Method for de-orbiting GEO (geostationary orbit) satellite by using residual propellant and helium gas
A kind of propellant and satellite technology, which is applied in transportation and packaging, space navigation equipment, space navigation aircraft, etc. It can solve the problems that have not yet been used, the calculation error of GEO satellite propellant is large, and the thrust of the propulsion subsystem is unstable. To achieve the effect of facilitating off-track strategy, facilitating adjustment, and reducing threats
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
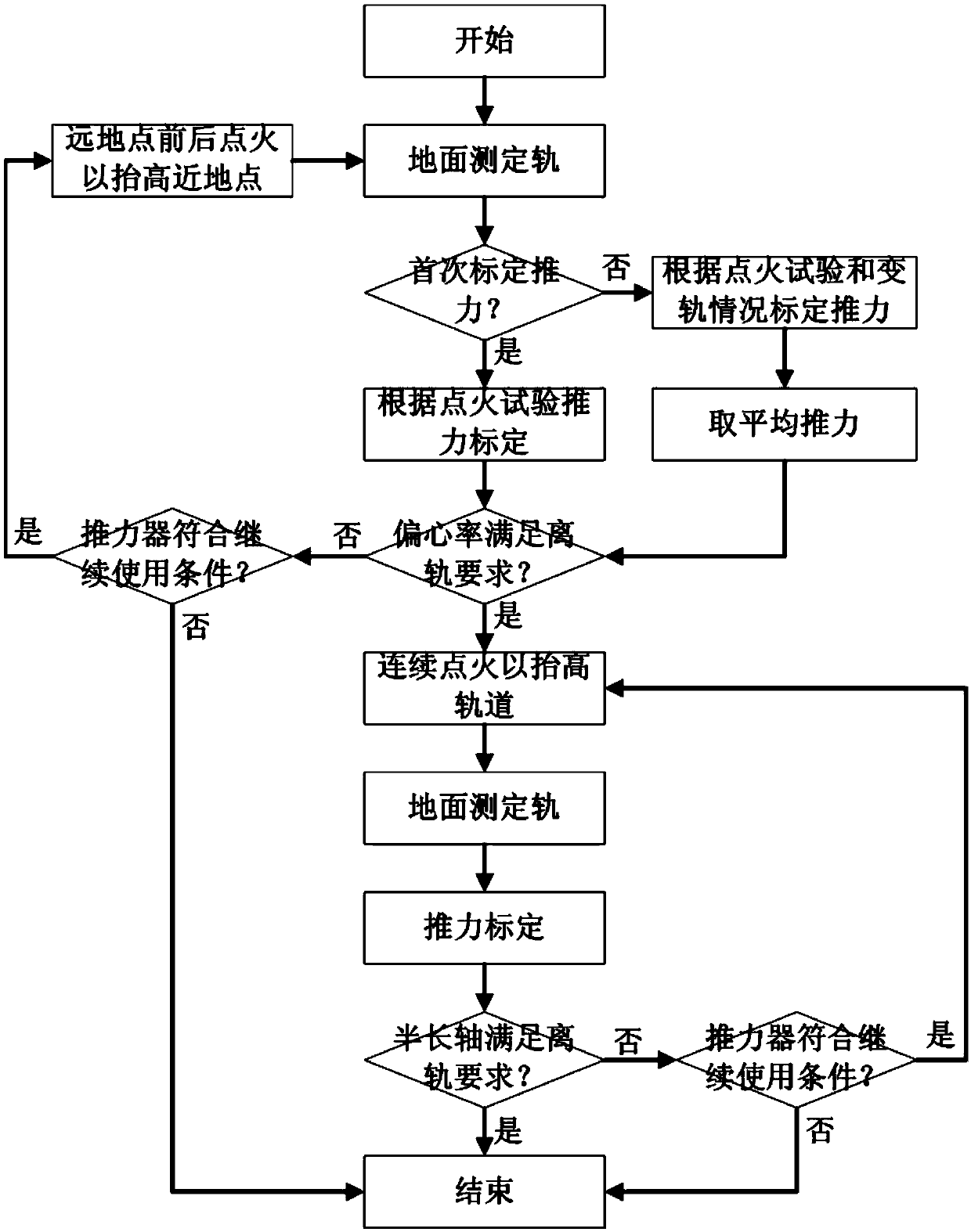
[0051] Such as figure 1 As shown, a kind of GEO satellite off-orbit method that utilizes residual propellant and helium that the present invention proposes, the steps are as follows:
[0052] (1) Measure the orbit of the GEO satellite on the ground, and output the number of orbit elements;
[0053] The ground station measures and determines the orbit of the GEO satellite, and outputs the semi-major axis, inclination, eccentricity, right ascension of ascending node, argument of perigee, and anomaly of the satellite.
[0054] (2) Thrust calibration: judge whether to perform thrust calibration for the first time, if it is the first time to perform thrust calibration, then enter step (3); otherwise, enter step (4);
[0055] (3) Carry out thrust calibration according to the thruster ignition test, and then enter step (6);
[0056] (4) Combined calibration: perform thrust calibration according to thruster ignition test and thrust calibration according to semi-major axis change;
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com