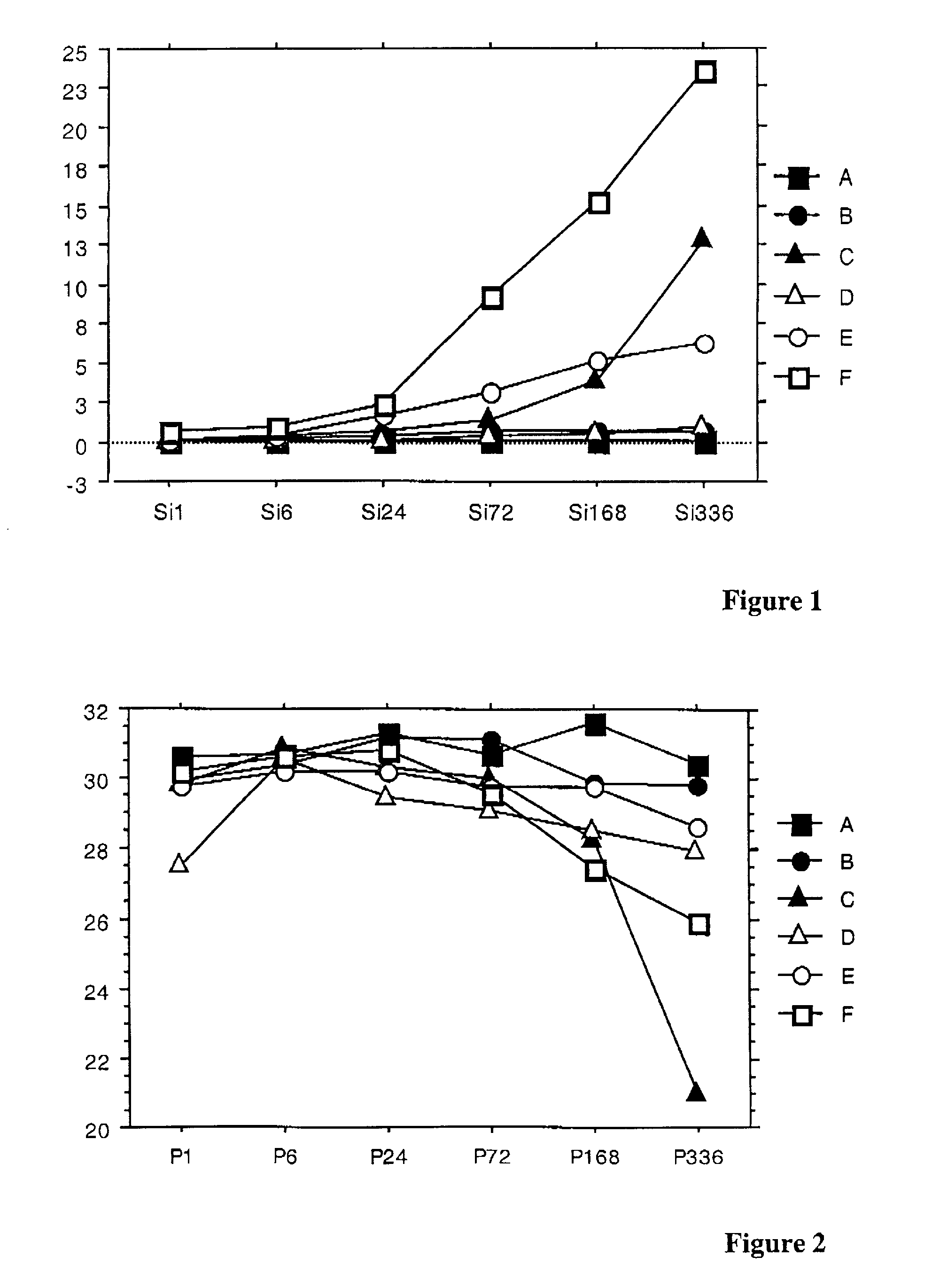
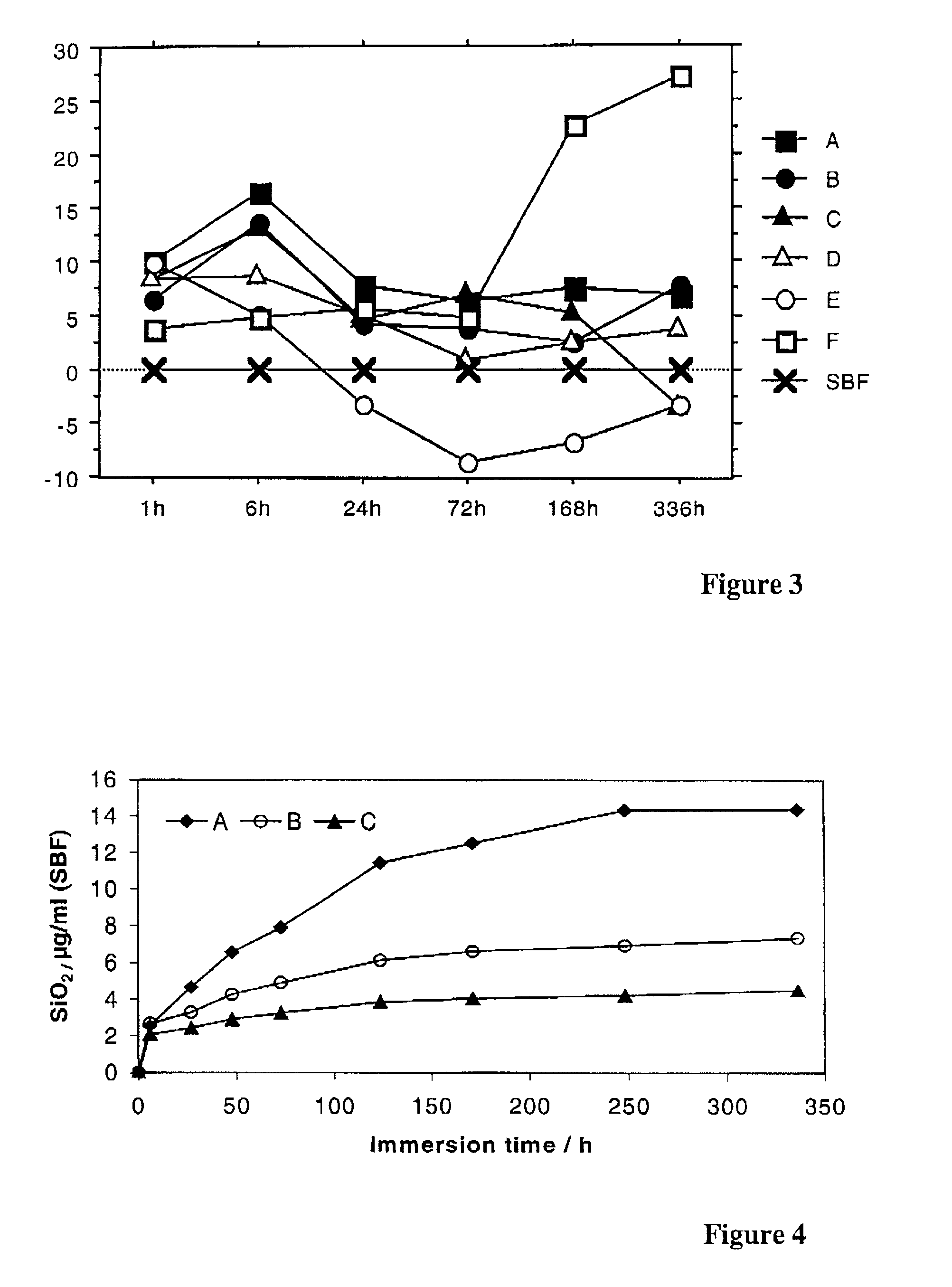
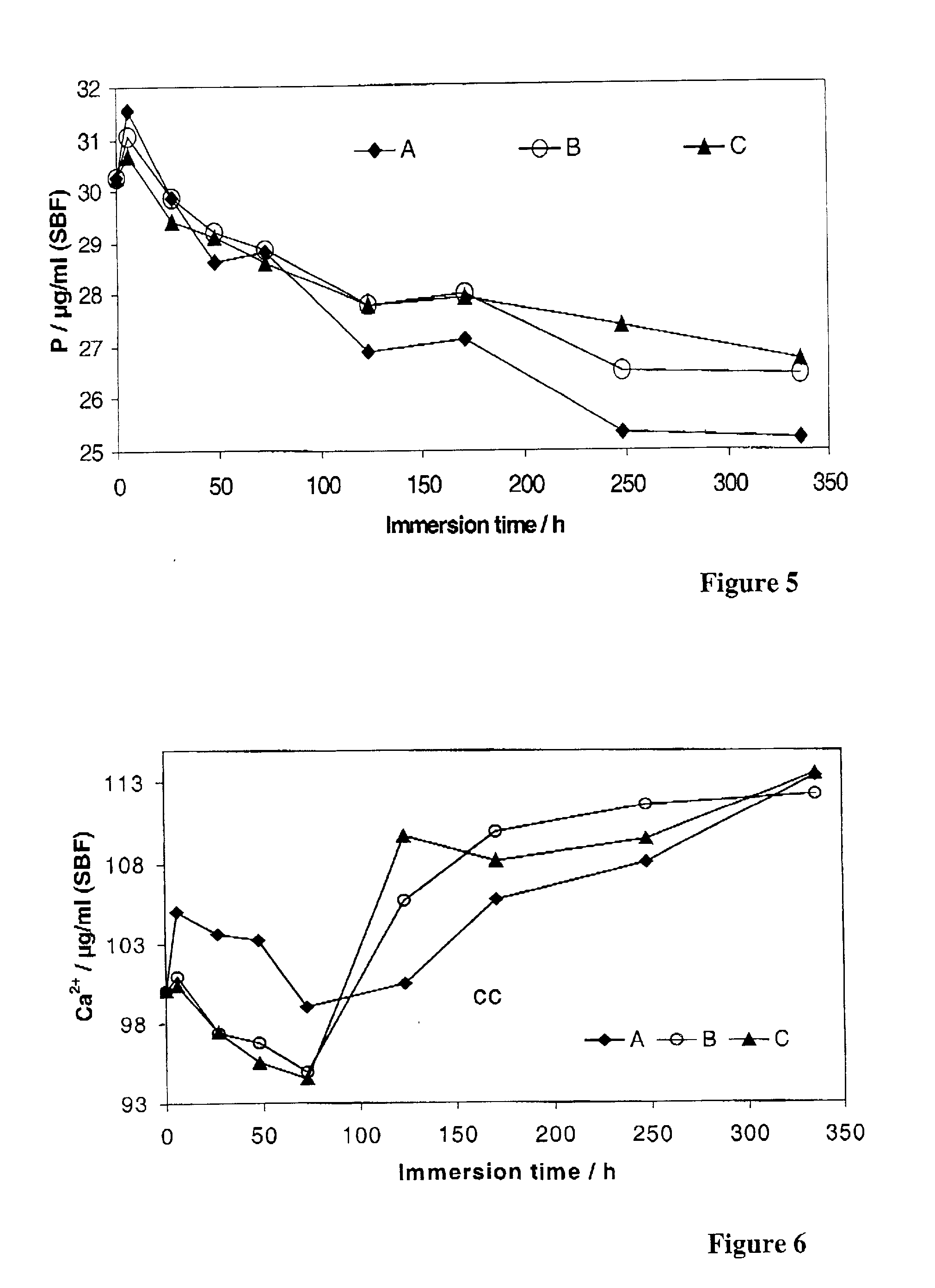
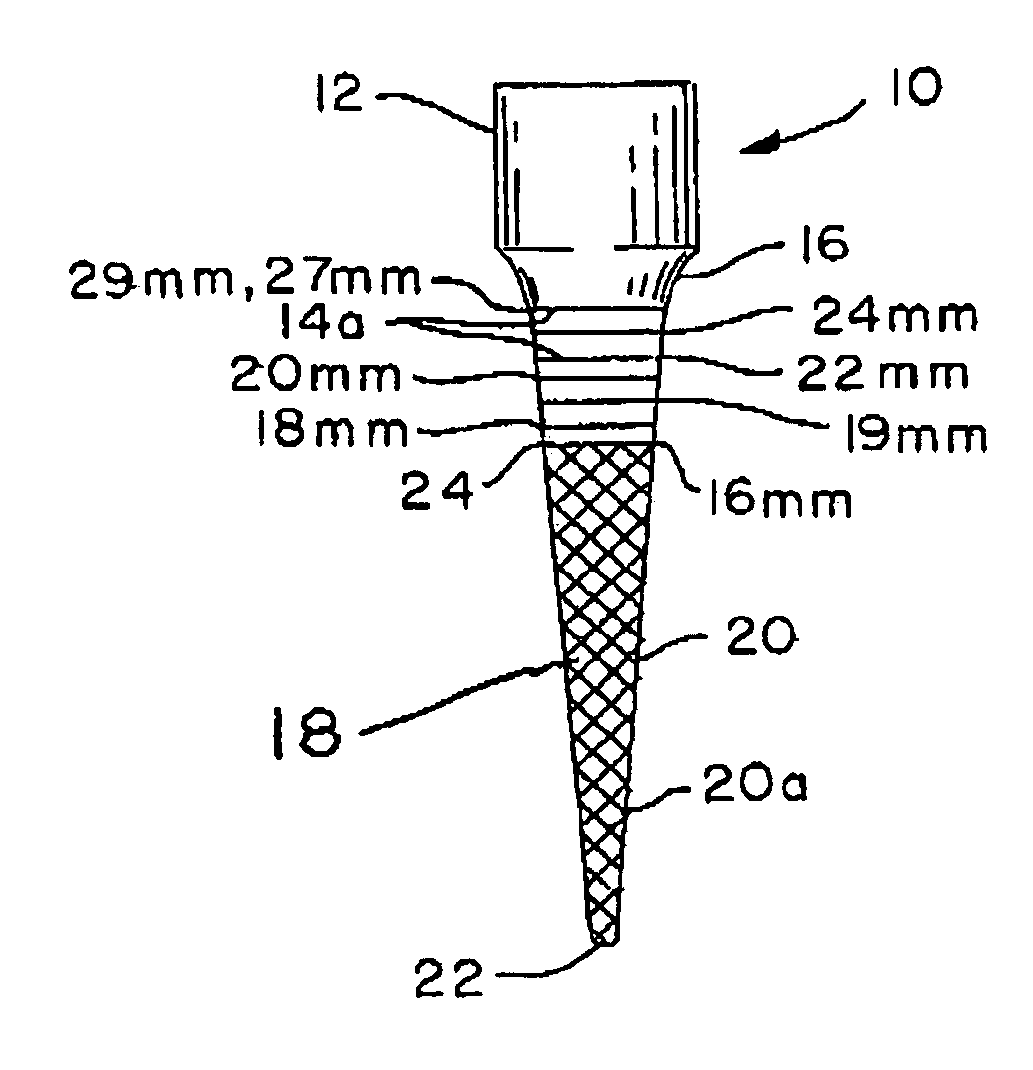
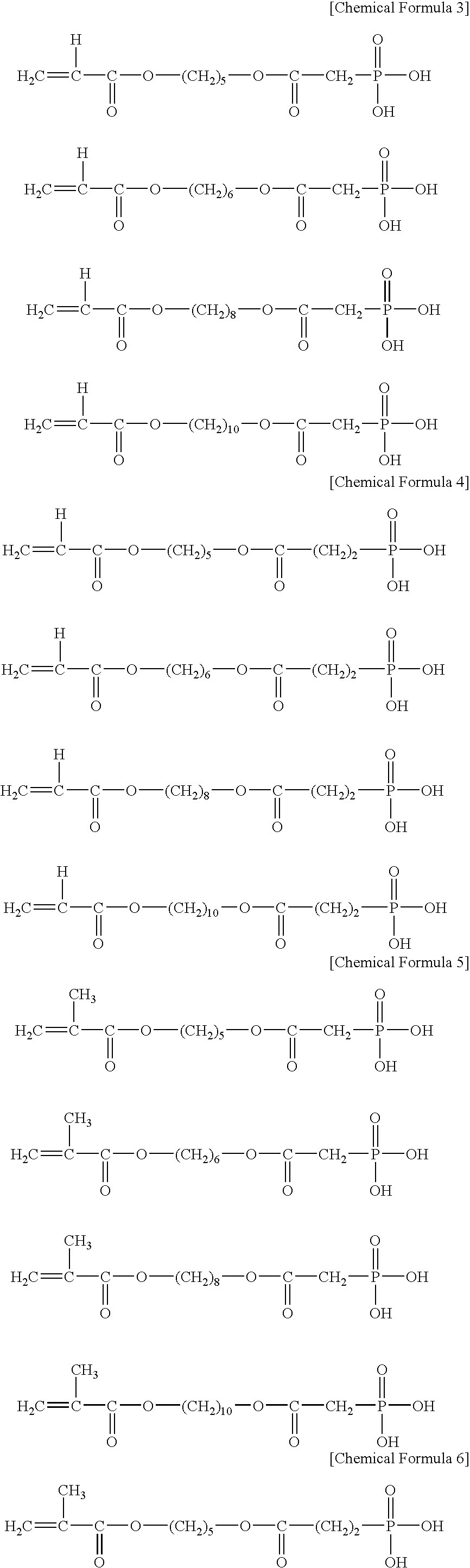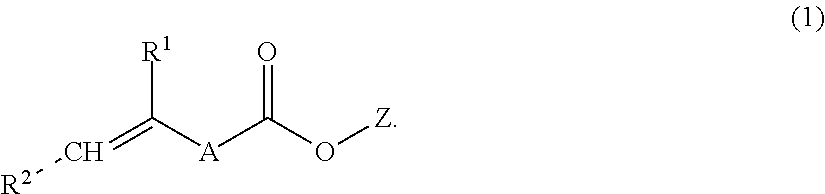Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
100 results about "Glass ionomers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A glass ionomer cement is a dental restorative material used in dentistry as a filling material and luting cement, including for orthodontic bracket attachment. Glass-ionomer cements are based on the reaction of silicate glass-powder (calciumaluminofluorosilicate glass)and polyacrylic acid, an ionomer.
Golf balls comprising glass ionomers, ormocers, or other hybrid organic/inorganic compositions
A golf ball comprising a core and a cover layer, wherein at least one of the core or cover layer comprises a hybrid material that contains fatty acid-modified glass ionomers, an ormocer or other inorganic-organic materials.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Two paste-type glass ionomer cement
ActiveUS20060247330A1High mechanical strengthWater sensitivityCosmetic preparationsImpression capsGlass ionomersWater based
An object of the present invention is to provide a paste-type cement composition which while retaining adhesion to tooth substance, biocompatibility, surface curability and fluorine sustained-releasability which are the characteristics derived from the conventional glass ionomer cement, reduces water sensitivity which is shortcoming of the conventional glass ionomer cement, enables simple mixing operation, does not adversely affect on the various properties of a cured cement depending on a difference in operators or a skill degree, and can afford various stable properties. There is provided a two paste-type glass ionomer cement comprising a resin-based paste containing a hydrophobic polymerizable monomer and a polymer of acidic group-containing polymerizable monomers which are insoluble to each other, and a water-based paste containing a hydrophilic polymerizable monomer and water which are soluble to each other, in which an acid reactive filler is contained in at least one of pastes.
Owner:SHOFU INC +1
Glass-ionomer cements containing amino acids
InactiveUS20050165136A1Good biocompatibilityImprove hydrophilicityImpression capsMedical preparationsGlass ionomersMedicine
Disclosed are ionomeric compositions and ionomeric cements containing the compositions. The cements are useful in dental and orthopedic medicine.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND +1
Glass ionomers for enhancing mineralization of hard tissue
The invention relates to glass ionomer for enhancing mineralization of hard tissue of mammals. The glass ionomer comprises, a inert biocompatible ceramic and a bioactive ceramic. The invention also relates to a method for enhancing mineralization of hard tissue of mammals with the aid of said glass ionomer. The invention further relates to the use of said glass ionomer for the preparation of products intended for treatment of defects of soft and hard tissue as well as the use of said glass ionomer for the preparation of a variety of products wherein the ability to enhance mineralization is advantageous.
Owner:NARHI TIMO +4
Two-part glass ionomer composition
InactiveUS20070254998A1Extended shelf lifeHigh strengthImpression capsWallsGlass ionomersWater soluble
Disclosed is a novel glass ionomer type dental cement composition comprising a first component comprising an aqueous solution of polymers made from monomers comprising acrylic acid, and a second, preferably substantially anhydrous, component comprising alkaline glass flux in a medium comprising water soluble / miscible monomers or pre-polymers, of such monomers, having at least one —OH group per molecule. The compositions offer more convenient handling, excellent reproducibility of desired properties of the cured material, improved strength, and extended shelf life.
Owner:SCI PHARMA INC
Dental paste glass ionomer cement composition
InactiveUS20070072957A1High affinityIncrease physical strengthImpression capsSpecial tyresColloidal silicaGlass ionomers
To give high mechanical strength, particularly compression strength, and excellent operationality in a two-paste system, a dental paste glass ionomer cement composition comprises a first paste comprising an α-β unsaturated carboxylic acid polymer, a filler that is not reacted with the α-β unsaturated carboxylic acid polymer and is not in a monodisperse state in water, a silica aqueous sol containing colloidal silica having an average particle diameter of 1 to 100 nm dispersed in a monodisperse state in water to an SiO2 concentration of 1 to 50% by weight, and water, in prescribed amounts respectively, and a second paste containing fluoroalumino silicate glass powder in a prescribed amount, where the second paste sometimes contains a thickening agent comprising a water soluble polymer material and water, or a polymerizable monomer having no acid group.
Owner:GC CORP
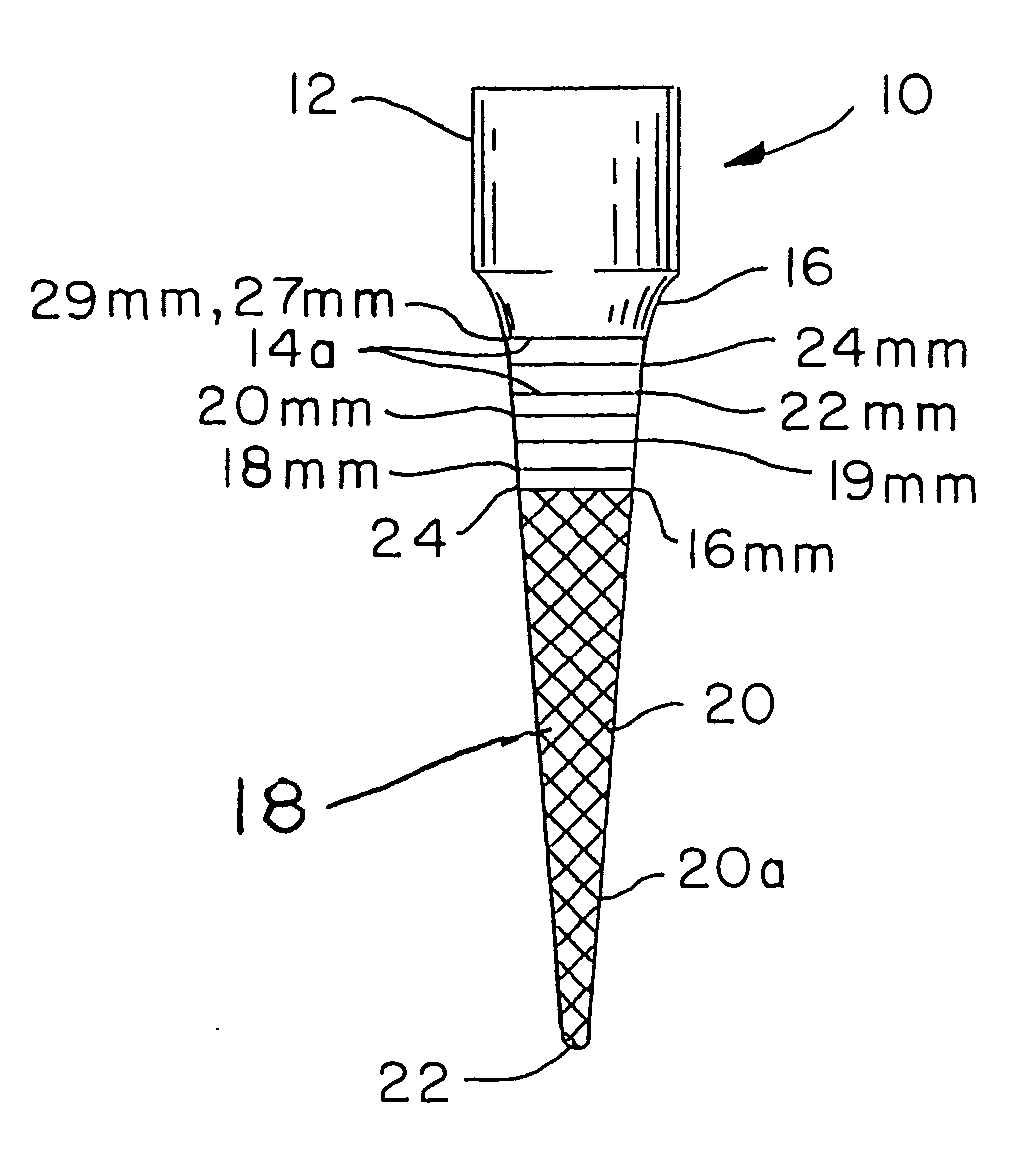
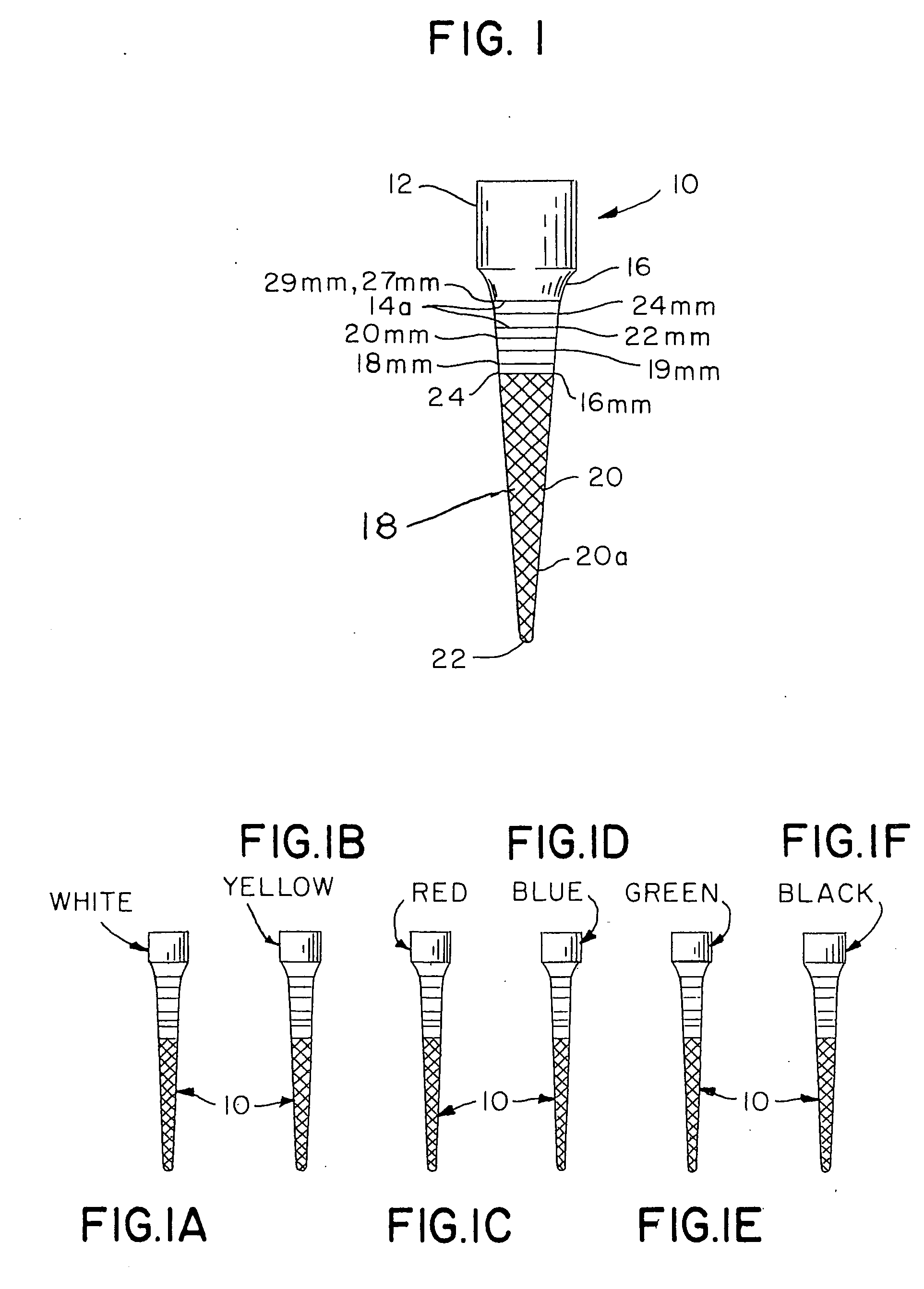
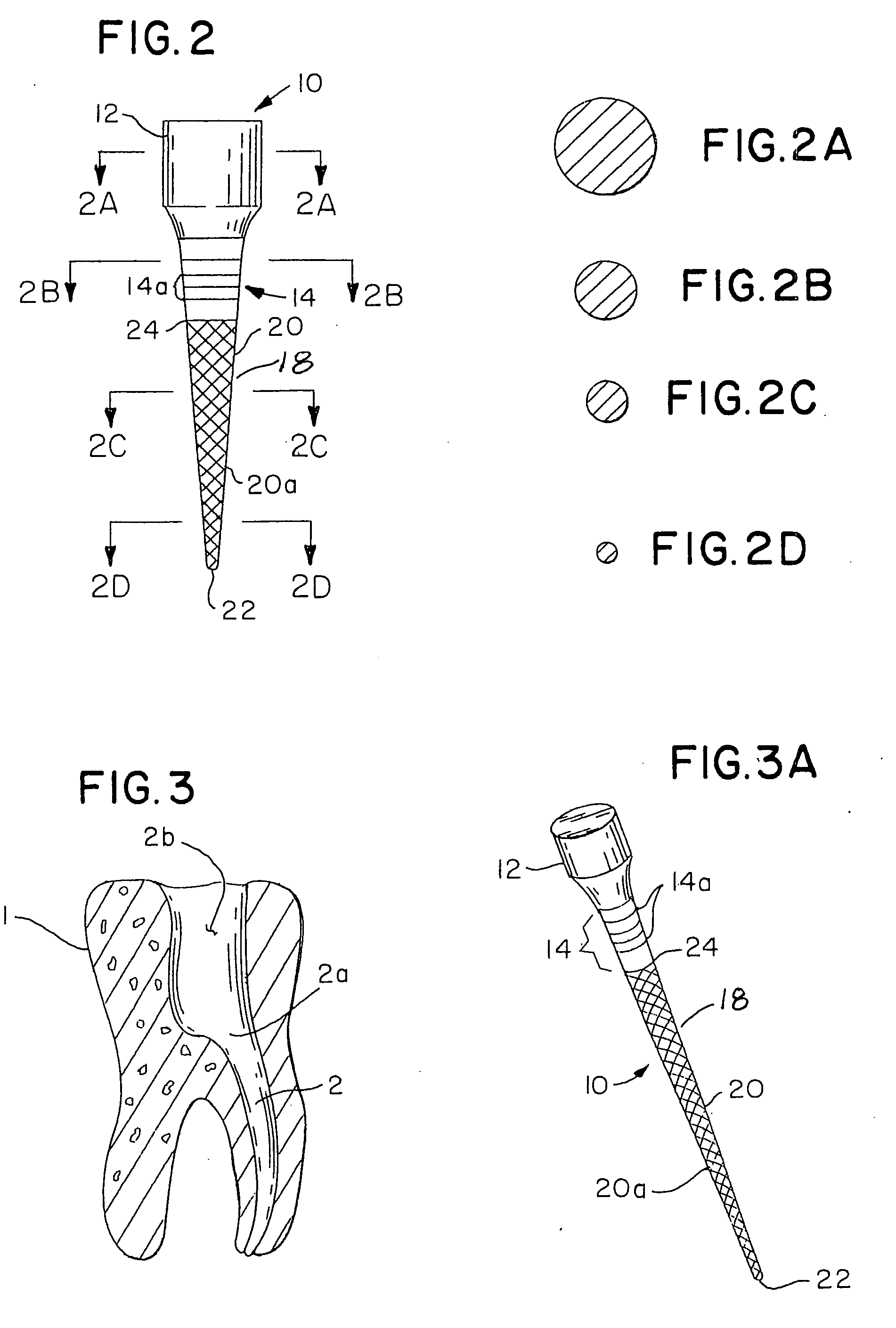
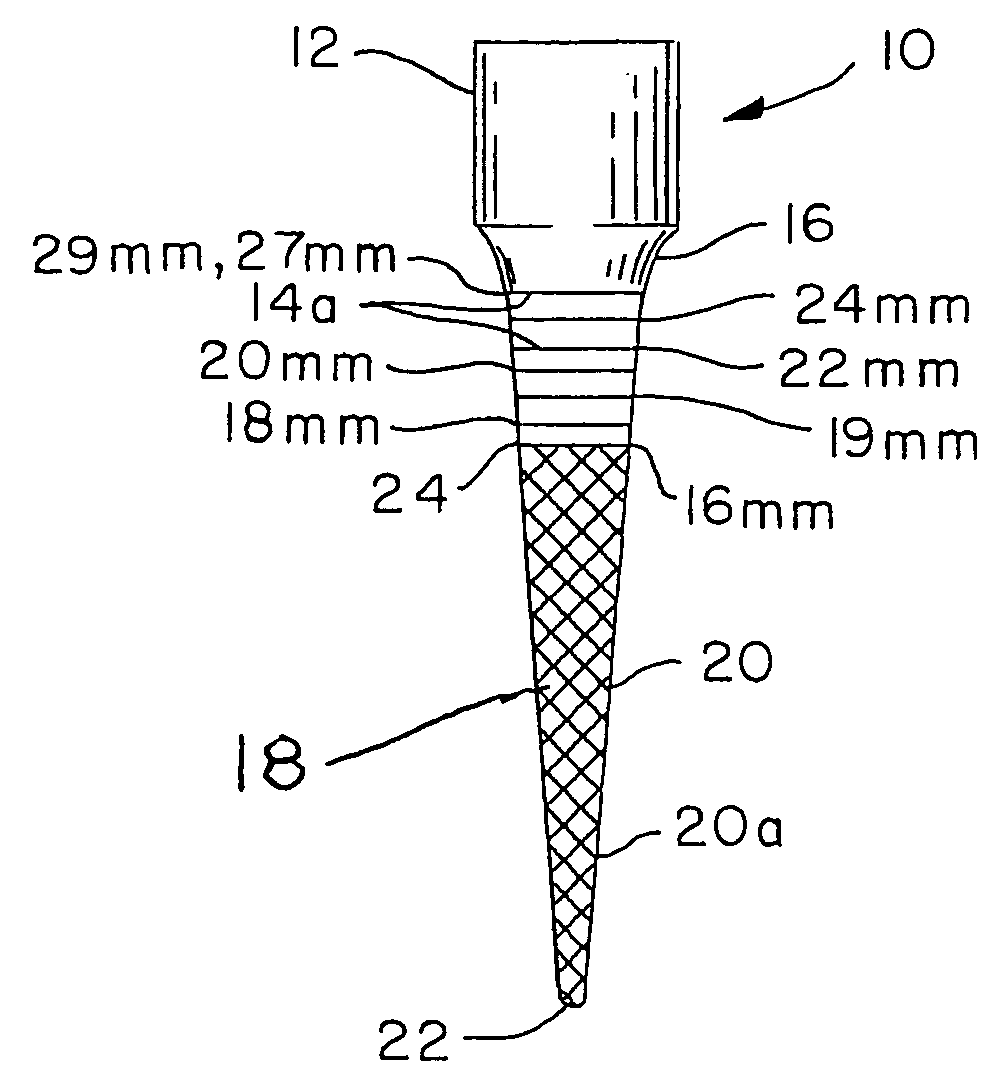
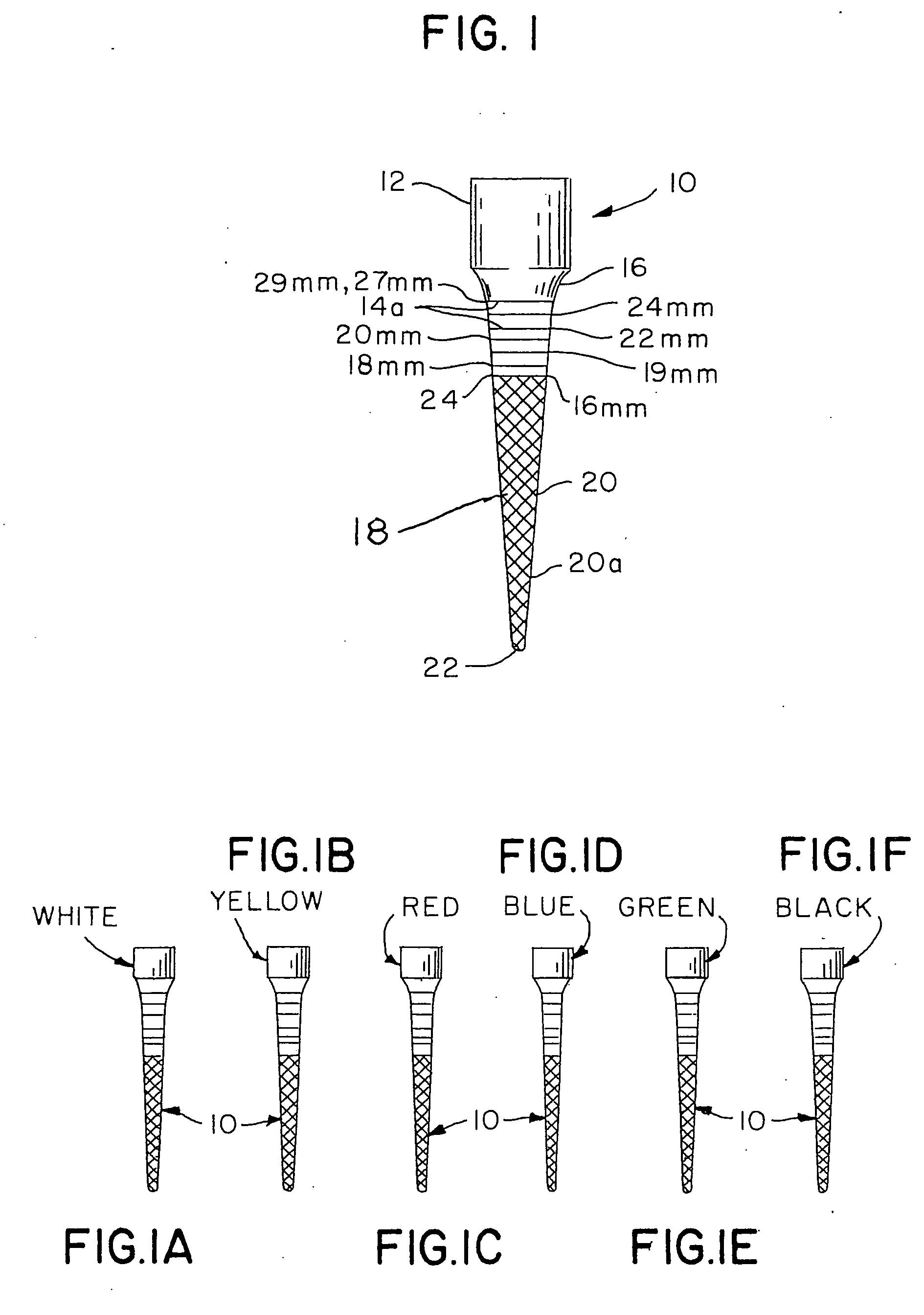
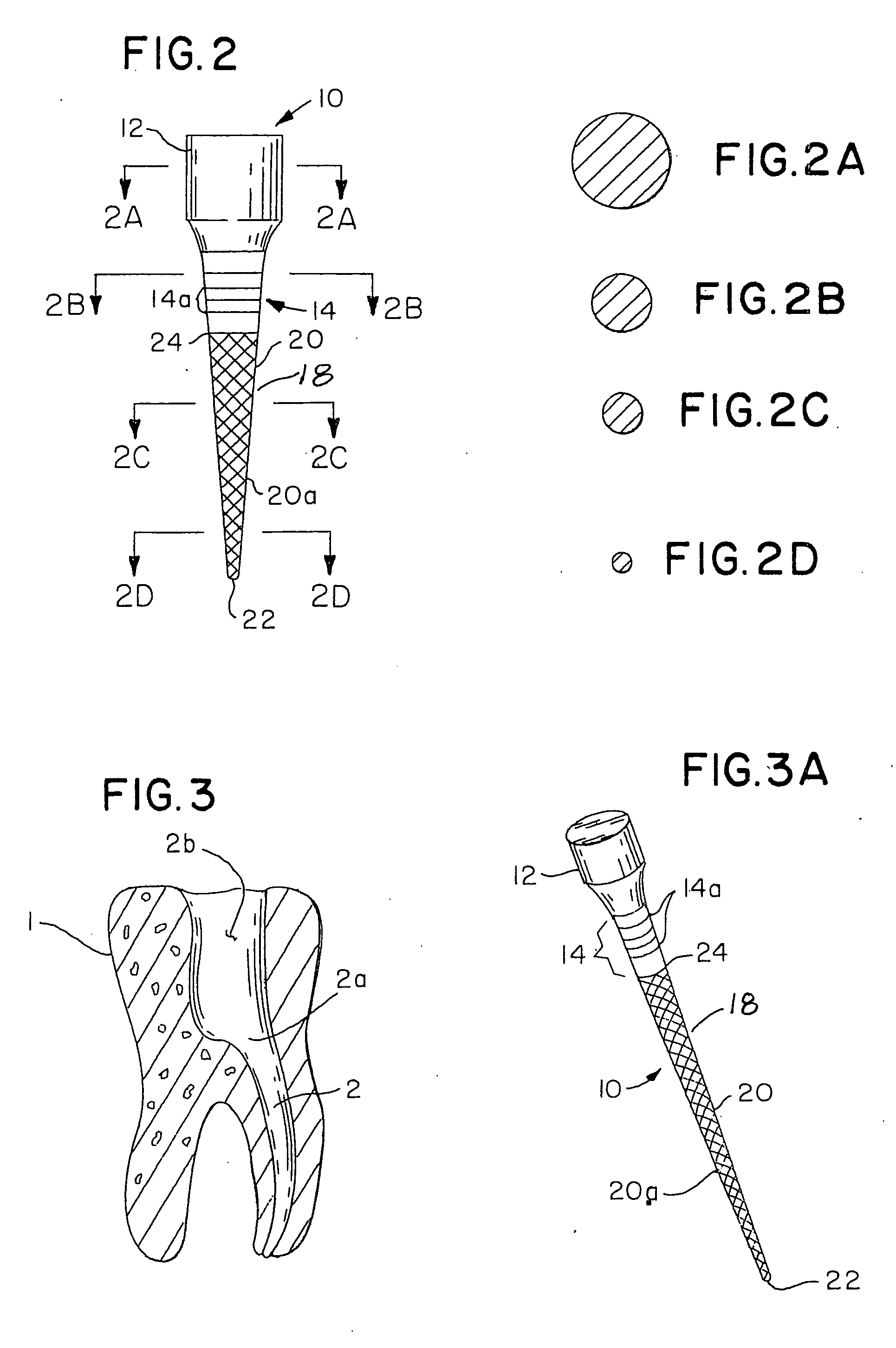
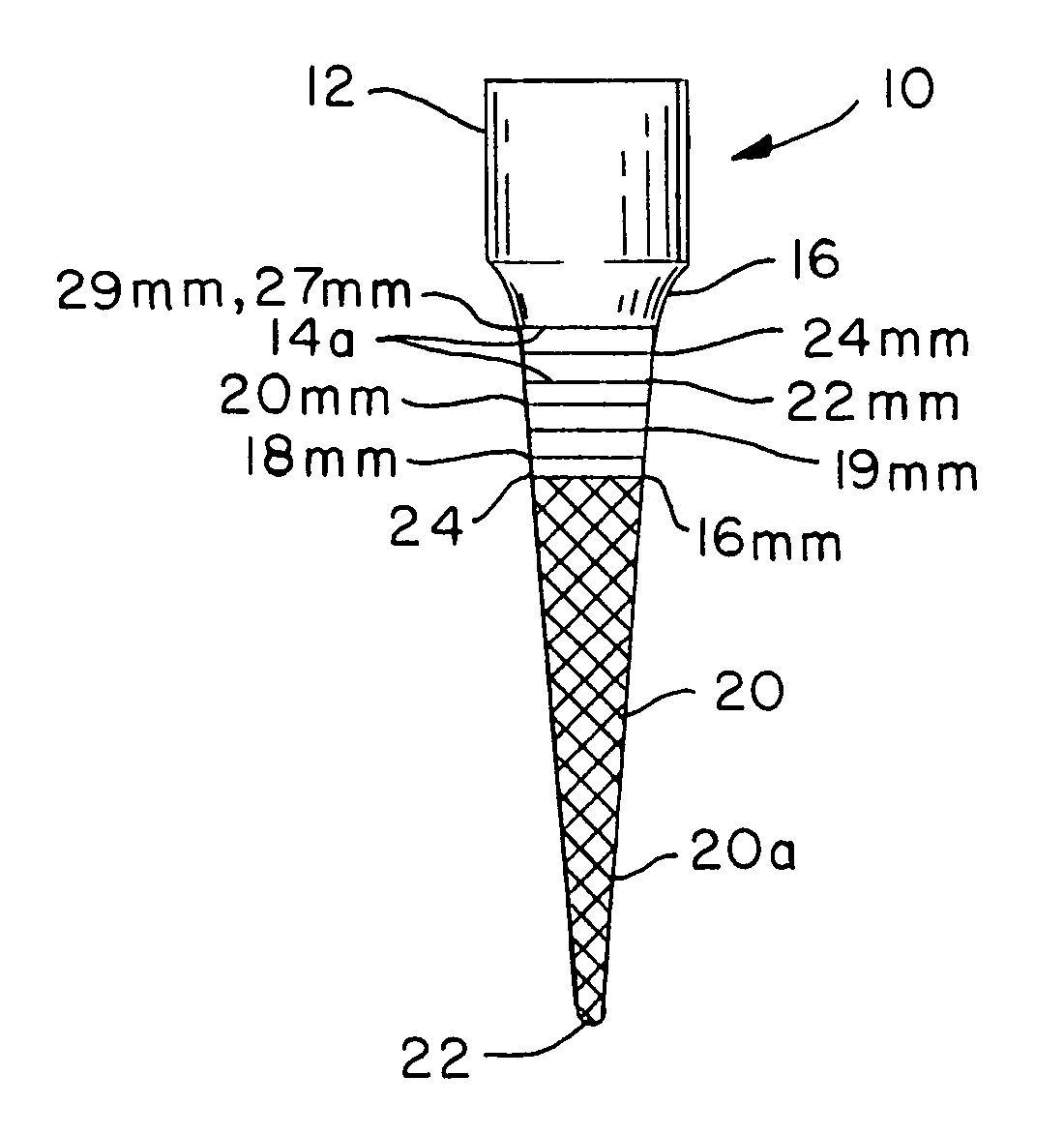
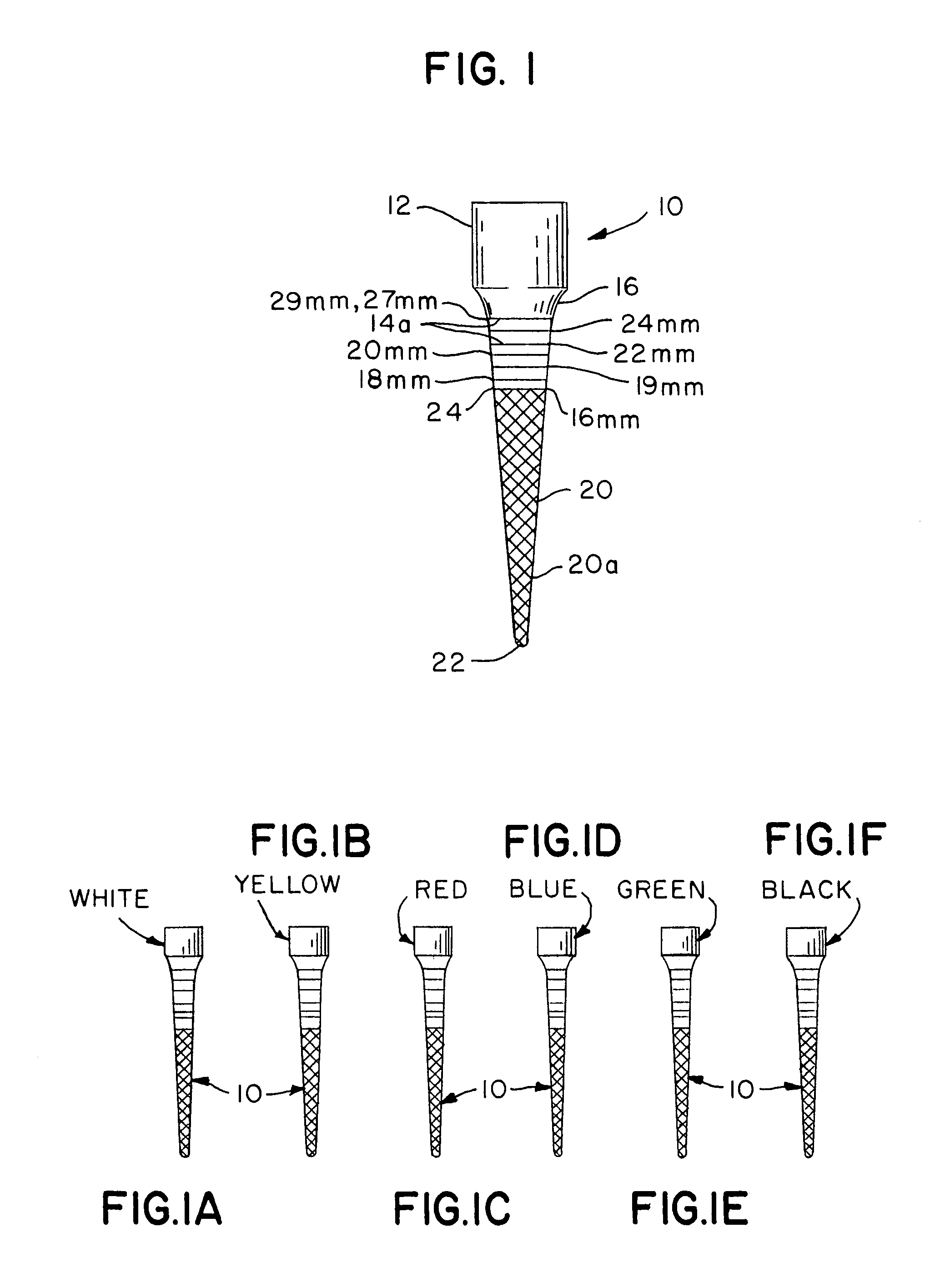
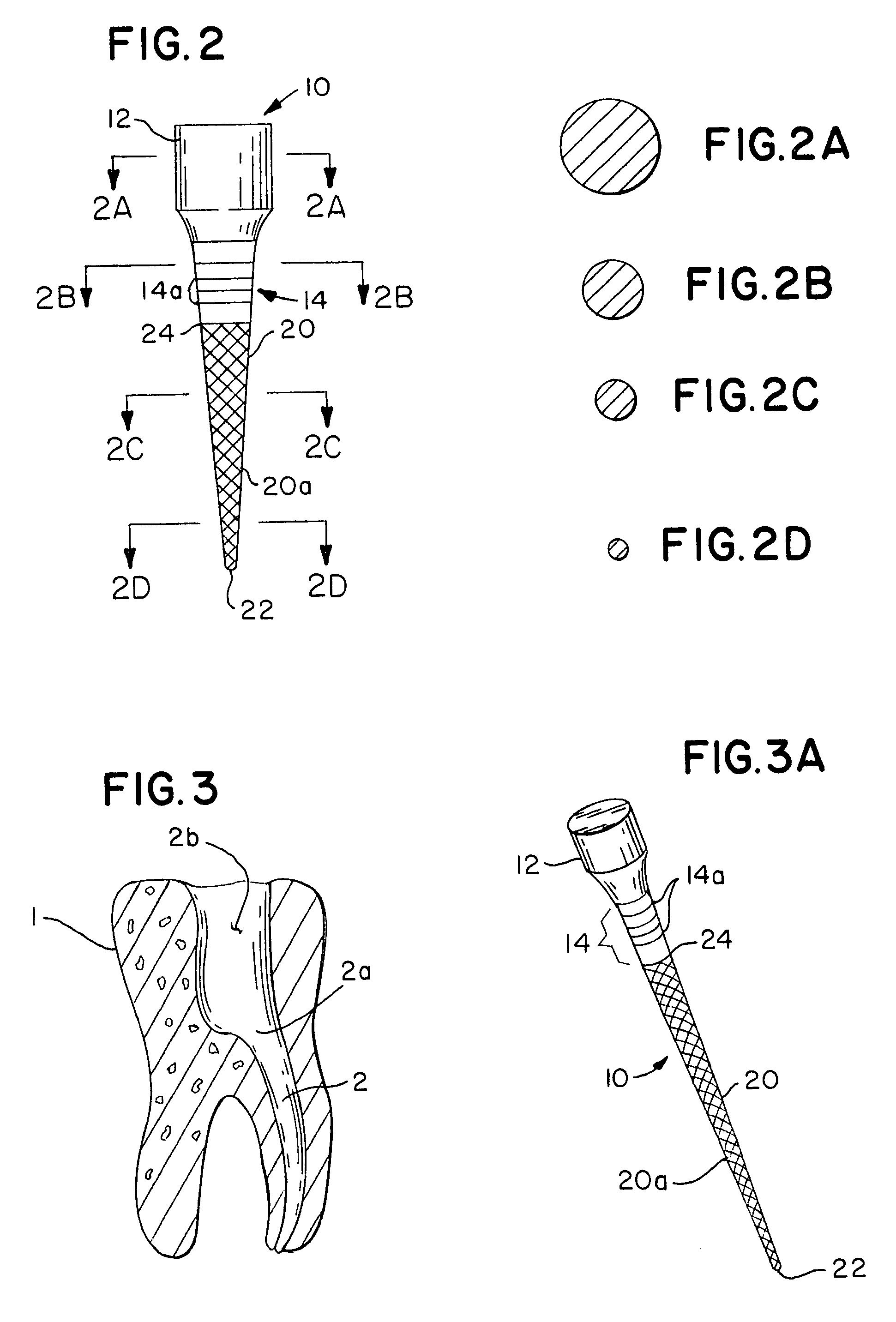
Integral gutta percha core/cone obturation technique
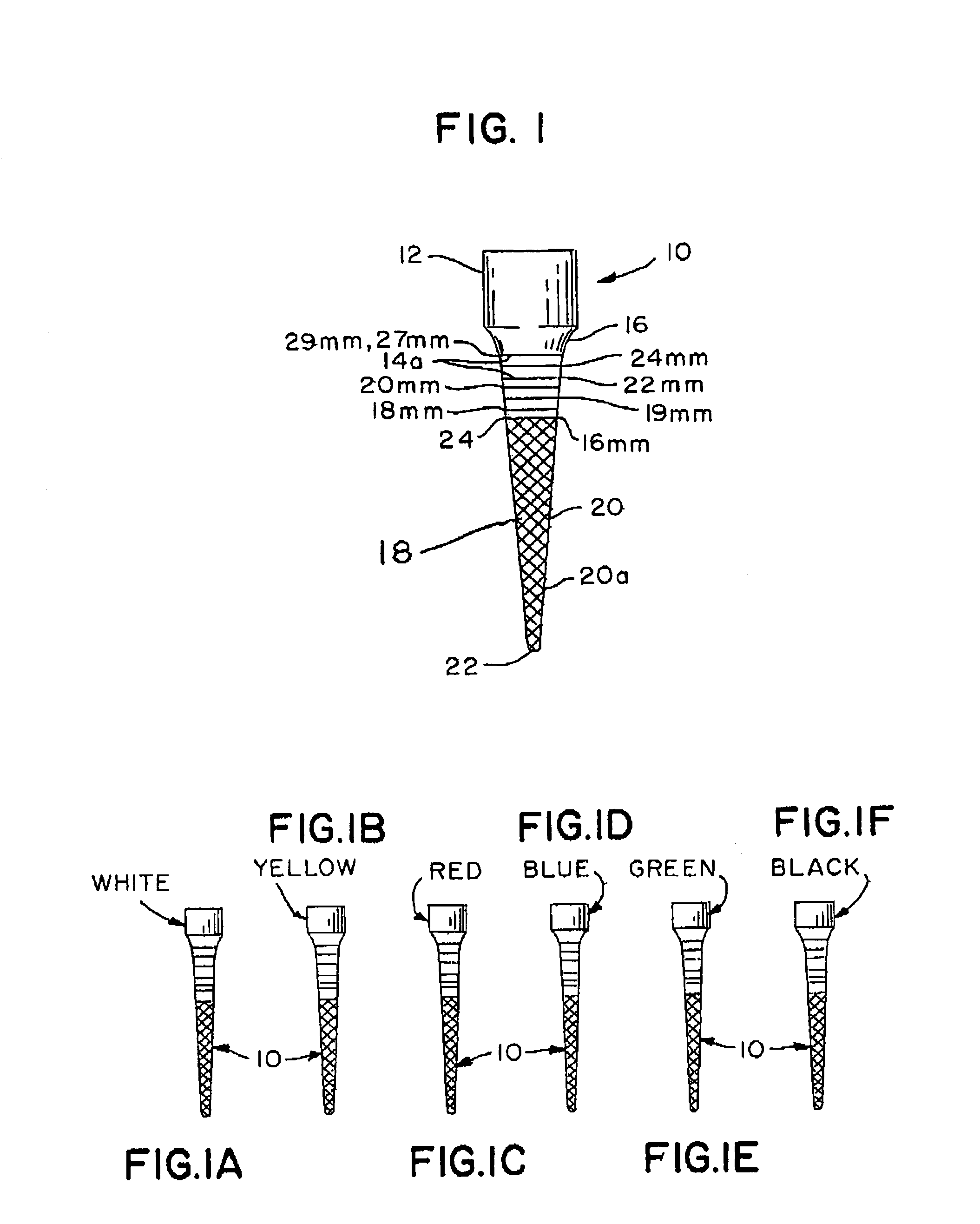
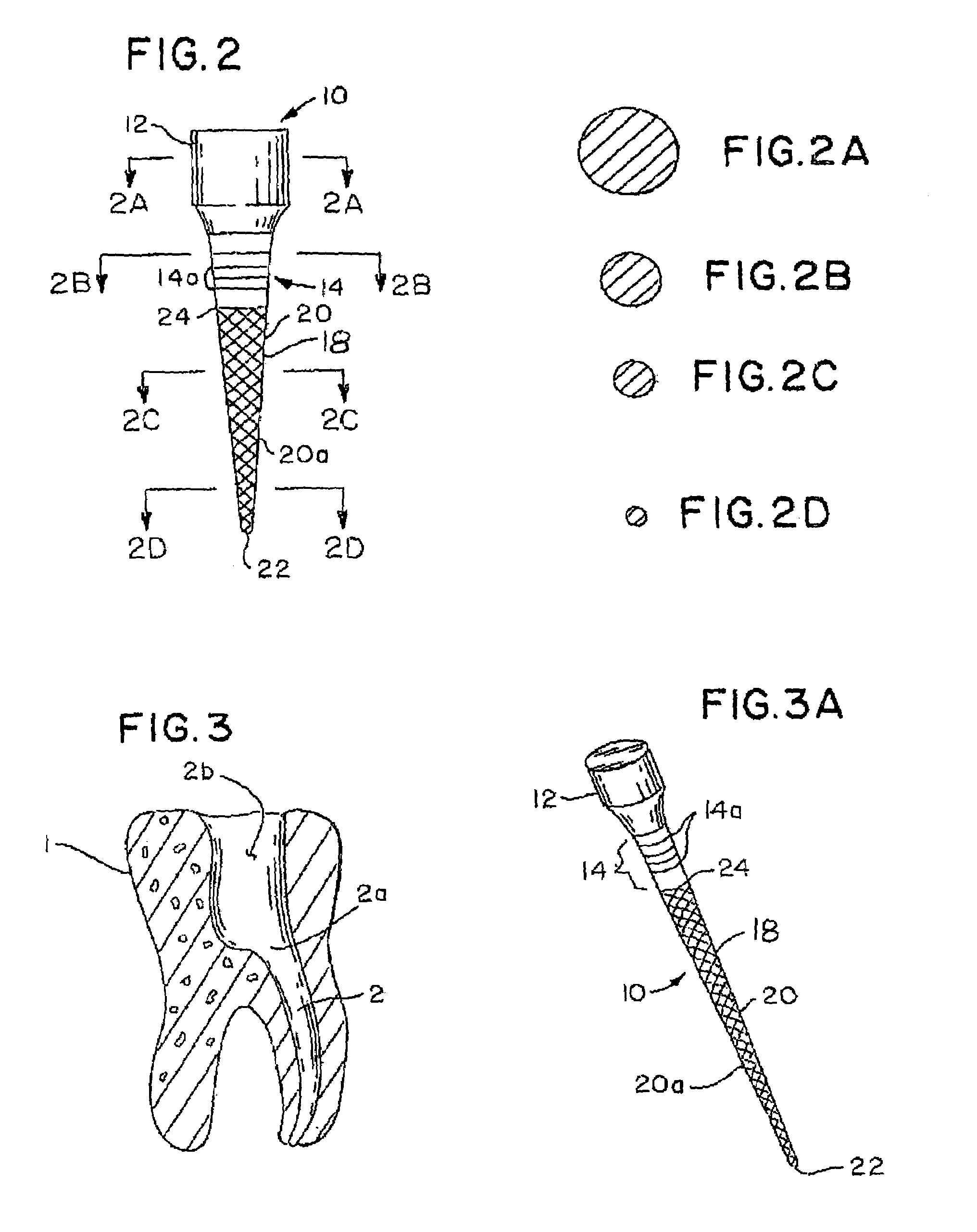
ActiveUS7021936B2Reduce leakageEasy to useImpression capsTeeth fillingGlass ionomersDelivery vehicle
An integral, one-piece silanated particle impregnated gutta percha core / cone technique employs a thin layer of a luting agent, such as glass ionomer cement with a machined gutta percha core / cone, precisely matches the preparation, thereby reducing leakage and achieving a hermetic seal. The hermetic seal is further enhanced by a mono-block bond that occurs between the silanated particles in the gutta percha and the appropriate chemical sealant. Optional cryogenic treatment of the gutta percha material changes its molecular weight, making it stiffer and conducive to forming an integral, one piece core / cone, without the need for a separate carrier core to install the tapered gutta percha core / cone within the root canal. Additionally, the tapered body of the core / cone may be reticulated in a slightly three dimensional texturized framework to increase surface area and therefore increase retention. Optional line demarcation indicia are also placed on the core / cone. Additionally, the head of the core / cone can be gripped by a delivery vehicle clasp.
Owner:ENDODONTIC EDUCATIONAL SEMINARS
Two paste-type glass ionomer cement
ActiveUS7488762B2Good biocompatibilityReduce disadvantagesCosmetic preparationsImpression capsWater basedGlass ionomers
An object of the present invention is to provide a paste-type cement composition which while retaining adhesion to tooth substance, biocompatibility, surface curability and fluorine sustained-releasability which are the characteristics derived from the conventional glass ionomer cement, reduces water sensitivity which is shortcoming of the conventional glass ionomer cement, enables simple mixing operation, does not adversely affect on the various properties of a cured cement depending on a difference in operators or a skill degree, and can afford various stable properties. There is provided a two paste-type glass ionomer cement comprising a resin-based paste containing a hydrophobic polymerizable monomer and a polymer of acidic group-containing polymerizable monomers which are insoluble to each other, and a water-based paste containing a hydrophilic polymerizable monomer and water which are soluble to each other, in which an acid reactive filler is contained in at least one of pastes.
Owner:SHOFU INC +1
Multiple use dental viscous material dispenser
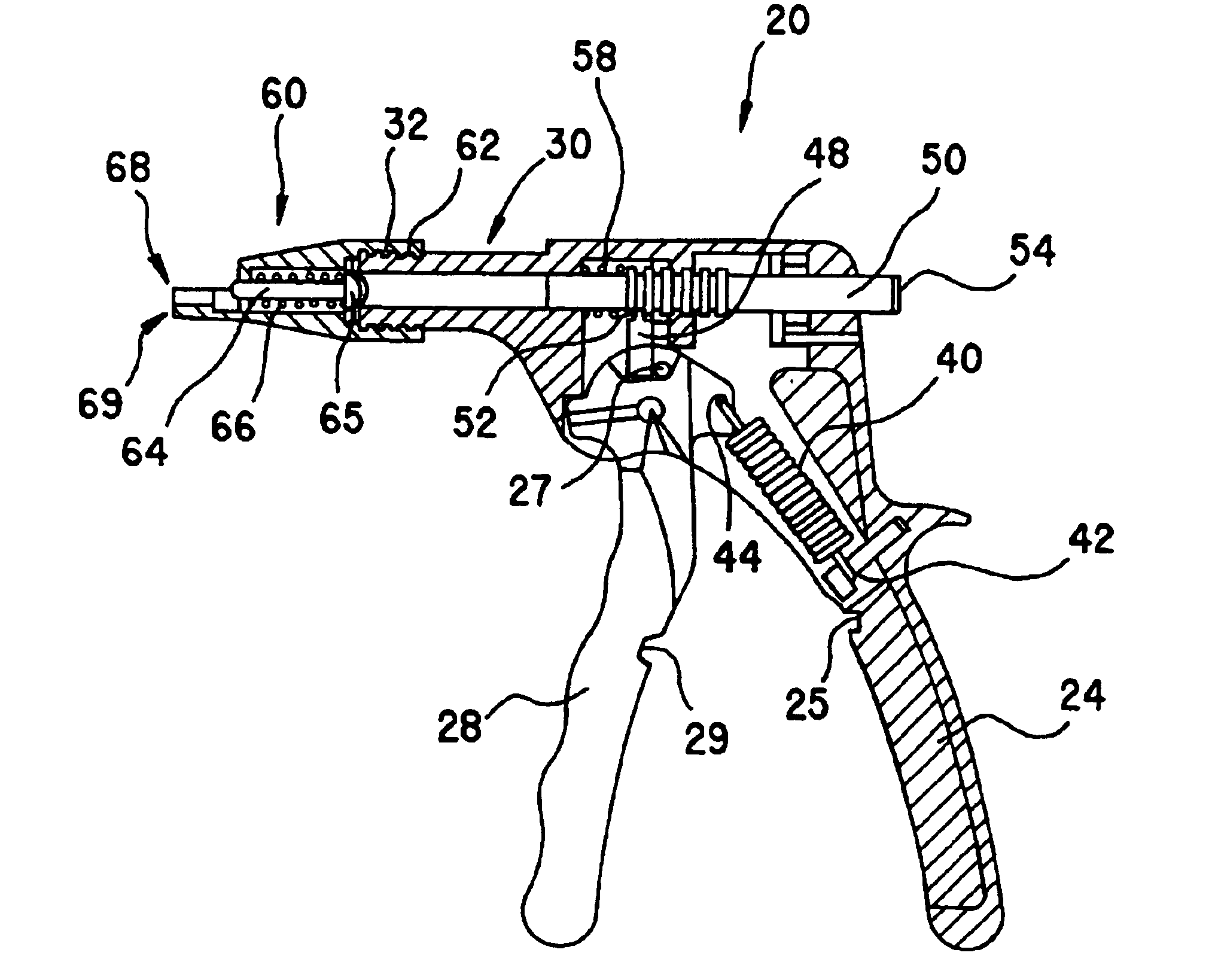
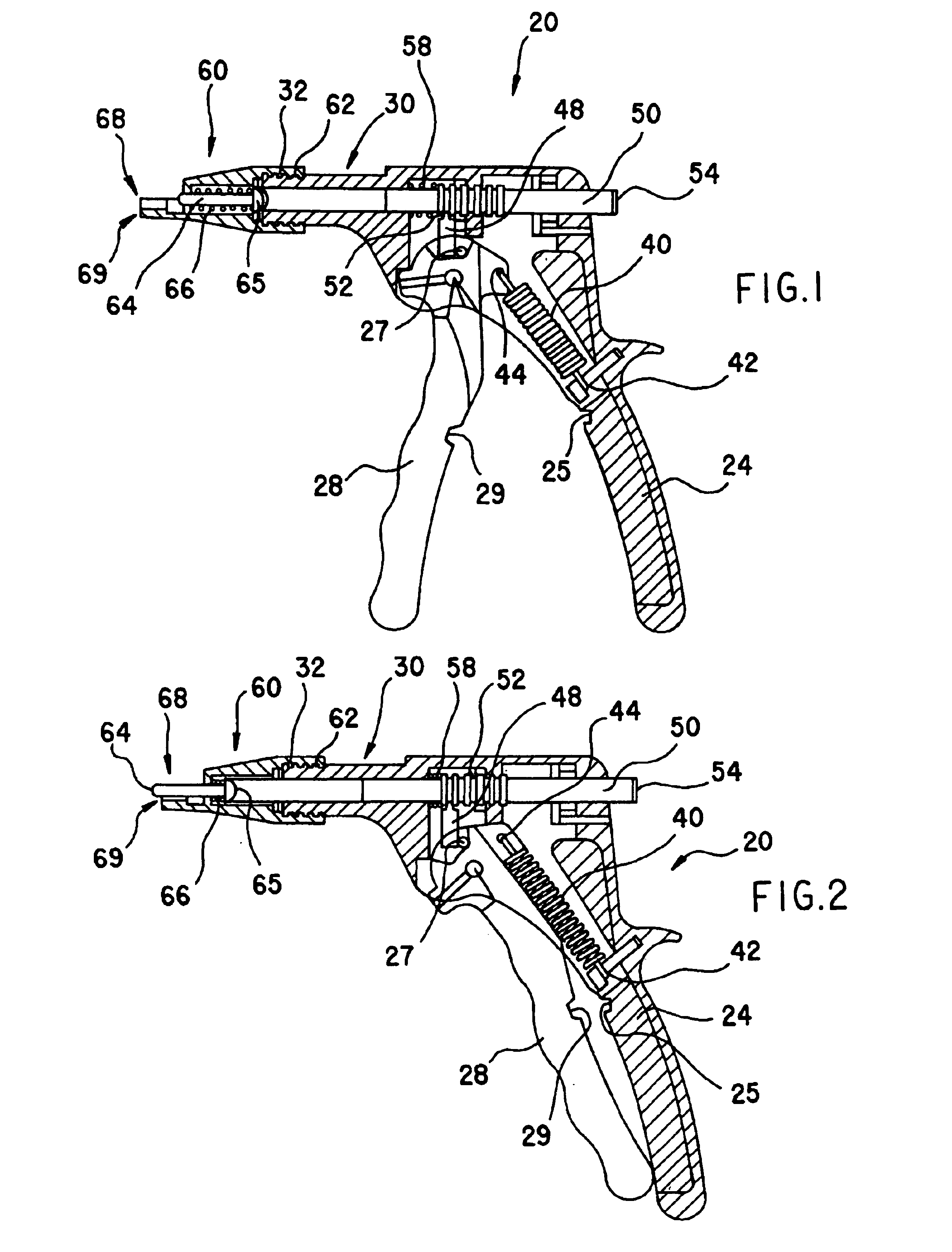
A viscous material dispenser, and dispenser system and kit, can include a dispenser without a dispensing tip and one or a plurality of separate dispensing tips that are removably attachable to the dispenser. The dispenser can be used with many different types of viscous material containing capsules and cartridges, such as those containing composites, dental cements, glass ionomers and the like. In embodiments, the dispenser can incorporate an integral activator for multi-component composition cartridges, such as glass ionomer cartridges.
Owner:CONFI DENTAL PRODS
Dental resin modified glass-ionomer composition
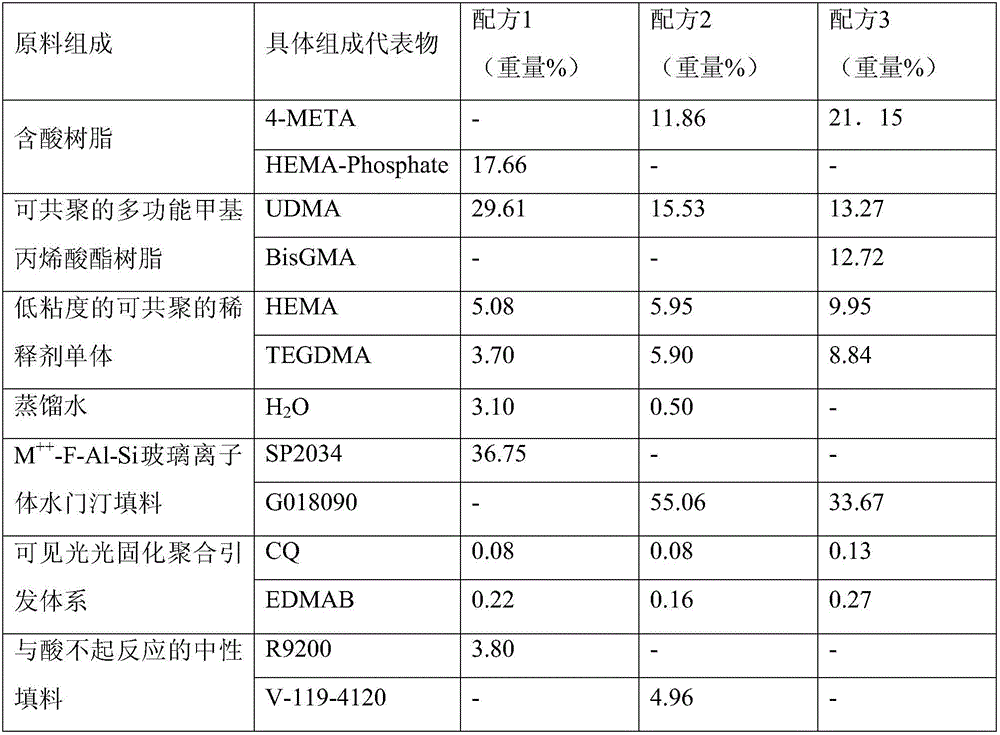
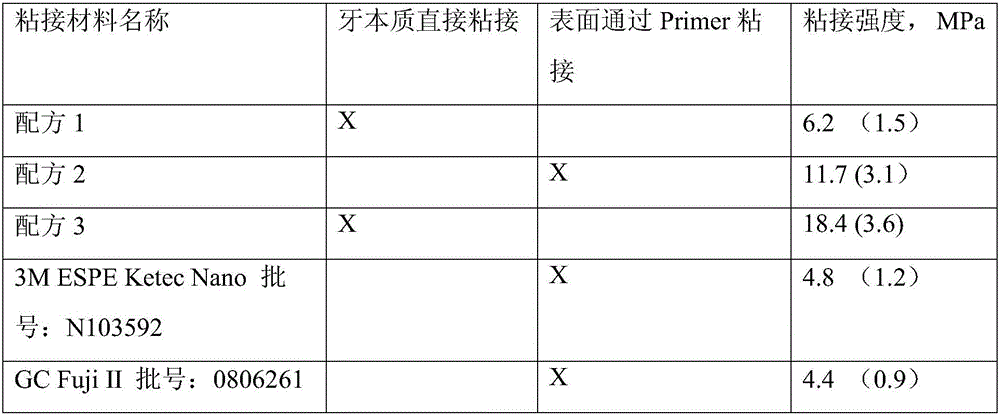
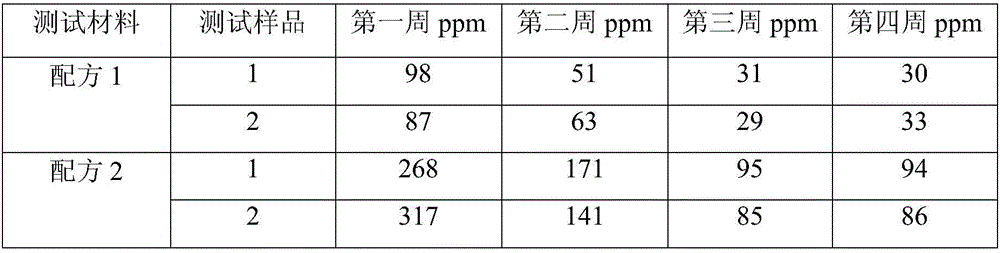
The dental resin modified glass-ionomer composition includes an acidic polymer; an acidic polymerizable monomer selected from 4-(meth)acryloxyalkyltrimellitic anhydride, 4-(meth)acryloxyalkyltrimellitic acid, and a combination thereof; a non-acidic polymerizable monomer; a fluoroaluminosilicate glass filler; water; and at least one polymerization initiator system. The dental resin modified glass-ionomer composition is useful for a dental restorative composition, an endodontic composition, and / or an orthodontic composition, and provides significantly enhanced adhesive property toward tooth structure.
Owner:THE KERR
Herbal bacteriostatic gel
InactiveCN107510768AGood curative effectEliminate gynecological problems quicklyAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsGlass ionomersSemen
The invention discloses a herbal bacteriostatic gel. The gel is mainly composed of the following components by weight percentage: 1.0-3.5% of troclat, 1.5-4.0% of sophora, 0.5-3.5% of Filia teng, 0.3-2.8% of a herba menthael extract, 0.4-3.0% of a motherwort extract, 40-65% of aloe gelvera, 0.3-2.0% of semen cnecos, 0.5-3.0% of radix angelicae sinensis, 0.1-3.0% of a fructus lonicerae extract, 0.3-2.3% of a cnidium extract, 0.1-1.2% of nano-silver, 0.8-1.2% of chlorhexidine acetate, 0.2-1.6% of vitamin E, 6-18% of glycerin, 0.8-2.0% of a glass ionomer cement, 0.5-3.0% of gel matrix carbomer, and 1.0-5.5% of triethanolamine. The herbal bacteriostatic gel provided by the invention adopts plants for antisepsis, is not added with any chemical preservative, and is safe. Through compatibility of all the components, the herbal bacteriostatic gel can balance flora, repair the microenvironment, does not change normal flora, is safer and healthier, has lasting and long-acting antibacterial and peculiar smell removing functions, and can quickly eliminate gynecological problems caused by various pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:吴鹏飞
Methods and compositions for preventing caries
InactiveUS20100247456A1Avoid developmentPrevention or treatment of cariesCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsGlass ionomersEpoxy
The present invention relates to an anti-caries composition that includes Silver Diamine Fluoride (SDF) and a carrier, and methods for using the composition. In particular, the composition includes SDF in an amount between about 1% and about 40% by weight; and a carrier (e.g., natural adhesive, a synthetic adhesive, a drying adhesive, an emulsion adhesive, silicone, copal, glass ionomer, cyanoacrylate, composite resin, latex, epoxy, silicone, polyurethane, denture adhesives, or variants thereof or any combination thereof.The methods of the present invention relate to arresting caries or reducing the number of active caries lesions. The steps include applying the anti-caries SDF composition to one or more tooth surfaces for about 1-5 minutes, and rinsing the composition from the tooth surface. Another method of the present invention relates to applying a SDF composition to the tooth surface, curing the composition, to thereby treat caries. Caries is arrested or the number of active caries lesions is reduced, as compared to an individual whose tooth surface is not subjected to the SDF composition.
Owner:FORSYTH DENTAL INFARY FOR CHILDREN
Integral gutta percha core/cone obturation technique
InactiveUS20060154213A1Reduce leakageEasy to useTeeth fillingTeeth cappingGlass ionomersDelivery vehicle
An integral, one-piece gutta percha core / cone technique employs a thin layer of a luting agent, such as glass ionomer cement with a machined gutta percha core / cone, precisely matches the preparation, thereby reducing leakage and achieving a hermetic seal. Optional cryogenic treatment of the gutta percha material changes its molecular weight, making it stiffer and conducive to forming an integral, one piece core / cone, without the need for a separate carrier core to install the tapered gutta percha core / cone within the root canal. Additionally, the tapered body of the core / cone may be reticulated in a slightly three dimensional texturized framework to increase surface area and therefore increase retention. Optional line demarcation indicia are also placed on the core / cone. Additionally, the head of the core / cone can be gripped by a delivery vehicle clasp.
Owner:KOCH KENNETH +1
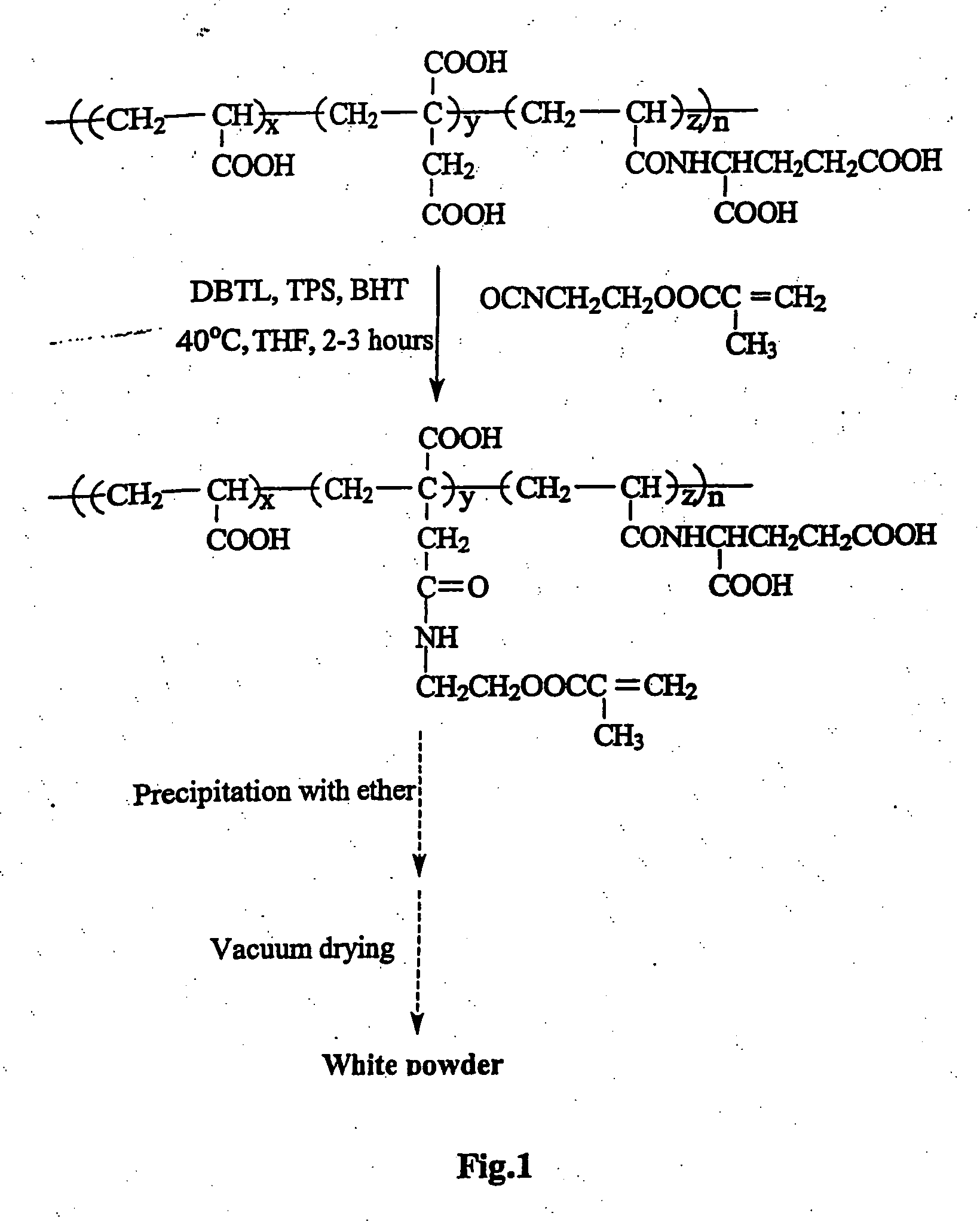
Polymer for a glass ionomer cement
ActiveUS20130289216A1High bonding strengthImprove stabilityImpression capsDentistry preparationsGlass ionomersCarboxylic acid
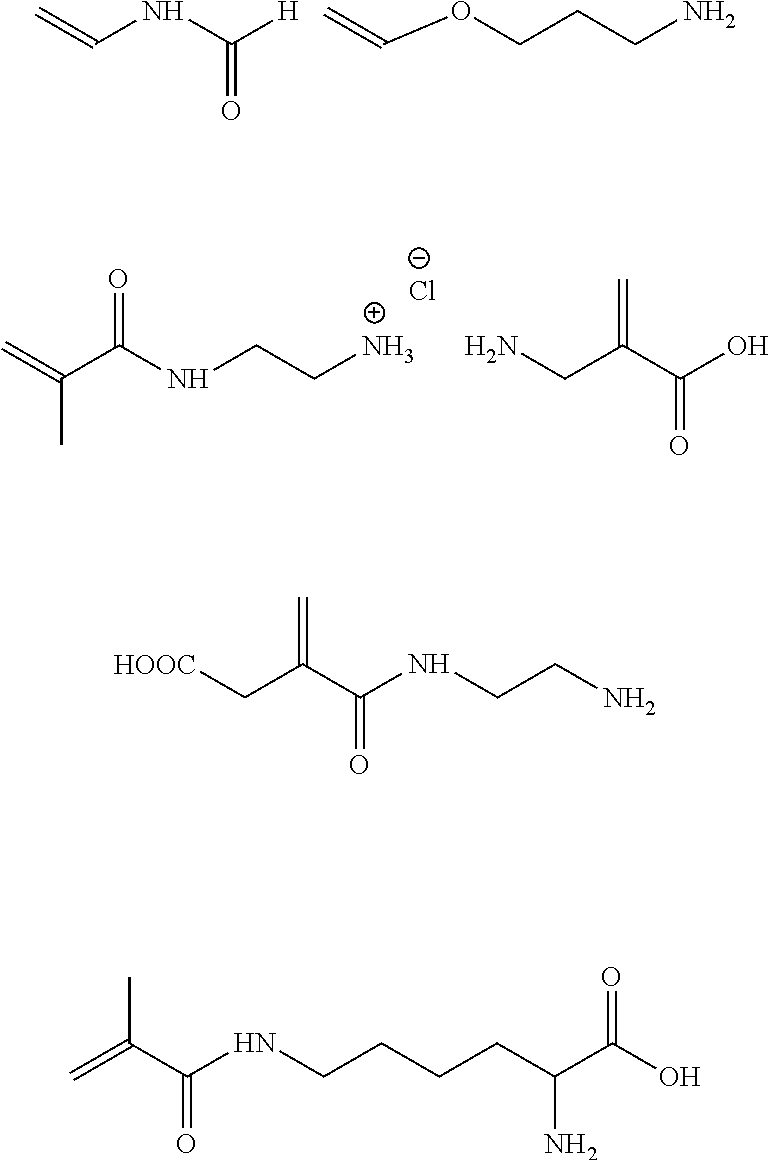
A process for producing a water-soluble, hydrolysis-stable, polymerizable polymer, comprising a) a step of copolymerizing a mixture comprising (i) a first copolymerizable monomer comprising at least one optionally protected carboxylic acid group and a first polymerizable organic moiety, and (ii) a second copolymerizable monomer comprising one or more optionally protected primary and / or secondary amino groups and a second polymerizable organic moiety, for obtaining an amino group containing copolymer; b) a step of coupling to the amino group containing copolymer a compound having a polymerizable moiety and a functional group reactive with an amino group of repeating units derived from the second copolymerizable monomer in the amino group containing copolymer obtained in the first step wherein the optionally protected amino group is deprotected, so that polymerizable pendant groups are linked to the backbone by hydrolysis-stable linking groups, and, optionally, a step of deprotecting the protected carboxylic acid group after step (a) or step (b), for obtaining a polymerizable polymer.
Owner:DENTSPLY SIRONA INC
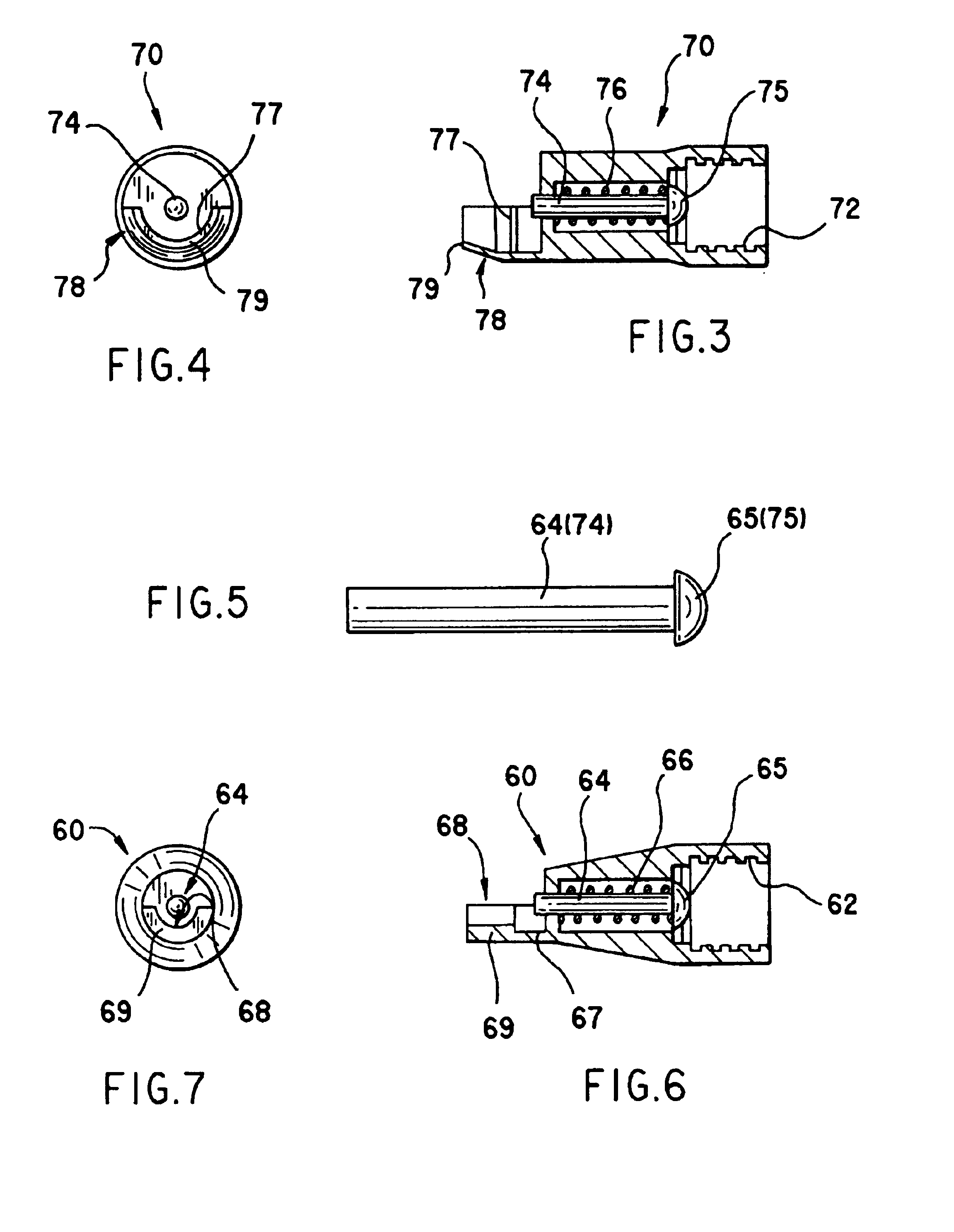
Nozzle for dental composition
InactiveUS20070031779A1Good storage stabilityReduce the number of partsLiquid surface applicatorsAmalgam presses/mixersGlass ionomersResin cement
To separate a catalyst for polymerizing a monomer contained in a liquid or paste dental composition containing at least a monomer, such as a dental resin cement, an autopolymerizing dental resin or a resin-reinforced dental glass ionomer cement, from the liquid or paste dental composition to thereby improve storage stability of the dental composition and reduce number of division of the dental composition, an extrusion nozzle for a dental composition mounted on one end of an extruder for extruding a liquid or paste dental composition containing at least a monomer, the extrusion nozzle contains a catalyst for polymerizing the monomer contained in the dental composition during extrusion, and the catalyst is attached to an inner wall of an extruding channel of the extrusion nozzle.
Owner:GC CORP
Integral gutta percha technique
InactiveUS20060154212A1Reduce leakageEasy to useTeeth fillingTeeth cappingGlass ionomersGutta-percha
An integral, one-piece silanated particle impregnated gutta percha core / cone technique employs a thin layer of a luting agent, such as glass ionomer cement with a machined gutta percha core / cone, precisely matches the preparation, thereby reducing leakage and achieving a hermetic seal. The hermetic seal is further enhanced by a mono-block bond that occurs between the silanated particles in the gutta percha and the appropriate chemical sealant. Optional cryogenic treatment of the gutta percha material changes its molecular weight, making it stiffer and conducive to forming an integral, one piece core / cone, without the need for a separate carrier core to install the tapered gutta percha core / cone within the root canal. Additionally, the tapered body of the core / cone may be reticulated in a slightly three dimensional texturized framework to increase surface area and therefore increase retention. Optional line demarcation indicia are also placed on the core / cone. Additionally, the head of the core / cone can be gripped by a delivery vehicle clasp.
Owner:KOCH KENNETH +2
Integral gutta percha technique
ActiveUS7097455B2Reduce leakageEasy to useImpression capsWheelchairs/patient conveyanceGlass ionomersGutta-percha
An integral, one-piece silanated particle impregnated gutta percha core / cone technique employs a thin layer of a luting agent, such as glass ionomer cement with a machined gutta percha core / cone, precisely matches the preparation, thereby reducing leakage and achieving a hermetic seal. The hermetic seal is further enhanced by a mono-block bond that occurs between the silanated particles in the gutta percha and the appropriate chemical sealant. Optional cryogenic treatment of the gutta percha material changes its molecular weight, making it stiffer and conducive to forming an integral, one piece core / cone, without the need for a separate carrier core to install the tapered gutta percha core / cone within the root canal. Additionally, the tapered body of the core / cone may be reticulated in a slightly three dimensional texturized framework to increase surface area and therefore increase retention. Optional line demarcation indicia are also placed on the core / cone. Additionally, the head of the core / cone can be gripped by a delivery vehicle clasp.
Owner:BATCHING SYST +2
Dental Adhesive Primer Composition
ActiveUS20090299006A1Good storage stabilityBonded firmlyDentistry preparationsMedical preparationsGlass ionomersNatural tooth
The present invention relates to a dental adhesive primer composition for use in dental fields employed to bond dental materials, such as restoration materials, dental crown materials, prosthetic materials, esthetic materials, orthodontic materials, preventive materials, core build-up materials and root canal materials, to ceramics, metals, resins, composite resins, glass ionomer cements, and hard biotissues (enamel or dentin of natural tooth). The present invention also relates to a dental adhesive primer composition including a dental adhesive composition which can be used not only in combination with another adhesive composition but also alone.
Owner:SHOFU INC
An adhesive coating composition for dentistry
InactiveCN101448479AFully curedImprove adhesionImpression capsDentistry preparationsGlass ionomersNatural tooth
The invention relates to an adhesive coating composition for dentistry applied to dentistry field, used to bond dental materials, such as restoration materials, tooth crown materials, prosthesis materials, beautifying materials, rectifying materials, preventing materials, supporter constructing materials or pulp canal materials and so on, onto ceramics, metals, resin, compound resin, glass ionomer cement, hard biological tissues (enamel or dentine of natural teeth) and so on. The invention provides an adhesive coating composition for dentistry including an adhesive composition for dentistry which cannot only be used with another adhesive composition together, but also can be used independently.
Owner:SHOFU INC
Glass ionomer sealed endodontic post
InactiveUS20060234190A1Reduce leakageEasy to useFastening prosthesisTooth crownsGlass ionomersSemi solid
A glass ionomer or resin modified glass ionomer coated blank is combined with glass ionomer or resin modified glass ionomer to create an integral mono-block post. prefabricated glass ionomer or resin modified glass ionomer post (with or without a coated blank) is cemented into the root canal with glass ionomer or resin modified glass ionomer, thereby creating a mono-block post as well as a mono-block core. The glass ionomer or resin modified glass ionomer cement is bonded to the canal wall and also through the bonding of the cement to the post surface of similar material. An alternate methodology involves syringing glass ionomer or resin modified glass ionomer in a malleable, semi-solid state into the post preparation space and a glass ionomer or resin modified glass ionomer coated blank is then inserted into the canal to a distance substantially equal to the depth of the post preparation.
Owner:ENDODONTIC EDUCATIONAL SEMINARS
Method for making dental prosthesis or dental prosthesis base material
InactiveUS20060076698A1Low costGood biocompatibilityDielectric heatingGlass shaping apparatusGlass ionomersMicrowave
A dental prosthesis, such as a crown, a bridge, inlay, onlay, a laminate veneer or an artificial tooth, or a dental prosthesis base material, such as an abutment, an abutment having a post, or a post, is made with a low cost in a short time by using dental glass ionomer cement, which is excellent in cost, mechanical strength and biocompatibility and has fluorine sustained releasability in general, by a method comprising steps of enclosing a mixture of dental glass ionomer cement into a mold in a shape fitting to the dental prosthesis or the dental prosthesis base material to be made, putting the mold into water, irradiating the whole mold with a microwave, and curing the dental glass ionomer cement in a short time, thereby a conventional problem of slow curing reaction in dental glass ionomer cement is solved.
Owner:HAMLIN DAVID ALAN
Dental composition
ActiveUS20120214900A1Improve flexural strengthHigh strengthImpression capsMedical preparationsParticulatesGlass ionomers
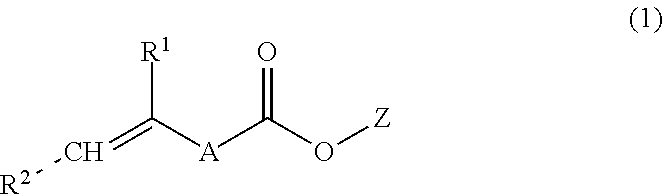
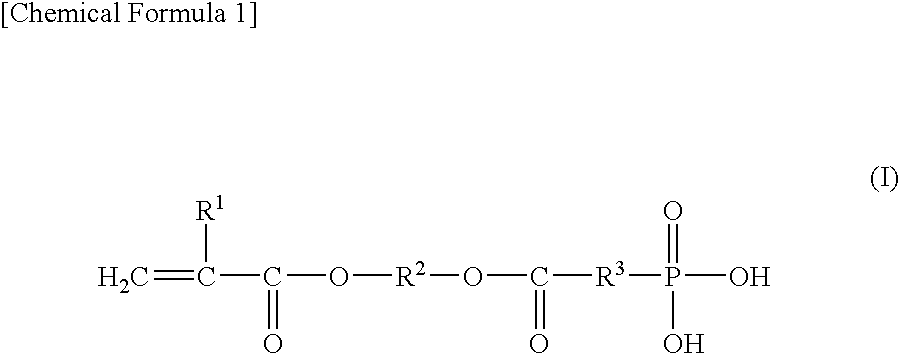
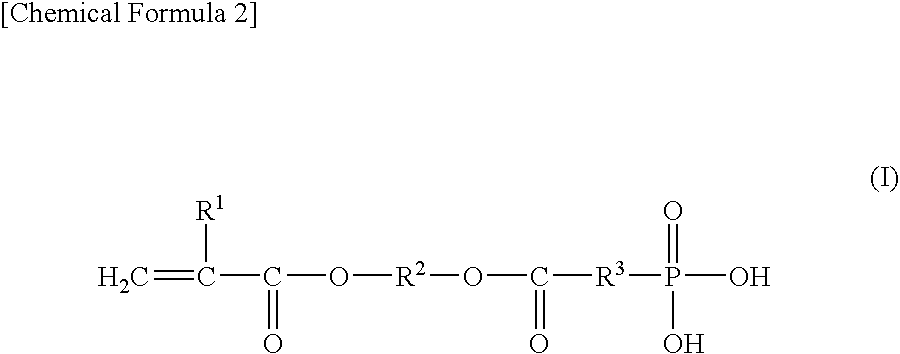
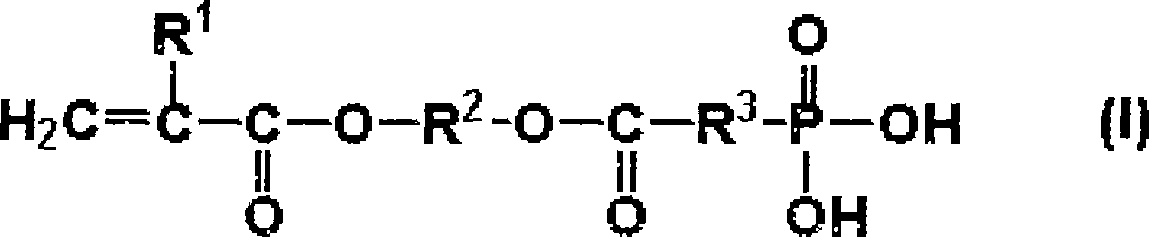
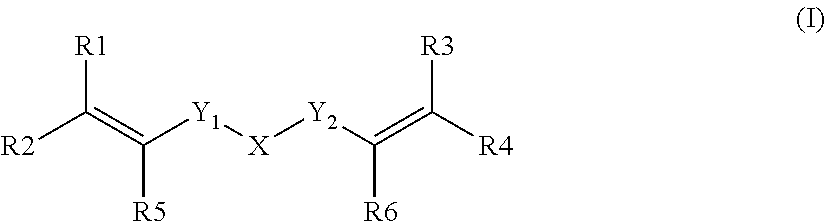
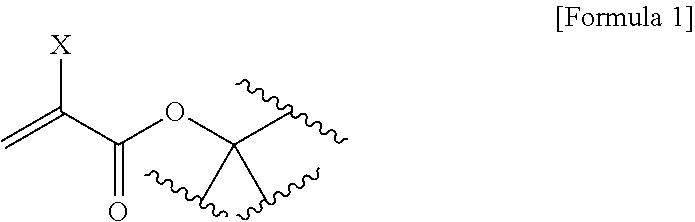
An aqueous dental glass ionomer composition comprising (a) a reactive particulate glass, (b) a linear or branched polymer comprising acidic groups, which is reactive with the particulate glass in a cement reaction, whereby the linear or branched polymer comprising acidic groups has a polymer backbone and optionally pendant groups, (c) optionally dispersed nanoparticles comprising grafted linear or branched polymer chains comprising acidic groups, and having a polymer backbone characterized in that a polymer backbone of the linear or branched polymer of component (b) and / or, if present, the grafted Sinear or branched polymer chains of component (c) are obtainable a process comprising (i) cyclopolymerizing or cyclocopolymerizing one or more compounds of the following formula (I).
Owner:DENTSPLY DETREY GMBH
Hard tissue regeneration material and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20140056948A1Good biocompatibilityHigh strengthBiocideCosmetic preparationsGlass ionomersFiber
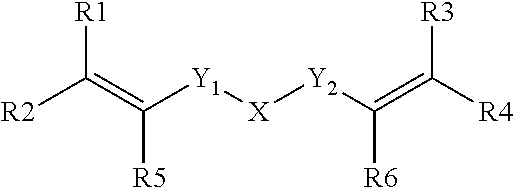
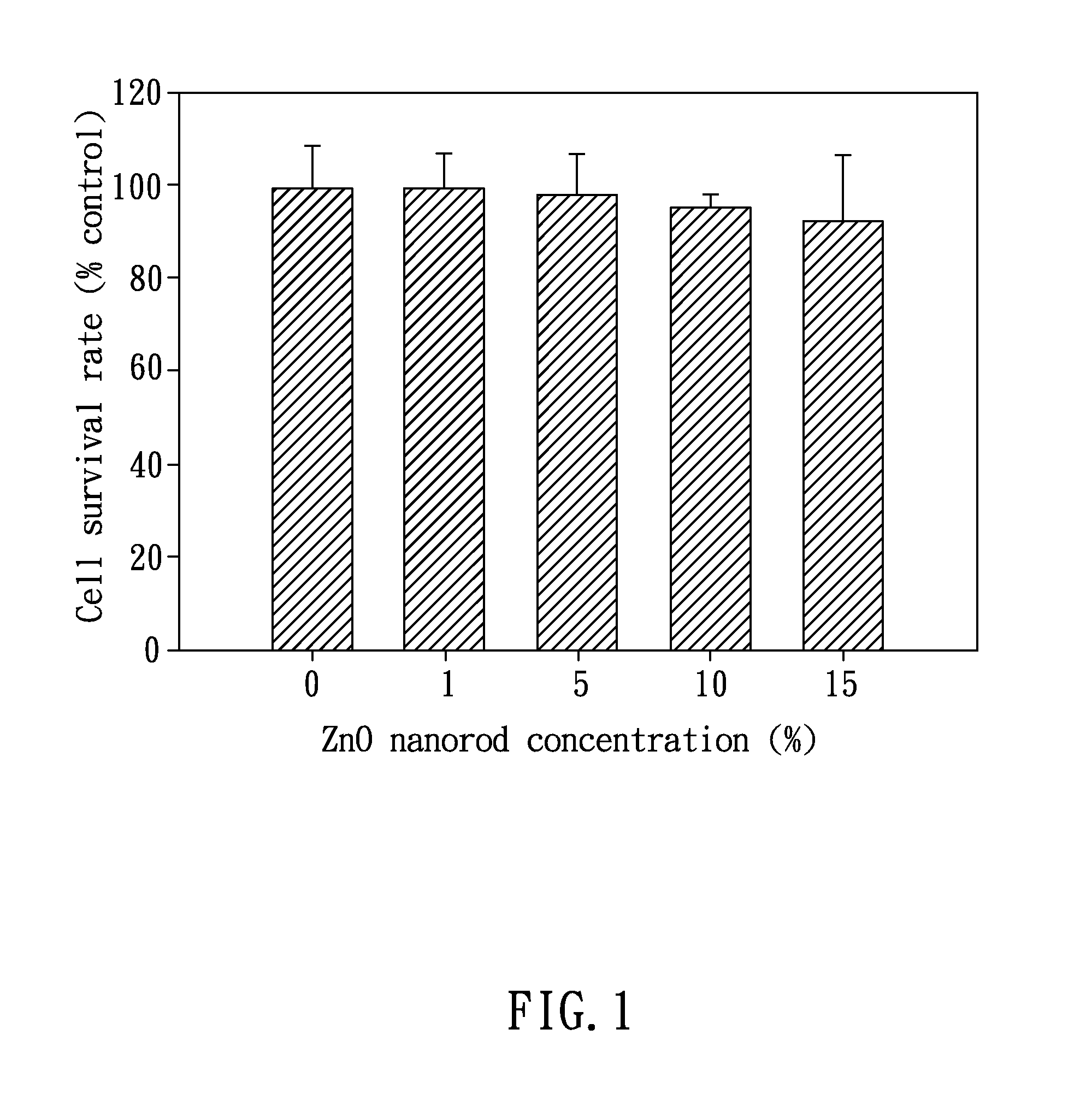
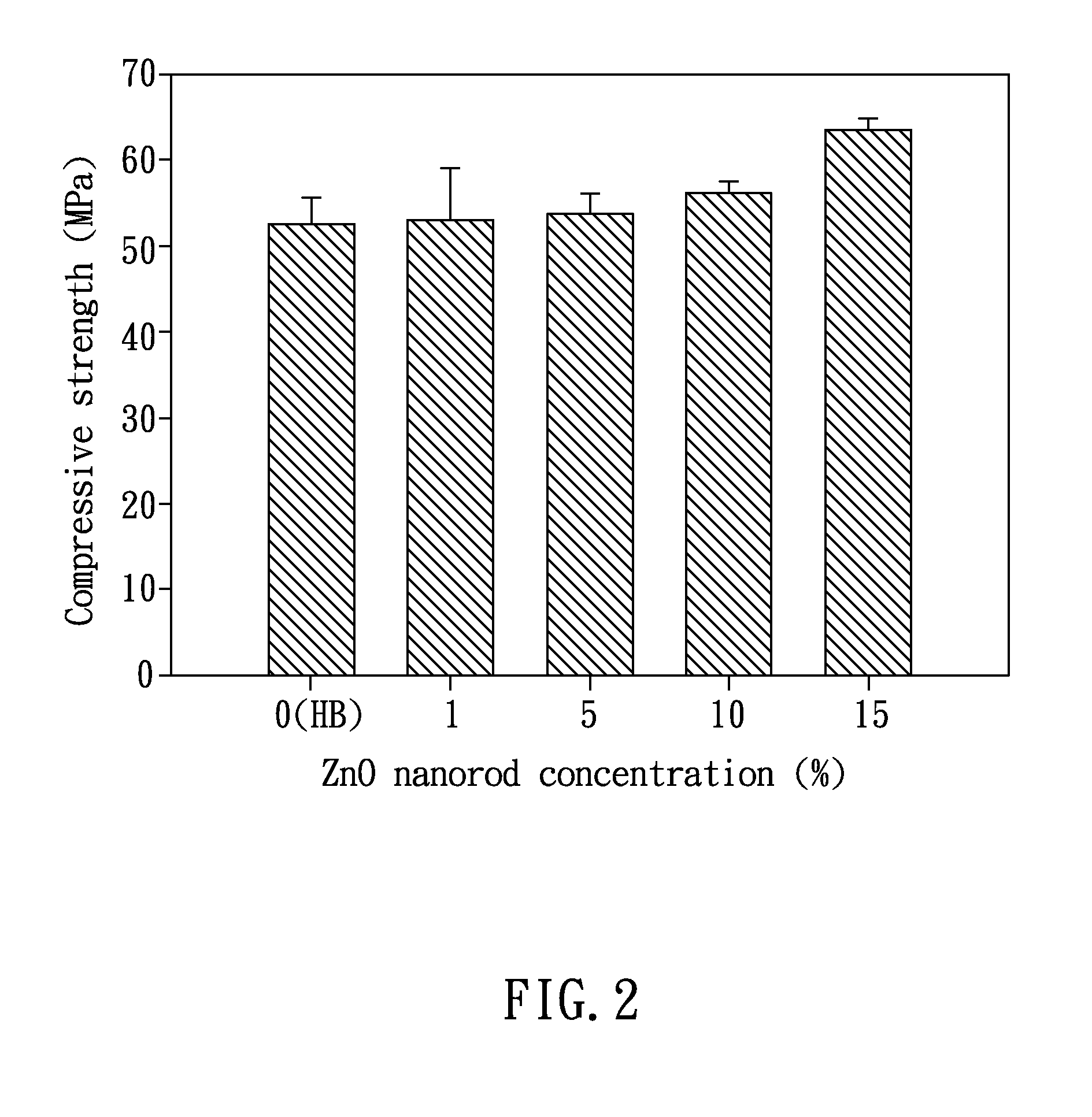
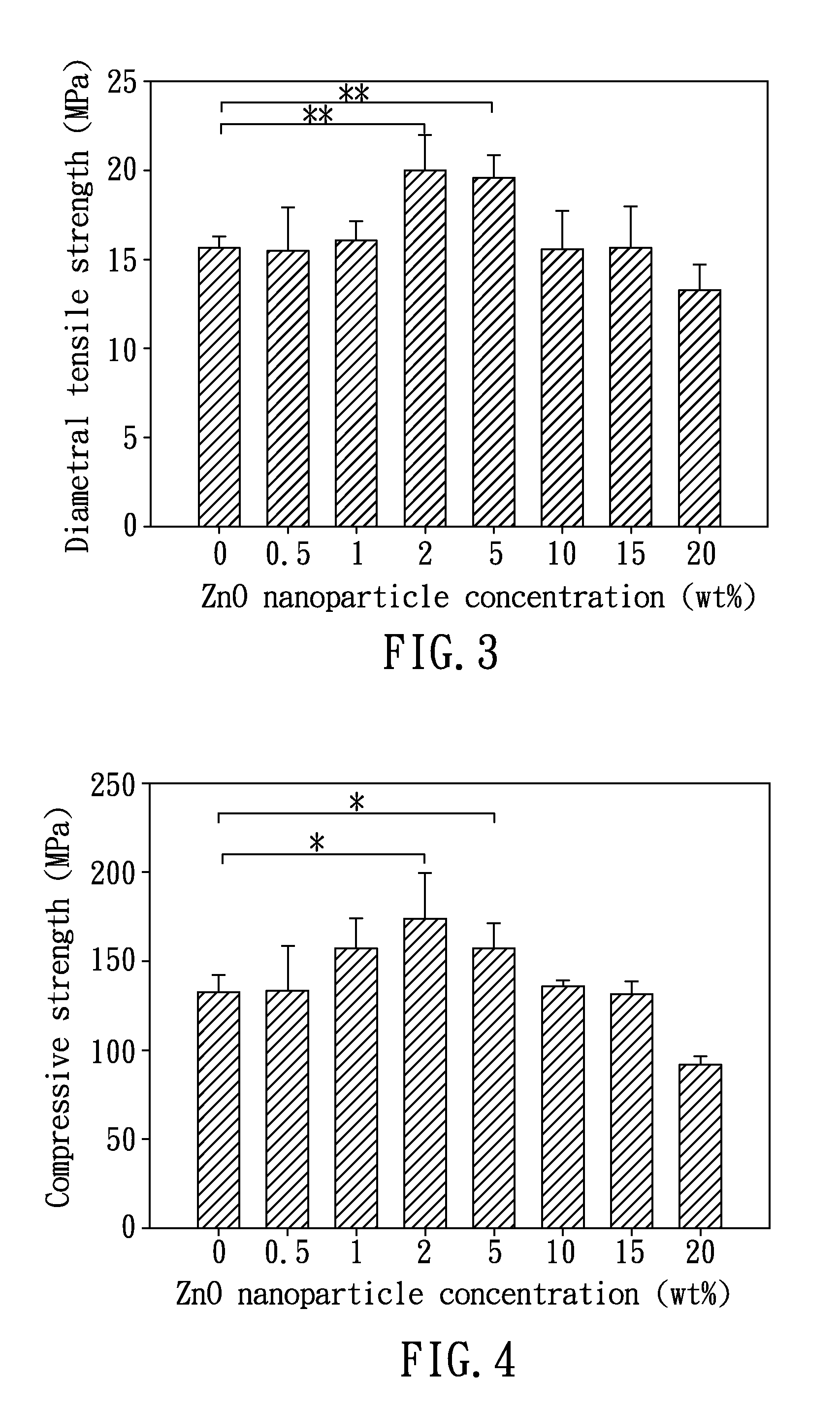
A hard tissue regeneration material and a method for manufacturing the same are disclosed. The hard tissue regeneration material of the present invention comprises: ZnO particles selected from the group consisting of crystallized ZnO particles, crystallized ZnO nanorods, nano-ZnO hollow fibers, and a combination thereof; and at least one selected from the group consisting of polycarboxylate cement, glass ionomer cements, and collagen.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
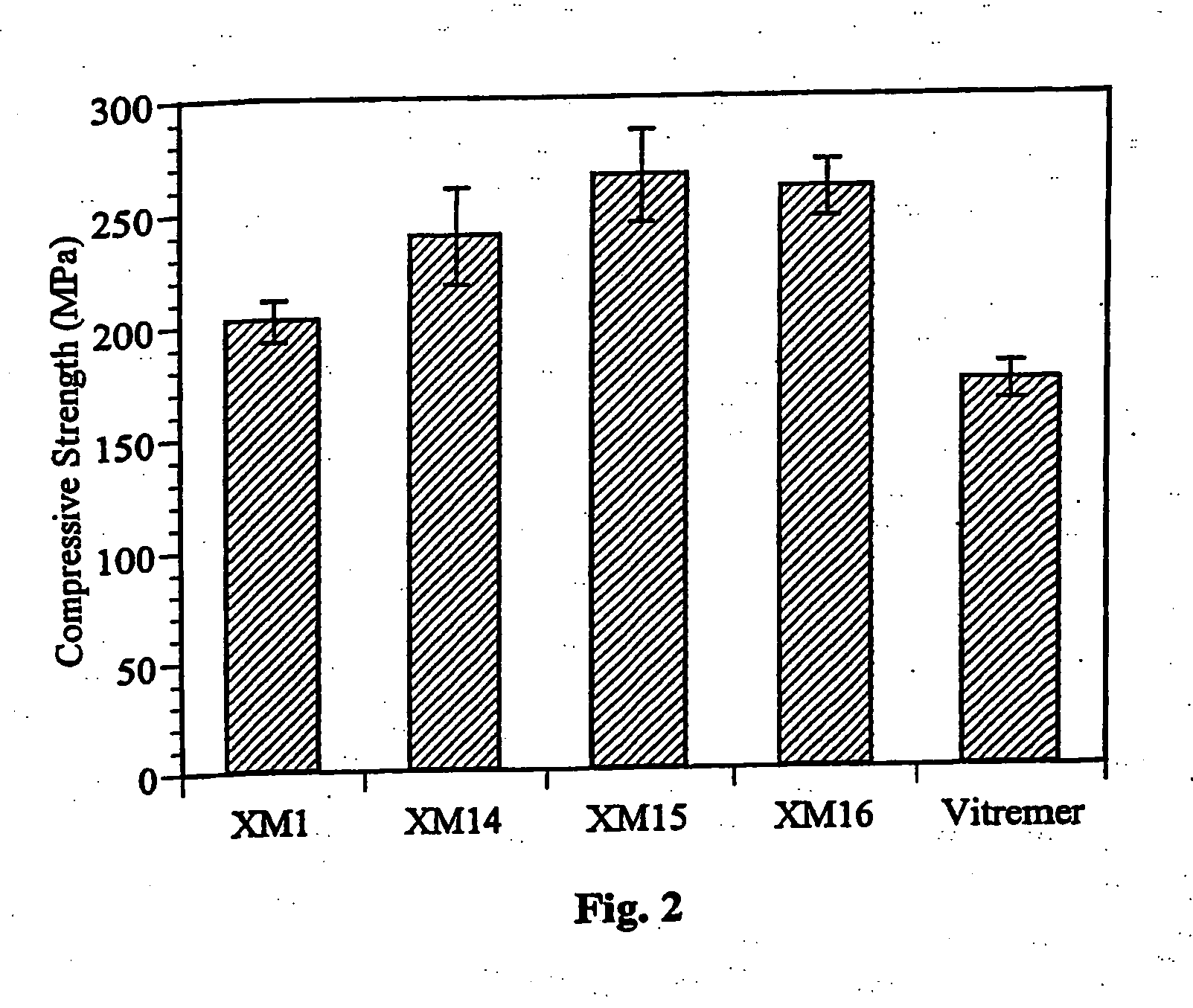
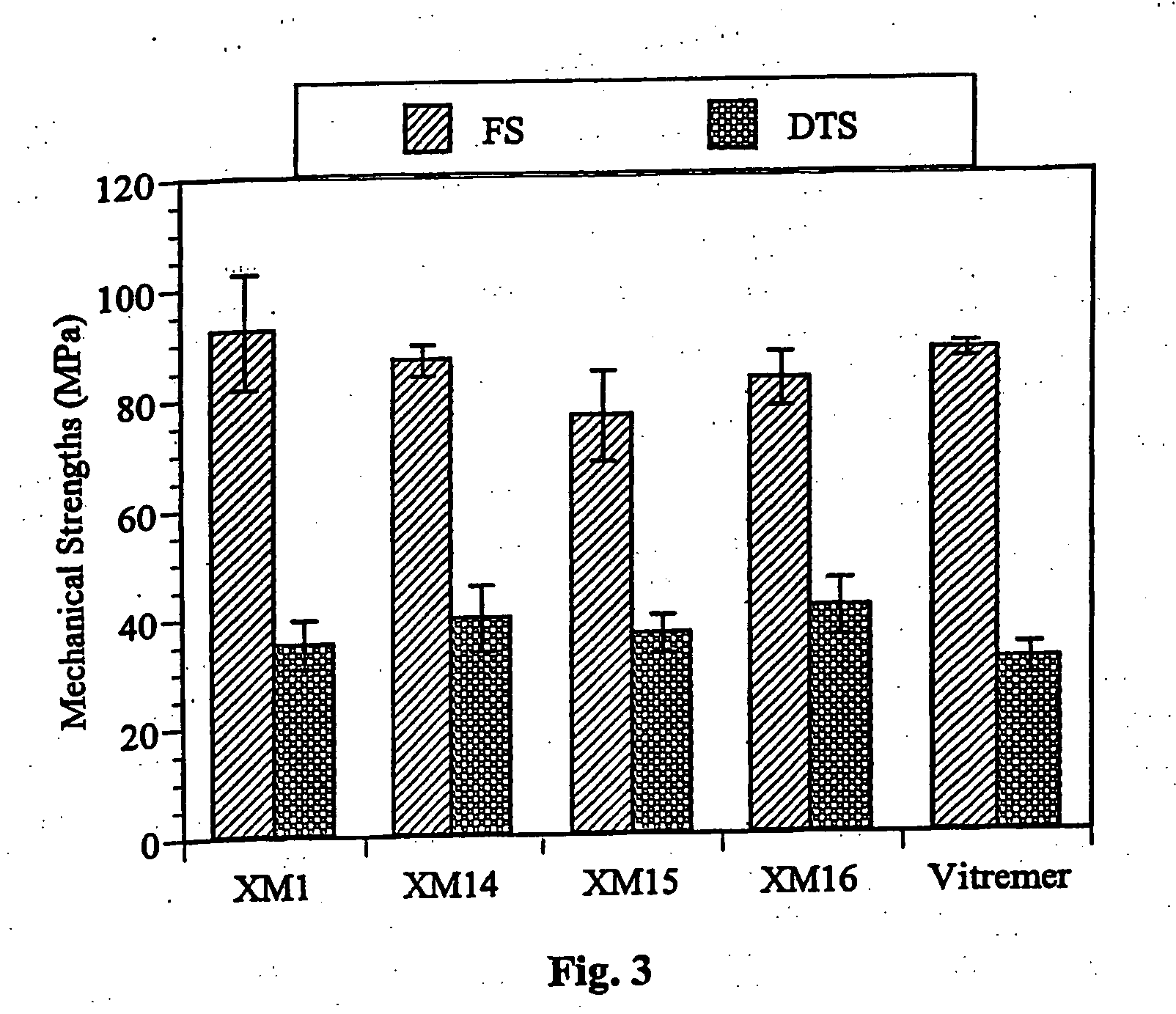
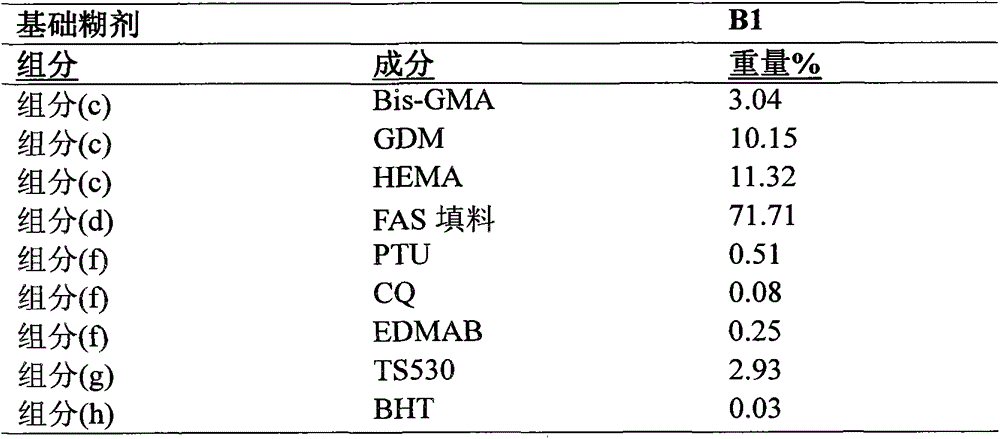
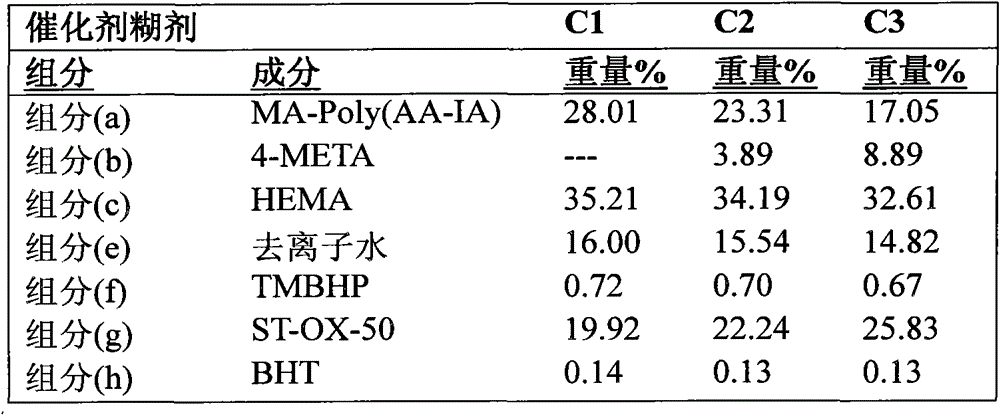
Aqueous dental glass ionomer composition
ActiveUS20180353391A1Improve mechanical propertiesImprove flexural strengthImpression capsDentistry preparationsGlass ionomersPolymer science
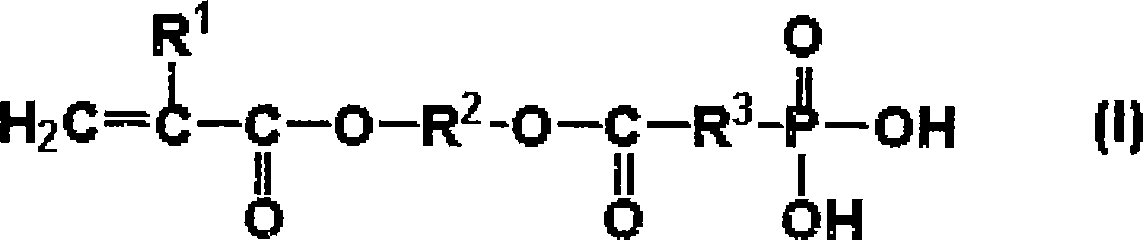
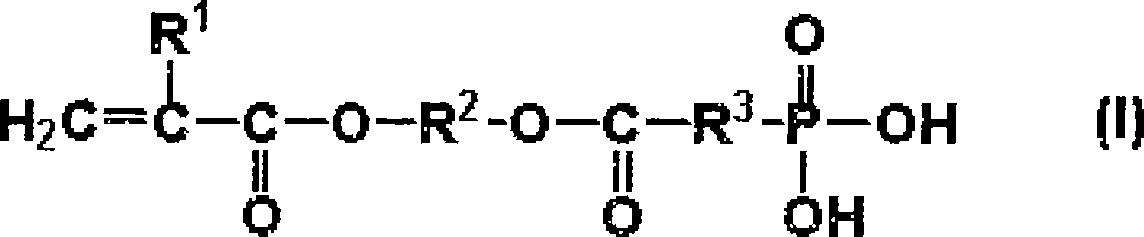
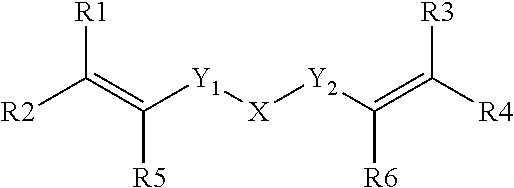
The present invention relates to an aqueous dental glass ionomer composition comprising(A) a reactive particulate glass,(B) a water-soluble, polymerizable polymer comprising acidic groups, which is reactive with the particulate glass in a cement reaction, whereby the polymerizable polymer has a polymer backbone and hydrolysis-stable pendant groups having one or more polymerizable carbon-carbon double bonds, wherein the polymerizable polymer is obtainable by a process comprisinga) a step of copolymerizing a mixture comprising(i) a first copolymerizable monomer comprising at least one optionally protected carboxylic acid group and a first polymerizable organic moiety, and(ii) a second copolymerizable monomer comprising one or more optionally protected primary and / or secondary amino groups and a second polymerizable organic moiety,for obtaining an amino group containing copolymer;b) a step of coupling to the amino group containing copolymer a compound having a polymerizable moiety and a functional group reactive with an amino group of repeating units derived from the second copolymerizable monomer in the amino group containing copolymer obtained in the first step, wherein the optionally protected amino group is deprotected, so that polymerizable pendant groups are linked to the backbone by hydrolysis-stable linking groups,and, optionally, a step of deprotecting the protected carboxylic acid group after step a) or step b), for obtaining a polymerizable polymer;(C) a hydrolysis-stable, water-soluble monomer having one polymerizable double bond and optionally a carboxylic acid group, said monomer having a molecular weight of at most 200 Da;(D) a polymerization initiator system; and(E) a polymerizable hydrolysis-stable crosslinker having at least two polymerizable carbon-carbon double bonds.
Owner:DENTSPLY SIRONA INC
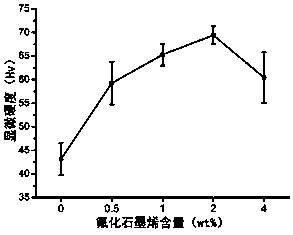
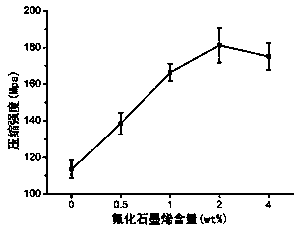
Novel dental glass ionomer cement/fluorinated graphene composite material
InactiveCN108245433AHigh mechanical strengthImprove wear resistanceImpression capsDentistry preparationsGlass ionomersSolubility
The invention discloses a novel dental glass ionomer cement / fluorinated graphene composite material. Traditional commonly-used dental glass ionomer cement powder and fluorinated graphene are used as raw materials, and uniformly mixed by mechanical ultrasonic blending, the traditional commonly-used dental glass ionomer cement powder and fluorinated graphene are uniformly dispersed in absolute ethanol in a certain proportion, the dispersion is ultrasonically promoted, uniform grinding is performed, and the ethanol is completely evaporated to obtain a new dental material, namely glass ionomer cement and fluorinated graphene mixed powder. The novel dental glass ionomer cement / fluorinated graphene composite material has the advantages of simple preparation method, simple equipment, low price and easy mass promotion. The novel dental material has high microhardness, high compressive strength, high abrasion resistance, and high antibacterial property, and does not affect the color, fluoride ion release property and solubility of the material, the quality of filling materials can be greatly improved, and the clinical application range of glass ionomer cement is expanded.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Dental glass-ionomer cement composition and method of preparing the same
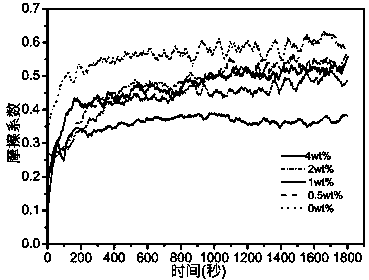
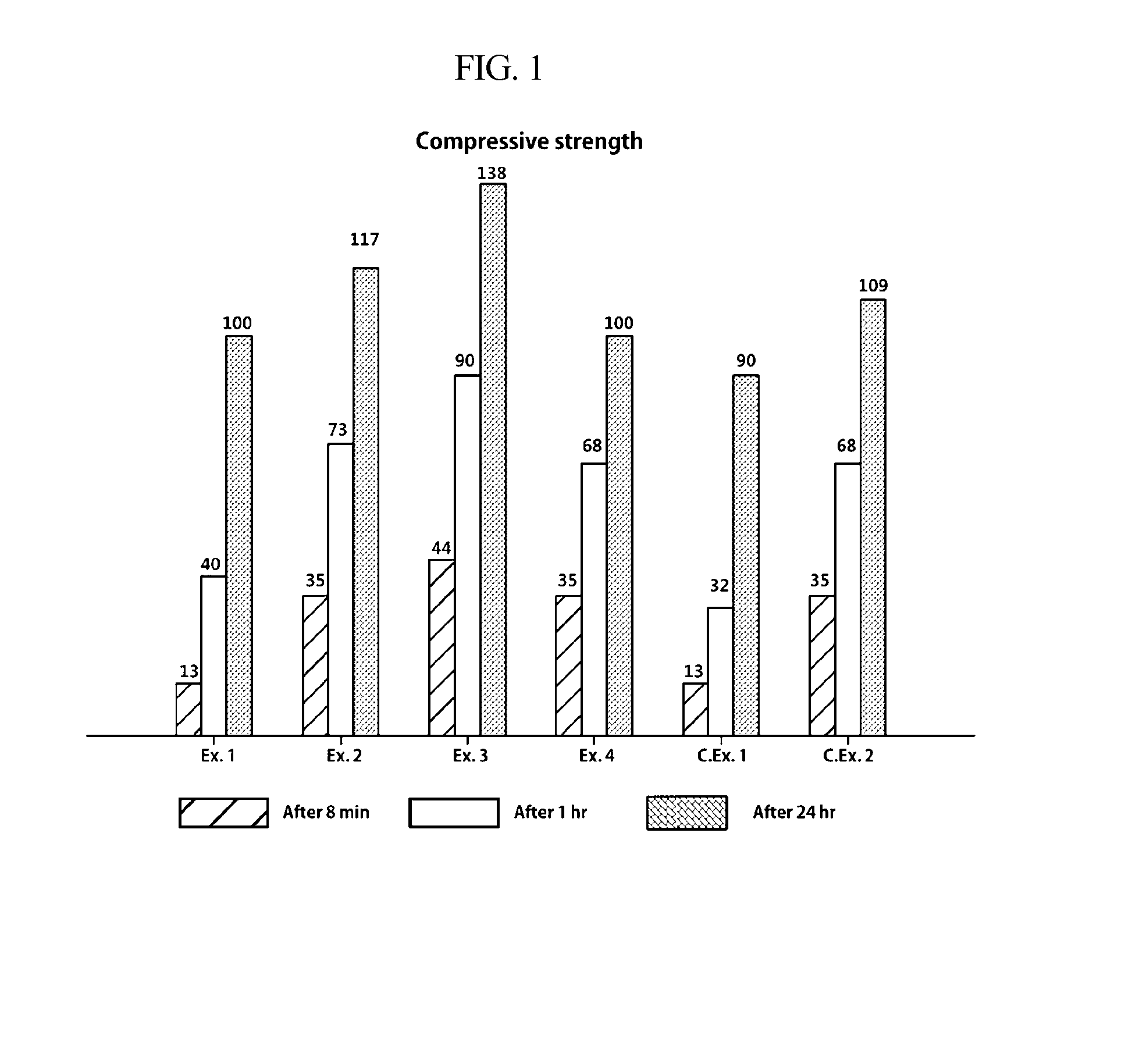
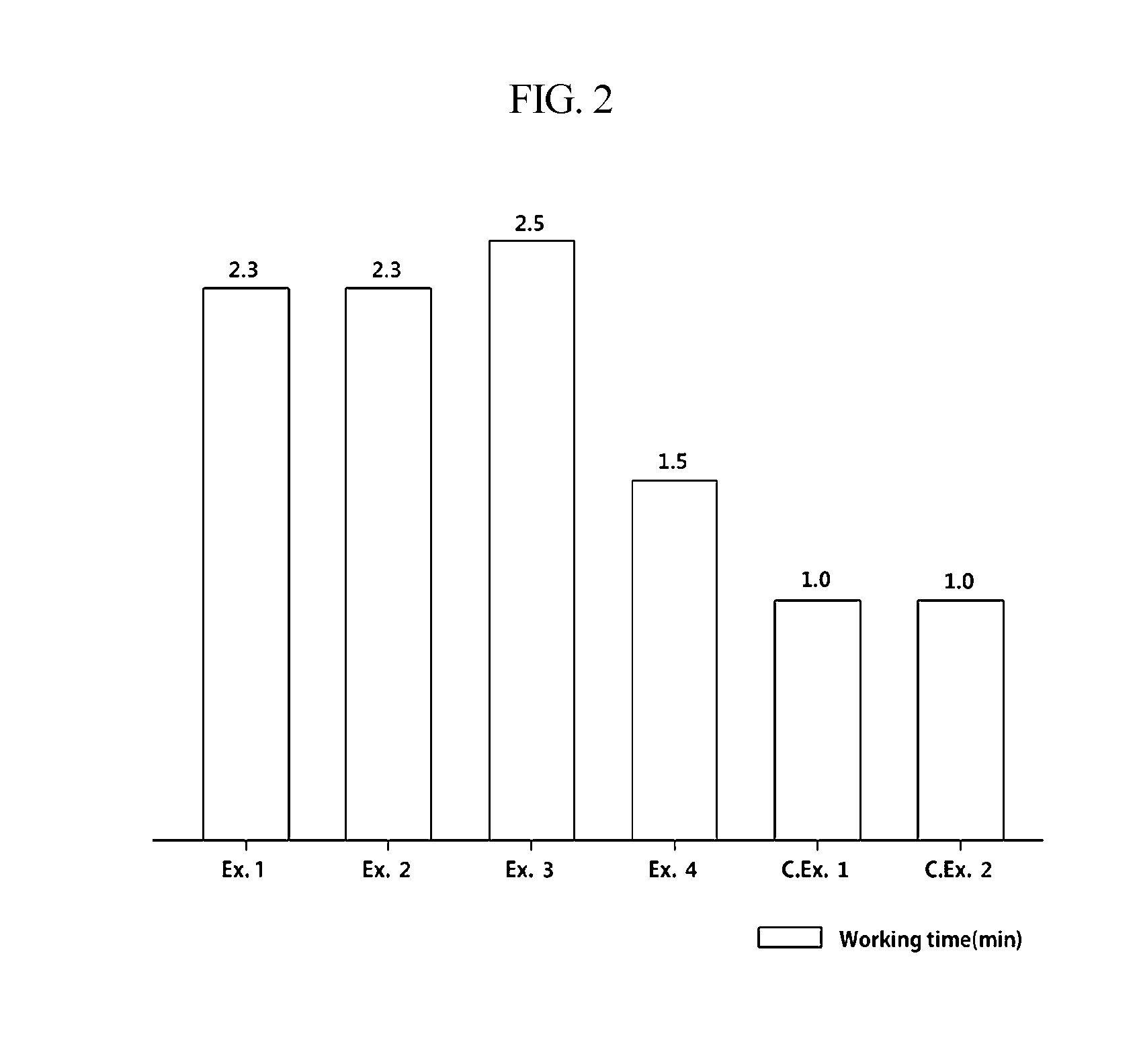
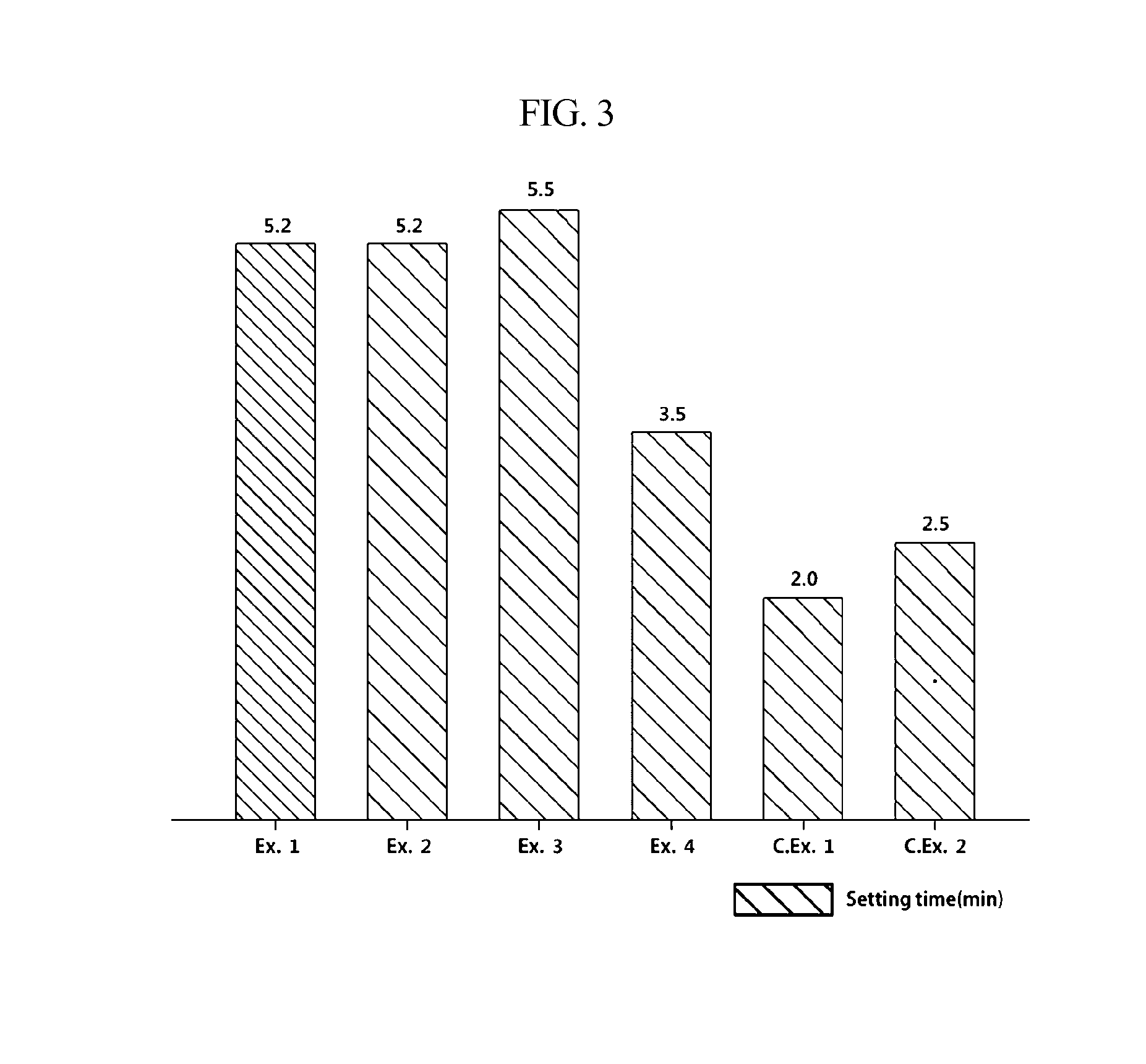
ActiveUS20160152795A1Increased initial strengthSufficient working timeImpression capsDentistry preparationsGlass ionomersCarboxylic acid
Disclosed is a dental glass-ionomer cement composition, which includes polycarboxylic acid, water, and a glass powder including a metal component that is able to form an ionic bond with a carboxyl group of polycarboxylic acid in the presence of water and having a polymer material that is applied on at least a portion of the surface of the glass powder. The dental glass-ionomer cement composition can guarantee sufficient working time and can exhibit increased initial strength.
Owner:SPIDENT
Glass powder of water-based glass ionomer cement and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102976618AUniform particle size distributionImprove retentionImpression capsDentistry preparationsGlass ionomersWater based
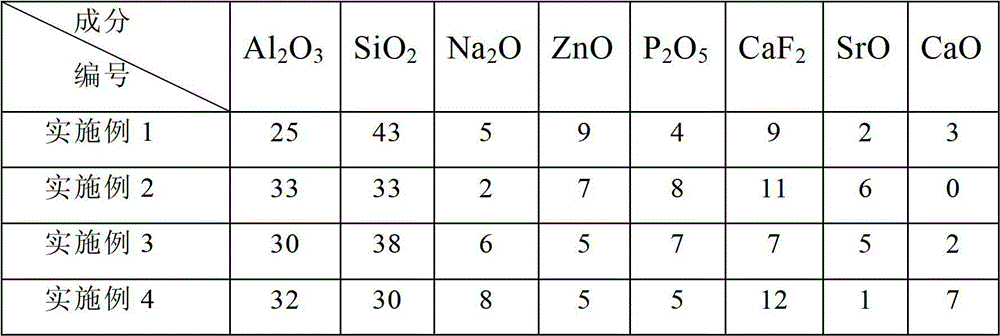
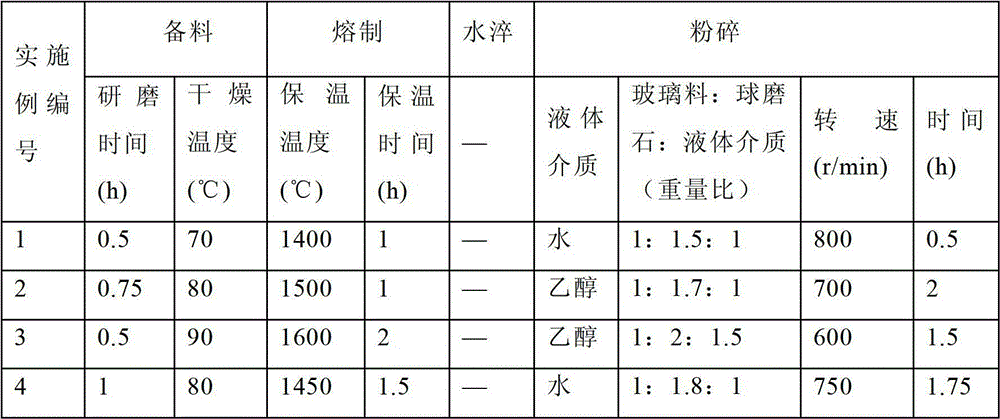
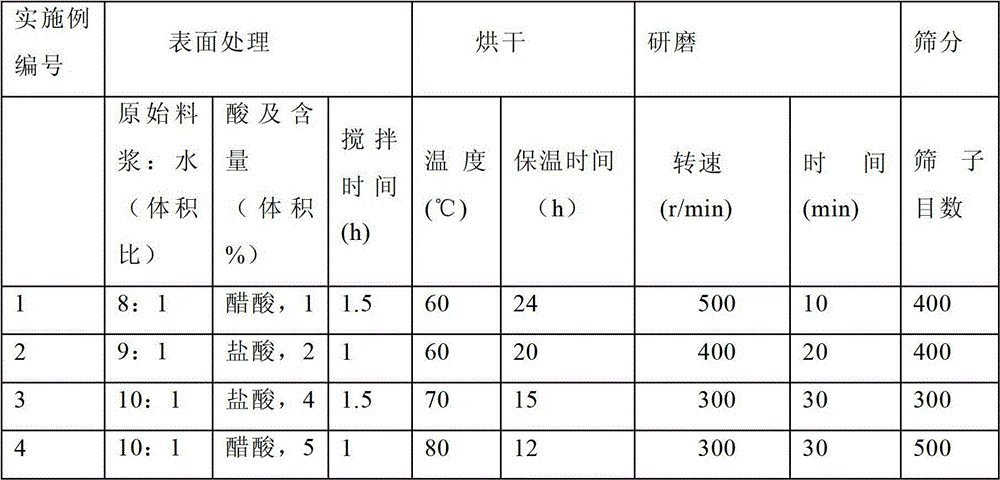
The invention discloses glass powder of water-based glass ionomer cement and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of inorganic non-metal materials. The powder is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by mass: 25-35% of Al2O3, 30-45% of SiO2, 5-8% of MO, 2-8% of Na2O, 5-10% of ZnO, 3-9% of P2O5 and 5-15% of CaF2, wherein MO is one of SrO and CaO or a mixture of the two. The preparation method of the powder sequentially comprises the following steps: preparing the raw materials, fusing, quenching with water, pulverizing, performing surface treatment, drying, grinding and screening. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the advantages of low cost, stable product quality, fine mechanical comprehensive properties, X ray rejection, continuous fluorion release and uniform particle size distribution, and is suitable for industrial mass production.
Owner:ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY & MATERIALS CO LTD +1
Filler for dental glass ionomer cement and method for manufacturing the same
Provided is a filler for dental glass ionomer cements, the filler to a surface of which a compound(s) having a carboxyl group(s) is / are bound via a silicon atom, for the purpose of providing: a filler suitable for dental glass ionomer cements that can provide a hardened cement having a high strength by being mixed with a dental glass ionomer cement composition, the filler that can be easily manufactured from a general inorganic powder as a raw material; and a manufacturing method of the filler for dental glass ionomer cements. The manufacturing method includes binding a carboxylic acid having an unsaturated double bond(s) exclusive of a (meth)acrylate compound to an inorganic powder whose surface is treated with a silane coupling agent having an unsaturated double bond(s).
Owner:GC CORP
Single-component photocuring composite with fluoride ion release property for dental restoration and application of composite
ActiveCN106726623AThickenEasy to useImpression capsDentistry preparationsGlass ionomersDental Adhesives
The invention discloses a single-component photocuring composite with the fluoride ion release property for dental restoration and application of the composite. The raw materials used for preparing the single-component photocuring composite with the fluoride ion release property for dental restoration comprise water soluble or at least partially water soluble acid molecule structure-containing polymeric resin monomers or oligomer or a mixture thereof, glass ionomer cement filler with the fluoride ion release property and a photocuring polymerization initiating system. The photocuring composite is the single-component photocuring composite, use is convenient, the fluoride ion release property is achieved, and meanwhile the mechanical and physical properties are achieved; the composite can be used as gasket materials under dental adhesives and other dental restoration materials, pit and fissure sealing materials on surfaces of teeth, tooth filling repair / restoration materials, post-core composition materials for dental crown restoration, root canal orifice sealing materials and photocuring orthodontic cement bonding materials and used for other dental treatment and restoration application.
Owner:日照沪鸽生物材料有限公司
Dental composition
ActiveUS20150297467A1Improve flexural strengthHigh strengthImpression capsDentistry preparationsParticulatesGlass ionomers
An aqueous dental glass ionomer composition comprising (a) a reactive particulate glass, and (b) a linear or branched polymer comprising acidic groups, which is reactive with the particulate glass in a cement reaction, whereby the linear or branched polymer comprising acidic groups has a polymer backbone and optionally pendant side chains, (c) optionally dispersed nanoparticles, and (d) optionally a low molecular compound, characterized in that the glass ionomer composition comprises—S.sub.xH groups, wherein x is an integer of from 1 to 6, which crosslink the particulate glass and / or the linear polycarboxylic acid and / or the optional dispersed nanoparticles and / or the optional low molecular compound.
Owner:DENTSPLY SIRONA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com