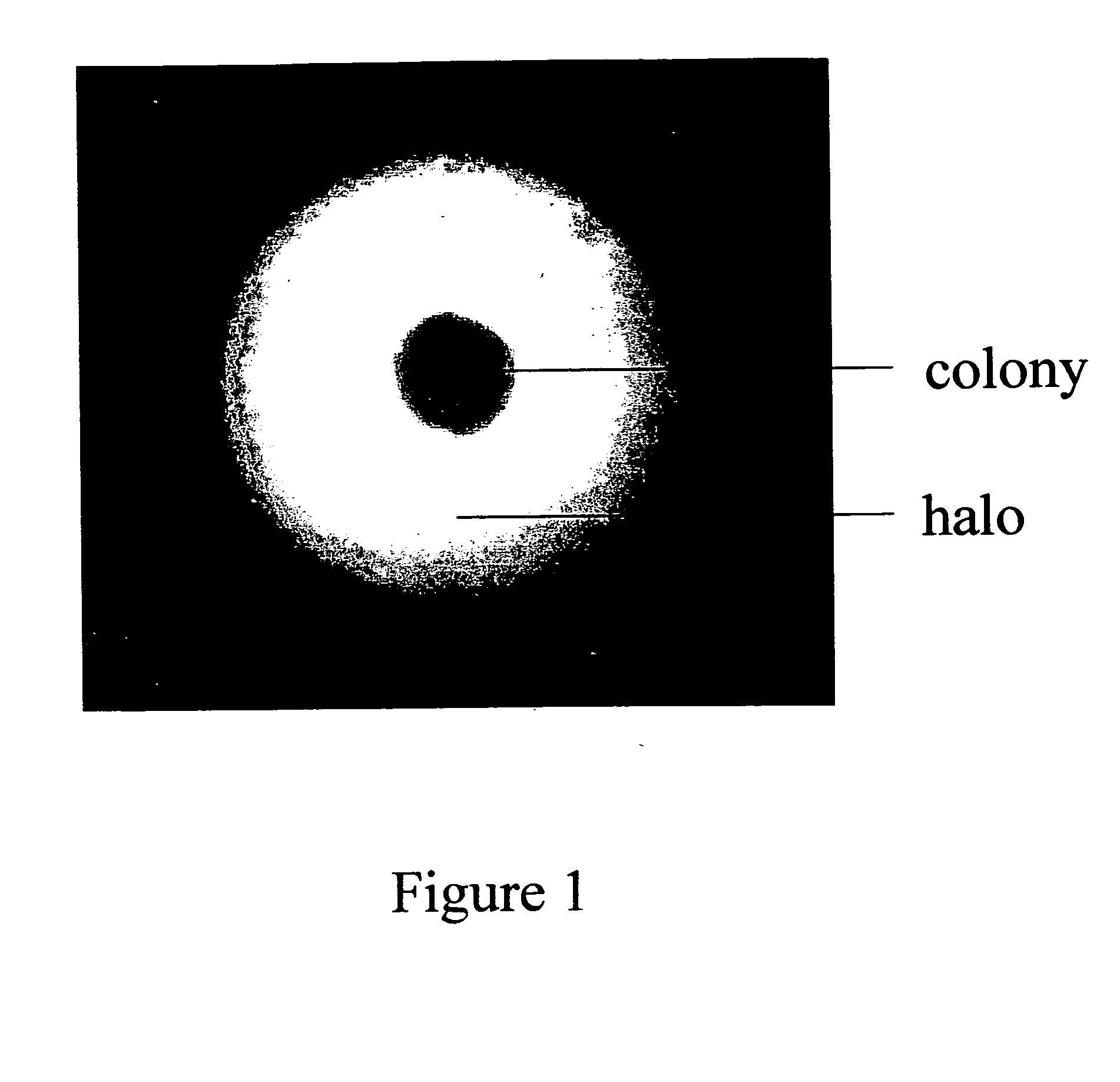
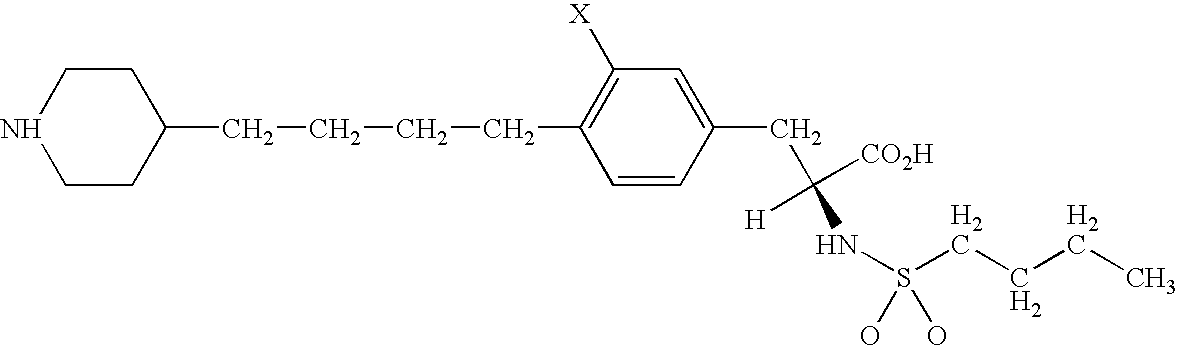
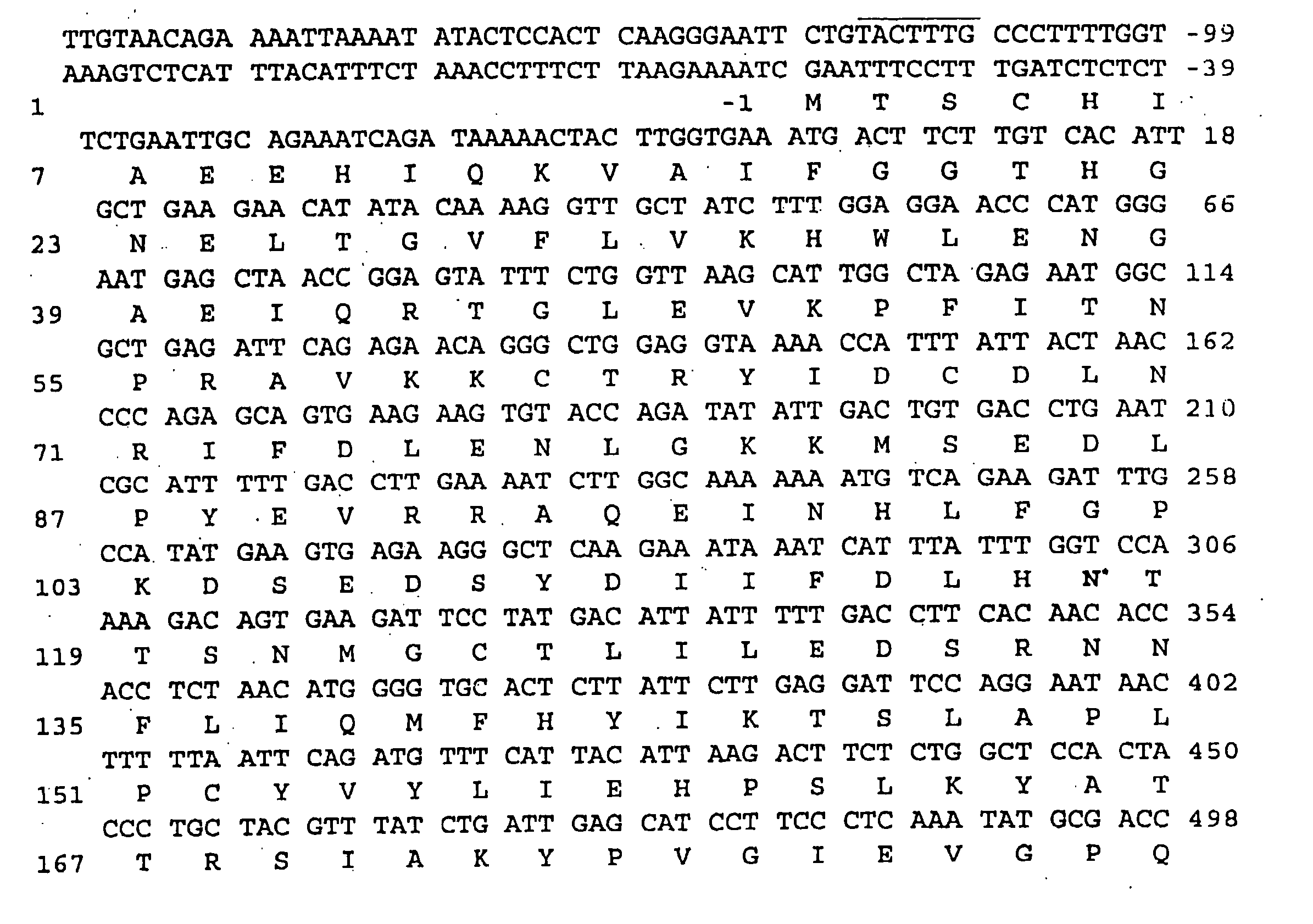
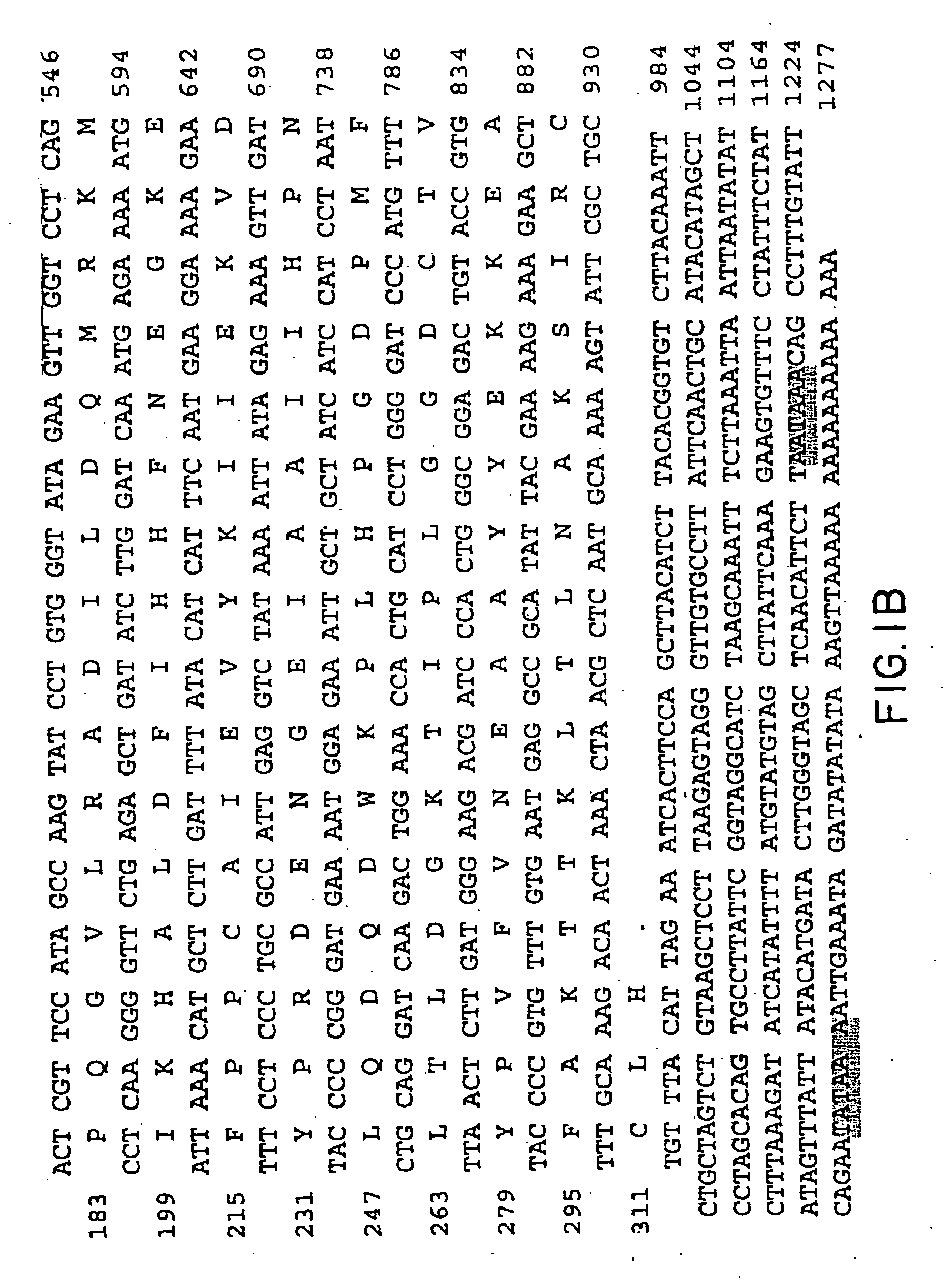
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
41 results about "Genetic screening method" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
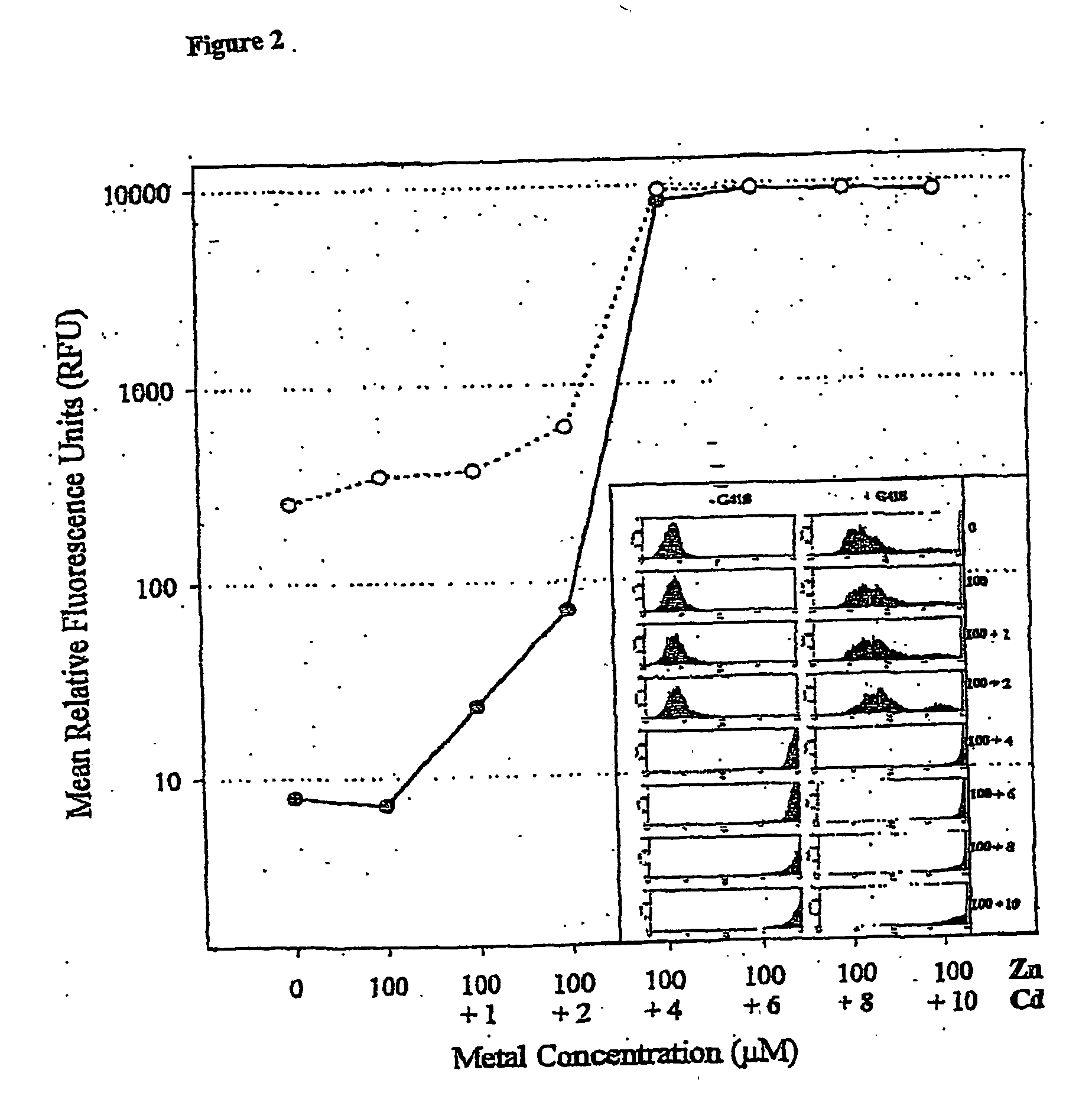
Rapid way to obtain high expression clones of mammalian cells using a methylcellulose and immunoprecipitation screening method
InactiveUS20050118652A1High throughput screeningImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsPeptide preparation methodsHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsScreening method
The invention provides a genetic screening method for identifying a transfected cell expressing the polypeptide of interest. The methods allows for high throughput screening of recombinant cells for elevated levels of expression of the polypeptide of interest. The invention also provides capture media, formulations and methods of making and using thereof.
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
Association of TSPYL polymorphisms with SIDDT syndrome
InactiveUS20050158754A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesScreening methodTestis specific
The identification of a novel mutation in the testis specific Y-like gene and association of the mutation with SIDDT syndrome are disclosed. Methods for diagnosing SIDDT syndrome are disclosed. Methods for identifying compounds for use in the diagnosis and treatment of disorders associated with mutation in the TSPYL gene are also disclosed. The invention therefore provides nucleic acid sequences, genes, polypeptides, antibodies, vectors containing the gene, host cells transformed with vectors containing the gene, animal models for the disease, methods for expressing the polypeptide, genetic screening methods and kits, diagnostic methods and kits.
Owner:THE CLINIC FOR SPECIAL CHILDREN
Aspartoacylase gene, protein, and methods of screening for mutations associated with canavan disease
Canavan disease, an autosomal recessive leukodystrophy, is caused by deficiency of aspartoacylase and accumulation of N-acetylaspartic acid in brain. Human aspartoacylase (ASP) cDNA spanning 1,435 bp has been cloned and expressed in E. coli. A base change, a854>c, has been found in 85% of the 34 Canavan alleles tested so far, which results in a missense glu285>ala mutation that is predicted to be part of the catalytic domain of aspartoacylase. The invention therefore provides nucleic acid sequences, genes, polypeptides, antibodies, vectors containing the gene, host cells transformed with vectors containing the gene, animal models for the disease, methods for expressing the polypeptide, genetic screening methods and kits, diagnostic methods and kits, methods of treating Canavan disease and methods of genetic therapy for the disease.
Owner:MIAMI CHILDRENS HOSPITAL RES INST
Single cell classification method, gene screening method and device thereof
InactiveUS20140206006A1Improve accuracyReduce stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsData setClassification methods
Provided are a single cell classification method, a gene screening method and a device for implementing the method. In that, the single cell classification method includes the following steps: sequencing the whole genomes of a plurality of single cell samples from the same group, respectively, so as to obtain reads from each single cell sample; aligning the reads from each single cell sample to the sequence of a reference genome, respectively, and performing data filtering on said reads; on the basis of the filtered reads, determining a consistent genotype of each single cell sample, in which consistent genotypes of all the single cell samples constitute an SNP dataset of said group; aimed at said each single cell, on the basis of the SNP dataset of said group, determining a corresponding genotype for each cell at a site corresponding to a position in an SNP dataset of the reference genome; and selecting an SNP site associated with cell mutation, and on the basis of the genotype of said single cell at the site, classifying said single cell.
Owner:BGI SHENZHEN CO LTD +1
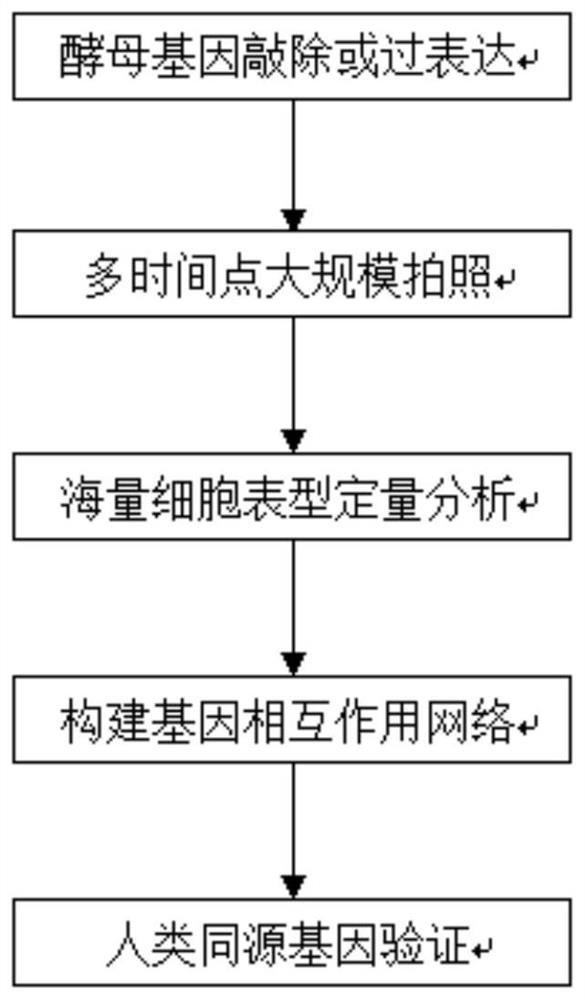
A high-throughput functional gene screening method and system for cell phenotypic image quantitative analysis
ActiveCN109815870AImprove accuracyImprove screening efficiencyImage analysisMaterial analysis by optical meansScreening methodFluorescence microscope
The invention discloses a high-throughput functional gene screening method and system for cell phenotypic image quantitative analysis, and belongs to the technical field of gene screening. The methodcomprises the steps of using a full-automatic fluorescence microscope to shoot a cell image of the phenotype to be screened and a cell image without the phenotype to be screened; respectively converting the images into a to-be-screened phenotype and a black-white binary image without the to-be-screened phenotype; then segmenting into an image containing a single phenotypic cell to be screened andan image containing a single phenotypic cell without being screened; taking the corresponding part of the image containing the single to-be-screened phenotypic cell in the cell image of the to-be-screened phenotypic cell as a positive training set, and taking the corresponding part of the image containing the single to-be-screened phenotypic cell in the cell image of the to-be-screened phenotypiccell as a negative training set to obtain a final model capable of identifying the cell phenotypic; and carrying out final model identification on the image of the knockout or overexpression cell of the to-be-screened gene to obtain the relevance between the to-be-screened gene and the phenotype. The method improves the screening efficiency and accuracy.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
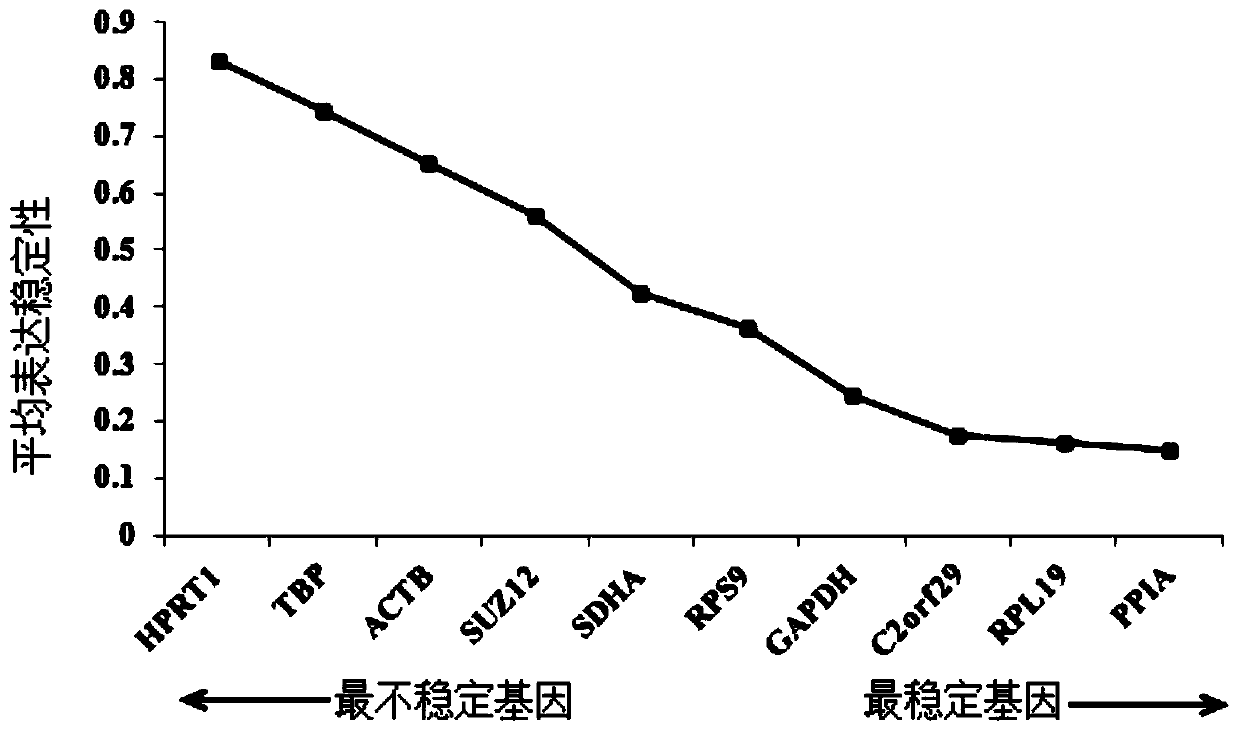
Reference gene screening method for stable expression of suaeda salsa under salt stress
ActiveCN110157776AImprove stabilityImprove reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationATPaseReference genes
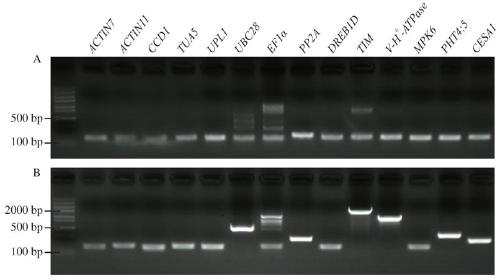
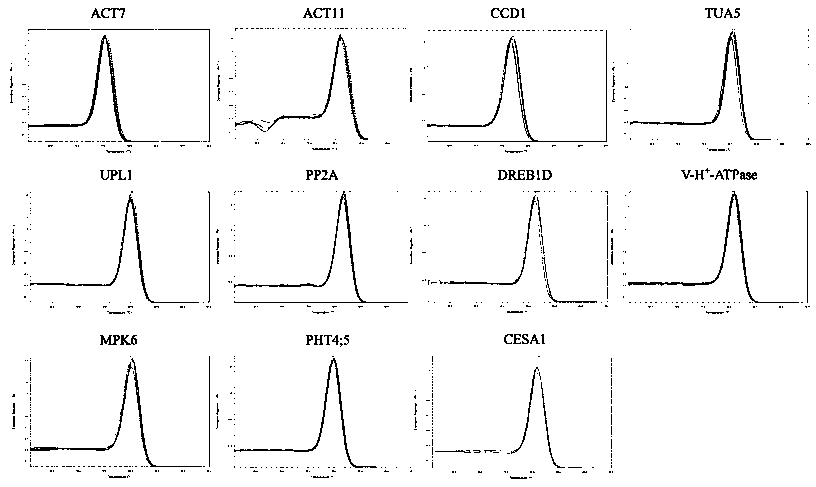
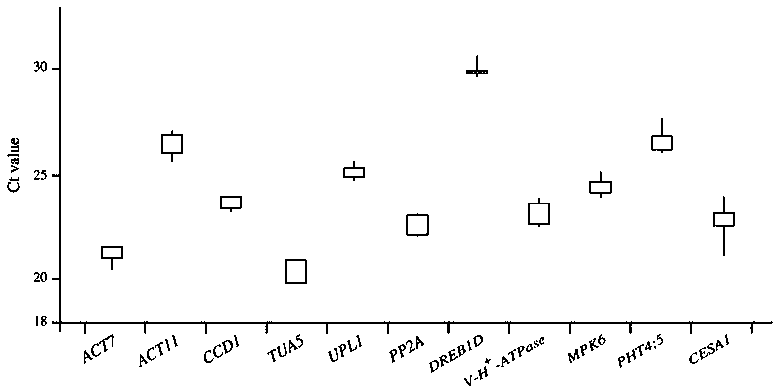
The invention discloses a reference gene screening method for stable expression of suaeda salsa under salt stress. According to transcriptome analysis results obtained in a laboratory and reported reference gene sequence information of other plants, fourteen reference gene candidates with relatively stable expression are preliminarily screened and named as ACT7, ACT1, CCD1, TUA5, UPL1, UBC28, EF1alpha, PP2A, DREB1D, TIM, V-H(+)-ATPase, MPK6, PHT4:5 and CESA1 respectively. For these gene candidates, corresponding amplification primers are designed and reference gene screening is conducted. Tengenes stably expressed in a gene expression profile of suaeda salsa are screened out as the reference genes of suaeda salsa under salt stress, and the stability and reliability of suaeda salsa gene expression analysis and research under salt stress conditions are easily improved. The method makes up for the defect of an existing method in which the use of a single reference gene can lead to errorsand deviations in experimental results, a more reliable conclusion can be obtained, and the method is of great significance for promoting the improvement and perfecting of molecular biological methods and revealing cell differentiation, development and morphogenesis.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD
Way to obtain high expression clones of mammalian cells using a methylcellulose with fluorescent protein a or g and fluorescent screening method
The invention provides a genetic screening method for identifying a transfected cell expressing the polypeptide of interest. The methods allows for high throughput screening of recombinant cells for elevated levels of expression of the polypeptide of interest using methylcellulose comprising fluorescent protein A or G to improve detection and cloning. The invention also provides capture media, formulations and methods of making and using thereof.
Owner:CENTOCOR ORTHO BIOTECH
Screening method of reference genes in skin tissue of sheep
The invention discloses a screening method of reference genes in a skin tissue of sheep, which relates to the technical field of biological engineering. The screening method comprises the steps that: a method of the reference genes is confirmed; a given amount of RNA (ribonucleic acid) extract is taken and diluted by 2-10 times by ddH2O (double-distilled water); a 50 nanograms / microlitre RNA sample is taken to serve as a template, and a cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) synthetic reagent kit is adopted for conducting inverse transcription to synthesize cDNA; the cDNA synthesized through the inverse transcription serves as a template, and six reference genes serve as primers; and finally, pairing variation analysis of normalized factors Vn / n+1 of the six reference genes are calculated based on a geNorm program, so as to decide the amount of the optimum reference genes. The screening method solves the problem that no screening method for GAPDH (reduced glyceraldehyde-phosphate dehydrogenase) genes in the skin tissue of a Chinese merino (Xinjiang type) serving as the reference genes is not available at present. Through the combination of the specificity of the SYBR Green I with double chain DNA to generate fluorescence, a real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection method of the SYBR Green I for the GAPDH genes in the skin tissue of the Chinese merino (Sinkiang type) is established.
Owner:新疆维吾尔自治区畜牧科学院畜牧科学研究所
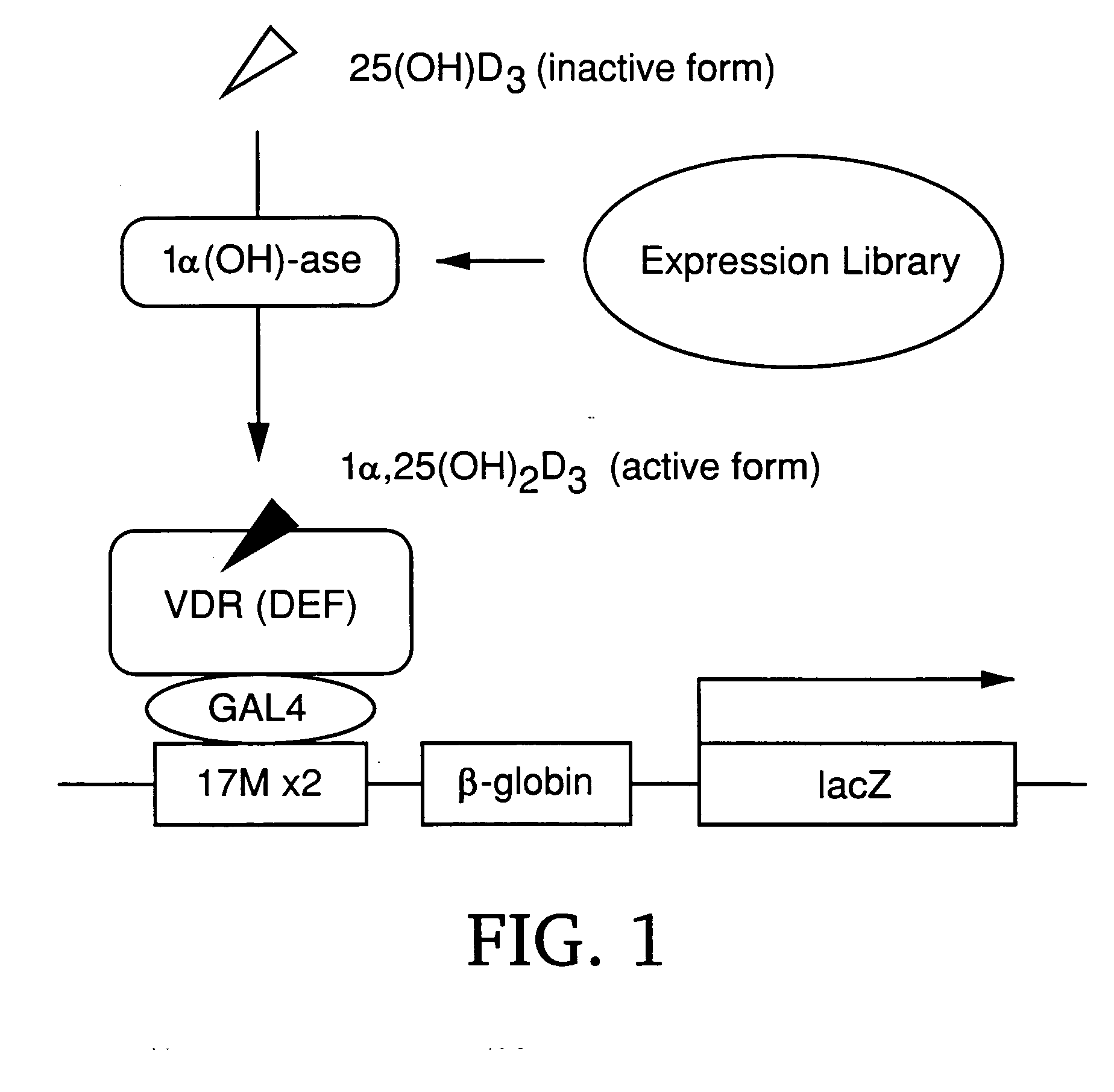
Gene screening method using nuclear receptor
InactiveUS20050042730A1Simple and efficientPromoting transcriptionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic screening methodGene screening
A system in which a ligand is formed by the expression of a polypeptide that converts a ligand precursor into a ligand, and the ligand thus formed binds to a nuclear receptor to thereby induce the expression of a reporter gene located downstream of the target sequence is constructed. Searching a gene library using this system can isolate a gene encoding a polypeptide capable of converting a ligand precursor into a ligand. This system, which takes the advantage of the transcriptional regulatory function of a nuclear receptor, enables screening a ligand that binds to a nuclear receptor and to examine whether or not a test compound is a ligand that binds to the nuclear receptor, and also screening genes that encode polypeptides capable of converting an inactive form of a wide range of transcriptional regulatory factors into an active form.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
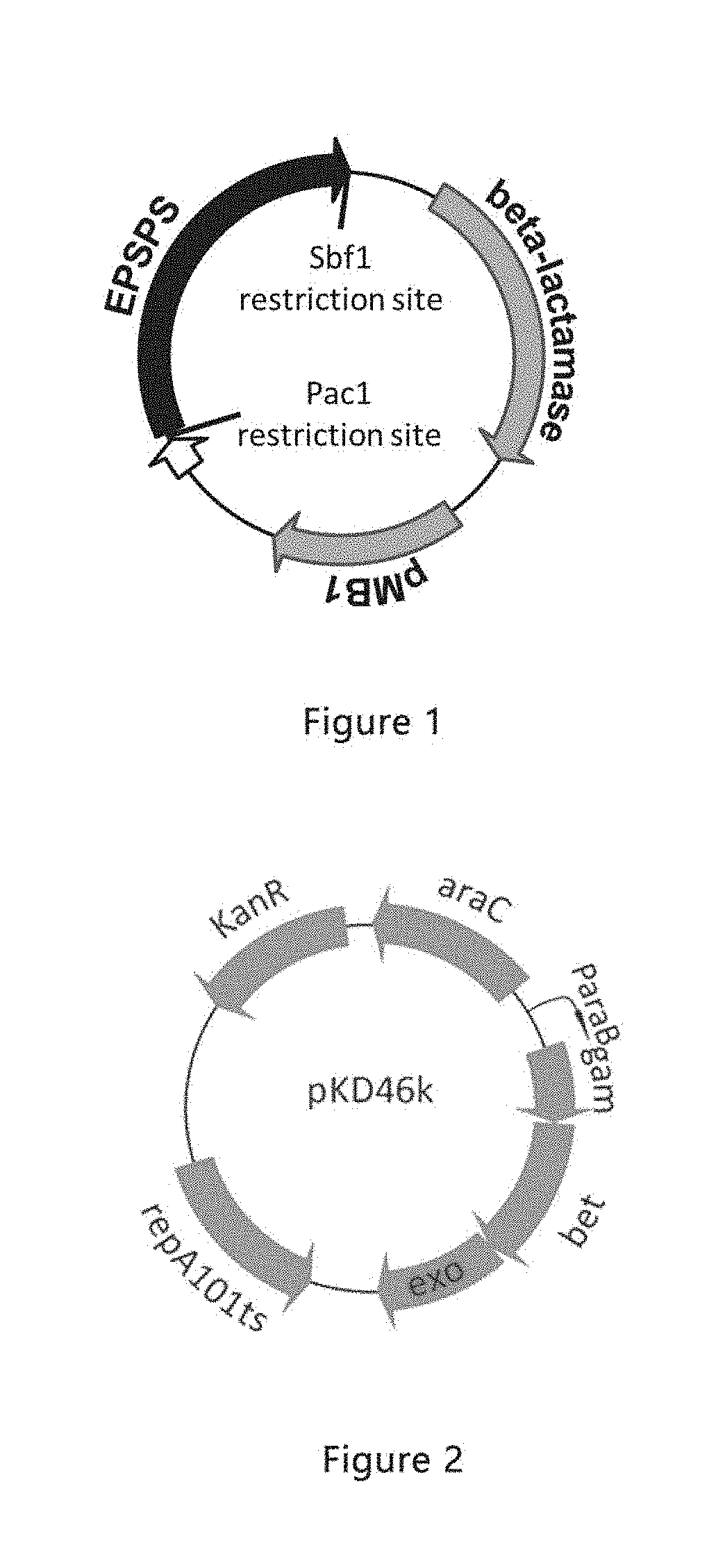
Glyphosate-resistant gene screening method, epsps mutant gene and deficient strain and use
ActiveUS20190144882A1Reproduce fastShort maintenance periodMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesResistant genesGlyphosate
Provided are a glyphosate-resistant gene screening method, an EPSPS mutant gene having glyphosate resistance screened by the method, an EPSPS and C-P Lyase deficient strain and a use thereof.
Owner:SICHUAN GEVOTO BIOTECH CO LTD
Plant genetic transformation screening carrier and application thereof
ActiveCN110408646ARich screening methodsReduce security risk concernsHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureHigh resistanceSocial benefits
The invention provides a plant genetic transformation screening carrier and an application thereof. The carrier uses an expression box containing a rice P450 gene(CYP81A6) as a screening label, bentazon or bensulfuron methyl is used as a screening agent for screening in the callus tissue stage, and the obtained plant is detected to be a genetically modified positive plant and has high resistance to herbicide. The plant genetic transformation carrier can be used as the genetically modified screening carrier, and through cooperation with other functional elements, in the genetically modified process, rice autogene is used, and exogenous screening label genes of bacterium sources and the like are not introduced, so that the genetically modified screening method for plants is enriched, the concern about security risks of genetically modified plants can also be reduced by public, promotion of business application of the genetically modified plants is facilitated, and the plant genetic transformation screening carrier has favorable market value and social benefits.
Owner:HAINAN BOLIAN RICE GENE TECH CO LTD
Genetic screening method for negative regulatory factor of streptomyces biosynthesis gene cluster
PendingCN108611361AReduce false positivesReduce verification effortMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid vectorMetaboliteBiosynthetic genes
The invention provides a screening method for a negative regulatory factor of a novel biosynthesis gene cluster of streptomyces. The screening method comprises the following steps: constructing a promoter-mediated reporting system of genes of self-interest in a streptomyces cell, then using a random mutation system based on a transposon Himar1 to mutate the streptomyces with the reporting system,intensively screening a mutant streptomyces strain to obtain a streptomyces strain with high expression of target genes, performing bacteriophage packaging on genomes of the streptomyces strain with high expression of target genes and screening out cosmids with randomly inserted fragments, sequencing DNA of the cosmids to determine the location of the randomly inserted fragments in the genomes ofthe streptomyces strain with high expression of target genes. The screening method, provided by the invention, is stable in screening environment, high in screening flux, low in false positive, high in efficiency, accurate and convenient to operate, and can be widely used in the field of high-yield screening and transformation of industrial streptomyces metabolites, and the screened and transformed streptomyces metabolites are high in yield, good in genetic stability and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Efficient genetic screening method
PendingUS20190330661A1Easy to handleImprove efficiencyHydrolasesStable introduction of DNADiseaseBarcode
A guide RNA comprising: a gRNA spacer sequence at the 5′ end of the guide RNA, wherein the spacer sequence is complementary to a target gene, a scaffold sequence that binds to Cas9, and an RNA capture and sequencing domain comprising: a barcode sequence, and a primer binding sequence; nucleic acids and vectors encoding the guide RNA; cells expressing the guide RNA; and a library comprising a plurality of guide RNAs. Also disclosed are methods of introducing a genetic perturbation into a cell, methods of assessing an effect of at least one genetic perturbation on RNA expression in a cell, methods of identifying nucleic acid sequences associated with a disease state and a method of identifying candidate therapeutic agents.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Screening method for tobacco antiviral regulatory genes and application of screening method
InactiveCN109610009AEasy accessSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionSequence analysisCDNA library
The invention provides a screening method for tobacco antiviral regulatory genes and an application of the screening method. The screening method comprises the following steps: firstly constructing atobacco cDNA library by using a virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) vector as a target vector, and performing homogenization treatment to obtain a VIGS-cDNA library capable of being directly used forgene silencing screening analysis; transforming VIGS-cDNA library plasmid into agrobacteria to obtain an agrobacterium library; performing spread plate culture on the agrobacterium library to obtain single colonies, performing VIGS silencing analysis on each single colony, and performing screening to obtain antiviral-related colonies; and performing sequencing analysis on genes corresponding to the screened antiviral-related colonies, performing homology analysis on the obtained sequences, and performing function prediction to obtain the antiviral regulatory genes. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple operation, no need to construct transgenic plants or mutants, short time consuming, comprehensive screening and high efficiency, is particularly suitable for screening of mutant lethal genes, and has broad application prospects.
Owner:GUIZHOU TOBACCO SCI RES INST
Screening method of reference genes for fluorescent quantitative detection of caruncle mucosa of pregnant cows and application of screening method
PendingCN109913533AOptimizing Pregnancy EstablishmentEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genesPregnancy Maintenance
The invention discloses screening method of reference genes for fluorescent quantitative detection of caruncle mucosa of pregnant cows and application of the screening method, and relates to the technical field of animal molecular biology. Suitable reference genes are screened out for the study on gene expression of caruncle mucosa of pregnant cows; the expression of genes playing a key role uponestablishing of a bond between the maternal cow and fetus can be truly reflected; key candidate genes of maternal-fetal interaction can be further applied to assist in the important reproductive mechanisms, such as cow pregnancy establishment, pregnancy recognition, and pregnancy maintenance.
Owner:WUHAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method of genetic screening using an amplifiable gene
InactiveUS20050142550A1Reduce productionHigh expressionVectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsGene Organization
The present invention pertains to genetic screening methods and related cells and genetic constructs. In particular, the invention relates to a method of screening cells for an alteration, typically an amplification, in the copy number of a nucleic acid of interest using an amplifiable nucleic acid linked to a reporter nucleic acid; a method of screening cells for increased expression of a polypeptide of interest derived from the nucleic acid of interest; and related cells and genetic constructs. The method allows for high throughput screening of recombinant cells expressing a polypeptide or protein of interest and, in particular, for screening of cells expressing the polypeptide or protein of interest at elevated levels.
Owner:UNISEARCH LTD
Homoeologous Region Determining Method by Homo Junction Fingerprint Method, Homoeologous Region Determining Device, and Gene Screening Method
InactiveUS20090155782A1Reduce in quantityExcellent characteristicsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenetic screening methodPolyploidies
To provide a method for efficiently searching for a recessive disease gene without needing any pedigree analysis. In a homoeologous region determining method, the following steps are conducted. It is determined whether or not the base constituting a polymorphic marker of a sample DNA of diploid or higher polyploidy is a homojunction. Homojunction region information representing the region of the sample DNA where polymorphic markers determined as continuous homojunctions acquired. If the continuous probability and / or continuous distance of the polymorphic markers contained in the homojunction region information satisfy a predetermined determination condition, the homojunction region is determined as a homoeologous region. A homoeologous region determining device and a gene screening method for identifying a disease susceptibility gene from the determined homoeologous region are also provided.
Owner:TOMY DIGITAL BIOLOGY +1
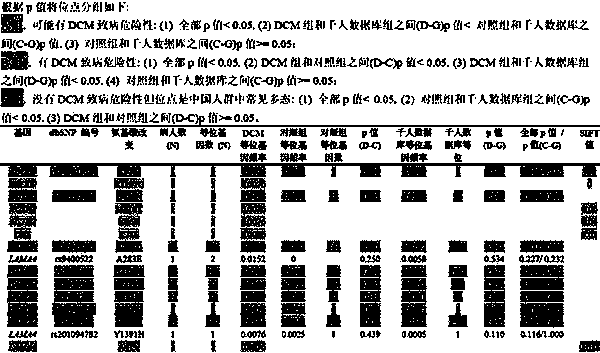
Kit for screening dilated cardiomyopathy
ActiveCN103509867BImprove survival rateImprove early detection rateMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseBiology
The invention relates to a kit for screening dilated cardiomyopathy. The detection genes of the kit are MYBPC3, SCN5A, MYH7 and MYPN. The present invention also provides the application of four genes MYBPC3, SCN5A, MYH7 and MYPN in preparing a kit for screening dilated cardiomyopathy. The advantages of the present invention are: the present invention screens out the most susceptible 4 sporadic dilated cardiomyopathy pathogenic genes in Chinese Han population, and develops an effective early diagnosis method and diagnostic kit for sporadic dilated cardiomyopathy in Chinese Han population, Effectively improve the early detection rate of patients with dilated cardiomyopathy, so as to achieve early treatment and improve the survival rate of patients; compared with the current expensive and inefficient genetic screening methods for dilated cardiomyopathy, the discovery of these four high-risk disease-causing genes It will make screening more targeted, thereby reducing testing costs and improving detection efficiency.
Owner:苏州科诺医学检验实验室有限公司
Goat F17 escherichia coli infection resisting gene screening method
PendingCN109797198AImprove the success rate of attacking poisonStrong targetingMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsDisease resistantGenetic screening method
The invention discloses a goat F17 escherichia coli infection resisting gene screening method which includes the steps: F17 escherichia coli infection diseased lamb and disease-resistant lamb screening and spleen and intestinal canal content sample acquisition; F17 escherichia coli infection diseased lamb and disease-resistant lamb spleen sample high-throughput sequencing; F17 escherichia coli infection diseased lamb and disease-resistant lamb spleen transcriptomics comparative analysis; F17 escherichia coli infection resisting gene (circRNA) screening and identifying. The goat F17 escherichiacoli infection resisting gene screening method is used for screening F17 escherichia coli infection resisting genes (circRNA) from disease-resistant lamb spleens in a targeted manner, is high in accuracy and pertinence and saves time.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Fungus genetic screening method based on marker gene
InactiveCN104846090ARich sourcesPermeableFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic screening methodSalt resistance
The invention discloses a fungus genetic screening method based on a marker gene. The method comprises the following steps of cloning an acceptor fungus HOG1 MAPK signal pathway key gene, establishing an acceptor fungus HOG1 MAPK signal pathway key gene knock-out vector, acquiring an acceptor fungus HOG1 MAPK signal pathway key gene knock-out mutant, determining permeability resistance and salt resistance of the acceptor fungus HOG1 MAPK signal pathway key gene knock-out mutant, and verifying the transformation by adopting the acceptor fungus HOG1 MAPK signal pathway key gene as a screening marker. By adopting the method, the source of the fungus genetic transformation screening marker is enriched, when the acceptor fungus does not have a plurality of screening markers, the requirement for carrying out the double-gene or multi-gene functional research can be met.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY +1
Method of screening reference genes to fluorescently quantitatively detect oviduct of pregnant cows and application of method
InactiveCN109971829AGuaranteed accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genesFluorescence
The invention discloses a method of screening reference genes to fluorescently quantitatively detect oviduct of pregnant cows and application of the method and relates to the technical field of animalmolecular biology. Suitable reference genes for the study on genetic expression of oviduct tissue of pregnant cows; the accuracy of fluorescent quantitative detection of the genetic expression of oviduct of the is forcibly guaranteed; important basis is provided for the further study on the regulatory mechanism of the oviduct of cows in early embryonic development phase.
Owner:WUHAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
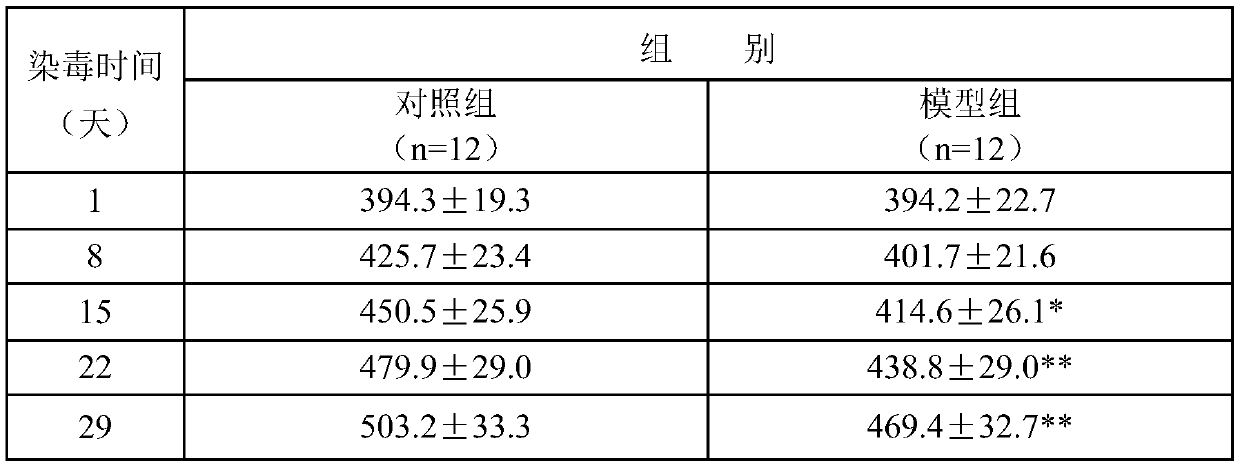
Method for establishing early liver injury model of passive smoking rats and method for screening related genes
The invention discloses a method for screening genes related to early liver injury of passive smoking rats. By the method, a rat passive smoking model is established. Through a liver gene chip technology, differential genes of early liver injury in passive smoking rats were screened out, and functional annotation and analysis of the differential genes are performed, thus providing gene-level discovery and explanation for liver injury caused by smoking. The established rat passive smoking model has higher scientificity and stronger reliability, is accurate in controlling the concentration of poisoned smoke, has short modeling period, is of great clinical significance, and can realize early detection and early prevention.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO JIANGXI IND CO LTD
Infectious etiologic agent detection probe and probe set, carreir, and genetic screening method
InactiveCN1539994ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBase JGenetic Examination
An infectious etiologic agent detection probe set which detects an infectious etiologic agent gene, includes a plurality of kinds of probes including oligonucleotide having base sequences selected from each of a plurality of groups selected from a first group including base sequences of SEQ ID Nos. 1 to 14 and complementary sequences thereof, a second group including base sequences of SEQ ID Nos. 15 to 24 and complementary sequences thereof, a third group including base sequences of SEQ ID Nos. 25 to 36 and complementary sequences thereof, a fourth group including base sequences of SEQ ID Nos. 37 to 47 and complementary sequences thereof, a fifth group including base sequences of SEQ ID Nos. 48 to 57 and complementary sequences thereof, a sixth group including base sequences of SEQ ID Nos. 58 to 68 and complementary sequences thereof, a seventh group including base sequences of SEQ ID Nos. 69 to 77 and complementary sequences thereof, an eighth group including base sequences of SEQ ID Nos. 78 to 85 and complementary sequences thereof, a ninth group including base sequences of SEQ ID Nos. 86 to 97 and complementary sequences thereof, and a 10th group including base sequences of SEQ ID Nos. 98 to 106 and complementary sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Selecting method of gene participating in transfection of exogenous DNA from sperm
The invention discloses a selecting method of gene participating in transfection of exogenous DNA from sperm, relates to a method for screening a gene participating in transfection of exogenous DNA from sperm, and aims at providing the method for screening the gene participating in transfection of the exogenous DNA from the sperm. The method comprises the following steps: 1 building a recombinant plasmid pGB-mCD4; 2 screening from a cDNA library to obtain a to-be-tested gene; 3 positively cloning the to-be-tested gene, extracting a yeast plasmid and amplifying; 4 transferring the plasmid pGB-mCD4 and the positively cloned yeast plasmid of the to-be-tested gene into a double-hybrid strain Y190 of the yeast; and 5 carrying out beta-galactosidase chromogenic reaction, if the chromogenic result becomes blue, judging to be positive, and analyzing, thereby obtaining the gene participating in the transfection of the exogenous DNA from the sperm. Through the method disclosed by the invention, the gene for transferring the exogenous DNA together with CD4 can be greatly and rapidly obtained; a new idea is developed for research on the sperm-mediated gene transfer mechanism; and a foundation is laid for building of simple, stable and efficient sperm-mediated genetically modified methodology.
Owner:赵永聚
Homozygote haplotype method
InactiveUS20090327203A1Reduce in quantityImprove recognition accuracyProteomicsFuzzy logic based systemsDiseaseHaplotype
To provide a method of efficiently searching for a disease sensitivity gene and an apparatus therefor. It is intended to provide: a method of determining a homoeologous region which comprises the polymorphism marker selection step of selecting a polymorphism marker usable as the subject of the homozygote determination, the homozygote determination step of determining whether or not bases constituting a specimen DNA which is a diploid or higher are homozygous, the homozygote haplotype data acquisition step of selecting exclusively polymorphism markers determined as homozygous and acquiring homozygote haplotype data of each specimen, the homozygous region data acquisition step of comparing the above-described homozygote haplotype data of two or more specimens and acquiring common homozygous region data, and the homoeologous region determination step of determining a common homozygous region satisfying definite homoeology requirements as a homoeologous region between the corresponding specimens for each common homozygous region data; and an apparatus and a gene screening method with the use of this method.
Owner:TOMY DIGITAL BIOLOGY +1
High-throughput functional gene screening method and system for quantitative analysis of cell phenotype images
ActiveCN109815870BFast recognitionRecognition speed is fastImage analysisMaterial analysis by optical meansCell phenotypeFluorescence microscope
The invention discloses a high-throughput functional gene screening method and system for quantitative analysis of cell phenotype images, and belongs to the technical field of gene screening. The images of cells with phenotypes to be screened and those without phenotypes to be screened are captured by a fully automatic fluorescence microscope; converted into black and white binary images of phenotypes to be screened and without phenotypes to be screened respectively; and then divided into individual phenotypes to be screened The image of the cell and the image containing a single cell without a phenotype to be screened; the corresponding part of the image containing a single cell with a phenotype to be screened in the image of a cell with a phenotype to be screened is used as a positive training set, which will contain a single cell without a phenotype to be screened The corresponding part of the cell image in the cell image without the phenotype to be screened is used as a negative training set, and the final model that can identify the cell phenotype is obtained; the image of the gene knockout or overexpression cell to be screened is identified by the final model, and the sample to be screened is obtained. Screening for association of genes with phenotypes. The method improves screening efficiency and accuracy.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Aspartoacylase gene, protein, and methods of screening for mutations associated with Canavan disease
Canavan disease, an autosomal recessive leukodystrophy, is caused by deficiency of aspartoacylase and accumulation of N-acetylaspartic acid in brain. Human aspartoacylase (ASP) cDNA spanning 1,435 bp has been cloned and expressed in E. coli. A base change, a854>c, has been found in 85% of the 34 Canavan alleles tested so far, which results in a missense glu285>ala mutation that is predicted to be part of the catalytic domain of aspartoacylase. The invention therefore provides nucleic acid sequences, genes, polypeptides, antibodies, vectors containing the gene, host cells transformed with vectors containing the gene, animal models for the disease, methods for expressing the polypeptide, genetic screening methods and kits, diagnostic methods and kits, methods of treating Canavan disease and methods of genetic therapy for the disease.
Owner:MIAMI CHILDRENS HOSPITAL RES INST
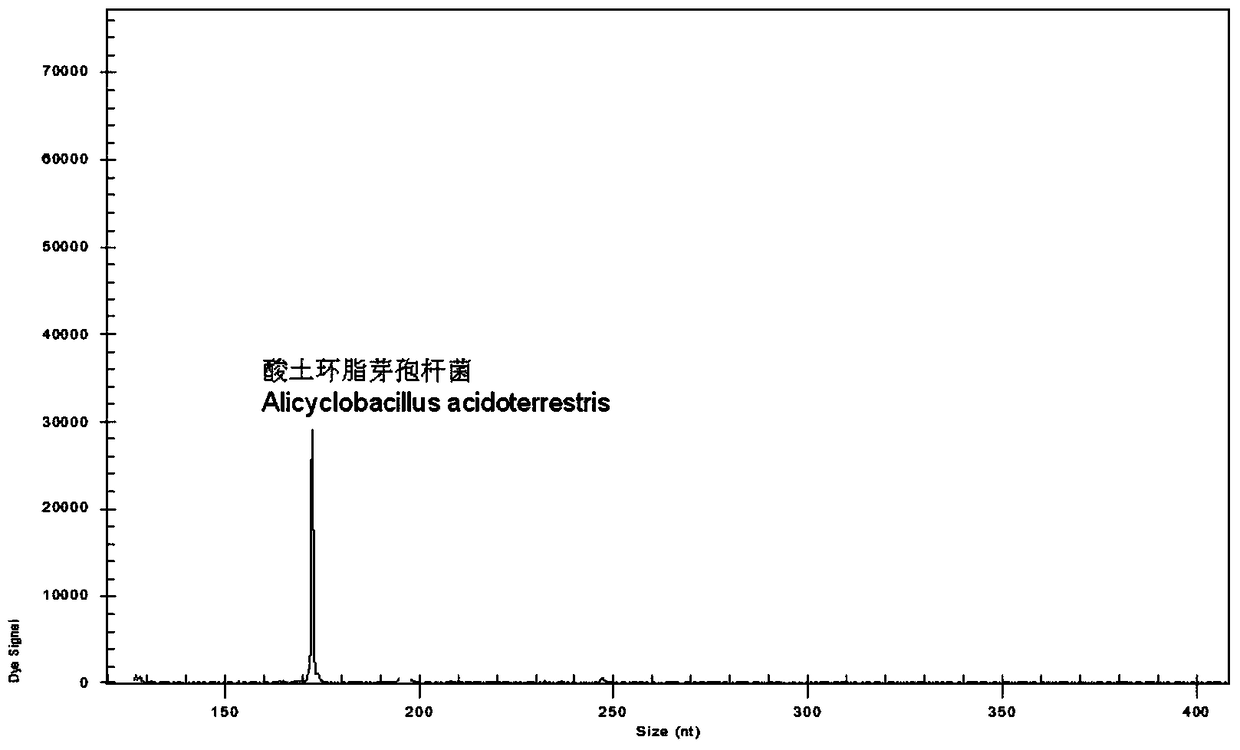
A rapid genetic screening method for simultaneous detection of four contaminating bacteria in juice drinks
ActiveCN105316413BEasy to operateThe test result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyMultiplex
The invention discloses a gene rapid screening method capable of simultaneously detecting contaminating bacteria in fruit juice drinks. The method includes the cultivation of juice beverage contaminating bacteria and DNA template extraction, and then through the combination of high-throughput multiplex PCR technology and high-resolution capillary electrophoresis separation technology, it is possible to detect whether the sample contains of contaminating bacteria. Compared with other current molecular biology detection methods based on PCR technology, the present invention can integrate and detect 4 kinds of fruit juice drink contaminating bacteria in one reaction, saving detection cost and detection time, and the detection time is reduced from 7 to 14 days shortened to 8h.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
A rapid genetic screening method for the simultaneous identification of multiple heat-resistant bacteria in fruit juice beverages
ActiveCN105316414BEasy to operateThe test result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyMultiplex
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Method for screening miR-3880 target gene
ActiveCN108504683AInhibit expressionMicroencapsulation basedMicrobiological testing/measurementBinding siteFluorescence
The invention discloses a method for screening a miR-3880 target gene. The method comprises the following steps of using a goat genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) as a template, utilizing a primer OGRI to perform amplification by PCR (polymerase chain reaction) under the existence of Taq DNA polymerase, buffer environment, Mg<2+> and dTNPs, and determining an obtained PCR product is a sequence ofa 3'UTR zone of the gene OGR1 (ovarian cancer G protein-coupled receptor 1); constructing a double-luciferase report system, detecting the activity of luciferase, and primarily identifying the miR-3880 target gene; adopting a RT-qPCR (real-time and quantitative polymerase chain reaction) method to detect the influence on the mRNA level of the gene OGR1 by an miR-3880 simulation matter; adopting aWestern blot method to detect the influence on the protein level of the gene OGR1 by the miR-3880 simulation matter. The method has the advantages that the existence of the 3'UTR zone of the gene OGR1and the binding sites of the miR-3880 are defined, the targeting regulating and control relationship between the miR-3880 and the target gene OGR1 is verified, the miR-3880 can be used for inhibitingthe expression of the gene OGR1 on mRNA and protein levels, and the gene OGR1 is further verified to be the miR-3880 target gene; a foundation is laid for the study on the influence on the mammogenesis and lactation functions of dairy goats.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com