Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "Recursive partitioning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
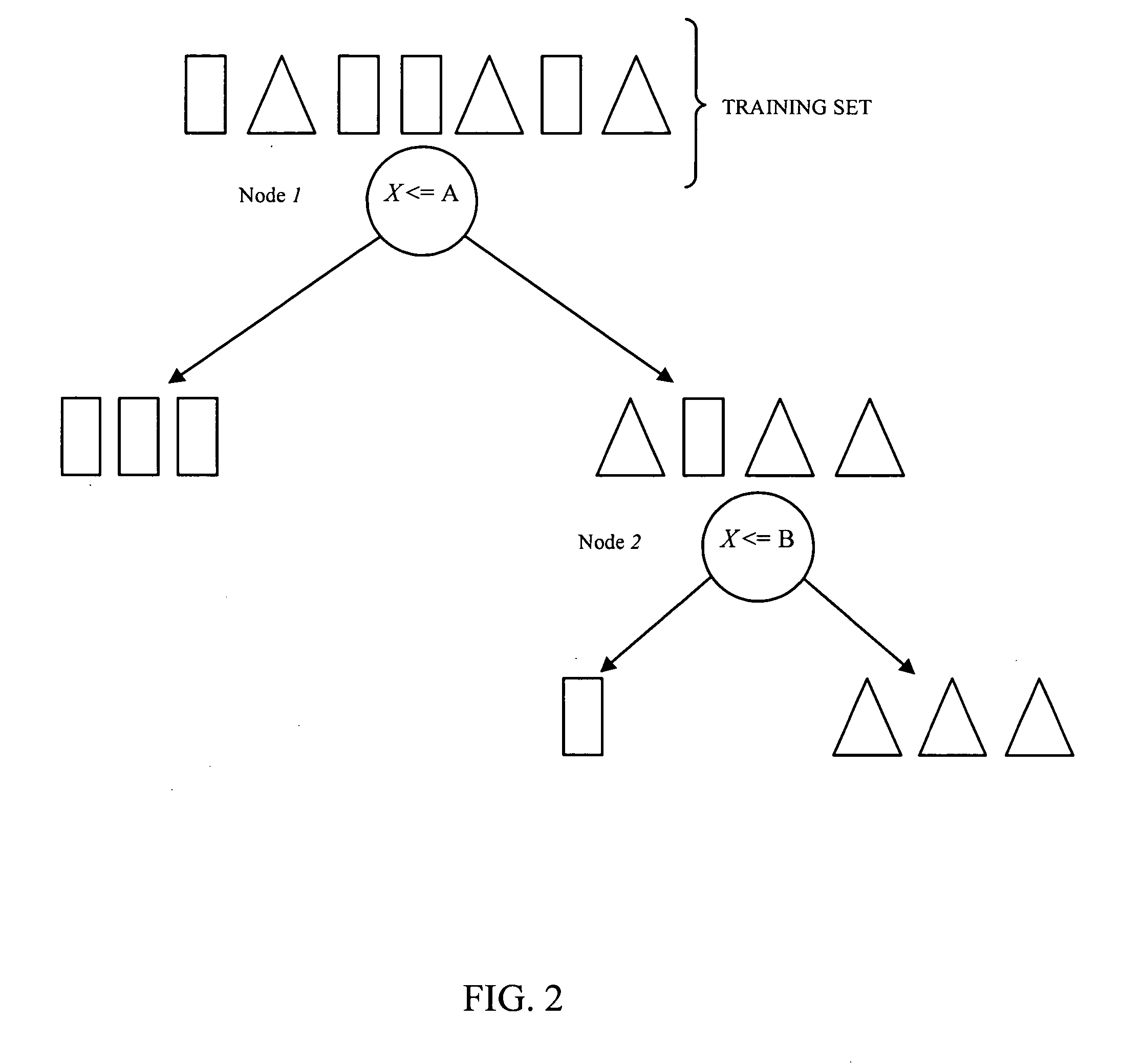
Recursive partitioning is a statistical method for multivariable analysis. Recursive partitioning creates a decision tree that strives to correctly classify members of the population by splitting it into sub-populations based on several dichotomous independent variables. The process is termed recursive because each sub-population may in turn be split an indefinite number of times until the splitting process terminates after a particular stopping criterion is reached.
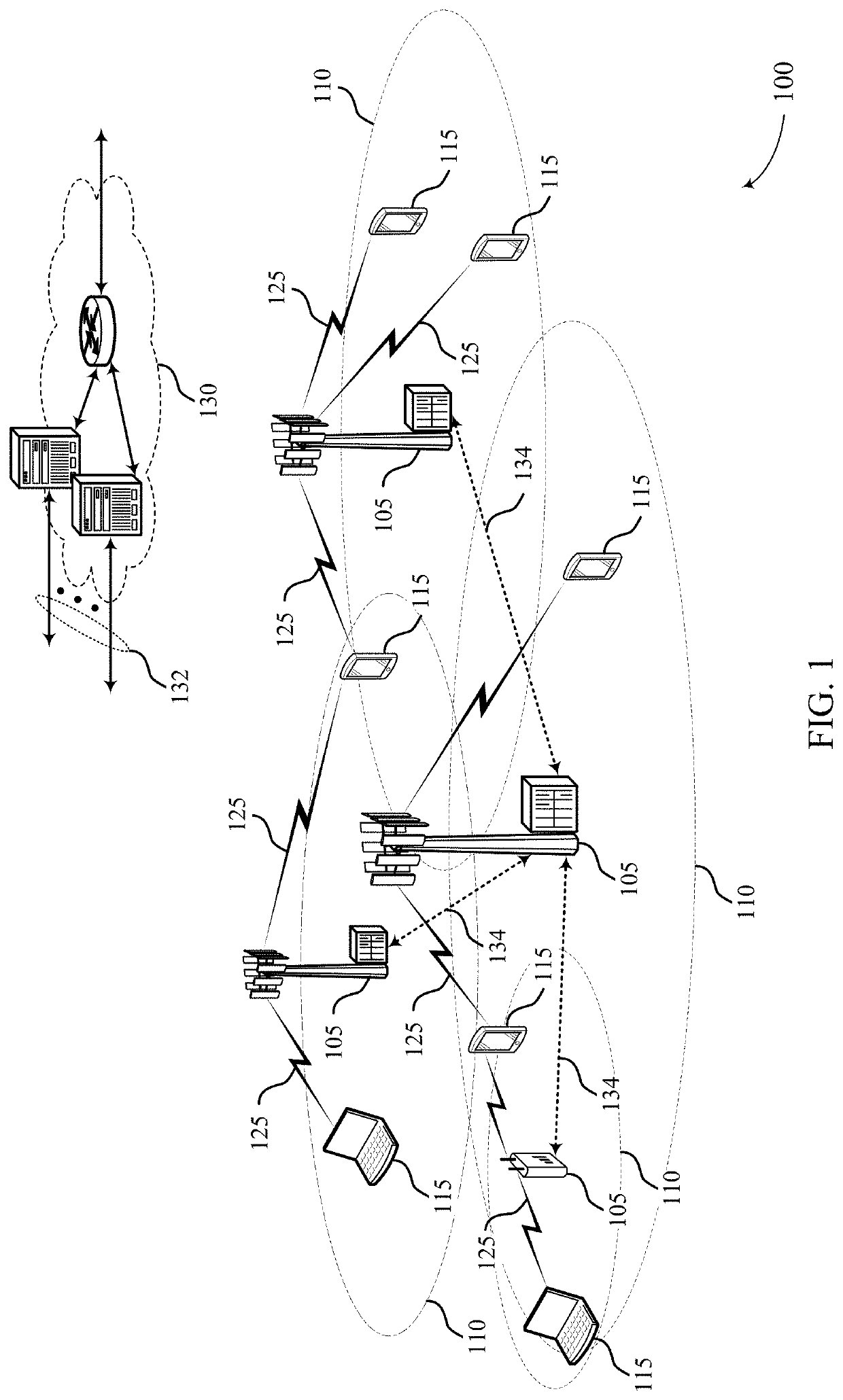
Method and System for Optimizing Industrial Furnaces (Boilers) through the Application of Recursive Partitioning (Decision Tree) and Similar Algorithms Applied to Historical Operational and Performance Data
InactiveUS20090125155A1Improve efficiencyMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlPrediction algorithmsNaive Bayes classifier
A method is provided for deriving optimized operating parameter settings for industrial furnaces of different designs as commonly used in power generation that will achieve robust and desirable operations (for example, low NOx and low CO emissions while maintaining specific furnace exit gas temperatures). The method includes the application of recursive partitioning algorithms to historical process data to identify critical combinations of ranges of operational parameter (combinations of settings) that will result in robust (low-variability) desirable (optimized) boiler performance, based on empirical evidence in the historical data. The method may include the application of various algorithms for recursive partitioning of data, as well as the consecutive application of recursive partitioning methods to prediction residuals of previous models (a methodology also known as boosting), as well as the application of other prediction algorithms that rely on the partitioning of data (support vector machines, naive Bayes classifiers, k-nearest neighbor methods).
Owner:HILL THOMAS +1
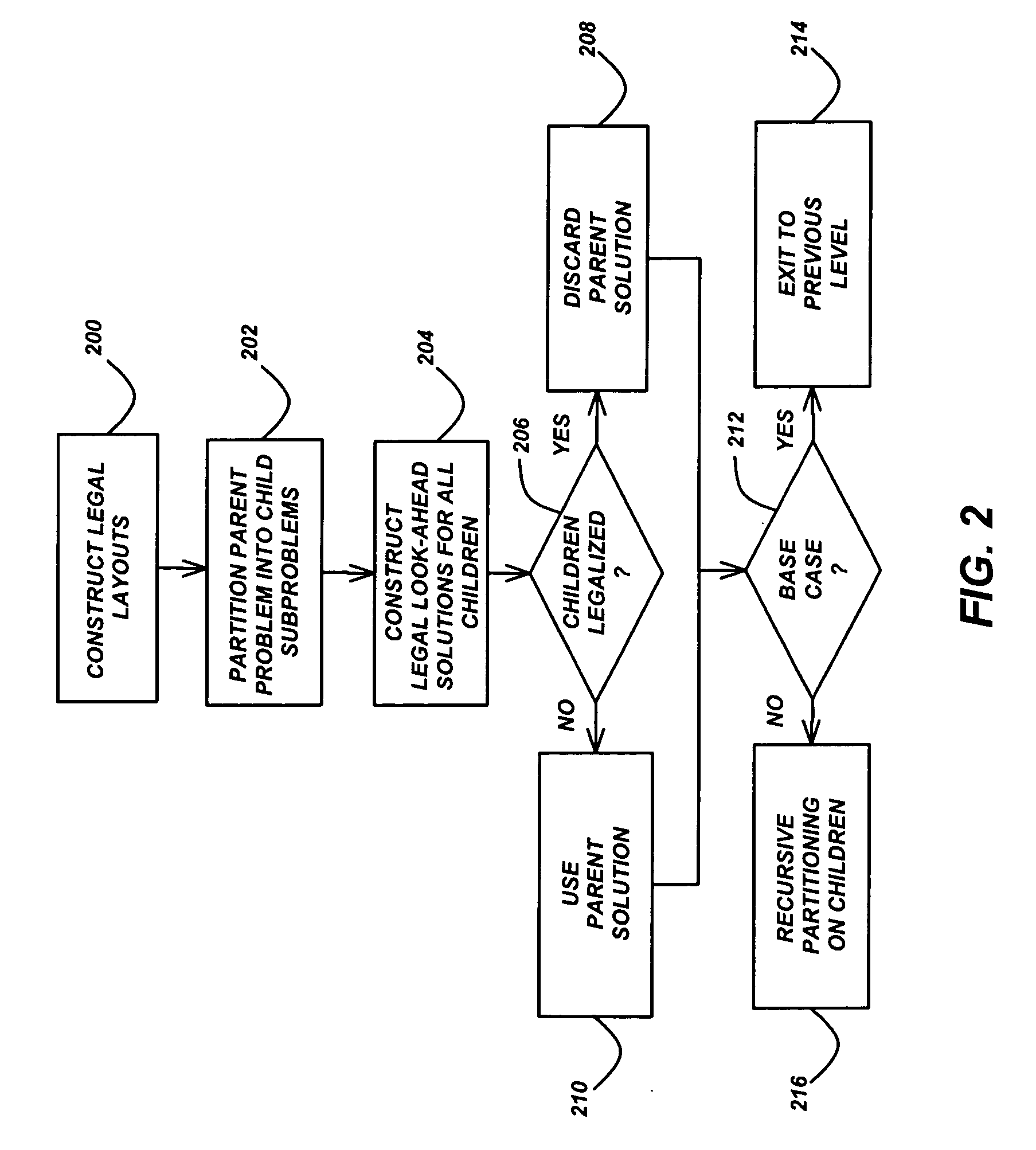
Circuit floorplanning and placement by look-ahead enabled recursive partitioning
InactiveUS20060190889A1Less run timeWirelength resultComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationBacktrackingSatisfiability
Placement or floorplanning of an integrated circuit is performed by constructing legal layouts at every level of a hierarchy of subsets of modules representing the integrated circuit, by scalably incorporating legalization into each level of the hierarchy, so that satisfiability of constraints is explicitly enforced at every level, in order to eliminate backtracking and post-hoc legalization.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
System and method for word-sense disambiguation by recursive partitioning
ActiveUS20060277045A1Special data processing applicationsSpeech synthesisWord-sense disambiguationVoice transformation
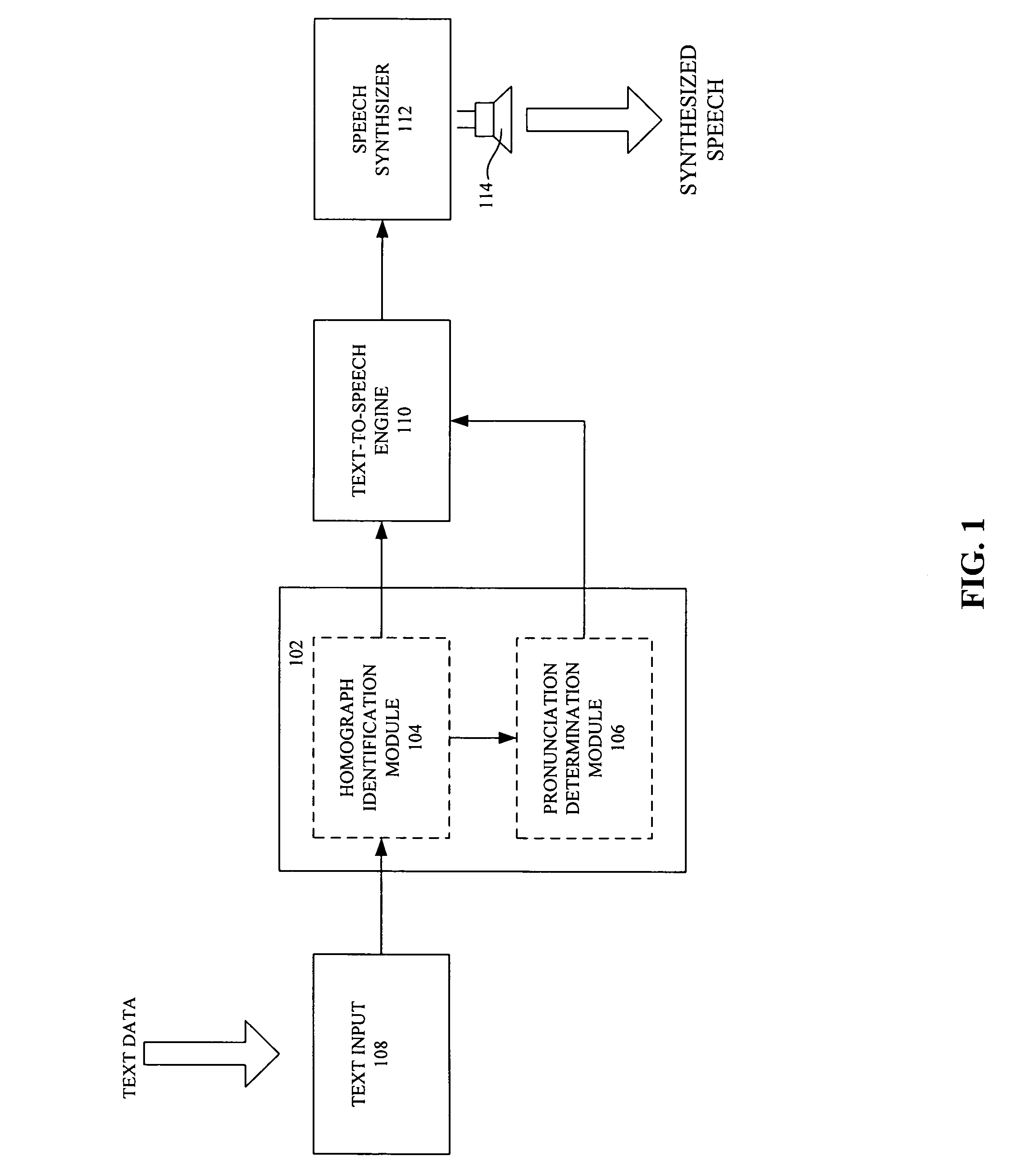
A device and related methods for word-sense disambiguation during a text-to-speech conversion are provided. The device, for use with a computer-based system capable of converting text data to synthesized speech, includes an identification module for identifying a homograph contained in the text data. The device also includes an assignment module for assigning a pronunciation to the homograph using a statistical test constructed from a recursive partitioning of training samples, each training sample being a word string containing the homograph. The recursive partitioning is based on determining for each training sample an order and a distance of each word indicator relative to the homograph in the training sample. An absence of one of the word indicators in a training sample is treated as equivalent to the absent word indicator being more than a predefined distance from the homograph.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
Image encoding method and image encoding device
InactiveCN101656880AEfficient compressionIncrease the compression ratioTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationImaging qualityImage compression
The invention discloses an image encoding method and an image encoding device. The method comprises the following steps: dividing domain blocks according to a value block scale range; performing isomorphic transformation on a matrix composed of 4 low frequency coefficients obtained by performing wavelet transformation on the domain blocks; performing recursive partitioning on value blocks until scale of the value blocks is less than the maximum scale; performing wavelet transformation on the value blocks to obtain 4 low frequency coefficients, calculating a value block direction K1 and a domain block direction K2, calculating a luminance factor and a shift factor and error thereof if the K1 is identical with the K2, and judging if the error is less than 5; if yes, writing position information of the value block and the domain blocks, transformation information and value block scale information into a code stream file, or performing quadtree partitioning on the value blocks; and writingending information into the code stream file when all the value blocks find corresponding domain blocks. The invention accelerates encoding speed and effectively improves compression ratio and decoded image quality, thus realizing effective image compression.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
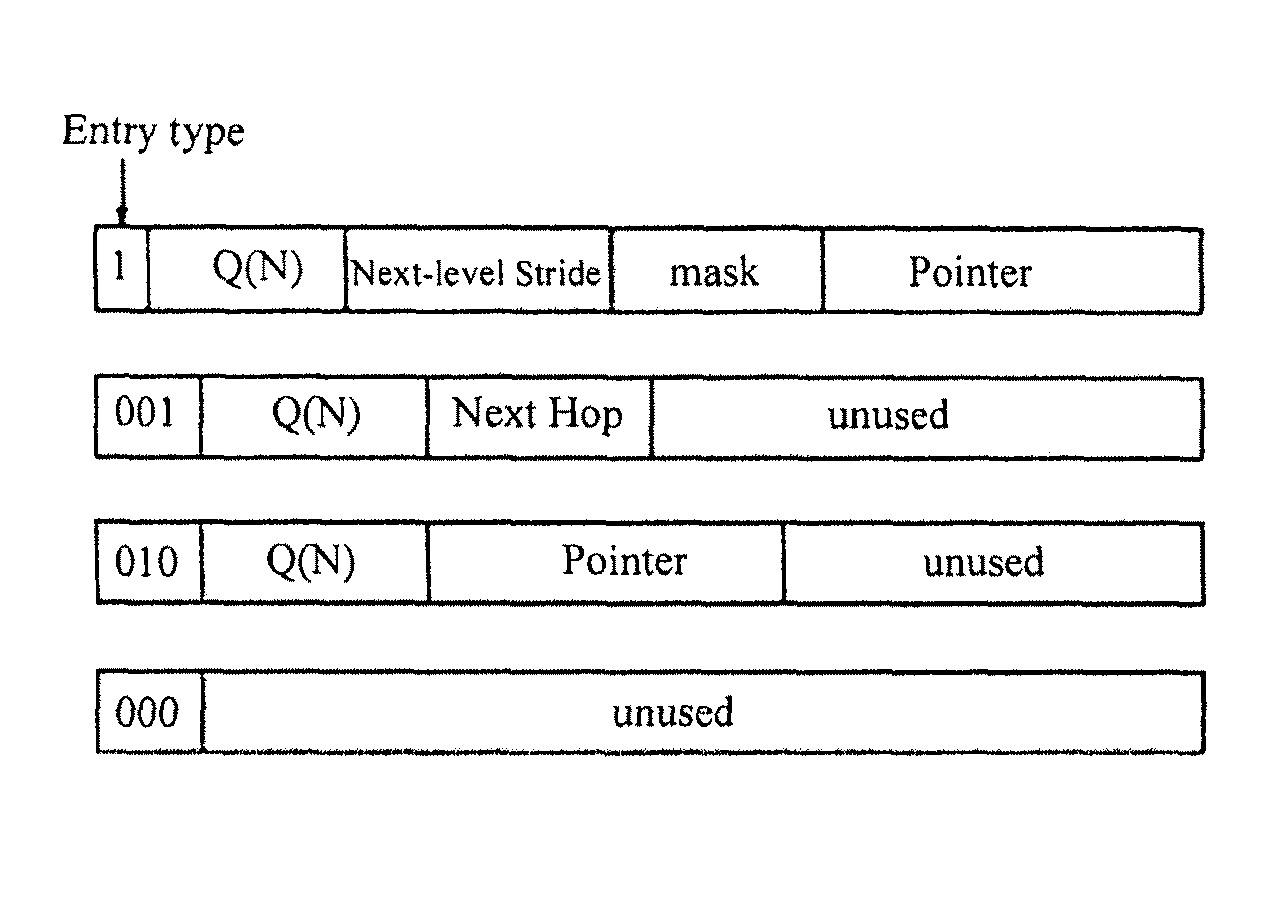
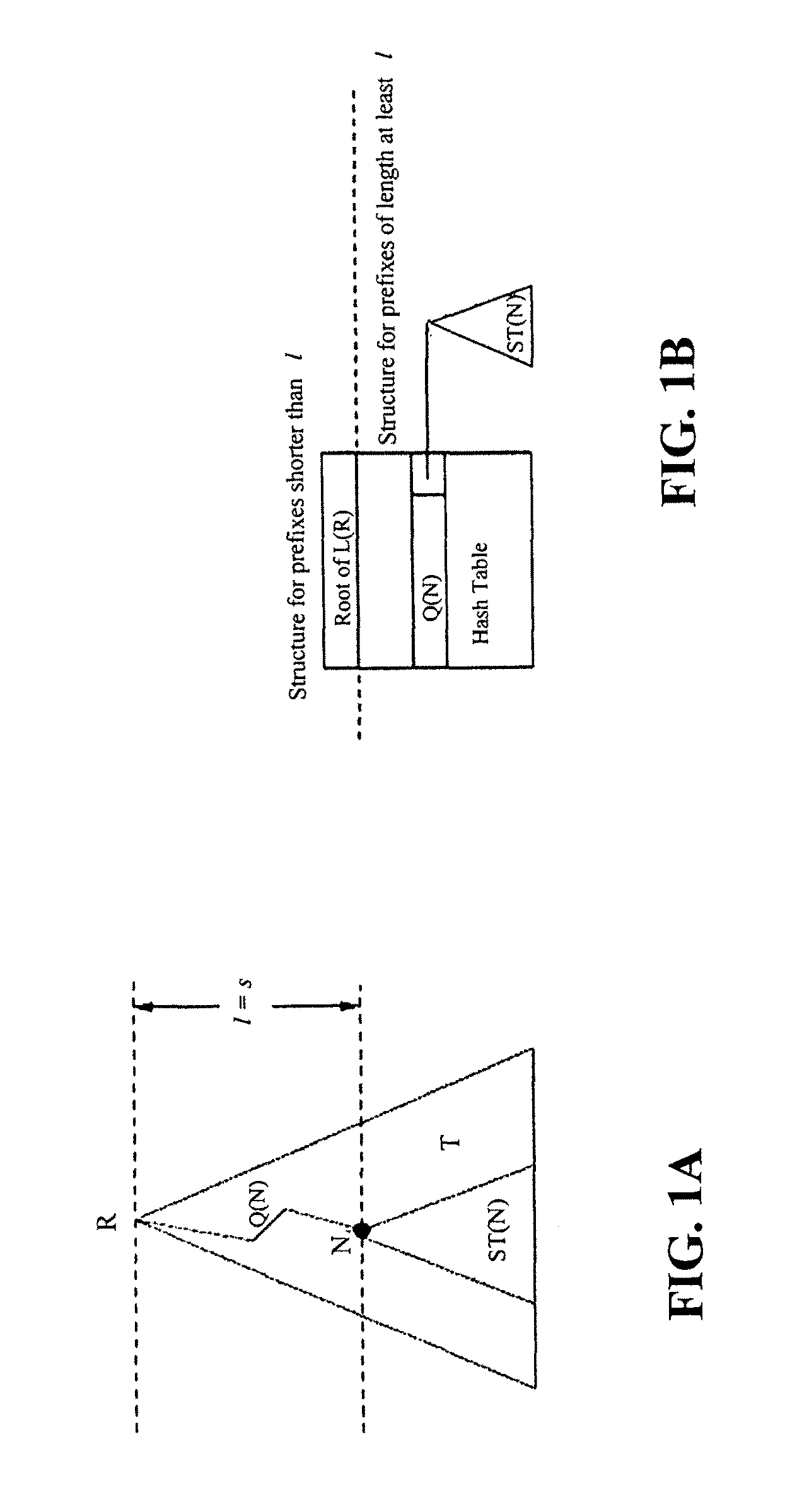
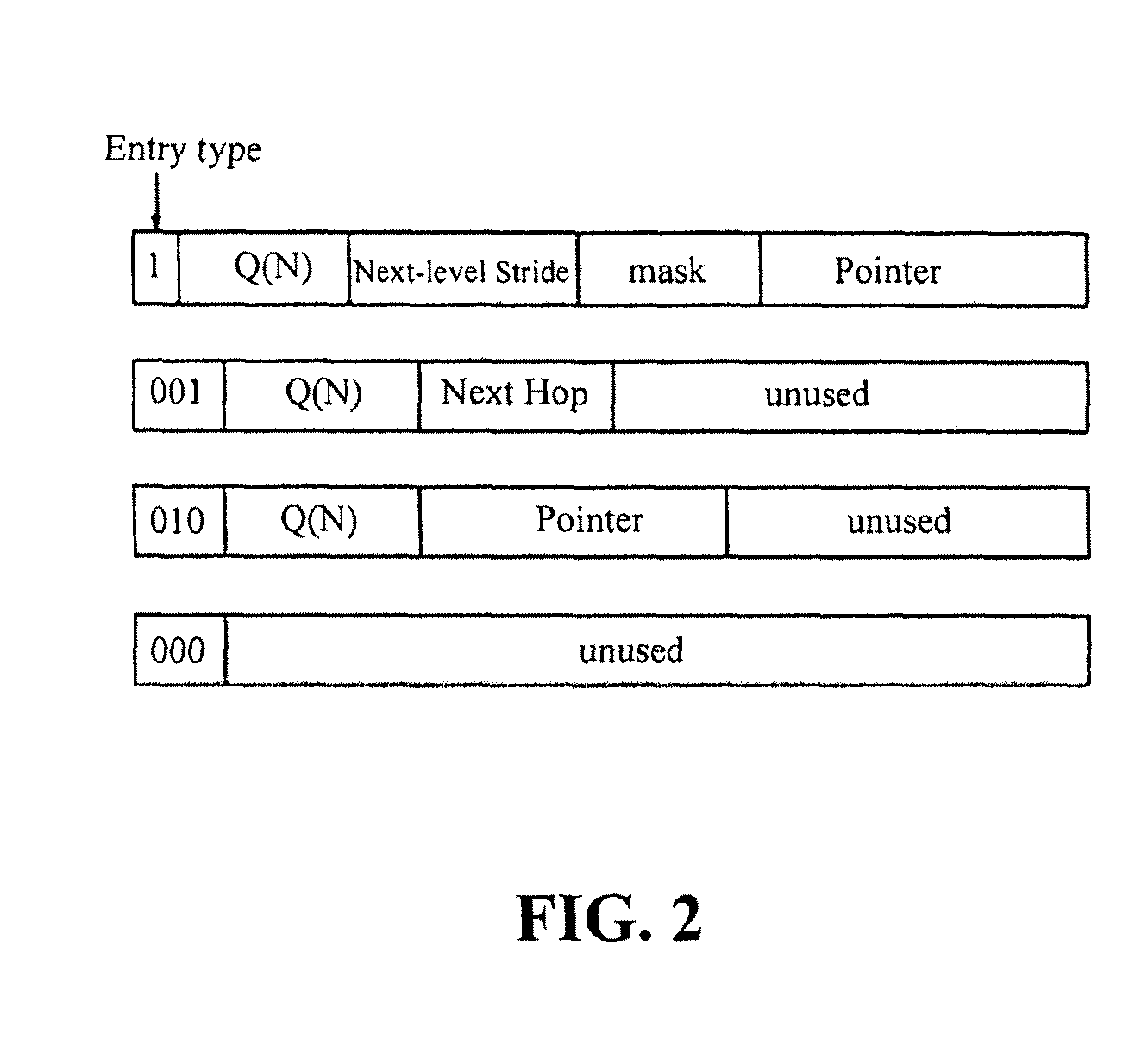
Recursively partitioned static IP router tables
InactiveUS7990979B2Less accessibleLess memory requiredData switching by path configurationIp routerPerfect hash function
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
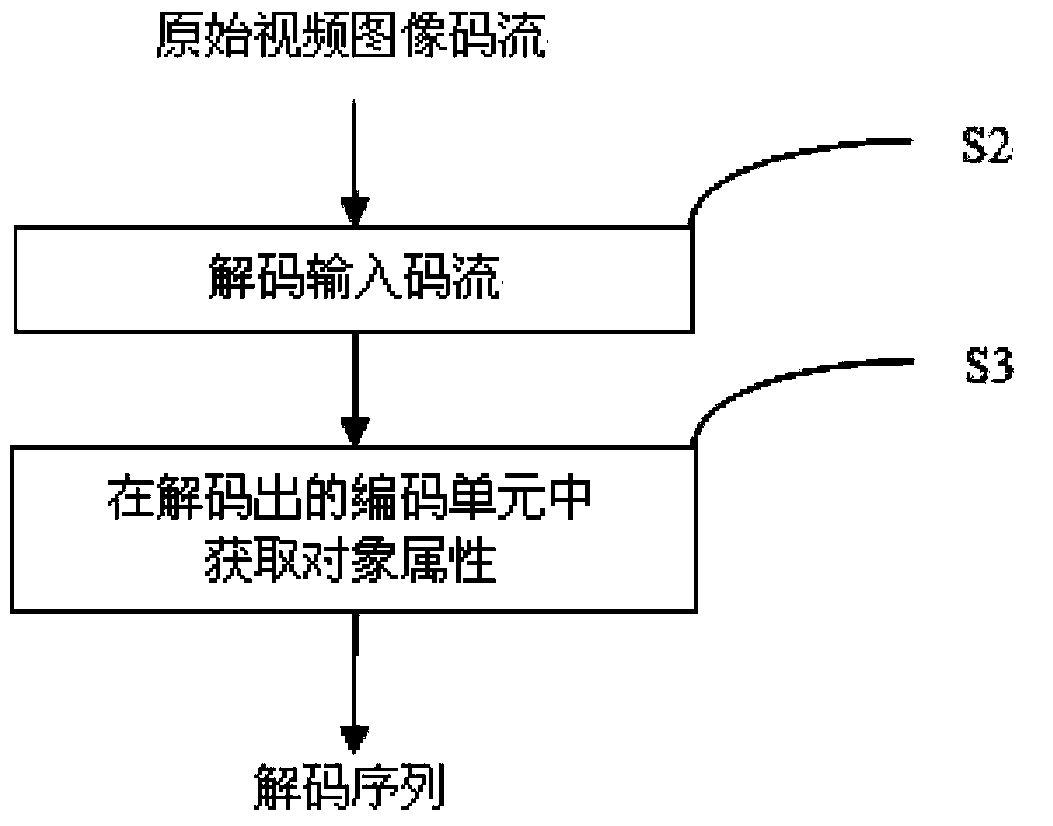
Extensible object notation method and device for use in video coder/decoder
The invention provides an extensible object notation method and device for use in a video coder / decoder. In a coding process, the object property of a coding unit is judged according to the partition structure and object information of the coding unit in order to write the object property into the bit stream of an output video; in a decoding process, the object property is decoded to obtain object information comprising shapes and locations. An extensible object notation device for use in the video coder / decoder is provided by using the method. For a maximum coding unit, recursive partitioning is performed according to a mode decision. For a coding unit of which partitioning is ended, a judgment on whether the coding unit belongs to an object is made. If the coding unit does not belong to the object, an identity coding module is entered to code an object index identity for the coding unit. If the coding unit belongs to the object, an object notation accuracy decision module is entered.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Hybrid mesh partition method with design of integrity of system-level packaging power supply
InactiveCN101976287AReduce the number of nodesMeet modeling needsSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringGrid partition
The invention relates to a hybrid mesh partition method in the field of electronic technologies, in particular to the hybrid mesh partition method with the design of integrity of a system-level packaging power supply. The hybrid mesh partition method comprises the following steps: (1) decomposing an irregular power supply / ground plane into a series of convex polygons by utilizing convex partition treatment; (2) obtaining an optimal rectangular mesh based on the recursive partitioning technology of the rectangular mesh, setting auxiliary ports on sides of the rectangular mesh, and establishing the transfer impedance relationship among the ports; (3) adopting a triangular mesh to fill the remaining structure, and carrying out modeling of an equivalent circuit for the triangular mesh; (4) establishing the electrical relationship among the ports at an interface of the rectangular mesh and the triangular mesh; and (5) solving simultaneous overall equations. The hybrid mesh partition method has the advantages of a wide range of applications, few internal nodes, high analysis precision and efficiency and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method of object location in airborne imagery using recursive quad space image processing
ActiveUS20100008565A1Wide applicabilityImprove accuracyCosmonautic vehiclesGeometric image transformationImaging processingGeolocation
A method and computer workstation are disclosed which determine the location in the ground space of selected point in a digital image of the earth obtained by an airborne camera. The image is rectangular and has four corners and corresponds to an image space. The image is associated with data indicating the geo-location coordinates for the points in the ground space corresponding to the four corners of the image, e.g., an image formatted in accordance with the NITF standard. The method includes the steps of: (a) performing independently and in parallel a recursive partitioning of the image space and the ground space into successively smaller quadrants until a pixel coordinate in the image assigned to the selected point is within a predetermined limit (Δ) of the center of a final recursively partitioned quadrant in the image space. The method further includes a step of (b) calculating a geo-location of the point in the ground space corresponding to the selected point in the image space from the final recursively partitioned quadrant in the ground space corresponding to the final recursively partitioned quadrant in the image space. The methods are particularly useful for geo-location from oblique reconnaissance imagery.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Method of object location in airborne imagery using recursive quad space image processing
ActiveUS8155433B2Wide applicabilityImprove accuracyCosmonautic vehiclesGeometric image transformationImaging processingGeolocation
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Method for screening compounds using consensus selection and multiple descriptor sets
InactiveUS20050239111A1Reduce false alarm rateMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningDrug biological activityComputer science
A method for screening compounds for biological activity is disclosed. A test library of compounds is selected. Then, a first analytical model is formed using a first recursive partitioning process. The first recursive partitioning process is performed on at least some of the compounds in the test library of compounds and uses a first descriptor set. Subsequent analytical models are formed using subsequent recursive partitioning processes using the digital computer and use multiple descriptor sets. A consensus compound set is determined using the first analytical model and one or more of the subsequent analytical models.
Owner:ICAGEN INC
Method and apparatus for pre-computing and using placement costs within a partitioned region for multiple wiring models
InactiveUS6910198B2Improve placement costRecord information storageMulti-objective optimisationTheoretical computer sciencePlacement method
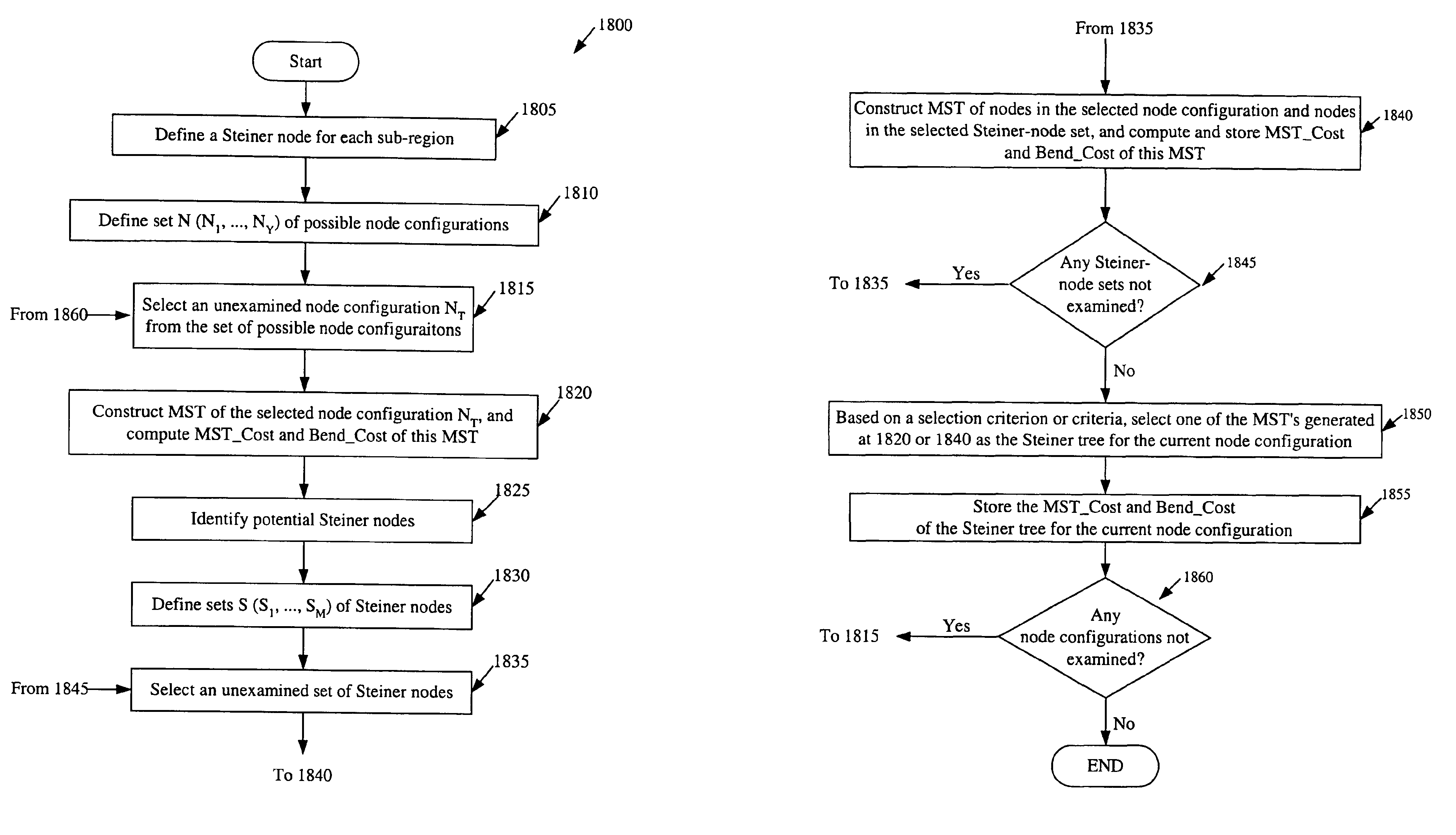
One embodiment of the invention is a recursive partitioning method that places circuit elements in an IC layout. This method initially defines a number of partitioning lines that divide an IC region into several sub-regions (also called slots). For a net in the region, the method then identifies the set of sub-regions (i.e., the set of slots) that contain the circuit elements (e.g., the pins of circuit modules) of that net. The set of sub-regions for the net represents the net's configuration with respect to the defined partitioning lines. Next, the placement method identifies attribute or attributes of a connection graph that models the net's configuration with respect to the partitioning lines. The connection graph for each net provides a topology of interconnect lines that connect the slots that contain the net's circuit elements. According to some embodiments of the invention, the connection graph for each net can have edges that are completely or partially diagonal.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
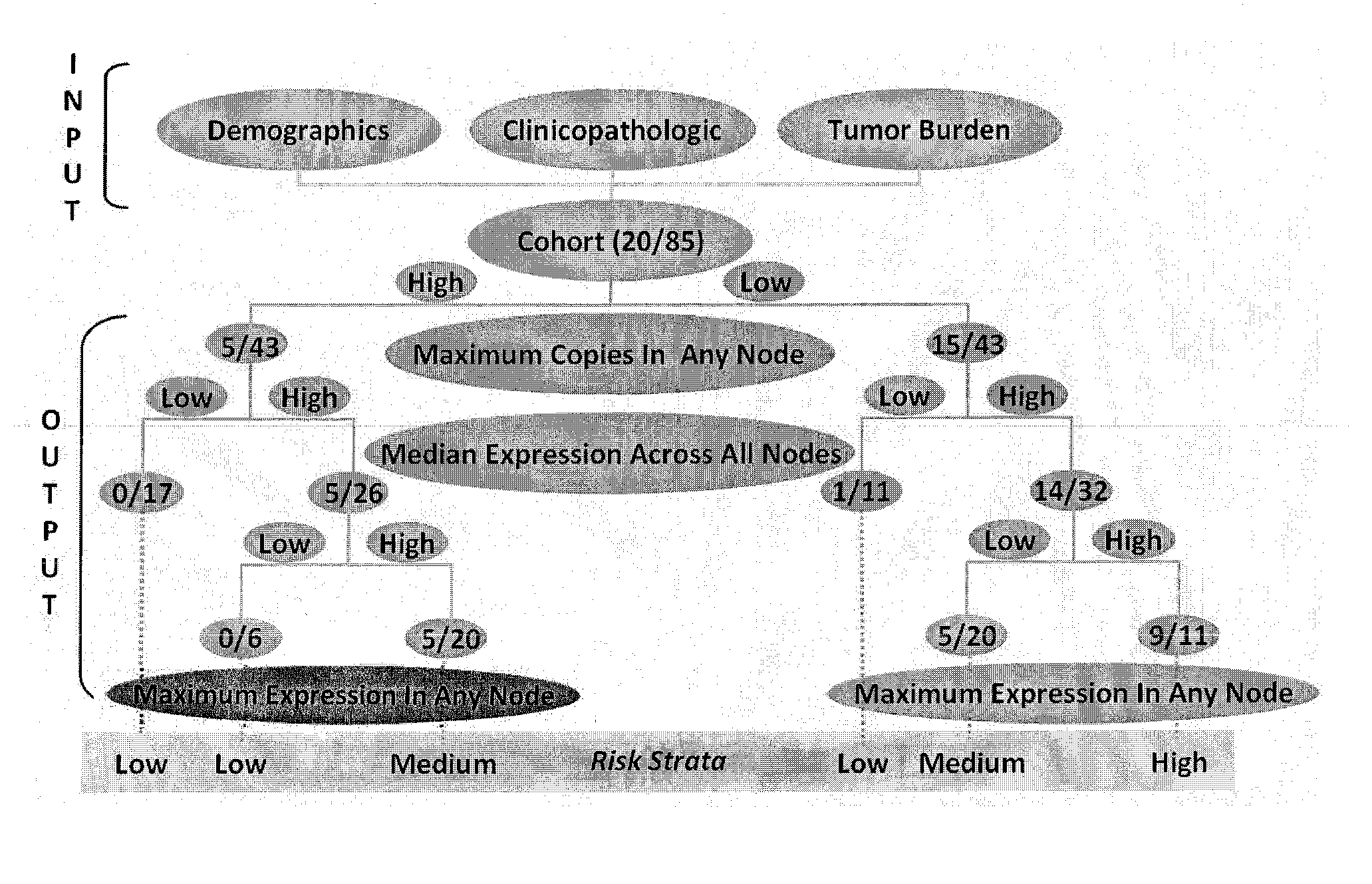
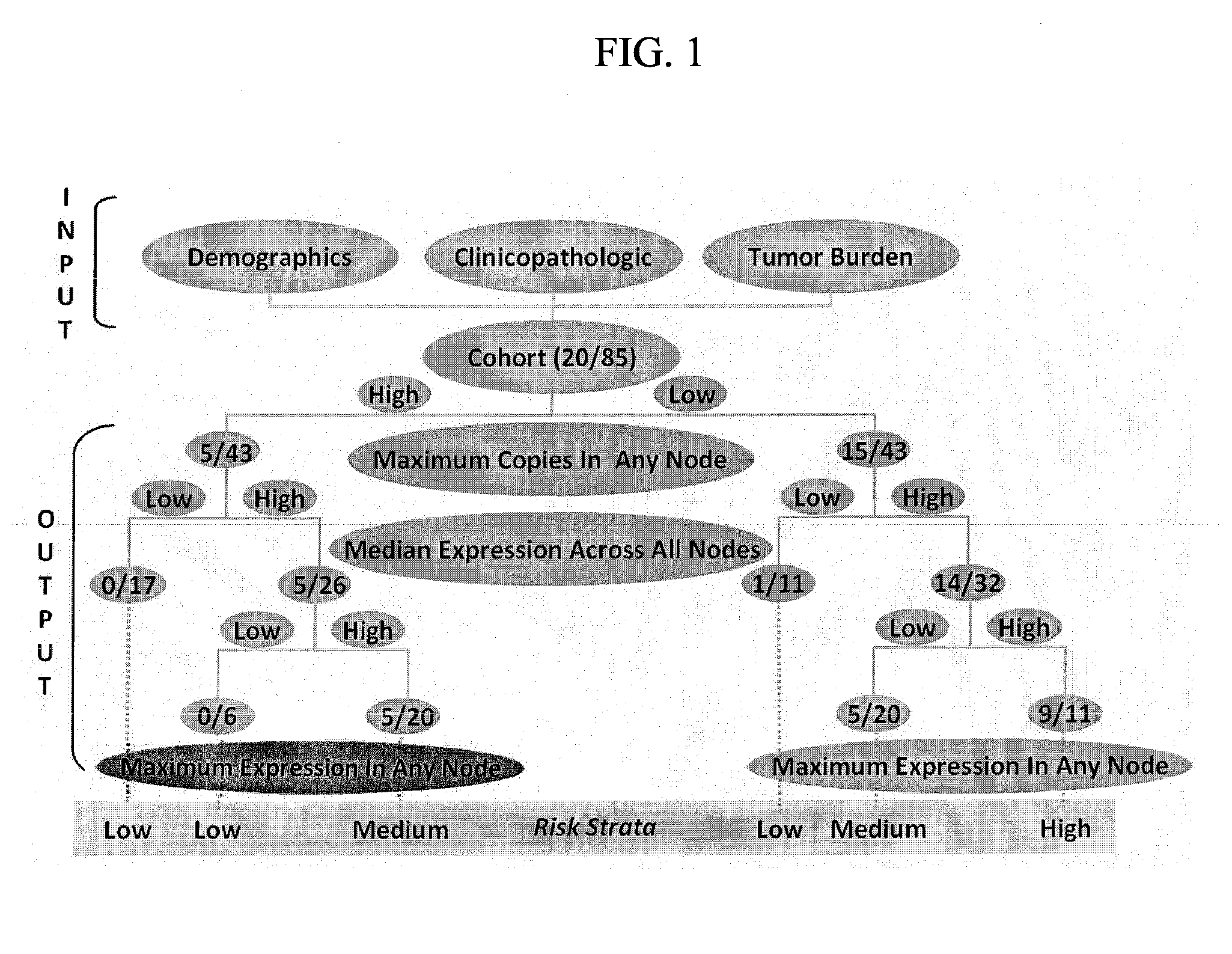
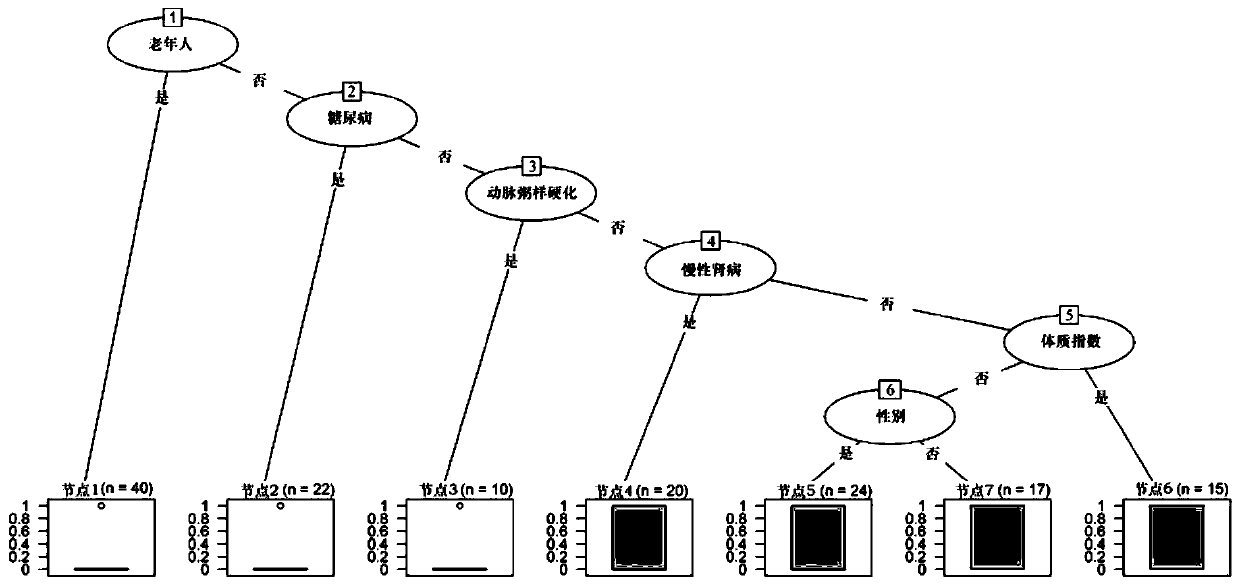
System for and method of determining cancer prognosis and predicting response to therapy
A database for predicting clinical outcomes based upon quantitative tumor burden in lymph node samples from an individual is provided. The database comprises data sets from a plurality of individuals. The data sets include clinical outcome data and data regarding number of lymph nodes evaluated, maximum number of biomarker detected in any single node, median normalized expression levels detected across all evaluated lymph nodes and the maximum normalized expression levels detected in any evaluated lymph nodes and the database also includes stratified risk categories based upon recursive partitioning of data. A system for predicting clinical outcomes based upon quantitative tumor burden in lymph node samples from an individual is provided which includes the database linked to a data processor, an input interface and an output interface. Method of preparing a database and method for predicting clinical outcome for a test patient based upon quantitative tumor burden in lymph node samples from an individual using a system that includes the database linked to a data processor, an input interface and an output interface. The method comprises measuring quantitative tumor burden in a plurality of lymph node samples from an individual, inputting the results into the system and processing with data in the database. The results of the processing of the data is the assignment of data test patient to a stratified risk category. Output is produced that displays test patient's identity and assigned stratified risk category.
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV
Method and apparatus for pre-computing and using multiple placement cost attributes to quantify the quality of a placement configuration within a partitioned region
InactiveUS6988256B2Record information storageComputer programmed simultaneously with data introductionAlgorithmLayout
One embodiment of the invention is a recursive partitioning method that places circuit elements in an IC layout. This method initially defines a number of partitioning lines that divide an IC region into several sub-regions (also called slots). For a net in the region, the method then identifies the set of sub-regions (i.e., the set of slots) that contain the circuit elements (e.g., the pins or circuit modules) of that net. The set of sub-regions for the net represents the net's configuration with respect to the defined partitioning lines. Next, the placement method identifies attribute or attributes of a connection graph that models the net's configuration with respect to the partitioning lines. The connection graph for each net provides a topology of interconnect lines that connect the slots that contain the net's circuit elements. According to some embodiments of the invention, the connection graph for each net can have edges that are completely or partially diagonal.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
System and method for word-sense disambiguation by recursive partitioning
ActiveUS8099281B2Special data processing applicationsPressure difference measurement between multiple valvesWord senseVoice transformation
A device and related methods for word-sense disambiguation during a text-to-speech conversion are provided. The device, for use with a computer-based system capable of converting text data to synthesized speech, includes an identification module for identifying a homograph contained in the text data. The device also includes an assignment module for assigning a pronunciation to the homograph using a statistical test constructed from a recursive partitioning of training samples, each training sample being a word string containing the homograph. The recursive partitioning is based on determining for each training sample an order and a distance of each word indicator relative to the homograph in the training sample. An absence of one of the word indicators in a training sample is treated as equivalent to the absent word indicator being more than a predefined distance from the homograph.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
Self-operated measuring unit for reaction of pupil aperture to light based on digital image processing
InactiveCN103445759ATest response effectAuxiliary detectionEye diagnosticsDigital signal processingMeasurement device
The invention provides a self-operated measuring unit for reaction of the pupil aperture to light based on digital image processing. The self-operated measuring unit consists of a uniform light stimulator, an infrared image acquisition module and pupil measuring software, wherein the uniform light stimulator is used for controlling hardware and a light source array to establish a photostimulation environment conforming to an International Society for Clinical Electrophysiological of vision (ISCEV) standard; the infrared image acquisition module is used for dynamically acquiring images and transmitting the images into a memory; the pupil measuring software is used for performing filtering processing and equilibrium processing on the images, performing recursive partitioning on the images according to a gray average and a variation proportion, extracting feature information including area, perimeter and circularity for judging whether the images are pupils of human eyes, and performing curve fitting, identification, and position and radius parameter extraction on verified pupils. According to the measuring unit provided by the invention, three kinds of stimulation light in red, white and blue conforming to the required strength of reaction of pupil to light can be generated, the size change of the reaction of pupil aperture to light is measured in real time, the shrinkage change rate of beam-focusing stimulation is calculated, and stability and accuracy are realized.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Mutual-information based recursive polar code construction
ActiveUS10523369B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsComputer hardwareMutual information
Decoding and encoding methods, systems, and devices for wireless communication are described. One method may include receiving a codeword over a wireless channel, the codeword being encoded using a polar code, identifying a set of repeated bit locations in the received codeword, and identifying a set of bit locations of the polar code used for information bits for the encoding. The set of bit locations may be determined based at least in part on recursively partitioning bit-channels of the polar code for each stage of polarization and assigning portions of a number of the information bits to bit-channel partitions of each stage of polarization based on a mutual information transfer function of respective aggregate capacities of the bit-channel partitions. The method may also include decoding the received codeword according to the polar code to obtain an information bit vector at the set of bit locations, and other aspects and features.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Hypertension medication recommendation model based on recursive partitioning calculation and construction method thereof
ActiveCN110751996AQuick selectionMedical data miningDrug and medicationsMedical recordRecommendation model
The invention discloses a hypertension medication recommendation model based on recursive partitioning calculation and a construction method thereof. The method comprises the steps: obtaining a hypertension data set through ICD coding, and analyzing and processing the data set to be in a standardized text medical record format; formatting a text medical record into a classification variable containing hypertension medication characteristics, and defining a model framework; dividing the data set into a test sample set and a verification sample set through an age stratified sampling method; based on the test sample set, calculating the fitting degree of the model and judging the complexity of medication nodes by using a recursive partitioning algorithm; establishing a model parameter pool, and setting parameter composition; and solving optimal model parameters based on the verification sample set to realize construction and optimization of the hypertension medication recommendation model. By means of big data analysis, recognition methods of different medication schemes in individualized application of hypertension patients are analyzed, and rapid selection of a single medication scheme or a combined medication scheme is achieved according to treatment classification characteristics of the patients.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
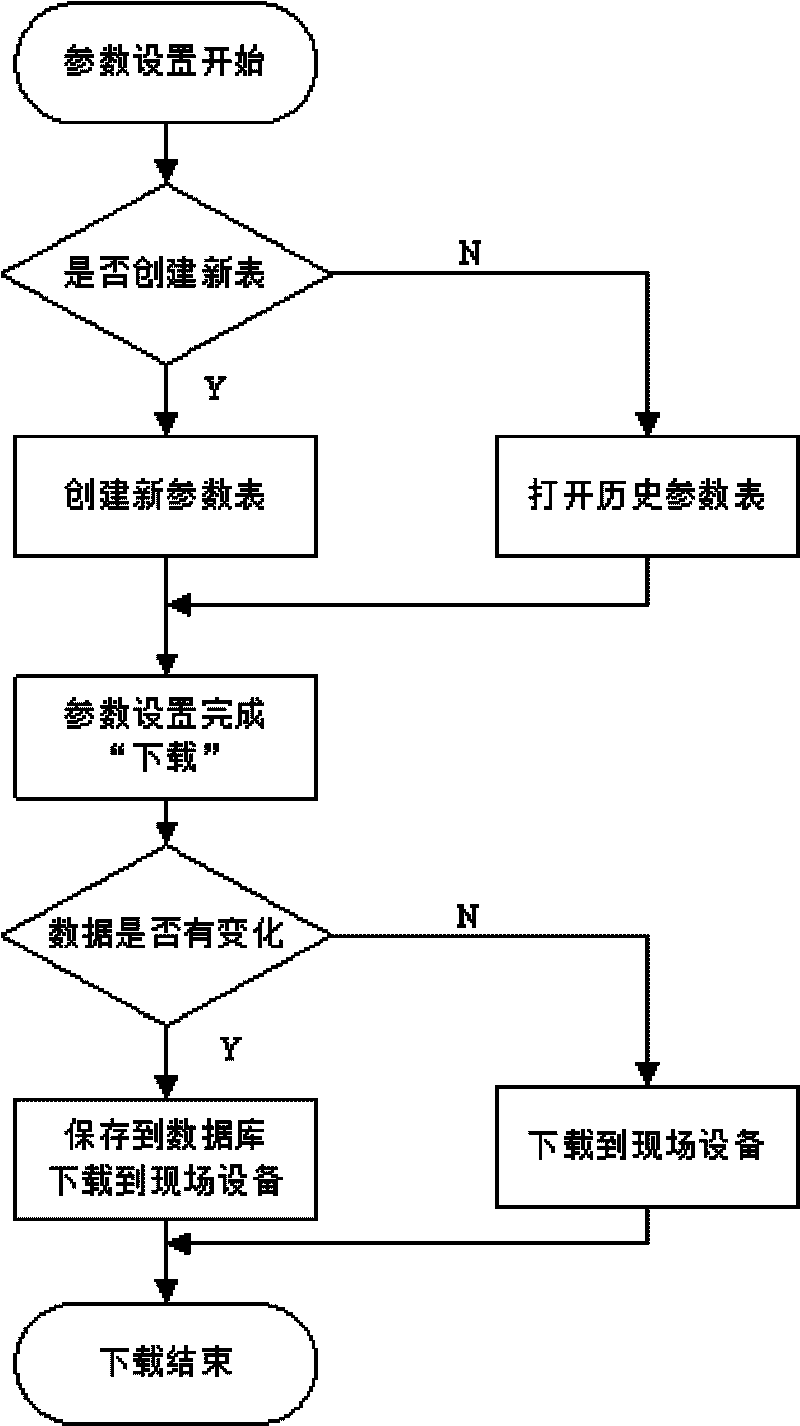
Computer automated measurement method of solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) electroconductance
InactiveCN101699299AImprove reusabilityCost-effectiveResistance/reactance/impedenceEngineeringField device
The invention provides a computer automated measurement method of solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) electroconductance, belonging to the technical field of chemical energy materal performance test, which is characterized by realizing parameter measurement selective setup of a programmable parameter table and dividing parameters in the programmable parameter table into two categories of measurement parameters and selective measurement parameters, namely whether the selective measurement parameters need to be measured can be selected; realizing multiple selection methods of measurement parameter download function for storing data in a database and field equipment; and realizing random-length seamless continual temperature programming process in a temperature increasing stage and adopting a method for downloading the temperature increasing stage in a recursive partitioning manner to solve the problem of extending the length of the temperature increasing stage limited by field temperature controller to cause the temperature increasing process to be in seamless and continual operation. The realization of the method changes the traditional manual measurement method, extends and enhances the self functions of the temperature controller, and leads the measurement system to have flexible operation efficiency, higher cost performance and high precision and efficiency of automatic measurement of the SOFC electroconductance.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
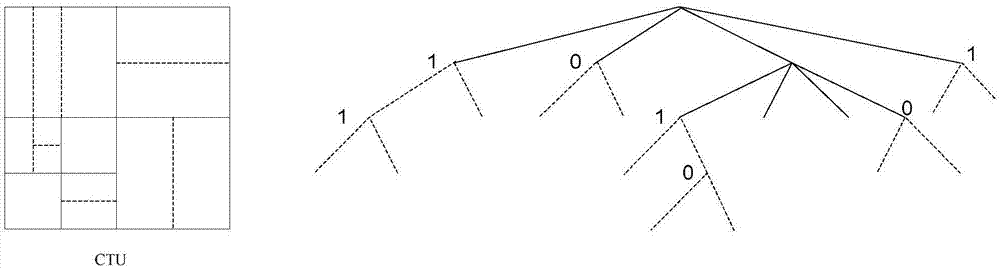
QTBT fast judgment method and system based on KB filter
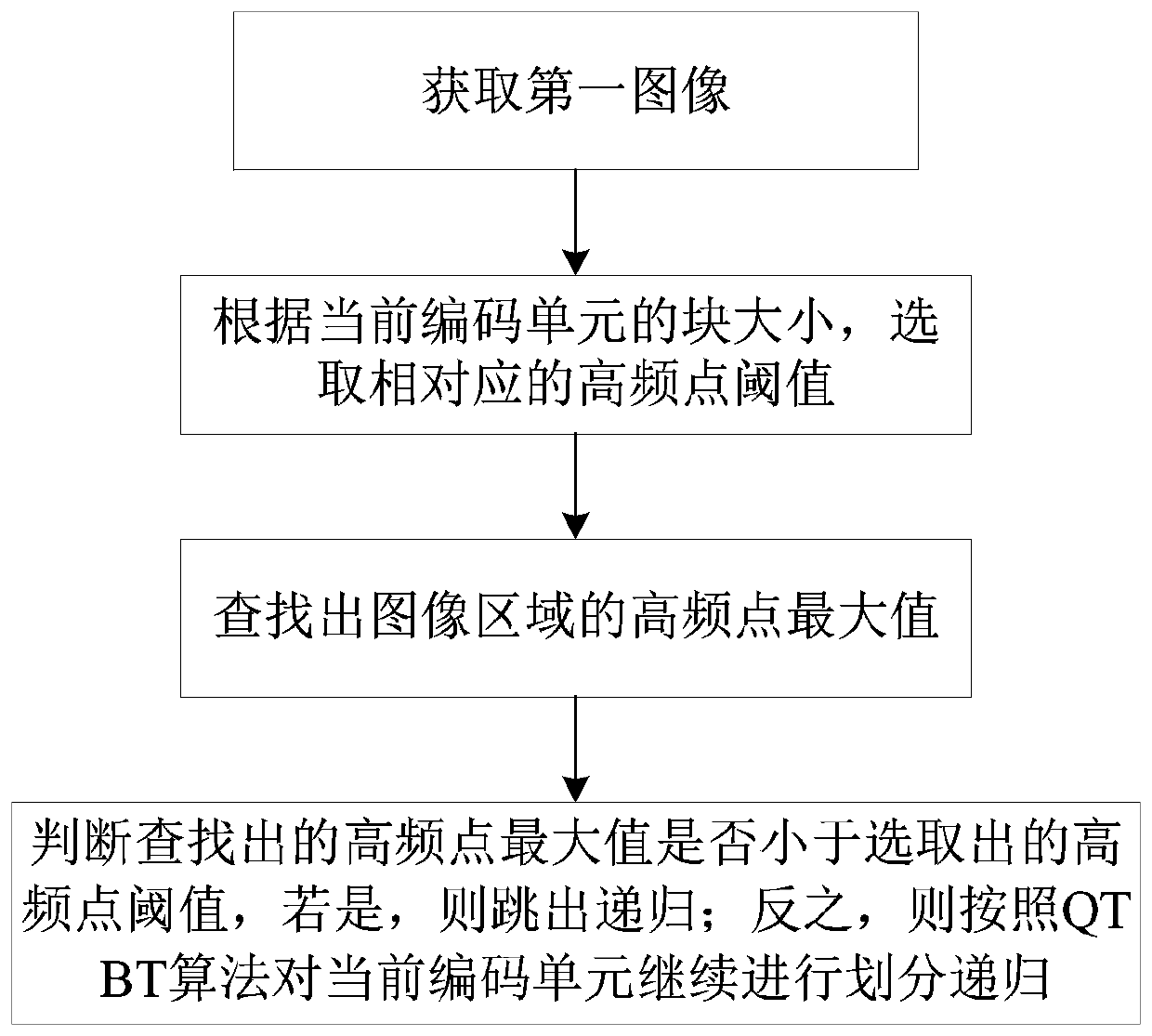
ActiveCN107197253AOperations that reduce division recursionShorten the timeDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionVideo encoding
The invention discloses a QTBT fast judgment method and system based on a KB filter. The system comprises an obtaining module, a selection module, a search module and a judgment module. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out filtering processing on a video frame image through the KB filter to obtain a filtered image; selecting a corresponding high frequency point threshold value; searching high frequency point maximum value of an image region; judging whether the searched high frequency point maximum value is smaller than the selected high frequency point threshold value; if so, jumping out of the current coding unit recursive partitioning program; or otherwise, carrying out recursive partitioning continuously on a current coding unit based on a QTBT algorithm. Through the method and system, whether the CU is subjected to recursive partitioning continuously can be pre-judged based on the image features, thereby greatly reducing video encoding time; and the QTBT fast judgment method and system based on the KB filter can be widely applied to the QTBT algorithm video coding field.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
HEVC intraframe coding method based on support vector radix
InactiveCN106412589AReduce computational complexityLow costDigital video signal modificationSupport vector machineCoding block
The invention discloses an HEVC intraframe coding method based on a support vector radix, which comprises the following steps of: 1, judging whether a current coded frame is a first frame, if not, directly jumping to the step 4, or directly carrying out quadtree recursive partitioning of an HEVC standard; 2, carrying out statistics on characteristic values under different coding depths and forming training samples; 3, according to the training samples obtained by statistics, training a support vector radix classifier; 4, carrying out extraction of a characteristic value on a current coding block, classifying the characteristic value by the support vector radix classifier obtained by the training samples, and determining a coding depth; 5, carrying out normal coding under the coding depth; and 6, if coding on a video sequence is completely finished, ending the operation, or jumping to the step 1 again. According to the HEVC intraframe coding method disclosed by the invention, on the basis of keeping reducing calculation complexity, hardware implementation cost is not additionally increased. Additional cost cannot be increased for manufacturing of hardware equipment, and meanwhile, power consumption also can be saved.
Owner:SICHUAN CHANGHONG ELECTRIC CO LTD
A Recursive Cutting Reactive Voltage Partitioning Control Method
InactiveCN103532139BRealize voltage partition controlEasy to controlAc network circuit arrangementsCouplingPower grid
The invention discloses a recursive cutting type zone control method of reactive voltage, belongs to the field of electrical power system safety analysis and operation control, and particularly relates to a node coupling relationship analysis and reactive voltage zone control method of an electrical power system. The problem that when the zone control method of the reactive voltage is applied to interconnected grids with non-uniform grid structures, the adaptability is poor is solved. The method comprises the steps as follows: a power supply node coupling relationship matrix and a voltage control sensitivity matrix HLG of power supply nodes to load nodes are calculated firstly; power supply nodes in a to-be-cut zone is divided into two groups, wherein one group has an intra-group coupling degree lager than Gamma (k), and the other group has an inter-group coupling degree smaller than Gamma (k); load nodes in the to-be-cut zone are merged into node sets of corresponding power supply nodes; whether sub-zones of the node sets meet the termination conditions of the sub-zones is judged, and if the termination conditions are met, the partition of nodes and sets is ended; then grid voltage of the zones is controlled, and operation control of the grid voltage of the zones is completed; otherwise, partition is performed continuously. The recursive cutting type zone control method of the reactive voltage is applicable to electrical power system safety analysis and operation control.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Image encoding method and image encoding device
InactiveCN101656880BEfficient compressionIncrease the compression ratioTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationImaging qualityImage compression
The present invention discloses an image encoding method and an image encoding device. The method comprises the following steps: dividing domain blocks according to a value block scale range; performing isomorphic transformation on a matrix composed of 4 low frequency coefficients obtained by performing wavelet transformation on the domain blocks; performing recursive partitioning on value blocks until scale of the value blocks is less than the maximum scale; performing wavelet transformation on the value blocks to obtain 4 low frequency coefficients, calculating a value block direction K1 and a domain block direction K2, calculating a luminance factor and a shift factor and error thereof if the K1 is identical with the K2, and judging if the error is less than 5; if yes, writing position information of the value block and the domain blocks, transformation information and value block scale information into a code stream file, or performing quadtree partitioning on the value blocks; and writing ending information into the code stream file when all the value blocks find corresponding domain blocks. The image encoding method and the image encoding device provided by the present invention accelerates encoding speed and effectively improves compression ratio and decoded image quality, thus realizing effective image compression.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
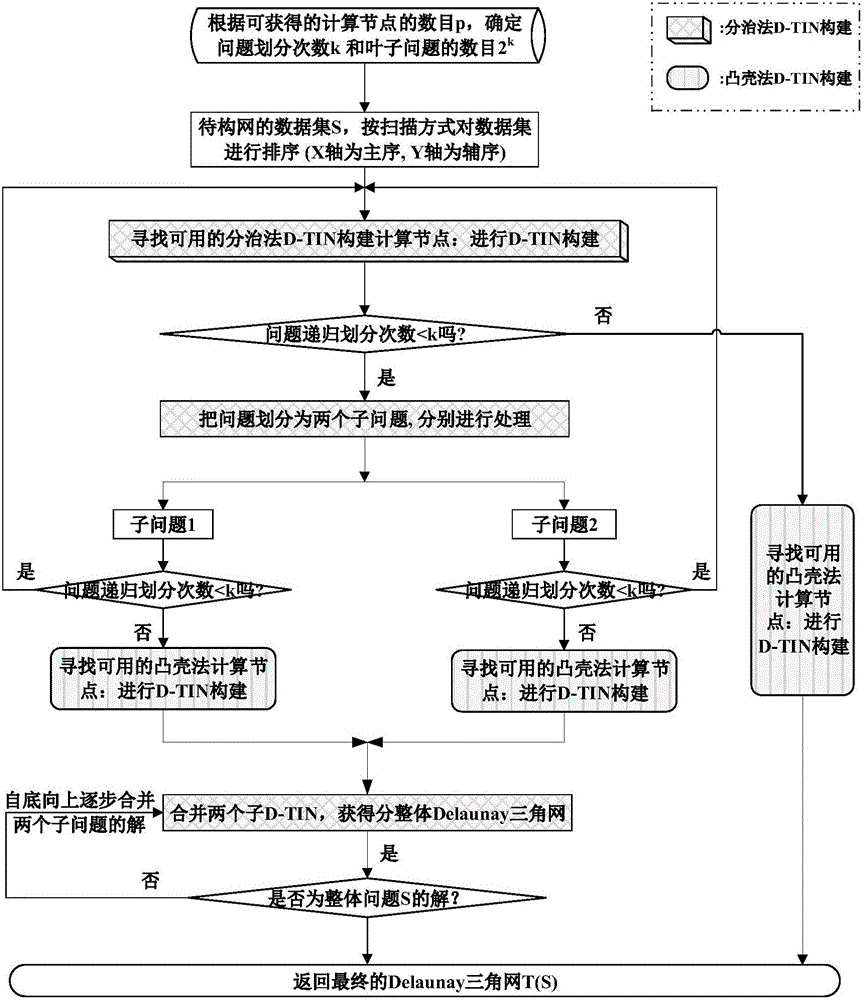
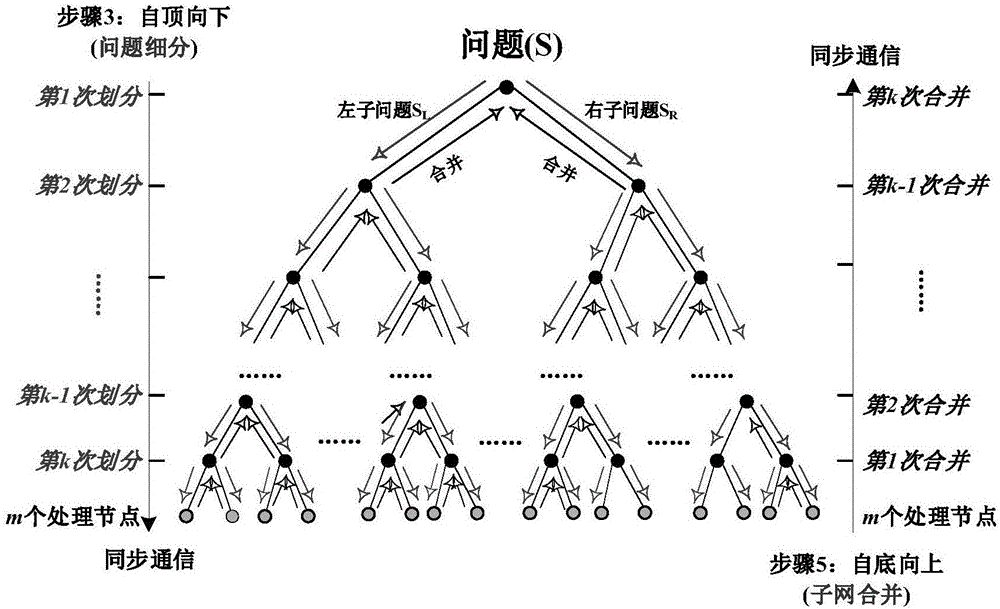
Efficient distributed and parallel Delaunay triangle construction method
InactiveCN106294985AImprove operational efficiencyImprove applicabilitySpecial data processing applicationsNODALData set
The invention discloses an efficient distributed and parallel Delaunay triangle construction method. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, determining the recursive partitioning frequency k of problem solving and the number 2k of leaf problems according to the scale p of a distributed and parallel computing environment; secondly, sorting data sets of to-be-solved problems with the scale of n in a flat scanning sequence mode; thirdly, performing gradual partitioning from top to bottom by adopting a partitioning strategy of a divide-and-conquer method, and recursively partitioning the to-be-solved problems with the scale of n into the 2k leaf problems; fourthly, performing convex-hull-method Delaunay triangular net parallel construction of sub-problems on the 2k leaf problems by using 2k parallel computing nodes; and finally, gradually combining solutions of the sub-problems from bottom to top by adopting a combination strategy of the divide-and-conquer method, and performing distributed and parallel combination processing by using t / 2 computing nodes during combination each time until a global solution of a global problem is obtained, wherein the number of the sub-problems is n. According to the method, the efficiency is remarkably improved.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Hypertension drug recommendation model based on recursive partition calculation and its construction method
ActiveCN110751996BQuick selectionMedical data miningDrug and medicationsMedical recordRecommendation model
The invention discloses a hypertension medication recommendation model based on recursive partitioning calculation and a construction method thereof. The method comprises the steps: obtaining a hypertension data set through ICD coding, and analyzing and processing the data set to be in a standardized text medical record format; formatting a text medical record into a classification variable containing hypertension medication characteristics, and defining a model framework; dividing the data set into a test sample set and a verification sample set through an age stratified sampling method; based on the test sample set, calculating the fitting degree of the model and judging the complexity of medication nodes by using a recursive partitioning algorithm; establishing a model parameter pool, and setting parameter composition; and solving optimal model parameters based on the verification sample set to realize construction and optimization of the hypertension medication recommendation model. By means of big data analysis, recognition methods of different medication schemes in individualized application of hypertension patients are analyzed, and rapid selection of a single medication scheme or a combined medication scheme is achieved according to treatment classification characteristics of the patients.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Algorithm to apply a predicate to data sets
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for analysing a pair of data sets with respect to a predicate, the predicate having a predicate criterion, each data set comprising one or more elements sorted according to the predicate criterion. The invention comprises recursive partitioning of the data sets in a parallel manner across multiple computing cores until a base case is reached. The invention is particularly suited for carrying out join, filter and sort operations on large data sets within database management systems.
Owner:BRYTLYT
A method for recursively splitting, transferring and reassembling files in a multi-stream and multi-homing environment
The invention discloses a method for file recursive subdivision, transmission and recombination under a multi-streaming and multi-homing environment. A sender is connected with a receiver through multiple links. The method comprises the following steps that: 1) before the sender sends a file, recursive subdivision is conducted to the file according to the quantity of connected links to subdivide the file into file fragments M with the same size, the file fragments M are numbered and coded, and the file fragments together with numbers and codes are sent to the receiver through the corresponding links; and 2) when the receiver receives the file fragments together with the numbers and the codes, the corresponding received file fragments are stored in a temporary folder according to the codes and the numbers of the file fragments and the directory structures of the temporary folder is created according to the codes and the numbers; and after all file fragments are received, all file fragments form a temporary folder with tree directory structures which are nested layer by layer in the receiver, the temporary folder is regarded as a tree root , the file fragments are regarded as leaves and the file fragments are combined by starting from the directory on the outermost layer through a binary-tree post-order traversal method to form the file. The method has the advantages of high file transmission efficiency, high network link dynamic adaptability and high simplicity and practicability.
Owner:SUZHOU INST FOR ADVANCED STUDY USTC
Scalable object representation method and device in video codec
The present invention proposes a scalable object representation method in a video codec. In the encoding process, the method determines the object attributes of the coding unit according to the division structure of the coding unit and the object information, so as to encode the object attributes into the output video In the decoding process, the object attributes are decoded to obtain object information including shape and position. Using this method, the present invention proposes scalable object representation means in video codecs. For a maximum coding unit, it is recursively divided according to the mode decision; for the coding unit that terminates the division, judge whether it belongs to the object: if it does not belong to the object, enter the identification coding module as its coding object index identification; if it belongs to the object, enter the object representation precision decision module.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method and device for protecting program memory space through precise partitioning
ActiveCN105677457AAvoid non-functioning situationsAvoid wastingSpecific access rightsTransaction processingComputer scienceDigital memory
The invention discloses a method and device for protecting program memory space through precise partitioning, and relate to the technical field of digital memory. The method comprises the steps that a first memory space is obtained according to the program memory space, the first memory space is processed to obtain a front end region and a rear end region, the front end region and the rear end region are subjected to recursive partitioning, and the access permission of sub-regions obtained through partitioning is set. The device comprises a first memory space generating module, a first judgment module, a first portioning module, a second judgment module, a front end region generating module, a rear end region generating module, a front end region processing module, a rear end region processing module, a third judgment module, a fourth judgment module, a front end region updating module and a rear end region updating module. The program memory space is protected through precise partitioning, the situation that due to inaccurate partitioning, the program cannot operate normally is avoided, and waste of system resources is avoided.
Owner:FEITIAN TECHNOLOGIES
A kind of qtbt fast judgment method and system based on kb filter
ActiveCN107197253BOperations that reduce division recursionShorten the timeDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionVideo encoding
The invention discloses a QTBT fast judgment method and system based on a KB filter. The system comprises an obtaining module, a selection module, a search module and a judgment module. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out filtering processing on a video frame image through the KB filter to obtain a filtered image; selecting a corresponding high frequency point threshold value; searching high frequency point maximum value of an image region; judging whether the searched high frequency point maximum value is smaller than the selected high frequency point threshold value; if so, jumping out of the current coding unit recursive partitioning program; or otherwise, carrying out recursive partitioning continuously on a current coding unit based on a QTBT algorithm. Through the method and system, whether the CU is subjected to recursive partitioning continuously can be pre-judged based on the image features, thereby greatly reducing video encoding time; and the QTBT fast judgment method and system based on the KB filter can be widely applied to the QTBT algorithm video coding field.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
An Efficient Distributed and Parallel Delaunay Triangle Construction Method
InactiveCN106294985BImprove operational efficiencyImprove applicabilitySpecial data processing applicationsNODALData set
The invention discloses an efficient distributed and parallel Delaunay triangle construction method. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, determining the recursive partitioning frequency k of problem solving and the number 2k of leaf problems according to the scale p of a distributed and parallel computing environment; secondly, sorting data sets of to-be-solved problems with the scale of n in a flat scanning sequence mode; thirdly, performing gradual partitioning from top to bottom by adopting a partitioning strategy of a divide-and-conquer method, and recursively partitioning the to-be-solved problems with the scale of n into the 2k leaf problems; fourthly, performing convex-hull-method Delaunay triangular net parallel construction of sub-problems on the 2k leaf problems by using 2k parallel computing nodes; and finally, gradually combining solutions of the sub-problems from bottom to top by adopting a combination strategy of the divide-and-conquer method, and performing distributed and parallel combination processing by using t / 2 computing nodes during combination each time until a global solution of a global problem is obtained, wherein the number of the sub-problems is n. According to the method, the efficiency is remarkably improved.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com