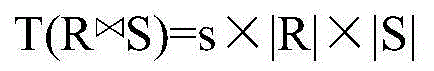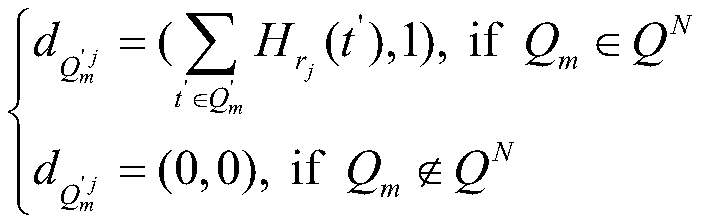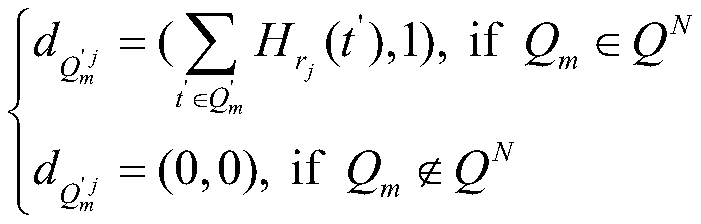Patents
Literature
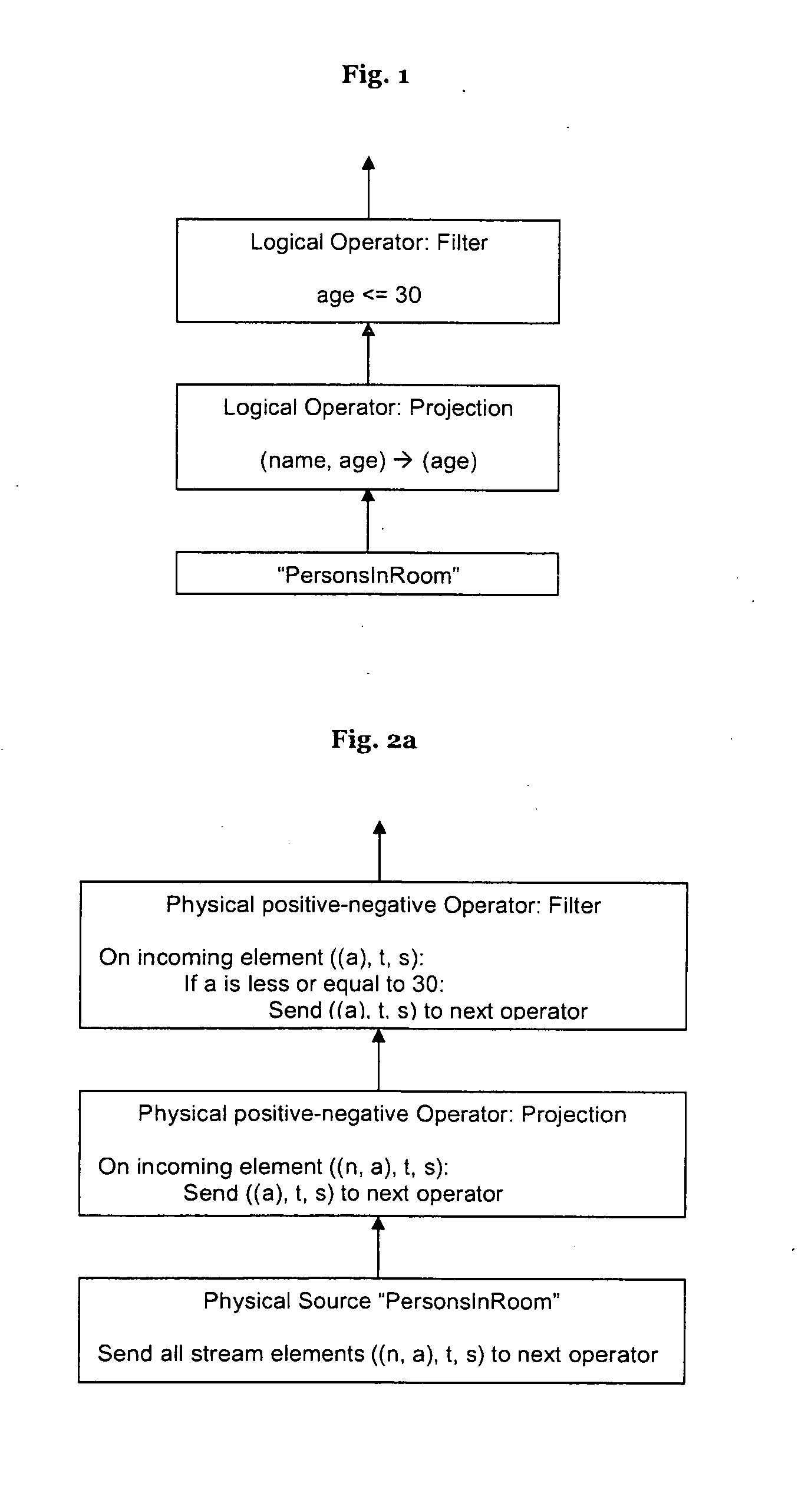
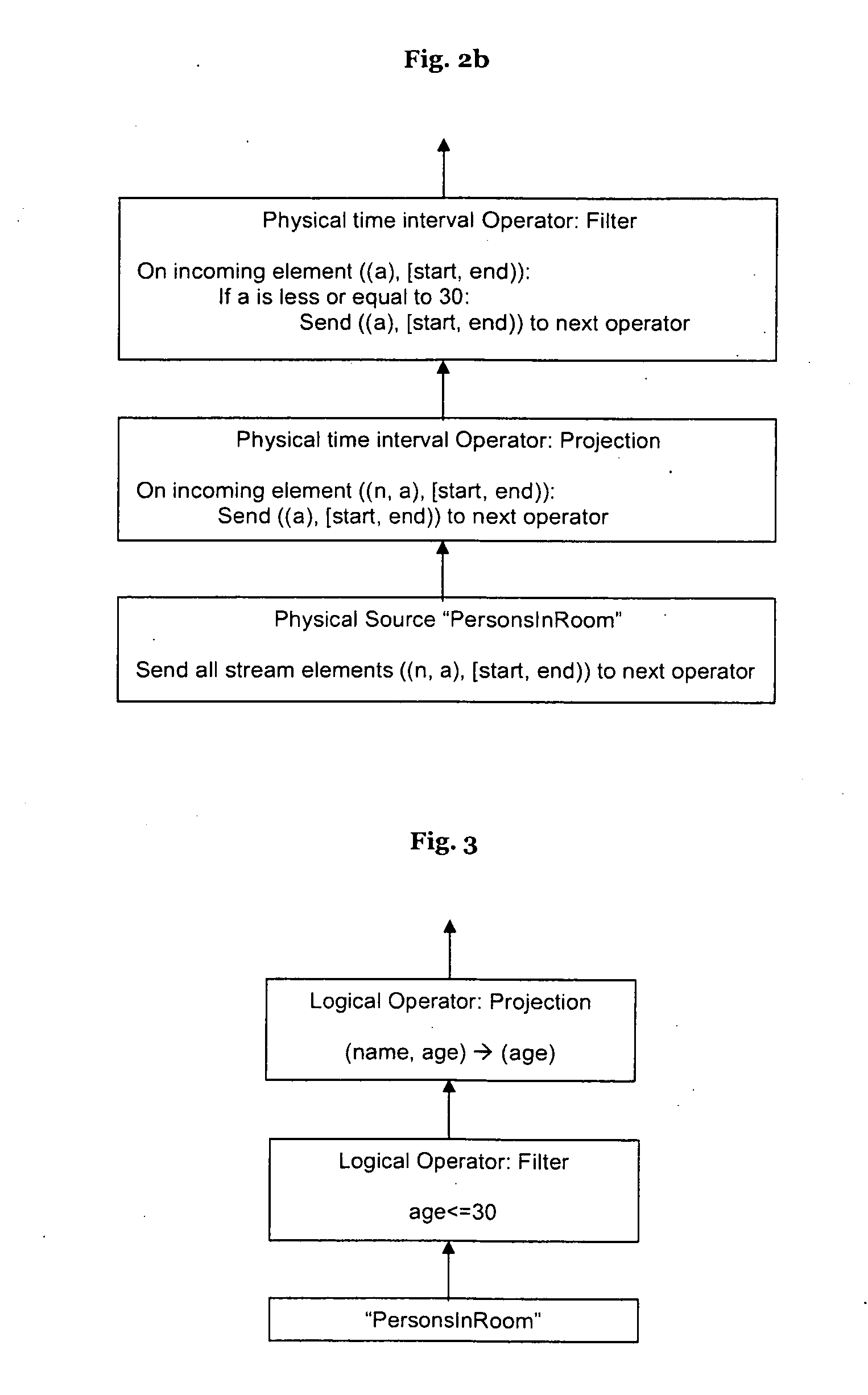
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
47 results about "Logical query" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
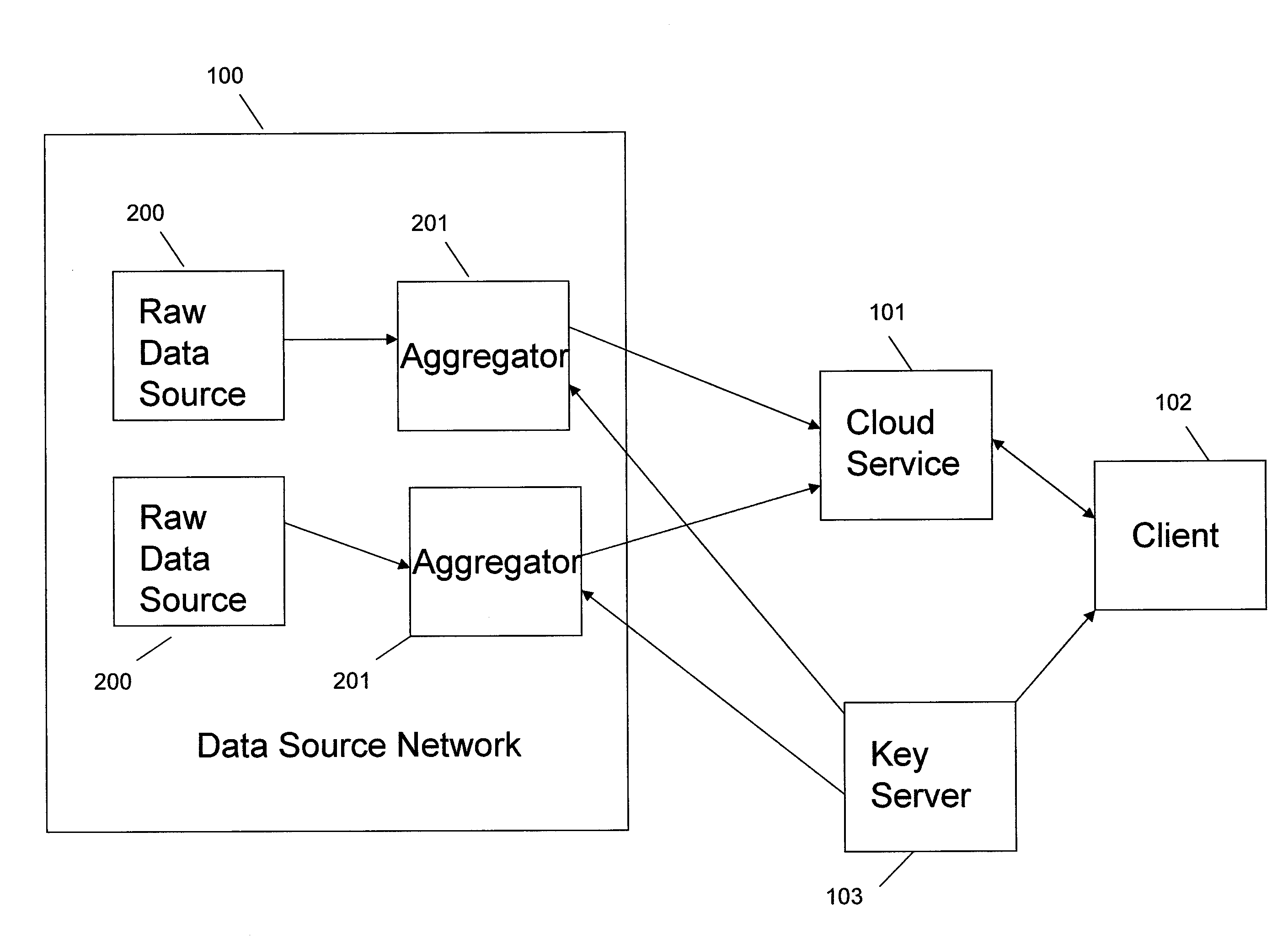
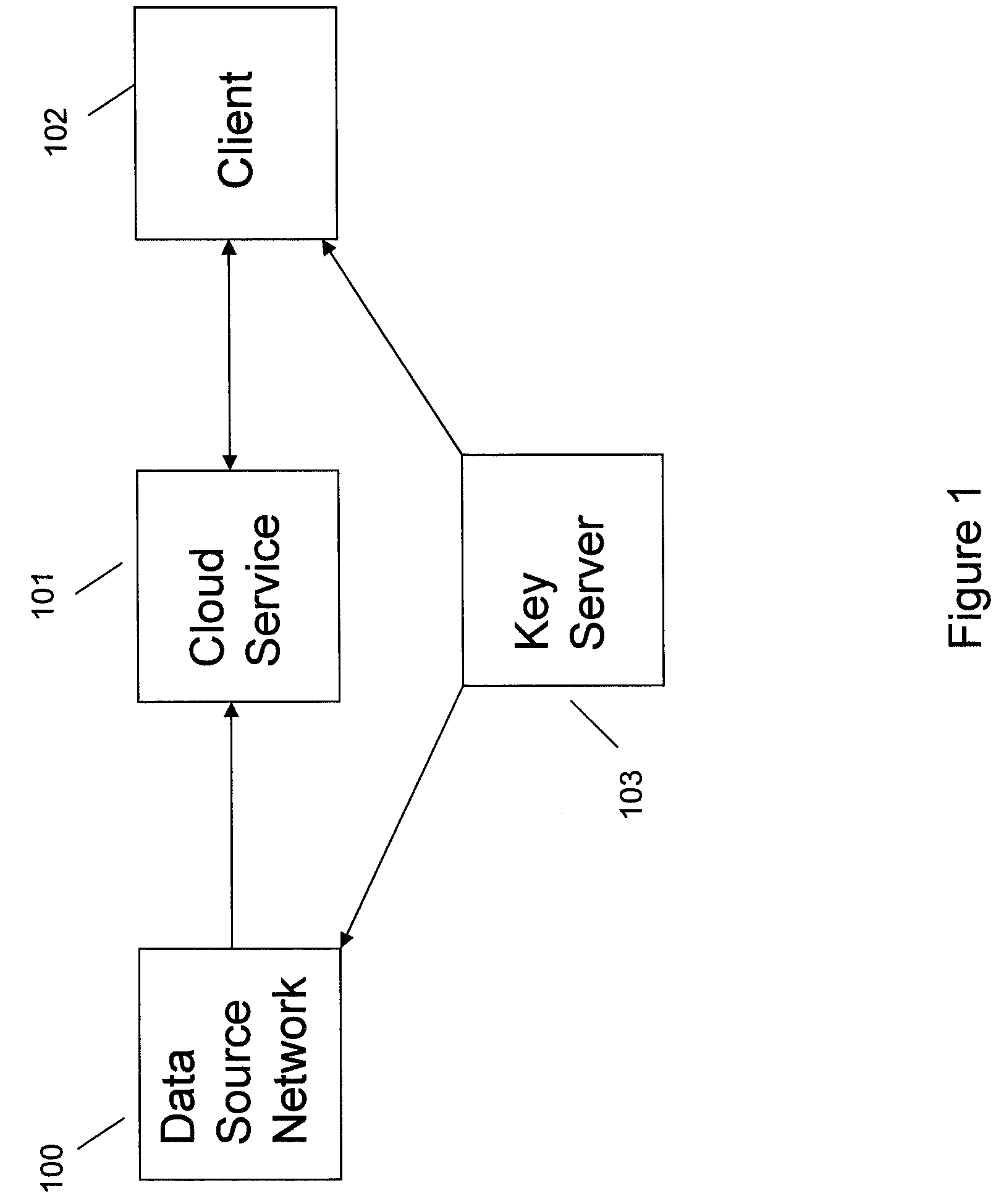
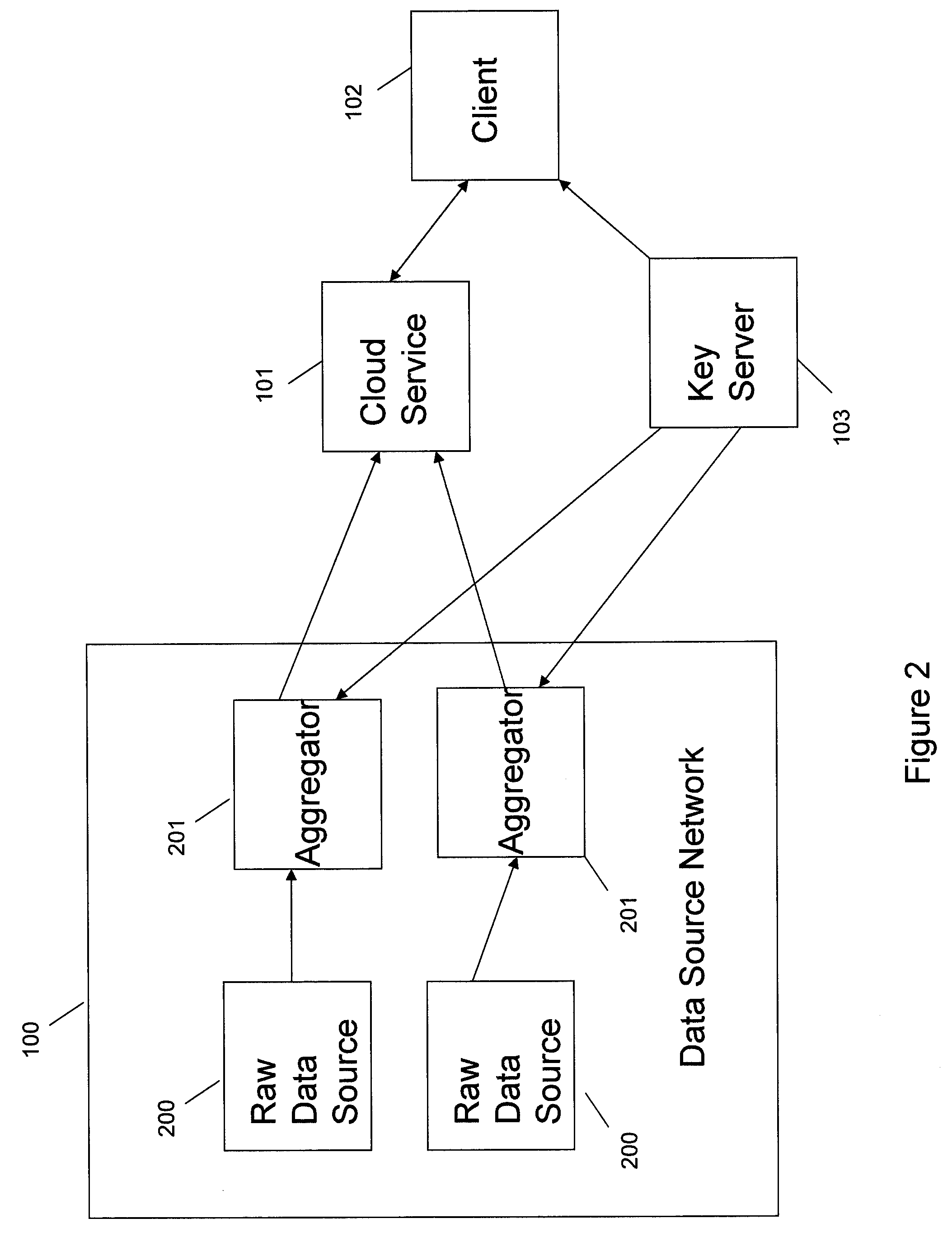
Systems and methods for communication, storage, retrieval, and computation of simple statistics and logical operations on encrypted data
InactiveUS20110264920A1Unauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringLogical queryData system
Systems and methods provide for a symmetric homomorphic encryption based protocol supporting communication, storage, retrieval, and computation on encrypted data stored off-site. The system may include a private, trusted network which uses aggregators to encrypt raw data that is sent to a third party for storage and processing, including computations that can be performed on the encrypted data. A client on a private or public network may request computations on the encrypted data, and the results may then be sent to the client for decryption or further computations. The third party aids in computation of statistical information and logical queries on the encrypted data, but is not able to decrypt the data on its own. The protocol provides a means for a third party to aid in computations on sensitive data without learning anything about those data values.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
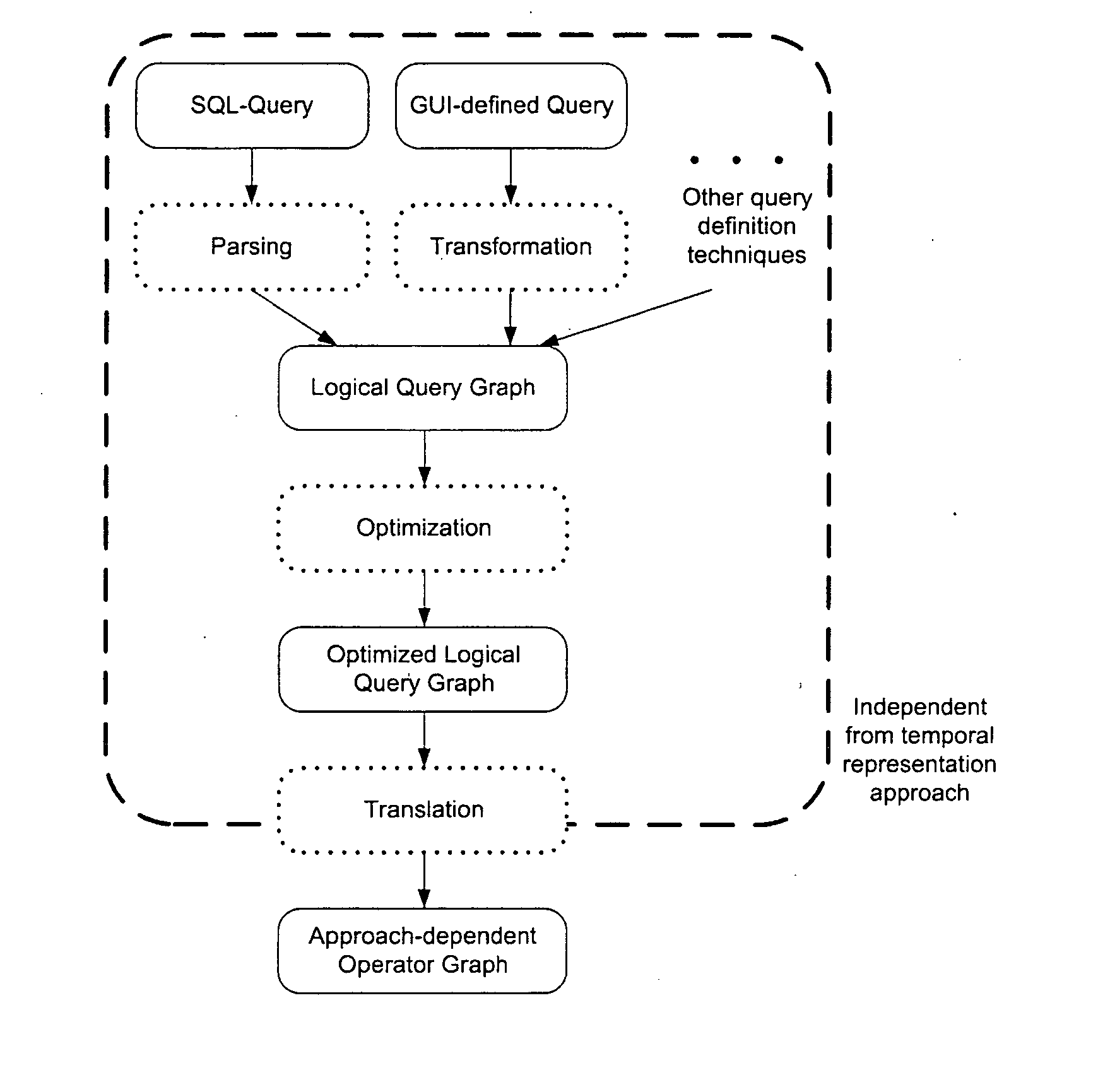
CEP engine and method for processing CEP queries
ActiveUS20120166469A1Reduce system loadEases interoperabilityDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsQuery planData stream
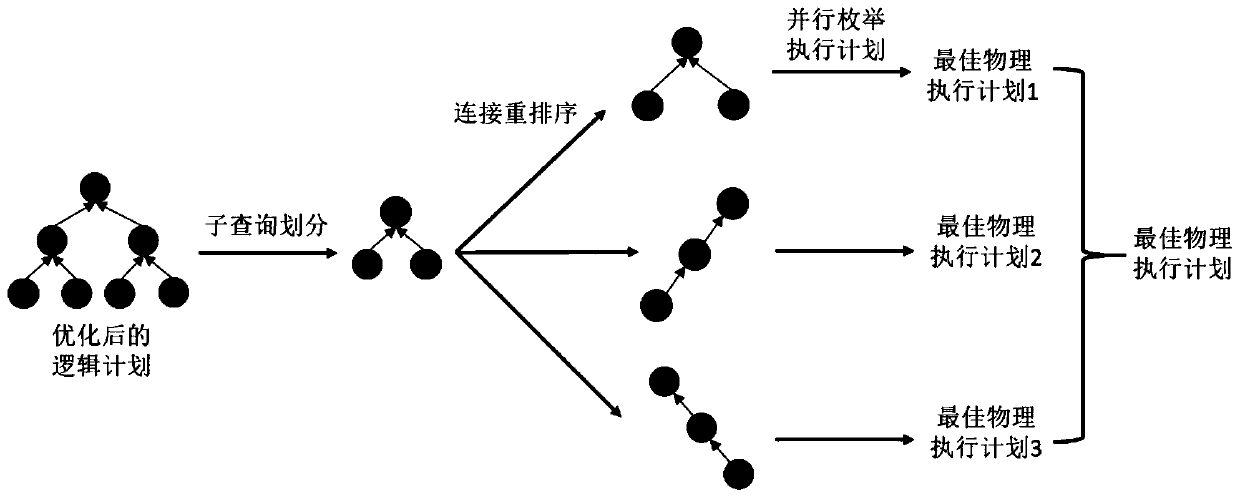
The present invention concerns a complex event processing (CEP) engine (1) for processing CEP queries (10) over data streams, wherein the CEP engine (1) comprises:a. a parser (100), adapted for parsing a received CEP query (10) into a logical query graph (20); andb. a translator (300), adapted for translating the logical query graph (20) into a physical query plan (30) in accordance with one of a plurality of data stream representations; whereinc. the logical query graph (20) is independent of the plurality of data stream representations.
Owner:SOFTWARE AG
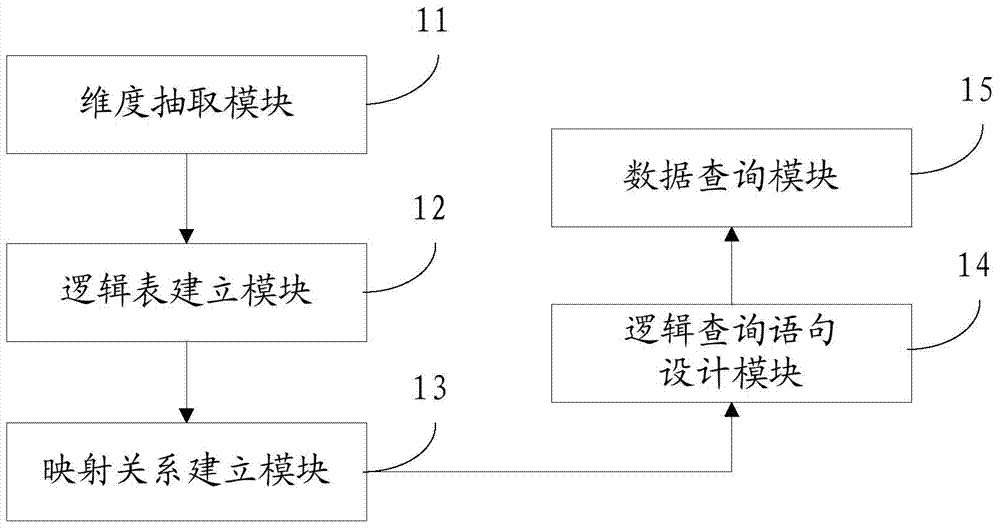
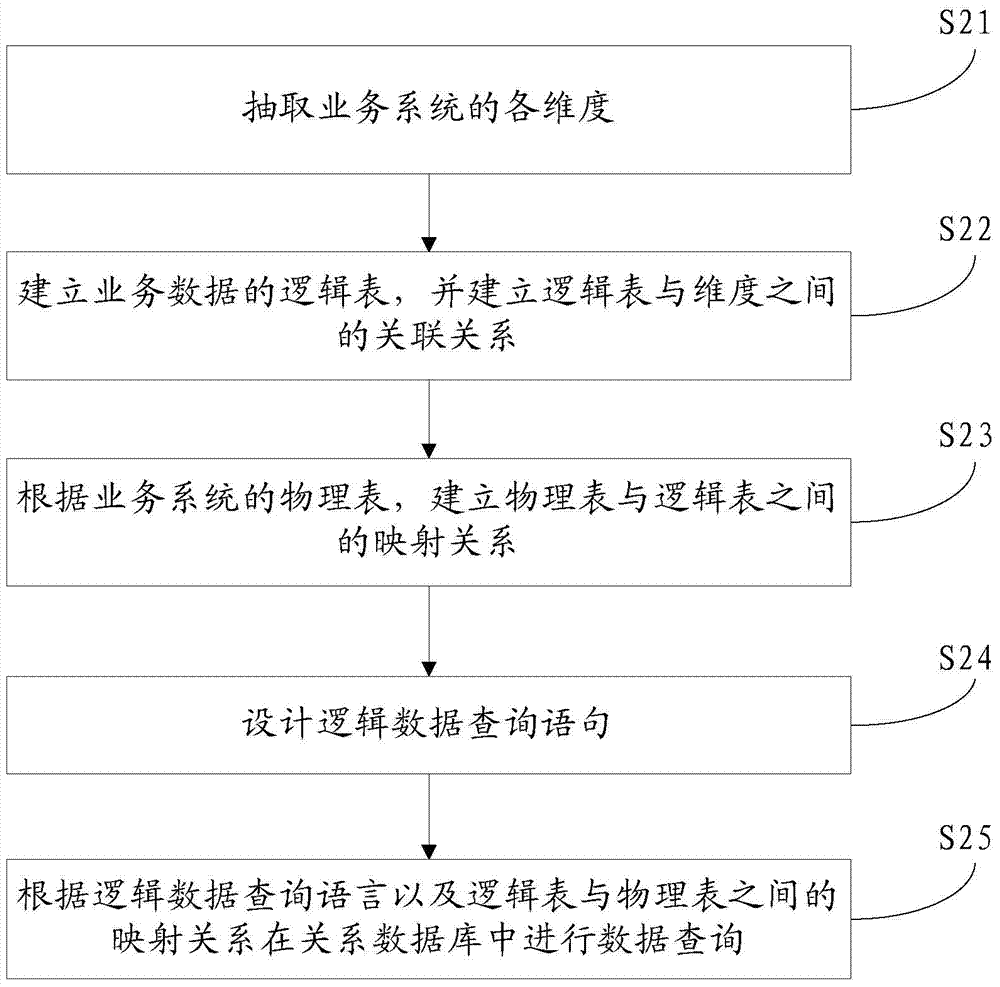
Data query method and system
InactiveCN103577590AImprove data structure understandabilityReduce couplingRelational databasesSpecial data processing applicationsLogical queryInto-structure
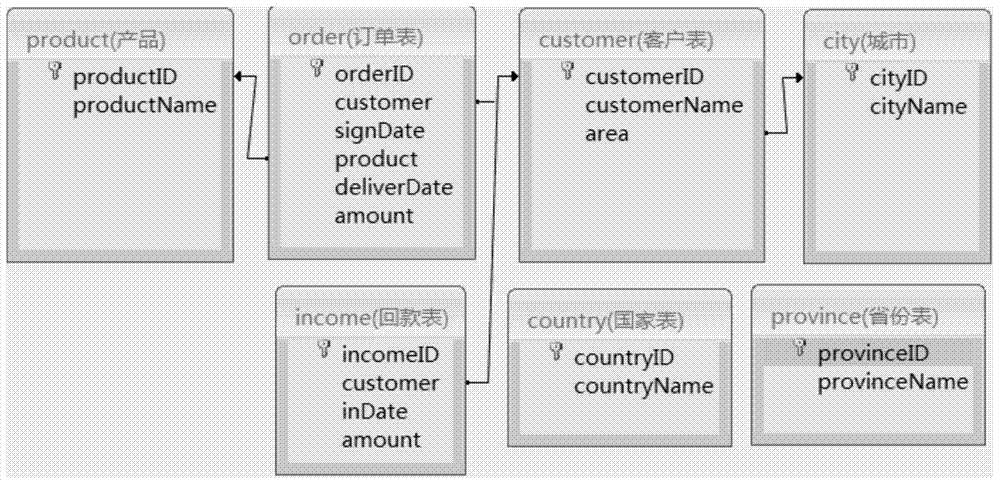
The invention discloses a data query method and system. The data query method includes the steps of firstly, extracting various dimensionalities in a business system, building a plurality of logical tables of business data for describing the business system, building incidence relations between the logical tables and the dimensionalities, then building mapping relations between a physical table and the logical tables according to the physical table of the business system, writing logical query statements according to the logical tables and a logical data query grammar defined according to a rule, finally, according to the mapping relations between the physical table and the logical tables, converting the logical query statements into structuring query statements, and executing the structuring query statements in a database to complete querying of the business data. According to the data query method and system, the complexity of data table understanding and writing can be reduced, and the understandability of a data structure of the business system is improved.
Owner:北京润乾信息系统技术有限公司
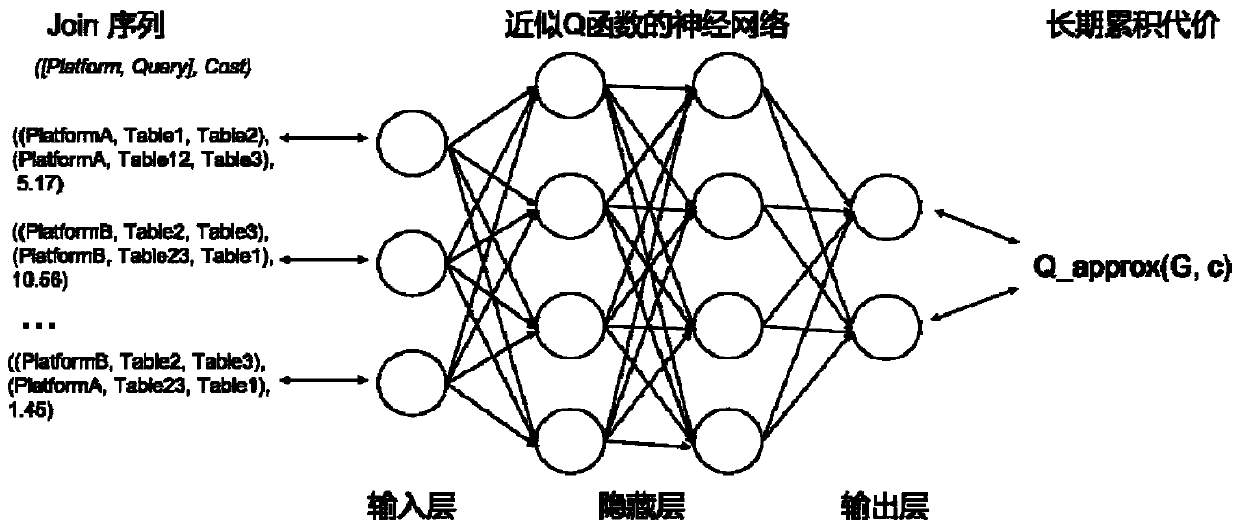
Node-level sub-queries in distributed databases
InactiveUS20100094851A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsLogical queryDistributed database
A database query is received that includes a logical query indicator at a distributed database node within a distributed network of databases. The logical query indicator includes at least one physical database query and at least one database node identifier that allows at least one distributed database node to identify at least one physical database to execute the physical database query against. It is determined that the at least one database node identifier matches a local node identifier. The at least one physical database query is executed against at least one local physical database table. A local query response is formed including data retrieved from the at least one local physical database table. The database query is responded to with at least the local query response. This abstract is not to be considered limiting, since other embodiments may deviate from the features described in this abstract.
Owner:IBM CORP
Structured cluster execution for data streams
ActiveUS10558664B2Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsQuery planData stream
A system for executing a streaming query includes an interface and a processor. The interface is configured to receive a logical query plan. The processor is configured to determine a physical query plan based at least in part on the logical query plan. The physical query plan comprises an ordered set of operators. Each operator of the ordered set of operators comprises an operator input mode and an operator output mode. The processor is further configured to execute the physical query plan using the operator input mode and the operator output mode for each operator of the query.
Owner:DATABRICKS INC
Structured cluster execution for data streams
A system for executing a streaming query includes an interface and a processor. The interface is configured to receive a logical query plan. The processor is configured to determine a physical query plan based at least in part on the logical query plan. The physical query plan comprises an ordered set of operators. Each operator of the ordered set of operators comprises an operator input mode and an operator output mode. The processor is further configured to execute the physical query plan using the operator input mode and the operator output mode for each operator of the query.
Owner:DATABRICKS INC
Method and apparatus for analyzing the effect of different execution parameters on the performance of a database query
InactiveUS20070143246A1Different execution performanceImprove executionDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsDatabase queryLogical query
A database application re-uses one or more query execution strategies for a given logical query, and saves historical data concerning query execution performance under differing execution parameters. The historical data is analyzed to identify environmental variables and / or imported variables which significantly affect execution performance. Preferably, an auxiliary data structure includes, for each of multiple execution strategies, a respective set of imported and environmental variables and respective average cost measure, such as execution time. An analytical tool compares multiple different strategies to identify imported and / or environmental variables which caused a different strategy to be used, and resultant average cost. Preferably, the tool can also compare variation within the same strategy.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for executing relation type calculating instruction in distributed way
ActiveCN105786808ARealize the irreparable gapSpecific program execution arrangementsSpecial data processing applicationsNODALLogical query
The objective of the invention is to provide a method and apparatus for executing relation type calculating instruction in distributed way. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a relation type calculating instruction that is formed by a plurality of distributed relation type calculating operators; generating a logic query tree corresponding to the relation type calculating instruction, wherein, the logic query tree comprises nodes corresponding to the distributed relation type calculating operators; and then, executing the logic query tree in a distributed way to obtain a query result corresponding to the relation type calculating instruction. Compared with prior art, the statements that haven't define standard operators in the distributed way into operators and relation type calculating instructions that can be processed in the distribution way to execute an execution method like an SQL statement in a distributed system, so that the gap between a traditional database and the distributed processing is avoided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG TMALL TECH CO LTD
Cross-platform unified big data SQL query method
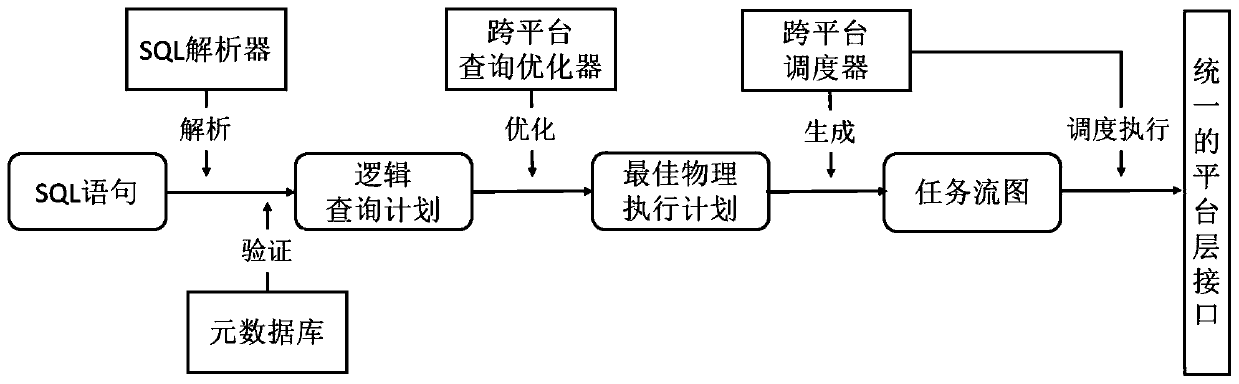
ActiveCN110059103AAddress usabilitySolve the unity problemEnergy efficient computingSpecial data processing applicationsExecution planLogical query
The invention discloses a cross-platform unified big data SQL (Structured Query Language) query method, which comprises the following steps of: expanding part of SQL semantics, and providing a unifiedcross-platform SQL query language for a user; enabling a unified SQL parser to parse the query statement submitted by the user into a logic query plan, and verifying the legality of the query statement according to the meta information stored in the unified meta database; enabling a cross-platform optimizer to optimize the structure and the connection sequence of the logic query plan and convertthe logic query plan into an optimal physical execution plan composed of a plurality of sub-queries bound with an execution platform; enabling a cross-platform scheduler to convert the optimal physical execution plan into a task flow graph, automatically schedule the task flow graph according to the dependency relationship among the tasks and execute all the tasks; designing a unified platform layer interface meeting cross-platform SQL query requirements, and shielding operation differences between different execution platforms. The cross-platform unified big data SQL query method solves the problems that an existing cross-platform query method is poor in usability, low in performance, large in data migration cost and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Building complex hierarchical queries
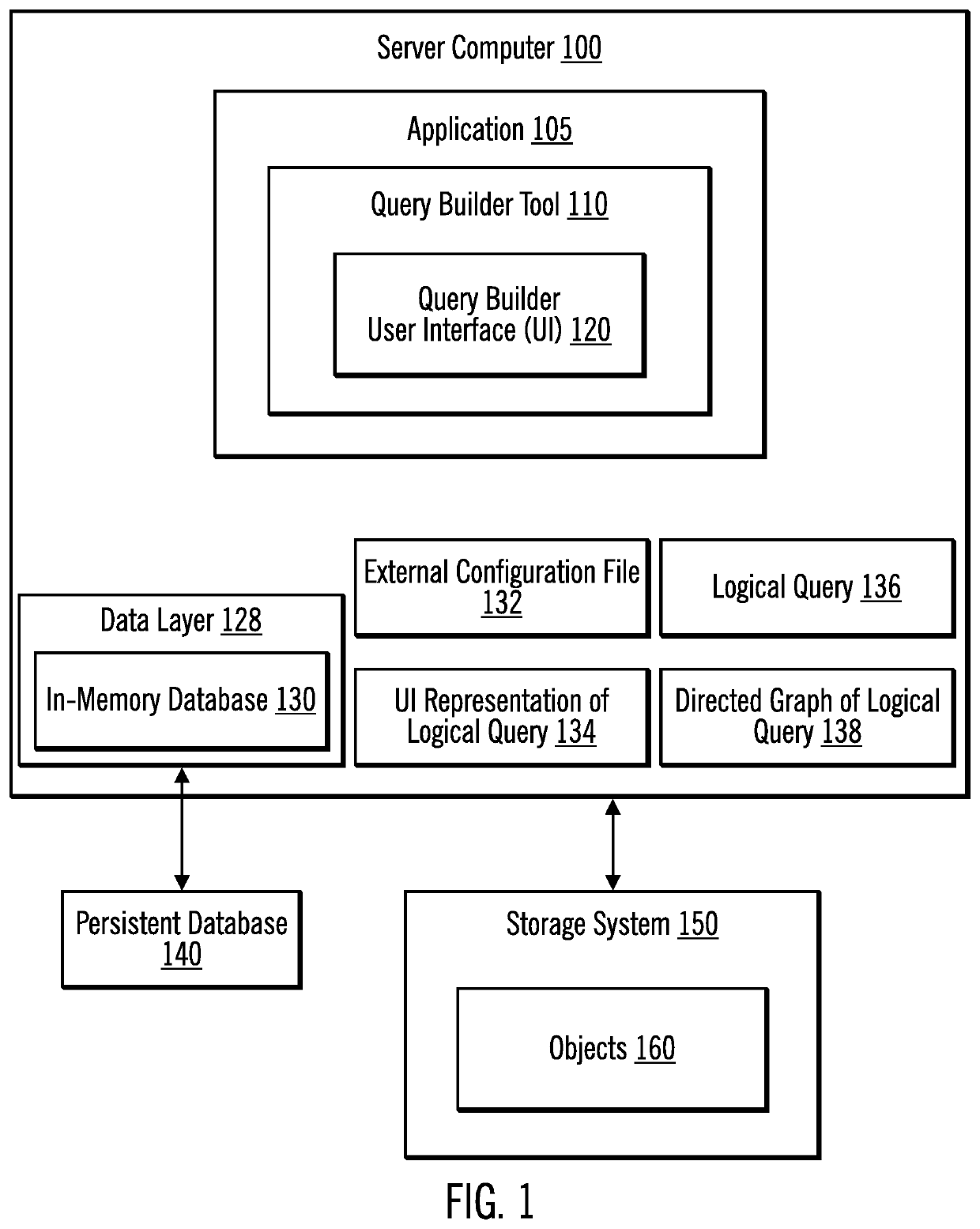
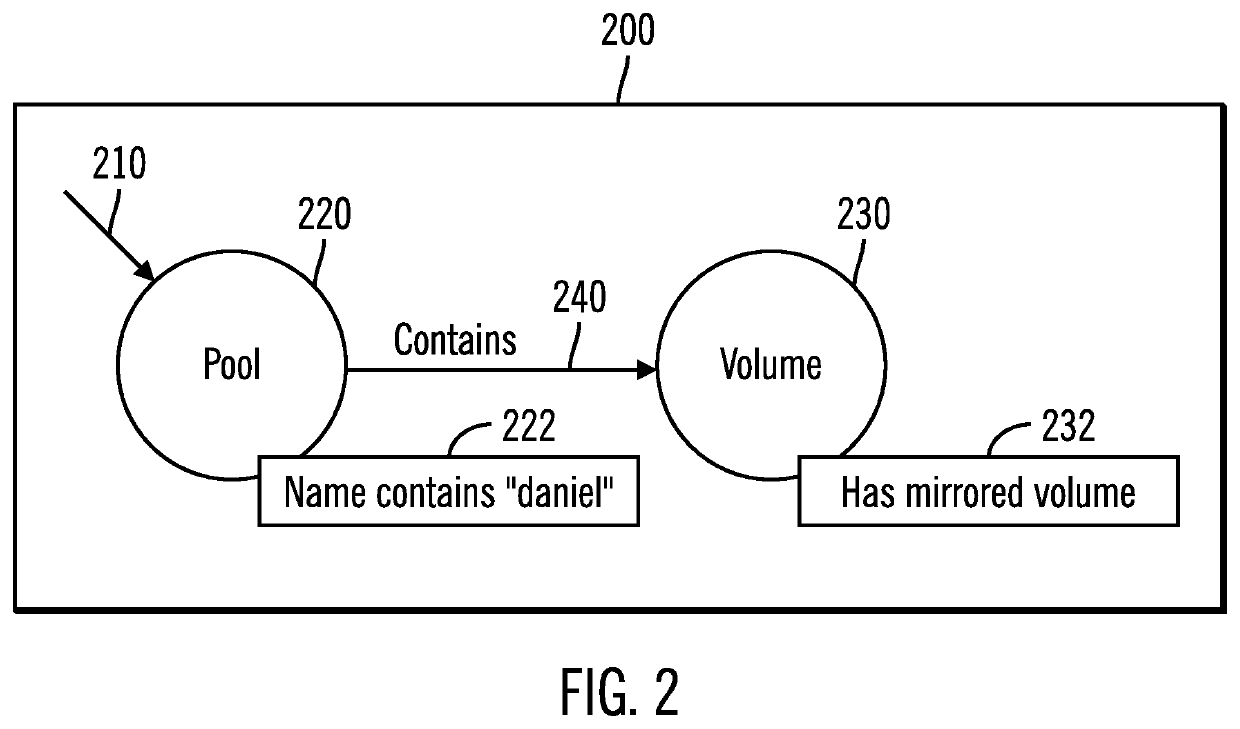
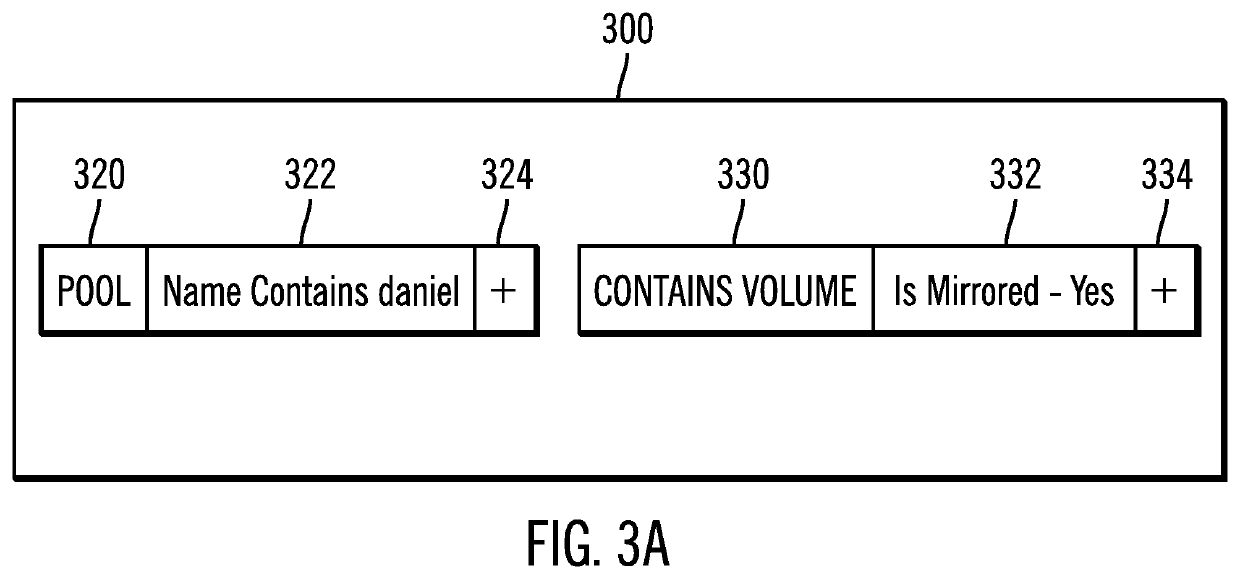
ActiveUS20170124146A1Avoid difficult choicesQuickly and easily visualizeDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsDirected graphLogical query
Provided are a computer program product, system, and method for building complex hierarchical queries. A User Interface (UI) representation of a logical query is received, wherein the UI representation describes object types, relationships between the object types, and attributes of the object types. The UI representation is translated to a logical query. The logical query is converted to data layer calls to retrieve objects having the object types, the relationships between the object types, and the attributes of the object types. The objects are received. Then, a directed graph is generated using the identified objects.
Owner:IBM CORP
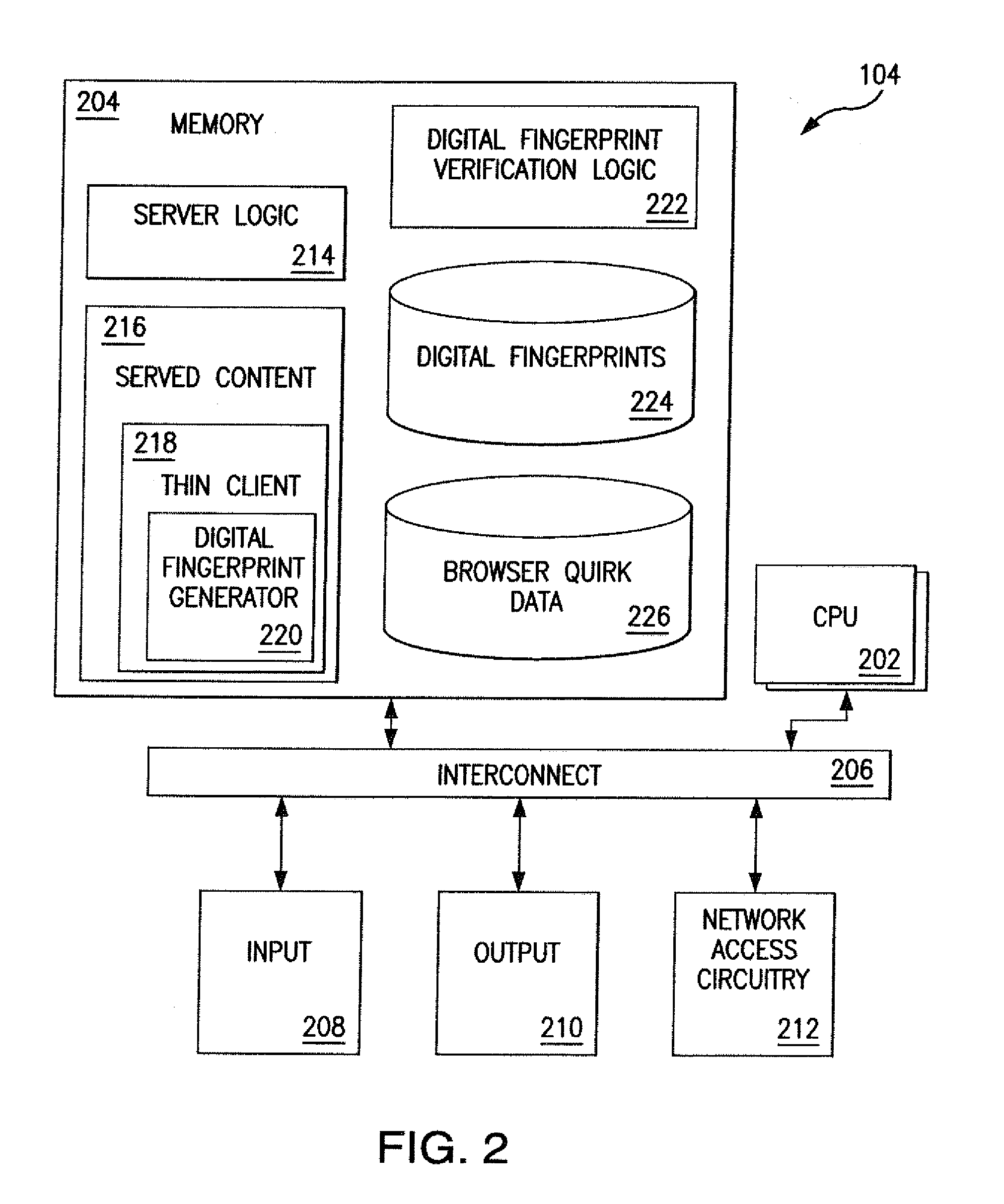
Detection of spoofing of remote client system information
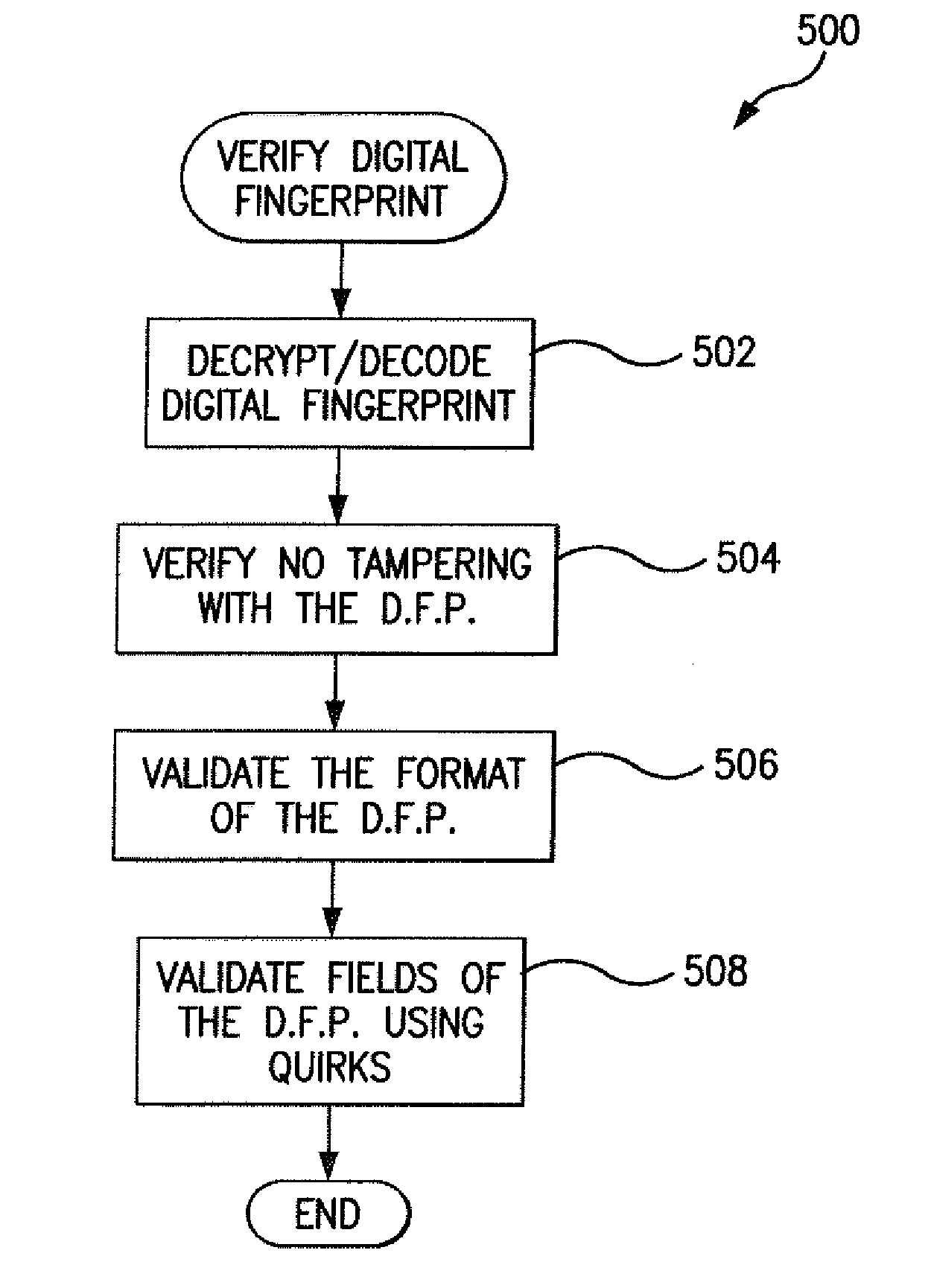
Digital fingerprint generation logic executed by a client device includes quirk-exposing logic configured to expose behavioral differences between various system configurations of client devices. The digital fingerprint generation logic queries a remote client device for system configuration, and generates a digital fingerprint of the client device that includes a system configuration characteristic reported by the client device in response to the query. Results of execution of the quirk-exposing logic are compared to expected results that are specific to the reported system configuration. If the results of execution do not match the expected results, the digital fingerprint is determined to have been spoofed.
Owner:ADSTRA INC
Systems and methods for communication, storage, retrieval, and computation of simple statistics and logical operations on encrypted data
InactiveUS8862895B2Digital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionLogical queryData system
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
SPARQL semantic data query optimization method based on connection cost
InactiveCN104834754AImprove experienceFast feedbackSpecial data processing applicationsDynamic planningLogical query
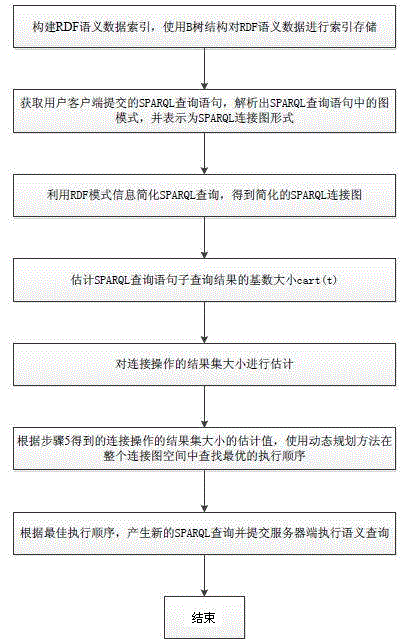
The invention provides a SPARQL semantic data query optimization method based on connection cost. According to the method, the RDF mode information to simplify SPARQL basic graph pattern is used, then a B tree structure is used for rapidly estimating SPARQL connection diagram nose sizes and edge weight values, the connection cost is used for estimating and finding the optimal logical query plan by combining a dynamic planning method, and therefore the query efficiency for improving RDF semantic data is improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Building complex hierarchical queries
ActiveUS10649989B2Avoid difficult choicesQuickly and easily visualizeOther databases indexingSpecial data processing applicationsObject typeLogical query
Provided are a computer program product, system, and method for building complex hierarchical queries. A User Interface (UI) representation of a logical query is received, wherein the UI representation describes object types, relationships between the object types, and attributes of the object types. The UI representation is translated to a logical query. The logical query is converted to data layer calls to retrieve objects having the object types, the relationships between the object types, and the attributes of the object types. The objects are received. Then, a directed graph is generated using the identified objects.
Owner:IBM CORP
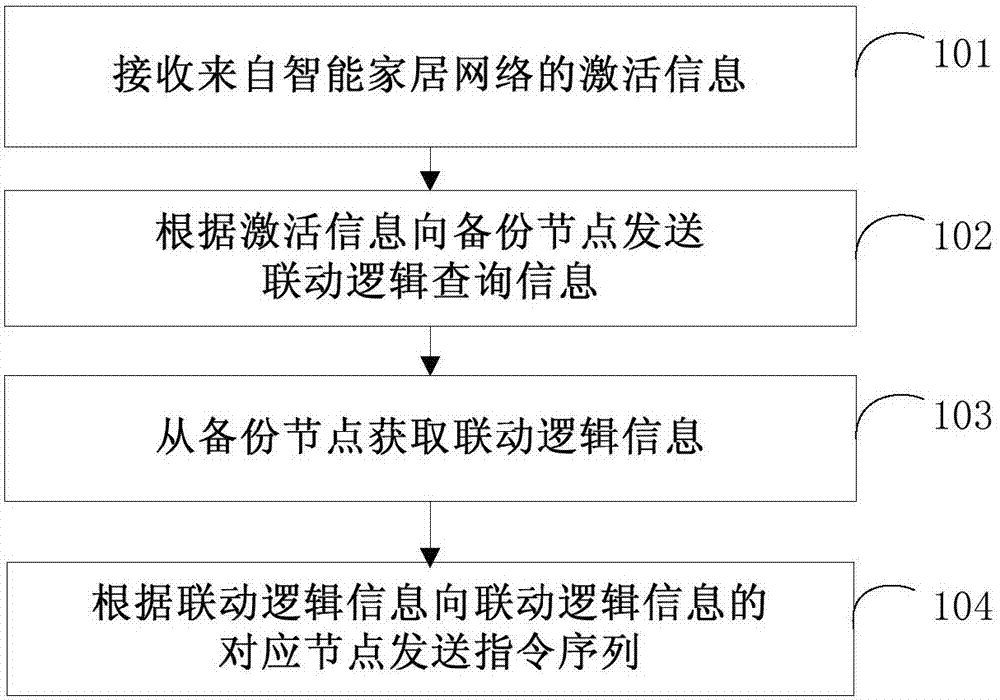
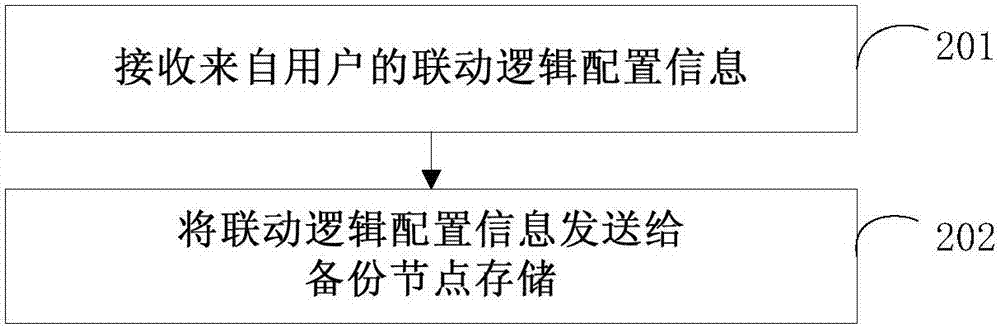
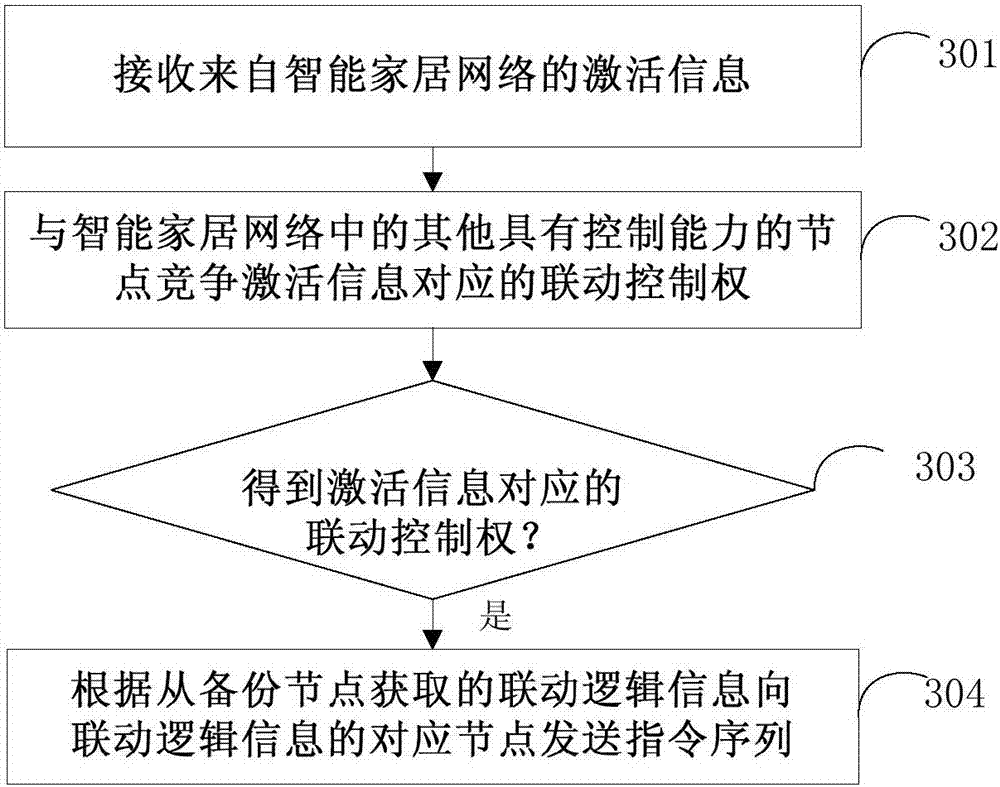
Smart home control method and node and node linkage method and system
ActiveCN107196829AReduce dependenceHome automation networksBiological activationInstruction sequence
The invention provides a smart home control method and node and a node linkage method and system, and relates to the field of smart home. The smart home control method comprises the steps that activation information from a smart home network is received; linkage logic inquiring information is transmitted to a backup node according to the activation information; the linkage logic information is acquired from the backup node; and an instruction sequence is transmitted to the corresponding node of the linkage logic information according to the linkage logic information so as to realize multi-node linkage. With application of the method, the node in the smart home network can inquire the linkage logic information from the backup node according to the activation information and the instruction sequent can be transmitted to the corresponding node according to the linkage logic information inquired from the backup node to realize multi-node linkage so that the dependence of the system on the center node can be reduced.
Owner:CHINA TELECOM CORP LTD
Query statement optimization method and apparatus
ActiveCN105701128AReduce in quantityImprove query efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsData warehouseLogical query
Embodiments of the invention disclose a query statement optimization method and apparatus, which relate to the technical field of data query and are used for solving the problem of occupation of a large amount of storage spaces caused by caching of historical logic query trees and corresponding query results of the query trees. The query statement optimization method provided by the embodiment of the invention comprises the steps of receiving n query statements; generating n logic query trees by the n query statements; according to a preset rule, adding version numbers for operands corresponding to operators in the n logic query trees; and optimizing the operators to reduce the number of physical tasks generated by the n logic query trees, wherein the operators belong to different logic query trees and the version numbers of the operands corresponding to the operators are same. The technical scheme provided by the embodiments of the invention can be used in a process that a big data query system performs batch query on a data warehouse.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
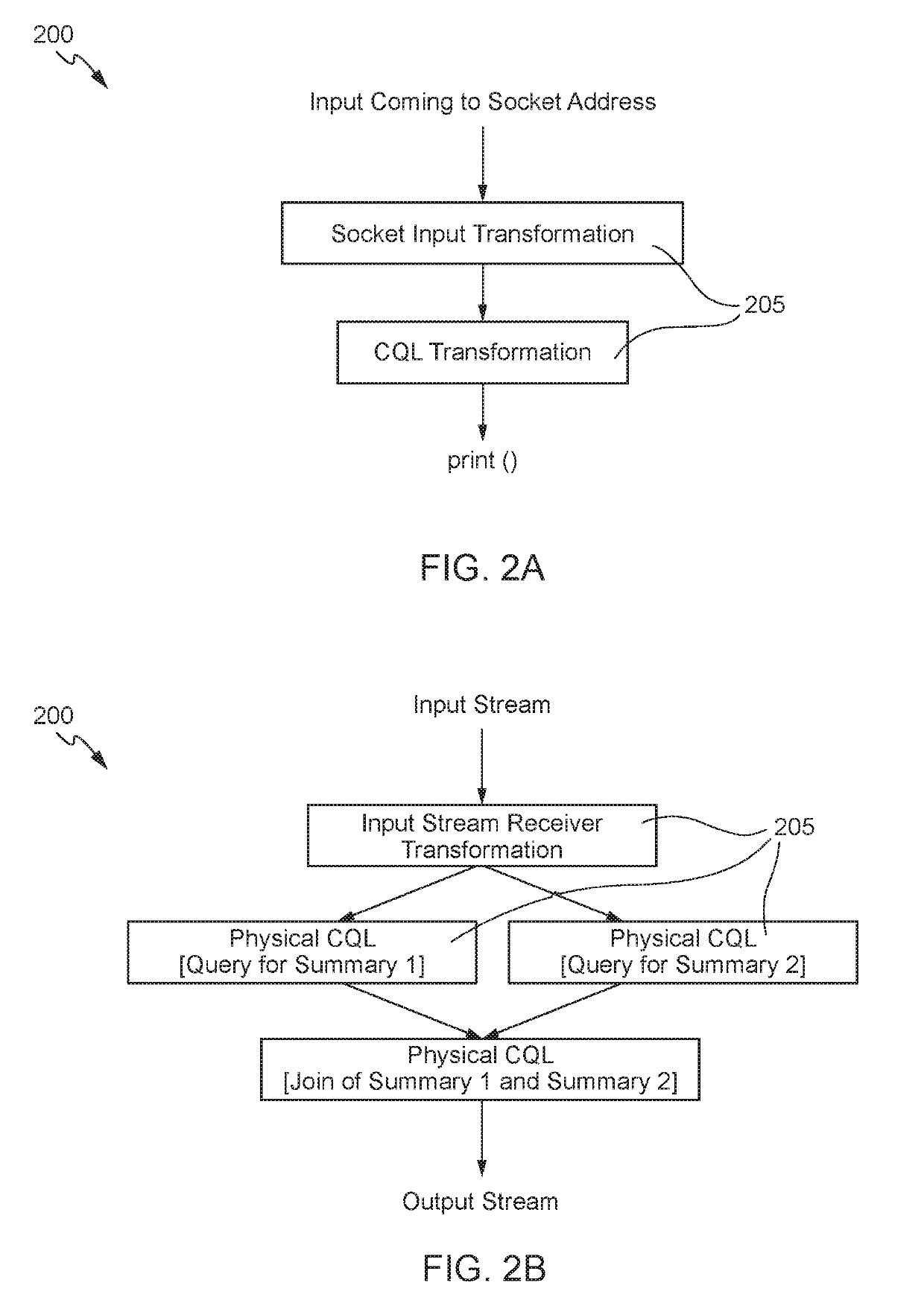
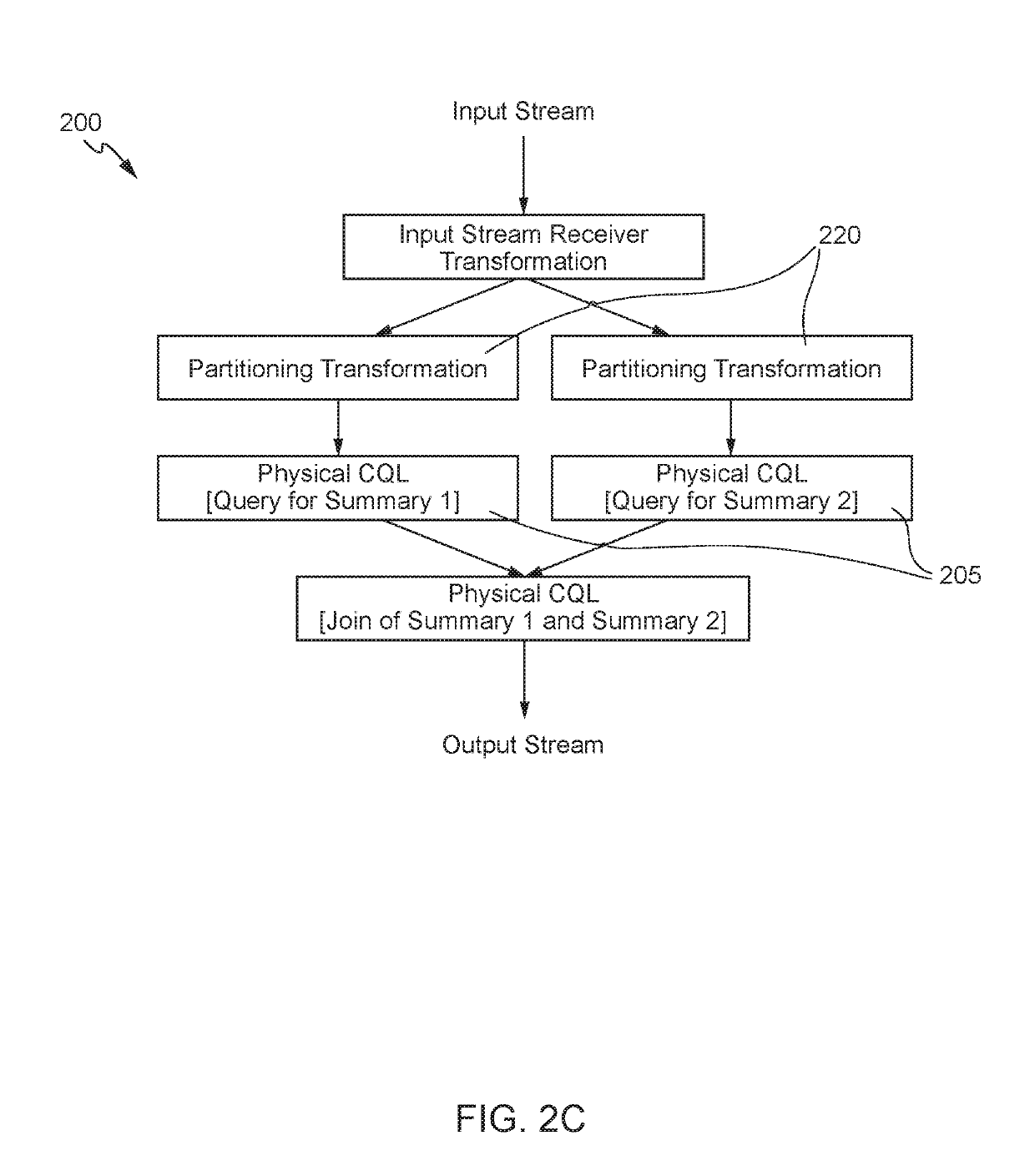
Logical queries in a distributed stream processing system
Techniques for implementing logical queries in a distributed stream processing system using automatic branching and joins. An exemplary technique includes determining a query is a logical query. The logical query includes two or more summaries based on different groups configured to execute in a single query stage of a stream analytics application. The technique further includes converting the logical query into one or more physical queries. The one or more physical queries are separated into individual query stages, and each of the query stages includes a summary from the two or more summaries that is based on an associated group. The technique further includes generating a directed acyclic graph for the one or more physical queries. The directed acyclic graph includes a physical query transformation for each of the individual query stages.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
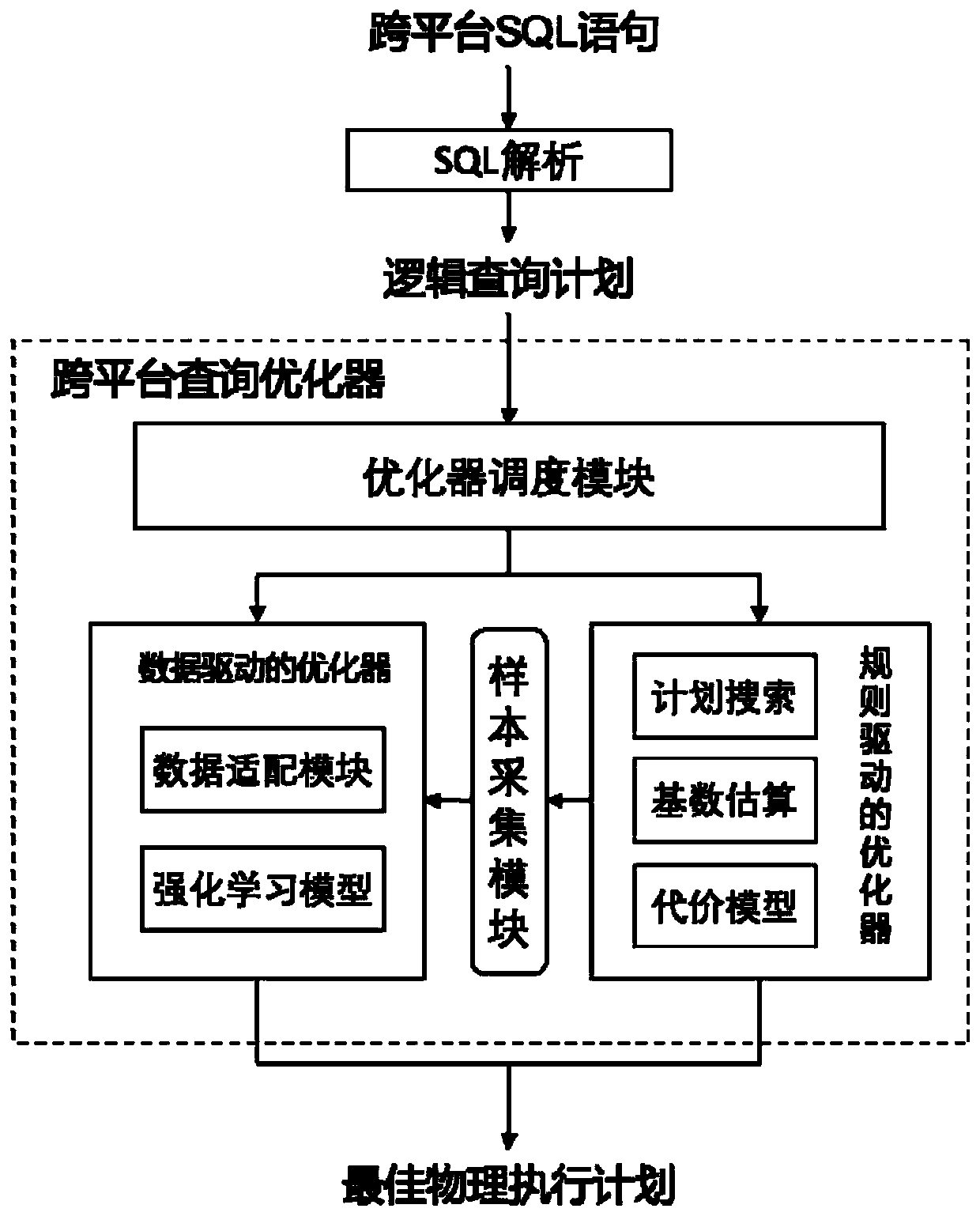
Rule-driven and data-driven combined cross-platform SQL query optimization method
ActiveCN111444220AAddress flexibilitySolve scalabilityDigital data information retrievalNeural architecturesExecution planQuery plan
The invention discloses a rule-driven and data-driven combined cross-platform SQL query optimization method. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, analyzing a cross-platform SQL statement into a logic query plan in a system; 2, enabling an optimizer scheduling module to schedule the most suitable optimizer to perform query optimization according to the characteristics of the logic queryplan; 3, enabling the rule-driven optimizer to perform plan search according to the rule, selecting an execution plan according to the cost model and the cardinal number estimation to obtain an optimal physical execution plan, and importing an optimization result into a sample collection module; and 4, converting the sample imported by the sample acquisition module into a training sample through adata adaptation module, performing reinforcement learning model training by using the training sample through a data-driven optimizer, and inputting query into the trained model to obtain an optimalphysical execution plan. The cross-platform SQL query optimization method solves the problems that an existing cross-platform SQL query optimization method is poor in expansibility, low in flexibility, poor in optimization effect and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Node-level sub-queries in distributed databases
InactiveUS9183260B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsLogical queryDistributed database
A database query is received that includes a logical query indicator at a distributed database node within a distributed network of databases. The logical query indicator includes at least one physical database query and at least one database node identifier that allows at least one distributed database node to identify at least one physical database to execute the physical database query against. It is determined that the at least one database node identifier matches a local node identifier. The at least one physical database query is executed against at least one local physical database table. A local query response is formed including data retrieved from the at least one local physical database table. The database query is responded to with at least the local query response. This abstract is not to be considered limiting, since other embodiments may deviate from the features described in this abstract.
Owner:IBM CORP
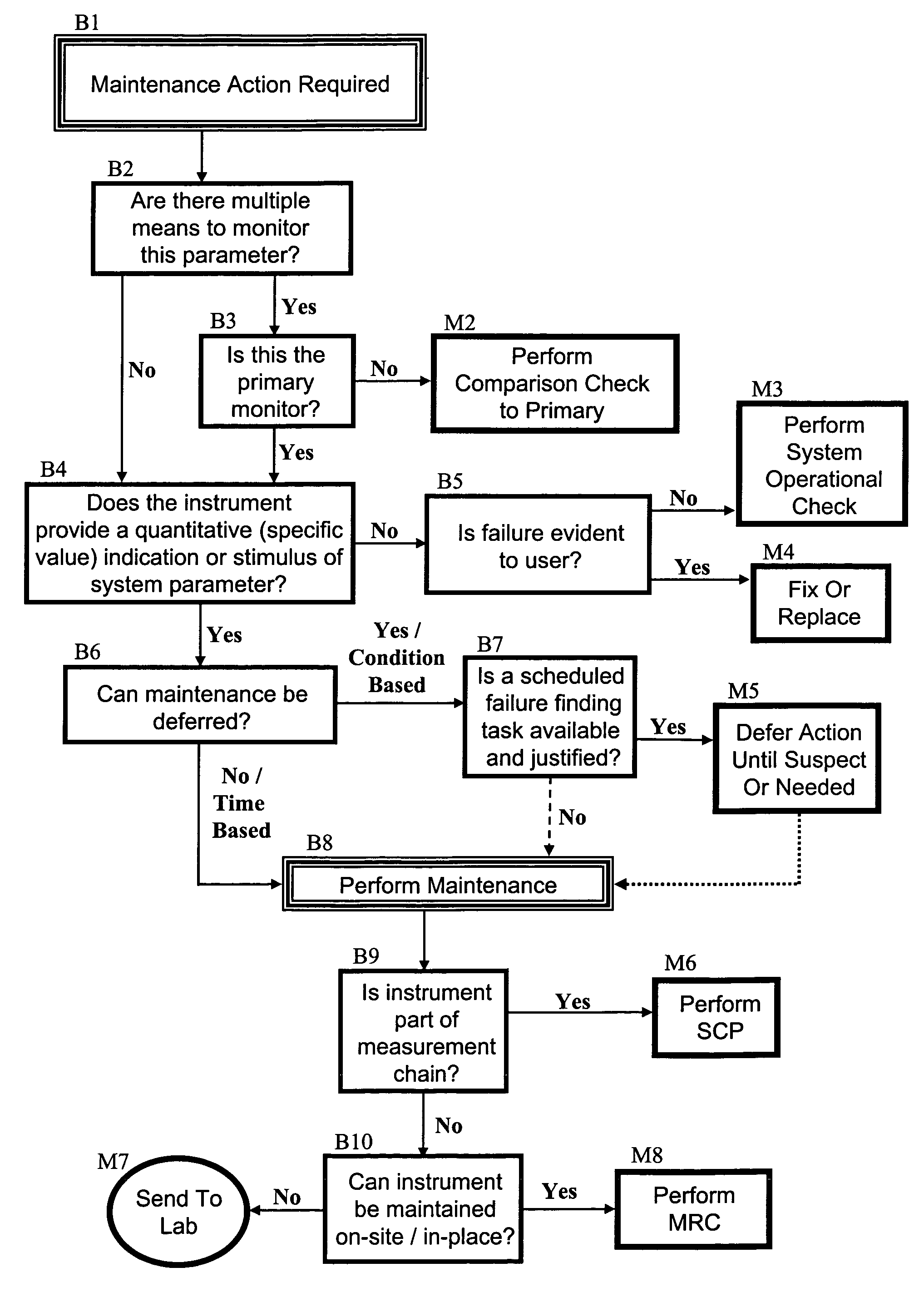
Installed instrumentation maintenance method
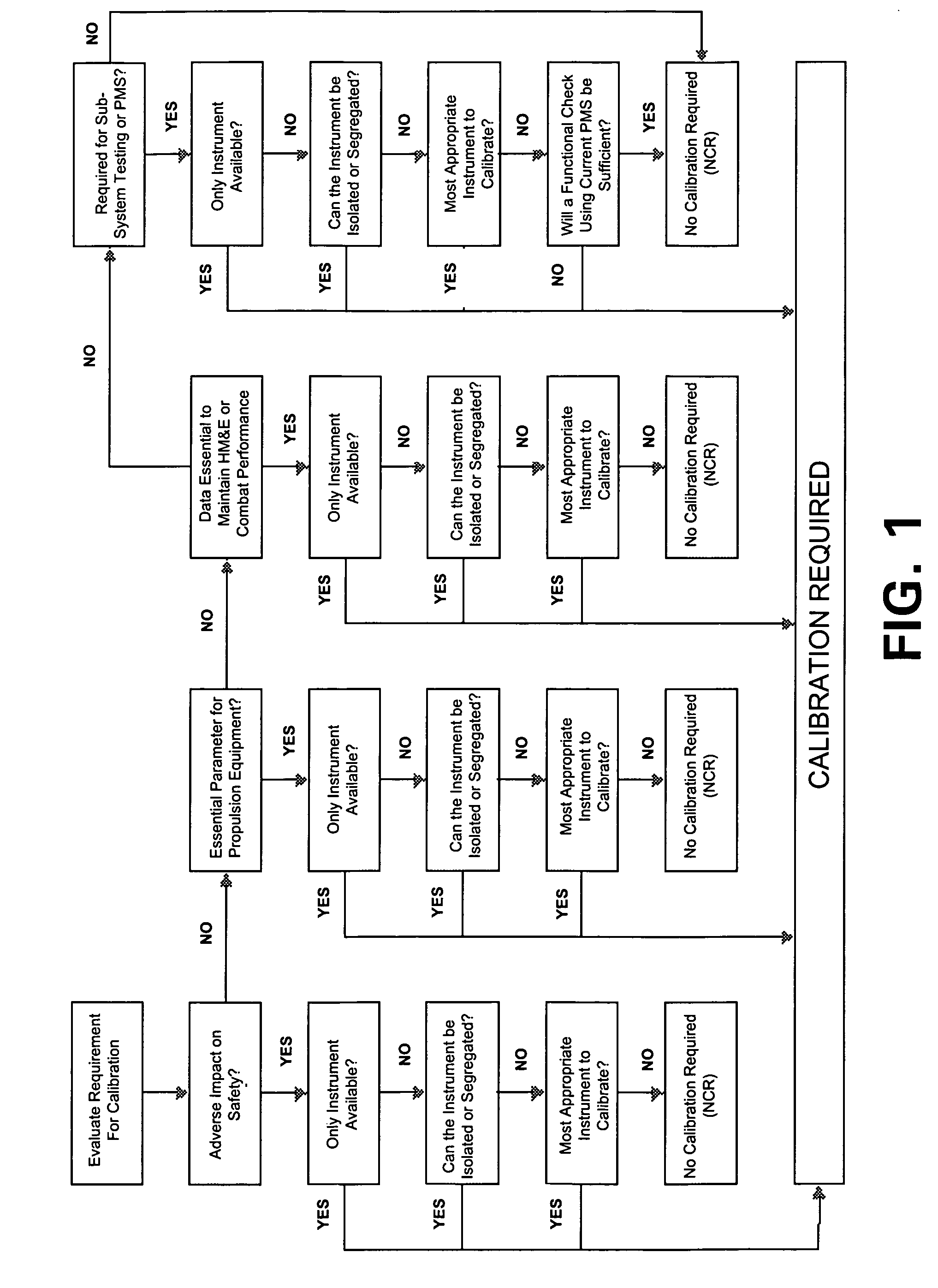
InactiveUS7280925B1Reduce calibrationReduce maintenancePlug gaugesNuclear monitoringOperational systemMaintenance strategy
The present invention's efficient and economical maintenance strategy for a system of operation (such as involving various kinds of instrumentation) features a unique decision-making logic that incorporates reliability-centered maintenance principles. The initial logical inquiry filters out the non-critical cases, i.e., those instruments the failure of which does not jeopardize or compromise safety, or the environment, or an important function or operation. The logical construct proceeds as to the remaining (unfiltered) instruments in a series of logical steps wherein the satisfaction of one or more given conditions by a subject instrument directs the practitioner to the appropriate maintenance action for the subject instrument. Possible maintenance actions include the following: comparison check of the instrument with respect to the primary instrument; system operational check; repair of the instrument; replacement of the instrument; maintenance deferral until a scheduled failure finding task; system calibration procedure; individual maintenance procedure (on-site or off-site).
Owner:MCDONNELL THOMAS
Lease management method and device based on block chain and electronic equipment
PendingCN112308690AReduce the difficulty of financingReduce investment riskFinanceDigital data protectionLogical queryFinancial transaction
The invention provides a lease management method and a device based on a block chain and electronic equipment. The method comprises the following steps: receiving a first smart contract calling transaction initiated by the financing leasing equipment; in response to the first calling transaction of the intelligent contract, calling contract state query logic in the intelligent contract corresponding to the financing leasing equipment, and querying a financing leasing contract corresponding to the identifier of the lessee in a financing leasing contract library maintained by the intelligent contract and corresponding to the financing leasing equipment, determining whether the contract state of the financing lease contract is an overdue non-repayment state; and if the contract state of the financing lease contract is an overdue non-repayment state, further calling a generation logic in the intelligent contract, and generating a service stop instruction for the financing lease equipment,so that the financing lease equipment stops providing service for the lessee when acquiring the service stop instruction.
Owner:ALIPAY (HANGZHOU) INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Parallel materialisation of a set of logical rules on a logical database
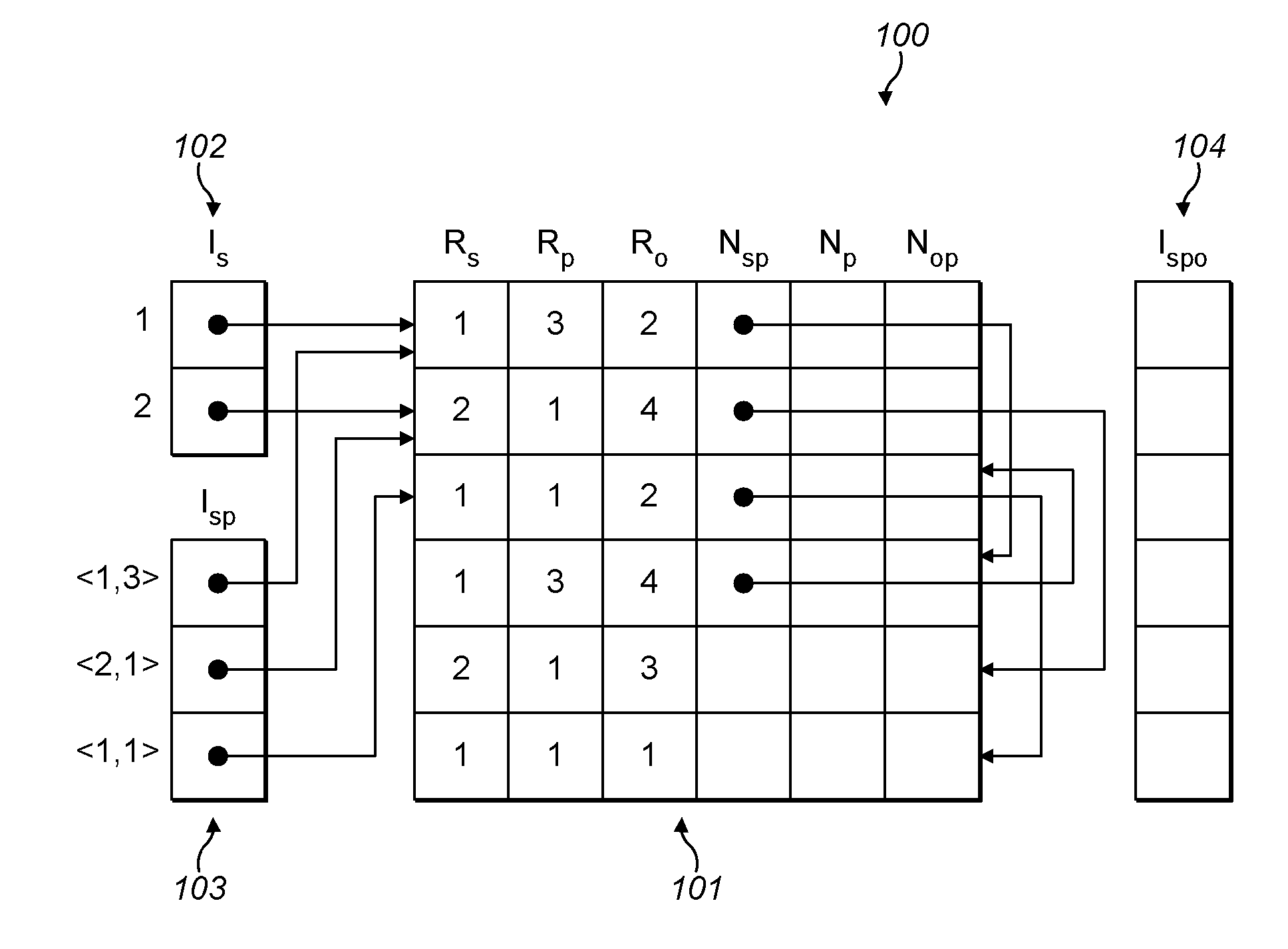
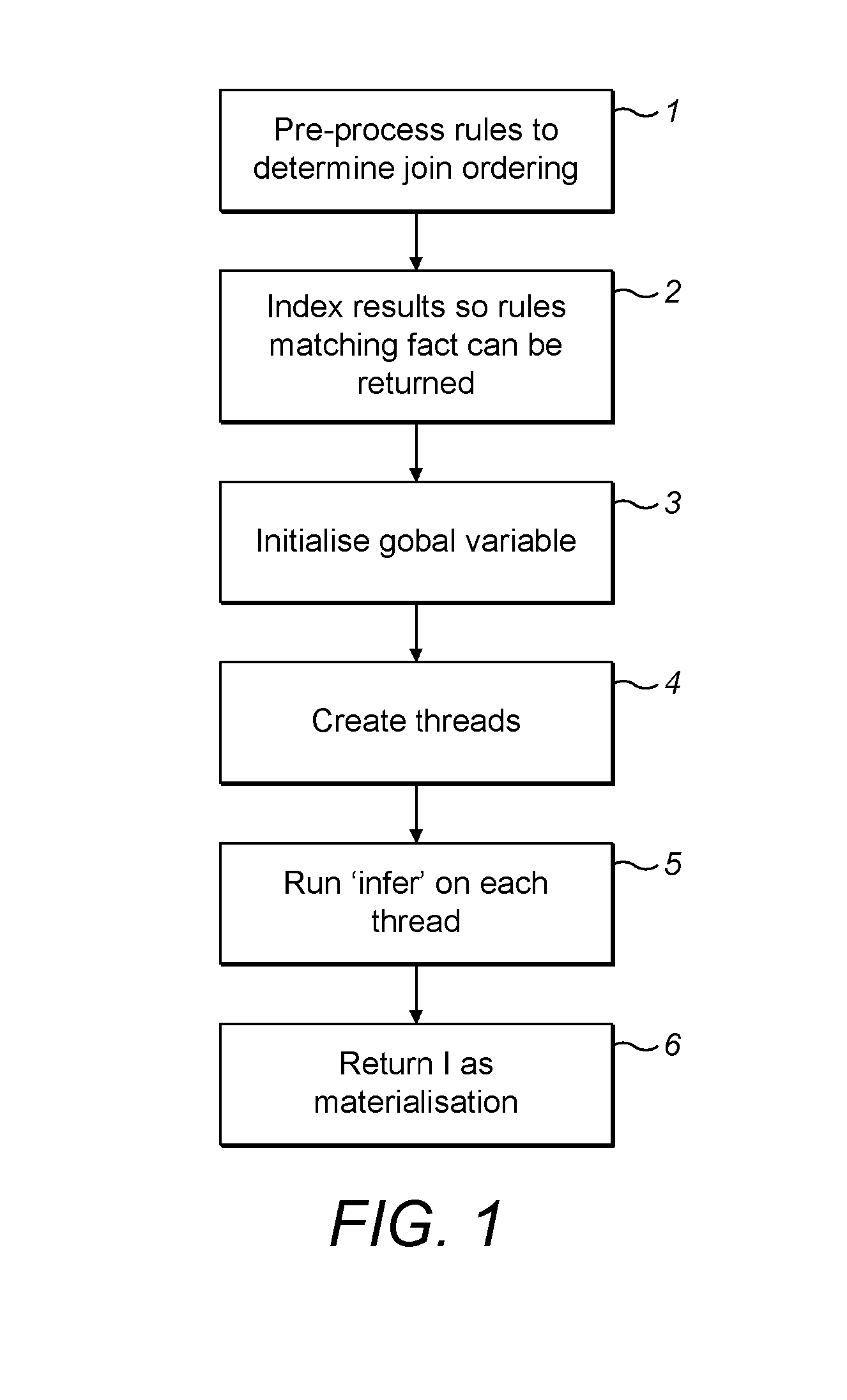
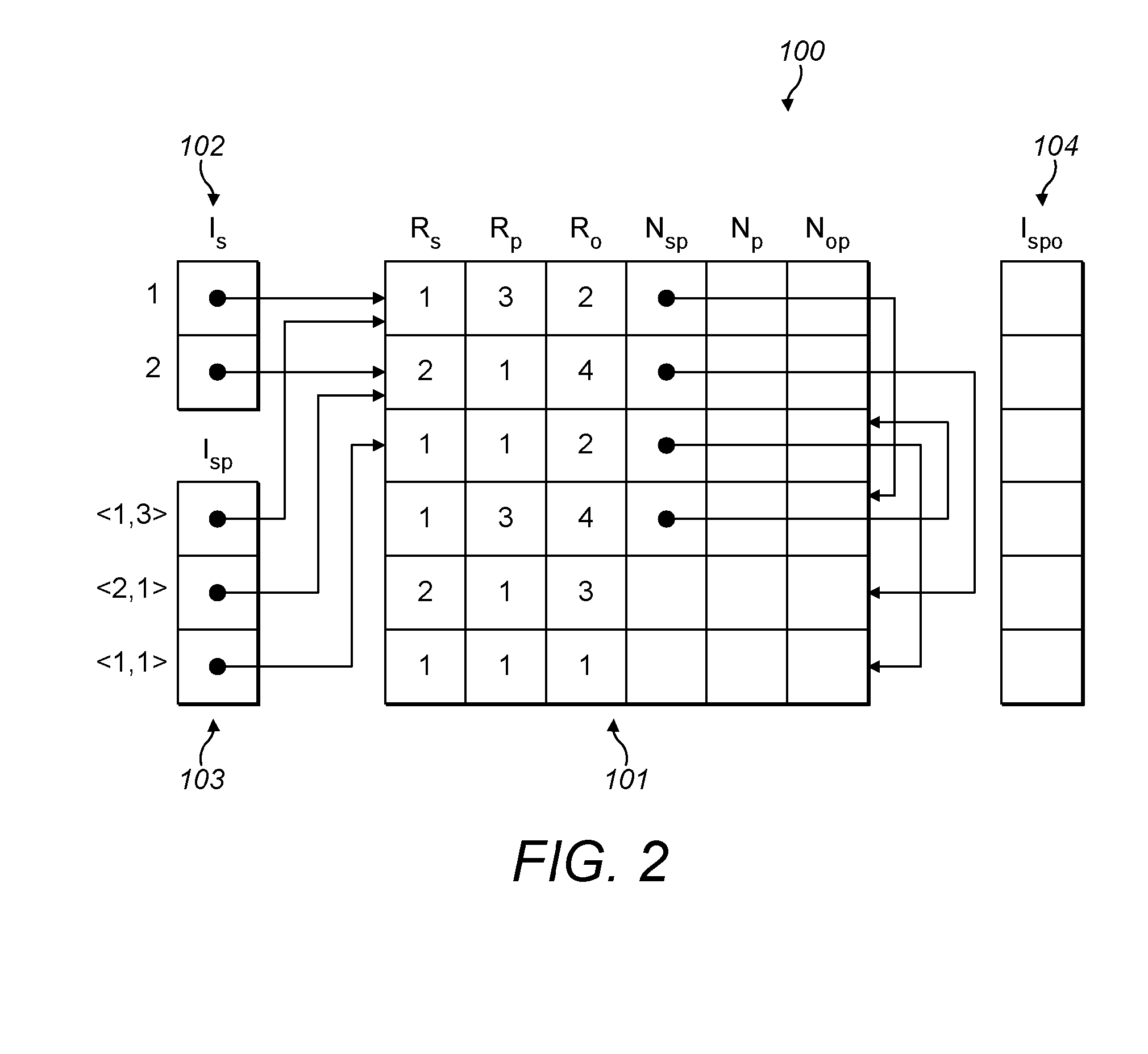
ActiveUS20160259796A1Efficient processingProvide accuratelyDigital data information retrievalInference methodsProgramming languageLogical query
A computer-implemented method of providing a materialisation of a set of logical rules on a logical database comprising a set of logical facts. Each of a plurality of parallel processing threads performs the following steps. A logical fact that has not previously been received by any thread is received by the thread. By applying any of the logical rules to the received logical fact and / or any of the logical facts received by any thread prior to the received logical fact, the thread determines whether a new logical fact is implied, and if so the new logical fact is added to the set of logical facts. The thread then repeats the above steps on any further logical facts in the set of logical facts that have not previously been received by any thread. When all threads are waiting for a new logical fact, the method has completed.
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD
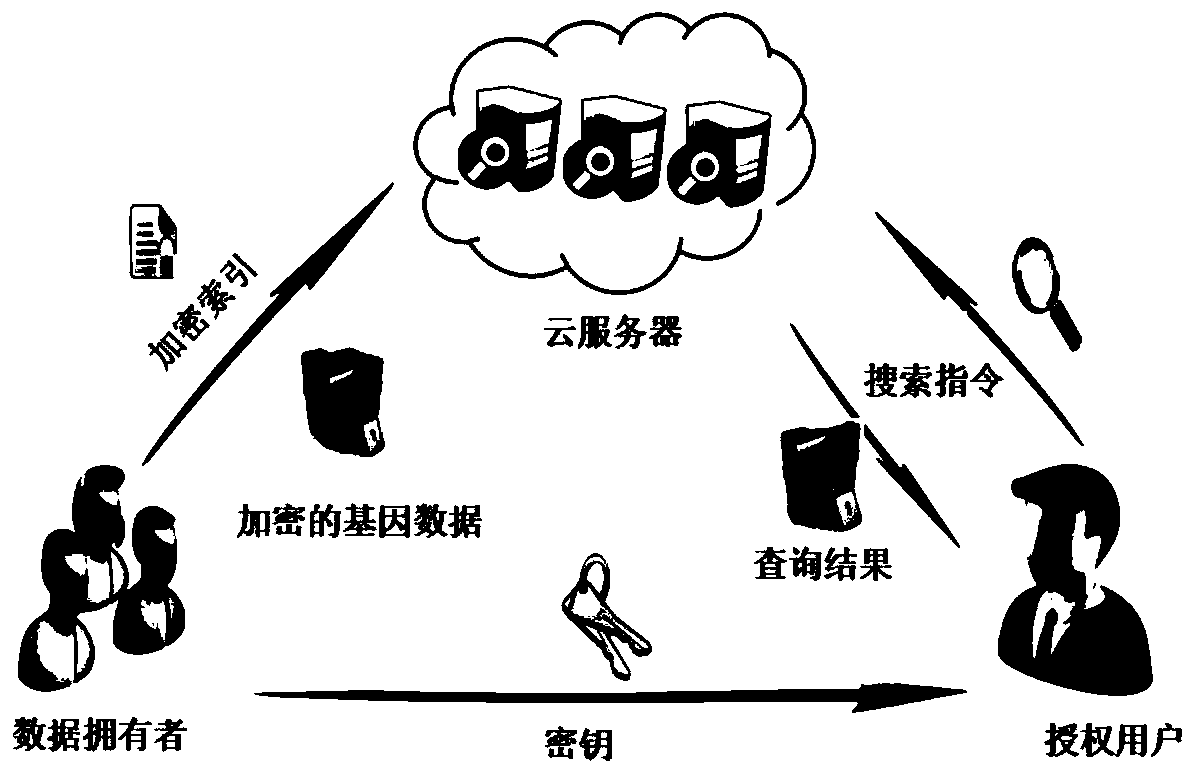
Gene data desensitization method for realizing efficient similarity query and access control
ActiveCN110263570AMeet individual query needsReduce in quantityKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data information retrievalPersonalizationAuthorization Mode
The invention belongs to the technical field of information security. The invention particularly provides a gene data desensitization method for realizing efficient similarity query and access control. The similarity query of large-scale gene data in a ciphertext environment is effectively supported; meanwhile, complex logic query is supported to meet the personalized query requirement of the user; according to the method, the authorization mode is flexible, different access authorities can be given to different data, reliable control over the data access authority of a user is achieved in the query process, in addition, a specific Hash function is adopted for compressing the data, the number of matched elements in the ciphertext state is remarkably reduced, and the query retrieval efficiency is further improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
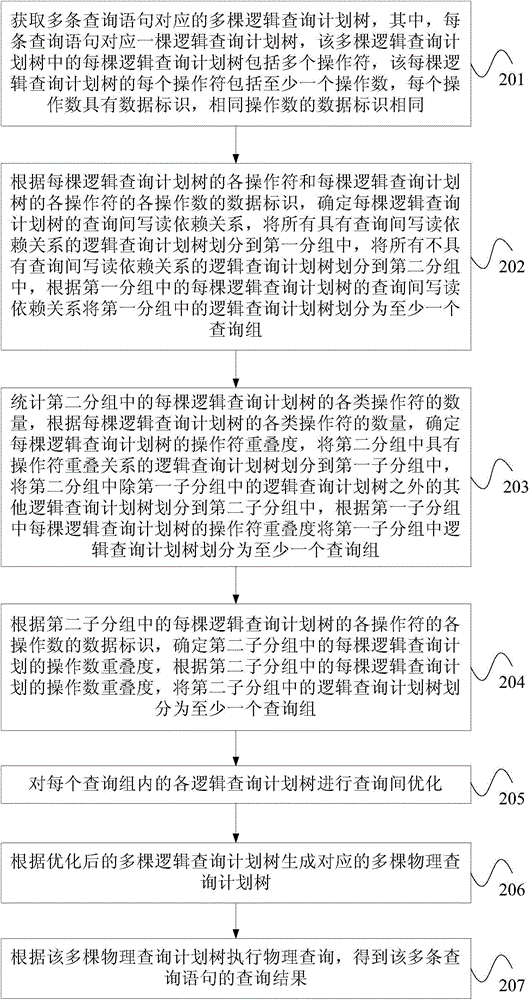
Batch data query method and device
ActiveCN105677683AImprove query efficiencyImprove opportunities for optimizationSpecial data processing applicationsQuery planProgram planning
The embodiment of the invention provides a batch data query method and a device. The method comprises following steps: obtaining multiple logic inquiry plan trees corresponding to multiple query statements; diving multiple query groups by all operators of each logical query plan tree, wherein logical query plan trees of each query group are in the relationships as follows: inter-query write-read dependency relationships; overlapping relationships between operators or operand overlapping relationships; optimizing inter-query logical query plan trees of each query group and generating multiple corresponding physical query plan trees based on multiple optimized query plan trees; and finally, executing physical obtaining query results of multiple sentences based on multiple physical query plan trees. The method helps to increase optimization opportunities between logical plan trees in query groups by grouping the multiple logical query plan trees. By performing inter-query optimization on the logical query trees of query groups, efficiency of batch data query is increased.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
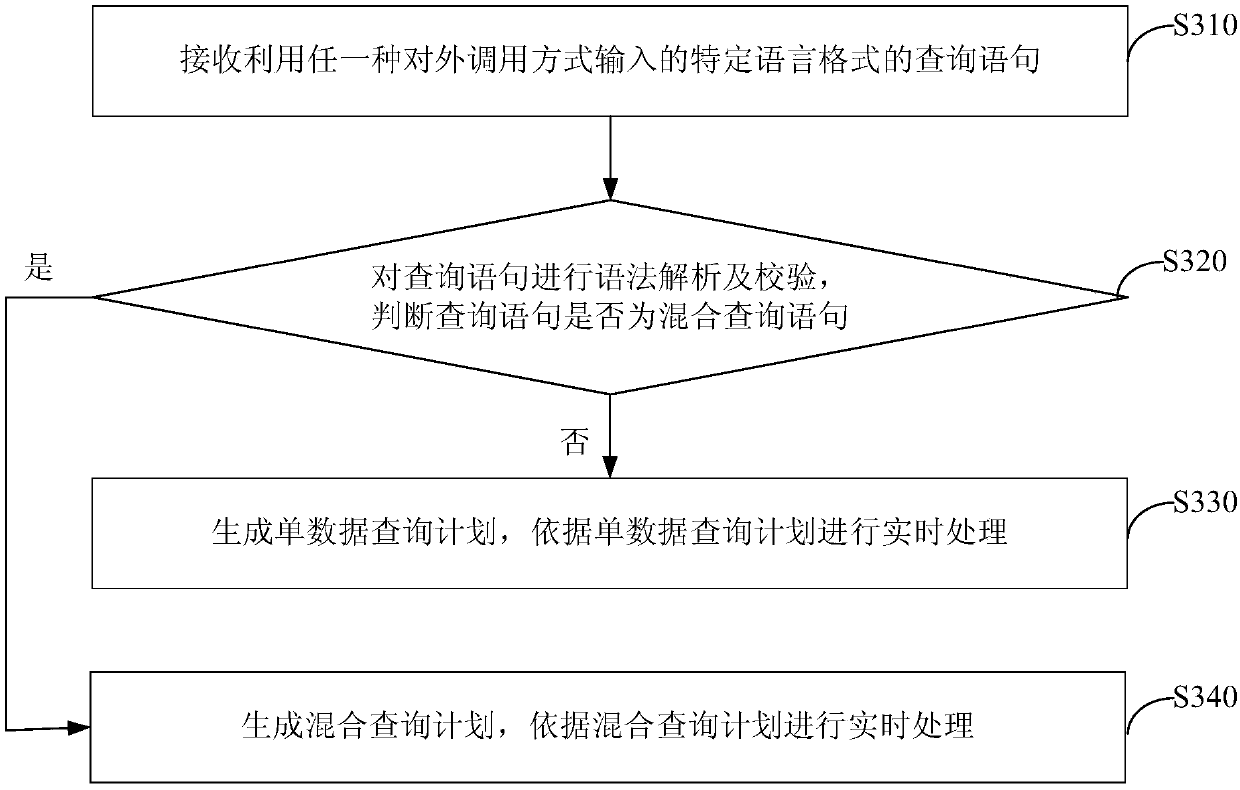
Big data processing system and method
PendingCN111221842AReduce learning costsImprove experienceDatabase management systemsSpecial data processing applicationsData processing systemQuery plan
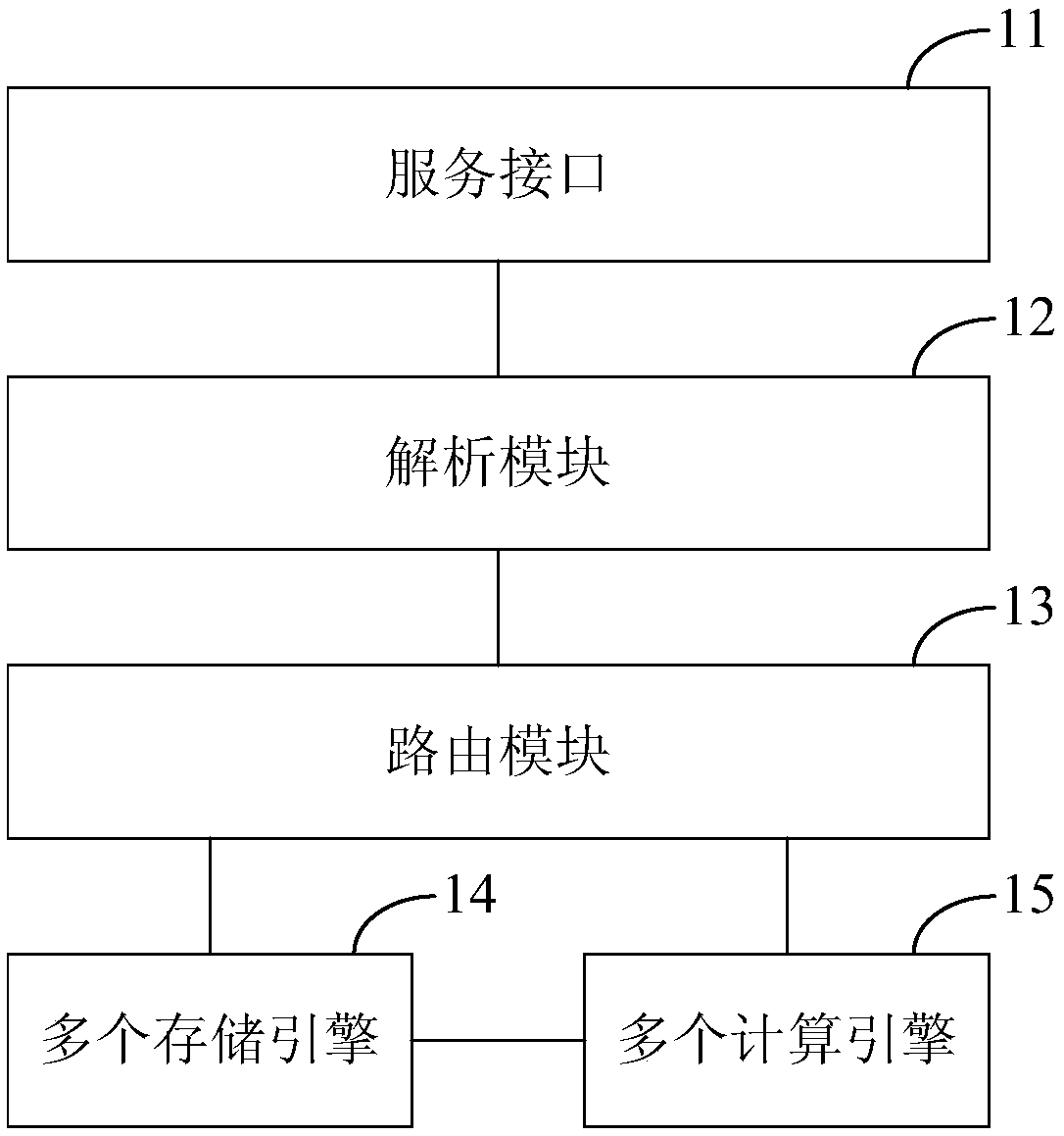
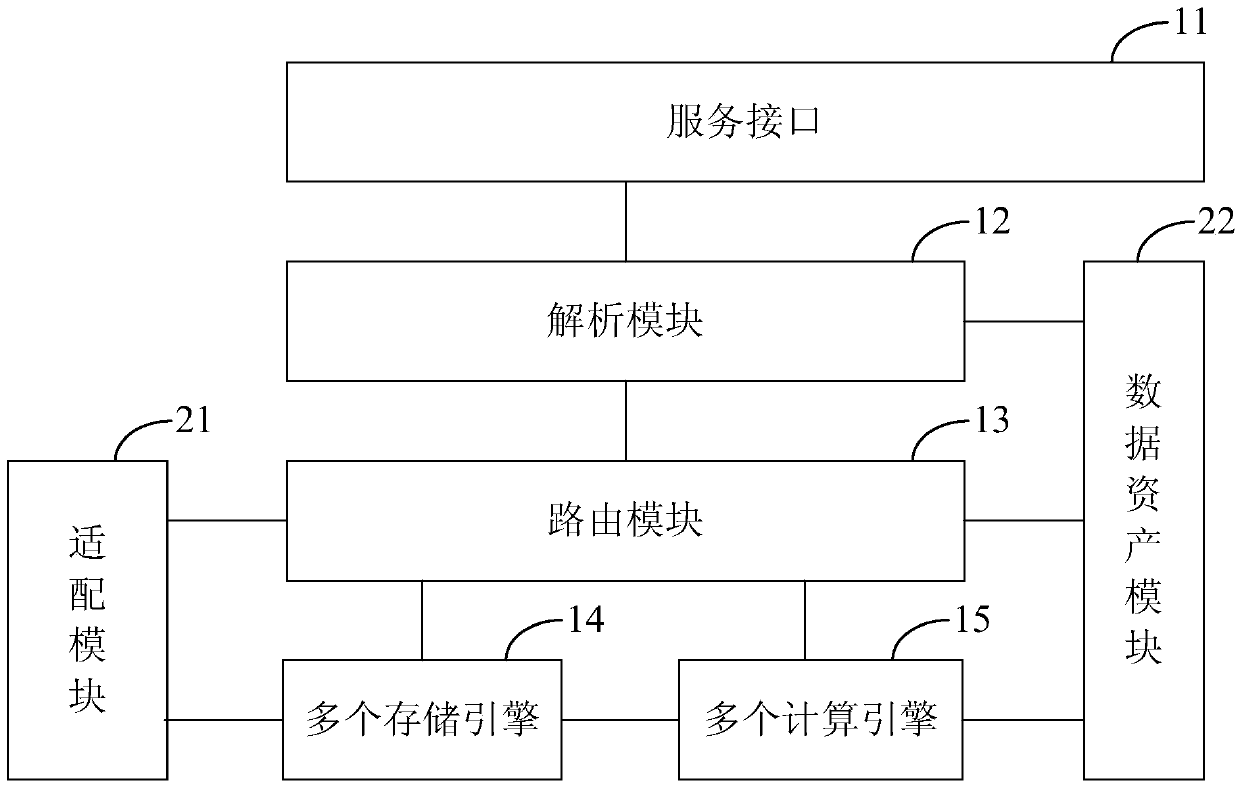
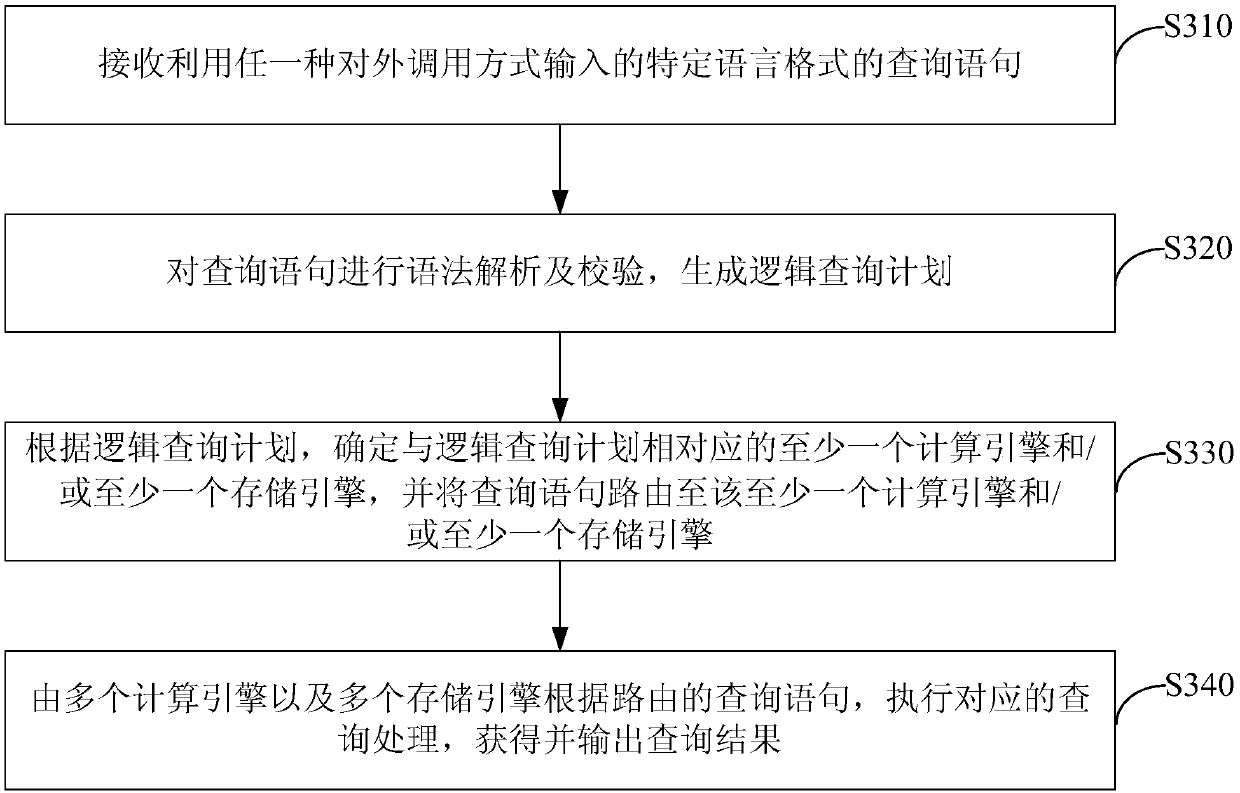
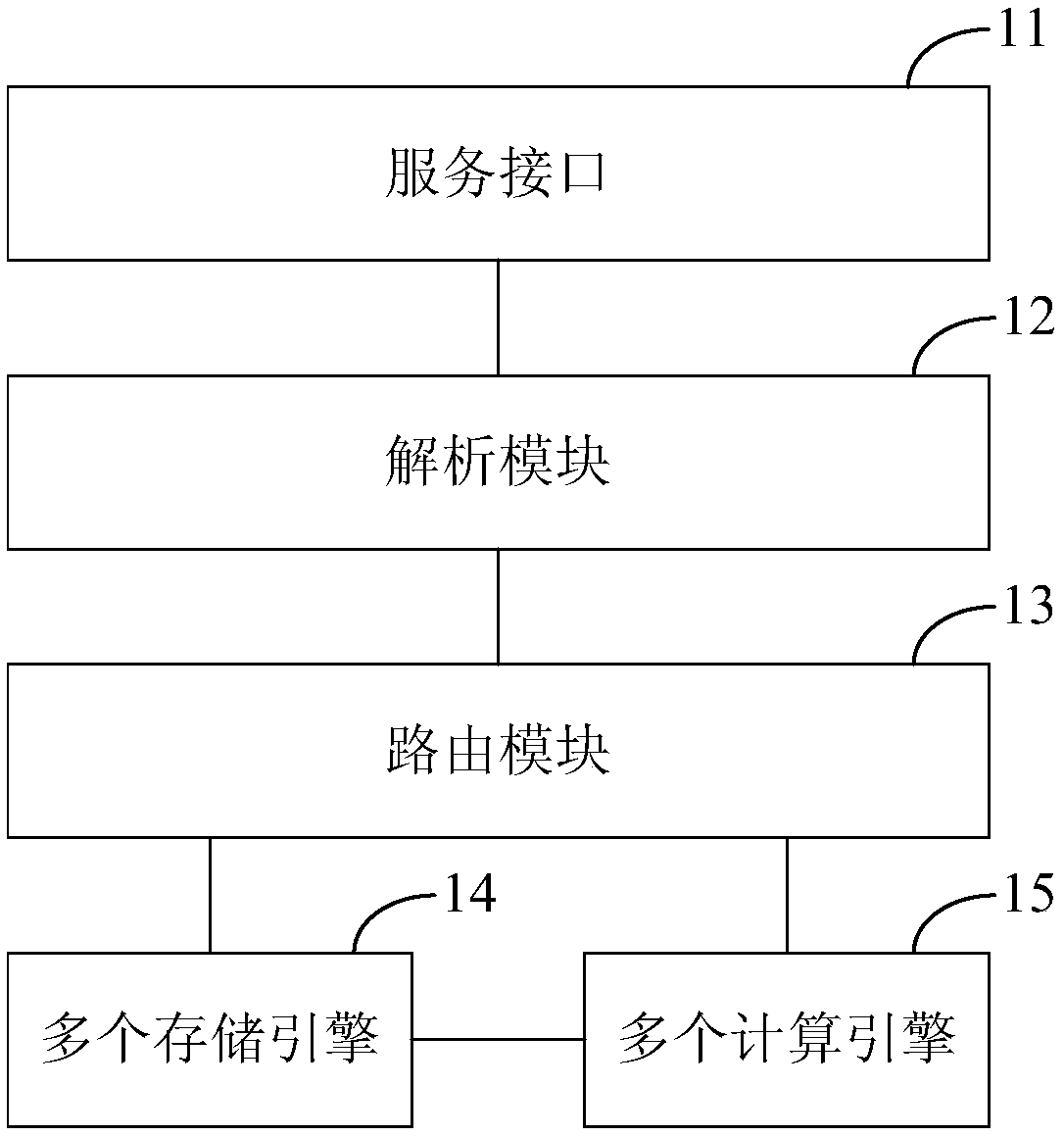
The invention discloses a big data processing system and method. The system comprises: a service interface which provides at least one external calling mode and is suitable for receiving a query statement in a specific language format, which is input by utilizing any external calling mode; an analysis module which is suitable for performing grammar analysis and verification on the query statementto generate a logic query plan; a routing module which is suitable for determining a calculation engine and / or a storage engine corresponding to the logic query plan according to the logic query plan,and routing the query statement to the calculation engine and / or the storage engine; and the plurality of computing engines and the plurality of storage engines which are suitable for executing corresponding query processing according to the query statement routed by the routing module, and obtaining and outputting a query result. By adopting the scheme, the user can process the big data only through the input query statement in the specific language format, so that the service logic of the user is decoupled from the calculation engine and the storage engine, the learning cost of the user isreduced, and the user experience is improved.
Owner:BEIJING QIHOO TECH CO LTD
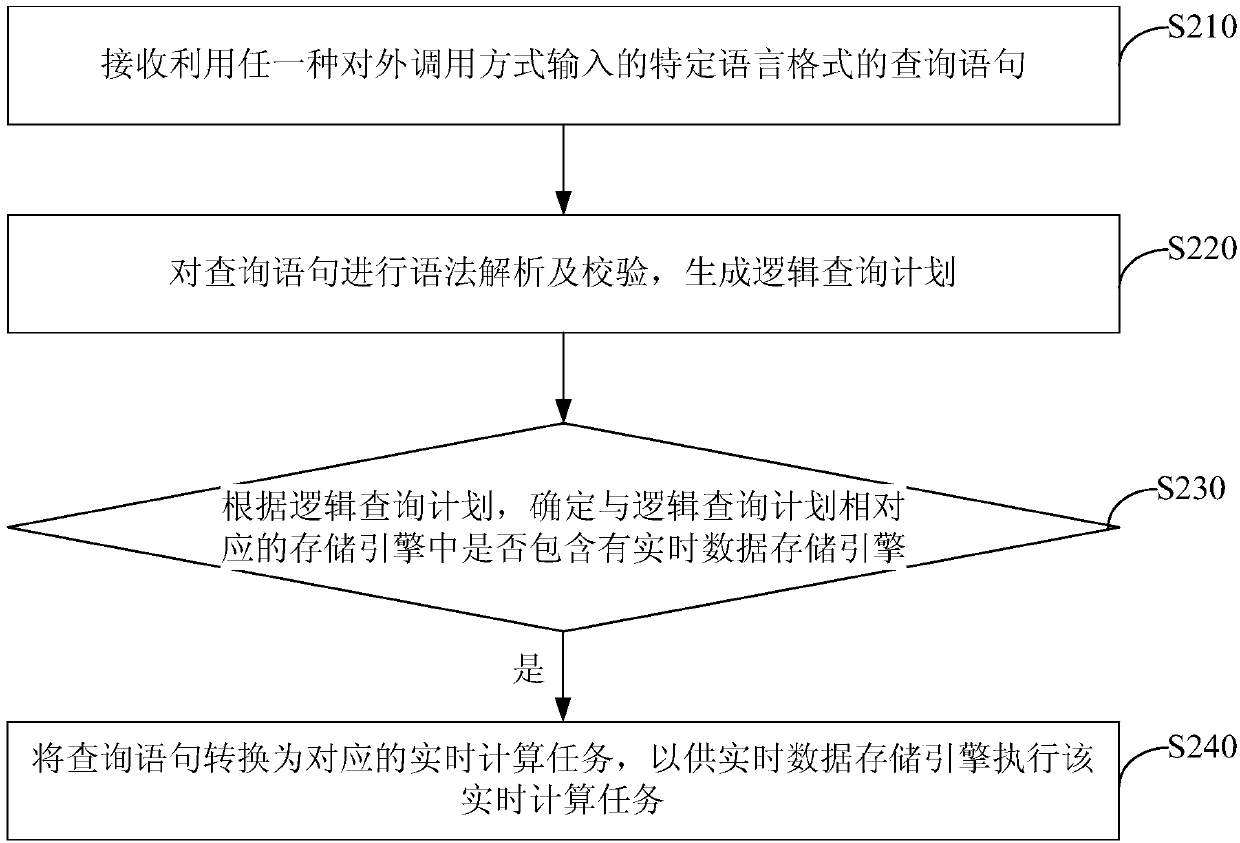
Real-time processing method and device based on big data
PendingCN111221841AReal-time processingReduce learning costsDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsProgramming languageQuery plan
The invention discloses a real-time processing method and device based on big data. The method comprises the following steps of: receiving a query statement in a specific language format, which is input by utilizing any external calling mode; carrying out grammar analysis and verification on the query statement, and generating a logic query plan; determining whether a storage engine correspondingto the logic query plan comprises a real-time data storage engine or not according to the logic query plan; and if so, converting the query statement into a corresponding real-time calculation task, so as to enable a real-time data storage engine to execute the real-time calculation task. By the adoption of the scheme, a user can process big data in real time only through the input query statementin the specific language format, the learning cost of the user for the real-time data storage engine is reduced, and maintenance of real-time processing services is facilitated.
Owner:BEIJING QIHOO TECH CO LTD
Device for controlling network user data
ActiveUS20140237579A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationLogical queryPassword
This utility model relates to devices for controlling (input, storage and deletion) network user data.The offered utility model is directed toward extending functional possibilities by virtue of organizing a system of pseudonyms (aliases), the possibility of grouping and assigning to aliases different groups of resources , including resources that enable communication with other clients in the network (e.g. a social network), presenting a real user with a plurality of aliases with the aim of sorting the resources of a network (e.g. a social network) by composition, which makes it possible for the user to set limits for access to different groups of resources with the aid of passwords. Resources of one type can be divided between different aliases according to access to said resources. For instance, different photo albums can be linked to different aliases; for this purpose, some albums will be accessible on the device if an alias without the password was used to access the system, while access to other albums can only be granted if the system was accessed using an alias with the password. Each of the aliases can be accompanied with a unique description of its characteristic attributes so that the user can be represented in the network as different identities.The utility model is implemented as follows. The system of aliases implies presenting a user with a plurality of aliases (nicknames) with the aim of sorting the computer network resources according to composition and access. Resources of one type can be divided between different aliases according to access to said resources. For instance, different photo albums can be linked to different aliases; for this purpose, some albums will be accessible on the device if an alias without the password was used to access the system, while access to other albums can only be granted if the system was accessed using an alias with the password.If required, a user has the option of searching from among the plurality of aliases linked to other users according to attributes which are of interest to the user, for example according to place of residence. The search option is ensured by the provision of an attribute search unit. A user enters a logic query for a search by means of an input unit, and then the attribute search unit produces a comparison of values for attributes set in the search query with values for the attributes of all of the aliases and from these selects those which correspond to the search criteria.
Owner:IKONOMOV ARTASHES VALERYEVICH
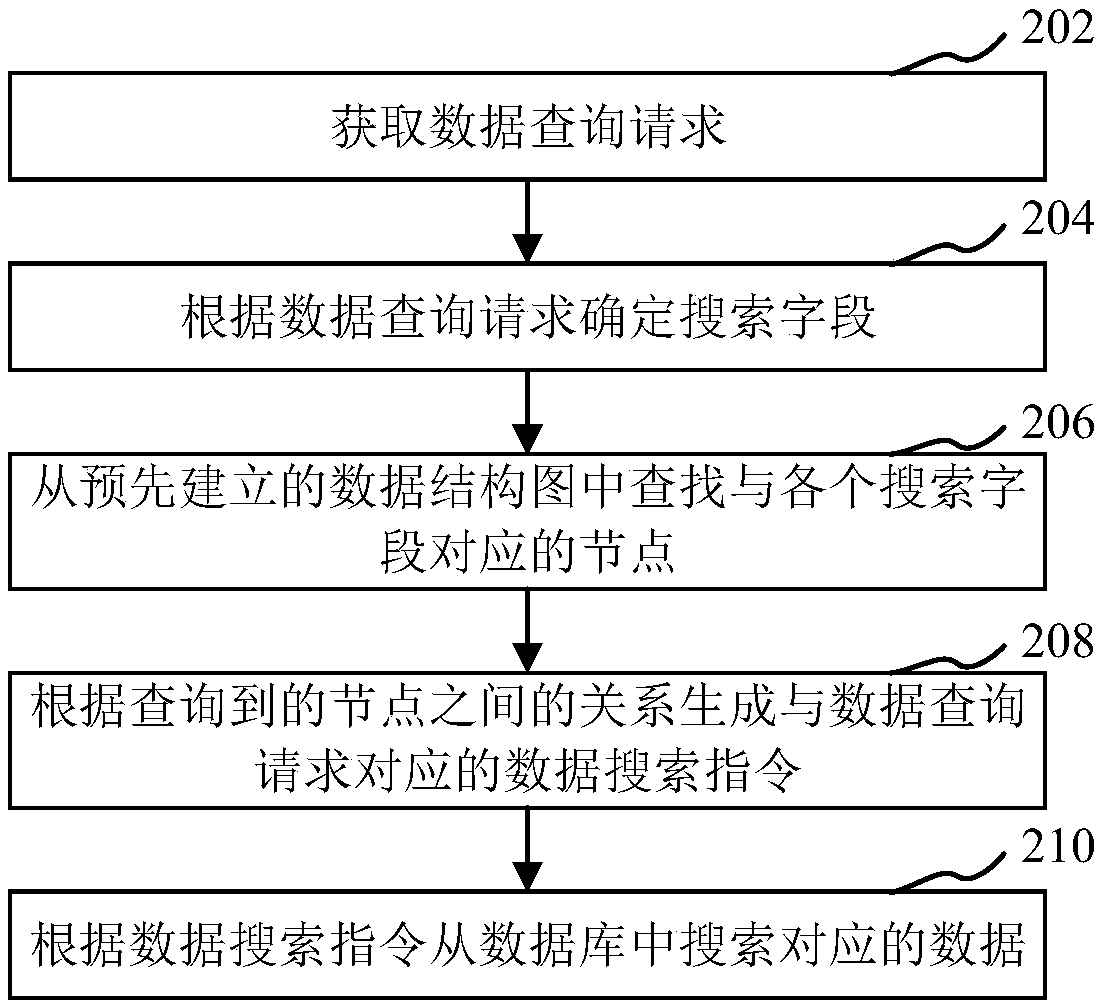
Search method, apparatus, computer device, and storage medium
ActiveCN109213775AImprove search efficiencySolve the problem that only supports single table queryDatabase queryingSpecial data processing applicationsLogical queryData query
The present application relates to a search method, apparatus, computer device and storage medium based on large data. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining a data query request; determining a search field according to the data query request; searching nodes corresponding to each search field from the pre-established data structure diagram; generating a data search instruction corresponding to the data query request according to the relationship between the queried nodes; the corresponding data is searched from the database according to the data search instruction. The searchmethod greatly improves the search efficiency, and the search method supports cross-table logical query, and the data corresponding to different search fields are stored in different tables, and can be directly queried at one time, which effectively solves the problem that only single table query is supported in the traditional technology.
Owner:ONE CONNECT SMART TECH CO LTD SHENZHEN
Distributed RDF stream data processing method, system and device and medium
ActiveCN111352961AImprove execution efficiencyReduce resource usageDigital data information retrievalEnergy efficient computingStreaming dataLogical query
The invention discloses a distributed RDF stream data processing method, system and device and a medium, and the method comprises the steps: configuring a logic operator, and deploying a big data stream processing distributed platform; obtaining a user query request; analyzing the user query request into a query statement in an algebraic form; processing the query statement in the algebraic form by adopting a greedy multi-path connection algorithm and the configured logic operator to generate a logic query plan; converting the logic query plan into a physical plan, wherein the physical plan can be executed and deployed by the big data stream processing distributed platform; based on the logic operator, performing distributed execution on the physical plan through the big data stream processing distributed platform to obtain a processing result stream. According to the method, parallel distributed query processing of the RDF stream data is realized, the execution efficiency is improved,the resource occupancy rate can be reduced, and the method can be widely applied to the technical field of computers.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method and device for determining target user based on user portrait data
PendingCN113282631AImprove general performanceMeet query needsDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsLogical queryEngineering
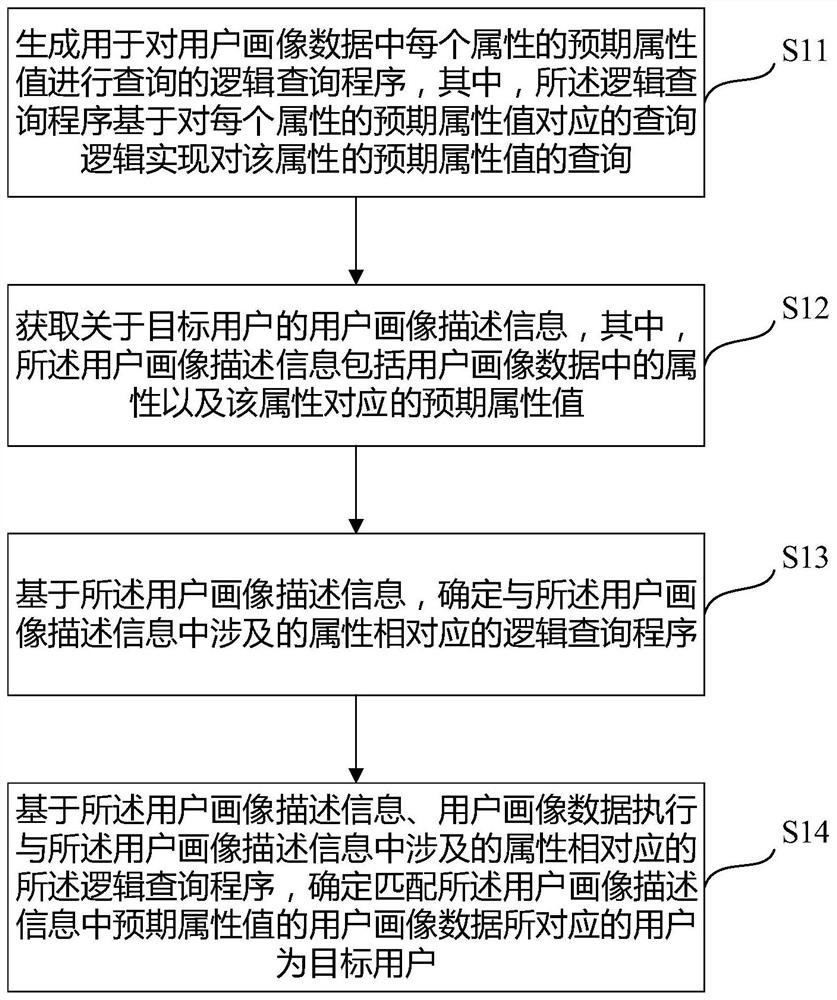
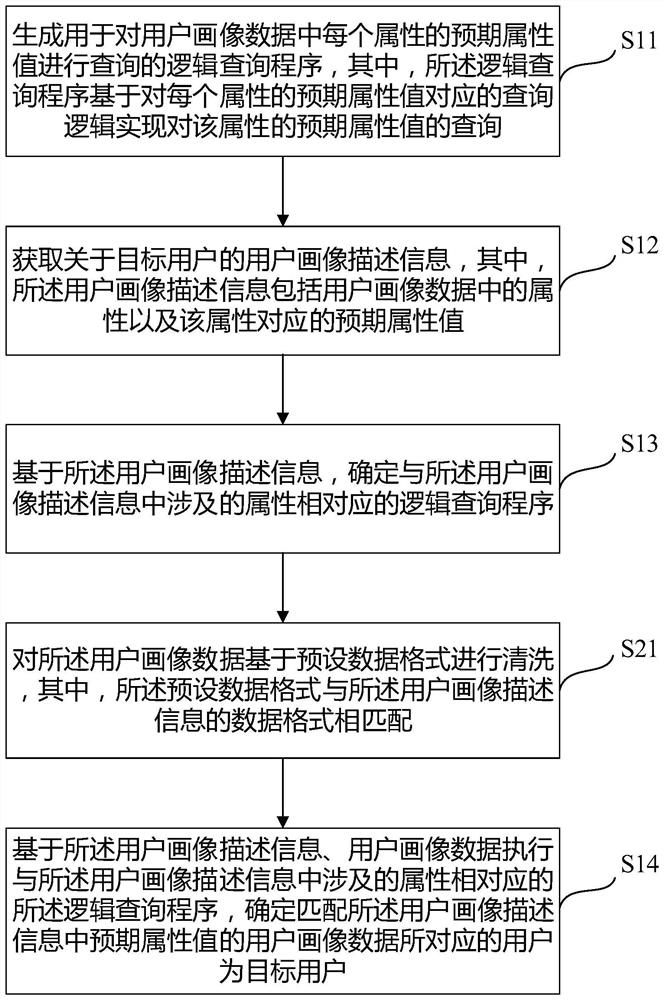
The invention aims to provide a method and equipment for determining a target user based on user portrait data, and the method comprises the steps: firstly generating a logic query program for querying an expected attribute value of each attribute in the user portrait data, then obtaining user portrait description information about the target user, and then determining a logic query program corresponding to the attribute involved in the user portrait description information based on the user portrait description information, and finally executing the logic query program corresponding to the attribute involved in the user portrait description information based on the user portrait description information and the user portrait data; and determining a user corresponding to the user portrait data matched with the expected attribute value in the user portrait description information as a target user. By means of the method, developers can develop a user portrait data screening tool with high universality, user portraits are not limited, the query requirements of various screening condition combinations are met, and beneficial effects are brought.
Owner:SHANGHAI BILIBILI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com