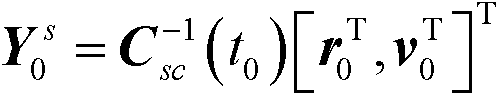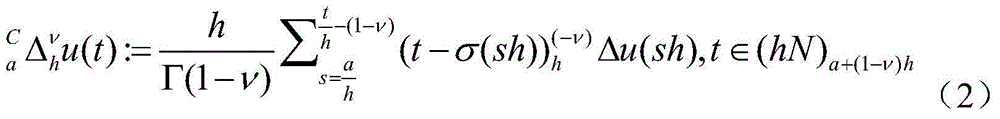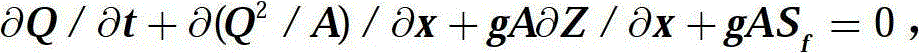Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
109 results about "Robin boundary condition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, the Robin boundary condition (/ˈrɒbɪn/; properly French: [ʁɔbɛ̃]), or third type boundary condition, is a type of boundary condition, named after Victor Gustave Robin (1855–1897). When imposed on an ordinary or a partial differential equation, it is a specification of a linear combination of the values of a function and the values of its derivative on the boundary of the domain.
Explosion Simulation in Finite Element Analysis
ActiveUS20100256957A1Reduce computing timeImprove userComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationProduction rateElement analysis
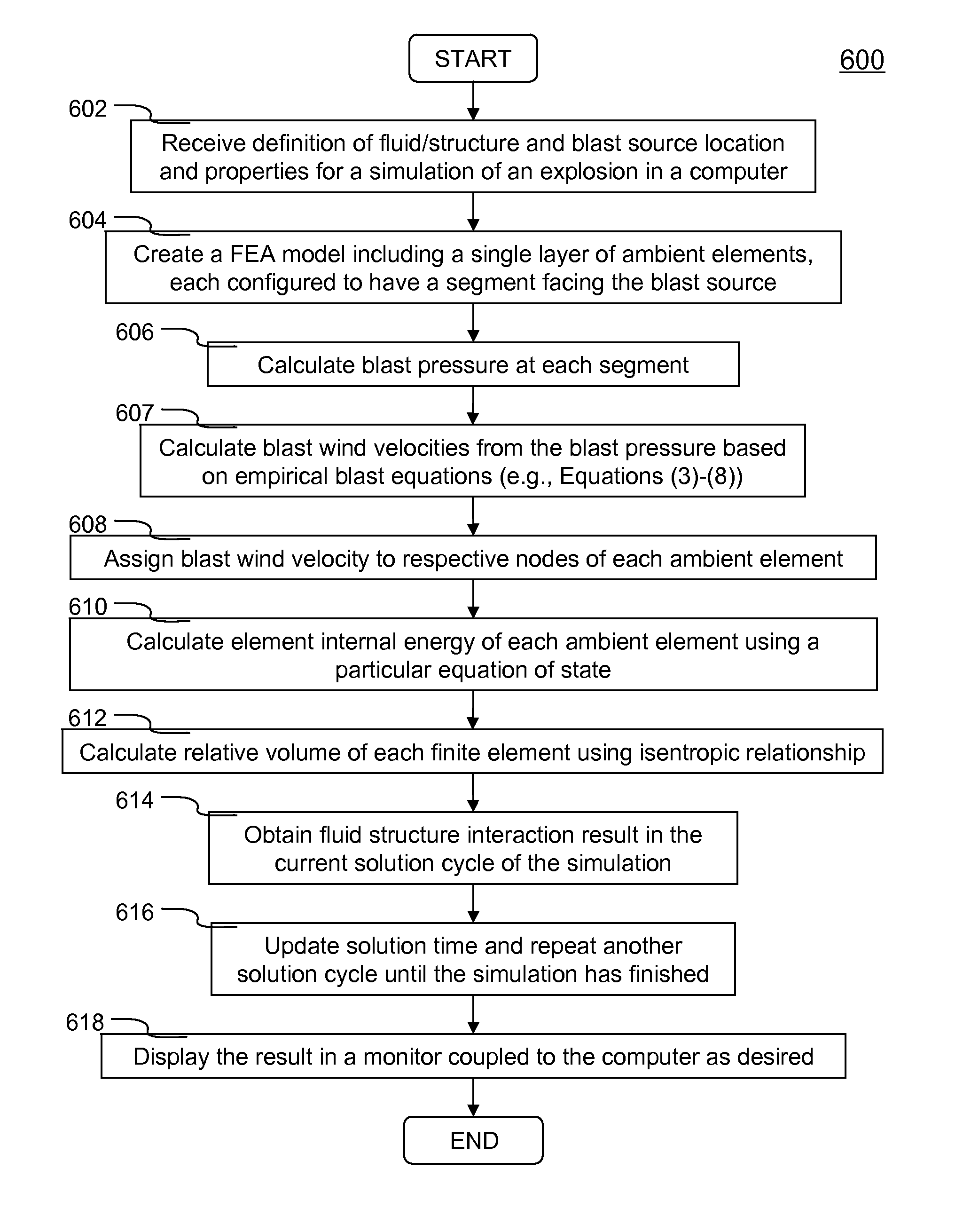
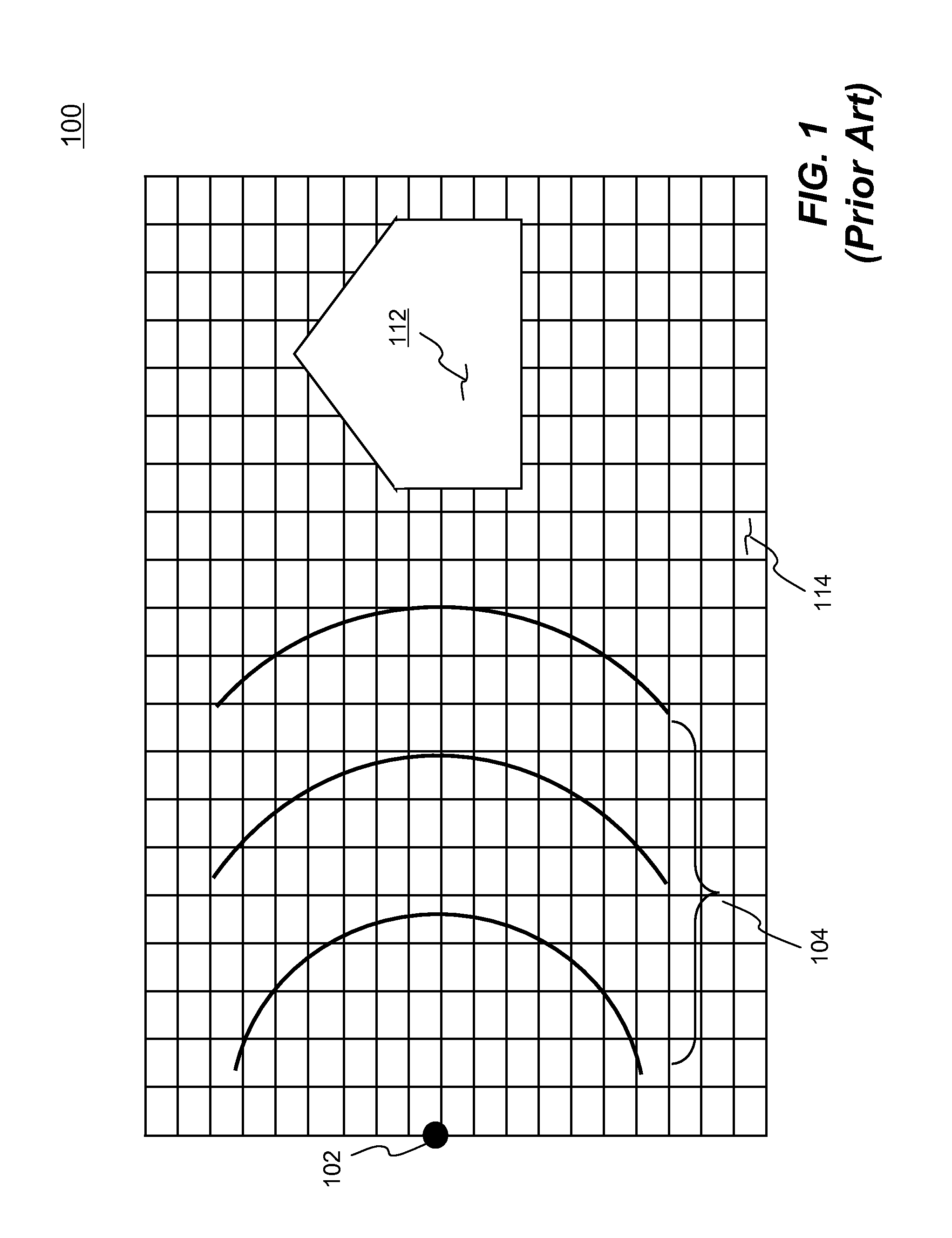
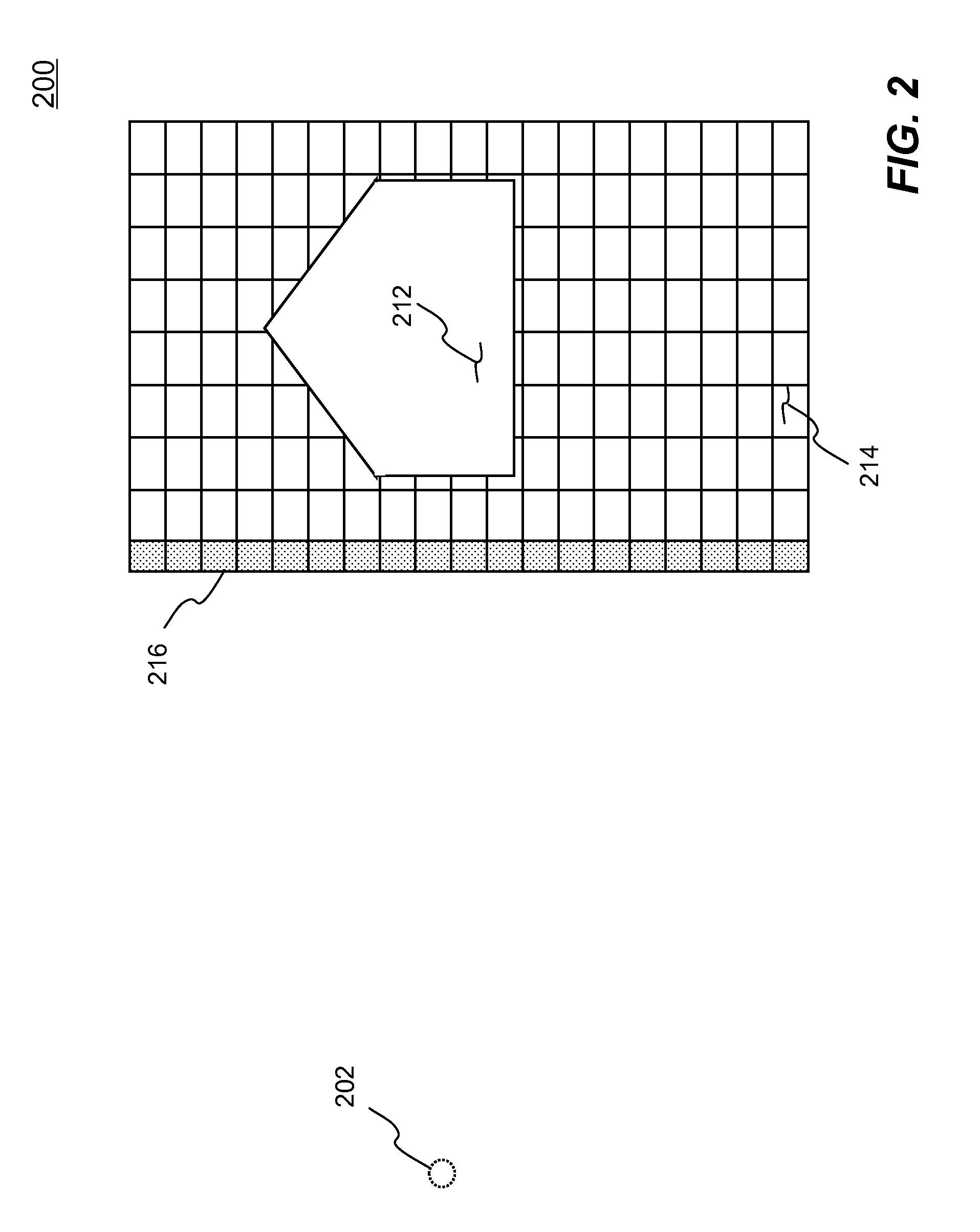
Systems and methods of simulating an explosion in time-marching finite element analysis are disclosed in the present invention. According to one aspect, a method is configured for increasing user (e.g., engineer or scientist) productivity by reducing computation time of simulating fluid-structure interaction due to an explosion. The method comprises a creation of a finite element analysis model that includes structure, surrounding fluid, a blast source of the explosion and a single layer of ambient elements each having a segment representing a boundary of the fluid facing the blast source. Each ambient element is associated with a particular finite element representing the fluid at the boundary. The ambient elements are configured to be situated between the blast source and the structure such that the simulation can be carried on a set of boundary conditions specified thereon. The boundary conditions comprise a set of nodal velocities that are determined from the empirical formula (e.g., Friedlander equation).
Owner:ANSYS
Structural dynamical model modification-based prestress recognition method
InactiveCN105740541AEasy to iterateEasy to identifyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionElement model
The invention discloses a structural dynamical model modification-based prestress recognition method, and relates to the prestress recognition of pre-tensioning structures. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a finite element model of a structure; converting the boundary condition such as clamped support or simple support into spring support in three or two directions, and applying an axial prestress at the same time; calculating a fixed frequency and a fixed vibration mode of the structure through commercial finite element software; carrying out test and recognition by utilizing a test modal analysis technology, so as to obtain the fixed frequency and the fixed vibration mode of the structure; and recognizing the spring support rigidity and prestress of the boundary at the same time on the basis of a model modification technology. The method is simple, high in recognition precision and convenient to operate; and through considering the influences of the boundary condition, the reliability is high. By taking MAC as a target function, the completeness of the test data is supplemented; the optimization through a genetic algorithm is more beneficial for obtaining the globally optimal solution; and the whole modification model can be automatically driven to carry out solving.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Interplanetary low-thrust transfer orbit design method based on polynomial approximation
InactiveCN102424119ARapid designReduce design difficultyCosmonautic componentsPerformance indexEngineering
The invention relates to an interplanetary low-thrust transfer orbit design method based on polynomial approximation. Firstly, variable initial value guess is designed, the initial value guess of the transfer orbit design is given, then, the beginning and tail end boundary conditions of a detector are calculated, next, a second type Chebyshev polynomial is adopted for fitting the transfer orbit of the detector, the performance indexes and the constrained conditions are calculated, finally, whether the feasibility conditions are met or not is judged according to the calculated thrust restriction in accordance with whether the calculated performance indexes meet the optimum conditions or not, if all requirements are met, the optimization is successful, the optimum transfer orbit is obtained, and if one requirement is not met, the initial value guess of the design variable in the first step is regulated until the optimization is successful. The method utilizes the Chebyshev polynomial for approximating the low-thrust transfer orbit shape, the time is used as the independent variable, and the flight time restriction is avoided. The polynomial factor is determined through the beginning and tail end orbit state restriction of the detector, and the method has the advantage that the fast design on the low-thrust transfer orbits in different task types can be realized according to the given beginning and tail end boundary conditions.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Heterogeneous cluster system for CFD simulation calculation and CFD calculation method
ActiveCN107122243ASolve the bottleneck problem of computing powerImprove operational efficiencyResource allocationDesign optimisation/simulationParallel computingHeterogeneous cluster
Embodiments of the present invention provide a heterogeneous cluster system for CFD simulation calculation and a CFD calculation method. The heterogeneous cluster system for CFD simulation calculation comprises a central processing unit (CPU) and a hardware accelerator. The CPU is configured to divide the received CFD task into task blocks, according to the attribute of the CFD task, the CFD boundary condition and the performance parameter of the hardware accelerator, determine the hardware accelerator for calculating the task blocks, and transmit the task blocks to the hardware accelerator; and the hardware accelerator is configured to receive and calculate task blocks transmitted by the CPU and transmit the calculation result to the CPU. According to the technical scheme of the embodiments of the present invention, by constructing the heterogeneous cluster system integrating the CPU, the GPU and the FPGA, calculation resources are intelligently deployed according to the attribute of the CFD task, so that the bottleneck problem of CFD simulation calculation is solved and the running efficiency of the CFD application is improved.
Owner:浙江远算科技有限公司
Anomalous diffusion simulation method based on discrete fraction order difference
InactiveCN104392127AKeep discrete memory effectsHigh expressionComplex mathematical operationsDiffusionMemory effect
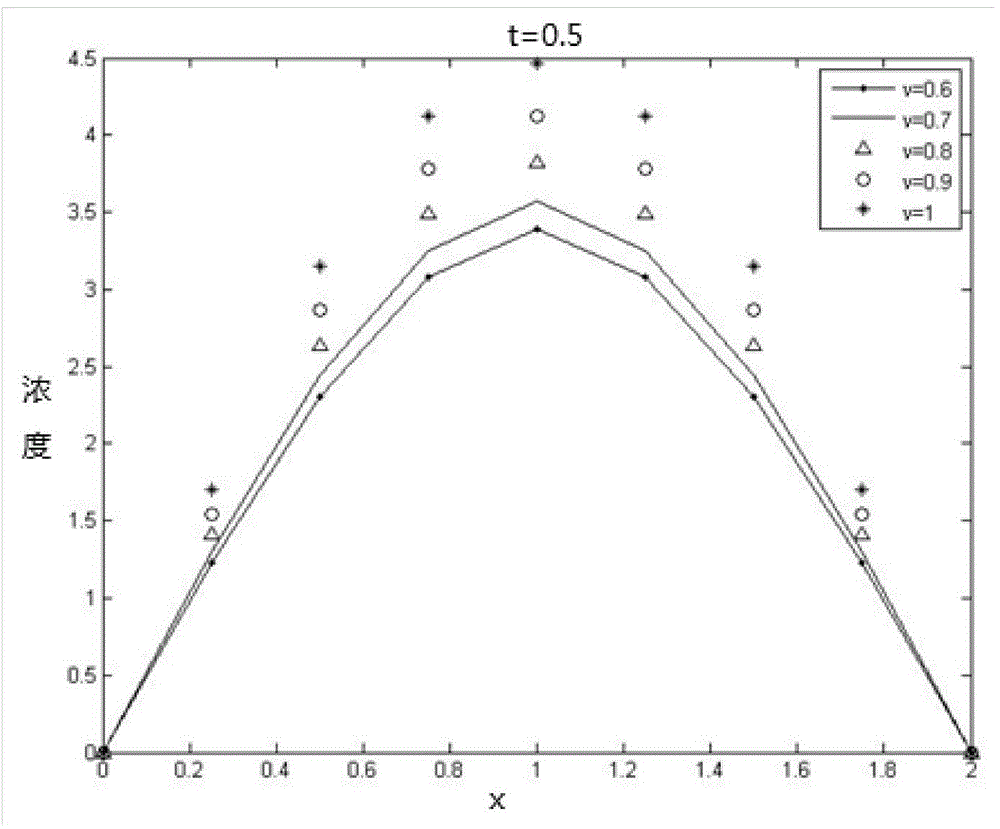
The invention discloses an anomalous diffusion simulation method based on a discrete fraction order difference. The anomalous diffusion simulation method based on the discrete fraction order difference includes: using a one dimension classical diffusion equation for describing a diffusion phenomenon; defining the discrete fraction order difference, using the discrete fraction order difference to discretize the one dimension classical diffusion equation, and performing numerical simulation according to initial boundary conditions. Compared with a diffusion model built by using a classical fraction order diffusion equation, a diffusion model built by using the anomalous diffusion simulation method based on the discrete fraction order difference is concise in expression, and convenient and fast in numerical simulation on the premise of maintaining discrete memory effects.
Owner:NEIJIANG NORMAL UNIV
Medium rough surface finite element electromagnetic simulation method based on integral boundary
InactiveCN103279600AImprove accuracyAvoid incomplete absorptionSpecial data processing applicationsRough surfaceFunctional methods
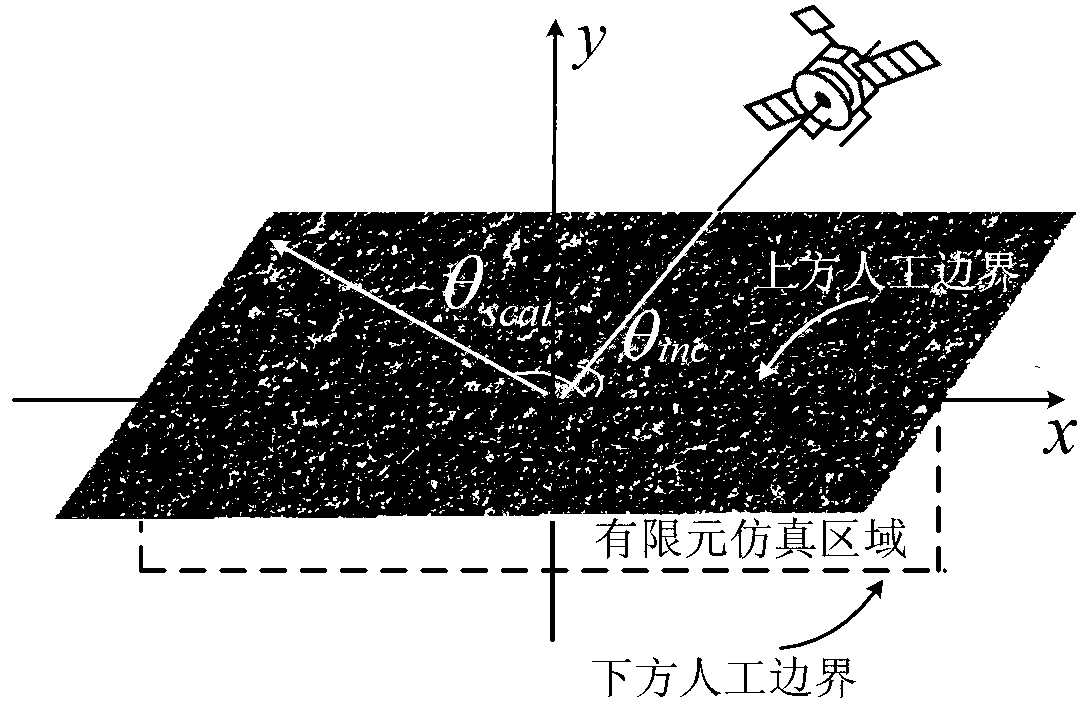
The invention discloses a medium rough surface finite element electromagnetic simulation method based on integral boundary. The medium rough surface finite element electromagnetic simulation method based on the integral boundary mainly solves the problem that similarity of inhomogeneous media and approximate absorbing boundary are difficult to solve by integral equation class methods. The medium rough surface finite element electromagnetic simulation method based on the integral boundary comprises the achieving steps of using a monte carlo method for obtaining a medium rough surface, carrying out truncation processing and scattering on the medium rough surface through an artificial boundary, acquiring a finite element equation of a simulation area according to a functional method inside the simulation area, using an integral equation method for obtaining integral boundary conditions outside the simulation area, forming an electromagnetic coupled equation through continuous conditions, and finally obtaining radar scattering parameters of the medium rough surface by solving an electromagnetic coupled matrix equation. Compared with the prior art, the medium rough surface finite element electromagnetic simulation method based on the integral boundary can be more easily used for simulating inhomogeneous medium electromagnetic problems than the integral equation class methods, can improve electromagnetic simulation precision compared with the approximate absorbing boundary, and can be used for acquiring the electromagnetic scattering parameters of medium rough surface unbounded area problems.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Forward computation method of motion equation of elastic wave on relief surface
InactiveCN102062875AImprove computing efficiencyFree Boundary Condition ImplementationSeismic signal processingTerrainWave equation
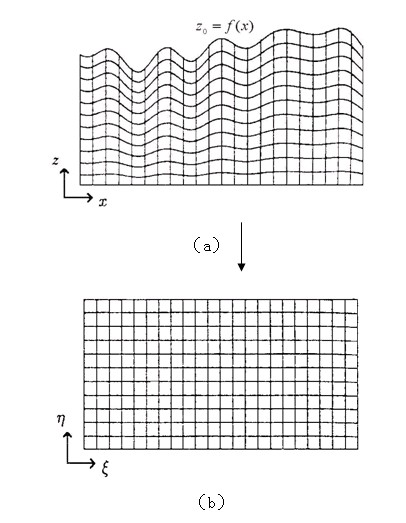
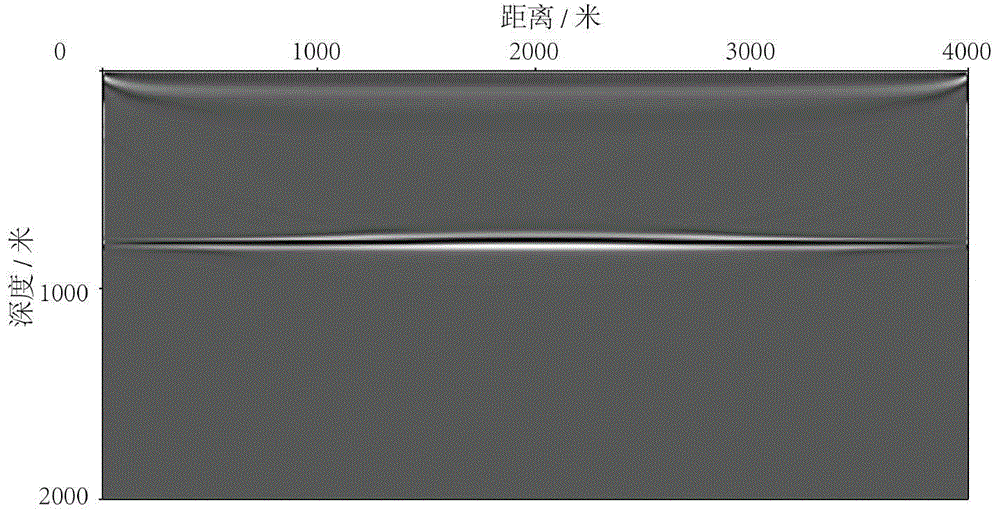
The invention discloses a forward computation method of a motion equation of an elastic wave on a relief surface, relating to the field of processing and explanation of the seismic exploration data of oil seismic exploration. The forward computation method comprises the following steps of: converting an irregular computational domain into a regular computational domain under a new coordinate system by utilizing longitudinal coordinate transformation; educing a free boundary condition under the new coordinate system on the basis of a zero-traction free boundary; and computing a seismic wave field positioned on the free boundary by adopting an implicit difference scheme. The forward computation method can process complex terrains, is adapted to the surface relief, also enhances the computing efficiency and can better implement the free boundary condition.
Owner:CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP CHUANQING DRILLING ENG CO LTD
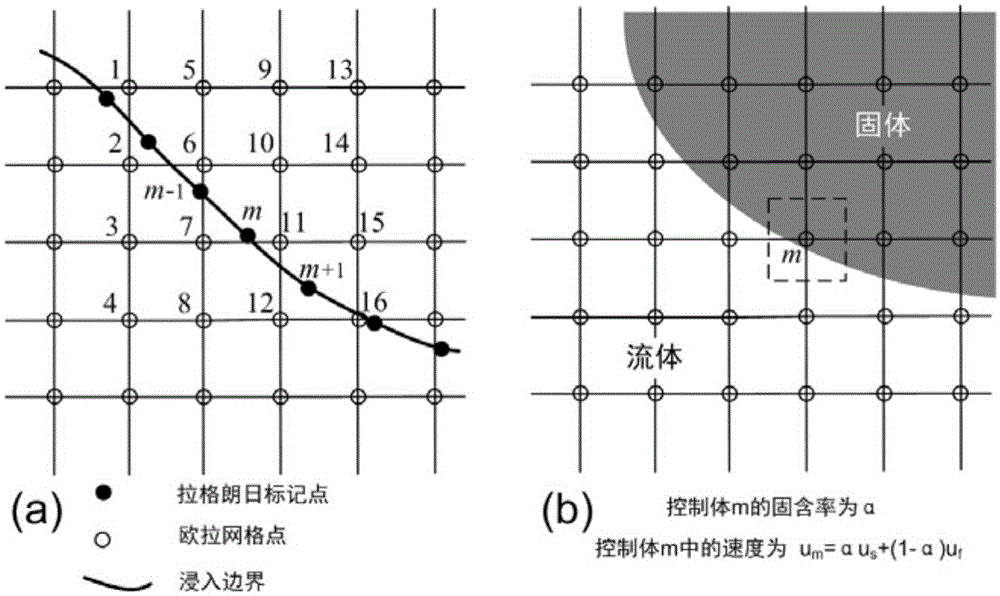
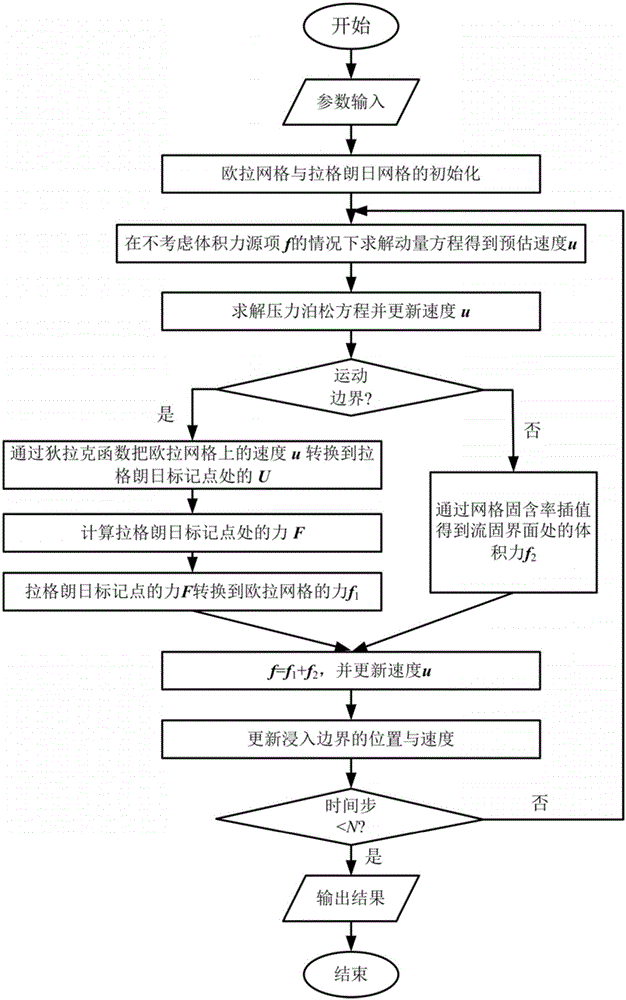
Stirred tank reactor simulation method based on immersed boundary method
ActiveCN105069184APromote generationReduce workloadSpecial data processing applicationsBoundary knot methodSolid particle
The present invention provides a stirred tank reactor simulation method based on an immersed boundary method. The method includes: a preparation phase including determination and setting of calculating parameters, generation of fluid grid files, generation of Lagrange mark point information, and preparation of calculating resources; numerical calculation: setting boundary conditions of computational domains and solving velocity fields and temperature fields based on fluid grids; combining with a discrete element method to achieve an interface analytic simulation of two-phase flow of particle flow, wherein the immersed boundary method is directly employed to apply non-slip boundary conditions to particle surfaces; a post-processing phase, and outputting information of each Euler mesh and information of each particle after a simulation is completed. According to the characteristics of different boundaries, in the calculation, the mixed immersed boundary method is employed to process, and the mass numerical simulation of turbulent flow in the stirred tank reactor is achieved through combination of large eddy simulation and high performance parallel computing technology. The simulation method may be applied to simulation of turbulent flow and simulation of solid particle suspension in the stirred tank reactor and the like.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
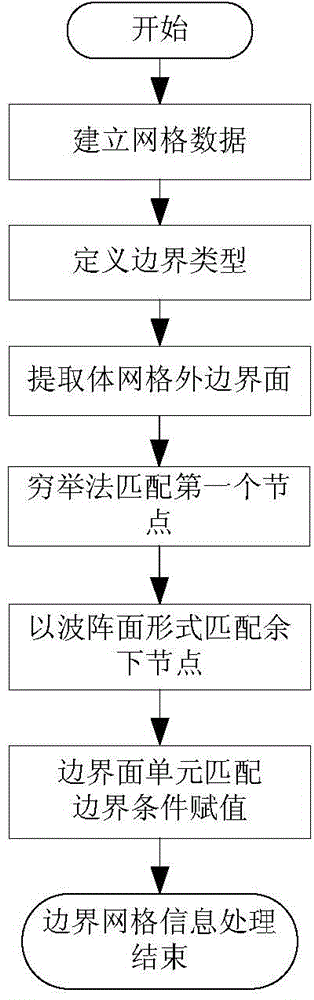
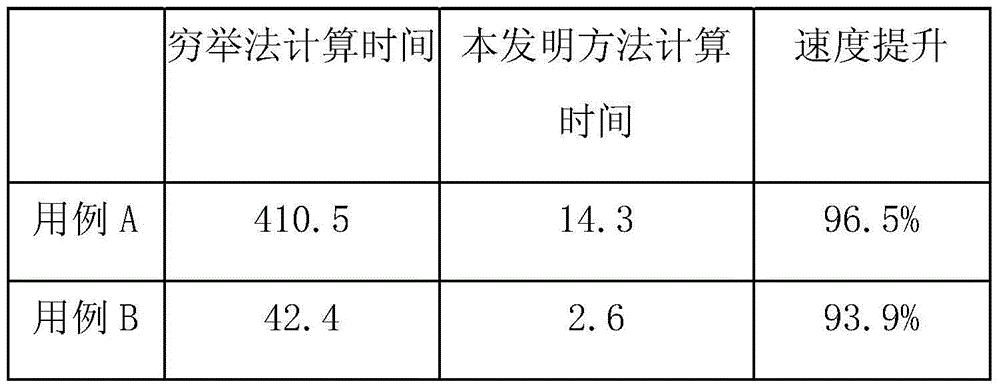
Grid boundary condition processing method of unstructured grid CFD computation
The invention belongs to the technical field of grid computation, and specifically relates to a grid boundary condition processing method of unstructured grid CFD computation. The method comprises the following steps: establishing grid information; defining a boundary type; extracting grid outer boundary information; realizing the matching of a first node through a method of exhaustion; matching the remaining nodes in a wave front form; matching a boundary surface unit; and assigning a boundary condition. According to the method, a method for rapidly matching between unstructured boundary surfaces and grid surfaces is utilized, so that the grid boundary conditions of unstructured grids in Tecplot form can be rapidly mapped to corresponding boundary surfaces of infield body grids, the rapid processing of boundary condition information of the unstructured grids can be realized and the computer time can be effectively decreased.
Owner:BEIJING LINJIN SPACE AIRCRAFT SYST ENG INST +1
Method for carrying out parallelization numerical simulation on hydrodynamic force conditions of river provided with cascade hydropower station
InactiveCN102722611AImprove versatilityImprove portabilitySpecial data processing applicationsInformation technology support systemEngineeringWater level
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
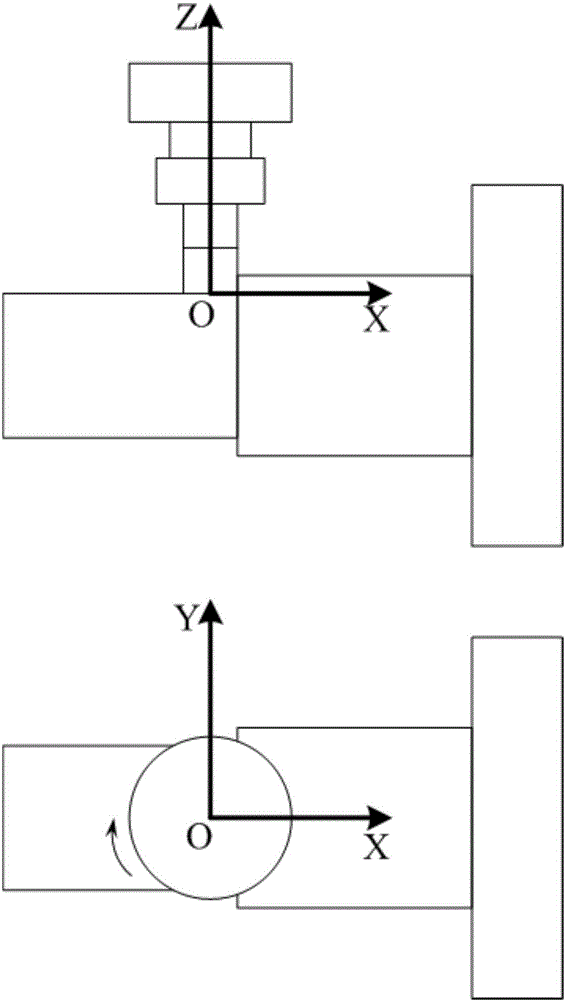
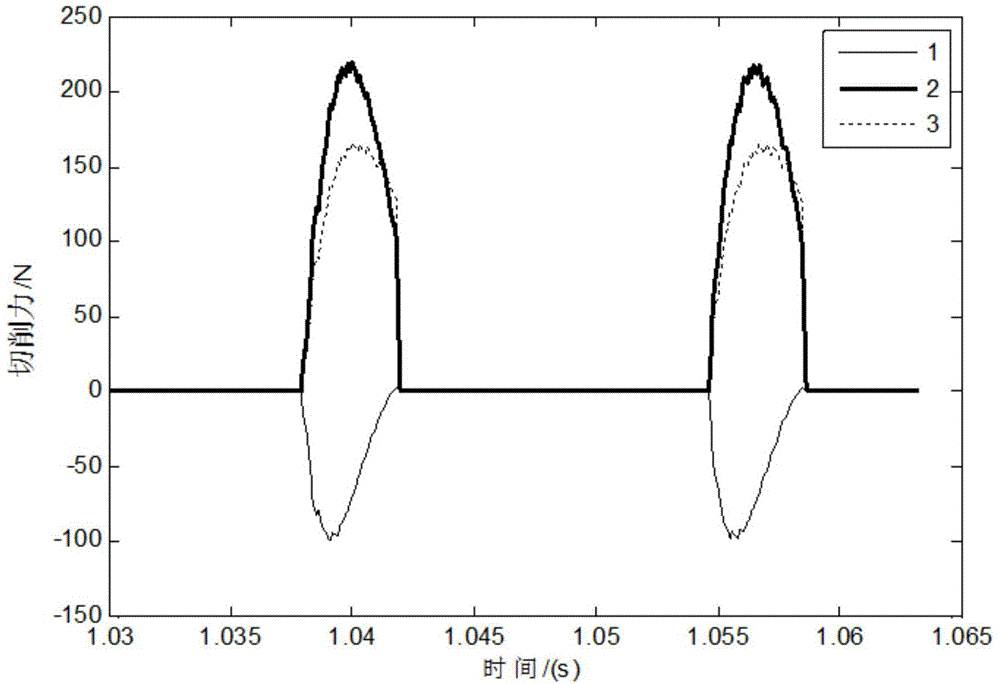
Modeling method for judging cutting force of orthogonal turn-milling machining end face on basis of boundary conditions
InactiveCN104794337AAccurately reflectHigh expressionSpecial data processing applicationsModel methodVirtual machining
The invention discloses a modeling method for judging the cutting force of an orthogonal turn-milling machining end face on the basis of boundary conditions. The method includes the five steps of firstly, establishing a tool coordinate system; secondly, dividing the tool end face into a plurality of microelements in the radial direction; thirdly, judging whether the microelements participate in cutting or not through the boundary conditions; fourthly, obtaining thickness of cuttings, and calculating the microelement cutting force on the basis of the thickness; fifthly, adding the cutting force on all the microelements participating in cutting to obtain the total cutting force. By means of the method for judging the cutting state of the microelements through a united boundary condition equation, the disadvantage that in the prior art, when the orthogonal turn-milling machining end face blade cutting force is predicted, the cutting progress needs to be divided into multiple stages to be discussed is avoided; due to the fact that the influences of jumping are taken into consideration, the prediction effect is more accurate. The expression is simple and easy to understand, the complex characteristic angle calculation is omitted, and the modeling method is suitable for development of virtual machining simulation systems and has good application aspects.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
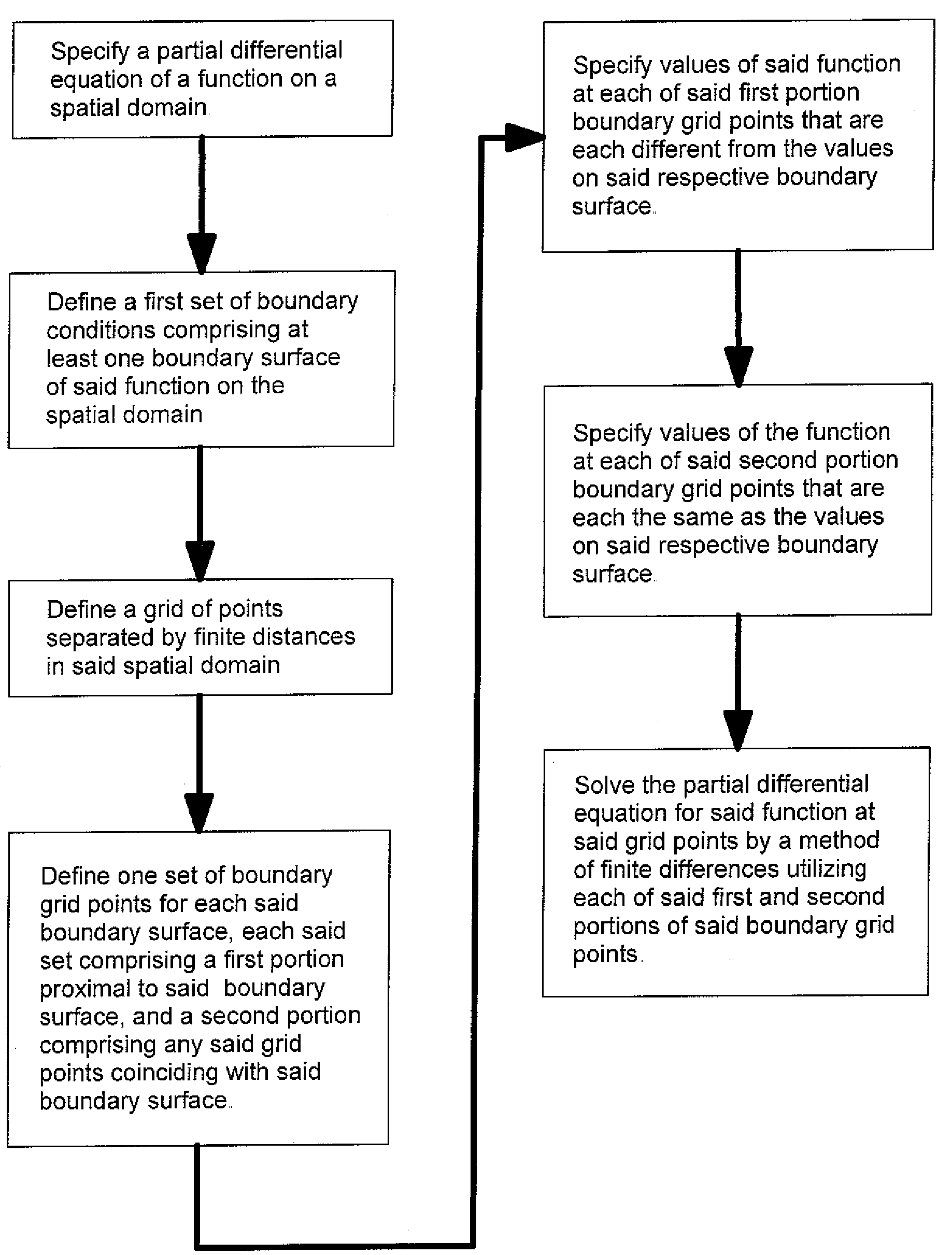
Finite differences methods
ActiveUS20090083356A1Improved accuracy in the calculation of the function fMeet growth requirementsDigital differential analysersDesign optimisation/simulationBoundary valuesDiscretization
The application of finite differences methods to solve boundary value problems typically involves a discretization of such a problem across an orthogonal array of discrete grid points. This leads to an array of difference equations which is solved numerically within the constraints of the boundary conditions to yield solutions at the grid point locations. However, the accuracy of the solutions is limited with conventional finite differences methods when the boundary conditions are not represented exactly within the orthogonal array of discrete grid points, as when the boundary conditions are curved or slanted surfaces. The invention described herein provides finite differences methods for solving boundary value problems more accurately than with conventional finite differences methods, particularly when curved or slanted boundary surfaces correspond to terminations of a known analytical function.
Owner:PERKINELMER U S LLC
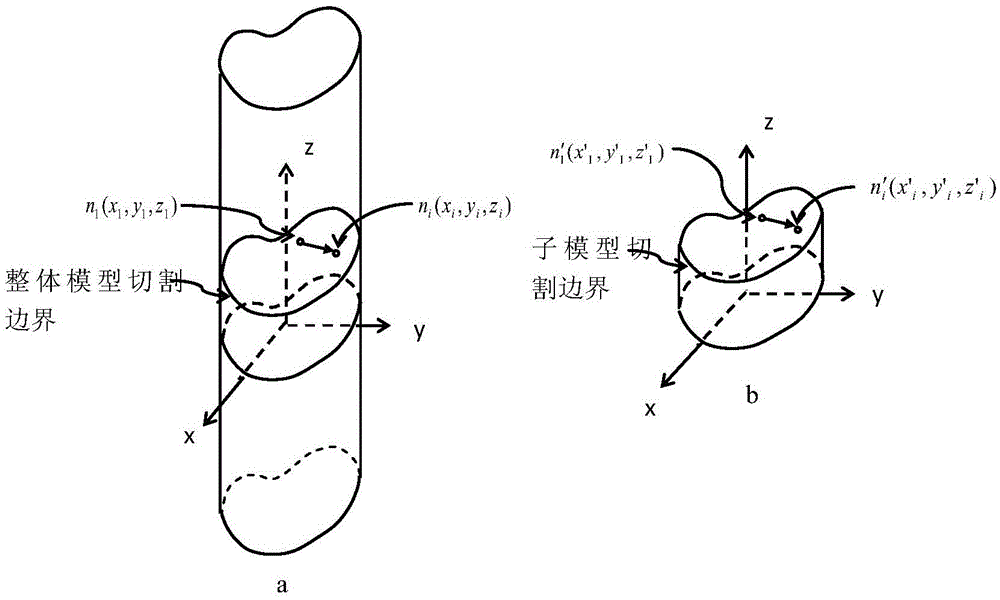
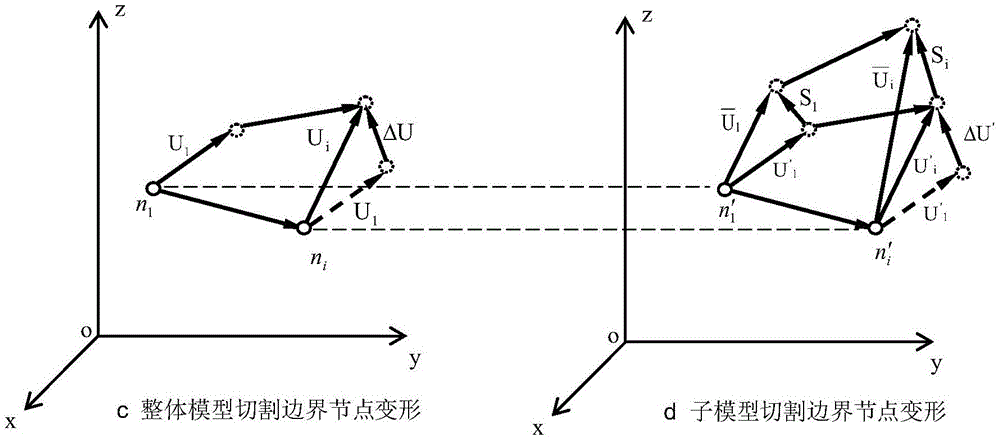
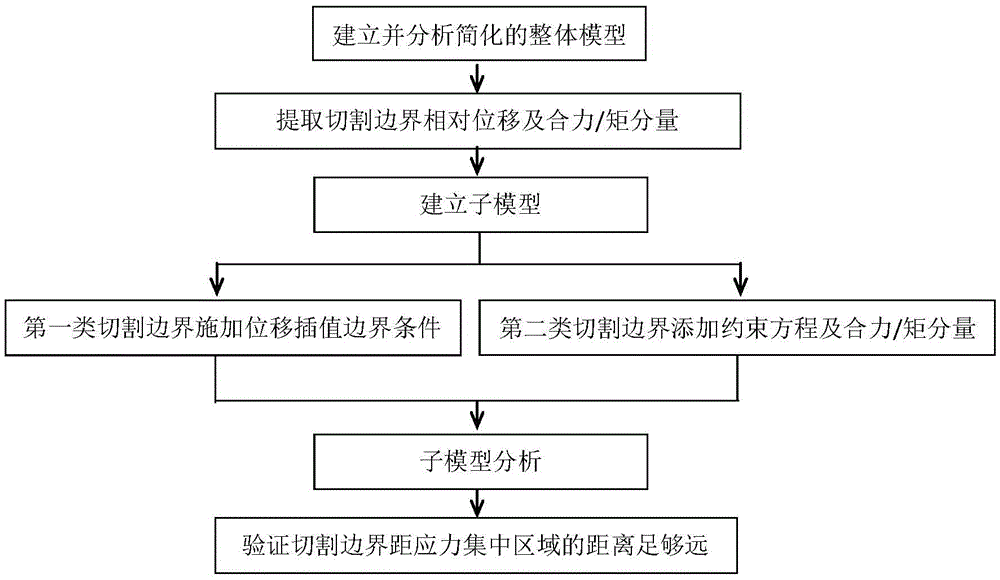
New submodel finite element analysis method based on cutting boundary deformation constraint
ActiveCN105550464APrecise structureAccurate forceDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsStress concentrationReduced model
The invention discloses a new submodel finite element analysis method based on cutting boundary deformation constraint. The content of the method comprises: building a complete machine simplified model, analyzing; carrying out postprocessing to cutting boundary nodes of the complete machine model; building a finite element model-a submodel of a partial structure; adding a deformation coupling constraint equation to the cutting boundary of the submodel, adding a displacement interpolation boundary condition and a force boundary condition; analyzing the submodel; and checking that the distance from a cutting boundary to a stress gathered region is far enough. The method of the invention is advantaged by that when applying the boundary conditions to the cutting boundary of the submodel, the displacement interpolation boundary condition is added to one part of the cutting boundary, the constraint equation and the force boundary condition are added to the other part; the accuracy of the boundary conditions of the submodel is ensured; compared with the traditional submodel finite element analysis method, in adoption of the new submodel finite element analysis method, the demand of the complete machine model is reduced; the complete machine model is greatly simplified; and the complete machine analysis efficiency and the calculation precision of the submodel are improved.
Owner:JIANGSU XCMG CONSTR MASCH RES INST LTD
Color conversion using barycentric projections
ActiveUS7423791B2Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsColor transformationRobin boundary condition
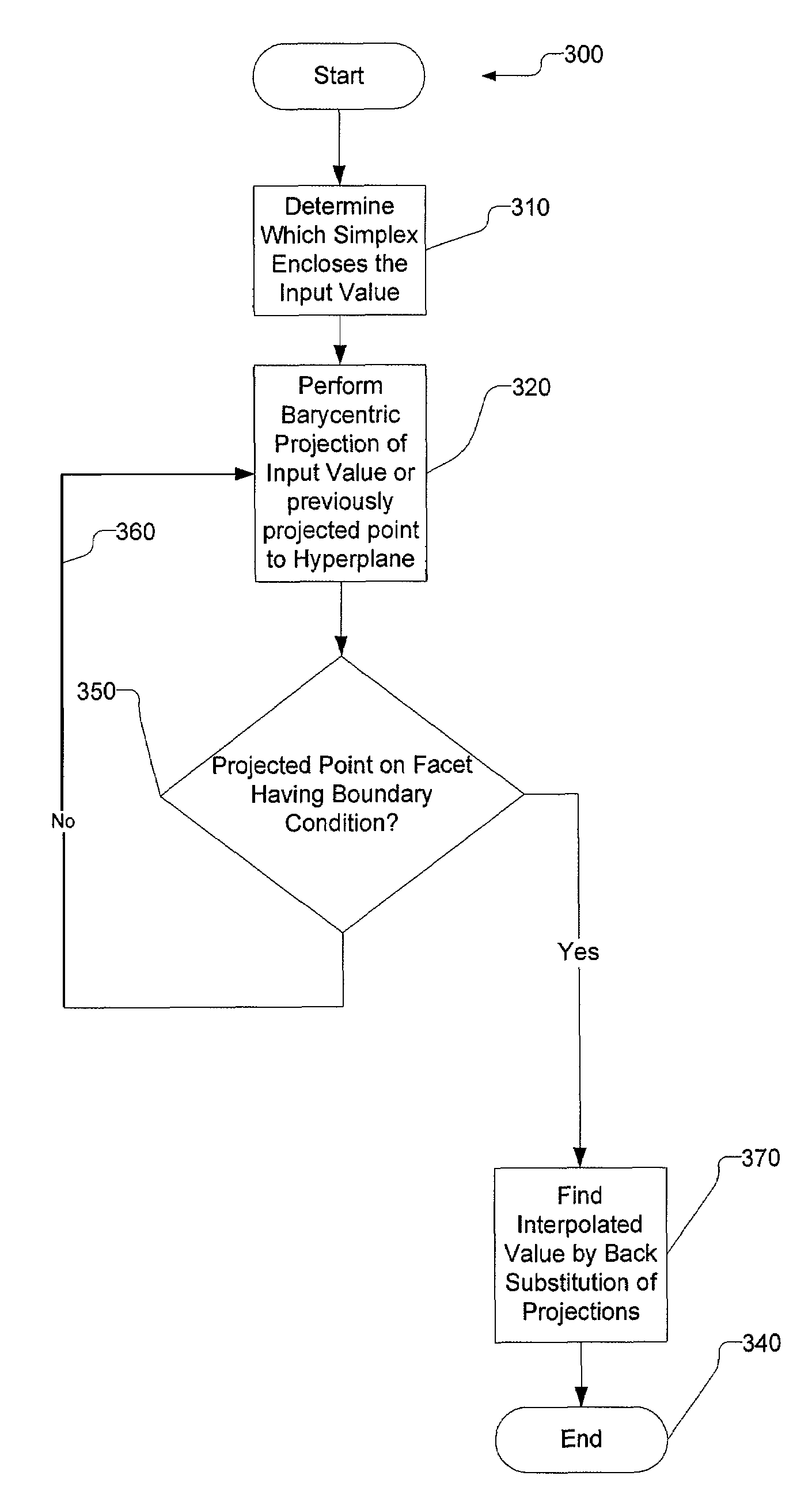
A method and apparatus for interpolating values for a color space from an input color value. A unit hypercube enclosing the input value is generated based on values from a look up table. A set of boundary conditions are then imposed on the unit hypercube. To perform the actual interpolation, an initial barycentric projection is performed from a selected vertex of the unit hypercube through the input value onto a boundary of the unit hypercube. If the projection satisfies one of the boundary conditions, an interpolated value is calculated using the projection by back substitution. If the initial projection does not satisfy a boundary condition, an intermediate value is generated from the previous projection and successive barycentric projections are performed using respectively different vertices of the unit hypercube through intermediate values onto a boundary of the unit hypercube until a projection satisfies one of the boundary conditions.
Owner:CANON KK +1
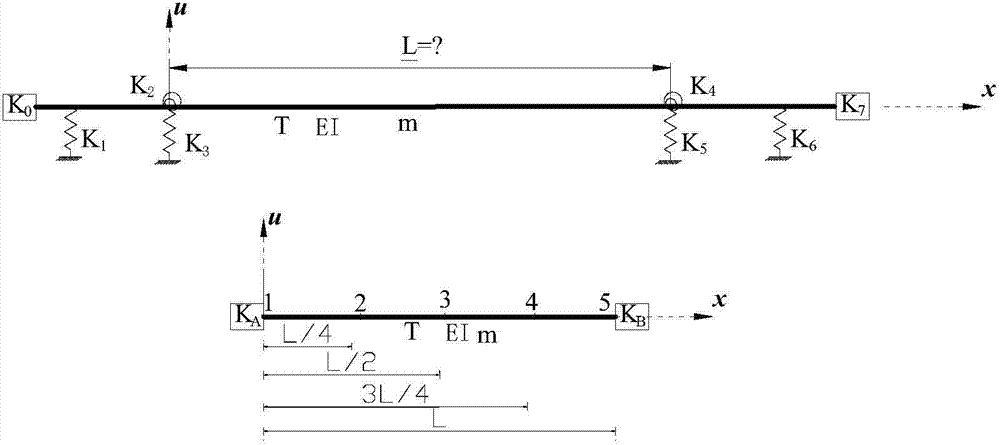
Method and device for cable force test in unknown boundary condition
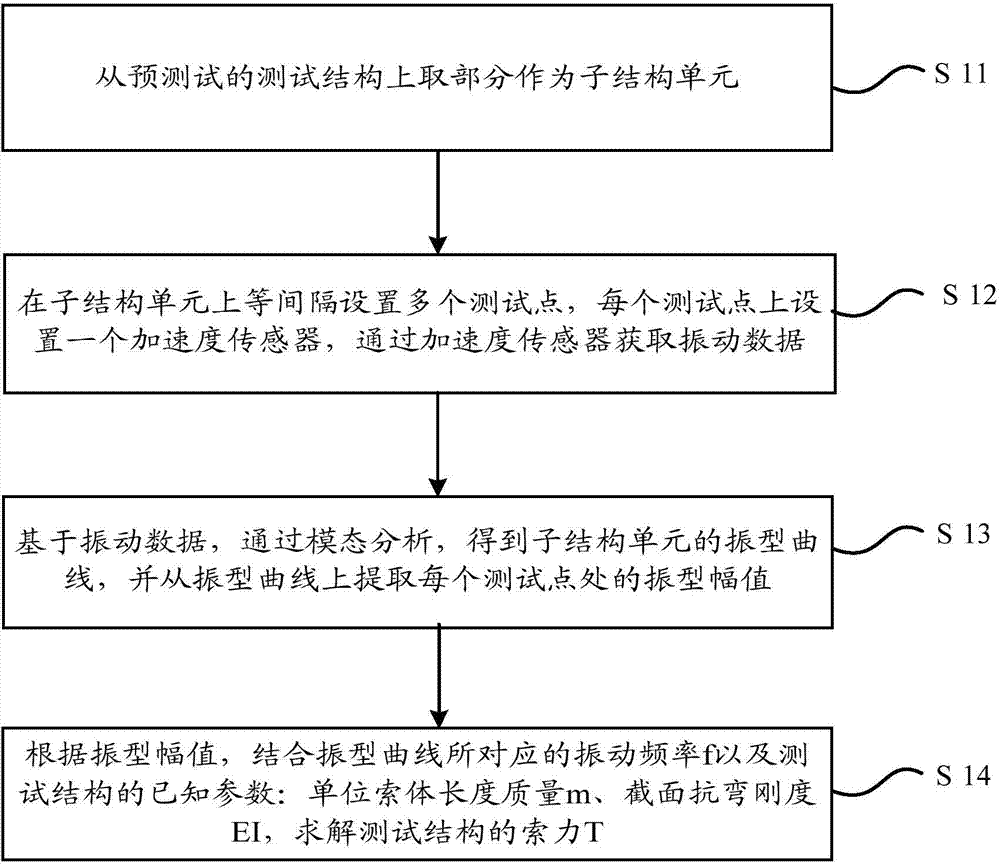
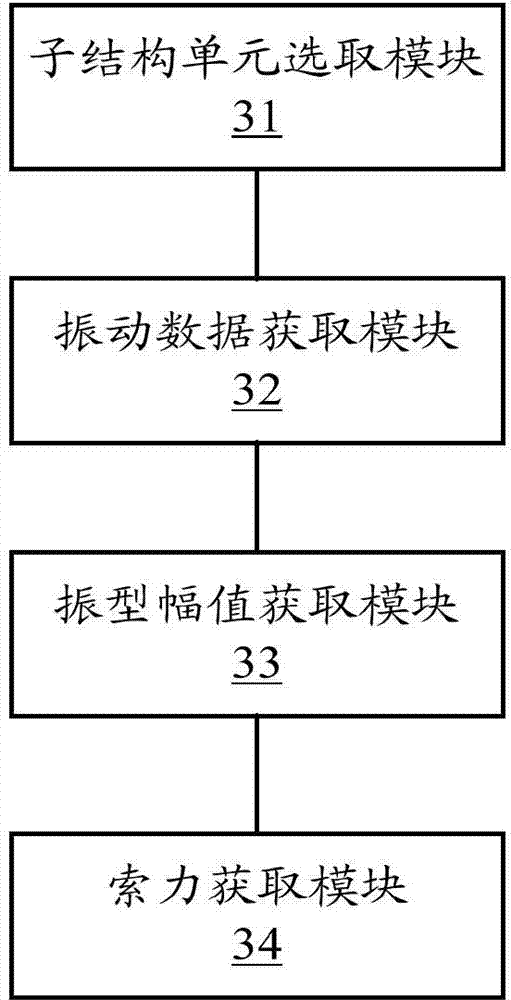
The invention relates to the technical field of cable force tests when boundary is unknown, and especially relates to a method and a device for a cable force test in an unknown boundary condition. The method comprises: taking a part from a pretest test structure, using the part as a substructure unit; arranging a plurality of test points at interval on the substructure unit, each test point being provided with an acceleration sensor, the test point obtaining vibration data through the acceleration sensor; based on the vibration data, through modal analysis, obtaining a vibration mode curve of the substructure unit, and extracting the vibration mode amplitude of each test point from the vibration mode curve; and according to the amplitude, combining with vibration frequency f corresponding to the vibration mode curve and known parameters of the test structure, solving the cable force T of the test structure. The cable force test method realizes cable force tests on a test structure whose boundary condition is unknown and cable pole calculation length is unknown. In the cable force test process, the method gives full consideration on influence of flexural rigidity of the test structure, so the obtained cable force is more accurate, and the device can the method can preferably satisfy actual measuring requirements of cable force tests.
Owner:徐辉 +1
Multi-loop cable steady-state temperature rise acquisition method adapting to various boundary conditions
ActiveCN106021189ASimple calculationAccurate calculationDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsHeat flowSteady state temperature
The invention relates to a multi-loop cable steady-state temperature rise acquisition method adapting to various boundary conditions. The method comprises the following steps: 1) constructing a multi-loop cable steady-state temperature rise model adapting to various boundary conditions according to a thermal field superposition principle; 2) acquiring an initial temperature rise matrix T<0> according to a set initial heat flow matrix Q<0>; 3) performing reduction according to the initial temperature rise matrix T<0> and the boundary conditions to form a reduced heat flow matrix Q<1>; 4) acquiring a next-step temperature rise matrix T<1> according to the reduced heat flow matrix Q<1>; and 5) judging whether a maximum difference value among all elements which correspond to the initial temperature rise matrix T<0> and the next-step temperature rise matrix T<1> is greater than a convergence threshold or not, if so, substituting T<0> with T<1> and returning to the step 3), and otherwise, judging that a current corresponding temperature rise matrix is a steady-state temperature rise matrix. Compared with the prior art, the multi-loop cable steady-state temperature rise acquisition method has the advantages of easiness and accuracy in calculation, high calculation efficiency, advanced algorithm, adaptability to various boundary conditions, and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
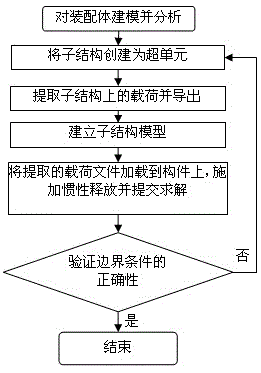
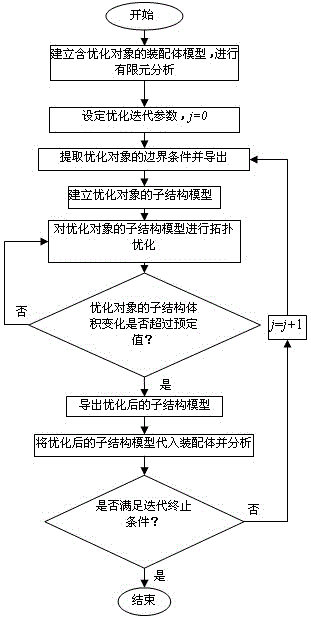
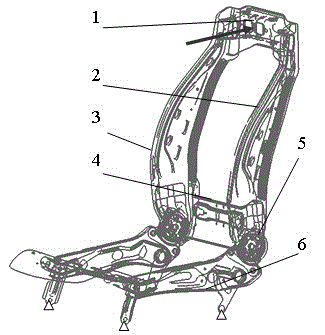
Component topology optimization design method for complex assembly
The invention relates to a component topology optimization design method for a complex assembly, and aims to solve the problem of difficulty in the determination of boundary conditions in a topology optimization design process for components of the complex assembly. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing and analyzing an assembly finite element model, and extracting and exporting the boundary conditions of a sub-structure which is a component to be optimized in the assembly model; loading the extracted boundary conditions onto the component to be optimized, and performing topology optimization on the component by utilizing a density method; when a change in the size of an optimization object exceeds a preset value, re-extracting the boundary conditions of the component, and continuing performing the topology optimization on the component; and when the optimization object is consistent with an iteration stopping condition, stopping optimization iteration to obtain a final optimal structure. An accurate optimal structure of the component can be obtained by accurately determining the boundary conditions of the component, and the problems of a plurality of design variables, inaccurate contact definition of combination parts between components and large calculated amount caused by the direct adoption of the assembly for the topology optimization design are solved.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
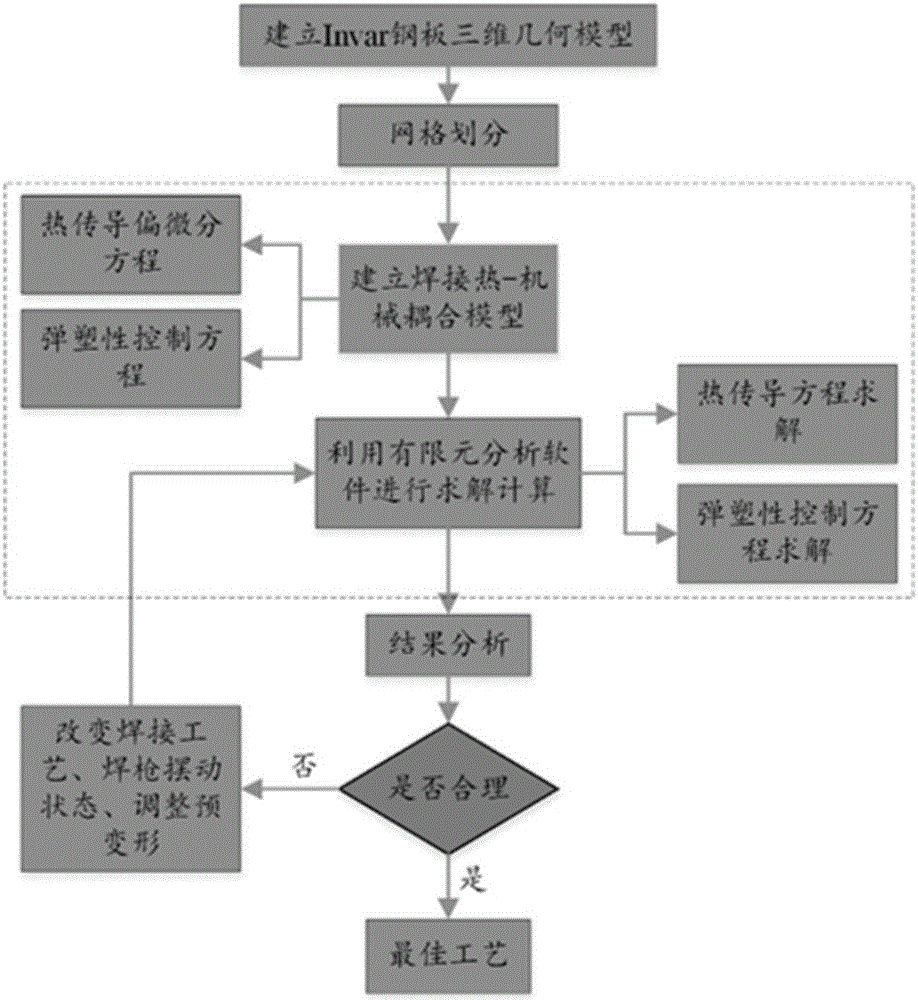
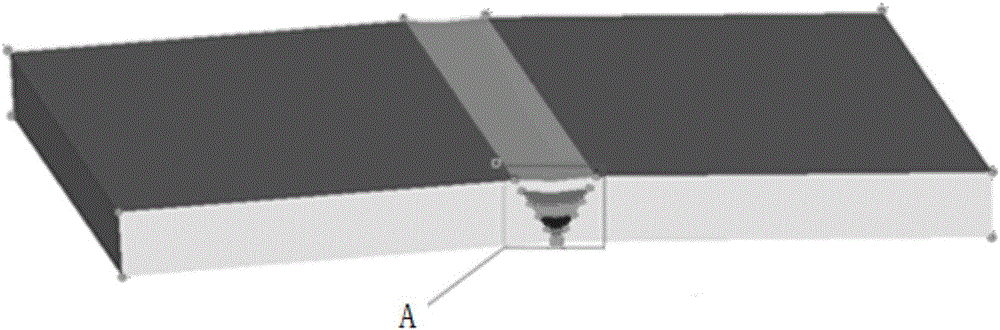
Invar steel PMIG weaving welding temperature field and deformation simulation method
InactiveCN105740577ASimple welding processReduce testing costsGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsPre deformationThick plate
The invention discloses an Invar steel PMIG weaving welding temperature field and a deformation simulation method.A thermal-mechanical coupling model used for analyzing an Invar steel thick plate temperature field and a stress strain field; through reasonably setting welding technology parameters, a swinging route and pre-deformation, the established coupling model is solved and calculated by the utilization of related finite element analysis software, the Invar steel temperature field and strain field distribution and deformation conditions under the corresponding welding technology parameters are obtained through loading and solving thermal boundary conditions and mechanical boundary conditions, and then the welding technology is instructed and optimized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
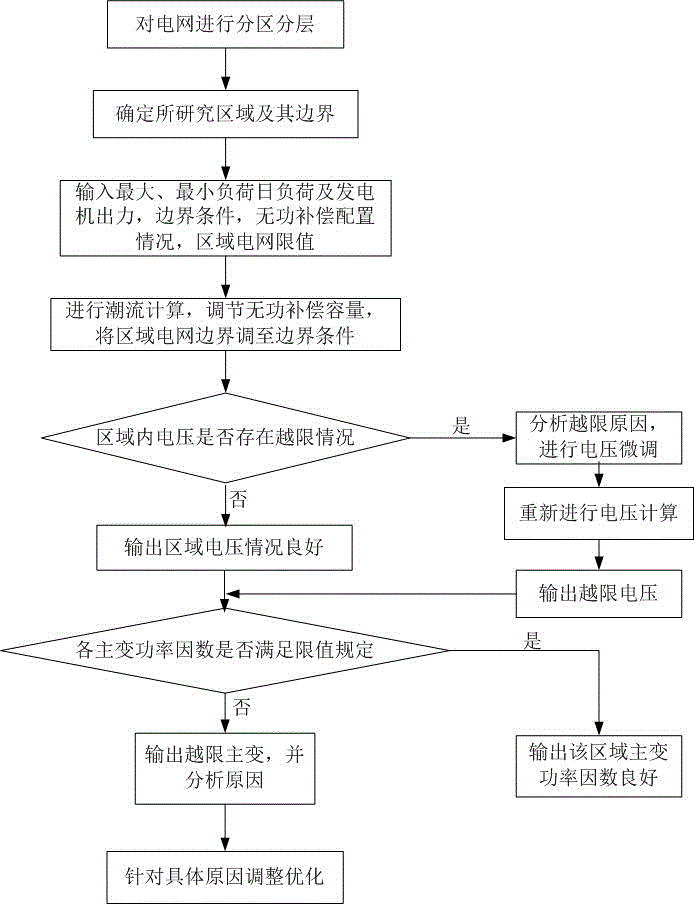
Layered and zoned reactive voltage analysis method based on boundary condition
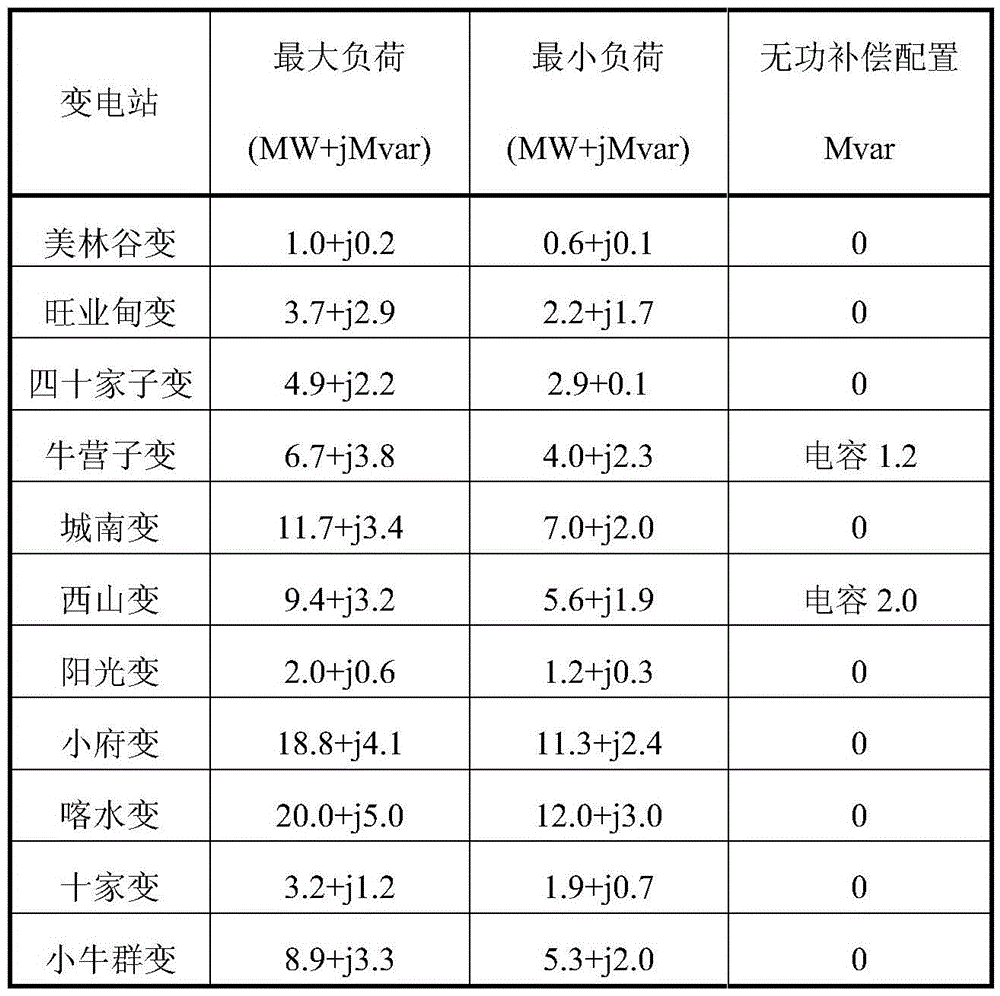
ActiveCN105490281AOptimization of reactive power distributionImprove analysis efficiencyAc network voltage adjustmentReactive power compensationTransformerLimit value
The invention belongs to the technical field of reactive voltage control of a power grid, in particular relates to a layered and zoned reactive voltage analysis method based on a boundary condition. The layered and zoned reactive voltage analysis method comprises the following steps of making the power grid layered and zoned; determining a researched zone and a boundary thereof; inputting maximum daily load, minimum daily load, output of a power generator, the boundary condition, a reactive compensation configuration condition and a limit value of a regional power grid; carrying out power flow calculation, adjusting reactive compensation capacity, and adjusting the boundary of the regional power grid to the boundary condition; judging whether an out-of-limit situation exists in the voltage in a region or not; and judging whether a power factor of each main transformer conforms to the stipulation of the limit value or not. According to the layered and zoned reactive voltage analysis method, reactive voltage correction and reactive voltage optimization can be fulfilled, the reactive voltage analysis efficiency of a large-sized power grid can be substantially improved, focused analysis can be conducted with regard to a local power grid, and the layered and zoned reactive voltage analysis method is suitably used for situations with relatively complete data of the local power grid and insufficient data of a large power grid; and the layered and zoned reactive voltage analysis method is easy to understand and implement, is proximate to actual running of the power grid, and is suitably for on-line application.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF EAST INNER MONGOLIA ELECTRIC POWER +1
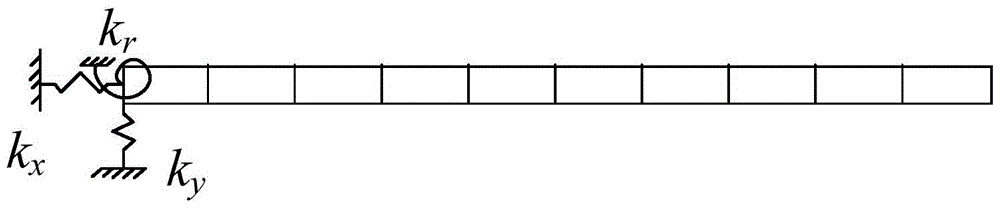
Method for analyzing vibration in structural surface of rectangular plate under non-uniform elastic constrained boundary condition
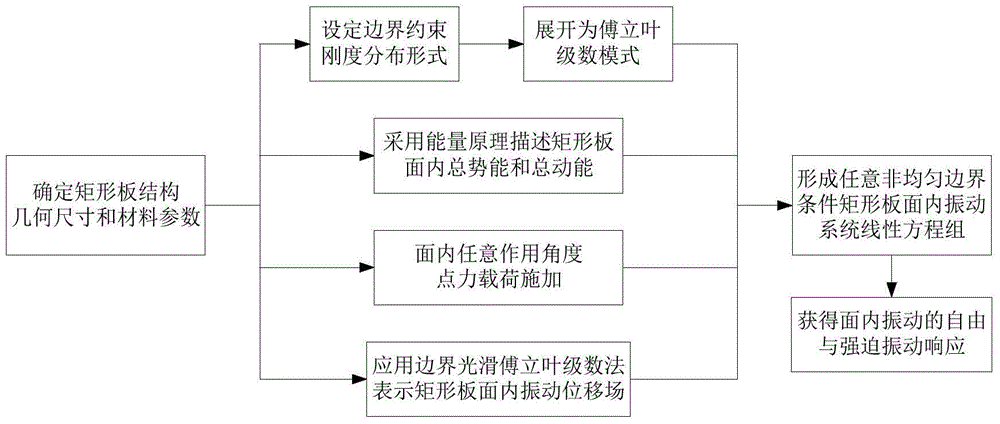
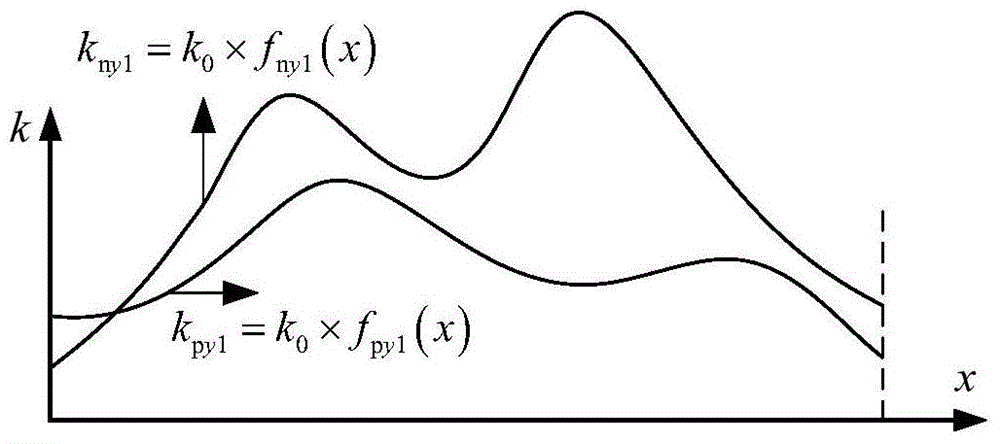
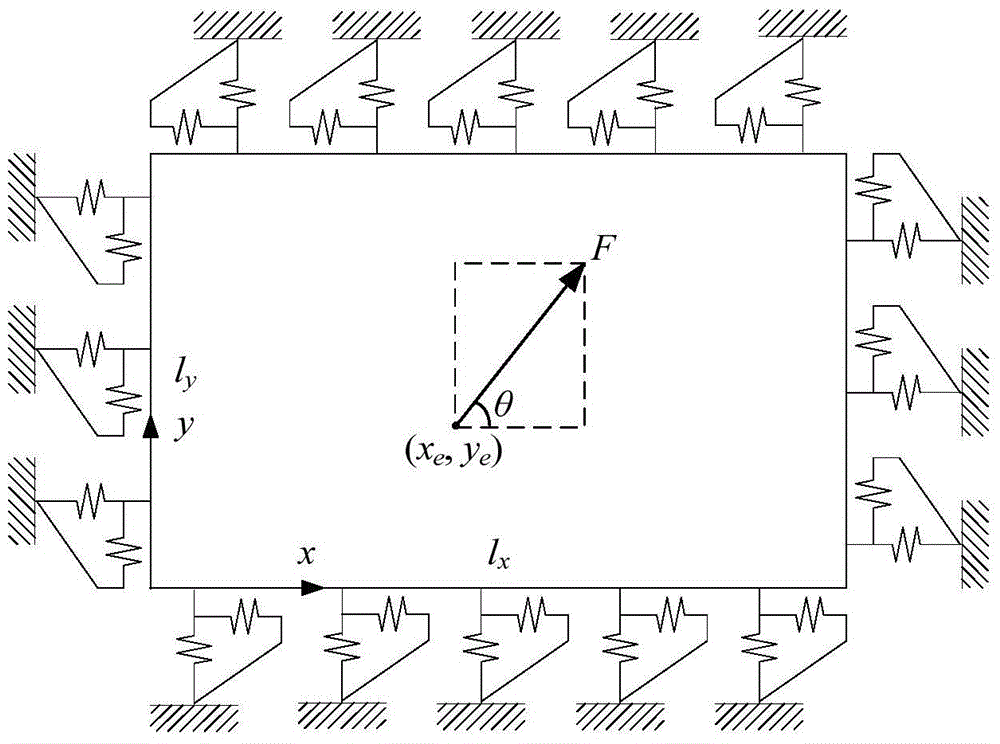
ActiveCN105205035AImprove general performanceFast convergenceComplex mathematical operationsStructure of the EarthFinite element method
The invention aims to provide a method for analyzing vibration in a structural surface of a rectangular plate under a non-uniform elastic constrained boundary condition. The method comprises the following steps: adopting Fourier series for unfolding the rigidity of a constraining linear spring in a non-uniform plane; adopting an energy principle for describing the vibration in the structural surface of the rectangular plate; applying a load in the plane at any acting angles to the structure of the rectangular plate; establishing the vibration displacement boundary smooth series in the structural surface of the rectangular plate; solving the system of vibration linear equations in the structural surfaces of any non-uniform boundary rectangular plates, thereby acquiring the vibration in the structural surface of the rectangular plate and forcing to respond and admit. Compared with the traditional methods, such as, the finite element method, and the like, the method provided by the invention has the advantage that the operation for the nodes is not required for the processing of the boundary condition in a non-uniform plane, so that the time for modeling and calculating is greatly saved. A rigidity distribution function of the spring can be adjusted for realizing any classic boundary conditions, uniform elastic constrained boundary conditions and non-uniform elastic constrained boundary conditions.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Rigid cylinder vortex-induced vibration testing device capable of achieving nonlinear boundary conditions
The invention aims at providing a rigid cylinder vortex-induced vibration testing device capable of achieving nonlinear boundary conditions. The rigid cylinder vortex-induced vibration testing device comprises nonlinear springs, a vertical restraining mechanism, a cylinder model, a support, a clamp, a supporting frame and a data collecting and analyzing processing part. The data collecting and analyzing processing part is used for collecting and analyzing vibration data of the cylinder model. The vertical restraining mechanism is composed of box iron, a cardan joint, a bolt and an aluminum alloy pipe. The adopted cardan joint has the advantages of being small in damping and flexible in structure. The vertical restraining mechanism is used for enabling vibration of the cylinder model to be kept in the same horizontal plane. A nonlinear boundary cylinder system is jointly composed of the vertical restraining mechanism, the support and the nonlinear springs. The rigid cylinder vortex-induced vibration testing device can be applied to rigid cylinder vortex-induced vibration tests of a circulating water channel or a towing tank, and the vortex-induced vibration mechanism under nonlinear rigidity such as contact between a seabed suspended span pipe and the seabed can be truly simulated.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
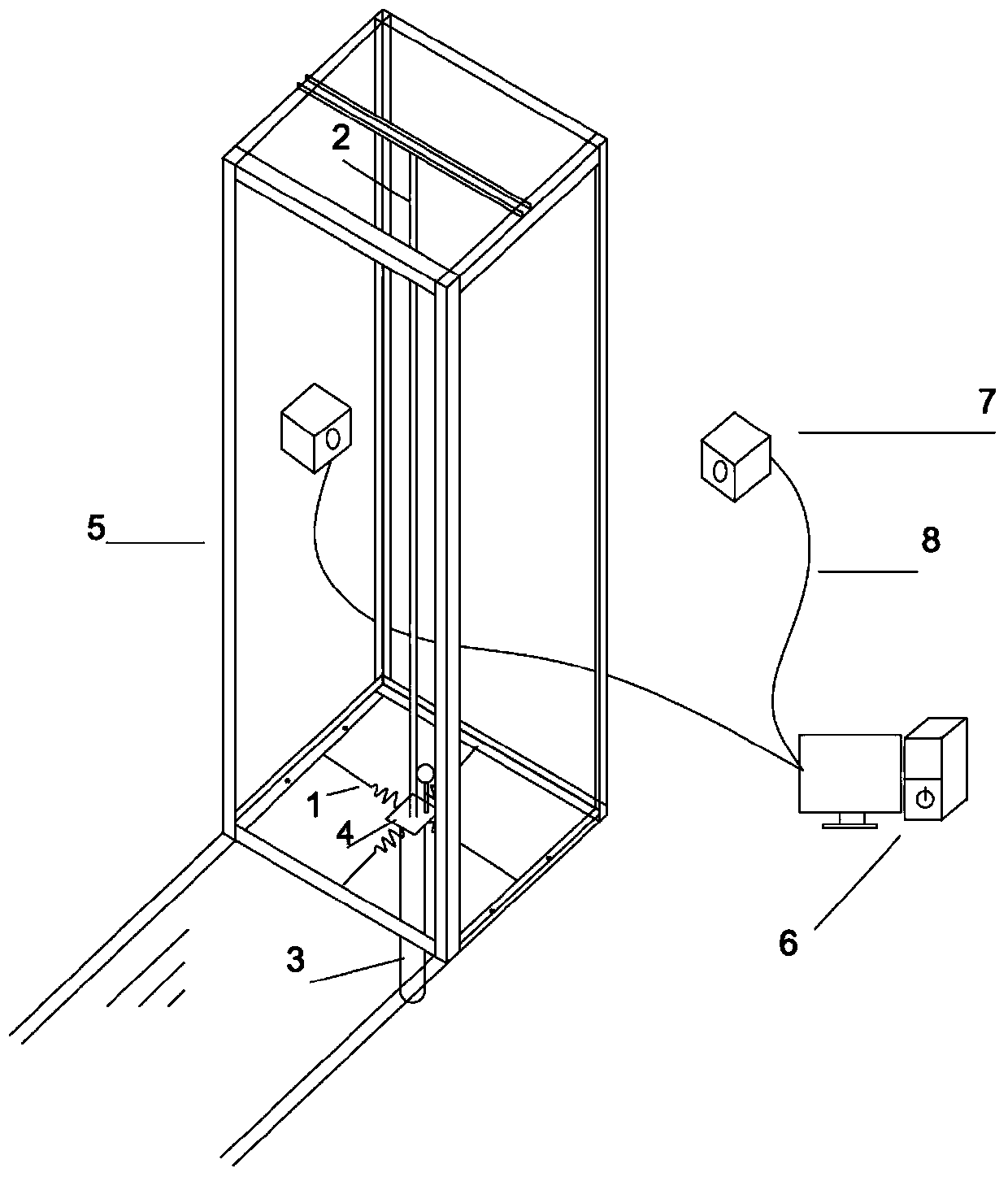
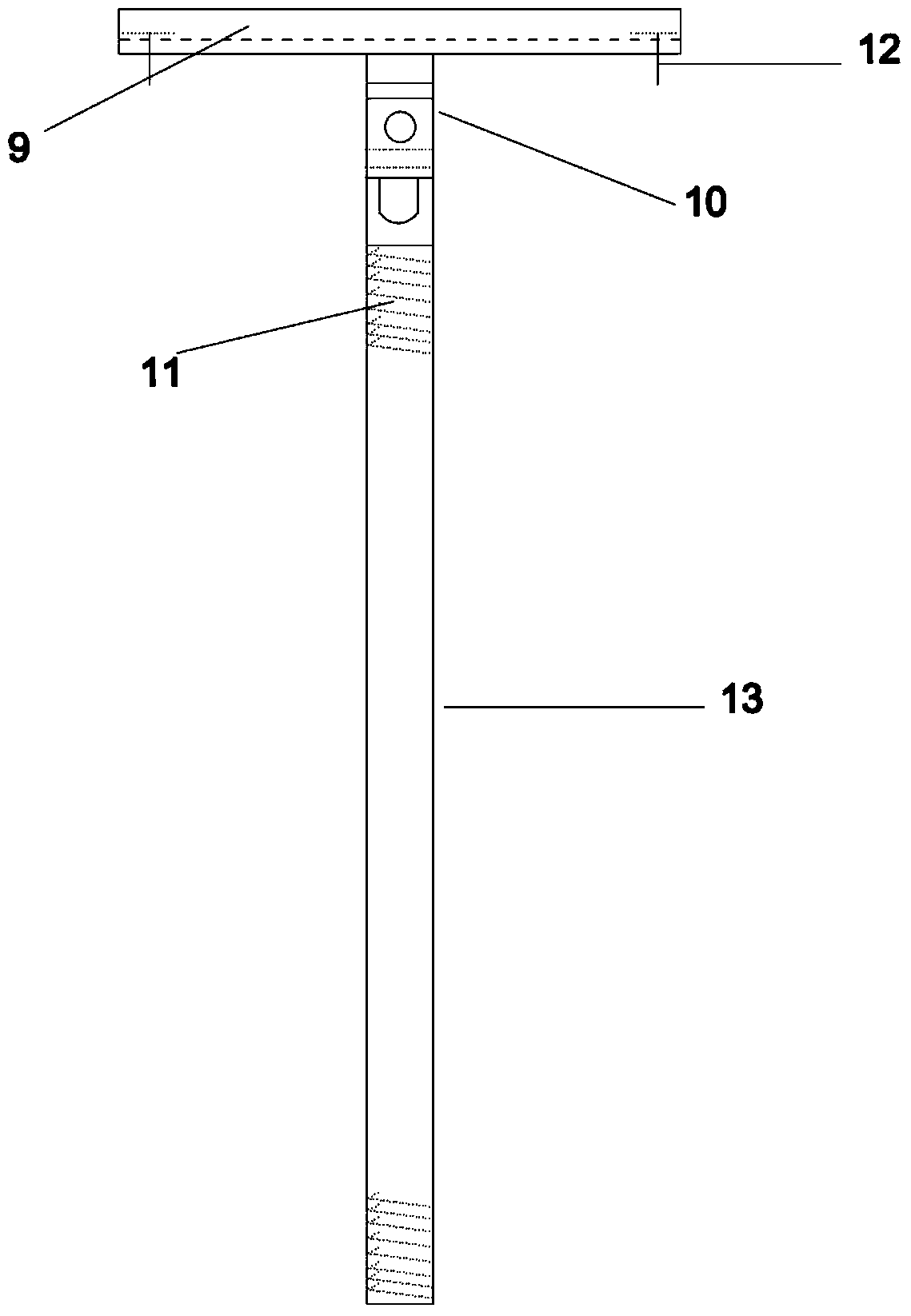
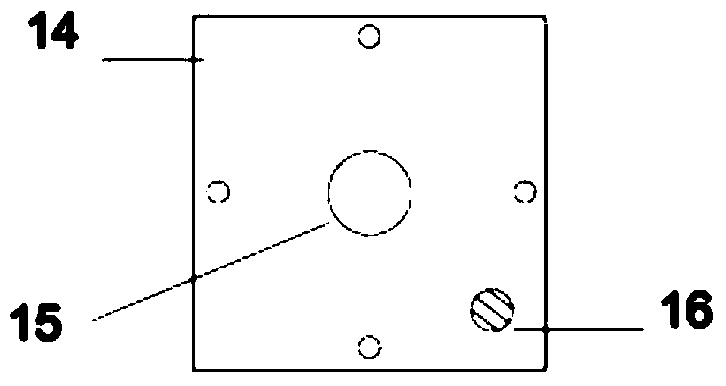
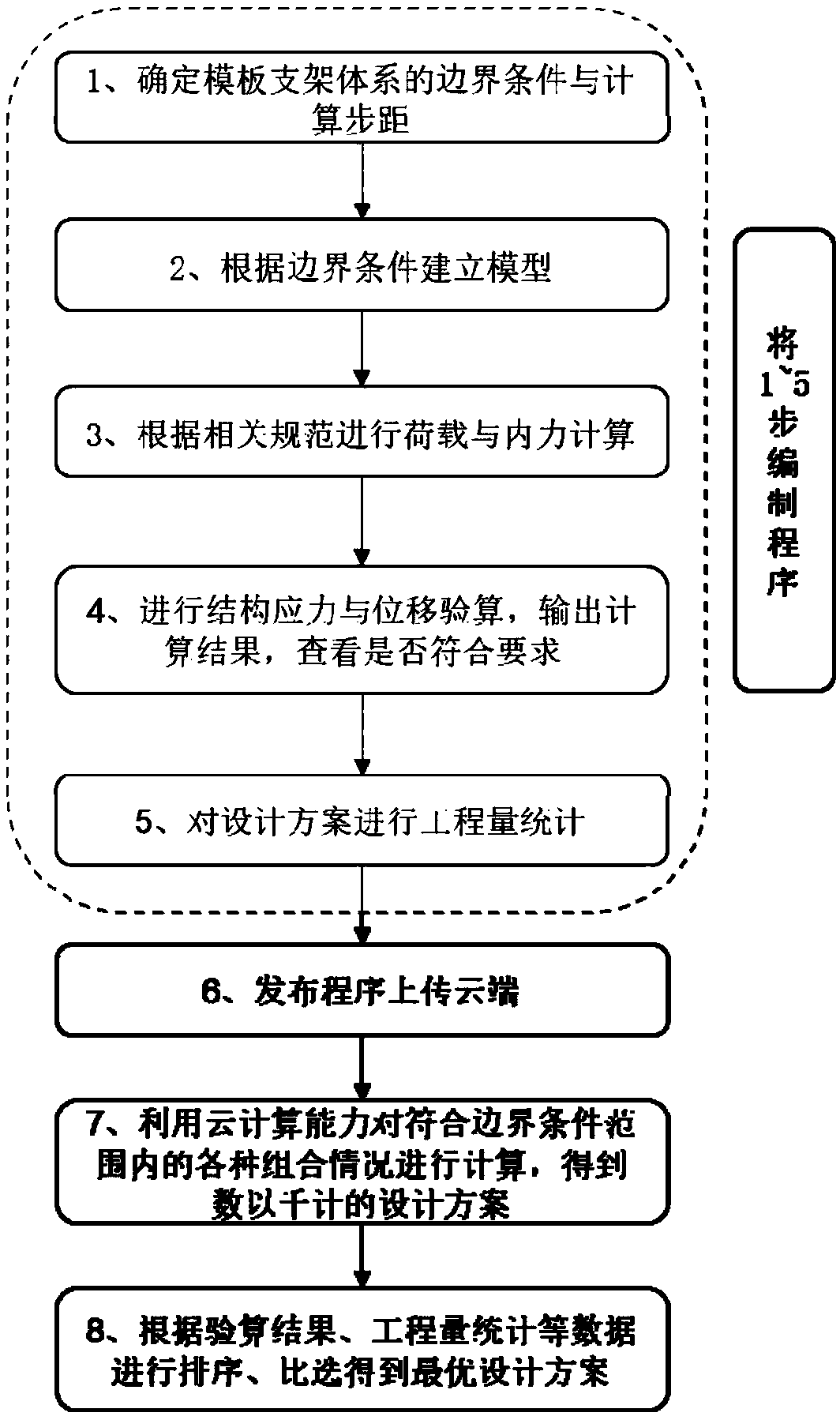
Formwork support system derivative design method
ActiveCN109359434ALow costImprove computing efficiencyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationSupporting systemEngineering
The invention relates to a formwork support system derivative design method. 1. Determine the boundary conditions and calculation steps of the formwork support system; 2, establish a parametric modelaccording to that boundary condition; 3, load and internal force calculation; 4. Checking the stress and displacement of the structure, outputting the calculation result to check whether it meets thedesign requirements; 5, count that engineering quantity of the design scheme; 6, upload that publishing program to the cloud; 7, compute various combinations according with that boundary conditions byusing the cloud computing capability, and obtaining thousands of design scheme; 8, arrange that statistical data of the project quantity according to the calculation result, and comparing and selecting the most design scheme. This method adopts the derivative design principle, according to the set boundary condition scope and the step distance request, compiles the program to construct the model,outputs the stress, the displacement and the project quantity statistical result, utilizes the cloud computing ability, has greatly improved the design efficiency, and reduced the engineering material, saves the cost.
Owner:BEIJING MUNICIPAL ROAD & BRIDGE
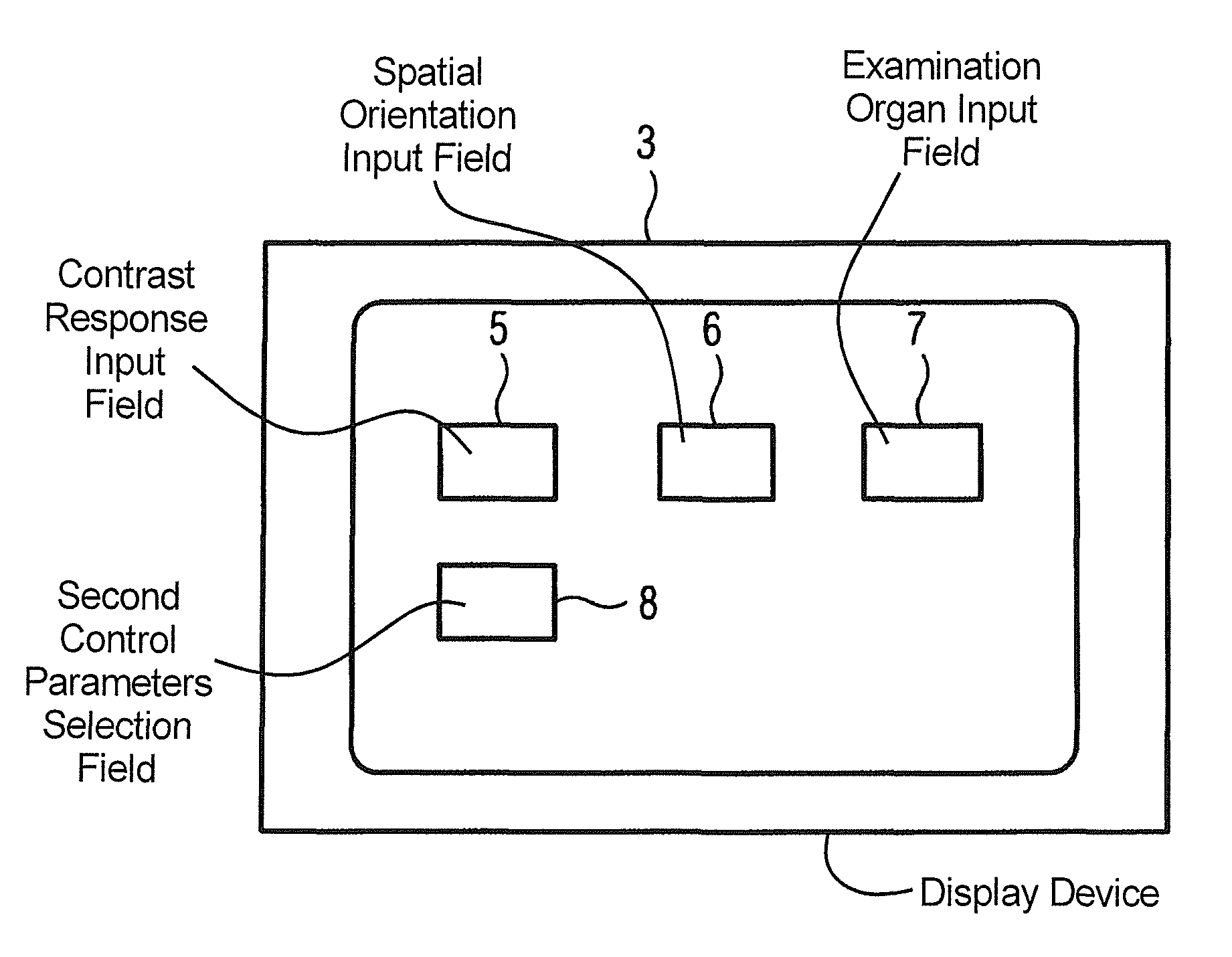
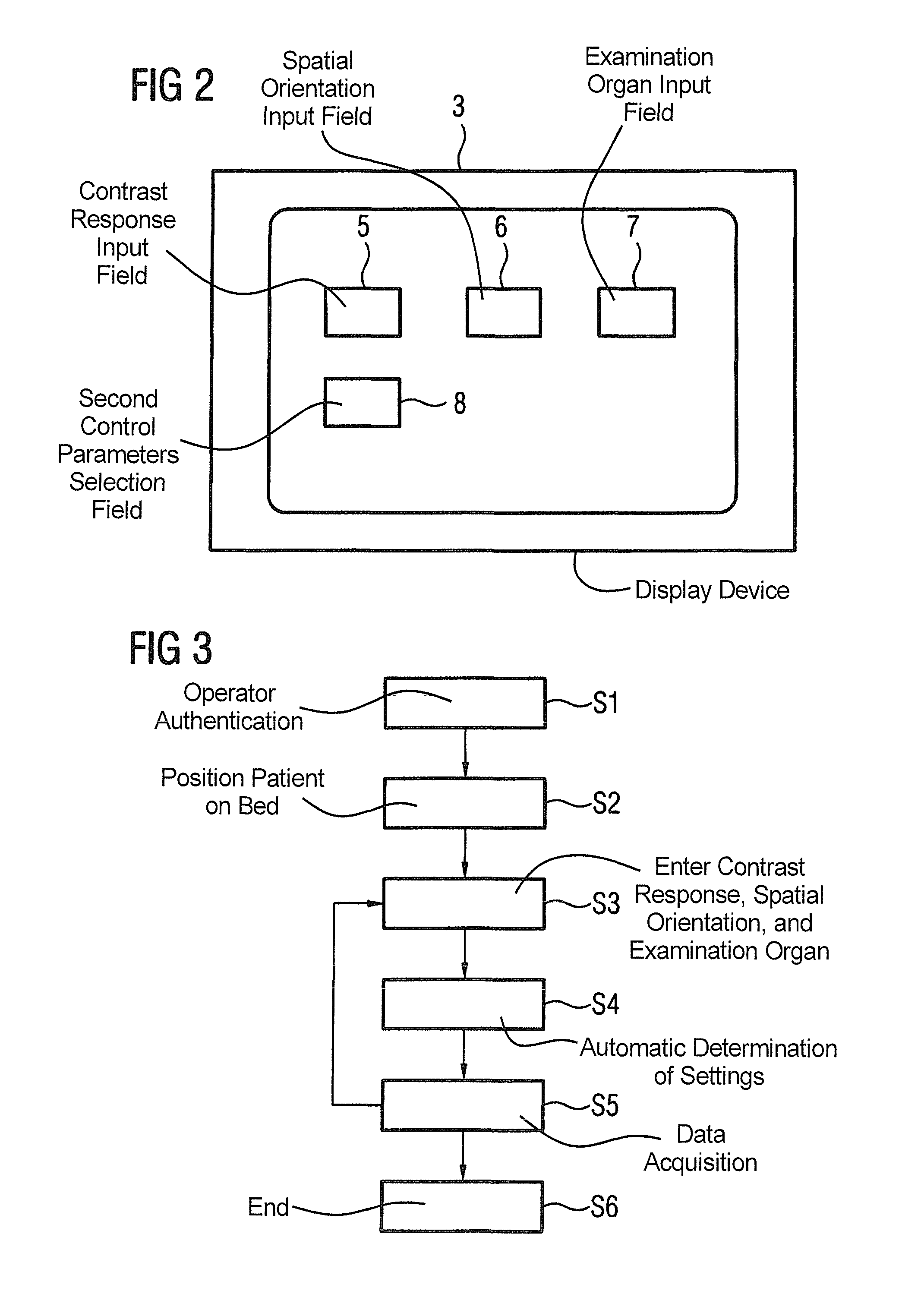
Streamlined diagnostic MR imaging requiring only three control parameters of operator selected boundary conditions
InactiveUS7990141B2Easy to measureSimplify creationMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringSpatial OrientationsData set
In a method for operation of a magnetic resonance system, at least one control device is fashioned for image data acquisition and corresponding components, and only three first control parameters defining primary boundary conditions are selected by an operator of the system, namely the contrast response, the spatial orientation of the at least one image data set to be acquired and the examination organ. Additional, second control parameters, required to control the components for image acquisition and defining secondary boundary conditions, are automatically determined by the control device using the first control parameters.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
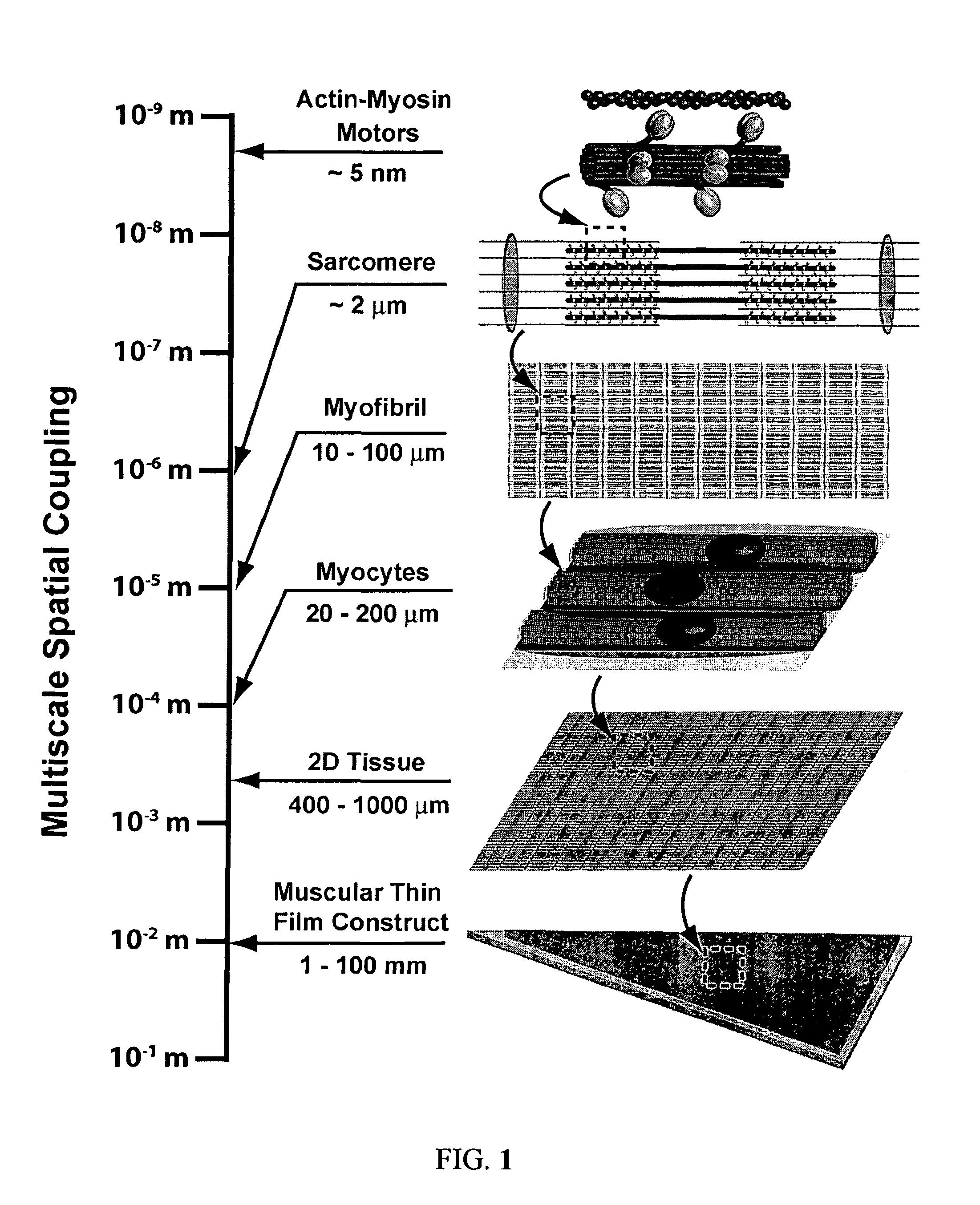
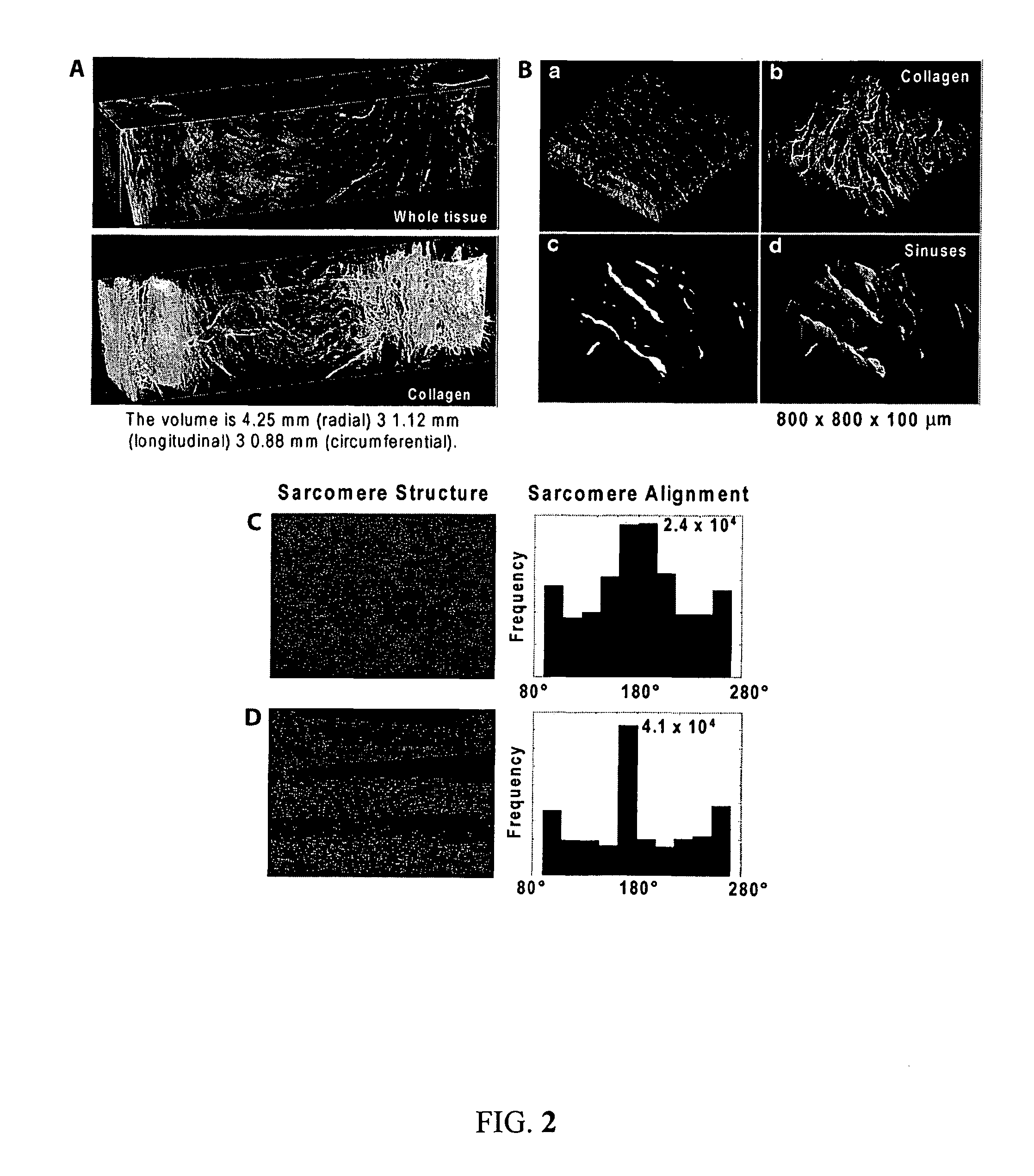
Boundary conditions for the arrangement of cells and tissues
ActiveUS9068168B2Maintain alignmentArtificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsMicrobiologyLocal environment
The present invention relates to the arrangement of one or more cells in a medium or on a substrate through the use of boundary conditions, which are changes in local environment compared to the medium or substrate alone or cause an alteration of cell response upon interaction of a cell with the boundary condition.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
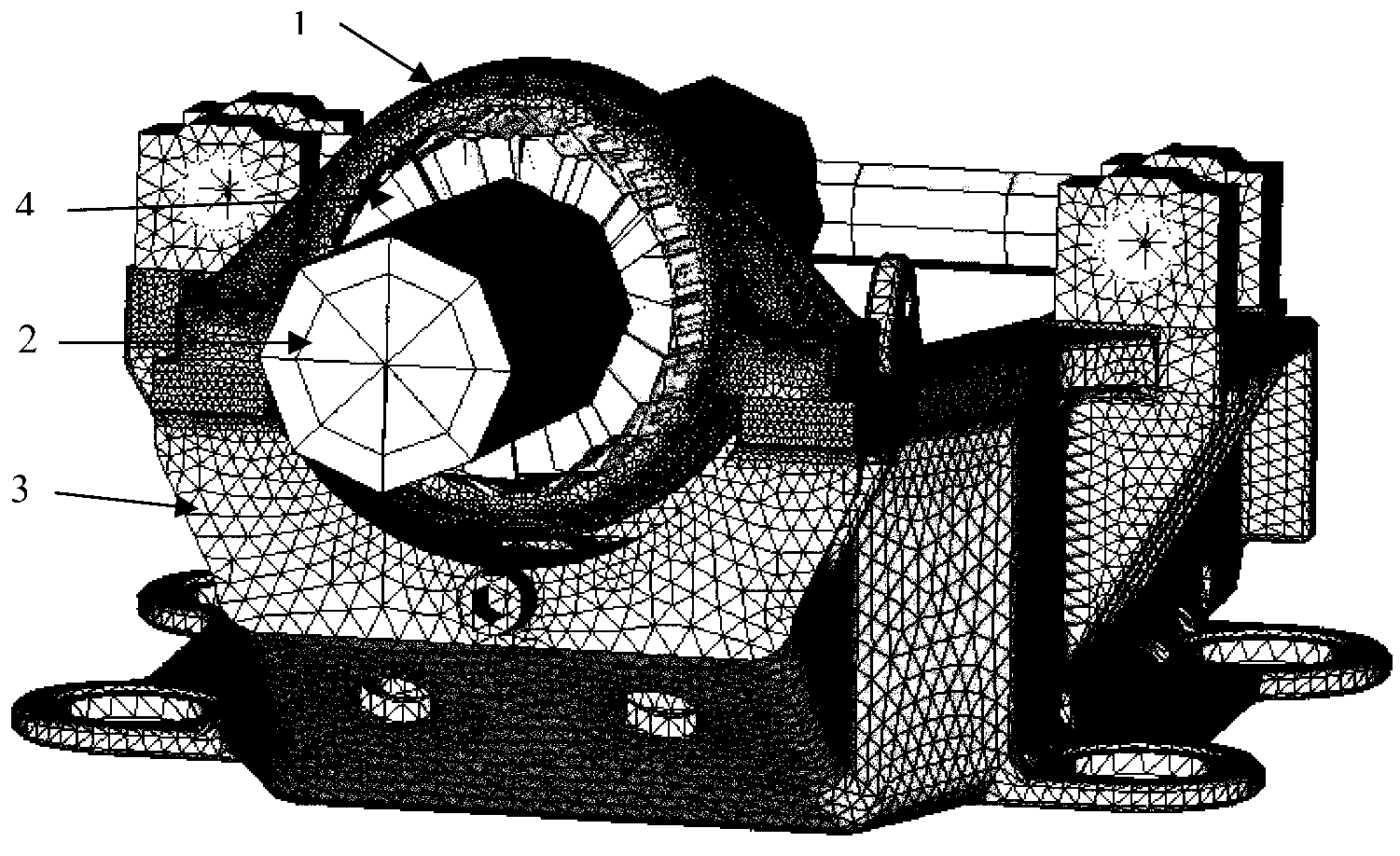
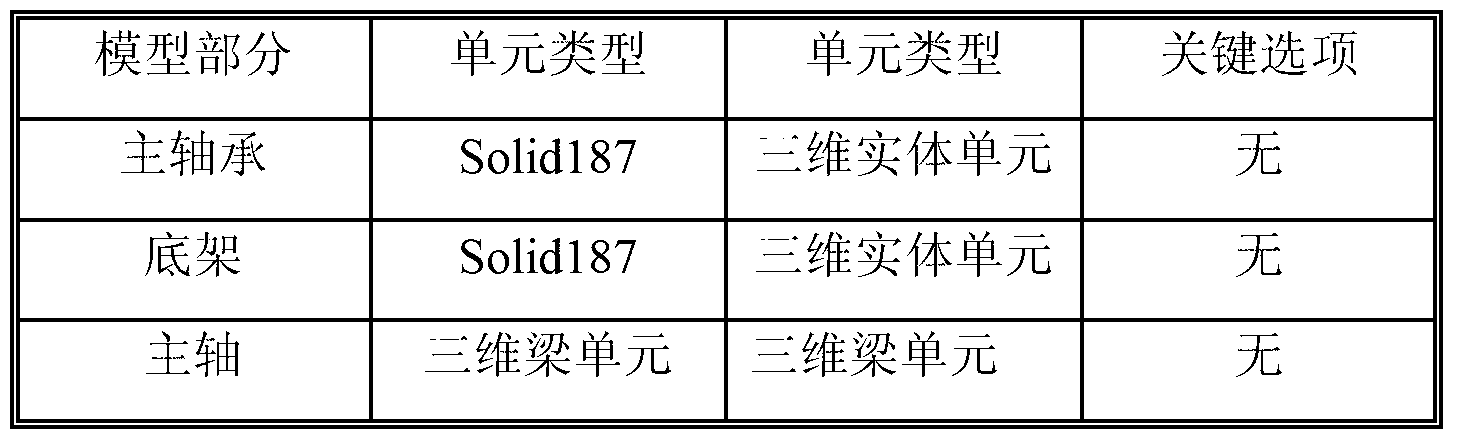
Calculation method for checking ultimate strength of fan underframe
InactiveCN103324805AWide applicabilitySimple calculationSpecial data processing applicationsStress conditionsFinite element analysis software
A calculation method for checking ultimate strength of a fan underframe includes: using finite element analysis software as a platform for modeling, performing finite element meshing, setting connecting structure load and boundary conditions, and calculating to obtain stress condition of the underframe. The step of setting the connecting structure load and boundary conditions includes: establishing nodes at the center of a hub and at the center of a bearing, connecting the nodes through a three-dimensional beam unit, and simulating spindle transfer load. A central point of a main bearing block is connected with an inner ring surface unit of the main bearing through a link unit which bears only pressure. The method has the advantages that calculated stress of the underframe and calculated danger positions are more accurate and the actual stress relation of the underframe is satisfied.
Owner:CHINA CREATIVE WIND ENERGY +3
Implementation method for mixed absorbing boundary condition applied to variable density acoustic wave equation
ActiveCN103698814AImproved the effect of suppressing border reflectionsSuppression is effectiveSeismic signal processingWave equationWave field
The invention relates to an implementation method for a mixed absorbing boundary condition applied to a variable density acoustic wave equation. The implementation method comprises the steps of dividing a whole simulation region into an internal region and a boundary region, calculating the wave field value of a sound wave of each absorbing boundary layer by using the variable density acoustic wave equation and a variable density AWWE (Arbitrary Wide-angle wave equation) respectively, and performing linear weighting on the two calculation results to obtain the wave field value of the sound wave of each absorbing boundary layer. On the basis of realizing a single variable density AWWE absorbing boundary layer and in 2D (2 dimensional) and 3D (3 dimensional) space coordinate systems, the wave field value of the sound wave of each absorbing boundary layer is calculated by respectively adopting a combination mode of processing edges of the variable density AWWE and processing angles of a modified 15-degree one-way wave equation, and a combination mode of processing faces of the variable density AWWE, the processing edges of the modified 15-degree one-way wave equation and the processing angles of a 5-degree one-way wave equation, and the mixed absorbing boundary condition of the variable density AWWE is realized. The implementation method can be widely applied to the numerical simulation of constant density and variable density acoustic wave equations.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
Three-dimensional finite element simulation method based on heat radiation boundary conditions
ActiveCN107577857AAccurate solutionQuick solveSpecial data processing applications3D modellingFinite element algorithmRadiation boundary conditions
The present invention belongs to the technical field of numerical analysis of three-dimensional thermal analysis and relates to a three-dimensional finite element simulation method based on heat radiation boundary conditions. The method comprises: carrying out modeling on a device to be subjected to the thermal analysis, introducing radiation boundary conditions into the heat conduction problem, and obtaining the finite element weak form of the heat radiation boundary conditions by adopting the method of Galerkin residual weighting; using the tetrahedral meshed model to select the second-orderlaminated basis function and the discrete finite element weak form equation, obtaining a finite element matrix and aright-end vector by cooperating with the Newton-Raphson iteration method, and integrating the final equation; and finally, by using the scientific nonlinear convergence criteria, through continuous iteration, quickly and accurately obtaining final numerical results.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A fitting method for calculating the main coefficients of the boundary conditions of a groove wall
ActiveCN109033548AGet the amount of interferenceEliminate local fluctuationsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsOriginal dataEngineering
The invention discloses a fitting method for calculating the main coefficients of the boundary conditions of a groove wall based on experimental data, aiming at solving the present situation of lacking accurate calculation of the transonic wind tunnel slot wall boundary condition coefficients. In this method, the least square solution of the overdetermined equations is obtained by fitting the experimental data of the pressure coefficient near the wall and the deflection angle along the flow direction, which exclude the bad points, and the number of the main systems in the boundary condition ofthe wall is obtained by the least square method. The invention needs to eliminate the bad points of the original data, and then subtracts the reference data of the empty wind tunnel from the pressurecoefficient to eliminate the local fluctuation caused by slotting; based on the pressure coefficient-deflection angle nonlinear correlation,an overdetermined equation is established, the least squaresolution of the overdetermined equations is obtained by using the pseudo-inverse of the coefficient matrix, and the number of coefficients of the gradient term, the first order term and the second order term of the deflection angle in the boundary condition of the channel wall is obtained. The invention can improve the accuracy of the boundary conditions of the groove wall and guide the aerodynamic design and correction of the groove wall.
Owner:INST OF HIGH SPEED AERODYNAMICS OF CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT +1
Immersed boundary implicit iterative solving method meeting no-slip boundary conditions and continuity conditions
InactiveCN107423511AInsufficient improvementImprove accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMomentumForce method
The invention discloses an immersed boundary implicit iterative solving method meeting no-slip boundary conditions and continuity conditions; the method mainly comprises the steps of using a viscous incompressible flow N-S control equation, expanding a momentum equation along a feature line to perform time discretization, using a finite element method to perform spatial discretization, and adding additional body force to the discretized control equation; using a direct force method to solve the additional body force so that interpolation speed on the boundary is equal to expected speed distribution; when a fractional step method is in use, dividing the additional body force into two parts according to whether it is coupled to pressure, and solving the two parts respectively; performing speed correction in iterative computation of the additional body force and pressure to obtain final flow field distribution. The problem of an existing immersed boundary method that no-slip boundary conditions and continuity conditions cannot be met at same time is solved; after the additional body force is divided into two parts, the cost of solving a component item uncoupled to the pressure is effectively reduced, and the computing efficiency of the immersed boundary method is improved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Reverse time migration method of carbonatite reservoir
InactiveCN104133987AEliminate boundary reflection interferenceReduce storage requirementsSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsReverse timeWave equation
The invention discloses a reverse time migration method of a carbonatite reservoir. By aiming at a phenomenon that a fracture-cavity pore construction of carbonatite is always companied with fracture and big-angle form distortion formed due to construction movement, the reverse time migration method is used for precisely depicting the carbonatite. A finite difference method is used for solving a wave equation to simulate a seismic wave field; a processing method for the wave field to transmit to a boundary adopts a PML (Perfectly Matched Layer) absorbing boundary condition; a seismic origin wave field recovery part adopts a reverse PML wave field recovery technology; and a calculation part adopts a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) parallel acceleration technology. The PML absorbing boundary condition is adopted, so that the invention can more effectively eliminate boundary reflection interference than a random boundary condition; since the reverse PML wave field recovery technology is adopted, compared with a traditional wave field storage strategy, the invention can greatly reduce requirements on a storage amount on the premise that a calculated amount is not increased, a wave field recovery effect is good, amplitude fading is avoided, and operation efficiency is improved by adopting the GPU parallel acceleration technology.
Owner:NORTHEAST GASOLINEEUM UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com