Dental resin modified glass-ionomer composition
A technology of acidic polymer and composition, applied in dentistry, dental preparation, dental prosthesis, etc., can solve the problem of low bonding strength of tooth structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
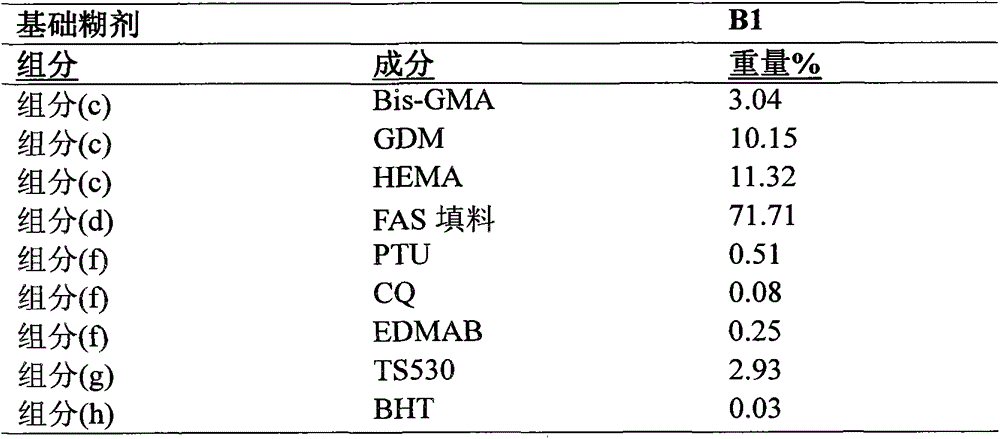
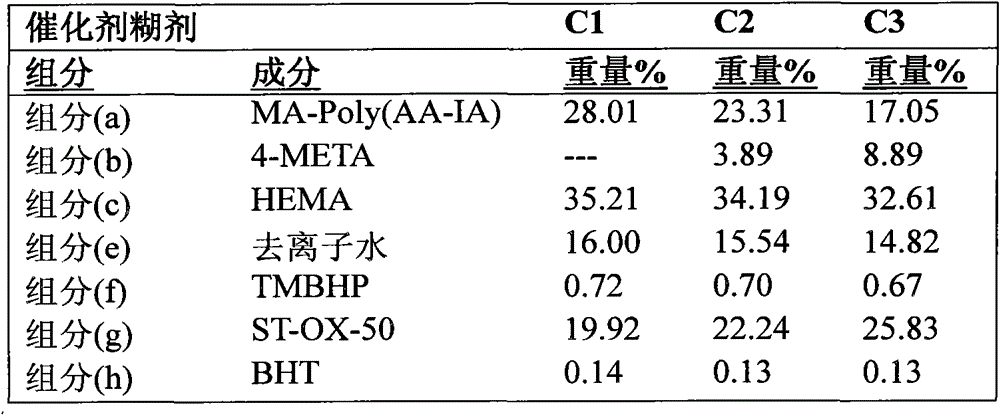
[0069] Comparative Example 1 comprising Base Paste (B1) and Catalyst Paste (C1) was prepared for comparison purposes and represents the prior art. The catalyst paste (C1) contains only the acidic polymer (component (a)) and does not contain any acidic polymerizable monomer (component (b)).
[0070] When the base paste (B1) was mixed with the catalyst paste (C1) through a double-barrel syringe equipped with a static mixer, the mixed material gelled after 1'55" (1 minute 55 seconds) and "Post hardening (or setting). The cured composition of Comparative Example 1 had a compressive strength of 120.0±9.5 MPa, a shear bond strength of 0.0±0.0 MPa to the dentin matrix, and a shear bond strength of 0.0±0.0 MPa to the enamel. It was not uncommon for each of the 6 samples tested in the comparative test to fail to obtain measurable shear bond strength. For low shear bond strength samples (eg < 2 MPa), the shear bond test method used here may be sensitive to the pressure introduced duri...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Base paste (B1) and catalyst paste (C2) make up the composition of Example 2. The catalyst paste (C2) contained 3.89% by weight of an acidic polymerizable monomer (component (b)) in addition to the acidic polymer (component (a)). When the base paste (B1) was mixed with the catalyst paste (C2) through a double-barrel syringe equipped with a static mixer, the mixed material gelled after 2'05" and hardened (or set) after 4'10". ). The cured composition of Example 2 had a compressive strength of 128.0±11.0 MPa, a shear bond strength of 9.4±4.3 MPa to the dentin matrix and a shear bond strength of 6.6±5.0 MPa to the enamel.
Embodiment 3
[0074] Base paste (B1) and catalyst (C3) make up the composition of Example 3. The catalyst paste (C3) contained 8.89% by weight of acidic polymerizable monomer (component (b)) in addition to the acidic polymer (component (a)). When the base paste (B1) was mixed with the catalyst paste (C3) through a double-barrel syringe equipped with a static mixer, the mixed material gelled after 2'12" and hardened (or set) after 4'18". ). The cured composition of Example 3 had a compressive strength of 123.6±13.9 MPa, a shear bond strength of 16.5±3.1 MPa to the dentin matrix, and a shear bond strength of 15.7±6.0 MPa to the enamel.
[0075]Examples 1-3 above illustrate the benefits of dental RMGI compositions of the present invention comprising both an acidic polymer and an acidic polymerizable monomer, providing significantly increased adhesion to tooth structures over the prior art. In particular, the combination of acidic polymer and acidic polymerizable monomer provides comparable c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com