Method for designing and selecting optical fiber for use with transmitter optical subassembly
A technology of optical subcomponents and transmitters, which is applied in the testing of optical components, machine/structural components, optics, etc., and can solve problems such as optical aberrations and fiber coupling power exceeding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
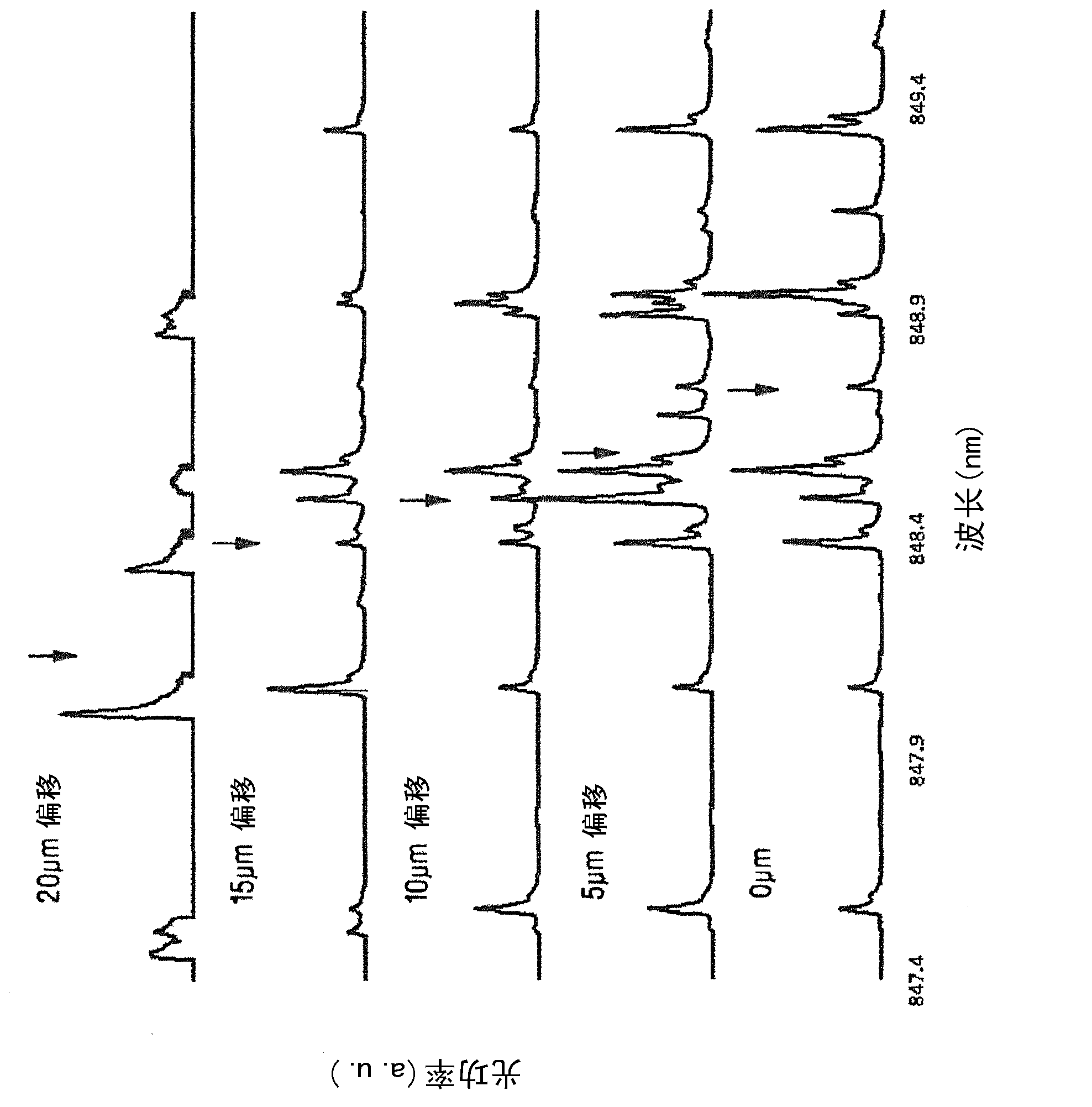
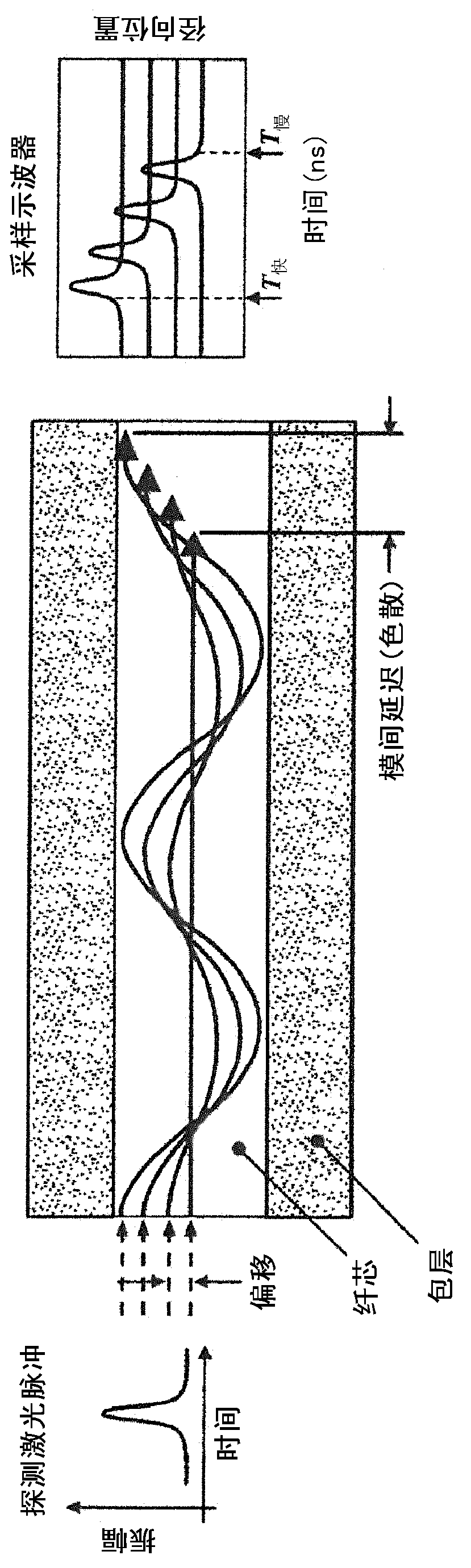
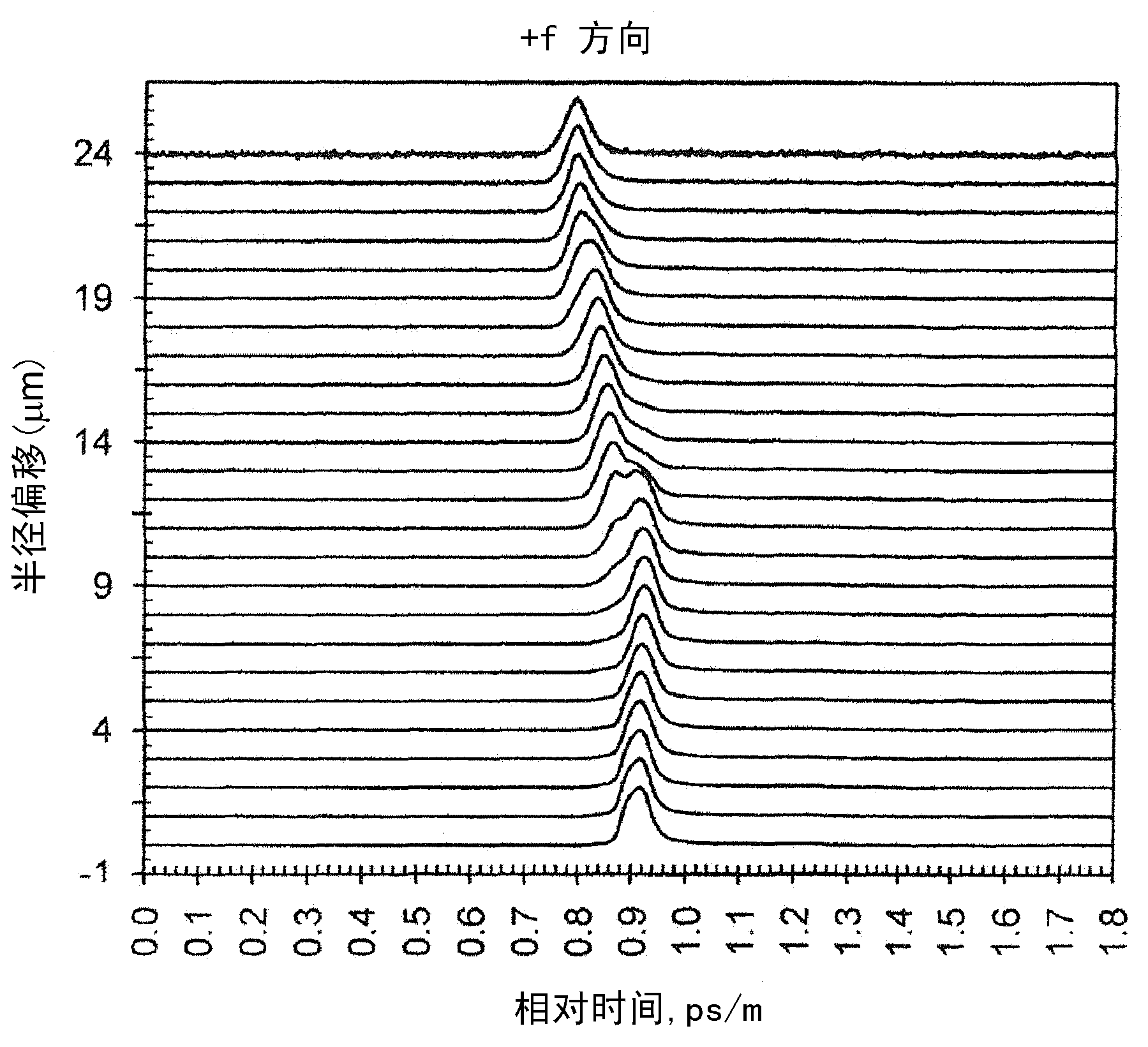
[0053] The present invention makes use of the discovery that due to the radially dependent wavelength emission pattern of the VCSEL and the way the light is coupled into the fiber, the fiber-coupled modes have a spectral composition that depends on the fiber radius and lead to non-negligible wavelength dispersion or material dispersion effect. figure 1 The spectra of various modes propagating in the MMF for five radial offsets on the fiber core are shown. The center wavelength or central wavelength of each radial spectrum is indicated by a downward arrow. Such as figure 1 As shown in , for this particular optical transmitter, on average, the center wavelength of the fiber mode shifts to shorter wavelengths for larger radial offsets. In addition to modal dispersion, this radial wavelength dependence causes the fiber modes to experience wavelength or material dispersion relative to each other. As a result, the refractive index profile must be modified to compensate for this...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com