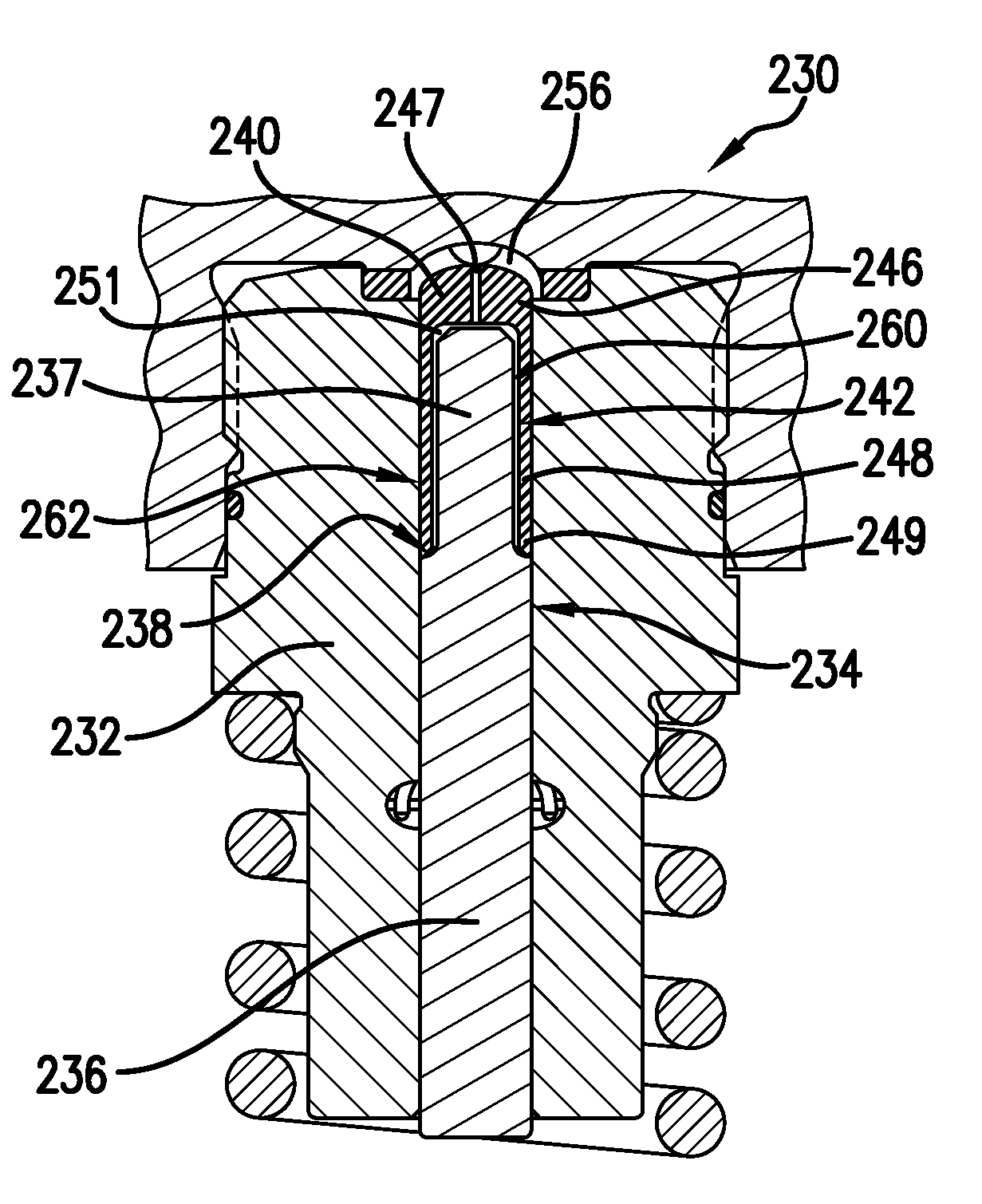
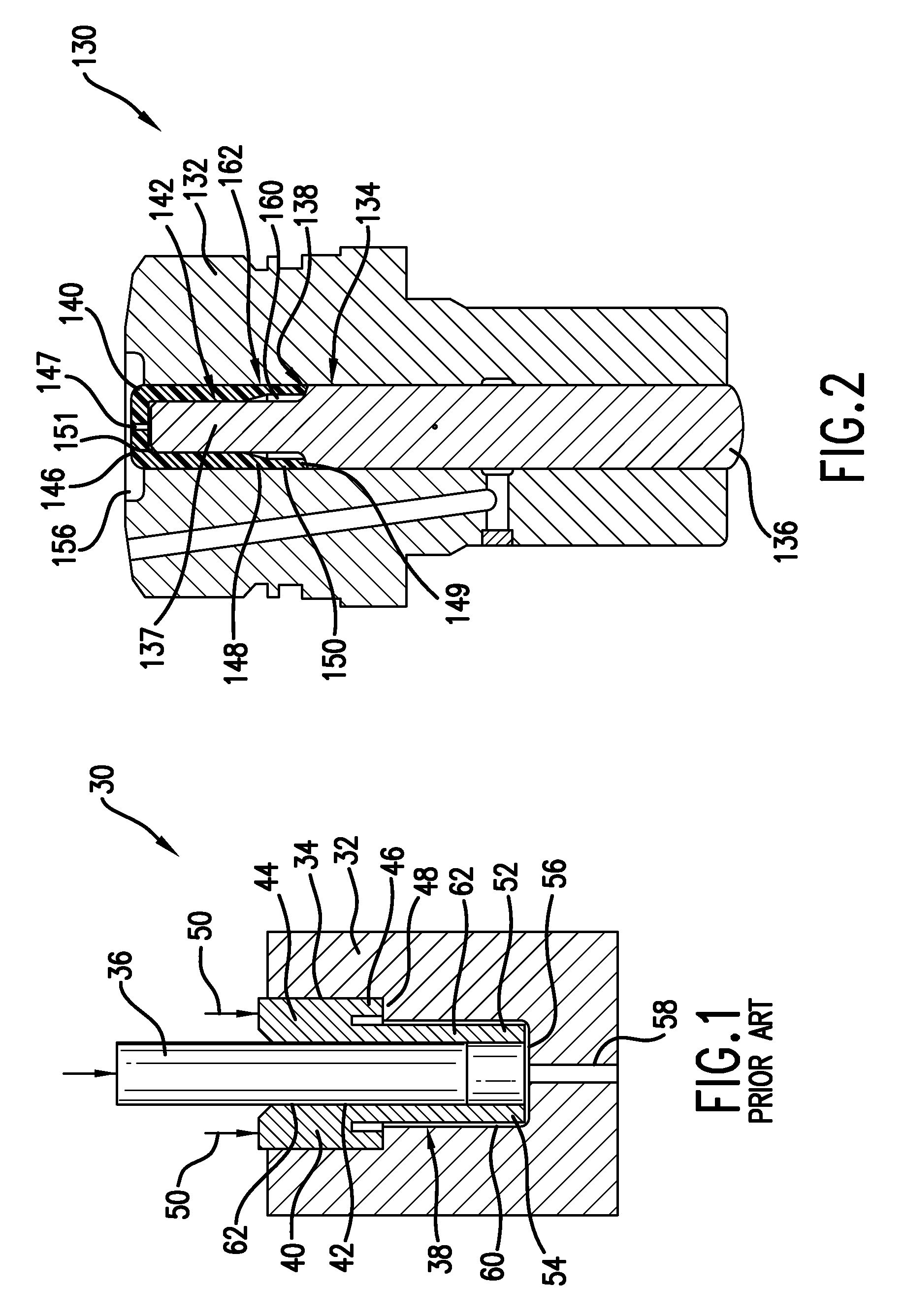
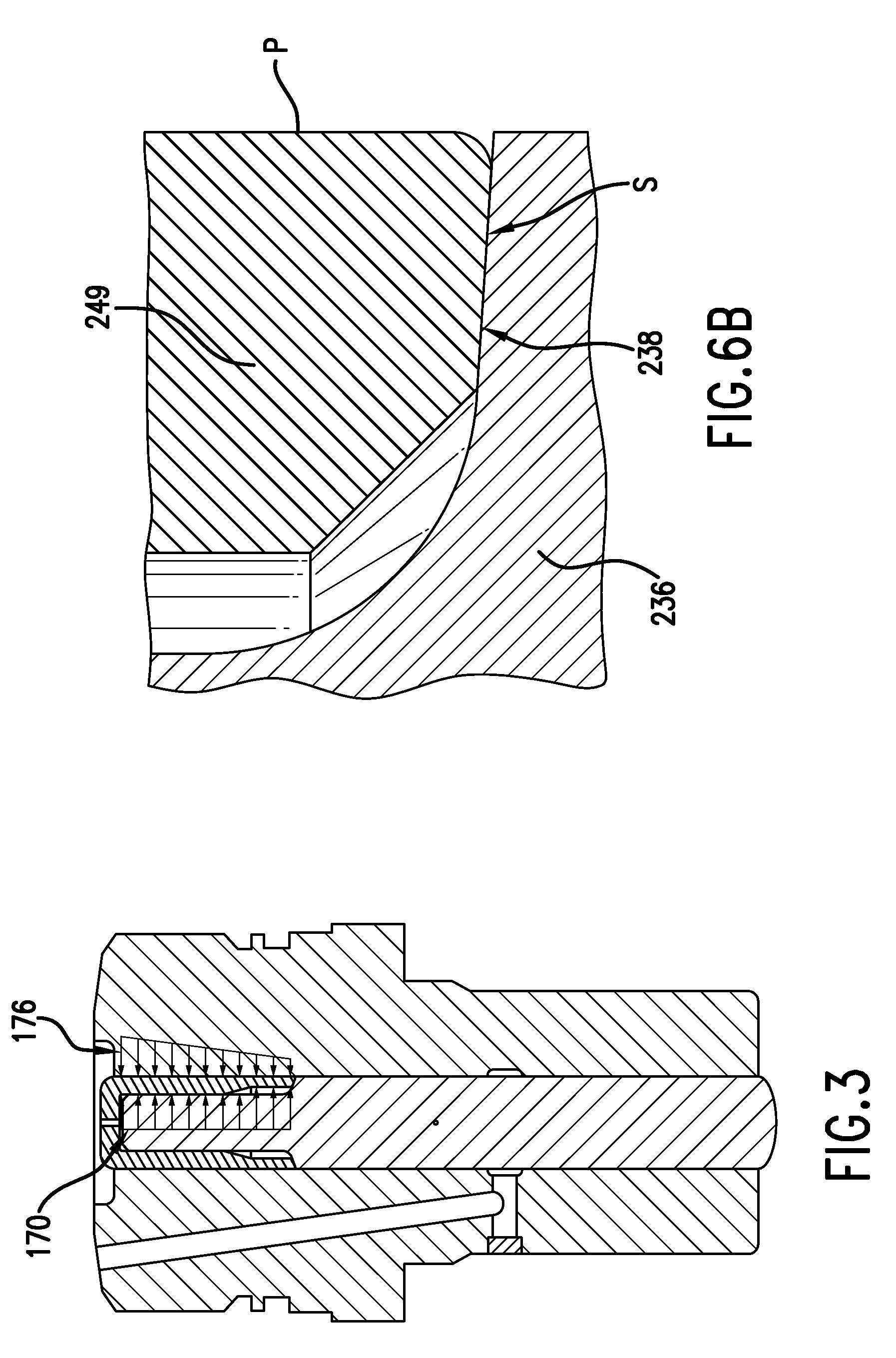
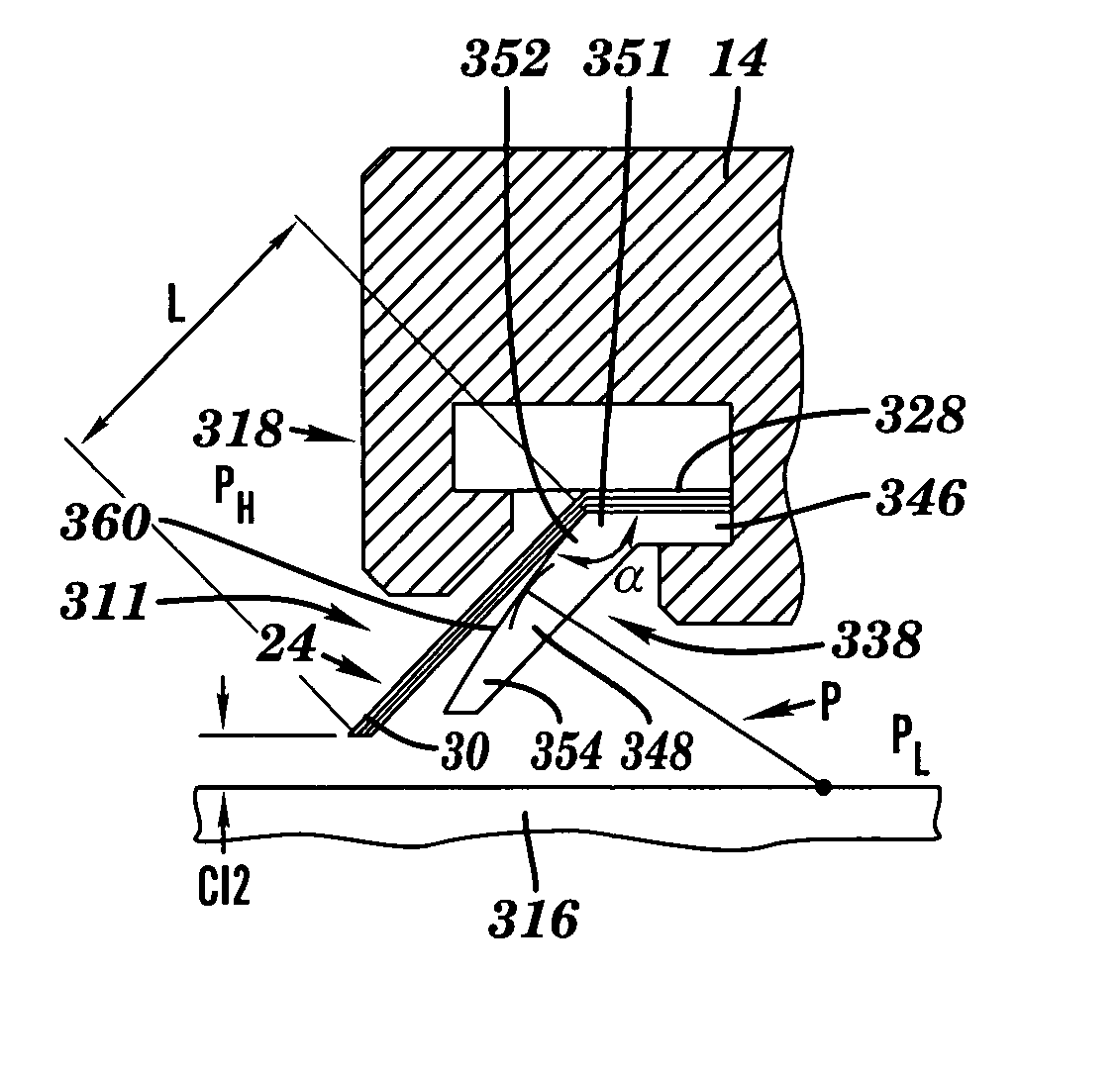
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
594 results about "Fluid leakage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The following are the most common causes of amniotic fluid leakage: Congenital infections or trauma: They weaken the membranes and facilitate their rupture. Amniocentesis: Even though the fissure heals over time and the leakage stops eventually, it can cause you to leak some fluid.
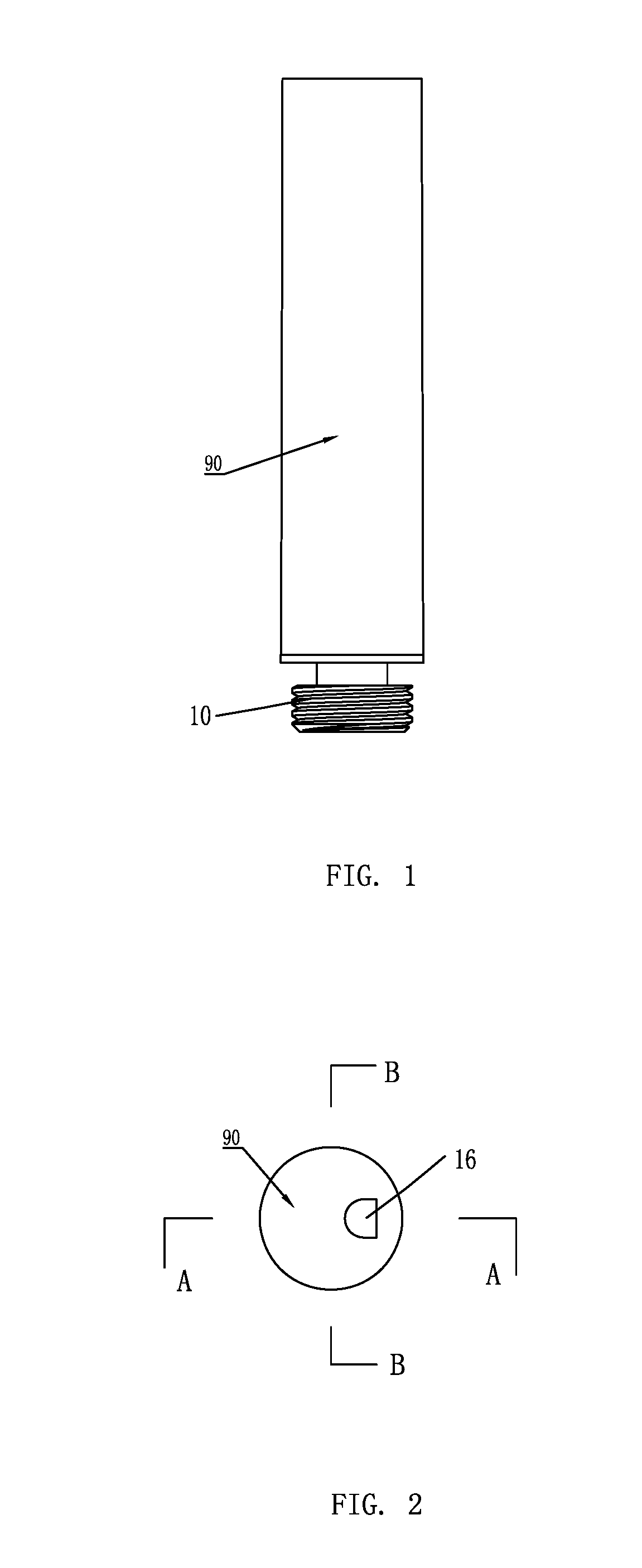
Electronic Cigarette and Mouthpiece Part Thereof
InactiveUS20130255675A1Easy to assembleEasy to manufactureRespiratory masksTobacco devicesMouth pieceEngineering
The present invention relates to an electronic cigarette and mouthpiece part thereof. The mouthpiece part includes within an inhaling shell: an aerosol passage, a reservoir, an atomizing device, and a guiding device for sealing the reservoir and guiding tobacco substance from the reservoir to the atomizing device for vaporization without fluid leakage. The guiding device includes a guiding plate and an absorption piece laminating each other. Tobacco substance penetrates the guiding plate and is absorbed and stored in the absorption piece for vaporization. The electronic cigarette includes the mouthpiece part and a power source part connecting each other. The electronic cigarette and mouthpiece part thereof facilitate assembling, improve guiding tobacco substance, and prevent fluid-leakage.
Owner:KIMREE HI TECH
Electronic cigarette and mouthpiece part thereof
InactiveUS20160143365A1Increase guideEasy to assembleOhmic-resistance electrodesTobacco pipesVaporizationEngineering
The present invention relates to an electronic cigarette and mouthpiece part thereof. The mouthpiece part includes within an inhaling shell: an aerosol passage, a reservoir, an atomizing device, and a guiding device for sealing the reservoir and guiding tobacco substance from the reservoir to the atomizing device for vaporization without fluid leakage. The guiding device includes a guiding plate and an absorption piece laminating each other. Tobacco substance penetrates the guiding plate and is absorbed and stored in the absorption piece for vaporization. The electronic cigarette includes the mouthpiece part and a power source part connecting each other. The electronic cigarette and mouthpiece part thereof facilitate assembling, improve guiding tobacco substance, and prevent fluid-leakage.
Owner:KIMREE HI TECH
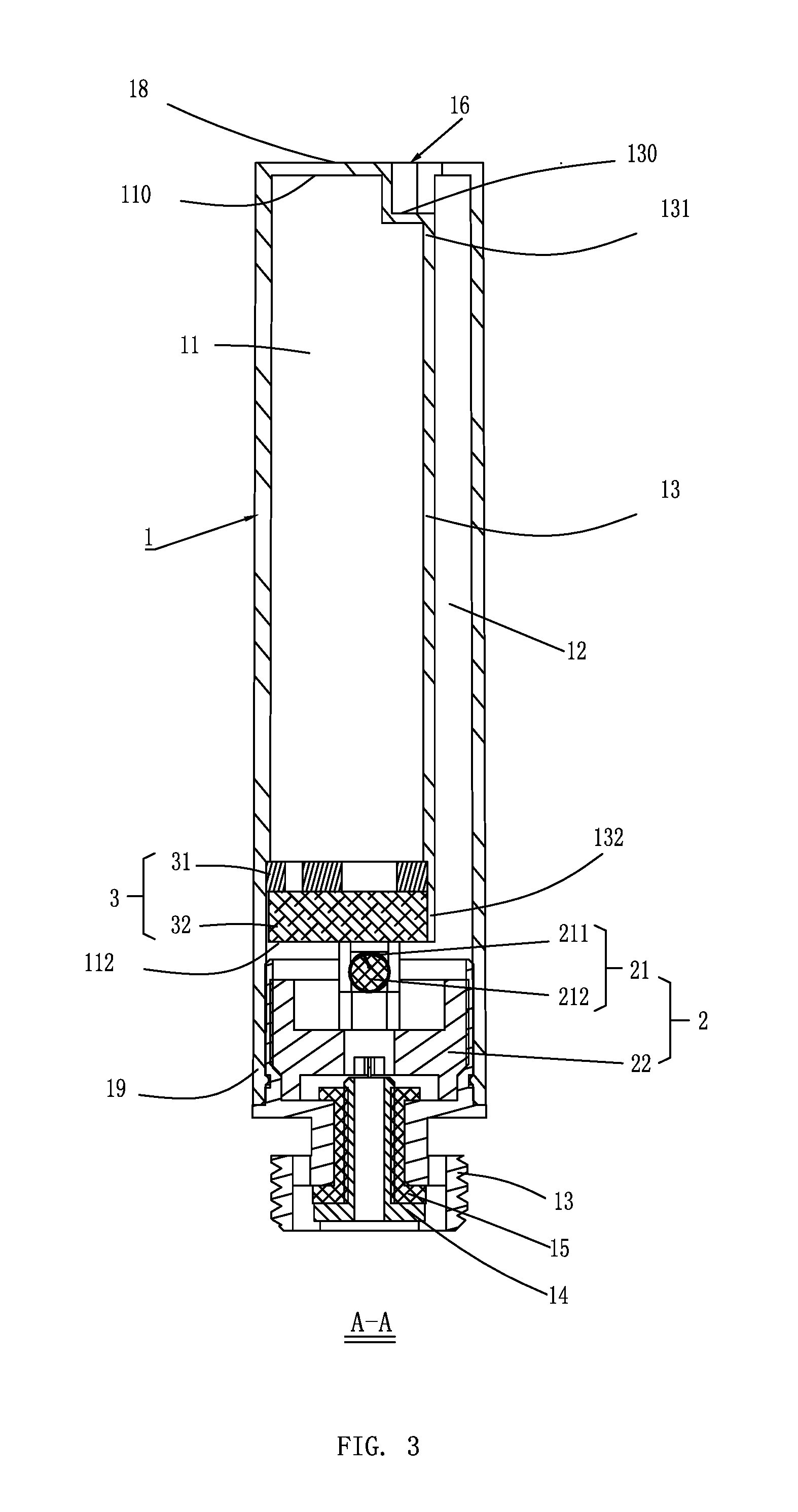
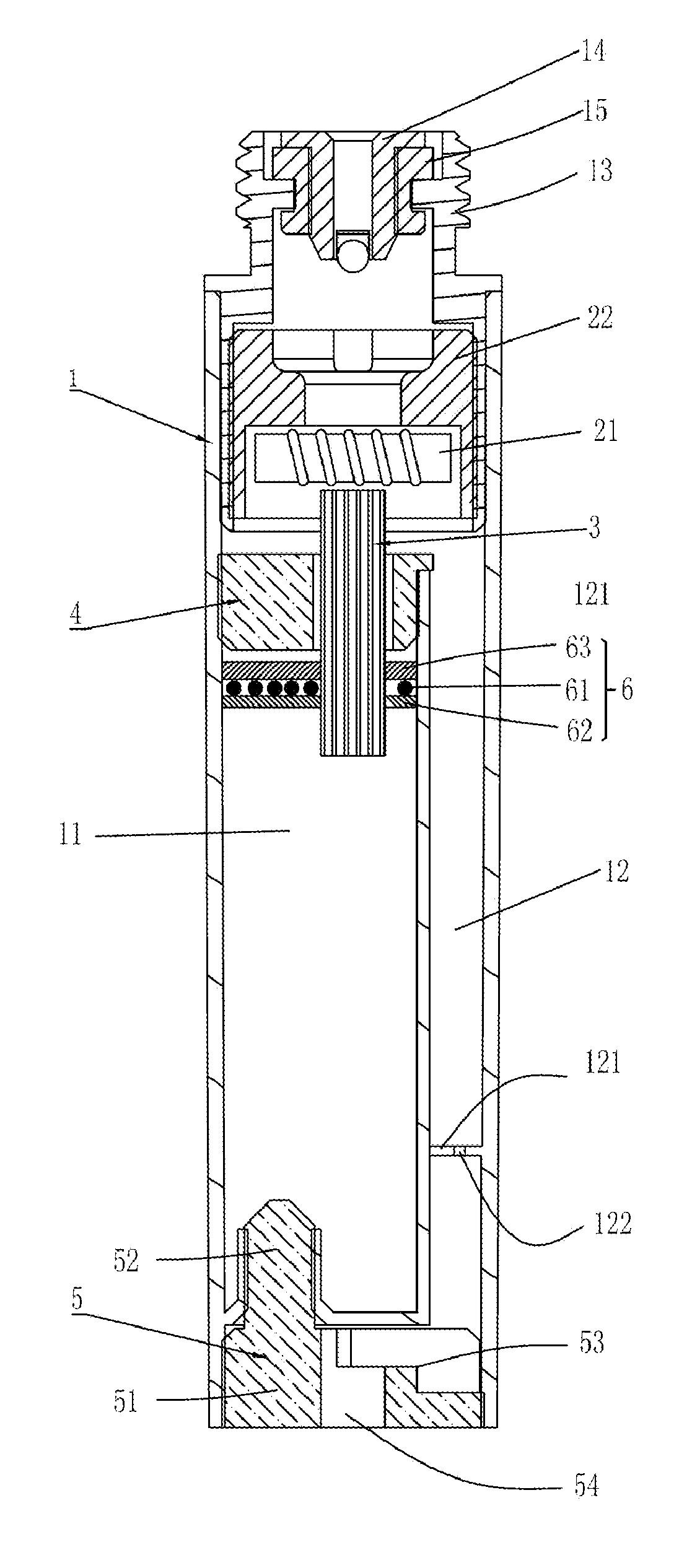
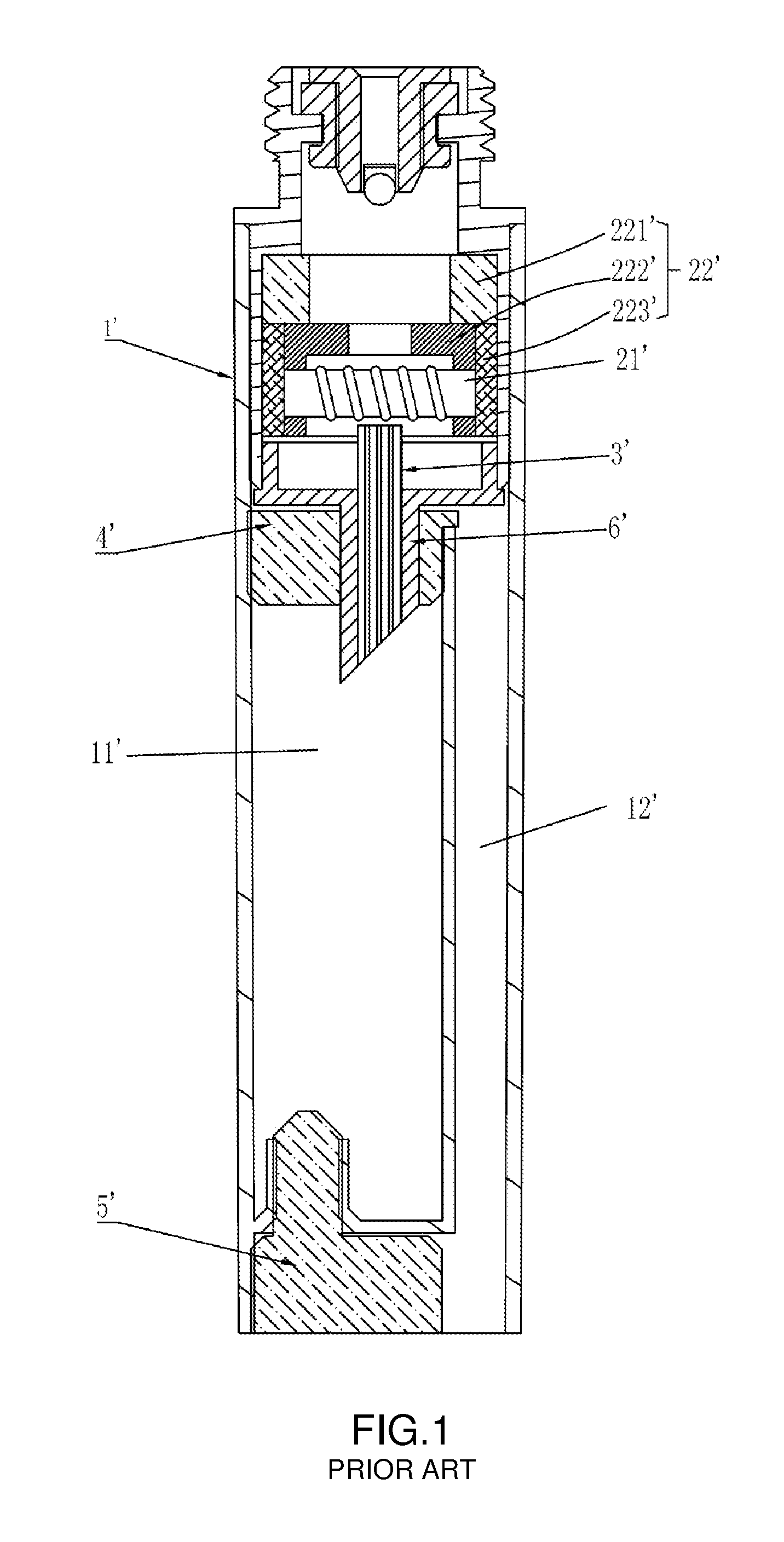
Mouthpiece device of electronic cigarette
InactiveUS20130160765A1Improve leak-proof effectEasy to manufactureTobacco treatmentTobacco smoke filtersElectronic cigaretteEngineering
The present invention relates to a mouthpiece device of electronic cigarette, includes an atomizing device for vaporizing tobacco substance into aerosol, a reservoir for storing tobacco substance and a guiding tube for guiding tobacco substance from the reservoir to the atomizing device, which are set in an shell. The guiding tube has one end inserted in the reservoir and the other end communicated with atomizing device. The mouthpiece device further includes a preheat device for heat solid tobacco substance in the reservoir to generate liquid. The preheat device is set in the end of the reservoir near the guiding tube, and seals solid tobacco substance in the reservoir. The present invention solves existing problems such as fluid leakage, complicate manufacturing, high cost, bad heat insulation and filtering aerosol; and obtains perfect leakage proof, simple manufacturing, lower cost, good heat insulation and well filtering aerosol.
Owner:HUIZHOU KIMREE TECH
Apical puncture access and closure system
A device, system, and method for providing access to, and sealing of, a body organ includes an implant device. An implant device has a main body having an internal access lumen, with a plurality of prongs extending from a distal end of the main body. The main body can include two lumens, one slidable within the other, to form a single continuous lumen with an adjustable length. The main body has an expanded configuration with an expanded diameter, and an unexpanded configuration with an unexpanded diameter. The prongs have a generally straight configuration where they extend distally of the distal end of the main body, and a bent configuration where the prongs bend around so that their tips extend proximally of the distal end of the main body. The device may include a hemostatic barrier to prevent fluid leakage therethrough when the main body is in the unexpanded configuration.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Barrier orifice valve for gas lift
ActiveUS20070181312A1Increase flow ratePrevent backflowPressure pumpsFluid removalEngineeringGas lift
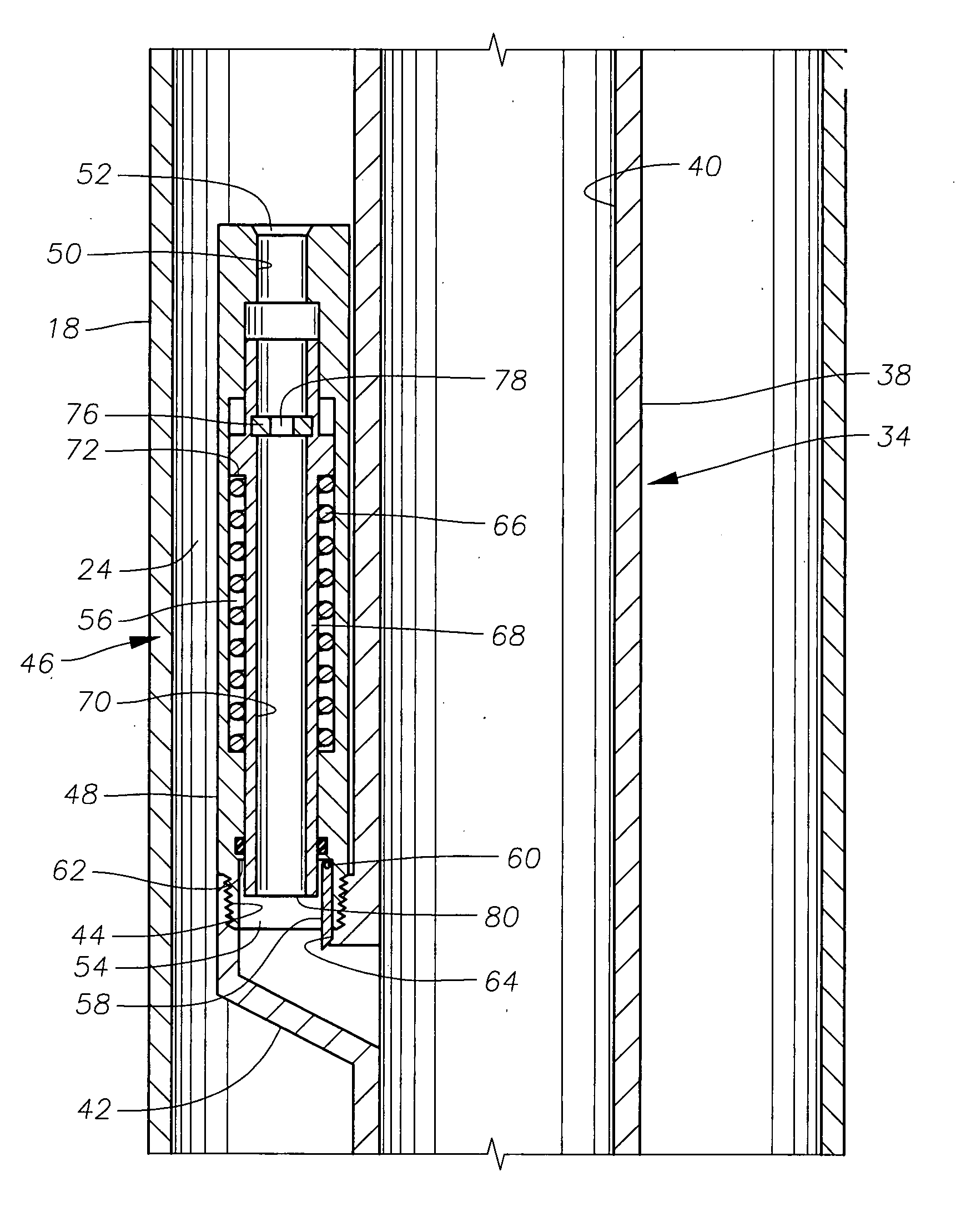
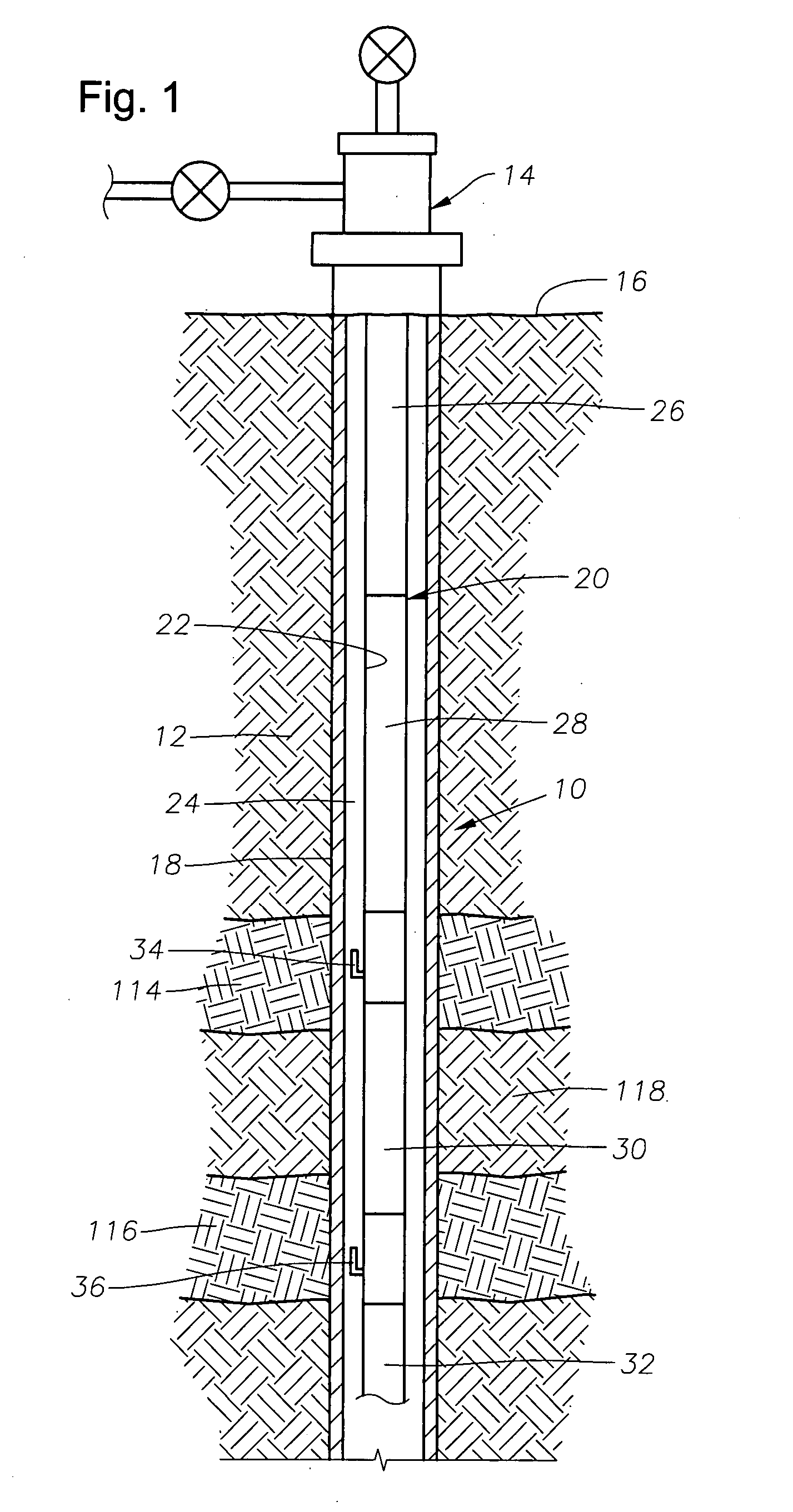
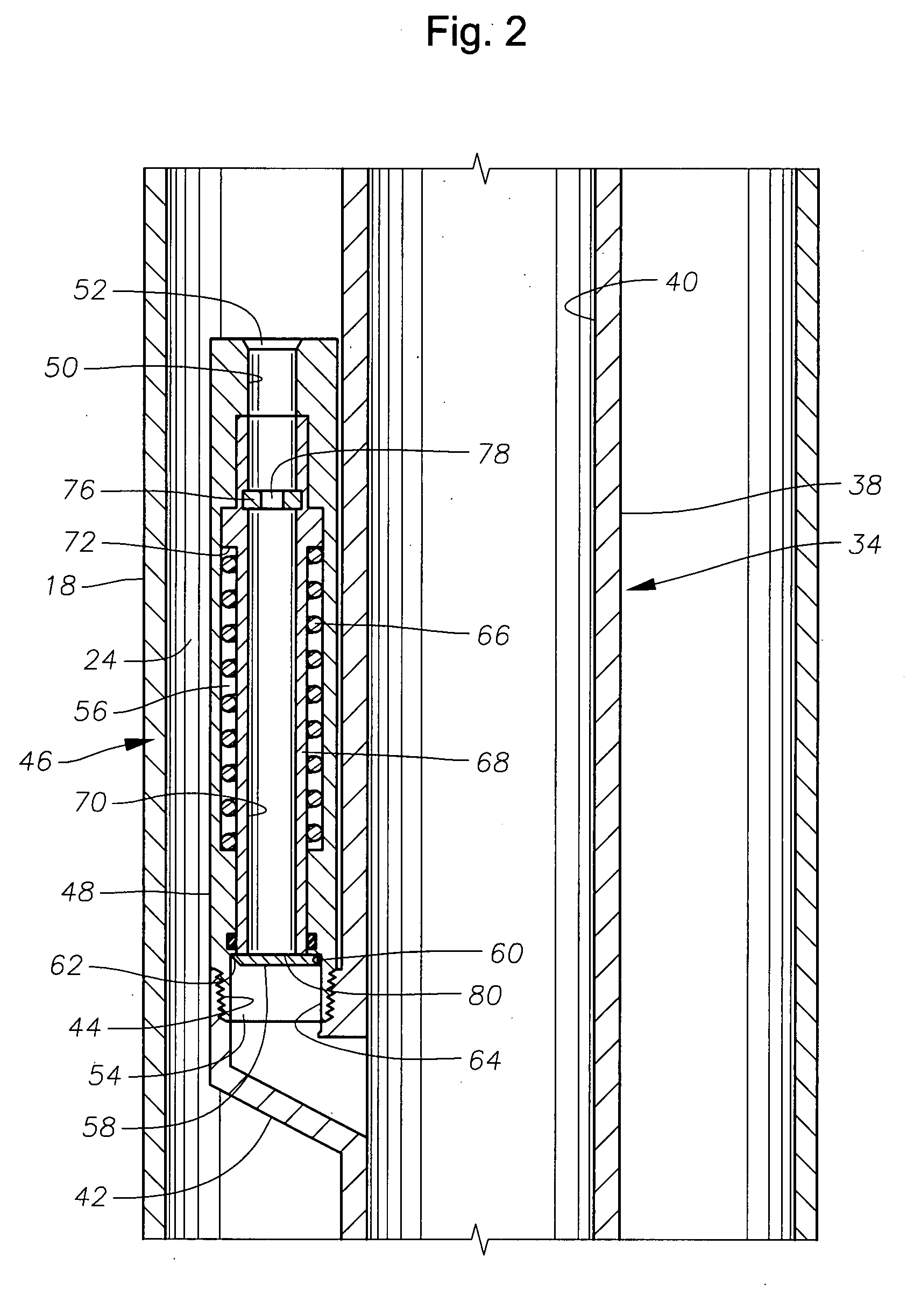
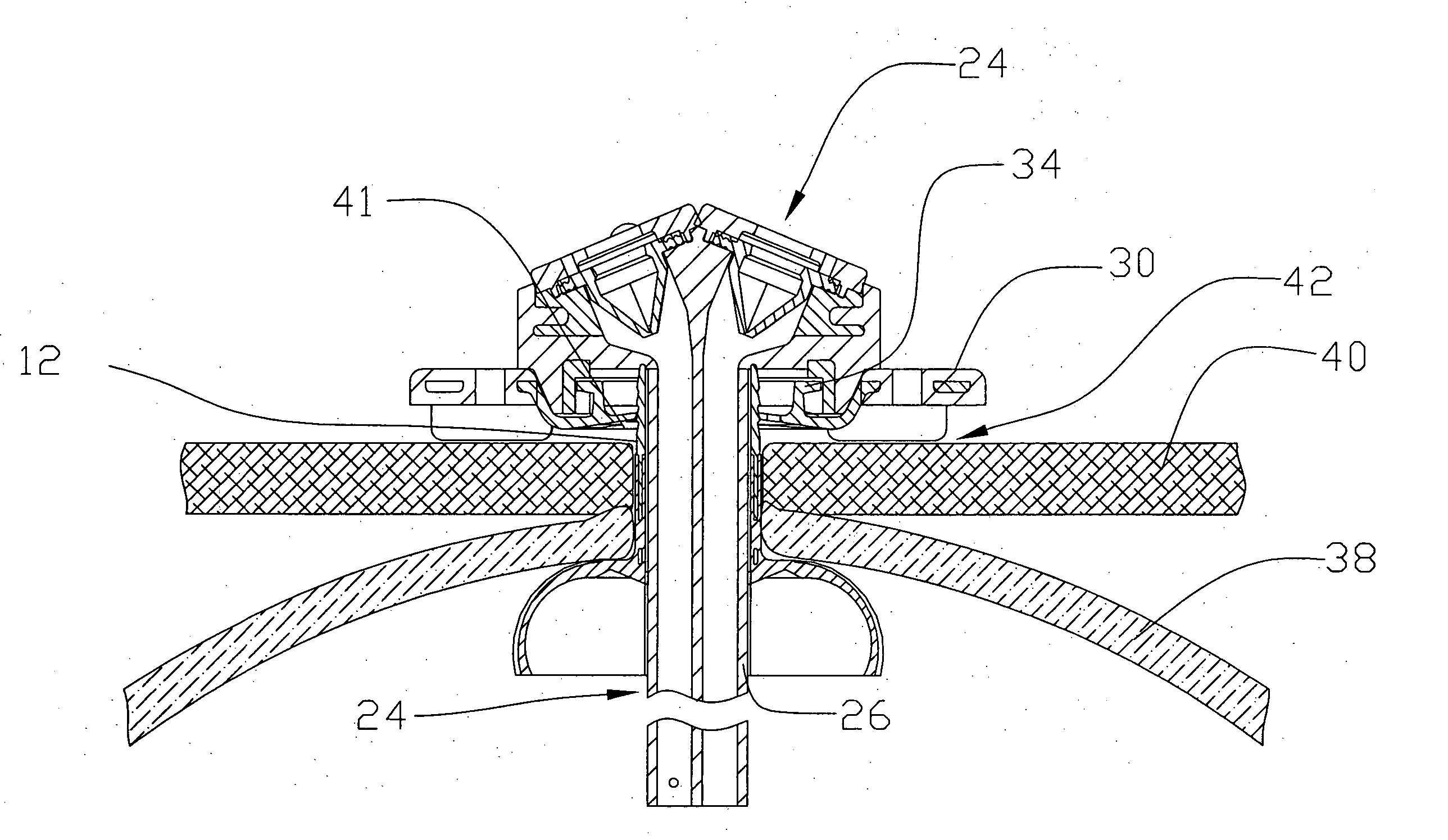
Gas lift valve designs and gas lift systems are described that feature a positive closure mechanism that is highly resistant to significant wear or damage that would result in fluid leakage. A pivotable flapper member is incorporated into a gas lift valve and used as a flow control mechanism. The flapper member provides a positive barrier to fluid flow from the production tubing to the annulus, even after substantial wear or damage.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Artificial stoma and method of use
A device for creating a channel between the stomach lumen and the abdominal surface of a patient. The device includes a tube and a first bolster. The tube has a proximal end, a distal end, and a wall, the wall having an inner surface and an outer surface, and each end having an opening therein. The first bolster is attached to the distal end of the tube and the tube is adapted to slidably receive a feeding device having a shaft, wherein at least a portion of the outer diameter of the shaft of the feeding device is substantially the same size as that of the inner wall of the tube. The first bolster is adapted to sealingly engage with the patient so as to minimize or avoid fluid leakage about the tube. The present invention is also directed to a method of using an artificial stoma.
Owner:AVENT INC
Vented, low-drip nursing nipple
A nipple assembly for a nursing bottle includes a nipple having a slit at the bottom of a concave depression in its tip acting as a fluid outlet valve. The nipple includes a flange seated on the rim of the bottle and held in place by a cap having a central opening through which the nipple extends. A threaded ring on the cap engages the threaded bottle neck with the outer circumferential edge of the nipple's flange compressed between the annular top and the rim of the bottle. The nipple flange includes vent apertures between its inner and outer circumferential edges, and a raised annular bead between its inner circumferential edge and the aperture. The annular bead provides a seal between flange and the cap that prevents fluid from leaking out the vent apertures when air pressure within the bottle is not substantially lower than ambient air pressure. When the air pressure inside the bottle falls below ambient air pressure as the infant suck fluid from the bottle, the annular bead moves away from the cap to break the seal, thereby permitting air to pass through the central opening and into the bottle via the vent apertures. The nipple includes one or more raised annular beads to provide tactile stimulation to a nursing infant and to improve the seal between the infant's lips and the nipple body to limit fluid leakage.
Owner:LEWIS JULIE MAUREEN +1
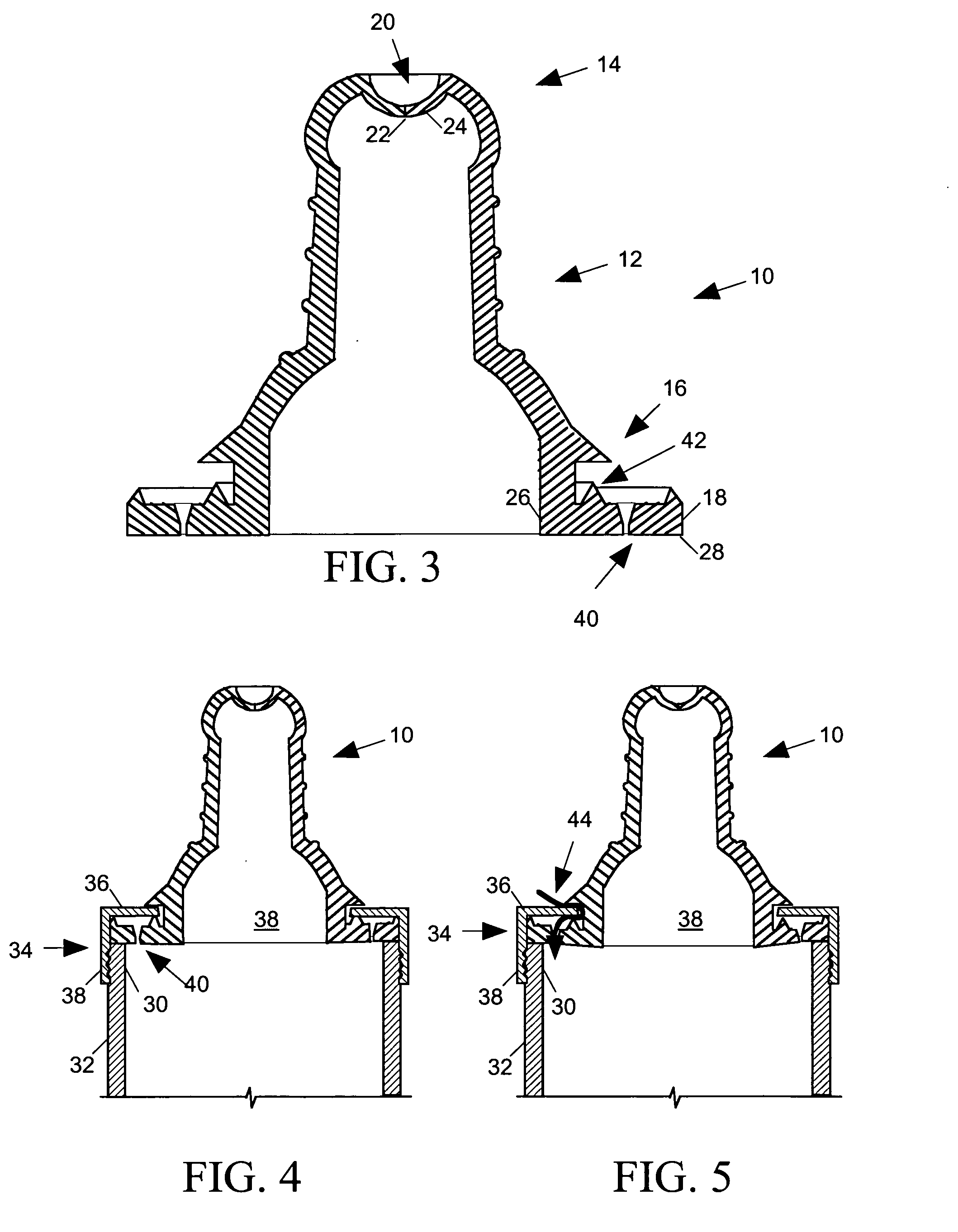
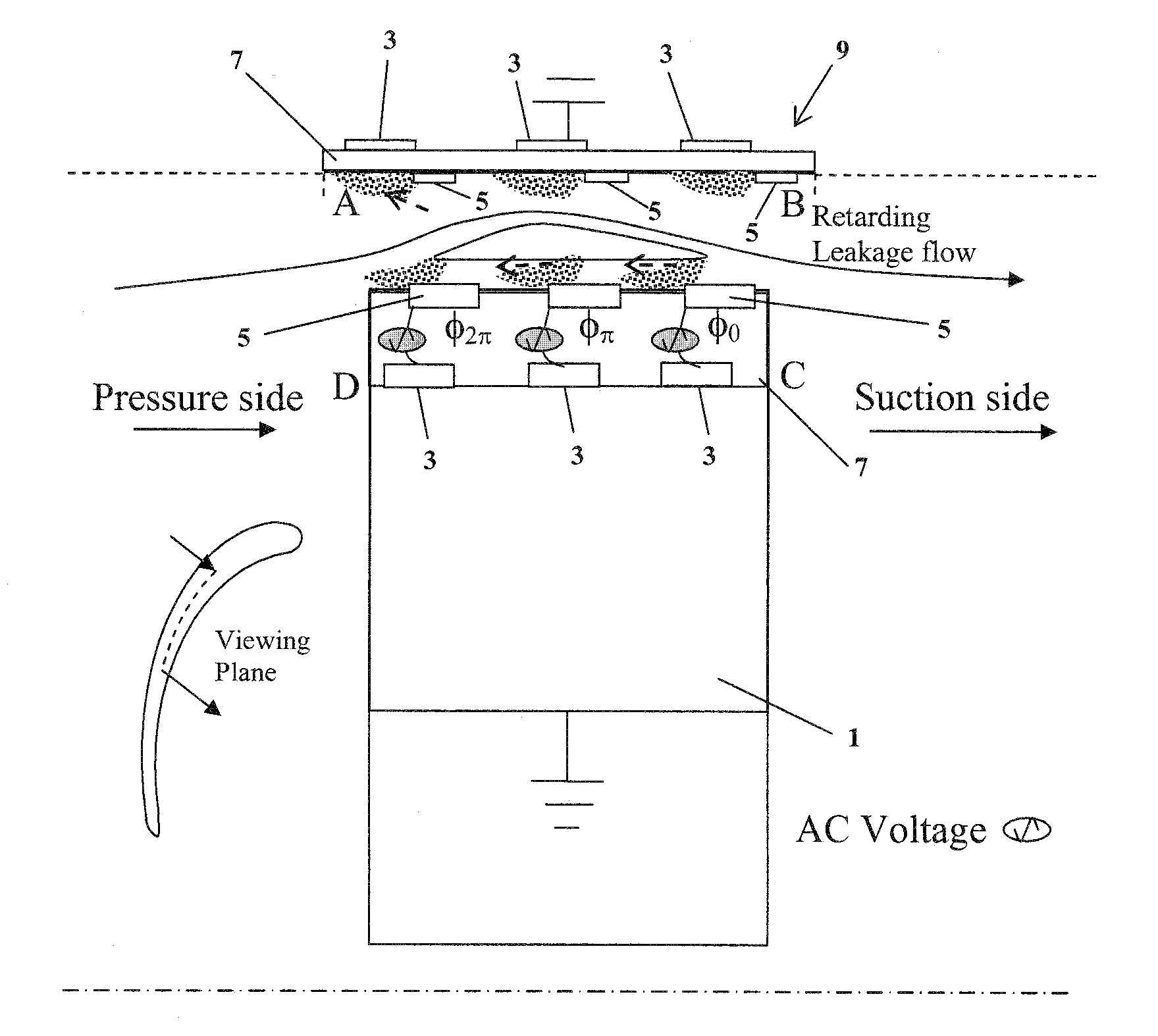
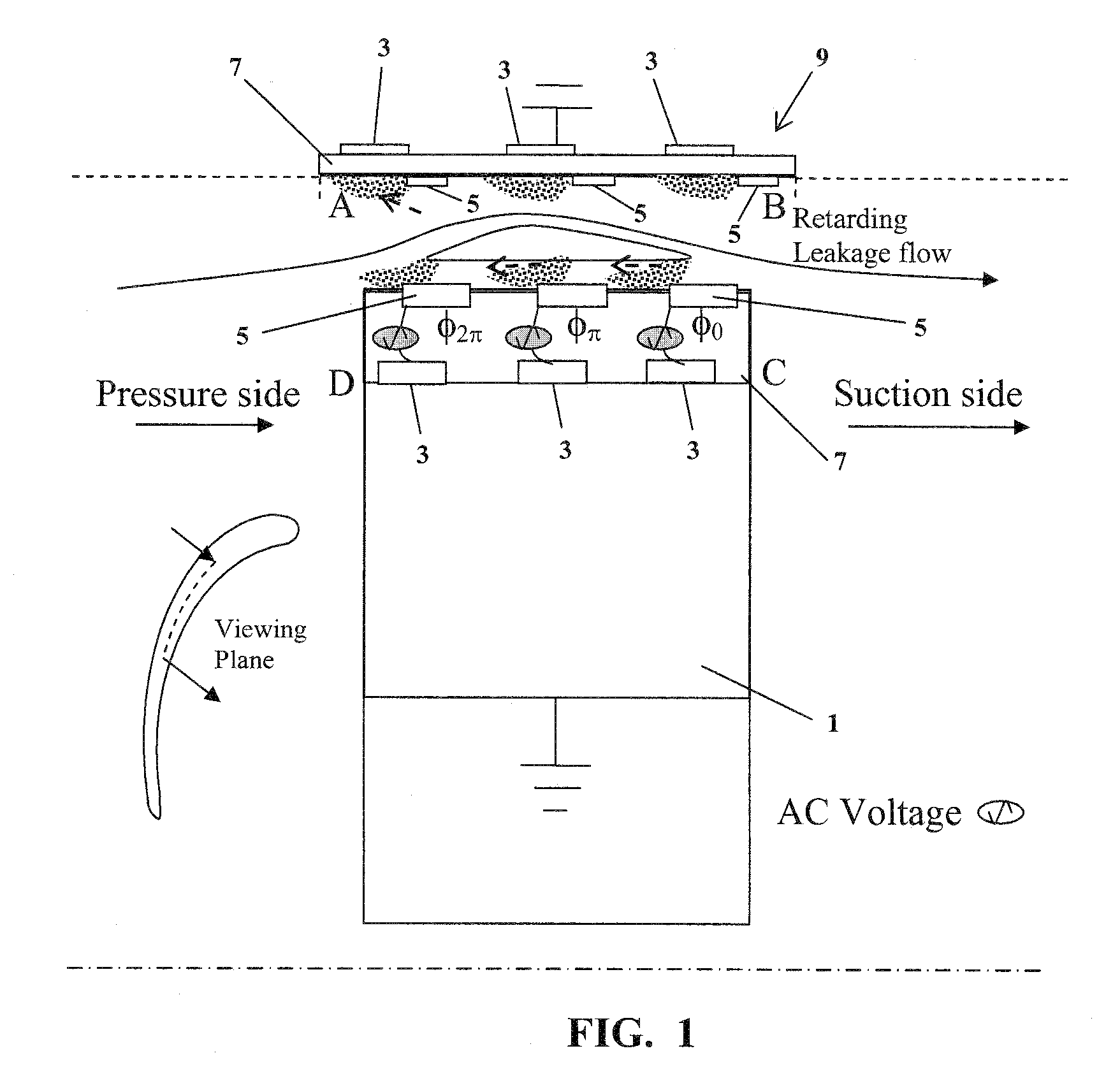
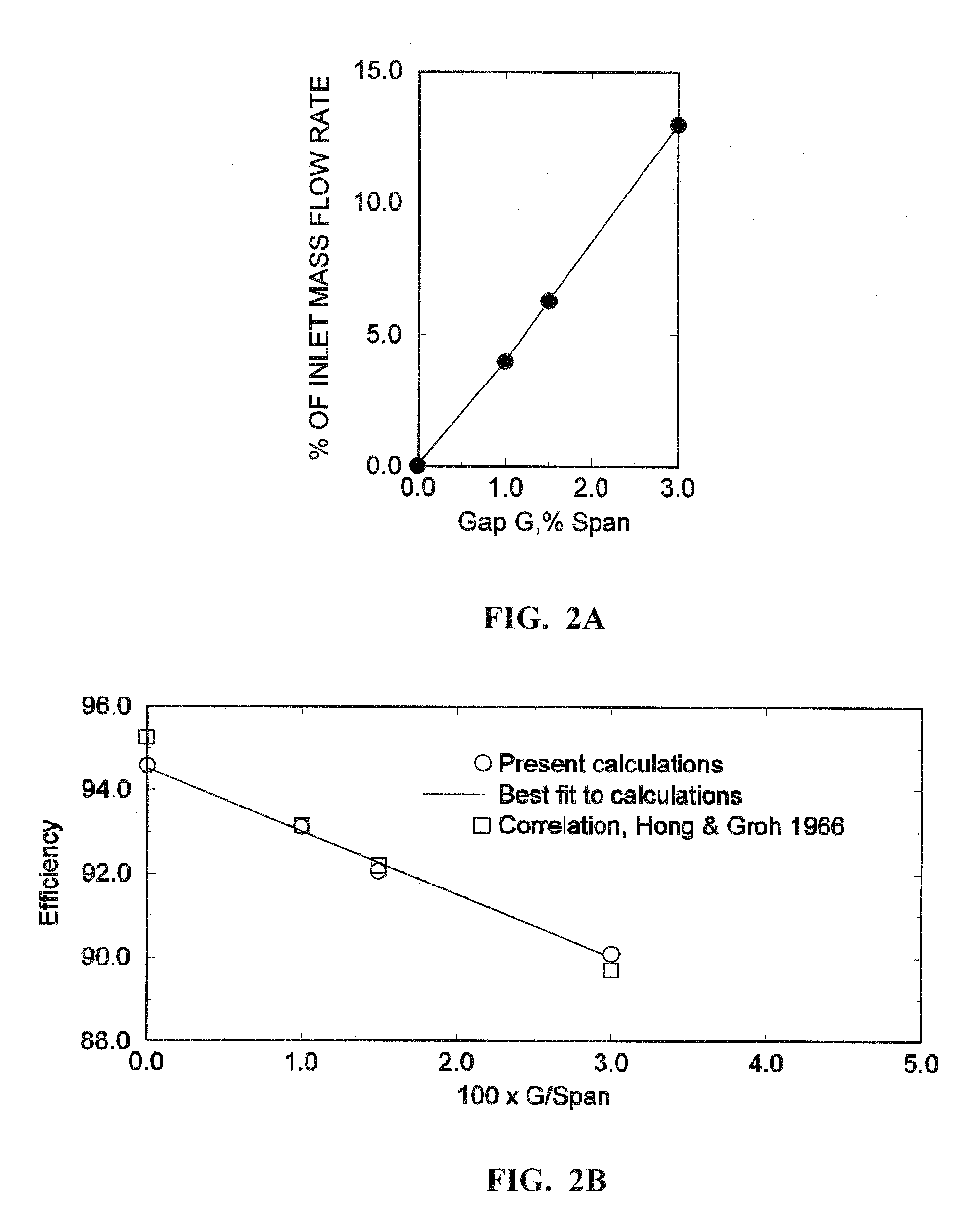
Electrodynamic Control of Blade Clearance Leakage Loss in Turbomachinery Applications
Electrodynamic control of fluid leakage loss is provided. Embodiments utilize electrohydrodynamic (EHD) principles to control and / or reduce leakage flow in turbomachinery. Electrodes can be used to provide a flow actuation mechanism inside the clearance gap for generating discharge. The electrodes can be positioned to have geometric asymmetry. Embodiments provide the electrodes on a turbine blade. The blade can have a DC power that can function as a square pulsed DC wave with the duty cycle equal to the blade passing frequency and the stator can be grounded. In an embodiment, the stator can have the actuator of the electrode-insulator assembly attached to the inside. In one embodiment, the actuators can be arranged just on the stator or casing. The phase and power supply to individual electrodes can be adapted as needed. In one embodiment, the phase can be lagged for accurate control of leakage flow. The control of the power supply to the electrodes can involve a closed control loop that monitors tip gap size.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Mouthpiece device of electronic cigarette
InactiveUS9072322B2Improve leak-proof effectEasy to manufactureTobacco treatmentTobacco smoke filtersMouth pieceElectronic cigarette
The present invention relates to a mouthpiece device of an electronic cigarette, includes an atomizing device for vaporizing tobacco substance into aerosol, a reservoir for storing tobacco substance and a guiding tube for guiding tobacco substance from the reservoir to the atomizing device, which are all set in a shell. The guiding tube has one end inserted in the reservoir and the other end communicated with atomizing device. The mouthpiece device further includes a preheating device for heating solid tobacco substance in the reservoir to generate liquid. The preheating device is set in the end of the reservoir near the guiding tube, and seals solid tobacco substance in the reservoir. The present invention solves existing problems such as fluid leakage, complicate manufacturing, high cost, bad heat insulation and filtering aerosol; and obtains perfect leakage proof, simple manufacturing, lower cost, good heat insulation and well filtering aerosol.
Owner:HUIZHOU KIMREE TECH
Monitoring seal system
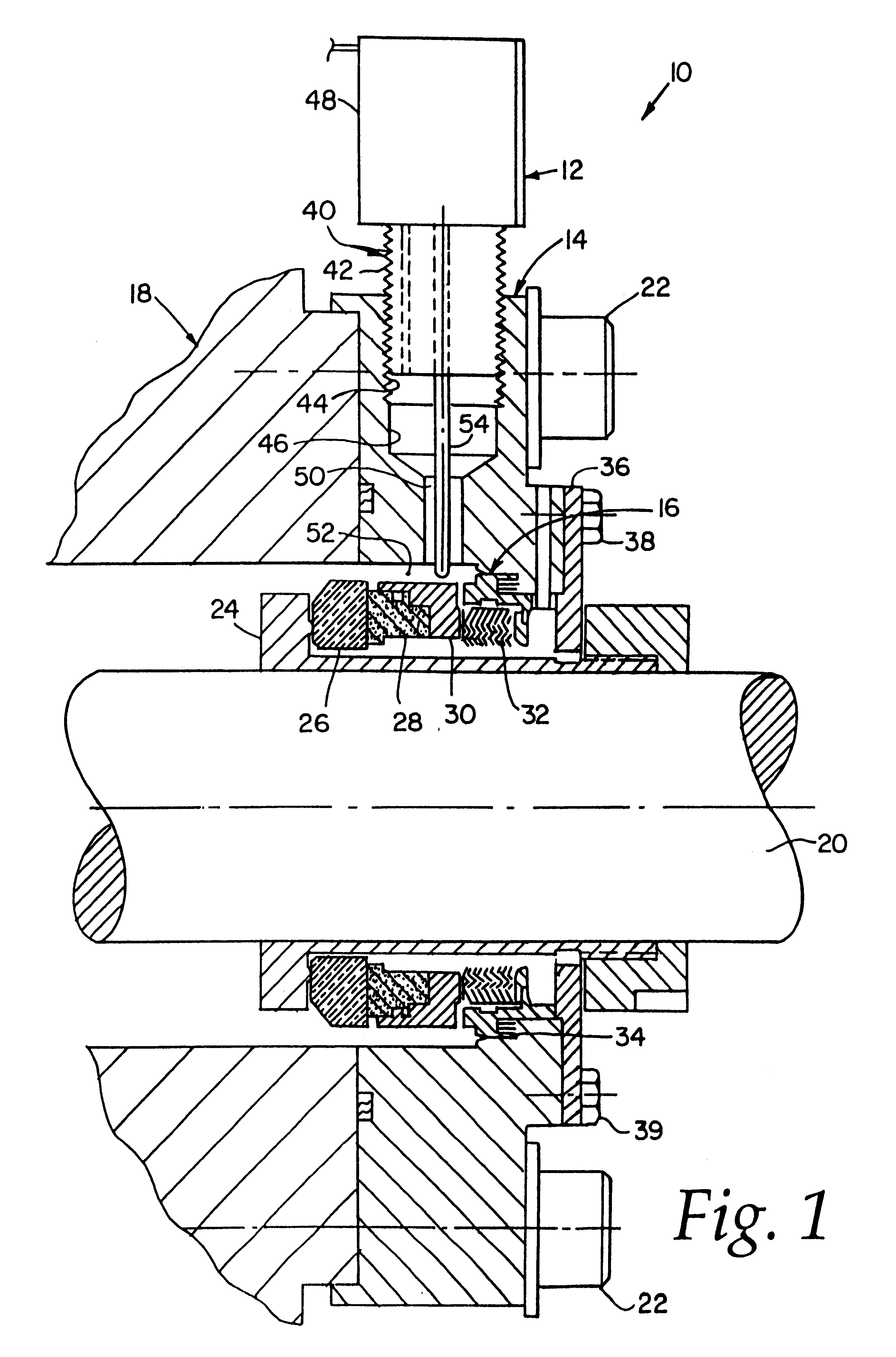
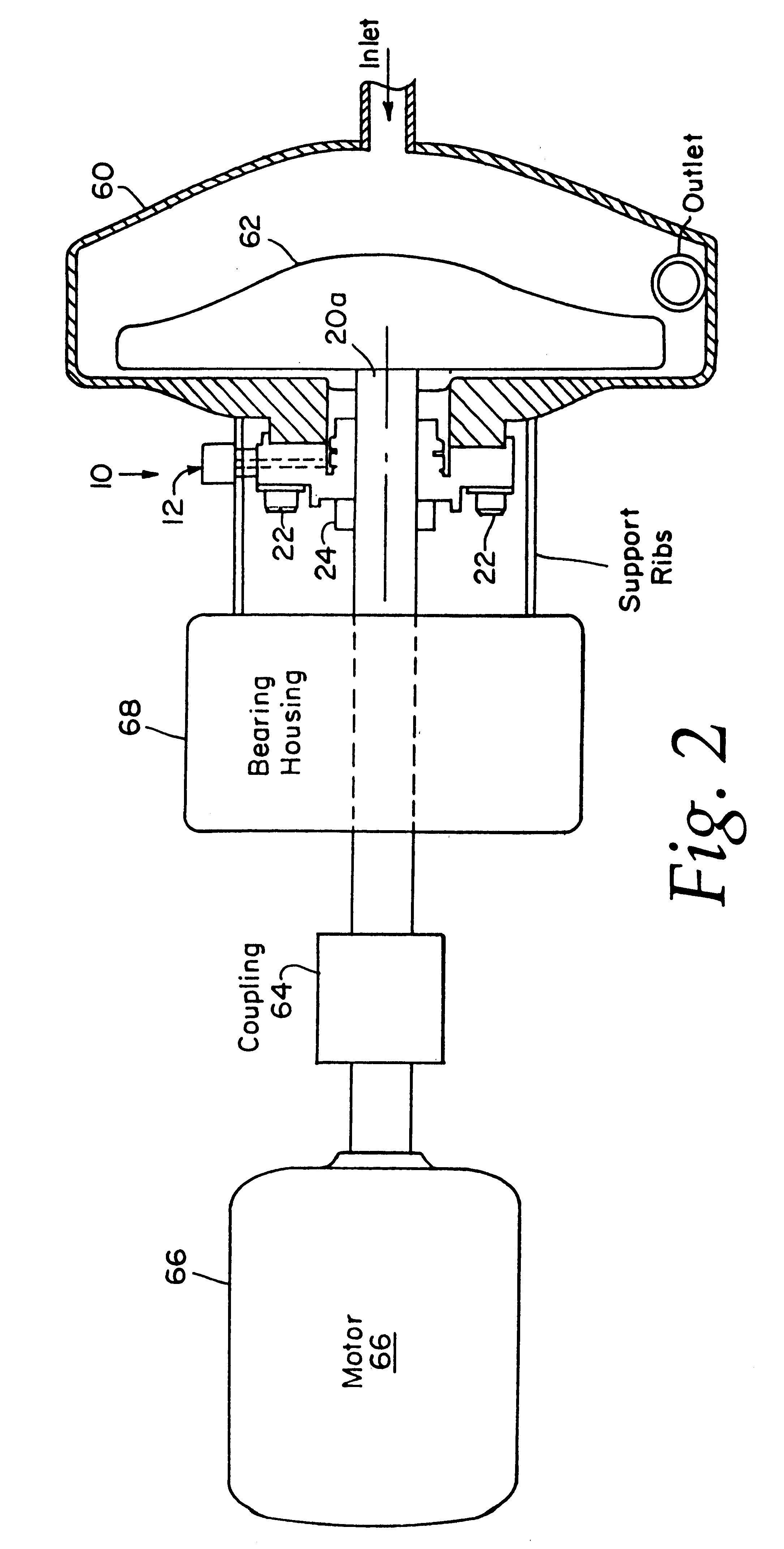
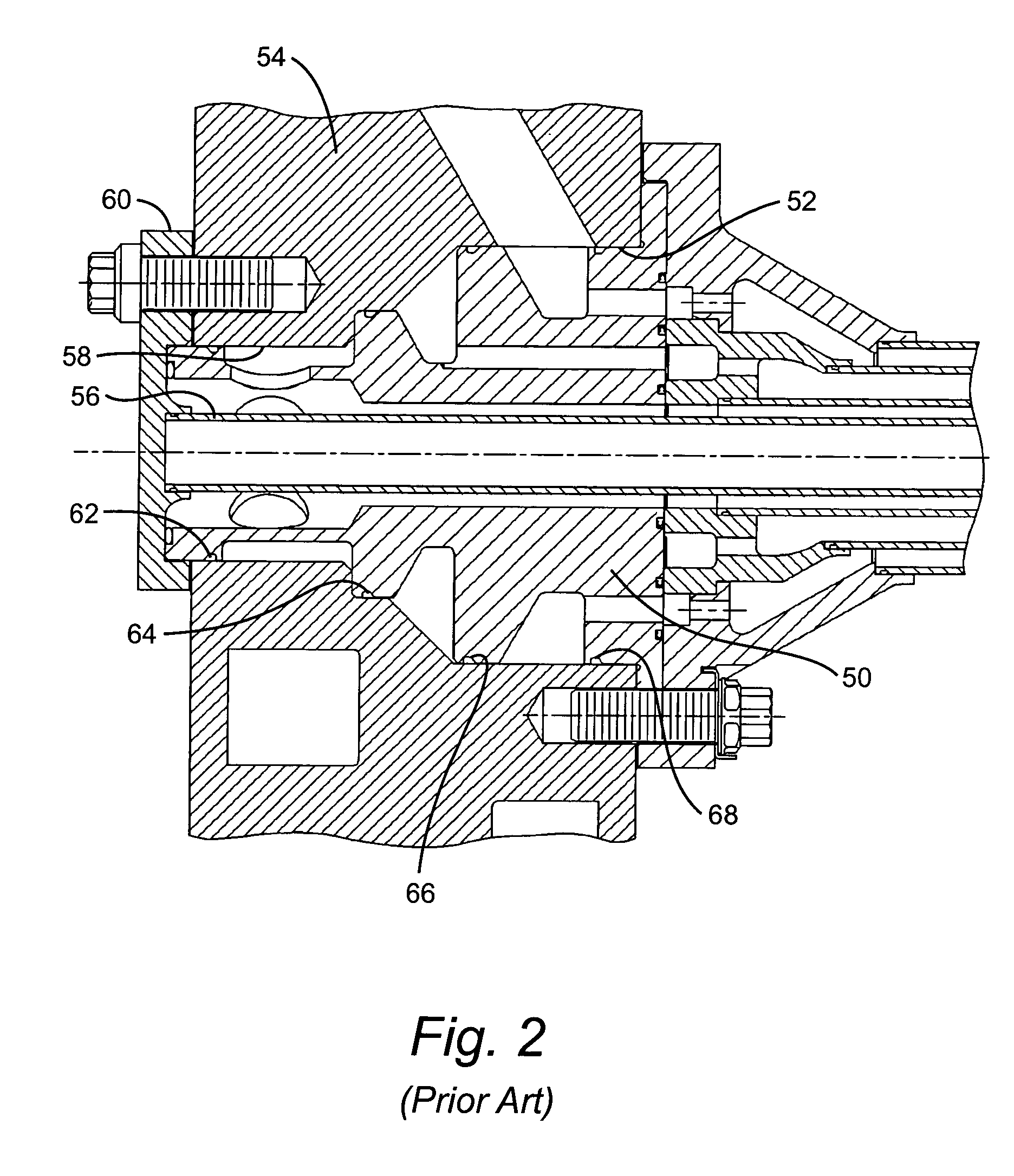
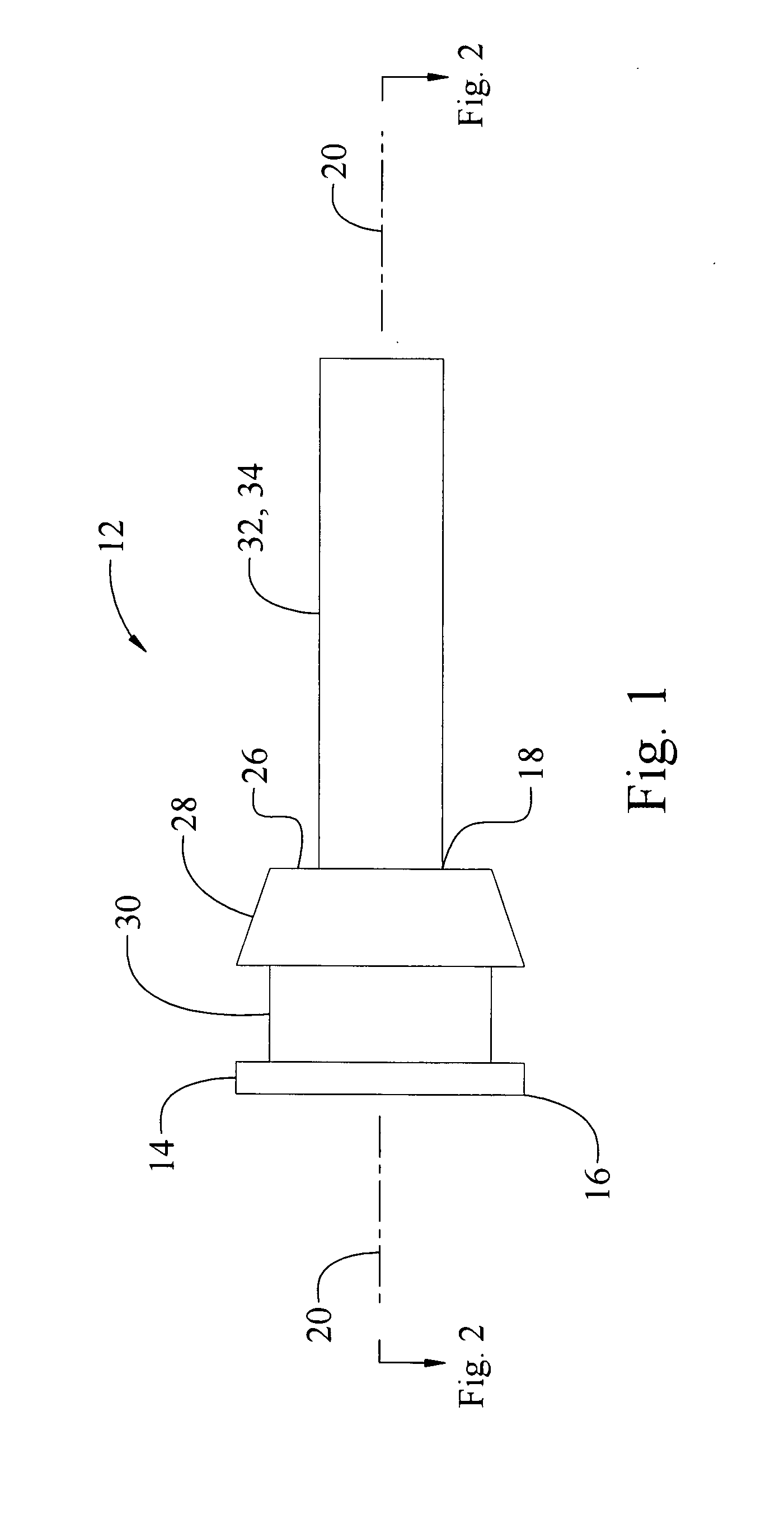
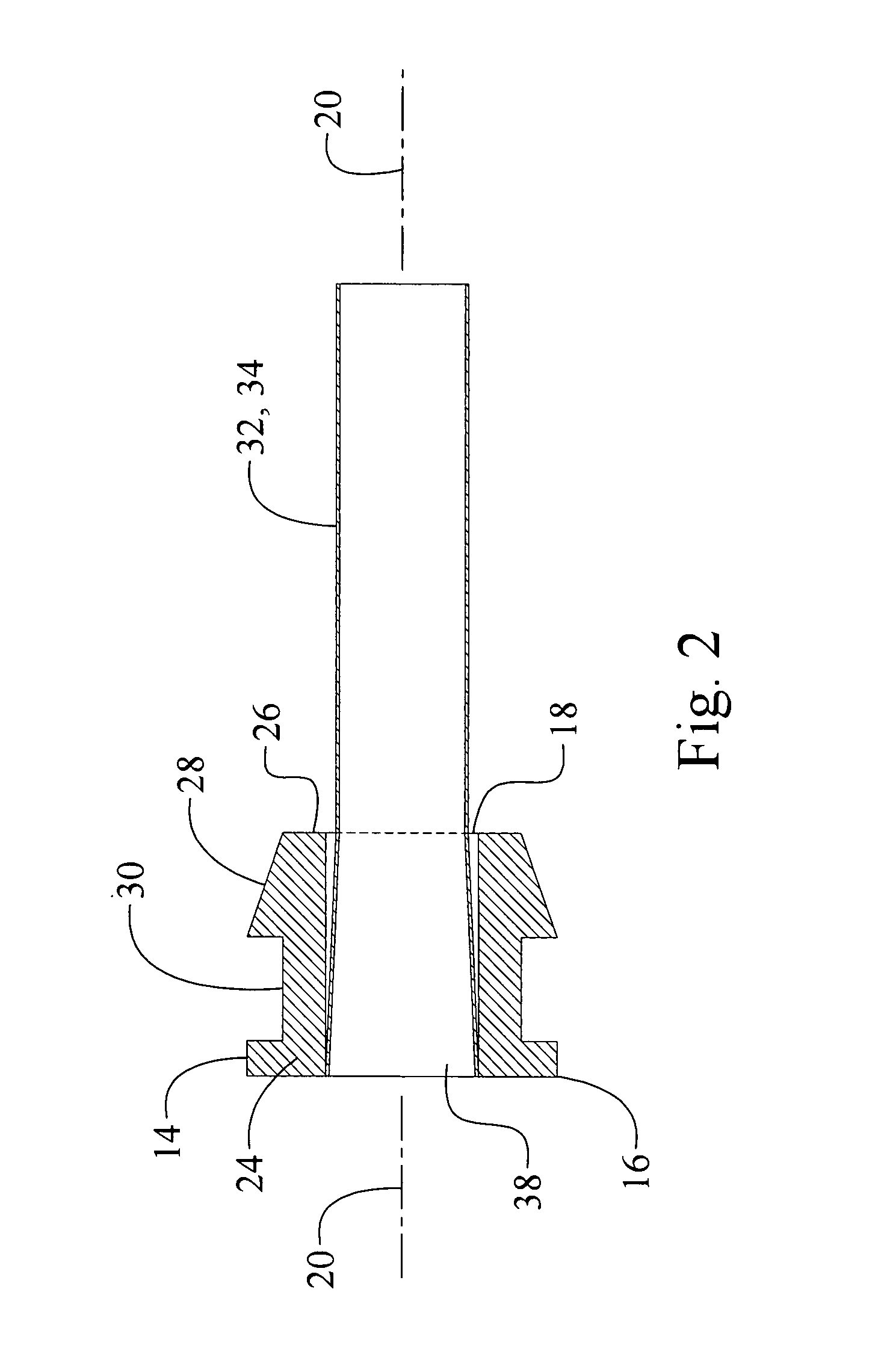
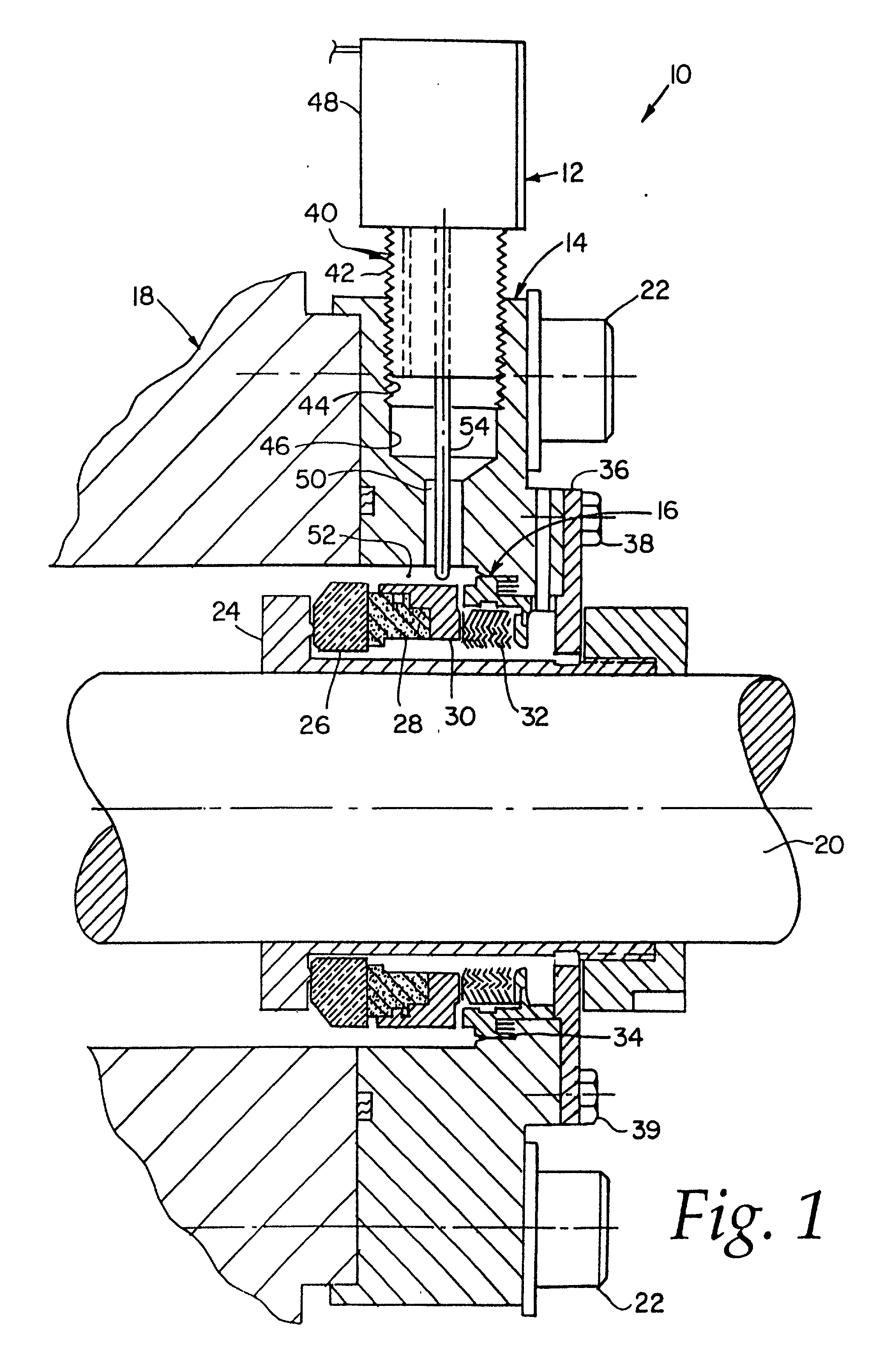
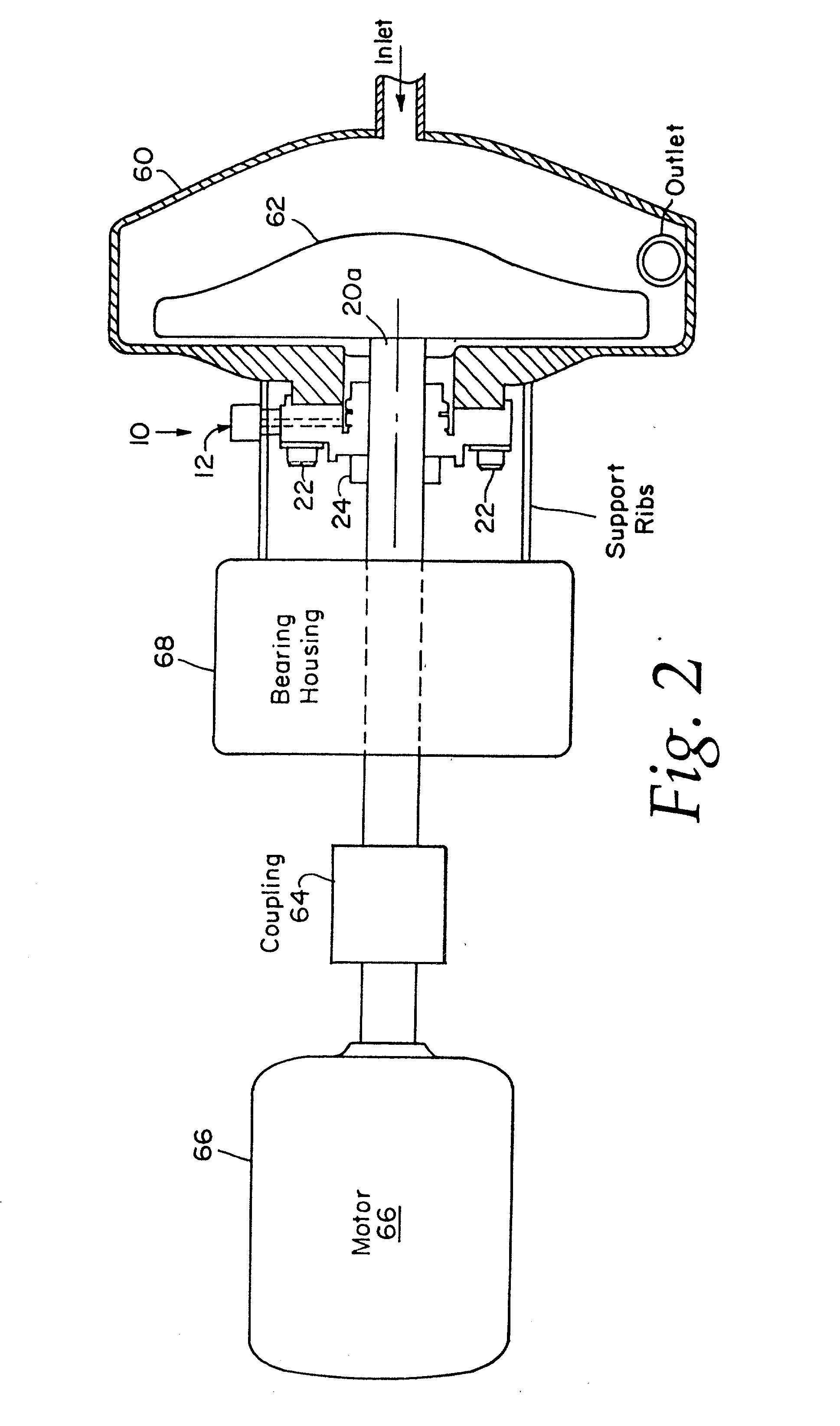
InactiveUS6626436B2Prevent liquid leakageEngine sealsPiston ringsEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A monitoring seal system comprises a seal housing, a seal assembly, a temperature sensor and a controller. The seal assembly sealingly engages a rotary shaft to prevent fluid leakage between the shaft and the housing. The seal assembly has at least one seal. The seal has a primary ring and a mating ring. The temperature sensor senses the temperature in the vicinity of the seal. The controller determines whether an upset condition has occurred based on at least the temperature in the vicinity of the seal.
Owner:JOHN CRANE INC
Apical puncture access and closure system
A device, system, and method for providing access to, and sealing of, a body organ includes an implant device. An implant device has a main body having an internal access lumen, with a plurality of prongs extending from a distal end of the main body. The main body can include two lumens, one slidable within the other, to form a single continuous lumen with an adjustable length. The main body has an expanded configuration with an expanded diameter, and an unexpanded configuration with an unexpanded diameter. The prongs have a generally straight configuration where they extend distally of the distal end of the main body, and a bent configuration where the prongs bend around so that their tips extend proximally of the distal end of the main body. The device may include a hemostatic barrier to prevent fluid leakage therethrough when the main body is in the unexpanded configuration.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
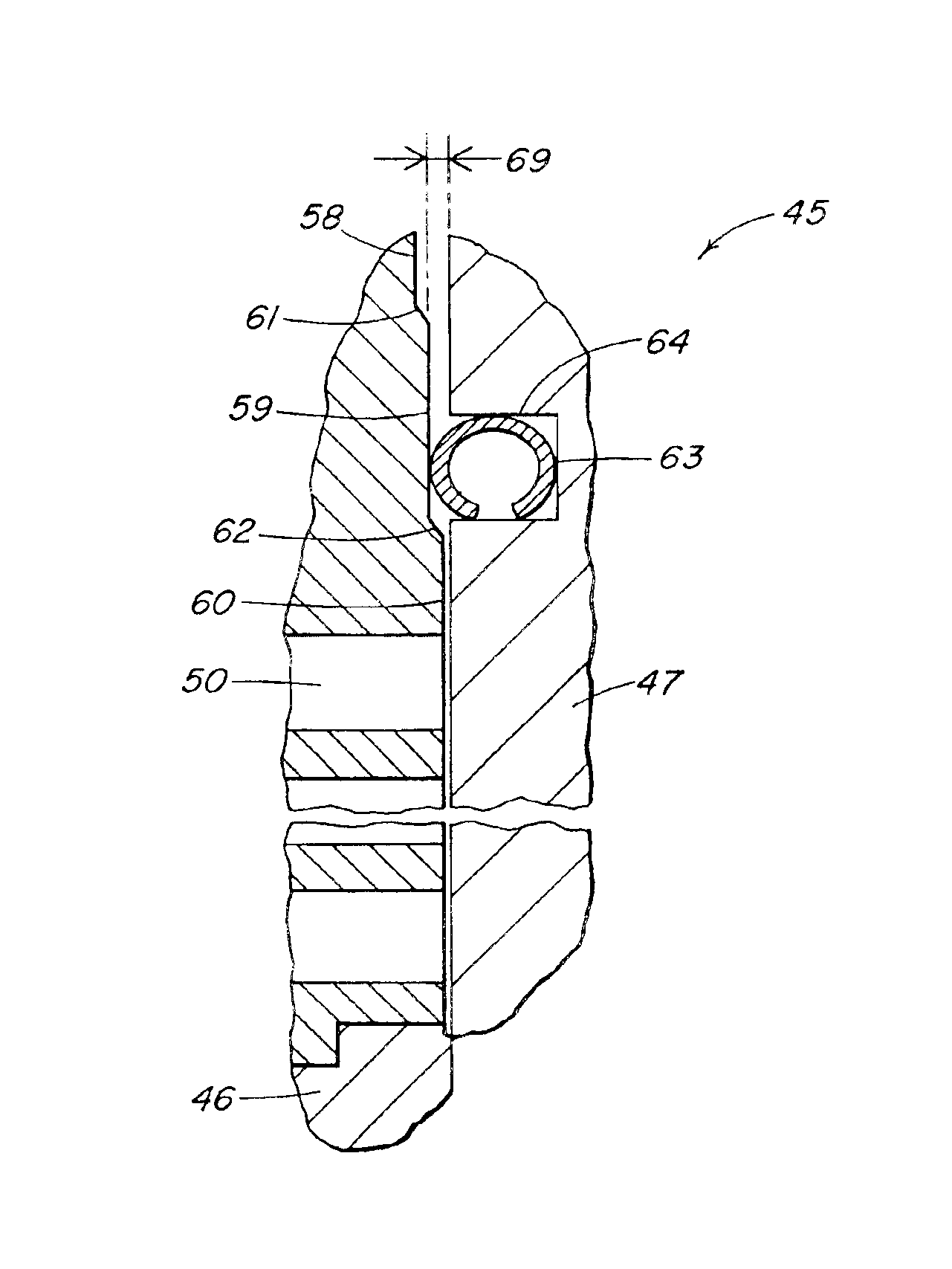
Rotary shaft monitoring seal system
InactiveUS6082737AEasy to installEasy to operateEngine sealsPiston ringsMechanical engineeringFluid leakage
A rotary shaft monitoring seal system includes a seal housing; a seal assembly in the housing for sealingly engaging a rotary shaft to prevent fluid leakage between the shaft and the housing; a monitoring port in the housing; and a detector assembly mounted in the port for sensing conditions in the vicinity of the seal assembly.
Owner:EG&G +1
Metal-glass sealing process
InactiveCN101531473AImprove air tightnessHigh insulation resistanceElectric connector introductionCapacitor housing/encapsulationWaxMetallic materials
The invention discloses a metal-glass sealing process, which comprises the following steps: according to the expansion coefficient of a metal upper cover being greater than the expansion coefficient of glass and the expansion coefficient of the glass being less than or equal to the thermal expansion coefficient of a metal mandril, selecting sealing glass powder; pressurizing the selected glass powder into a glass blank by a mould, and dewaxing and forming the glass blank in a furnace; respectively putting a metal material and the glass blank into a deoiling solution for treatment, and washing and drying the metal material and the glass blank after the deoiling; and assembling the metal upper cover, the metal mandril and the formed glass blank in a graphite mould, and sintering the assembled graphite mould in a sintering furnace. The metal and glass products sealed by the metal-glass sealing process have good sealing strength, good leakproofness with the leak rate less than 10 <-10>m <3>. Pa / s, and good leakproofness at a high temperature, and can solve the problems of fluid leakage, poor consistency and the like of consumer products. The metal-glass sealing process has strong operability and good consistency of the prepared products, and meets the requirement of mass production.
Owner:西安华泰有色金属实业有限责任公司
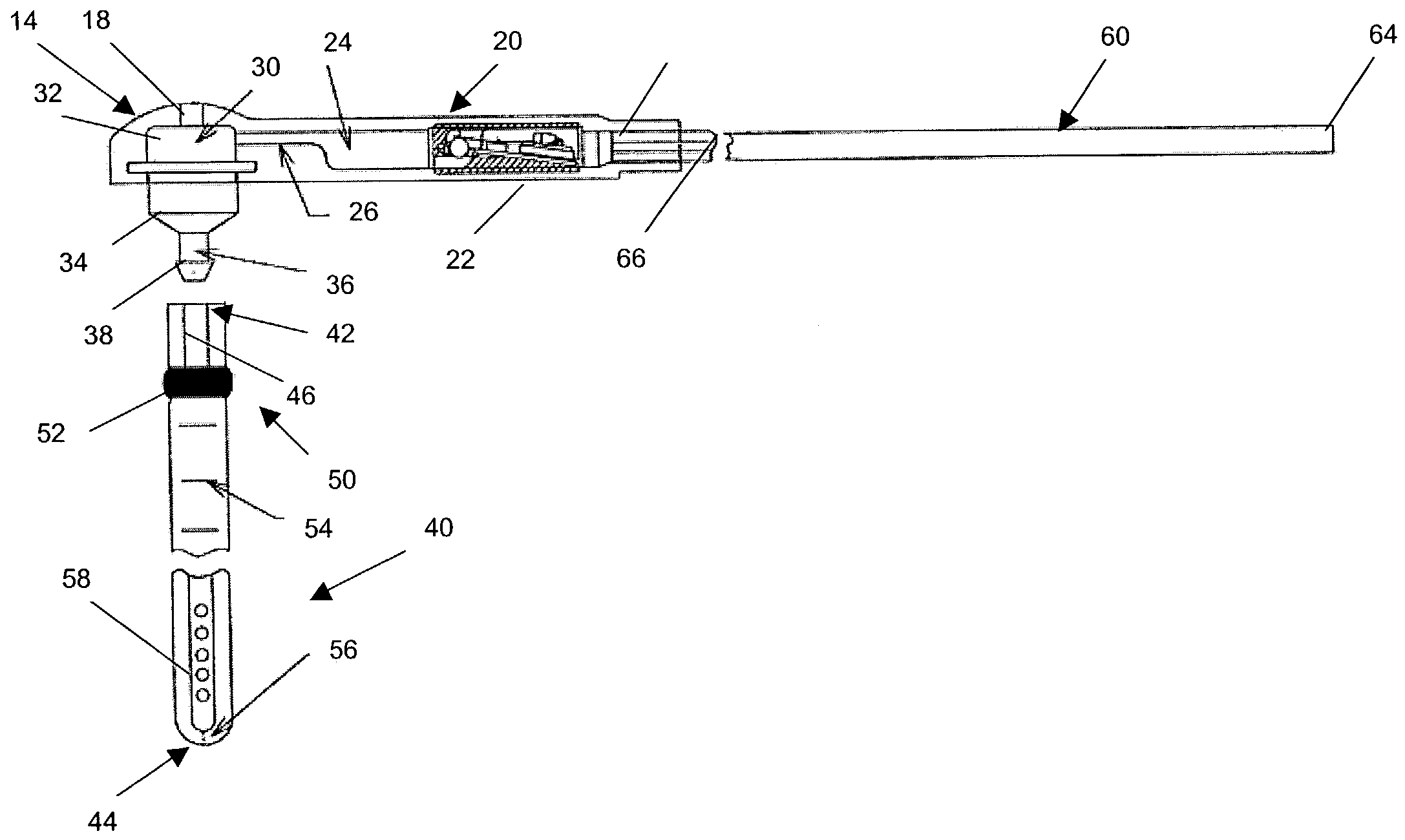
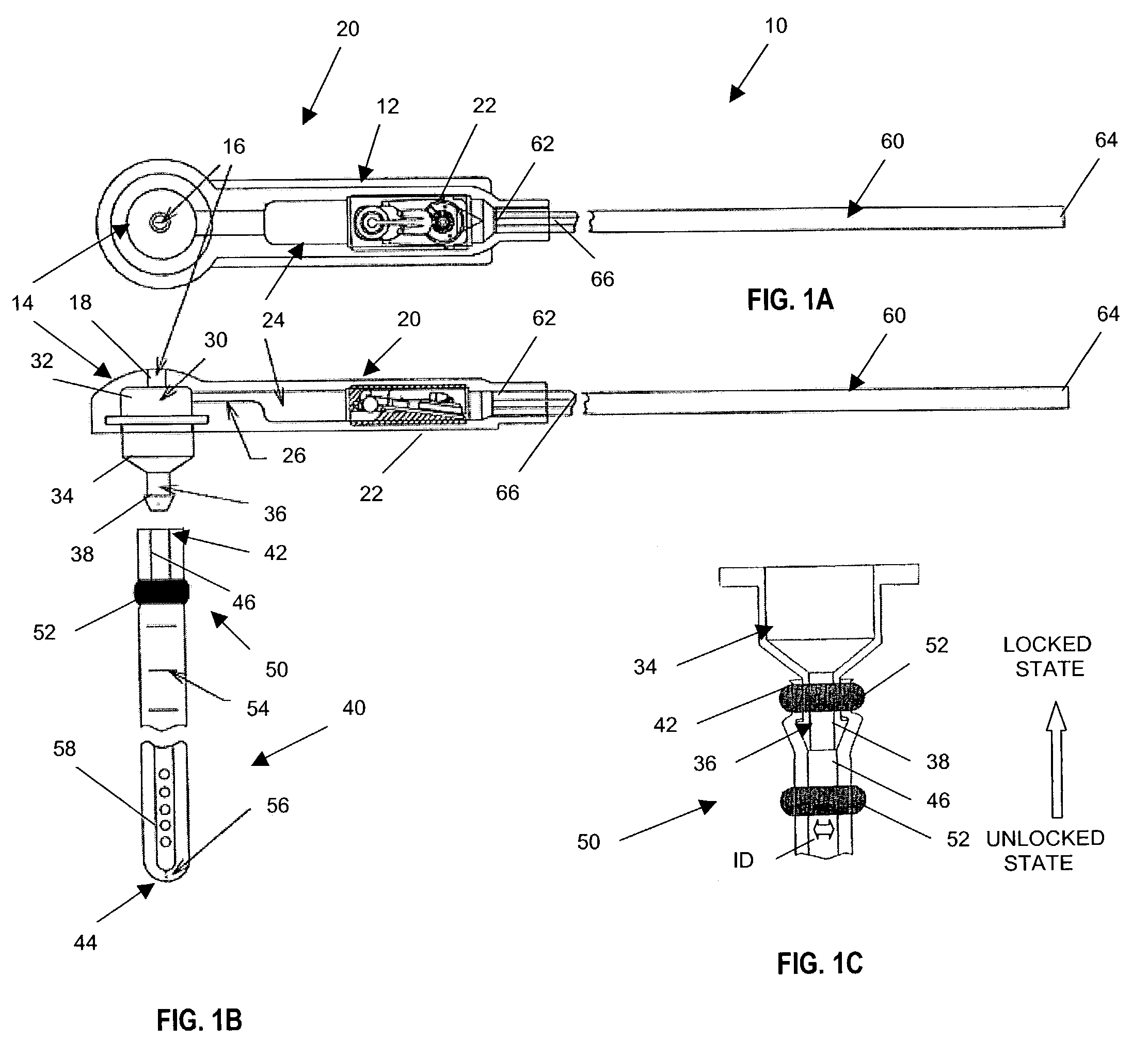
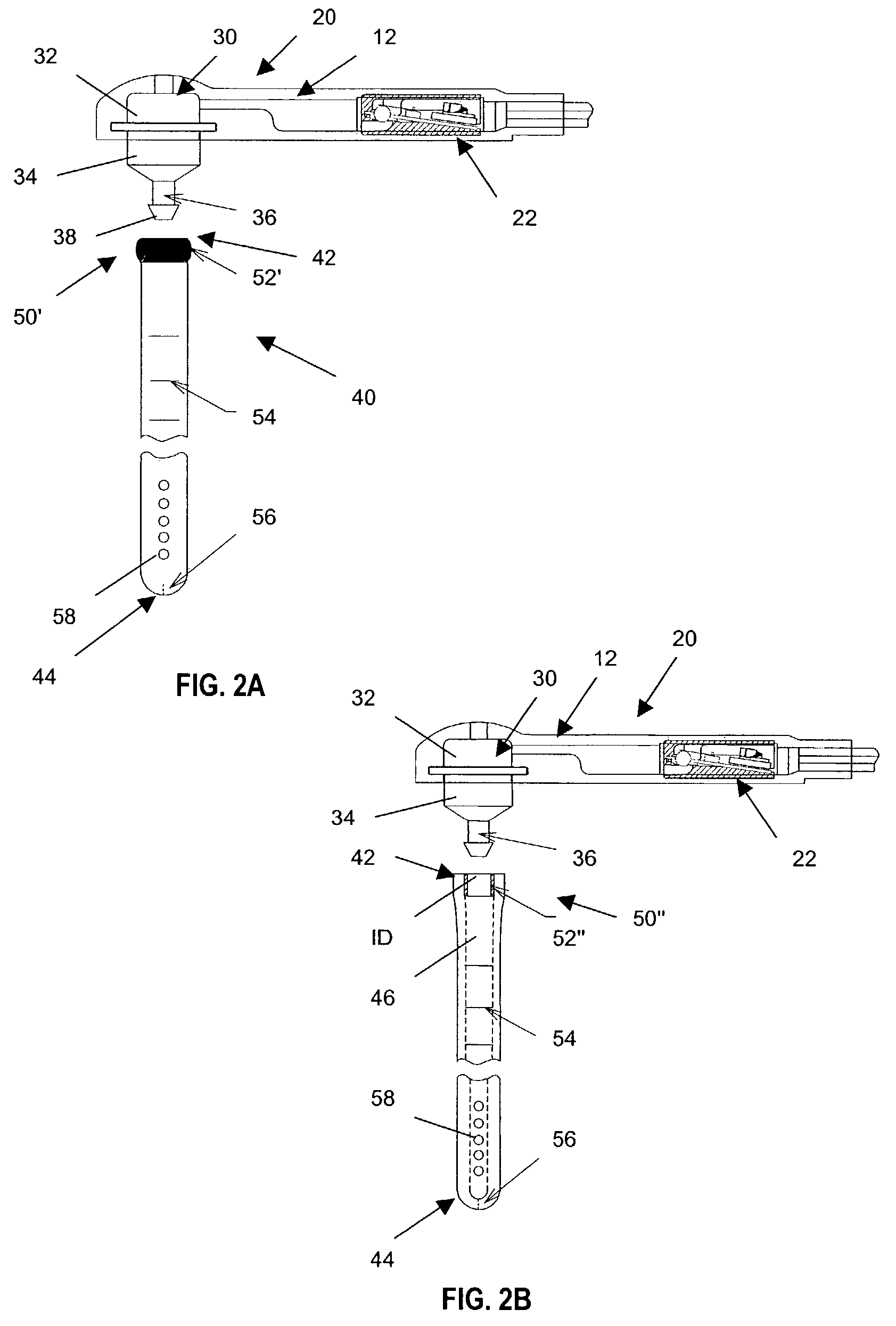
Hydrocephalus shunt system with endoscopic placement features
ActiveUS7235060B2Easy and fast assemblyFacilitate entryEar treatmentWound drainsMini invasive surgeryAdhesive
A shunt system for controlling the flow of fluid from one region of a patient to a different region of the patient's body. The shunt system includes endoscopic placement features so that the system can be placed endoscopically in a minimally invasive surgery. Also provided is a single fluid flow control device having flow control characteristics previously obtainable only by connecting in series two or more shunt system components. In addition, the shunt system includes a selectively engageable locking mechanism that allows the system to be assembled quickly and easily, without the need for sutures or adhesives. The present assembly process minimizes the possibility of any unintended fluid leakage from the device.
Owner:INTEGRA LIFESCI SWITZERLAND SARL
Multi-use torque fitting and compressible ferrule
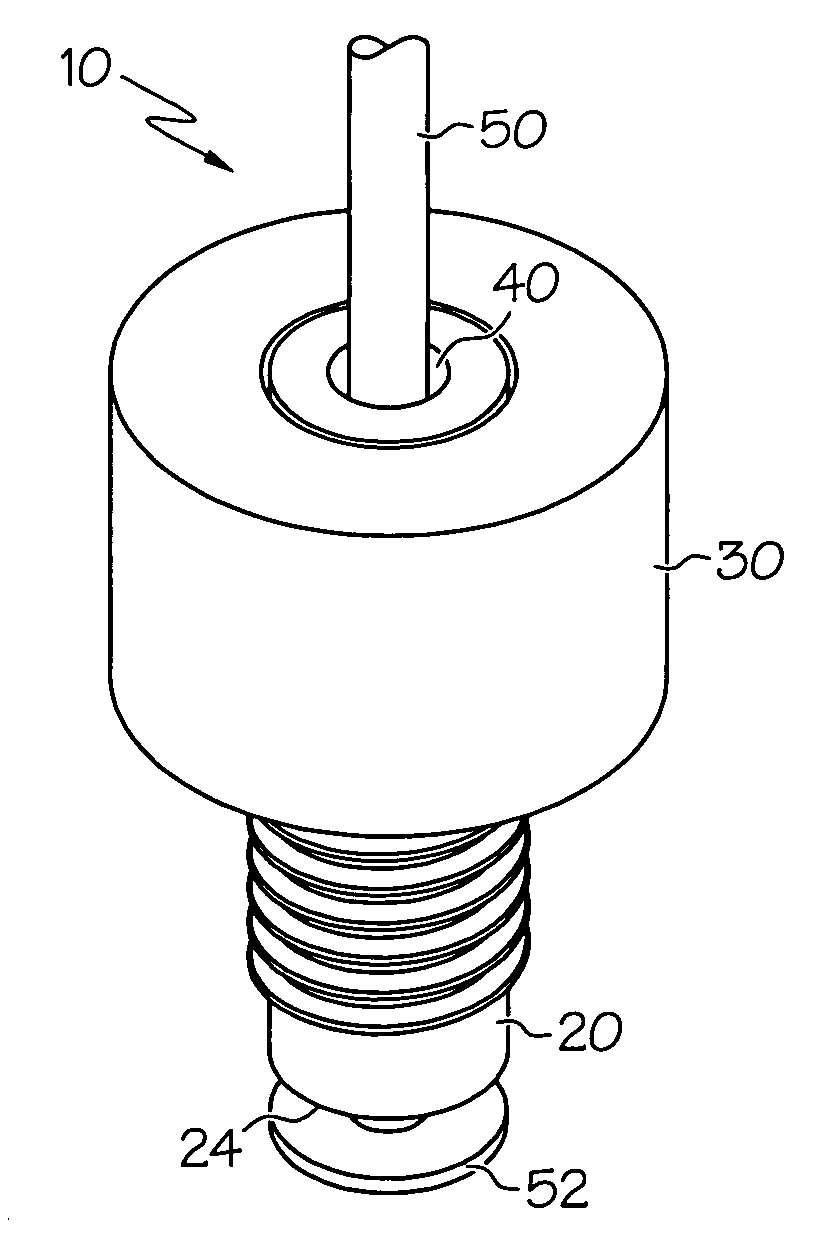
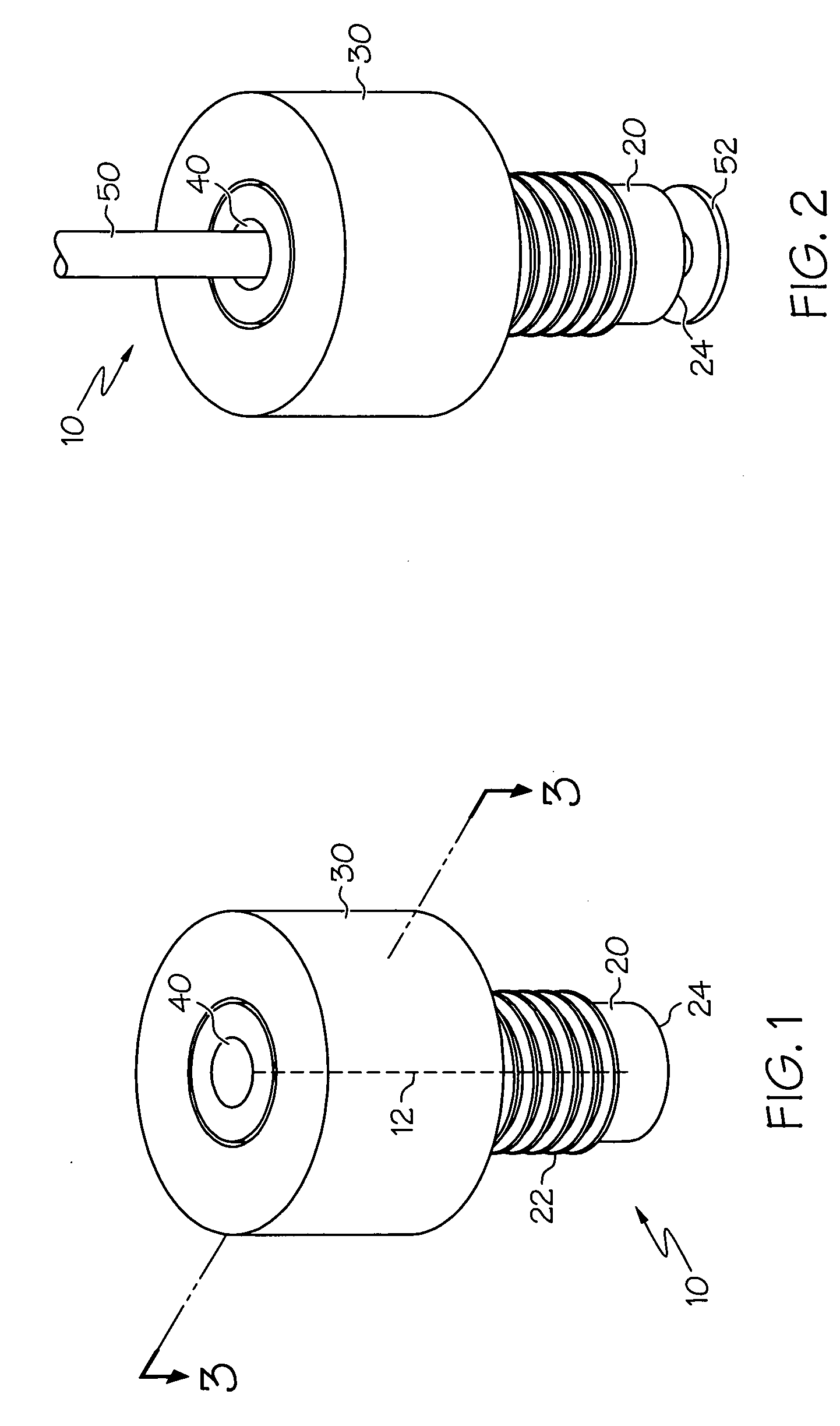
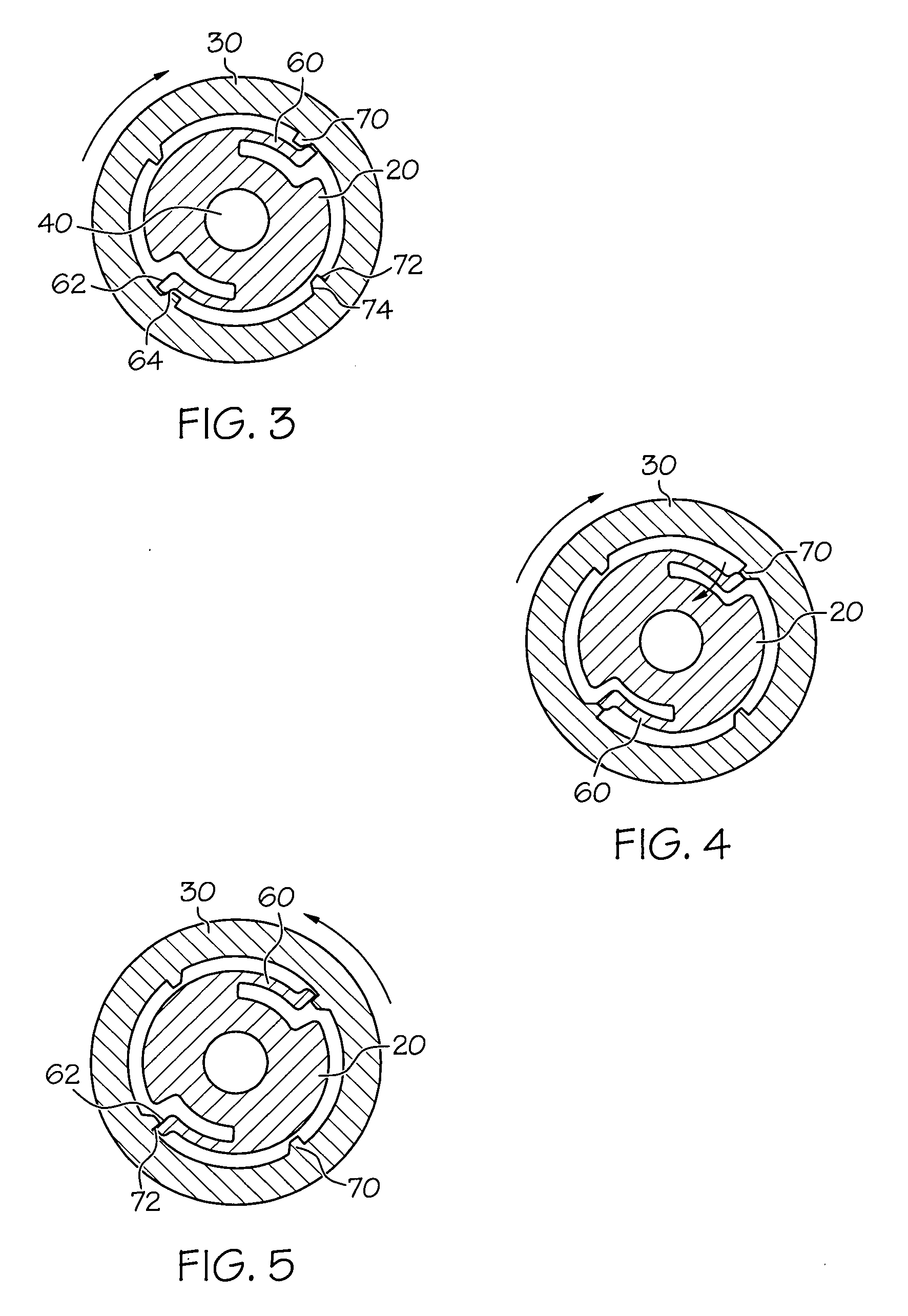
ActiveUS20090218813A1Prevent substantial fluid leakageEnable flexionFluid pressure sealed jointsJoints with sealing surfacesEngineeringScrew thread
Embodiments of the present invention generally relate to an assembly comprising a multi-use torque fitting, a length of tubing, and a compressible ferrule, wherein the assembly is configured to couple an end of the length of tubing to a port of a fluid-handling device in a hermetically sealed or substantially leak-proof manner. Generally, the fitting is configured to provide a degree of compression to the compressible ferrule sufficient to prevent substantial fluid leakage at the ferrule / port interface. This fitting generally comprises a threaded body portion and a torque-limiting body portion, wherein the threaded body portion and the torque-limiting body portion are arranged substantially concentrically along a longitudinal axis of the fitting.
Owner:DIBA IND
Diverter valve
InactiveUS6978795B2Flow on effectOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMultiple way valvesEngineeringPressure difference
A diverter valve comprises a housing having inlets, a first outlet, and a second outlet. The inlets are connected to hot and cold water supplies, and mixing of the hot and cold water occurs both inside the housing and inside a mixing chamber external to the valve. The first outlet is connected to a spout, and the second outlet is connected to a spray unit. A valve element is mounted in the housing, movable between a closed position and an open position with respect to the first outlet. A piston member comprising a first piston at the bottom end of the valve element, and a second smaller piston at the top end of the valve is responsive to pressure differential between the second outlet and the inlet for movement to a first and second position. When a lower pressure exists at the second outlet, the piston member moves to the second position, closing off the first outlet. The valve also includes a flow regulator to regulate the flow through the second outlet. Fluid is directed into the flow regulator by channels running through the bottom piston. The flow regulator allows pressure to build up inside the valve, providing an increased closure force on the second outlet when the first outlet is open. An inverted cup washer prevents fluid leakage from the second exit by any other route than through the flow regulator. Build up of water inside this cup washer pushes it against the housing, providing an anti-knocking mechanism. The diverter valve may be included in a faucet assembly along with a separate isolated channel for filtered water.
Owner:TCL MFG
Artificial stoma and method of use
A device for creating a channel between the stomach lumen and the abdominal surface of a patient. The device includes a tube and a first bolster. The tube has a proximal end, a distal end, and a wall, the wall having an inner surface and an outer surface, and each end having an opening therein. The first bolster is attached to the distal end of the tube and the tube is adapted to slidably receive a feeding device having a shaft, wherein at least a portion of the outer diameter of the shaft of the feeding device is substantially the same size as that of the inner wall of the tube. The first bolster is adapted to sealingly engage with the patient so as to minimize or avoid fluid leakage about the tube. The present invention is also directed to a method of using an artificial stoma.
Owner:AVENT INC
Side-arm Port Introducer
InactiveUS20100063360A1Minimize fluid leakageEasy to introduceFallopian occludersCannulasSide armSurgical device
A self-sealing introducer is disclosed that allows easy introduction of a catheter into a working channel of a surgical instrument while minimizing fluid leakage before, during and after catheter insertion.
Owner:CYTYC CORP
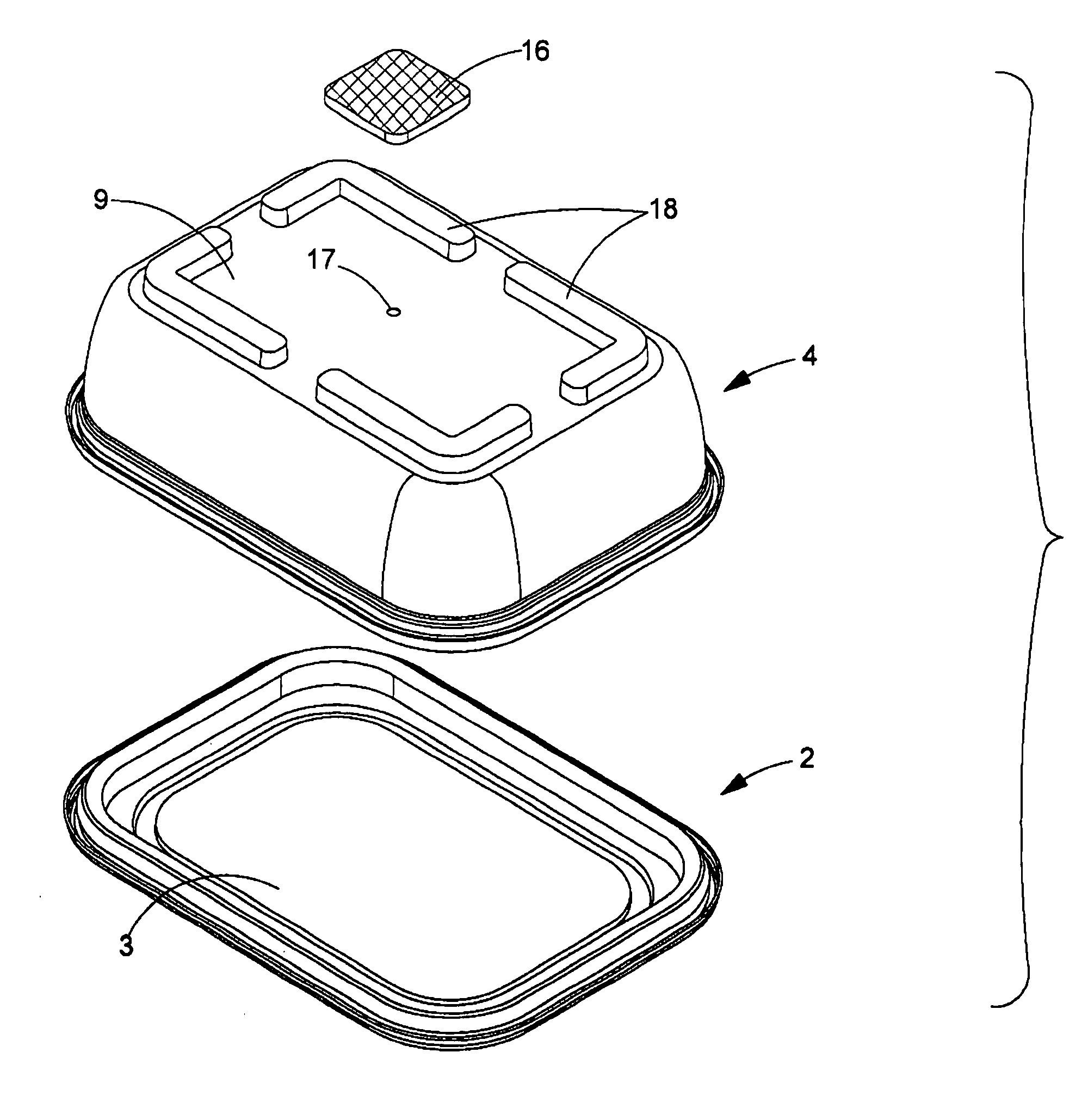
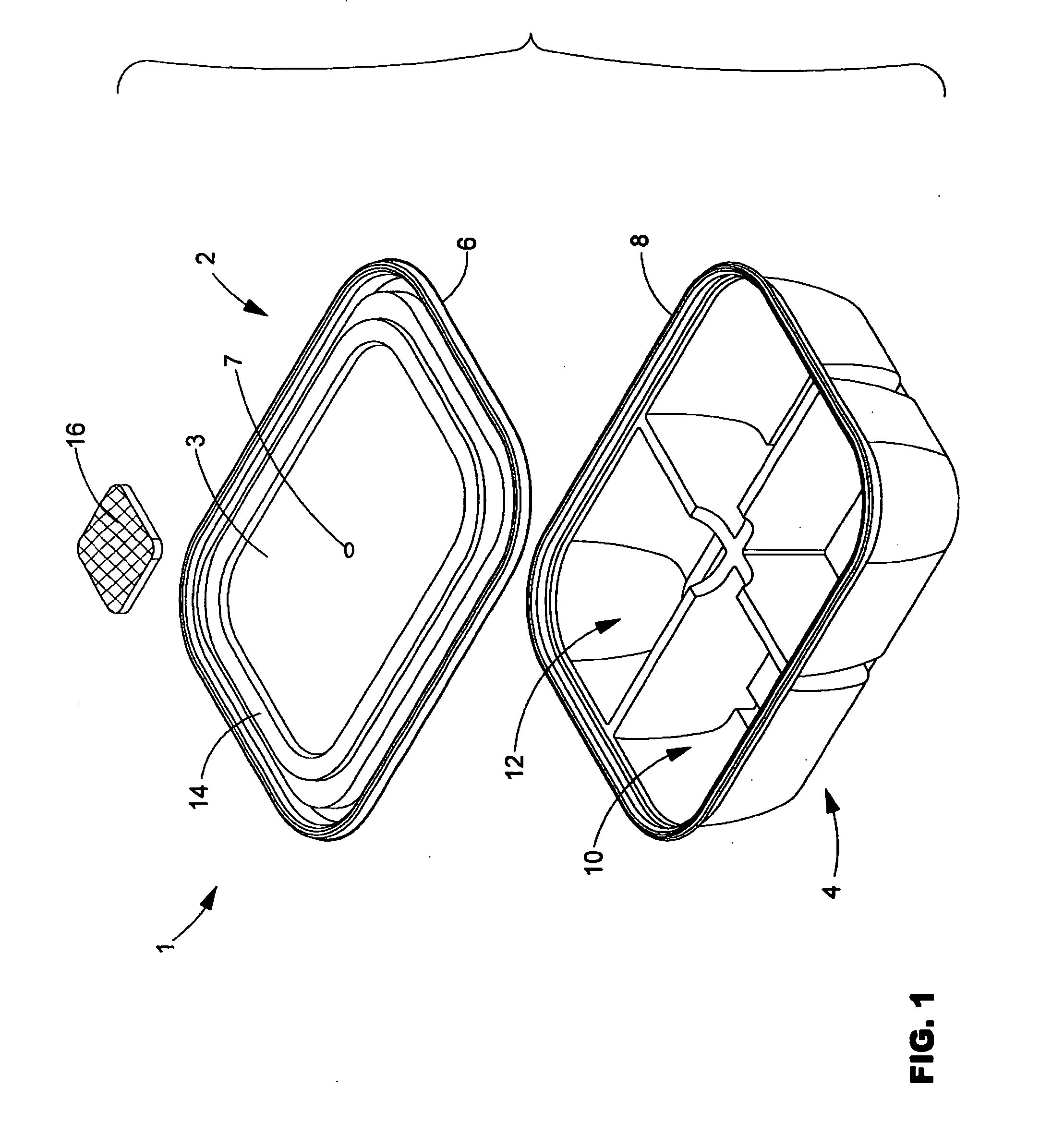
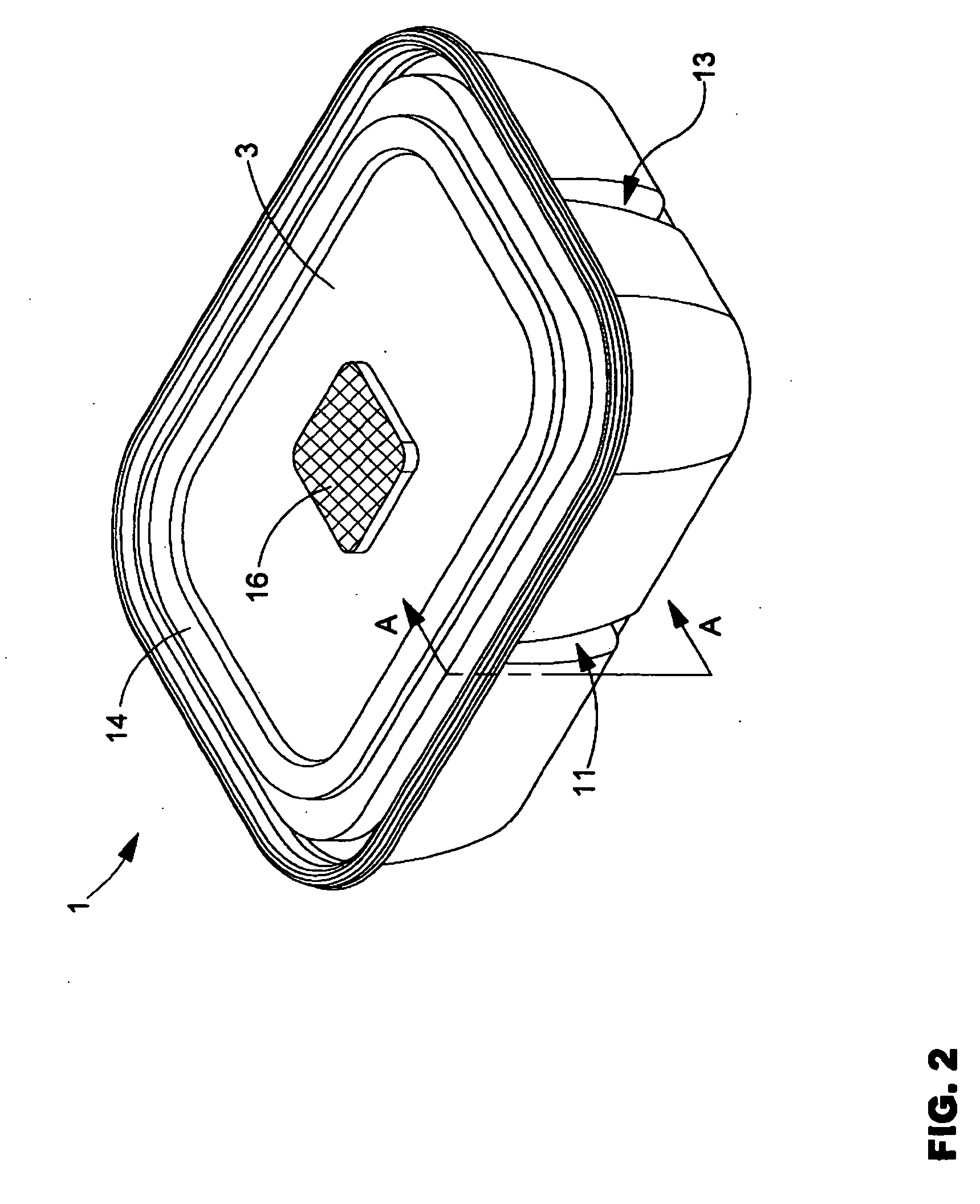
Food container with breathable patch
InactiveUS20080116098A1Freshness is promotedResistance to and sanitationLidsTray containersFoam food containerAdhesive
Owner:PACTIV PACKAGING
Control valve trim and bore seal
InactiveUS6851658B2Less stringent partReduced actuator forcePressure relieving devices on sealing facesValve members for absorbing fluid energyControl valvesActuator
An ANSI Leakage Class V control valve having consistent shut off characteristics with a reduced actuator force required to open and close the valve is provided. The trim arrangement of the control valve includes a valve cage having a multi-contoured inner surface. The multi-contoured inner surface can include a plurality of surfaces. The multi-contoured surface can include first, second, and third perimeter surfaces, and a first transition surface disposed between and coupling the first and second perimeter surfaces, and a second transition surface disposed between and coupling the second and third perimeter surfaces. The valve also includes a valve plug disposed at one end of a valve stem. The valve plug controls the fluid flow through the valve. The valve plug includes an opening through the plug for equalizing pressure across the valve plug. An annular channel is formed within a wall of the valve plug and is sized to accommodate a sealing ring. The sealing ring engages the second perimeter surface to form a fluid seal that substantially hinders fluid leakage through the valve.
Owner:FISHER CONTROLS INT LLC
Turbine combustor endcover assembly
ActiveUS20050005610A1Easy maintenanceMaintenance freeEngine sealsContinuous combustion chamberCombustorEngineering
The endcover assembly for a combustor includes an endcover having an aperture, an insert disposed in the stepped bore opening through an internal face of the endcover, a fuel cartridge extending through the insert and aperture and a seal cover on the external face of the endcover. Seal cover / endcover annular seals are disposed in registering axial cavities to seal against fluid leakage externally of the endcover assembly. Generally C-shaped and W-shaped seals are disposed in the cavities between the stepped shoulders of the insert and aperture to seal against leakage through the internal face of the endcover. The seals maintain sealing engagement during assembly and thermal distortion during turbine usage.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
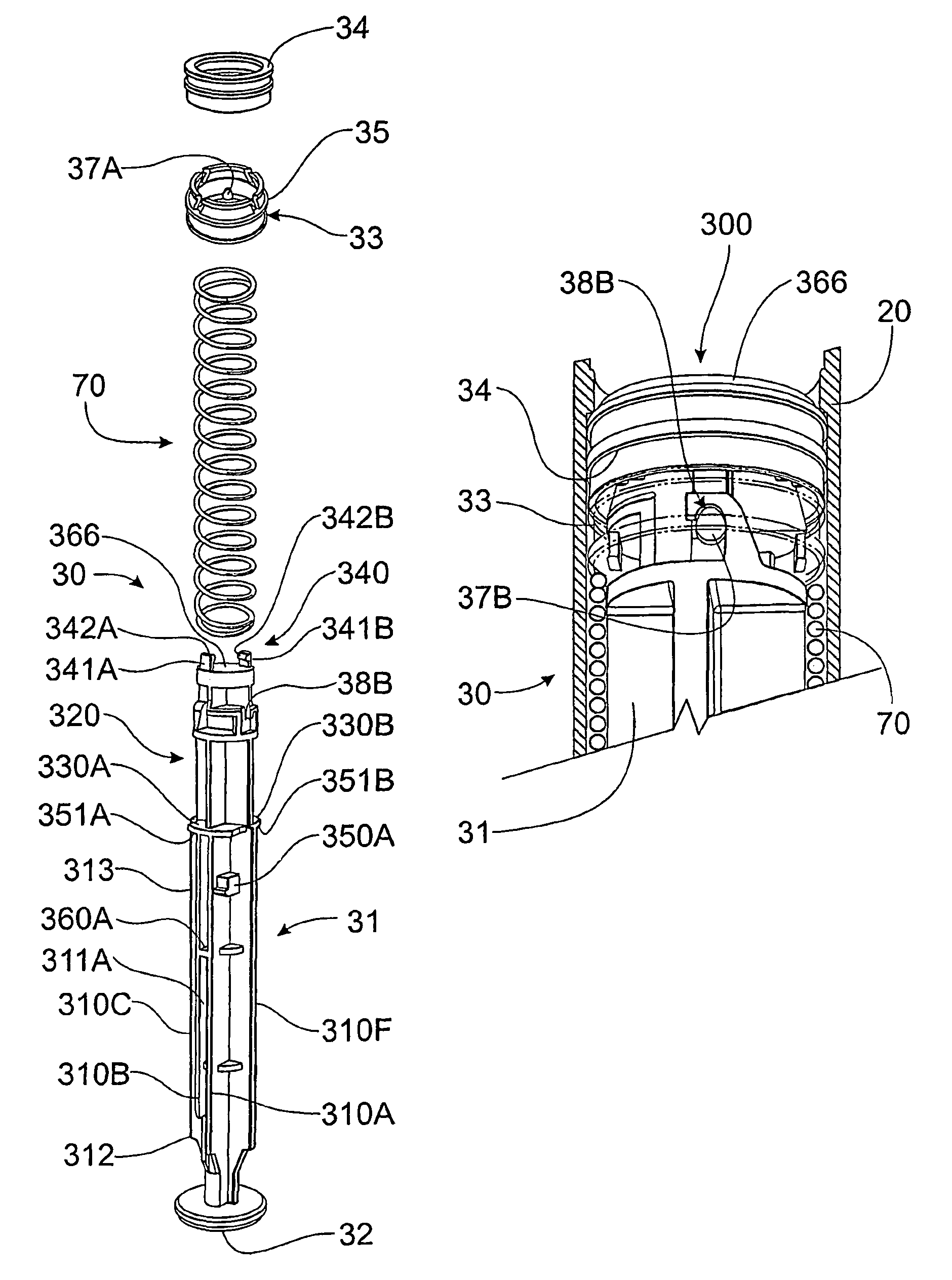
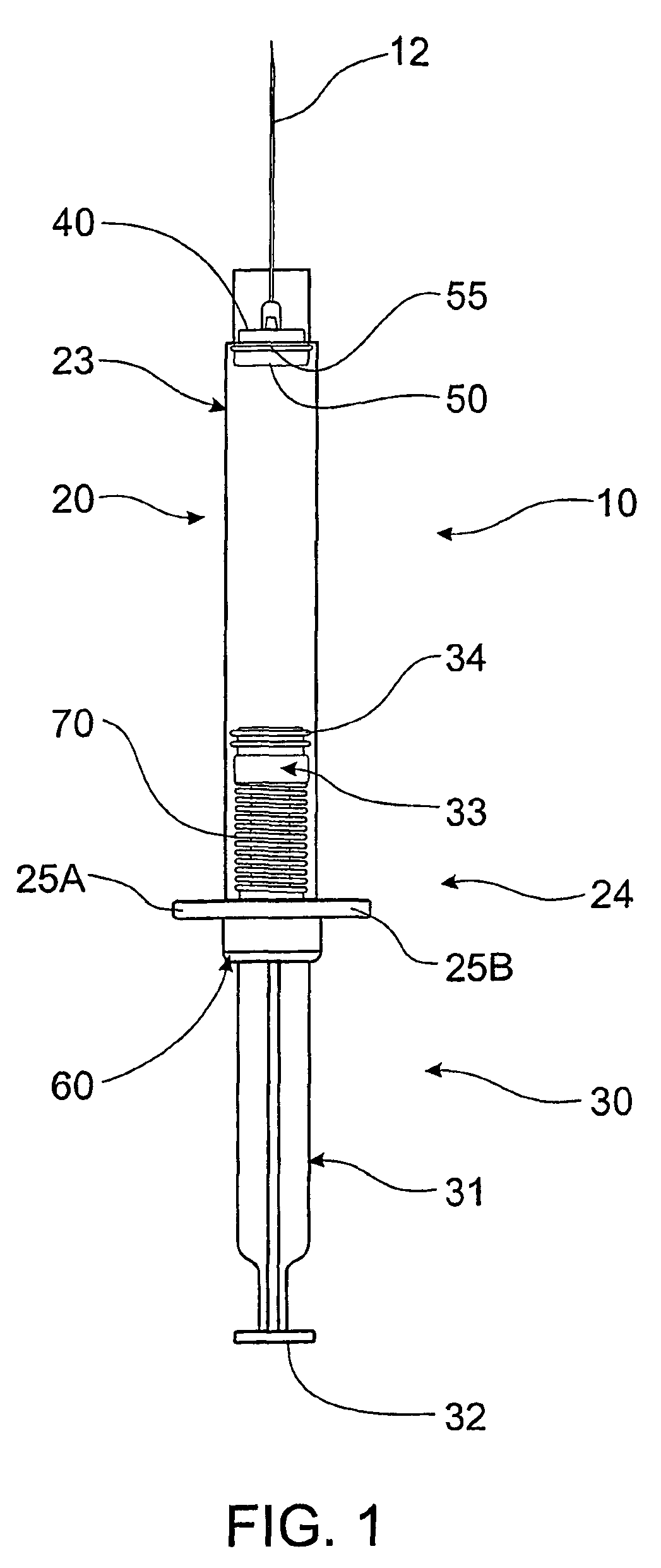
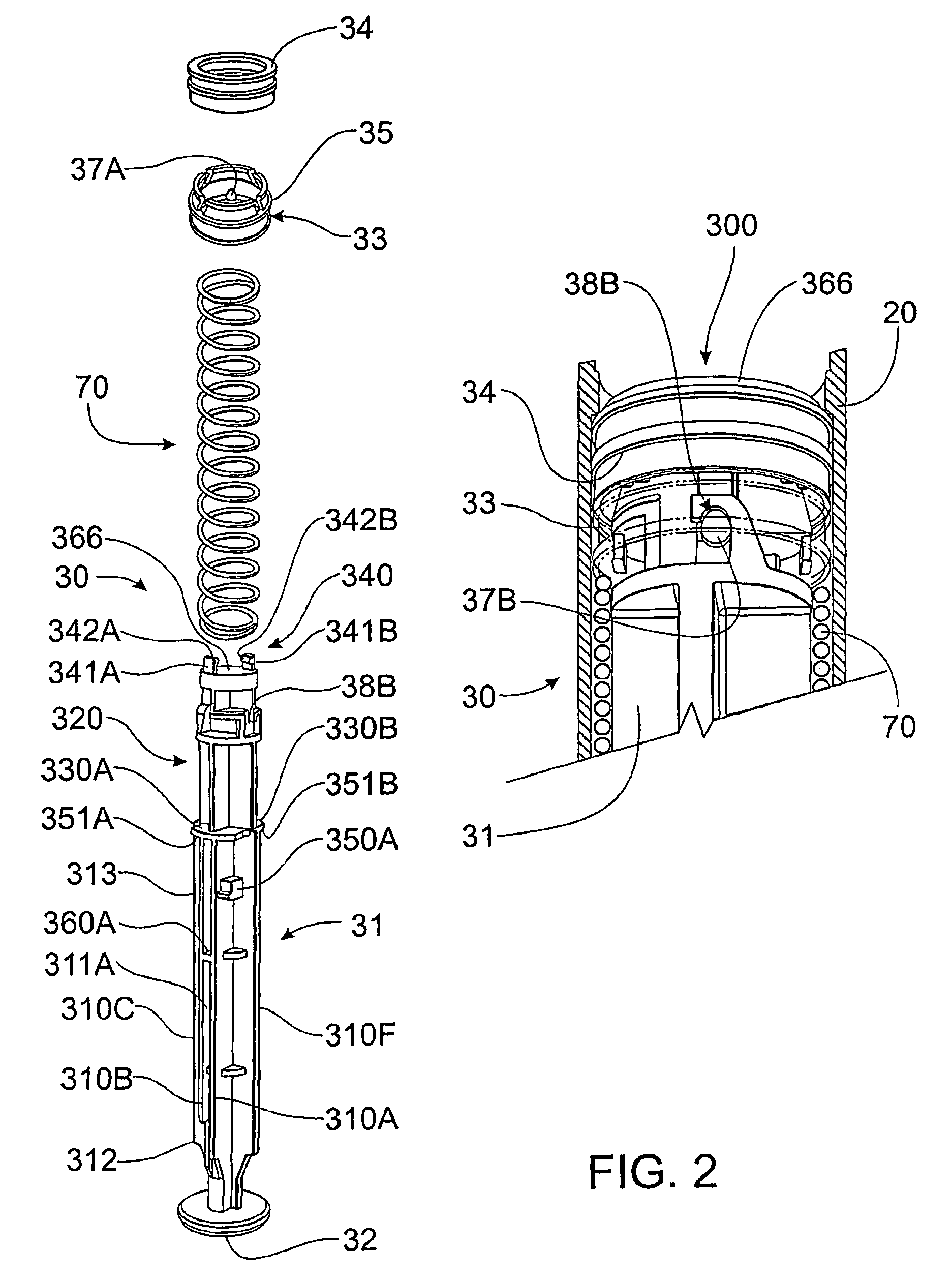
Retractable syringe with plunger disabling system
ActiveUS8002745B2Spring can be largeSmoother “ feel ”Infusion syringesInfusion needlesSyringe needleBiomedical engineering
A retractable syringe includes a barrel, a collar mounted to the barrel, a retraction spring and a needle mount. The plunger includes a first plunger member and a second plunger member that are releasably coupled to initially compress the spring. The second plunger member further includes a seal to prevent fluid leakage between plunger and barrel. After depression of the plunger to deliver the syringe fluid contents, the first plunger member engages the needle mount with needle attached thereto and is rotatably uncoupled from the second plunger member to allow decompression of the retraction spring, which forces retraction of the first plunger member, needle mount and needle engaged therewith. The first plunger member and the collar include elements that co-operatively disable subsequent depression or withdrawal of the plunger. Following retraction of the first plunger member, the second plunger member and seal prevent refilling and re-use of the syringe.
Owner:UN HOLDINGS LLC
Low leakage plunger assembly for a high pressure fluid system
InactiveUS20080224417A1Minimize fuel leakageImprove efficiencyEngine sealsLeakage preventionFluid controlReciprocating motion
A fluid control device for use in a high pressure fluid system, the device including a device body with a cavity and a high pressure circuit, a plunger positioned for reciprocal movement in the cavity, and a leakage reduction cap mounted to the plunger for reducing fluid leakage flow. In one implementation, the leakage reduction cap includes a flexible portion positioned between the device body and the plunger, and defining an annular clearance gap between the leakage reduction cap and the device body. The flexible portion of the leakage reduction cap resiliently flexes radially outwardly in response to fluid pressure forces to reduce the annular clearance gap so as to minimize fluid leakage flow through the annular clearance gap.
Owner:CUMMINS INC
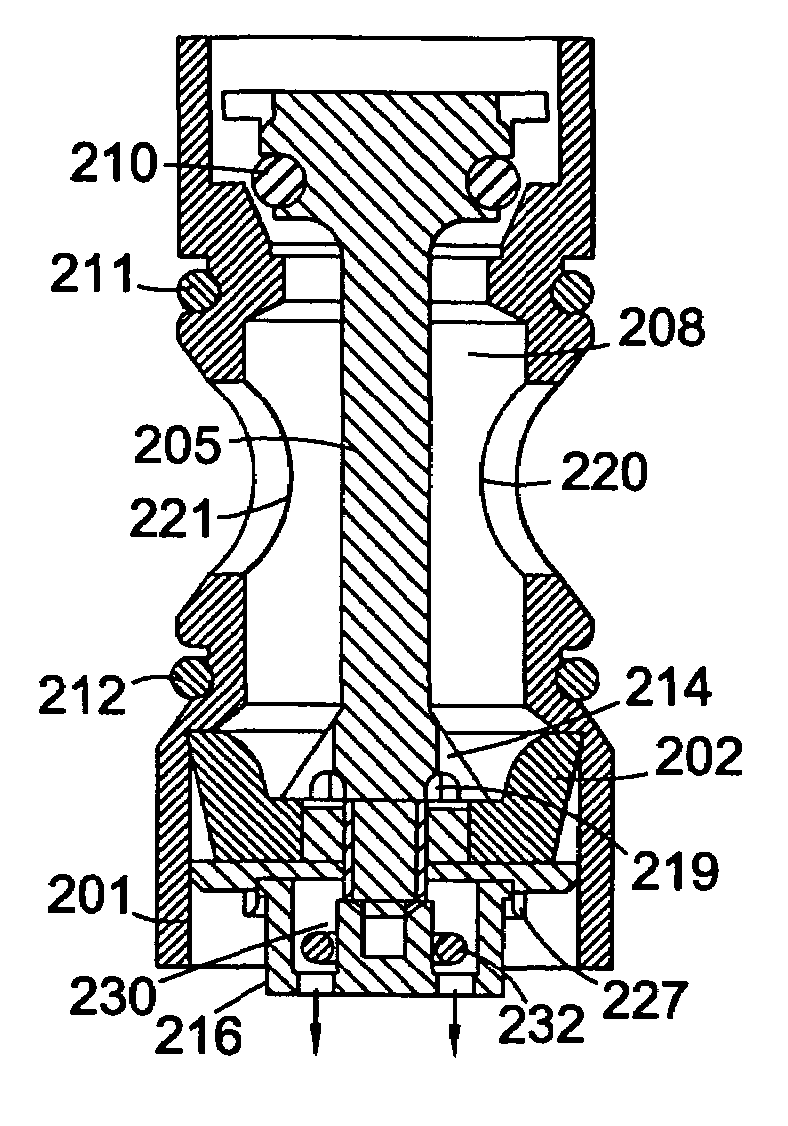
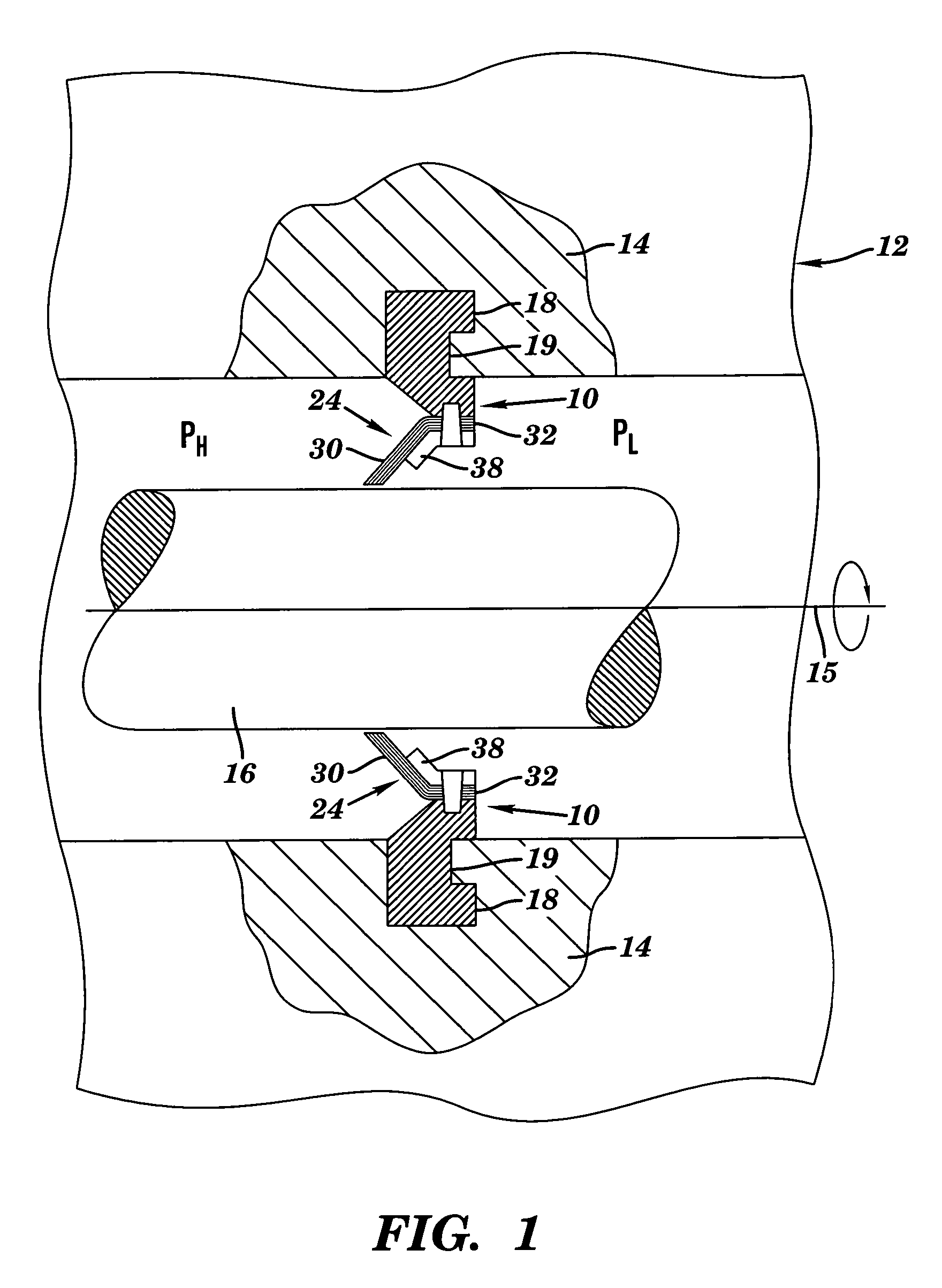
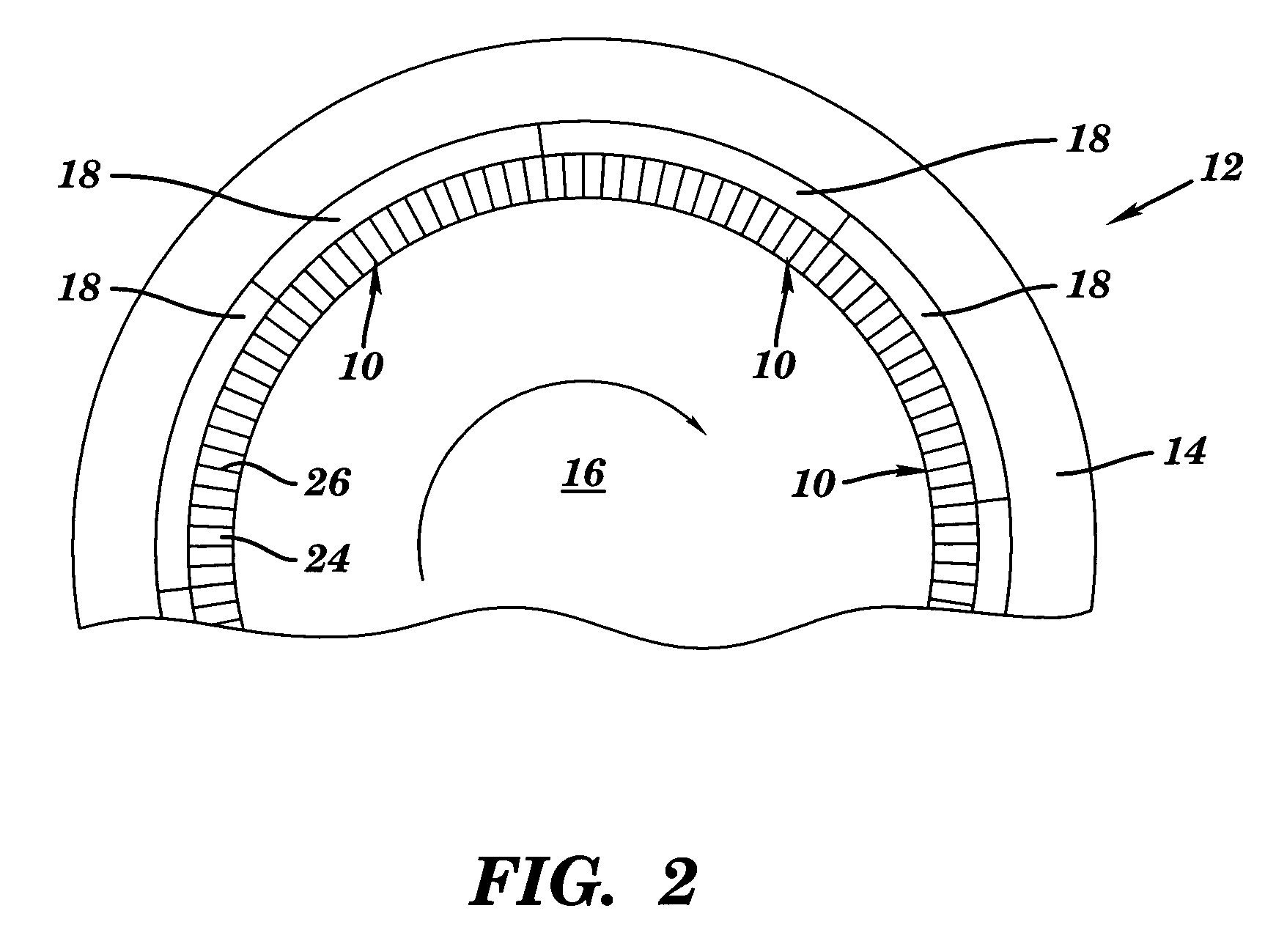
Seal assembly and rotary machine containing such seal
A seal assembly which, among other applications, may be used for sealing fluid leakage between a steam or combustion (gas) turbine rotor and a turbine stator body. The seal assembly includes elements having a plurality of spaced leaf seal members with slots therebetween. Each leaf seal member is angled out-of-plane between a fixed end and a free end thereof, and the free ends slidably engage the rotatable component. In one embodiment, the fixed ends of each leaf seal member are positioned substantially perpendicular to a longitudinal axis of the rotating component. A support may be provided supporting the free end such that it contacts a distal end of the support in an operative state and is out of contact with the distal end in an inoperative state. Seal members may include two different materials having different coefficients of thermal expansion.
Owner:CMG TECH
Apparatus for selectively establishing a needleless injection port on iv tubing, and associated methods
ActiveUS20120130305A1Avoid missing wasteMedical devicesCombustion enginesNeedle Free InjectionInjection port
Apparatus enables one or more needleless injection ports to be established on IV tubing as needed. An IV tubing-engaging portion secures the apparatus about the tubing. A puncturing member establishes fluid communication between the IV line and a sealing member on the apparatus. Connecting a syringe to the sealing member establishes fluid communication between the IV line and the syringe, enabling an injection to be made. When the syringe is withdrawn, the sealing member reseals to prevent fluid leakage from the IV line.
Owner:B BRAUN MELSUNGEN AG
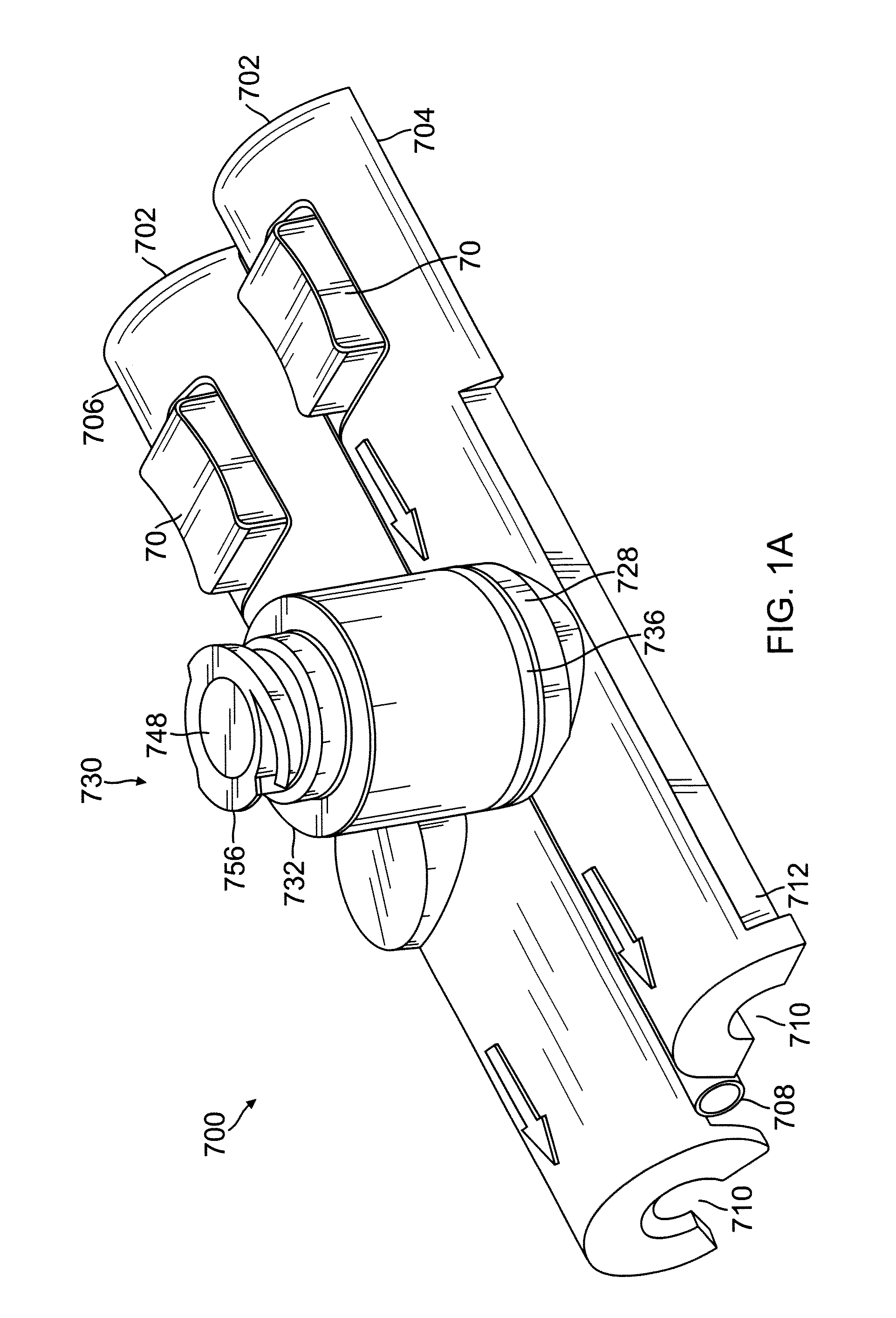
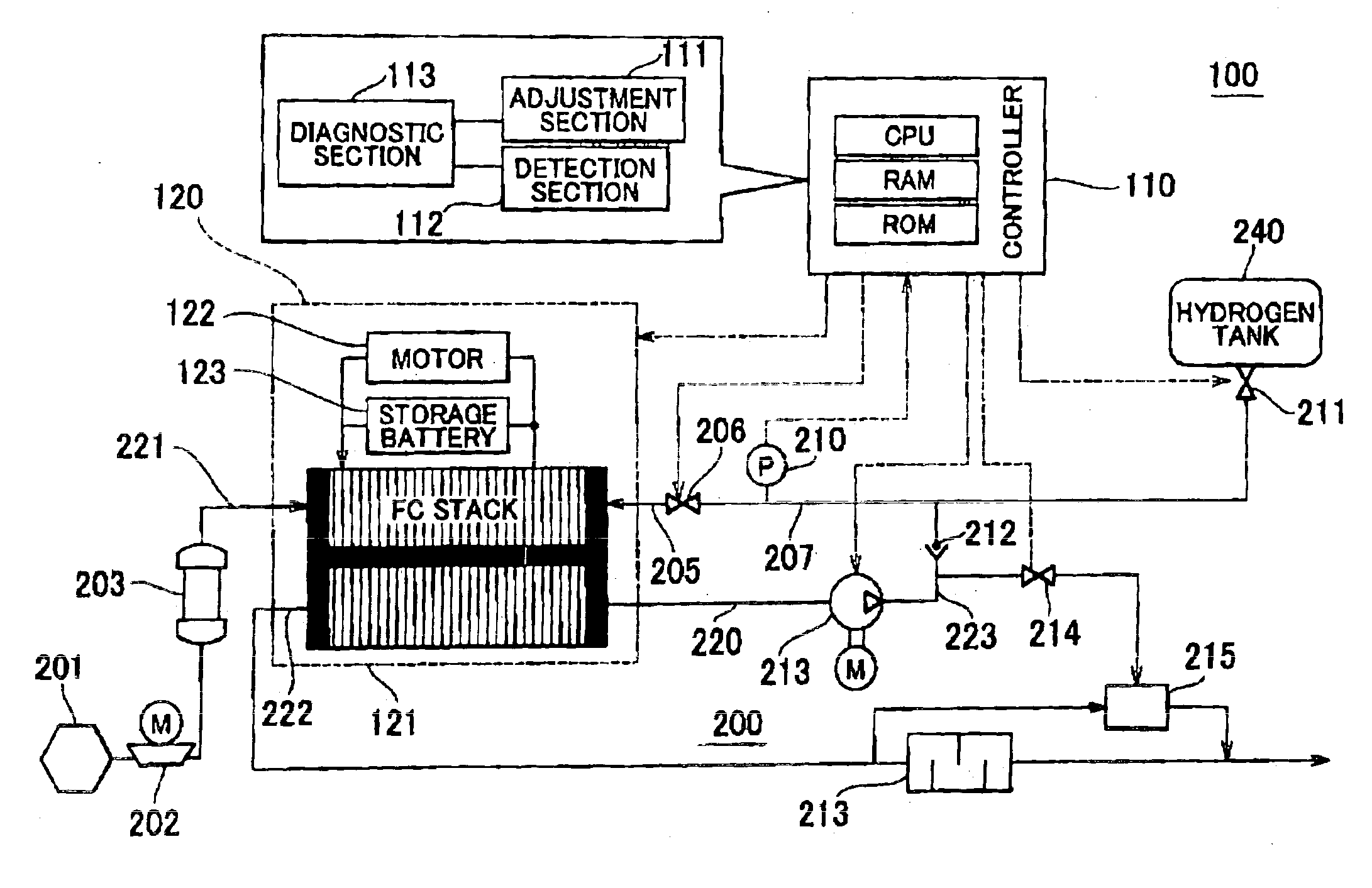
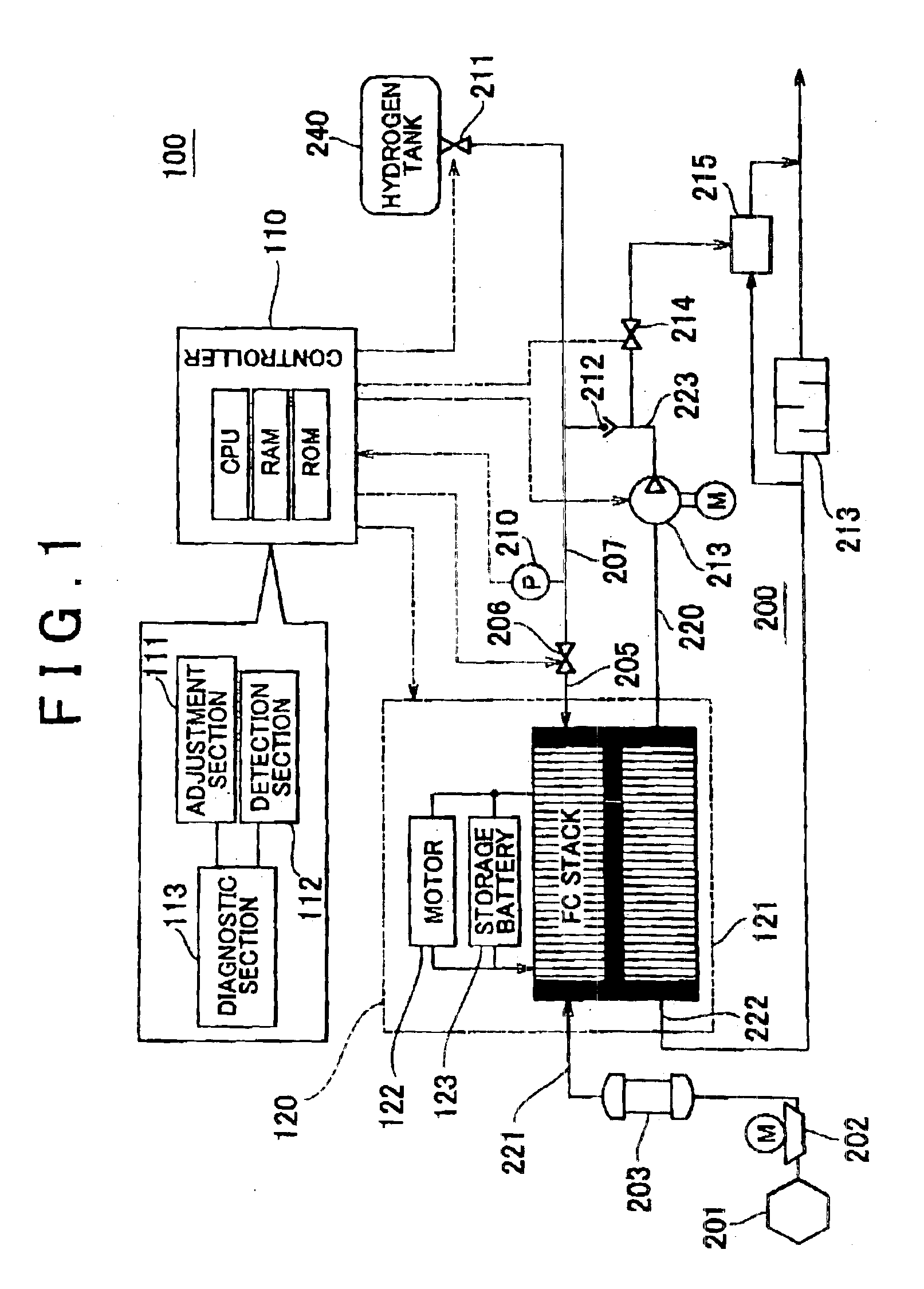
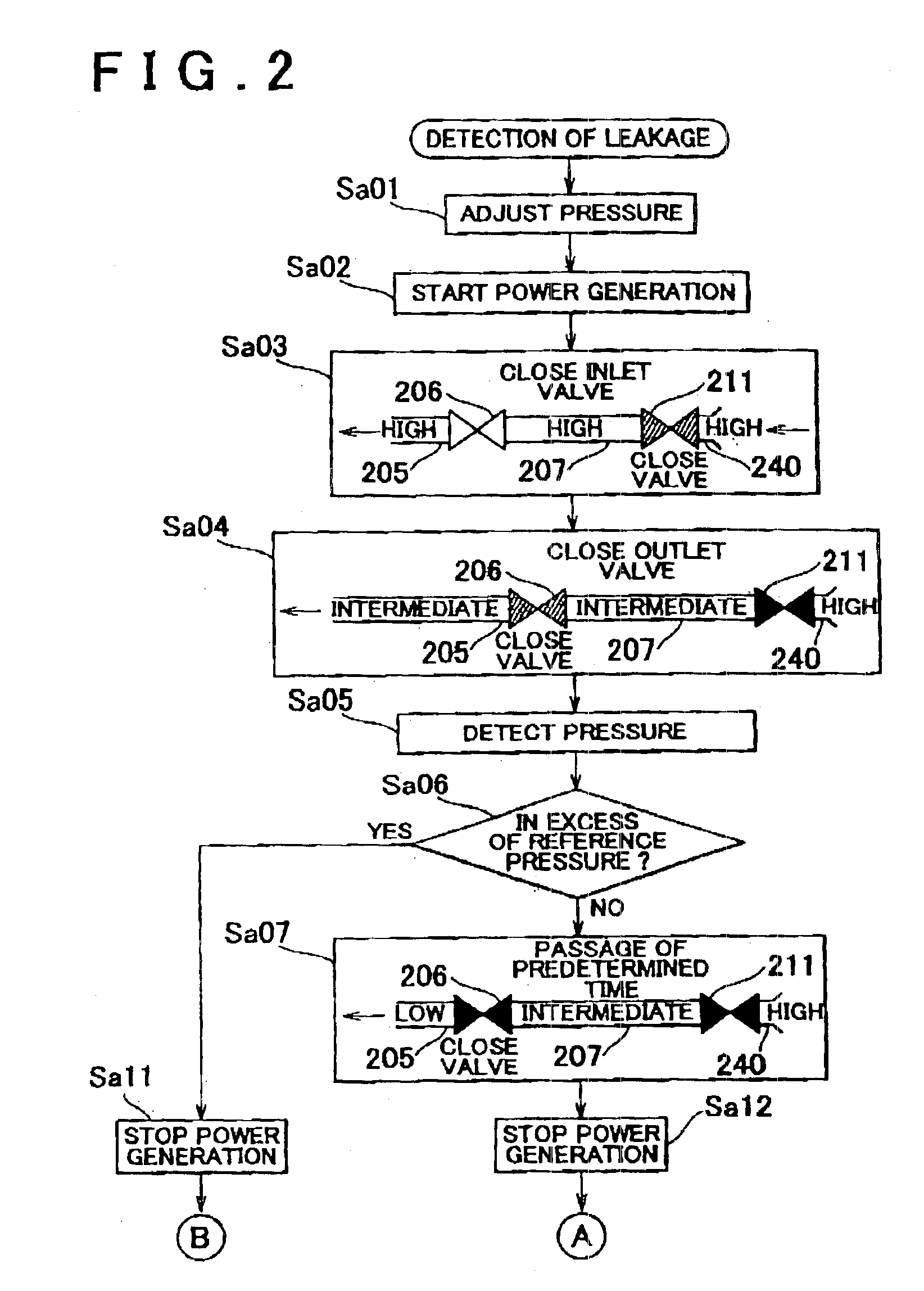
Fluid leakage detection apparatus and fluid leakage detection method
ActiveUS6851298B2Detects leakageEnsure correct executionDetection of fluid at leakage pointMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateInlet valveEngineering
In a fluid leakage detection apparatus, hydrogen is supplied from a hydrogen tank to an FC stack of a fuel cell via first and second pipes. An inlet valve is provided between the hydrogen tank and the first pipe, and an outlet valve is provided between the first pipe and the second pipe. A controller serves to control valve opening a valve closing operation of the inlet and outlet valves, respectively. Those valves are closed in a state where the pressure within the hydrogen tank is made lower than the pressure within the first pipe, and the pressure within the second pipe is made lower than the pressure within the first pipe by operating those valves. Thereafter, the increase or decrease in the pressure within the first pipe is detected by a pressure gauge such that the leakage in the inlet valve or the outlet valve is determined. This makes it possible to detect the leakage both in the inlet valve and the outlet valve at the same time.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
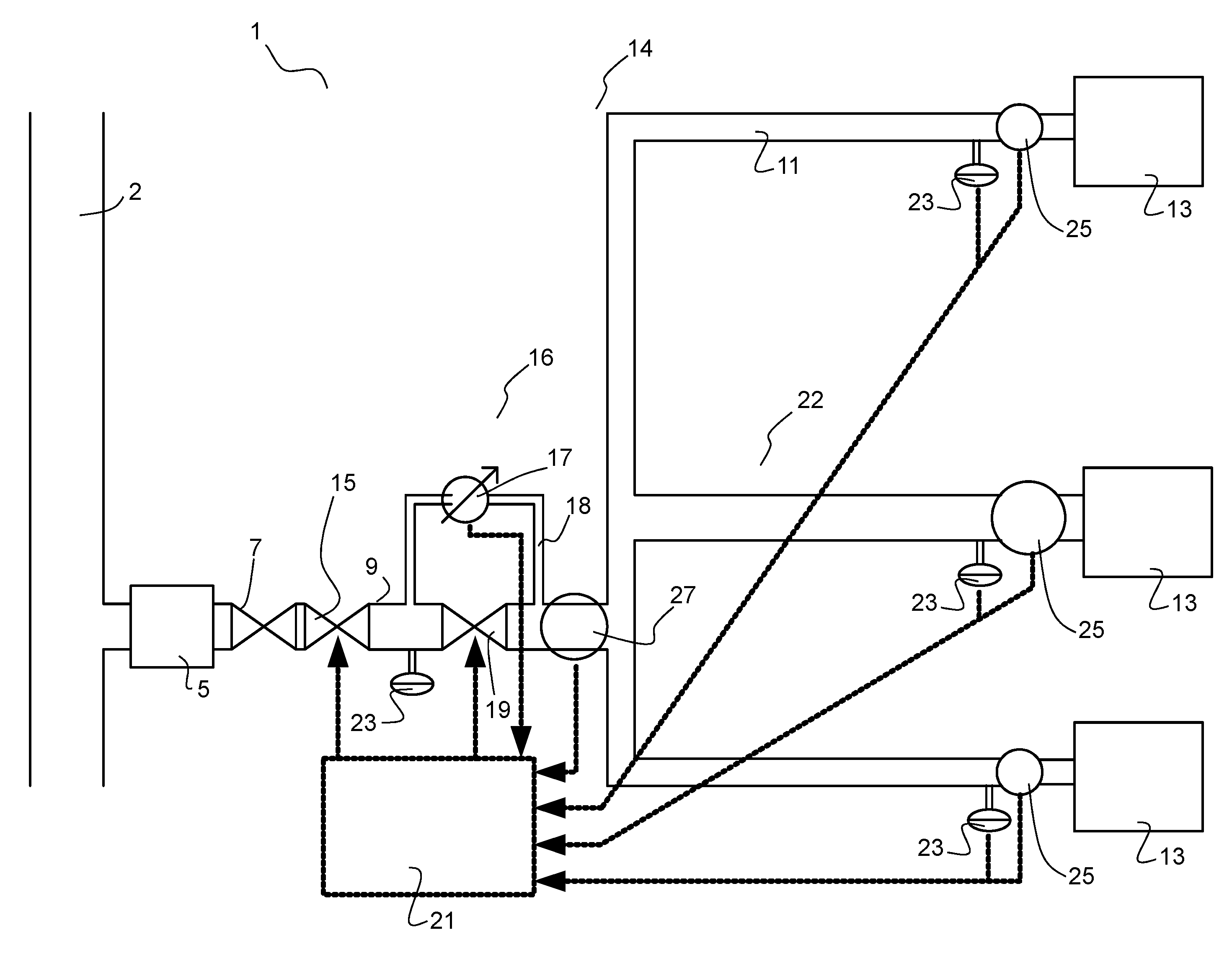
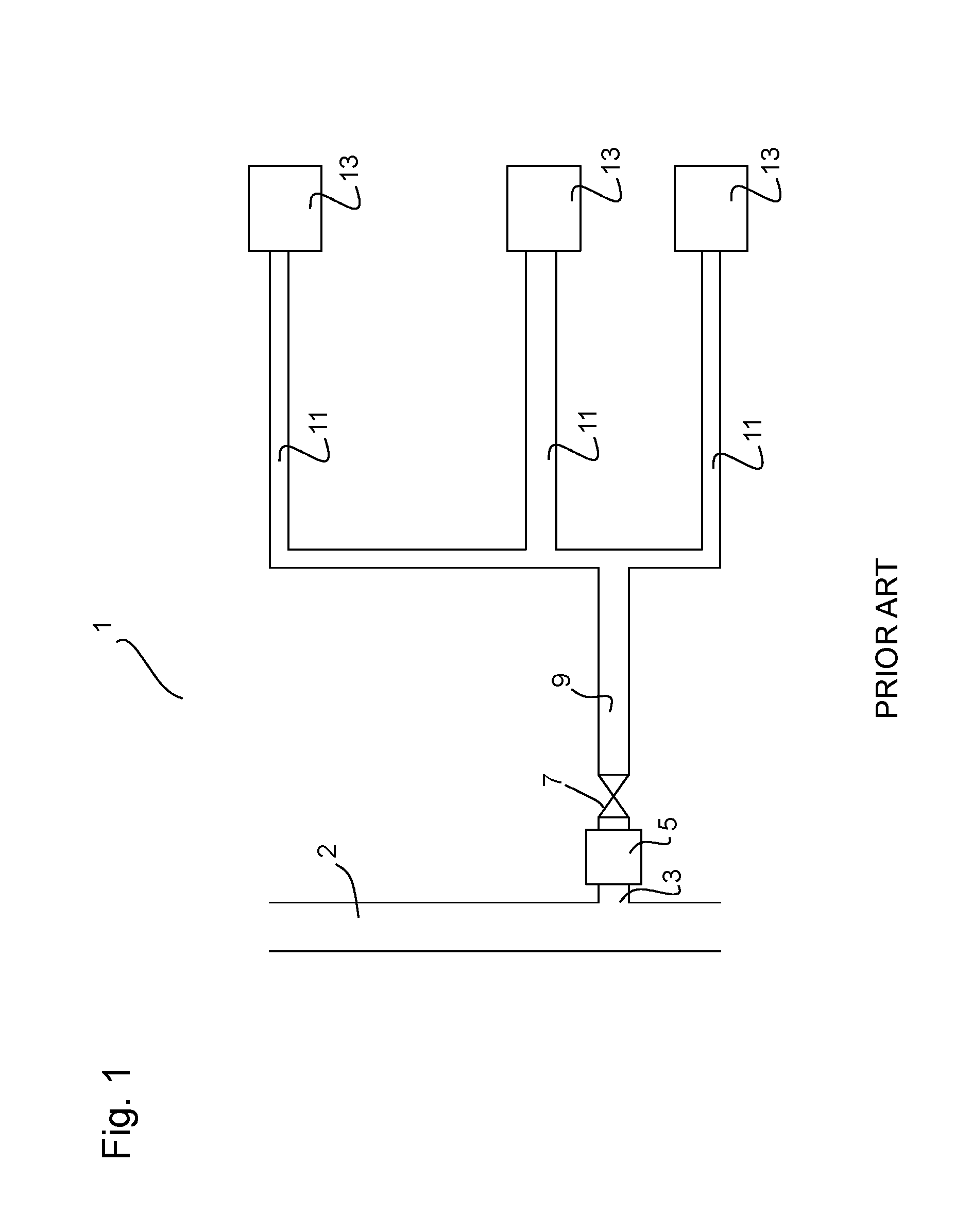
Fluid leakage detection system
InactiveUS20130291974A1Short response timeReliable detectionMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateValve members for absorbing fluid energyLeak detectionStreamflow
Fluid-leakage detection system (14) for a domestic fluid distribution installation (1), comprising: a main fluid feed pipe (9) connected to at least one item of fluid consuming equipment (13) through a corresponding secondary pipe (11), a cutoff valve (15) for cutting off the main feed pipe (9) in the event of the detection of any leak, a small-leak detection device (16) activated in the case of zero global consumption, a flow meter (25) on the secondary pipe of each item of consuming equipment (13) for establishing the state of the global consumption.
Owner:CLEVERGAS HLDG
Flexible walled cannula
InactiveUS7846134B1Reduce liquid leakageHeal fastAdditive manufacturing apparatusEye surgerySurgical operationGrommet Insertion
A flexible walled cannula apparatus and method of use comprising a uniquely deformable cannula tube and head in combination with a uniquely shaped obturator which allows the use of heretofore unusable larger gauge surgical instruments while providing a self sealing incision. The apparatus and method of use provides a preassembled obturator and cannula assembly with which the surgeon forms an incision or channel, inserts the cannula tube, and through the cannula inserts surgical instruments to perform a surgical operation. The apparatus and method of use is especially suited for ophthalmic surgical operations. Alternative embodiments for use with even larger diameter instruments utilize a uniquely designed valve having leaflets which prevent bodily or other fluid leakage from the cannula when an instrument is not inserted.
Owner:SYNERGETICS
Monitoring seal system
InactiveUS20010030396A1Prevent liquid leakageEngine sealsPiston ringsElectrical and Electronics engineeringFluid leakage
A monitoring seal system comprises a seal housing, a seal assembly, a temperature sensor and a controller. The seal assembly sealingly engages a rotary shaft to prevent fluid leakage between the shaft and the housing. The seal assembly has at least one seal. The seal has a primary ring and a mating ring. The temperature sensor senses the temperature in the vicinity of the seal. The controller determines whether an upset condition has occurred based on at least the temperature in the vicinity of the seal.
Owner:JOHN CRANE INC
Fiber optic sensing device and method
A device includes a stationary, rotary component, and a fiber optic sensing system. The fiber optic sensing system includes a cable having one or more fiber optic sensors disposed on the stationary component, the rotary component, or combinations thereof. The fiber optic sensing system is configured to detect one or more first parameters including temperature, strain, pressure, vibration, torque; or combinations thereof related to the stationary component, the rotary component, or combinations thereof. The one or more first parameters is used to determine one or more second parameters including thermal expansion, clearance, fluid flow rate variation, condensation, fluid leakage, thermal loss, life, thermal stress, or combinations thereof related to the stationary component, the rotary component, or combinations thereof.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com