Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
59 results about "Optical interleaver" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
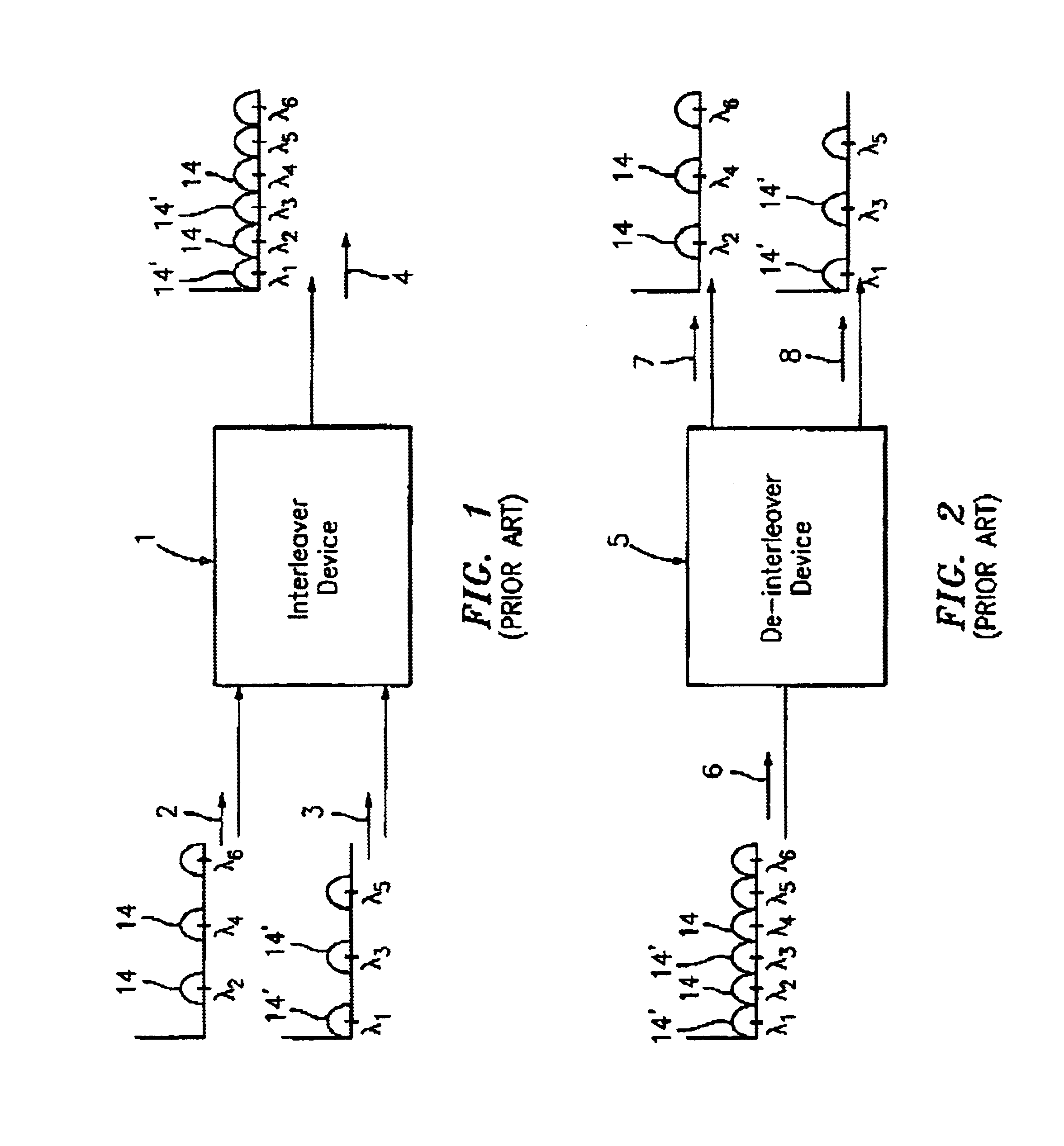
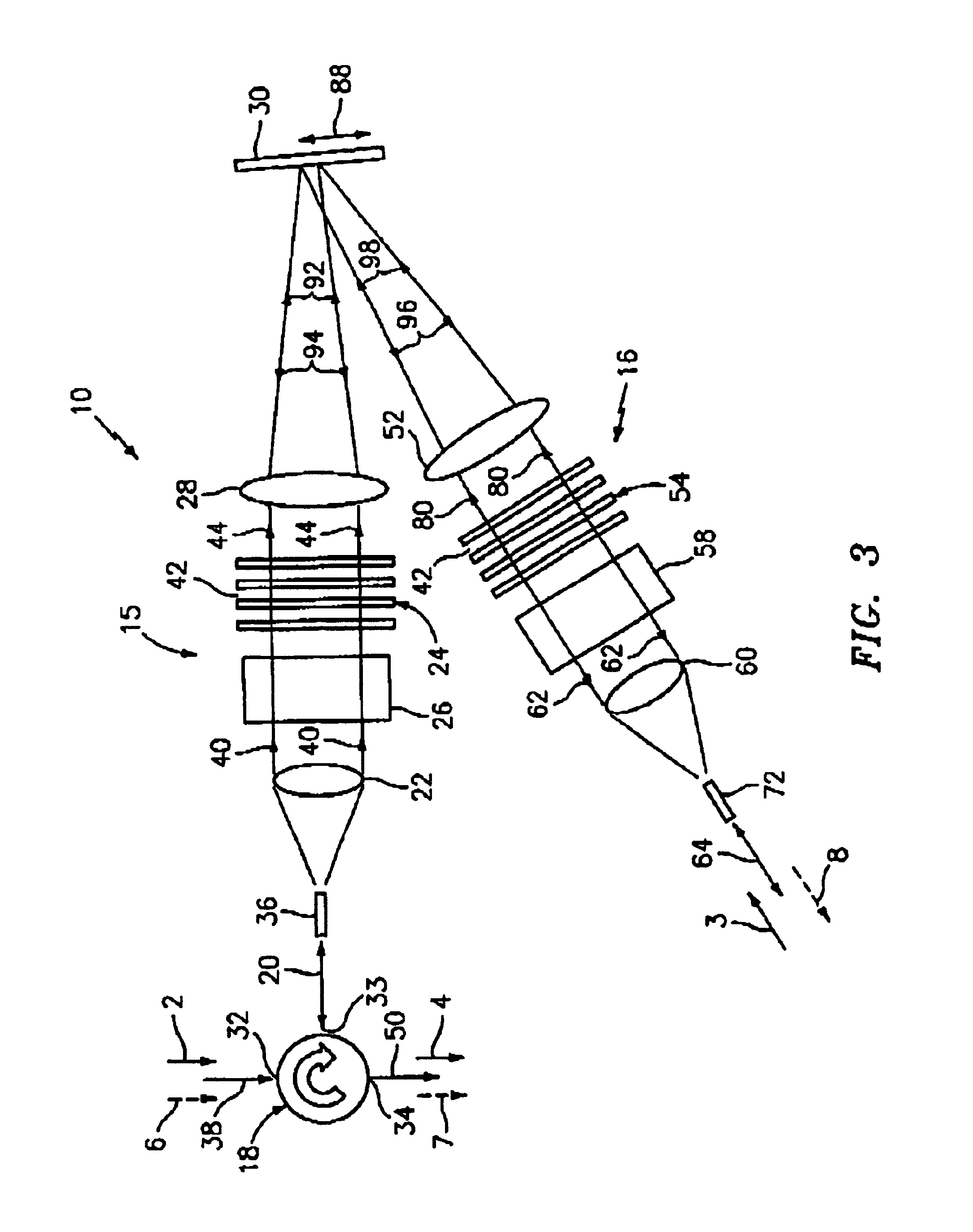
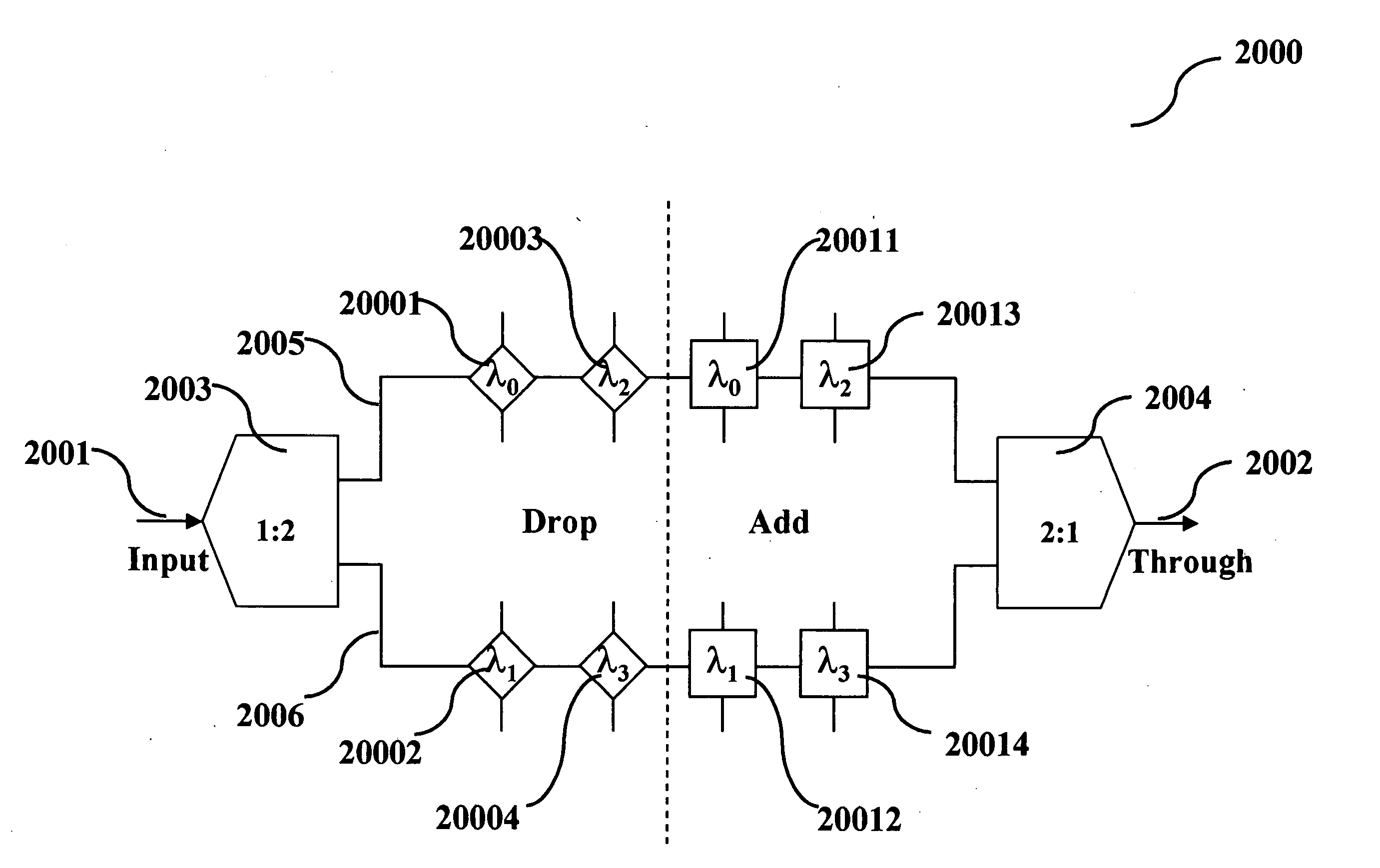
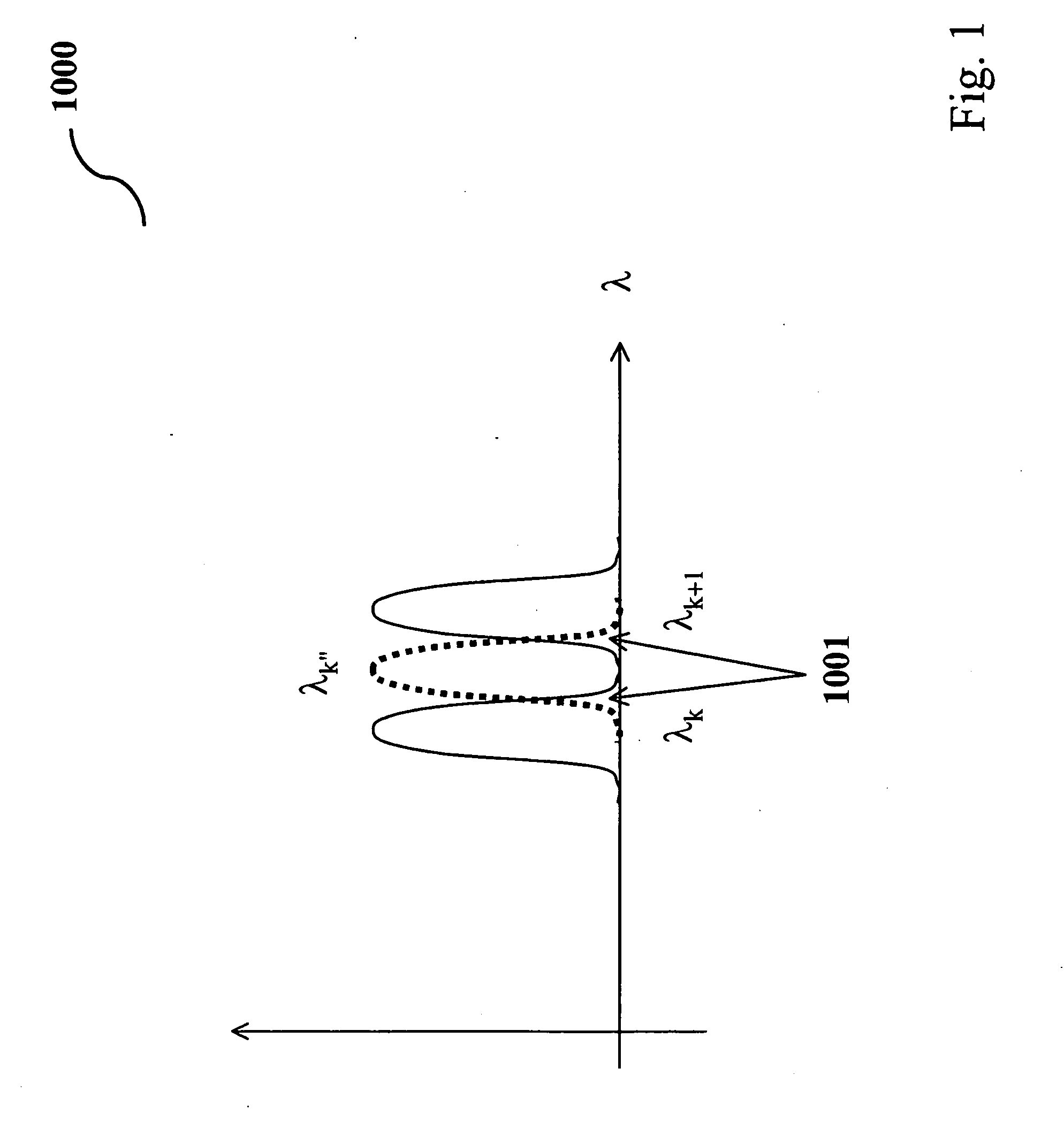
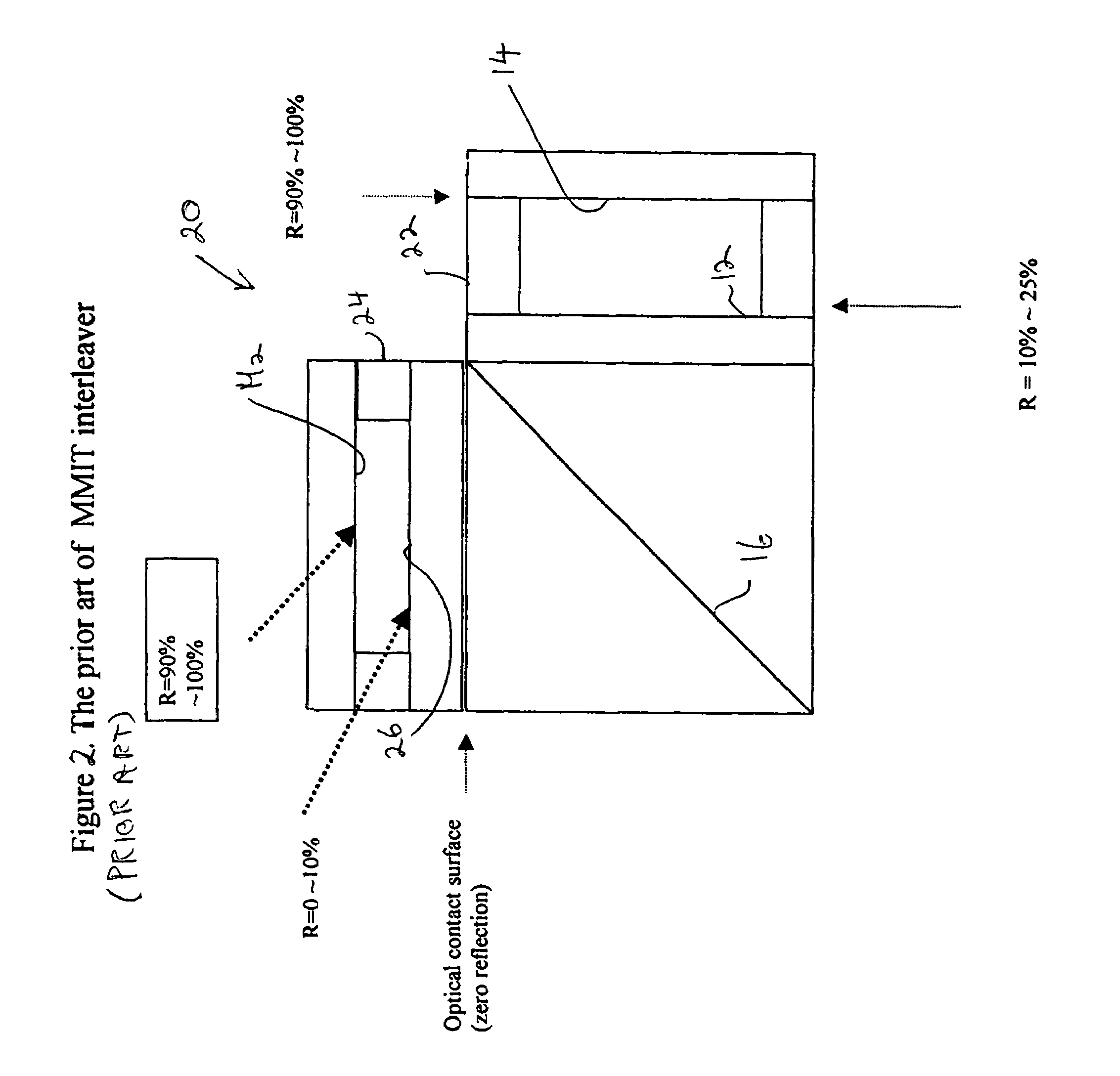
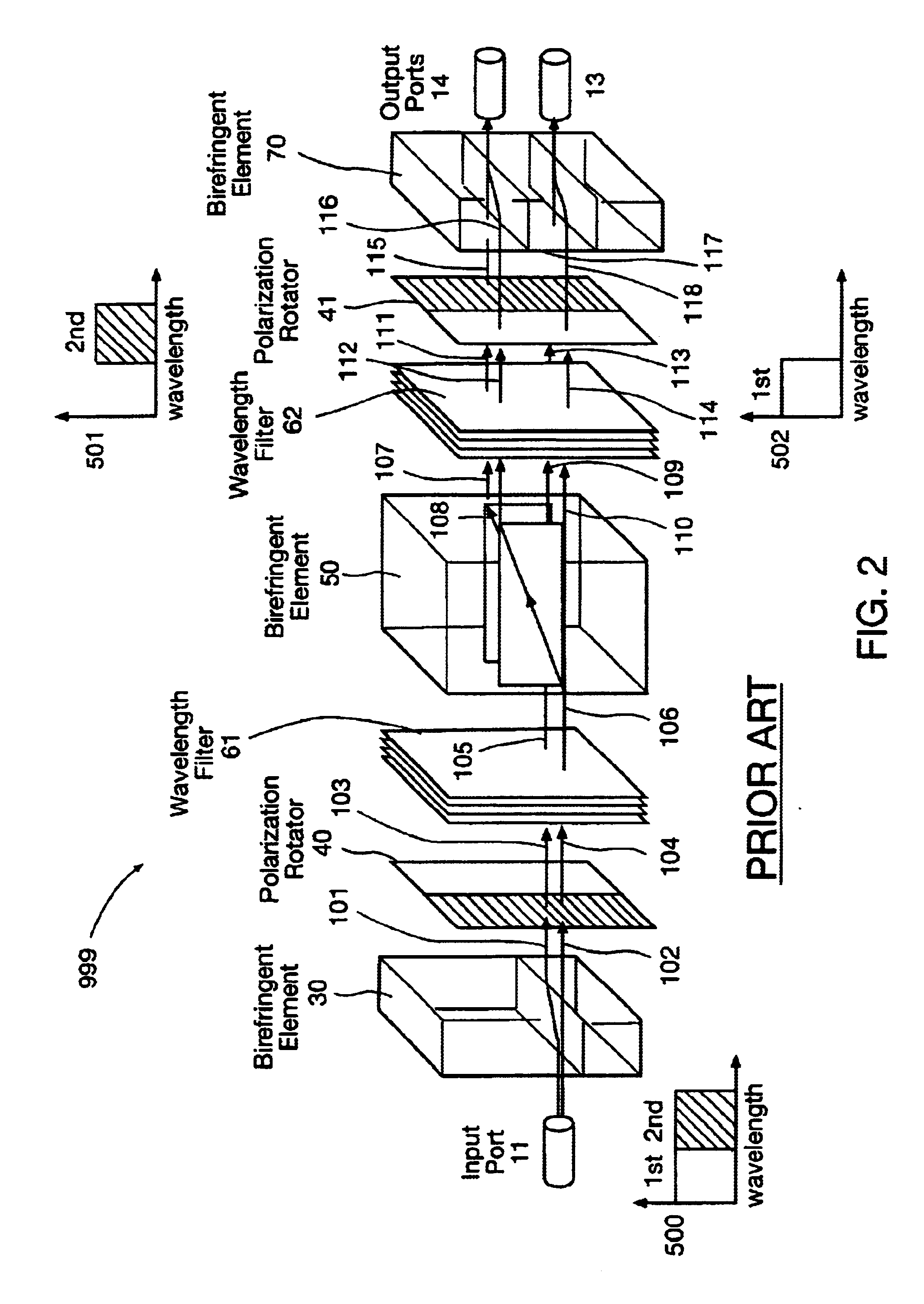
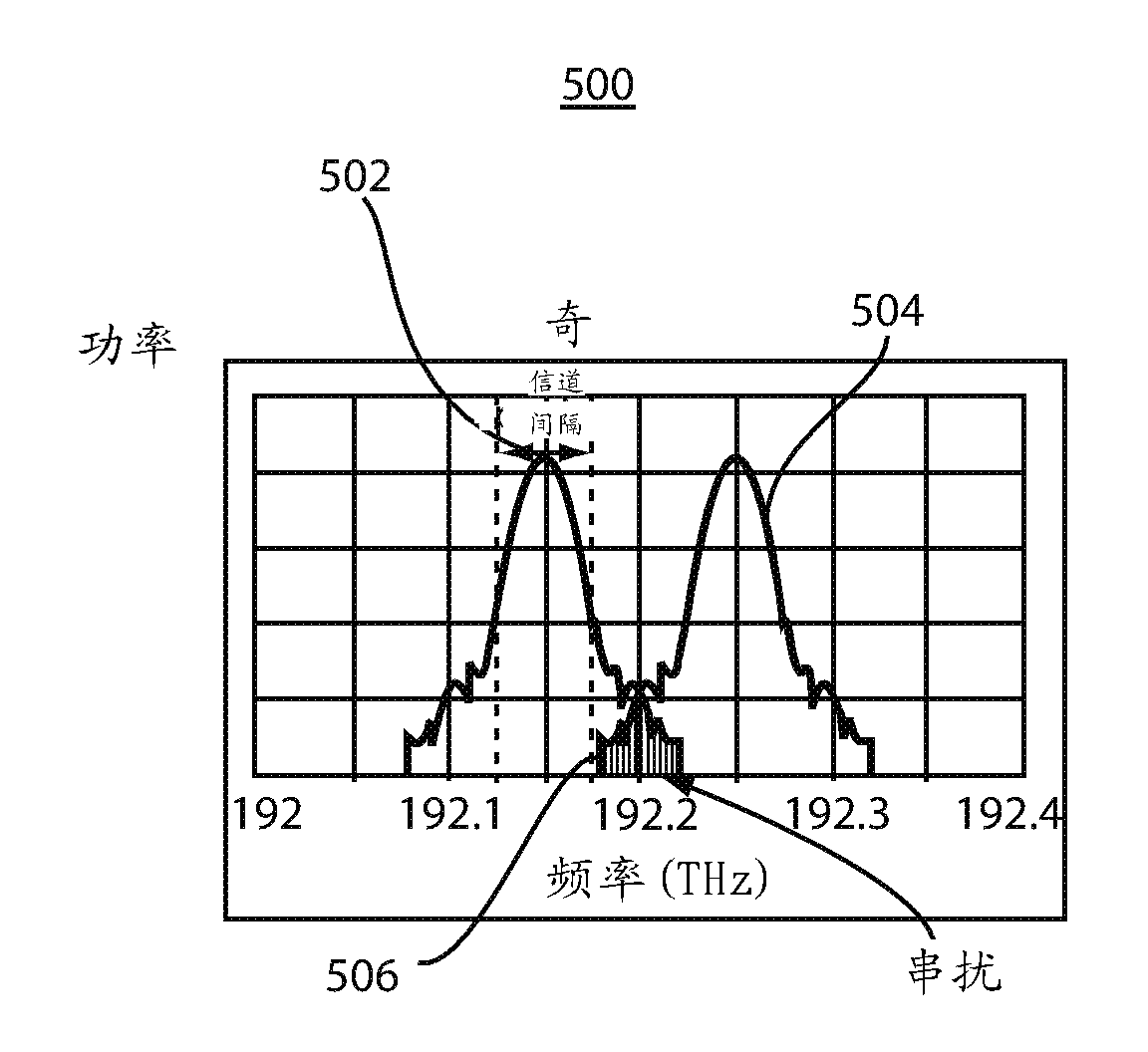
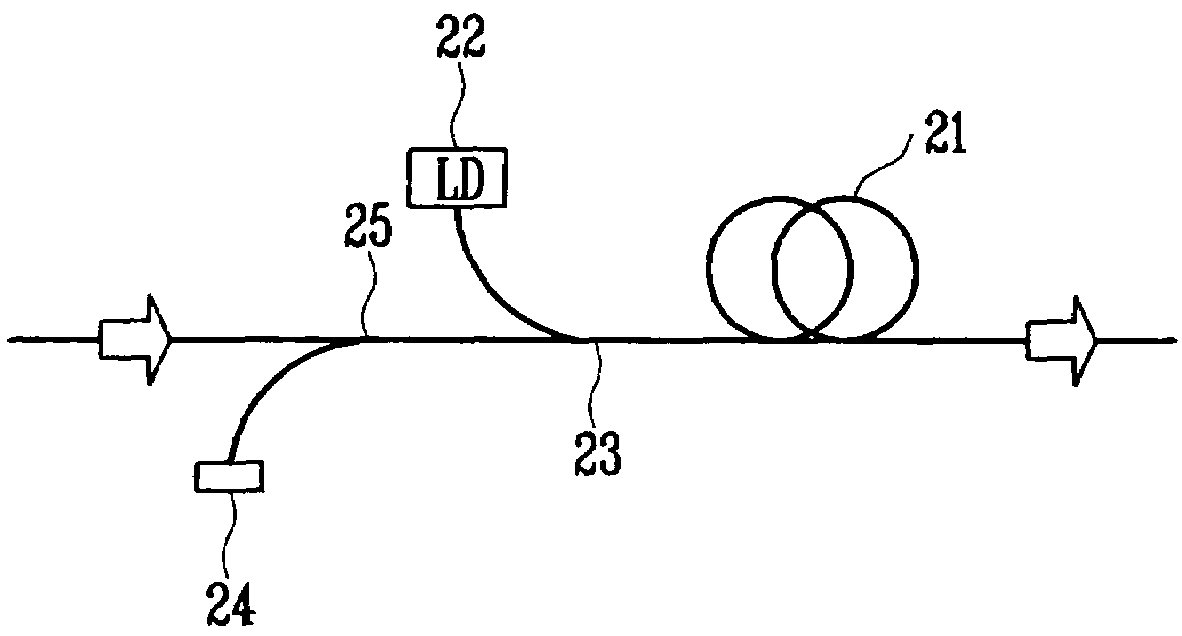
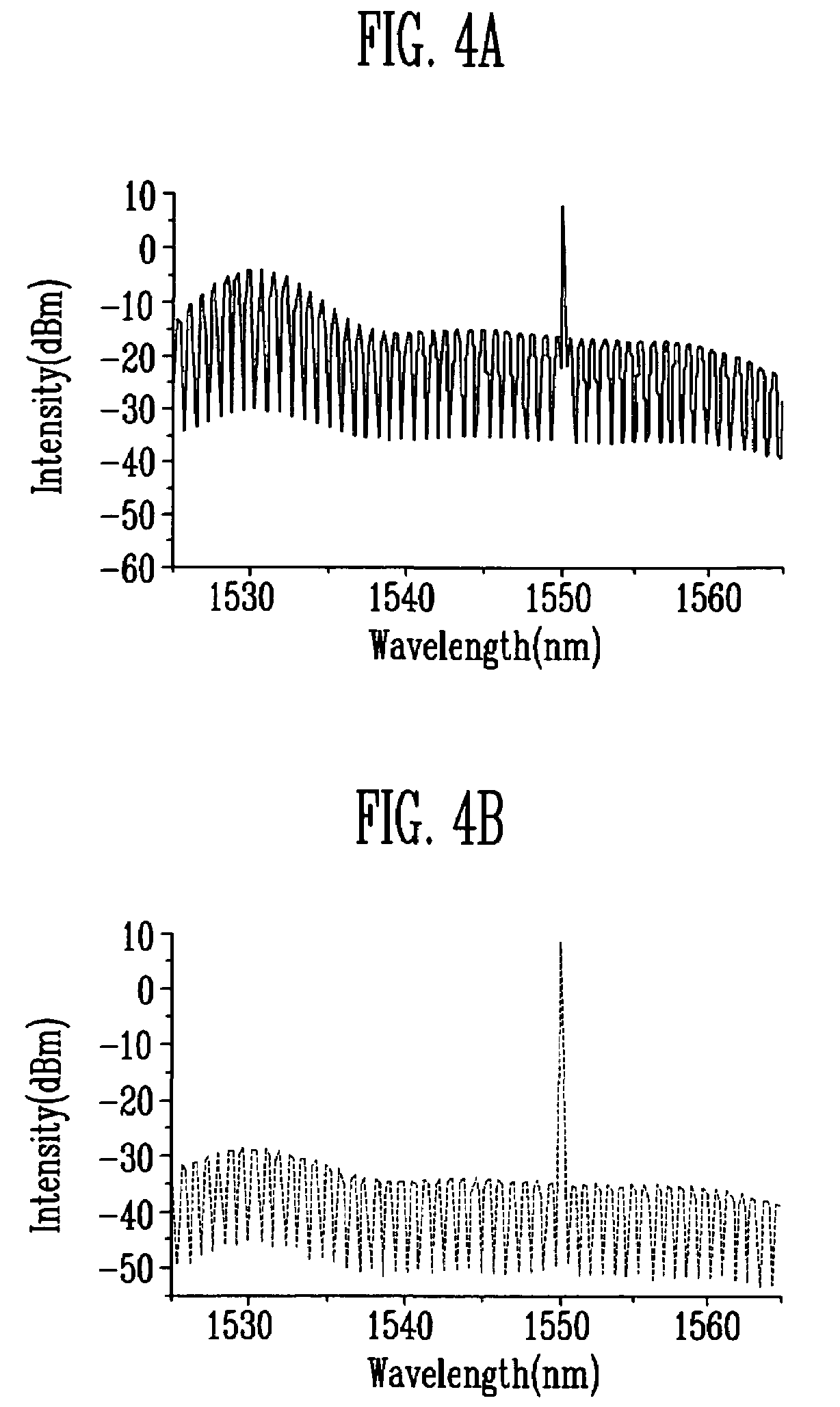
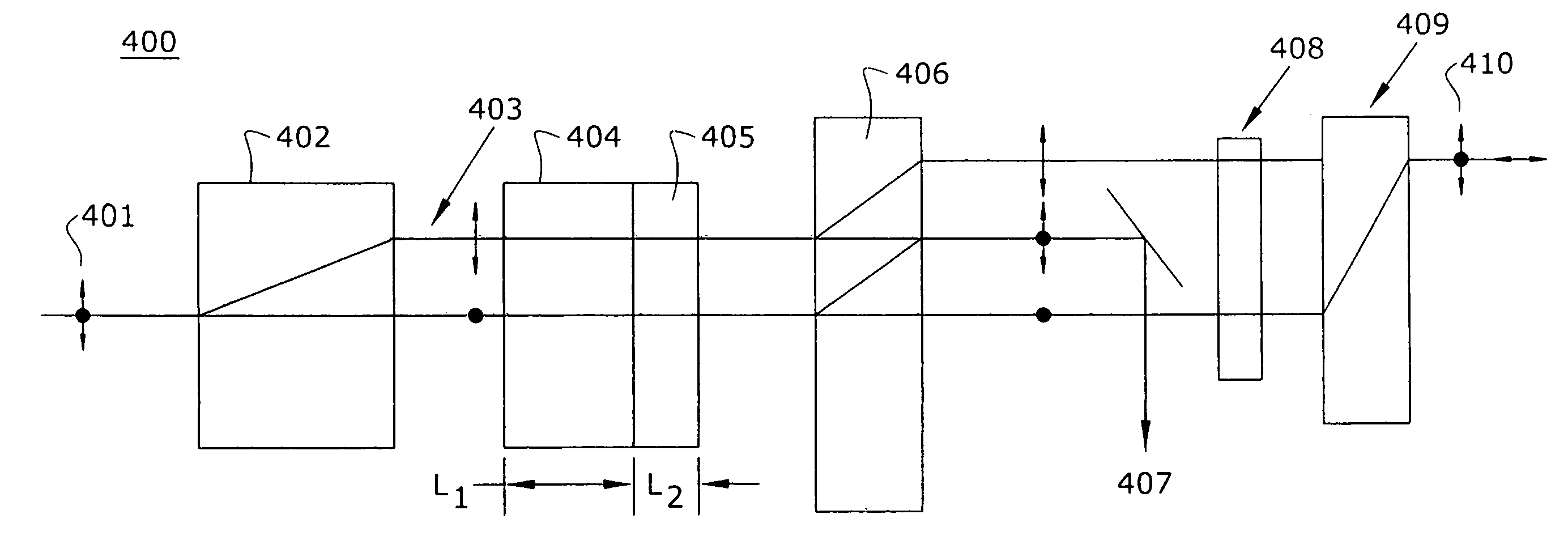
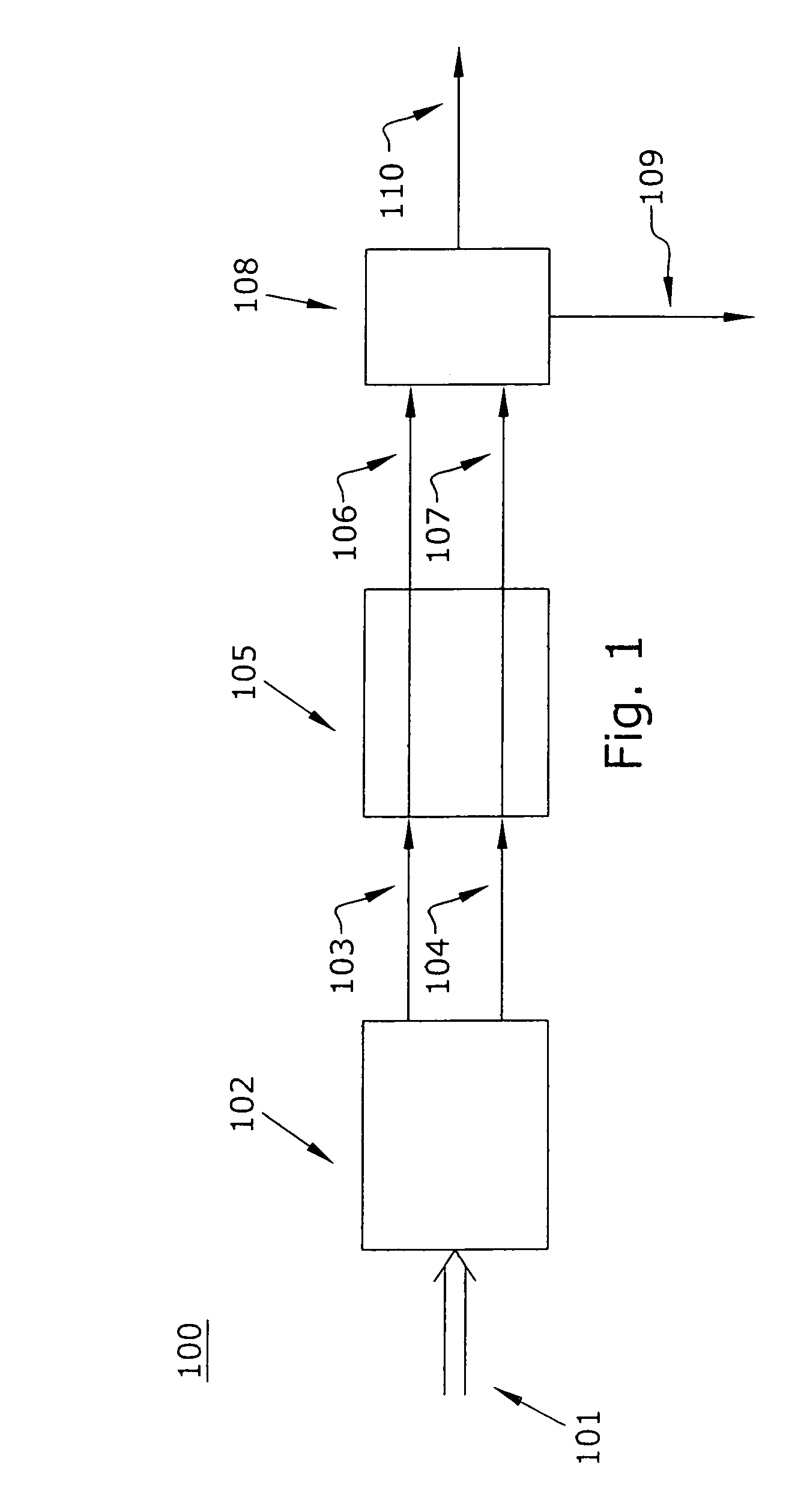
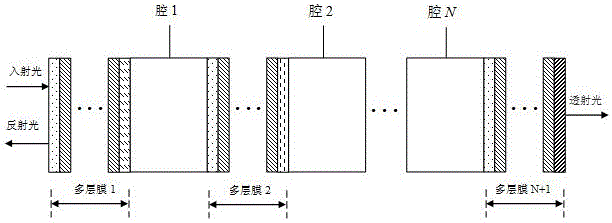
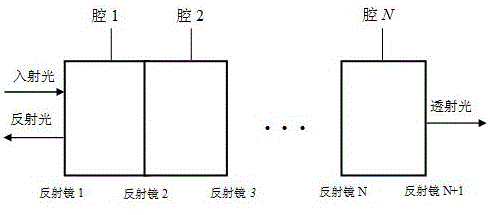
An optical interleaver is a 3-port passive fiber-optic device that is used to combine two sets of dense wavelength-division multiplexing (DWDM) channels (odd and even channels) into a composite signal stream in an interleaving way. For example, optical interleaver takes two multiplexed signals with 100 GHz spacing and interleaves them, creating a denser DWDM signal with channels spaced 50 GHz apart. The process can be repeated, creating even denser composite signals with 25 GHz or 12.5 GHz spacing.
Spectrum division multiplexing for high channel count optical networks
InactiveUS20020126291A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsUsing optical meansFrequency spectrumPath length
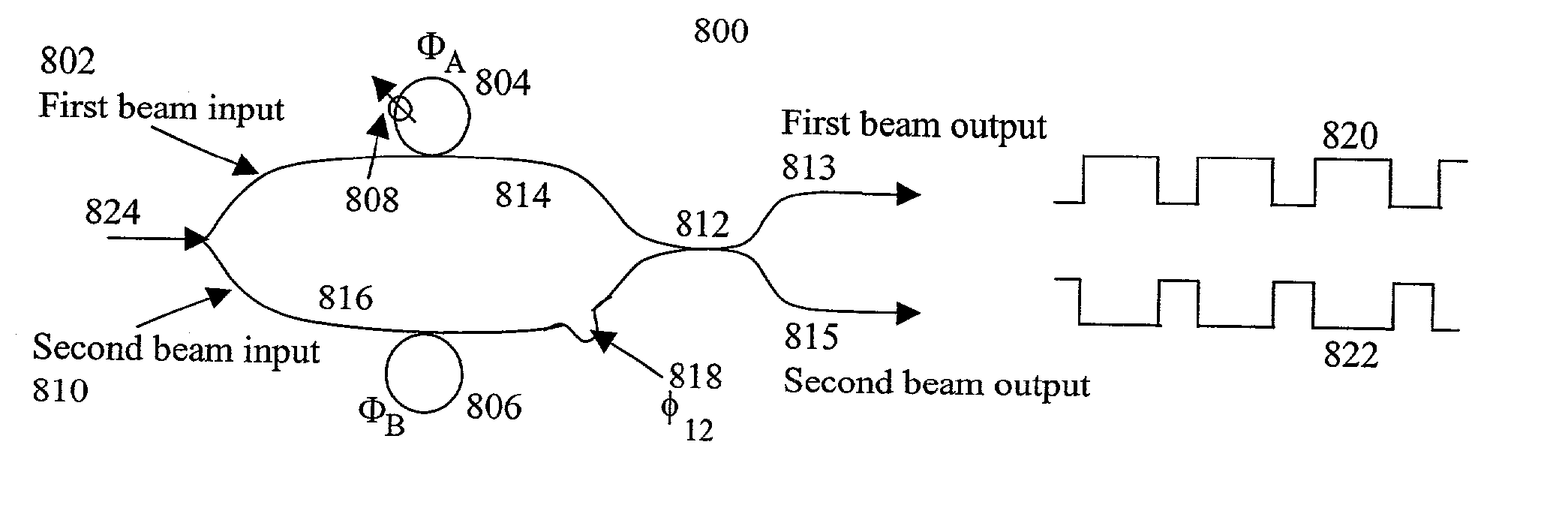
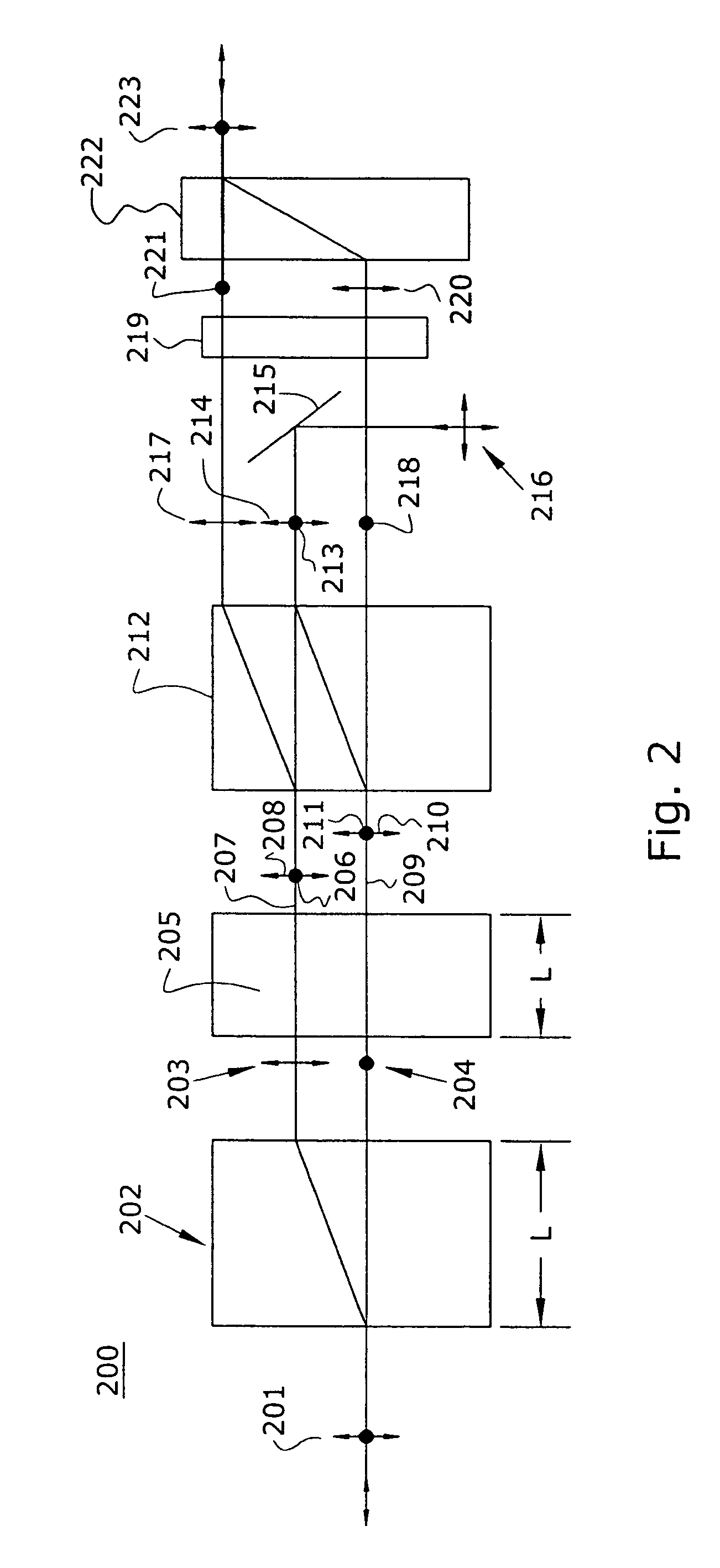
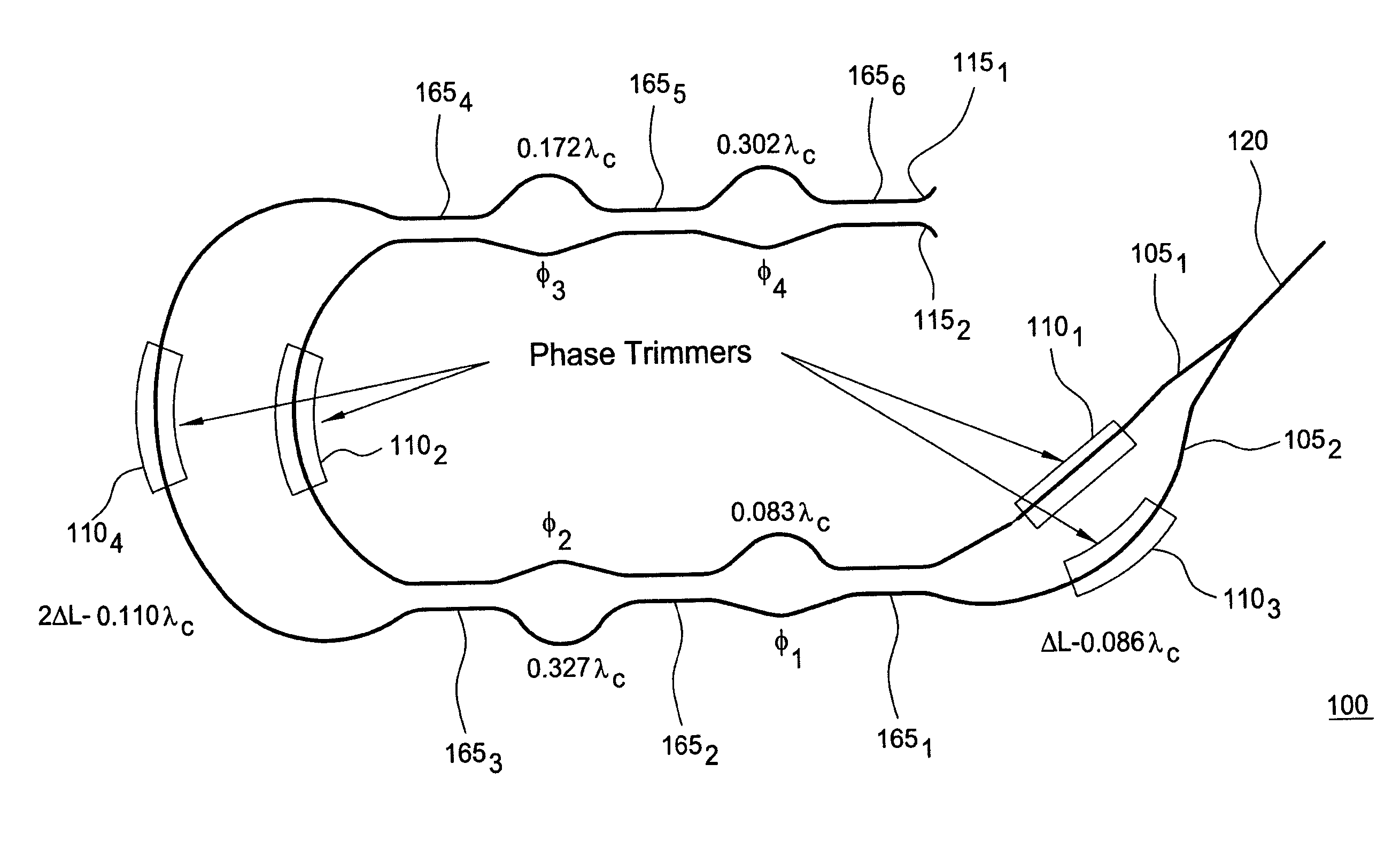
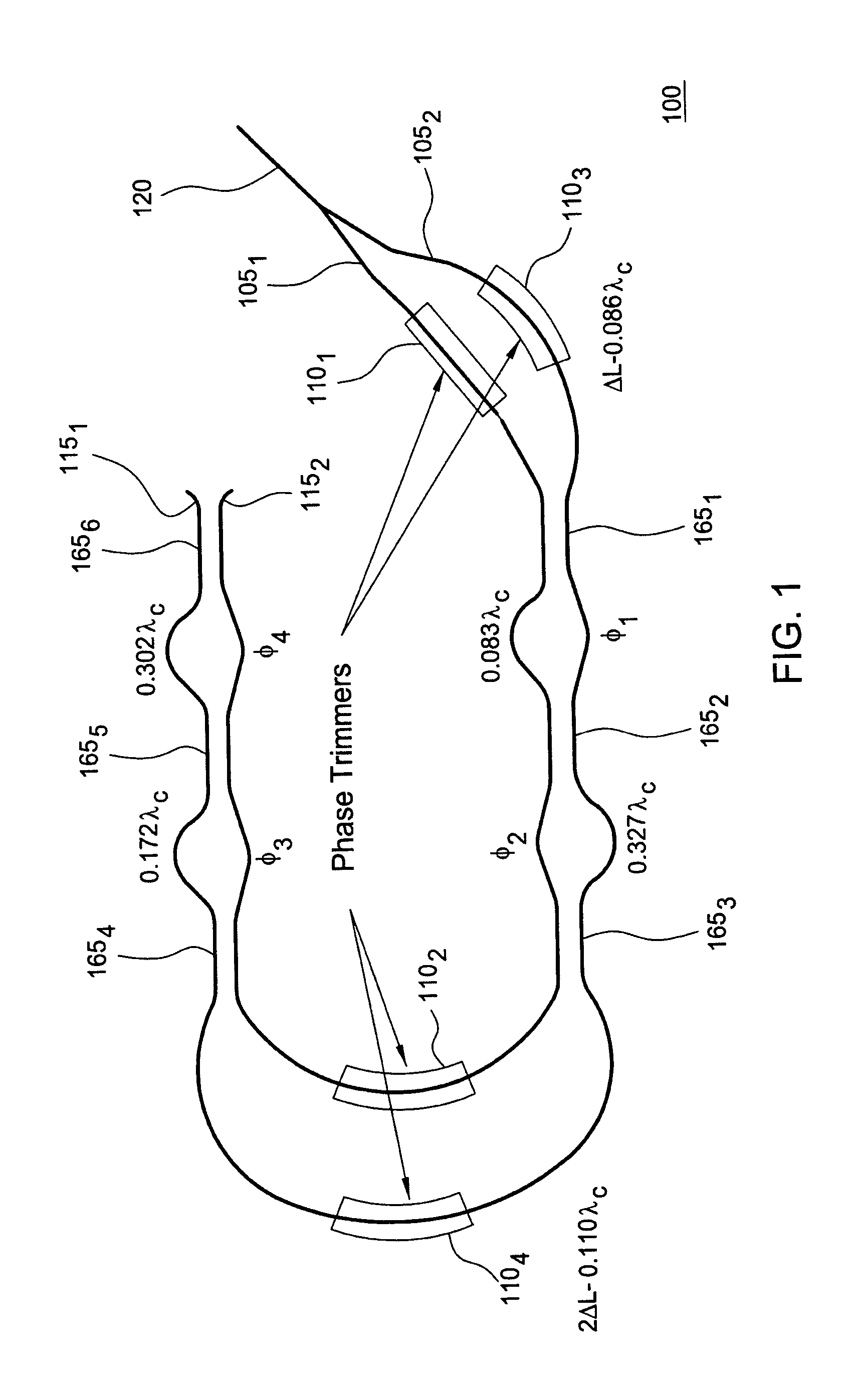
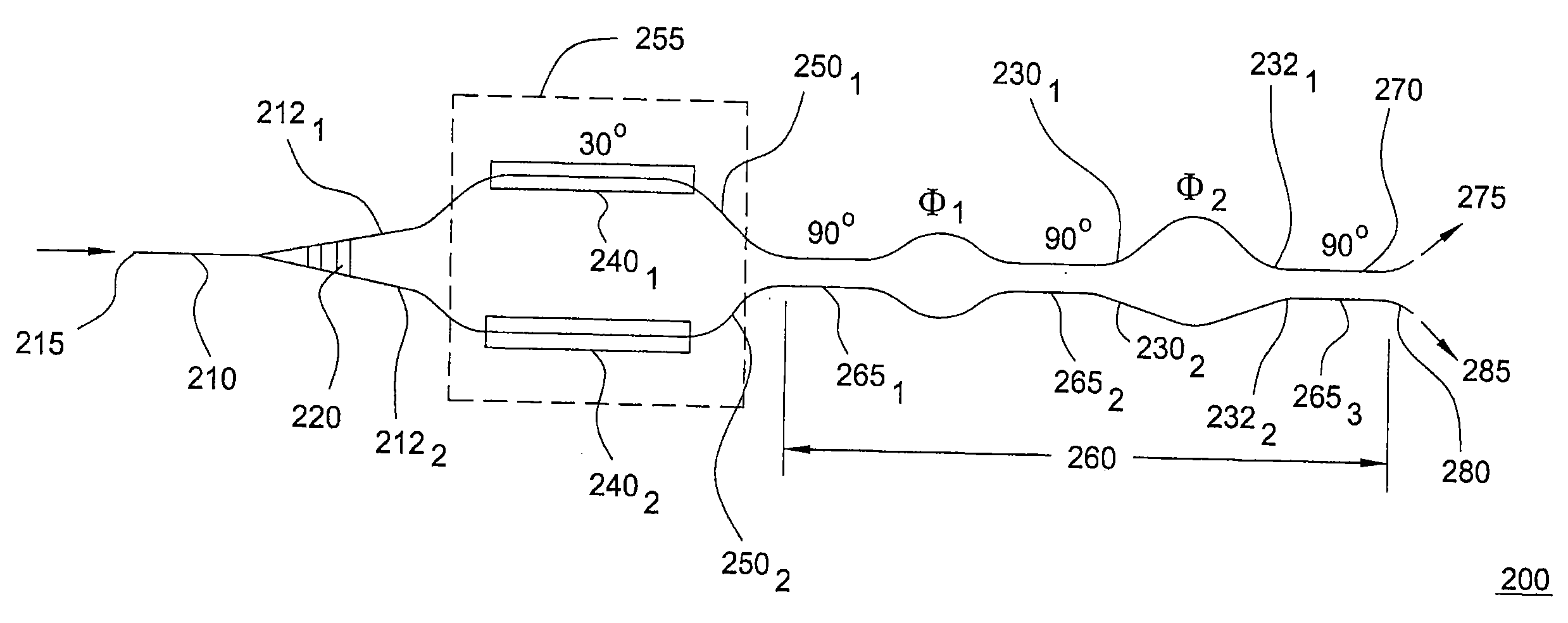
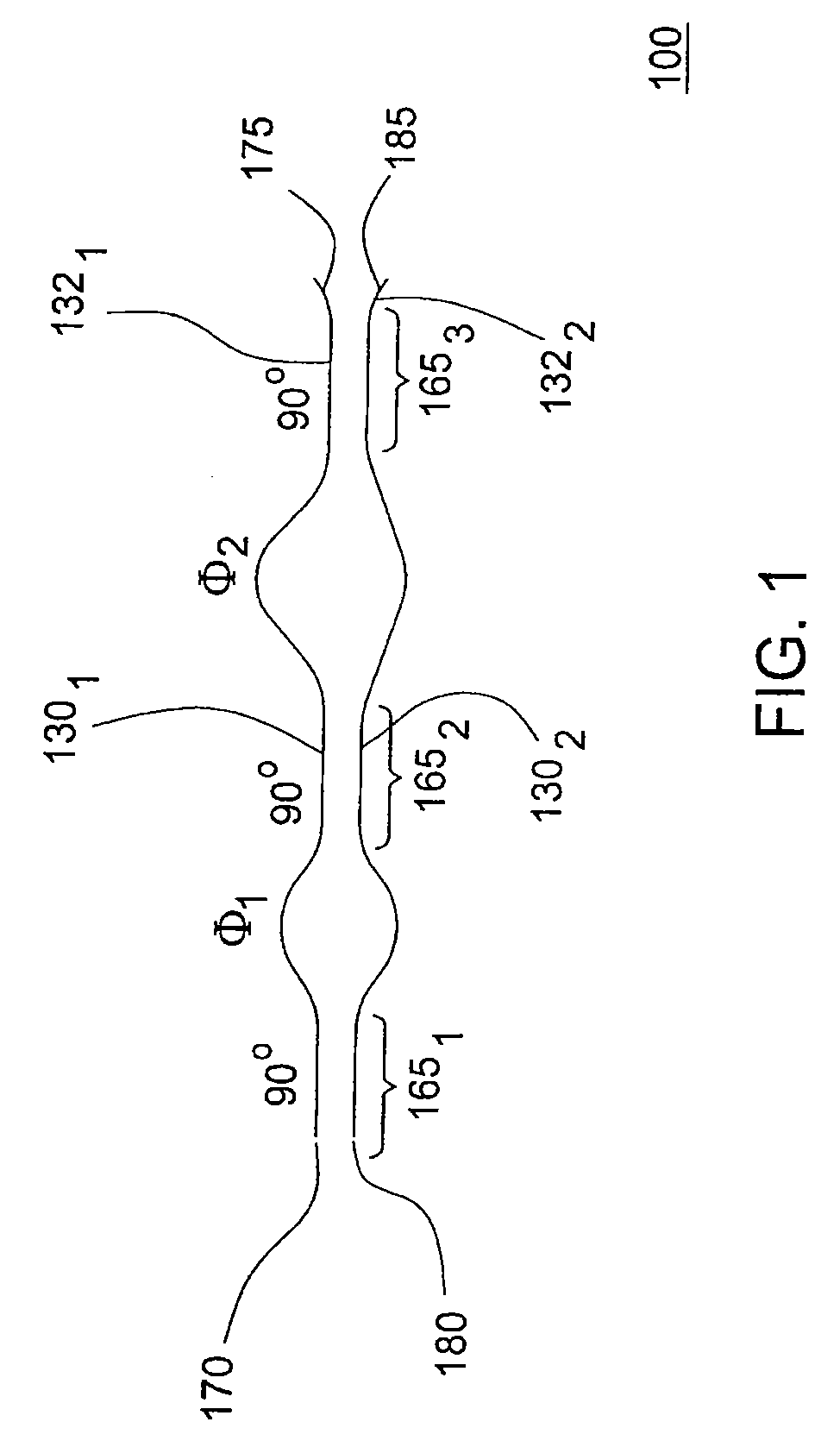
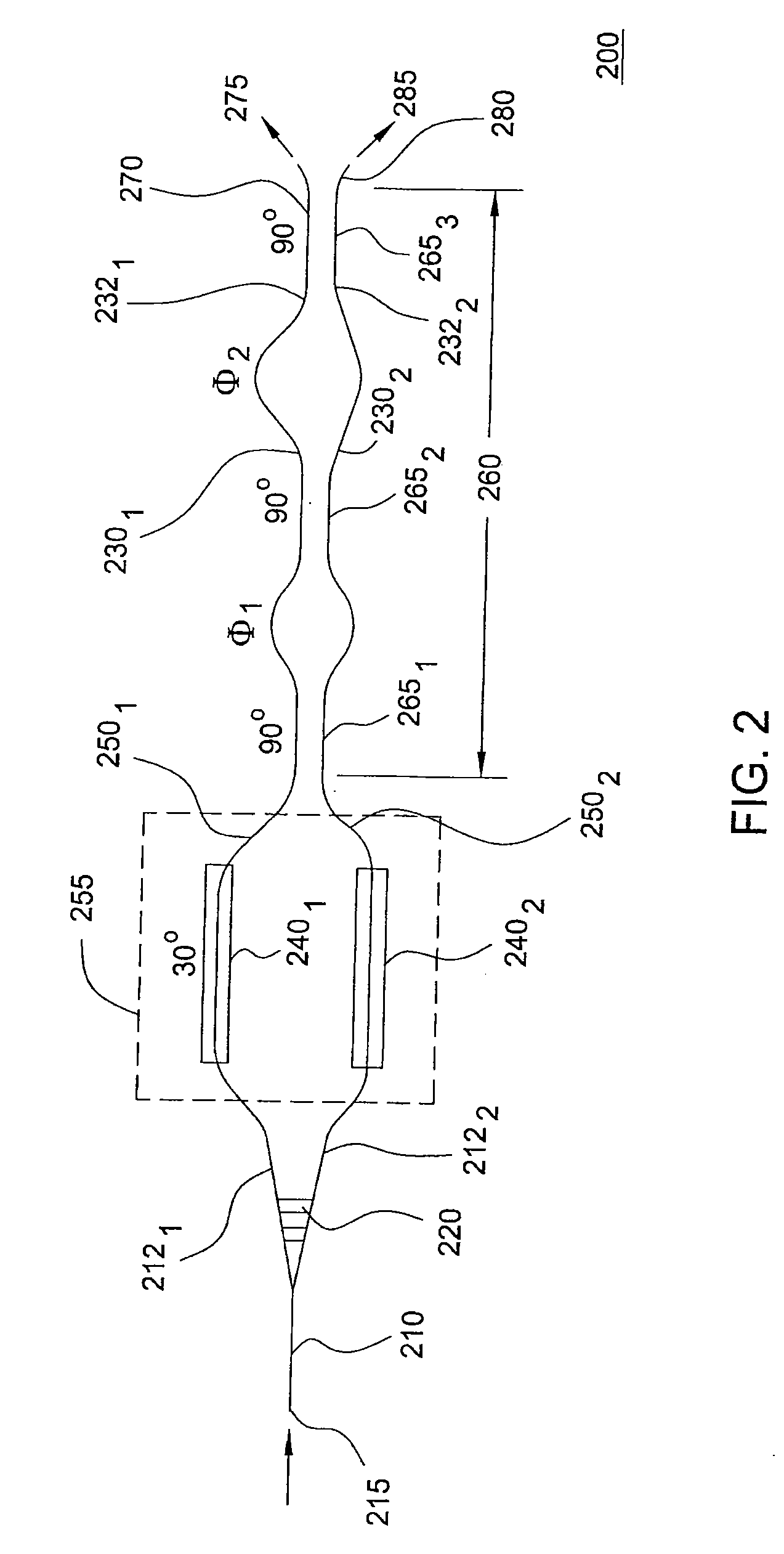
An optical interleaver comprising: an interferometer which includes a coupler, a first phase shifter and a combiner; wherein the coupler splits incident light into a first light beam and a second light beam and couples the first light beam and the second light beam to the first phase shifter; wherein the first phase shifter includes a first light propagation element that propagates the first light beam along a first path between the coupler and the combiner and that includes a second light propagation element that propagates the second light beam along a second path between the coupler and the combiner, the first and second paths having different path lengths that contribute to a phase shift between light of the first light beam propagated along the first path and light of the second light beam propagated along the second path; wherein the combiner couples the first light beam with and the second light beam; a second phase shifter which receives first light beam light propagated along the first path between the coupler and the combiner and imparts a first wavelength dependent variation in phase to the received first light beam light; a third phase shifter which receives second light beam light propagated along the second path between the coupler and the combiner and imparts a second wavelength dependent variation in phase to the received second light beam light.
Owner:NEXFON CORP
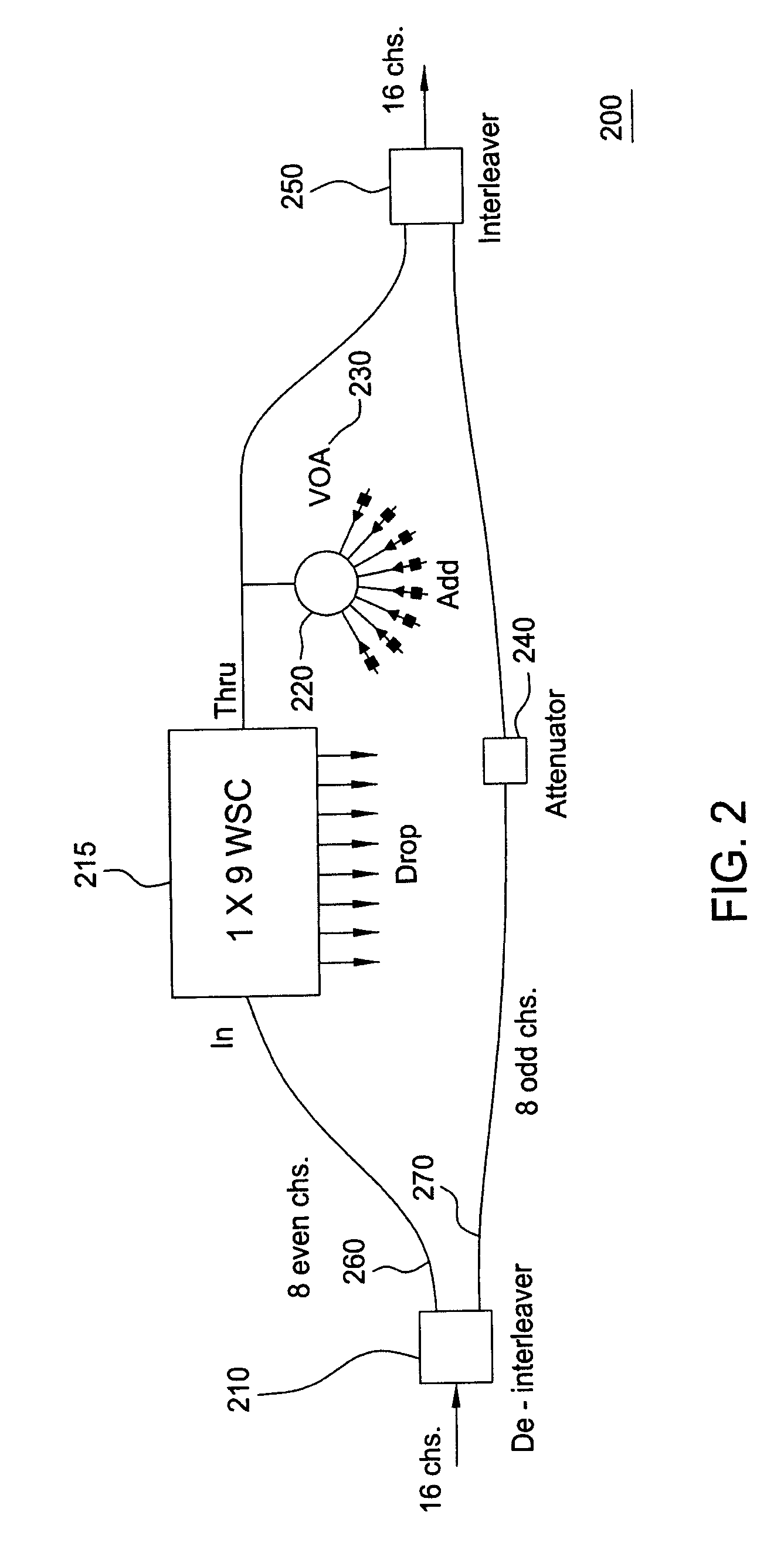
Roadm systems and methods of operation
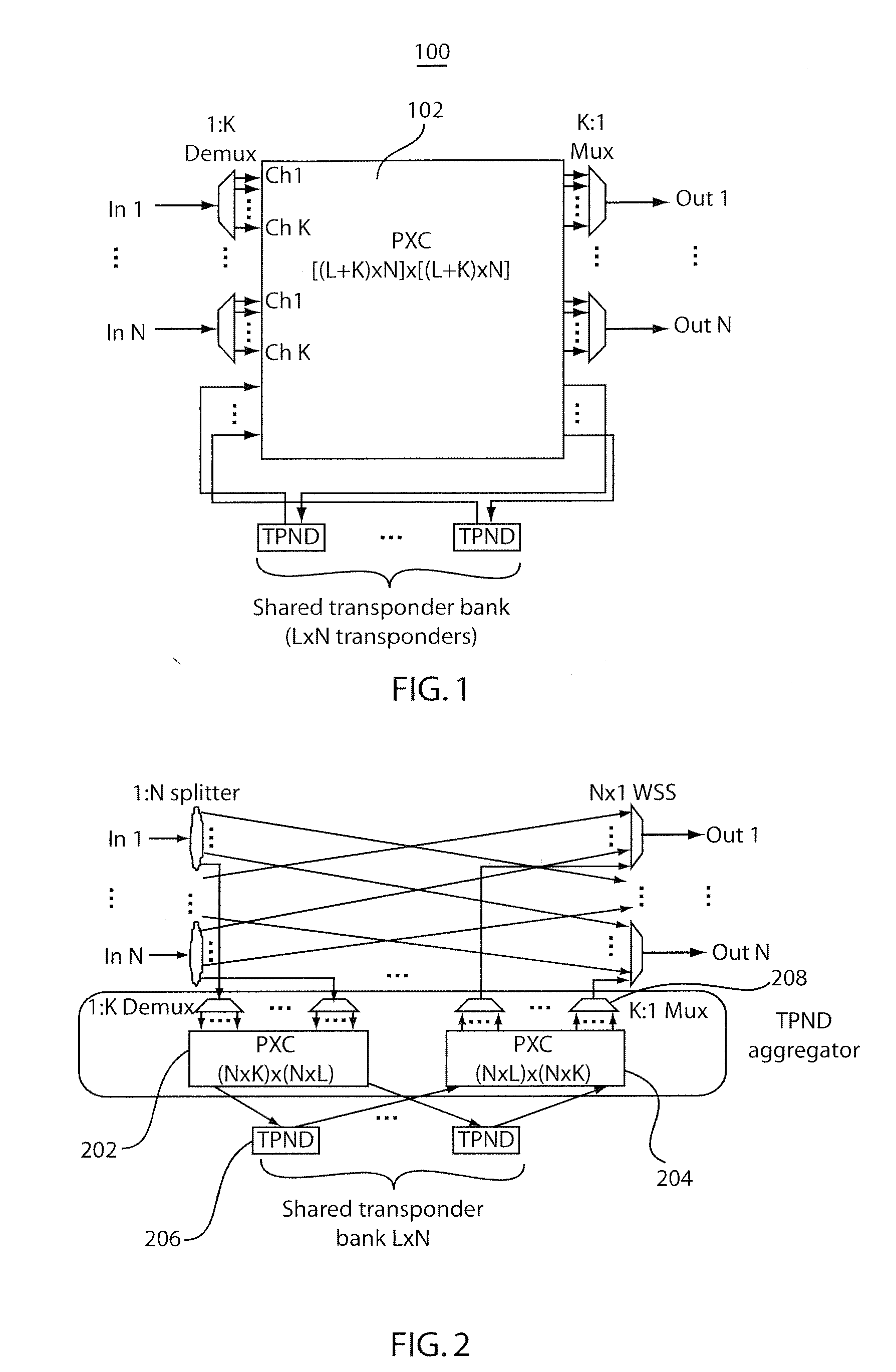
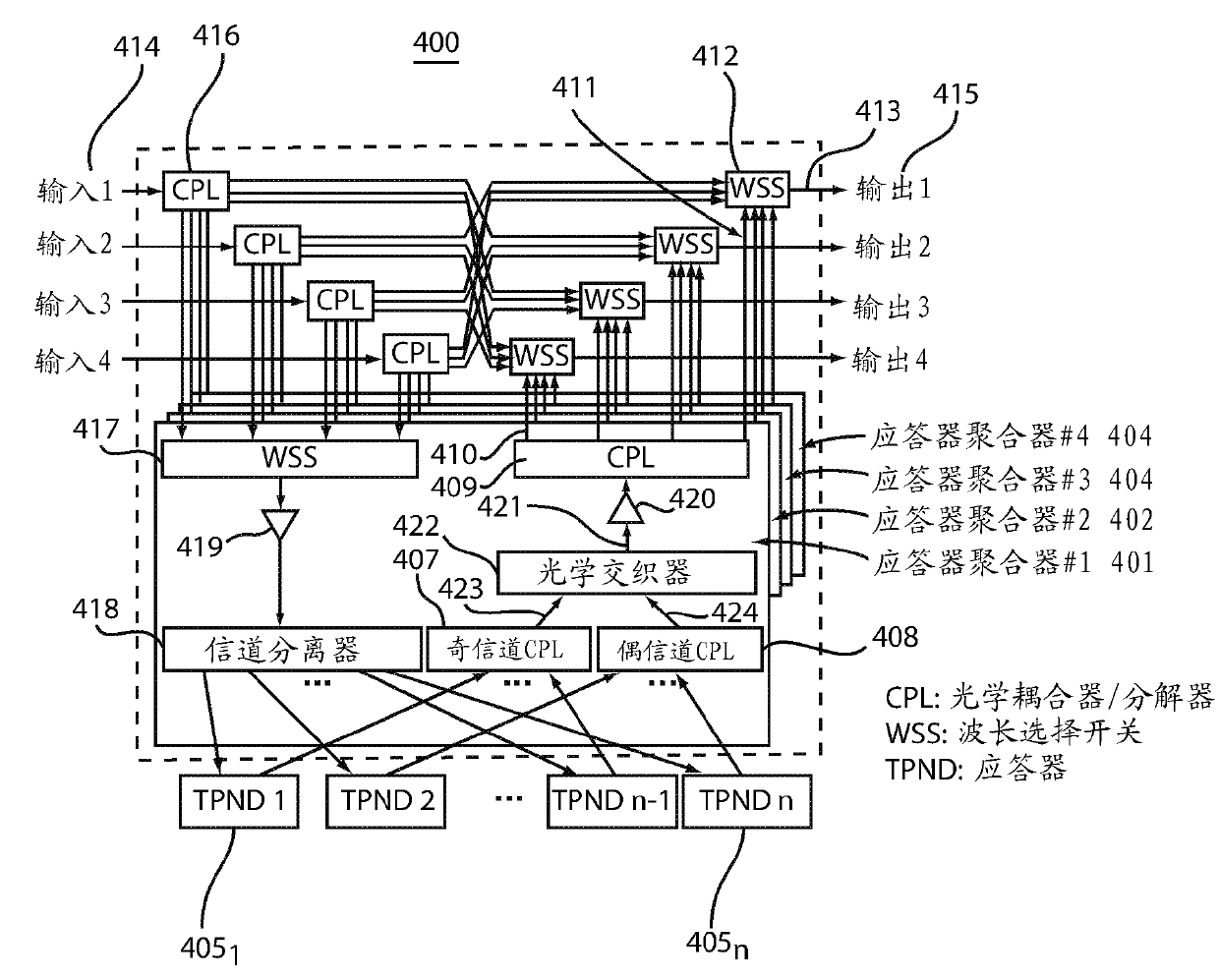
InactiveUS20110262143A1Facilitate flexible add/dropIncrease the cost of useWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultimode transmissionSignal onEngineering
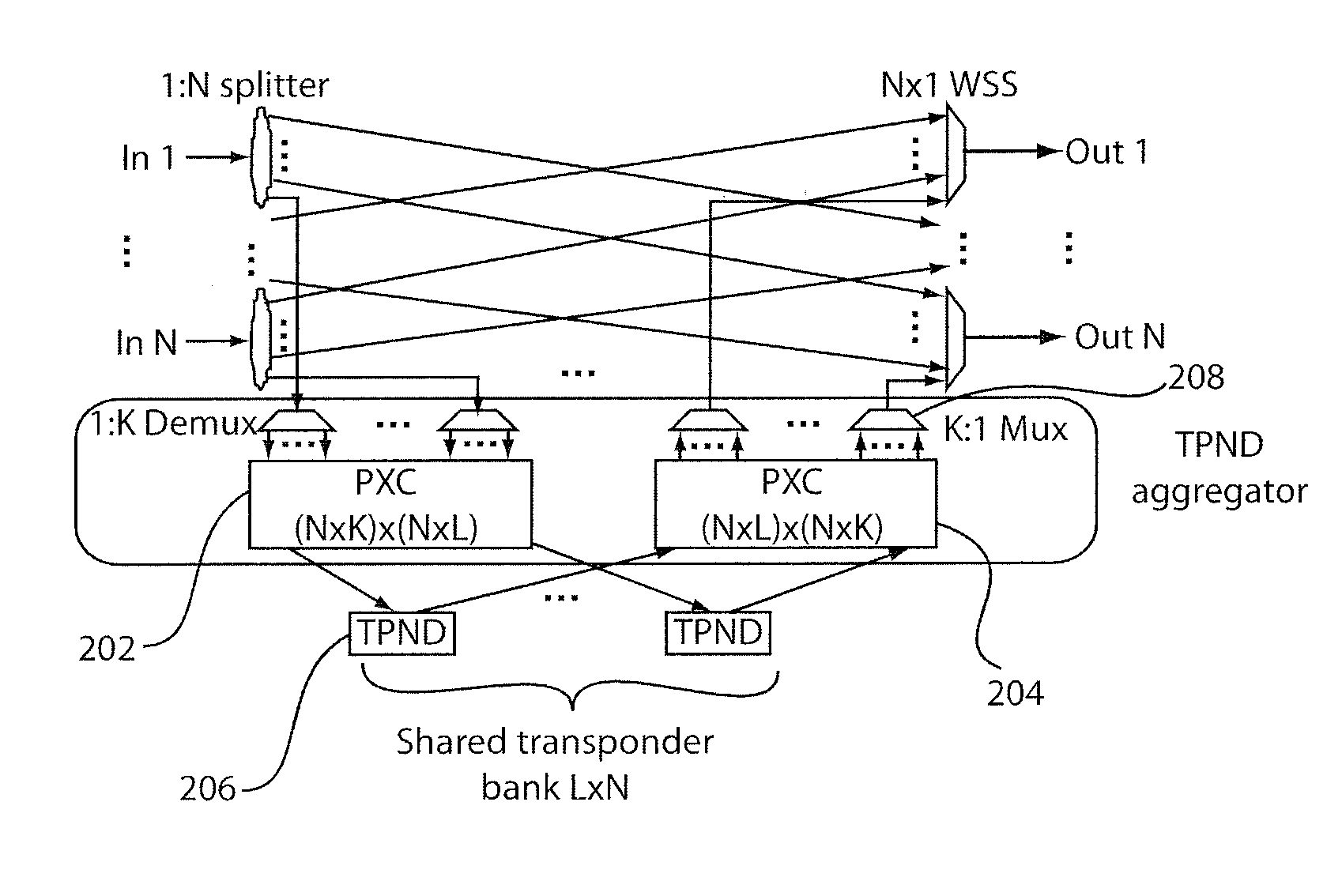
ROADM node systems and methods of operation are disclosed. ROADM node systems may include transponder aggregators including transponders to add signals for switching through the ROADM node. The transponder aggregators include optical couplers constrained that are from coupling added signals on adjacent channels for simultaneous use. The ROADM system may include an optical interleaver that can provide an additional filtering function for the coupled signals prior to transmission of the signals on a WDM network.
Owner:NEC LAB AMERICA +1
Optical interleaver/deinterleaver device having an array of micro-mirrors
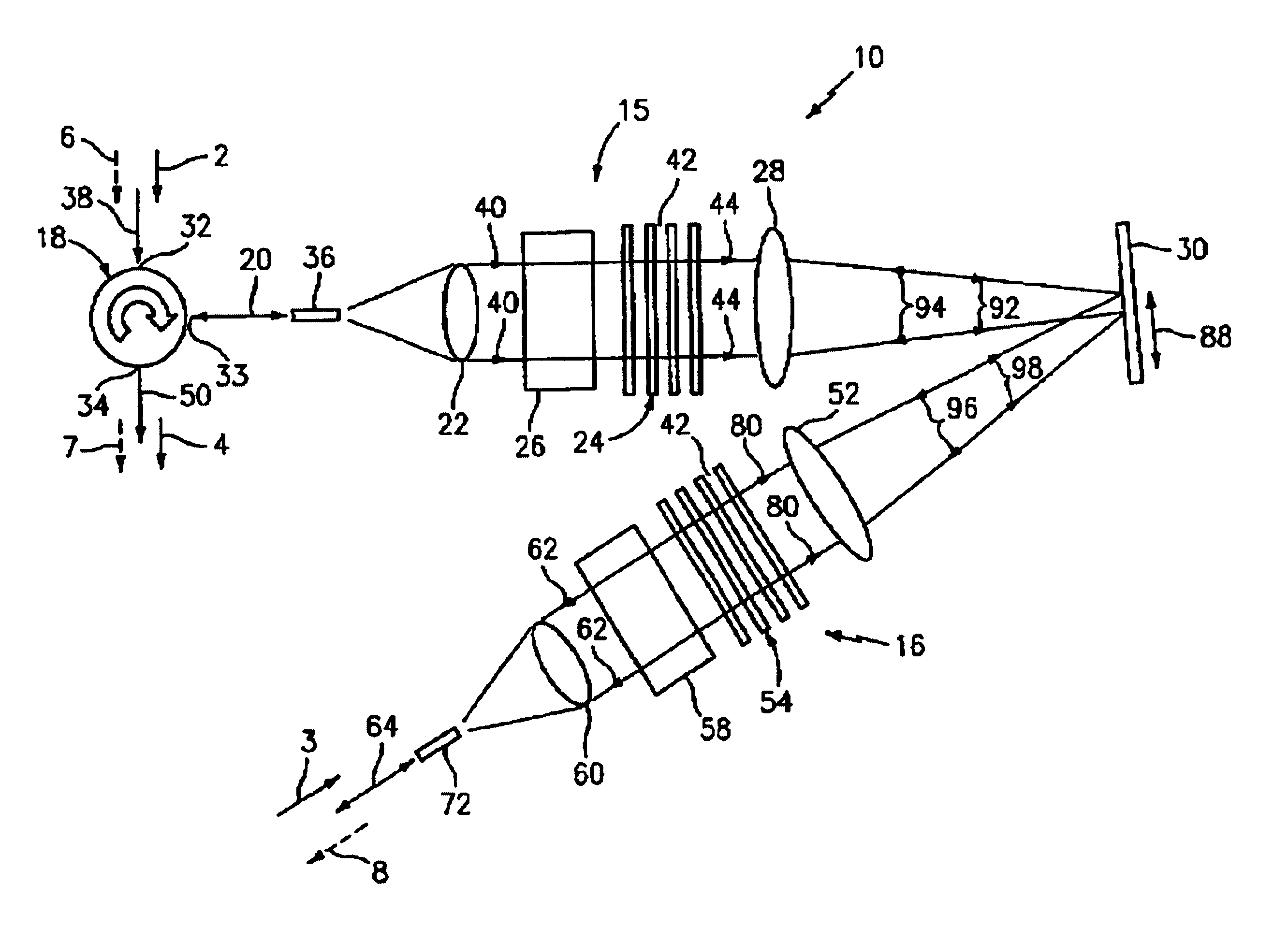
A reconfigurable optical interleaver / deinterleaver device combines / separates a pair of optical input signals from and / or to an optical WDM input signal. The interleaver device includes a spatial light modulator having a micro-mirror device with a two-dimensional array of micro-mirrors that flip between first and second positions in a “digital” fashion in response to a control signal provided by a controller in accordance with a switching algorithm and an input command. A pair of collimators, diffraction gratings and Fourier lens collectively collimate, separate and focus the optical input channels and optical add channels onto the array of micro-mirrors. Each optical channel is focused on a plurality of micro-mirrors of the micro-mirror device, which effectively pixelates the optical channels.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Intra-Channel Equalizing Optical Interleaver
ActiveUS20090162066A1Suppress Intersymbol InterferenceWavelength-division multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationChannel densityIntersymbol interference
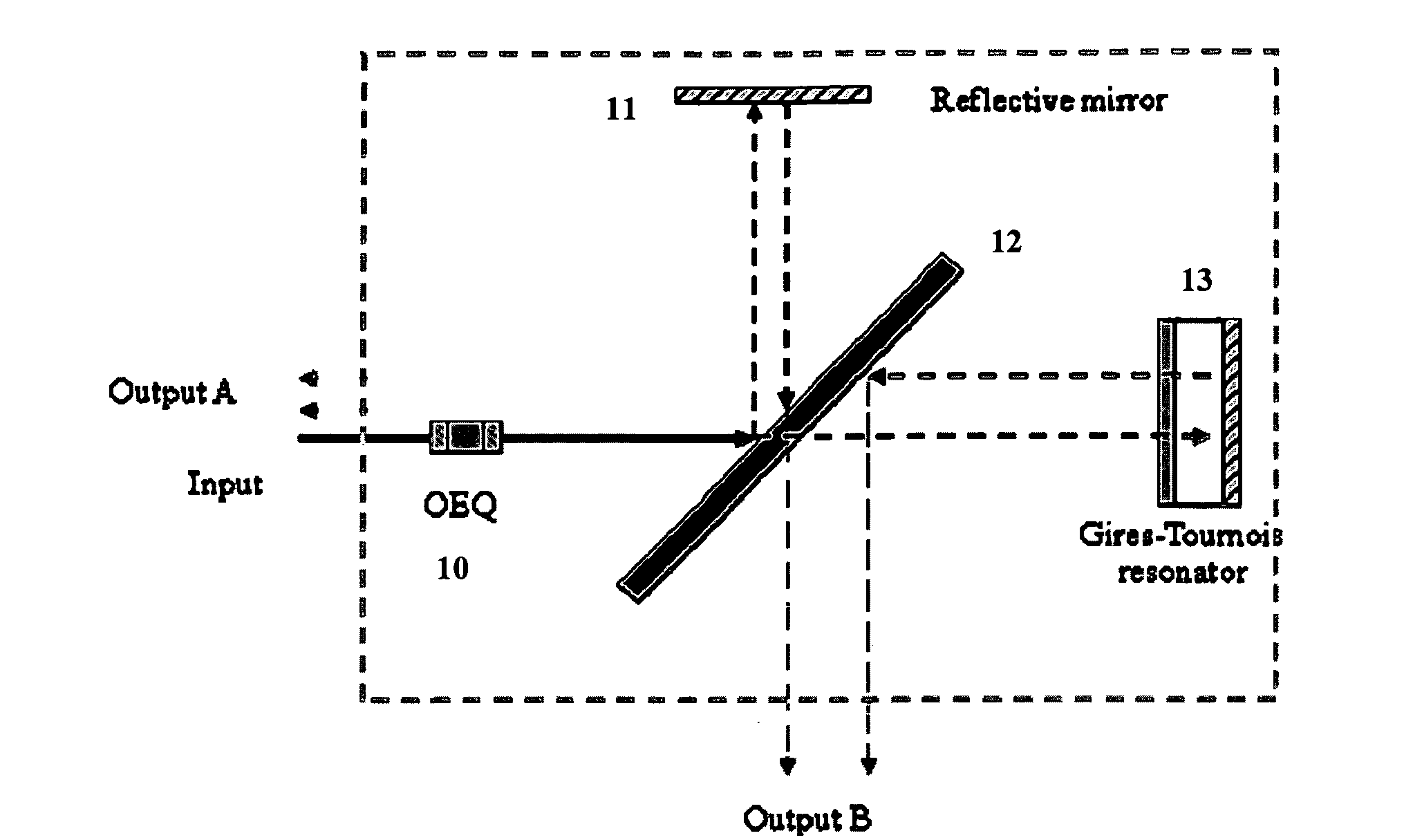
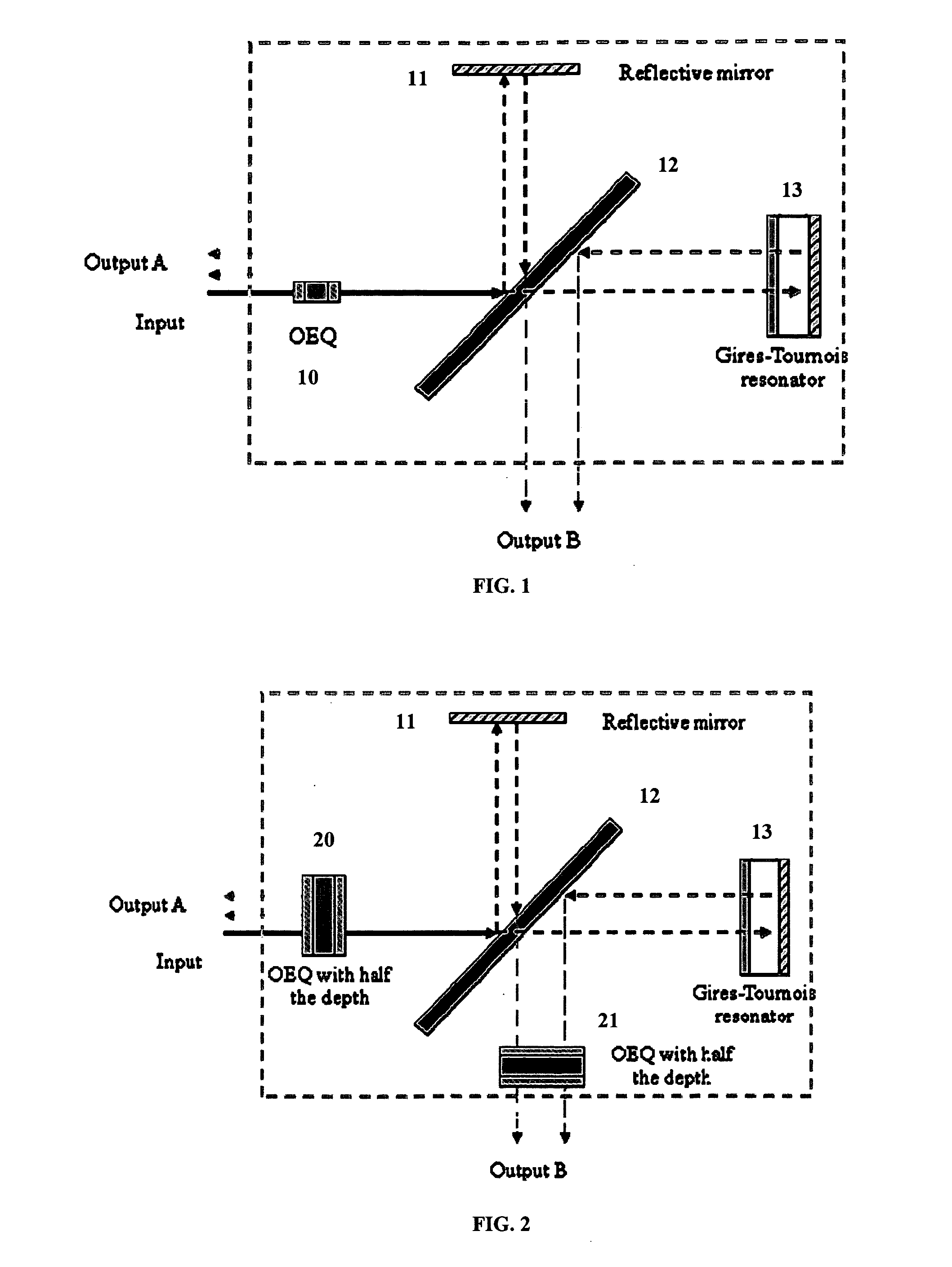
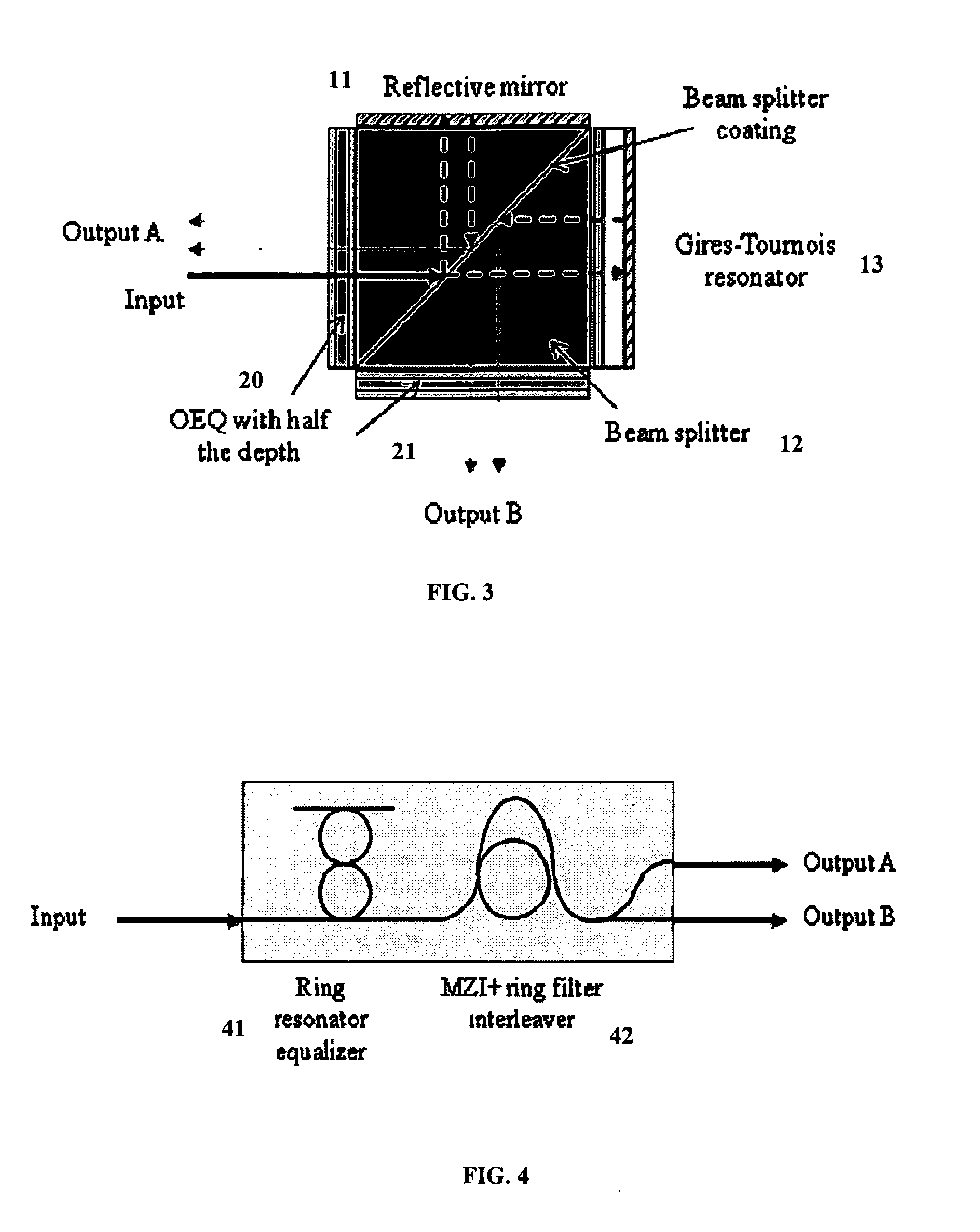
An apparatus includes an interleaver configuration for at least one of combining or separating odd and even channel groups to achieve channel density doubling; and an optical equalizer for suppressing inter symbol interference within the channels to provide intra-channel equalizing in the optical path, the equalizer being integrated into the interleaver. Preferably, optical equalizer and interleaver are integrated together as a single monolithic device, the optical equalizer includes a passband that has a dip in the channel center to achieve a raised-cosine filtering profile in the optical signal path to achieve inter-symbol interference ISI suppression, and the equalizer includes integration into the optical path of the interleaver to realize a monolithic device combining or separating odd and even channel groups to achieve channel density doubling. Preferably, also, the optical equalizer includes a first equalizer with half the depth of required ripple dips at both a first output port and an input port and a second equalizer with half the depth of required ripple dips at a second output port.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
Optical interleaver and filter cell design with enhanced clear aperture
InactiveUS7173763B2Improve integrityEasy to packMultiplex system selection arrangementsPrismsMultiplexerOptical processing
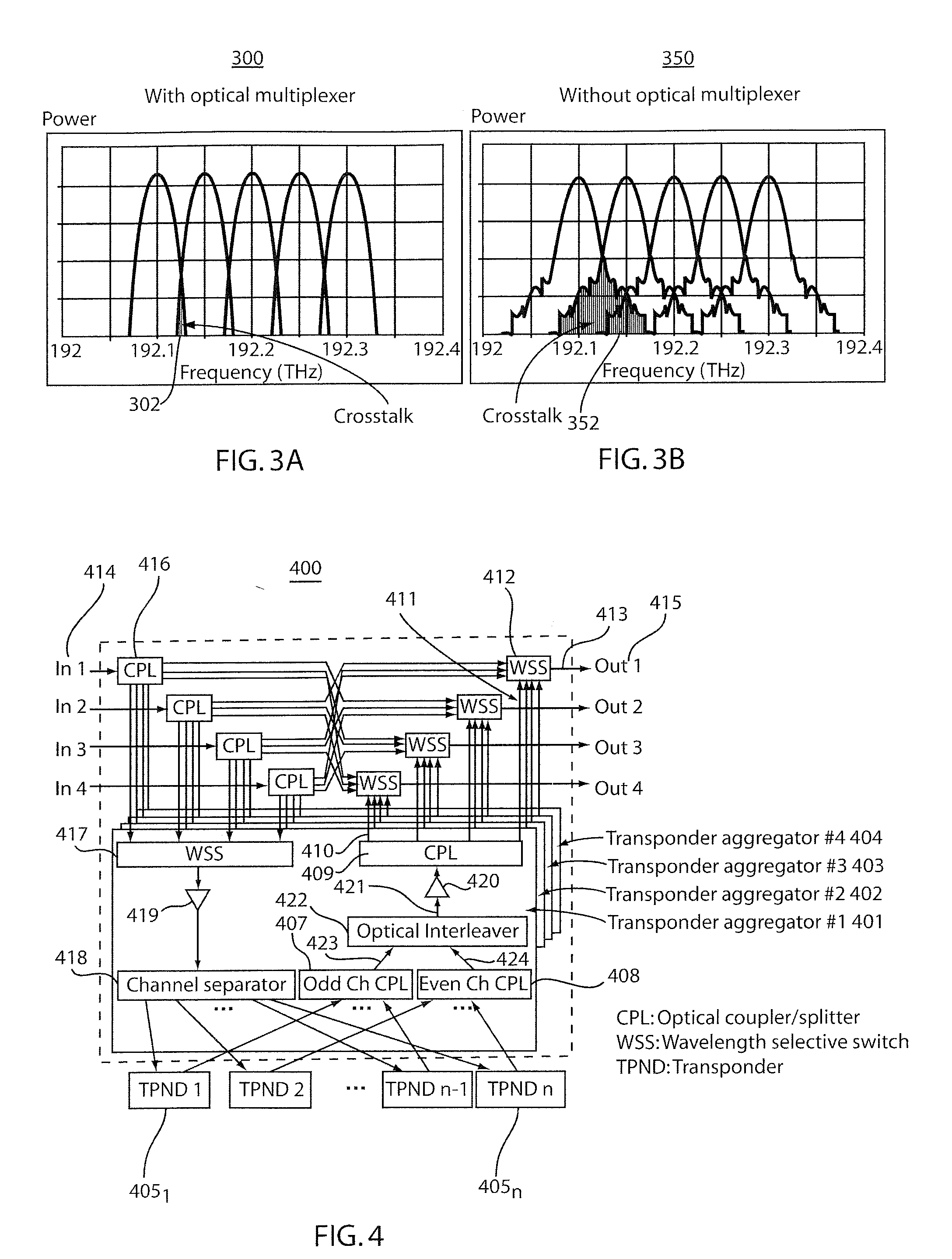
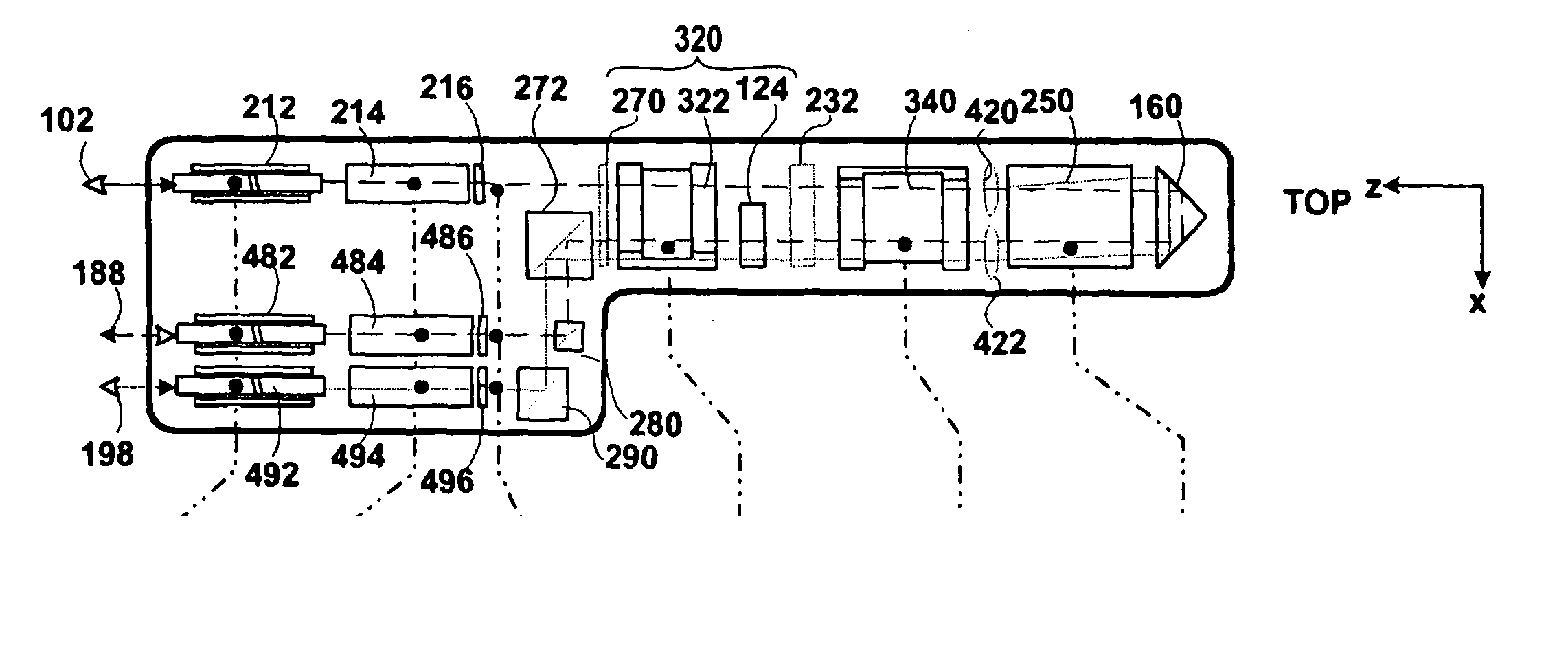
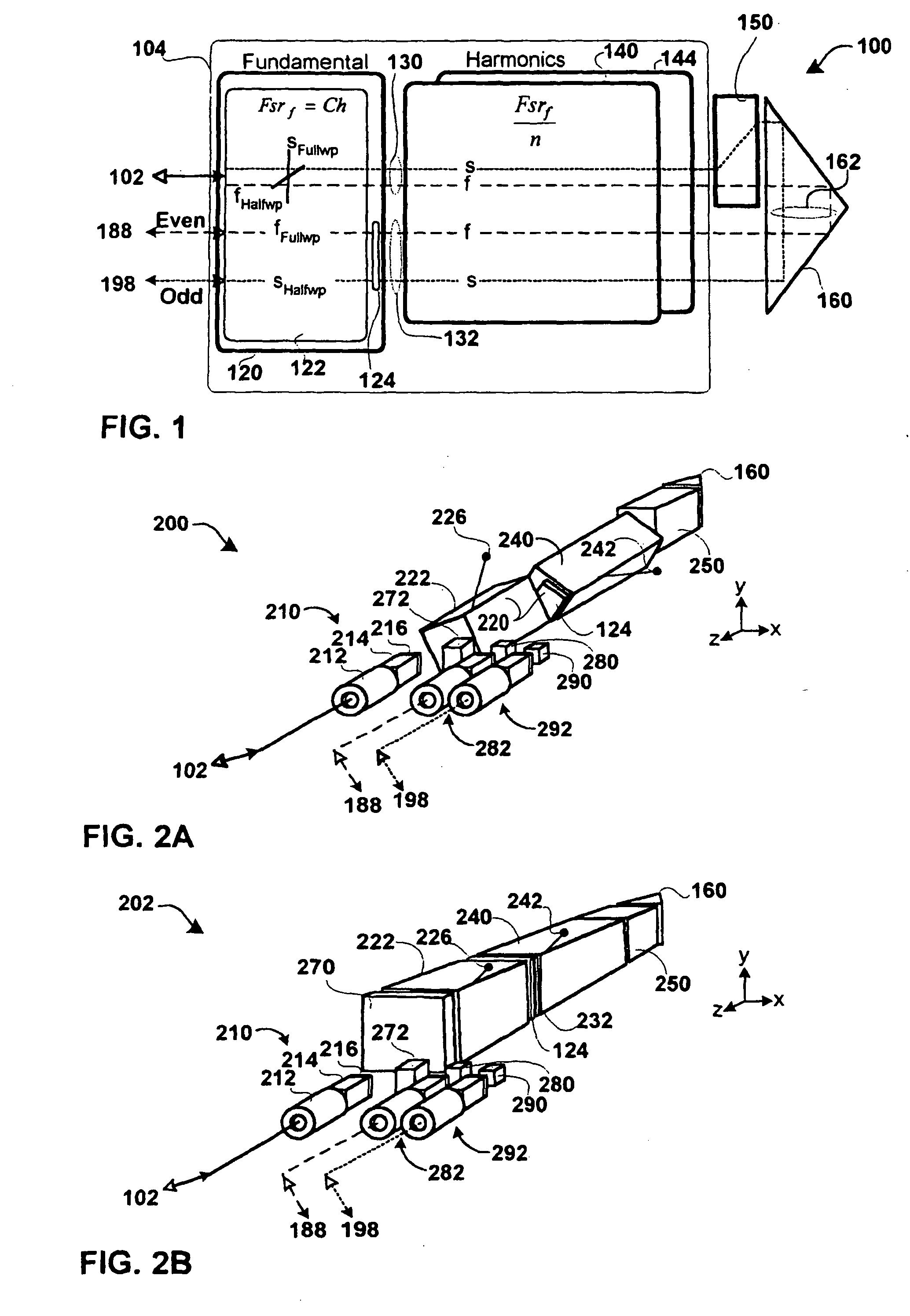
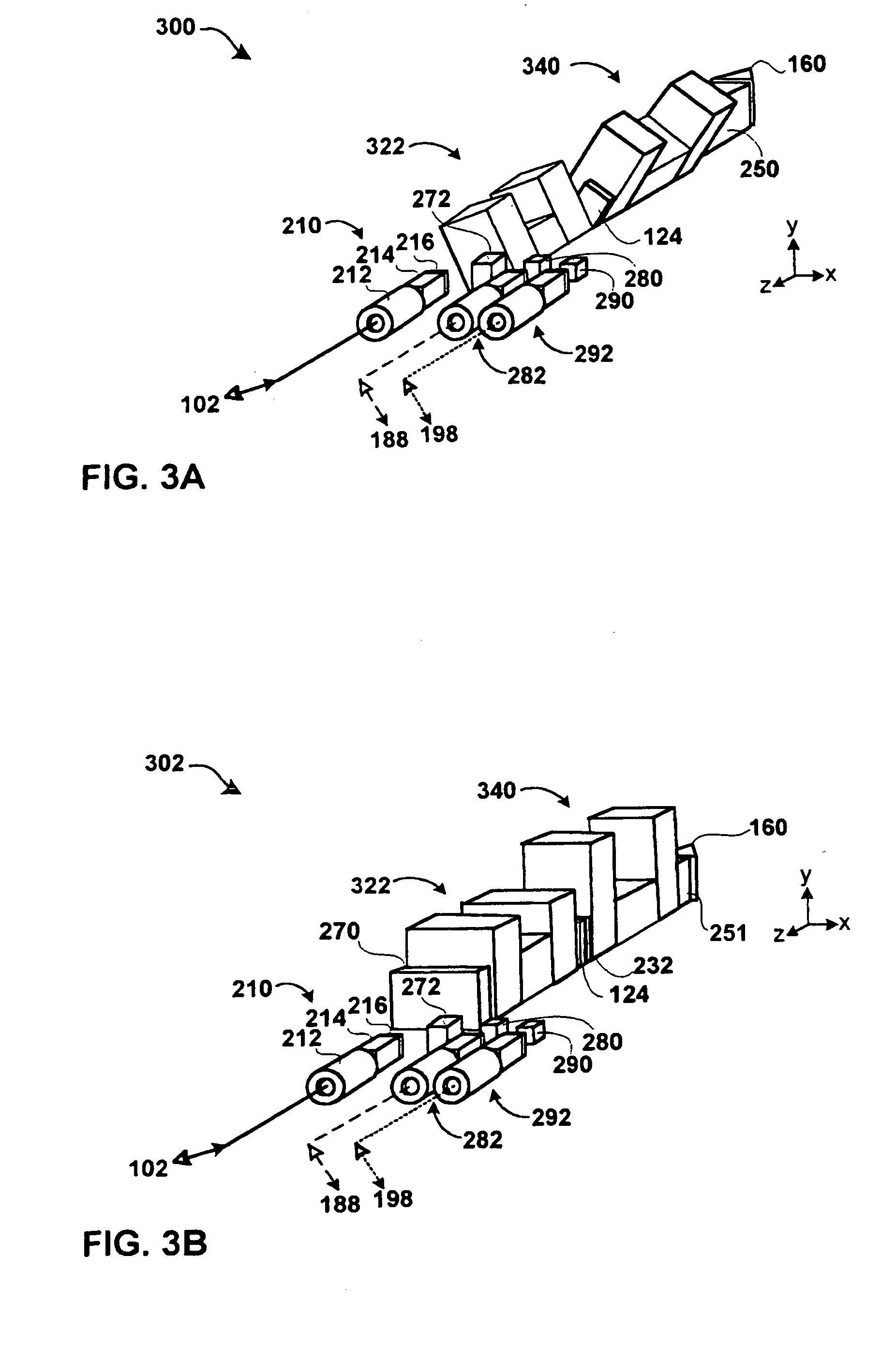
An optical interleaver for use in a range of telecommunications applications including optical multiplexers / demultiplexers and optical routers. The optical device includes an optical processing loop which allows multi-stage performance characteristics to be achieved with a single physical filtration stage. Optical processing on the first leg and second legs of the loop is asymmetrical thereby improving the integrity of the optical signals by effecting complementary chromatic dispersion on the first and second legs. A fundamental filter cell within the interleaver filters optical signals propagating on each of the two legs of the optical loop which intersects the fundamental filter cell.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Wavelength division multiplexing add/drop system employing optical switches and interleavers
An optical add / drop multiplexer (OADM) having reduced crosstalk is disclosed. The OADM uses an optical interleaver to separate channels of a wavelength division multiplexed signal into a plurality of branches. The branches then separately act on the widely spaced channels to add or drop channels. After the add / drop function is completed, the channels on the branches are recombined.
Owner:INTERGRATED OPTICS COMM
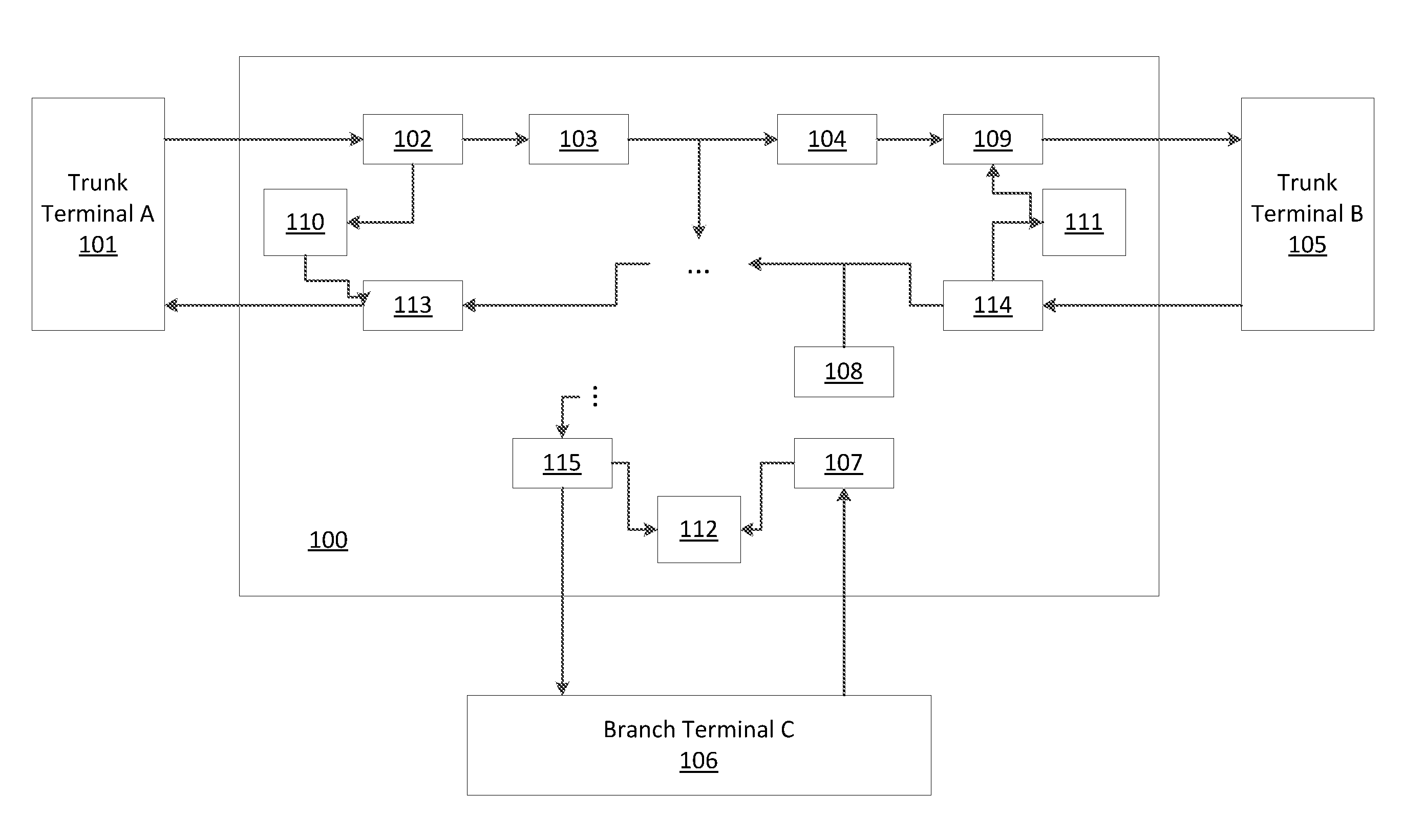
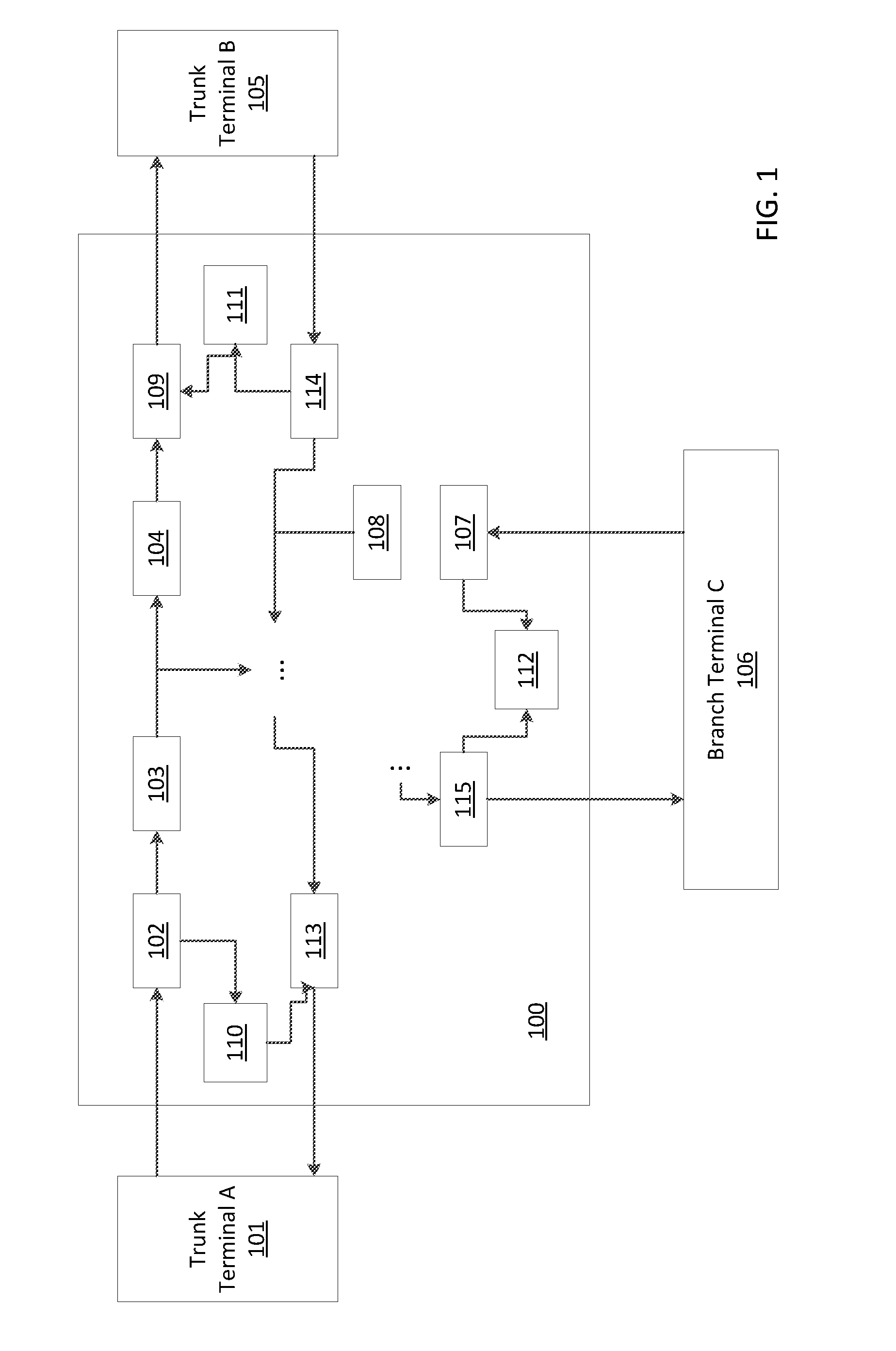
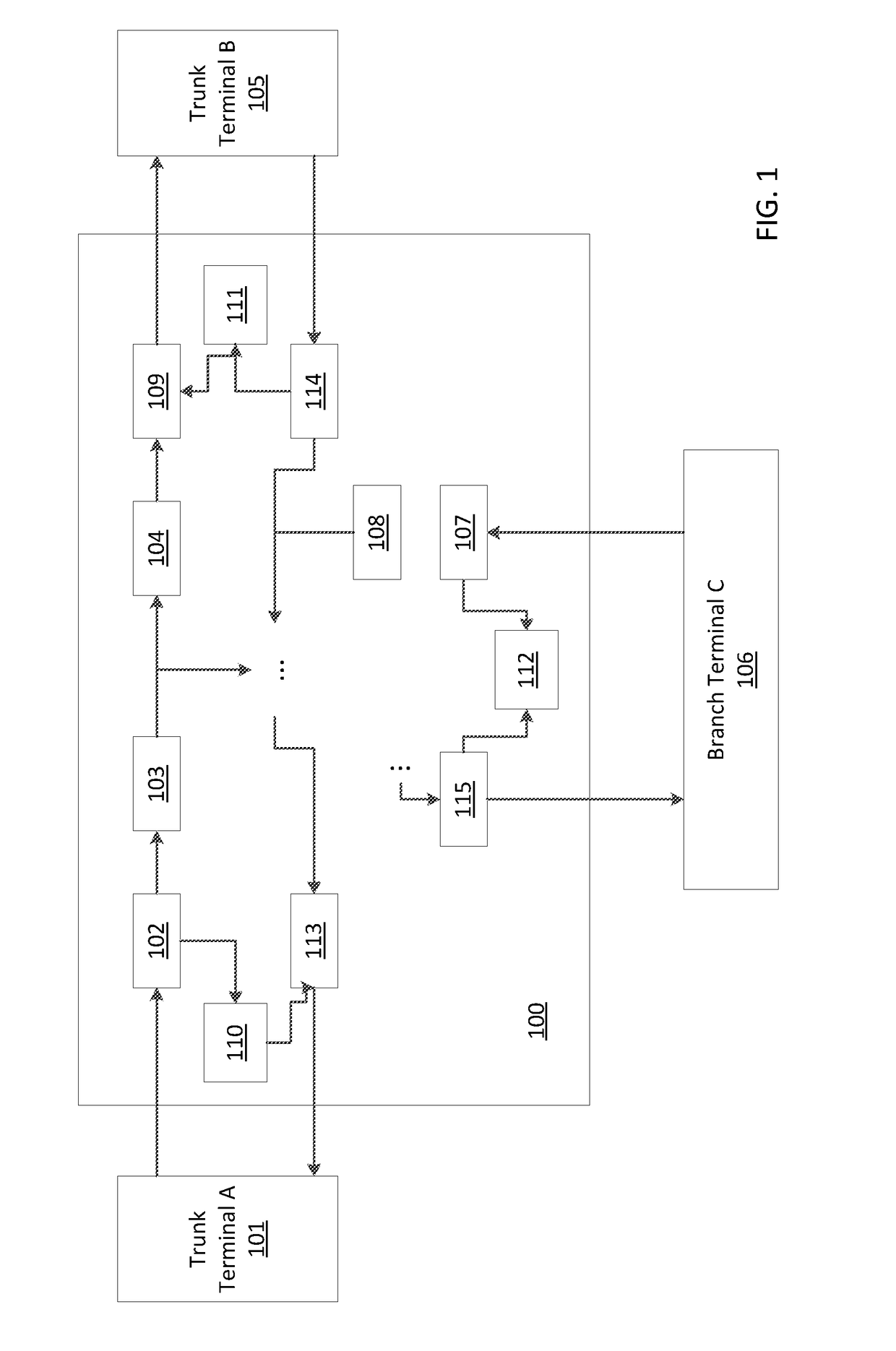
Submarine reconfigurable optical add/drop multiplexer with passive branching unit
ActiveUS20150043920A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic network arrangementsUnit systemEngineering
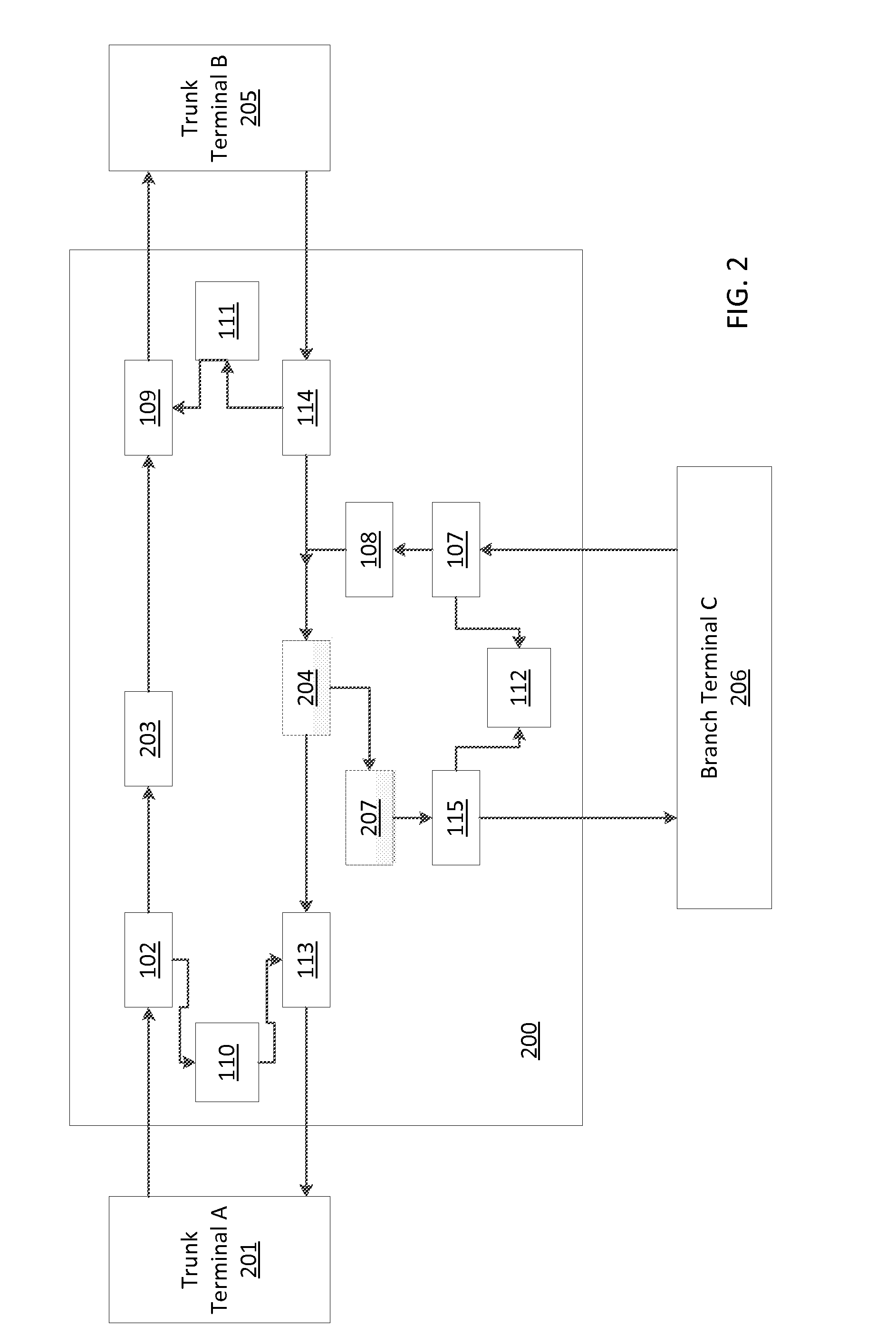
Systems and methods for data transport, including submarine reconfigurable optical add / drop multiplexers, branching units configured to receive signals from trunk terminals (TTs), and dummy light filters configured to pass useful signals through the filters, and to reflect dummy light. Optical interleavers are configured to separate useful signals into two or more groups of optical channels, and the optical channels are set to a frequency of either a left or a right portion of a total channel bandwidth. De-interleavers merge signal groups together from trunk terminals, and lasers at each of the transponders at the source terminals are configured to adjust a destination of a channel by fine tuning a frequency or wavelength of the one or more signals.
Owner:NEC CORP
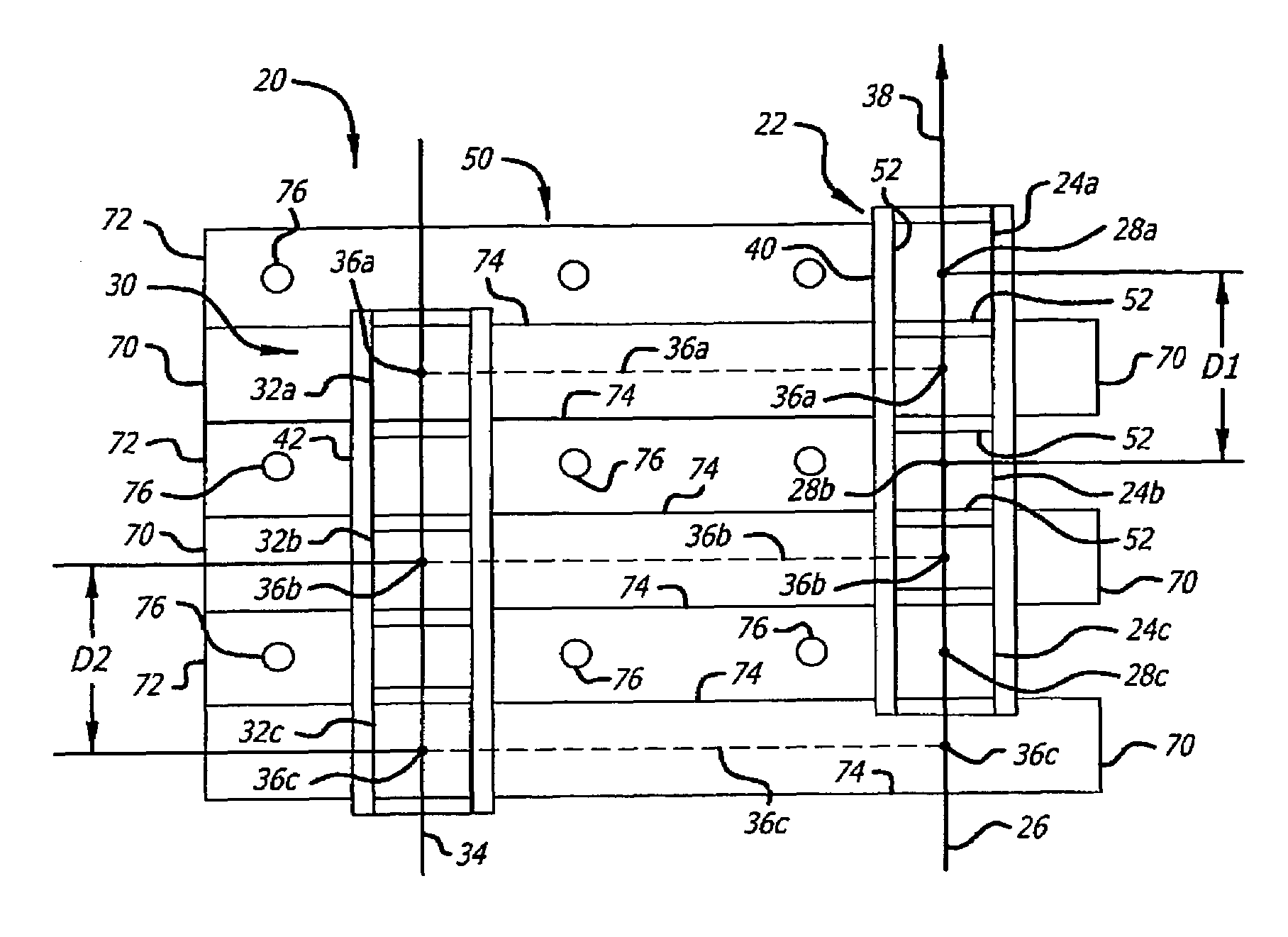
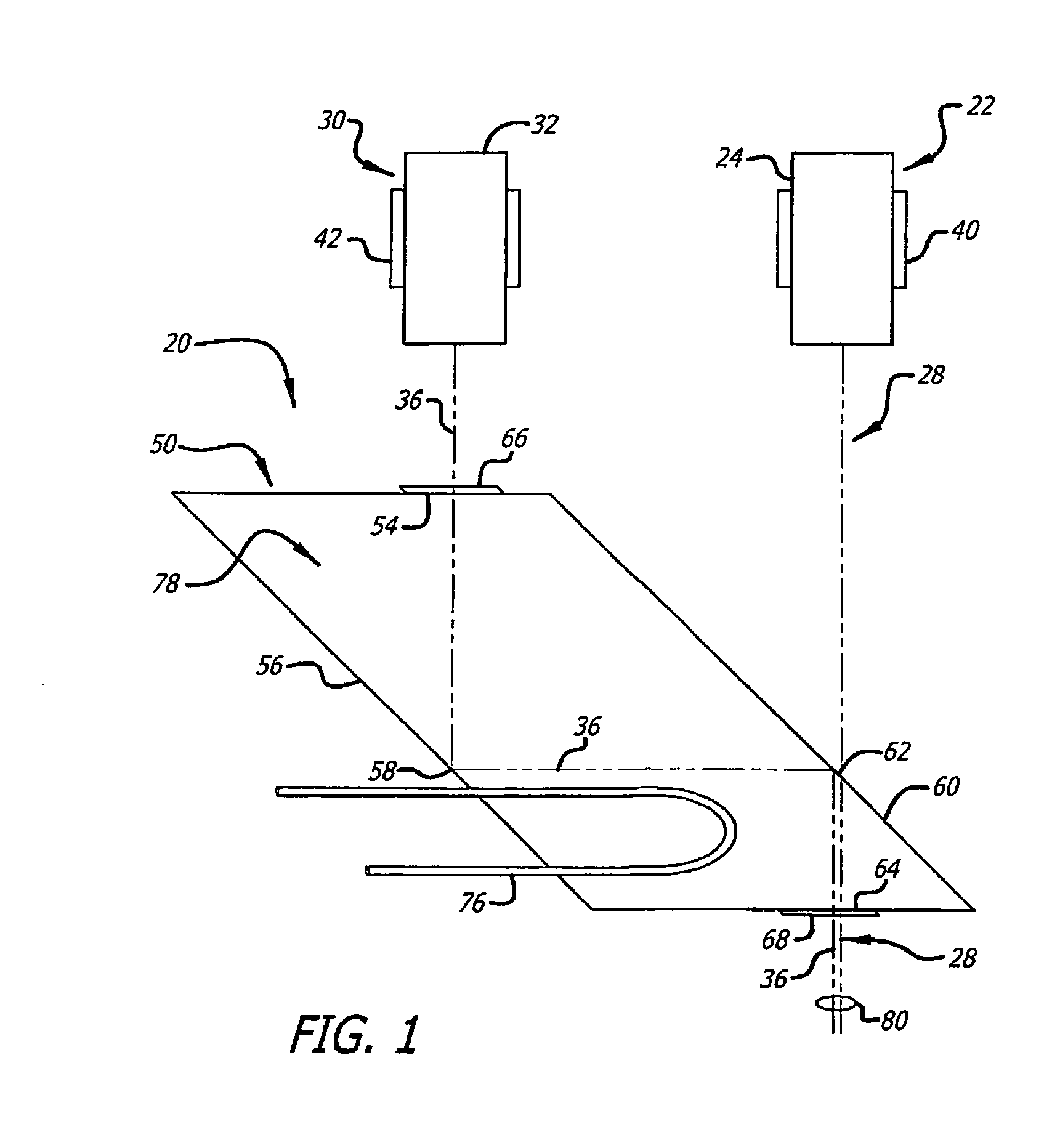
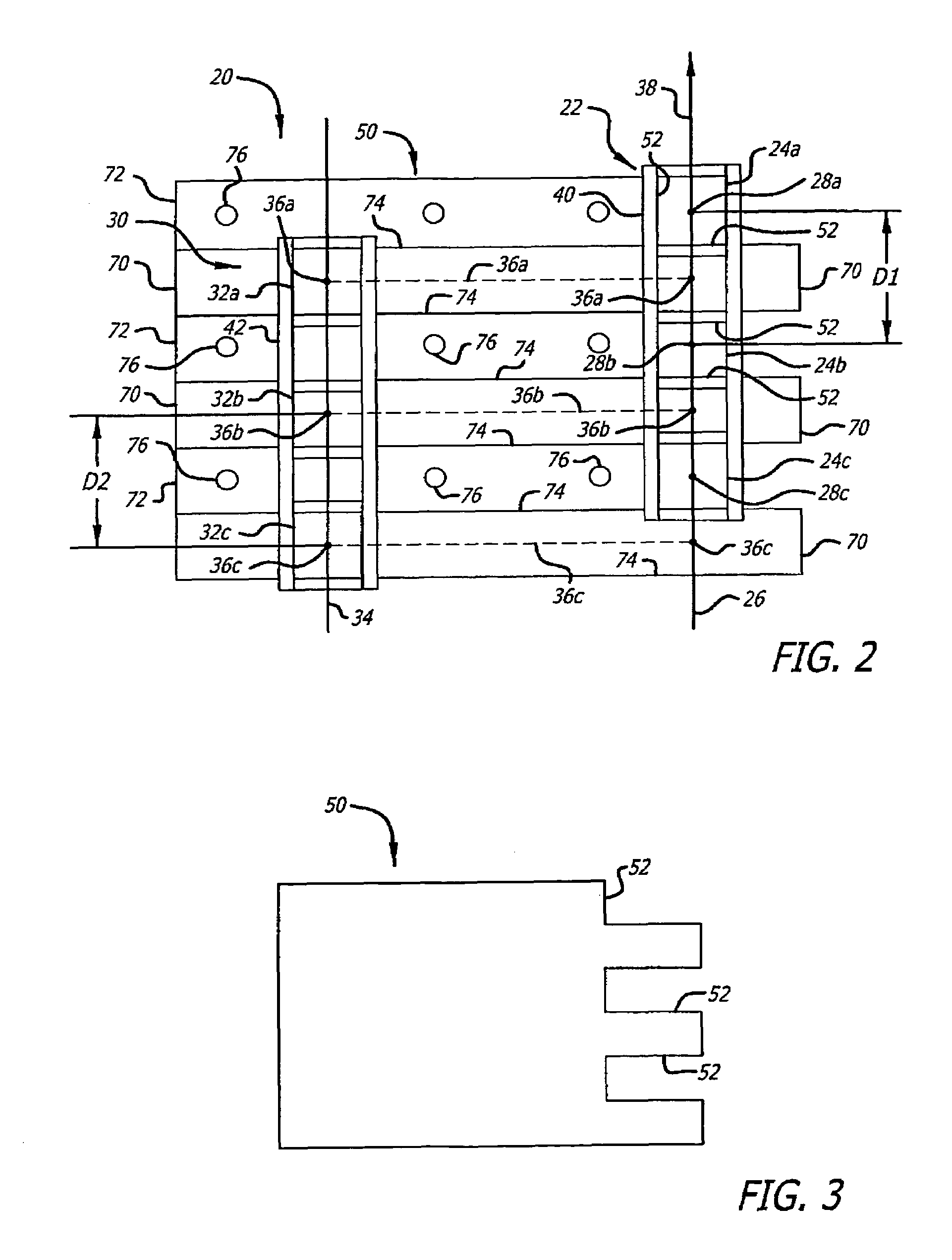
Optical communication system and method for generating dark return-to zero and DWDM optical MM-Wave generation for ROF downstream link using optical phase modulator and optical interleaver
InactiveUS7761012B2Significant valueInexpensive solutionWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmittersSignal onOptical communication
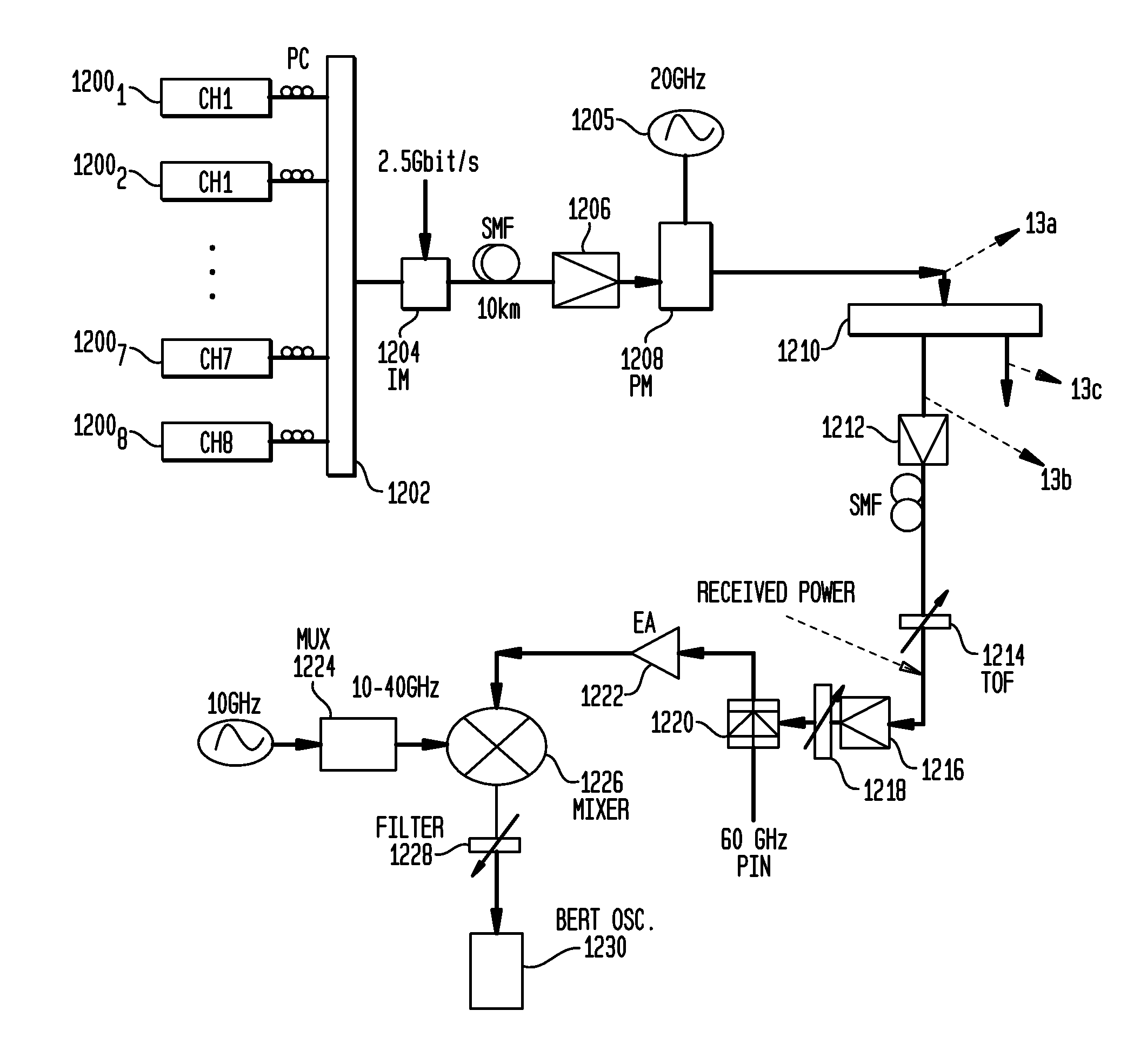
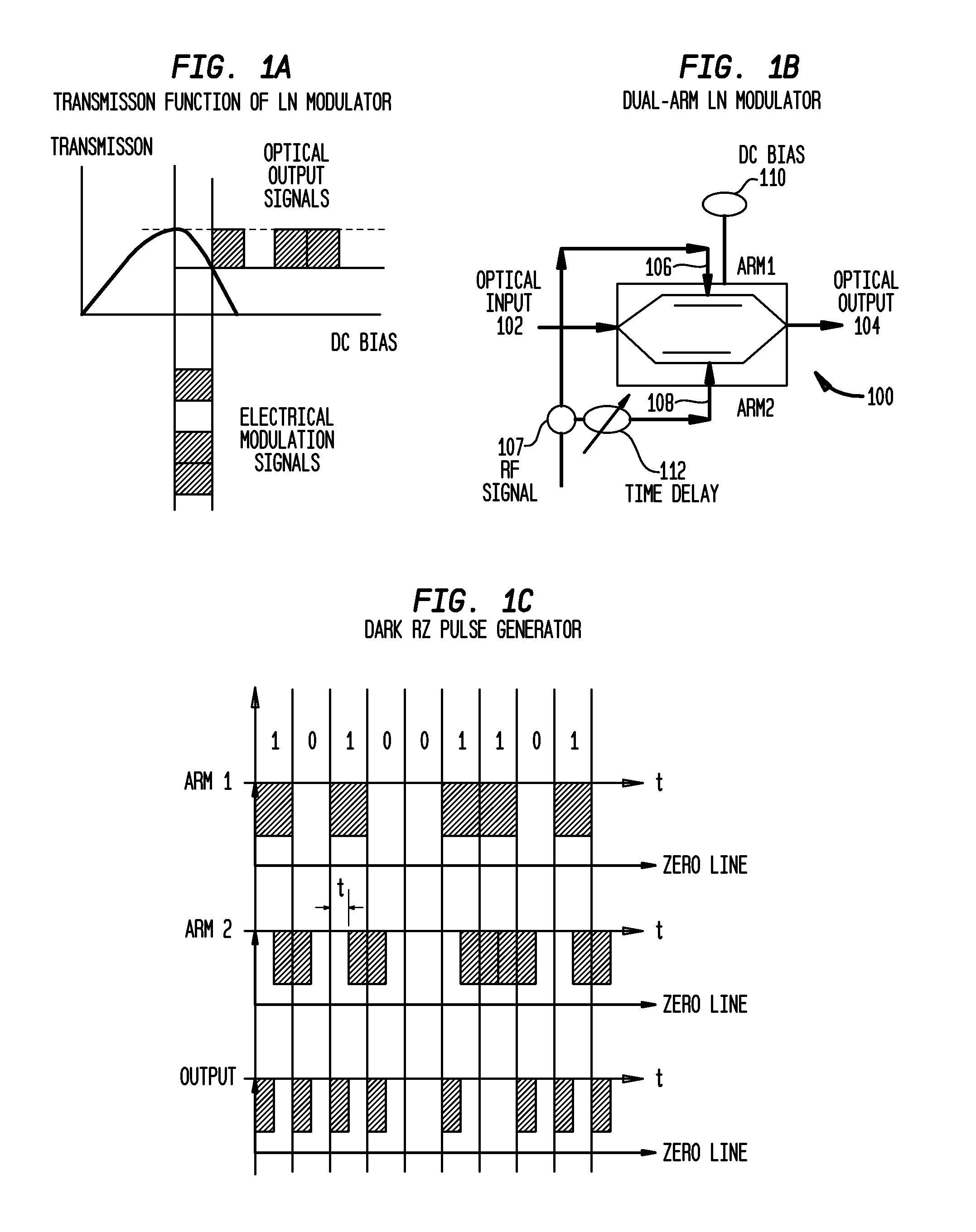
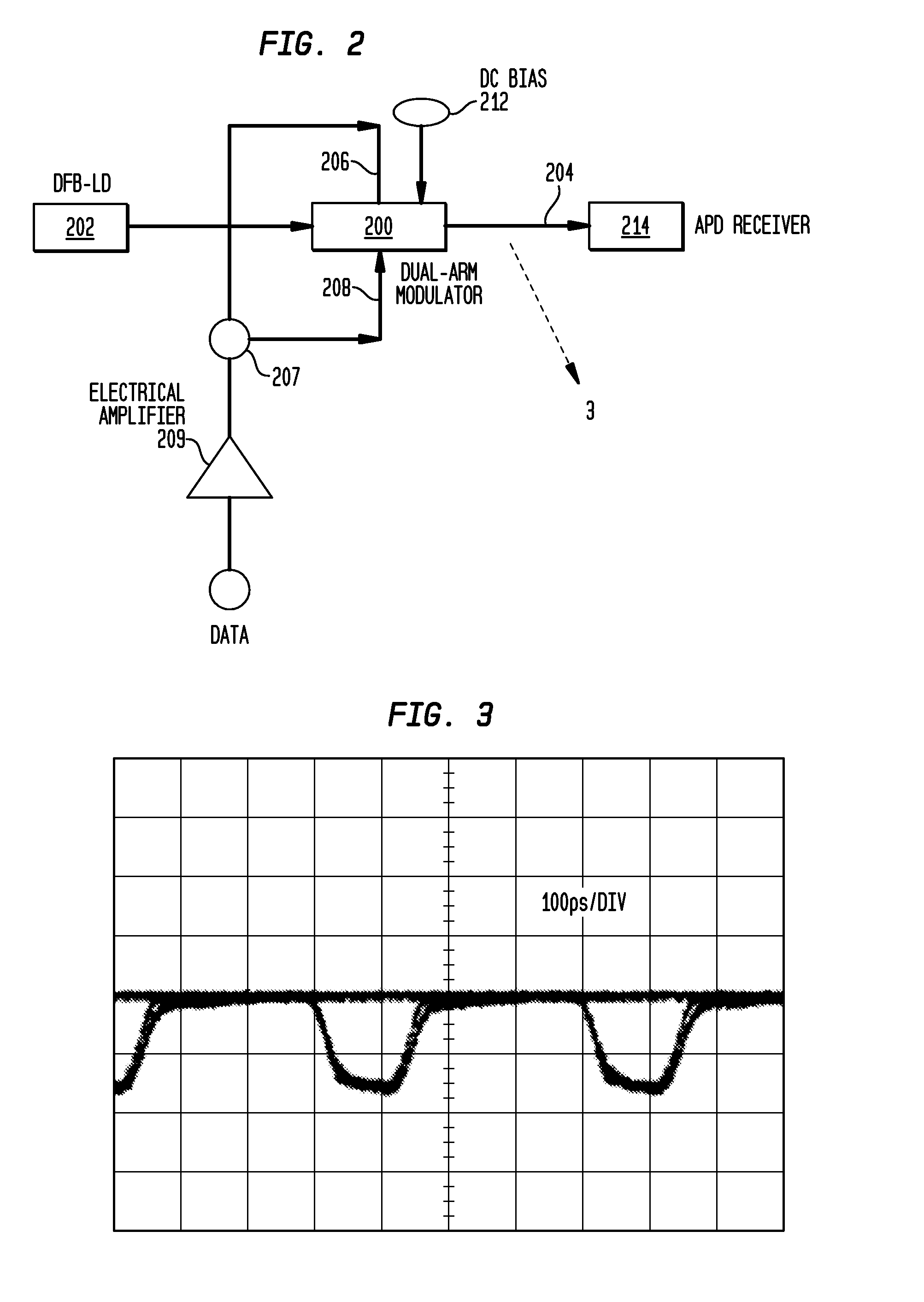
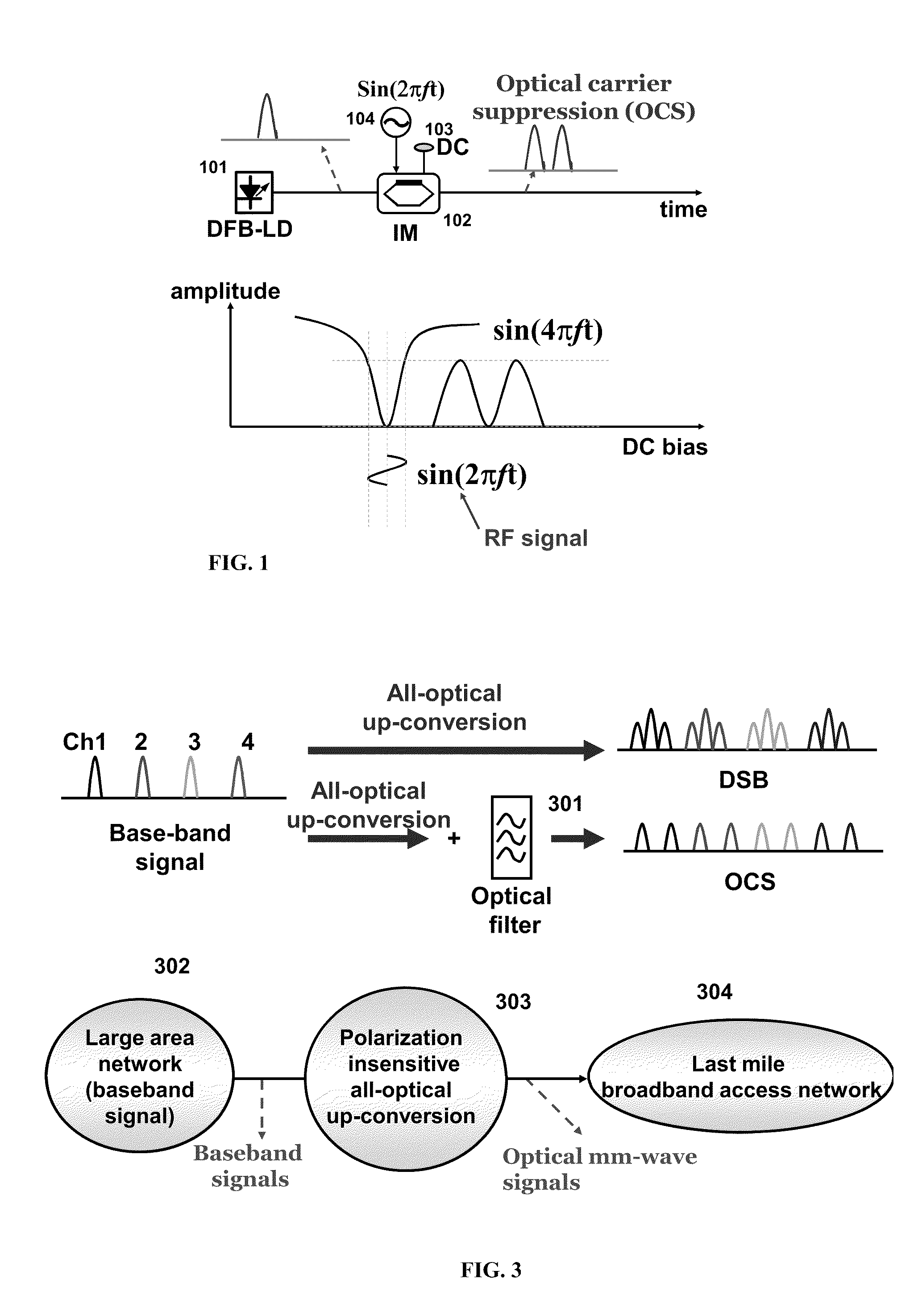
A method of generating a dark-RZ pulse in an optical communications system with a dual-arm modulator by setting a direct current bias on the modulator to a specific value such that an output optical power from the modulator achieves a maximum value when the RF signals on the first and second arms of the modulator are off and maintaining the direct current bias at the specific value and applying RF signals to the first and second arms of the modulator and delaying one of the RF signals applied to one of the first and second arms relative to the other of the RF signals such that a dark-RZ pulse is generated with a duty cycle based on the delay. Another aspect of the invention provides a method for generating dense wave division multiplexing (DWDM) optical mm-waves in an optical transmission system by phase modulated DWDM optical signal and applying the phase modulated DWDM optical signal to an input port of an optical interleaver, the optical interleaver having a specified bandwidth to suppress the optical carriers and convert the DWDM optical signal to DWDM optical mm-waves; and amplifying the DWDM optical mm-waves and transmitting the DWDM optical mm-waves over single mode fiber (SMF).
Owner:NEC CORP
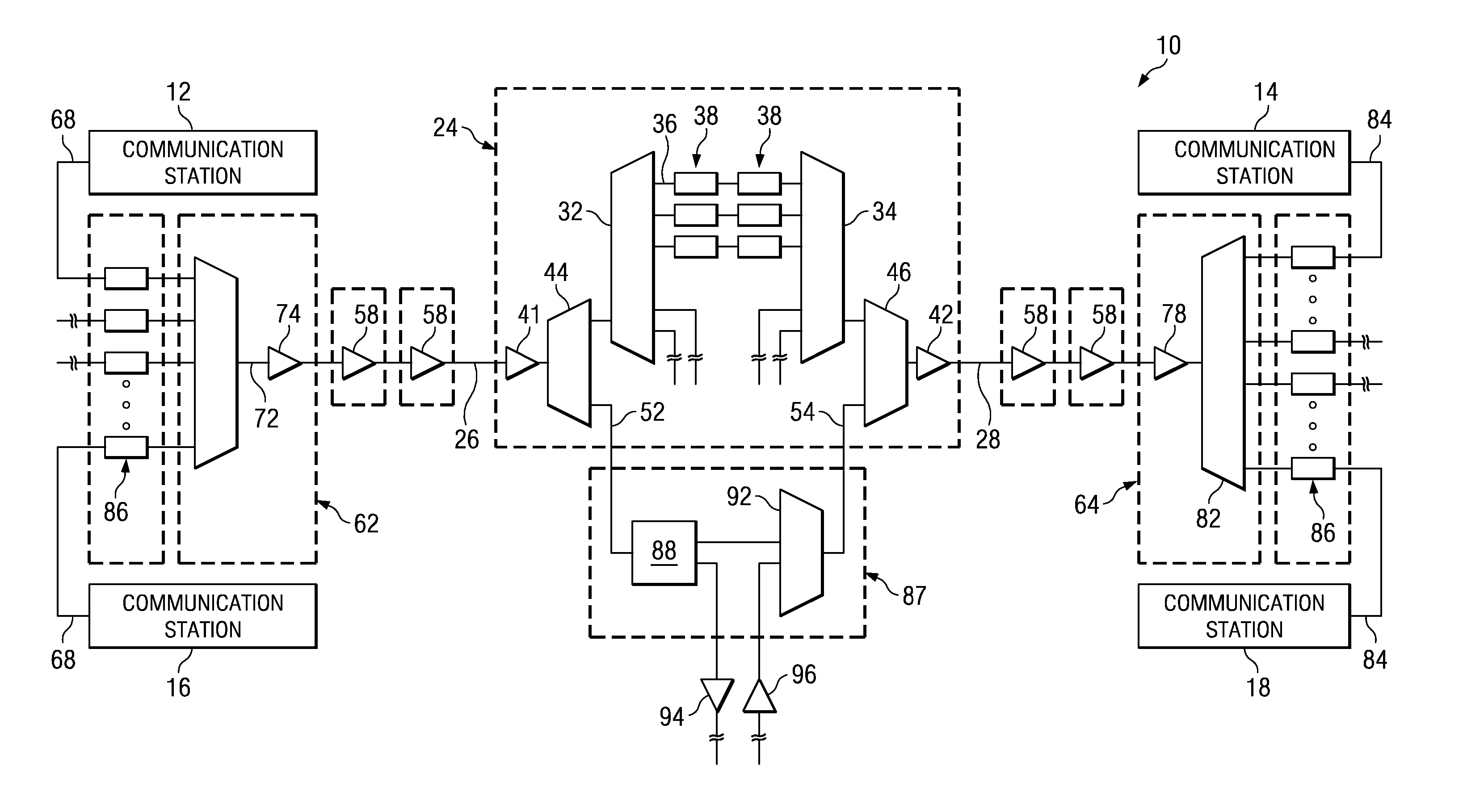
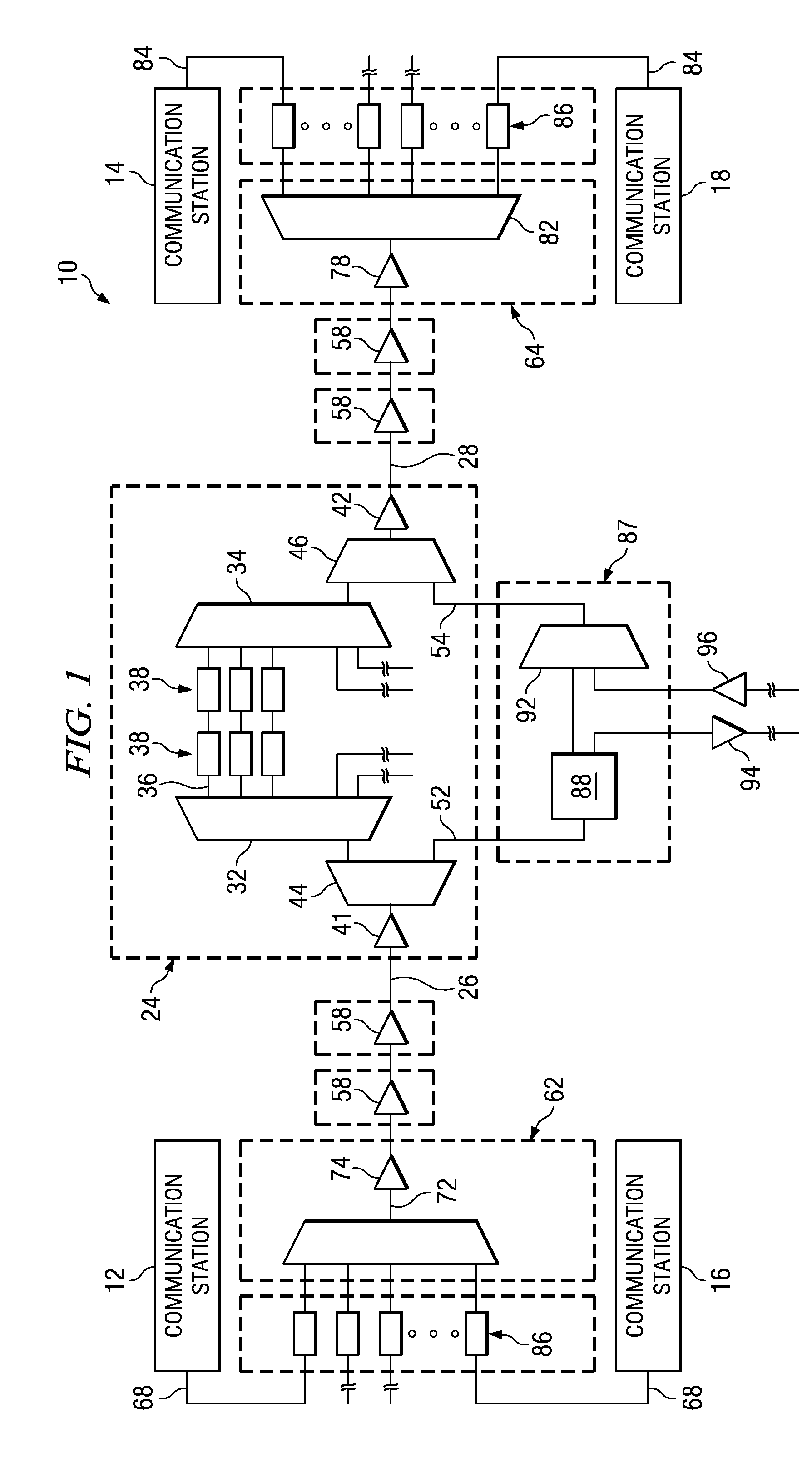
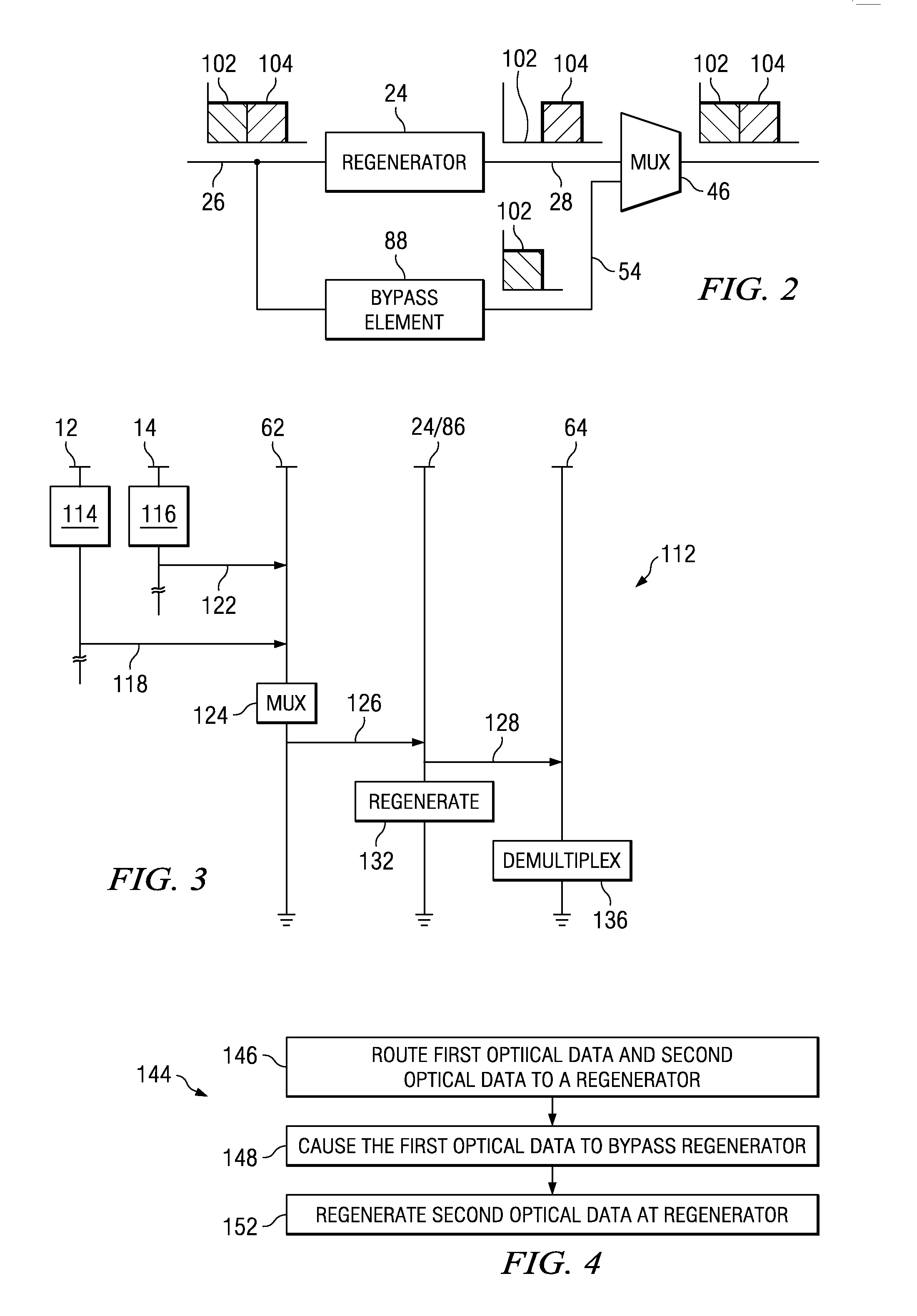
Optical network regenerator bypass module and associated method
InactiveUS20070058986A1Regeneration of optical dataWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic repeatersCommunication endpointOptical communication
An optical bypass element for an optical communication system. The optical bypass element, formed of an optical interleaver, is positioned in parallel with a regenerator. Data requiring regeneration is caused to be provided to the regenerator while data not requiring regeneration is bypassed about the regenerator by way of the optical bypass element. Once bypassed around the regenerator and once regenerated at the regenerator, the respective data is recombined and subsequently routed to communication endpoints.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Amplified spontaneous emission reflector-based gain-clamped fiber amplifier
InactiveUS20060082865A1Wide dynamic rangeCladded optical fibreFibre transmissionGratingFiber amplifier
Provided is an all-optical gain-clamped fiber amplifier, comprising transmission and isolation means for periodically transmitting an optical signal or reflecting amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) back to a gain medium. The transmission and isolation means can be embodied by an optical interleaver or a number of optical fiber Bragg gratings. Accordingly, an optical signal can be amplified across the entire C-band, and an ASE reflector-based gain-clamped fiber amplifier having a wider dynamic range than conventional amplifiers can be implemented.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Variable dispersion step-phase interferometers
InactiveUS20050270544A1Avoid reflectionsUsing optical meansCoupling light guidesOptical interferometerPhysics
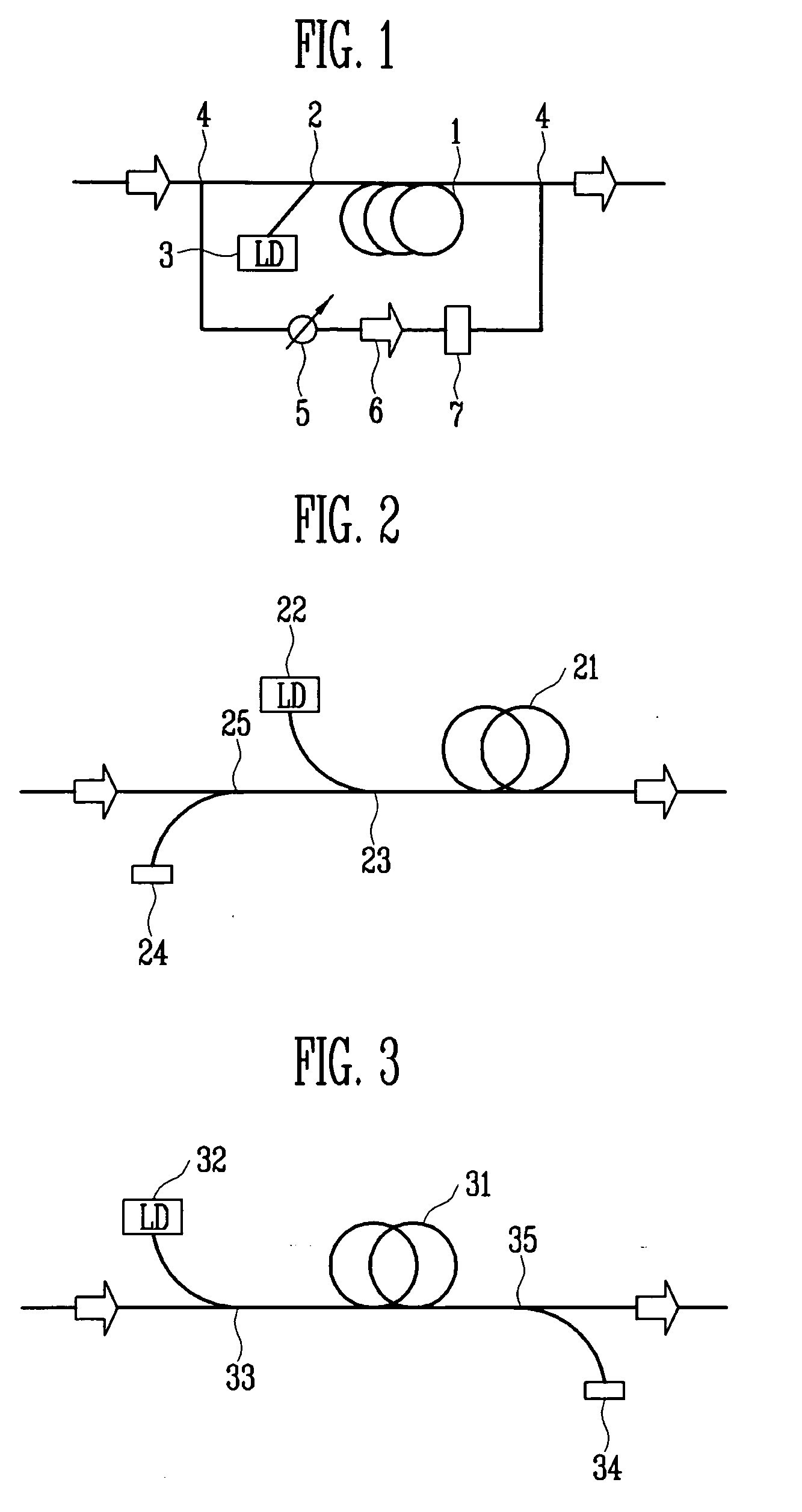
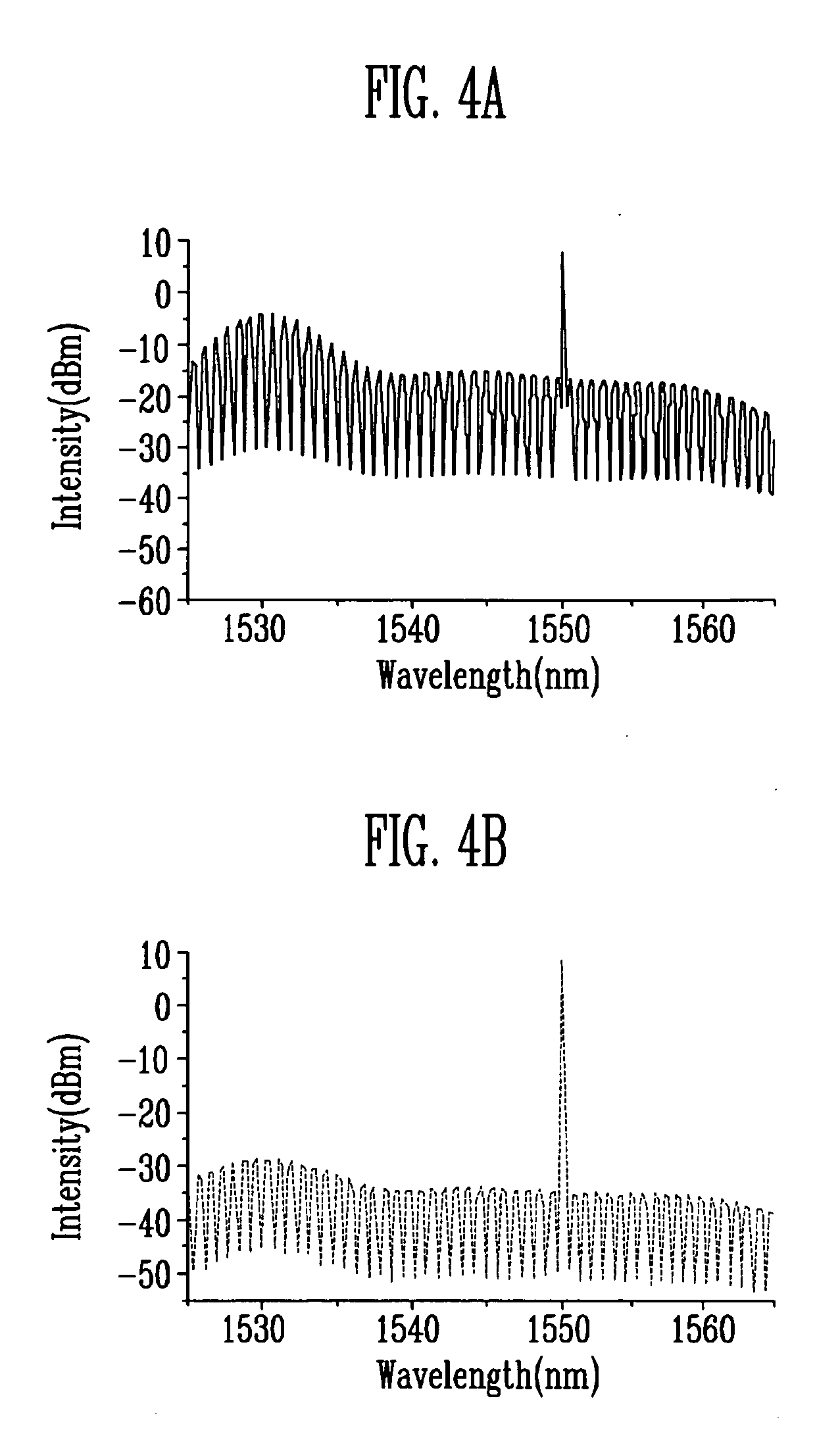
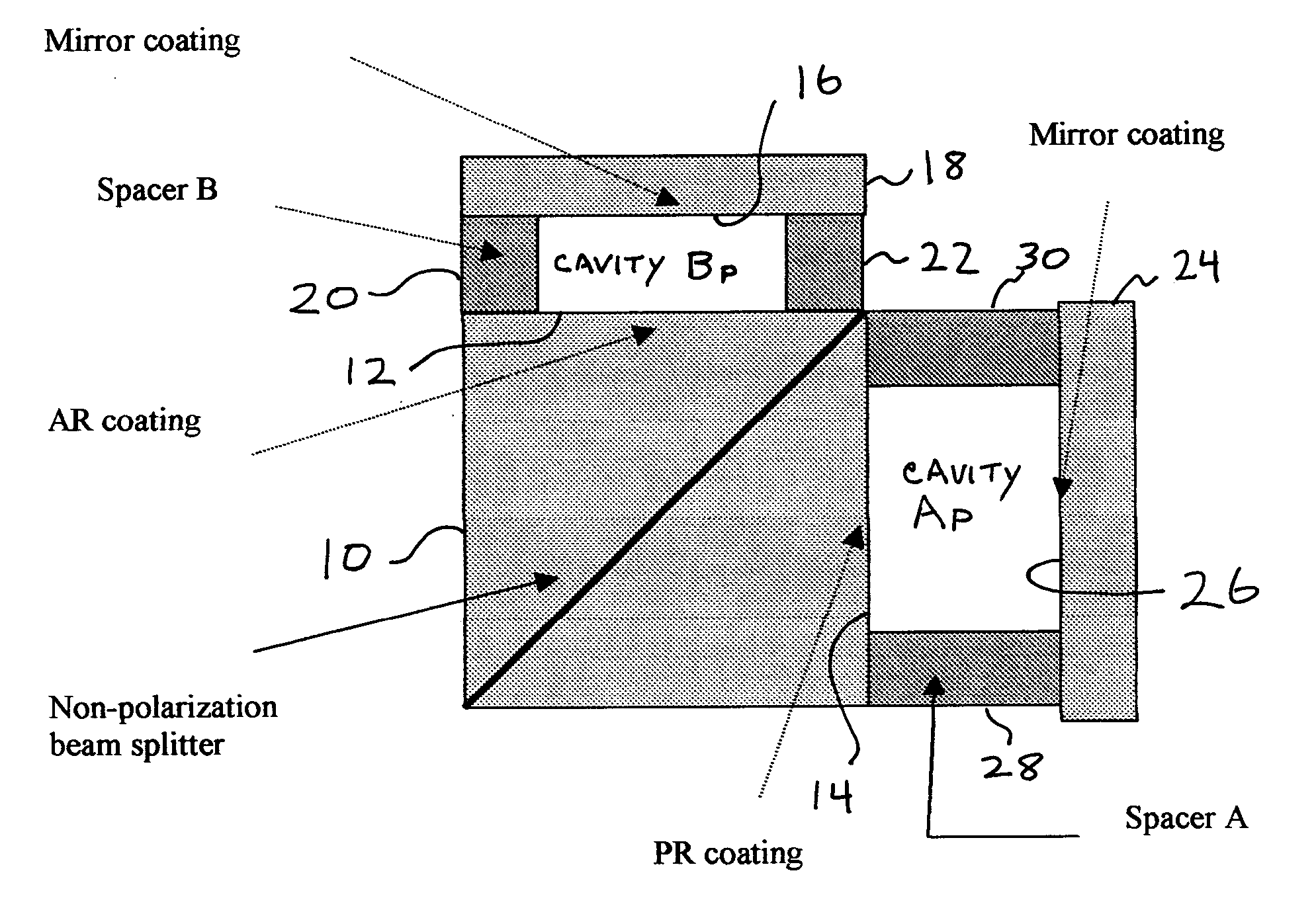
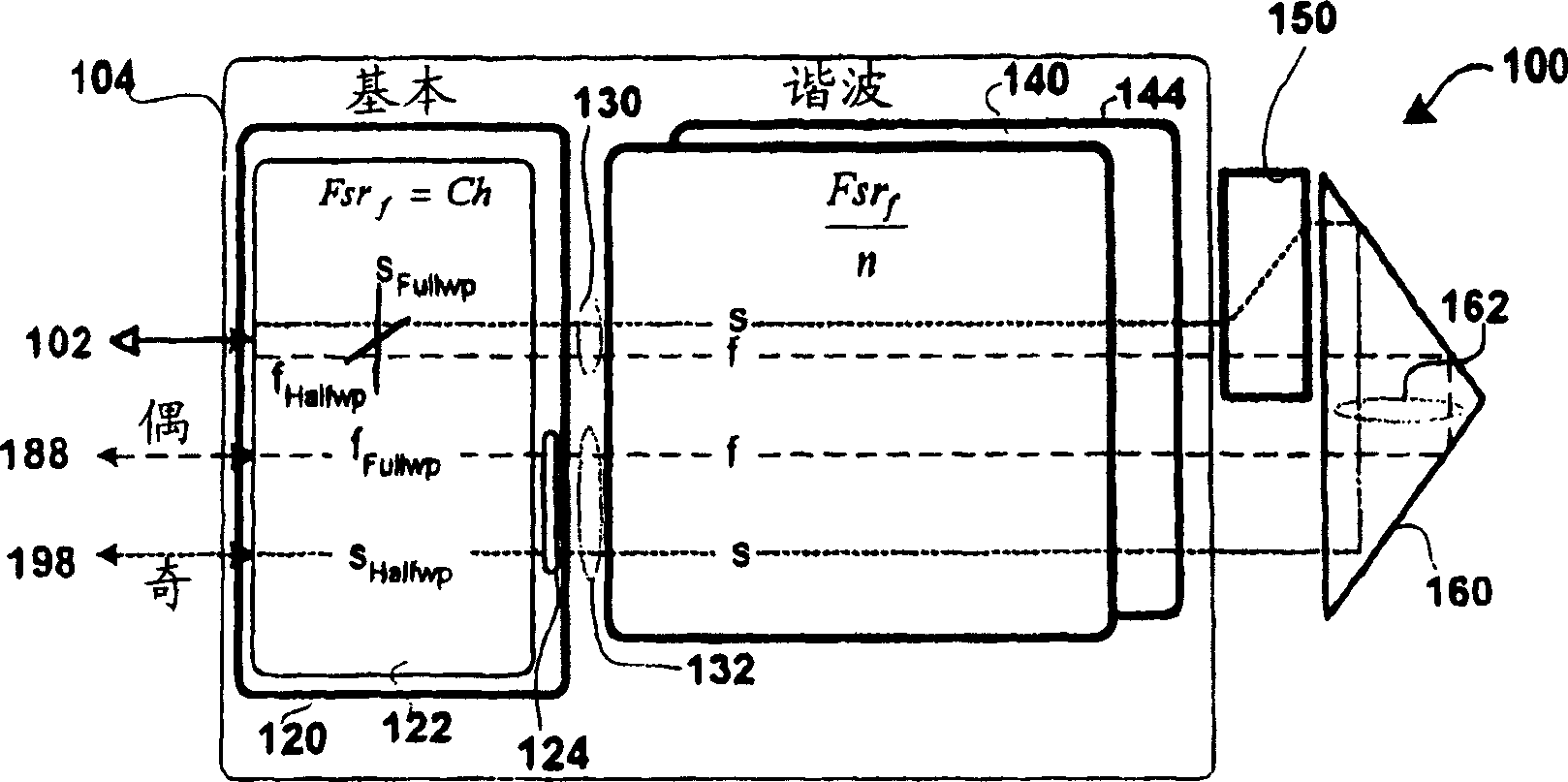
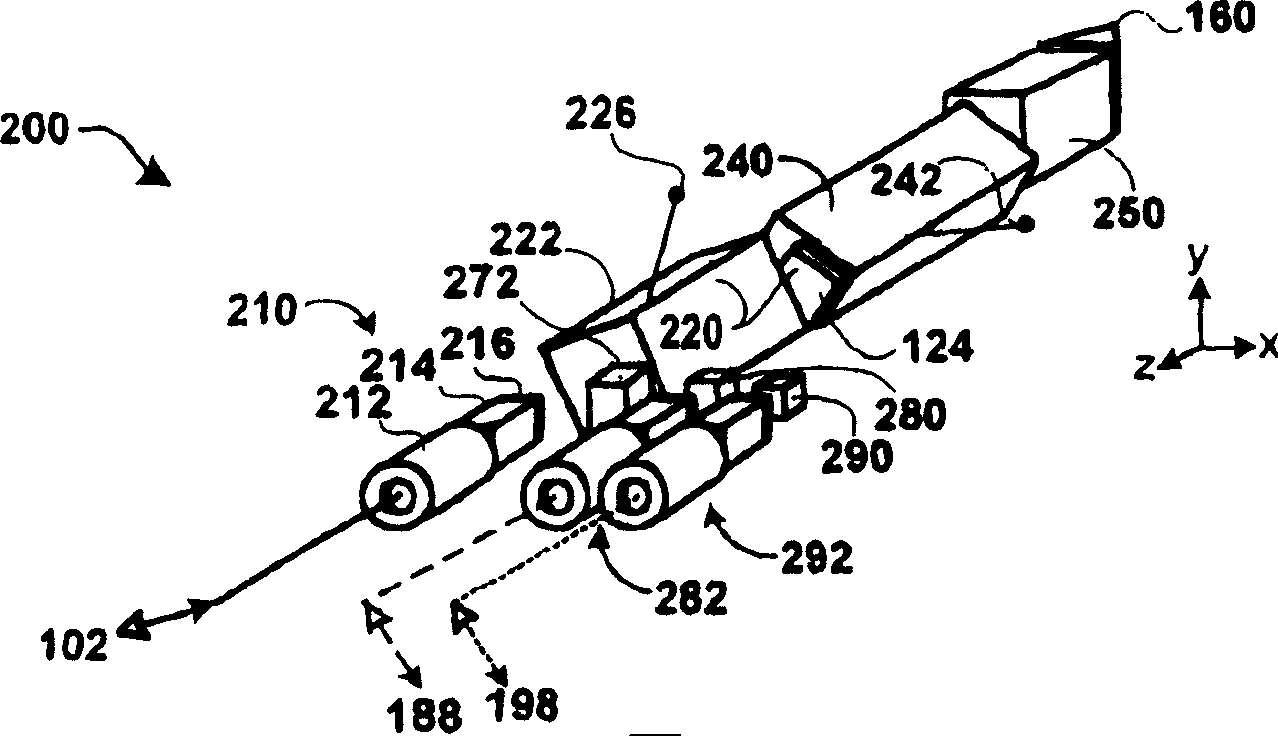
Optical interferometers with variable dispersion are shown. These interferometers are useful as optical interleavers and through the control of their design, are made to have negative and near-zero dispersion. The N-type interleaver has a negative dispersion slope near the center of the pass band. The Z-type interleaver has a dispersion that is close to zero within the pass band. These interleavers can be arranged in various systems to produce low dispersion optical networks. The non-linear phase etalons in the N- and Z-type interleavers taught herein contribute to the device dispersion. The N-Type interleaver includes a linear cavity length that is 1.5 times that of a non-linear cavity. The Z-type interleaver includes two non-linear cavities that are out of phase with each other such that the net dispersion is close to zero.
Owner:OPTOPLEX CORP
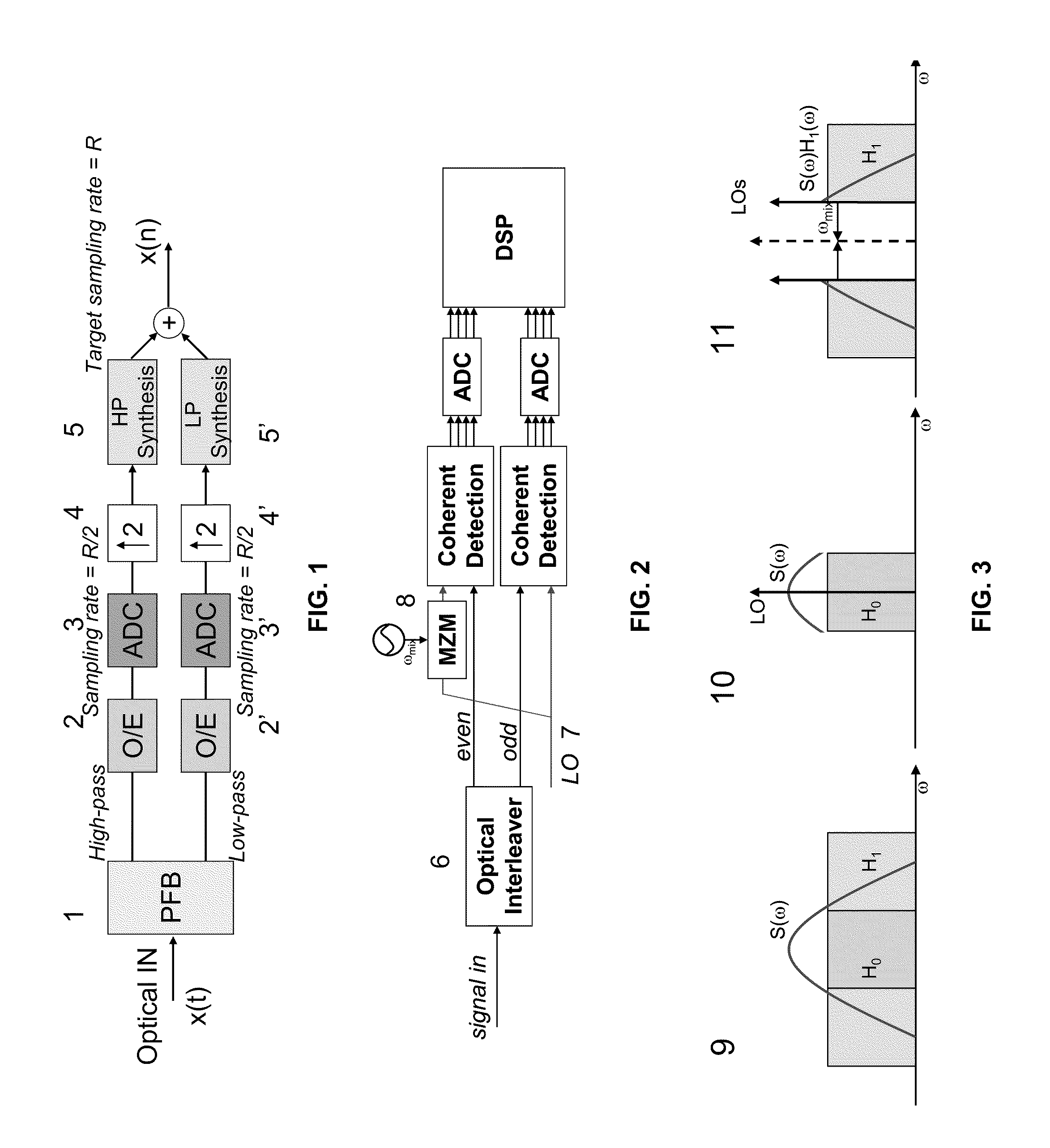
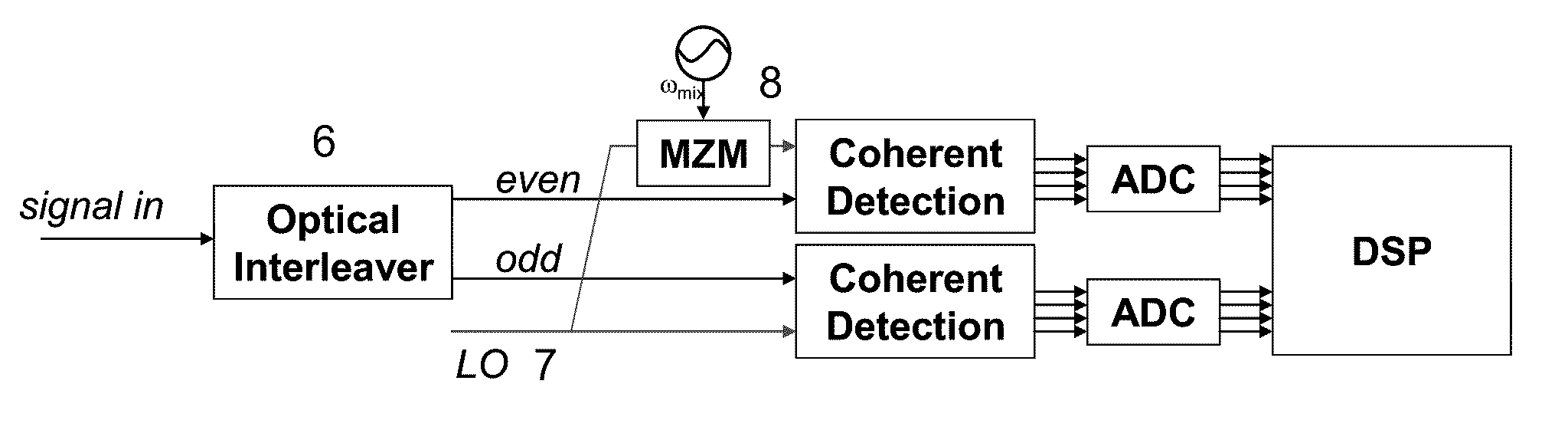
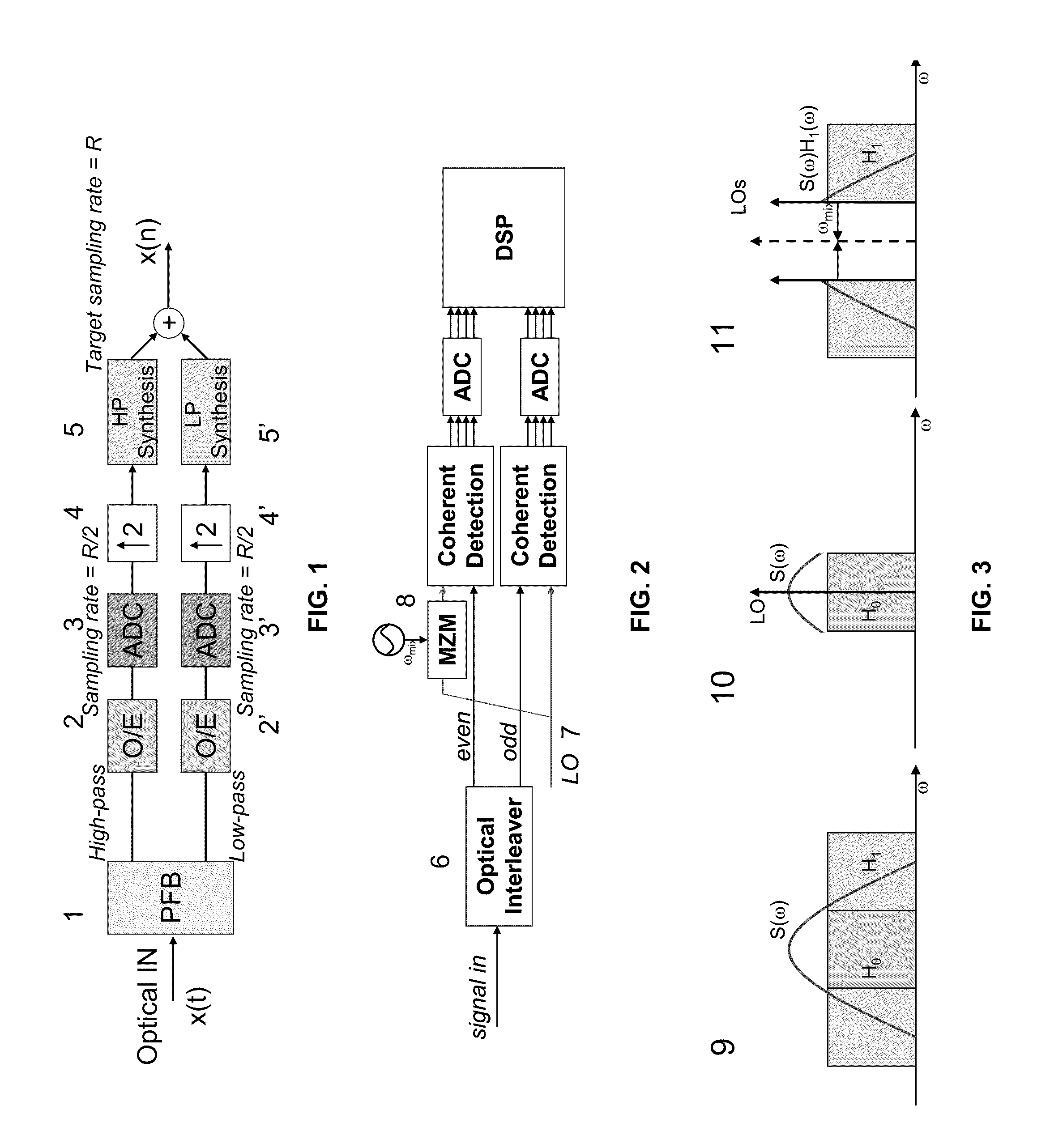
Parallel digital coherent detection using symmetrical optical interleaver and direct optical down conversion
A method includes modulating lightwaves to provide first and second OFDM signal sidebands at a first polarization direction and first and second OFDM signal sidebands at a second polarization direction, and combining sidebands that are oppositely positioned and joined from the first and second OFDM signal sidebands at each polarization direction to provide a polarization multiplexing OFDM signal.
Owner:NEC CORP
Optical interleaver, filter cell, and component design with reduced chromatic dispersion
InactiveUS20050041290A1Improve integrityEasy to packMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexerOptical processing
An optical interleaver for use in a range of telecommunications applications including optical multiplexers / demultiplexers and optical routers. The optical device includes an optical processing loop which allows multi-stage performance characteristics to be achieved with a single physical filtration stage. Optical processing on the first leg and second legs of the loop is asymmetrical thereby improving the integrity of the optical signals by effecting complementary chromatic dispersion on the first and second legs. A fundamental filter cell within the interleaver filters optical signals propagating on each of the two legs of the optical loop which intersects the fundamental filter cell.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
One-dimensional membrane cavity structure-based different-bandwidth optical interleaver
InactiveCN101806938ASimple structureReduce manufacturing costCoupling light guidesRefractive indexOptical thin film
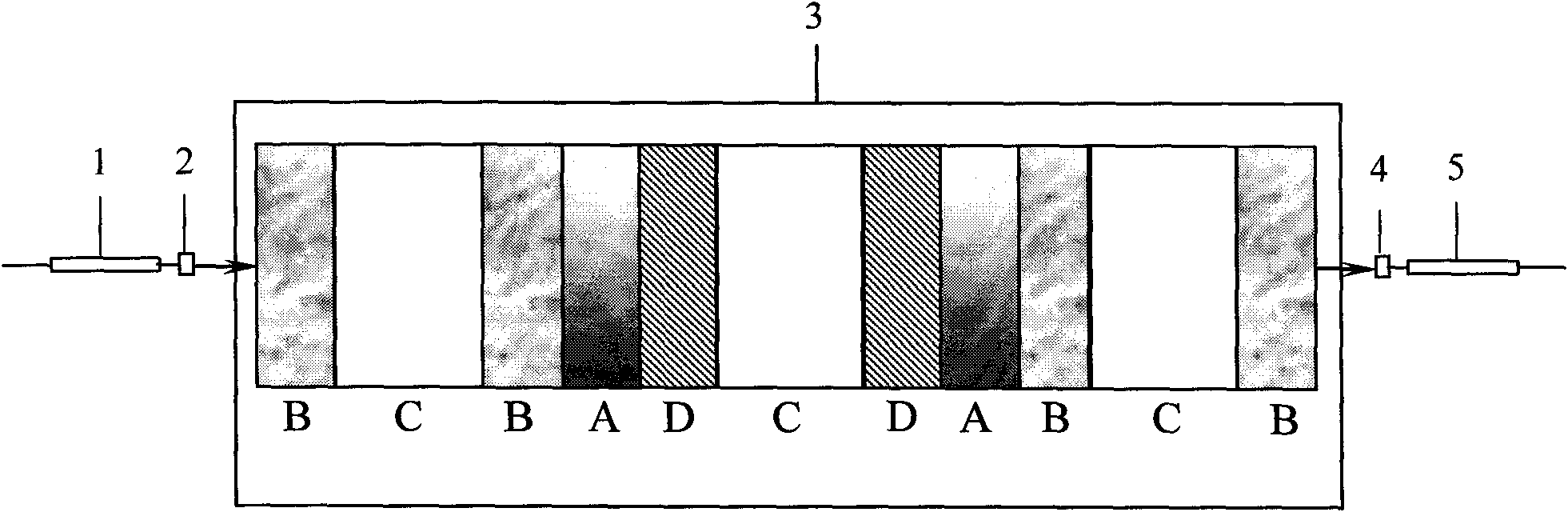
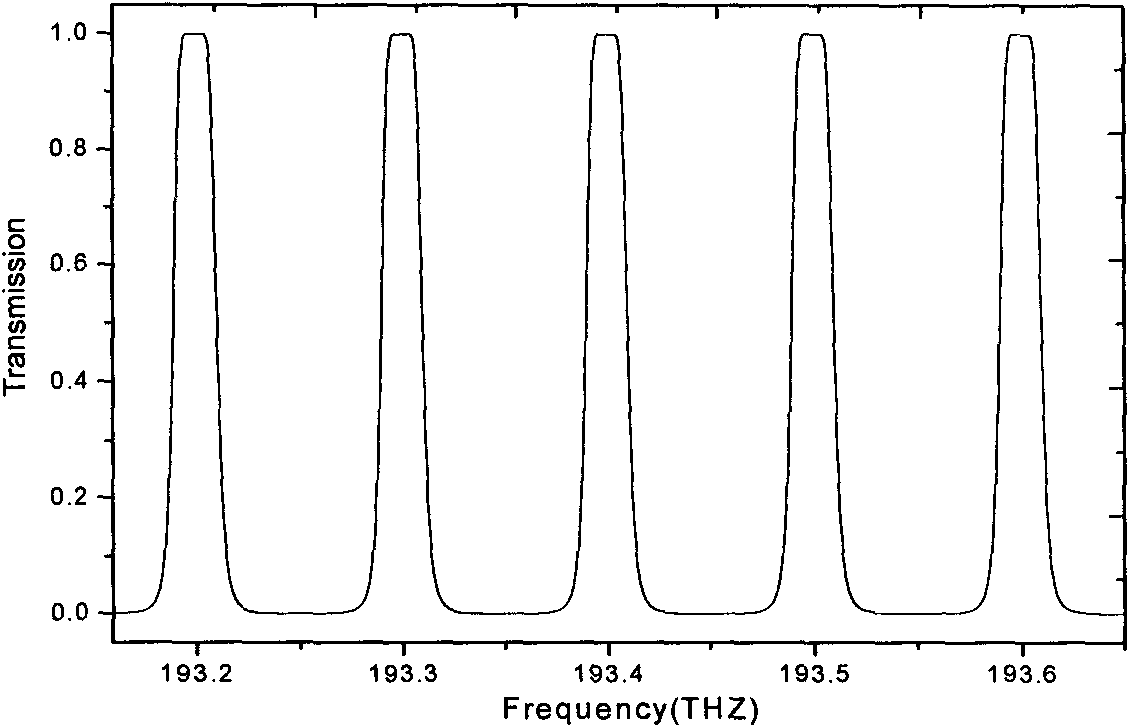
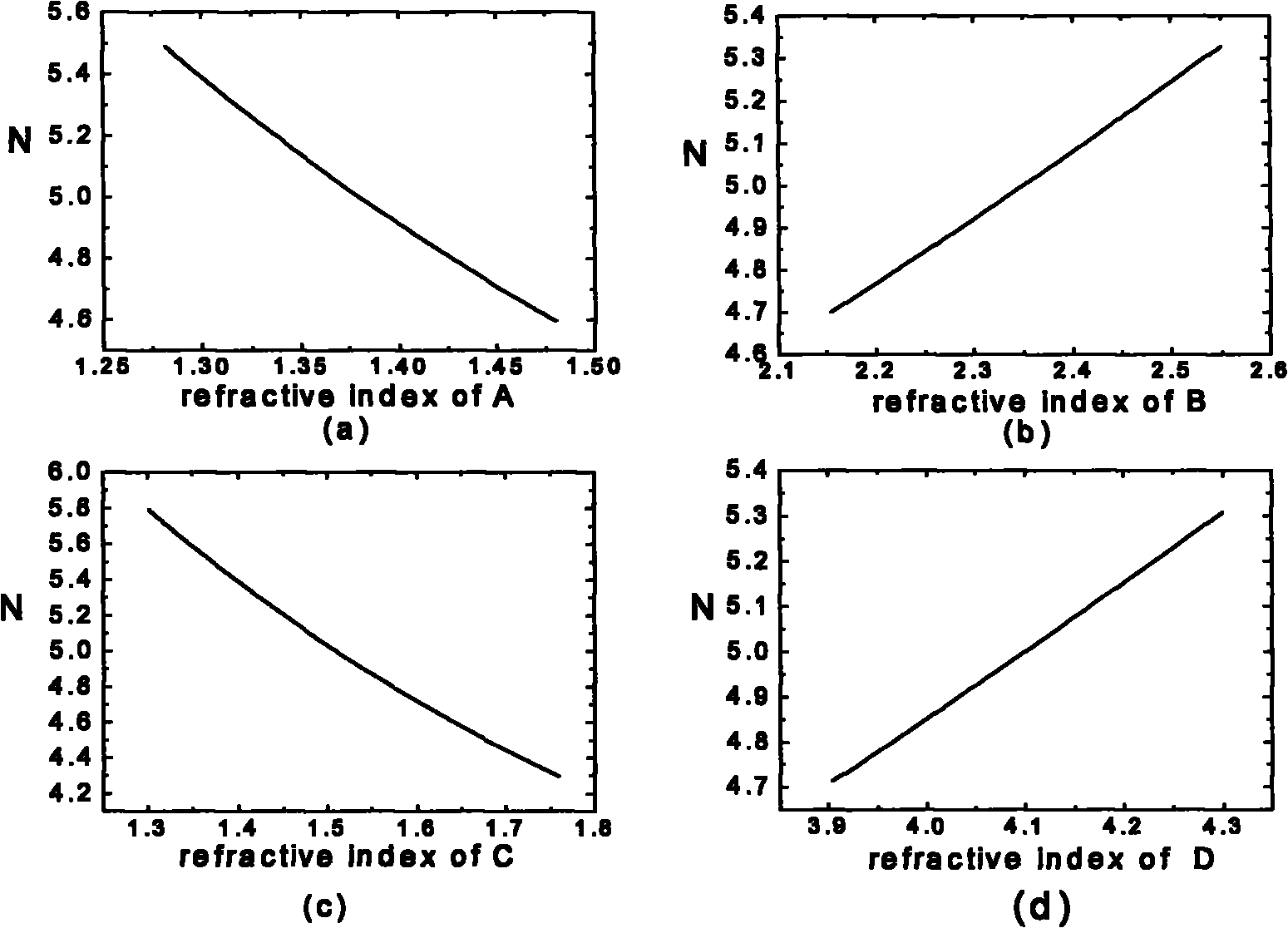
The invention discloses a one-dimensional membrane cavity structure-based different-bandwidth optical interleaver. The interleaver comprises an input optical fiber, a collimating lens, eleven optical dielectric layers, a focusing lens and an output optical fiber and is characterized in that: along the forward direction of a light beam, the eleven optical dielectric layers orderly comprise: a first layer and an eleventh layer of B-type dielectric layers, a second layer and a tenth layer of C-type dielectric layers, a third layer and a ninth layer of the B-type dielectric layers, a fourth layer and an eighth layer of A-type dielectric layers, a fifth layer and a seventh layer of D-type dielectric layers and a sixth layer of a C-type dielectric layer; the C dielectric layers are isotropical optical glass; the A, B and D dielectric layers are optical thin films with different refractive indexes; the optical thicknesses of the A, B and D dielectric layers are all 1 / 4 of a central wavelength; and the expression of the optical thickness of the C dielectric layer is C / (2*delta f). The interleaver has the characteristics of low cost, high performance and high reliability; and both a pass band and a stop band have flat filter characteristics, so the interleaver is used for performing the selection of wavelength signals, noise filter of an optical amplifier, gain equalization and the like in a wave division multiplex communication system.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
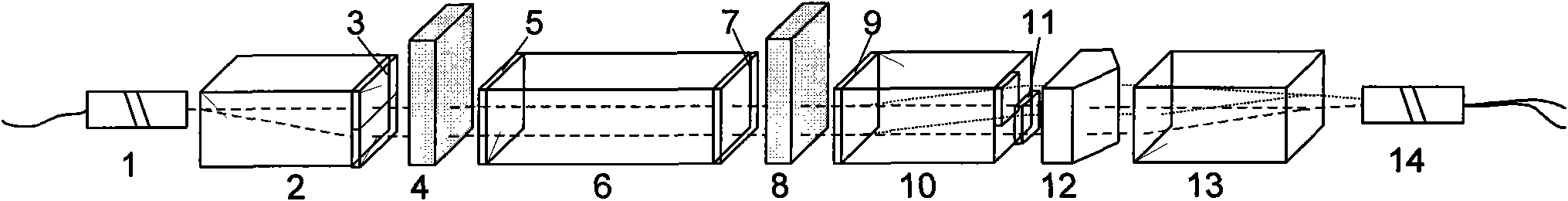
Step-phase interferometric optical interleaver
InactiveUS7408713B1Reducing contribution to phase errorEliminate errorsRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryCoated surfaceOptical axis
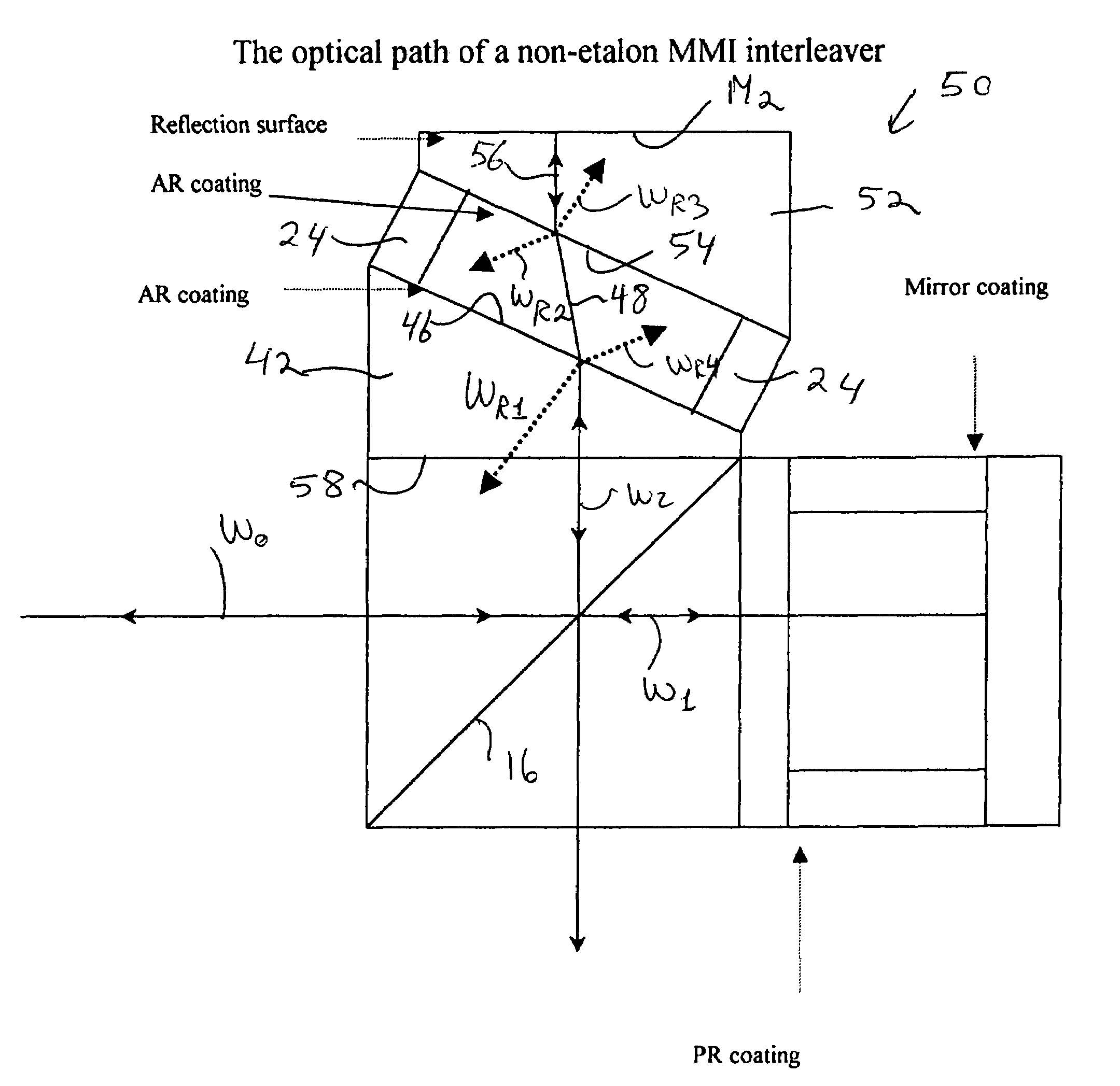
The cavity in the mirror arm of a conventional interleaver is replaced by a wedge integral with the beamsplitter structure of the interleaver. Thus, the light reflected from the AR-coated surface of the wedge is dispersed away from the optics of the device. The beam emerging from the wedge surface is directed toward a tilted mirror that reflects it totally on-axis. As a result of the diversion of the light reflected from the wedge surface and the non-parallel disposition of the wedge surface with respect to the mirror, phase errors are virtually eliminated. In another embodiment, a second wedge is used with a second antireflective surface disposed in parallel to the first wedge's antireflective surface, and with a mirror normal to the optical axis of the device.
Owner:OPTOPLEX CORP
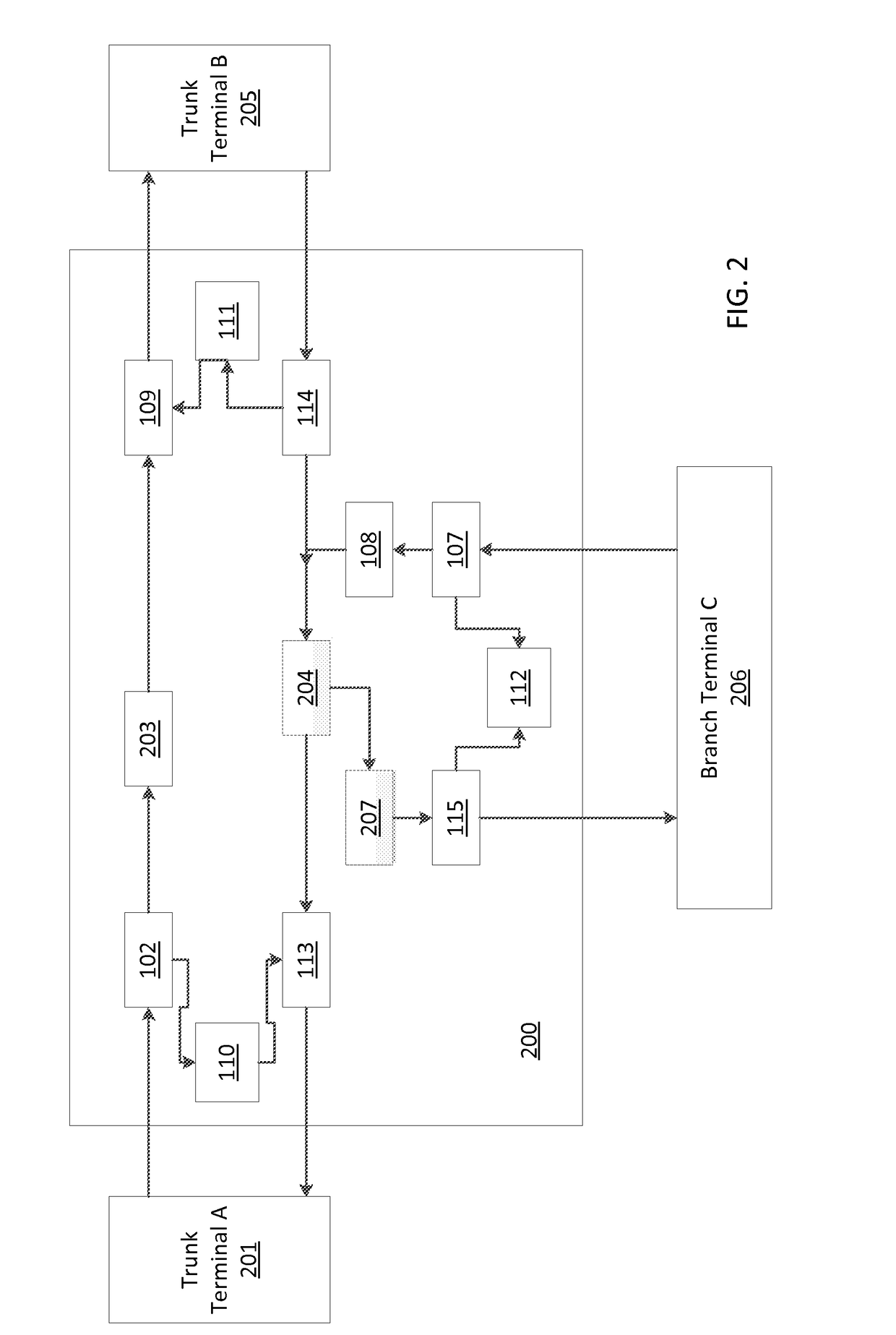
Submarine reconfigurable optical add/drop multiplexer with passive branching unit
Systems and methods for data transport, including submarine reconfigurable optical add / drop multiplexers, branching units configured to receive signals from trunk terminals (TTs), and dummy light filters configured to pass useful signals through the filters, and to reflect dummy light. Optical interleavers are configured to separate useful signals into two or more groups of optical channels, and the optical channels are set to a frequency of either a left or a right portion of a total channel bandwidth. De-interleavers merge signal groups together from trunk terminals, and lasers at each of the transponders at the source terminals are configured to adjust a destination of a channel by fine tuning a frequency or wavelength of the one or more signals.
Owner:NEC CORP
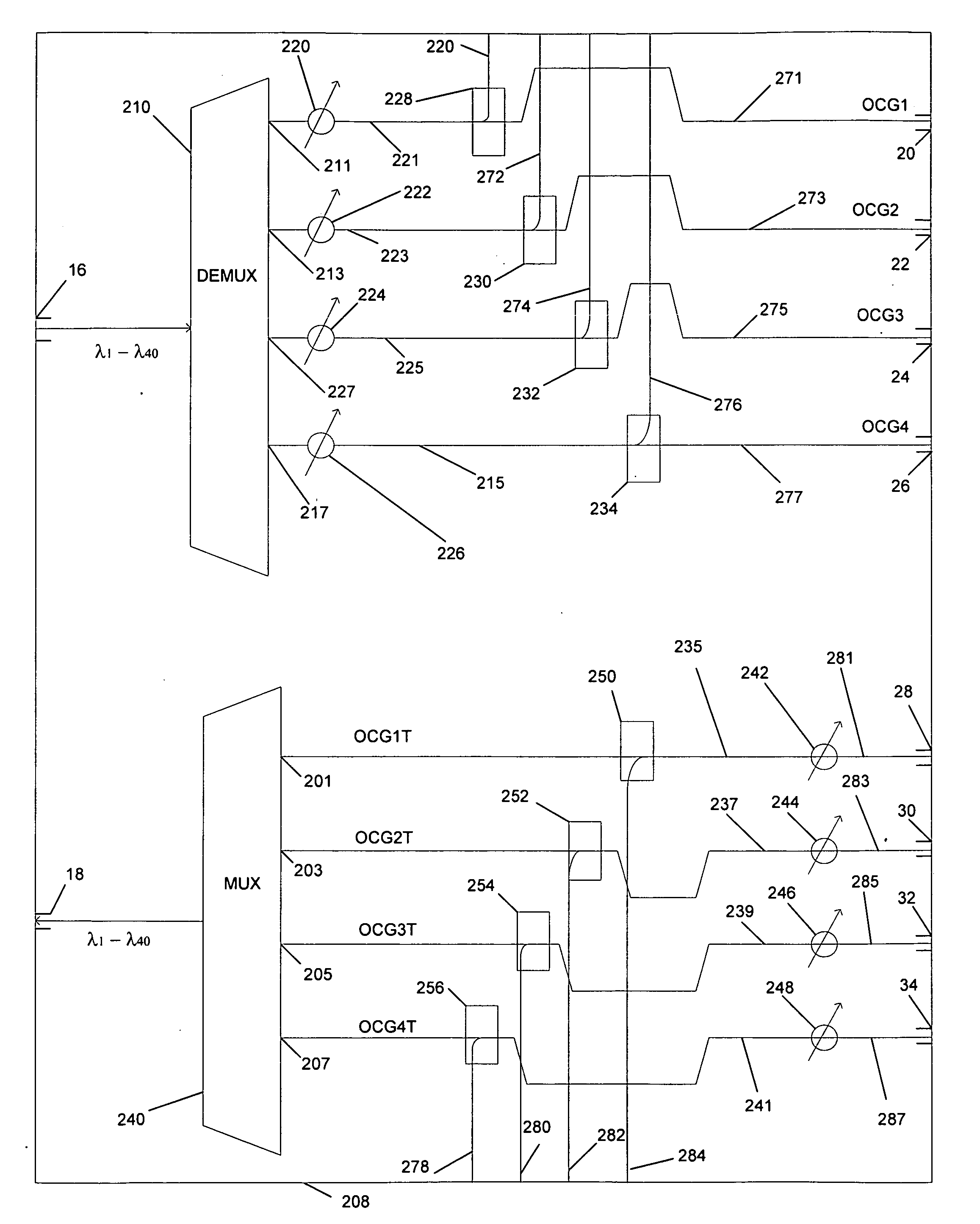
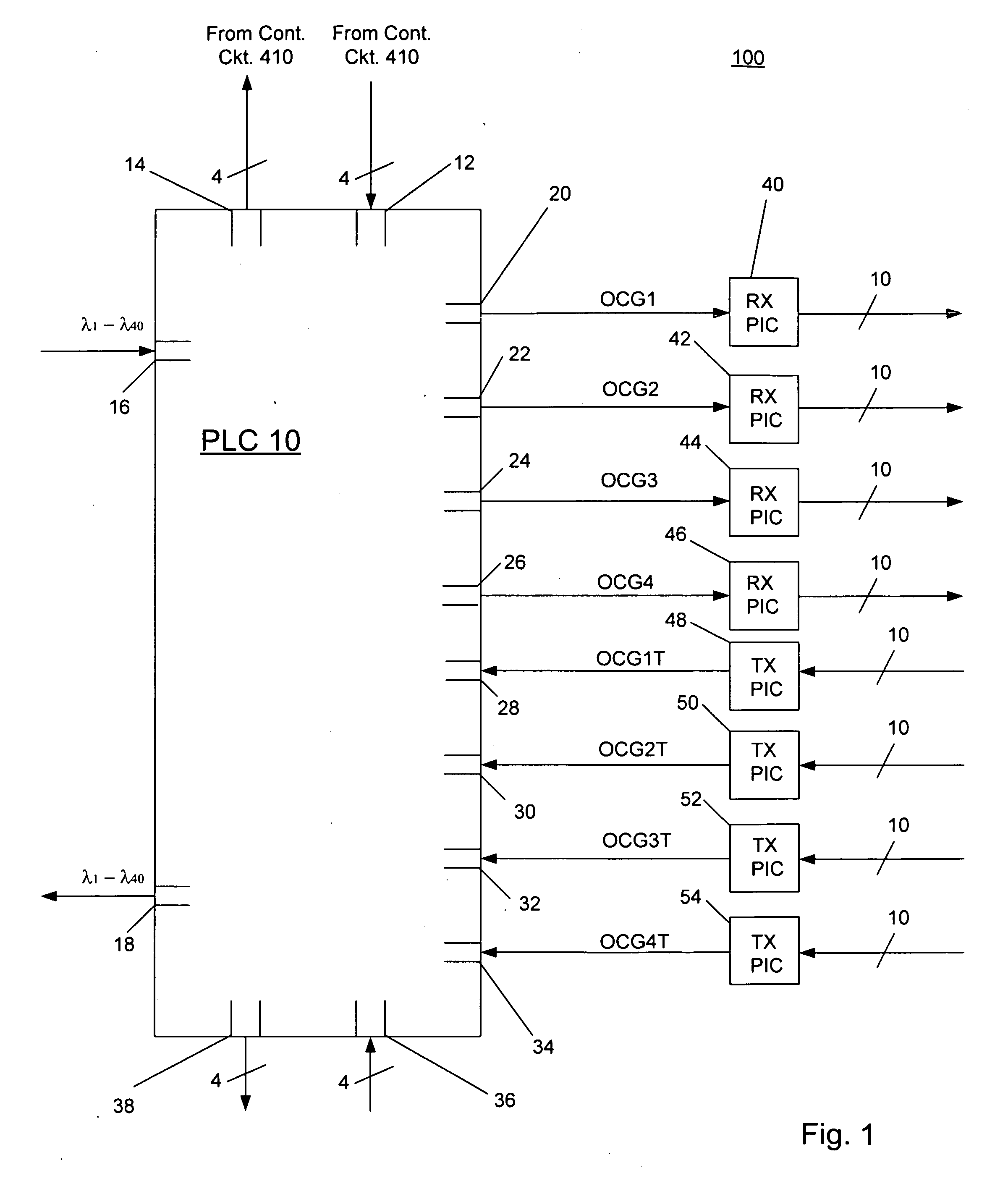
Planar lightwave circuit
Consistent with the present disclosure optical interleaver and deinterleaver circuits are integrated onto a substrate. The inputs to the interleaver and the outputs of the deinterleaver are each coupled to a corresponding variable optical attenuator (VOA) and optical tap, which are also provided on the substrate. The optical taps supply a portion of the output of each VOA to a corresponding photodetector. A control circuit, which is coupled to the photodetector, in turn, supplies a control signal to each VOA based on the output of the photodetector. Accordingly, optical multiplexing and demultiplexing components, as well as monitoring and power regulating components are provided on the same chip. Such a chip may be compact, relatively inexpensive, and has reduced power consumption compared to optical multiplexer and demultiplexer equipment including discrete components.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Parallel Digital Coherent Detection Using Symmetrical Optical Interleaver and Direct Optical Down Conversion
ActiveUS20100266282A1Polarisation multiplex systemsSecret communicationPolarization multiplexedSideband
A method includes modulating lightwaves to provide first and second OFDM signal sidebands at a first polarization direction and first and second OFDM signal sidebands at a second polarization direction, and combining sidebands that are oppositely positioned and joined from the first and second OFDM signal sidebands at each polarization direction to provide a polarization multiplexing OFDM signal.
Owner:NEC CORP
Light source having spatially interleaved light beams
A light source includes a first set of first beam sources having parallel output beams lying in a first-beam-source plane and a second set of second beam sources having parallel output beams lying in a second-beam-source plane. The first-beam-source output beams are parallel to the second-beam-source output beams, but are spatially offset in a direction perpendicular to the first-beam-source output beams. A spatial optical interleaver disposed receives the first-beam-source output beams and the second-beam-source output beams. The first-beam-source output beams pass unimpeded through a set of first-beam openings in the spatial optical interleaver, and the second-beam-source output beams are reflected parallel to the first-beam-source output beams and in the first-beam-source plane.
Owner:RAYTHEON CANADA LTD
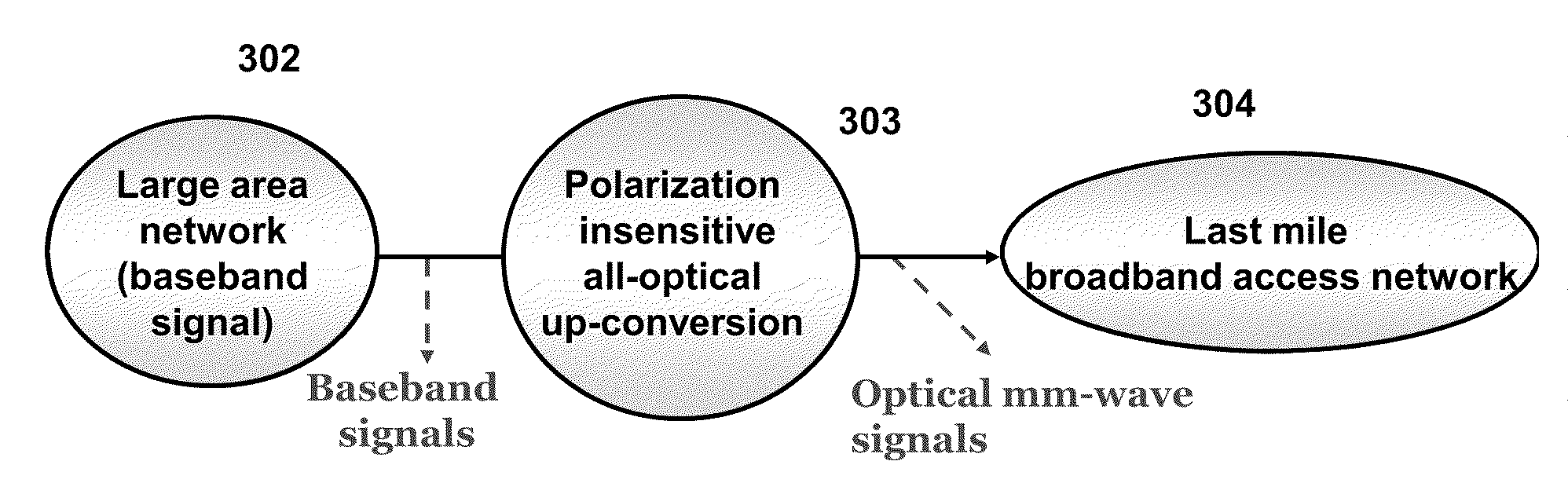
All Optical Up-Conversion System
ActiveUS20100046962A1Electromagnetic transmission non-optical aspectsRadio-over-fibreCarrier signalLaser light
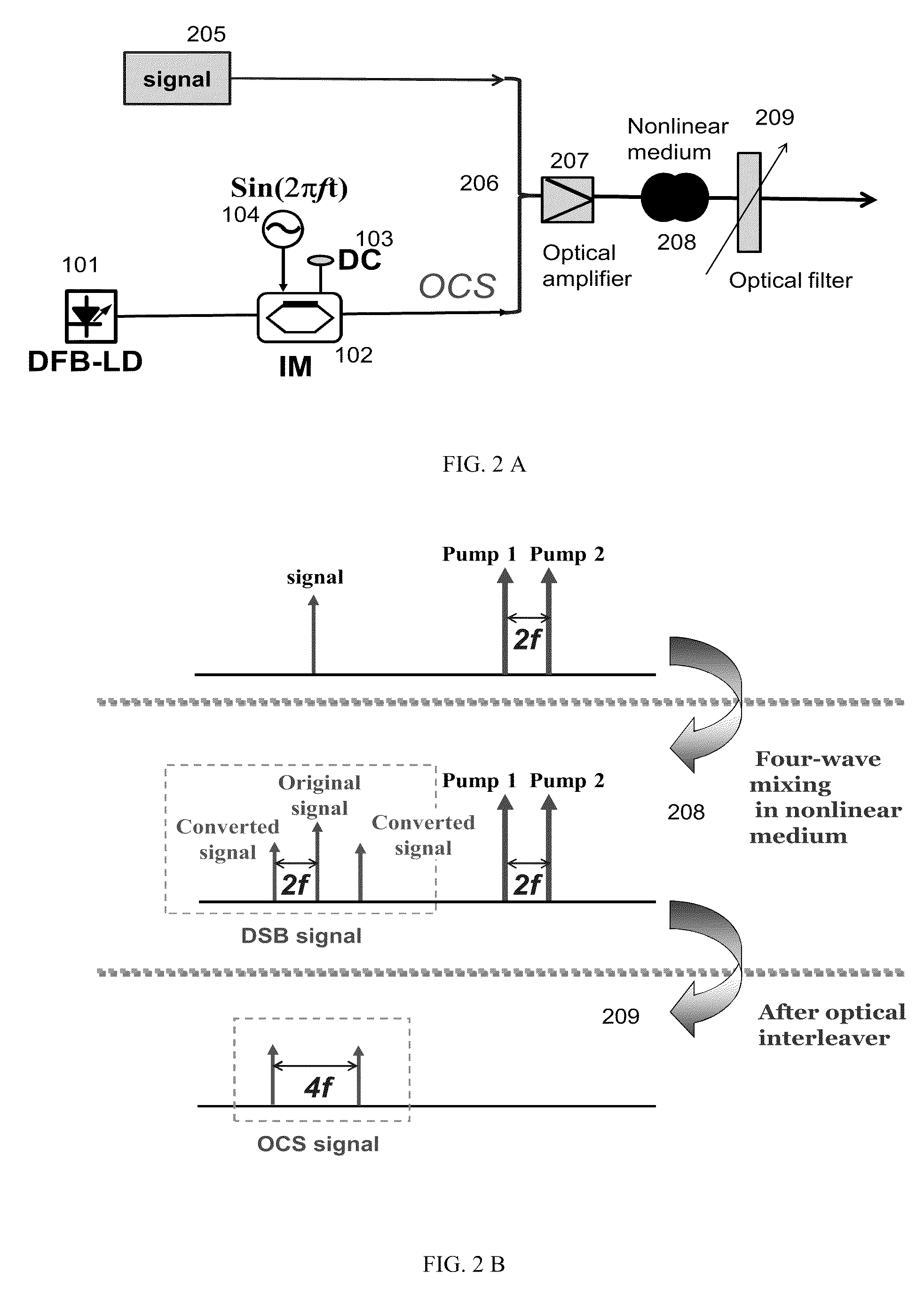
An optical system for providing all-optical up-conversion of a baseband signal including an all-optical up-converter responsive to baseband signals to provide corresponding dual sideband signals about a suppressed optical carrier, said dual sideband signals each having the same polarization direction, being phase locked, having the same optical power and having a fixed frequency spacing; and an optical filter for filtering the carrier signals and providing wavelength division multiplexed signals without optical carriers. In a preferred embodiment, the all-optical up-converter includes an intensity modulator for generating two pump lightwaves that are carrier suppressed in response to the intensity modulator receiving a laser light source and being driven by an RF signal, wherein the intensity modulator is DC biased at a null point, an optical combiner for combining the baseband signal and the two pump lightwaves, a nonlinear medium for four wave mixing the baseband signal and two pump lightwaves to generate the baseband signal and corresponding dual sideband signals, and an optical interleaver for removing the baseband signal and two pump lightwaves to provide said sideband signals about the suppressed optical carrier.
Owner:NEC CORP
Wide passband optical interleaver
InactiveUS6917760B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesEngineeringChannel spacing
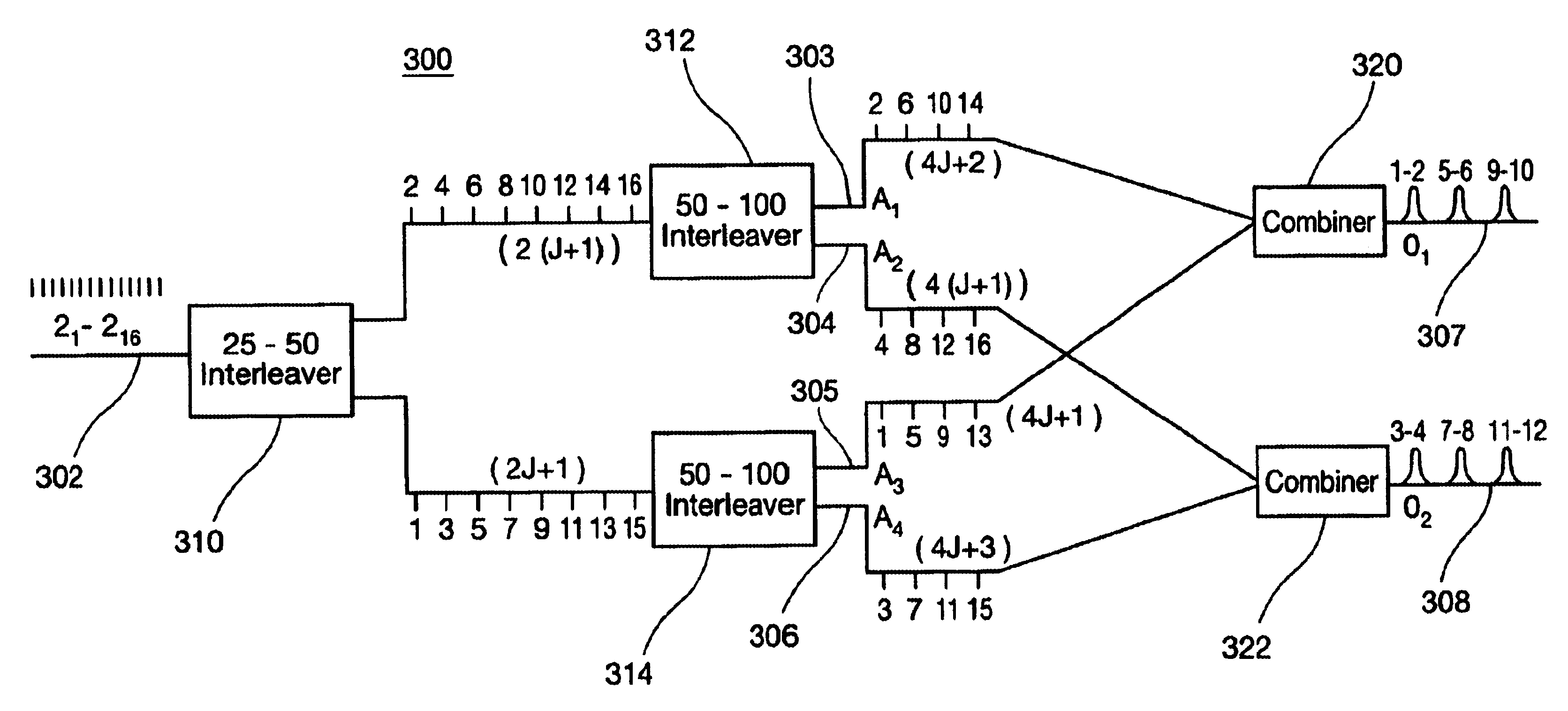
A method and apparatus is provided for reformatting or interleaving a WDM signal that includes a plurality of optical channels having a first bandwidth and a first channel spacing. The method begins by receiving the WDM signal and dividing it into first and second subsets of optical channels each having a second channel spacing. Next, the first subset of optical channels are divided into third and fourth subsets of optical channels each having a third channel spacing. In addition, the second subset of optical channels is divided into fifth and sixth subsets of optical channels each having a fourth channel spacing. The third and fifth subsets of optical channels are combined to generate a first output WDM signal, while the fourth and sixth subsets of optical channels are combined to generate a second output WDM signal.
Owner:WAVESPLITTER TECH INC
Wide passband optical interleaver
ActiveUS7496253B2Increase effective bandwidthBandwidthCoupling light guidesTransmission coefficientPhysics
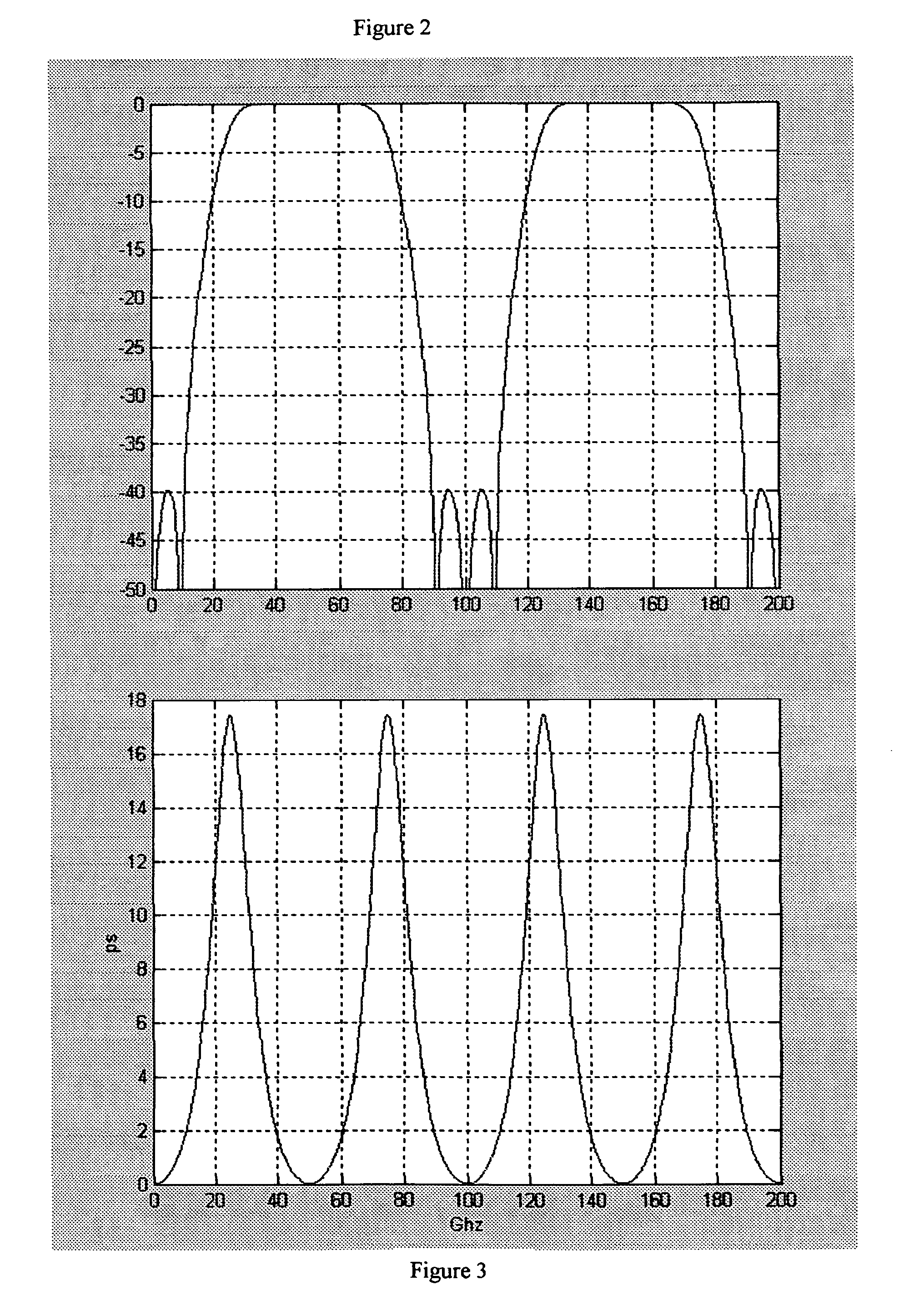
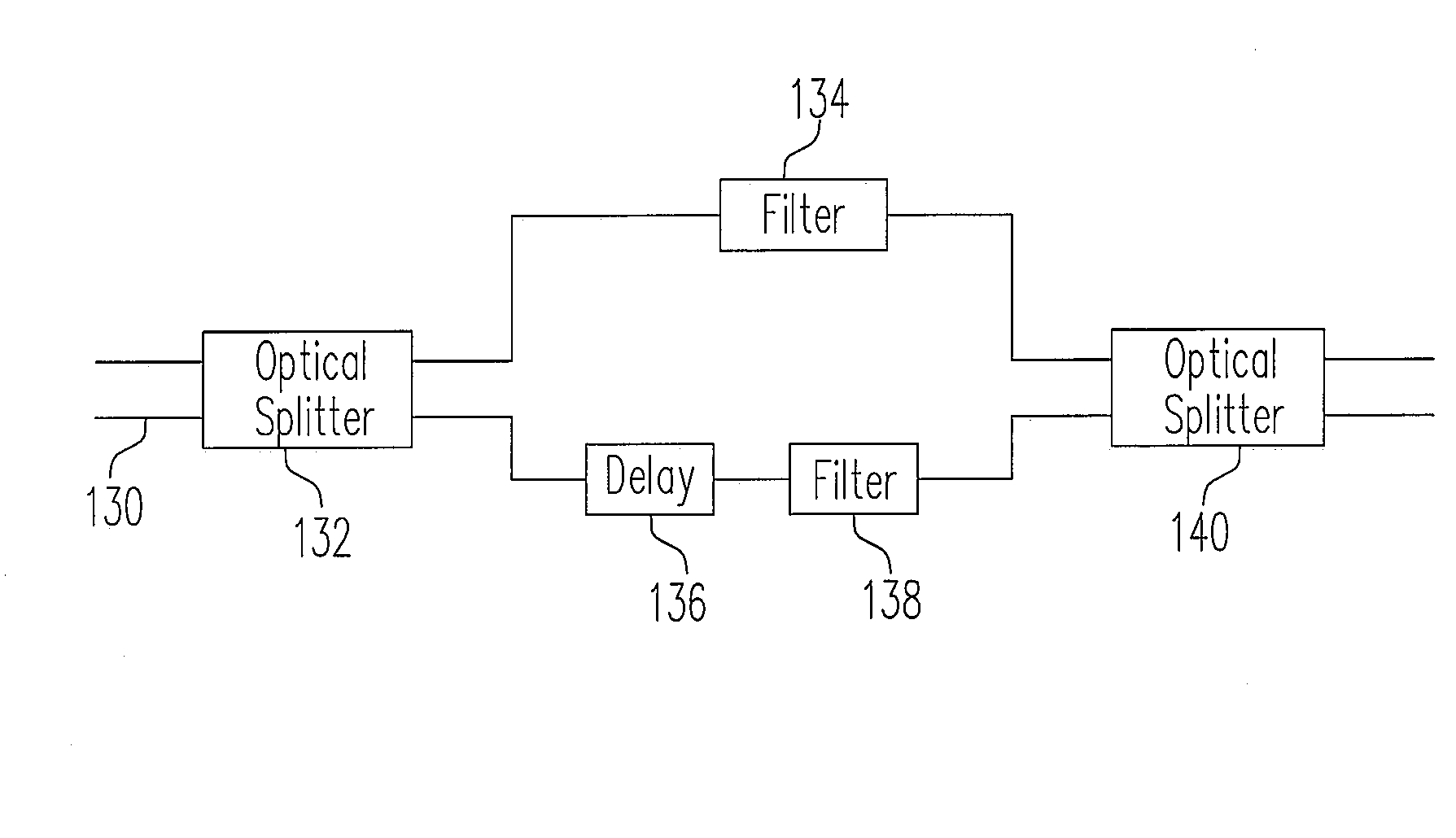
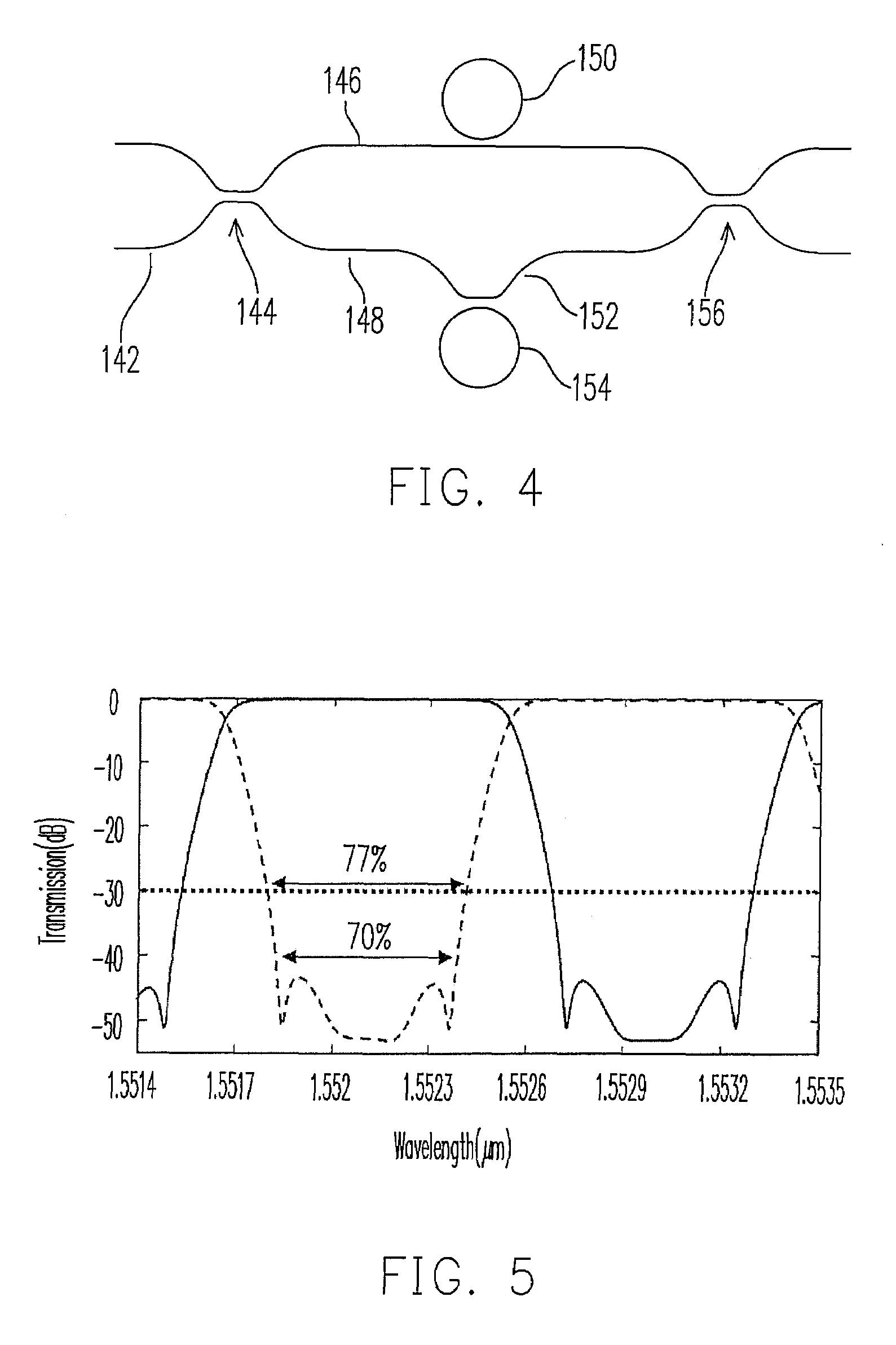
A wide passband optical interleaver includes a first optical splitter, having a first output terminal and a second output terminal. A first optical route is coupled to the first output terminal. A second optical route is coupled to the second output terminal. A delay is coupled on the second optical route. A second optical splitter having two input terminals is receiving the first optical route and the second optical route. A plurality of optical filter respectively having transmission coefficients ρi is coupled to the first optical route and the second optical route. The transmission coefficients ρi are determined by satisfying a desired quantity of effective group delay ratio T, defined asT=∑iSi1-ρi1+ρi,whereSiis+1or-1.where Si is +1 or −1.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
ROADM systems and methods of operation
InactiveCN102640439AWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultimode transmissionSignal onOptical coupler
ROADM node systems and methods of operation are disclosed. ROADM node systems may include transponder aggregators including transponders to add signals for switching through the ROADM node. The transponder aggregators include optical couplers constrained that are from coupling added signals on adjacent channels for simultaneous use. The ROADM system may include an optical interleaver that can provide an additional filtering function for the coupled signals prior to transmission of the signals on a WDM network.
Owner:NEC LAB AMERICA
Optical interleaver, filter cell, and component design with reduced chromatic dispersion
An optical interleaver for use in telecommunications applications includes an optical multiplexer / demultiplexer and an optical router, the optical device including optical processing circuitry capable of achieving multi-level performance characteristics using a single physical filtering stage. The optical processing is asymmetrical on the first and second segments of the loop, thereby improving the integrity of the optical signal by compensating for dispersion on the first and second segments. A basic filter unit within the interleaver filters the optical signal propagating on each of the two segments of the optical circuit intersected by the filter unit.
Owner:FINISAR SHANGHAI INC
Amplified spontaneous emission reflector-based gain-clamped fiber amplifier
Provided is an all-optical gain-clamped fiber amplifier, comprising transmission and isolation means for periodically transmitting an optical signal or reflecting amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) back to a gain medium. The transmission and isolation means can be embodied by an optical interleaver or a number of optical fiber Bragg gratings. Accordingly, an optical signal can be amplified across the entire C-band, and an ASE reflector-based gain-clamped fiber amplifier having a wider dynamic range than conventional amplifiers can be implemented.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Optical interleaver
In accordance with an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, an optical device includes an interleaver / deinterleaver, which includes a passive thermal compensator, wherein an optical signal which transverses the optical device undergoes substantially no temperature induced frequency drift over a desired temperature range.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Integrateable optical interleaver and de-interleaver
A proposed integrateable optical interleaver includes an input Y-branch coupler and at least two multi-section optical couplers. The multi-section optical couplers of the interleaver include at least three substantially similar optical couplers, adjacent ones of the optical couplers interconnected via at least one set of waveguides. The interleaver of the present invention comprises a highly compact and fabrication-robust form that is capable of being integrated onto a single planar lightwave circuit.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Integrateable Optical Interleaver and De-Interleaver
A proposed integrateable optical interleaver includes an input Y-branch coupler and at least two multi-section optical couplers. The multi-section optical couplers of the interleaver include at least three substantially similar optical couplers, adjacent ones of the optical couplers interconnected via at least one set of waveguides. The interleaver of the present invention comprises a highly compact and fabrication-robust form that is capable of being integrated onto a single planar lightwave circuit.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Optical interleaver with adjustable high speed isolation and centre wavelength
The invention discloses an optical interleaver with adjustable high speed isolation and centre wavelength. A single optical fiber collimator, a first polarization displacement crystal, a first half wave plate group, a first electro light delay plate, a quarter-wave plate, a double refraction crystal, a second half wave plate group, a second electro light delay plate, a third half wave plate group, a second polarization displacement crystal, a fourth half wave plate group, a ridge prism, a third polarization displacement crystal and a double optical fiber collimator are sequentially put in the direction of the same horizontal optical path; parallel beams separated by the second polarization displacement crystal are collimated by the fourth half wave plate group, the ridge prism, the third polarization displacement crystal and coupled to the double optical fiber collimator; the high speed adjustment of the channel separation of the optical interleaver is realized by controlling the first electro light delay plate; the high speed adjustment of the centre wavelength of the optical interleaver is realized by controlling the second electro light delay plate. The invention realizes the high speed adjustment of the isolation and the centre wavelength of the optical interleaver, and is characterized by the compact structure, the low cost, the stable performance, etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
One-dimensional film-cavity type unequal bandwidth optical interleaver design method
ActiveCN106054318ASimple structureHigh flatnessOptical light guidesDielectricDigital signal processing
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com