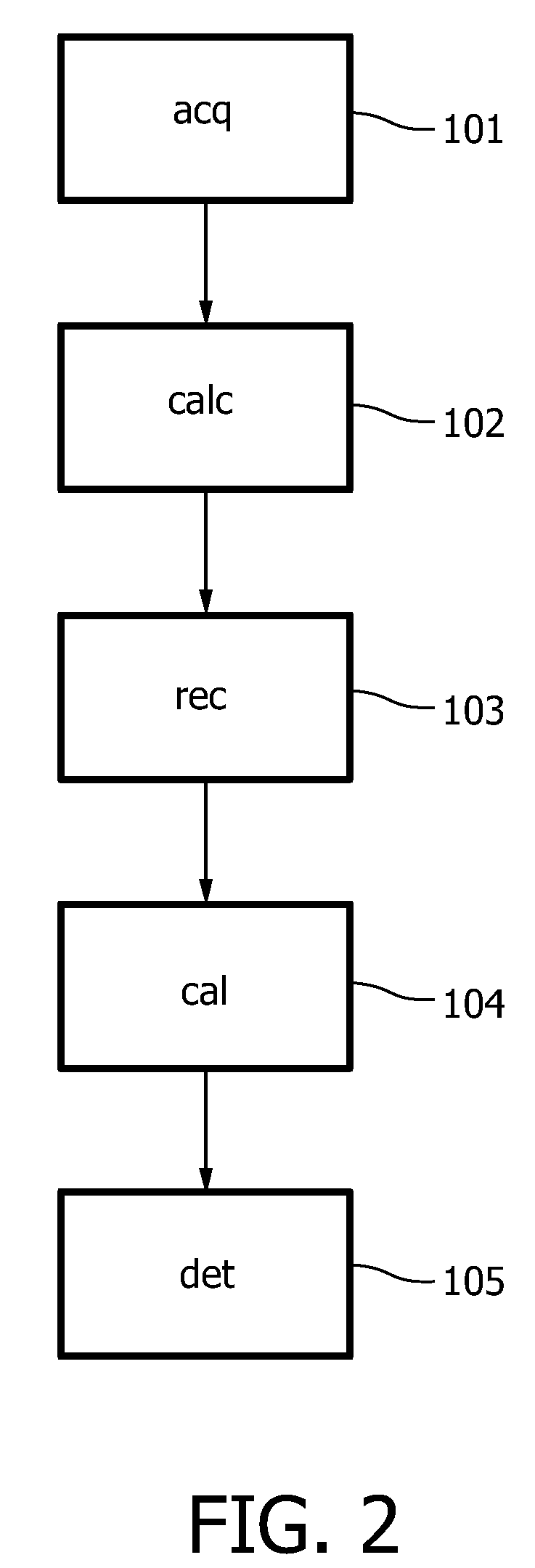
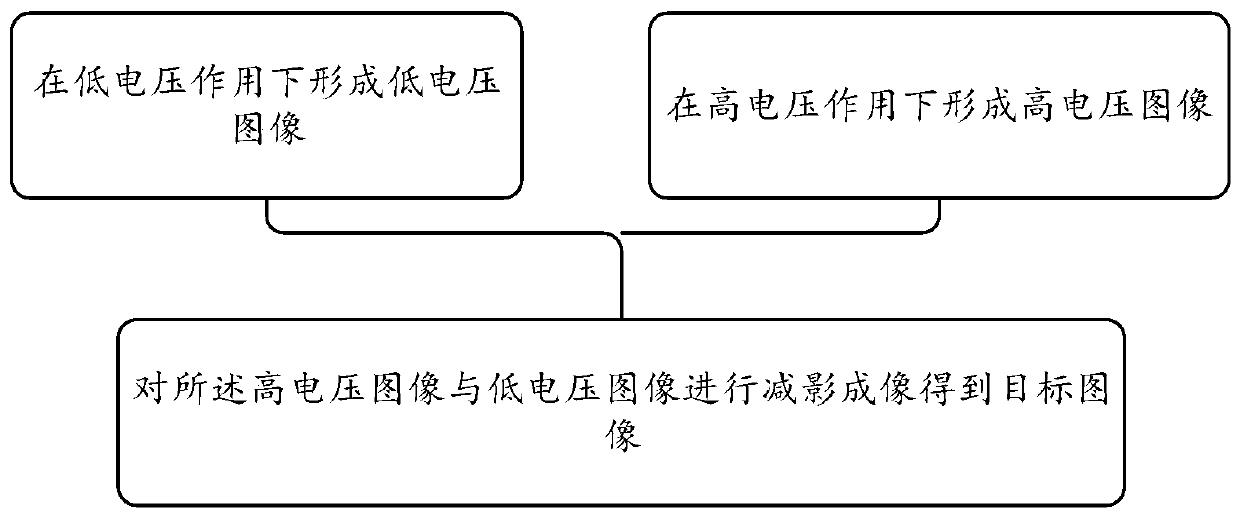
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
45 results about "K-edge" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
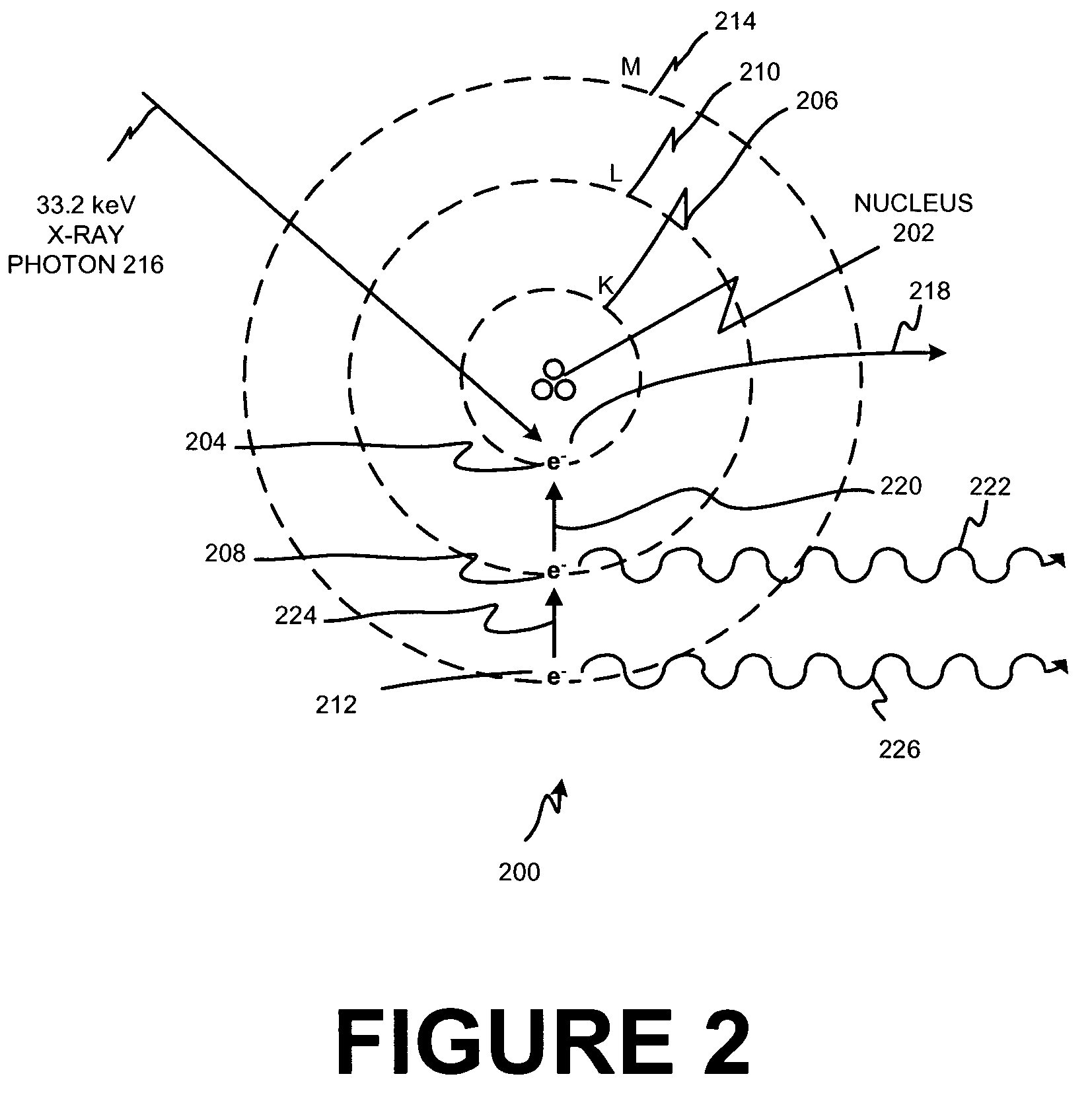
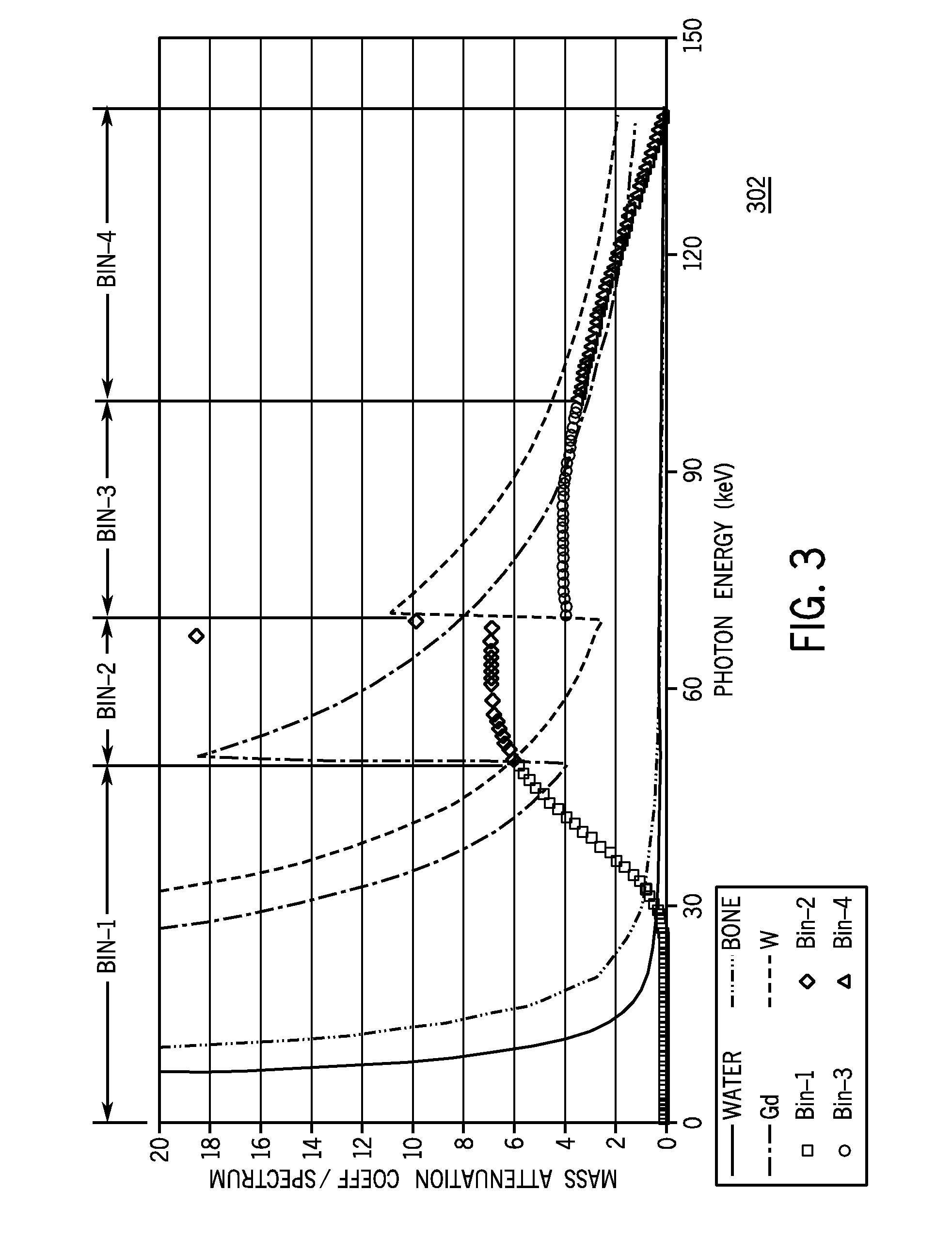
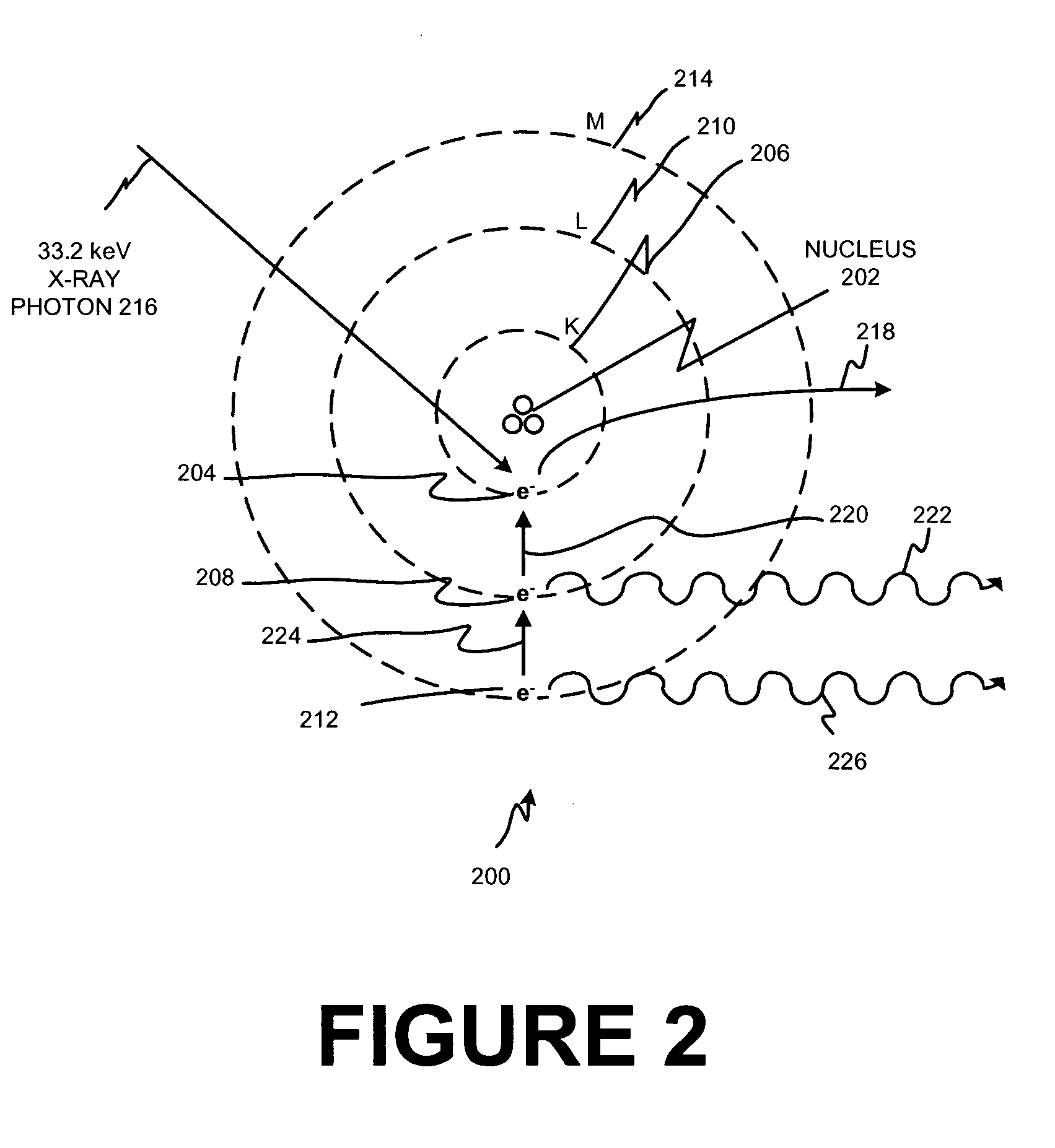
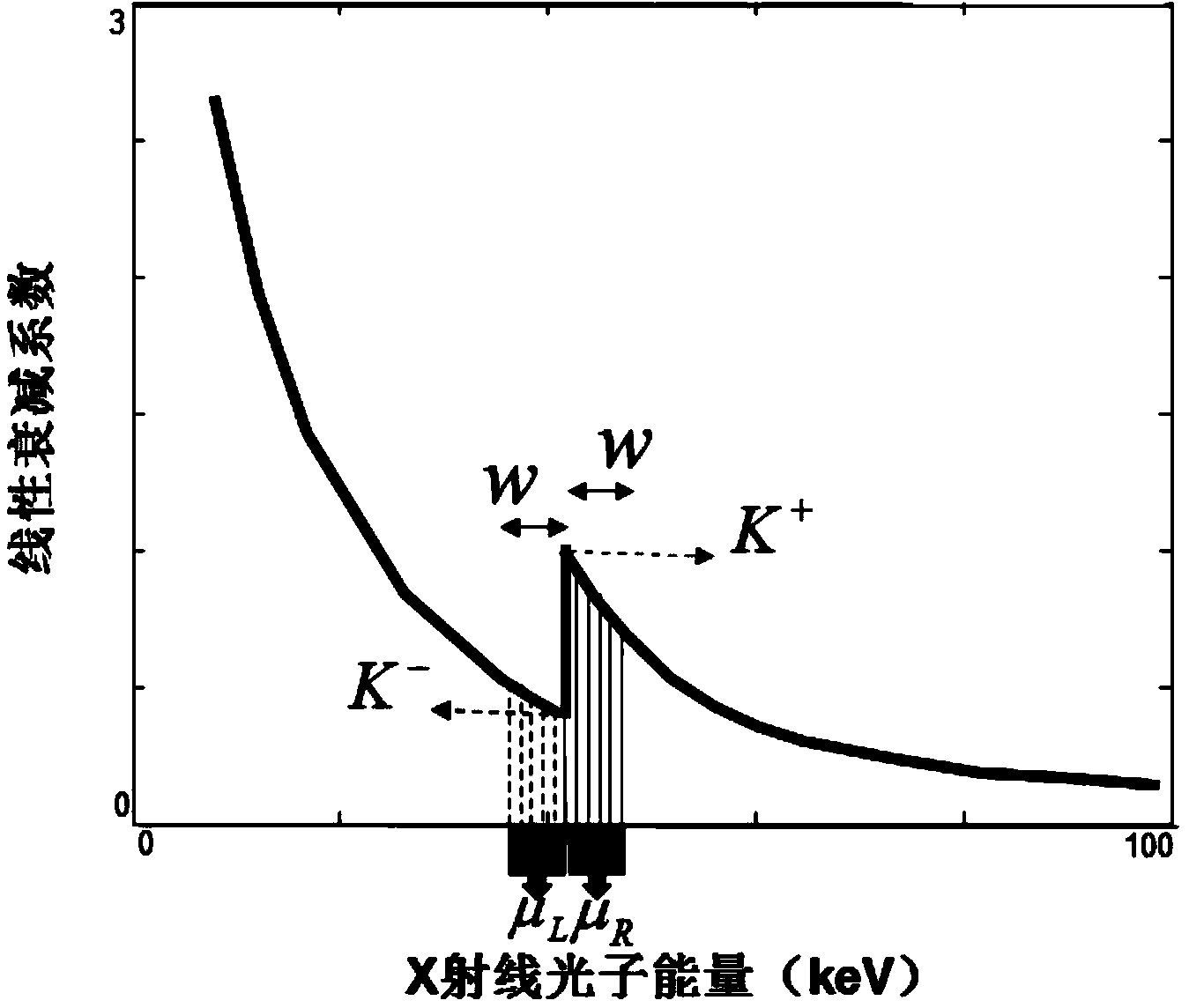
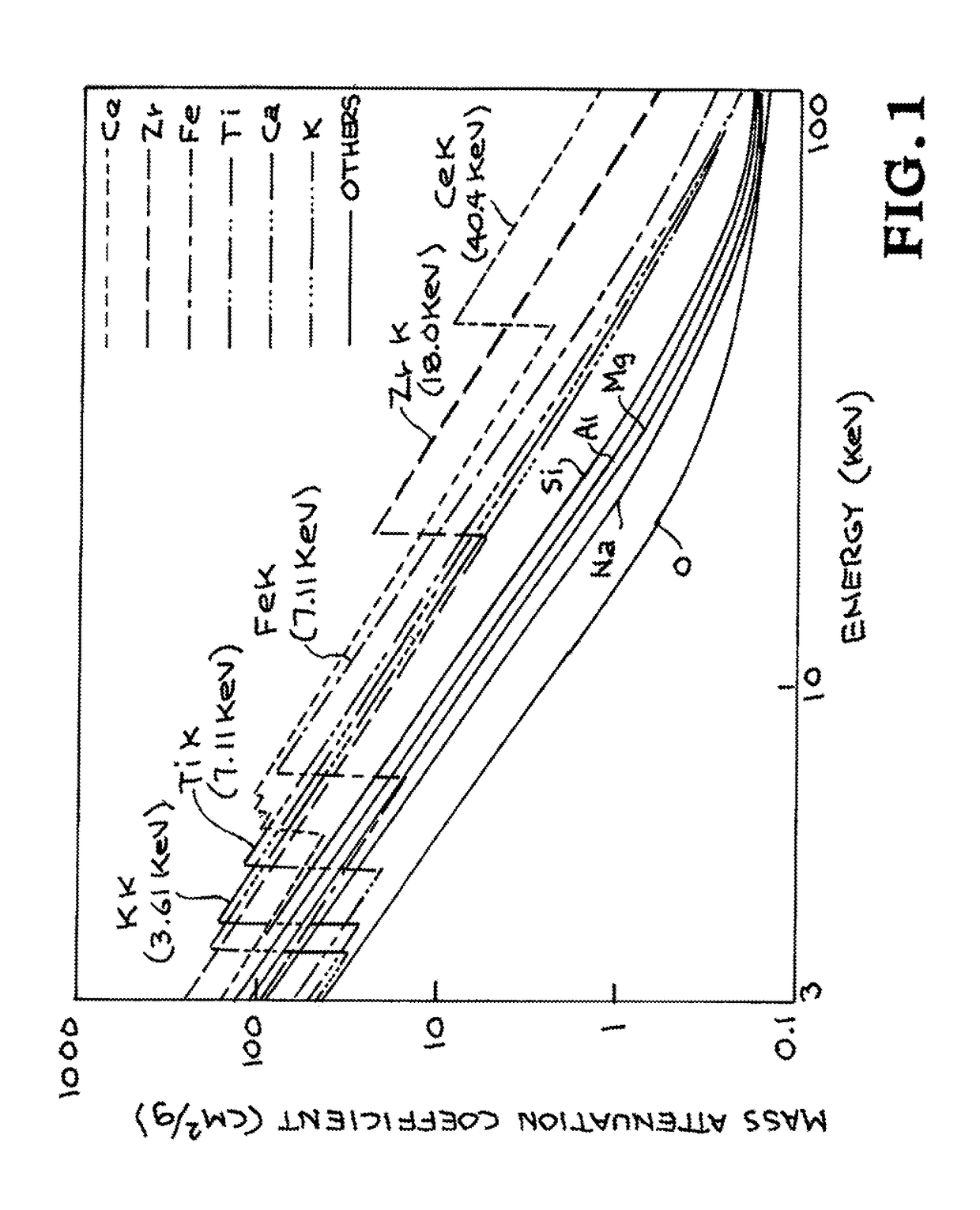
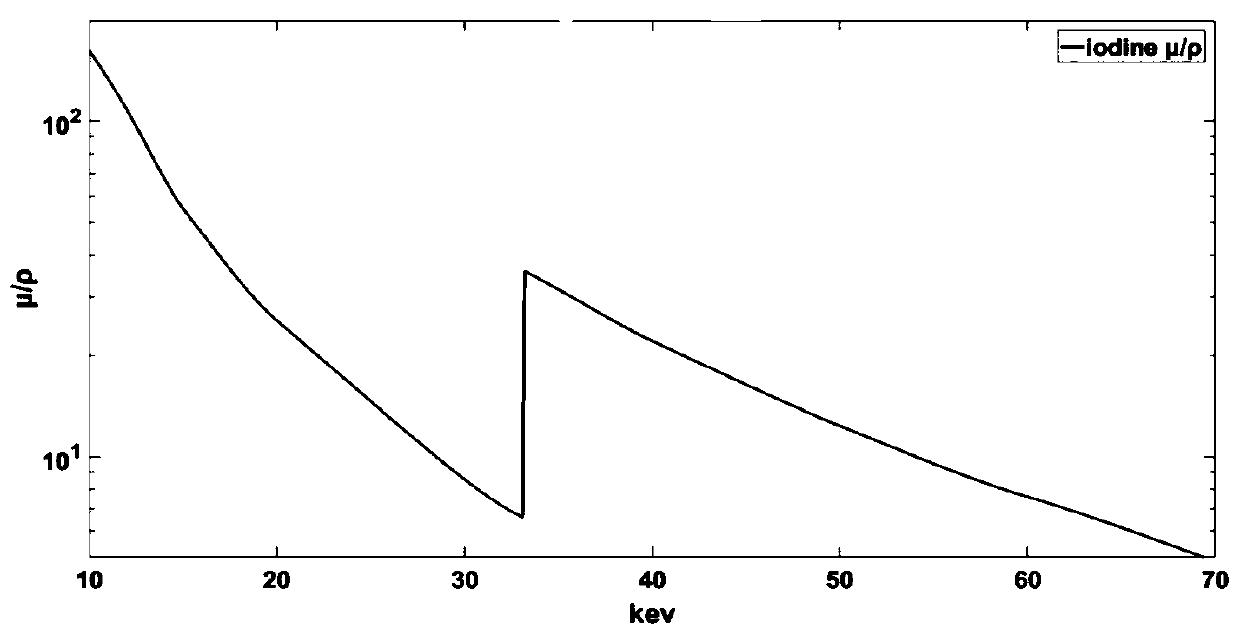
K-edge is the binding energy of the K-shell (innermost, using X-ray notation) electron of an atom. There is a sudden increase in the attenuation coefficient of photons occurring at a photon energy just above the binding energy of the K-shell electron of the atoms interacting with the photons. This sudden increase in attenuation is due to photoelectric absorption of the photons. For this interaction to occur, the photons must have more energy than the binding energy of the K-shell electrons (K-edge). A photon having an energy just above the binding energy of the electron is therefore more likely to be absorbed than a photon having an energy just below this binding energy.
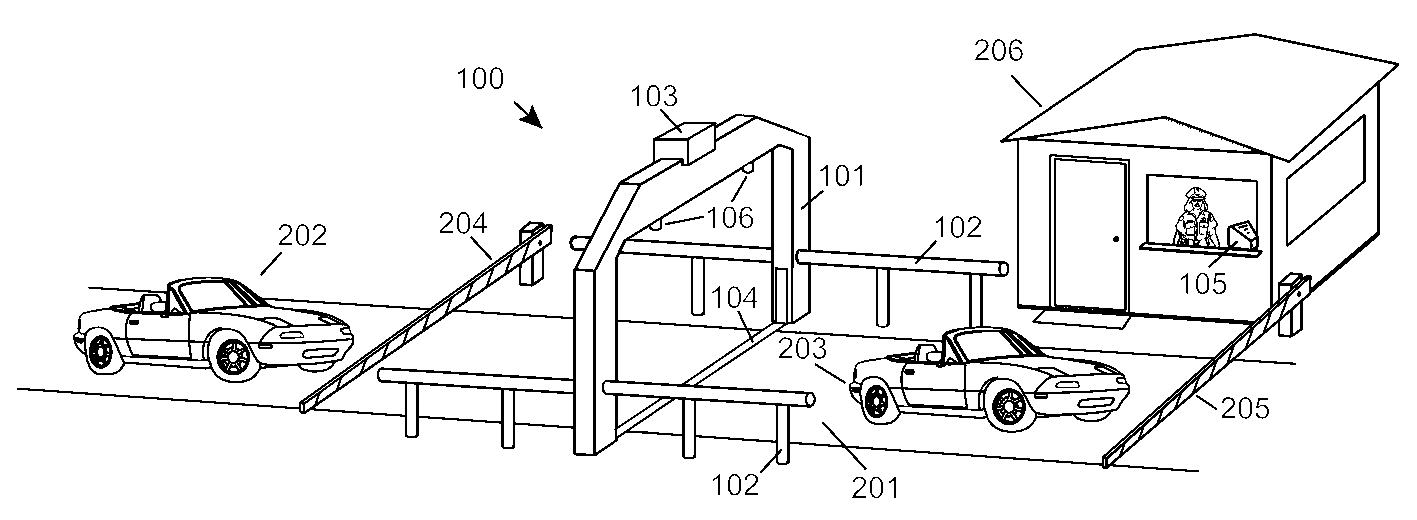
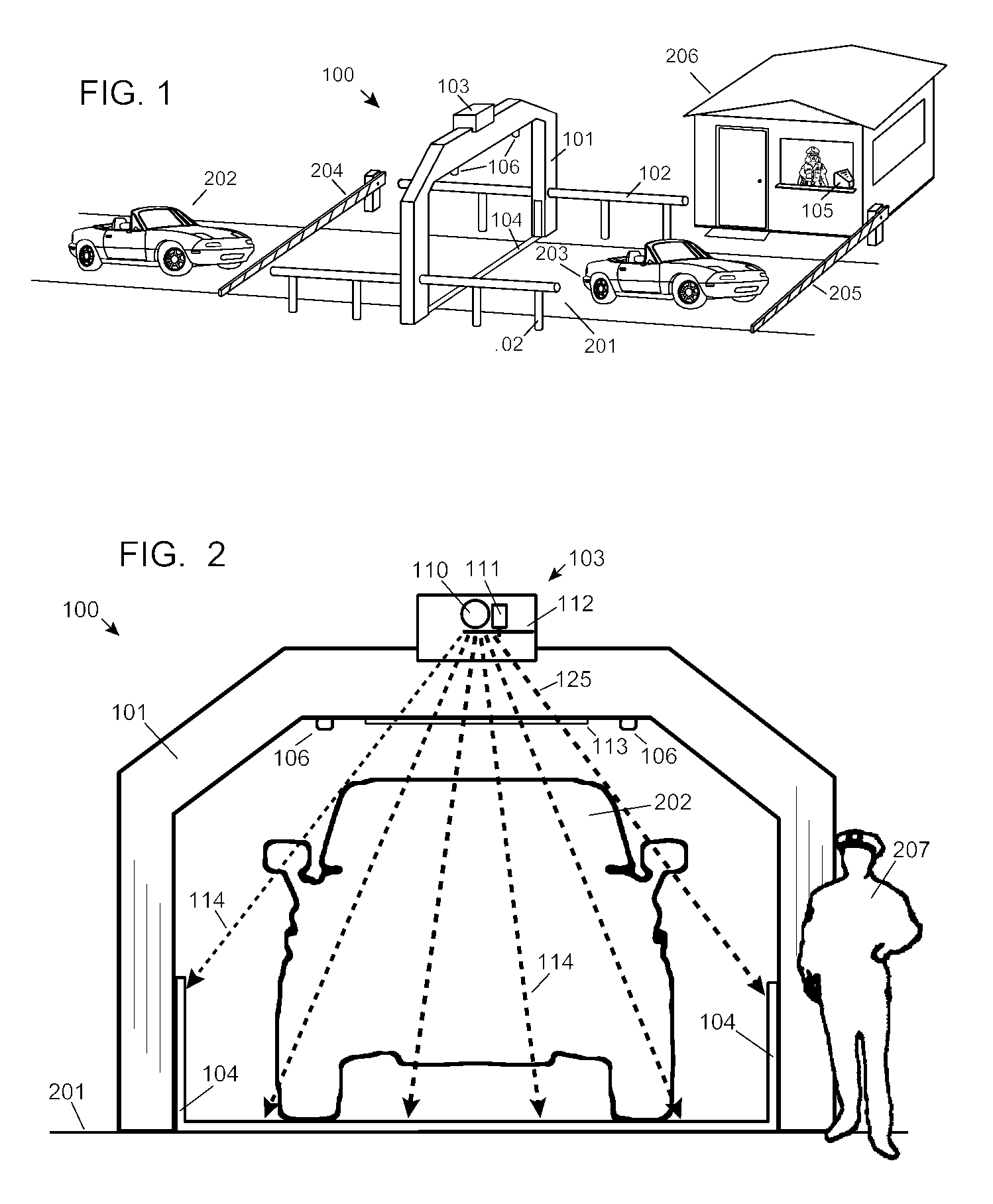
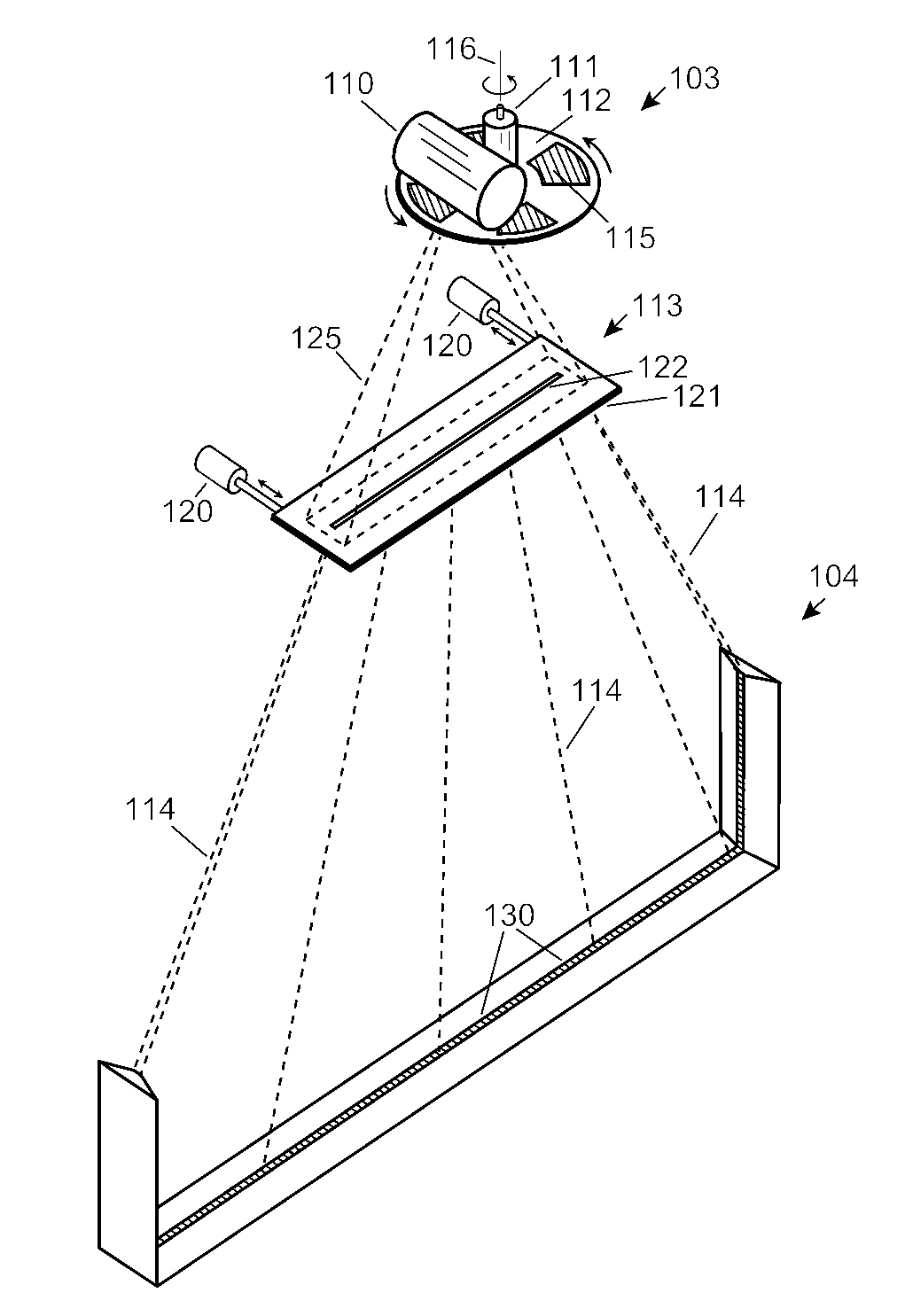
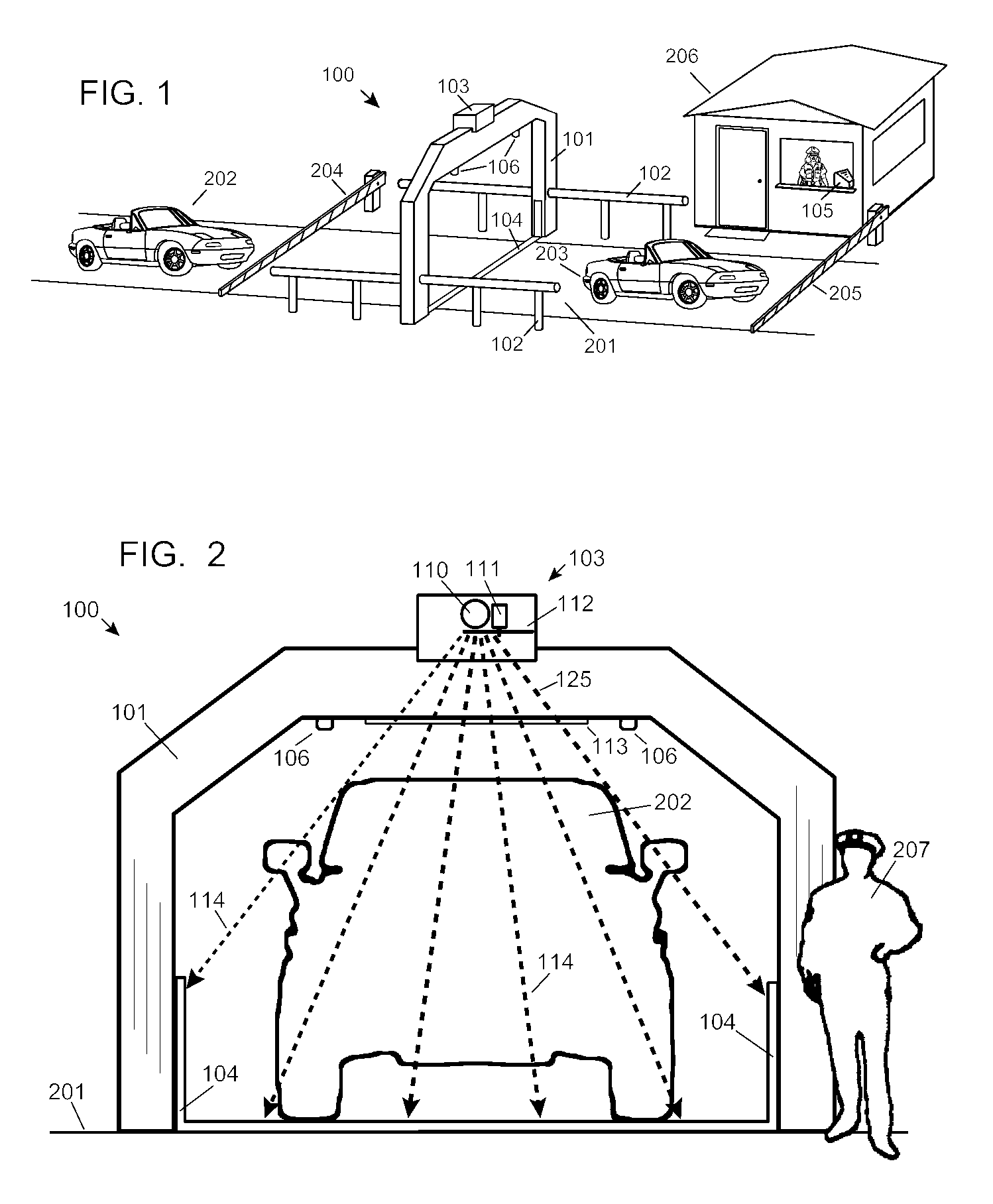
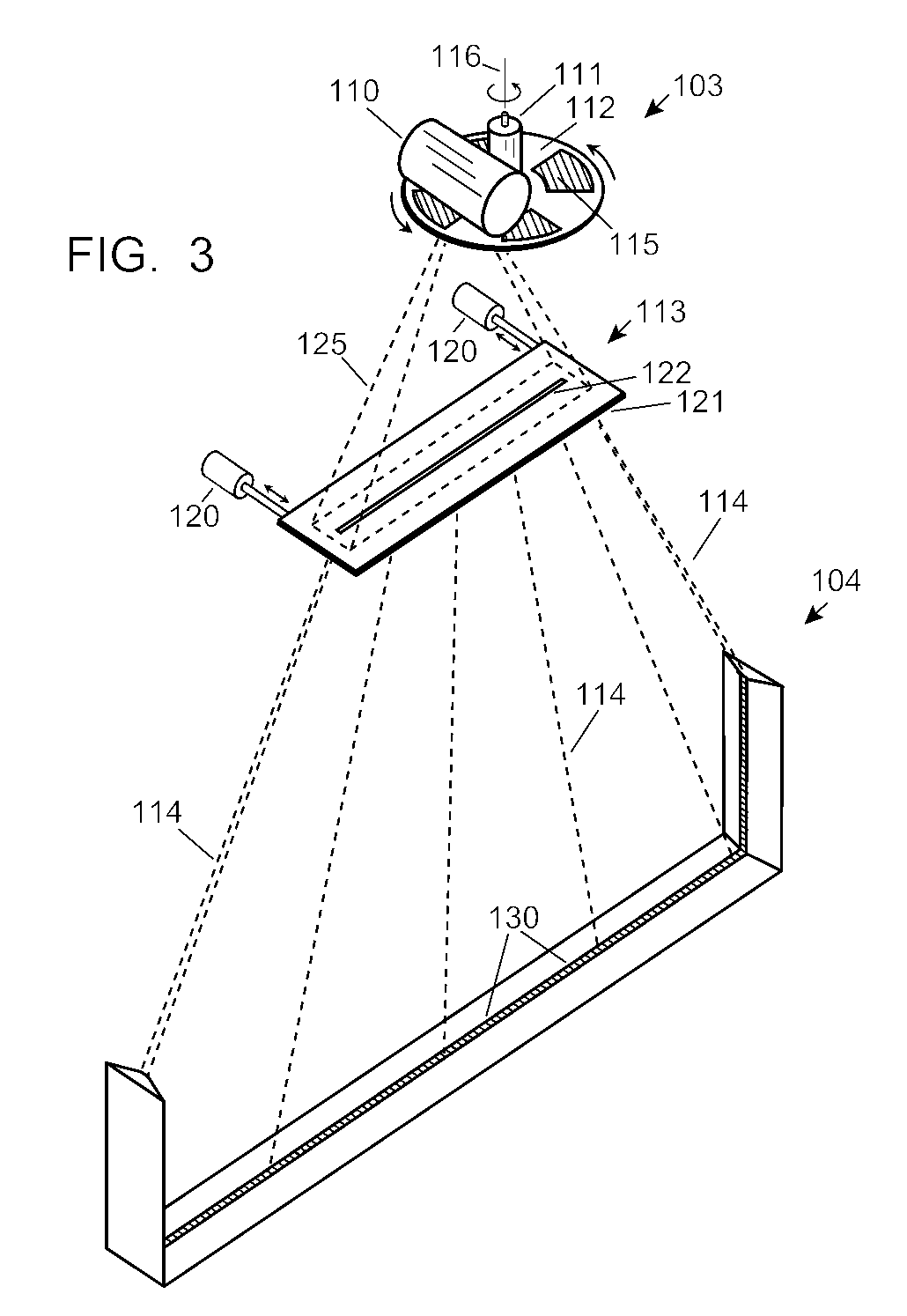
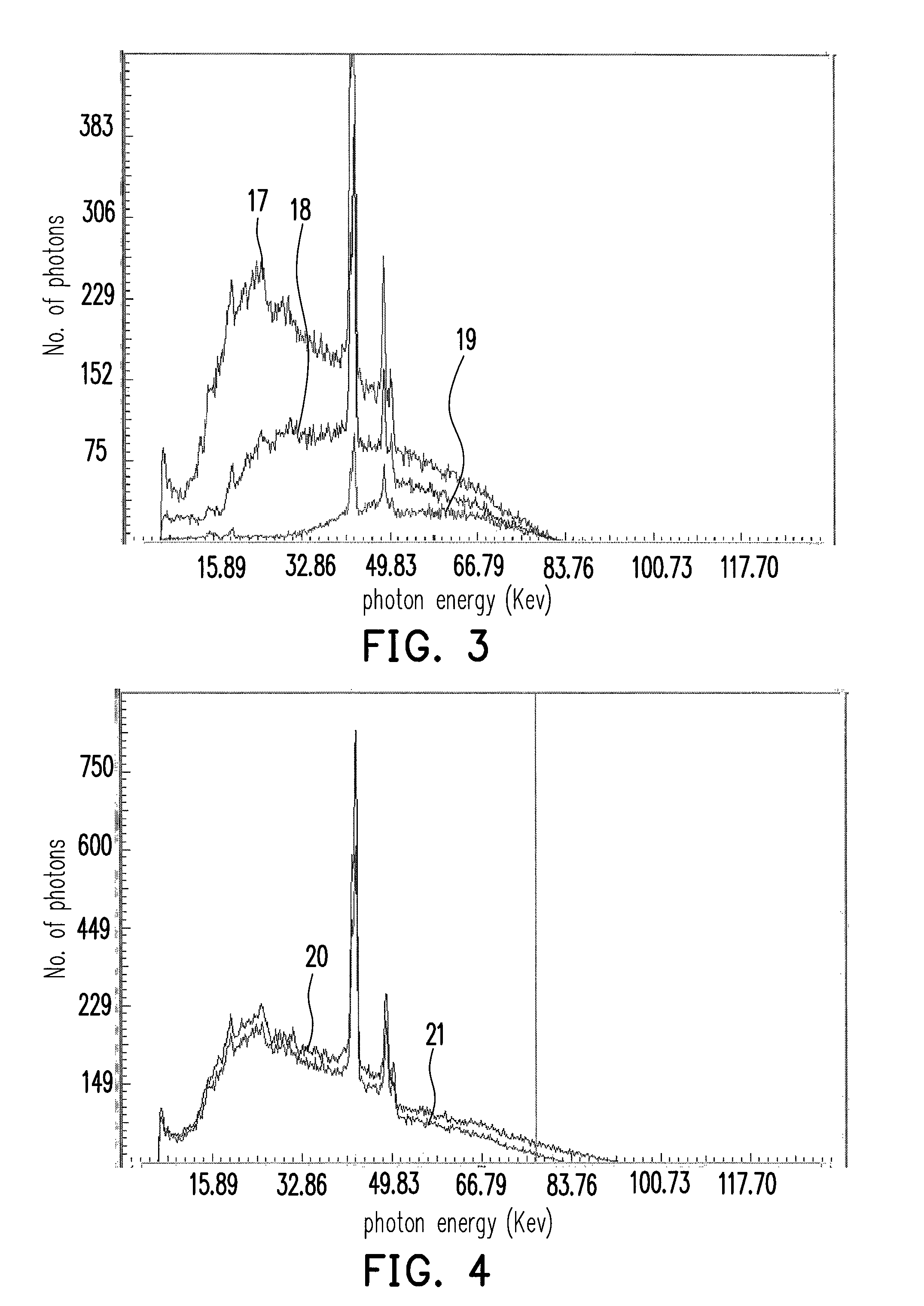
Automobile scanning system
ActiveUS7742568B2Easy to checkUniform exposureX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationAtomic elementHigh energy
A dual-energy x-ray imaging system searches a moving automobile for concealed objects. Dual energy operation is achieved by operating an x-ray source at a constant potential of 100 KV to 150 KV, and alternately switching between two beam filters. The first filter is an atomic element having a high k-edge energy, such as platinum, gold, mercury, thallium, lead, bismuth, and thorium, thereby providing a low-energy spectrum. The second filter provides a high-energy spectrum through beam hardening. The low and high energy beams passing through the automobile are received by an x-ray detector. These detected signals are processed by a digital computer to create a steel suppressed image through logarithmic subtraction. The intensity of the x-ray beam is adjusted as the reciprocal of the measured automobile speed, thereby achieving a consistent radiation level regardless of the automobile motion. Accordingly, this invention provides images of organic objects concealed within moving automobiles without the detritus effects of overlying steel and automobile movement.
Owner:LEIDOS
Automobile Scanning System
ActiveUS20090086907A1Easy to checkUniform radiation exposureX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationAtomic elementHigh energy
A dual-energy x-ray imaging system searches a moving automobile for concealed objects. Dual energy operation is achieved by operating an x-ray source at a constant potential of 100 KV to 150 KV, and alternately switching between two beam filters. The first filter is an atomic element having a high k-edge energy, such as platinum, gold, mercury, thallium, lead, bismuth, and thorium, thereby providing a low-energy spectrum. The second filter provides a high-energy spectrum through beam hardening. The low and high energy beams passing through the automobile are received by an x-ray detector. These detected signals are processed by a digital computer to create a steel suppressed image through logarithmic subtraction. The intensity of the x-ray beam is adjusted as the reciprocal of the measured automobile speed, thereby achieving a consistent radiation level regardless of the automobile motion. Accordingly, this invention provides images of organic objects concealed within moving automobiles without the detritus effects of overlying steel and automobile movement.
Owner:LEIDOS
Diagnostic imaging two non k-edge basis materials plus n k-edge contrast agents
ActiveUS20080137803A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingData acquisitionK-edge
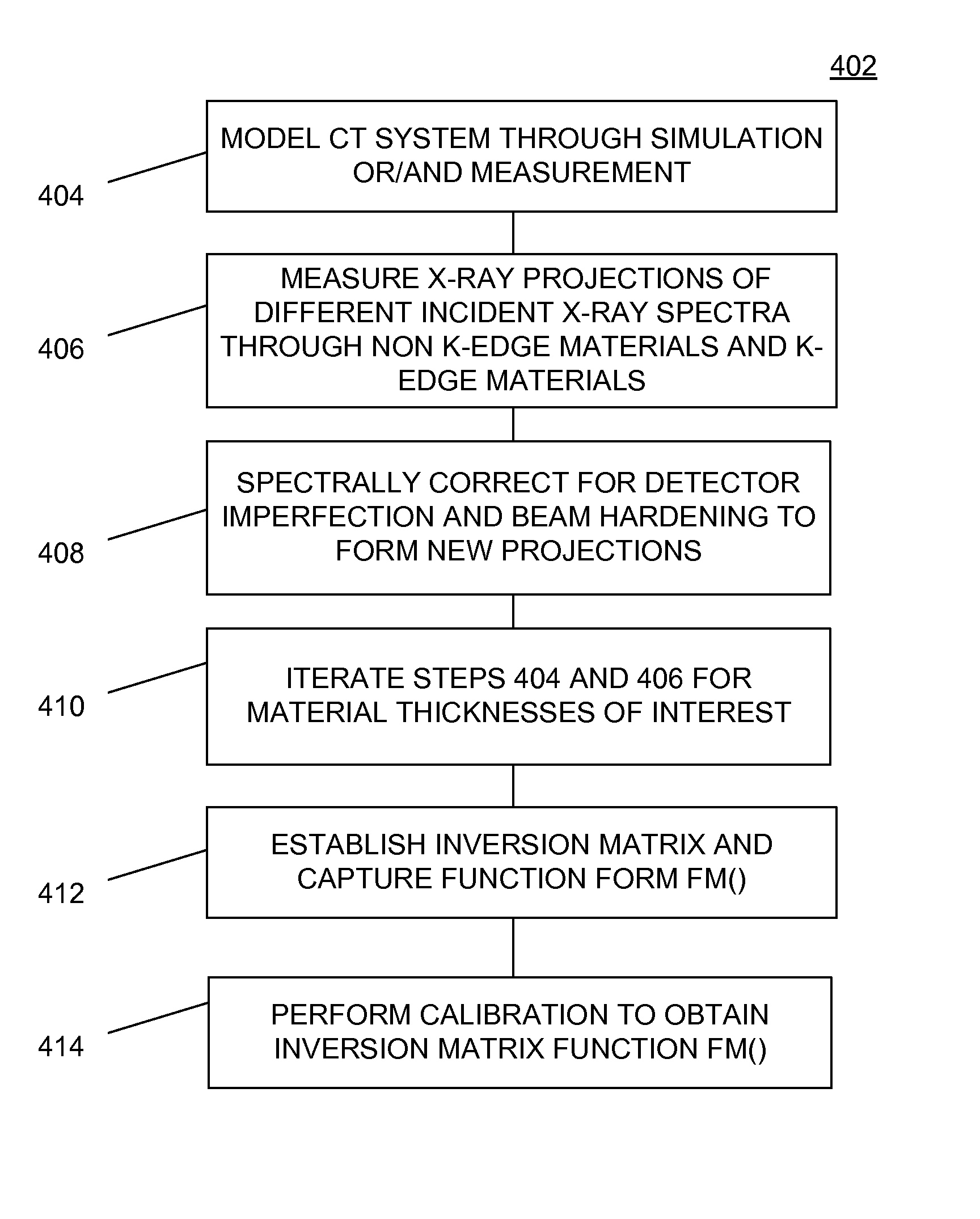
A diagnostic imaging system in an example comprises a high frequency electromagnetic energy source, a detector, a data acquisition system (DAS), and a computer. The high frequency electromagnetic energy source emits a beam of high frequency electromagnetic energy toward an object to be imaged and be resolved by the system. The detector receives high frequency electromagnetic energy emitted by the high frequency electromagnetic energy source. The DAS is operably connected to the detector. The computer is operably connected to the DAS and programmed to employ an inversion table or function to convert N+2 measured projections at different incident spectra into material specific integrals for N+2 materials that comprise two non K-edge basis materials and N K-edge contrast agents. N comprises an integer greater than or equal to 1.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for basis material decomposition with k-edge materials
InactiveUS20090052621A1Improve accuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsUltrasound attenuationAttenuation coefficient
A diagnostic imaging system includes a high frequency electromagnetic energy source that emits a beam of high frequency electromagnetic energy toward an object to be imaged, a detector that receives high frequency electromagnetic energy emitted by the high frequency electromagnetic energy source, and a data acquisition system (DAS) operably connected to the detector. A computer is operably connected to the DAS and is programmed to generate corresponding sets of projection values for three or more energy spectra through employment of attenuation coefficients of three or more basis materials to simulate responses of the diagnostic imaging system to a plurality of lengths of the three or more basis materials wherein the three or more basis materials comprise two or more non K-edge basis materials and one or more K-edge basis materials.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
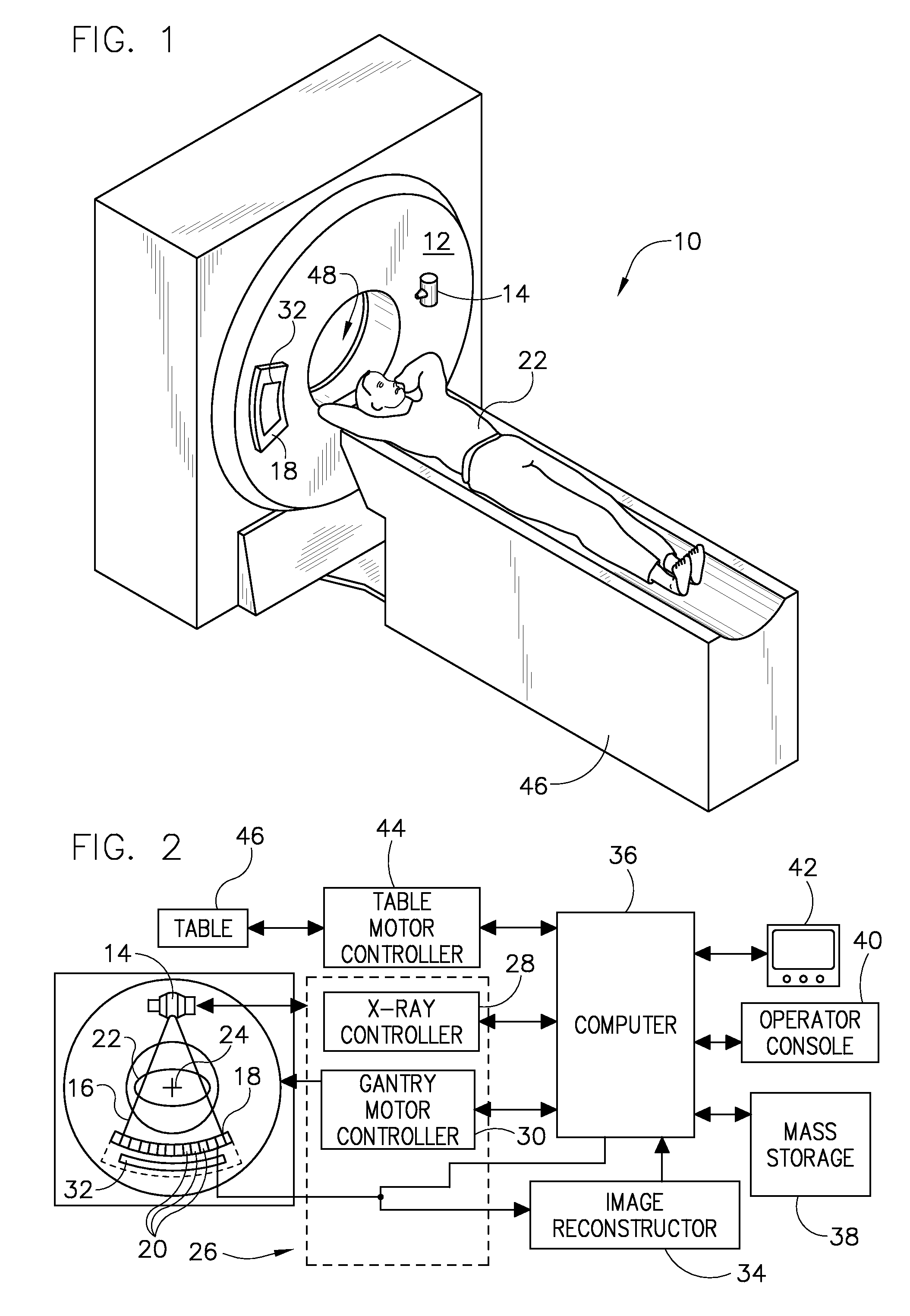
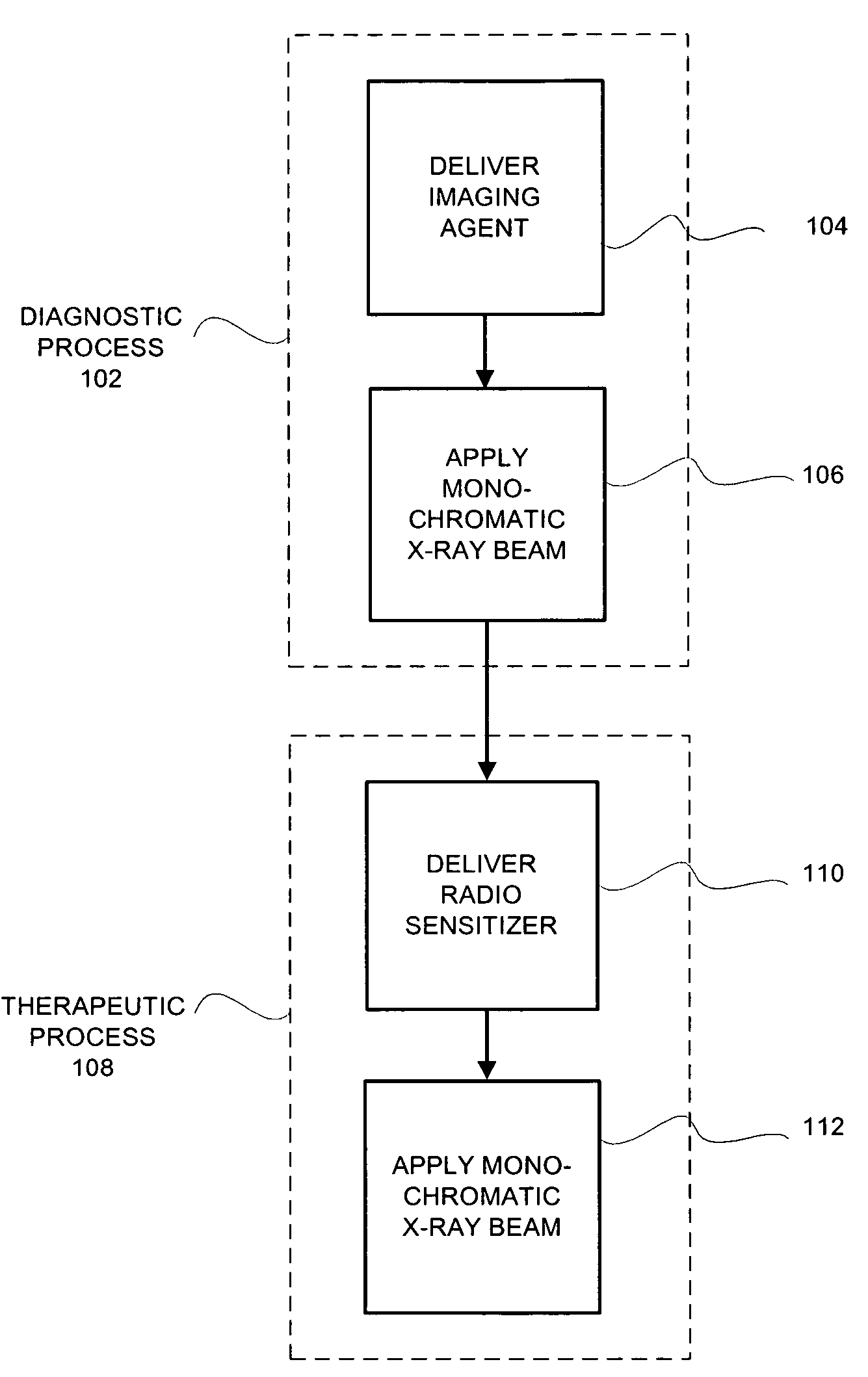
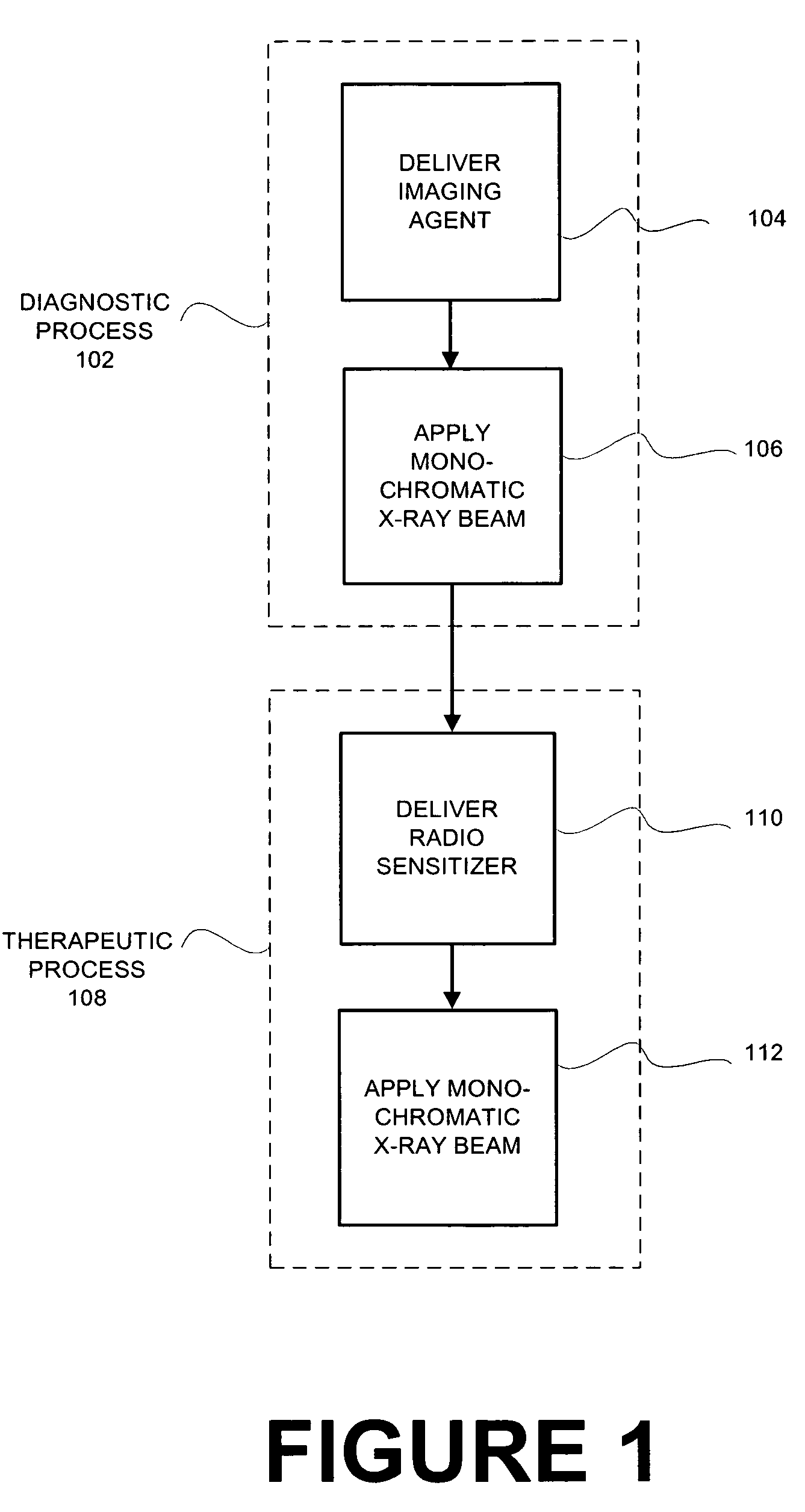
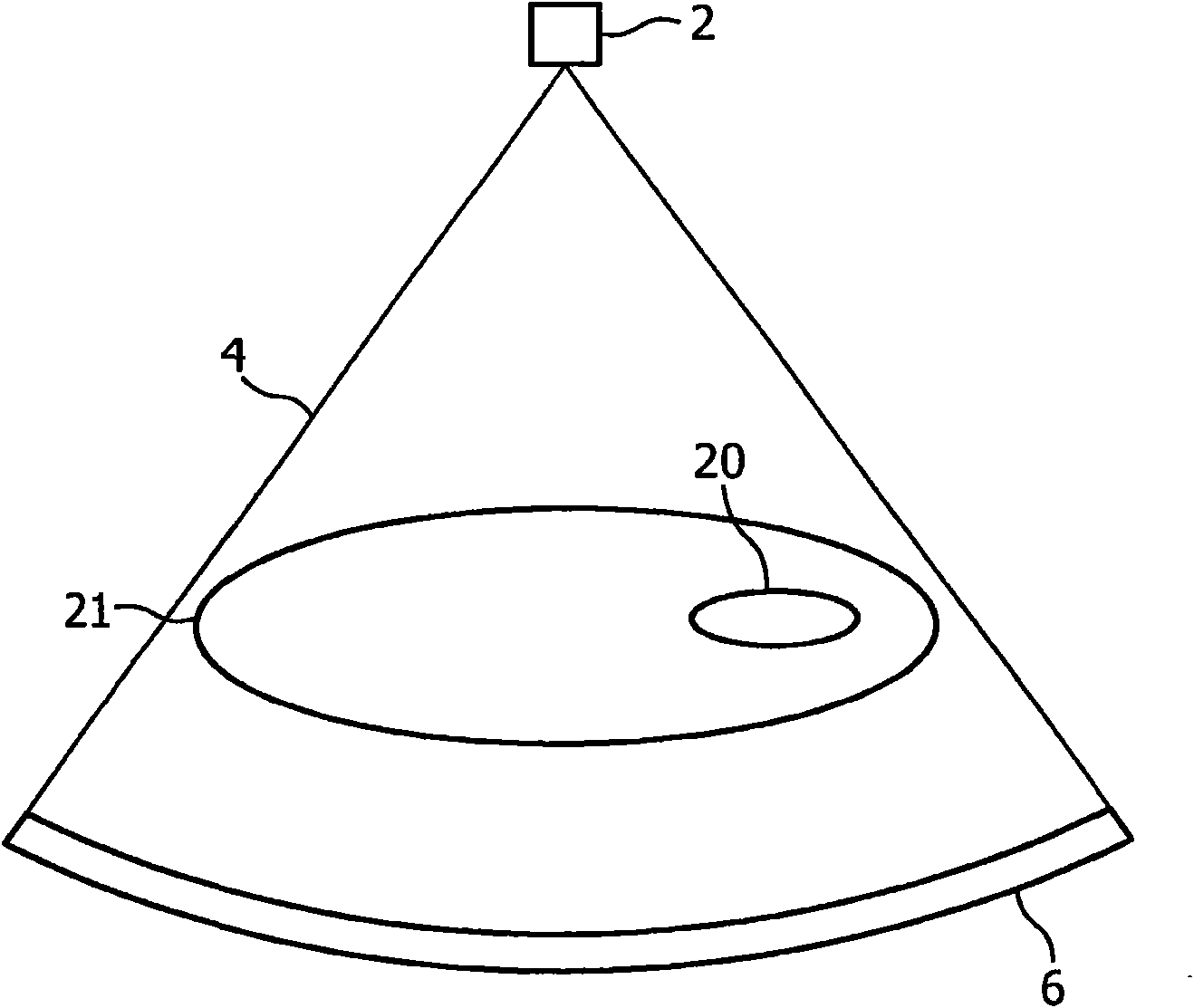
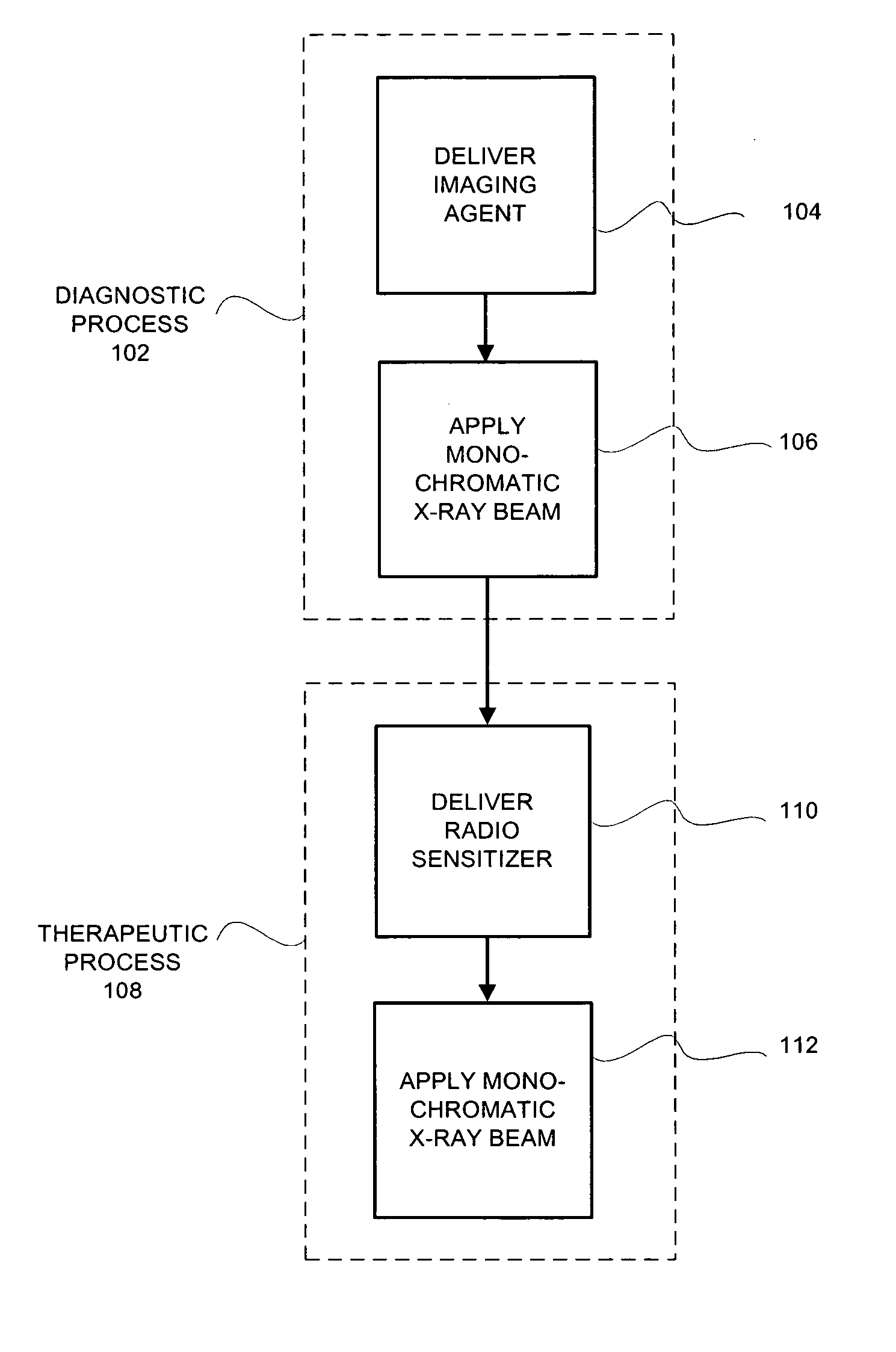
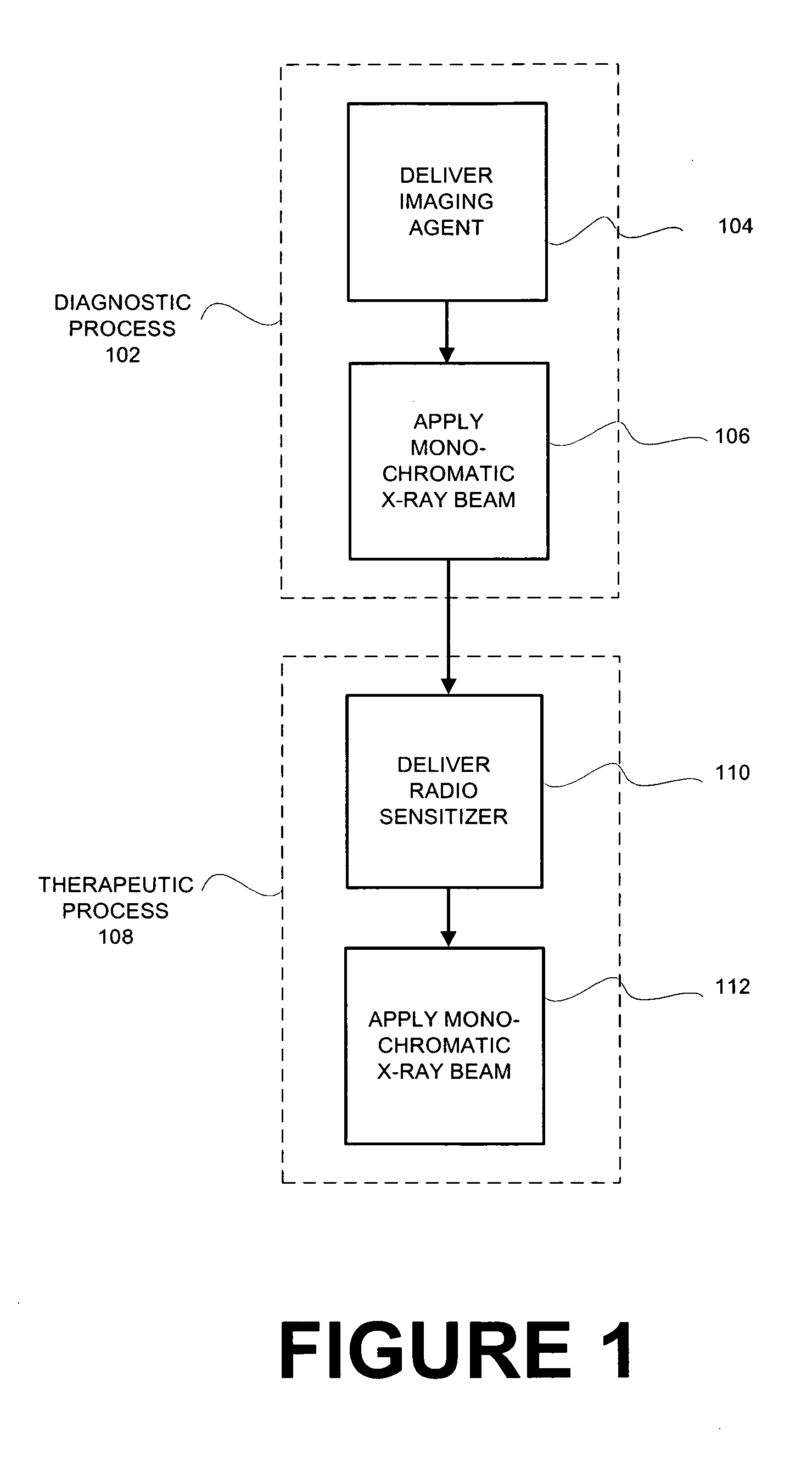
System and method for monochromatic x-ray beam therapy
InactiveUS7486984B2Cathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingRadioactive preparation carriersX-ray beam therapyRadiation sensitizers
In embodiments of the invention, a radiosensitizer or other agent is relatively uniformly accumulated in the cells of a tumor. An external monochromatic x-ray beam, which is tuned to a predetermined energy level associated with k-edge effects in the agent, is then directed to the tumor. The monochromatic x-ray beam activates the release of additional localized radiation from the agent. The additional radiation destroys the DNA of at least some tumor cells, making those tumor cells incapable of reproduction and repair. In embodiments of the invention, a single monochromatic x-ray beam source is used for both imaging and radiotherapy.
Owner:MXISYST
Lane line detection method
ActiveCN104268860AInitialization parameter insensitiveImprove robustnessImage analysisImaging processingAlgorithm
The invention discloses a lane line detection method, and belongs to the technical field of image processing. The lane line detection method comprises the steps that first a pre-processed image is horizontally divided into K edge image blocks, the height scale of the edge image block at the bottom end and the entire image is [1 / 4,1 / 3], and two or more pairs of straight lines which are closest to a vanishing line are determined under the determined vanishing line to be used as candidate line pairs of the current edge image block; then the weights of the candidate line pairs are calculated, the straight line with the maximum weight of the edge image blocks of the candidate line pairs is taken as the only lane line segment pair of the current edge image block based on the weights of the candidate line pairs; at last, the lane line of a current frame image is output based on the end points of the lane line segment pairs of all the edge image blocks. The method is used for detecting lane lines, the method is not sensitive to initialization parameters, the robustness of detection is high, and a good detecting effect can be achieved under the bad conditions of dark light, lane line loss, shadows and the like.
Owner:HOPE CLEAN ENERGY (GRP) CO LTD
Contrast phantom
A contrast phantom for assessing the characteristic, exposure-related signal and noise response and dynamic range of an image recording and detection system. The contrast phantom is composed of an absorber medium having a sudden K-edge absorption change of the mass attenuation coefficient for at least one photon energy level in-between the mean and maximum energies of the lowest energy spectrum it is subjected to. The invention further provides a method for assessing the characteristic, exposure-related signal and noise response and dynamic range of an image recording and detection system with the aforementioned contrast phantom.
Owner:AGFA NV
Radioscopy using kalpha gadalinium emission
InactiveUS20040017889A1Improve accuracyReduce radiationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsHuman bodyX-ray
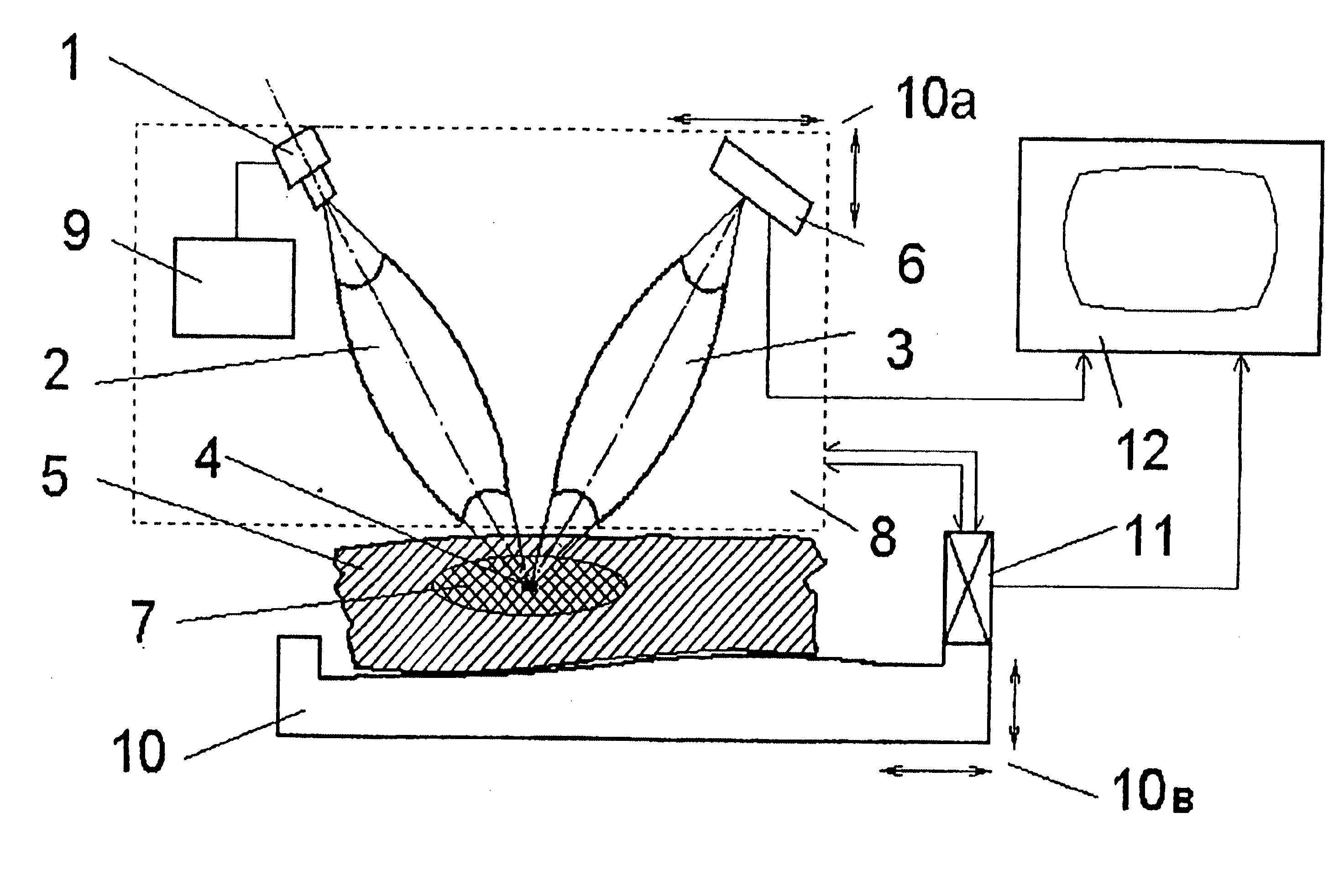
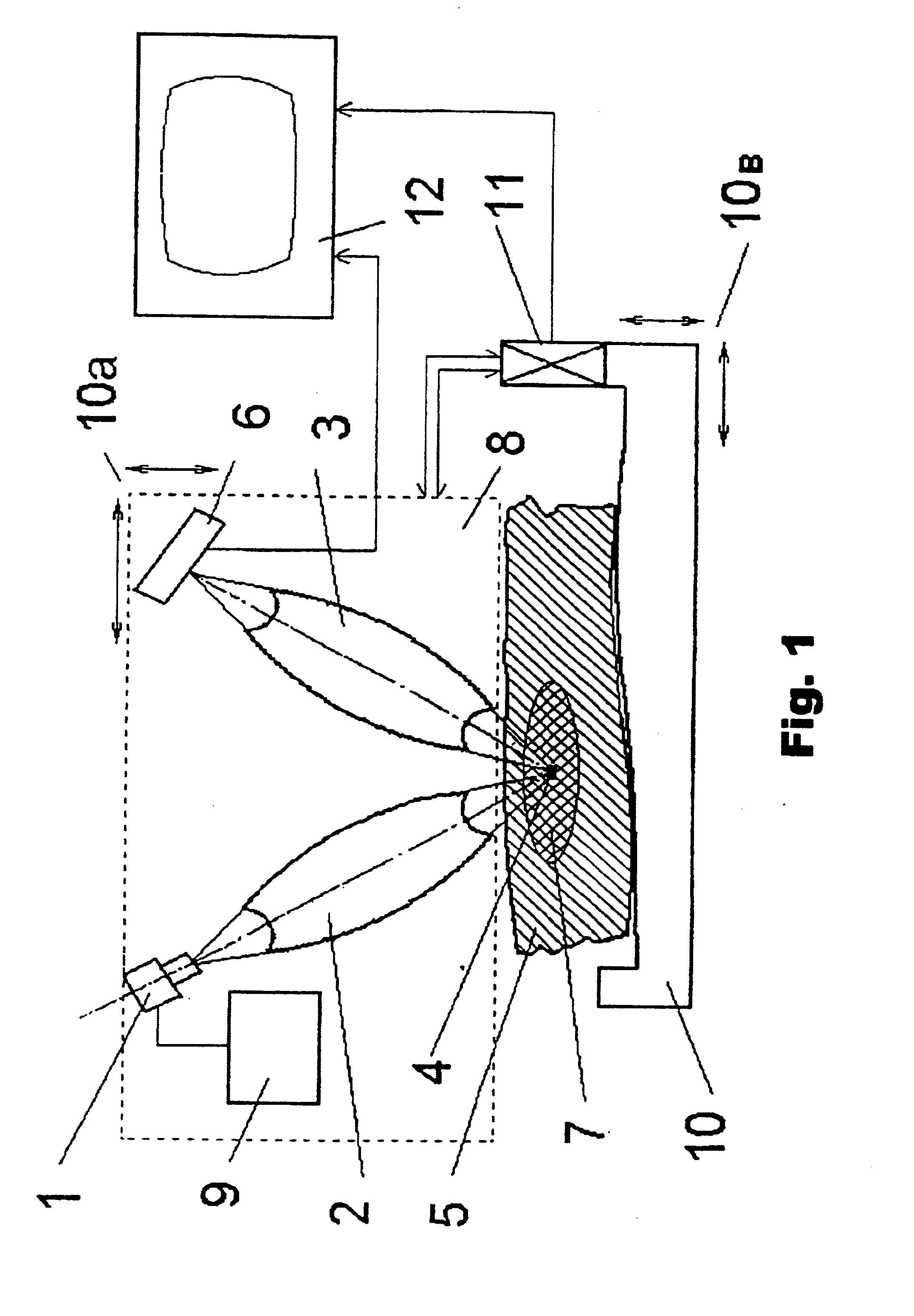
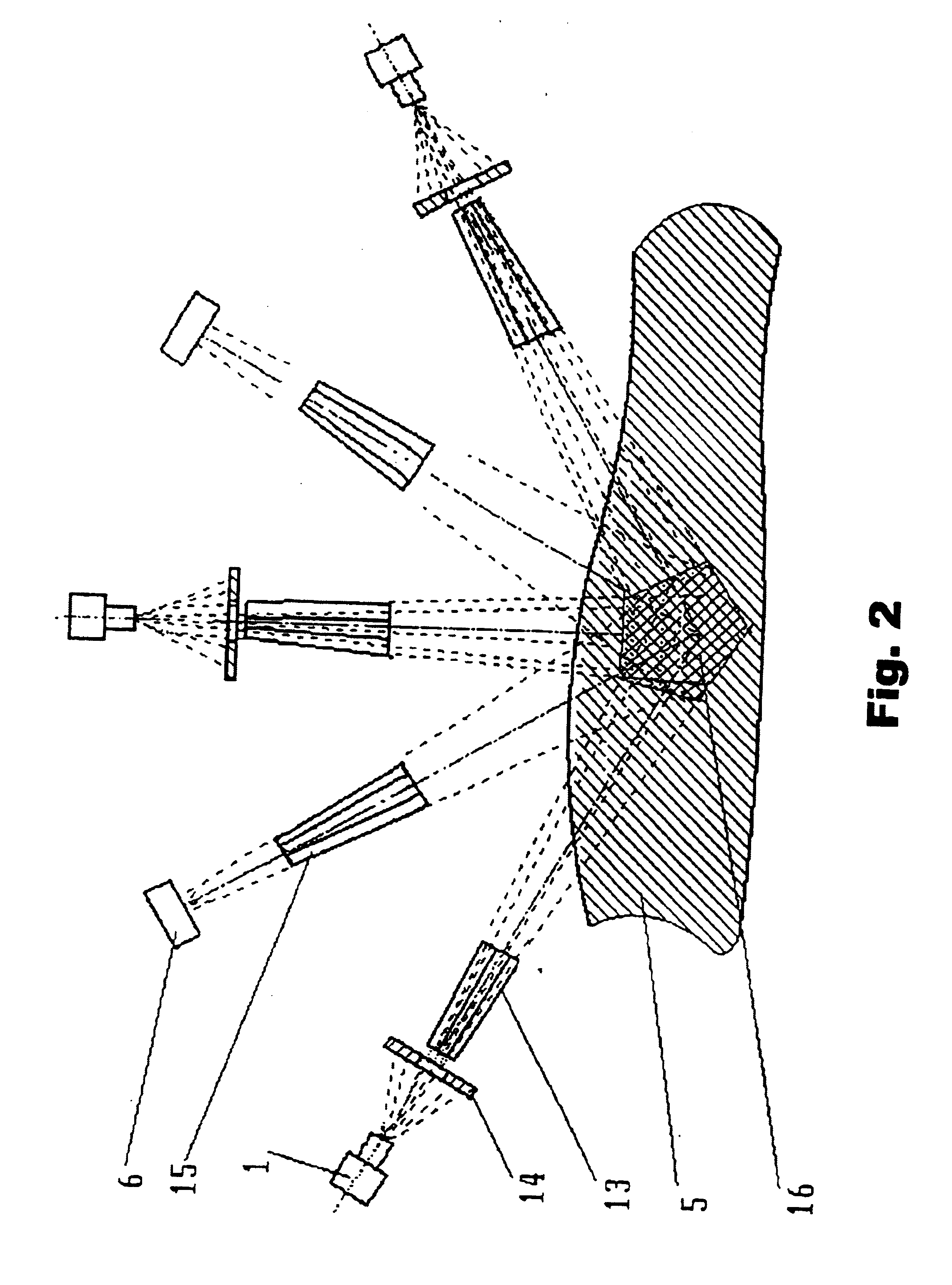
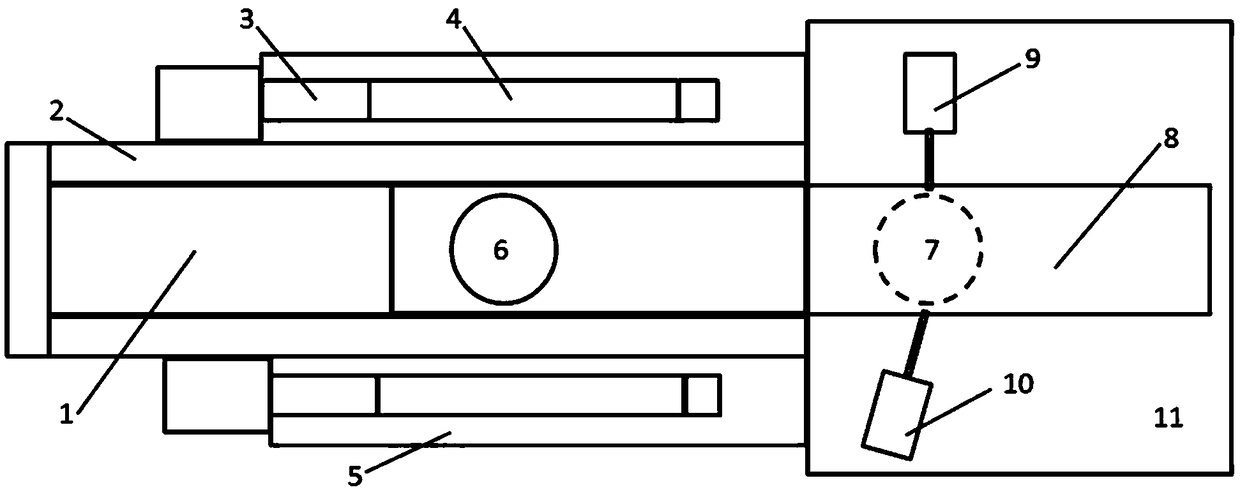
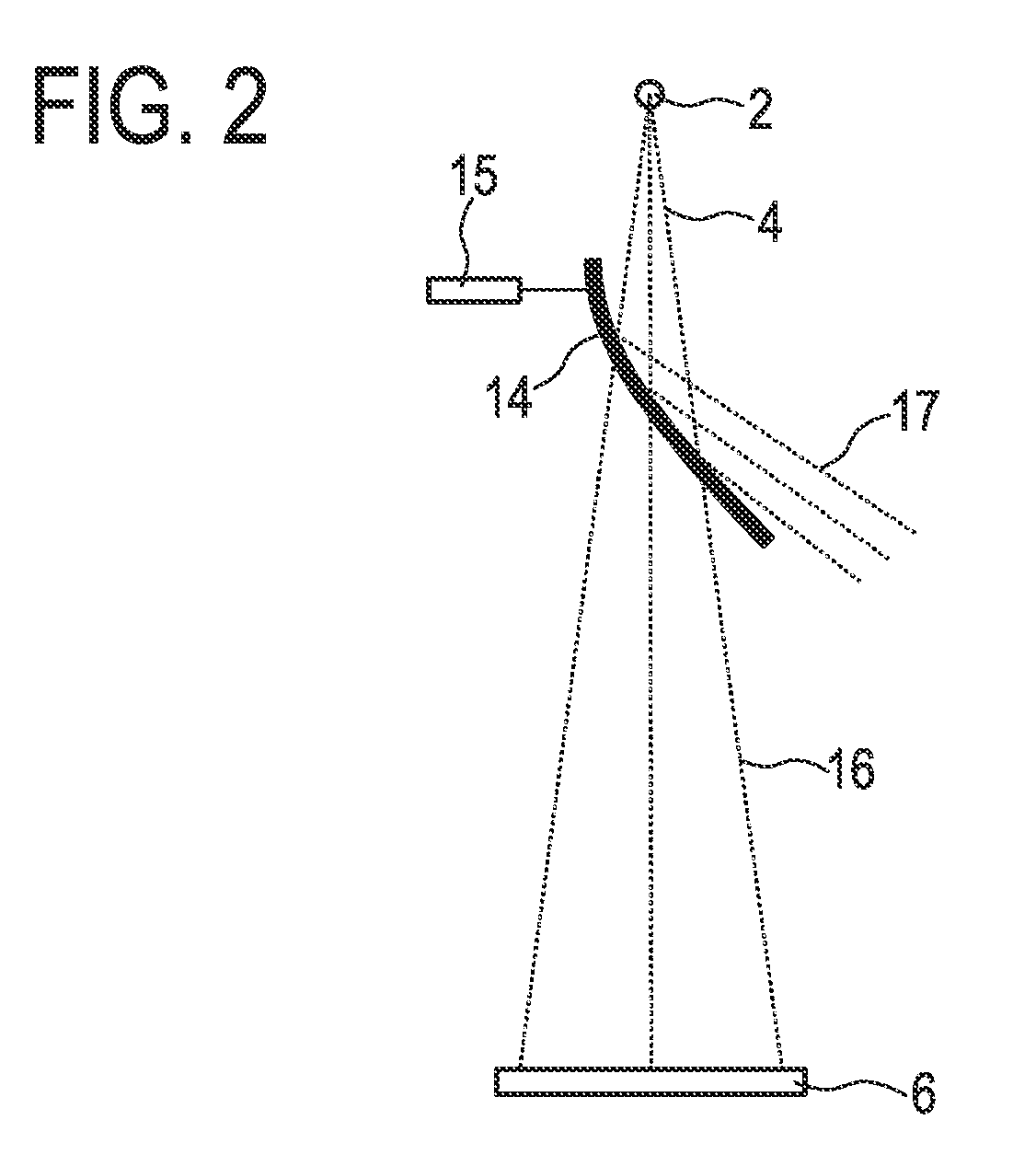
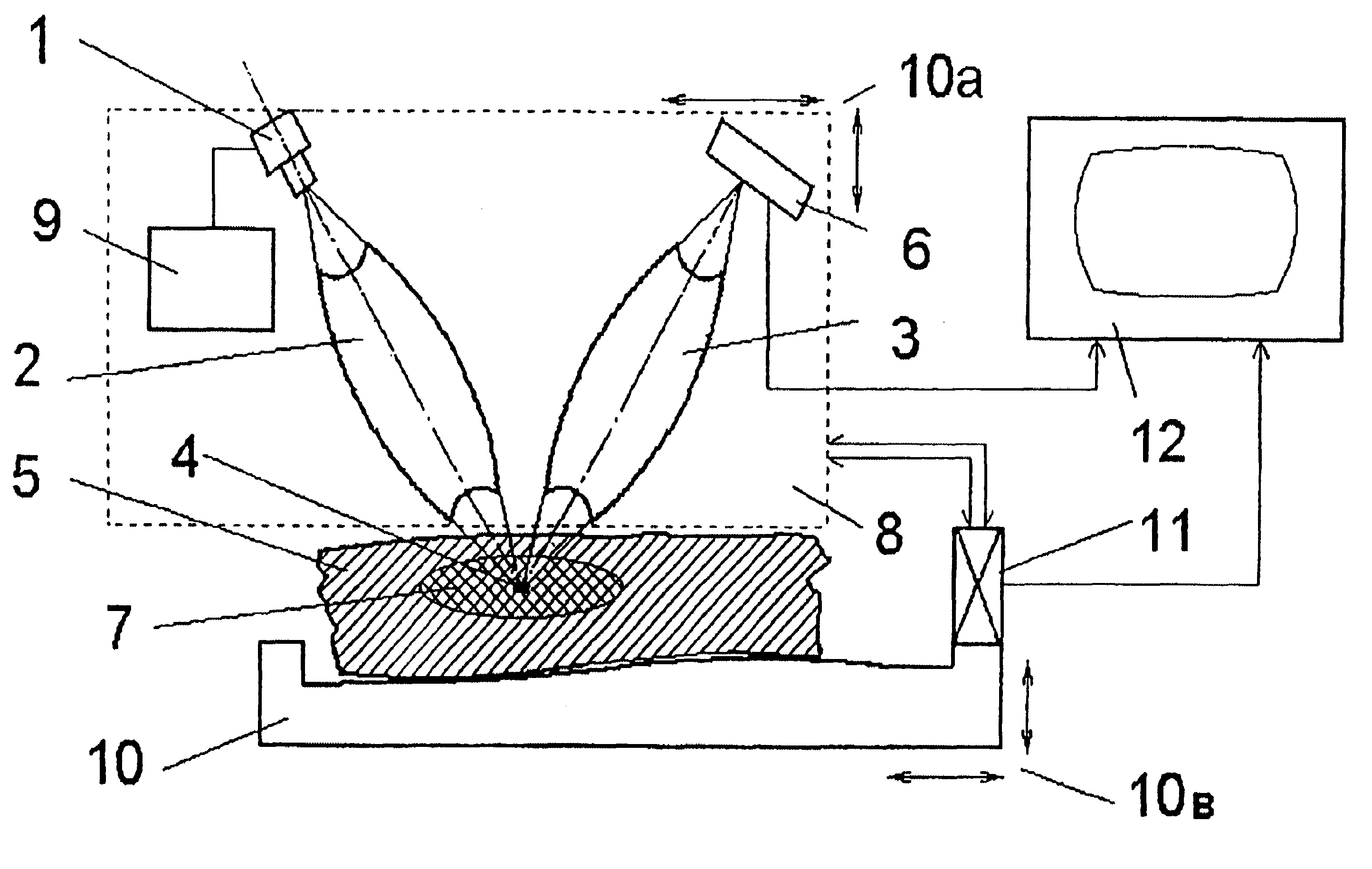
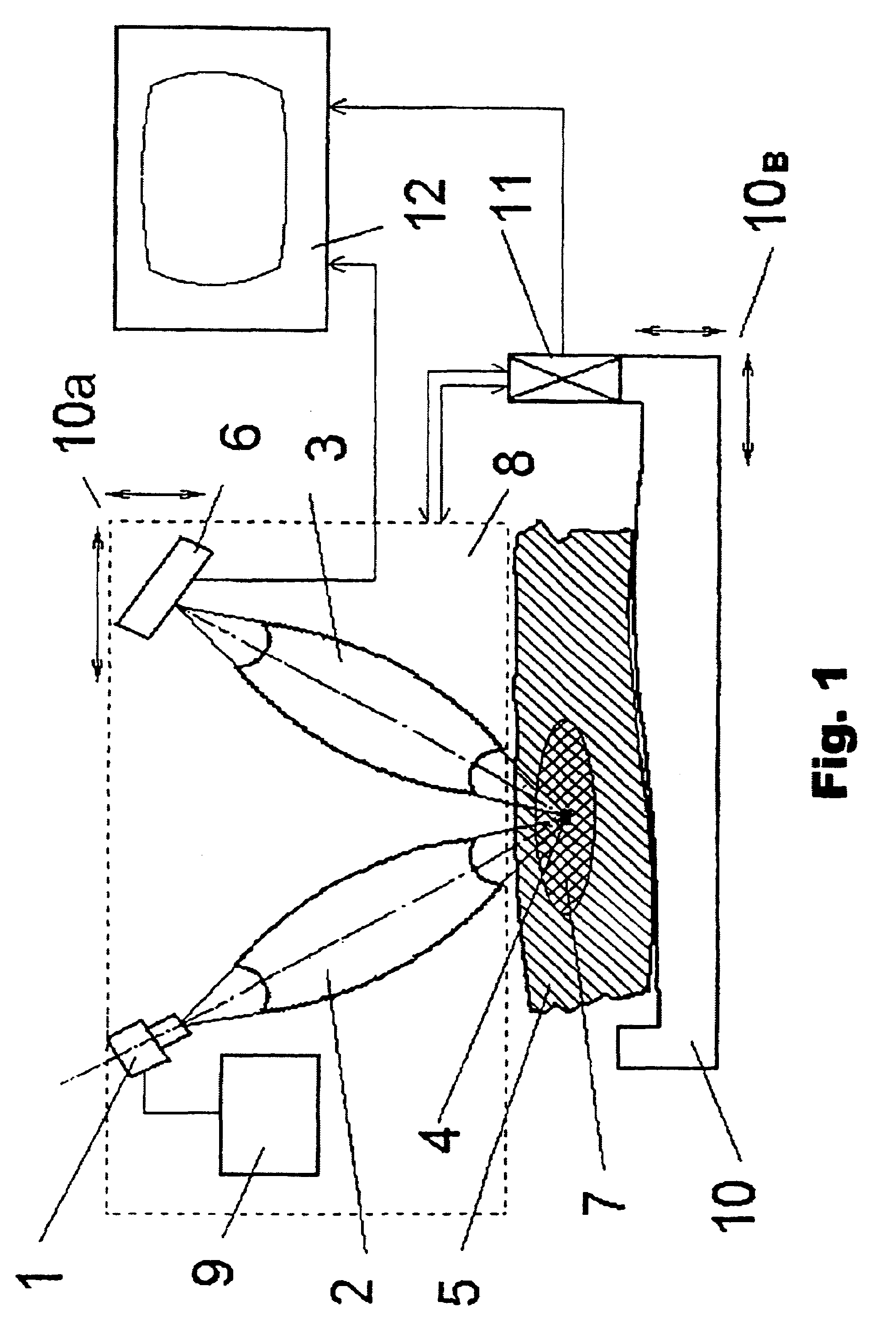
The methods proposed comprise detection of gadolinium presence in tissues and organs of human body, utilized in refining the position of malignant neoplasm and radiation treatment of said neoplasm with the purpose of damaging its cells. In order to determine the refined position of the malignant neoplasm discovered in the result of preceding diagnostics, scanning is performed of part (7) of patient body (5) in which said neoplasm is located, after introduction of gadolinium into the patient body. The scanning is performed by displacement of zone (4) of radiation concentration created by intersection of several X-ray beams having radiation energy corresponding to K-edge of gadolinium atoms absorption. The refined information is acquired using detectors (6) sensitive to Kalpha-radiation of gadolinium atoms, to which secondary radiation is transported arising in zone (4) of concentration. Then scanning is performed of region of the malignant neoplasm location utilizing the same means as in the first stage. At that, sources (1) of X-ray radiation are switched with control means (9) into elevated intensity mode, sufficient for radiation damage of the malignant neoplasm tissues. To transfer radiation from the sources into zone of concentration, and secondary radiation-to the detectors, different combinations are used of collimators, X-ray lenses (2, 3) and half-lenses, constituting together with sources and detectors a roentgenooptical system (8).
Owner:KUMAKHOV MURADIN ABUBEKIROVICH
Diagnostic imaging two non K-edge basis materials plus N K-edge contrast agents
ActiveUS7756239B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingData acquisitionK-edge
A diagnostic imaging system in an example comprises a high frequency electromagnetic energy source, a detector, a data acquisition system (DAS), and a computer. The high frequency electromagnetic energy source emits a beam of high frequency electromagnetic energy toward an object to be imaged and be resolved by the system. The detector receives high frequency electromagnetic energy emitted by the high frequency electromagnetic energy source. The DAS is operably connected to the detector. The computer is operably connected to the DAS and programmed to employ an inversion table or function to convert N+2 measured projections at different incident spectra into material specific integrals for N+2 materials that comprise two non K-edge basis materials and N K-edge contrast agents. N comprises an integer greater than or equal to 1.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
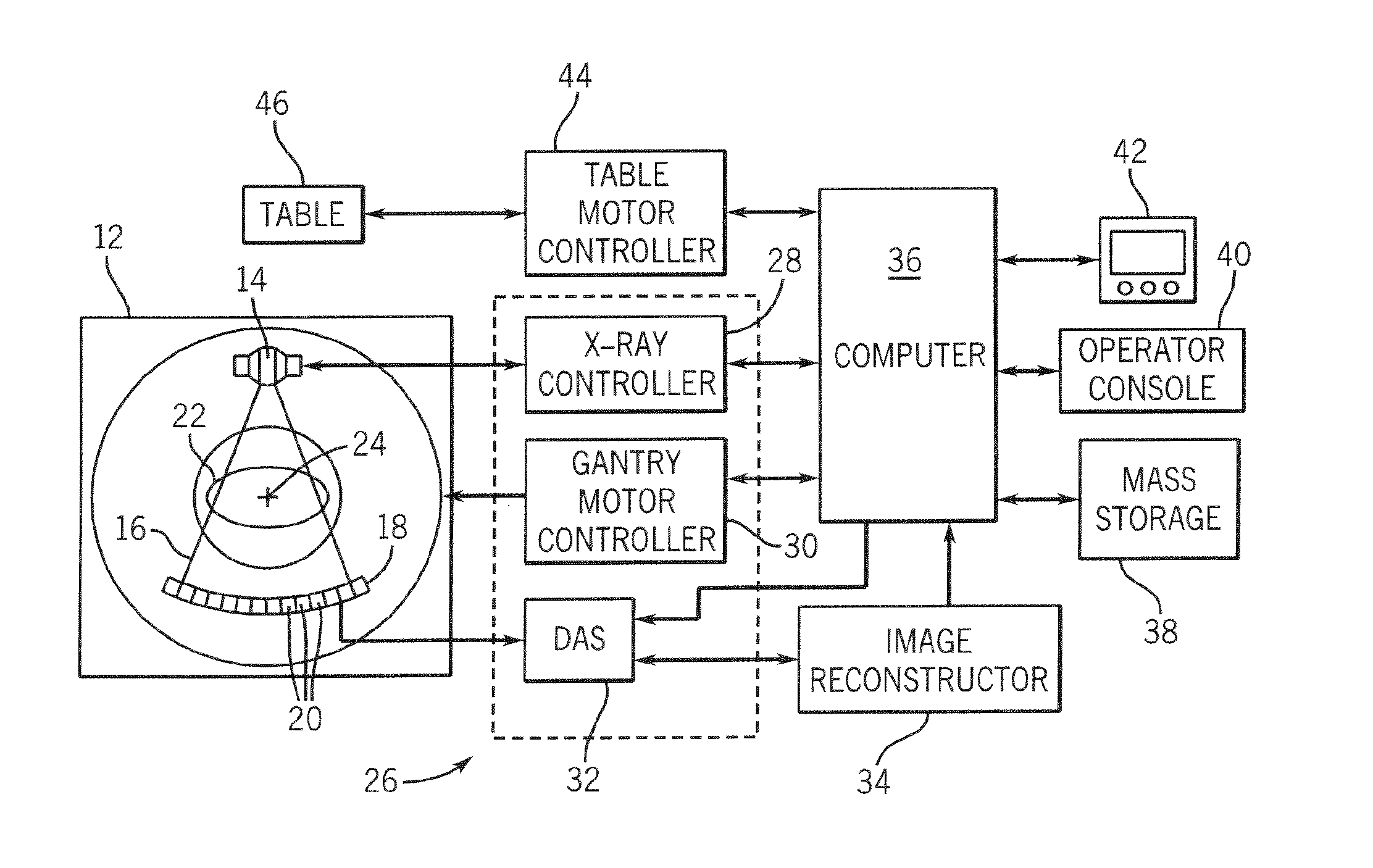
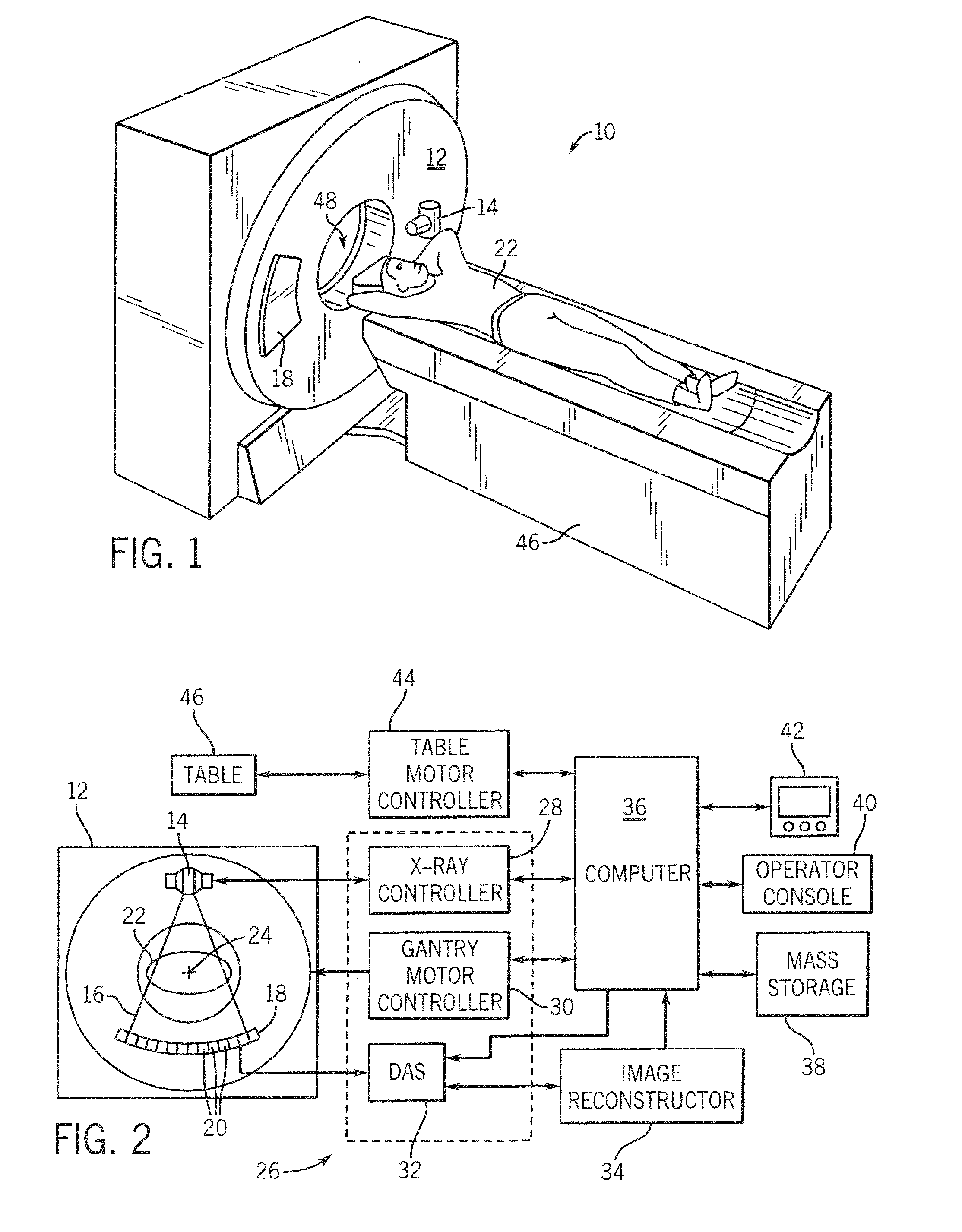
Ct imaging system
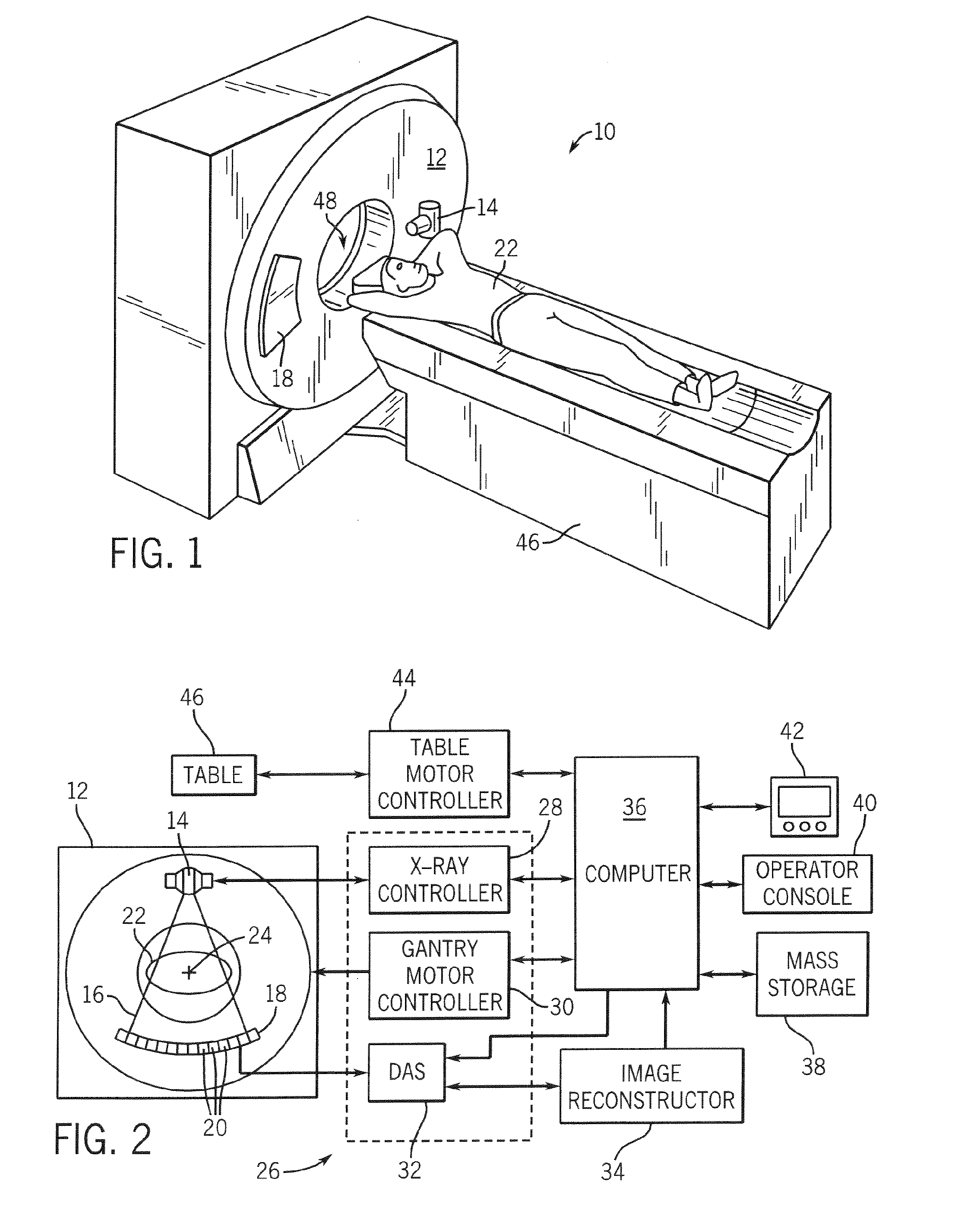
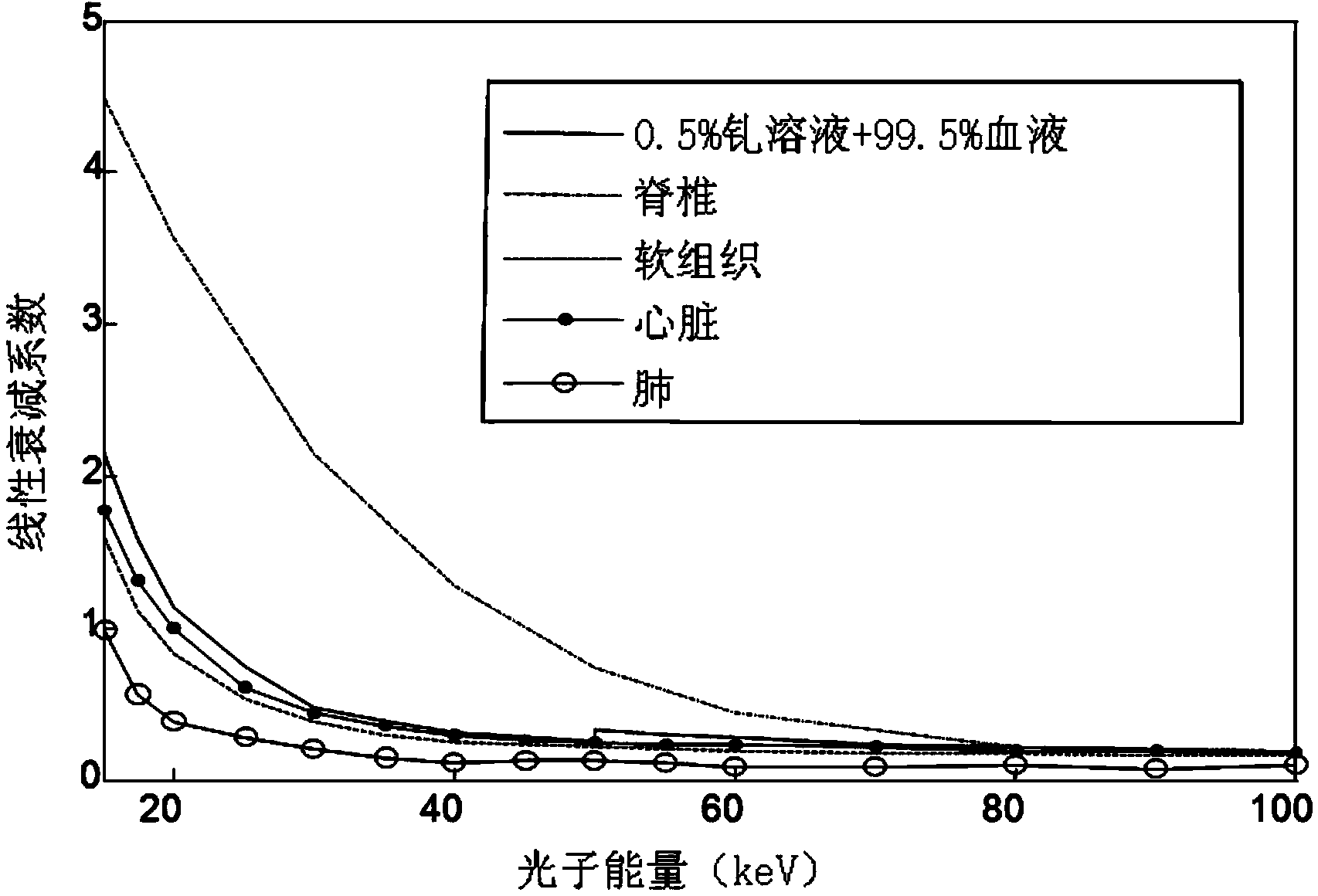
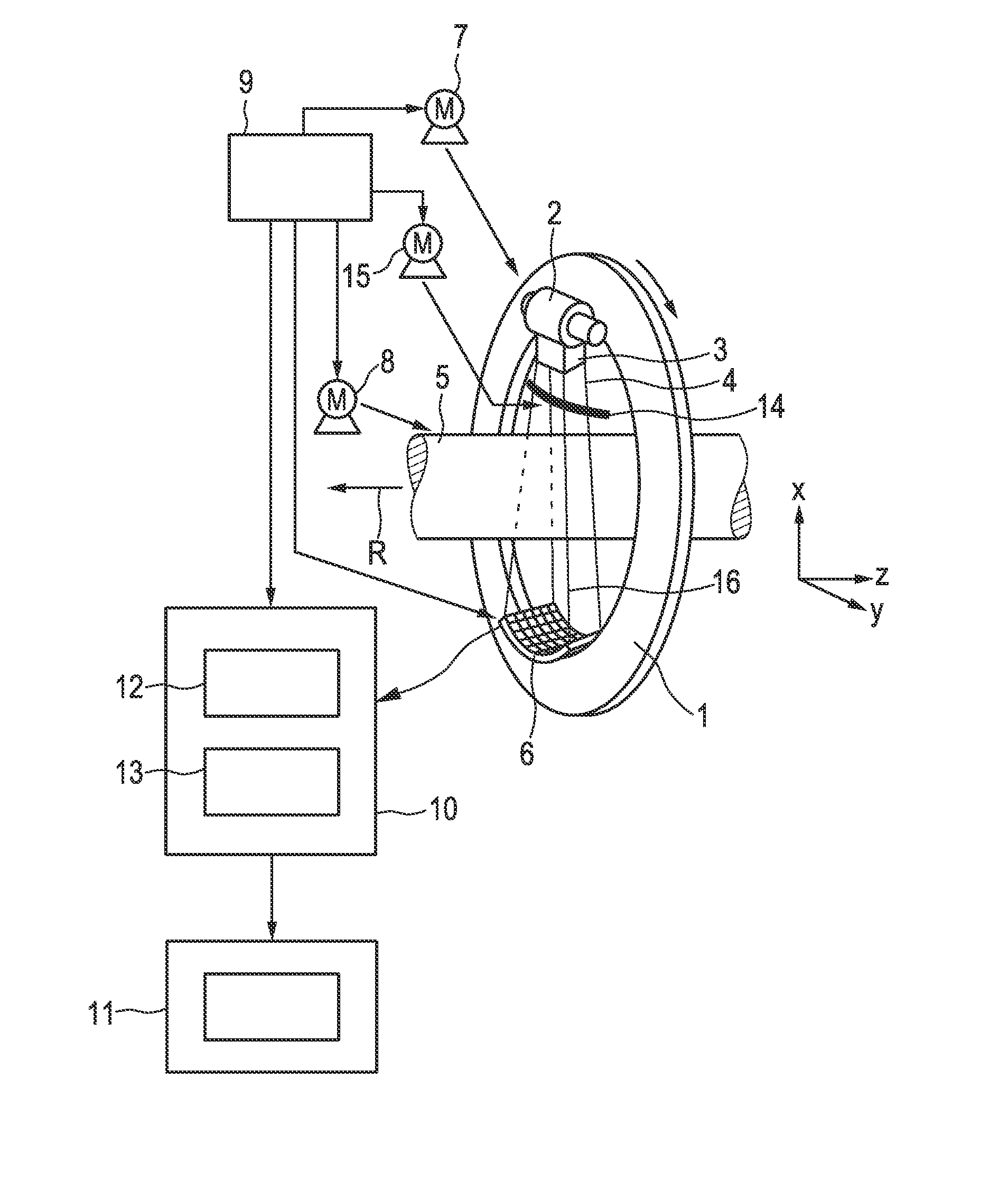
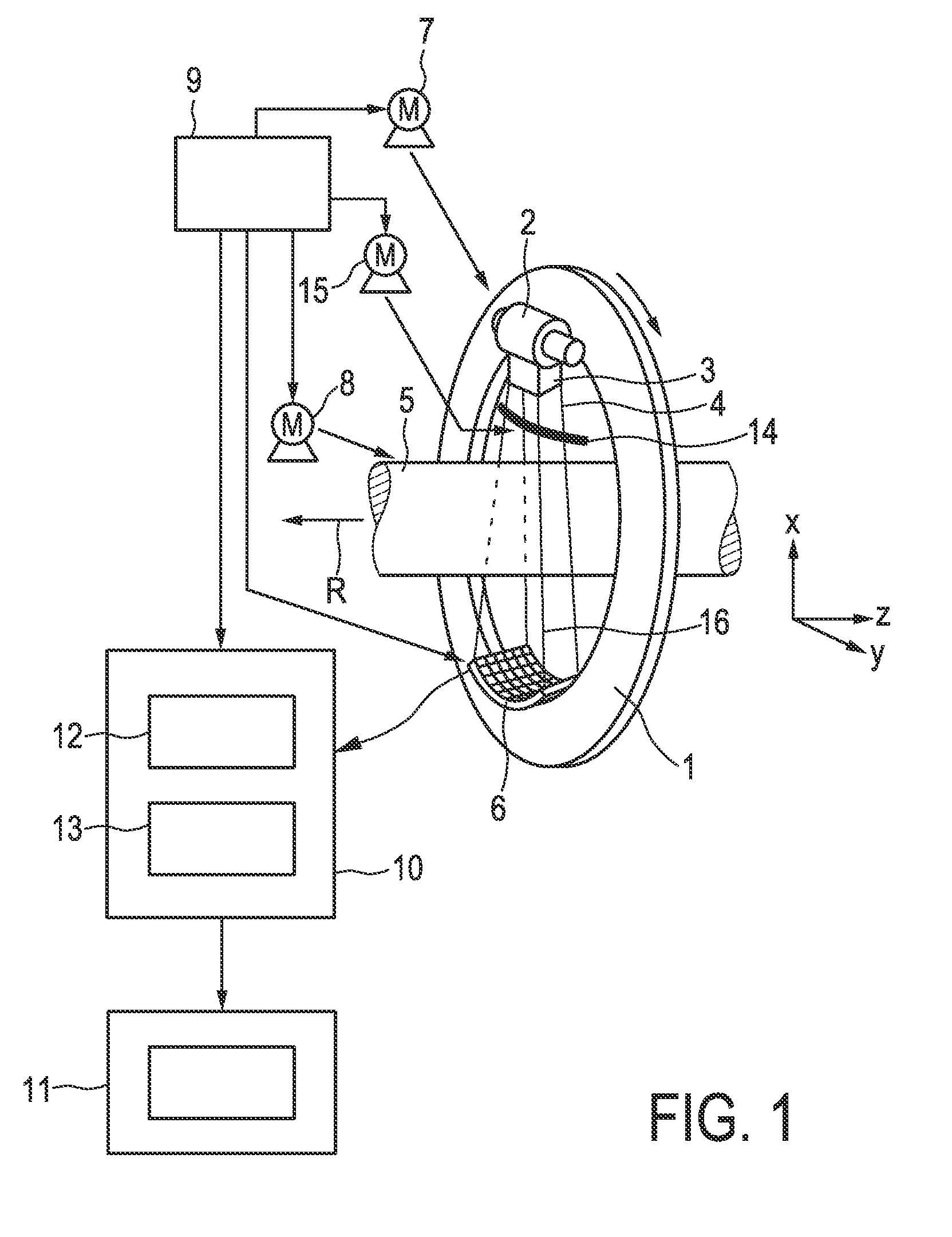
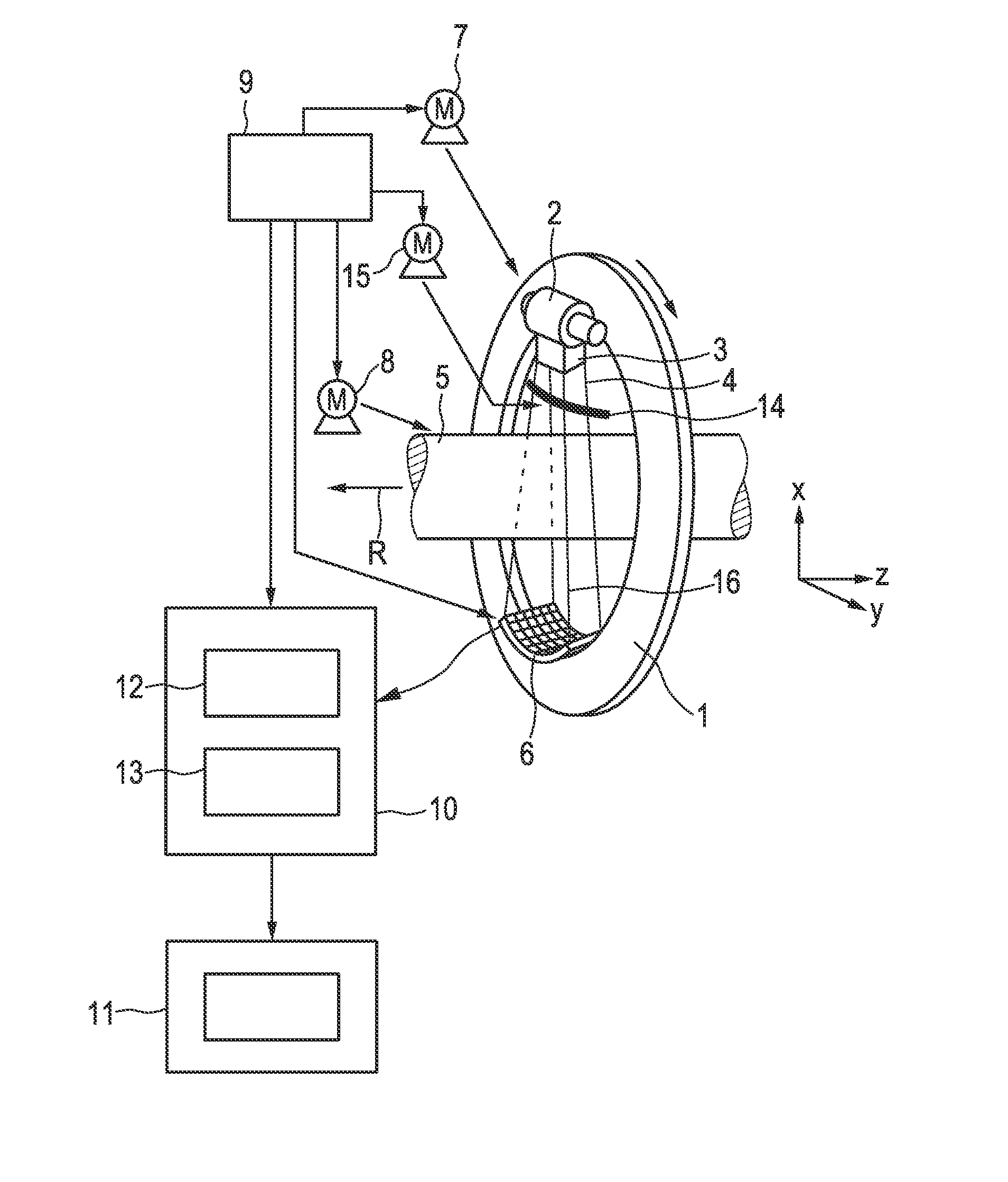
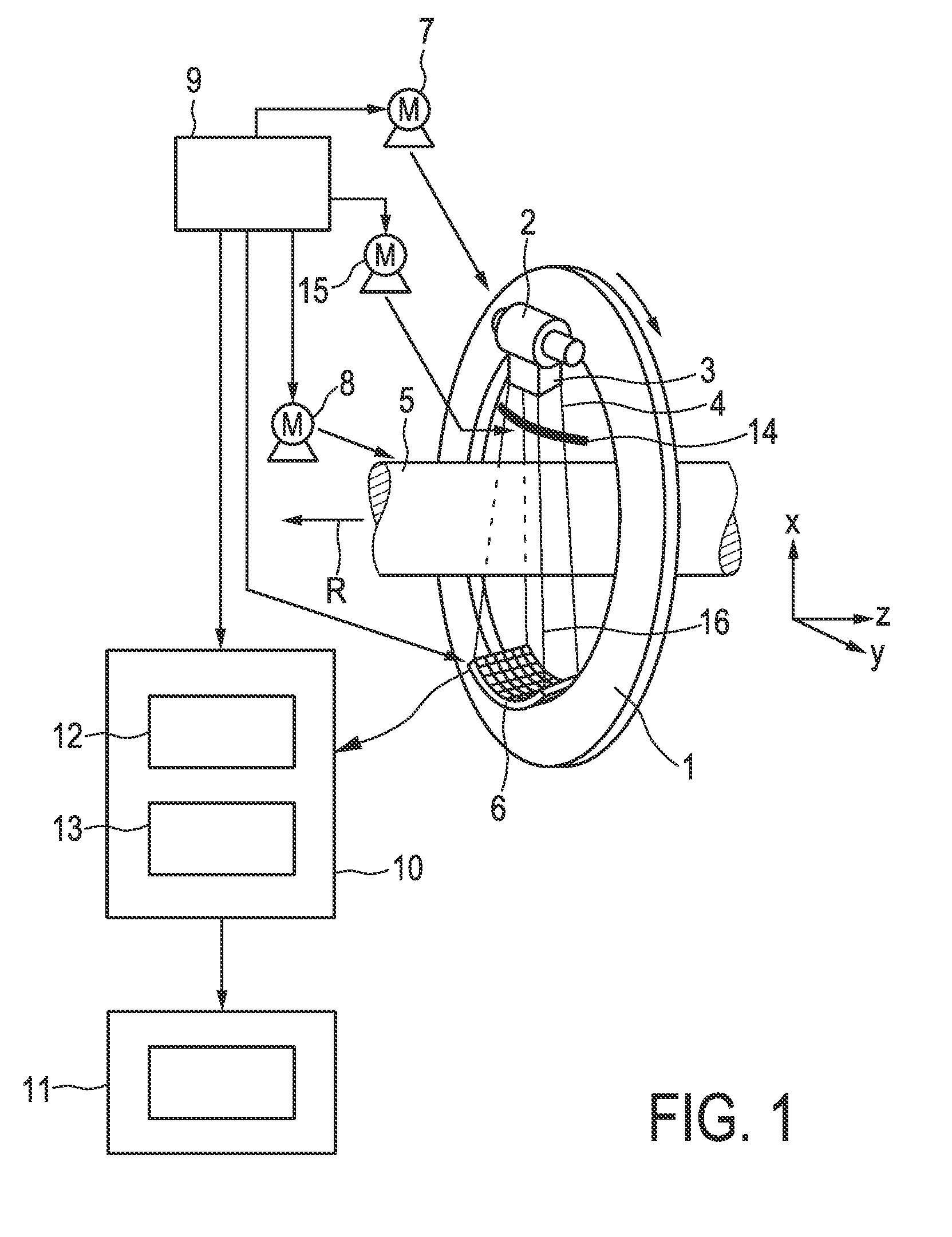
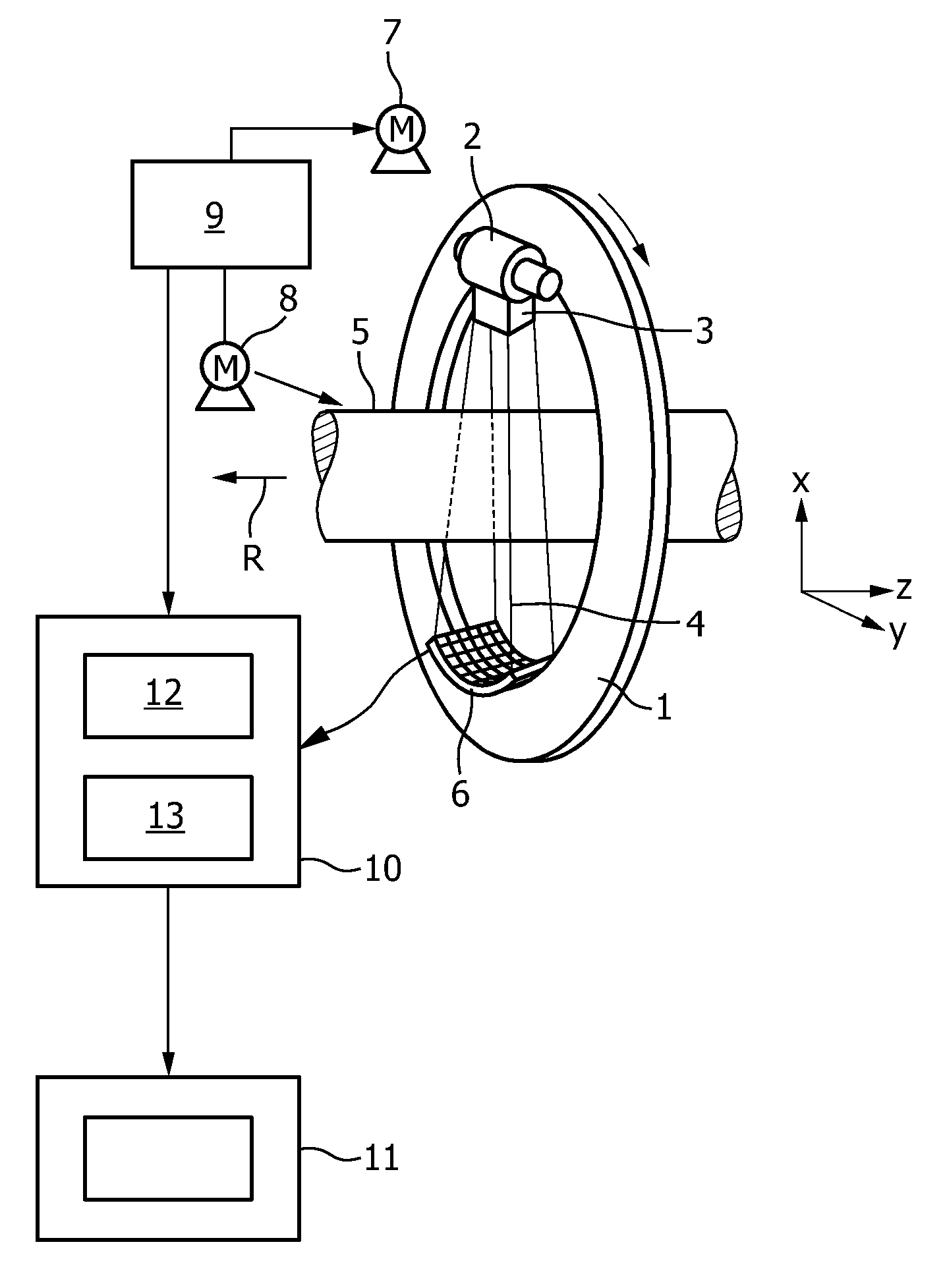
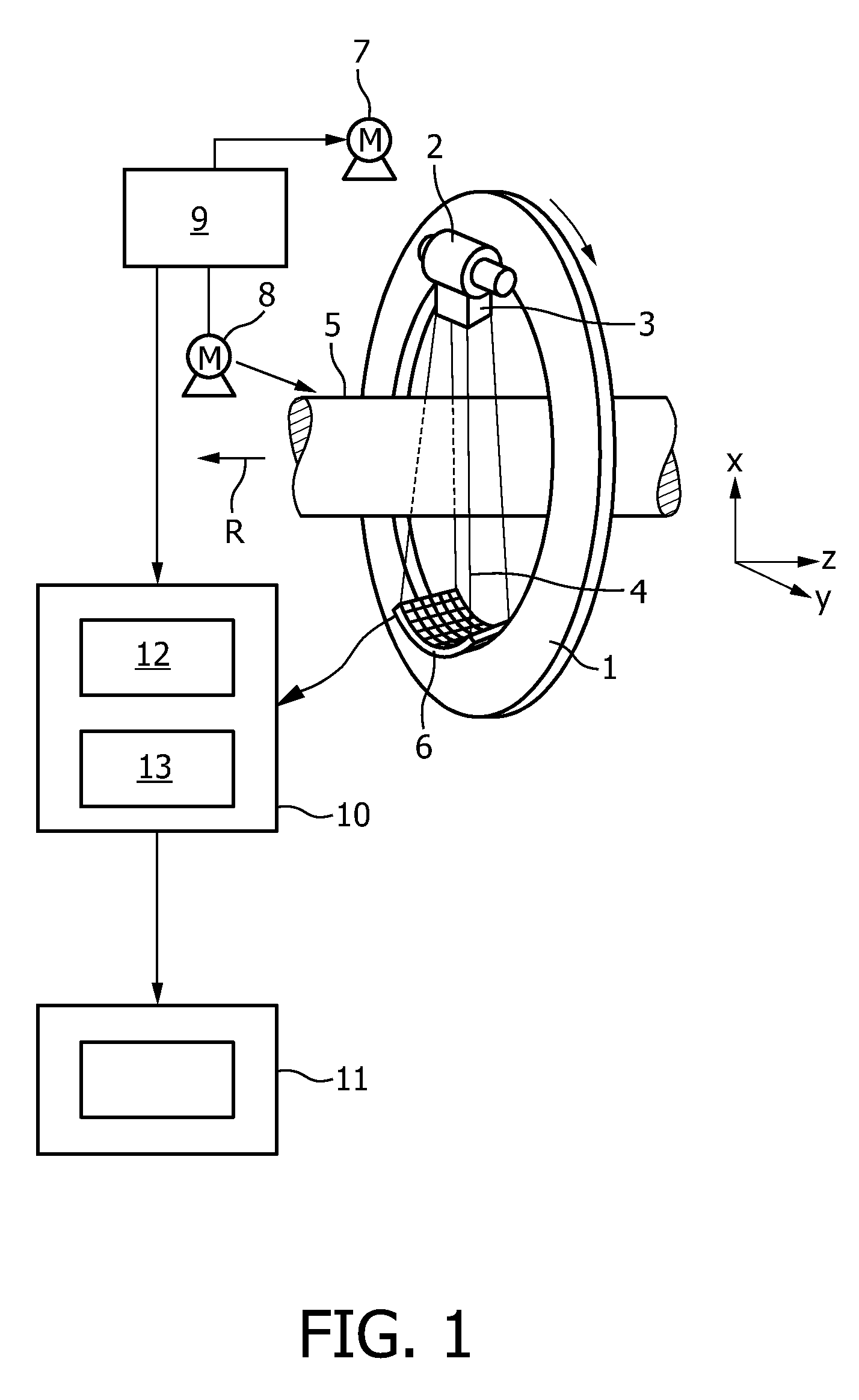
The invention relates to a CT imaging system for determining the flow of a substance within an object, wherein the CT imaging system comprises a polychromatic X-ray source and an energy-resolving X-ray detector for obtaining detection signals depending on the X-ray radiation after passing through the object. A calculation unit (12) determines a k-edge 5 component of the substance from the detection signals, and a reconstruction unit (13) reconstructs a time series of k-edge image from the determined k-edge component. A flow determination unit (14) determines flow values indicative for the flow within the object from the time series of k-edge images.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
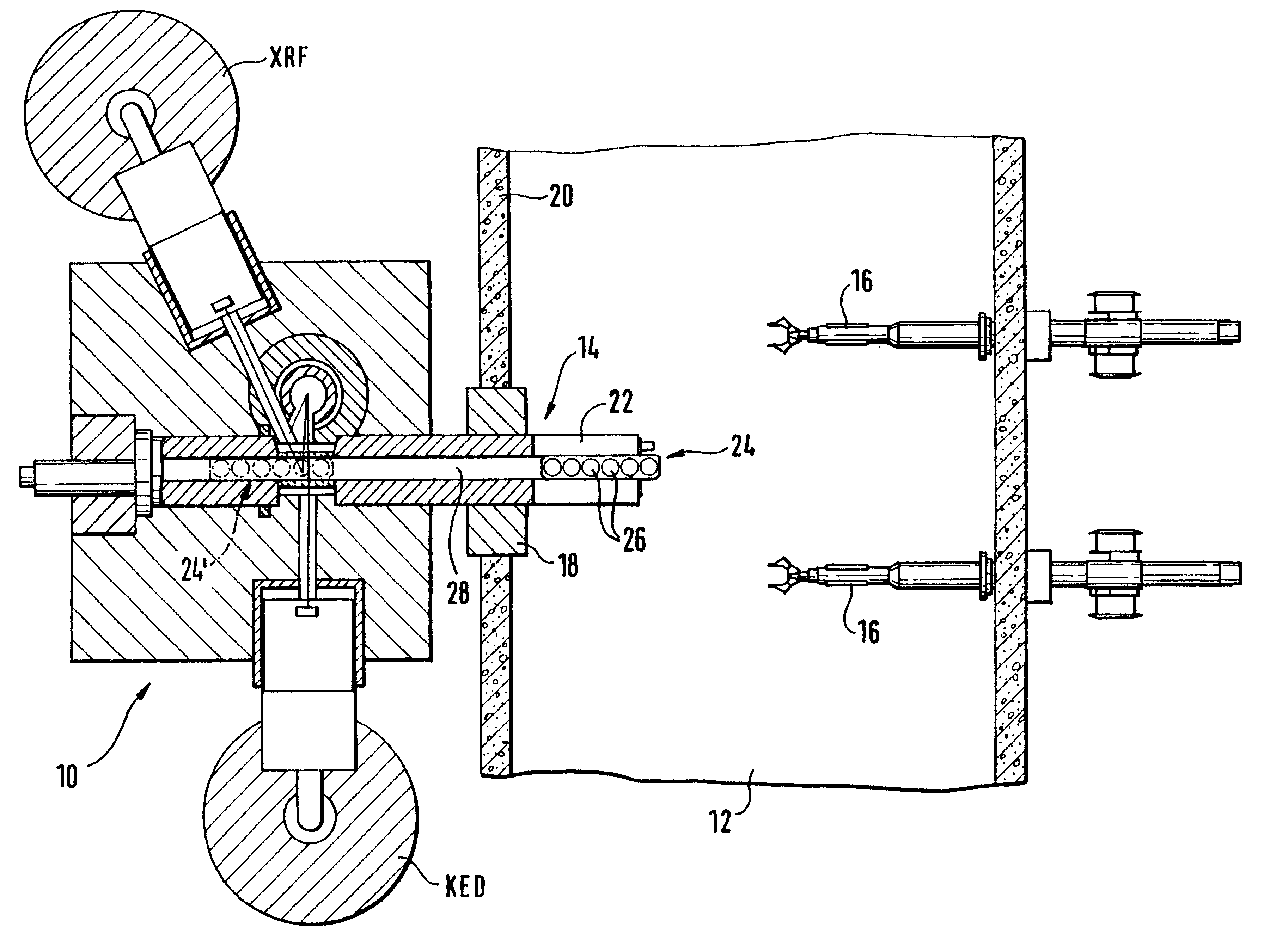
Sample changer for transferring radioactive samples between a hot cell and a measuring apparatus
InactiveUS6630679B1Operating reliability can be highHigh positioning accuracyWithdrawing sample devicesNuclear monitoringCouplingRadioactive waste
A sample changer for transferring radioactive samples between a hot cell (12) and a measuring apparatus (10), as e.g. a hybrid K-edge densitometer, comprises a transfer channel (28) axially extending through a tubular containment (22) between the charging / discharging port and the measuring window section D. A recipient (24), with at least one compartment (100) for receiving therein a radioactive sample, is arranged in the transfer channel (28) so as to be movable therethrough. A threaded spindle (44) is rotatably housed in a spindle channel (42) below the transfer channel (28). A coupling (46) passing in a sealed manner through the closed rear end section connects a stepping motor (34) to the threaded spindle (44). A longitudinally guided support carriage supports the magazine (24) and engages the threaded spindle (44), so as to be subjected to a translational movement upon rotation of the spindle (44).
Owner:EURON COMMUNITY EC
Imaging system for imaging an object
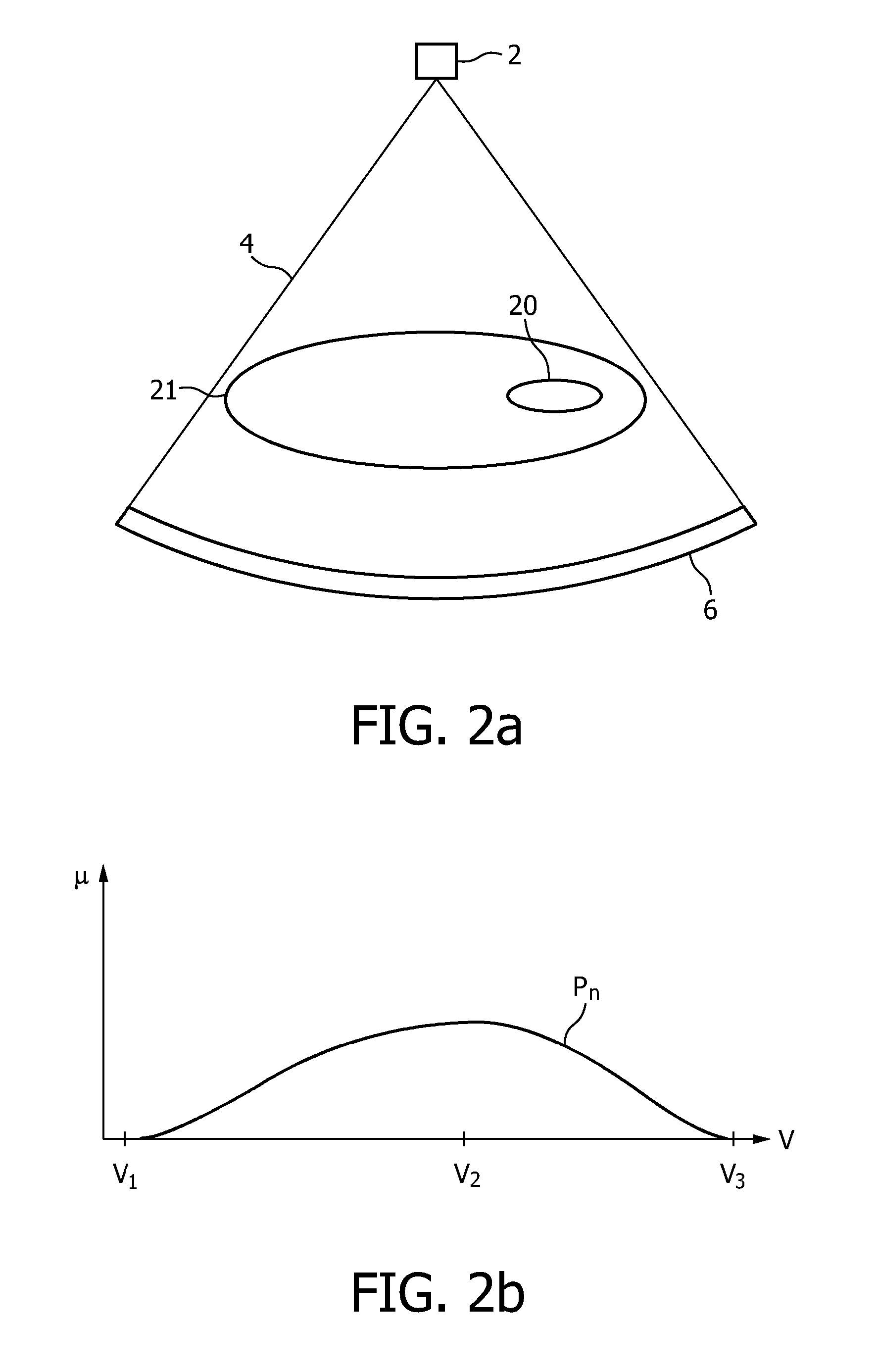
The present invention relates to an imaging system for imaging an object (20) comprising a polychromatic radiation source (2) and an energy resolving radiation detector (6). The imaging system comprises further a driving device for moving the object (20) and the radiation source (2) relatively to each other, in order to acquire truncated projections from different directions. A calculation unit determines a k-edge component at least of one of the object (20) and a substance within the object (20) from the truncated projections and determines non-truncated projections from the determined k-edge component. A reconstruction unit constructs the object using the non-truncated projections.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
System and method for monochromatic x-ray beam therapy
InactiveUS20050259787A1Cathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingRadioactive preparation carriersX-ray beam therapyRadiation sensitizers
In embodiments of the invention, a radiosensitizer or other agent is relatively uniformly accumulated in the cells of a tumor. An external monochromatic x-ray beam, which is tuned to a predetermined energy level associated with k-edge effects in the agent, is then directed to the tumor. The monochromatic x-ray beam activates the release of additional localized radiation from the agent. The additional radiation destroys the DNA of at least some tumor cells, making those tumor cells incapable of reproduction and repair. In embodiments of the invention, a single monochromatic x-ray beam source is used for both imaging and radiotherapy.
Owner:MXISYST
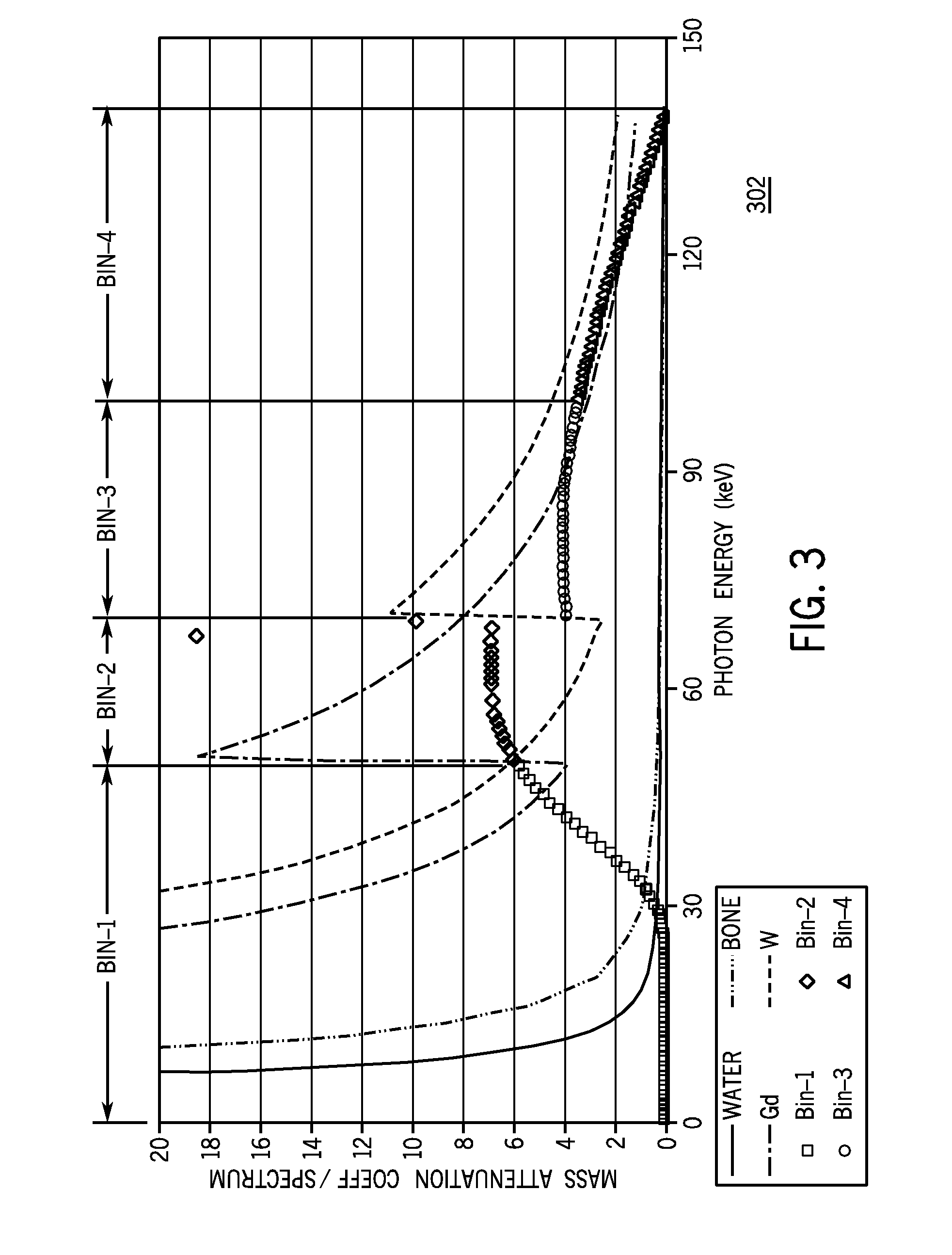
Optimized K-edge imaging method
InactiveCN103530849ANoise minimizationBig contrast differenceImage enhancement2D-image generationNoise levelX-ray
The invention discloses an optimized K-edge imaging method. According to the method, imaging is performed at front and rear X-ray energy sections of K-edge to improve the known material imaging contrast. The widths of the front and rear X-ray energy sections of the K-edge determine the contrast and the noise level of two energy spectrum CT (Computed Tomography) images; aiming at the problem of way of setting the widths of the front and rear X-ray energy sections of the K-edge, a signal difference to noise ratio (SDNR) is introduced as an optimization criterion; under the constraint of the optimization criterion, the width of the optimal X-ray energy section is selected, and then K-edge imaging is performed. According to the imaging method, the greatest contrast difference can be obtained while the miniaturization of noise of two reconstructed energy spectrum CT image interesting regions is guaranteed, so that the purpose of improving the known material imaging contrast is achieved. The method can be used for the field of biomedical CT imaging.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
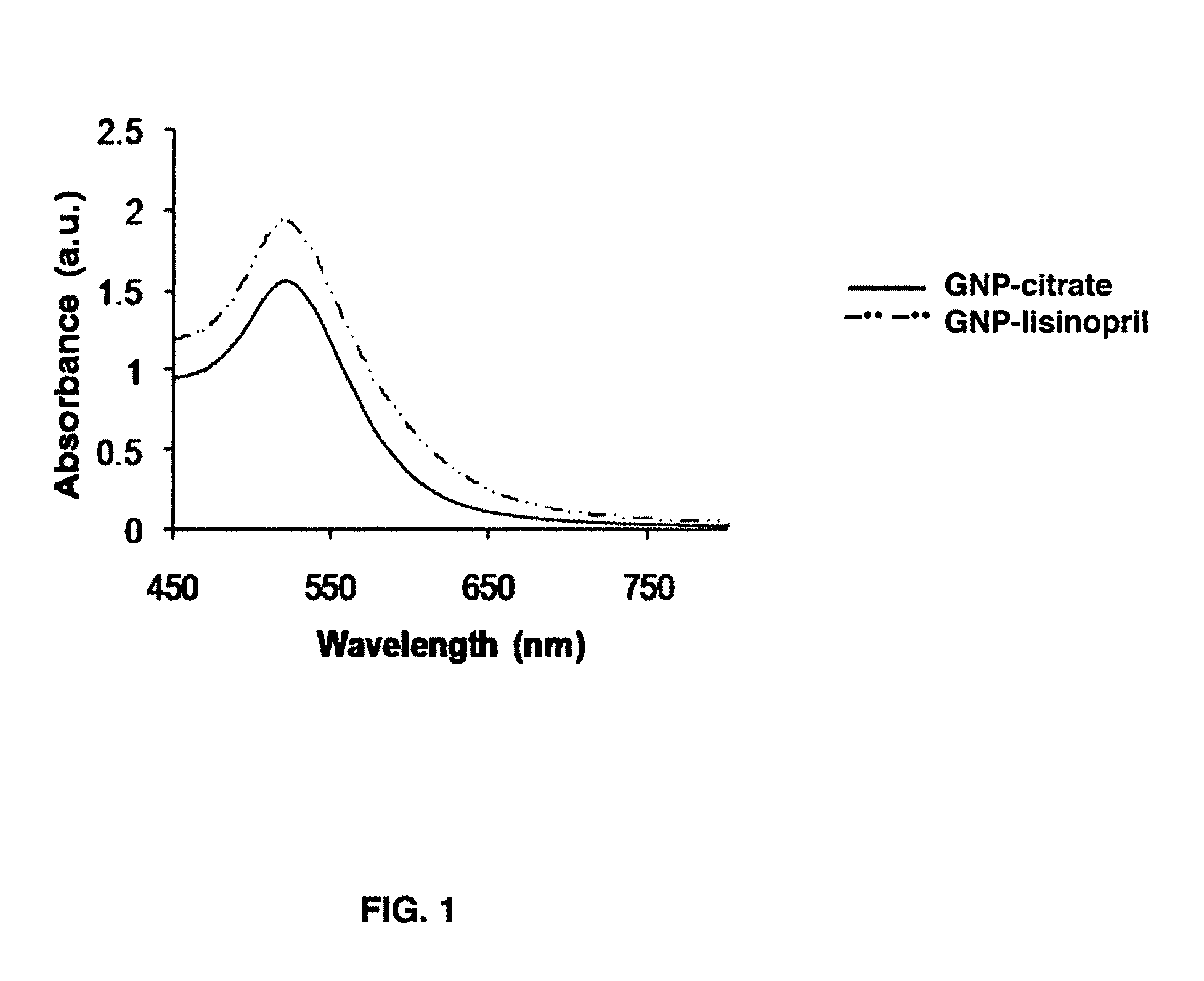
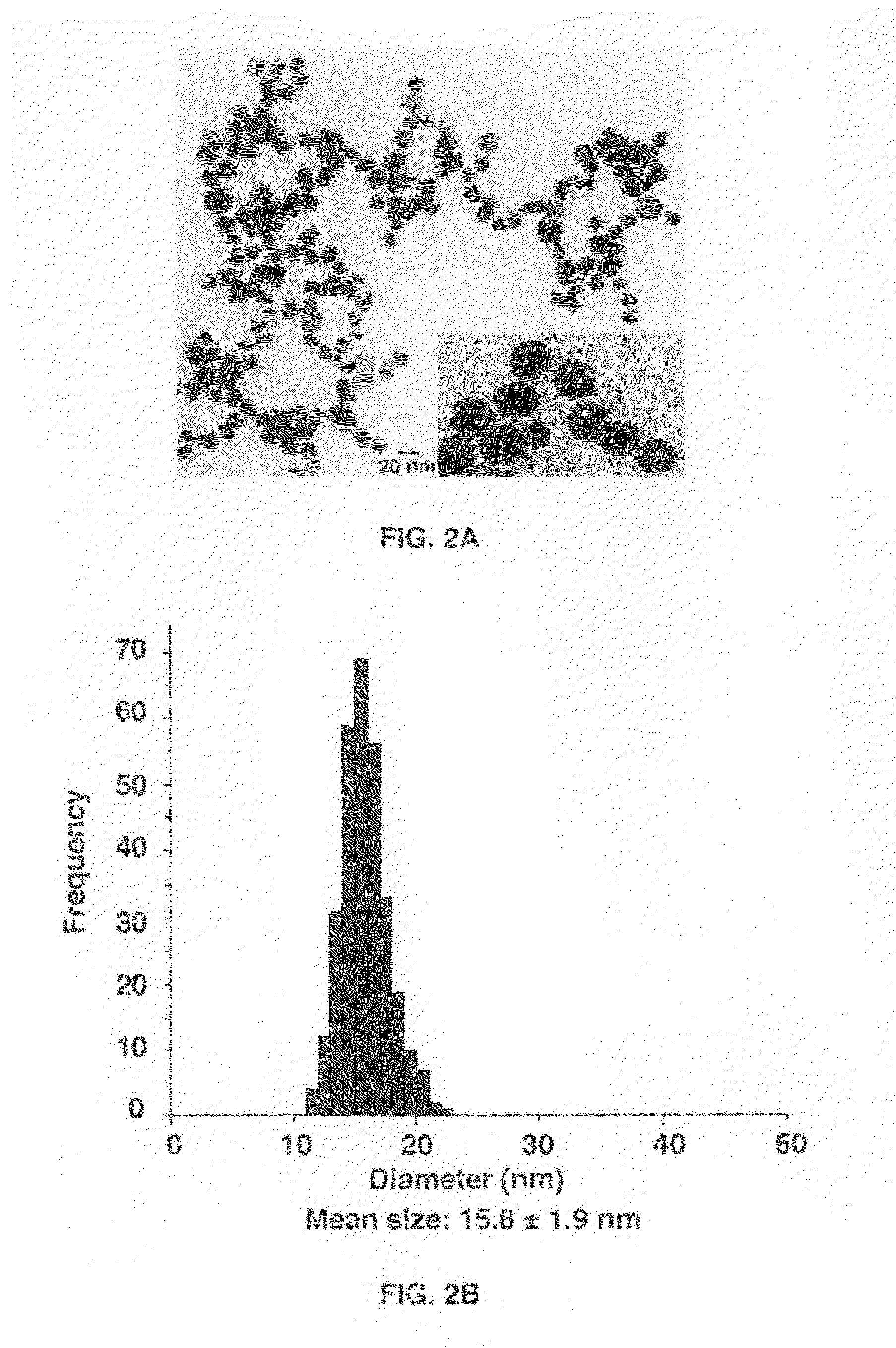
Gold nanoparticle imaging agents and uses thereof
Overexpression of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) has been associated with a number of pathophysiologies, including those associated with cancer and the cardiovascular system. Thus, targeted imaging of ACE is of crucial importance for monitoring tissue ACE activity as well as treatment efficacy. To this end, lisinopril-coated gold nanoparticles were prepared to provide a new type of probe for targeted molecular imaging of ACE by tuned K-edge computed tomography (CT) imaging.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY
Transmission type x-ray tube and reflection type x-ray tube
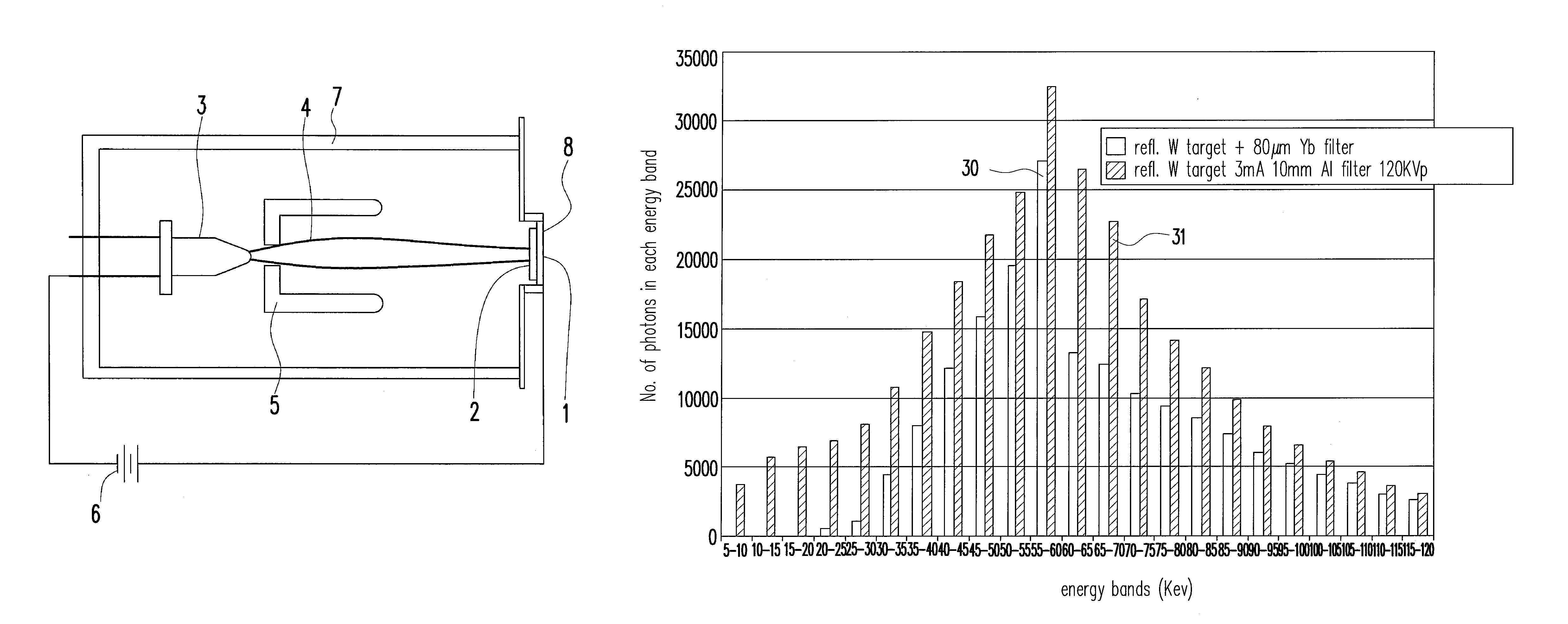
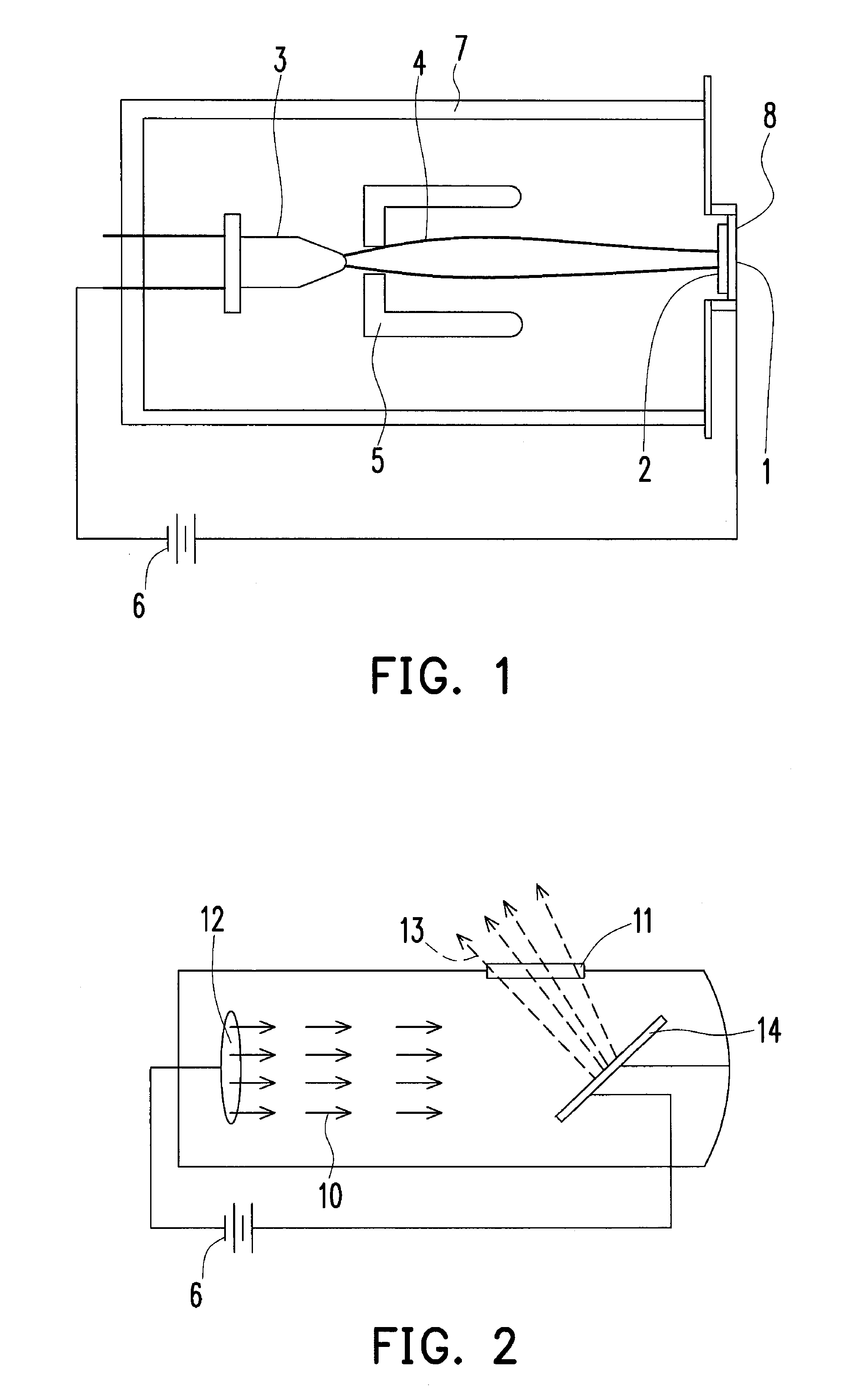
ActiveUS20130108024A1Reduce x-radiationReduce intensityX-ray tube electrodesX-ray tube vessels/containerX-rayFilter material
The present invention provides a transmission type X-ray tube and a reflection type X-ray tube. The transmission type X-ray tube comprises a target and a filter material. The target has at least one element which produces X-rays as being excited. The X-rays comprise characteristic Kα and Kβ emission energies of the element for producing images of an object impinged by the X-rays. The filter material through which the X-rays pass has a k-edge absorption energy that is higher than the Kα emission energies and is lower than the Kβ emission energies. The thickness of the filter material is at least 10 microns and less than 3 millimeters.
Owner:NANORAY BIOTECH CO LTD
1AF feed liquid measuring equipment
InactiveCN108919330ARealize simultaneous quantitative measurementRealize analysisX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentNeutron radiation measurementElectronic systemsFluorescence
The invention belongs to the technical field of 1AF feed liquid measurement, and particularly relates to 1AF feed liquid measurement equipment. The 1AF feed liquid measurement equipment comprises a hybrid K edge / X fluorescence measuring device, and a passive neutron measuring device is arranged at an inlet of a measuring chamber (8) of the hybrid K edge / X fluorescence measuring device. The passiveneutron measuring device includes a measuring channel (1), a plurality of He3 neutron tubes (4) and an electronic system, wherein the measuring channel (1) is connected to an inlet of the measuring chamber (8) and can pass through a 1AF feed liquid sample (6), the He3 neutron tubes (4) are arranged on the periphery of the measuring channel (1), and the electronic system is connected to the He3 neutron tubes (4). The 1AF feed liquid measurement equipment is based on an existing hybrid K edge / X fluorescence technology, by adding the neutron measuring device, the simultaneous quantitative measurement and analysis of Cm, Pu and U are realized, and a technical approach for subsequent development of the passive neutron analysis of uranium and plutonium content in waste cladding is provided.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Medical x-ray examination apparatus and method for k-edge imaging
ActiveUS20110103550A1Improve abilitiesHigh sensitivityRadiation/particle handlingCharacter and pattern recognitionX-rayK-edge
The present invention relates to a medical X-ray examination apparatus and method for performing k-edge imaging of an object of interest including material showing k-edge absorption. To allow the use of conventional detector technology, which does not suffer from the limitation to provide very high k-rate capabilities a method is proposed comprising the steps of:emitting polychromatic X-ray radiation (4; 4a, 4b),Bragg filtering said polychromatic X-ray radiation by a Bragg filter such that radiation (16) transmitted through said Bragg filter (14; 14a, 14b) passes through said object (5),detecting X-ray radiation after passing through said object (5),acquiring projection data at at least two different Bragg reflection angles of said Bragg filter (14; 14a, 14b), andreconstructing a k-edge image from the acquired projection data.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
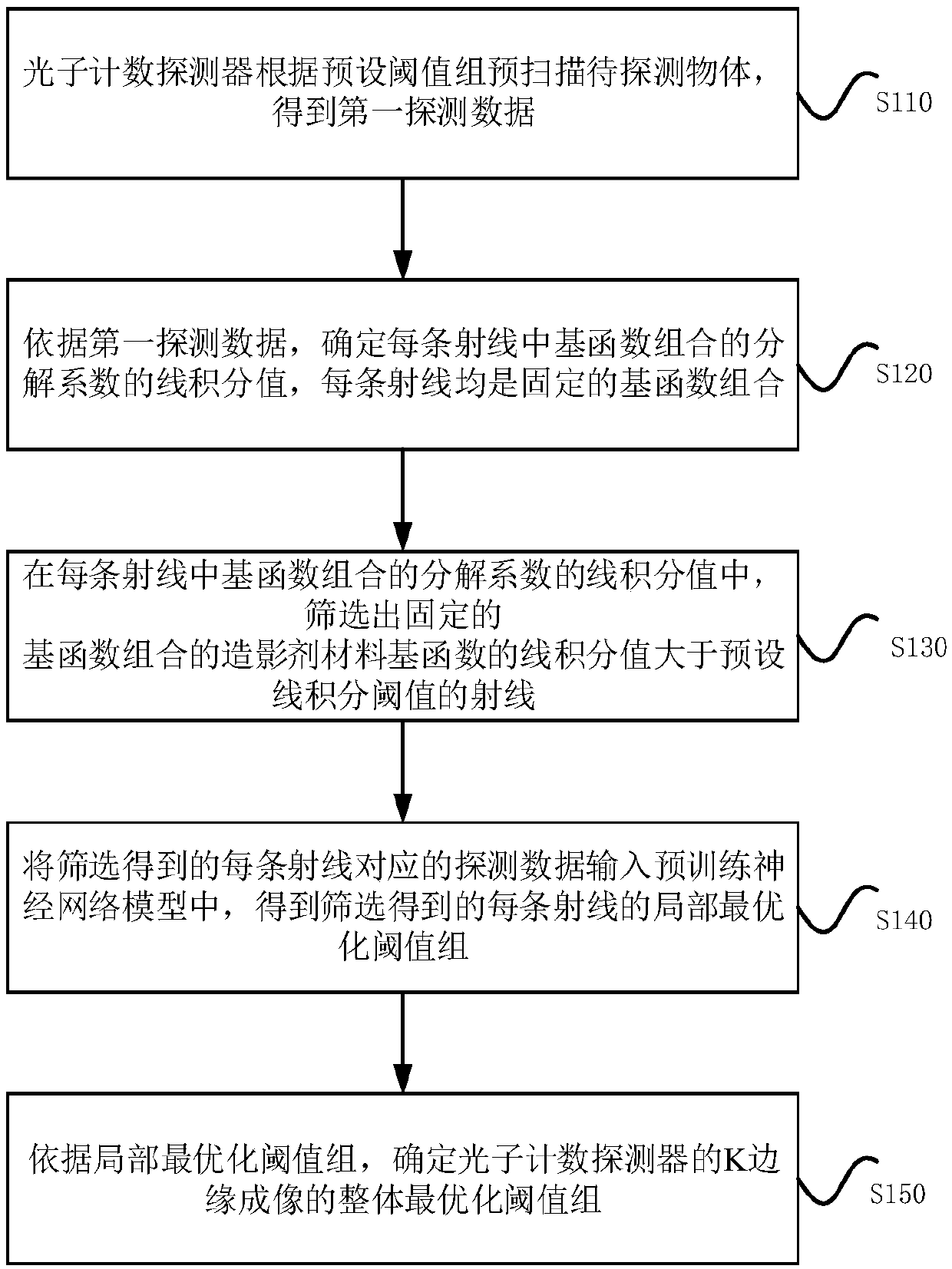
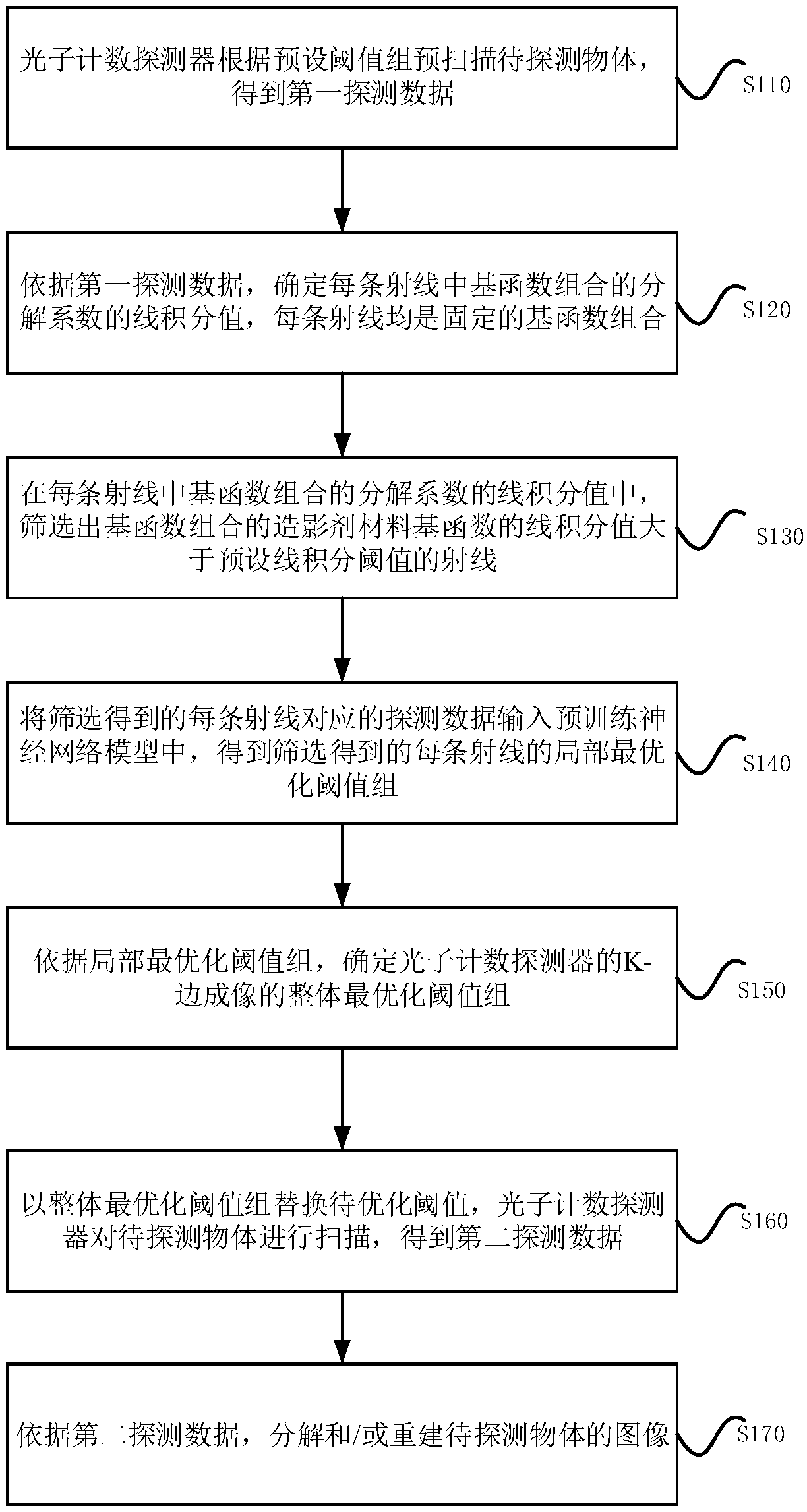
Threshold optimization method and device based on K edge imaging, equipment and medium
ActiveCN110836901AReduce harmImprove efficiencyTelevision system detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationNetwork modelContrast medium
The embodiment of the invention discloses a threshold optimization method and device based on K edge imaging, equipment and a medium. The method comprises the following steps of: pre-scanning a to-be-detected object by a photon counting detector according to a preset threshold group to obtain first detection data; according to the first detection data, determining the line integral value of the decomposition coefficient of the basis function combination in each ray, wherein each ray is a fixed basis function combination; in the linear integral values of the decomposition coefficients of the basis function combination in each ray, screening out the rays of which the linear integral values of the contrast agent material basis functions of the basis function combination are greater than a preset linear integral threshold value; inputting the screened detection data corresponding to each ray into a pre-trained neural network model to obtain a screened local optimal threshold group of eachray; and determining the overall optimal threshold group of K edge imaging of the photon counting detector according to the local optimal threshold group.
Owner:NUCTECH CO LTD +1
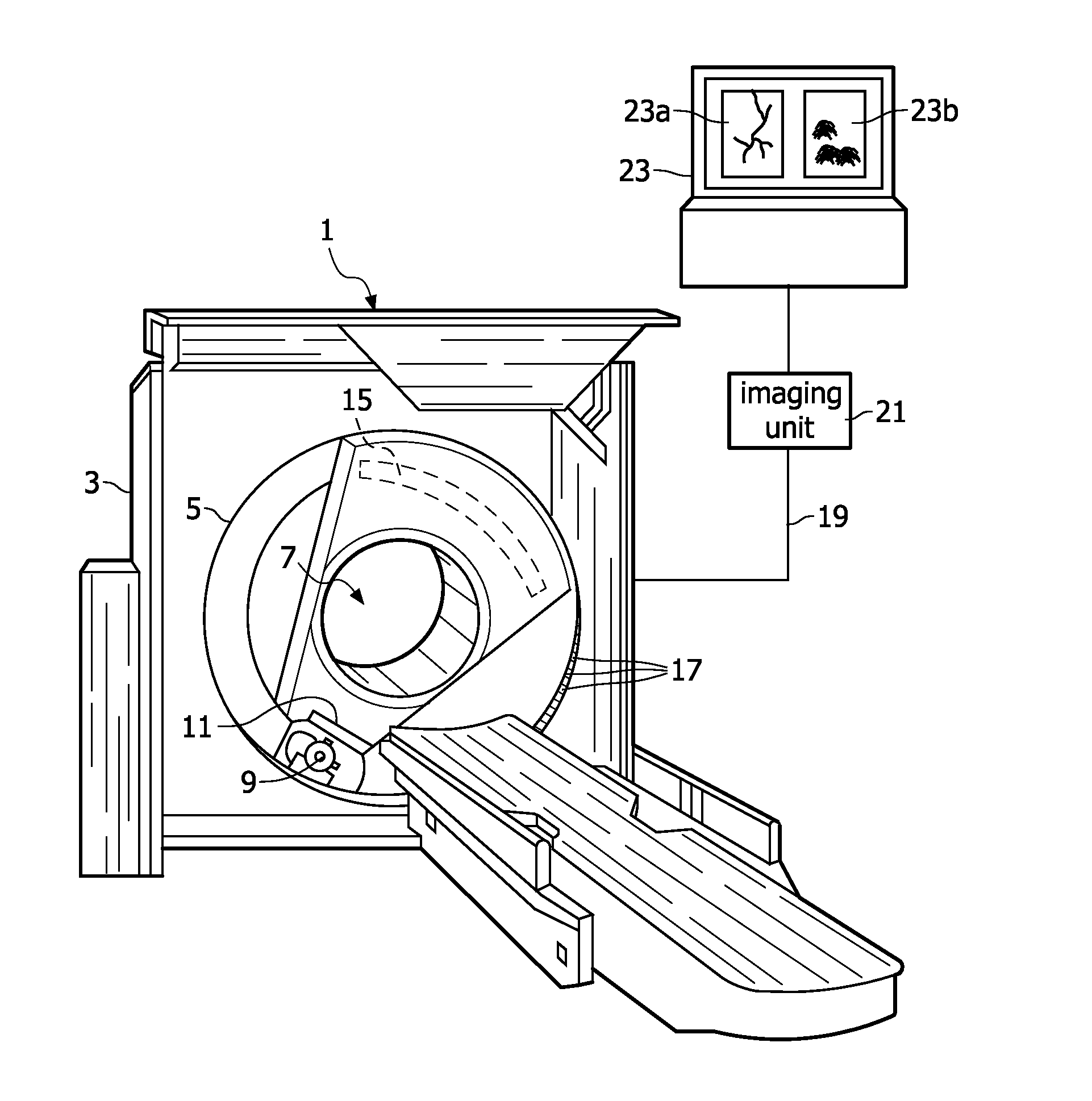
Medical X-ray examination apparatus for performing K-edge imaging
ActiveUS7894569B2High sensitivityReduce spacingMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayX-ray absorption spectroscopy
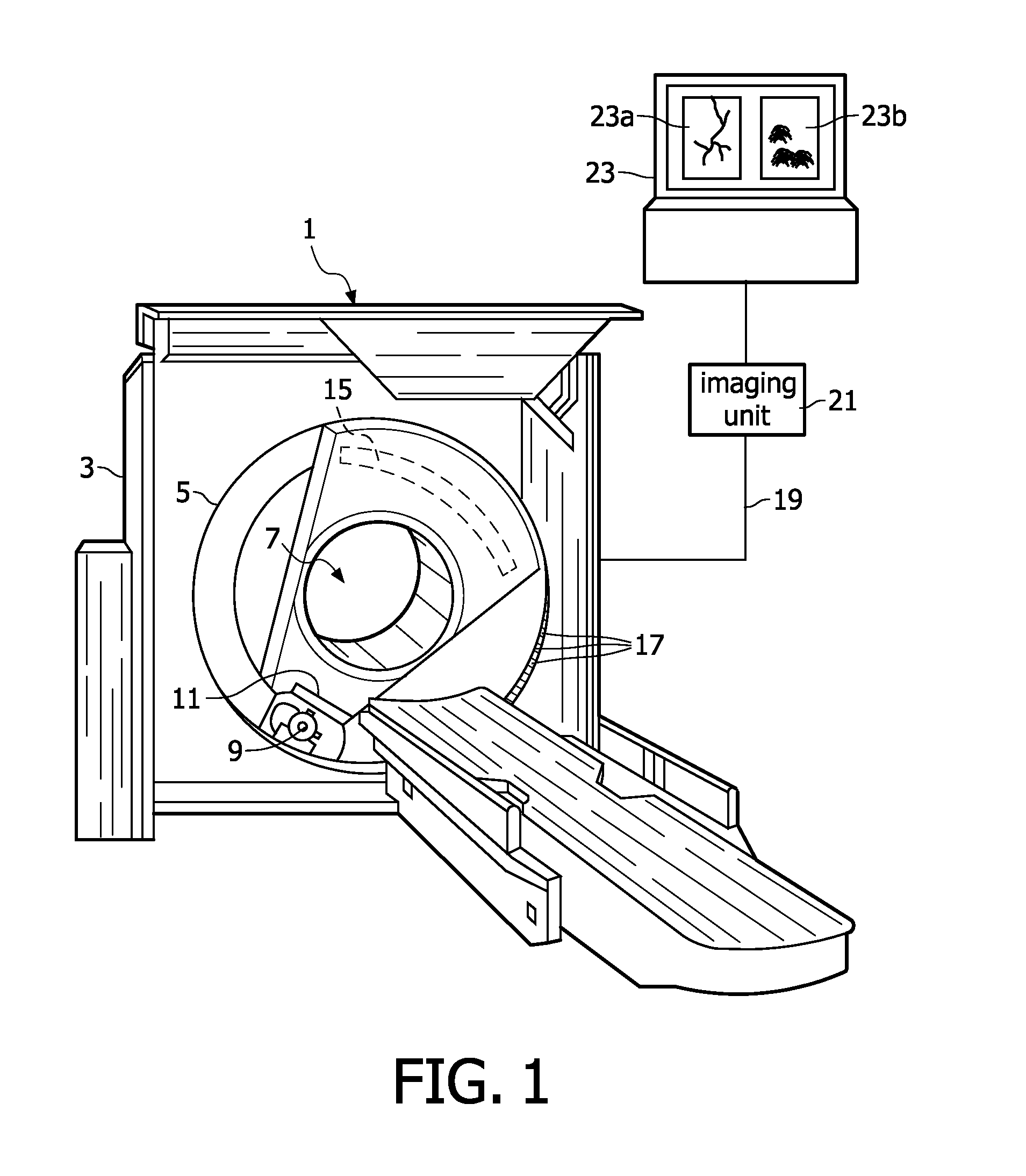
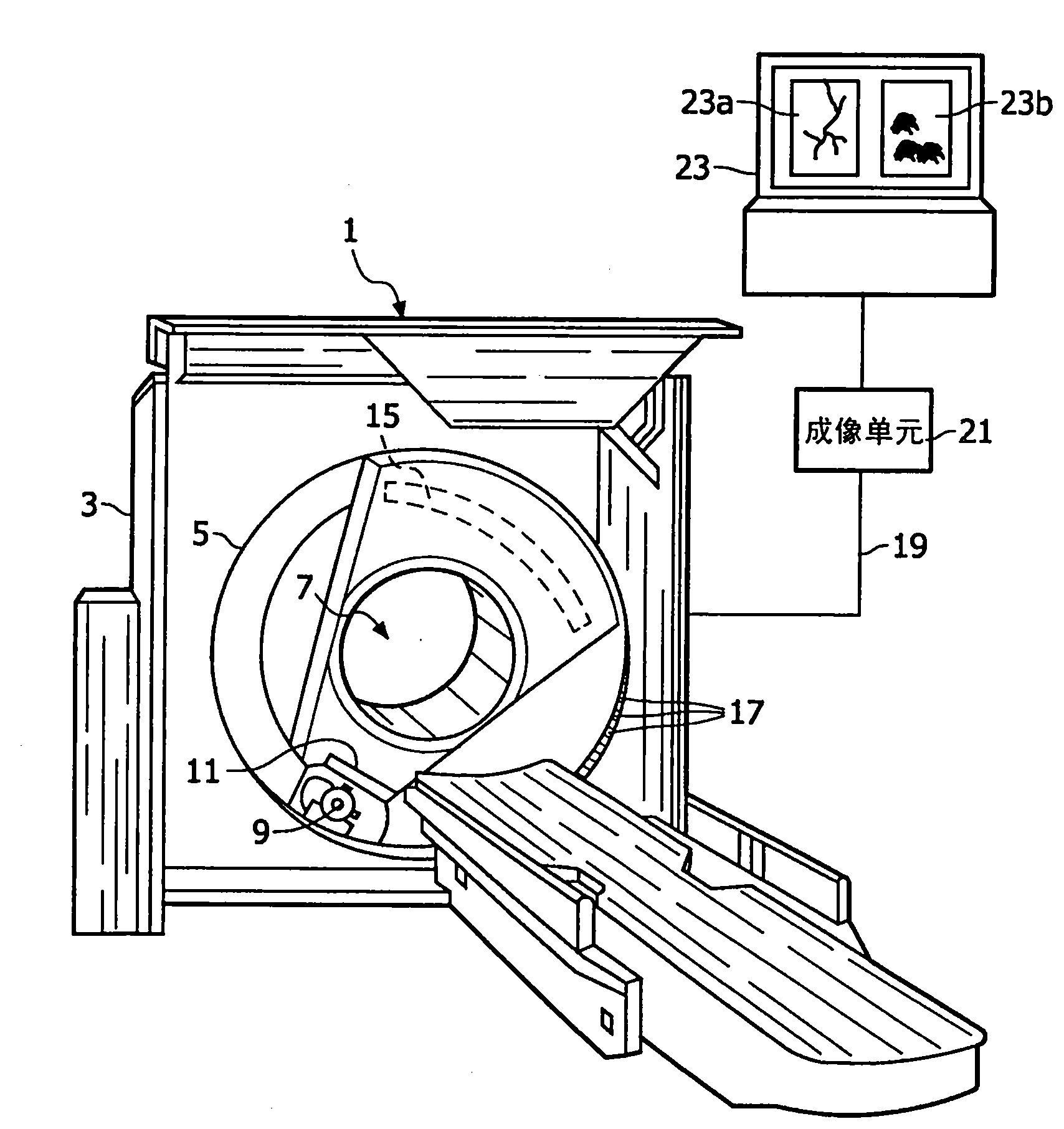
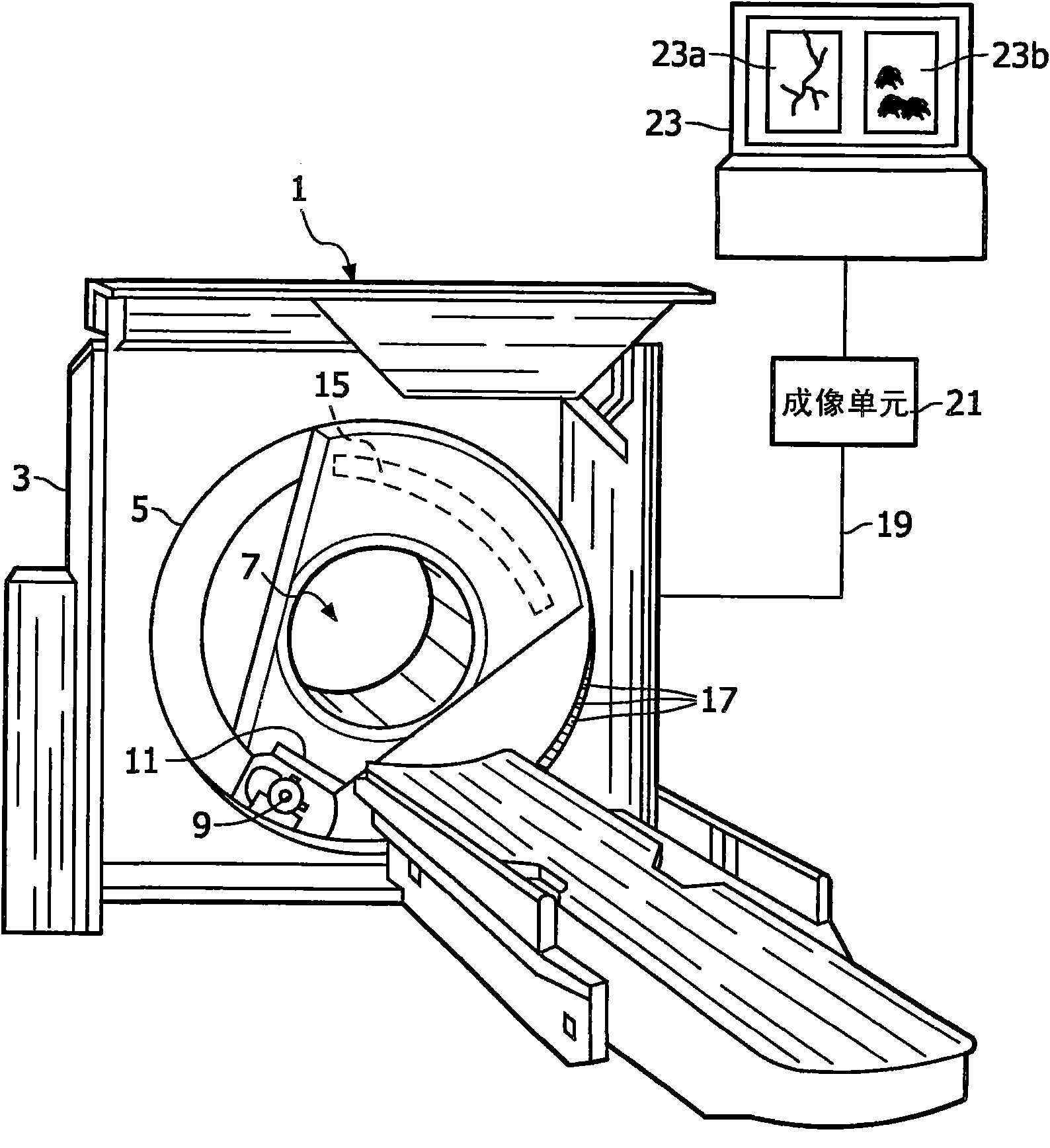
The invention relates to a medical X-ray examination apparatus (1) for performing K-edge imaging. The medical X-ray examination apparatus (1) comprises an imaging unit (21), which is configured to spectrally decompose an X-ray absorption spectrum to image the X-ray absorption spectrum as a conventional X-ray absorption image (23a) and a K-edge absorption image (23b). The conventional X-ray absorption image (23a) includes data elements representing the anatomical background of an object of interest. The K-edge absorption image (23b) includes data elements representing quantitative information of local densities of material showing K-edge absorption within the object of interest. The imaging unit (21) comprises a spatial resolution reducer for reducing the spatial resolution of the K-edge absorption image, so that with a medical X-ray examination apparatus according to the invention an increased sensitivity of the selective imaging of a K-edge absorption image is achieved as compared to the sensitivity of the selective imaging of a K-edge absorption image of a known medical X-ray examination apparatus.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Medical X-ray examination apparatus and method for k-edge imaging
ActiveUS8229060B2Improve abilitiesHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayX-ray
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Device and method for mapping the distribution of an x-ray fluorescence marker
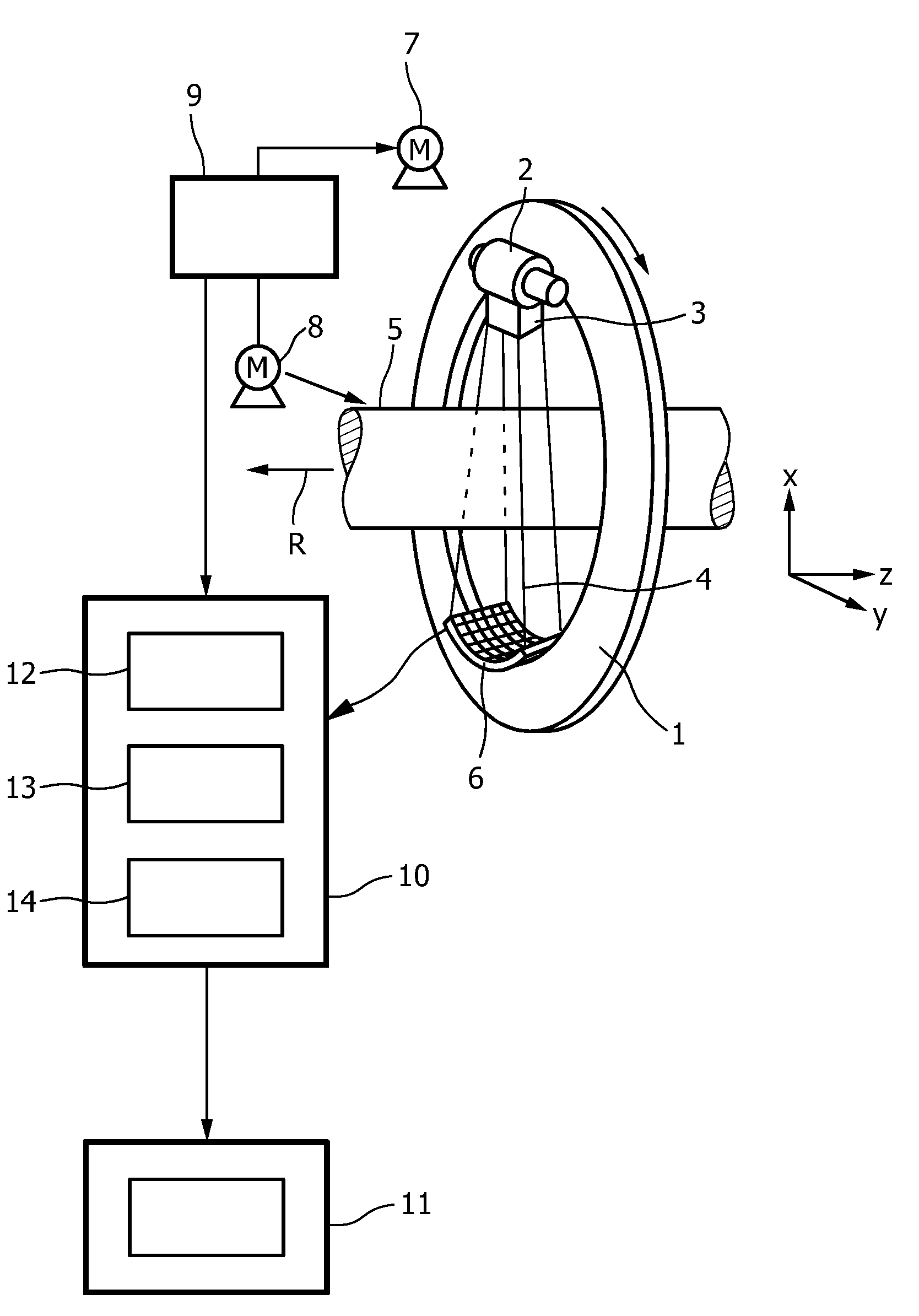
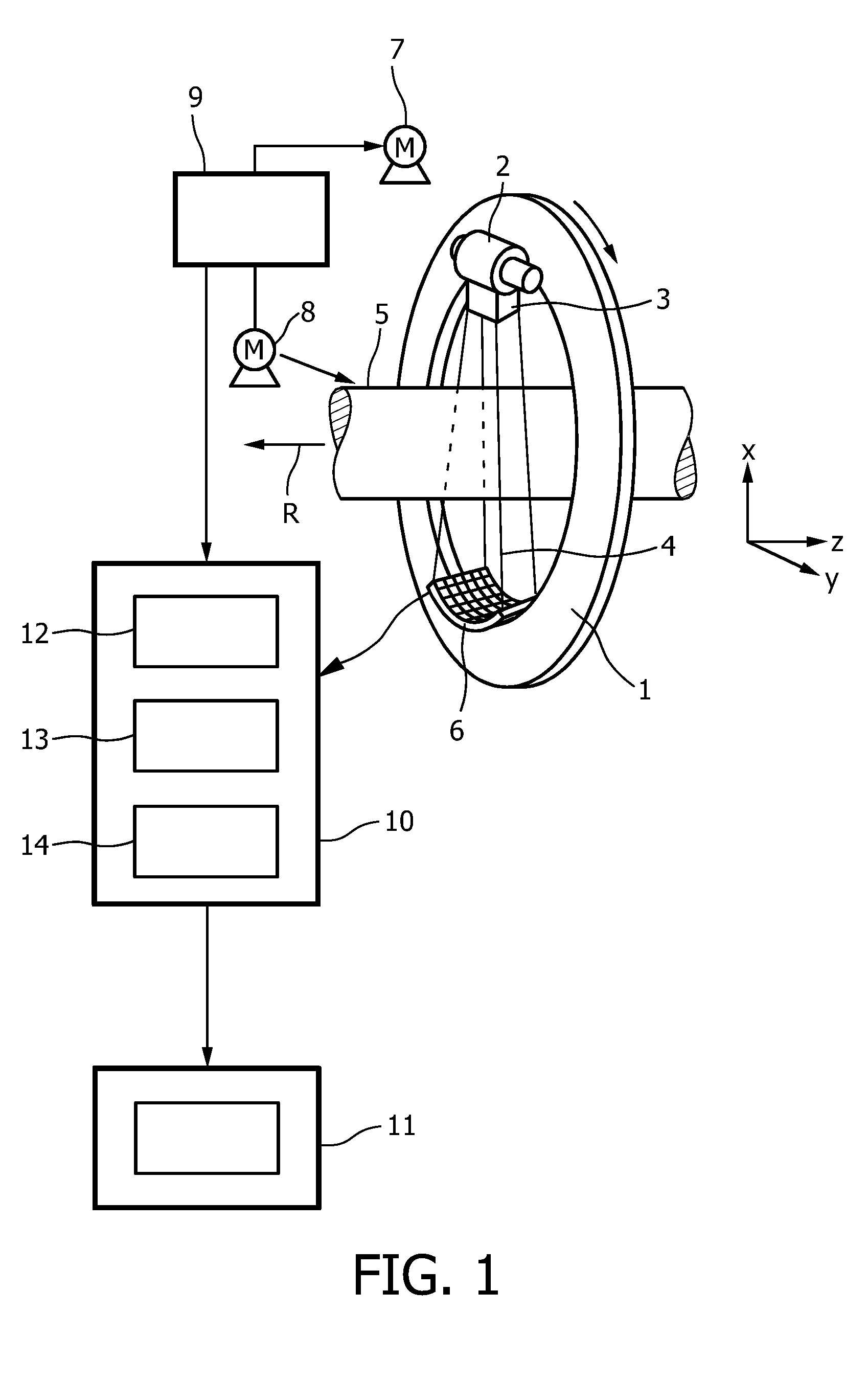
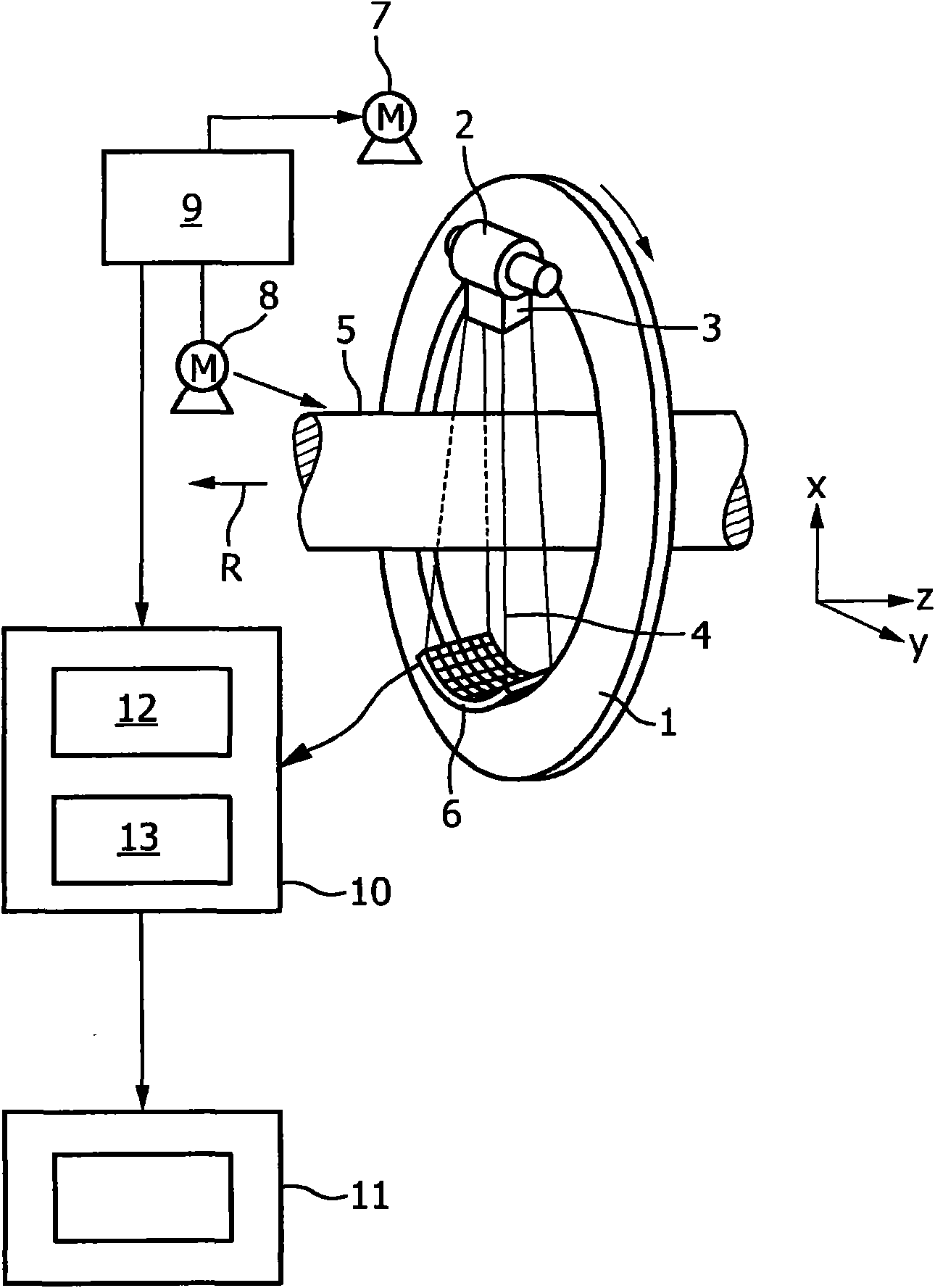
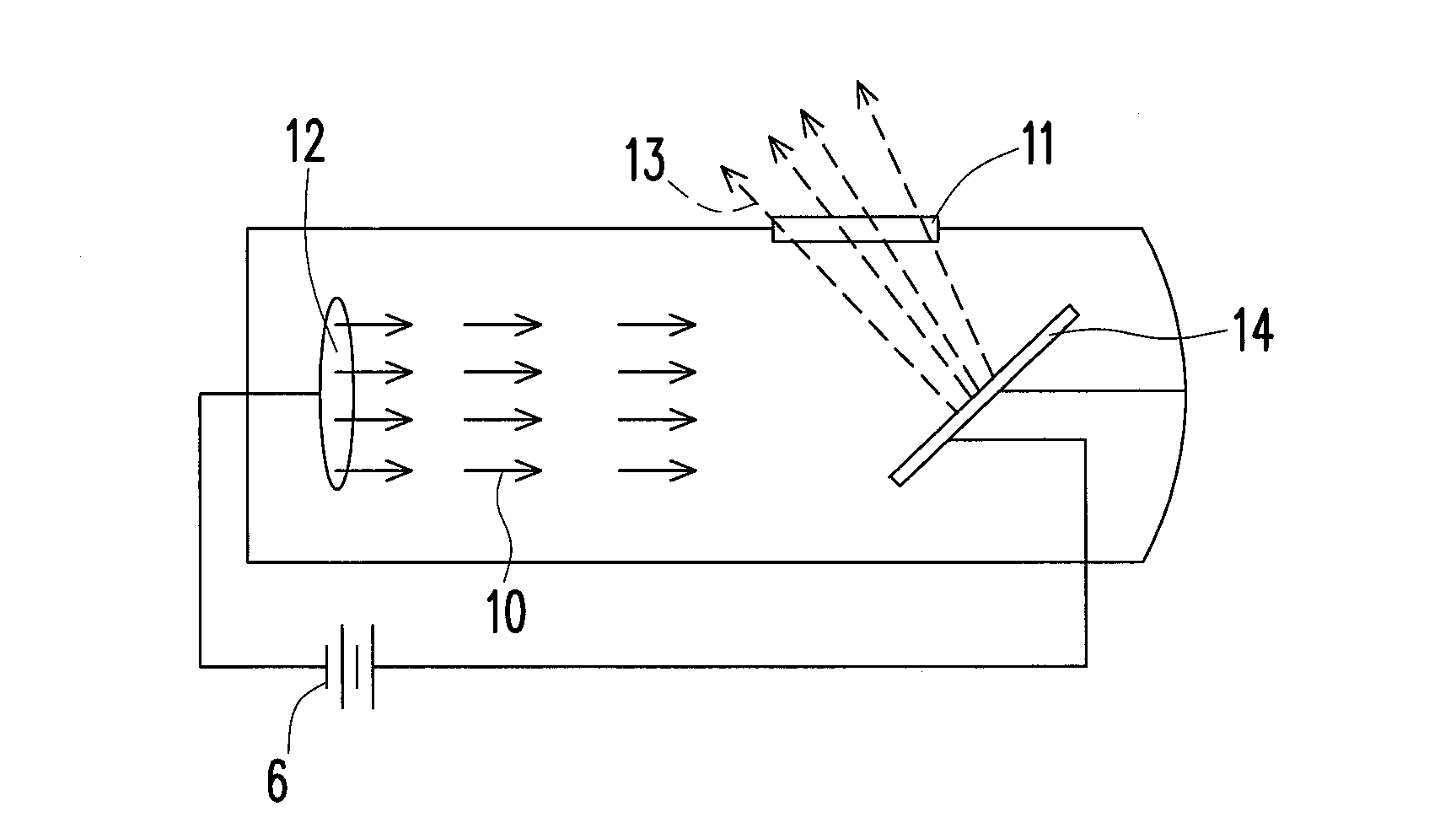
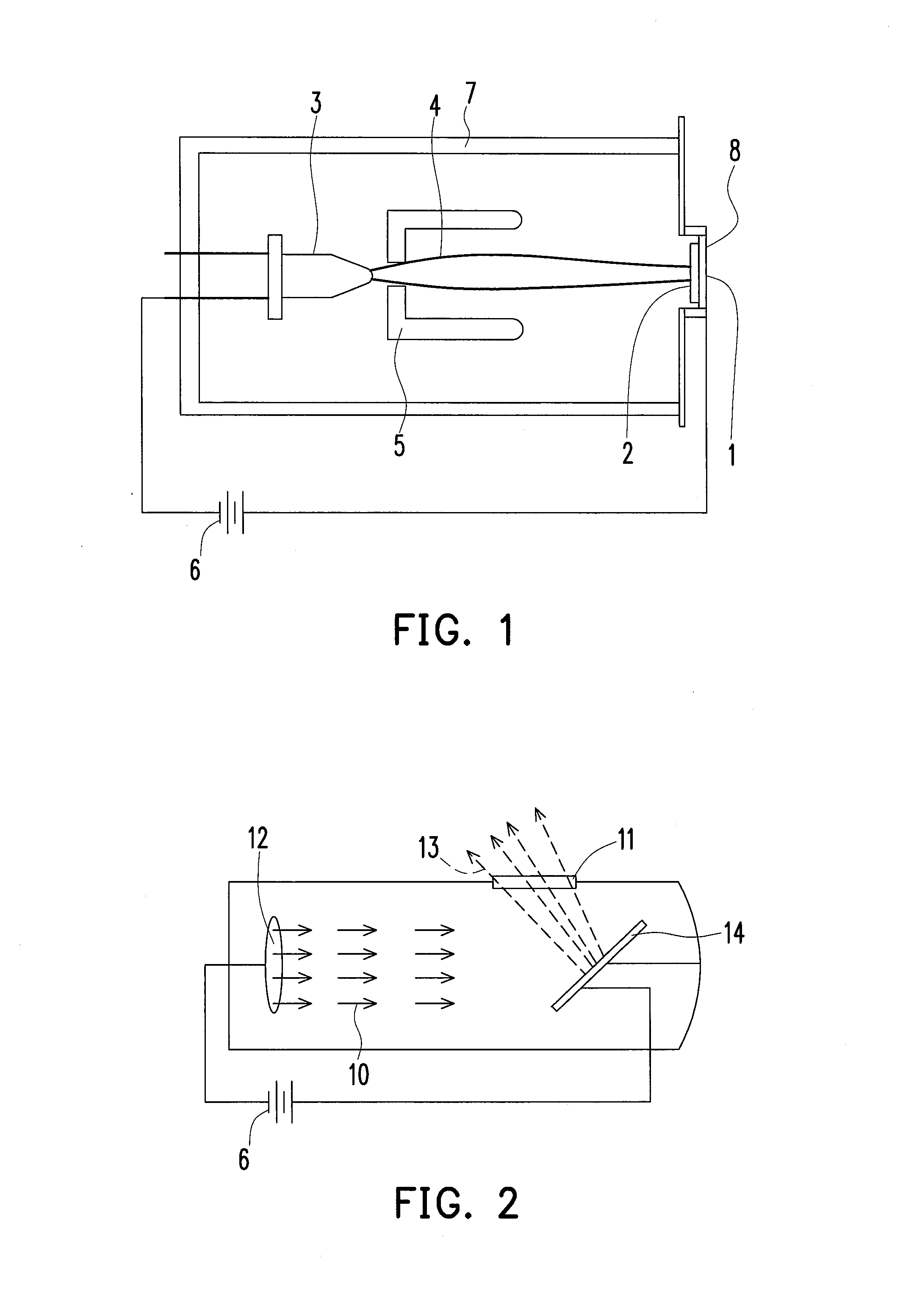
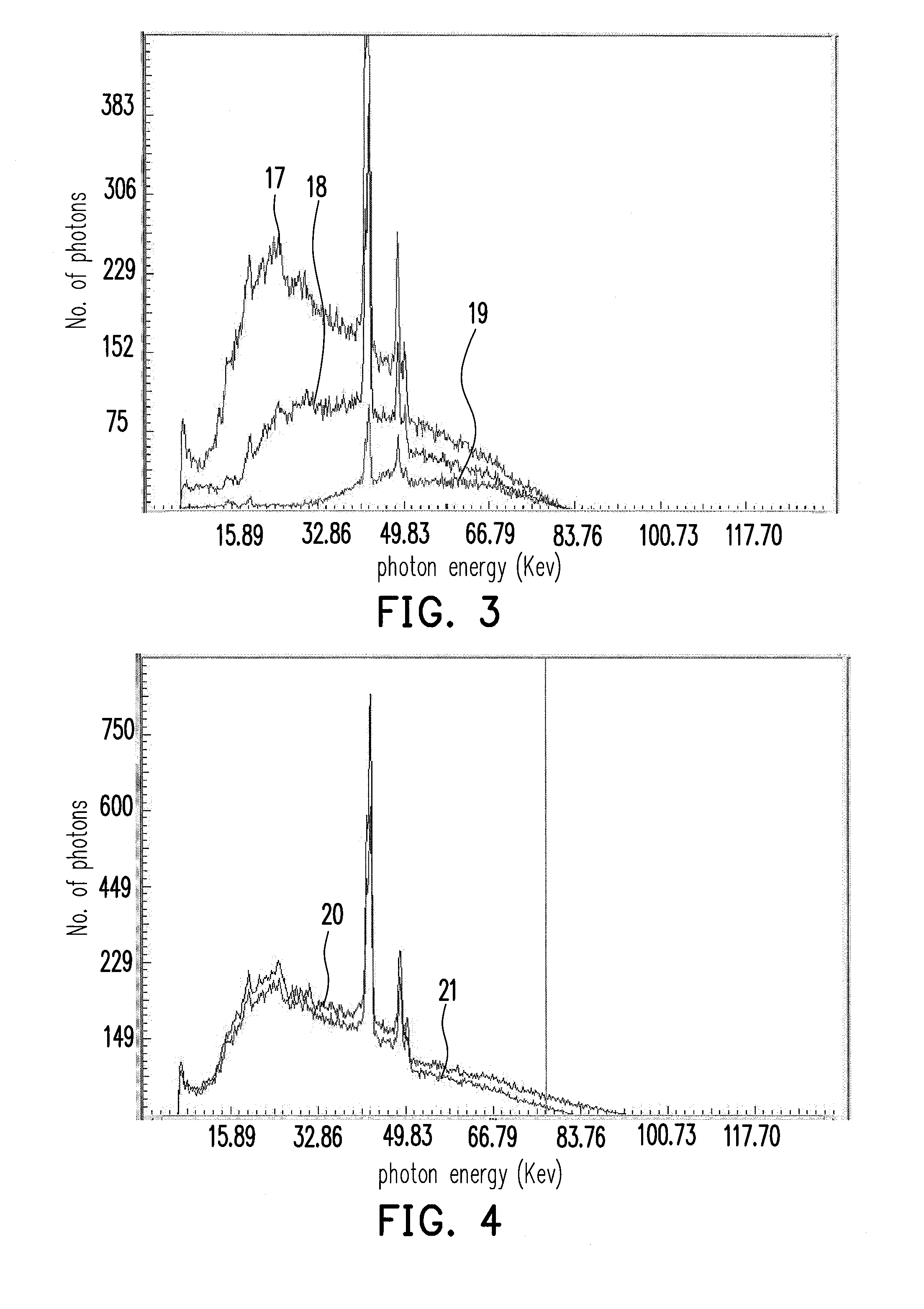
The invention relates to a method and a device for determining the distribution of an X-ray fluorescence (XRF) marker (16) in a body volume (14). The body volume (14) is irradiated with a beam of rays (12) from an X-ray source (10) with a first ray component with a quantum energy just above and a second ray component with a quantum energy just below the K-edge of the XRF marker (16). Secondary radiation emitted from the body volume (14) is detected in a location-resolved way by a detector (30). To separate the X-ray fluorescence components in the secondary radiation from background radiation, the body volume is irradiated for a second time with a beam of rays from which the first ray component has been substantially removed by a filter (22) made from the material of the XRF marker.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Imaging system for imaging an object
ActiveUS7852978B2Improve image qualityLess artefactMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingK-edgeImage system
The present invention relates to an imaging system for imaging an object (20) comprising a polychromatic radiation source (2) and an energy resolving radiation detector (6). The imaging system comprises further a driving device for moving the object (20) and the radiation source (2) relatively to each other, in order to acquire truncated projections from different directions. A calculation unit determines a k-edge component at least of one of the object (20) and a substance within the object (20) from the truncated projections and determines non-truncated projections from the determined k-edge component. A reconstruction unit constructs the object using the non-truncated projections.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Transmission type X-ray tube and reflection type X-ray tube
ActiveUS9036786B2Reduce intensityImprove image qualityX-ray tube electrodesX-ray tube vessels/containerSoft x rayX-ray
Owner:NANORAY BIOTECH CO LTD
Methods for 2-color radiography with laser-compton x-ray sources
ActiveUS20170241920A1Improve image contrastReduce X-ray doseMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-rayX ray image
High-contrast, subtraction, x-ray images of an object are produced via scanned illumination by a laser-Compton x-ray source. The spectral-angle correlation of the laser-Compton scattering process and a specially designed aperture and / or detector are utilized to produce / record a narrow beam of x-rays whose spectral content consists of an on-axis region of high-energy x-rays surrounded by a region of slightly lower-energy x-rays. The end point energy of the laser-Compton source is set so that the high-energy x-ray region contains photons that are above the k-shell absorption edge (k-edge) of a specific contrast agent or specific material within the object to be imaged while the outer region consists of photons whose energy is below the k-edge of the same contrast agent or specific material. Scanning the illumination and of the object by this beam will simultaneously record and map the above edge and below k-edge absorption response of the object.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Piezoelectric ceramic, method for producing piezoelectric ceramic, and piezoelectric ceramic electronic component
ActiveUS10193054B2Limited insulation resistance dropImprove piezoelectric performanceImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesX-ray absorption spectroscopyCrystal structure
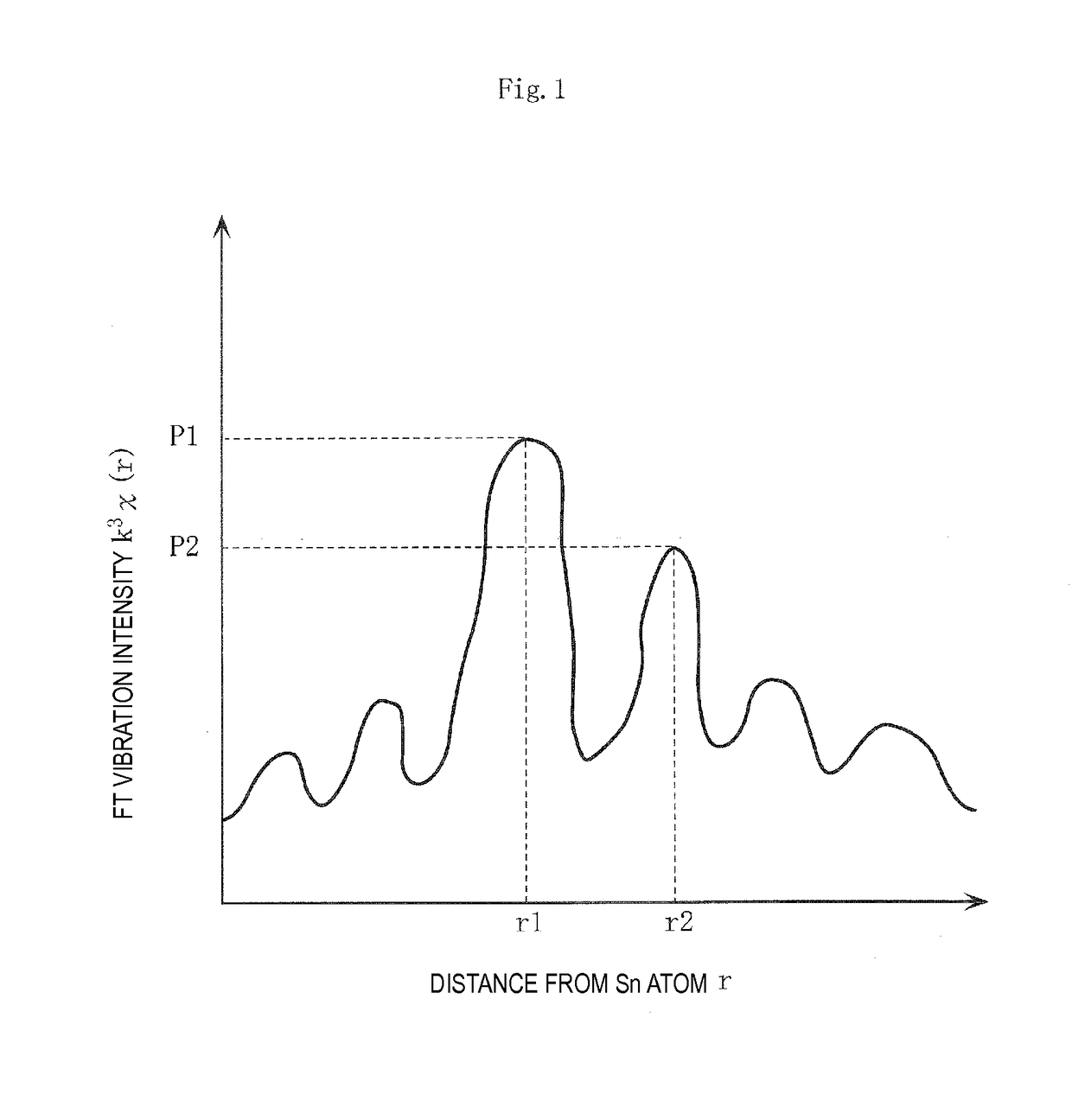
A piezoelectric ceramic that contains an alkali niobate compound as its main ingredient. The alkali niobate compound has a perovskite crystal structure represented by AmBO3 and contains an alkali metal. There exists Sn in part of site A, and Zr in part of site B. A radial distribution function obtained from a K-edge X-ray absorption spectrum of Sn has a first peak intensity P1 at a first distance from a Sn atom and a second peak intensity P2 at a second distance from the Sn atom. The second distance is greater than the first distance, and the peak intensity ratio P1 / P2 is 2.7 or less.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
CT imaging system
ActiveUS7813472B2Quality improvementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayK-edge
The invention relates to a CT imaging system for determining the flow of a substance within an object, wherein the CT imaging system comprises a polychromatic X-ray source and an energy-resolving X-ray detector for obtaining detection signals depending on the X-ray radiation after passing through the object. A calculation unit (12) determines a k-edge 5 component of the substance from the detection signals, and a reconstruction unit (13) reconstructs a time series of k-edge image from the determined k-edge component. A flow determination unit (14) determines flow values indicative for the flow within the object from the time series of k-edge images.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
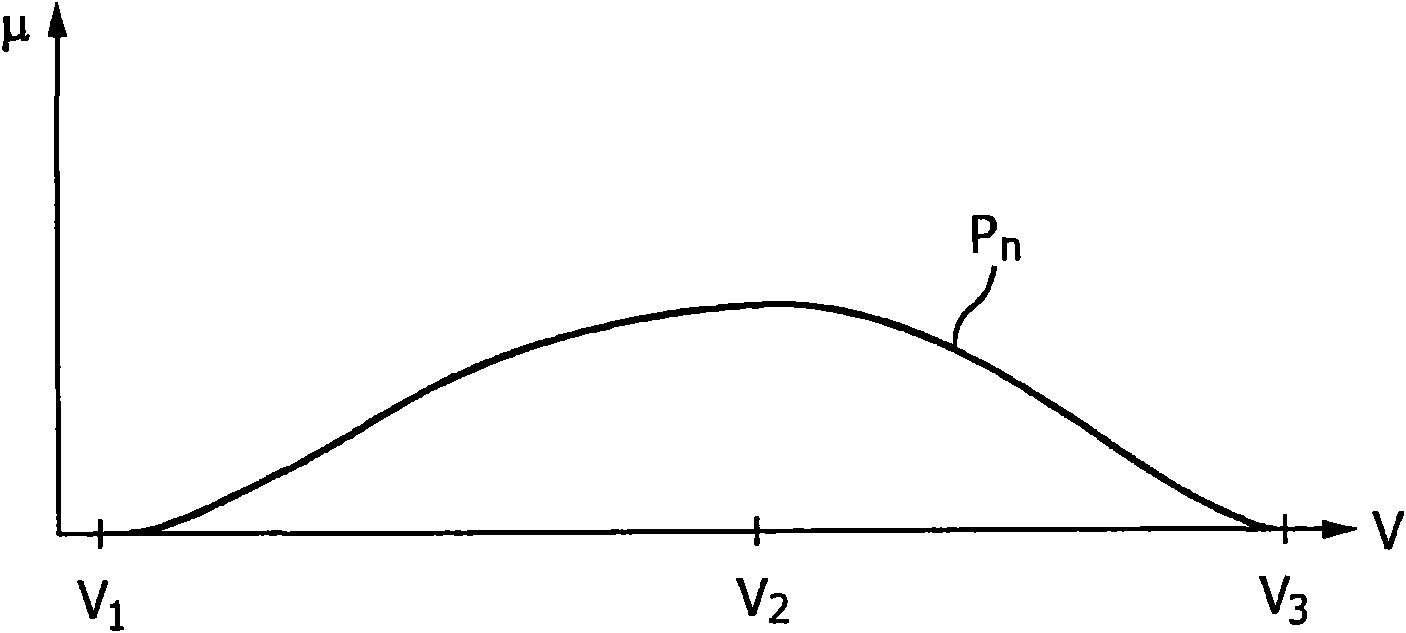
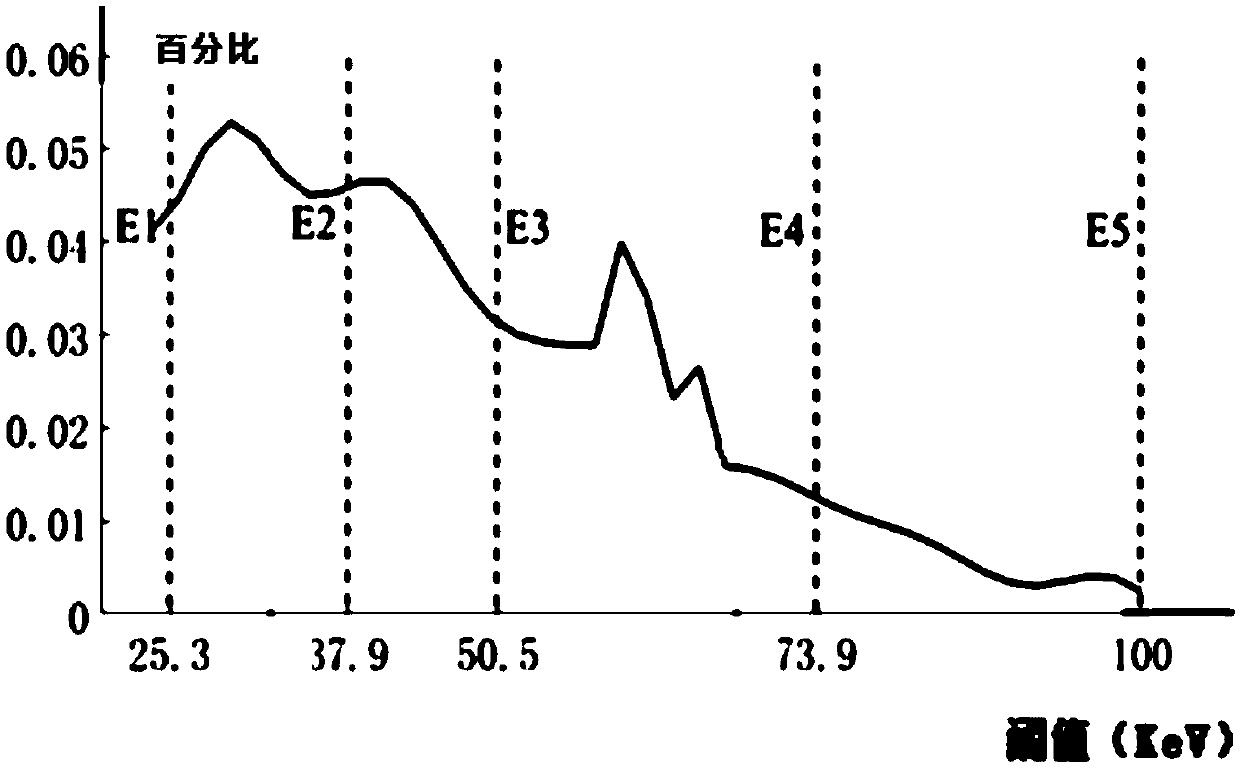
K-edge imaging method
ActiveCN110006932AImprove image qualityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAttenuation coefficientEnergy window
The invention relates to the technical field of imaging, and provides a K-edge imaging method. The K-edge imaging method comprises the steps of acquiring the energy resolution of a detector, and determining a Gaussian convolution kernel according to the energy resolution; obtaining a theoretical attenuation coefficient curve; obtaining a first smooth attenuation coefficient curve according to theGaussian convolution kernel and the theoretical attenuation coefficient curve; obtaining a second smooth attenuation coefficient curve according to the first smooth attenuation coefficient curve in combination with spectral information in an energy window; and selecting positions of the energy window according to the second smooth attenuation coefficient curve. When the position of the energy window is selected, the influences of the energy resolution of the detector and the spectral information in the energy window are considered, and the positions of the energy window with the maximum attenuation coefficient difference can be well selected under different energy window width requirements, so that subtraction imaging is carried out by using the difference of K-absorption edge as much as possible, and the optimal image quality is obtained.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Radioscopy using Kalpha gadolinium emission
InactiveUS7315757B2Precision therapyImprove accuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsX-rayNeoplasm
The methods comprise detection of gadolinium in human tissues and organs by refining the position of malignant neoplasm and radiation treatment of the neoplasm in order to damage its cells. Refined position of the malignant neoplasm is determined by introducing gadolinium into the patient body and scanning part of the patient body in which the neoplasm is located. The scanning is performed by displacement of zone of radiation concentration created by intersection of several X-ray beams having radiation energy corresponding to K-edge of gadolinium atoms absorption. The refined information is acquired using detectors sensitive to Kα-radiation of gadolinium atoms, to which secondary radiation is transported arising in zone of concentration. Scanning is performed of the region of the malignant neoplasm location utilizing the same means as in the first stage. Sources of X-ray radiation are switched with control means into elevated intensity mode, sufficient for radiation damage of the malignant neoplasm tissues.
Owner:KUMAKHOV MURADIN ABUBEKIROVICH
Medical x-ray examination apparatus for performing k-edge imaging
ActiveCN101868183AReduce spatial resolutionImprove signal-to-noise ratioComputerised tomographsTomographyConventional X-RayX-ray
The invention relates to a medical X-ray examination apparatus (1) for performing K-edge imaging. The medical X-ray examination apparatus (1) comprises an imaging unit (21), which is configured to spectrally decompose an X-ray absorption spectrum to image the X-ray absorption spectrum as a conventional X-ray absorption image (23a) and a K-edge absorption image (23b). The conventional X-ray absorption image (23a) includes data elements representing the anatomical background of an object of interest. The K-edge absorption image (23b) includes data elements representing quantitative information of local densities of material showing K-edge absorption within the object of interest. The imaging unit (21) comprises a spatial resolution reducer for reducing the spatial resolution of the K-edge absorption image, so that with a medical X-ray examination apparatus according to the invention an increased sensitivity of the selective imaging of a K-edge absorption image is achieved as compared to the sensitivity of the selective imaging of a K-edge absorption image of a known medical X-ray examination apparatus.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com