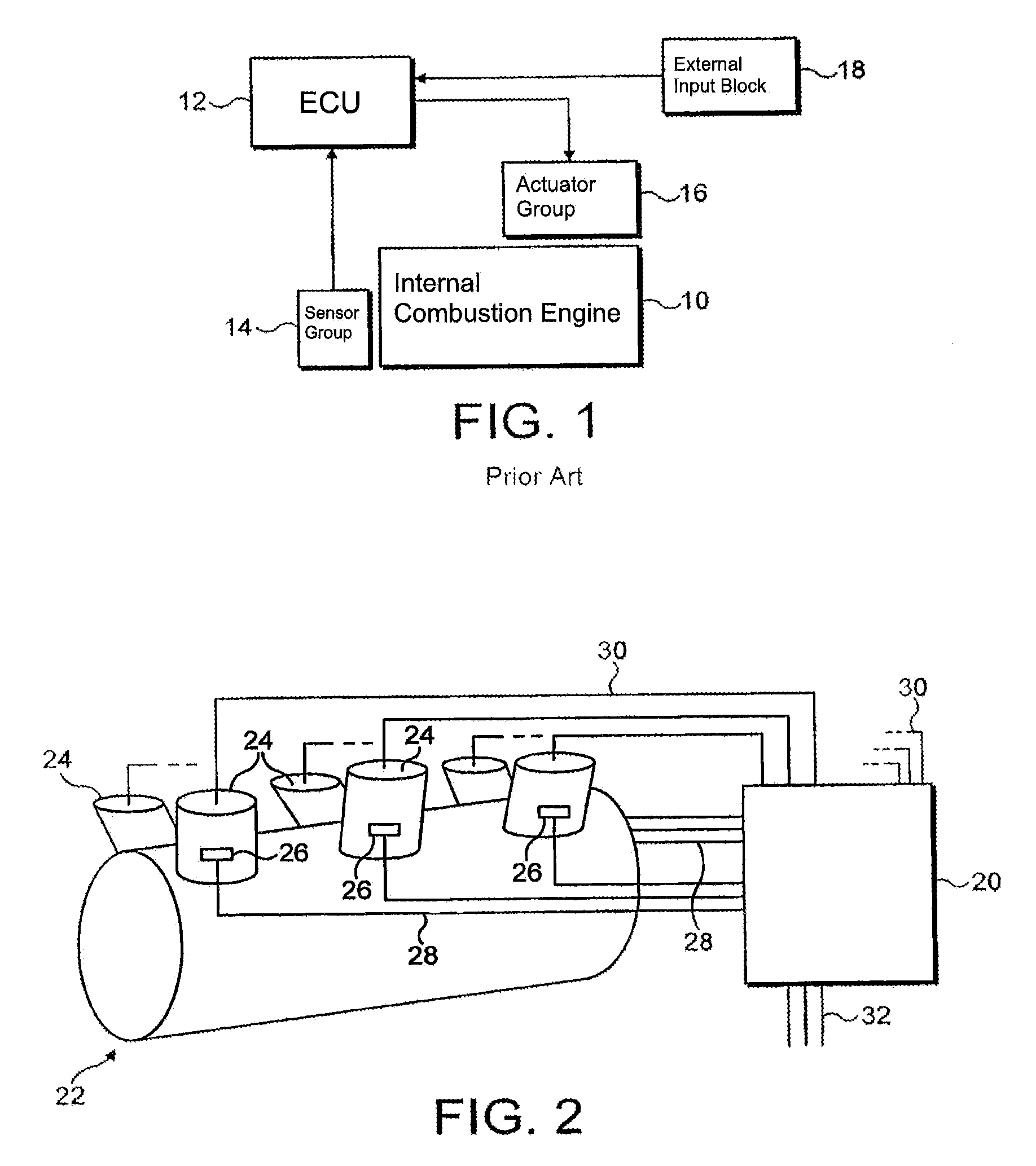
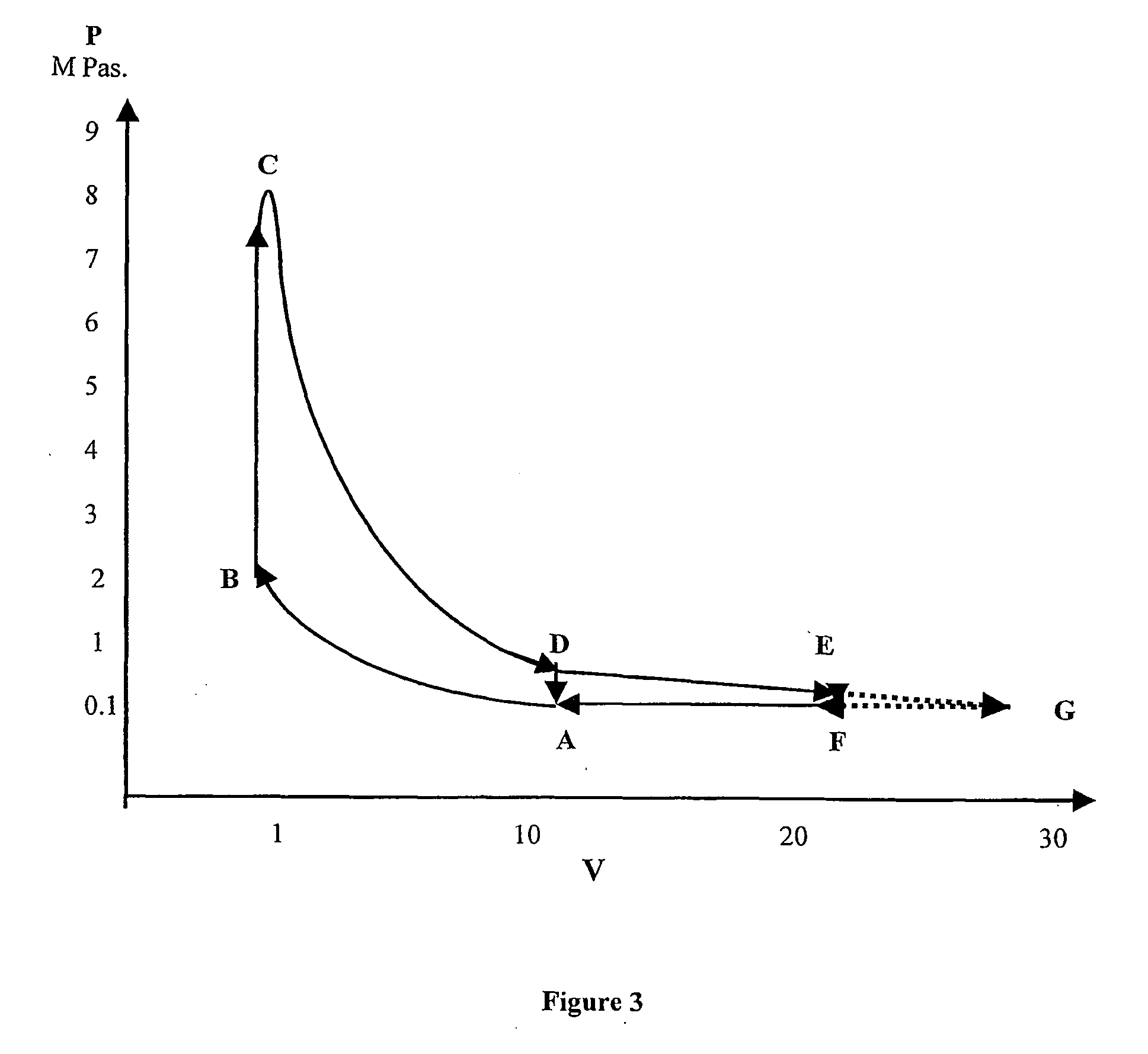
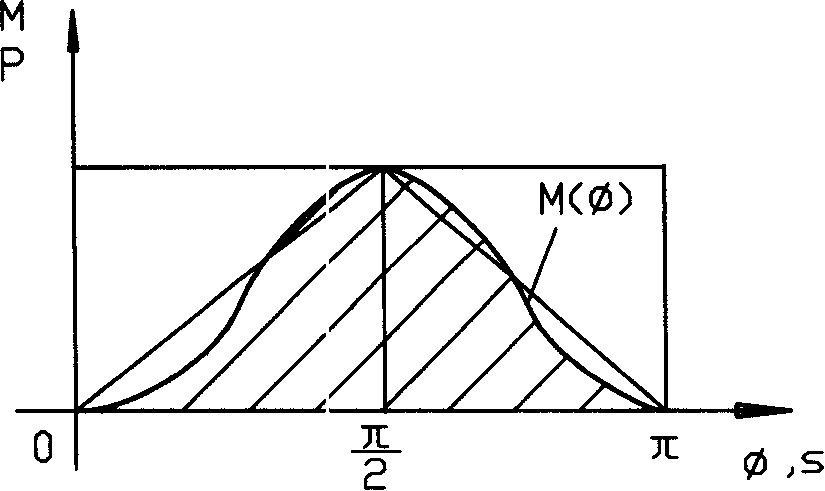
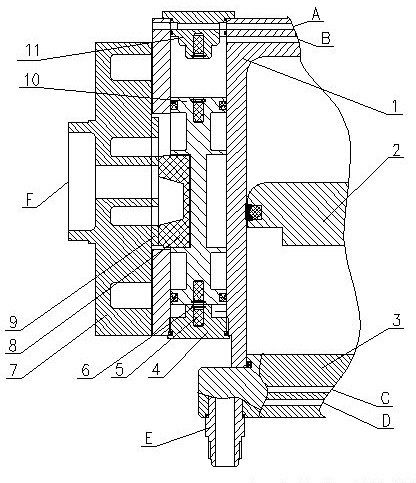
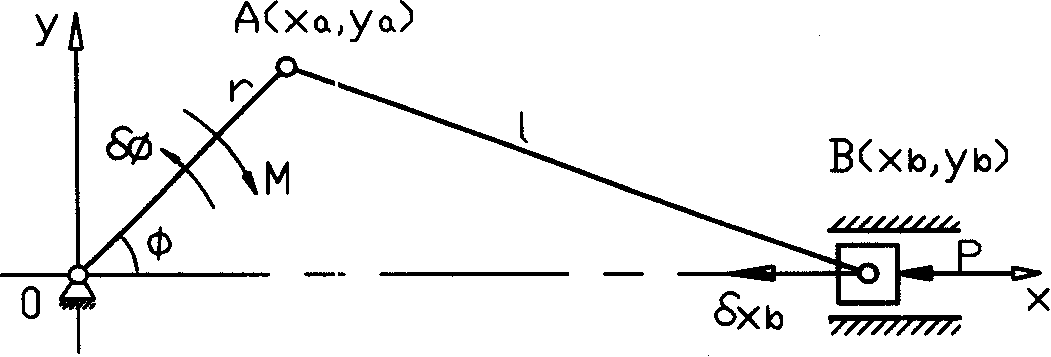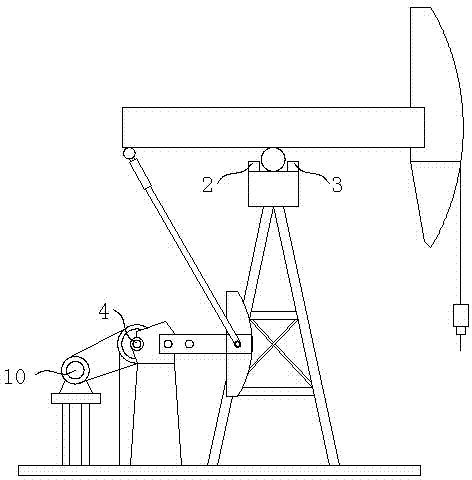Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
122 results about "Dead centre" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
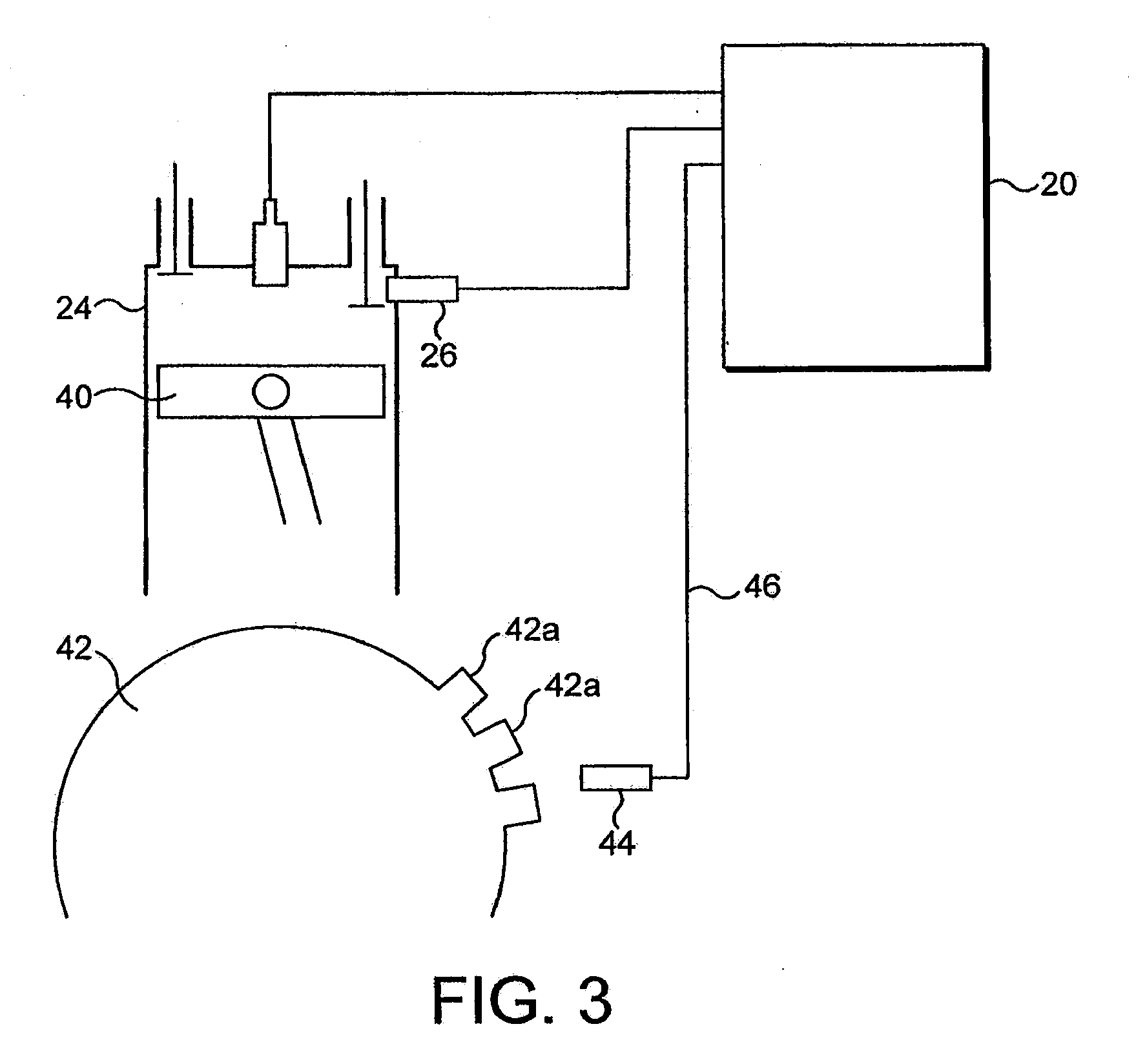
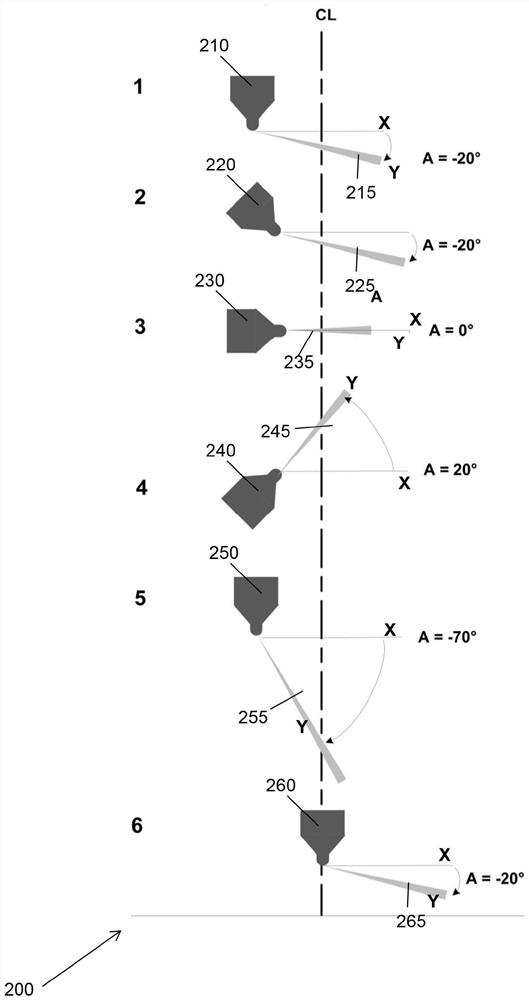
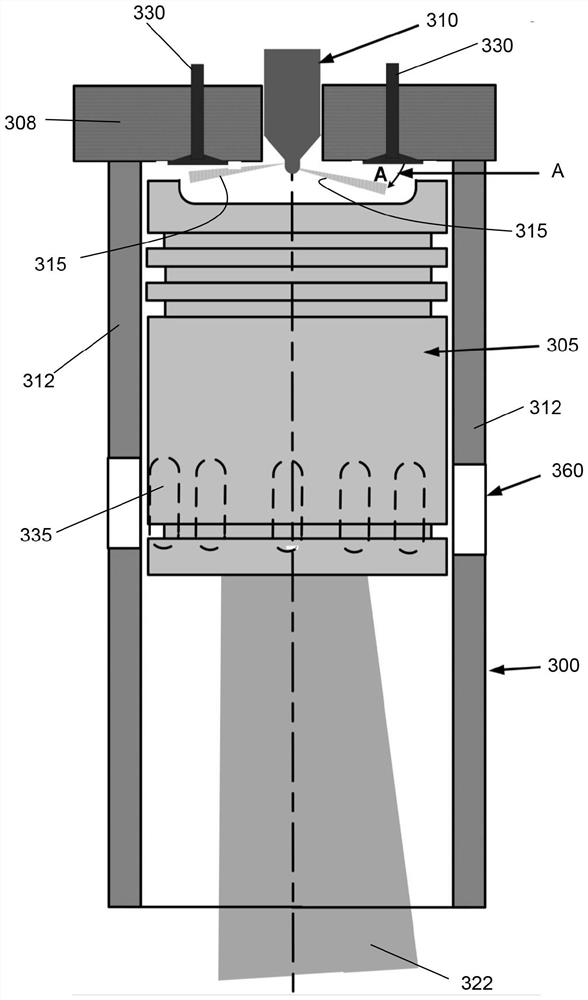
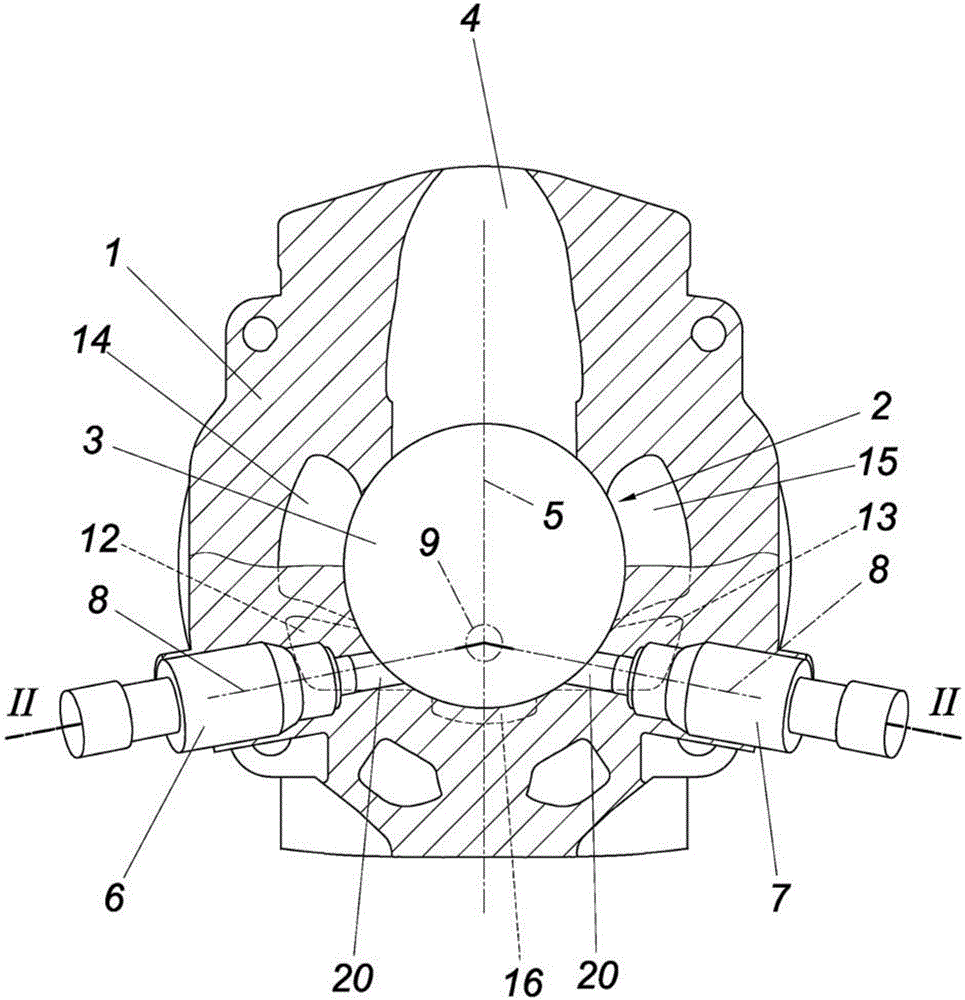
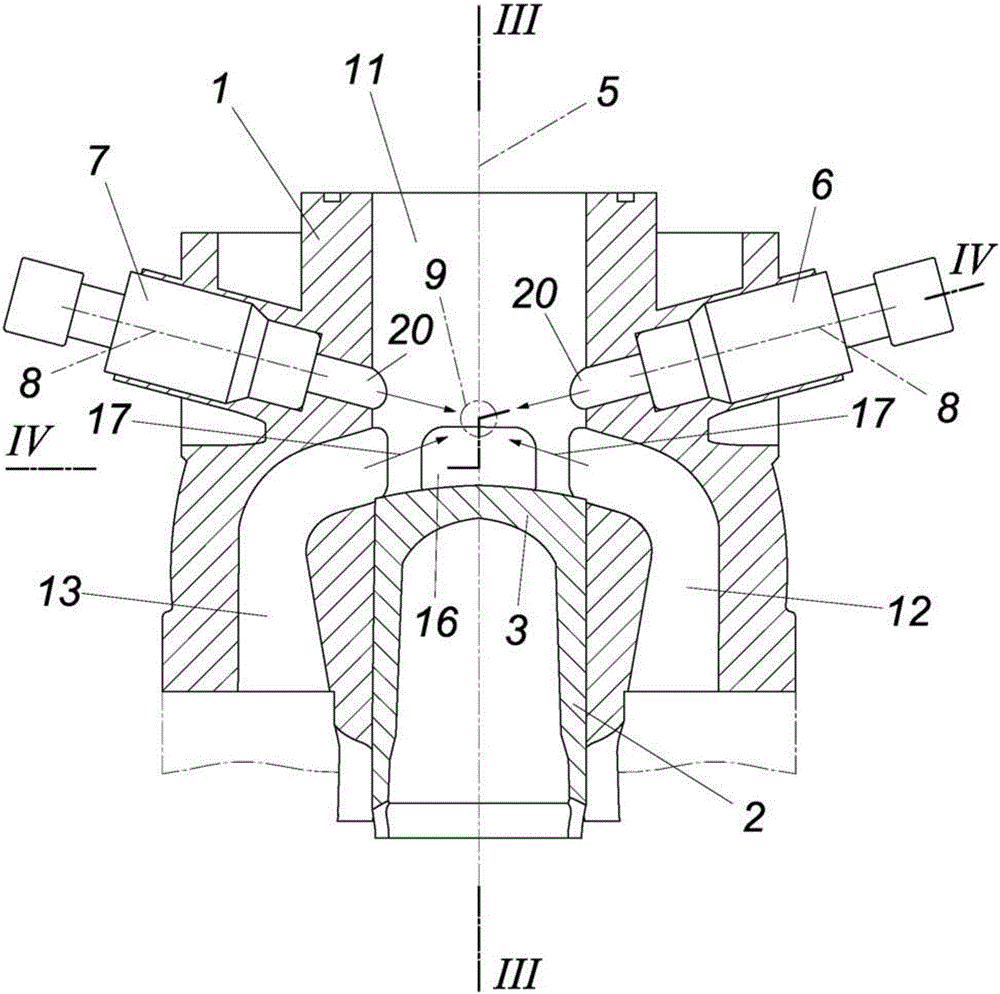
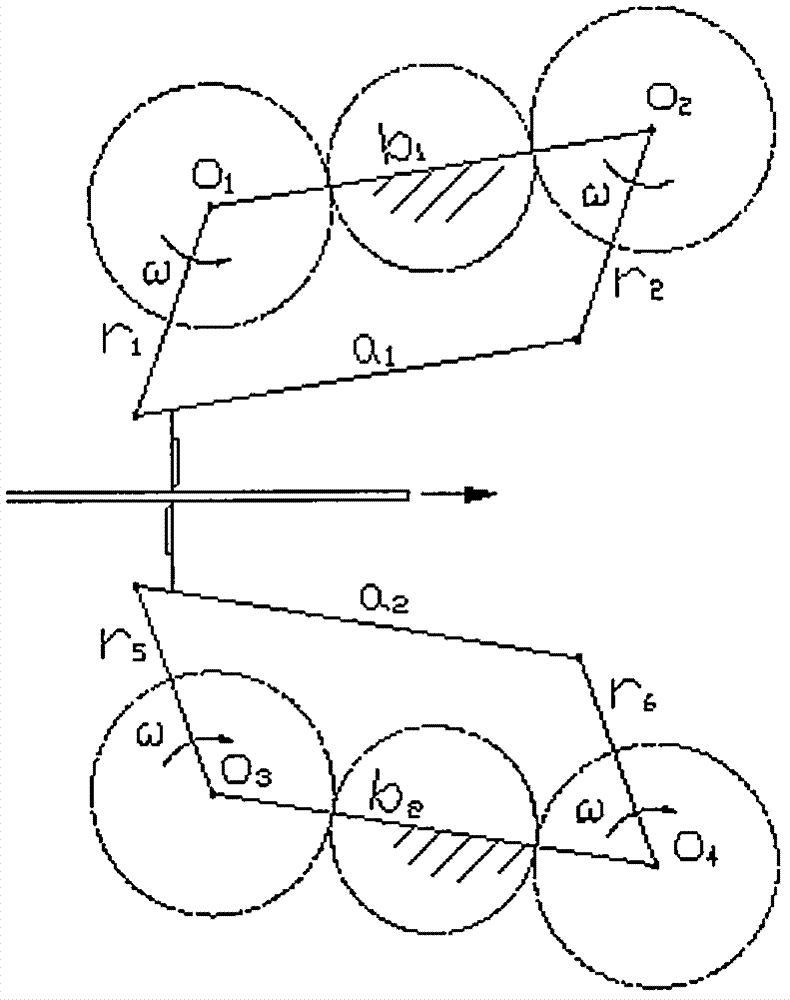
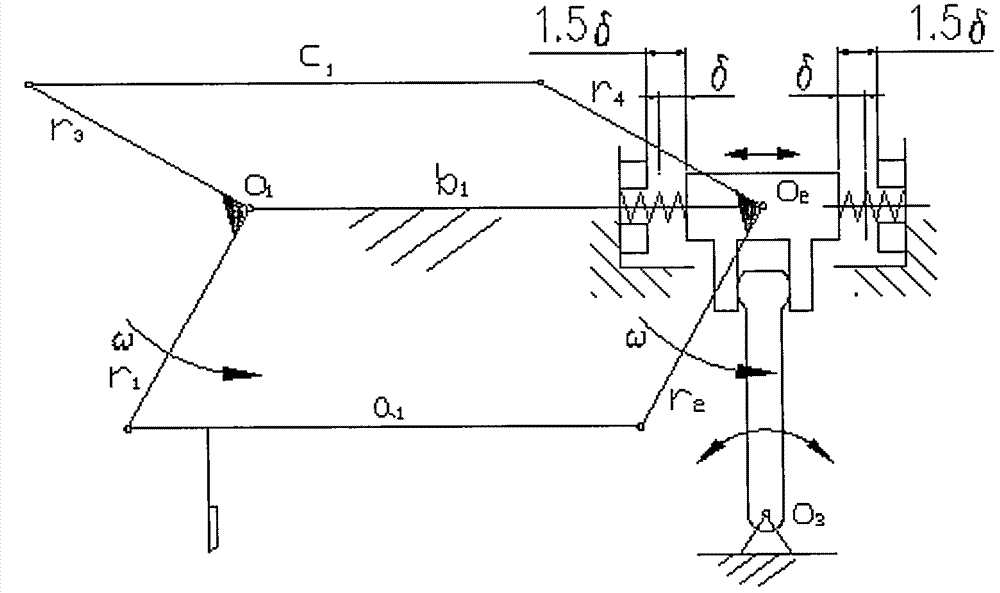
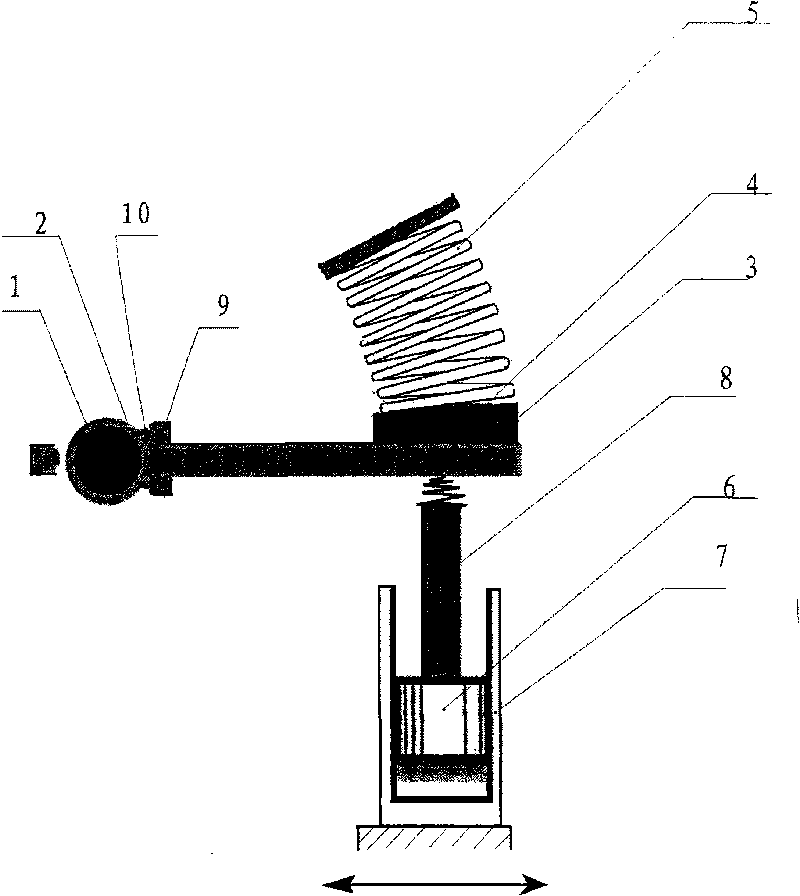
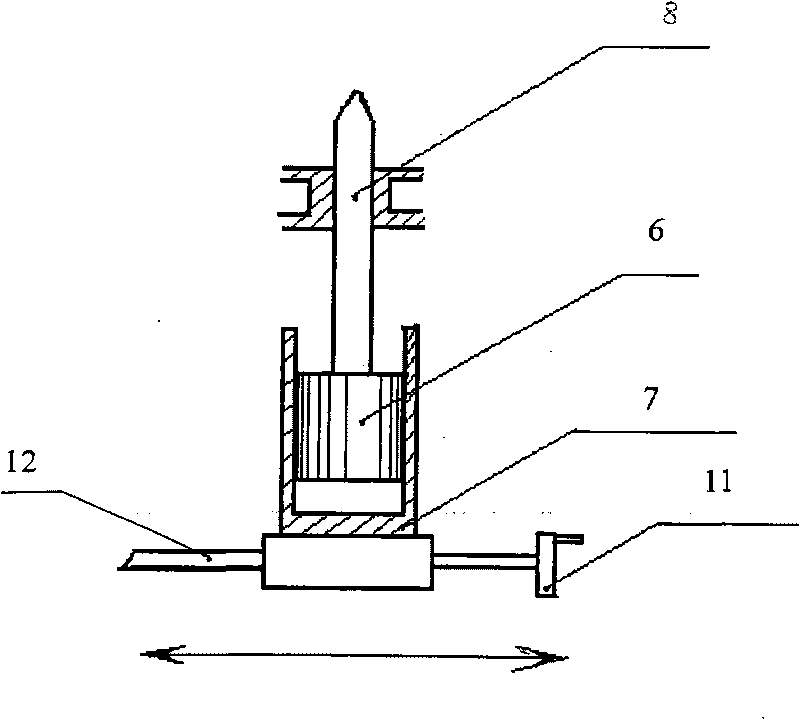
In a reciprocating engine, the dead centre is the position of a piston in which it is either farthest from, or nearest to, the crankshaft. The former is known as top dead centre (TDC) while the latter is known as bottom dead centre (BDC).
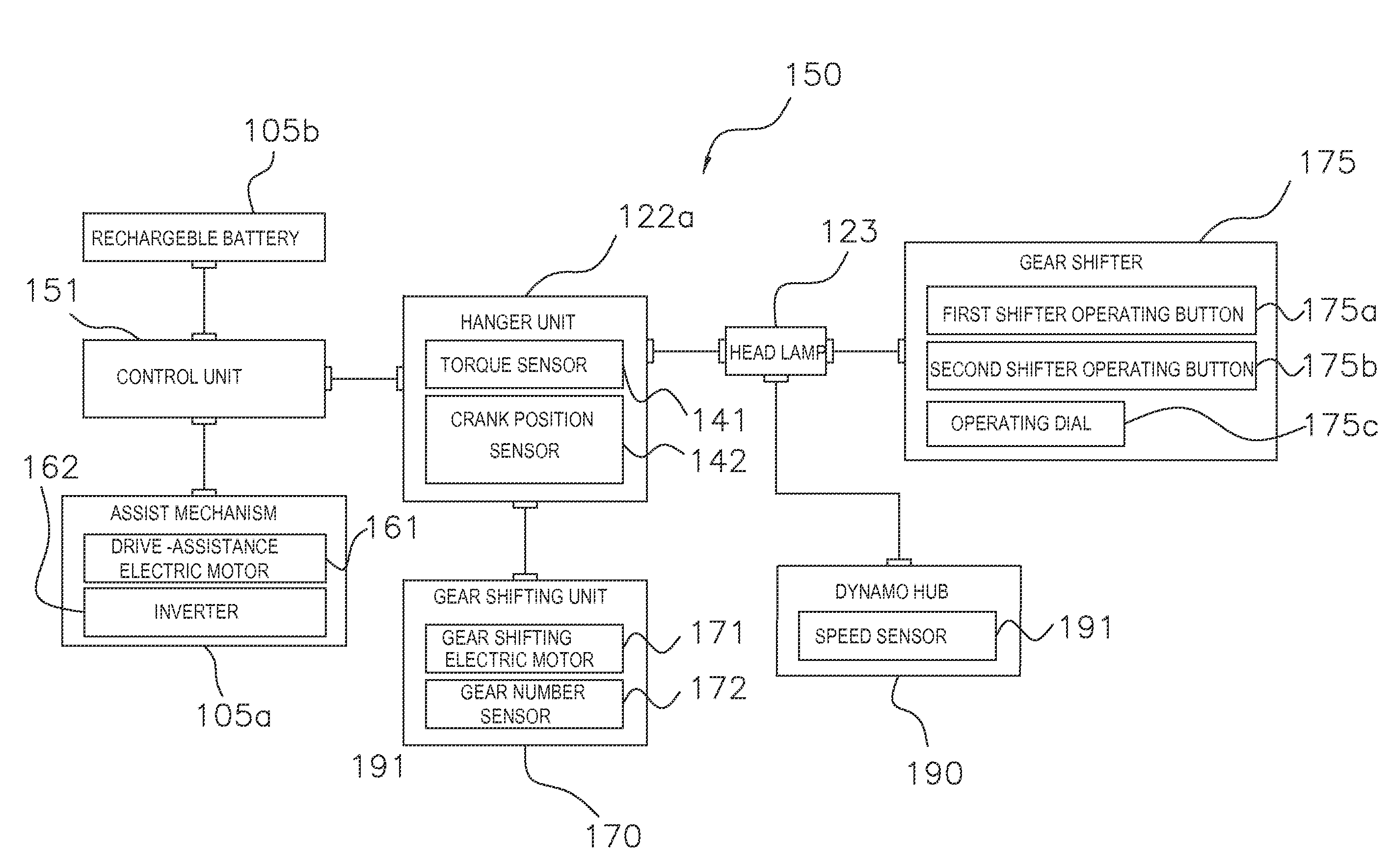
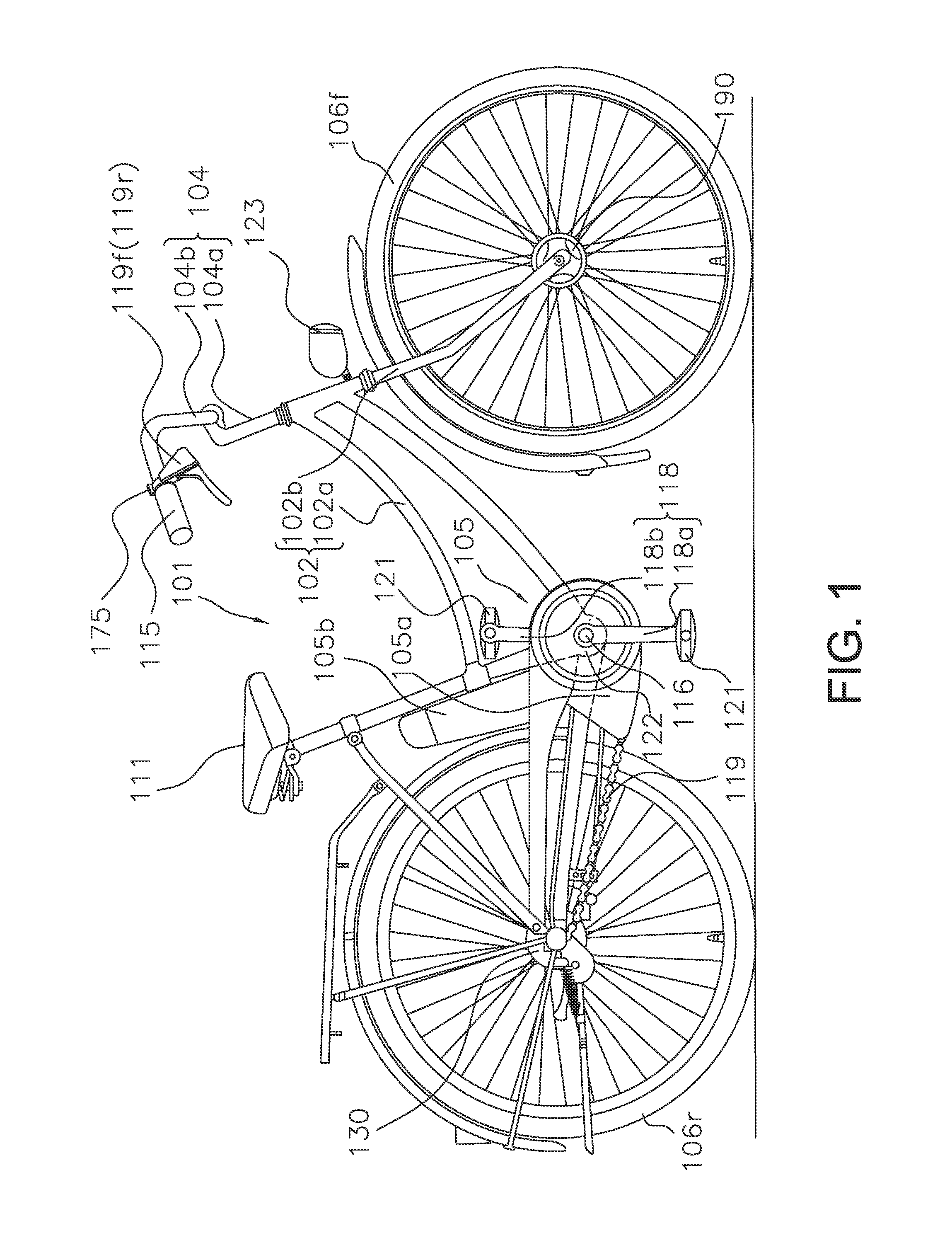
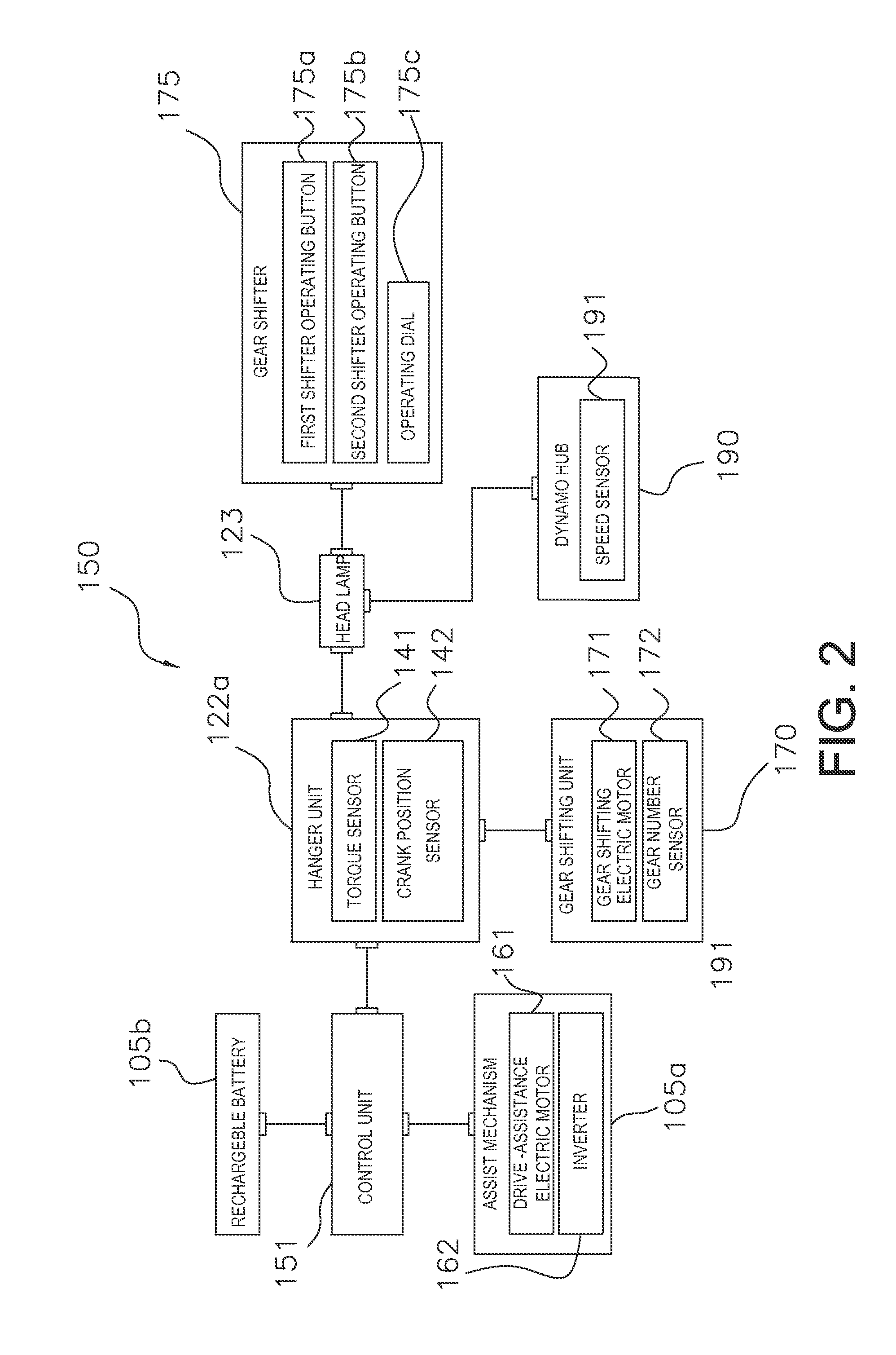
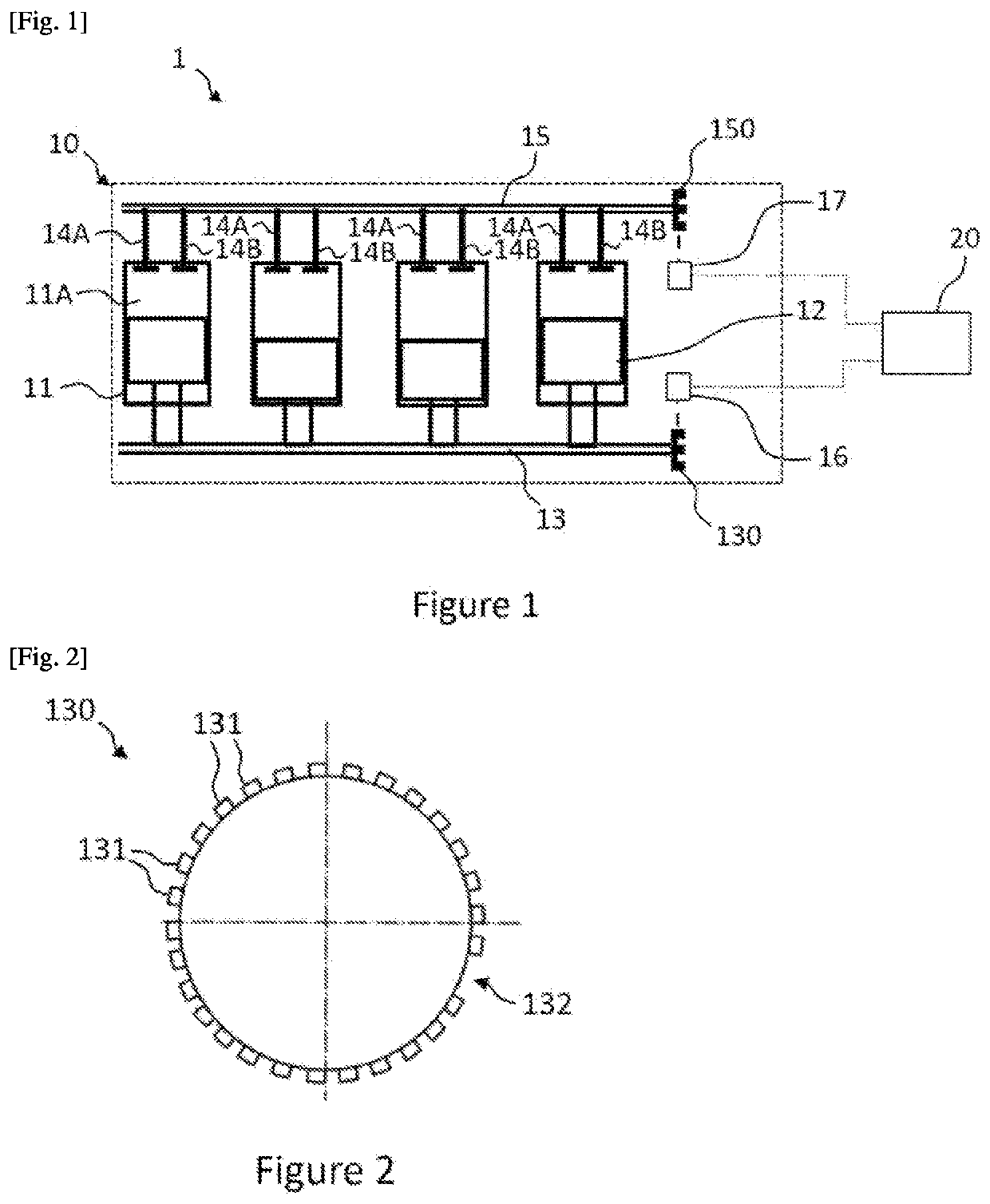
Bicycle drive apparatus
ActiveUS20130054065A1Guaranteed uptimeTension of chain is smallDigital data processing detailsCycle control systemsMicrocomputerTop dead center
A bicycle drive apparatus includes a bicycle crankset, a bicycle transmission, a drive assistance electric motor and a microcomputer. The microcomputer includes an output control section. The output control section has a first control and a second control that makes an output of the drive assistance electric motor smaller than an output of the drive assistance electric motor occurring during the first control only upon determining a crank arm of the bicycle crankset is positioned within a prescribed range of at least one of a top dead center position and a bottom dead center position of the bicycle crankset. The output control section is configured to vary the output of the drive assistance electric motor according to a pedaling force. The output control section switches from the first control to the second control upon receiving a shift command to shift the transmission.
Owner:SHIMANO INC
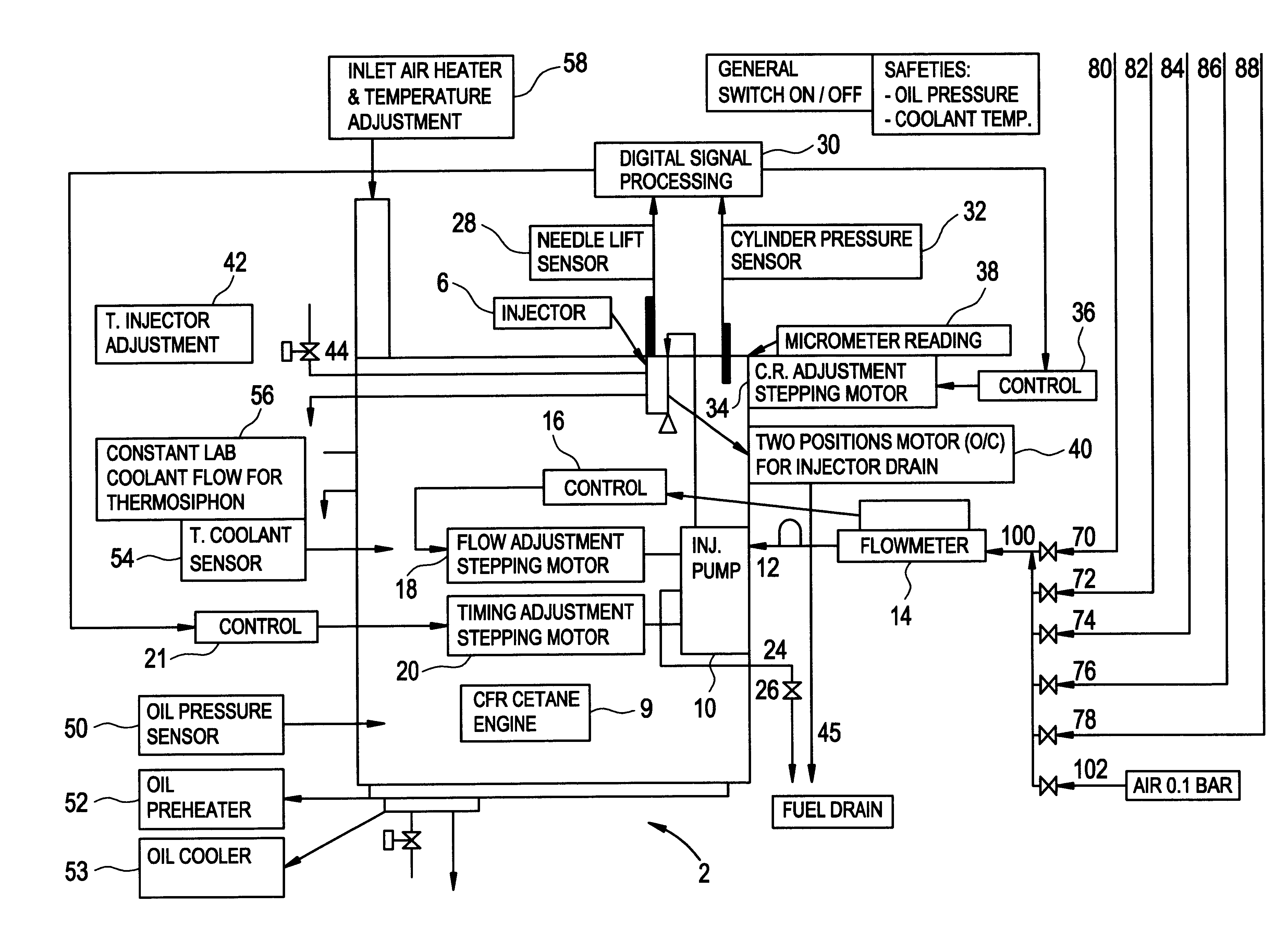
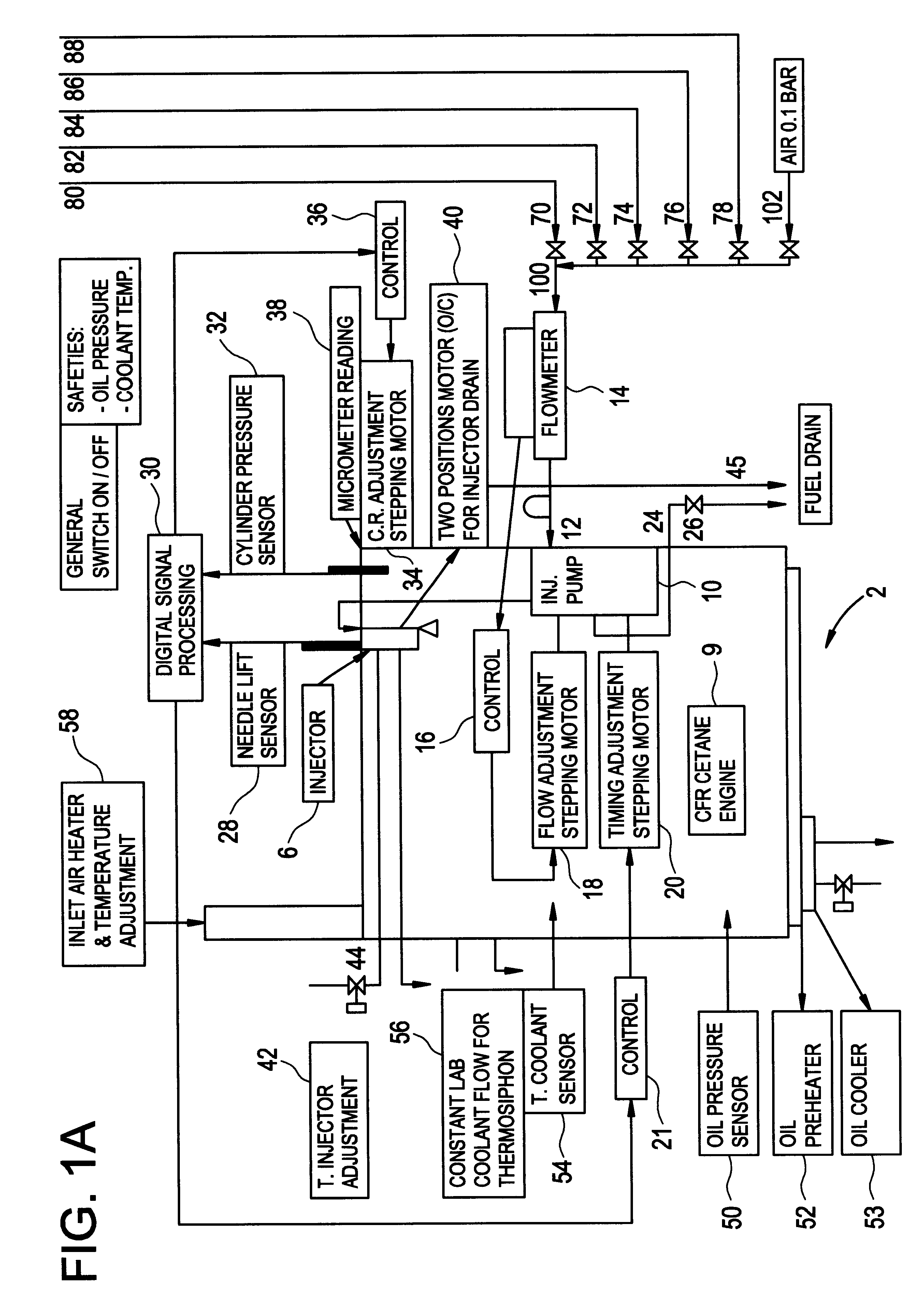
Method and apparatus for measuring cetane number of diesel fuel
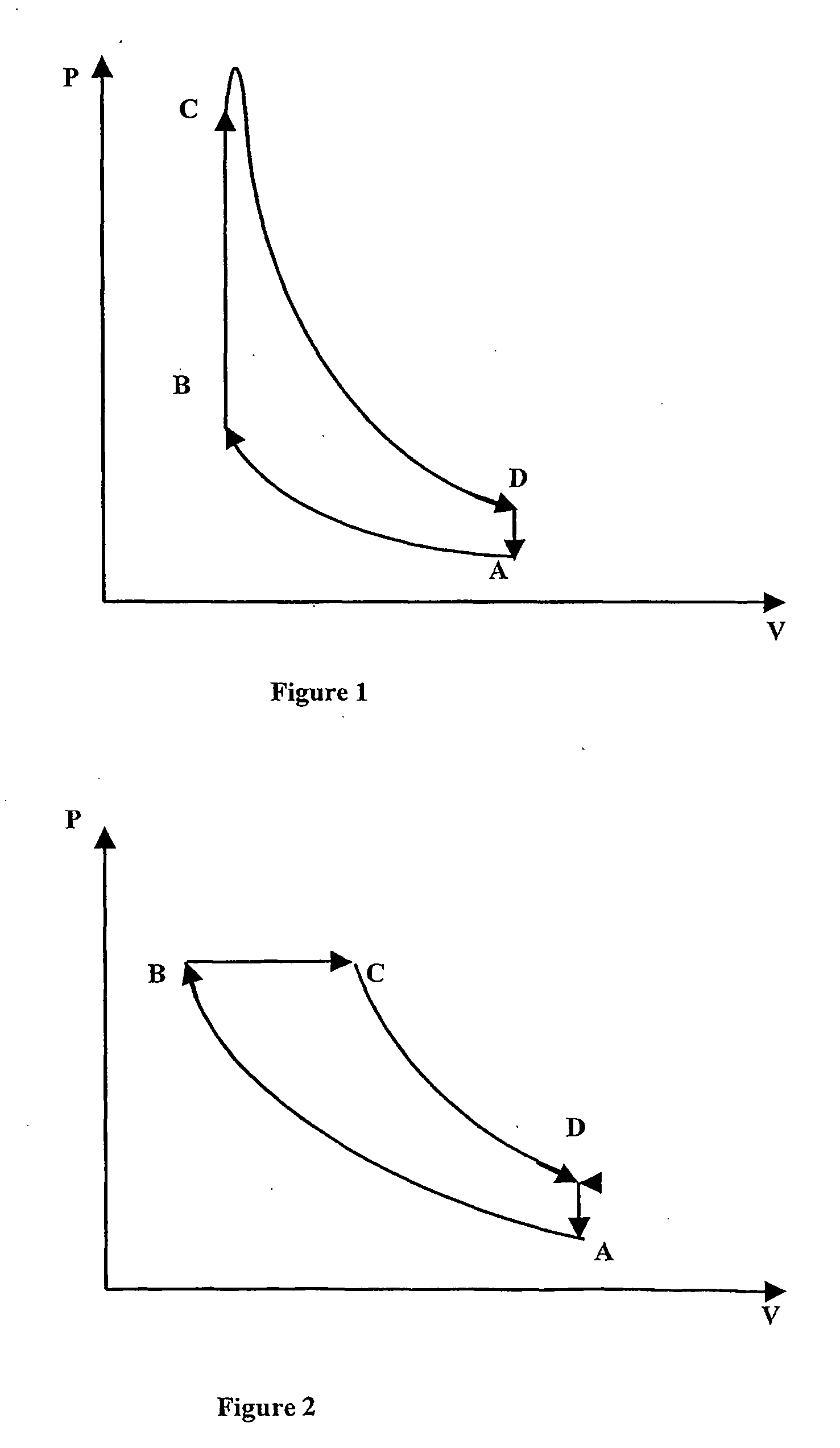
A method of continually measuring the cetane number of a diesel fuel, the method comprising the steps of:(a) providing a diesel engine having means for selectively supplying at least three diesel fuels to the engine, a first actuator for varying the injection timing of the engine, a second actuator for varying the fuel flow of the engine, and a third actuator for varying the compression ratio of the engine;(b) providing a first supply of a diesel fuel of known cetane number, a second supply of a diesel fuel of different known cetane number and a third supply of a diesel fuel of unknown cetane number to be measured, the third supply being connected to a diesel fuel blending system;(c) in a first cycle selectively and alternately supplying the first, second and third supplies to the diesel engine, and for each supply, controlling the first actuator to achieve an injection timing of a predetermined angle before top dead centre, controlling the second actuator to achieve a predetermined fuel flow and controlling the third actuator to achieve a predetermined diesel fuel ignition delay by varying the compression ratio of the engine;(d) determining the cetane number of the third supply by linear interpolation of the pre-chamber plug positions, corresponding with the respective compression ratio values, for the three supplies; and(e) periodically repeating steps (c) and (d) in further cycles to yield a series of cetane number values of the third supply.
Owner:FINA RES SA
Engine Management
An in-cylinder pressure sensor obtains a high resolution pressure curve for each cylinder cycle allowing the various data to be derived for improved monitoring and control of operation of the engine. A more accurate measure of work done by the engine is obtained allowing more accurate estimation of the vehicle torque and hence real torque control. In addition, engine losses can be more accurately calculated and the estimates corrected yet further by obtaining an accurate top dead centre position for the engine cylinders.
Owner:CORNWELL RICHARD CHARLES ELLIOT +6
Hydraulic overload protecting device and pressing machine with hydraulic overload protecting device
InactiveCN104314885AHigh modulus of elasticityWork reliablyMechanical apparatusPressesWorking pressureGas spring
The invention discloses a hydraulic overload protecting device of a gas spring energy accumulator with a manual oil pumping function. The hydraulic overload protecting device and a slide block hydraulic cushion form a closed loop. A plunger is driven by a pneumatic proportional pressurizing piston to extrude oil liquid in a system, so that the pressure of the oil liquid of the slide block hydraulic cushion reaches the required working pressure value from the initial pressure. When a pressing machine is overloaded, a pressure indicator transmits a signal to enable an electromagnetic valve to act to switch an air channel, the proportional pressurizing piston drives the plunger to quickly move to restore, a pressurizing cavity is communicated with a pressure-releasing cavity, and the oil liquid in the slide block hydraulic cushion is quickly released to the gas spring energy accumulator. After a pressing machine slide block is overloaded to surpass a bottom dead centre, the oil liquid of the gas spring energy accumulator can be automatically supplemented back into the slide block hydraulic cushion, and the initial working state is quickly restored. Once an overload failure is cleared, the pressing machine can immediately normally work again according to a program. The pressing machine with the hydraulic overload protecting device is reliable in work and long in maintenance-free period.
Owner:杭震
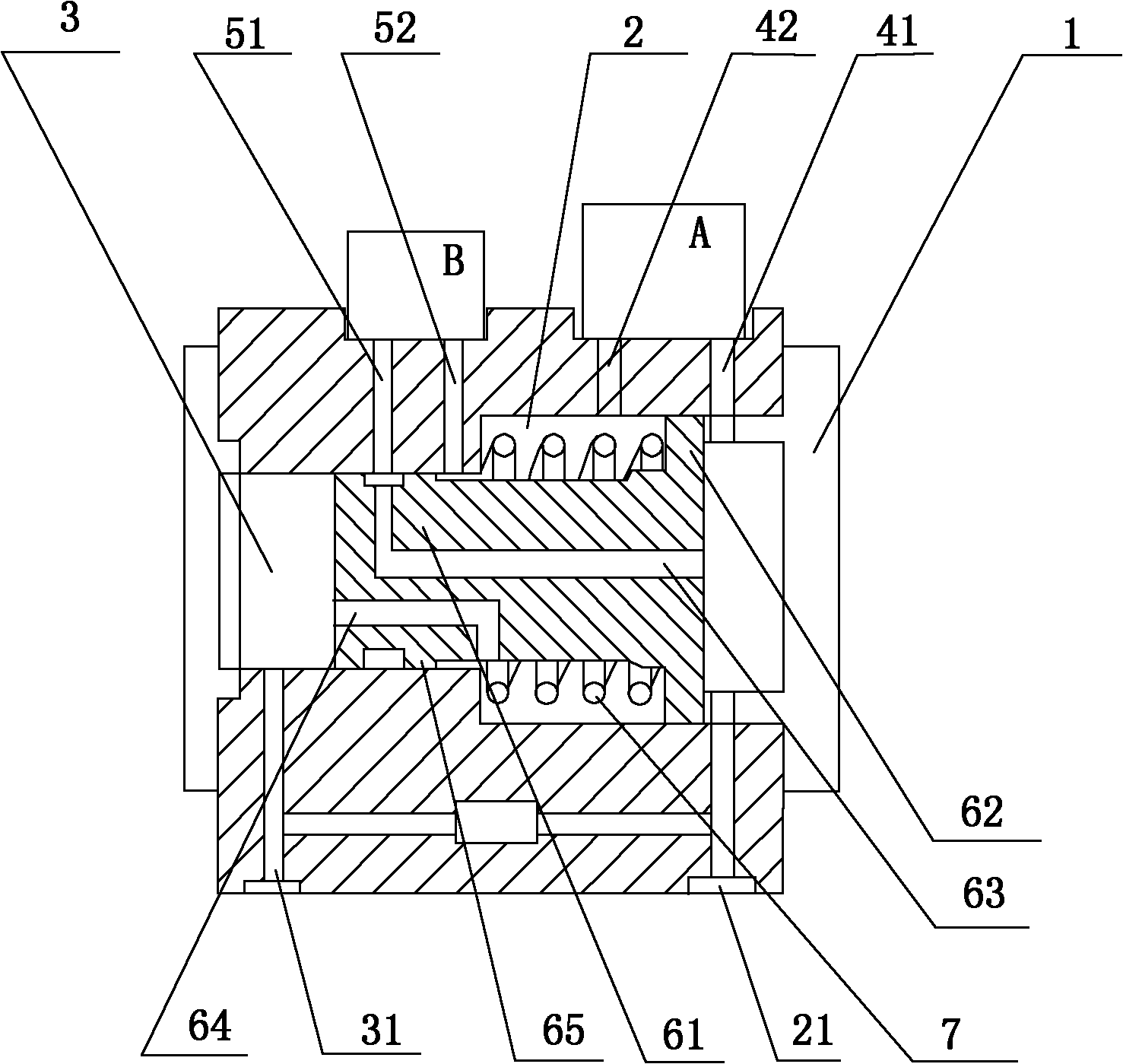
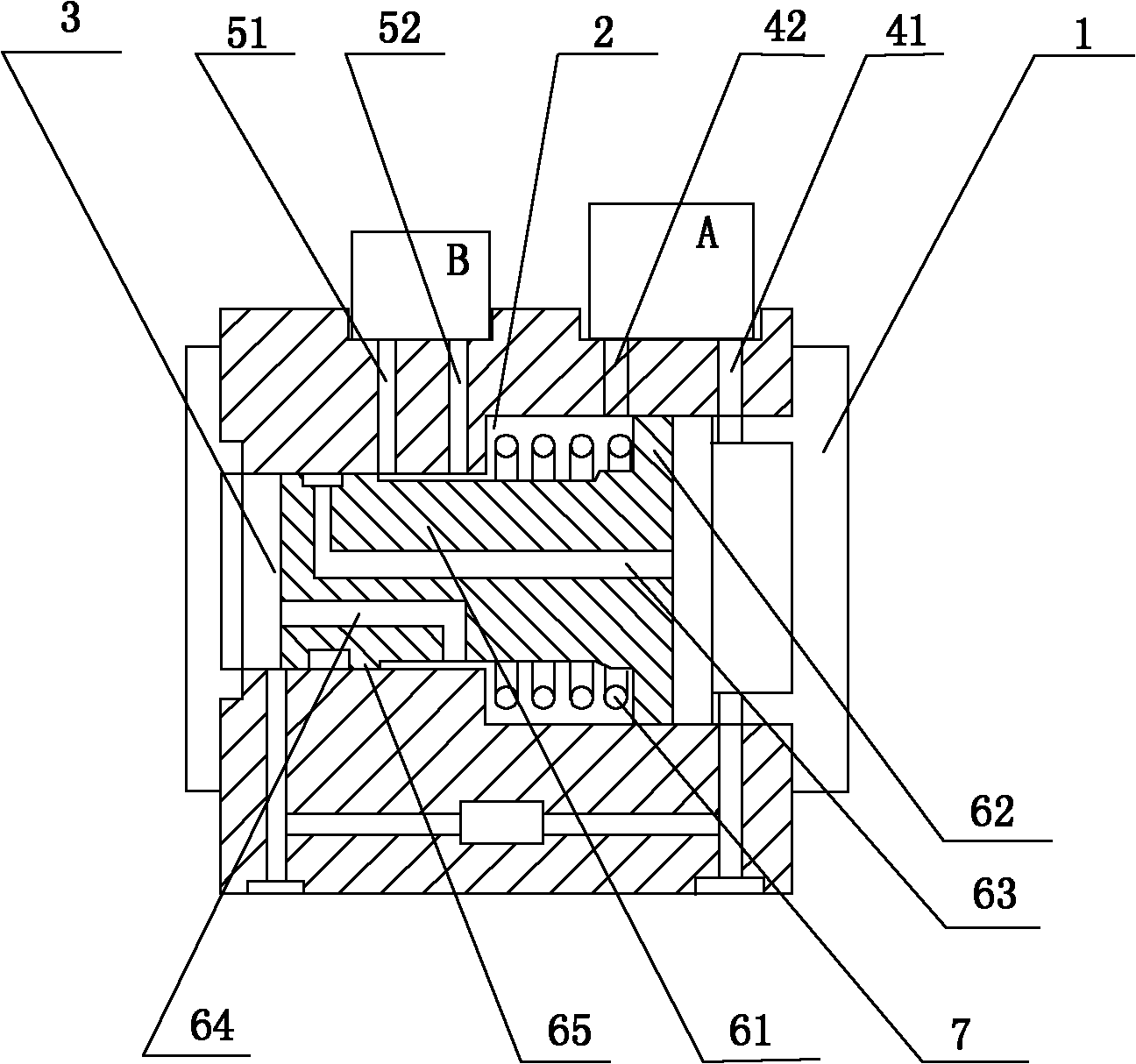
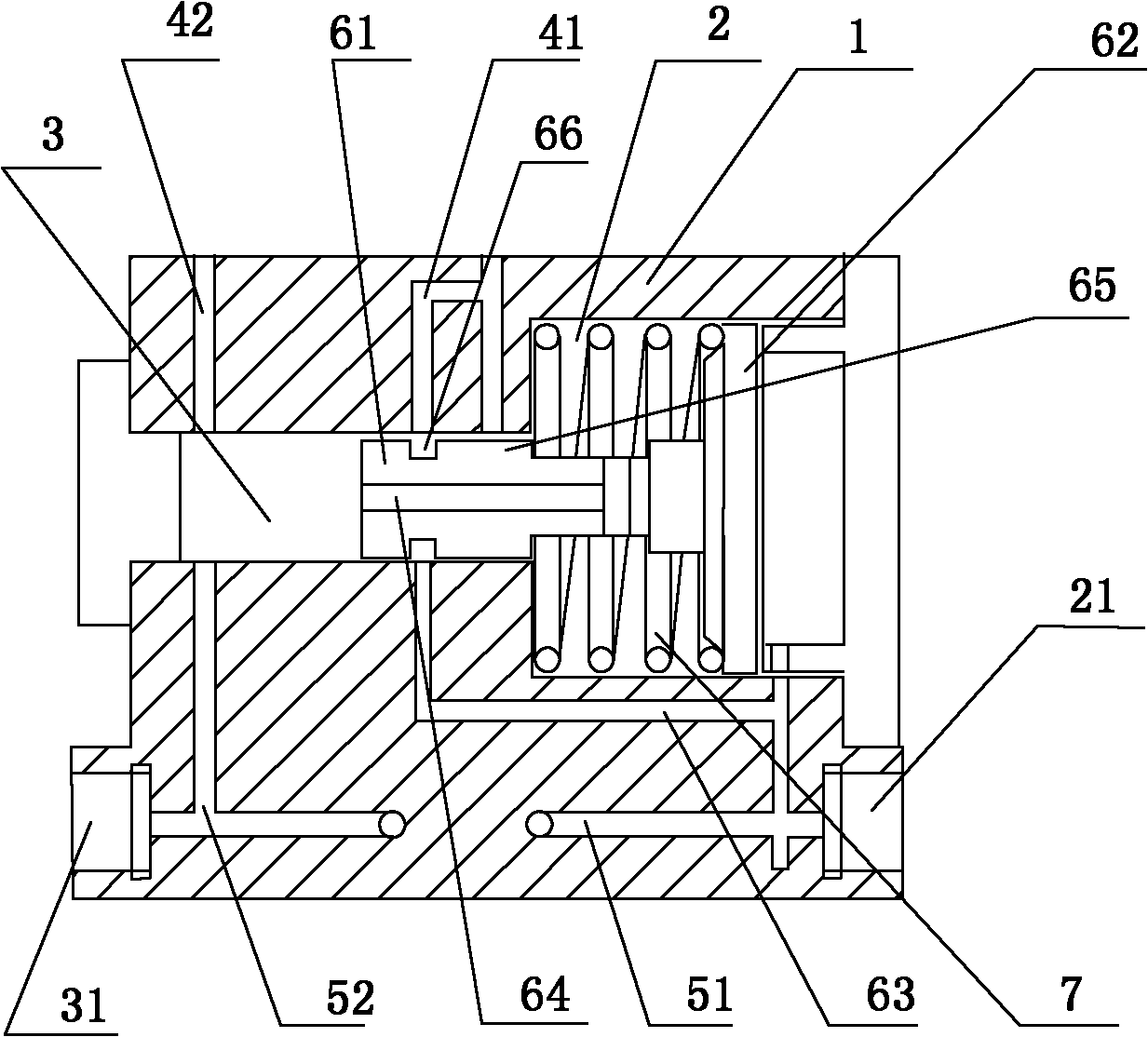
Flow transmitter provided with double differential pressure sensors and pressure difference measurement method
InactiveCN101819052ALarge rangeVolume/mass flow by differential pressureElastic componentDifferential pressure
The invention discloses a differential pressure type flow transmitter provided with two differential pressure sensors. The flow transmitter is characterized in that a piston consisting of a cylinder and a head flange is arranged in an outer shell; a big cavity is partitioned into high and low pressure regions by the head flange of the piston; the piston is provided with an elastic component; the outer shell is provided with measurement holes of a high pressure difference measurement module (A) and a low pressure difference measurement module (B); high and low pressure measurement holes of thehigh pressure difference measurement module (A) ensure that two dead centre positions for compression and ejection of the elastic component are positioned in high and low pressure regions respectively; when the elastic component is not compressed, the high pressure measurement hole of the low pressure difference measurement module (B) is connected with the high pressure region; the elastic component is compressed to the dead centre position, the piston is moved to the end and the connecting channel is cut off. The transmitter can automatically switch the working channel of the low pressure difference measurement module (B) according to the pressure difference size so as to change the operating state of the low pressure difference measurement module (B) and protect the low pressure difference module; and meanwhile, the measurement range can be expanded by effectively using two pressure difference measurement modules.
Owner:无锡求信流量仪表有限公司
Press machine driven by servo motor
The invention discloses a press machine driven by a servo motor. The press machine comprises a cross beam body and a base, wherein a stand column is connected between the cross beam body and the base; the base is provided with a working platform and a lower die; a sliding block is connected with a transmission mechanism used for driving the sliding block to make reciprocating motion up and down; the transmission mechanism comprises the servo motor arranged on the top of the cross beam body, a zero-backlash elastic coupler, a speed reducer, and a gear mechanism, an eccentric gear and an eccentric connecting rod mechanism which are arranged in the cross beam body; the servo motor is connected with the speed reducer by the zero-backlash elastic coupler; an output gear of the speed reducer is meshed with the gear mechanism; the gear mechanism is connected with the eccentric gear which is connected with the eccentric connecting rod mechanism; the eccentric connecting rod mechanism is connected with the sliding block by a sliding block connector; and the speed reducer is provided with a mechanical brake. The press machine has the advantages that the energy consumption and the maintenance cost are reduced; the stamping motion and the forming force can be freely adjusted and accurately controlled; and full-load bottom dead centre pressure maintaining can be realized on any kinetic characteristic curve of the sliding block.
Owner:JIER MACHINE TOOL GROUP
Mechanical pressure machine control method for slider stopping at certain point
ActiveCN1951682AReduce the number of adjustmentsHigh positioning accuracyPressesMachine controlEngineering
The invention relates to a method for controlling the compressor sliding block to stop at dead position. Wherein, it uses the rotation coder as the crank angle / block strike sensor of mechanical compressor, to feed collected angle information to the electric cam controller; the controller based on the crank angle information outputs cam signal, based on the passed angle in fixed time of crank to calculate out the crank speed. The invention is characterized in that: based on the brake angles of last two sliding blocks, it finds the incline factor of angle-speed curvature; when the compressor first operates in one sliding block speed, based on said factor, it can find the present brake angle; when the speed is stable, the brake angle will be automatically compensated referring to the shift from last brake angle; the brake angles in different speeds are stored; when the electric cam receives brake signal, based on preset speed to inquire database, and find out present brake angle; when block reaches said brake angle, outputting the brake signal.
Owner:NANJING ESTUN AUTOMATION CO LTD
Oil supply for an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7753024B2Increase supplyReliable functionDrip lubricationLiquid coolingReciprocating motionInternal combustion engine
The invention relates to an oil supply for an internal combustion engine, comprising an oil supply device for the supply of oil to a piston, reciprocating in a cylinder. The oil supply device is embodied such that at least at a point at which the piston is in the region of bottom dead centre, oil is introduced directly into a region below the piston, by means of the oil supply device, in particular, beneath the piston crown and within the piston skirt. The oil supply device thus comprises at least one tube element, extending into a region beneath the piston crown. The tube element terminates as close as possible to a gudgeon pin, when the piston is at bottom dead center. A targeted lubrication of the mechanically and thermally highly loaded gudgeon pin can thus be guaranteed. It is also possible by means of the oil supply to supply transfer ports of a two-stroke engine with oil, counteracting a tendency to coke up.
Owner:WACKER NEUSON SE
Spherical compressor
ActiveCN103541892AEasy to processHigh precisionRotary piston pumpsRotary piston liquid enginesProcess errorEngineering
The invention discloses a spherical compressor which comprises a cylinder body (7), a cylinder cover (6), a piston (1), a piston shaft (5), a rotary table (2), a main shaft (4), a housing (12), a compression disc (13) and a center pin (3), wherein the rigidity of each part of the piston (1), the rotary table (2), the piston shaft (5) and the cylinder cover (6) is not more than that of the main shaft (4), and the rigidity of at least one part of the piston (1), the rotary table (2), the piston shaft (5) and the cylinder cover (6) is less than that of the main shaft (4). According to the spherical compressor, the clamping stagnation problem of a rotor in a movement process, caused by dead points, friction factors, processing errors and the like of a mechanism movement of the spherical compressor is fundamentally solved; the invention is suitable for spherical compressors which are different in sizes and uses different mediums.
Owner:XIAN ZHENGAN ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
Sheet hole punching device
InactiveUS20120297951A1Maintain positionReduce loadElectrographic process apparatusMetal working apparatusRotational axisPunching
A sheet hole punching device has a device frame; a plurality of punching members arranged in first and second groups, and arranged linearly on the device frame; a driving rotation shaft; a driving motor reciprocally rotating the driving rotation shaft; a gear mechanism transmitting a rotation of the driving rotation shaft; cam mechanisms converting the rotational movement; and a motor control device. The gearing mechanism includes drive gears disposed on the drive rotational shaft, and receiving gears disposed on the punching members to engage with the drive gears. The cam mechanisms include cam followers and cylindrical cams. The cylindrical cam has a V-shaped groove cam to reciprocate each of the punching members between an upper dead point and a lower dead point. The punching members are rotated in one direction to punch holes in first sheets, and subsequently rotated in a reverse direction to punch holes in following sheets.
Owner:SEIKO CORP
Piston-chamber hydro-gravity engine
InactiveCN102498287ASolve environmental problemsSolve energy problemsHydro energy generationEngine componentsEngineeringCam
A piston-chamber hydro-gravity engine capable of converting the stagnant volume of the liquid matter of sea, lake, pond or artificially made hydro container, to a moving volume of liquid matter that flows back upon itself and in meanwhile exploits this motion as a working agent to produce mechanical kinetic power, capable of being used for mechanical production of kinetic work for hydro-electricity generation, or to be used multi-purposely for other energy needs that demand mechanical kinetic force sufficient to solve energy production problems worldwide forever beneficial to the economy and, friendly to the environment, consisting of particular accessories of mechanisms embodied in a single system of mutual successive co-operation by exploiting gravity, that is the hydro-container (7),; capable of creating the means of exploiting the gravity-hydro-static tension of squashing compression exist within the volume of liquid matter of the sea, lake, pond or artificially made containers, the cylinder-chamber (15) and piston-chamber (1) these convert the stagnant gravity- hydro-static tension of force into a fluctuating homo-acting and counter-acting to gravity hydro-gravity-moving-force of action, that compels the piston-chamber (1) to reciprocate, the hermetically sealed vessel crank-cam-shaft chamber (8) operating as a participator in creating the means of the system piston-chamber hydro-gravity engine's function and meanwhile participating in the embodiment system that converts the reciprocating motion of piston-chamber (1), to a rotating motion capable of being used multi-purposely,; where for the piston-chamber hydro-gravity engine to function it is necessary for the hydro-gravity force of action of conduits (19) to be less than the hydro-gravity force of action of piston-chamber (1), the area where conduits (19) adjusted hermetically fixed at the trunk of the cylinder-chamber (15) to be under the B.D.C. of piston-chamber (1).
Owner:斯特法诺斯・恩图科利亚诺斯 +1
Arrangement and method to measure cylinder pressure in a combustion engine
InactiveUS20040118182A1Simple and inexpensive meanInternal-combustion engine testingRapid change measurementEngineeringInternal combustion engine
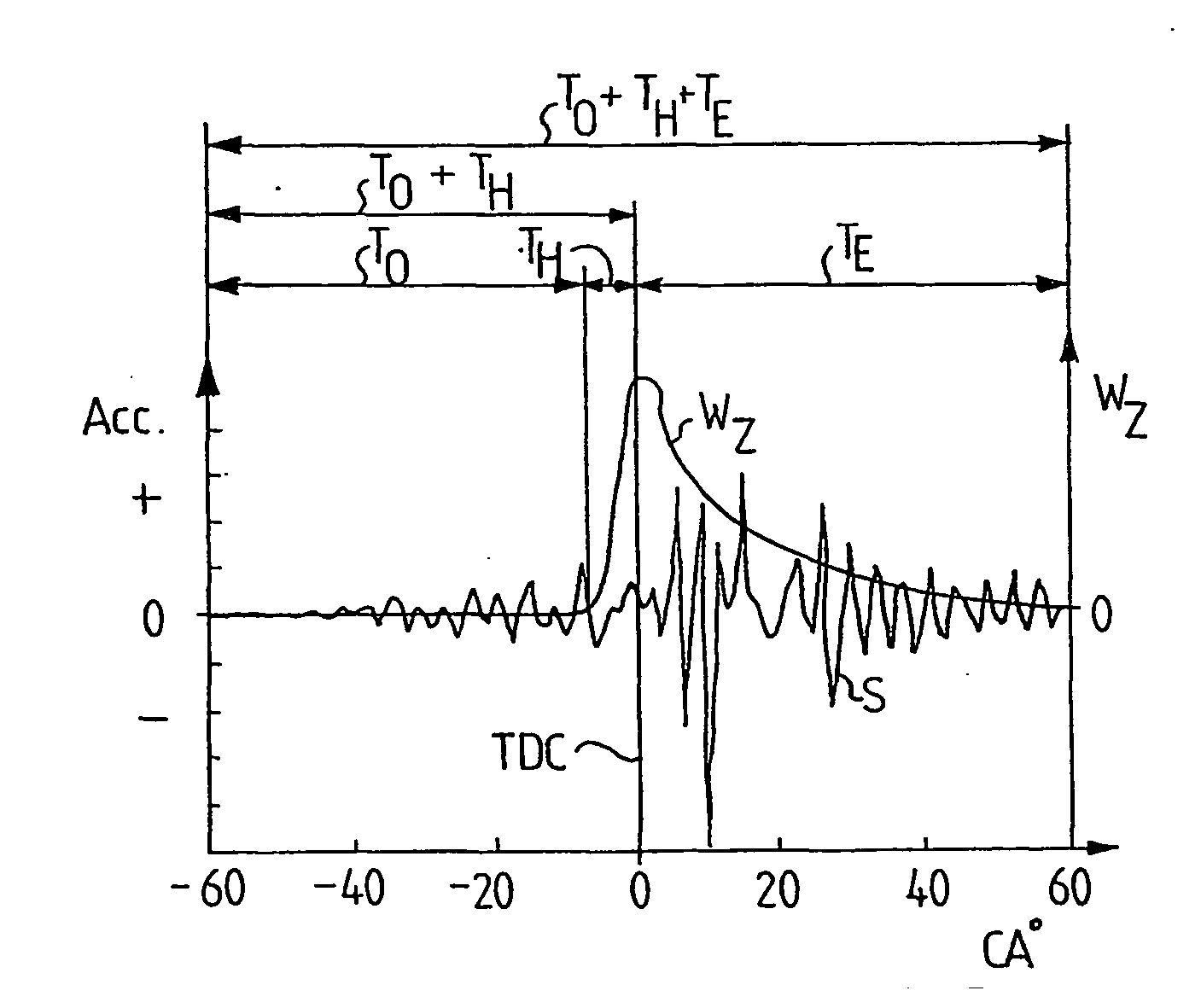
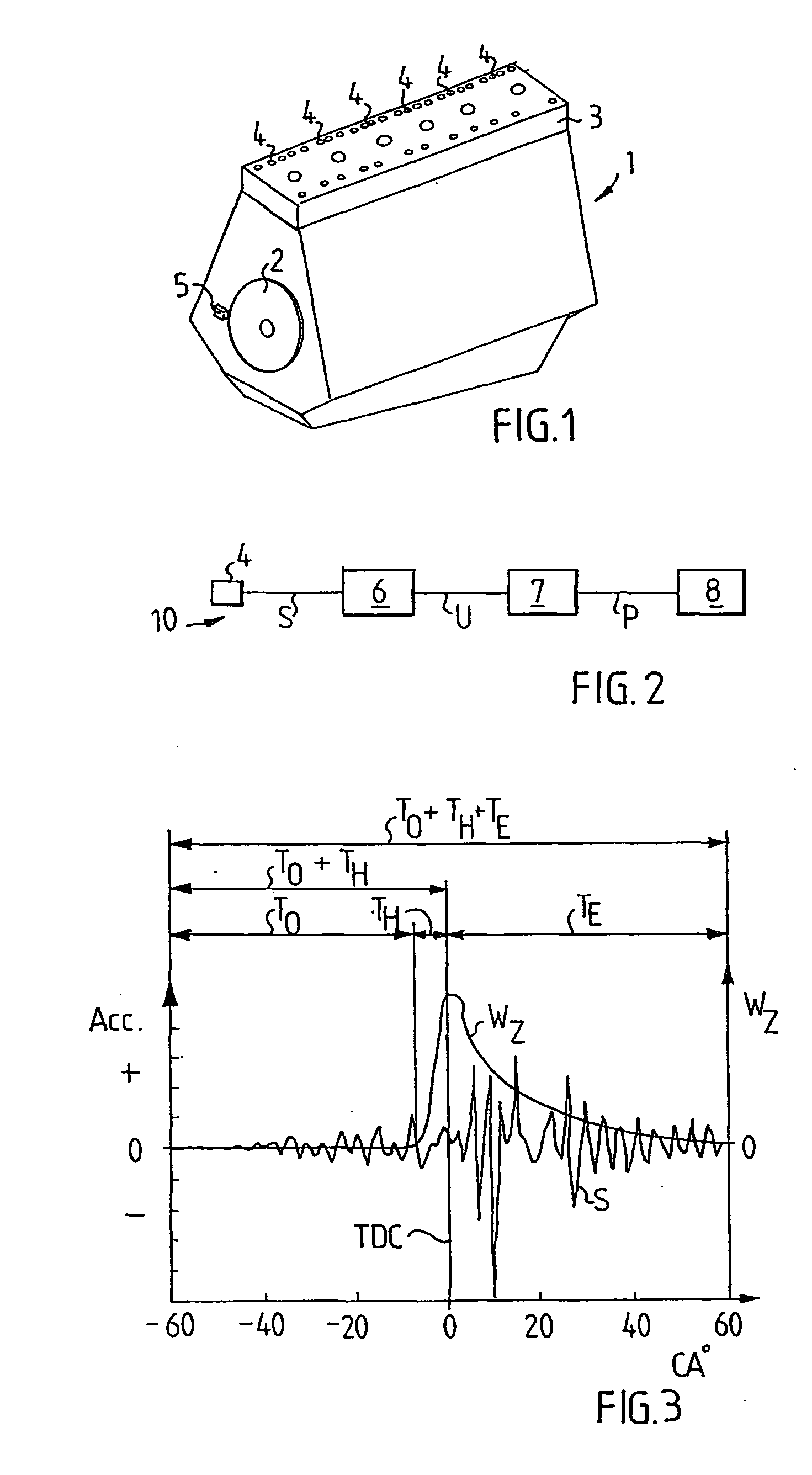
The pressure in a cylinder of a combustion engine is determined on the basis of vibrations in the engine which are generated during movement of the piston. A vibration signal (S) from a vibration sensor (4) situated on a cylinder is filtered in the region about the piston's top dead centre position, at the transition from compression to expansion, in a special filter (6) in which a half Hanning filter acts upon the vibration signal after the piston's top dead centre position. The filtered signal (U) is thereafter converted to a pressure signal (P) on the basis of an established relationship between vibration and pressure. The half Hanning filter has a significantly shorter time window (TH) than the exponential filter. The novel filter (6) cleans the vibration signal in an advantageous manner and makes more reliable pressure determination possible.
Owner:SCANIA CV AB
Apparatus to improve the efficiency of internal combustion engines, and method thereof
ActiveUS20100024750A1Good environmental performanceImprove efficiencyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineEngineering
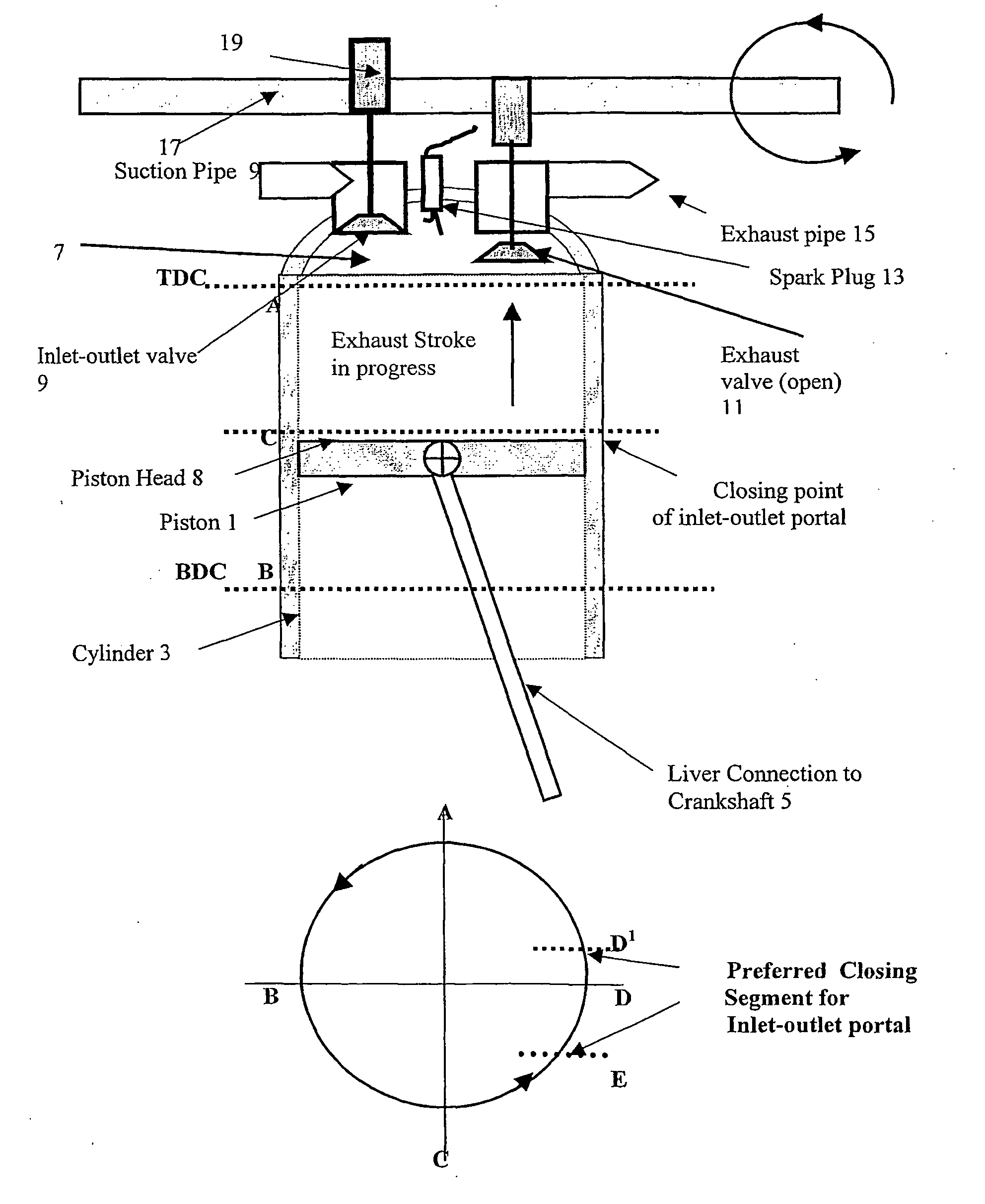
Method and apparatus for controlling the volume of air or air and non-combusted fuel mixture inside a combustion chamber and cylinder of an internal combustion engine. The apparatus includes an inlet-outlet portal having open and closed states and connected to air or air and non-combusted fuel source(s), and a combustion chamber with reduced volume. The inlet-outlet portal is controlled, when open, to permit air or air and non-combusted fuel mixture to enter or enter and exit the combustion chamber and cylinder and when closed to prevent air or air and non-combusted fuel mixture from entering or exiting the chamber and cylinder, in which the volume of air or air and non-combusted fuel mixture located inside the chamber and cylinder when the inlet-outlet portal closes, is less than the volume of the combustion chamber and cylinder defined when the piston is at the bottom dead centre position inside the cylinder when the inlet-outlet portal is closed.
Owner:HAWAR TECH LTD
Non-round annular wheel crankless engines
InactiveCN101158316AEliminate work lossIncrease conversion rateMachines/enginesTime delaysWork cycle
The invention provides a piston-typed engine without crankshaft, moment dead point, or time delay ignition, mainly comprising a cylinder body, a piston, a piston pin, a non-round internal gear, a mainshaft gear, a mainshaft, a cam, a cam roller, etc. When the piston supplies work, the piston pushes the non-round internal gear to move and pushes the mainshaft gear engaged with the non-round internal gear to rotate, and the power is output from the mainshaft; meanwhile, the other mainshaft gears are driven to drive respective non-round gear engaged with the mainshaft gear to move, in order to implement the working cycles of each cylinder of sucking, pressing, bursting, and discharging. As the thrust force of the non-round internal gear is always tangent to a reference circle of the mainshaft gear and the torque is not changed with the rotation angle of the mainshaft gear, the output torque of the mainshaft is improved to the most extent, the torque of the crankshaft is avoided to be changed with the rotation angle of the crankshaft, the work loss caused by moment dead point and time delay ignition are avoided; the conversion rate of the power can theoretically reach 100%; the output torque, the output power of the mainshaft and the power performance of the engine are greatly improved, and the fuel consumption and pollution discharge are reduced by more than a half.
Owner:张连奎
Pneumatic two-position four-way reversing valve
InactiveCN102418798AOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMultiple way valvesFour-way valveEngineering
The invention relates to a pneumatic two-position four-way reversing valve. A traditional built-in two-position four-way reversing valve of a pneumatic motor can stop at a dead-point position in the operating process, i.e. an air-inlet cavity of an air-distributing chamber is directly communicated with an air-discharging opening through a slide block to cause a spraying machine to stop working, and a dead-point phenomenon is strictly prohibited to appear on the spraying machine on an automatic spraying flow line. In the invention, aiming at the deficiency, on the basis of a traditional two-position four-way valve, permanent magnets are inlaid in a reversing piston, an upper end-cover hole and a lower end-cover hole, and the dead-point difficult problem of the two-position four-way valve appearing in the reversing process is solved through the change of magnet forces and friction forces.
Owner:CHONGQING CHANGJIANG COATING EQUIP
Super-tonnage lifting extension and retraction system and control method for all-ground crane
PendingCN109368500ARealize speed regulationImprove synchronicityServomotor componentsServomotorsEnergy lossElectricity
The invention discloses a super-tonnage lifting extension and retraction system and control method for an all-ground crane. The outlet pressure of a multi-path valve bank is compared with the outlet pressure of a pump through a super-tonnage lifting controller, a current value used for controlling an electric proportional overflow valve in a hydraulic source is output, and a pressure cut-off valveof a constant-pressure variable pump is changed, so that the outlet pressure of the constant-pressure variable pump and the outlet pressure of the multi-path valve blank are maintained at a constantpressure difference value. In this way, the super-tonnage lifting amplitude can be changed through the system and method, and an oil cylinder has good synchronicity and speed regulation performance when extending and retracing; prompting or automatic tensioning is achieved in use when the oil cylinder retracts, the speed can be automatically decreased when the oil cylinder approaches an upper deadpoint and a lower dead point, system impact is reduced, and the safety and stability of the system are improved; and the output flow is matched with the flow required by a load, the response speed ofthe system is ensured while the energy loss of the system is reduced, and the controllability of the system is improved.
Owner:臧其亮
Two-cycle combustion engine
InactiveUS20110220059A1Lower hydrocarbon emissionsScavenging losses can be preventedInternal combustion piston enginesCylinder headsCylinder headCrankcase
The invention relates to a two-cycle combustion engine, comprising at least one cylinder (1) accommodating a piston (2) and provided with a cylinder head, a crankcase (10) which is in fluid connection with the cylinder (1) by way of transfer ports (12 to 16) which are disposed symmetrically opposite of one another with respect to a diametral plane (5) of the cylinder (1) that is determined by the axis of an exhaust port (4), and two injection nozzles (6, 7) for fuel disposed symmetrically with respect to said diametral plane (5), the nozzle axes (8) of which intersect one another above the piston crown (3) in the diametral plane (5) in the bottom dead centre position of the piston (2). In order to create advantageous scavenging conditions, it is proposed that the nozzle axes (8) intersect one another on the side of the cylinder axis facing away from the exhaust port (4) and extend at least approximately in the outflow direction (17) of the transfer ports (12, 13) respectively provided on the opposite side of the diametral plane (5), and the piston (2) comprises a casing opening (21) for injecting fuel into the crankcase (10) on at least one circumferential side facing the injection nozzles (6, 7).
Owner:GANGLMAYR JOSEF
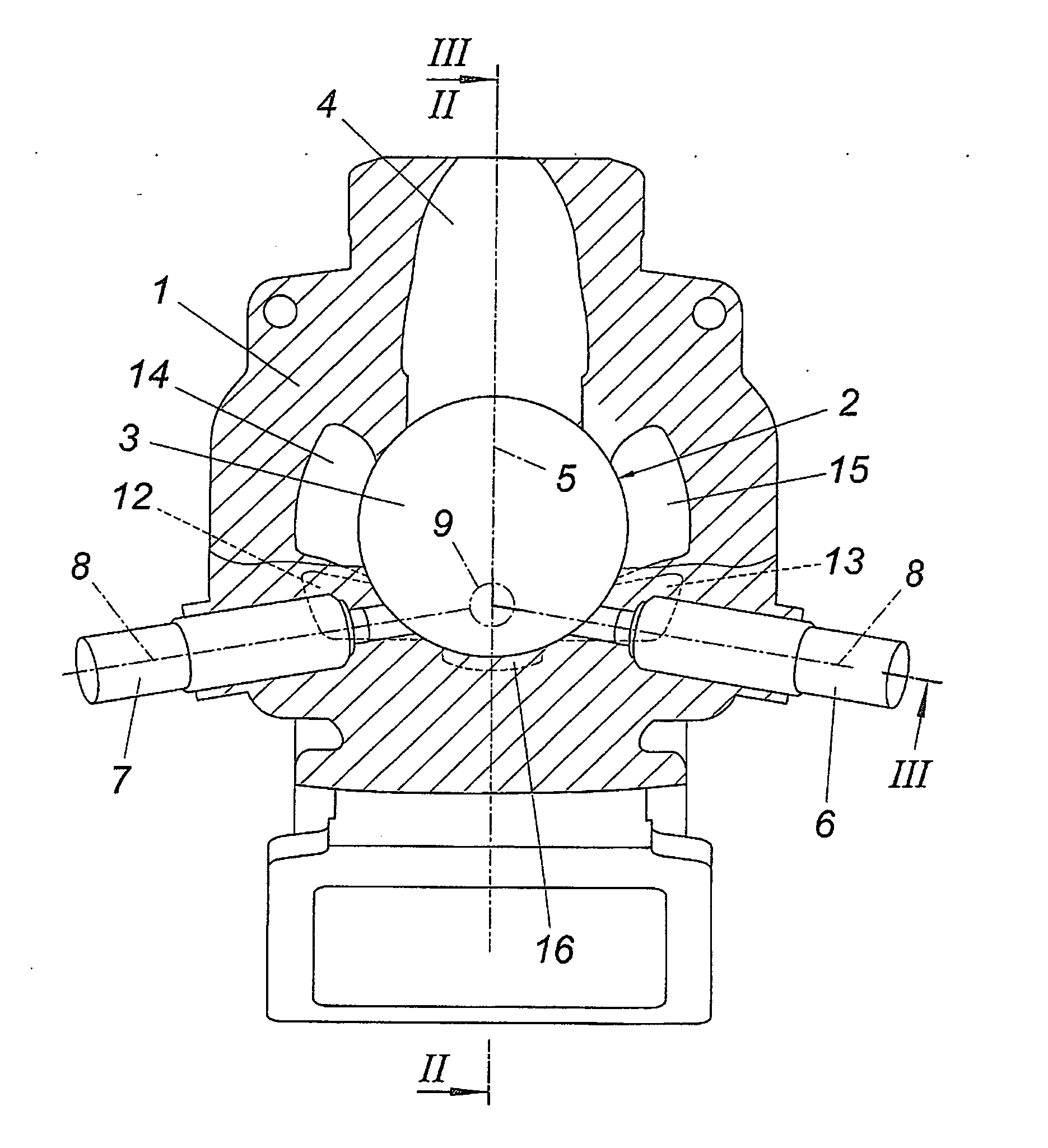
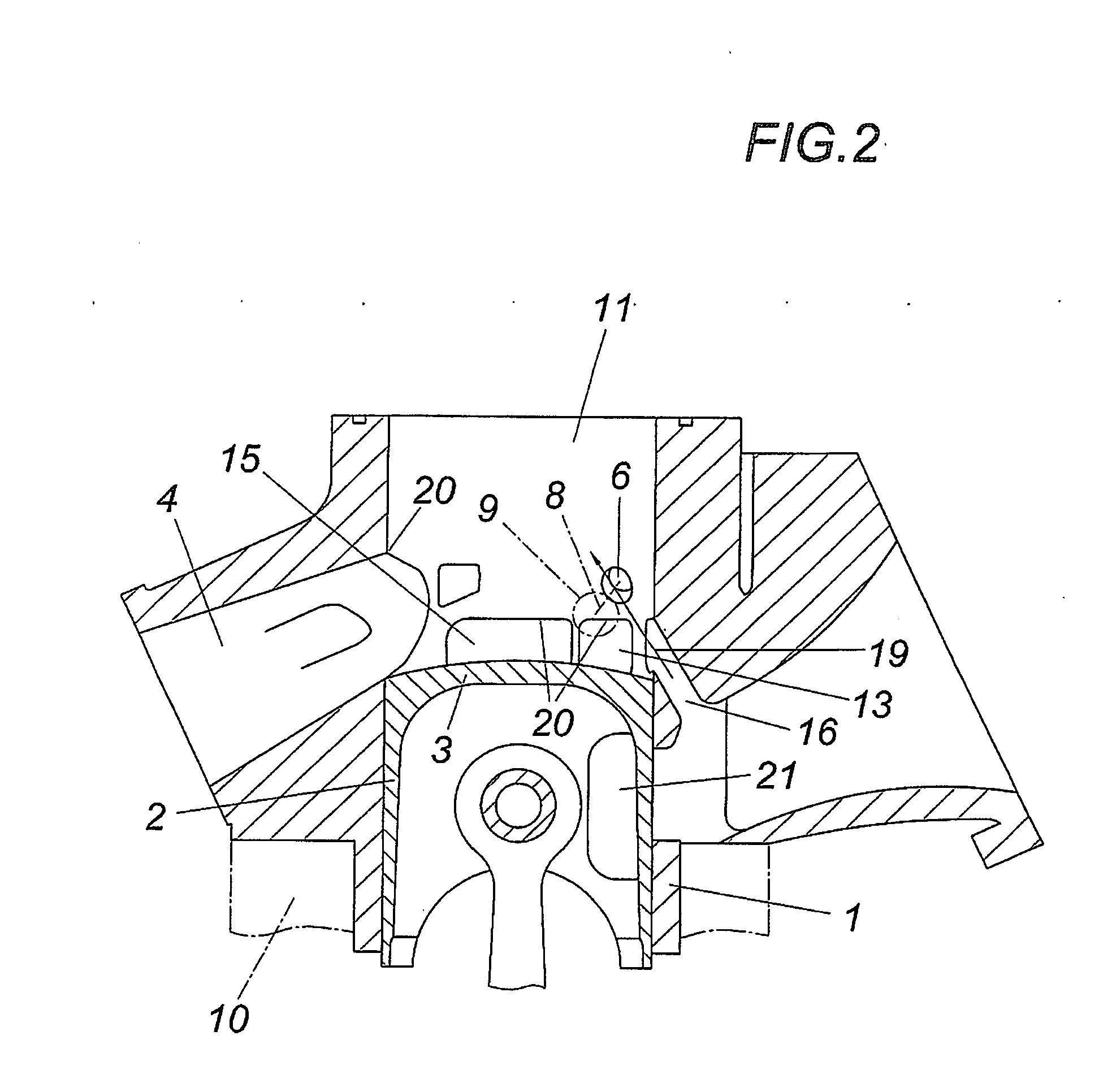
Cylinder assembly and piston for a longitudinally flushed stroke piston combustion engine
InactiveCN102691565AAvoid damageDamage no longer occursValve arrangementsCylinder headsCombustion chamberPiston ring
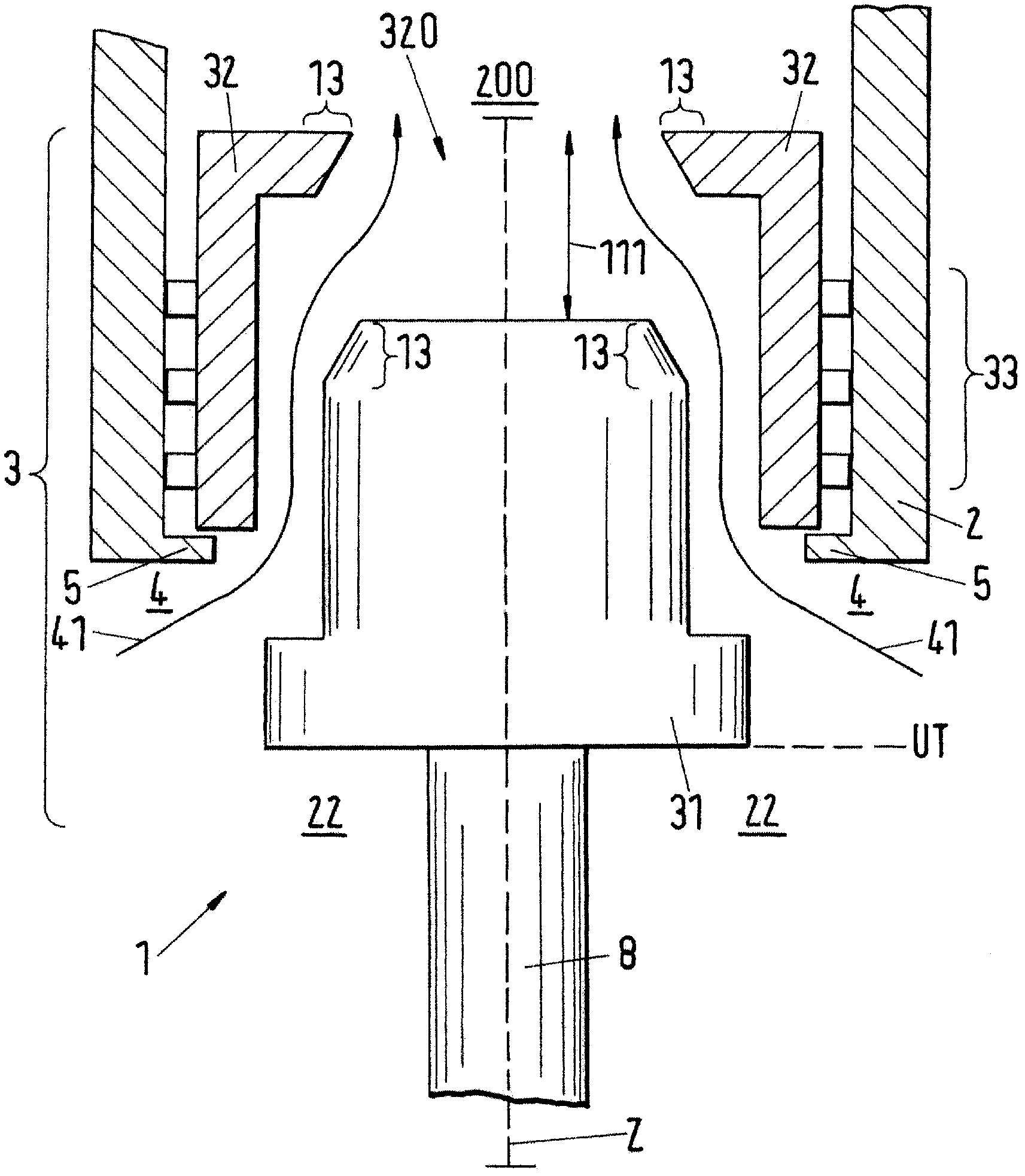
The invention relates to a cylinder assembly 1 for a longitudinally flushed stroke piston combustion engine and especially to a large-size two-stroke diesel generator moving slowing and flushing longitudinally. The cylinder assembly 1 includes an air cylinder provided with a combustion room 200 and an entrance area 22. A piston 3 moving back and forward long a cylinder axis Z is installed between an upper dead point and a lower dead point in the cylinder 2. And a flushing air entrance 4 is arranged in the cylinder 2 to facilitate to lead the flushing air 4 into the combustion room 200. The cylinder arrangement comprises a piston (3) which is provided as two piece piston. A mantle piston (32) is provided with a piston ring (33), where a main piston (31) is positioned in the mantle piston. A retaining device is provided at a cylinder for the mantle piston. The rinsing air (41) is introduced from an inlet area (22) to a combustion chamber (200) by the rinsing air opening (320) of the mantle piston.
Owner:WAERTSILAE SCHWEIZ AG
Monorail crane separable toothed rail driving device suitable for large gradient
ActiveCN113620171APrevent slippingAvoid problems such as slippingTravelling gearCranesMarine engineeringGear wheel
The invention discloses a monorail crane separable toothed rail driving device suitable for a large gradient. The separable toothed rail driving device comprises a driving mechanism, a walking mechanism, a four-bar mechanism, a connecting mechanism, a meshing rail plate and a transition rail plate; the driving mechanism comprises driving motors, meshing gears, bearing rods and a bearing supporting plate; the walking mechanism comprises walking wheels, clamping wheels, a shell and telescopic supporting rods; the four-bar mechanism comprises first rockers, connecting rods, a second rocker and an oil cylinder; and the connecting mechanism comprises a fixing plate, connecting plates and a connecting bolt. When a monorail crane runs to a ramp, the oil cylinder drives the four-bar mechanism in advance to feed the meshing gears into a transition rail, the meshing gear is adjusted to a dead point state, and the telescopic supporting rods are locked. After the monorail crane enters the ramp, the meshing gears are matched with the meshing rail plate mounted on the ramp to provide auxiliary driving for the monorail crane to climb. The driving device overcomes the defect of insufficient power when the monorail crane operates at a large slope, and stable and safe operation of the auxiliary driving device is realized by virtue of the characteristics of dead points of the telescopic supporting rods and the four-bar mechanism.
Owner:XUZHOU LIREN MONORAIL TRANSPORTATION EQUIP CO LTD
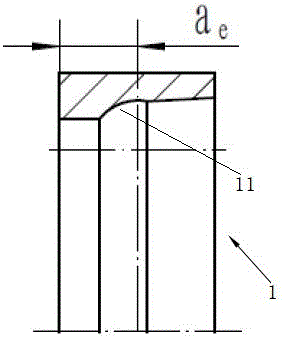
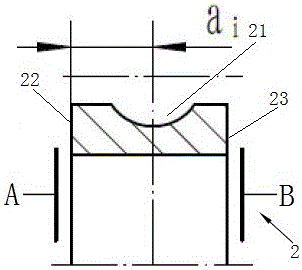
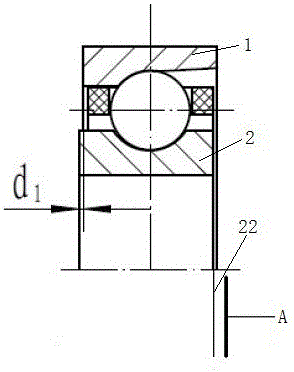
Angular contact ball bearing, bearing assembly, manufacturing method and assembling method thereof
ActiveCN106224374AReduce processing difficultyAvoid grindingBall bearingsBearing componentsBall bearingEngineering
The invention relates to an angular contact ball bearing, a bearing assembly, a manufacturing method and an assembling method thereof. The center of a bearing inner ring groove manufactured by the manufacturing method provided by the invention is not certainly located at the dead centre of an inner ring but can be close to the first end of the inner ring, so that the machining difficulty is reduced by way of permitting machining deviation. Meanwhile, when the manufactured inner ring fits an outer ring based on the first end, the convex value of a manufacturing bearing I is a positive value. When the manufactured inner ring fits the outer ring based on the second end, the convex value of a manufacturing bearing II is a negative value. Therefore, proper bearings can be selected to be correspondingly assembled by measuring the convex values of the bearings, so that coping of the convex values of the bearings is avoided.
Owner:LUOYANG BEARING RES INST CO LTD
Method of injecting ammonia fuel into a reciprocating engine
InactiveCN113039355APromote combustionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberExhaust valve
A method of injection of liquid or gaseous ammonia fuel into a reciprocating engine that includes at least two cylinders, each cylinder including a piston that moves reciprocally within that cylinder, each cylinder having a head location at one end located opposite to a compression end of the piston and defining a combustion chamber therebetween, the cylinder including at least one inlet valve through which combustion gases are fed into the combustion chamber and at least one exhaust valve through which spent combustion gases egress the combustion chamber, the piston moving the cylinder in a cycle between top dead center where the piston is located closest to the head location and bottom dead center where the piston is located furthest from the head location, and including at least one fuel injector located at or in the head location, and wherein the method comprises: injecting the ammonia fuel into the combustion chamber of each cylinder as at least one fuel jet with a timing of: after the at least one exhaust valve of the respective cylinder is substantially closed; and before the respective piston moves to at most 35 degrees, preferably at most 45 degrees, prior to top dead centre.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Method for operating a two-stroke otto engine
InactiveCN105917106AUniform wearEvenly distributedElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberMomentum
The invention relates to a method for operating a two-stroke Otto engine comprising at least one cylinder (1) that receives a piston (2); a crankcase (10) which is fluidically connected to the combustion chamber (11) of said cylinder (1) by means of overflow channels (12, 13, 14, 15, 16) on either side of a diameter plane (5) of the cylinder (1) which is determined by the axis of an outlet channel (4); and two fuel injection nozzles (6, 7) that are arranged either side of said diameter plane (5) and whose nozzle axes (8) extend, in the bottom-dead centre position of the piston (2), above the piston base (3) and at least approximately in the outlet flow direction (17, 18) of the overflow channels (12, 14: 13, 15) each provided on the opposite sides of said diameter plane (5), the fuel being injected with reduced momentum into the combustion chamber (11) of the cylinder (1) via only one of the injection nozzles (6, 7) per working cycle when idling and in the lower part-load range.
Owner:罗兰・柯克伯格
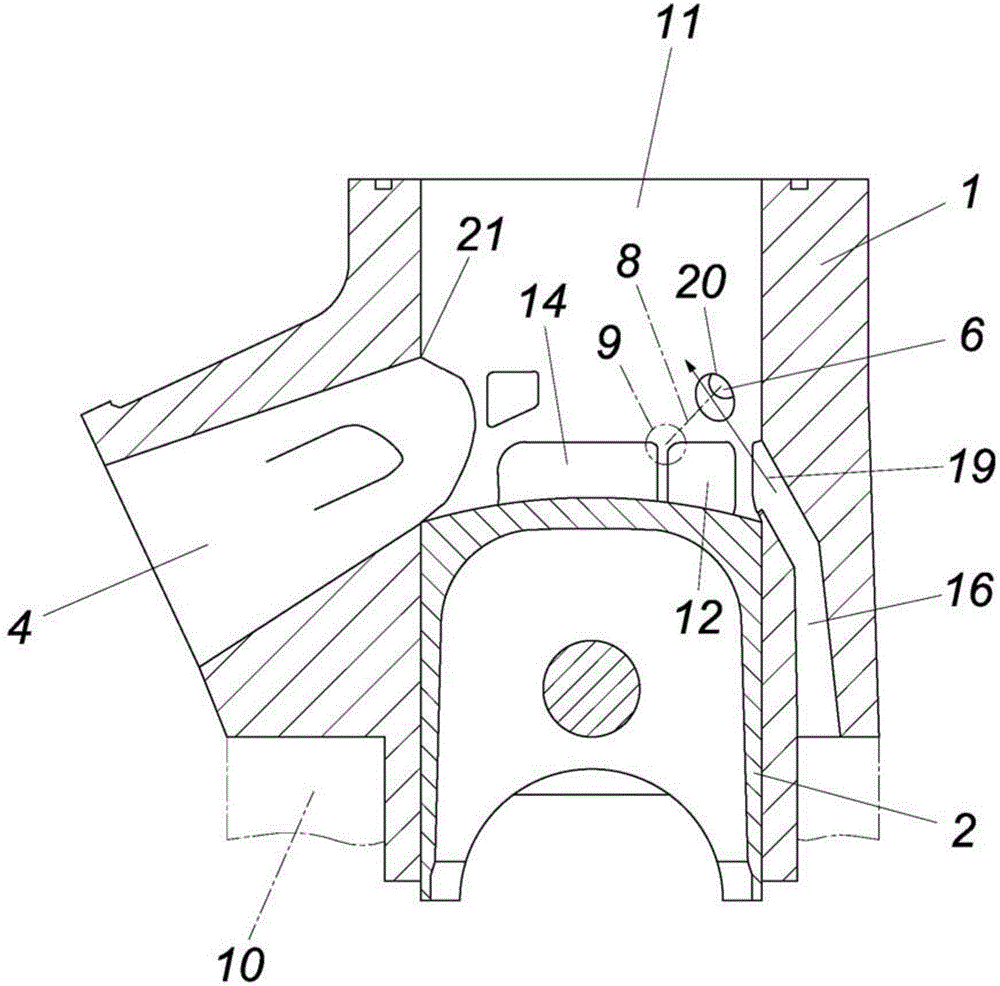
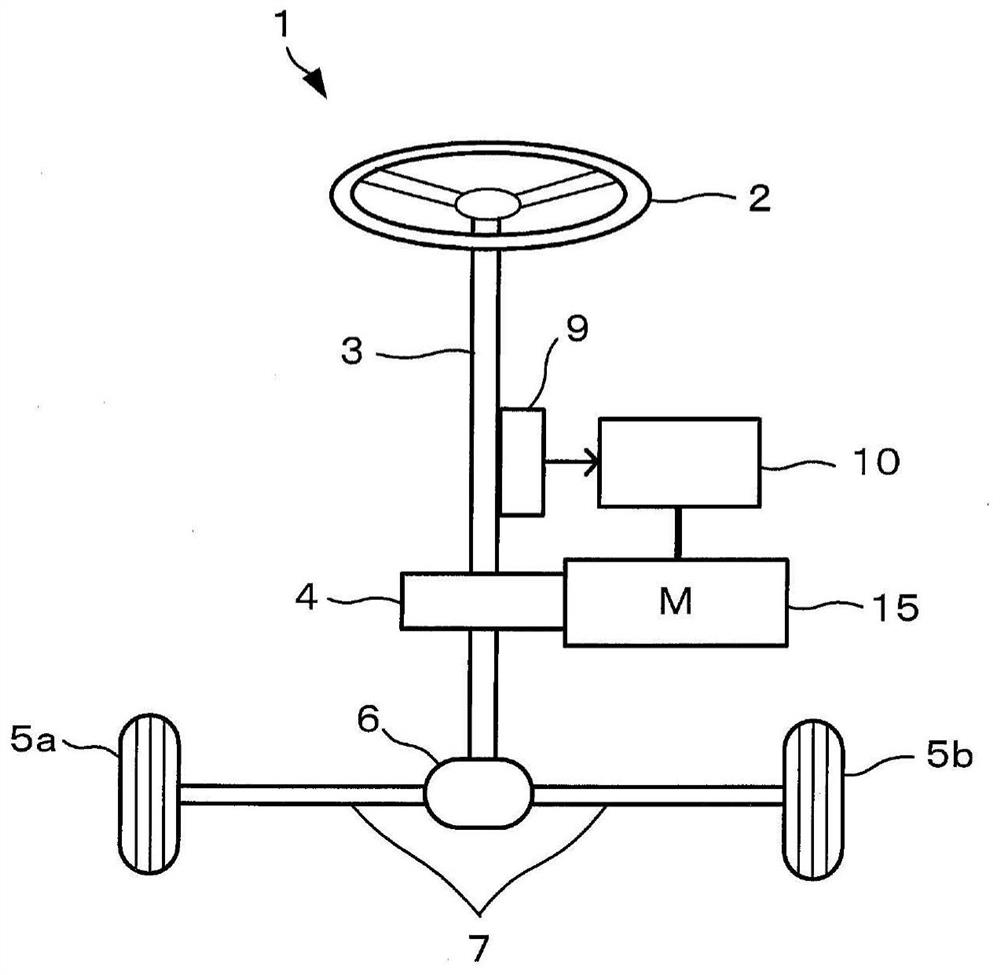
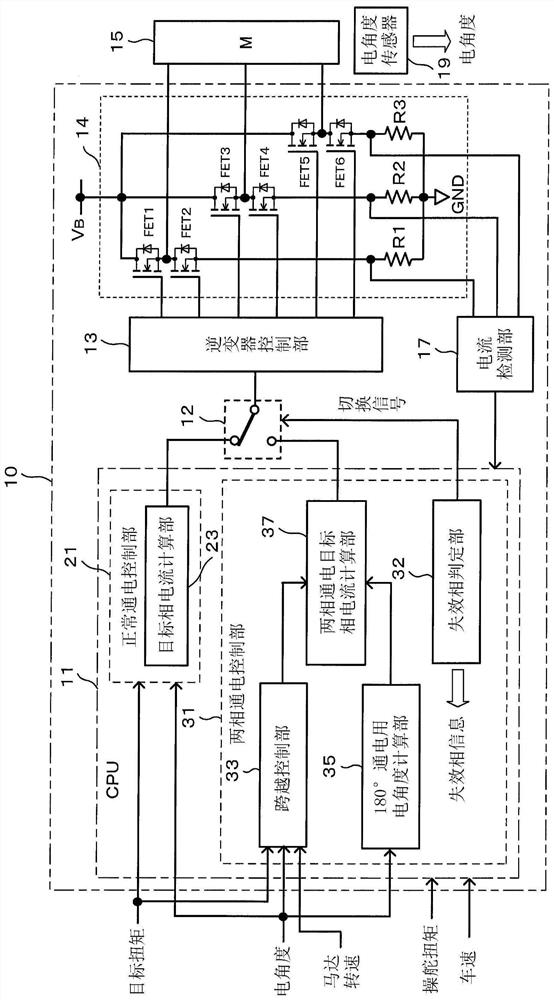
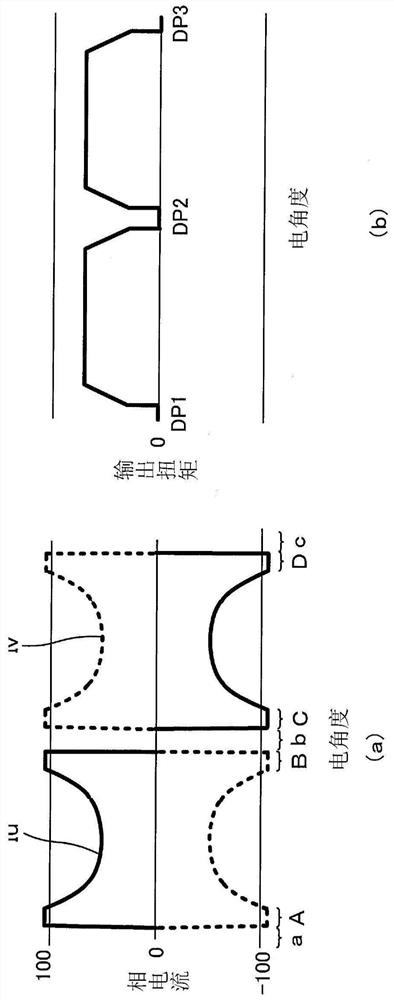
Motor energization control method
The invention provides a motor energization control method capable of continuing to drive a motor to cross a dead point even if a phase failure occurs. When a phase failure has occurred, if the electrical angle is located at a predetermined angle earlier than a torque dead point at which the output torque is zero, and if the rotational speed and steering torque of the electric motor (15) satisfy predetermined conditions, the electrical angle is returned, a phase current is passed in the opposite direction until the first electrical angle ([theta] 4) is reached, and the electric motor (15) is rotated in the opposite direction. Then, a phase current is passed in the forward direction, the electric motor (15) is rotated forward until a second electrical angle (theta5) is reached, and controlis performed so as to straddle the torque dead center by maintaining a sufficient angular velocity.
Owner:NIDEC ELESYS
Intelligent image positioning intermissive pumping controller
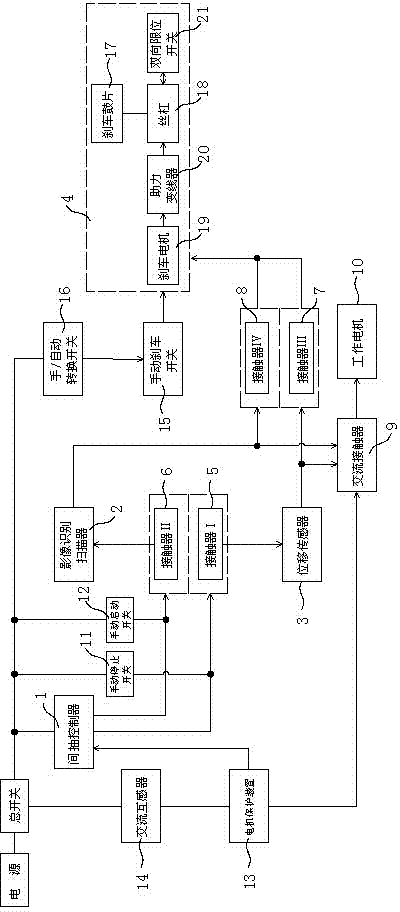
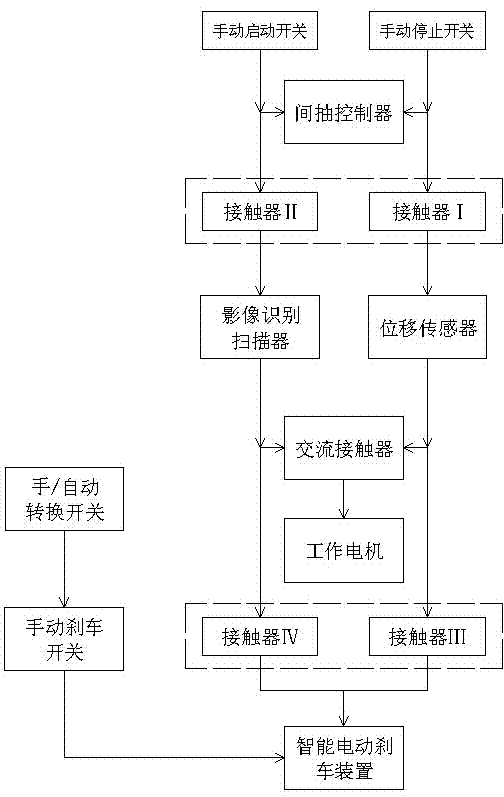
InactiveCN104730954AHigh degree of automationStrong precisionProgramme control in sequence/logic controllersEngineeringAlternating current
The invention relates to the field of auxiliary equipment of oil pumping units, in particular to an intelligent image positioning intermissive pumping controller. The intelligent image positioning intermissive pumping controller is composed of an intermissive pumping controller, a brake device, an image recognizer and a positioning sensor, wherein the intermissive pumping controller, the brake device and the image recognizer are installed on an oil pumping unit, the positioning sensor is arranged at a support point of a walking beam of the oil pumping unit, a power source, a total switch, the intermissive pumping controller, a contactor I, the positioning sensor, a contactor III and the brake device are sequentially connected in a circuit, the intermissive pumping controller, a contactor II, the image recognizer, a contactor IV and the brake device are sequentially connected in a circuit, the positioning sensor and the image recognizer are both connected to a work motor through an alternating current contactor, the contactor I and the contactor II are interlocked, and the contactor III and the contactor IV are interlocked. The image recognizer and the positioning sensor are added based on an original intermissive pumping controller, the on-site conditions can be recognized through the image recognizer when a well is started and stopped, and the positioning sensor can detect whether the movement state of the oil pumping unit reaches an upper / lower dead center and enables the oil pumping unit to be accurately stopped at the upper / lower dead center.
Owner:洪继波
Double-crank flying shear mechanism with instinct of automatically eliminating mechanism movement dead points
InactiveCN103752937APass without hindranceSynchronous slidingStock shearing machinesDriving apparatusEngineeringCrankshaft
The invention relates to a double-crank flying shear mechanism with an instinct of automatically eliminating mechanism movement dead points. One of two cranks of the mechanism is movable, and at least two corresponding bearing blocks supporting the moving crank become sliders, and can be driven by the moving crank to move on a body. In order to ensure the sliders to synchronize on one side during movement, a mechanical synchronizer is arranged. An axis of the moving crank is ensured to be always parallel to an axis of the non-moving crank. Therefore, necessary conditions are created for a novel shearing mechanism to easily cross the mechanism movement dead points. The problem that two sets of past shearing mechanisms in specifications cannot cross the mechanism movement dead points easily is solved satisfactorily. The novel fly shear mechanism is mainly used for shearing metal in movement just like the past shearing mechanisms, thereby still belonging to mechanical equipment in the metallurgy industry. Whether or not the related principle of the novel mechanism can be further applied to other occasions is still unclear at present.
Owner:王利霞 +2
New-principle super energy-saving engine
The invention provides a super energy-saving engine, which mainly achieves the purpose of saving energy on a large scale while keeping or producing high power in two ways. The first way is that internal energy consumption phenomena, including included angle dispersion, included angle friction and dead point counteraction existing in a traditional crankshaft engine are eliminated through a lever structure or a straight tooth structure; and the second way is that residual energy is recovered, stored and recombined through a resonance phenomenon of a resonance device, and main energy is superposed, accumulated and amplified to achieve the purpose of further saving energy. In the super energy-saving engine, a periodic driving force, which is output by a cylinder part and is the same as or similar to the fixed frequency of a resonant part, acts on a lever or an inertia hammer in a mechanical or electronic control mode, so that the lever or the inertia hammer of the resonant part performs resonant movement; and working is carried out again after a certain resonant movement, namely after the collection, storage and accumulation of certain energy. In the engine, the expansion force and shock wave force generated by the fuel combustion of the cylinder part, and the energy collected and recombined by the resonant part together generate a torque to drive a rotating shaft to rotate at most of the time so as to achieve the purposes of saving force and saving oil.
Owner:杨兴隆
Piston pump and relative control method
ActiveUS10914295B2Easy and economical can be manufactured and implementedFluid parameterPositive displacement pump componentsTop dead centerSolenoid valve
A piston pump for feeding a liquid in a vehicle having at least one piston, which is configured to cyclically slide inside a housing between a top dead centre and a bottom dead centre. The liquid is usually fed along a main feeding direction from a suction duct to a delivery duct. The piston pump has two solenoid valves, which are each arranged in the suction duct and in the delivery duct, respectively, and are designed to be operated by an electronic control unit so as to reverse the liquid feeding direction from the main feeding direction to a secondary feeding direction opposite the main liquid feeding direction and / or so as to adjust the cylinder capacity of the piston pump. The piston is operated by an electromechanical actuator, in particular comprising an electromagnet.
Owner:MARELLI EURO SPA
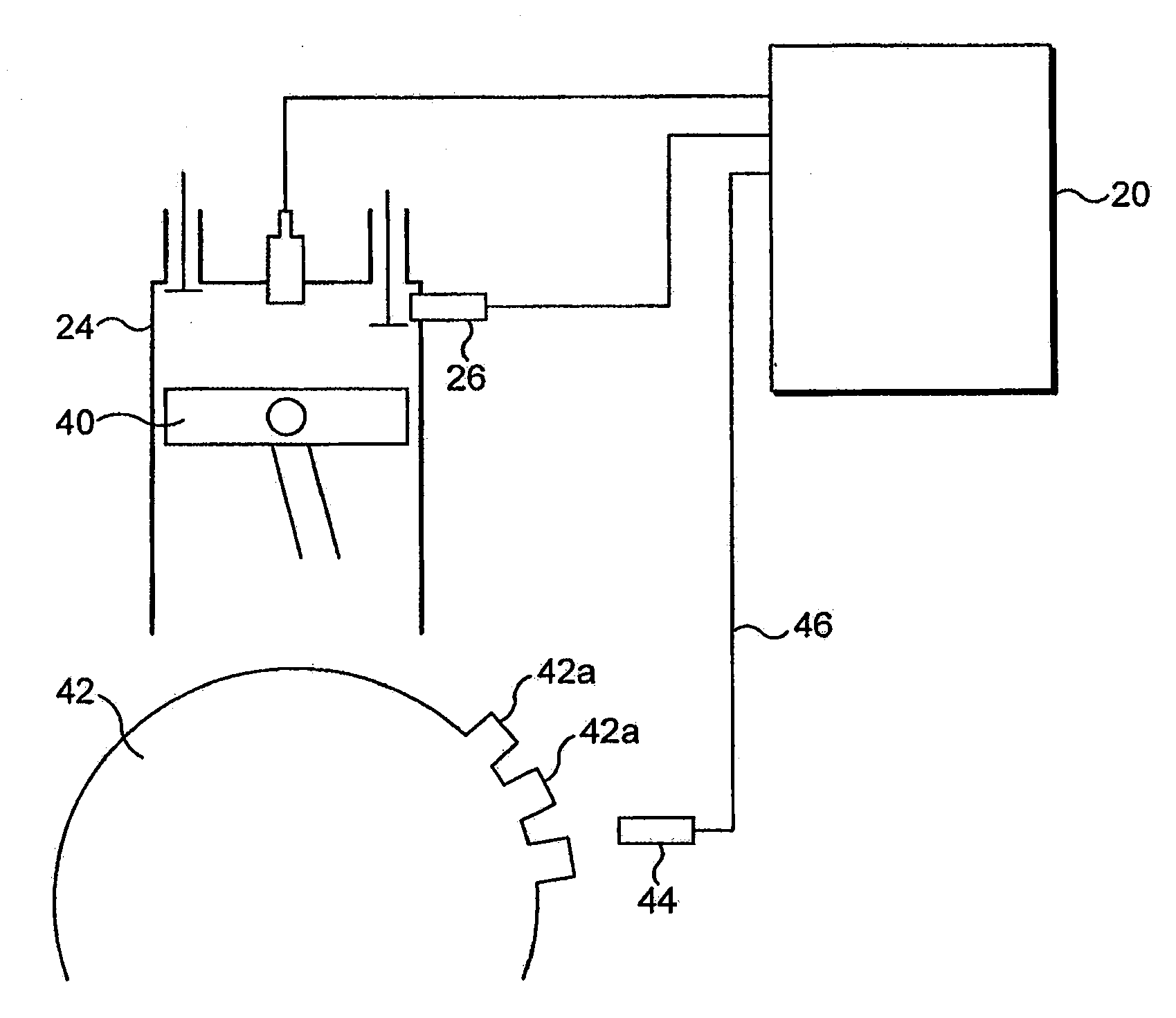
Validation of a signal from a crankshaft sensor
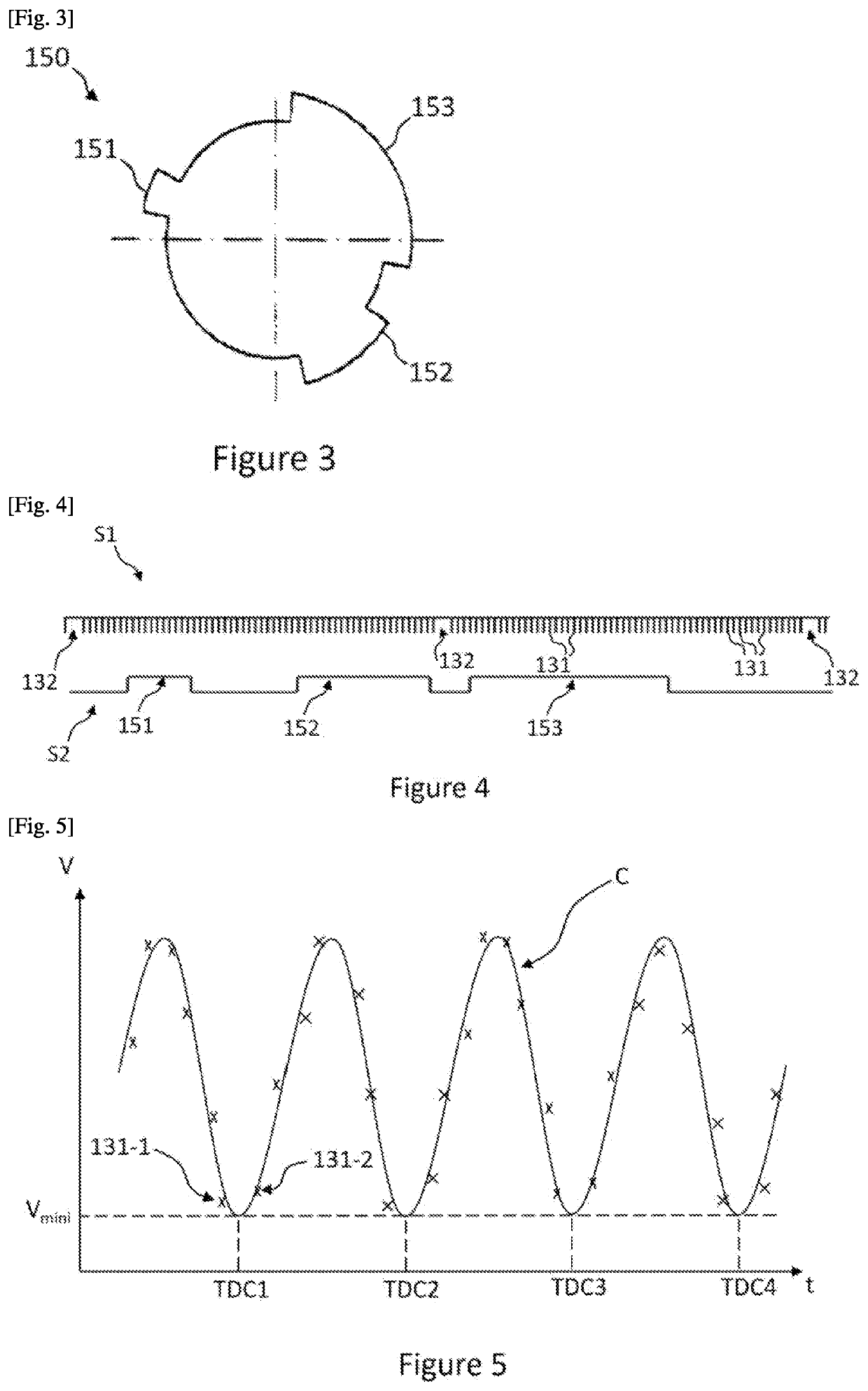
ActiveUS20220228536A1Quick fixGuaranteed uptimeValve arrangementsElectrical controlTop dead centerGear wheel
The invention relates to a method for switching between a degraded mode and a normal mode for establishing the angular position of an internal combustion engine (10) of a vehicle (1), the method comprising the steps of, in degraded mode, detecting the free space and the teeth of the toothed wheel (130) of the crankshaft (13) during the rotation of the crankshaft (13) from the signal generated by the crankshaft sensor (16), establishing the angular positions of the crankshaft (13) corresponding to the minimum rotation speeds of the top dead centres established, and switching to normal mode when, for each top dead centre, the deviation between the angular position of the crankshaft (13) and a reference position is less than a position threshold for at least one revolution of the crankshaft (13).
Owner:VITESCO TECH GERMANY GMBH
Device and method for accurately measuring dead point on crankshaft of diesel engine
PendingCN109341503AImprove assembly efficiencyImprove assembly qualityInternal-combustion engine testingUsing electrical meansCylinder headEngineering
The invention discloses a device for accurately measuring a dead point on a crankshaft of a diesel engine. The device comprises a guide rod, a positioning guide cylinder, a permanent magnet combination, a Hall sensor, a sensor support, and a signal processor. The positioning guide cylinder is positioned in an injector mounting hole of a cylinder head. The middle of the guide rod and the positioning guide cylinder are in clearance fit. The bottom of the guide rod abuts against the top surface of a piston. The permanent magnet combination is fixed on the top end of the guide rod. The Hall sensoris vertically supported on the upper portion of the sensor support, and the lower end of the Hall sensor is opposite to the center of the top end of a permanent magnet. The method comprises the stepsof: (1) installing the permanent magnet combination, the guide rod, and the positioning guide cylinder; (2) detecting the position of the dead point on the crankshaft. The measurement precision of the dead point on the crankshaft of the diesel engine can be increased to 0.1 degree to 0.2 degree by the device and the method for accurately measuring the dead point on the crankshaft of the diesel engine. The device, for accurately measuring the dead point on the crankshaft of the diesel engine with only once detection during the diesel engine assembling process, is efficient, and is easy to operate, thereby improving the assembling efficiency and the assembling quality of the diesel engine.
Owner:CSSC MARINE POWER
Structure for preventing formation of dead point for cam wheel and strapping device using the same
ActiveUS11111039B2Preventing the generations of unexpected dead points from interrupting the work flowImprove work efficiencyBinding material applicationBundling machine detailsDrive wheelCam
A structure for preventing the formation of a dead point for a cam wheel includes a driving wheel with a pressing portion provided at one side thereof for pushing a pushed portion of the cam wheel. When the cam wheel is moved over a distance while rotating simultaneously, a cam portion of the cam wheel pushes one end of the swinging piece. When the one end of the swinging piece is pushed to be apart from the outer periphery of the cam wheel, a restoring piece axially pushes the cam wheel back to its original position. A strapping device includes the above structure, a housing, a first transmission assembly, a second transmission assembly and a third transmission assembly. Tensioning of a circular strap, rapid friction bonding and cutting are sequentially performed by the transmissions of the first to third assemblies, respectively.
Owner:PANTECH INT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com