Two-dimensional blade profile optimization design method and device based on self-adaptive grid
An adaptive grid and optimization design technology, applied in design optimization/simulation, geometric CAD, etc., can solve problems such as unfavorable engineering implementation, not specifying the means of capturing shock wave parameters, and poor solution robustness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
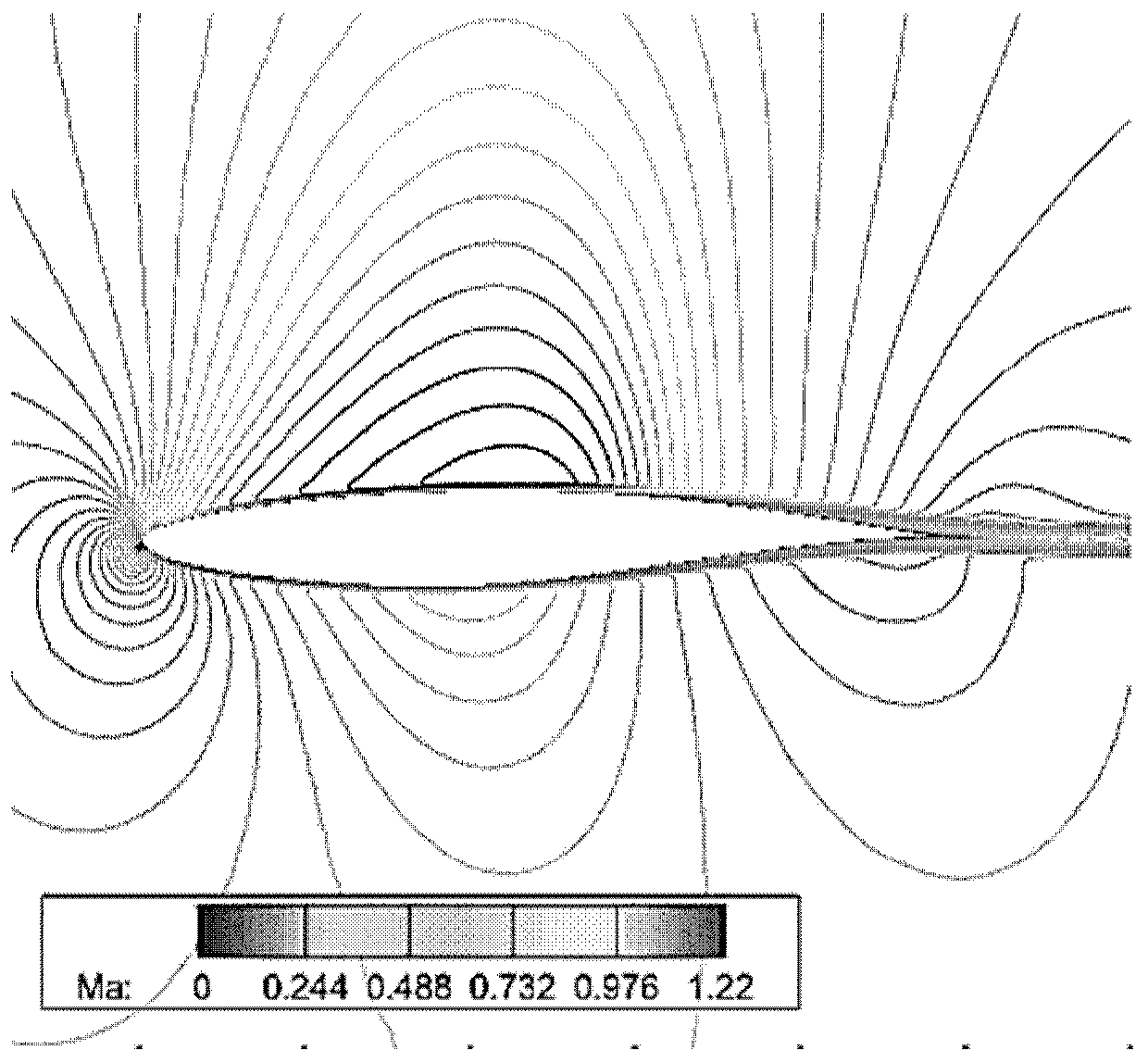
[0111] like Figure 7 As shown, for the compressor blade, the deflection angle is relatively small, and 3 to 5 control points (quadratic to quartic spline curves) are used to generate the main profile of the compressor (such as suction surface, pressure surface profile) Can get better results. Taking the rotor37 of the compressor rotor disclosed by NASA as an example, the blade shape at 50% of the blade height of the rotor is used as the original blade shape, and its aerodynamic performance is optimized so that the angle of attack range is as large as possible and the total pressure loss is as small as possible. And there needs to be a certain surge boundary, and an optimized airfoil shape with small loss and fluctuation within the working range.
[0112] The optimization objective function is defined as:
[0113]
[0114] Among them, ω D is the total pressure loss coefficient at the design point; Δβ 1 is 2ω D The difference between the corresponding positive and negat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com