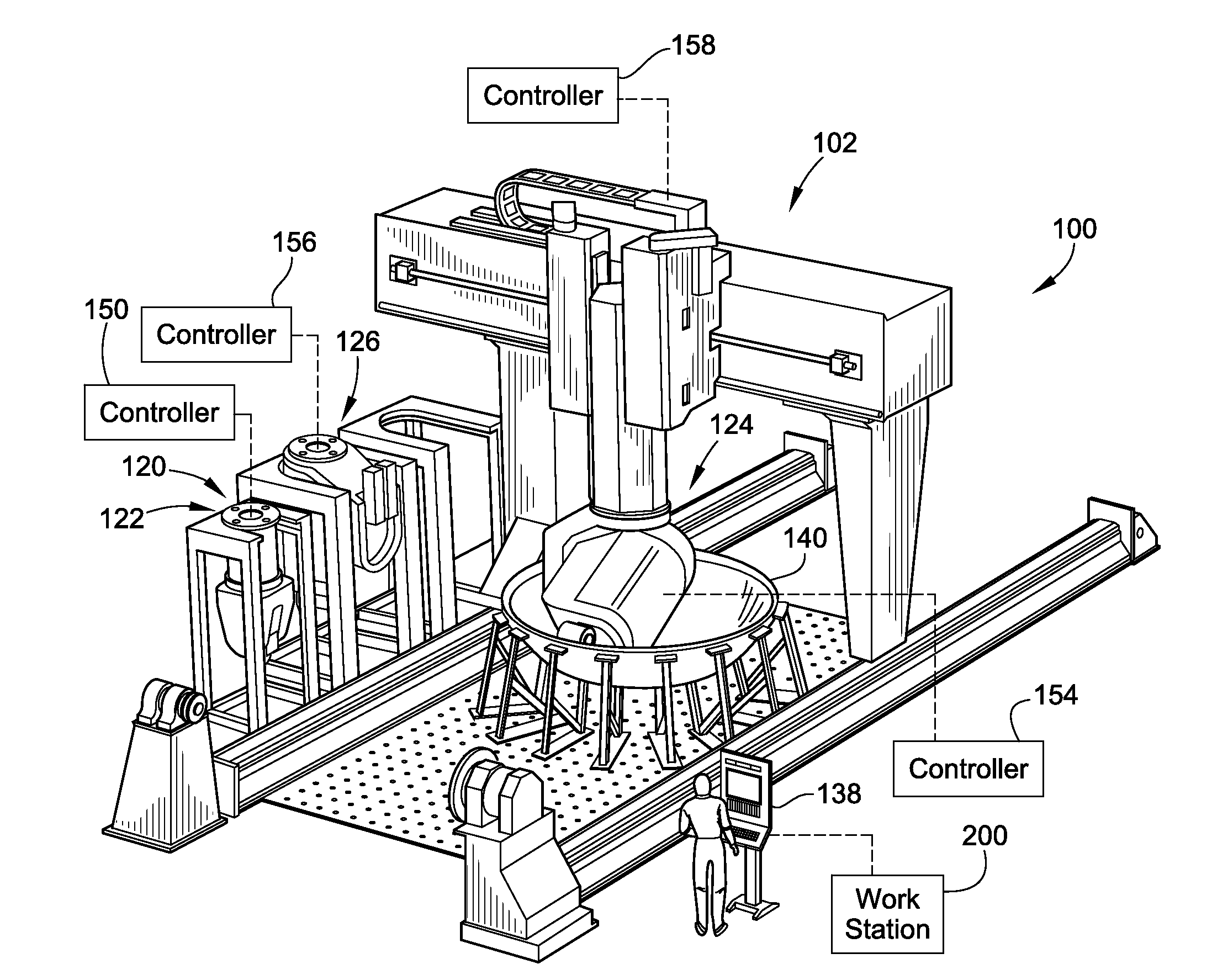
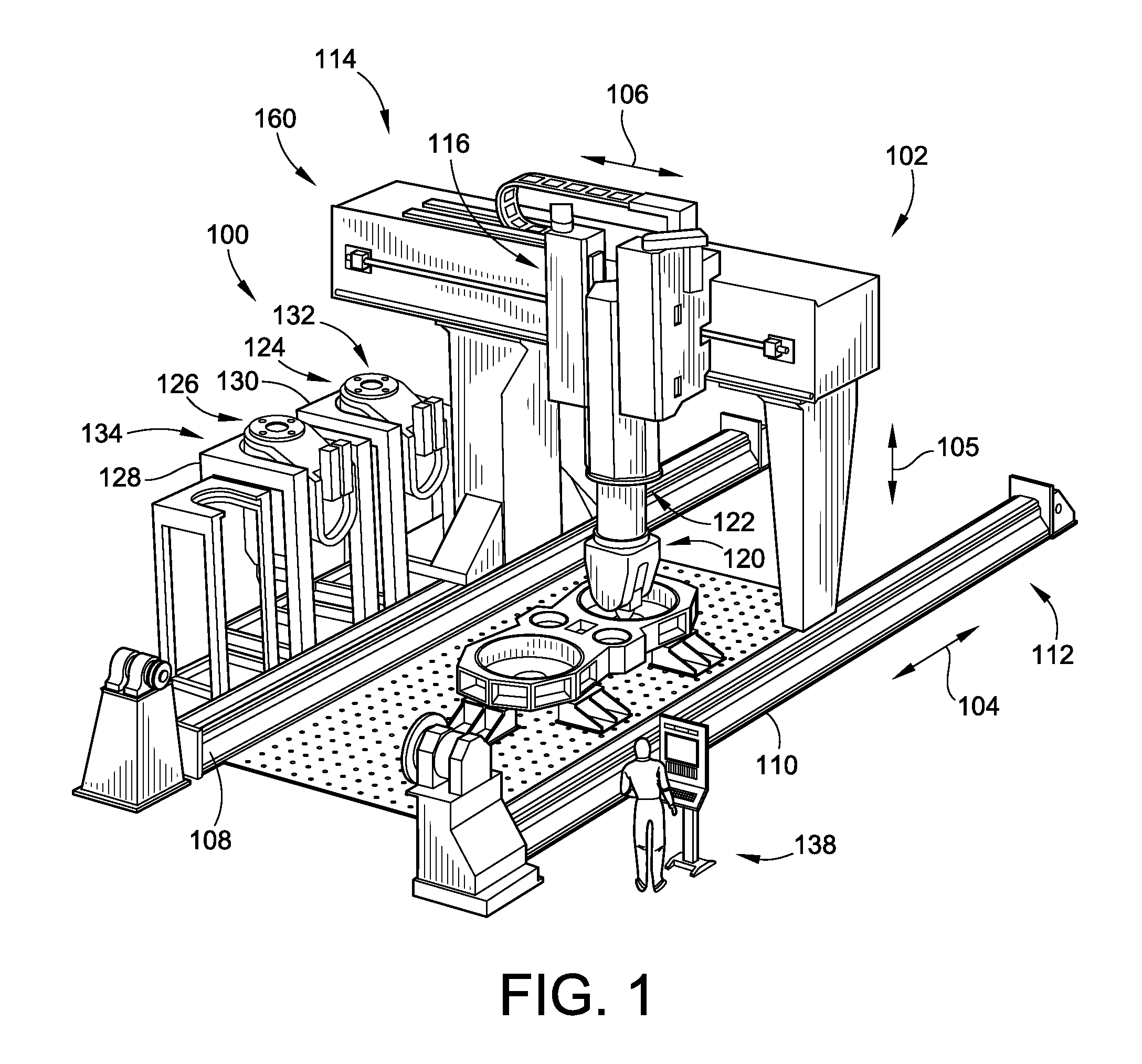
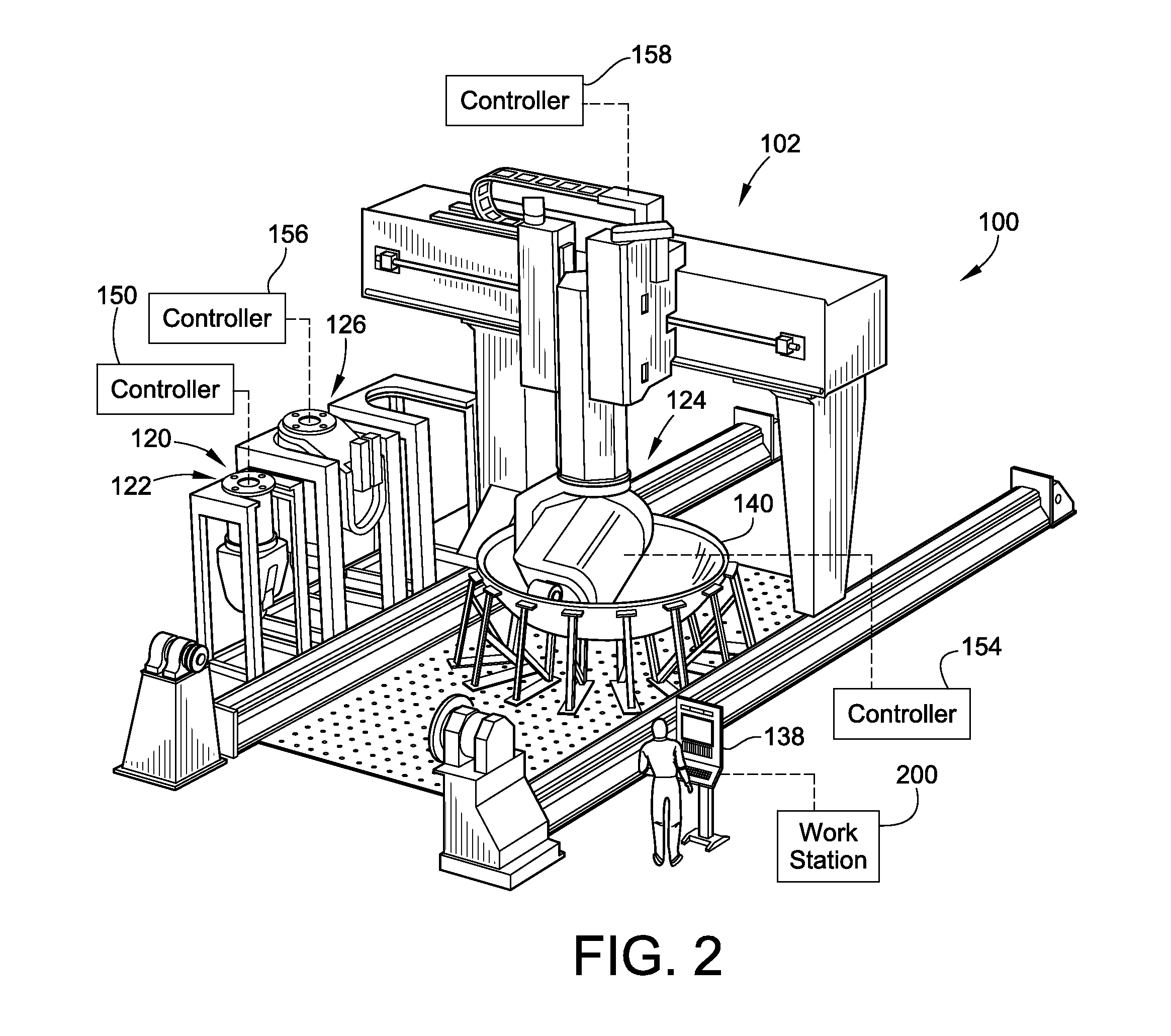
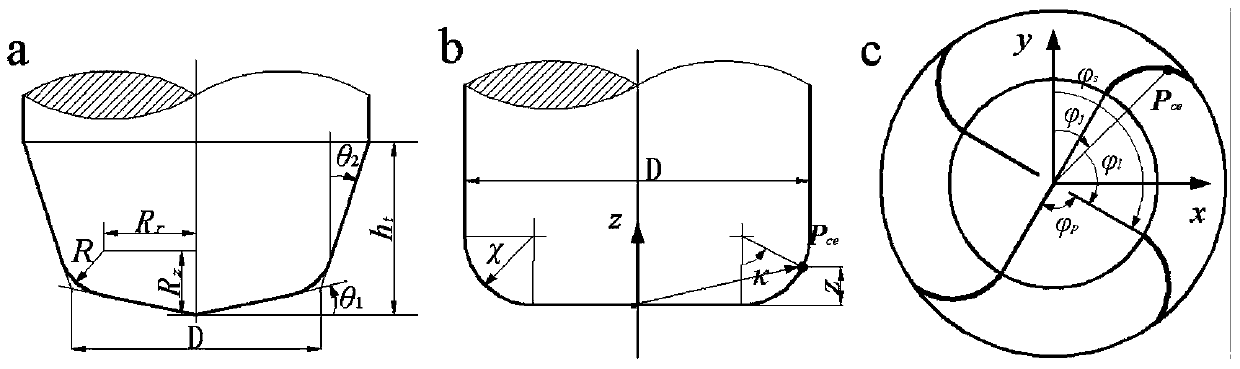
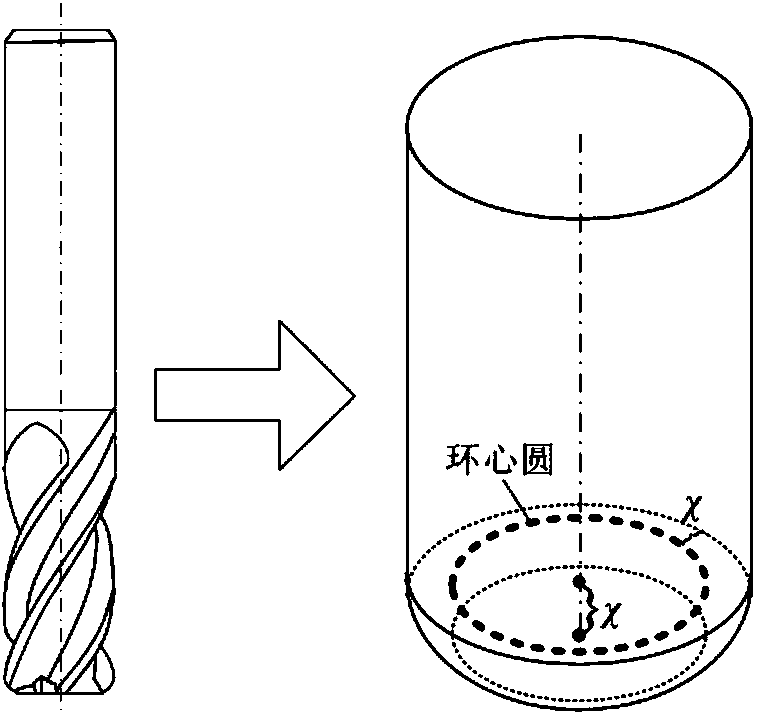
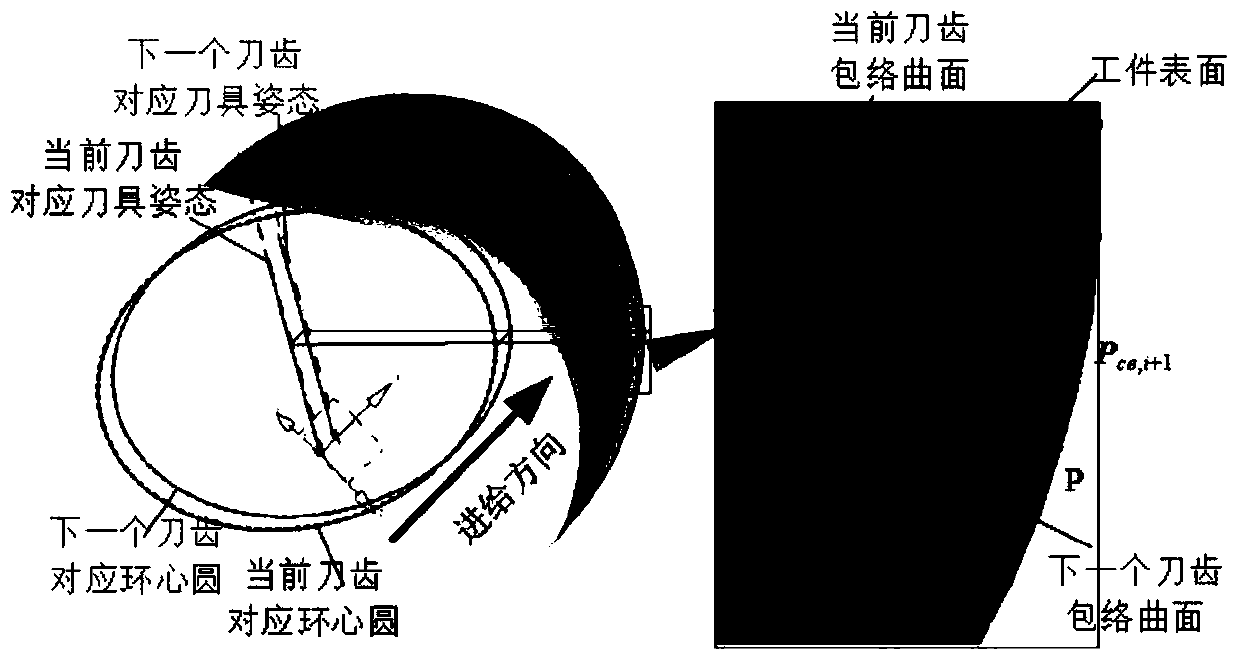
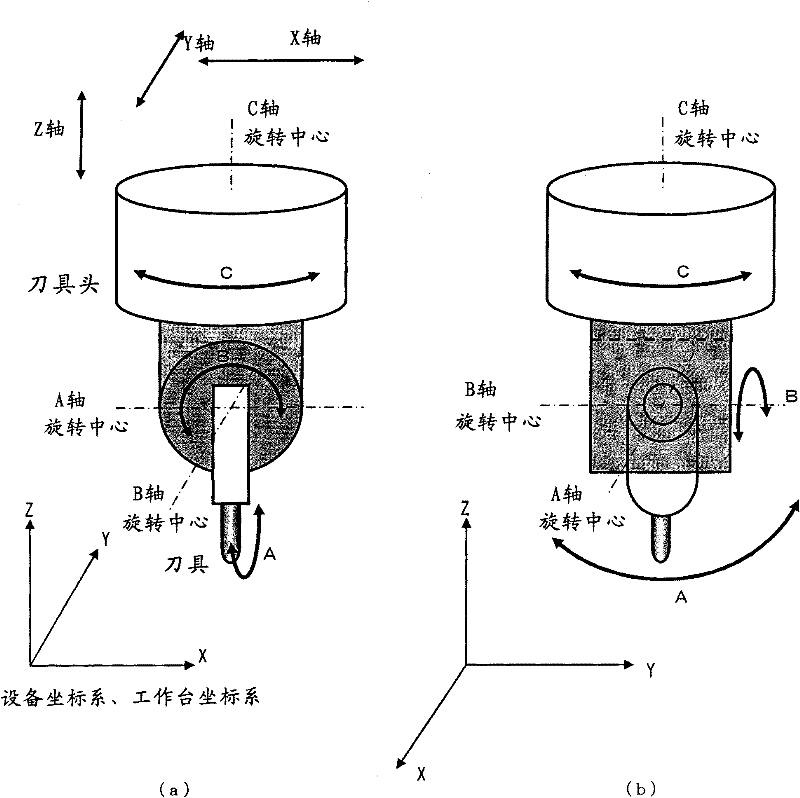
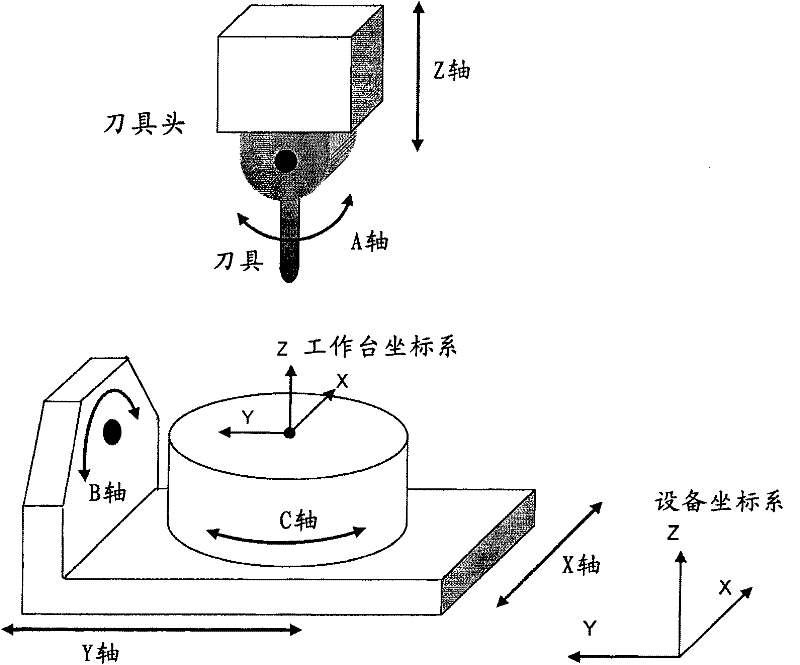
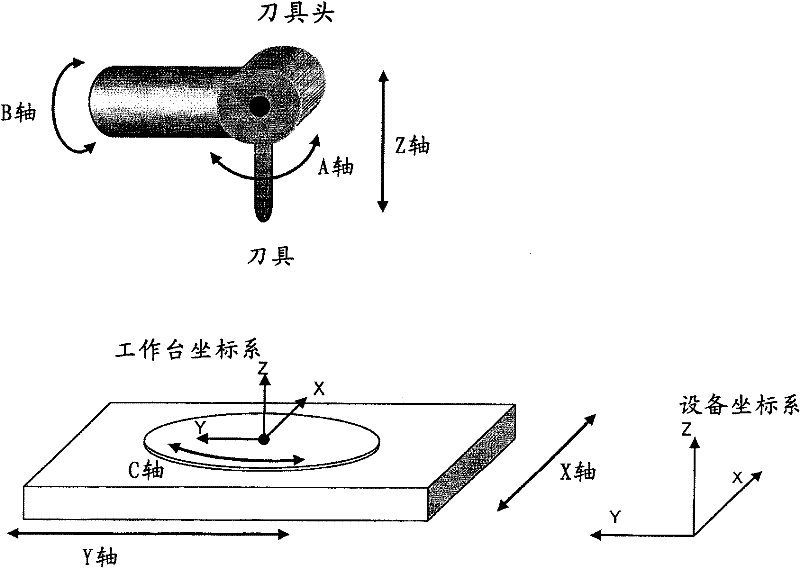
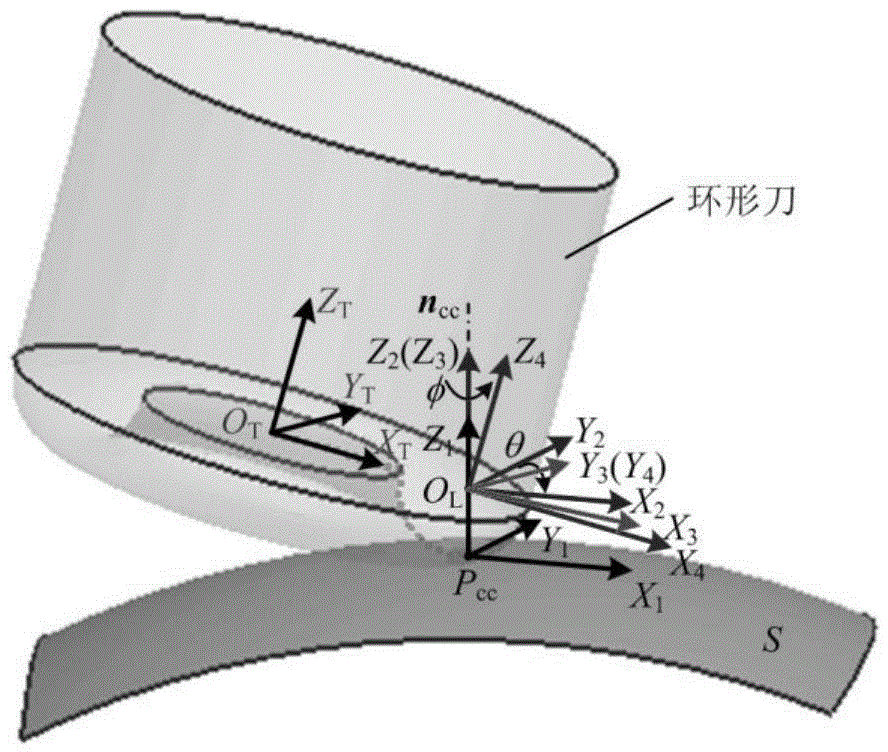
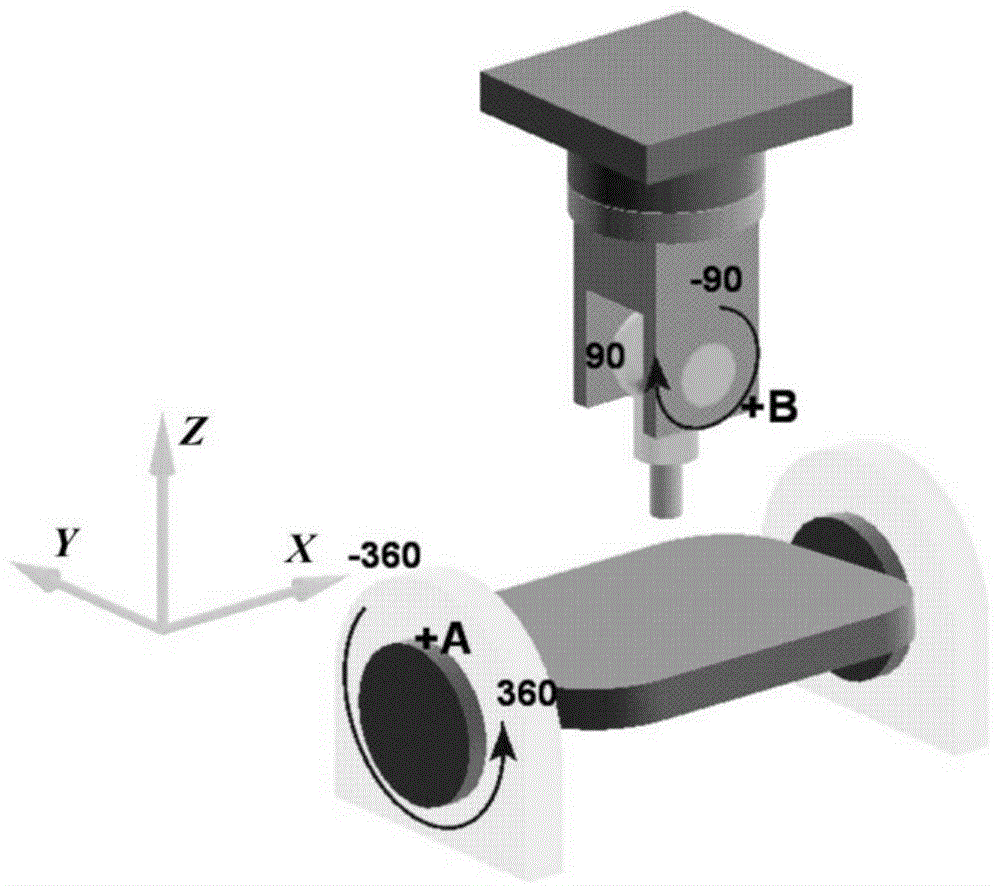
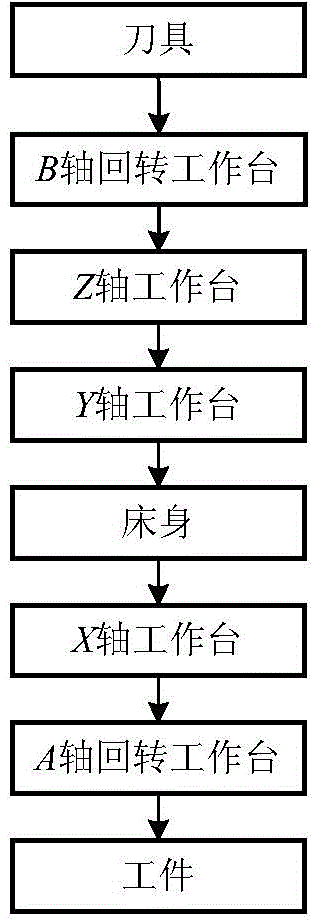
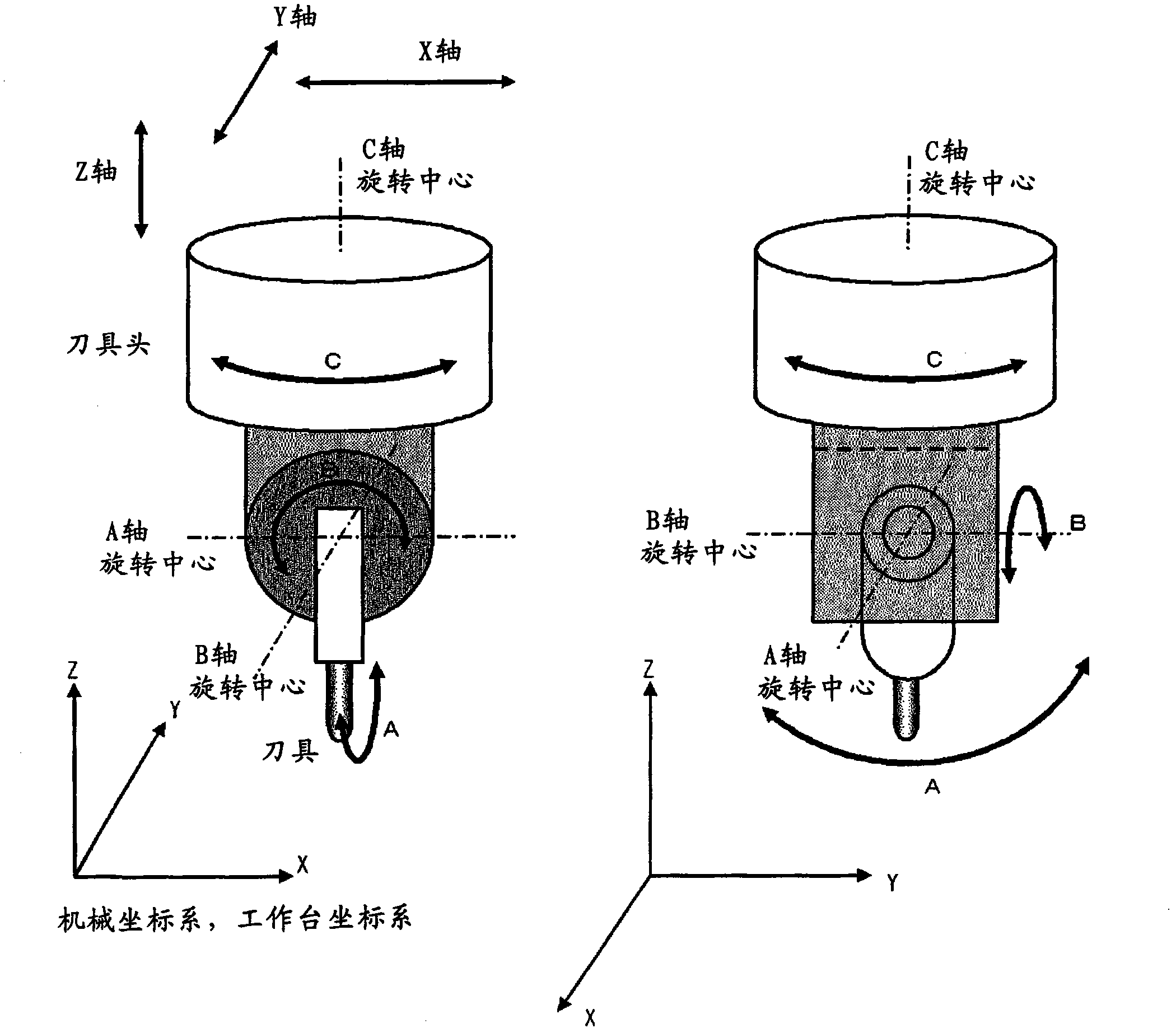
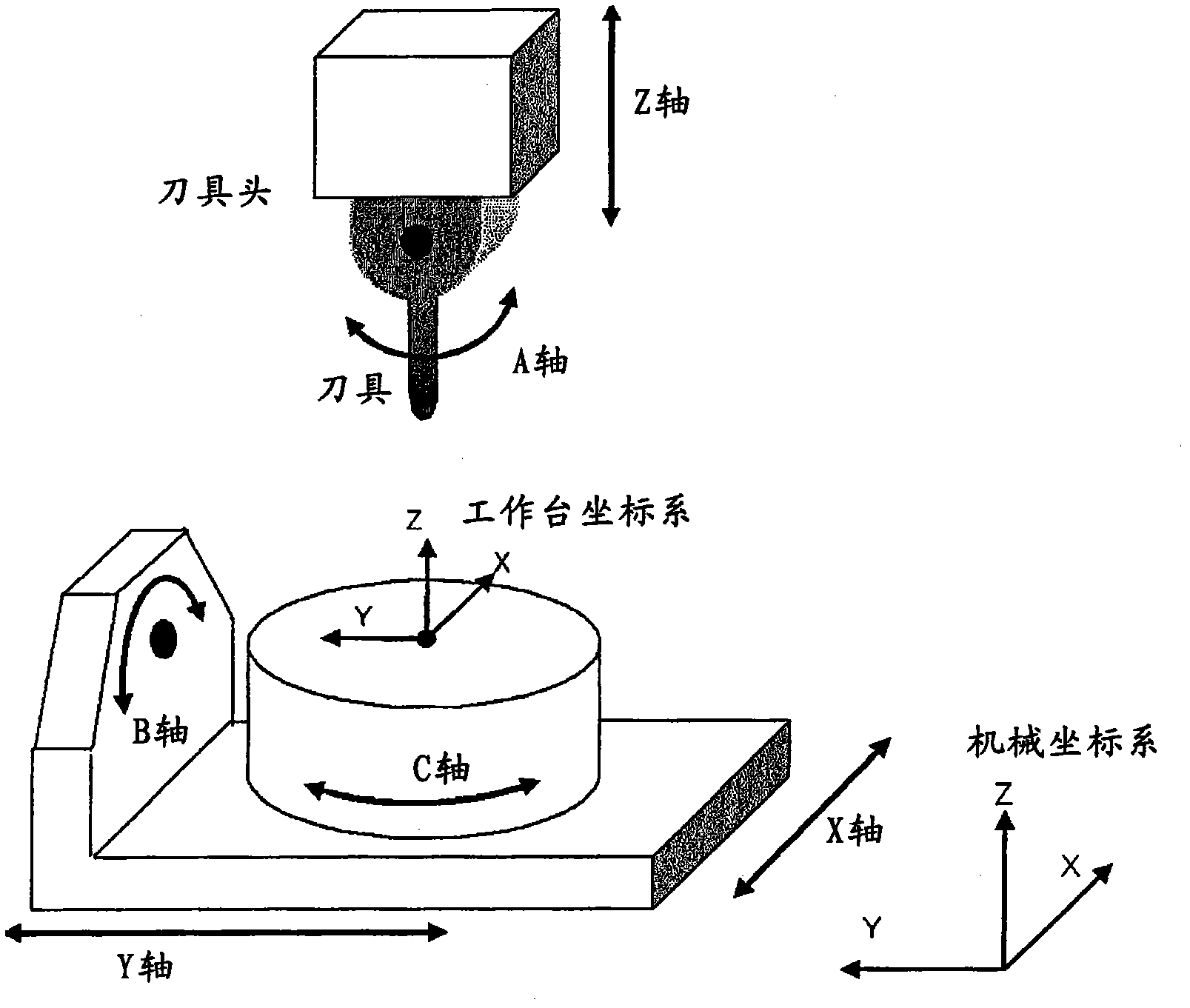
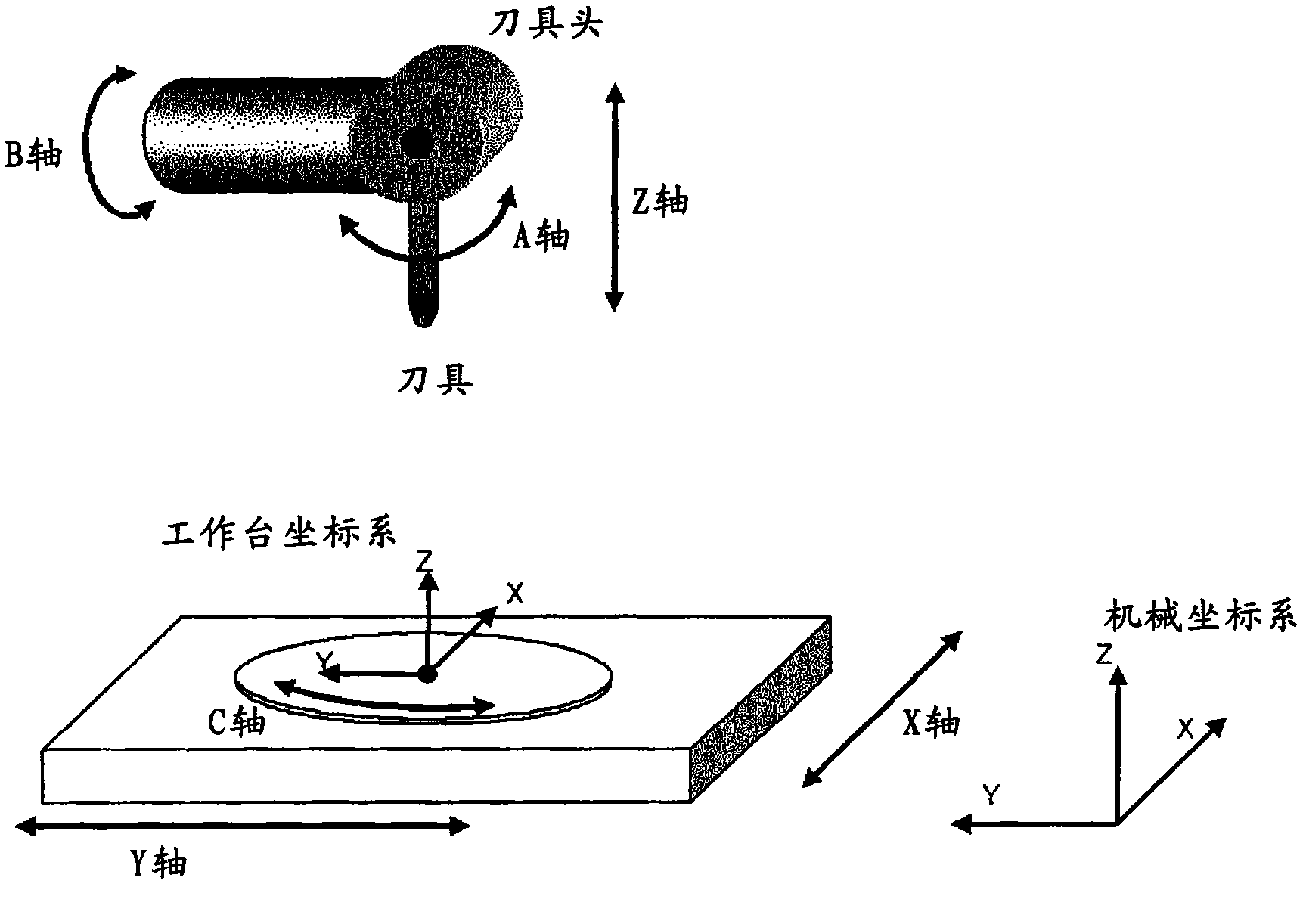
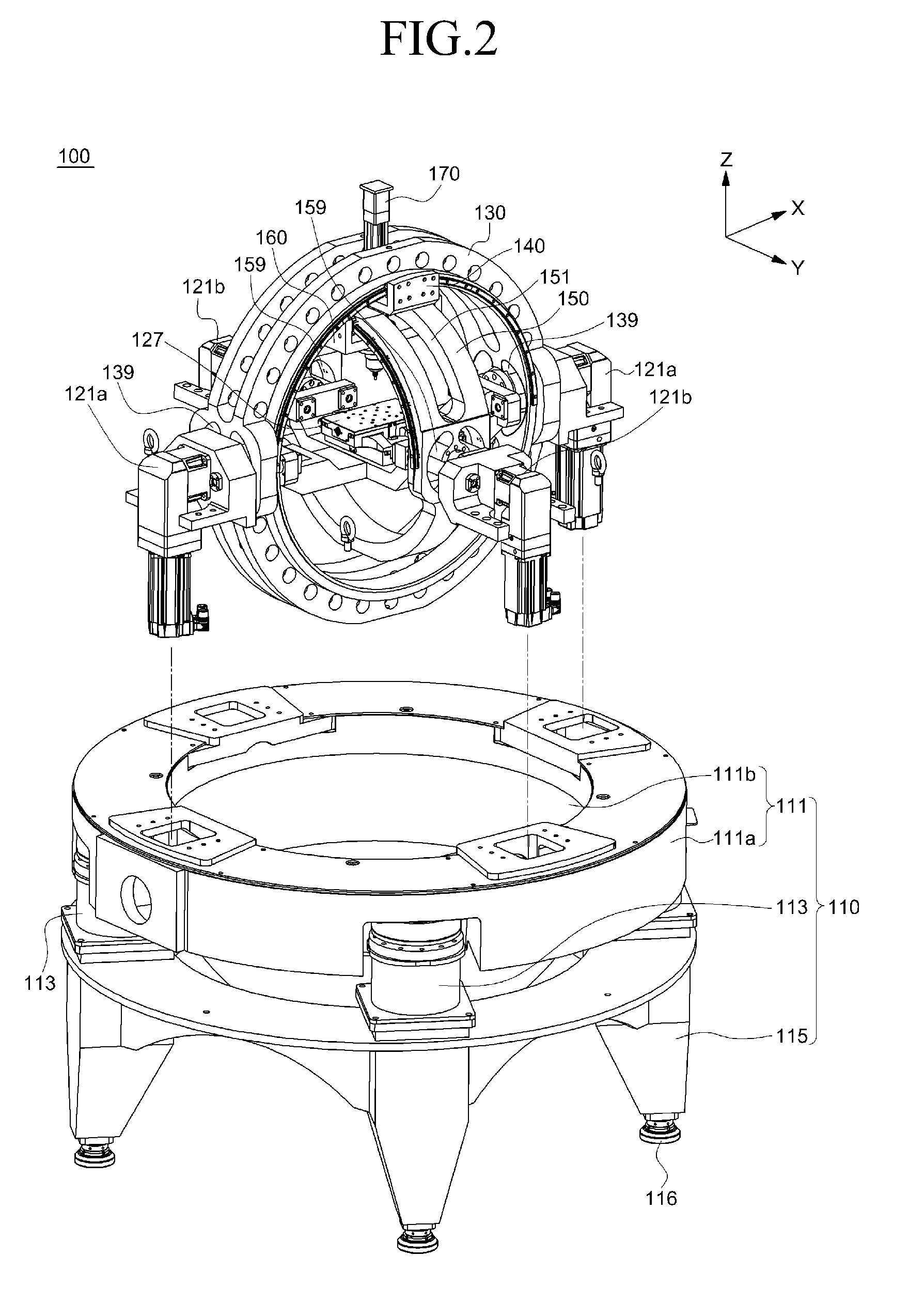
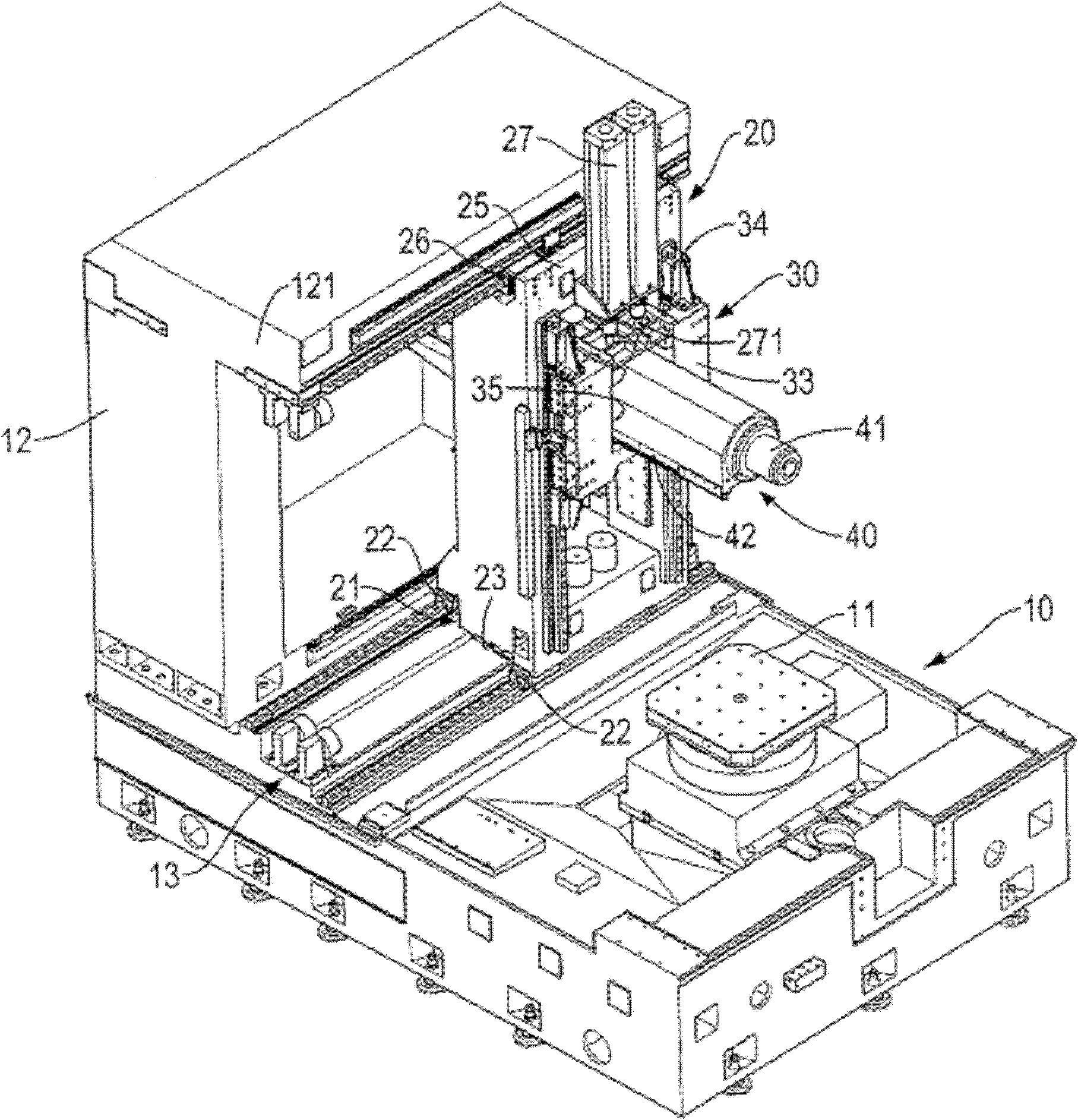
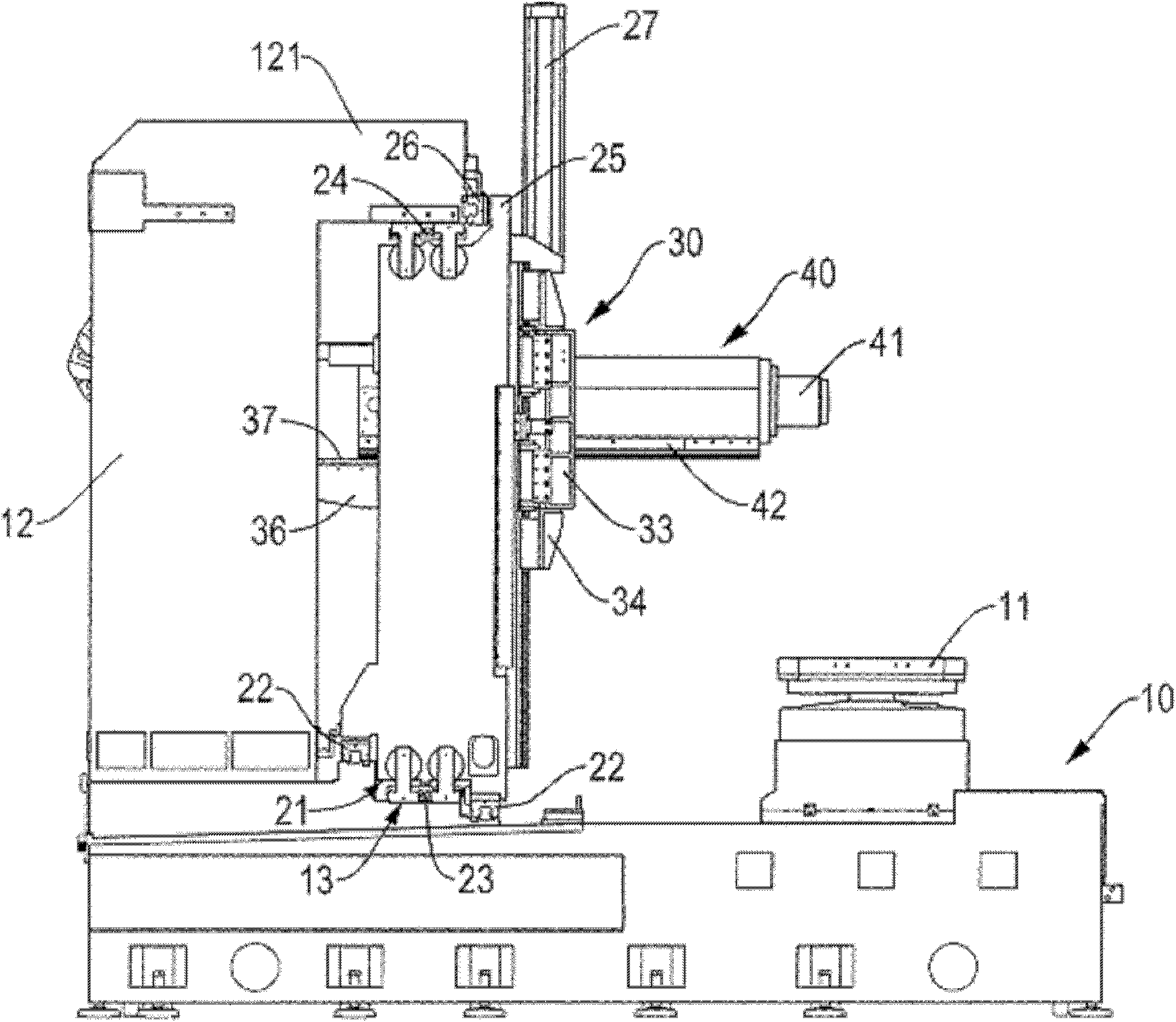
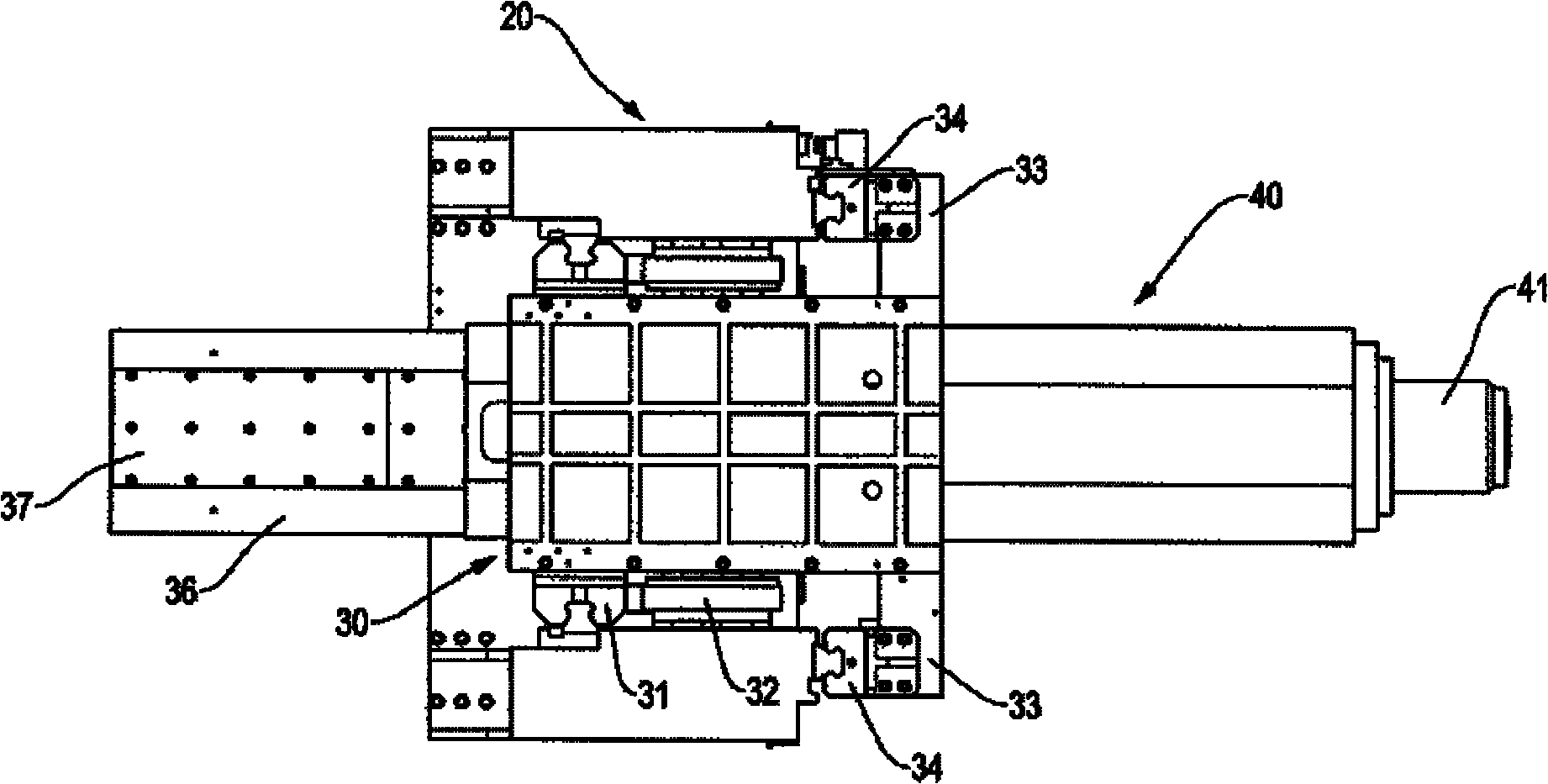
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
185 results about "Multiaxis machining" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Multiaxis machining is a manufacturing process that involves tools that move in 4 or more directions and are used to manufacture parts out of metal or other materials by milling away excess material, by water jet cutting or by laser cutting. This type of machining was originally performed mechanically on large complex machines. These machines operated on 4, 5, 6, and even 12 axes which were controlled individually via levers that rested on cam plates. The cam plates offered the ability to control the tooling device, the table in which the part is secured, as well as rotating the tooling or part within the machine. Due to the machines size and complexity it took extensive amounts of time to set them up for production. Once computer numerically controlled machining was introduced it provided a faster, more efficient method for machining complex parts.
Digital manufacturing of removable oral appliances
InactiveUS20060003292A1Improved of final shapeReduce trimming timeMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesOthrodonticsDental ArticulatorsCentric occlusion
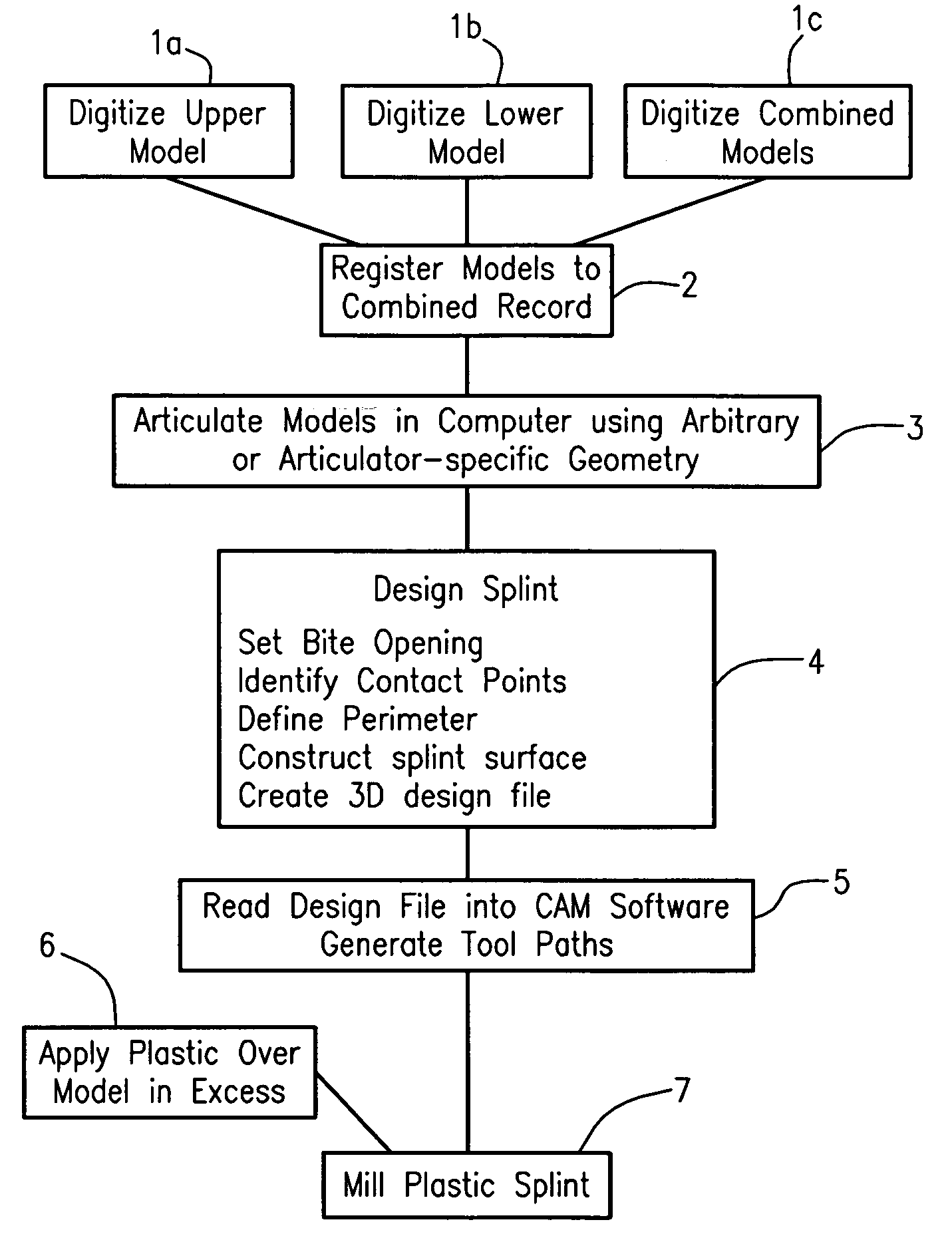
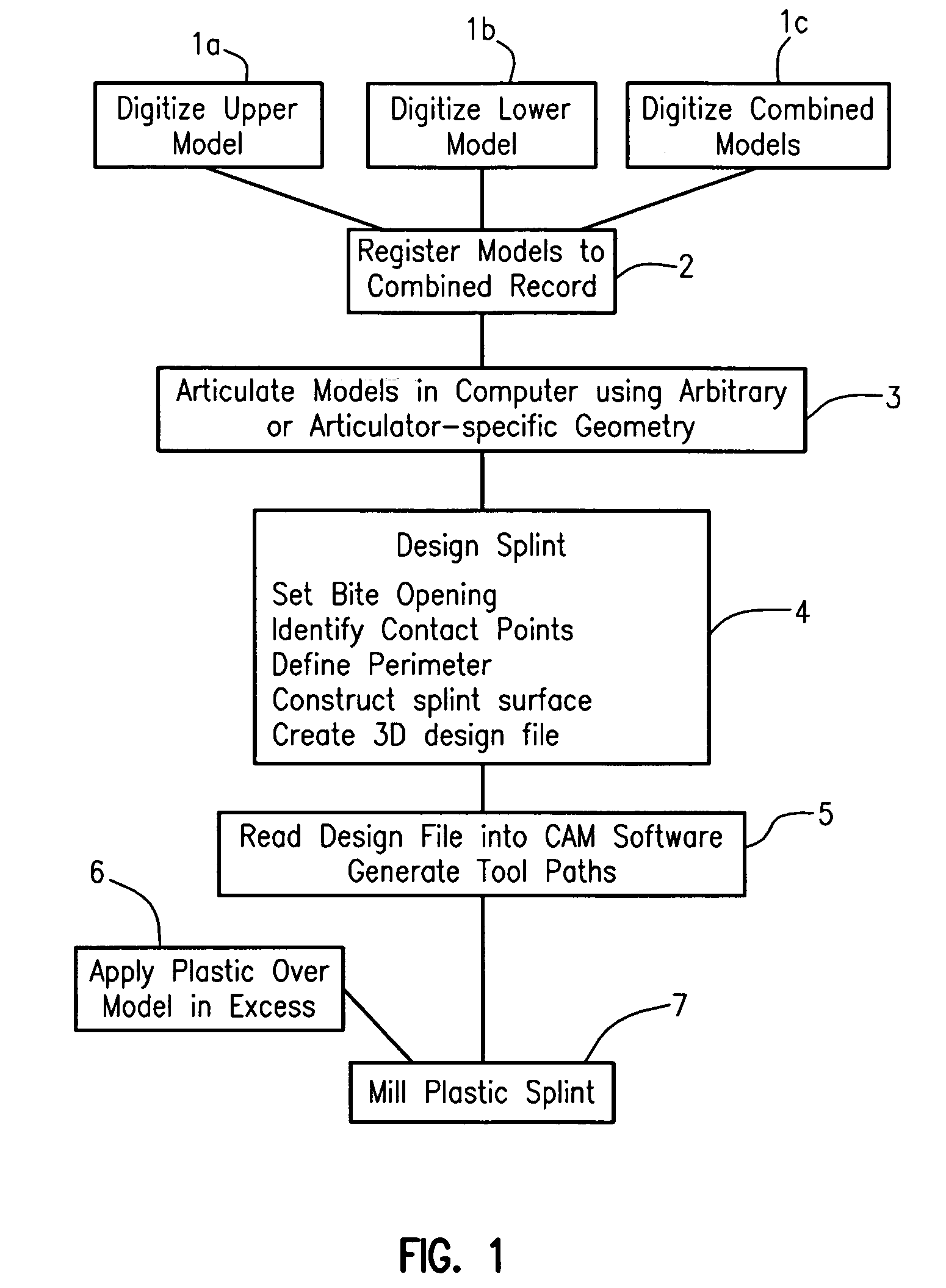
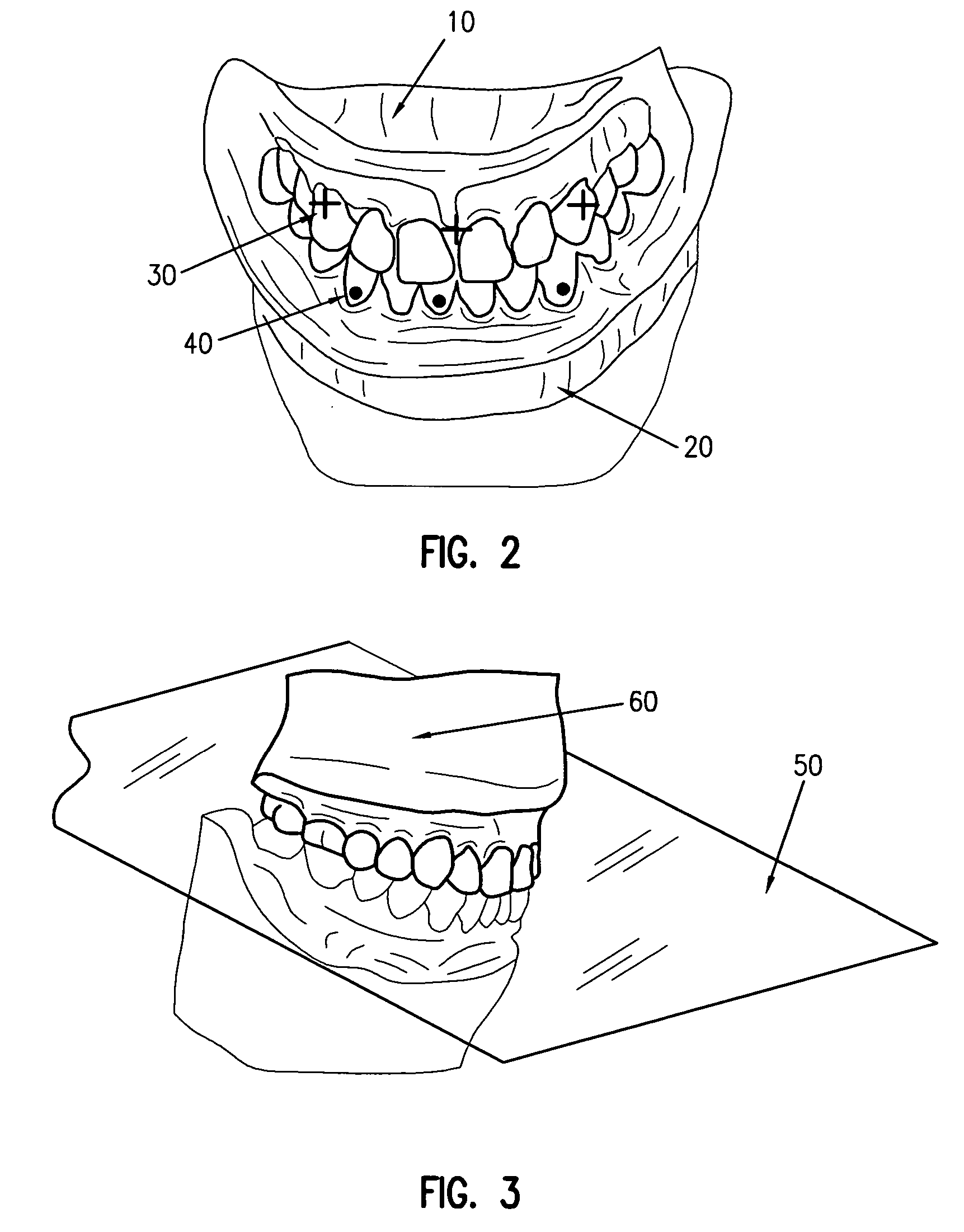
A digitally-based method is described for the design and production of customized removable dental appliances. The plastic component of custom appliances is designed using software, and milled directly over a plaster model of the dentition. A patient's upper, lower, and bite-registered arches are digitized, registered to a bite or centric occlusion position, and articulated in software using either an average geometry or the geometry of a specific articulator. Appliance design is performed by defining the desired plastic surfaces and margins as dictated by the relative movement and positions of the arches as functionally required for a specific appliance. Standard CAM software is used to read the design file and command a multiaxis machine center to mill the plastic while directly on a plaster model.
Owner:GREAT LAKES ORTHODONTICS
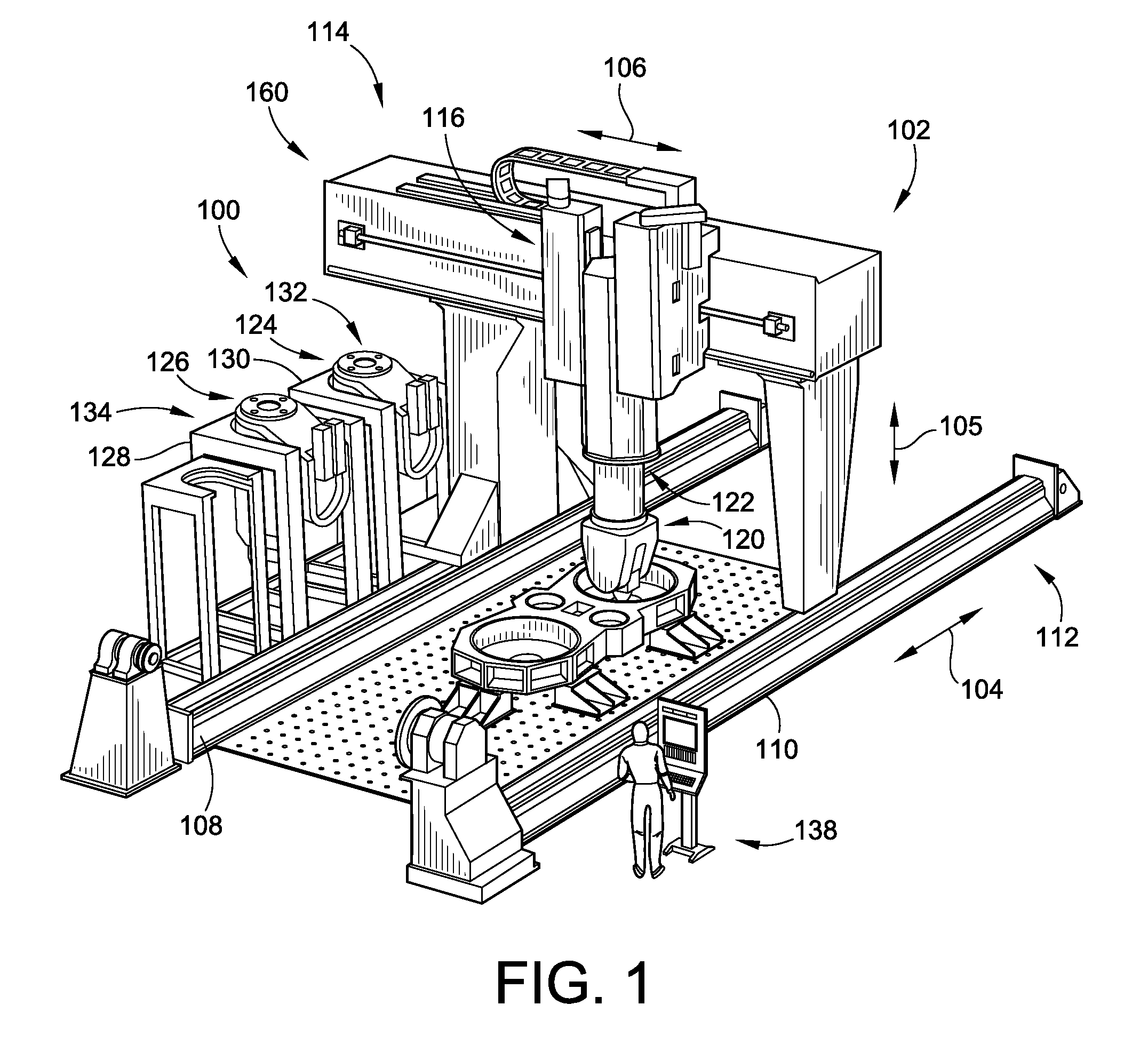
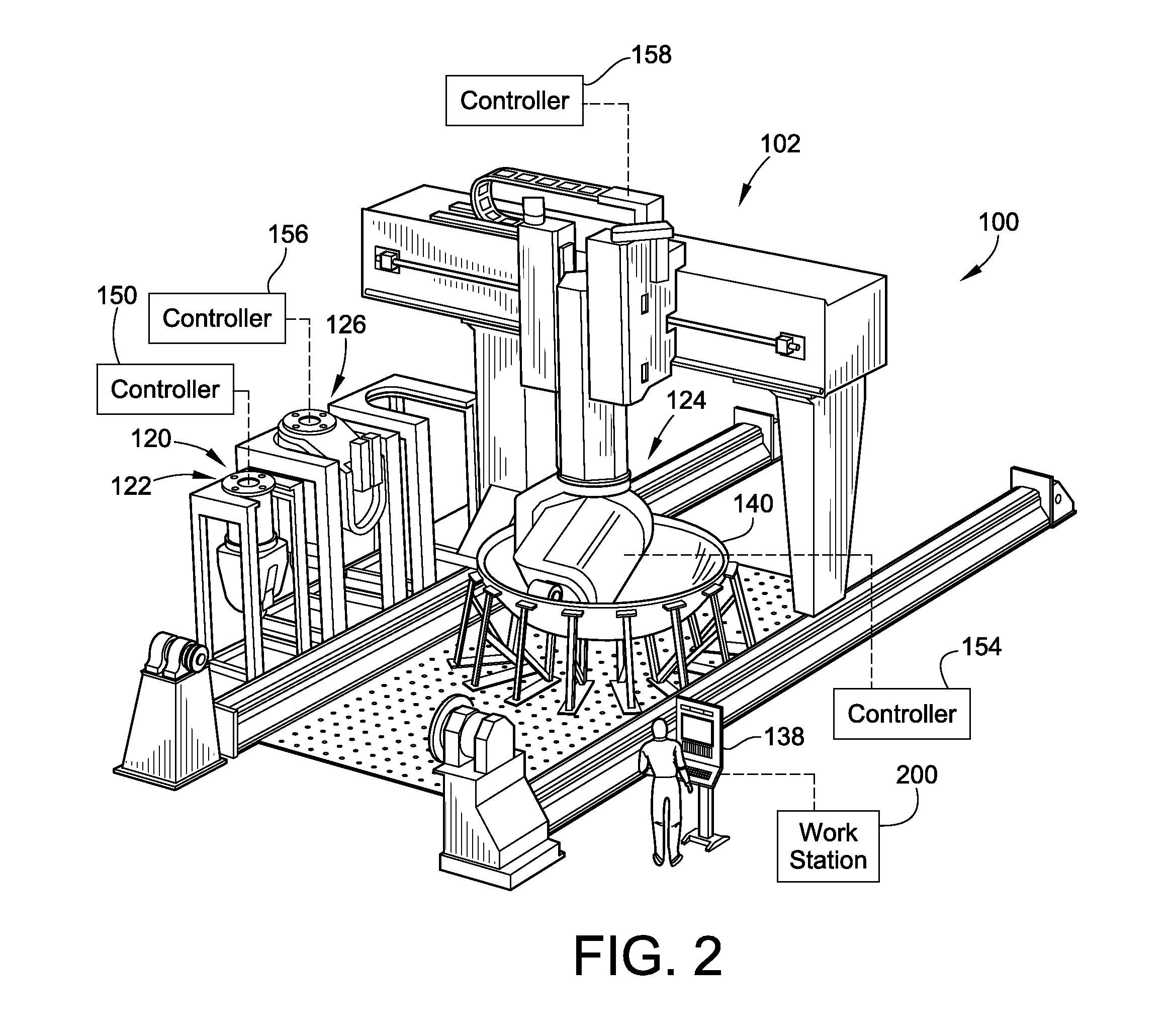
Manufacturing process and apparatus having an interchangeable machine tool head with integrated control
ActiveUS8954180B2Efficient transferAutomatic control devicesTool changing apparatusFiberDegrees of freedom
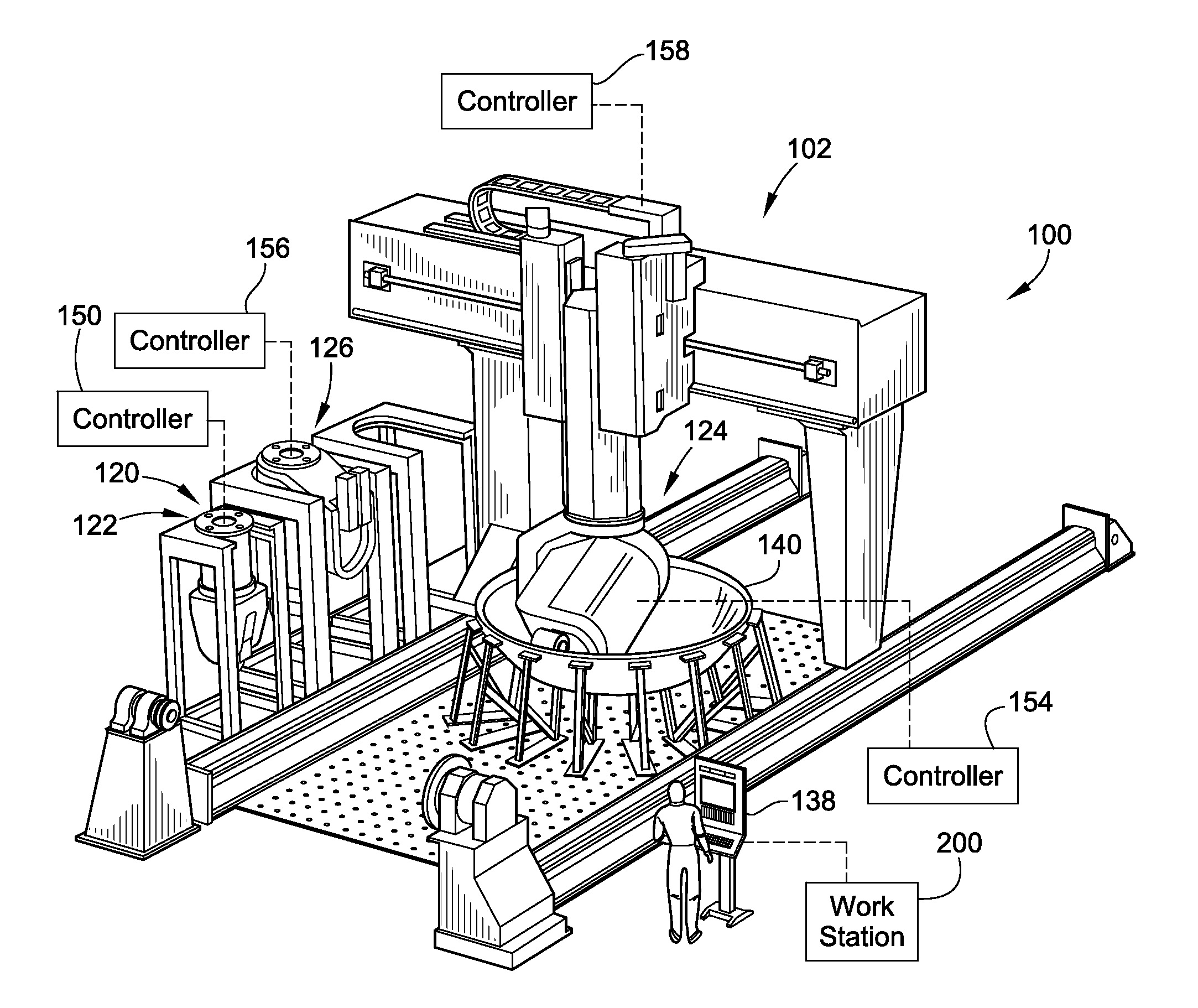
A modular manufacturing system and methods of using are provided. The modular manufacturing system includes a plurality of manufacturing heads that perform different manufacturing processes. These heads may include multi-axial machining heads, fiber placement heads including fiber tow and fiber tape lay-up heads. The heads are fixably attachable to a single positioning system that can manipulate the various heads along a plurality of different degrees of freedom relative to a tool or material blank.
Owner:INGERSOLL MACHINE TOOLS
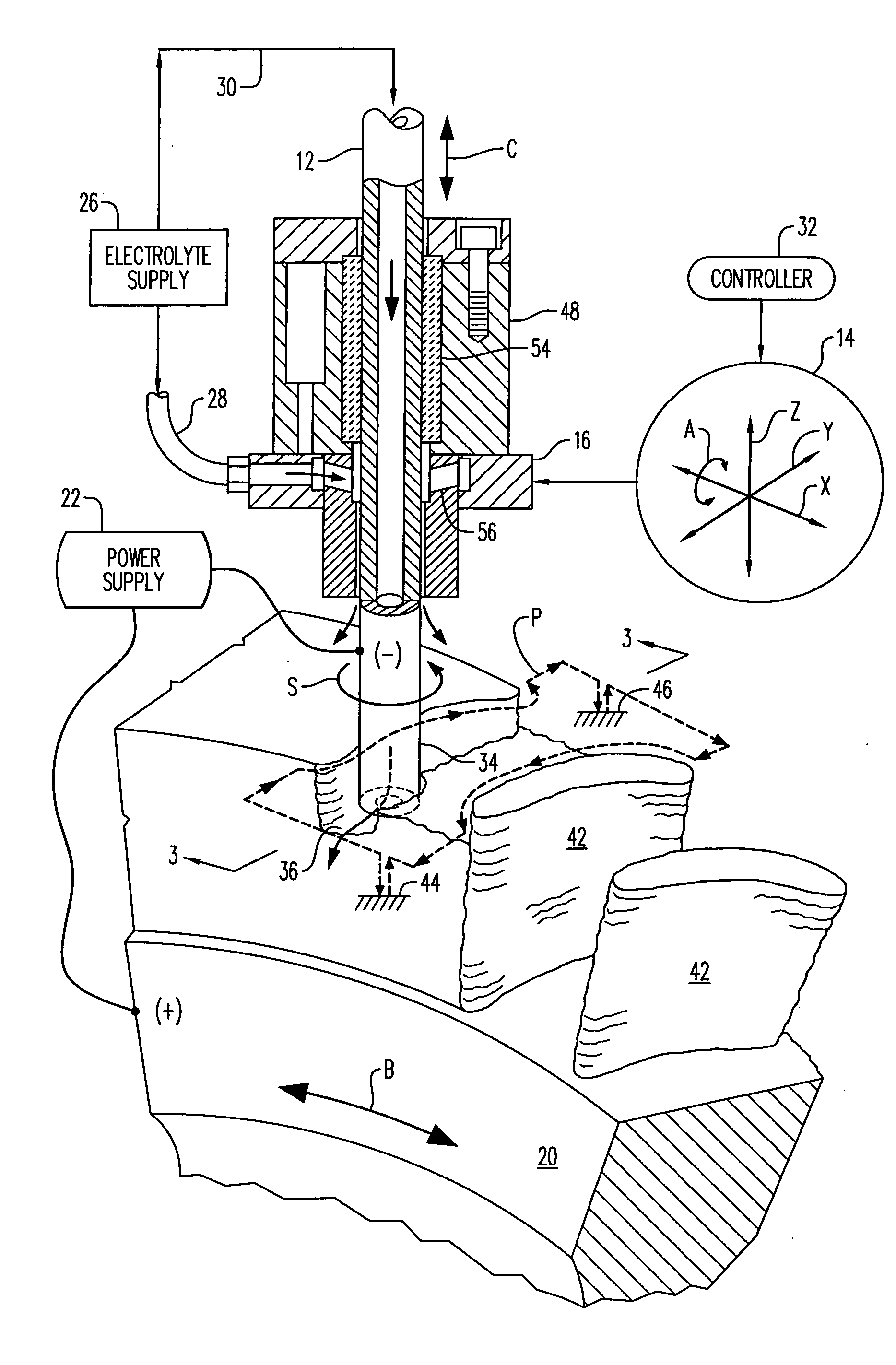
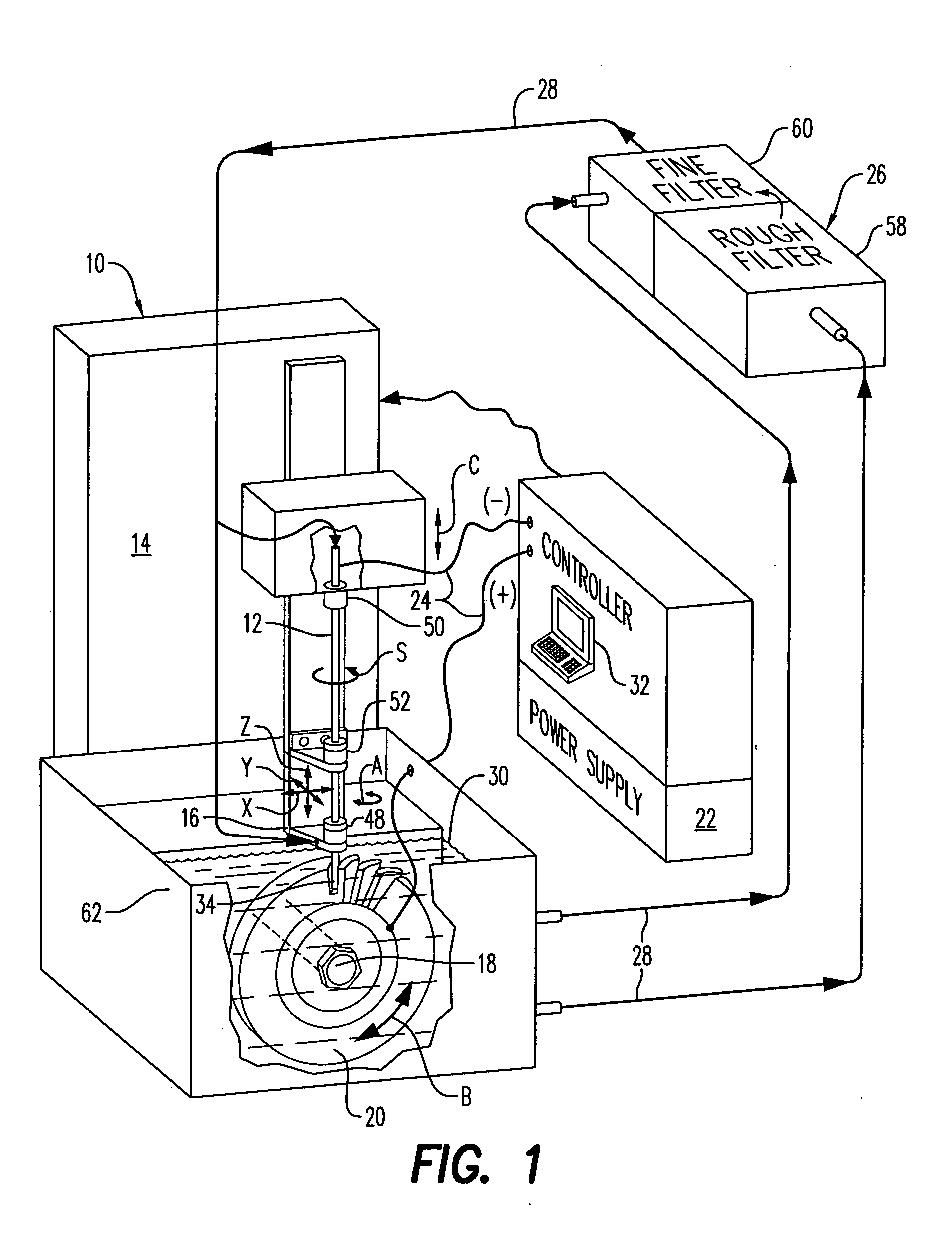
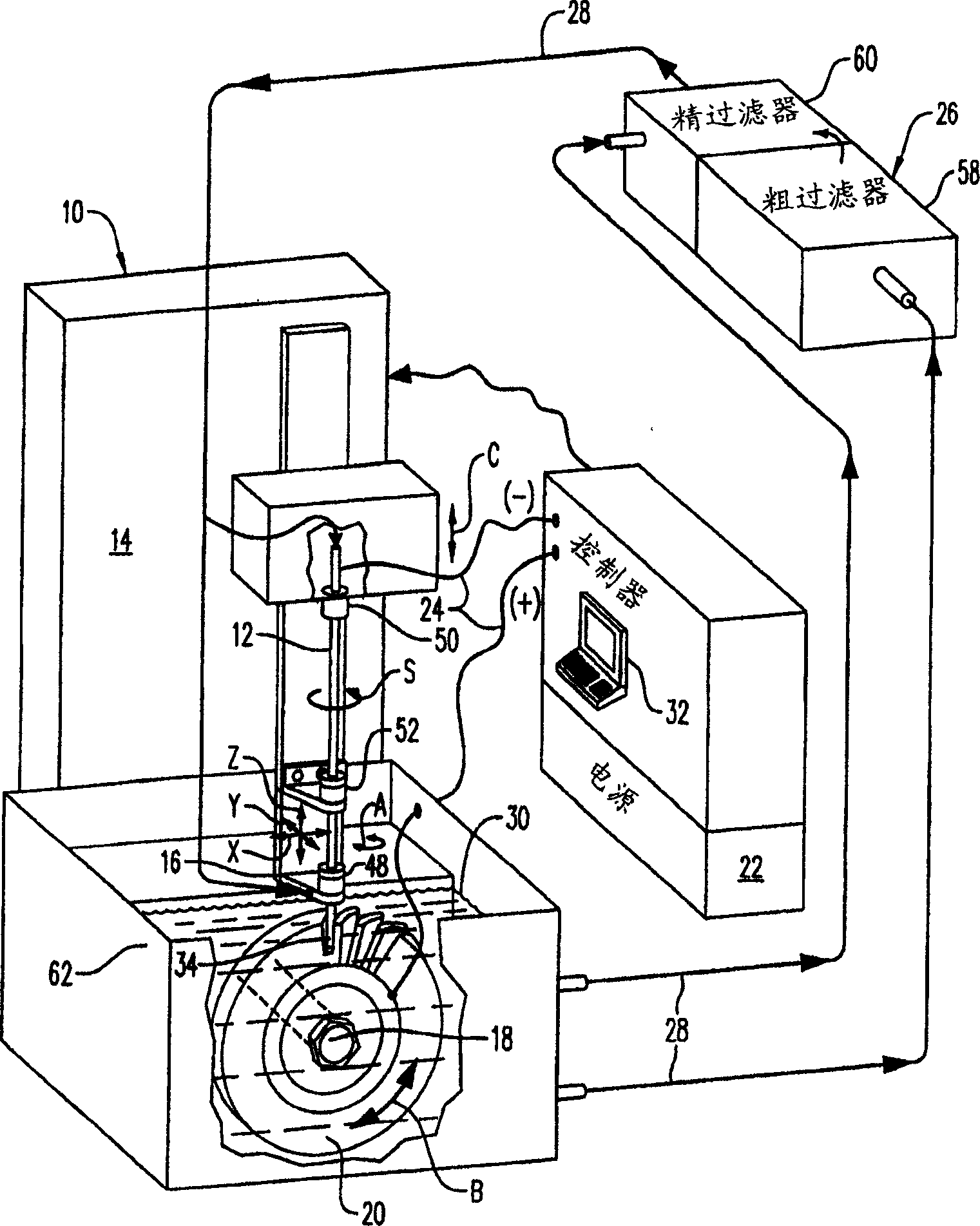
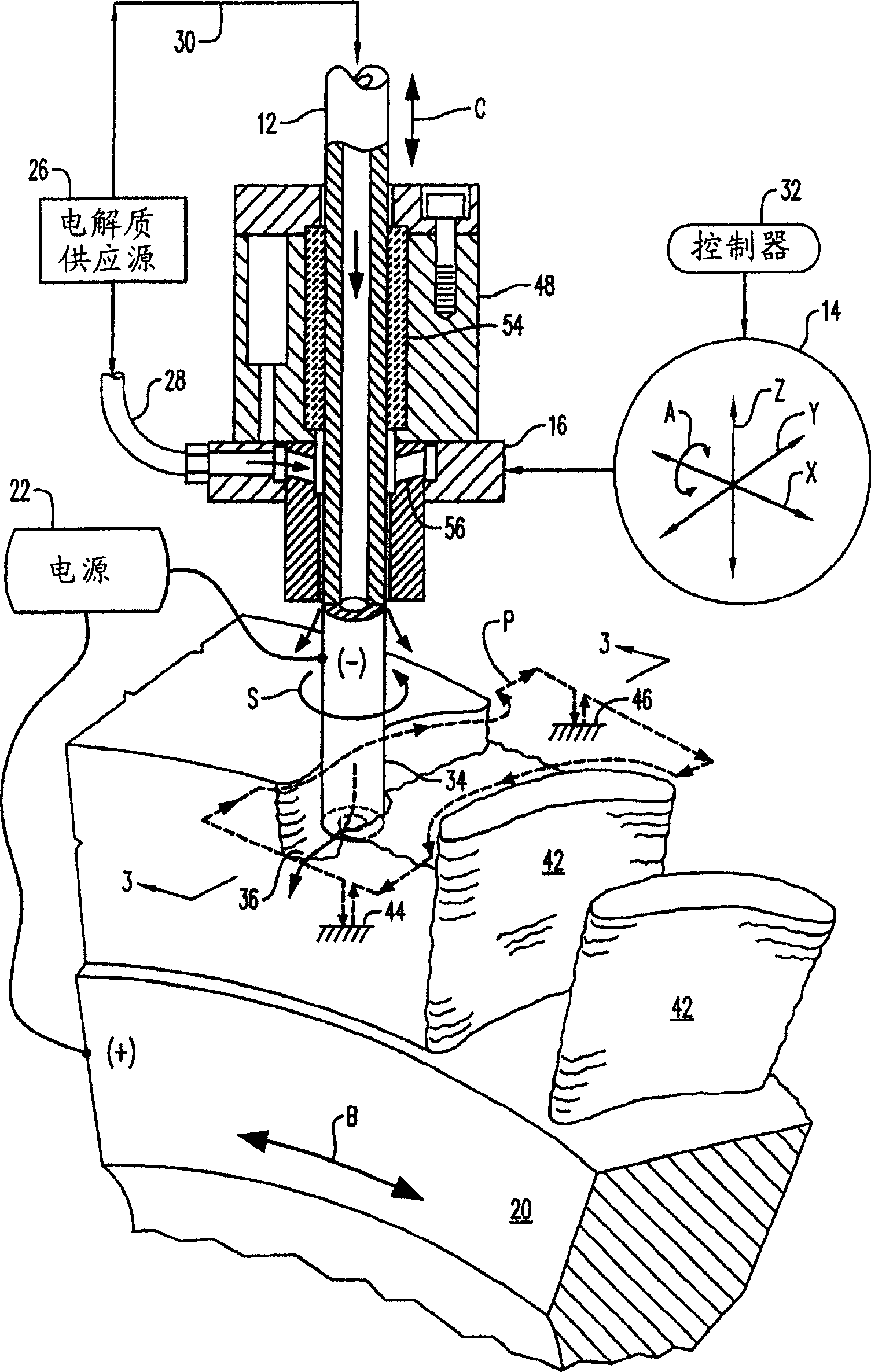
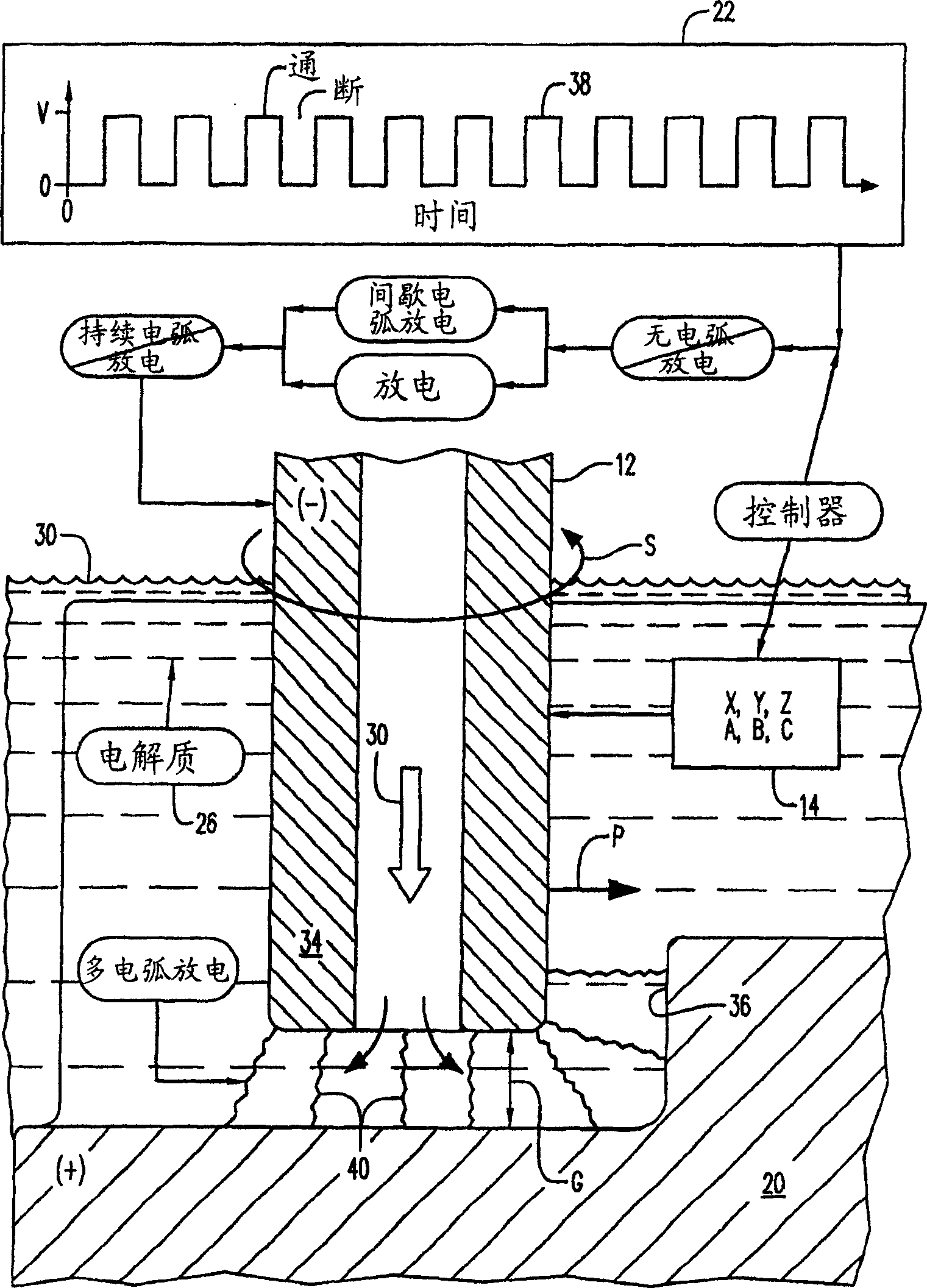
Distributed arc electroerosion
InactiveUS20050247569A1Easy to processMachining electrodesElectrolysis componentsElectricityEngineering
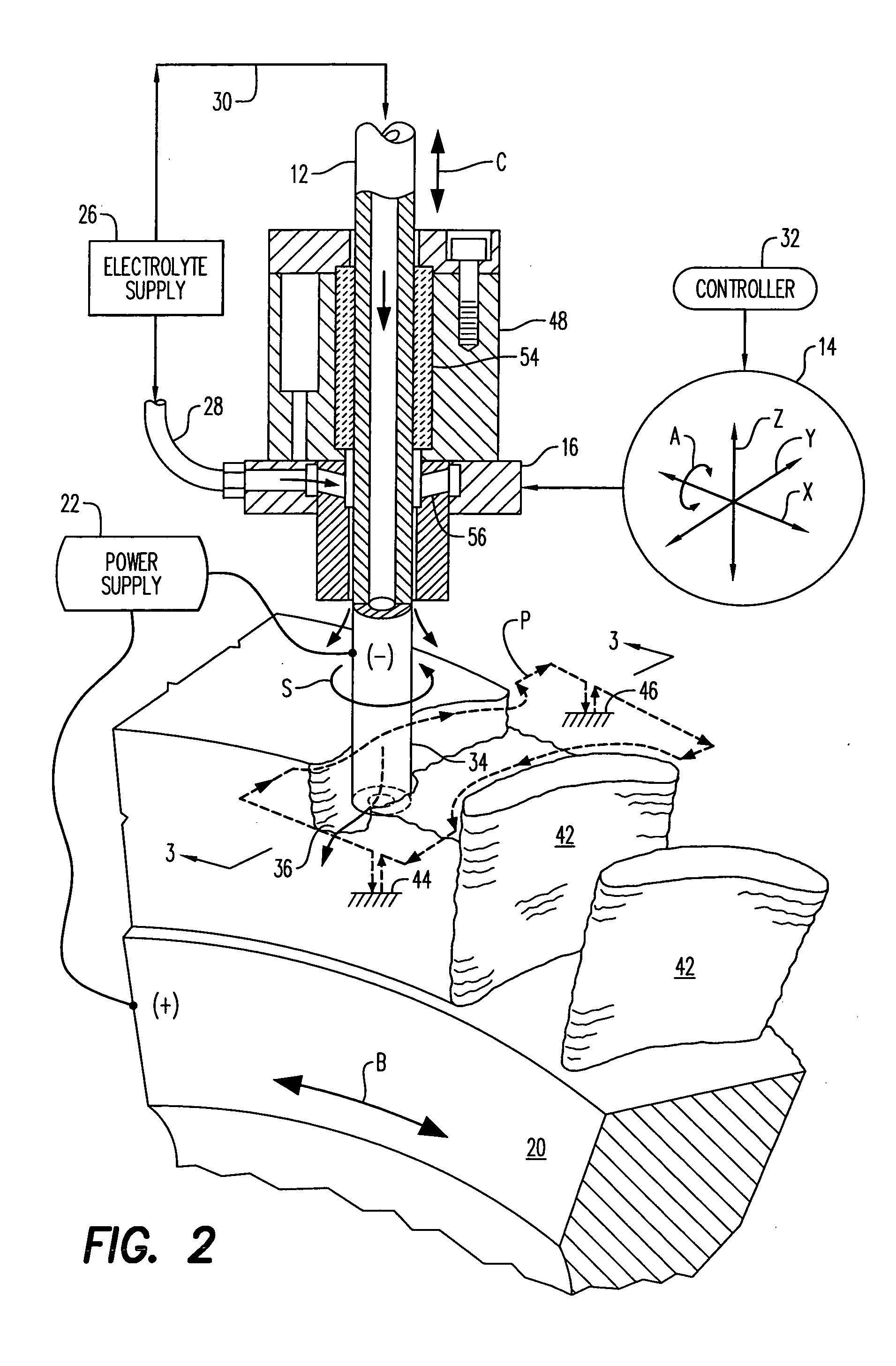
An electroerosion apparatus includes a tubular electrode supported in a tool head in a multiaxis machine. The machine is configured for spinning the electrode along multiple axes of movement relative to a workpiece supported on a spindle having an additional axis of movement. A power supply powers the electrode as a cathode and the workpiece as an anode. Electrolyte is circulated through the tubular electrode during operation. And, a controller is configured to operate the machine and power supply for distributing multiple electrical arcs between the electrode and workpiece for electroerosion thereof as the spinning electrode travels along its feedpath.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Flexible rail multiaxis machine tool and method
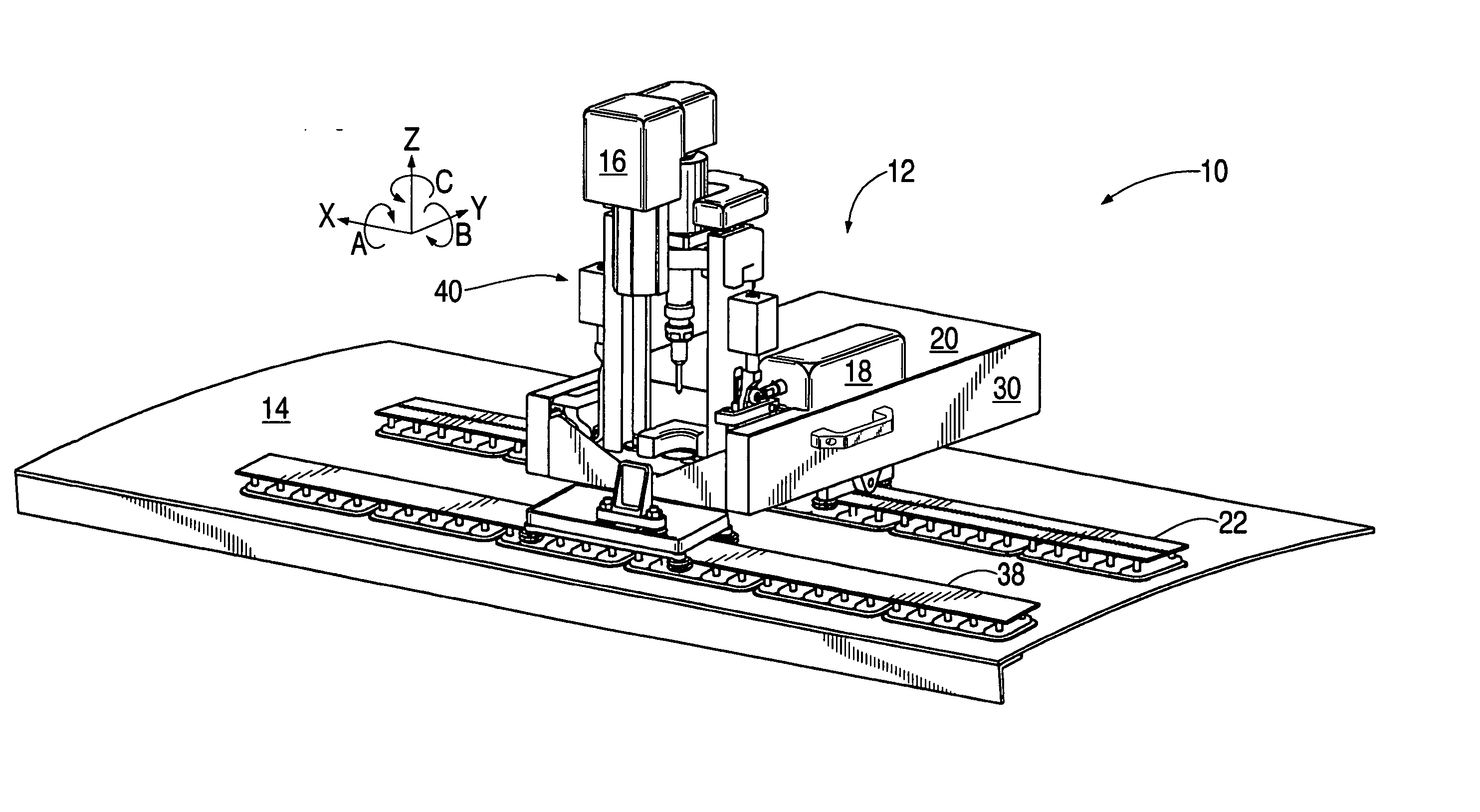
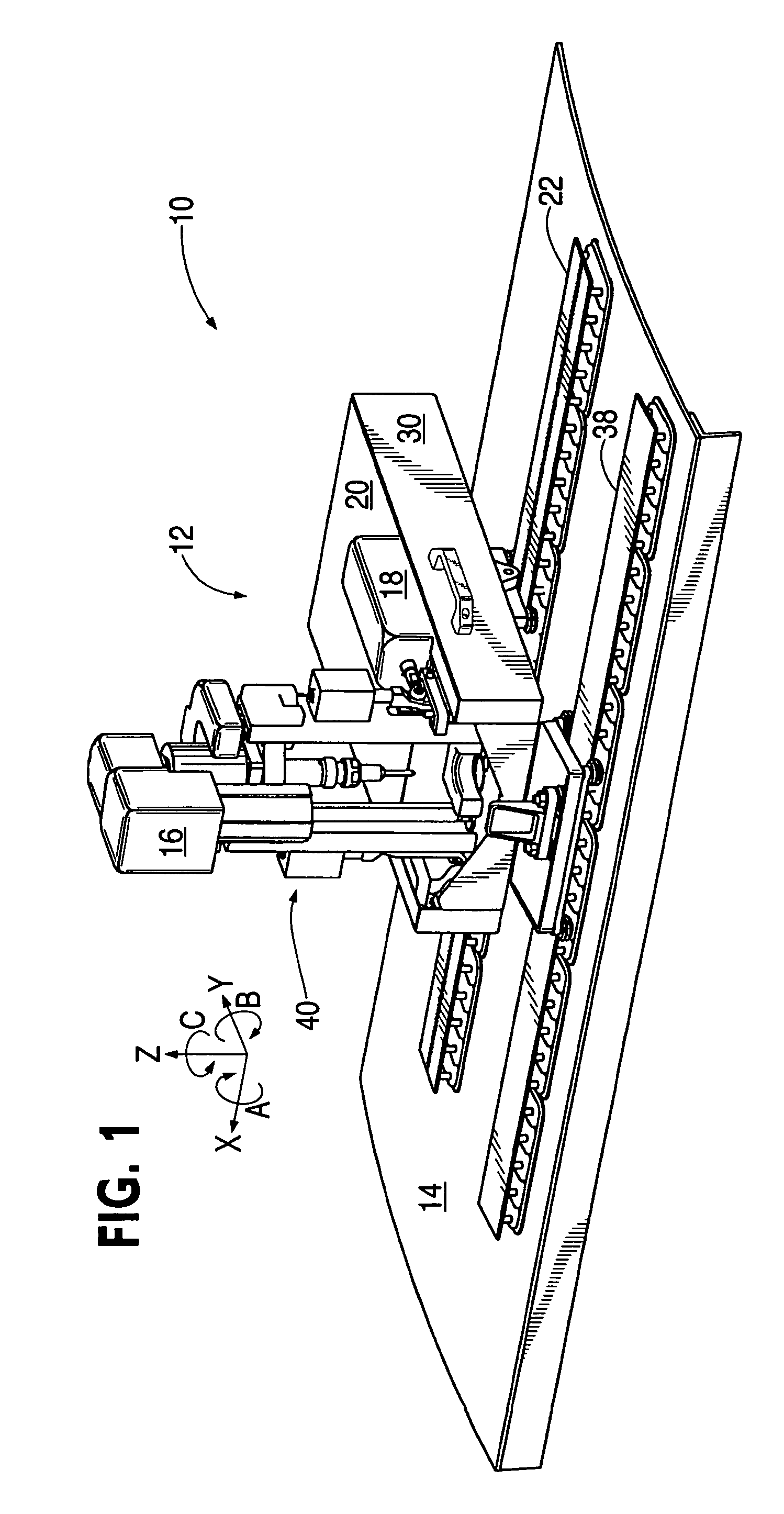
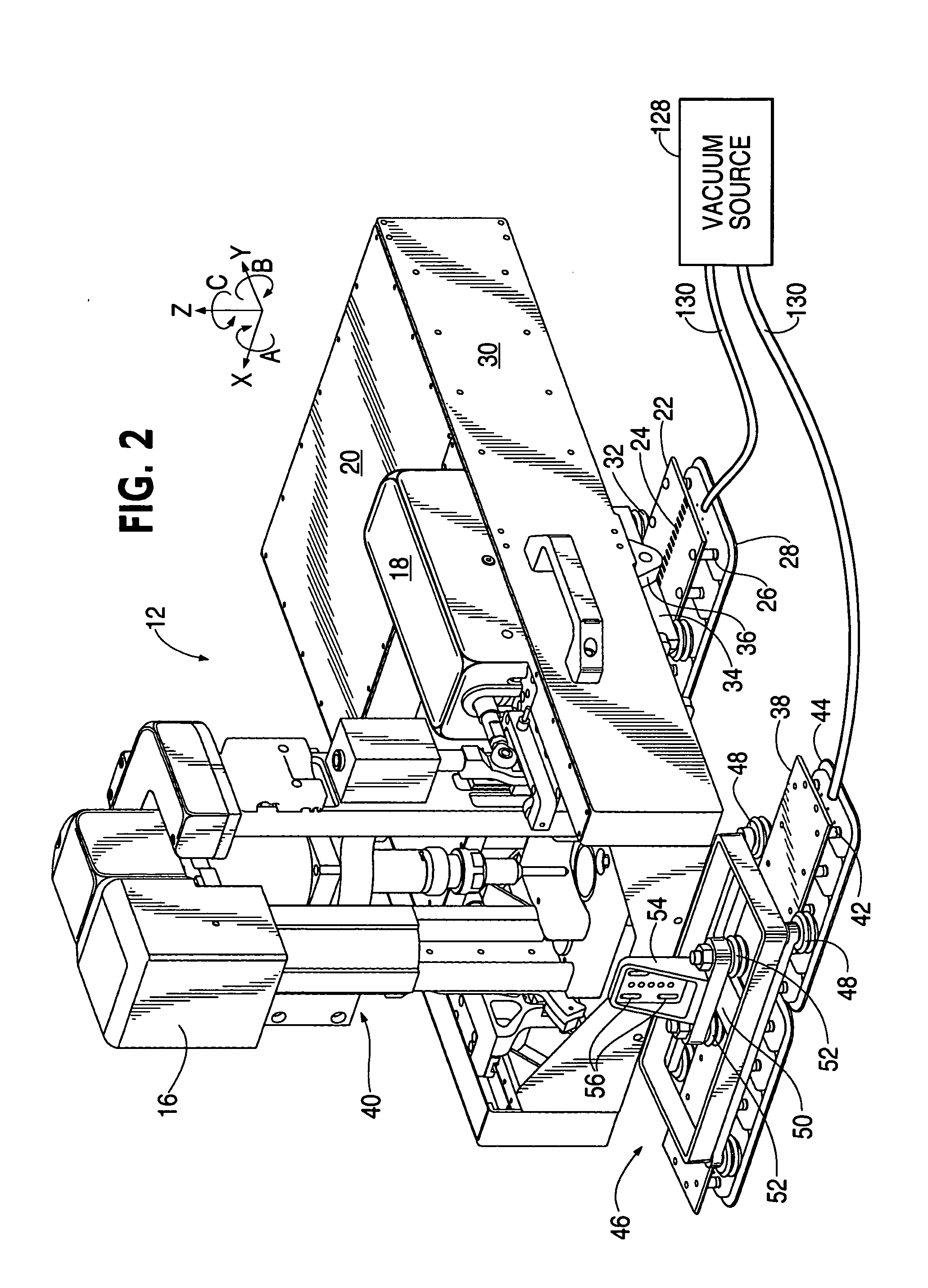
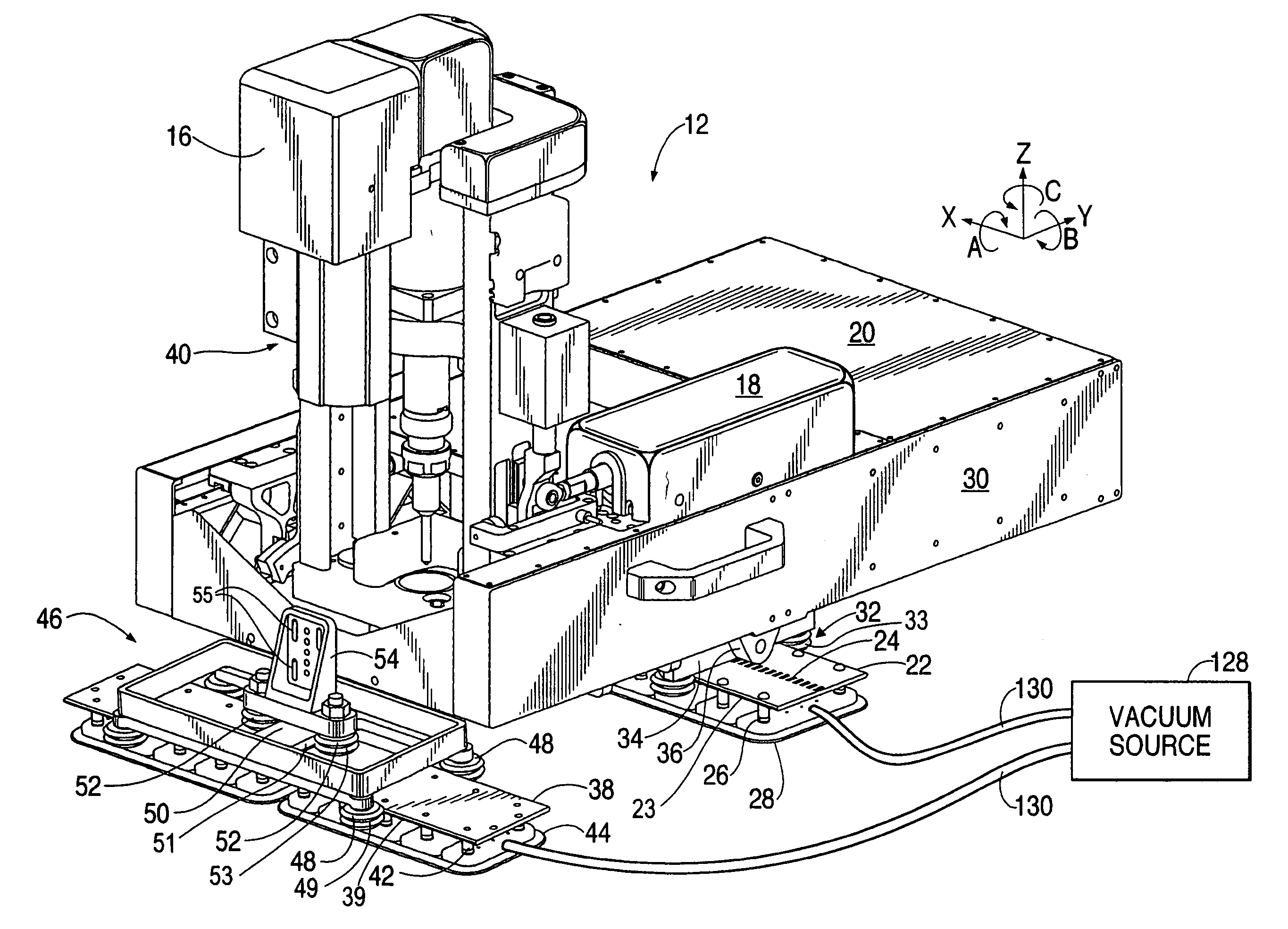
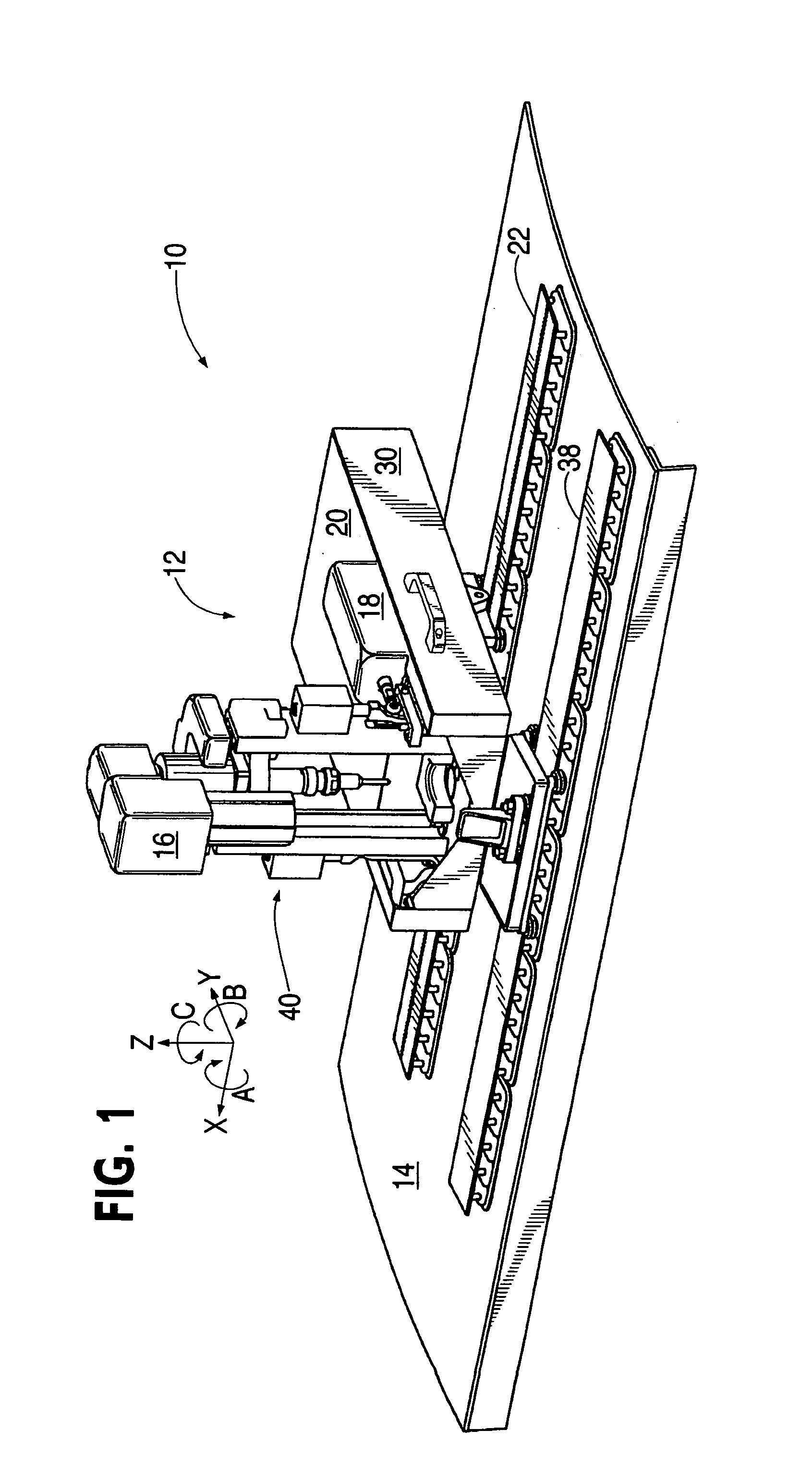
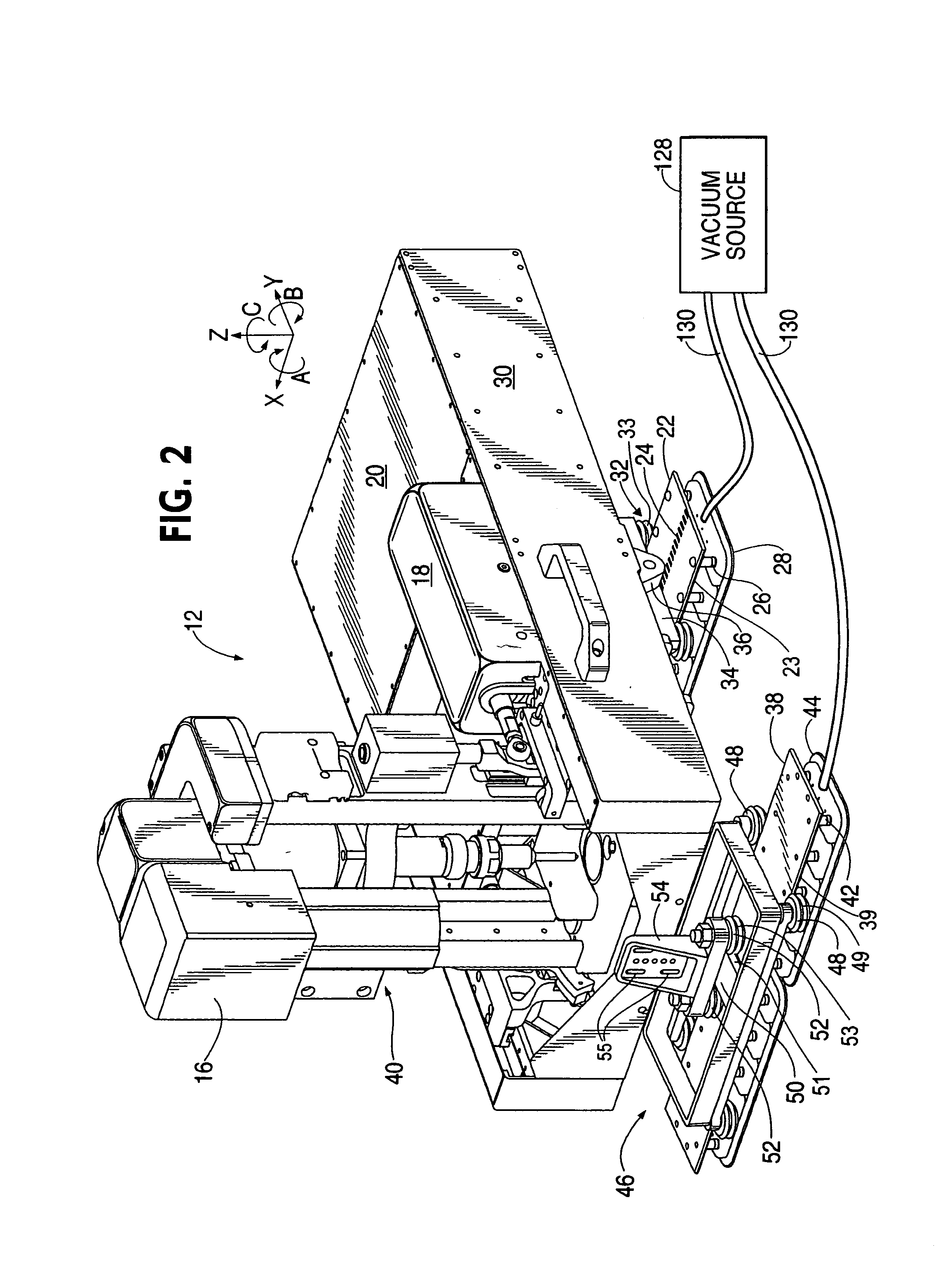
ActiveUS20050265798A1Readily demountedDrilling/boring measurement devicesThread cutting machinesOrbitMultiaxis machining
A flexible rail machine tool couples temporarily to a structure by vacuum cups and positions a tool head at any desired point over an area. The toolhead can perform operations such as drilling, bolt insertion, and acquisition of dimension data. The flexible rail can conform to surface curvature in one or more axes. Tool head perpendicularity to the structure can be sensed and adjusted as needed. The as-attached position of the rail may be compensated for through coordinate transformation, allowing holes, for example, to be placed with substantial precision.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Flexible rail multiaxis machine tool and method
ActiveUS7216408B2Readily demountedMilling machinesOther manufacturing equipments/toolsEngineeringMultiaxis machining
A flexible rail machine tool couples temporarily to a structure by vacuum cups and positions a tool head at any desired point over an area. The toolhead can perform operations such as drilling, bolt insertion, and acquisition of dimension data. The flexible rail can conform to surface curvature in one or more axes. Tool head perpendicularity to the structure can be sensed and adjusted as needed. The as-attached position of the rail may be compensated for through coordinate transformation, allowing holes, for example, to be placed with substantial precision.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Ball-end cutter multi-axis machining cutter axis vector optimization method
ActiveCN104102171AImprove processing efficiencyImprove processing qualityNumerical controlCutter locationStructural engineering
The invention discloses a ball-end cutter multi-axis machining cutter axis vector optimization method. The method includes the following steps that: at first, a relationship equation between cutter location optimization variables and cutter location data is constructed, and at the same time, a movement transformation equation between the cutter location data and machine tool rotation axis angles is constructed, and therefore a relationship equation between the cutter location optimization variables and the machine tool rotation axis angles can be derived; then, a cutter axis vector computational formula of ball-end cutter multi-axis machining complex curved surfaces can be obtained through solving the above equations; and finally, the ball-end cutter multi-axis machining cutter axis vector optimization method is rendered based on the above steps. With the ball-end cutter multi-axis machining cutter axis vector optimization method adopted, large fluctuation of machine tool rotation axes in a machining process can be avoided, and the movement of the machine tool axes is more stable and smooth, and therefore, machining quality and machining efficiency of the curved surfaces can be improved. The ball-end cutter multi-axis machining cutter axis vector optimization method has a certain practical application value.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Methods and Apparatus for Electroerosion
An electroerosion apparatus comprising: an electrode, a multiaxis machine, an electrolyte supply including a conduit for circulating an electrolyte, and a controller in operative communication with the multiaxis machine and configured for distributing intermittent multiple electrical arcs between the electrode and a workpiece. The multiaxis machine comprises a tool head configured to support and to spin the electrode, and a spindle configured to support a workpiece. The electrolyte comprises an anti-rusting agent, a defoaming agent, a lucent additive, a burst additive, a surface active medium, a lubricant, and water, and has a conductivity of about 0.1 milliSiemens to about 30 milliSiemens. In one embodiment, the method of electroerosion machining a workpiece comprises: creating relative motion between a spinning electrode and a workpiece; circulating an electrolyte around the spinning electrode, and distributing multiple electrical arcs between the electrode tip and the workpiece.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Distributed arc electroerosion
An electroerosion apparatus (10) includes a tubular electrode (12) supported in a tool head (16) in a multiaxis machine (14). The machine (14) is configured for spinning the electrode (12) along multiple axes of movement relative to a workpiece (20) supported on a spindle having an additional axis of movement. A power supply (22) powers the electrode (12) as a cathode and the workpiece (20) as an anode. Electrolyte (30) is circulated through the tubular electrode (12) during operation. And, a controller (32) is configured to operate the machine (14) and power supply (22) for distributing multiple electrical arcs between the electrode (12) and workpiece (20) for electroerosion thereof as the spinning electrode travels along its feedpath.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Impeller machining cutter-axis vector control method based on five-axis interference-free cutter axis control line
ActiveCN103433804AAvoid global interferenceQuality improvementAutomatic control devicesFeeding apparatusImpellerRotational axis
The invention discloses an impeller machining cutter-axis vector control method based on a five-axis interference-free cutter axis control line. The method is used for solving the technical problem that a machined impeller machined through an existing impeller machining cutter-axis vector control method is poor in quality. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the steps that a cutter axis selection border is generated, a curve projection surface where the cutter axis control line is located is determined, the offset surface of an impeller to be machined is expanded along the tangential direction of an air inlet edge and the tangential direction of an air exhaust edge, and an five-axis interference-free cutter axis control line is constructed to determine the cutter axis vector of any cutter location point. Because the angle between the cutter axis and the rotating shaft of the impeller is singly and evenly changed from the air inlet edge to the air exhaust edge, minimal swinging changes of the cutter axis surrounding the rotating shaft are achieved, minimal angle changes of the cutter axis surrounding the rotating shaft of the impeller are achieved, and two rotating shafts of a machine tool evenly and slowly rotate in the five-axis machining process; the whole blade-type surface multi-axis machining can be achieved through the cutter axis control line, the interference-free cutter axis vector determination of the whole impeller curved blade surface is achieved, and the method is simple; meanwhile, overall interference of the cutter axis is avoided, and the quality of the machined impeller is improved.
Owner:西安三航动力科技有限公司
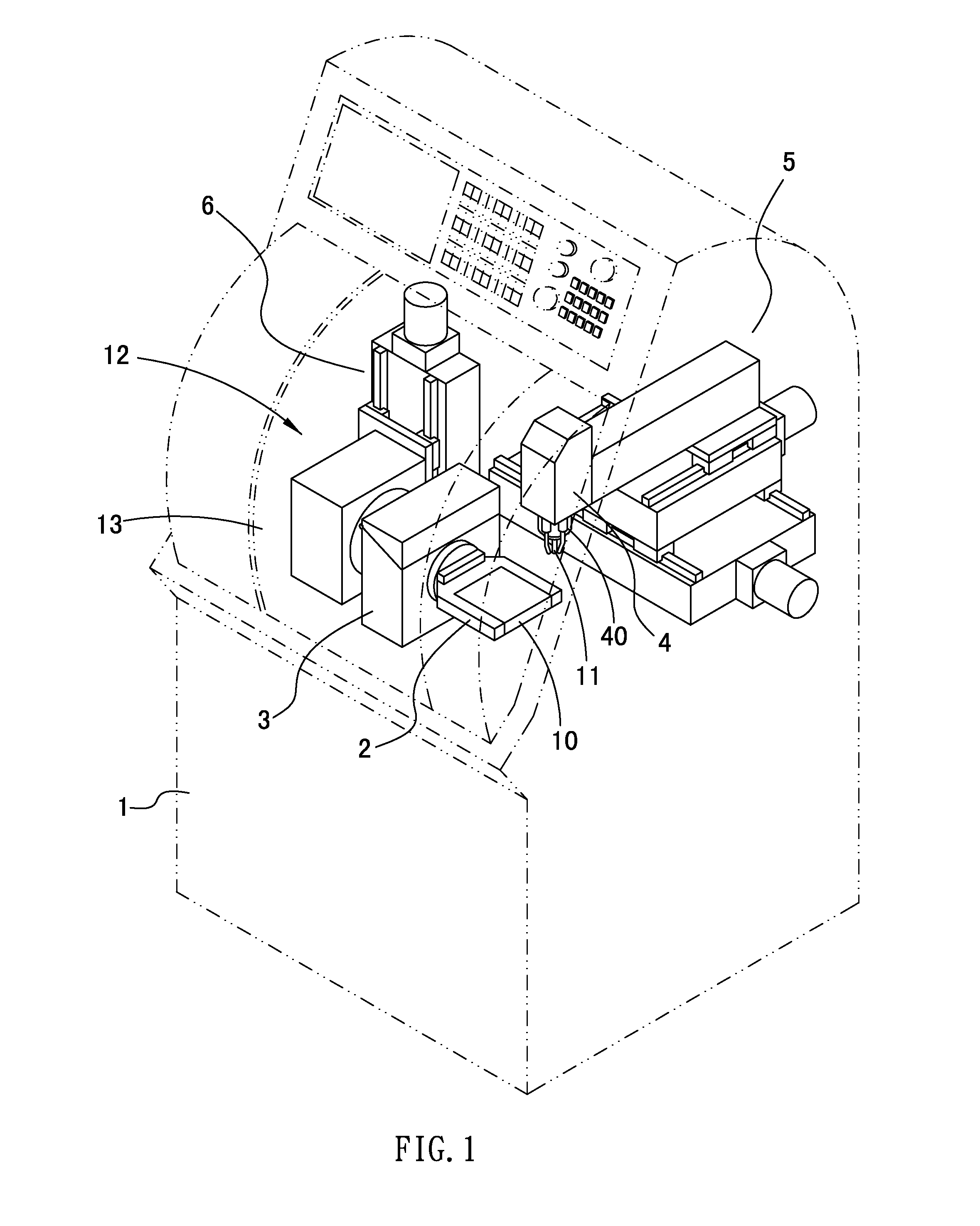
Multi-spindle machining machine with tool changing mechanism
InactiveUS20110083307A1Low production costReduce sizing costsDrilling machinesTransportation and packagingRotational axisEngineering
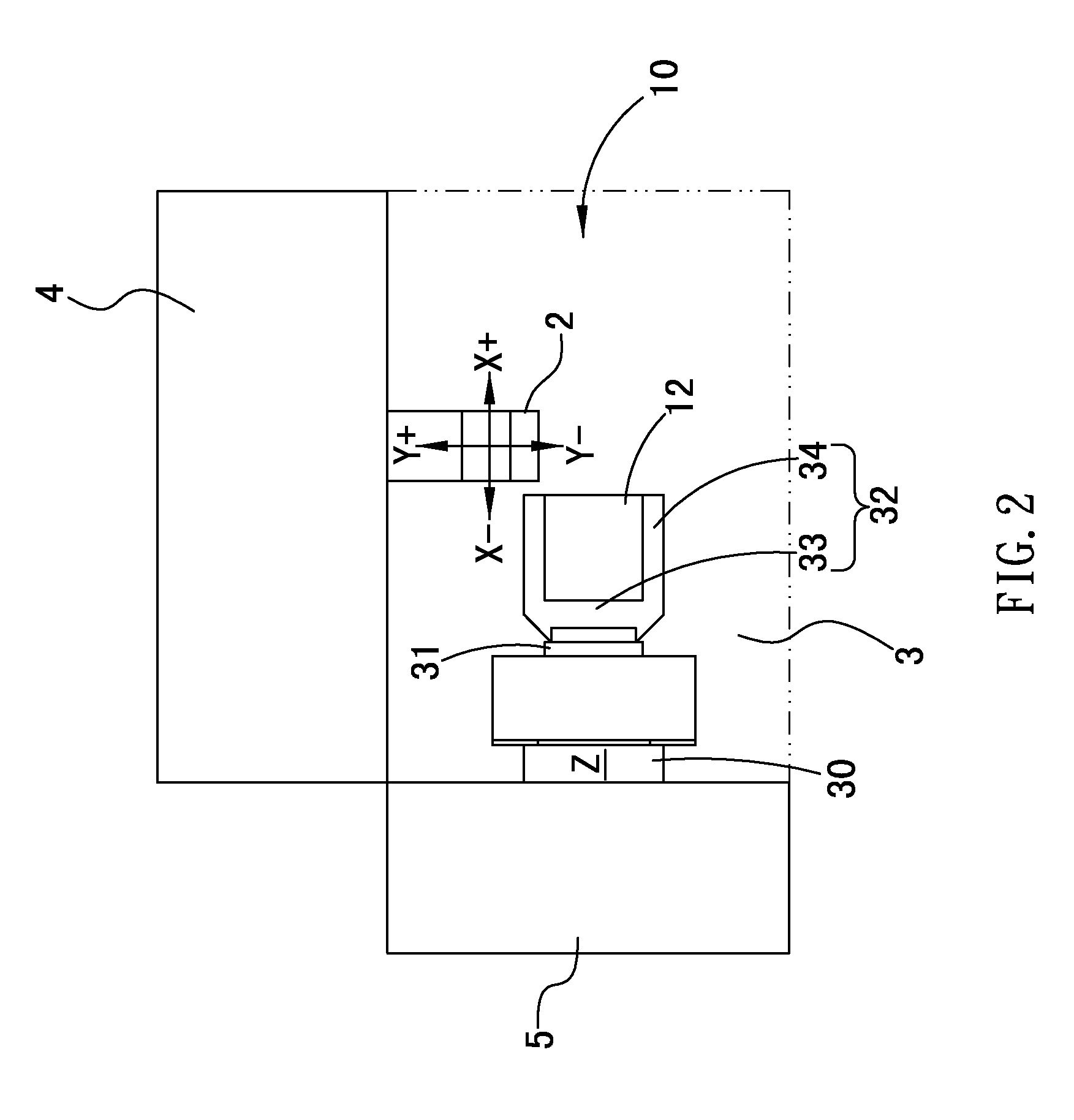
A multi-spindle machining machine with a tool changing mechanism comprising a base; a carrier including a seat to move in Z axis, a rotary shaft fixed on the seat laterally to drive the seat to rotate in A axis, and a fixing holder coupled to an end portion of the rotary shaft to fix a workpiece; a tool changing mechanism including a mount mounted to the rotary shaft to rotate with the rotary shaft and a monitor fixed on the seat to measure a length of the tool clamped on the driving spindle, and including a plurality of slots to receive the tools respectively; a working head moving above the carrier and the tool changing mechanism in X and Y axes and including a driving spindle mounted on a lower end thereof to rotate axially, and the lower end of the driving spindle allowing to engage and disengage the tool.
Owner:SHENQ FANG YUAN TECH
Manufacturing process and apparatus having an interchangeable machine tool head with integrated control
ActiveUS20120035754A1Efficient transferAutomatic control devicesTool changing apparatusFiberDegrees of freedom
A modular manufacturing system and methods of using are provided. The modular manufacturing system includes a plurality of manufacturing heads that perform different manufacturing processes. These heads may include multi-axial machining heads, fiber placement heads including fiber tow and fiber tape lay-up heads. The heads are fixably attachable to a single positioning system that can manipulate the various heads along a plurality of different degrees of freedom relative to a tool or material blank.
Owner:INGERSOLL MACHINE TOOLS
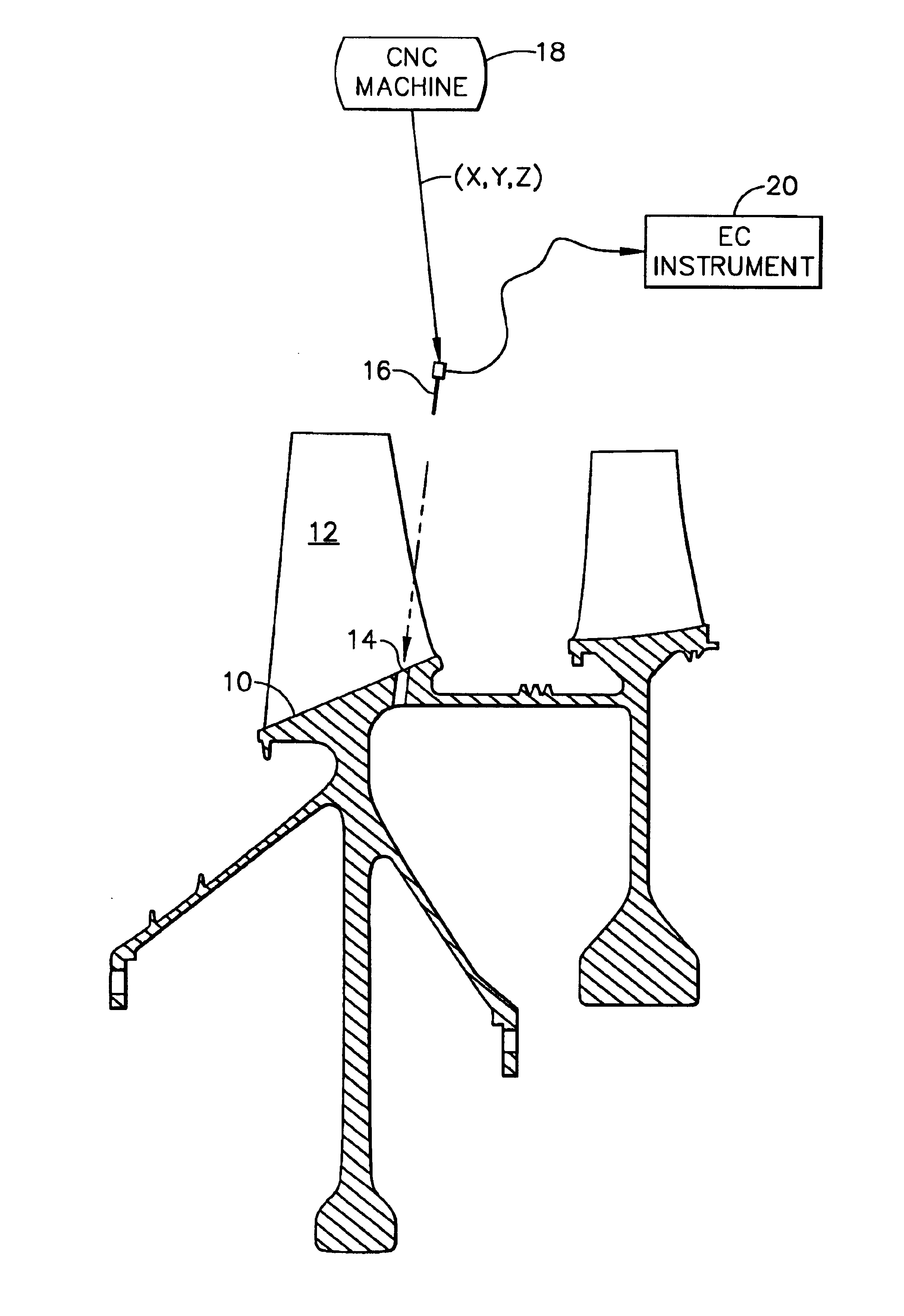
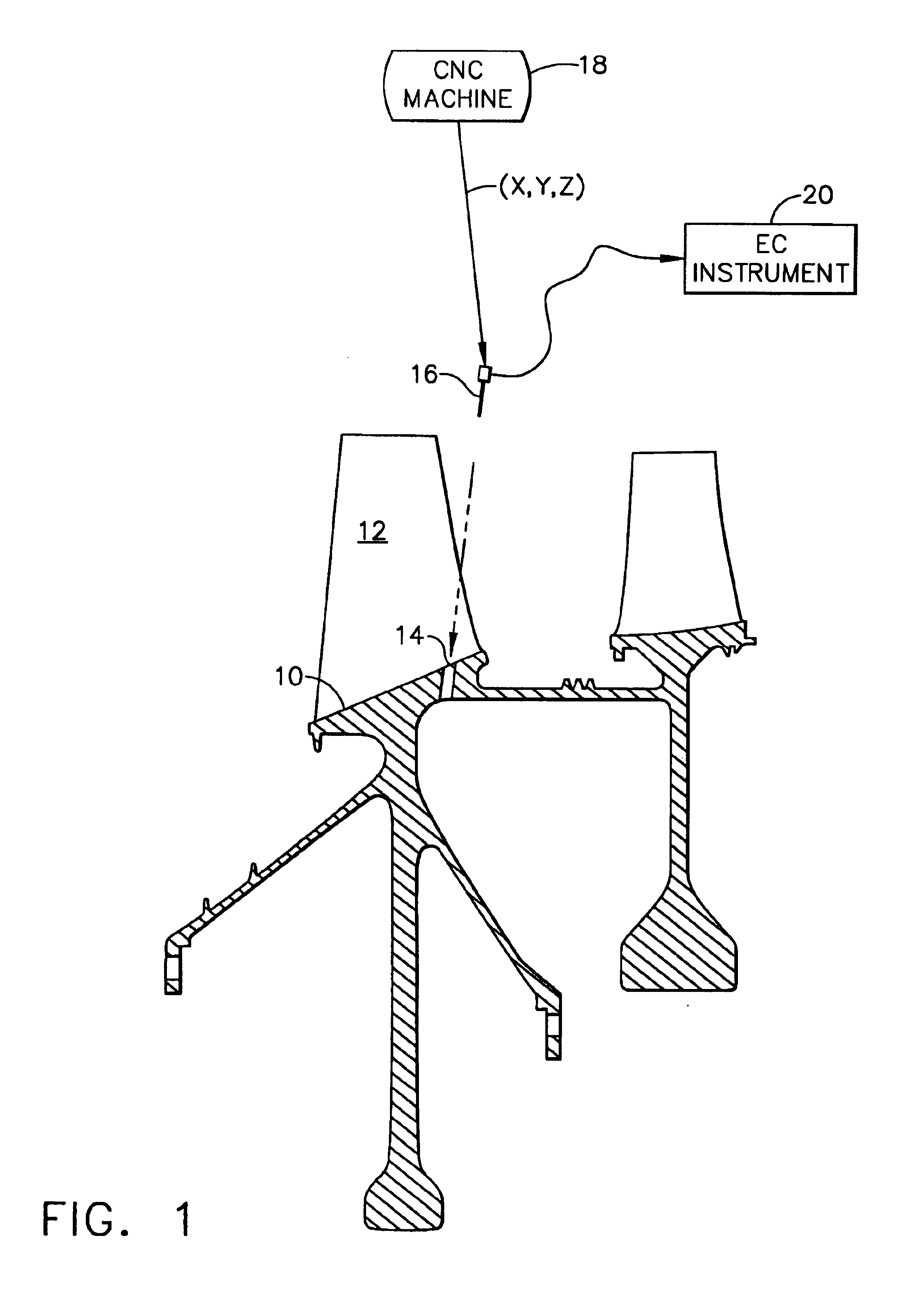
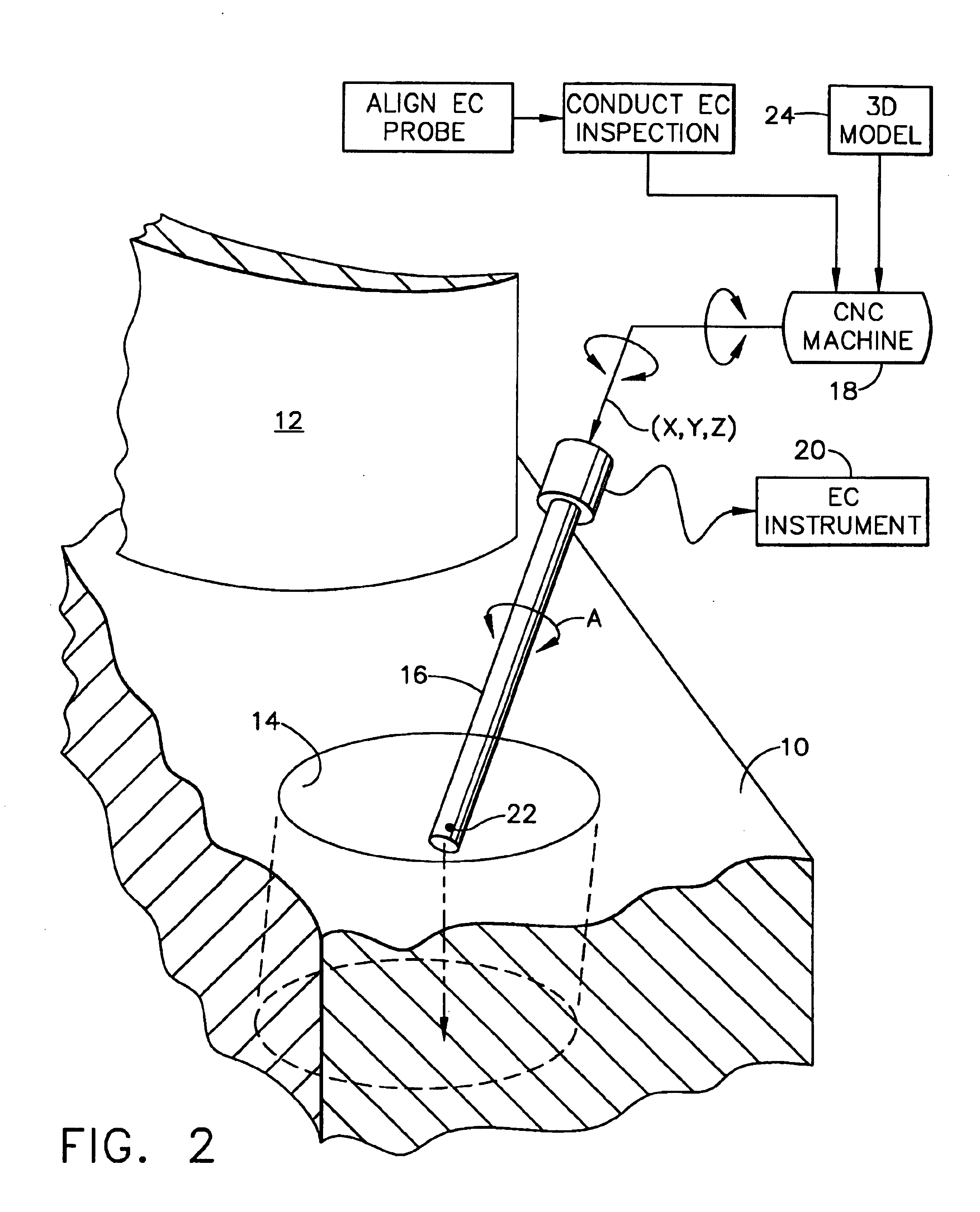
Eddy current inspection method
ActiveUS6907358B2Simple methodEliminate needCharacter and pattern recognitionElectric/magnetic contours/curvatures measurementsEddy currentNumerical models
A specimen is mounted in a multiaxis machine. An eddy current probe is also mounted in the machine for multiaxis movement relative to the specimen. The probe is aligned in situ with a target in the specimen by direct contact therebetween at multiple alignment sites corresponding with a numerical model of the specimen. Eddy current inspection of the target may then be conducted by moving the probe along multiple inspection sites of the target corresponding with the specimen model.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
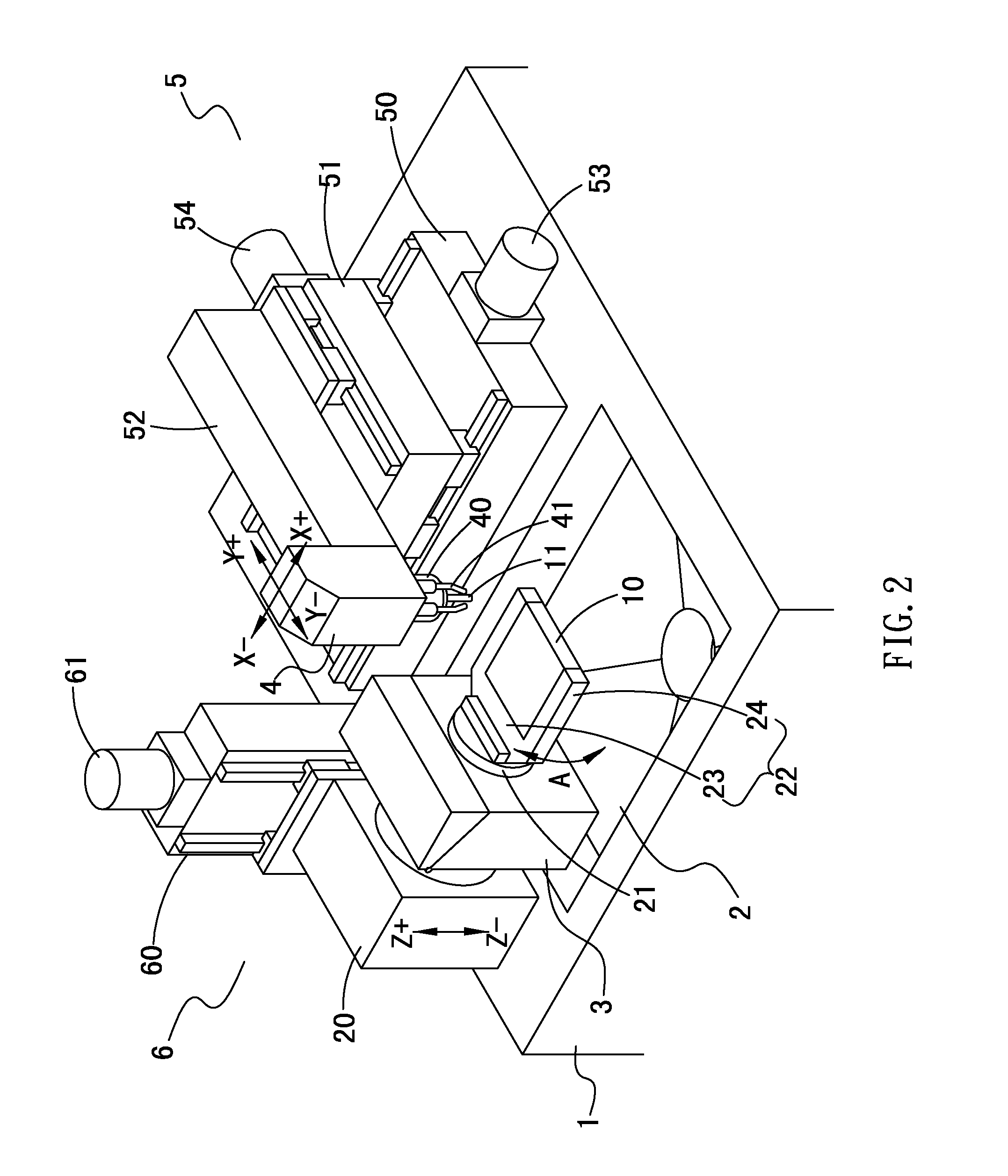
Multi-spindle machining machine
InactiveUS20110085863A1Low production costReduce sizing costsThread cutting machinesAttachable milling devicesRotational axisEngineering
A multi-spindle machining machine comprises a base including a working room to move a tool and a workpiece; a working head including a driving spindle disposed on a lower end thereof to clamp the tool; a carrier including a seat fixed on one side of the working room, a rotary shaft mounted on the seat laterally to drive the seat to rotate in an axial direction, a fixing holder connected to the rotary shaft to fix the workpiece to the fixing holder; a lateral driving device disposed on the base and located on one side of the working room in a horizontal direction to drive the working head to move in X and Y axes; a vertical driving device disposed on the base and located on another side of the working room in a lateral direction to drive the seat to move in Z axis direction.
Owner:SHENQ FANG YUAN TECH
Multi-axis machining center structure
ActiveCN103213034AImprove rigidityQuick placementTool changing apparatusMilling machinesEngineeringMulti axis
The invention relates to a vertical multi-axis machining center structure machine tool, which comprises an integrated machine tool body, two cross beams, a saddle, a multi-axis spindle box, a first transmission mechanism, a second transmission mechanism and a third transmission mechanism, wherein the integrated machine tool body comprises a base and two side walls, and a detachable fixed worktable is arranged on the base; the two cross beams are respectively arranged on the two side walls, and the saddle is fixedly arranged at the inner side of one cross beam; the first transmission mechanism drives the multi-axis spindle box to move along aY-axis direction, and the second transmission mechanism drives the multi-axis spindle box to move along an X-axis direction; and the third transmission mechanism drives the multi-axis spindle box to move along the Z-axis direction. The vertical multi-axis machining center structure machine tool not only adapts to machining a plurality of types of parts, but realizes simultaneously machining a plurality of parts, so the machining efficiency is greatly improved, and the machining time is shortened; and each cross beam adopts a gantry structure on the vertical multi-axis machining center structure, and the transmission mechanisms control the multi-axis spindle box to move back and forth, left and right and up and down.
Owner:河北力准机械制造有限公司
Tool deflection modeling method for multi-axis machining system
ActiveCN104182631AVariation law of accurate deviationThe compliance model is accurateProgramme controlComputer controlDrive shaftEngineering
The invention discloses a tool deflection modeling method for a multi-axis machining system. The tool deflection modeling method includes establishing a new non-deformable cutting thickness model, and a cutting force prediction model of arc-tool variable-posture milling by the vector method; establishing a flexibility model of a machine transmission shaft by the equivalent column method and a comprehensive flexibility model of the machining system by force ellipsoid method and coordinate system transformation; finally utilizing the cutting force model in the process of variable-posture machining and the flexibility model at the tail end of the multi-axis machining system to obtain a tool deflection model. In the tool deflection modeling method, the non-deformable cutting thickness model of a new tool cutting blade and the comprehensive flexibility model of the multi-axis machining system are used to obtain a more accurate tool deflection change law during machining, so that the tool postures during multi-axis machining and machining parameters such as feed speed and spindle revolving speed are optimized, tool deflection is controlled, and quality of machined surfaces of workpiece is improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Numerical Control Device For Multi-axis Processing Machine Used For Processing Inclined Plane
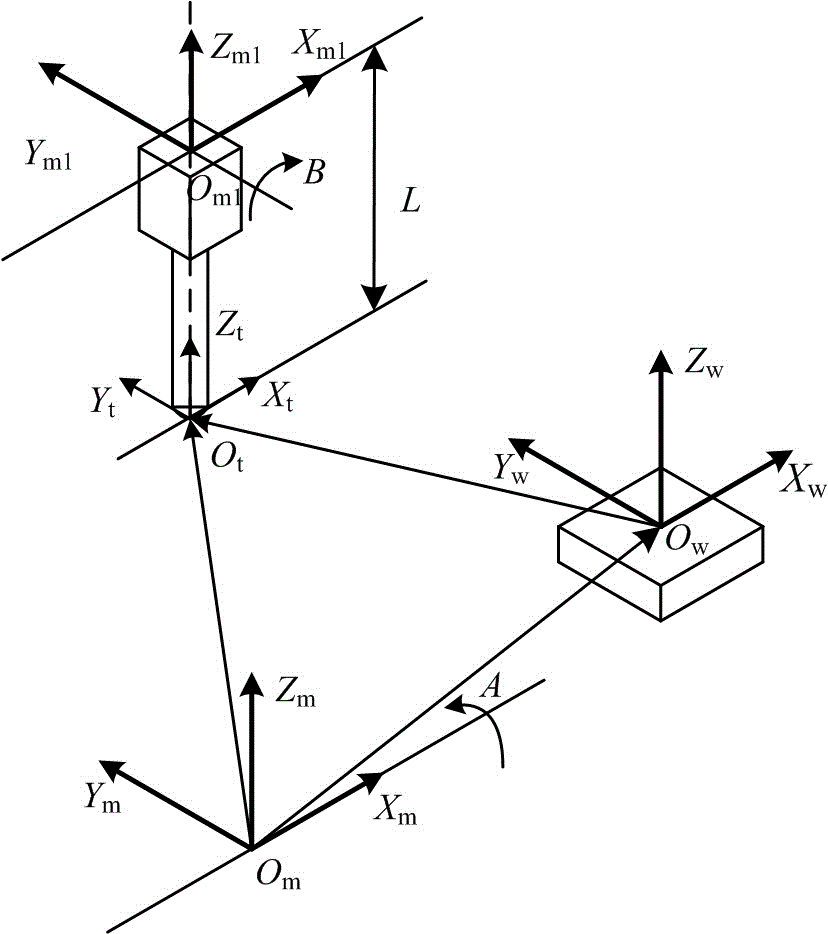
The invention provides a numerical control device for a multi-axis processing machine used for a processing inclined plane. Inclined planes of a work piece are processed through controlling three linear axles relatively to a position of the work piece installed on the working table and controlling three rotary axles relative to a direction of the work piece. A three rotary axle operation part composed of an analyzing unit calculates positions of the three rotary axles to make a coordinate system (a knife coordinate system) on a knife and moving along with the movement of the knife to be parallel with a characteristic coordinate system indicating a coordinate system of the inclined plane on the work piece. The three rotary axle are driven to calculated positions.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Tool path generating method for multi-axis machining complex curved surface of constraint circular tool based on motion of machine tool
ActiveCN104678888AImprove processing efficiencyImprove processing qualityTotal factory controlNumerical controlNumerical controlTransformation equation
The invention discloses a tool path generating method for a multi-axis machining complex curved surface of a constraint circular tool based on the motion of a machine tool. The method explains by taking head and table five-axes numeric control machine tools as an example and comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a relation equation between a tool position design variable and tool position data as well as a motion transformation equation between the tool position data and a rotating shaft of the machine tool, and further deducing a relation equation between the tool position design variable and the rotating shaft of the machine tool; secondly, analyzing and discussing the equations, and deducing a formula of solving another two variables by using any two variables in a known equation set, thereby obtaining a tooth position calculation formula for the multi-axis machining complex curved surface of the constraint circular tool; on the basis, giving out the basic principle and the calculation flow of a tooth path generation algorithm for the multi-axis machining complex curved surface of the constraint circular tool. The test result shows that by using the algorithm, great change of the rotating shaft of the machine tool can be avoided, the feed speed of a motion shaft of the machine tool is improved, and higher processing quality of the curved surface can be obtained; the algorithm has certain actual application value.
Owner:CHANGHE AIRCRAFT INDUSTRIES CORPORATION
Numerical value control device controlling multi-shaft processor located on a cutter front point position
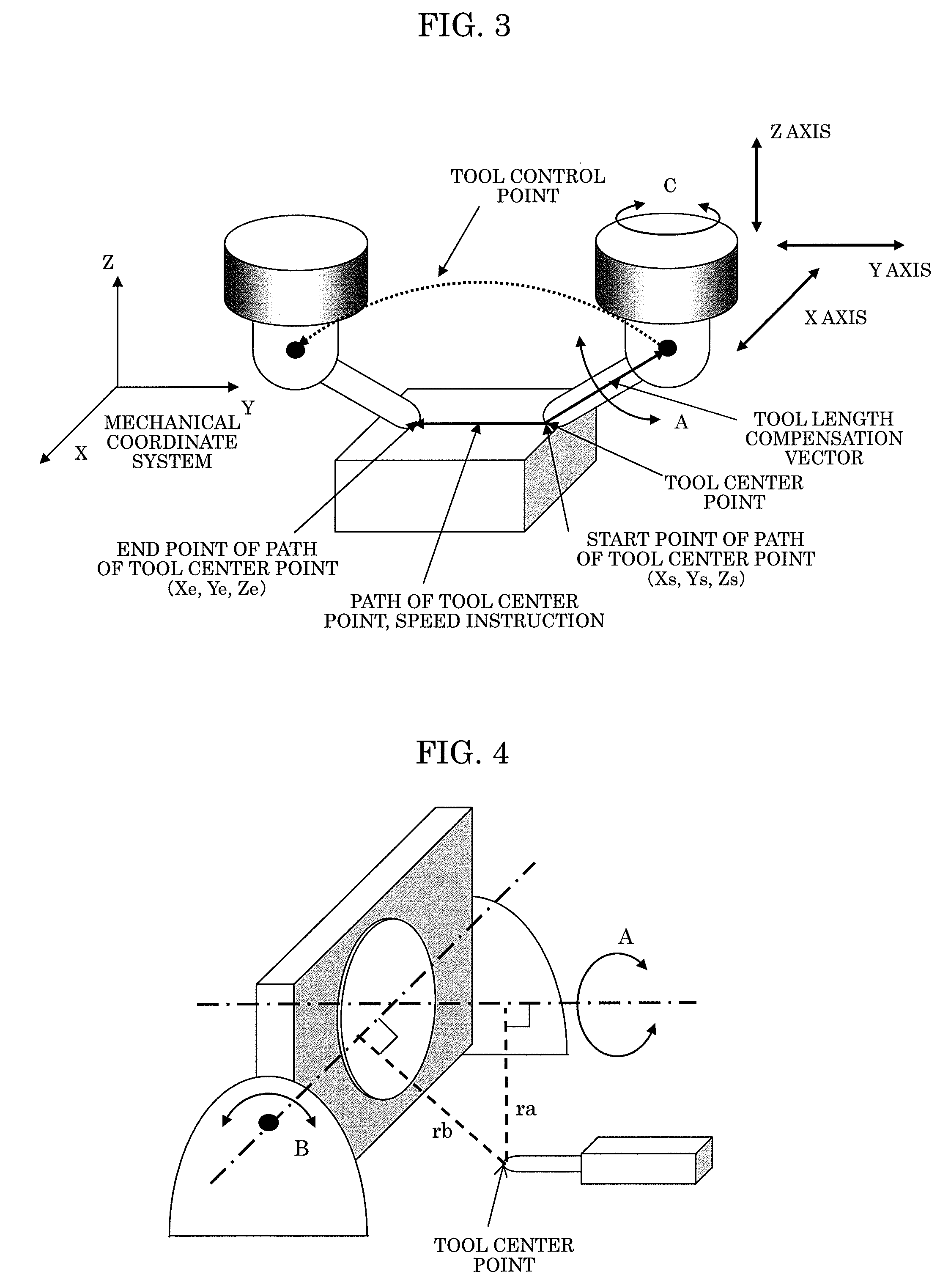
The invention provides a numerical value control device, which controls a multi-shaft processor having three linear shafts and three rotary shafts. A path on a cutter front point is instructed and interpolated on a workbench coordinate system. The rotary shafts are meanwhile instructed and interpolated. According to the linear shaft position, the rotary shaft position of the interpolated cutter front point position and the cutter length rectified vector, the linear shaft position and the rotary shaft position of the control points as the mechanism coordinate system are calculated. Then the linear shafts and the rotary shafts are driven to obtain the position.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Trajectory optimization method of singular region by virtue of five-axis machining
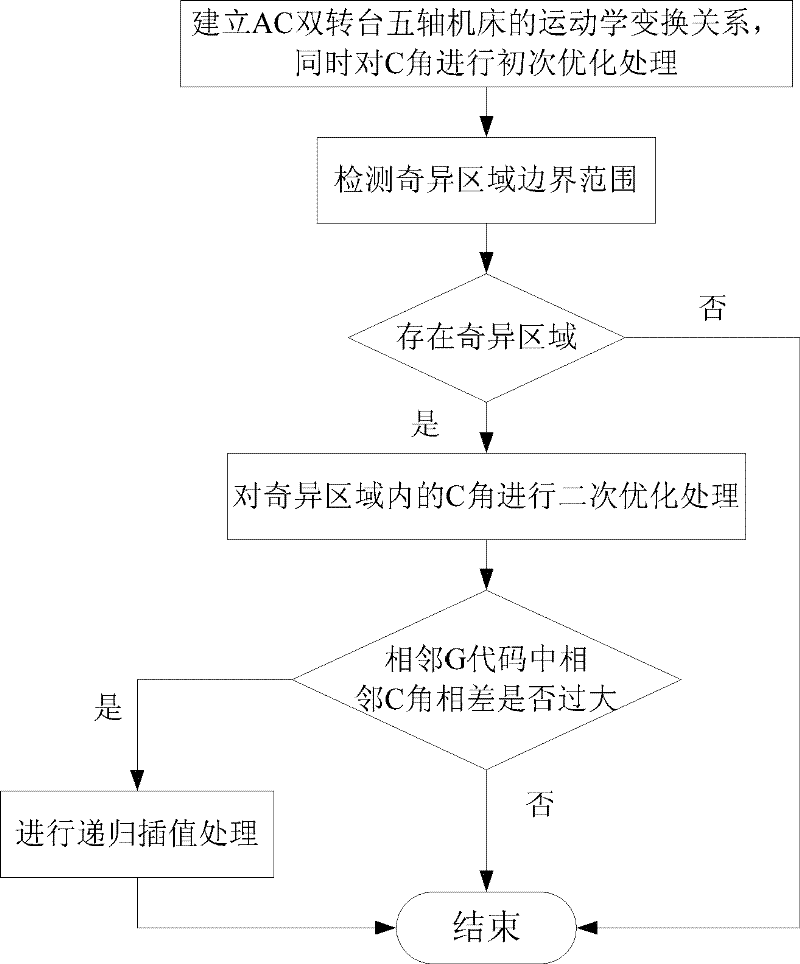
ActiveCN102528554AReduce speed mutationReduce excessive non-linear errorsAutomatic control devicesFeeding apparatusEngineeringAlternating current
The invention relates to a processing method of a singular region by virtue of five-axis machining. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a kinematics conversion relationship of an AC (alternating current) dual-rotary-table five-axis machine tool, carrying out primary optimization treatment on a C-axle rotation angle while inverse kinematics changes so as to obtain cutter shaft data, and traversing the cutter shaft data; in the traversing process of the cutter shaft data, detecting the boundary range of the singular region by using a method based on a Jacobian matrix condition number; carrying out secondary optimization treatment on a singular point and a C angle nearby the singular point within the boundary range of the singular region to obtain new cutter shaft data; and carrying out recursion interpolation treatment on a subinterval with still larger C angle change between the two adjacent lines in the new cutter shaft data to obtain the final cutter shaft data. By adopting the method provided by the invention, velocity jump of a rotation shaft in the singular region can be effectively reduced, overlarge non-linear errors generated by the velocity jump can be reduced, the processing precision can be improved, and the machine tool as well as parts and components can be effectively protected.
Owner:中国科学院沈阳计算技术研究所有限公司
Multi-axis numerical control machining tool motion planning method based on process system rigidity characteristic
ActiveCN101870073AAnalyzing the distribution of stiffness propertiesImprove the level of application technologyAutomatic control devicesFeeding apparatusProcess systemsNumerical control
The invention relates to a multi-axis numerical control machining tool motion planning method based on a process system rigidity characteristic. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a multi-axis numerical control equipment process system comprehensive rigidity model through a Jacques matrix method and a finite element method; establishing a three-dimensional space force ellipsoid according to the rigidity field model; optimizing the cutting feed direction according to the rigidity performance index of all control points by taking the force ellipsoid axial length corresponding to the cutting feed direction at any control point in a complex curved surface as the rigidity performance index; and optimizing the cutter orientationtool gesture according to the rigidity performance index of all control points by taking the shortest force ellipsoid axial length corresponding to the cutter orientationtool gesture at any control point. The invention makes up the defect that only the geometrical condition is considered in the traditional multi-axis machining motion planning, can realize the multi-axis machining tool motion planning based on the comprehensive rigidity characteristics of a multi-axis numerical control equipment process system and the geometric constraint condition, and adds a new method for the large-scale complex curved surface multi-axis numerical control machining motion planning.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Numerical controller having speed control function for multi-axis machining device
ActiveUS20120221141A1Stable speedSpecial data processing applicationsNumerical controlMulti axisRelative Change
When a numerical controller executes a tool-center-point control in which a path of a tool center point with respect to a workpiece is instructed, and the workpiece is machined along the instructed path based on a speed instruction, the numerical controller sets the speed instruction so that the speed instruction is a synthesis speed with respect to a synthesis distance of a relative moving distance between the workpiece and a tool center point and a tool-direction changing distance due to a relative change in a tool direction with respect to the workpiece by a rotary axis. The numerical controller interpolates a position of a linear axis and a position of a rotary axis by the tool-center-point control according to the synthesis speed and drives the linear axis and the rotary axis to the position of the linear axis and the position of the rotary axis created by the interpolation.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Machining method for rear shaft neck of aerial turbofan engine
The invention discloses a machining method for a rear shaft neck of an aerial turbofan engine, and belongs to the technical field of precision machining of components for an aerial engine. The method comprises the following steps: blank machining, coarse machining, flow detection, semi-finishing, surface corrosion, thermal treatment, finishing, five-axis machining, excircle grinding, cleaning detection and machining completion. According to the machining method provided by the invention, problems can be discovered in real time during the machining process through multi-step machining and detection of branch operation, the deformation is controlled, the method is beneficial to discovering the defects of die forging blanks of the components, schemes of solving and dealing with the problems can be quickly performed, and the machining efficiency and quality of products are ensured. Moreover, the strength of the components can be ensured and the materials can be saved by adopting die forging blanks; moreover, the multi-step machining and detection of branch operation are adopted, and are also beneficial to controlling overhigh production cost caused by production defects; the machining method is further convenient to design special measuring tools and clamping tools, so that the machining efficiency and quality of components are ensured.
Owner:GUIZHOU ZUNYI CHI YU PRECISION MACHINERY MFG
Variable machine tool capable of multi-axis machining
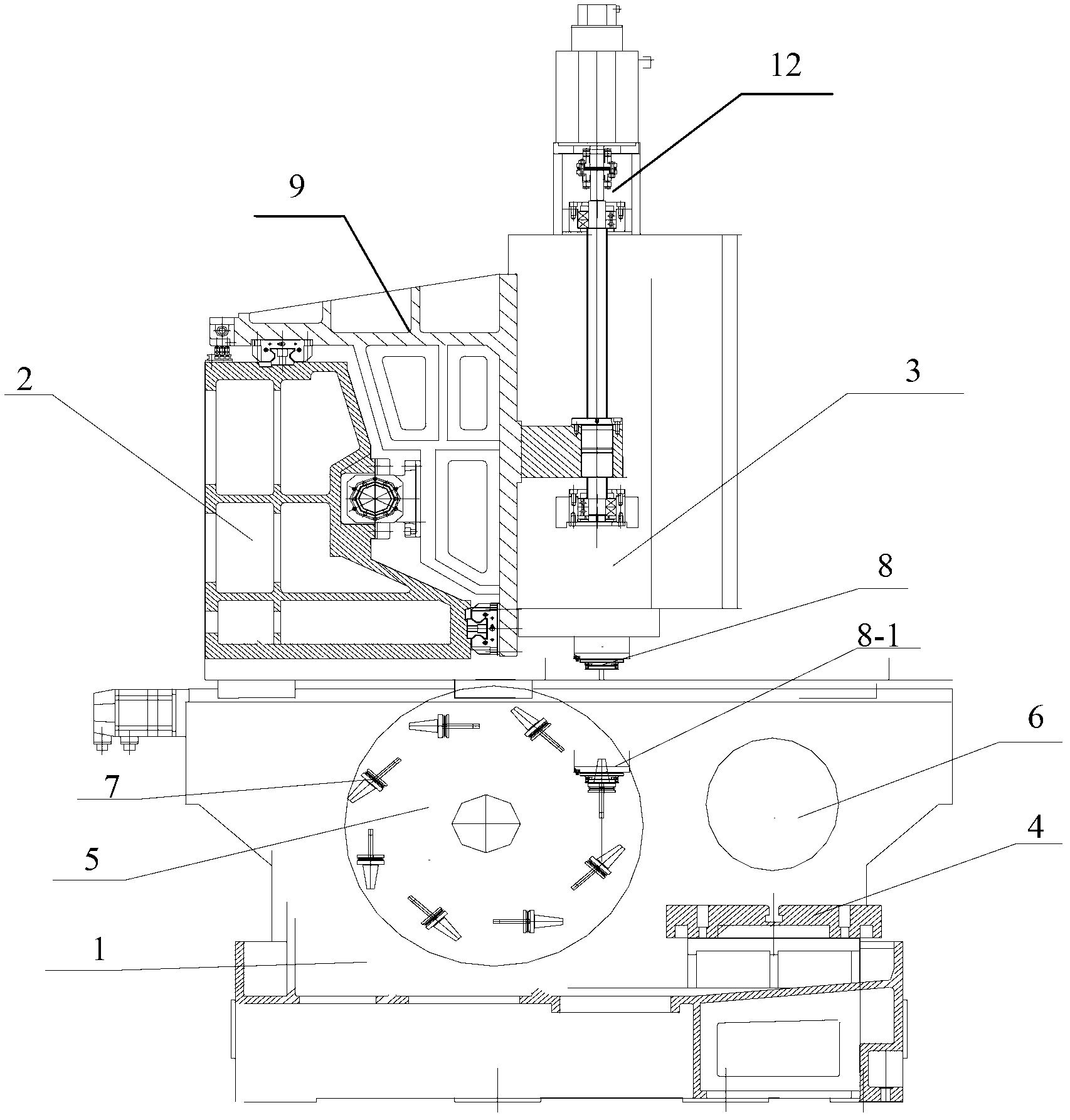
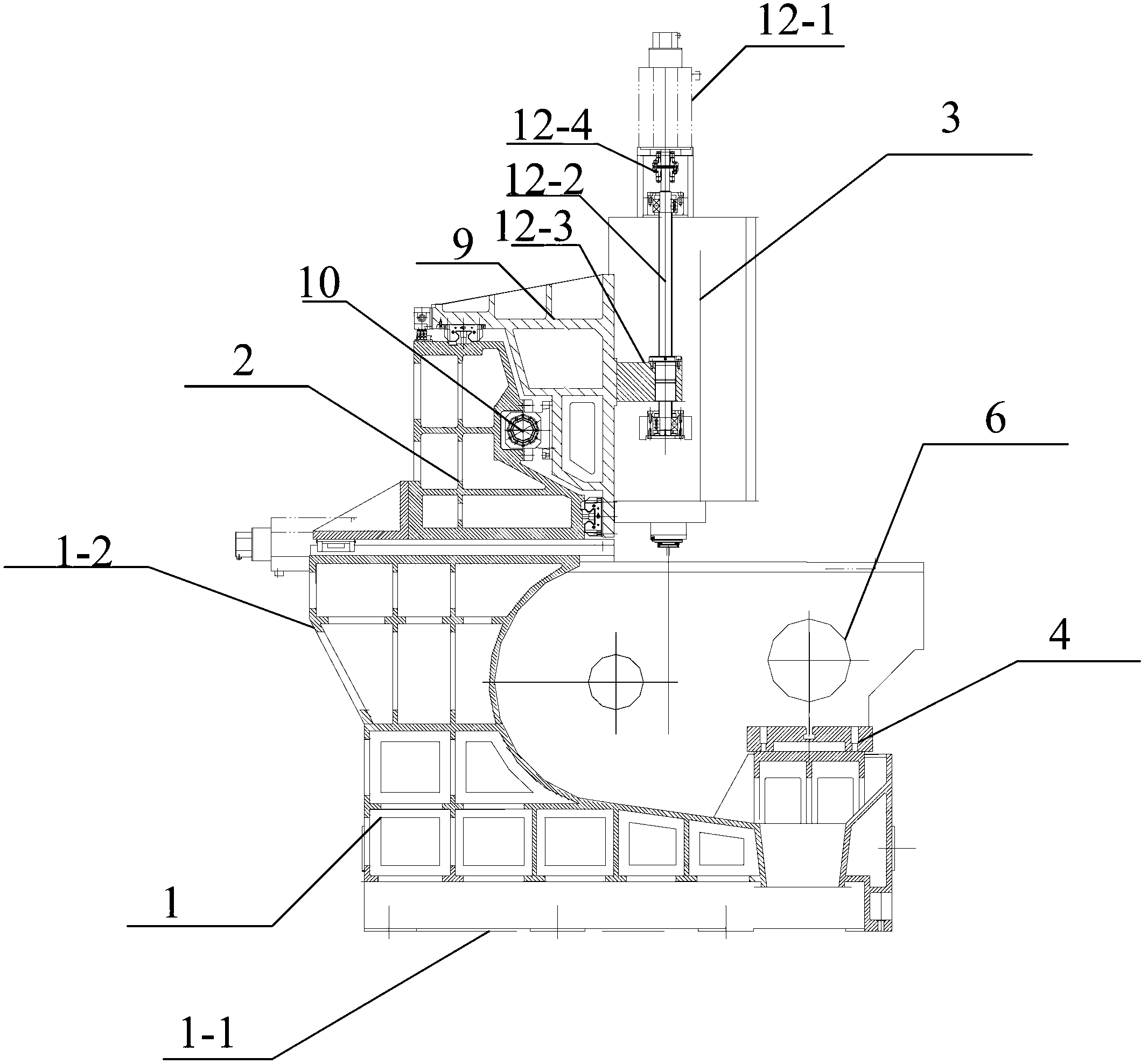
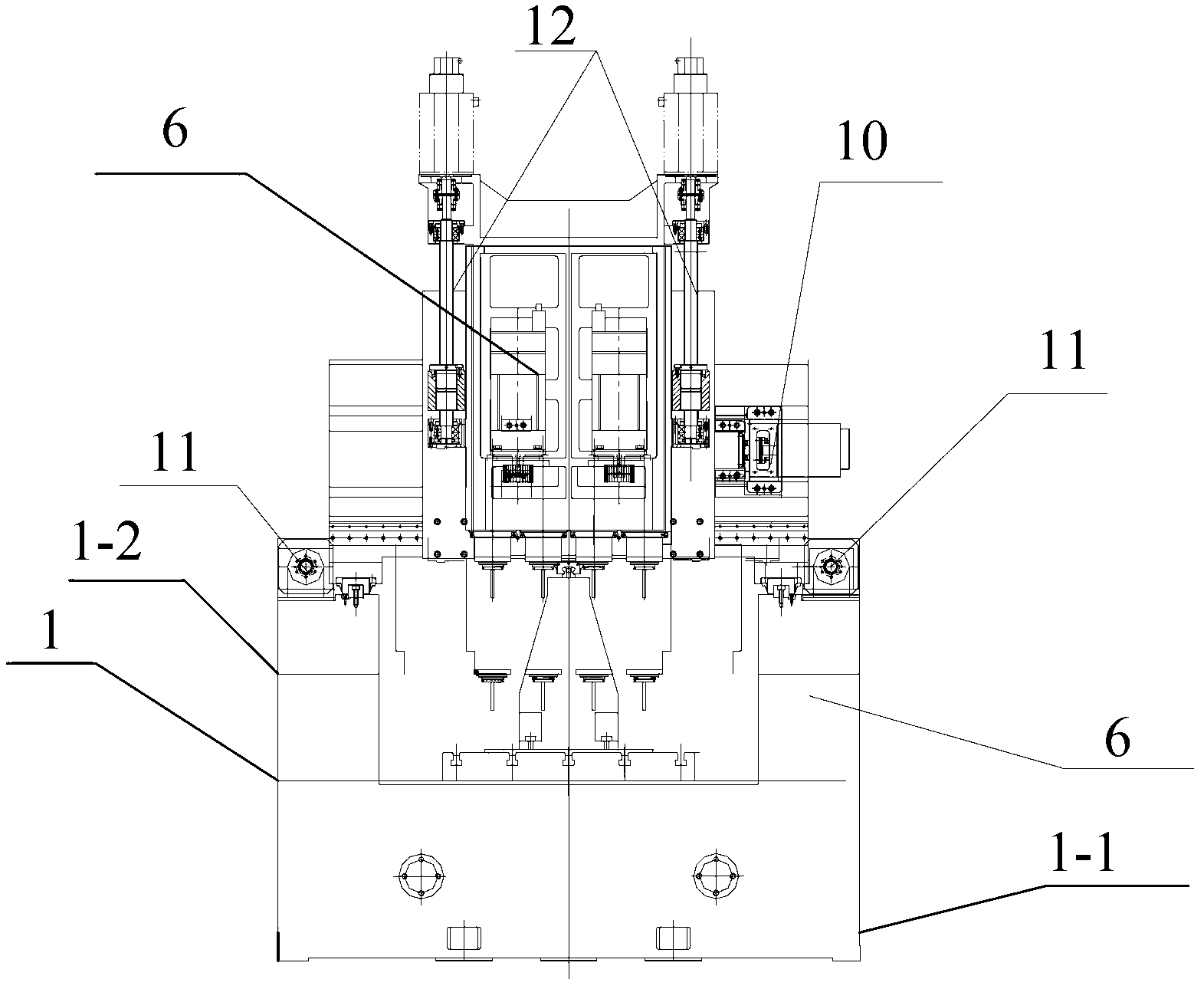
ActiveUS20140023450A1Easy to processSimple configurationMilling machinesOther manufacturing equipments/toolsEngineeringMulti axis
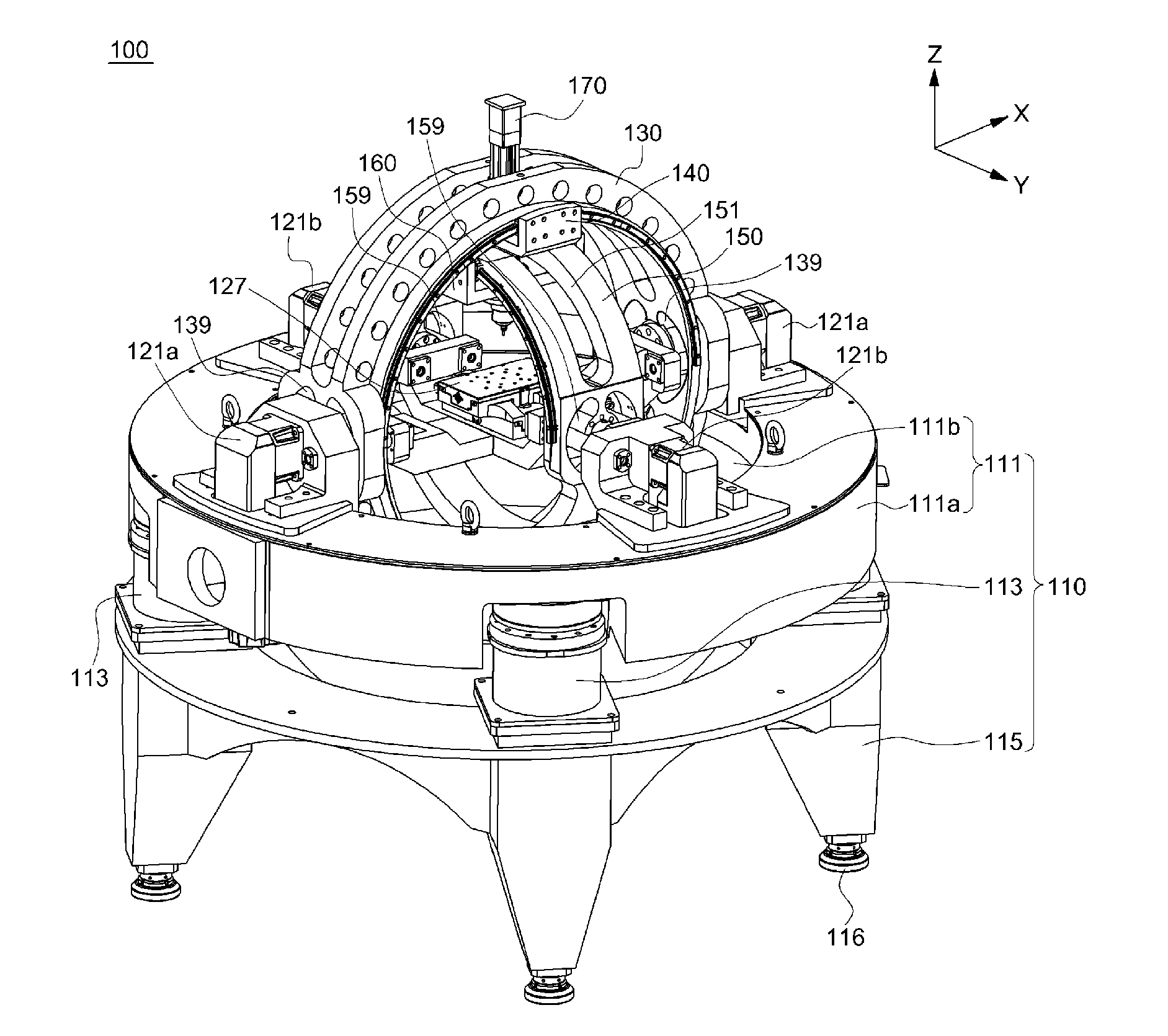
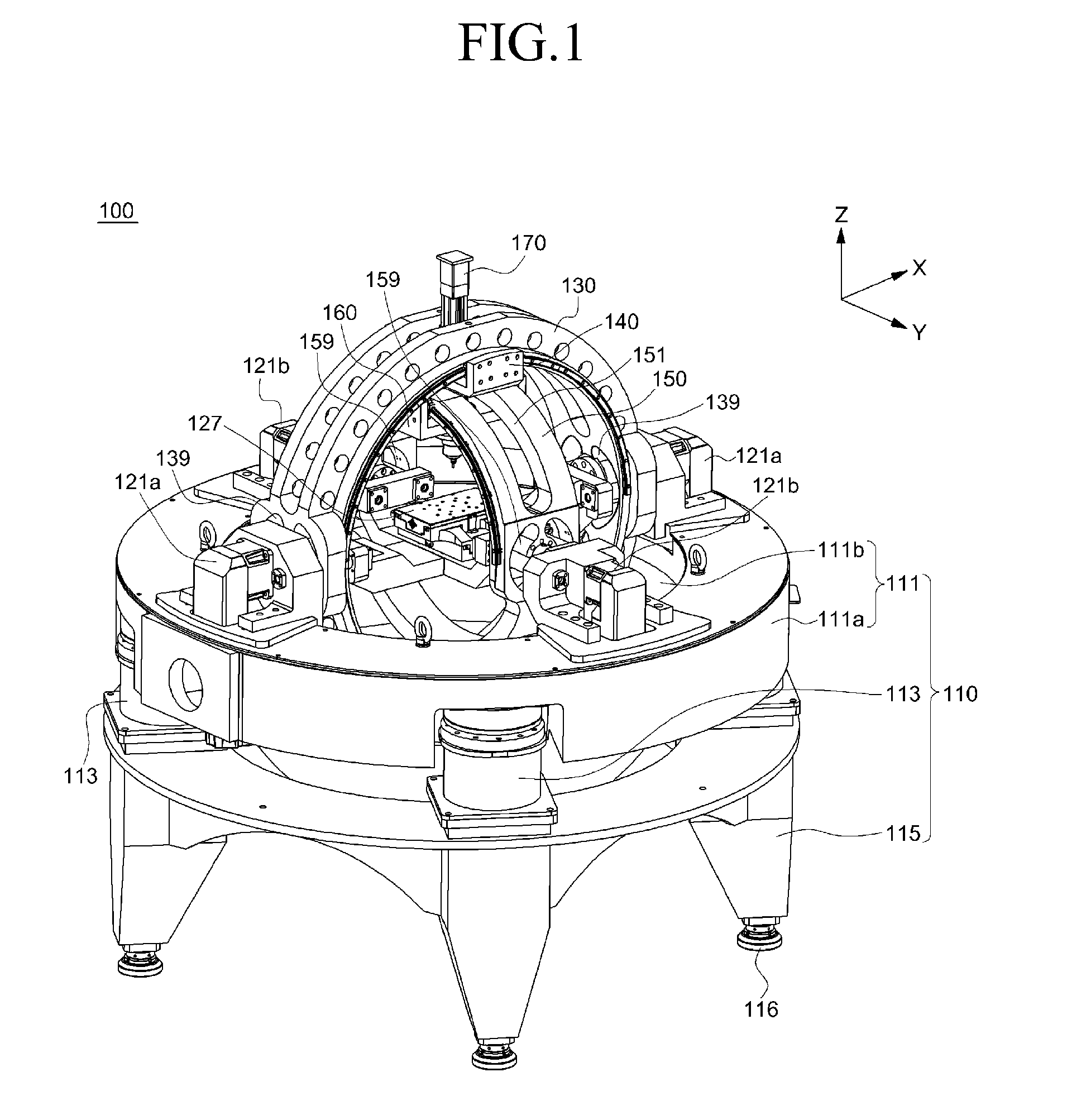
According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, a variable machine tool capable of multi-axis machining includes: a base frame; a first rotating frame rotating on the base frame and comprising a first sliding member sliding along a circumference while being contact-supported through an interior diameter; a second rotating frame cross-disposed inside the first rotating frame to rotate in a direction crossing the first rotating frame, and comprising a second sliding member sliding along a circumference while being contact-supported through an interior diameter; and a spindle of which position and posture displacement is adjusted when the first sliding member and the second sliding member slide by interworking with rotation of the first rotating frame and the second rotating frame, the spindle being installed while passing through the first sliding member and the second sliding member.
Owner:KOREA INST OF MASCH & MATERIALS
Novel multiaxis machining machine
InactiveCN102328234AAid in diffusionReduce the impactFeeding apparatusLarge fixed membersElectric machineryControl theory
The invention relates to a novel multiaxis machining machine which comprises a chassis, a vertical type stand, a cutter bit box and a spindle head seat, wherein a workbench for bearing a workpiece is arranged at one side of the chassis, and an erectly arranged base which is a square framework with an inner space is arranged at the other side of the chassis; a combined part is extended from the top end of the base to the direction of the workbench; the chassis is provided with a three-layer step part under the combined part; the three-layer step part sequentially climbs upwards from the workbench to the base; the vertical type stand is a square framework body; a corresponding combined step is formed on a position at the bottom of the vertical type stand, corresponding to the three-layer step part on the chassis; first horizontal linear guides are respectively arranged between the front end of the combined step and the rear end of the combined step as well as between the first step of the three-layer step part and the third step of the three-layer step part; one first linear guide is set to be high, and the other first linear guide is set to be low; and a first horizontal linear electric motor is arranged between the middle end of the combined step and the second step of the three-layer step part, therefore, a first horizontal feeding mechanism is formed between the vertical type stand and the three-layer step part of the chassis.
Owner:四川欧曼机械有限公司
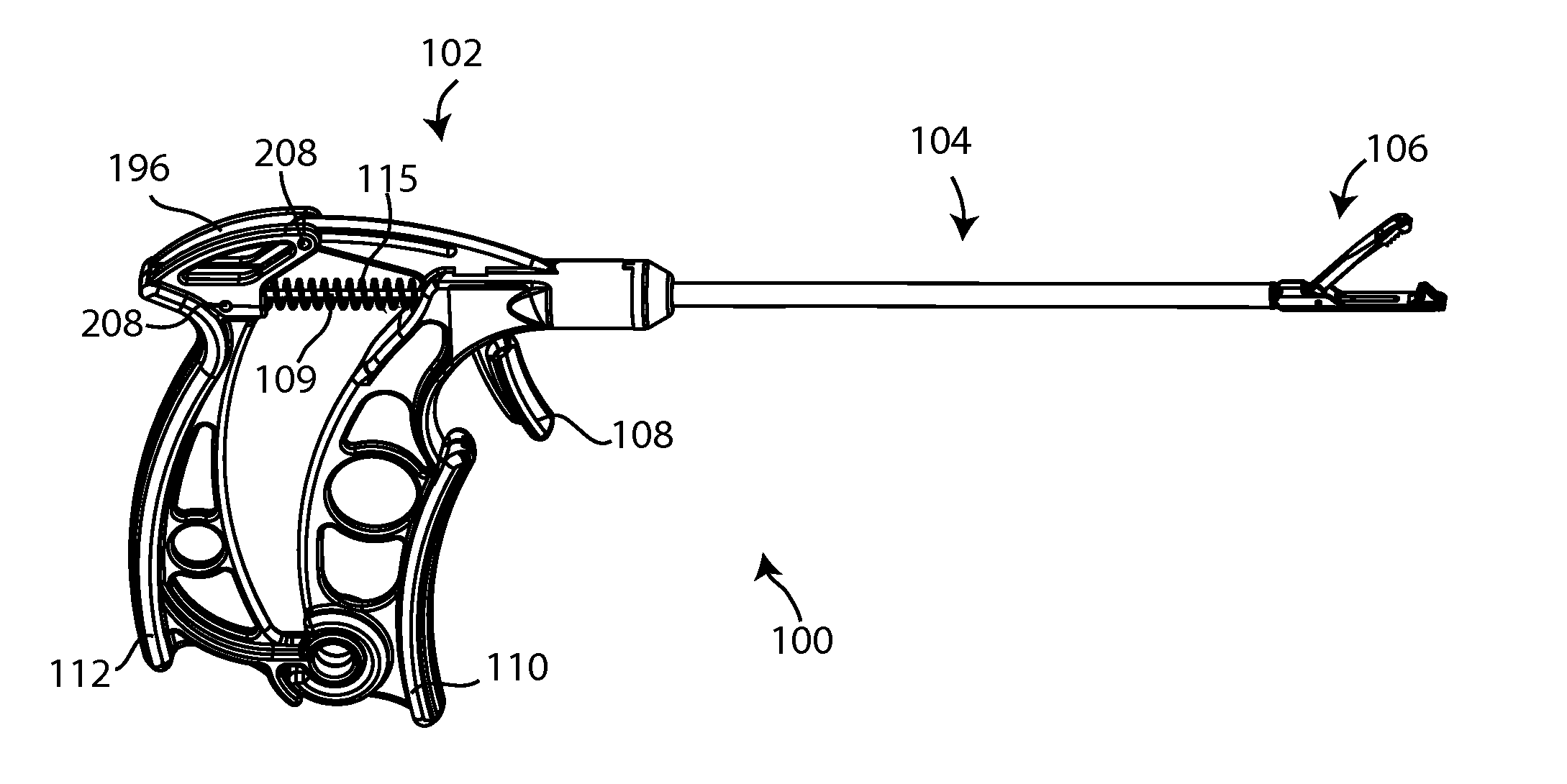
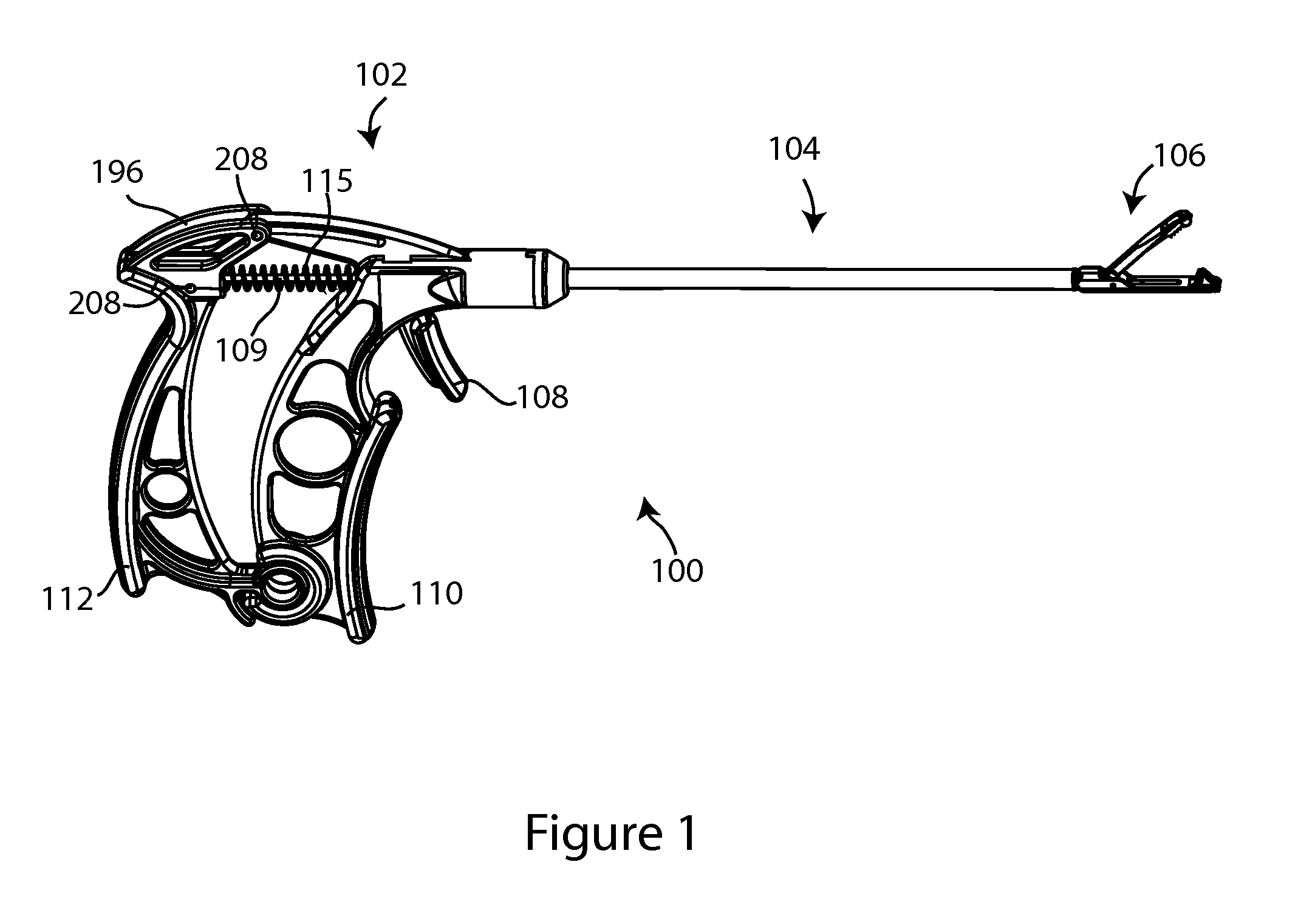
Suture passers
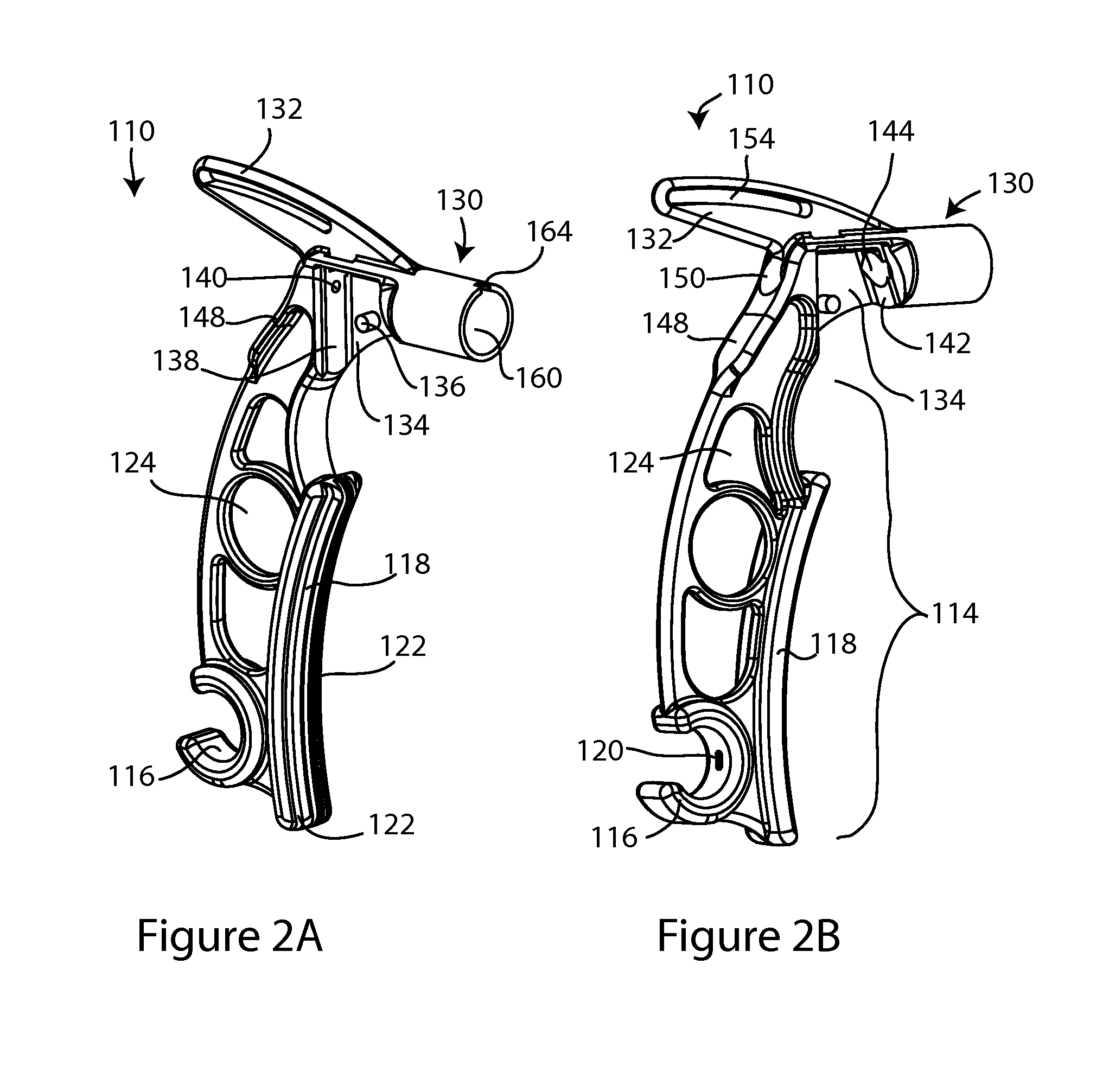
Suture passers which include a handle assembly, shaft assembly, and jaw assembly. In one embodiment, the handle assembly includes first and second handles joined at a hinge, the second handle pivotable relative to the first handle and guided by an arcuate guiding feature concentric to the hinge. The jaw assembly includes upper and lower jaws, the lower jaw including an open needle track. The open needle track includes entry, tangential and exit segments, each of which is directly visible, directly accessible, and directly inspectable. The lower jaw can be manufactured as a single piece, using a single manufacturing process, which may be injection molding or multi-axis machining. When manufactured by multi-axis machining, all features of the lower jaw may be machined without removal of the jaw piece from the multi-axis machine. Methods of suture passer manufacture and assembly which may provide significant cost savings are disclosed.
Owner:IMDS CORPORATION
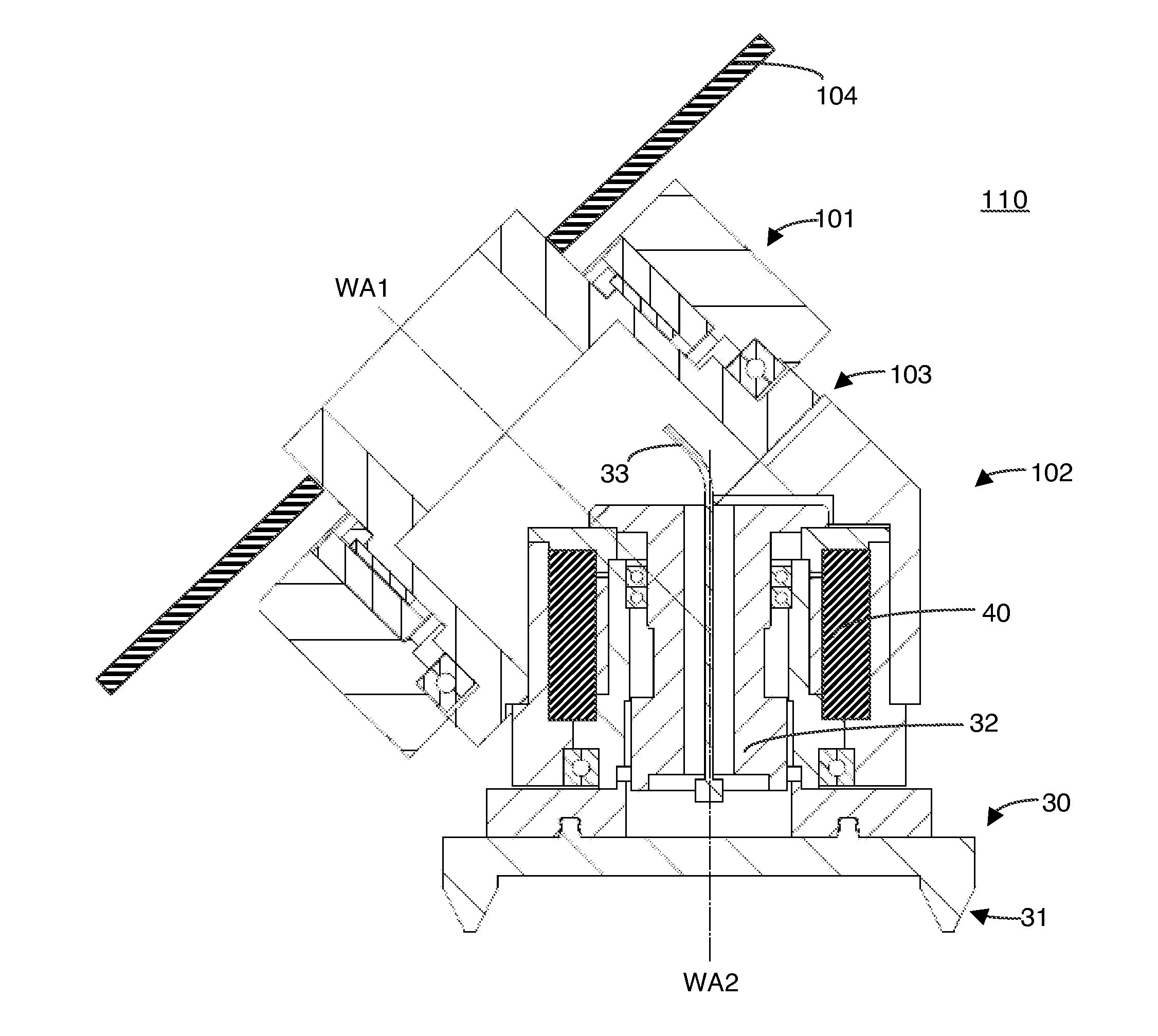
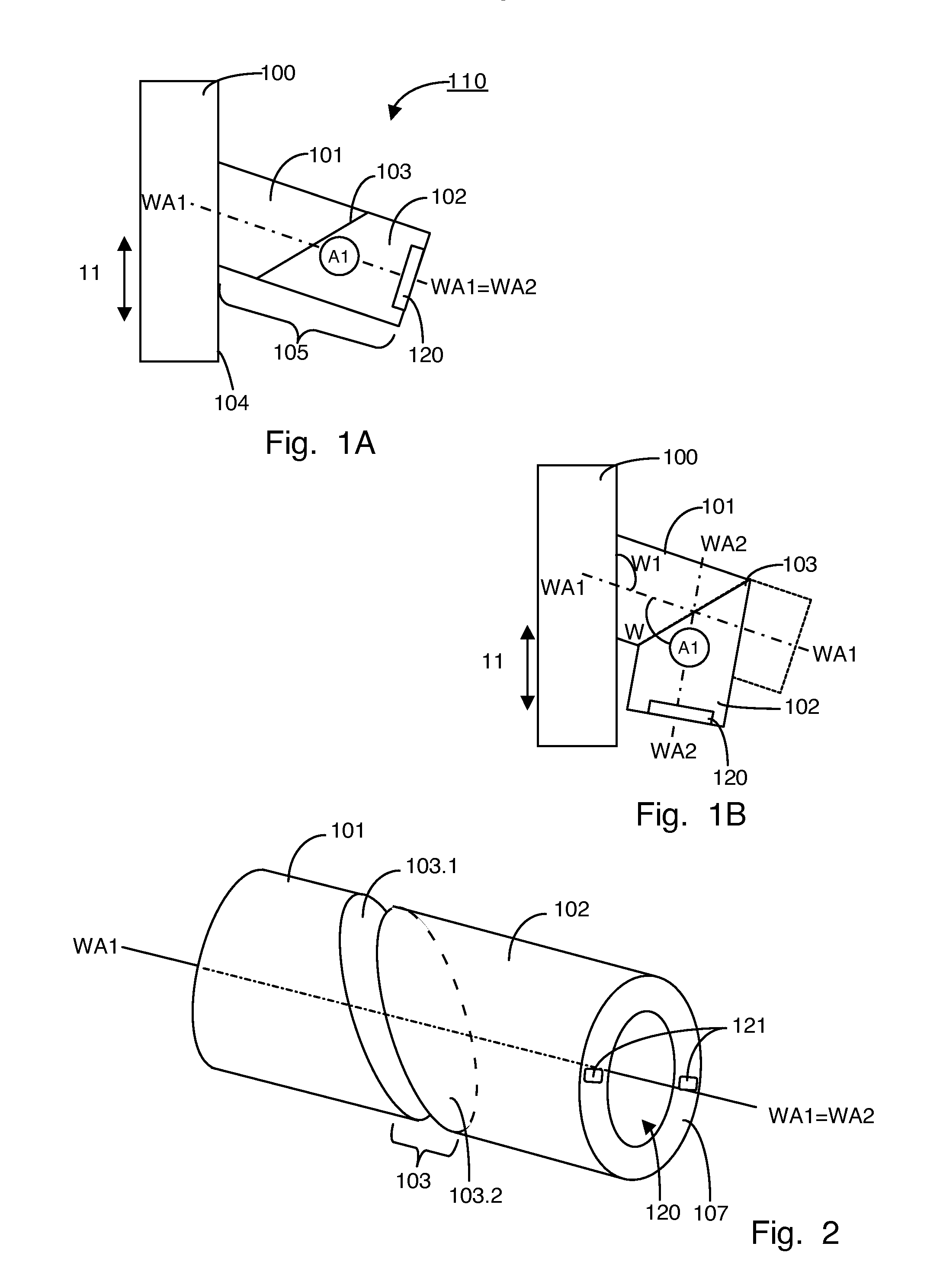
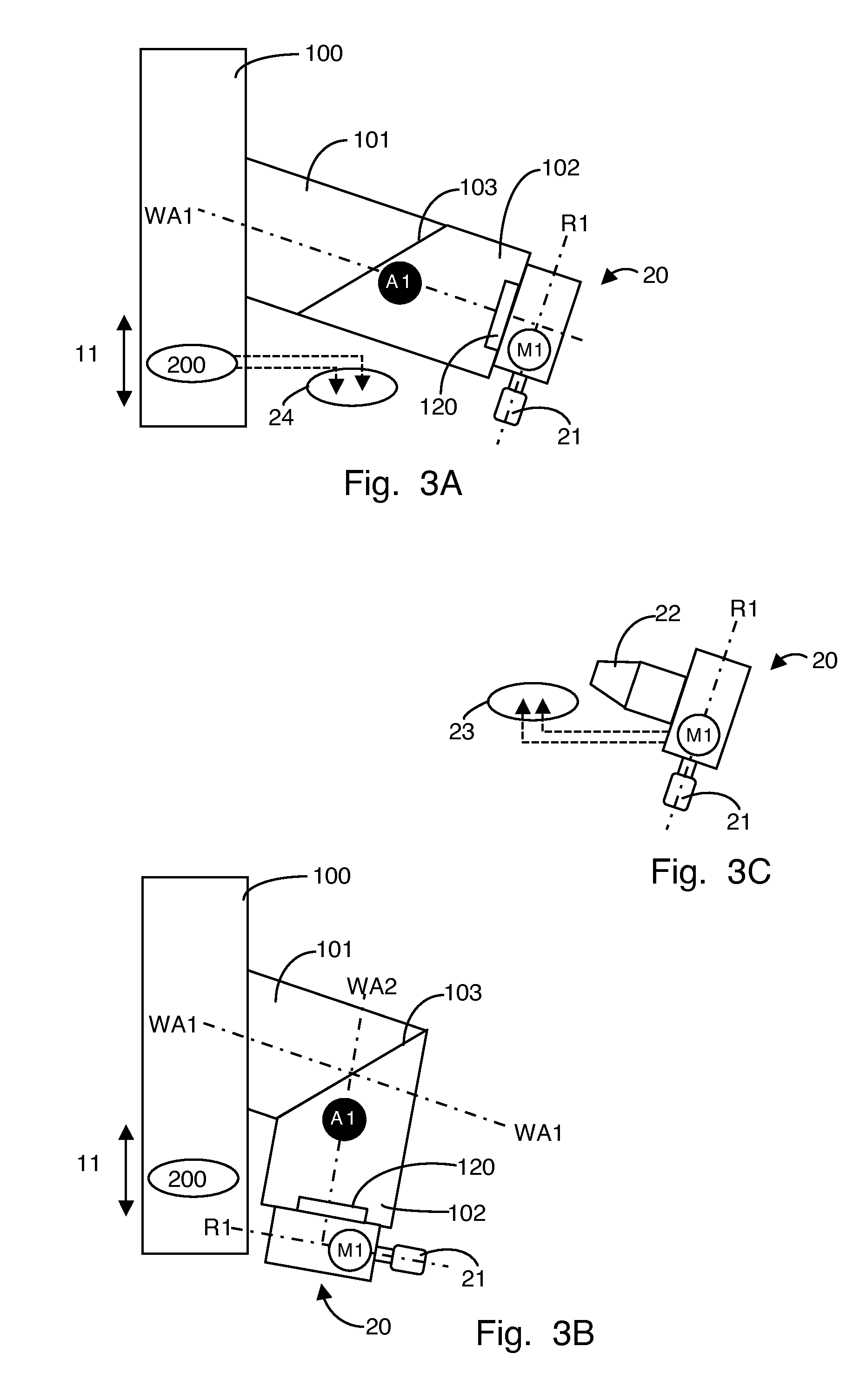
Tool head for use in a multiaxis machine, multiaxis machine having such a tool head, and use of such a machine
InactiveUS20110058913A1Precision properties are not negatively impairedMore flexibly usableAttachable milling devicesMilling machinesMilling cutterElectric machine
Tool head (110) for use in a multiaxis machine (100), the tool head (110) comprising a spindle body, which has two elements (101, 102). These elements (101, 102) are rotatably connected with one another via a corresponding coupling (103), the first element (101) having a first longitudinal axis (WA1) and the second element (102) having a second longitudinal axis (WA2), which are transferable from a stretched position into an angled position depending on the rotational position. A first drive (A1) is seated in or on the spindle body. A receptacle device (120) is provided, which is situated on the second element (102). This receptacle device (120) is used for fastening a motor spindle (20), a motor (M1), which is integrated in the motor spindle (20), being able to be supplied with power via the second element (102) and via electrical connection means of the receptacle device (120). The receptacle device (120) is also used for fastening a milling tool (30), which is drivable using the first drive (A1).
Owner:KLINGELNBERG AG
Multi-axis cascade connection direct driving PCB (printed circuit board) drilling machine
InactiveCN103921314AImprove drilling accuracyImprove stabilityMetal working apparatusHigh loadMotion system
The invention discloses a multi-axis cascade connection direct driving PCB drilling machine. The multi-axis cascade connection direct driving PCB drilling machine comprises a bed, a the bed is provided with a beam, the beam is provided with a beam motor fixing plate, an X-axis linear motor is arranged between the beam and the beam motor fixing plate, the bed is provided with a plurality of cascade connection drilling hole structures connected through cascade connection shafts, every cascade connection drilling hole structure comprises a drilling hole assembly and a Z-axis linear motor, the bed is provided with a Y-axis motion platform, and a Y-axis linear motor is arranged between the bed and the Y-axis motion platform. The multi-axis cascade connection direct driving PCB drilling machine is designed by taking factors such as manufacturing cost, operating cost and machinability into consideration, solves the problems of high load and high vibration due to high-speed driving, achieves optimum compatibility among a control system, a motion system and a mechanical system, can meet requirements of high-quality multi-level drilling hole machining, and overcomes technology defects of low accuracy and poor stability of multi-axis drilling hole machining compared to single-axis machining by improving the cascade structure so as to further improve multi-axis machining accuracy as well as maintain high machining efficiency.
Owner:HANS LASER TECH IND GRP CO LTD +1
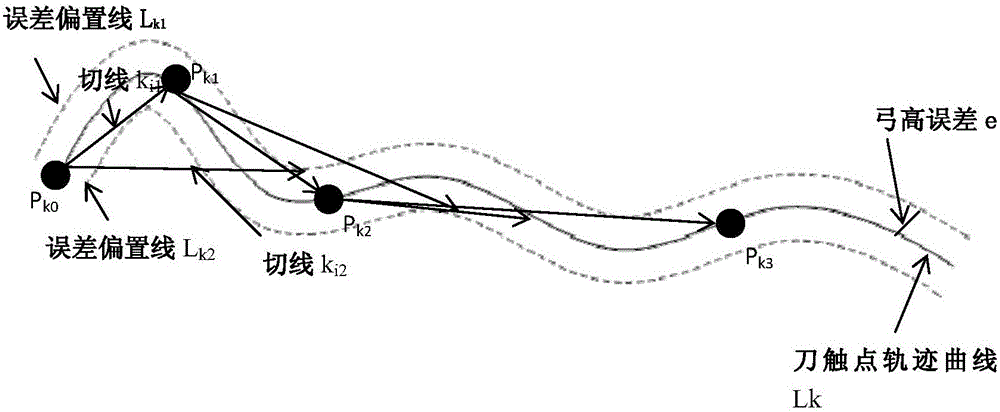
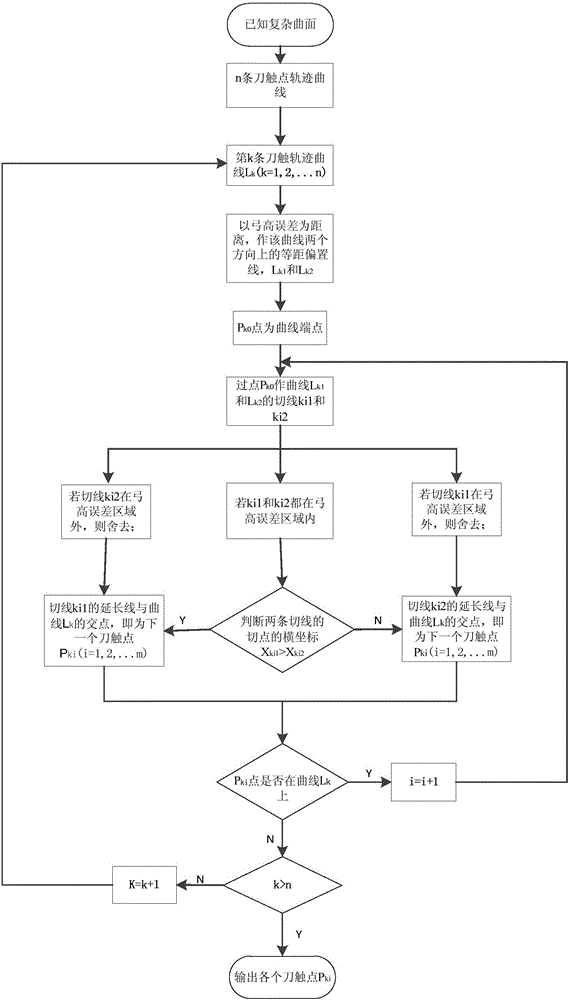
Equal-chord-error variable-step tangent interpolation method
The invention belongs to the field of a numerical control technology and especially relates to an equal-chord-error variable-step tangent interpolation method. The method is mainly used in multi-axis machining tool-path planning work, is suitable for surface curvature variable self-adaptative adjustment of machining step-length, realizes maximization of machining step-length within chord error range, can be used to obtain the fewest curve discretization segments and has high machining efficiency. By a new equal-chord-error step-length method, a tool path track is determined. Chord errors within each approximation line segment are uniform and consistent. Machining precision is high.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Multi-spindle machining machine with tool changing mechanism
InactiveUS8308621B2Reduce productionSmall sizeSpeed/accelaration controlFeeding apparatusEngineeringMultiaxis machining
A multi-spindle machining machine with a tool changing mechanism comprising a base; a carrier including a seat to move in Z axis, a rotary shaft fixed on the seat laterally to drive the seat to rotate in A axis, and a fixing holder coupled to an end portion of the rotary shaft to fix a workpiece; a tool changing mechanism including a mount mounted to the rotary shaft to rotate with the rotary shaft and a monitor fixed on the seat to measure a length of the tool clamped on the driving spindle, and including a plurality of slots to receive the tools respectively; a working head moving above the carrier and the tool changing mechanism in X and Y axes and including a driving spindle mounted on a lower end thereof to rotate axially, and the lower end of the driving spindle allowing to engage and disengage the tool.
Owner:SHENQ FANG YUAN TECH
Method and apparatus for non-spindle multi-axis machining
ActiveUS9101991B1Increase chanceEliminate the effects ofPlaning/slotting toolsPlaning/slotting machinesSurface finishMaterial removal
A non-spindle multi-axis machining center (600) and method for forming a part using a non-rotating cutting tool (400) for removing material from a non-rotating workpiece within a three-dimensional work envelope. The non-spindle machining center makes obsolete the use of mills for profiling operations without the need to rotate the cutting tool to produce sufficient torque to remove material. Instead, the cutting tool (400) applies a linear cutting force to the workpiece along a one-, two-, or three-dimensional cutting path with sufficient impact to remove material by means of controlled fracturing instead of plastic deformation. Also, without the need to rotate, neither the cutting tool nor the part are constrained in shape by axial symmetry. Therefore, parts without restrictions in shape can be produced with higher material removal rates and finer surface finishes than by milling or turning.
Owner:TENNINE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com