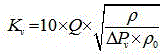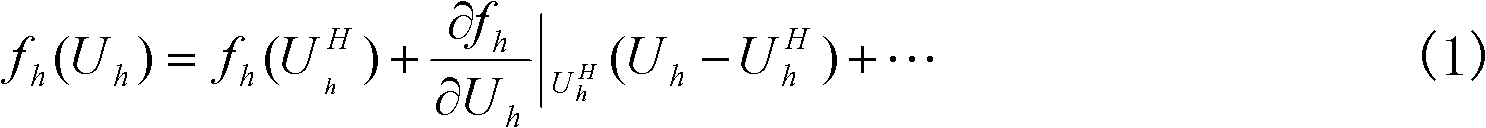Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
46 results about "Mesh adaptation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mesh adaptation, often referred to as Adaptive Mesh Refinement (AMR), refers to the modification of an existing mesh so as to accurately capture flow features.
CFD simulation and grid self-adaption based valve flow coefficient calculating method
ActiveCN105677964AAccurately predict circulation capacityEnrich flow field detailsSpecial data processing applicationsComputing MethodologiesQuality by Design
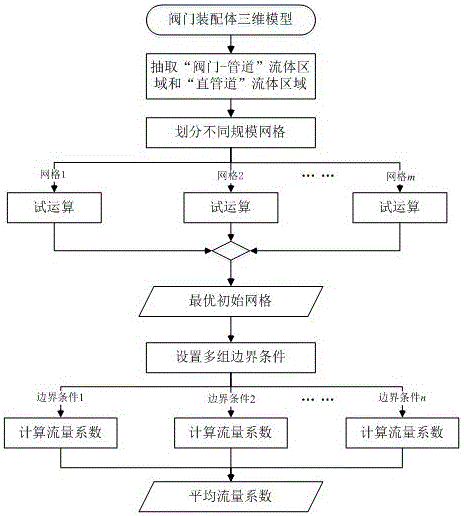
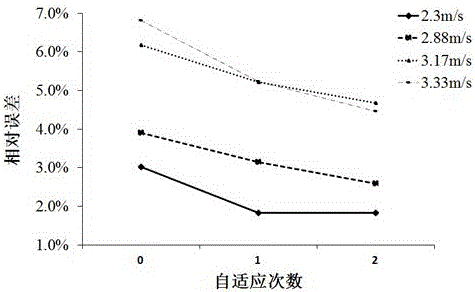
The invention discloses a CFD simulation and grid self-adaption based valve flow coefficient calculating method. The CFD simulation and grid self-adaption based valve flow coefficient calculating method comprises the main steps that a 'valve-pipe' flow field model and a 'straight pipeline' flow field model are extracted based on a valve assembly body three-dimensional model; initial grids are divided for the flow field models, wherein multiple groups of initial grids different in scale are divided for the 'valve-pipe' flow field model; trial operation is performed by applying the groups of initial grids respectively, the change tends with grid scales of the obtained pressure differences are compared to select optimal initial grids; the optimal initial grids are applied to set different boundary conditions, and simulating calculation of corresponding flow coefficients is performed by combining a grid self-adaption technology; finally, the arithmetic average of the obtained flow coefficients is obtained to serve as a valve flow coefficient prediction result. The CFD simulation and grid self-adaption based valve flow coefficient calculating method can more rapidly and flexibly predict the flow capacity of a valve under various conditions, shorten a development period and improve the design quality and can effectively improve the calculation accuracy and reduce the dependence on specialization level of operators.
Owner:JIANGSU SHENTONG VALVE +1
A method for self-adapted load balance scheduling of the video grid
InactiveCN1997031AReduce interaction overheadImprove scalabilityPulse modulation television signal transmissionTransmissionPeak valueSelf adaptive
This invention relates to one visual network self-adaptive load even transfer method in computer multi-media field, which comprises the following steps: generating dynamic area corporation member list, service point virtual organization point list and belong service point provider list; after customer sends requires, network grid door automatically set its direction to service points and judging whether the real servo satisfies the service quality requires; if yes, ending this transfer; if not, according to dynamic area load value to judge whether the service point satisfies the service needs.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Adaptive concrete mesoscopic modeling method
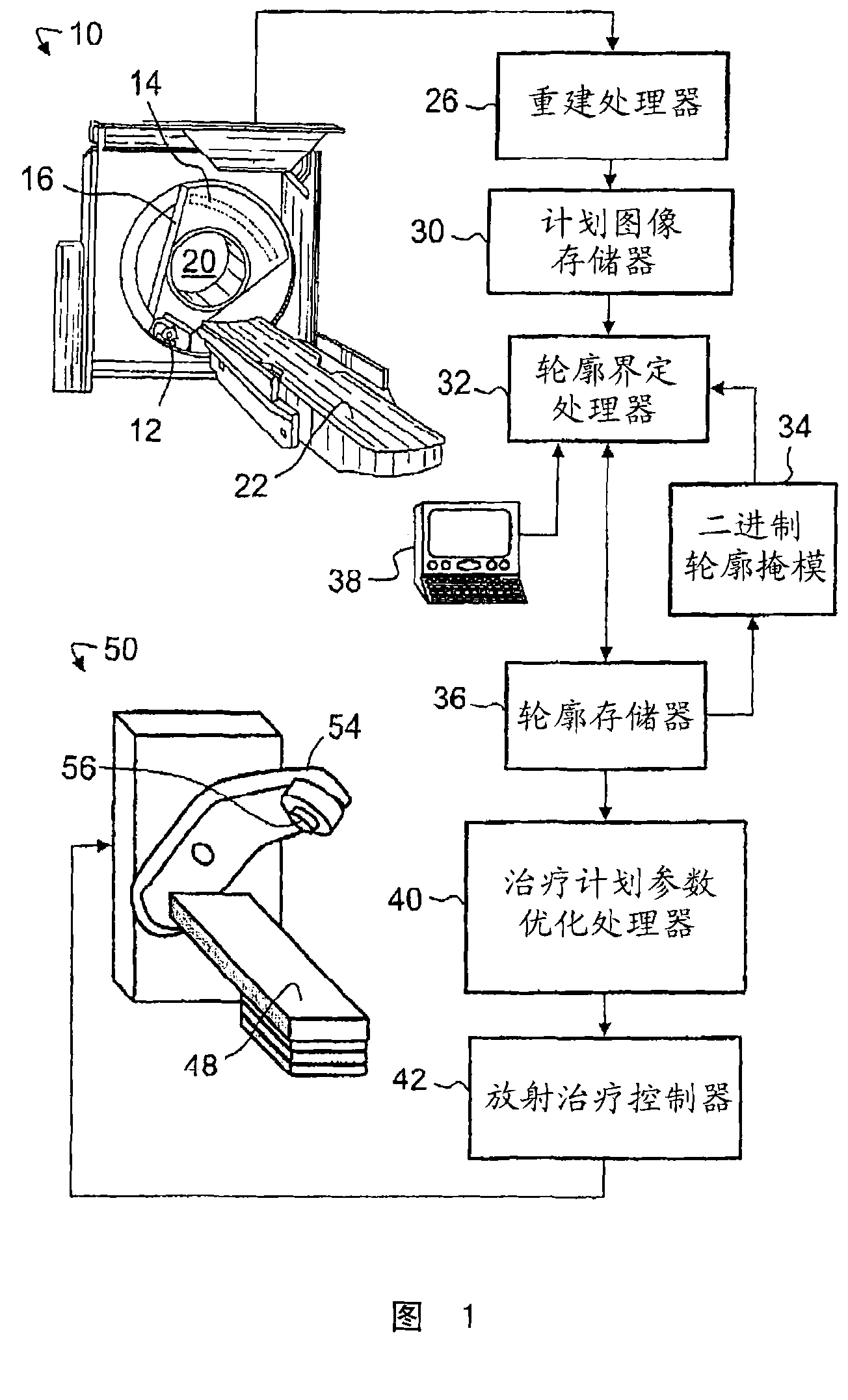
ActiveCN107918706AImprove computing efficiencyBatch Numerical Simulation ConvenienceDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSlurryCement mortar
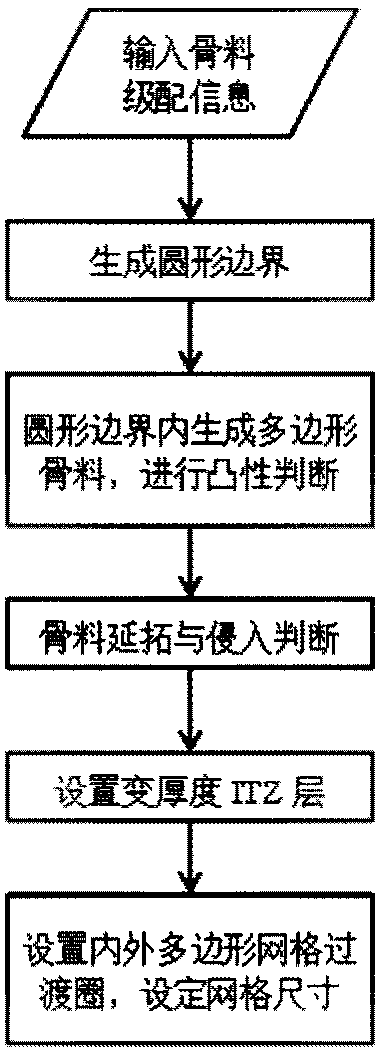
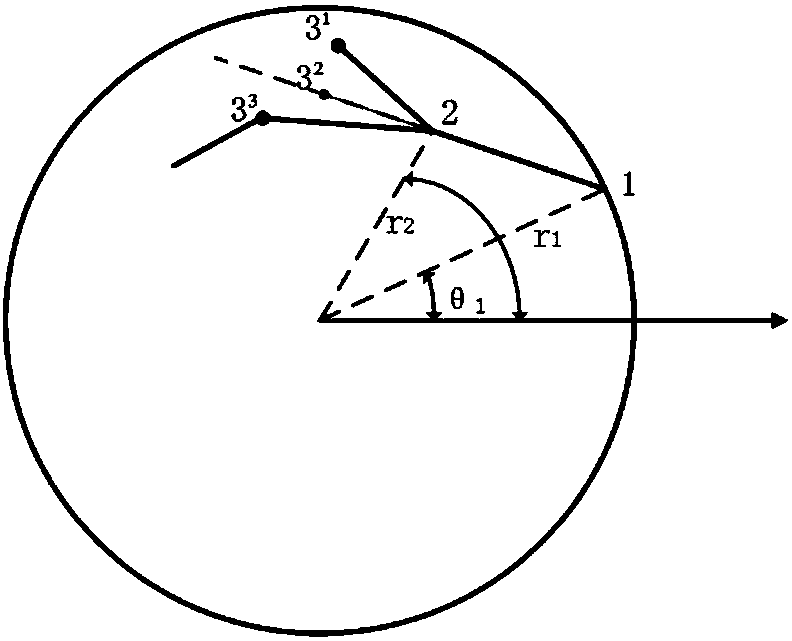
The present invention discloses an adaptive concrete mesoscopic modeling method. The method comprises the following steps: 1) generating a required circular boundary according to the concrete aggregate gradation, generating convex polygonal aggregates within a circular boundary, carrying out prolongation on the area of the convex polygonal aggregate, and determining prolongation point intrusion atthe same time to generate a convex polygonal aggregate concrete model; and 2) setting an inner polygon mesh transition circle inside each convex polygon aggregate, setting an outer polygon mesh transition circle between an aggregate-slurry interface transition zone and the cement mortar, adjusting the polar radius of the aggregate to obtain vertex coordinates of the aggregate-slurry interface transition zone and the inner and outer mesh transition circles, setting the thickness of the aggregate-slurry interface transition zone according to the aggregate particle size, setting the mesh size onthe inner and outer mesh transition circles, and obtaining a mesh-adaptive concrete multi-phase mesoscopic model. According to the method disclosed by the present invention, the random placement of aggregates and the generation of adaptive meshes in the mesoscopic model can be realized, the calculation efficiency can be improved while ensuring the calculation accuracy of different regions withinthe model.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
BESO topological optimization method based on dynamic evolution rate and adaptive grid and application of BESO topological optimization method
ActiveCN111737839ASmall amount of calculationImprove calculation accuracyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelElement analysis
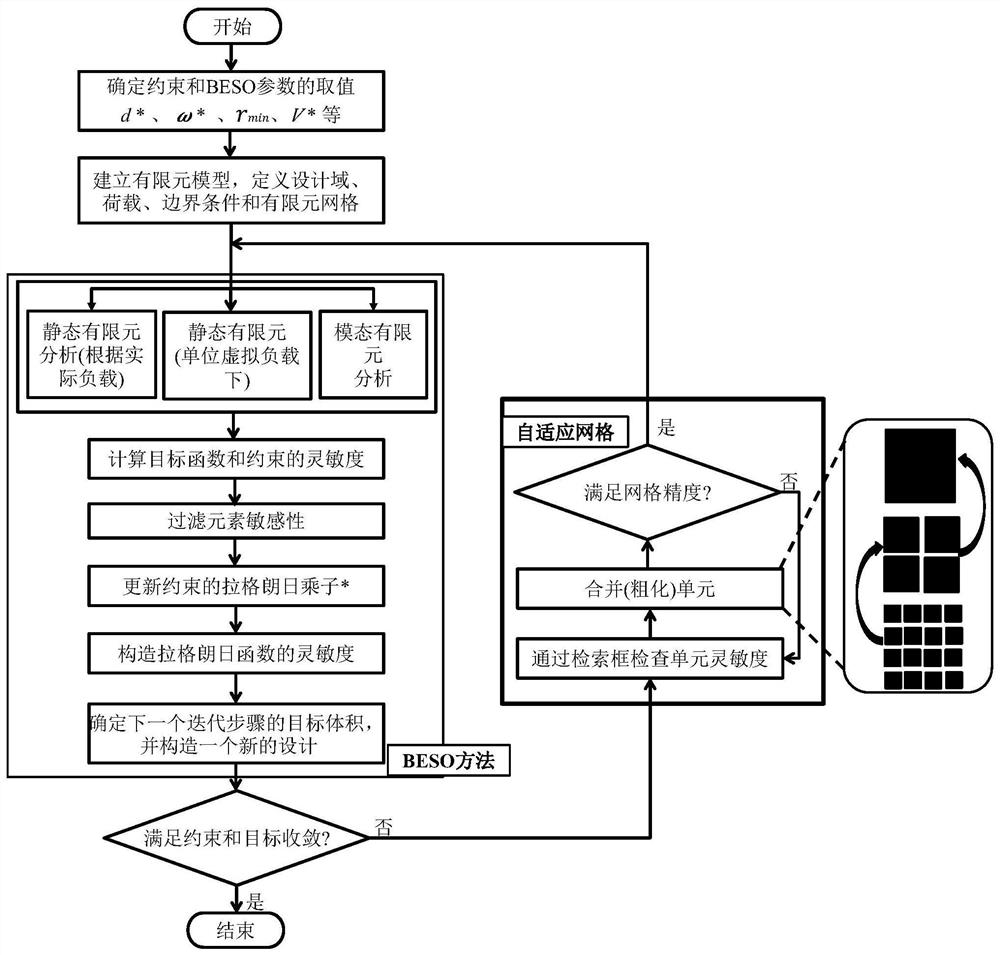
The invention discloses a BESO topological optimization method based on a dynamic evolution rate and an adaptive grid and application thereof, and the method comprises the steps: building a finite element model for a to-be-topologically optimized basic structure, and defining a design domain, a load, a boundary condition and a grid size; determining a constraint value and BESO necessary parameters; performing finite element analysis on the structure after mesh division, and calculating unit sensitivity under a target function and a constraint condition; filtering the unit sensitivity and updating the constrained Lagrange multiplier, and constructing the sensitivity of a Lagrange function; determining an evolution rate of the current iterative step based on a dynamic evolution rate functionof a Logistic function according to the volume rate of the current iterative step; and updating a design variable according to a set constraint function, judging whether constraint conditions and convergence conditions are met or not, if not, performing grid adaptive updating, then performing unit updating, and stopping iteration until the constraint conditions and the convergence conditions aremet. According to the invention, the calculation amount of single finite element analysis and the number of iterations required by topological optimization are effectively reduced while high calculation precision is ensured, so that the total calculation time consumption of topological optimization is greatly reduced.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
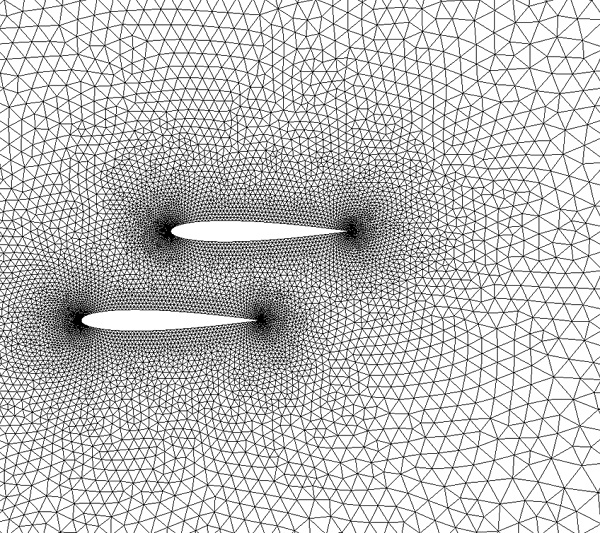
Two-dimensional blade profile optimization design method and device based on self-adaptive grid
ActiveCN110851929AReduce workloadAccurate captureGeometric CADSustainable transportationAlgorithmSimulation
The invention discloses a two-dimensional blade profile optimization design method and device based on a self-adaptive grid. The method for solving the two-dimensional blade profile flow field based on the adaptive grid comprises the following steps: drawing an initial grid for a two-dimensional blade profile, and performing viscosity calculation on the two-dimensional blade profile flow field toobtain flow field data corresponding to each node of the initial grid so as to form an initial flow field; and sniffing the initial flow field, marking grid nodes which do not accord with a thresholdcondition by utilizing a characteristic quantity detector, carrying out grid self-adaption until all the grid nodes meet the threshold condition, and finishing accurate calculation of the two-dimensional blade profile flow field to obtain an accurate response output value of a target function. A user does not need a high-precision solver, and the first-order precision to the second-order precisionprovided by common commercial computing software can meet requirements; at the position where the flow field change gradient is large, better robustness can be achieved through low-order solving; thegrid encryption position is determined through characteristic quantity detection, global encryption is avoided, the calculated amount is reduced, and the method has engineering practical use value.
Owner:INST OF ENGINEERING THERMOPHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
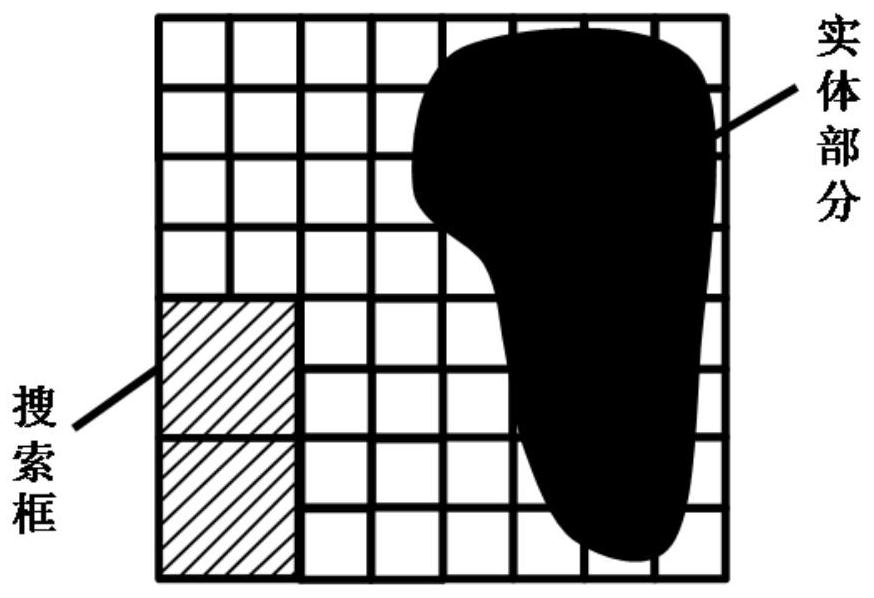
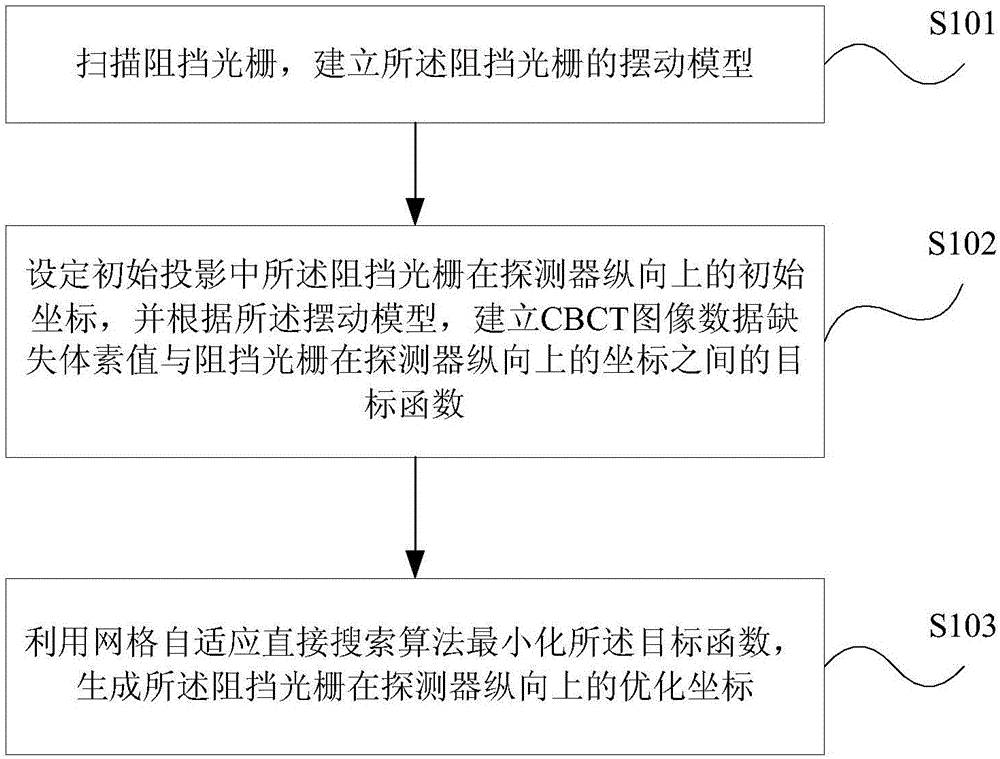
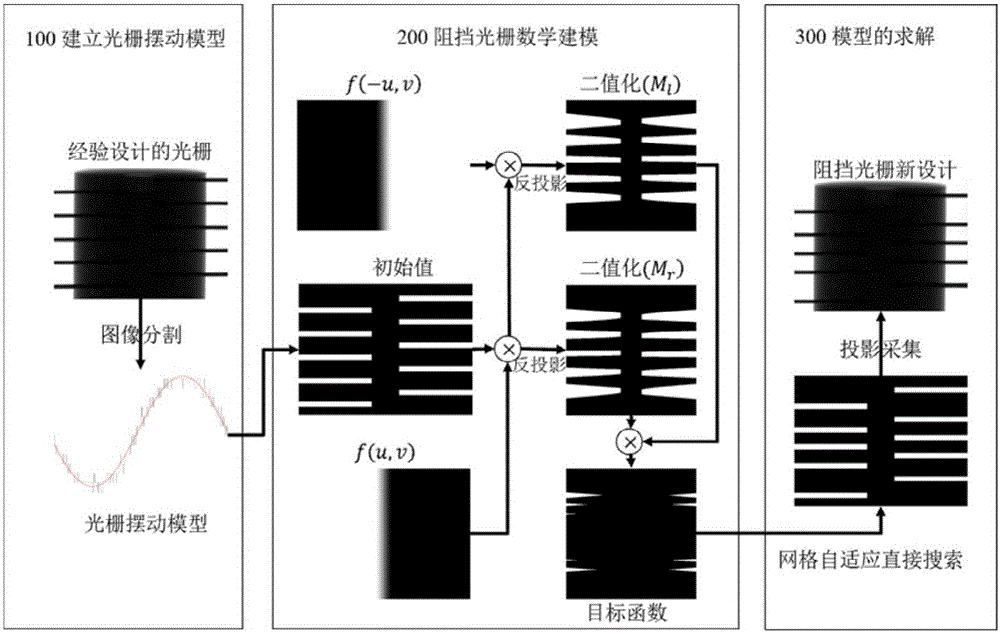
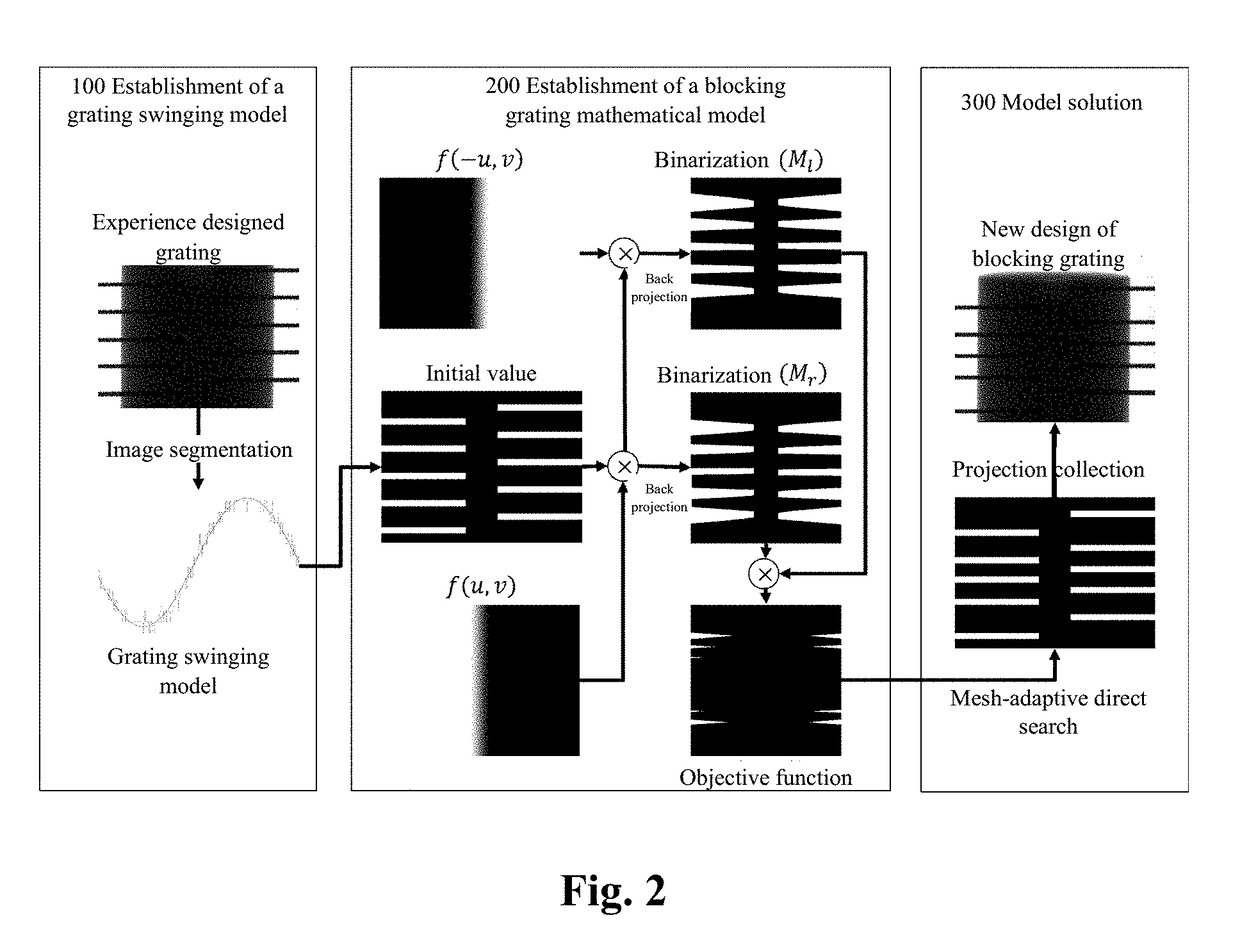
Blocking optical grating optimization method and device for scattering correction of cone-beam CT (computed tomography) image
The present invention provides a blocking optical grating optimization method and device for the scattering correction of a cone-beam CT (computed tomography) image. The method includes the following steps that: a blocking optical grating is scanned, and the swing model of the blocking optical grating is established; the initial coordinates of the blocking optical grating in the longitudinal direction of a detector in an initial projection are set, and an objective function between the data missing voxel value of the CBCT image and the coordinates of the blocking optical grating in the longitudinal direction of the detector is established; and the objective function is minimized by using a mesh adaptive direct search algorithm, so that the optimized coordinates of the blocking optical grating in the longitudinal direction of the detector can be generated. According to the brand new scattering correction method which does not require source compensation and is suitable for clinical CBCT in the present invention, mathematical optimization modeling is performed for data loss in an image field caused by the blocking optical grating; influence on a reconstructed image caused by the blocking device is quantitatively evaluated; the geometric optimal structure of the blocking device is solved by means of the mesh adaptive direct search method; and a solid theoretical basis is established for blocking device measurement-based scattering correction methods.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
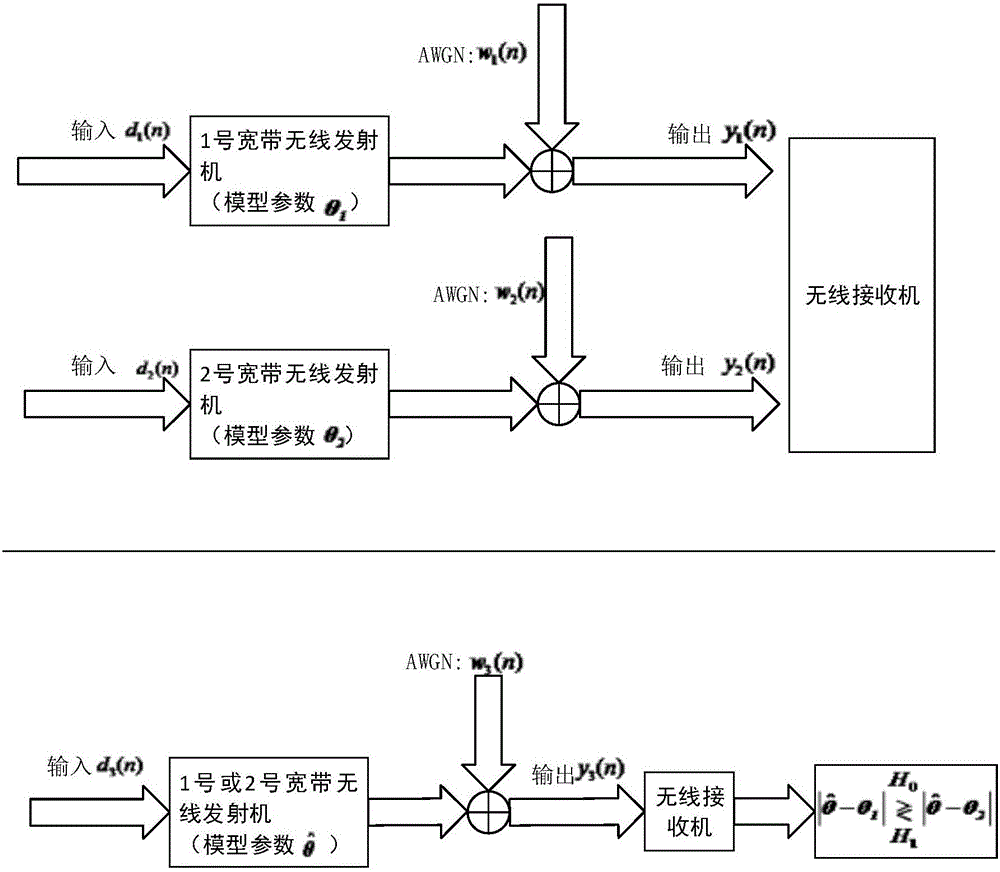
Method for identifying broadband wireless transmitter based on Hammerstein-Wiener model
The invention discloses a method for identifying a broadband wireless transmitter based on the Hammerstein-Wiener model: the first step: modeling the broadband wireless transmitter; the second step: using an improved adaptive niche genetic algorithm (or grid adaptive direct search (mads) algorithm, adaptive niche genetic algorithm and other model identification algorithms) carry out Hammerstein-Wiener model parameter identification, and obtain the estimated model parameter vector; the third step: broadband wireless transmitter identification. The invention has strong global optimization and local optimization capabilities, and has the advantages of good robustness and high identification accuracy, and its effectiveness is verified in the identification of broadband wireless transmitters.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
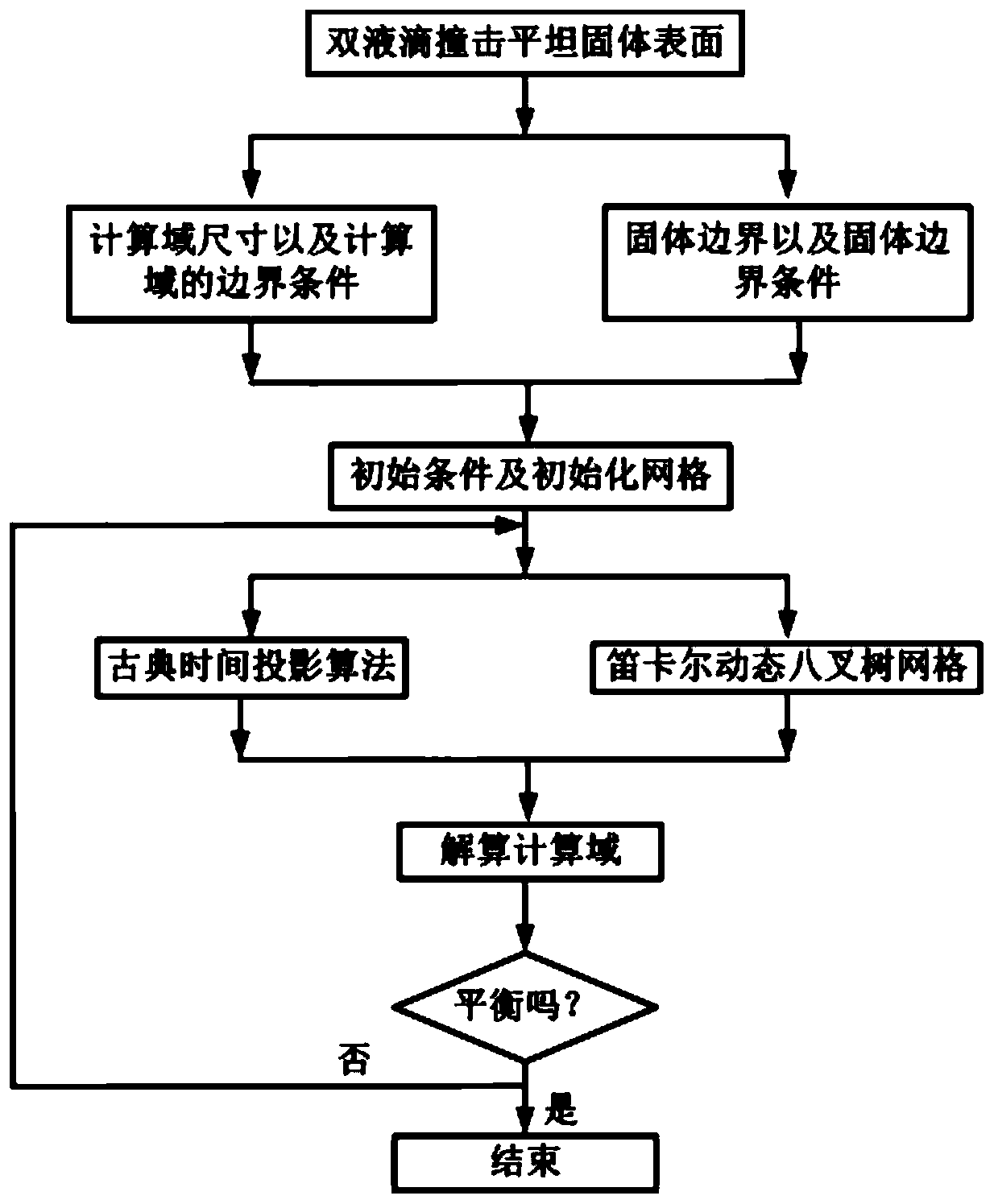
Numerical simulation test method for impacting flat solid surface by double liquid drops based on VOF and dynamic grid self-adaption
InactiveCN111144003ARealize simulationExact Numerical Calculation MethodDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingAdaptive refinementEngineering
The invention discloses a numerical simulation test method for impacting a flat solid surface by double liquid drops based on VOF and dynamic grid self-adaptation. The method comprises the steps thatfirstly, an ideal computational domain size is defined in gerris software, and boundary conditions of a computational domain are determined; secondly, importing a solid boundary and defining a solid boundary condition; secondly, assigning an initial condition, and giving an initialization grid; furthermore, a Cartesian grid dynamic self-adaptive refining function is used; then, resolving the wholecalculation domain, and outputting a corresponding calculation result; and finally, importing the output calculation result into the simulation result of the visualized gerris in the text. Accordingto the method, the numerical simulation method for impacting the flat solid surface by the double liquid drops based on VOF and dynamic grid self-adaptation is achieved, the flowing process of impacting the flat solid surface by the double liquid drops is obtained, and an accurate numerical calculation method is provided for analyzing the flowing rule and flow state characteristics of the flat solid surface by the double liquid drops.
Owner:ANHUI POLYTECHNIC UNIV MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL COLLEGE
Circular foundation pit stability analysis method based on limit analysis upper limit theorem
PendingCN112069574AStability solutionImprove calculation accuracyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationMathematical modelArchitectural engineering
The invention discloses a circular foundation pit stability analysis method based on a limit analysis upper limit theorem, belongs to the technical field of geotechnical foundation pit engineering stability analysis, takes a circular foundation pit as a research object, and comprises the following steps: according to the actual situation of the circular foundation pit, drawing up basic informationfor performing circular foundation pit stability; dispersing the circular foundation pit by adopting a triangular three-node plastic unit; generating a constraint control equation obeying a limit analysis upper limit theorem; establishing an upper limit finite element method mathematical optimization model for solving the stability of the circular foundation pit; performing numerical solution ofthe mathematical model of the circular foundation pit stability upper limit finite element method; and introducing a local grid adaptive encryption technology to automatically carry out local grid encryption on the damaged area. Compared with a traditional limit equilibrium analysis method, the method has higher calculation precision; compared with a finite element method, the method neglects theconstitutive relation of the material, so that the calculation speed and efficiency are higher.
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF TECH
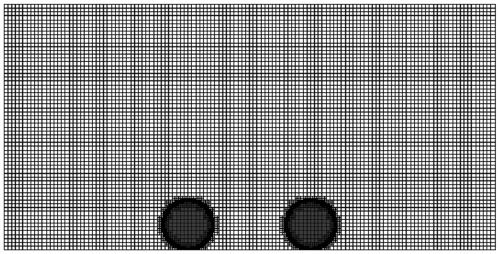
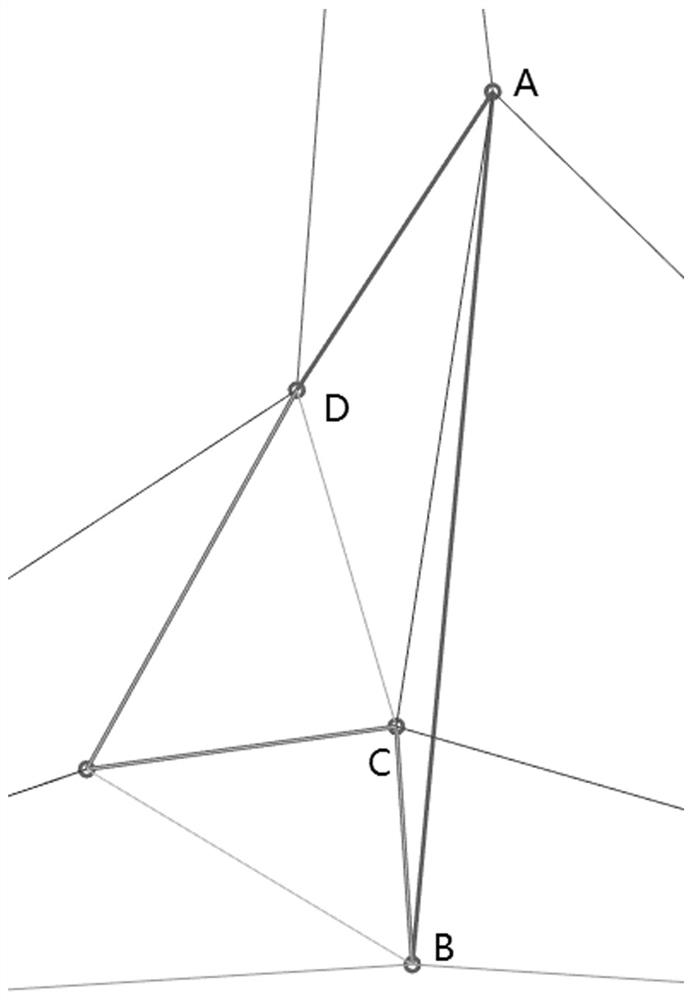
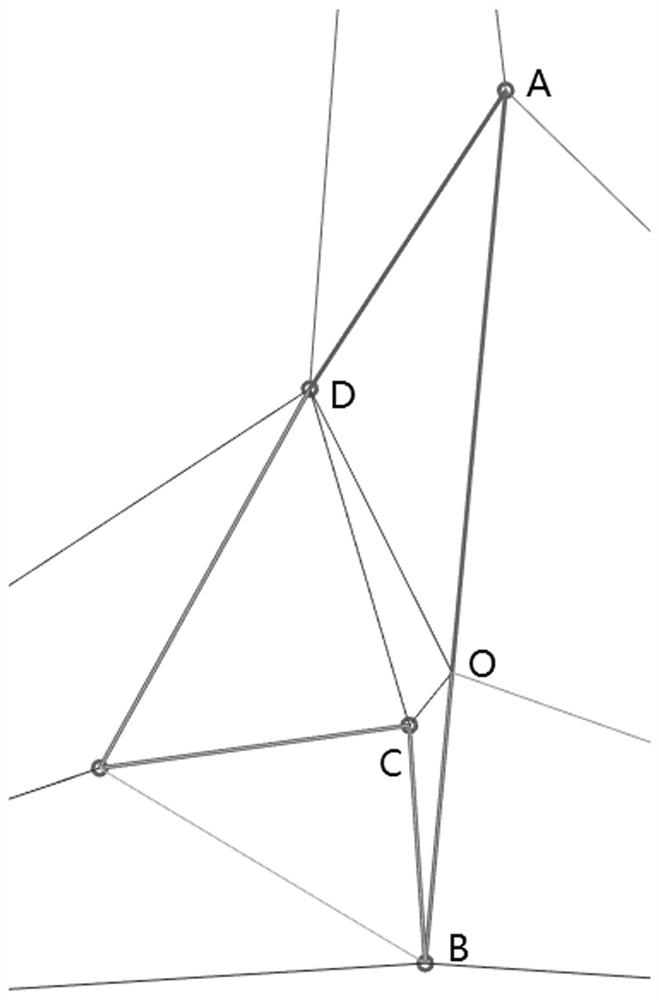
Self-adaptive subdivision method and system for polygonal unstructured grids of integrated circuit layout
ActiveCN111767688AHigh precisionImprove efficiencyCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsComputational scienceVery large scale integrated circuits
The invention relates to a self-adaptive subdivision method and system for polygonal unstructured grids of an integrated circuit layout. The method comprises the following steps: sequentially inserting eccentric midpoints into existing grids according to lost and eroded polygonal edges so as to recover the lost polygonal edges and eliminate the eroded polygonal edges; determining to-be-subdividedtriangles according to a set ratio / minimum angle threshold value; and sequentially inserting the centers of the eccentric circles of the to-be-subdivided triangles into the existing grids to eliminatethe to-be-subdivided triangles, wherein recovering of lost polygon edges, eliminating of eroded polygon edges and eliminating of to-be-subdivided triangles are performed in an interlacing manner until no lost and eroded polygon edges and to-be-subdivided triangles exist in the polygon unstructured grids of the integrated circuit layout so as to finally form a new unstructured grid of the super-large-scale integrated circuit layout, so that the problem that in the prior art, due to redundancy generated by newly-inserted nodes, local grids are too dense is solved, the grid subdivision precisionand the numerical calculation efficiency are improved, and the calculation memory is reduced.
Owner:北京智芯仿真科技有限公司
Self-adaptive grid disturbance domain updating acceleration method for aircraft aerodynamic characteristic prediction
ActiveCN113850008AOptimize technical approachImprove acceleration performanceGeometric CADSustainable transportationShock waveAlgorithm
The invention discloses a self-adaptive grid disturbance domain updating acceleration method for aircraft aerodynamic characteristic prediction, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, providing a novel data format for coupling storage of a self-adaptive grid and a dynamic computational domain so as to realize efficient storage and traversal of dynamic computational domain information on the self-adaptive grid; secondly, establishing a self-adaptive detector capable of identifying characteristic units which are positioned in a detached strong shock wave region and are slow in convergence and the like; thirdly, establishing a self-adaptive strategy of the anisotropic encrypted grid in the decoupled strong shock wave region, which can accelerate convergence and can minimize calculation increment; and finally, establishing coupling logic of adaptive grid encryption and dynamic computational domain updating and an algorithm thereof, and proposing a self-adaptive grid disturbance domain updating acceleration method. According to the method, the acceleration effect of an existing disturbance domain updating method can be further improved; compared with a traditional global updating method, the method can provide a technical approach for optimizing the grid and the computational domain at the same time for aerodynamic characteristic prediction of the aircraft.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
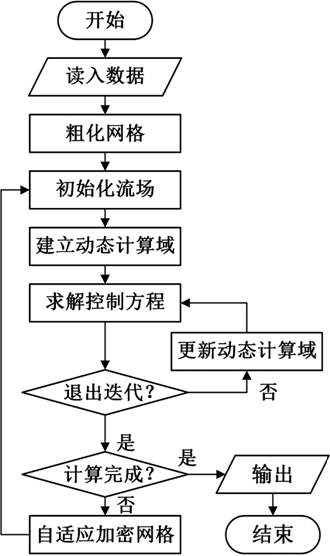
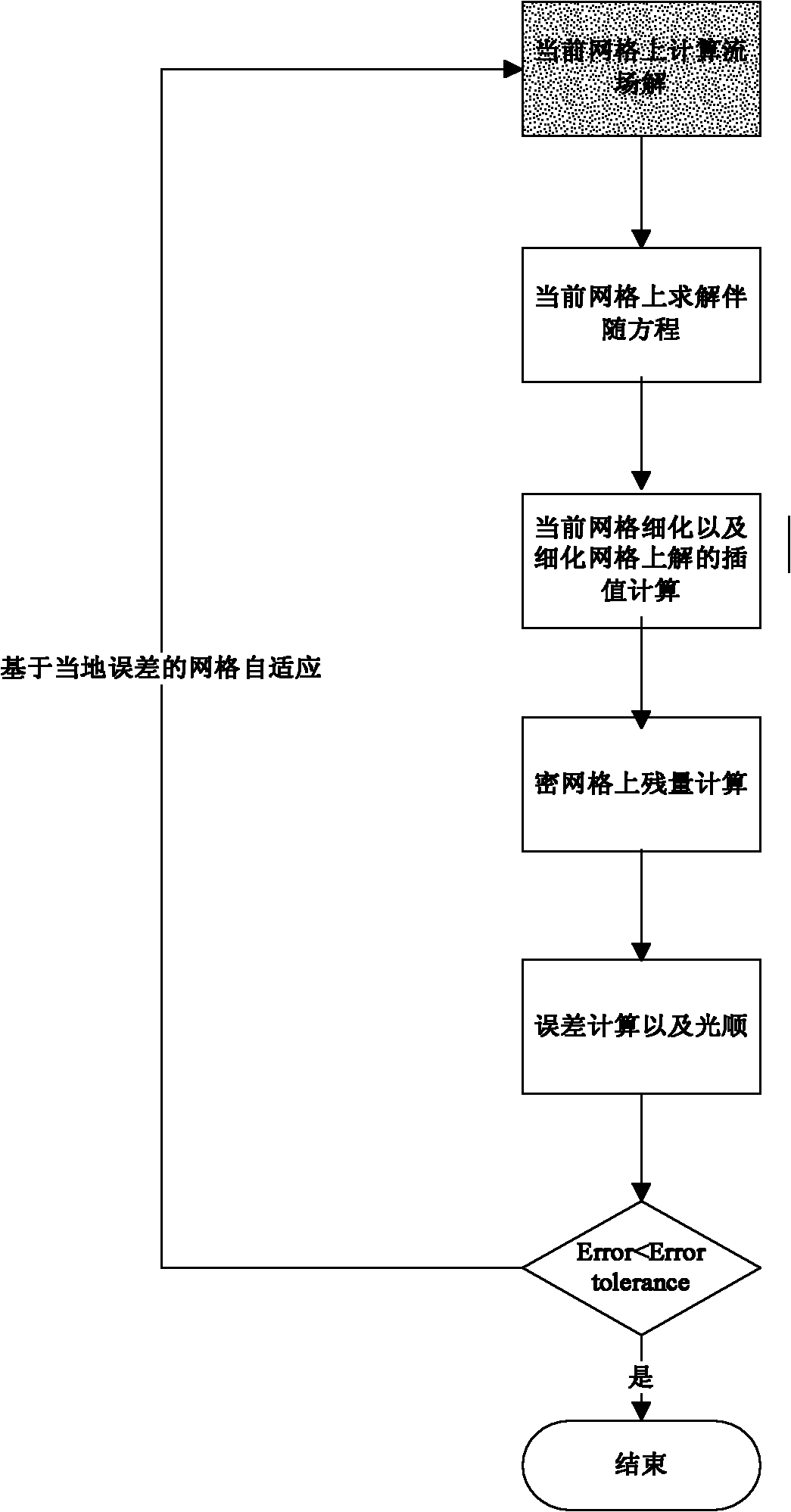
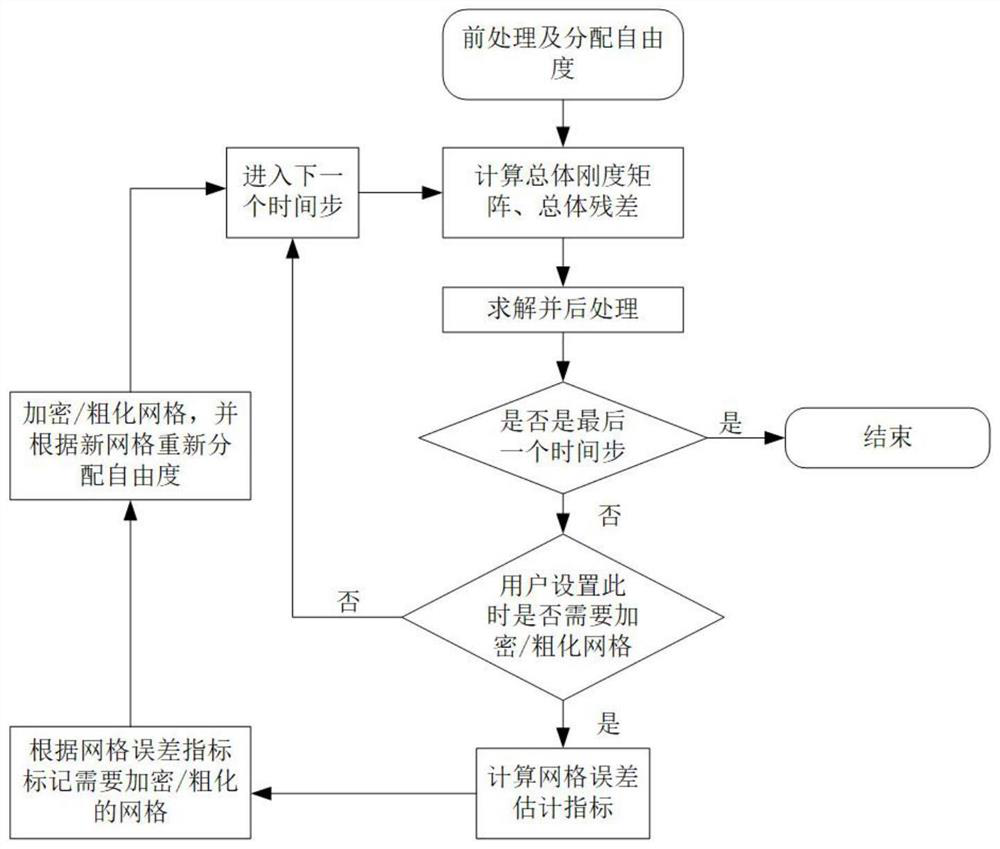
Grid self-adaptive method based on error estimation
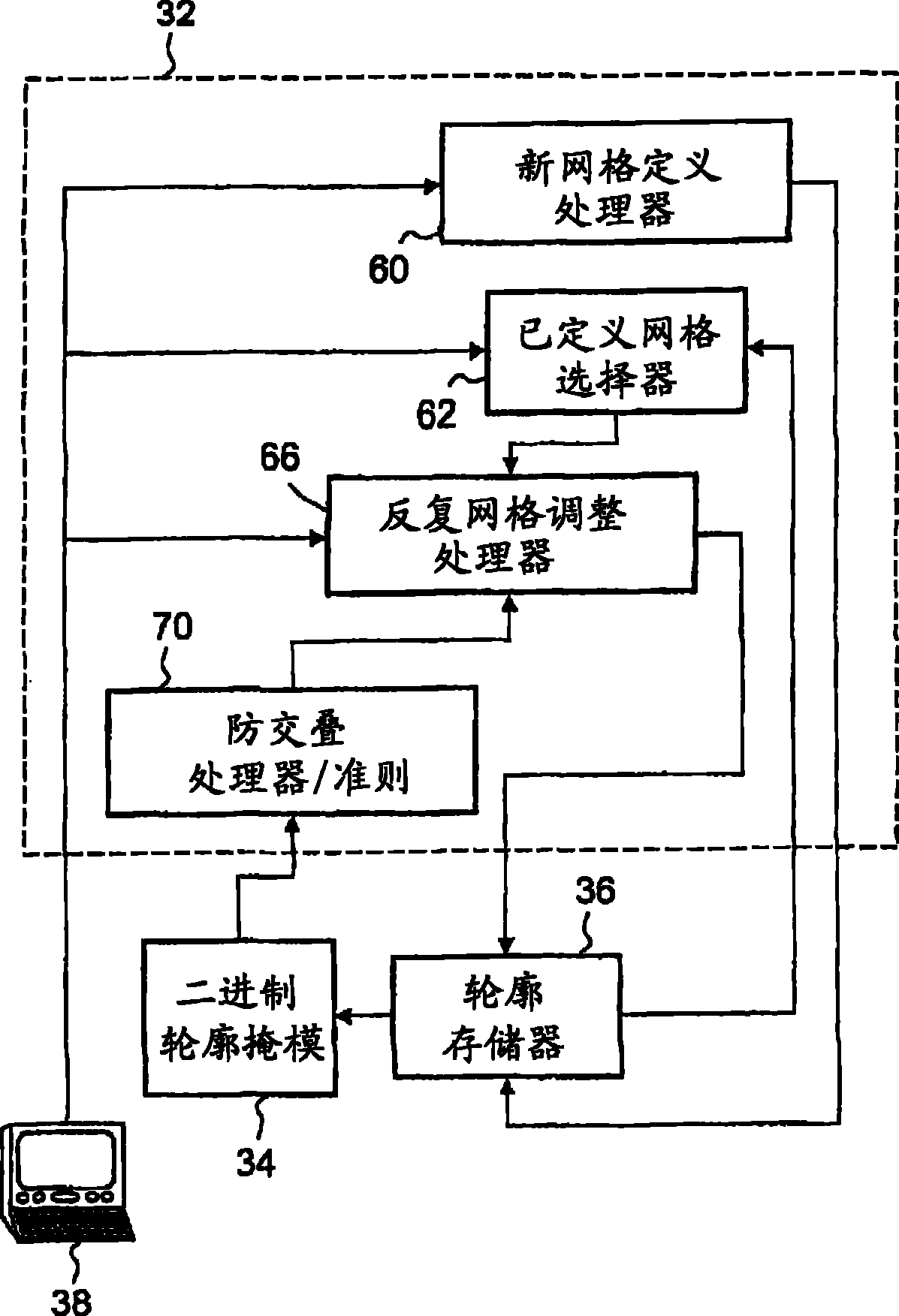
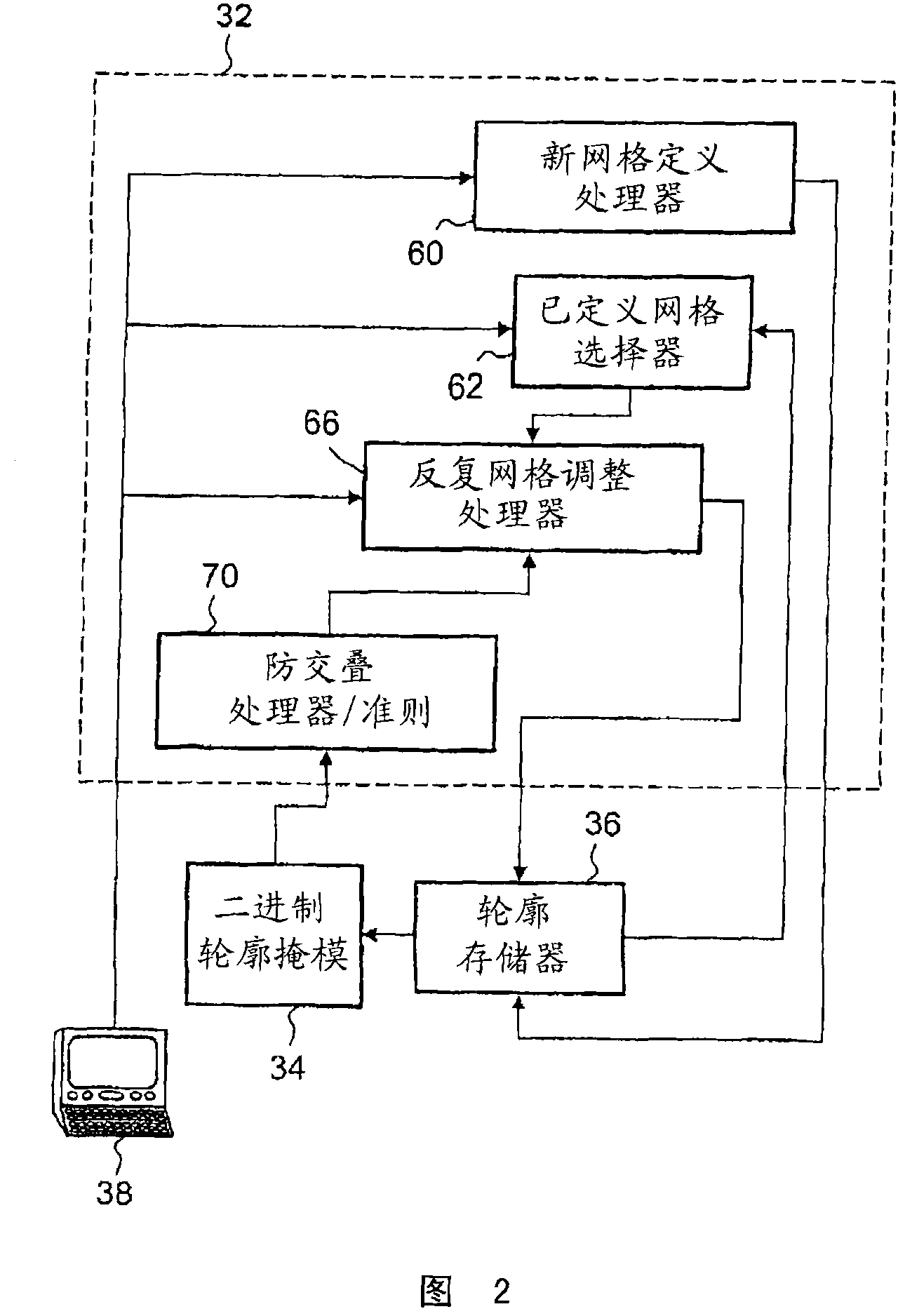
InactiveCN102043887AImplement adaptive fine-grained encryptionImprove high-precision computing capabilitiesSpecial data processing applicationsErrors and residualsGrid cell
The invention relates to a grid self-adaptive method based on error estimation, comprising the following steps: 1) determining a target function; 2) obtaining a flow field solution and an adjoint solution based on the current grids of the target function; 3) constructing fine grids corresponding to the current grids; 4) interpolating the corresponding quantity of the current grids in the fine grids, and constructing an interpolation operator from a current grid solution to a fine grid solution; 5) calculating the residual amount of the flow field on the fine grids; and 6) carrying out error estimation and fairing, if the error is more than a set error, marking the current grids for fining, and returning to the step 2) after the fining is finished, and if the error is less than the set error, avoiding fining on the current grids. By utilizing the grid self-adaptive method, the error of the target function can be estimated according to the specified target function as well as a flow field control equation and the solutions of an adjoint equation thereof under the specific flow condition, self-adaptive local grid refinement is carried out according to the error, and then the calculation of the target function with higher accuracy is realized on the self-adaptive grids.
Owner:AVIC NO 631 RES INST
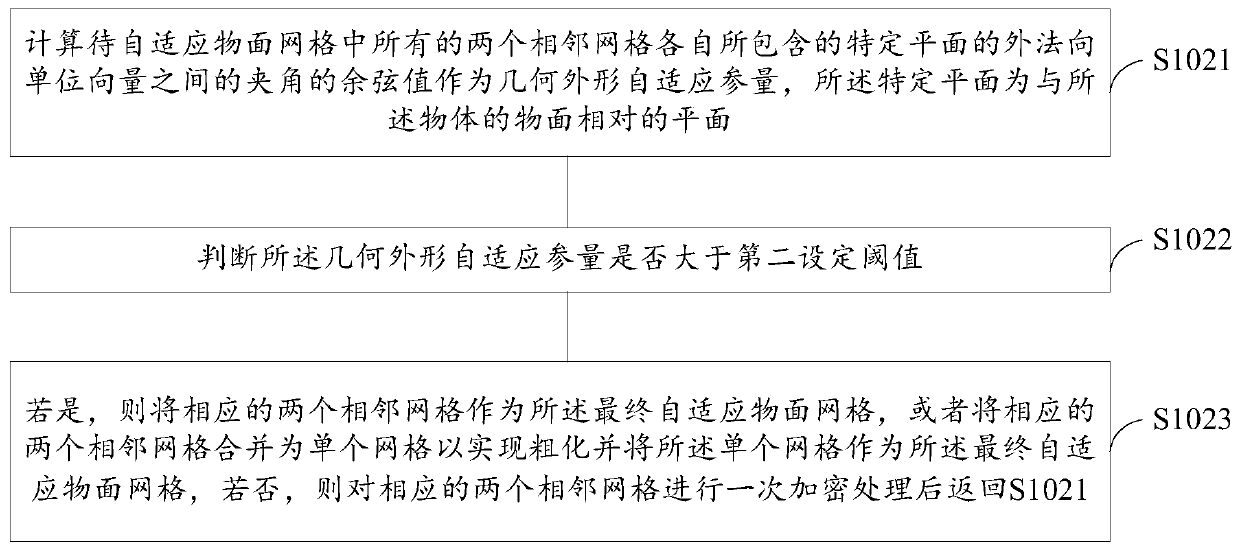
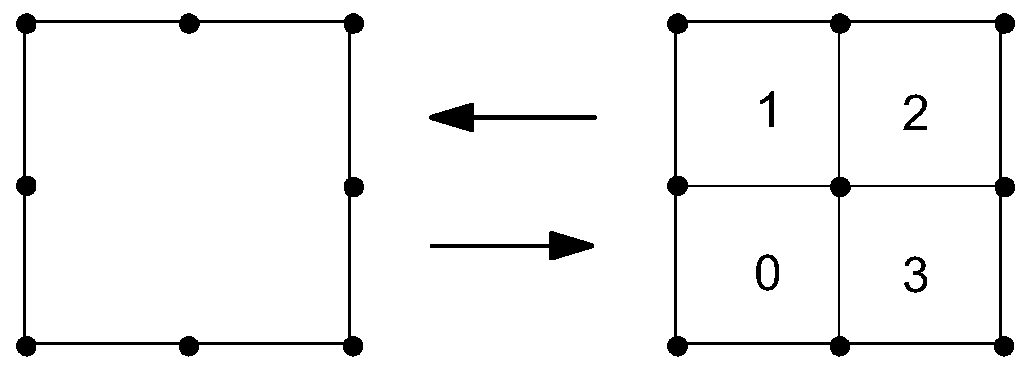
Right-angle grid self-adaptive modeling method suitable for grid Boltzmann method
ActiveCN111489447AReduce in quantityRealize computingDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsModelSimClassical mechanics
The embodiment of the invention discloses a right-angle grid self-adaptive modeling method suitable for a grid Boltzmann method. The modeling method comprises the following steps: S101, dividing a root grid unit into right-angle sub-grid units to obtain an initial grid comprising an initial object plane grid and an initial flow field grid; S102, performing right-angle grid self-adaptive processingon the initial object plane grid to obtain a final self-adaptive object plane grid, and taking the final self-adaptive object plane grid and the initial flow field grid as an initial calculation grid; S103, solving the flow field by adopting a lattice Boltzmann method based on the current calculation grid to obtain a current flow field calculation result, and obtaining a flow field calculation adaptive parameter based on the current flow field calculation result; S104, judging whether all flow field calculation self-adaptive parameters are smaller than a first set threshold value or not; S105, if so, taking the current flow field calculation result as a final flow field calculation result, and if not, carrying out right-angle grid adaptive processing on the current flow field grid, takingthe current flow field grid and the final adaptive object plane grid as a new calculation grid, and returning to the step S103.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
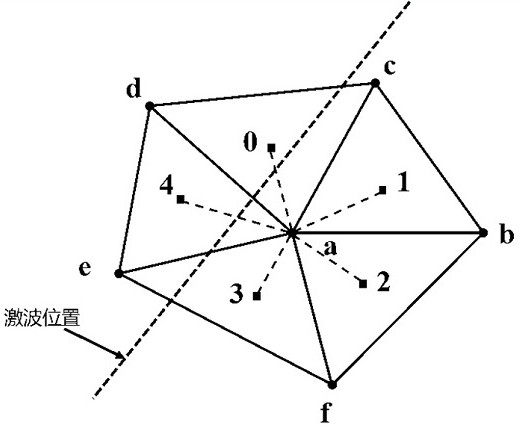
Variable difference and relative displacement-based r-type grid adaptive movement method and equipment
ActiveCN112665820AMobile synchronizationEliminate movement effectsAerodynamic testingMesh adaptationMesh point
The invention discloses a variable difference and relative displacement-based r-type grid adaptive movement method and equipment, two kinds of parameters including the variable difference of normalized grid points and the relative displacement of the grid points are used as a weight function for calculating the movement of the grid points, and the following movement of the grid points is realized by adding the weight function, namely the relative displacement of the grid points. The influence of the magnitudes and dimensions of the two types of parameters on the movement amount of the grid points is eliminated by normalizing, a new combined weight is formed by the two types of parameters so as to determine the displacement of the grid points near the shock wave, and the displacement information of the grid points near the shock wave is transmitted to the adjacent grid points of the grid points. Several rows of grid points near the shock wave can synchronously move to the shock wave position. By normalizing the physical quantity and the grid point position movement amount, the influence of two types of parameter values and dimensions on the grid point movement amount is eliminated, the grid points at the shock wave position can be effectively close to the shock wave position, and meanwhile it can be guaranteed that several rows of grid points near the shock wave synchronously move to the shock wave position.
Owner:CALCULATION AERODYNAMICS INST CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
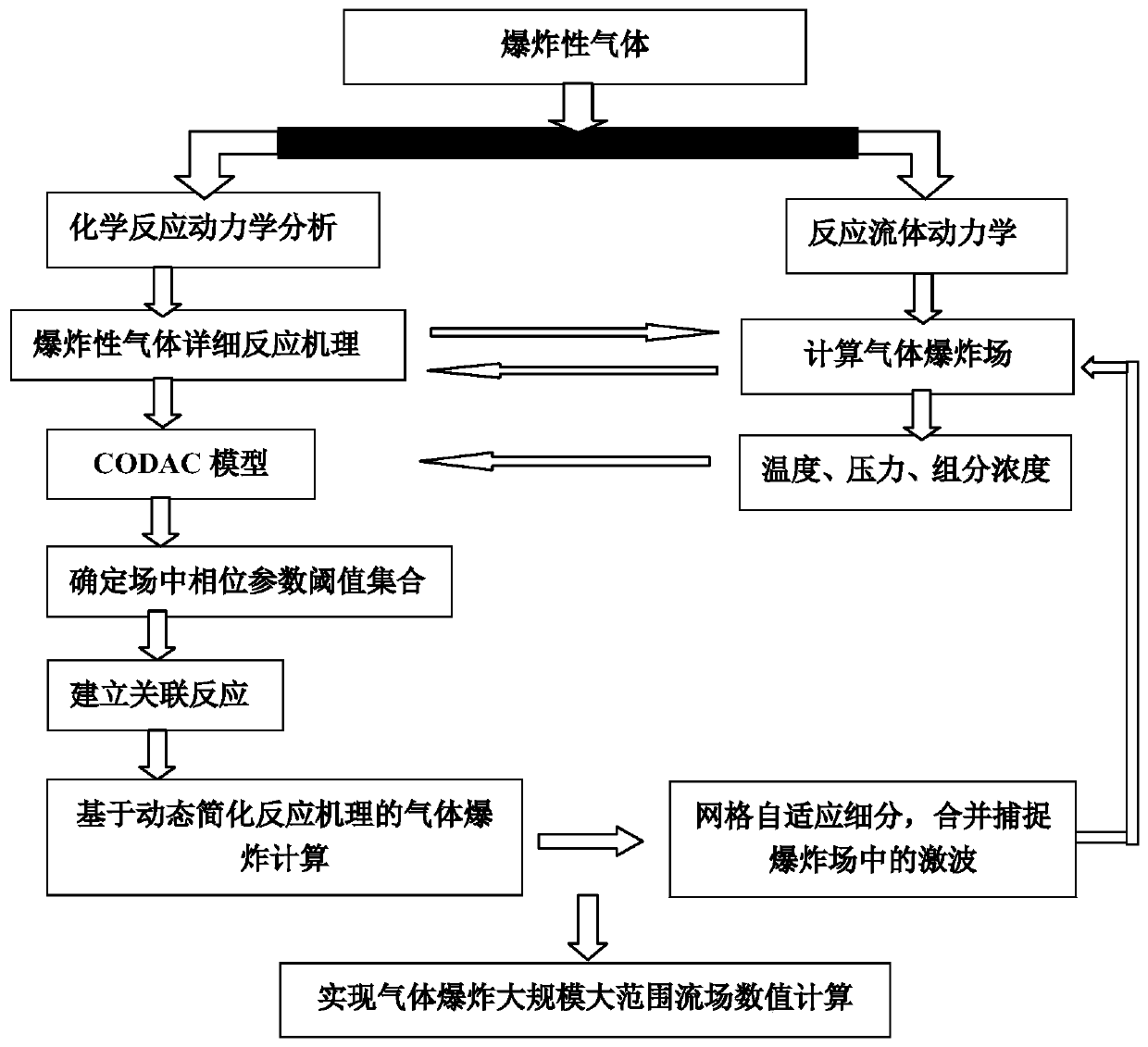
Gas explosion simulation method based on self-adaptive simplified reaction and mesh subdivision
ActiveCN106503379AReduced responseImprove computing efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsShock waveChemical reaction kinetics
The invention discloses a gas explosion simulation method based on a self-adaptive simplified reaction and mesh subdivision. The gas explosion simulation method is characterized by comprising the steps that explosive gas component attributes are determined; chemical reaction kinetics analysis is conducted on explosive gas, and an explosive gas detailed reaction mechanism; a phase parameter threshold set in an explosion field generated through explosion is determined by adopting the detailed reaction mechanism obtained through a self-adaptive simplified reaction method; self-adaptive mesh subdivision is conducted on areas high in pressure and density gradient in the explosion field, and shock waves in the explosion field and time-space evolution of shock wave temperature, pressure and component concentration are captured. According to the method, the problem that gas explosion safety large-scale simulation is low in computing efficiency in real explosion accident site calculation can be solved.
Owner:京工博创(北京)科技有限公司
A new method of structural mesh generation
ActiveCN109461209AAchieving AdaptivenessImplement local encryptionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTriangulationSelf adaptive
The invention provides a novel structural mesh generation method, which is based on an existing Delaunay triangulation technology to generate a structural mesh. Firstly, the discrete point set and boundary information of the computational region are obtained by reading the model data. Secondly, Delaunay triangulation is applied to the computational region. Then, the triangular mesh is used to generate the transitional mesh: the optimized Voronoi diagram; Finally, the transitional mesh element type is judged, and the mesh element is divided by the central circle method to generate the structured mesh. The invention can realize the automatic generation of the structural mesh of the complex region, and has high calculation precision, and reduces the dependence on human being compared with thetraditional method. Delauny triangulation technology is a mature unstructured mesh generation technology, which can generate adaptive and locally refined high-quality mesh for complex regions efficiently and quickly. This method adopts triangulated mesh as background mesh, so it can also realize mesh adaptation and local refinement.
Owner:CALCULATION AERODYNAMICS INST CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
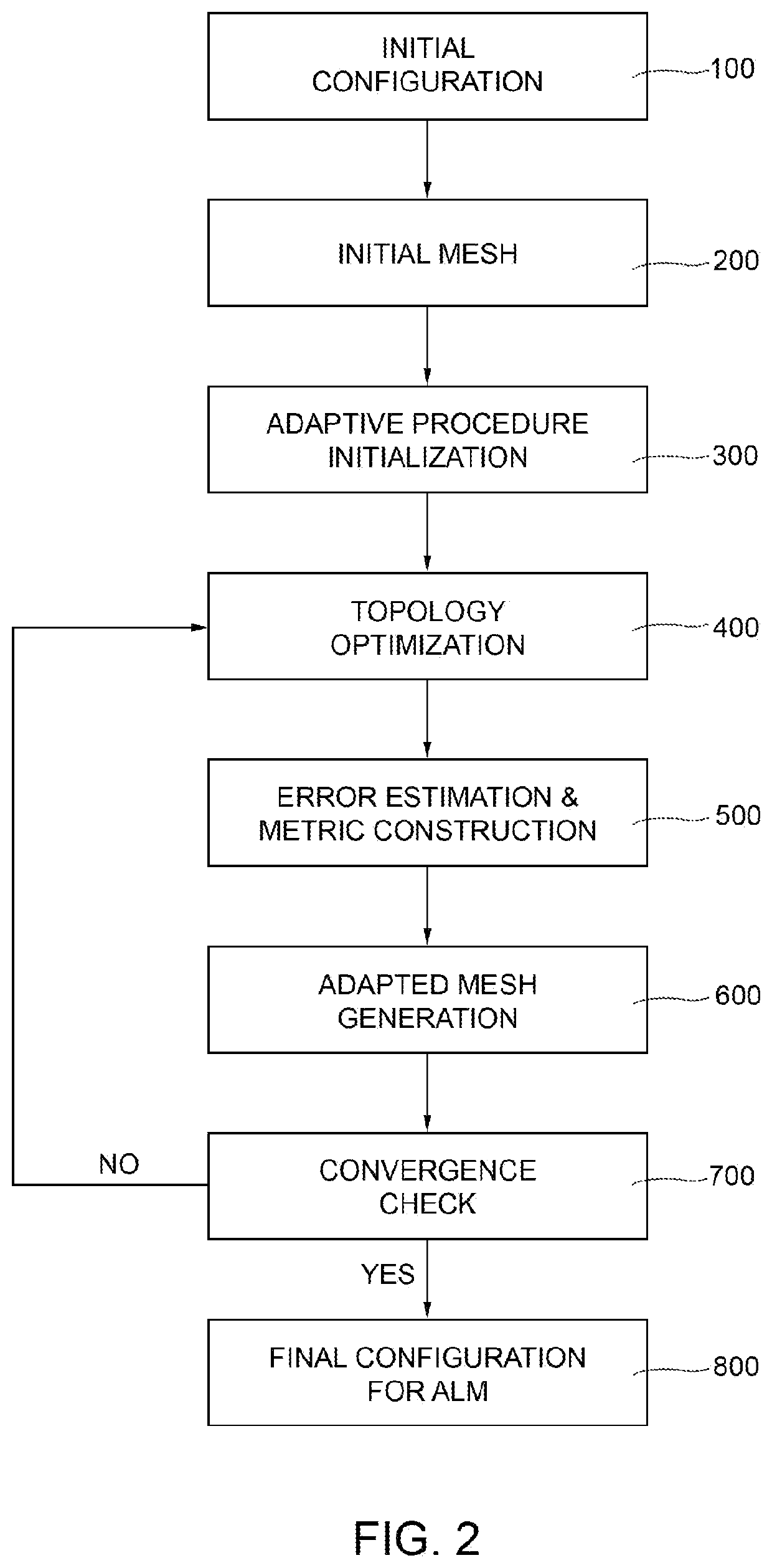
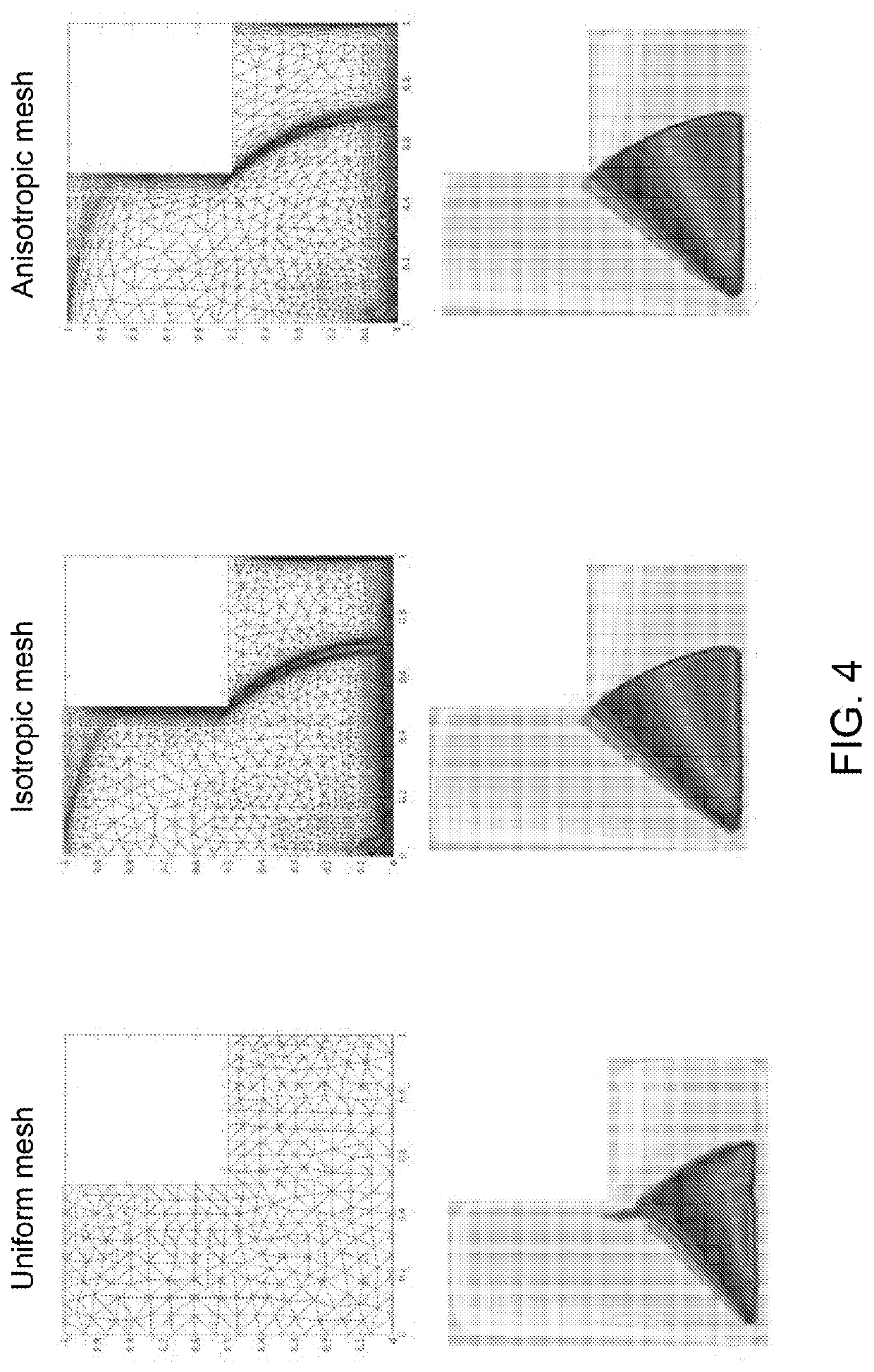
Adaptive Topology Optimization For Additive Layer Manufacturing
InactiveUS20210034800A1Reduce computing costGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
A computer-aided FEM-based structure design system is provided that operates to:acquire an initial structure design configuration comprising:a design domain (Ω),an applied load (f), andconstrained, unconstrained and loaded areas (ΓD, ΓF, ΓN);compute an initial mesh (Th0) of the design domain (Ω);compute a topologically optimized structure model by iterating, until a termination criterion is fulfilled:computing an optimized structure topology by properly implementing the SIMP (Solid Isotropic Material with Penalization) algorithm based on a density function (ρ) that represents the distribution of the material in the structure;computing an anisotropic recovery-based a posteriori error estimator (η) that quantifies the error between the gradient of the exact structure material density (ρ) and the gradient of the FEM-computed approximation thereof,computing a metric (Mk+1) for anisotropic mesh adaptation based on the anisotropic recovery-based a posteriori error estimator (η), andcomputing an adapted anisotropic mesh (Thk+1) based on the metric (Mk+1).
Owner:THALES ALENIA SPACE ITAL SPA +1
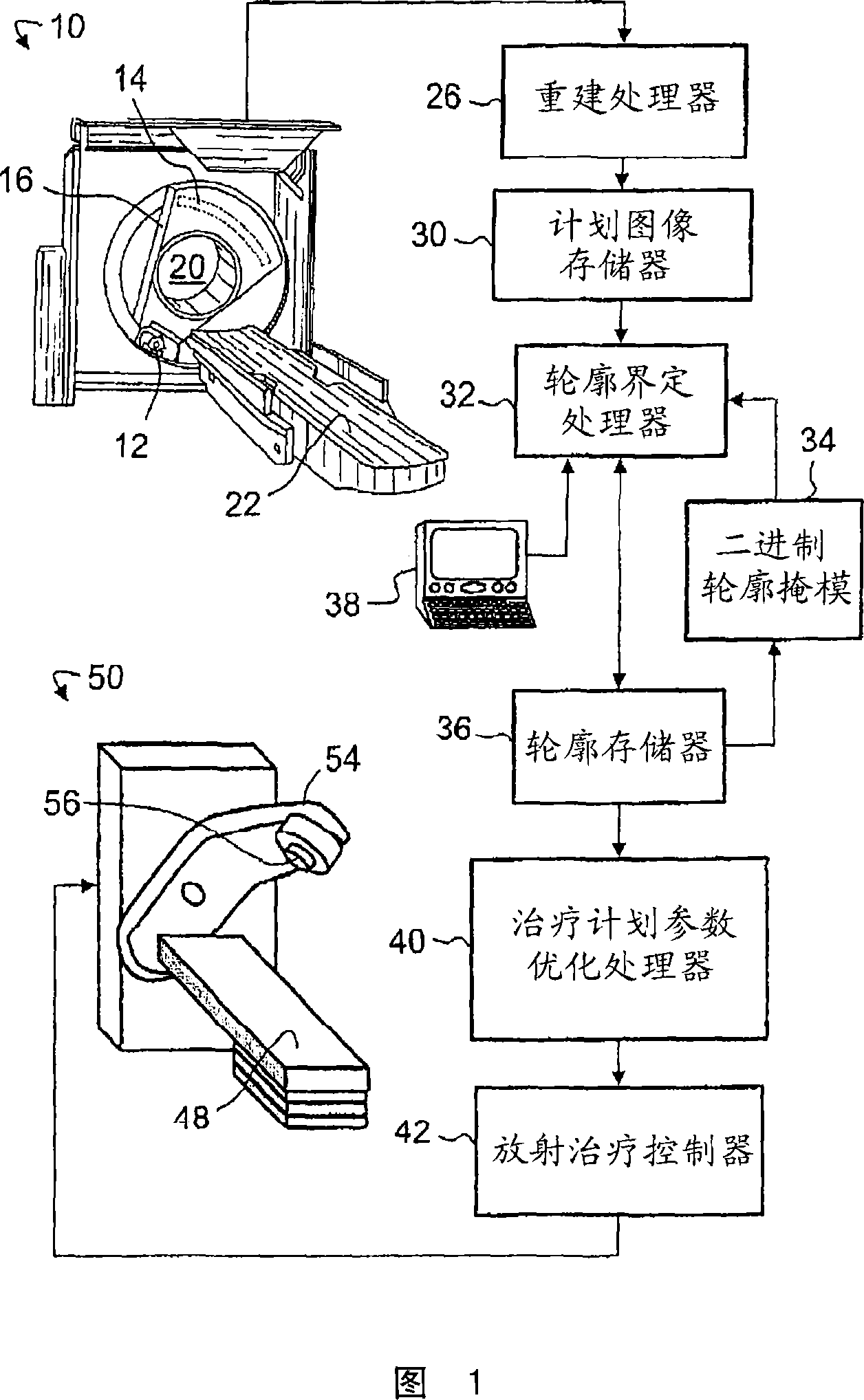
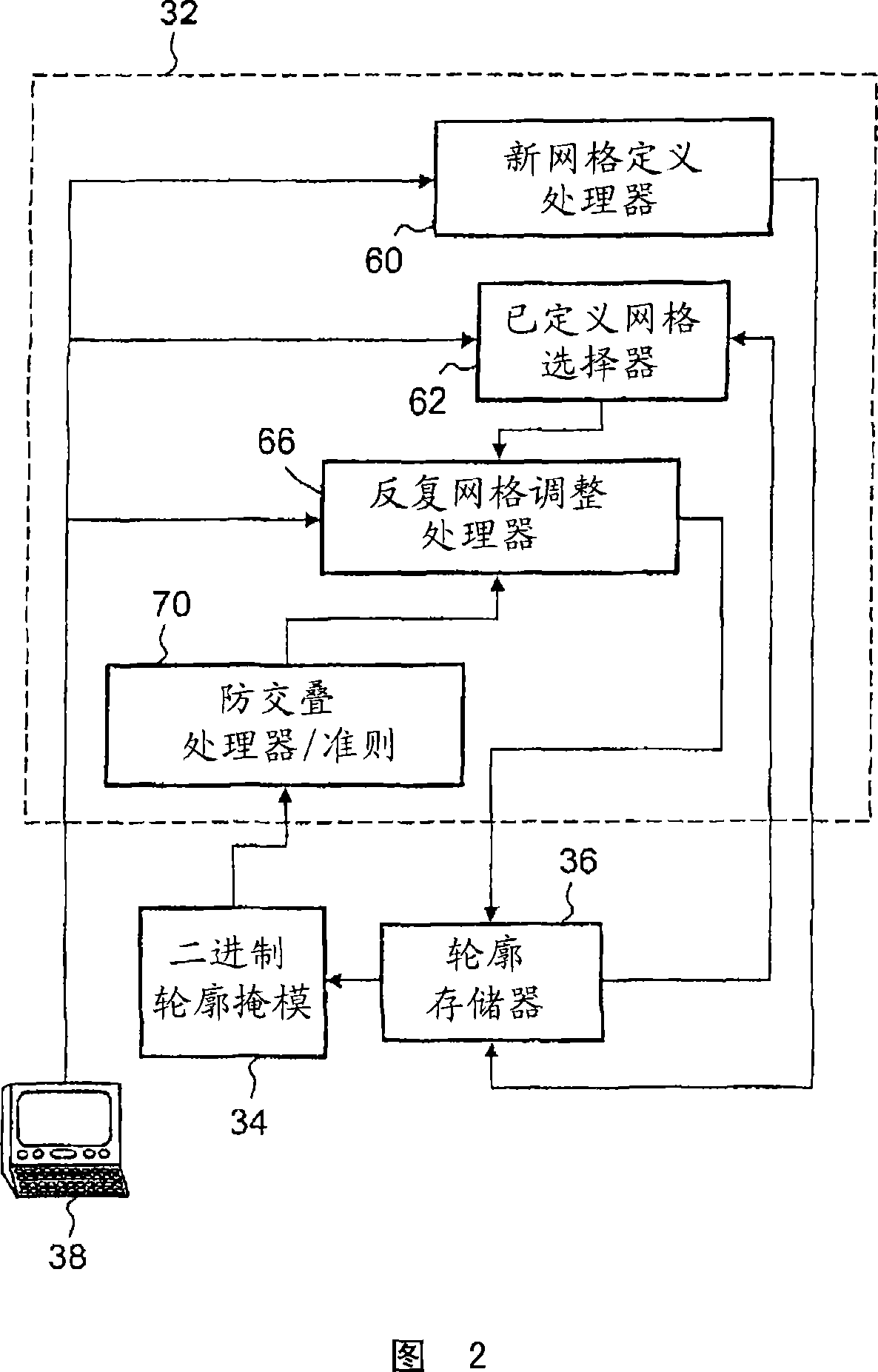
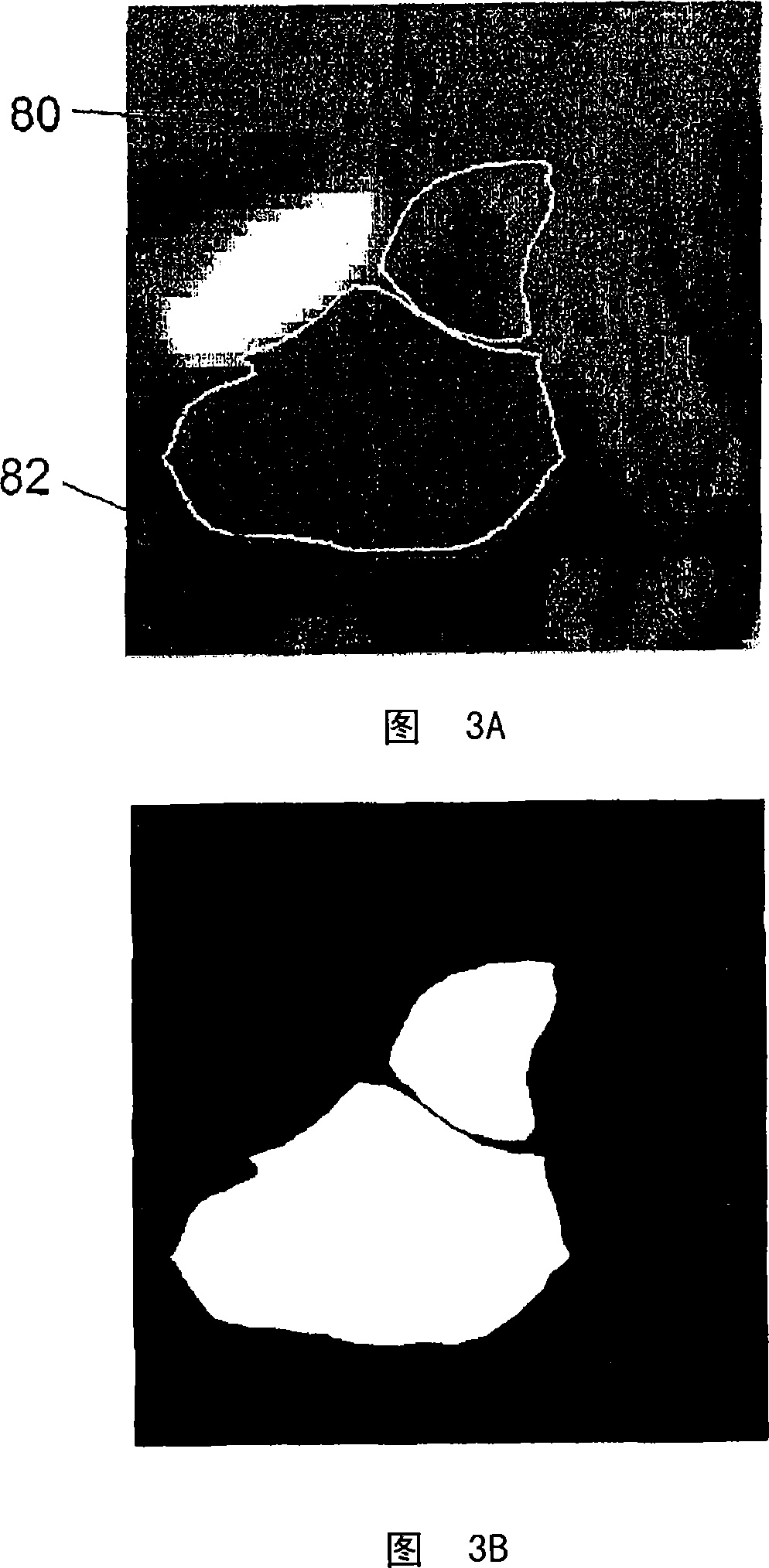
Segmentation based on region-competitive deformable mesh adaptation
ActiveCN101002231AImprove stabilityAvoid overlapping contoursImage enhancementImage analysisImaging FeatureImage segmentation
An image segmentation method segments a plurality of image features in an image. The plurality of image features are segmented non-simultaneously in succession. The segmenting of each image feature includes adapting an initial mesh to boundaries of the image feature. The segmenting of each image feature further includes preventing the adapted mesh from overlapping any previously adapted mesh.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
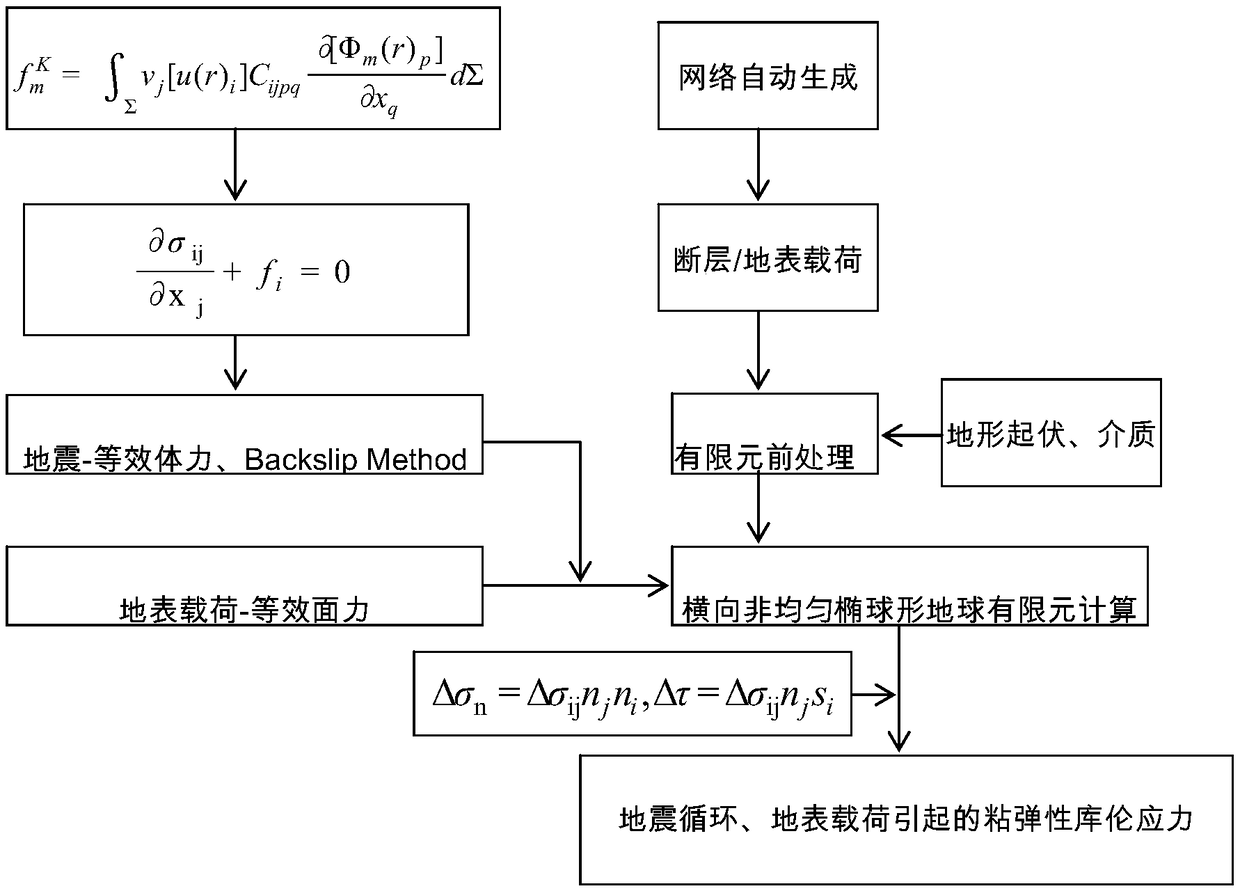
Non-uniform ellipsoid earth earthquake and ground surface load coulomb stress calculation method
ActiveCN109270590AComputationally comprehensive and accurateComprehensive and accurate stress changesGeological measurementsEarth surfaceLandform
The invention discloses a non-uniform ellipsoid earth earthquake and ground surface load coulomb stress calculation method. According to the method, seismic shear dislocation and ground surface load are respectively equivalent to a body force item and a surface force item in finite element calculation; and calculation accuracy is guaranteed with a local grid adaptive encryption technology. With the method adopted, the coulomb stress change of the coulomb stress of an earthquake, including inter-seismic, co-seismic and post-seismic coulomb stress, and coulomb stress change caused by ground surface load, such as the loading and unloading of topographic erosion, glacial ablation and reservoir water pumping and impounding can be calculated. The method includes the following specific steps of:equivalent substitution of seismic shear dislocation and ground surface load; grid adaptive encryption; viscoelastic maxwell volume fractional constitutive recursive realization; lateral non-uniform ellipsoidal earth implementation; and automatic calculation by a program. The method of the invention is more comprehensive and accurate in calculation, and embodies the whole process of the earthquakeand volcanic coulomb stress change of the shallow superficial sphere of the earth.
Owner:NAT INST OF NATURAL HAZARDS MINISTRY OF EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT OF CHINA
Segmentation based on region-competitive deformable mesh adaptation
ActiveCN101002231BAvoid overlappingImprove stabilityImage enhancementImage analysisImaging FeatureImage segmentation
An image segmentation method segments a plurality of image features in an image. The plurality of image features are segmented non-simultaneously in succession. The segmenting of each image feature includes adapting an initial mesh to boundaries of the image feature. The segmenting of each image feature further includes preventing the adapted mesh from overlapping any previously adapted mesh.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
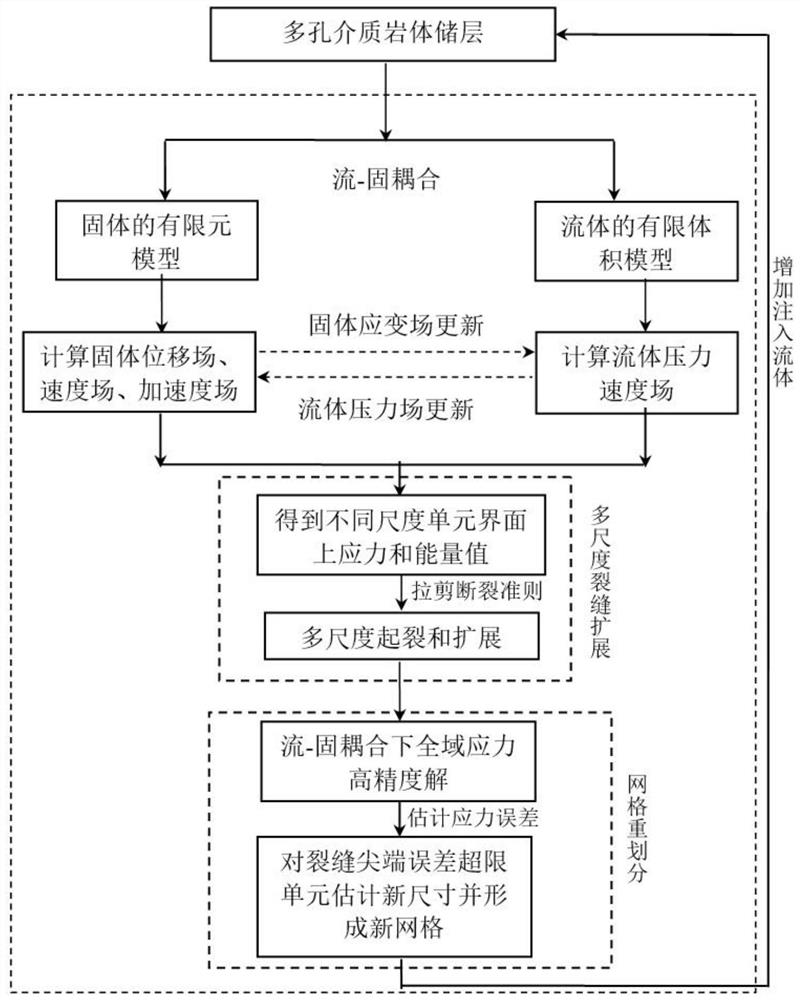
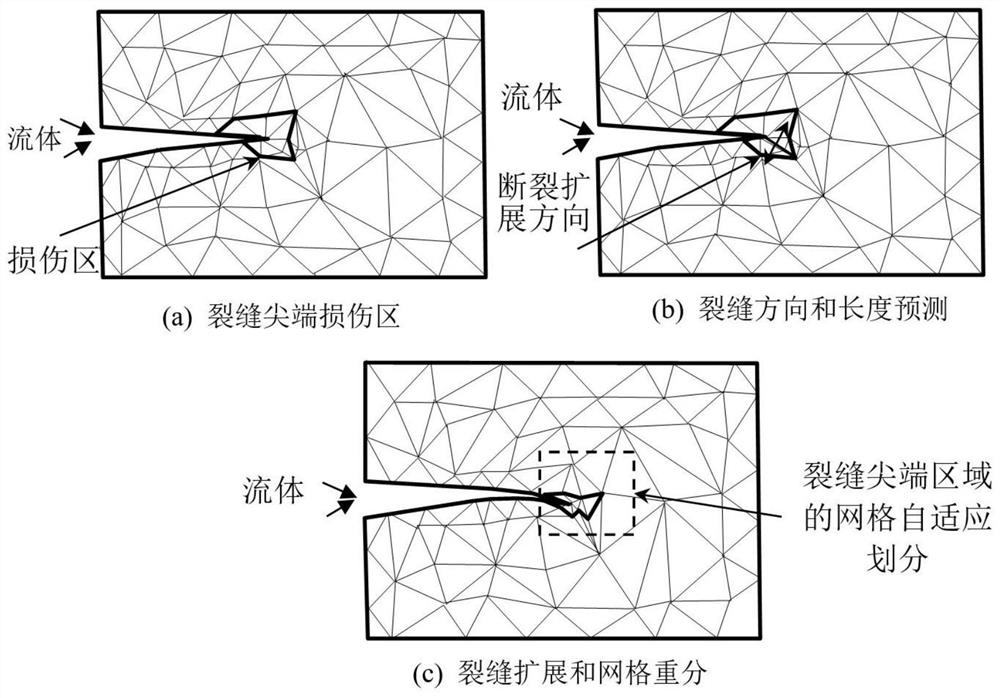
Grid adaptive method for multi-scale expansion of hydraulic fracturing crack
PendingCN113919201AEfficient Multiscale Scaling BehaviorAchieving fully coupled discretizationFluid removalDesign optimisation/simulationEngineeringHydraulic fracturing
The invention discloses a grid adaptive method for multi-scale expansion of a hydraulic fracturing crack. The grid adaptive method comprises the following steps of fluid-solid coupling result calculation, multi-scale fracture judgment, stress error estimation and grid re-division. The coupling method based on the finite element, the discrete element and the finite volume method overcomes the difficulty of high-precision simulation of the multi-scale problem in a traditional numerical method, the multi-scale extension behavior of the hydraulic fracturing fracture network can be effectively simulated, the simulation result is more accurate and effective, the Darcy law is integrated into the model, the percolation effect is considered, fluid leakage is controlled, complete coupling discretization of single-phase flow in the fractured porous medium is achieved through a finite volume method, the problem of grid division of a traditional finite element in a fracture tip area is solved, the difficulties in the aspects of large-scale fractures of an engineering model and small-scale fractures of a laboratory model are solved, and the problem that it is difficult to reliably and effectively solve the multi-scale expansion of the hydraulic fracturing crack is solved.
Owner:王永亮
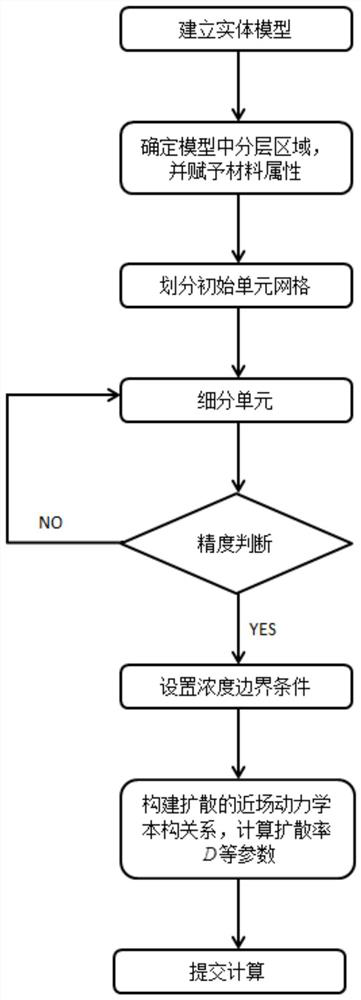
Near-field dynamic modeling method for composite mass diffusion problem
ActiveCN108319774AHigh precisionImprove adaptabilityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsModel parametersEntity model
The invention discloses a near-field dynamic modeling method for a composite mass diffusion problem. The method comprises the following steps of 1, building an entity model; 2, cutting the entity model, determining layering and mixing region positions of materials in the model, and giving corresponding material attributes to the regions; 3, dividing the entity model into unit grids; 4, setting concentration boundary conditions of the entity model; 5, on the basis of mass diffusion near-field dynamic constitutive relation, integrating model parameters, determining a calculation method for concentration changes of a diffusing substance in a composite in the entity model, and calculating operation parameters of all units in the entity model; 6, performing submission calculation. The modelingmethod is high in precision and good in grid adaptability, all the parameters in the model are preprocessed, the operation complexity can be greatly lowered, and an algorithm is greatly optimized; themodeling method and the operation process are large in adaptability and applicable to many problems.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method and apparatus for optimizing blocking grating for cone beam ct image scattering correction
ActiveUS20180132807A1Accurate signalIncrease the number ofRadiation diagnostics testing/calibrationRadiation diagnostic image/data processingVoxelGrating
A method and apparatus for optimizing a blocking grating for cone beam CT image scattering correction, wherein the method comprises: scanning a blocking grating to establish a swinging model thereof; setting initial coordinates of the blocking grating along a longitudinal direction of a detector in an initial projection, and establishing an objective function between CBCT image data missing voxel values and the coordinates of the blocking grating along the longitudinal direction of the detector according to the swinging model; minimizing the objective function with a mesh-adaptive direct search algorithm to generate optimized coordinates of the blocking grating along the longitudinal direction of the detector. The present disclosure proposes a brand new scattering correction method not requiring any source compensation, performs a mathematical optimization modeling of the data missing caused by the blocking grating in the image domain, quantitatively evaluates the influence on the reconstructed image by a blocker, solves a geometric optimal structure of the blocker using a mesh-adaptive direct search algorithm, and lays a solid theory foundation for the scattering correction method based on the blocker measurement.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
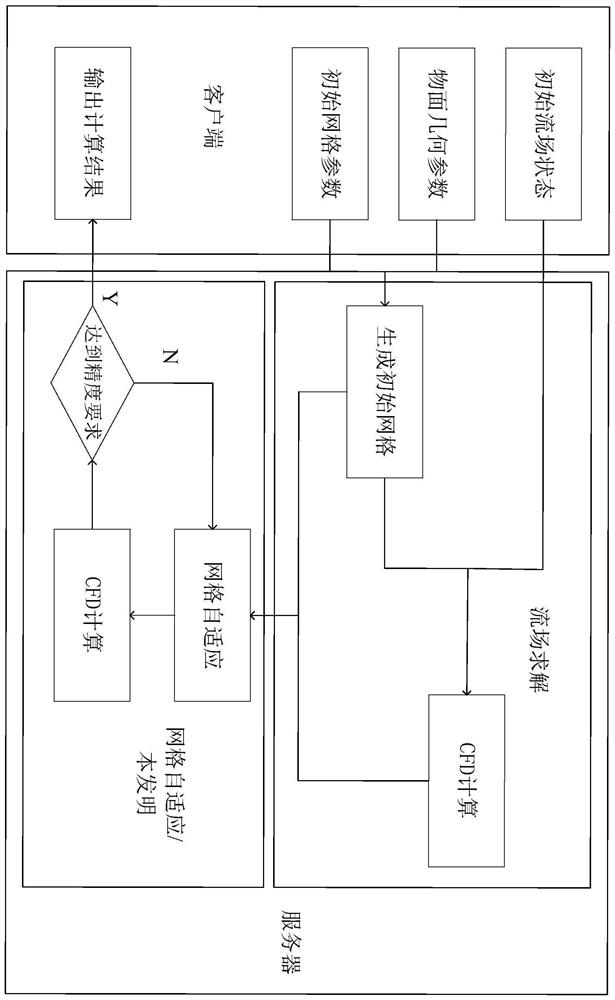
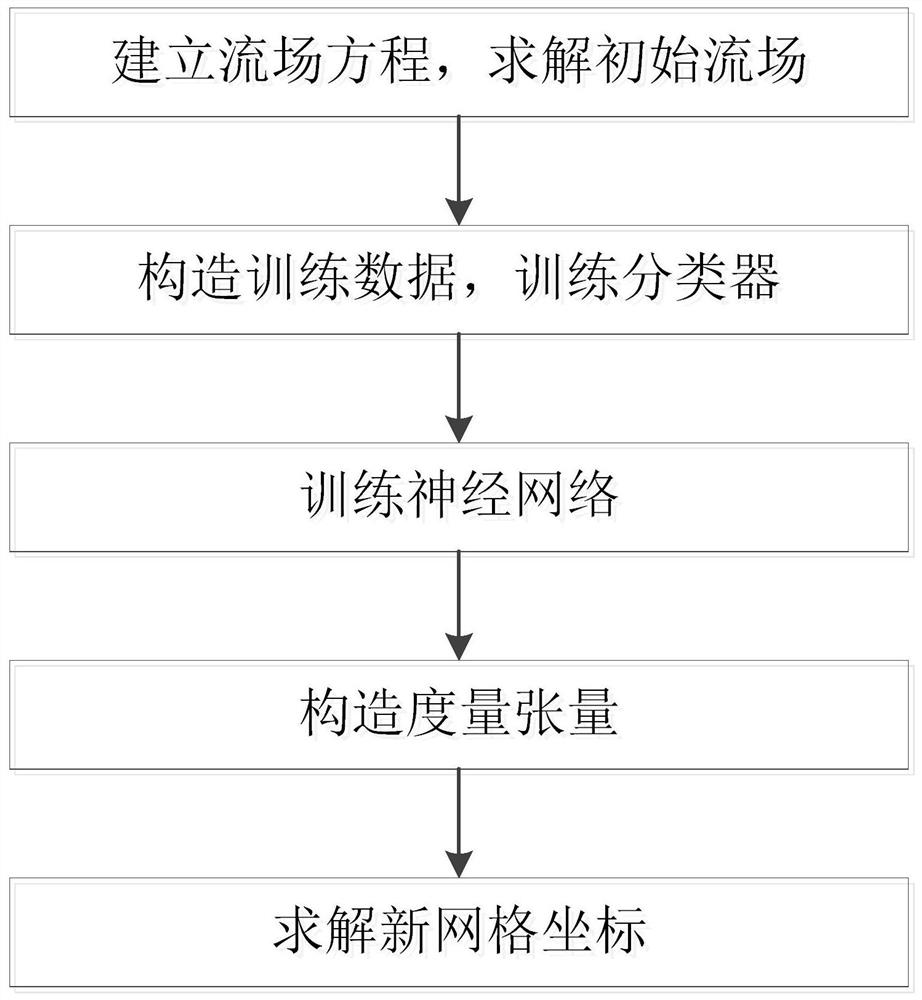
Grid adaptive method for high-precision flow field analysis
PendingCN113221475AImprove efficiencyIncrease profitEnsemble learningCharacter and pattern recognitionSimulationField analysis
The embodiment of the invention discloses a grid adaptive method for high-precision flow field analysis, relates to the field of flow field numerical simulation of fluid mechanics, and can improve the efficiency of a whole flow field analysis system and also improve the utilization rate of computing resources. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a flow field equation and calculating an initial flow field according to flow field information set by a client; constructing training data to train an AdaBoost classifier to classify grid nodes, and training a neural network for flow field solution prediction; constructing a measurement tensor by using the initial flow field solution and the classification result, and obtaining a new grid by constructing a grid equation; and predicting a flow field solution on the new grid by using a neural network for moving grid nodes in the next round, and returning a finally obtained result to a customer service end. The method is suitable for industrial design related to flow field numerical simulation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method for self-adapted load balance scheduling of the video grid
InactiveCN100581173CReduce interaction overheadImprove scalabilityPulse modulation television signal transmissionTransmissionPeak valueSelf adaptive
This invention relates to one visual network self-adaptive load even transfer method in computer multi-media field, which comprises the following steps: generating dynamic area corporation member list, service point virtual organization point list and belong service point provider list; after customer sends requires, network grid door automatically set its direction to service points and judging whether the real servo satisfies the service quality requires; if yes, ending this transfer; if not, according to dynamic area load value to judge whether the service point satisfies the service needs.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
A Gas Explosion Simulation Method Based on Adaptive Simplified Reaction and Mesh Subdivision
InactiveCN106503379BReduced responseImprove computing efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsShock waveChemical reaction kinetics
Owner:京工博创(北京)科技有限公司
Adaptive Correction Method of Model Mesh under Extremely Compressive Deformation
ActiveCN113221406BPrevent termination of computationPrevent extrusionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmEngineering
The invention relates to a method for self-adaptive correction of model grids under the condition of extreme compression and deformation. coordinates; calculate the updated coordinate position of the node correction; find the code of the grid unit where the node will fall, and perform linear interpolation on the displacement field of the node in the x and z directions according to the positions of the four nodes that make up the grid unit, and get The new coordinates of the nodes; traverse the grid units, and find the corresponding grid unit codes according to the new coordinates, and at the same time obtain the center coordinates of the grid units, linearly interpolate the stress and strain of the units where the new coordinates of all nodes are located, and obtain the strain information, and store the stress and strain information into the extra variables of the unit; re-traverse the nodes, and update the node coordinate position and node displacement information; re-traverse the grid unit, and update the unit stress and strain information.
Owner:POWERCHINA HUADONG ENG COPORATION LTD
A Peridynamic Modeling Method for Mass Diffusion Problems in Composite Materials
ActiveCN108319774BHigh precisionImprove adaptabilityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsStructural engineeringEntity model
The invention discloses a near-field dynamic modeling method for a composite mass diffusion problem. The method comprises the following steps of 1, building an entity model; 2, cutting the entity model, determining layering and mixing region positions of materials in the model, and giving corresponding material attributes to the regions; 3, dividing the entity model into unit grids; 4, setting concentration boundary conditions of the entity model; 5, on the basis of mass diffusion near-field dynamic constitutive relation, integrating model parameters, determining a calculation method for concentration changes of a diffusing substance in a composite in the entity model, and calculating operation parameters of all units in the entity model; 6, performing submission calculation. The modelingmethod is high in precision and good in grid adaptability, all the parameters in the model are preprocessed, the operation complexity can be greatly lowered, and an algorithm is greatly optimized; themodeling method and the operation process are large in adaptability and applicable to many problems.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Grid self-adaptive finite element method for simulating martensite phase transformation
ActiveCN112131762AReduce in quantityReduce the total number of degrees of freedomDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMartensite transformationElement model
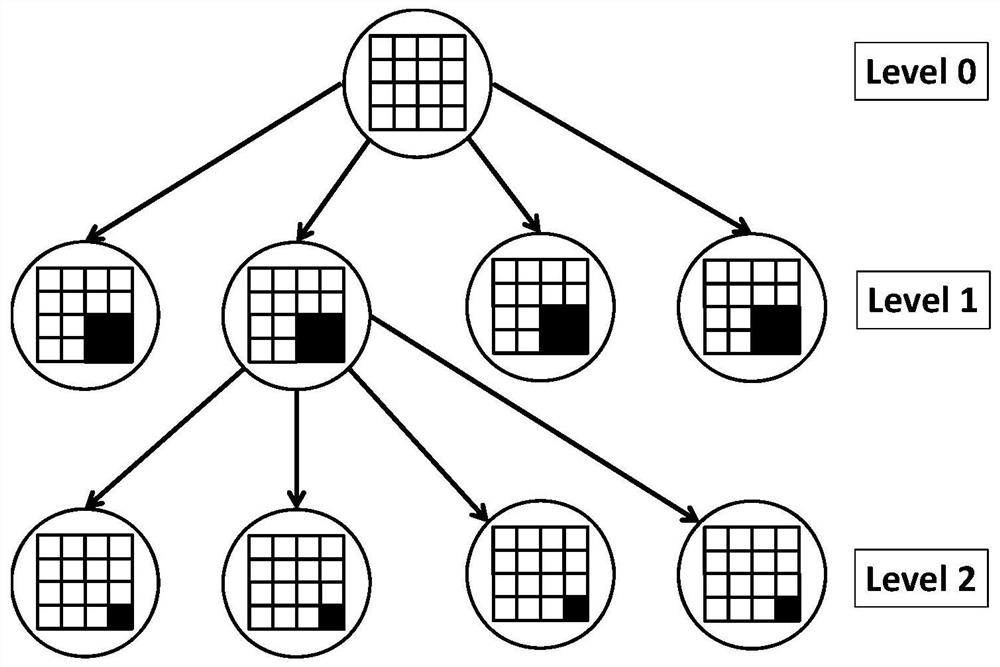
The invention discloses a grid self-adaptive finite element method for simulating martensite phase transformation, and is applied to the field of industrial production simulation design and scientificresearch of shape memory alloys. A martensite phase transformation phase field finite element model is established, proper grid unit posteriori error estimation is set, grid units needing to be encrypted / coarsened are marked, and the encryption / coarsening step is executed, so that the effects of effectively tracking a martensite variant interface, encrypting grids at the interface and coarseningthe grids at a non-interface are achieved; under the condition of keeping the calculation precision, the total number of degrees of freedom of a solution required by phase field simulation calculationis reduced, the calculation efficiency is effectively improved, and the simulation research process is promoted. The method provided by the invention can effectively and dynamically track the dynamically changed martensite variant interface, requires fewer computing resources and computing time, and can effectively improve the computing efficiency and promote the simulation research process.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
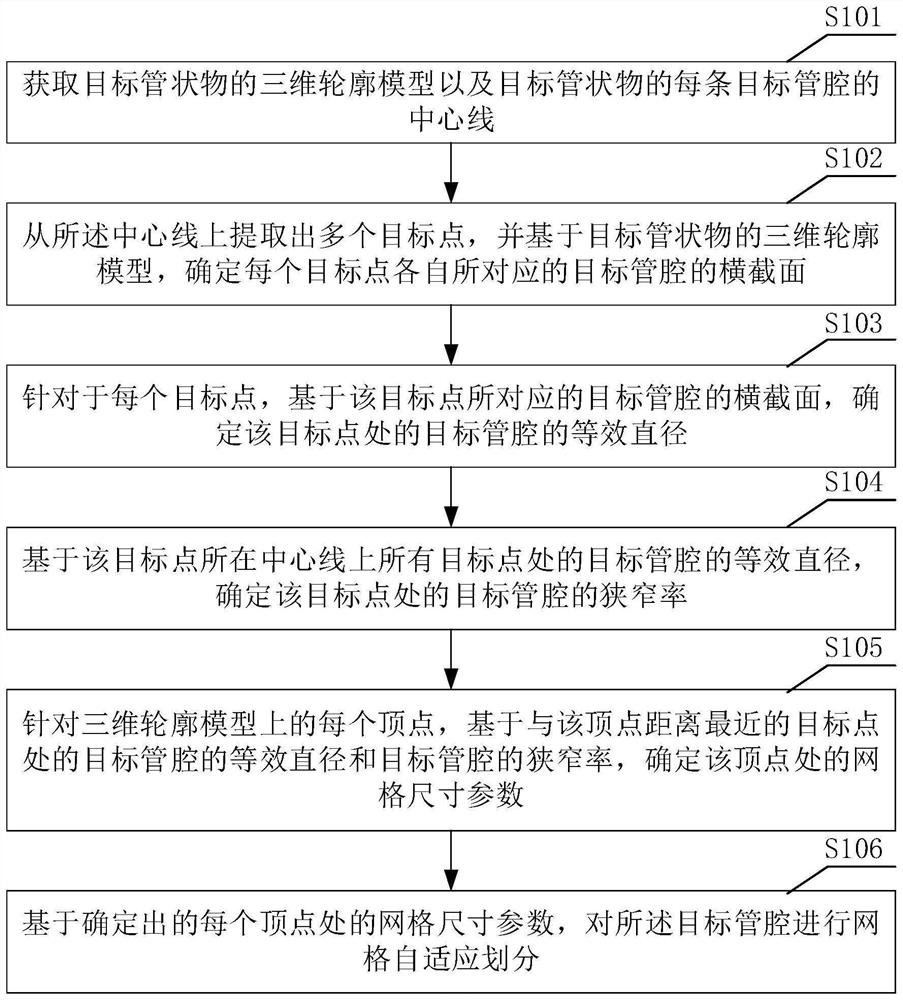
Adaptive grid division method and device for tubular object and storage medium
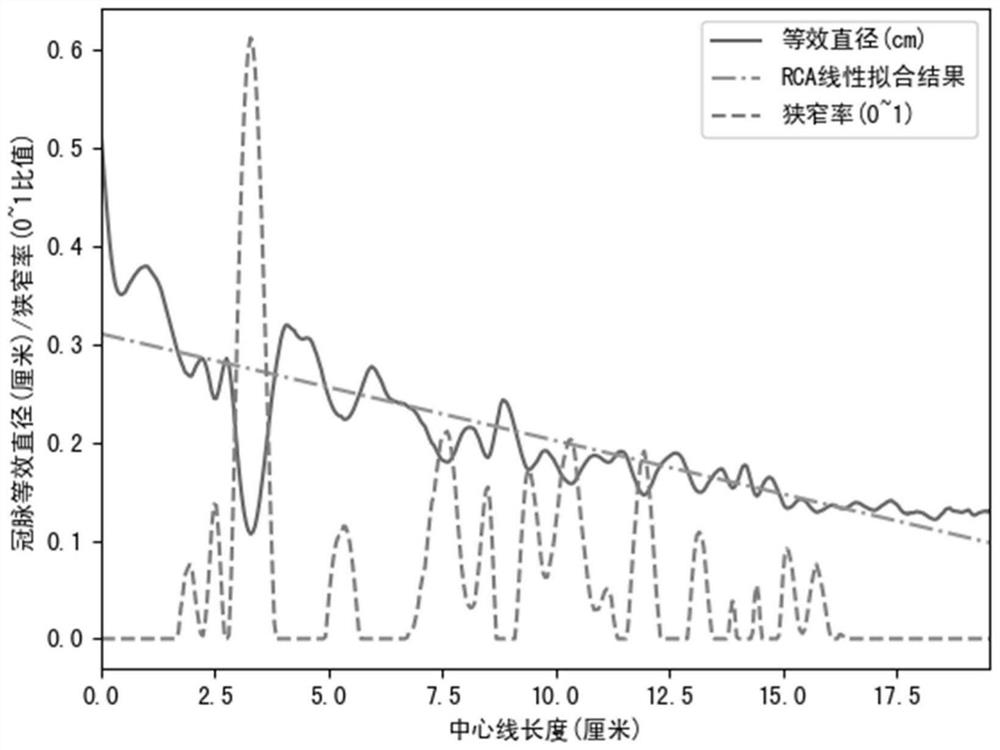
PendingCN114861564AReduce the numberSmall amount of calculationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringComputer vision
The invention provides a tubular object grid adaptive division method. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a three-dimensional contour model of a target tubular object and a center line of each target lumen of the tubular object; extracting a plurality of target points from the center line, and determining the cross section of the target lumen of the tubular object corresponding to each target point; for each target point, determining an equivalent diameter of a tubular target lumen at the target point and a stenosis rate of the tubular target lumen at the target point; for each vertex on the three-dimensional contour model, determining a grid size parameter at the vertex based on the equivalent diameter and the stenosis rate of a tubular object target lumen at a target point closest to the vertex; and based on the determined grid size parameter at each vertex, performing grid adaptive division on the target lumen of the tubular object. In this way, the size parameters of the grids are adaptively set according to the equivalent diameter and the stenosis rate of the target lumen of the tubular object, and full-automatic grid adaptive division is achieved.
Owner:SHENZHEN RAYSIGHT INTELLIGENT MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com