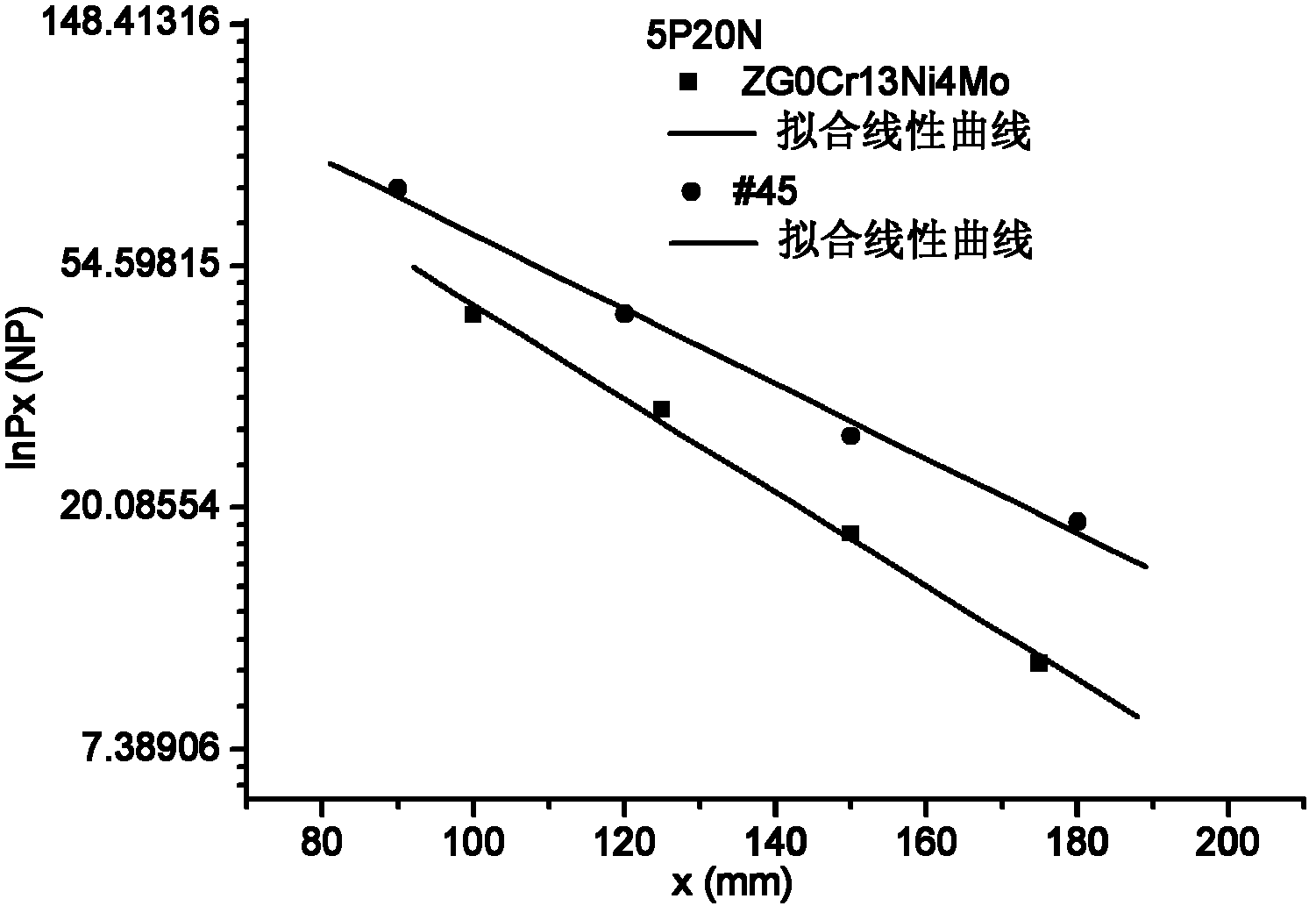
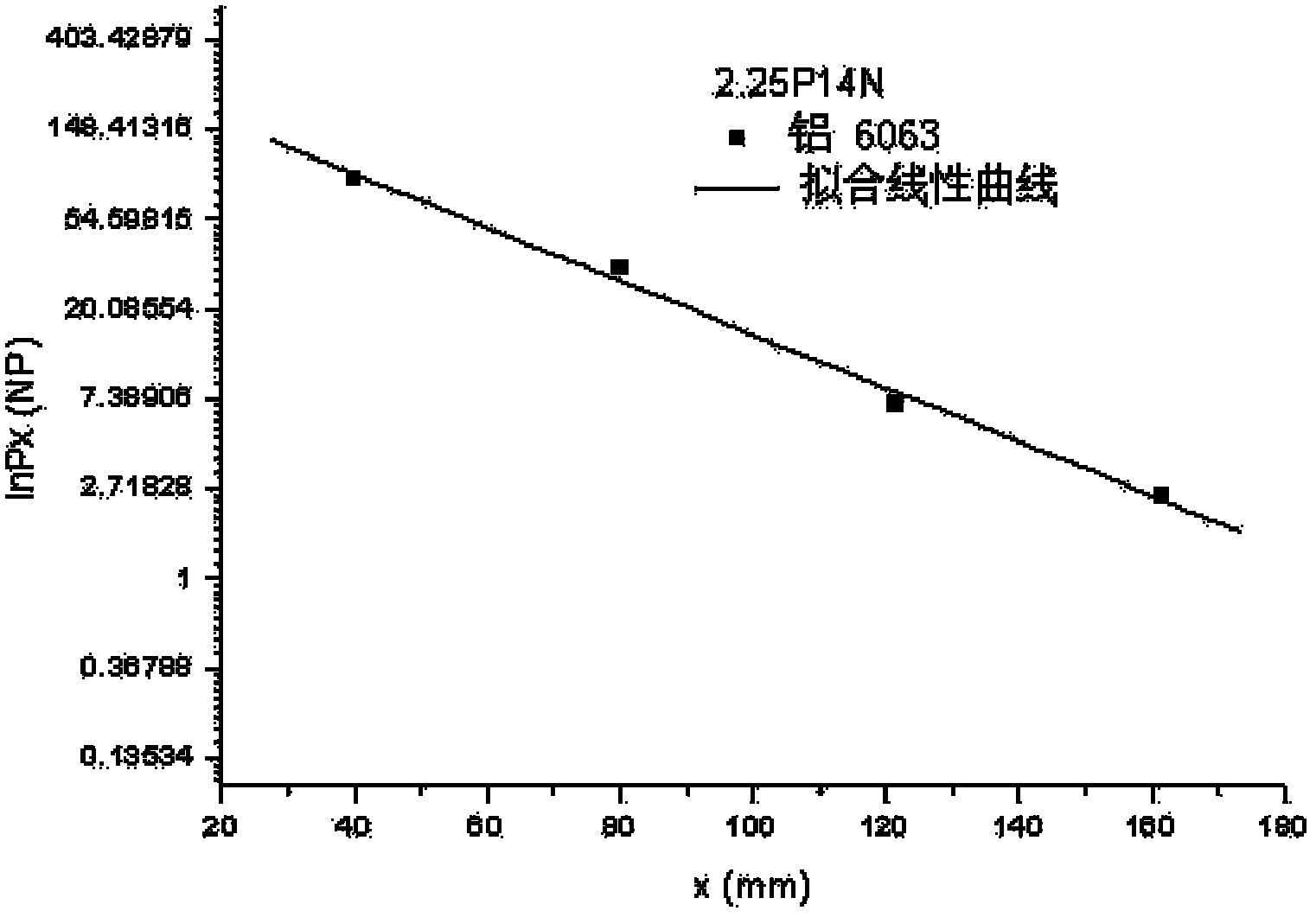
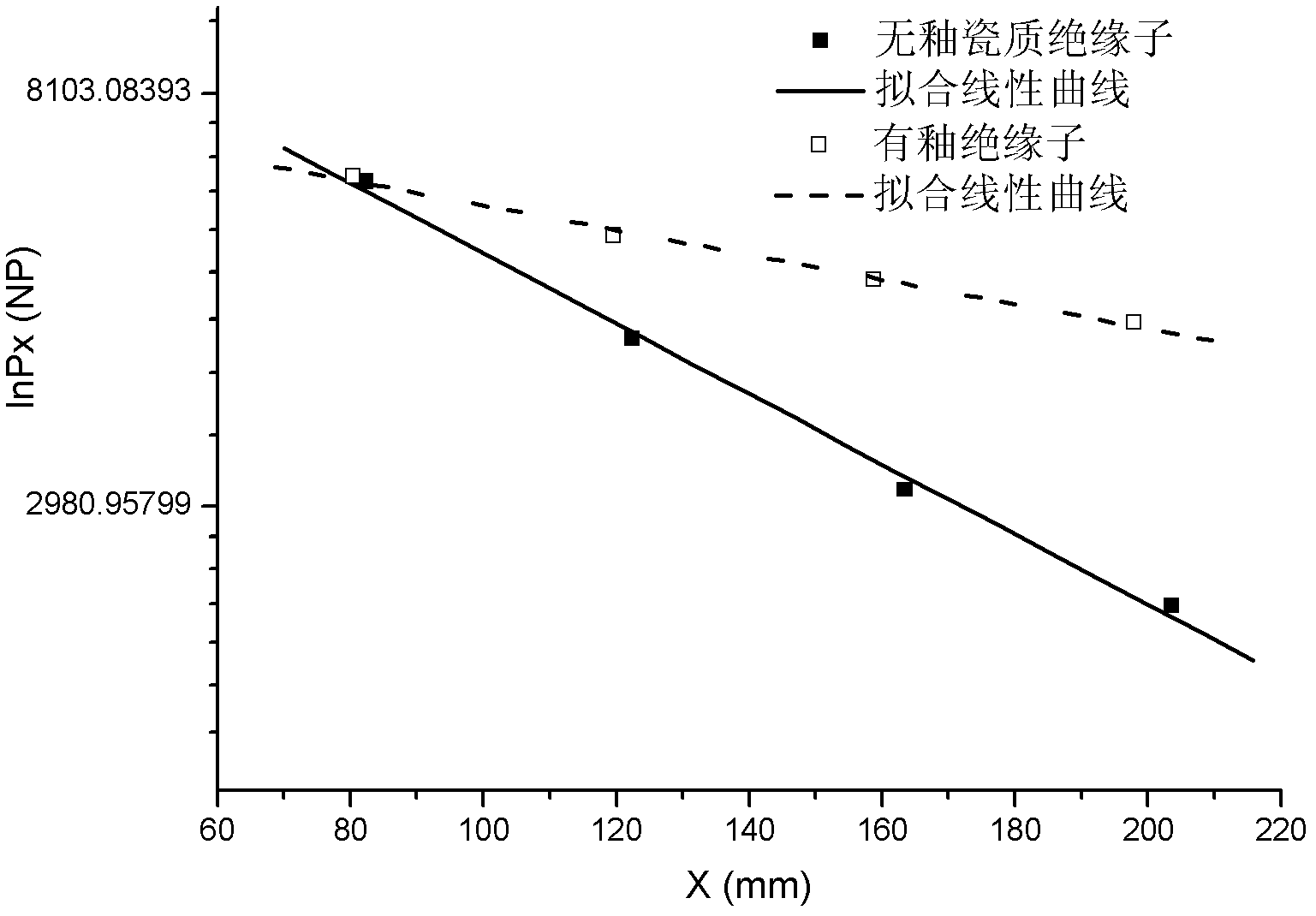
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
44 results about "Mass attenuation coefficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The mass attenuation coefficient, mass extinction coefficient, or mass narrow beam attenuation coefficient of the volume of a material characterizes how easily it can be penetrated by a beam of light, sound, particles, or other energy or matter. In addition to visible light, mass attenuation coefficients can be defined for other electromagnetic radiation (such as X-rays), sound, or any other beam that attenuates. The SI unit of mass attenuation coefficient is the square metre per kilogram (m²/kg). Other common units include cm²/g (the most common unit for X-ray mass attenuation coefficients) and mL⋅g⁻¹⋅cm⁻¹ (sometimes used in solution chemistry). "Mass extinction coefficient" is an old term for this quantity.
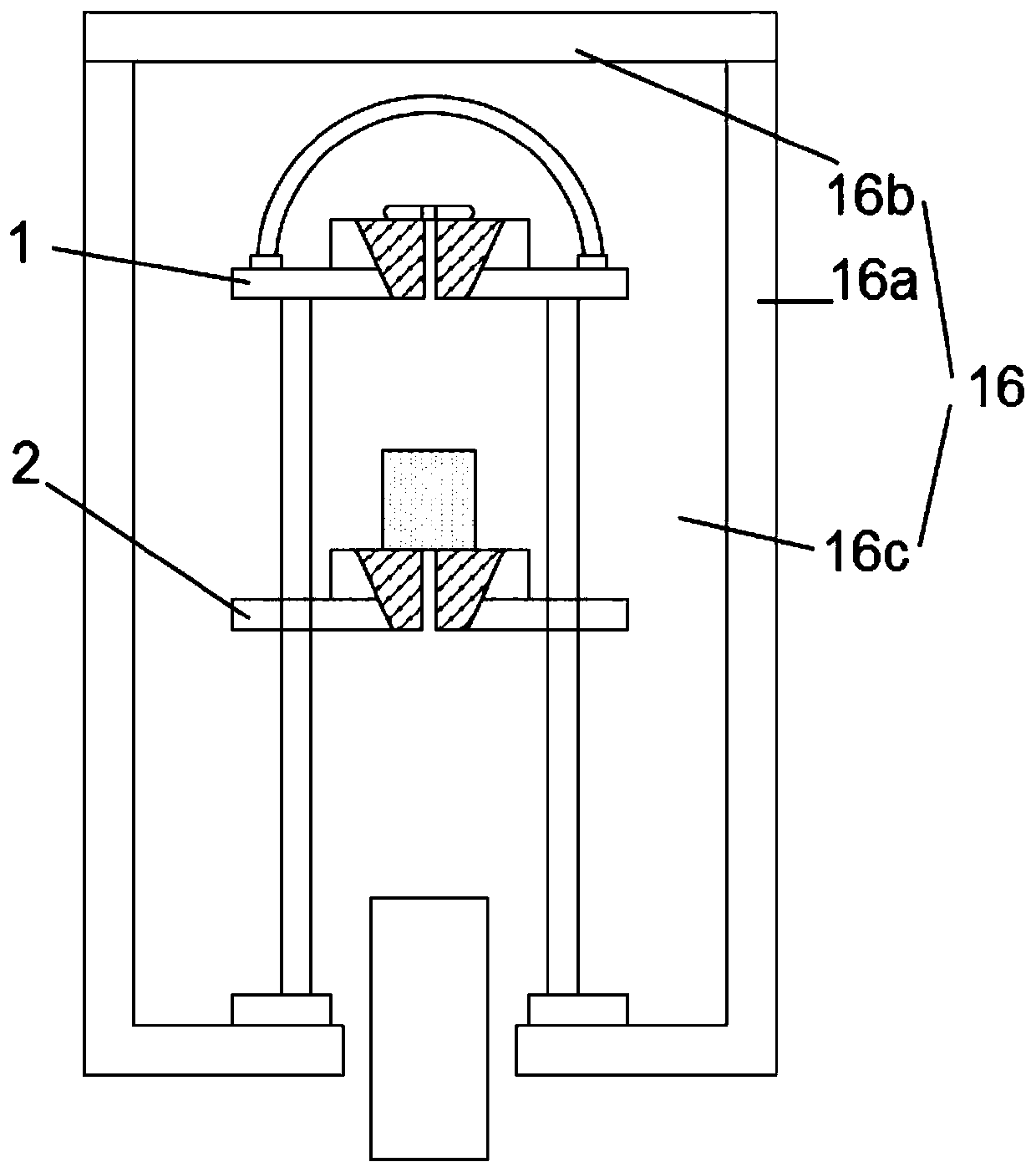
Radiopaque bioabsorbable occluder
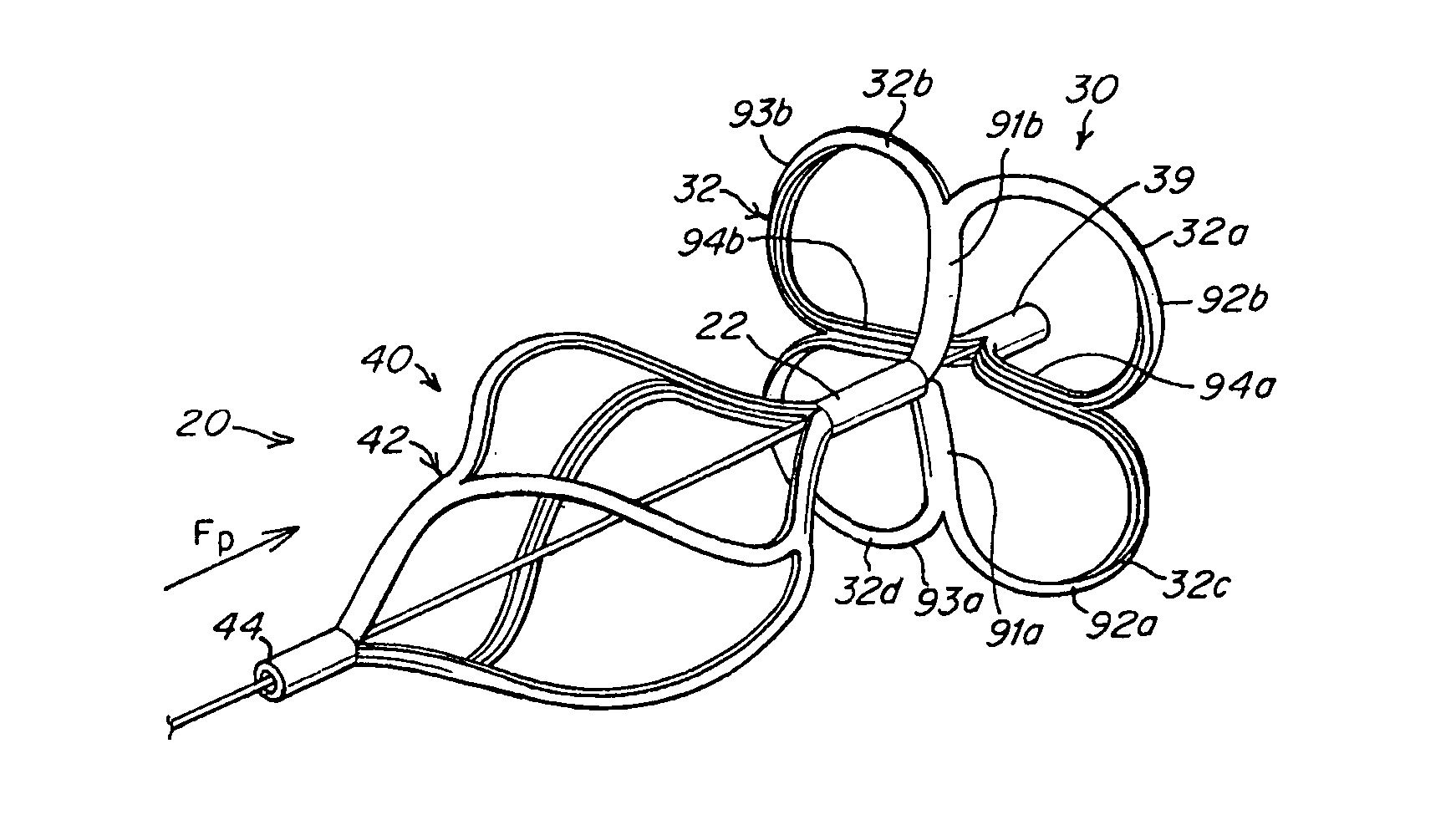
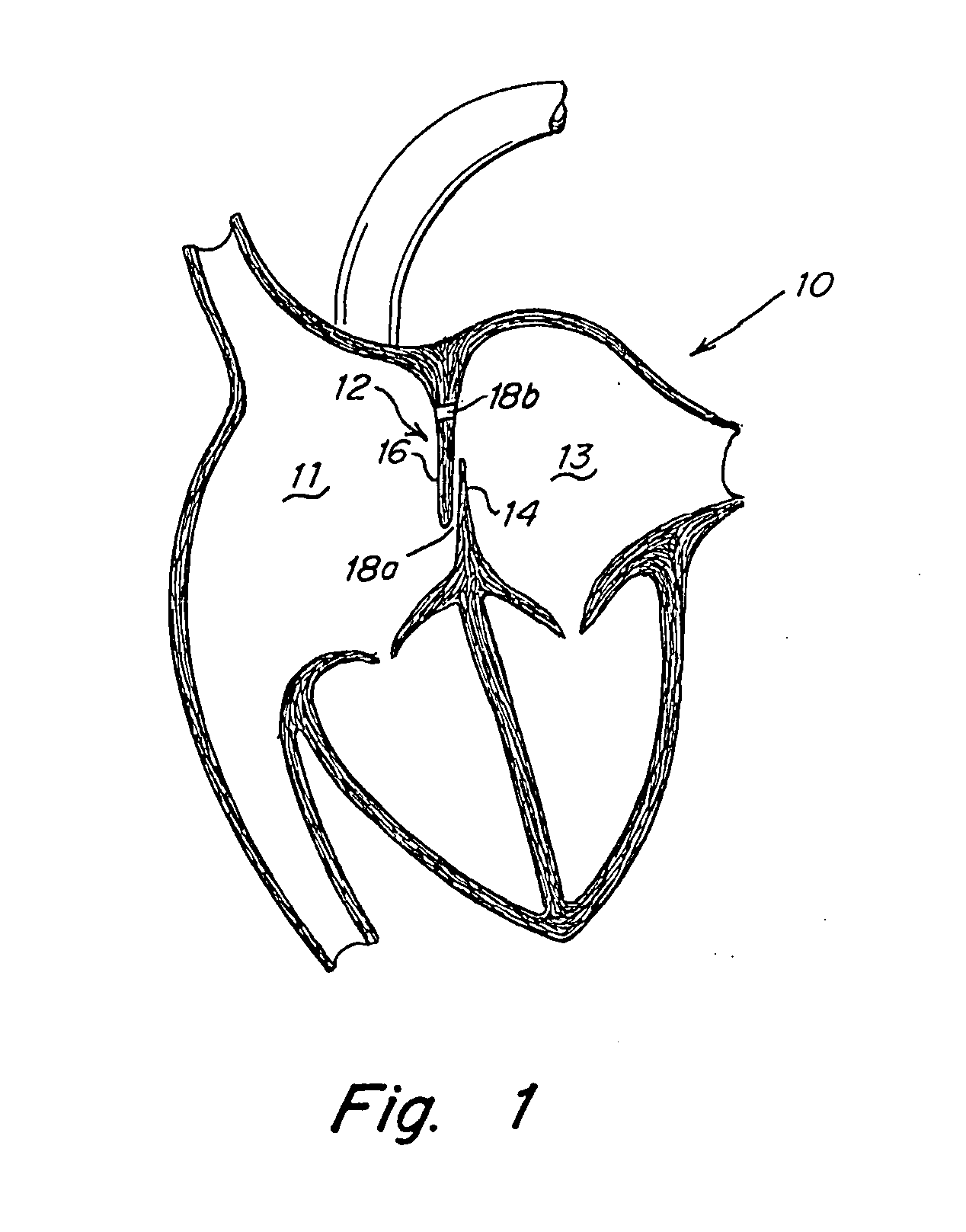
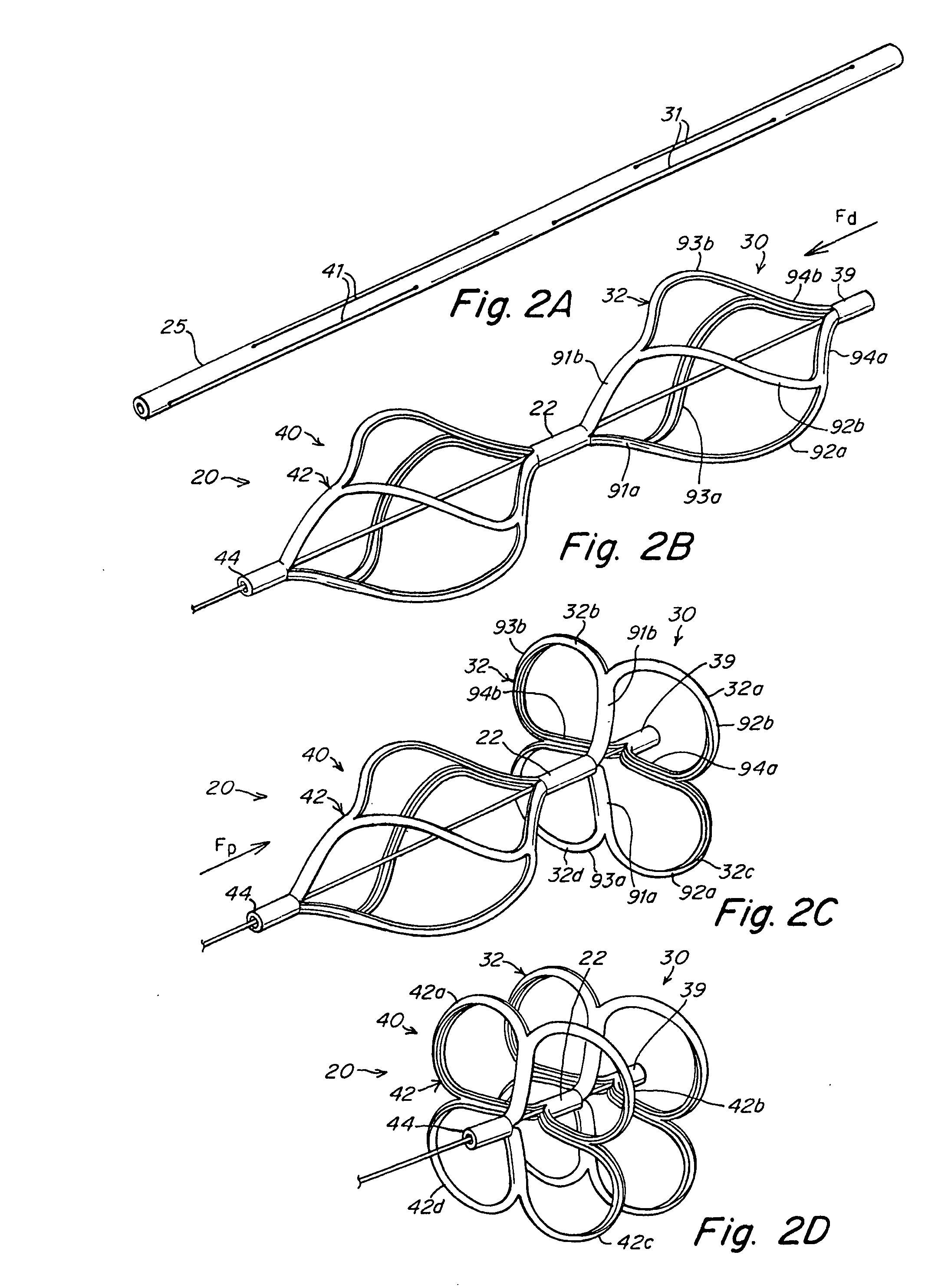
The present invention provides an occluder for a biological defect, such as an atrial septal defect (ASD) or a patent foramen ovale (PFO). The occluder is at least partially formed of a radiopaque, bioabsorbable material. In some embodiments, the occluder is formed from a tube, which is cut to produce struts in each side. Upon the application of force, the struts deform into loops. The radiopaque, bioabsorbable material is a blend of a biocompatible radiopaque material with a bioabsorbable material. In some embodiments, the radiopaque material may have a mass attenuation coefficient greater than about 1.2 cm2 / gm and / or a linear attenuation coefficient greater than about 9 cm−1. In some embodiments, the radiopaque material is tungsten. In some embodiments, the bioabsorbable material may have a molecular weight greater than about 300,000. In some embodiments, the bioabsorbable material is a polymer.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Ultrasonic attenuation spectrum based mixed solid particle size and concentration measurement method
InactiveCN104849183ASimple structureSmall structureParticle size analysisParticle suspension analysisSolid massUltrasonic attenuation
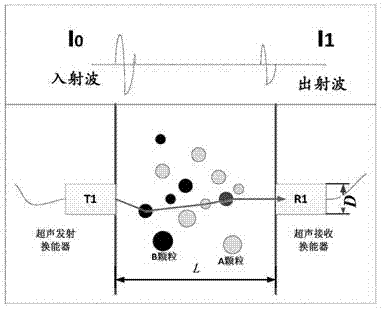
The invention relates to an ultrasonic attenuation spectrum principle based method for measuring the average particle size and concentration of two types of mixed solid particles in a liquid or gas medium. The ultrasonic attenuation spectrum principle based method comprises the following steps of step 1, measuring an experimental measurement ultrasonic attenuation spectrum alpha (f) under the condition that the two types of solid particles A and B are located in a measurement area, wherein f is the ultrasonic frequency; step 2, calculating an acoustic attenuation coefficient Kext of the particle and acoustic wave effect; step 3, determining whether the particles are A particles or B particles and determining whether phonons are absorbed or scattered through the acoustic attenuation coefficient; step 4, calculating a scattering emergence angle theta M1 of the scattered phonons; step 5, continuing to calculate a theoretical ultrasonic attenuation spectrum through a result of the step 4; step 6, establishing an objective function according to the theoretical ultrasonic attenuation spectrum and the experimental measurement ultrasonic attenuation spectrum to solve the particle size and volume concentration. The ultrasonic attenuation spectrum based mixed solid particle size and concentration measurement method can be applied to the two types of mixed solid particles and laboratory scientific research and the online measurement and the application of the industrial field can be implemented.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Material composition detection from effective atomic number computation
ActiveUS20090304249A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationCharacter and pattern recognitionUltrasound attenuationMonochromatic color
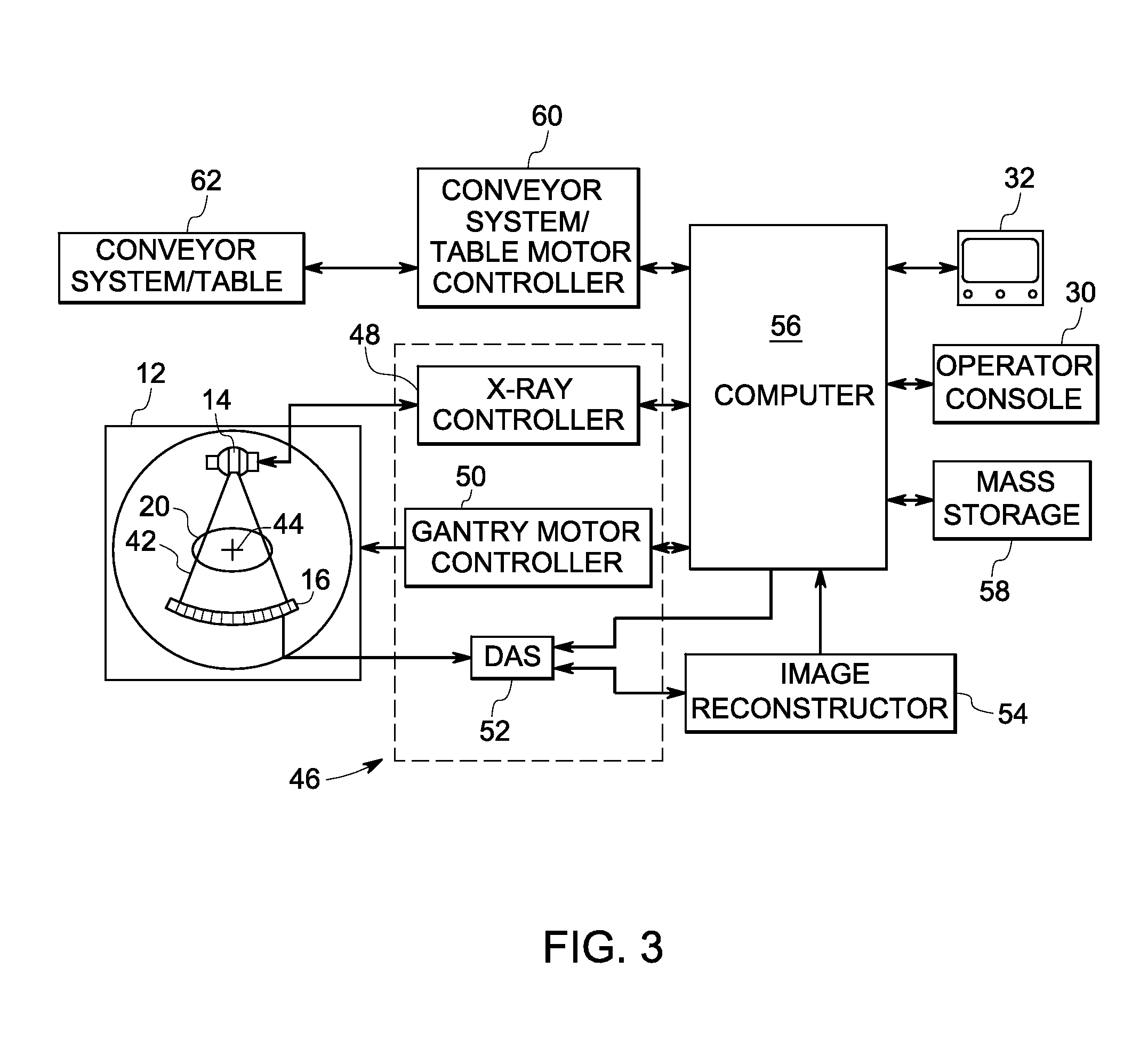
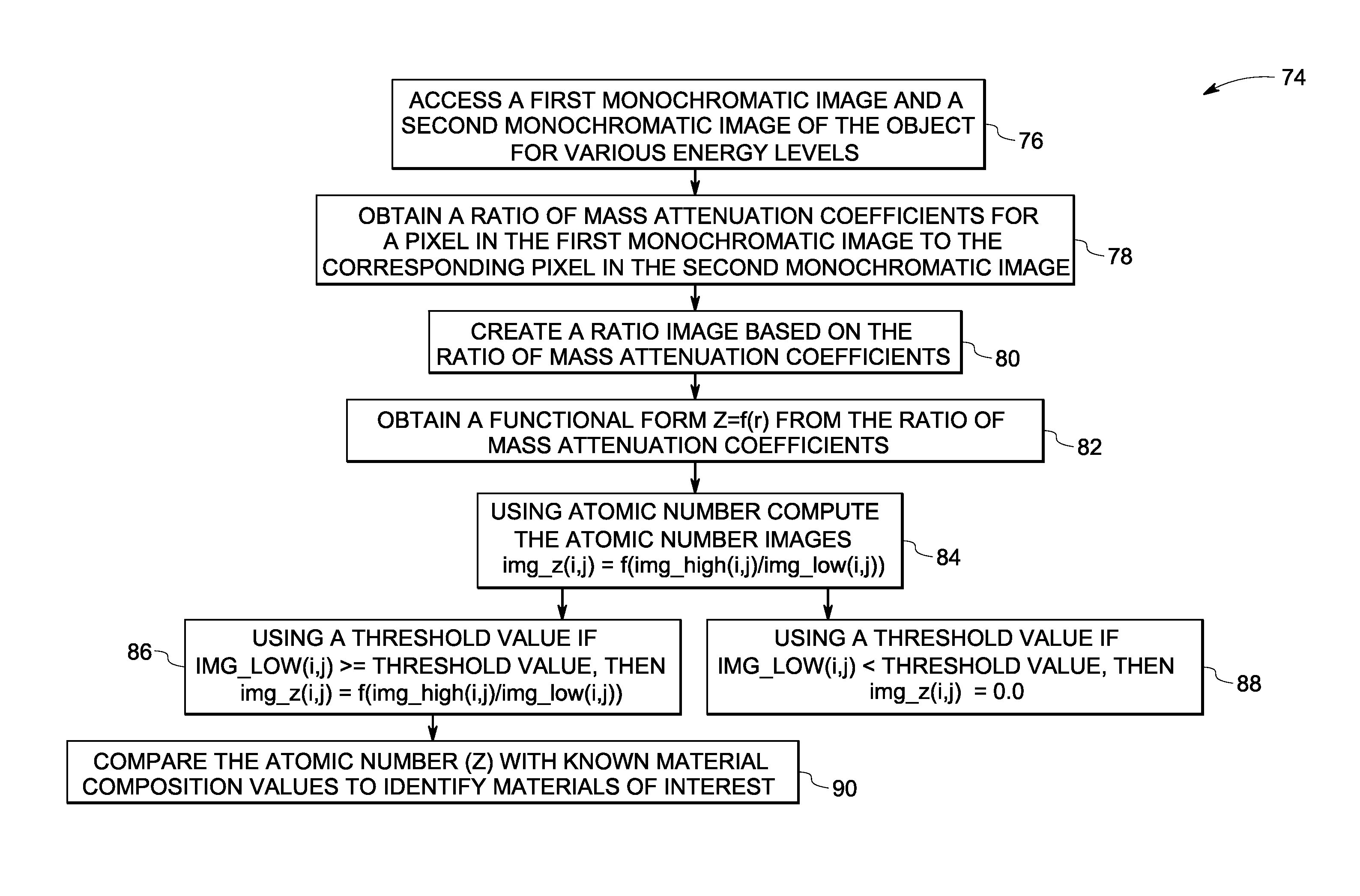
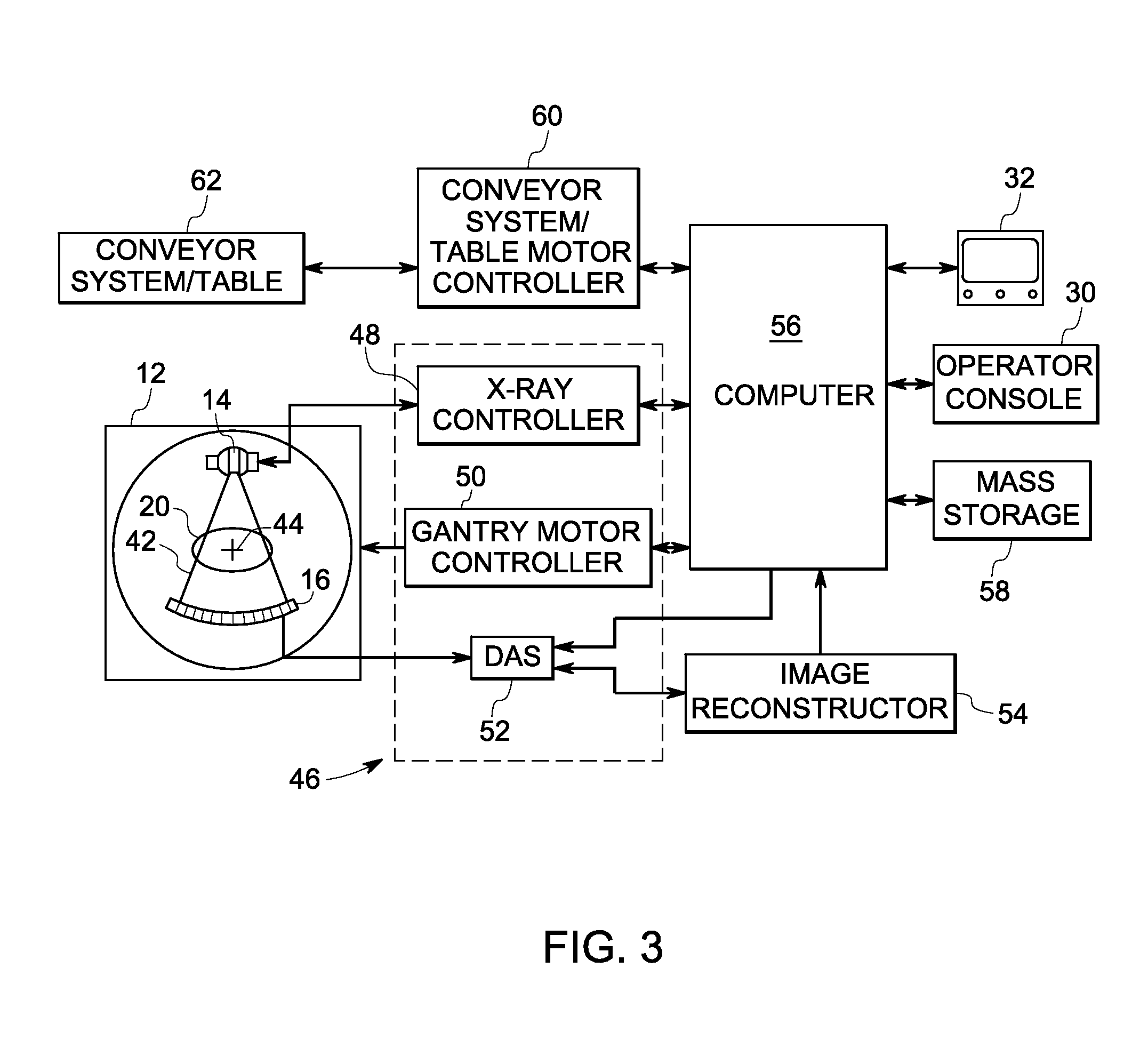
A technique is provided for computing an atomic number of materials forming an object imaged by a radiological modality. The method includes accessing a first monochromatic image and a second monochromatic image of the object, the first monochromatic image acquired at a first energy level and the second monochromatic image acquired at a second energy level. A ratio of the mass attenuation coefficients between the first monochromatic image and the second monochromatic image may be obtained. The atomic number for a material of the object may be computed based upon the ratio of mass attenuation coefficients.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
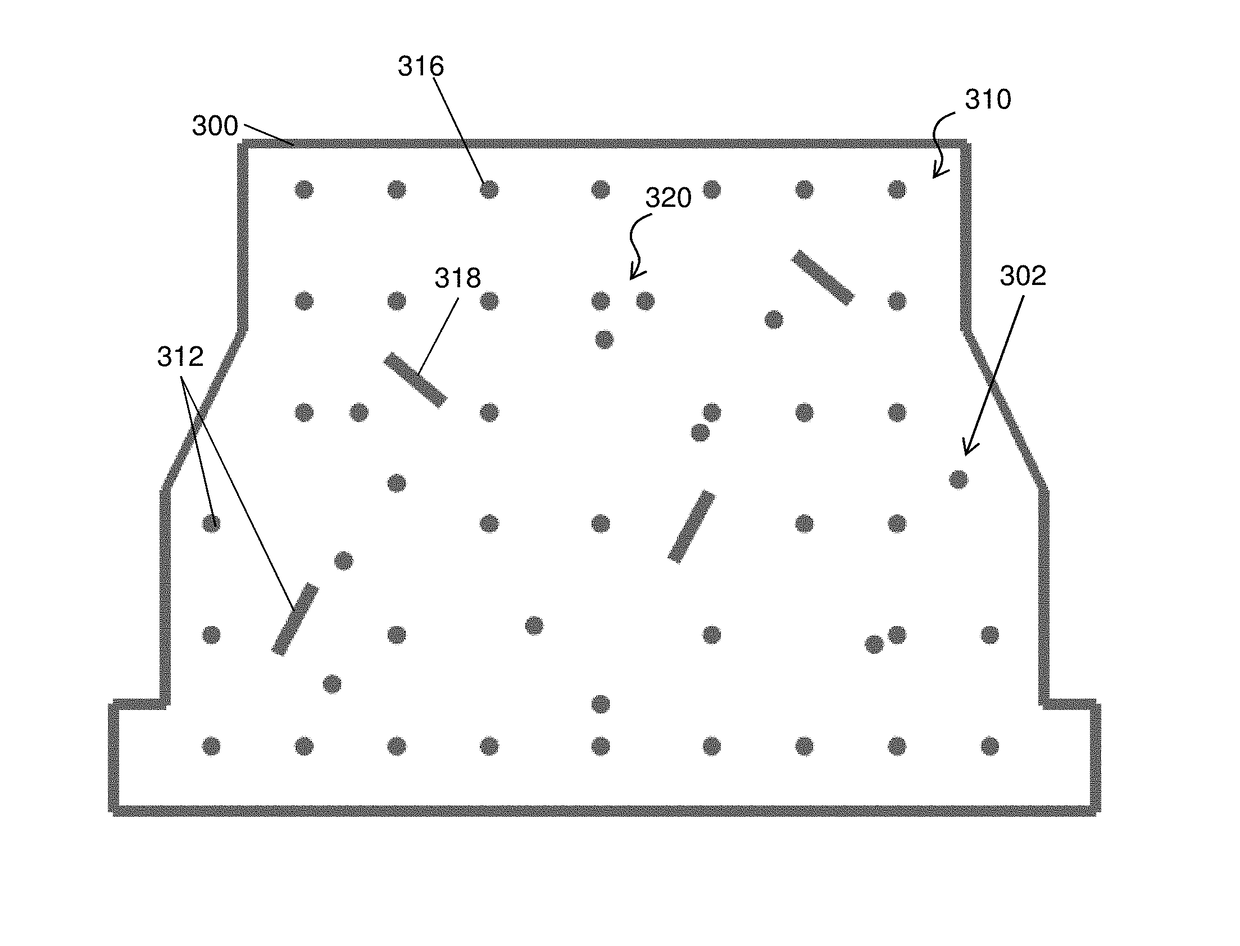
Contrast phantom
A contrast phantom for assessing the characteristic, exposure-related signal and noise response and dynamic range of an image recording and detection system. The contrast phantom is composed of an absorber medium having a sudden K-edge absorption change of the mass attenuation coefficient for at least one photon energy level in-between the mean and maximum energies of the lowest energy spectrum it is subjected to. The invention further provides a method for assessing the characteristic, exposure-related signal and noise response and dynamic range of an image recording and detection system with the aforementioned contrast phantom.
Owner:AGFA NV
Material composition detection from effective atomic number computation
ActiveUS8218837B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationCharacter and pattern recognitionUltrasound attenuationMonochromatic color
A technique is provided for computing an atomic number of materials forming an object imaged by a radiological modality. The method includes accessing a first monochromatic image and a second monochromatic image of the object, the first monochromatic image acquired at a first energy level and the second monochromatic image acquired at a second energy level. A ratio of the mass attenuation coefficients between the first monochromatic image and the second monochromatic image may be obtained. The atomic number for a material of the object may be computed based upon the ratio of mass attenuation coefficients.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Sounding laser full waveform data-based diffuse attenuation coefficient extraction method and system
ActiveCN106802289AImprove calculation accuracyScattering properties measurementsUltrasound attenuationScattering function
The invention discloses a sounding laser full-waveform data-based diffuse attenuation coefficient extraction method and system. The method comprises the following steps: filtering to obtain effective laser sounding points from full-waveform data in sounding laser data; extracting emission intensity and echo intensity of each effective laser sounding point obtained by filtering from the full-waveform data, and after extracting the echo intensity, generating a water body back scattering function corresponding to a water body back scattering waveform according to an algorithm; selecting a plurality of time point pairs with a preset time interval from the water body back scattering function corresponding a single laser sounding point, and calculating an initial diffuse attenuation coefficient of each time point pair; taking an average value of the initial diffuse attenuation coefficients of all the time point pairs as a final diffuse attenuation coefficient of the laser sounding points. According to the invention, the diffuse attenuation coefficient value can be calculated by using the full-waveform data of the single sounding points, and echo intensity information and a depth value of each sounding point do not need to be acquired, the calculation accuracy of the diffuse attenuation coefficient is high.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
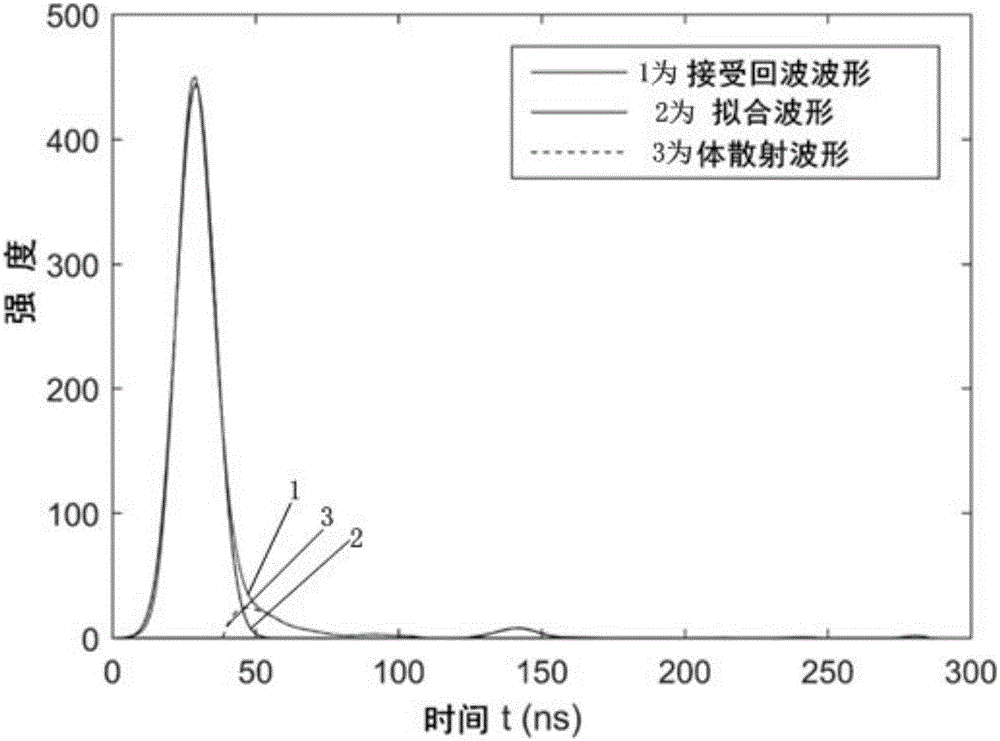
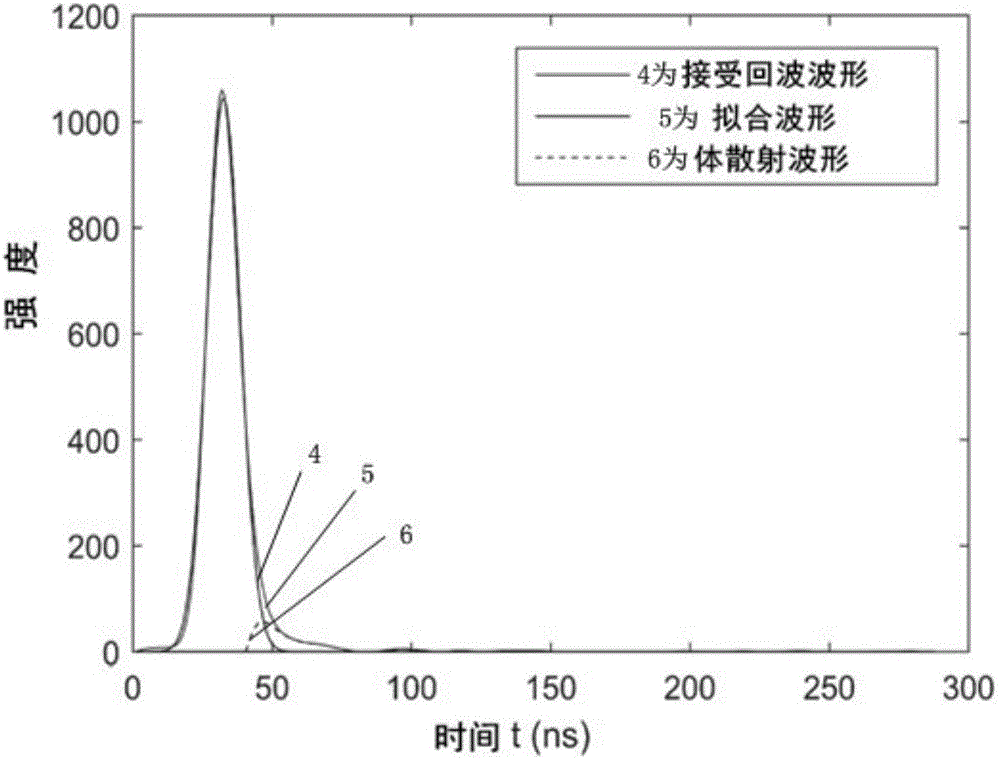
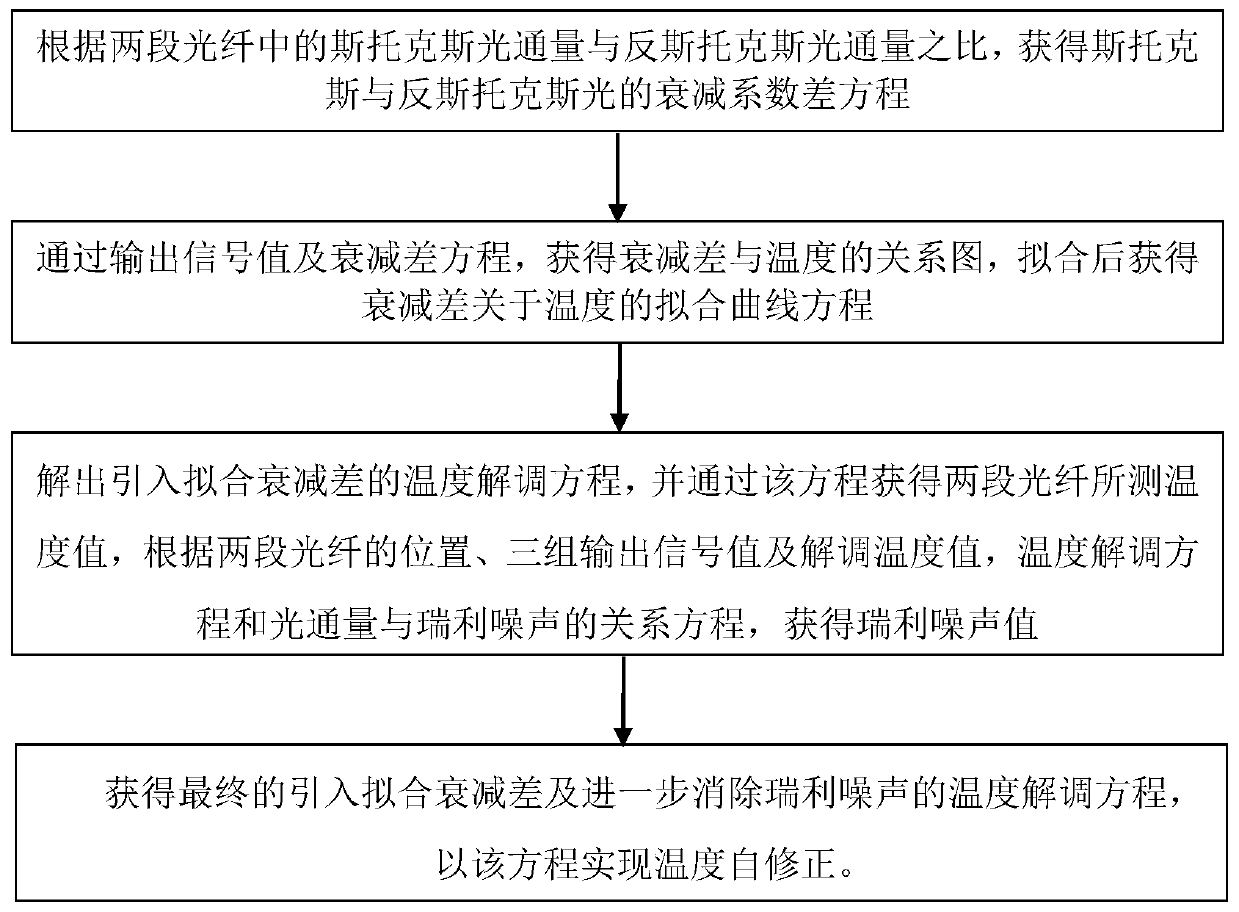
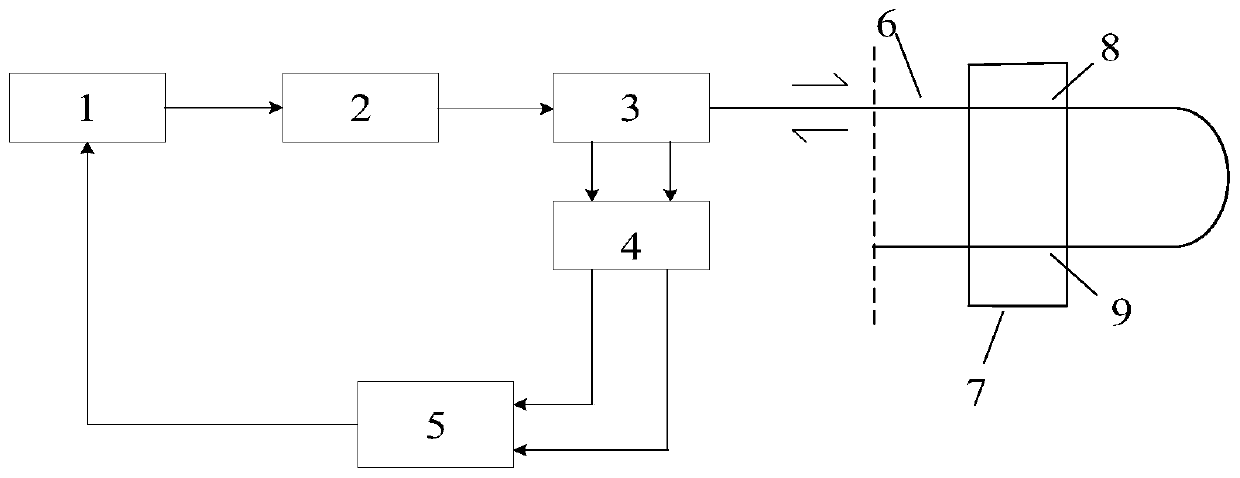
Fit attenuation difference temperature self-correction method for distributed optical fiber Raman temperature measurement system
ActiveCN110231106ASatisfy accurate detectionIncrease temperature correctionThermometers using physical/chemical changesThermometer testing/calibrationLuminous fluxEqualization
The invention relates to a fit attenuation difference temperature self-correction method for a distributed optical fiber Raman temperature measurement system. According to the invention, a Stokes light and anti-Stokes light attenuation coefficient difference equation is obtained by a temperature demodulation principle; a fit curve equation of an attenuation coefficient difference relative to a temperature is obtained by a fit curve; a temperature demodulation equation is obtained by a ratio of the fit curve equation to luminous flux; after demodulation, primary correction on a temperature is implemented; then Rayleigh noise is solved by combining a relationship between Stokes light and anti-Stokes light signals and the Rayleigh noise; further a corrected temperature demodulation formula isobtained; and after demodulation, secondary correction is implemented. The temperature self-correction aim is fulfilled; and compared to a conventional method of eliminating the Rayleigh noise, the fit attenuation difference temperature self-correction method improves temperature correction, implements accurate measurement on the temperature, avoids an error problem caused by approximate equalization processing on Stokes light and anti-Stokes light attenuation coefficients, and meets accurate detection on temperatures of a mine goaf and an adjacent old goaf.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
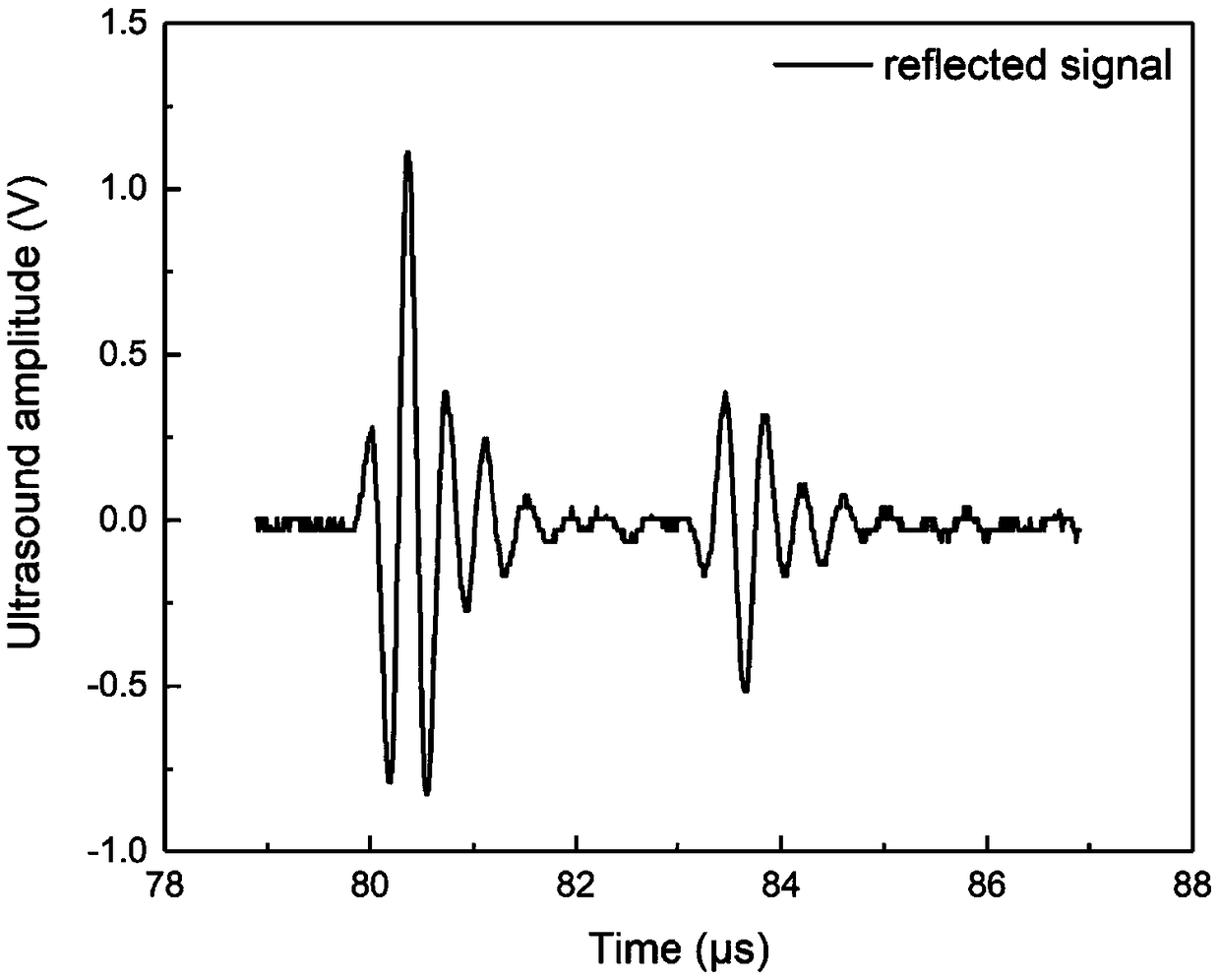
Method for measuring ultrasonic attenuation coefficient of solid material
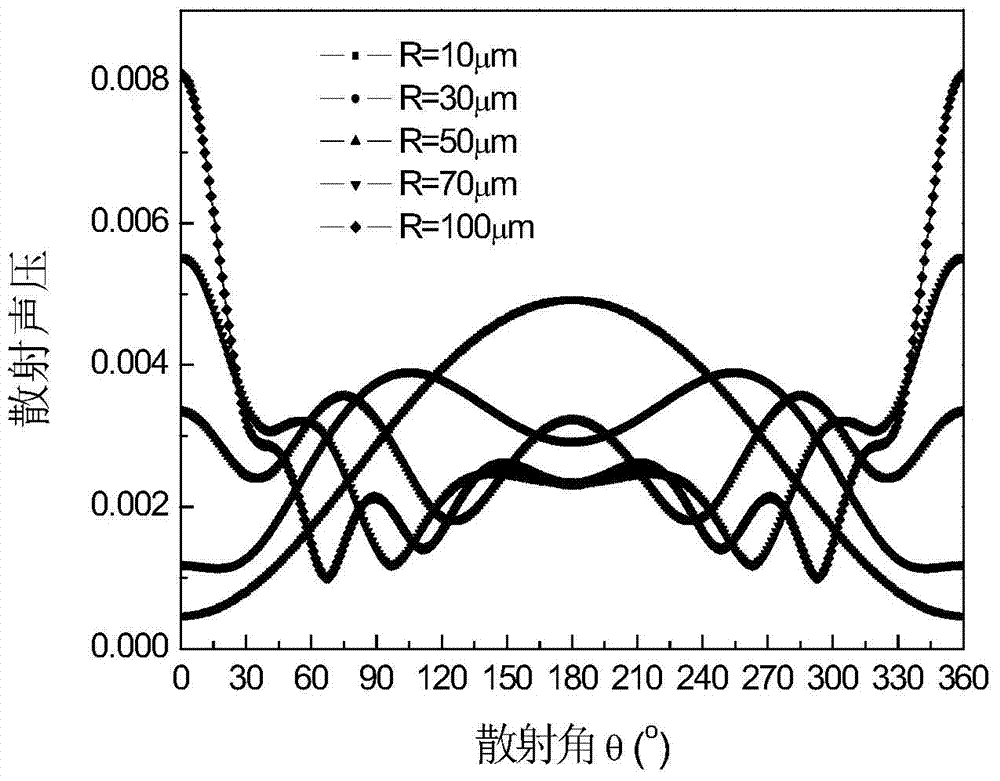
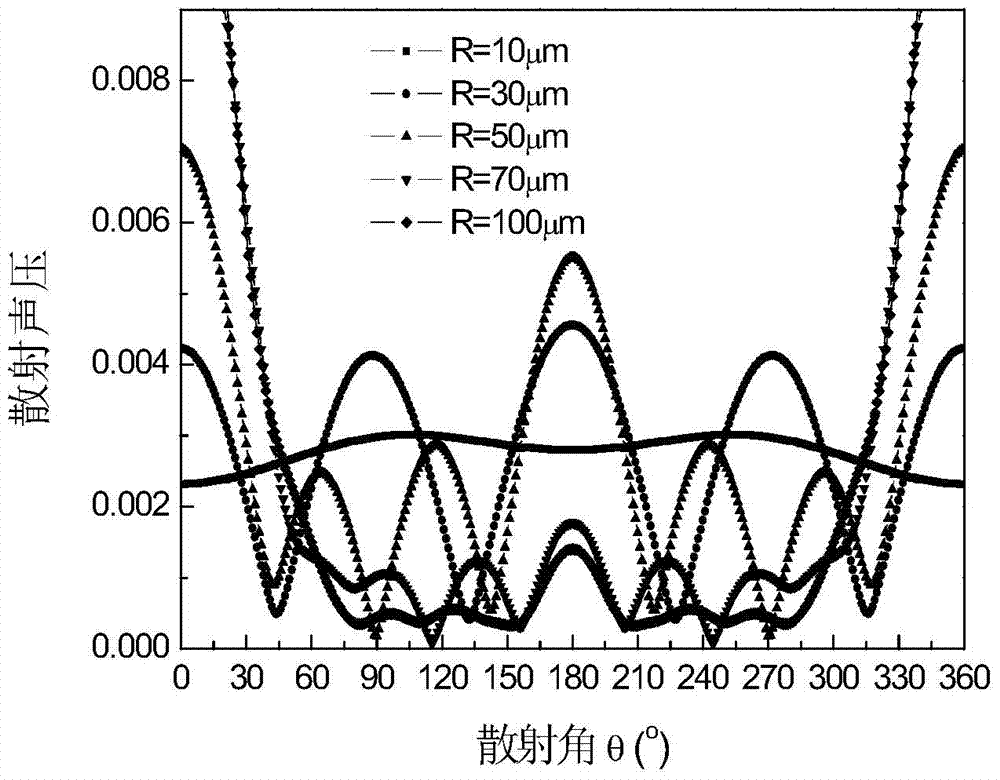
InactiveCN102621224AThe principle is simpleEasy to operateAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic attenuationSound pressure
The invention discloses a method for measuring the ultrasonic attenuation coefficient of a solid material. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting a solid material required to be measured for serving as a sample; selecting an ultrasonic detection instrument, and tuning the ultrasonic detection instrument by using the solid material required to be measured; performing ultrasonic detection on the solid material required to be measured by adopting the adjusted ultrasonic instrument and the conventional ultrasonic detection method, and at least recording the sound pressure amplitudes and sound path values of four times of ultrasonic echo waves; establishing a sound pressure and sound path product logarithmic function and sound path curve chart by adopting the conventional method according to the recorded sound pressure amplitudes and sound path values of the ultrasonic echo waves; and performing linear fitting by using the established curve chart and fitting a linear function relationship, wherein a linear function gradient is the ultrasonic attenuation coefficient of a field measured solid material. The method can be used for measuring the ultrasonic attenuation coefficient of a solid material without performing special processing, and has the characteristics of easiness, safety, reliability and high sensitivity.
Owner:湖南省湘电锅炉压力容器检验中心有限公司 +1
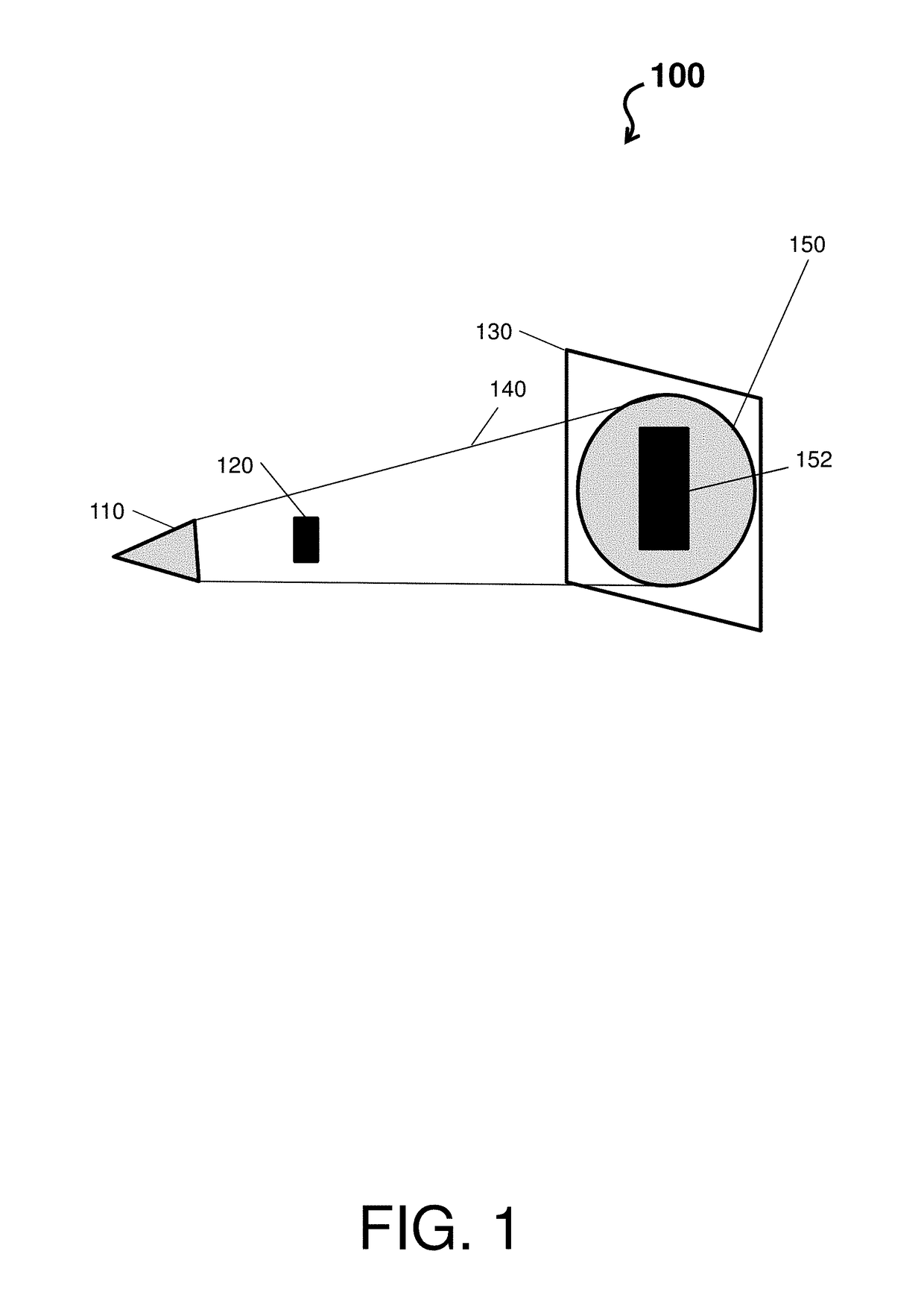
Radiography flat panel detector having a low weight x-ray shield and the method of production thereof
InactiveUS20160322411A1Reduce weightEasy to handleSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesX-ray shieldChemical synthesis
A radiography flat panel detector and a method of producing the flat panel detector including, in a scintillating or photoconductive layer, an imaging array, -a substrate, and an X-ray absorbing layer including a chemical compound having a metal element with an atomic number of 20 or more and one or more non-metal elements. The X-ray absorbing layer has a dimensionless absorption exponent of greater than 0.5 for gamma ray emission of Am241 at about 60 keV, whereinAE(Am241 60 keV)=t*(k1e1+k2e2+k3e3+ . . . )and AE(Am241 60 keV) represents the absorption exponent of the X-ray absorbing layer relative to the about 60 keV gamma ray emission of Am241; t represents the a thickness of the X-ray absorbing layer; e1, e2, e3, . . . represent concentrations of the elements in the X-ray absorbing layer; and k1,k2,k3 . . . represent mass attenuation coefficients of the elements. If the chemical compound is a scintillating phosphor, a layer is present between the X-ray absorbing layer and the substrate and has a transmission for light of 10% or lower at the wavelength of the light emission of the chemical compound.
Owner:AGFA HEALTHCARE NV
Method for analyzing underwater light transmission characteristic
The invention discloses a method for analyzing an underwater light transmission characteristic. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1, layering a water body in a depth direction, acquiring absorption coefficient values and scattering coefficient values which correspond to different layers, and calculating diffusion attenuation coefficients of the corresponding layers according to the absorption coefficient value and scattering coefficient value of each layer; 2, calculating the transmissivity of each layer according to the diffusion attenuation coefficient of each layer, multiplying the transmissivity of each layer to obtain the whole transmissivity of a water body communication channel, and correcting the whole transmissivity by adopting a truncation error to obtain the corrected whole transmissivity; and 3, outputting the transmission characteristic of the water body communication channel according to an attenuation situation of the water body. According to the method for analyzing the underwater light transmission characteristic, the communication channel transmission characteristic of light in the water is analyzed by using a vertical distribution model of chlorophyll concentration; and compared with the conventional attenuation coefficient model, the attenuation coefficient model has the advantages that the attenuation coefficients at different depths are not required to be measured through experiments, and the method is simple and is easy to apply.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Method for inversing sea-bottom attenuation coefficient by using modal dispersion curve energy difference
ActiveCN105631194AInversion realizationAccurate estimateInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsSound sourcesEngineering
The present invention relates to a method for inversing a sea-bottom attenuation coefficient by using a modal dispersion curve energy difference, wherein inversion of a sea-bottom attenuation coefficient is implemented by using amplitude energy information of a modal dispersion curve. The present invention provides a method for inversing a sea-bottom attenuation coefficient by using an energy difference of a modal dispersion curve of two bombs, so as to estimate a sea-bottom attenuation coefficient of an experimental sea area. The method provided by the present invention focuses on inversion of a neritic zone by using a dispersion effect generated by a wide-band explosive sound source during propagation in neritic zones. The method comprises: firstly, placing a receiving hydrophone at a certain depth; then delivering explosive sound sources with the same model number parameter (considered as generating the same signal during explosion) on the same straight line and at different distances, so as to receive time-frequency maps of two explosive sound sources; then processing the time-frequency maps of the two explosive sound sources by using a warping transformation, so as to obtain a transmission energy difference of first four stages of a modal dispersion curve; and finally inversing a sea-bottom attenuation coefficient by using a modal dispersion curve energy difference.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Pulse-laser-based rapid measurement method of attenuation coefficient and scattering albedo of semi-transparent medium
ActiveCN103389272AQuick measurementFast measurementScattering properties measurementsOmegaRadiation measurement
The invention discloses a pulse-laser-based rapid measurement method of an attenuation coefficient and scattering albedo of a semi-transparent medium, belongs to the technical field of semi-transparent medium radiation measurement, and solves the problem of low measurement speed of the semi-transparent medium radiation measurement method on the basis of an inverse problem solving. A black coating is coated at the surface of one side of a to-be-tested semi-transparent test-piece; a gaussian pulse laser beam is utilized to vertically enter the surface of one side of the test-piece without the coating; a time-domain hemisphere reflection signal of the semi-transparent medium is measured by adopting a single photon counter; the attenuation coefficient beta of a to-be-tested medium and the value of the scattering albedo omega of the to-be-tested medium are set; the least square difference is formed by an estimation value of the time-domain hemisphere reflection signal and the time-domain hemisphere reflection signal of the semi-transparent medium measured by the single photon counter; whether the difference is smaller than the threshold is judged; if so, the set attenuation coefficient beta of the to-be-tested medium and the scattering albedo omega of the to-be-tested medium are taken as results. The rapid measurement method is suitable for the semi-transparent medium radiation measurement.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
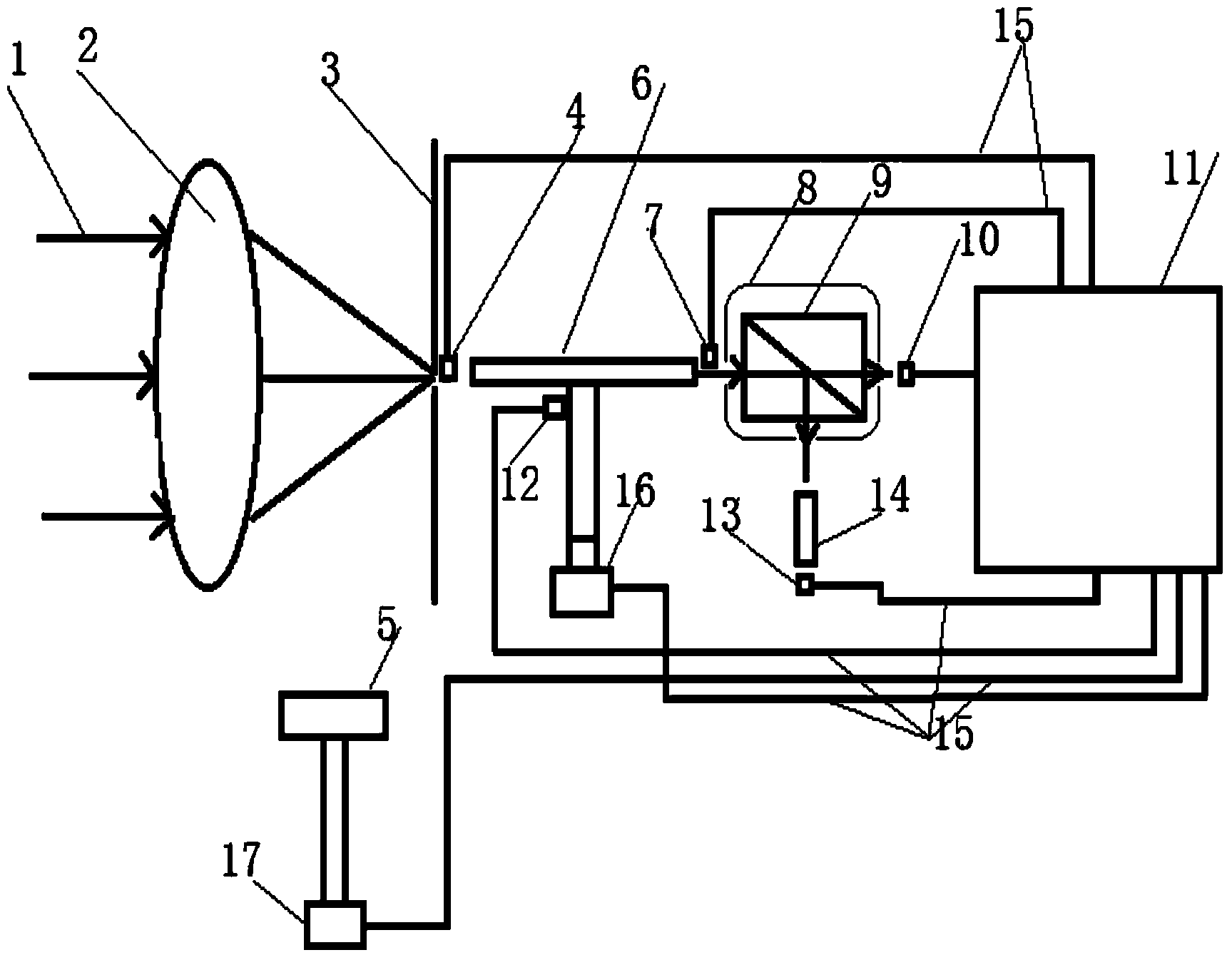
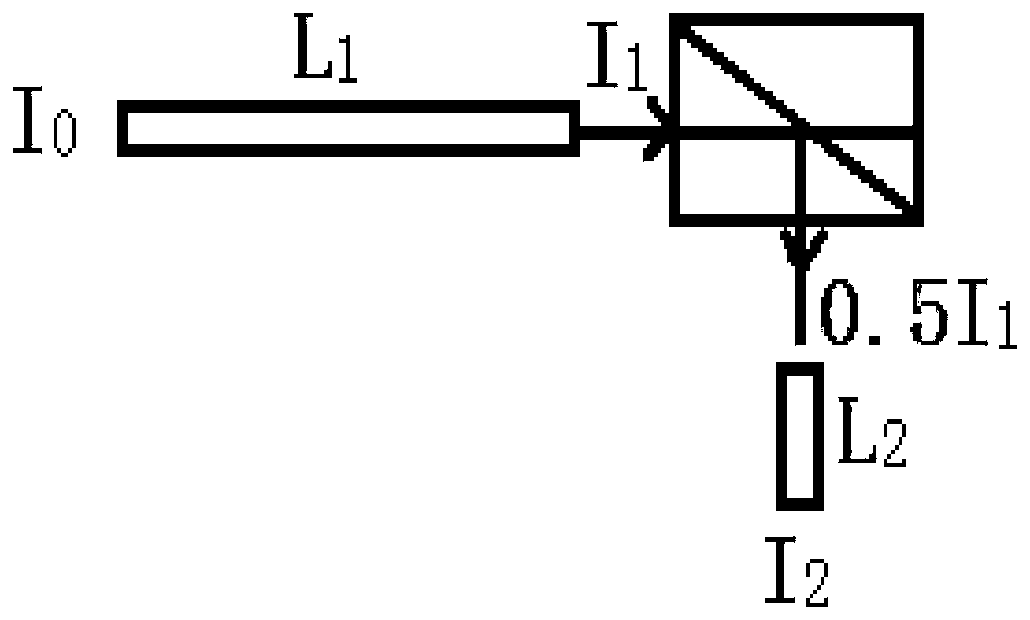
Experimental device for measuring numerical apertures and attenuation coefficients of light-guide fibers
ActiveCN103558011ASolve different problemsFusion simpleTesting optical propertiesFiberUltrasound attenuation
The invention provides an experimental device for measuring the numerical apertures and the attenuation coefficients of light-guide fibers. The experimental device comprises a light source, a focusing device (2), a plurality of light intensity sensors, a collimator (5), a shading box (8), a semi-reflexivity semi-transparent lens (9), a processor (11), an angle sensor (12), a first actuating device (16) and a second actuating device (17). The experimental device measures a first optical fiber (6) to be measured and a second optical fiber (14) to be measured which are the same in structure and different in length. The experimental device has two working modes, namely the numerical aperture mode and the attenuation coefficient mode, is capable of being conveniently switched between the two modes, and then measures the numerical apertures and the attenuation coefficients of the optical fibers to be measured.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Sound velocity-attenuation coefficient integrated detection method for polymer
ActiveCN108896664AEasy to operateEasy to calculateAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSonificationTest sample
The invention discloses a sound velocity-attenuation coefficient integrated detection method for a polymer. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) allowing an ultrasonic probe to emit ultrasonic waves directly towards a to-be-detected sample; (2) collecting reflection echoes on the upper and lower surfaces of the sample, and calculating amplitude spectrums of the reflection echoes, wherein one side, directly facing the ultrasonic probe, of the sample is defined as the upper surface, and one side, opposite to the ultrasonic probe, of the sample is defined as the lower surface; and (3) calculating an ultrasonic transmission speed of the to-be-detected sample, the thickness of the sample and the attenuation coefficient of the sample according to the amplitude spectrums of the reflection echoes. The detection method is easy in operation, convenient in calculation and low in detection cost, the tested sample is not damaged, the online monitoring can be easily realized, and the sound speed, attenuation coefficient and wall thickness of a polymer part can be simultaneously detected.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
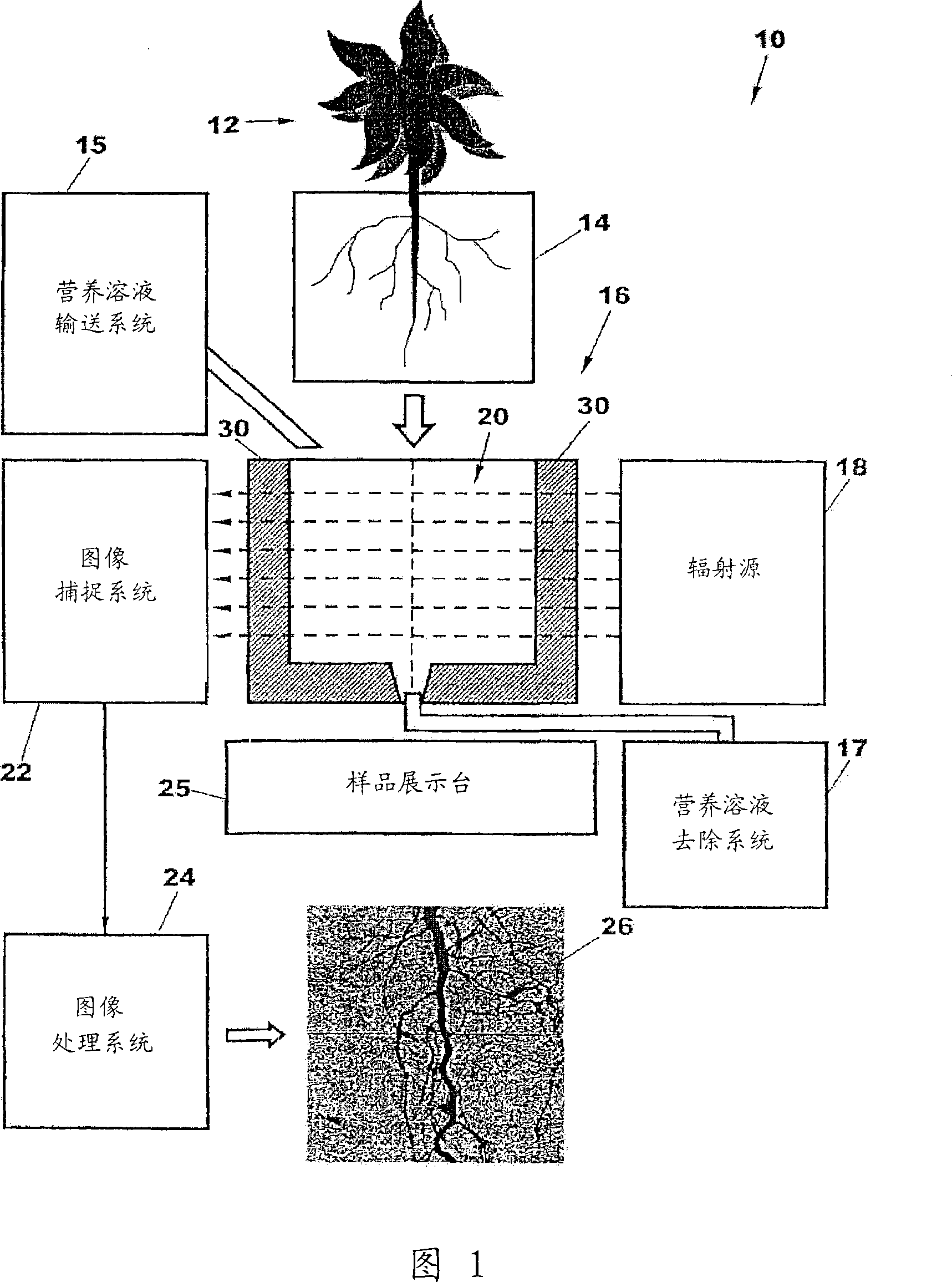
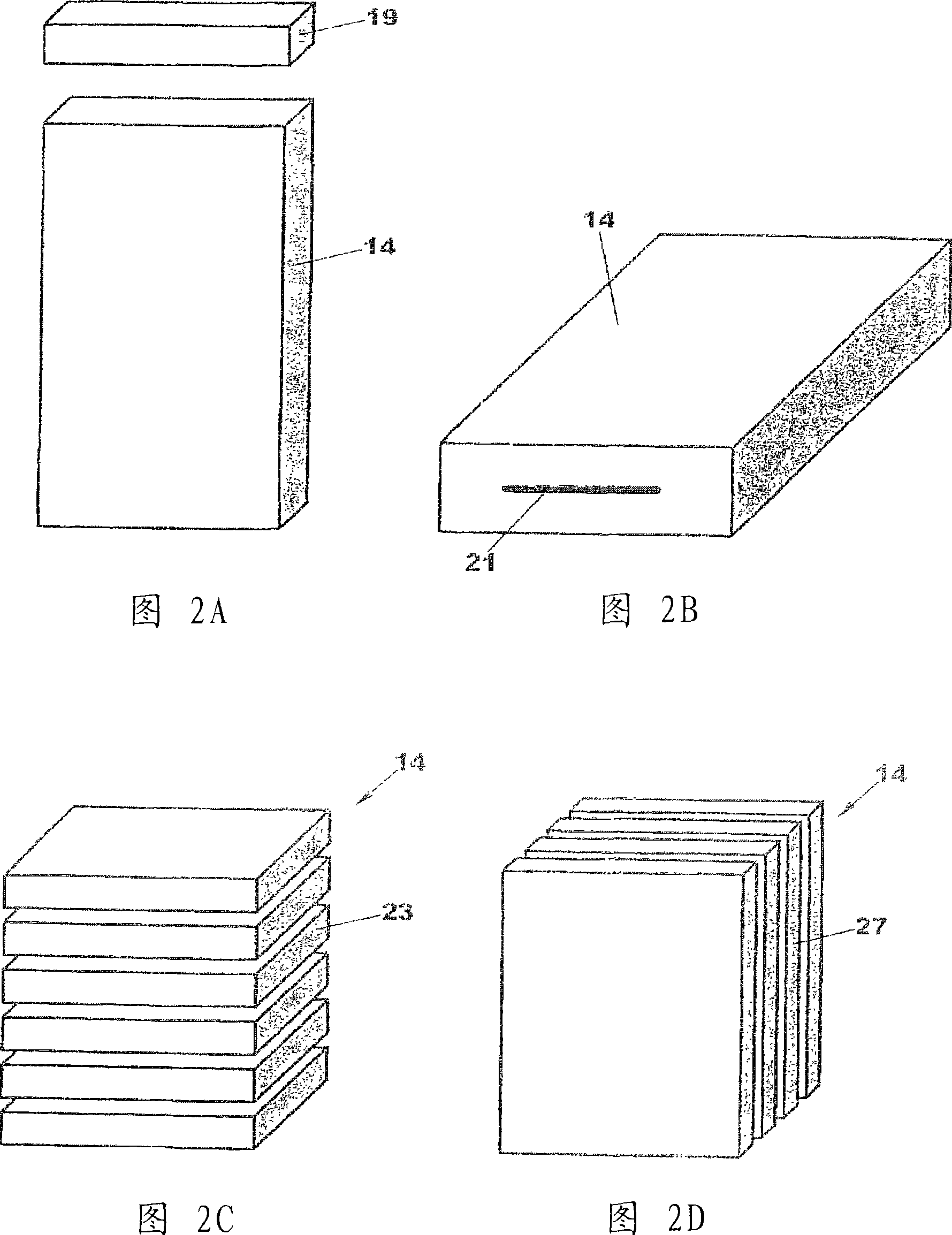
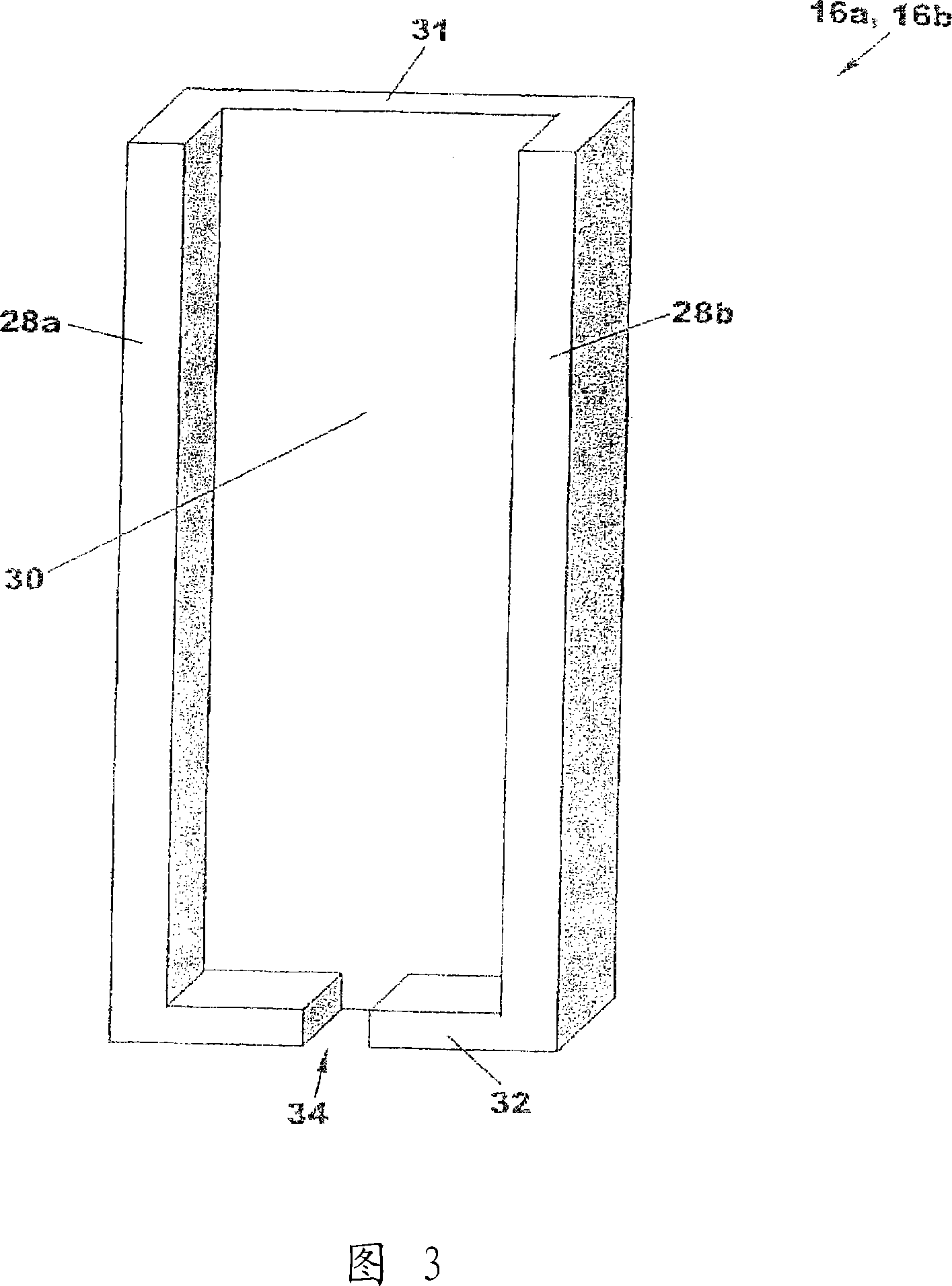
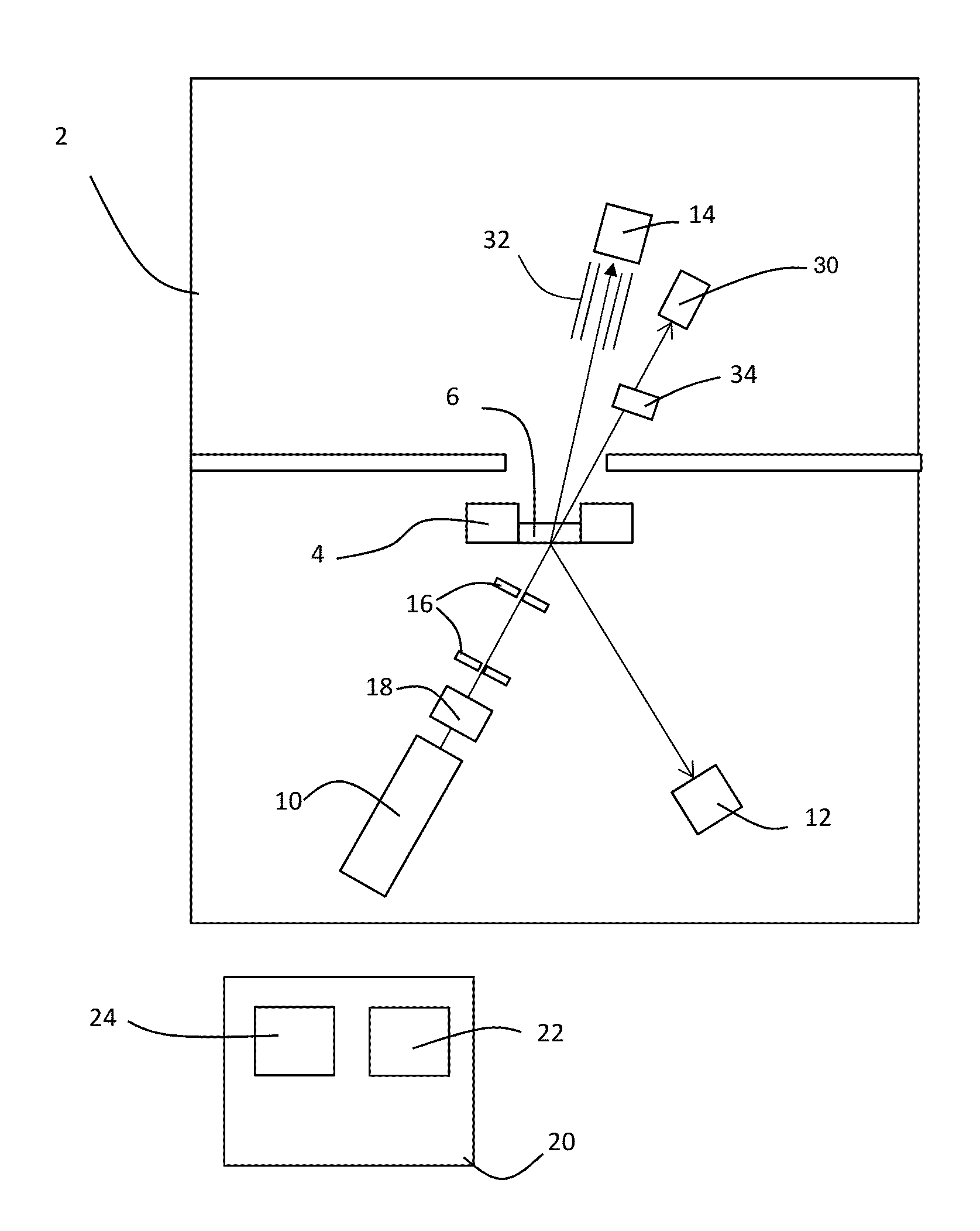
Plant root characterization system
ActiveCN101170898ASo as not to damagePlant phenotype modificationHorticulture methodsPlant rootsX-ray
An apparatus and method for nondestructively acquiring images of a plant root system is described. The apparatus includes a substrate for supporting the plant root system, a container for holding the substrate, an x-ray radiation source for generating x-ray radiation and directing the radiation to pass through the plant root system, and an x-ray image capture system for receiving the x-ray radiation having passed through the plant root system and for generating an image of the plant root system based on the radiation. The x-ray radiation source generates x-ray radiation having an energy level in the range of about 8 keV to about 20 keV. In this energy range, the attenuation of the x-ray radiation due to air is minimized and the contrast between the root system and the container and substrate is sufficiently high to provide a resolvable image. The substrate and container are preferably formed of materials having a low mass density, such as less than about 3 pounds per cubic foot, and a low x-ray mass attenuation coefficient. The low density materials of the substrate and the container introduce comparatively low attenuation of the x-ray radiation when compared to the attenuation introduced by the roots, thereby enhancing the visibility of the root system in the image.
Owner:PHENOTYPE SCREENING CORP
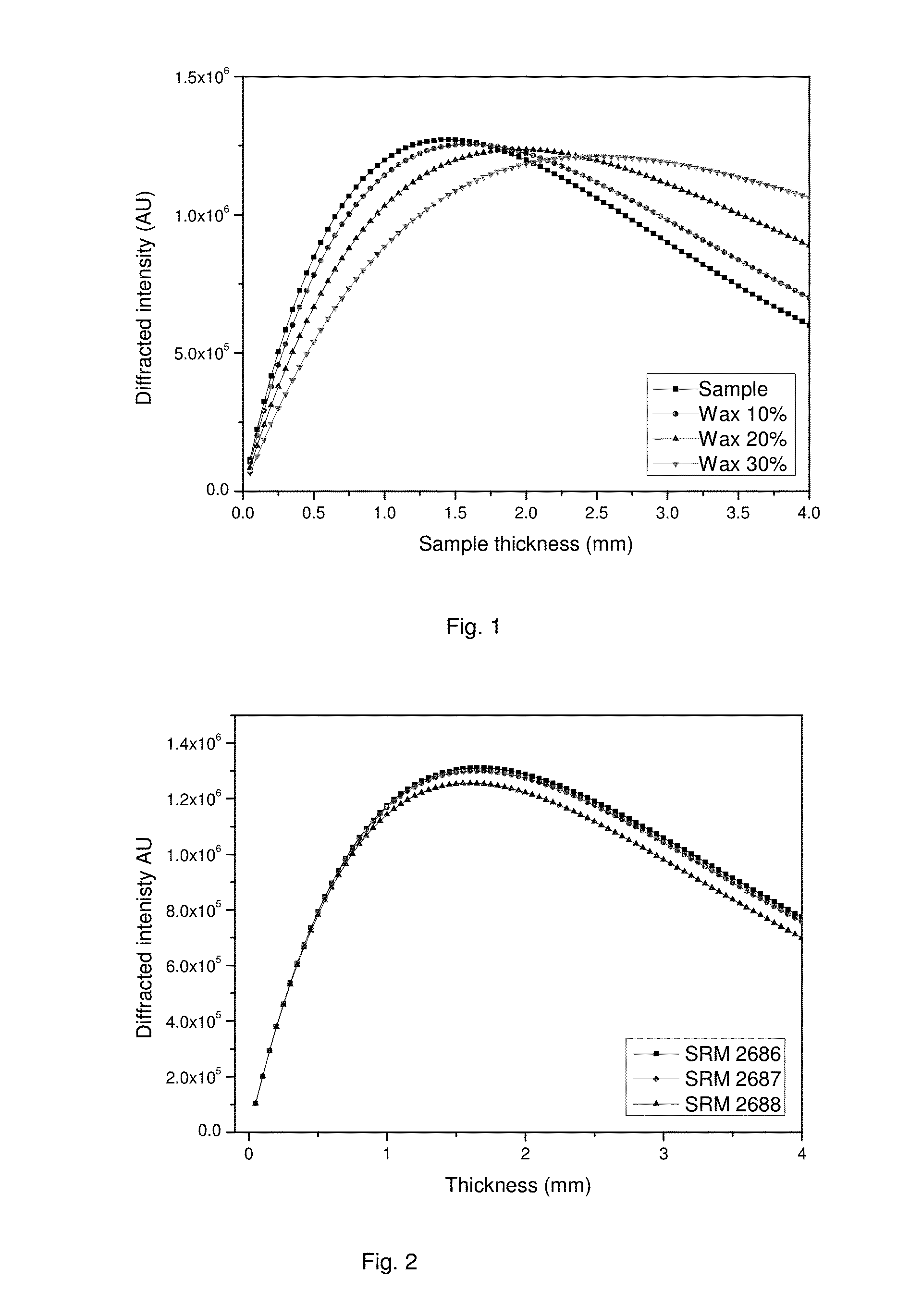
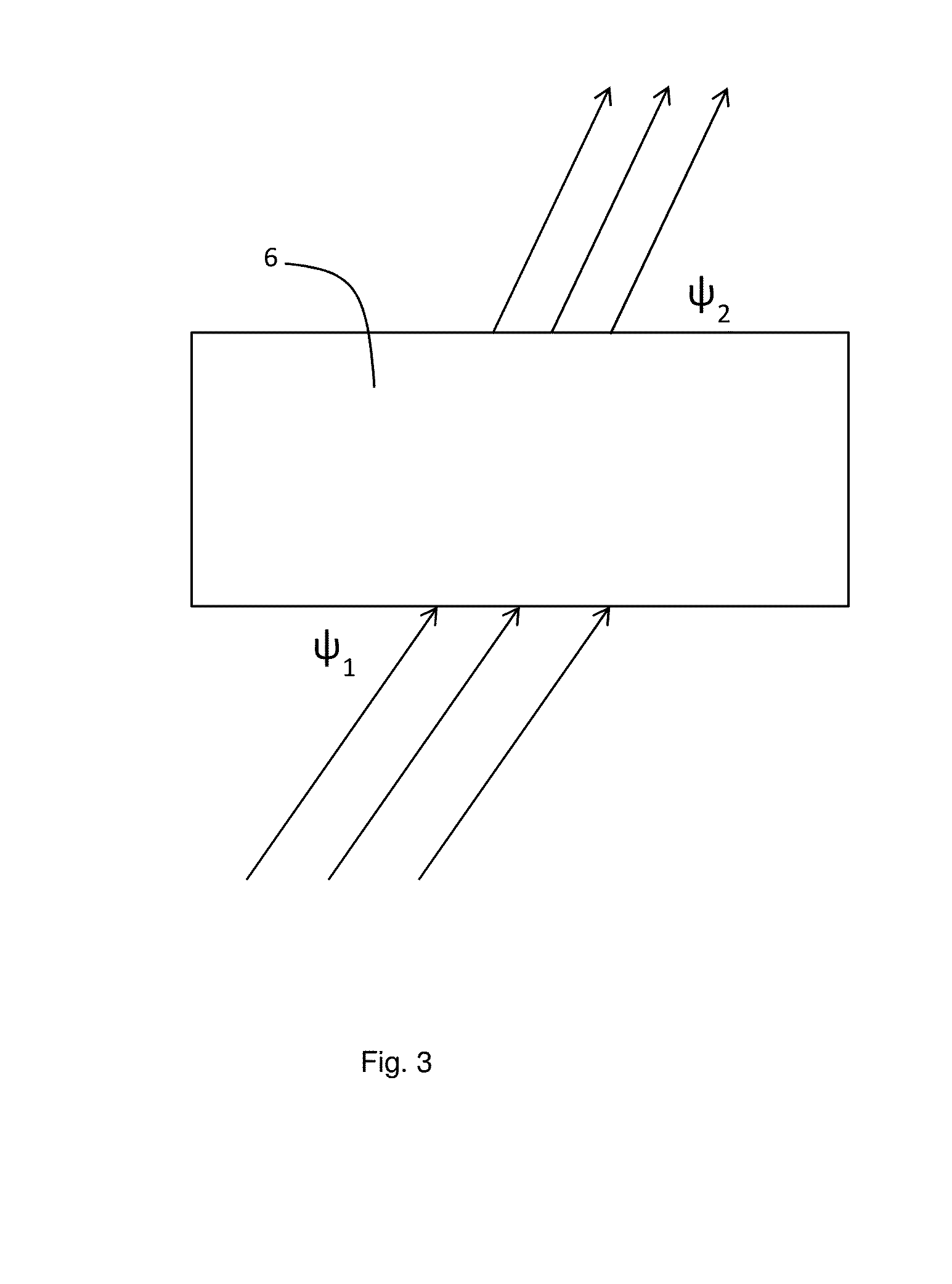
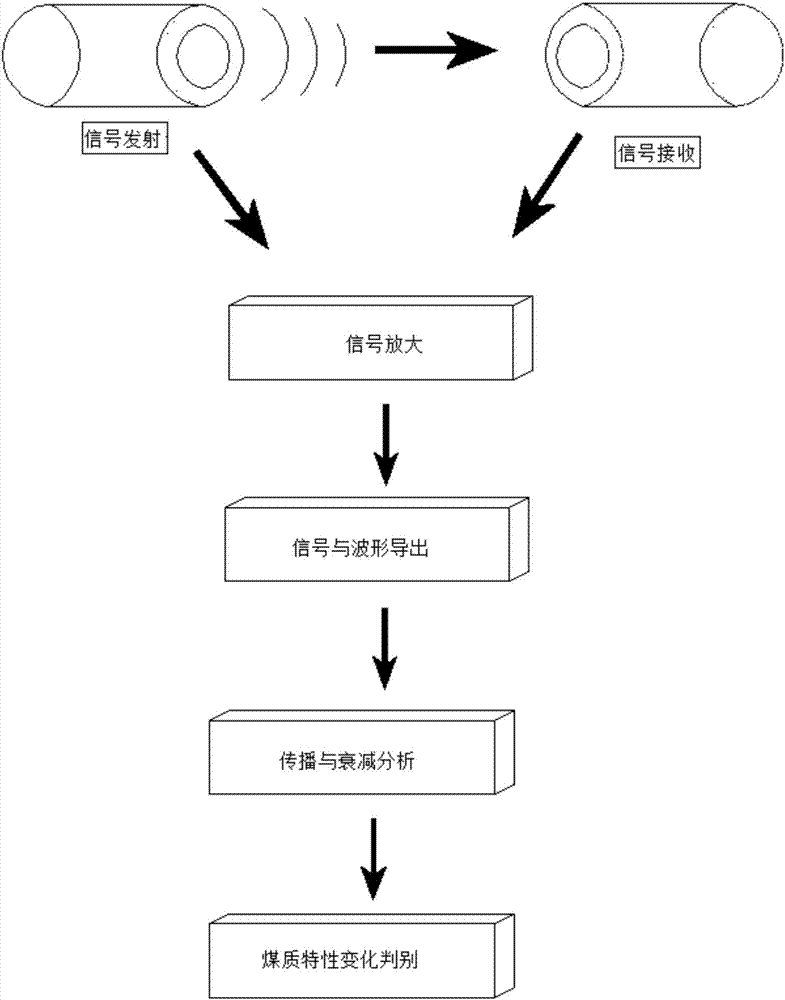
Quantitative X-ray Analysis - Matrix thickness correction
ActiveUS20160258890A1Quantitative measurementShorten the timeUsing wave/particle radiation meansMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionUltrasound attenuationElemental composition
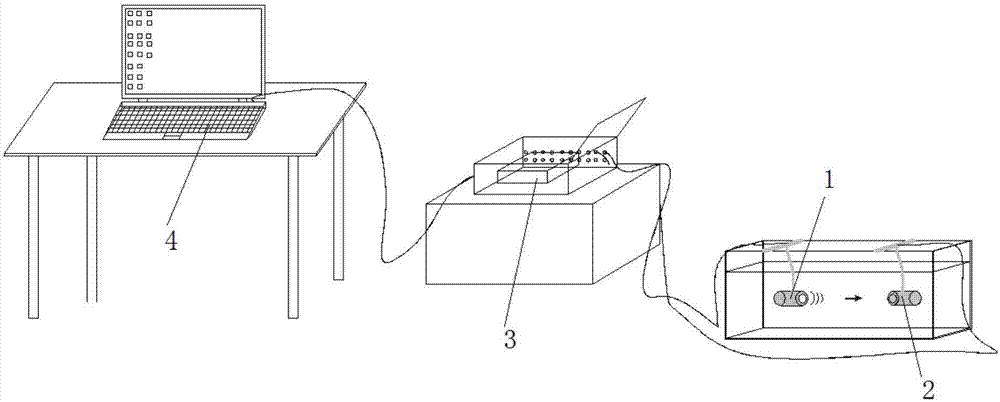
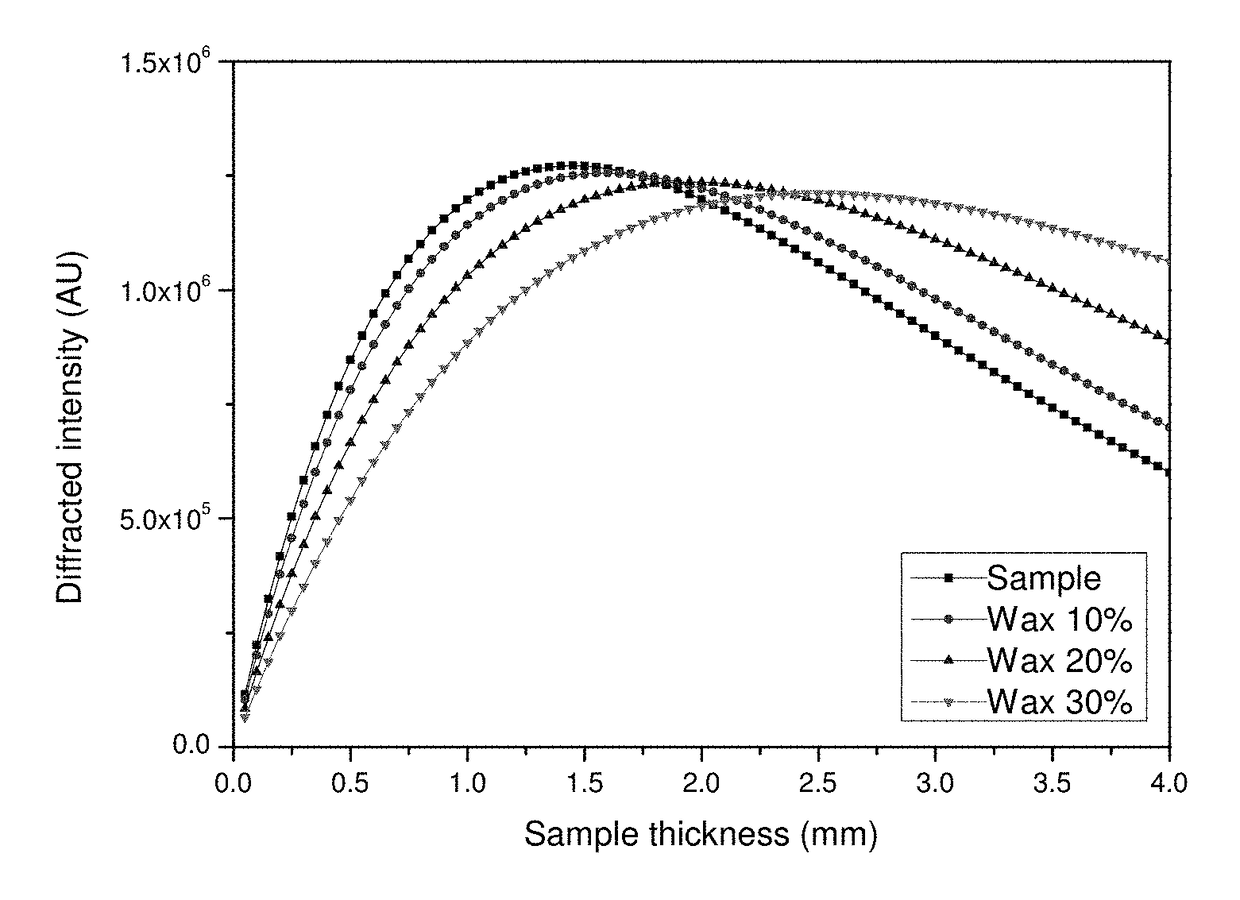
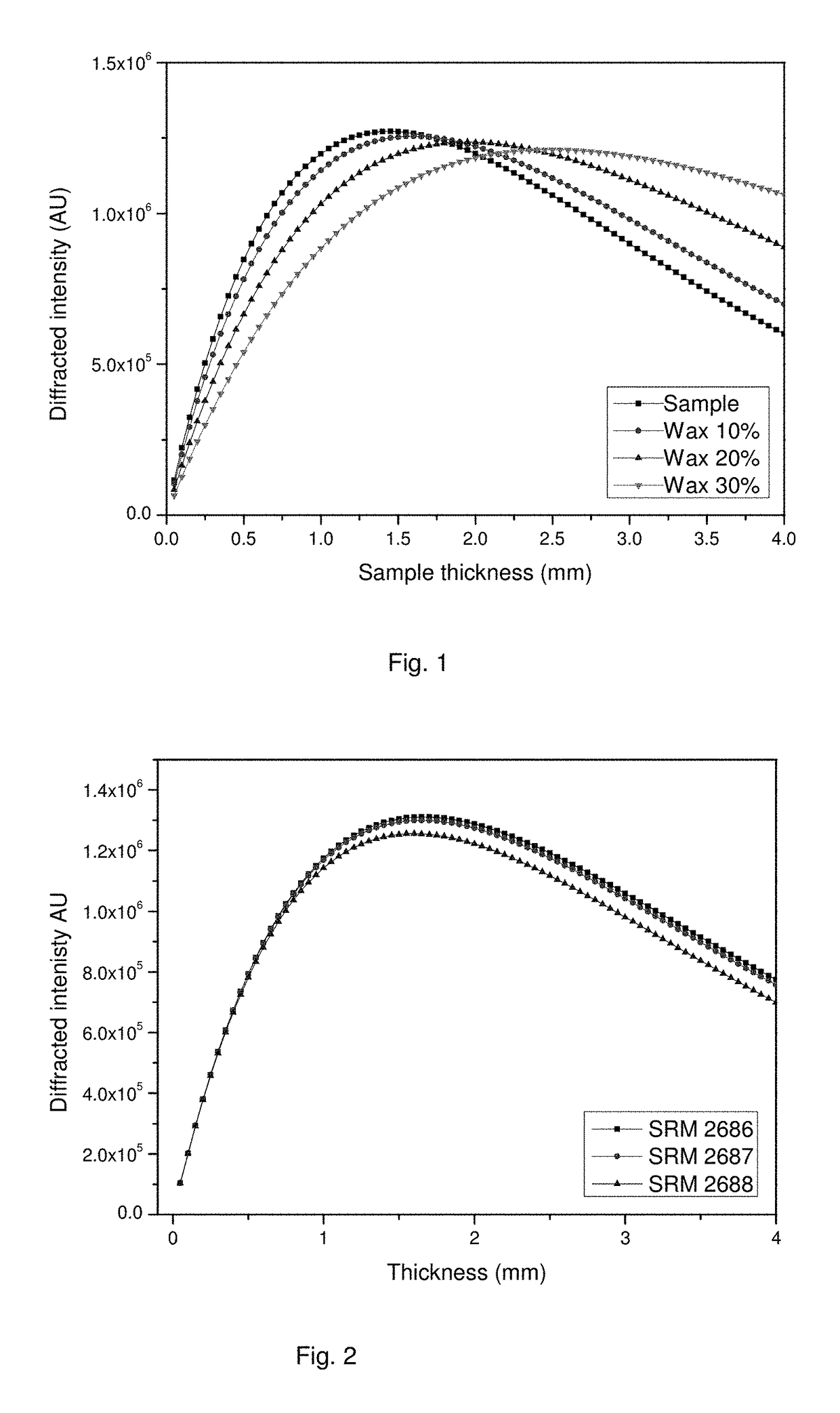
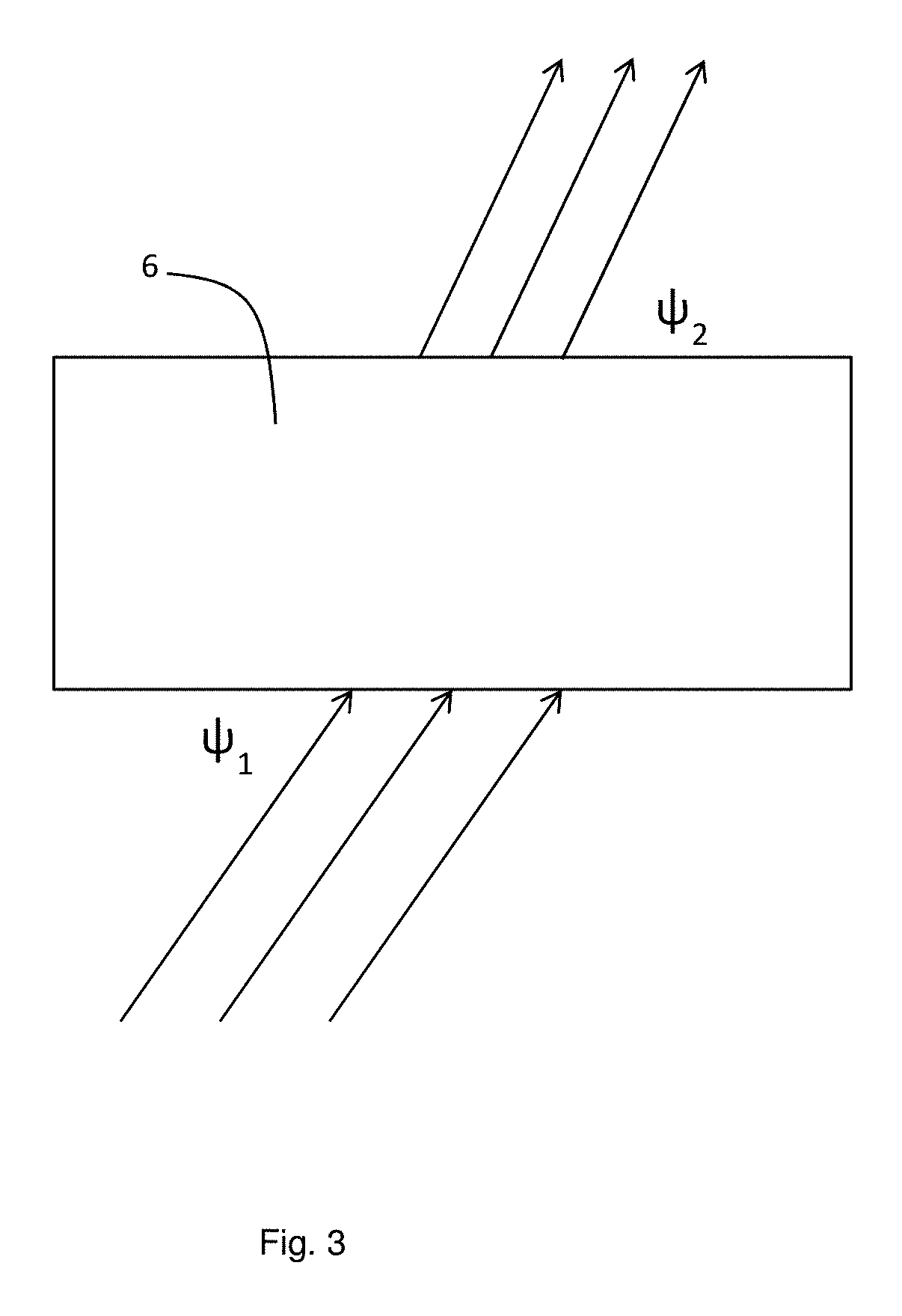
Quantitative X-ray analysis is carried out by making X-ray fluorescence measurements to determine the elemental composition of a sample and a correction measurement by measuring the transmitted intensity of X-rays at an energy E transmitted directly through the sample without deviation. An X-ray diffraction measurement is made in transmission by directing X-rays from an X-ray source at the energy E onto a sample at an incident angle ψ1 to the surface of the sample and measuring a measured intensity Id(θfl) of the diffracted X-rays at the energy E with an X-ray detector at an exit angle ψ2 corresponding to an X-ray diffraction peak of a predetermined component. A matrix corrected X-ray intensity is obtained using the measured X-ray intensity in the X-ray diffraction measurement, the correction measurement and the mass attenuation coefficient of the sample calculated from the elemental composition and the mass attenuation coefficients of the elements.
Owner:PANALYTICAL BV
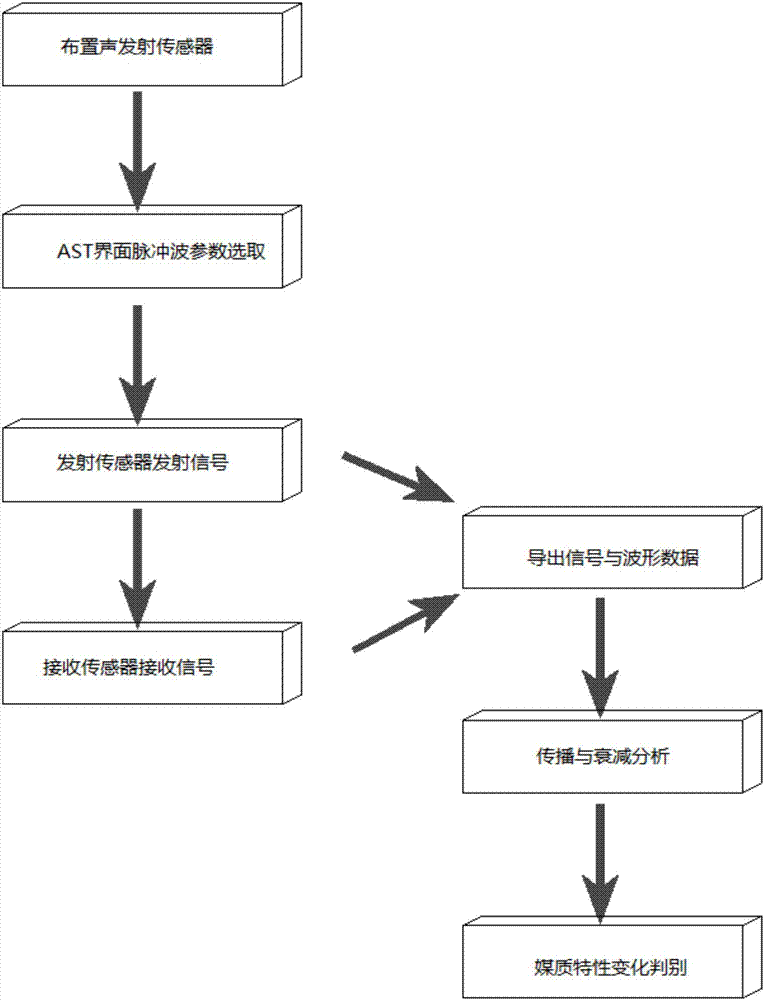
Nondestructive testing method for testing soil characteristics of soil complex through acoustic emission
InactiveCN107991392AAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSoil characteristicsAcoustic emission
The invention relates to a nondestructive testing method for testing soil characteristics of a soil complex through acoustic emission. Multiple pairs of acoustic emission sensors and acoustic reception sensors are reasonably arranged in a medium or on the surface of a material, a reception signal probe receiving surface of each acoustic reception sensor and an emission surface of each acoustic emission sensor are arranged oppositely, the distance between each acoustic emission sensor and each acoustic reception sensor is S, the propagation velocity v=S / t of impulse waves is calculated, the attenuation coefficient alpha of the impulse waves is calculated, the characteristic change of the medium is judged according to the propagation velocity V and the attenuation coefficient alpha of the impulse waves, the main frequency of emission waves is determined according to an acoustic emission spectrogram, and the characteristics of the medium are judged according to the main frequency and theattenuation coefficient alpha obtained through testing. The acoustic emission sensors and the acoustic reception sensors are arranged on the to-be-tested medium, the characteristic change of the physical mechanics of a soil mass is obtained by use of the tested propagation velocity and the attenuation coefficient of the impulse waves. The technology is simple, convenient and flexible to operate.
Owner:NANJING HYDRAULIC RES INST
Quantitative X-ray analysis—matrix thickness correction
ActiveUS9784699B2Shorten the timeUsing wave/particle radiation meansMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionUltrasound attenuationElemental composition
Quantitative X-ray analysis is carried out by making X-ray fluorescence measurements to determine the elemental composition of a sample and a correction measurement by measuring the transmitted intensity of X-rays at an energy E transmitted directly through the sample without deviation. An X-ray diffraction measurement is made in transmission by directing X-rays from an X-ray source at the energy E onto a sample at an incident angle ψ1 to the surface of the sample and measuring a measured intensity Id(θfl) of the diffracted X-rays at the energy E with an X-ray detector at an exit angle ψ2 corresponding to an X-ray diffraction peak of a predetermined component. A matrix corrected X-ray intensity is obtained using the measured X-ray intensity in the X-ray diffraction measurement, the correction measurement and the mass attenuation coefficient of the sample calculated from the elemental composition and the mass attenuation coefficients of the elements.
Owner:PANALYTICAL BV
Neutron imaging method for natural gas hydrate sediment triaxial mechanical test
PendingCN110567814AIncrease cold neutron contentRealize digital image outputMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesResponse processImage resolution
The invention provides a method capable of carrying out high-precision imaging on an internal structure of a natural gas hydrate sediment triaxial mechanical test. The method is characterized in thatthe distinction degree of natural gas hydrate, natural gas and water molecules is enhanced, the imaging resolution of the internal structure of natural gas hydrate sediment is improved and high-precision imaging of the structure in the natural gas hydrate triaxial mechanical test process is achieved by reducing the energy of neutron beams and improving the mass attenuation coefficient of neutron beams based on the fact that the molecular structure size of hydrate is close to the wavelength of cold neutrons. By means of the method, the creep and relaxation rules in the natural gas hydrate sample forming and decomposing process can be obtained, and the dynamic response process of reservoir stability after natural gas hydrate development can be known easily. The method is characterized in that the distinction degree of natural gas hydrate, natural gas and water molecules is enhanced, the imaging resolution is improved and high-precision imaging of the natural gas hydrate dynamic gatheringand dispersing process is realized by reducing the energy of neutron beams and improving the mass attenuation coefficient of neutron beams based on the fact that the molecular structure size of hydrate is close to the wavelength of cold neutrons.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
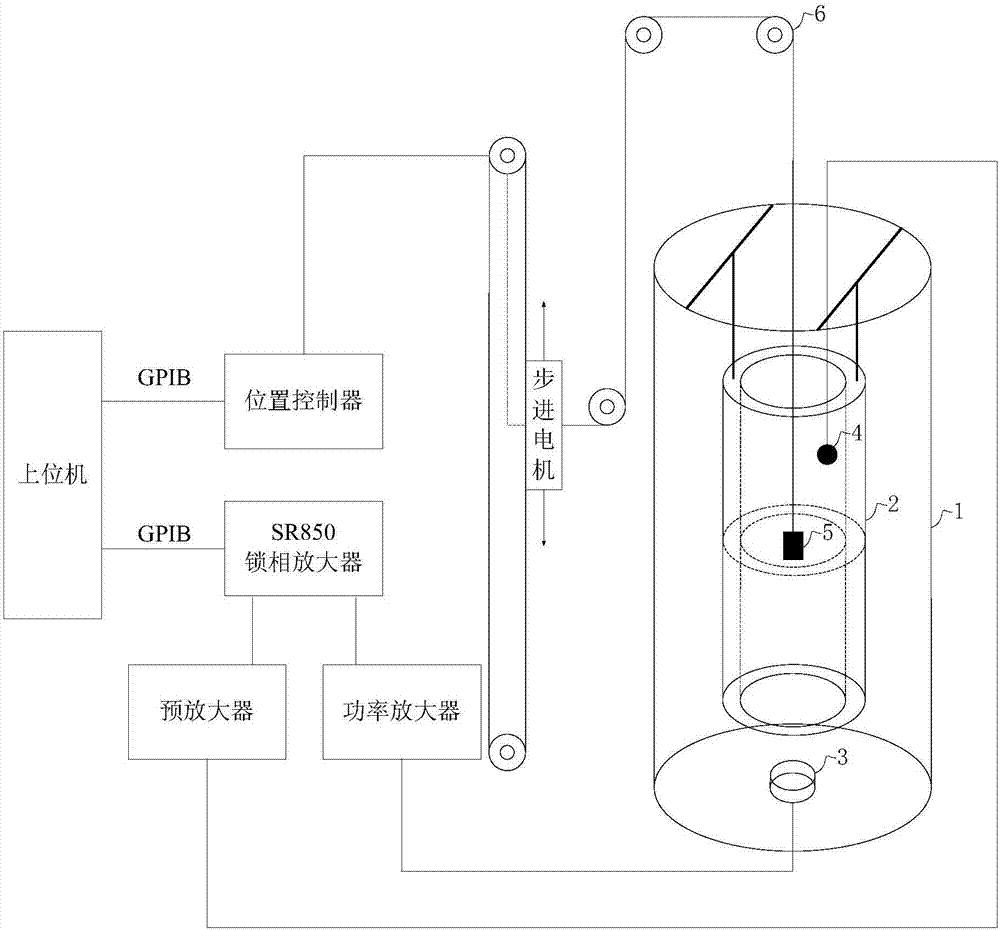
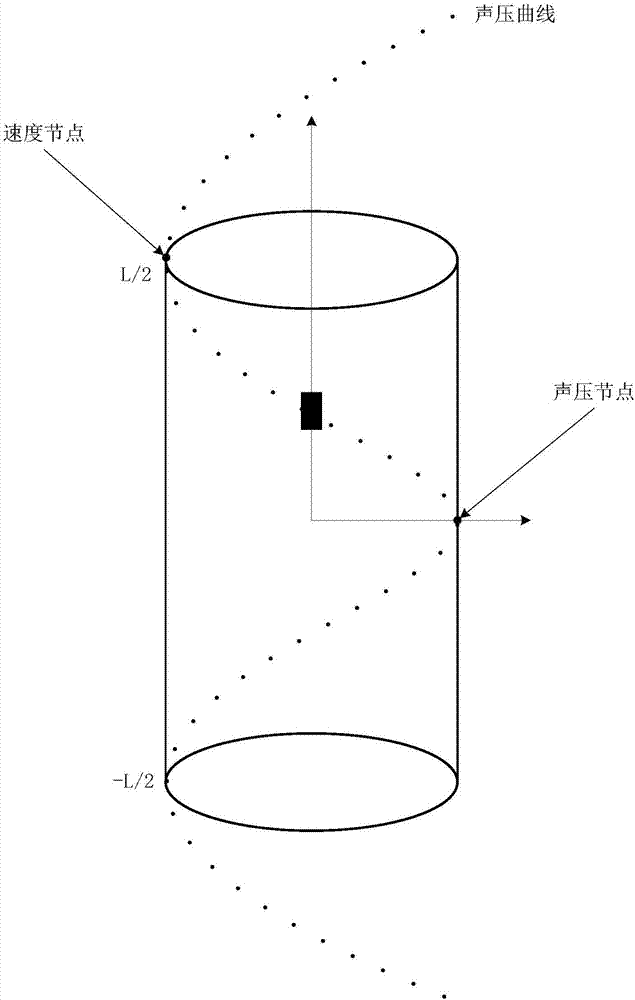
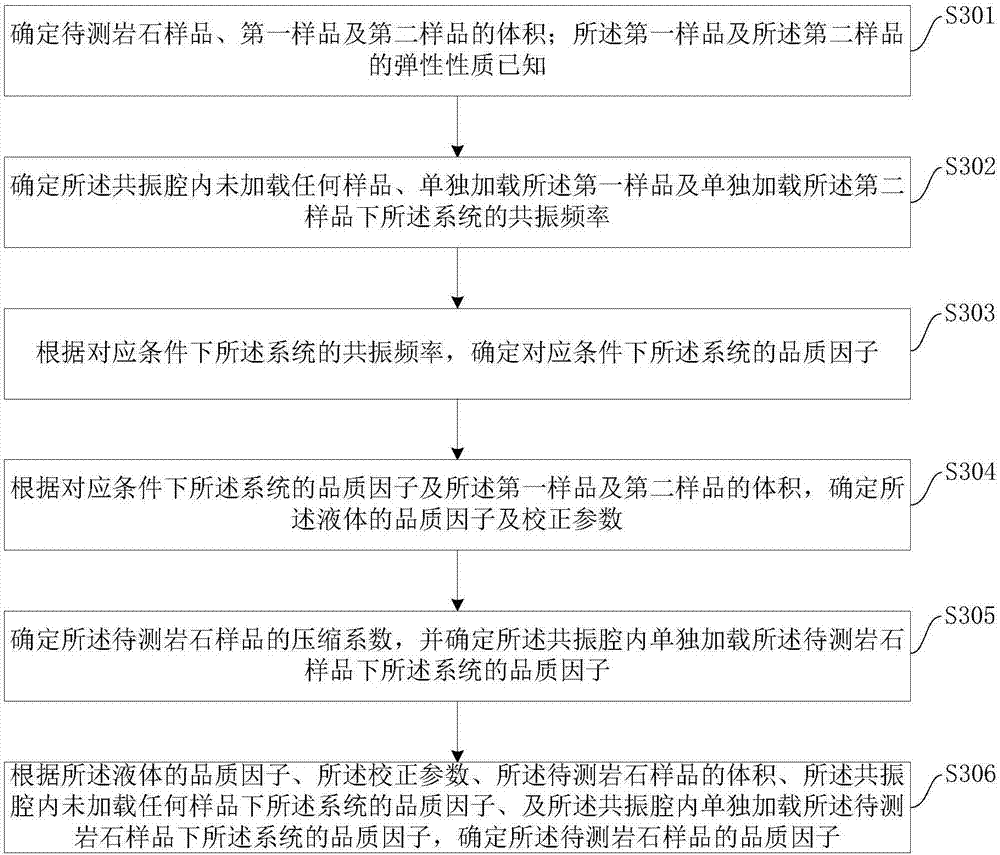
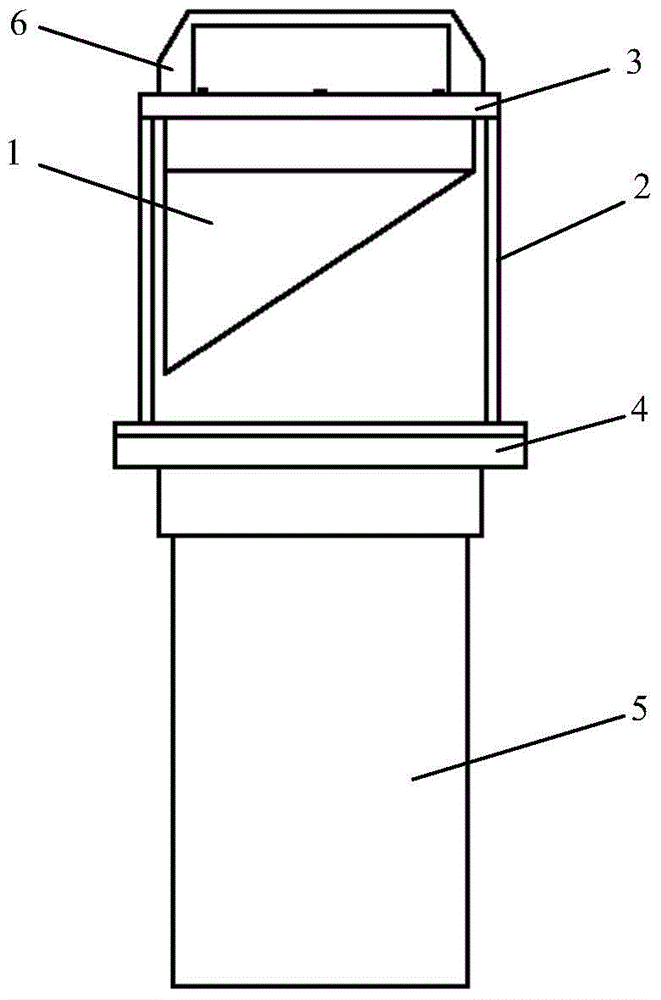
Method and system for measuring rock attenuation coefficient
ActiveCN107389794ARealize measurementImprove practicalityAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesHydrophoneAcoustic wave
The embodiment of the invention provides a method and a system for measuring a rock attenuation coefficient. The system comprises an opening container, a vibration source, a resonance chamber, a hydrophone, a phase-lock amplifier and an upper computer, wherein the opening container is used for containing a solution used as a sound bearing medium; the vibration source is used for generating a sound wave signal for driving the system to resonate; the resonance chamber is immersed in the solution and is used for outputting resonance sound pressure field signals generated in the resonance process of the system; the resonance sound pressure field signals comprise the resonance sound pressure field signals under the states of loading no sample, singly loading a first sample, singly loading a second sample and singly loading a rock sample in the resonance chamber; the hydrophone is arranged in the resonance chamber and is used for collecting the resonance sound pressure field signals; the phase-lock amplifier is used for outputting a vibration source stimulating signal to the seismic source, performing phase-lock treatment on the seismic source stimulating signal and the resonance sound pressure field signals collected by the hydrophone and then supplying to the upper computer; the upper computer is used for acquiring a quality factor of the rock sample according to the signal supplied by the phase-lock amplifier. According to the method and the system, the measuring practicability and the measuring efficiency of the rock attenuation coefficient can be improved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
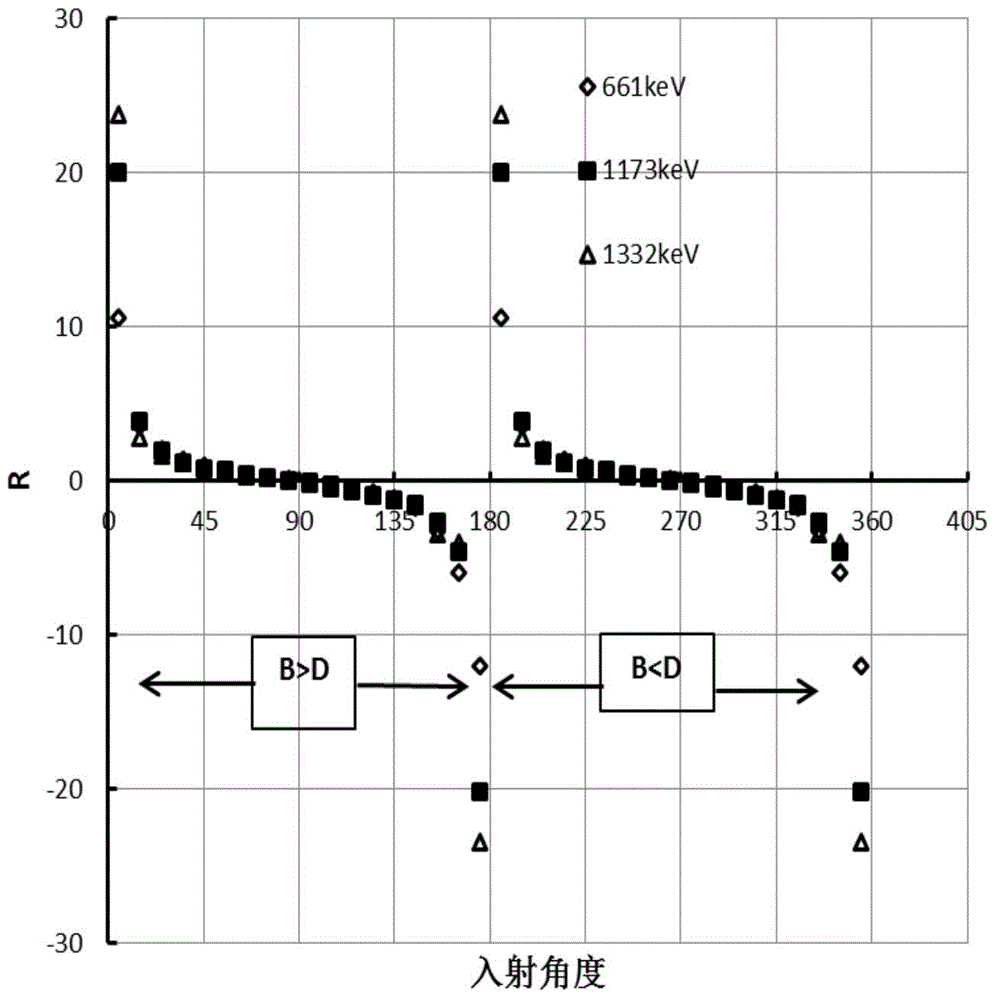
Shielding body assembly used for gamma radioactive source orientation measurement and ray incident angle measurement method
ActiveCN105700001AChange direction response characteristicsLocation determinationX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentReduced doseGamma ray
The invention belongs to the radiation measurement technical field and relates to a shielding body assembly used for gamma radioactive source orientation measurement and a ray incident angle measurement method. The shielding body assembly comprises a shielding barrel covering a measuring probe; the shielding barrel is made of a material which has a large mass attenuation coefficient for gamma rays; the upper part of the shielding barrel is of a solid cylindrical structure; the lower part of the shielding barrel is of a hollow diagonal beveled cylindrical structure; after being unfolded, the hollow diagonal beveled cylindrical structure is an isosceles triangle; and the measuring probe is arranged in the hollow beveled cylindrical structure. Combined with a background automatic deduction algorithm, the measurement method can quickly determine the position of a radioactive source and a radioactive hot area in a nuclear terrorist incident, and avoid harm caused by radiation and reduce doses to which operating personnel is subjected.
Owner:CHINA INST FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
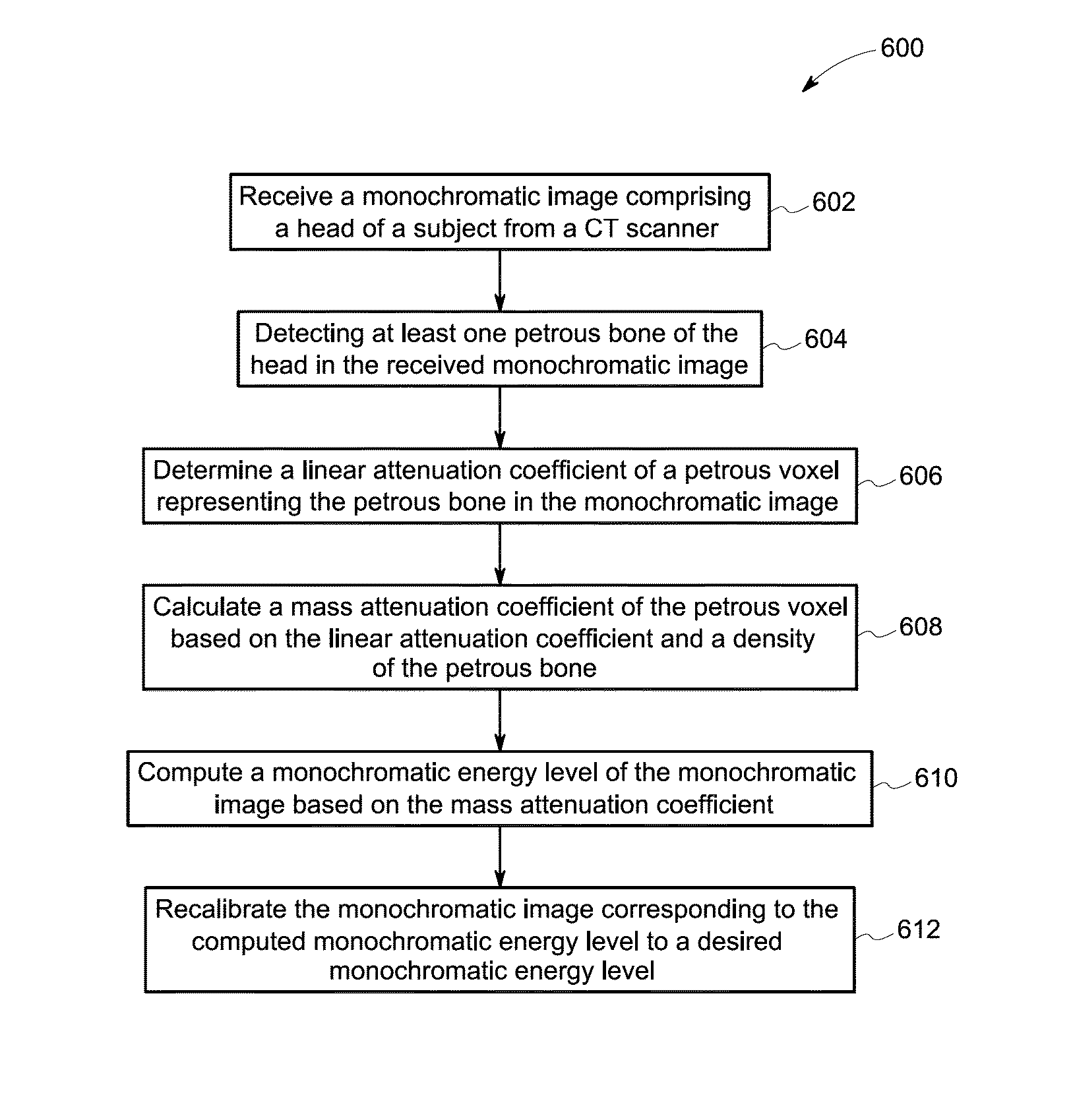
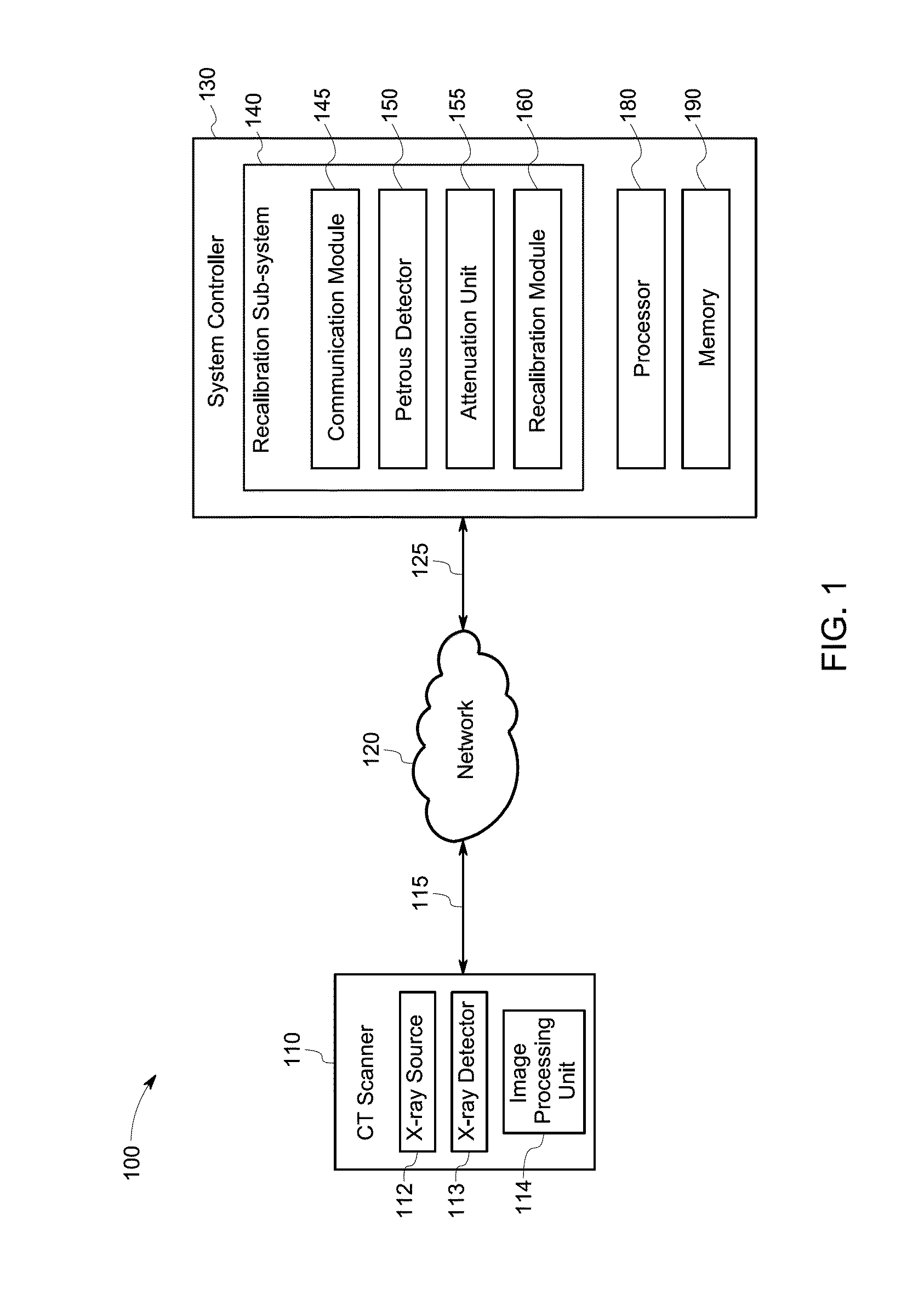
System and method for recalibrating a monochromatic image
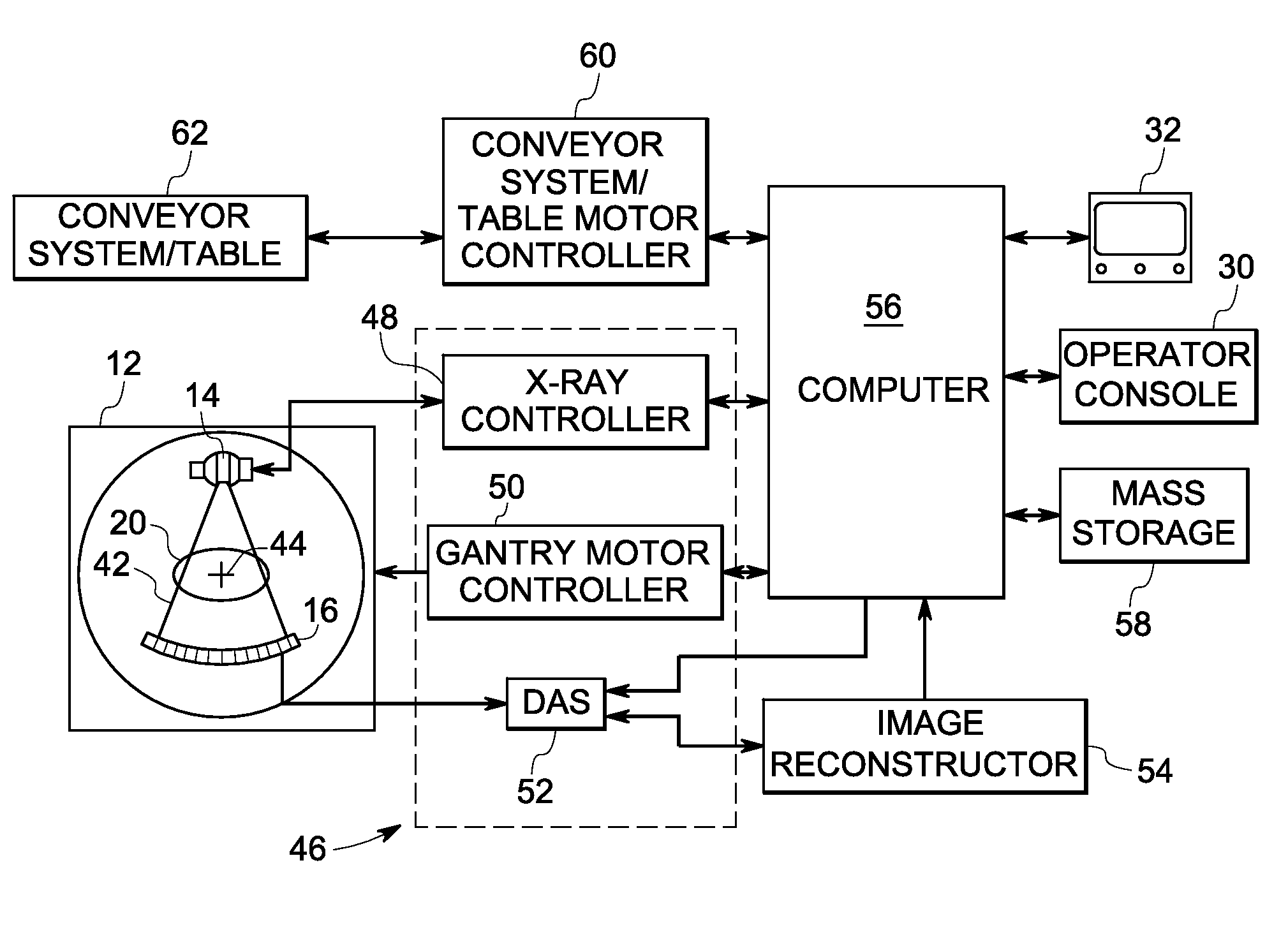
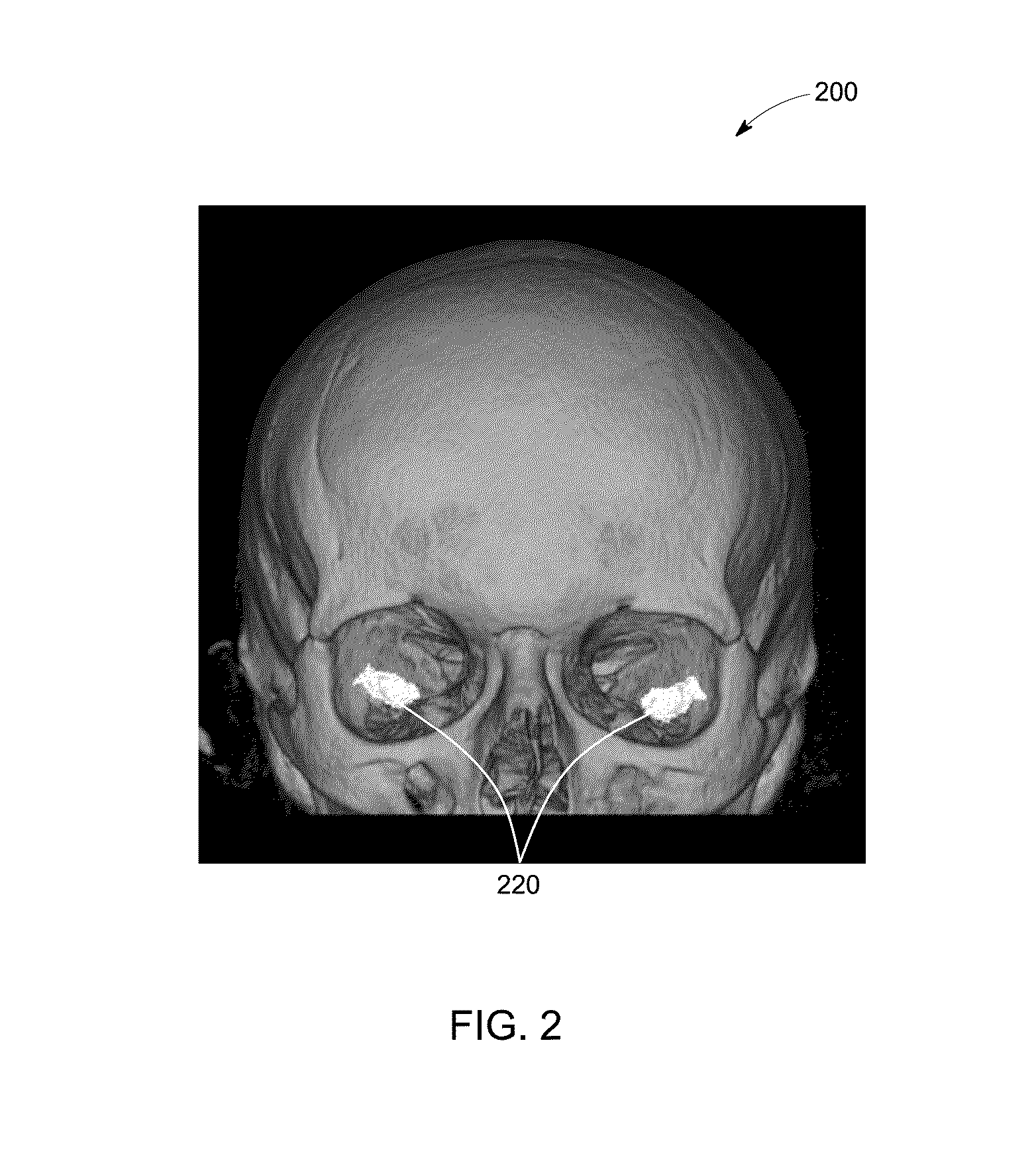
A method includes receiving a monochromatic image comprising a head of a subject from a Computed Tomography (CT) scanner and detecting a petrous bone of the head in the monochromatic image. The method further includes determining a linear attenuation coefficient of at least one petrous voxel representing the petrous bone and calculating a mass attenuation coefficient of the petrous voxel based on the linear attenuation coefficient and a density of the petrous bone. The method also includes computing a monochromatic energy level of the monochromatic image based on the mass attenuation coefficient of the petrous voxel and recalibrating the monochromatic image corresponding to the computed monochromatic energy level to the desired monochromatic energy level.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
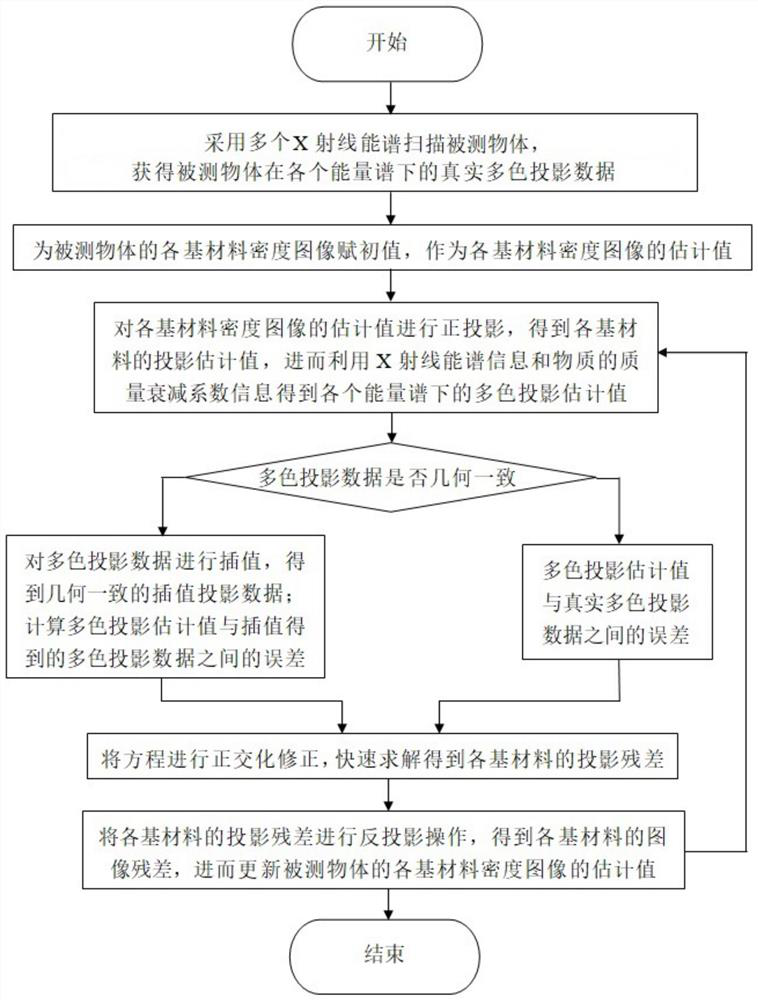
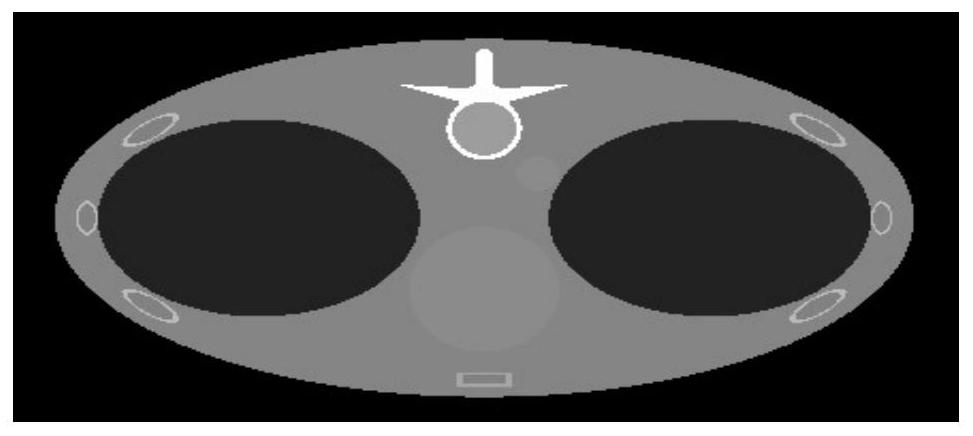
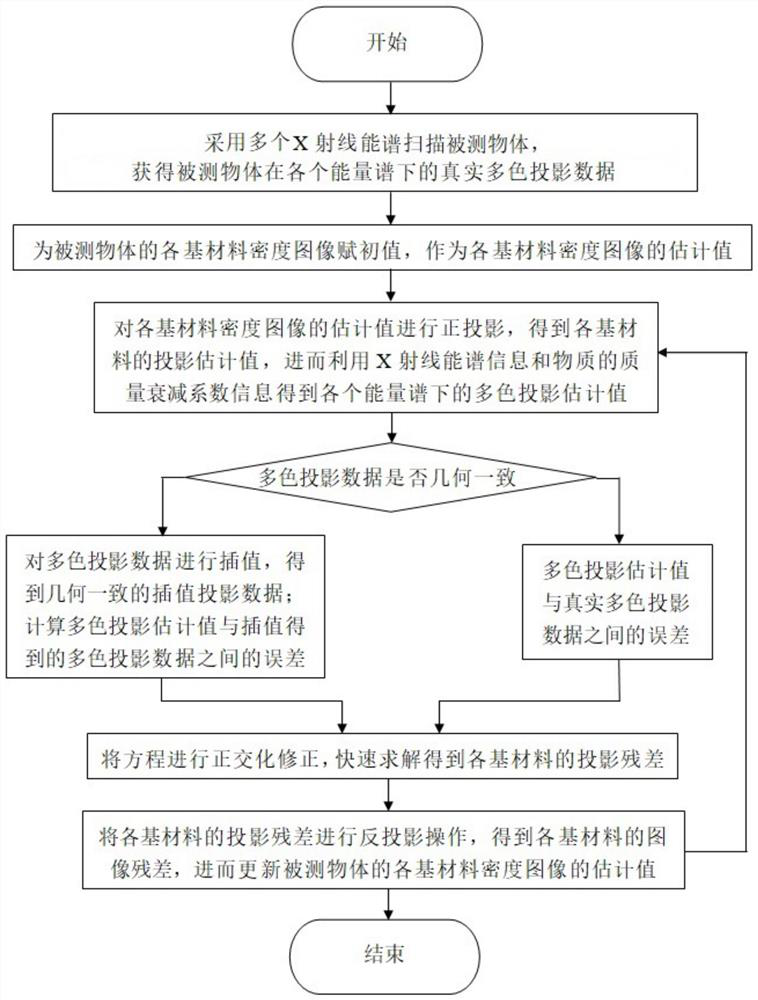
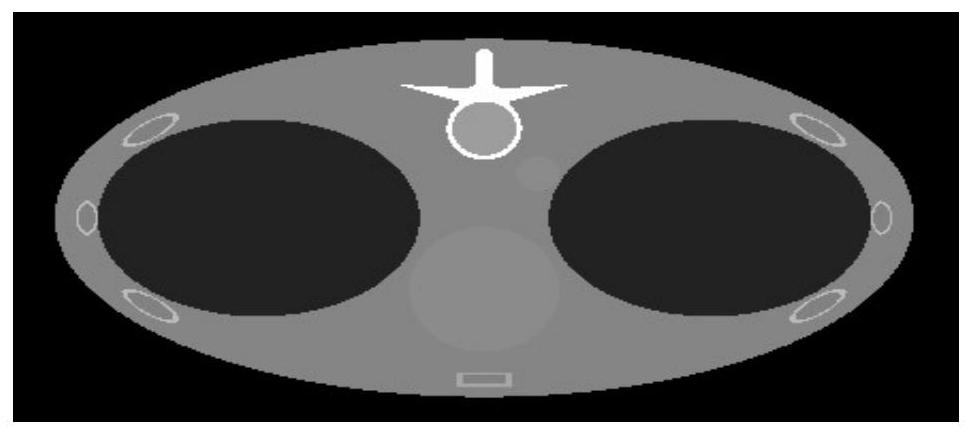
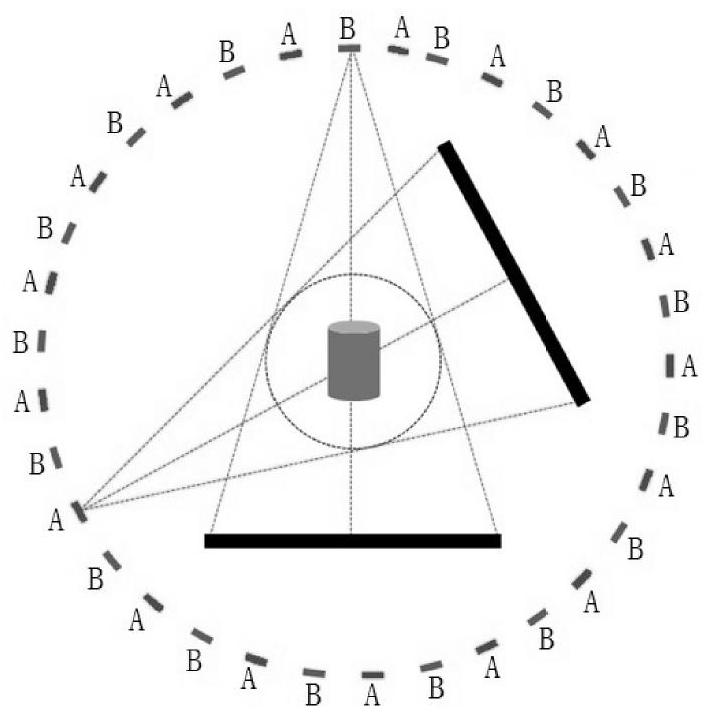
Energy spectrum CT multi-base material rapid iterative decomposition method based on equation orthogonal correction
ActiveCN111915695AImprove reconstructed image qualityFast convergenceImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses an energy spectrum CT multi-base material rapid iterative decomposition method based on equation orthogonal correction, and the method comprises the steps: 1, scanning a measured object through employing different X-ray energy spectrums to acquire the multi-color projection data of the measured object; 2, assigning an initial value to each base material density image of themeasured object; 3, performing orthographic projection on the estimated value of the density image of each base material, and obtaining a multi-color projection estimated value according to the X-rayenergy spectrum information and the mass attenuation coefficient information of the substance; 4, calculating an error between the multi-color projection estimated value and the multi-color projection data, and solving the projection residual error of each base material by utilizing orthogonal correction; 5, obtaining an image residual error of each base material, and updating an estimated valueof a density image of each base material of the measured object; and 6, repeating the steps 3 to 5 until a termination condition is met. According to the invention, a plurality of base material density images of the measured object can be reconstructed according to the acquired multi-color projection data of the plurality of energy spectrums.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
CT enhanced imaging method and system for three-dimensional structure of natural gas hydrate
InactiveCN112213336AAttenuation coefficient increasesAttenuation coefficient unchangedMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationIce waterMethane gas
The invention belongs to the technical field of hydrates, particularly relates to a CT enhanced imaging method and system for a three-dimensional structure of a natural gas hydrate, and aims to solvethe problems of poor observation and positioning precision and low observation precision of the three-dimensional structure of the natural gas hydrate due to small gray difference of CT images in imaging of the three-dimensional structure of the natural gas hydrate in the prior art. According to the CT enhanced imaging method for the three-dimensional structure of the natural gas hydrate, the sediment containing the natural gas hydrate is fully filled with the aqueous solution containing the intervention enhancer, and the intervention tracer dissolved in water improves the mass attenuation coefficient mu / rho difference value of X-rays in the natural gas hydrate, ice, water and methane gas; meanwhile, the X-ray mass energy absorption coefficient muen / rho difference value of the natural gashydrate, ice, water and methane gas is increased, then the linear attenuation coefficient received by the detector is changed, and the imaging resolution of all components of the natural gas hydrate sediment is increased.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
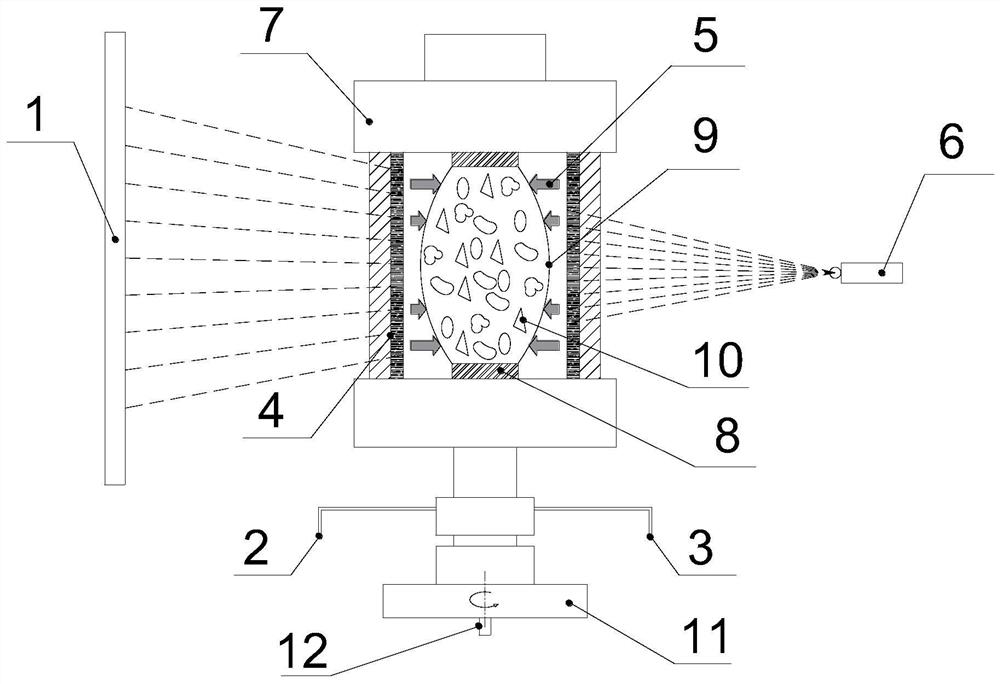
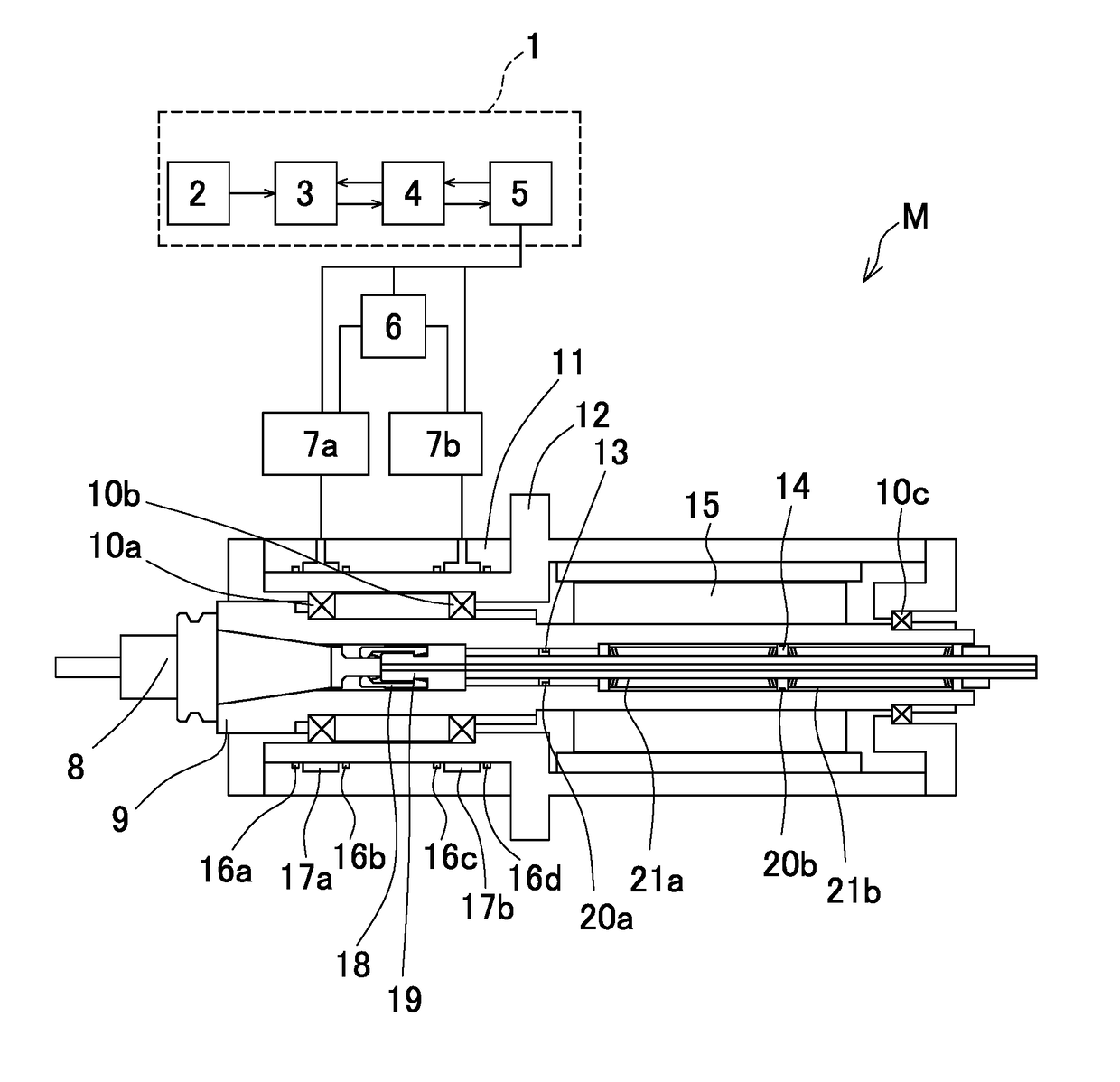
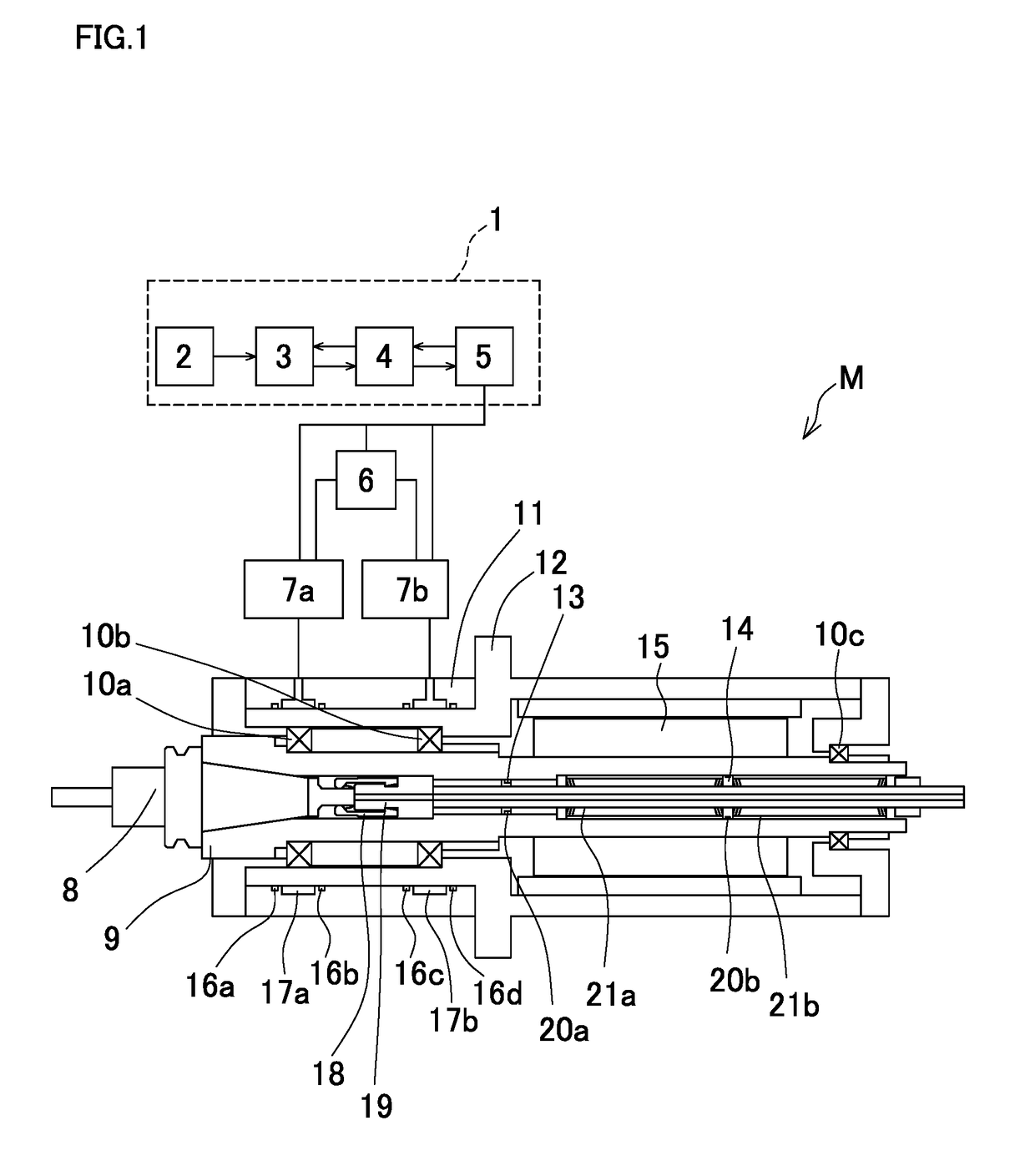
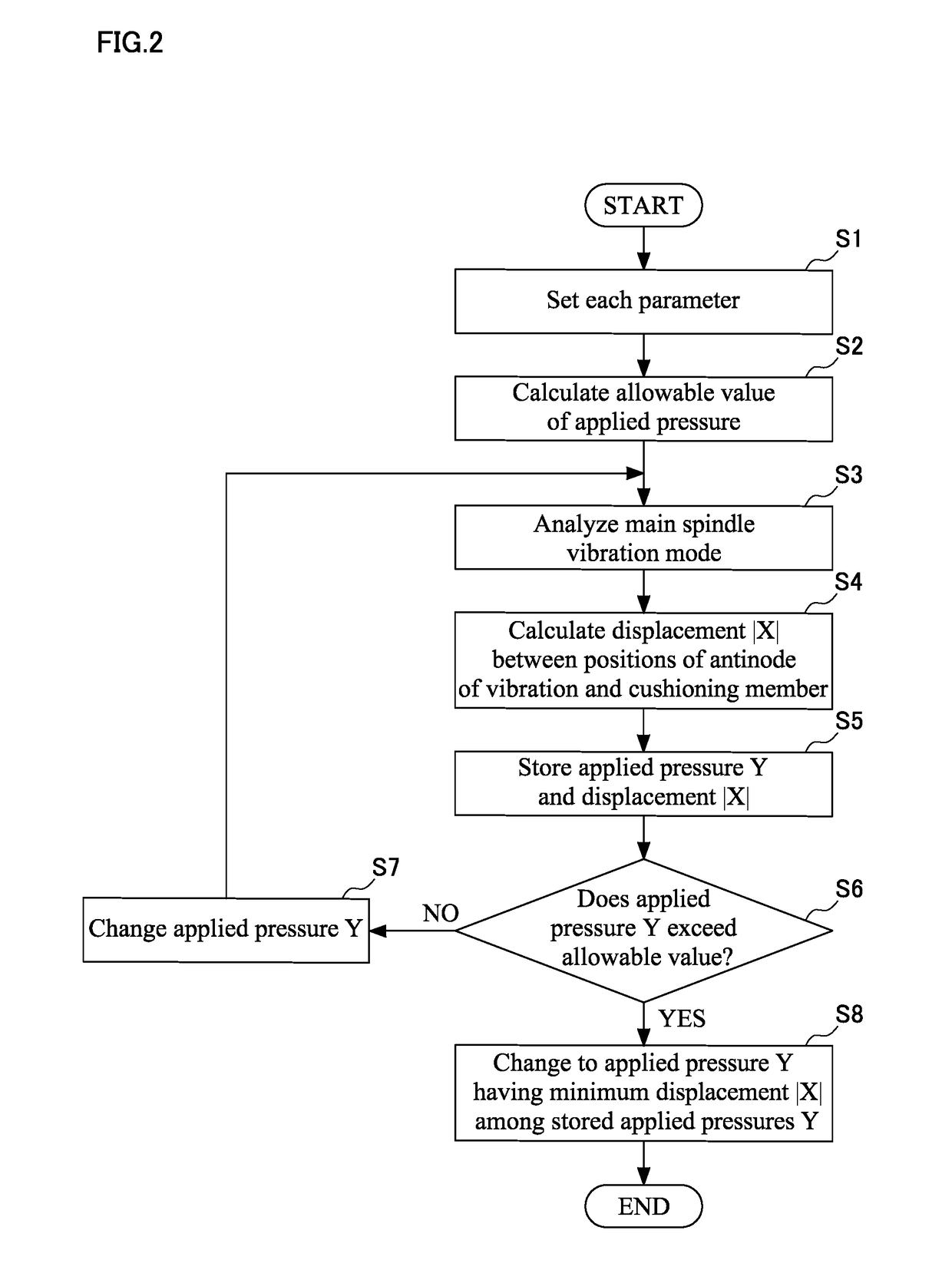
Main spindle device for machine tool
ActiveUS20180021904A1Reduce processReduce vibrationRotating vibration suppressionRolling contact bearingsEngineeringMachine tool
A main spindle device for a machine tool includes a main spindle, a cushioning member, and an arithmetic unit. The cushioning member is disposed on a position where a vibration displacement of a rotator exists. The arithmetic unit uses data of a tool to be used to analyze a vibration mode in a free vibration of the rotator based on a support rigidity of a bearing, masses of respective parts of the rotator including the tool, an attenuation coefficient, and an equation of motion derived from rigidity and inertia by a rotation. An outer diameter of a sleeve positioned outside the bearing is changed such that a position of an antinode of the vibration or a position on which a vibration displacement exists in the vibration mode matches a position of the cushioning member inside the main spindle to change a preload on the bearing.
Owner:OKUMA CORP
Liquid metal radiation shielding coating material and preparation method thereof
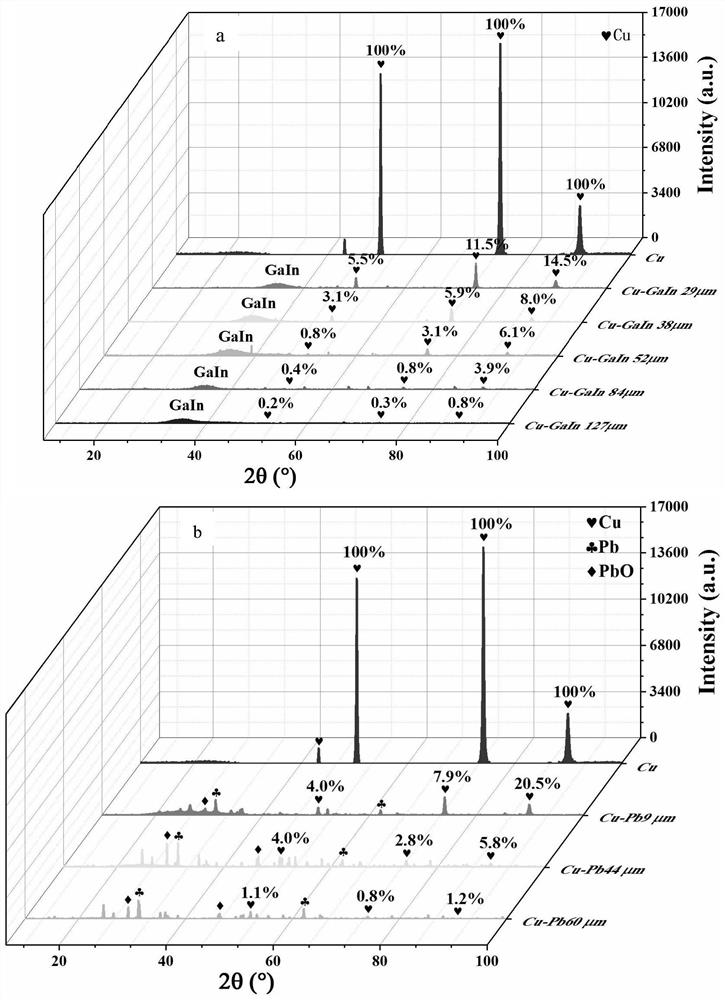
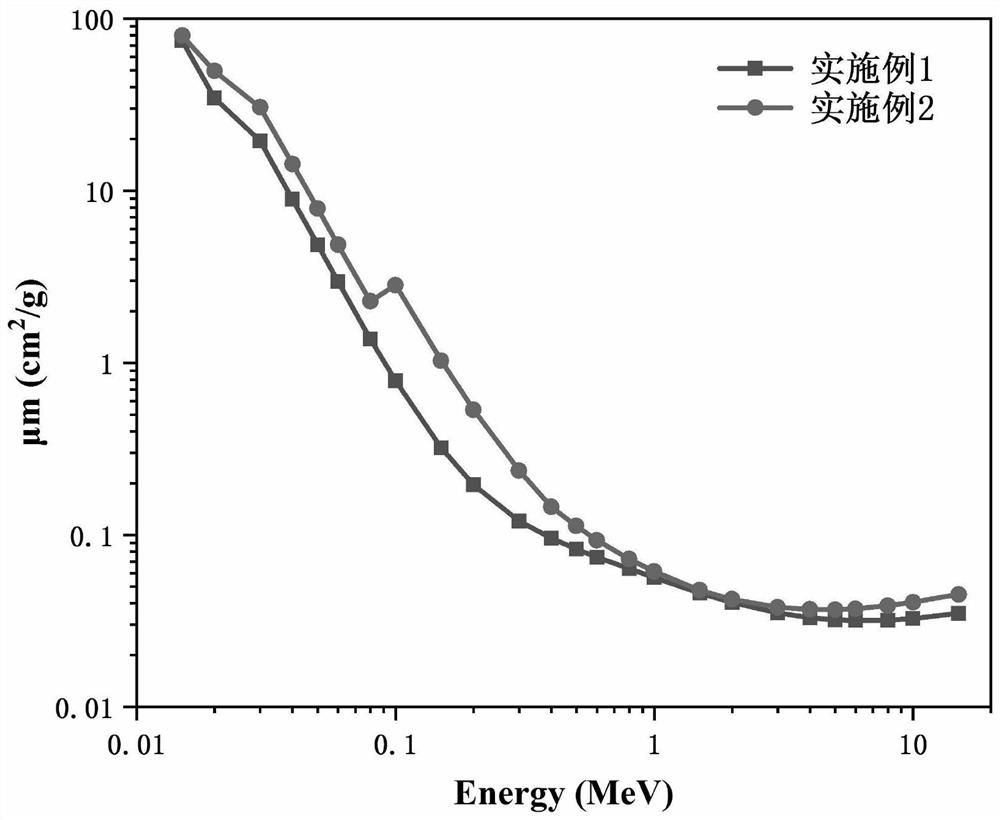
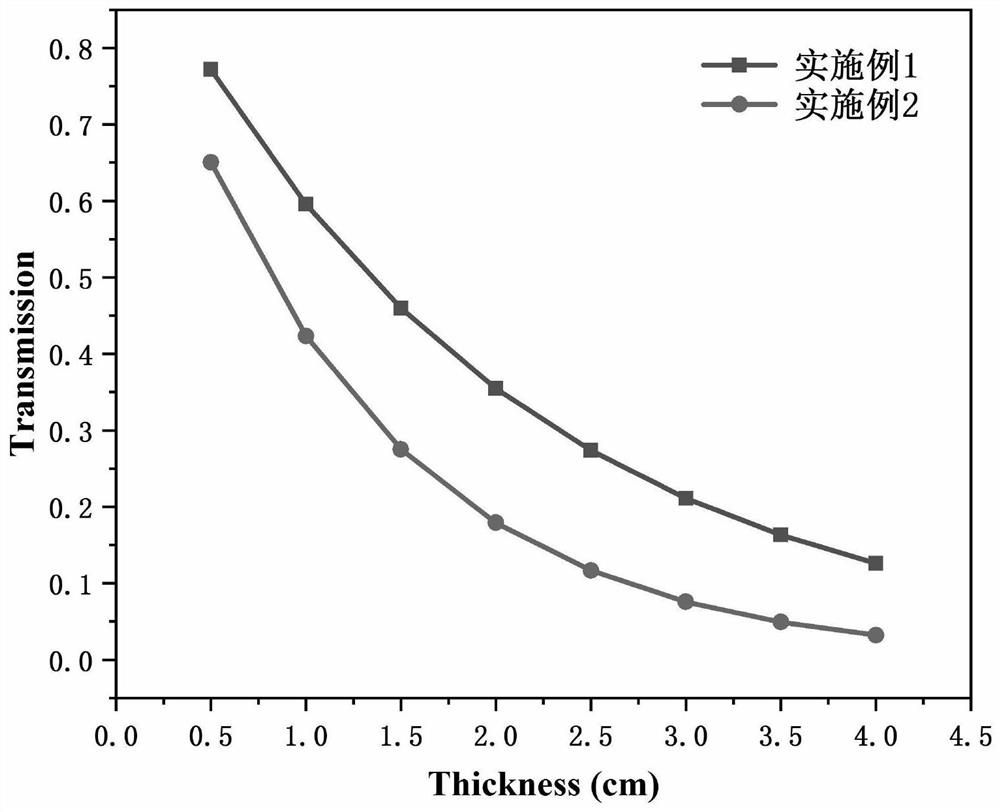
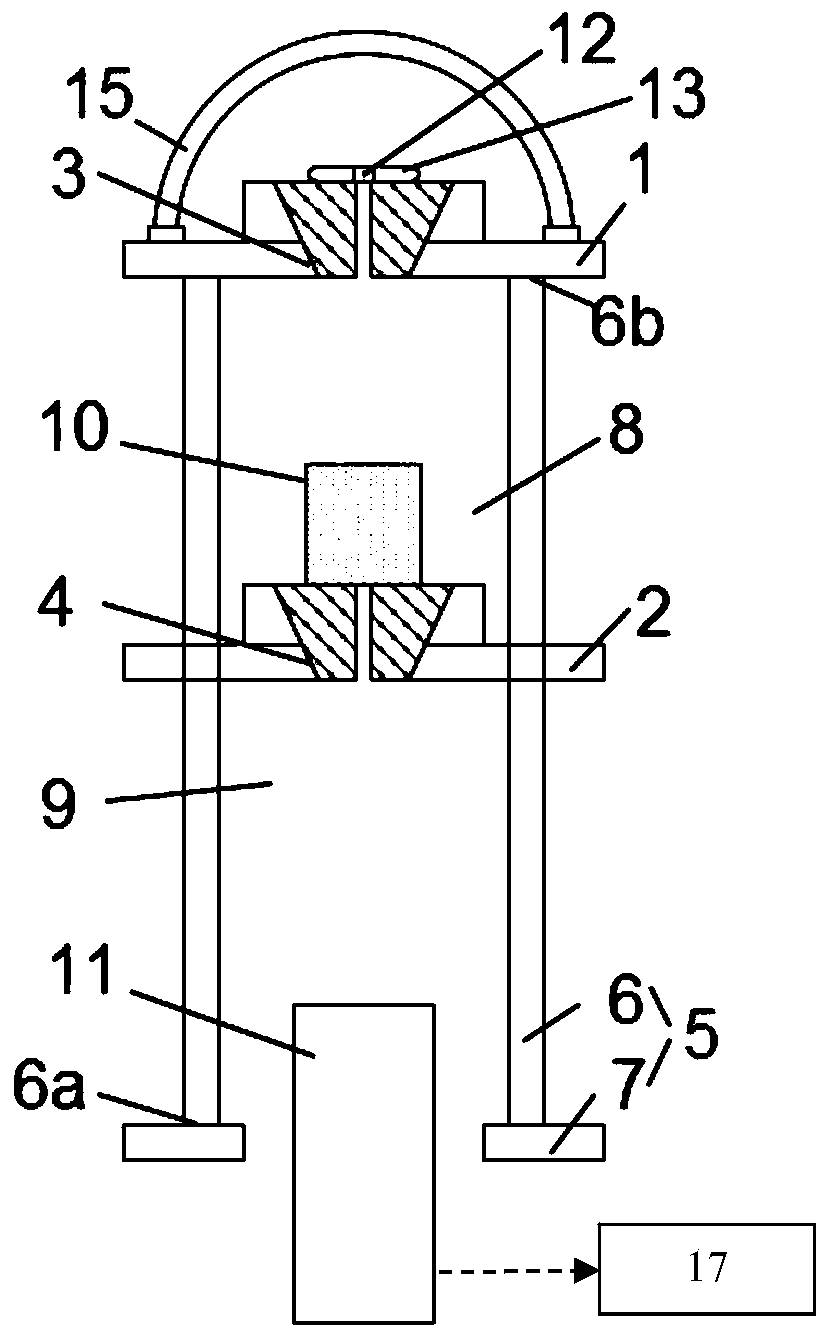
InactiveCN113025088AGood mass attenuation coefficientLight in massCoatingsLiquid metalRadiation shield
The invention relates to a liquid metal radiation shielding coating material and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of materials. In terms of the molar weight of the coating material being 100, the coating material is GaxIn100-x-GayIn80-ySn20, GazIn40-zSn20Bi20 or GavInwSn20Bi20Zn20, x is 20-80, y is 20-50, z is 10-20, v is 15-25, and w is 15-25. The low-melting-point liquid metal radiation shielding coating material has a good mass attenuation coefficient, and the mass of the low-melting-point liquid metal radiation shielding coating material can be reduced by about 13% compared with that of traditional lead under the same mass attenuation coefficient.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Mass attenuation measurement method and device based on gamma-ray full-energy peak
PendingCN111380879ADirect measurement of mass attenuation coefficientVerify reliabilityMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationCounting rateNuclear engineering
The invention relates to a mass attenuation measurement method based on a gamma-ray full-energy peak. The method at least comprises the steps of 1, configuring a radioactive source and a detector, arranging an empty sample box for placing a sample to be detected between the radioactive source and the detector, enabling radioactive rays generated by the radioactive source to enter the detector in atransmission mode in the set direction, promoting the detector to generate first data, arranging a sample to be detected between the radioactive source and the detector, enabling the radioactive raysgenerated by the radioactive source to enter the detector in a mode of penetrating through the sample to be detected when being transmitted along the set direction, and promoting the detector to generate second data; and acquiring a first counting rate n1 (E) based on the first data, acquiring a second counting rate n2 (E) based on the second data, and enabling the mass attenuation coefficient [mu]m (E) of the sample to be detected to the radioactive source to be expressed through a formula shown in the description, wherein h is the thickness of the sample to be detected.
Owner:NAT INST OF METROLOGY CHINA
Radiographic and computed tomography inspection Anti-counterfeit security
A structure for preventing a scan by a beam is provided. The structure includes a primary material forming the structure. The primary material includes a first mass attenuation coefficient enabling the primary material to be penetrated by the beam. The structure also includes a matrix of dense particles within the primary material. The dense particles include secondary materials different than the primary material. The secondary materials comprise a subsequent mass attenuation coefficient that is greater than the first mass attenuation coefficient of the primary material. The subsequent mass attenuation coefficient enables the dense particles to attenuate the beam to distort the scan.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
A method for measuring light absorption attenuation coefficient of water body
InactiveCN105510250BEasy to operateReduce mistakesColor/spectral properties measurementsUltrasound attenuationOptoelectronics
The invention provides a water body light absorption and attenuation coefficients measurement method. The method comprises the following steps: 1) light emitted by same light source is divided into three paths; 2) the following measurement can be carried out simultaneously; a first path of an optical signal is input to an absorption channel, passes through a water body to-be-measured to generate a first feedback light signal, the light signal is received for being as an absorption channel measure result; a second path of the optical signal is input to an attenuation channel, passes through the water body to-be-measured to generate a second feedback light signal, the light signal is received for being as an attenuation channel measure result; a third path of the optical signal is directly output to obtain a third feedback light signal, the light signal is received for being as a reference optical path measure result; and 3) according to the absorption channel measure result, the attenuation channel measure result and the reference optical path measure result, light absorption coefficients and attenuation coefficients of the water body can be obtained. According to the invention, in-situ measurement of an absorption spectrum of the water body can be carried out, operation is simple, error is little, and the method provides a good technical case for accurately measuring the attenuation coefficients and the absorption coefficients of the water body such as seawater.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A Fast Iterative Decomposition Method for Energy Spectral CT Multi-base Materials Based on Equation Orthogonal Correction
ActiveCN111915695BImprove reconstructed image qualityFast convergenceImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionComputational physicsStatistical physics
The invention discloses a fast iterative decomposition method for energy spectrum CT multi-base materials based on equation orthogonalization correction. The method includes: step 1, using different X-ray energy spectra to scan the measured object, and obtain the multi-base material of the measured object. color projection data; step 2, assign initial values to the density images of each base material of the measured object; step 3, perform orthographic projection on the estimated values of the density images of each base material, and use the X-ray energy spectrum information and the mass attenuation coefficient of the substance information, obtain the estimated value of multi-color projection; step 4, calculate the error between the estimated value of multi-color projection and multi-color projection data, and use orthogonal correction to solve the projection residual of each base material; step 5, obtain the image residual of each base material difference, and update the estimated value of each base material density image of the measured object; step 6, repeat steps 3 to 5 until the termination condition is satisfied. The invention can reconstruct a plurality of base material density images of the measured object from the multicolor projection data of the collected energy spectrums.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com