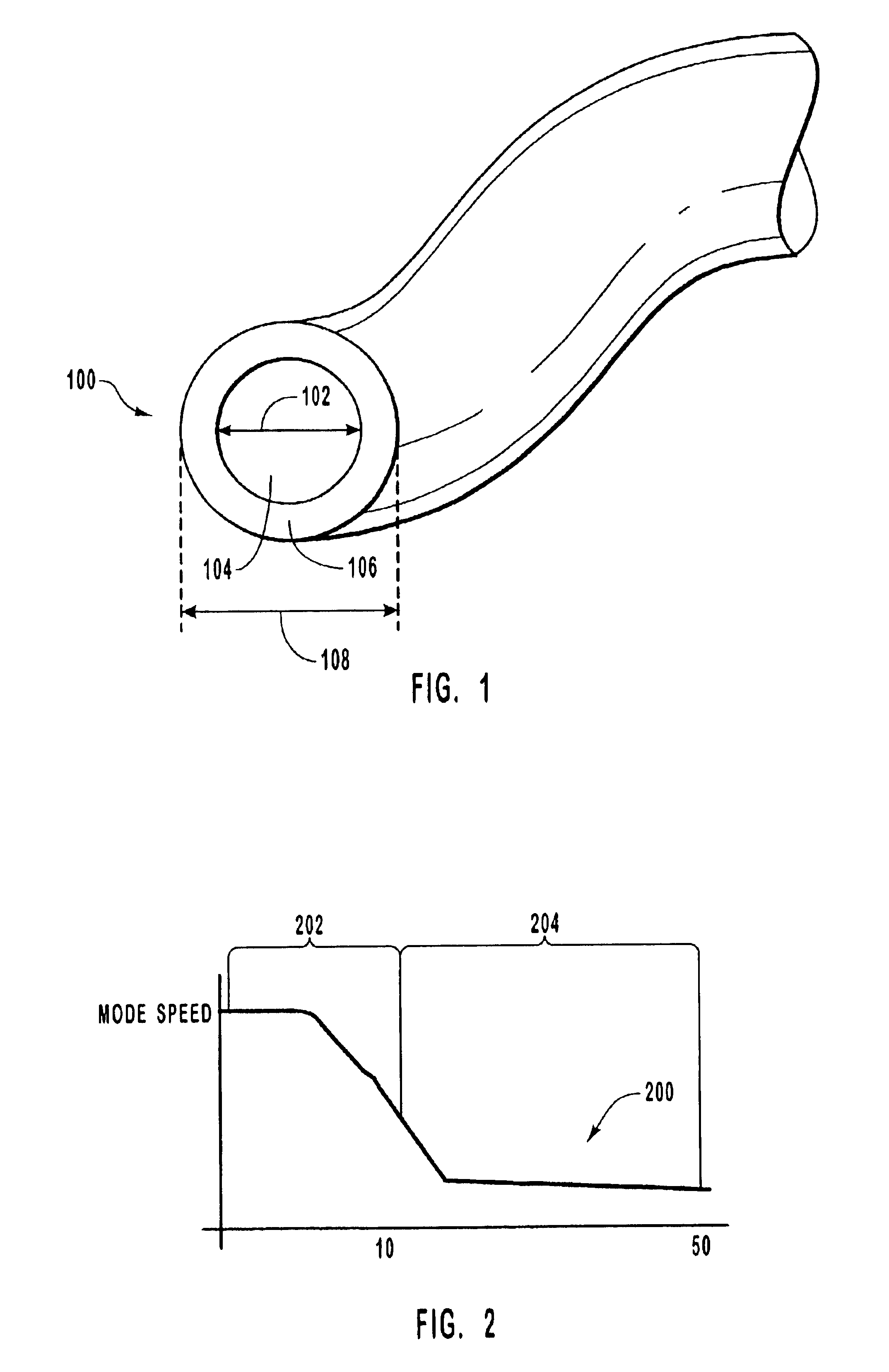
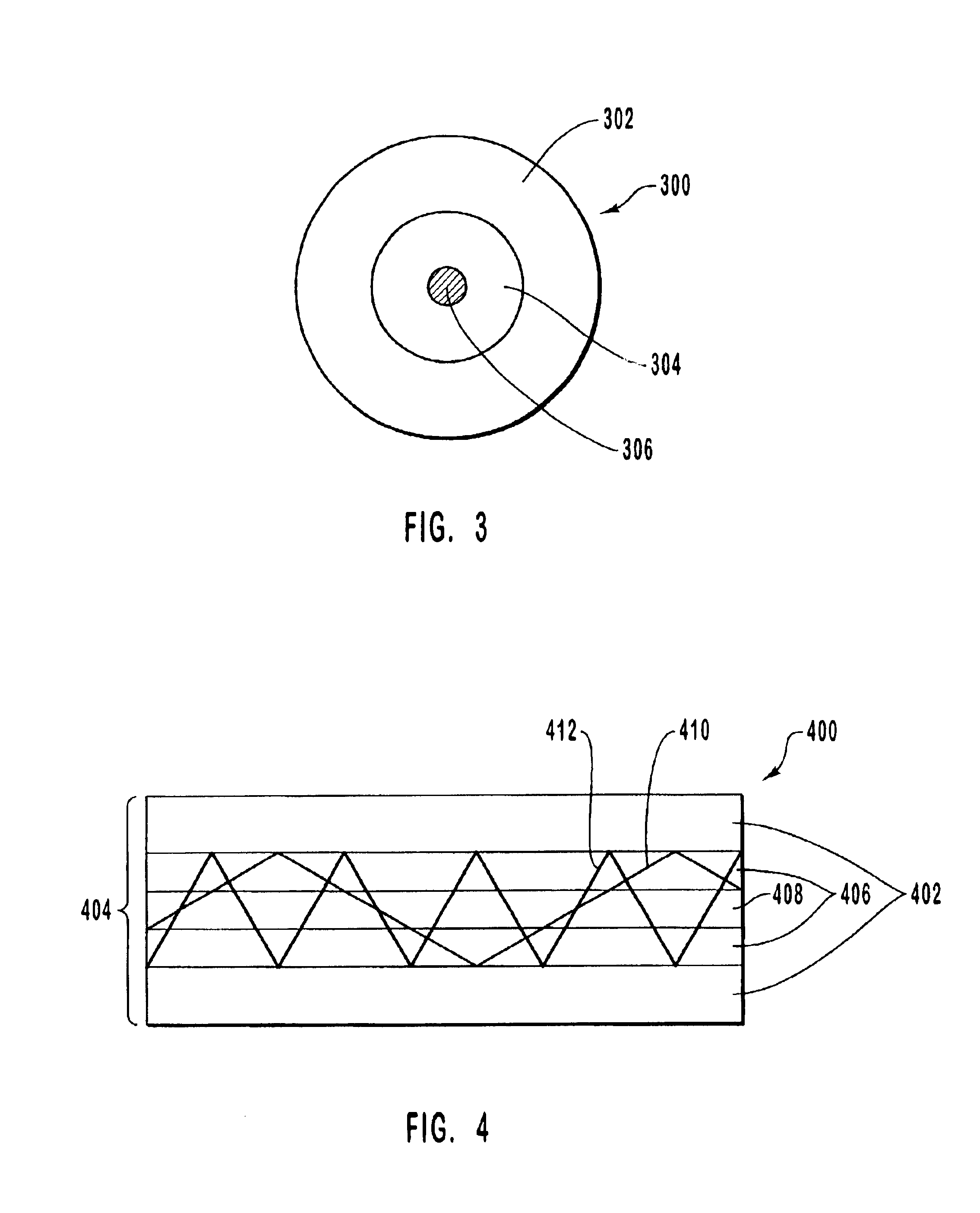
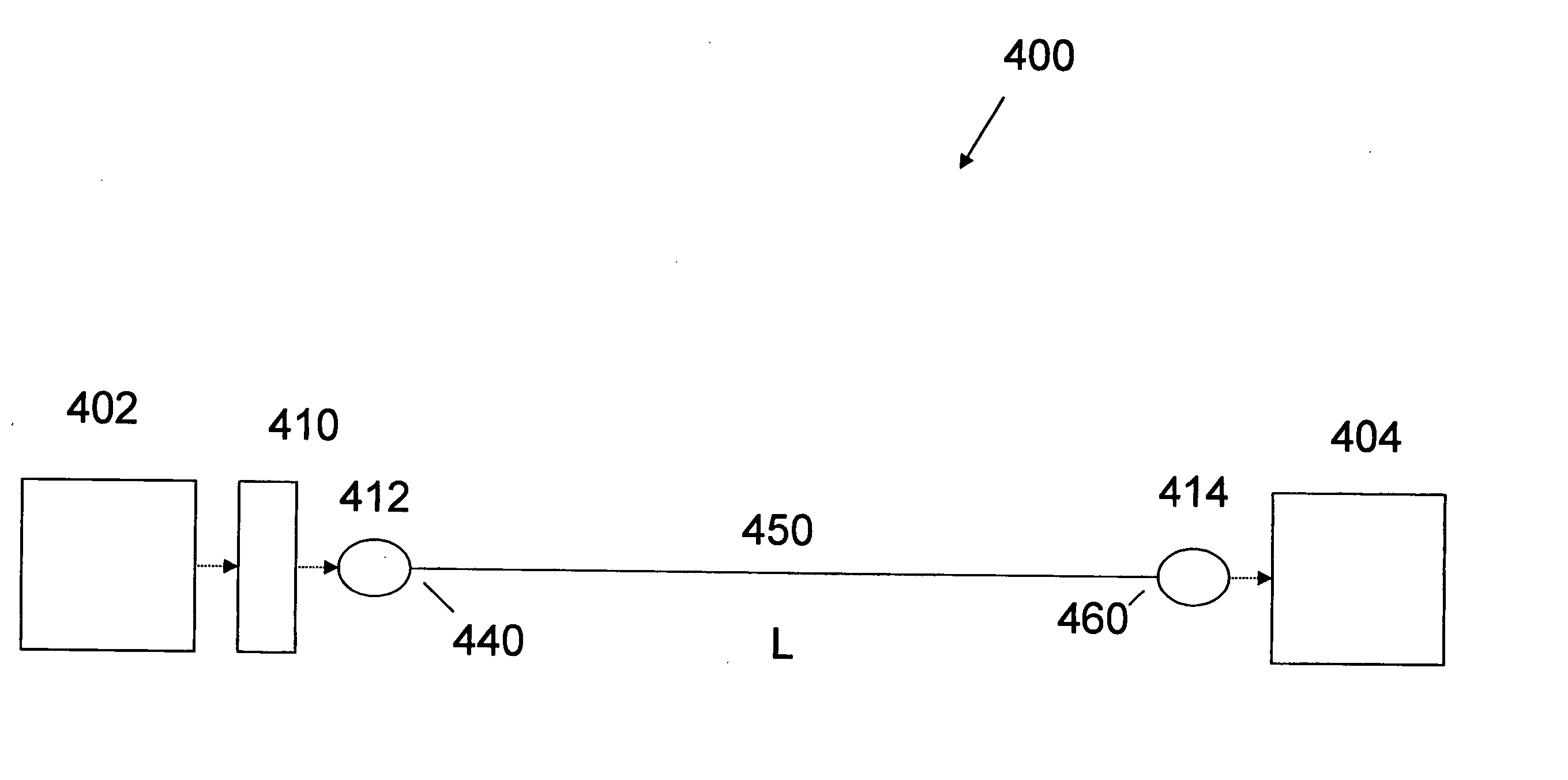
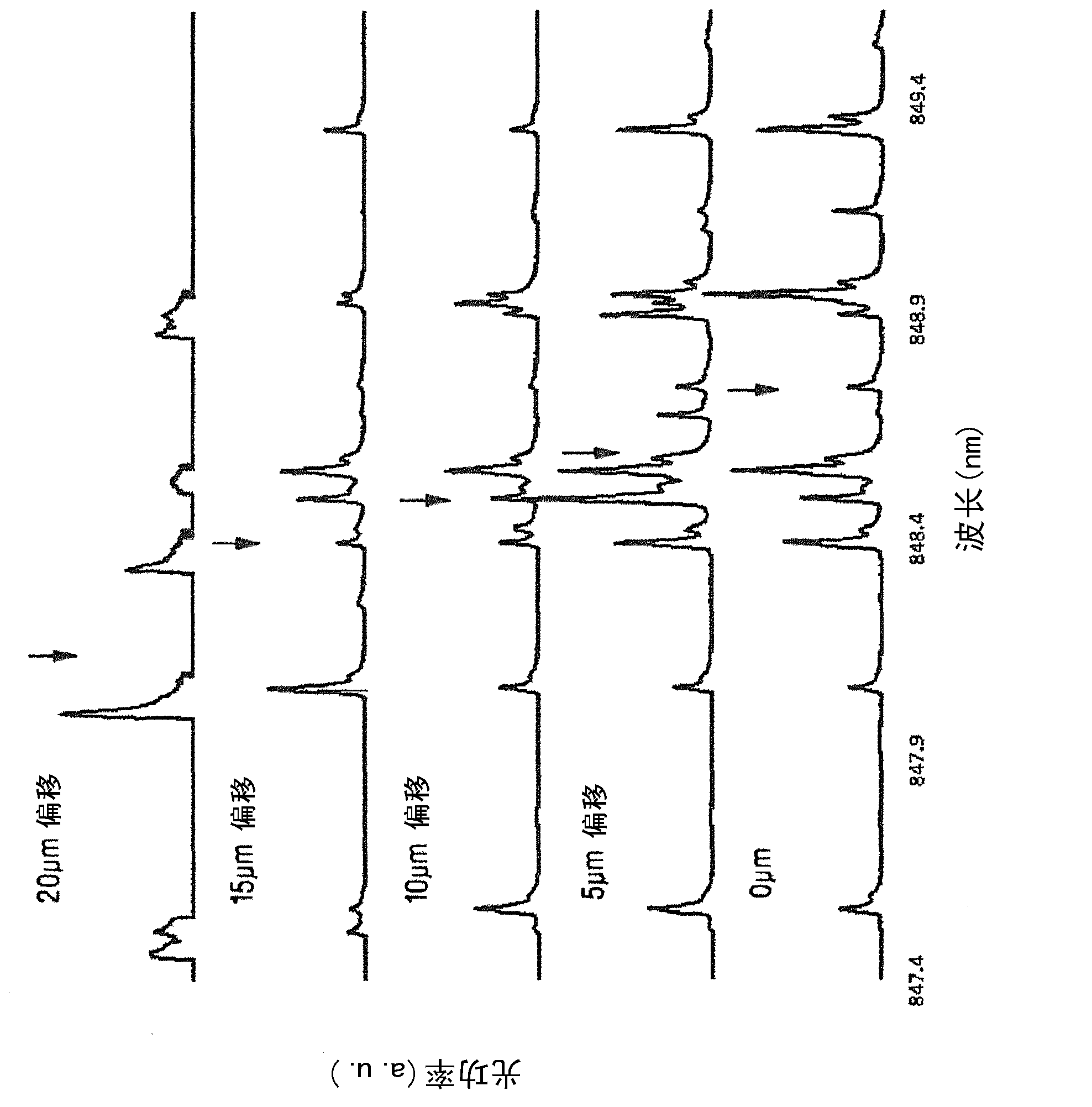
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
52 results about "Modal dispersion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
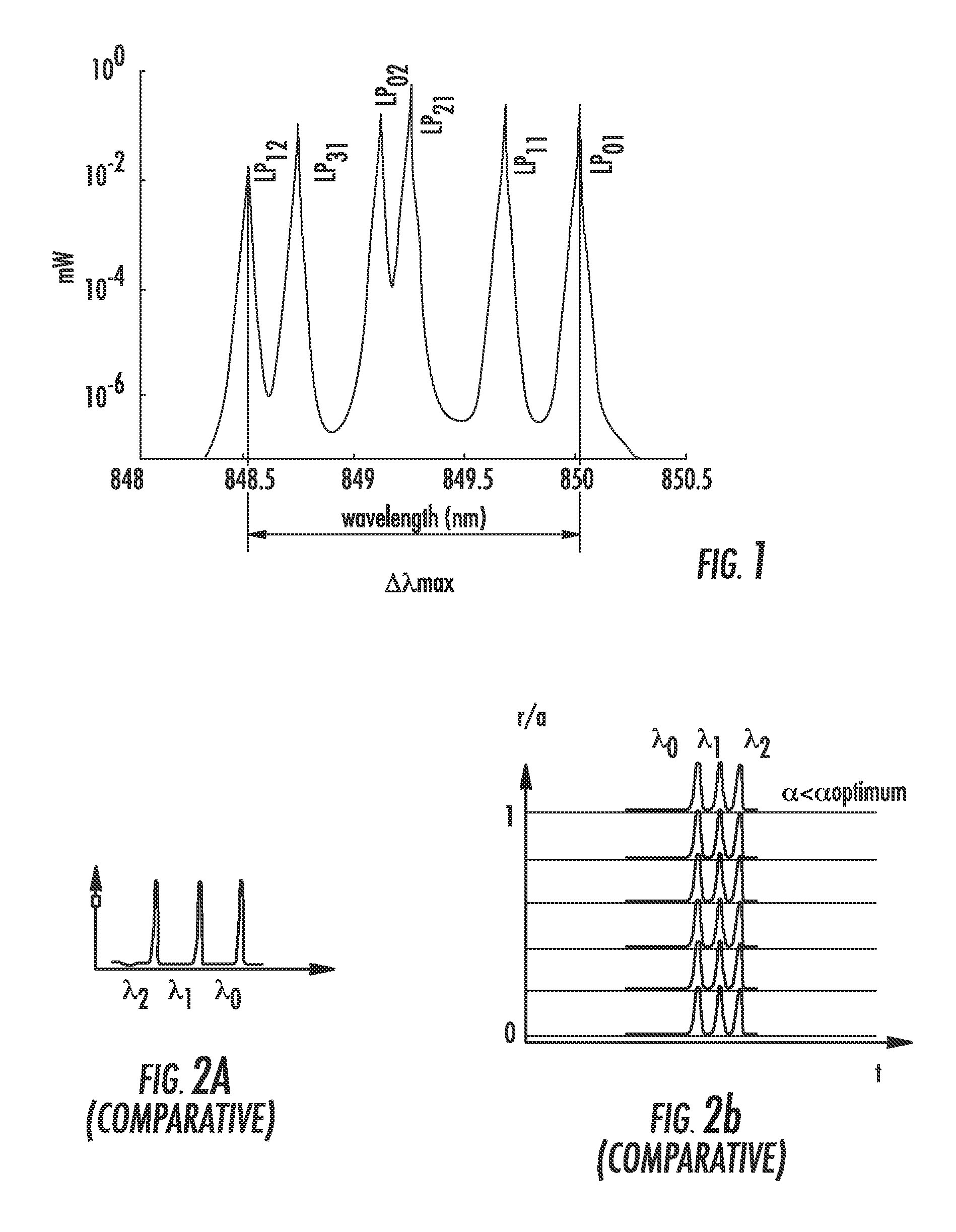
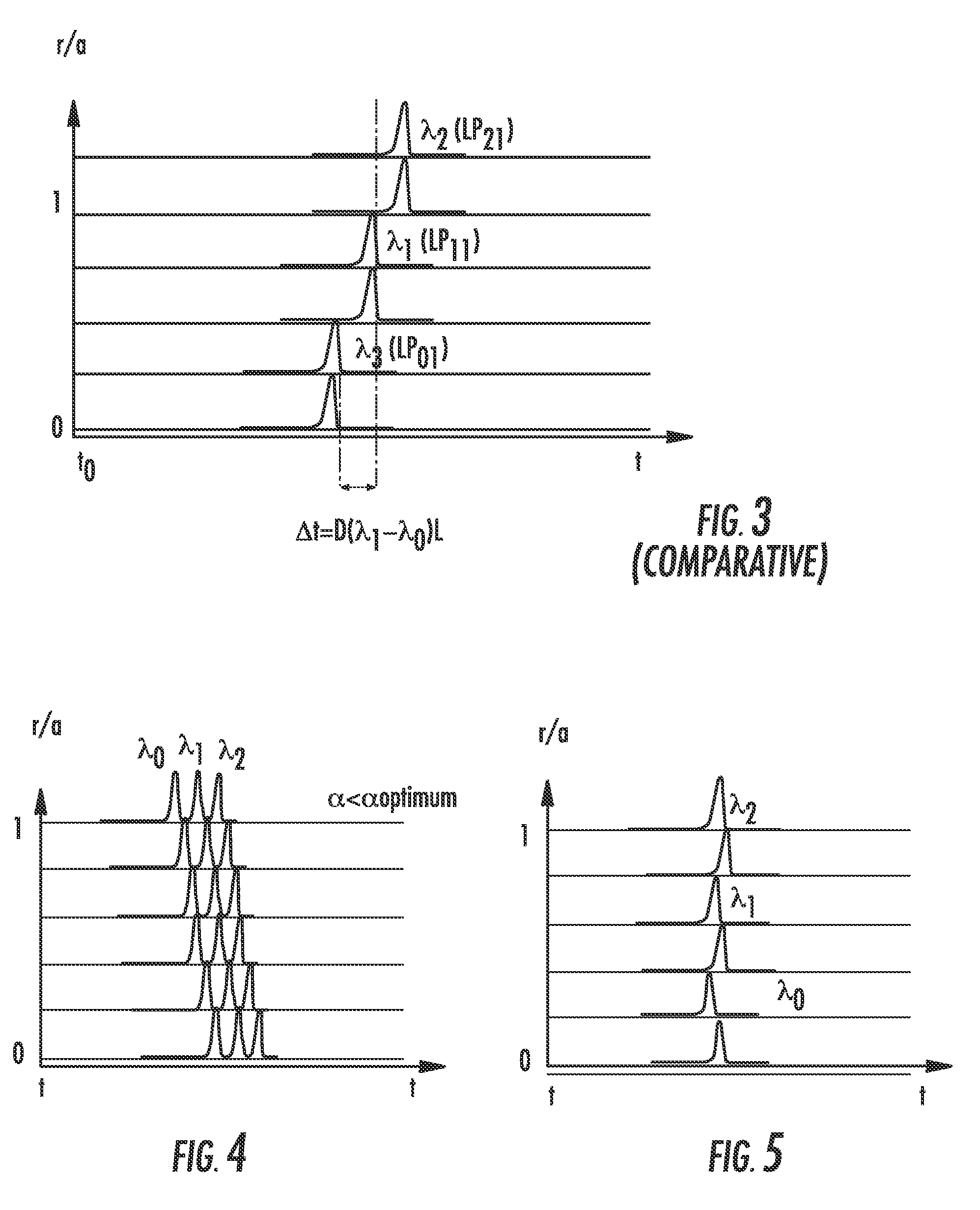
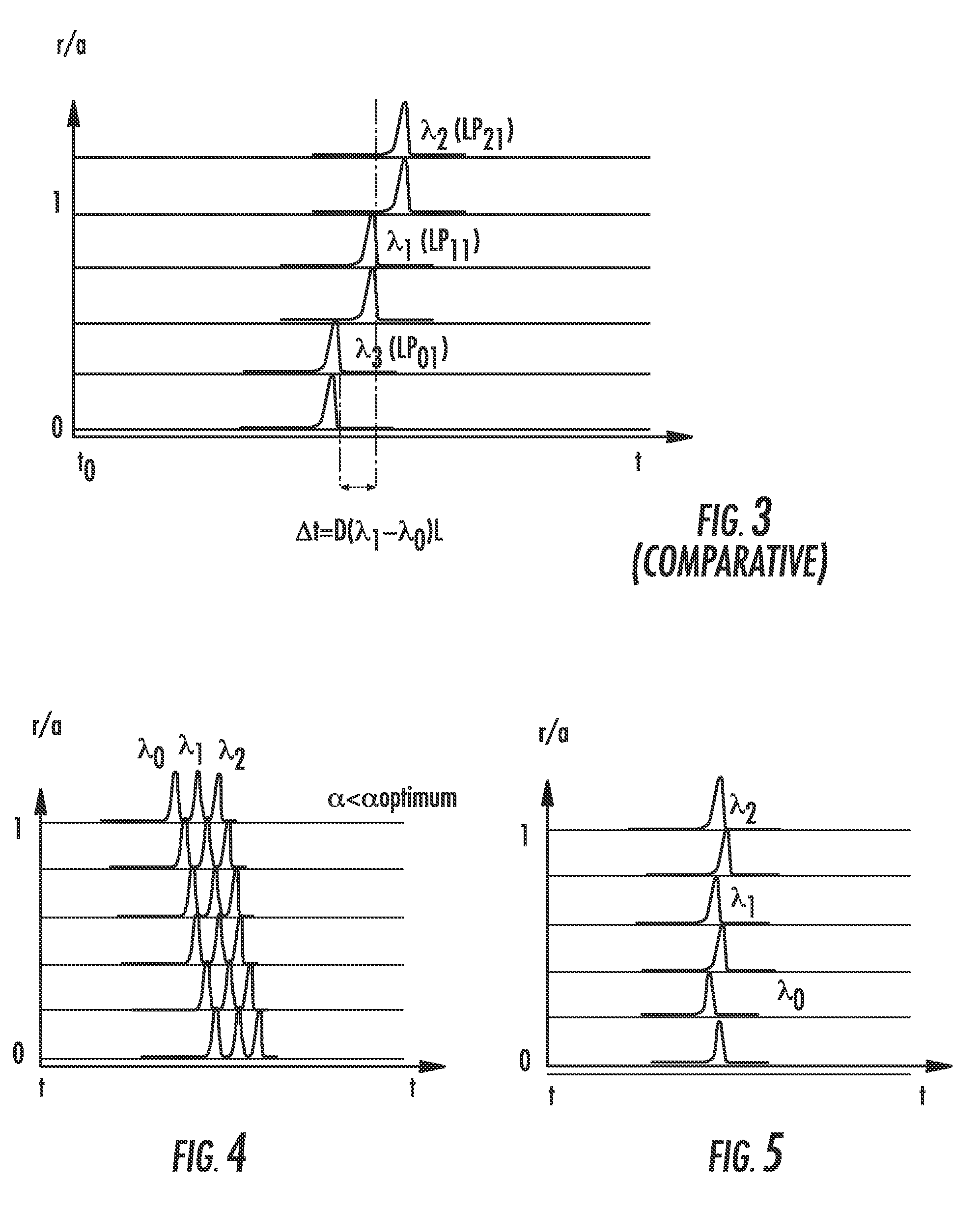
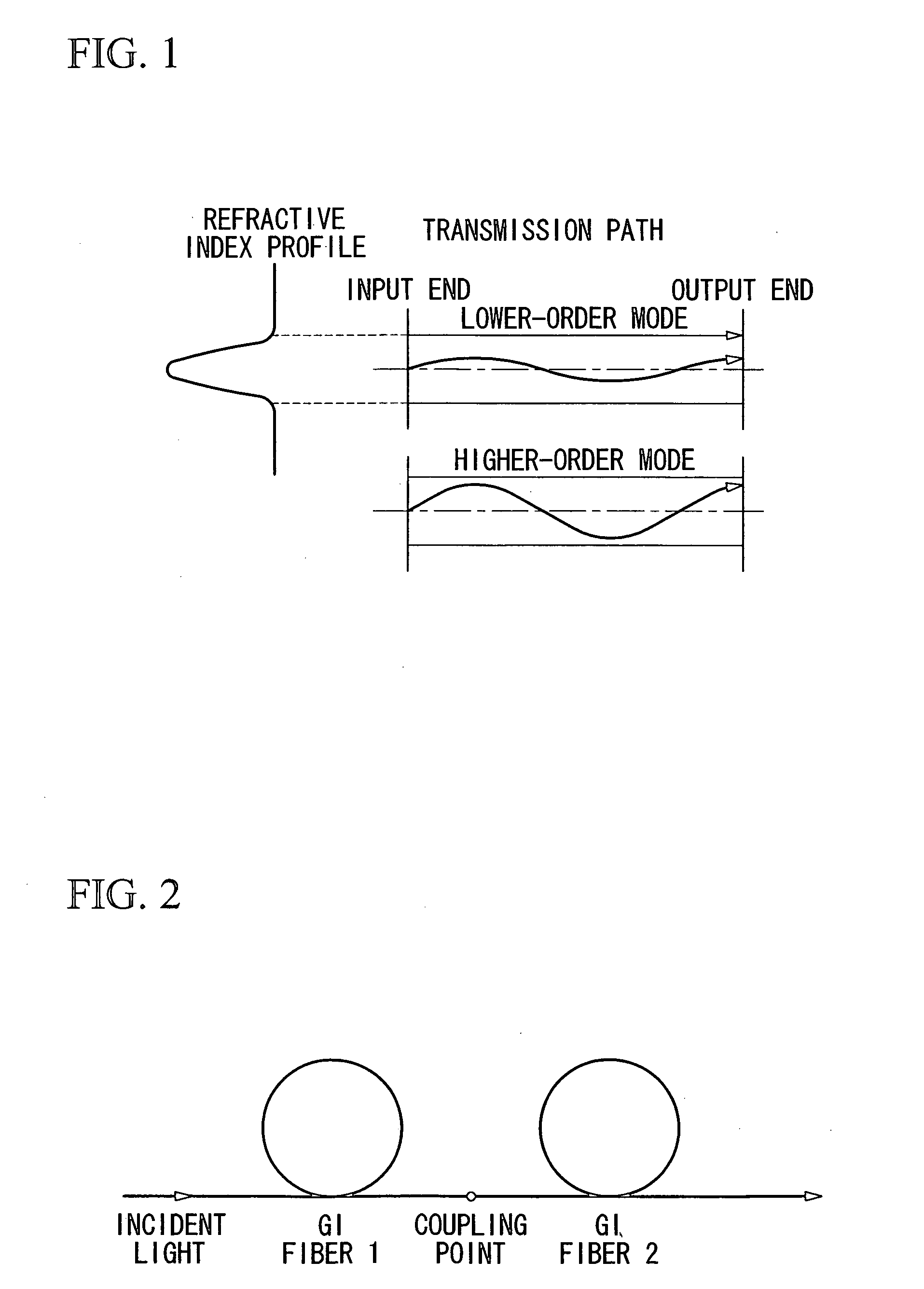
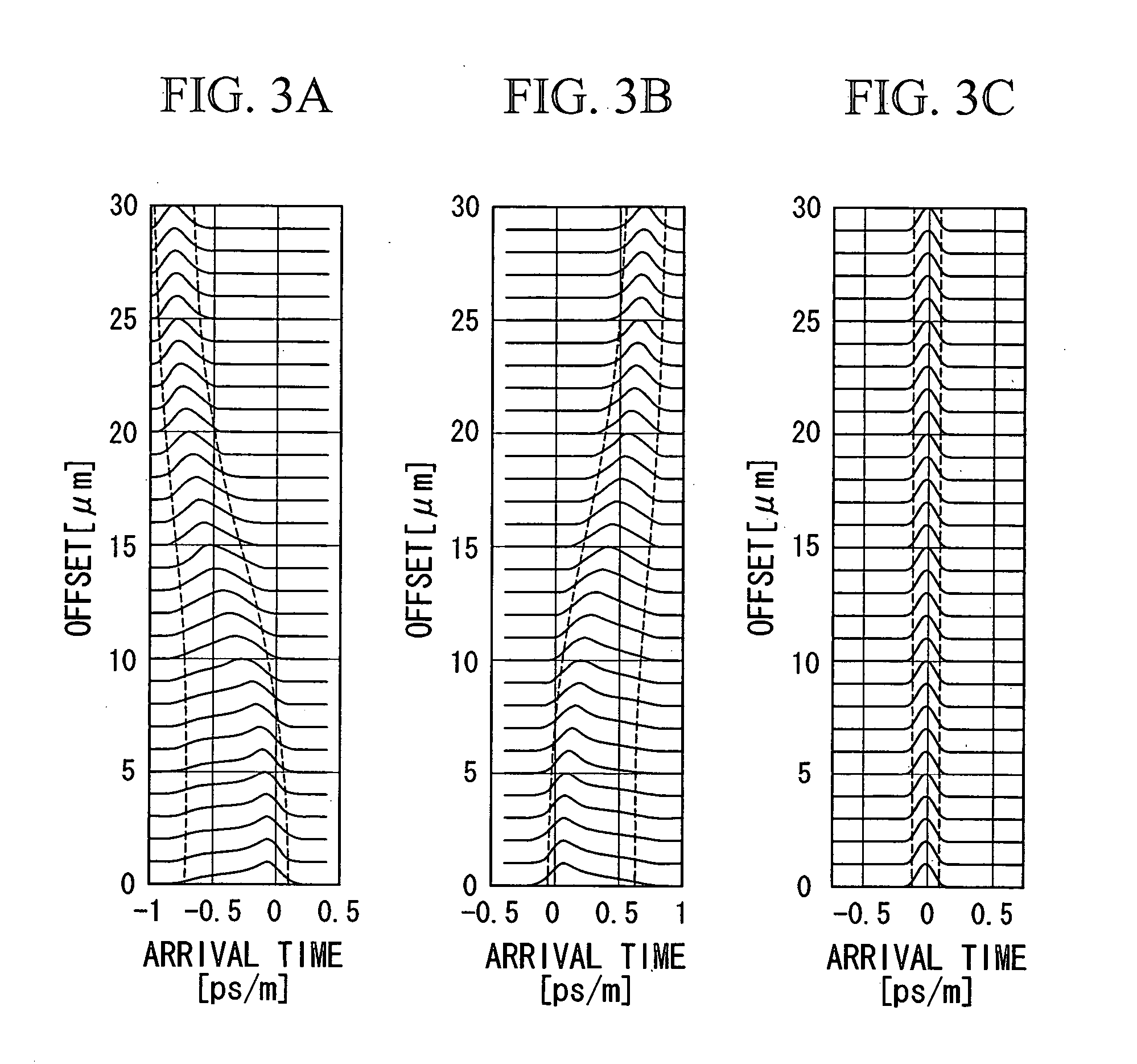
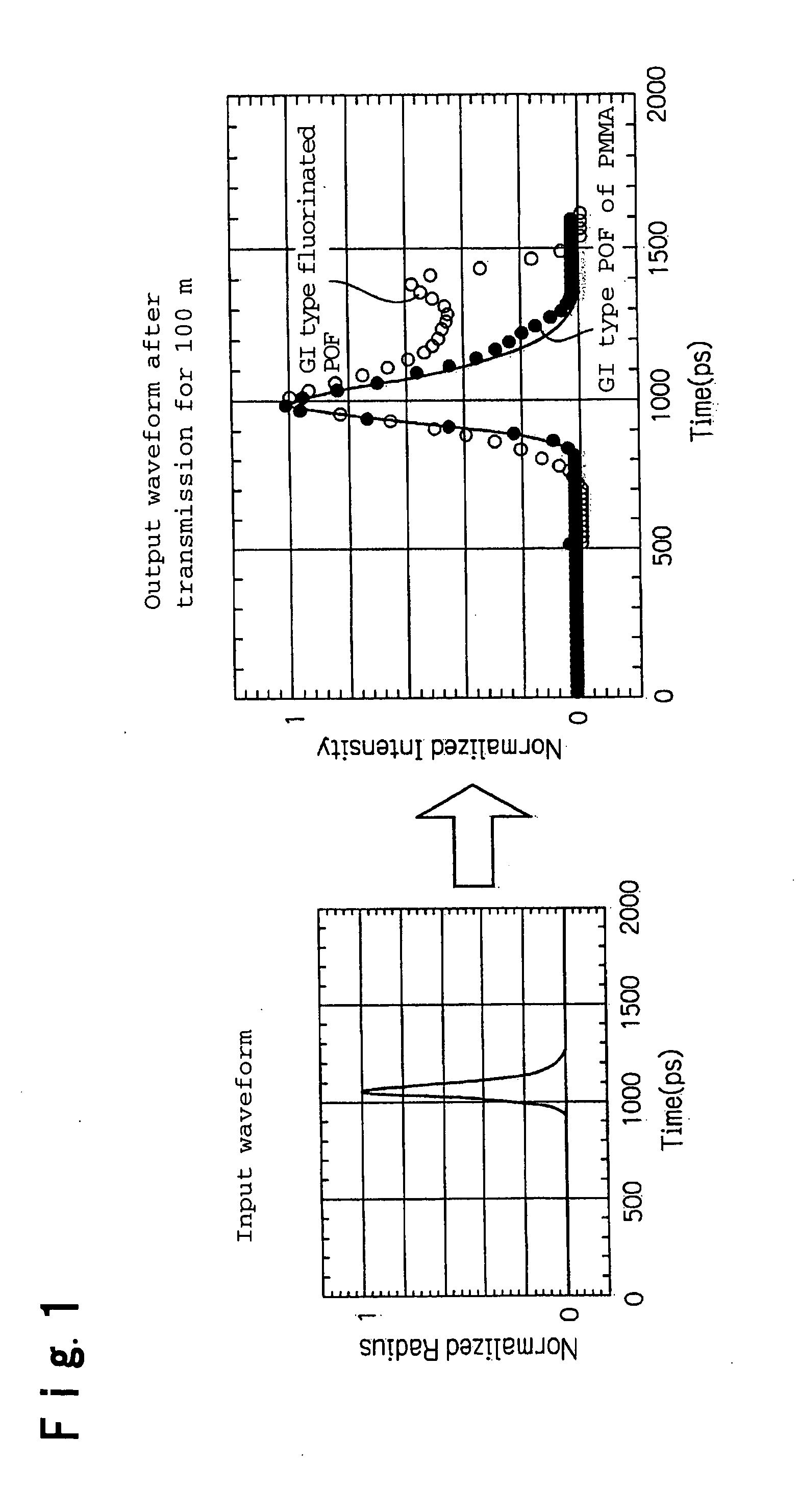
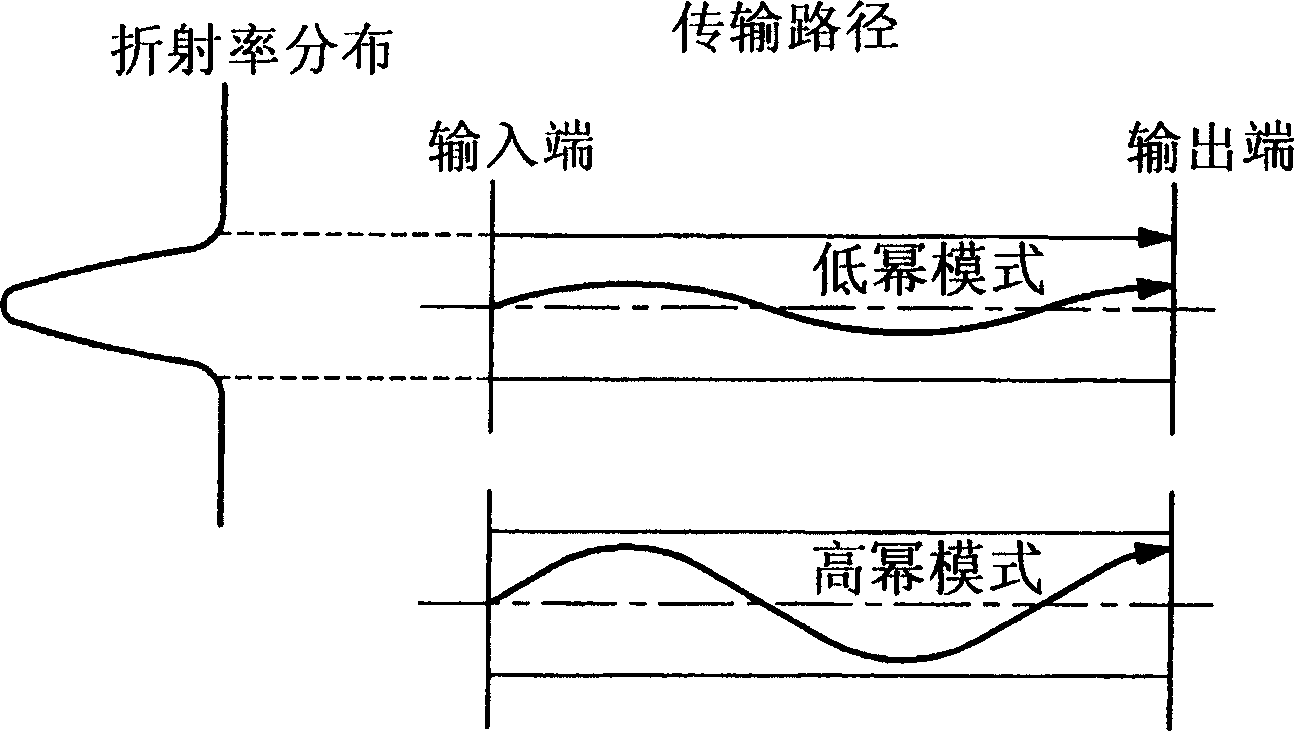
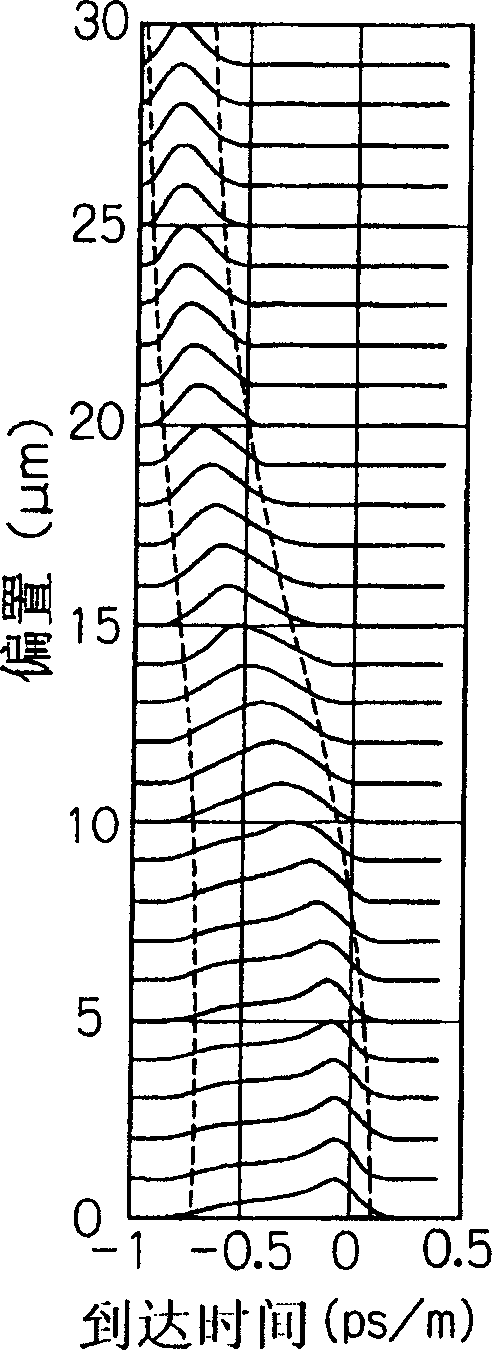
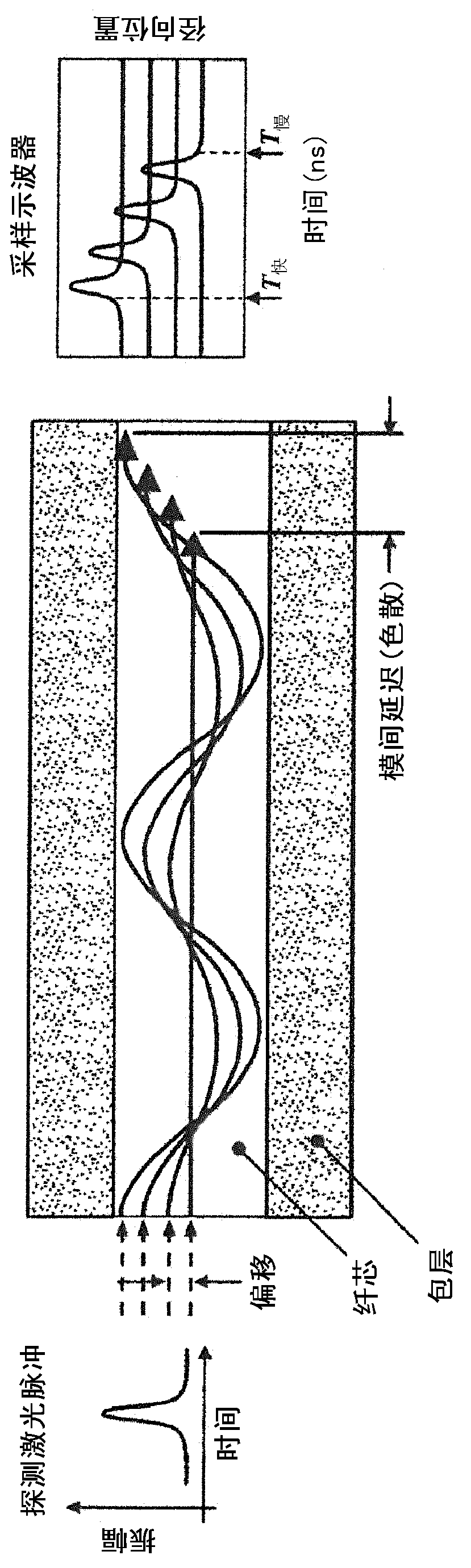
Modal dispersion is a distortion mechanism occurring in multimode fibers and other waveguides, in which the signal is spread in time because the propagation velocity of the optical signal is not the same for all modes. Other names for this phenomenon include multimode distortion, multimode dispersion, modal distortion, intermodal distortion, intermodal dispersion, and intermodal delay distortion.
Multimode Optical Fibers
ActiveUS20100028020A1Cladded optical fibreWavelength-division multiplex systemsModal dispersionPhysics
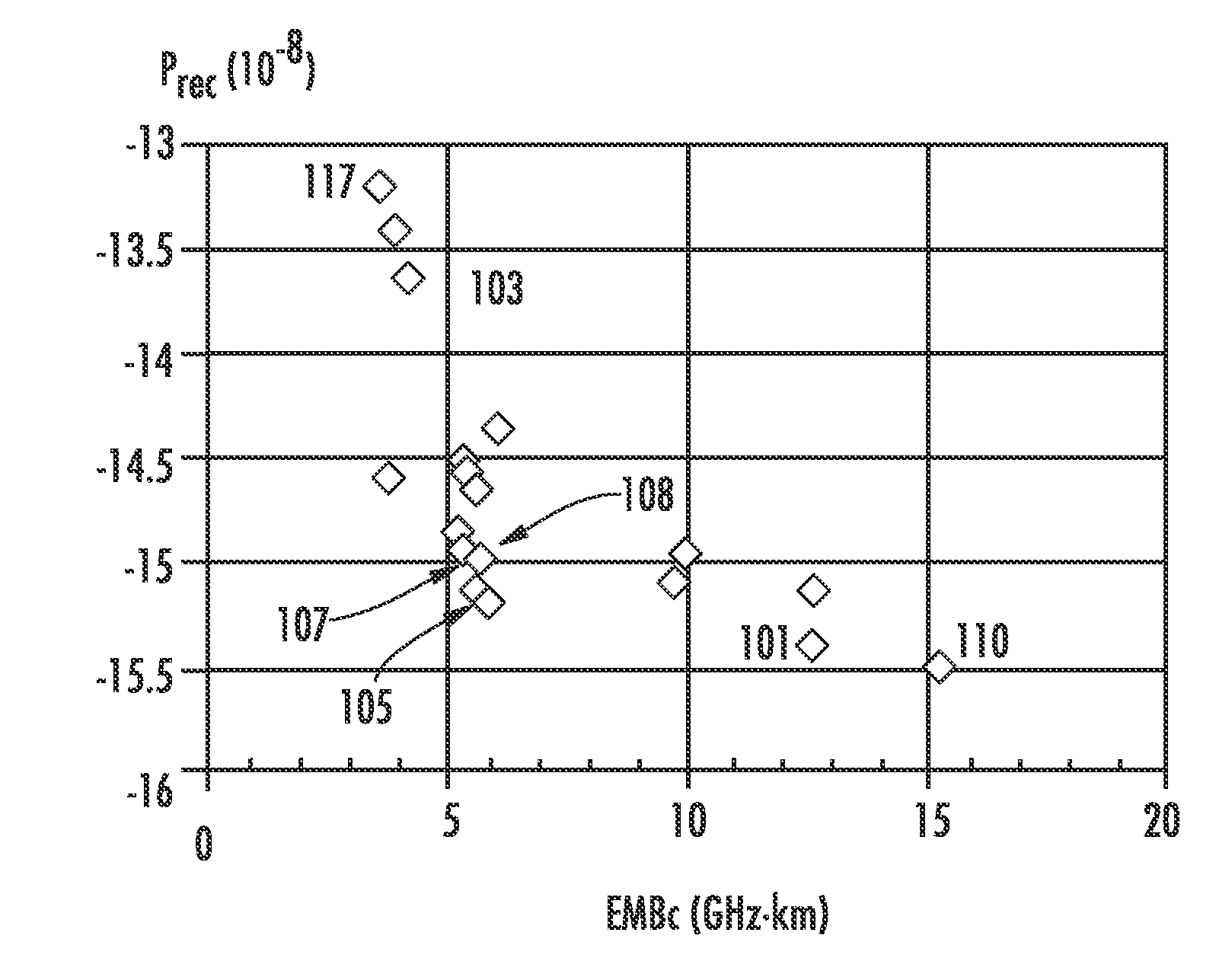
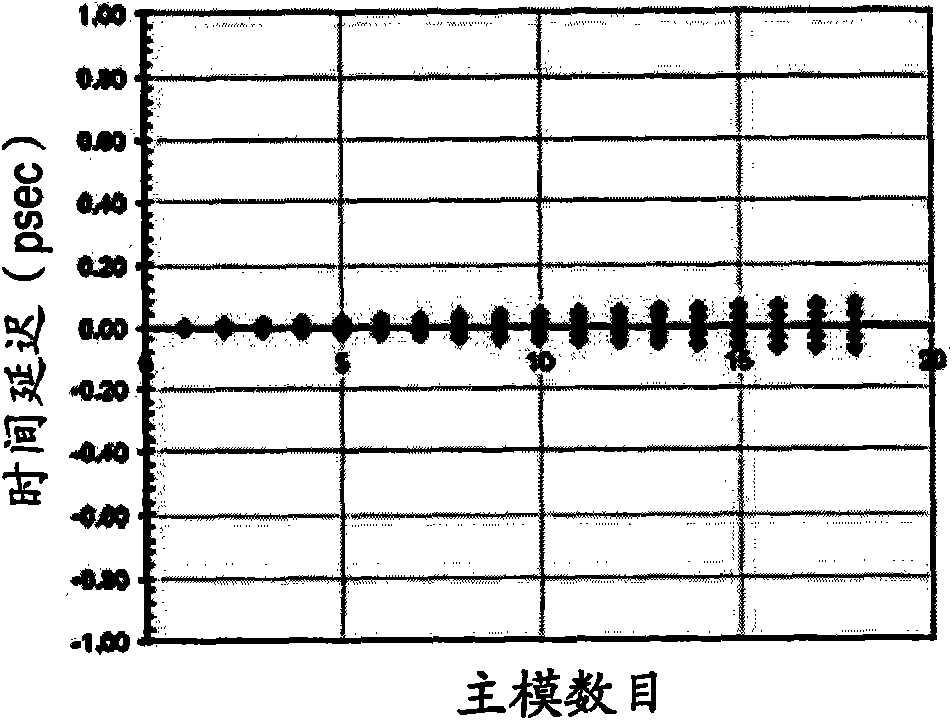
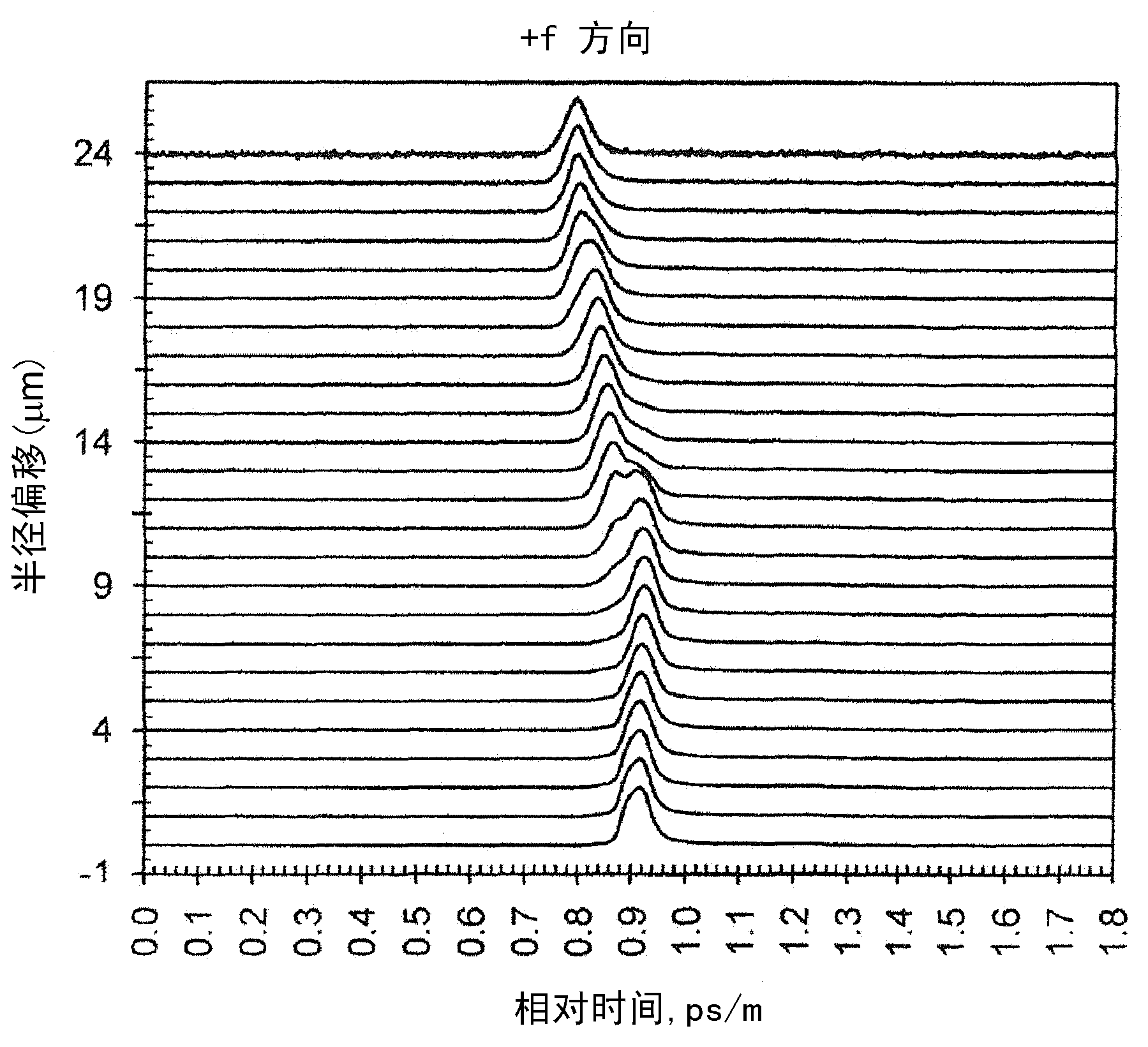
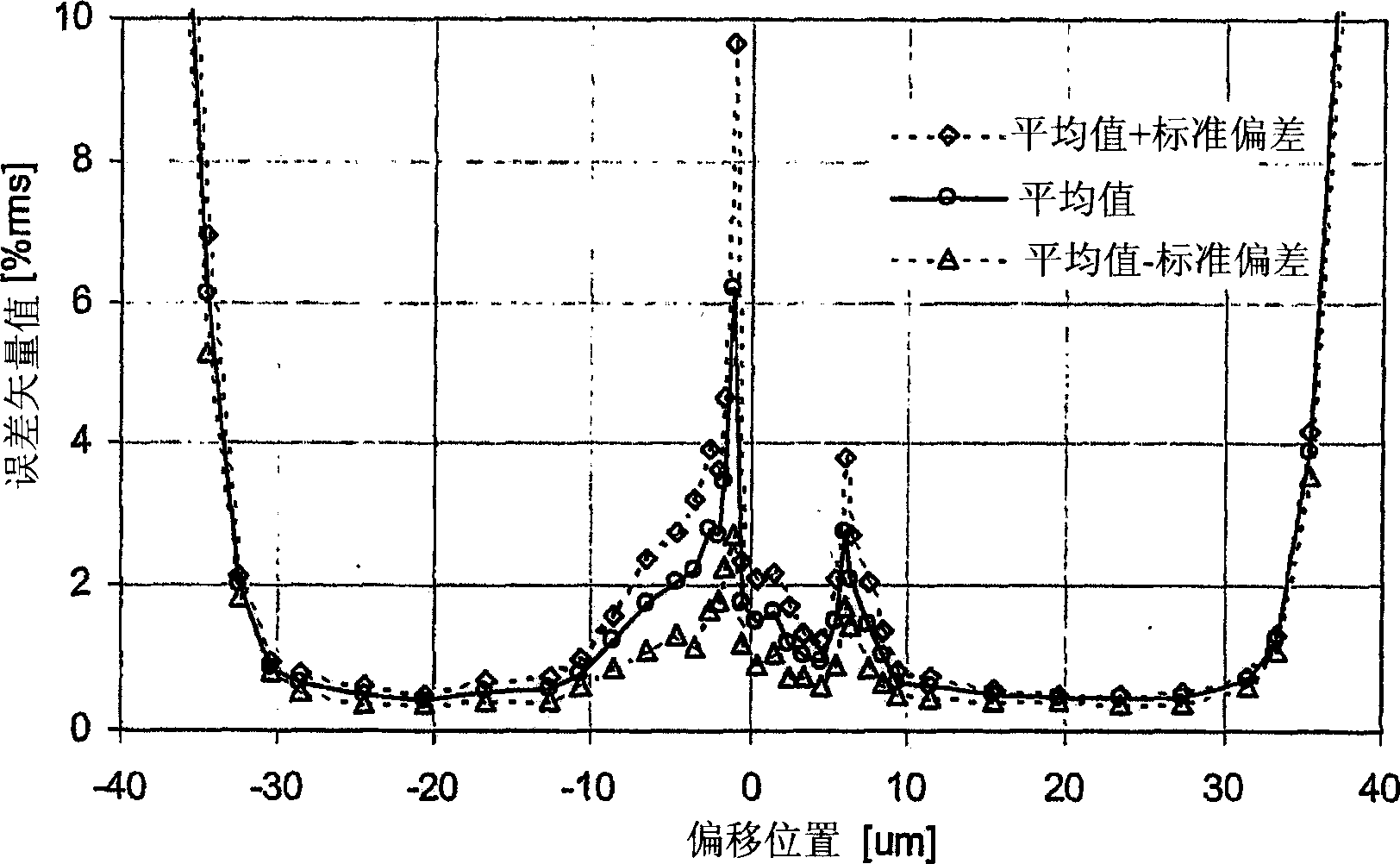
A multimode optical fiber has an equivalent modal dispersion value (DMDinner&outer) of less than 0.11 ps / m for (Δλmax×D)>0.07 ps / m as measured on a modified DMD graph. The modified DMD graph accounts for chromatic dispersion to ensure that the multimode optical fiber has a calculated effective bandwidth EBc greater than 6000 MHz-km when used with multimode transverse sources.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Wavelength Multiplexed Optical System with Multimode Optical Fibers
ActiveUS20100021170A1Minimize modal dispersionReduced Modal DispersionWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultimode transmissionModal dispersionLength wave
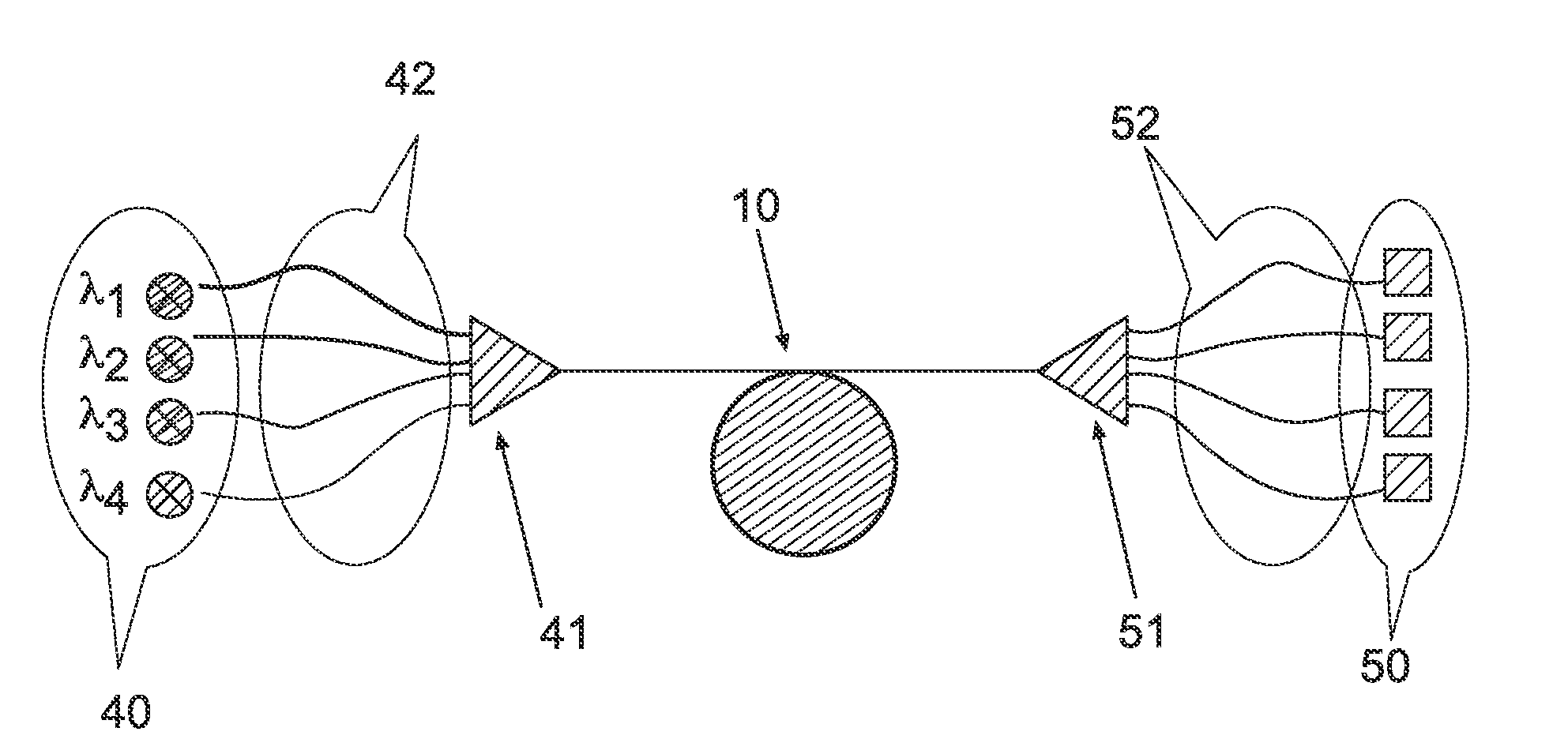
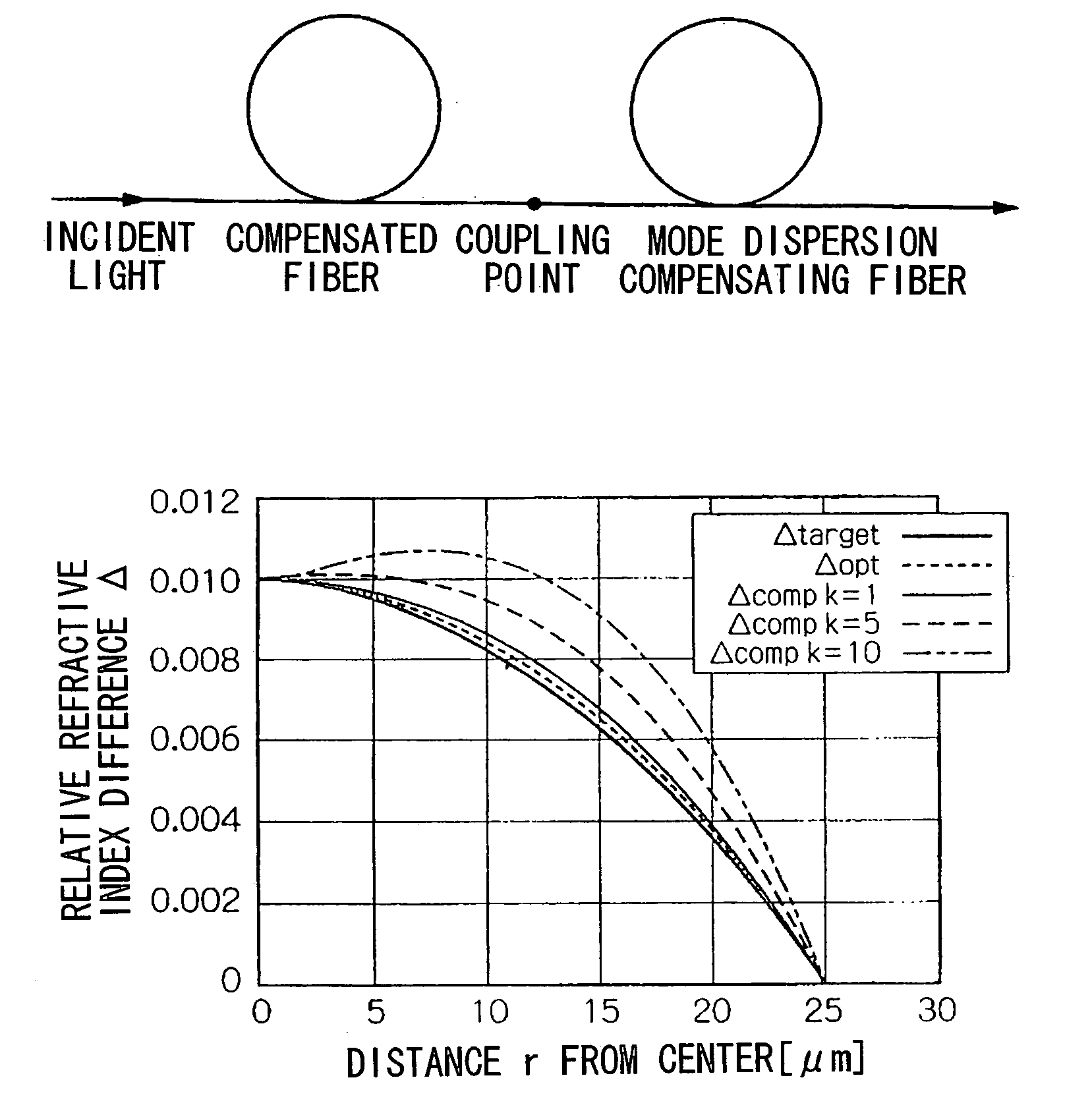
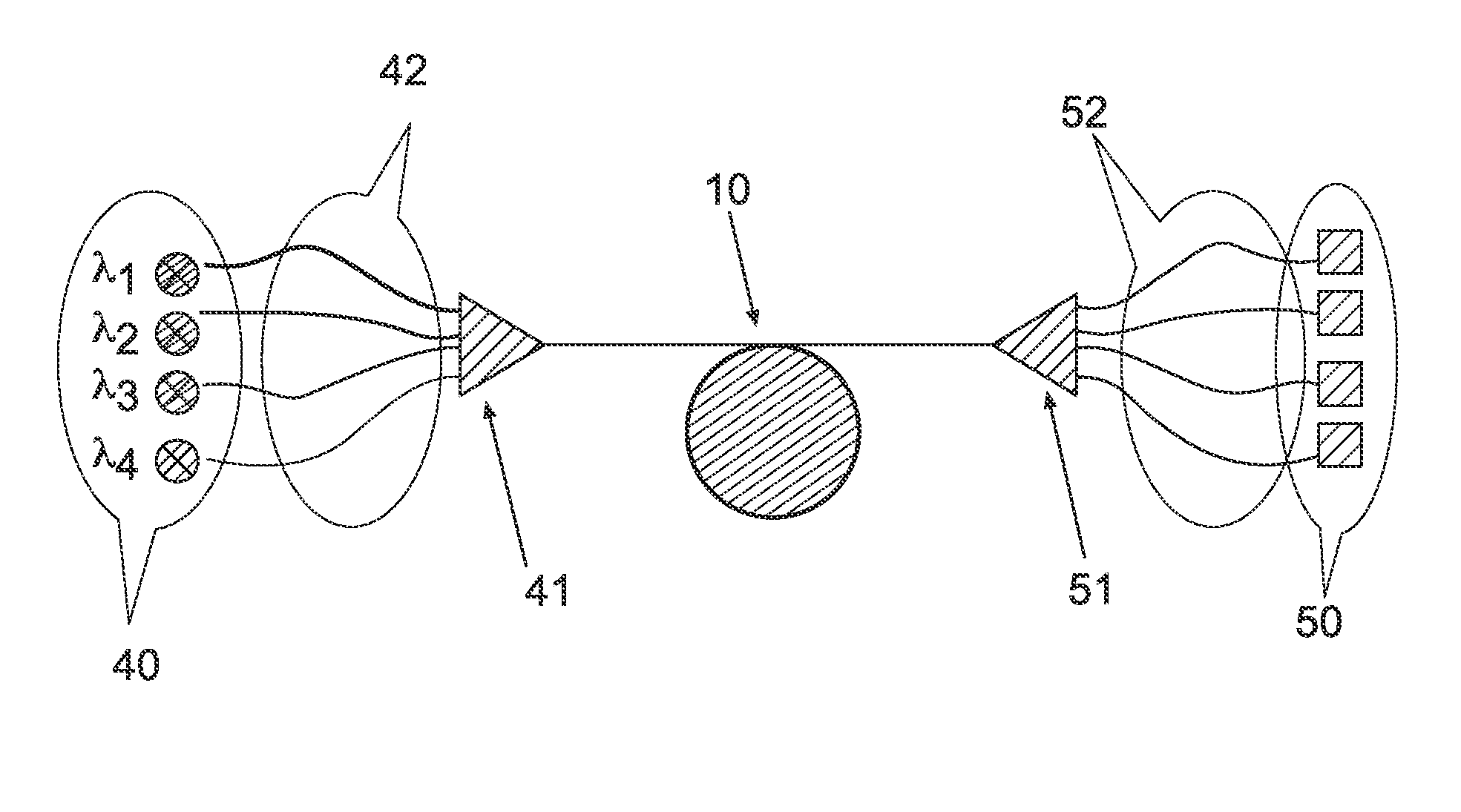
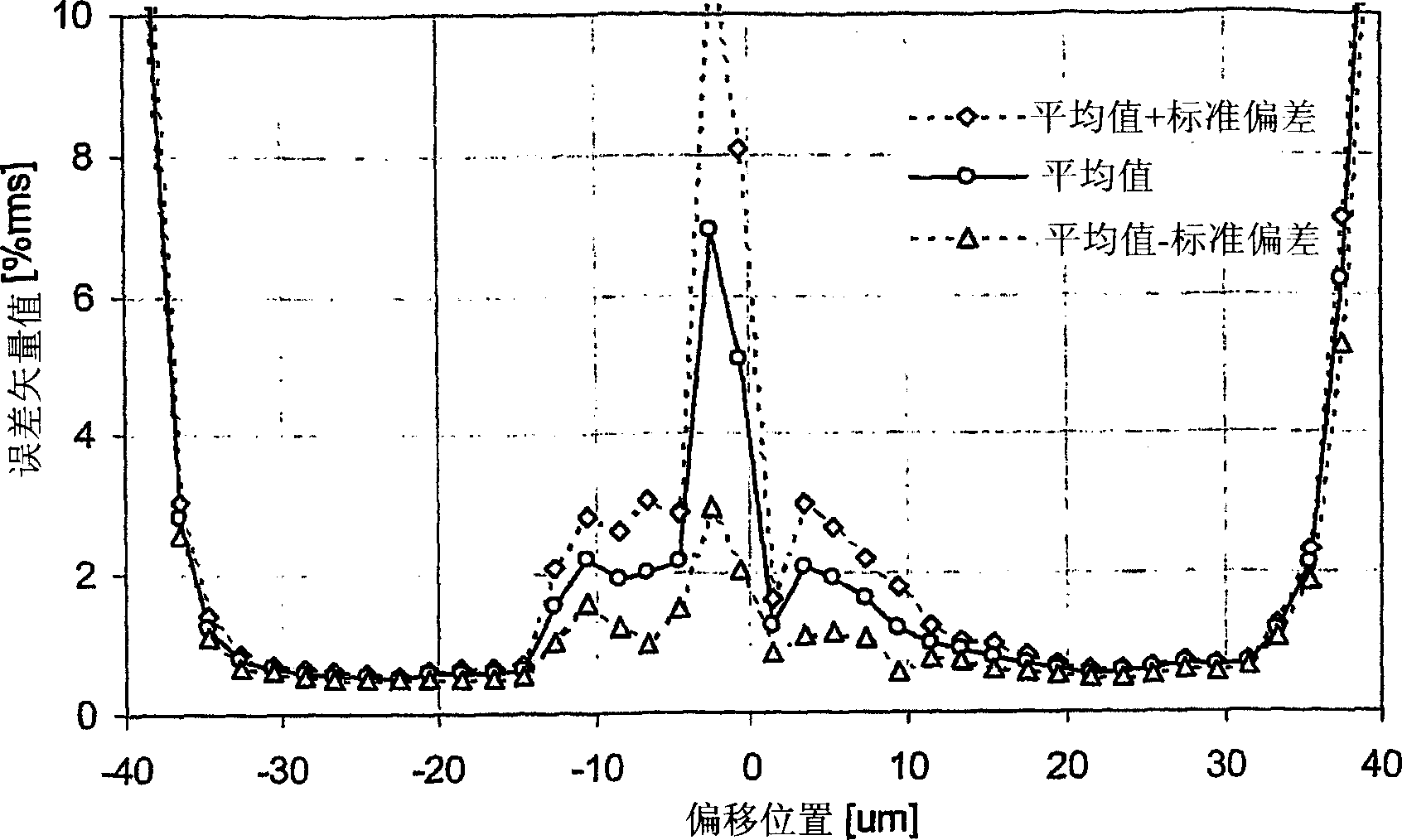
The present wavelength multiplexed optical system includes a multimode optical fiber that transmits wavelength multiplexed optical signals and a plurality of multimode modal dispersion compensation optical fibers. Each modal dispersion compensation optical fiber can transmit one of the multiplex wavelengths, and each modal dispersion compensation optical fiber has an optimized index profile such that the modal dispersion for the transmitted wavelength is approximately inversely equal to the modal dispersion induced in the multimode optical fiber. The wavelength multiplexed optical system facilitates an increased bitrate without reducing bandwidth.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Multimode optical fibers
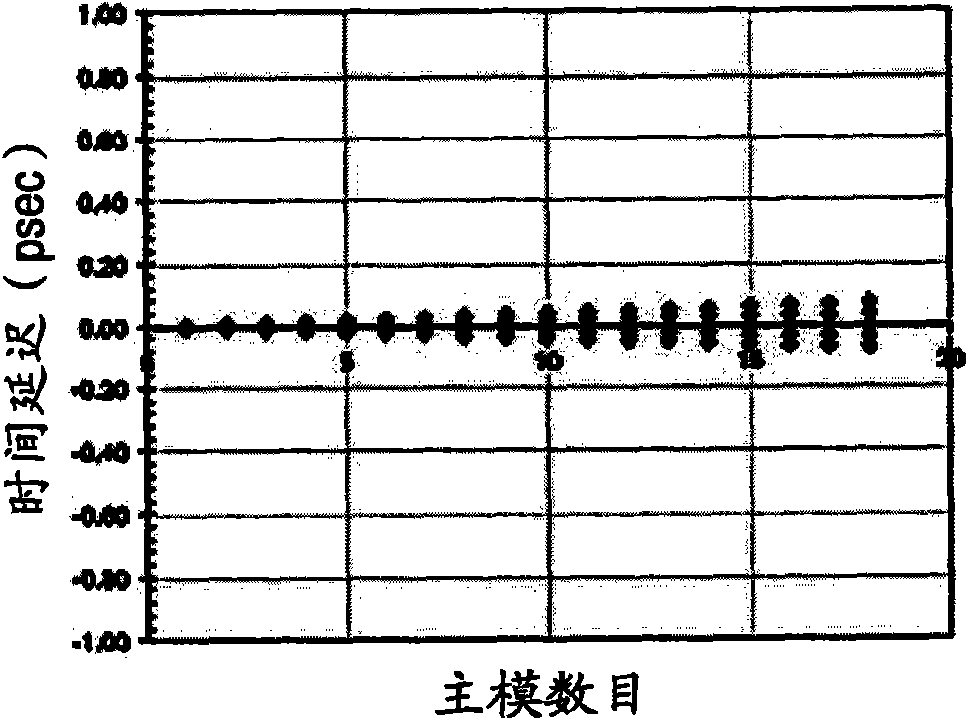
A multimode optical fiber has an equivalent modal dispersion value (DMDinner&outer) of less than 0.11 ps / m for (Δλmax×D)>0.07 ps / m as measured on a modified DMD graph. The modified DMD graph accounts for chromatic dispersion to ensure that the multimode optical fiber has a calculated effective bandwidth EBc greater than 6000 MHz-km when used with multimode transverse sources.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
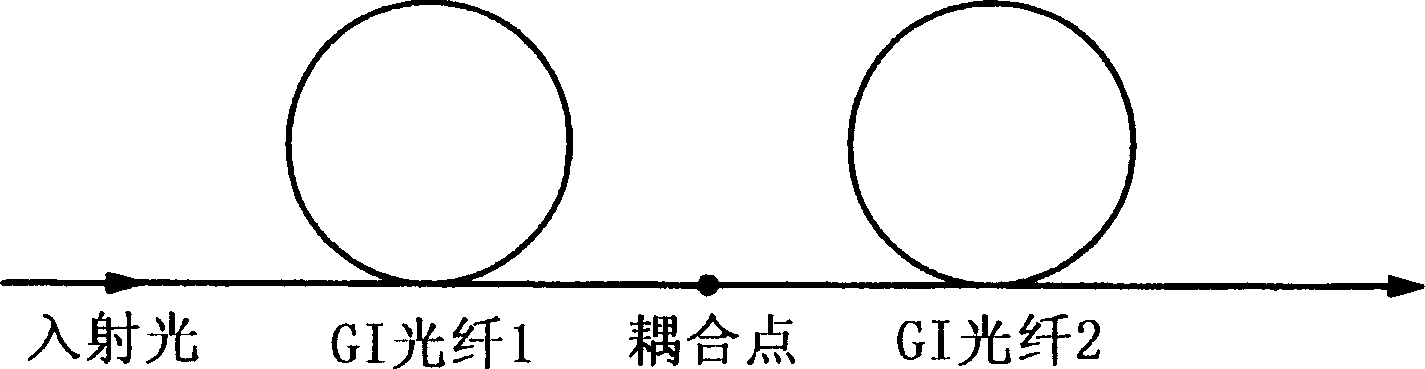
Method for compensating modal dispersion in multimode optical fiber transmission path
ActiveUS20060034573A1Well formedFormed over a long distance easily and at low-costCladded optical fibreCoupling light guidesModal dispersionEngineering
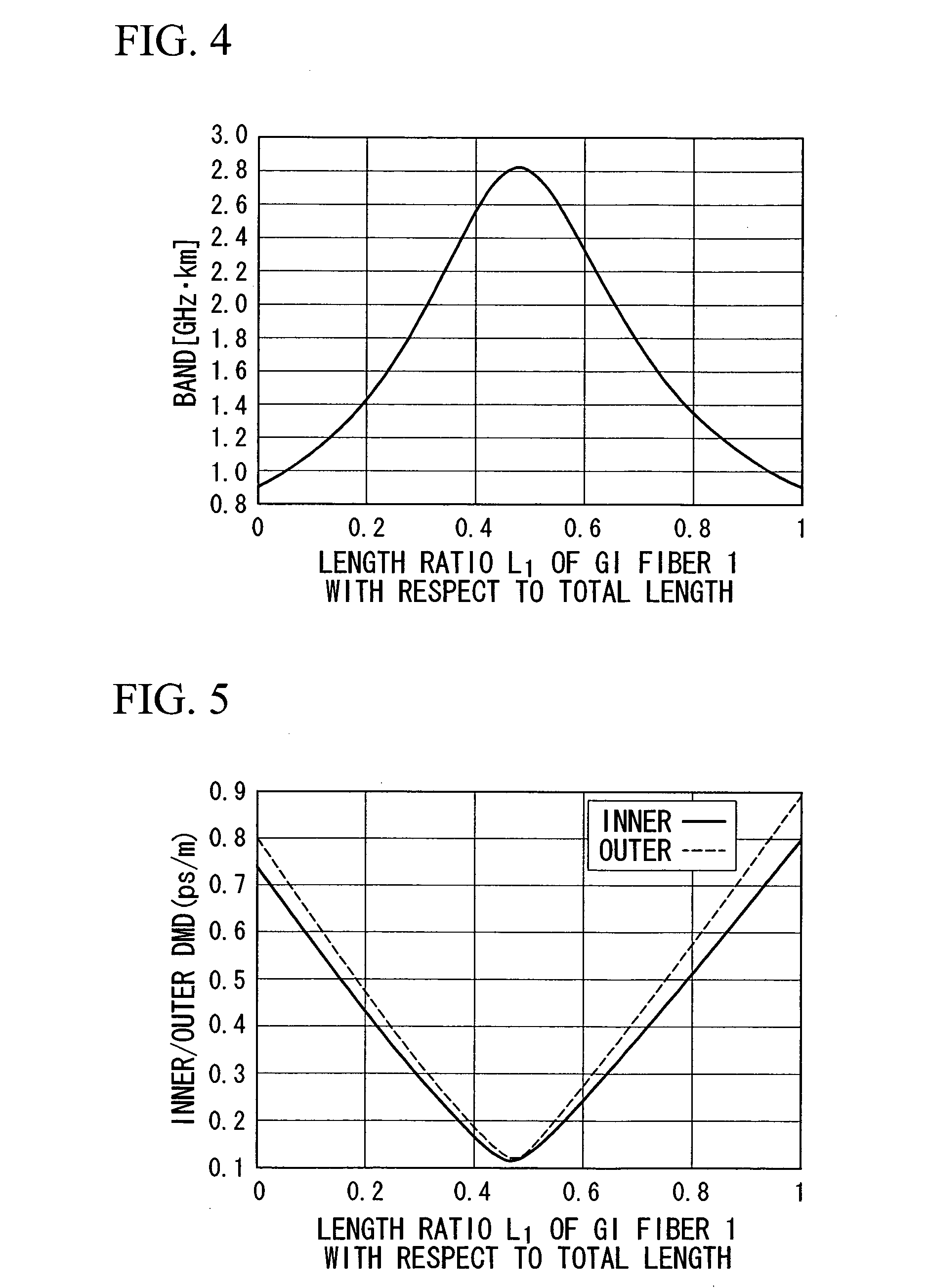
In an optical transmission path including multimode optical fibers, modal dispersion is reduced so that signal light can be transmitted at high speed and across a broad band, at low-cost and over a long distance. To reduce modal dispersion, when the transmission path is constructed by coupling a plurality of multimode optical fibers, a length ratio for the multimode optical fibers that obtains the maximum band of the optical transmission path is determined, and the multimode optical fibers are coupled according to this length ratio. The multimode optical fibers that are used have specific refractive index profiles as mode dispersion-compensating fibers. The compensated fiber and the mode dispersion-compensating fiber are coupled with specific lengths.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Method for compensating modal dispersion in multimode optical fiber transmission path
ActiveUS7139457B2Well formedFormed over a long distance easily and at low-costCladded optical fibreCoupling light guidesFiberModal dispersion
In an optical transmission path including multimode optical fibers, modal dispersion is reduced so that signal light can be transmitted at high speed and across a broad band, at low-cost and over a long distance. To reduce modal dispersion, when the transmission path is constructed by coupling a plurality of multimode optical fibers, a length ratio for the multimode optical fibers that obtains the maximum band of the optical transmission path is determined, and the multimode optical fibers are coupled according to this length ratio. The multimode optical fibers that are used have specific refractive index profiles as mode dispersion-compensating fibers. The compensated fiber and the mode dispersion-compensating fiber are coupled with specific lengths.
Owner:FUJIKURA LTD
Spatially resolved equalization and forward error correction for multimode fiber links
InactiveUS6847760B2Reduce impactWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical mode multiplex systemsFiberSpatially resolved
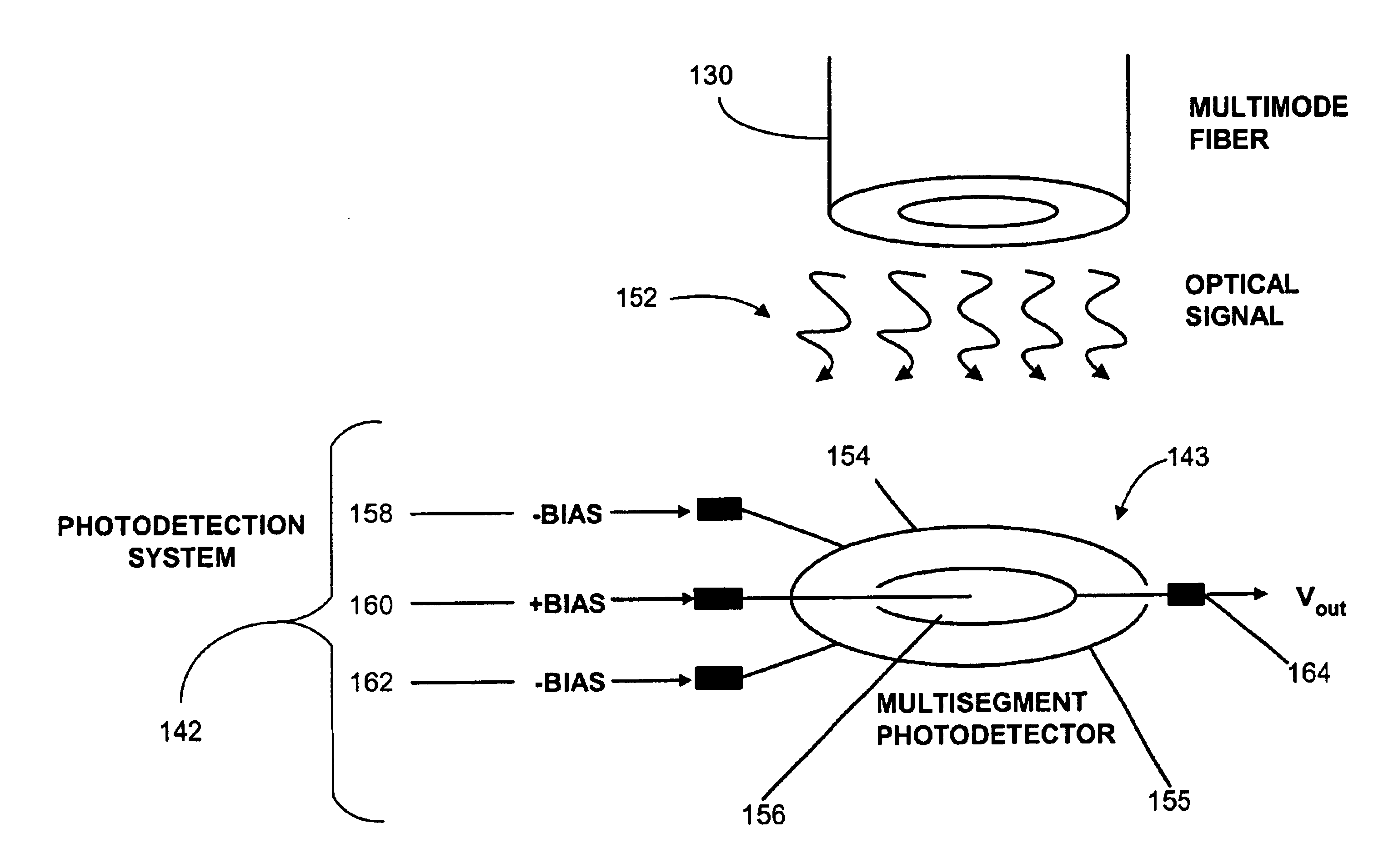
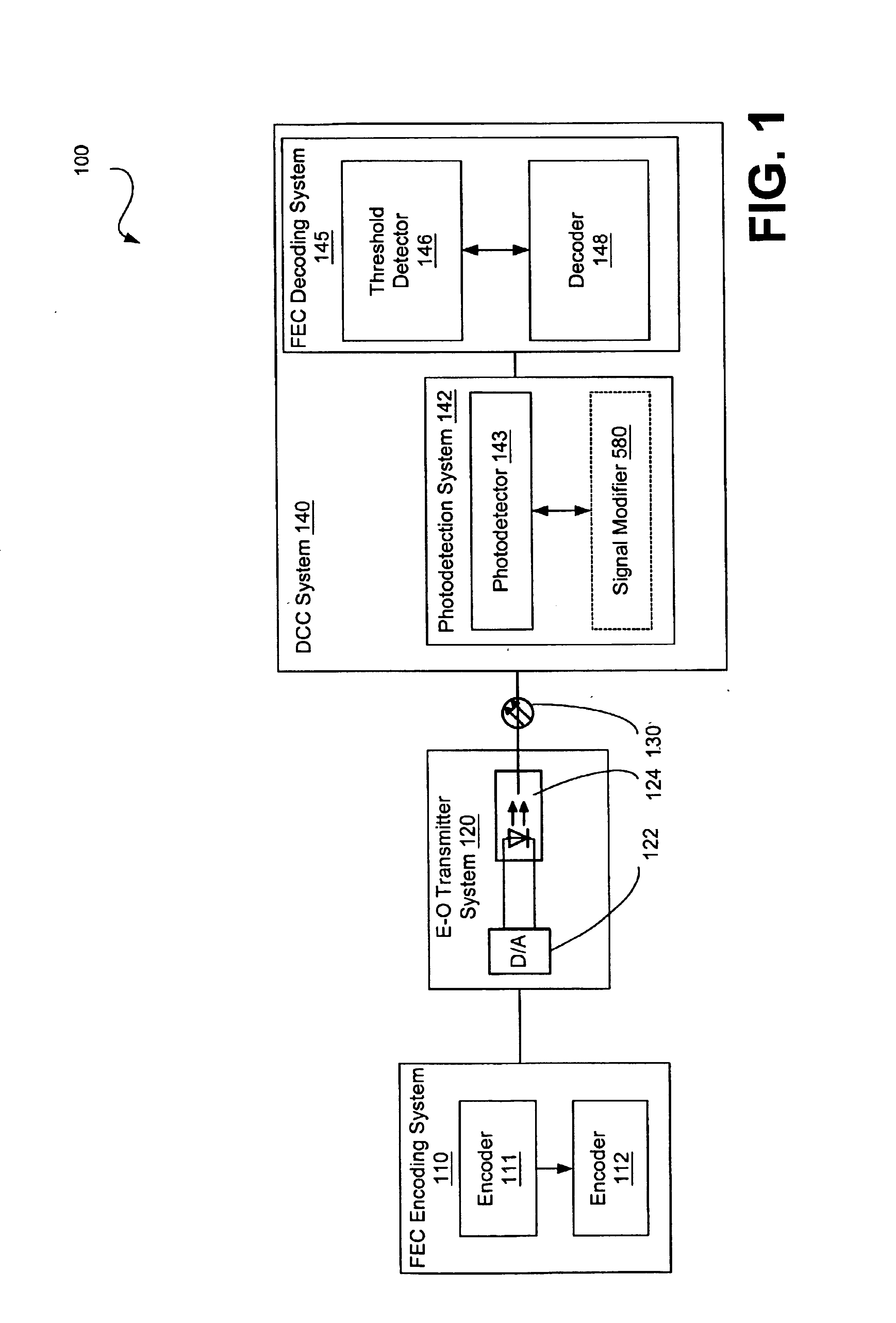
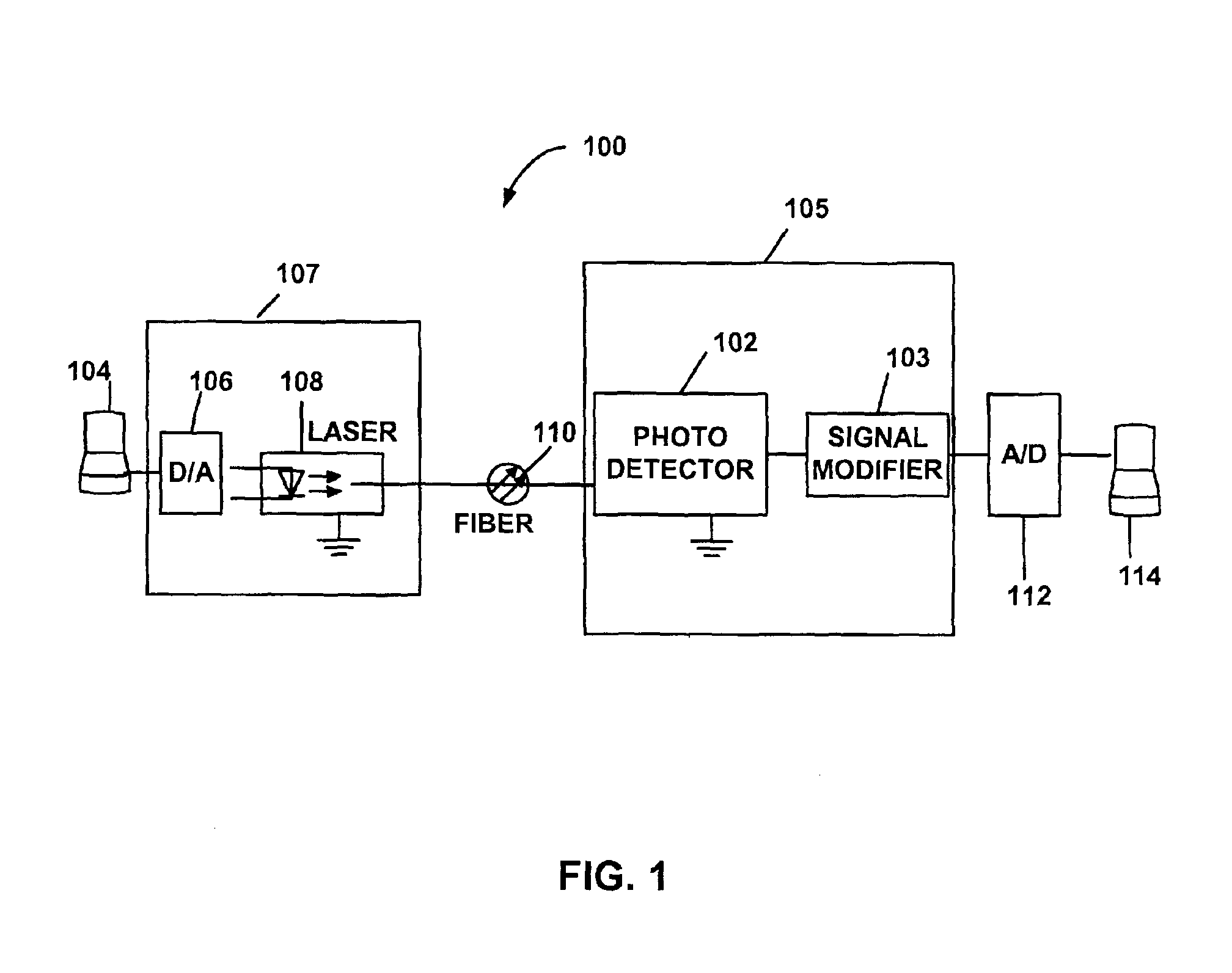
A system is described that includes a system for correcting modal dispersion and errors in an optical fiber system. The system includes a multisegment photodetector coupled to an end of an optical fiber for detecting optical signals exiting the optical fiber and for converting the optical signals to an electrical output, the multisegment photodetector including a plurality of photodetector regions configured such that one of the plurality of photodetectors regions intercepts a mode in a manner distinct from another of the plurality of photodetectors. The system also includes logic configured to receive a resultant signal output from the photodetector regions and provide forward error correction decoding of the resultant signal.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Dielectric particles in optical waveguides for improved performance
InactiveUS20040013376A1Increase concentrationSmall sectionCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideModal dispersionWaveguide
Owner:CABOT MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Plastic optical fiber
InactiveUS20050207714A1Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideUltrasound attenuationModal dispersion
A plastic optical fiber low in attenuation in a high order mode and small in mode dispersion, is presented. The plastic optical fiber comprises at least a core and a clad surrounding the core, characterized in that the core has a refractive index which gradually decreases from the core center towards the outside in the radial direction of the plastic optical fiber, and the refractive index of the clad is lower than the refractive index of the core center and higher than the refractive index of the core periphery.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD +1
Method for compensating modal dispersion in multimode optical fiber transmission path
In an optical transmission line consisting of a multimode optical fiber, the mode dispersion of the optical transmission line is reduced in order to permit a wide-band optical signal to be transmitted at high speed, over a long distance and at low costs. When a plurality of multimode optical fibers are connected together to form a transmission line for the purpose of reducing a mode dispersion, length ratios between the respective multimode optical fibers that can maximize the band of this optical transmission are determined, and they are connected together at the length ratios. In addition, a multimode optical fiber having a specific refractive index profile is used as a mode dispersion compensating fiber. Also, a compensated fiber and a compensating fiber each having a specific length are connected together.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
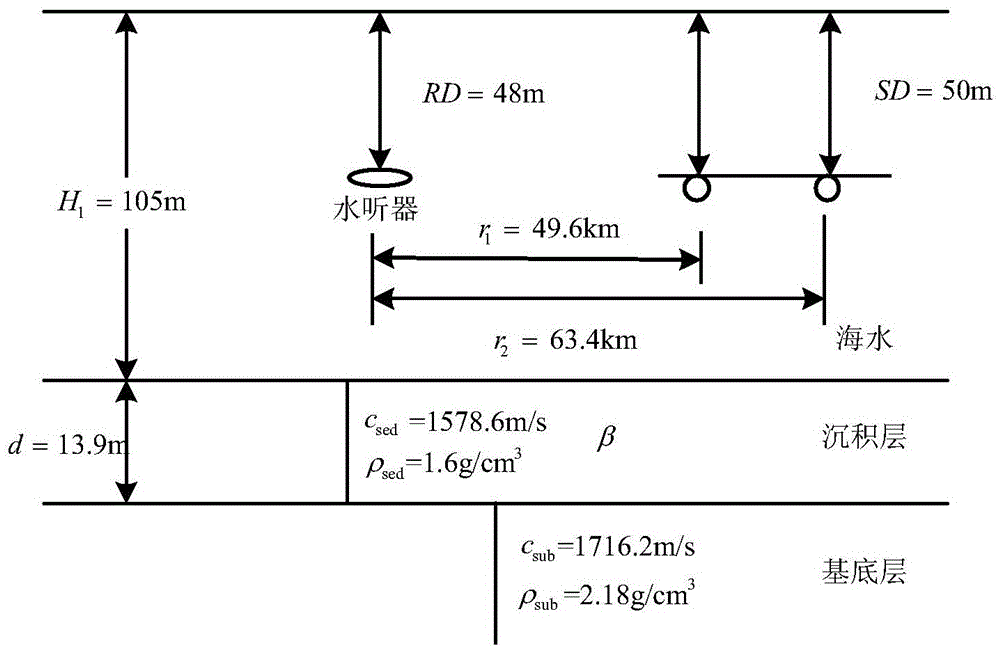
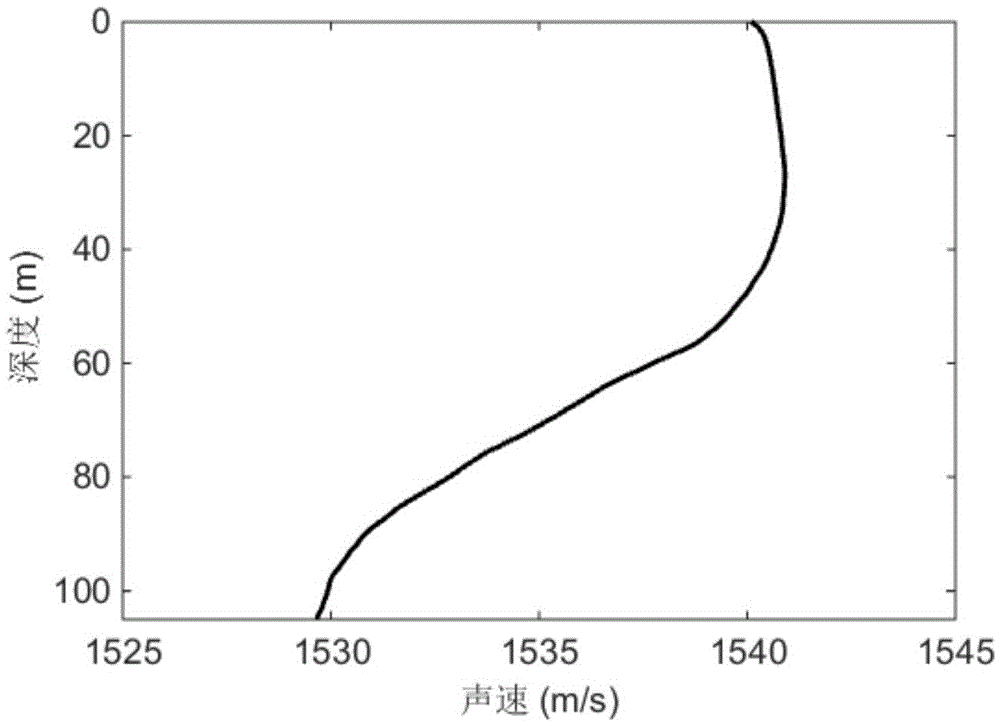
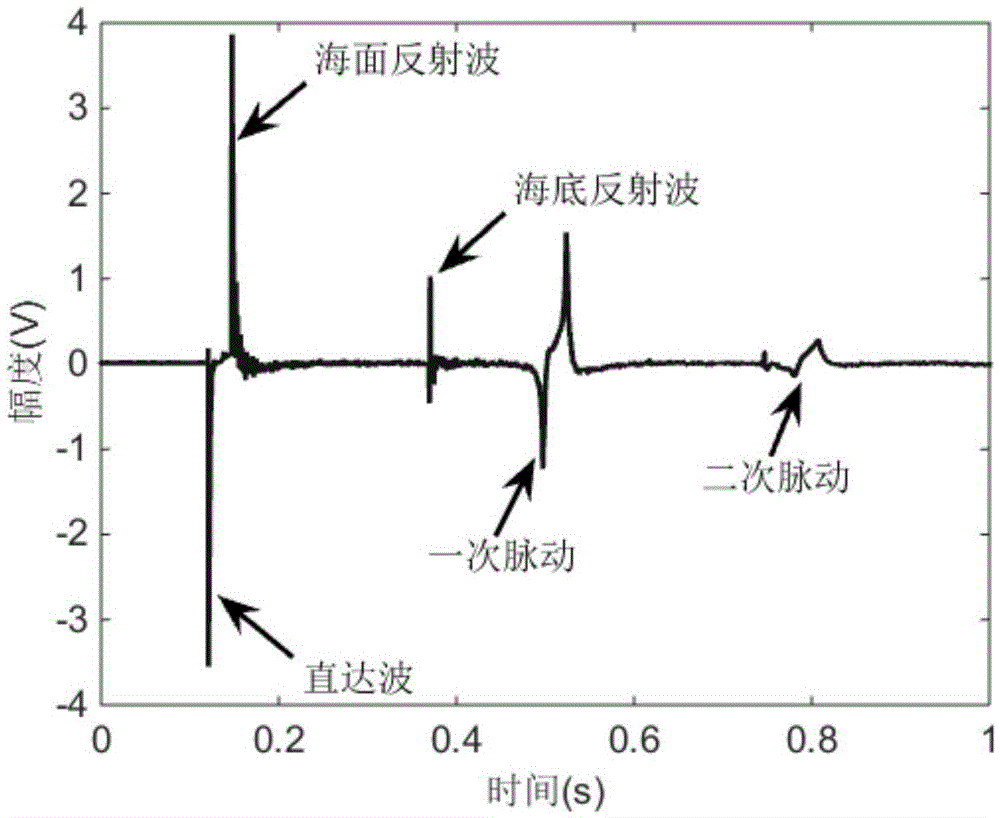
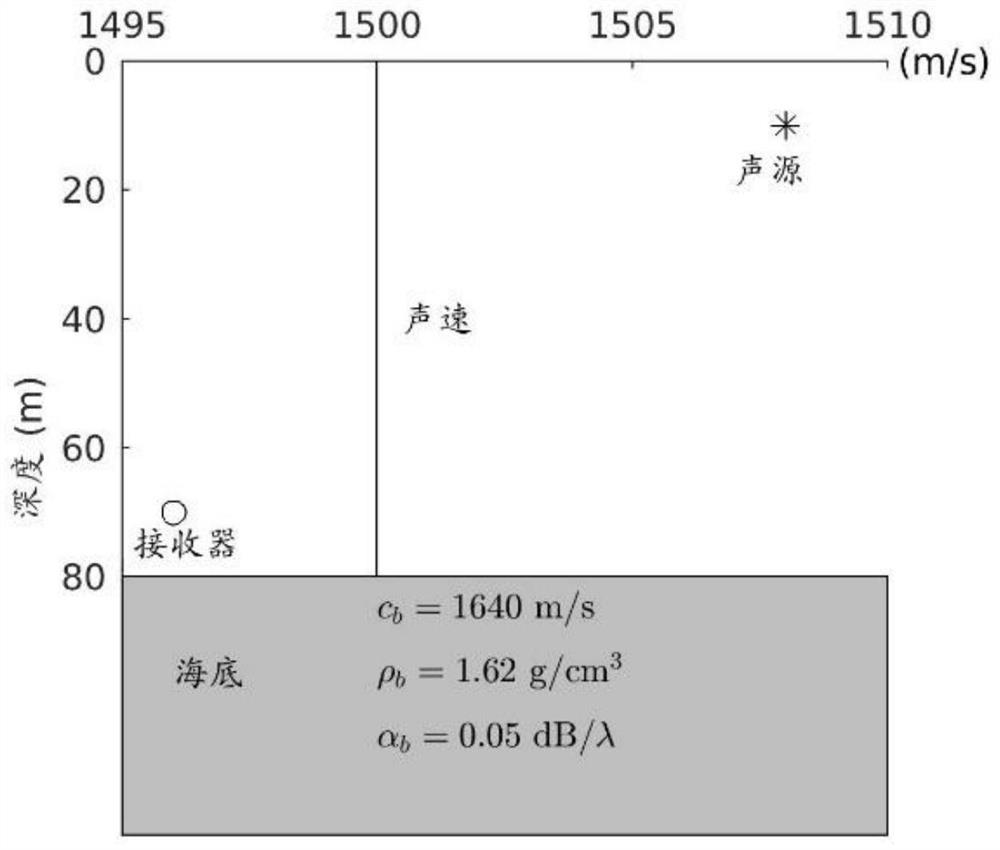
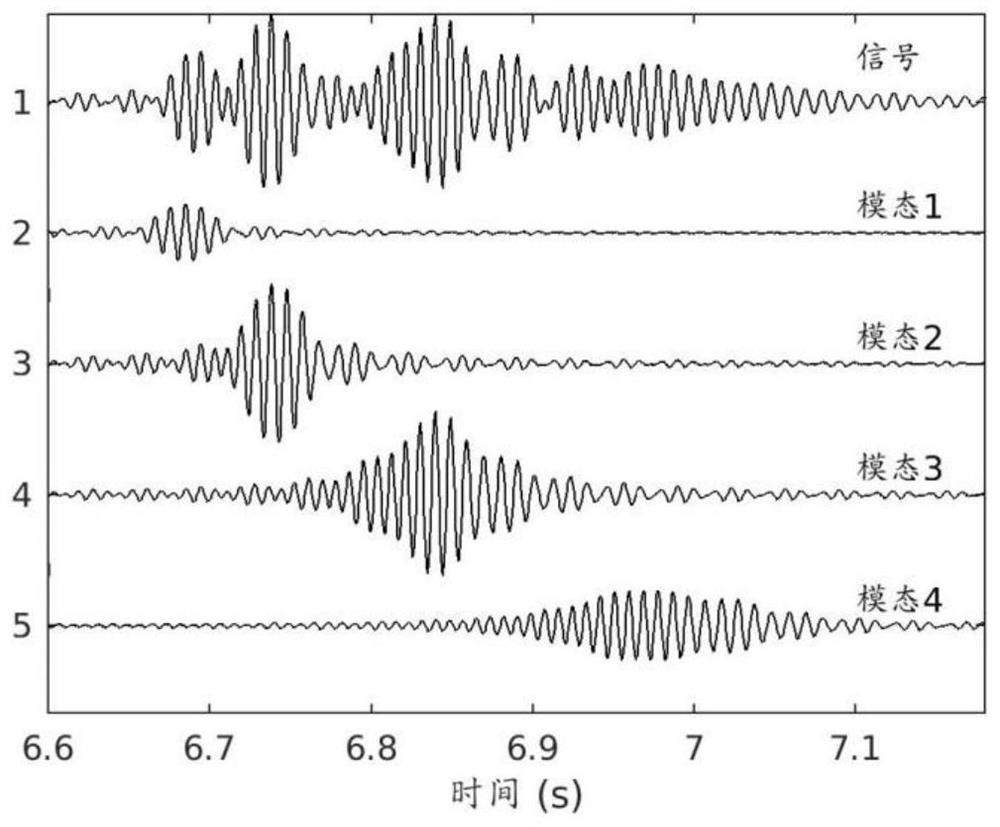
Method for inversing sea-bottom attenuation coefficient by using modal dispersion curve energy difference
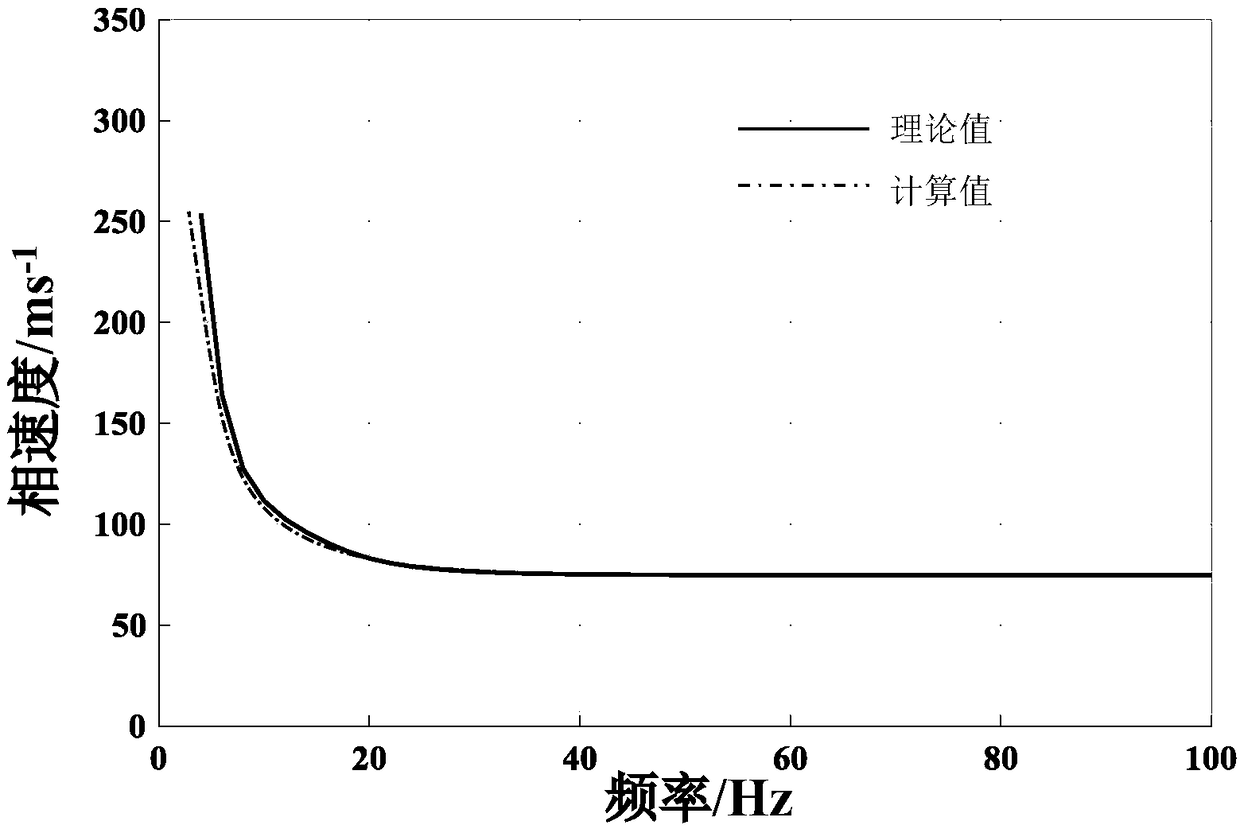
ActiveCN105631194AInversion realizationAccurate estimateInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsSound sourcesEngineering
The present invention relates to a method for inversing a sea-bottom attenuation coefficient by using a modal dispersion curve energy difference, wherein inversion of a sea-bottom attenuation coefficient is implemented by using amplitude energy information of a modal dispersion curve. The present invention provides a method for inversing a sea-bottom attenuation coefficient by using an energy difference of a modal dispersion curve of two bombs, so as to estimate a sea-bottom attenuation coefficient of an experimental sea area. The method provided by the present invention focuses on inversion of a neritic zone by using a dispersion effect generated by a wide-band explosive sound source during propagation in neritic zones. The method comprises: firstly, placing a receiving hydrophone at a certain depth; then delivering explosive sound sources with the same model number parameter (considered as generating the same signal during explosion) on the same straight line and at different distances, so as to receive time-frequency maps of two explosive sound sources; then processing the time-frequency maps of the two explosive sound sources by using a warping transformation, so as to obtain a transmission energy difference of first four stages of a modal dispersion curve; and finally inversing a sea-bottom attenuation coefficient by using a modal dispersion curve energy difference.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
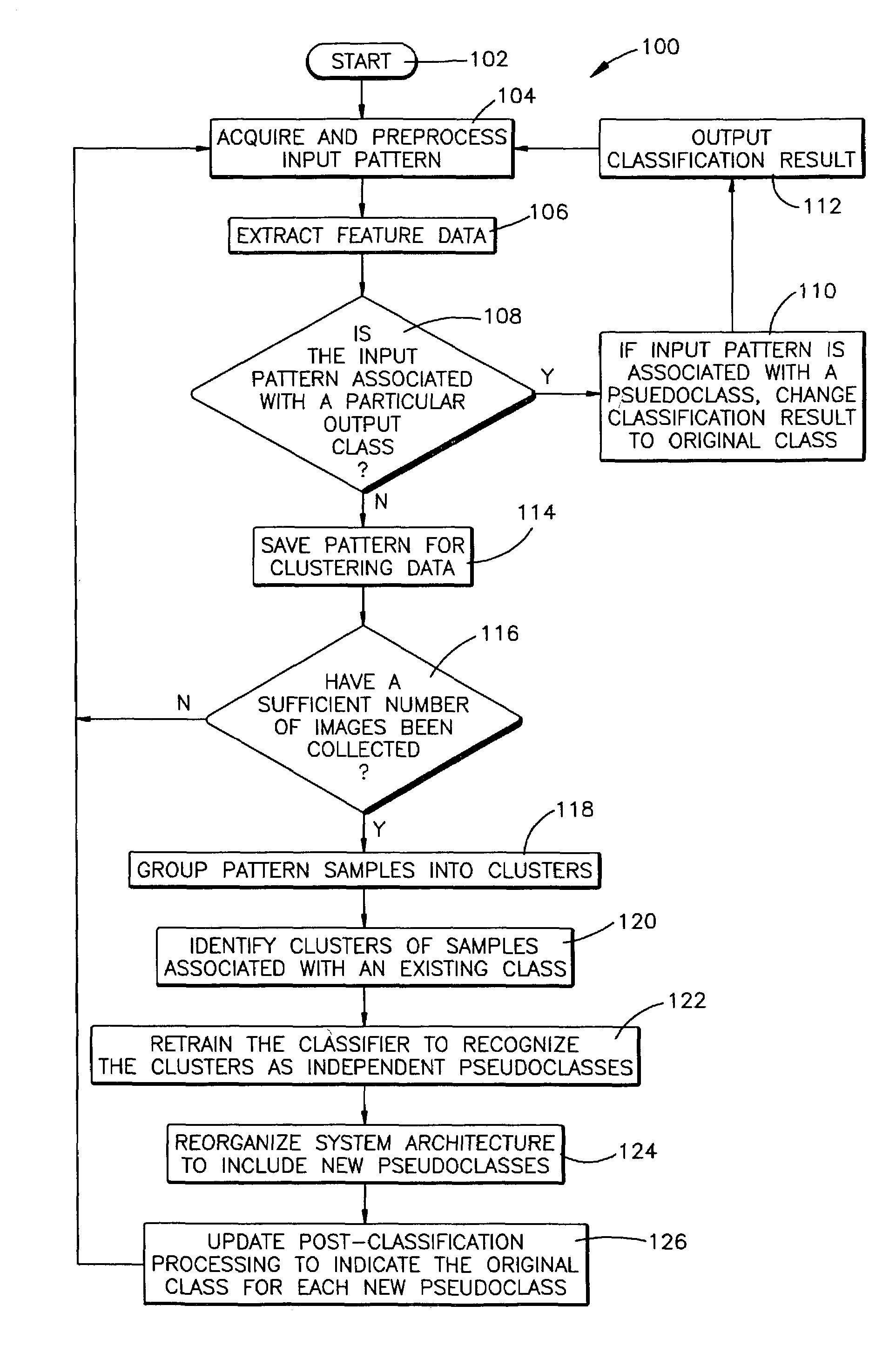
Method and computer program product for identifying output classes with multi-modal dispersion in feature space and incorporating multi-modal structure into a pattern recognition system
A method and computer program product are disclosed for identifying output classes with multi-modal dispersion in feature space and incorporating multi-modal structure into a pattern recognition system architecture. A plurality of input patterns, determined not to be associated with any of a set of at least one represented output class by a pattern recognition classifier, are rejected. The rejected pattern samples are grouped into clusters according to the similarities between the pattern samples. Clusters that contain samples associated with a represented output class are identified via independent review. The classifier is then retrained to recognize the identified clusters as output pseudoclasses separate from the represented output class with which they are associated. The system architecture is reorganized to incorporate the output pseudoclasses. The output pseudoclasses are rejoined to their associated class after classification.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Segmented photodetectors for detection and compensation of modal dispersion in optical waveguides
InactiveUS6870152B2Optimize allocationRadiation pyrometryPhotoelectric discharge tubesElectricityPhotovoltaic detectors
Systems for detection and compensation of modal dispersion in an optical fiber system including a multisegment photodetector coupled to an end of an optical fiber for detecting optical signals exiting the optical fiber and for converting the optical signals to an electrical output are provided. A representative multisegment photodetector includes a plurality of photodetector regions configured such that each of the plurality of photodetectors detects a portion of the plurality of optical signals exiting the end of the optical fiber and modifies the signal to reduce the affects of modal dispersion. Other systems are also provided.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Wavelength multiplexed optical system with multimode optical fibers
ActiveCN101621349AWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultimode transmissionMultiplexingModal dispersion
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Wavelength multiplexed optical system with multimode optical fibers
ActiveUS8879920B2Minimize modal dispersionReduced Modal DispersionWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultimode transmissionModal dispersionLength wave
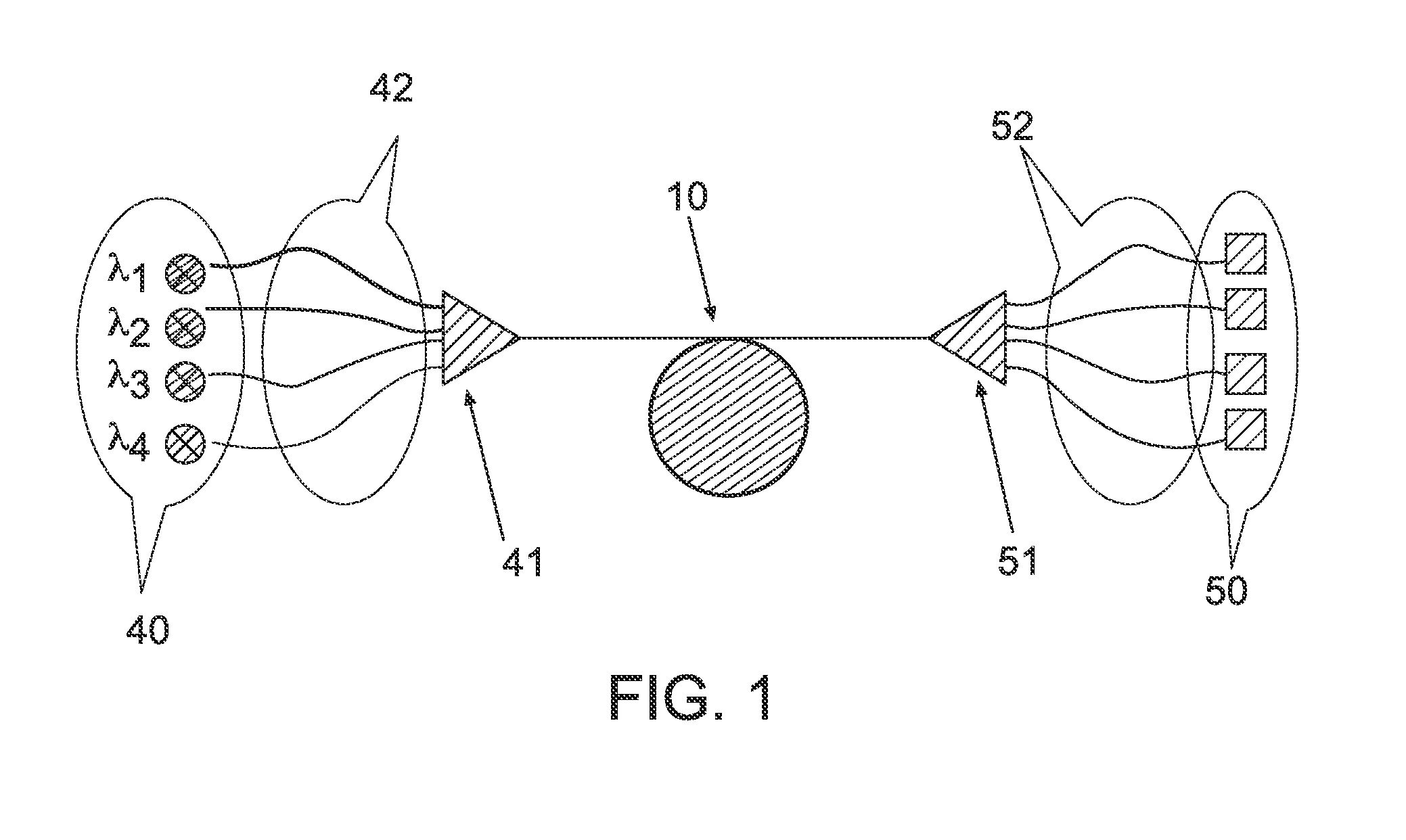
The present wavelength multiplexed optical system includes a multimode optical fiber that transmits wavelength multiplexed optical signals and a plurality of multimode modal dispersion compensation optical fibers. Each modal dispersion compensation optical fiber can transmit one of the multiplex wavelengths, and each modal dispersion compensation optical fiber has an optimized index profile such that the modal dispersion for the transmitted wavelength is approximately inversely equal to the modal dispersion induced in the multimode optical fiber. The wavelength multiplexed optical system facilitates an increased bitrate without reducing bandwidth.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Ultra-miniature broadband polarization beam splitter based on two-slit interference
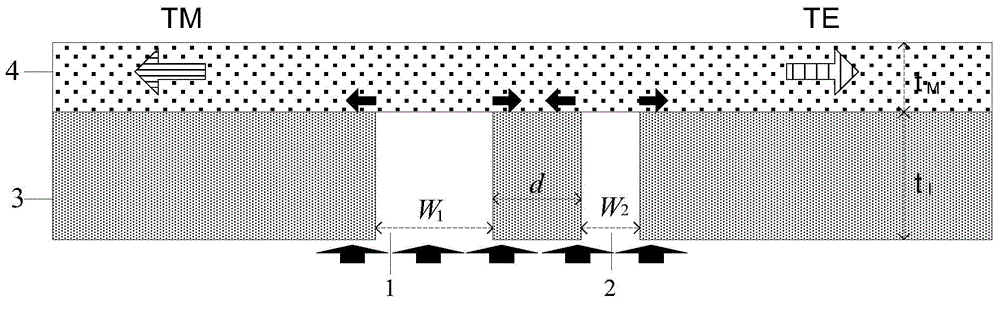
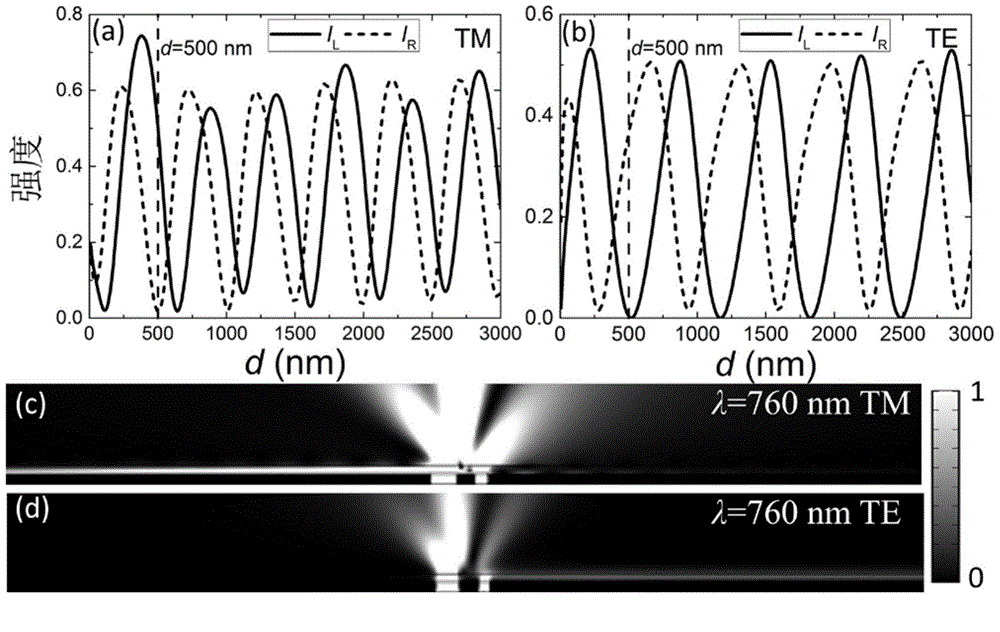
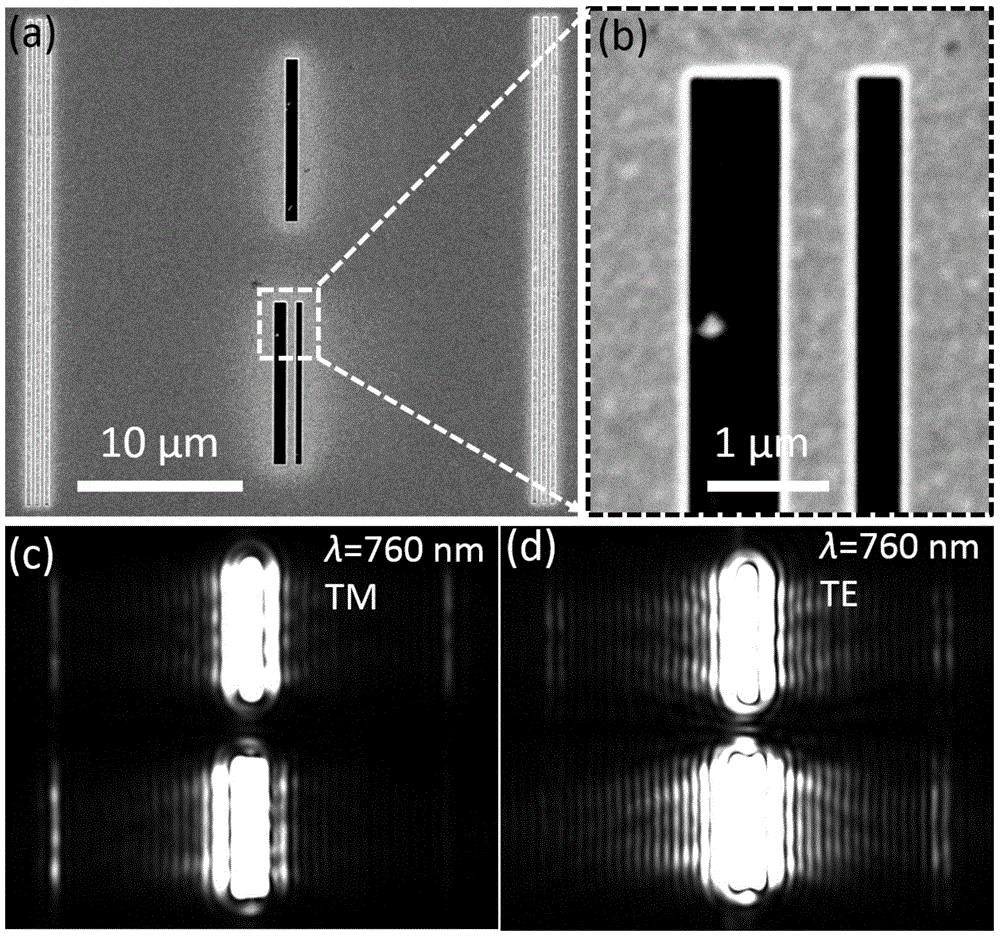
InactiveCN104614796AAchieve directional excitationAchieving Polarization BeamsplittingPolarising elementsNano structuringModal dispersion
The invention discloses an ultra-miniature broadband polarization beam splitter based on two-slit interference. A medium thin film covers a metal two-slit structure; when an incident light irradiates the metal two-slit structure from the back, each slit is capable of activating a TM mode and a TE mode supported by an air-medium-metal composite waveguide; the total field intensity of the waveguide mode in each direction is the coherent superposition of the separately activated modes of two slits; because two slits are different in width, the interference state in the opposite direction can be opposite and the oriented activation of the waveguide mode can be realized; further, the composite waveguide has great modal dispersion, two polarization modes perpendicular to each other can be propagated along the opposite direction and the polarization beam splitting is realized. A ultra-miniature polarization beam splitter is realized on the metal two-slit structure; the two-slit interference is capable of regulating field distribution in a metal nano structure, is important to the nano surface plasmon polariton devices and is important to an integrated loop.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Multiple mode fiber with mode discrimination
InactiveUS6876805B2Reduces and eliminates low order modeRange of propagation is reducedOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesFiberModal dispersion
An optical fiber for reducing modal dispersion and increasing both travel distance and transmission speed. A core center is formed in the core of the optical fiber. The core center is doped with impurities, is hollow, or is pulled at a lower temperature to increase diffraction of the core center. The core center discriminates the low order modes such that only the high order modes are present in the optical fiber. Because the low order modes are absorbed or otherwise discriminated against, the range of propagation constants is reduced and modal dispersion is likewise reduced. High order modes can be launched in the optical fiber using a lens whose center portion is obscured or by using a diffractive lens to couple a source to the optical fiber.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Method and apparatus for mitigation of modal dispersion effects in multimode fiber
InactiveUS20060093260A1Reduced Modal DispersionReduce the impactWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesEngineeringCoarse wavelength division multiplexing
A method for mitigating modal dispersion in a multimode optical fiber involves launching a diffractionless optical beam, such as a Bessel beam, into a multimode optical fiber. A fiber optical transmission system includes a multimode optical fiber transmission medium having an input end and an output end, an optical signal transmitter in communication with the input end of the multimode optical fiber medium, means for converting the optical signal into a diffractionless optical signal, means for launching the diffractionless optical signal in the input end of the multimode optical fiber transmission medium, means for outputting the propagated optical signal from an output end of the multimode fiber transmission medium, and a receiver that receives the optical signal from the output means. Fiber optic communication systems employing the invention embodiments include point-to-point transmission links, local area networks and WDM systems including coarse wavelength division multiplexing and dense wavelength division multiplexing systems.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Method for designing and selecting optical fiber for use with transmitter optical subassembly
ActiveCN103154691AImprove performanceTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsMultimode transmissionModal dispersionEngineering
A method for compensating for both material or chromatic dispersion and modal dispersion effects in a multimode fiber transmission system is provided. The method includes, but is not limited to measuring a fiber-coupled spatial spectral distribution of the multimode fiber laser transmitter connected with a reference multimode fiber optical cable and determining the amount of chromatic dispersion and modal dispersion present in the reference multimode fiber optic cable. The method also includes, but is not limited to, designing an improved multimode fiber optic cable which compensates for at least a portion of the chromatic dispersion and modal dispersion present in the reference multimode fiber optic cable resulting from the transmitter's fiber-coupled spatial spectral distribution.
Owner:PANDUIT
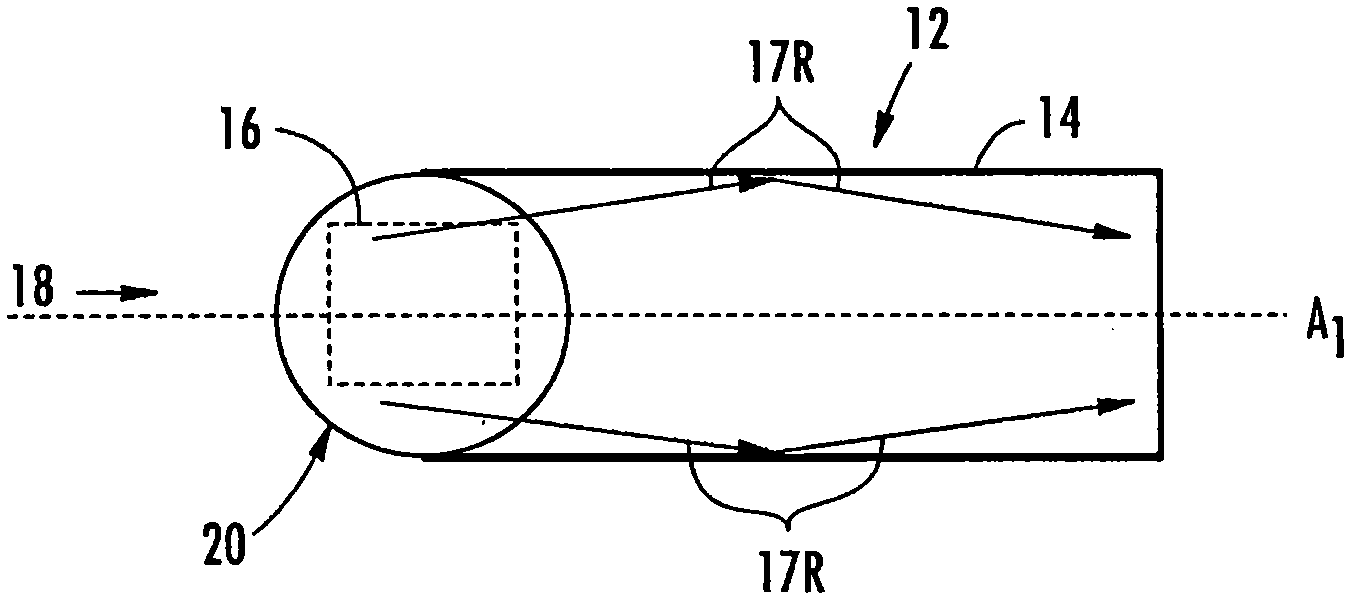
Optical fiber end structures for improved multi-mode bandwidth, and related systems and methods
Multi-mode optical fiber apparatuses, multi-mode optical fibers, and related methods for improving fiber link bandwidth are disclosed. One or more end structures can be disposed on an optical fiber end of a multi-mode optical fiber to improve link bandwidth by reducing and / or eliminating modal dispersion. Modal dispersion can be caused by higher-order modes or modes in an optical fiber being excited by received light. Modal dispersion can limit the bandwidth of an optical fiber link. In certain embodiments, end structures for multi-mode optical fibers are disclosed for reducing the launch angle of light in an optical fiber to reduce modal dispersion. In other embodiments, end structures for multi-mode optical fibers are disclosed for reducing or eliminating coupling astigmatism. In other embodiments, end structures for multi-mode optical fibers are disclosed for directing higher order modes or groups away from an optical detector to reduce or eliminate modal dispersion. In one embodiment, a prism structure is disposed on the source end of the multi-mode optical fiber. In other embodiments a convex profile lens is disposed at the source and detector ends of the fiber.
Owner:CORNING INC
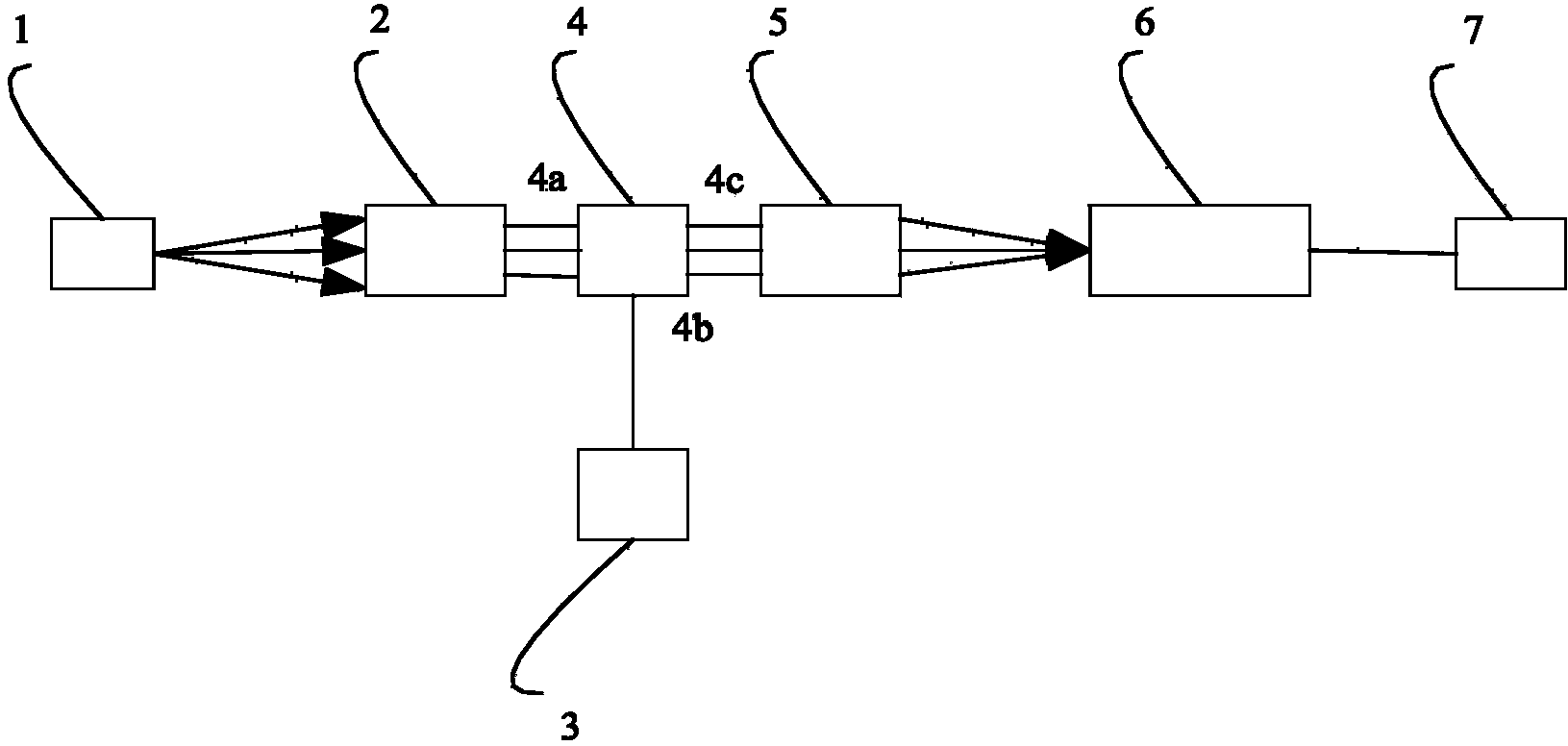
Optical correlator based on modal dispersion
InactiveCN103856266AReduce lossSolve the difficulty of choosingDistortion/dispersion eliminationMultimode transmissionSpatial light modulatorFocal position
The embodiment of the invention provides an optical correlator based on modal dispersion, and belongs to the field of optical fiber communication. The optical correlator based on modal dispersion is characterized in that a light source (1) is located at the focal position of a convergent lens (2), the back of the convergent lens (2) is a light input port (4a) of a spatial light modulator (4), an electric input port (4b) of the spatial light modulator (4) is connected with a signal source (3), the back of a light output port (4c) of the spatial light modulator is a convergent lens (5), the focal position of the convergent lens is the input end of a multi-mode optical fiber (6), and the output end of the multi-mode optical fiber (6) is connected with a photoelectric detector (7). The optical correlator based on modal dispersion is basically characterized in that the modal dispersion of the multi-mode optical fiber is used for manufacturing the correlator and has the advantage of being simple in structure, and the optical fiber is short, so that the energy loss in the transmission process of light signals is reduced. The light source bears the signals to be detected, the use of a high-speed modulator is avoided, and system cost is avoided. The use of the multi-mode light source overcomes the defect that an existing optical correlator based on modal dispersion has a high requirement for the bandwidth of the light source, and the optical correlator based on modal dispersion has broad application prospects on the aspect of light signal processing.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Anti-polarizing mode chromatic dispersion (PMD), system
InactiveCN1487315APMD reductionIncrease torqueGlass fibre drawing apparatusOptical light guidesFiberModal dispersion
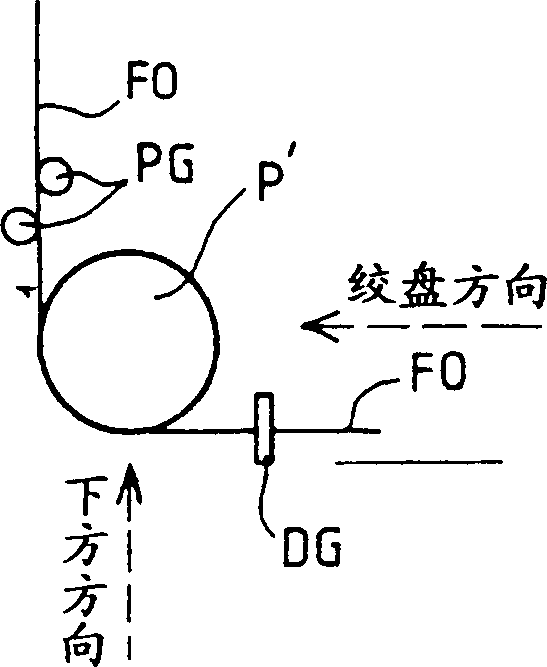
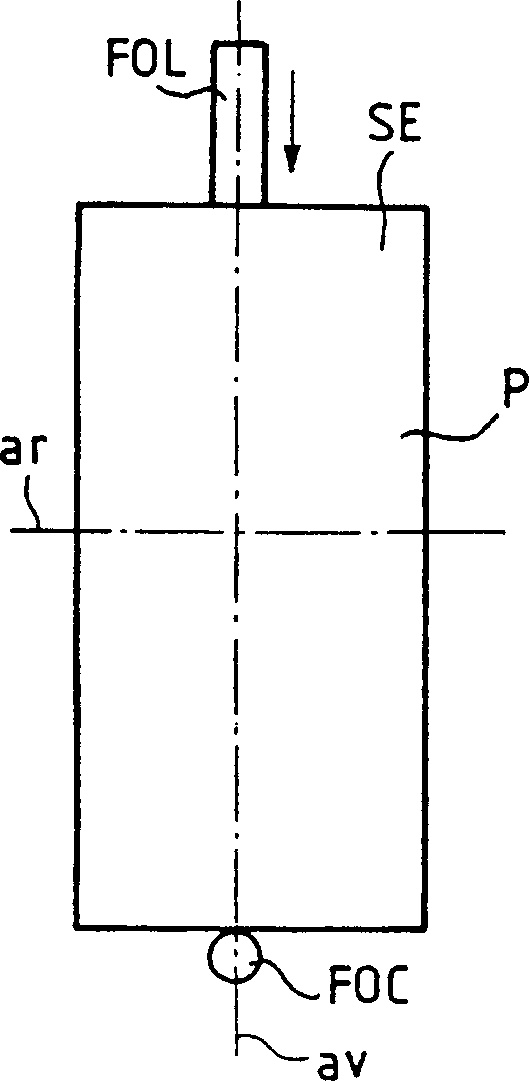
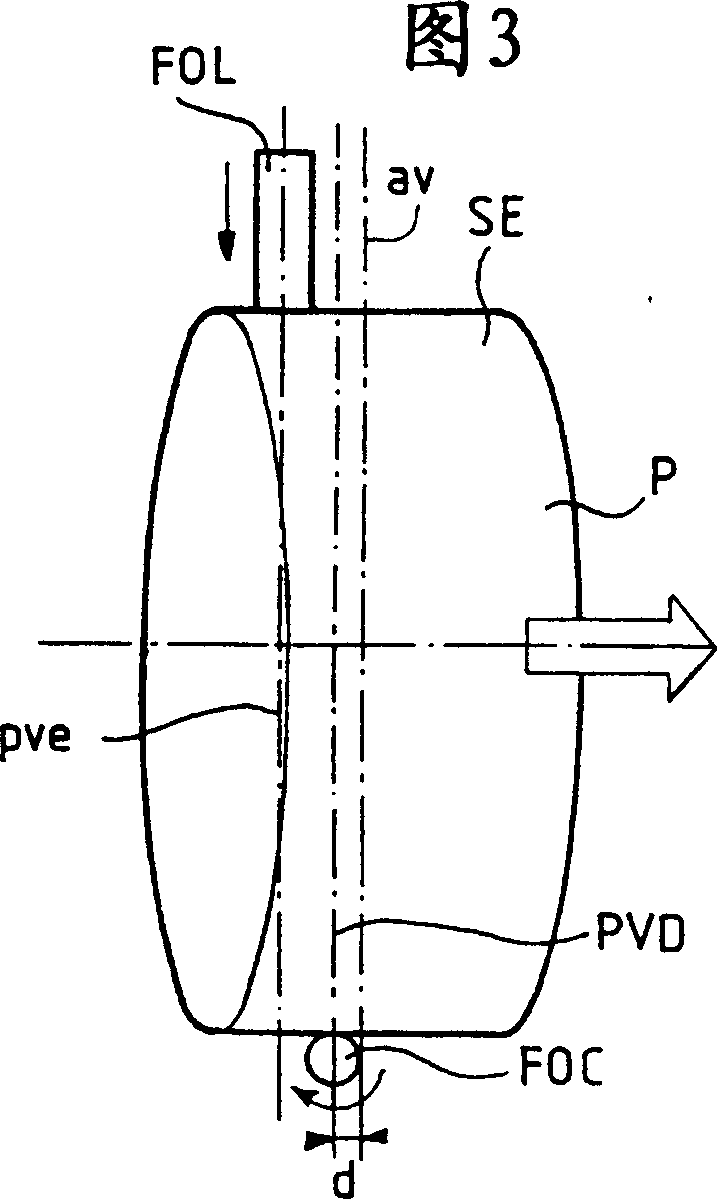
Anti-PMD (Polarization Modal Dispersion) system comprises a pulley (P') oscillating in rotation. The pulley applies, during the formation of an optical fiber (FO), alternately in the clockwise and anti-clockwise directions, a torsion couple to the fiber so as to diminish its PMD. At least part of the external surface (SE') of the pulley in contact with the fiber during its formation is convex. An Independent claim is also claimed for the pulley used in the anti-PMD system.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
An optical communication system for wireless radio signals
InactiveCN1723640ARadio transmission for post communicationRadio-over-fibreOptical radiationRefractive index
A method of transmission of radio signals over all types of graded-index multimode fibre is provided. The method comprises launching optical radiation into the core of the multimode fibre away from the centre of the core so as to strongly excite a subset of the available modes of the multimode fibre. The subset of modes excited are within a small number of mode groups and thus have similar propagation constants leading to a reduction in modal dispersion and modal interference and smoothing of the frequency response passband region beyond the fibres specified 3dB base band bandwidth assisting RF transmission and recovery from this region
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE OF LONDON +1
A Parallel Optical Fiber Angled Coupling Component
ActiveUS20190196114A1Increasing optical signal transmission distance in opticalReduction in inter-modal dispersionCoupling light guidesModal dispersionCoupling
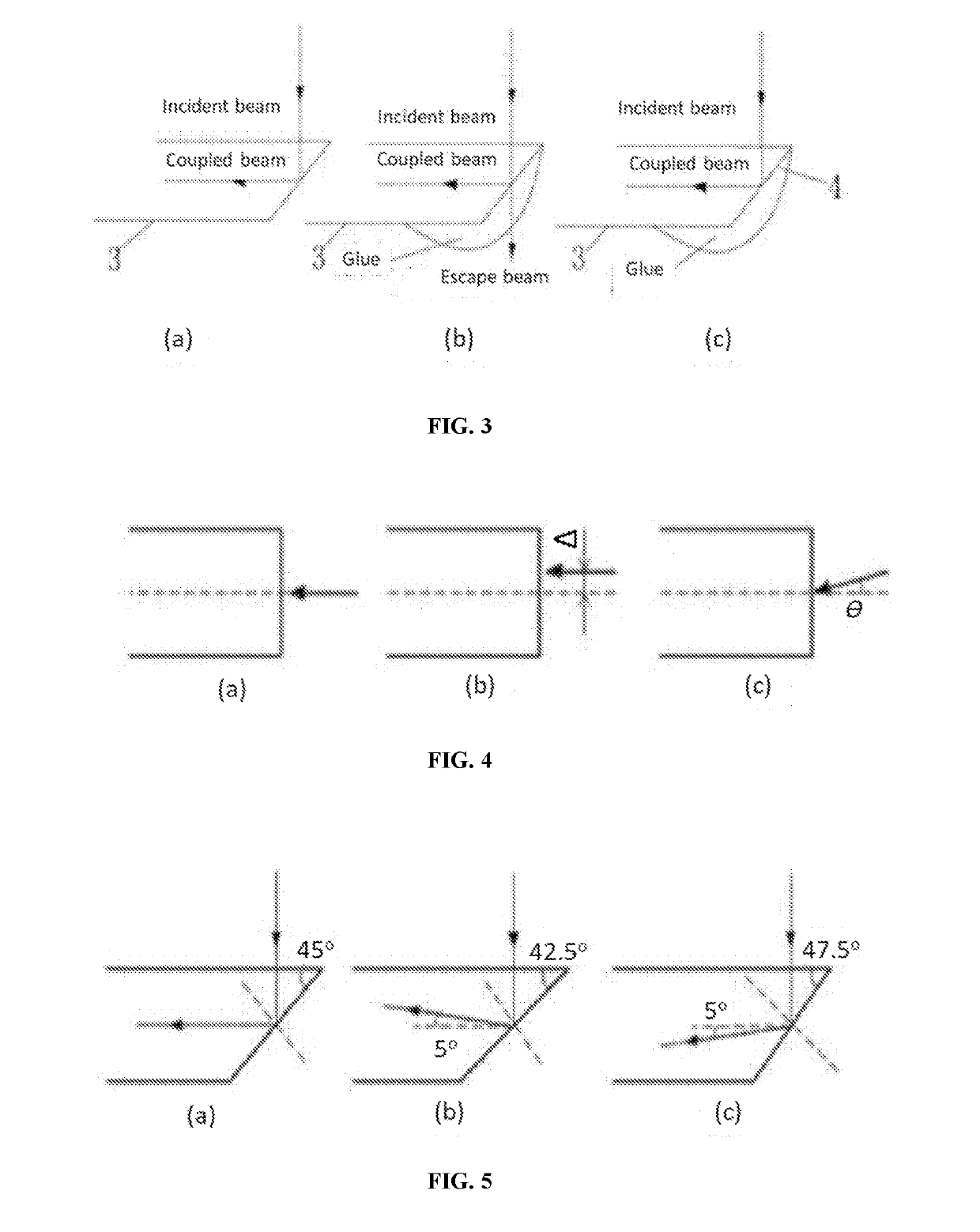
A parallel optical fiber angled coupling component, which is used for parallel coupling of optical signal between the optical fiber array and the laser array, comprises an optical fiber positioning substrate, a cover plate and a plurality of optical fibers. The end face of the optical fiber is polished into a bevel with an inclination of 42.5° or 47.5°, and the bevel of the optical fiber is coated with a metal reflective film. This invention has the following beneficial effects: The end face of the optical fiber is polished into a bevel with an inclination of 42.5° or 47.5° to reduce inter-modal dispersion and increase the transmission distance of the optical signal in the subsequent optical fiber; the bevel of the optical fiber is coated with a metal reflective film, so as to ensure high reflectivity even if the bevel of the optical fiber is covered with glue.
Owner:SENKO ADVANCED COMPONENTS
Multimode optical fiber systems with adjustable chromatic modal dispersion compensation
ActiveUS8977091B2Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingCoupling light guidesModal dispersionLength wave
Multimode optical fiber systems with adjustable chromatic modal dispersion compensation are disclosed, wherein the system includes a VCSEL light source and primary and secondary optically coupled multimode optical fibers. Because the VCSEL light source has a wavelength spectrum that radially varies, its use with the primary multimode optical fiber creates chromatic modal dispersion that reduces bandwidth. The compensating multimode optical fiber is designed to have a difference in alpha parameter relative to the primary multimode optical fiber of −0.1≦Δα≦−0.9. This serves to create a modal delay opposite to the chromatic modal dispersion. The compensation is achieved by using a select length of the compensating multimode optical fiber optically coupled to an output end of the primary multimode optical fiber. The compensating multimode optical fiber can be configured to be bend insensitive.
Owner:CORNING INC
Covert acoustic communications through solid propagation channels using spread spectrum coding and adaptive channel pre-distortion
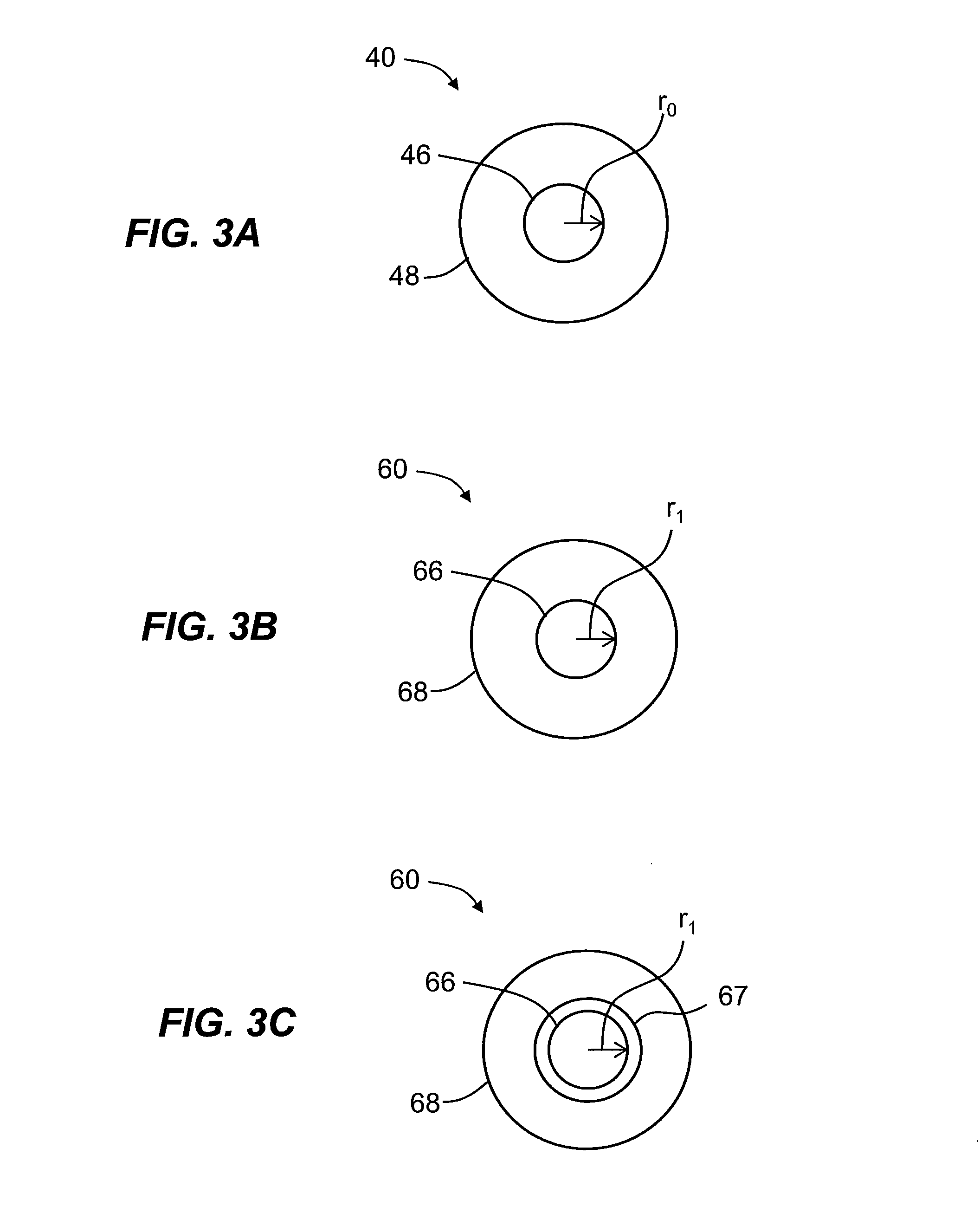
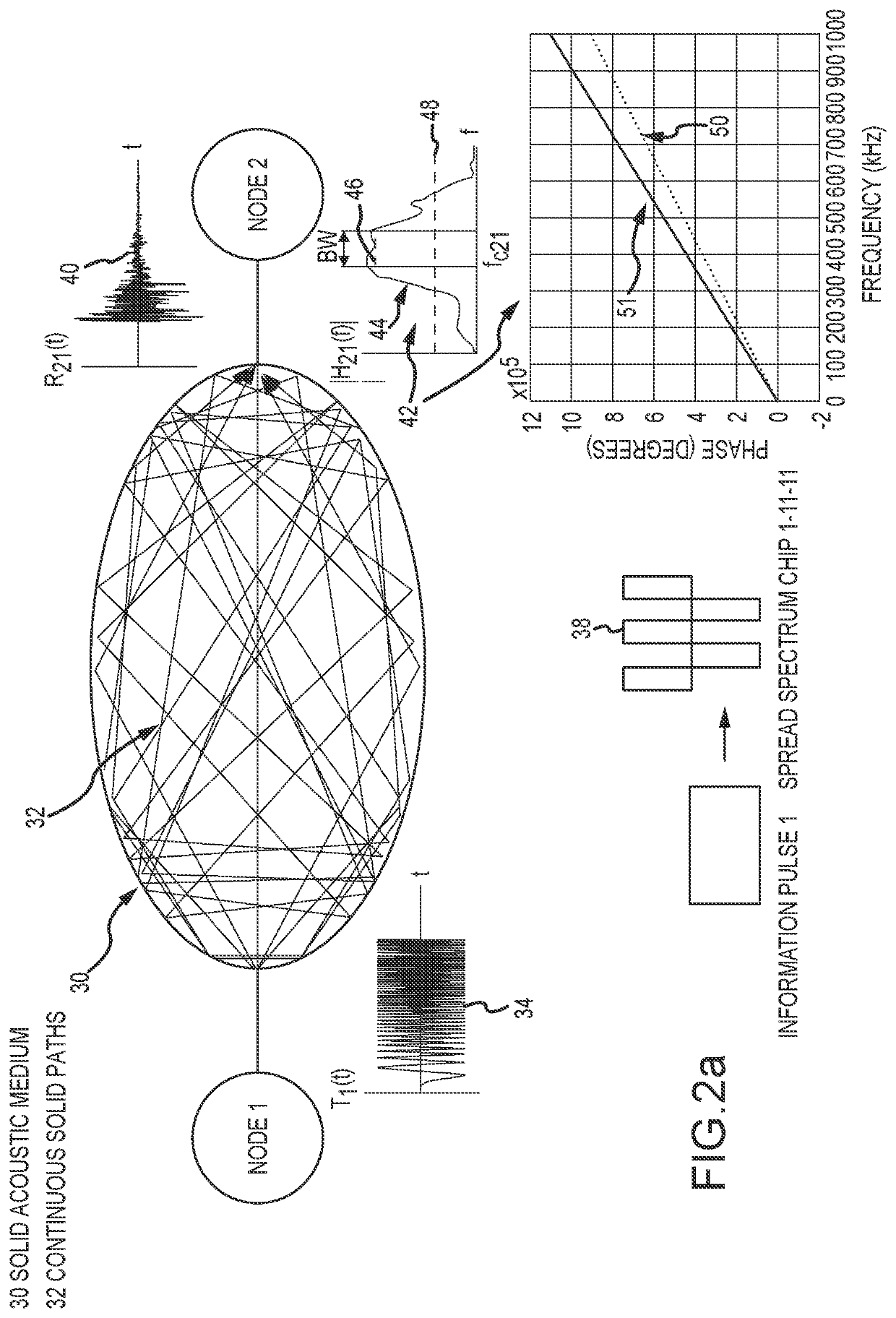
ActiveUS11108429B1Avoid problemsBaseband system detailsSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionFrequency spectrumModal dispersion
Covert acoustic communications (CAC) through solid propagation channels that connect node pairs is achieved by encoding signals using spread spectrum coding techniques that position the encoded signal at a center frequency fc within a narrow frequency bandwidth BWNB in which the amplitude of the channel response H(f) between each node pair is relatively high. The channel response H(f), bandwidth BWNB and center frequency fc, and accordingly the signal data rate will adapt for each node pair and possibly each side of the node pair. A pre-distortion filter 1 / H(f) pre-distorts the encoded signal over bandwidth BWNB to compensate for material and modal dispersion and multipath between the node pair. This technique avoids the problems associated with frequency dependent attenuation of the continuous solid path and allows for simultaneous transmission and reception of signals among the multiple node pairs.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
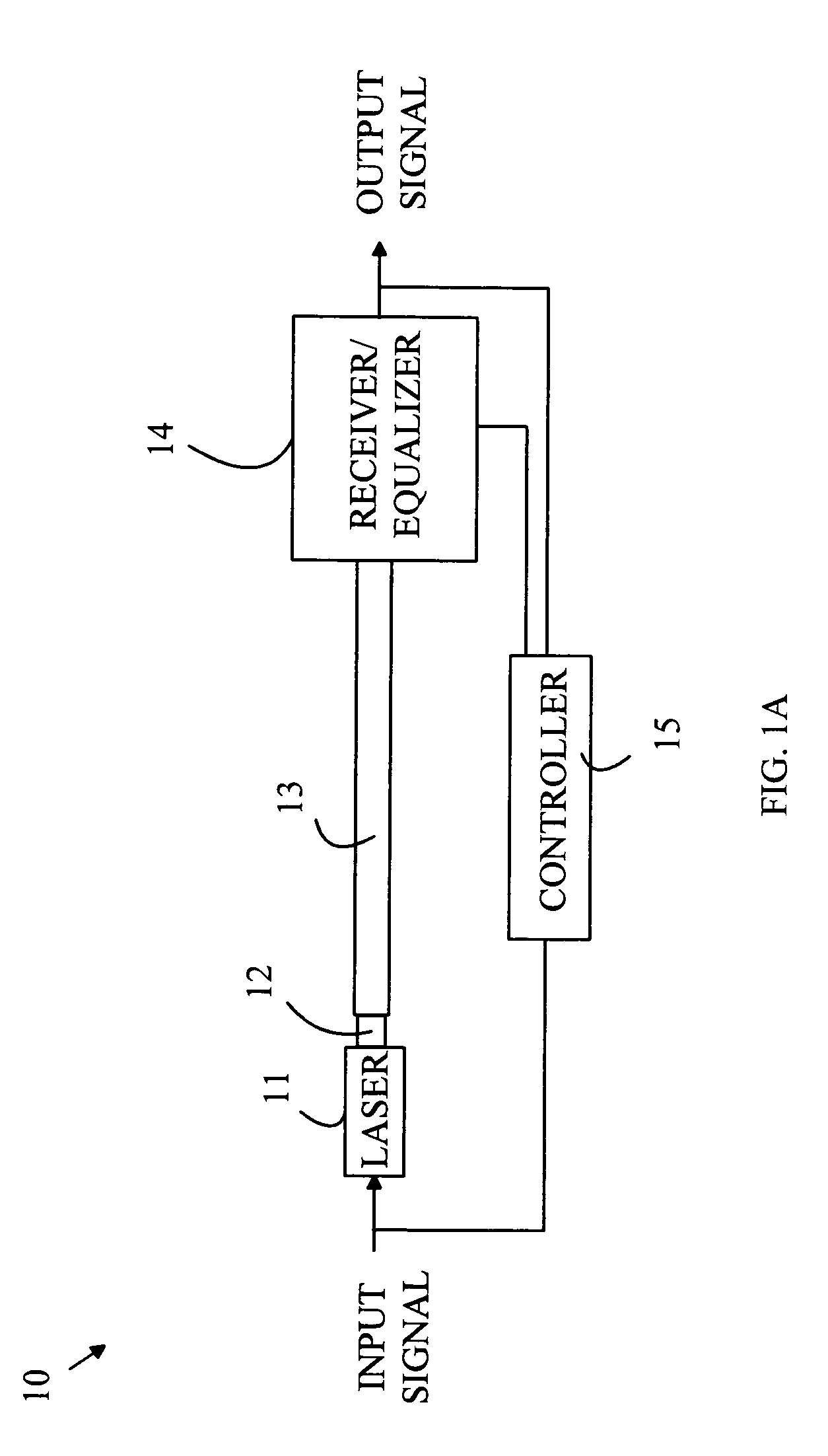
Communications system employing single-mode lasers and multimode optical fibers
InactiveUS20060039656A1Reduced Modal DispersionTime stableLaser detailsSemiconductor laser optical deviceCommunications systemModal dispersion
An optical transmission system having a single mode laser that generates an optical signal that is carried by a multimode optical fiber to a receiver is disclosed. The single mode laser has an emitting aperture from which the optical signal is routed to the input end of the multimode optical fiber. The receiver receives light from the output end of the optical fiber. The receiver includes an equalizer that corrects the received light for modal dispersion introduced by the multimode optical fiber. Light leaving the emitting aperture of the laser is introduced into the multimode optical fiber in a pattern that excites a subset of the plurality of optical transmission modes thereby reducing the modal dispersion introduced into the light signal and stabilizing the dispersion in time. The improved dispersion enables further correction of the dispersion through the utilization of equalization techniques.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Hybrid single and multimode optical fiber for a home network
ActiveCN103492918AEasy to manufactureLow costOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingModal dispersionOptical power
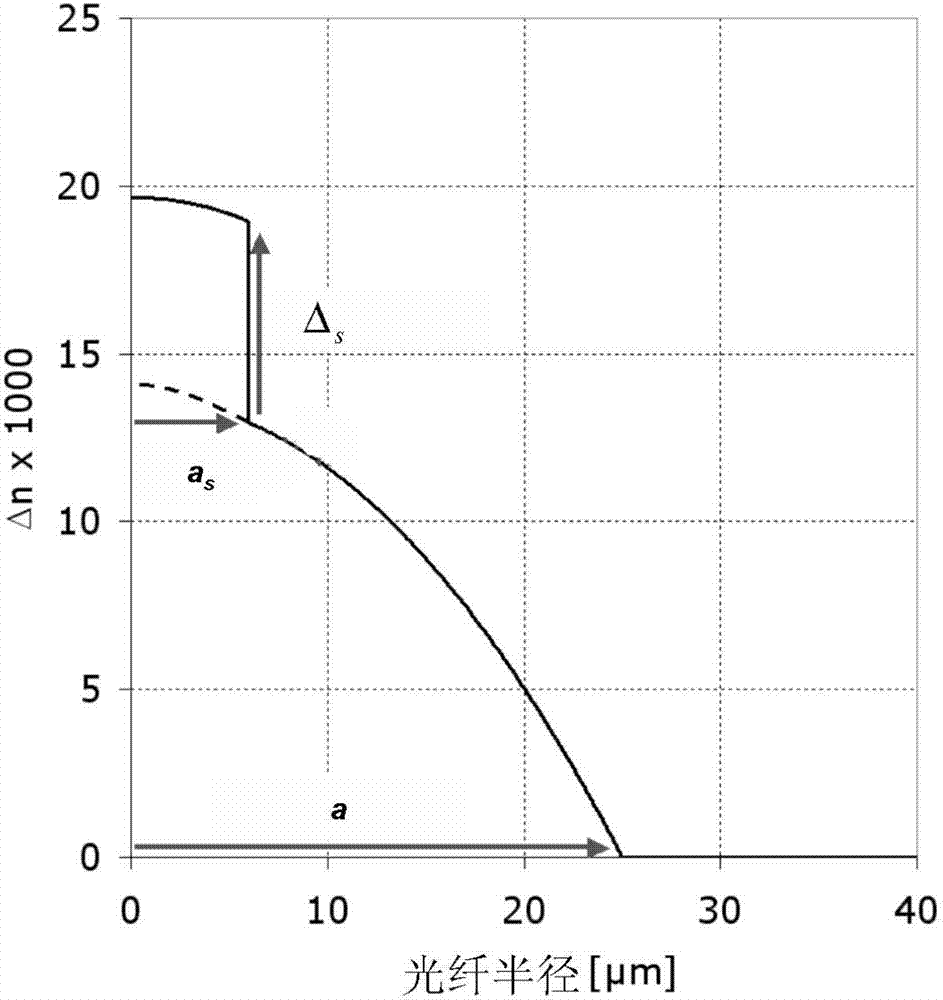
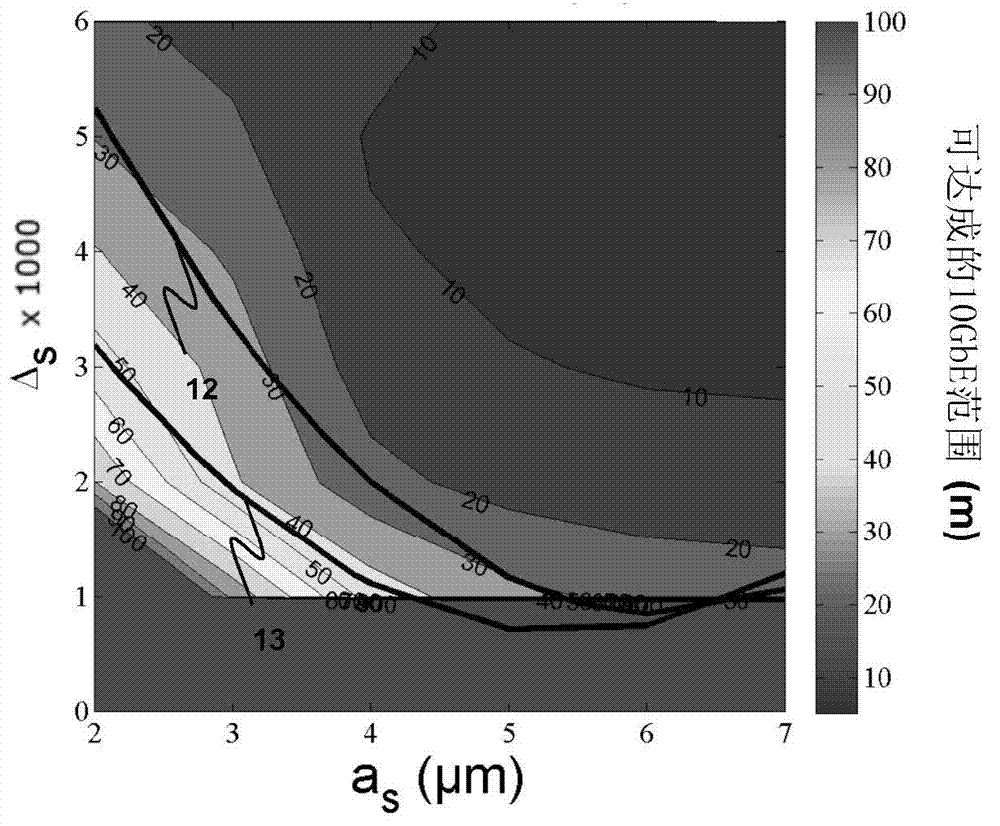
The invention relates to a hybrid optical fiber that includes a multi-segmented optical core exhibiting a refractive graded-index profile typically used to support multimode transmission in which a step-index is added at the center of the optical core, the profile parameters (a s ) and (” s ) of this step-index being tuned so as to provide an optical fiber that transmits both error free multimode optical signals and error free single-mode optical signals. The implementation of such a refractive index profile n(r) of the optical core, as well as the choice of an adequate value of the parameters (a s ) and (” s ) lead to adapt the fundamental mode of the optical fiber such that the optical power coupled into the fundamental mode is maximized at the wavelength of the single-mode transmission, 1550 nm for example, while preserving a relatively reduced modal dispersion at the wavelength of the multimode transmission, 850 nm for example.
Owner:德拉卡康泰克私营有限责任公司
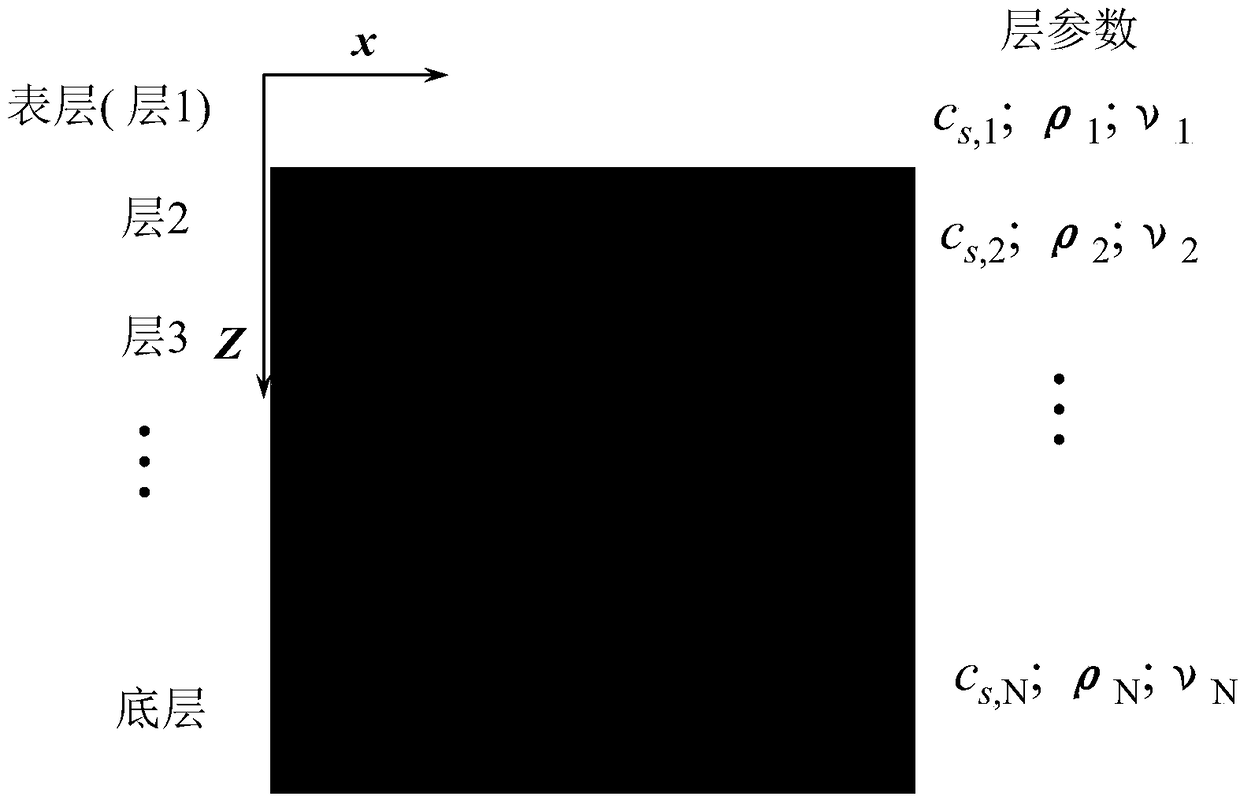
An analytical algorithm for the dispersion curves of Rayleigh wave fundamental modes in a regular layered semi-infinite body is presented
ActiveCN109101684ASimple calculationCalculation speedDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsRelative energyPoisson's ratio
The invention relates to an analytical algorithm of Rayleigh wave base order modal dispersion curve in a regular layered semi-infinite body, a regular layered semi-infinite body consists of a uniformbottom layer with an infinite depth of the lower layer, and at least one uniform layer covering the bottom layer, wherein the shear wave velocities of each layer increase with the depth of the layer.The analytical algorithm comprises the following steps: 1, calculating the vertical displacement mode function of Rayleigh waves in the uniform semi-infinite body from the surface Poisson's ratio of the regular layered semi-infinite body; 2, calculating the relative energy of the fundamental mode Rayleigh wave in each layer of the regular layere semi-infinite body according to the displacement vibration mode function, and correcting the relative energy in each layer by utilize the material mechanical parameter difference of the relative surface layer of each layer; 3, taking the relative energy in each layer as a weight function, calculating an average value of the weight function weighted with the shear wave velocity or the Rayleigh wave velocity of each layer and the total relative energy, and obtaining an analytical expression of the phase velocity of the Rayleigh wave base order mode in a regular layered semi-infinite body.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Method and apparatus for mitigation of modal dispersion effects in multimode fiber
InactiveUS7215847B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesEngineeringCoarse wavelength division multiplexing
A method for mitigating modal dispersion in a multimode optical fiber involves launching a diffractionless optical beam, such as a Bessel beam, into a multimode optical fiber. A fiber optical transmission system includes a multimode optical fiber transmission medium having an input end and an output end, an optical signal transmitter in communication with the input end of the multimode optical fiber medium, means for converting the optical signal into a diffractionless optical signal, means for launching the diffractionless optical signal in the input end of the multimode optical fiber transmission medium, means for outputting the propagated optical signal from an output end of the multimode fiber transmission medium, and a receiver that receives the optical signal from the output means. Fiber optic communication systems employing the invention embodiments include point-to-point transmission links, local area networks and WDM systems including coarse wavelength division multiplexing and dense wavelength division multiplexing systems.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
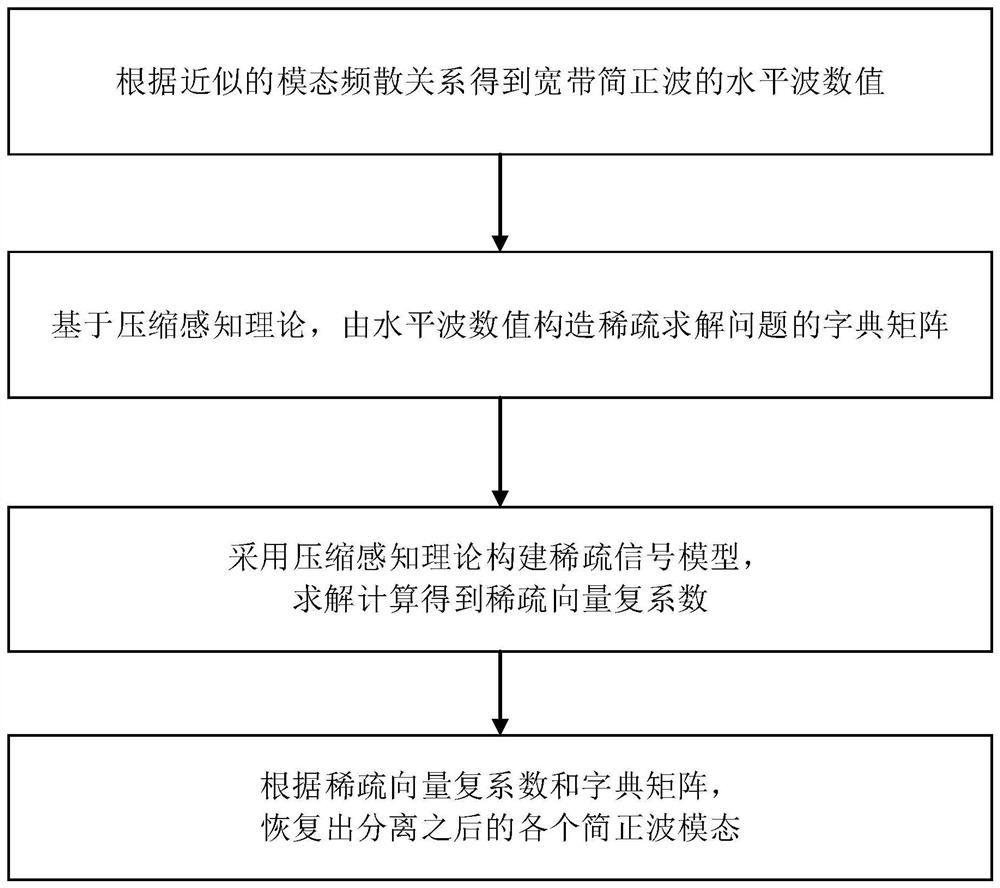
Single hydrophone normal wave modal separation method and system based on compressed sensing
ActiveCN112784412AWide range of applicable scenariosDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsSound pressureSeabed
The invention relates to the technical field of underwater acoustic signal processing, in particular to a single hydrophone normal wave modal separation method and system based on compressed sensing, and the method comprises: obtaining a horizontal wave value of a broadband normal wave according to an approximate modal dispersion relation; based on a compressed sensing theory, constructing a dictionary matrix of a sparse solving problem by horizontal wave values; according to the dictionary matrix and a broadband frequency domain sound pressure vector received by the single hydrophone, constructing a sparse signal model by adopting a compressed sensing theory, and solving and calculating by utilizing a compressed sensing implementation algorithm to obtain a sparse vector complex coefficient; and, according to the sparse vector complex coefficient and the dictionary matrix, recovering each separated normal wave mode. The method is wider in applicable scene and can be suitable for the condition that refraction type and reflection type normal positive waves exist at the same time under the negative gradient hydrological condition, and the known accurate seawater sound velocity profile and seabed parameters are not needed.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com