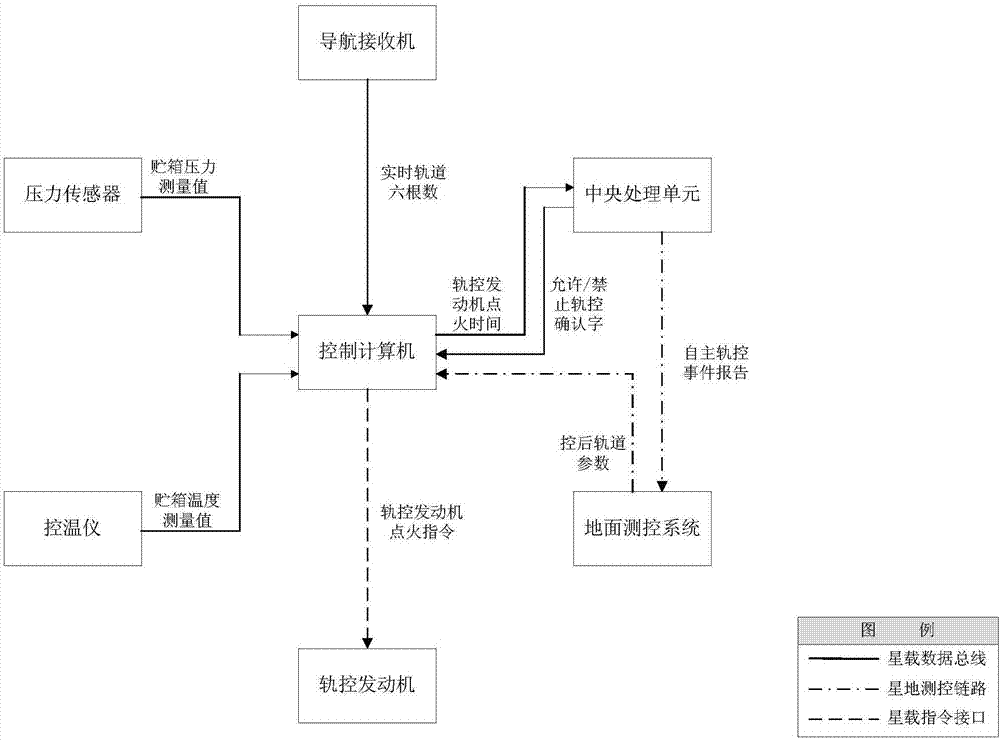
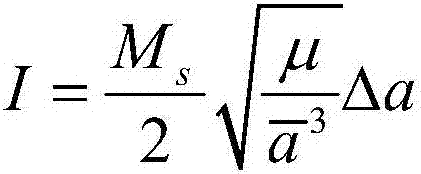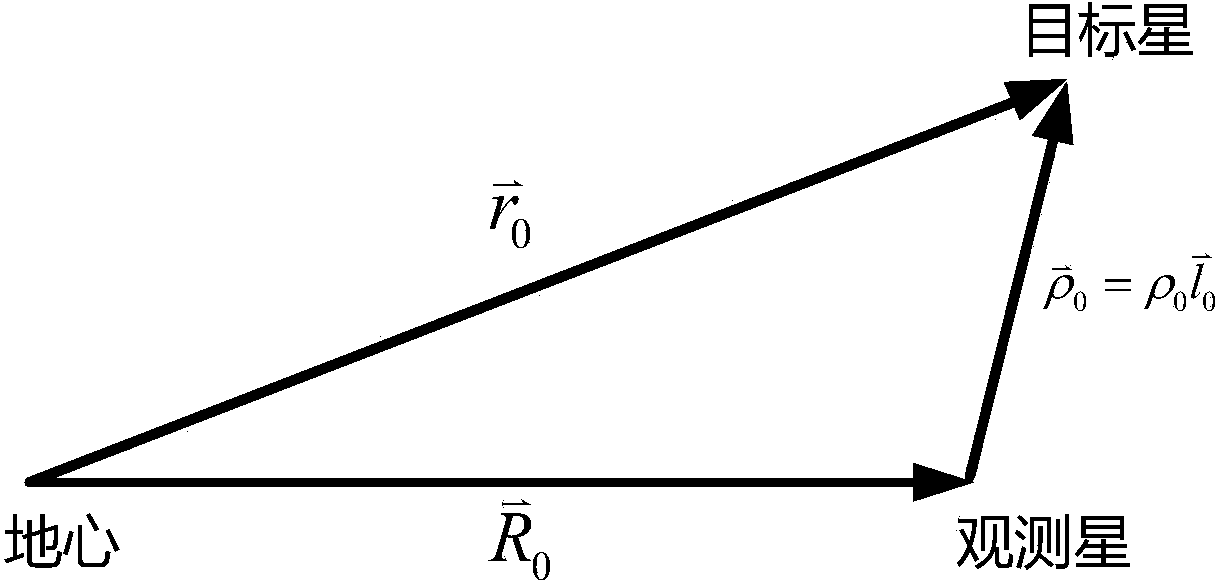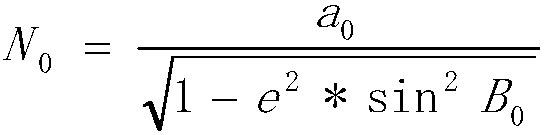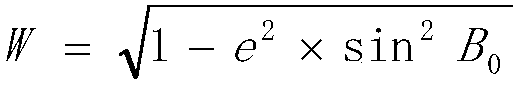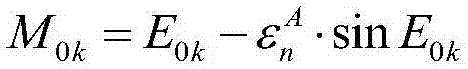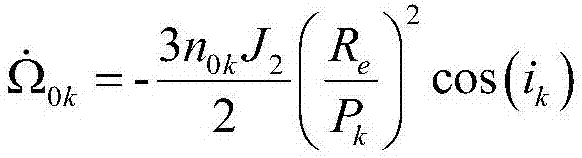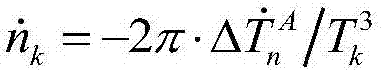Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
77 results about "Semi-major axis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
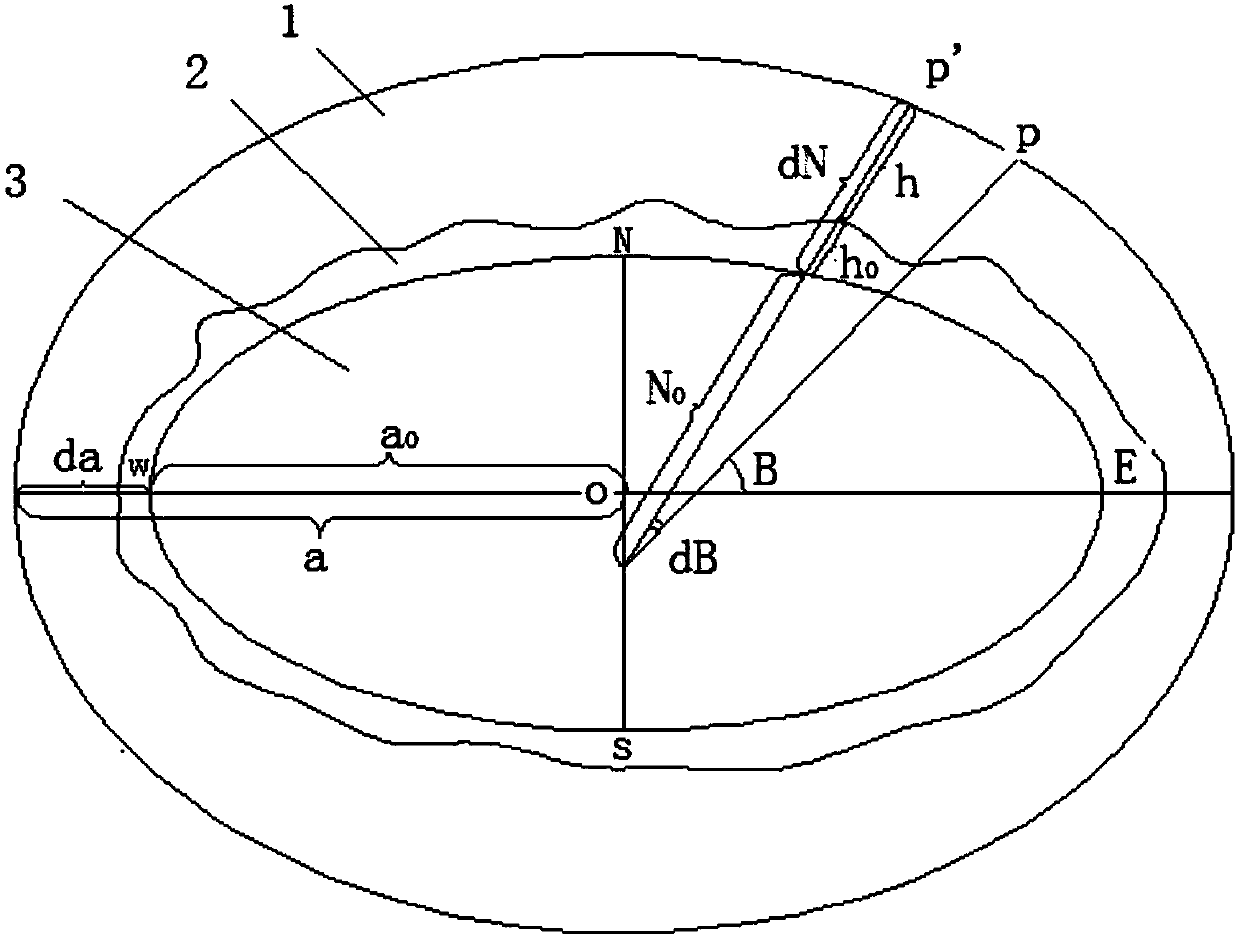
In geometry, the major axis of an ellipse is its longest diameter: a line segment that runs through the center and both foci, with ends at the widest points of the perimeter. The semi-major axis (more properly, major semi-axis) is one half of the major axis, and thus runs from the centre, through a focus, and to the perimeter. The semi-minor axis (more properly, minor semi-axis) of an ellipse or hyperbola is a line segment that is at right angles with the semi-major axis and has one end at the center of the conic section. For the special case of a circle, the lengths of the semi-axes are both equal to the radius of the circle.
Method and a system for launching satellites on non-coplanar orbits, making the use of gravitational assistance from the moon
InactiveUS6059233AMinimize energy usageAccurate acquisitionLaunch systemsArtificial satellitesEllipseAerogravity assist
A first satellite is placed practically directly by a launcher on a first final orbit. A second satellite is placed on the same launcher is initially transferred to a highly elliptical waiting orbit whose semi-major axis points to intercept the torus formed by the sphere of influence of the moon on its orbit, and then during a maneuver at the perigee of the highly elliptical orbit, the second satellite is transferred to lunar transfer orbit. Changes in the perigee altitude and the inclination of an intermediate orbit on which the second satellite is to be found are obtained mainly by gravitational reaction in the sphere of influence of the moon, and during a last maneuver, the second satellite is placed on a final orbit having orbital parameter values that are quite different from those of the orbital parameters of the first final orbit.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
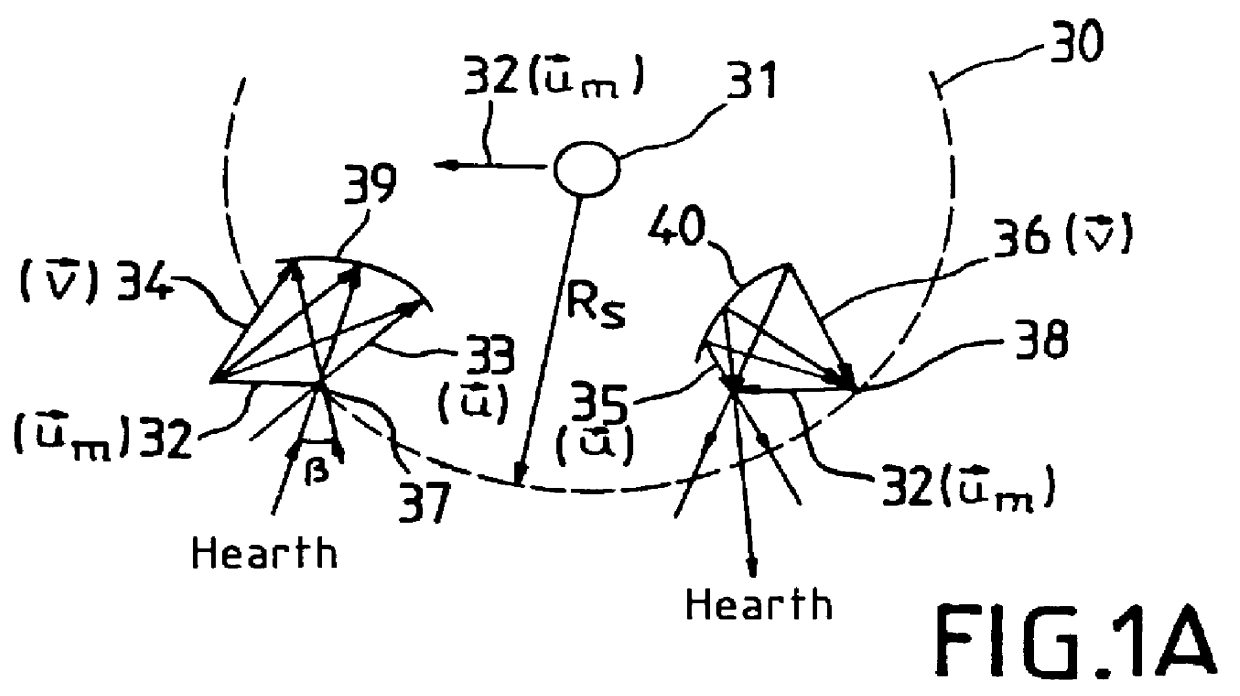
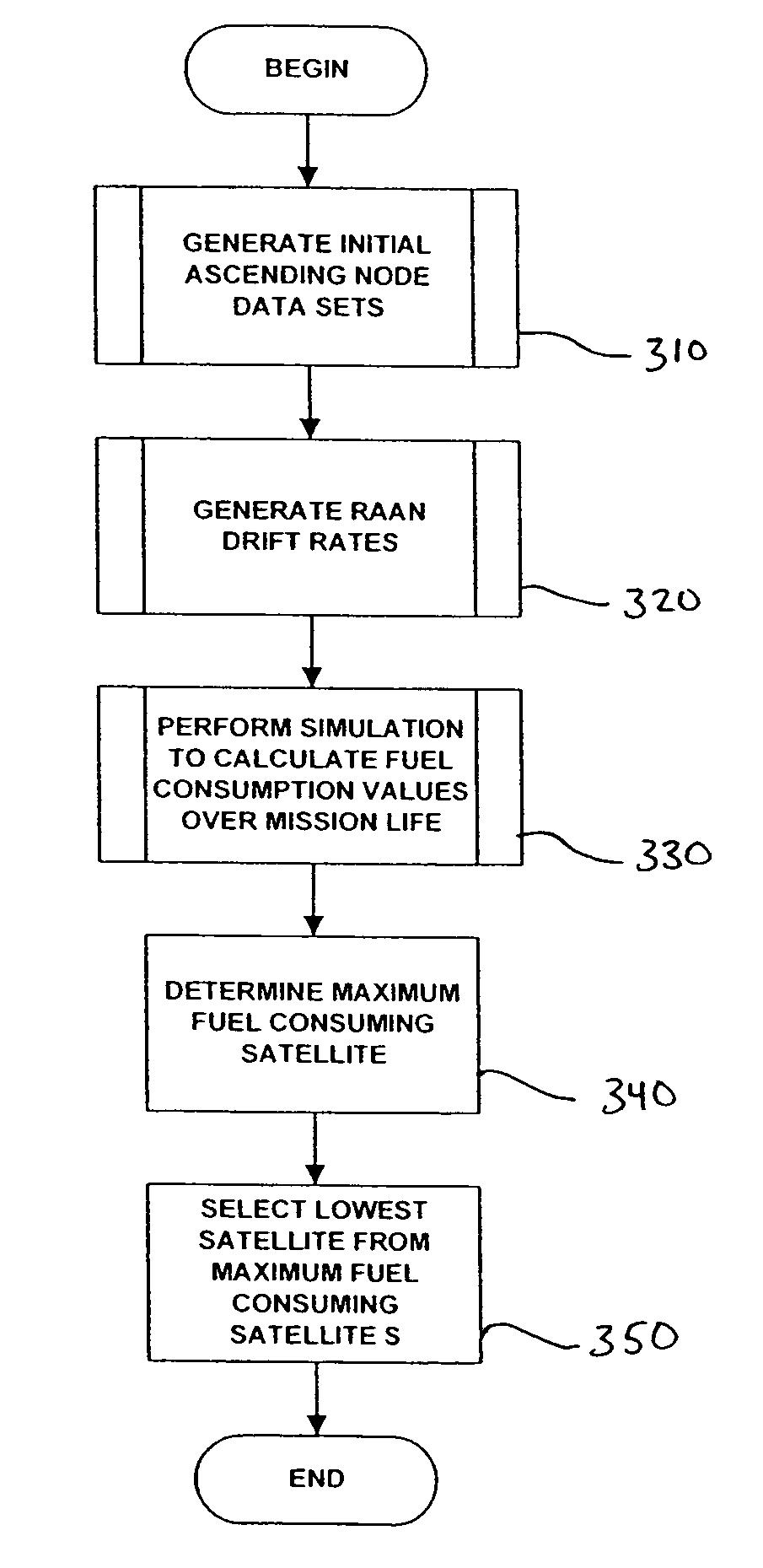
Stationkeeping optimization for inclined elliptical satellite orbit constellations
ActiveUS7720604B1Reduce fuel consumptionMinimum consumptionInstruments for comonautical navigationCosmonautic partsEllipseSatellite orbit
A satellite constellation optimized for stationkeeping fuel consumption is provided. The satellite constellation includes a plurality of satellites, each satellite having a corresponding inclined elliptical orbit, each orbit having an initial right ascension of ascending node (“RAAN”) value, a RAAN drift rate, a semi-major axis, an eccentricity, an argument of perigee and an inclination. Each satellite has a fuel consumption value required to maintain the RAAN drift rate, the semi-major axis, the eccentricity, the argument of perigee and the inclination of the corresponding orbit. The initial RAAN value and the RAAN drift rate for each orbit correspond to a minimized fuel consumption value for the satellite having the highest fuel consumption value. The initial RAAN value and RAAN drift rate may be determined by calculating, for each possible data combination of an initial RAAN value for each orbit and a RAAN drift rate for the constellation, a fuel consumption value for each satellite in the constellation, and selecting, from the fuel consumption values thus determined, the data combination corresponding to a lowest fuel consumption for a highest fuel-consuming satellite.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
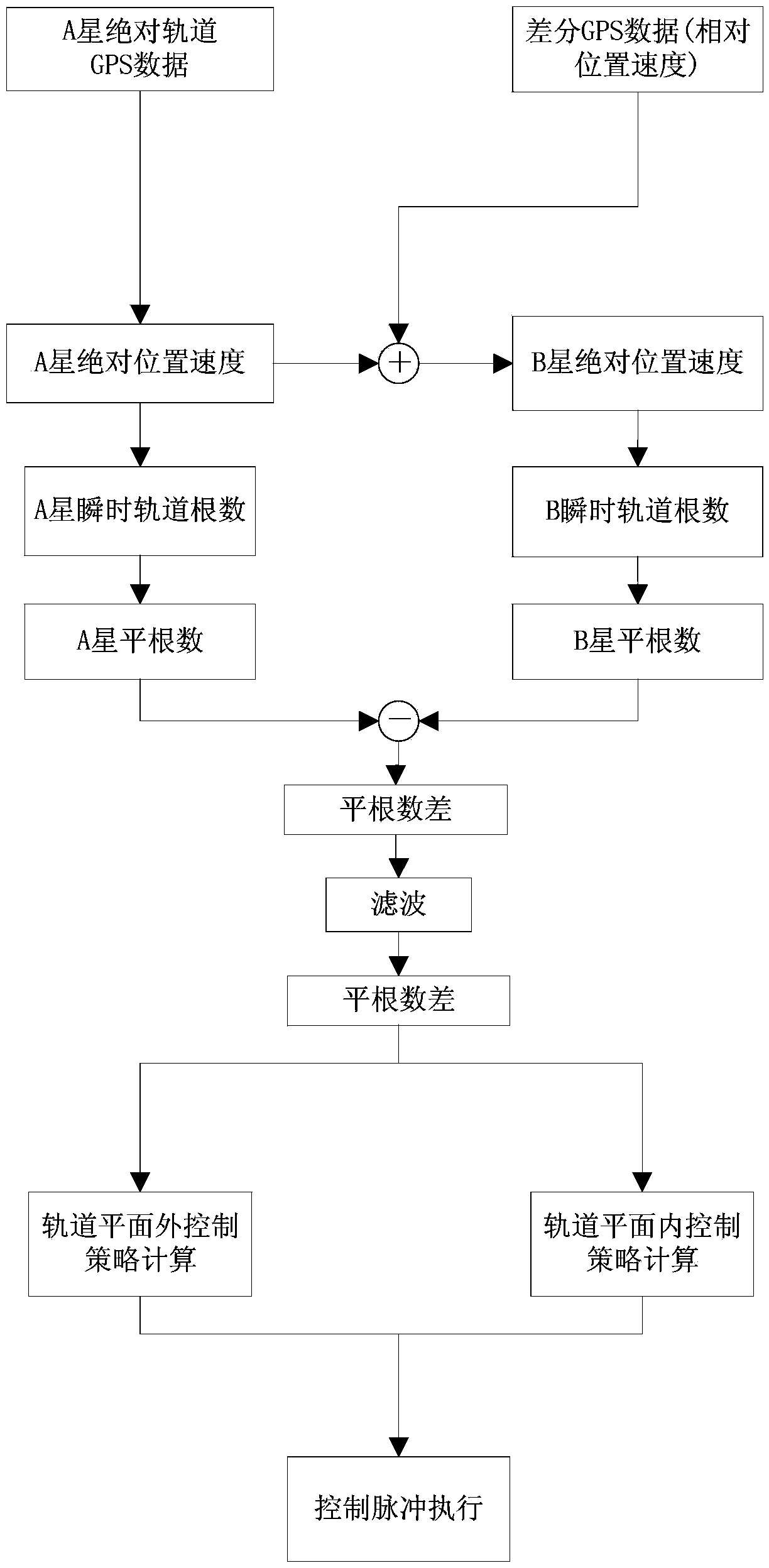
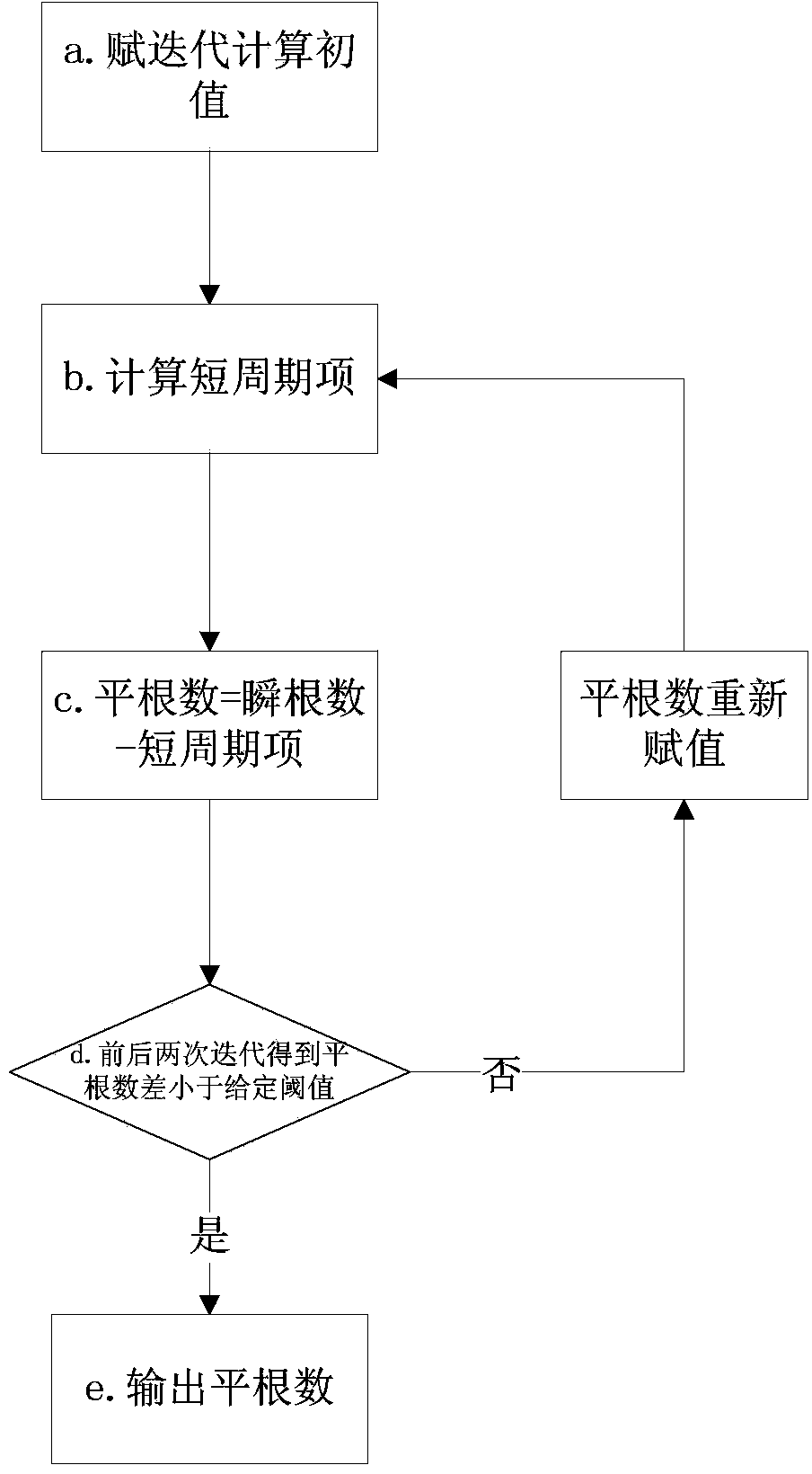
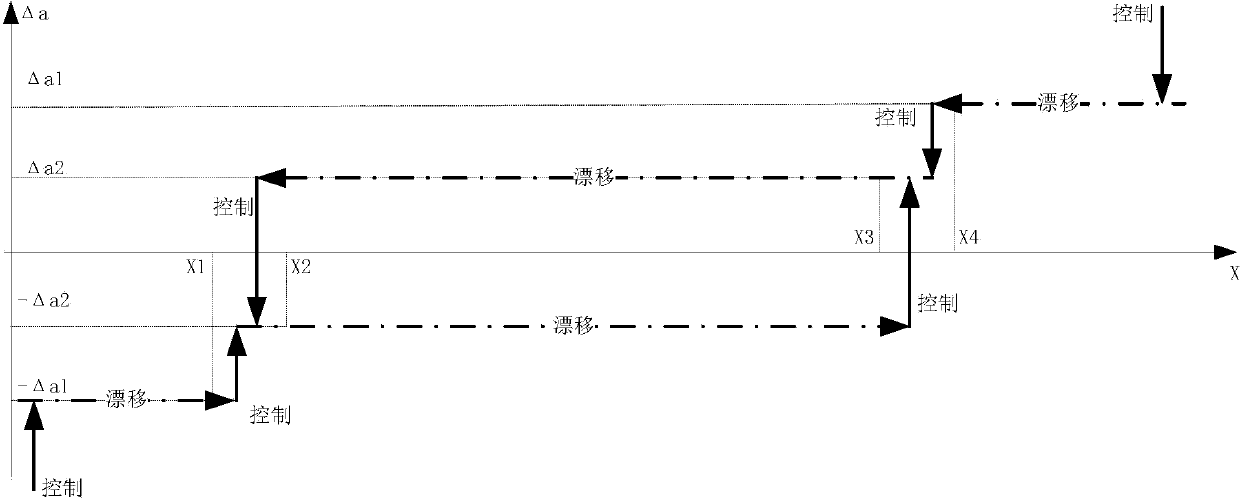
Autonomous formation flight control method for satellites
ActiveCN104142686ALong-term change controlDrift speed is smallAttitude controlRelative orbitRelative motion
The invention discloses an autonomous formation flight control method for satellites. Formation flight control is carried out through relative orbit mean elements, and due to the fact that a long-term trend of relative movement between the satellites is accurately reflected through the relative orbit mean elements, long-term changes of the relative movement can be well controlled with the method. The autonomous formation flight control method is characterized in that a mean semi-major axis difference control strategy in an orbital plane is designed, the mode that control targets are set in a partitioned mode is adopted, and it is guaranteed that the drift speeds within control zones are low; when outside the control zones, the control targets can return to the control zones at high speeds. According to the autonomous formation flight control method, due to the mode that small-pulse air injecting is used for orbit control multiple times, and a momentum wheel is used for posture control, influences of posture air injection control on orbits are reduced, and the orbit control execution accuracy is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
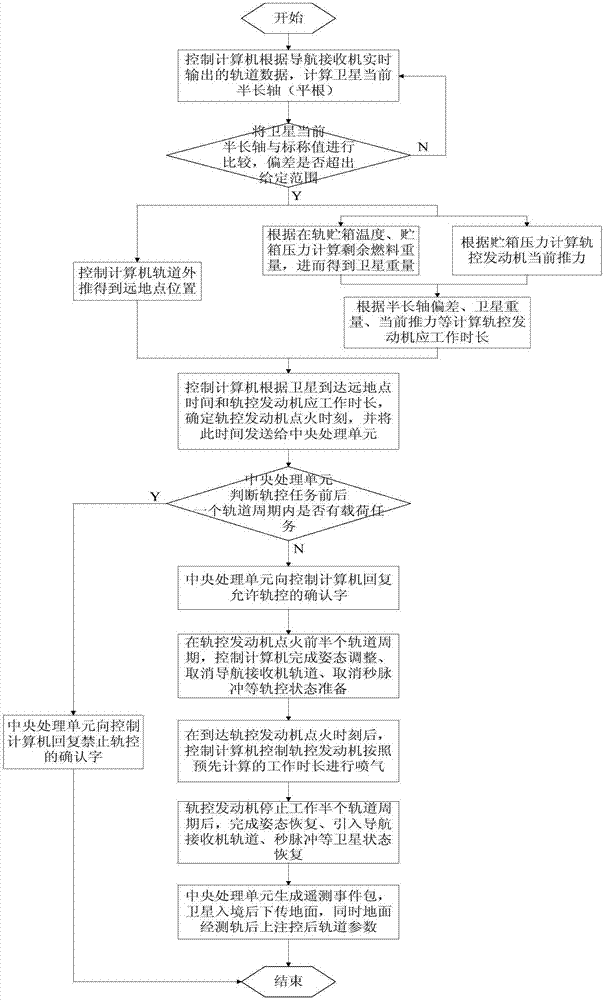
Autonomous orbit control method for low-orbit remote sensing satellite
ActiveCN107031868AFlexible useImprove efficiencyCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusNatural satelliteControl impulse
The invention discloses an autonomous orbit control method for a low-orbit remote sensing satellite. The autonomous orbit control method comprises the following steps that firstly, the deviation between a current orbit semi-major axis and a nominal orbit semi-major axis is calculated on orbit in real time; secondly, the length of working time of an orbit-control engine is acquired according to orbit-control impulse, an apogee position is acquired through orbit extrapolation calculation autonomously, the time that the satellite arrives at the apogee position is taken as an orbit-control center moment, and the moment that the engine begins to ignite and the moment of brennschluss are acquired according to the length of working time of the orbit-control engine and the orbit-control center moment; and thirdly, the orbit-control engine is controlled to ignite autonomously according to the moment that the engine begins to ignite in the second step, then the orbit-control engine is controlled to conduct brennschluss autonomously according to the brennschluss moment in the second step, and finally the low-orbit remote sensing satellite completes state recovery. According to the autonomous orbit control method for the low-orbit remote sensing satellite, on-orbit autonomous compensation of the orbit semi-major axis error can be achieved on the condition without ground station support, the ground operation control cost of the satellite is lowered, and abilities of autonomous management and autonomous operating of the satellite are promoted.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
Gravity-gradient-invariant-based method for estimating orbit element
ActiveCN107065025AStrong autonomyImprove anti-interference abilityGravitational wave measurementState parameterDecomposition
The invention provides a gravity-gradient-invariant-based method for estimating an orbit element. The method comprises: step one, carrying out preparation work; step two, carrying out decomposition of an ideal gravity gradient tensor under an east-noth-up (ENU) coordinate system and obtaining feature values; step three, solving decomposition of a measuring epoch J2 model gravity field tensor under the ENU coordinate system and obtaining feature values; step four, solving all measuring epochs r and phi by using feature values of a J2 gravity gradient matrix; step five, calculating an initial orbit element by using the r and phi; and step six, carrying out orbit element smoothing. Therefore, with utilization of the gravity gradient matrix invariant information measured during the satellite operating process, a geometrical distance between the satellite and the earth's core and the latitude of the earth's core are obtained by iterative solution; a measurement equation that uses a semi-major axis, an eccentricity ratio, an orbit inclination angle, a perigee depression angle, and a true anomaly in an orbital element as state parameters is provided by using an obtained data as an observed quantity; and a perturbation kinetic equation of the orbital element is introduced innovatively and five orbital elements are estimated by using a batching least square method. The gravity-gradient-invariant-based method has advantages of high autonomous degree, high anti-interference capability, and low building cost and the like and has advantages that the traditional method does not have in the deep space exploration field.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Satellite orbit maintenance and control method based on two lines of radicals
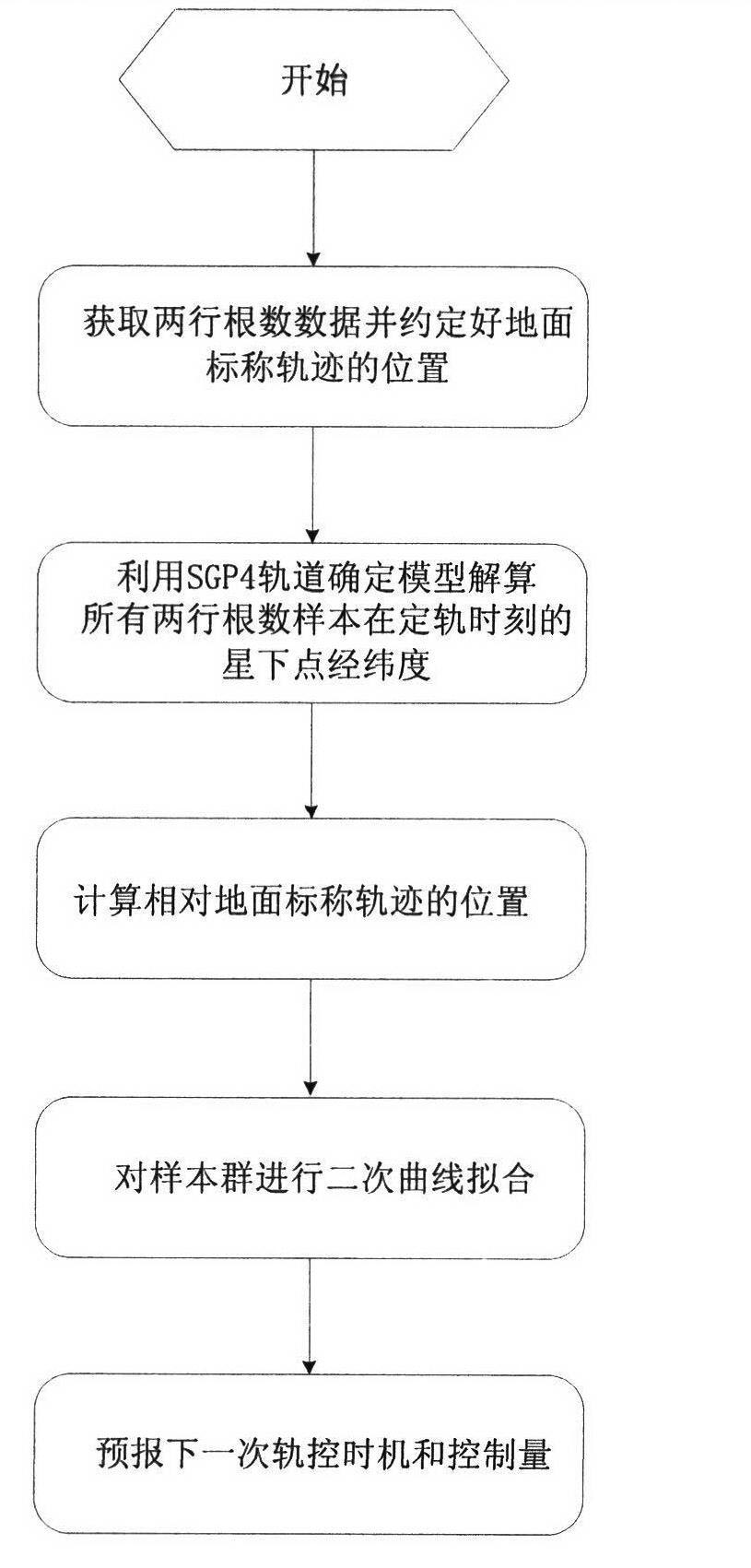
ActiveCN102591343AGood serviceFacilitate maintenance of control forecastsPosition/course control in two dimensionsUltrasound attenuationGeographical latitude
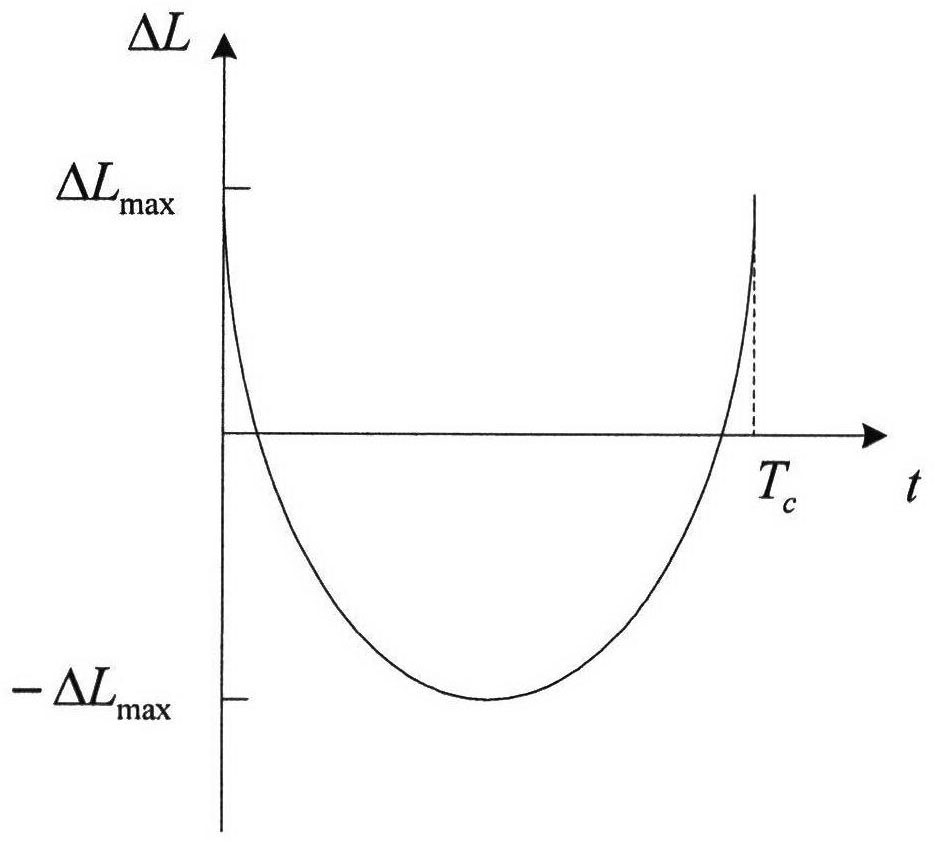
The invention relates to a satellite orbit maintenance and control method based on two lines of radicals, which comprises the following steps of: calculating two lines of radical data disclosed by a satellite by utilizing a SGP4 orbit determination model, calculating and obtaining a geographical latitude and a geographical longitude of a sub-satellite point of the satellite and comparing with an agreed ground nominal track. Through taking the duration of a first sample opposite to an orbit epoch moment as an independent variable and taking the ground track distance difference as a variable, all samples are subjected to quadratic curve fitting by using an average method; the difference delta at between an actual value of a satellite orbit semi-major axis and a nominal value by a latest sample moment as well as the average attenuation rate of the satellite orbit semi-major axis within the time interval of the sample are calculated and obtained through a fitting polynomial coefficient; and finally, the next orbit control time Tc as well as the control quantity delta af required to be used are predicted and obtained by utilizing a fitted secondary curve and an allowable drift range [-delta Lmax and delta Lmax] to ensure that the position of an actual ground track within the satellite next drift period opposite to a ground nominal track is within the allowrable drift range.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
Low-earth-orbit satellite orbit designing method for quickly revisiting discrete targets
InactiveCN103675832ARapid repeat reconnaissanceClarify requirements for side-looking pointing capabilityArtificial satellitesElectromagnetic wave reradiationHigh latitudeLongitude
Disclosed is a low-earth-orbit satellite orbit designing method for quickly revisiting discrete targets. The method includes (1), determining an inclination angle of a satellite orbit, wherein the inclination angle is not lower than the highest latitude Lmax of a ground target; (2), selecting a round orbit as the satellite orbit, wherein eccentricity ratio is 0; (3), executing a reconnaissance mission according to the ground target, determining a regression cycle of the orbit, utilizing the regression cycle to determine a semi-major axis of the satellite orbit, and then determining height of the orbit; (4), according to corresponding orbit ascending node longitude when sub-satellite points of an orbit ascending section and an orbit descending section of the satellite orbit pass the ground target, respectively determining ideal satellite orbit ascending node longitude of the orbit ascending section and the orbit descending section, performing optimization aiming at enabling the sum of designed satellite orbit ascending node longitude and a difference value of the ideal satellite orbit ascending node longitude of the orbit ascending section and the orbit descending section of the ground target, and determining ascending node longitude of the satellite orbit to be L; (5), utilizing the orbit inclination angle, the round orbit and the eccentricity ratio thereof, the orbit height and the ascending node longitude of the satellite orbit to complete designing of the satellite orbit.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
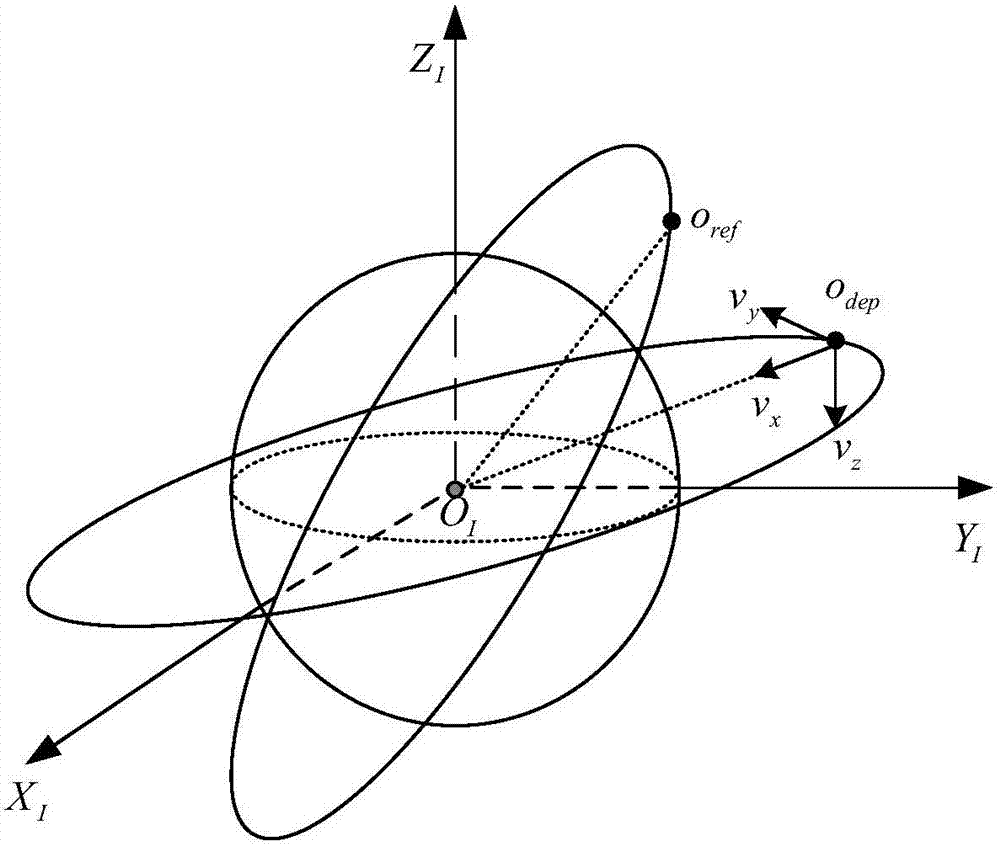
Satellite flying-around formation configuration initialization method under engineering constraint condition
ActiveCN108438255AClear processStrong engineering achievabilityCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusIn planeOut of plane
The invention provides a satellite flying-around formation configuration initialization method under an engineering constraint condition. The satellite flying-around formation configuration initialization method under the engineering constraint condition comprises the steps that (1) formation concomitant satellites are made to gradually approach a formation primary satellite by using natural perturbation; (2) when the situation that an inter-satellite distance is less than the acting distance of an inter-satellite link occurs, a satellite-borne carrier differential GNSS receiver can output measuring data and output a navigation result to carry out in-plane control on the formation concomitant satellites; (3) when the inter-satellite distances are completely less than the acting distances of the inter-satellite links, out-of-plane control is carried out in a prioritized manner; (4) the in-plane control is carried out according to a relative navigation result to further reduce inter-satellite semi-major axis deviation so as to preliminarily form a flying-around formation configuration; and (5) when the inter-satellite distances are less than a threshold, in-plane and out-of-plane parameter combined control is carried out according to the relative navigation result to correct the formation configuration so that the inter-satellite semi-major axis deviation and inter-satellite distance tangential deviation are eliminated to form the final target flying-around formation configuration.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
Tangential low-thrust in-orbit circular orbit calibration method based on (Global Navigation Satellite System) GNSS precise orbit determination
ActiveCN103940431AThe method calibration results are accurateMethod calibration results are reliableInstruments for comonautical navigationApparatus for force/torque/work measurementNODALIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
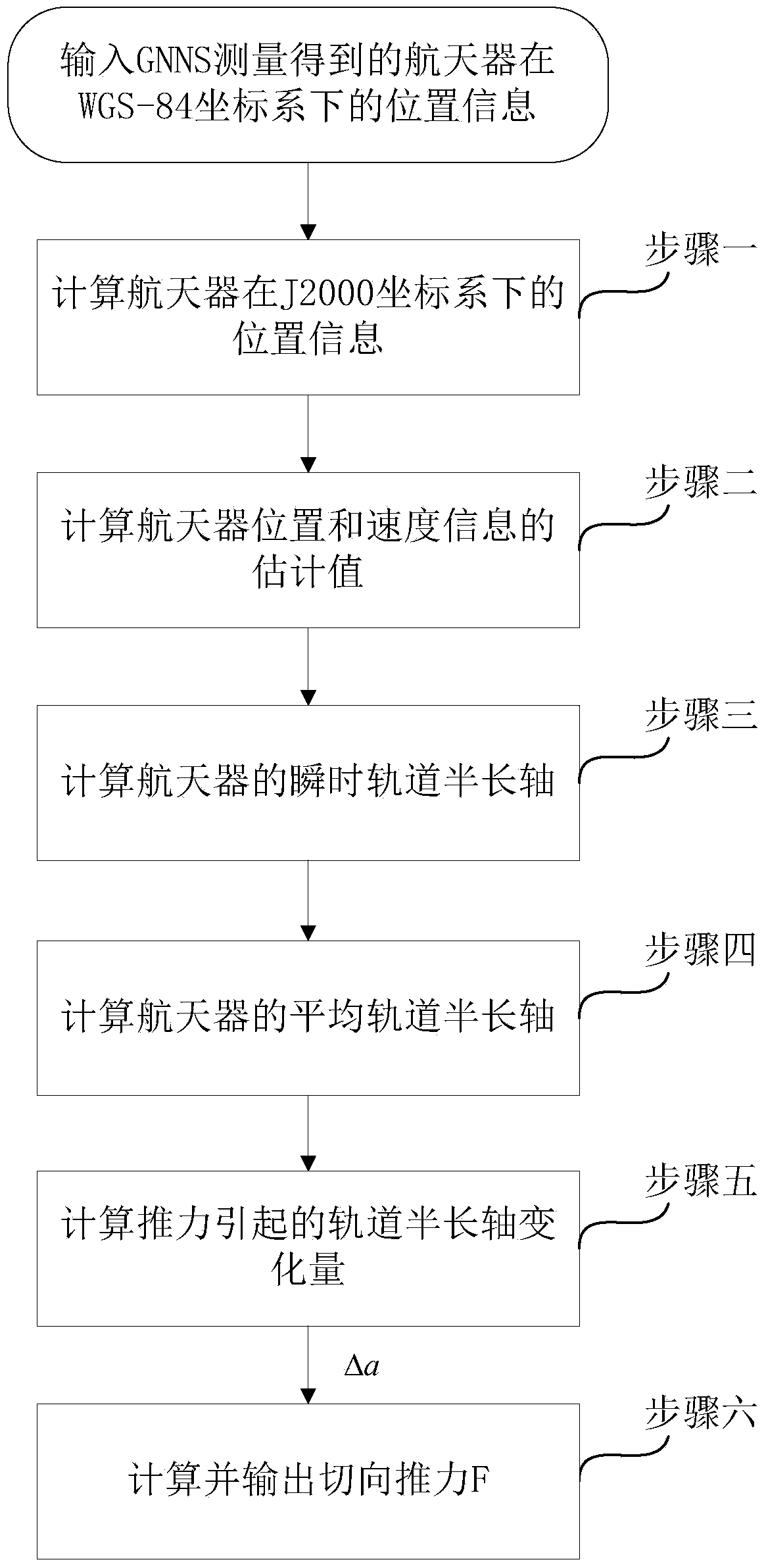
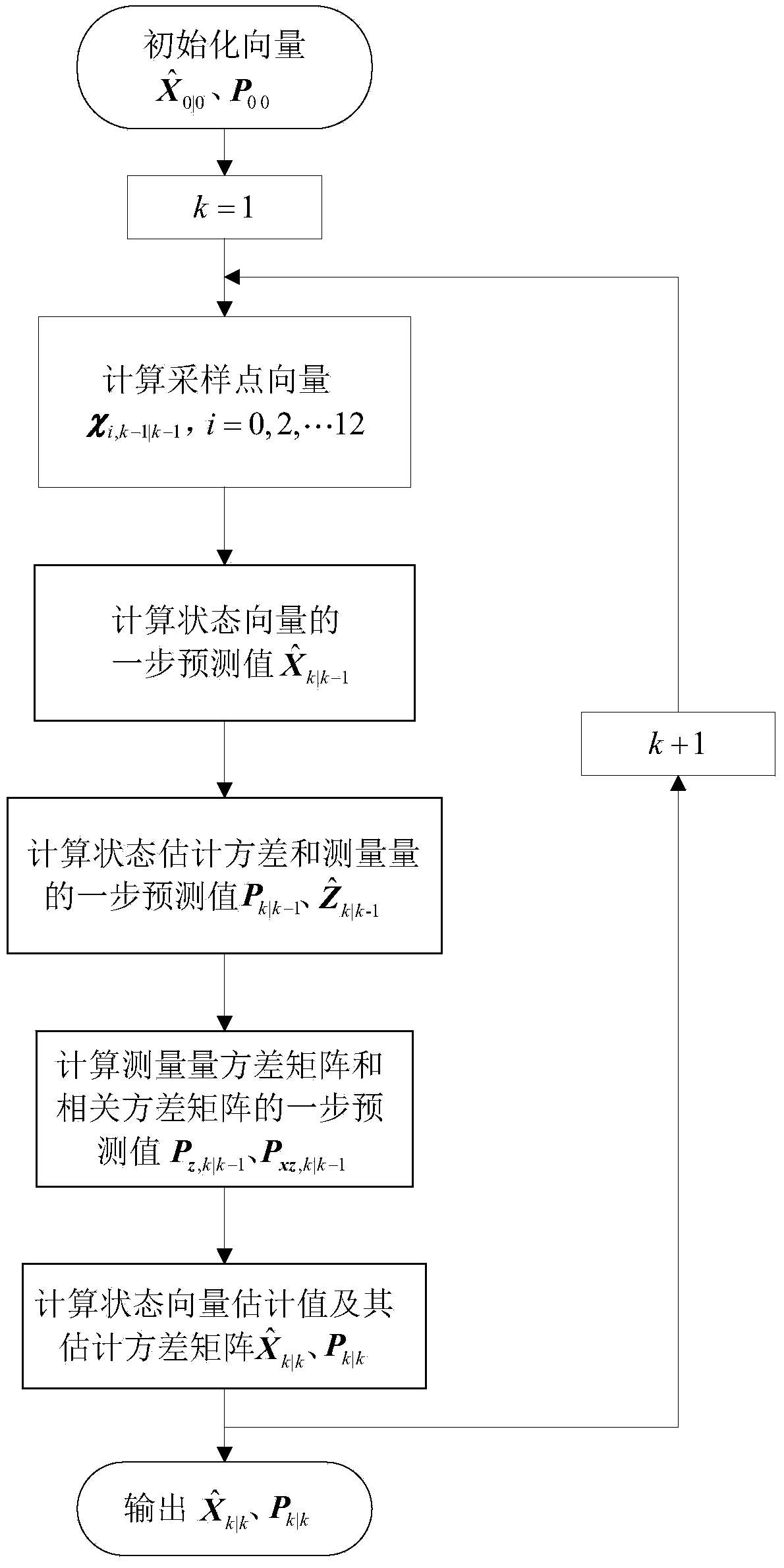
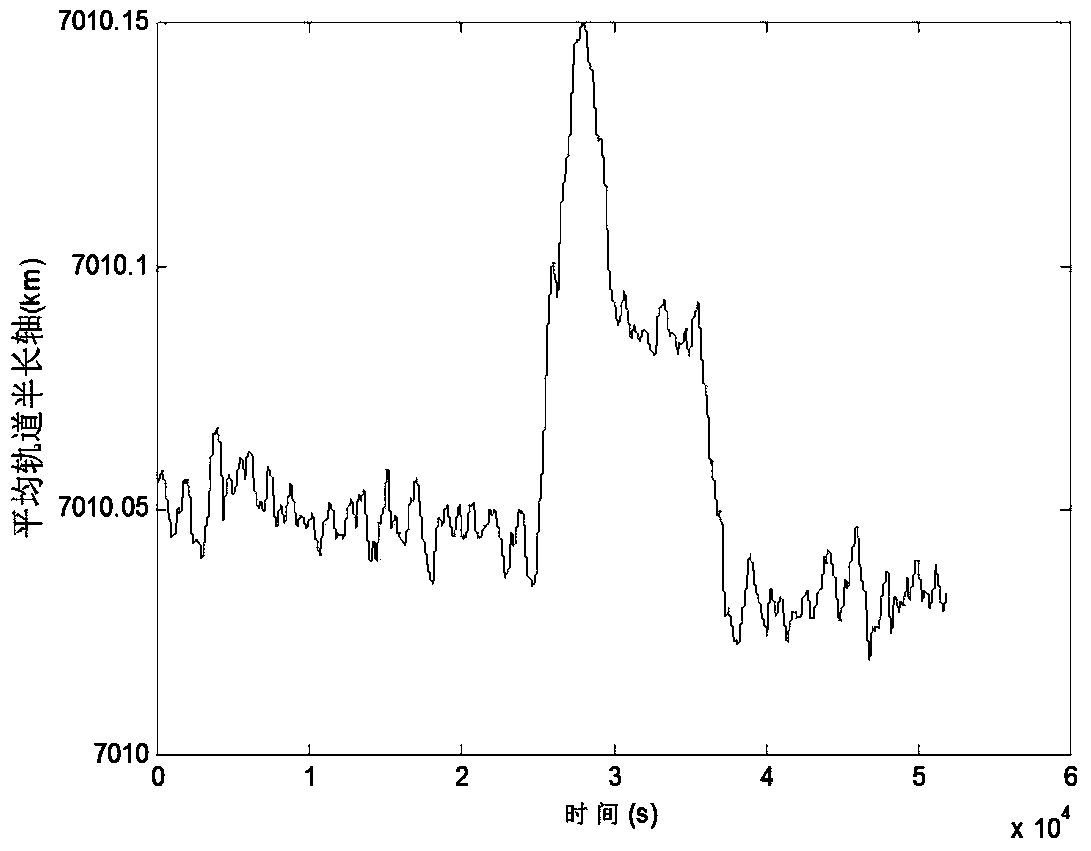
The invention provides a tangential low-thrust in-orbit circular orbit calibration method based on (Global Navigation Satellite System) GNSS precise orbit determination. The calibrated tangential thrust F is used for controlling a spacecraft orbit, and the tangential low-thrust in-orbit circular orbit calibration method is characterized by comprising the following steps: measuring by utilizing a GNSS to obtain the spacecraft position information, and performing a Unscented Kalman filtering method to obtain estimated values of spacecraft position and velocity information under a J2000 coordinate system; calculating an instantaneous orbit semi-major axis of a spacecraft according to the estimated values of the spacecraft position and the velocity information; averaging the instantaneous orbit semi-major axis in the orbital nodal period before each measurement moment to obtain the average orbit semi-major axis at the moment; and subtracting the average orbit semi-major axes before and after the action of the tangential thrust of a circular orbit to obtain orbit semi-major axis variation delta a, and calculating the tangential thrust calibration value of the circular orbit according to the delta a. In the calculation process, the GNSS is completely used to obtain the real-time orbital data without data support of a ground station, and the calibration method has accurate and reliable result and simplicity in calculation and is easy to realize.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
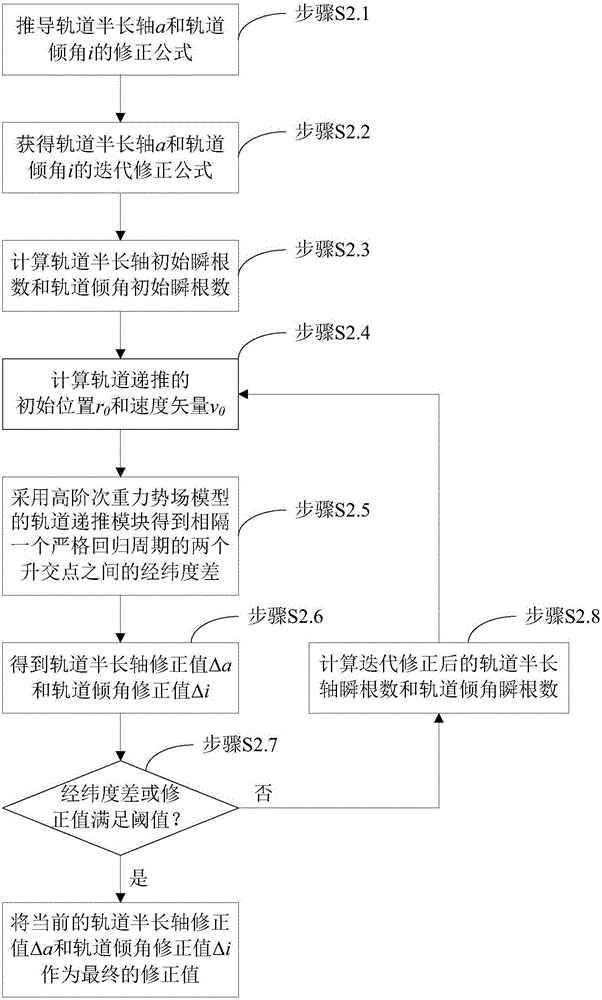
Method for determining strictly-regressive orbit of near-earth satellite
InactiveCN106092105AHigh precisionInstruments for comonautical navigationEarth satellitePotential field
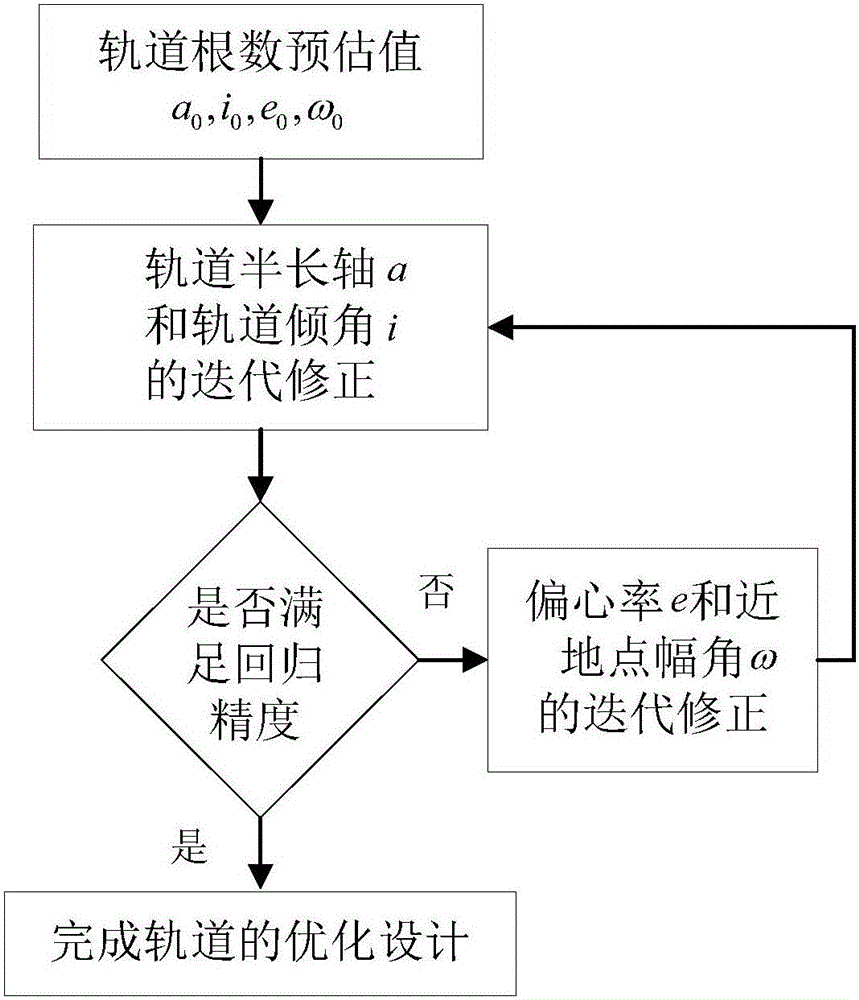
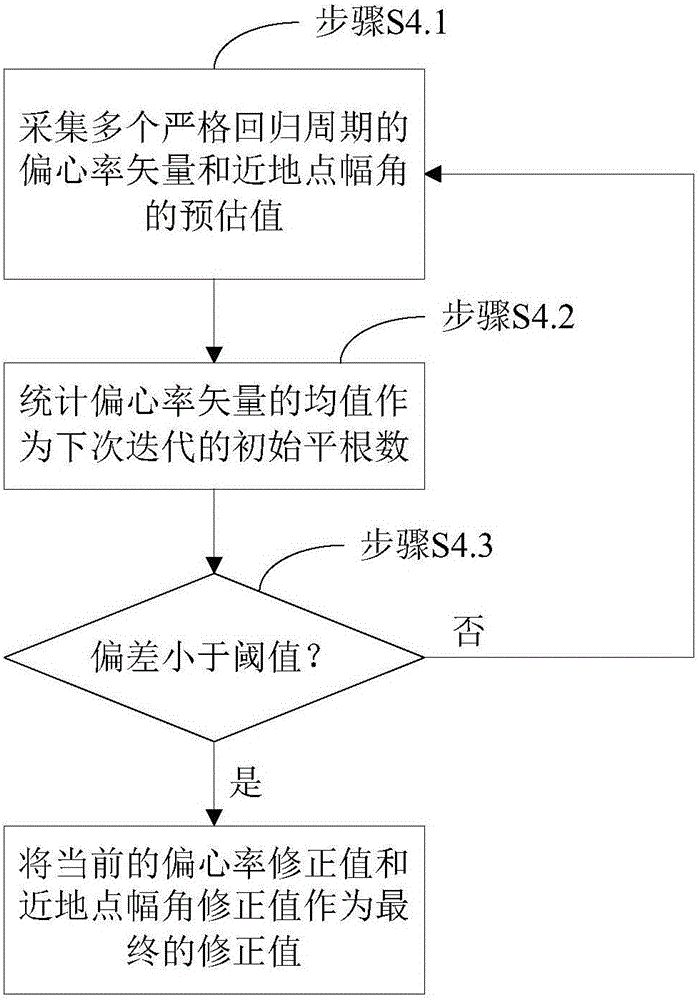
A method for determining strictly-regressive orbit of a near-earth satellite is disclosed. The method comprises: on the basis that an orbit element prediction value of a regressive orbit in a low-order gravity potential field, combining an orbit semi-major axis a and an orbit inclination angle i, performing repeated iteration correction on the orbit semi-major axis a and the orbit inclination angle i according to the relationship of the orbit semi-major axis a and the orbit inclination angle i with the longitude and latitude of a sub-satellite point and based on an orbit recursion module of a high-order gravity potential filed module, combining an eccentricity ratio e and a perigee argument omega, and performing repeated irritation correction on the eccentricity ratio e and the perigee argument omega by employing an average process according to the characteristics of a vector limit cycle of the eccentricity ratio until the regression precision of an ascending node satisfies a preset value. The method determines the strictly-regressive orbit of the near-earth satellite based on high-precision orbit dynamics, the determined orbit possesses relatively high regression precision for a space target point, and compared with a conventional method based on a low-order gravity potential field, the high-precision orbit dynamics is relatively close to reality and possesses relatively high application value.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
Design method of service track providing ontrack service for satellite constellations
InactiveCN101916114AReduced mobility requirementsShorten speedPosition/course control in three dimensionsNatural satellitePhase difference
The invention provides a design method of a service track which provides an ontrack service for integral satellite constellations by using a few track service spacecrafts within limited time. In the design method, by utilizing the characteristic of constellation configuration, one track service spacecraft is arranged on each constellation track surface by taking the track surfaces as units, an elliptical service track which is in coplanar intersection with corresponding tracks of the constellations in a mode of a single intersection point, and the semi-major axis and eccentricity of the single-intersection point elliptical service track and phase difference among target satellites on the corresponding tracks of the constellations meet a certain relation, so that the single track service spacecraft is intersected with different target satellites on the corresponding tracks of the constellations when passing through the intersection points of the tracks every time to perform each ontrack service operation. Based on the constellation target service tasks, the relative speed that the track service spacecrafts are intersected with the target satellites is small and the duration of time windows is long, and the design method has excellent adaptability to different ontrack service tasks.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Sub-satellite point circular geosynchronous orbit design method
InactiveCN103678787AMeet the needs of multi-angle earth observationSpecial data processing applicationsNatural satelliteGeosynchronous orbit
Disclosed is a sub-satellite point circular geosynchronous orbit design method. The method includes: (1) analyzing and determining sub-satellite point circular geosynchronous orbit generating conditions including that (1.1) an orbital semi-major axis is 42164km, (1.2) a satellite drifts back and forth in the north-south direction every day, (1.3) the satellite drifts back and forth in the east-west direction every day, (1.4) the distance of north-south direction drift is equal to that of east-west direction drift, and (1.5) the satellite passes the equator twice every day with relative distance of sub-satellite points when the satellite passes the equator twice equal to east-west direction drift distance of the satellite; (2) according to the conditions in the step (1), determining orbital parameters, satisfying the five conditions at the same time, namely the orbital semi-major axis a, eccentricity ratio e, inclination angle i, right ascension of ascending node Omega, argument of perigee omega and true anomaly theta. Design of a sub-satellite point circular geosynchronous orbit is completed by utilizing the determined orbital parameters.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
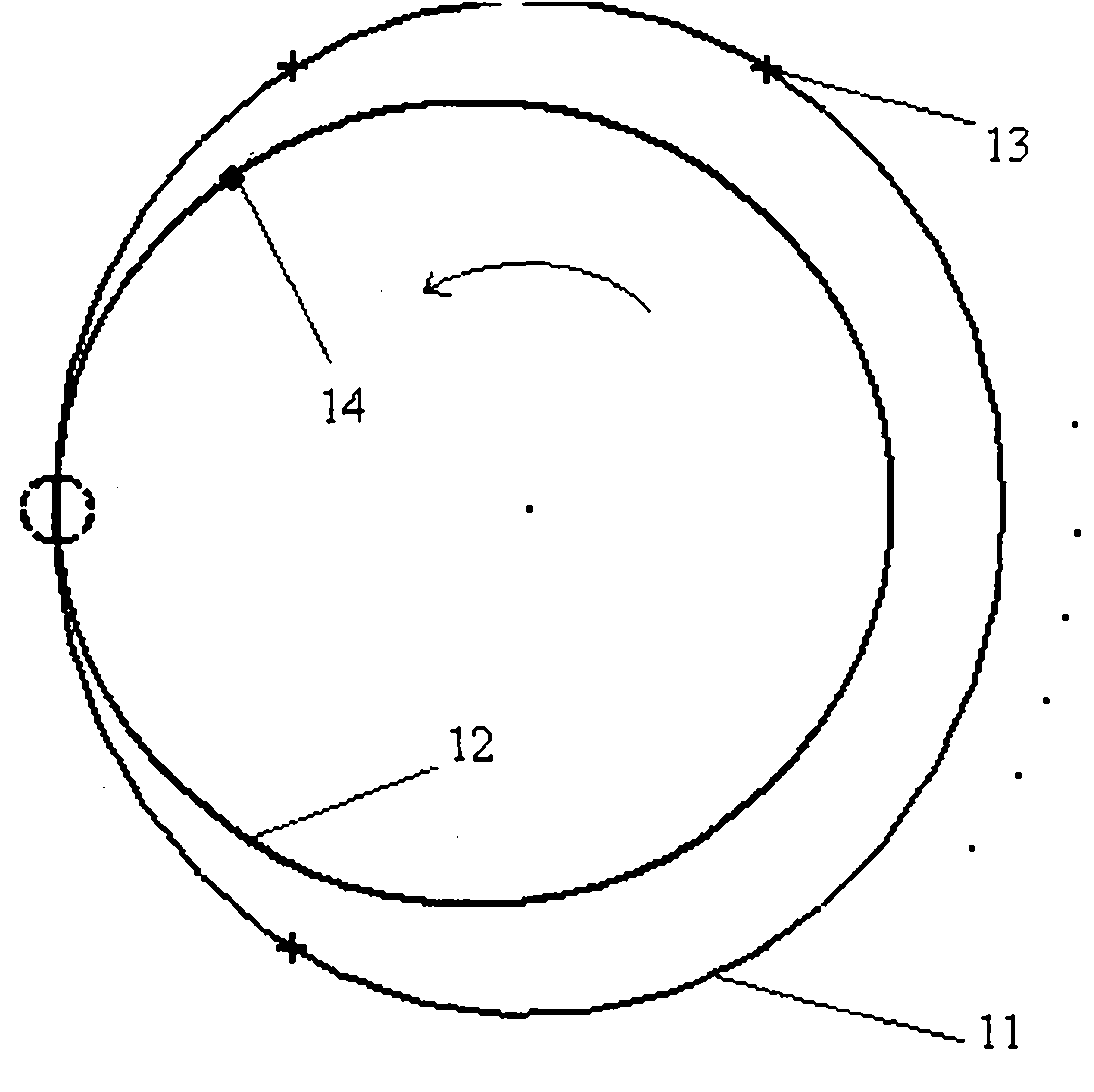
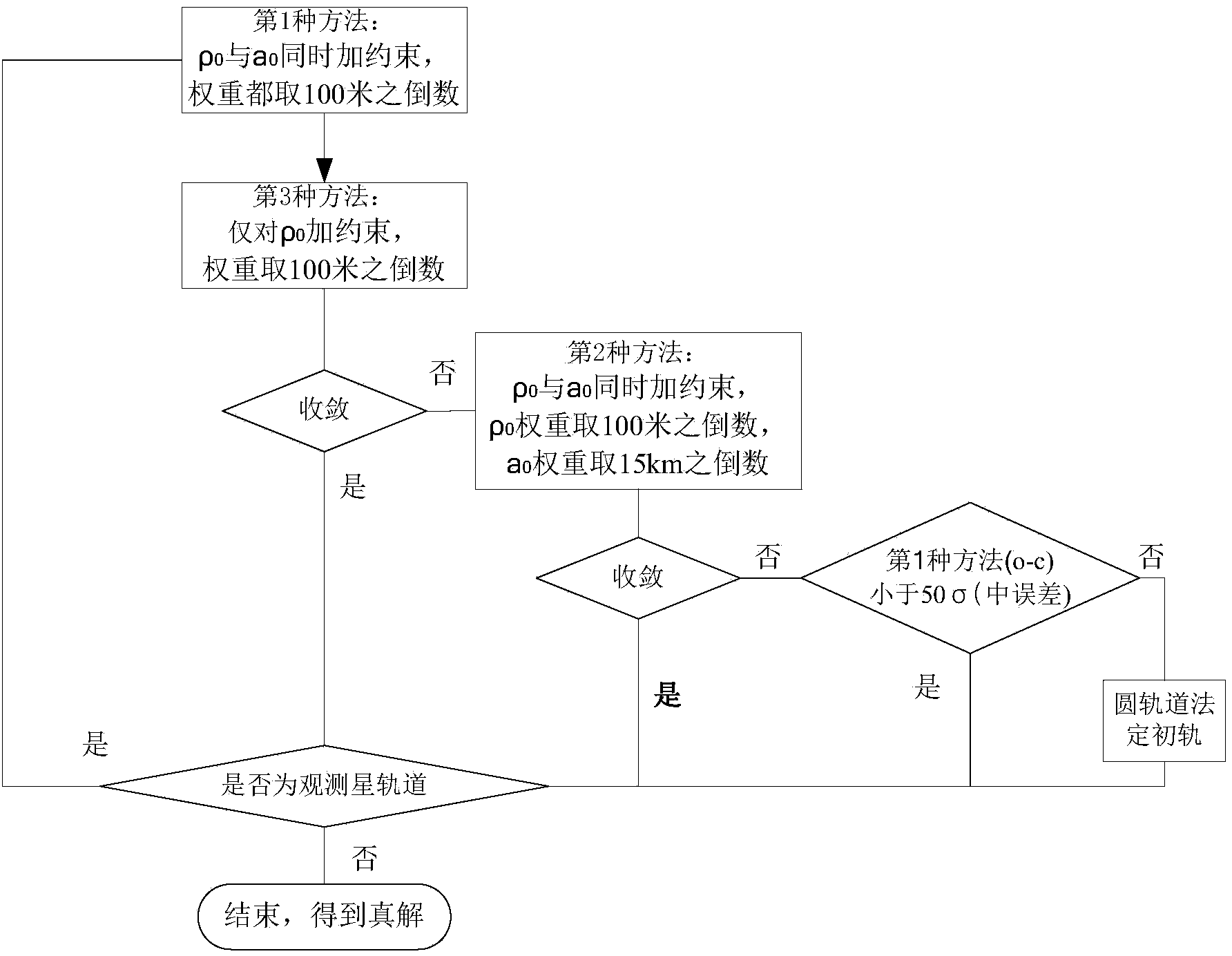
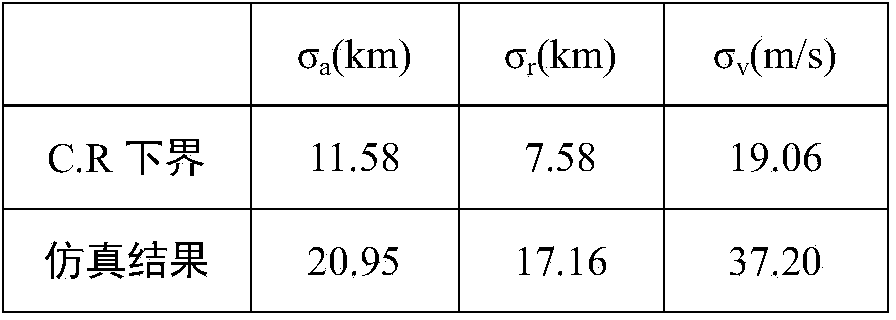
Method for determining preliminary orbit of low-orbit target satellite according to space-based satellite angle measurement data
The invention discloses a method for determining a preliminary orbit of a low-orbit target satellite according to space-based satellite angle measurement data. According to the method, a condition equation of the unit vector (please see the specification for the symbol) of the target satellite relative to an observation satellite is obtained according to the angle measurement data of the high-speed motion low-orbit target satellite relative to the low-orbit observation satellite; the condition equation of measured distance rho <0> (please see the specification for the formula) is obtained on the premise that the condition equation is constrained, and an iterative solution is obtained to serve as the initial values, position (please see the specification for the symbol) and speed (please see the specification for the symbol), of the next step of iteration by selecting a certain step length and adding certain weights to rho <0> in the constraint equation and the semi-major axis a <0> of the target satellite, then iterative calculation is conducted till convergence to obtain the preliminary orbit of the target satellite, spurious solutions are blocked out and a genuine solution is obtained, and then the position and speed of the target satellite are determined. According to the method, by attaching the constraint condition to the solution target, the generation of spurious solutions caused by the high-speed dynamic nature of the target satellite relative to the observation satellite and the lack of distance observed quantity is avoided, the calculation procedure is successfully converged to be close to the genuine solution, and an orbit determination result is made to be close to the lower bound of a theoretical optimum solution C.R.
Owner:SHANGHAI ENG CENT FOR MICROSATELLITES
Satellite constellation implementation method for implementing communication by utilizing recursive orbit
ActiveCN107980210AReduce co-channel interferenceRealize coexistence at the same frequencyCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsGeostationary orbitIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
The invention relates to a satellite constellation implementation method for implementing communication by utilizing a recursive orbit, and the method comprises the steps: a regression period, an orbital semi-major axis, an inclination of an orbit, an eccentricity ratio and an argument of perigee of the orbit are determined; the number of satellites and orbital planes are determined as n; right ascension of ascending node and a mean anomaly of a first satellite are determined, and according to service needs of the satellite, right ascension of ascending node and mean anomaly of following satellites are determined in sequence; a geostationary orbiting satellite network set that needs to be coordinated and the width of a non-geostationary satellite to geostationary satellite interference protection band are determined; all set satellites successively passes the top in the air along a same fixed orbit are seen at any position of the ground, and when multi-coverage is formed, users on theground can see a plurality of satellites; and if satellite trails pass the interference protection band for the geostationary satellite, when present accessed satellite enters the protection band, theusers on the ground switch to another satellite that does not in the protection band to continuously implement communication.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
GNSS Ephemeris with Graceful Degradation and Measurement Fusion
InactiveUS20110071808A1High precisionComputation using non-denominational number representationSatellite radio beaconingHarmonicEphemeris
A method for providing an extended propagation ephemeris model for a satellite in Earth orbit, the method includes obtaining a satellite's orbital position over a first period of time, applying a least square estimation filter to determine coefficients defining osculating Keplarian orbital elements and harmonic perturbation parameters associated with a coordinate system defining an extended propagation ephemeris model that can be used to estimate the satellite's position during the first period, wherein the osculating Keplarian orbital elements include semi-major axis of the satellite (a), eccentricity of the satellite (e), inclination of the satellite (i), right ascension of ascending node of the satellite (Ω), true anomaly (θ*), and argument of periapsis (ω), applying the least square estimation filter to determine a dominant frequency of the true anomaly, and applying a Fourier transform to determine dominant frequencies of the harmonic perturbation parameters.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
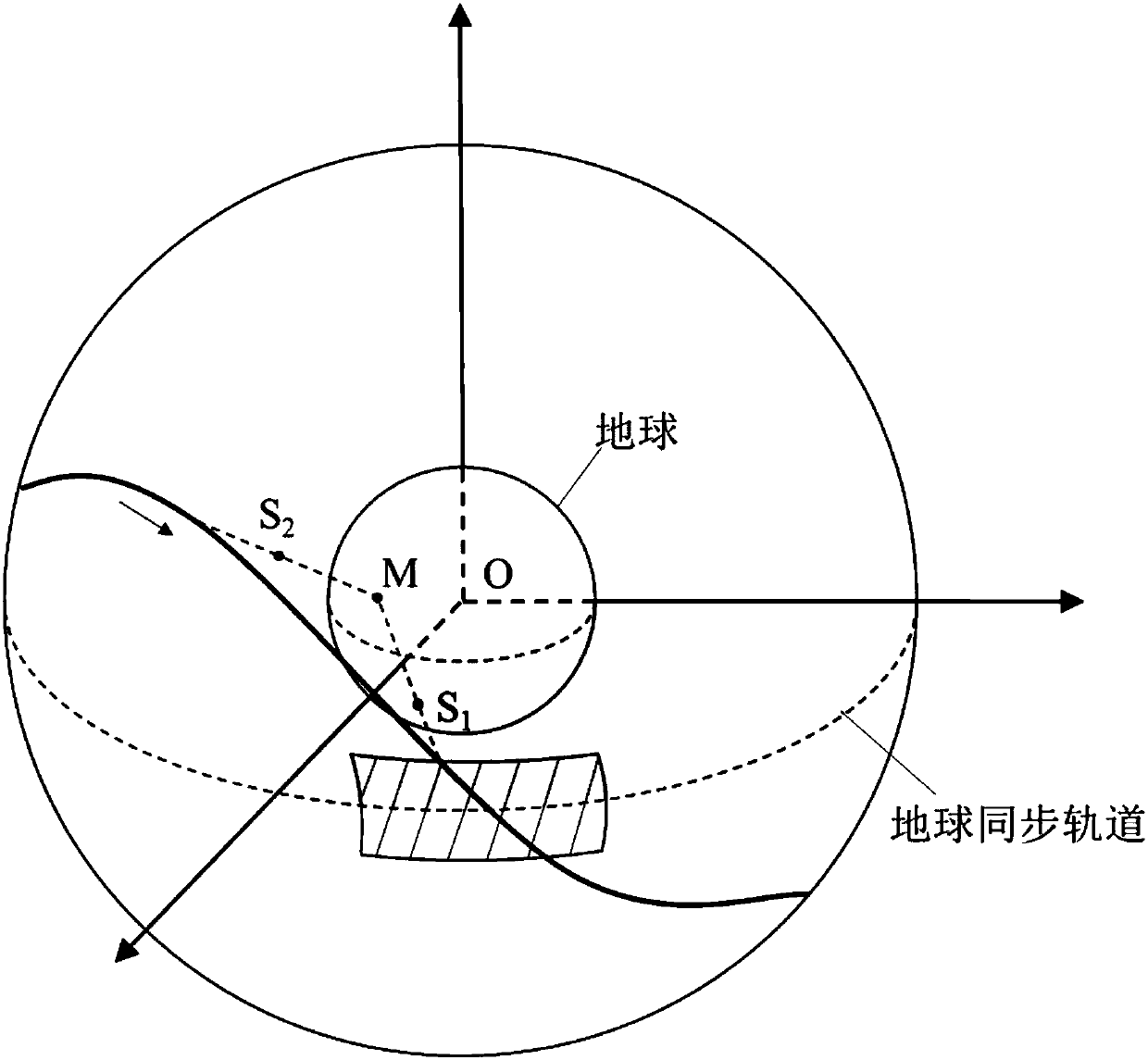
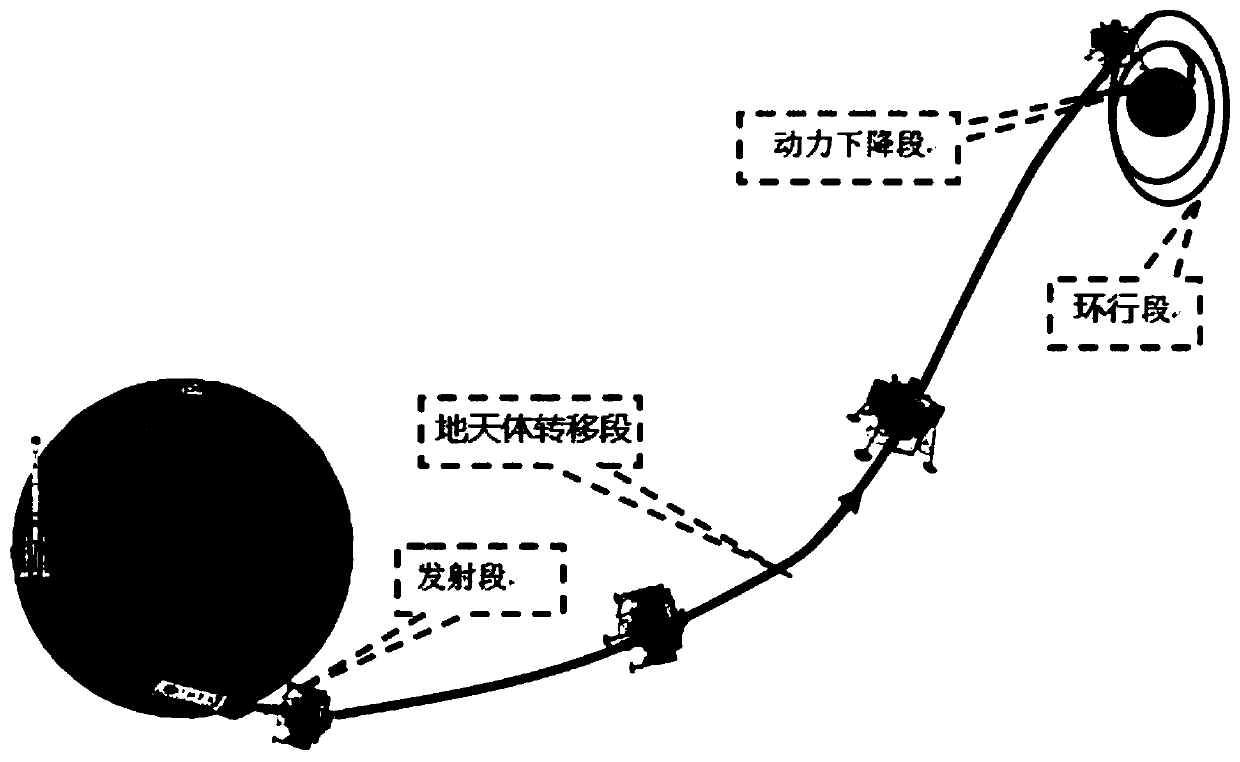
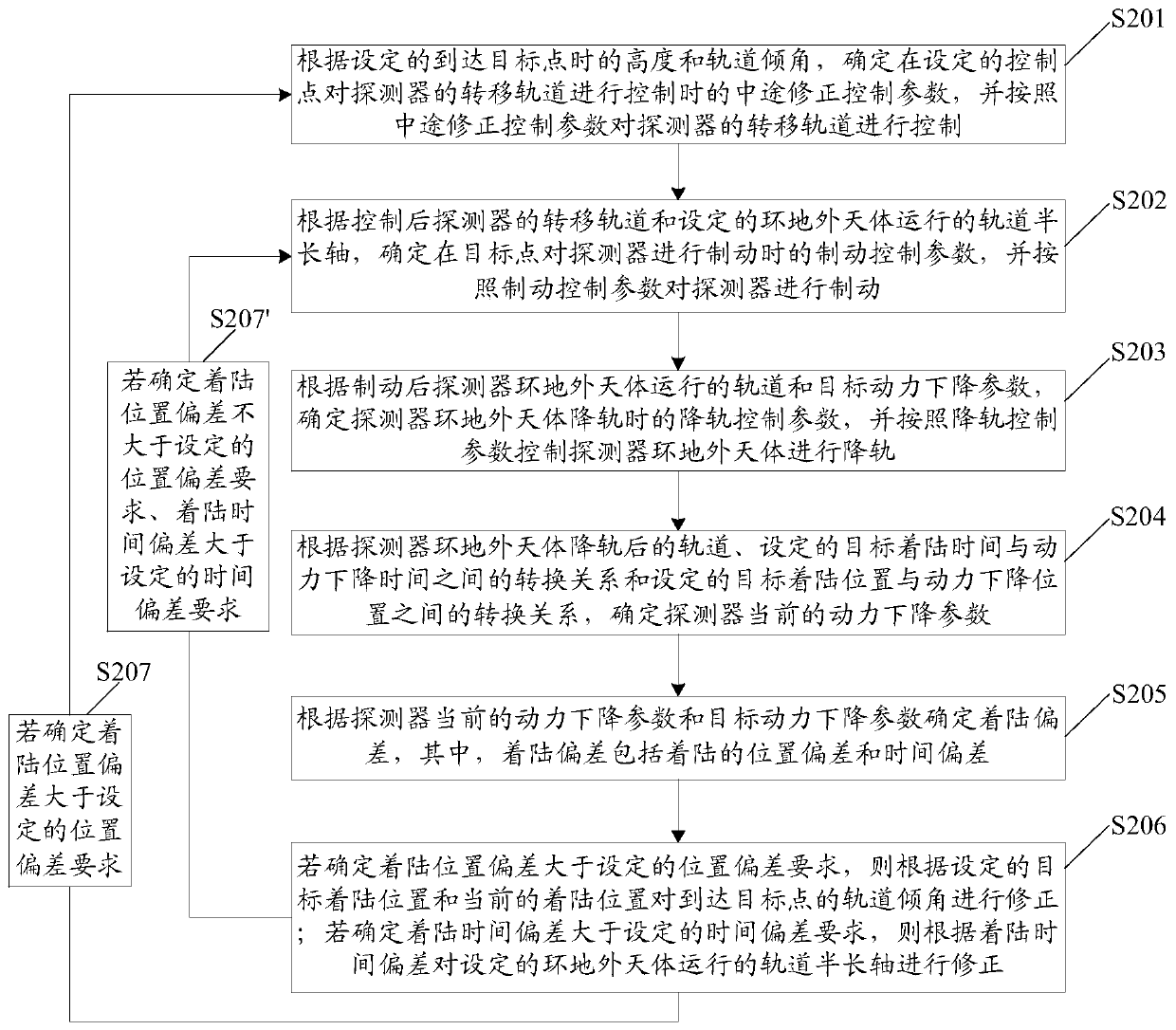
Method and device for controlling prober to land on object outside earth
The invention discloses a method and device for controlling a prober to land on an object outside the earth, and belongs to the technical field of spaceflight. The method comprises the steps that midcourse correction control parameters at set control points are determined according to the set height and the set orbit inclination when a target point is reached, a transfer orbit of the prober is controlled according to the midcourse correction control parameters, brake control parameters are determined according to the controlled transfer orbit and the set orbit semi-major axis, and the prober is controlled to conduct braking according to the brake control parameters; inbound pass control parameters are determined according to the braked orbit and target power lowering parameters, and the prober is controlled to conduct inbound pass according to the inbound pass control parameters; power lowering parameters are determined according to the orbit subjected to inbound pass, the landing deviation is determined according to the power lowering parameters and the target power lowering parameters, and the orbit inclination and / or the orbit semi-major axis are / is corrected according to the landing deviation; the landing position deviation is larger than the set position deviation, the step of determining the midcourse correction control parameters is executed; and when only the landing time deviation is larger than the set time deviation, the step of determining the brake control parameters is executed.
Owner:中国人民解放军63920部队
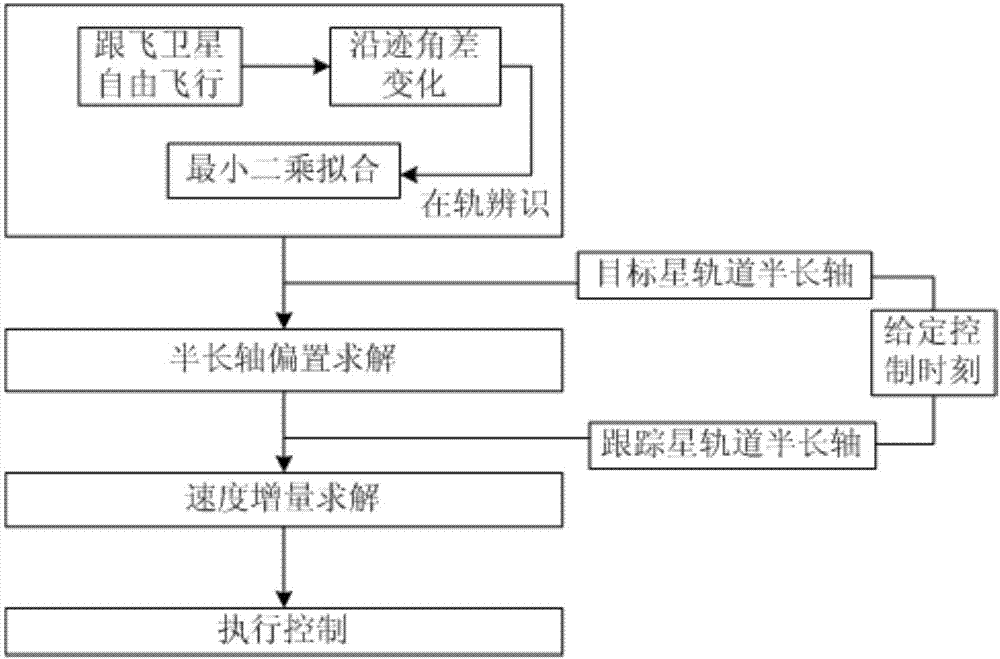
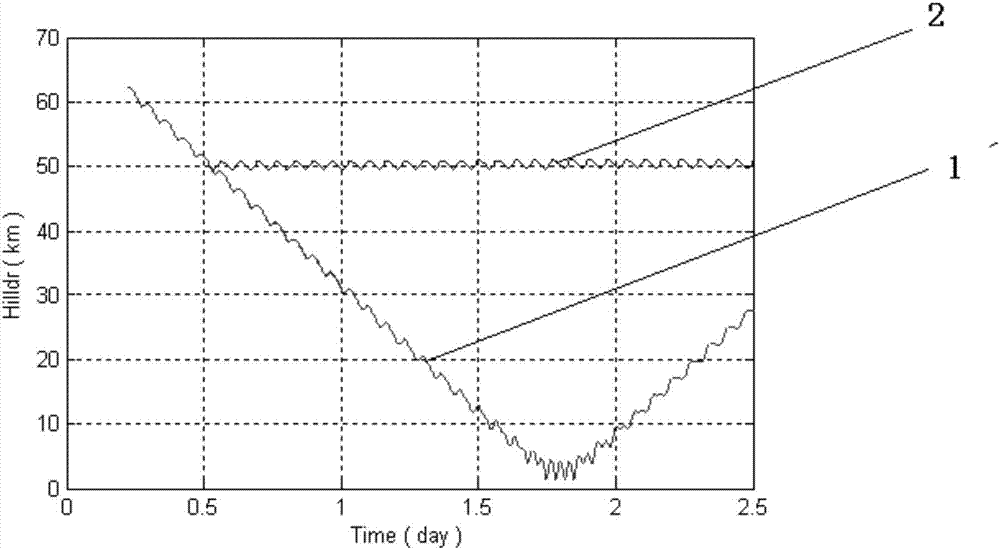
Satellite flight-tracking secular perturbation compensation method based on on-orbit parameter identification and offset
ActiveCN107168372AIncrease flexibilityReduce fuel loadPosition/course control in three dimensionsBurnupOrbit
The invention provides a satellite flight-tracking secular perturbation compensation method based on on-orbit parameter identification and offset, and the method comprises the following steps: 1, carrying out the on-orbit identification of an along-track angle relative drift rate; 2, calculating an orbit semi-major axis offset of a tracking satellite at a given control moment based on the along-track angle relative drift rate obtained at step 1; 3, giving an orbit semi-major axis of the tracking satellite at the control moment, and obtaining the velocity increment, needed by the orbit semi-major axis offset control, of the tracking satellite according to an orbit dynamical model. The method is advantageous in that the (1), the method has no requirements for the control time, and improves the flexibility of formation keeping control; (2), the method is low in control burnup, and effectively reduces the fuel load of a satellite formation; (3), the method can achieve the long-time natural maintaining through one control operation, and reduces the control frequency.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
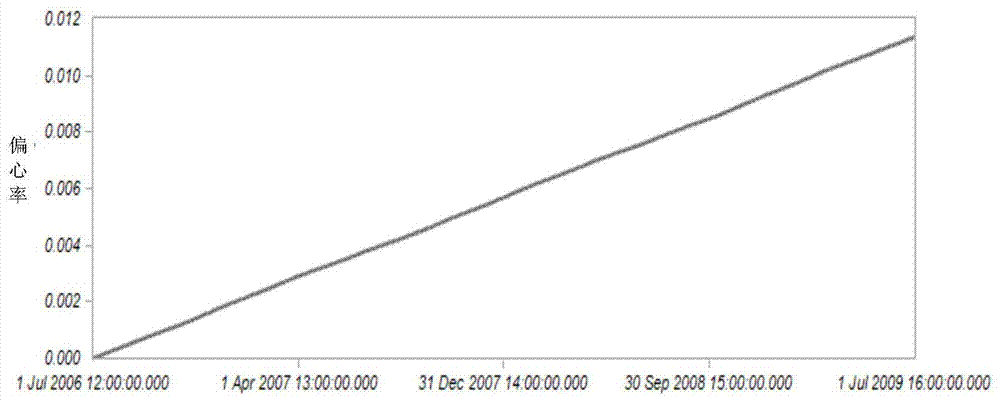
Method for designing eccentricity ratio prebias of critical inclination nearly-circular orbit
ActiveCN103678814ATo overcome the shortcomings of gradually increasing eccentricityReduce eccentricitySpecial data processing applicationsNatural satellitePulse rate
The invention provides a method for designing eccentricity ratio prebias of a critical inclination nearly-circular orbit, and belongs to the technical field of satellite orbits. The method comprises the steps that firstly, the mean elements of the six parameters of the eccentricity ratio, the argument of perigee, the mean anomaly, the ascending node right ascension, the orbit semi-major axis and the orbit inclination are transformed into instant elements; then, the instant elements are substituted into STK satellite simulation software for orbit calculation, and the instant elements of the six parameters in the tail period of the service life are obtained; the instant elements are transformed into the mean elements, the mean element prebias amount of the eccentricity ratio is designed to be half of the mean element of the eccentricity ratio in the tail period of the service life at last, and the mean element of the argument of perigee is designed to be 180 degrees. The eccentricity ratio of the tail period of the service life can be reduced by half to overcome the defect that the eccentricity ratio of the nearly-circular orbit of the critical inclination is gradually enlarged.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
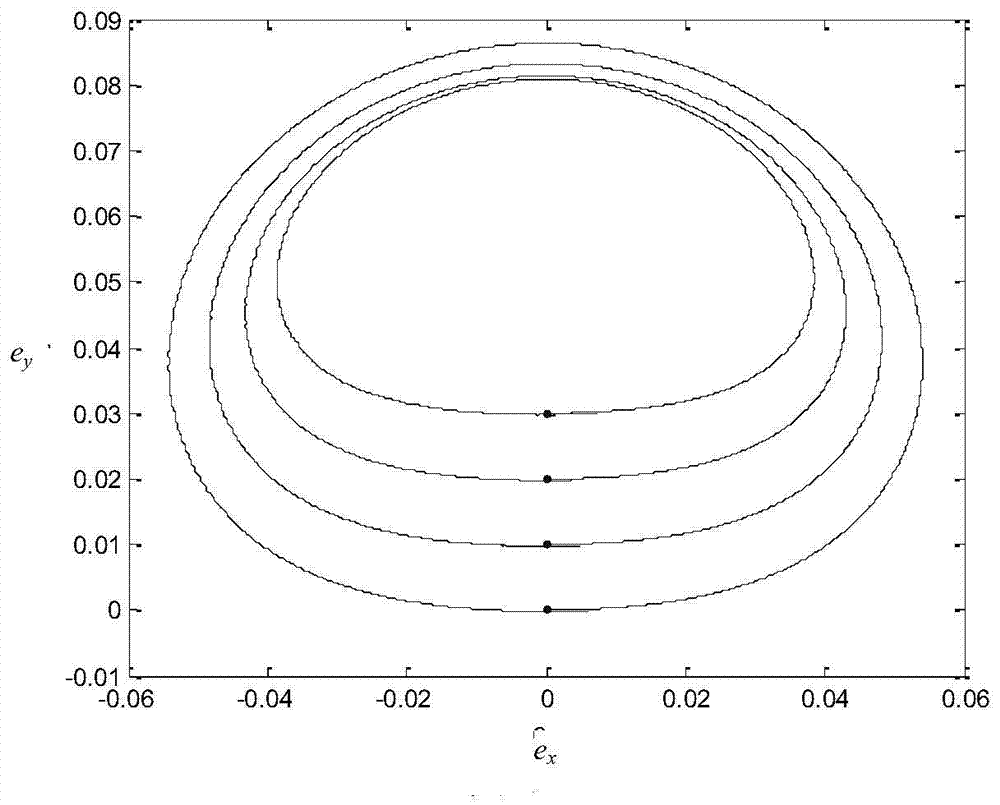
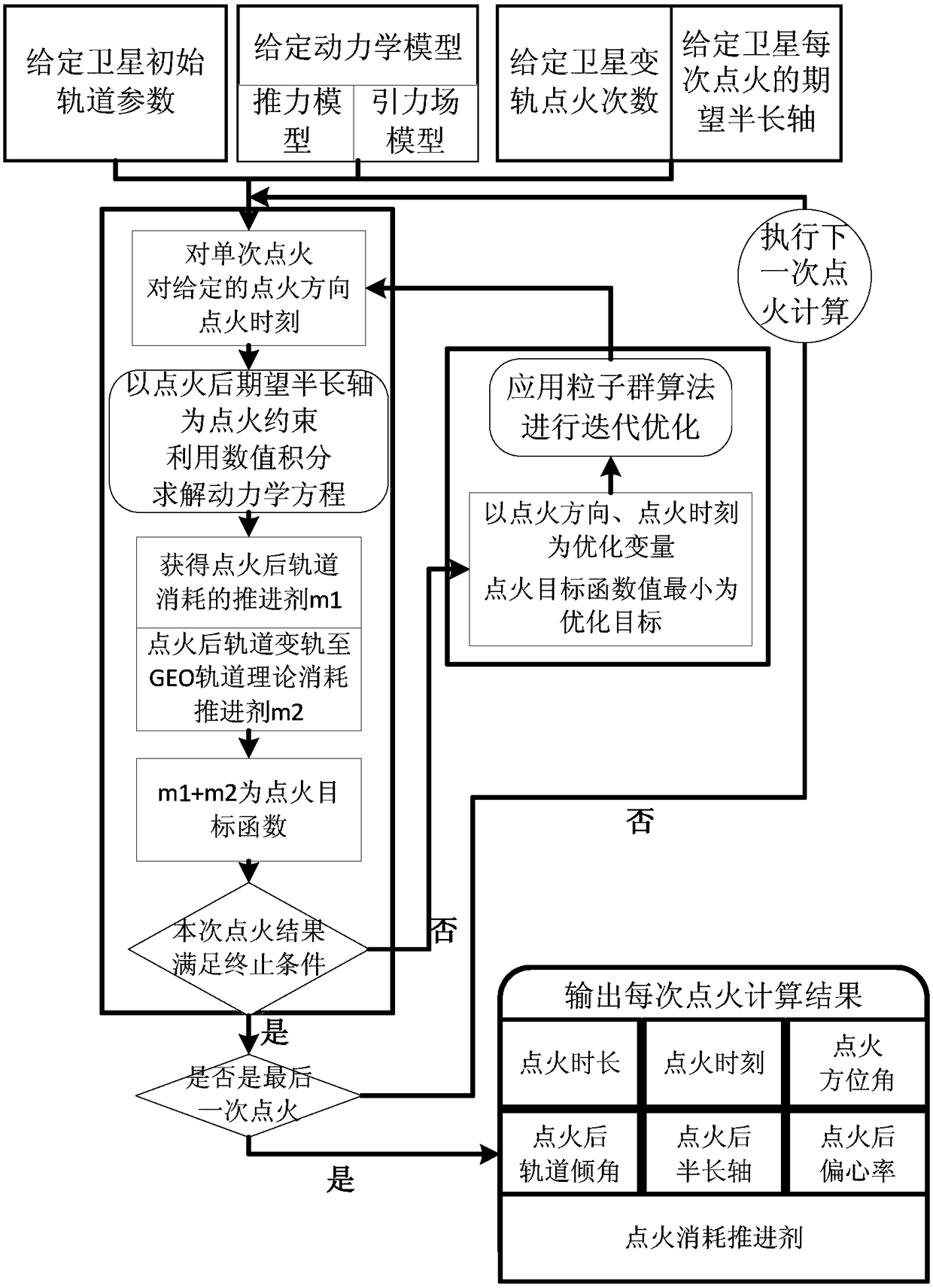
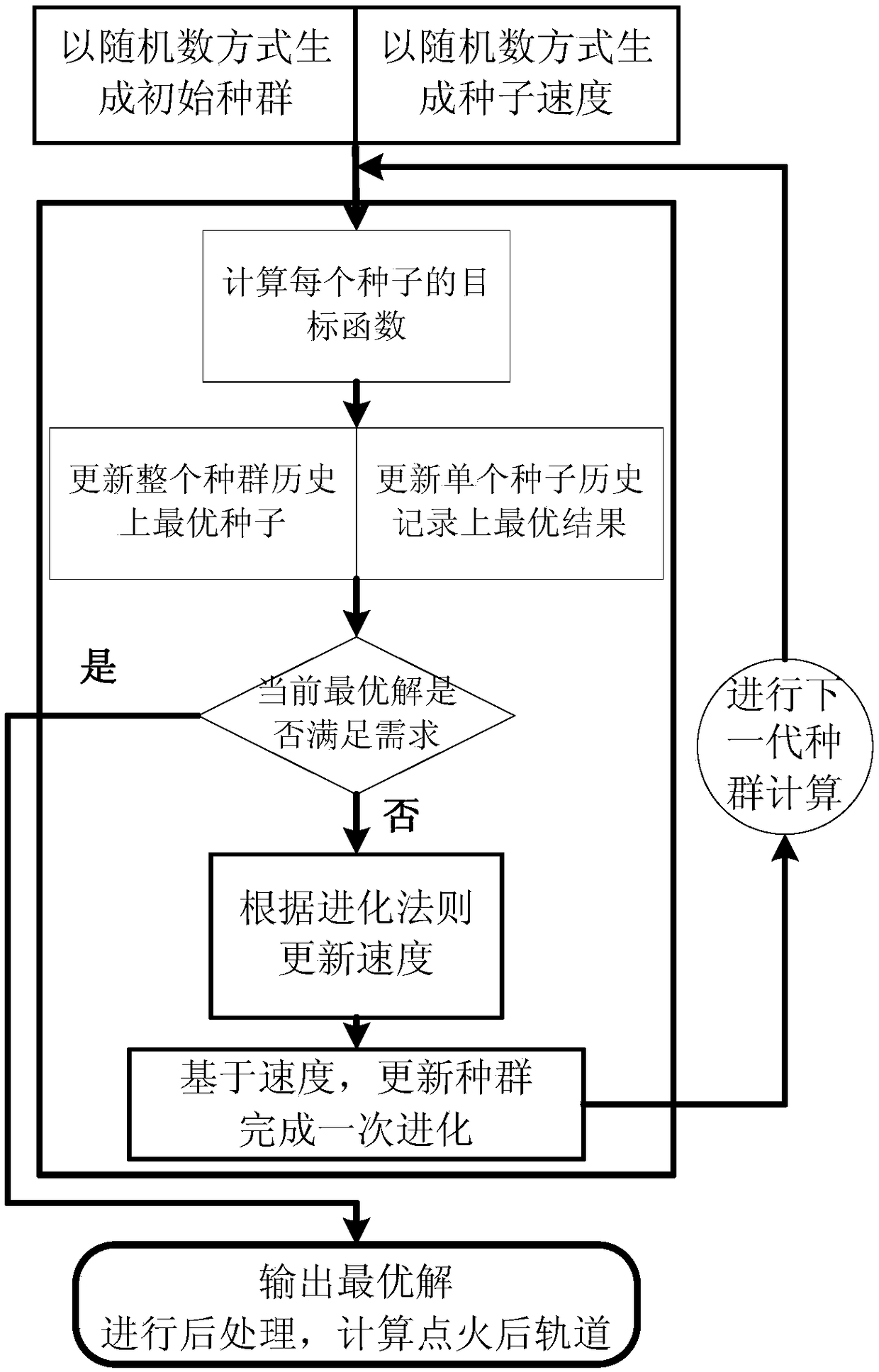
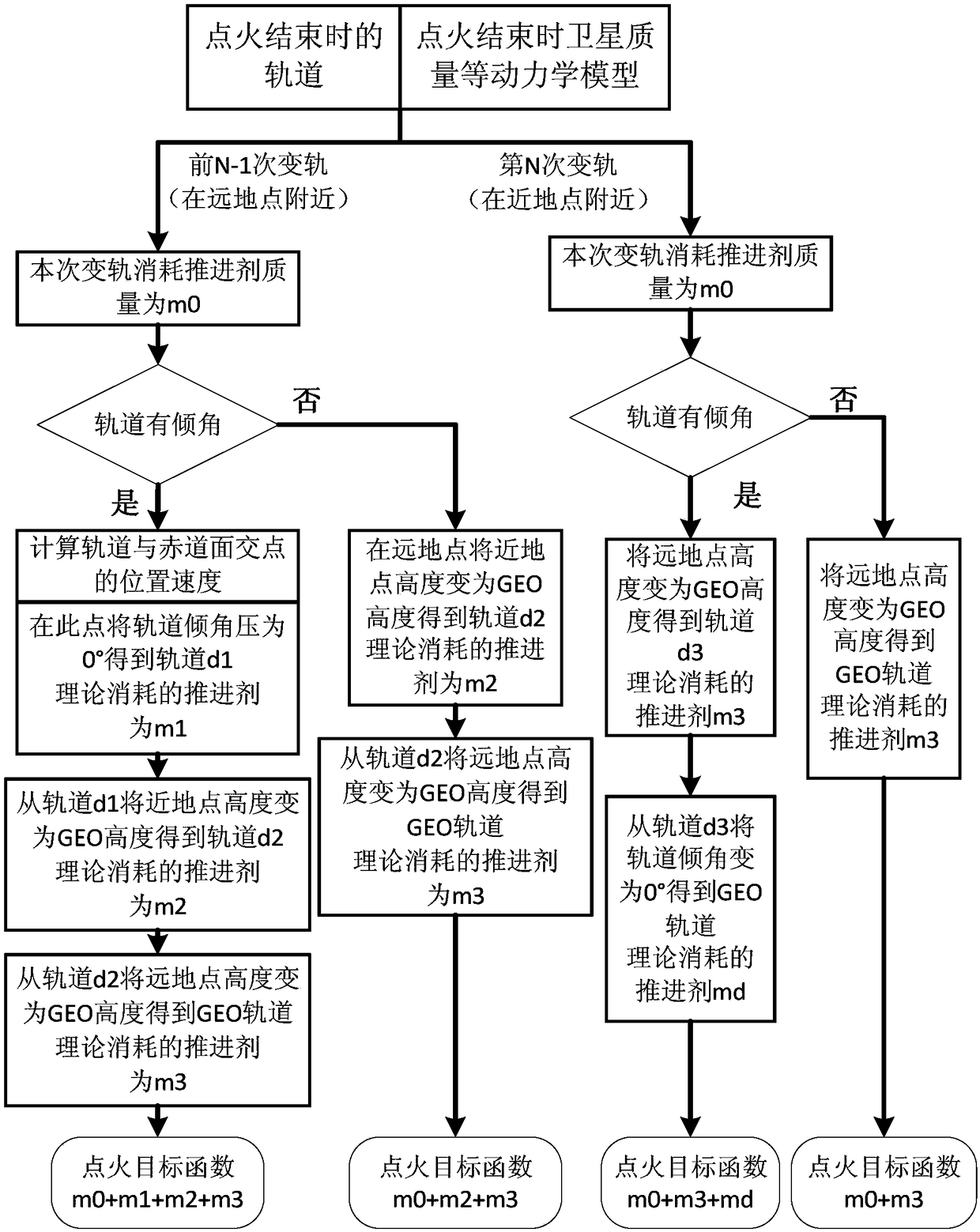
GEO-satellite orbit-transfer strategy computing method and system based on particle swarm algorithm and medium
ActiveCN108216687AEasy accessImprove computing efficiencyCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusEvolutionary computationIgnition timing
The invention discloses a GEO-satellite orbit-transfer strategy computing method and system based on the particle swarm algorithm and a medium. The GEO-satellite orbit-transfer strategy computing method includes the following steps that a satellite original orbit parameter, a satellite dynamical model, the ignition number N required when an orbit of a satellite is transferred to a GEO and semi-major-axis expected values after every-time ignition are preset; according to the satellite orbit parameter and the satellite dynamical model of every-time ignition, every-time ignition timing and the every-time ignition direction serve as optimization variables, the semi-major-axis expected values after every-time ignition serve as constraints, and every-time ignition optimization is carried out according to the particle swarm algorithm to obtain an every-time ignition optimization result. According to the GEO-satellite orbit-transfer strategy computing method and system based on the particle swarm algorithm and the medium, the ignition timing and the ignition direction serve as the optimization variables, propellant consumption serves as an objective function, original particle populationsare set, evolutionary computation is carried out according to the algorithm, expectation solutions are more rapidly obtained, and computing efficiency is improved.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
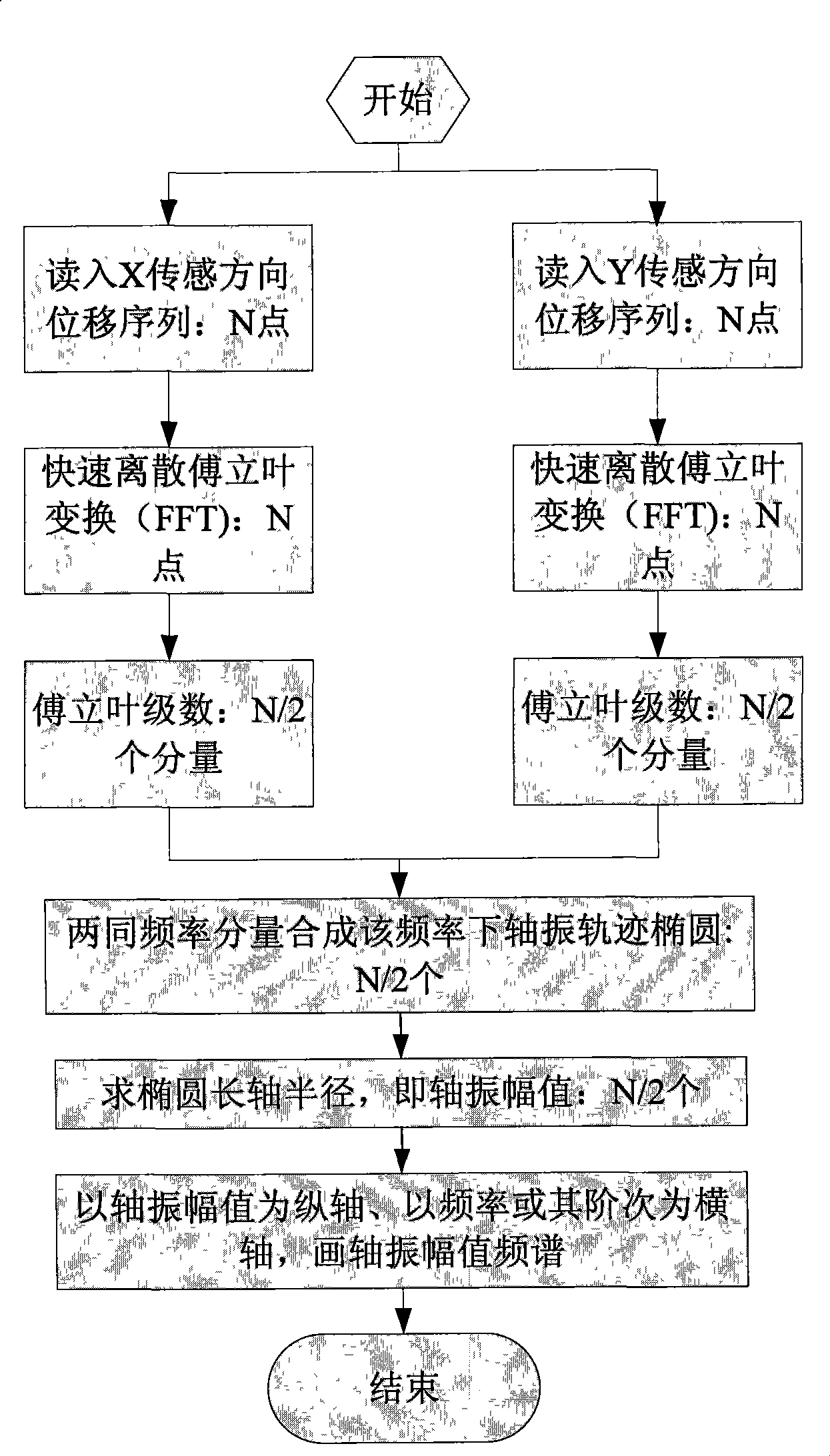
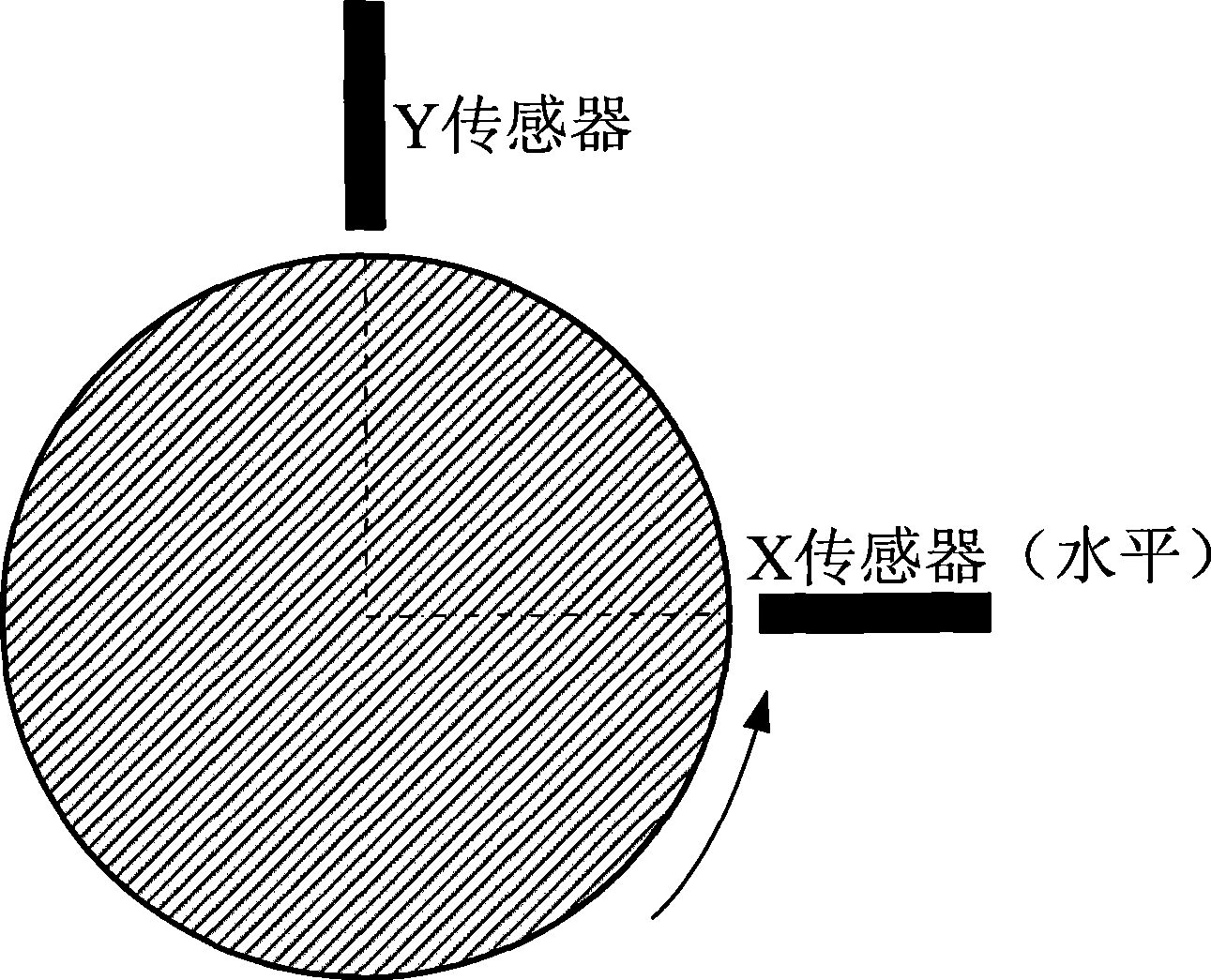
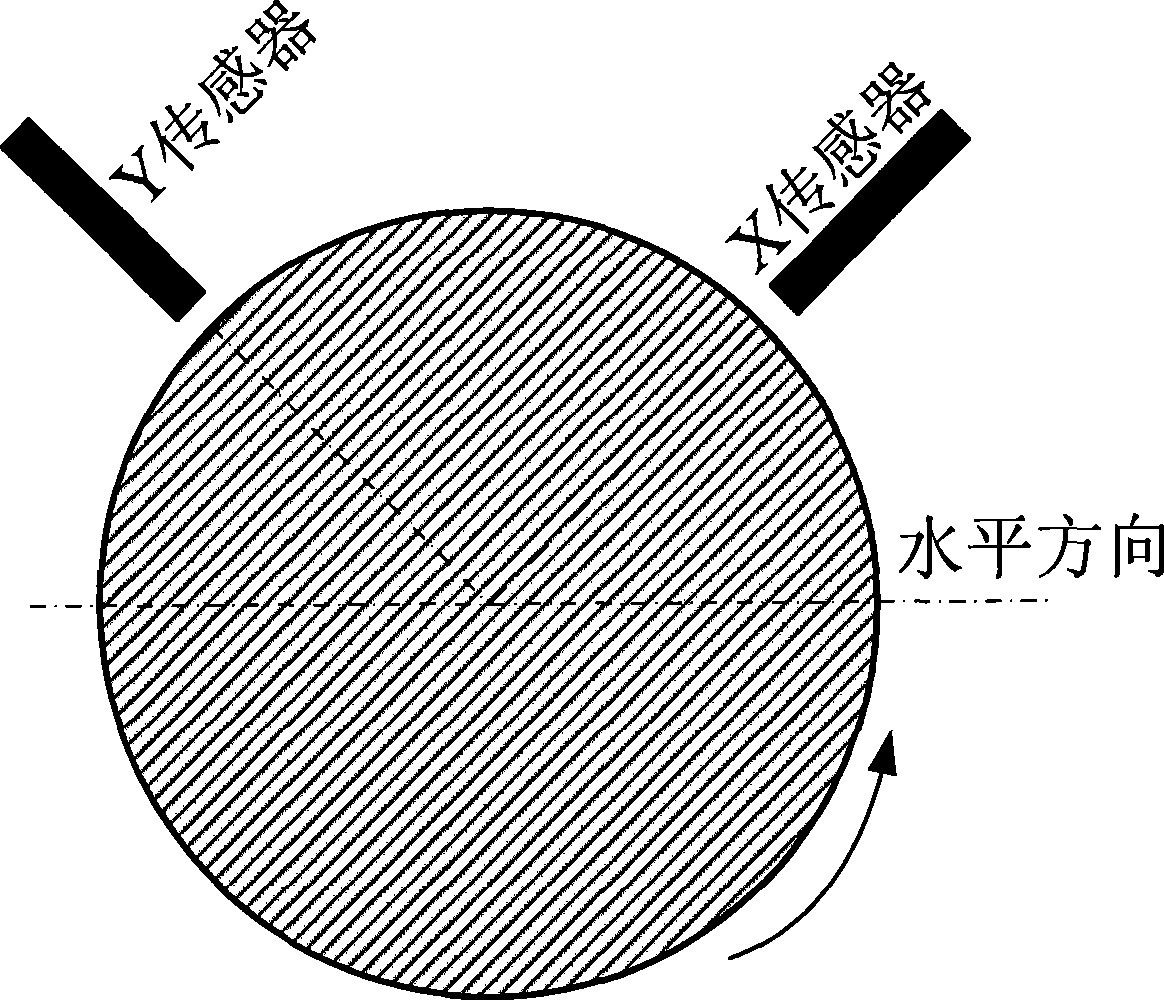
Amplitude frequency spectrum used for mechanical rotor single cross section shaft vibration analysis
InactiveCN101368870ASubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementVibration testingFrequency spectrumHarmonic
The invention relates to an amplitude spectrum used for mechanical rotor single-section shaft vibration analysis; the production of the amplitude spectrum comprises the following steps: (1), importing the synchronously acquired displacement signal sequences x and y of two vertical directions of a section of a rotating shaft; (2), processing fast discrete Fourier transformation on the two signal sequences, respectively; (3), evaluating the respective Fourier series according to the two signal discrete Fourier transformation results; (4), in the two obtained Fourier series, synthesizing the sine wave harmonic component of the x-signal with the sine wave harmonic component of the y-signal under each frequency so as to obtain an axis orbit ellipse, also known as Lissajous figure; (5), calculating the size of the semi-major axis of the synthesized ellipse under each frequency, namely, the size of the shaft amplitude on the section under each frequency; (6), and taking the frequency or the order as the horizontal axis, and taking the shaft amplitude as the longitudinal axis to map out the amplitude spectrum. Each shaft amplitude stands for the actual size of the shaft vibration of the section under the corresponding frequency and is not affected by the mounting direction of the sensor.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Mechanical arm autonomous robust singularity avoidance method for improving path tracking performance
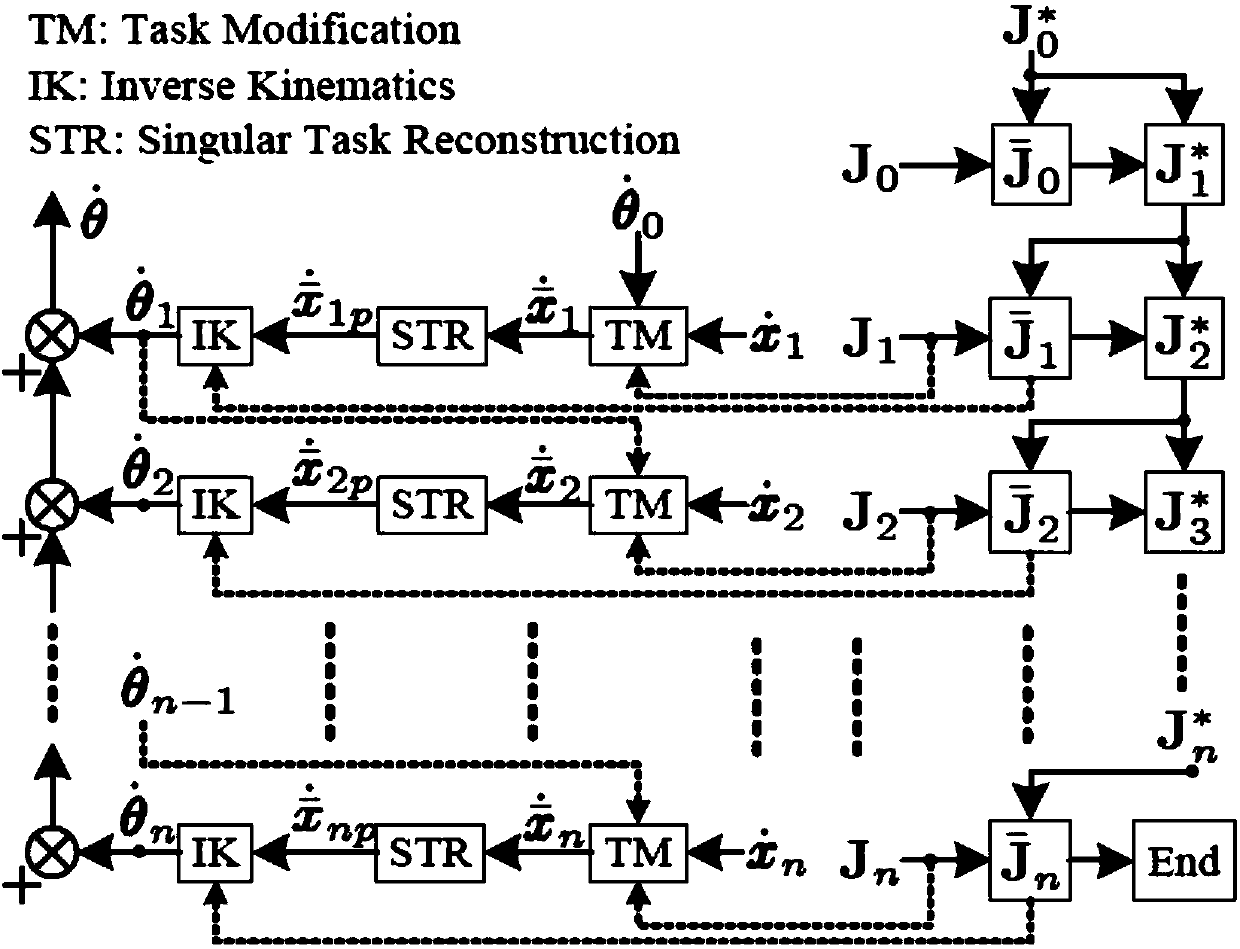
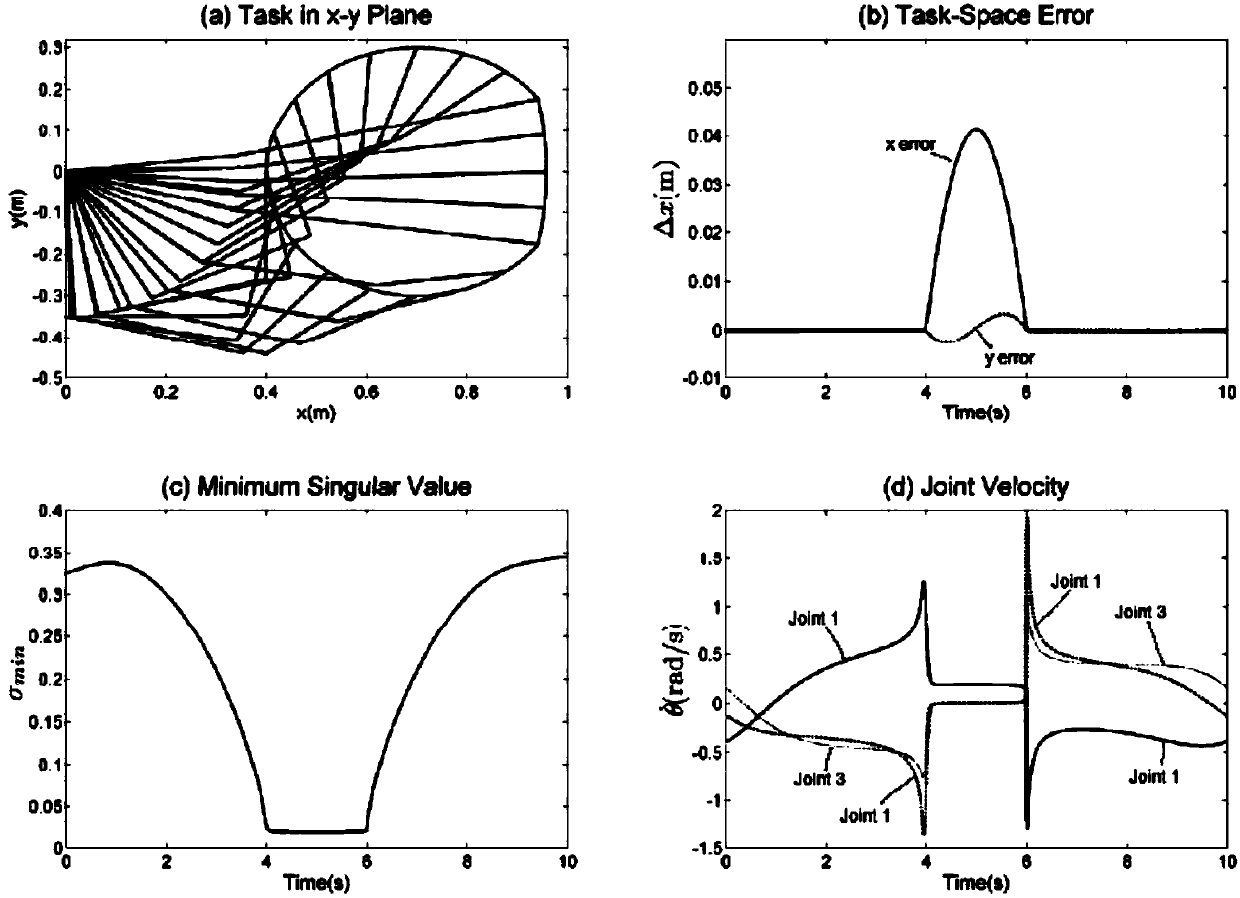
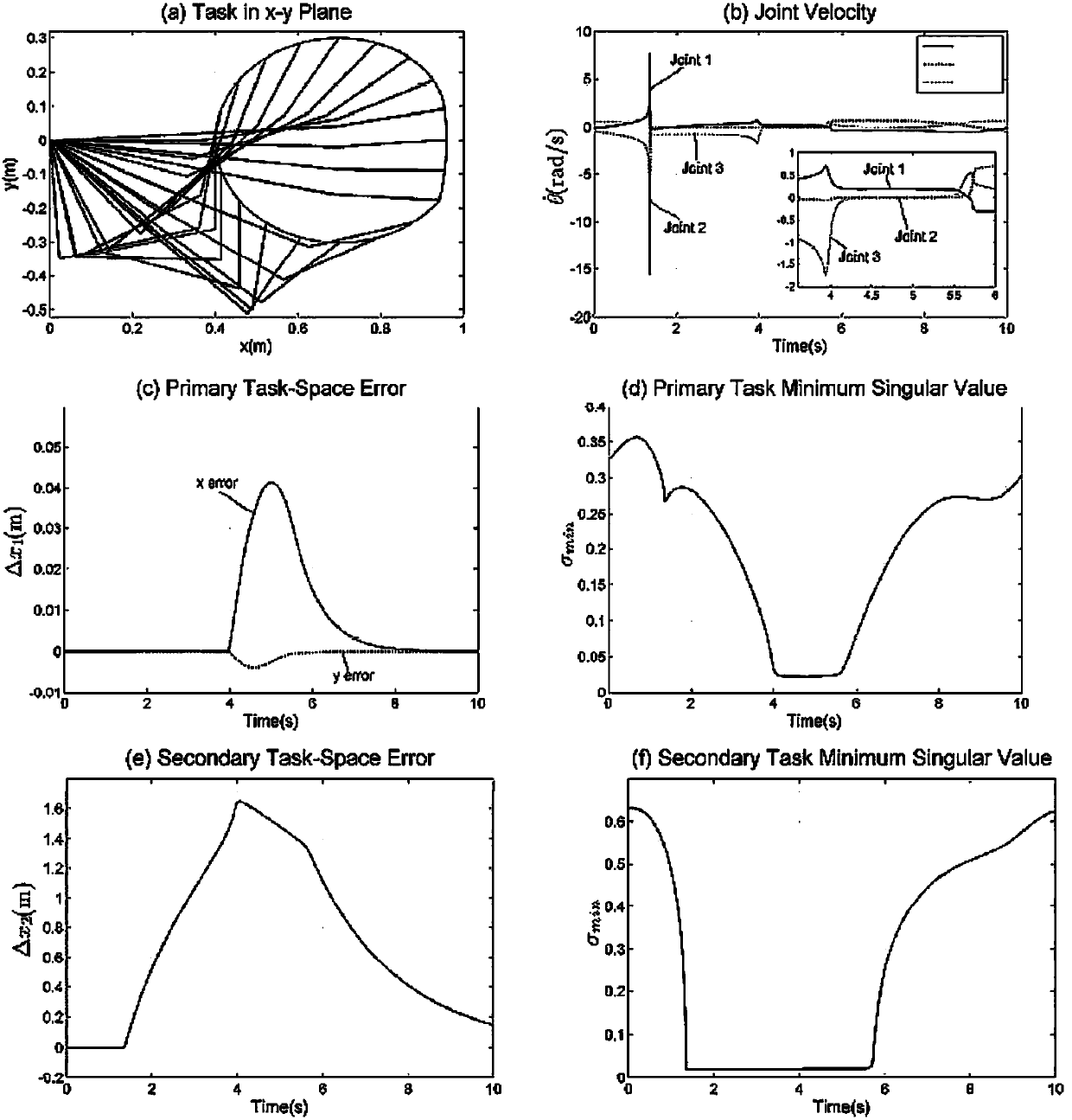
ActiveCN108247631AGuaranteed tracking effectEasy to trackProgramme-controlled manipulatorUnitary matrixEngineering
The invention discloses a mechanical arm autonomous robust singularity avoidance method for improving path tracking performance. The method comprises the steps that a maneuverable ellipsoid of a mechanical arm is built according to an inverse kinematics model of the mechanical arm and a mechanical arm speed model, wherein the semi-major axis of the maneuverable ellipsoid is in the direction of theU longitudinal row of a unitary matrix, and the length of the semi-major axis corresponds to singular value of a Jacobian matrix; and then the path of an end effector is amended in the mth spindle direction of the maneuverable ellipsoid, and the singularity avoidance path of the mechanical arm is built. The method can be used for planning the autonomous singularity avoidance path of the mechanical arm, can keep the tracking performance of the path, and can also achieve the multi-task singularity avoidance path planning on the basis of task priority based on the method.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV +1
Method for de-orbiting GEO (geostationary orbit) satellite by using residual propellant and helium gas
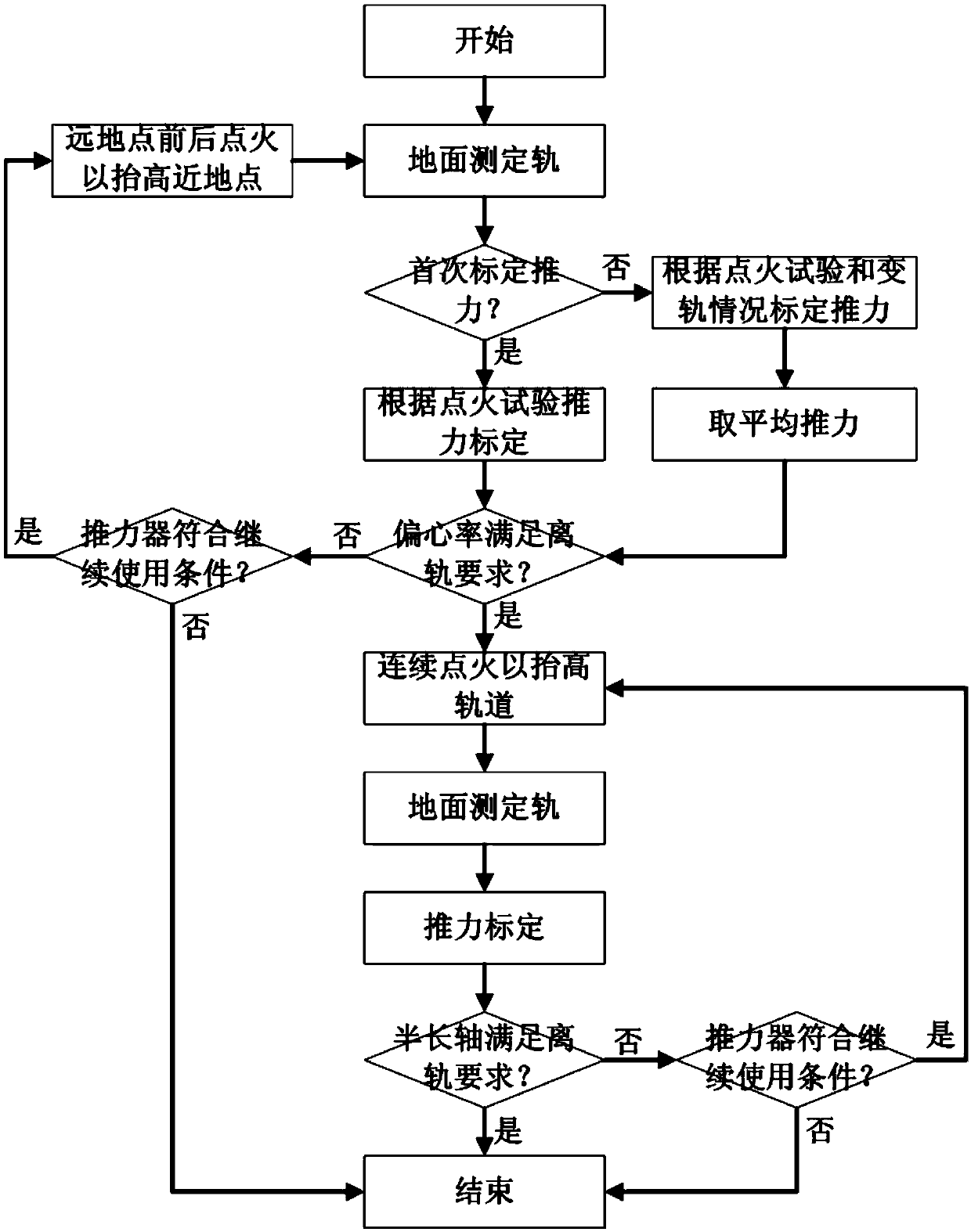
ActiveCN109515758AReduce threatUnlimited off-orbit operationsCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusNatural satelliteEngineering
A method for de-orbiting a GEO satellite by using residual propellant and helium gas comprises the steps: (1) determining an orbit on the ground; (2) performing thrust calibration: thrust calibrationis performed according to an ignition test of a thruster under different conditions, or combined calibration is performed to obtain a first calibrated thrust; 3) judging whether the eccentricity ratioof the orbit meets the de-orbiting requirement or not, and then judging whether the thruster meets the use condition or not; (4) lifting the perigee, lifting the orbit, measuring the orbit again andperforming combined calibration to obtain a second calibration thrust; and (5) judging whether the semi-major axis of the orbit meets the de-orbiting requirement or not, and then judging whether the thruster meets the use condition or not. In a de-orbiting process, the method can fully utilize the residual propellant and helium gas, lift the semi-long axis of the orbit as much as possible, and reduce the threat to other GEO satellites.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
Compensation elevation plane or mean elevation plane-based 3-degree zoning coordinate conversion system
InactiveCN107908808AMeet the precision requirementsVerify correctnessGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationCoordinate changeClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a compensation elevation plane or mean elevation plane-based 3-degree zoning coordinate conversion system. By research on a geodetic coordinate change law of a control point ona reference ellipsoid, a compensation elevation plane or a testing zone and a mean elevation plane of a city, a calculation method for a semi-major axis of a new ellipsoid after adoption of the compensation elevation plane or the testing zone and the mean elevation plane of the city, a calculation method for a geodetic latitude correction number and new geodetic latitude of the ground control point, and a calculation method for calculating direct and inverse computation parameters by taking the compensation elevation plane or the testing zone, the mean elevation plane of the city, the semi-major axis of the ellipsoid and first eccentricity as arguments are derived. Compared with the prior art, the control point is transferred to the compensation elevation plane or the testing zone and themean elevation plane of the city from the CGCS2000 ellipsoid according to calculation formulae for the direct and inverse computation parameters; high-precision coordinate conversion of geodetic coordinates and plane coordinates can be realized; and a conversion mode is also suitable for a 1980 Xi an coordinate system, a 1954 Beijing coordinate system and local independent coordinate systems.
Owner:SHANDONG JIAOTONG UNIV
Anti-corrosion mobile floating island
ActiveCN106564571ASmooth sailingReduce shockWatercraft hull designShip vibration reductionSeakeepingEngineering
The invention relates to an anti-corrosion mobile floating island. The anti-corrosion mobile floating island comprises a working platform, a plurality of first buoys, a plurality of second buoys and a connecting component, wherein the connecting component is used for fixedly connecting the working platform, the plurality of the first buoys and the plurality of the second buoys; the connecting component comprises a plurality of first connecting units; and each first connecting unit comprises a first connecting column and a second connecting column, wherein two ends of the first connecting column are fixedly connected with the working platform and the side surface of one first buoy, respectively; the radial section of the first connecting column is elliptical; elliptical semi-major axis where the first connecting column is placed is vertical to the axial direction of the first buoy; two ends of the second connecting column are fixedly connected with the side surface of one first buoy and the side surface of one second buoy, respectively; the radial section of the second connecting column is elliptical; the elliptical semi-major axis where the second connecting column is placed is vertical to the axial direction of the first buoy; and the axial direction of the second connecting column of each first connecting unit is coincided with the axial direction of the first connecting column. The anti-corrosion mobile floating island provided by the invention has the advantage of good seakeeping capability.
Owner:深圳市海斯比浮岛科技开发有限公司
Design method for airship returning back to predetermined fall point recursive orbit
The invention provides a design method for an airship returning back to a predetermined fall point recursive orbit. According to the design method for the airship returning back to the predetermined fall point recursive orbit, a sub-satellite point can accurately pass a predetermined fall point by selecting a rail mean anomaly, a rail satisfies recursive characteristics by adjusting the rail semi major axis, a double-layer iteration solution process for two parameters of the rail semi major axis and the rail mean anomaly is established, design parameters which are mutually matched with the rail inclination angle, the rail semi major axis and the rail mean anomaly are obtained, and an airship sub-satellite point track is guaranteed accurately passing through the predetermined fall point at every recursive period.
Owner:中国人民解放军63920部队
Satellite position and speed forecasting method based on GLONASS almanac parameters
InactiveCN107238846AReduce complexitySmall amount of calculationSatellite radio beaconingAngular velocitySatellite orbit
The invention discloses a satellite position and speed forecasting method based on GLONASS almanac parameters. The method of the invention utilizes the GLONASS almanac parameters to estimate the satellite position and the speed at a quick pace and with small computation amount. According to the invention, based on the satellite orbit kinetic principle and the orbital element representing method for the satellite position and speed and according to the GLONASS almanac parameters, the orbital parameters and their changing rates at the observation period such as the average angular velocity, the semi-major axis, the eccentric anomaly, the mean anomaly, and the ascending node right ascension can be worked out so as to seek the latitude amplitude, the latitude amplitude changing rate, the radial vector and the radial vector changing rate. In this manner, the position and the speed of the satellite in the orbital coordinate system can be worked out; and according to the coordinate conversion formula, the position and the speed of the satellite in the PZ-90 coordinate system can be worked out finally.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Autonomous orbit maintaining method of satellite based on increment on-line estimation
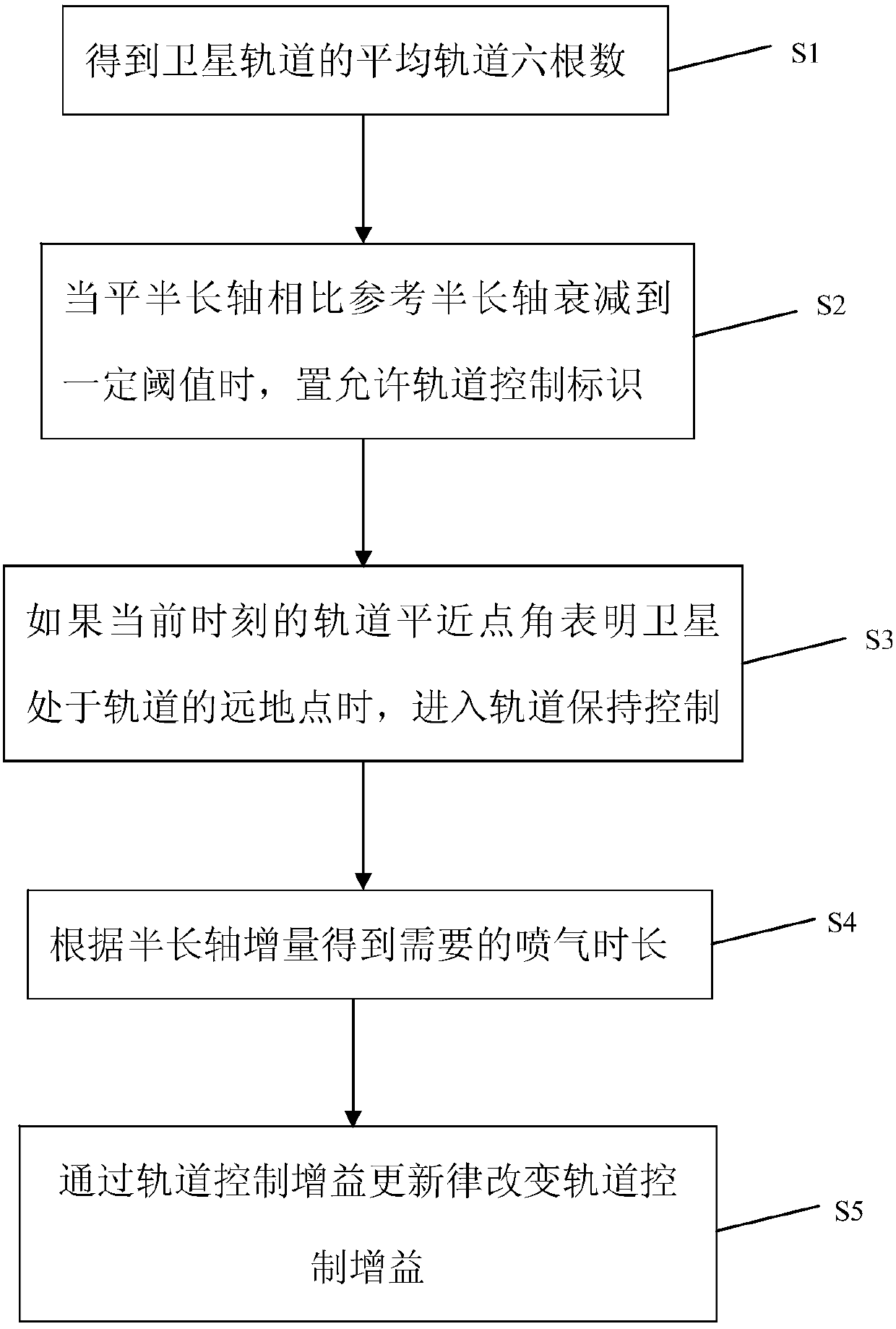
ActiveCN107554820AReduce precisionSmall amount of calculationSpacecraft guiding apparatusNatural satelliteSatellite orbit
The invention discloses an autonomous orbit maintaining method of a satellite based on increment on-line estimation. The autonomous orbit maintaining method comprises the following steps of S1, acquiring six average orbit instantaneous elements of a satellite orbit; S2, compared with a referring semi-major axis, when an average semi-major axis is attenuated to a certain threshold, placing an orbitcontrol allowing mark; S3, if an orbit mean anomaly of at current moment indicates that the situation that the satellite is located at a far point away from the orbit, entering the orbit keeping control; S4, if in the first control cycle of the orbit keeping control, according to the attenuate degree of the current orbit average semi-major axis, performing calculating to obtain the required increment of the semi-major axis; adopting orbit control increment which can be updated on-line to calculate the jet duration of the orbit control, if not in the first control cycle of the orbit keeping control, judging whether the jet duration of the current orbit control achieves the jet duration of the orbit control or not, and if not, continuing performing jetting, or else, placing an orbit controlfinishing mark, and exiting the orbit control; and S5, calculating deviation between the change quantity of a target semi-major axis and the actual variation of the semi-major axis, and changing theorbit control increment through an update rule of the orbit control increment.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
Low-thrust phase modulation maneuvering method among coplanar circular orbits
InactiveCN102508999AImprove design efficiencySimplify complexitySpecial data processing applicationsNonlinear systems of equationsComputer science
The invention discloses a low-thrust phase modulation maneuvering method among coplanar circular orbits. The method comprises the following steps of: calculating an initial phase difference; 2, calculating a maneuvering parameter of an internal and external spinning strategy; and 3, determining a phase modulation maneuvering parameter. According to the method, a phase relation between a tracking spacecraft and a target spacecraft is described by mean anomalies of the orbits, so that a relation of parameters, such as the initial phase difference, a thrust direction and the like, is acquired; two feasible phase modulation strategies are acquired according to a characteristic of a phase modulation task on the basis of the relation, so that the complexity of an algorithm is simplified; a nonlinear equation group which is met by the phase modulation turnaround time and a mean semi-major axis is built by using an orbit meaning technology; and the equation group can be solved through simple Newton iteration, so that the robustness of the algorithm is enhanced, and the design efficiency is improved. In the method, a method for quickly judging a phase modulation direction is provided, so that a rational and feasible initial value forecast is supplied to a precise design of a low-thrust phase modulation orbit.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Orbit control method by utilizing interference accumulation angular momentum self balance
ActiveCN103076809AAchieving Disturbance Angular Momentum Self-balancingEasy to adjustPosition/course control in three dimensionsOrbital periodMomentum
The invention discloses an orbit control method by utilizing the interference accumulation angular momentum self balance. The method comprises the following steps that the starting offset angular momentum is built at the starting moment of the satellite orbit control; the orbit control time Tp of the satellite by utilizing an orbit control thruster in each orbit control process is determined; and in one orbit period of the satellite, M orbit control points are uniformly selected for carrying out orbit control. After the orbit control method is adopted, the goal that the interference accumulation angular momentum generated by utilizing the orbit control thruster in the orbit semi-major axis regulating process is used for controlling the satellite orbit is realized.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Method for adjusting fixed point position of satellite stationary orbit
InactiveCN108614575AReduce control errorEasy to controlCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsOrbitSatellite
The invention discloses a method for adjusting a fixed point position of a satellite stationary orbit. The method comprises: S1, calculating orbital transit time of a satellite according to a transferinitial point, an end point and maximum transfer time; S2, calculating a semi-major axis changing amount of a satellite secondary pulse with harmonic term perturbation; S3, calculating a secondary pulse considering tesseral harmonic term perturbation; and S4, calculating a cubic pulse considering the tesseral harmonic term perturbation. Therefore, a problem of low fixed point position adjustmentprecision of the stationary orbit satellite is solved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF ELECTRONICS SYST ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com