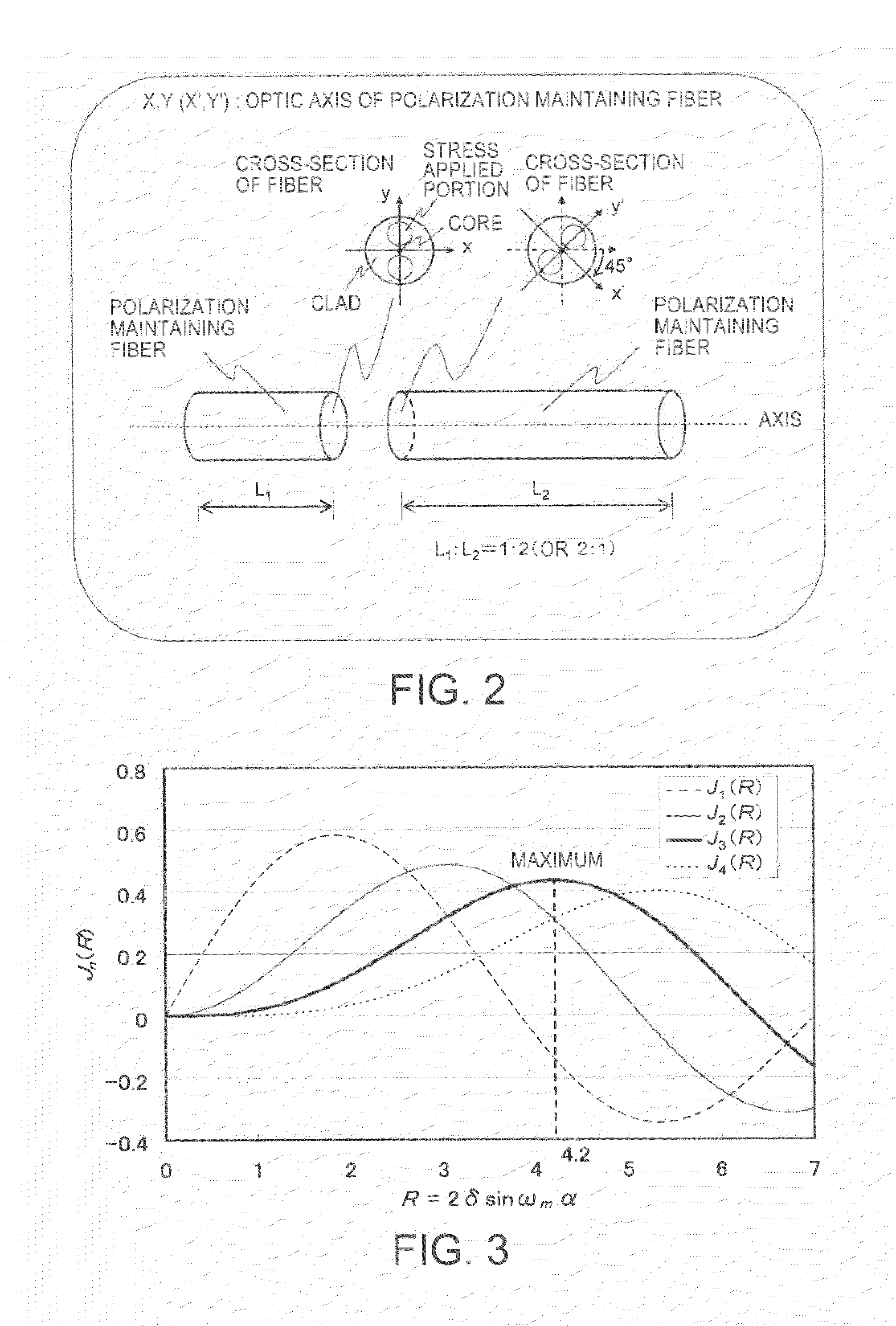
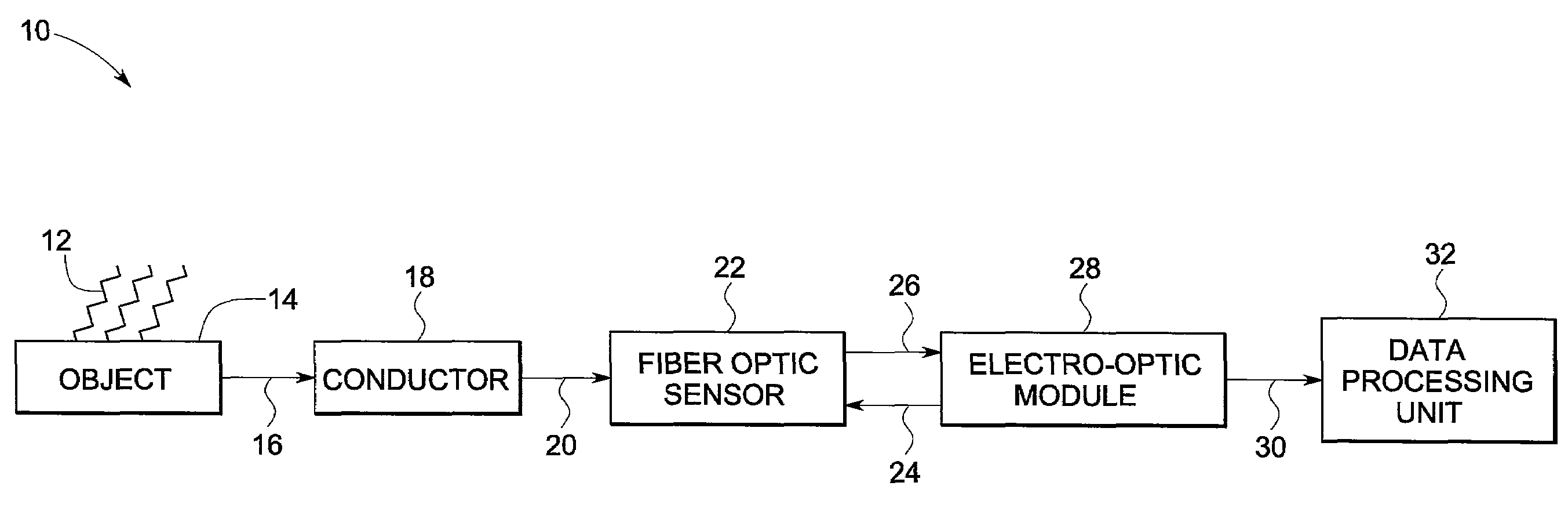
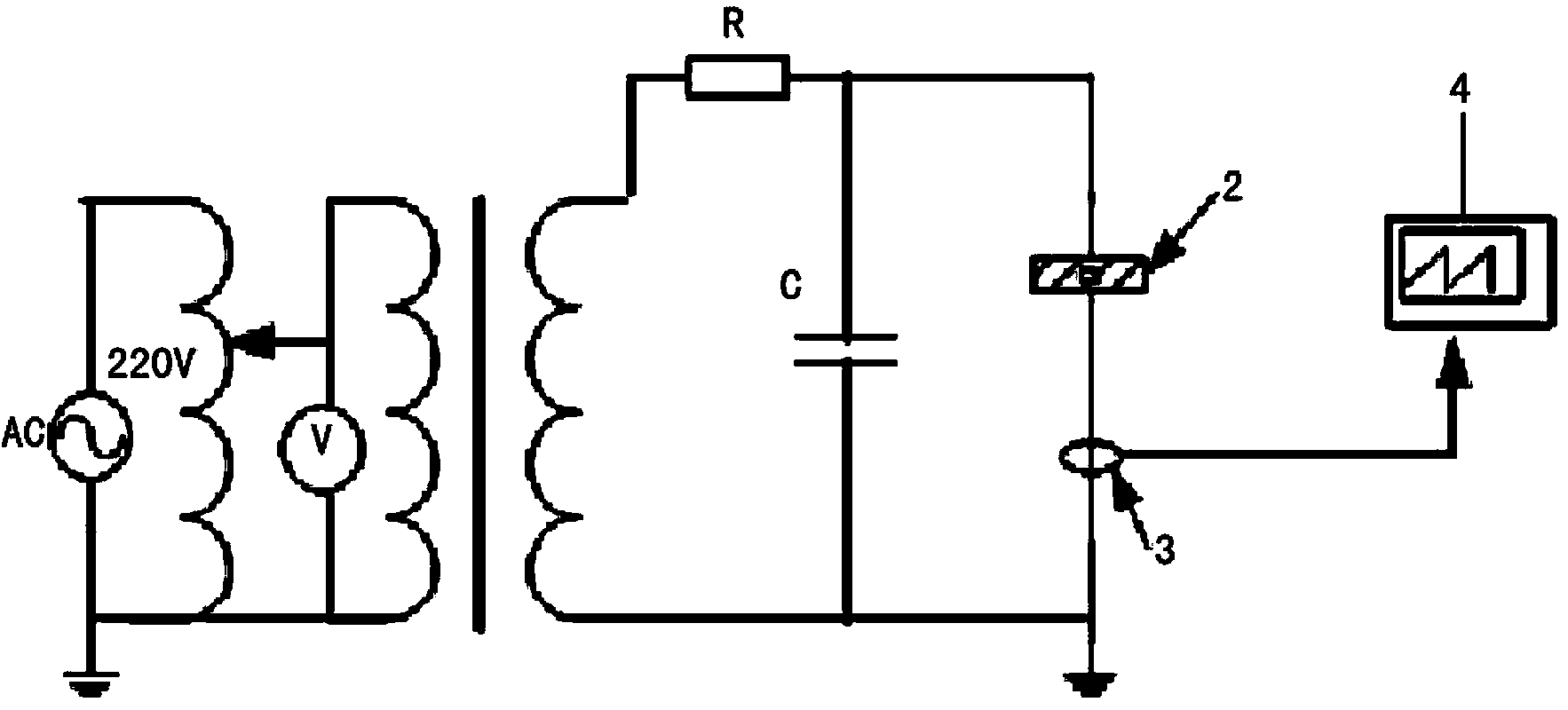
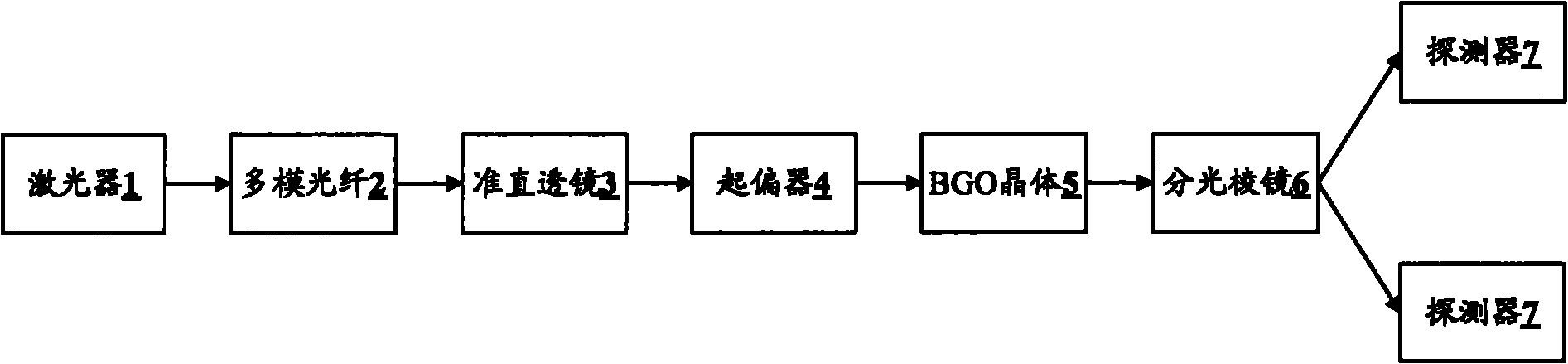
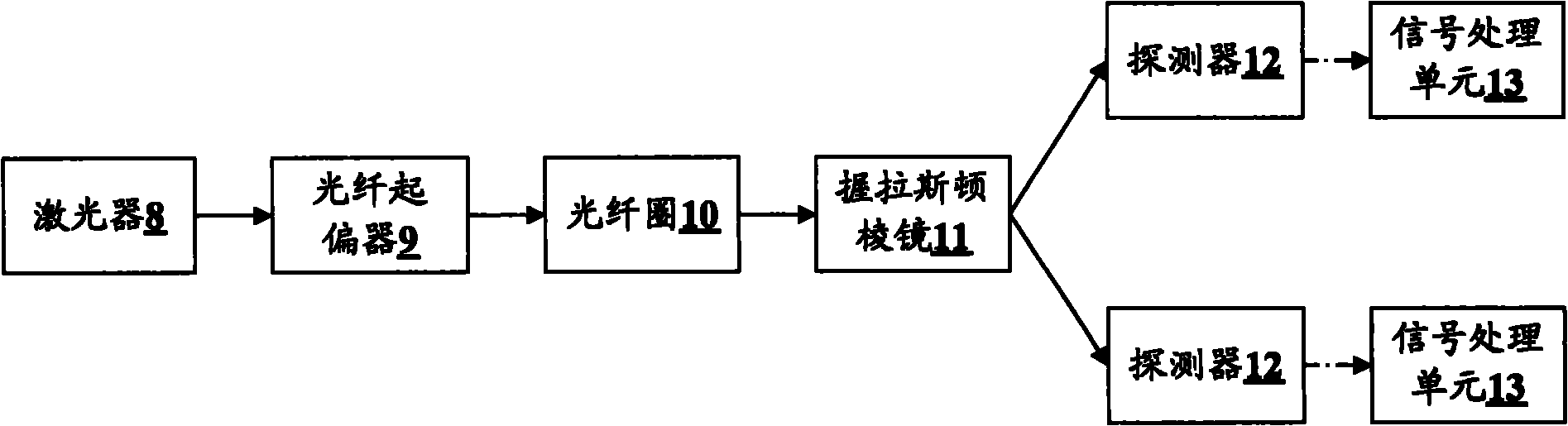
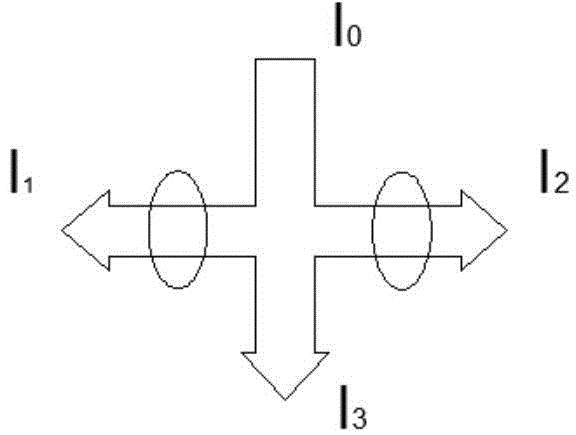
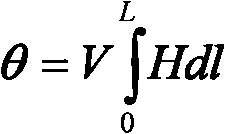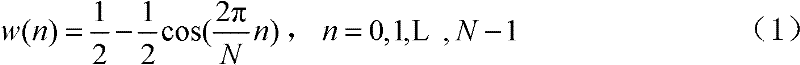Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
203 results about "Fiber optic current sensor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
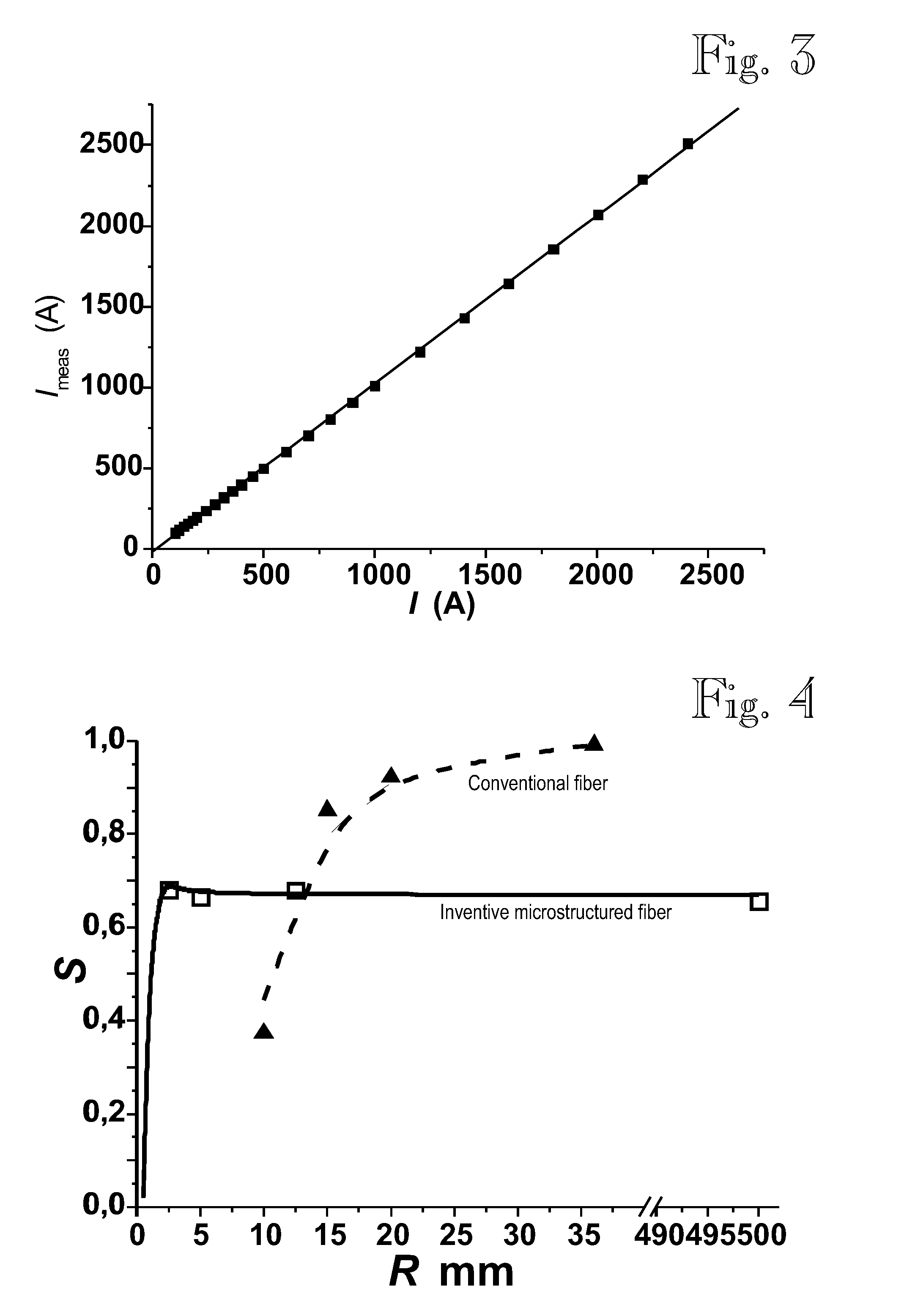
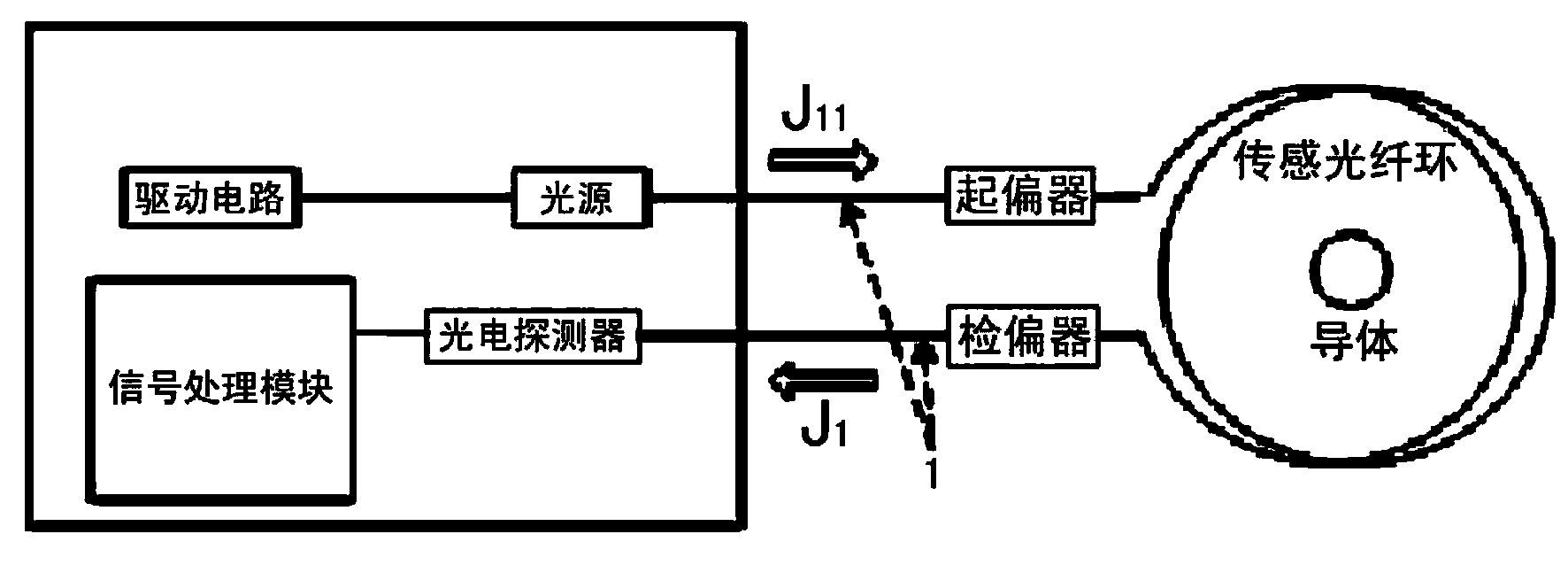
A fiber-optic current sensor (FOCS) is a current sensor for measuring direct current. By using a single-ended optical fiber around the current conductor that utilizes the magneto-optic effect (Faraday effect), FOCS measures uni- or bidirectional DC currents of up to 600 kA within ±0.1% of the measured value.
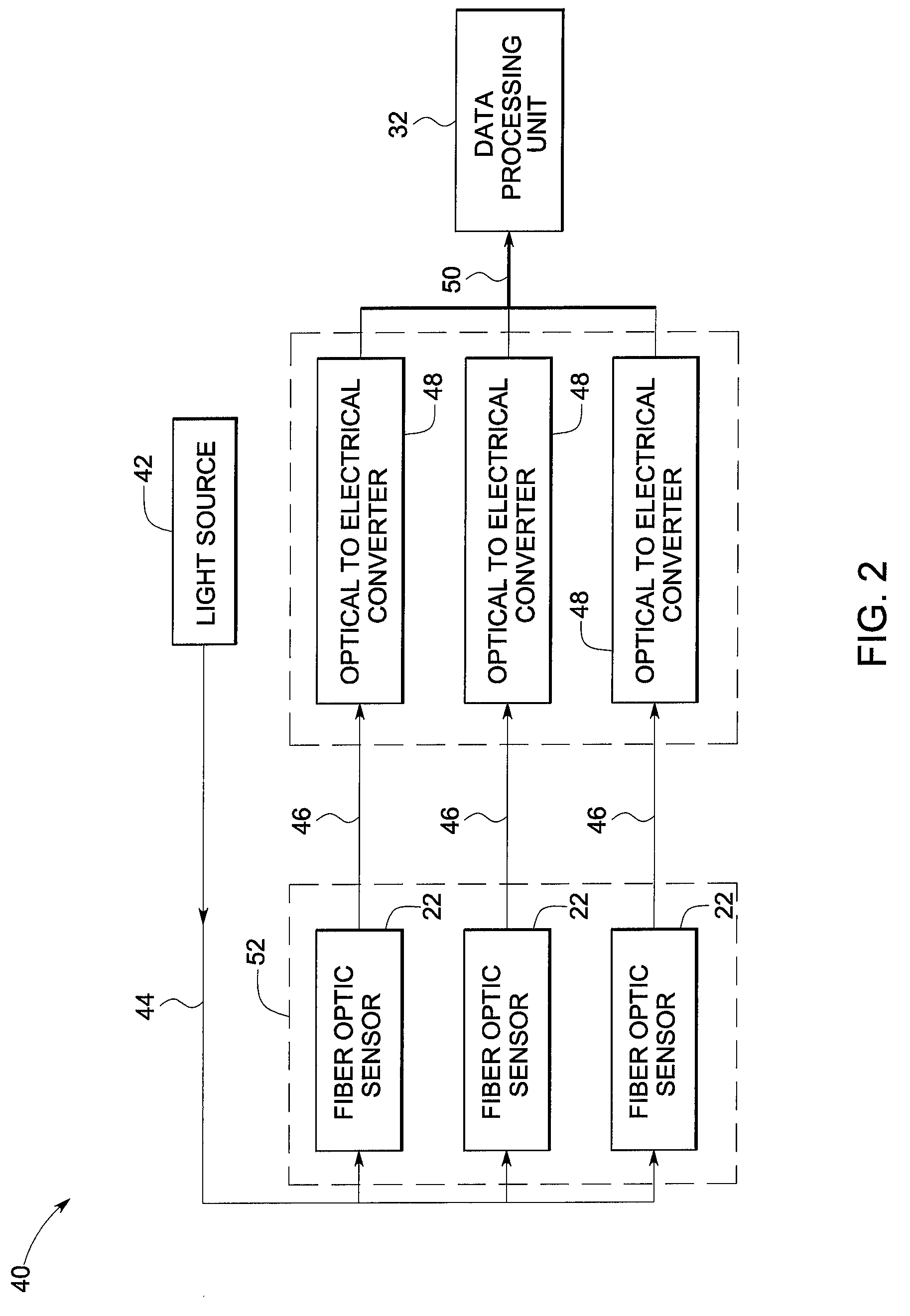
Power inverter with optical isolation
InactiveUS6972972B2Conversion constructional detailsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPower inverterElectronic switch
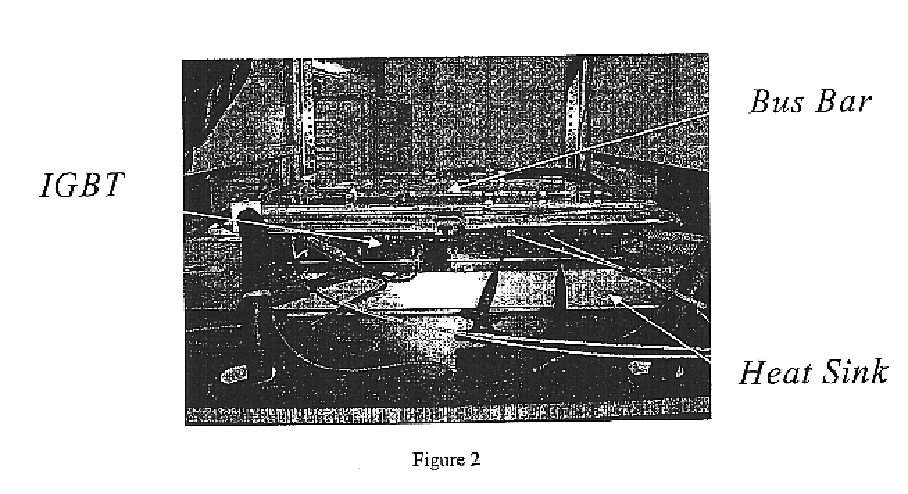
An optically isolated power electronic power conversion circuit that includes an input electrical power source, a heat pipe, a power electronic switch or plurality of interconnected power electronic switches, a mechanism for connecting the switch to the input power source, a mechanism for connecting comprising an interconnecting cable and / or bus bar or plurality of interconnecting cables and / or input bus bars, an optically isolated drive circuit connected to the switch, a heat sink assembly upon which the power electronic switch or switches is mounted, an output load, a mechanism for connecting the switch to the output load, the mechanism for connecting including an interconnecting cable and / or bus bar or plurality of interconnecting cables and / or output bus bars, at least one a fiber optic temperature sensor mounted on the heat sink assembly, at least one fiber optic current sensor mounted on the load interconnection cable and / or output bus bar, at least one fiber optic voltage sensor mounted on the load interconnection cable and / or output bus bar, at least one fiber optic current sensor mounted on the input power interconnection cable and / or input bus bar, and at least one fiber optic voltage sensor mounted on the input power interconnection cable and / or input bus bar.
Owner:ALRAK INC
Digital closed loop type optical fiber current sensor
ActiveCN101957399AHigh sensitivityImprove dynamic rangeCurrent/voltage measurementVoltage/current isolationCurrent transducerNoise level
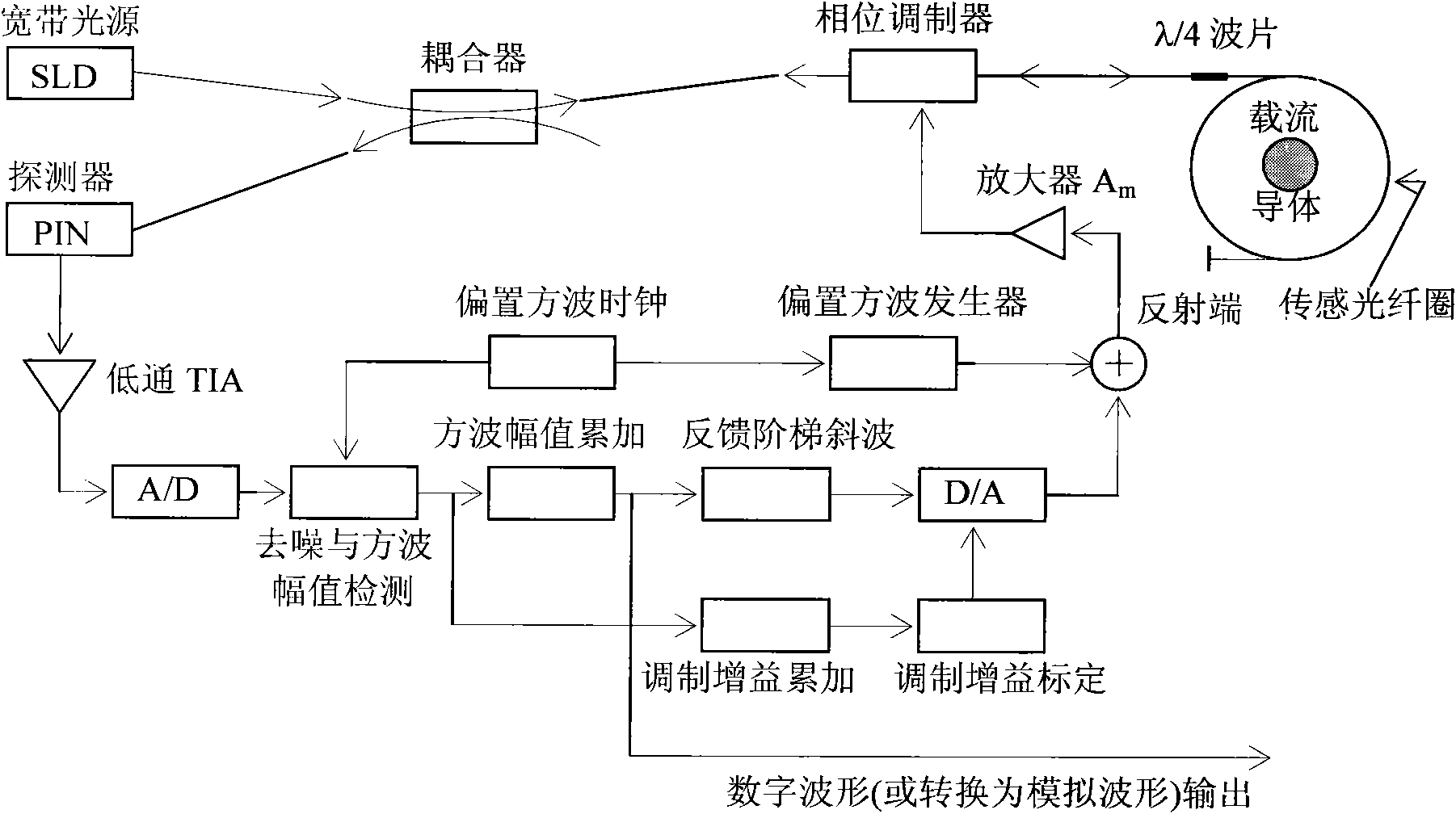
The invention provides a digital closed loop type optical fiber current sensor. A modulation signal of a light wave phase modulator of a sensor optical path system is an amplitude modulation square wave; a signal processing system extracts any harmonic wave of amplitude modulation square wave current output by a photoelectric transducer and extracts tested current information from the current; a pre-amplifier of the signal processing system is a transimpedance amplifier TIA, and the bandwidth is below 1 / 650 when the square wave transient amplitude value (prior art) is directly extracted from the amplitude modulation square wave, so that thermal noise output by the pre-amplifier and the shot noise level are also reduced to be below 1 / 650 of the prior art; and current-voltage conversion gain of the transimpedance amplifier TIA is not determined by the resistance of a feedback network of the TIA, so that a low-resistance resistor is adopted in the feedback network of the TIA while the high current-voltage conversion gain is ensured, and the thermal noise of the resistor which accounts for a significant proportion in the level of the noise output by the TIA is reduced to be negligible.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Detecting apparatus for detecting lightning strike, wind turbine blade equipped with the same, wind turbine generator, method for detecting lightning strike
InactiveUS20120133146A1Simple and inexpensive and highly reliable configurationReliably determinedInstallation of lighting conductorsEngine fuctionsLightning strikeElectrical conductor
A lightning-strike detecting apparatus comprises: receptors (lightning members) that are provided at a plurality of locations on a wind turbine blade; lightning conductors that extend from these receptors to guide lightning-strike current to ground; a plurality of optical-fiber current sensors that are provided on the respective lightning conductors, detect lightning-strike current flowing in the lightning conductors, and output an optical signal; an optical signal converter that receives the individual optical signal output from these optical-fiber current sensors, converts the optical signals to the respective characteristic electrical signals, and outputs the electrical signals; and a controller that identifies the type of the electrical signal input from the optical signal converter, determines a lightning-strike spot on the basis of the type, and reports the lightning-strike spots.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
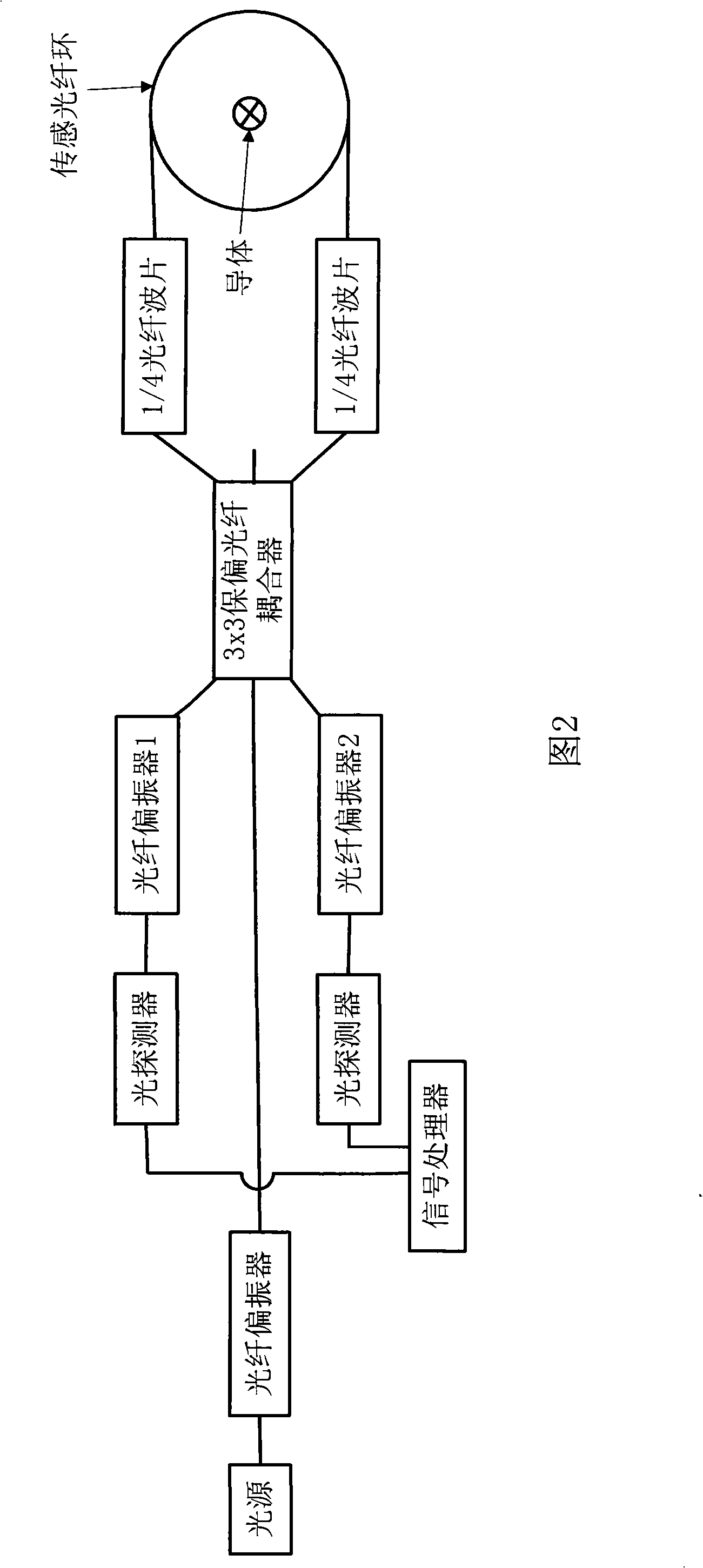
Full optical fiber current sensor
InactiveCN101320055AEliminate imperfectionsEliminate measurement errorsVoltage/current isolationOptical light guidesFiber couplerPhase difference
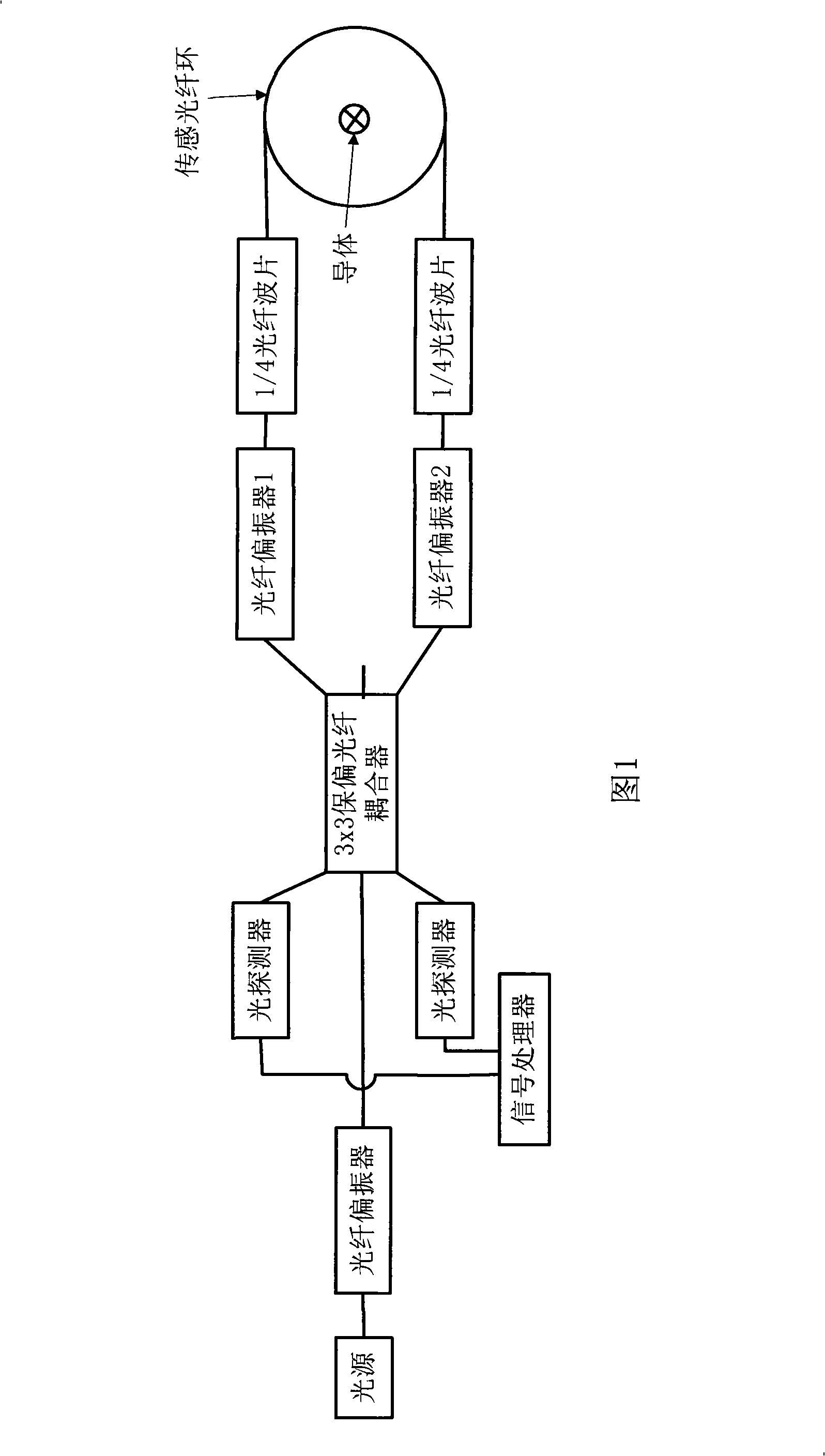
The invention discloses an all-fiber current sensor consists of a 3x3 polarization-maintaining fiber coupler. One embodiment of the invention, a straight-through type interferometric all-fiber current sensor, comprises a light source, a 3x3 polarization-maintaining fiber coupler, fiber polarizers, a 1 / 4 fiber wave sheet and a transduction fiber ring. The light source is connected with one end of the 3x3 polarization-maintaining fiber coupler; the two ports of the 3x3 polarization-maintaining fiber coupler are respectively connected with two fiber polarizers; and the other ends of the two fiber polarizers are respectively connected with the transduction fiber ring by the 1 / 4 fiber wave sheet; one port of the 3x3 polarization-maintaining fiber coupler is vacant; and the rest two ports of the 3x3 polarization-maintaining fiber coupler are respectively connected with a signal processor by two photoelectric detectors. In addition, another embodiment of the invention, a reflection type interferometric all-fiber current sensor, also uses the 3x3 polarization-maintaining fiber coupler. The all-fiber current sensor avoids phase differences made artificially and makes the current transduction system woke more stably.
Owner:上海康阔光智能技术有限公司
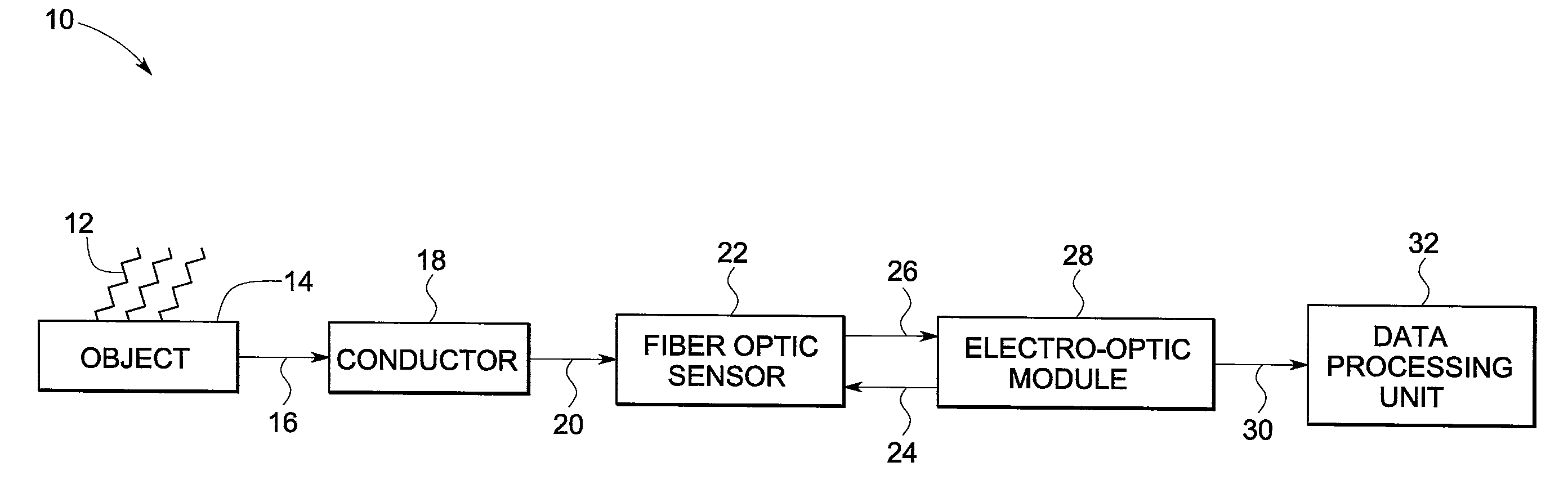
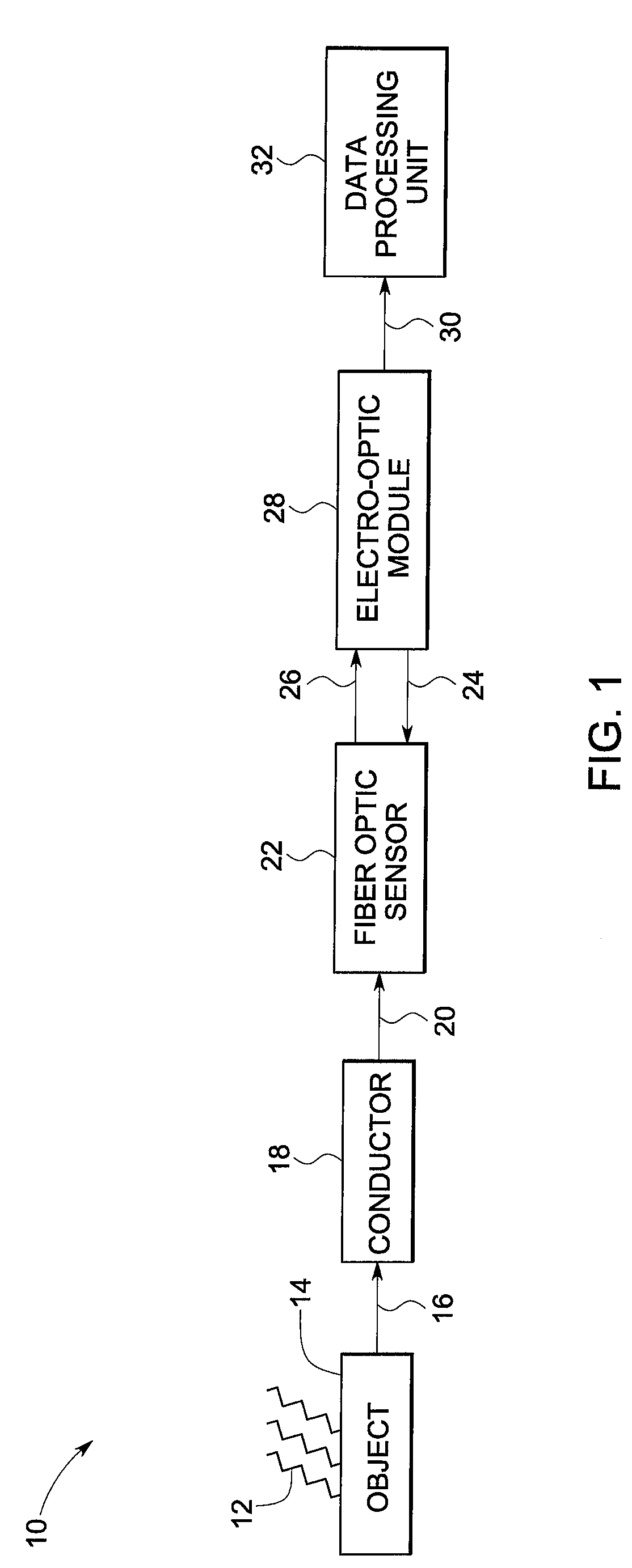
System and method for detecting lightning
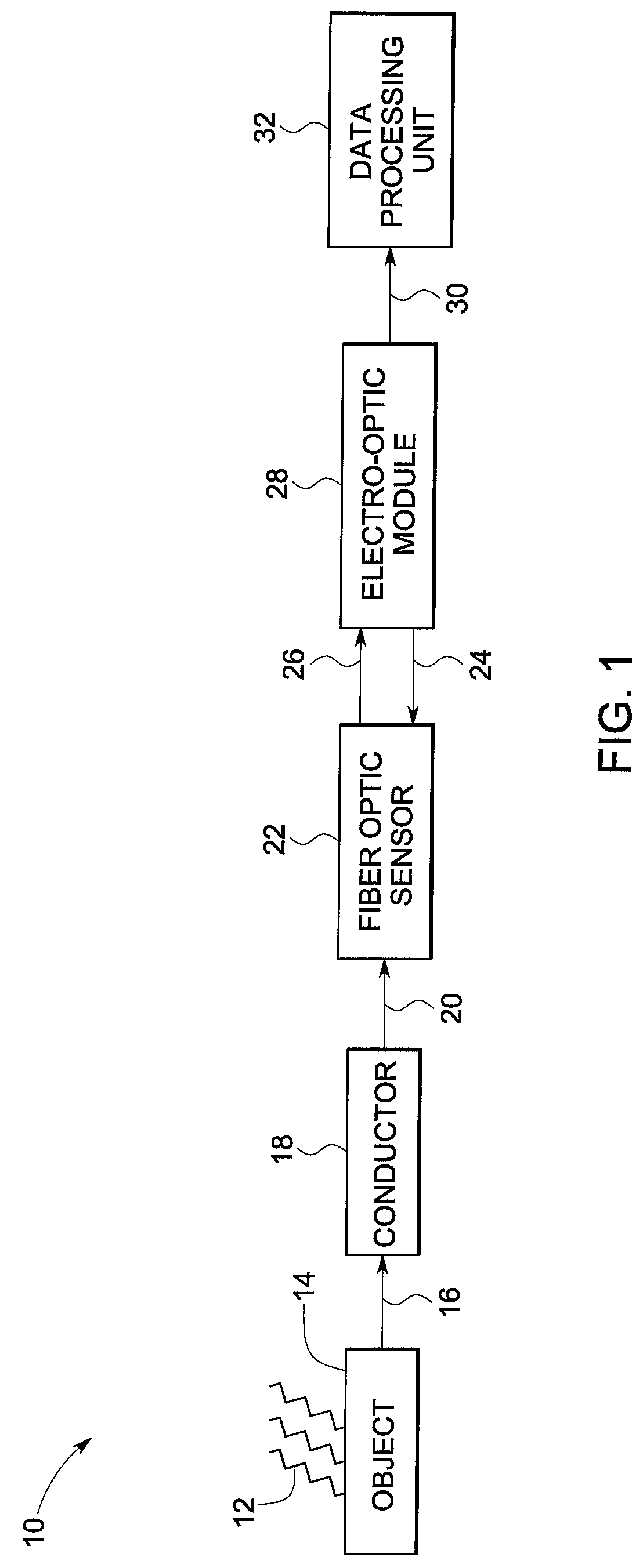
A system for lightning detection is provided. The lightning detection system includes a conductor configured to receive a lightning strike and transmit a lightning induced current. The system also includes a fiber optic current sensor configured to detect multiple lightning parameters from the lightning induced current and to modulate a beam of radiation in response thereto. The system further includes an electro-optic module configured to receive and convert said beam of radiation from the fiber optic current sensor to an electrical signal.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
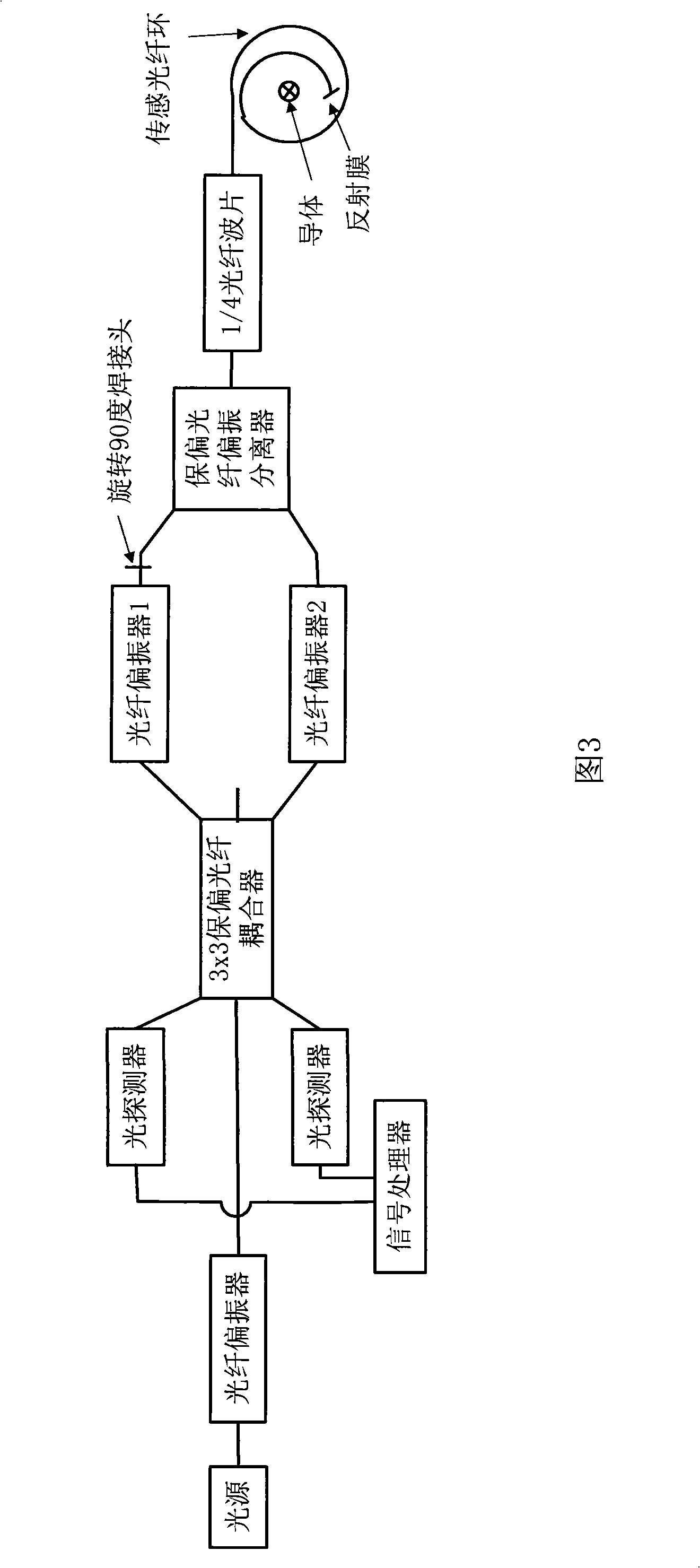
Sensing fiber used in reflective all-fiber current sensor
InactiveCN101876723ADoes not affect normal workReduce speedCladded optical fibreCurrent/voltage measurementPolarization-maintaining optical fiberCurrent sensor
The invention discloses a sensing fiber used in a reflective all-fiber current sensor. The sensing fiber comprises a polarization-preserving fiber, wherein the polarization-preserving fiber comprises a non-rotating section, a rotation-starting section and a uniform rotation section in turn; and a reflective film is plated at the tail end of the uniform rotation section. The sensing fiber has the characteristics of simple manufacturing and low cost.
Owner:COMCORE OPTICAL TECH
Sagnac interferometer-type fiber-optic current sensor
InactiveUS20110141478A1Current measurements onlyUsing optical meansPower flowSignal processing circuits
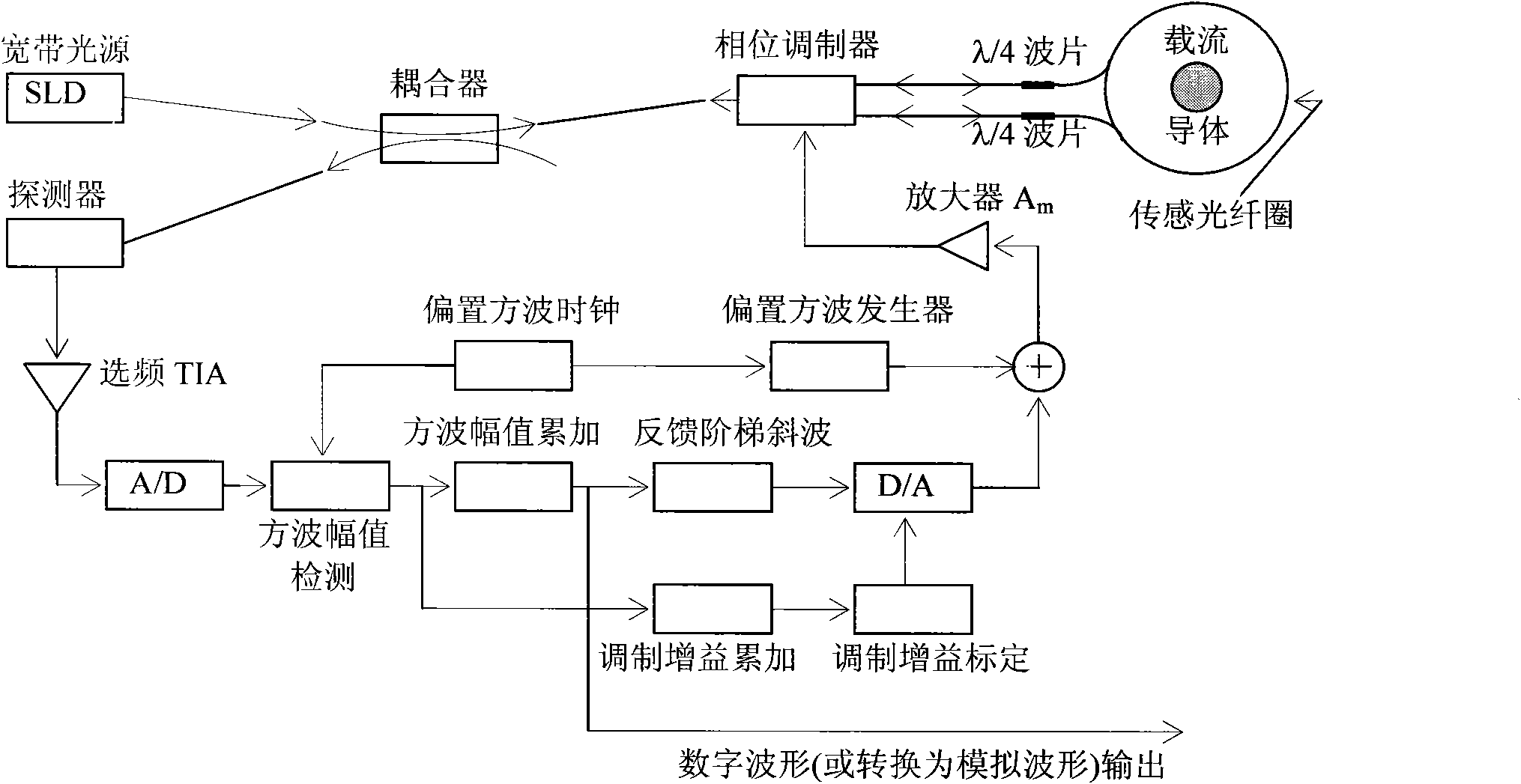
In one embodiment, a Sagnac interferometer-type fiber-optic sensor includes a synchronous detection circuit to carry out synchronous detection of detected light signal with a phase modulation angular frequency of a phase modulator. A signal processing circuit calculates and outputs the magnitude of current to be measured using the signal detected in the synchronous detection circuit. A phase modulator driving circuit controls the driving of the phase modulator. The phase modulator driving circuit controls a phase modulation depth of the phase modulator so that the amplitude of the second-order harmonics and the fourth-order harmonics obtained by carrying out the synchronous detection of the detected light signal with the phase modulation angular frequency becomes the same.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Fiber current sensor
ActiveCN103777063ARealize measurementShorten the lengthVoltage/current isolationMeasurement using digital techniquesFiberCurrent sensor
The invention brings forward a fiber current sensor. The fiber current sensor comprises an optical path unit and an FP cavity which are connected through a polarization maintaining fiber. A quarter wave-plate is connected between the polarization-maintaining fiber and the FP cavity; the optical path unit comprises a light source, an optical circulator, a fiber polarizer and an optical phase modulator which are successively connected; the optical circulator is also connected with a signal processing unit through a photoelectric detector; the FP cavity comprises a polarization-maintaining coupler, a first Faraday rotating mirror, a second Faraday rotating mirror, and a sensing fiber for connecting with a current lead to be detected; one end of the sensing fiber is connected with the first Faraday rotating mirror; the other end of the sensing fiber is connected with one port at one side of the polarization-maintaining coupler; and two ports at the other side of the polarization-maintaining coupler are respectively connected with the second Faraday rotating mirror and the quarter wave-plate. The sensor provided by the invention can improve the precision of current measurement, especially for the measurement of low currents, so that a feasible method is provided for current measuring engineering of the fiber current sensor.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Fiber optic current sensor system and method for detecting lightning
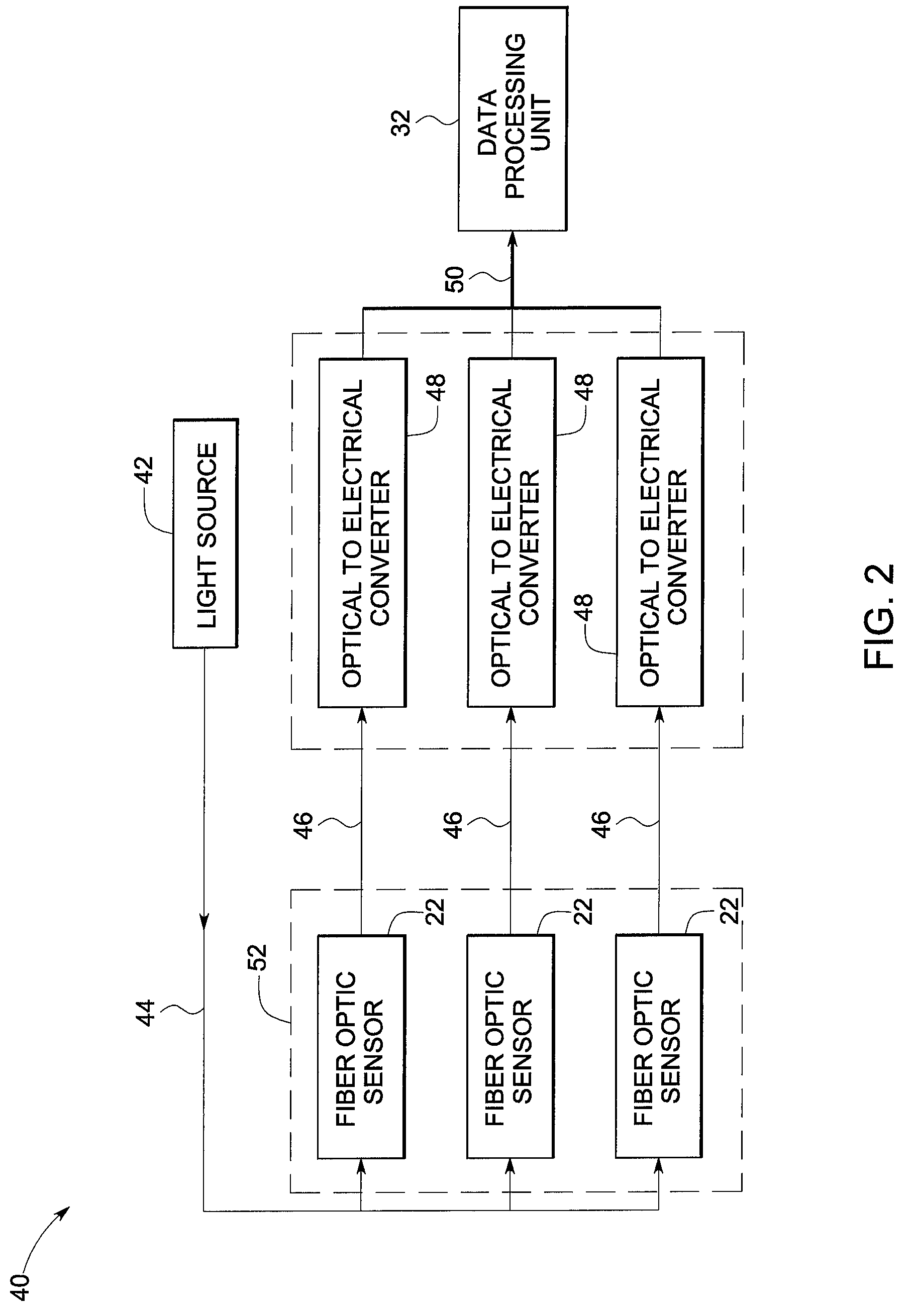
A system for lightning detection is provided. The lightning detection system includes a conductor configured to receive a lightning strike and transmit a lightning induced current. The system also includes a fiber optic current sensor configured to detect multiple lightning parameters from the lightning induced current and to modulate a beam of radiation in response thereto. The system further includes an electro-optic module configured to receive and convert the beam of radiation from the fiber optic current sensor to an electrical signal.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Fiber optic current sensor
ActiveUS20120286767A1Increased sensitivity and precisionReduce sensitivityElectrical testingMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesPhotodetectorCurrent sensor
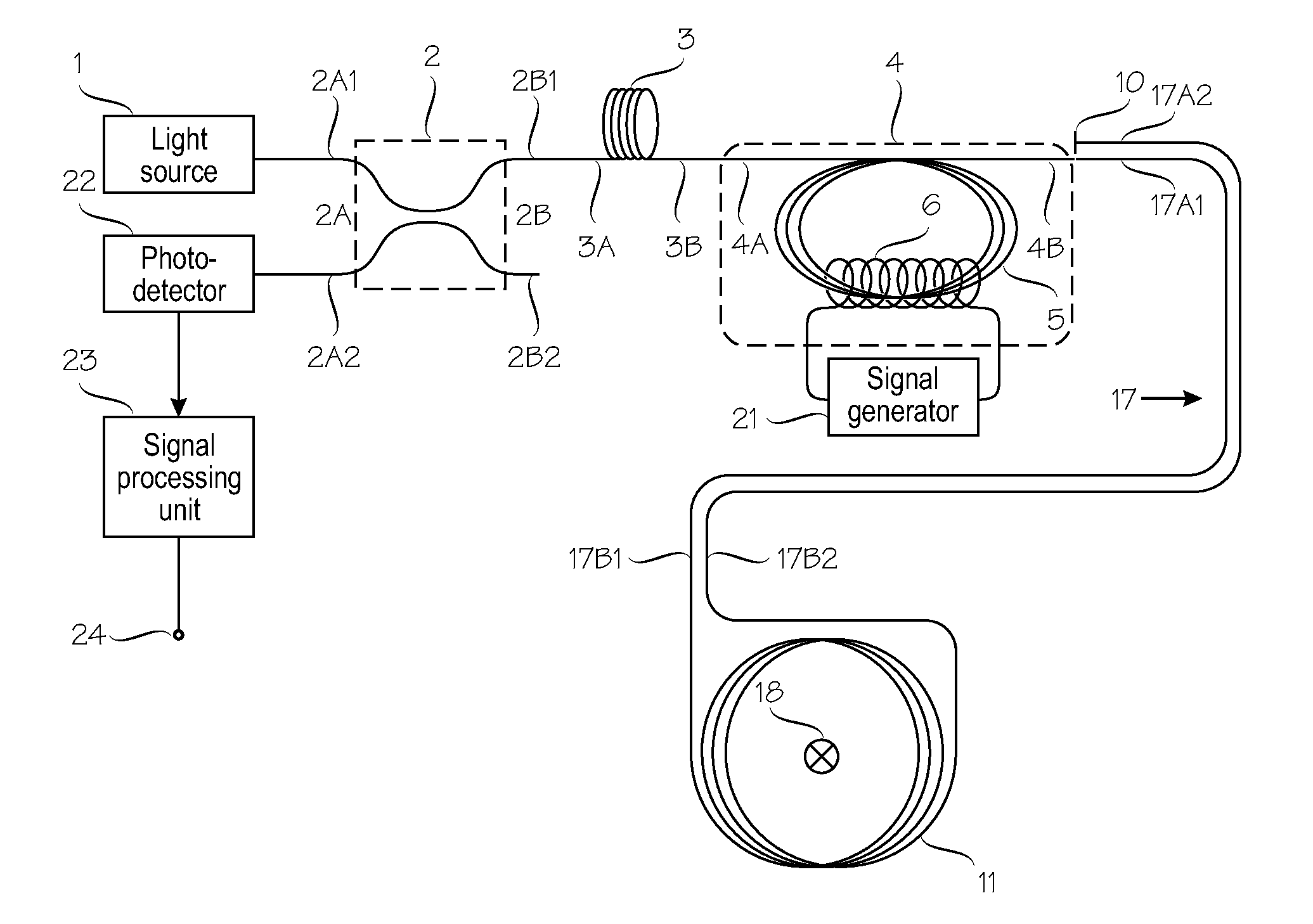
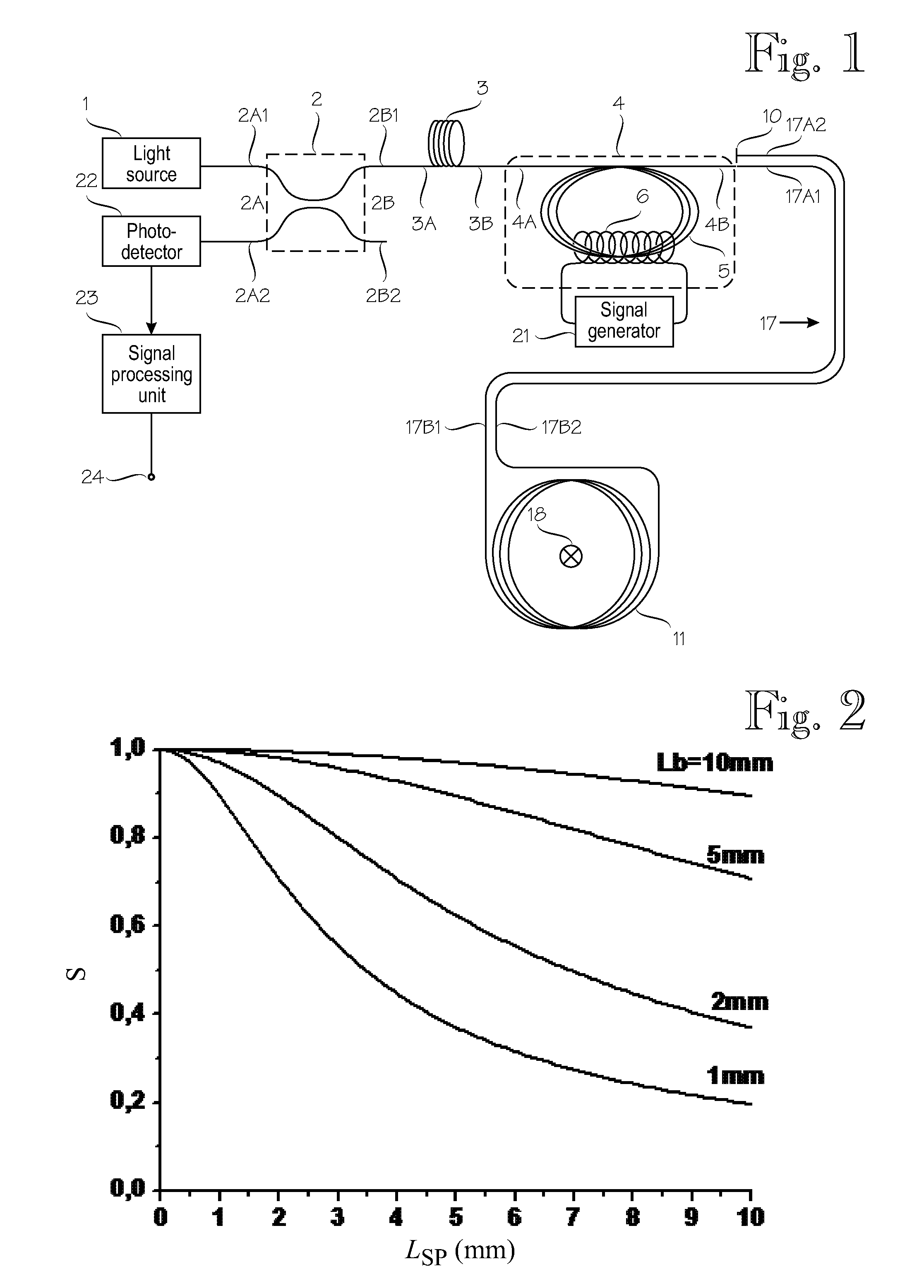
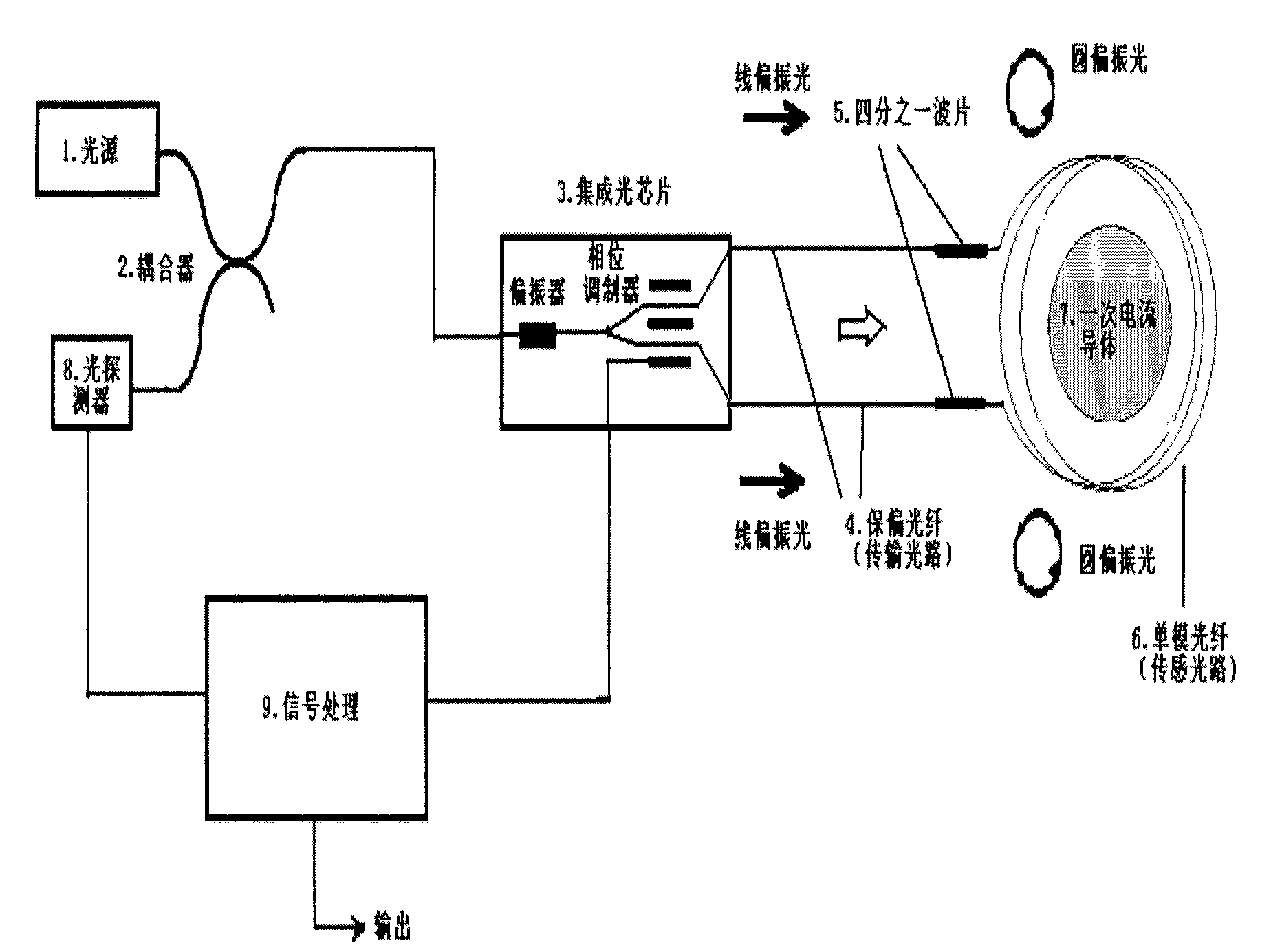
A Fiber-optic current sensor for sensing electric current carried in an electric conductor (18). Its optical section comprises: a light source (1); a directional coupler (2) with two ports (2A, 2B) of two arms each; a radiation polarizer (3); a polarization modulator (4); a fiber line (17) coupled to a current-sensing fiber loop (11); a mirror (10); and a photodetector (22). The first port of the coupler (2) is coupled to the light source (1) and to the photodetector (22). Its second port is coupled via the radiation polarizer (3) to the polarization modulator (4). The polarization modulator comprises a magneto-sensitive element (5), around which a solenoid (6) is wound. The fiber loop (11) comprises a magneto-sensitive optical fiber with embedded linear birefringence. An electronic section comprises a signal generator (21) which drives the solenoid (6); and a signal processing unit which receives the optical signal from the photodetector (22).
Owner:CLOSED PROFOTECH CJSC PROFOTECH
Method for preparing sensitive coil of reflection type optical fiber current sensor
ActiveCN101408559AImprove stabilityGood shock and vibration resistanceCurrent/voltage measurementVoltage/current isolationFiberCurrent sensor
The invention relates a method for making a sensor coil of a reflective optical fiber current sensor. A groove which takes the shape of the spiral of Archimedes is processed on a ring-shaped metallic framework, and sensitive fiber is wound in the groove; after filled with fiber paste and fixed, the groove is sealed; finally, the stress on the sensitive fiber is released by temperature ictus and vibration, thus causing the state of the sensitive fiber to be stable. The method of the invention can ensure that the sensitive fiber coil has good stability even under certain perturbation and can guarantee the ideal measuring precision; meanwhile, in the method of the invention, the metallic framework is adopted, so as to reduce the making difficulty and cost and realize the consistency of winding easily with respect to the technique.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE TIMES OPTICAL ELECTRONICS TECH
All optical-fiber current sensor based on magnetic fluid and multi-mode interference and detection method
InactiveCN103592495AOvercome instability flawsReduce volumeCurrent/voltage measurementFiberBeam splitter
The invention discloses an all optical-fiber current sensor based on magnetic fluid and a multi-mode interference structure. The all optical-fiber current sensor comprises a signal detection unit and a sensing unit. The signal detection unit comprises an SLD light source, a 50:50 optical fiber beam splitter, an adjustable optical fiber attenuator, a photoelectric balance detector, a data collection card, a computer, a power-on coil and a programmable power source. The sensing unit comprises a multi-mode coreless optical fiber arranged in a quartz capillary tube, the portion between the quartz capillary tube and the multi-mode coreless optical fiber is filled with magnetic fluid, the two ends of the multi-mode coreless optical fiber are respectively connected with single-mode input and output optical fibers in a welding mode, and the two ends of the quartz capillary tube are sealed by optical solidification glue. According to the all optical-fiber current sensor based on magnetic fluid and the multi-mode interference structure, the sensitivity of the magnetic field generated by the magnetic fluid to the currents and the multi-mode interference theory are used, the change relation between light intensity and currents is directly detected and output to achieve the purpose of detecting currents, and the defect that the polarized light detection method adopted by a traditional all optical-fiber current sensor is not stable is overcome.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Reflection-type Sagnac interference fiber current sensor
InactiveCN102426280AReduce technical difficultyReduce system costVoltage/current isolationCurrent sensorEngineering
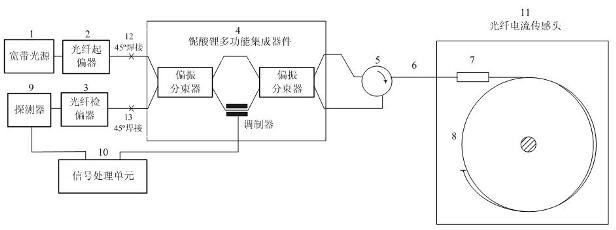
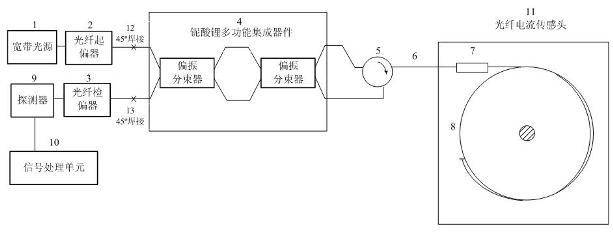
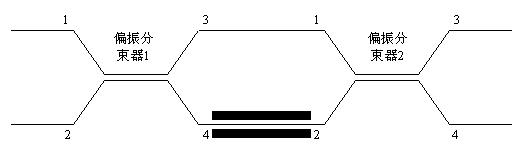
The invention discloses a reflection-type Sagnac interference fiber current sensor. The sensor comprises: a broadband light source, a fiber polarizer, a fiber polarization analyzer, a lithium niobate multifunctional integration device, a fiber loop device, a polarization-maintaining transmission cable, a quarter wave plate, a sensing fiber, a photoelectric detector and a signal processing unit. The lithium niobate multifunctional integration device, which is formed by two polarization beam splitters, is a Mach-Zehnder phase adjusting system. The structure can realize passive bias and can realize active modulation. By using the sensor of the invention, technical difficulty of an active modulation scheme of the interference fiber current sensor can be substantially reduced. Simultaneously, unification of an optical path structure of the two schemes: the passive bias of the fiber current sensor and the active modulation can be realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Optical fiber current sensor based on ring cavity ring-down spectroscopy technology
InactiveCN104950162ASimple manufacturing processHigh measurement accuracyCurrent/voltage measurementVoltage/current isolationSpectrographCurrent sensor
The invention provides an optical fiber current sensor based on the ring cavity ring-down spectroscopy technology, and belongs to the field of optical fiber sensing and magnetic fluid materials. The sensor comprises a tunable laser, an electro-optical modulator, a waveform generator, an optical isolator No.1, a 2*2 coupler No.1, a current sensing unit, an optical isolator No.2, a time-delay single mode fiber, a 2*2 coupler No.2, a high-speed photoelectric detector and a spectrograph, wherein the 2*2 coupler No.1, the current sensing unit, the optical isolator No.2, the time-delay single mode fiber and the 2*2 coupler No.2 are combined to form a ring cavity. The sensor has the advantages of being practical, reliable, ingenious in design, high in measurement precision and convenient for tuning.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Novel optical fibre current sensor system
InactiveCN101672865AEasy to installReduce volumeCurrent/voltage measurementCoupling light guidesCurrent sensorEngineering
The invention provides a novel optical fibre current sensor system, comprising a control unit and a sensing head connected with the control unit through a sensing optical cable. The sensing head comprises an electric cable and a sensing optical cable winding the electric cable; a sensing optical fibre and a reference optical fibre are encapsulated in the sensing optical cable; magnetostrictive materials are coated on the sensing optical fibre; the control unit comprises a laser, an optical fibre coupler connected with the laser, a reflector connected with the optical fibre coupler through thesensing optical cable, a photoelectric converter connected with the optical fibre coupler, a data processor connected with the photoelectric converter and a signal collector connected with the data processor and used for collecting output signals of the data processor and transmitting the signals to a computer for analysis and processing. The system adopts the optical fibre as the sensing medium and has the characteristics of high sensitivity, small volume, anti-electromagnetic interference, high-voltage resistance, favorable safety, and the like when compared with the traditional current sensor.
Owner:SHANGHAI BOOM FIBER SENSING TECH
Miniature optical fiber current sensor probe and making method thereof
InactiveCN101915865AQuick responseWith insulationCladded optical fibreVoltage/current isolationFiberGrating
The invention relates to a miniature optical fiber current sensor probe and a making method thereof. The probe is formed by butt welding a D type fiber bragg grating (9) sputtered with a TbDyFe thin film (10) and an uncoated reference grating (8) with the same central wavelength as the D type fiber bragg grating (9), wherein the D type fiber bragg grating (9) sputtered with the TbDyFe thin film is formed by sputtering a layer of giant magnetostrictive material TbDyFe thin film on a fiber bragg grating with polished sides, and the thickness of the thin film is 2-20 mum. The miniature optical fiber current sensor probe is made by combining a magnetostrictive TbDyFe thin film sensitive to a magnetic field with an anti-electromagnetic interference D type fiber bragg grating. Because a magnetic-control sputtering process, a heat processing process and a temperature compensation technique are adopted, the accuracy and the sensitivity of a sensor are greatly improved, and the volume of the sensor probe is greatly reduced, thereby the sensor probe is beneficial to the miniaturization of an optical fiber current sensor.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
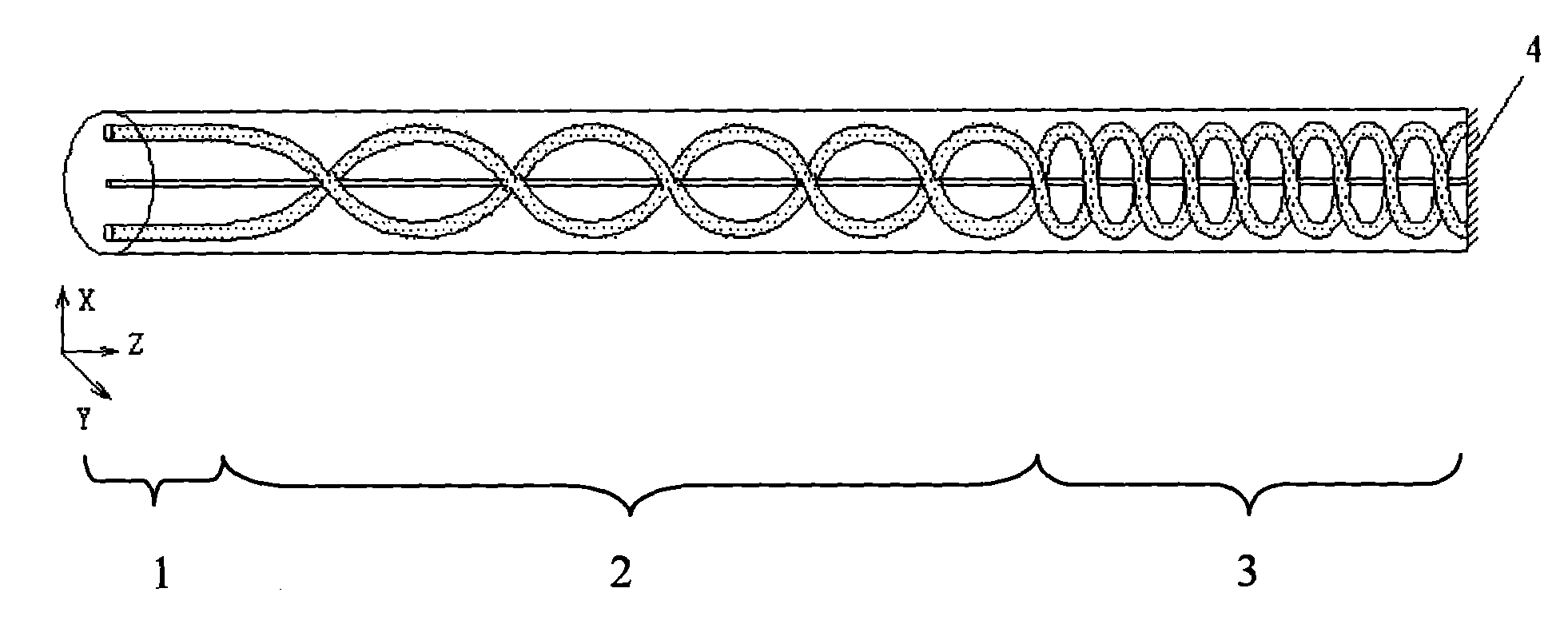
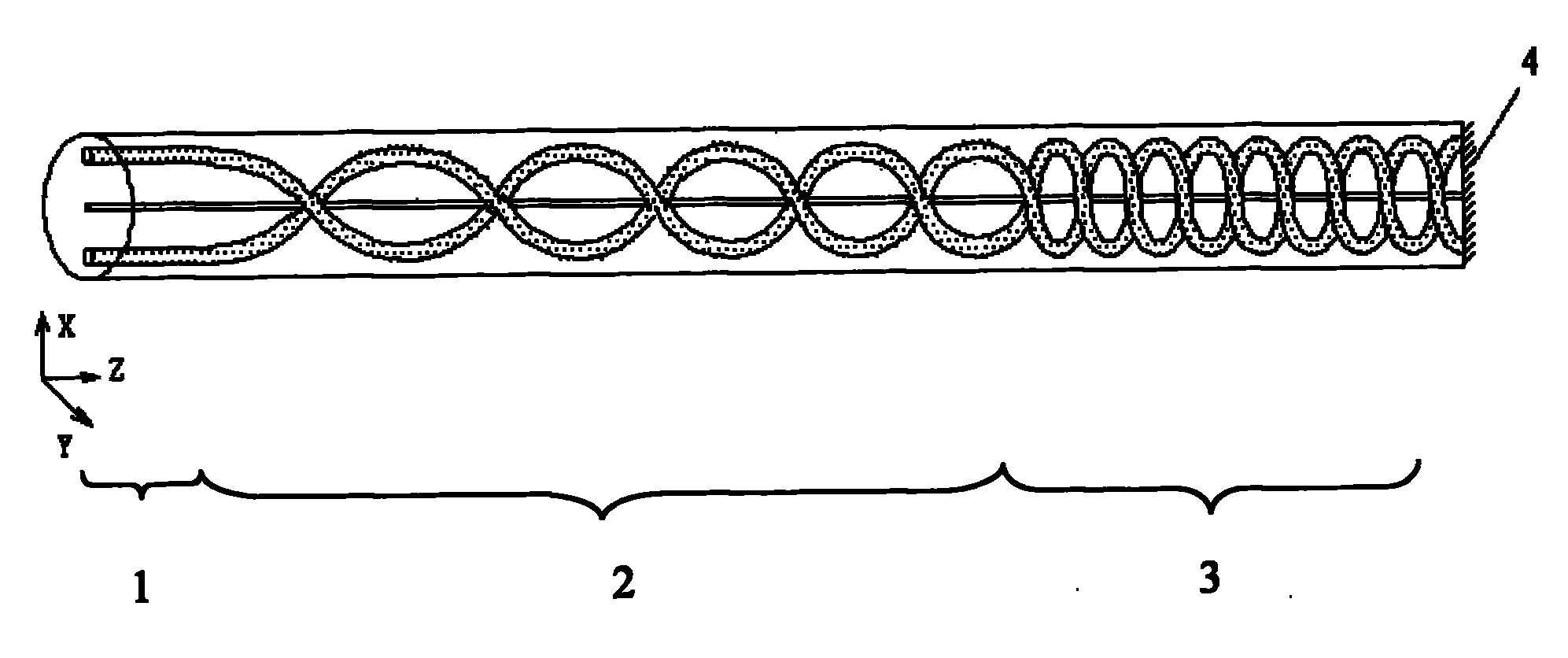
Sensing fiber, sensing fiber ring and through-type all-fiber current sensor
ActiveCN102393546AGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed stabilityOptical fibre with polarisationCurrent/voltage measurementAnti jammingPower flow
The invention discloses a sensing fiber which comprises a spiral velocity ascending portion, a spiral velocity keeping portion and a spiral velocity descending portion in turn, wherein the spiral velocity ascending portion and the spiral velocity descending portion are symmetric, and have the same length and symmetrically same spiral velocity. The invention also discloses a sensing fiber ring made of the sensing fiber, wherein the start point of a spiral velocity ascending portion and the start point of a spiral velocity descending portion of the sensing fiber ring are superposed on a spatial diameter position; and the end point of the spiral velocity ascending portion and the end point of the spiral velocity descending portion are superposed on a spatial diameter position. The sensing fiber disclosed by the invention has the same thread pitch on any symmetric positions, and the sensing fiber ring made of the sensing fiber is equivalent to a closed loop, thus the anti-jamming performance of the sensing fiber ring and the current accuracy and stability of a tested bus are ensured. The invention also discloses a through-type all-fiber current sensor.
Owner:上海康阔光智能技术有限公司
Method for manufacturing full-fiber quarter wave plate
InactiveCN101620287ASimple preparation processImprove welding success ratePolarising elementsVoltage/current isolationCurrent sensorEngineering
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a full-fiber quarter wave plate. A Sagnac interferometer type full-fiber current transformer comprises modules such as a sensing light path, a transmission fiber from a high-voltage part of 110kV to 550kV to 1,000kV to a control room of a power station, a signal processing electronic circuit, an interface circuit of a merging unit and the like, accords with the standard of IEC 60044-8, and is applicable to the industry of electric transmission and transformation and other situations for measuring high current. A full-fiber current sensor realizes current sensing by changing a phase of circularly polarized light of a (gauge outfit) in a sensitive coil through the current. The method for manufacturing the quarter wave plate, namely a key component for realizing mutual conversion of linearly polarized light and circularly polarized light in the full-fiber current transformer comprises the steps of selecting a wave plate, welding the wave plate, a transmission light path and the sensing light path, and protecting welding spots.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINYUE METER FACTORY
Fiber-optic current sensor
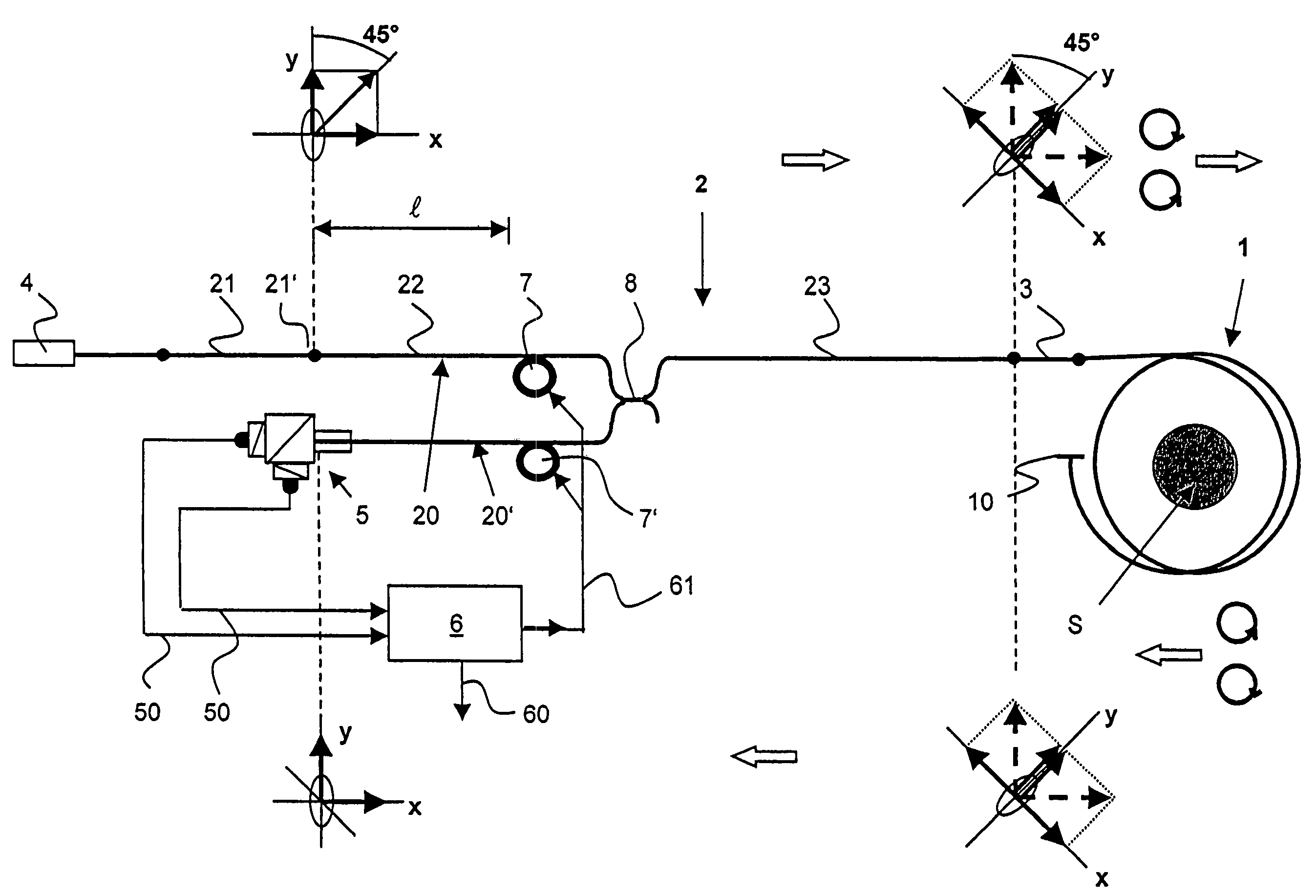
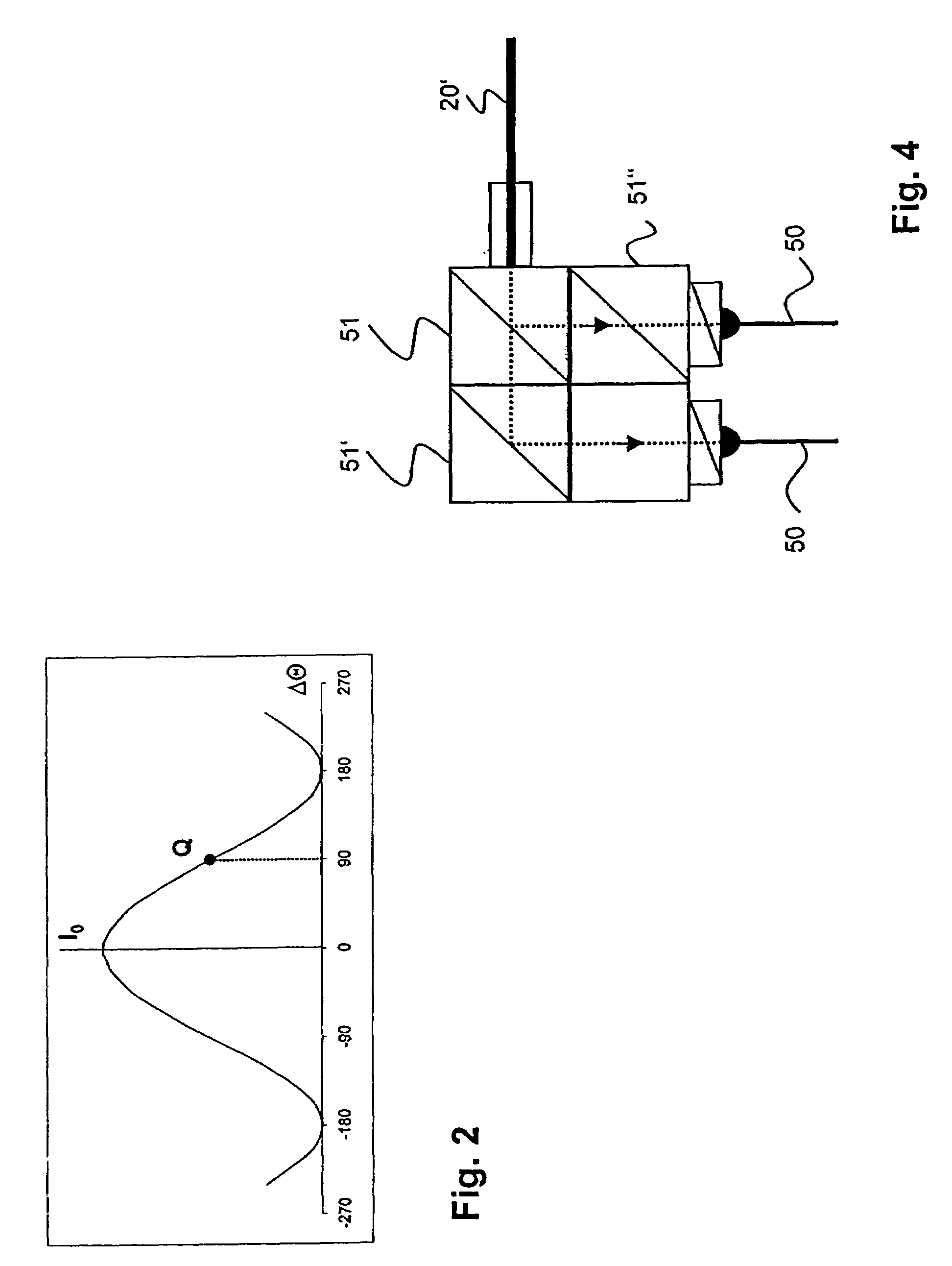
InactiveUS7075286B2Improve long-term stabilityRadiation pyrometryCurrent/voltage measurementFiberPhase shifted
Owner:ABB RES LTD
Temperature Compensated Fiber-Optic Current Sensor
ActiveUS20150115934A1Reduce the impactReduce impactCurrent/voltage measurementElectrical testingFiberCurrent sensor
In a fiber-optic current sensor, a 22.5° Faraday rotator, which is part of the sensing fiber coil, determines the working point of the sensor. The coil is operated with substantially linearly polarized light or incoherent substantially left and right circularly polarized light waves. In one arrangement, a polarization beam splitter generates two optical signals that vary in anti-phase with changing current. A signal processor determines the current from the two anti-phase signals. Appropriately detuned and oriented fiber-optic half-wave or quarter-wave retarders before the fiber coil are used to reduce or cancel the adverse effects of temperature and bend-induced birefringence on the measurement signal. Moreover, the temperature may be derived from the difference in the bias of the anti-phase signals and may be used to cancel temperature effects in the signal processor.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
Electric power system harmonics analysis method based on multilayered feedforward neural network
InactiveCN102353839AImprove accuracyAccurate amplitudeSpectral/fourier analysisNeural learning methodsElectric power systemFourier transform on finite groups
The invention discloses an electric power system harmonics analysis method based on a multilayered feedforward neural network in the electric power system signal testing technology field. In the invention, an electric power system voltage or current signal is obtained through an optical fiber voltage sensor or an optical fiber current sensor, single hidden layer of the multilayered feedforward neural network is established; an excitation function is a sine and a cosine function and a variable parameter is a harmonic amplitude and an angular frequency; a Hanning window is performed to an obtained electric power system signal; and then discrete fourier transform (DFT) is performed; the sine and cosine component amplitude of each corrected subharmonic and the harmonic angular frequency are taken as an initial weight value of the neural network; an RPROP algorithm training is employed on the basis of the initial weight value; the amplitude and the frequency of the each subharmonic can be acquired according to the trained weight value. By using the method of the invention, accuracy of a calculating result is high and a speed is fast. The harmonic wave analysis accuracy at short sampling time can be greatly raised. A principle is simple and the method is easy to be realized.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Capacitive equipment partial discharge detection method based on optical fiber current sensor
InactiveCN103869224AAccurate detectionKeep abreast of insulation agingTesting dielectric strengthSpecial data processing applicationsSystem testingMathematical model
The invention discloses a capacitive equipment partial discharge detection method based on an optical fiber current sensor. The capacitive equipment partial discharge detection method based on the optical fiber current sensor mainly comprises the following steps: establishing a mathematical model of the optical fiber current sensor; designing the structure of the optical fiber current sensor; analyzing and testing the performance of the optical fiber current sensor; testing a local discharge experiment system. According to the capacitive equipment partial discharge detection method based on the optical fiber current sensor, which is disclosed by the invention, the defects of poor antijamming capability, low reliability, small applicable range and the like in the prior art can be overcome, and the advantages of good antijamming capability, high reliability and big applicable range can be realized.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
All-fiber current sensor and polarization state control method thereof
ActiveCN101968508AAngle error is smallAvoid the effects of birefringenceCurrent/voltage measurementVoltage/current isolationCurrent sensorPolarizer
The invention discloses an all-fiber current sensor and a polarization state control method thereof. The all-fiber current sensor comprises a laser device, a fiber loop assembly for sensing the change of a current magnetic field, a first polarization controller arranged at the input end of the fiber loop assembly, a second polarization controller arranged at the output end of the fiber loop assembly, a fast polarization state detector and a high pass filter which are sequentially arranged. Being different from the all-fiber current sensor in the prior art, the invention has no polarizer and analyzer, but directly detects the change of polarization state on the equator of a Poincare sphere based on the principal state principle and filters temperature interference and other environmental interferences by means of the filter.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
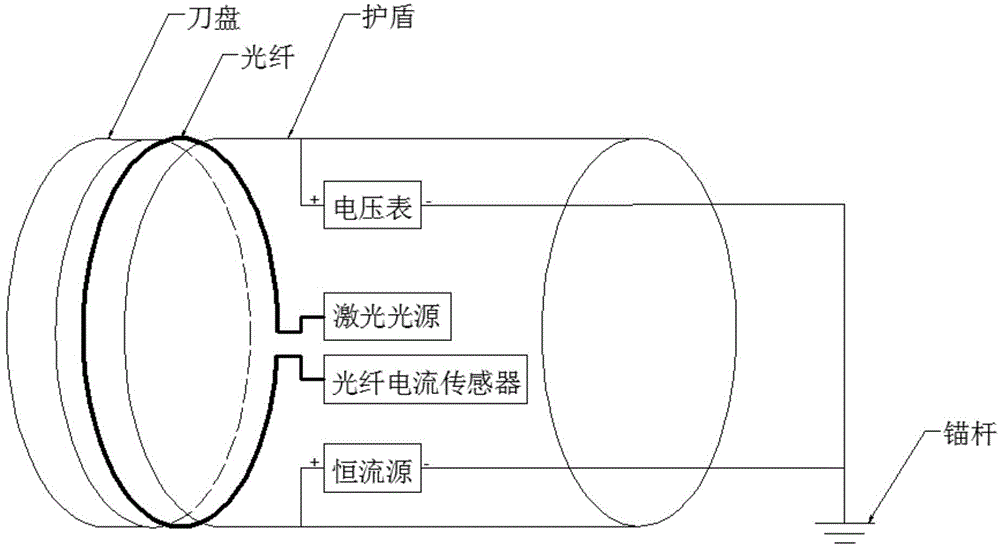
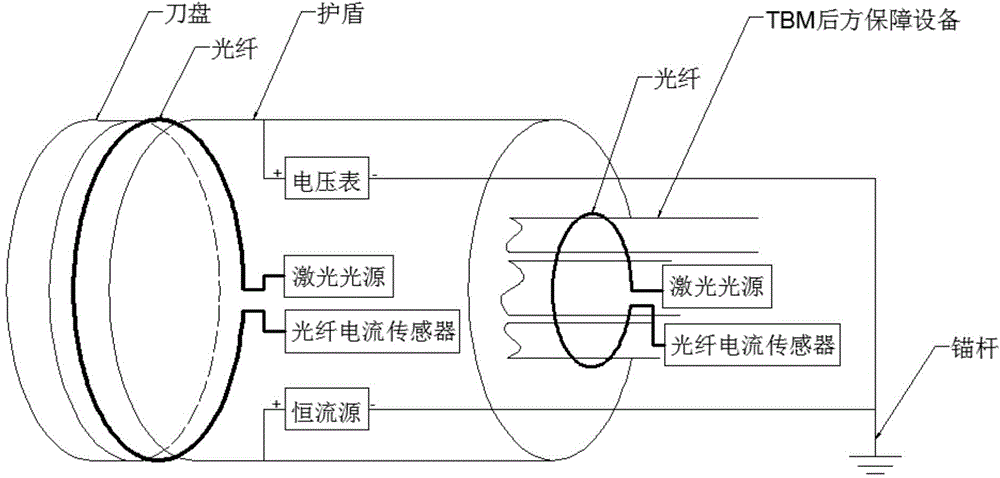
Bore-tunneling electrical ahead monitoring device based on optical fiber current sensor, and detection method thereof
InactiveCN104932023ABypassing the challenge of uninterrupted measurementMeet analysis requirementsWater resource assessmentElectric/magnetic detectionElectrical resistance and conductanceVoltmeter
The invention discloses a bore-tunneling electrical ahead monitoring device based on an optical fiber current sensor, and a detection method thereof. The bore-tunneling electrical ahead monitoring device is composed of a constant current source, a voltmeter, a laser light source, the optical fiber current sensor and an anchor rod. A tunneling part of a tunnel boring machine (TBM) is supplied with a constant current I, a circle of an optical fiber winds around the rear part of a cutterhead and the rear part of a shield, the magnitude of current on each of the cutterhead, the shield and TBM rear guaranteeing equipment can be obtained by using the optical fiber current sensor, and voltage on the shield is measured for calculating apparent resistance of a geologic body, so as to judge water content and rock class of the geologic body. Compared with the traditional bore-tunneling electrical ahead monitoring method, the bore-tunneling electrical ahead monitoring device based on the optical fiber current sensor omits a great deal of pre-insulating operation.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Ring cavity type all-fiber current sensor
InactiveCN104597304ASimple structureShorten the lengthCurrent/voltage measurementVoltage/current isolationPhase shiftedCurrent sensor
The invention relates to a ring cavity type all-fiber current sensor, including a phase modulator, a delay coil, a 1 / 4 wave plate and a fiber ring cavity which are sequentially arranged on the light path of incident light, wherein the fiber ring cavity, the 1 / 4 wave plate, the delay coil and the phase modulator are also sequentially arranged on the light path of return light; the fiber ring cavity includes a sensing fiber and a coupler, the port on one side of the coupler is connected with the 1 / 4 wave plate, two ports on the other side of the coupler are respectively connected with two ends of the sensing fiber, and the splitting ratio of the coupler is 1:99 to 15:85. According to the ring cavity type all-fiber current sensor, the Faraday phase shift caused by current can be significantly increased, and meanwhile the cost is reduced and the small current measurement accuracy and measurement range of the fiber current sensor are improved.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER SCI RES INST OF GUIZHOU POWER GRID CO LTD +1
Sensor probe for fiber-based current sensor
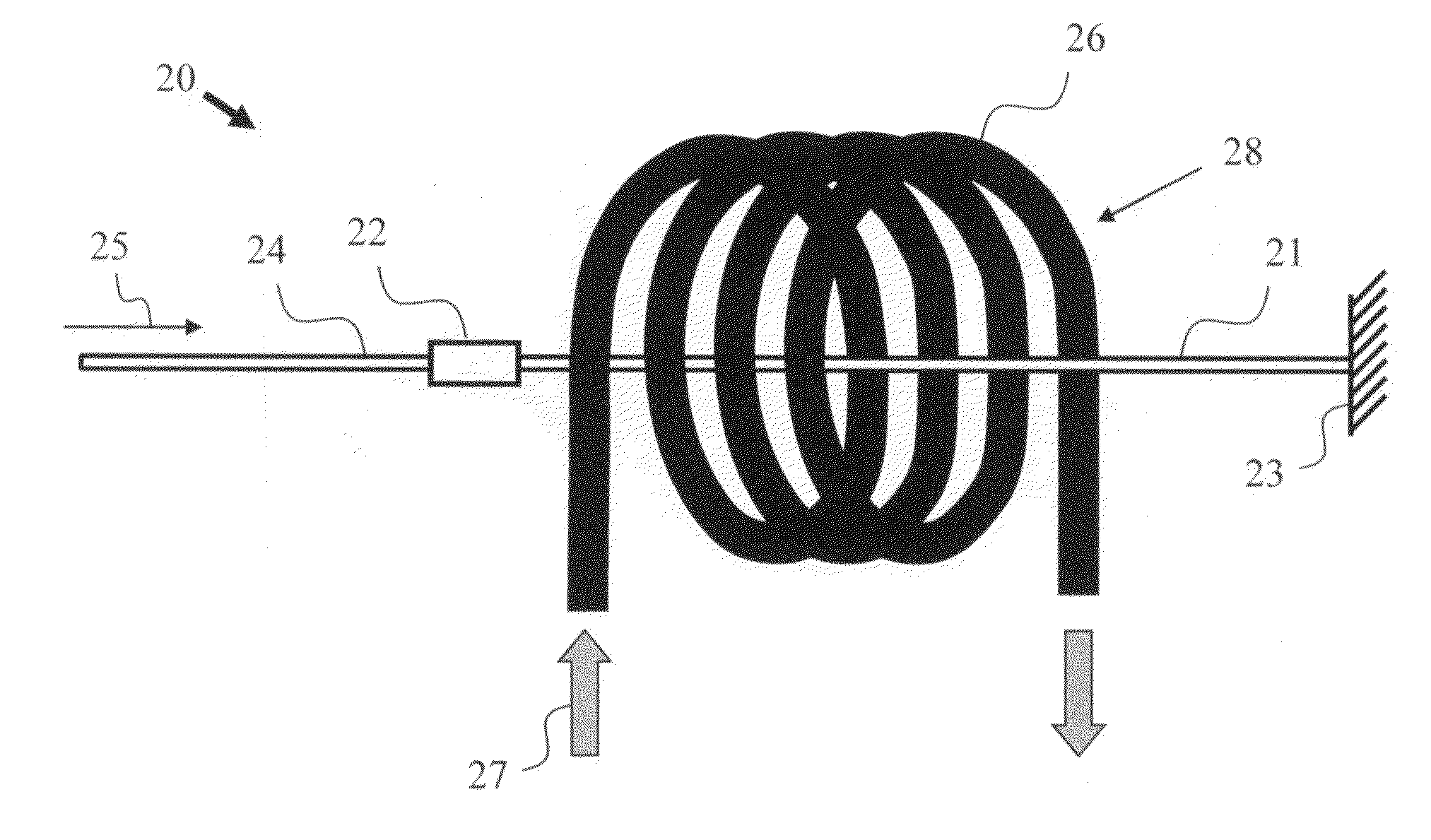
InactiveUS20100141955A1Manufacture of electrical instrumentsUsing optical meansFiberElectrical conductor
Embodiments of the present invention provide a sensor probe for fiber-based electric current sensors. The sensor probe includes a conductor of spiral shape and a relatively straight optical fiber being placed at a through-hole formed by the spiral shape conductor. An electric current conveyed by the spiral shape conductor causes polarization direction of a light traveling along the optical fiber to rotate. By detecting the amount of rotation that the light experiences at the ends of the optical fiber, the amount of current carried by the spiral shape conductor is determined. Method of making the sensor probe is also disclosed.
Owner:HUANG YONG
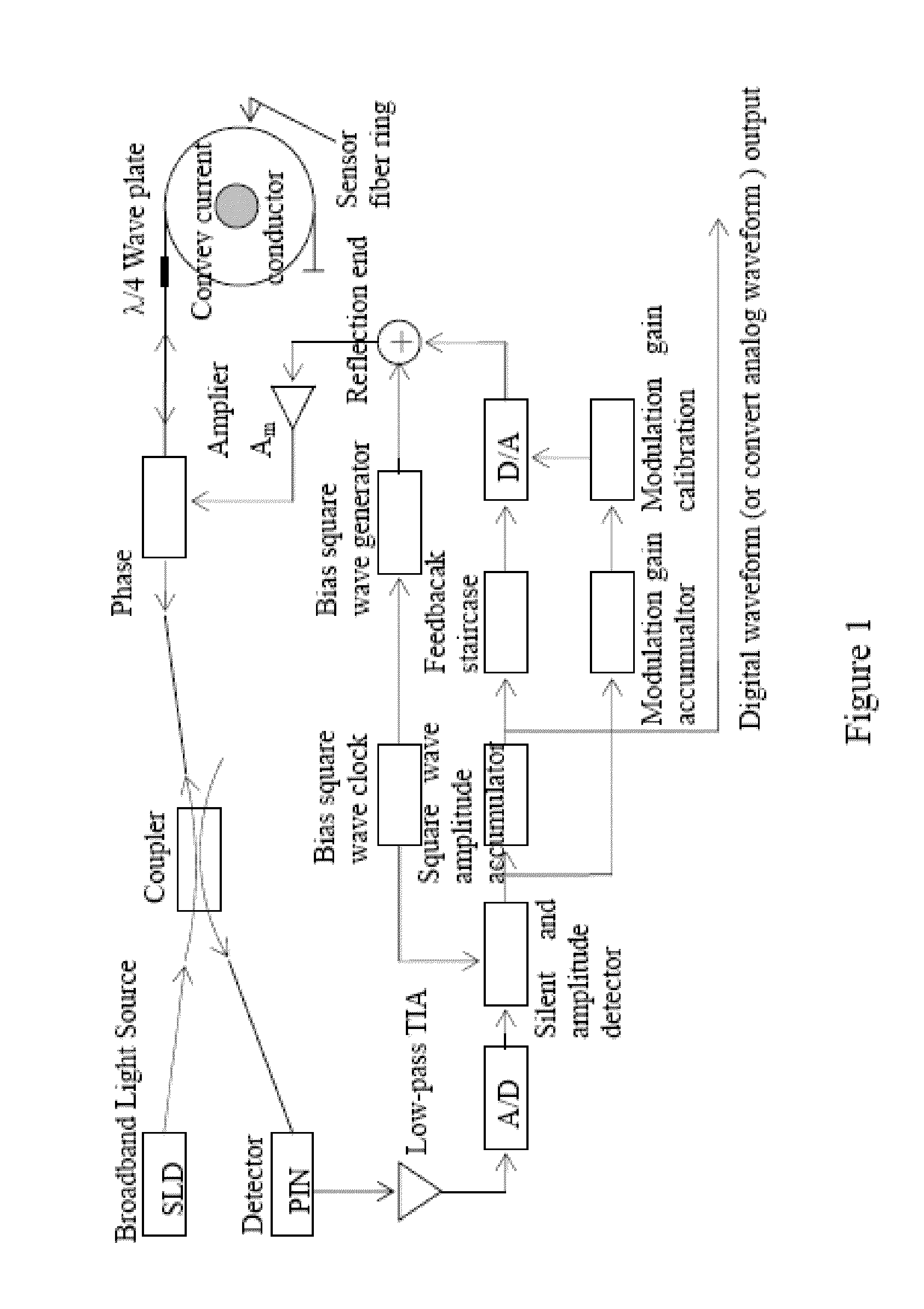
Digital closed-loop fiber optical current sensor
InactiveUS20130278241A1Reduce noise power level of closed-loopHigh bandwidthResistance/reactance/impedenceVoltage-current phase angleFiberClosed loop
This present inversion provides a digital closed-loop fiber optical current sensor. The modulation signal of the optical wave “phase modulator” of the fiber optical current sensor system is modulation square wave, signal processing system extracts any harmonic wave of the photoelectric converter output modulation square waves, and extracts the measured current information from it. The preamplifier of signal processing system is transimpedance amplifier TIA, the bandwidth is extracted 1 / 650 instantaneous amplitude square wave directly from the modulation square wave (existing), thus the thermal noise of the preamplifier output and shot noise level is reduced to the existing technology of below 1 / 650; the current-voltage gain of transimpedance amplifier TIA does not depend on the feedback network resistance, thus it can have high current-voltage conversion gain and use low resistance in the feedback network TIA at the same time. So it can reduce resistance thermal noise to negligible that is accounted for a large proportion of TIA output noise.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Polarization insensitive current and magnetic sensors with active temperature compensation
ActiveCN107085130ADetection advantageAvoid electromagnetic interferenceCurrent/voltage measurementThermometers using physical/chemical changesCurrent sensorLight beam
The ivnention discloses a current sensor based on optical sensing and a corresponding temperature sensor. The current sensor comprises: a light source, a first transmission fiber, an optical current sensor probe comprising a beam shifter, a Faraday material, an output beam shifter, a second transmission fiber, an optical detection unit and a measurement module. According to the invention, a polarization insensitive current and magnetic sensor and a system thereof adopting active temperature compensation can ensure sensing precision, measurement range and stability of the optical fiber current sensor when sensing the circuit.
Owner:姚晓天 +1
Optical fibre electric current sensor all-optical fibre sensing head
InactiveCN101216508AEasy to disassembleImprove anti-electromagnetic interference performanceVoltage/current isolationTurn angleCurrent sensor
The invention discloses a full optical fiber sensing head of optical fiber current sensor, which is designed to solve the problems of the prior sensing head such as inconvenience in achieving field installation and detachment. The f sensing head of the invention comprises a beam, a turning angle member, an adjusting member, a connection angle member and a hose. The beam comprises a first lower beam, a first upper beam, a second lower beam, a second upper beam, a third lower beam, a third upper beam, a fourth lower beam and a fourth upper beam. The turning angle member comprises a turning angle A lower plate, a turning angle A lower plate, a turning angle B lower plate, a turning angle B upper plate, a first bending angle lower plate, a first bending angle upper plate, a second bending angle lower plate and a second bending angle upper plate. The connection angle member comprises a connection angle A lower plate, a connection angle A upper plate, a connection angle B lower plate and a connection angle B upper plate. The adjusting member comprises an A adjusting member, a B adjusting member, a C adjusting member and a D adjusting member with the same structures. The full optical fiber sensing head of the invention can be installed and detached on live line with short detachment time. By adopting modularization design ideal, the invention can achieve miniaturized structure design to effectively reduce the weight and the size of the sensing head configuration.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Interference type fiber optic current sensor based on magneto-optic modulation
ActiveCN103197119AReduce technical difficultyCurrent/voltage measurementVoltage/current isolationEngineeringPolarizer
The invention discloses an interference type fiber optic current sensor based on magneto-optic modulation. The interference type fiber optic current sensor based on the magneto-optic modulation comprises a broadband light source, a fiber optic polarizer, a fiber optic coupler, a Faraday magneto-optic modulator, a round polarization-maintaining transmission optical cable, a sensing fiber ring, a photoelectric detector and a signal processing unit. The non-reciprocal magneto-optic modulation avoids the using of a large quantity of polarization-maintaining delay lines, and modulation speed can be decreased at the same time. Due to the using of the round polarization-maintaining transmission optical cable, the polarization state of light is well controlled, and alignment of a polarization main shaft is not needed during welding. According to the interference type fiber optic current sensor based on the magneto-optic modulation, technical difficulty of an active modulation scheme of the interference type fiber optic current sensor can be greatly reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com