Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "Pantoea sp." patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
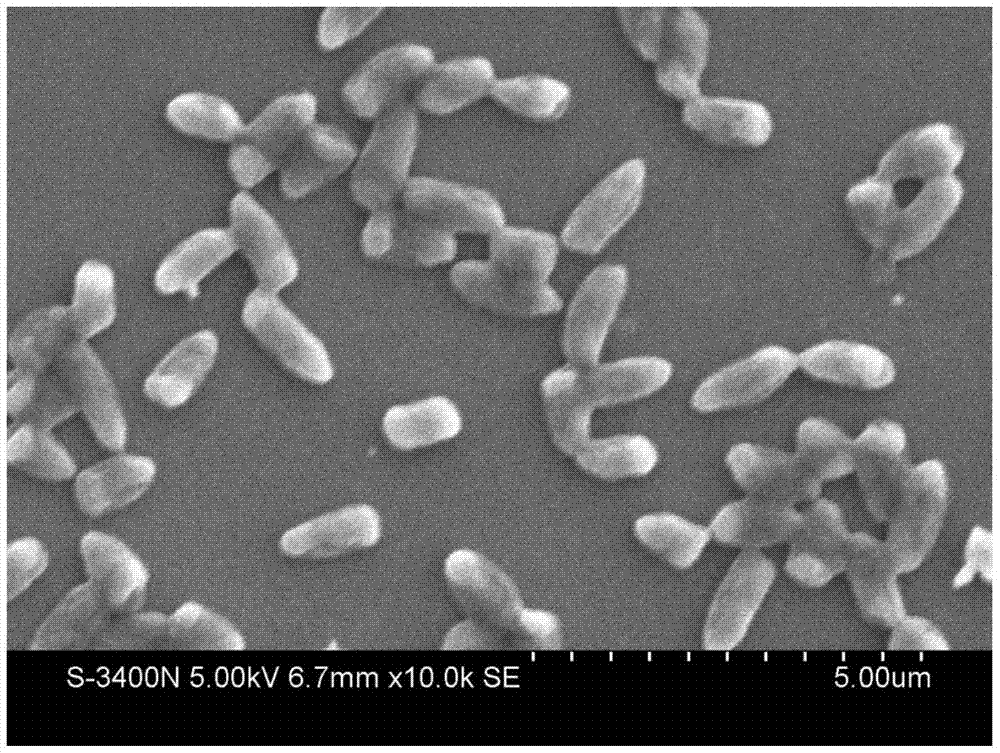
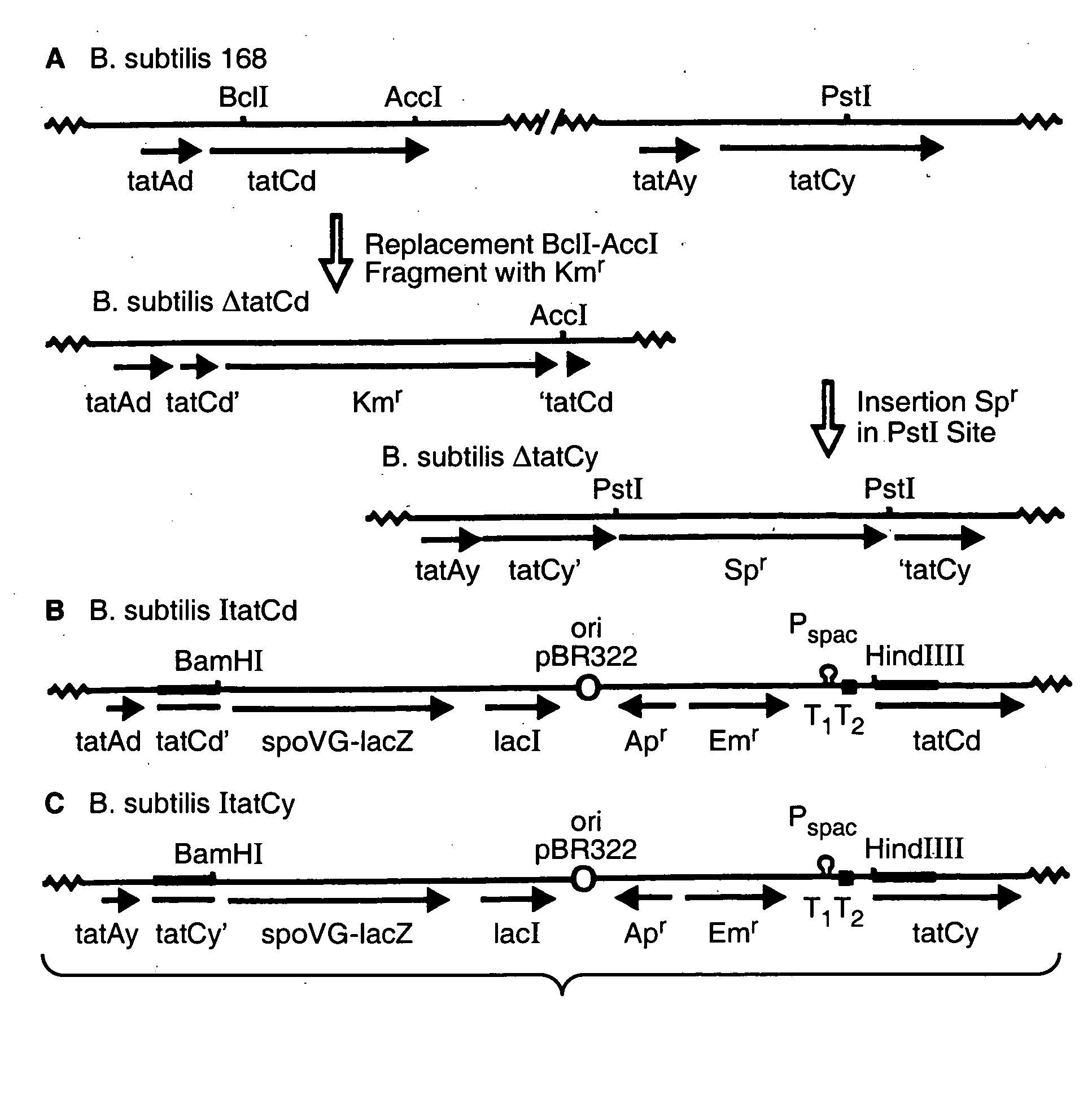
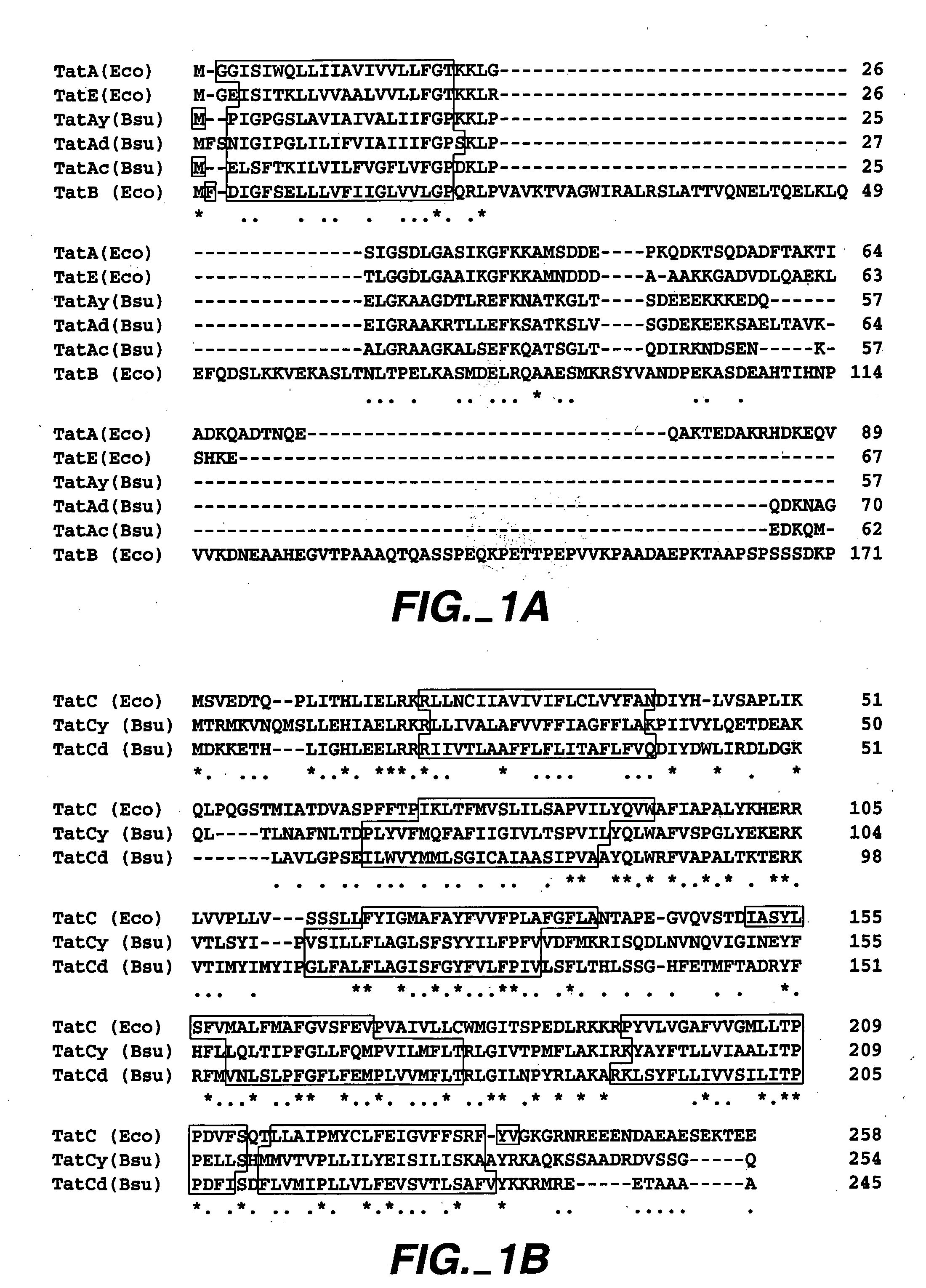
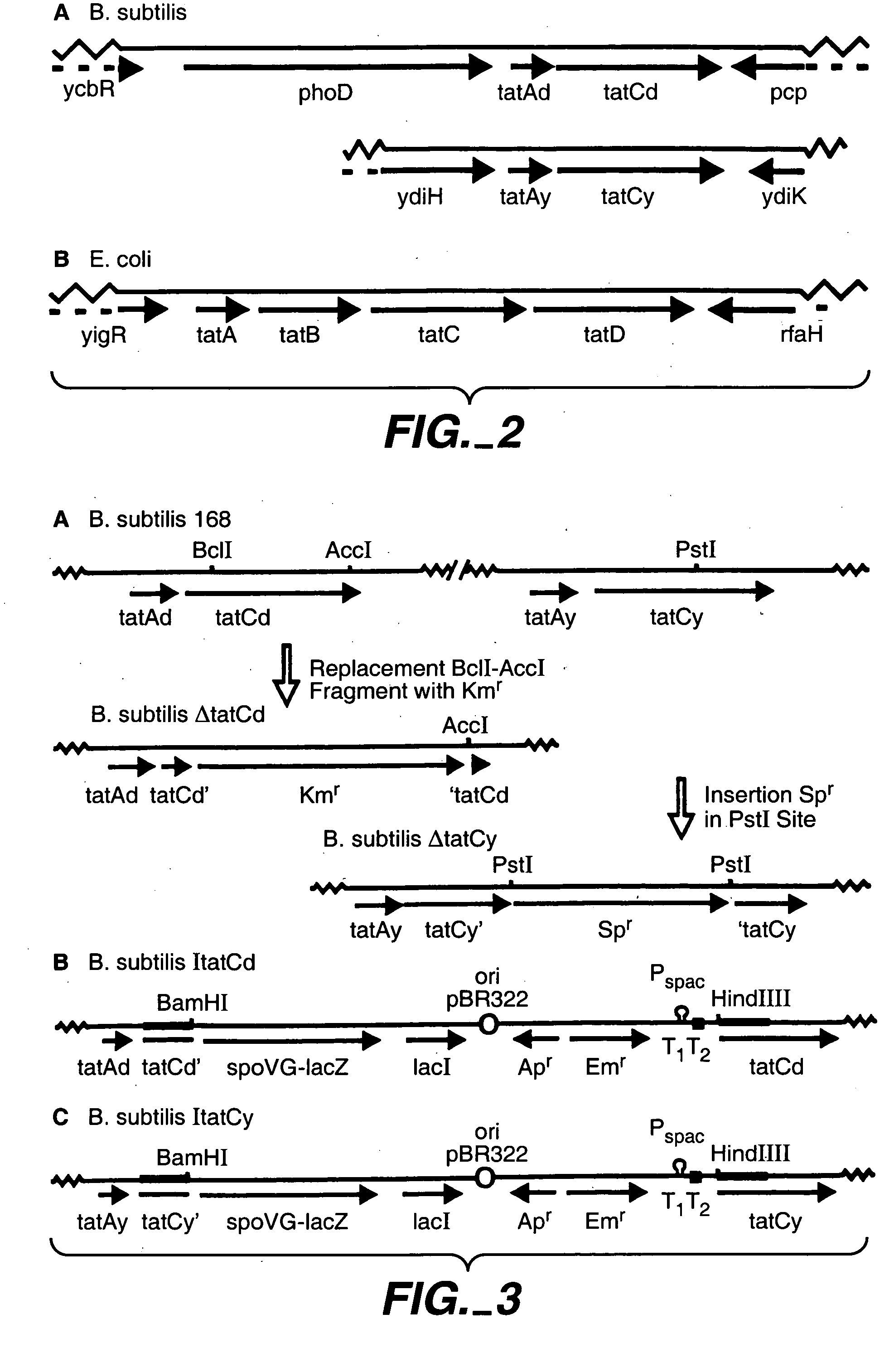
Twin-arginine translocation in Bacillus
Described herein are methods to enhance protein secretion in a host cell. In preferred embodiment, the host cell is a gram-positive microorganism such as a Bacillus. In another preferred embodiment, the host cell is a gram-negative microorganism. Preferably the gram-negative microorganism is an Escherichia coli or a member of the genus Pantoaea. Protein secretion may be enhanced by the overexpression of protein components of the Tat pathway. Alternatively, secretion of foreign proteins can be selectively enhanced by forming a chimeric polypeptide comprising a tat signal sequence and the protein of interest. In a preferred embodiment, the tat signal sequence is selected from phoD or LipA.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Sugarcane endogenous nitrogen-fixing Pantoea bacteria and application thereof
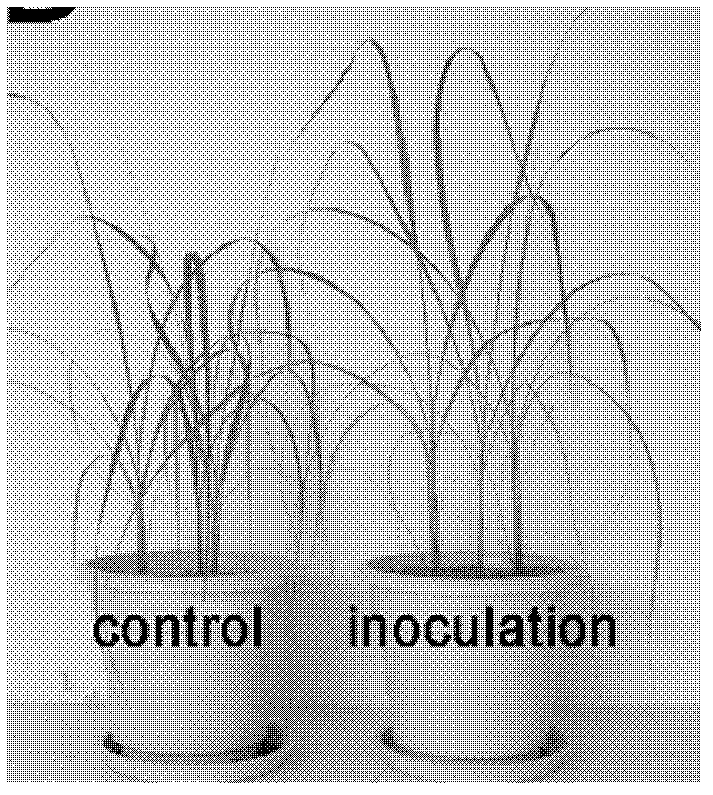
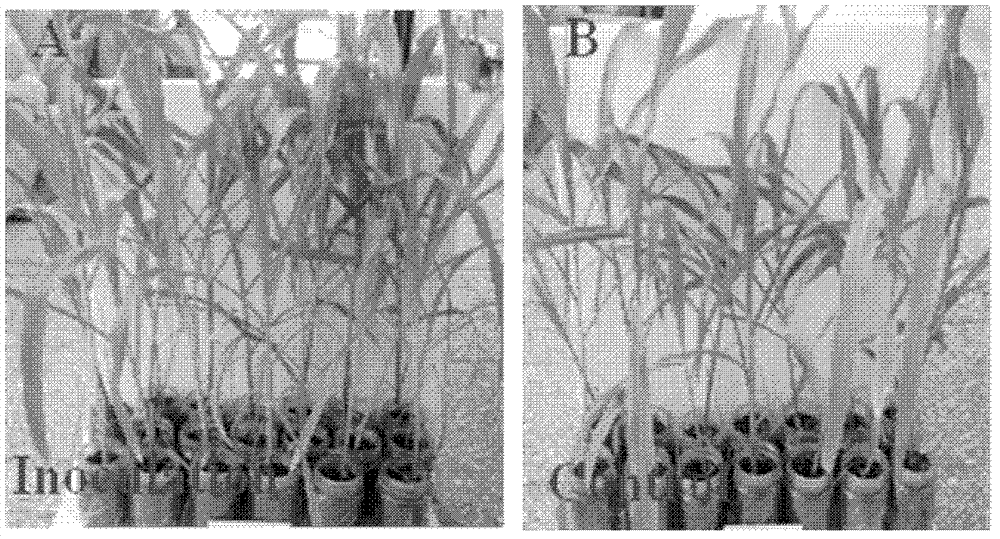
The invention relates to a sugarcane endogenous nitrogen-fixing bacteria strain and an application thereof. The classification of the strain is named as Pantoea sp.NN08200 with a preservation number of CGMCC NO.5438. The strain disclosed herein can significantly promote the growth of plants and revisiting various plant pathogenic fungi. According to the invention, after inoculating the strain to sugarcane to conduct tissue culture plantlet for 50 days, dry weight of the plants and the total nitrogen content are respectively increased by 46.74% and 41.5% over blank control group, the nitrogen fixation efficiency is 12.85%; the dry weight of the overground part of corn seedling of the inoculated strain NN08200 is increased by 74.5% over control group, the dry weight of the underground part is increased by 84.6%, the plant height is increased by 16.3%, the chlorophyll content is increased by 29.2%, and the nitrogen content is increased by 27.0%. The strain has the effects of association nitrogen fixation, production of hormone, and the like for promoting the growth of plants, and can be applied for producing nitrogen-fixing microbial agents and bio-organic fertilizers with the effects of promoting growth and inhibiting plant diseases.
Owner:MICROBIOLOGY RES INST GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
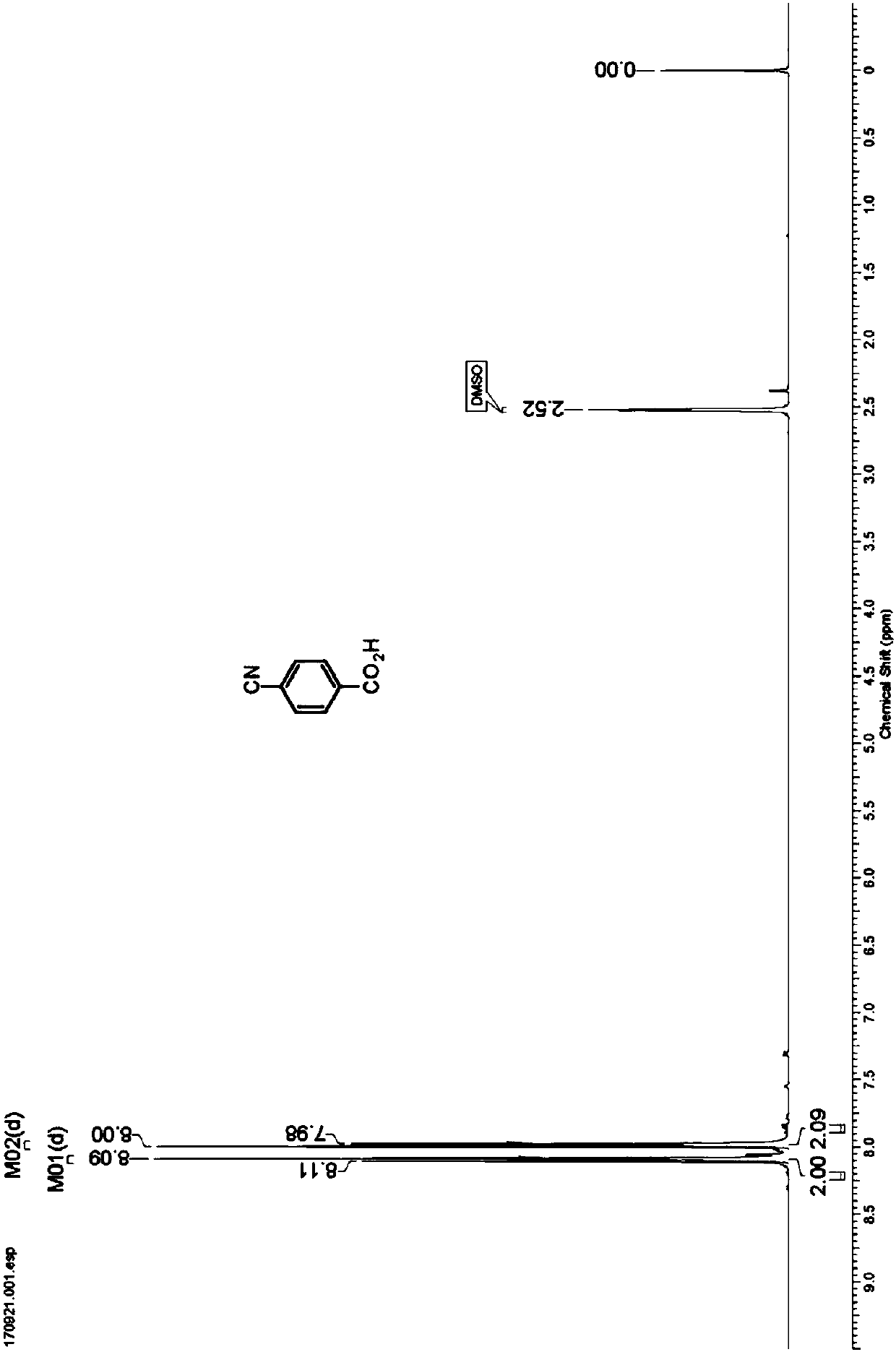
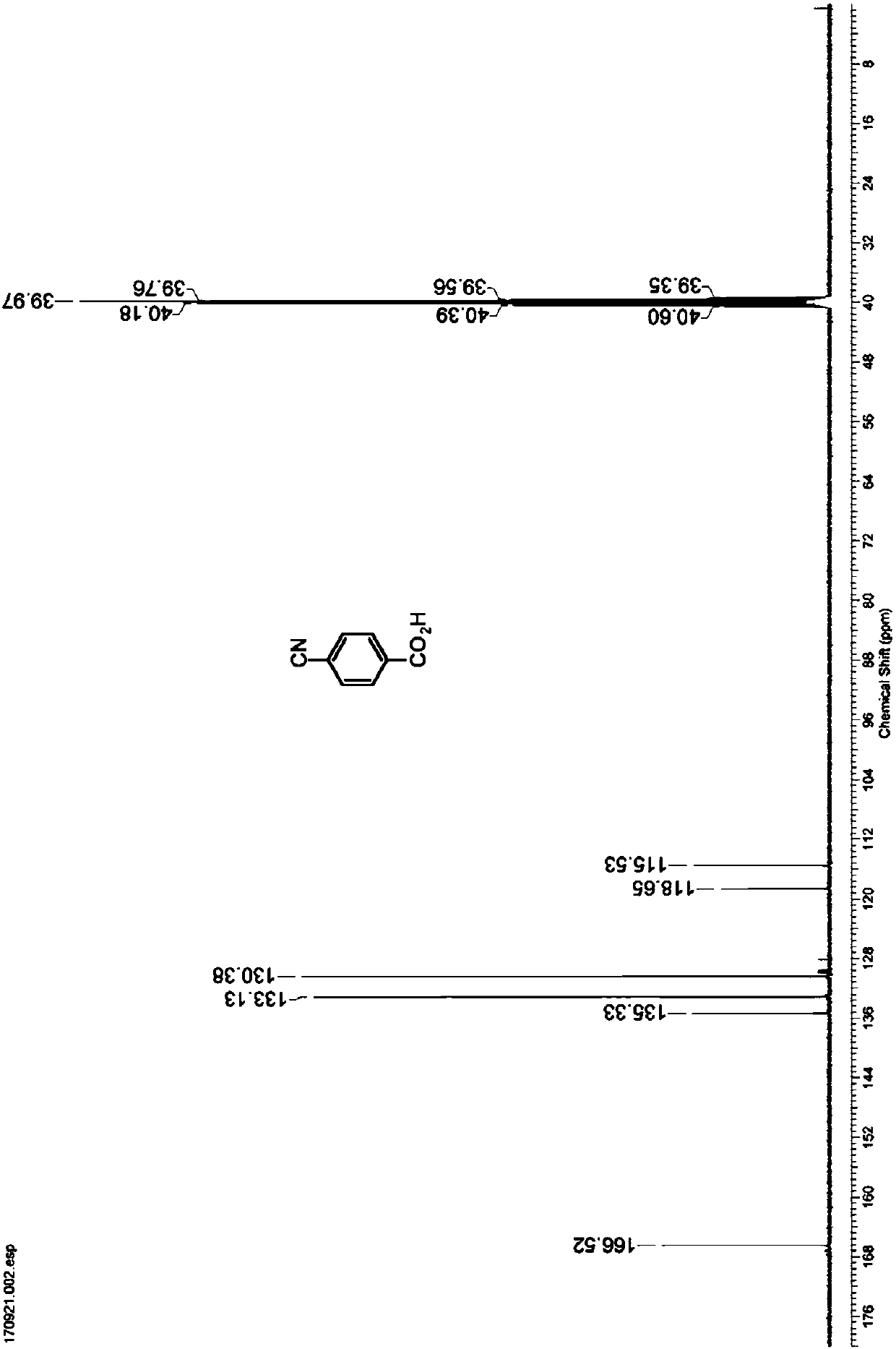
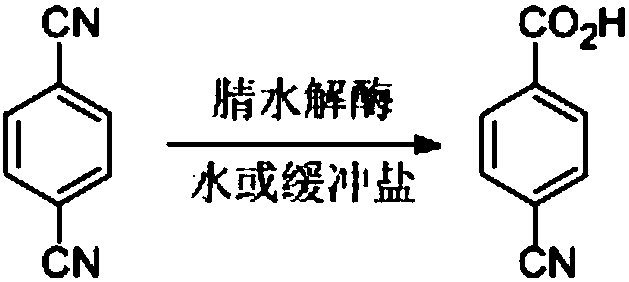
Nitrilase capable of preparing paracyanobenzoic acid by hydrolyzing p-benzenedicarbonitrile
ActiveCN107641622AMild reaction conditionsQuick responseHydrolasesFermentationArabidopsis thalianaPollution
The invention discloses a nitrilase N1 derived from pantoea sp.AS-PWVM4 and a gene thereof, a nitrilase N2 derived from arabidopsis thaliana and a gene thereof, a nitrilase N3 derived from acidovoraxfacilis 72W and a gene thereof, a nitrilase N4 derived from leptolyngbya sp. and a gene thereof, a nitrilase N5 derived from brassica oleracea var.oleracea and a gene thereof and a nitrilase N6 derived from camelina sativa and a gene thereof, and a method for preparing paracyanobenzoic acid as p-aminomethylbenzoic acid intermediate by using the nitrilase as a biological catalyst; resting cells ofthe corresponding nitrilases can be used for catalyzing 100g / L of substrate; the conversion rate is greater than 99%; the method has the obvious characteristics of mild reaction conditions, no pollution and simple process route, and has broad industrial application prospects.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
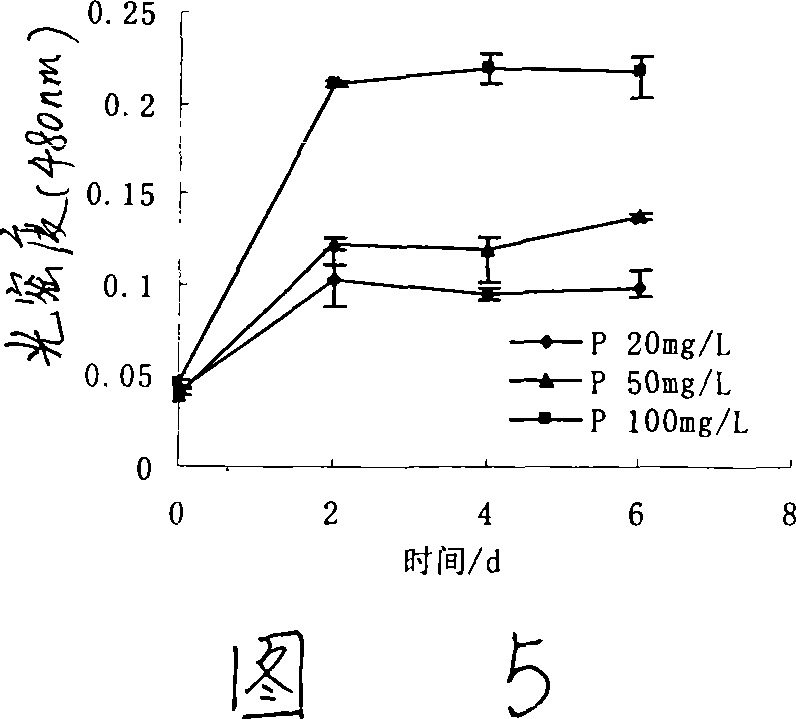
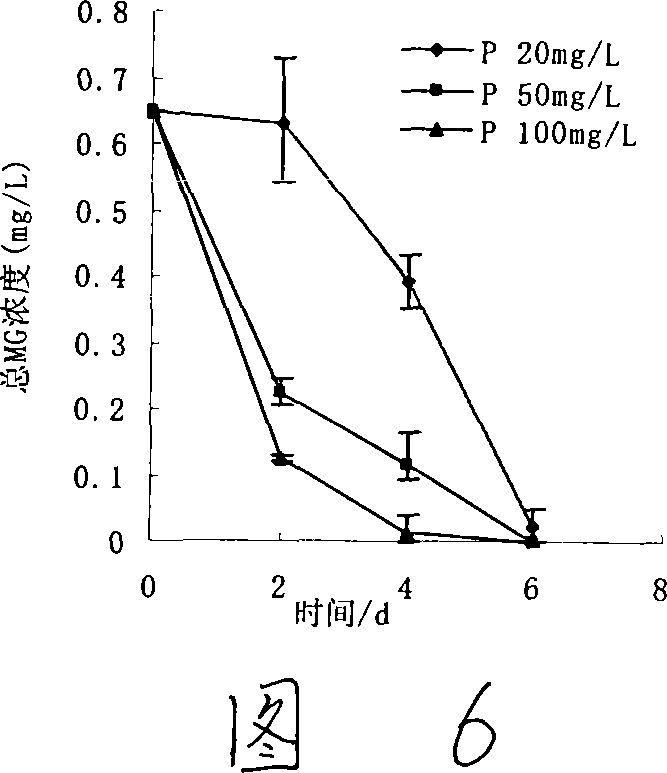
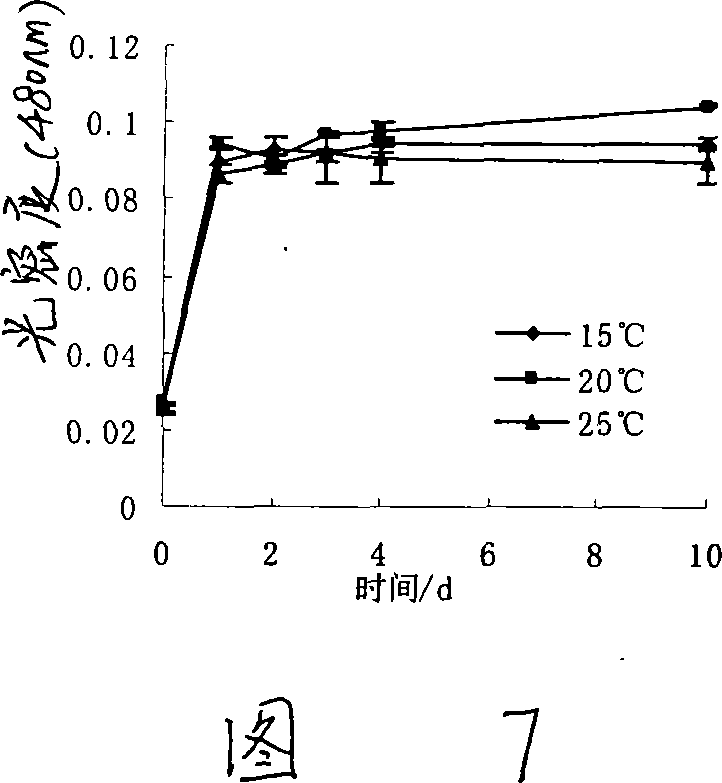
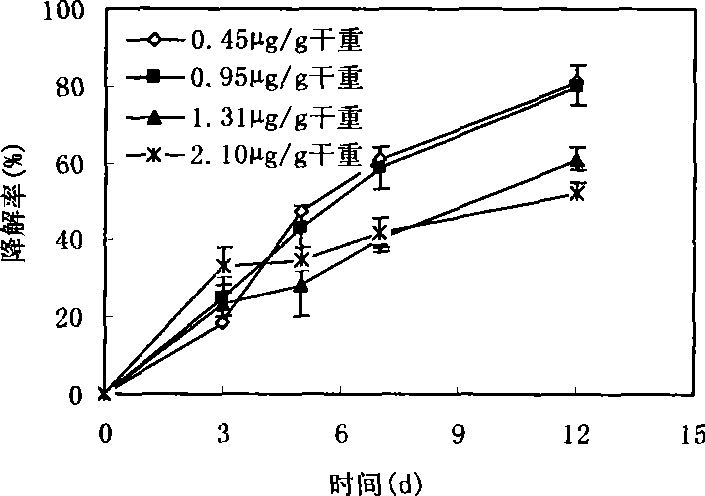
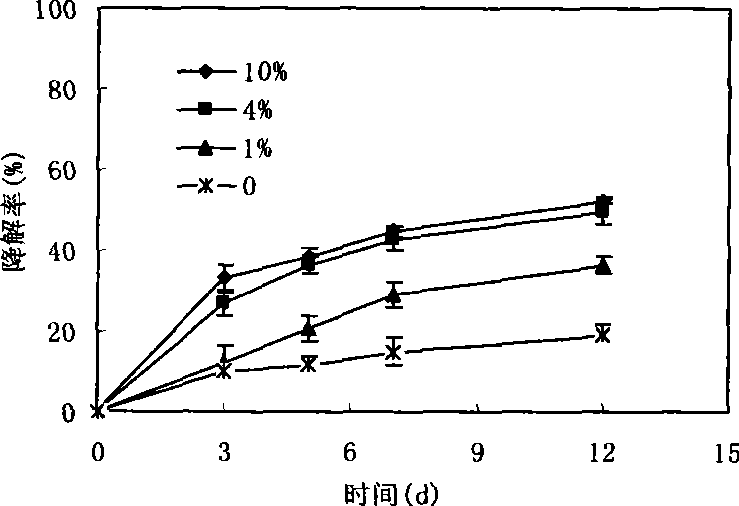
Pantoea sp, M3, and method for degrading malachite green
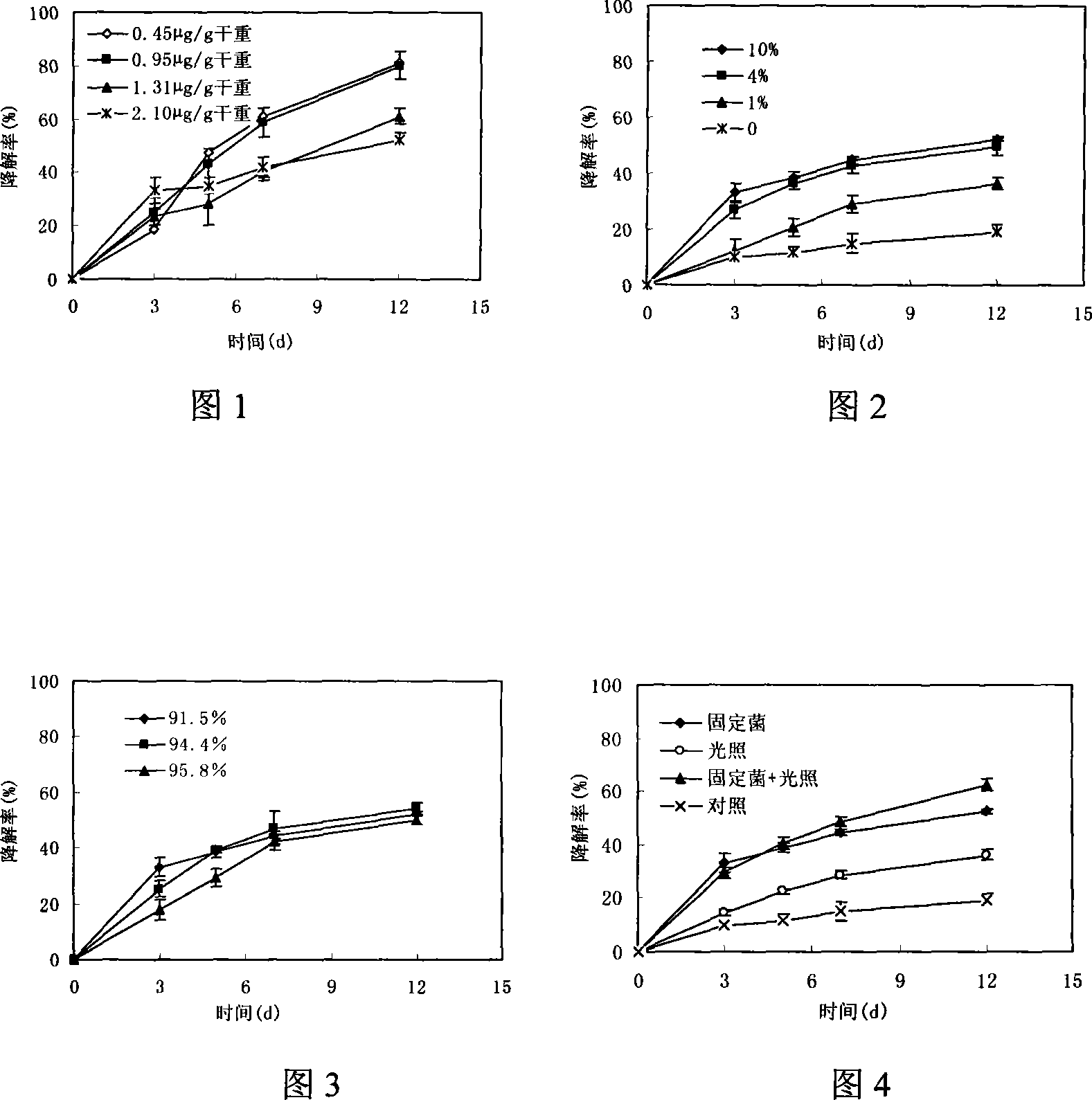
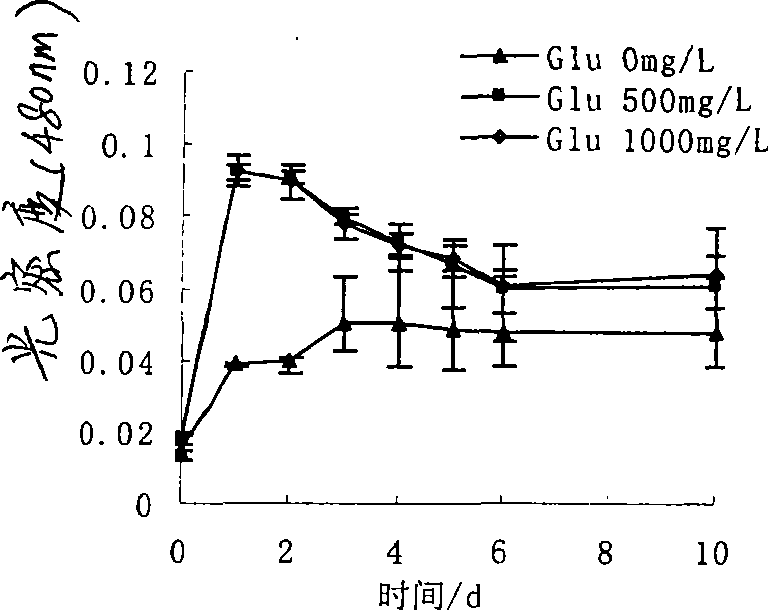
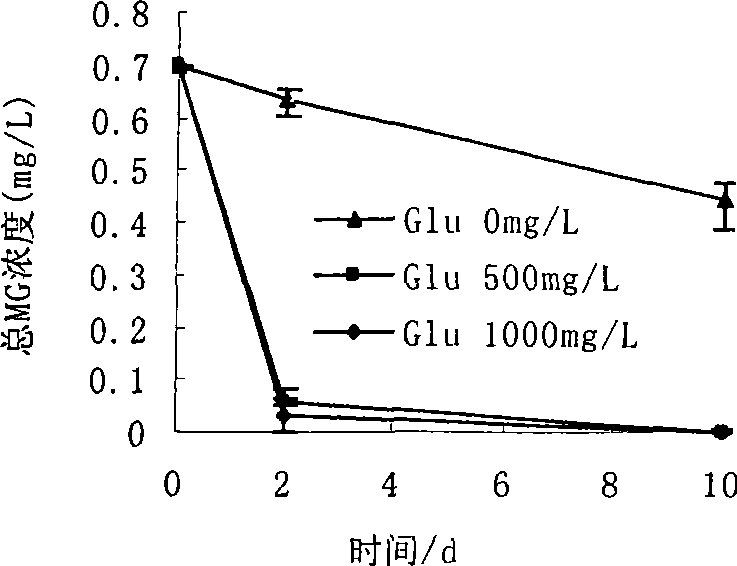
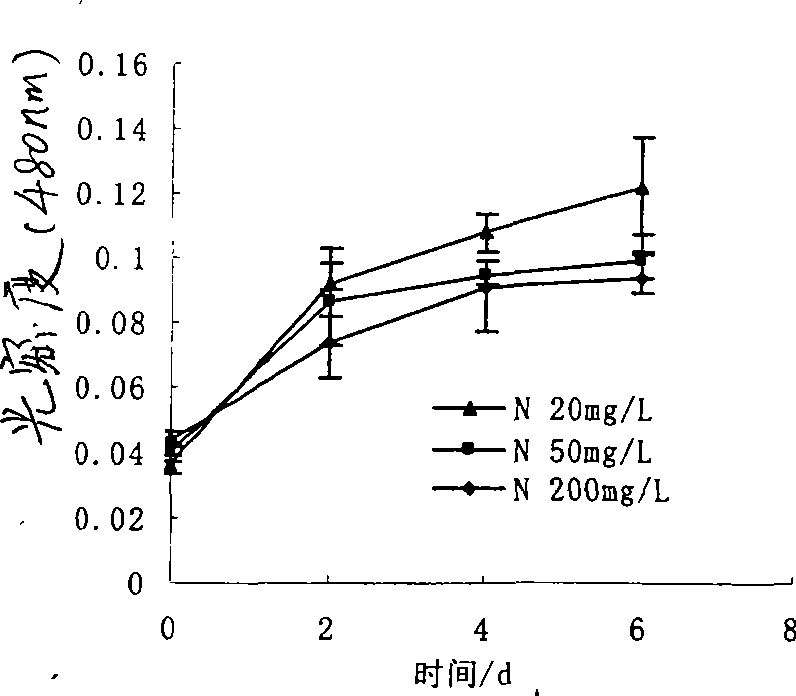
This invention discloses Pantoea sp. M3 (CCTCC No.M207022) with the ability to degrade malachite green. Logarithmic phase Pantoea sp. M3 2-4 wt. % is added into sterile degradation medium containing 0.5-5 mg / L malachite green, and cultured at 20-30 deg.C for 5-10 days to degrade malachite green. The degradation medium with a pH value of 6.0-8.0 comprises: glucose 0.5-1 g / L, NaCl 0.01-0.1 g / L, MgSO4 0.01-0.1 g / L, NH4NO3 0.02-0.1 g / L, K2HPO4 0.01-0.1 g / L, KH2PO4 0.01-0.1 g / L, and yeast extractum 0.06-0.3 g / L. Pantoea sp. M3 can effectively remove residual malachite green and leucomalachite green in water body for fishery. The degradation rate of Pantoea sp. M3 for 0.5-2 mg / L malachite green is higher than 90%.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Immobilized biological agent and method for degrading bice green contamination of cultivation aquifer
InactiveCN101134954APromote degradationEfficient removalBacteriaOn/in organic carrierCross-linkMalachite green
The present invention is one kind of immobilized microbial preparation and the method of degrading malachite green pollutant in aquiculture water therewith. The immobilized microbial preparation is prepared with Pantoea sp. M3 strain as effective component and through the following steps: 1. inoculating M3 seed to enrichment culture medium, culturing at 30-37 deg.c and 150 rpm for 18-30 hr, centrifuging, and washing with phosphate buffer to obtain concentrated bacterial suspension; 2. dissolving sodium alginate in water through heating, cooling to room temperature, mixing with the concentrated bacterial suspension; 3. dropping the mixture into 5 % concentration CaCl2 solution to form calcium alginate pellets and cross-linking to fix at 4-8 deg.c; and 4. washing the calcium alginate pellets with phosphate buffer. The present invention has high malachite green pollutant eliminating rate.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES INSITUTE OF JIANGSUPROVINCE
Rice endophyte (Pantoea sp. Sd-1) for efficiently degrading lignin
InactiveCN102978142AEfficient degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicrobiology
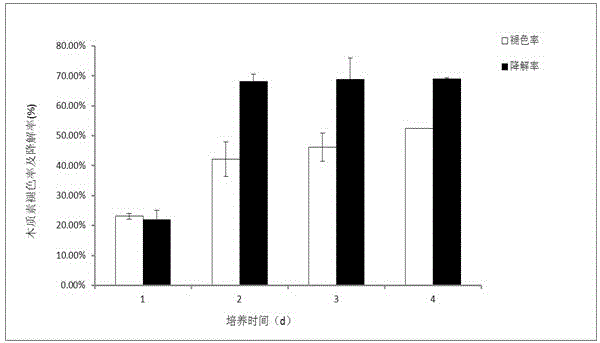
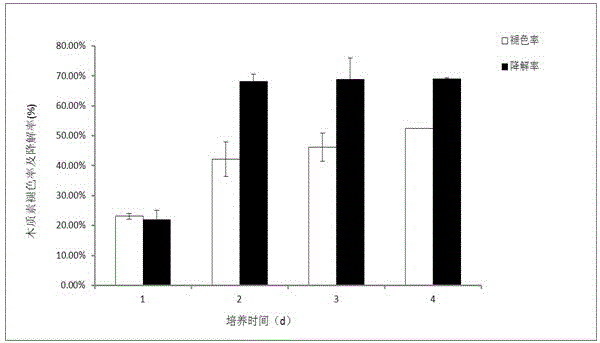
The invention discloses a rice endophyte (Pantoea sp. Sd-1) for efficiently degrading lignin and the preservation number of the Pantoea sp. Sd-1 is CGMCC No. 6698. The Pantoea sp. Sd-1 is a bacterial strain which can grow on a culture medium with alkali lignin as a unique carbon source. After the Pantoea sp. Sd-1 is cultured for four days in a liquid culture medium containing 3g / L alkali lignin and supplemented with 1% of glucose and 0.5% of peptone, the fading rate and the degradation of lignin respectively reach 52.38% and 69.06%. And in a liquid culture medium containing 10g / L rice straws and supplemented with 1% of glucose and 0.5% of peptone, the degradation of straws can reach 54.51 at most.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
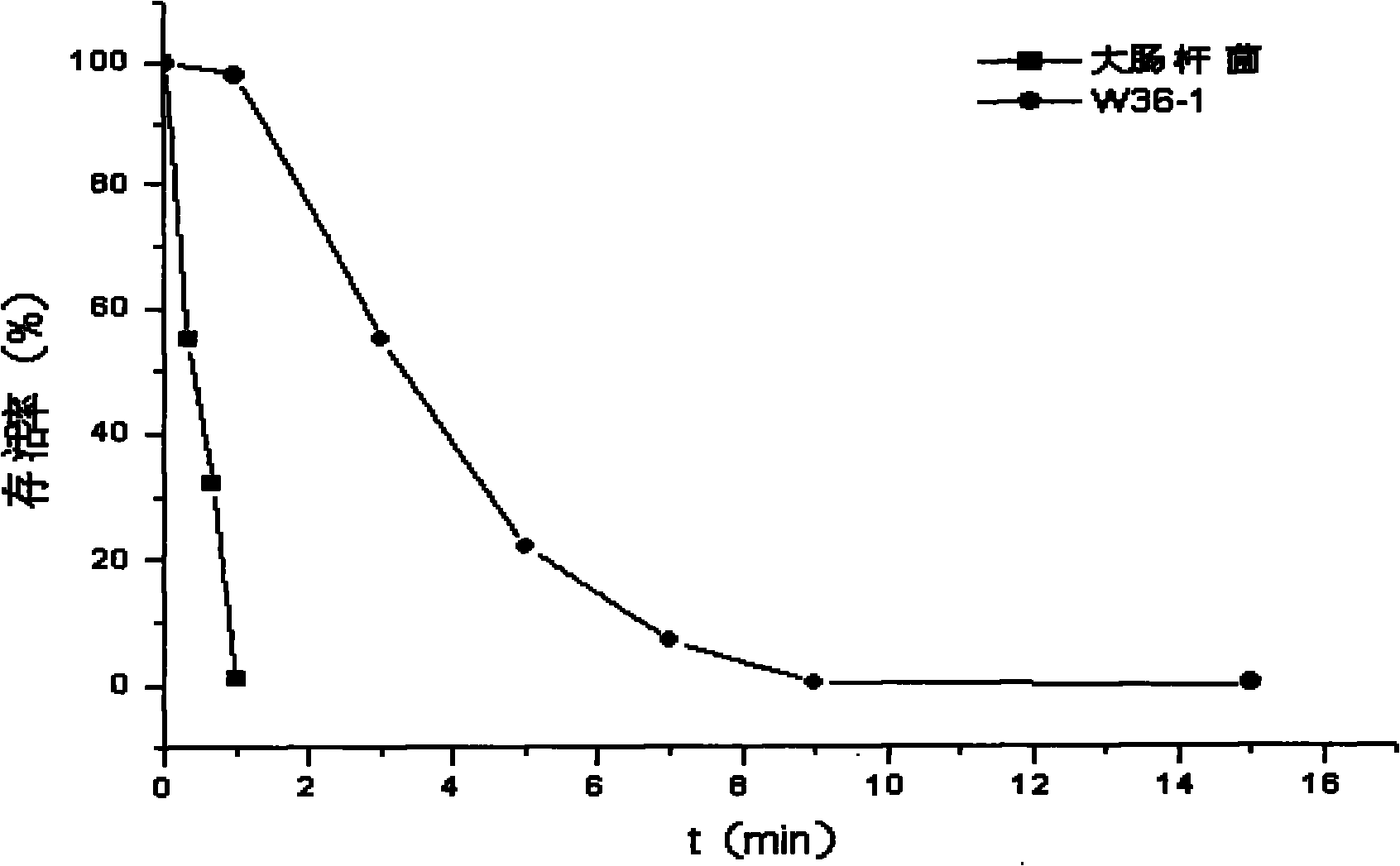
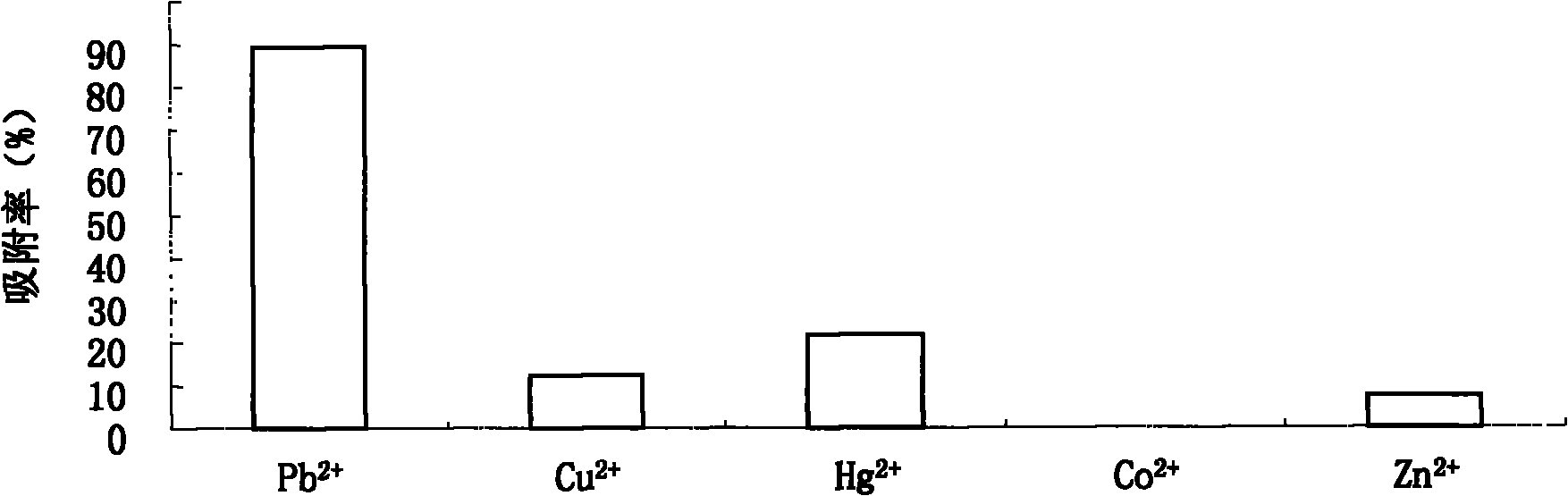
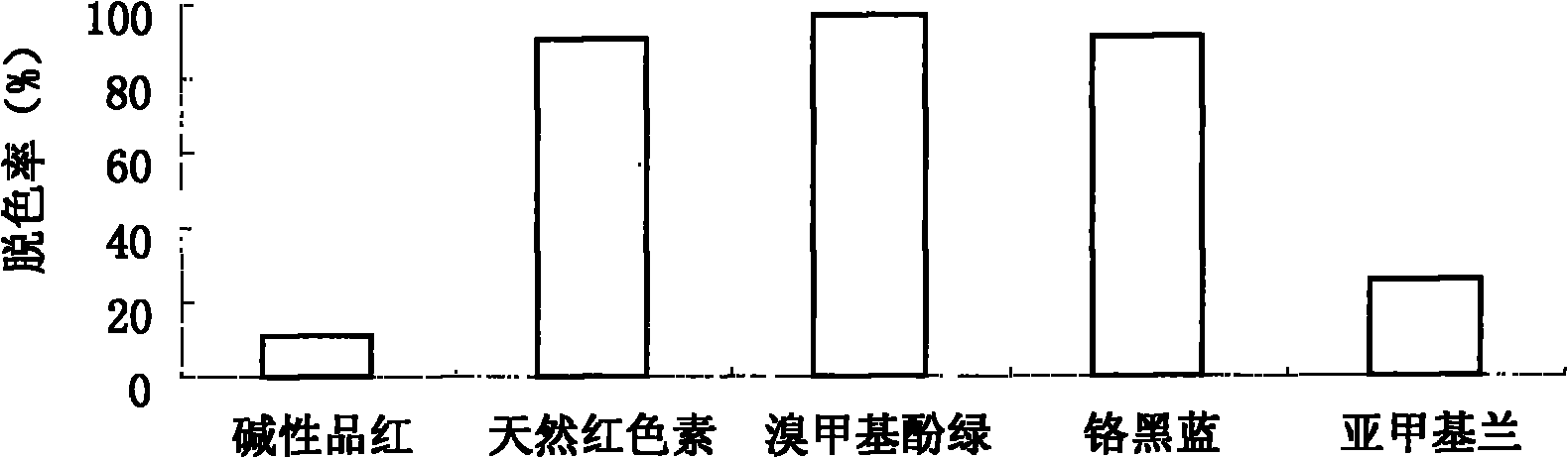
Radiation resistant pantoea sp. W36-1 and application thereof in environmental engineering
InactiveCN101864379AHigh flocculation activityHigh decolorization rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesRadiation resistantWastewater
The invention discloses pantoea sp. W36-1, of which the preservation number is CGMCC No. is 3701, a flocculant prepared by the pantoea sp. W36-1 and application of the flocculant in removal of suspensions, dyeing agents and heavy metal in waste water. Extracellular products of the bacteria have an obvious absorption peak at 200 to 250nm, and polysaccharide solution can remove 54.89 percent of free groups in the bacteria. The method for preparing the pantoea sp. W36-1 comprises the following steps of: performing fermentation culture of the bacteria strain for 48 hours, centrifuging 100ml of fermentation solution at a rotation speed of 6,000r / min for 10 minutes, adding absolute ethanol, of which the volume is 1.5 times that of supernatant, into the supernatant, uniformly mixing the absolute ethanol and the supernatant standing the mixed solution at the temperature of 4 DEG C overnight, centrifuging the precipitate, washing the precipitate by 70-percent ethanol for 2 to 3 times, and then drying the precipitate to obtain the finished product. The flocculent activity of the fermentation culture product of the pantoea sp. W36-1 is 81.7 to 83.15 percent, the yield of the pantoea sp. W36-1 is 6g / L and can be widely used for removing suspensions, dyeing agents, heavy metal and the like in waste water.
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for Producing an L-Amino Acid Using a Bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae Family
The present invention provides a method for producing L-amino acid using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, particularly a bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia or Pantoea, which has been modified to enhance the expression of the bssR gene, which encodes a regulator of biofilm through signal secretion.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Pantoea strain and application thereof
ActiveCN107058149AIncrease nitrogen, phosphorusIncrease PotassiumPlant growth regulatorsBiocidePhosphatePotassium
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Dye molecule detection method
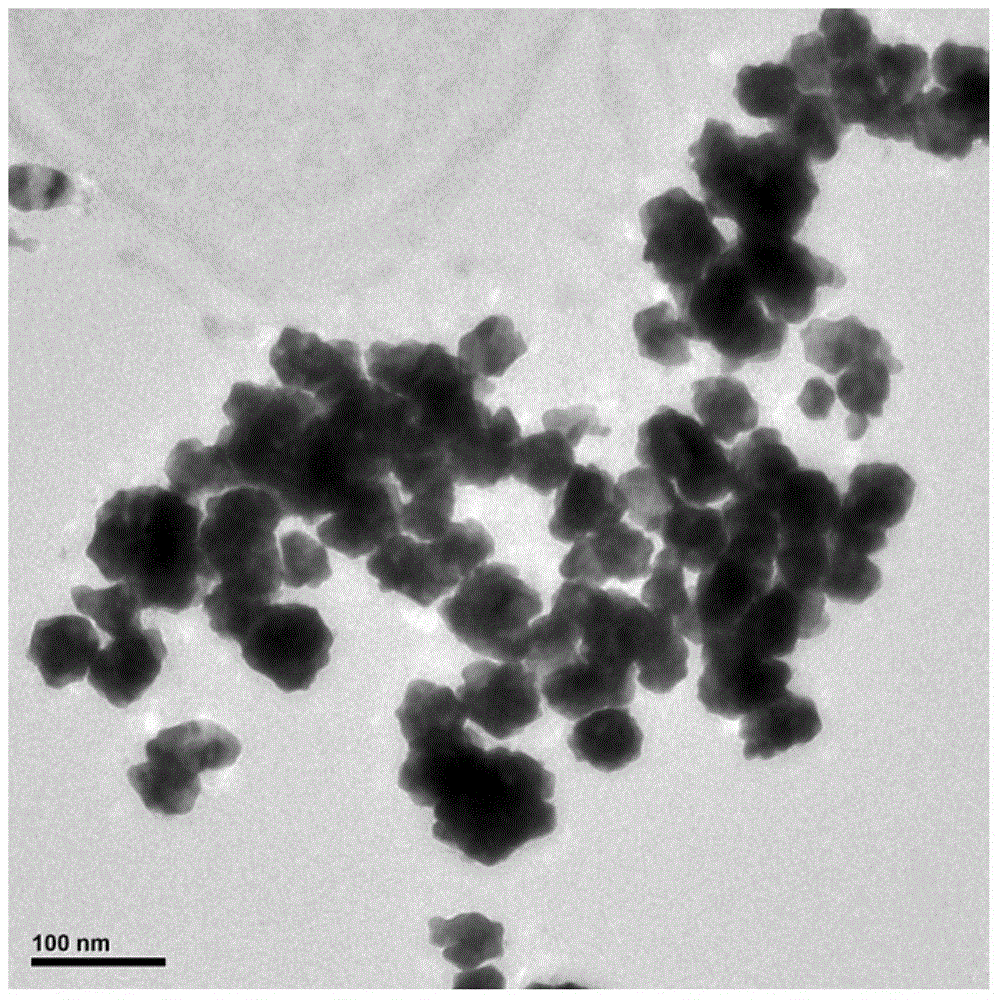
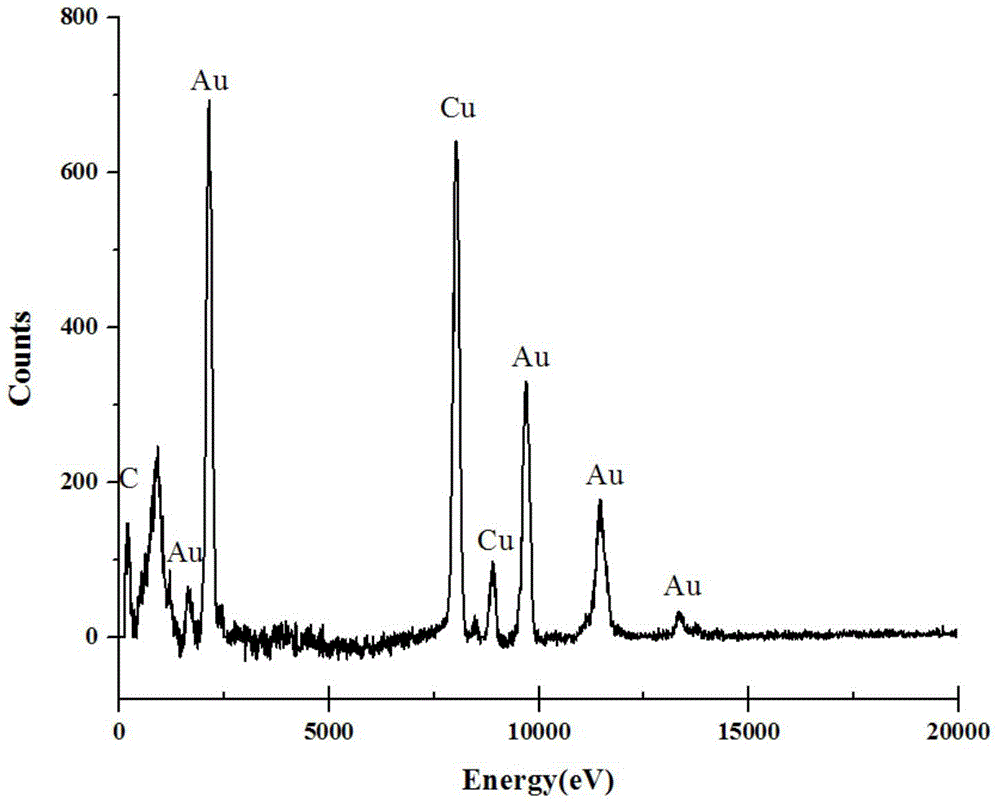
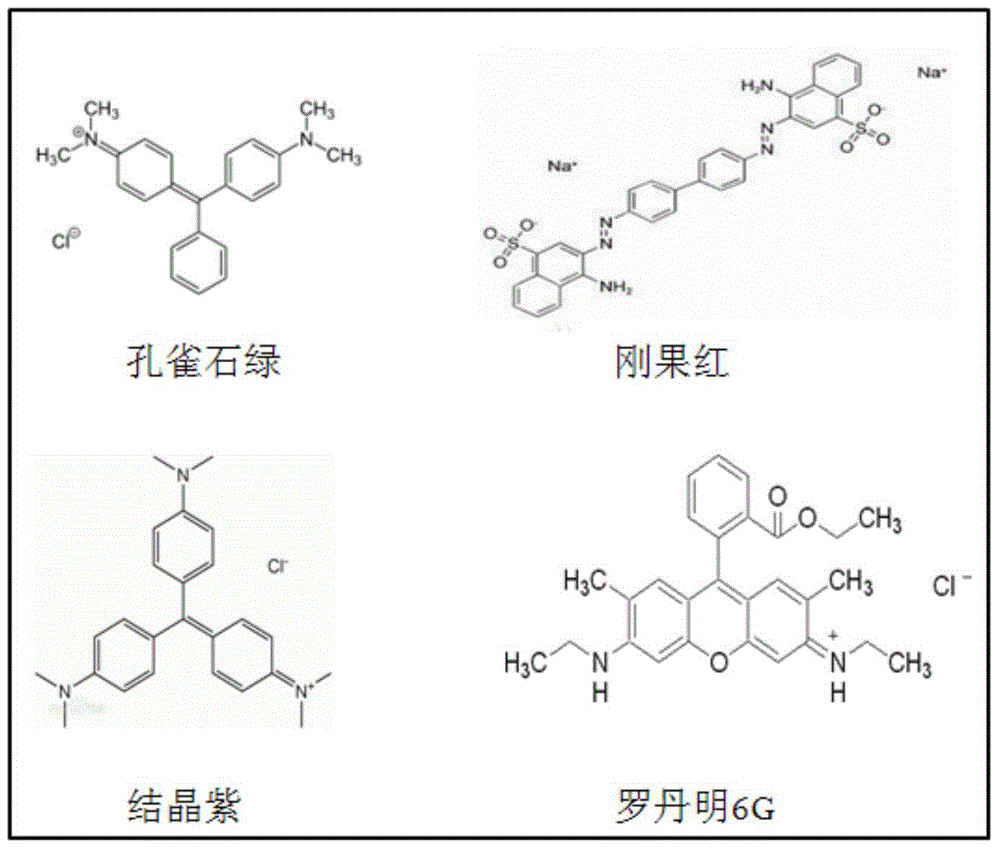
A dye molecule detection method includes the steps of (1) synthesizing gold nano particles through a method of in-situ reduction of chloroauric acid with a bacteria strain Pantoea sp.IMH; (2) with the gold nano particles as a surface enhanced Raman substrate, mixing the gold nano particles with dye molecules; and (3) detecting a Raman characteristic peak of the dye molecules through a portable Raman spectrometer, thereby achieving the detection of four kinds of dye molecules.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cellulose degradation composite flora and application thereof in decomposing phellinusribis bran
PendingCN111471617AStable structurePromote degradationFungiBio-organic fraction processingBiotechnologyCellulose
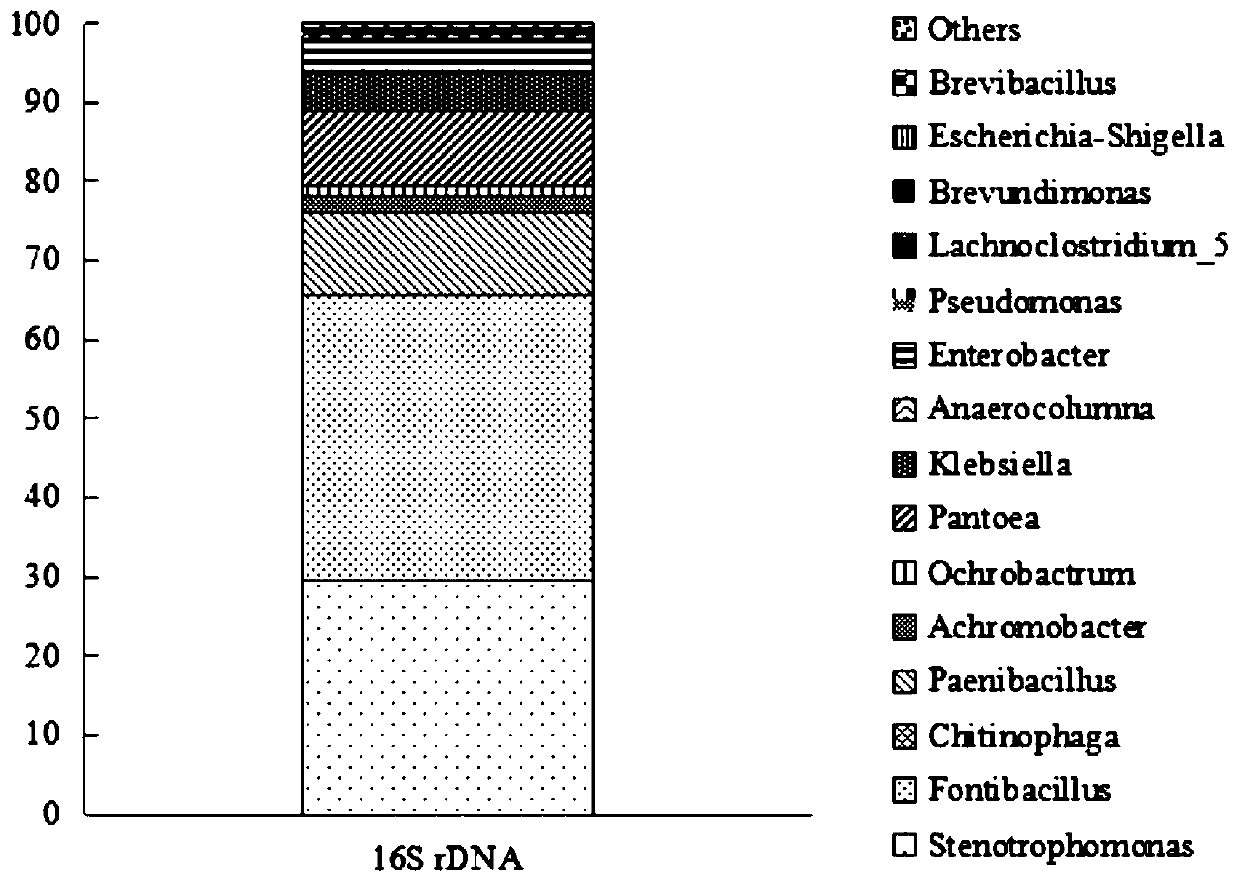
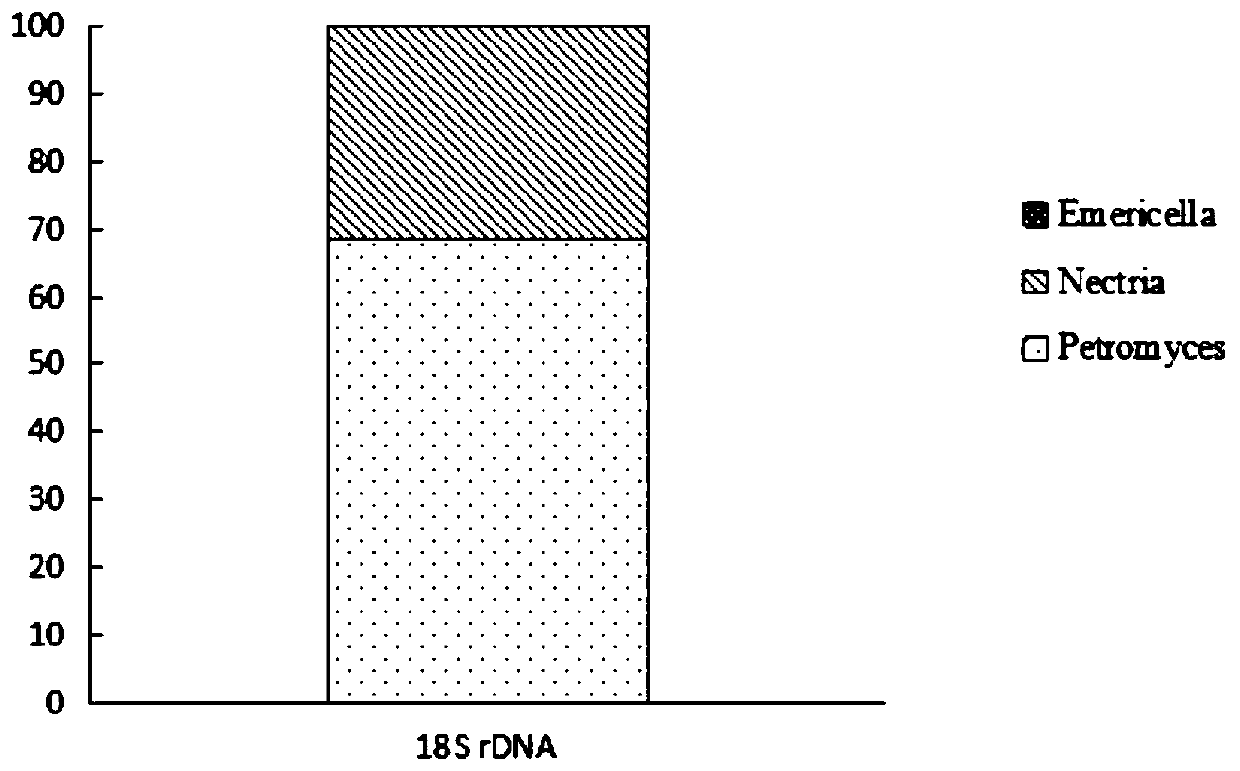
The invention relates to a cellulose degradation composite flora which is composed of bacterial species and fungal species. The composite flora horizontal bacterial community is mainly composed of fontibacillus, stenotrophomonas, paenibacillus and pantoea; and the fungal community is mainly composed of petromyces and nectria. The composite flora is obtained by adopting a subculture continuous culture method; wheat straw is added into a Mandels culture medium to serve as a unique carbon source and is obtained by screening litters under a perennial pinus sylvestris forest in a Maowusu sandy land; and the composite flora can be used for innocent treatment and resource utilization of agricultural wastes such as phellinusribis bran. The method overcomes the defects of low efficiency, poor constant value, weak competitive capacity with indigenous microorganisms, non-ideal practical application effect and the like of cellulose degrading bacteria in practical application in the prior art, is suitable for decomposing and composting phellinusribis bran which is difficult to degrade, and can quickly and efficiently realize harmless treatment and resource utilization of the agricultural wastesdifficult to decompose.
Owner:MICROBIOLOGY INST OF SHAANXI
Microorganism aerobiotically reducing arsenic high-effectively
InactiveCN104974948AIncrease awarenessDeepen understandingBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnterobacter agglomeransMicroorganism
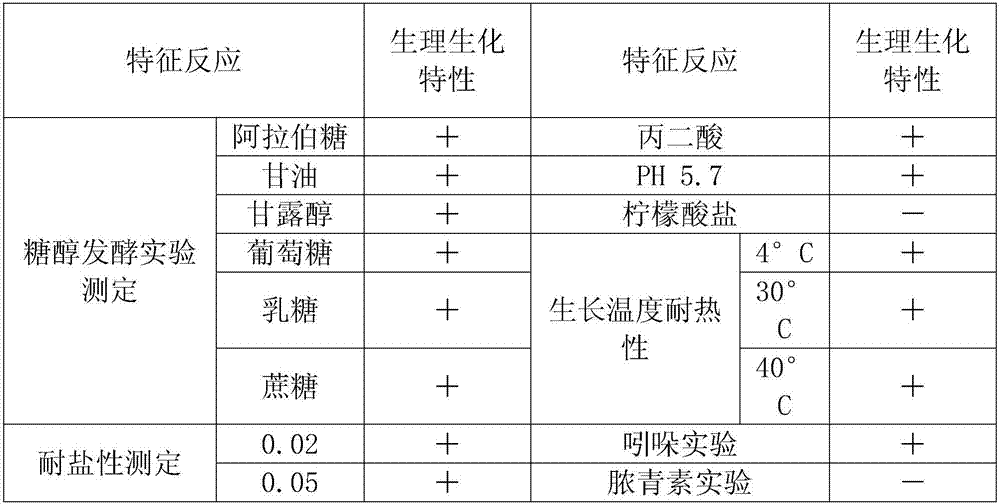
The invention relates to a microorganism aerobiotically reducing arsenic high-effectively, which is separated from a high-arsenic pollution region in Inner Mongolia, China. 16S rDNA identification proves that the microorganism belongs to pantoea agglomerans and is named Pantoea sp.IMH. A bacterial strain of the microorganism is assigned the accession number CGMCC No.8825. The microorganism is wide in pH and temperature ranges of growth, is very high in tolerance on trivalent arsenic and pentavalent arsenic, and can reduce more than 90% of the pentavalent arsenic in 36 h under an aerobiotical culture condition.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Organic solid waste high-temperature aerobic composting strain and application thereof
ActiveCN112760274AFast filtrationHigh temperature resistanceBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaMicroorganismFeces
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental microorganisms, and particularly relates to an organic solid waste aerobic composting strain. The organic solid waste aerobic composting strain is identified as Pantoea sp., and has the preservation number of CCTCC NO: M 2020973. The pantoea Pantoeasp.BK-PP311 is resistant to high temperature, has the capacity of efficiently degrading organic matters and quickly decomposing, and can be applied to the high-temperature aerobic composting treatment process of organic solid wastes such as food wastes, kitchen wastes, fruit and vegetable wastes, livestock and poultry breeding feces, municipal sludge and the like, so that quick composting and resource utilization of the organic solid wastes are realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
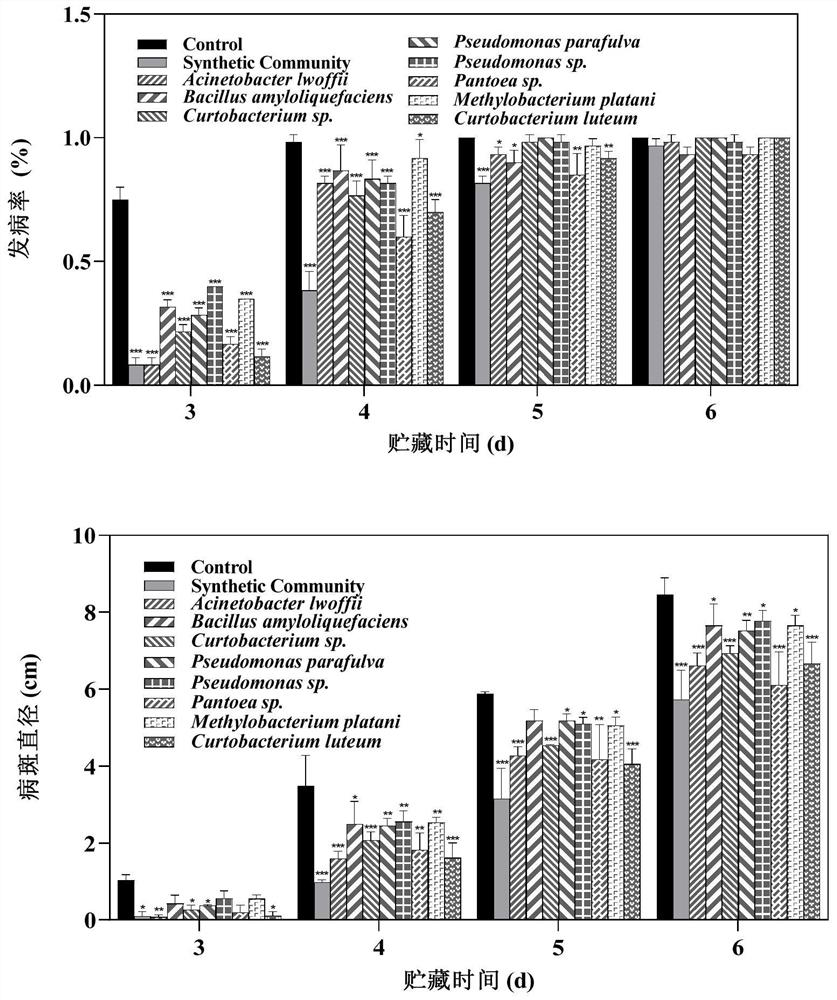
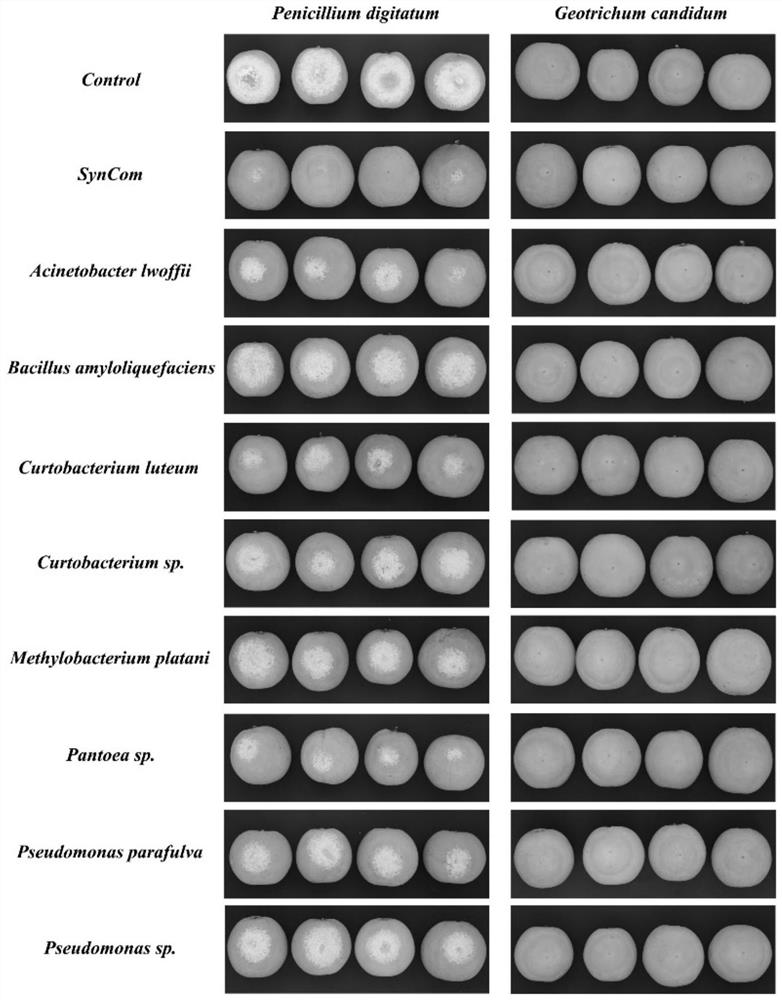
Bacterial synthetic community and application thereof in preparation of biological control agent for controlling postharvest diseases of citrus fruits
PendingCN112695002AThe effect of early onset is obviousThe effect of disease control is weakenedFruit and vegetables preservationBacteriaBiotechnologyCitrus volkameriana
The invention discloses a bacterial synthetic community, which is composed of eight bacteria, namely Acinetobacter lwoffii, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, Curptobacterium luteum, Curptobacterium sp., Methylobacterium platani, Pantoea sp., Pseudomonas parasulva and Pseudomonas sp., compared with a single bacterial strain, the bacterial synthetic community can better control the occurrence and progress of citrus green mold and sour rot, can more enduringly control diseases, can be used for preparing a biological control agent for controlling postharvest diseases of citrus fruits, has good application potential. A new thought and method are provided for controlling the postharvest diseases of the citrus fruits, and the application range of the bacterial synthetic community is widened.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Radiation resistant pantoea sp. W36-1 and application thereof in environmental engineering
InactiveCN101864379BHigh flocculation activityHigh decolorization rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesRadiation resistantPolysaccharide
The invention discloses pantoea sp. W36-1, of which the preservation number is CGMCC No. is 3701, a flocculant prepared by the pantoea sp. W36-1 and application of the flocculant in removal of suspensions, dyeing agents and heavy metal in waste water. Extracellular products of the bacteria have an obvious absorption peak at 200 to 250nm, and polysaccharide solution can remove 54.89 percent of free groups in the bacteria. The method for preparing the pantoea sp. W36-1 comprises the following steps of: performing fermentation culture of the bacteria strain for 48 hours, centrifuging 100ml of fermentation solution at a rotation speed of 6,000r / min for 10 minutes, adding absolute ethanol, of which the volume is 1.5 times that of supernatant, into the supernatant, uniformly mixing the absoluteethanol and the supernatant standing the mixed solution at the temperature of 4 DEG C overnight, centrifuging the precipitate, washing the precipitate by 70-percent ethanol for 2 to 3 times, and thendrying the precipitate to obtain the finished product. The flocculent activity of the fermentation culture product of the pantoea sp. W36-1 is 81.7 to 83.15 percent, the yield of the pantoea sp. W36-1 is 6g / L and can be widely used for removing suspensions, dyeing agents, heavy metal and the like in waste water.
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
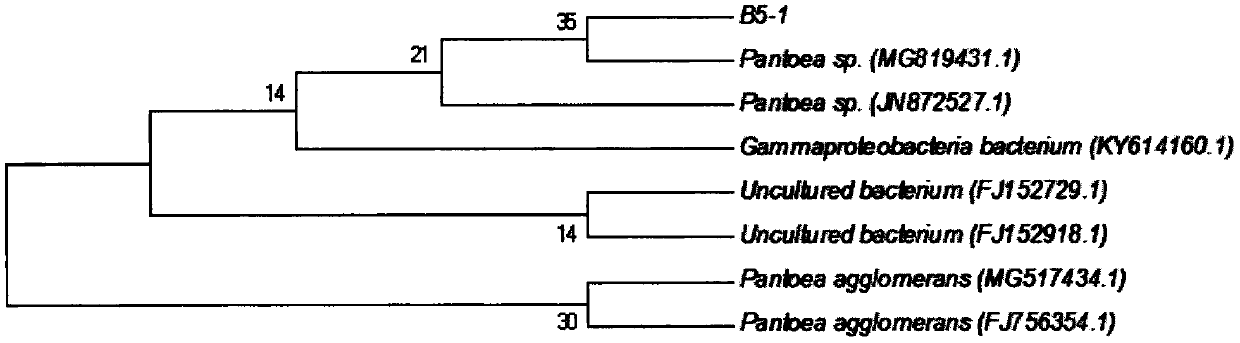
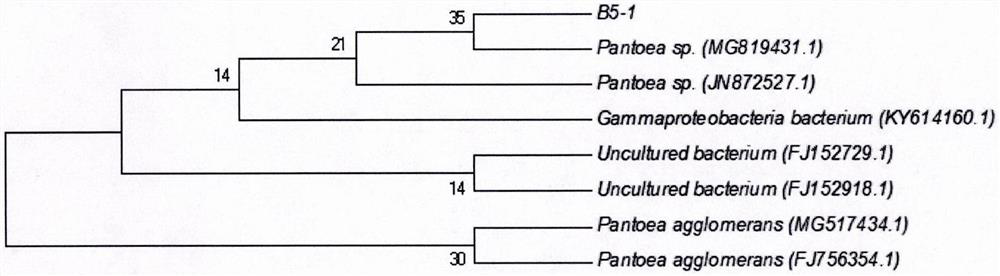
Pantoea with good degradation effect on cellulose
The invention discloses pantoea with a good degradation effect on cellulose, and belongs to the technical field of microbiology. The pantoea is characterized in that a strain B5-1 is isolated from frozen soil collected from the Mohe county of the Daxinganling region of the Heilongjiang province by using an enrichment culture method, and the strain B5-1 can fully degrade straw with thickness of 10cm within 72 days; the strain B5-1 is directly isolated by a sodium carboxymethylcellulose slab, through physiological, biochemical and 16S rDNA identification, the strain B5-1 is identified as the Pantoea, and the preservation date of the strain is November 30, 2018; the preservation number is CGMCC No.16848; and degradation experiments show that the strain B5-1 has a good degradation effect on the cellulose.
Owner:HARBIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Cymbopogon citratus fragrance-producing endophytic bacterium
The invention discloses an endophytic bacterium pantoea sp. CcSh-1 generating volatile fragrant substance, and the preservation number is CGMCCNo.8715. The bacterium strain comes from the sheath part of matured cymbopogon citratus, is easy to culture, and is capable of generating refreshing and pleasing fragrance after being grown on a solid medium for 2-3 days, and the fragrant substance is identified to contain a citral composition. The bacterium provides a new microbe source for replacing plant raw materials producing perfumes.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Pantoea for conversion of resveratrol to ε-glutin and uses thereof
ActiveCN108865916BHigh yieldNo pollution in the processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyVitis vinifera
Owner:天津市尖峰天然产物研究开发有限公司
A nitrilase that can hydrolyze terephthalonitrile to p-cyanobenzoic acid
The invention discloses nitrilase N1 and its gene derived from Pantoea sp. ) nitrilase N3 and its gene, Leptolyngbya sp. nitrilase N4 and its gene, Brassica oleracea var. oleracea nitrilase N5 and its gene and Camelina sativa nitrilase N6 and its gene, and using the nitrilase as a biocatalyst to prepare p-aminomethylbenzoic acid intermediate p-cyanobenzoic acid. The resting cells of the corresponding nitrilase can catalyze 100g / L of the substrate, and the conversion rate is greater than 99%. The method has the remarkable characteristics of mild reaction conditions, no pollution, simple process route, etc., and has great industrial application prospects.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Immobilized biological agent and method for degrading bice green contamination of cultivation aquifer
InactiveCN101134954BPromote degradationEfficient removalBacteriaOn/in organic carrierCross-linkMalachite green
The present invention is one kind of immobilized microbial preparation and the method of degrading malachite green pollutant in aquiculture water therewith. The immobilized microbial preparation is prepared with Pantoea sp. M3 strain as effective component and through the following steps: 1. inoculating M3 seed to enrichment culture medium, culturing at 30-37 deg.c and 150 rpm for 18-30 hr, centrifuging, and washing with phosphate buffer to obtain concentrated bacterial suspension; 2. dissolving sodium alginate in water through heating, cooling to room temperature, mixing with the concentrated bacterial suspension; 3. dropping the mixture into 5 % concentration CaCl2 solution to form calcium alginate pellets and cross-linking to fix at 4-8 deg.c; and 4. washing the calcium alginate pellets with phosphate buffer. The present invention has high malachite green pollutant eliminating rate.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES INSITUTE OF JIANGSUPROVINCE
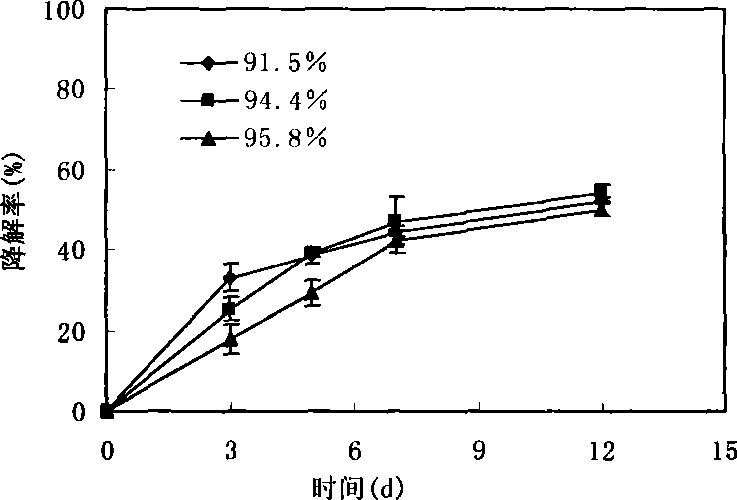
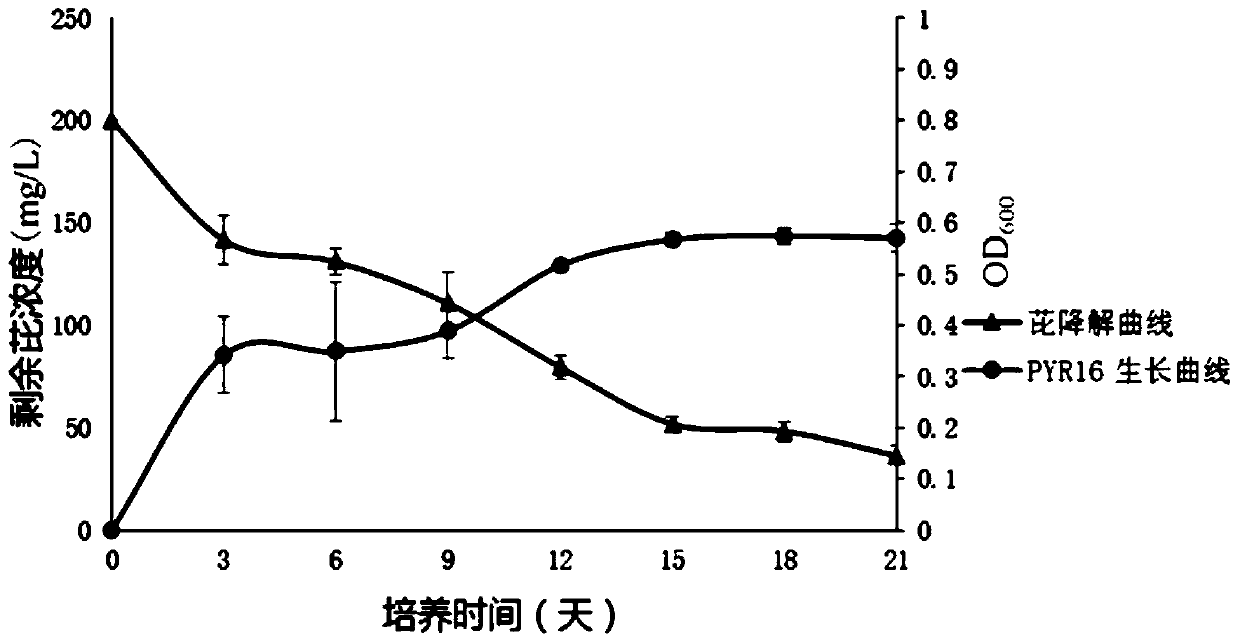
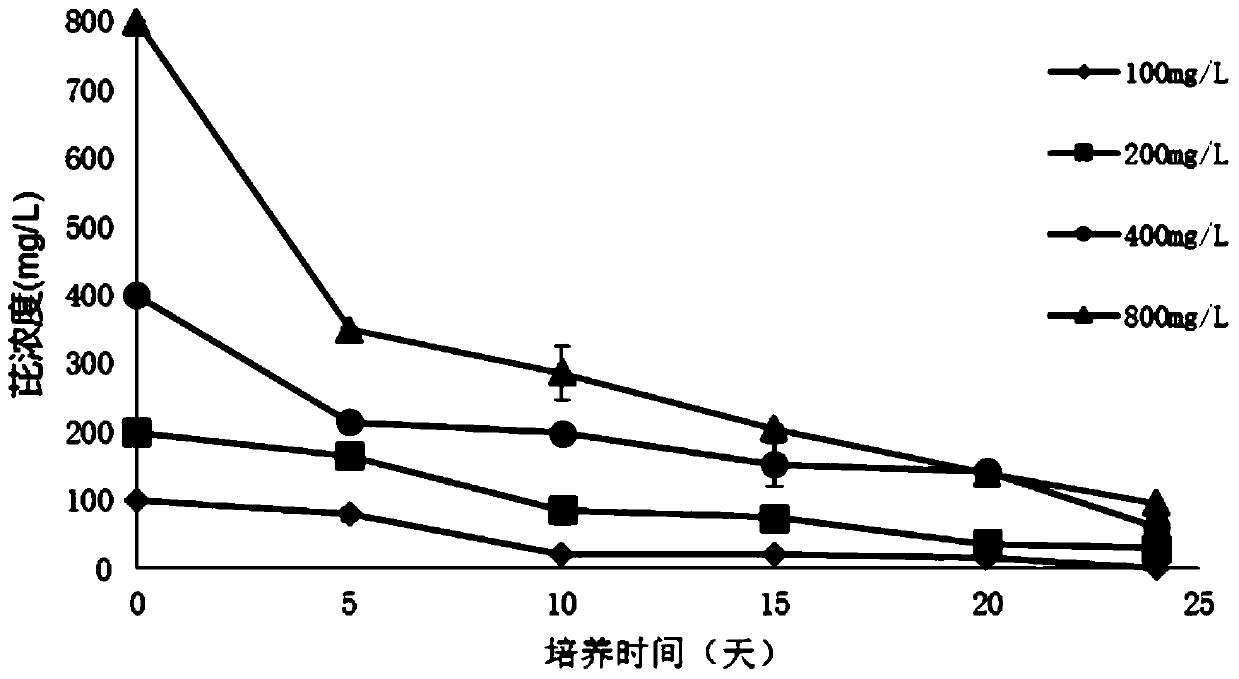
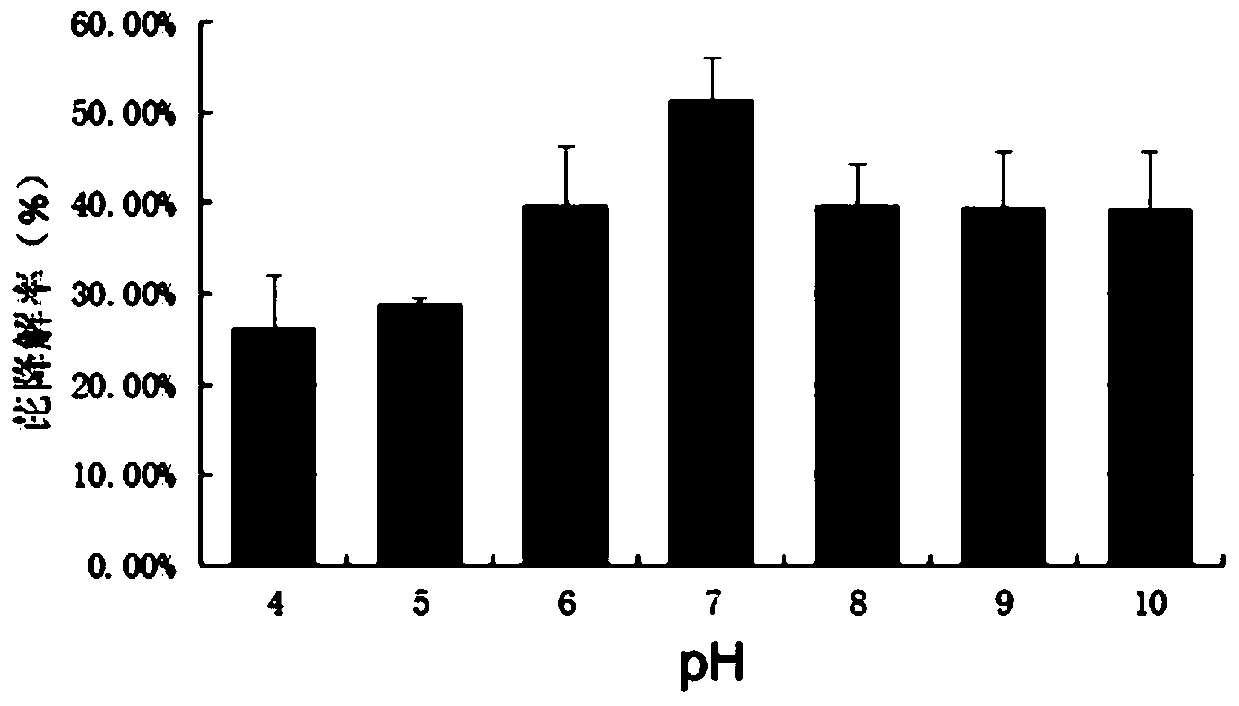
A strain of Pantoea degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons organic pollutants
ActiveCN105950501BWide temperature adaptabilitySuitable for clearingBacteriaWater contaminantsPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonMicroorganism
The invention discloses a strain of Pantoea sp. PYR16 that degrades organic pollutants of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, which belongs to the field of restoration and treatment of microorganisms and environmental organic pollutants. The strain is preserved in the China Typical Culture Collection Center, and the preservation number is : CCTCC NO: M2016227. The bacterial strain disclosed by the invention can efficiently degrade various polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, has extensive environmental adaptability and heavy metal resistance, and can be colonized in harsh environments to repair soil or water bodies compounded by heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Rice endophyte (Pantoea sp. Sd-1) for efficiently degrading lignin
InactiveCN102978142BEfficient degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicrobiology
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
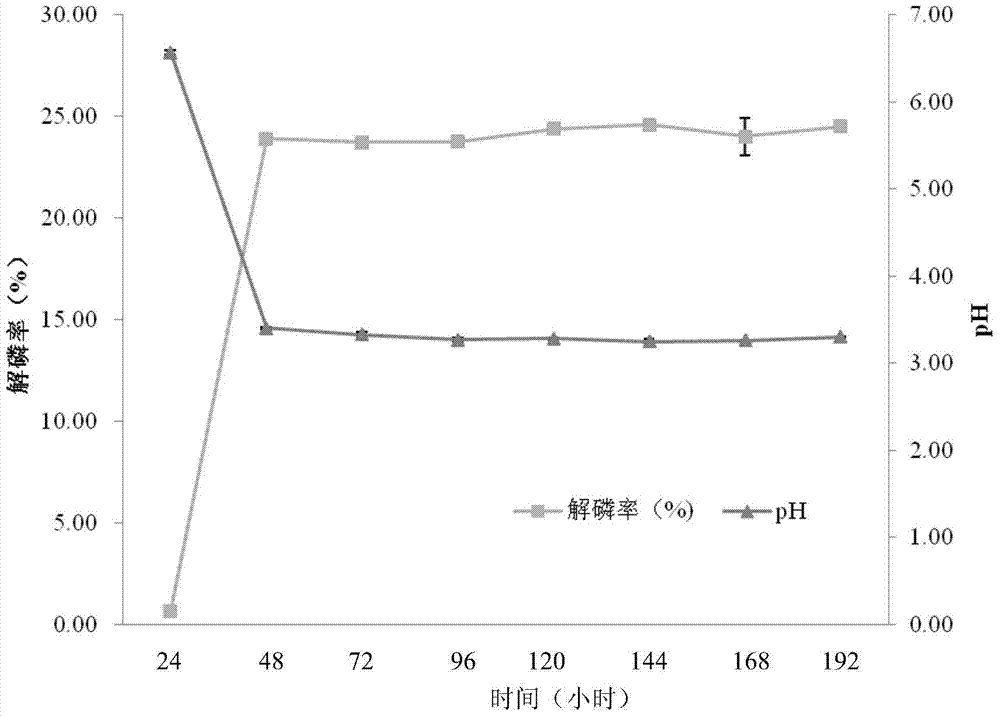
A kind of pantoea degrading organic phosphorus and inorganic phosphorus and its application
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Method for Producing L-Methionine Using a Bacterium of the Genus Pantoea
ActiveUS20210054425A1Production of L-methionine by fermentationIncrease productionFermentationGenus PantoeaMicrobiology
The present invention provides a method for producing L-methionine by fermentation using a bacterium belonging to the genus Pantoea which has been modified to overexpress the rarD gene or a mutant gene thereof.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Pantoea agglomerans with molluscicidal activity and application thereof
InactiveCN104531554AEfficient killingEasy to prepareBiocideBacteriaEnterobacter agglomeransOncomelania
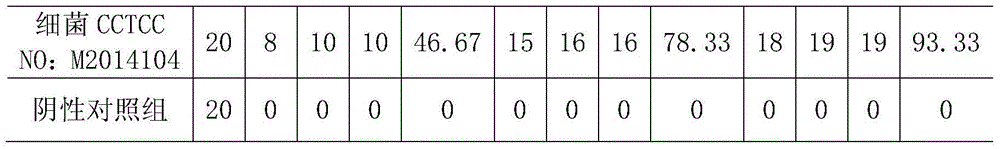
The invention discloses pantoea agglomerans (Pantoea agglomerans C4) with the molluscicidal activity and application thereof. The biological preservation number of the pantoea agglomerans is CCTCC NO: M2014104; bacteria with the preservation number of CCTCC NO:M2014104 are pantoea bacteria and are screened from tee leaves; and oncomelania can be rapidly and effectively killed. The pantoea agglomerans has the advantages that the new bacteria for killing the oncomelania is provided; the pantoea agglomerans can be used as a biological oncomelania killing agent directly; and compared with a traditional chemical oncomelania killing agent, the biological oncomelania killing agent prepared with the bacteria with the preservation number of CCTCC NO: M2014104 is simple in preparation method, low in cost and environment-friendly.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
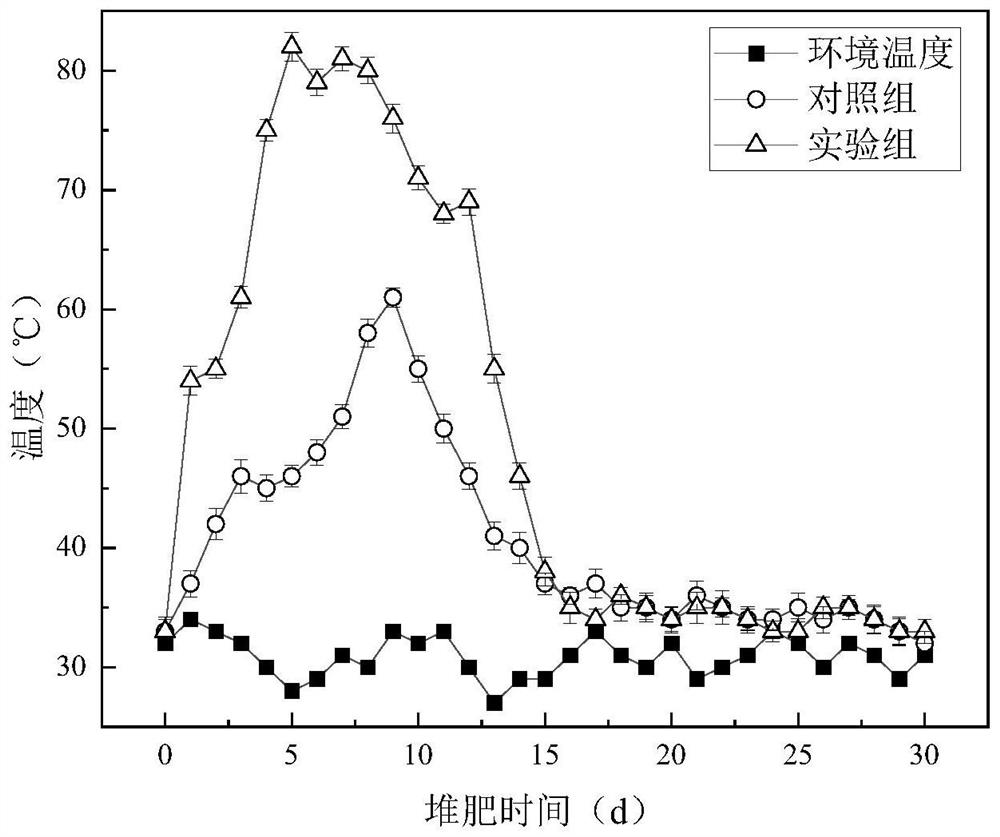
Composite microbial agent and application thereof in biogas residue high-temperature aerobic composting
ActiveCN114480215ASpeed up the composting processIncrease the maximum temperatureBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
The invention relates to the technical field of environmental microorganisms, in particular to a compound microbial agent and application thereof in high-temperature aerobic composting of biogas residues. The compound microbial agent is prepared from the following components: Geobacillus variotii G6-1, Acinetobacter piteti pittii AP-16, Pantoea sp. BK-PP311 (Pantoea sp. BK-PP311), and Geobacillus kaustophilus FWGK-JYJ1 (Bacillus kaustophilus FWGK-JYJ1), and the compound microbial agent is prepared from the following raw materials: Geobacter variotii G6-1, Acinetobacter piteti pittii AP-16, Pantoea sp. BK-PP311, Geobacter kaustophilus FWGK-JYJ1, Pantoea sp. The compound microbial agent is used for high-temperature aerobic composting of biogas residues, can improve the highest temperature of a compost body, prolong the high-temperature period, quickly decompose organic matters, shorten the composting time and improve the decomposition degree of materials and the quality of organic fertilizers, and has relatively high application value.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
A strain capable of degrading soil residual quinclorac
InactiveCN107217014BReduce economic lossBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationBiotechnologyGenus Pantoea
The invention discloses a quinclorac-degrading bacterium and its application. A quinclorac-degrading bacterium J7 provided by the present invention belongs to Pantoea ( Pantoea sp.), was deposited in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), and the preservation date was March 16, 2017, and the preservation number was CCTCC M 2017131. It was identified as Pantoea by using 16S rDNA. The bacterium is a Gram-negative bacterium, and the colony is pale yellow, smooth, round, and with neat edges. The fungus has the function of degrading quinclorac, and can prevent tobacco from being injured by quinclorac.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV +1
A strain of Pantoea with good degrading effect on cellulose
ActiveCN110643530BPromote degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCarboxymethyl cellulose
A Pantoea with good degrading effect on cellulose belongs to the technical field of microbiology, and is characterized in that: the bacterial strain B5-1 is isolated from the frozen soil collected in Mohe County, Daxing'an Mountains, Heilongjiang Province by using the enrichment culture method. B5‑1 can fully degrade straw with a thickness of 10 cm within 72 days; the strain B5‑1 was directly isolated from the sodium carboxymethyl cellulose plate, and the strain B5‑1 was identified as Pantoea sp., strain storage date: November 30, 2018; storage number: CGMCC No.16848; degradation experiments show that the strain B5‑1 has a good cellulose degradation effect.
Owner:HARBIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Strain capable of degrading residual quinclorac in soil
InactiveCN107217014AReduce economic lossBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationNicotiana tabacumPhytotoxicity
The invention discloses quinclorac degradation bacterium and application thereof. The quinclorac degradation bacterium J7 provided by the invention belongs to pantoea sp. and is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC); the preservation date is March 16, 2017 and the preservation number is CCTCC M2017131; the quinclorac degradation bacterium is identified to be pantoea sp. by 16S rDNA. The bacterium is a Gram-negative bacterium and has a light yellow bacterial colony, a smooth and round surface and an ordered edge. The bacterium has a function of degrading quinclorac and can be used for preventing and controlling phytotoxicity, caused by the quinclorac, on tobaccos.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV +1
Pantoea sp, M3, and method for degrading malachite green
This invention discloses Pantoea sp. M3 (CCTCC No.M207022) with the ability to degrade malachite green. Logarithmic phase Pantoea sp. M3 2-4 wt. % is added into sterile degradation medium containing 0.5-5 mg / L malachite green, and cultured at 20-30 deg.C for 5-10 days to degrade malachite green. The degradation medium with a pH value of 6.0-8.0 comprises: glucose 0.5-1 g / L, NaCl 0.01-0.1 g / L, MgSO4 0.01-0.1 g / L, NH4NO3 0.02-0.1 g / L, K2HPO4 0.01-0.1 g / L, KH2PO4 0.01-0.1 g / L, and yeast extractum 0.06-0.3 g / L. Pantoea sp. M3 can effectively remove residual malachite green and leucomalachite green in water body for fishery. The degradation rate of Pantoea sp. M3 for 0.5-2 mg / L malachite green is higher than 90%.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com