Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
51 results about "Cryptographic primitive" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cryptographic primitives are well-established, low-level cryptographic algorithms that are frequently used to build cryptographic protocols for computer security systems. These routines include, but are not limited to, one-way hash functions and encryption functions.
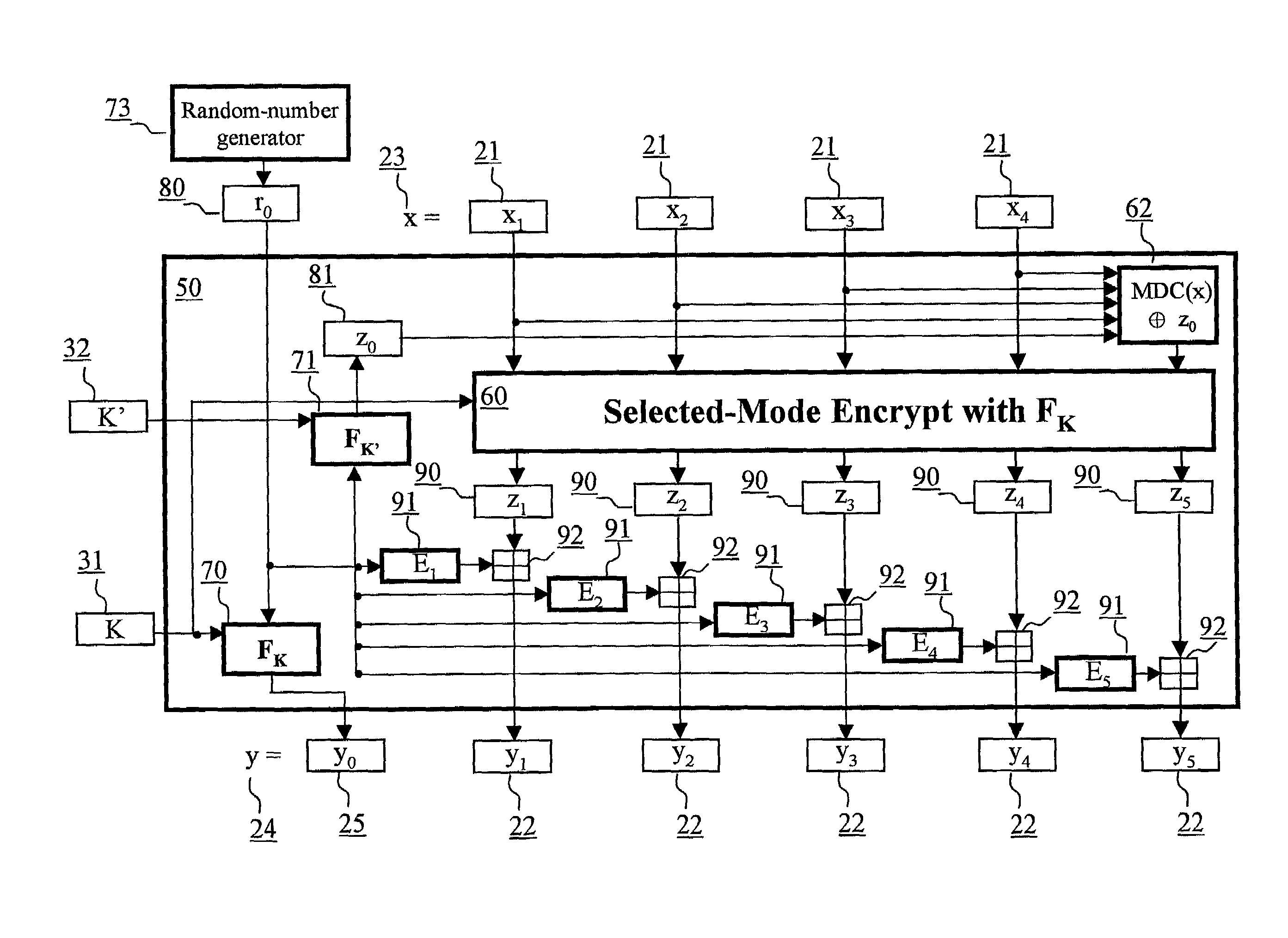
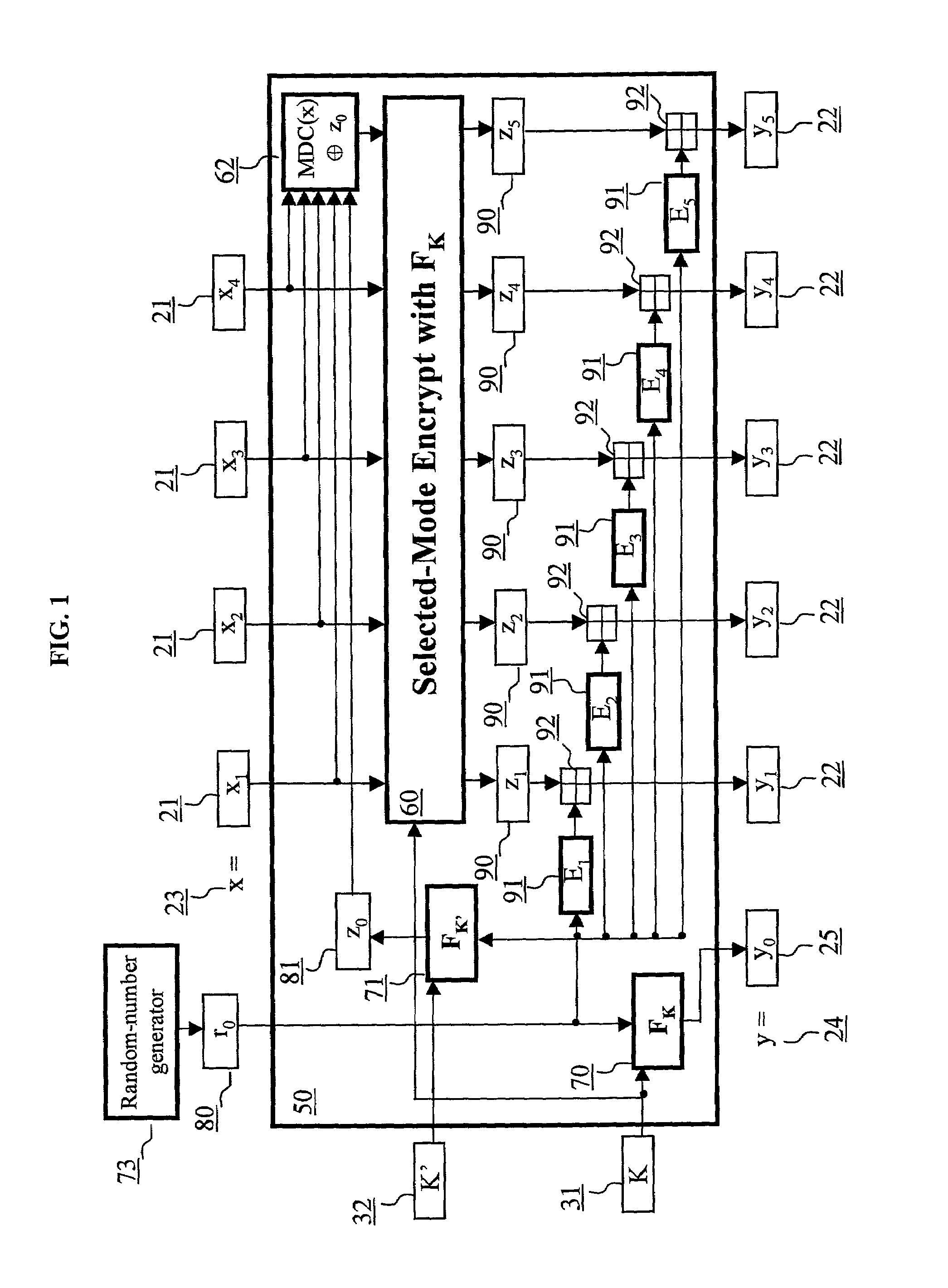
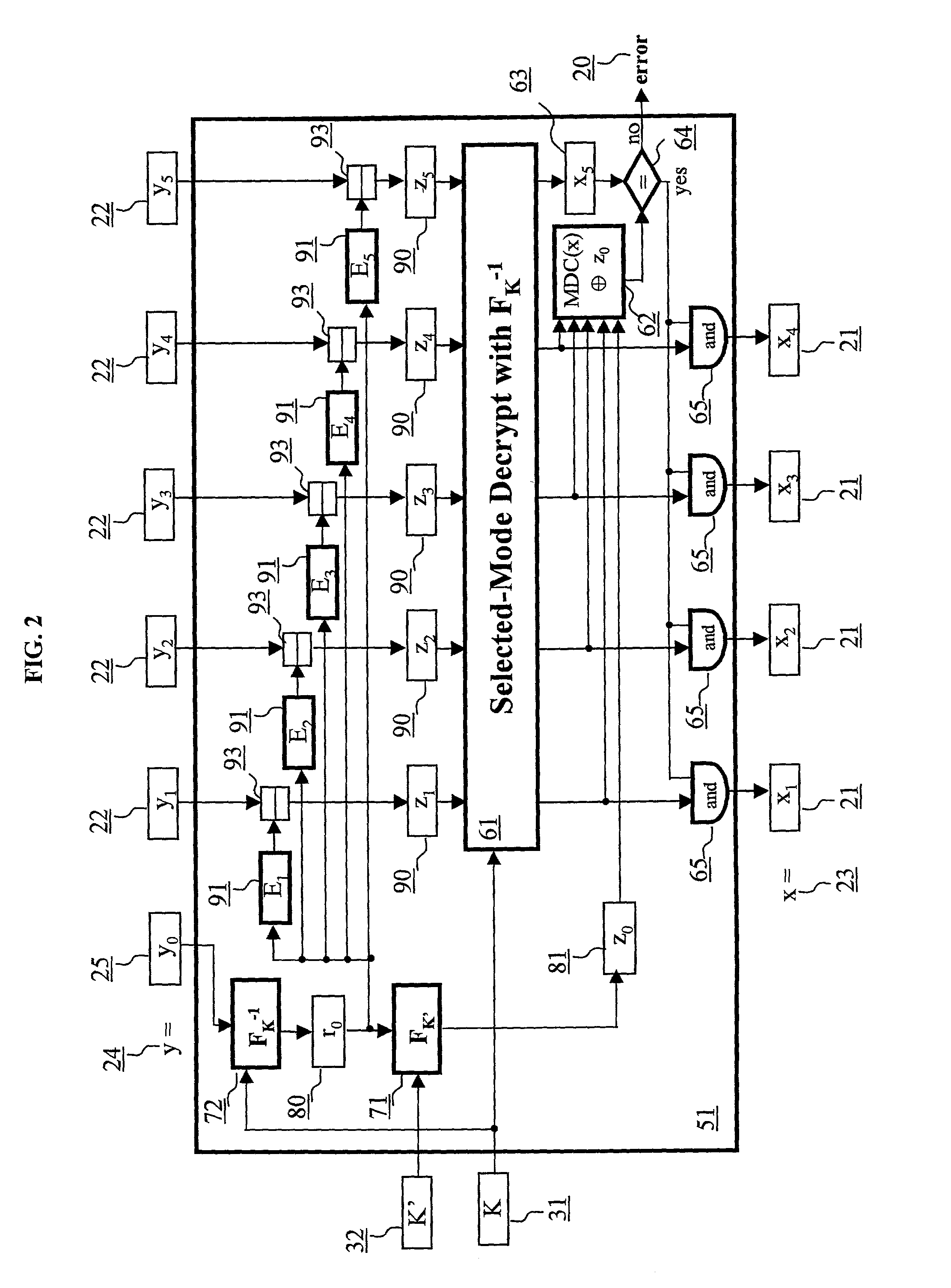
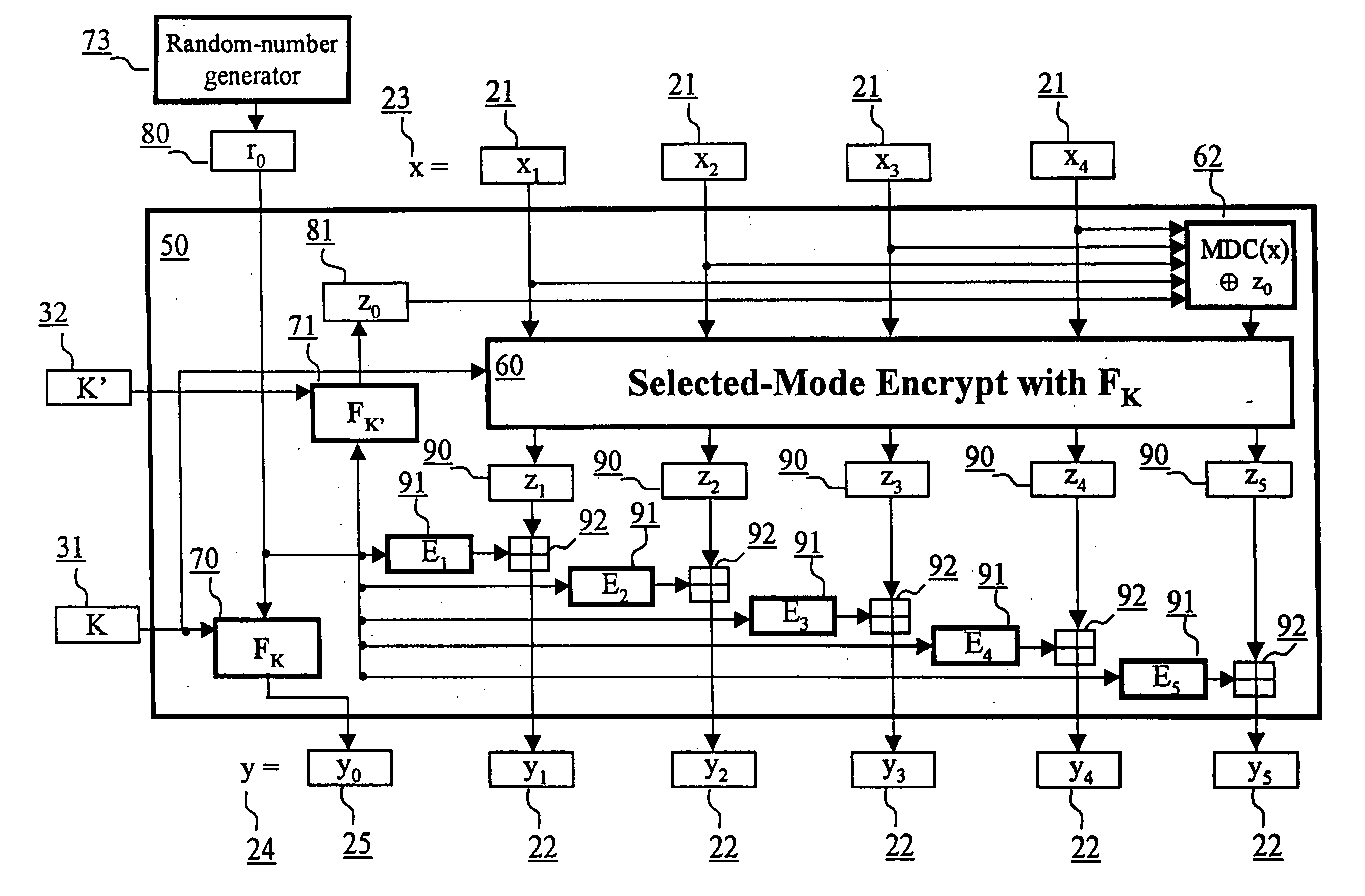
Block encryption method and schemes for data confidentiality and integrity protection
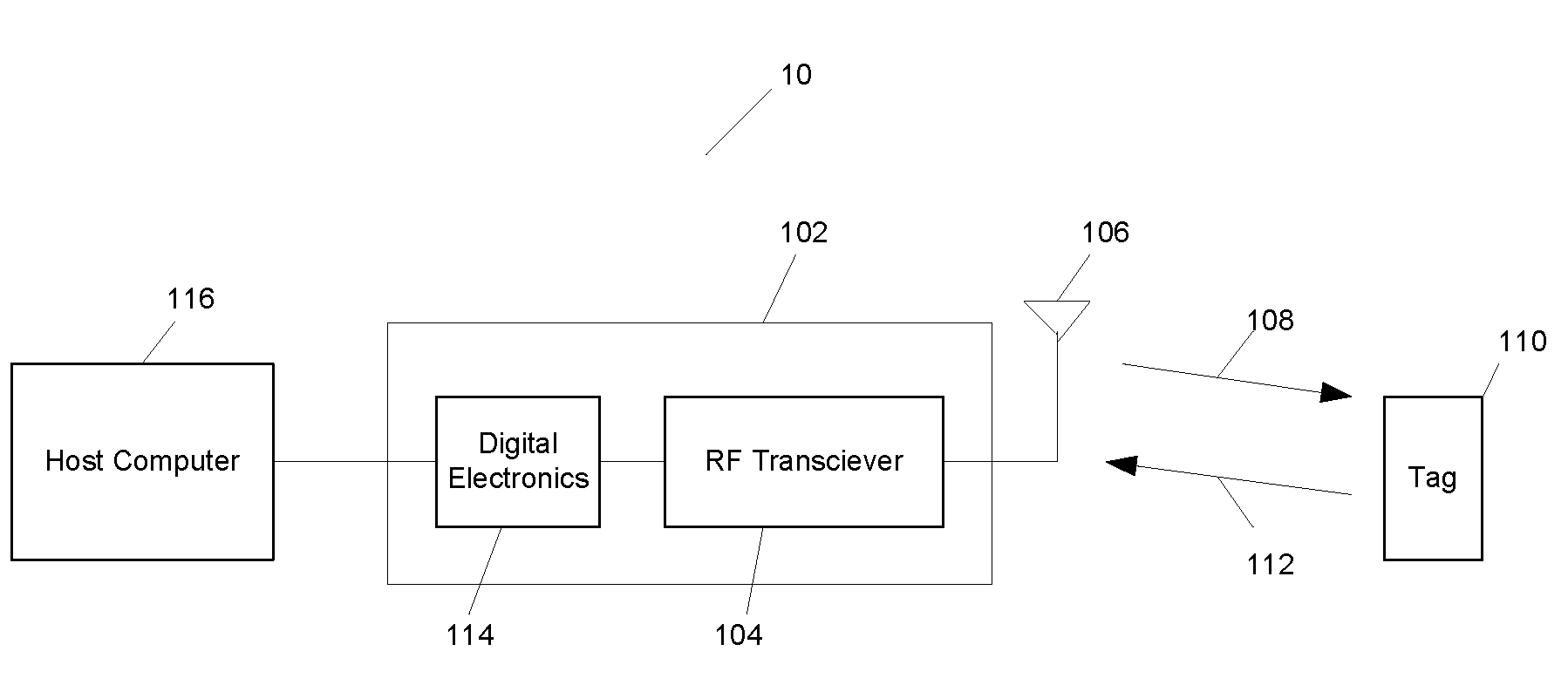
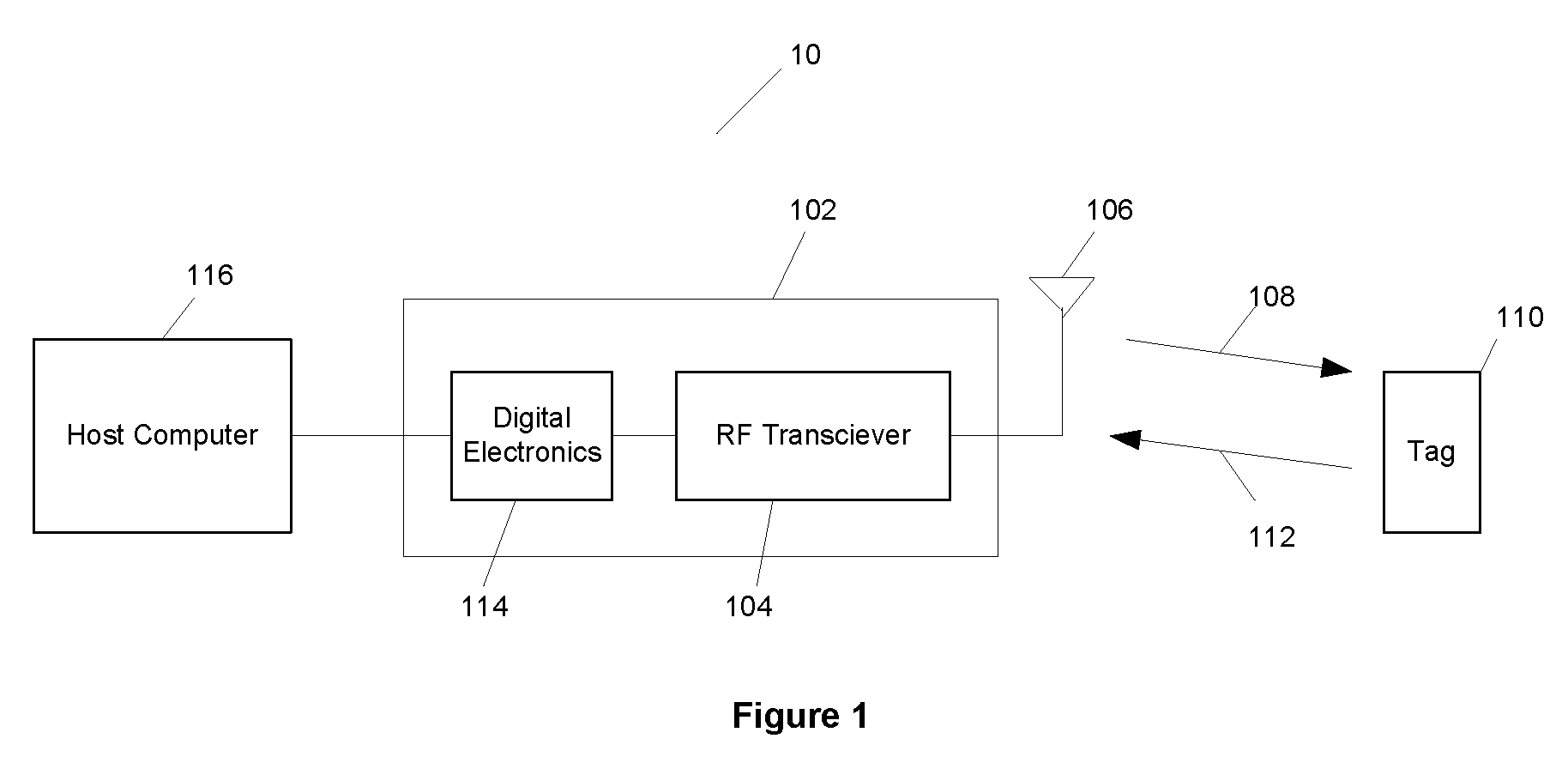
ActiveUS6973187B2Encryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesUser identity/authority verificationPower applicationComputer hardware
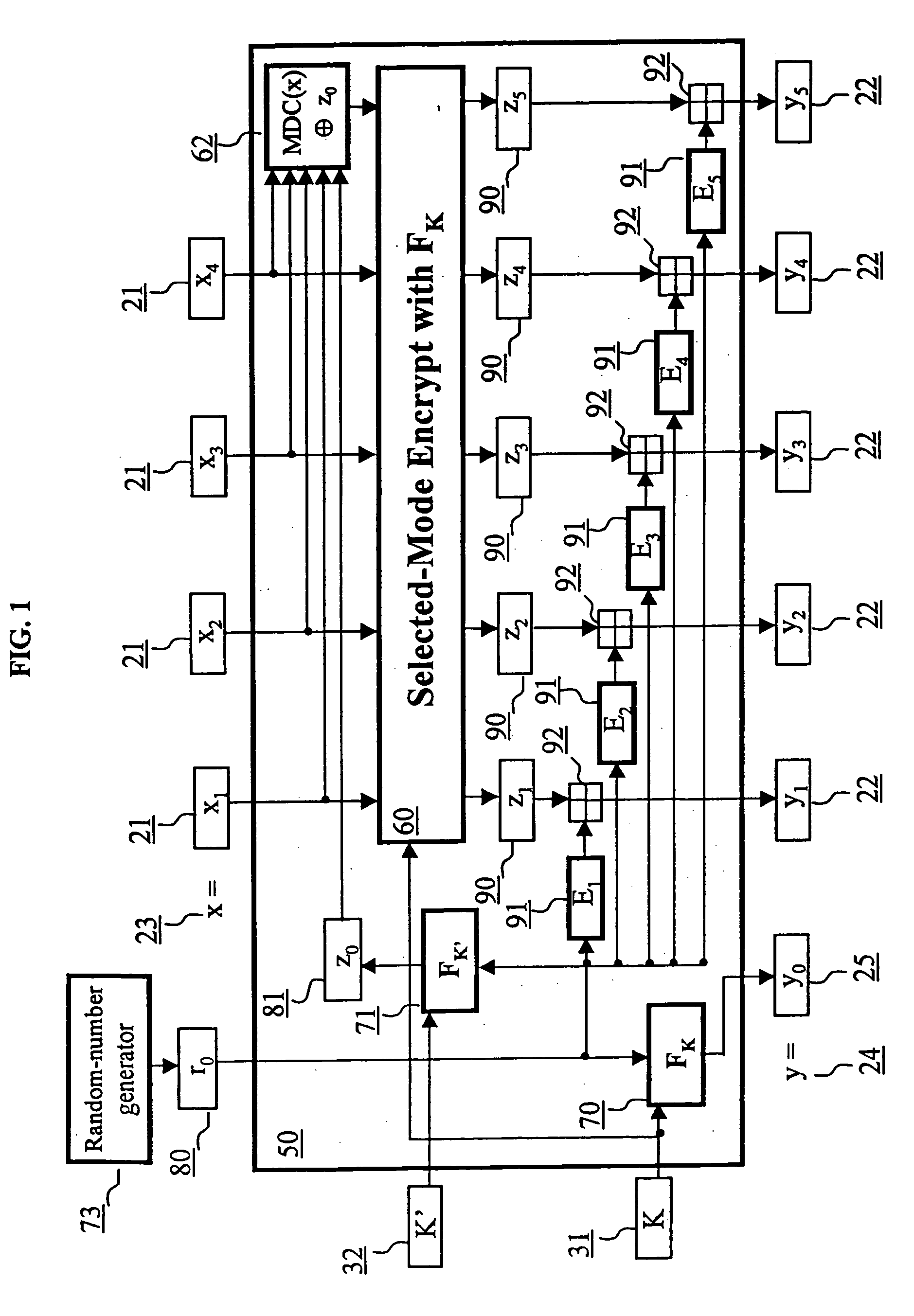
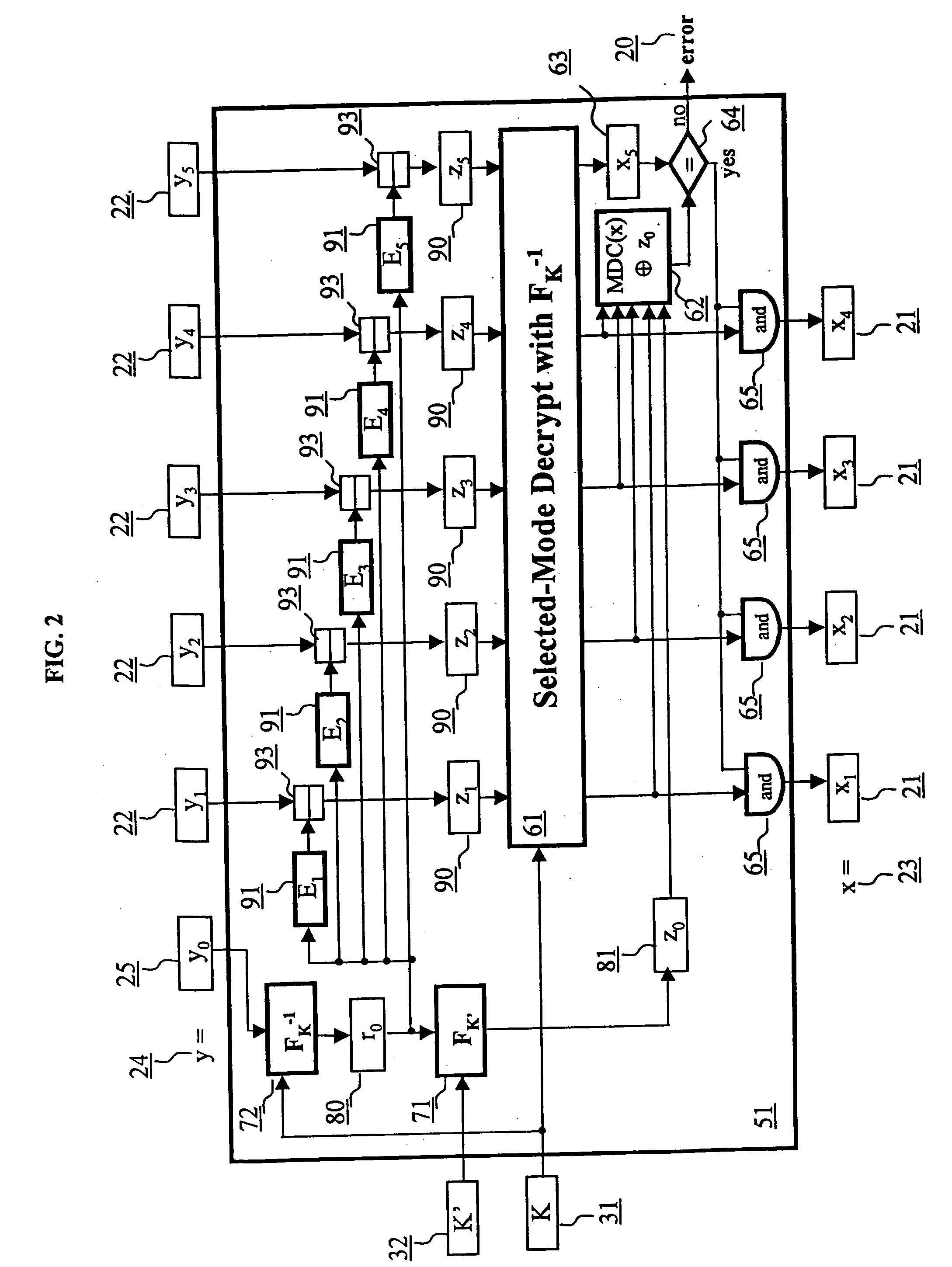
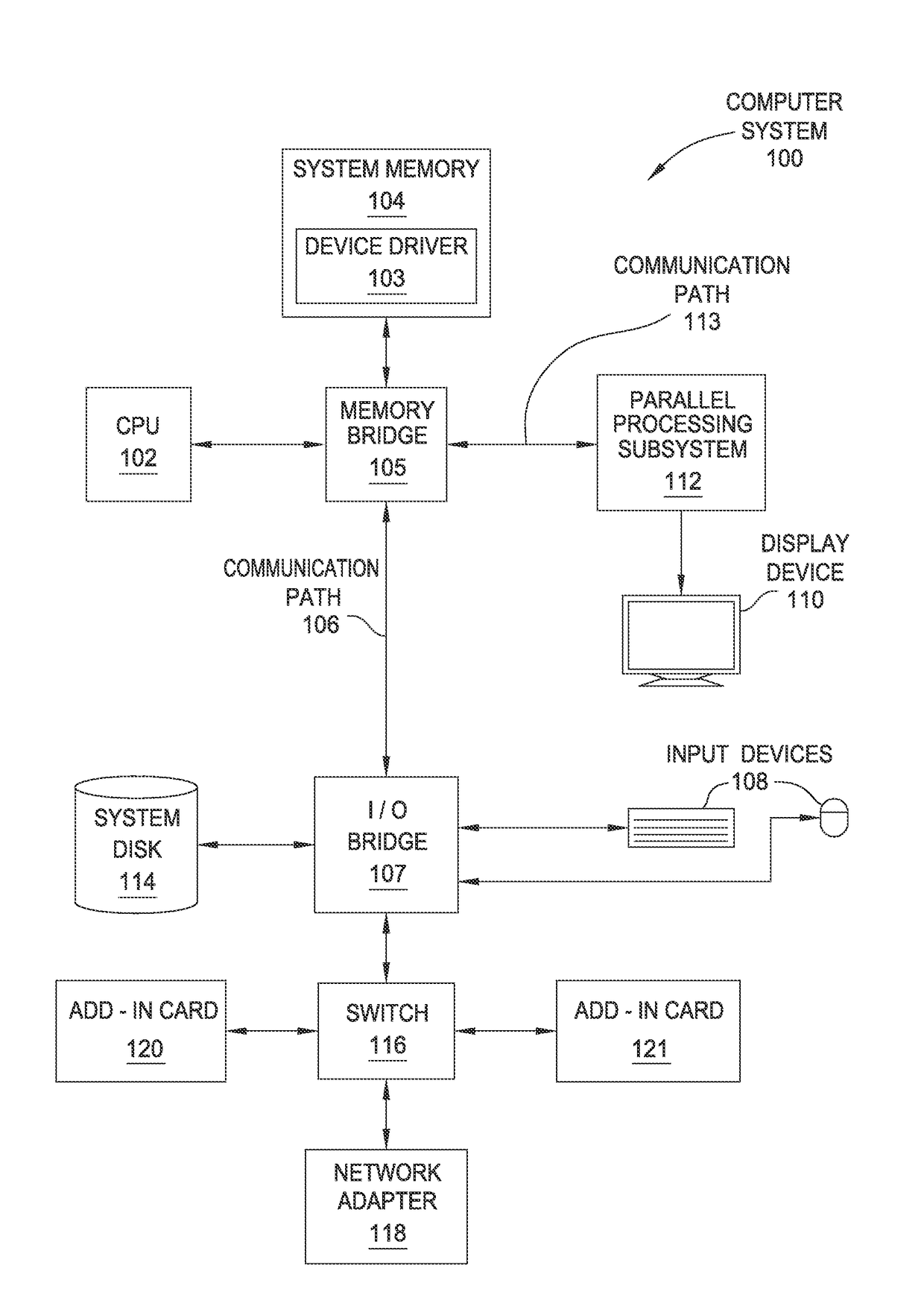
A block encryption method and schemes (modes of operation) that provide both data confidentiality and integrity with a single cryptographic primitive and a single processing pass over the input plaintext string by using a non-cryptographic Manipulation Detection Code function for secure data communication over insecure channels and for secure data storage on insecure media. The present invention allows, in a further aspect, software and hardware implementations, and use in high-performance and low-power applications, and low-power, low-cost hardware devices. The block encryption method and schemes of this invention allow, in yet a further aspect, encryption and decryption in parallel or pipelined manners in addition to sequential operation. In a yet further aspect, the block encryption method and schemes of this invention are suitable for real-time applications.
Owner:VDG
Block encryption method and schemes for data confidentiality and integrity protection
InactiveUS20060056623A1Encryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesUser identity/authority verificationPower applicationComputer hardware
Owner:VDG
Method and apparatus for time-lapse cryptography
ActiveUS20100185863A1Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageThird partyCiphertext
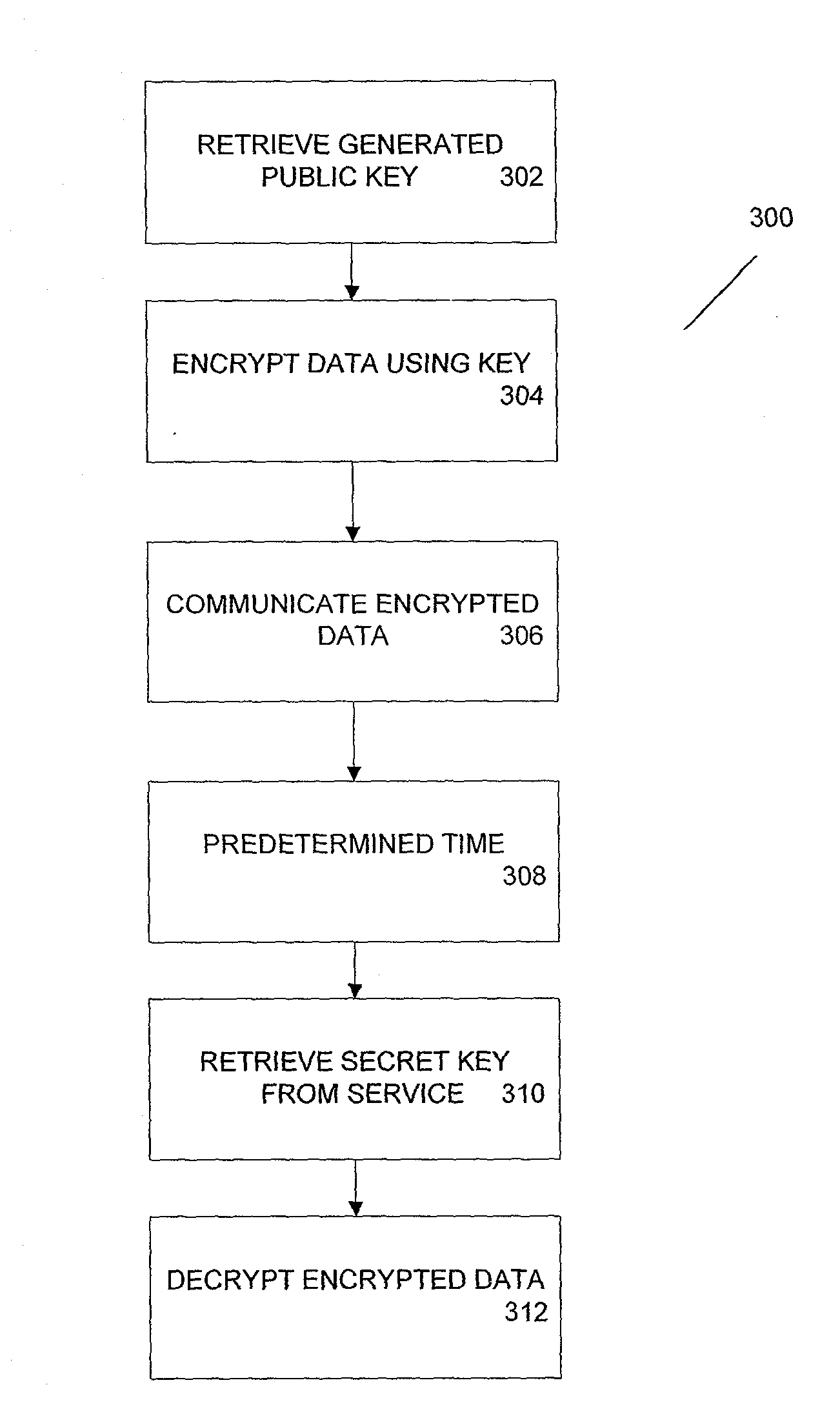
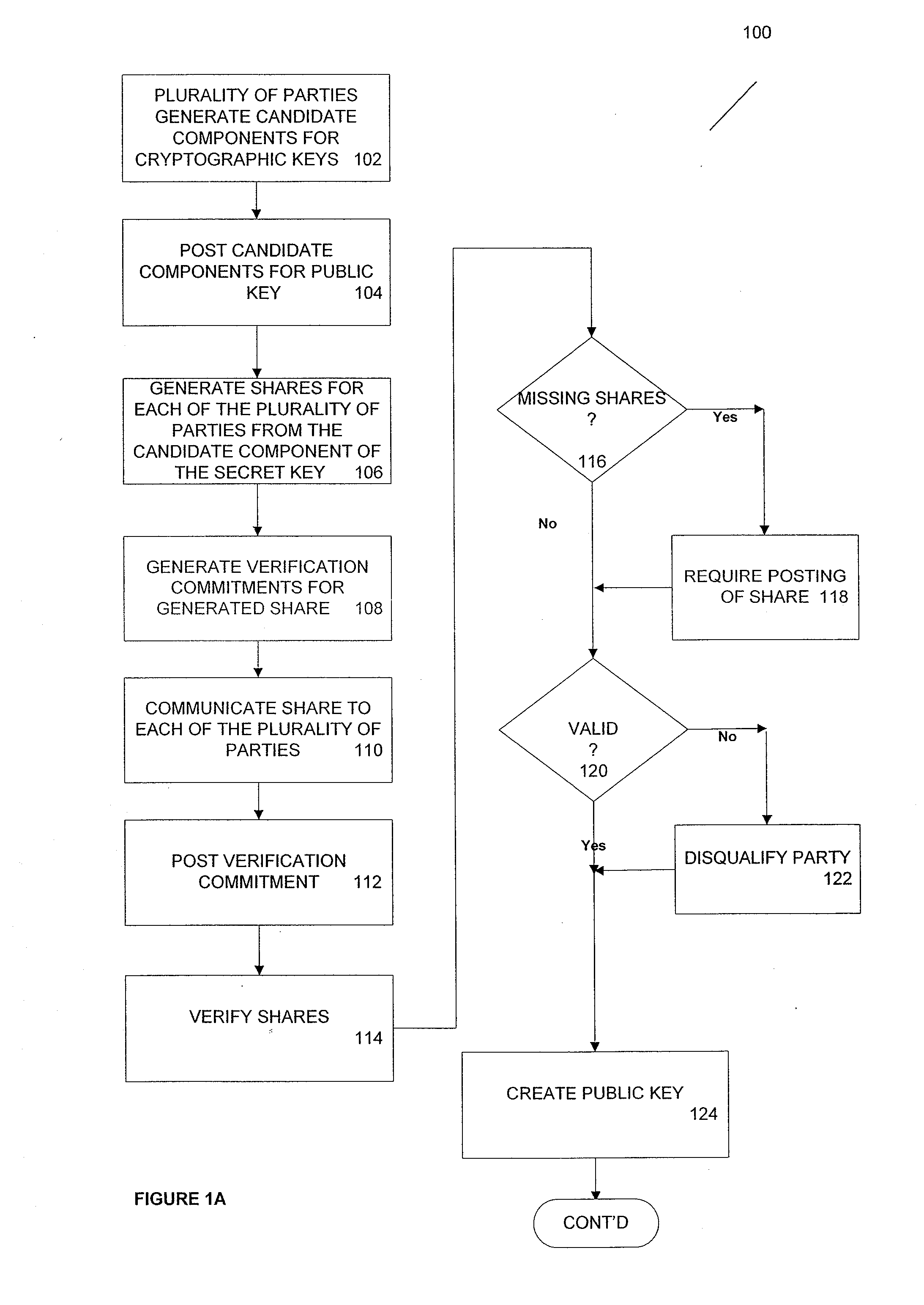
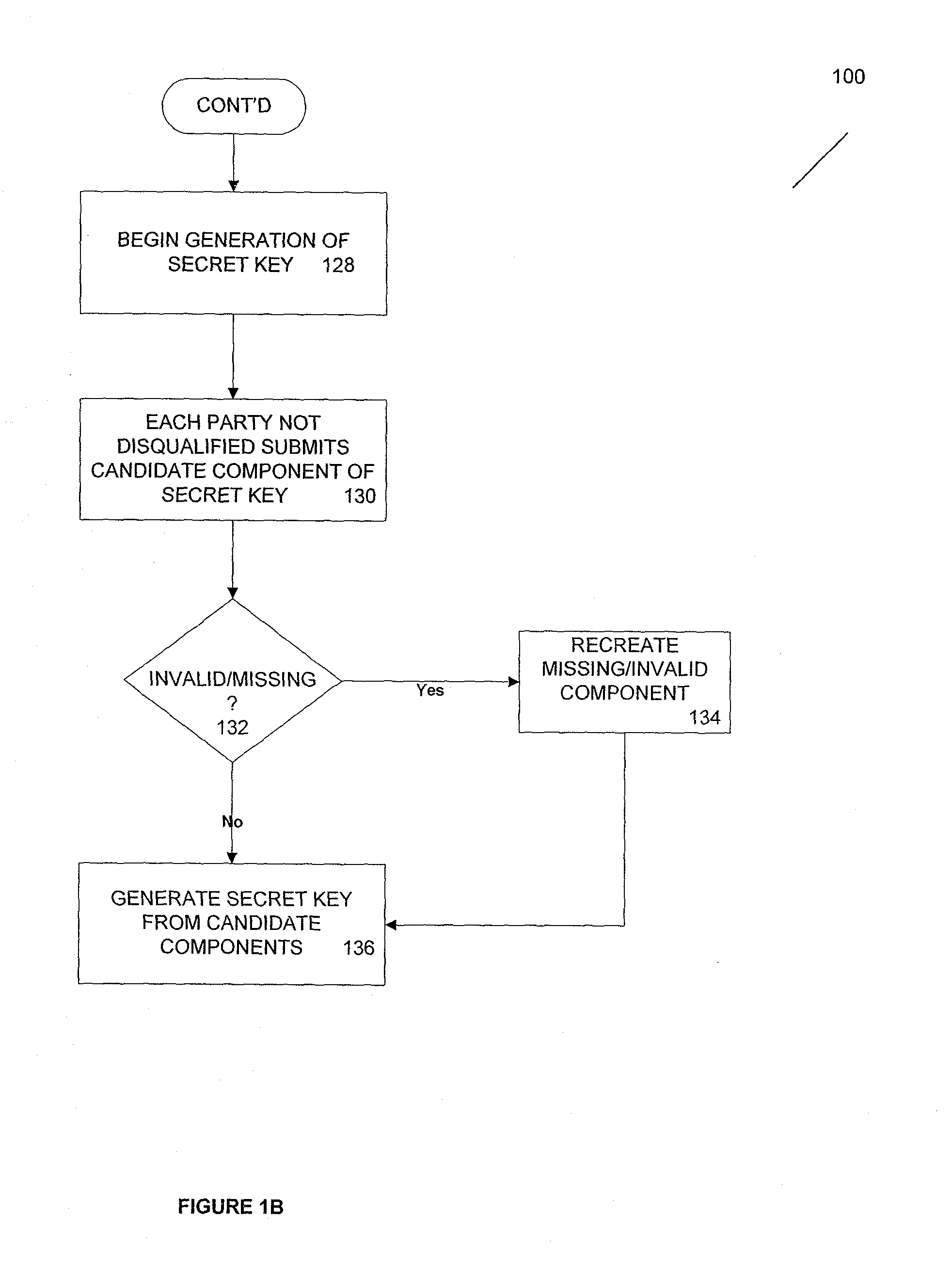
According to one aspect, provided is a construction and specification for an implementation of a new cryptographic primitive, “Time-Lapse Cryptography”, with which a sender can encrypt a message so that it is guaranteed to be revealed at an exact moment in the future, even if this revelation turns out to be undesirable to the sender. In one embodiment, a Time-Lapse Cryptography Service is provided (“the Service”) based on a network of parties. Senders encrypt their messages with this public key whose secret key is not known to anyone—not even a trusted third party—until a predefined and specific future time T+δ, at which point the secret key is constructed and published. In one example, the secret key can only be known after it is constructed. At or after that time, anyone can decrypt the cipher text using this secret key. Other embodiments describe other applications of such a service, for example, one embodiment is used in sealed bid auctions, others in insider stock sales, clinical trials, and electronic voting, among a variety of possible implementations. In one embodiment, a method for cryptographic encoding is provided, including generation of cryptographic key components by a plurality of parties, where participation of the parties is verified. A public key is constructed from a plurality of key components,
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
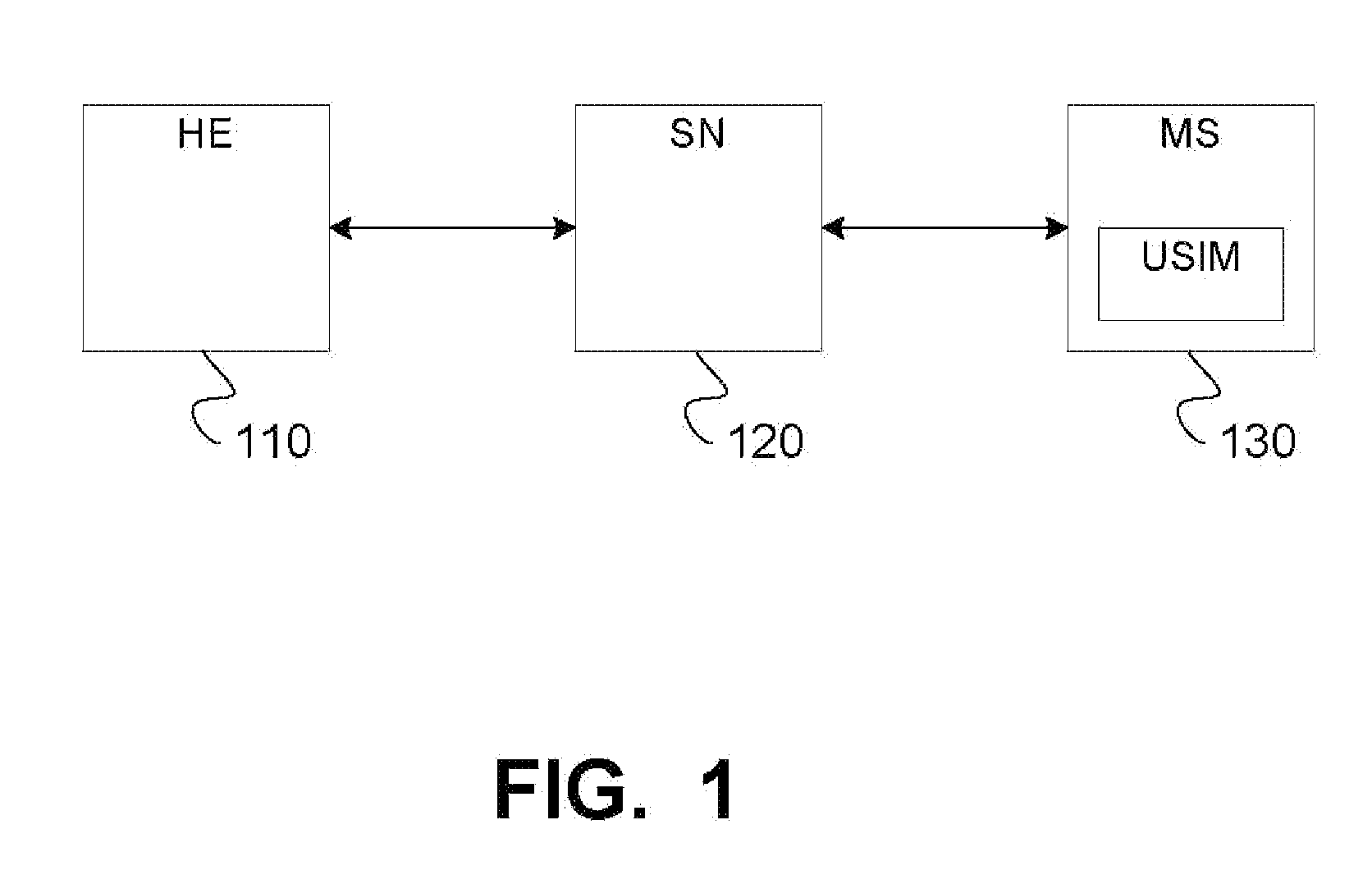
Cryptographic techniques for a communications network
InactiveUS7131006B1Efficiently authenticatingKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationHome environmentAuthentication
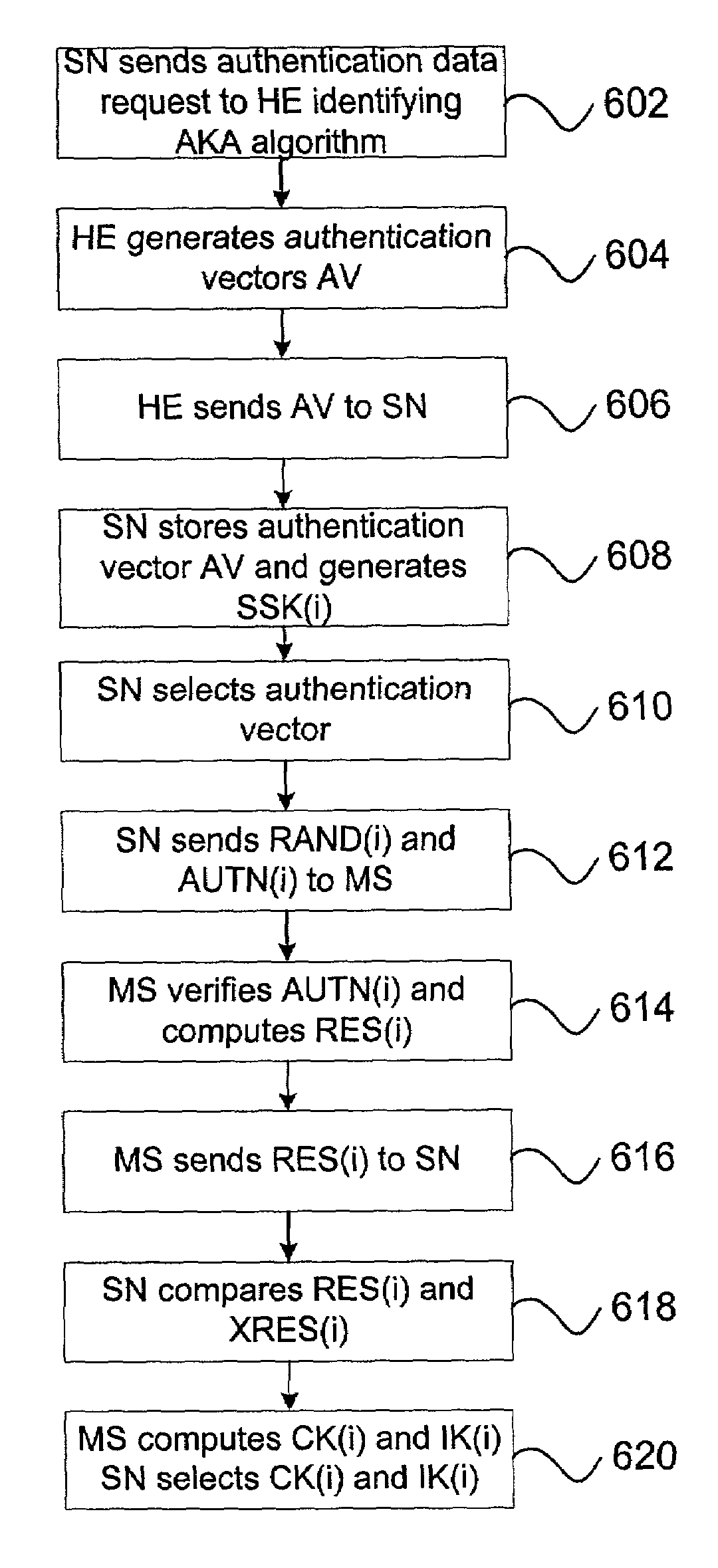
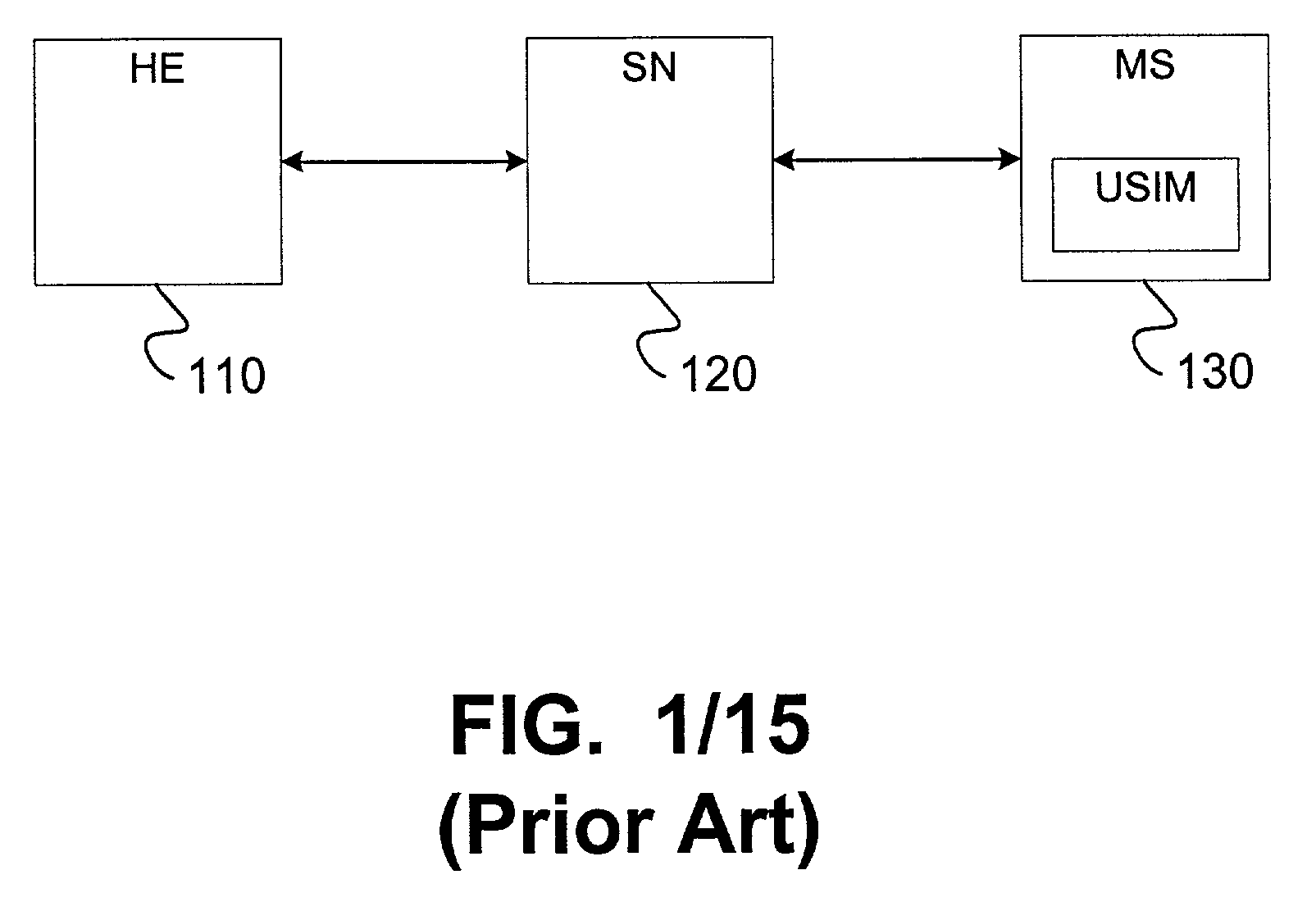
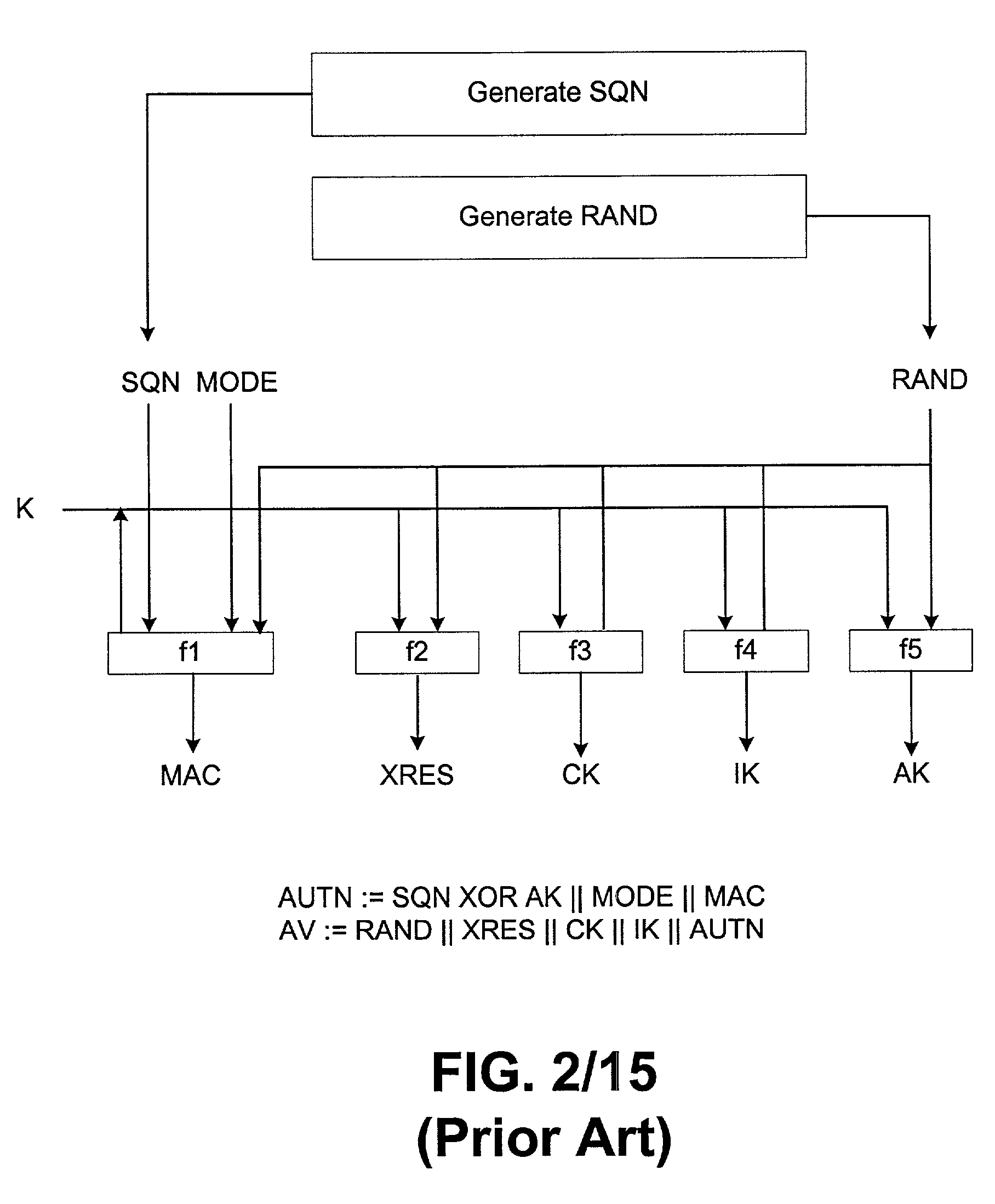
Techniques are described for enabling authentication and / or key agreement between communications network stations and service networks. The techniques described include the negotiation and use of a cryptographic primitive shared between a service network and a home environment of a station. The techniques described also feature a key usage indicator, such as a sequence number, maintained by the service network and a station. Comparison of the key usage indicators can, for example, permit efficient authentication of the service network.
Owner:VERIZON LAB
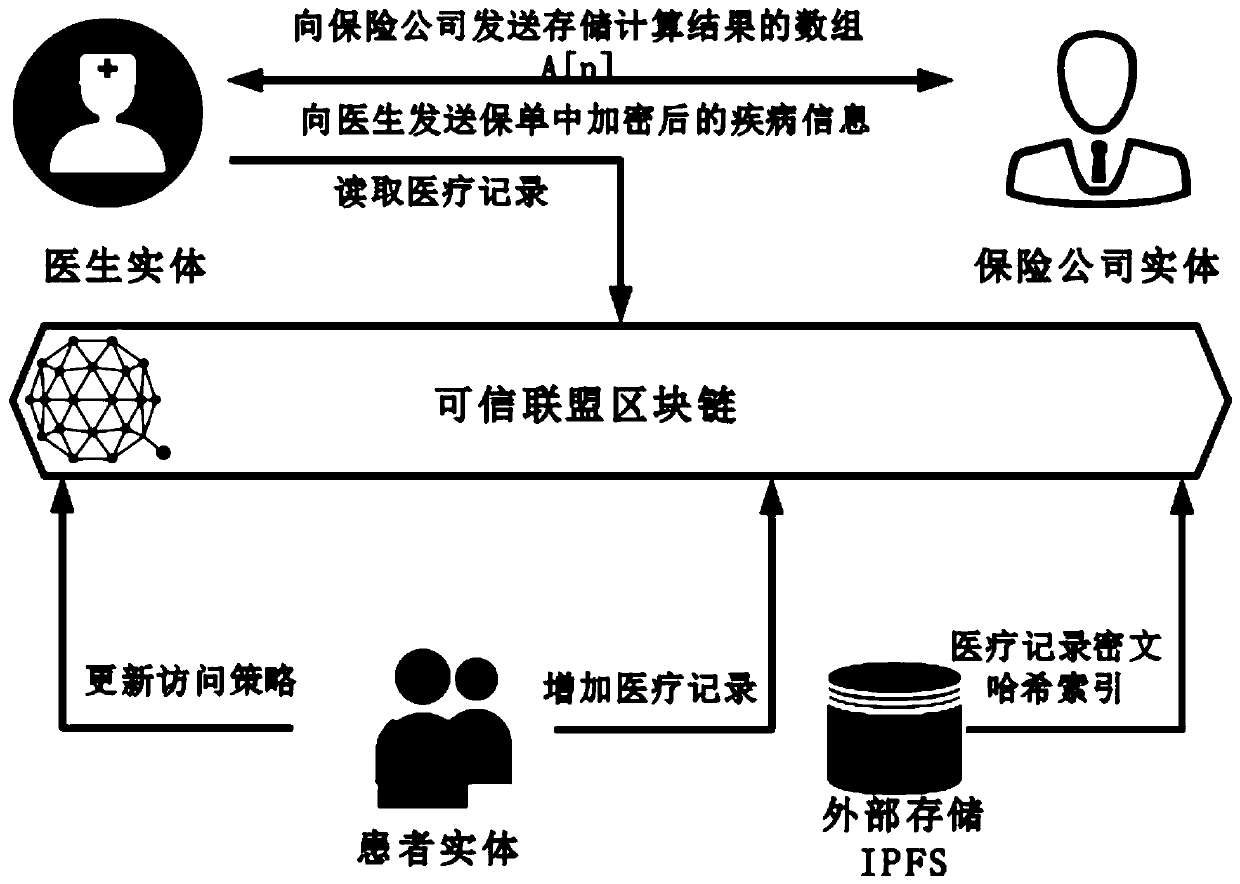
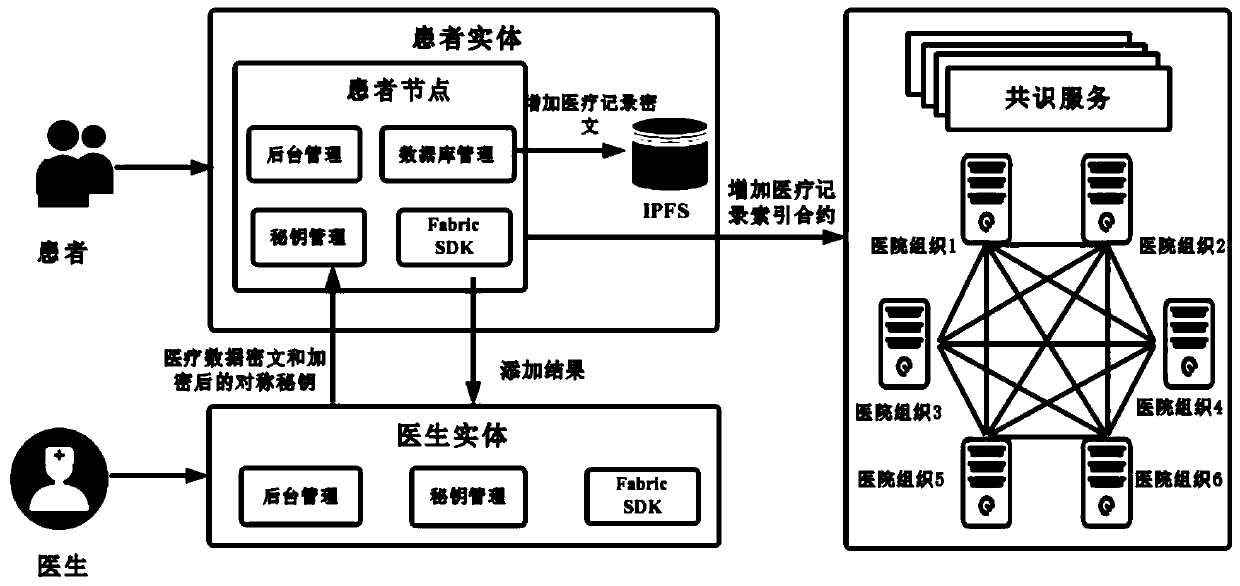
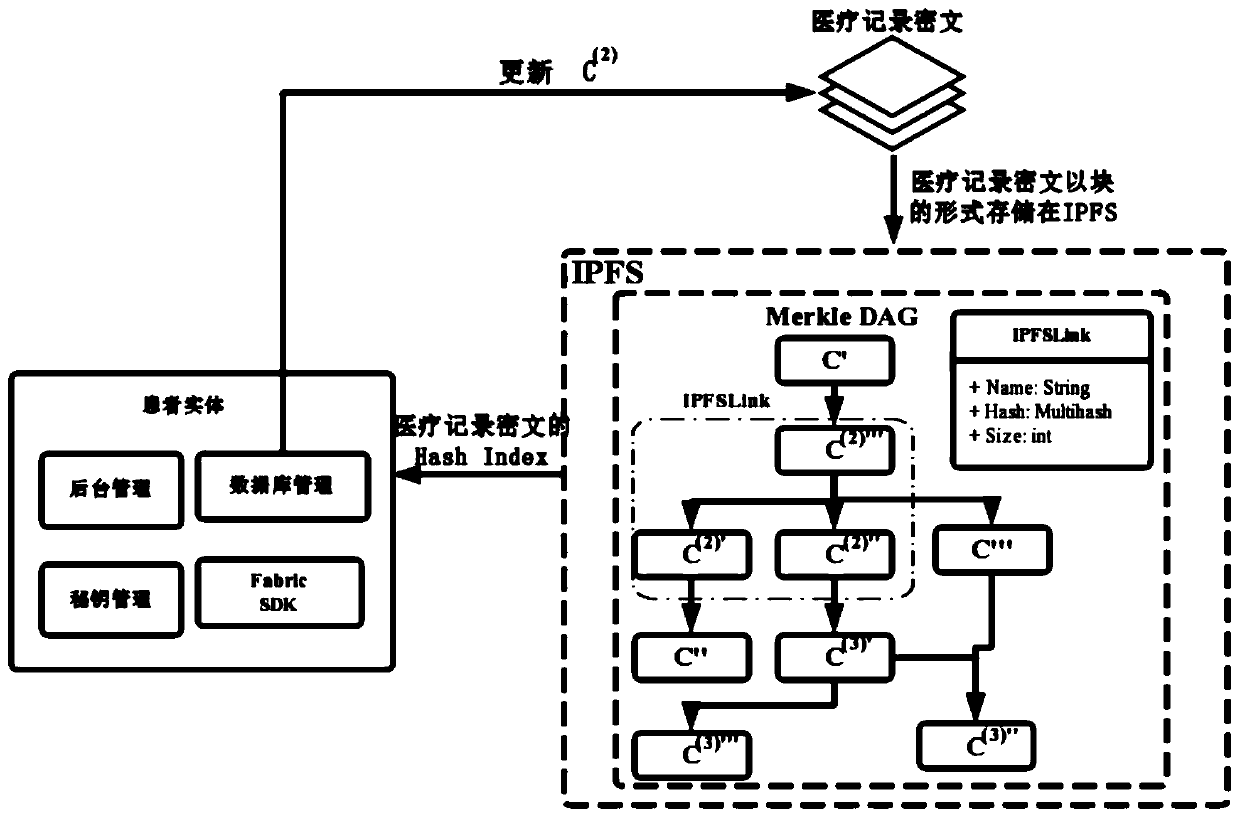
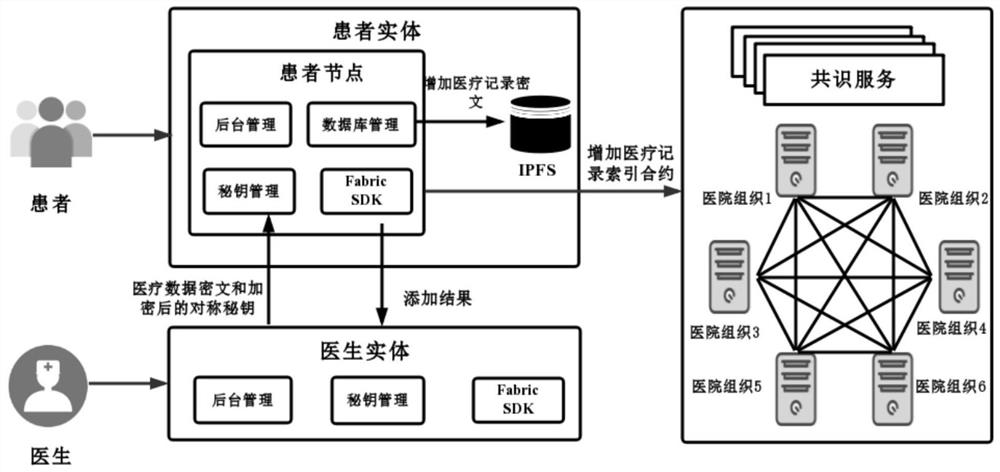
Medical record storage, sharing and security claim settlement model and method based on a block chain
ActiveCN110008746AGuaranteed privacyIncrease resistanceDigital data protectionPatient healthcareMedical recordThird party
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical data management, and relates to a medical record storage, sharing and security claim settlement model and method based on a block chain. Firstly, credible sharing of medical data of patients among medical institutions is achieved through the blockchain technology, and a lifelong medical record is established for the patients; based on a Hashchain type storage structure, the medical data cannot be tampered; secondly, an improved CP-ABE-based cryptographic primitive SHDPCPC-CP-ABE is proposed, security encryption and fine-grained access control on the medical data are realized, and a patient can conveniently and efficiently access and authorize a medical institution to read the medical data; and finally, a Paillier homomorphic encryption technology is utilized to realize safe medical insurance claim settlement, and the privacy of the patient is protected when the patient interacts with a third-party non-medical institution. According to the invention, security, confidentiality, reliability and integrity of medical data can be realized, and confidential sharing of private data is supported.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
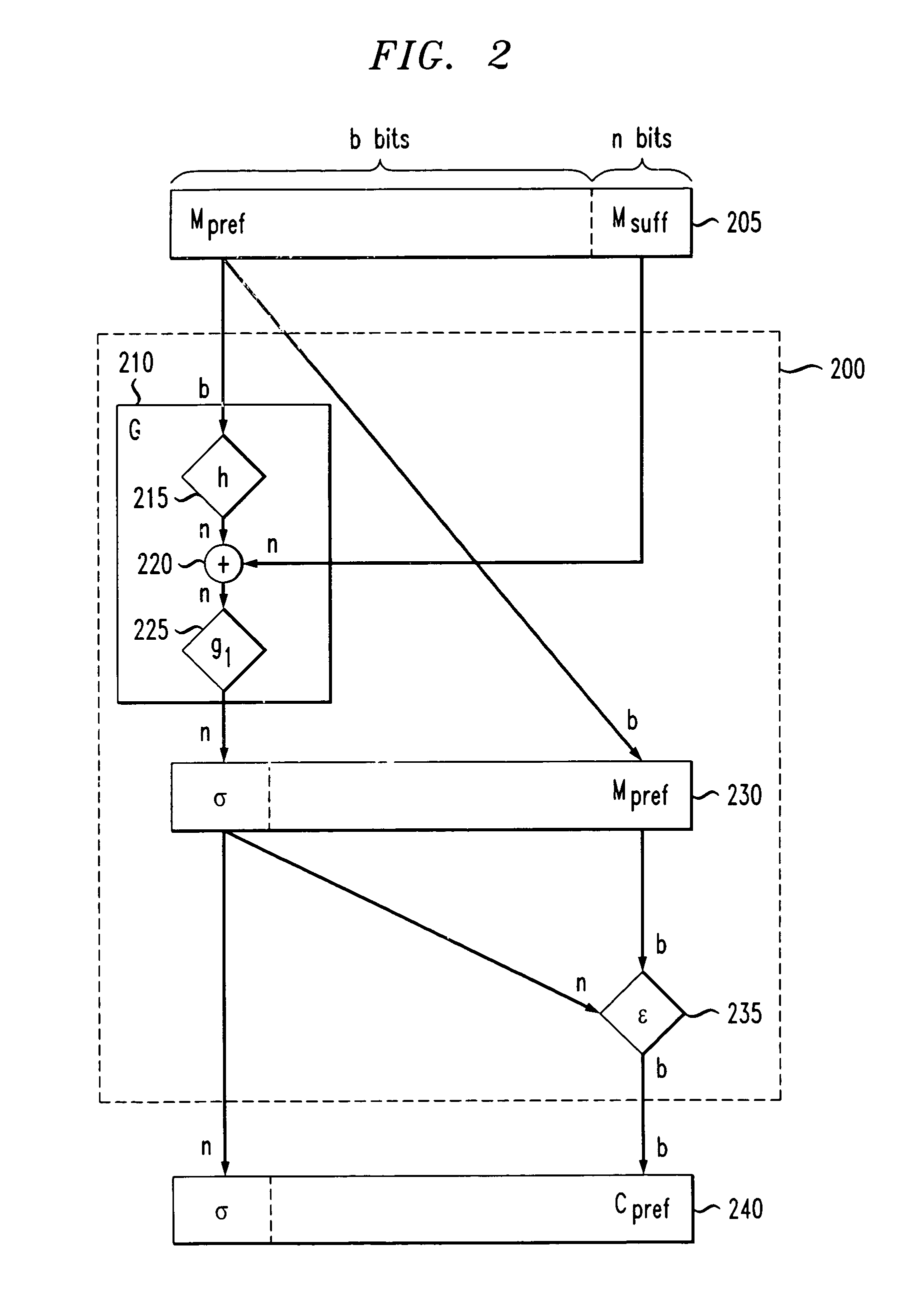
Constructions of variable input length cryptographic primitives for high efficiency and high security
ActiveUS7221756B2Improve securityEfficient constructionEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareHash function
A hash function is applied to a prefix of a VIL input. The output is added to a suffix of the input. A block cipher is applied to results of the addition. An encryption function is performed on the prefix. The final output is the output of the block cipher and the encryption function. In a second encryption technique, a hash function is applied to an input, and the output of the hash function has first and second portions. A block cipher is applied to the second portion. The output of the block cipher is added to the first portion, and a second function is applied to the result of this first addition. The output of the second function is added to the second portion. An inverse hash function is then applied to the output of the first and second additions, creating an encrypted output.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
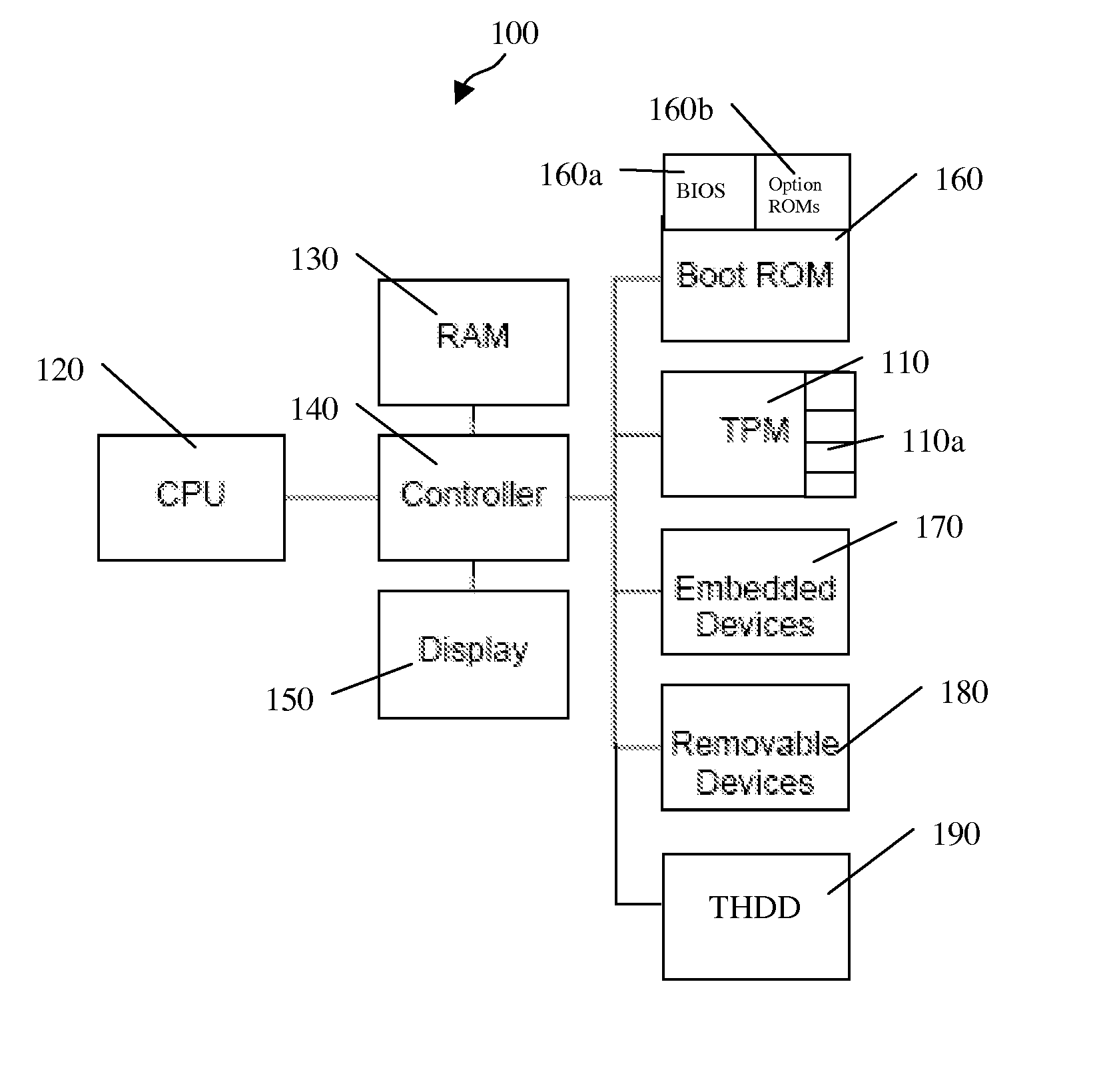
Method and system for using a trusted disk drive and alternate master boot record for integrity services during the boot of a computing platform
InactiveUS20090172378A1Digital computer detailsComputer security arrangementsHard disc driveEngineering
A trusted hard disk drive (“THDD”) contains cryptographic primitives and support functions in a trusted partition (“TP”). In particular, a master boot record (“MBR”) of the THDD is replaced with an alternative MBR and the normal MBR is stored elsewhere on the THDD. The program(s) loaded from the alternative MBR performs measurements of the TP. The TP, in turn, performs all necessary measurements of the MBR, a personal computer platform's OS, and the OS-present applications, including a platform trust service (“PTS”) kernel. The program(s) also performs functions to clear the PC platform's state such that any events that occurred prior to its execution do not alter the functionality of the OS-present applications. This may include clearing the PC's microprocessor, system memory and cache, for example. DRTM types of system resets may also be performed after the PC's OS has booted to force system clears without requiring OS or VMM infrastructure.
Owner:WAVE SYST
A privacy-preserving, mutual puf-based authentication protocol
ActiveUS20190026457A1Improve reliabilityKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer hardwareDigitization
An authentication protocol using a Hardware-Embedded Delay PUF (“HELP”), which derives randomness from within-die path delay variations that occur along the paths within a hardware implementation of a cryptographic primitive, for example, the Advanced Encryption Standard (“AES”) algorithm or Secure Hash Algorithm 3 (“SHA-3”). The digitized timing values which represent the path delays are stored in a database on a secure server (verifier) as an alternative to storing PUF response bitstrings thereby enabling the development of an efficient authentication protocol that provides both privacy and mutual authentication.
Owner:STC UNM
System and method for secure preservation and long term archival of electronic documents
InactiveUS20050235140A1The process is simple and effectiveUser identity/authority verificationElectronic documentTimestamp
A method and system for long term electronic document archiving. The system collects a certificate revocation information for a certificate from a certificate authority that indicates the validity of the certificate used in an electronic document. The certificates are collected from a certificate authority. The system then generates at least two layers of signature and timestamp from the electronic document, certificate revocation information collected, and the collected certificate. Cryptographic primitives of different strength are used, and the two layers of signature and timestamp generated have different cryptographic strengths. The signature is generated using a system signing key whereas the timestamp is generated by an external entity. A digital aging token is then formed by combining the original electronic document, certificate revocation information, and certificate collected to the layers generated.
Owner:HONG KONG THE UNIV OF
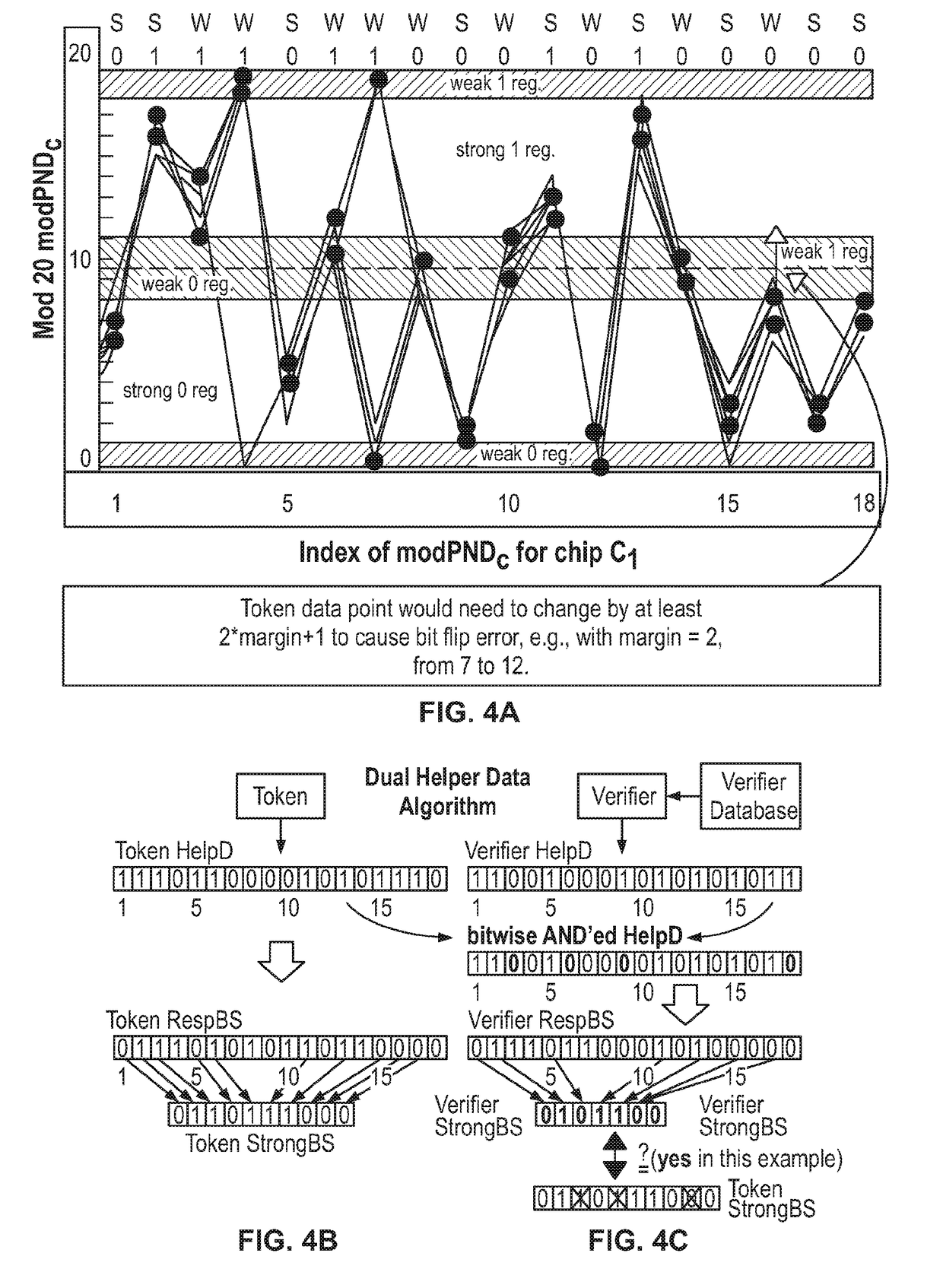
Leakage-Resilient Garbled Circuit Generation Using Reduced Memory Hardware Token
ActiveUS20120076302A1Multiple keys/algorithms usageSecret communicationClient-sideSymmetric-key algorithm
A garbled circuit is generated for a client in a leakage-resilient manner with a reduced memory requirement. The garbled circuit is used for secure function evaluation between the client and a server. The garbled circuit is generated with a reduced storage requirement by obtaining a token from the server; querying the token gate-by-gate, wherein for each gate of the garbled circuit, the token generates new wire garblings and stores them with the client using a Stream Cipher and interacts with the leakage-protected area to generate a garbled table for the gate; and receiving the garbled circuit from the token. The token comprises a leakage-protected area. The Stream Cipher is leakage-resilient and can be a symmetric-key cryptographic primitive that has a secret key as an input and generates an unbounded stream of pseudorandom bits as an output. The number of evaluations of the Stream Cipher is kept to a substantial minimum.
Owner:RPX CORP
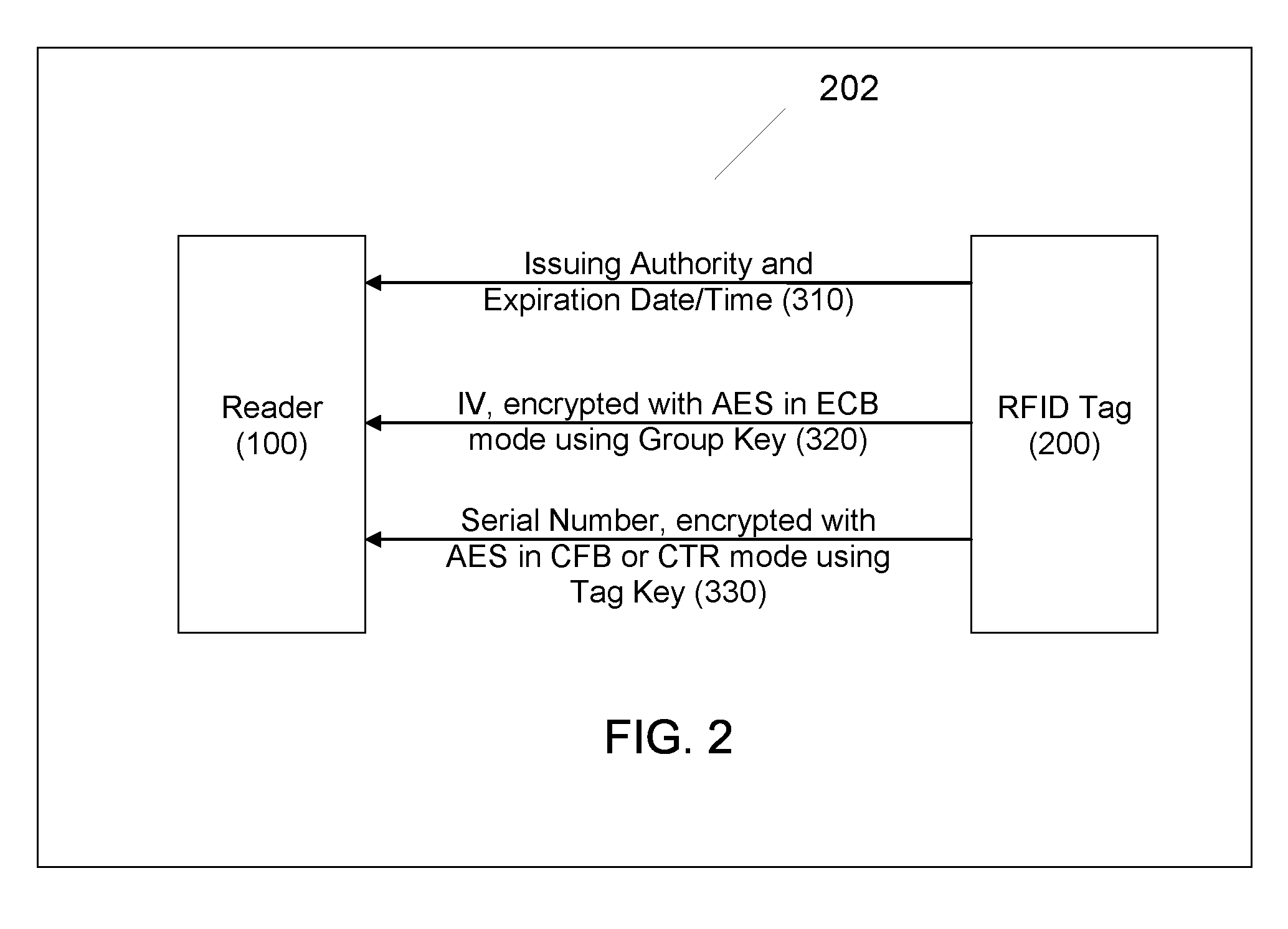
Systems and methods for preventing transmitted cryptographic parameters from compromising privacy
ActiveUS20090122986A1Improve privacyKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageGroup keyCipher
A method for secure cryptographic communication comprises transmitting information that identifies a group key from a first device to a second device. The method further comprises, in the first device, using the group key to encrypt an input vector, transmitting the encrypted input vector, encrypting privacy-sensitive information using a device key, an encryption algorithm, and the input vector, and transmitting the encrypted privacy-sensitive information to the second device.
Owner:SMART COSMOS SOLUTIONS INC
Cryptographic techniques for a communications network
InactiveUS20080032669A1Efficiently authenticatingKey distribution for secure communicationUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionHome environmentComputer science
Techniques are described for enabling authentication and / or key agreement between communications network stations and service networks. The techniques described include the negotiation and use of a cryptographic primitive shared between a service network and a home environment of a station. The techniques described also feature a key usage indicator, such as a sequence number, maintained by the service network and a station. Comparison of the key usage indicators can, for example, permit efficient authentication of the service network.
Owner:VERIZON LAB
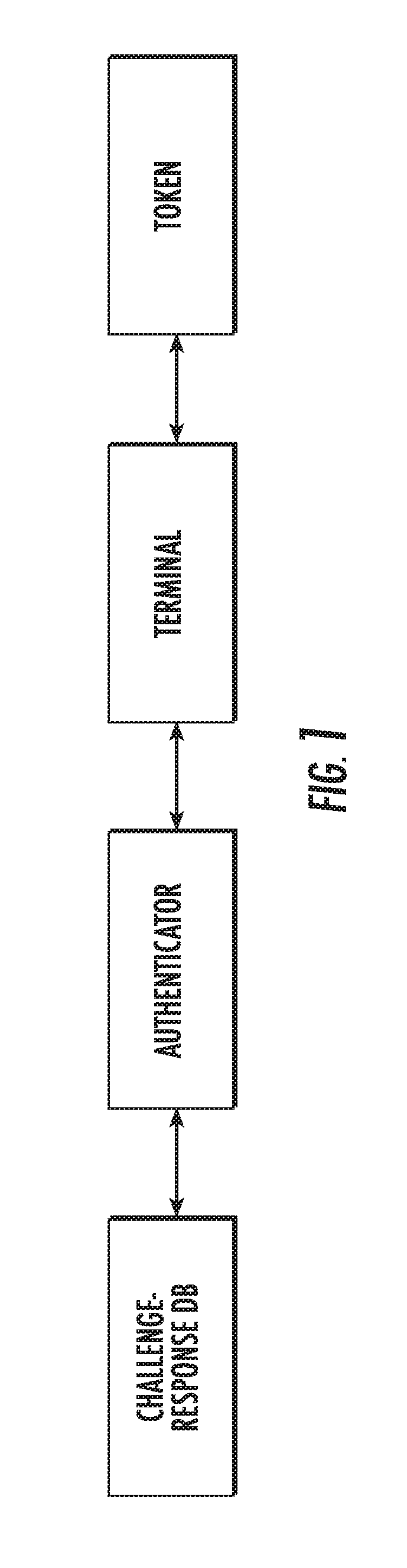
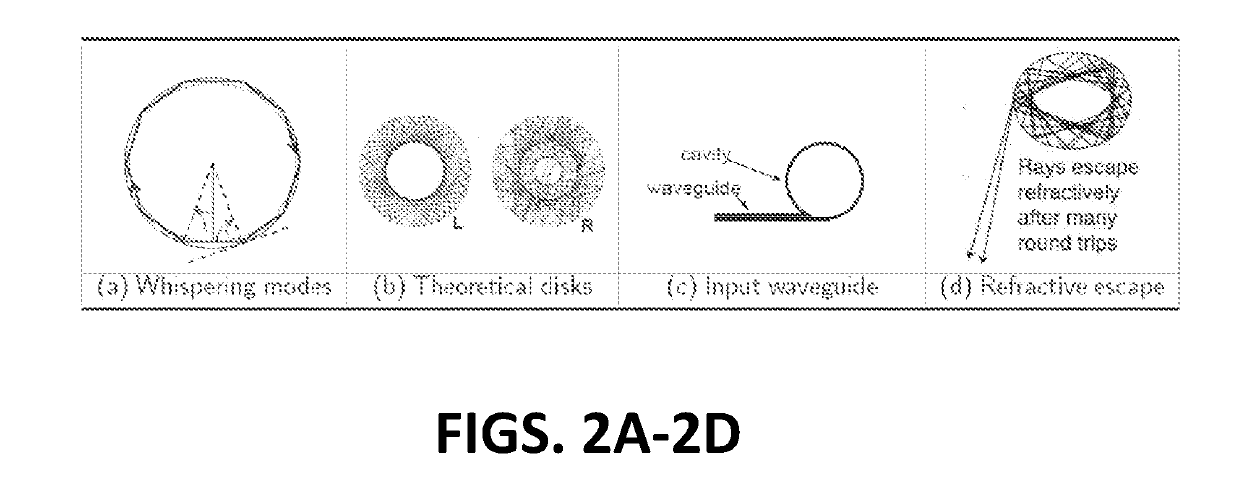
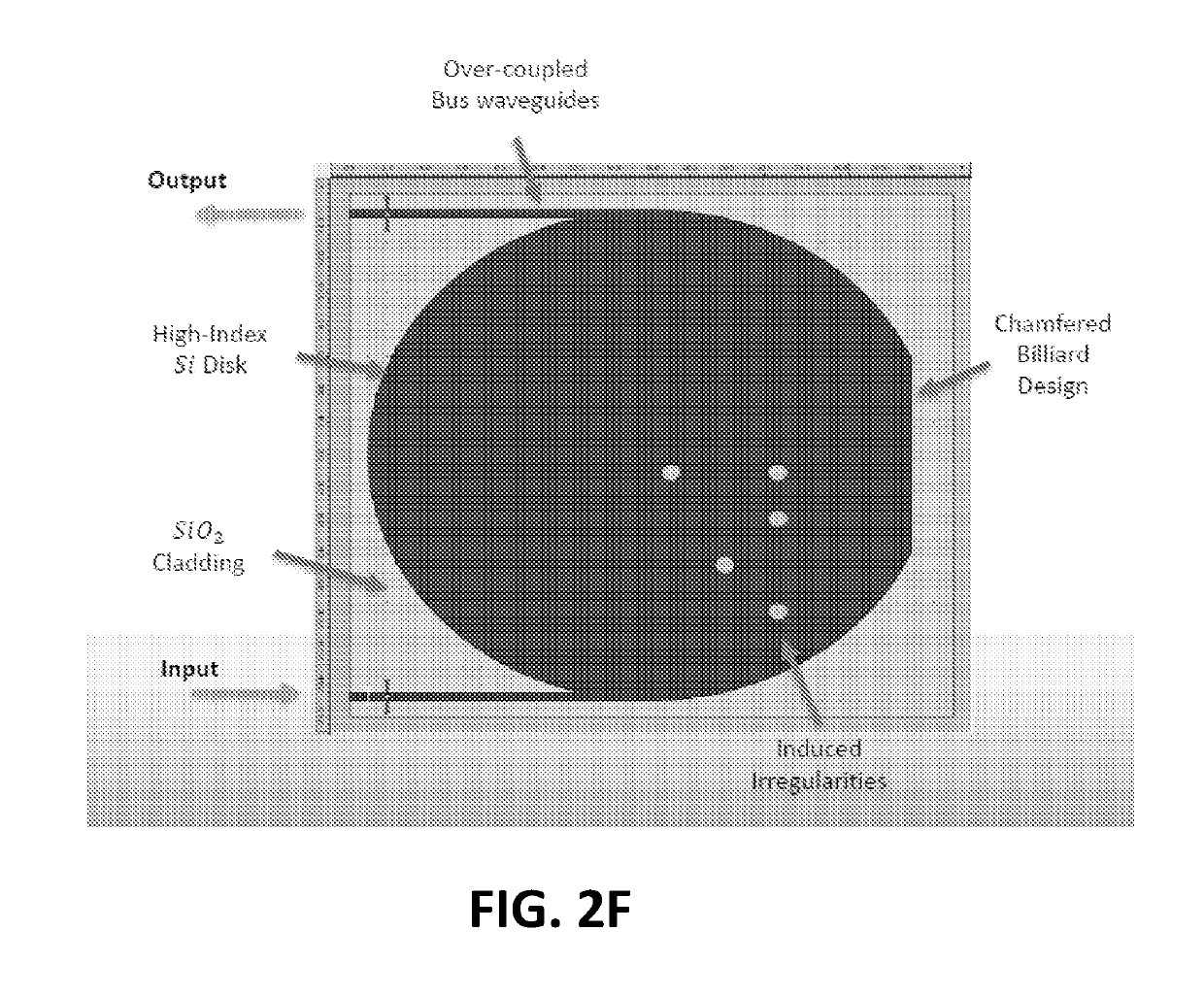
System and method for physical one-way function authentication via chaotic integrated photonic resonators
ActiveUS20190156066A1User identity/authority verificationInternal/peripheral component protectionDigital signal processingPhotonics
A system and method is provided for a cryptographic primitive and authentication protocol comprised of micro-cavity resonators at optical wavelengths. A micro-cavity resonator is illuminated with an optical challenge signal and the cavity returns an output response that is dependent on the input signal. Digital signal processing is performed on the output signal to generate a corresponding digital representation. This process is repeated for variations of the input signal with its digital output being stored in a database. A user or object claiming an identity presents a token to the system. The system selects a subset of the available challenge-response pairs and presents the challenges to the token. The system compares the digitized responses with the original responses expected for that token. The system will approve or deny the claimed identity corresponding to the presented token.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
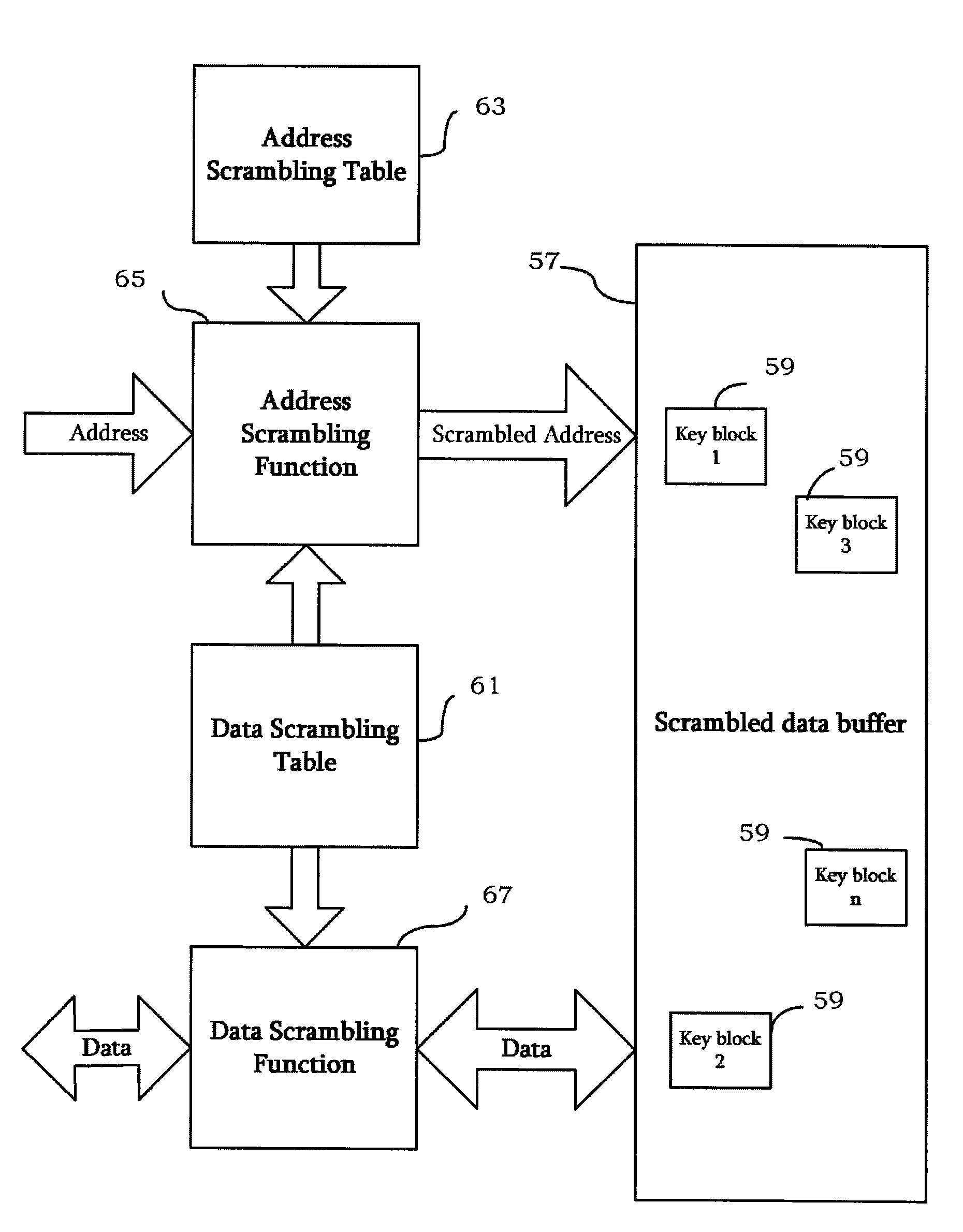
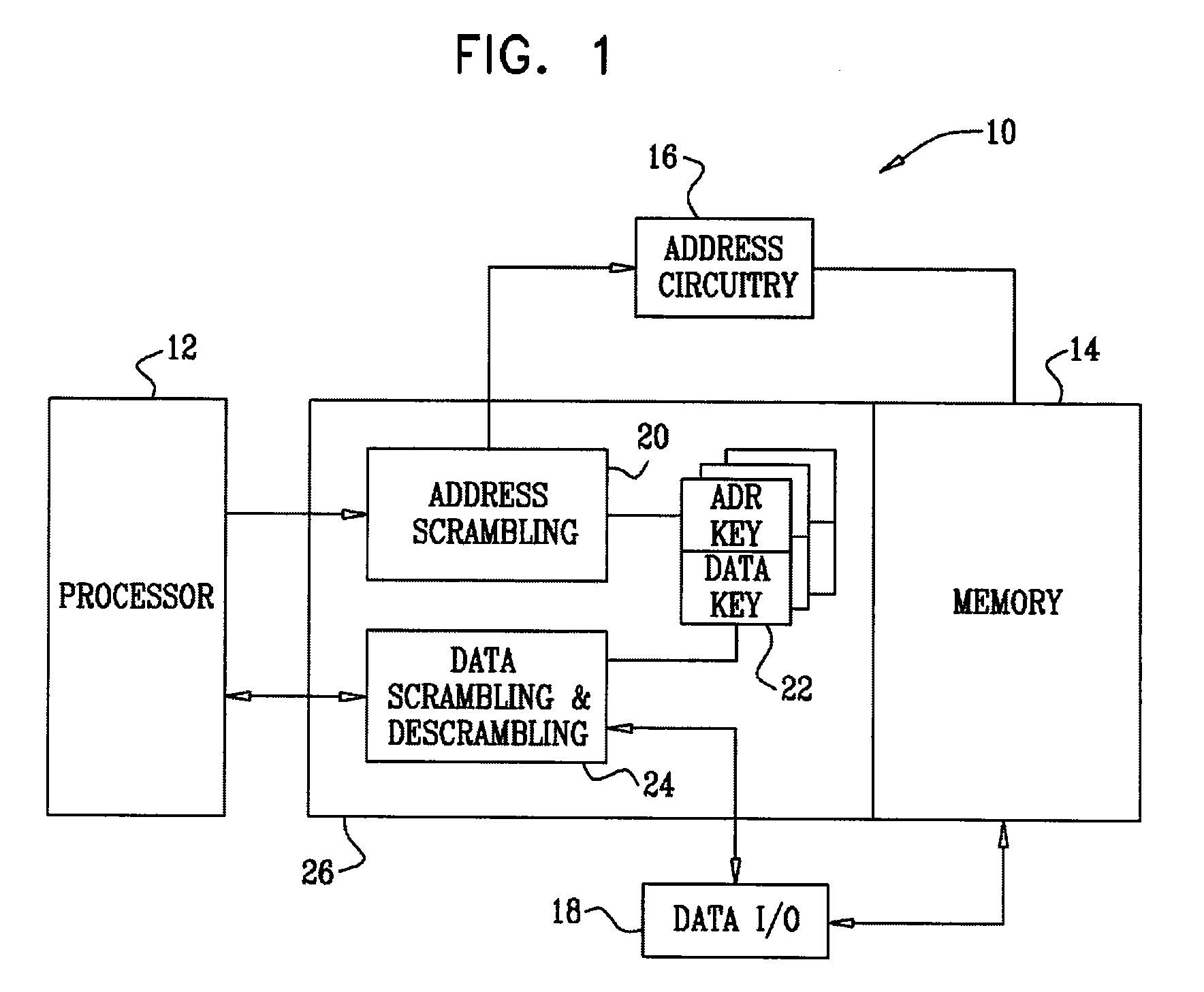
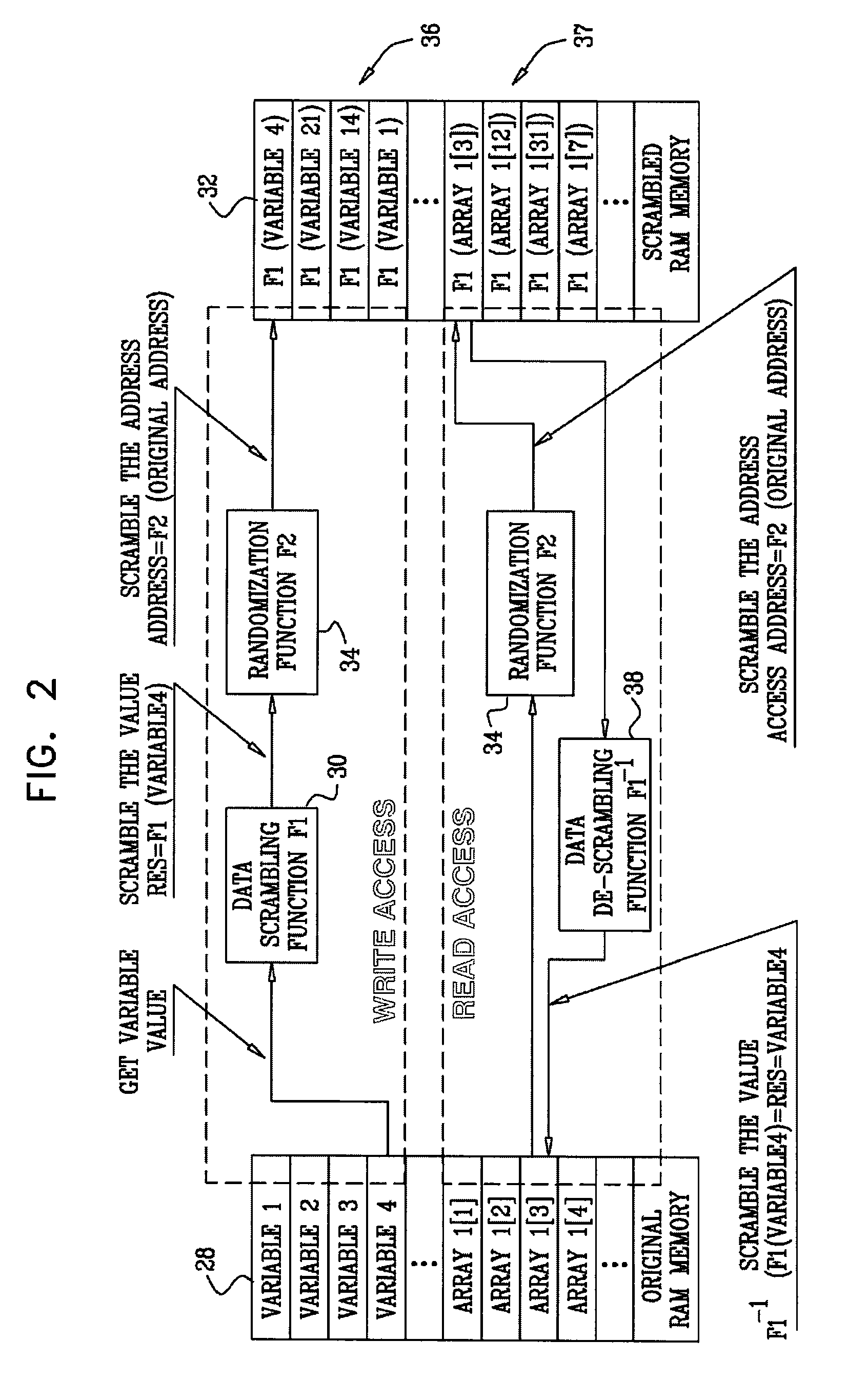
Memory randomization for protection against side channel attacks
InactiveUS8195957B2Unauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringComputer hardwareMemory address
Side channel attacks against a computing device are prevented by combinations of scrambling data to be stored in memory and scrambling the memory addresses of the data using software routines to execute scrambling and descrambling functions. Encrypted versions of variables, data and lookup tables, commonly employed in cryptographic algorithms, are thus dispersed into pseudorandom locations. Data and cryptographic primitives that require data-dependent memory accesses are thus shielded from attacks that could reveal memory access patterns and compromise cryptographic keys.
Owner:SANDISK IL LTD
Security protocol analysis method and device
InactiveCN102195771AEnhance message processing capabilitiesAutomate analysisSecret communicationSecuring communicationPasswordSecure state
The invention discloses a security protocol analysis method and a security protocol analysis device. The security protocol analysis method mainly comprises the following steps of: initializing a security protocol, generating a subsequent state by adopting a subsequent generation algorithm, judging whether the subsequent state is an insecure state, giving a path from an initial state to the subsequent state if the subsequent state is the insecure state, and finishing a flow if the subsequent state is not the insecure state, wherein an attacker knowledge analysis algorithm introducing special algebraic properties is called by the subsequent generation algorithm for attacker deduction problems. In the security protocol analysis method provided by the invention, the processing of the algebraic properties of password operators is added, and the message processing capability of DY attackers, so attacks caused by the algebraic properties can be detected; and the method is applied to most of current security protocol analysis in which password primitives with the special algebraic properties are used, and the success rate of the analysis is greatly increased.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
Imprinting an identification certificate
InactiveUS7174459B2Quantity minimizationLarge capacityDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationOne-way functionComputer security
A system and method for using imprinting as part of a security function that involves a user, for a security and / or identification mechanism. Imprinting is preferably used for cryptographic primitives, for determining a one-way function that operates at least partially according to a characteristic and / or function of the human brain.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
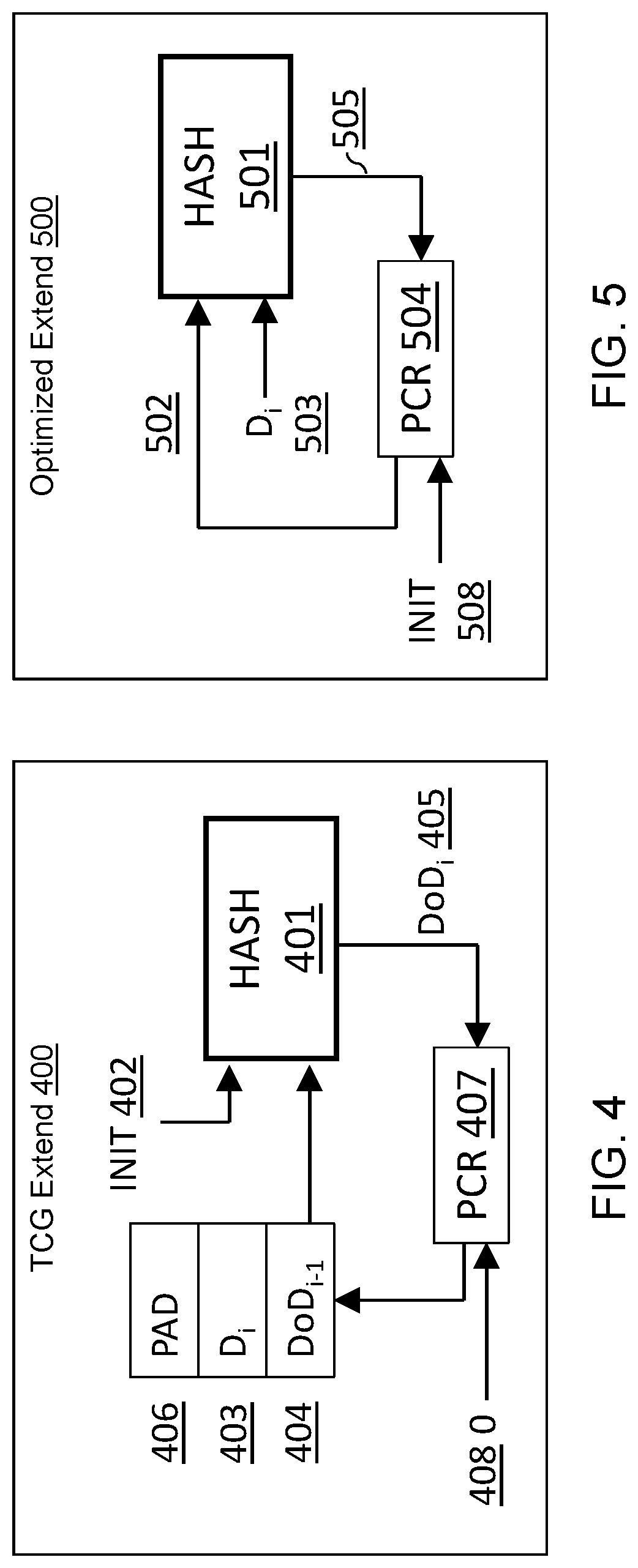
System and Method for Measuring and Reporting IoT Boot Integrity
ActiveUS20190363888A1Increase overheadEnsure integrityUser identity/authority verificationComputer security arrangementsMicrocontrollerComputer printing
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to an improved system and method of producing, recording and reporting boot integrity measurements of an Internet of Things (“IoT”) computing device to resource (such as an on-chip software module, an external software module, a printer, a network router, or a server), so the resource can confirm that the IoT computing device can be trusted before access to the resource is granted. Embodiments provide a new and less expensive architecture for reliably collecting and relaying device state information to support trust-sensitive applications. Embodiments leverage crypto-acceleration modules found on many existing microprocessors and microcontroller-based IoT devices, while introducing little additional overhead or additional circuitry. Embodiments provide a Root of Trust module comprising integrated internal control logic that functions as a secure on-chip wrapper for cryptographic primitive modules, which provide secure storage and reporting of the host's platform integrity measurements.
Owner:CYBER PACK VENTURES INC
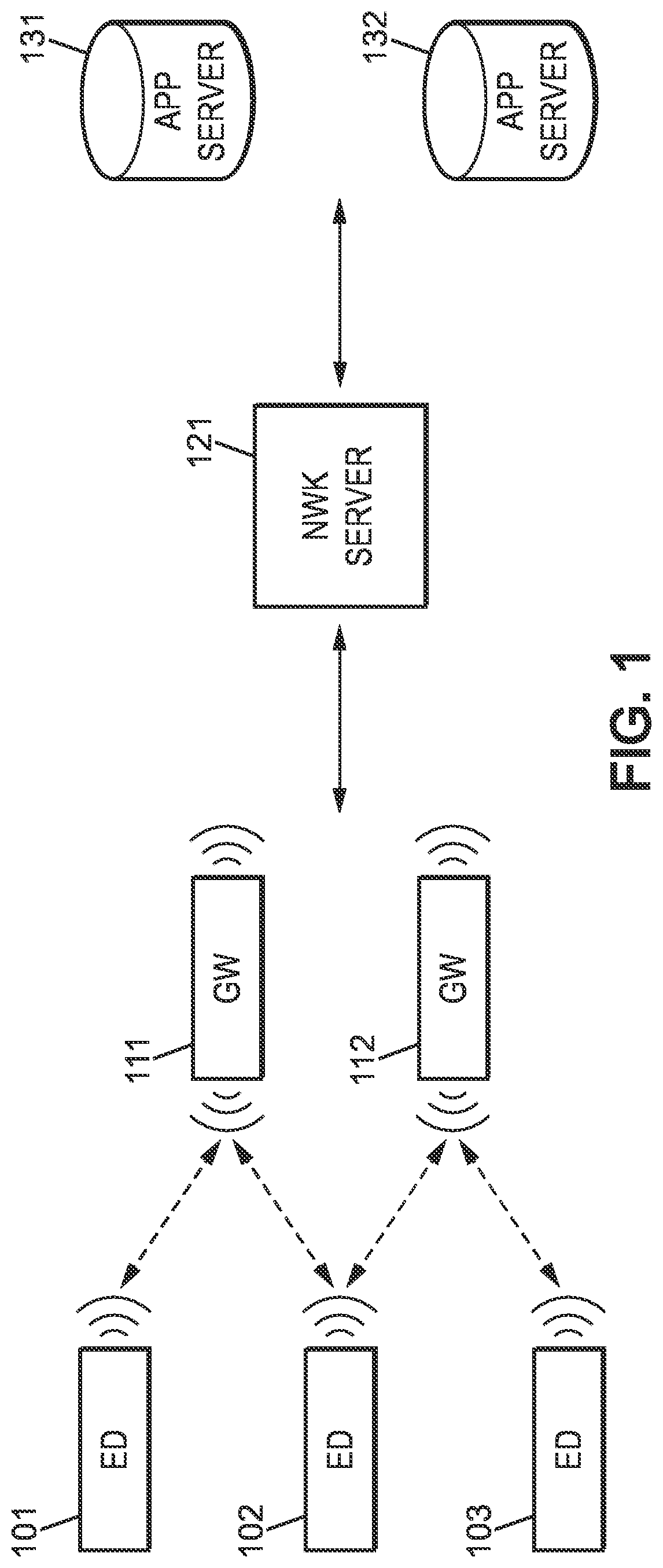
Communication interface for a low power wide area network, wireless device and server using such communication interface
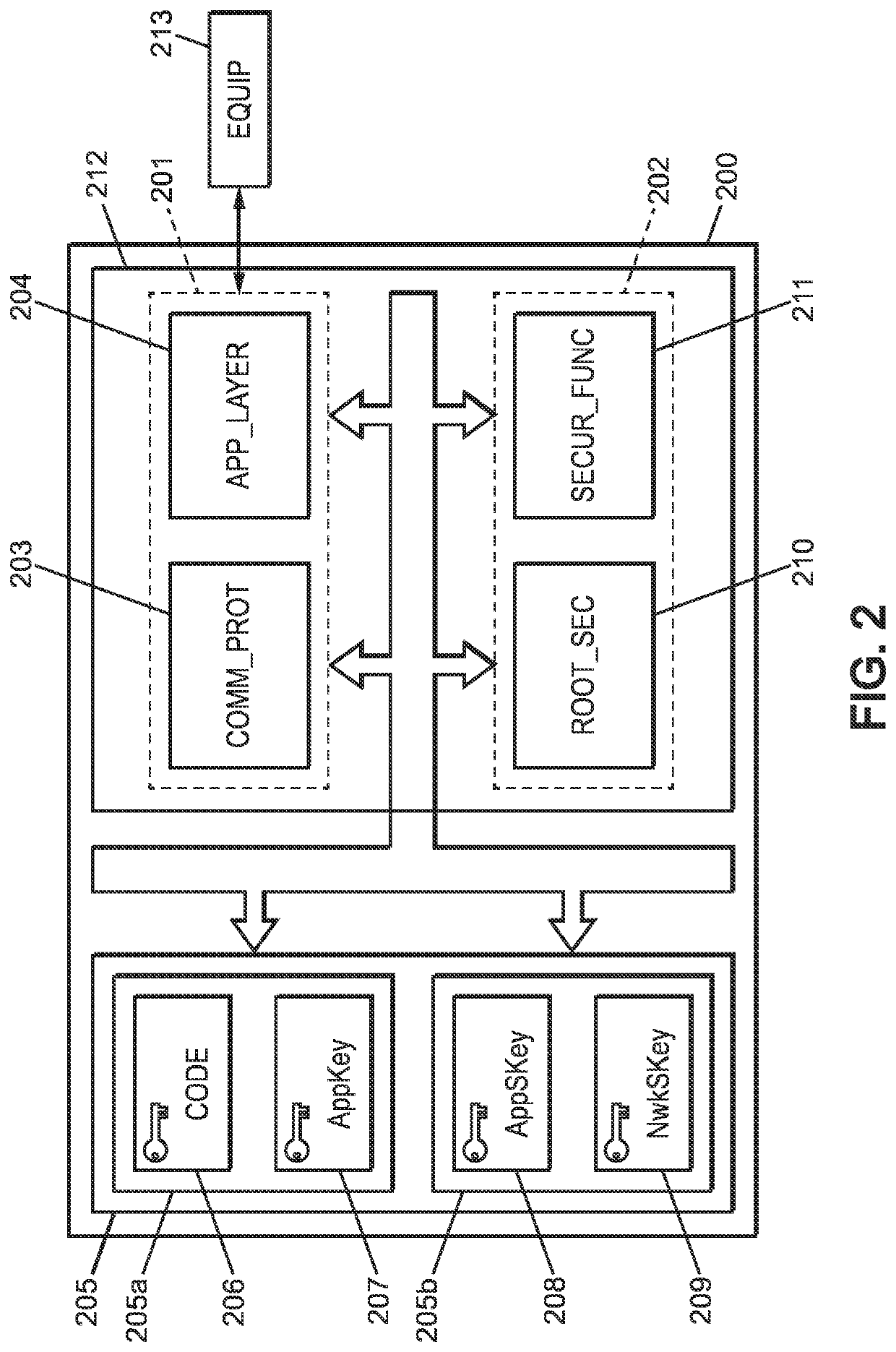
ActiveUS20190394172A1Low hardware costLow costKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationCommunication interfaceProtocol stack
The present invention relates to a communication interface (200) for supporting communication between a wireless device (101, 102, 103) and a server (121) over a low power wide area network, LPWAN, comprising: an untrusted execution part (201) configured to operate in accordance with an LPWAN communication protocol stack (203) including at least one secured LPWAN protocol using cryptographic primitives; a memory (205) for storing computer code (206) and at least one cryptographic key (207, 208, 209) in an encrypted form; a trusted execution part (202) incorporating a root secret (210) for decrypting the at least one cryptographic key (207 208, 209) from the memory (205), wherein the trusted execution part (202) is configured to execute the cryptographic primitives of the at least one secured LPWAN protocol using the decrypted cryptographic key and computer code (206) from the memory (205).
Owner:ACTILITY
Method for secure delivery of digital content
InactiveUS20110066857A1User identity/authority verificationTelevision systemsTamper resistanceHash function
Methods and apparatus for the secure and copy-proof distribution of digital content are disclosed. In a preferred embodiment of the invention cryptographic primitives (encryption algorithms, message-authentication codes, hash functions, random-number generators, etc.) are used in a novel security protocol. The invention may be utilized to protect a first-run movie that has been digitized in accordance with one of the current or forthcoming MPEG standards (e.g., MPEG-7). Content receivers or users first register their boxes. This registration information is stored in a secure database. When a subscriber registers, he then receives a box (interface to his player) that has been initialized to contain a number of tamper-proof secrets that are shared between the station and that particular box. The station stores an encrypted version of the digital content. This encrypted version ultimately arrives at some unprotected storage medium local to the player. Upon demand, the station delivers to the box the use-once computational ability to decrypt the content and display it on the player or terminal.
Owner:PASCALS POCKET
All-photon cryptographic primitive preparation method based on high-throughput perovskite micro-single crystal array
PendingCN113186600AImprove encoding performanceIncrease randomnessMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthDot matrixSingle crystal
The invention relates to the technical field of perovskite single-crystal photoelectric devices, in particular to an all-photon cryptographic primitive preparation method based on a high-flux perovskite micro-single-crystal array. The method comprises the following steps of: regulating and controlling the atmosphere of a high-flux micro-droplet evaporation recrystallization solvent to control the environment humidity and the temperature of a hot plate; and by means of a solution method, successfully achieving one-step evaporation self-assembly on a patterned array substrate, so as to efficiently prepare the shape-controllable high-flux perovskite nanorod single crystal array. Laser emission information and characteristics of the crystal array are collected and successfully applied to establishment of the all-photon cryptographic primitive PUF, and encryption and decryption of encrypted transmission information are achieved. The excellent chemical / structural stability of the high-flux all-inorganic perovskite single crystal dot matrix provides innate advantages for stable formation and reading of the password primitive, the preparation method is simple, the operation is flexible, and the high-flux perovskite single crystal array is certainly promoted to enter a new step in the application of the all-photon password primitive.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Primitives for fast secure hash functions and stream ciphers
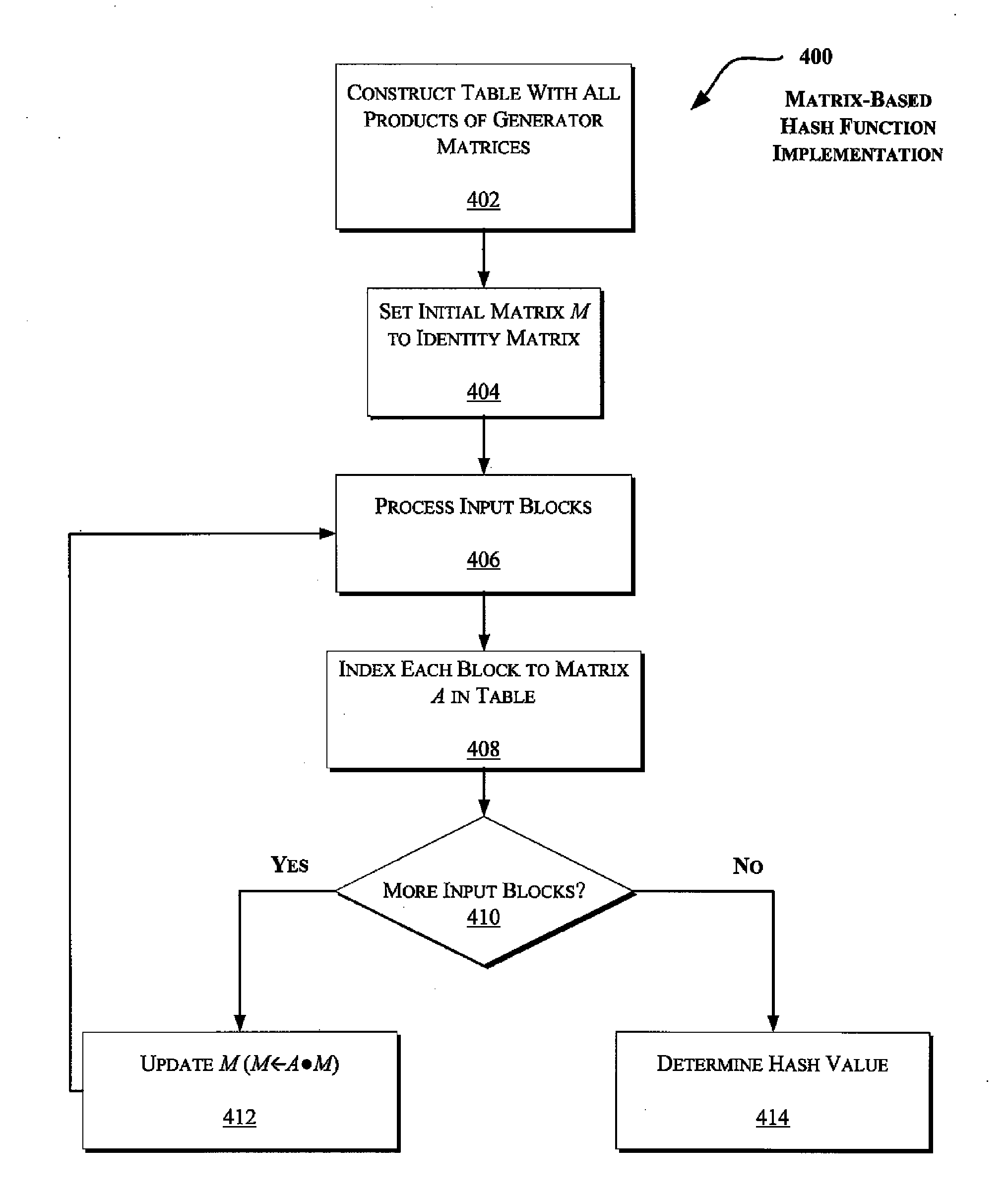
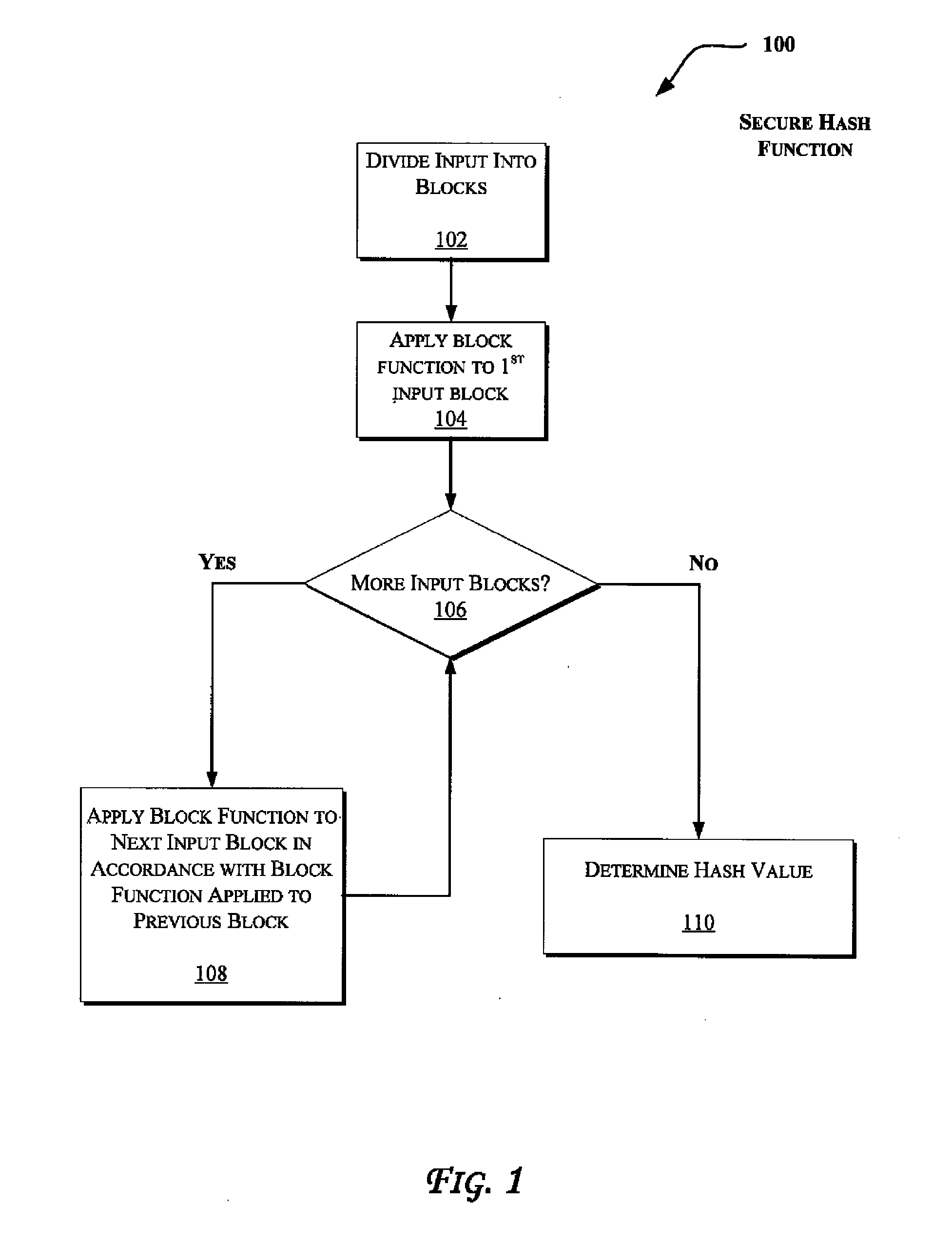
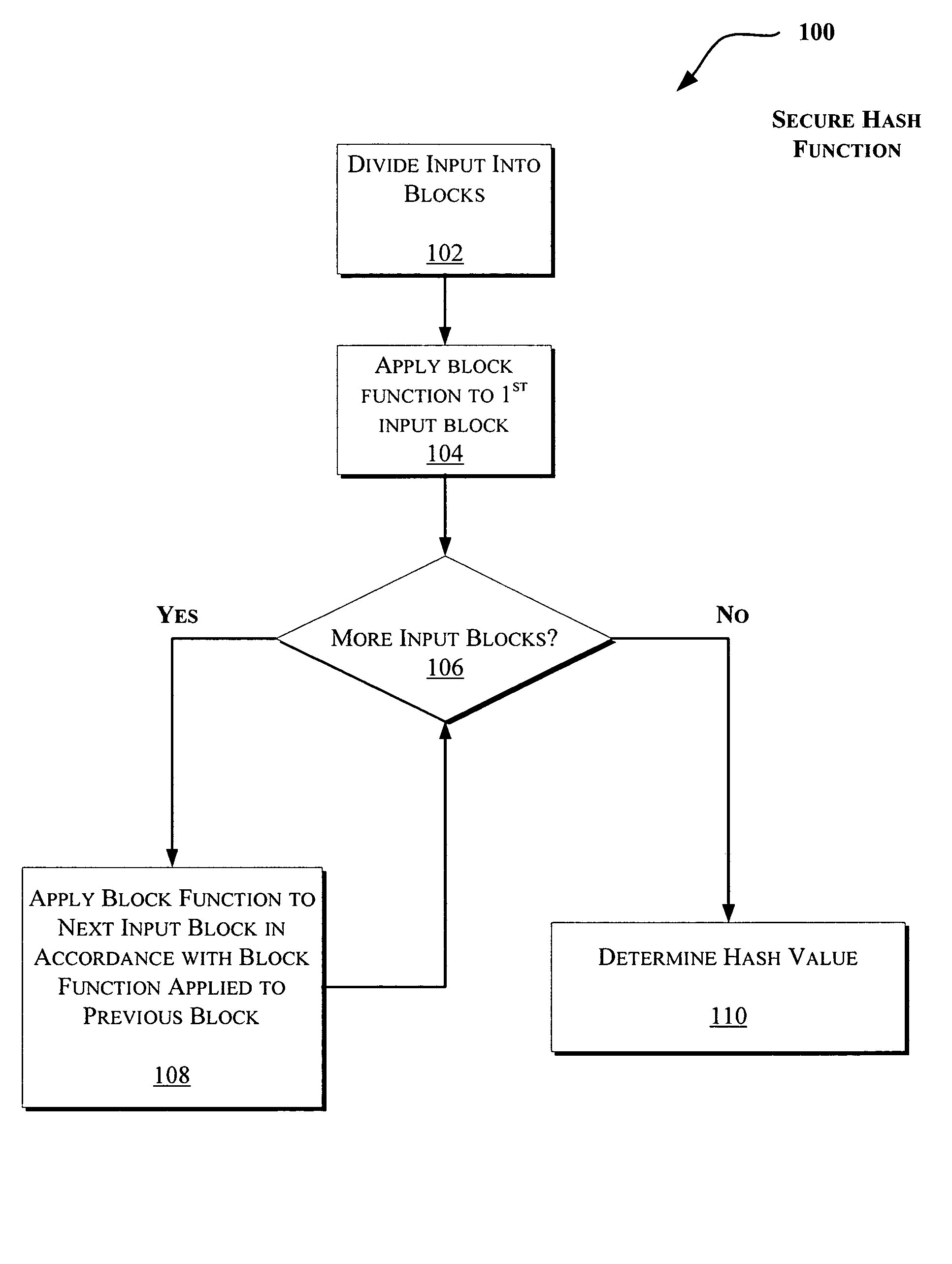
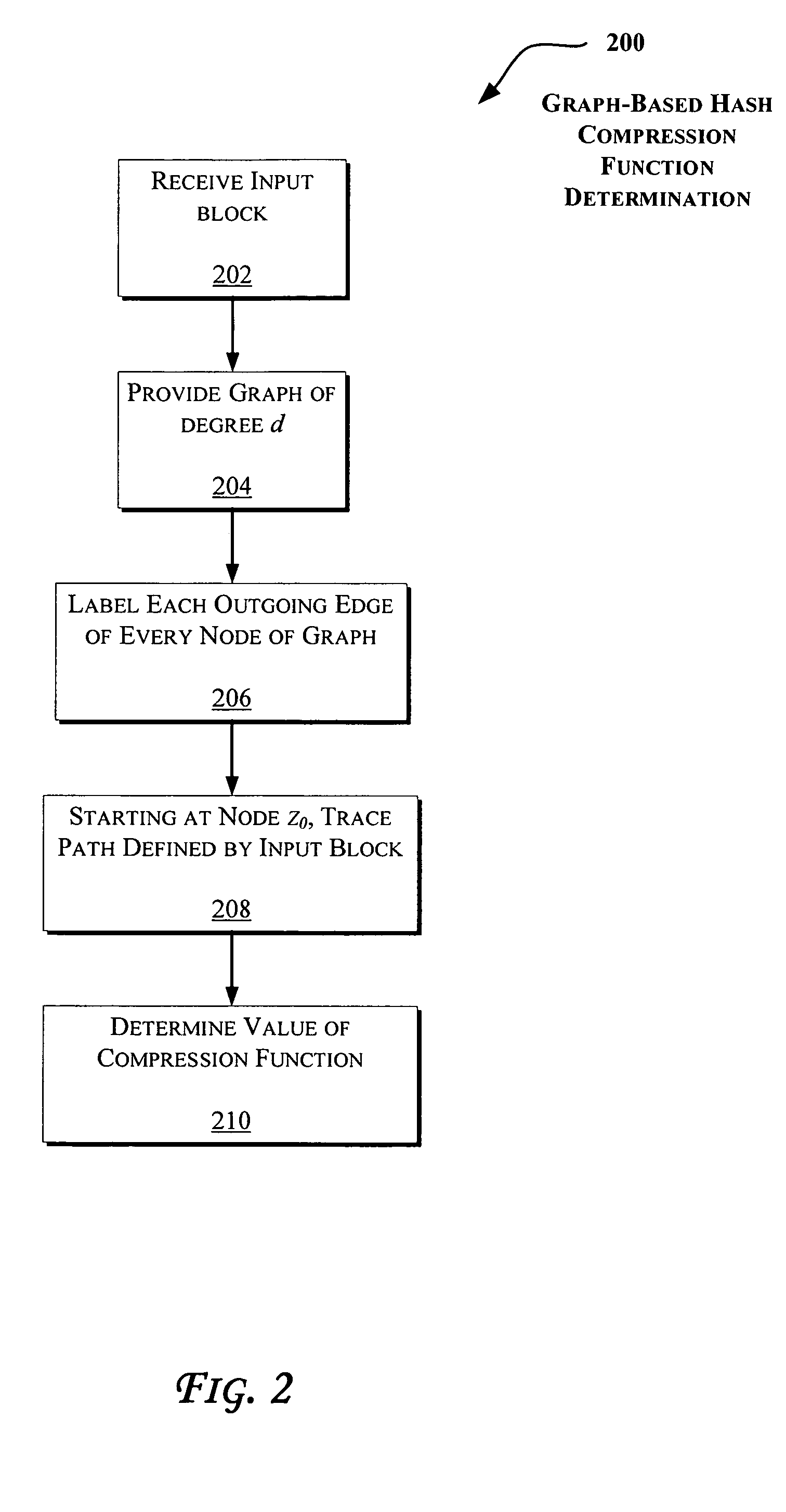
InactiveUS7933404B2Efficient implementationLarge girthEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputation using non-contact making devicesHash functionSecret code
Techniques are disclosed to enable efficient implementation of secure hash functions and / or stream ciphers. More specifically, a family of graphs is described that has relatively large girth, large claw, and / or rapid mixing properties. The graphs are suitable for construction of cryptographic primitives such as collision resistant hash functions and stream ciphers, which allow efficient software implementation.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Weak-leakage and high-efficiency exposing encryption method
ActiveCN108234108AImprove computing efficiencyEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesPlaintextComputer hardware
The invention belongs to the field of cryptography, and specifically relates to a weak-leakage and high-efficiency exposing encryption method. The method comprises a triplet of initialization, encryption and comparison algorithm, which is expressed as (the formula is described in the specification); and for each exposing encryption scheme, a certain amount of plaintext information leakage is followed. The information leaked by the exposing encryption meeting the ideal security is a size relationship of a plaintext corresponding to a ciphertext. By adoption of the weak-leakage and high-efficiency exposing encryption method, on the basis of meeting high efficiency, the leakage information is reduced as much as possible, that is, only the plaintext size relationship, the plaintext highest different bit equal mode and the partial information of the highest different bits of the plaintext are leaked. In the construction of the scheme, only two efficient cryptographic primitives, namely a pseudo-random function and a hash function are used, so that the entire scheme is executed efficiently.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
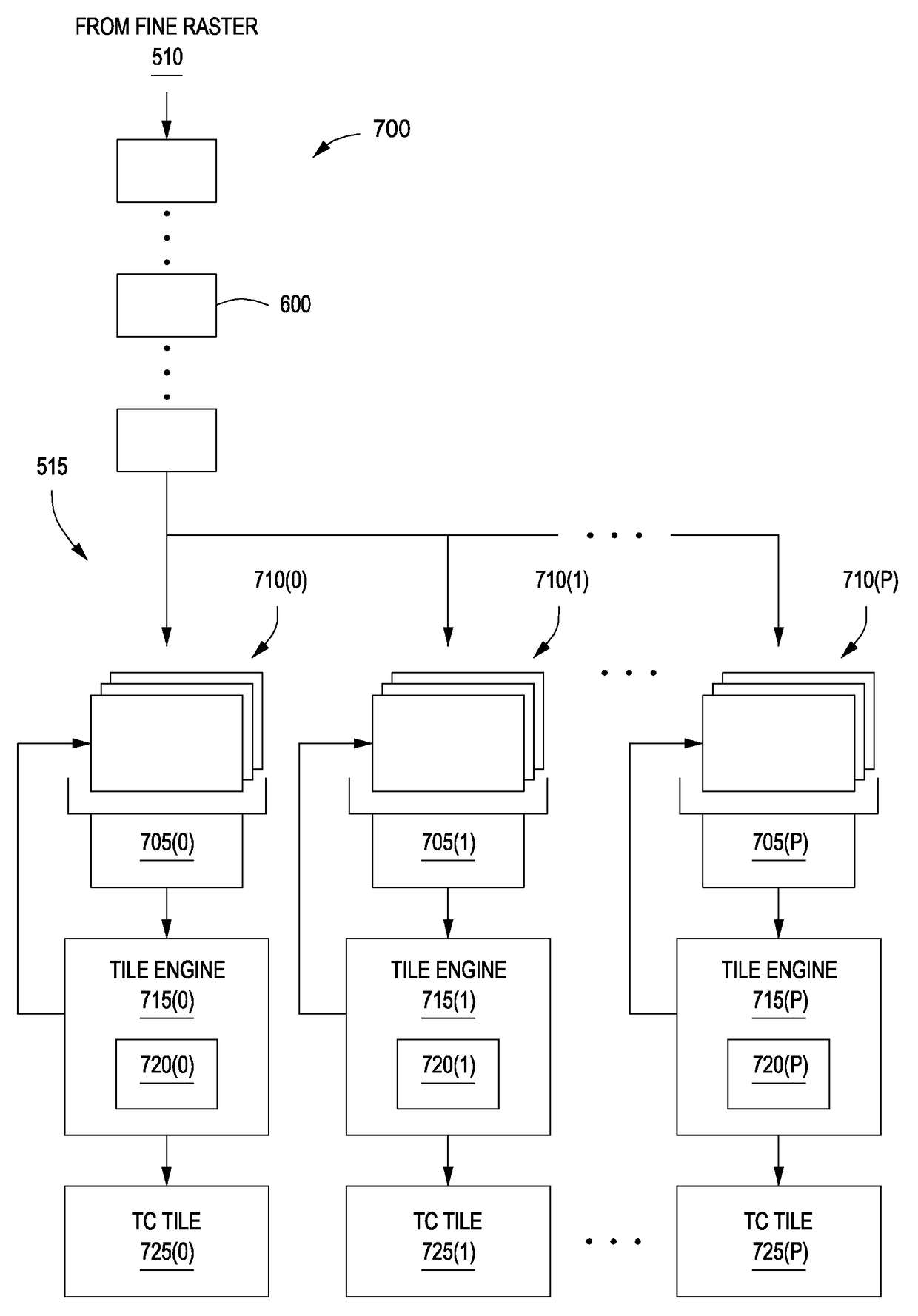
Techniques for maintaining atomicity and ordering for pixel shader operations
ActiveUS20170116700A1Not limitedImage memory managementProcessor architectures/configurationComputational scienceRead-modify-write
A tile coalescer within a graphics processing pipeline coalesces coverage data into tiles. The coverage data indicates, for a set of XY positions, whether a graphics primitive covers those XY positions. The tile indicates, for a larger set of XY positions, whether one or more graphics primitives cover those XY positions. The tile coalescer includes coverage data in the tile only once for each XY position, thereby allowing the API ordering of the graphics primitives covering each XY position to be preserved. The tile is then distributed to a set of streaming multiprocessors for shading and blending operations. The different streaming multiprocessors execute thread groups to process the tile. In doing so, those thread groups may perform read-modify-write operations with data stored in memory. Each such thread group is scheduled to execute via atomic operations, and according to the API order of the associated graphics primitives.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Method for preparing cryptographic primitive based on perovskite crystal and application thereof
ActiveCN113259115AStrong randomnessMore recognizable pixelsPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsCryptographic primitiveAtomic physics
The invention relates to a method for preparing cryptographic primitives based on perovskite crystals and application thereof, and the method comprises the steps that different chips with component segregation perovskite crystals are prepared, the fluorescence emission spectrum of a target array on the perovskite crystal chips is scanned and read, according to the number of emission peaks of the target array, array patterns are divided into four types: one emission peak, two emission peaks, three emission peaks, and four or more emission peaks, and the coding rules that the pattern of one emission peak is 00, the pattern of two emission peaks is 01, the pattern of three emission peaks is 10, and the pattern of four or more emission peaks is 11 are set; all patterns on the target array are converted into a binary coding array composed of 0 and 1, namely cryptographic primitives of the target array are formed, and the cryptographic primitives can be used for constructing a computer cryptographic security system. The method for preparing the password primitives based on the perovskite crystals has the technical effects of being high in randomness, unclonable, rapid in coding and capable of being produced on a large scale at low cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Primitives for fast secure hash functions and stream ciphers
InactiveUS7289629B2Efficient implementationLarge girthUser identity/authority verificationSecret communicationComputer hardwareHash function
Techniques are disclosed to enable efficient implementation of secure hash functions and / or stream ciphers. More specifically, a family of graphs is described that has relatively large girth, large claw, and / or rapid mixing properties. The graphs are suitable for construction of cryptographic primitives such as collision resistant hash functions and stream ciphers, which allow efficient software implementation.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and device for establishing session keys
The present invention relates to a method and a device for establishing a session key between a source entity and a target entity in a communication network comprising a plurality of communicating entities. The method which is based on the use of symmetric cryptographic primitives offers each entity of the session a protection against attacks by denial of service by the establishment of a session in four or five exchanges of messages.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
System and method for measuring and reporting IoT boot integrity
ActiveUS10924282B2Ensure integrityIncrease overheadUser identity/authority verificationComputer security arrangementsMicrocontrollerComputer printing
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to an improved system and method of producing, recording and reporting boot integrity measurements of an Internet of Things (“IoT”) computing device to resource (such as an on-chip software module, an external software module, a printer, a network router, or a server), so the resource can confirm that the IoT computing device can be trusted before access to the resource is granted. Embodiments provide a new and less expensive architecture for reliably collecting and relaying device state information to support trust-sensitive applications. Embodiments leverage crypto-acceleration modules found on many existing microprocessors and microcontroller-based IoT devices, while introducing little additional overhead or additional circuitry. Embodiments provide a Root of Trust module comprising integrated internal control logic that functions as a secure on-chip wrapper for cryptographic primitive modules, which provide secure storage and reporting of the host's platform integrity measurements.
Owner:CYBER PACK VENTURES INC
Techniques for maintaining atomicity and ordering for pixel shader operations
ActiveUS10019776B2Image memory managementProcessor architectures/configurationComputational scienceRead-modify-write
A tile coalescer within a graphics processing pipeline coalesces coverage data into tiles. The coverage data indicates, for a set of XY positions, whether a graphics primitive covers those XY positions. The tile indicates, for a larger set of XY positions, whether one or more graphics primitives cover those XY positions. The tile coalescer includes coverage data in the tile only once for each XY position, thereby allowing the API ordering of the graphics primitives covering each XY position to be preserved. The tile is then distributed to a set of streaming multiprocessors for shading and blending operations. The different streaming multiprocessors execute thread groups to process the tile. In doing so, those thread groups may perform read-modify-write operations with data stored in memory. Each such thread group is scheduled to execute via atomic operations, and according to the API order of the associated graphics primitives.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Blockchain-based medical record storage, sharing and secure claim settlement model and method
ActiveCN110008746BGuaranteed privacyIncrease resistanceDigital data protectionPatient healthcareMedical recordConfidentiality
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical data management, and relates to a medical record storage, sharing and security claim settlement model and method based on a block chain. Firstly, credible sharing of medical data of patients among medical institutions is achieved through the blockchain technology, and a lifelong medical record is established for the patients; based on a Hashchain type storage structure, the medical data cannot be tampered; secondly, an improved CP-ABE-based cryptographic primitive SHDPCPC-CP-ABE is proposed, security encryption and fine-grained access control on the medical data are realized, and a patient can conveniently and efficiently access and authorize a medical institution to read the medical data; and finally, a Paillier homomorphic encryption technology is utilized to realize safe medical insurance claim settlement, and the privacy of the patient is protected when the patient interacts with a third-party non-medical institution. According to the invention, security, confidentiality, reliability and integrity of medical data can be realized, and confidential sharing of private data is supported.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Error detection
PendingUS20210266146A1Error preventionEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer networkPacket generator
A data transmitter is disclosed. The data transmitter includes a digest generator configured in response to receiving a set of data from a data source to generate a digest from the set of data using a cryptographic primitive. The data transmitter further includes a packet generator configured to generate a series of one or more packets carrying the set of data for transmission, wherein each packet in the series includes a header, the set of data, a footer and the digest.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS AMERICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com