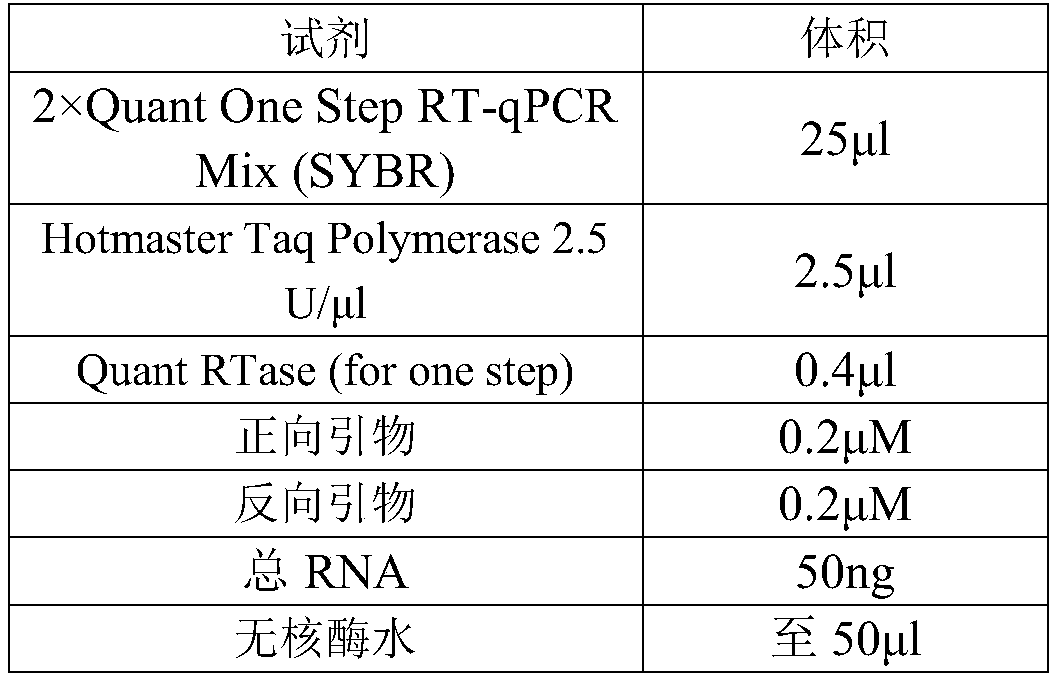
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
43 results about "Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A squamous cell carcinoma arising from the oral cavity. It affects predominantly adults in their fifth and sixth decades of life and is associated with alcohol and tobacco use. Human papillomavirus is present in approximately half of the cases. It is characterized by a tendency to metastasize early to the lymph nodes. When the tumor is small, patients are often asymptomatic. Physical examination may reveal erythematous or white lesions or plaques. The majority of patients present with signs and symptoms of locally advanced disease including mucosal ulceration, pain, difficulty with speaking, chewing, and swallowing, bleeding, weight loss, and neck swelling. Patients may also present with swollen neck lymph nodes without any symptoms from the oropharyngeal tumor. The most significant prognostic factors are the size of the tumor and the lymph nodes status.
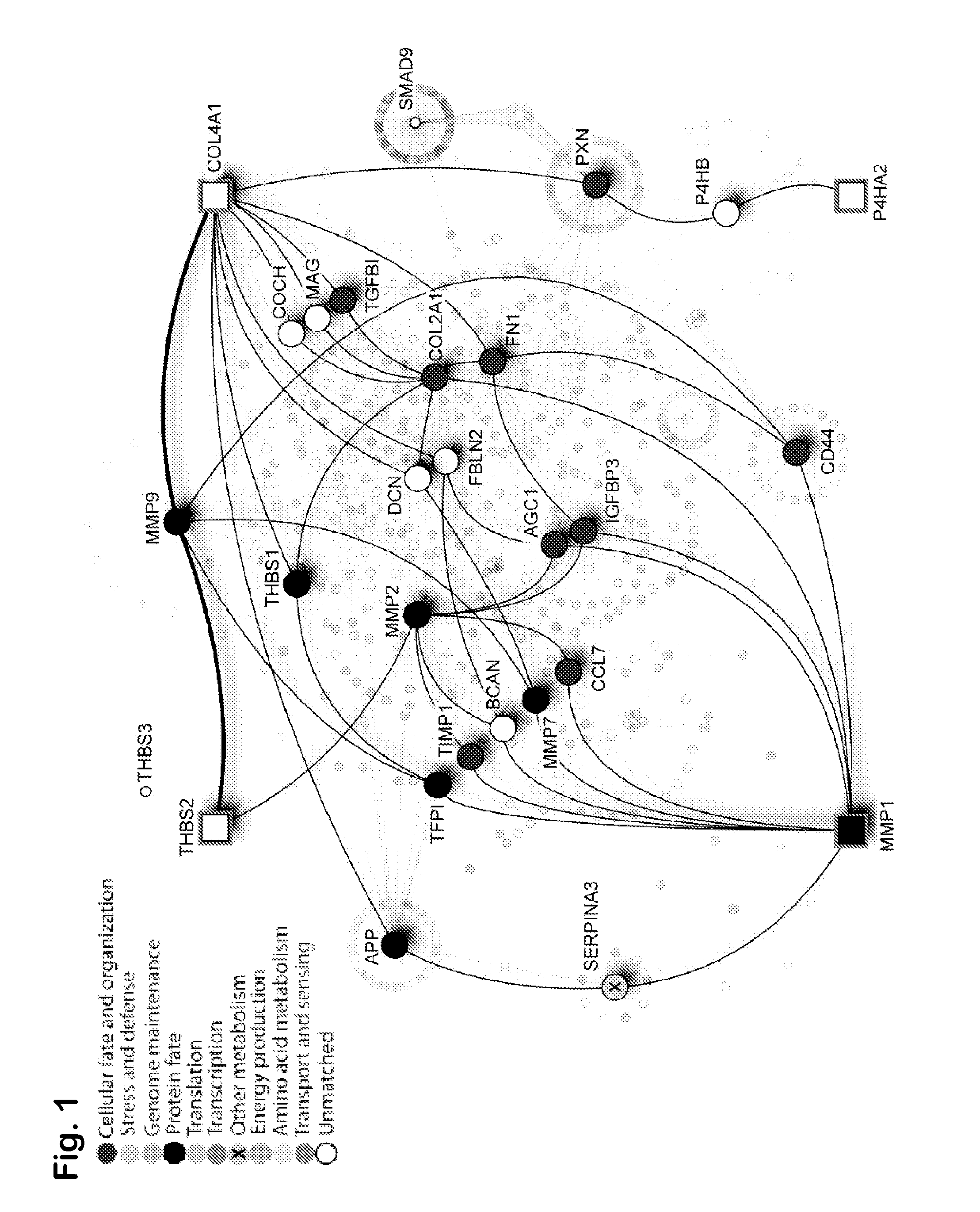
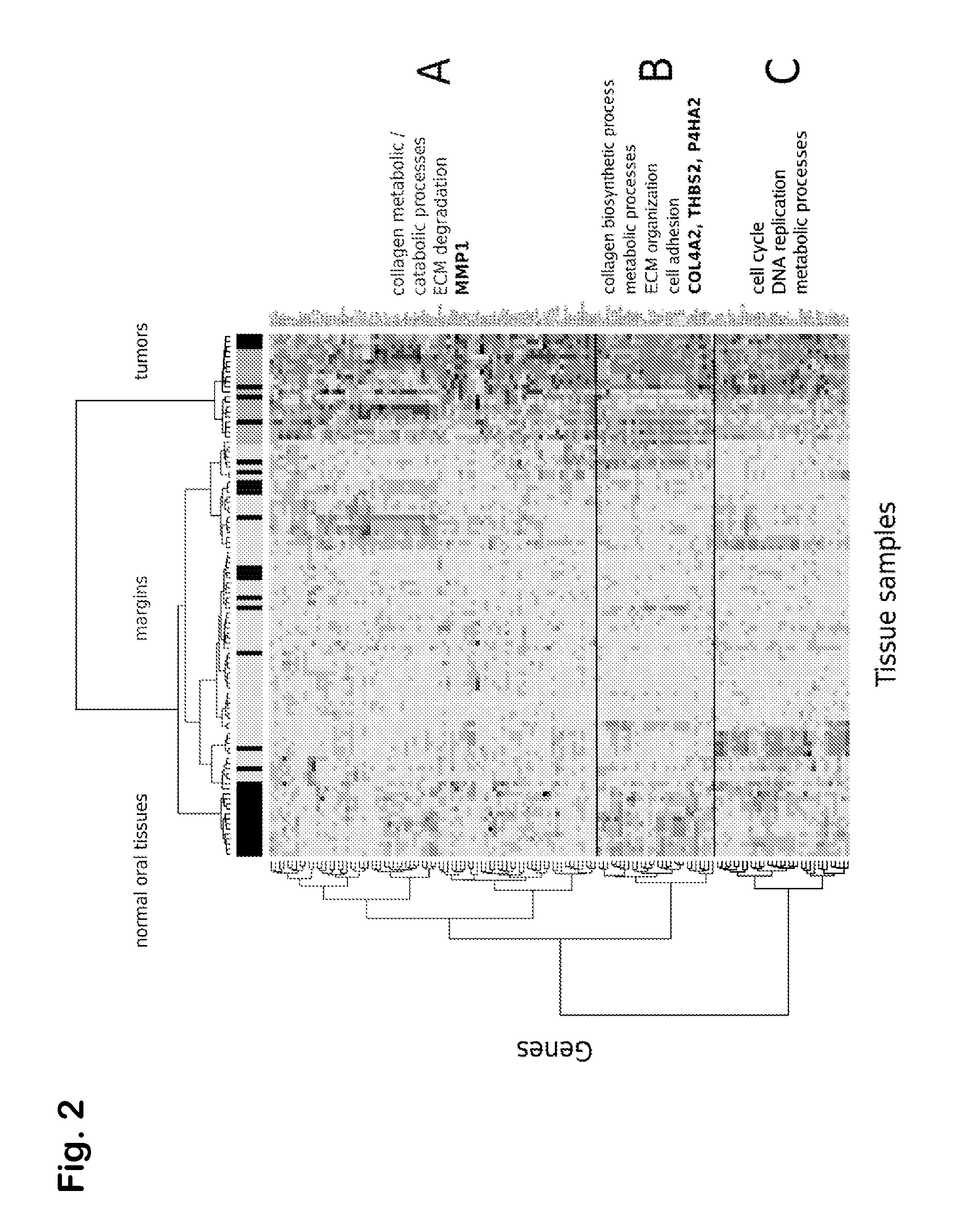
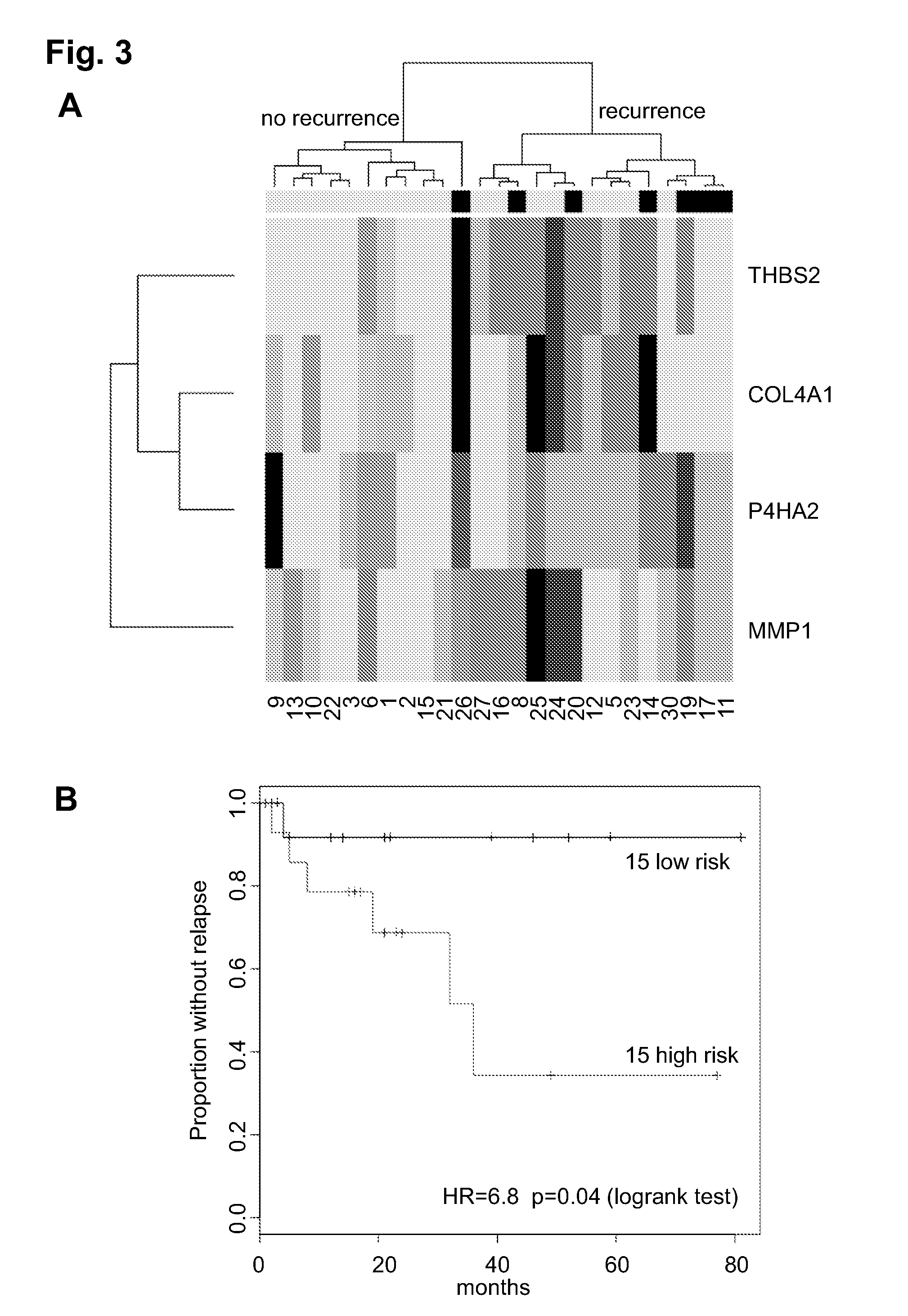
Prognostic signature for oral squamous cell carcinoma
InactiveUS20130303826A1Raise the possibilityImprove expression levelMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningPrognostic signatureSquamous Carcinomas
The present disclosure describes methods and compositions for diagnosing or predicting likelihood of a OSCC recurrence in a subject having undergone OSCC resection comprising: a) determining an expression level of one or more biomarkers selected from Table 4, 5 and / or 7, optionally MMP1, COL4A1, THBS2 and / or P4HA2 in a test sample from the subject, the one or more biomarkers comprising at least one of THBS2 and P4HA2, and b) comparing the expression level of the one or more biomarkers with a control, wherein a difference or a similarity in the expression level of the one or more biomarkers between the test sample and the control is used to diagnose or predict the likelihood of OSCC recurrence in the subject In particular, the present disclosure describes methods and compositions using a four-gene biomarker signature that can predict recurrence of oral squamous cell carcinoma in subjects that have histologically normal surgical resection margins.
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK
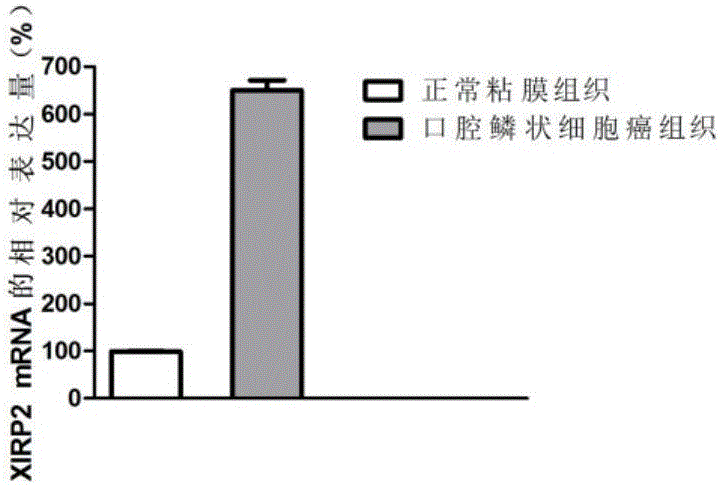
OSCC (oral squamous cell carcinoma) biomarker and application thereof
ActiveCN106435002AAchieve early diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisSquamous CarcinomasFhit gene
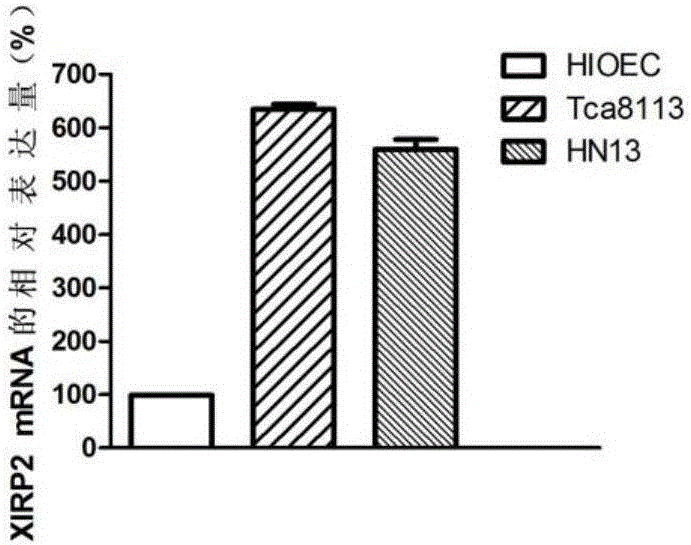
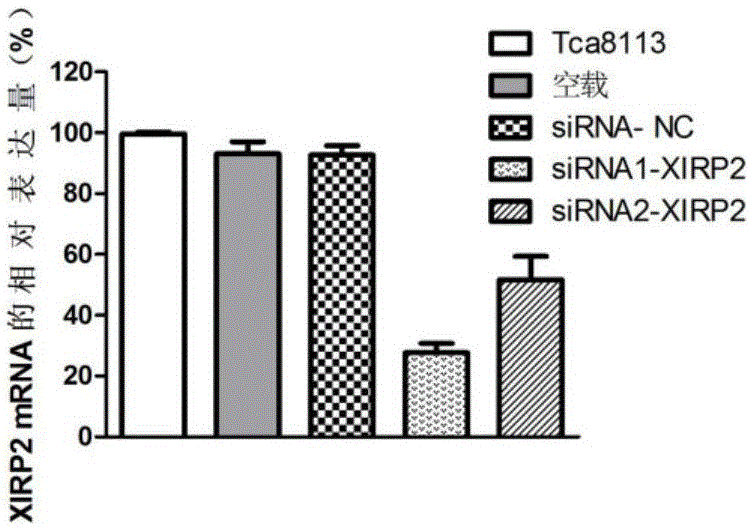
The invention discloses an OSCC (oral squamous cell carcinoma) biomarker and an application thereof. The biomarker is XIRP2, an experiment proves that an XIRP2 gene expresses up regulation in OSCC tissue, and the silent XIRP2 gene can reduce transcription and translation of the gene to inhibit excessive proliferation of OSCC cells. The invention provides the application of the gene or an expression product of the gene in diagnosis and treatment of OSCC.
Owner:BEIJING MEDINTELL BIOMED CO LTD
Oral cavity squamous carcinoma diagnosis reagent, reagent kit and preventing and controlling medicament
InactiveCN101246169AImprove survival rateGood control effectMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingAbnormal tissue growthApoptosis
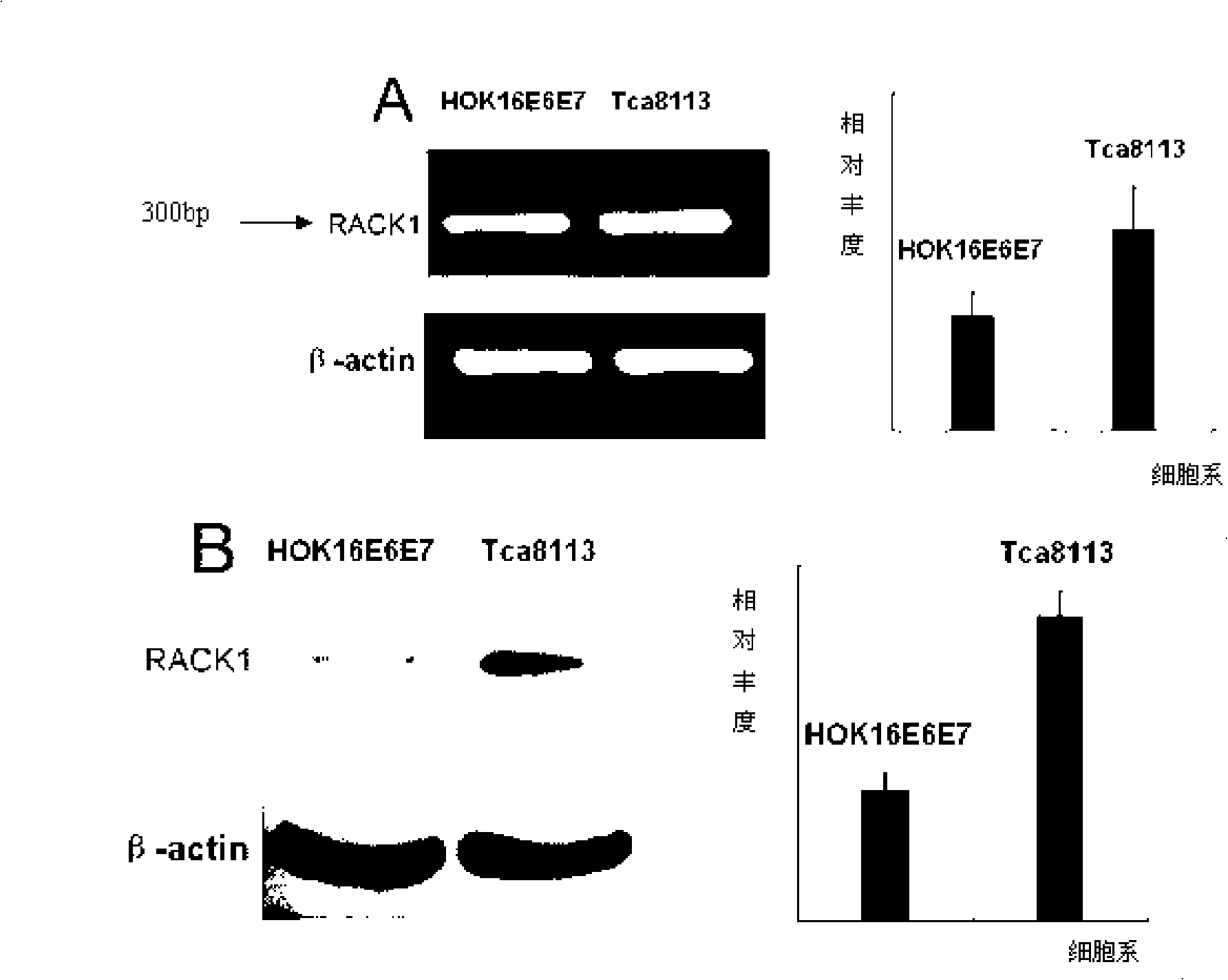
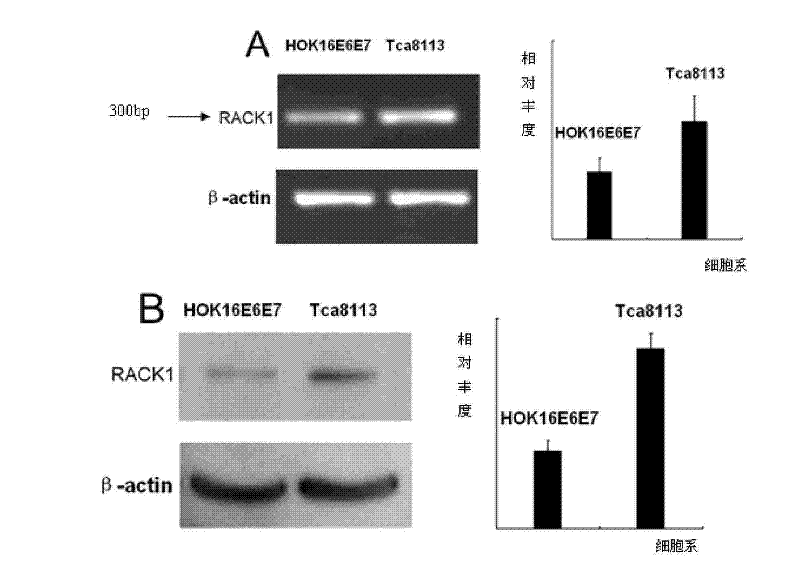
The invention belongs to the field of the tumor molecular biological, particularly relating to an oral squamous cell carcinoma diagnostic reagent, kits and medicine. The invention solves the technical problem that the existing medicine and reagent can not early diagnose oral squamous cell carcinoma and can not prevent oral carcinogenesis effectively. The invention oral squamous cell carcinoma diagnostic reagent contains the reagent which can detect expression level of protein RACK1 (activated protein kinase C receptor) and its mRNA content. The oral squamous cell carcinoma kits can be obtained with regular technology. By using the method of screening oral squamous cell carcinoma medicine, the medicine can be screened for preventing oral squamous cell carcinoma medicine, for example: by screen, obtaining effective RACK1 gene and RNA interference molecular, moreover the RNA interference result first reveals the functions of the RNA interference molecular in oral neoplasms apoptosis regulation and oral neoplasms apoptosis treatment, with broad application prospect.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Molecular subtyping of oral squamous cell carcinoma to distinguish a subtype that is unlikely to metastasize
InactiveUS20130225420A1Significant likelihoodMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningSquamous CarcinomasDentistry
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
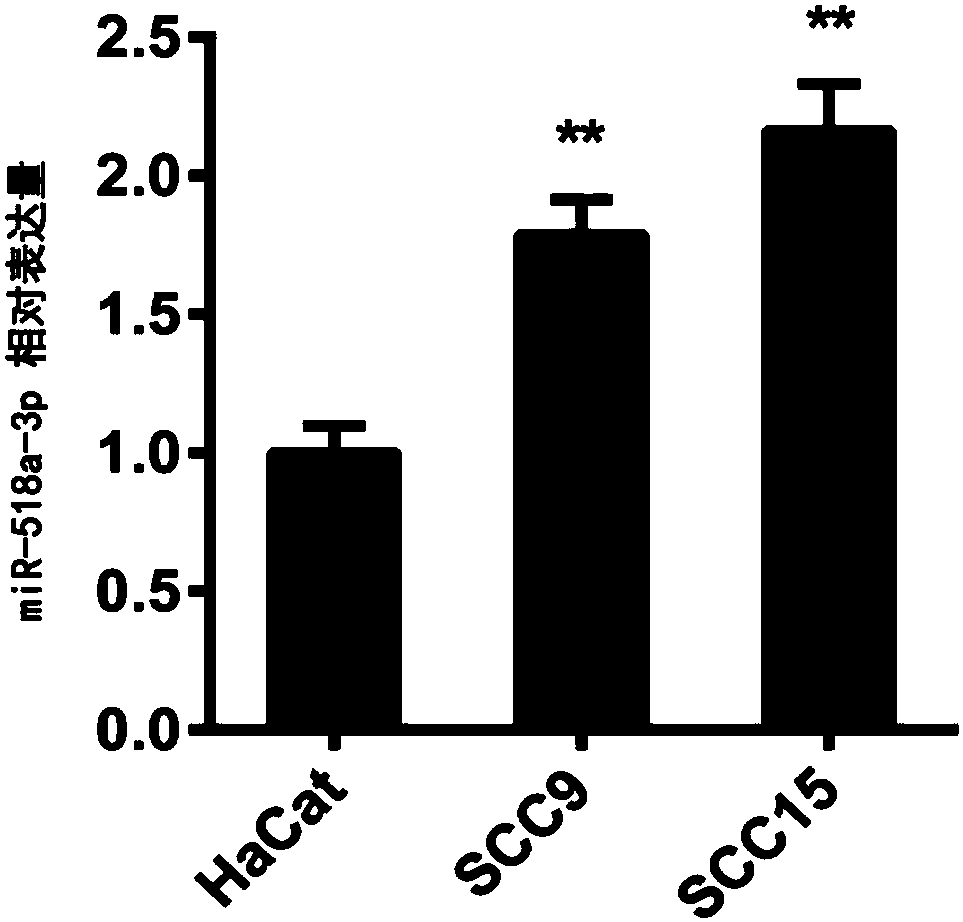
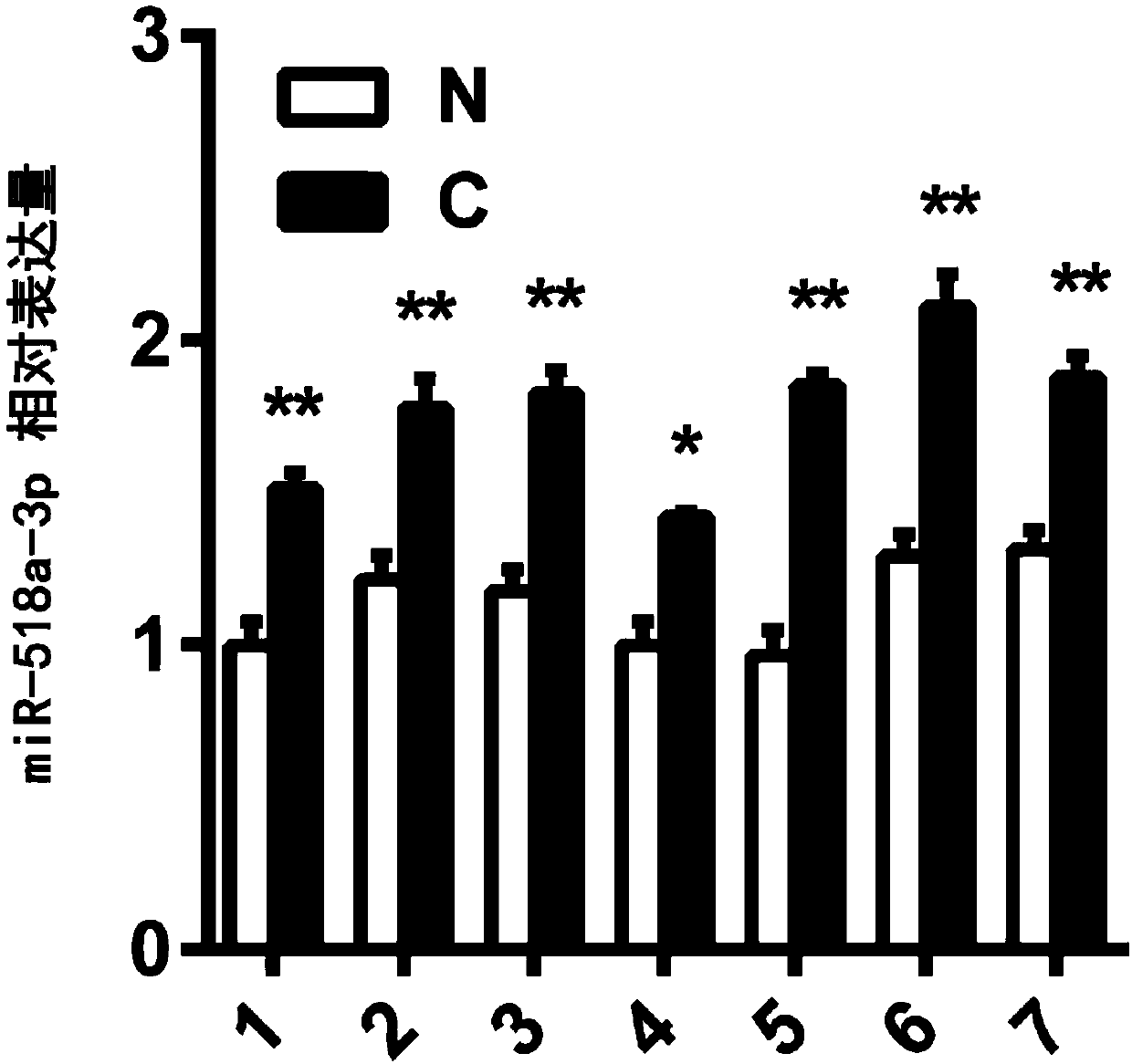
Application of miR-518a-3p in diagnosis of oral carcinoma
InactiveCN107604066AMicrobiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsSquamous CarcinomasFluorescence
The invention relates to an application of miR-518a-3p in diagnosis of oral carcinoma, in particular to the application of miR-518a-3p and a precursor of miR-518a-3p in preparation of oral squamous cell carcinoma diagnosis preparations. MiRNA microarray data analysis is performed on oral squamous cell carcinoma and adjacent normal tissue with an SAM (selectively amplified microsatellite) method. MiRNA with significant differential expression is screened out, and miR-518a-3p as a novel molecular diagnostic marker associated with the oral squamous cell carcinoma is found. Further, experimental results of fluorescence quantitative PCR verify high expression of miR-518a-3p in oral squamous cell carcinoma tissue and the cell line of the oral squamous cell carcinoma. The novel molecular marker is provided for accurate clinical diagnosis of the oral carcinoma, and a foundation is laid for subsequent development of oral squamous cell carcinoma molecular diagnosis products.
Owner:XIANGYA STOMATOLOGICAL HOSPITAL CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method of detection and diagnosis of oral and nasopharyngeal cancers
InactiveUS20110236314A1Improve the immunityImprove durabilityOrganic active ingredientsFermentationSquamous CarcinomasNasopharyngeal carcinoma
The present invention relates to cancer and in particular to oral and nasopharyngeal cancers. In particular, the present invention relates to a method of detection and diagnosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) and nasopharyngeal cancers by determining the expression levels of certain genes. The method comprising (a) determining in a biological sample from the patient the amount of the expression level of at least one gene selected from the group consisting of GNA-12 and IFITM3; and (b) comparing the determined expression levels of said genes in said biological sample with the level in a reference. The invention also relates to polypeptides, antibodies and nucleic acids of the invention for use in medicine and a kit for performing the invention.
Owner:CANCER RES INITIATIVES FOUND
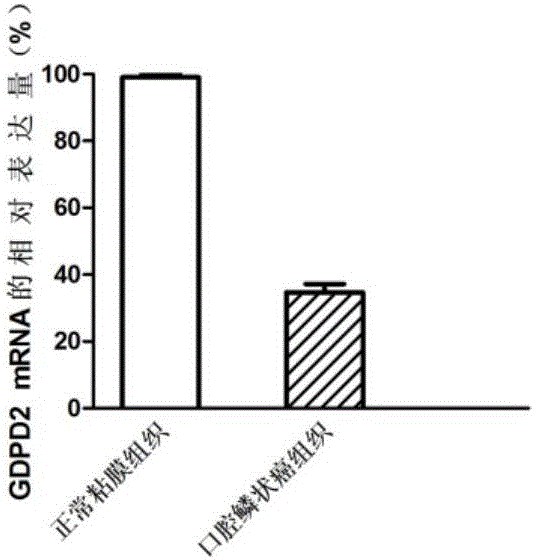
Application of molecular marker to diagnosis and treatment of oral squamous cell carcinoma
ActiveCN106755372APeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellSquamous Carcinomas
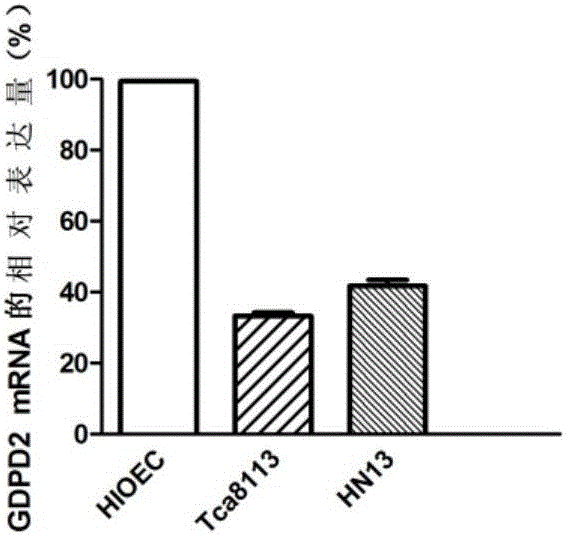
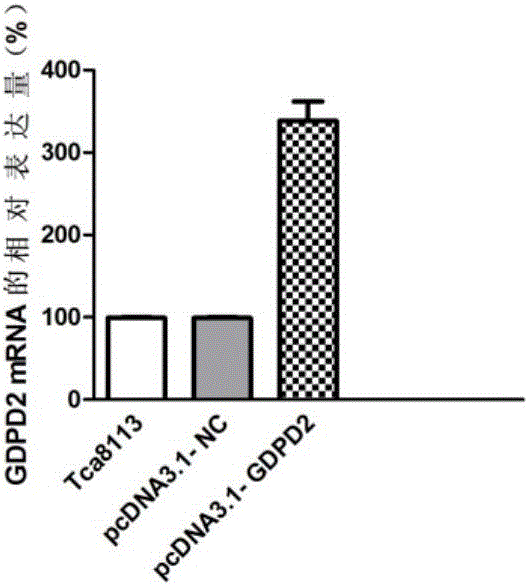
The invention discloses application of a molecular marker to the diagnosis and the treatment of an oral squamous cell carcinoma. A biomarker is GDPD2; discovered through a qPCR (quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction) experiment, the expression of a GDPD2 gene in tissue and a cell of the oral squamous cell carcinoma is regulated down; the GDPD2 gene overexpression can inhibit the proliferation of the cell and decrease the attack rate of a carcinoma cell. The invention provides application of an accelerant of the GDPD2 to the diagnosis and treatment of the oral squamous cell carcinoma; meanwhile, the invention also discloses a method for inhibiting the cell from proliferating.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
Deep learning method for identifying oral squamous cell carcinoma based on visual features
ActiveCN111369501AAvoid interferenceAccurate identificationImage enhancementImage analysisOral Cavity Squamous Cell CarcinomaNetwork model
The invention discloses a deep learning method for identifying oral squamous cell carcinoma based on visual features. The method comprises the following steps: 1) establishing a development set and atest set; 2) constructing a data training sample; 3) training a target detection network model; 4) performing batch initial positioning on the oral photos of the development set through the target detection model, and constructing a classification network data sample by using the positioned photo area; 5) expanding classification network data samples; 6) the DenseNet is used as a backbone networkof the classification network, and the DenseNet is improved, so that the model is more concentrated in difficult samples of wrong classification; the oral squamous cell carcinoma detection method hasthe advantages that the oral squamous cell carcinoma can be detected from the oral photos by the aid of the oral squamous cell carcinoma detection method, the oral squamous cell carcinoma detection sensitivity is high, the oral squamous cell carcinoma detection specificity is good, and the oral squamous cell carcinoma detection method is suitable for detecting and screening various oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method of stable fluorescence labeling of living cells of oral squamous cell carcinoma
InactiveCN103675262ARich experimental meansBroaden the field of studyDisease diagnosisMedicineFluorescence
Owner:步荣发 +1
Oral cavity squamous carcinoma diagnosis reagent, reagent kit and preventing and controlling medicament
InactiveCN101246169BGood control effectImprove survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingAbnormal tissue growthApoptosis
The invention belongs to the field of the tumor molecular biological, particularly relating to an oral squamous cell carcinoma diagnostic reagent, kits and medicine. The invention solves the technical problem that the existing medicine and reagent can not early diagnose oral squamous cell carcinoma and can not prevent oral carcinogenesis effectively. The invention oral squamous cell carcinoma diagnostic reagent contains the reagent which can detect expression level of protein RACK1 (activated protein kinase C receptor) and its mRNA content. The oral squamous cell carcinoma kits can be obtained with regular technology. By using the method of screening oral squamous cell carcinoma medicine, the medicine can be screened for preventing oral squamous cell carcinoma medicine, for example: by screen, obtaining effective RACK1 gene and RNA interference molecular, moreover the RNA interference result first reveals the functions of the RNA interference molecular in oral neoplasms apoptosis regulation and oral neoplasms apoptosis treatment, with broad application prospect.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
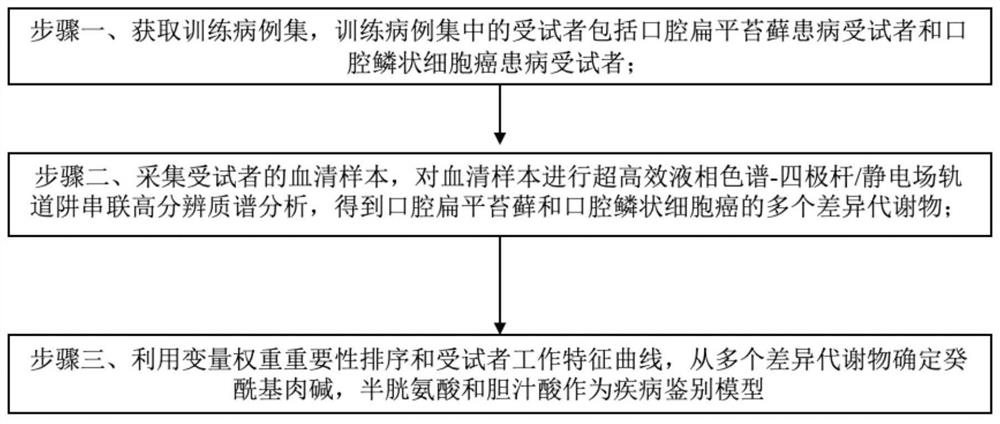
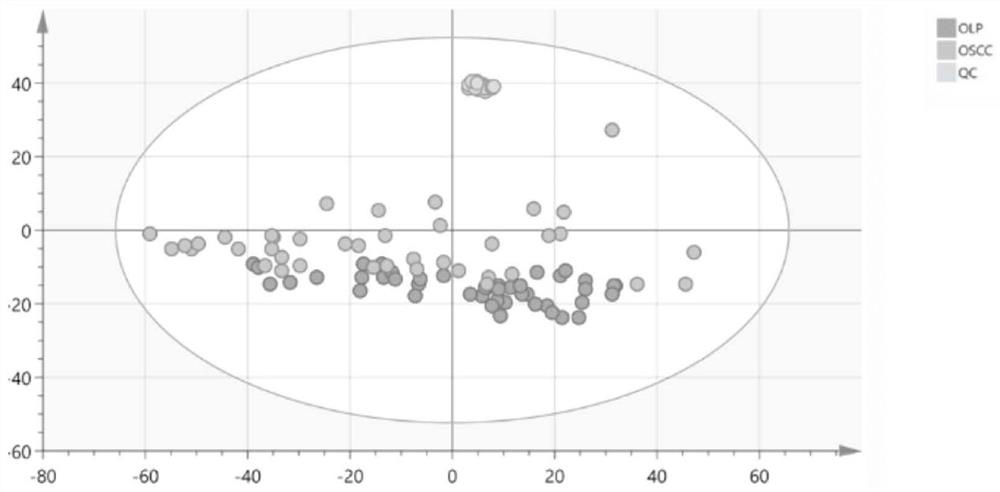
Construction method of disease identification model, marker and application thereof
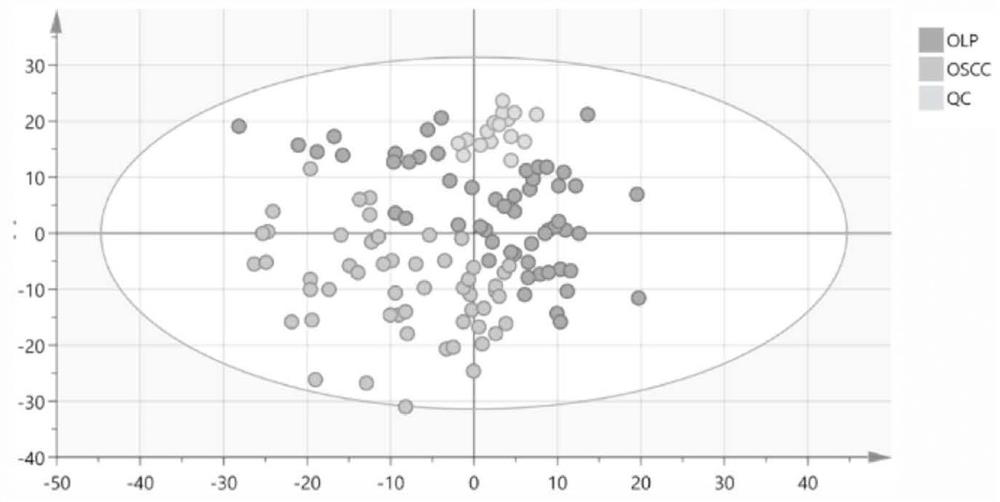
The invention provides an auxiliary marker for identifying diseases. The auxiliary marker consists of decanoyl carnitine, cysteine and bile acid. The invention also provides a construction method of adisease identification model, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, acquiring a training case set, the subjects in the training case set comprising oral lichen planus disease subjects andoral squamous cell carcinoma disease subjects; secondly, collecting serum samples of the subjects, and carrying out ultra-high performance liquid chromatography quadrupole / electrostatic field orbitraptandem high-resolution mass spectrometry analysis on the serum samples to obtain a plurality of differential metabolites of oral lichen planus and oral squamous cell carcinoma; and thirdly, determining decanoyl carnitine, cysteine and bile acid from the plurality of differential metabolites as a disease identification model by utilizing variable weight importance sorting and a subject working characteristic curve. The invention provides a disease identification model which can be used for identifying and distinguishing oral lichen planus and oral squamous cell carcinoma in the early stage andhas the advantages of being minimally invasive and high in accuracy.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZHENGZHOU UNIV
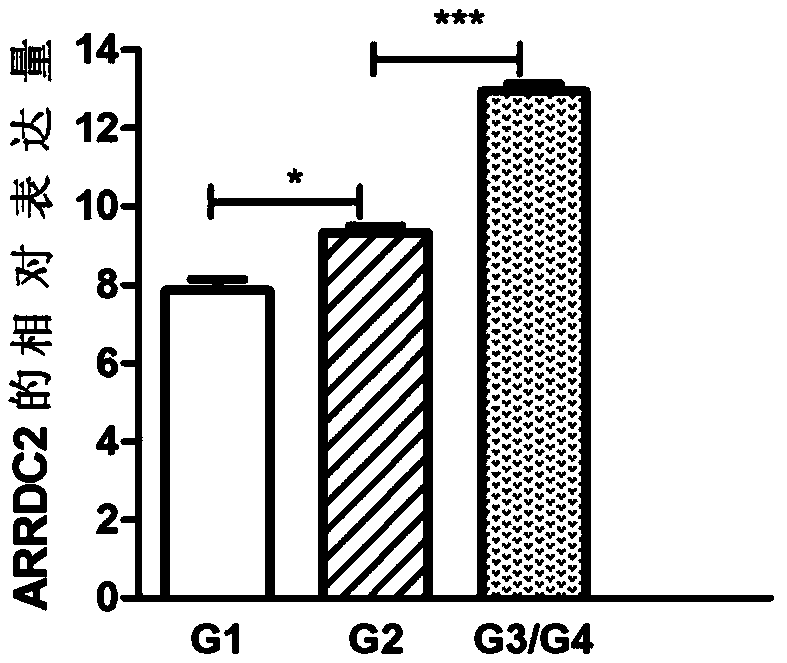
Application of ARRDC2 in evaluating development process of oral squamous cell carcinoma
ActiveCN109439760ARealize individualized treatmentAvoid overtreatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisSquamous CarcinomasCurative effect
The invention discloses an application of ARRDC2 in evaluating the development process of oral squamous cell carcinoma. According to the invention, by means of high throughput sequencing and bioinformatics analysis, gene ARRDC2, which indicates significant changes in different development processes of the tumor, is screened, and ARRDC2 is suggested, as a marker molecule, to be applied to determination of the development of the oral squamous cell carcinoma, prediction of the prognosis of the tumor and guiding of therapeutic plans and curative effect monitoring.
Owner:XIANGYA STOMATOLOGICAL HOSPITAL CENT SOUTH UNIV
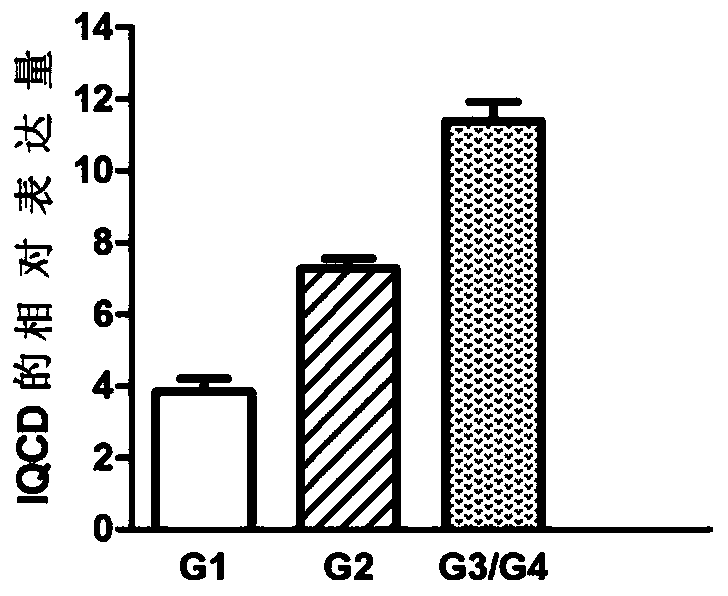
Target gene for diagnosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma and application thereof
InactiveCN109880906ARealize individualized treatmentAvoid overtreatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisSquamous CarcinomasTherapeutic effect
The invention discloses a target gene for diagnosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma and application thereof. By screening genes with an expression level related to a tumor differentiation level, the expression of genes in tumor tissues in each differentiation level is determined, so that the differentiation level of a tumor is determined, thereby accurately and objectively predicting the tumor prognosis, guiding the formulation of a treatment plan and monitoring a therapeutic effect.
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL OF HEBEI MEDICAL UNIV
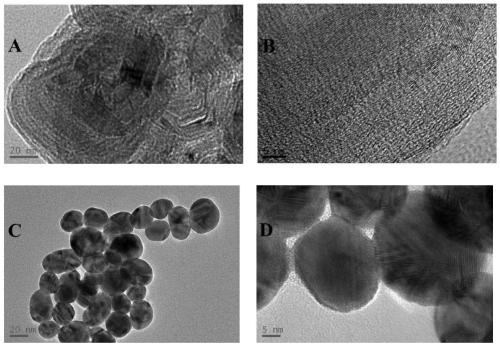
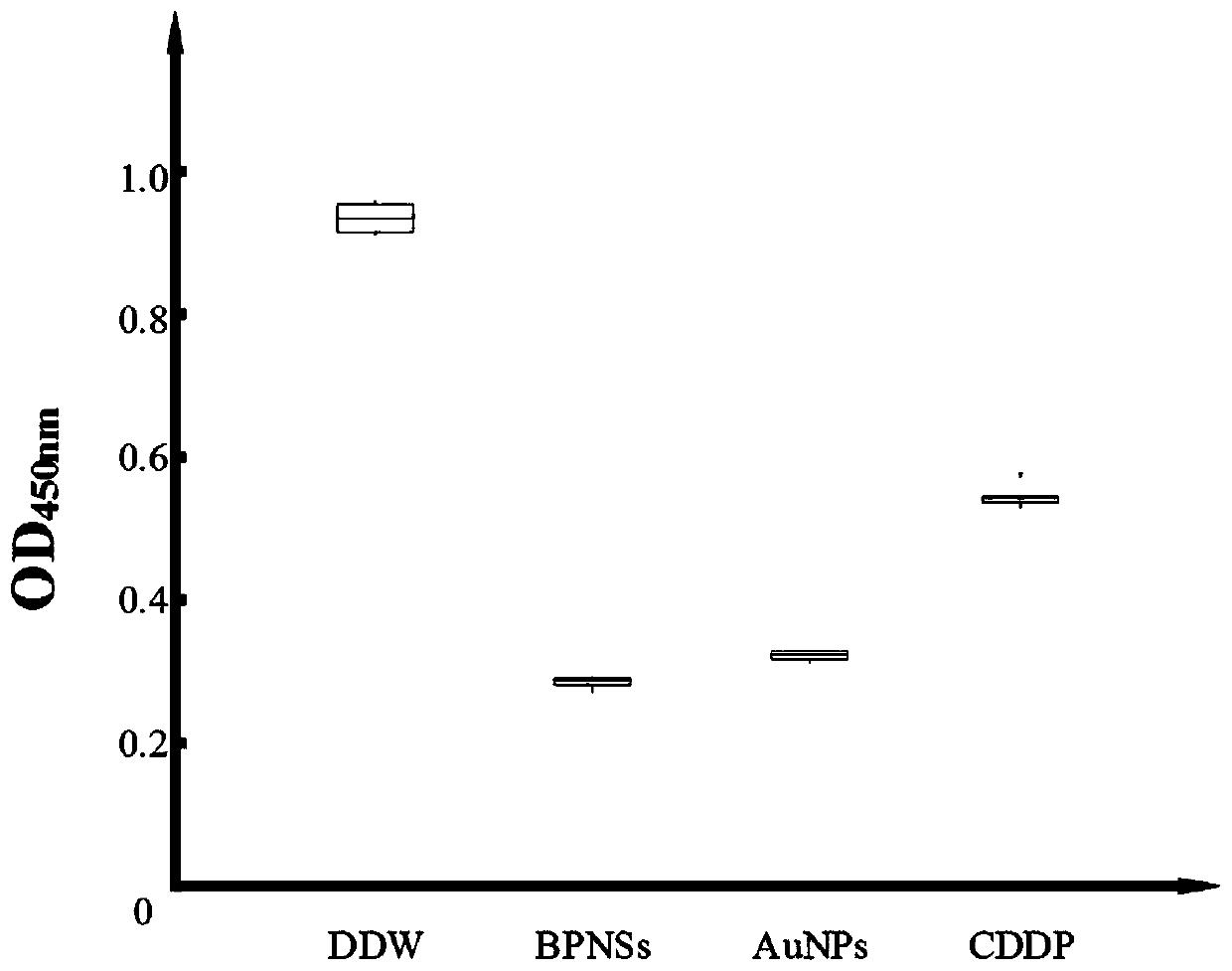
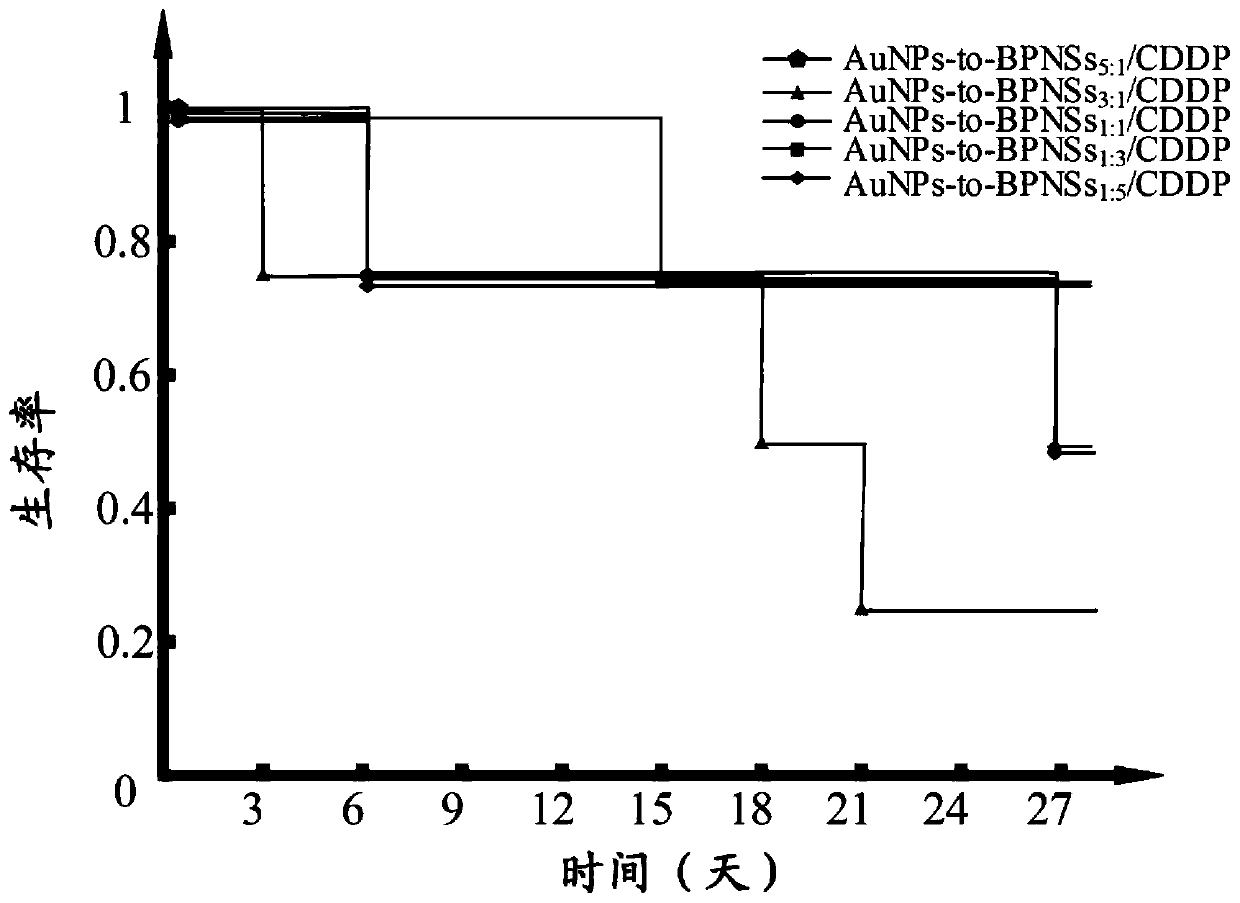
Black phosphorus nanosheet/gold nanoparticle composite material and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN111529508AHigh efficiency loadExcellent treatmentInorganic active ingredientsPhotodynamic therapySquamous CarcinomasCombined treatment
The invention discloses a black phosphorus nanosheet / gold nanoparticle composite material and a preparation method and application thereof. In the black phosphorus nanosheet / gold nanoparticle composite material, the mass percentage of the black phosphorus nanosheet is greater than or equal to 16.7%, a gold nanoparticle solution is added into dispersion liquid including the black phosphorus nanosheet, and thus the black phosphorus nanosheet / gold nanoparticle composite material can be obtained through ultrasonic oscillation. The black phosphorus nanosheet / gold nanoparticle composite material provided by the invention can efficiently load cis-platinum chemotherapeutic drugs, can realize photo-thermal, photodynamic and chemotherapeutic combined treatment on oral squamous cell carcinoma, and has excellent treatment effect.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
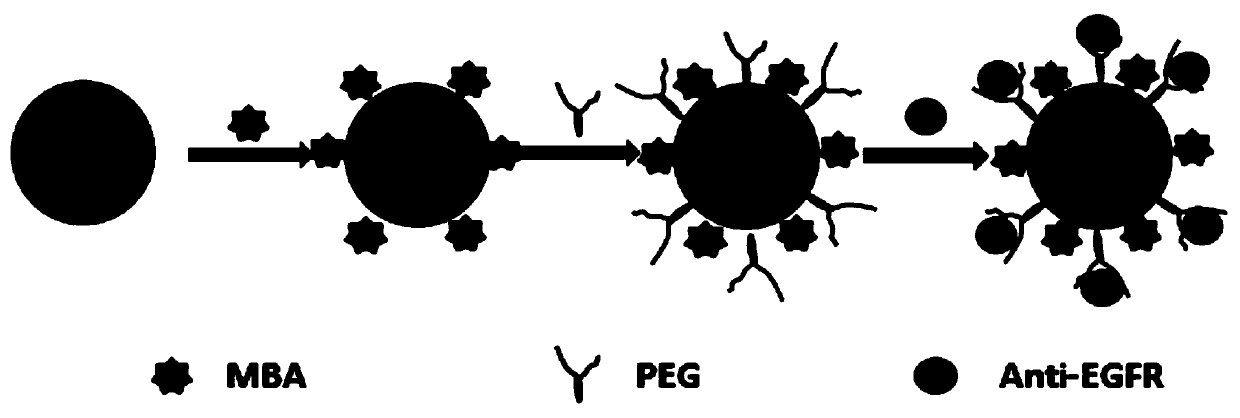
Nanoparticles for Raman spectrum detection of oral squamous cell carcinoma tumor cells and preparation method thereof
The invention provides nanoparticles for Raman spectrum detection of oral squamous cell carcinoma tumor cells. The nanoparticles for Raman spectrum detection of the oral squamous cell carcinoma tumorcells are prepared from nanoscale gold particles and 4-mercaptobenzoic acid, alpha-sulfydryl-omega-carboxyl polyethylene glycol and an EGFR antibody through response. The nanoparticles for Raman spectrum detection of oral squamous cell carcinoma tumor cells can be combined with the characteristics of the oral squamous cell carcinoma tumor cells, so that specific Raman signals are obtained, and theoral squamous cell carcinoma tumor cells are rapidly and accurately detected in real time in situ; compared with traditional frozen pathological tissue section examination, the time is saved, accuracy is improved, and a novel detection method for detecting whether oral squamous cell carcinoma cells remain or not in clinical operations is provided.
Owner:拉曼兄弟(深圳)科技发展有限公司
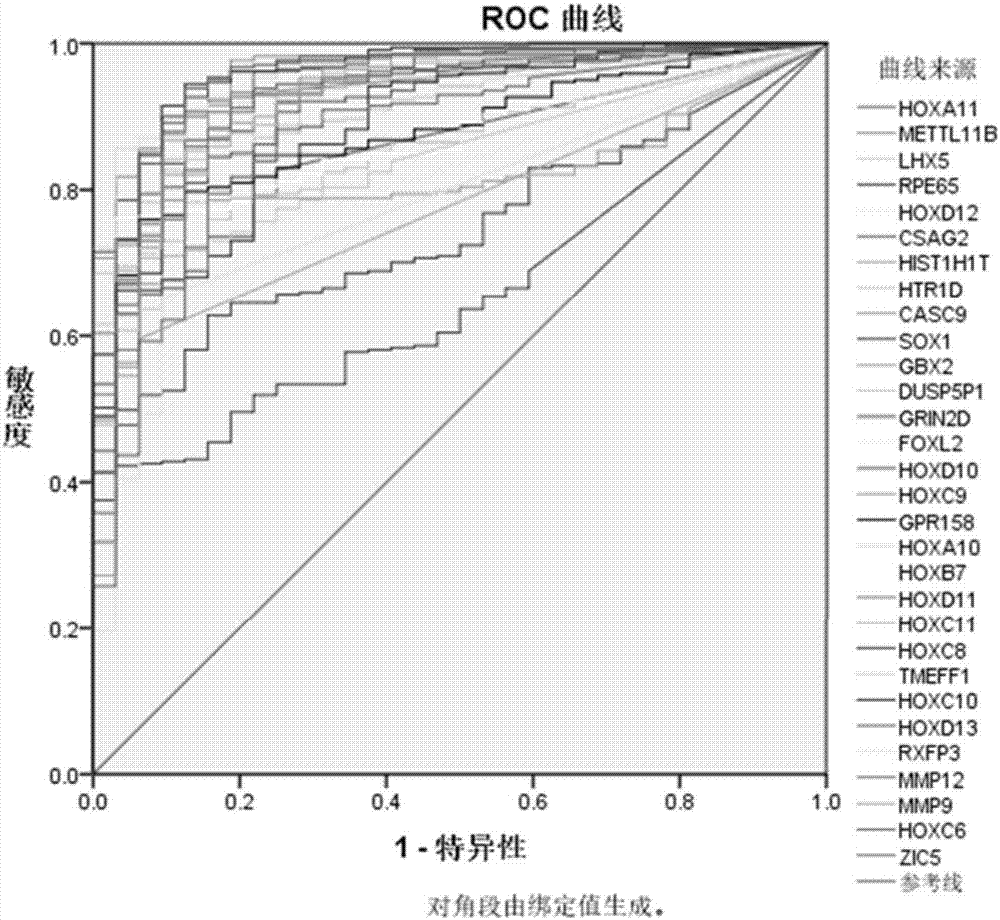
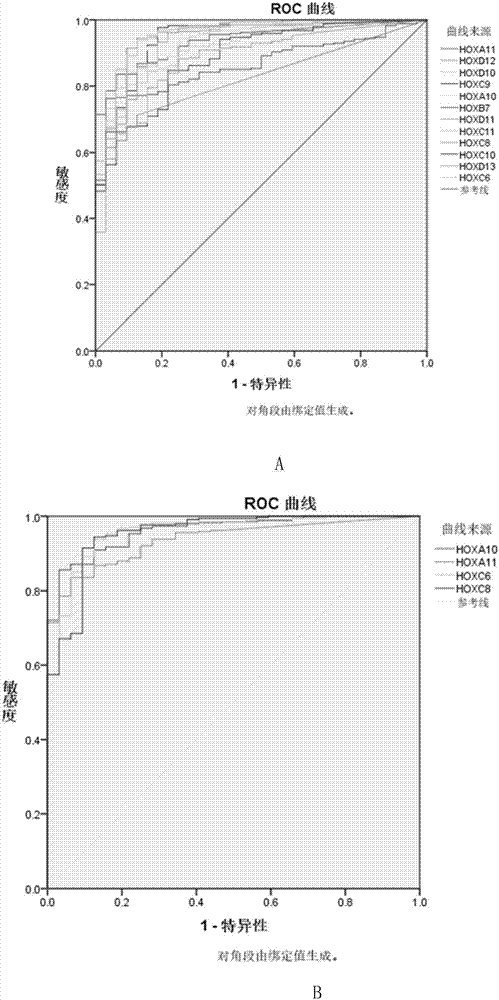
Reagent kit for diagnosing oral squamous cell carcinoma
ActiveCN107422123ASignificant technological progressSensitivity advantageMaterial analysisOral tissueSquamous Carcinomas
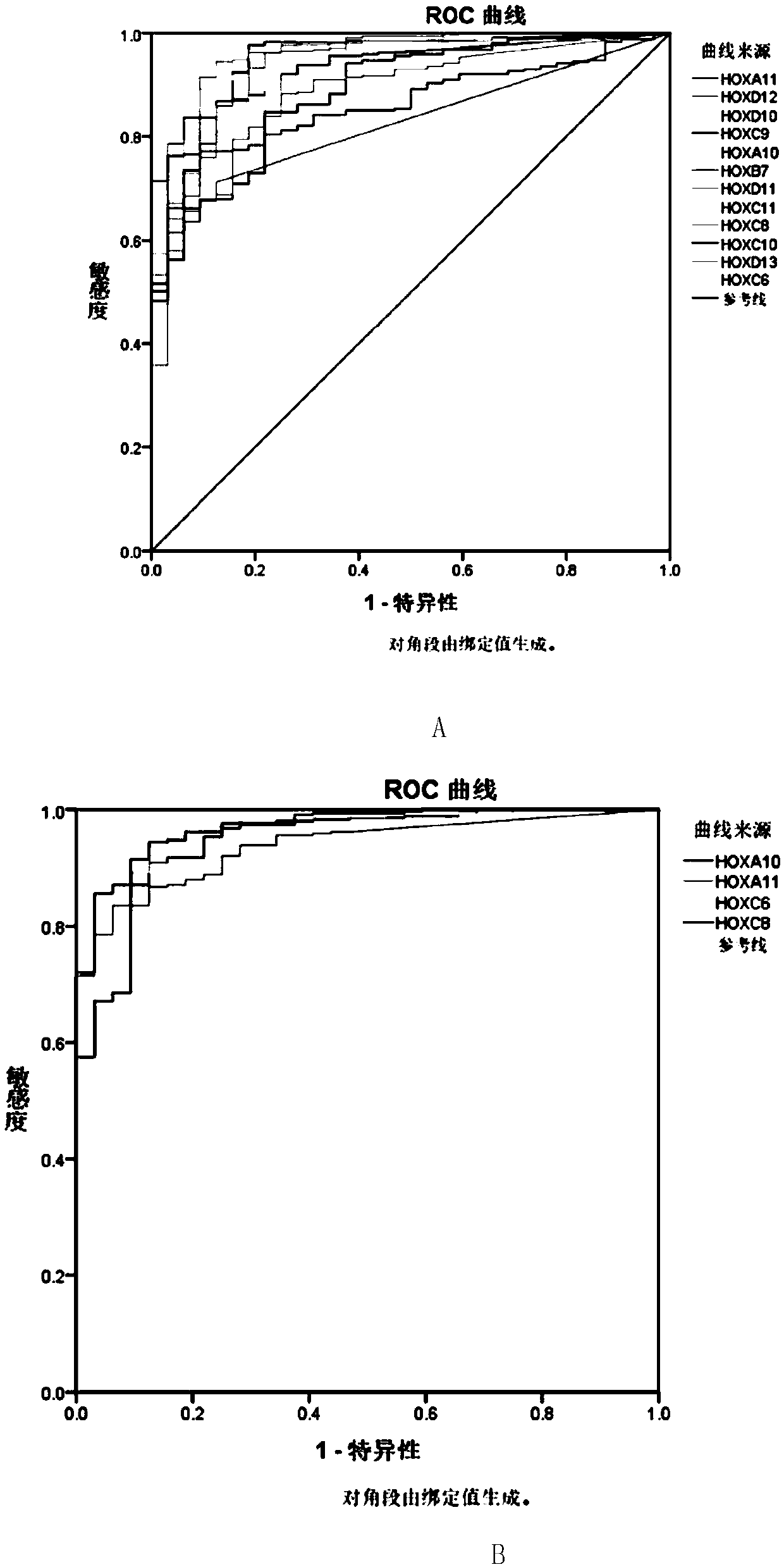
The invention provides a reagent kit for diagnosing oral squamous cell carcinoma. The reagent kit comprises specific antibodies for detecting HOXA10, specific antibodies for detecting HOXA11, specific antibodies for detecting HOXC6 or compositions with more than one or two optional specific antibodies for detecting the expression quantities of HOXC8. The reagent kit has the advantages that sequencing results for mRNA [messenger RNA (ribonucleic acid)] of the oral squamous cell carcinoma and normal oral tissues in TCGA (the cancer genome atlas) databases are statistically analyzed, data of 32 cases of normal oral tissues and 341 cases of oral squamous cell carcinoma tissues are incorporated, obvious difference of expression of partial genes in HOX families in the oral squamous cell carcinoma and the normal tissues is discovered, and accordingly the reagent kit is suitable to be applied to diagnosing the oral squamous cell carcinoma; expression of genes in the HOX families is detected in oral squamous cell carcinoma tissue pathological sections by the aid of immunohistochemical processes, and accordingly positive expression of the genes in the oral squamous cell carcinoma and application values of the genes in diagnosis can be determined.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
Marker related to malignant degree of oral squamous cell carcinoma and application thereof
InactiveCN109055558AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisSquamous CarcinomasPoorly differentiated
The invention discloses an SIX4 gene used as a molecular marker for assessing the malignant degree of oral squamous cell carcinoma. High-throughput sequencing and QPCR studies show that the content ofthe SIX4 gene in high differentiated oral squamous cell carcinoma is lower than that in low differentiated oral squamous cell carcinoma. According to the research results, the invention can also develop a kit for assessing the malignant degree of oral squamous cell carcinoma, which has a remarkable detection effect and can be widely popularized and applied in clinic.
Owner:SUINING CENT HOSPITAL
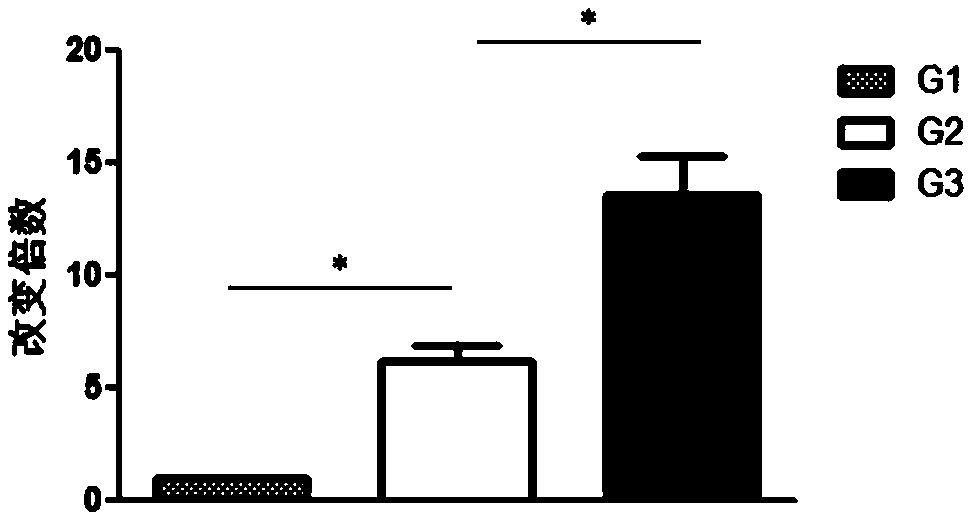
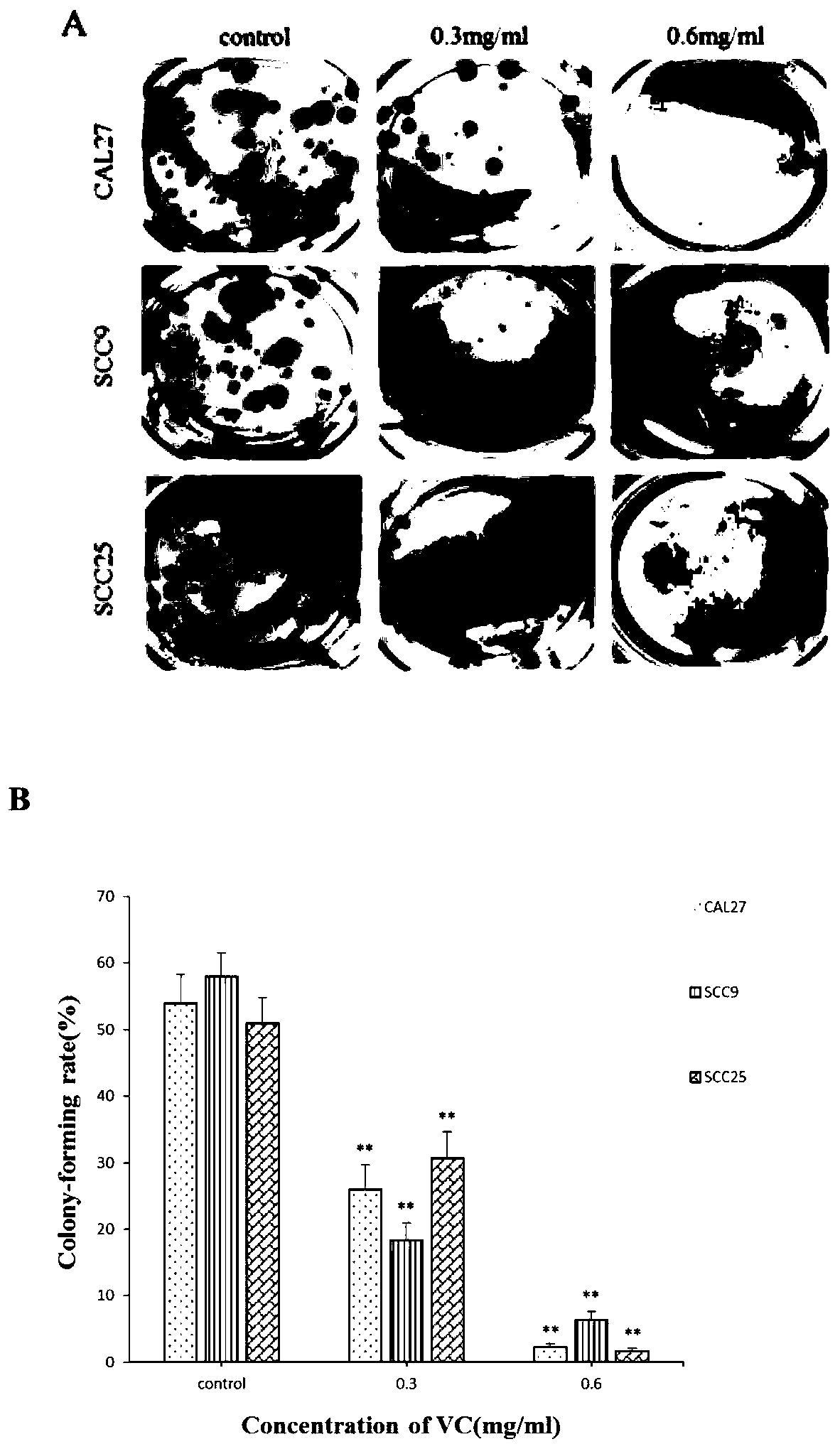
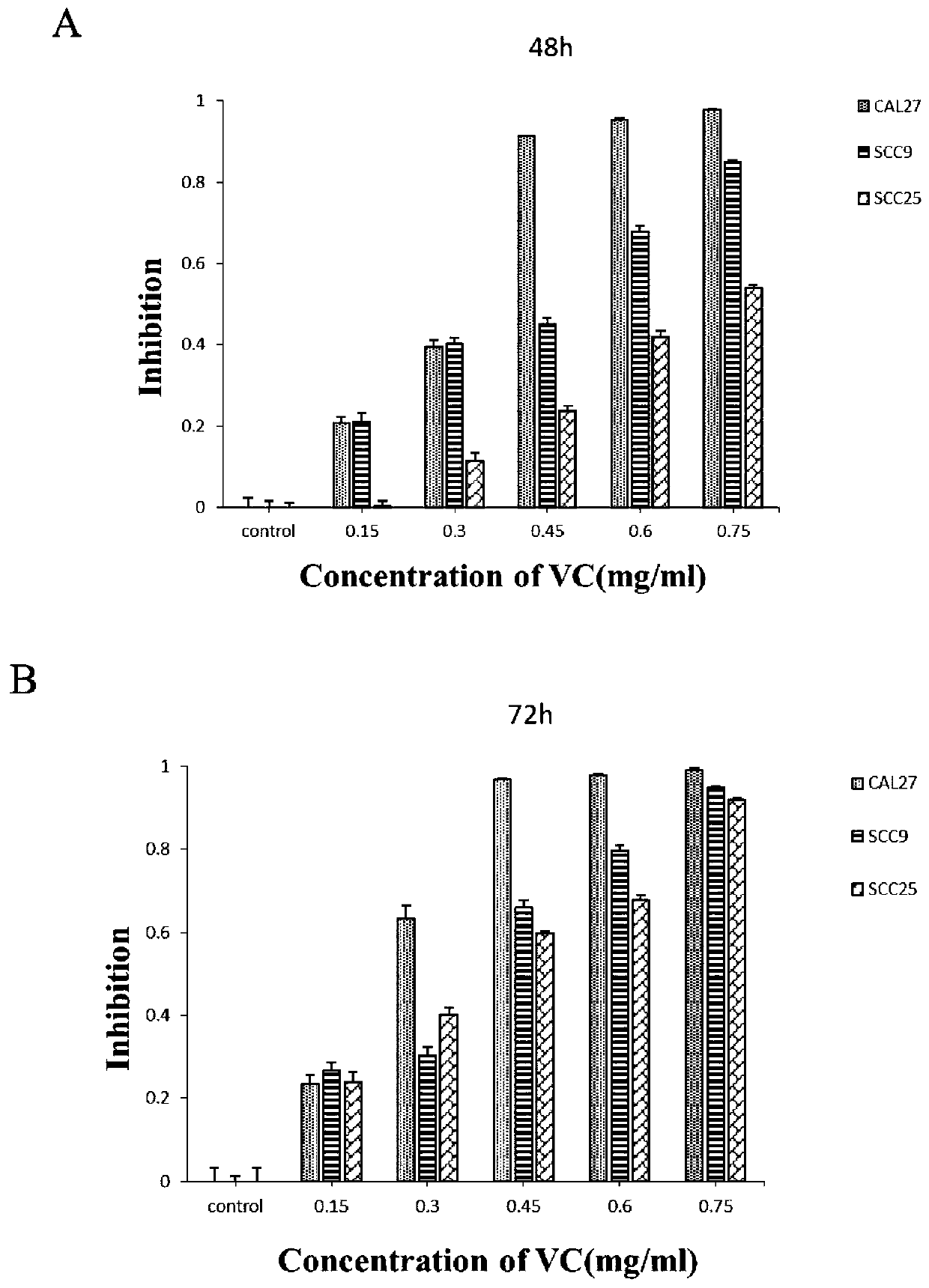
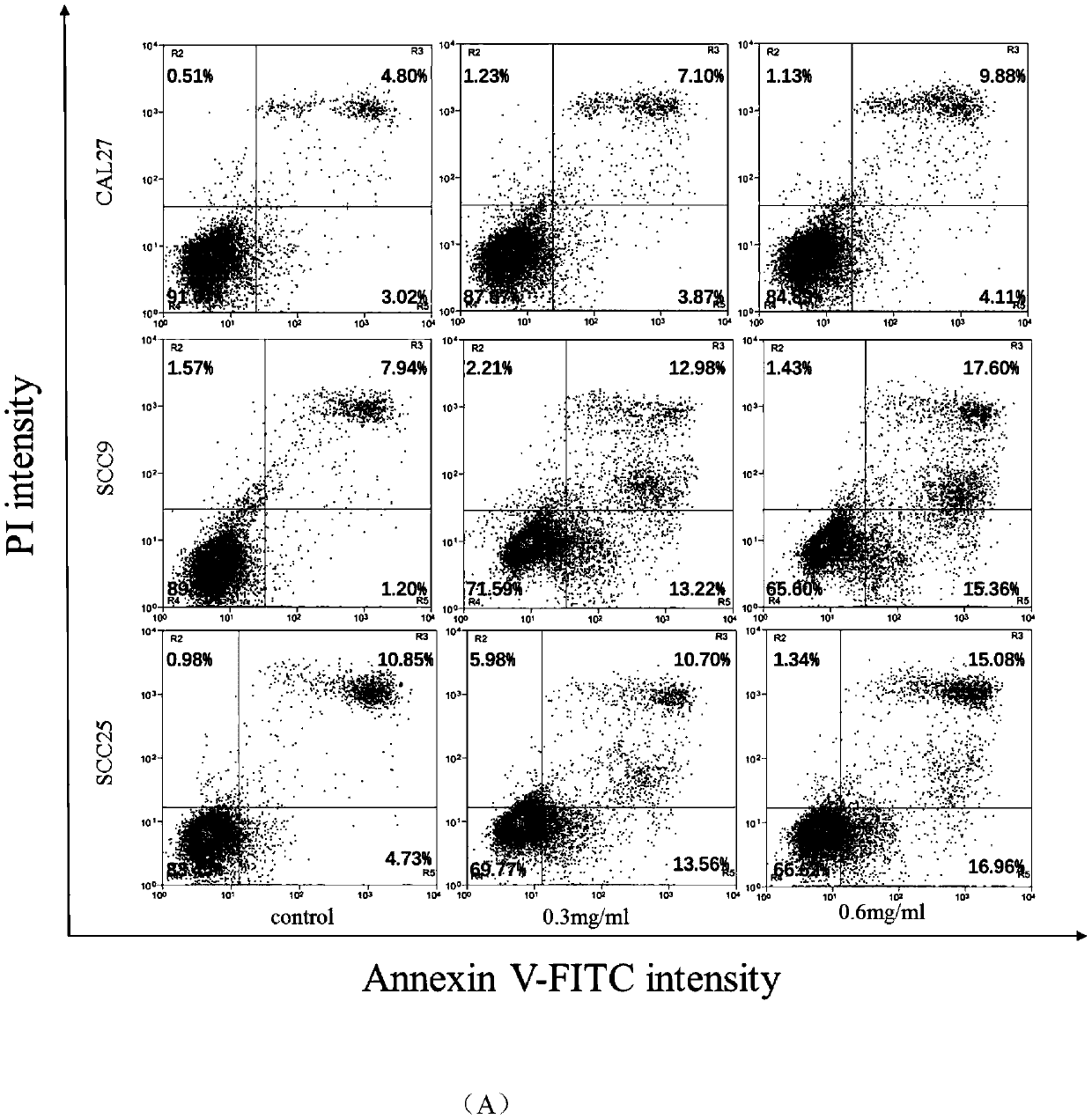
Application of vitamin C in preparation of products for inhibiting human oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC)
InactiveCN110169966AEasy accessSmall side effectsOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemVitamin CSquamous Carcinomas
The invention relates to the technical field of biological medicines, and provides application of vitamin C in preparation of products for inhibiting human oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). The products for inhibiting the human OSCC comprise drugs for treating the human OSCC, and health care food or health care drink for preventing the human OSCC. It is verified by cell experiments and animal experiments that the vitamin C can inhibit the growth of human OSCC cells, increases the apoptosis of the human OSCC cells, inhibits the growth of nude mouse transplanted tumors at the same time, and is better in inhibitory effect on tumors in combination with cis-platinum, so that it is shown that the vitamin C has the effect of inhibiting the human OSCC. Therefore, the vitamin C is to become a novel drug for inhibiting the human OSCC, and new exploration is provided for the prevention or treatment of the human OSCC.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGZHENG HOSPITAL
Application of verbascoside in preparation of medicine for treating oral squamous cell carcinoma
InactiveCN106619664AOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismIntraperitoneal routeSquamous Carcinomas
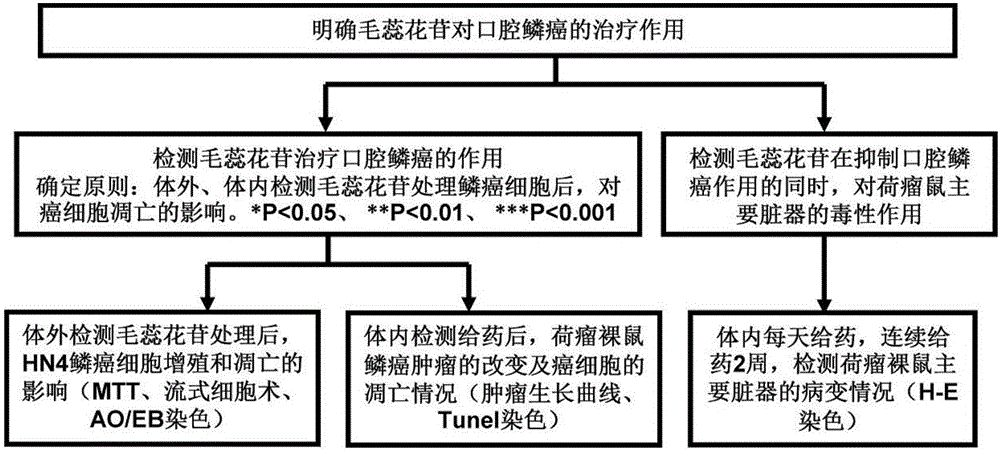
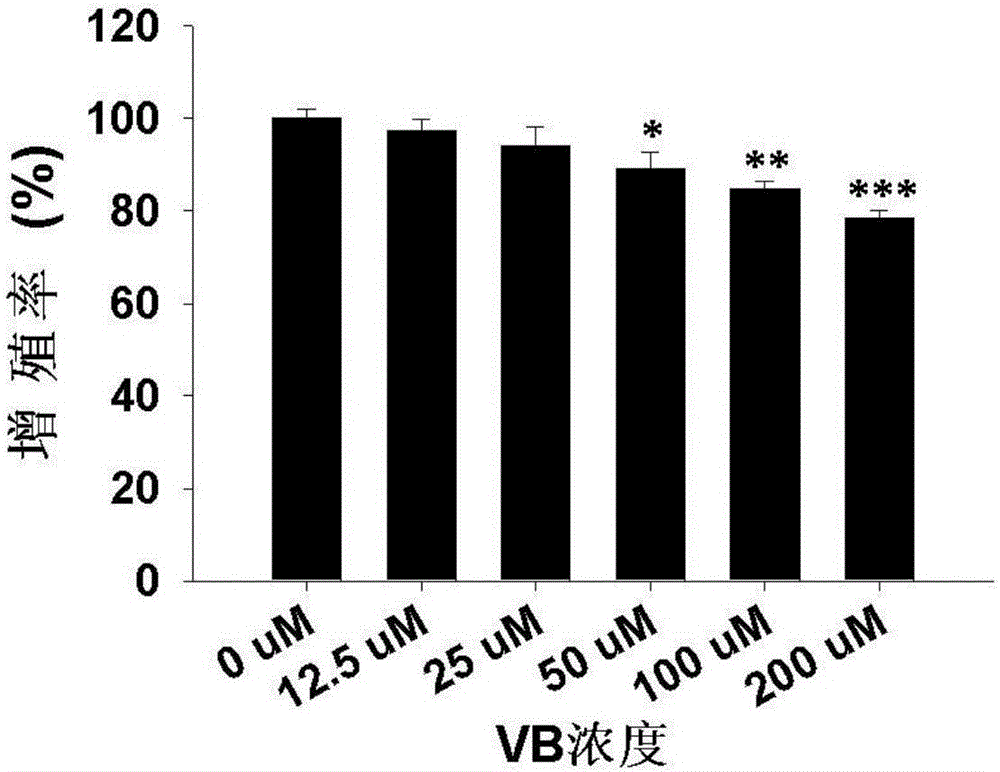
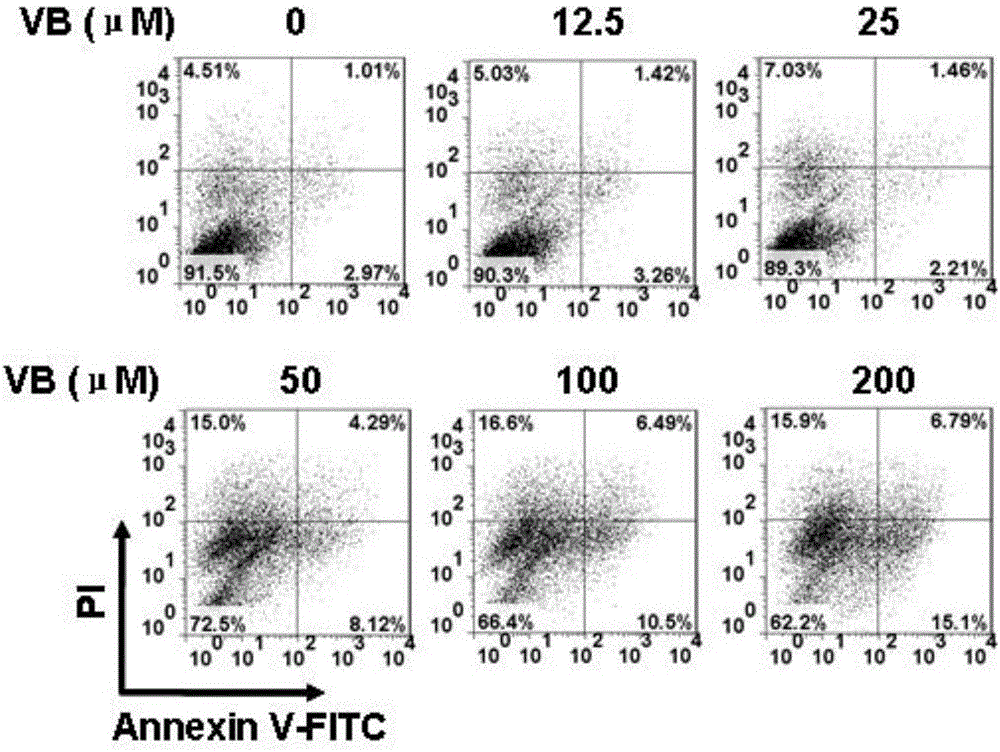
The invention provides an application of verbascoside in preparation of a medicine for treating oral squamous cell carcinoma. By intraperitoneal injection of verbascoside into a tumor-bearing mouse with oral squamous cell carcinoma, it is observed that the verbascoside can effectively inhibit the growth of oral squamous cell carcinoma tumors by promoting tumor cell apoptosis. Moreover, the verbascoside provided by the invention, at cell and animal levels, achieves an effect of effectively resisting squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting proliferation of HN4 cells of the oral squamous cell carcinoma and inducing apoptosis of the HN4 cells.
Owner:AFFILIATED STOMATOLOGICAL HOSPITAL OF NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
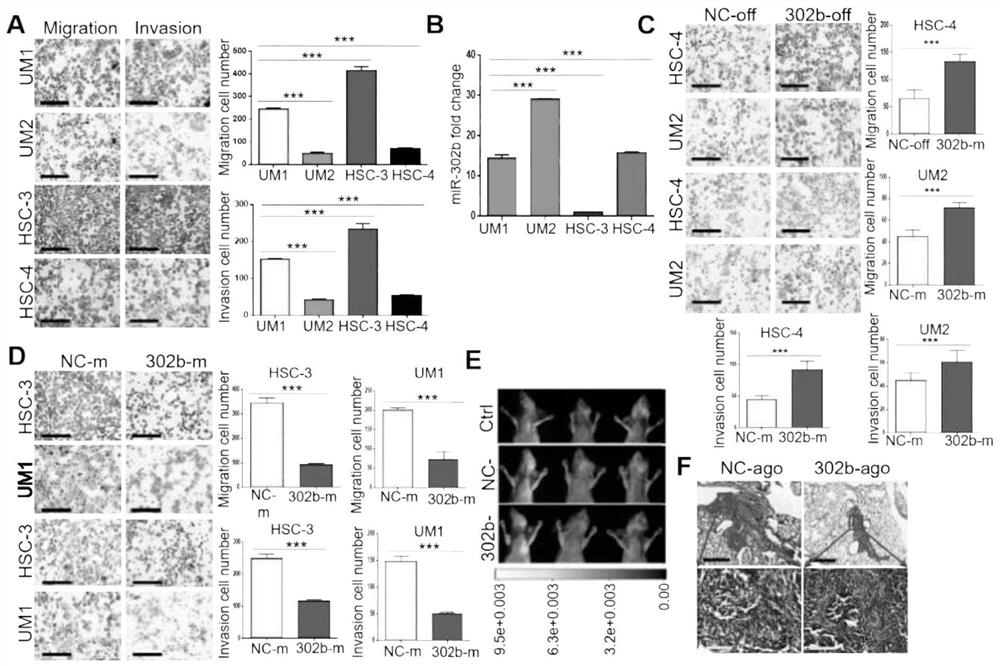
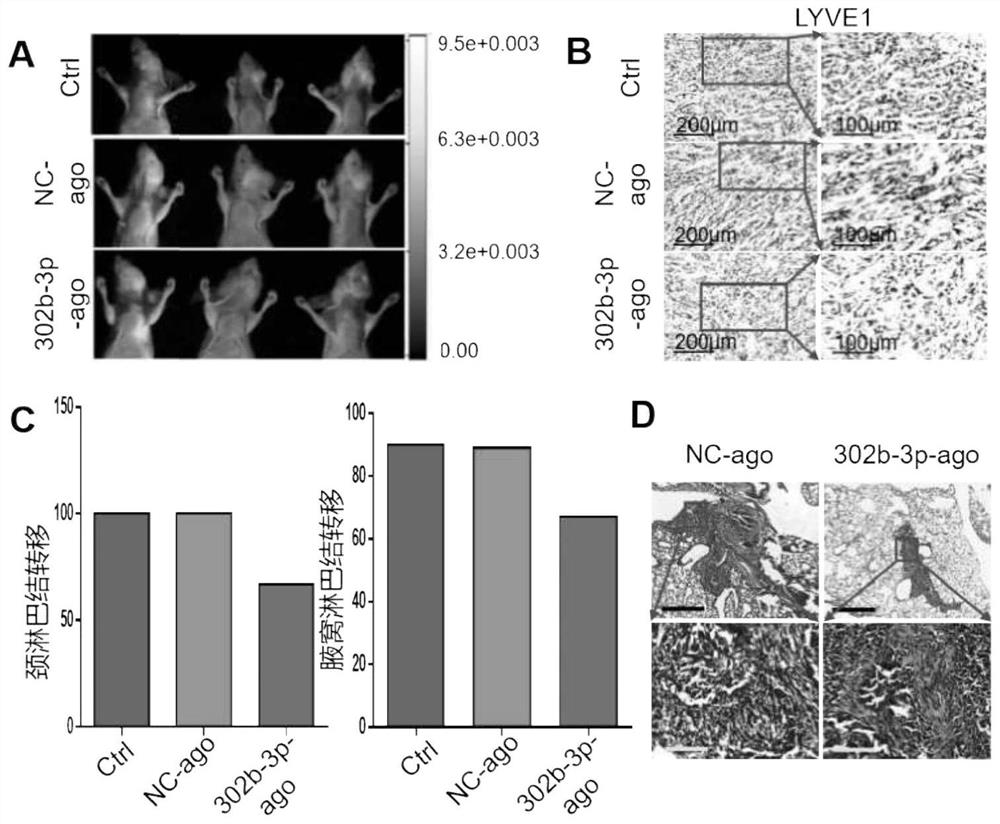
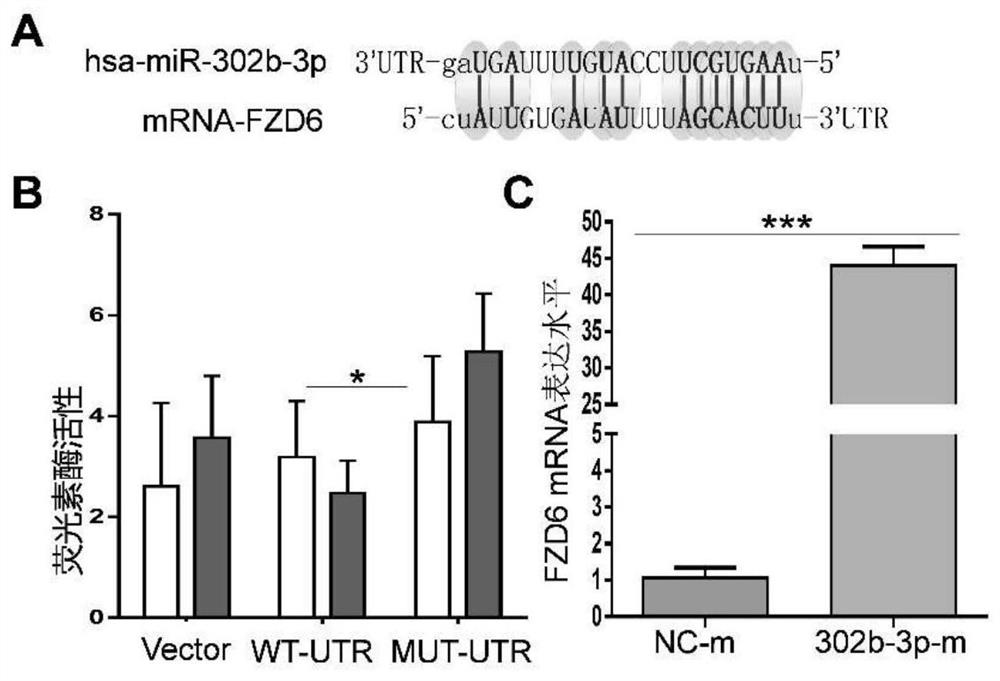
Application of miR-302b-3p as anti-tumor marker of oral squamous cell carcinoma
PendingCN113577309AImprove the level ofPrevent invasionOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementParanasal Sinus CarcinomaSquamous Carcinomas
The invention discloses application of miR-302b-3p as an anti-tumor marker of oral squamous cell carcinoma, and belongs to the field of tumor diagnosis and treatment. The application is divided into two aspects: firstly, the miR-302b-3p detection reagent is used for preparing a diagnostic kit for the invasiveness and / or migration of the oral squamous cell carcinoma, and secondly, the miR-302b-3p or a miR-302b-3p precursor is used as an active ingredient for preparing a medicine for delaying the invasion and / or migration of the oral squamous cell carcinoma. The application provides a new direction for diagnosis and treatment of oral squamous cell carcinoma, and has a very good application prospect.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
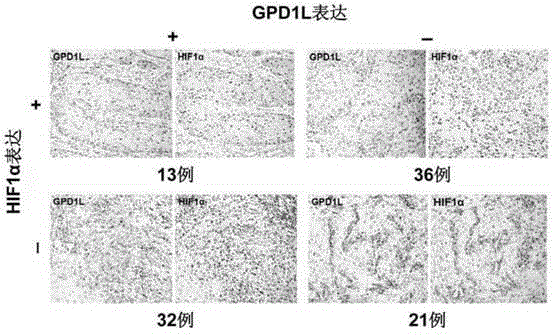
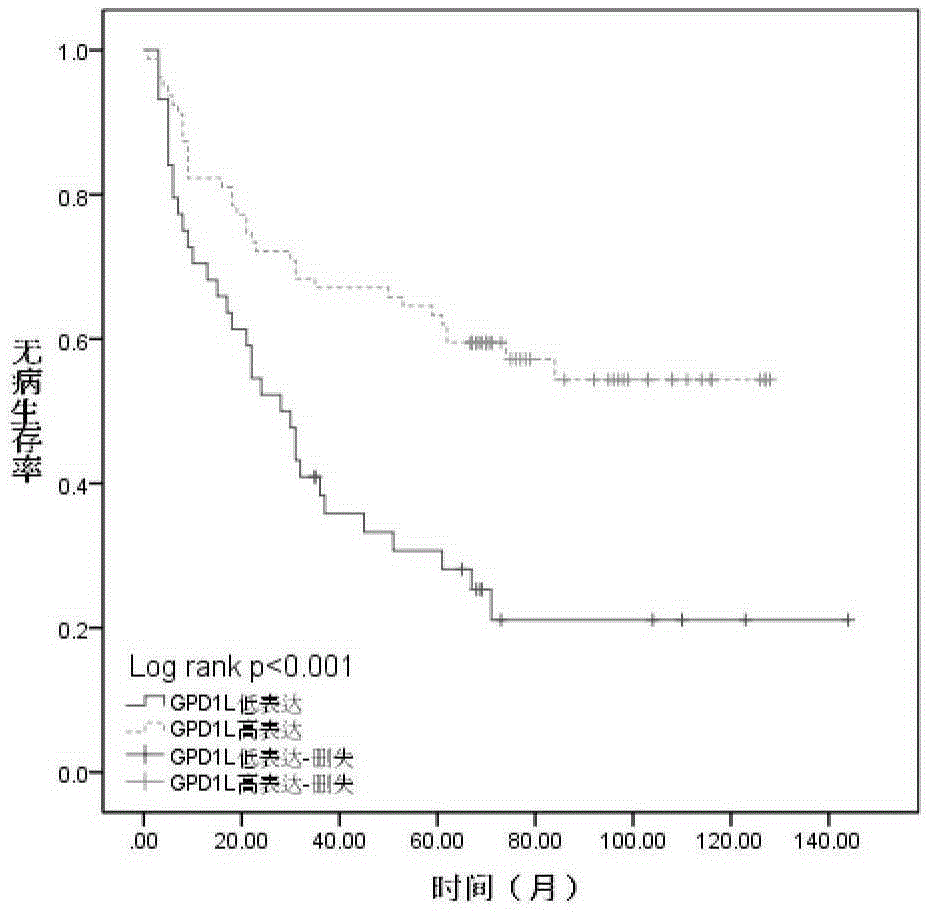
Biomarkers and their application in oral squamous cell carcinoma
ActiveCN104267191BIncreased sensitivityImprove featuresDisease diagnosisBiological testingNode metastasisSquamous Carcinomas
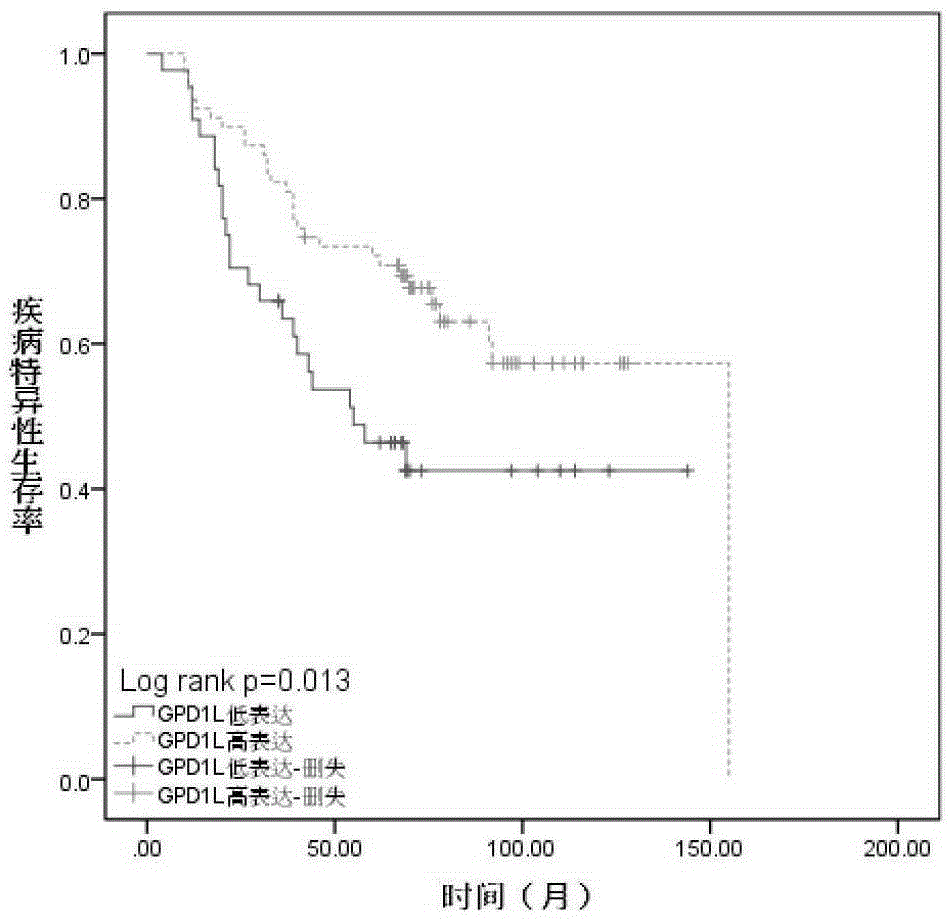
The invention provides a biological marker of oral cavity oropharynx squamous-cell carcinoma and application of the biological marker. The biological marker is GPD1L and / or HIF1 alpha, and especially a combination of the GPD1L and the alpha. According to the invention, by detecting expression levels of the GPD1L and / or the HIF1 alpha, oral cavity oropharynx squamous-cell carcinoma auxiliary diagnosis, oral cavity oropharynx squamous-cell carcinoma patient prognosis, and / or prognosis cervical lymph node metastasis prediction can be performed.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SCHOOL OF STOMATOLOGY
Mouse-derived oral squamous cell carcinoma cell strain, and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN113201495ASolve the problem of poor tumor formation effectCompound screeningCell dissociation methodsCarcinoma cell lineSquamous Carcinomas
The invention discloses a mouse-derived oral squamous cell carcinoma cell strain,and a preparation method and application thereof, and the preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, adding 4-nitroquinoline-N-oxide into mouse drinking water, inducing mouse oral squamous cell carcinoma, and obtaining mouse oral squamous cell carcinoma tumor tissues; carrying out digestion and primary culture on the mouse tumor tissue to obtain mouse tumor primary cells; selecting a monoclonal cell from the primary cells by adopting a monoclonal screening method; and purifying the monoclonal cells, carrying out continuous passage, and screening out a cell strain to obtain the mouse oral squamous cell carcinoma cell strain. The mouse squamous cell carcinoma cells can form tumors on both immunodeficient nude mice and immune-healthy C57BL / 6J mice, so that the problem that the existing human oral squamous cell carcinoma cell line has poor tumor forming effect on immune-healthy mice is solved; the invention has an important value in establishment of a tumor immune mouse model and research of a subsequent interaction mechanism of a tumor and an immune system.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
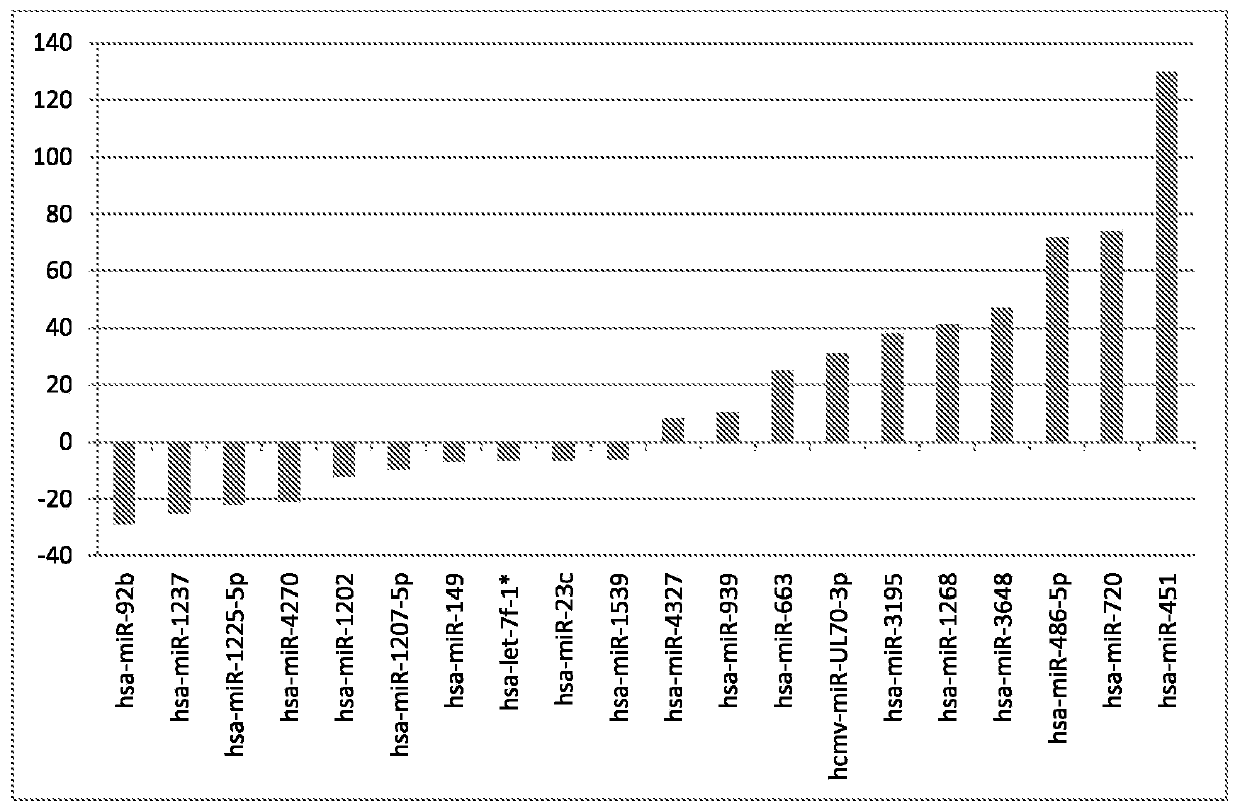
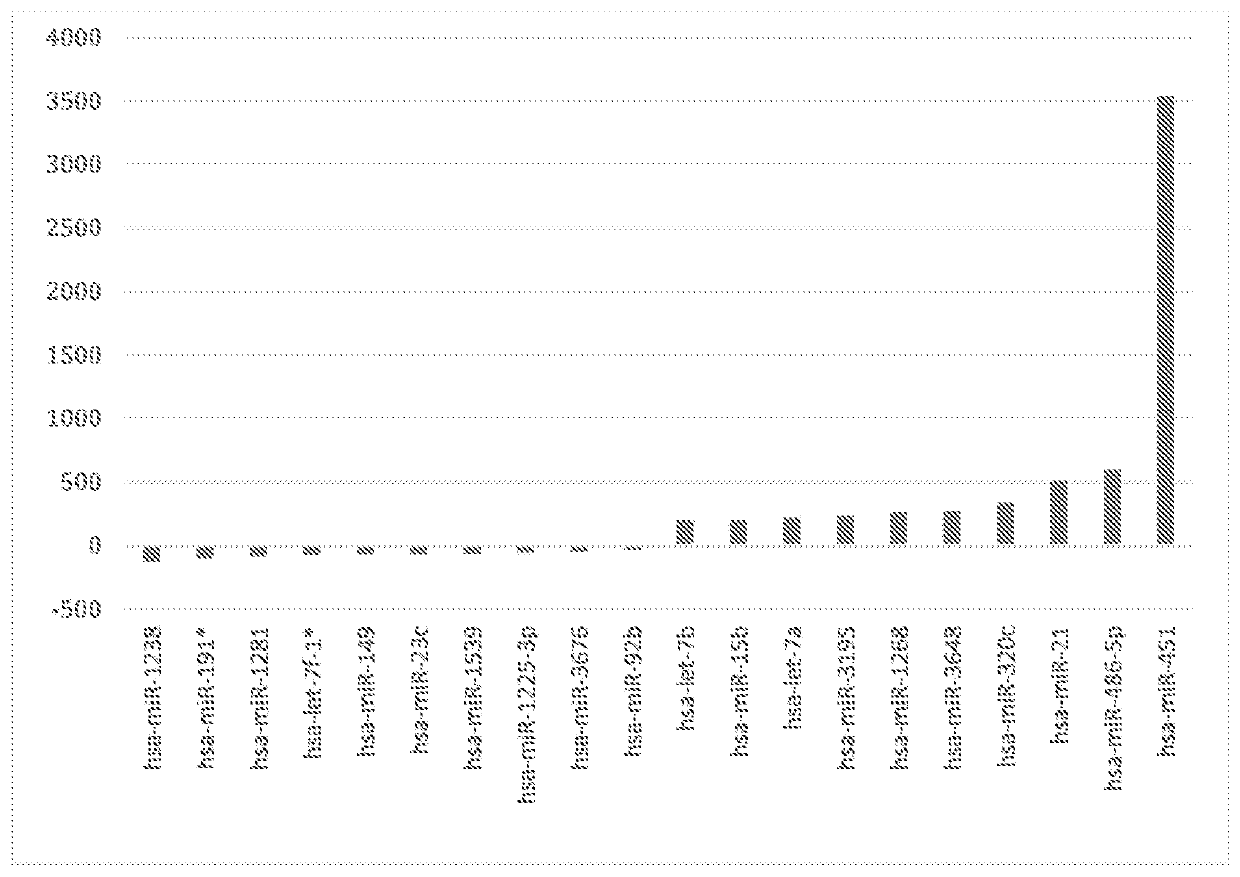
Biomarkers of oral, pharyngeal and laryngeal cancers
Provided herein are methods for detecting a head and neck cancer of the oral cavity or throat, optionally oral squamous cell carcinoma, comprising executing the step of determining the expression of two or more miRNA in a biological sample obtained from a subject, wherein the two or more miRNA are selected from the group consisting of hsa-let-7a, hsa-miR-16, hsa-miR-21, hsa-miR-451, hsa-miR-486-5pand hsa-miR-92a- 3p, and wherein the level of expression of said two or more niiRNAs in the biological sample relative to the level of expression of said two or more miRNAs in one or more cancer-freereference samples is indicative of the presence of a head and neck cancer of the oral cavity or throat of the subject.
Owner:N 特兰 +1
Construction methods, markers and applications of disease identification models
Provides an auxiliary marker for disease identification consisting of decanoylcarnitine, cysteine and bile acids. The present invention also provides a method for constructing a disease identification model, which includes: step 1, obtaining a training case set, and the subjects in the training case set include oral lichen planus patients and oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. In step 2, the serum sample of the subject is collected, and the serum sample is subjected to ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole / electrostatic field orbitrap tandem high-resolution mass spectrometry analysis to obtain oral lichen planus and oral squamous cell carcinoma. Multiple differential metabolites; step 3, using variable weight importance ranking and receiver operating characteristic curves to determine decanoylcarnitine, cysteine and bile acids from multiple differential metabolites as a disease discrimination model. The invention provides a disease identification model, which can identify and distinguish oral lichen planus and oral squamous cell carcinoma at an early stage, and has the advantages of minimally invasive and high accuracy.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Application of Cranemenine in Biomedicine
ActiveCN109432118BEnhanced inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsSquamous CarcinomasObstructive chronic bronchitis
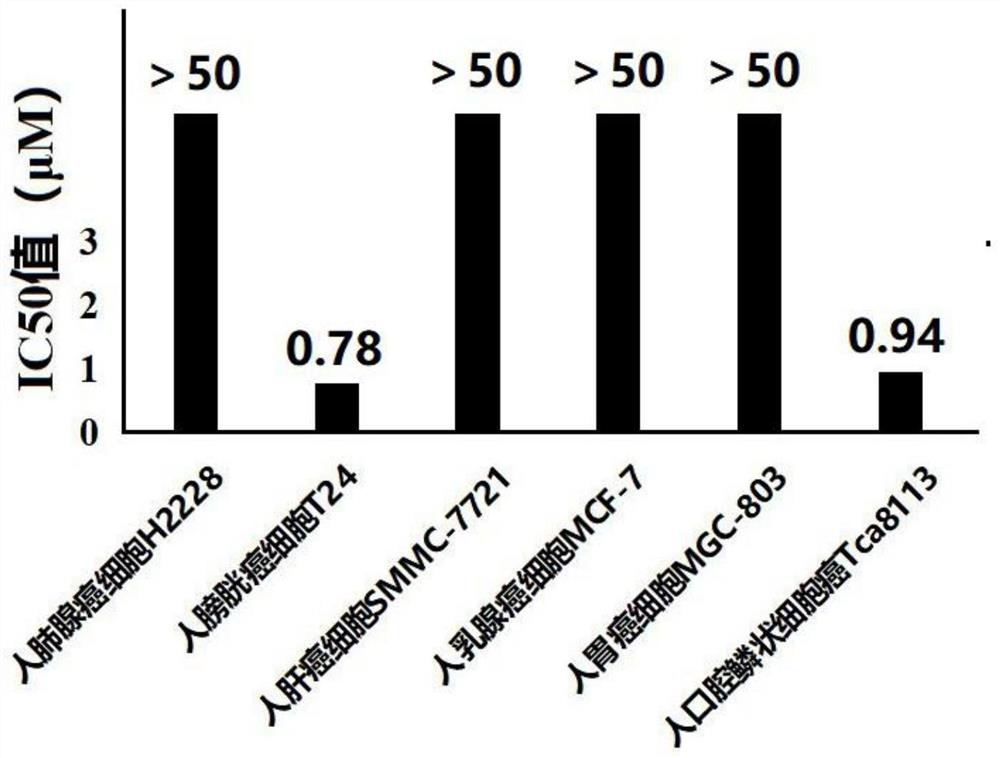
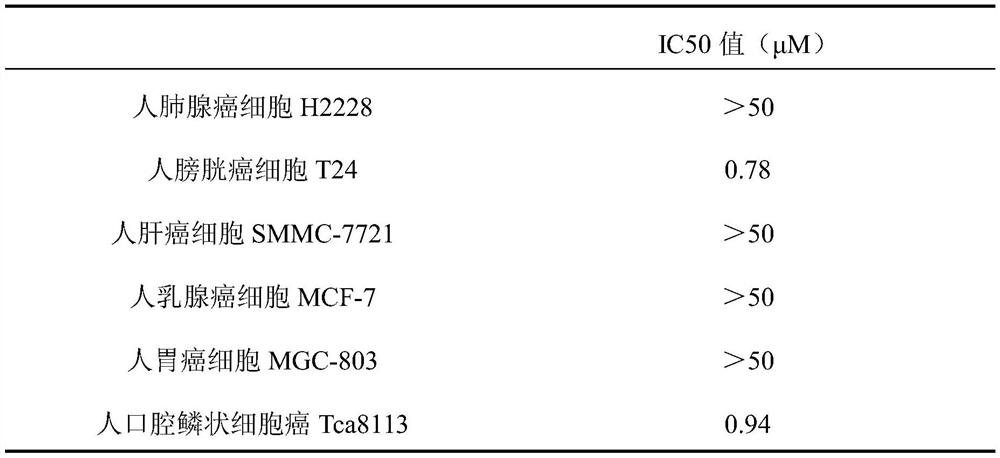
The invention discloses application of argyreia aceta alkali in biological medicines. The whole herb of argyreia aceta has medicinal value, and argyreia aceta is widely distributed in many places of Guangxi, such as Guigang, Yulin, Fangcheng Gang and Wuming, and is used as a traditional Chinese medicine for treating acute and chronic bronchitis, tuberculosis, liver cirrhosis, nephritis edema, sores and furuncles, acute mastitis, skin eczema, traumatic bleeding and other symptoms. The argyreia aceta alkali is a chemical component separated from argyreia aceta. According to the invention, through the tests for the proliferation inhibition effect of the argyreia aceta alkali on human lung adenocarcinoma cell H2228, human bladder cancer cell T24, human hepatoma carcinoma cell SMMC-7721, humanbreast cancer cell MCF-7, human gastric carcinoma cell MGC-803 and human oral squamous cell carcinoma Tca8113, the argyreia aceta alkali is found to have an excellent inhibiting effect on human bladder cancer cell T24 and human oral squamous cell carcinoma Tca8113 and has no obvious inhibiting effect on other tested tumor cells, so that the argyreia aceta alkali can be used for preparing drugs fortreating bladder cancer or oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Owner:北京麦迪海药业有限责任公司
A deep learning method for identifying oral squamous cell carcinoma based on visual features
ActiveCN111369501BAccurate classificationImage enhancementImage analysisSquamous CarcinomasSquamous Cell Cancers
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
A kit for diagnosing oral squamous cell carcinoma
ActiveCN107422123BSignificant technological progressSensitivity advantageMaterial analysisOral tissueMessenger RNA
The invention provides a reagent kit for diagnosing oral squamous cell carcinoma. The reagent kit comprises specific antibodies for detecting HOXA10, specific antibodies for detecting HOXA11, specific antibodies for detecting HOXC6 or compositions with more than one or two optional specific antibodies for detecting the expression quantities of HOXC8. The reagent kit has the advantages that sequencing results for mRNA [messenger RNA (ribonucleic acid)] of the oral squamous cell carcinoma and normal oral tissues in TCGA (the cancer genome atlas) databases are statistically analyzed, data of 32 cases of normal oral tissues and 341 cases of oral squamous cell carcinoma tissues are incorporated, obvious difference of expression of partial genes in HOX families in the oral squamous cell carcinoma and the normal tissues is discovered, and accordingly the reagent kit is suitable to be applied to diagnosing the oral squamous cell carcinoma; expression of genes in the HOX families is detected in oral squamous cell carcinoma tissue pathological sections by the aid of immunohistochemical processes, and accordingly positive expression of the genes in the oral squamous cell carcinoma and application values of the genes in diagnosis can be determined.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
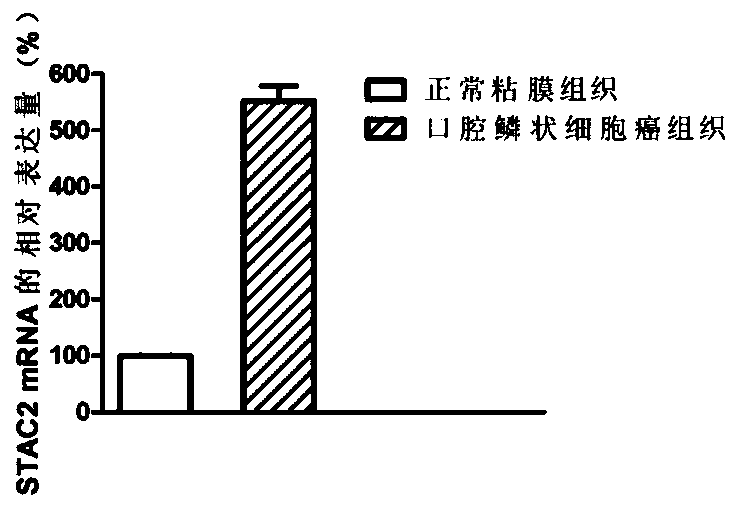
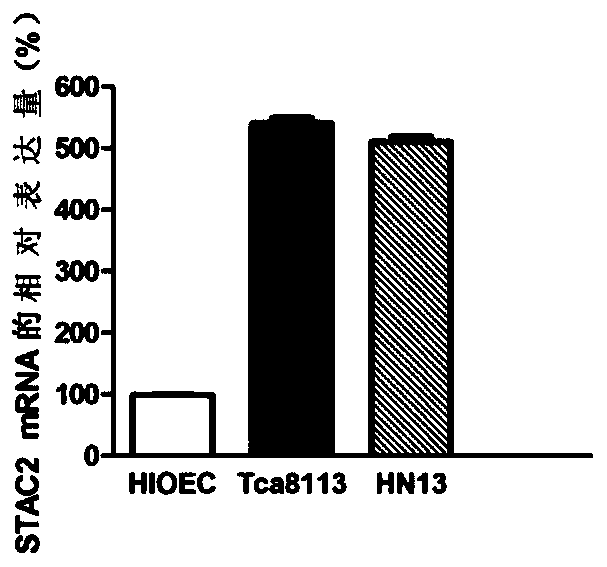
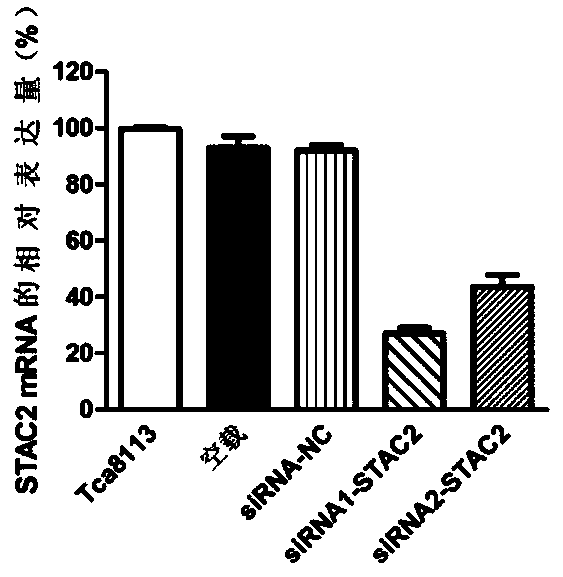
Application of molecular marker stac2 in oral squamous cell carcinoma
ActiveCN106520992BAchieve early diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsOvarian Squamous Cell CarcinomaSquamous Cell Breast Carcinoma
The invention discloses application of a molecular marker STAC2 to oral squamous cell carcinoma. Experimental results show that STAC2 is highly expressed in a patient with oral squamous cell carcinoma; and a STAC2-specific siRNA for silencing STAC2 so as to reduce expression of STAC2, so proliferation of oral squamous cell carcinoma is inhibited. Thus, STAC2 can be applied to research on the pathogenesis of oral squamous cell carcinoma and is applicable as a molecular target to clinical diagnosis and treatment of oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Owner:BEIJING MEDINTELL BIOMED CO LTD
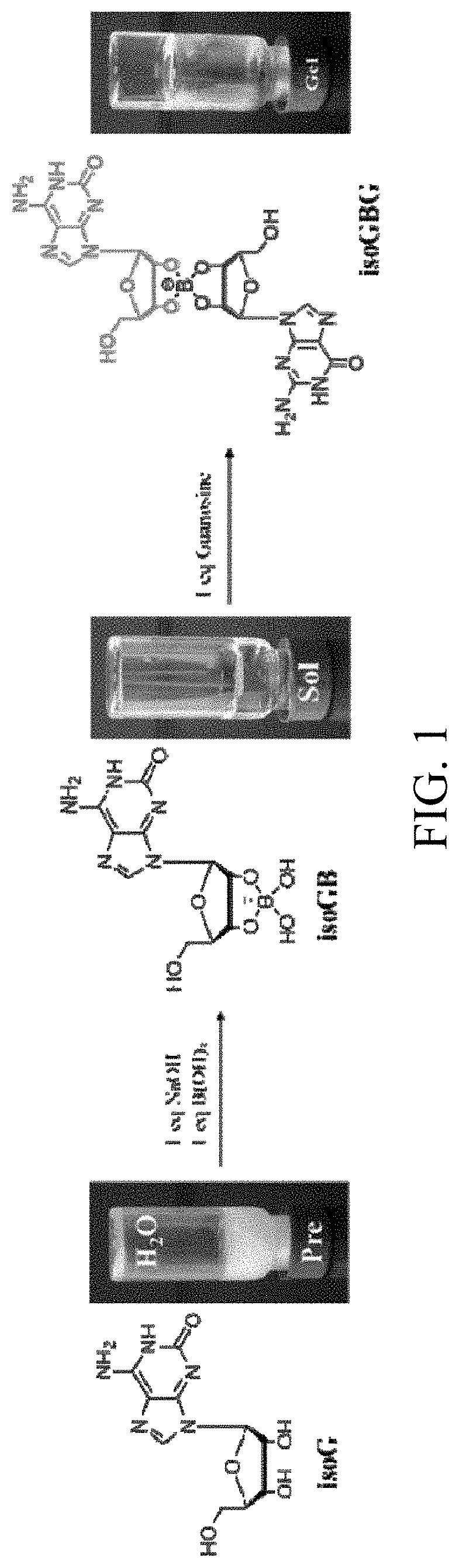
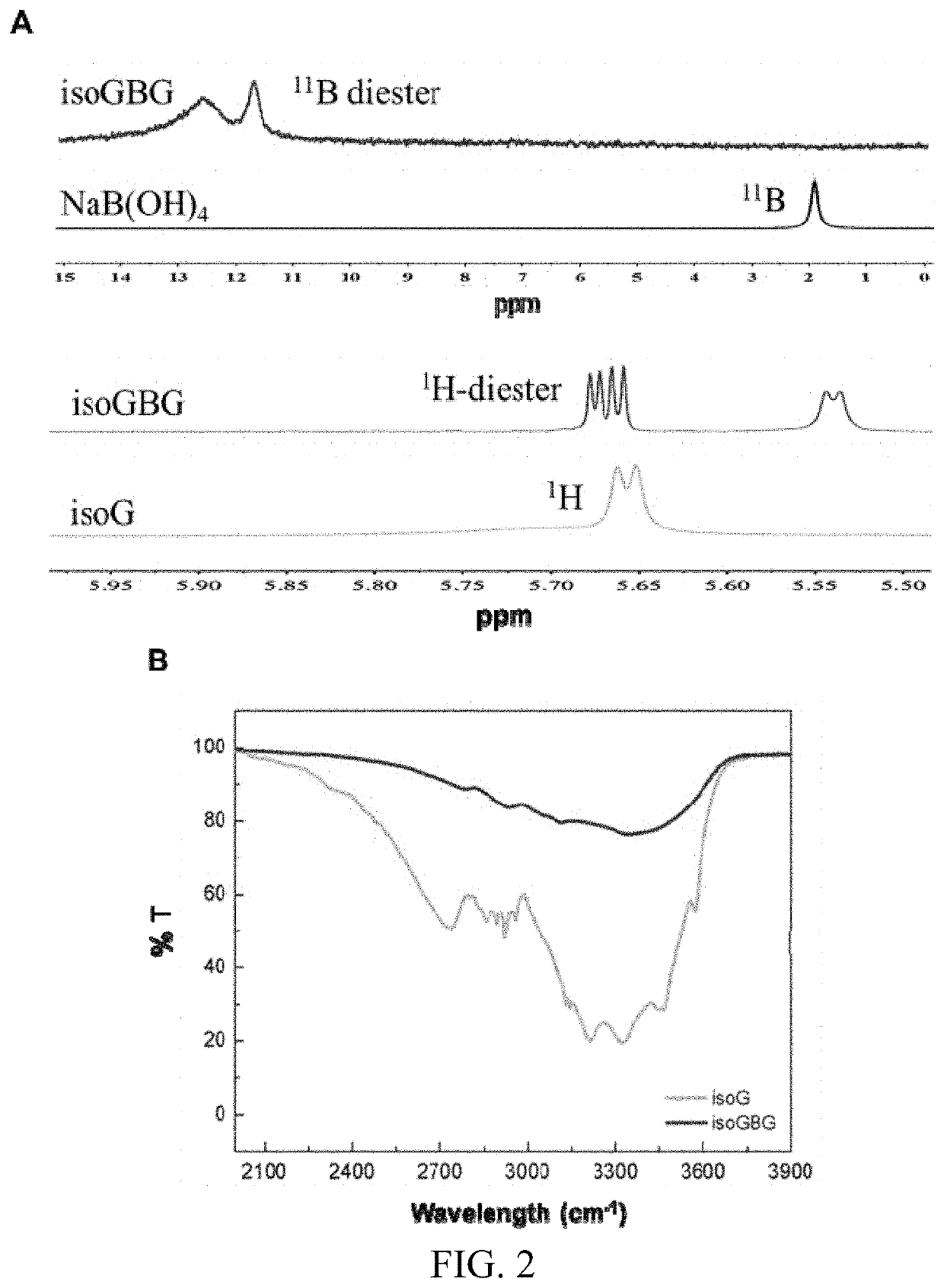
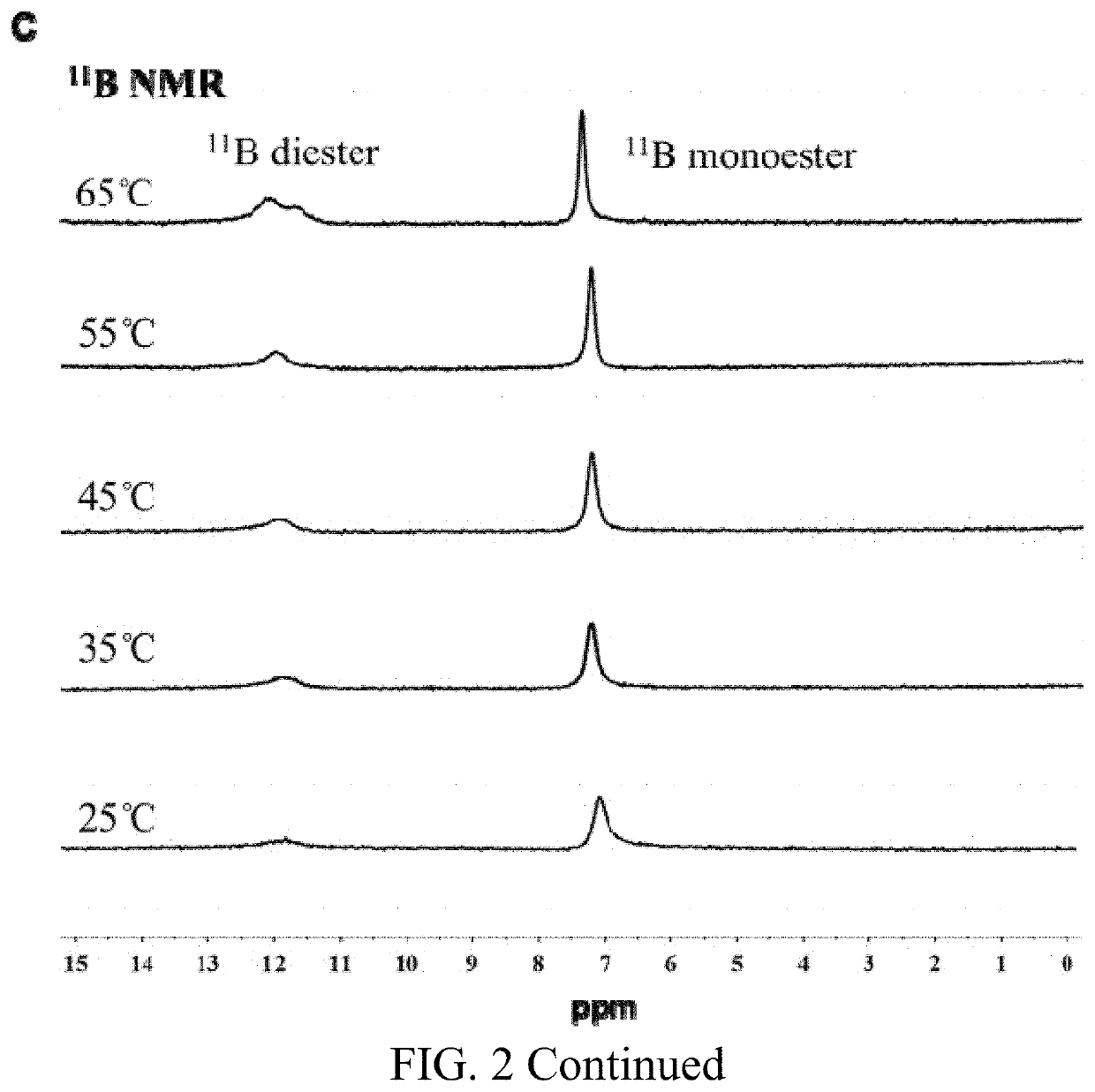
Bifunctional nucleoside hydrogel, preparation method therefor and use thereof
PendingUS20220218605A1Prevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesSquamous CarcinomasOncology
A bifunctional nucleoside hydrogel is formed by dissolving isoguanosine, guanosine and a borate in water or an aqueous solution and then crosslinking same. The bifunctional nucleoside hydrogel integrates a carrier and a drug effect and has a significant inhibitory effect on the activity of tumor cells, and in particular has a significant inhibitory effect on the activity of cells related to lung cancer, glioma, osteoma, colon cancer, breast cancer, oral squamous cell carcinoma and tongue squamous cell carcinoma, of which the inhibitory effect on the activity of cells related to oral squamous cell carcinoma is the best. Therefore, the bifunctional nucleoside hydrogel has potential application prospects in preparing anti-tumor drugs, and particularly, same can provide a new approach for treating oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Oral squamous cell carcinoma differentiation degree prediction system
PendingCN113112459AStrong resolutionIncreased sensitivityImage analysisMedical imagesDiseaseSquamous Carcinomas
The invention discloses an oral squamous cell carcinoma differentiation degree prediction system, and belongs to the field of disease diagnosis and artificial intelligence. The system comprises an input module, a prediction module and an output module. The input module is used for inputting pathological section image data; the prediction module is internally provided with an OfficientNets model; and the output module is used for outputting the slice map which is subjected to region marking according to the differentiation degree. The prediction system is high in prediction accuracy of the differentiation degree of the oral squamous cell carcinoma, and is superior to an existing method for predicting other cancers through deep learning.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com