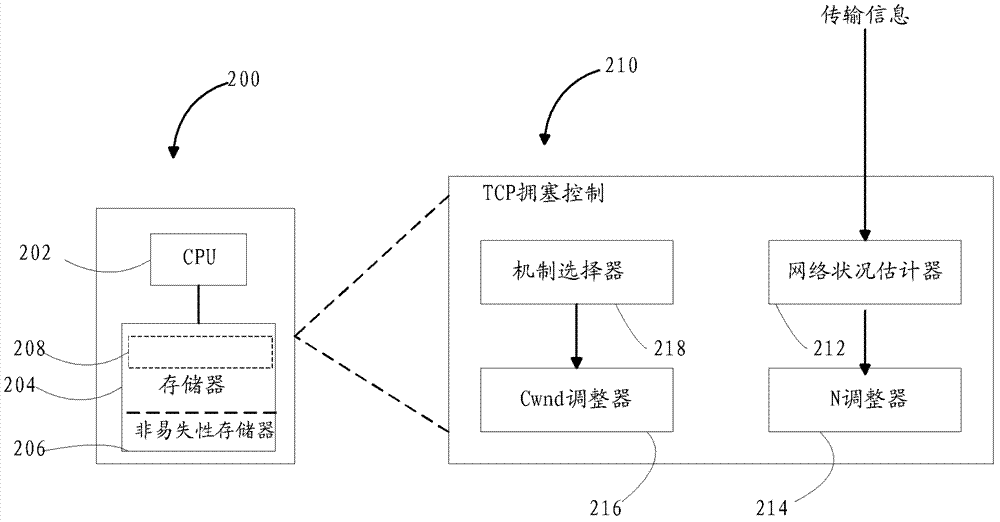
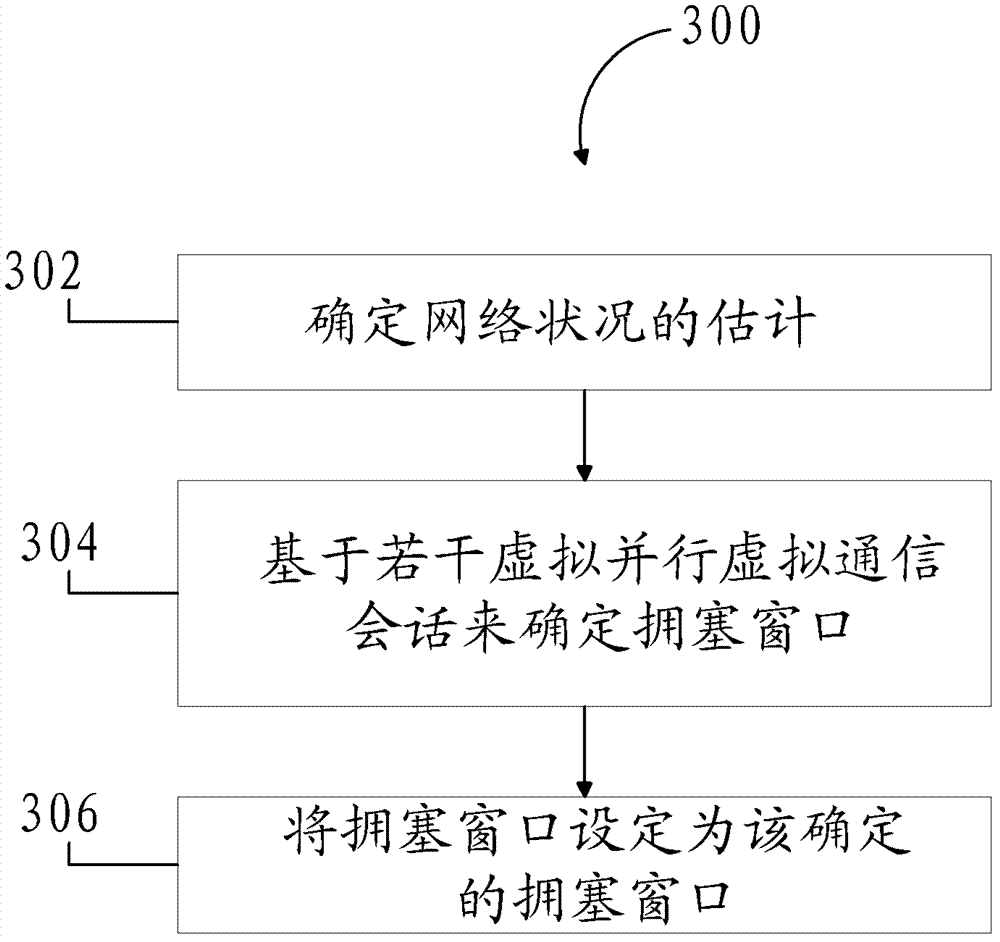
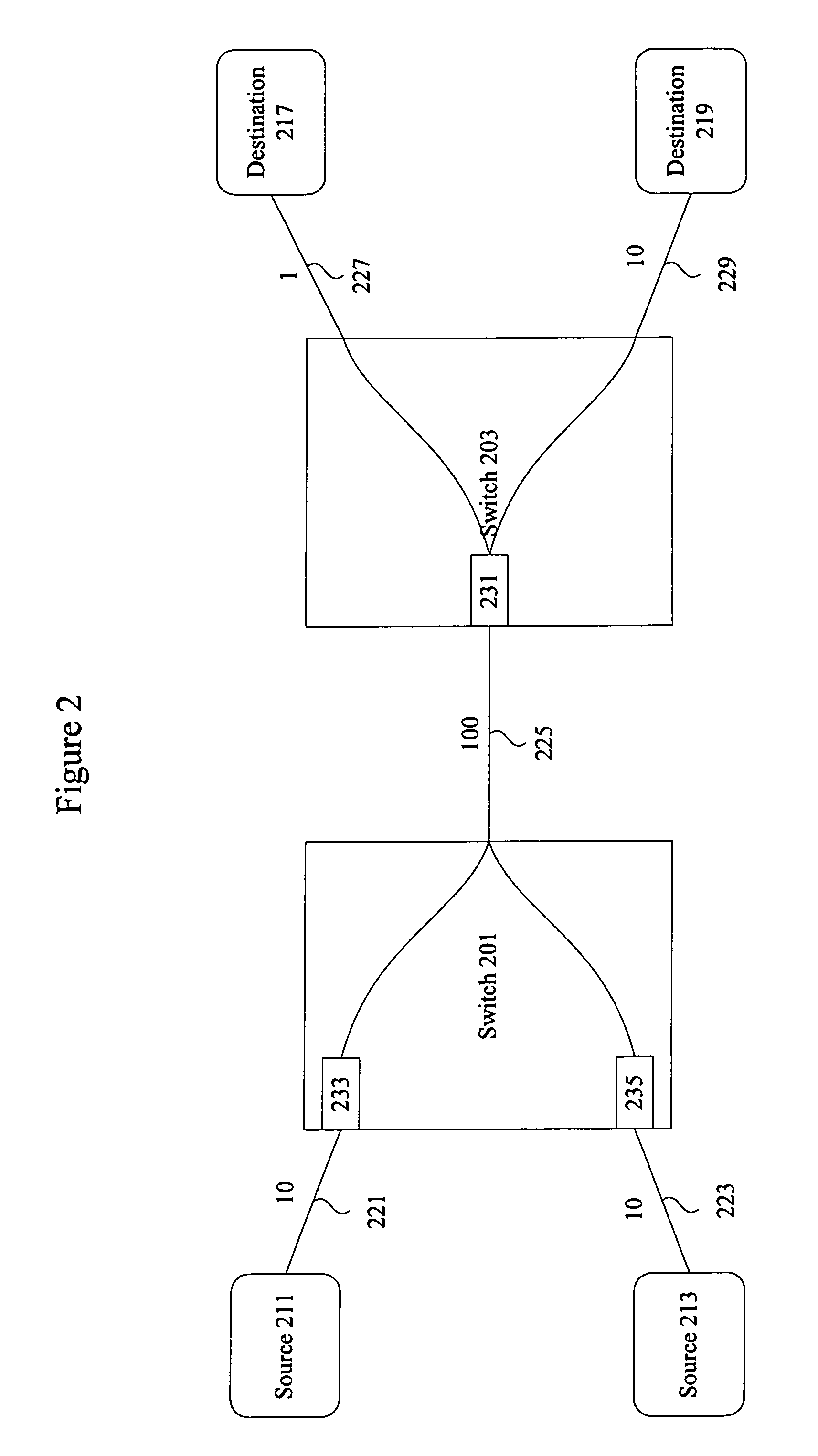
Tcp congestion control for heterogeneous networks
A congestion control mechanism for TCP communication sessions is described. The congestion control mechanism adjusts the size of the congestion window based on a number, N, of parallel virtual connections. The number N of parallel virtual connections used to determine the congestion window is dynamically adjusted based on an estimation of the network condition.
Owner:NANJING YUYAN INFORMATION TECH
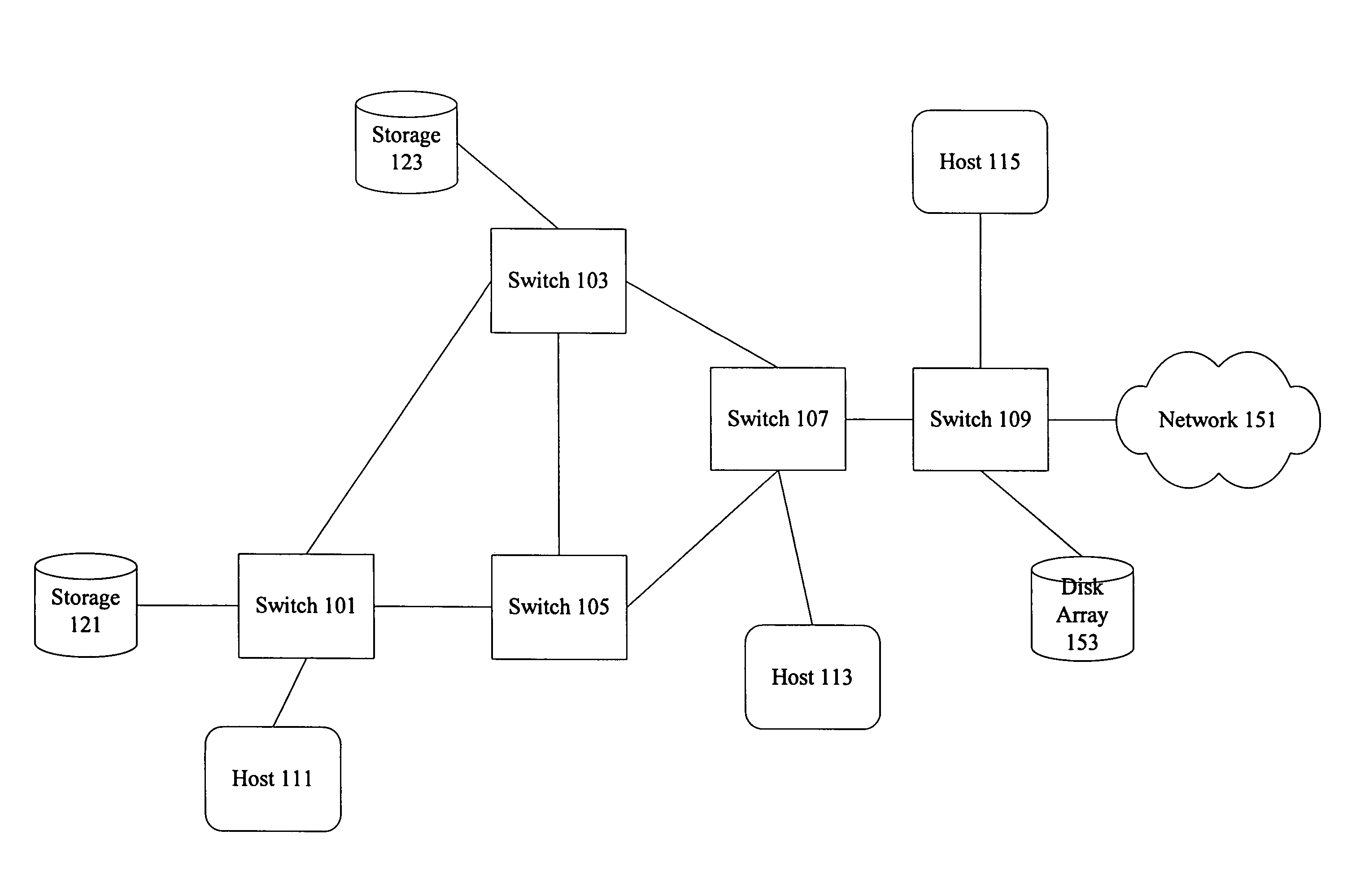
End-to-end congestion control in a Fibre Channel network
ActiveUS7734808B1Reduce stepsError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsFiberEnd to end congestion control
Methods and devices are provided for controlling congestion in a network such as a Fibre Channel network. According to some implementations, a node within a network fabric detects congestion caused by an edge device outside of the fabric and notifies the edge device of the congestion. The edge device applies a congestion reaction mechanism in response to the notification. In some implementations, the congestion reaction mechanism is applied on a per-exchange basis, in order to mitigate congestion caused by a particular operation.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Systems and methods for providing quality of service precedence in TCP congestion control
Systems and methods for dynamically controlling bandwidth of connections are described. In some embodiments, a proxy for one or more connections may allocate, distribute, or generate indications of network congestion via one or more connections in order to induce the senders of the connections to reduce their rates of transmission. The proxy may allocate, distribute, or generate these indicationsin such a way as to provide quality of service to one or more connections, or to ensure that a number of connections transmit within an accepted bandwidth limit. In other embodiments, a sender of a transport layer connection may have a method for determining a response to congestion indications which accounts for a priority of the connection. In these embodiments, a sender may reduce or increase parameters related to transmission rate at different rates according to a priority of the connection.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Quality of service (QOS) congestion control handling
InactiveUS20190281491A1Unable to supportNetwork traffic/resource managementParticular environment based servicesQuality of serviceTelecommunications link
Aspects of the disclosure relate to a method of operating a scheduled entity for wireless communication. In some aspects, the scheduled entity determines to modify a first quality of service (QoS) level for a data transmission from the first device to a second device, wherein the first device is configured to communicate with the second device through a direct wireless communication link, and wherein the first QoS level is requested by an application of the first device. The scheduled entity modifies the first QoS level to a second QoS level, wherein the direct wireless communication link is able to support the second QoS level and is unable to support the first QoS level. The scheduled entity transmits the data transmission based on the second QoS level.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
TCP parameter adjusting method applicable to wireless self-organized network
InactiveCN101662842AImprove throughputEasy to adjustNetwork topologiesWireless network protocolsCongestion windowState parameter
The invention belongs to the technical field of network communication, relating to a TCP parameter adjusting method applicable to a wireless self-organized network, wherein the method comprises the steps of adjusting the size of a congestion window, slow starting a threshold value and a RTO value. The method specifically comprises the steps: by adopting a cross-layer mechanism, differentiating a movable lost package from non-movable lost package at a link layer zone, and feeding back a judging result to a network layer; expanding a routing protocol at the a network layer, transmitting a package lost reason hop by hop, and transmitting expanded TCMP control information to a TCP layer; and at the TCP layer, according to the judging result and the ICMP control information of the package lostreason, adjusting a TCP congestion mechanism and corresponding status parameters to enter into different running status. The method improves the congestion control performance of the TCP, and is applicable to a wireless Ad Hoc network with an AODV routing protocol. The method is taken as an effective and practical technical scheme, thereby having good application foreground.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Link adaptation-based heterogeneous network TCP congestion control method
ActiveCN105024940AImprove fairnessImprove link utilizationData switching networksCongestion windowPacket loss
The invention provides a link adaptation-based heterogeneous network TCP congestion control method. According to the method, an adaptive growth factor is introduced to an exponential type window growth function, so that window growth rate can be matched with link status, and in a packet loss differentiation strategy, an adaptive queue threshold is adopted to improve the performance of a TCP in a wireless environment; the window growth rate and a back-off strategy are adaptively adjusted according to links, so that the degradation of the transmission performance of the TCP caused by different link bandwidth, the difference of time delay and high packet loss can be avoided; a strategy for accelerating the convergence of a congestion window is adopted, and only a transmitting-end TCP needs to be modified, and therefore, the method can be gradually deployed on and applied to the Internet; and according to performance analysis and evaluation, the fairness of TCP congestion control algorithms, the utilization rate of the links and the fairness of end-to-end round-trip delay can be improved.
Owner:重庆珂荧科技有限公司
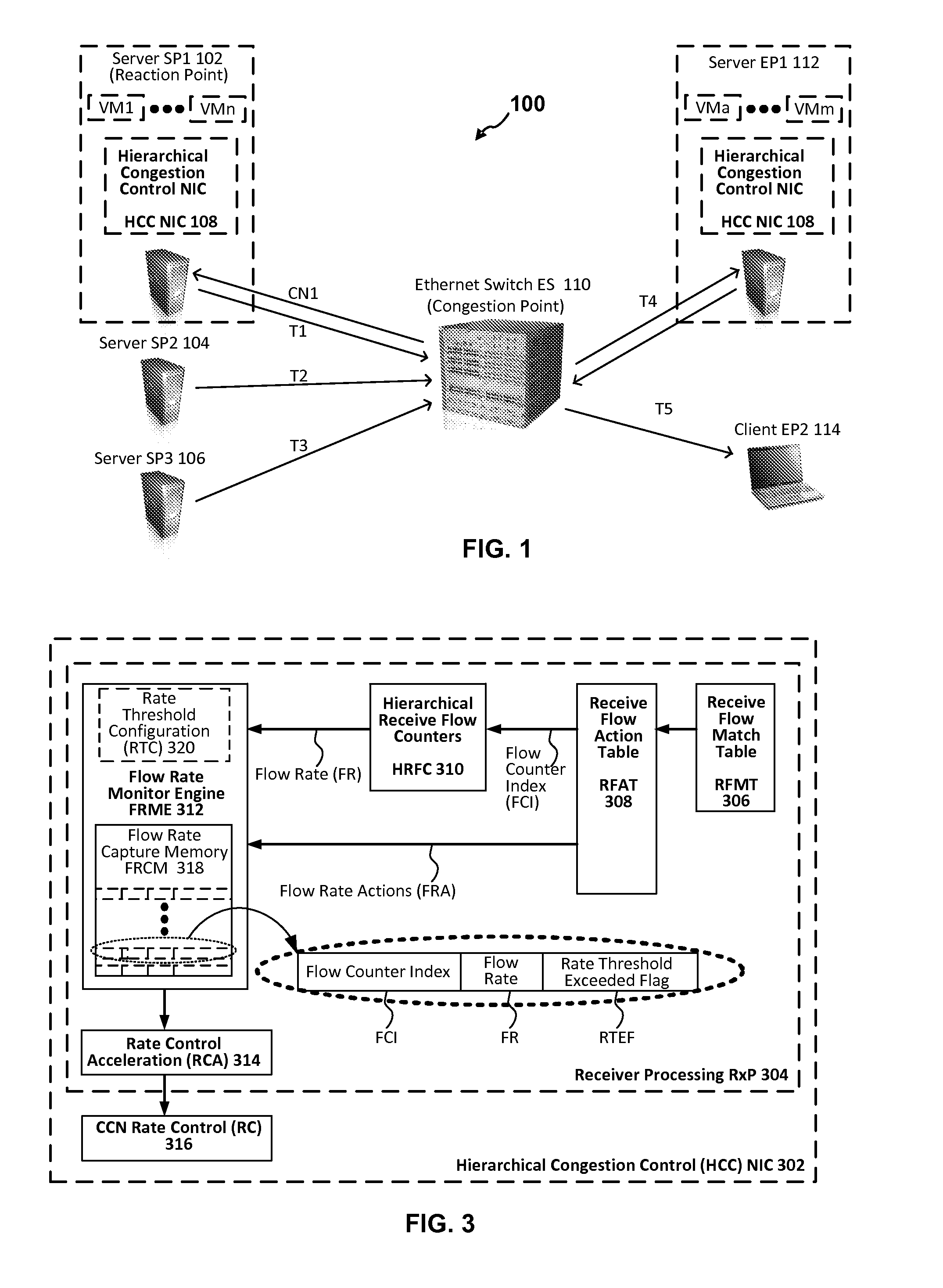
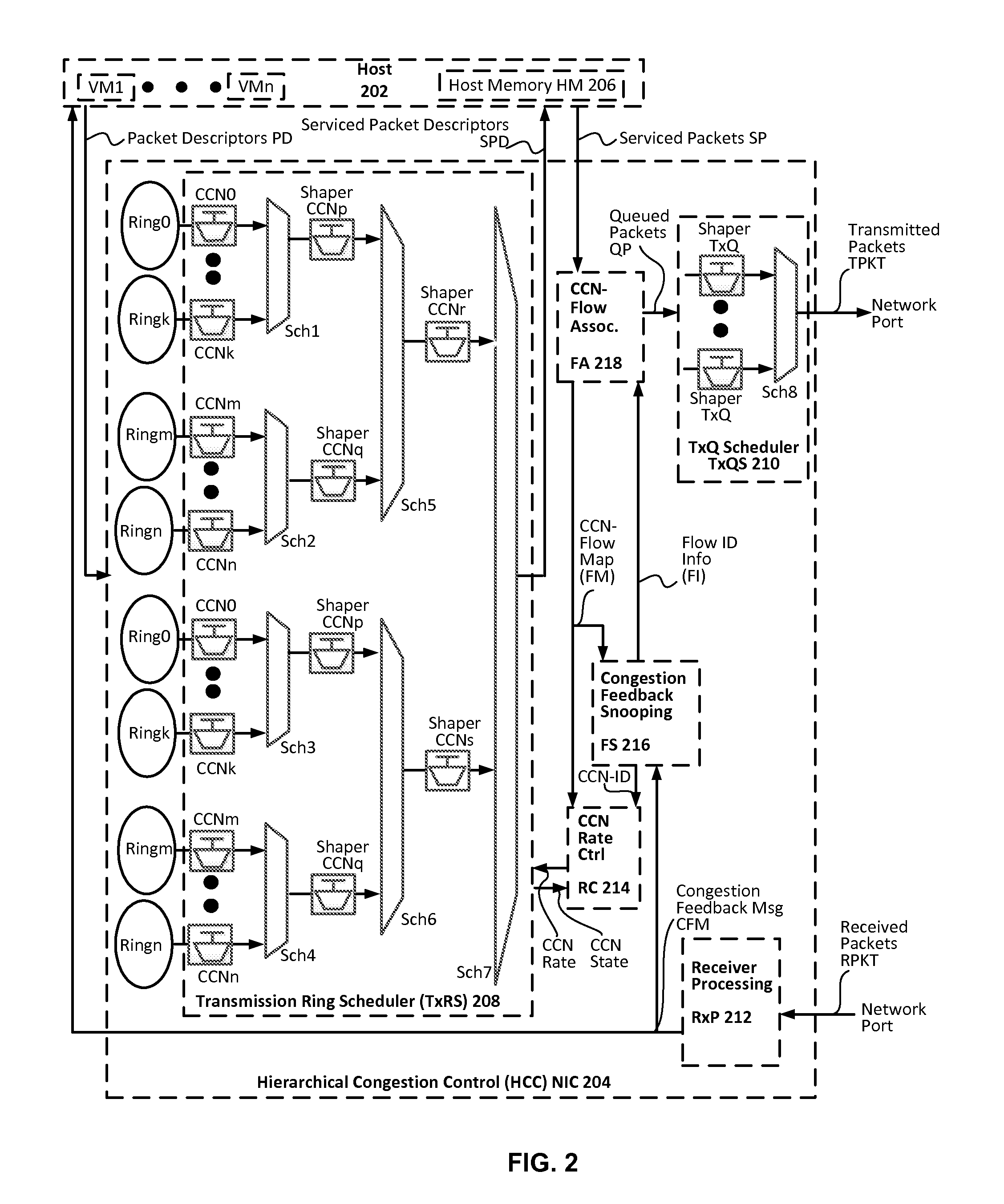
Hierarchical congestion control with congested flow identification hardware
ActiveUS20150172193A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsControl flowTraffic capacity
Hierarchical congestion identification and control hardware supports multi-level congestion control at flow, tenant and virtual machine (VM) levels. Hardware implementation expedites response to congestion notifications and frees-up processor bandwidth. A hierarchy of transmit shapers in a transmit ring scheduler isolate rate adjustments for flows, tenants and VMs. The hierarchy of shapers provide a hierarchy of congestion control nodes to control flows and aggregate flows. Hardware quickly associates congested flows with shapers before or after receiving a congestion notification. The associations may be used by any flow control algorithm to selectively rate-control shapers to control flow rates. Shaper associations and configured states, scheduler configuration, congestion states, thresholds and other flow information may be stored and monitored to filter data flows that need attention and to raise alerts at flow, tenant and VM levels. Congestion control occurs fast and without packet modification, queue or ring switching or queue accumulation.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
TCP congestion control based on bandwidth estimation techniques
InactiveUS7925775B2Reduce loss rateControl congestionError prevention/detection by using return channelMultiple digital computer combinationsTraffic capacityTransport control protocol
Systems and methods are described for controlling congestion, such as within the transport control protocol (TCP) based on bandwidth estimation techniques which provide explicit indications of back-to-back packet traffic. In response to registered back-to-back traffic, receiver-side bandwidth estimation techniques are exploited to enhance the congestion control behavior of TCP based networks. By way of example, a sender marks packets in the header or by changing segment size within a packet to indicate whether the packet is being sent back-to-back. A receiver utilizes the explicit back-to-back information, optionally in conjunction with other back-to-back packet estimation techniques, when estimating available bandwidth and setting congestion parameters. In addition a mechanism for controlling the length of packet trains is described which is based on modulating the transmission of delayed acknowledgements, such as sending acknowledgements upon receipt of a selected number of packets.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
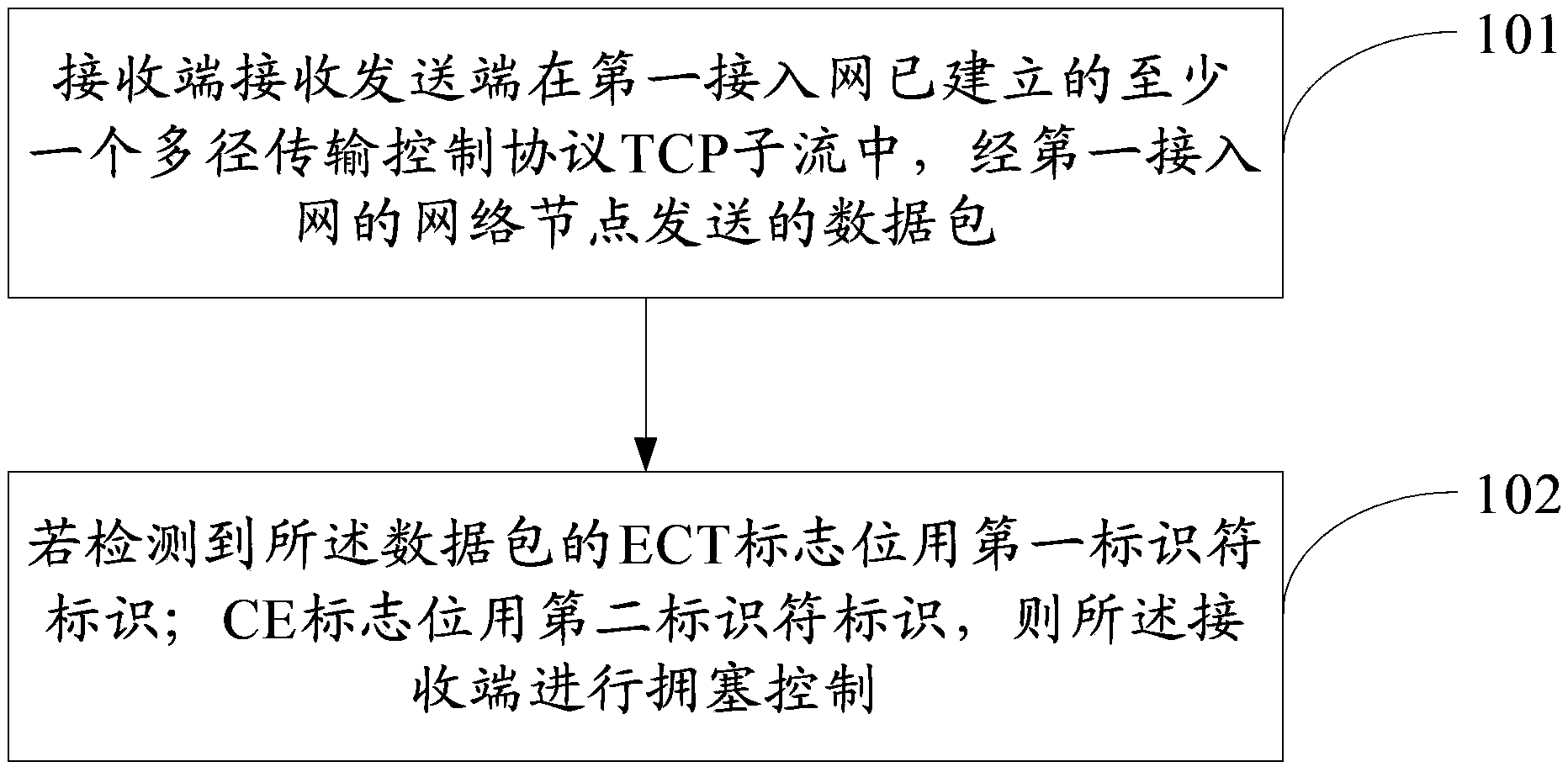
Method, device and system for multi-path TCP congestion control
ActiveCN103581035AImprove data transfer efficiencyNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching networksCongestion windowAccess network
The embodiment of the invention provides a method, device and system for multi-path TCP congestion control, and relates to the field of communication. The method, device and system are used for carrying out congestion control before congestion occurs and improve efficiency of data transmission. The method comprises the steps that a data packet sent by a network node of a first access network in at least one multi-path TCP substream constructed in the first access network by a sending end is received by a receiving end; if it is detected that the data packet supports explicit congestion, a transmission ECT zone bit of an ECN is identified by a first identifier; a CE zone bit is identified by a second identifier, and congestion control is carried out on the receiving end; an ECN feedback ECE zoon bit of the data packet is identified by a third identifier; a CWR zoon bit is identified by a fourth identifier. The method, device and system are suitable for congestion control of networks.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
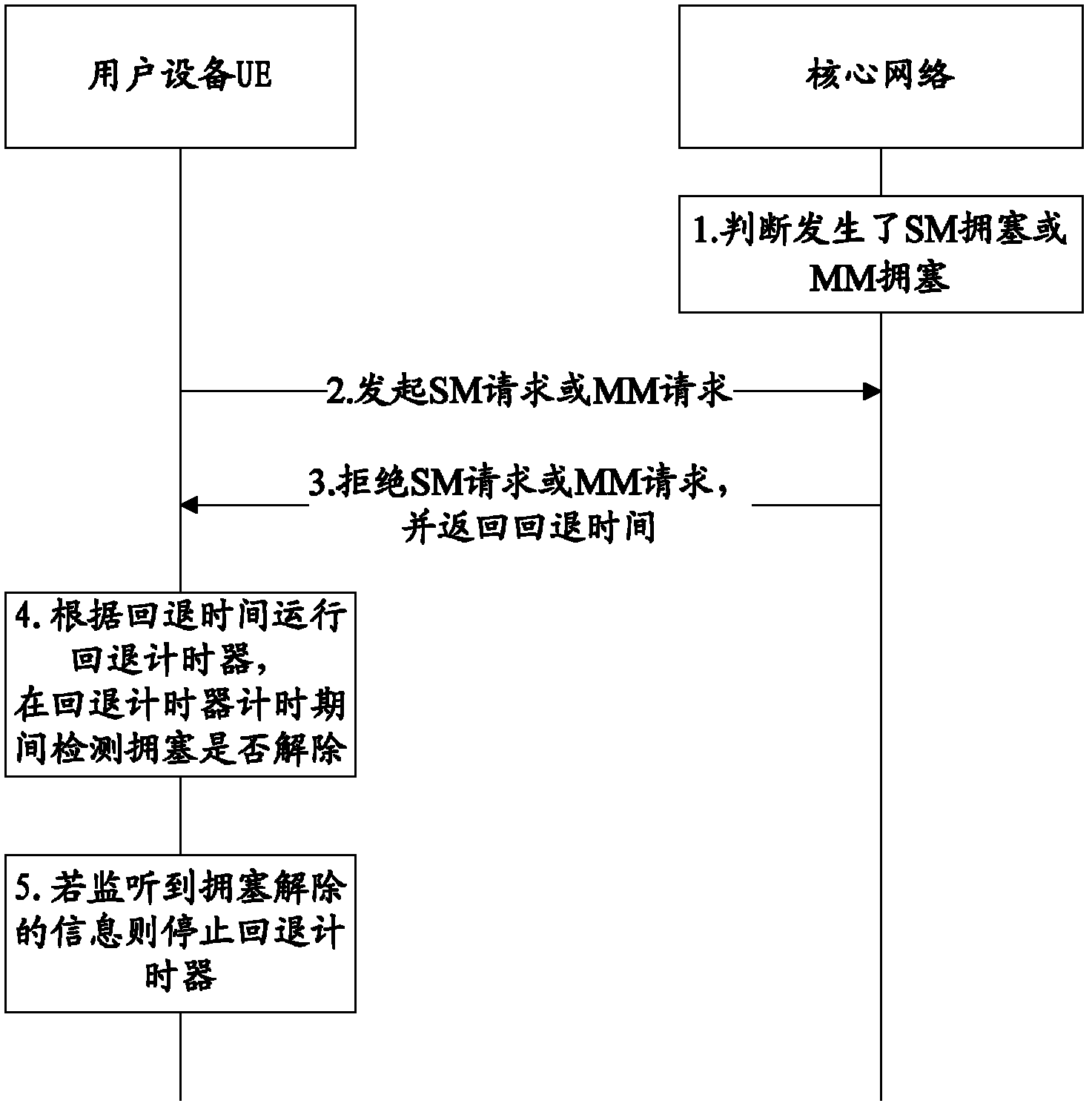
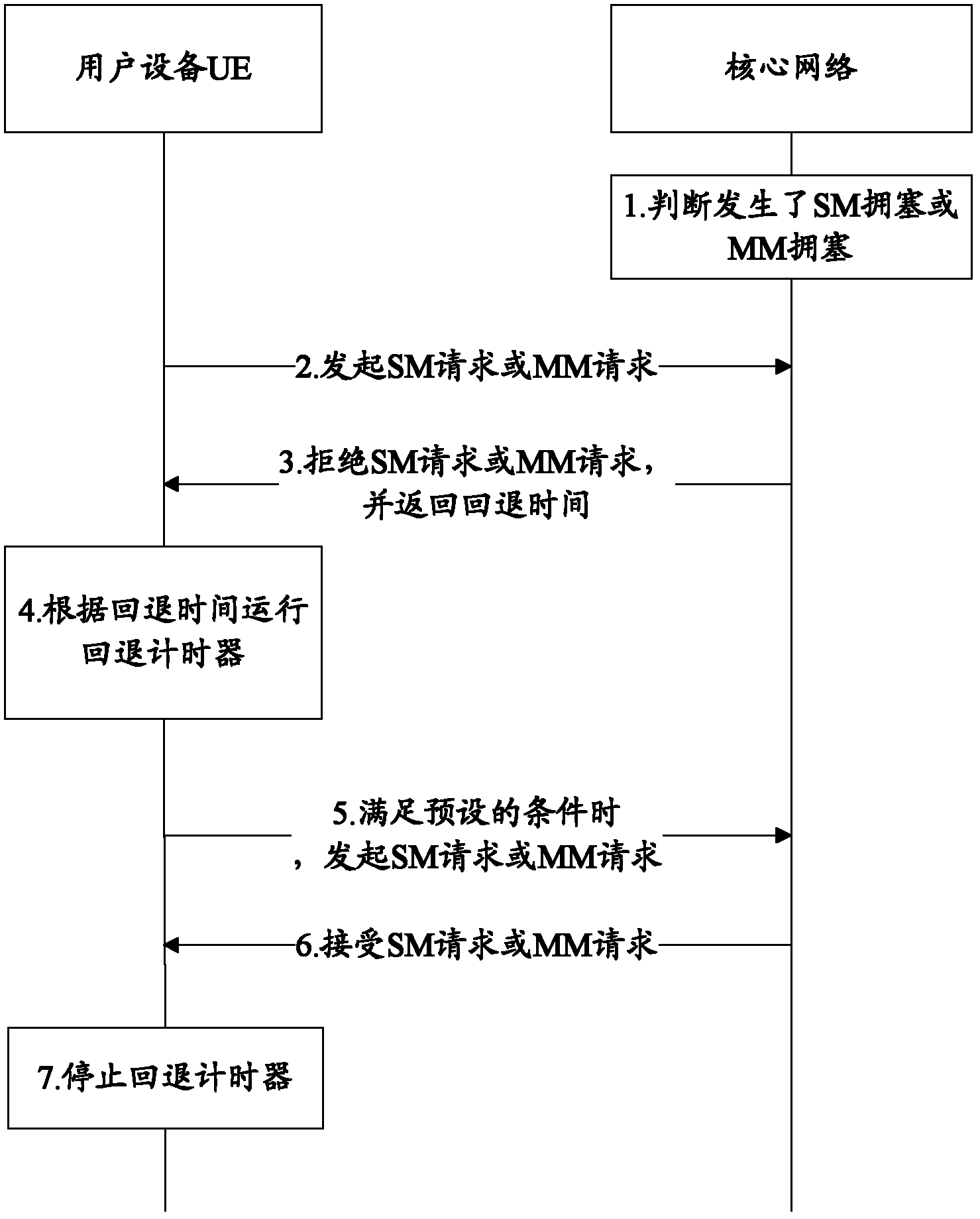
Method and device for congestion control and user equipment
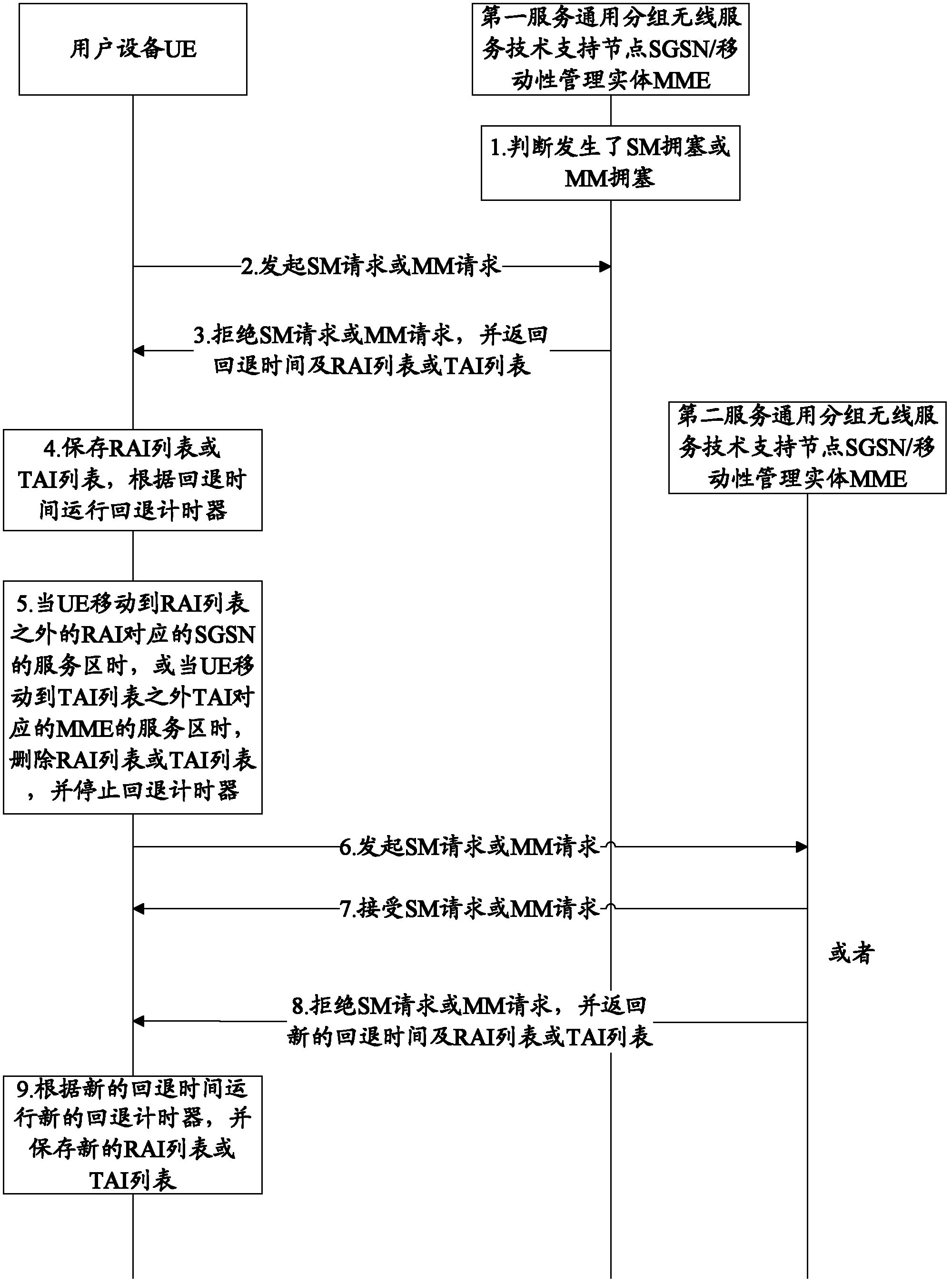
ActiveCN102868634ANetwork traffic/resource managementData switching networksSession managementMobility management
The invention is applicable to the communication field and provides a method and a device for congestion control and user equipment. The method comprises the steps that: the user equipment UE initiates a session management (SM) request or a mobility management (MM) request to a core network; the UE receives a rejection message, containing back-off time, sent by the core network due to SM congestion or MM congestion; and the UE runs a back-off timer according to the back-off time, monitors information of congestion release during the running of the back-off timer, and stops running the back-off timer when the information of congestion release is monitored. According to the invention, the UE monitors information of SM congestion release or MM congestion release during the running of the back-off timer so that the UE can timely acquire the information of network congestion release.
Owner:GLOBAL INNOVATION AGGREGATORS LLC
Dynamically optimized transport system
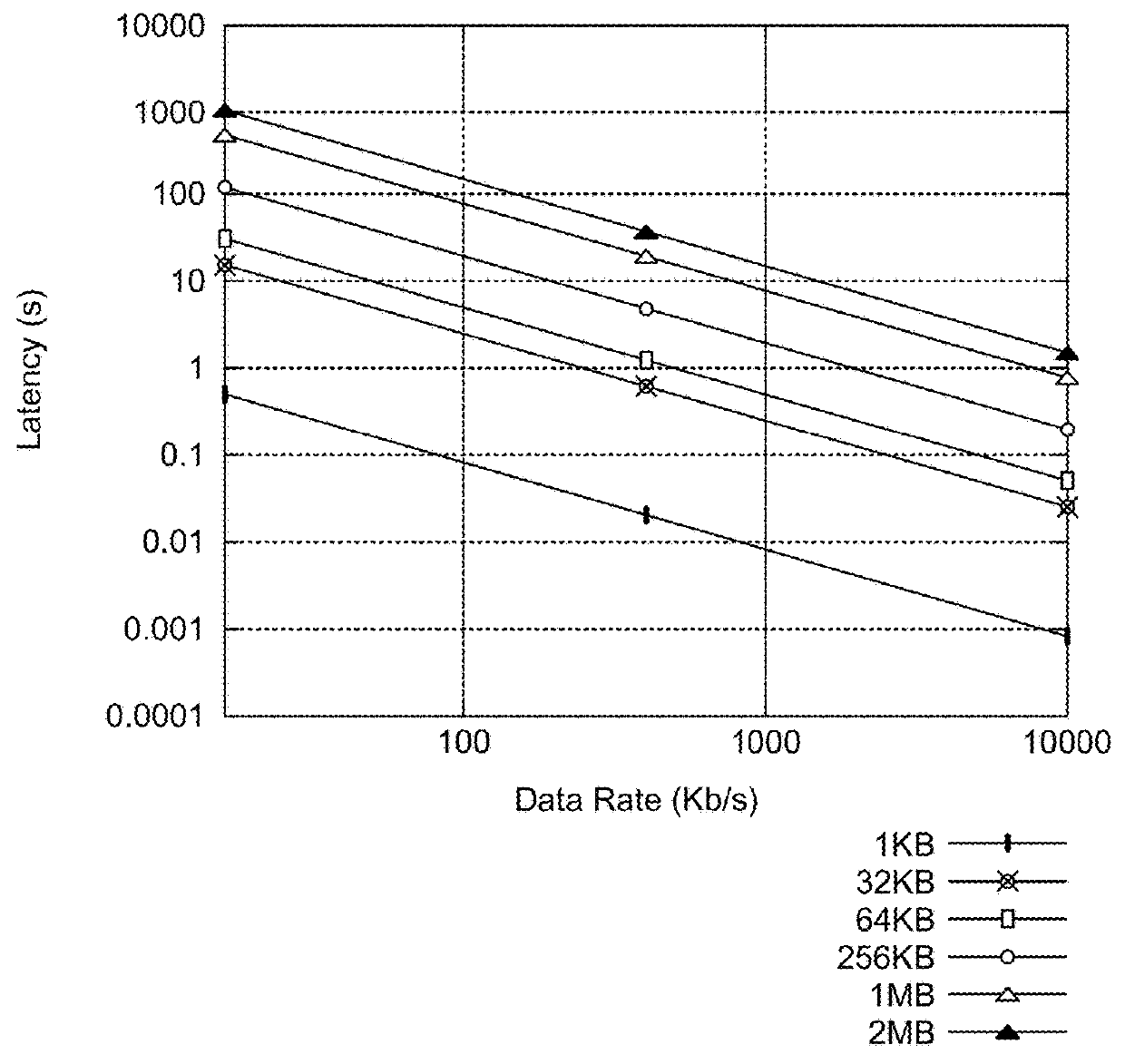
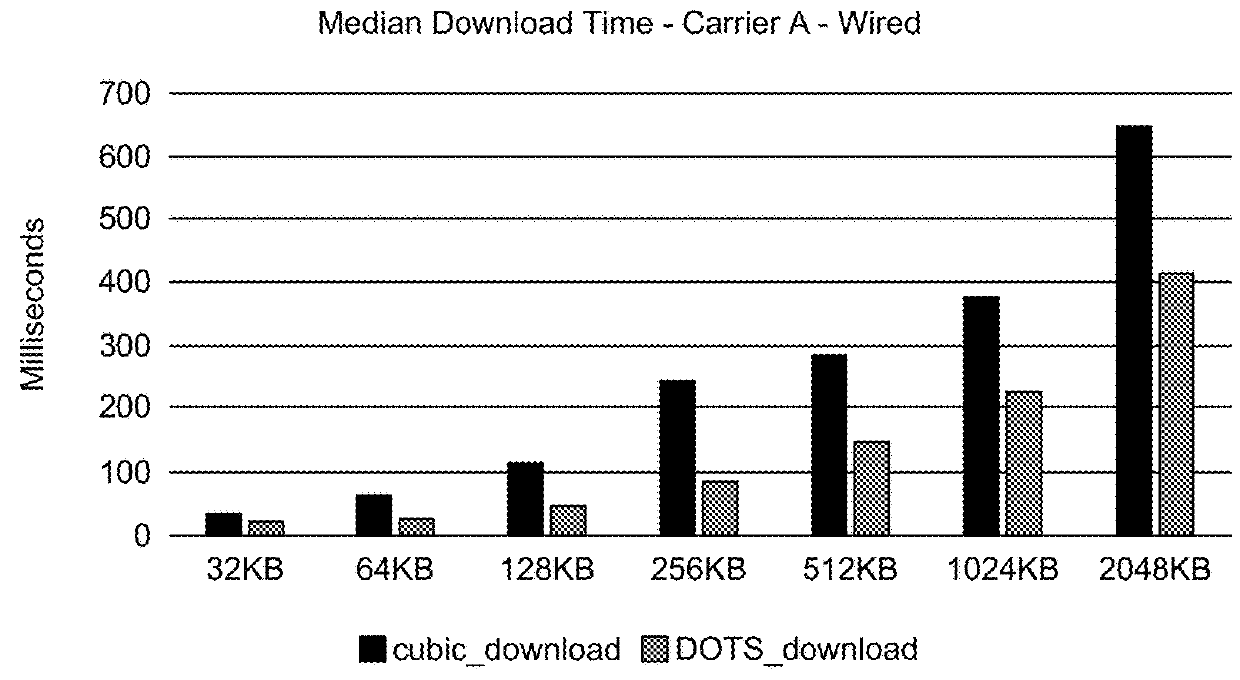
InactiveUS10043137B1Easy to operateSpeed maximizationWeb data indexingMachine learningCongestion windowTransport system
A congestion control mechanism is described that is specifically designed to enhance the operation of TCP communication sessions for the delivery of web content. The congestion control mechanism dynamically adjusts the size of the congestion window in a manner that maximizes the speed of content delivery for web page requests in a cellular network. The dynamic window size adjustments, including the initial congestion control window size, are adaptive, changing as cellular network conditions change, and in a manner that is not possible with conventional TCP congestion control mechanisms that were not explicitly designed to accelerate content in cellular networks. The congestion control mechanism also learns from previous experience with a particular end user device address and network, and applies its learning to set its initial values and subsequent behavior to more optimal levels for the particular end user device and network.
Owner:NUUBIT INC
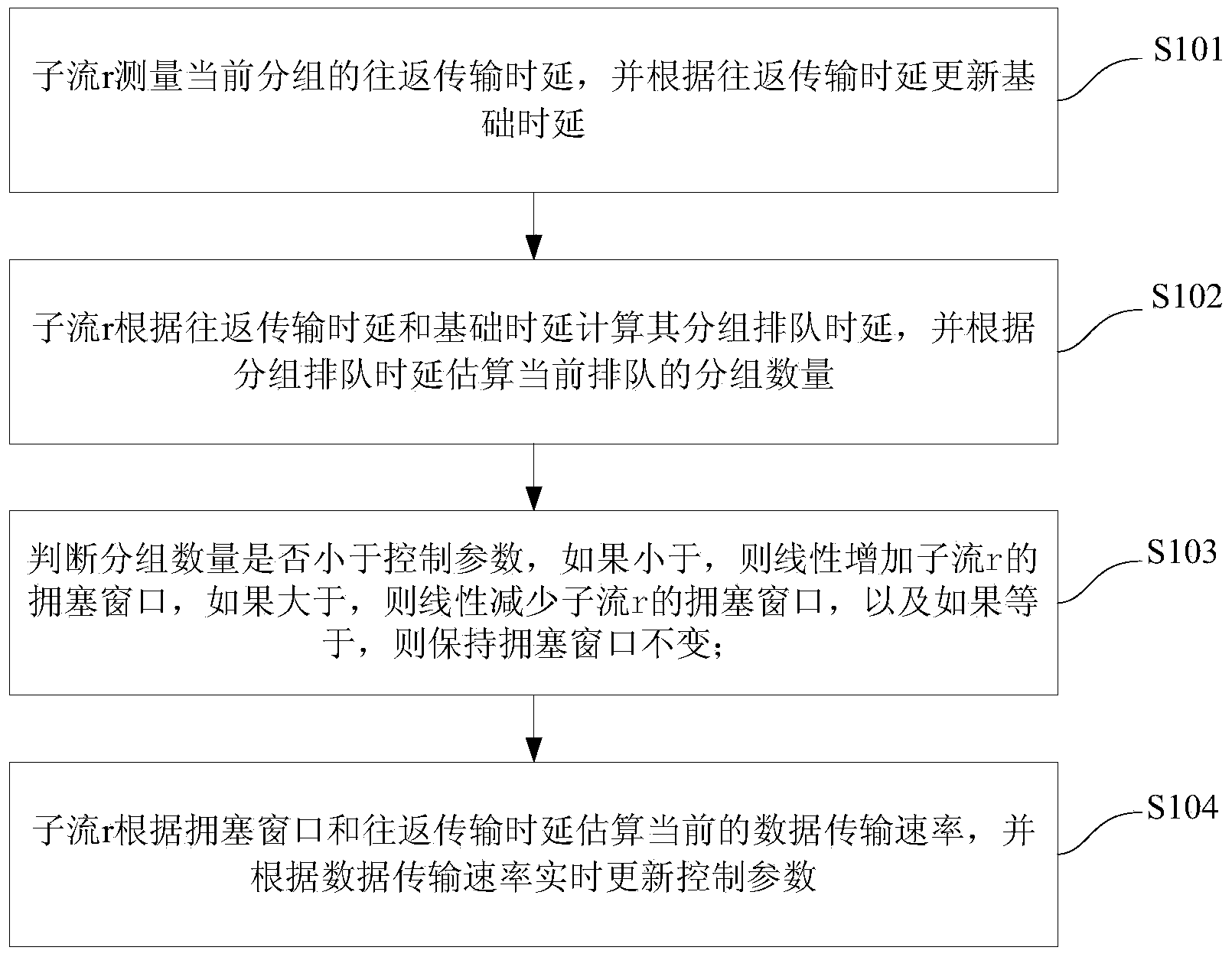
Multi-path TCP congestion control method based on packet transmission delay
InactiveCN103888367AReduce computing costLoad balancingData switching networksCongestion windowGranularity
The invention provides a multi-path TCP congestion control method based on packet transmission delay. The method includes the following steps that round-trip transmission delay rttr of a current packet is measured through substream r, and a base delay base RTTr is updated according to the rttr; the queuing delay qr of packets is calculated through the substream r according to the rttr and the base RTTr, and the number diffr of the packets queuing currently is estimated according to the qr; whether the diffr is smaller than a control parameter alpha r is judged, if the diffr is smaller than the alpha r, congestion windows cwndr of the substream r are increased linearly, if the diffr is larger than the alpha r, the congestion windows cwndr of the substream r are reduced linearly, and if the diffr is equal to the alpha r, the congestion windows cwndr remain unchanged; the current data transmission rate is estimated by means of the substream r according to the cwndr and the rttr, and the control parameter alpha r is updated in real time according to the data transmission rate. The method has the advantages that calculation cost is low, load balance granularity is small, compatibility is high and expansibility is high.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com