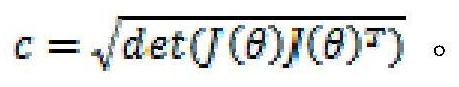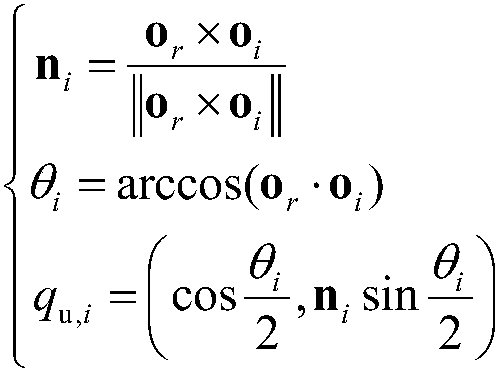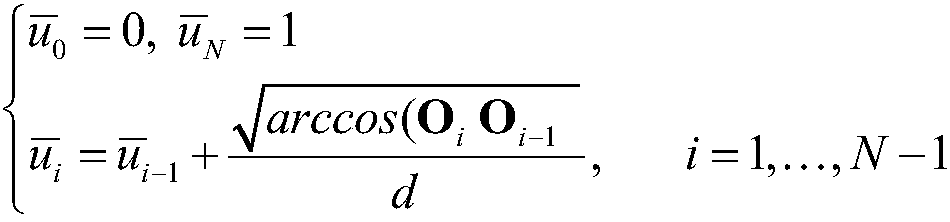Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
45 results about "Singularity avoidance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
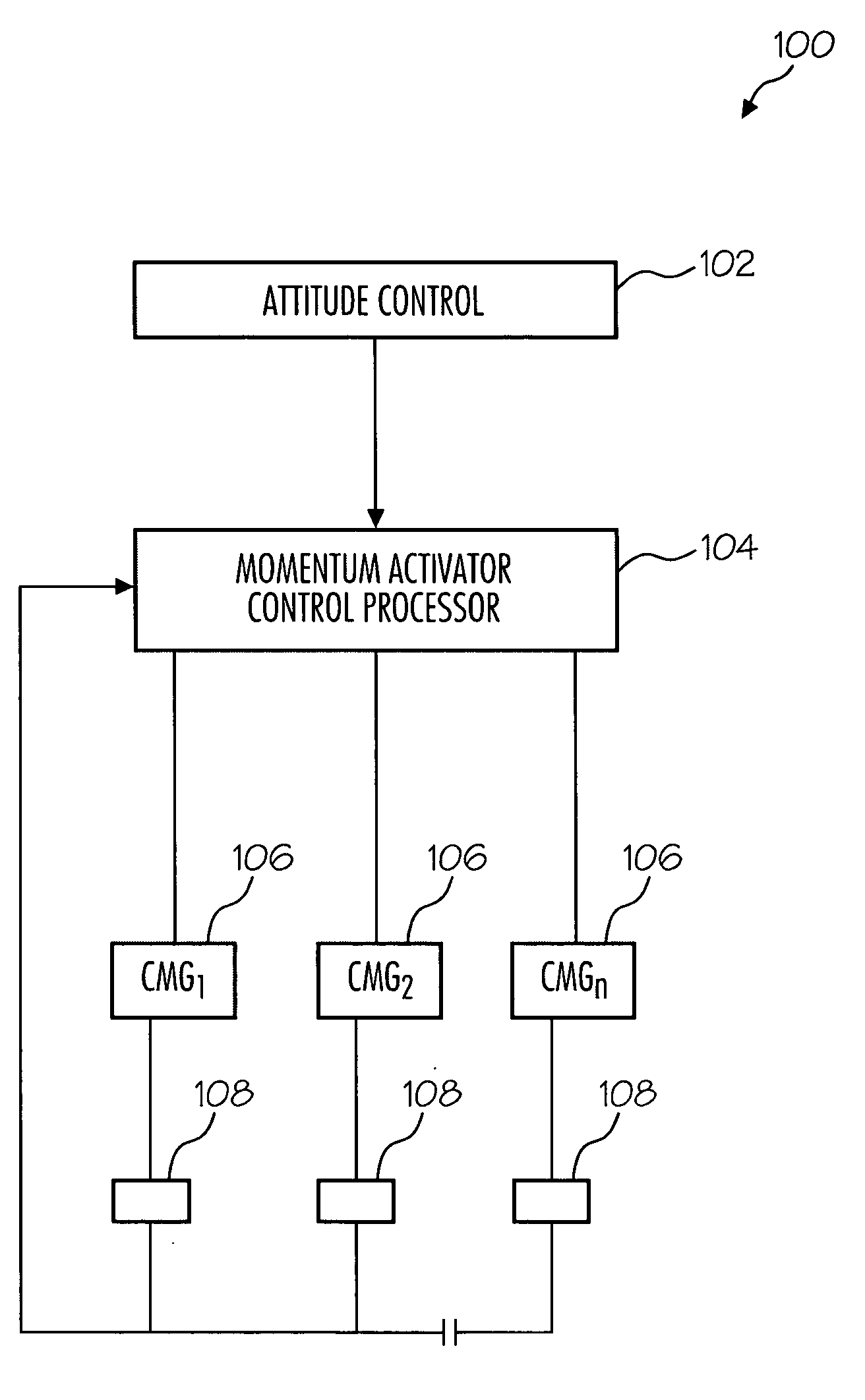
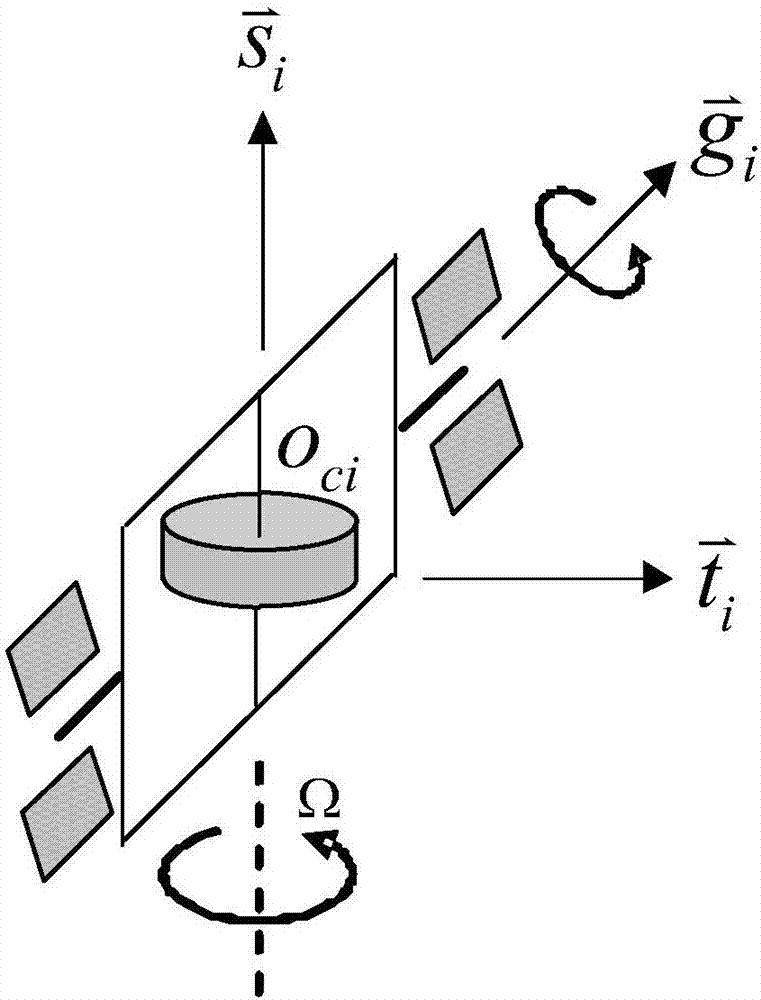
Method and system for CMG array singularity avoidance
ActiveUS20060027708A1Cosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsPresent methodSingularity avoidance
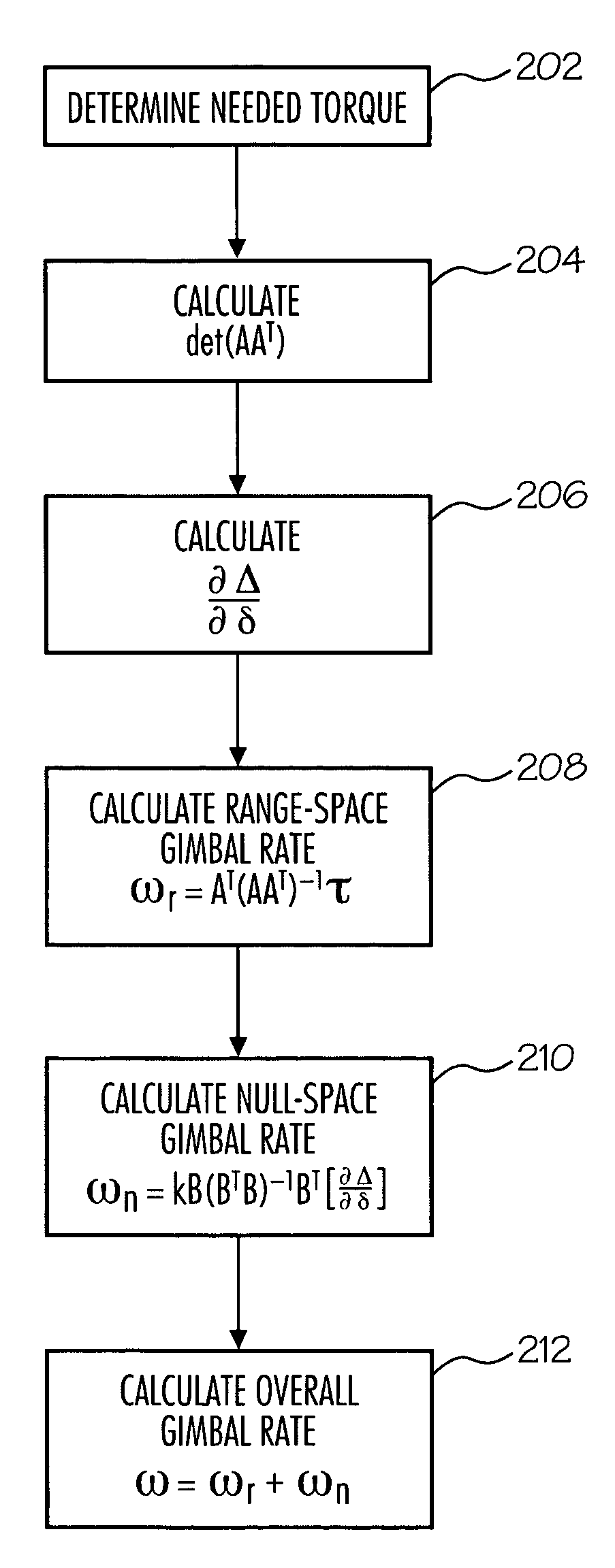
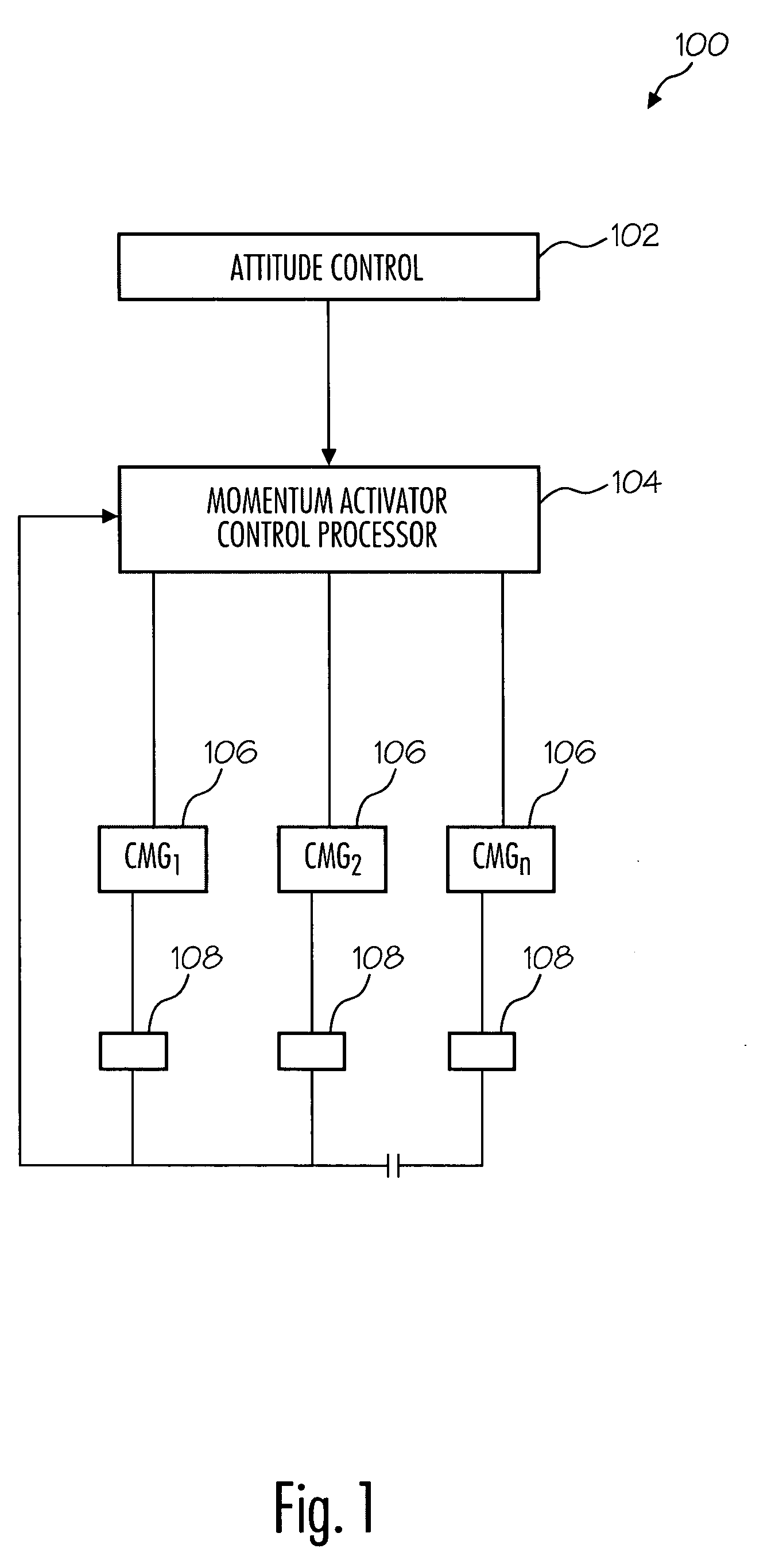
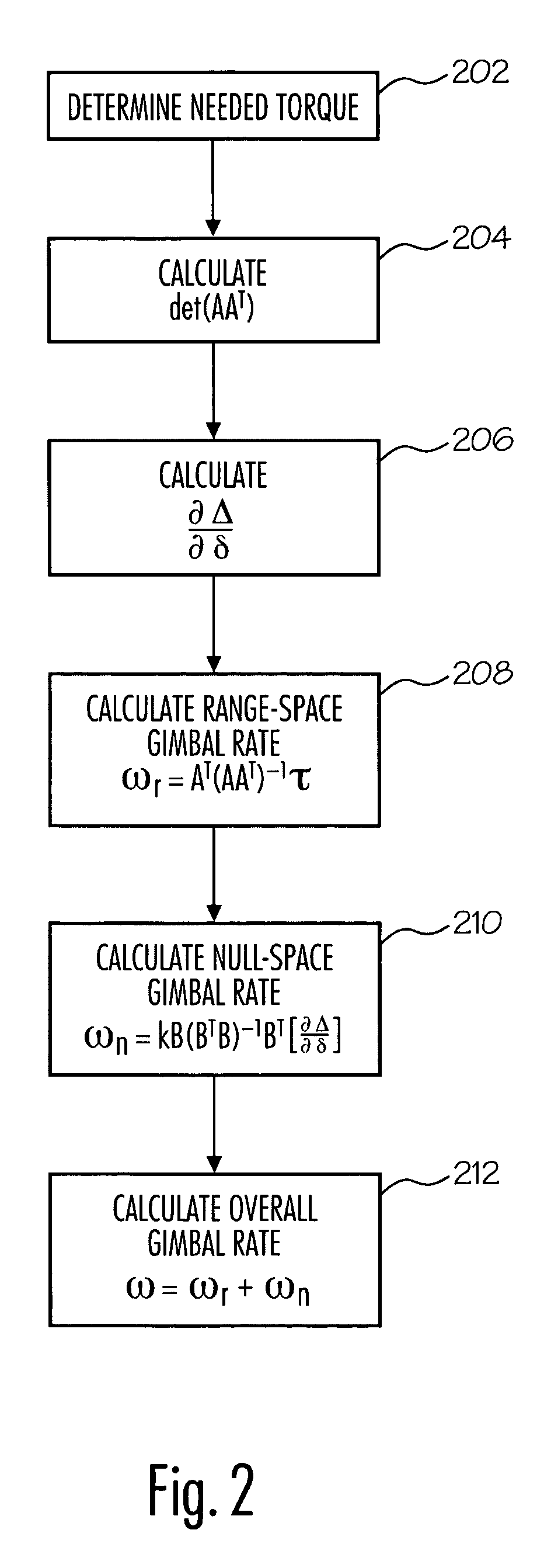
The present method provides a method for avoiding singularities in the movement of CMGs in an array of CMGs in a spacecraft. In a first step, a torque command representing a desired torque to produce an attitude adjustment for the spacecraft is received. Next, a range-space gimbal rate required to produce the desired torque based on the desired torque and a Jacobian matrix is calculated. Then, a null-space gimbal rate that assists in the avoidance of singularities is calculated. The total gimbal rate command is determined by summing the range-space gimbal rate and the null-space gimbal rate. Then, the total gimbal rate command is provided to the CMGs to produce the total gimbal rate.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
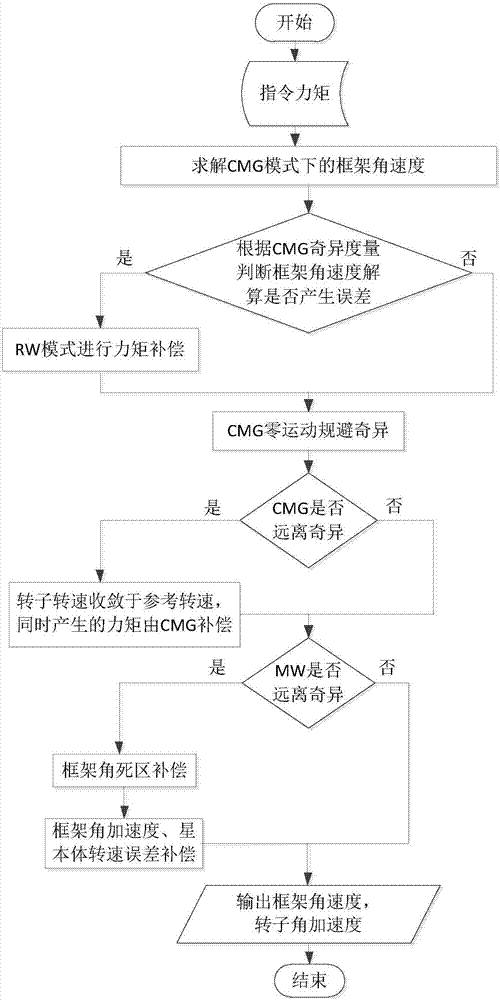
Angular momentum management method for variable-speed control moment gyroscope
The invention relates to an angular momentum management method for a variable-speed control moment gyroscope (VSCMG). A technical scheme is described as follow. An angular momentum management algorithm for the VSCMGs is designed to mainly solve the following problems: mixed mode instruction torque output based on singularity measurement, zero-motion rotor wheel speed balance, zero-motion frame configuration singularity avoidance, frame angular velocity dead-zone nonlinear processing and neglected item compensation, and gives corresponding theoretical analysis. The mixed mode of the VSCMGs gives full scope to the large torque output of the control moment gyroscope and large-angle fast attitude maneuver operation can be achieved by using the steering law. The present invention provides a novel VSCMGs angular momentum management algorithm which is improved significantly in torque output accuracy, angular velocity tracking, and frame singularity avoidance compared with a conventional angular momentum management algorithm, and which has a good engineering value.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
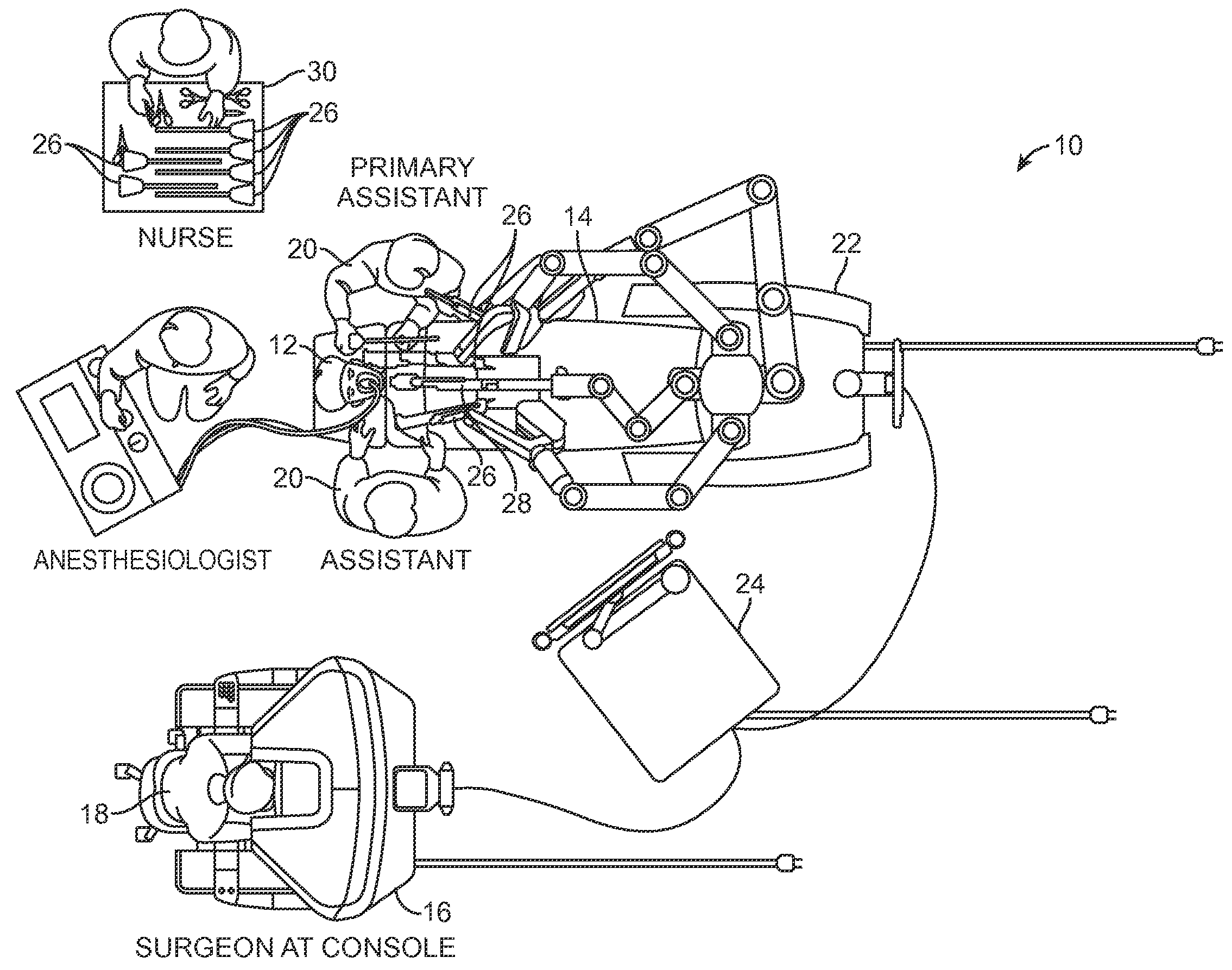
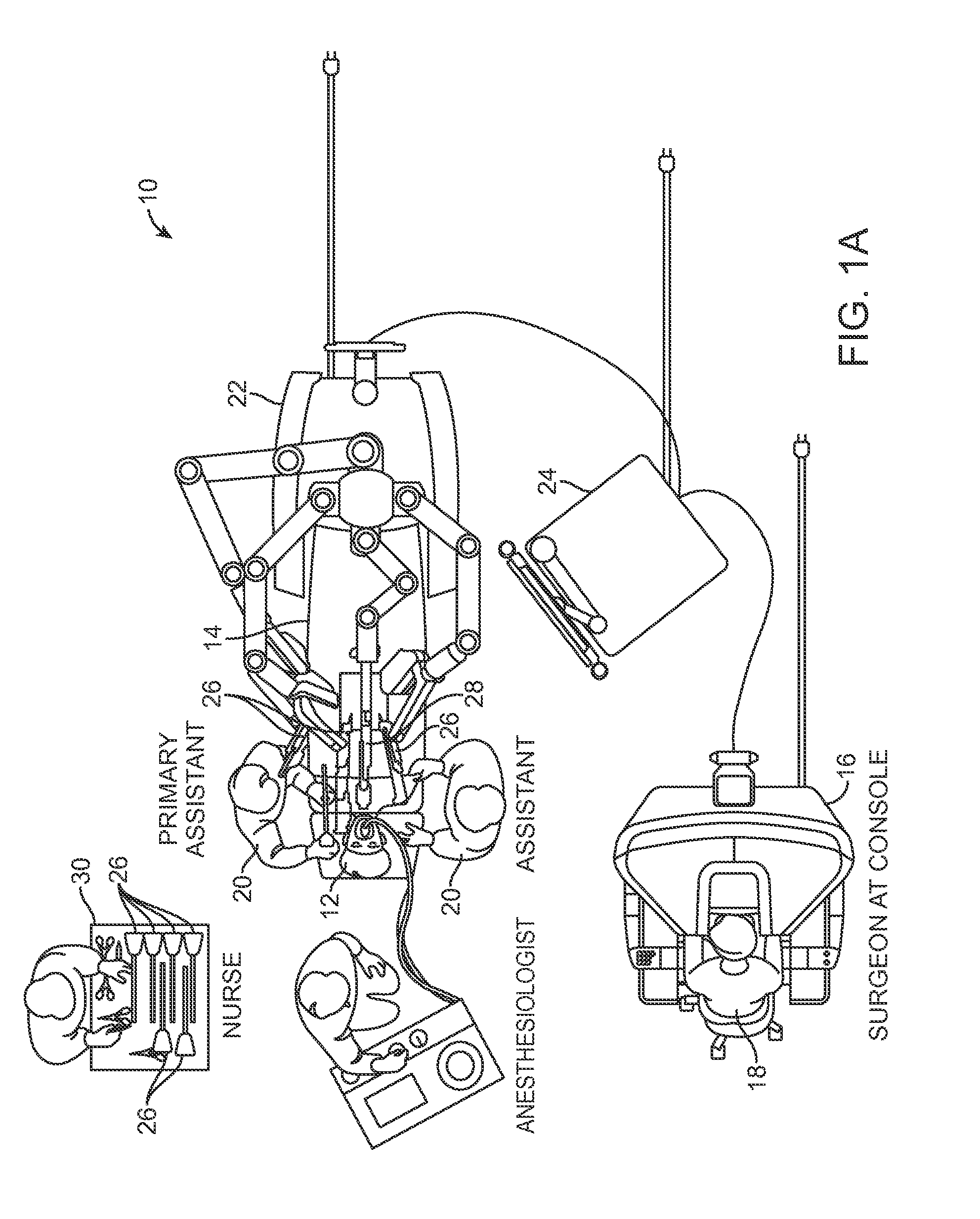
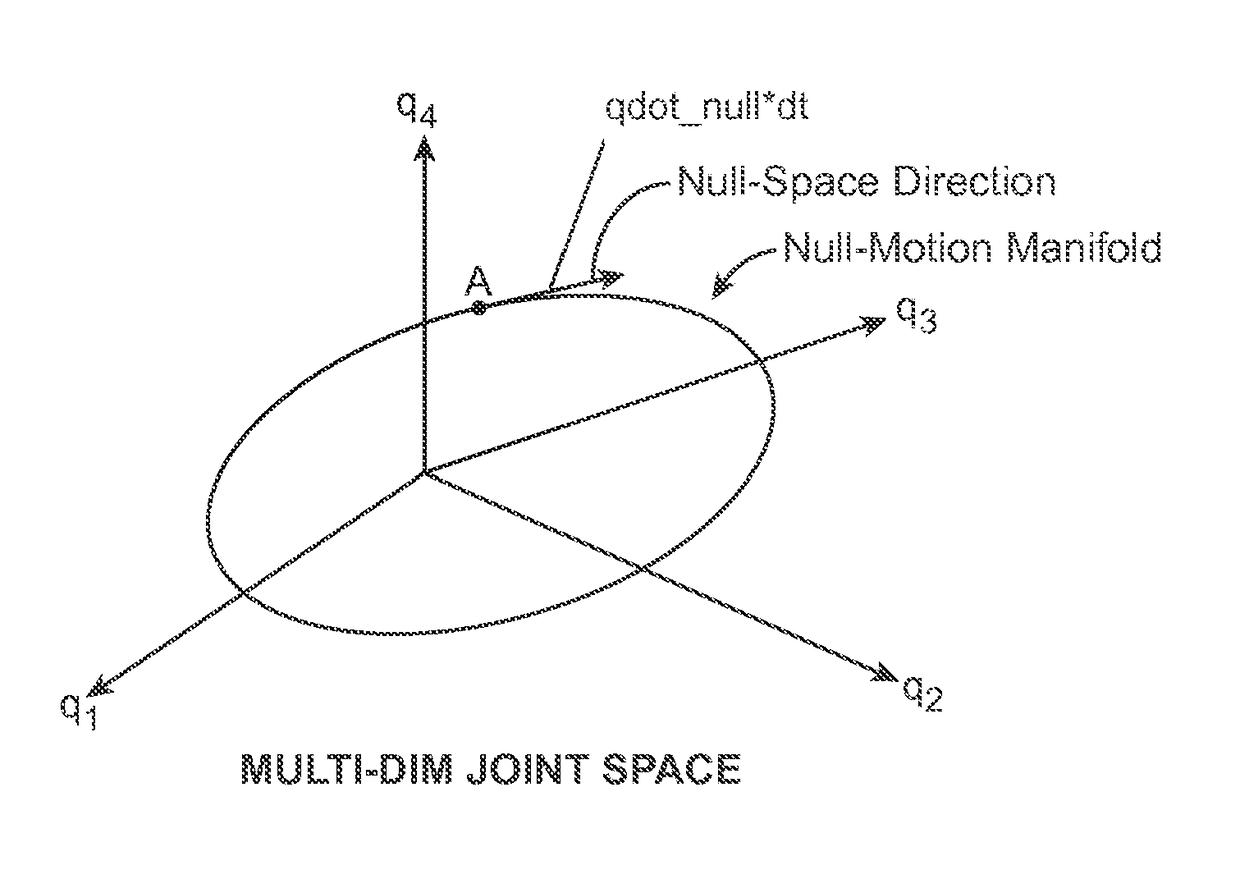
System and methods for managing multiple null-space objectives and SLI behaviors
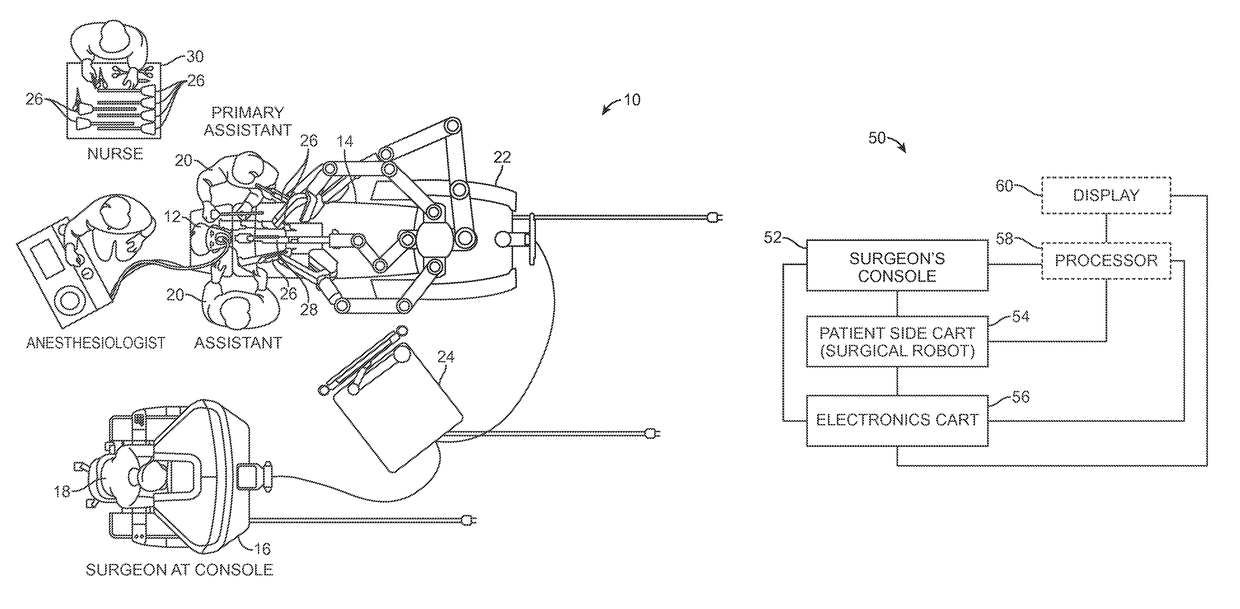
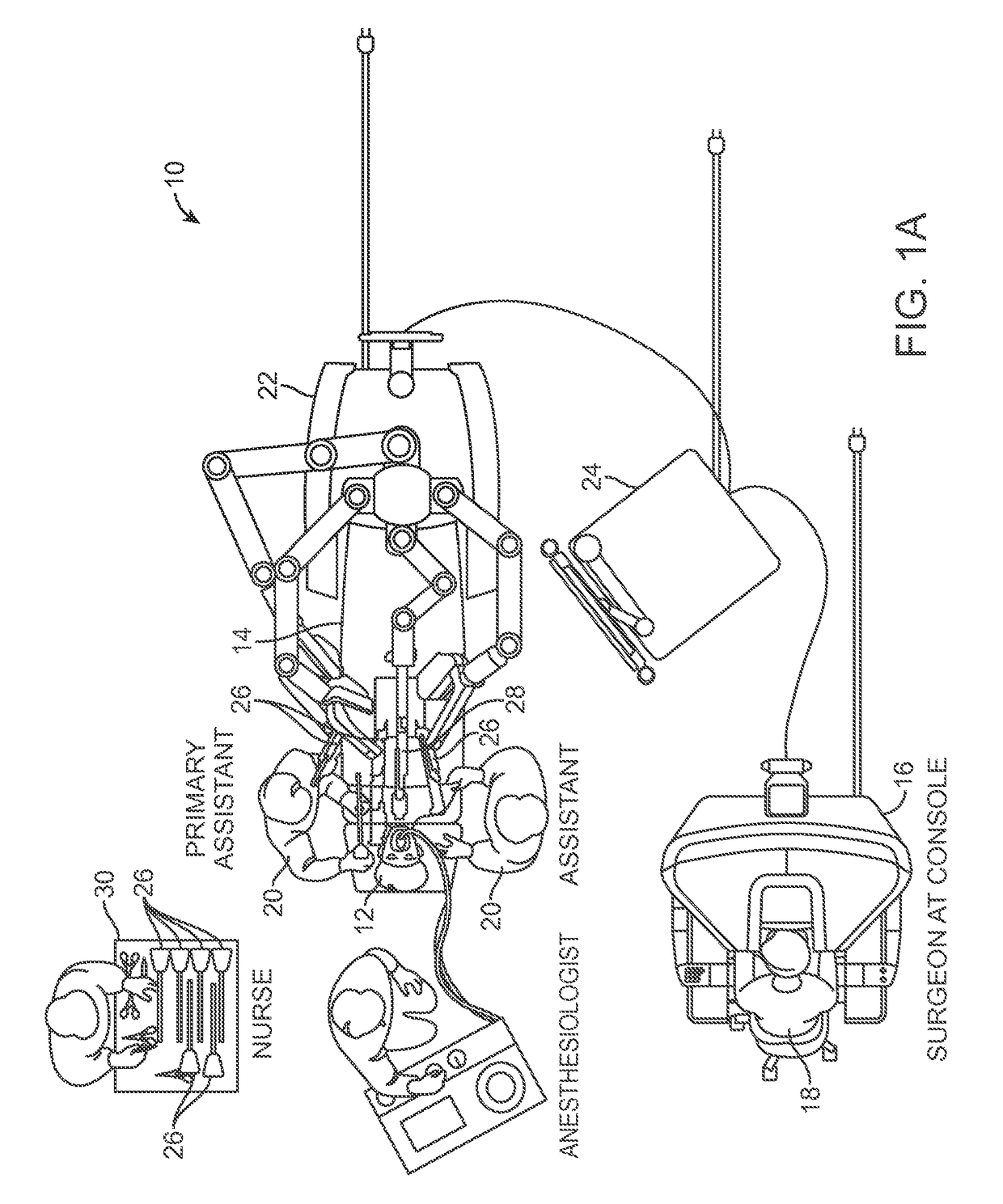
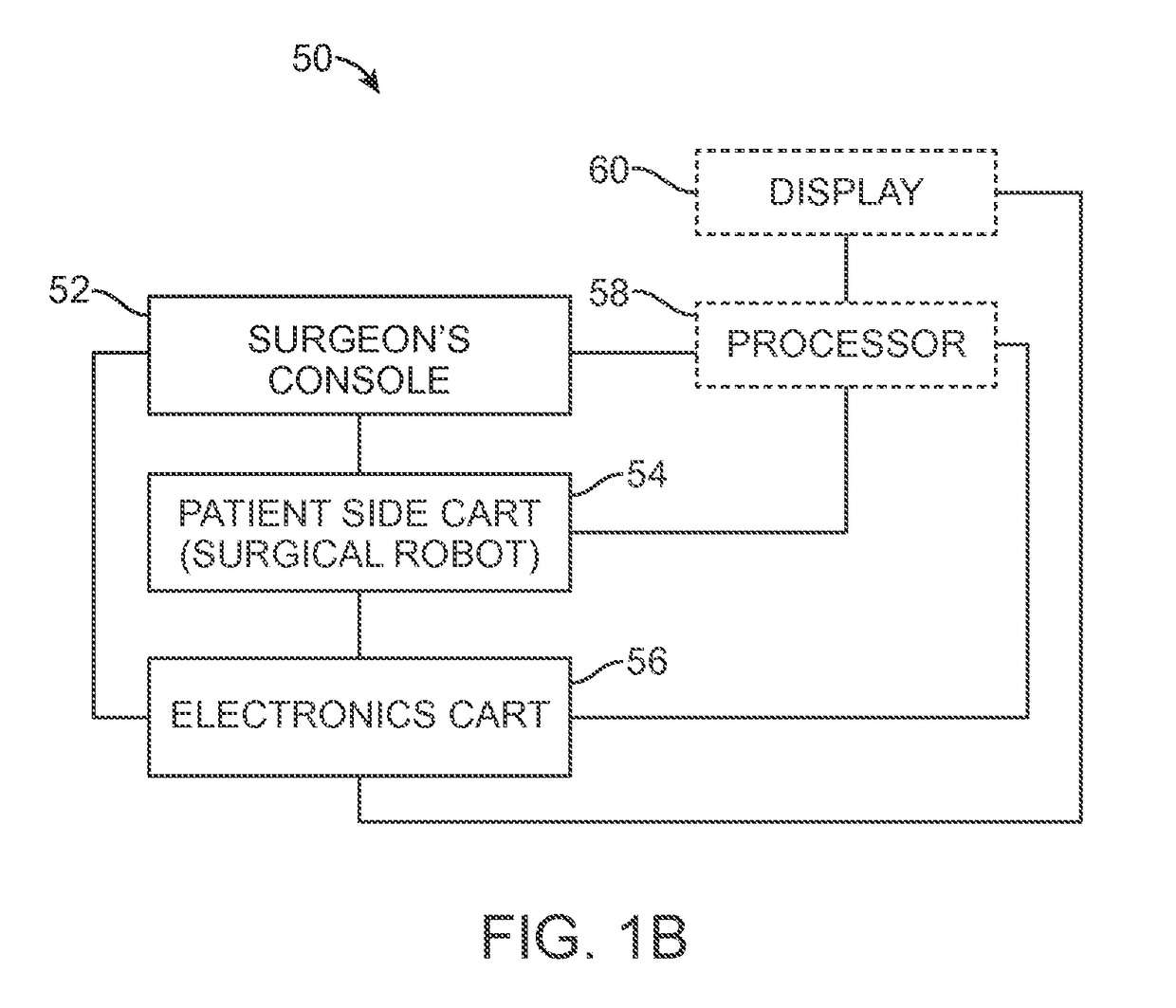
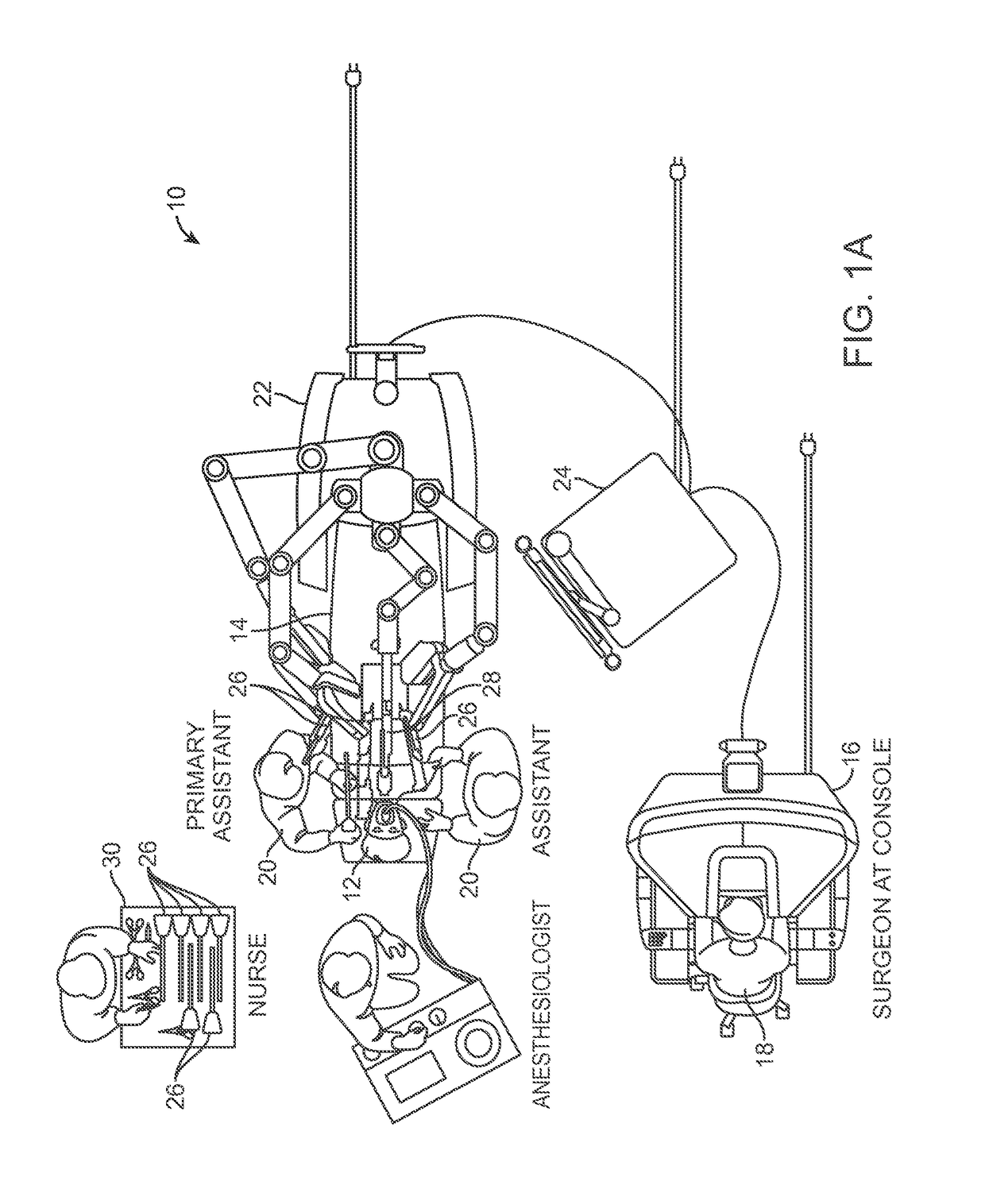
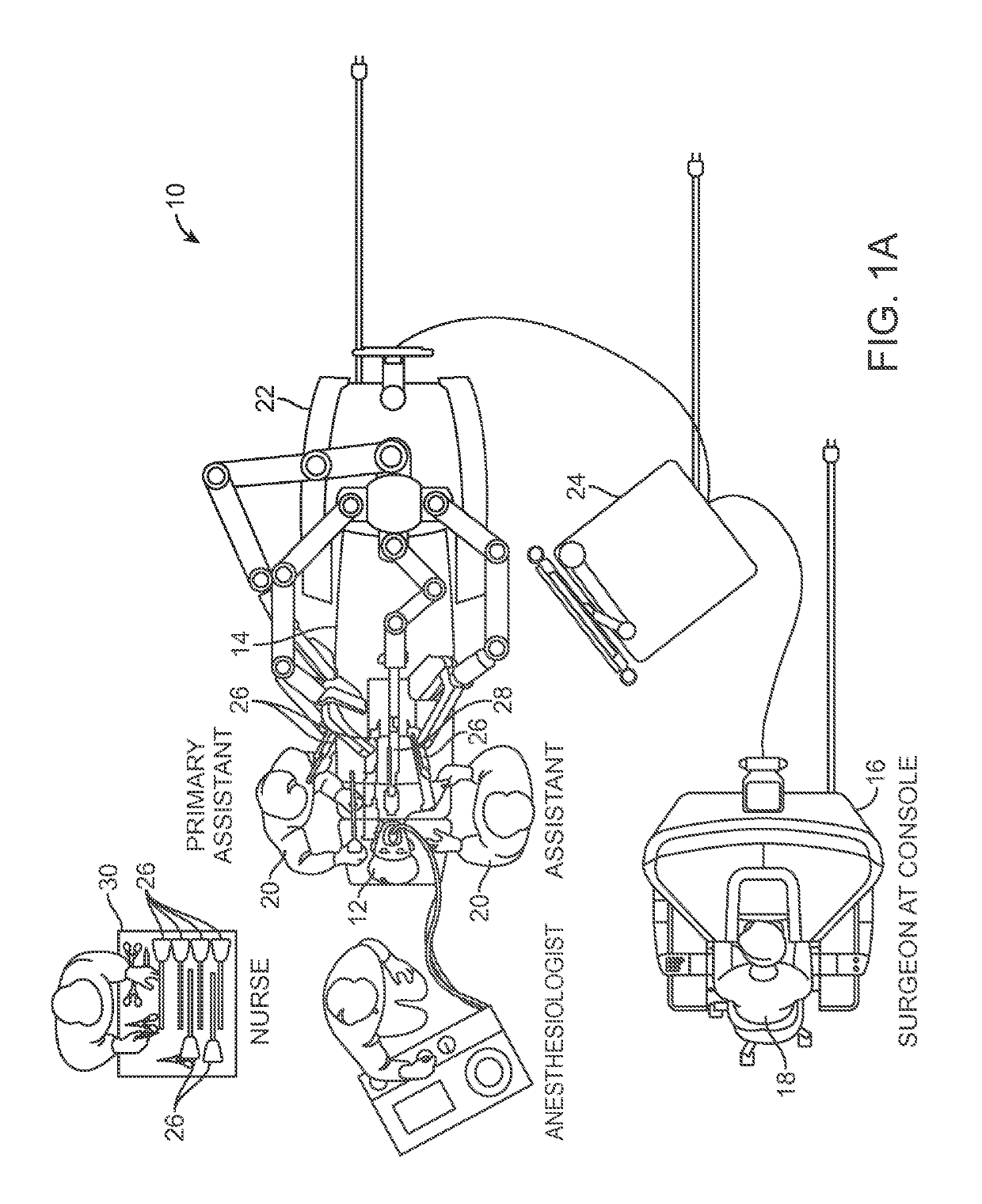
ActiveUS9510911B2Highly configurableExtended range of motionProgramme-controlled manipulatorSurgical robotsSingularity avoidanceEngineering
Devices, systems, and methods for providing commanded movement of an end effector of a manipulator concurrent with a desired movement of one or more joints of the manipulator according to one or more consolidated null-space objectives. The null-space objectives may include a joint state combination, relative joint states, range of joint states, joint state profile, kinetic energy, clutching movements, collision avoidance movements, singularity avoidance movements, pose or pitch preference, desired manipulator configurations, commanded reconfiguration of the manipulator, and anisotropic emphasis of the joints. Methods include calculating multiple null-space movements according to different null-space objectives, determining an attribute for each and consolidating the null-space movements with a null-space manager using various approaches. The approaches may include applying weighting, scaling, saturation levels, priority, master velocity limiting, saturated limited integration and various combinations thereof.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Teleoperated robot for flood-welding operations
ActiveUS20170232615A1Inhibition effectAvoid heatingProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorJoystickVisual perception
A remote controlled, tele-operated welder includes a multi-axis robot arm, video cameras, sensors a specialized control station that allows an operator to perform flood-fill welding operations at a remote location to avoid the heat, smoke and other environmental effects produced through typical flood-welding operations. The operator accesses the control unit (OCU) using a GUI and mouse, keyboard, joystick, or other custom controls, and observe the piece via the cameras (visual, thermal, or other) placed in the welding station via a feed displayed on the OCU display(s). Audio, video, and / or tactile feedback may be provided to indicate arm, welder, or other system status, for collision warning and arm motion singularity avoidance. Augmented reality informational graphic / textual overlays may provide guidance to an operator, and the apparatus may further include the ability to repeat series of steps needed to handle flood-weld on a given piece, repeatedly across many pieces.
Owner:HAMMOCK DARRYL
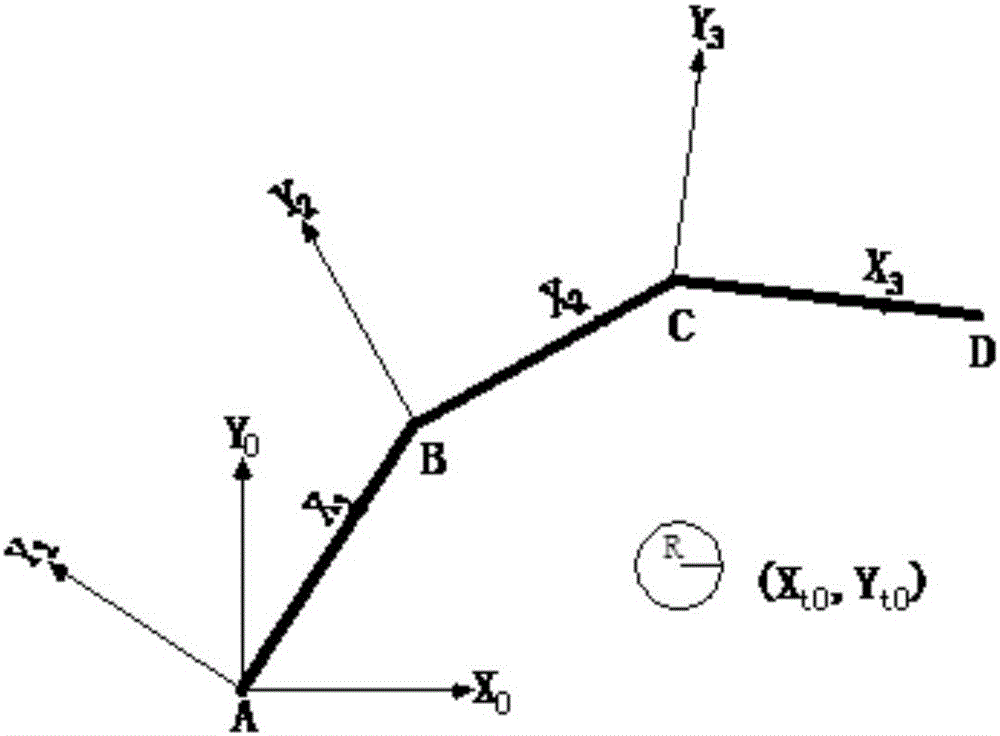
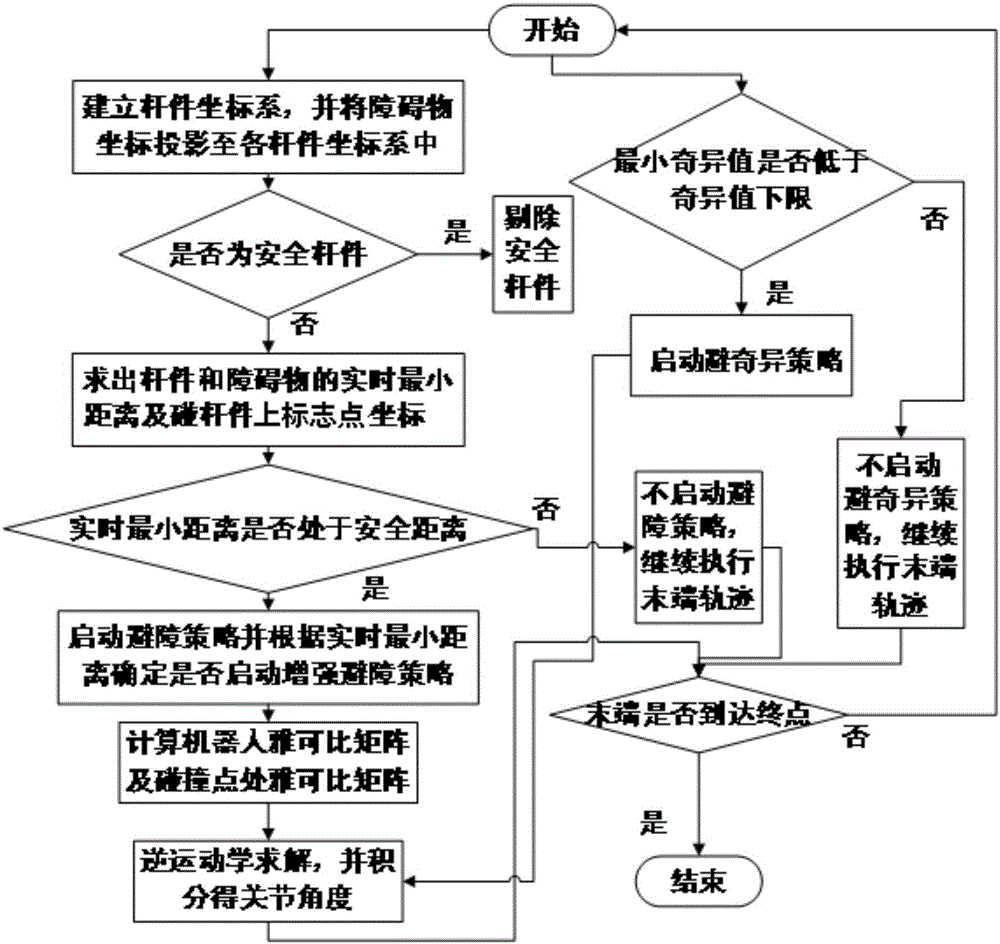
A path programming method for a plane redundancy robot to avoid obstacles and avoid singularities
InactiveCN105700527AReduce risk of collaborationImprove assembly qualityPosition/course control in two dimensionsSimulationPlanning approach
A path programming method for a plane redundancy robot to avoid obstacles and avoid singularities relates to the field of robot motion control, and especially relates to a plane redundancy robot to avoid obstacles and avoid singularities. The invention aims to solve problems that risk of hurting working personnel by existing plane redundancy robots exists in a cooperation process and the speed of joints will exceed a robot allowance scope when the end of the robot moves to a singular position. The method of the invention is carried out according to the following steps: the method of the invention relates to threads which are carried out simultaneously: the first thread relates to several steps of path programming to avoid obstacles; and the second thread relates to various steps of path programming to avoid singularities. The method of the invention ca simultaneously complete the path programming method of obstacle avoidance and singularity avoidance, so that in a cooperation process, collaborator avoidance can be completed, and avoiding of singular configuration of the robot can also be realized to reduce risks of man-machine cooperation and raise the assembling quality. The method of the invention can be applied to the field of robot motion control.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
System and method for managing multiple null-space objectives and constraints
ActiveUS10029367B2Highly configurableExtended range of motionProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsSpatial managementEngineering
Devices, systems, and methods for providing commanded movement of an end effector of a manipulator concurrent with a desired movement of one or more joints of the manipulator according to one or more consolidated null-space objectives. The null-space objectives may include a joint state combination, relative joint states, range of joint states, joint state profile, kinetic energy, clutching movements, collision avoidance movements, singularity avoidance movements, pose or pitch preference, desired manipulator configurations, commanded reconfiguration of the manipulator, and anisotropic emphasis of the joints. Methods include calculating multiple null-space movements according to different null-space objectives, determining an attribute for each and consolidating the null-space movements with a null-space manager using various approaches. The approaches may include applying weighting, scaling, saturation levels, priority, master velocity limiting, saturated limited integration and various combinations thereof.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
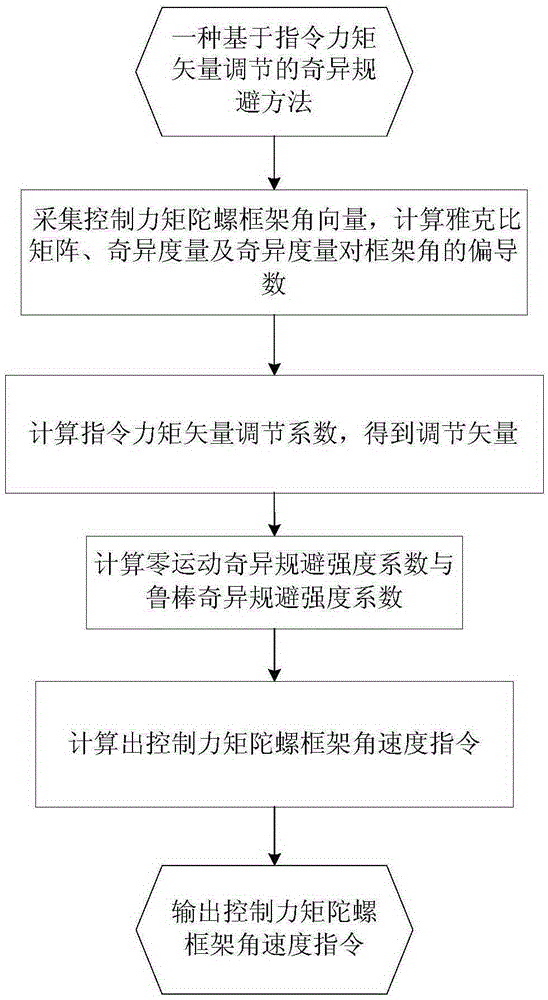
Control moment gyro singularity avoidance method based on instruction moment vector adjustment
ActiveCN105388902AEasy to chooseSolve the "locked" problemCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsAttitude controlAngular velocity
A control moment gyro singularity avoidance method based on instruction moment vector adjustment comprises the steps of first acquiring a frame angular vector of control moment gyros, then calculating a Jacobian matrix, a singularity metric value and an instruction moment vector adjustment coefficient of a control moment gyro motion equation, next obtaining a control moment instruction adjustment vector and a zero motion singularity avoidance strength coefficient based on a control moment instruction given by an attitude controller, and finally obtaining a control moment gyro frame angular velocity instruction vector based on the control moment instruction adjustment vector and the zero motion singularity avoidance strength coefficient so as to control the moment gyro frame angular velocity. The invention overcomes the situation in which a moment instruction coincides with a particular direction thereof when a frame is "locked", thereby making separation impossible; solves the problem of a "locked" frame angle during singularity avoidance in the prior art; and achieves effective avoidance of the control moment gyro singularity.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Mechanical arm autonomous robust singularity avoidance method for improving path tracking performance
ActiveCN108247631AGuaranteed tracking effectEasy to trackProgramme-controlled manipulatorUnitary matrixEngineering
The invention discloses a mechanical arm autonomous robust singularity avoidance method for improving path tracking performance. The method comprises the steps that a maneuverable ellipsoid of a mechanical arm is built according to an inverse kinematics model of the mechanical arm and a mechanical arm speed model, wherein the semi-major axis of the maneuverable ellipsoid is in the direction of theU longitudinal row of a unitary matrix, and the length of the semi-major axis corresponds to singular value of a Jacobian matrix; and then the path of an end effector is amended in the mth spindle direction of the maneuverable ellipsoid, and the singularity avoidance path of the mechanical arm is built. The method can be used for planning the autonomous singularity avoidance path of the mechanical arm, can keep the tracking performance of the path, and can also achieve the multi-task singularity avoidance path planning on the basis of task priority based on the method.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV +1
Teleoperation system fractional order sliding mode synchronous control method based on event trigger mechanism
ActiveCN112621759AReduce buffetingIncrease freedomProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorSystem parametersIndustrial engineering
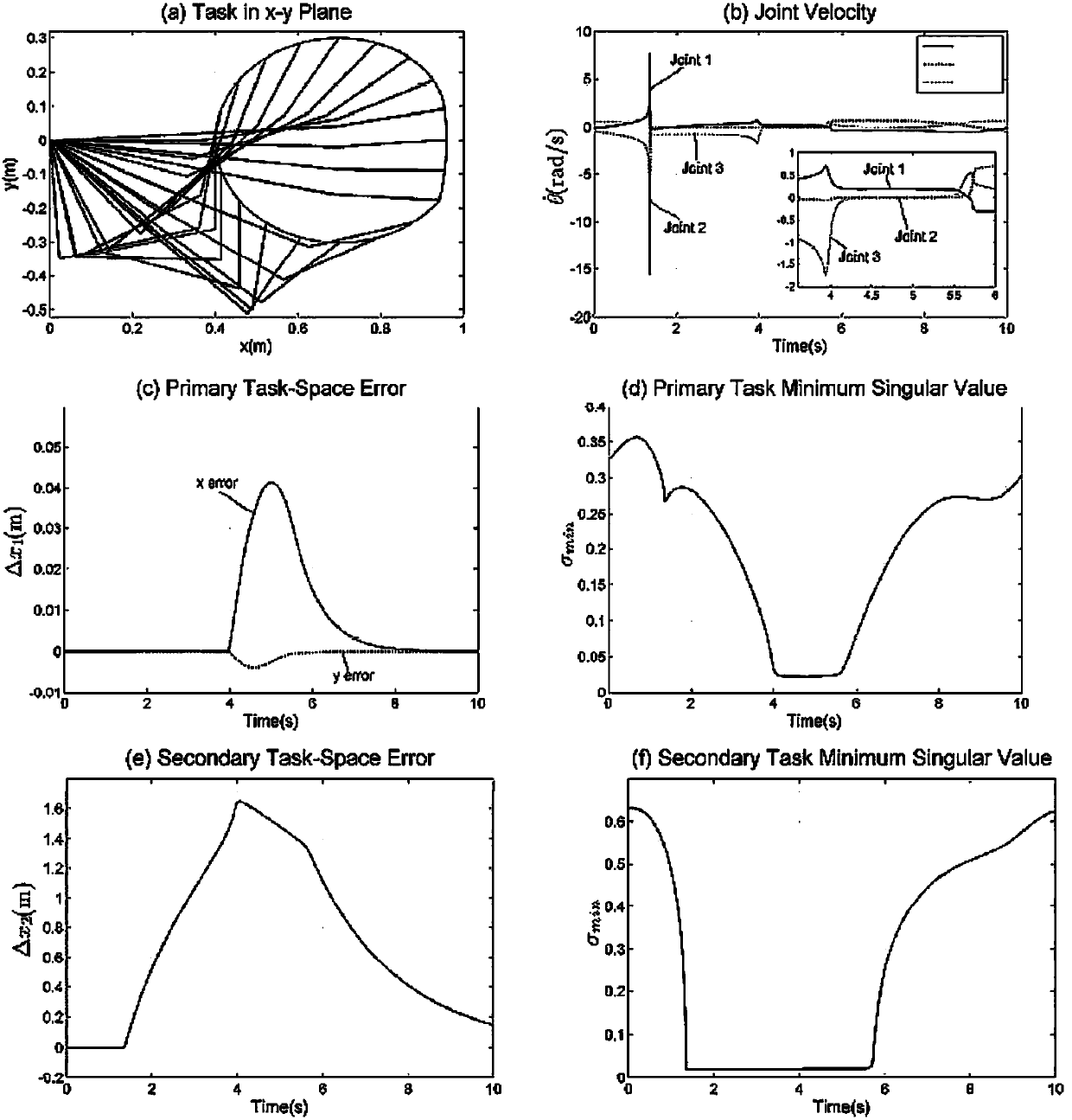
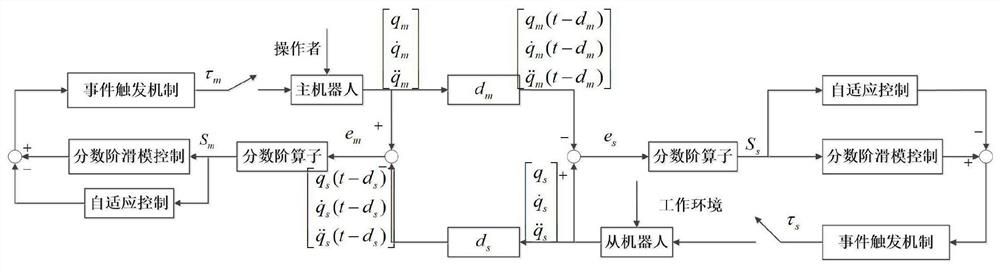
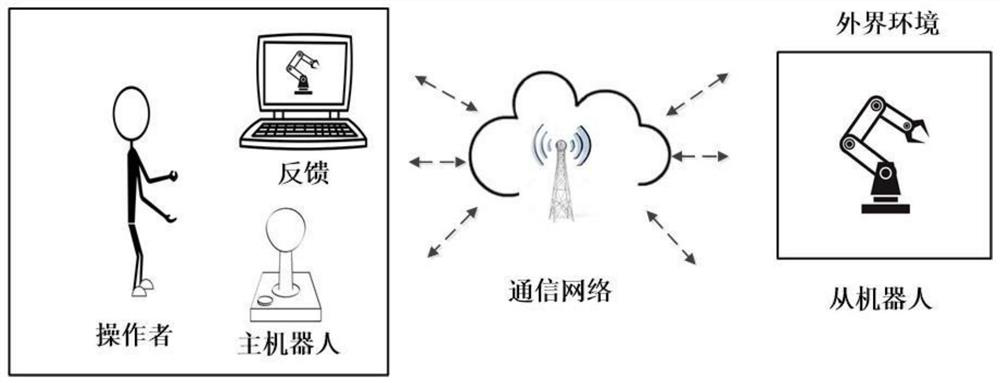
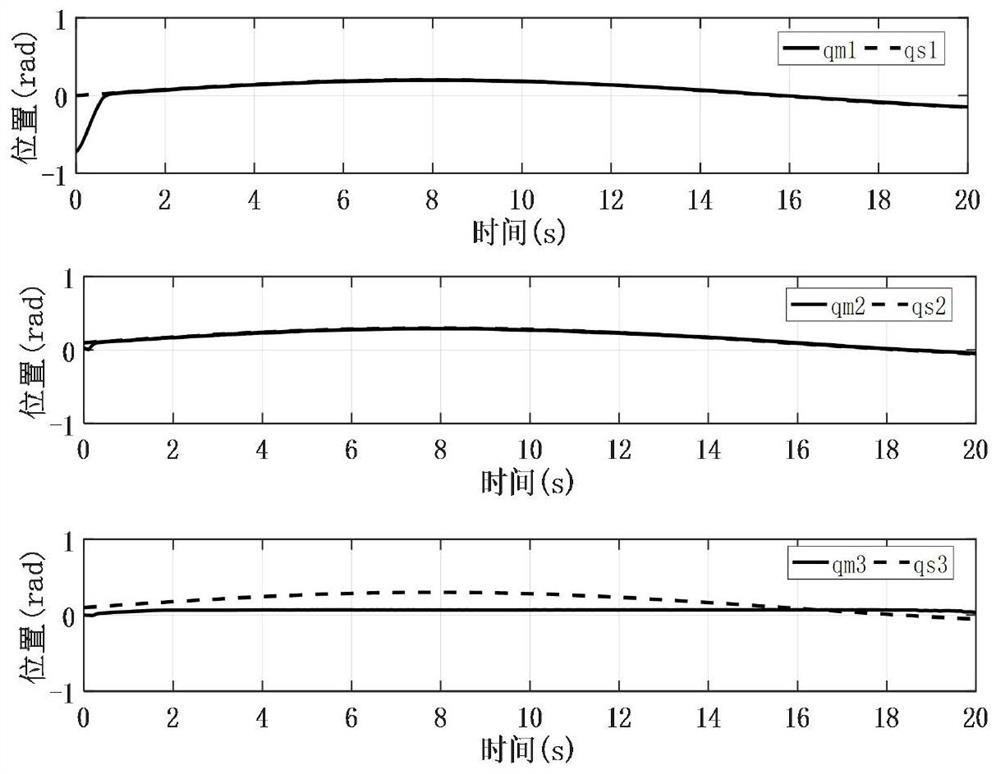
The invention provides a teleoperation system fractional order sliding mode synchronous control method based on an event trigger mechanism. The method comprises the steps: building a kinetic model of a teleoperation system through considering external disturbance and parameter uncertainty; selecting master and slave robots, interactively establishing a teleoperation system through a communication network, and determining system parameters of the kinetic model; designing a fractional order nonsingular fast terminal sliding mode surface equation by utilizing the position tracking error and the fractional order calculus; setting trigger event conditions of master and slave robot information interaction, and designing an adaptive fractional order nonsingular fast terminal sliding mode controller based on a sliding mode; and designing a Lyapunov function for stability analysis, and proving the boundness of a closed-loop state signal of the system. According to the teleoperation system fractional order sliding mode synchronous control method, the singular problem can be solved, the degree of freedom of the controller is expanded, the convergence speed is increased, the control precision is improved, the buffeting problem existing in the integer-order sliding mode surface is reduced, the applicability is higher, the occupation of network bandwidth and communication resources is reduced, and the resource utilization rate is increased.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
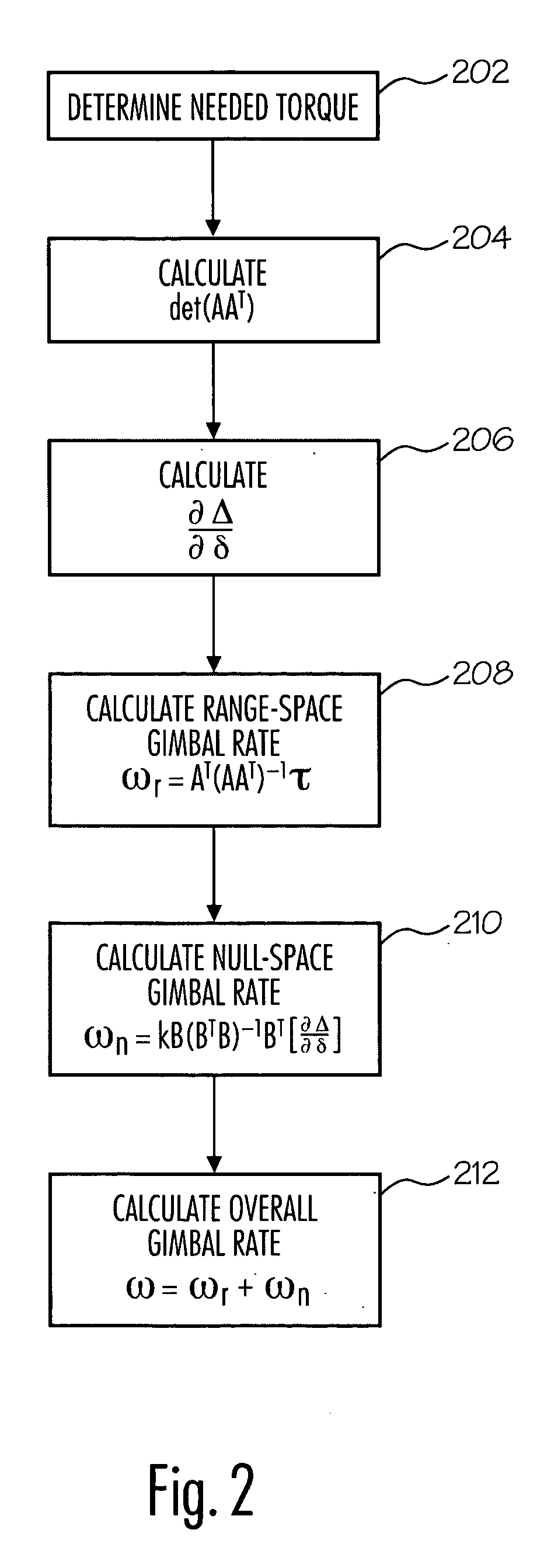
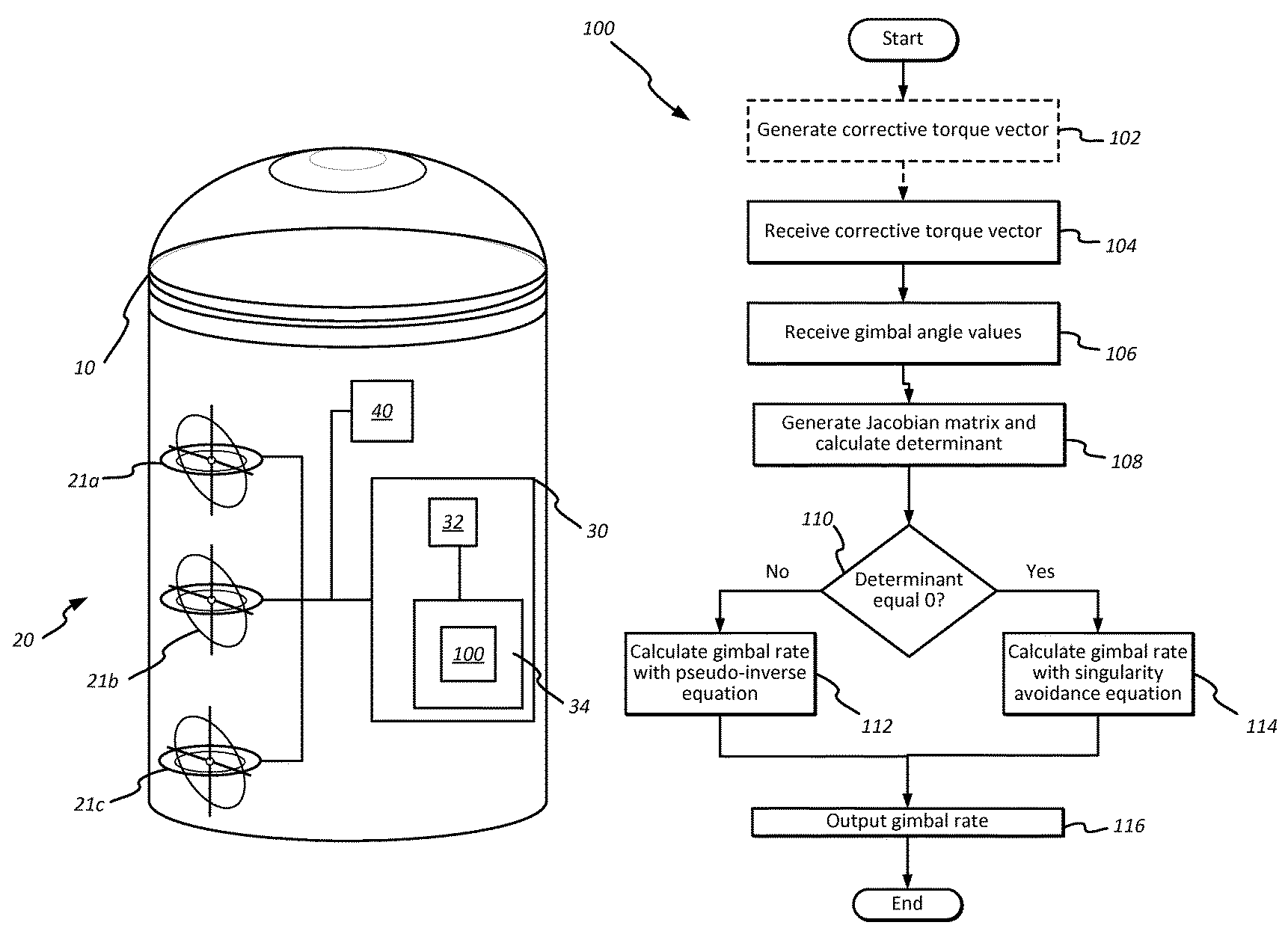
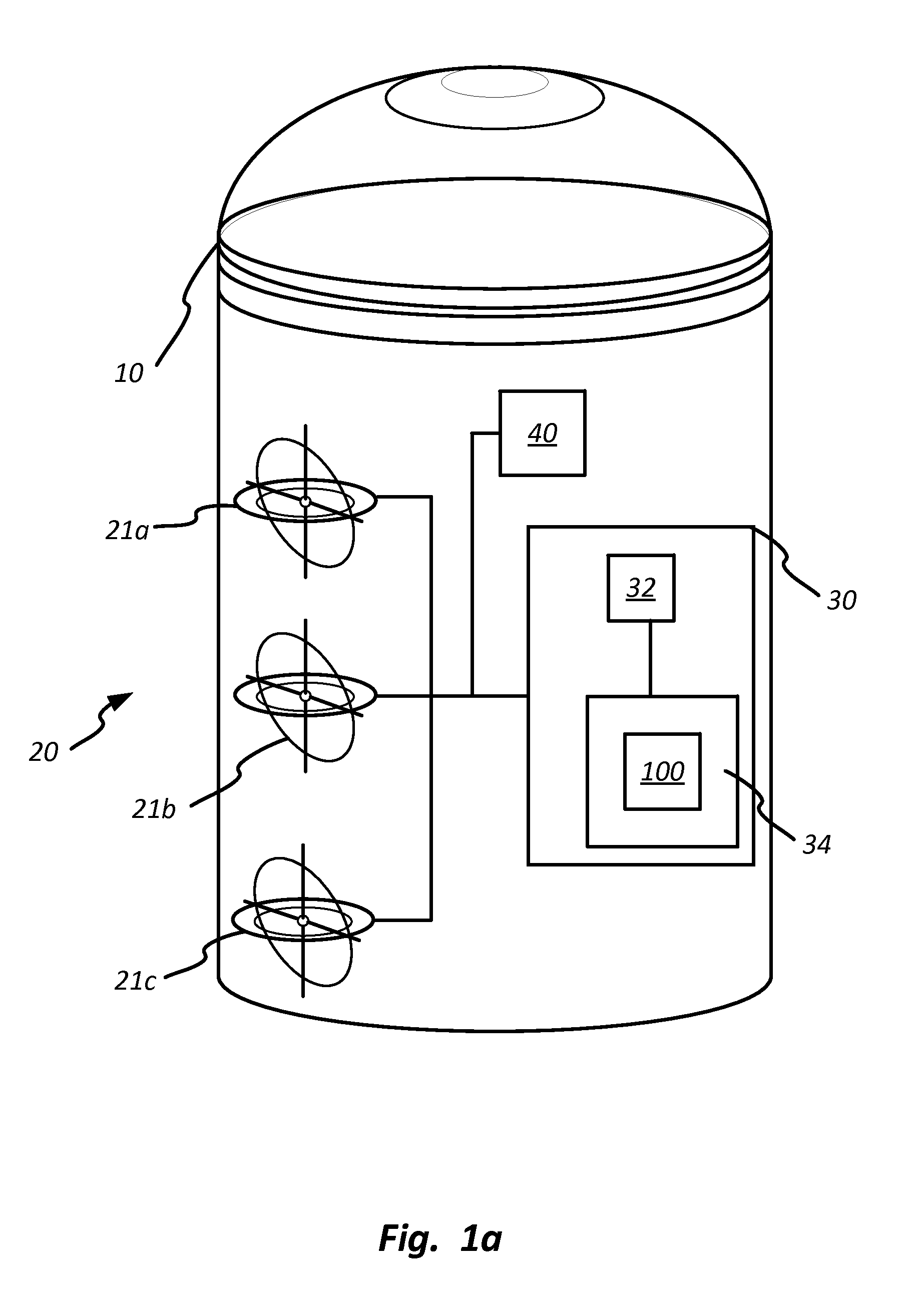
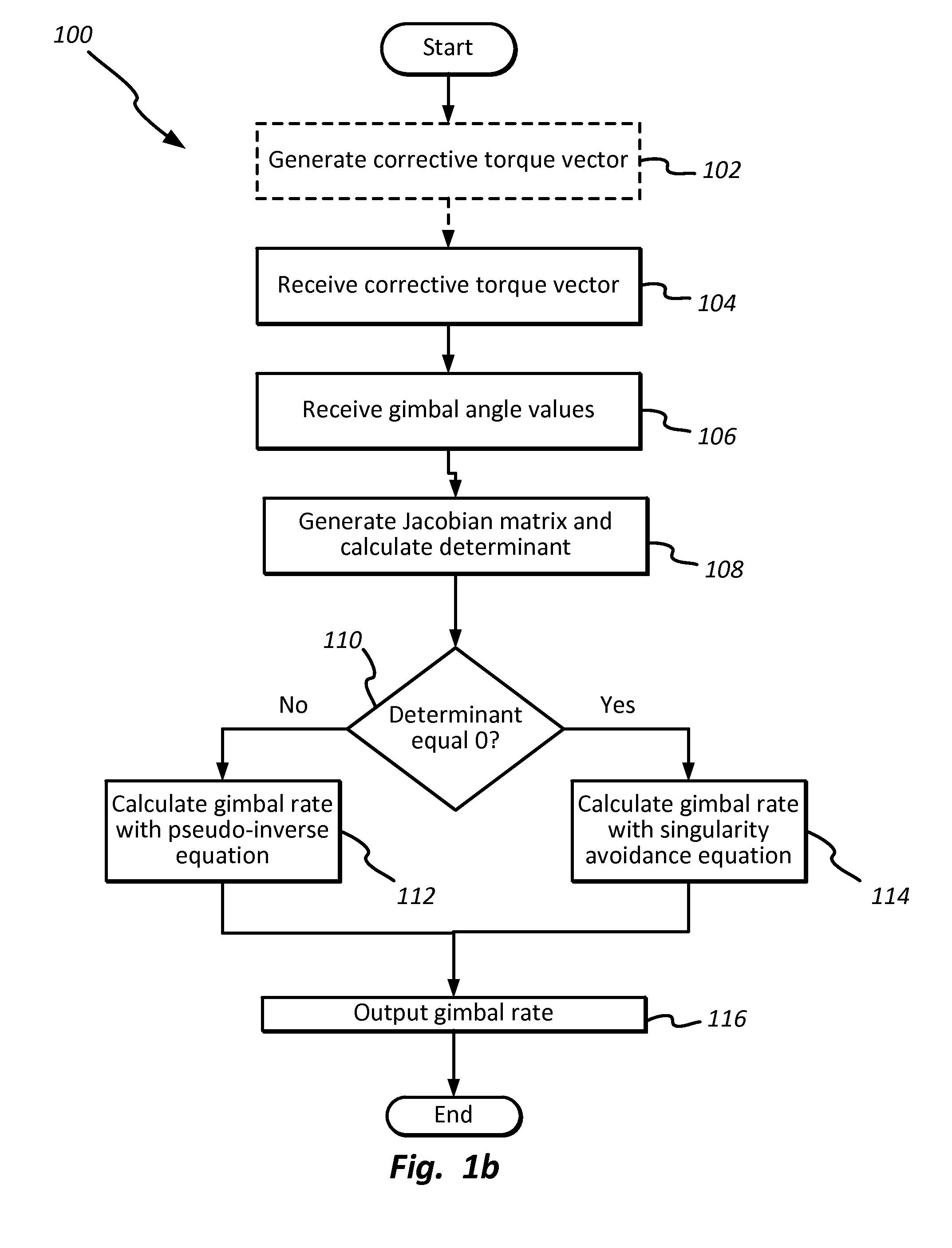
Method and apparatus for singularity avoidance for control moment gyroscope (CMG) systems without using null motion
ActiveUS9567112B1Avoid singularitiesMechanical apparatusCosmonautic vehiclesSingularity avoidanceSteering law
A method is described for avoiding gyroscopic singularities during attitude correction to a system, such as a spacecraft having a CMG array. The method receives a corrective torque vector μ and gimbal angle values δ for each of at least three gimbals within the CMG array. The method generates a Jacobian matrix A as a function of gimbal angle values δ. The method calculates a determinant D of Jacobian matrix A. If the determinant is not equal to zero, it is not singular, and the method calculates a gimbal rate {dot over (δ)} using a pseudo-inverse steering law equation. If the determinant is equal to zero, it is singular, and the method calculates a gimbal rate {dot over (δ)} using a singularity avoidance steering law equation. The gimbal rate {dot over (δ)} is output and can be applied to a CMG array resulting in applied torque to a spacecraft and attitude correction.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
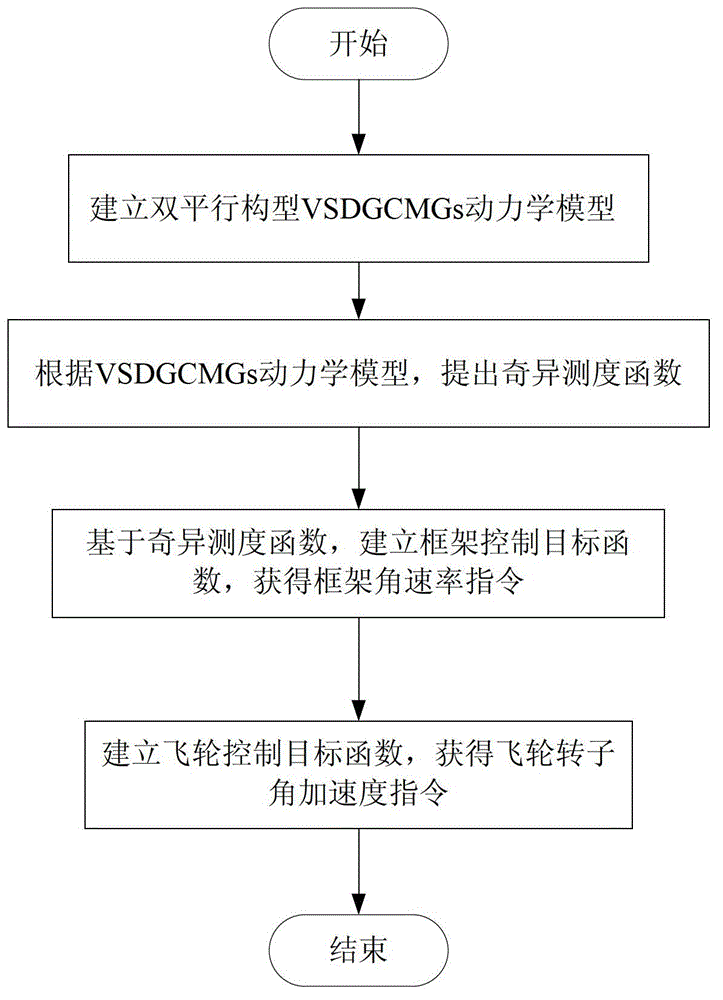
Design method of double parallel configuration VSDGCMGs singularity avoidance steering law
ActiveCN102749846ASmooth changeGuaranteed output torque accuracyAttitude controlAdaptive controlSingularity avoidanceSteering law
The invention discloses a design method of double parallel configuration VSDGCMGs singularity avoidance steering law, which comprises the steps of: firstly creating a dynamical model of double parallel configuration VSDGCMGs, and then, analyzing the singularity states of the double parallel configuration VSDGCMGs, finally, creating a framework control target function based on a singularity measure function, creating a flywheel control target function based on rotating speed balance, and designing the double parallel configuration VSDGCMGs singularity avoidance steering law comprehensively considering the singularity avoidance, energy consumption and rotating speed balance. The design method disclosed by the invention can effectively guarantee the output moment precision of the double parallel configuration VSDGCMGs and lay the foundation for agile maneuver attitude control of spacecrafts.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
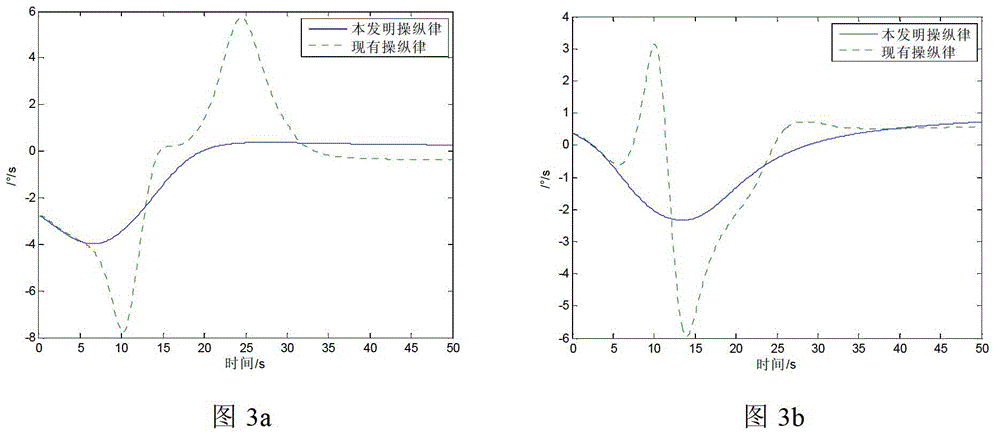
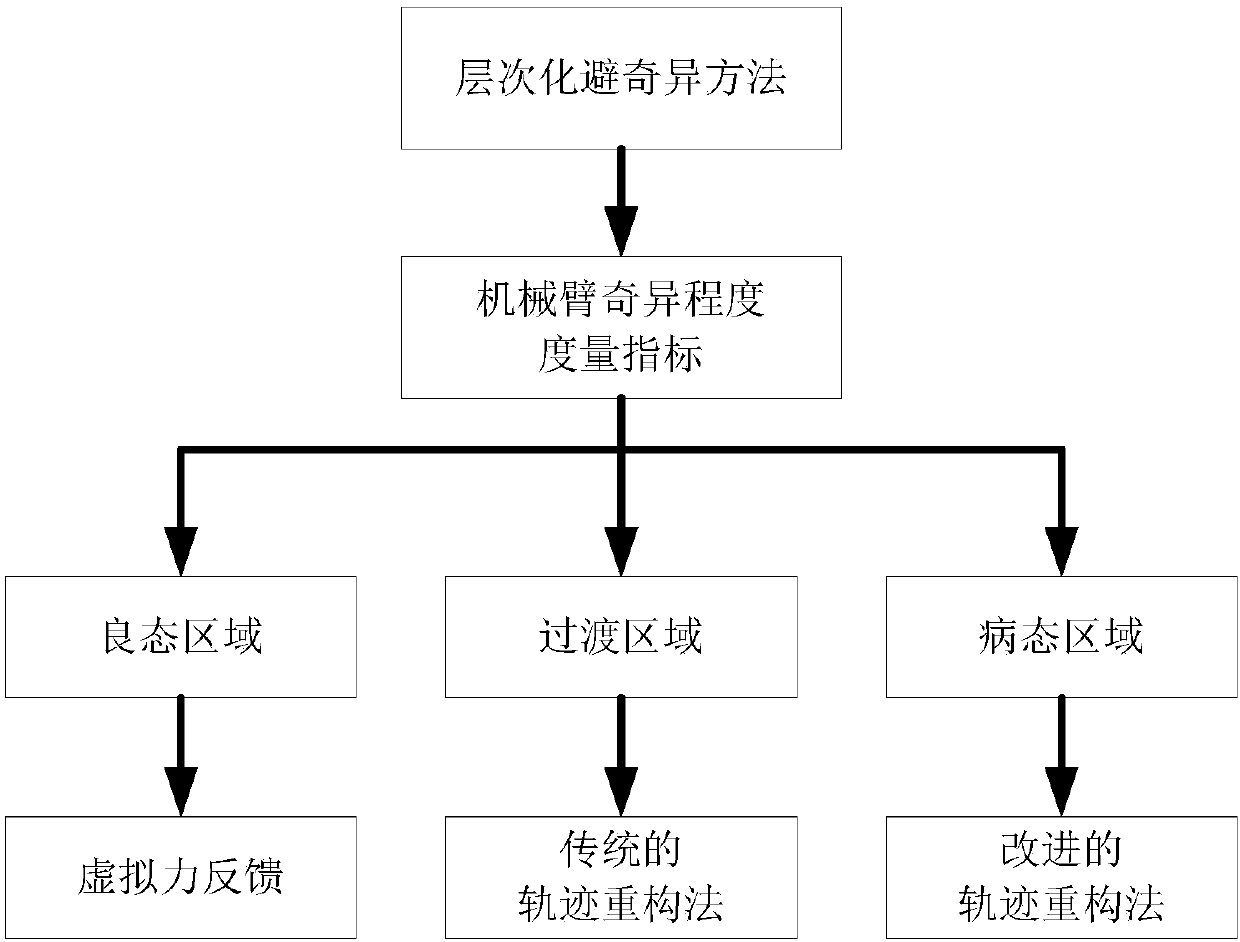
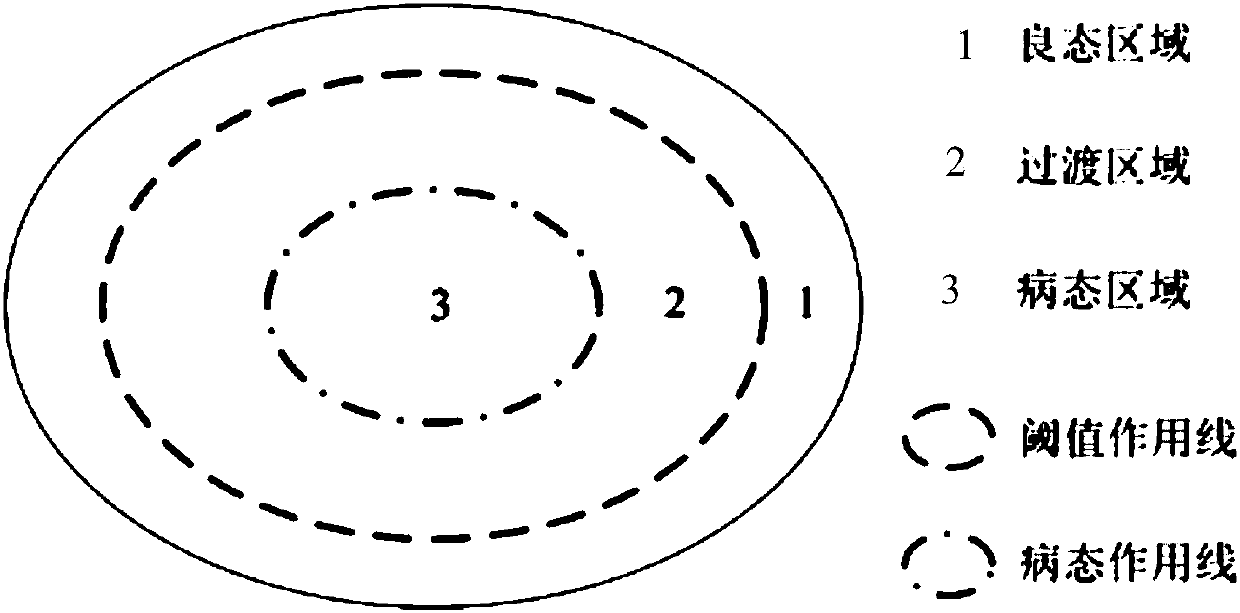
Layering singularity avoidance method of remotely operating mechanical arm
ActiveCN107831680AGuaranteed movement trajectoryProgramme control in sequence/logic controllersSingularity avoidanceReconstruction method
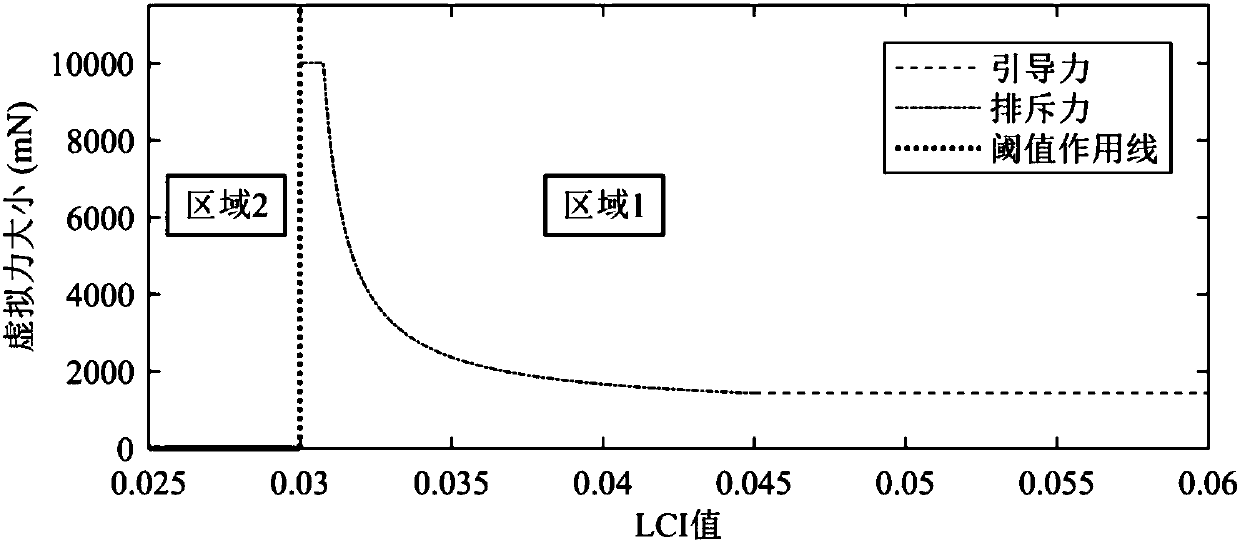
A layering singularity avoidance method of a remotely operating mechanical arm belongs to the field of robot remote operation. The invention aims to solve the problem that in the existing mechanical arm movement process, a single method is adopted to avoid singularity, and the normal motion trail of the mechanical arm cannot be effectively ensured. The singularity avoidance layer of operation state of the mechanical arm is divided into a good region, a transition area and a sick area according to the local condition sequence of a mechanical arm singularity degree measurement index. When the mechanical arm operates in a good area, the movement of an operator of a main end is guided in a virtual force feedback mode; when the mechanical arm operates in the transition area, a traditional trackreconstruction method is adopted to reconstruct the tail end track of the mechanical arm; and when the mechanical arm operates in a sick area, the tail end track of the mechanical arm is reconstructed by adopting an improved track reconstruction method. The method is used for avoiding singularity of a mechanical arm.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for confirming motion mode of corresponding free node at singular configuration part of hinge bar system mechanism
The invention discloses a method for confirming the motion mode of a corresponding free node at a singular configuration part of a hinge bar system mechanism. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out second-order derivation on a coordination function which is dependent from a mechanism to describe the corresponding free node variable quantity, to judge whether the second-order derivative is equal to zero or not at the singular configuration place, if the second-order derivative is equal to zero, the corresponding free node at the singular configuration part can move like a limiting mechanism; and if the second-order derivative is not equal to zero, the corresponding free node can move like a first-order infinite small mechanism. According to the method, the motion mode of the corresponding free node at the singular configuration place of the hinge bar system mechanism can be confirmed, the motion mode of the mechanism at the singular configuration place can be basically confirmed, the method is high in operability, the basis is provided for the singularity avoidance and the structure design of the novel space structure, and the research of the mechanism singularity and the motion bifurcation has an important impelling action, so that the method is wide in application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
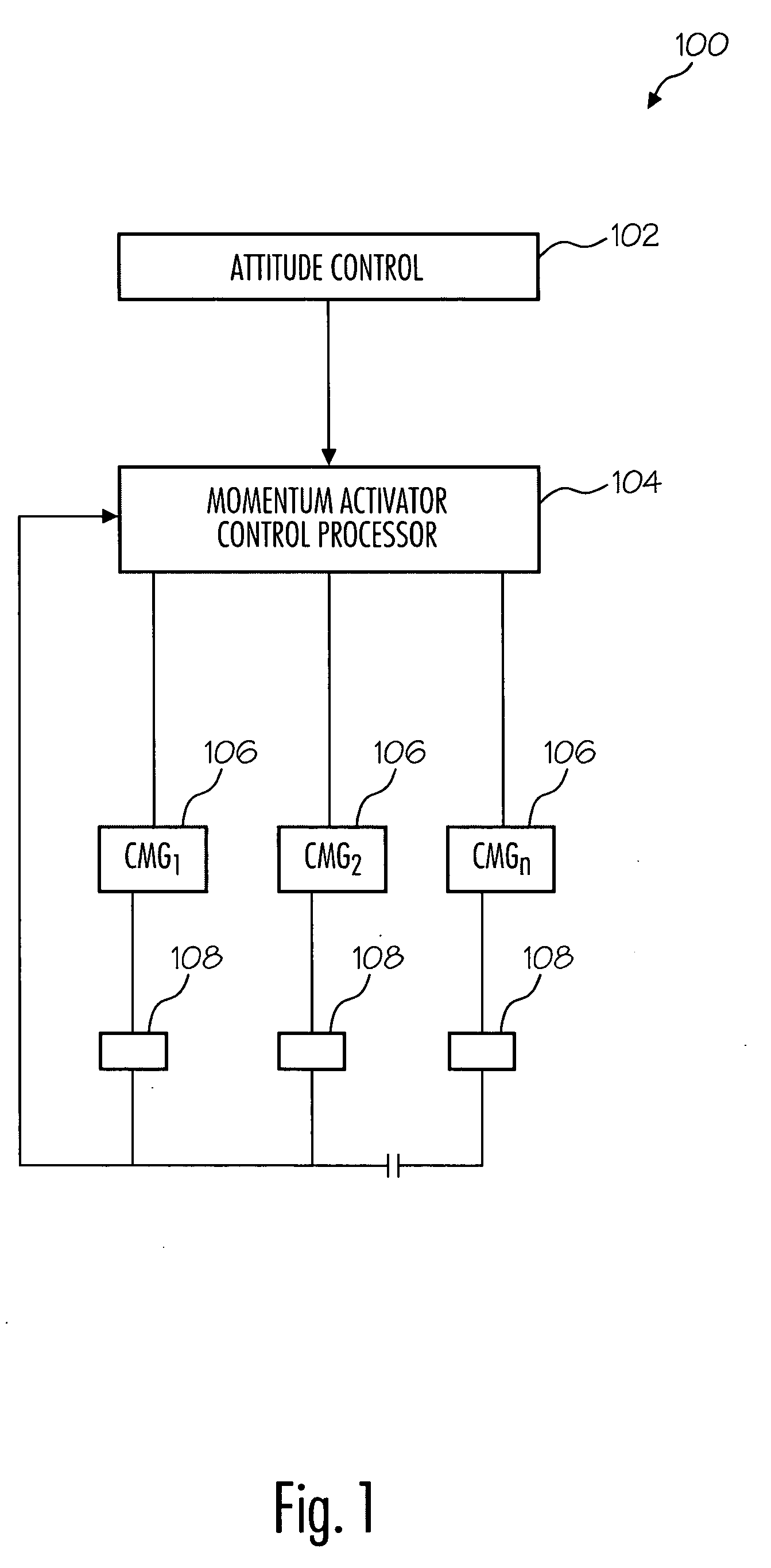
Method and system for CMG array singularity avoidance
ActiveUS7246776B2Cosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsPresent methodSingularity avoidance
The present method provides a method for avoiding singularities in the movement of CMGs in an array of CMGs in a spacecraft. In a first step, a torque command representing a desired torque to produce an attitude adjustment for the spacecraft is received. Next, a range-space gimbal rate required to produce the desired torque based on the desired torque and a Jacobian matrix is calculated. Then, a null-space gimbal rate that assists in the avoidance of singularities is calculated. The total gimbal rate command is determined by summing the range-space gimbal rate and the null-space gimbal rate. Then, the total gimbal rate command is provided to the CMGs to produce the total gimbal rate.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
System and method for managing multiple null-space objectives and constraints
ActiveUS20180243906A1Highly configurableExtended range of motionProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorSpatial managementEngineering
Devices, systems, and methods for providing commanded movement of an end effector of a manipulator concurrent with a desired movement of one or more joints of the manipulator according to one or more consolidated null-space objectives. The null-space objectives may include a joint state combination, relative joint states, range of joint states, joint state profile, kinetic energy, clutching movements, collision avoidance movements, singularity avoidance movements, pose or pitch preference, desired manipulator configurations, commanded reconfiguration of the manipulator, and anisotropic emphasis of the joints. Methods include calculating multiple null-space movements according to different null-space objectives, determining an attribute for each and consolidating the null-space movements with a null-space manager using various approaches. The approaches may include applying weighting, scaling, saturation levels, priority, master velocity limiting, saturated limited integration and various combinations thereof.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
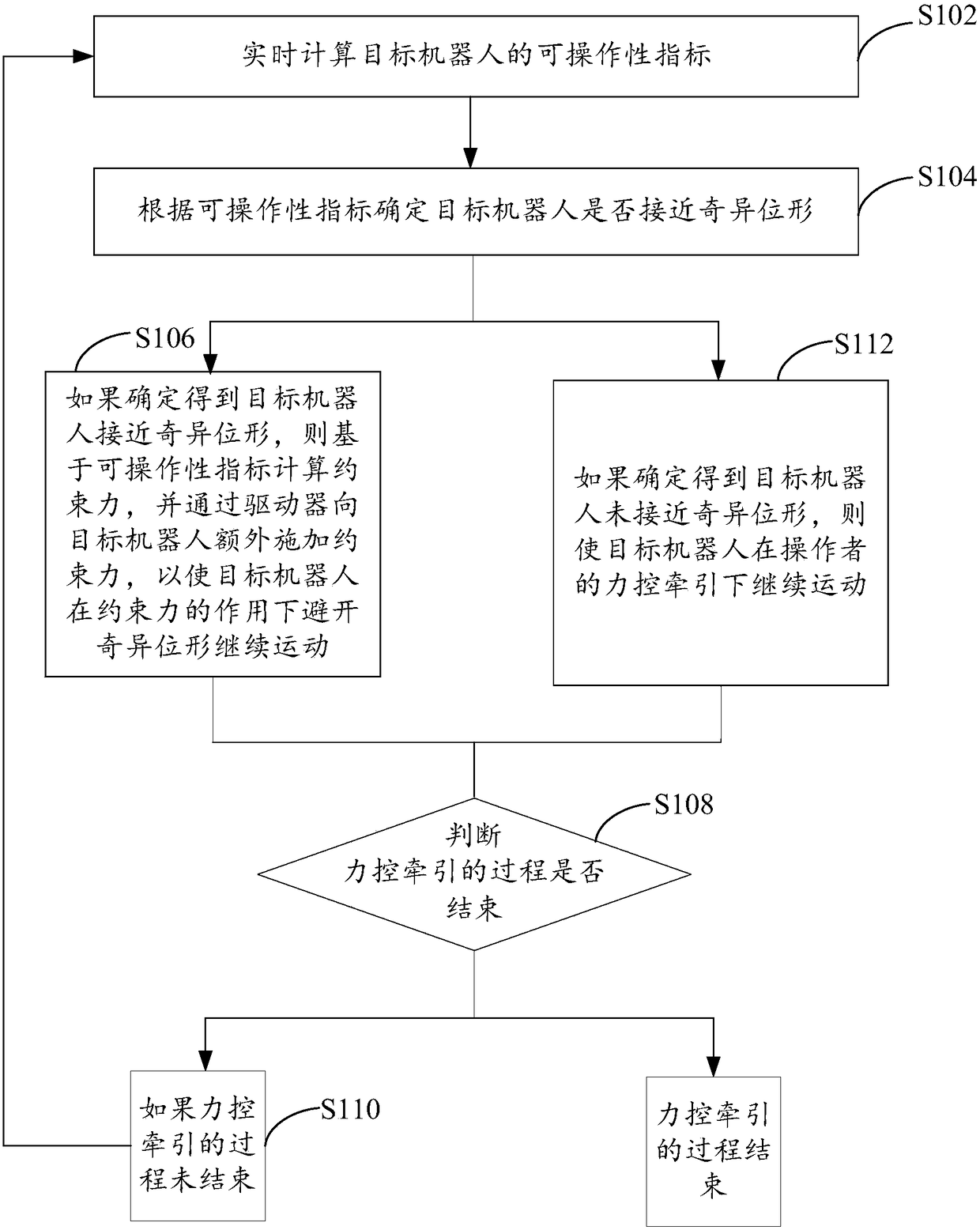
Singularity avoidance method and device in force-controlled traction process for robot
ActiveCN108608427AAvoid reachingReduced operating experienceProgramme-controlled manipulatorSimulationOperability
The invention provides a singularity avoidance method and device in a force-controlled traction process for a robot. The method comprises the following steps: calculating the operability indexes of the target robot in real time; determining whether the target robot approaches to a singularity configuration or not according to the operability indexes; and if the target robot is determined to approach to the singularity configuration, calculating a constraint force on the basis of the operability indexes, and additionally applying the constraint force onto the target robot through a driver, so that the target robot avoids the singularity configuration and continues to move under the effect of the constraint force. The method is capable of effectively preventing the robot from arriving at thesingularity configuration, and enabling the force-controlled traction process to be continuously carried out, so that the operation experience of force-controlled traction is improved, the operationefficiency of the force-controlled traction is increased, and the technical problems of low operation efficiency and poor operation experience of force-controlled traction due to the alarming and stopping of a robot, which are caused by that an operator drags the robot to a singularity configuration, are alleviated.
Owner:SIASUN CO LTD
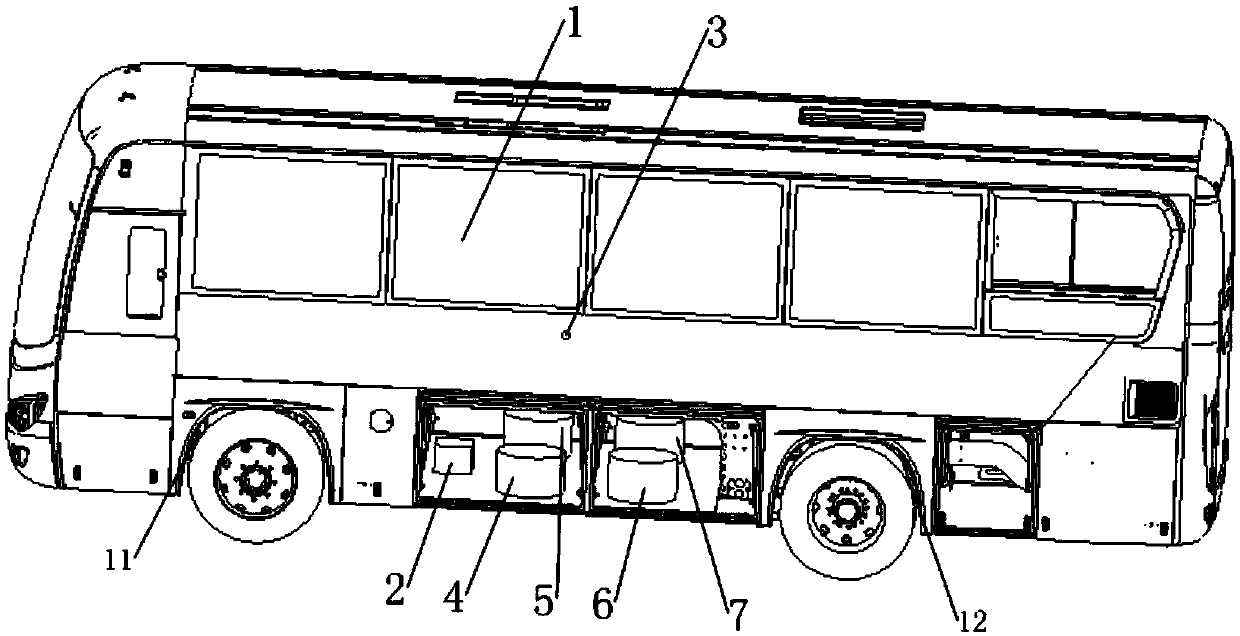
Vehicle anti-rollover method based on control moment gyroscope
ActiveCN110412995AWon't fall overAvoid singularity problemsAttitude controlRolloverMeasurement device
The invention relates to the field of vehicle rollover prevention, in particular to a vehicle anti-rollover method based on a control moment gyroscope. When a vehicle turns or is under external interference stimulation, a measurement device detects the response of the vehicle, the own suspension mechanism dynamics of the vehicle can be combined to estimate the state of the vehicle through a vehicle rollover model, the control moment gyroscope generates torques of thousands of N.m for keeping the balance of a vehicle body, and therefore, the vehicle is free from rollover under any situation even under a collision situation. A rollover judgment system can accurately estimate the tilt state of the vehicle so as to judge vehicle rollover. Meanwhile, the own mechanism characteristics of the vehicle are fully considered. Through a continuous anti-rollover moment output by the control moment gyroscope, the vehicle is free from rollover under any situation even under the collision situation, and a corresponding control algorithm can guarantee singularity avoidance and accurate moment output.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU YUTONG BUS CO LTD
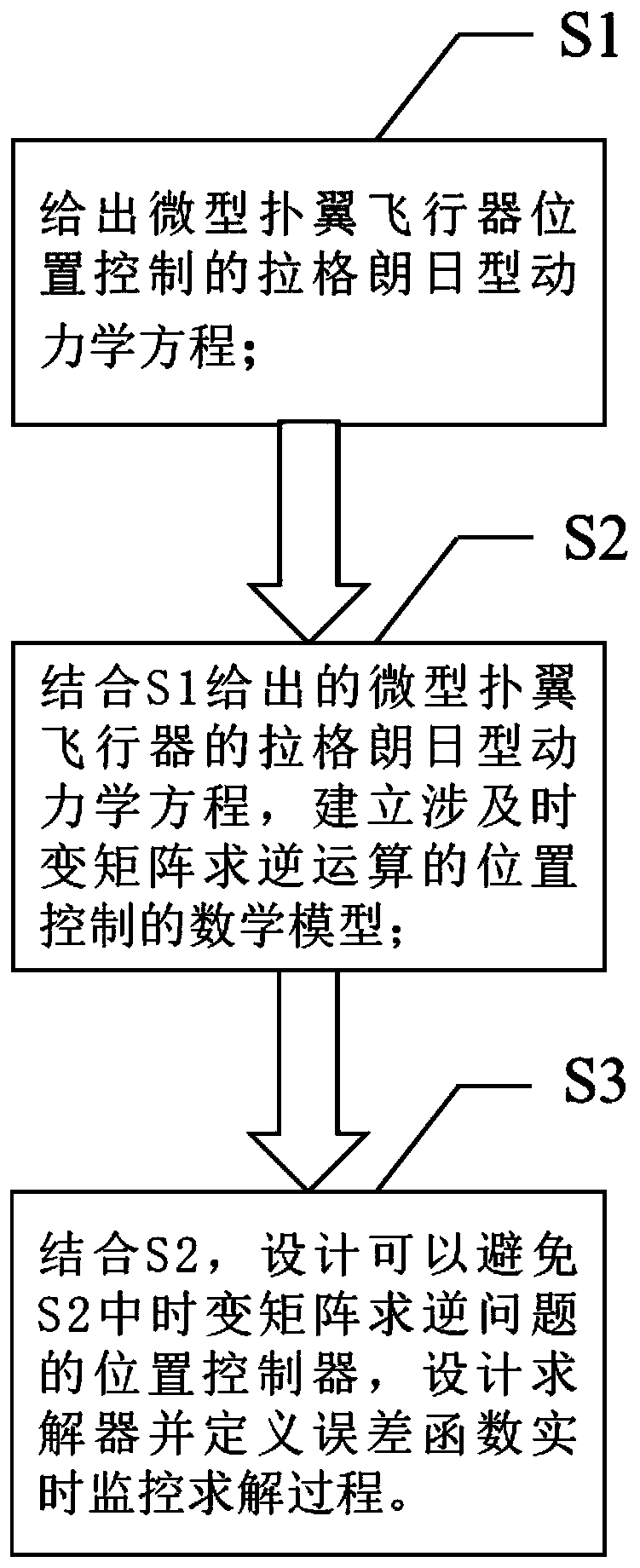
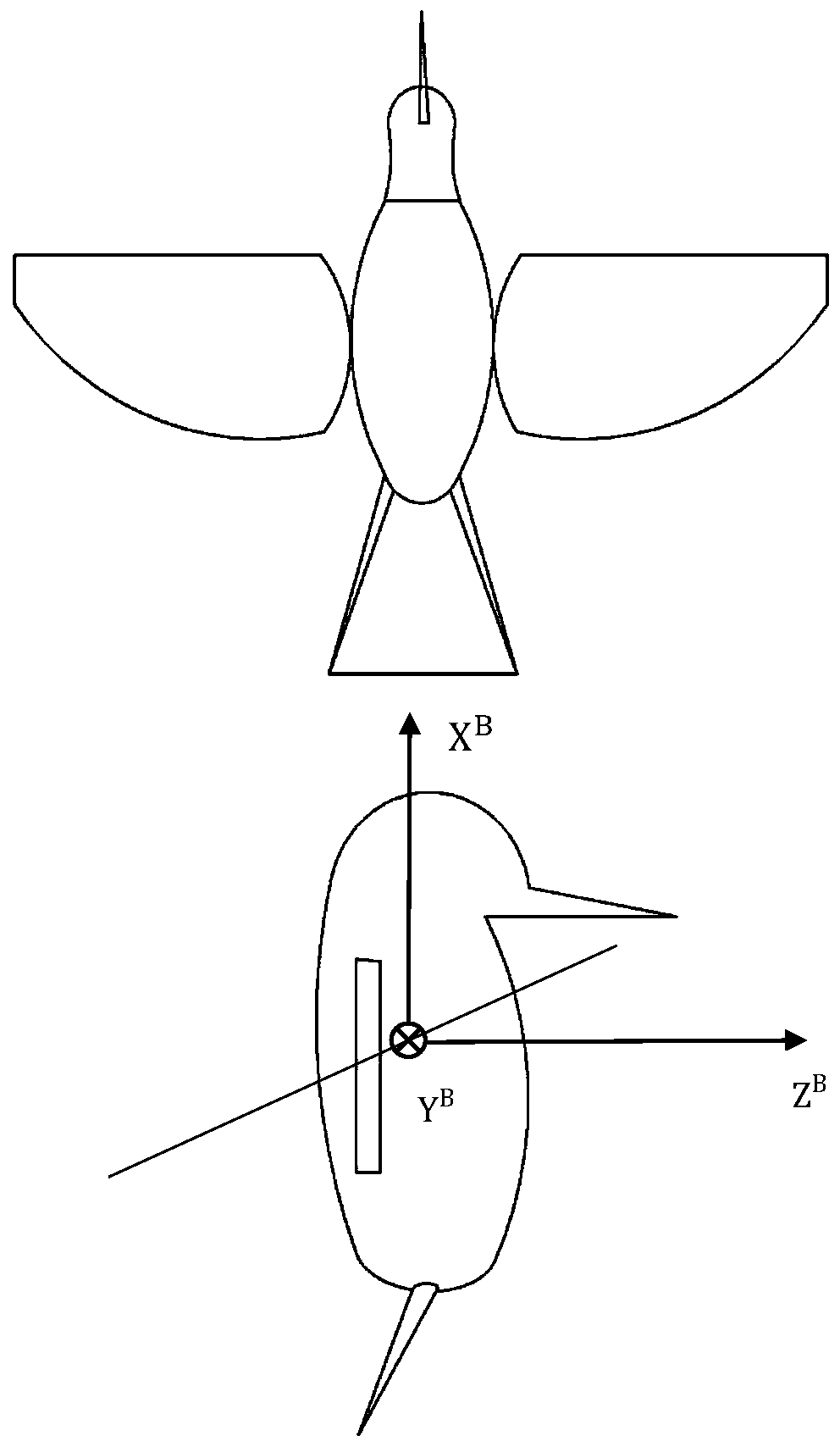
Position tracking control method for miniature ornithopter capable of avoiding singular state
ActiveCN111240357AAvoid Position Tracking ControlsRealization of position tracking controlSustainable transportationPosition/course control in three dimensionsComputation complexityMathematical model
The invention provides a position tracking control method for a miniature ornithopter capable of avoiding singular state. The method comprises the following steps: 1) giving a Lagrange type kinetic equation for position control of the miniature ornithopter; 2) in combination with the Lagrange type kinetic equation of the miniature ornithopter given in the step 1), establishing a mathematical modelof position control related to time-varying matrix inversion operation; and 3) in combination with the step 2), designing a position controller capable of avoiding the time-varying matrix inversion problem in the step 2), designing a solver, and defining an error function to monitor the solving process in real time. The method skillfully avoids the time-varying matrix inversion operation in the algorithm solving process, and reduces the calculation complexity.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
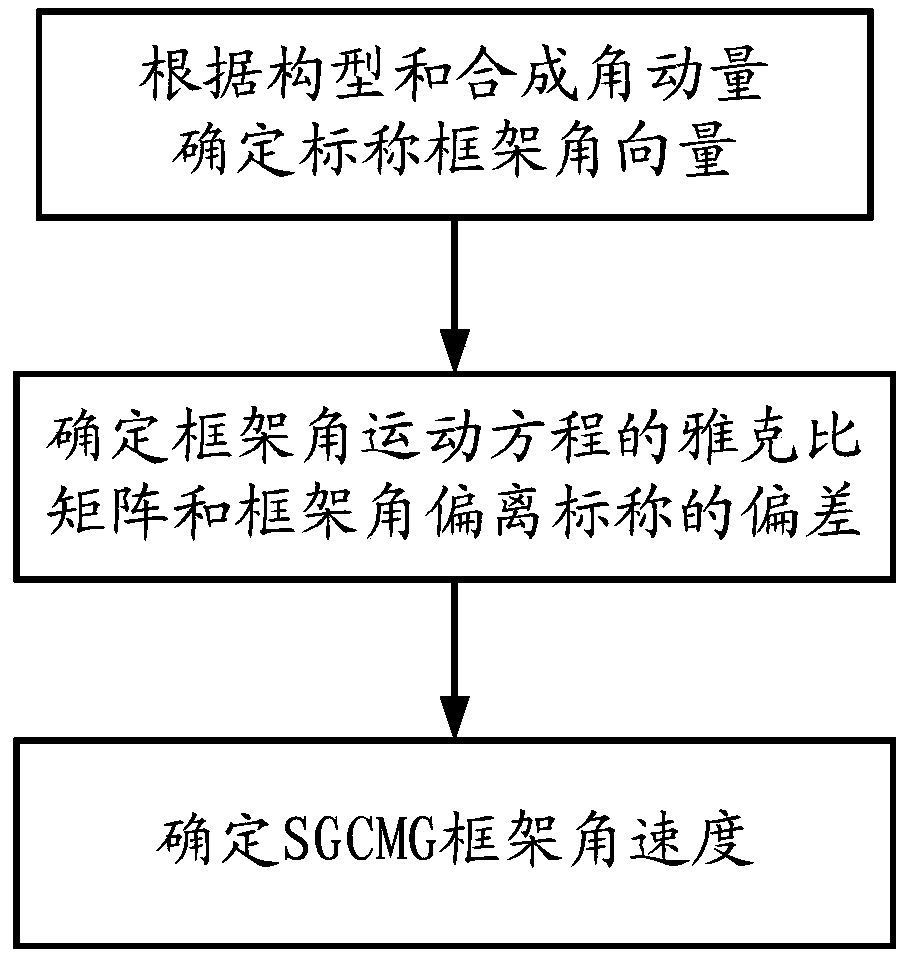
Method for determining gimbal angular velocity of SGCMGs
ActiveCN110723316ASolve the problem of losing attitude maneuver abilityHarmonized Singularity AvoidanceCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusSingularity avoidanceAttitude control
Disclosed is a method for determining the gimbal angular velocity of SGCMGs. The method includes the steps of firstly, determining a nominal gimbal angular vector of the configurations of the n SGCMGsaccording to the configurations and synthesis angular momentum of the n SGCMGs; secondly, determining the Jacob of a gimbal angular motion equation and the deviation of each gimbal angle deviating from nominal according to the gimbal angle of each SGCMG; and thirdly, determining a gimbal angular velocity instruction of the SGCMGs according to the Jacob determined in the step 2) and the deviation,determined in the step 2), of each gimbal angle deviating from nominal. By considering the distance of each gimbal angle deviating from nominal, the gimbal angular instruction amplitude and moment output deviation, the method has the abilities of singularity avoidance in attitude maneuvering and gimbal nominal position returning after maneuvering, the contradiction between the CMG gimbal singularity avoidance and the attitude control moment is resolved, and the high maneuvering performance at the arbitrary attitude can be ensured.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
System and method for managing multiple null-space objectives and constraints
ActiveUS20170136624A1Highly configurableExtended range of motionProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorSpatial managementEngineering
Devices, systems, and methods for providing commanded movement of an end effector of a manipulator concurrent with a desired movement of one or more joints of the manipulator according to one or more consolidated null-space objectives. The null-space objectives may include a joint state combination, relative joint states, range of joint states, joint state profile, kinetic energy, clutching movements, collision avoidance movements, singularity avoidance movements, pose or pitch preference, desired manipulator configurations, commanded reconfiguration of the manipulator, and anisotropic emphasis of the joints. Methods include calculating multiple null-space movements according to different null-space objectives, determining an attribute for each and consolidating the null-space movements with a null-space manager using various approaches. The approaches may include applying weighting, scaling, saturation levels, priority, master velocity limiting, saturated limited integration and various combinations thereof.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Method for confirming motion mode of corresponding free node at singular configuration part of hinge bar system mechanism
The invention discloses a method for confirming the motion mode of a corresponding free node at a singular configuration part of a hinge bar system mechanism. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out second-order derivation on a coordination function which is dependent from a mechanism to describe the corresponding free node variable quantity, to judge whether the second-order derivative is equal to zero or not at the singular configuration place, if the second-order derivative is equal to zero, the corresponding free node at the singular configuration part can move like a limiting mechanism; and if the second-order derivative is not equal to zero, the corresponding free node can move like a first-order infinite small mechanism. According to the method, the motion mode of the corresponding free node at the singular configuration place of the hinge bar system mechanism can be confirmed, the motion mode of the mechanism at the singular configuration place can be basically confirmed, the method is high in operability, the basis is provided for the singularity avoidance and the structure design of the novel space structure, and the research of the mechanism singularity and the motion bifurcation has an important impelling action, so that the method is wide in application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
System and method for managing multiple null-space objectives and constraints
ActiveUS10513031B2Highly configurableExtended range of motionProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsSingularity avoidanceEngineering
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
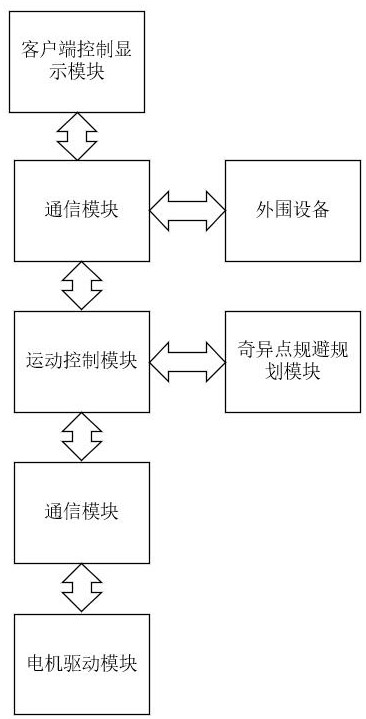
General avoidance method and system for singular point of mechanical arm
ActiveCN113601512AOmit transform solverGuaranteed inverseProgramme-controlled manipulatorSingularity avoidanceJoint angle
The invention discloses a general avoidance method and system for a singular point of a mechanical arm, and belongs to the technical field of avoidance of singular points of mechanical arms. The technical problem to be solved is to provide the improvement of the general avoidance method for the singular point of the mechanical arm. According to the technical scheme for solving the technical scheme, the method comprises the following steps that a kinematic model of the mechanical arm is established, a reference joint coordinate system is established, the spinor of each joint is calculated according to the spinor theory, and a Jacobian matrix is solved; a condition number is calculated by using a joint angle value of a tracing point and the Jacobian matrix; the condition number is used for judging whether the mechanical arm is close to the singular point or not, and after it is judged that the mechanical arm is about to approach the singular point, the mechanical arm uses a singularity avoidance algorithm to calculate a singularity avoidance tracing point till the condition number of the Jacobian matrix of the generated tracing point meets the state of being away from the singular point and the tracing point returns to an original Cartesian trajectory again; and after the singularity avoidance trajectory is planned, smoothing processing and trajectory interpolation are conducted on the planned singularity avoidance trajectory, and a final singularity avoidance trajectory is obtained; The invention is applied to the mechanical arm.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for Avoiding Singular Points in Five-Axis Machining Tool Trajectory
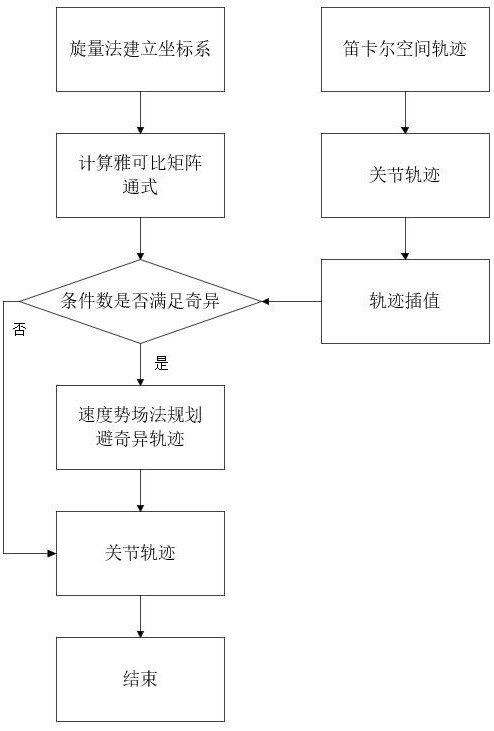
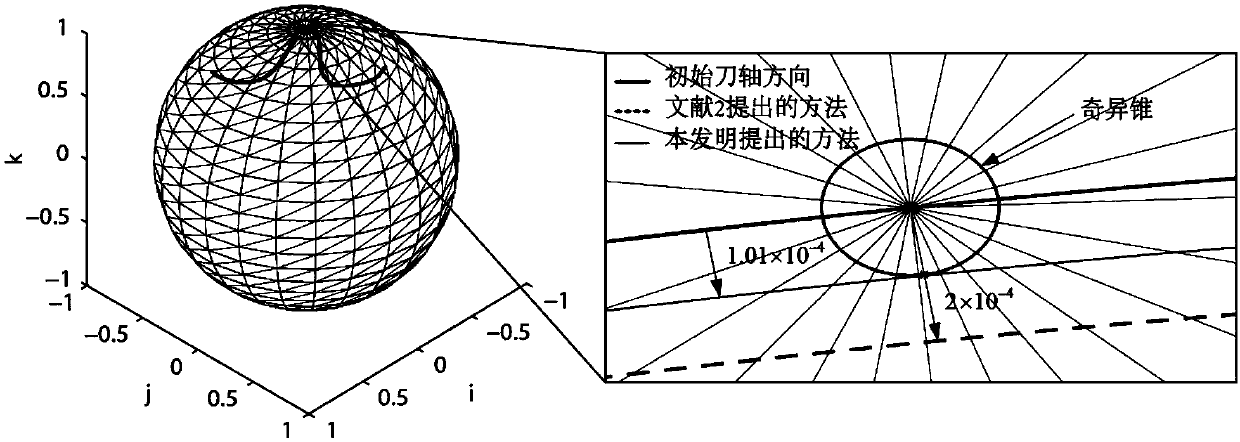
ActiveCN106843144BReduce distortionLarge machining errorNumerical controlQuaternionLinear representation
The invention discloses a method for avoiding singular points of a five-axis machining tool feeding track, which aims at solving the technical problem of low machining accuracy in the existing method for avoiding the singular points of the five-axis machining tool feeding track. The method adopts the technical scheme with the following steps of using a quaternion to express a conversion relationship between the tool axis direction and the reference direction, and projecting the quaternion onto a P plane, wherein a singular cone in the P plane corresponds to a singular circle with center of circle at the origin point; using a B spline to interpolate a projecting point in a two-dimensional plane; establishing a constraint optimization problem again, wherein a target function is a sum of squares of increments of control top points, the constraint is the distance between the point of the B spline to the origin point in the P plane to be greater than the radius of the singular circle, and an initial value of the control top point is the control top point of the B spline obtained by interpolation; linearly expressing the constraint of the constraint optimization problem by the increment of the control top point of the B spline, and using a quadratic programming theory to solve an optimal solution of the optimizing problem. The method has the advantage that the common constraint optimization problem is converted into the quadratic programming problem, so that the processing accuracy is guaranteed.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
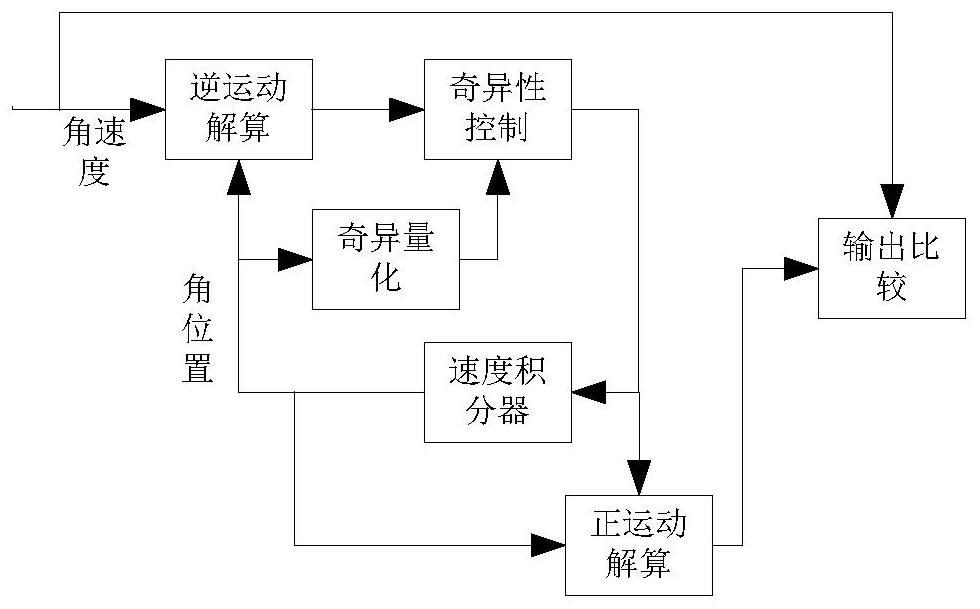
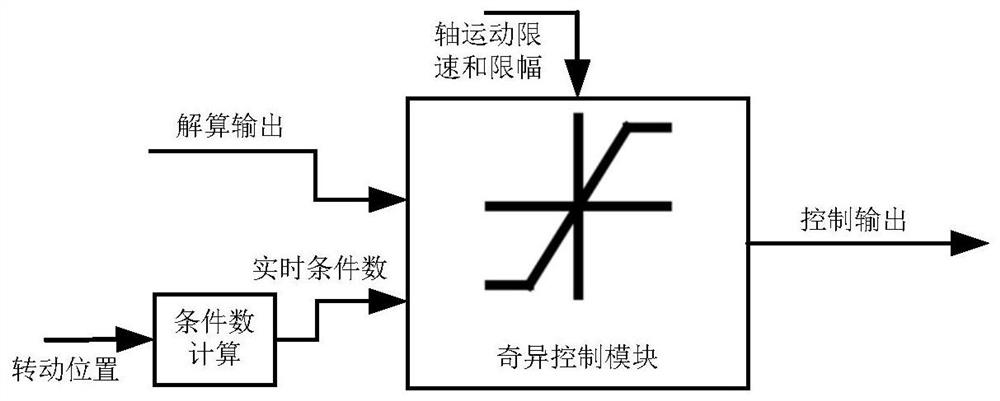
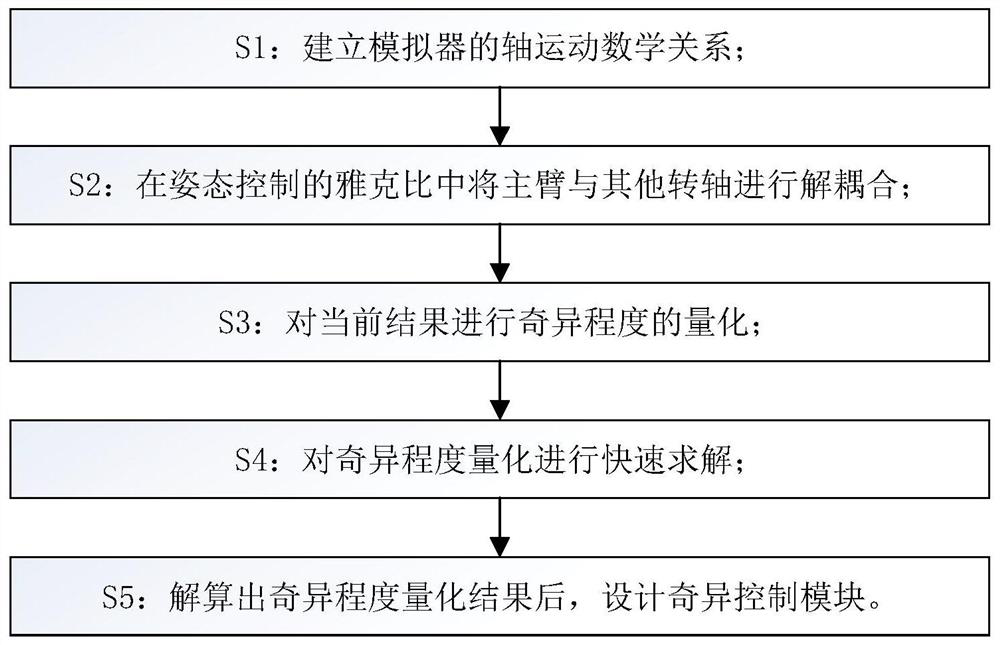
Multi-axis coupling motion singularity control method for continuous load simulator
ActiveCN111813139AAvoid Mutation SituationsImprove stabilityAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsAttitude controlSimulation
The invention discloses a multi-axis coupling motion singularity control method for a continuous load simulator. The method comprises the following steps: S1, establishing an axis motion mathematicalrelationship of the simulator; S2, decoupling the main arm from other rotating shafts in the Jacobian of attitude control; S3, quantifying the singular degree of the current result; S4, carrying out quick solving on the quantification of the singular degree; and S5, after a singular degree quantification result is solved, designing a singular control module. According to the method, singular pointtransition is carried out under the condition that the shaft motion stroke is fully utilized; and the sudden change of the vicinity of the singular point due to the limitation of the mechanical rangeof the shaft is avoided in a mode of reducing the proportion of the control instruction, so that the stability and fidelity of flight simulation are improved.
Owner:GENERAL ENG RES INST CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
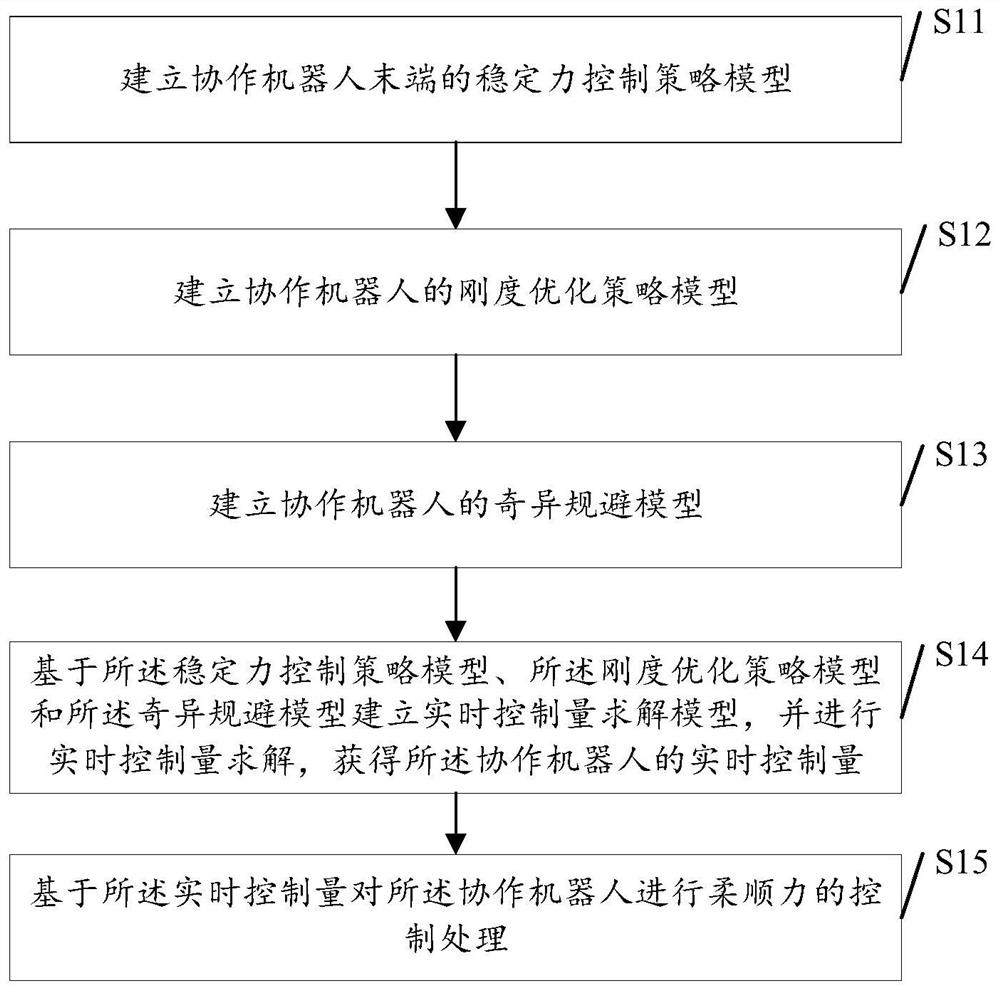
Compliant force control method and system for collaborative robot
PendingCN114260896AIncrease stiffnessMeet the joint angleProgramme-controlled manipulatorCollaborative roboticsSingularity avoidance
The invention discloses a compliance control method and system for a collaborative robot, and the method comprises the steps: building a stable force control strategy model of the tail end of the collaborative robot; establishing a rigidity optimization strategy model of the collaborative robot; establishing a singularity avoidance model of the collaborative robot; establishing a real-time control quantity solution model based on the stable force control strategy model, the rigidity optimization strategy model and the singularity avoidance model, and performing real-time control quantity solution to obtain the real-time control quantity of the collaborative robot; and controlling the compliance of the collaborative robot based on the real-time control quantity. In the embodiment of the invention, high-precision control on the contact force can be realized, and the rigidity of the collaborative robot system can be improved in real time, so that flutter is inhibited; the system can be effectively prevented from falling into a singular position type, and meanwhile the joint angle and angular velocity limitation of the robot is met.
Owner:INST OF INTELLIGENT MFG GUANGDONG ACAD OF SCI
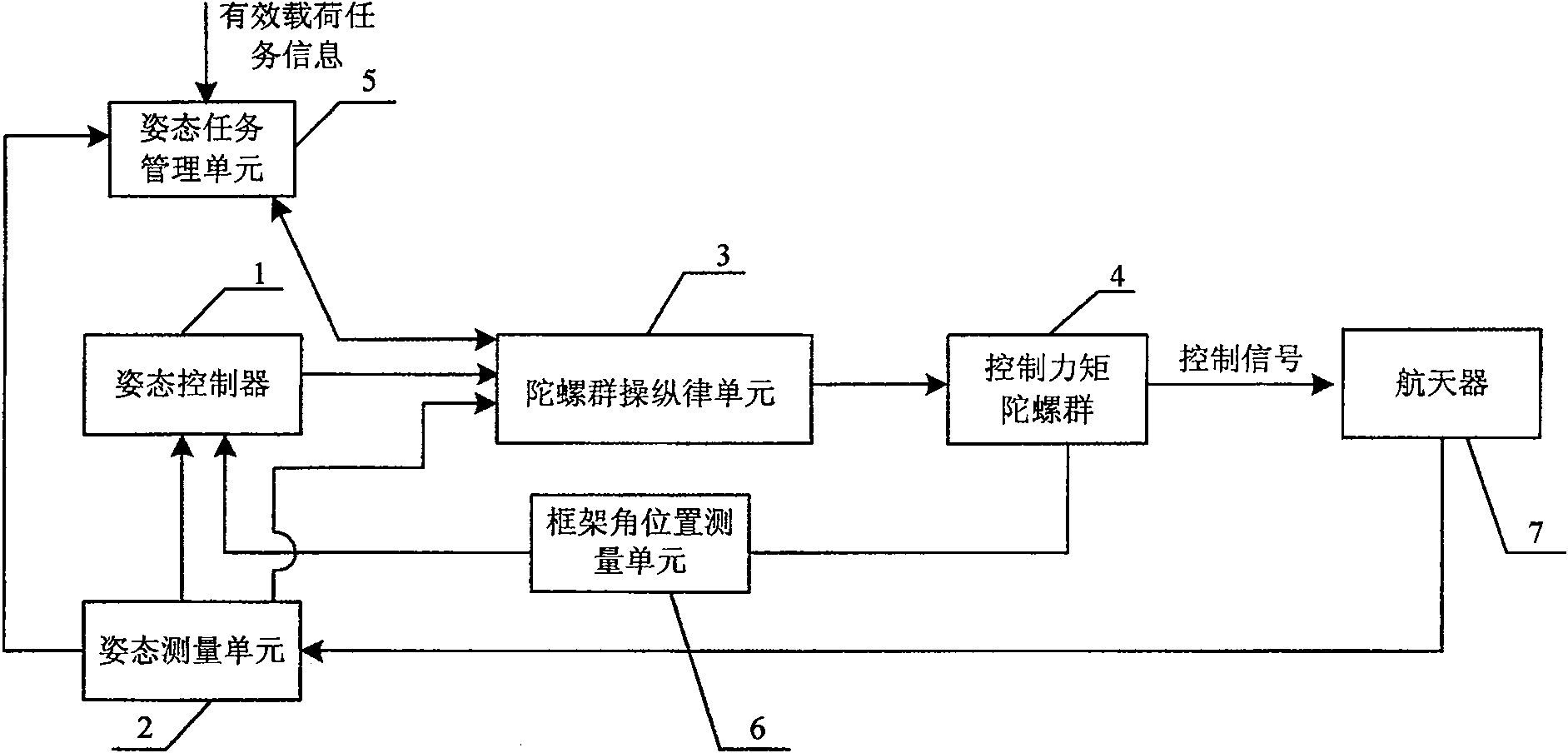
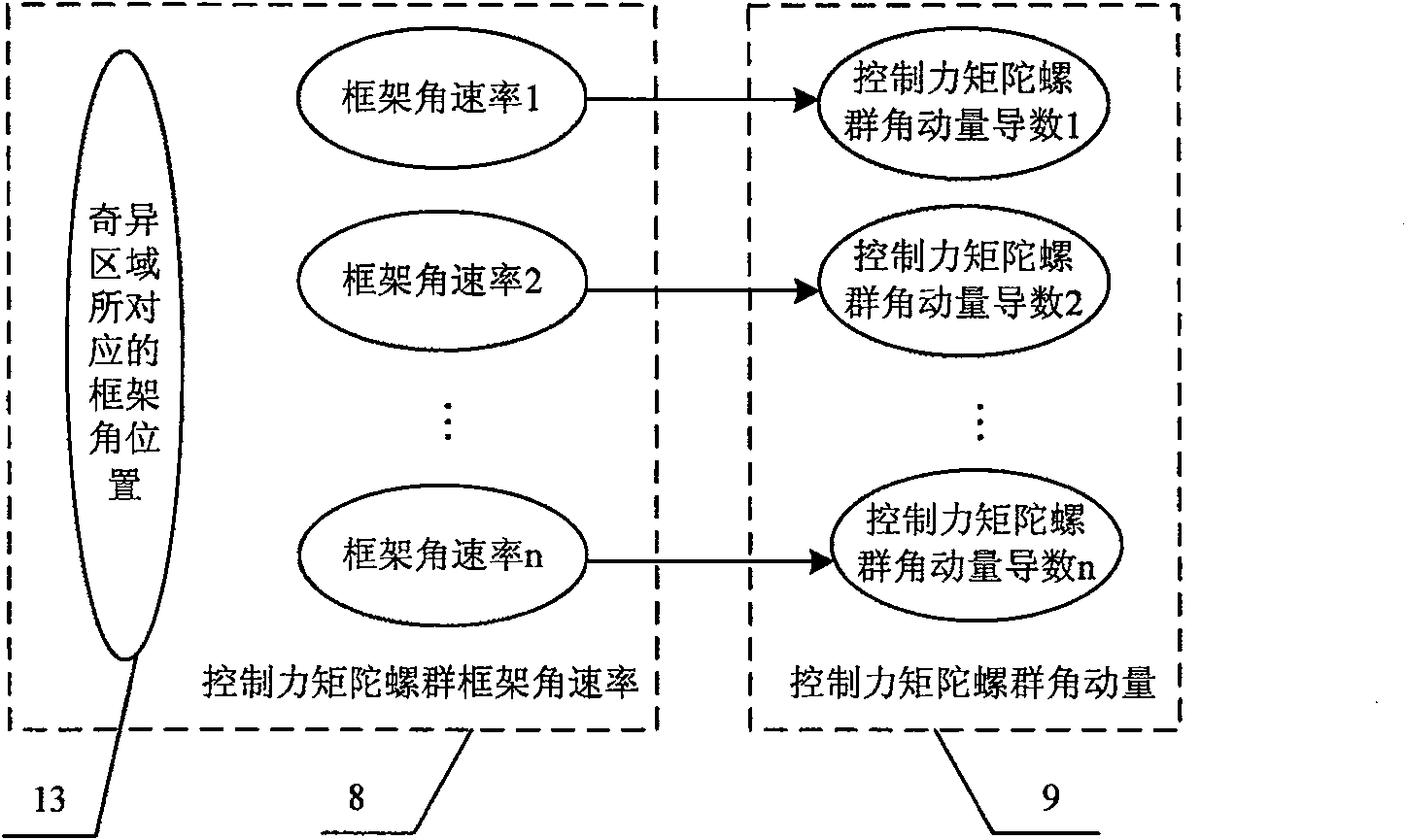
Steering law singularity avoidant spacecraft attitude control system
ActiveCN100565405CChange the output torqueAchieve high precision controlSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsAttitude controlControl signalSpacecraft attitude control
A spacecraft attitude control system for maneuvering law singularity avoidance, comprising an attitude task management unit, an attitude controller, an attitude measuring unit, a gyro group maneuvering law unit, a frame angle position measuring unit, a control moment gyro group and a spacecraft. The gyro group maneuvering law unit calculates the frame angular rate of the control moment gyro group through the control moment gyro angular momentum table, zero motion algorithm and pseudo-inverse maneuvering law algorithm, and uses the angular rate value as the given signal of the control moment gyro group, In order to improve the control accuracy of spacecraft attitude. The present invention introduces a steering law design method based on the look-up table method to select the frame angular rate and the initial value of the frame angular position, realizes the precise torque output of the control moment gyroscope group, and avoids the pseudo-inverse maneuvering law calculation method to obtain the control moment gyroscope frame angular rate The singularity problem generated in the process avoids the "deadlock" problem that occurs when the zero-motion algorithm and the robust pseudo-inverse steering law are iteratively calculated.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
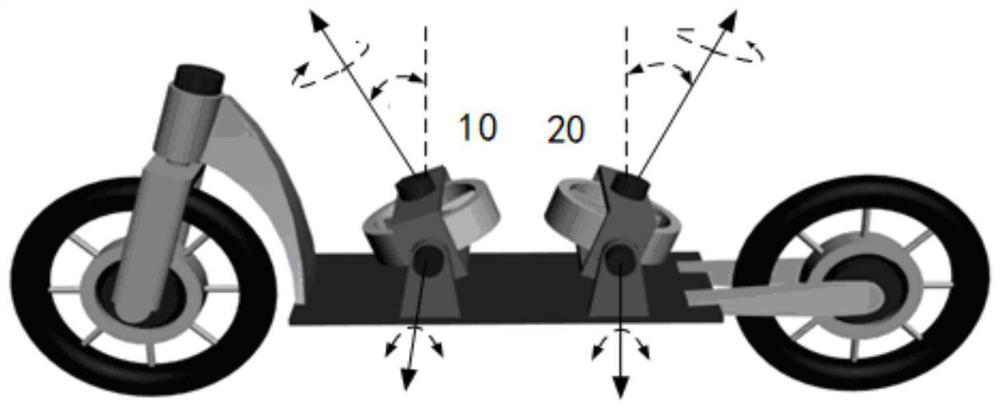
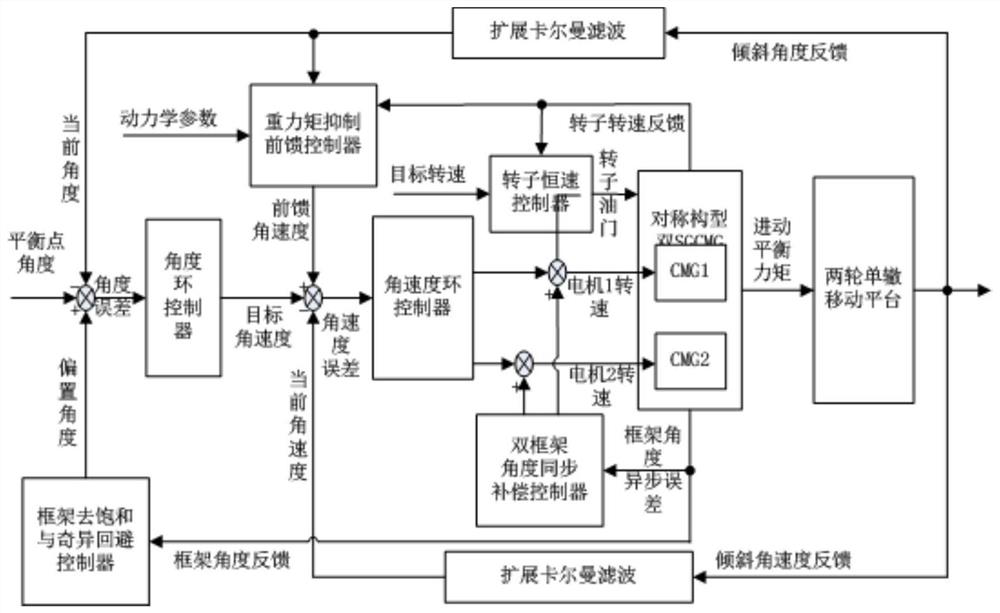
Static balance control system and method for two-wheeled single-track carrier
ActiveCN113093822AReal-time balance controlImprove the ability to resist external disturbancesElectric energy managementSpeed/accelaration control using electric meansControl systemElectric machinery
The invention provides a two-wheel single-track carrier static balance control system and method. The two-wheel single-track carrier is of a double-SGCMG parallel symmetrical structure, the two-wheel single-track carrier static balance control system is provided with a first frame motor, a second frame, a first control moment gyroscope and a second control moment gyroscope, the first control moment gyroscope and the second control moment gyroscope correspond to the first frame motor and the second frame respectively, and the first frame motor is provided with a first rotor; the second frame has a second rotor; the two-wheeled single-track vehicle static balance control system comprises a frame desaturation and singularity avoidance controller which executes the following calculation and control of calculating a frame angle error; calculating a bias angle for realizing frame desaturation and singularity avoidance based on the frame angle error; a bias angle being added to the input of the angle loop controller.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
A Spacecraft Attitude Control Method for Controlling Moment Gyro Singularity Avoidance
ActiveCN105223961BPrecise torque outputLower launch costsAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsSpacecraft attitude controlOptimal control
Owner:BEIJING MECHANICAL EQUIP INST
Fixed-time adaptive neural network sliding mode control method for nonlinear systems
ActiveCN112987567BSolve chattering problemsSolve the speed problemAdaptive controlDynamic modelsNetwork control
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com