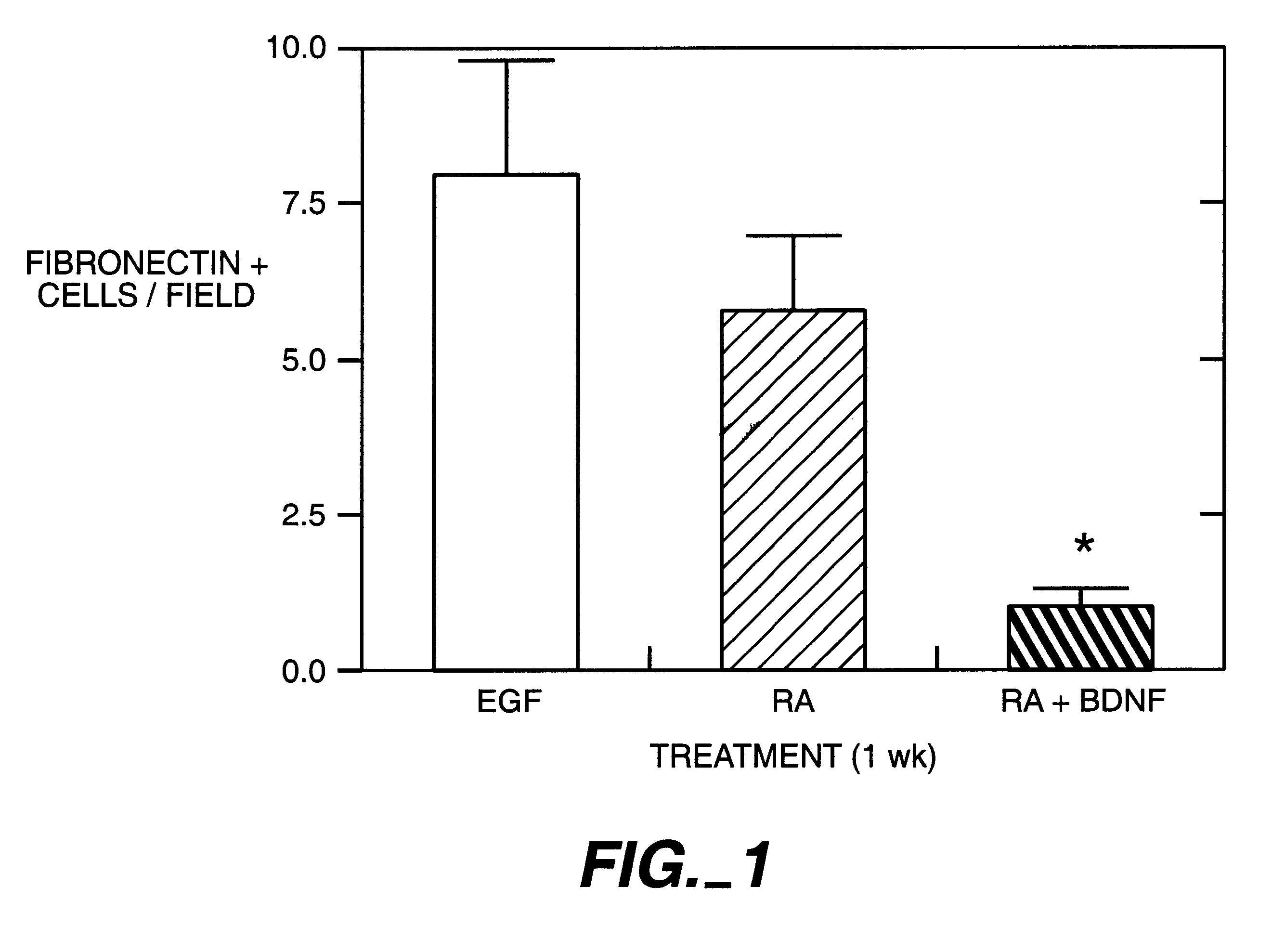
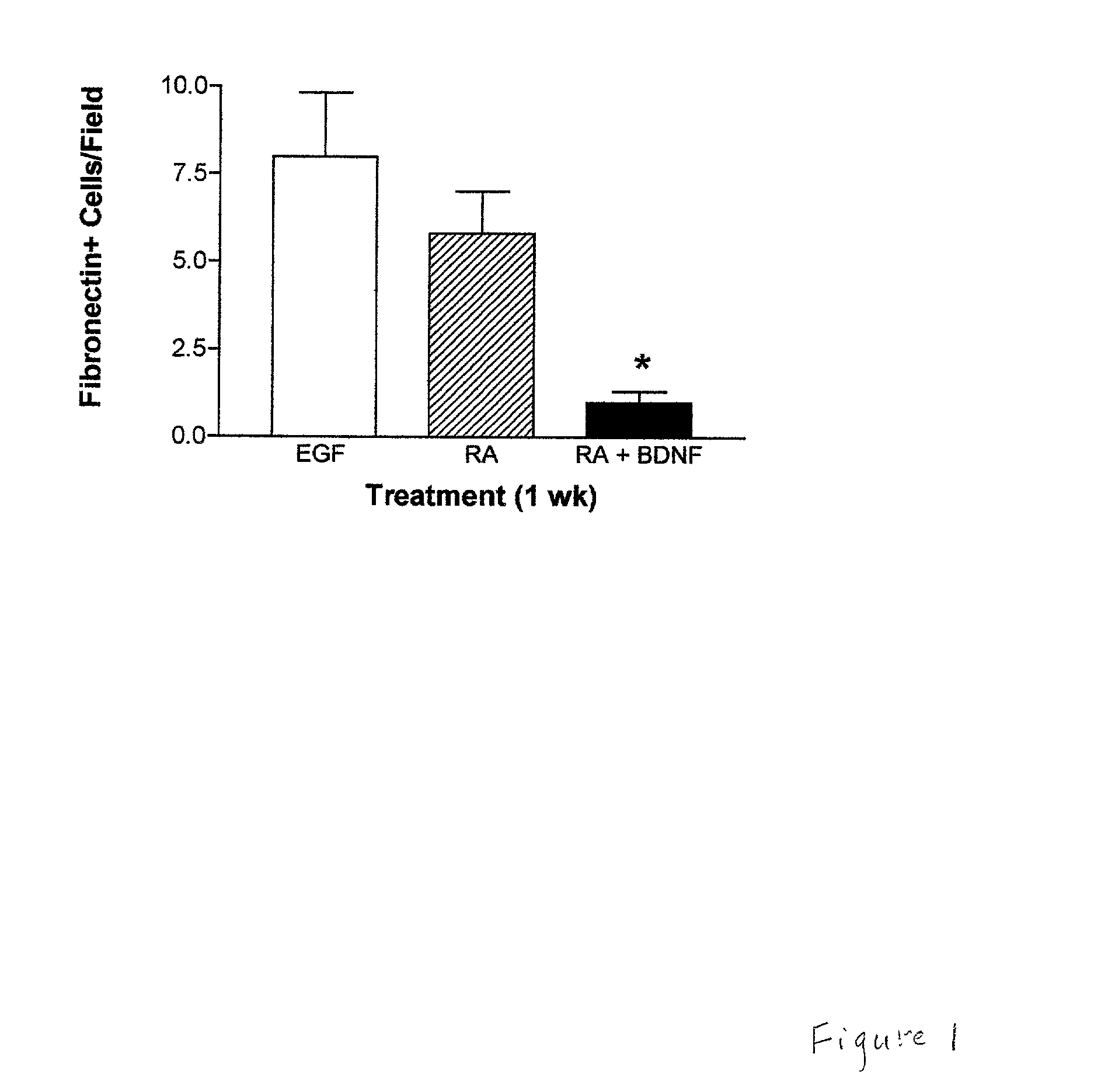
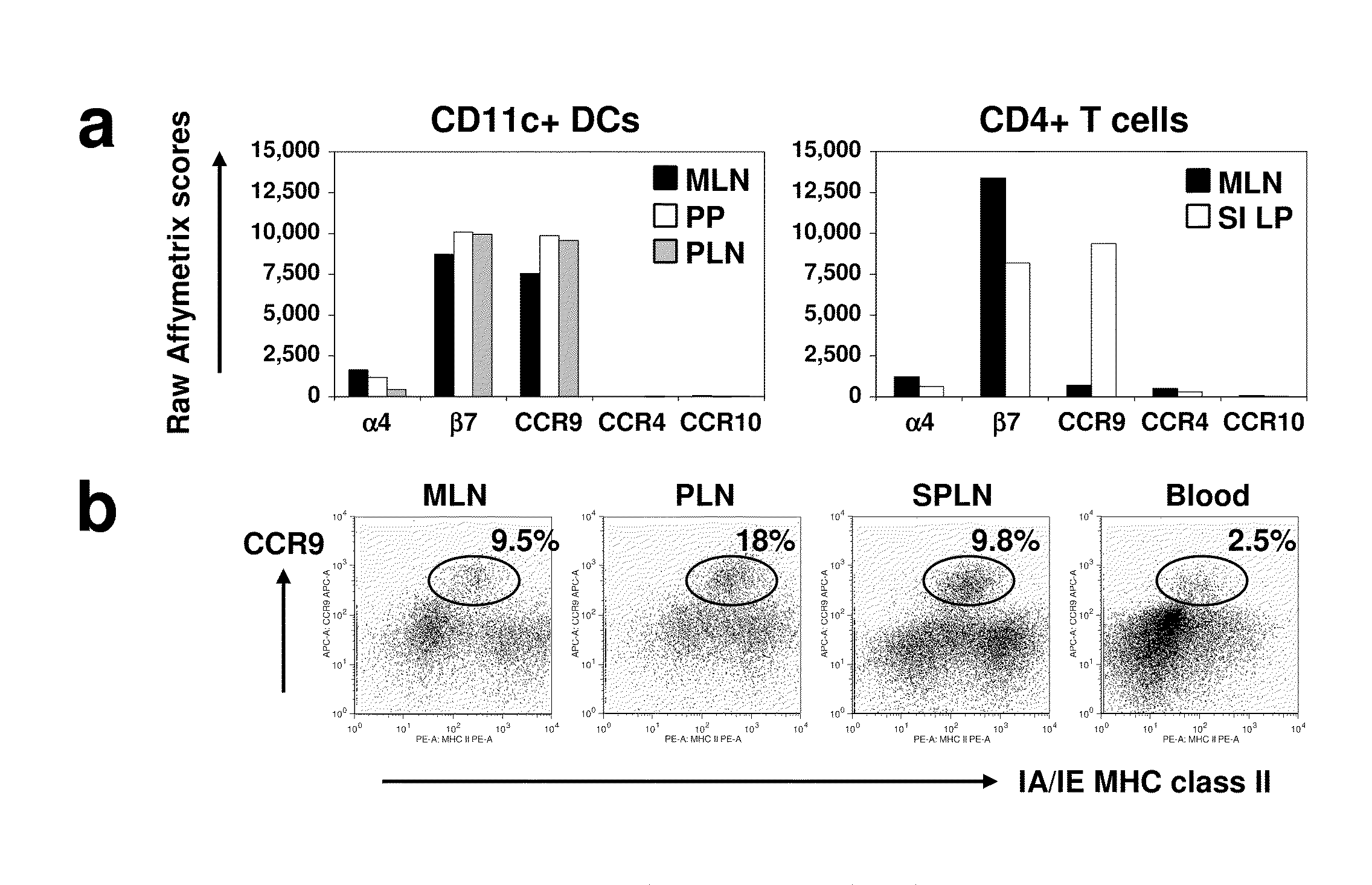
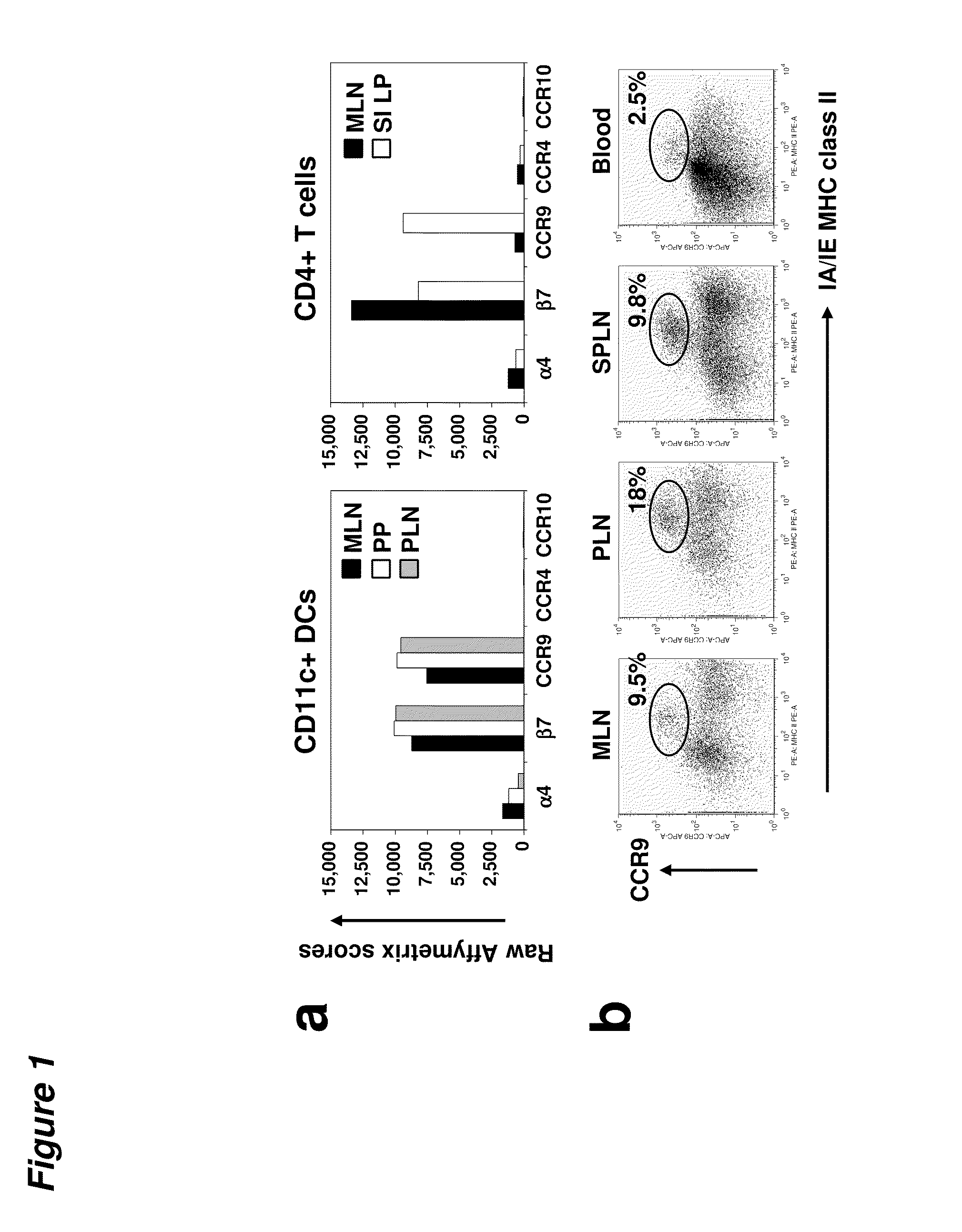
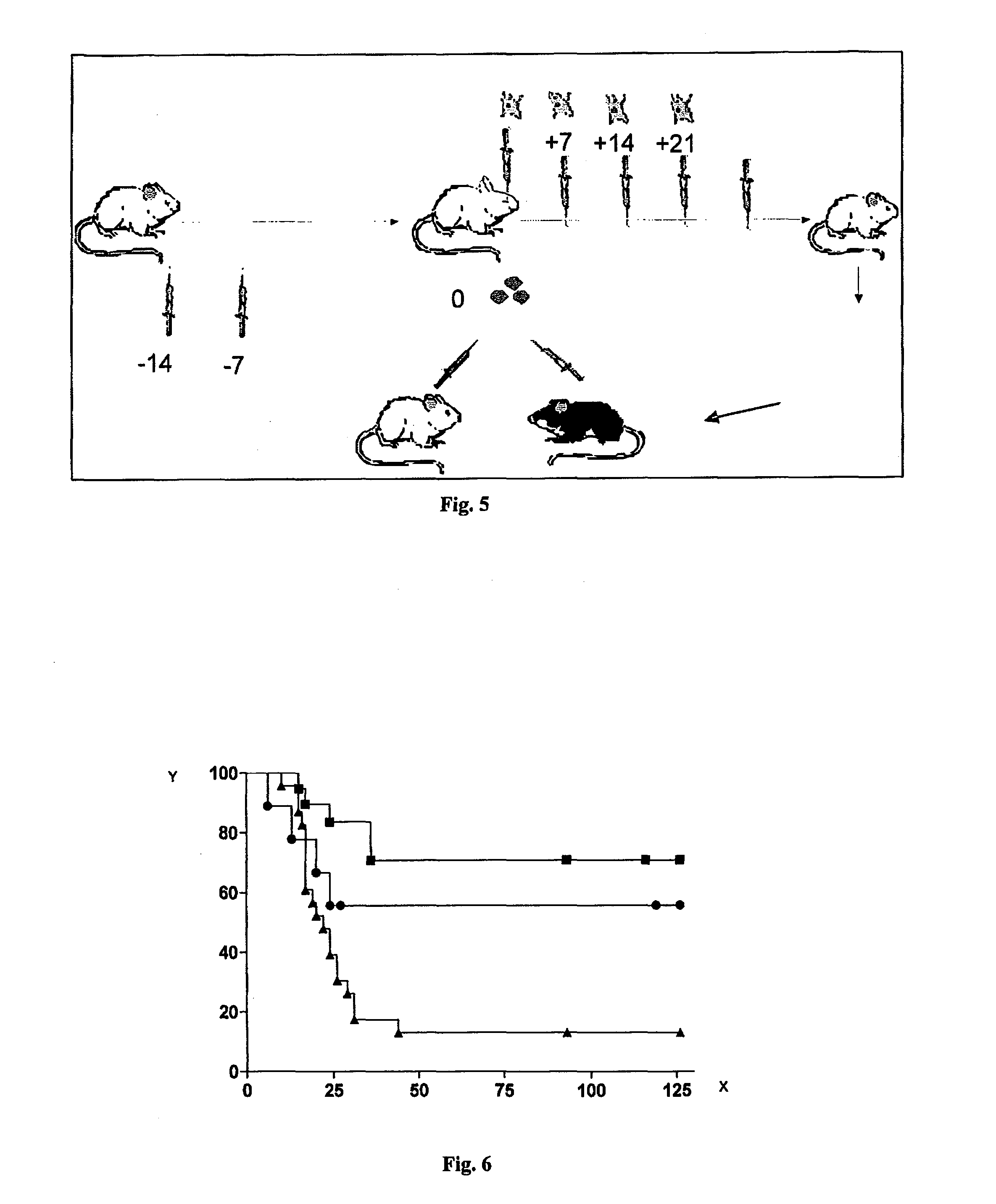
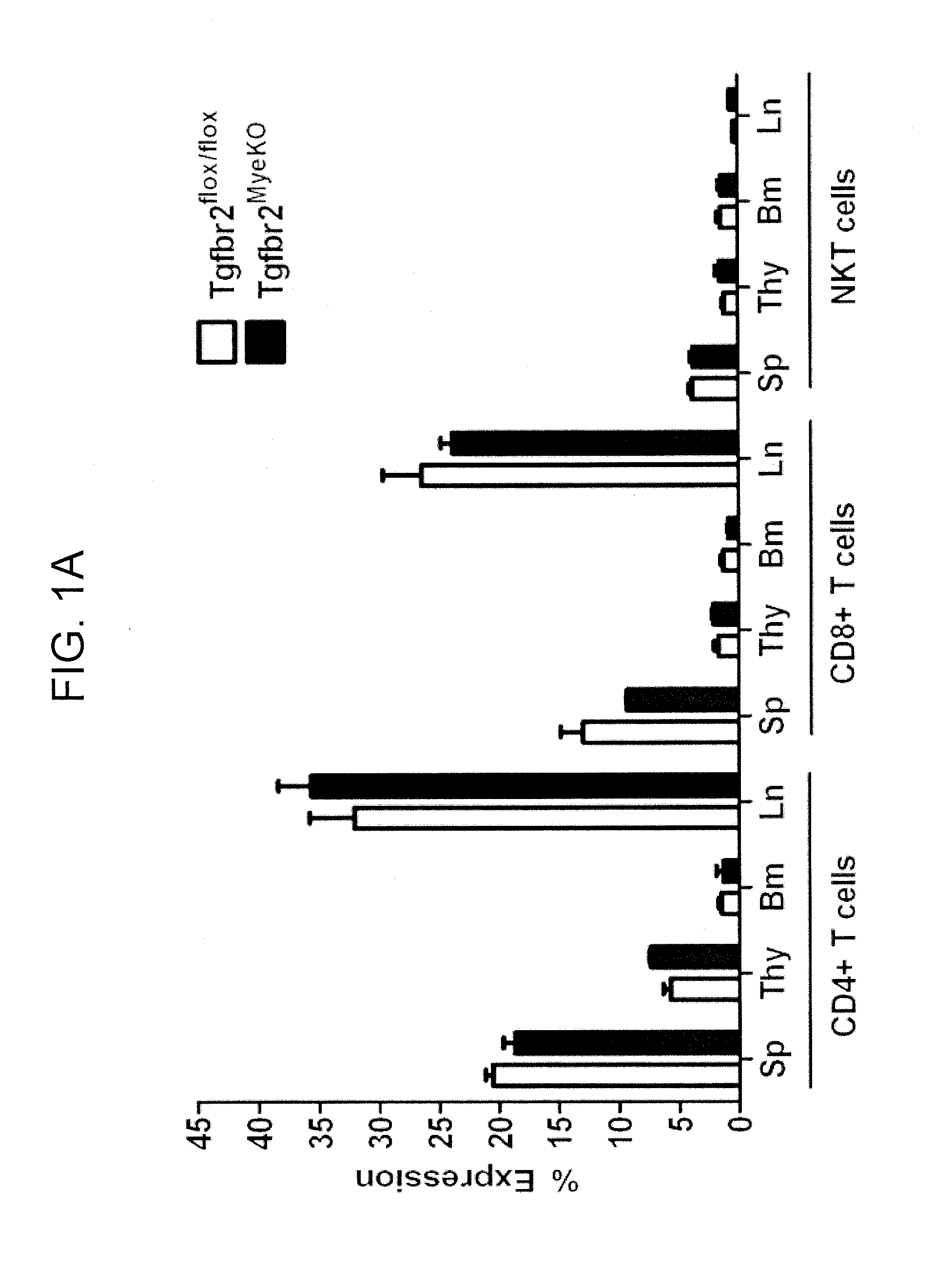
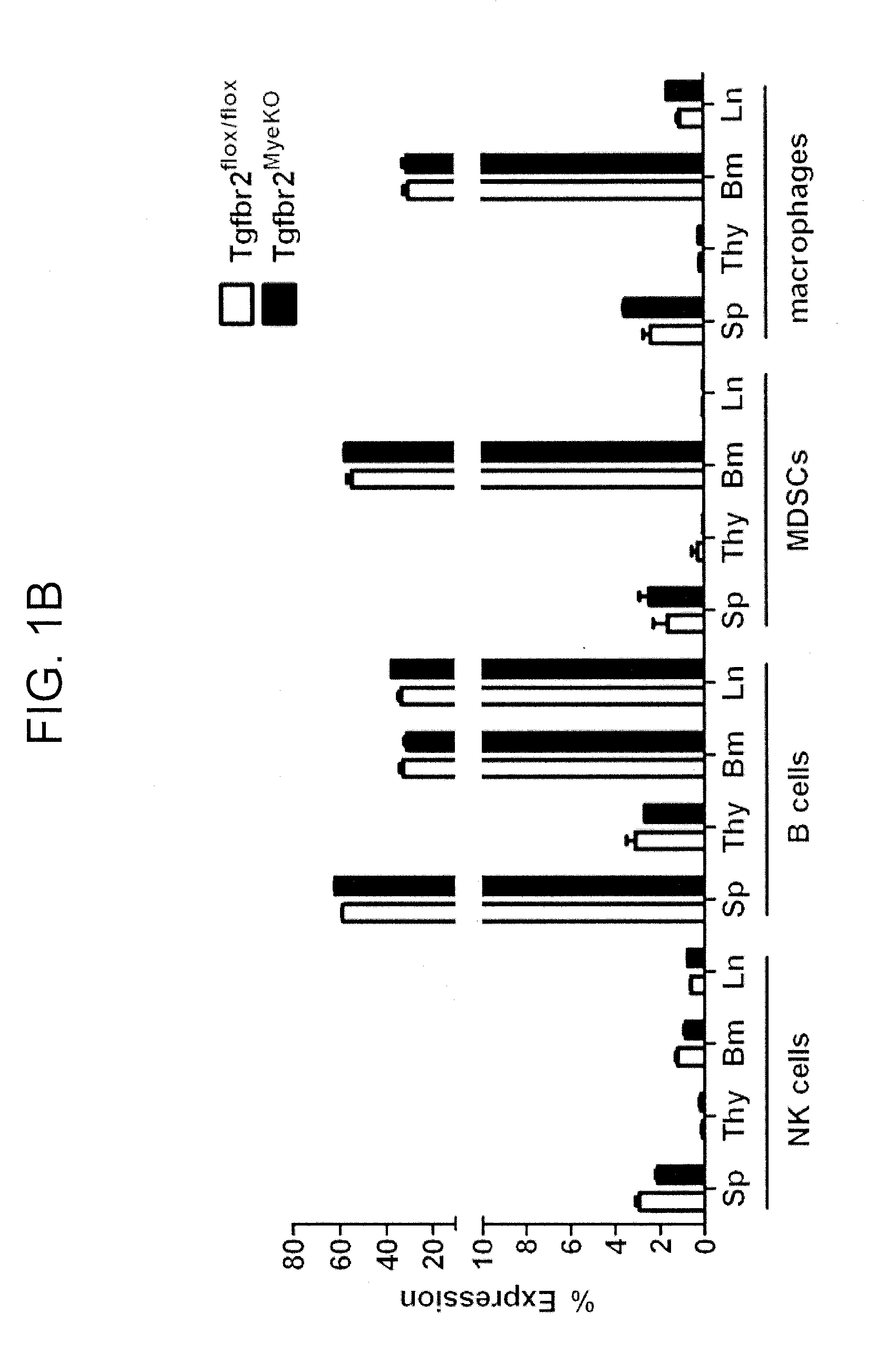
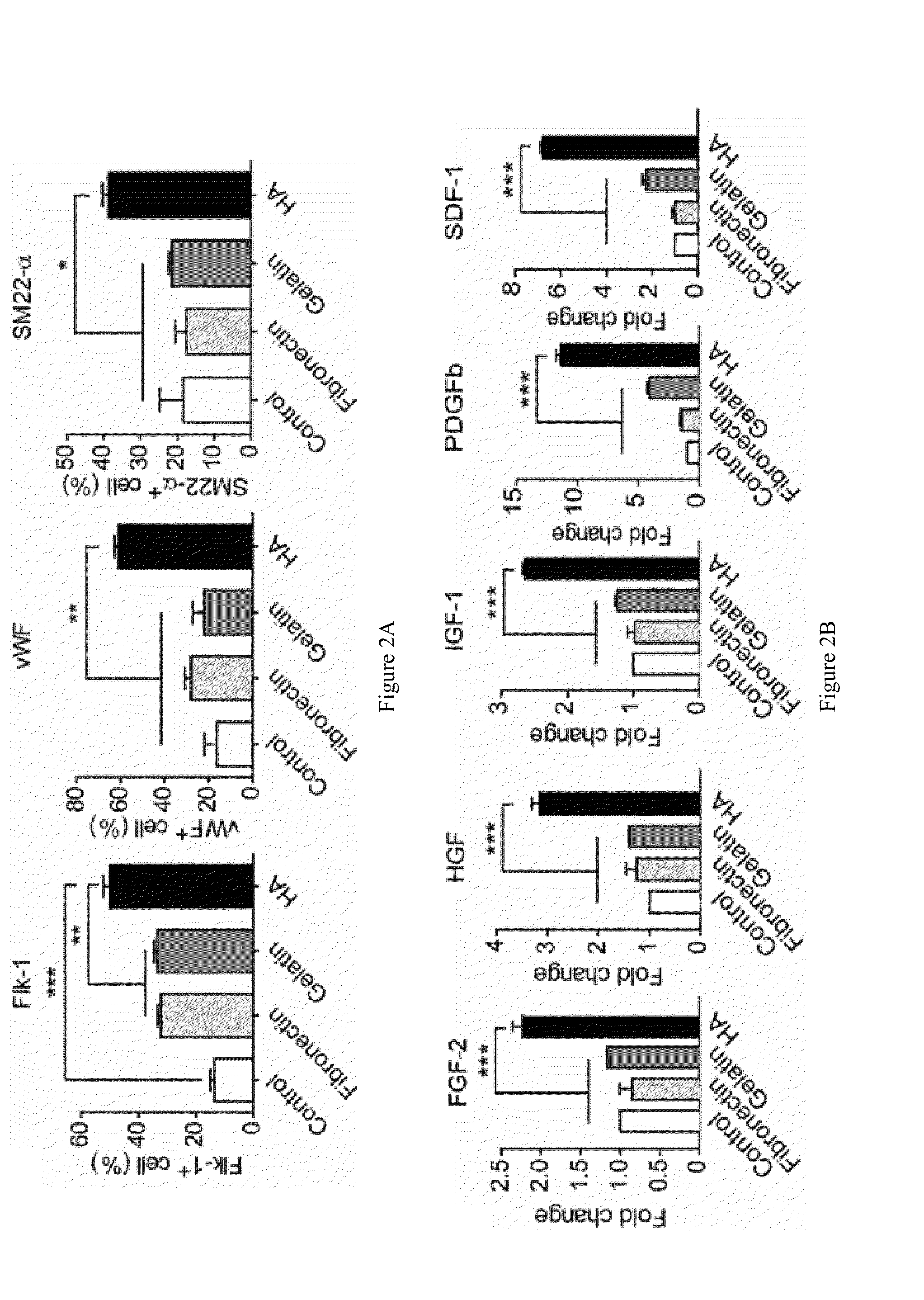
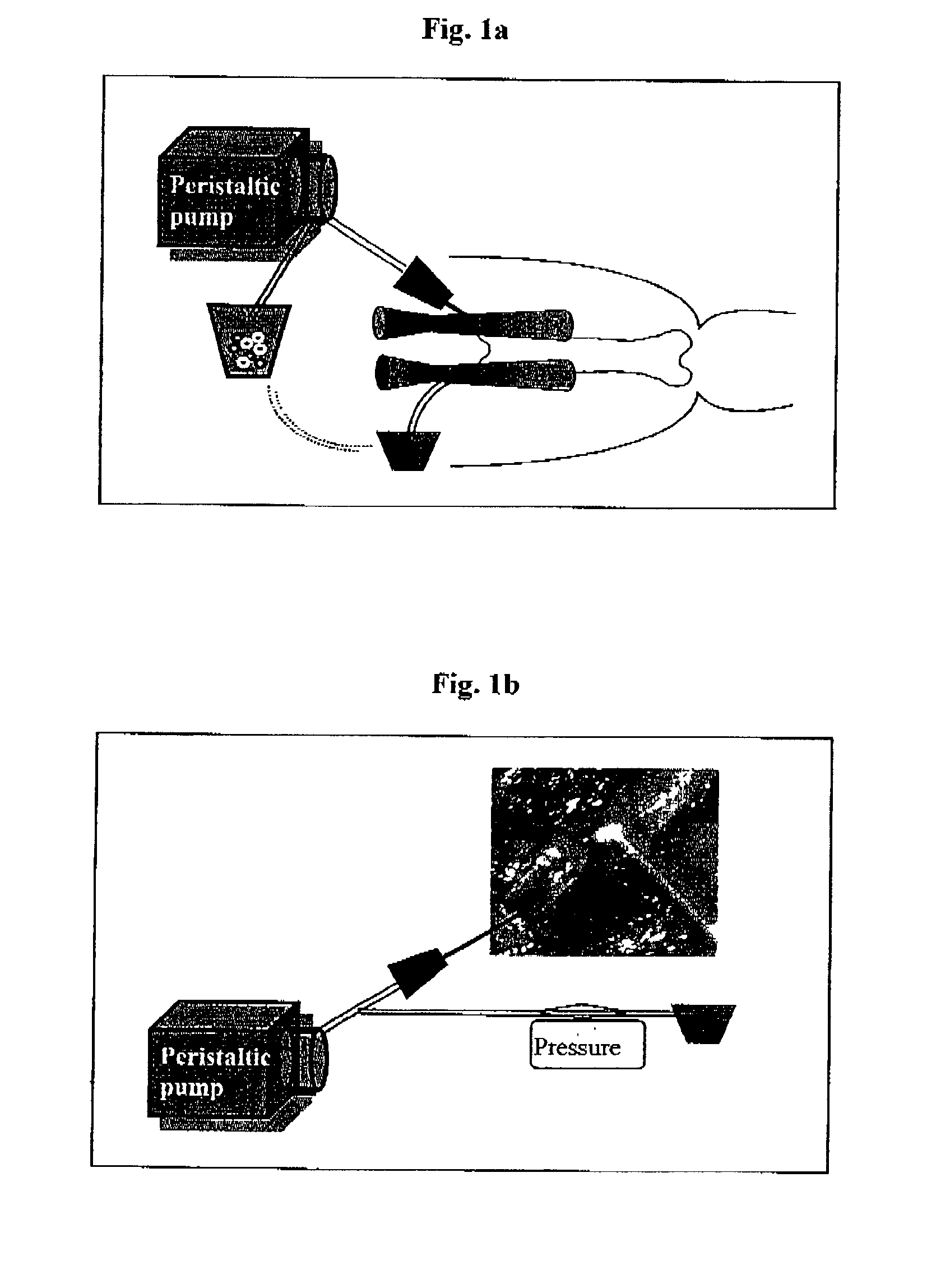
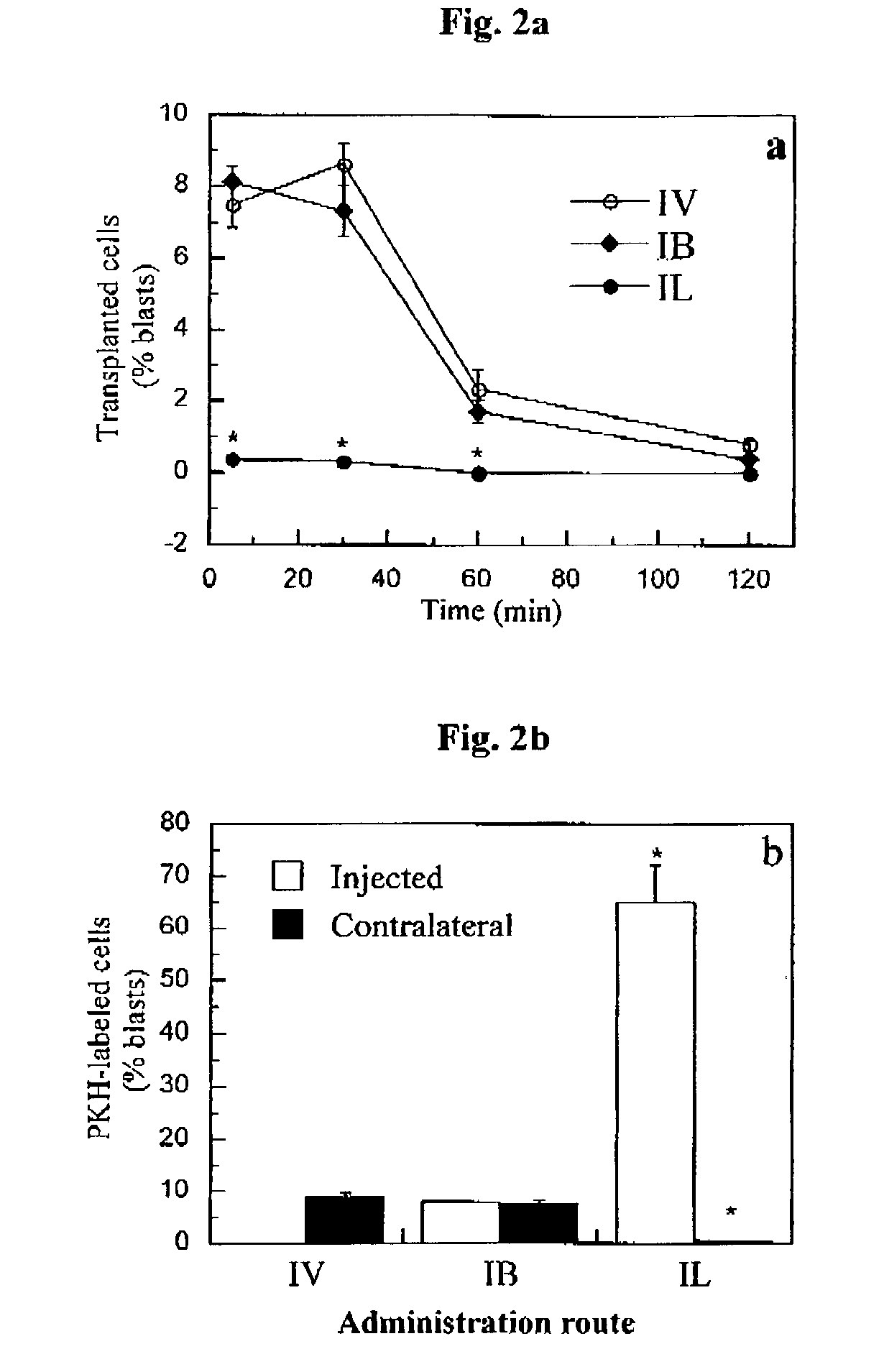
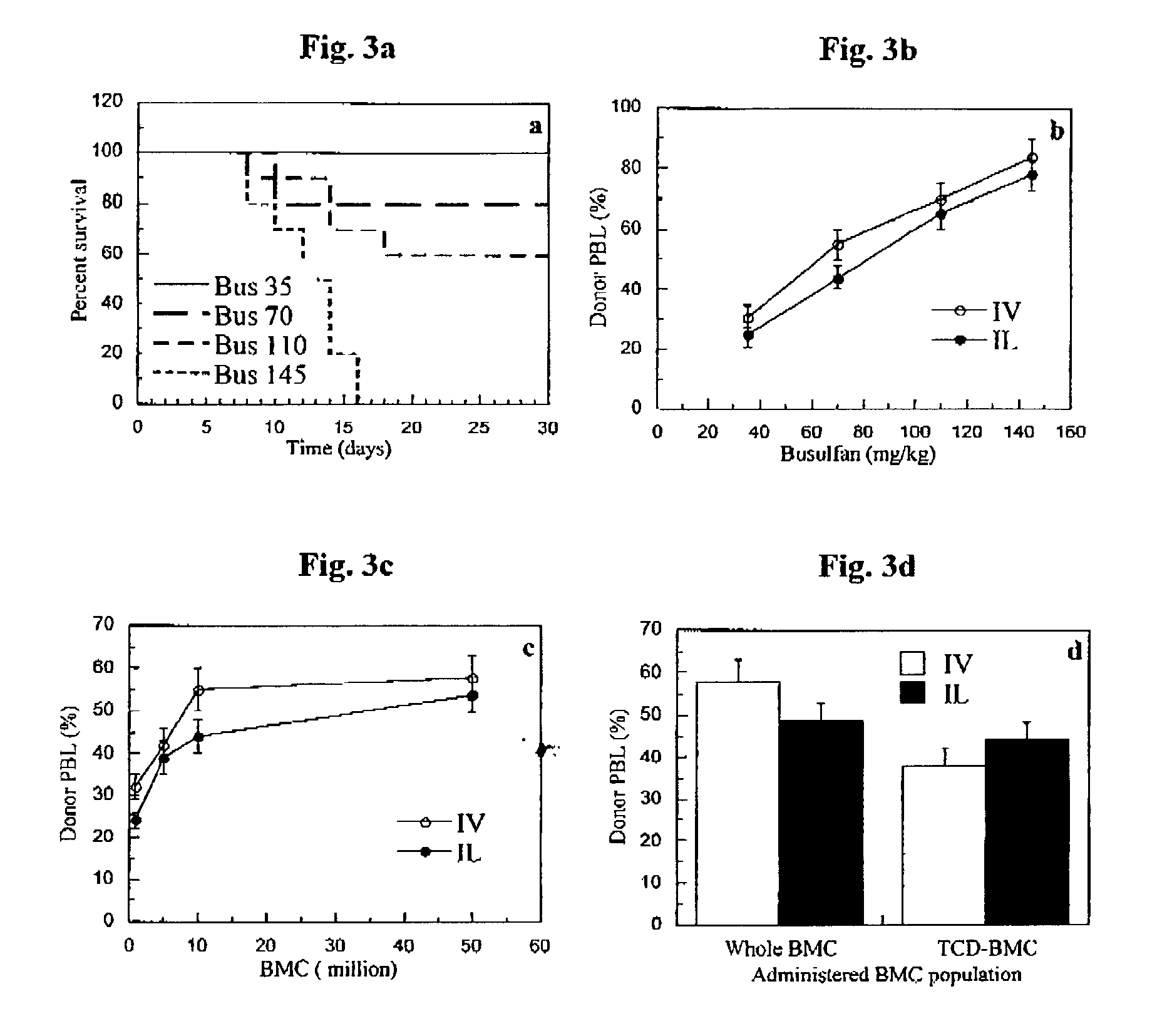
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
76 results about "Myelocyte" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A myelocyte is a young cell of the granulocytic series, occurring normally in bone marrow (can be found in circulating blood when caused by certain diseases).
Bone marrow cells as a source of neurons for brain and spinal cord repair
Owner:SOUTH FLORIDA UNIVESITY OF
Bone marrow cells as a source of neurons for brain and spinal cord repair
Bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC) differentiate into neuron-like phenotypes in vitro and in vivo, engrafted into normal or denervated rat striatum. The BMSC did not remain localized to the site of the graft, but migrated throughout the brain and integrated into specific brain regions in various architectonic patterns. The most orderly integration of BMSC was in the laminar distribution of cerebellar Purkinje cells, where the BMSC-derived cells took on the Purkinje phenotype. The BMSC exhibited site-dependent differentiation and expressed several neuronal markers including neuron-specific nuclear protein, tyrosine hydroxylase and calbindin. BMSC can be used to target specific brain nuclei in strategies of neural repair and gene therapy.
Owner:SOUTH FLORIDA UNIVESITY OF
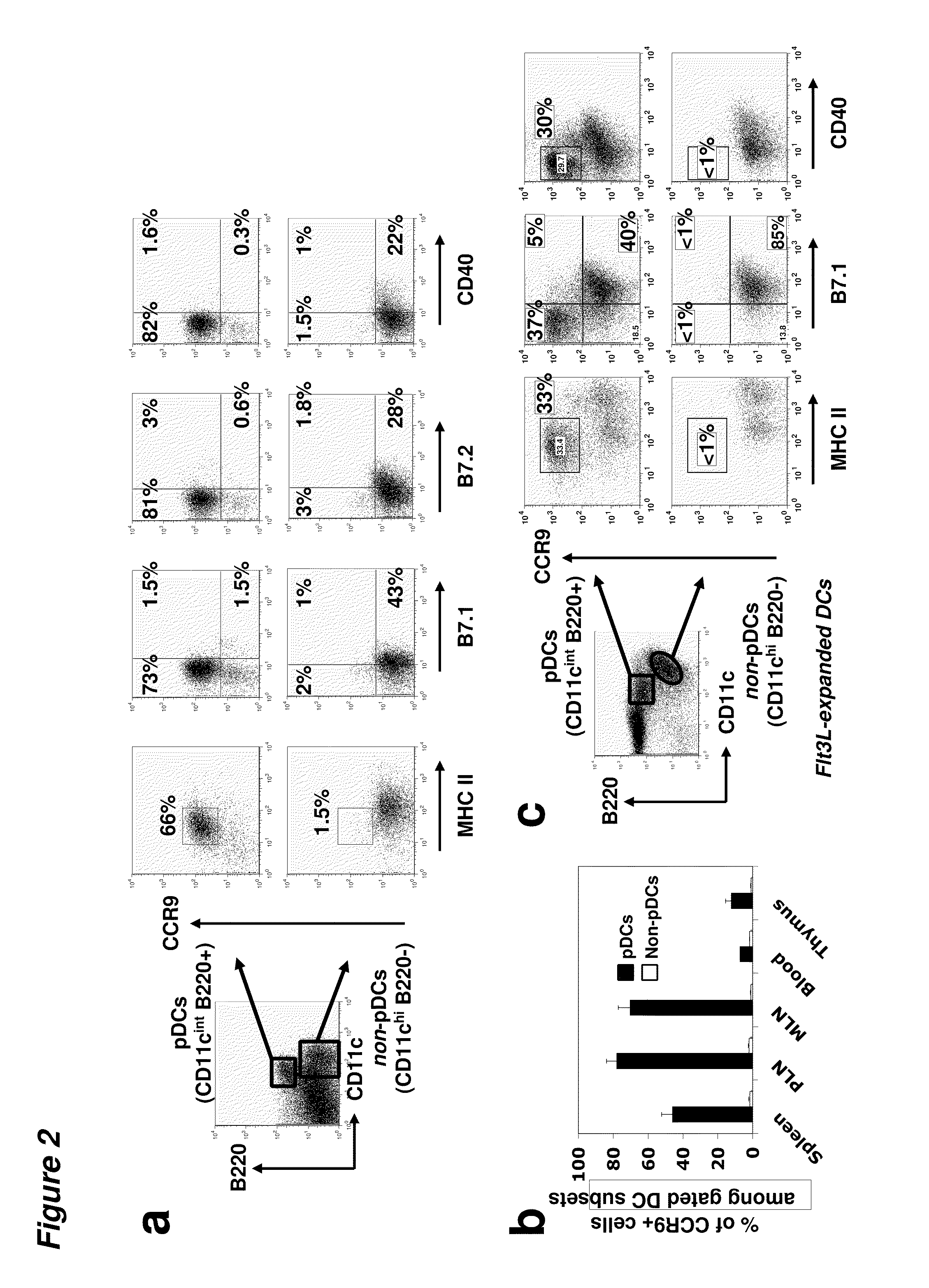
Tolerogenic populations of dendritic cells
InactiveUS20100080816A1Snake antigen ingredientsArtificial cell constructsAutoimmune responsesCMKLR1
Tolerogenic populations of dendritic cells are provided, where the dendritic cells are characterized by expression of select tissue-specific homing receptors including the chemokine receptors CCR9; or CMKLR1; or the integrin CD103. The dendritic cells may be conventional / myeloid or plasmacytoid dendritic cells. The cells may be isolated from lymphoid tissue, from blood, or from in vitro culture, e.g. bone marrow culture, etc. Methods are provided for their identification, isolation and targeting in immunotherapeutic interventions in suppressing inflammatory disorders including autoimmunity, transplantation responses and allergic diseases. In some embodiments dendritic cell populations are fixed to render them immunosuppressive, thus allowing the cells to be typed and banked for future use.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
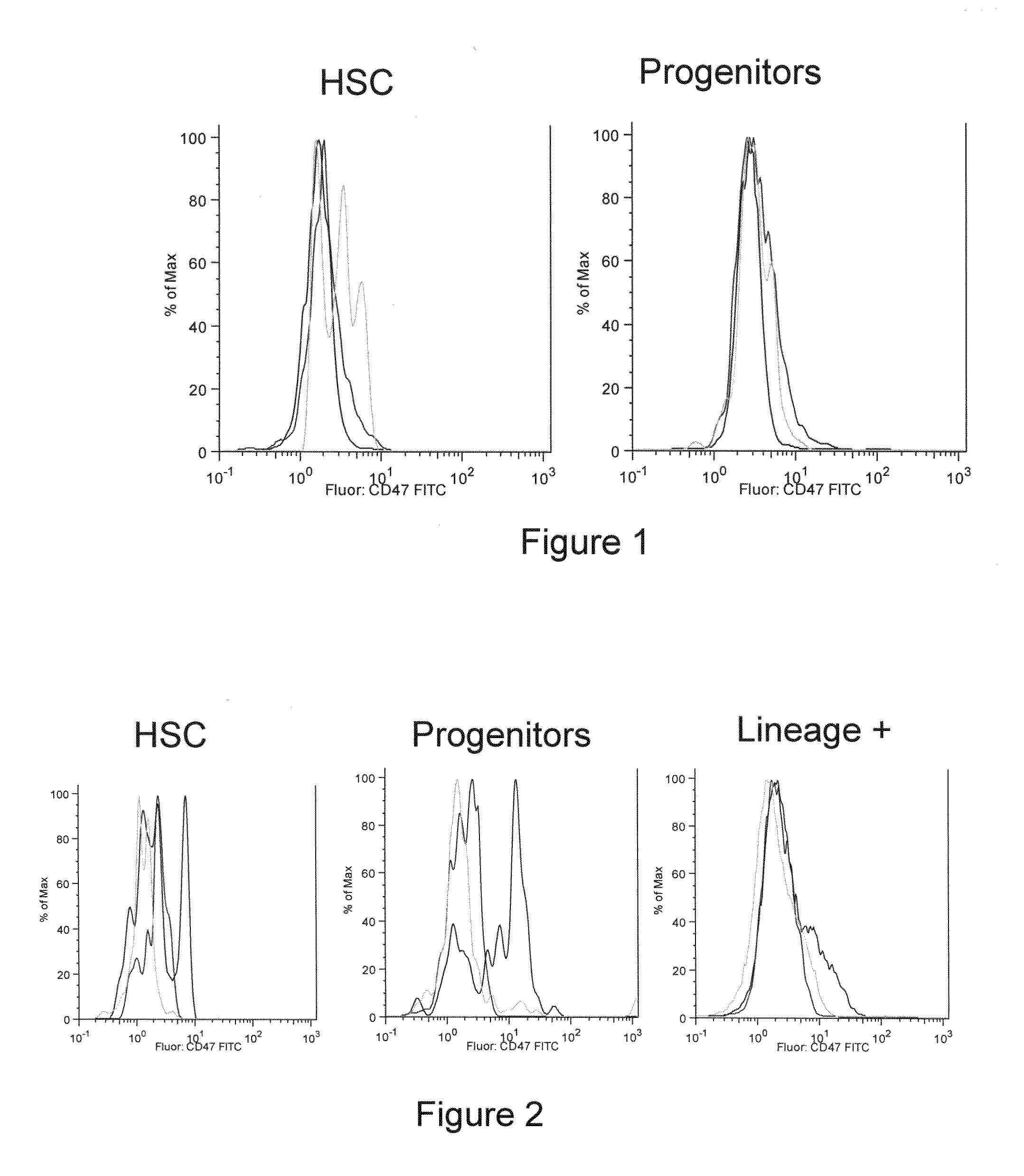
Methods for manipulating phagocytosis mediated by CD47
InactiveUS20090191202A1Enhance phagocytosisPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsHematopoietic cellSolid tumor
Methods are provided to manipulate phagocytosis of cells, including hematopoietic cells, e.g. circulating hematopoietic cells, bone marrow cells, etc.; and solid tumor cells. In some embodiments of the invention the circulating cells are hematopoietic stem cells, or hematopoietic progenitor cells, particularly in a transplantation context, where protection from phagocytosis is desirable. In other embodiments the circulating cells are leukemia cells, particularly acute myeloid leukemia (AML), where increased phagocytosis is desirable.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
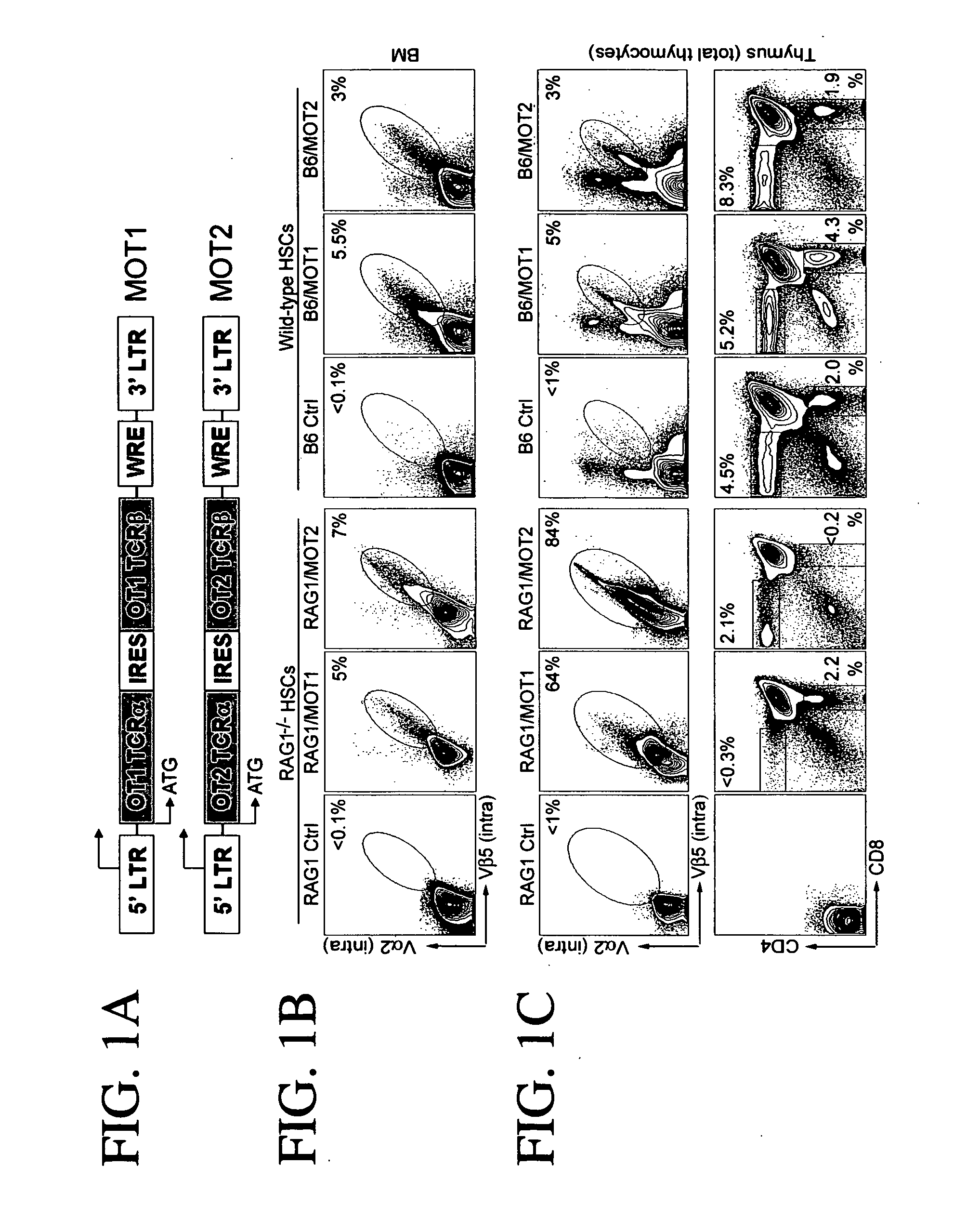
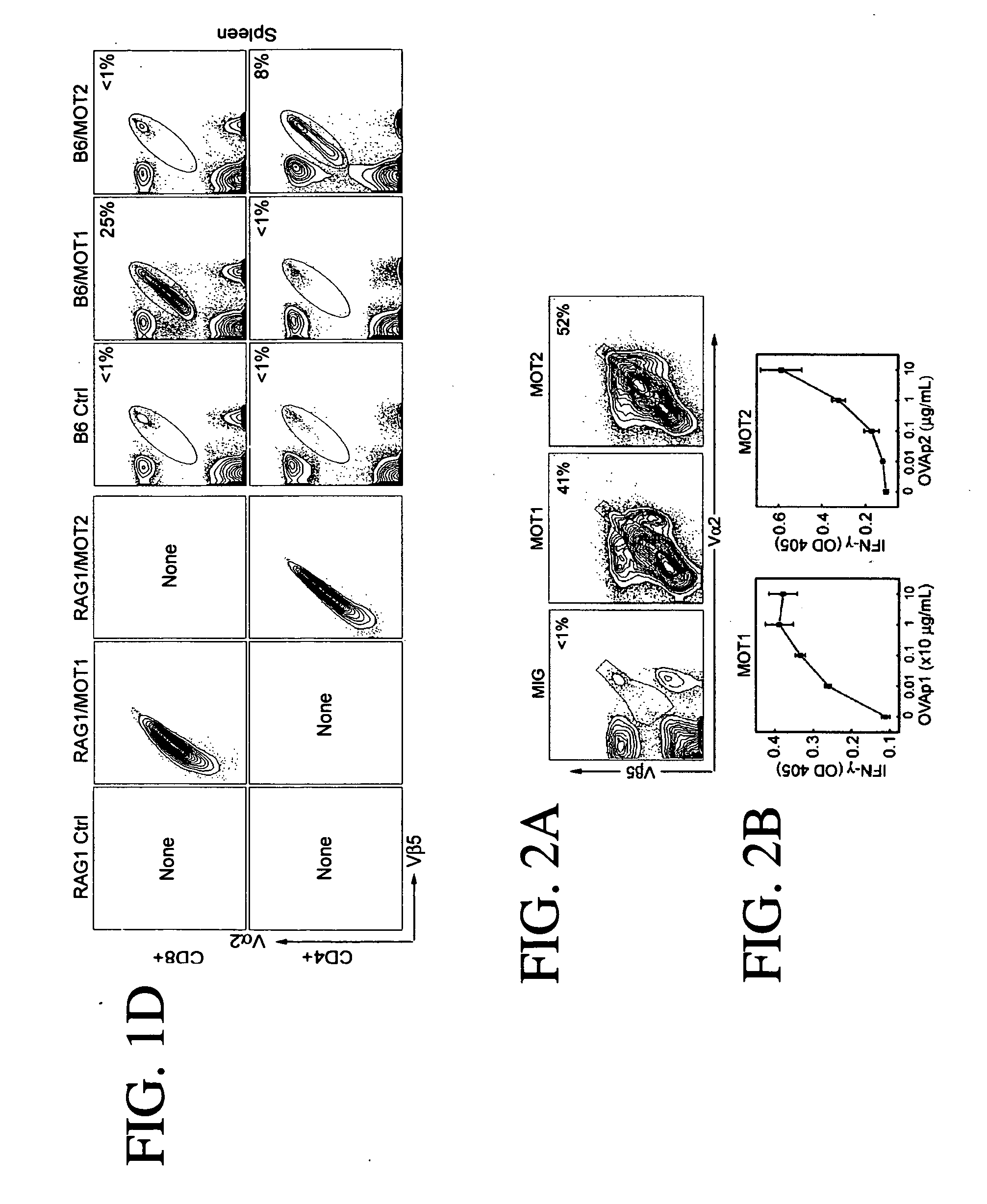
Antigen specific T cell therapy
Provided are methods for generating immune cells of the desired type and specificity in a host. The methods may be used to treat a disease or disorder, such as a tumor in a patient. Target cells, preferably hematopoietic stem cells such as primary bone marrow cells are transfected with a polynucleotide encoding a T cell receptor with the desired specificity. The transfected cells are then transferred to the host where they develop into mature, functional immune cells. The source of the T cell receptor can determine the stem cell's fate. Thus transfecting stem cells with TCRs from cytotoxic cells will lead to the generation of cytotoxic T cells in the host, while TCRs from helper cells will produce helper cells. Both arms of T cell immunity can be generated simultaneously in a host. Additionally, the immune response to the desired antigen can be further stimulated by immunizing the host with the antigen.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Induction of Myocardial Cell From Mammalian Bone Marrow Cell or Cord Blood-Derived Cell and Fat Tissue
InactiveUS20070212676A1Improve securityEasy to getCell differentiationMicrobiological testing/measurementCord blood stem cellCardiac muscle
This invention provides a method for differentiating mammalian bone marrow cells or cord blood-derived cells into myocardial precursor cells and / or myocardial cells by culturing said bone marrow cells or cord blood-derived cells with cells isolated from mammalian fat tissues or a culture supernatant thereof.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
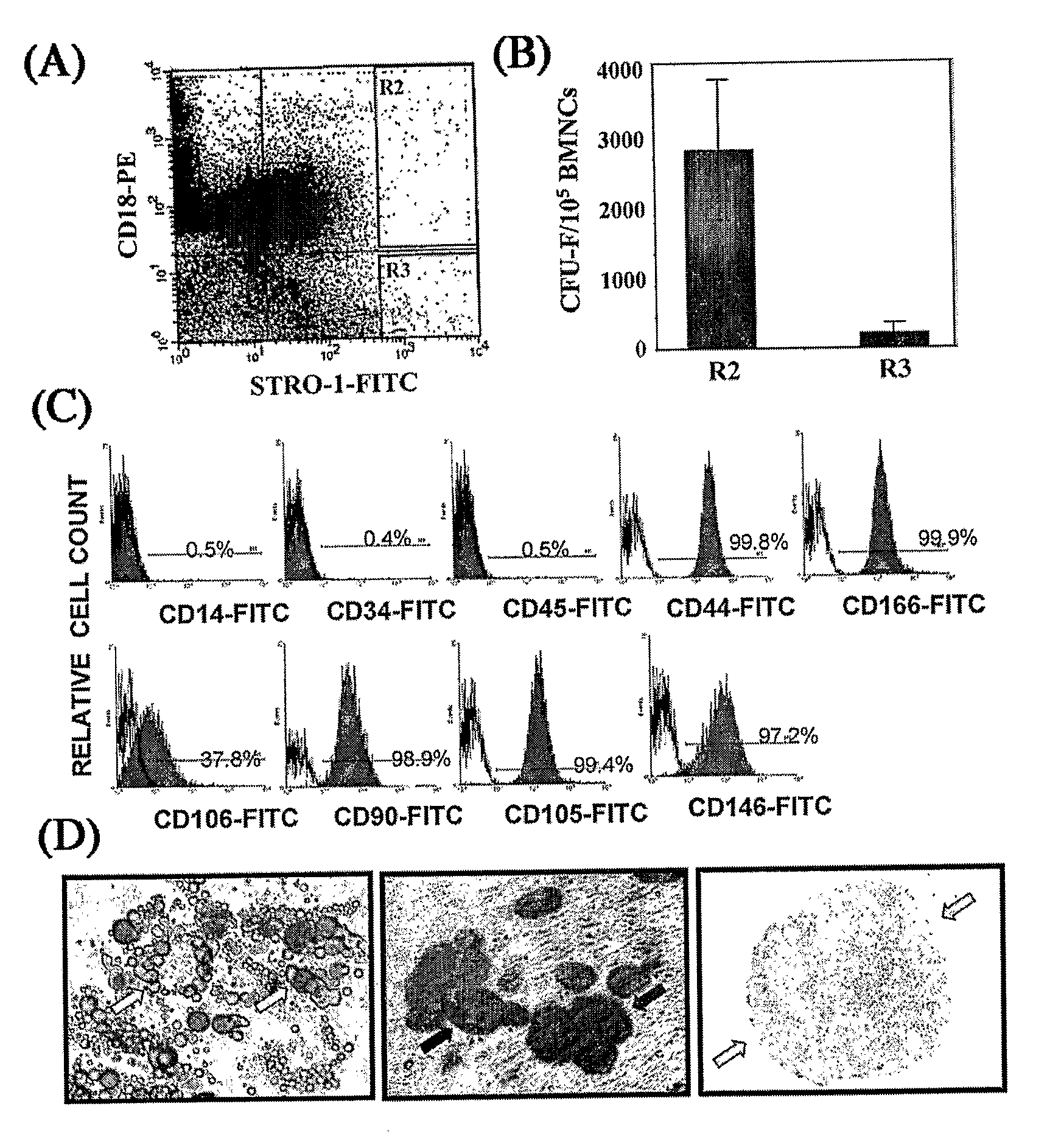
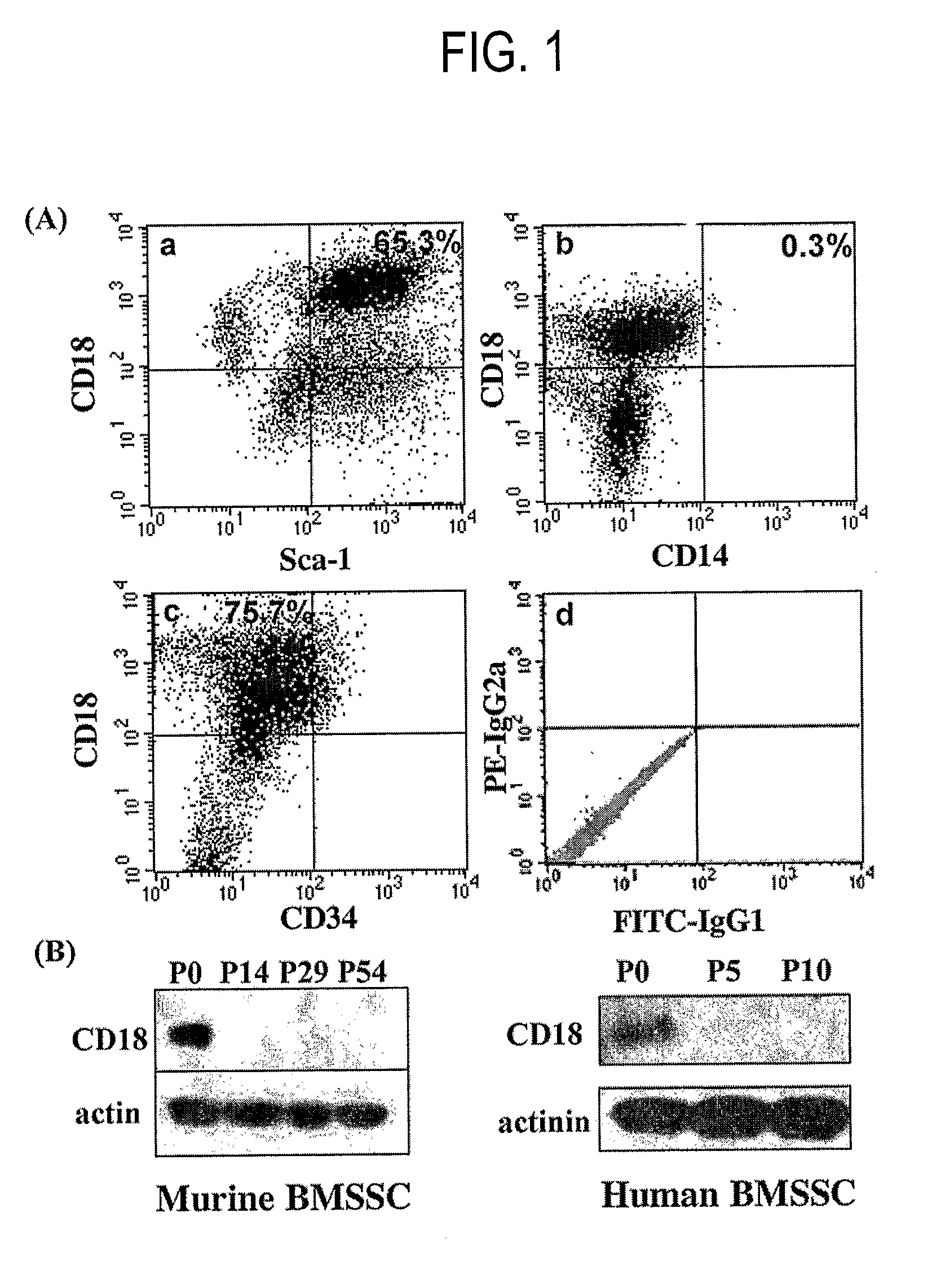
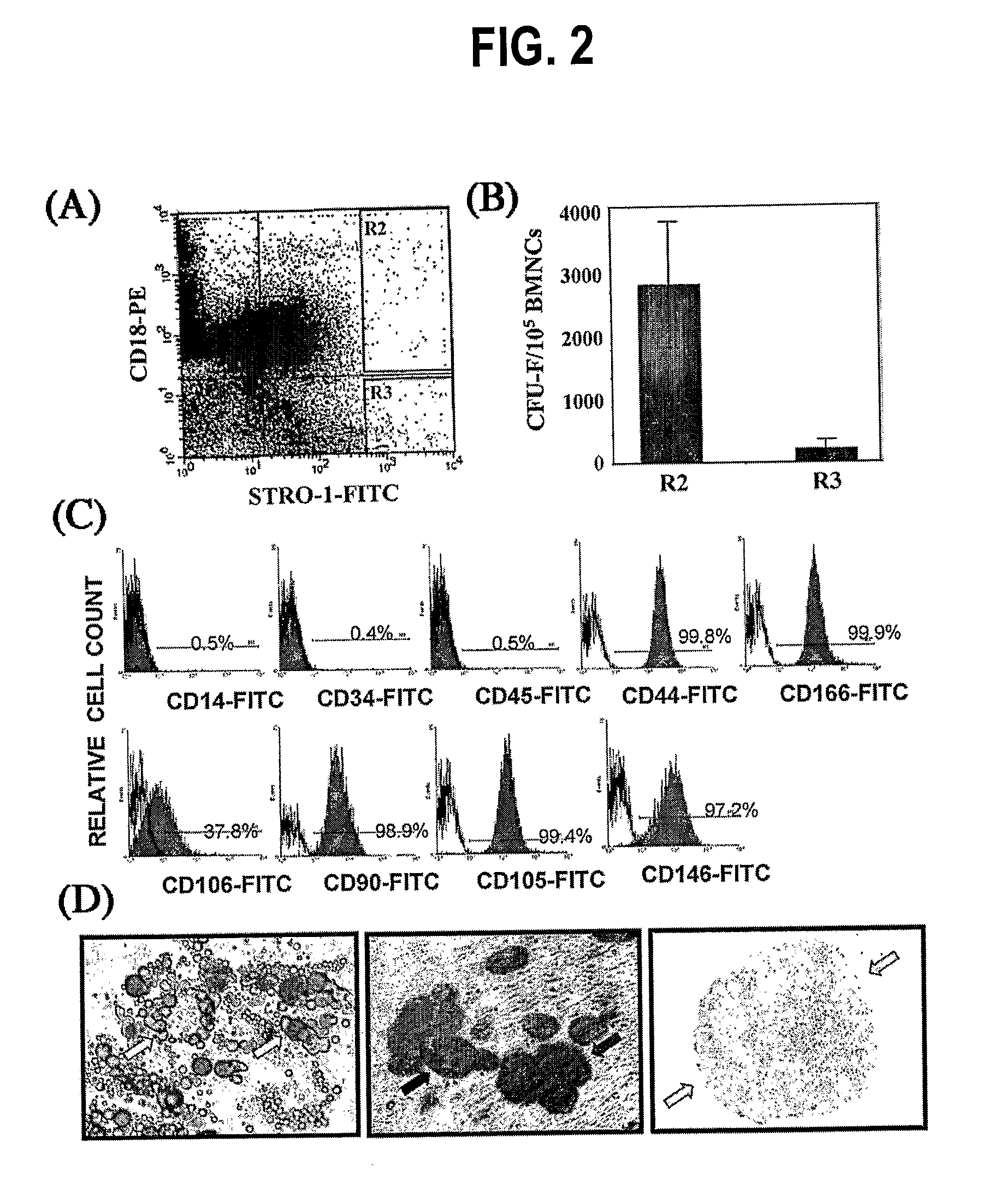
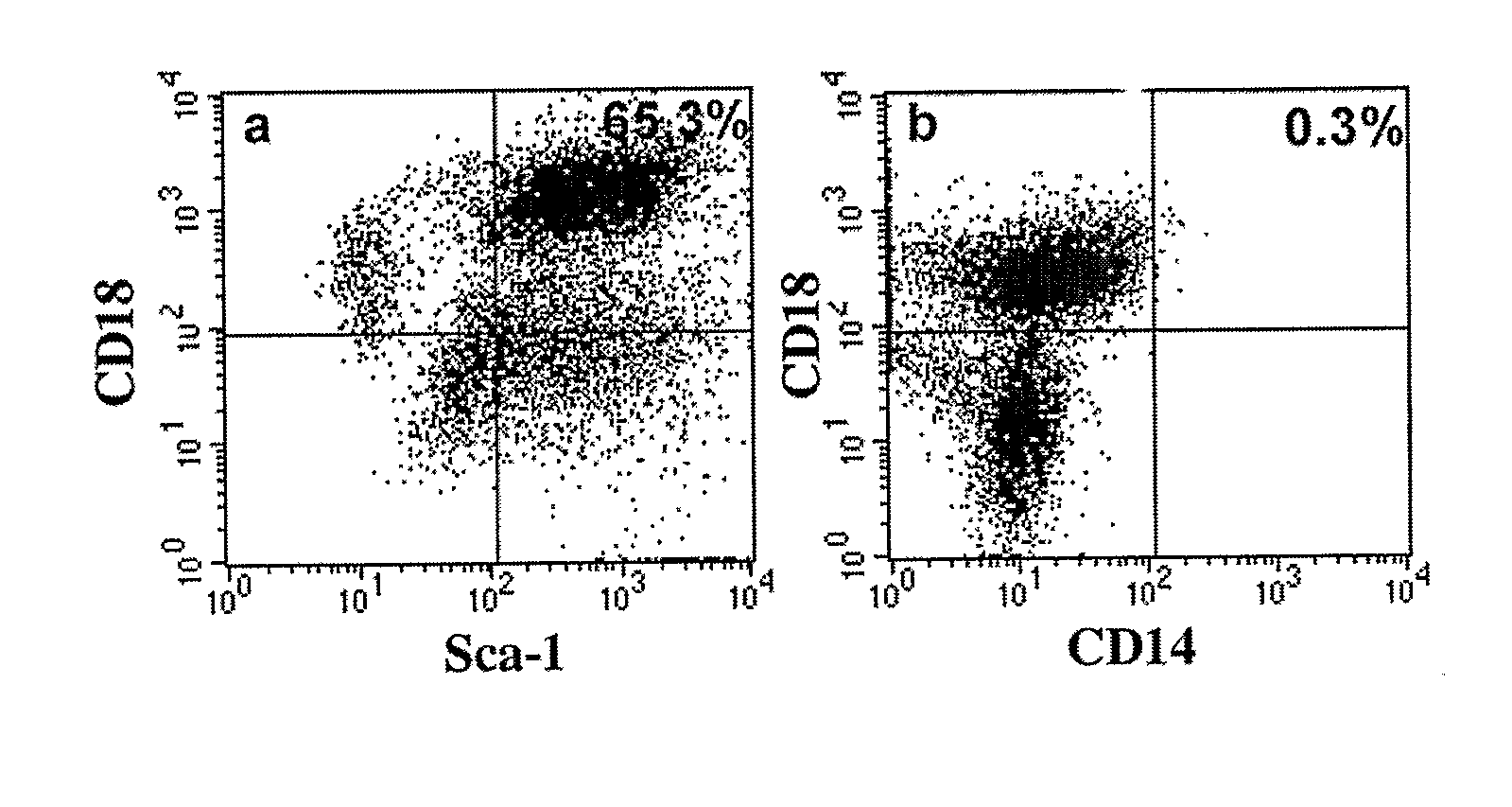
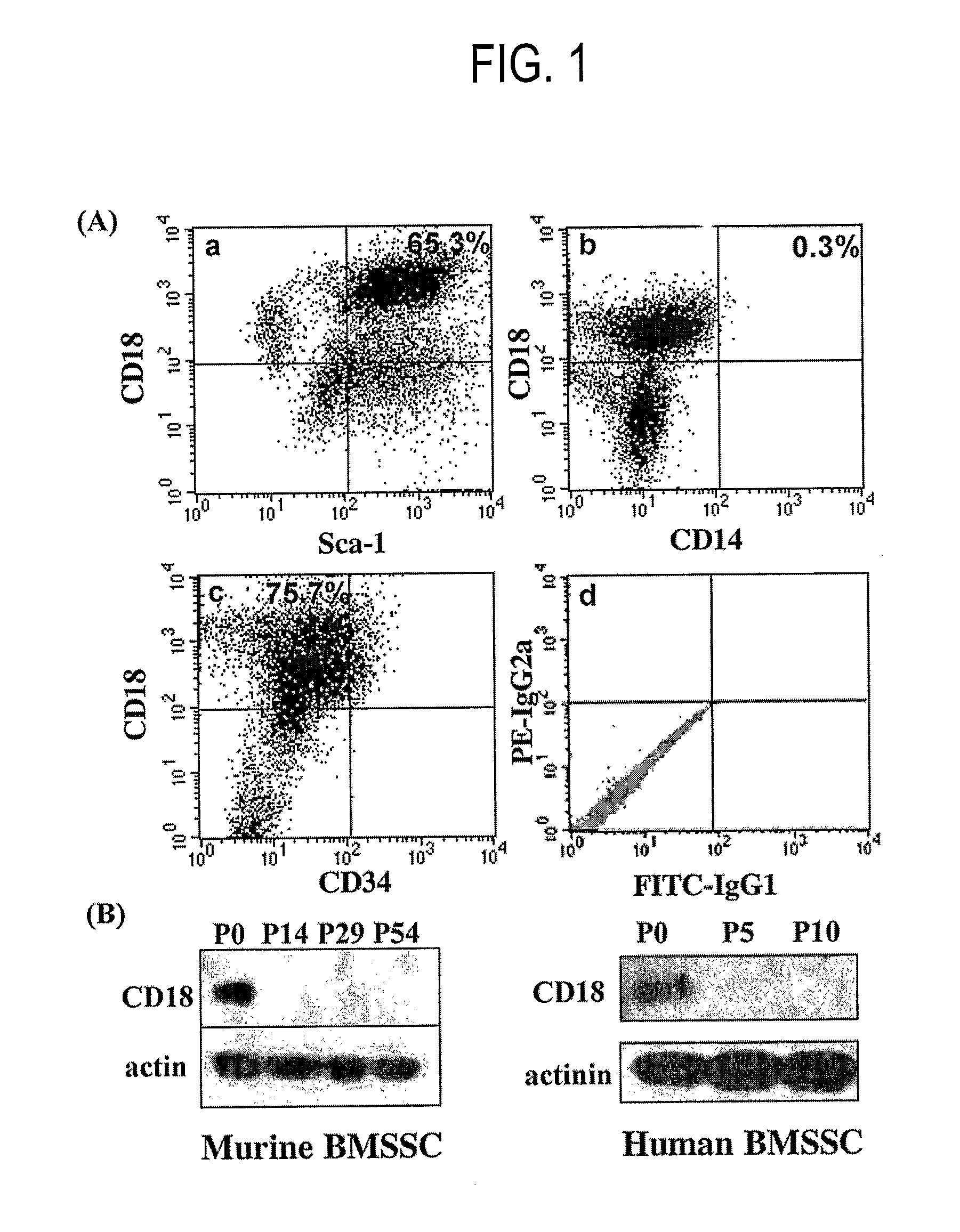
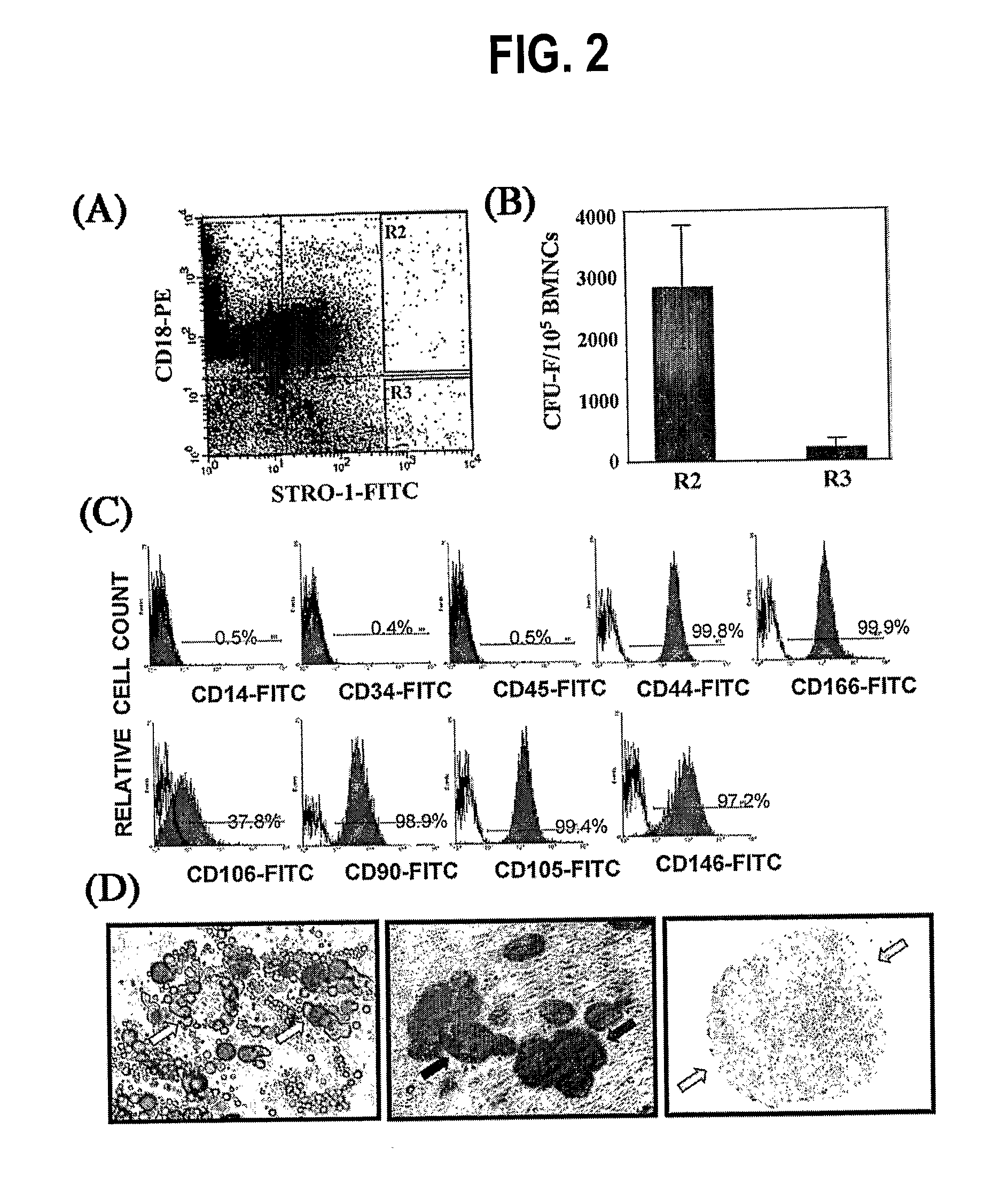
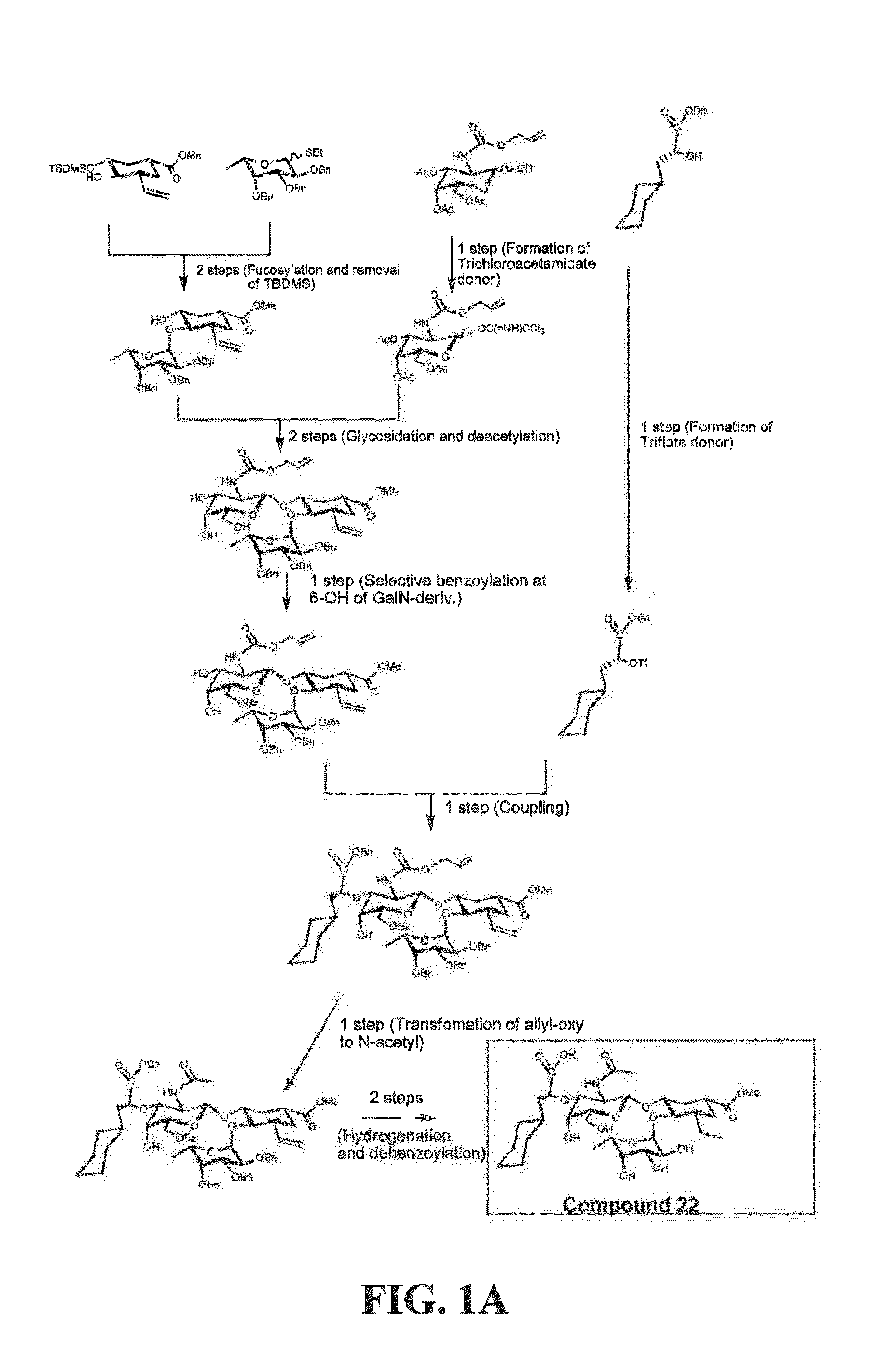
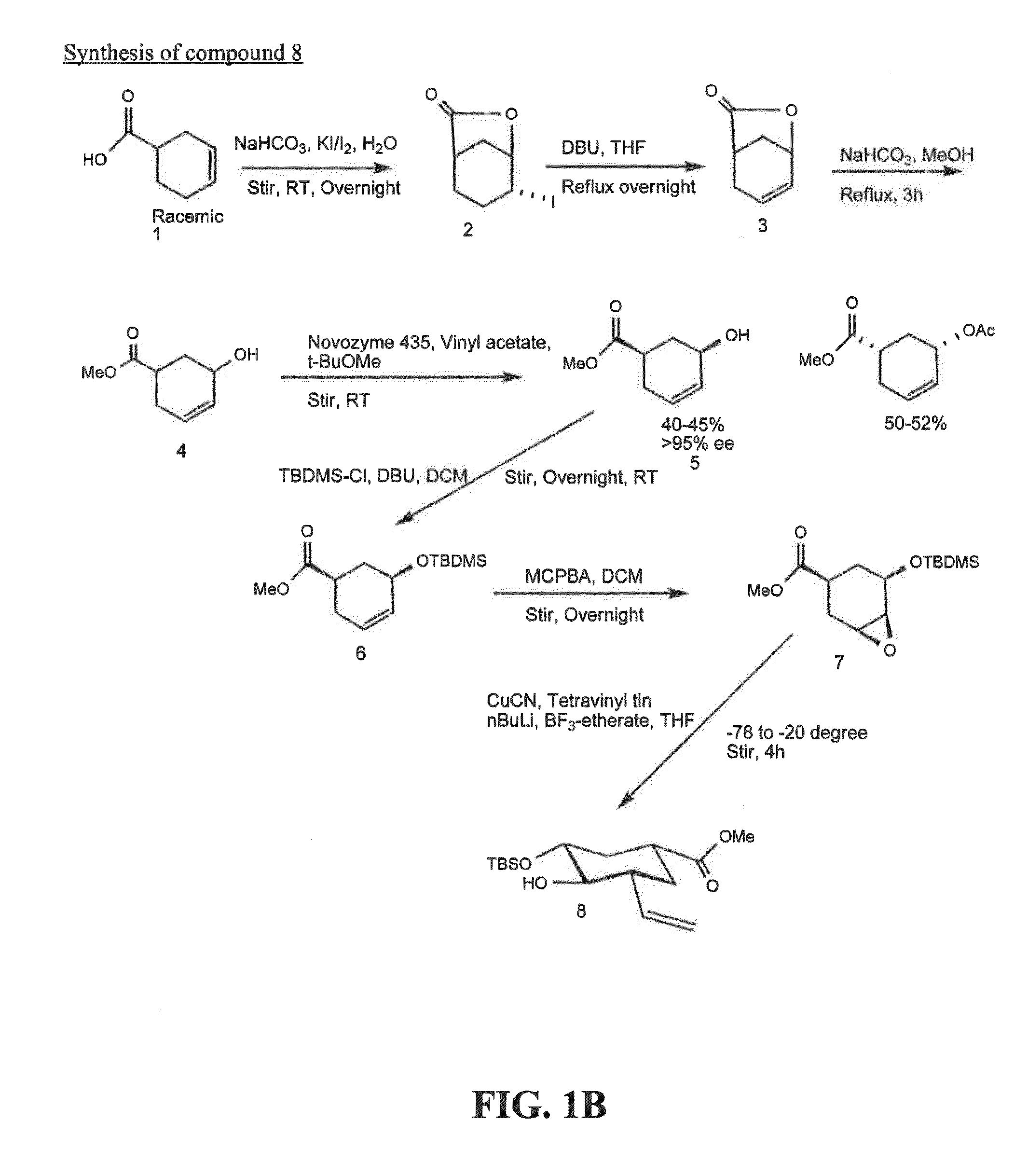
Integrin CD18 is a novel stromal stem cell marker and functions to promote osteogenesis
InactiveUS7732126B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsImmunoperoxidase StainingCancer research
The present invention is directed to a new bone marrow stromal stem cell (BMSSC) marker, CD18, for use in selecting a population of cells enriched in BMSSCs, from bone marrow cells, adipose cells, or peripheral blood. The invention is further directed to methods for selecting a population of cells enriched in BMSSCs based on the selective expression of CD18 on their surface, using techniques known in the art such as fluorescent assisted cell sorting, an immunomagnetic method, flow microfluorimetry, immunofluorescence, immunoperoxidase staining, radioimmunoassay and immunoaffinity chromatography. The invention is further directed to the BMSSCs isolated based on CD18 expression, and their use to treat various diseases. In one aspect, the HMSSCs are transformed with a vector having a normal gene for CD18, and the transformed BMSSCs are administered to treat bone degenerative diseases and diseases of bone involving abnormal expression of CD18 expression of CD18.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Generating teeth from bone marrow cells
The present invention is based on the discovery that teeth primordia can be generated using bone marrow cells and that bone marrow cells may be employed to generate teeth without the need for purification and expansion of a population of cells.
Owner:ODONTIS
Isolation of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells
InactiveUS20120142102A1Symptoms improvedMicrobiological testing/measurementCell culture supports/coatingCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
Human umbilical cord blood (UCB) contains mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) that have higher multipotentiality than adult marrow-derived MSCs. However, it has been difficult to obtain these cells because the frequency of MSCs in UCB is extremely rare (0.4-30 out of 1×108 mononuclear cells). To date, the isolation of MSCs has depended upon their plastic-adhesion capacity. Some “true” MSCs could be missed because their ability to adhere to plastic may be poor. Previous studies demonstrated extracellular matrix (ECM) made by bone marrow cells enhanced MSC attachment and proliferation, and retained their stem cell properties. The present invention provides methods for isolating MSCs from umbilical cord blood by adherence to an ECM and uses for the isolated stem cells.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method for enhancing proliferation or differentiation of a cell using ob protein
InactiveUS7074397B1Easy to implantFacilitates mobilizationPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesMyelopoiesisIn vivo
Uses for WSX ligands in hematopoiesis are disclosed. In particular, in vitro and in vivo methods for stimulating hematopoiesis (e.g., myelopoiesis, erythropoiesis and especially, lymphopoiesis) using a WSX ligand (e.g., anti-WSX receptor agonist antibodies or OB protein), and optionally another cytokine, are described.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Monoclonal antibodies to antigens expressed by hematopoietic facilitatory cells
InactiveUS6013519AImprove abilitiesQuick identificationAnimal cellsHybrid cell preparationHigh level expressionMonoclonal antibody
The present invention relates to monoclonal antibodies (MAb) to hematopoietic facilitatory cells (FC). In particular, it relates to MAb against antigens expressed by murine FC, methods of generating the antibodies, and methods of using the same. MAb directed to markers that are expressed specifically or at higher levels by FC than by most other bone marrow cells have a wide range of applications, including but not limited to, rapid isolation of FC, identification of FC in a donor cell preparation, and molecular cloning of the genes encoding the corresponding target antigens.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
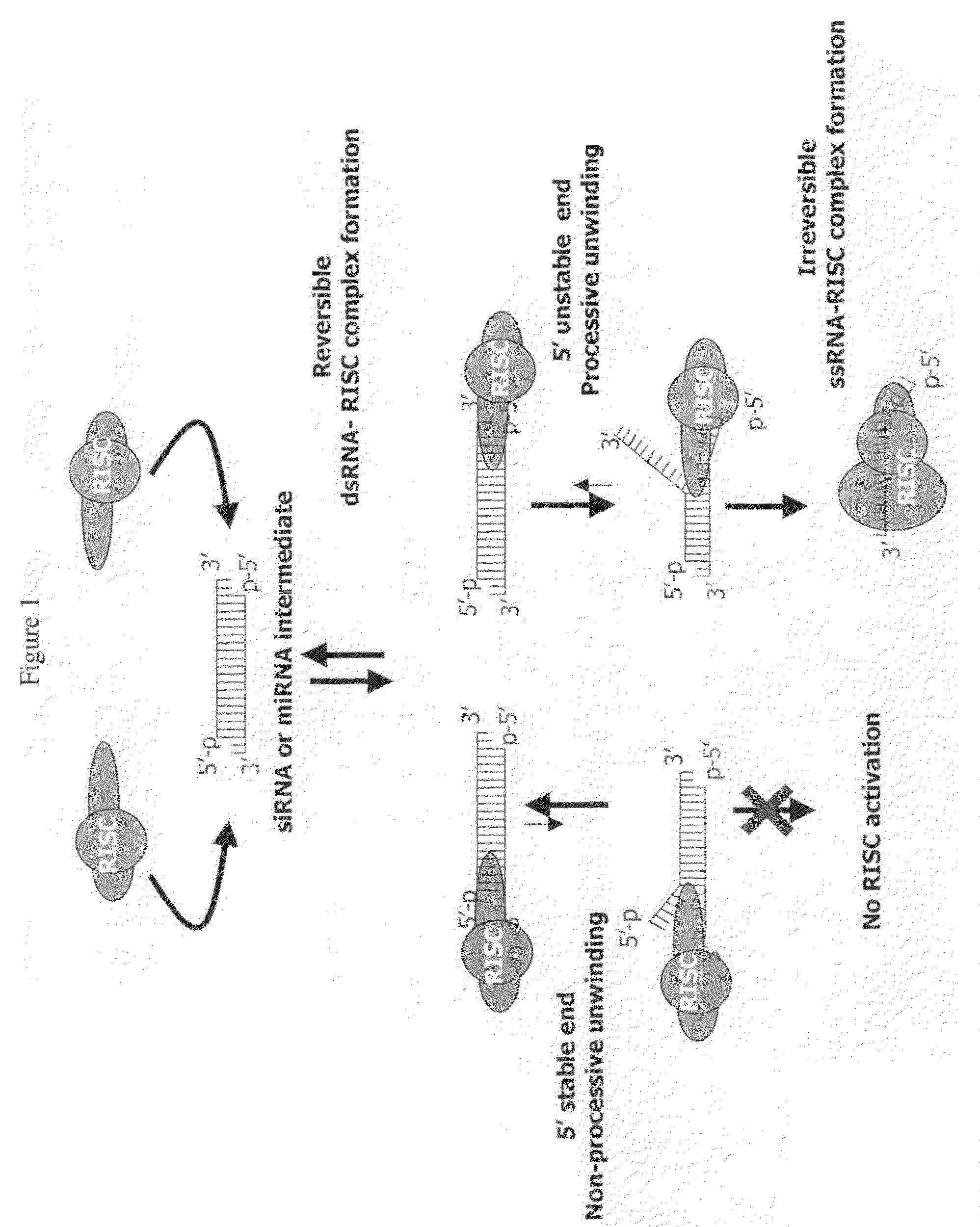
siRNA targeting v-myc myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog (MYC)
InactiveUS7951935B2Improve efficiencyGood curative effectSugar derivativesActivity regulationViral OncogeneSilent gene
Efficient sequence specific gene silencing is possible through the use of siRNA technology. By selecting particular siRNAs by rational design, one can maximize the generation of an effective gene silencing reagent, as well as methods for silencing genes. Methods, compositions, and kits generated through rational design of siRNAs are disclosed including those directed to MYC.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCIENTIFIC INC
Methods of Regenerating Cartilage
The present disclosure relates to methods of regenerating cartilage. In an embodiment, a method includes initiating a release of precursor cells, including bone marrow cells and progenitor cells, into a cartilage defect; and applying a population of exogenous cells to the cartilage defect. The exogenous cells, selected from a group including chondrocytes, synoviocytes, fat pad cells, chondroprogenitor cells, mesenchymal stem cells, and any combination thereof, induce the precursor cells to form cartilage tissue through a release of factors by the exogenous cells. The factors stimulate the precursor cells to form cartilage cells. The cartilage cells then form cartilage tissue. The factors are selected from a group including transforming growth factors, fibroblast growth factors, platelet-derived growth factors, insulin-like growth factors, epidermal growth factors, interleukins, and any combination thereof. Other methods of regenerating cartilage are also disclosed.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Closed system separation of adherent bone marrow stem cells for regenerative medicine applications
ActiveUS20130101561A1Elicit neuronal and astrocytic differentiationMinimally invasiveBiocideBone marrow stroma cellsCell adhesionBone Marrow Stem Cell
A method for isolating and processing bone marrow derived stem cells, including the steps of: (a) collecting a biological sample containing adherent bone marrow stem cells in a receptacle with interior walls coated with a cell-adherent substrate; (b) incubating the bone marrow cells on the adherent substrate so that a layer of adherent bone marrow stem cells adheres to the substrate; (c) washing any non-adherent cells from the substrate; and (d) collecting the bone marrow stem cell layer. Isolation kits and use of bone marrow cells harvested for cell therapies are also described.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Bone marrow transplantation for treatment of stroke
InactiveUS20090162327A1Reduces functional deficitRelieve symptomsBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseNeural cell
There is provided a treatment for patients suffering from neurodegenerative disease or neural injury including the steps of transplanting cultured bone marrow cells into the spinal cord or brain or injecting intravascularly bone marrow cells of a patient in need. Also provided is a method of activating the differentiation of neural cells in an injured brain including the steps of transplanting bone marrow cells adjacent to the injured brain cells and activating the endogenous central nervous system stem cells to differentiate into neurons. A method of treating injured brain or spinal cord cells is also provided including the steps of transplanting bone marrow cells near the injured brain cells and generating new neurons at the location of transplantation. A method of treating injured brain or spinal cord cells with a composite of MSCs and neurospheres.
Owner:HENRY FORD HEALTH SYST
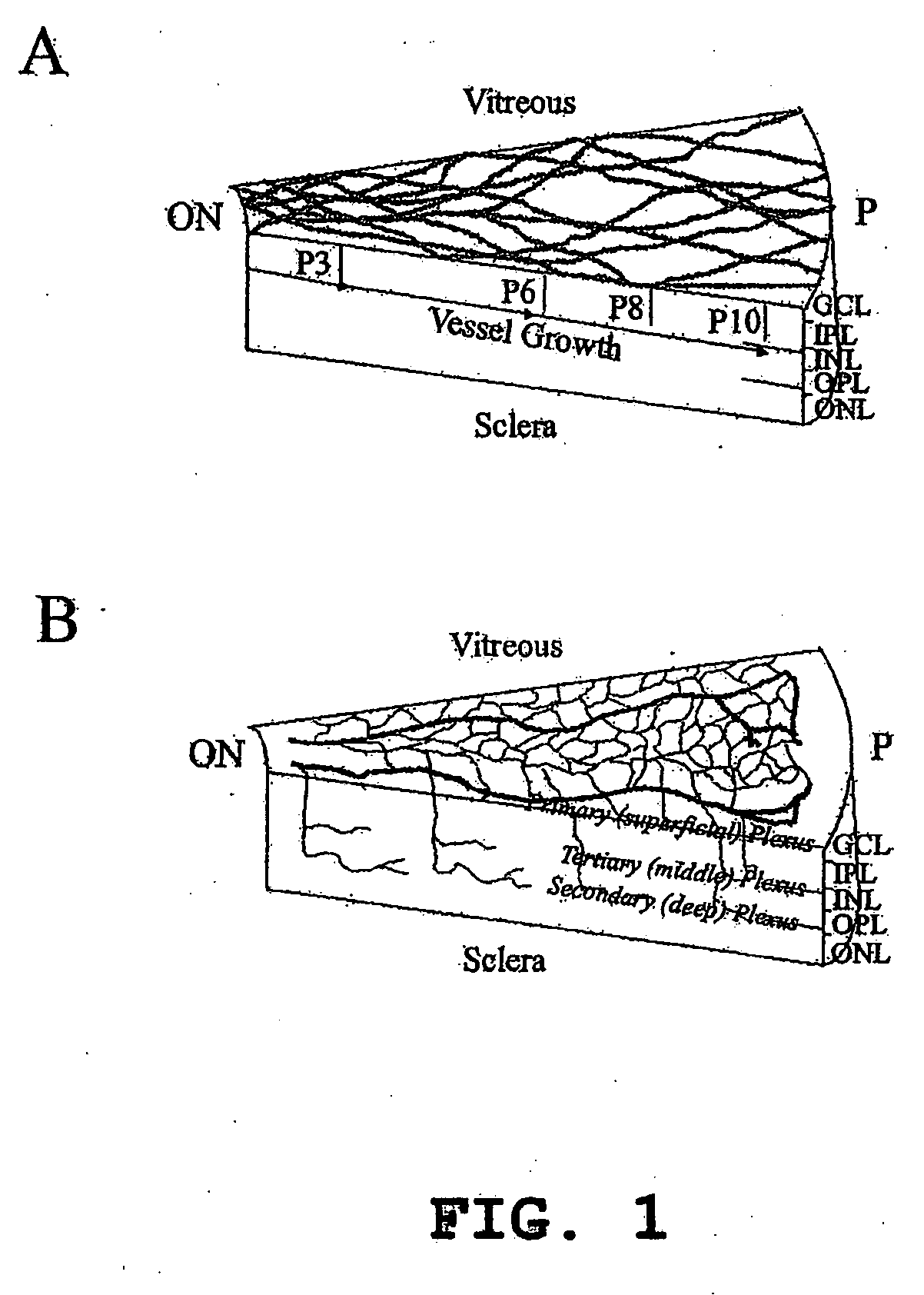
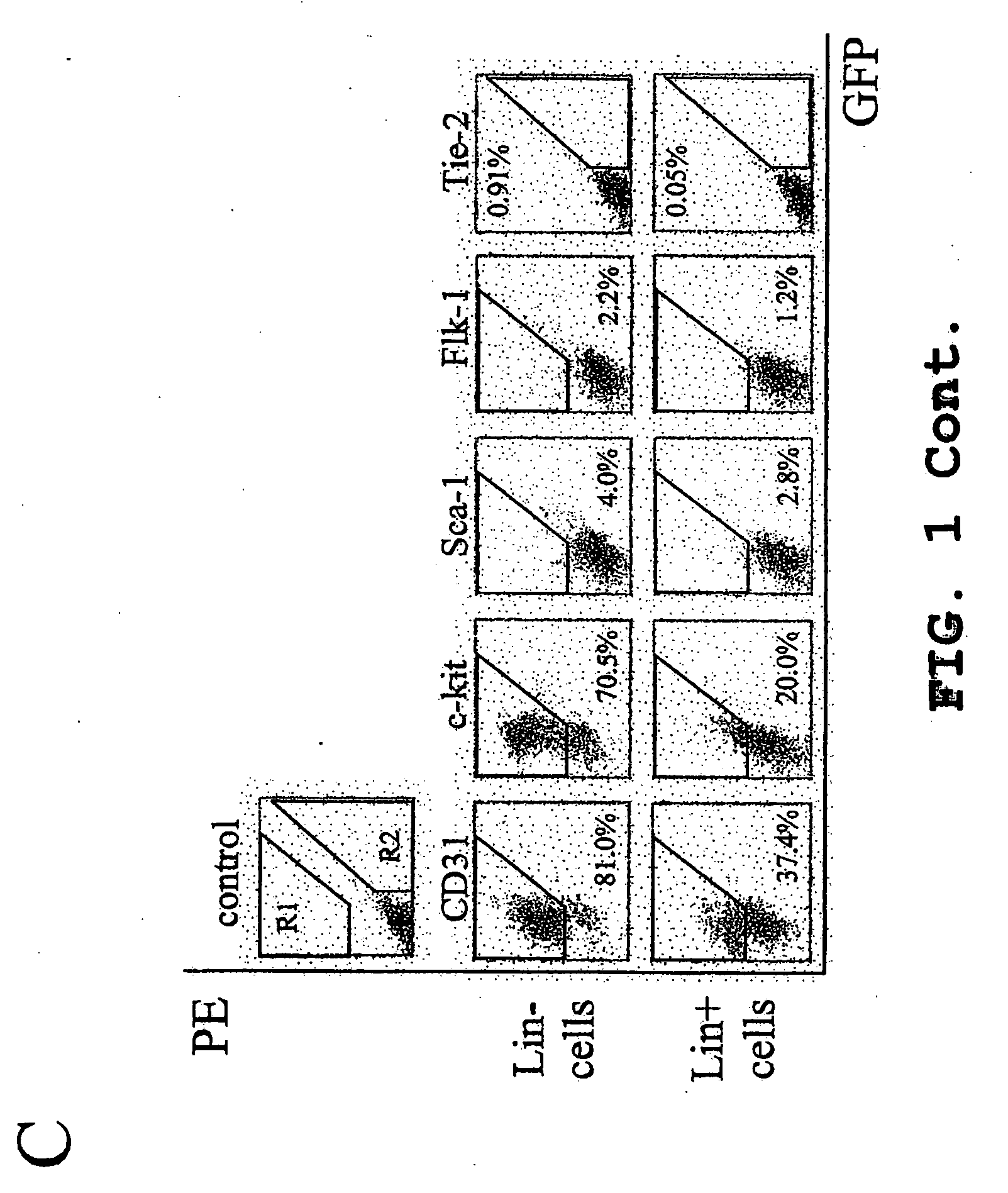
Isolated myeloid-like cell populations and methods of treatment therewith
The present invention provides an isolated myeloid-like cell population comprising a majority of cells that are lineage negative, and which express both CD44 antigen, CD11b antigen, and hypoxia inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α). These cells have beneficial vasculotrophic and neurotrophic activity when intraocularly administered to the eye of a mammal, particularly a mammal suffering from an ocular degenerative disease. The myeloid-like cells are isolated by treating bone marrow cells, peripheral blood cells or umbilical cord cells with an antibody against CD44 (hyaluronic acid receptor), against CD11b, CD14, CD33, or against a combination thereof and using flow cytometry to positively select CD44 and / or CD11b expressing cells therefrom. The isolated myeloid-like bone marrow cells of the invention can be transfected with a gene encoding a therapeutically useful protein, for delivering the gene to the retina.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
New use of anti-impaludism medicament hydroxyl chloroquine
InactiveCN101428025AMinimize or control damageClear anti-inflammatory activityOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsHydroxychloroquineLysosome
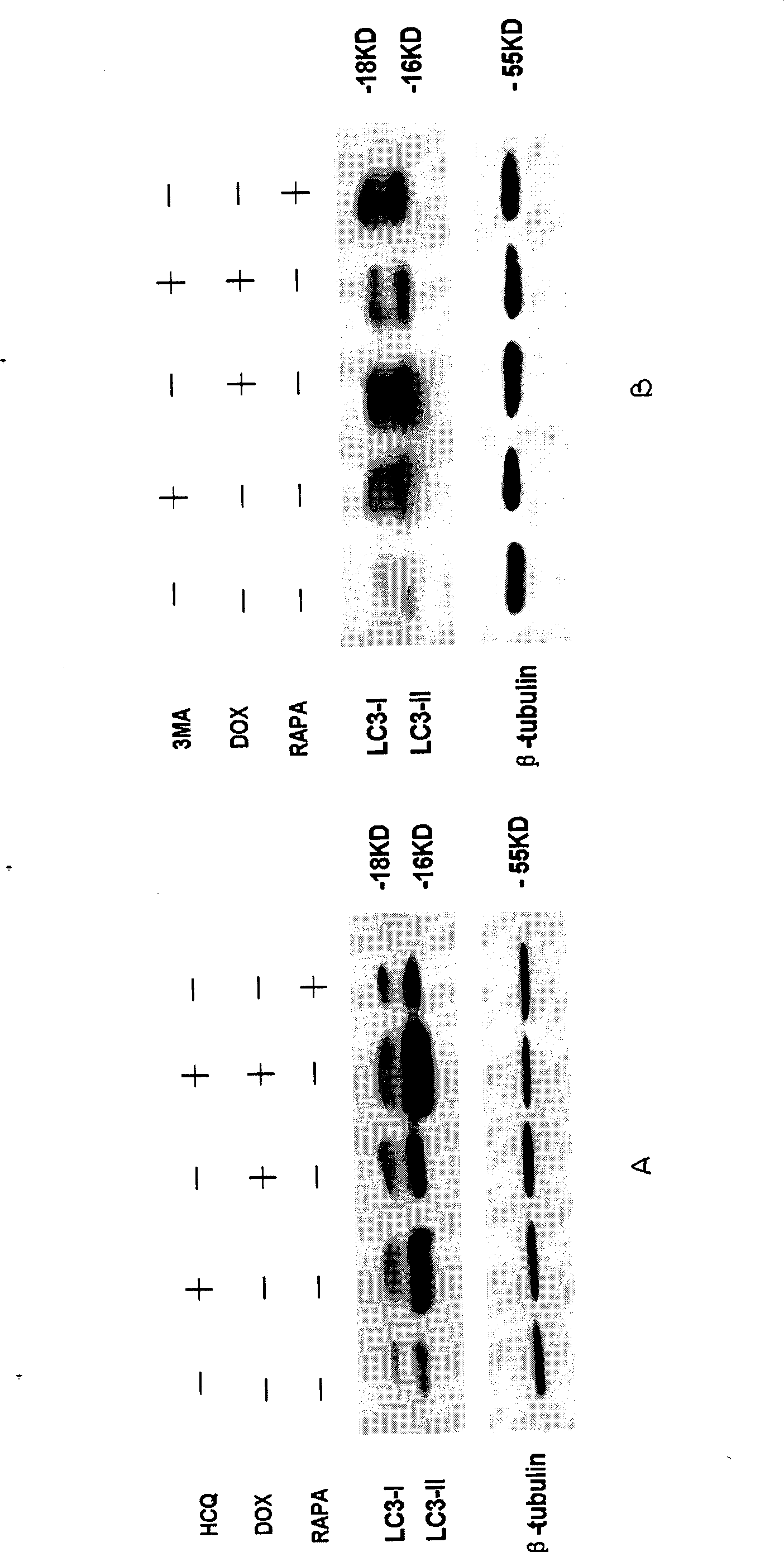
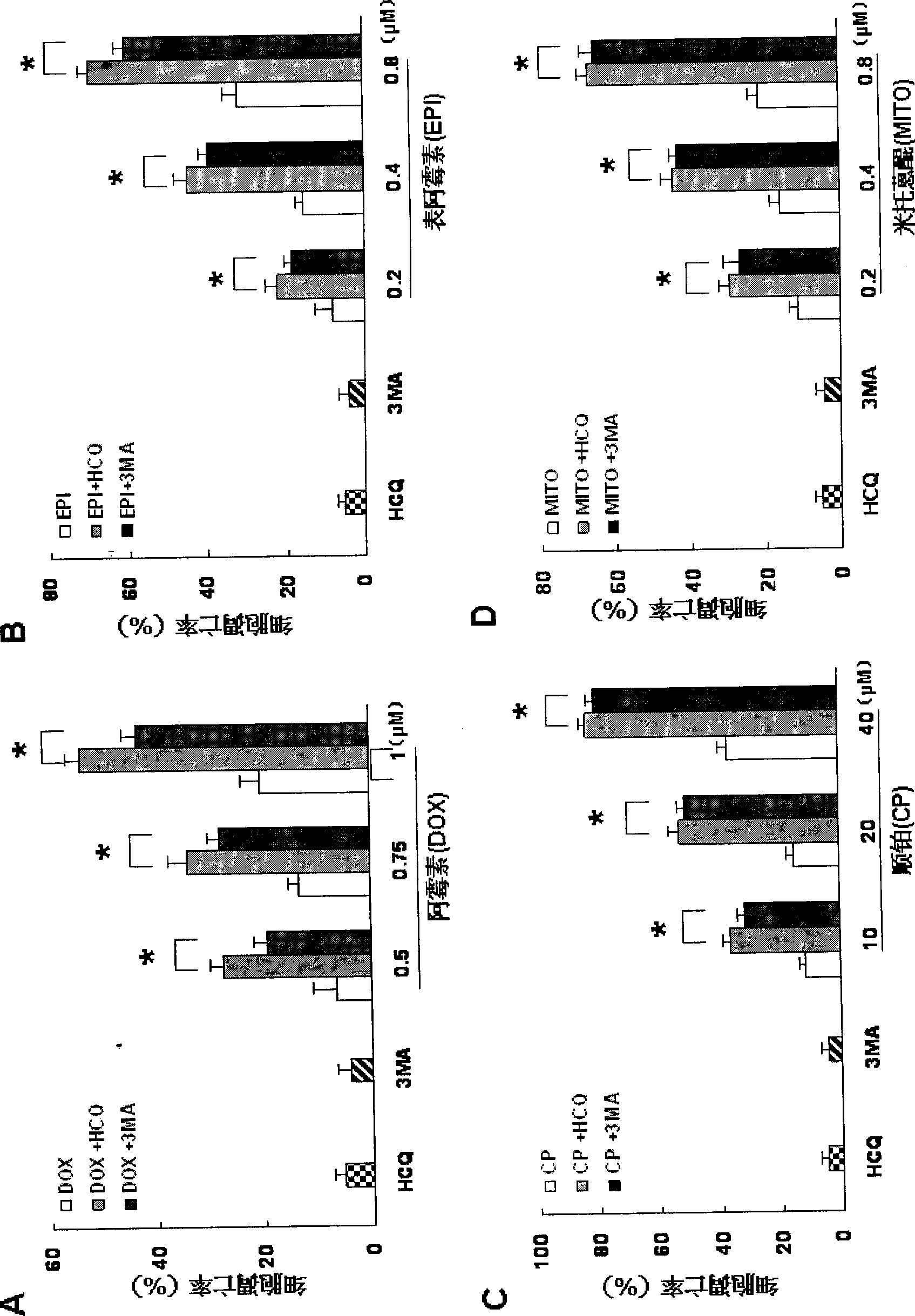
The invention relates to the novel usage of an antimalarial medicine, in particular to the novel usage of hydroxychloroquine having sensitivity enhancing effect on various chemical anti-multiple myeloma medicaments. The novel usage is characterized in the application of hydroxychloroquine in treatment of multiple myeloma through chemotherapeutic medicaments. The hydroxychloroquine can obviously enhance the killing activity of chemotherapeutic medicines such as doxorubicine, epidoxorubicin, cis-platinum and mitoxantrone to multiple myeloma cells, and the killing activity thereof is realized by inhibiting the myeloma cell autophagy signals by hydroxychloroquine. Hydroxychloroquine can induce the quantity of the autophagy lysosomes of the multiple myeloma cells to be increased and the expression of the autophagy-associated albumen LC3-II to be increased.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
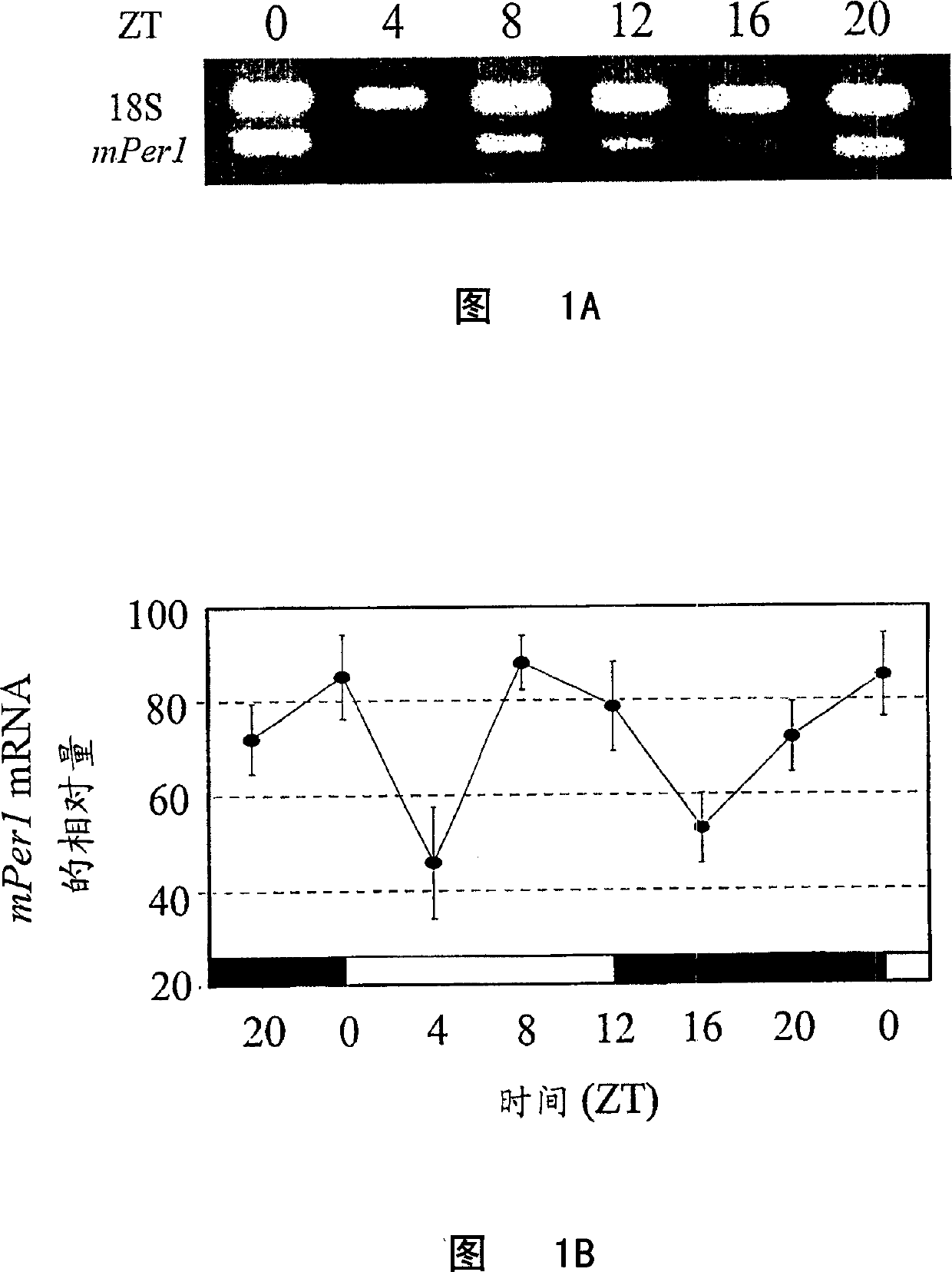
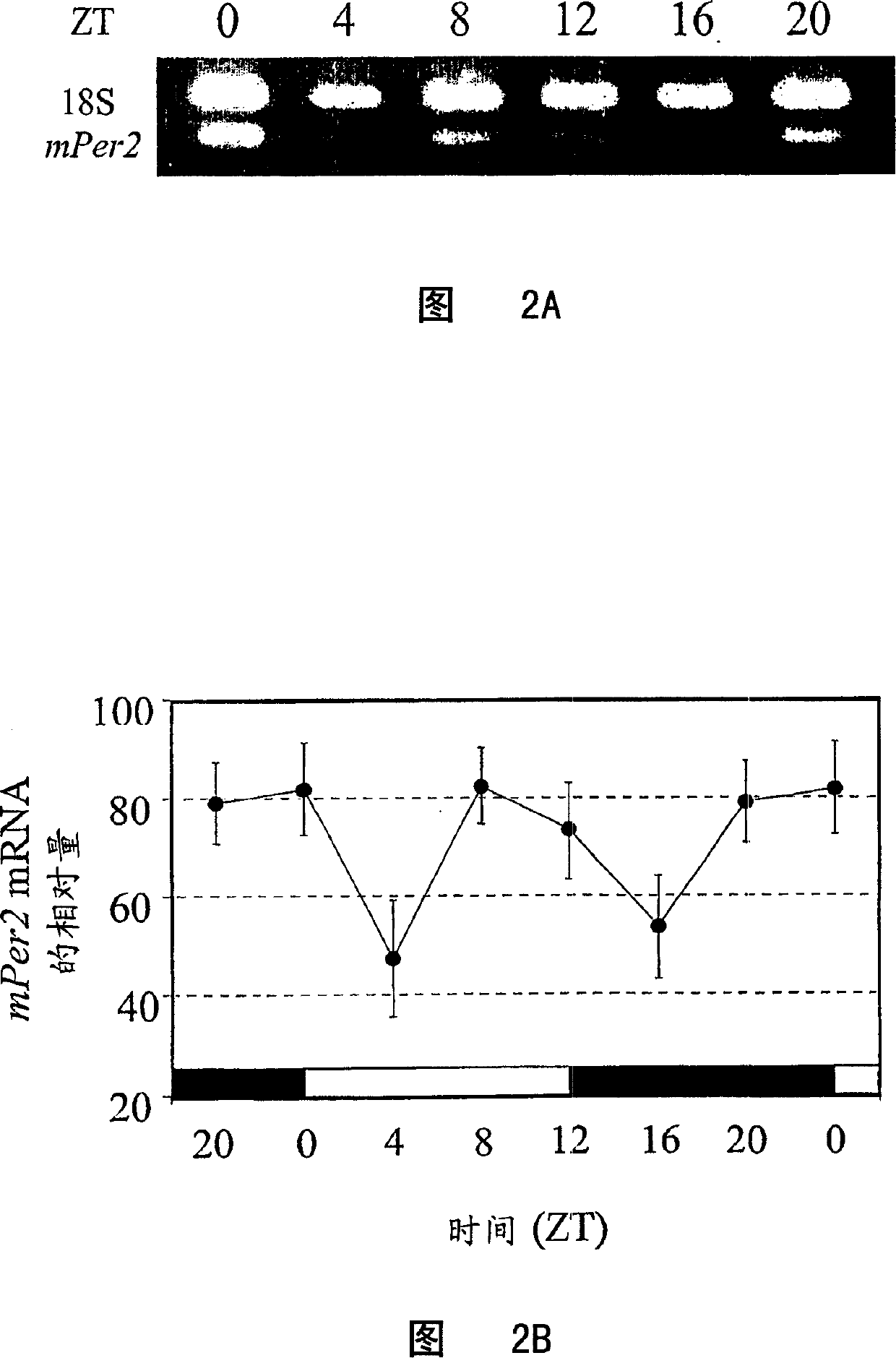
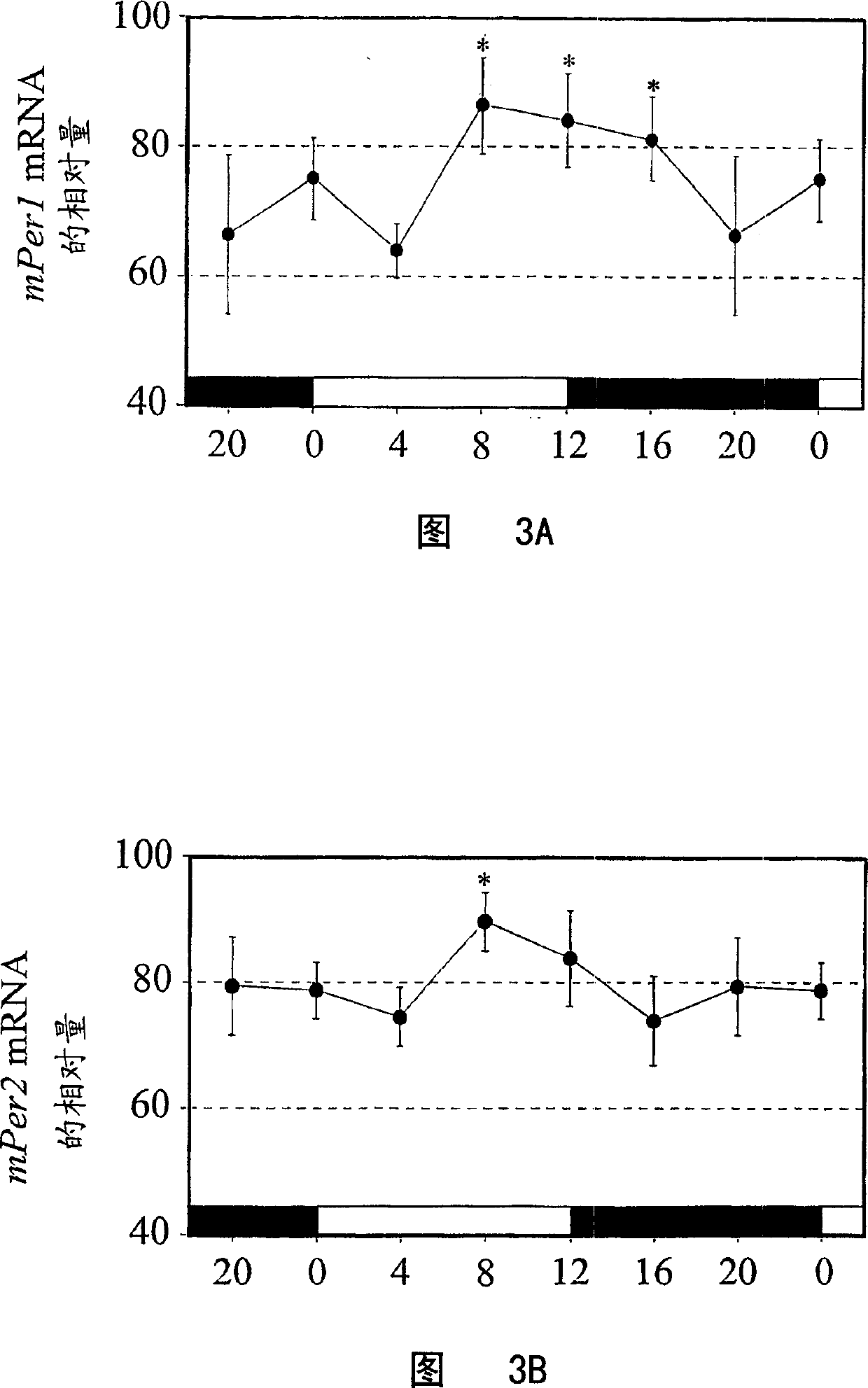
Circadian control of stem/progenitor cell self-renewal and differentiation and of clock controlled gene expression
Manipulation of the circadian clock system by providing suitable cells with the circadian clock system under conditions that effectively control myeloid cell development, stem cell self-renewal, differentiation and / or function, and clock-controlled gene expression with E-box sequences in the regulatory region , A method for controlling bone marrow cell development, stem cell self-renewal, differentiation and / or function, and a clock with an E-box sequence in the regulatory region to control gene expression. Additionally, in vitro engineered tissues are disclosed that include a plurality of cells or cell types in intimate contact with each other to form the tissue, these cells or cell types having properties that have been modulated to regulate the growth, development and and / or functional rhythmic clock system.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Integrin CD18 is a Novel Stromal Stem Cell Marker and Functions to Promote Osteogenesis
InactiveUS20070248998A1Easy to detectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsImmunoperoxidase StainingCancer research
The present invention is directed to a new bone marrow stromal stem cell (BMSSC) marker, CD18, for use in selecting a population of cells enriched in BMSSCs, from bone marrow cells, adipose cells, or peripheral blood. The invention is further directed to methods for selecting a population of cells enriched in BMSSCs based on the selective expression of CD18 on their surface, using techniques known in the art such as fluorescent assisted cell sorting, an immunomagnetic method, flow microfluorimetry, immunofluorescence, immunoperoxidase staining, radioimmunoassay and immunoaffinity chromatography. The invention is further directed to the BMSSCs isolated based on CD18 expression, and their use to treat various diseases. In one aspect, the HMSSCs are transformed with a vector having a normal gene for CD18, and the transformed BMSSCs are administered to treat bone degenerative diseases and diseases of bone involving abnormal expression of CD18 expression of CD18.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES +1
E-selectin antagonist compounds, compositions, and methods of use
ActiveUS20150110808A1Reduce the possibilityReduce the likelihood of occurrencePigmenting treatmentBiocideDiseaseAptamer
Methods and compositions using E-selectin antagonists are provided for the treatment and prevention of diseases and disorders treatable by inhibiting binding of E-selectin to an E-selectin ligand. Described herein are E-selectin antagonists including, for example, glycomimetic compounds, antibodies, aptamers and peptides that are useful in methods for treatment of cancers, and treatment and prevention of metastasis, inhibiting infiltration of the cancer cells into bone marrow, reducing or inhibiting adhesion of the cancer cells to endothelial cells including cells in bone marrow, and inhibiting thrombus formation.
Owner:GLYCOMIMETICS
Method for treating a condition with neural progenitor cells derived from whole bone marrow
A method is described for generating a clinically significant volume of neural progenitor cells from whole bone marrow. A mass of bone marrow cells may be grown in a culture supplemented with fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2) and epidermal growth factor (EGF). Further methods of the present invention are directed to utilizing the neural progenitor cells cultured in this fashion in the treatment of various neuropathological conditions, and in targeting delivery of cells transfected with a particular gene to diseased or damaged tissue.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Induction of myocardial cell from mammalian bone marrow cell or cord blood-derived cell and fat tissue
InactiveUS8093047B2Easily inducingCurb riskCell differentiationMicrobiological testing/measurementCord blood stem cellCardiac muscle
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells generated in vitro
InactiveUS20120225038A1BiocideArtificial cell constructsMyeloid-derived Suppressor CellBone Marrow Stem Cell
A population of myeloid-derived suppressor cells and the culture procedure to obtain these in vitro starting with bone marrow cells of mice, other animals and human beings, in the presence of specific cytokine combinations used to determine concentrations, is provided.
Owner:IST ONCOLOGICO VENETO
Methods and compositions for expanding T regulatory cells
InactiveCN101378783AHigh affinityEfficient signal transductionCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsDendritic cellAutoimmune disease
The present invention provides methods and compositions for expanding Treg cells ex vivo or in vivo using one or more conjugates comprising a costimulatory moiety that stimulates at least one of three signals involved in Treg cell development and / or using dendritic cells pulsed with antigens and modified to display TGF-beta, or hematopoetic stem cells or bone marrow cells modified to display TGF-beta. The methods and compositions are useful, for example, in the treatment and prevention of autoimmune disease, including Type 1 diabetes and in preventing foreign graft rejection, as well as to establish mixed chimerism, induce tolerance to autoantigens, alloantigens or xenoantigens, beta cell regeneration, prevention of foreign graft rejection, and treatment of a genetically inherited hematopoietic disorder.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
Methods and compositions for expanding T regulatory cells
InactiveUS7745215B2Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAutoimmune conditionDendritic cell
The present invention provides methods and compositions for expanding Treg cells ex vivo or in vivo using one or more conjugates comprising a costimulatory moiety that stimulates at least one of three signals involved in Treg cell development and / or using dendritic cells pulsed with antigens and modified to display TGF-β, or hematopoetic stem cells or bone marrow cells modified to display TGF-β. The methods and compositions are useful, for example, in the treatment and prevention of autoimmune disease, including Type 1 diabetes and in preventing foreign graft rejection, as well as to establish mixed chimerism, induce tolerance to autoantigens, alloantigens or xenoantigens, beta cell regeneration, prevention of foreign graft rejection, and treatment of a genetically inherited hematopoietic disorder.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
Reduction of tgf beta signaling in myeloid cells in the treatment of cancer
InactiveUS20130045188A1Inhibit transferReduce signalingOrganic active ingredientsFungiLymphatic SpreadNucleic acid sequencing
Methods of inhibiting metastasis in cancer patients are provided, wherein the methods comprise reducing TGFβ signaling, for example, by reducing TGF receptor II expression in myeloid cells. Vectors comprising a TGFβ receptor II RNAi nucleic acid sequence operably linked to a myeloid specific promoter also are provided. A method of diagnosing cancer in an individual by determining TGFβ receptor II expression in myeloid cells in the individual is provided. Additionally, a method of modulating TGFβ activity in myeloid cells in a cancer patient comprising administering a regulator of at least one of the GSK3 and PI3K pathways to the patient is provided.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Methods and Compositions Comprising Hyaluronan for Enhancing Bone Marrow Cell Therapy
InactiveUS20130315878A1Improves heart performancePrevents ventricular dilatationBiocideUnknown materialsProgenitorVascular disease
Disclosed herein are methods and compositions for treating cardiovascular disease and damaged cardiac tissue which employ at least one hyaluronan (HA) compound and one or more cells selected from the group consisting of stem cells, precursor cells, progenitor cells, committed cells, mature somatic cells, and recombinant cells.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
Method of inducing immune tolerance via blood/lymph flow-restricted bone marrow transplantation
ActiveUS7138144B2Reduced doses of bone marrow cellsPreventing graft-versus-host diseaseBiocideGenetic material ingredientsImmune toleranceLymph flow
Owner:CELLECT BIOTECH
Generating teeth from bone marrow cells
The present invention is based on the discovery that teeth primordia can be generated using bone marrow cells and that bone marrow cells may be employed to generate teeth without the need for purification and expansion of a population of cells.
Owner:ODONTIS
Preparation method of bone marrow chromosome G band
InactiveCN108168968AMulti-lengthIncrease the lengthPreparing sample for investigationWhite blood cellTurbidity
The invention discloses a preparation method of a bone marrow chromosome G band. The method comprises the following steps: (1) performing bone marrow white cell counting, determining the inoculation amount and culture time of bone marrow blood according to the result of the white blood cell counting; (2) inoculating the bone marrow blood into a bone marrow cell culture medium for culturing; (3) adding colchicine to the bone marrow cell culture medium to stop the culturing; (4) collecting a bone marrow cell culture, preparing the bone marrow cell culture into cell suspension, and adjusting theturbidity of the cell suspension to 2-3 McFarland turbidity; (5) dropping the cell suspension on a glass slide, burning the slide glass for 10 to 15 seconds, and after burning of the glass slide, baking the slide glass; and (6) treating the baked glass slide, and dyeing the glass slide with a Giemsa dye to obtain a G-banding chromosome sample. A bone marrow chromosome prepared by the method is inthe form of a long rod, and is well dispersed without crossover, and banding is clearly visible.
Owner:济南金域医学检验中心有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com