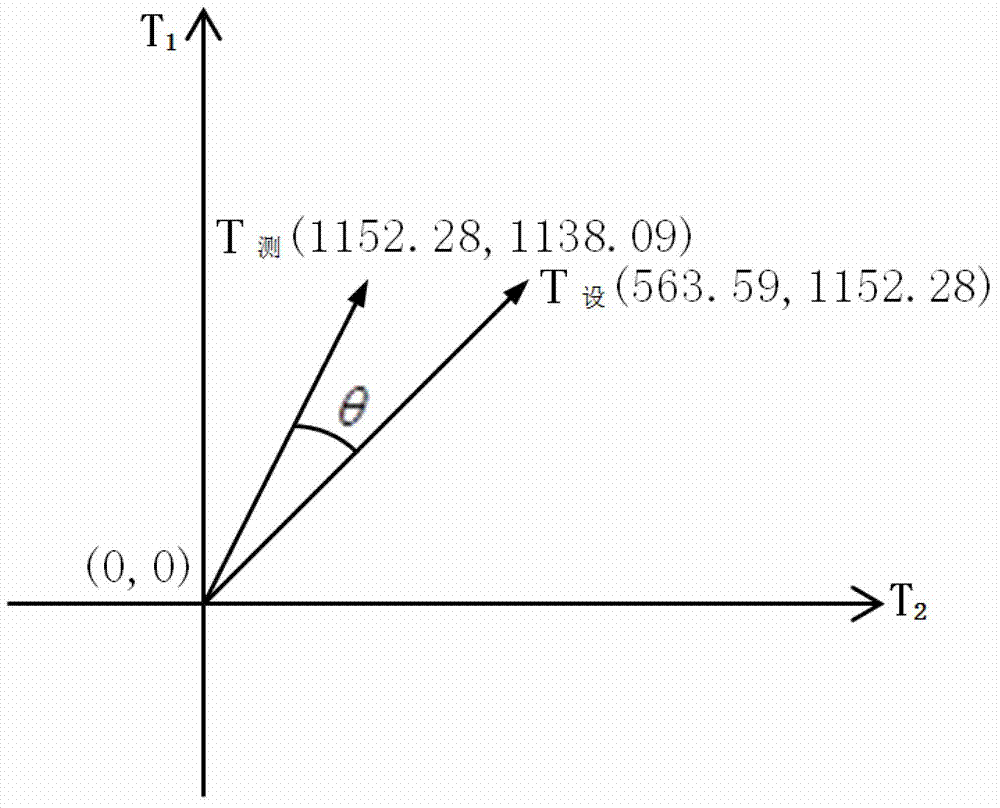Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
143 results about "Combustion instability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Combustion instability. Combustion instabilities are physical phenomena occurring in a reacting flow (e.g., a flame) in which some perturbations, even very small ones, grow and then become large enough to alter the features of the flow in some particular way.
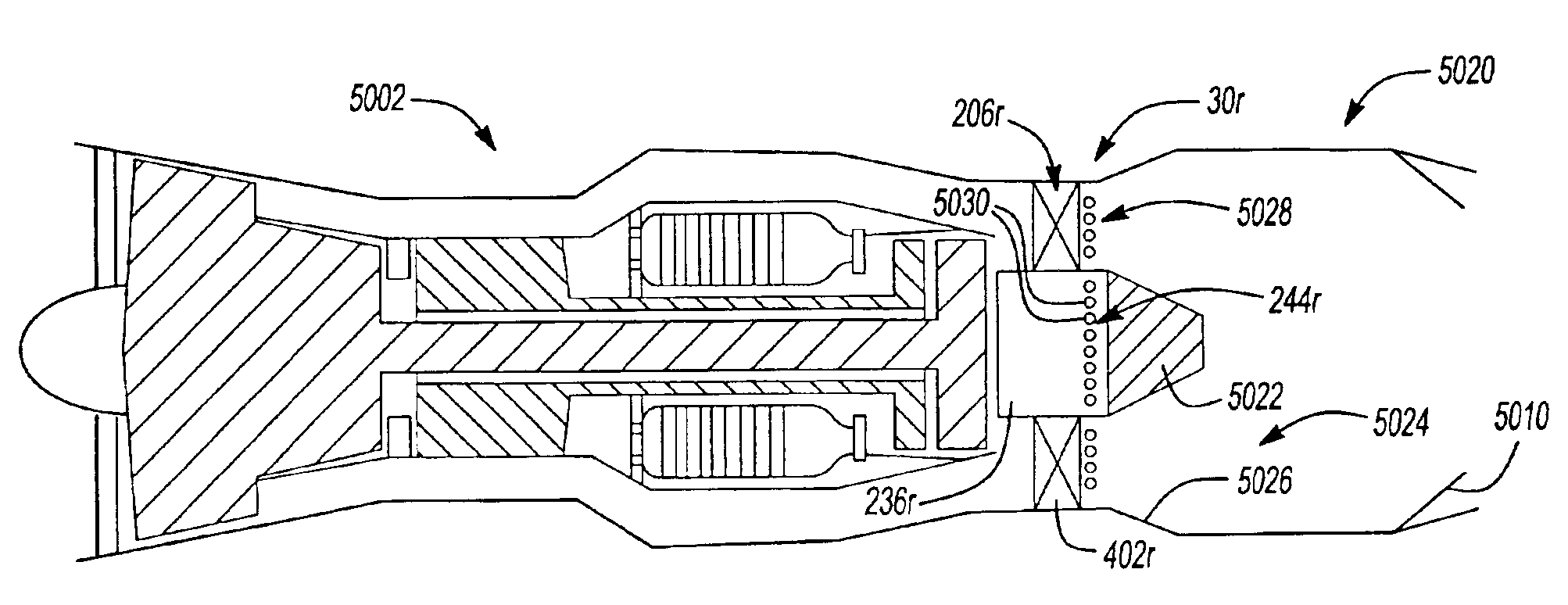
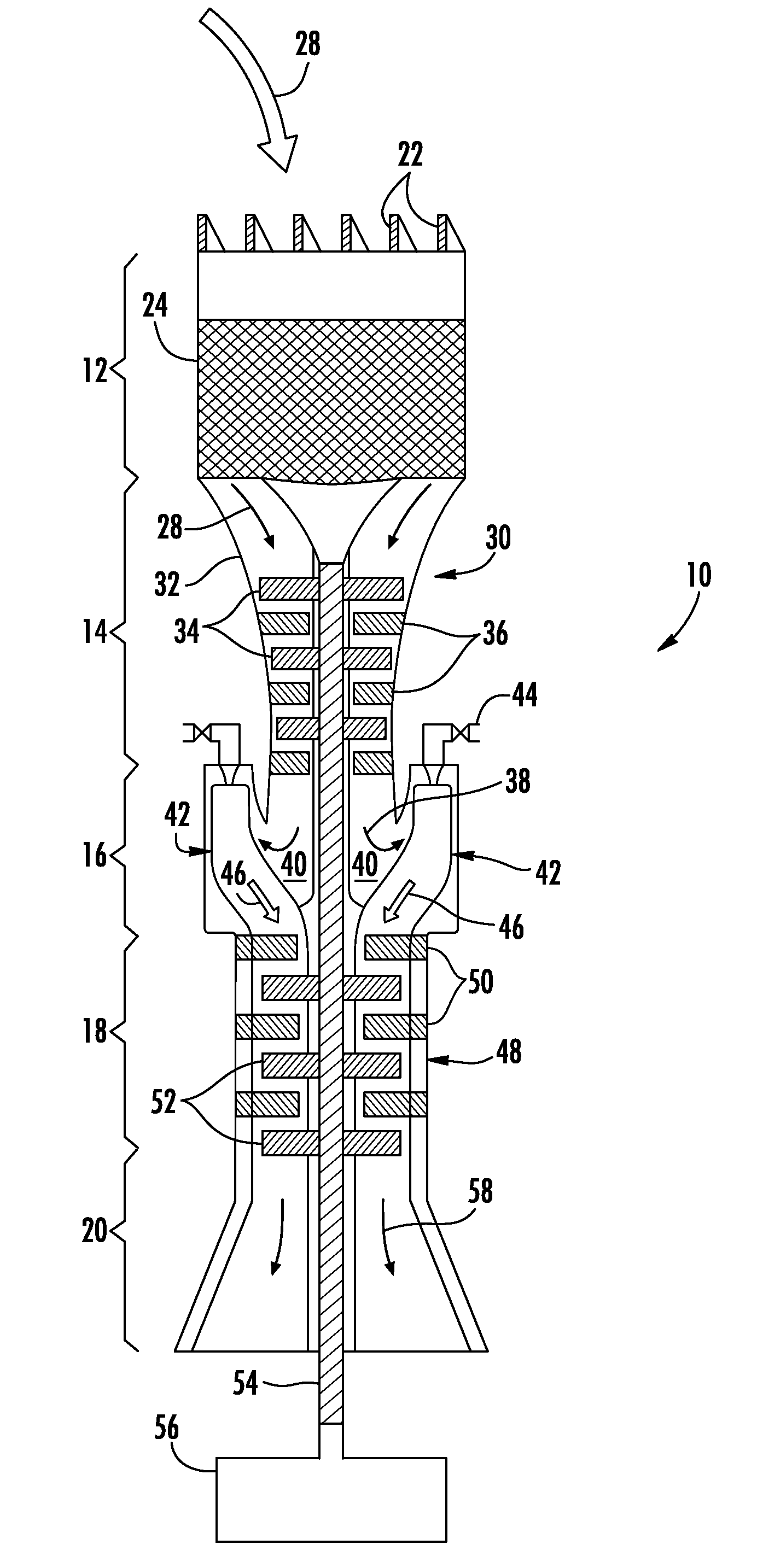
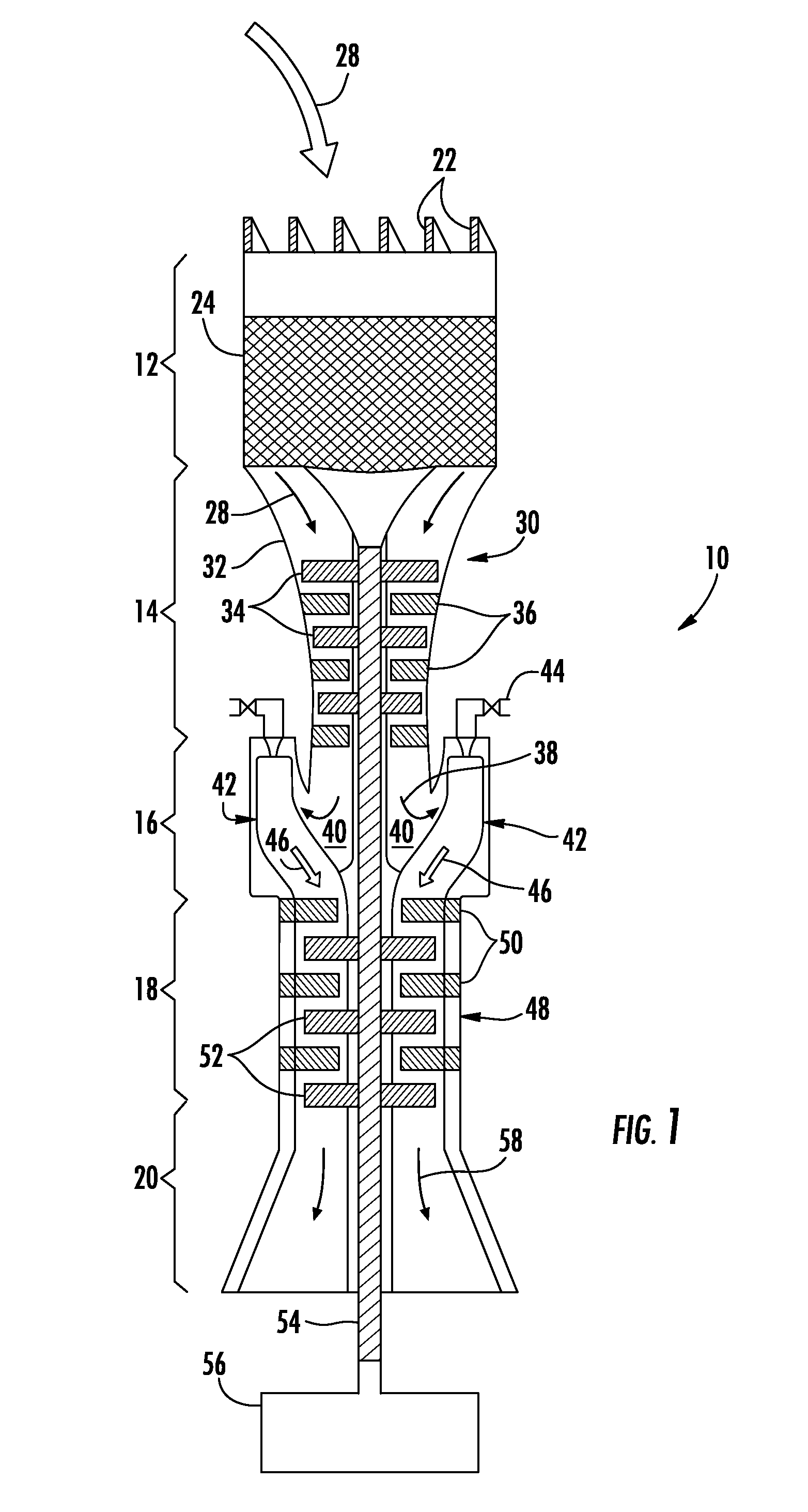
Compact swirl augmented afterburners for gas turbine engines
InactiveUS6895756B2Efficient flame propagationBurn quicklyTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsContinuous combustion chamberCombustion instabilityCombustion chamber
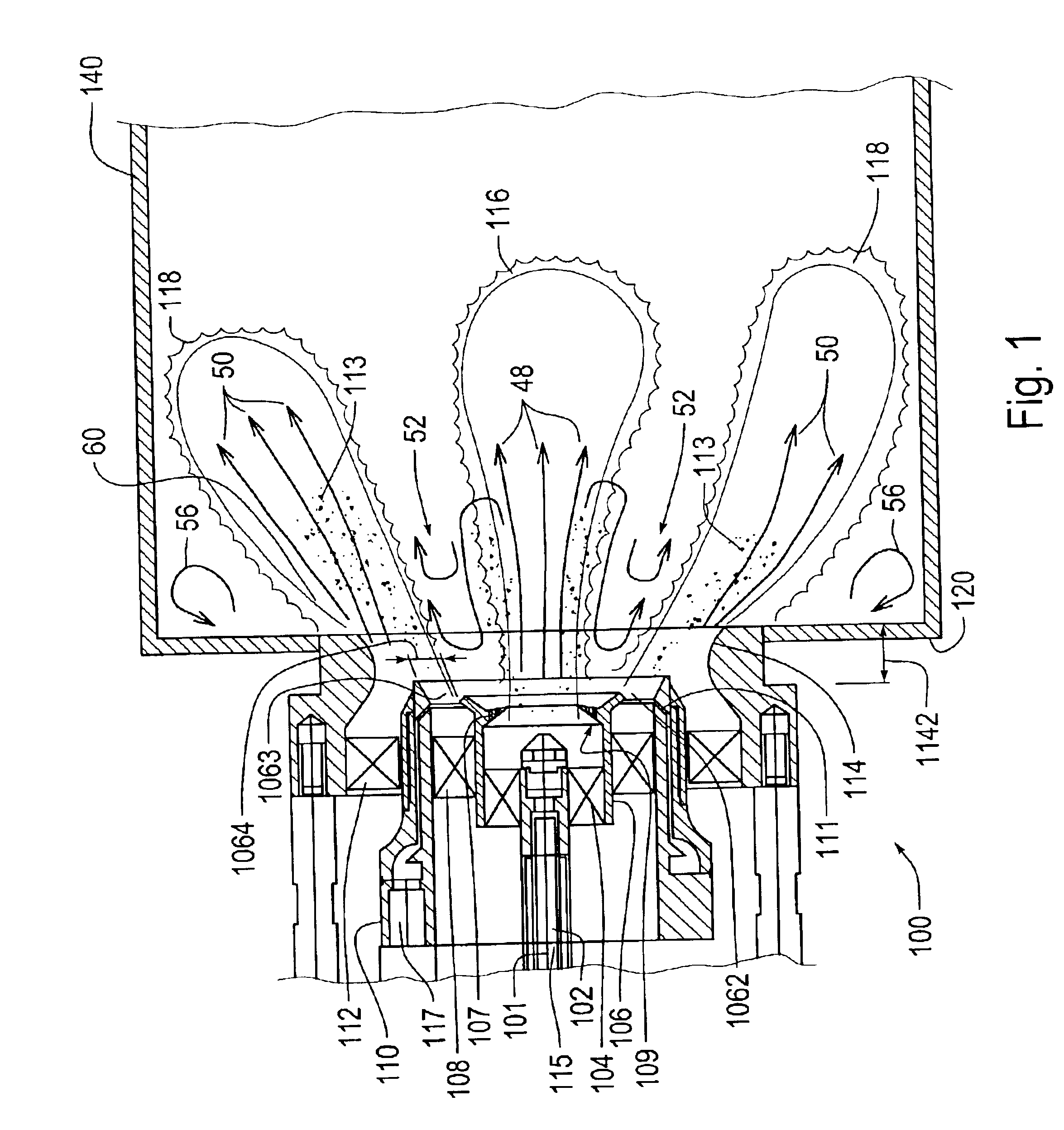
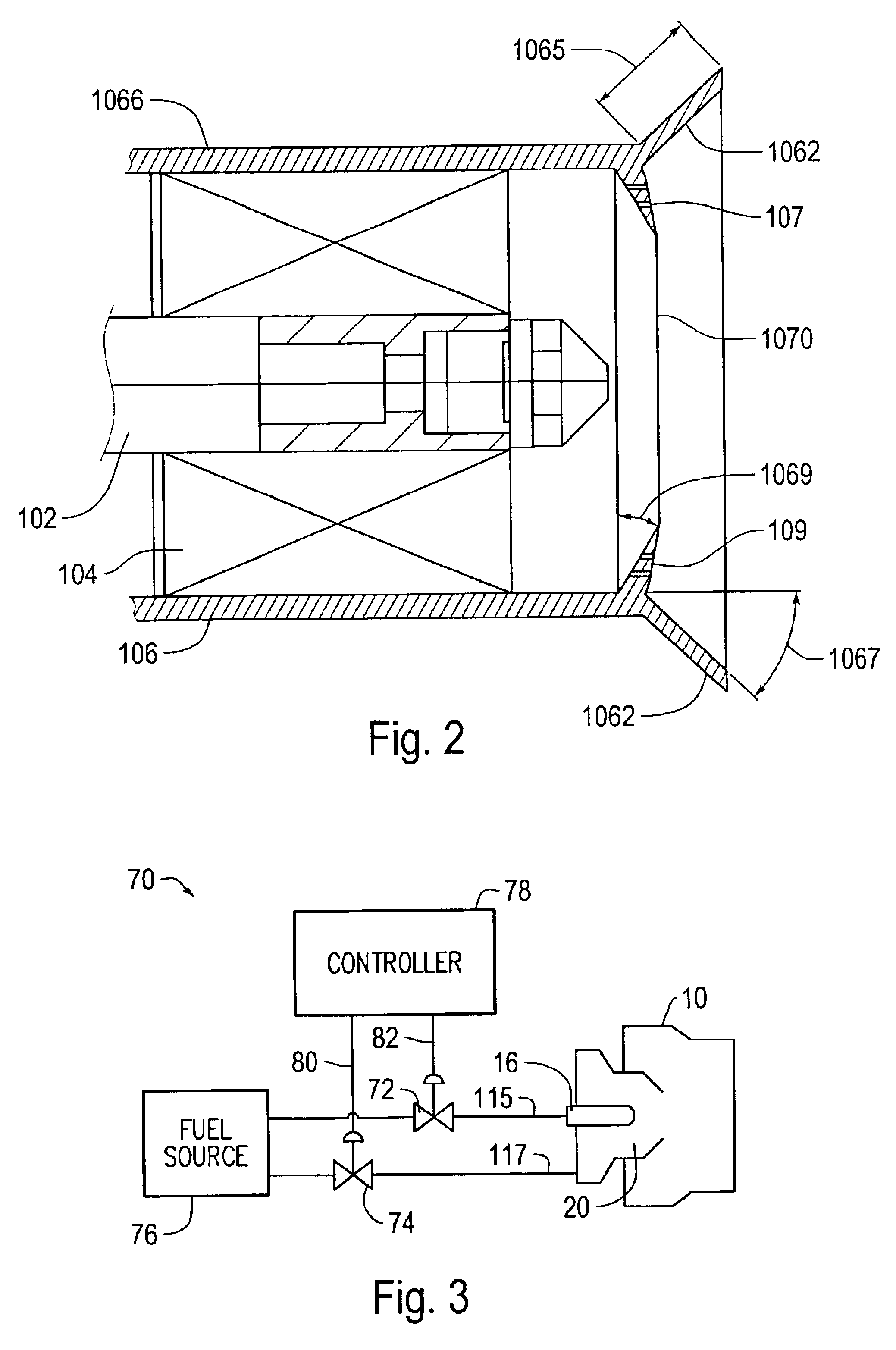
An afterburner apparatus that utilizes a novel swirl generator for rapidly and efficiently atomizing, vaporizing, as necessary, and mixing a fuel into an oxidant. The swirl generator converts an oxidant flow into a turbulent, three-dimensional flowfield into which the fuel is introduced. The swirl generator effects a toroidal outer recirculation zone and a central recirculation zone, which is positioned within the outer recirculation zone. These recirculation zones are configured in a backward-flowing manner that carries heat and combustion byproducts upstream where they are employed to continuously ignite a combustible fuel / oxidizer mixture in adjacent shear layers. The recirculation zones accelerate flame propagation to allow afterburning to be completed in a relatively short length. Inherent with this swirl afterburner concept are design compactness, light weight, lower cost, smooth and efficient combustion, high thrust output, wide flammability limits, continuous operation at stoichiometric fuel / oxidizer mixture ratios, no combustion instabilities, and relatively low pressure losses.
Owner:THE BOEING CO +1
Piloted airblast lean direct fuel injector with modified air splitter
ActiveUS6986255B2Improve combustion efficiencyEmission reductionBurnersContinuous combustion chamberCombustion instabilityInjector
A fuel injector system that reduces and / or eliminates combustion instability. The fuel injector system includes a pilot fuel injector, a pilot swirler that swirls air past the pilot fuel injector, a main airblast fuel injector having an aft end, inner and outer main swirlers that swirl air past the main airblast fuel injector, and an air splitter located between the pilot swirler and the inner main swirler. The air splitter includes at least one aft end cone angled radially outboard and axially positioned downstream of the main airblast fuel injector aft end. The air splitter divides a pilot air stream exiting the pilot swirler from an inner main air stream exiting the inner main swirler to create a bifurcated recirculation zone.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Method and apparatus for detecting combustion instability in continuous combustion systems
Owner:WOODWARD GOVERNOR CO
Periodic equivalence ratio modulation method and apparatus for controlling combustion instability
InactiveUS6059560AReduce pollutant emissionsReduce instabilityTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsPulsating combustionCombustion instabilityStable state
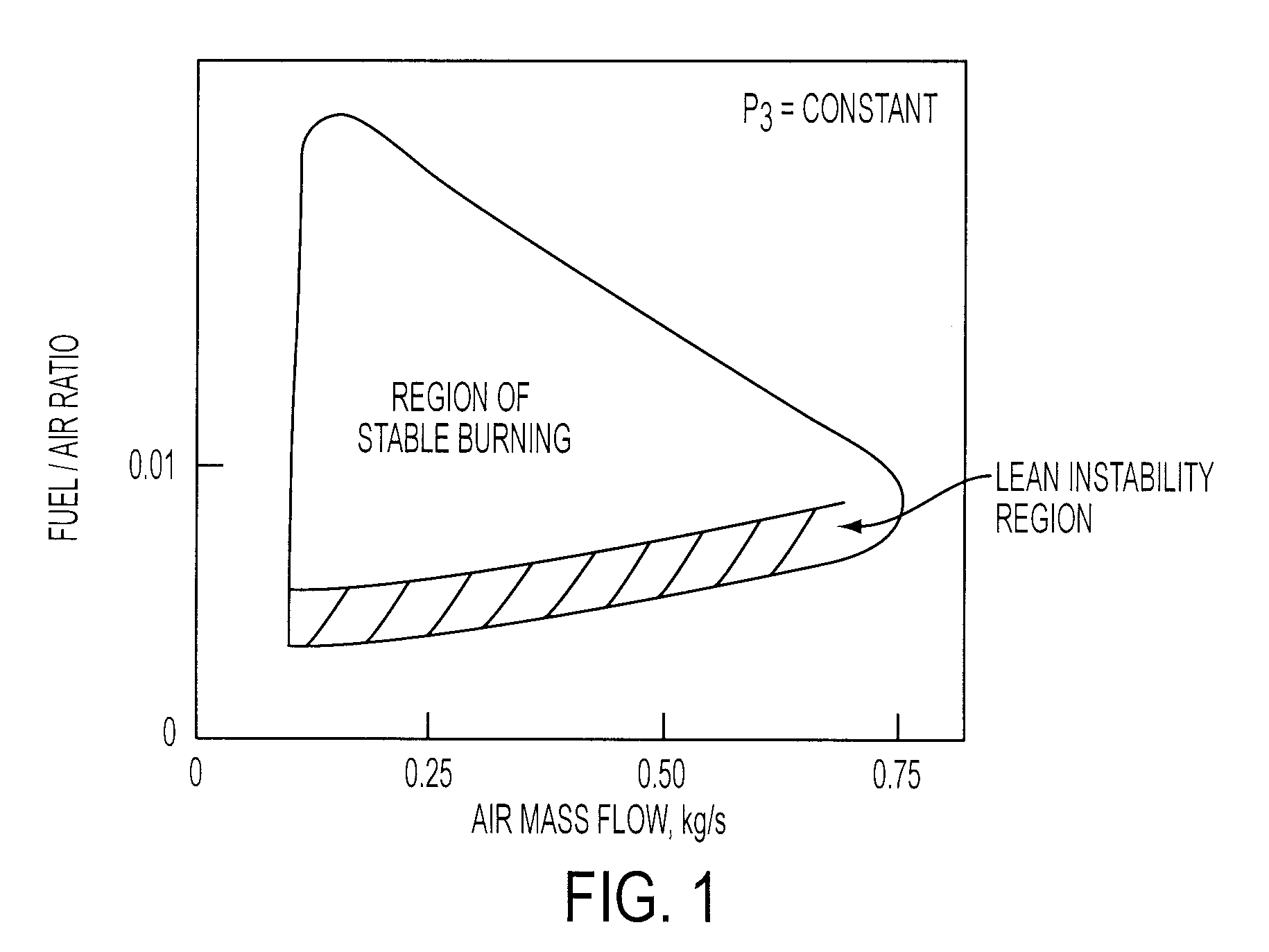
The periodic equivalence ratio modulation (PERM) method and apparatus significantly reduces and / or eliminates unstable conditions within a combustion chamber. The method involves modulating the equivalence ratio for the combustion device, such that the combustion device periodically operates outside of an identified unstable oscillation region. The equivalence ratio is modulated between preselected reference points, according to the shape of the oscillation region and operating parameters of the system. Preferably, the equivalence ratio is modulated from a first stable condition to a second stable condition, and, alternatively, the equivalence ratio is modulated from a stable condition to an unstable condition. The method is further applicable to multi-nozzle combustor designs, whereby individual nozzles are alternately modulated from stable to unstable conditions. Periodic equivalence ratio modulation (PERM) is accomplished by active control involving periodic, low frequency fuel modulation, whereby low frequency fuel pulses are injected into the main fuel delivery. Importantly, the fuel pulses are injected at a rate so as not to affect the desired time-average equivalence ratio for the combustion device.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
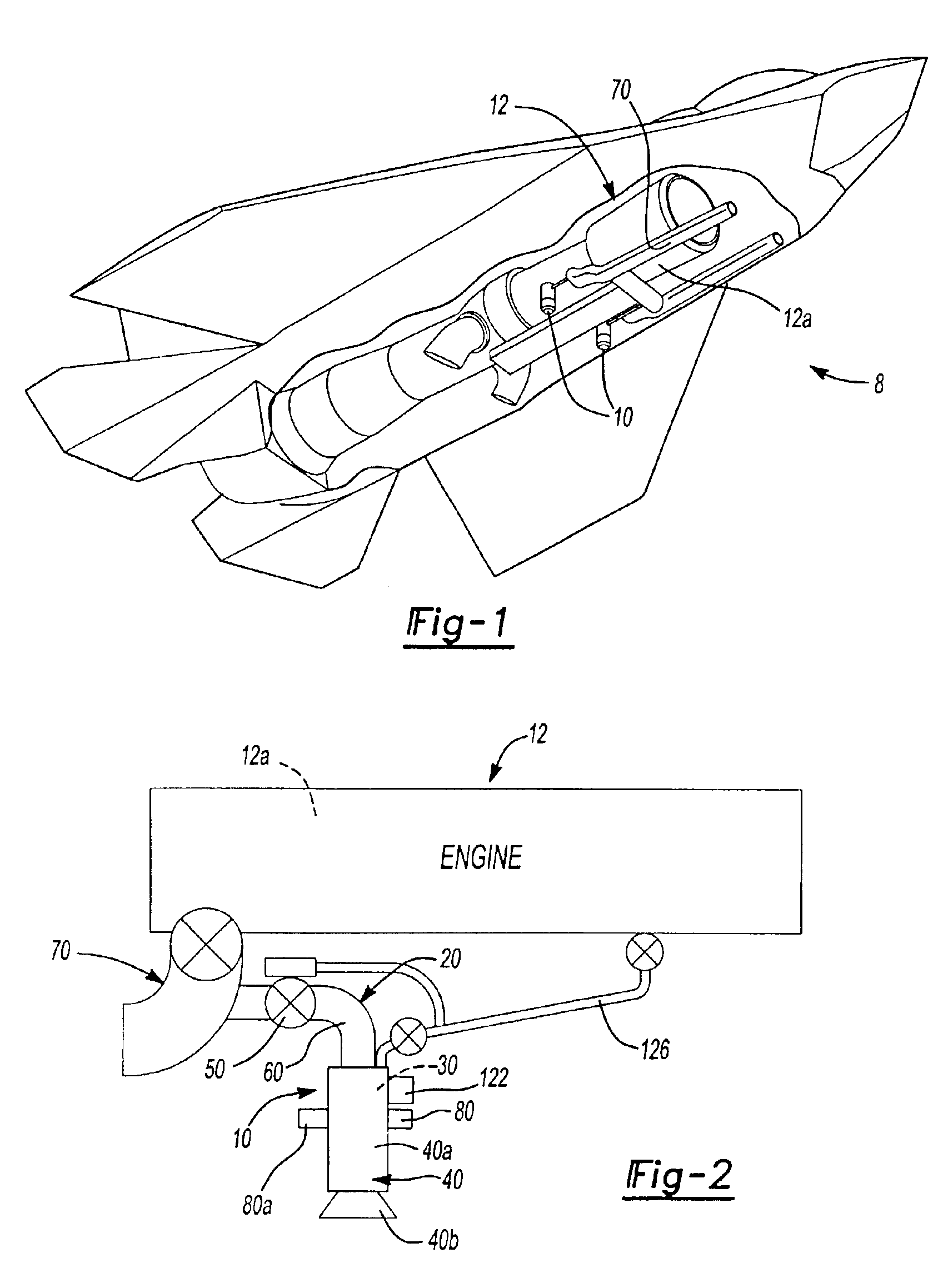
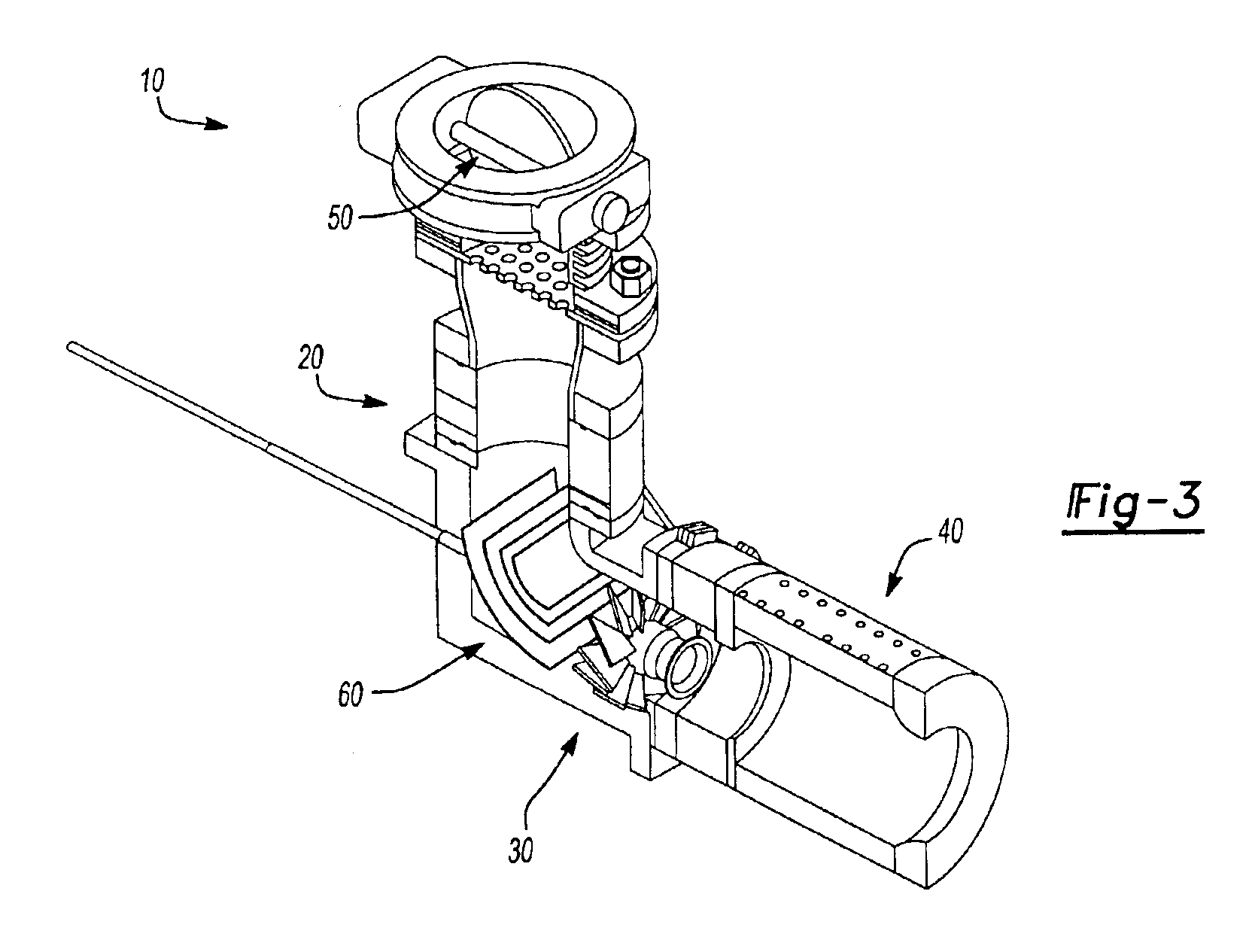
Methods and systems for modulating fuel flow for gas turbine engines
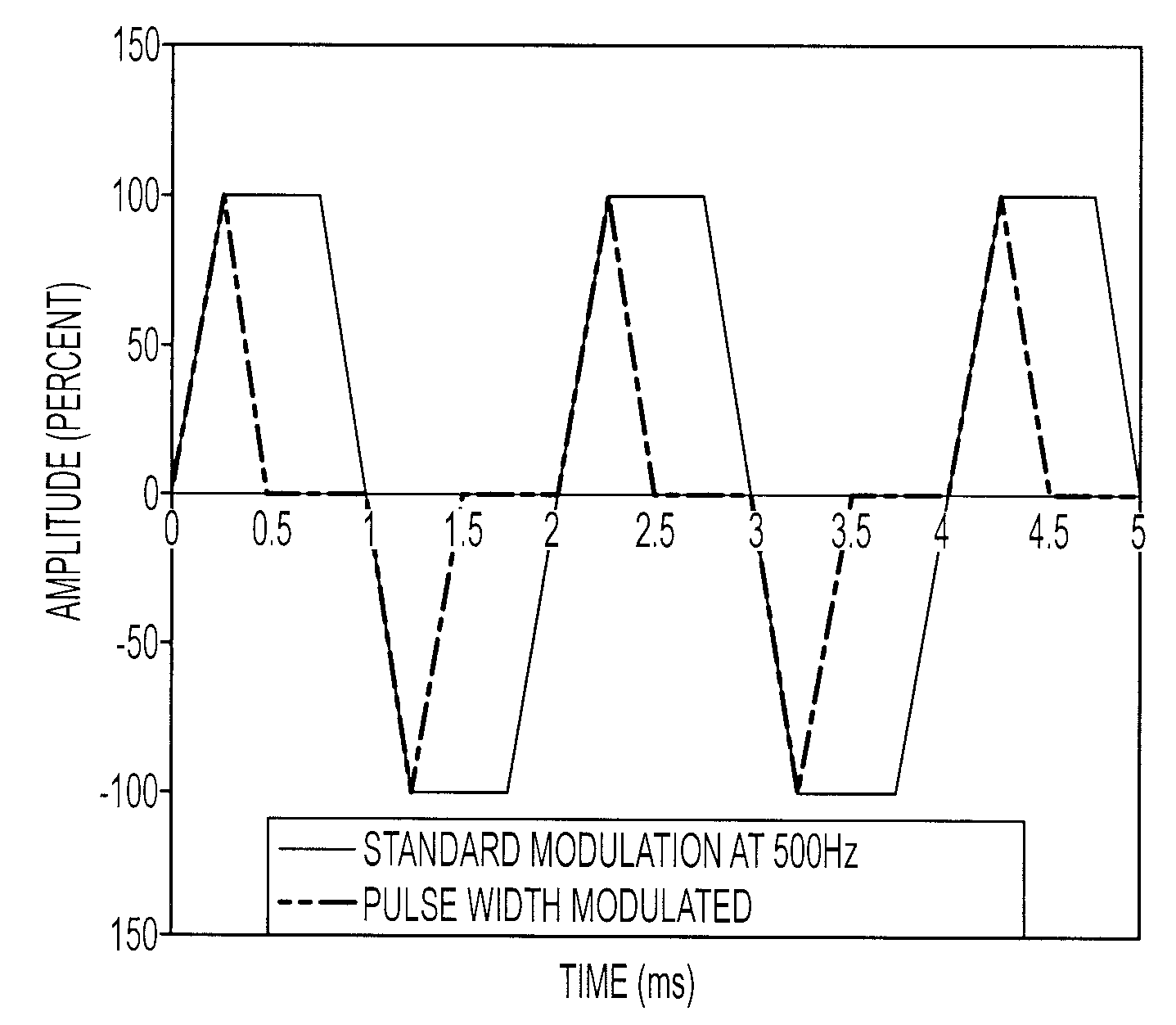
ActiveUS20090204306A1Magnitude is minimisedReduce the amplitudeAnalogue computers for vehiclesContinuous combustion chamberCombustion instabilityCombustion
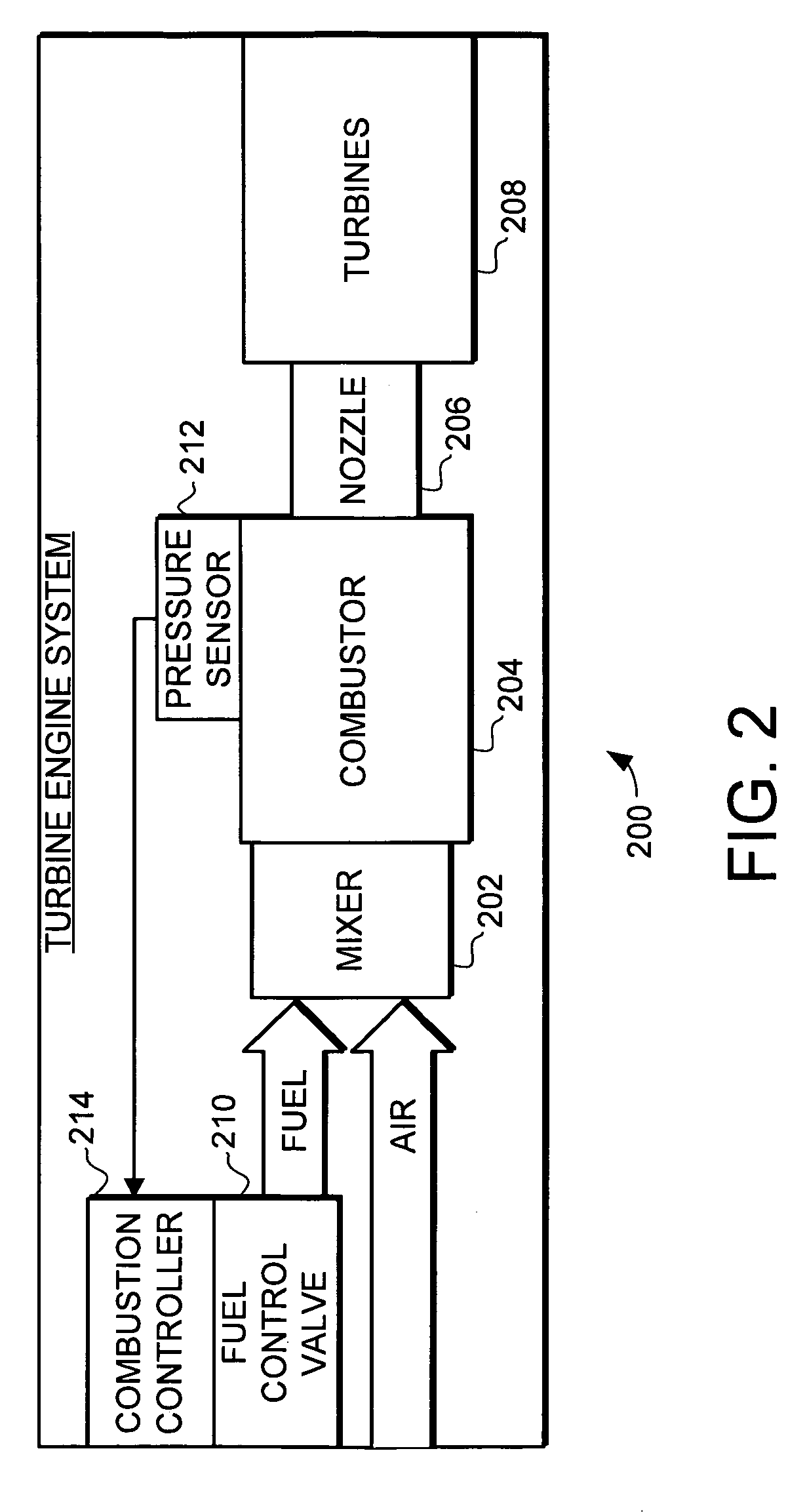
A method of combustion stability control for a gas turbine engine is provided, and includes the steps of receiving by a stability controller, information regarding environmental and operating conditions, and comparing the environmental and operating conditions to pre-programmed information to determine if a likelihood of combustion instability exists. The method further includes the steps of determining optimal fuel modulation frequency and amplitude for the environmental condition to reduce combustion instability, if a likelihood of combustion instability exists, and actuating at least one fuel modulation valve to, at the optimal fuel modulation frequency and amplitude, reduce combustion instability, if a likelihood of combustion instability exists. Systems for modulating fuel flow are also provided.
Owner:COLLINS ENGINE NOZZLES INC
Compact swirl augmented afterburners for gas turbine engines
InactiveUS20060230764A1Promotes rapid and efficient atomization and mixingBurn quicklyTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsContinuous combustion chamberCombustion instabilityFlame propagation
An afterburner apparatus that utilizes a novel swirl generator for rapidly and efficiently atomizing, vaporizing, as necessary, and mixing a fuel and an oxidant. The swirl generator converts an oxidant flow into a turbulent, three-dimensional flowfield into which the fuel is introduced. The swirl generator effects a toroidal outer recirculation zone and a central recirculation zone, which is positioned within the outer recirculation zone. These recirculation zones are configured in a backward-flowing manner that carries heat and combustion byproducts upstream where they are employed to continuously ignite a combustible fuel / oxidizer mixture in adjacent shear layers. The recirculation zones accelerate flame propagation to allow afterburning to be completed in a relatively short length. Inherent with this swirl afterburner concept are design compactness, light weight, lower cost, smooth and efficient combustion, high thrust output, wide flammability limits, continuous operation at stoichiometric fuel / oxidizer mixture ratios, no combustion instabilities, and relatively low pressure losses.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
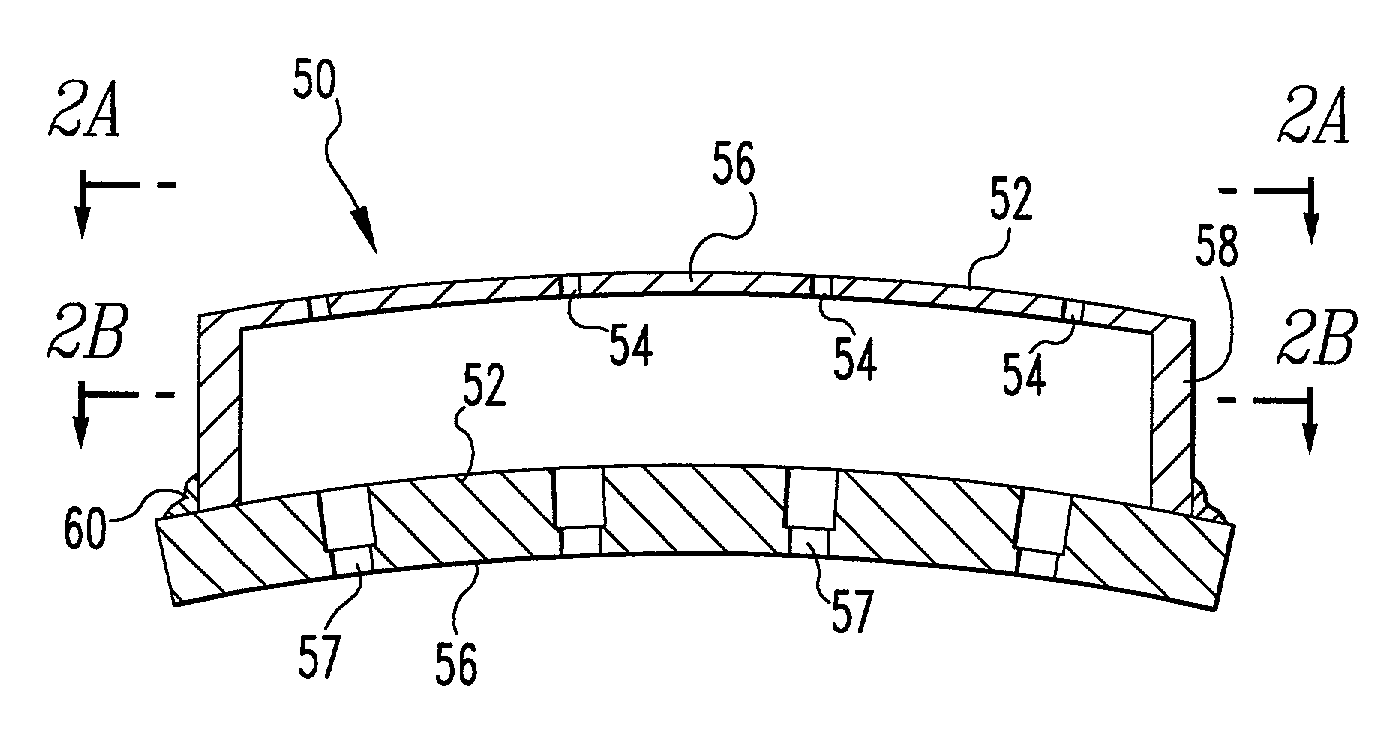
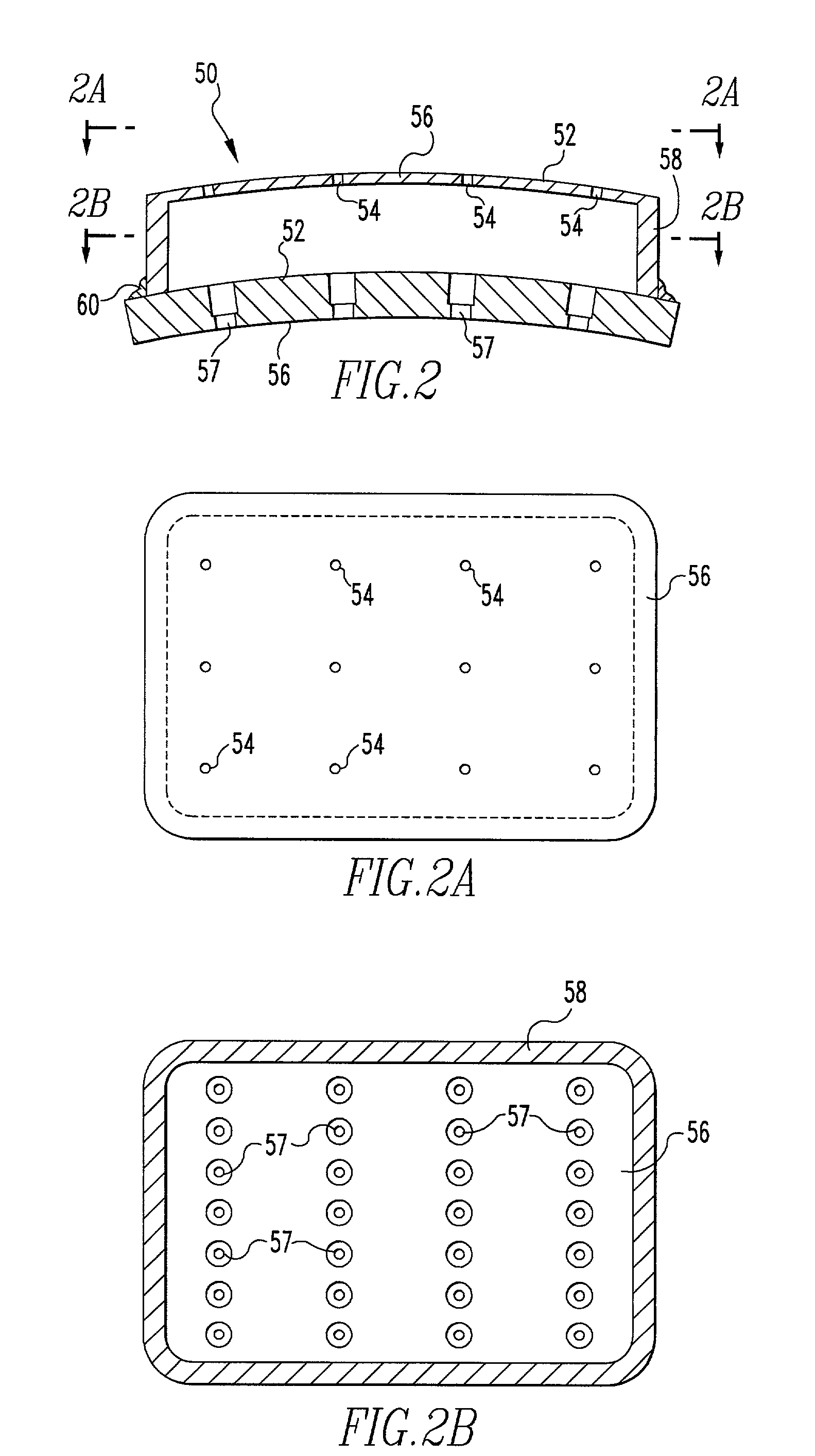
Resonator adopting counter-bored holes and method of suppressing combustion instabilities
ActiveUS20050166596A1Suppress instabilityAdd additional massBurnersContinuous combustion chamberCombustion instabilityResonator
A resonator for damping pressure waves or instabilities in a system supported by acoustic energy wherein the resonator adopts the use of counter-bored openings on the downstream side of the resonator within the flow path of the system. The resonator includes a first member and a second member where the second member includes a plurality of openings therethrough with each hole having a counter-bore on its upstream side. The first member has a size substantially smaller than the diameter of said flow path and a first plurality of openings therethrough. The openings are in fluid communication with the flow path. The second member has a size generally equal to the first member and a second plurality of openings therethrough, which openings are in fluid communication with the flow path.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Combination combustion chamber
ActiveCN105953265AEnhanced blendingImprove flame stabilityContinuous combustion chamberCycloneCombustion instability
The invention relates to a combination combustion chamber. A combustion chamber head part consists of a main combustion stage and a pre-combustion stage; the main combustion stage consists of a single-grade axial cyclone, a main combustion stage nozzle and a venturi pipe; and the pre-combustion stage consists of double concave cavities and a pre-combustion stage nozzle. The main combustion stage adopts a single-oil-way centrifugal nozzle, and enables fuel to reach needed concentration and particle size distribution through pressure atomization. The pre-combustion stage adopts an evaporation pipe type nozzle; and the fuel is sprayed to an evaporation pipe for primary atomization through a straight spraying nozzle, and performs secondary atomization and evaporation mixing in the evaporation pipe under an air shearing effect. The combination combustion chamber not only can achieve the purpose of reducing the pollutant discharge in a low-pollution combustion chamber, but also can solve the problems of small-state combustion instability and large-stage visible smoke in a high-temperature-rise combustion chamber so as to widen stable working range of the high-temperature-rise combustion chamber through classified combustion, in particular special structural design and arrangement mode of the pre-combustion stage and the main combustion stage.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
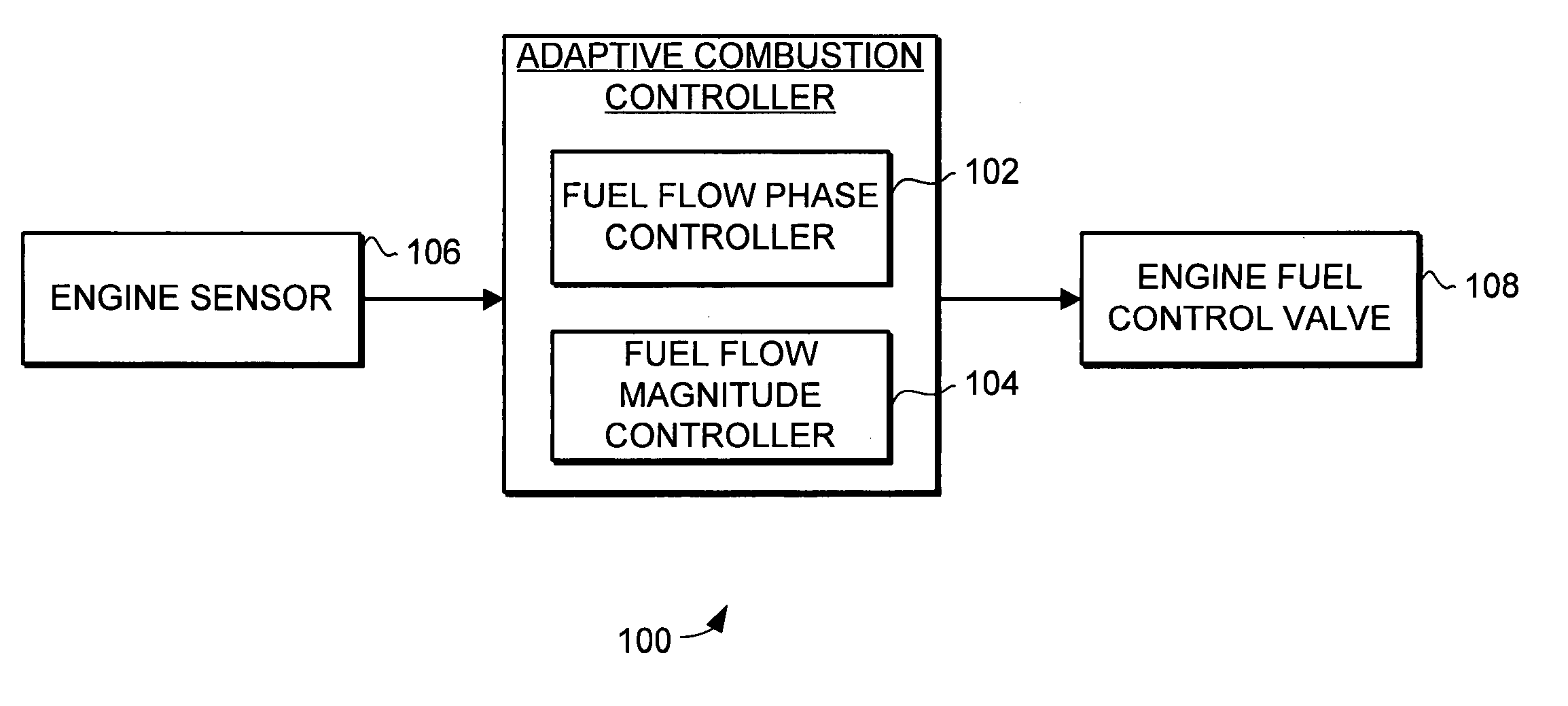
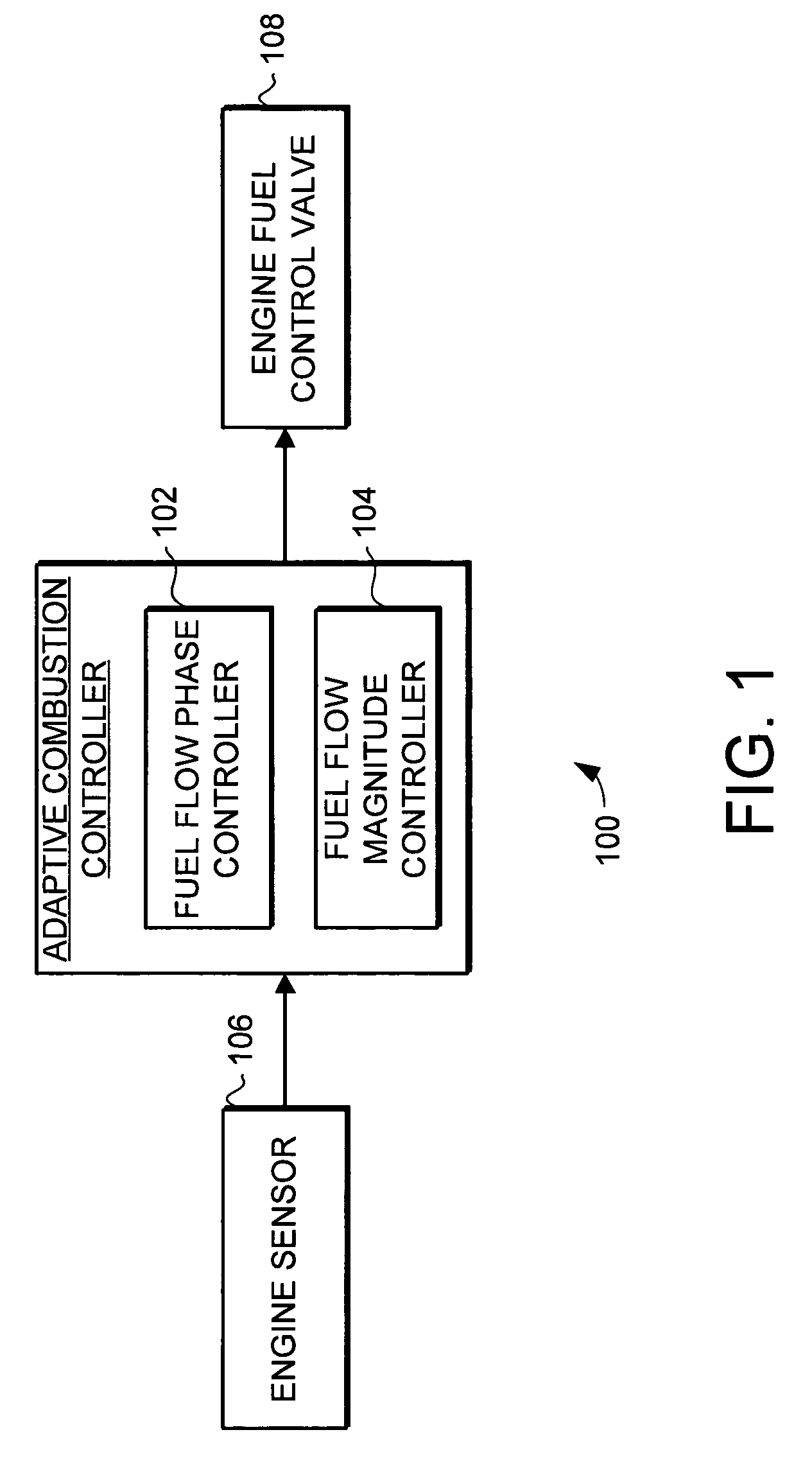
System and method for turbine engine adaptive control for mitigation of instabilities
InactiveUS20060213200A1Reduce combustion instabilityReduce instabilityGas turbine plantsTurbine/propulsion fuel controlCombustion instabilityInstability
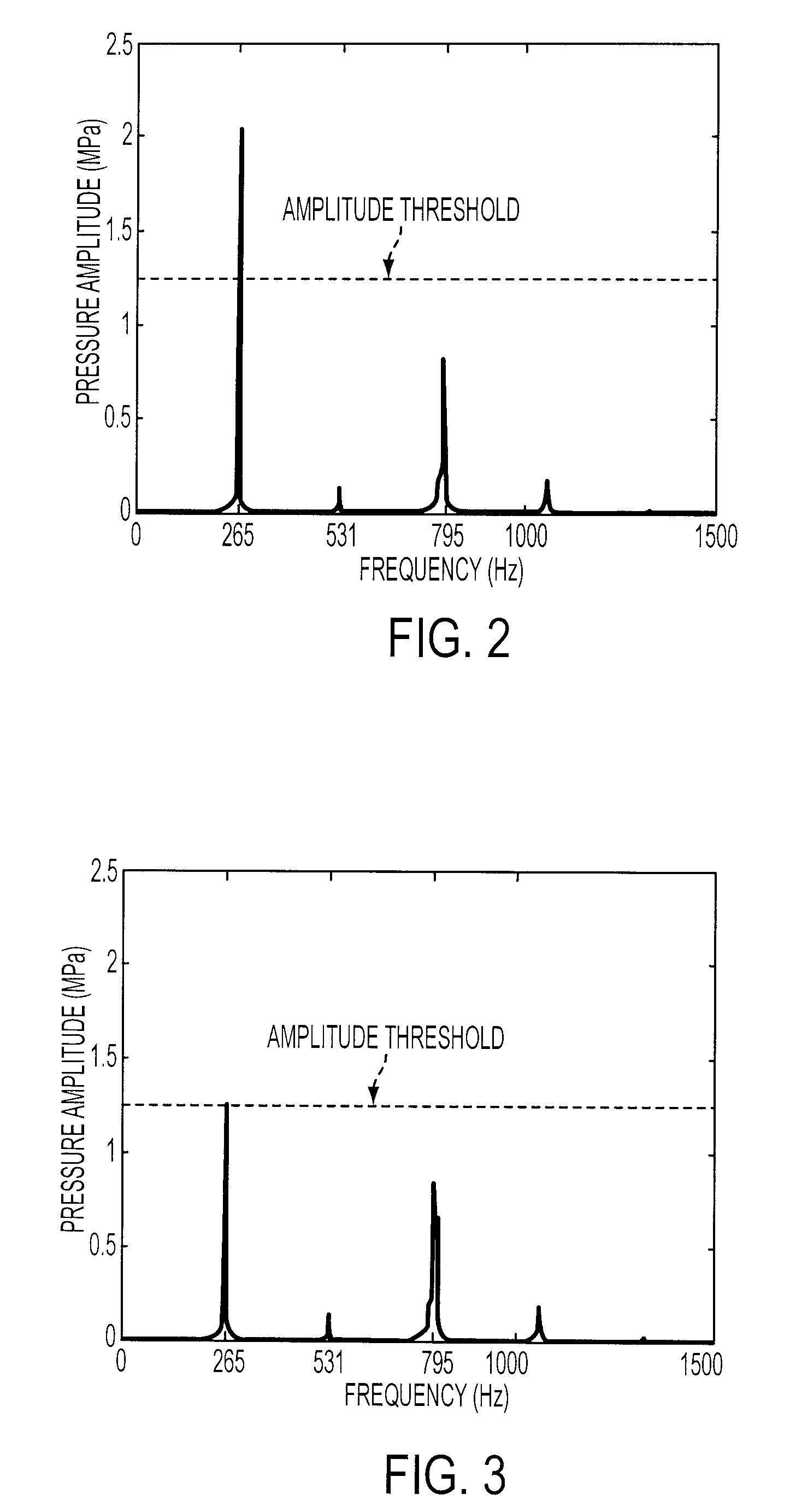
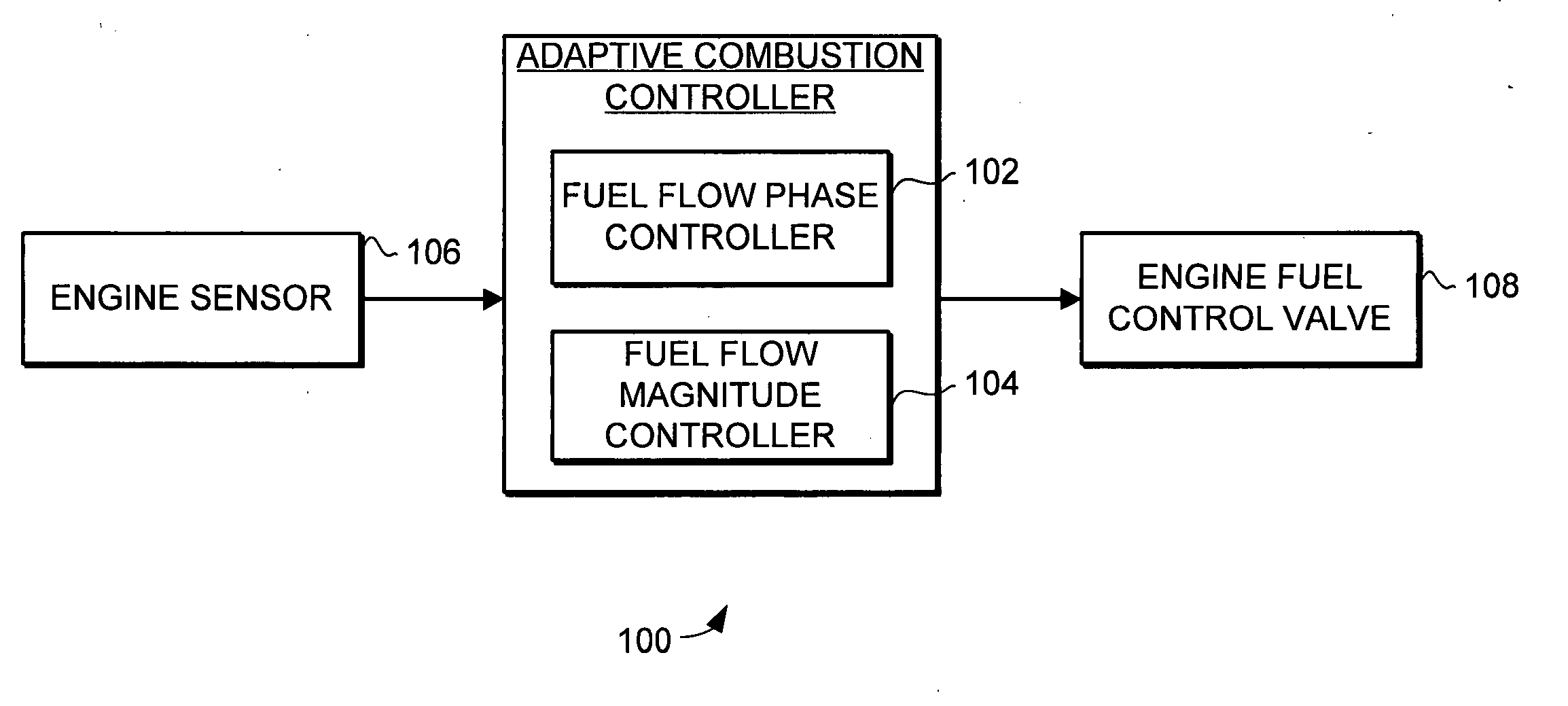
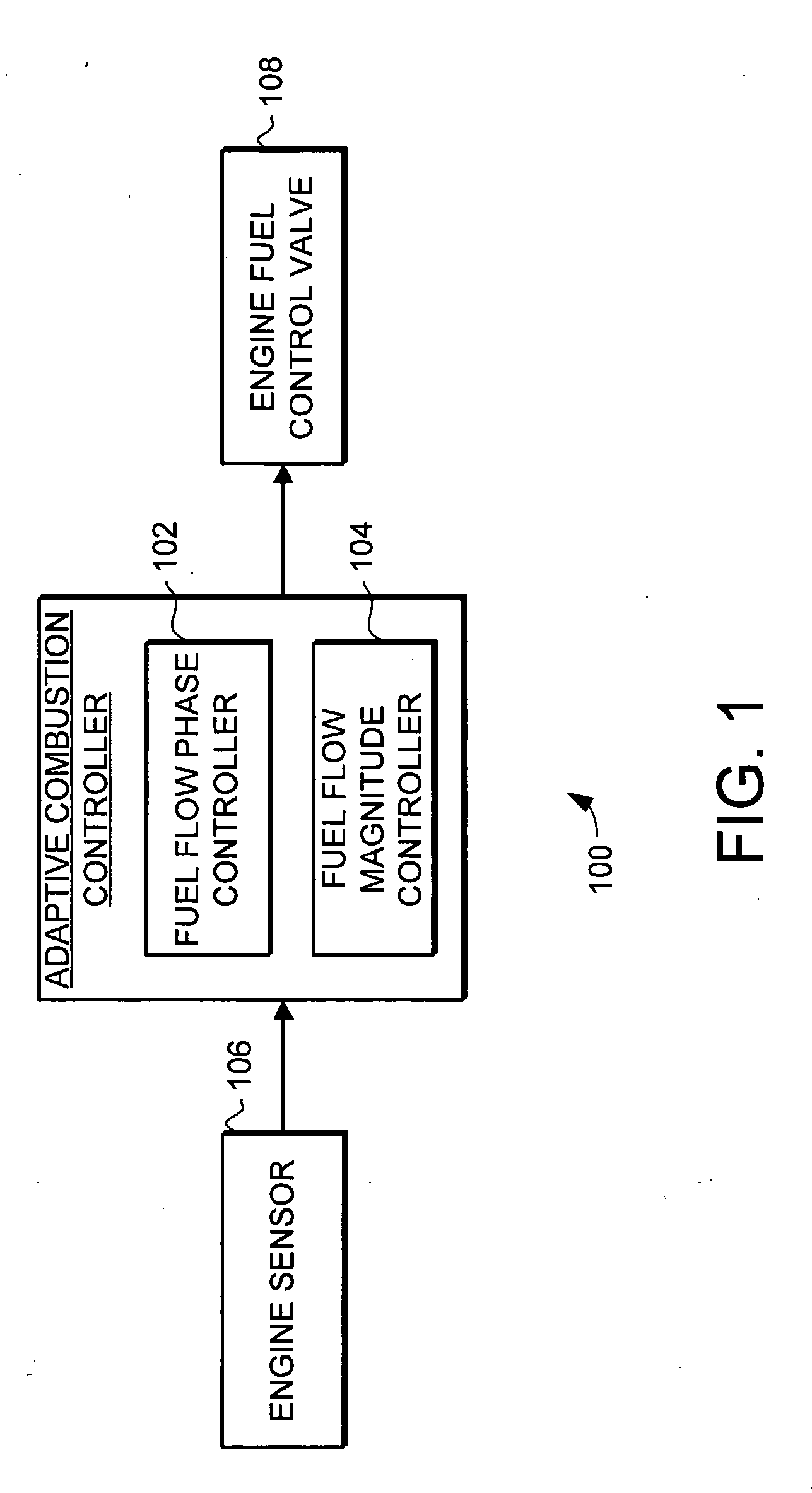
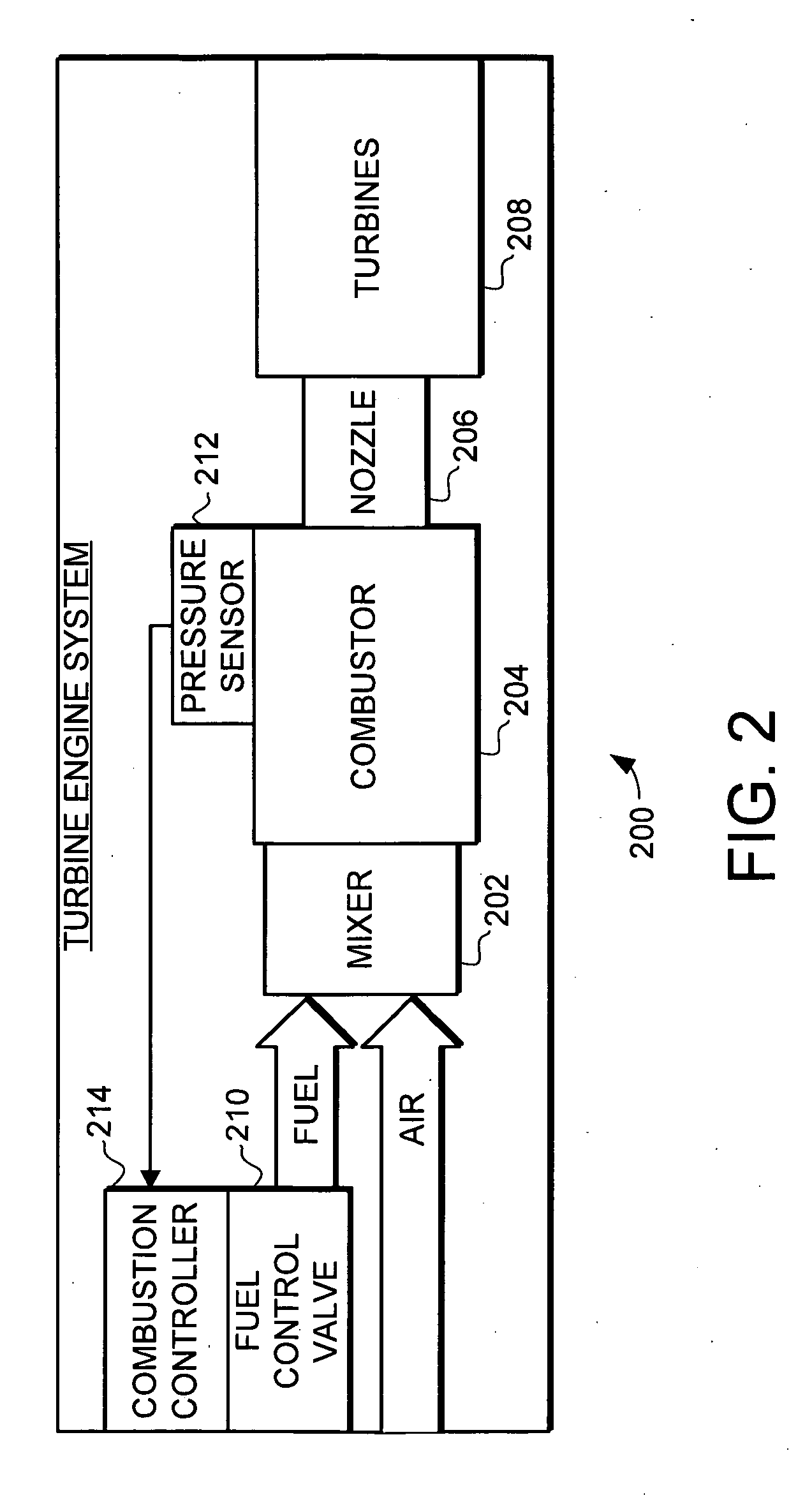
The present invention provides an adaptive combustion controller and method for a turbine engine. The adaptive combustion controller and method modulates the fuel flow to the turbine engine combustor to reduce combustion instabilities. In particular, the adaptive combustion controller includes a fuel flow phase controller and a fuel flow magnitude controller. The adaptive combustion controller receives sensor data from the turbine engine. In response to the sensor data the fuel flow phase controller adjusts the phase of the modulated fuel flow to reduce instabilities in the combustor. Likewise, in response to the sensor data the fuel flow magnitude controller adjusts the magnitude of the modulated fuel flow to further reduce the instabilities in the combustor. By modulating the fuel flow to the combustor, and adaptively adjusting the phase and magnitude of the modulated fuel flow, the adaptive combustion controller is able to effectively reduce combustion instabilities.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Variable amplitude double binary valve system for active fuel control
InactiveUS20090077945A1Reduce size and weight and complexity and costMinimizing amplitudeContinuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion fuel valvesCombustion instabilityPhase shifted
A method of controlling combustion stability in a turbine engine having combustion stability control capability includes the steps of providing at least one pair of pulsating valves, mutually arranged in parallel with respect to fuel flow provided to a combustor of the turbine engine, detecting an amplitude and frequency of a pressure wave of at least one periodic combustion instability, selecting an amplitude, frequency and first phase shift, with respect to the pressure wave, of resultant fuel pulsations to reduce the amplitude of the pressure wave, translating the selected amplitude into a second, relative phase shift between each pulsating valve of at least one pair of pulsating valves, and commanding each pulsating valve of at least one pair of pulsating valves to operate at the selected frequency and a relative second phase shift with respect to one another, to yield a resultant fuel pulsation at the selected amplitude, frequency and first phase shift, with respect to the detected pressure wave of combustion instability.
Owner:DELAVAN
System and method for turbine engine adaptive control for mitigation of instabilities
InactiveUS7406820B2Gas turbine plantsTurbine/propulsion fuel controlCombustion instabilityInstability
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Multi-mode multi-fuel combustion system
InactiveCN102278216AGuaranteed high power densityAvoid fireElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCombustion instabilityCombustion system
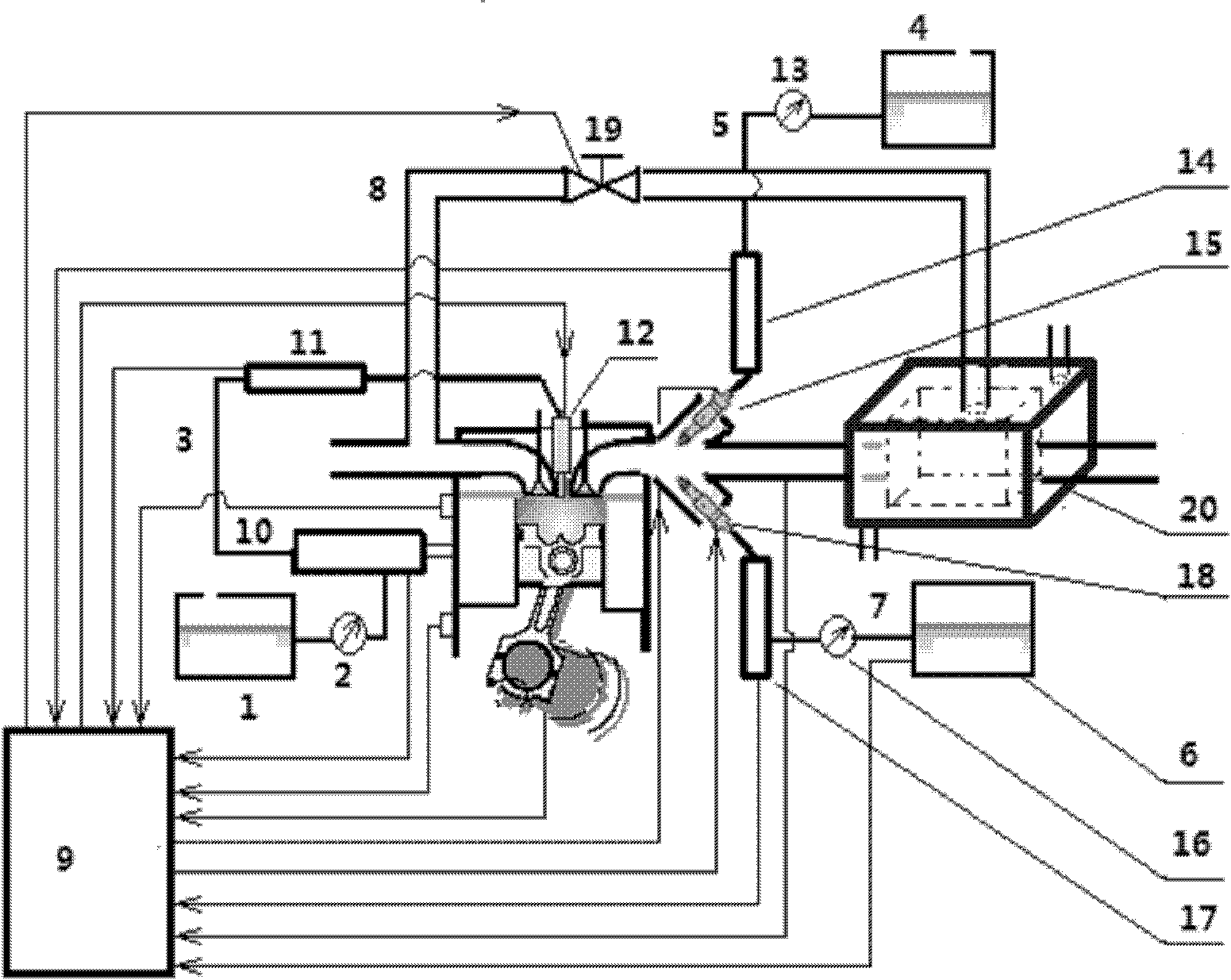
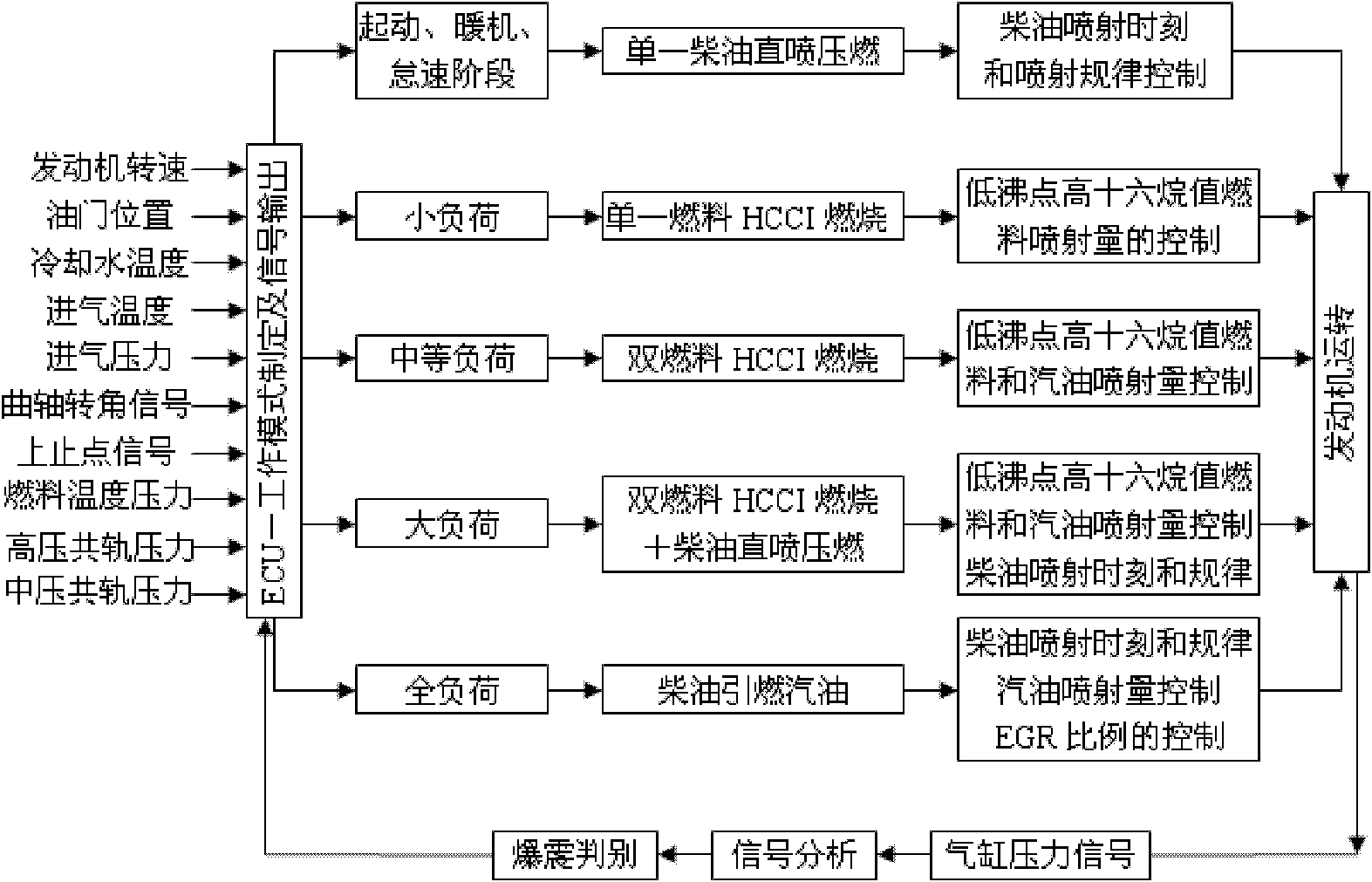
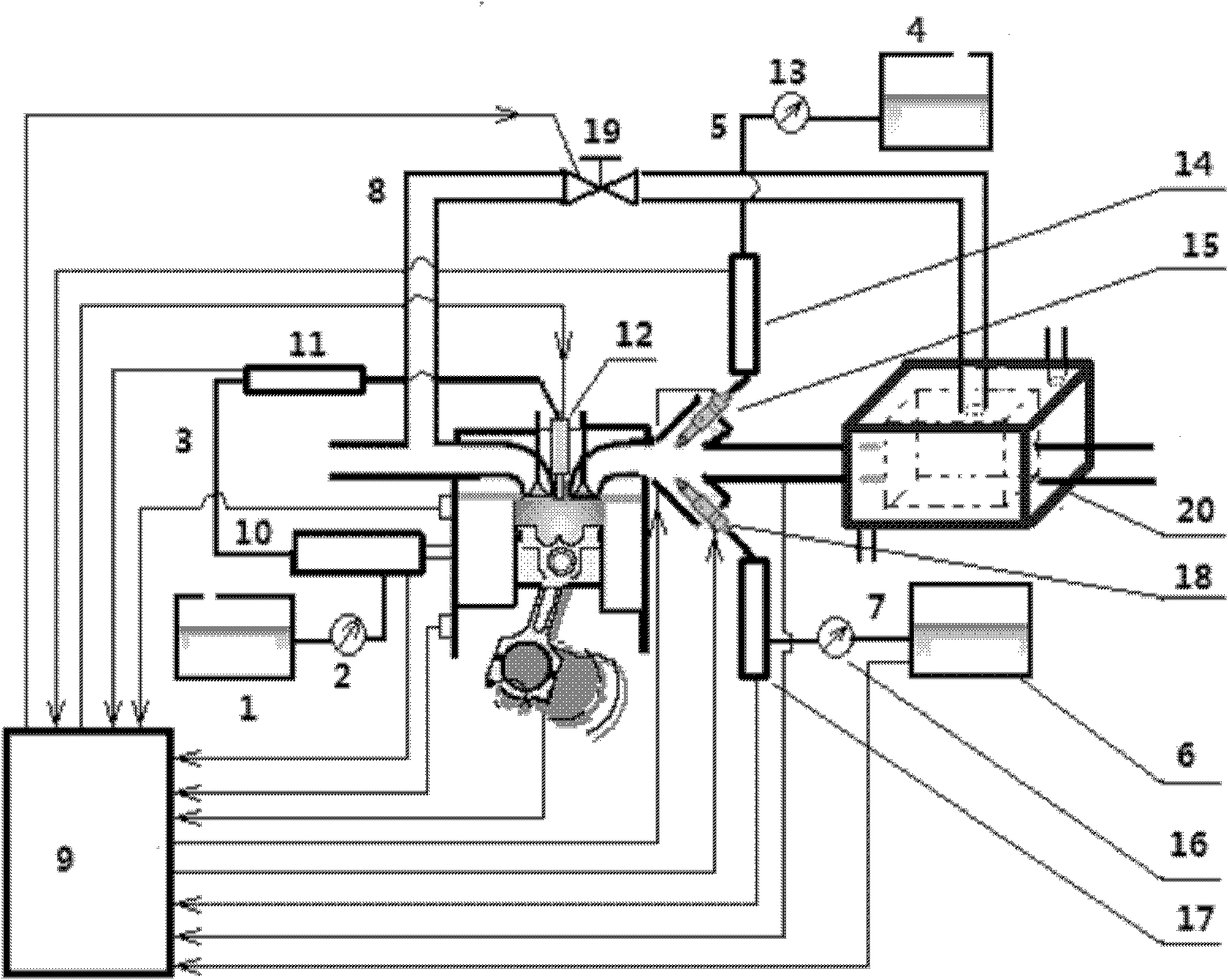
A multi-mode multi-fuel combustion system in the technical field of internal combustion engines, comprising: a diesel fuel tank, a diesel filter, a diesel high-pressure common rail injection system, a first auxiliary fuel tank, a first common rail gas port injection system, a second auxiliary fuel tank, Second common rail port injection system, cooled exhaust gas recirculation and electronic control unit. The invention can avoid the problems of ignition and combustion instability, poor combustion efficiency, and high emissions of hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide in the low-temperature cold start stage of the spark ignition combustion mode; it can realize smooth switching of various modes; as long as the existing engine is simply operated High-efficiency and ultra-low emissions in the full load range are achieved through technological transformation.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Resonator adopting counter-bored holes and method of suppressing combustion instabilities
InactiveUS7194862B2Add additional massSuppress energyBurnersContinuous combustion chamberCombustion instabilityCombustion
A resonator for damping pressure waves or instabilities in a system supported by acoustic energy wherein the resonator adopts the use of counter-bored openings on the downstream side of the resonator within the flow path of the system. The resonator includes a first member and a second member where the second member includes a plurality of openings therethrough with each hole having a counter-bore on its upstream side. The first member has a size substantially smaller than the diameter of said flow path and a first plurality of openings therethrough. The openings are in fluid communication with the flow path. The second member has a size generally equal to the first member and a second plurality of openings therethrough, which openings are in fluid communication with the flow path.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
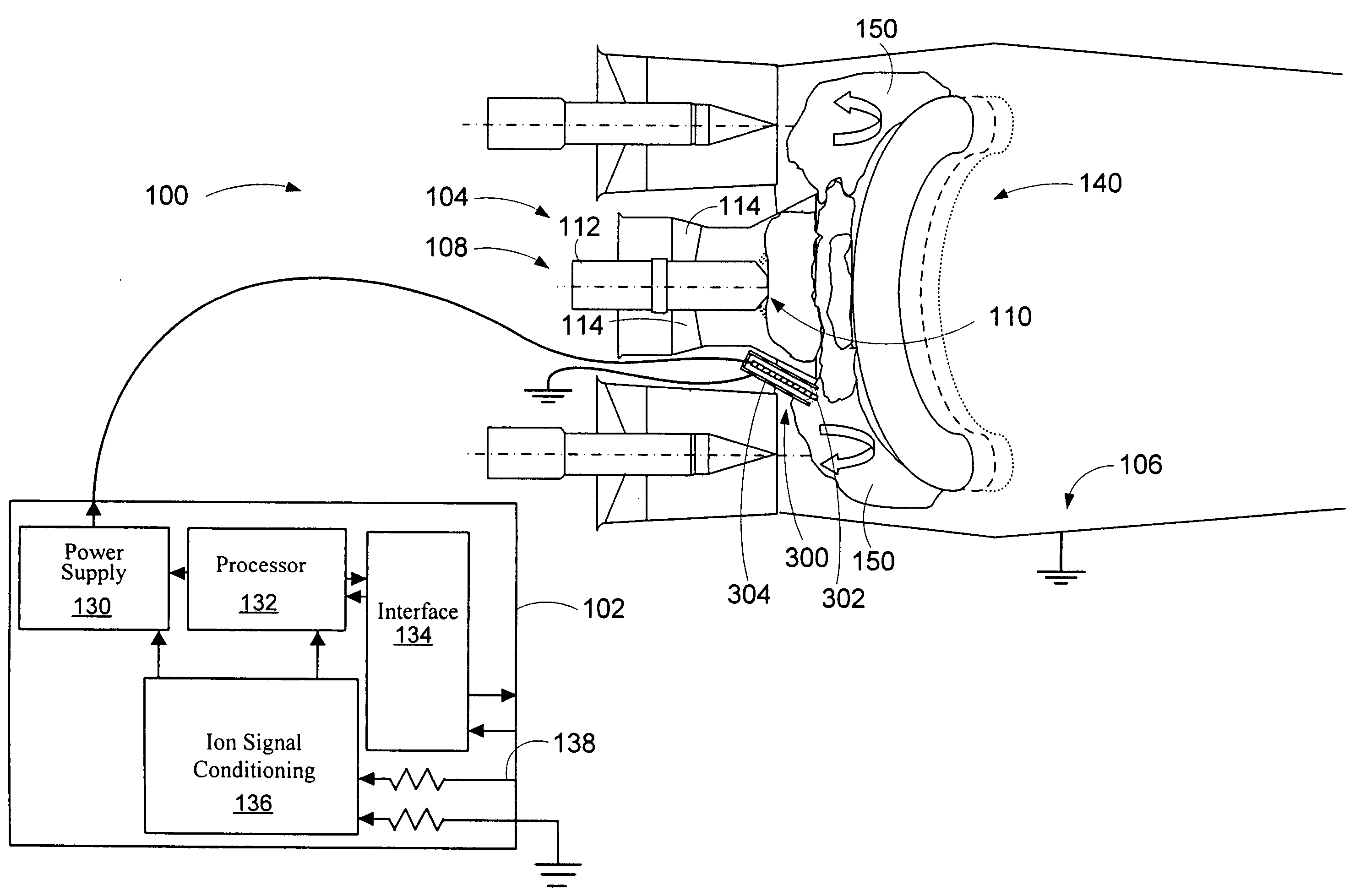
Method and apparatus for detecting combustion instability in continuous combustion systems
InactiveUS20060000260A1Restore stabilityBurnersFuel supply regulationCombustion systemCombustion instability
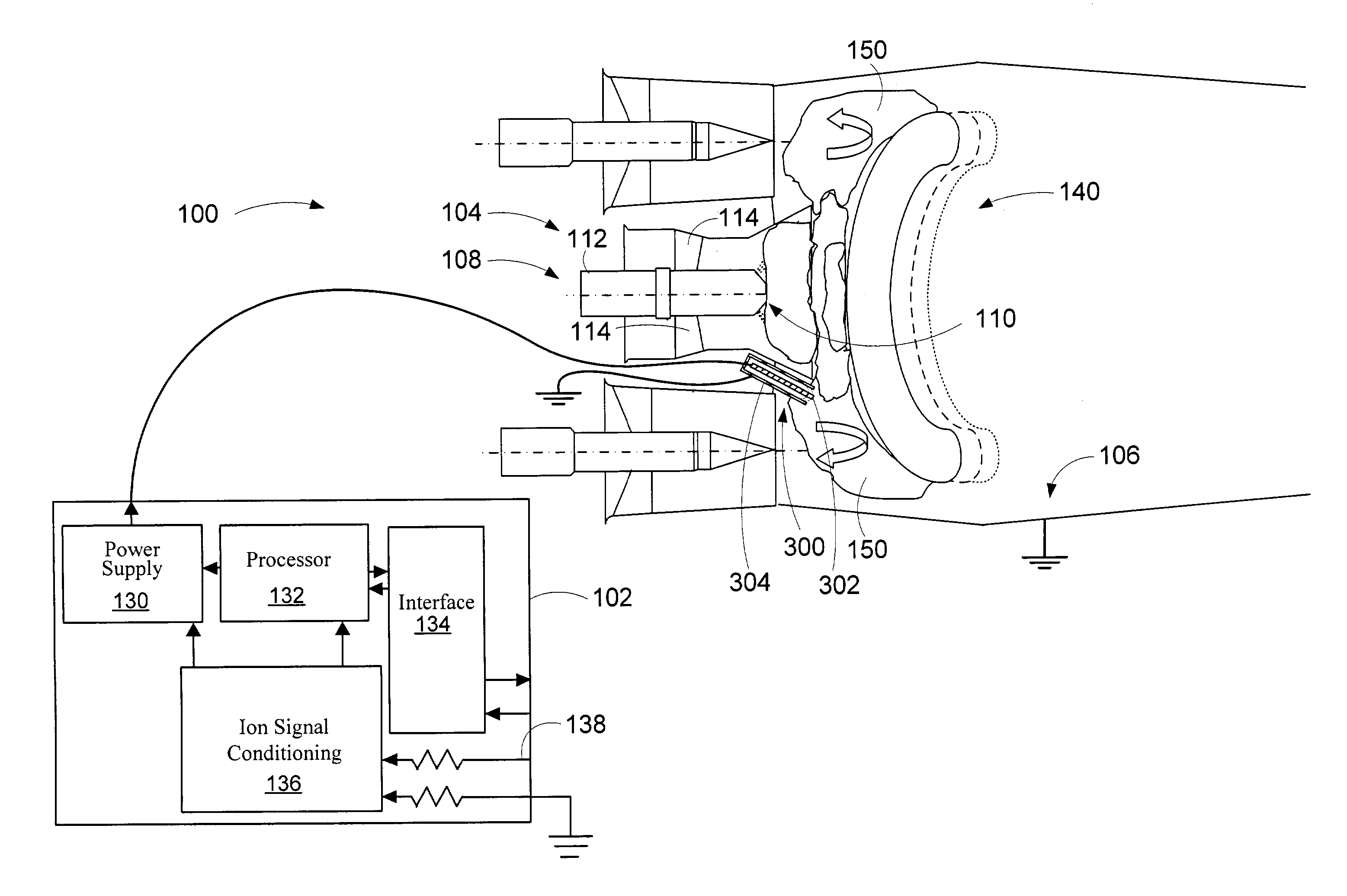
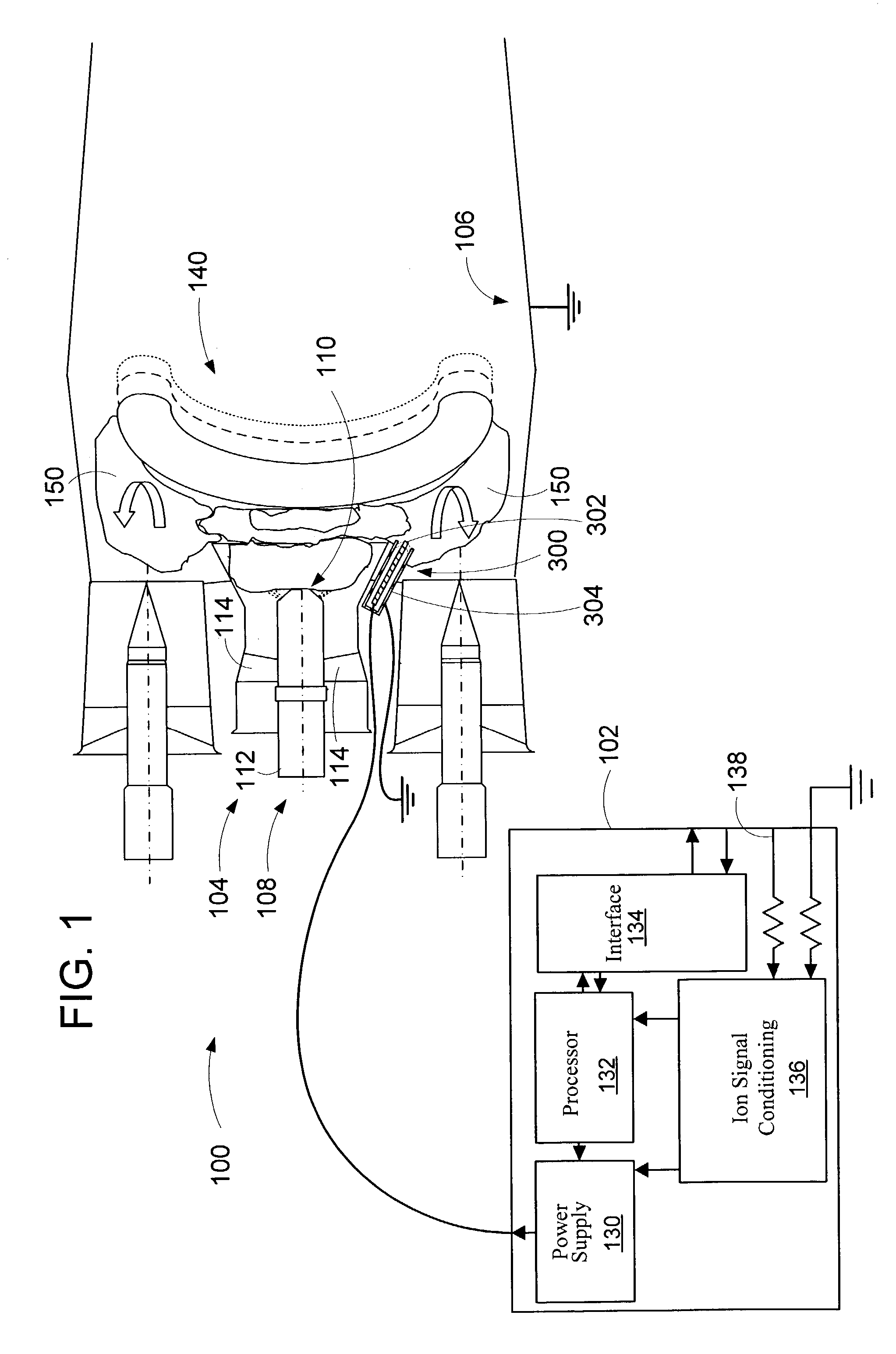
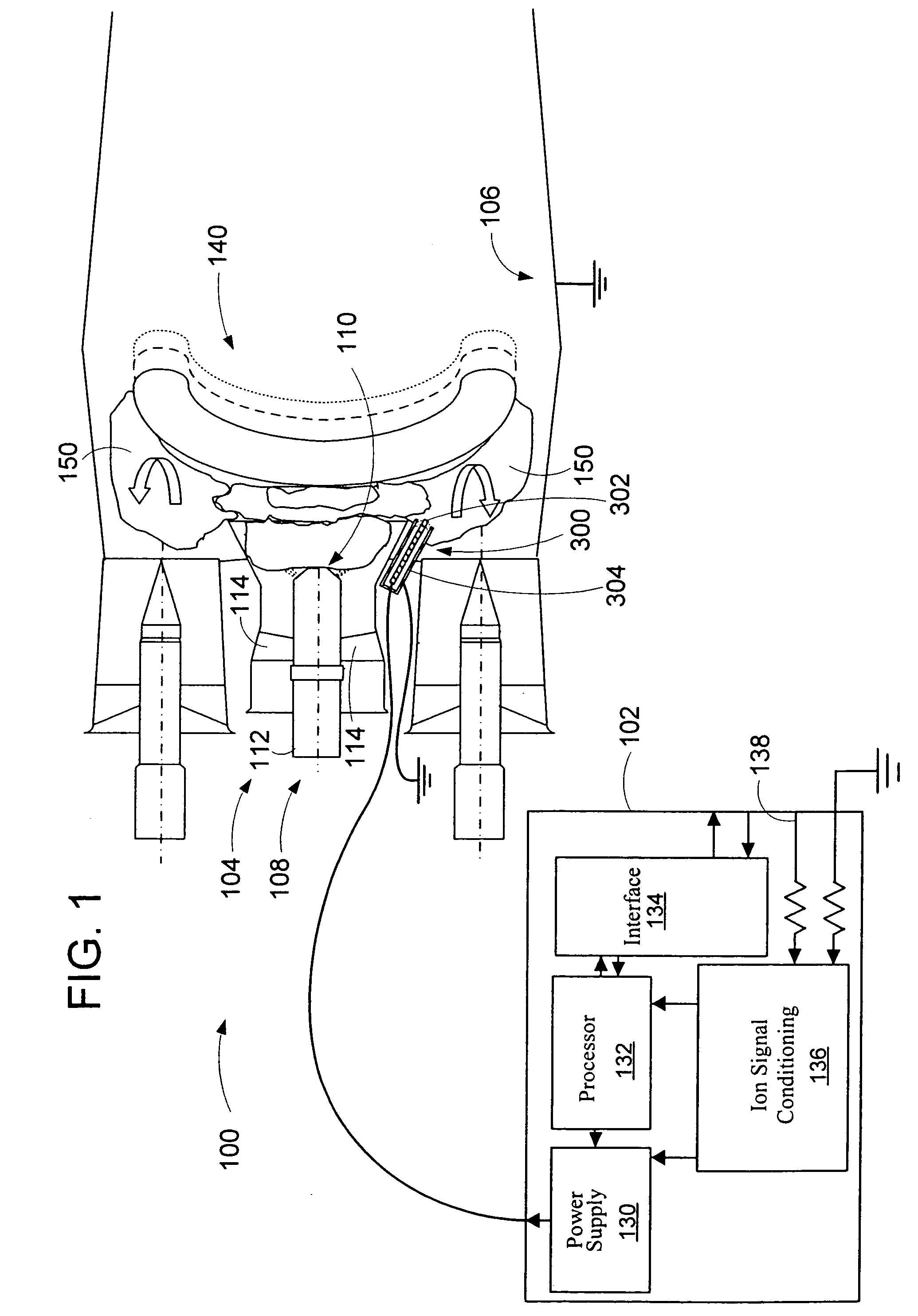
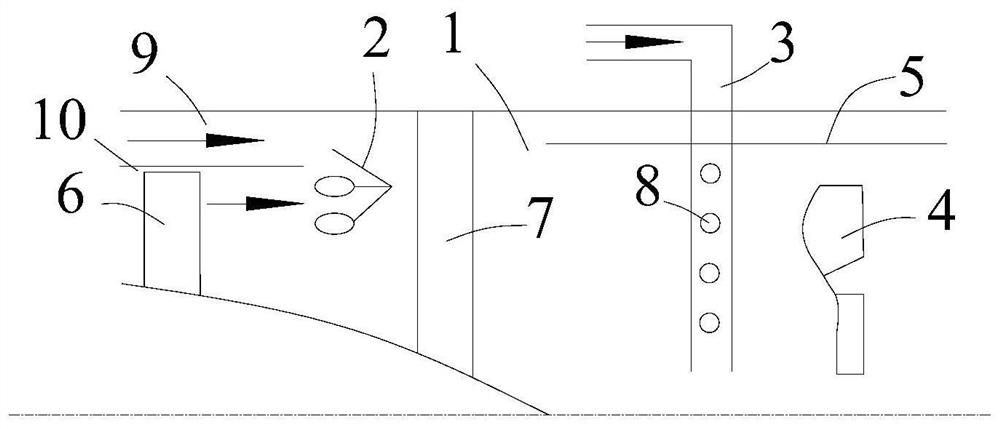
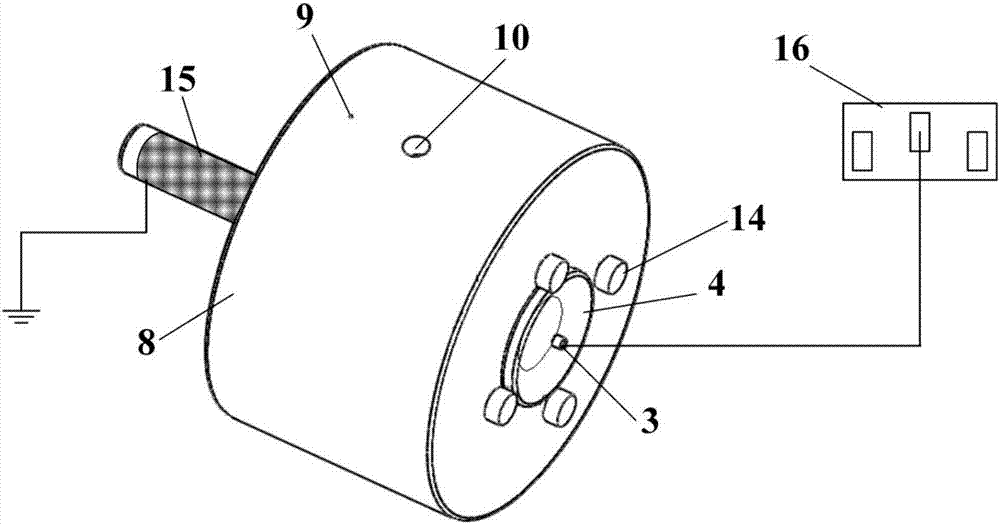
An apparatus and method to sense the onset of combustion stability is presented. An electrode is positioned in a turbine combustion chamber such that the electrode is exposed to gases in the combustion chamber. The electrode may be integrated with an igniter. A control module applies a voltage potential to the electrode and detects a combustion ionization signal and determines if there is an oscillation in the combustion ionization signal indicative of the occurrence of combustion stability or the onset of combustion instability. The control module broadcasts a notice if the parameters indicate the combustion process is at the onset of combustion instability or broadcasts an alarm signal if the parameters indicate the combustion process is instable. Combustion parameters are adjusted to drive the combustion process towards stability.
Owner:WOODWARD GOVERNOR CO
Method for representing and diagnosing combustion instability
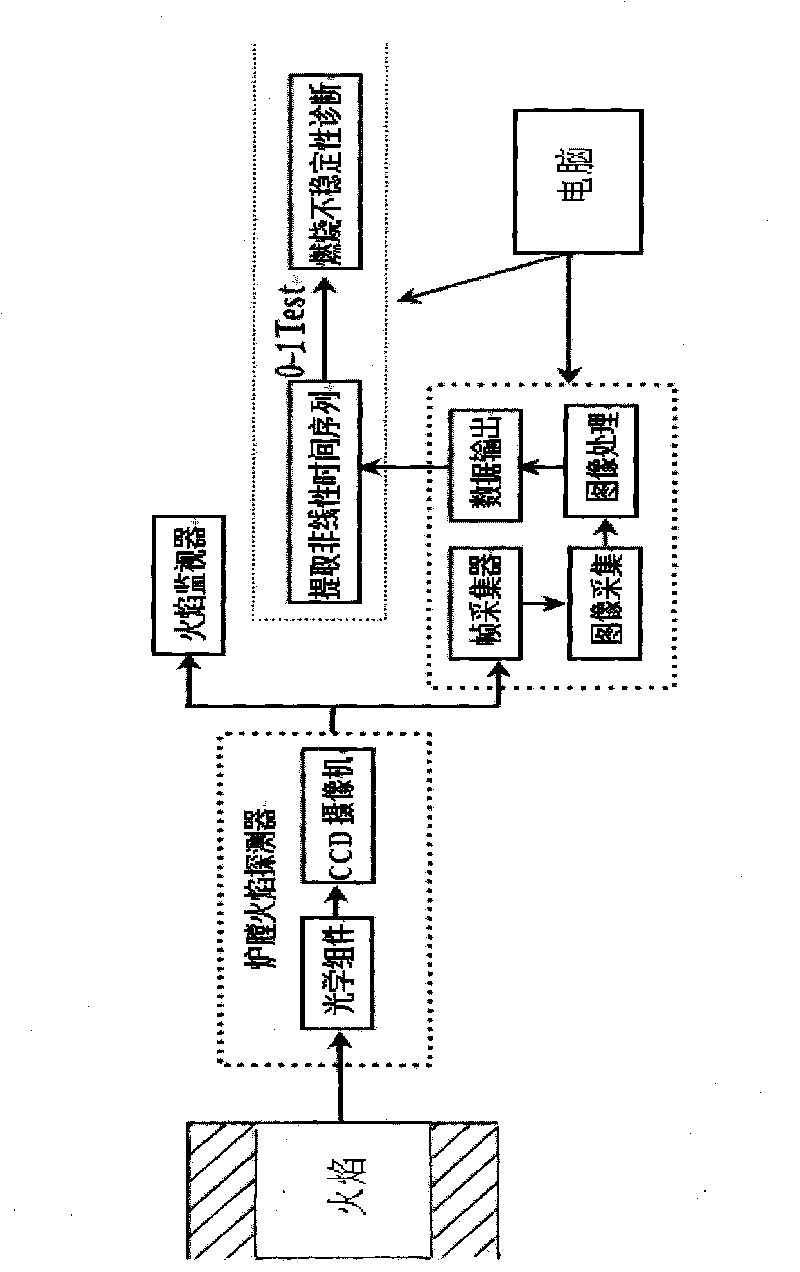
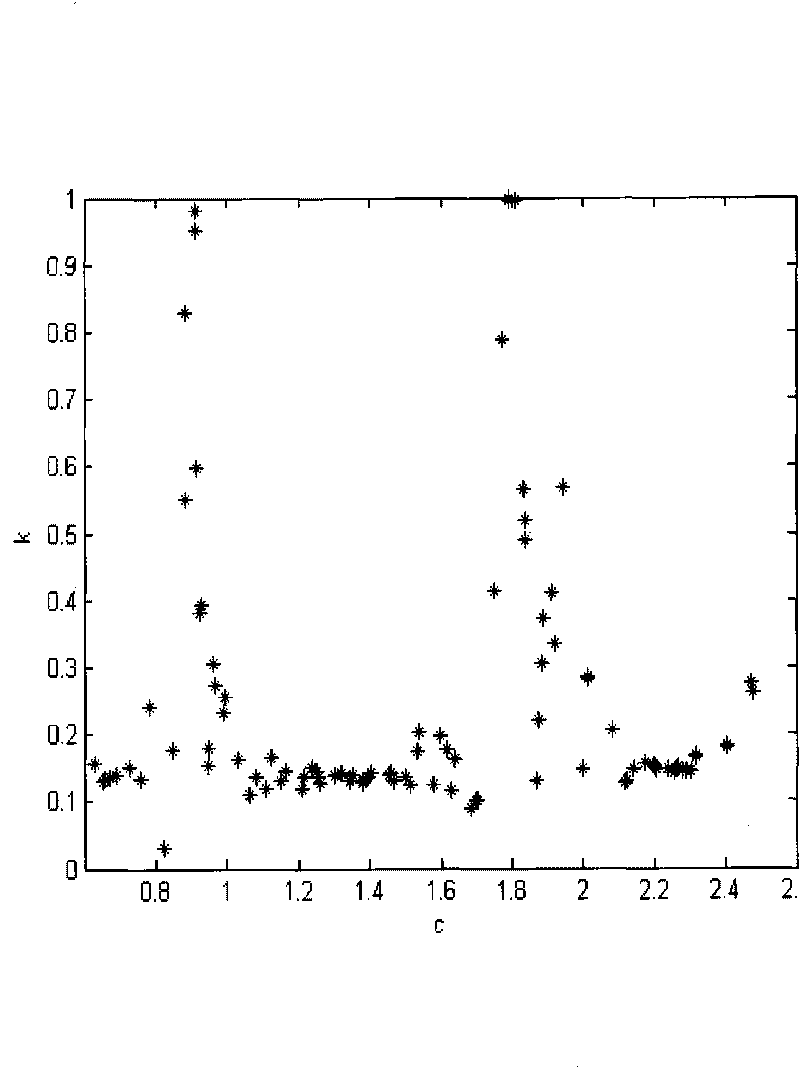
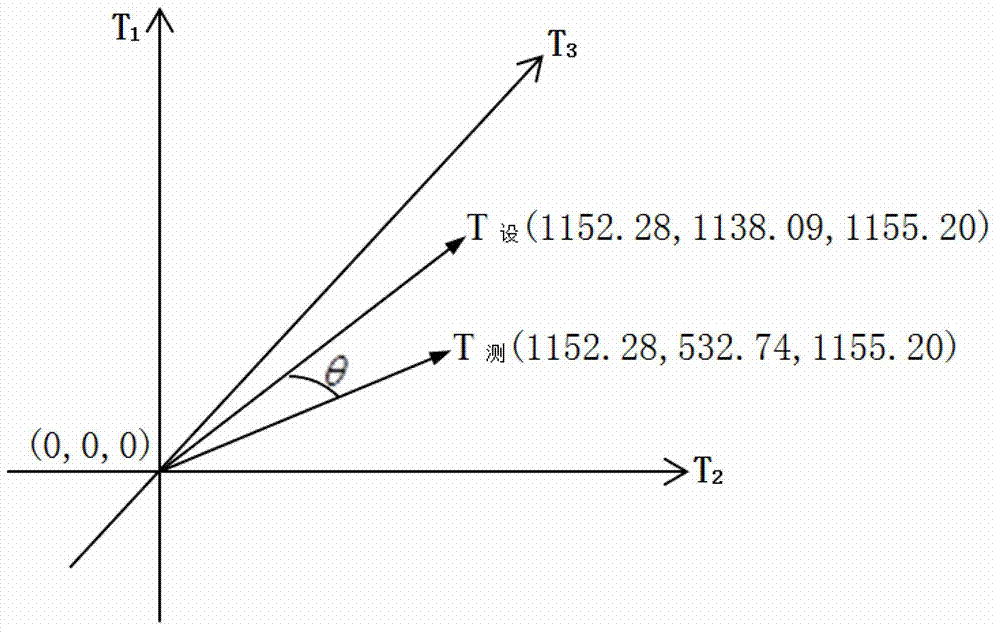
InactiveCN101750152AThe method is simple and feasibleTimely detectionRadiation pyrometryCharacter and pattern recognitionCombustion instabilityPower station
The invention discloses a method for representing and diagnosing combustion instability, which is mainly applied to real-time monitoring, process and safety control technology of combustion equipment, such as a power station boiler, an industrial boiler and the like related to the combustion instability. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) acquiring a real-time pattern by utilizing a color CCD camera and an image acquisition card; (2) performing gray processing on the real-time pattern through digital image processing; and (3) extracting a sparse sample of a nonlinear time sequence of the pretreated flame real-time pattern. The detected result is acquired by a method for judging chaos 0-1 Test of a nonlinear power system so as to judge the combustion instability. The method is used for detecting the flame instability of any combustion equipment, is simple and practicable, can nimbly, rapidly and reliably detect the combustion situation in a combustion chamber in real time, provides a reliable and practical method for diagnosing the combustion instability of the combustion equipment, such as the power station boiler, the industrial boiler and the like.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
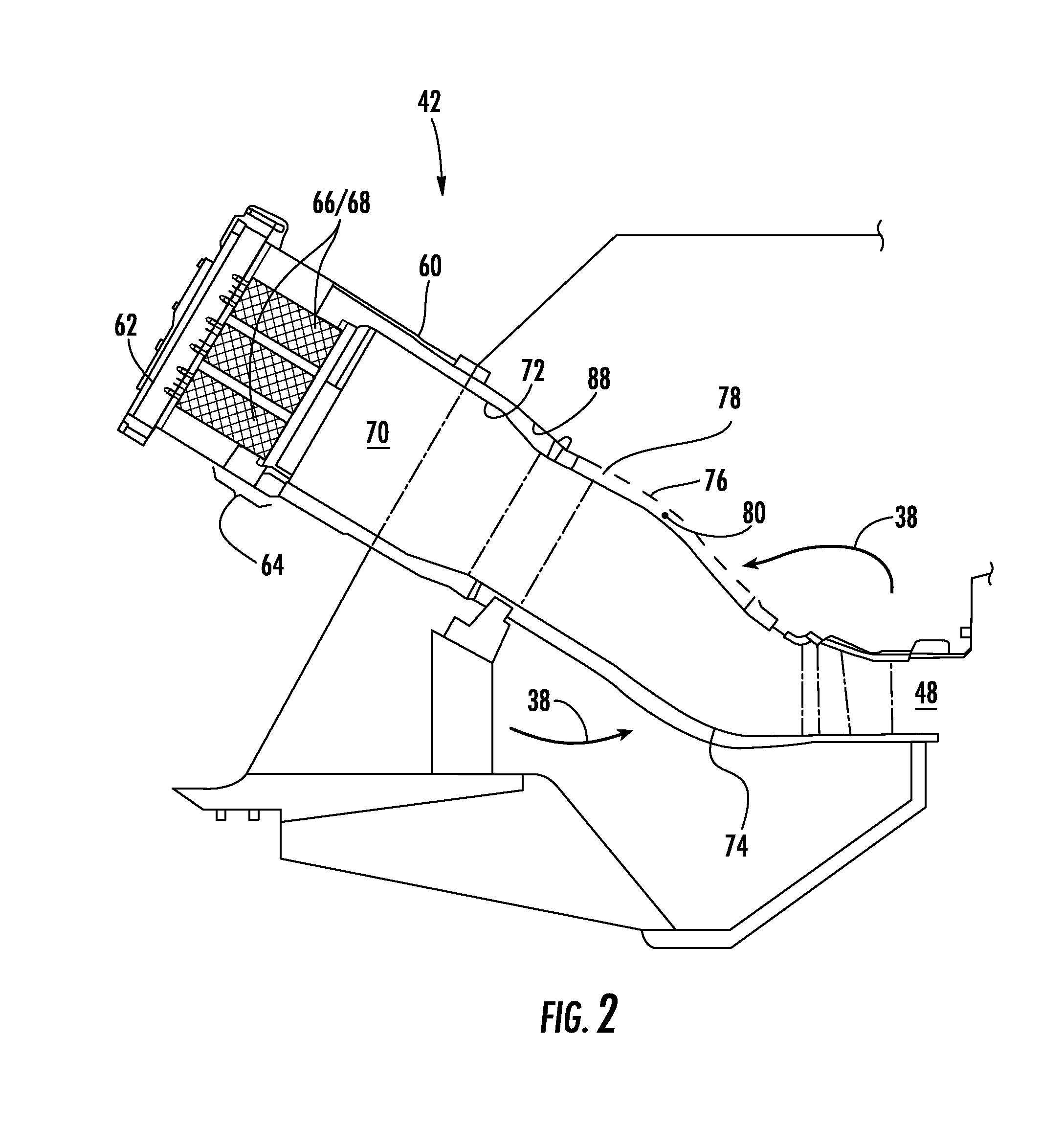
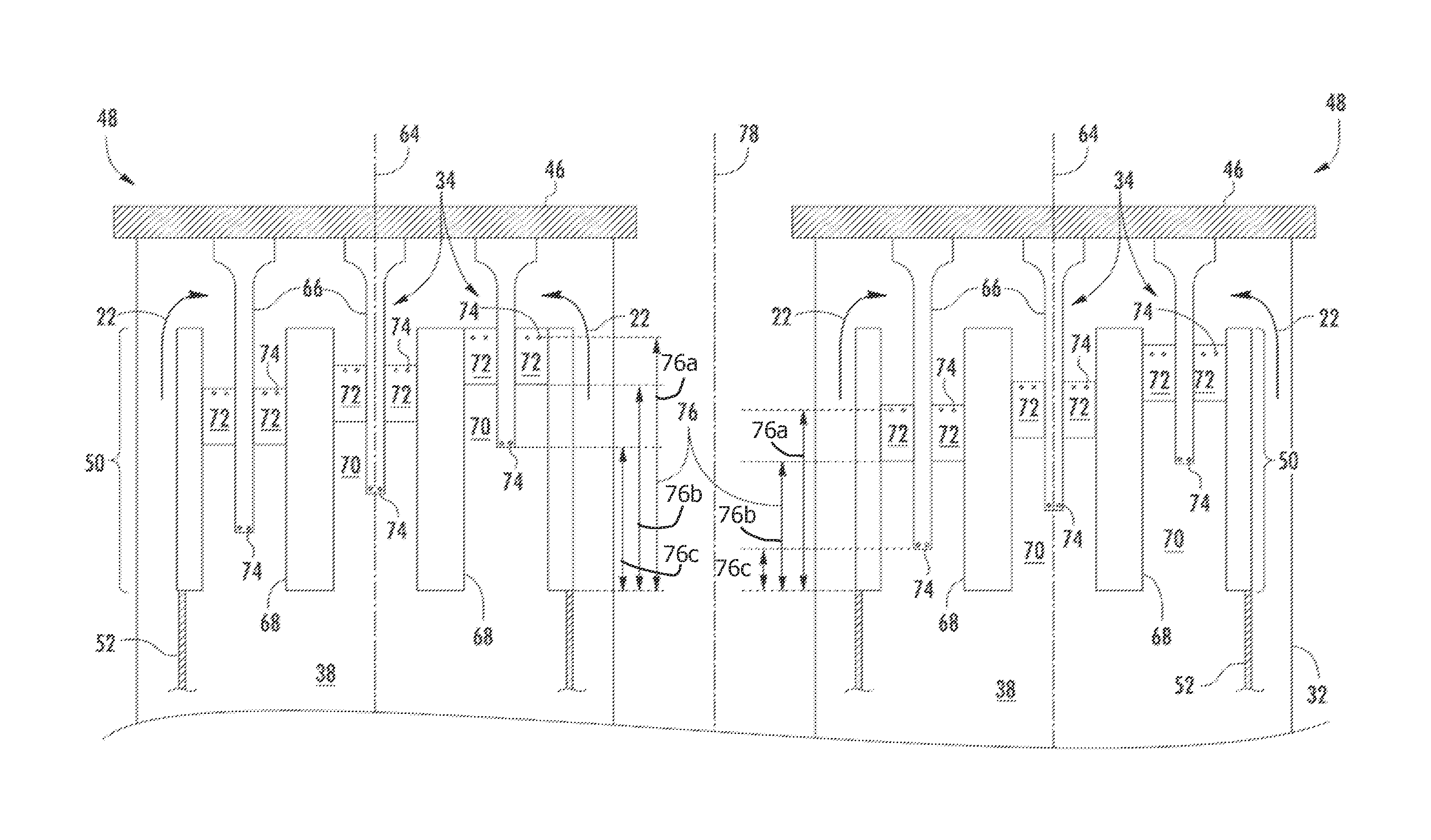
System and method for suppressing combustion instability in a turbomachine
InactiveUS20100192578A1Suppress instabilityImprove instabilityContinuous combustion chamberGas turbine plantsCombustion instabilityCombustion chamber
A system for suppressing combustion instability in a turbomachine includes at least one combustion chamber operatively connected to the turbomachine, and at least one pre-mixer mounted to the at least one combustion chamber. The at least one pre-mixer is configured to receive an amount of fuel and an amount of air that is combined and discharged into the at least one combustion chamber. In addition, the turbomachine includes a combustion instability suppression system operatively associated with the at least one pre-mixer. The combustion instability suppression system is configured to create a combustion asymmetry. The combustion asymmetry facilitates combustion instability suppression in the turbomachine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
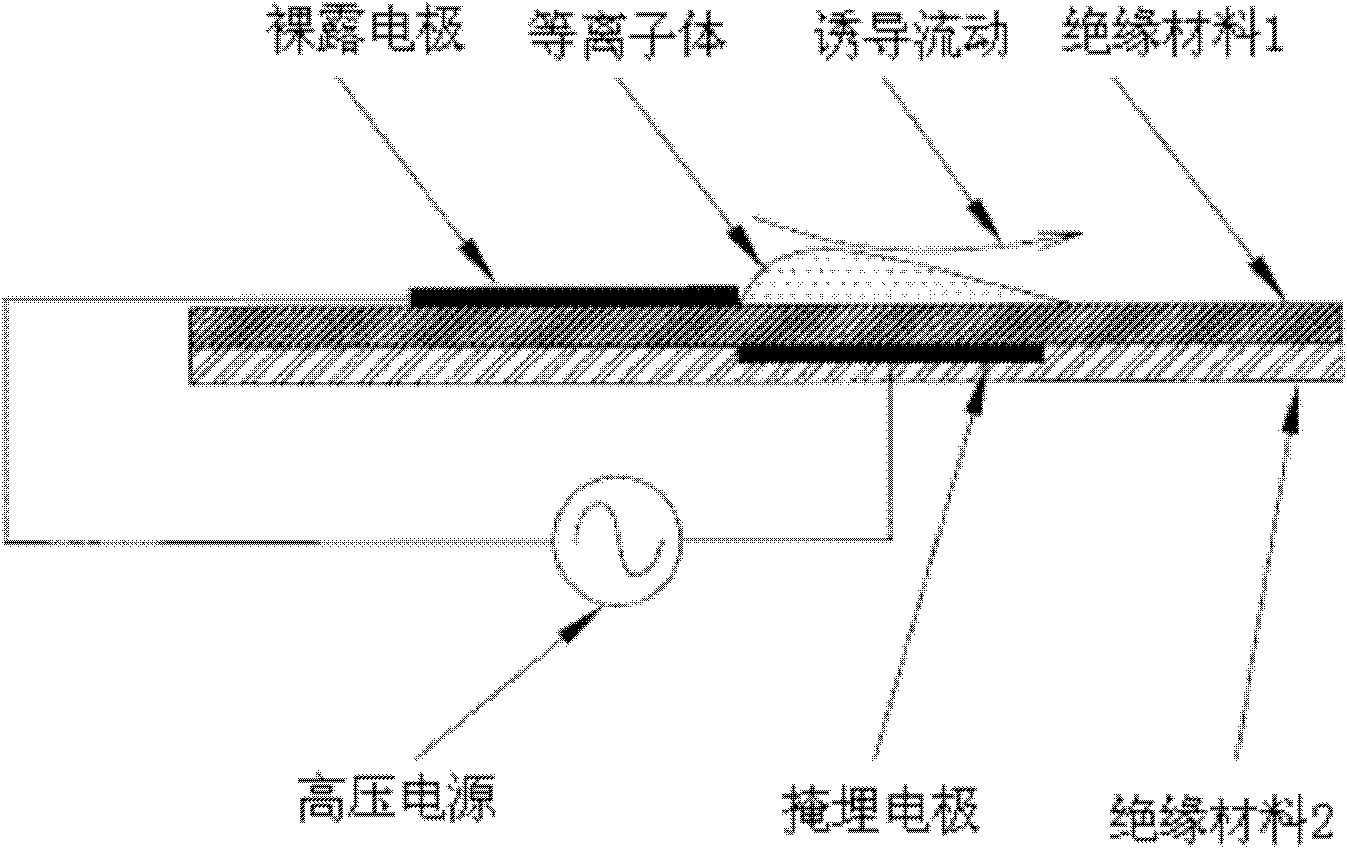
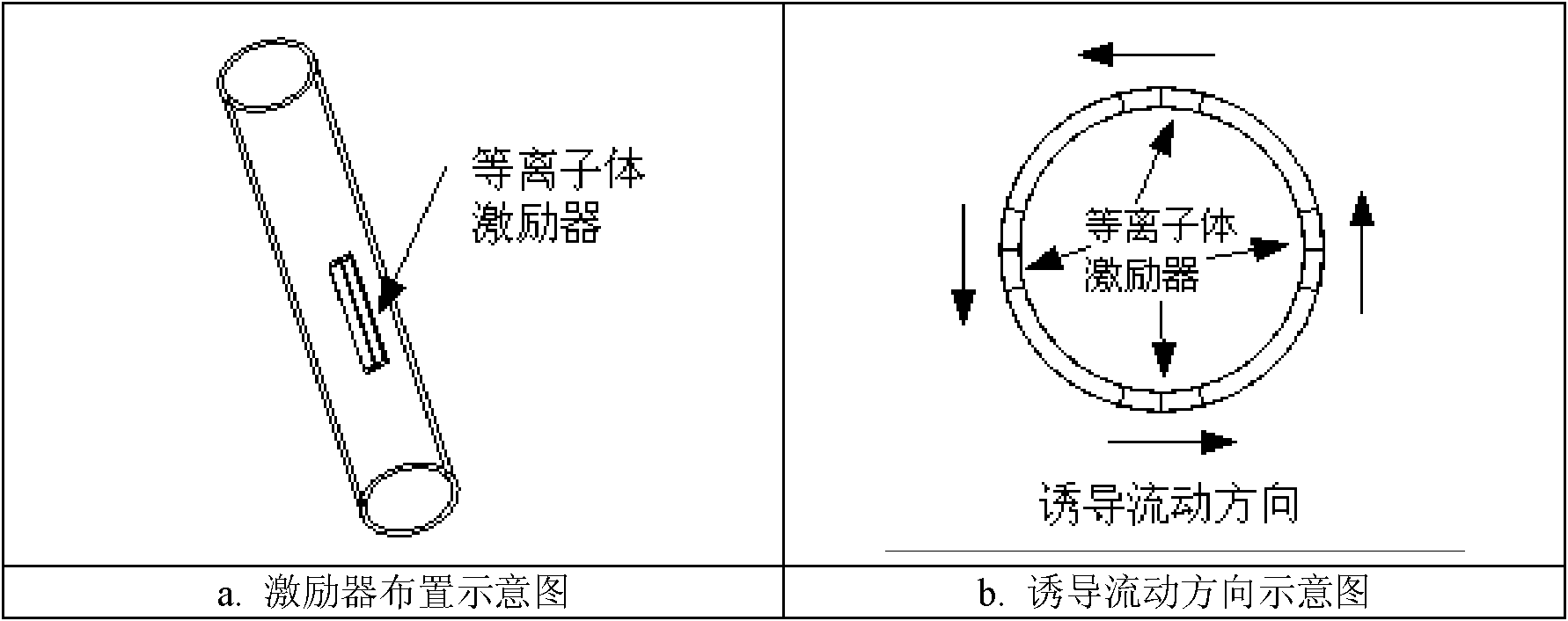
Dielectric barrier discharge plasma axial rotational flow device
The invention discloses a dielectric barrier discharge plasma axial rotational flow device which is used for stabilizing and supporting combustion of a burner. The device comprises a plurality of groups of plasma exciters, a nozzle outlet segment and a high-voltage power supply, wherein the plurality of groups of plasma exciters are uniformly distributed on the nozzle outlet segment along a circumferential direction. By applying plasma excitation of appropriate strength at the nozzle outlet segment of the burner, on one hand, the device can have an effect of increasing rotational flow of air, on the other hand, active radical is generated by ionization of the air, so that the effects of stabilizing and supporting combustion and improving combustion efficiency are achieved, and the device is favorable for solving the problems of aviation gas turbine blowout, and difficulty in ignition and combustion instability during combusting low-heat value gas of a ground gas turbine. The dielectric barrier discharge plasma axial rotational flow device has the advantages of simple and compact structure, rapid reaction, low energy consumption and the like.
Owner:INST OF ENGINEERING THERMOPHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Premixing injector for gas turbine engines
InactiveUS20070277528A1Extend your lifePreserve longevity of premixingBurner safety arrangementsContinuous combustion chamberCombustion instabilityCombustion chamber
A premixing injector for use in gas turbine engines assists in the lean premixed injection of a gaseous fuel / air mixture into the combustor of a gas turbine. The premixing injector is designed to mix fuel and air at high velocities to eliminate the occurrence of flashback of the combustion flame from the reaction zone into the premixing injector. The premixing injector includes choked gas ports, which allow the fuel supply to be decoupled from any type of combustion instability which may arise in the combustor of the gas turbine and internal passages to provide regenerative cooling to the device.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC +1
Premixing injector for gas turbine engines
InactiveUS7870736B2Reduce equivalence ratioBurner safety arrangementsContinuous combustion chamberCombustion instabilityHigh velocity
A premixing injector for use in gas turbine engines assists in the lean premixed injection of a gaseous fuel / air mixture into the combustor of a gas turbine. The premixing injector is designed to mix fuel and air at high velocities to eliminate the occurrence of flashback of the combustion flame from the reaction zone into the premixing injector. The premixing injector includes choked gas ports, which allow the fuel supply to be decoupled from any type of combustion instability which may arise in the combustor of the gas turbine and internal passages to provide regenerative cooling to the device.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC +1
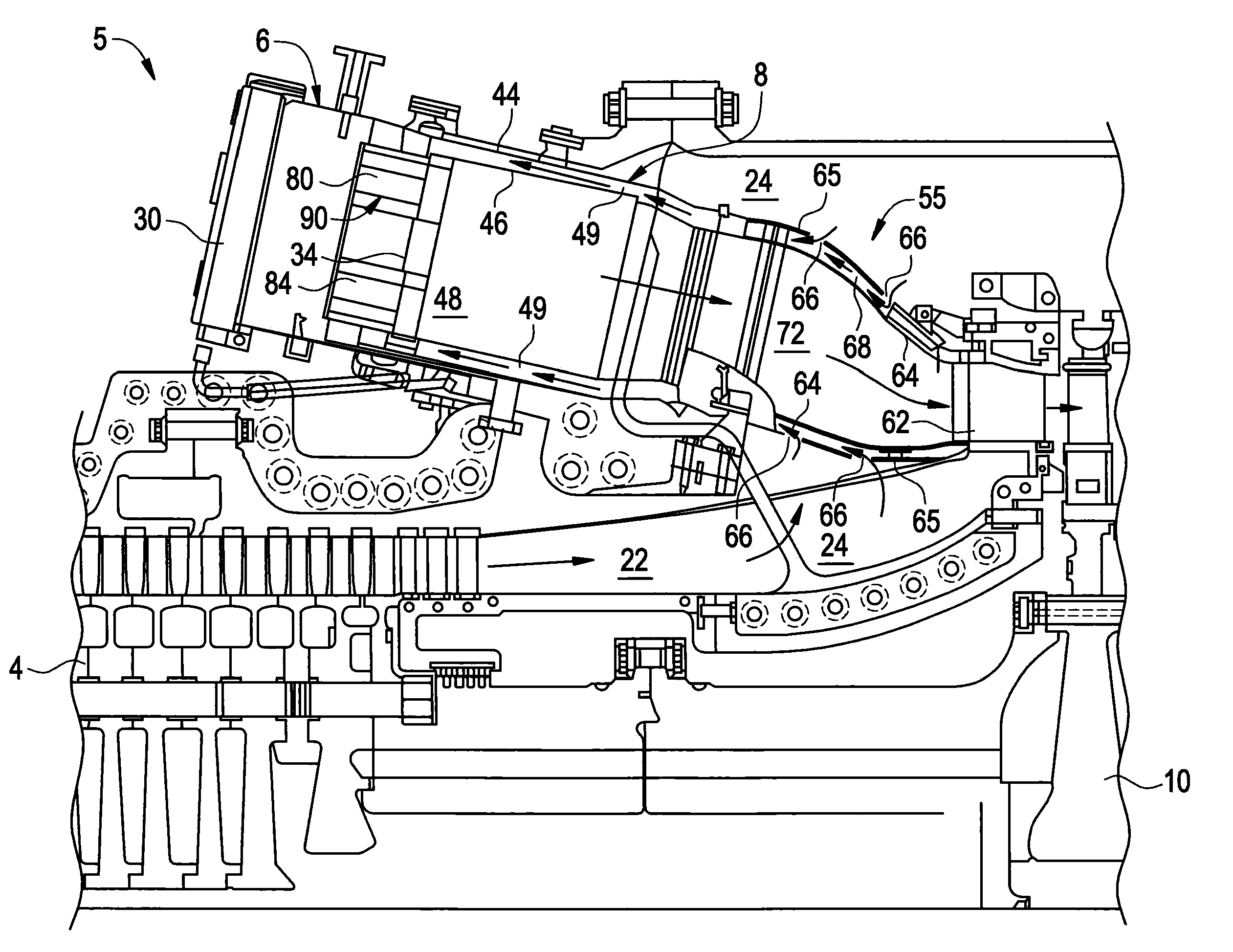
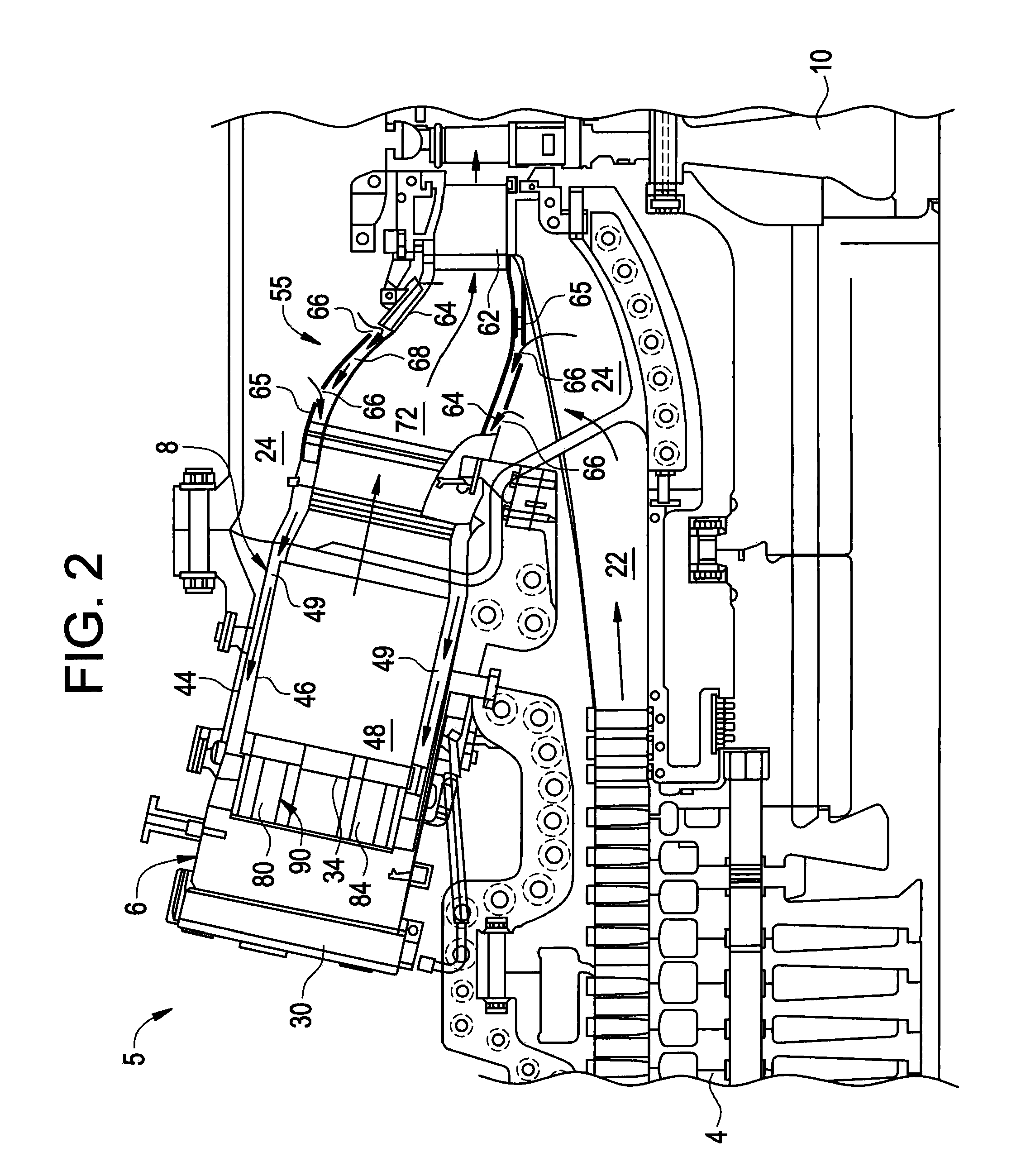
System and method for suppressing combustion instability in a turbomachine
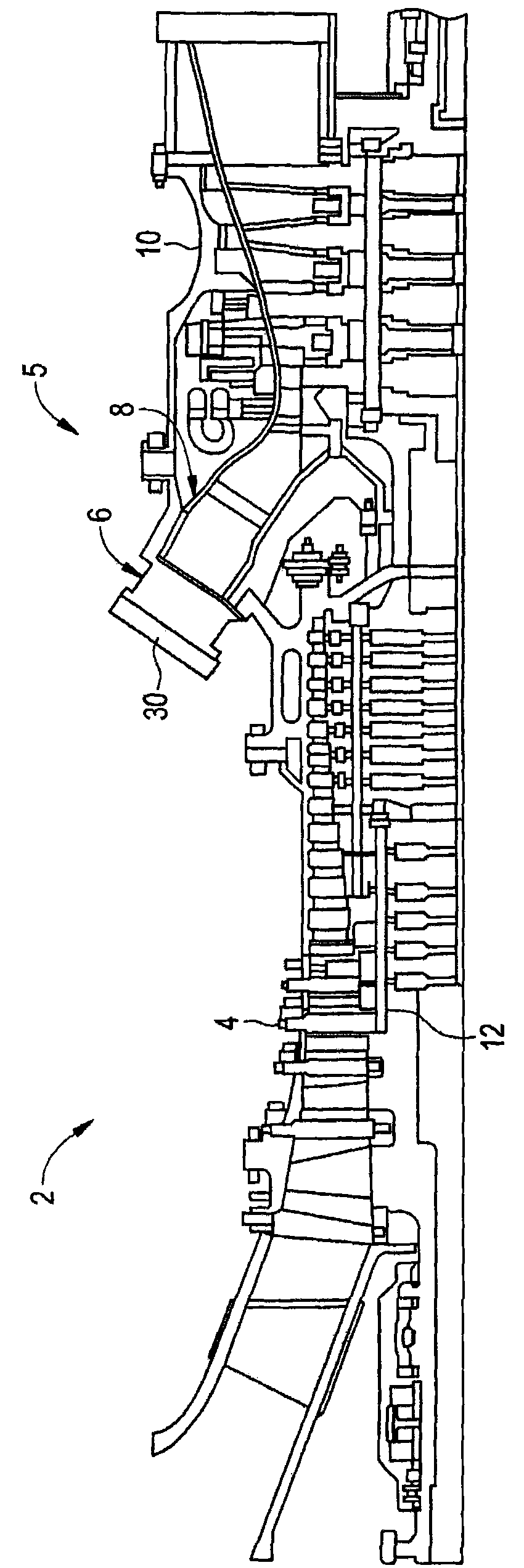
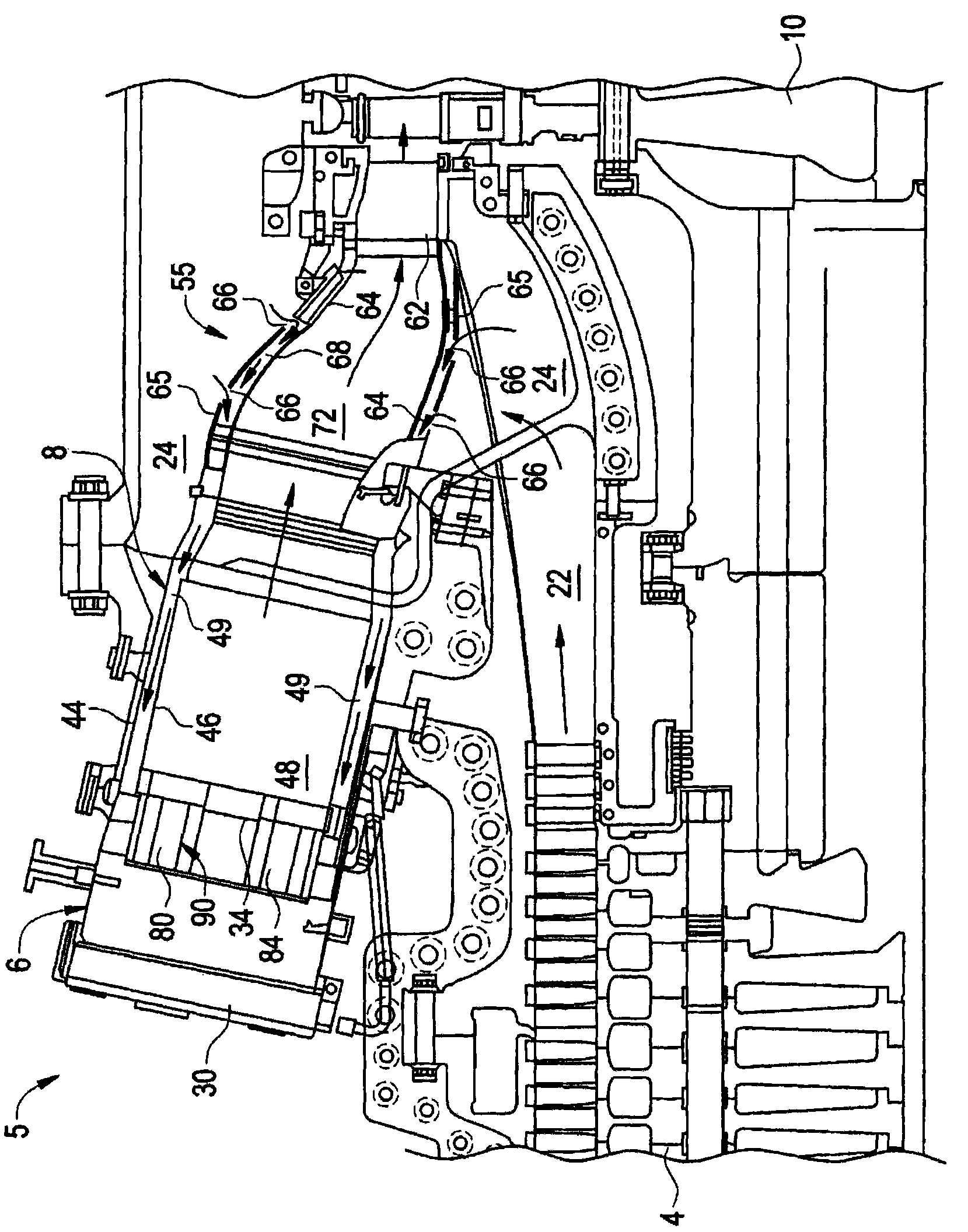
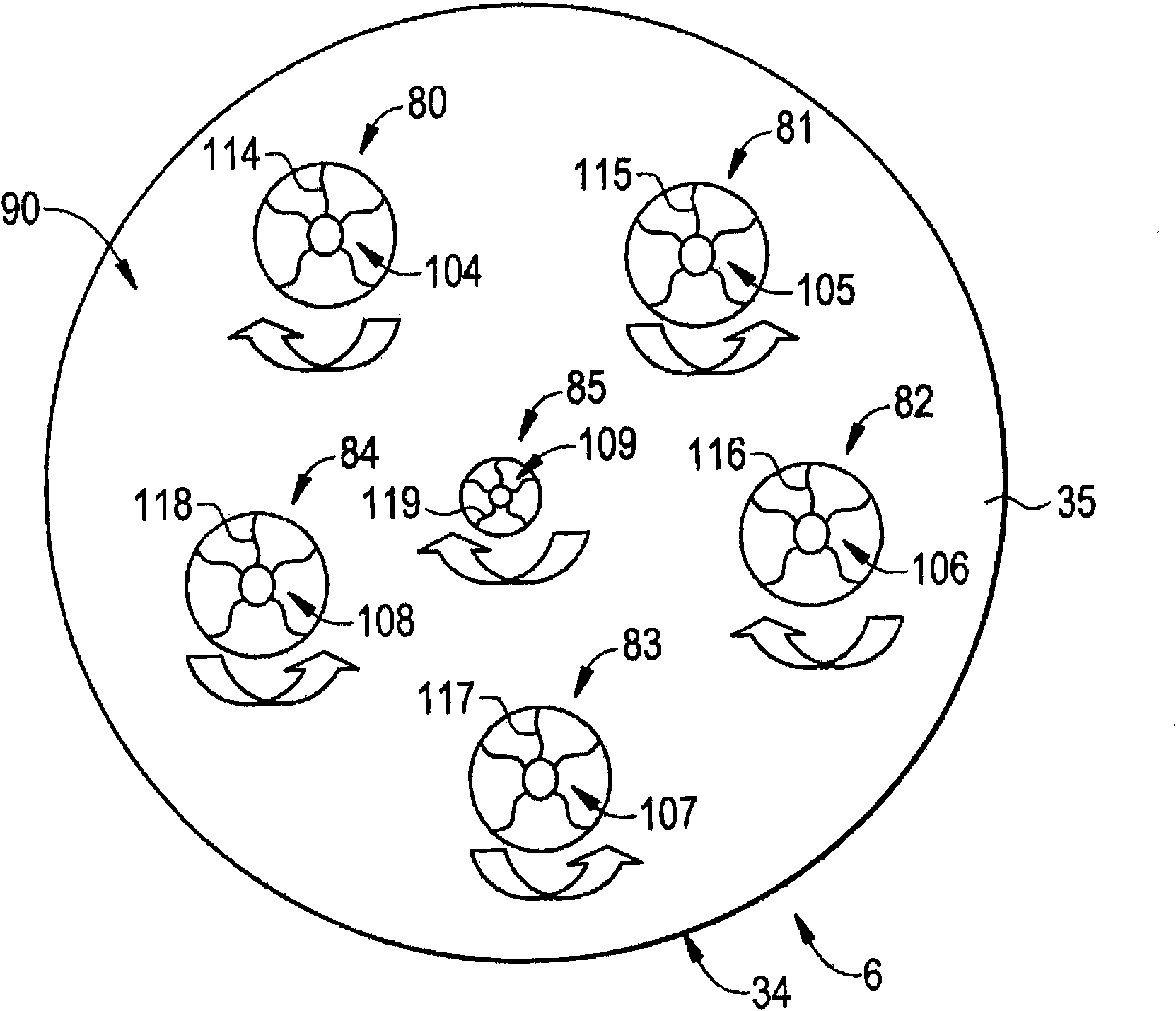
InactiveCN101818907ASuppresses combustion instabilityContinuous combustion chamberCombustion instabilityCombustion chamber
The invention relates to a system and a method for suppressing combustion instability in a turbomachine. The system for suppressing combustion instability in a turbomachine (2) includes at least one combustion chamber (48) operatively connected to the turbomachine (2), and at least one pre-mixer (80-85) mounted to the at least one combustion chamber (48). The at least one pre-mixer (80-85) is configured to receive an amount of fuel and an amount of air that is combined and discharged into the at least one combustion chamber (48). In addition, the turbomachine (2) includes a combustion instability suppression system (90) operatively associated with the at least one pre-mixer (80-85). The combustion instability suppression system (90) is configured to create a combustion asymmetry. The combustion asymmetry facilitates combustion instability suppression in the turbomachine (2).
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for monitoring and protecting combustion of gas turbine by adopting air exhaust temperature dispersity
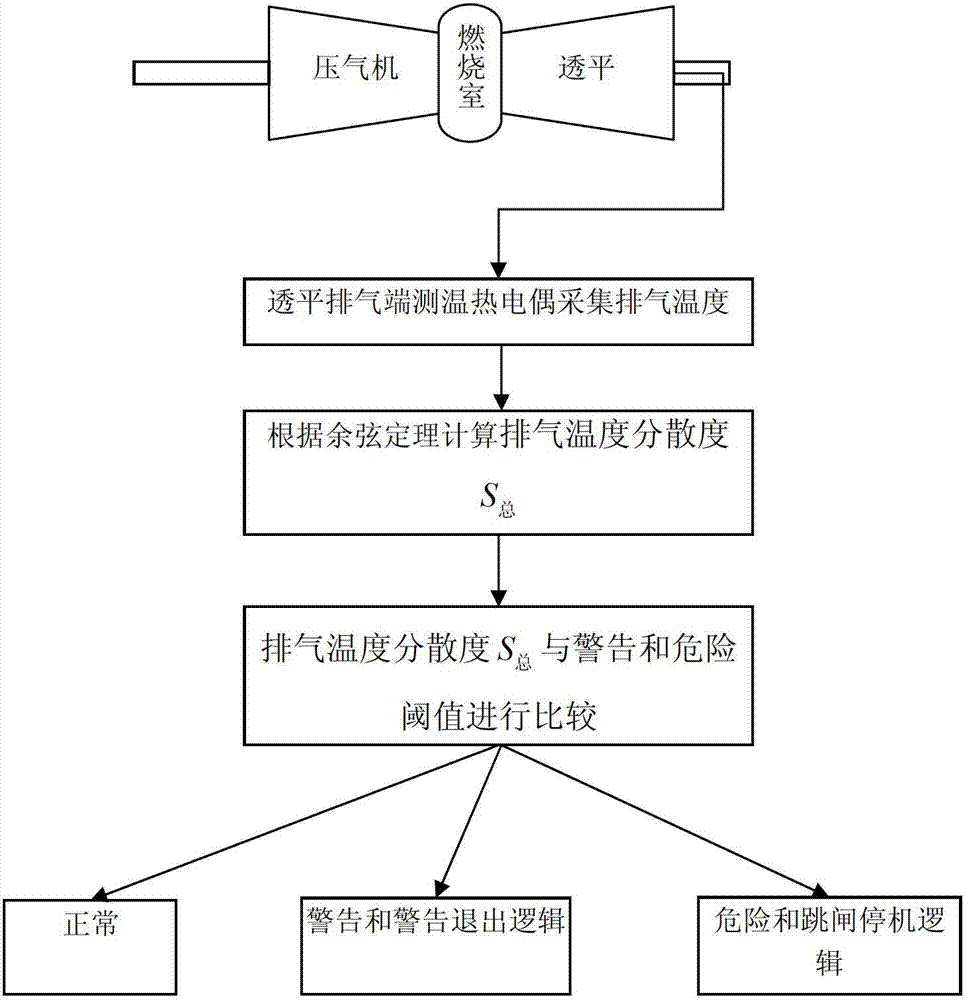
ActiveCN103195583AReduce dangerous accidentsReduce distractionsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsGas turbine plantsDispersityCombustion instability
The invention discloses a method for monitoring and protecting the combustion of gas turbine by adopting gas exhaust temperature dispersity, and relates to a protecting method for preventing a gas turbine from being damaged for combustion instability during the running process after being in an active service. The method comprises the following steps of: installing a plurality of temperature measuring thermocouples at the turbine air exhaust end of the gas turbine, and acquiring a gas exhaust temperature dispersity through temperature measuring thermocouple collecting signals by adopting a multi-dimensional space cosine law, thereby predicting the combustion stability of a combustion chamber indirectly; establishing the alarm logic and alarm exit logic of combustion monitoring and protection of the gas turbine according to the gas exhaust temperature dispersity; and establishing the dangerous tripping logic of combustion monitoring and protection of the gas turbine. Compared with the traditional method, the method for monitoring and protecting the combustion of gas turbine by adopting gas exhaust temperature dispersity provided by the invention is simple in design, is easy to expand, cannot increase the work load additionally because of the variation of the number of temperature measurement thermocouples, is also simple and convenient in calculation, and is high in real-time performance; and meanwhile the algorithm is high in anti-interference capability, and can effectively lower the influences to monitoring and protection effectiveness by working condition variation of noises and the gas turbine effectively.
Owner:CHINA UNITED GAS TURBINE TECH CO LTD
Real-time detection and control method of instability of flame in industrial furnace
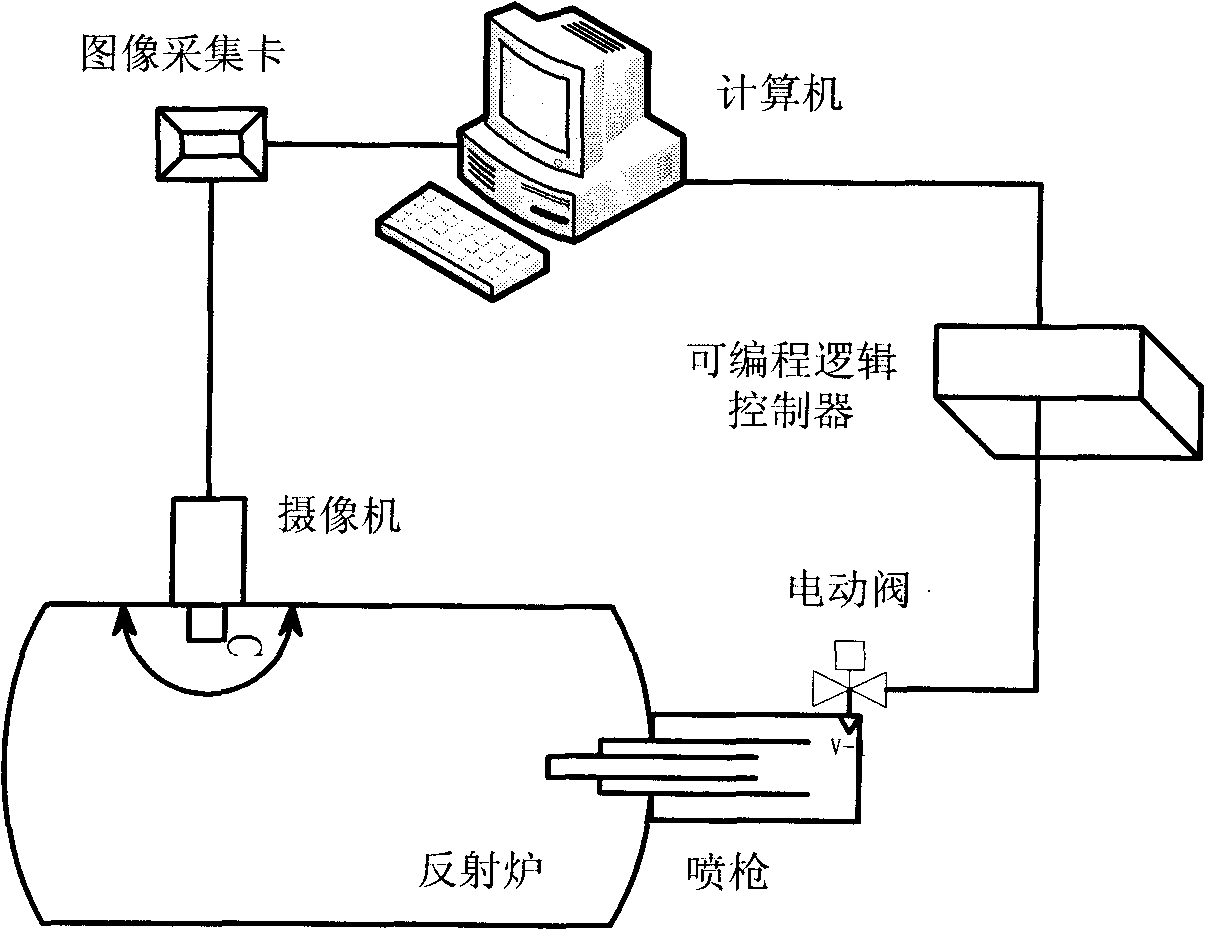
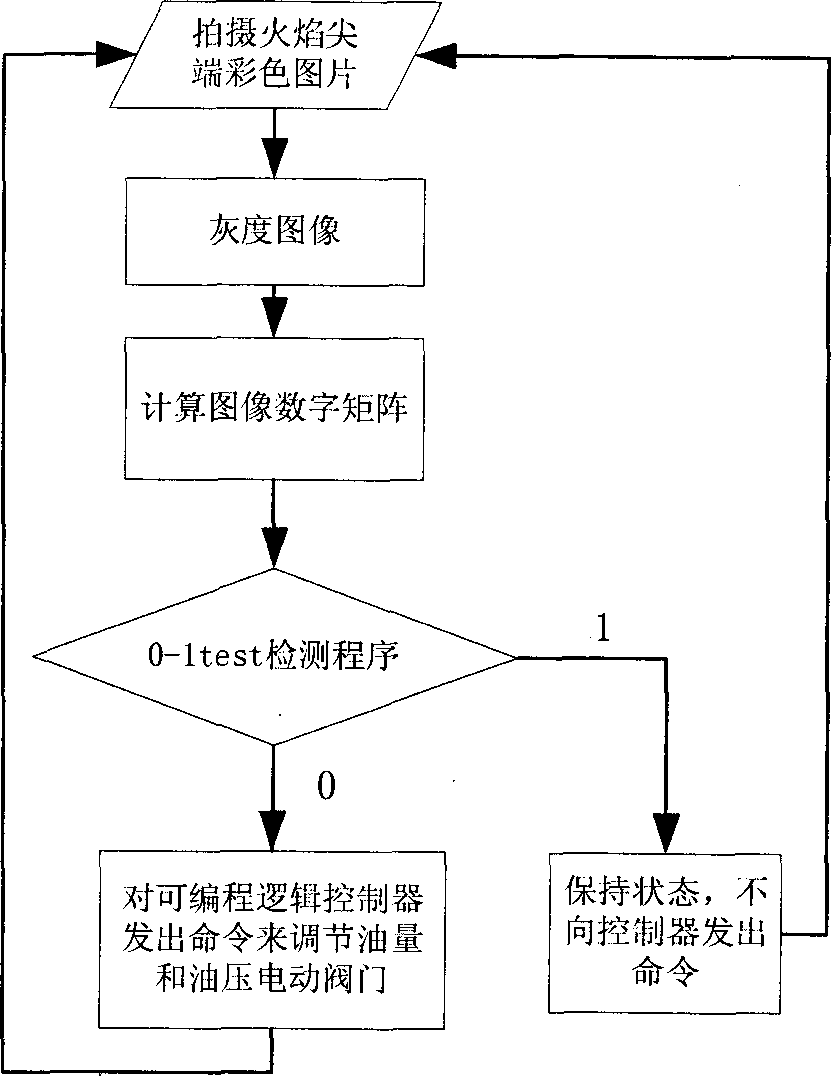
InactiveCN101806548ATimely detectionSensitive detectionControl devices for furnacesColor imageCombustion instability
The invention relates to a real-time detection method of instability of flame in an industrial furnace, which comprises the following steps: acquiring a color picture of the point of the flame, and inputting the picture into a supervisory control computer; converting the color image into a gray level image firstly, and then, converting the gray level image into a digital matrix; computing the characteristic value of the digital matrix by using 0-1 test programs compiled in the computer to judge whether the flame has a chaos phenomenon or not; sending a command by a programmable logic controller according to the judged result of the step to enable a regulator to regulate oil mass and oil pressure to enable the flame to reach a chaos state, and regulating the sizes of electrically operated valves of oil mass and oil pressure by utilizing programs; and continuously carrying out judgment repeatedly, and controlling the whole combustion process. The control method is simple and easy and can be used for sensitively, quickly and reliably detecting the combustion condition in a combustion chamber in real time. The invention provides a reliable and practical control method for diagnosis and active control of combustion instability of combustion equipment such as power station boilers, industrial furnaces and the like.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
System and method for reducing modal coupling of combustion dynamics
InactiveUS20140137561A1Reducing modal coupling of combustion dynamicContinuous combustion chamberGas turbine plantsCombustion instabilityWorking fluid
A system for reducing modal coupling of combustion dynamics includes a plurality of combustors, and at least one fuel injector in each of the plurality of combustors. The system also includes structure for dithering a combustion instability frequency in at least one combustor in the plurality of combustors. A method for reducing modal coupling of combustion dynamics includes flowing a compressed working fluid at a temperature to a plurality of combustors and flowing a fuel to at least one fuel injector in each of the plurality of combustors. The method further includes dithering at least one of the temperature of the compressed working fluid flowing to the plurality of combustors or the fuel flow to the at least one fuel injector in at least one combustor in the plurality of combustors.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for reducing modal coupling of combustion dynamics
ActiveUS9151502B2Reduce coherenceFrequency instabilityTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsContinuous combustion chamberCombustion instabilityCombustion chamber
A system and method for reducing combustion dynamics includes first and second combustors, and each combustor includes a fuel nozzle and a combustion chamber downstream from the fuel nozzle. Each fuel nozzle includes an axially extending center body, a shroud that circumferentially surrounds at least a portion of the axially extending center body, a plurality of vanes that extend radially between the center body and the shroud, a first fuel port through at least one of the plurality of vanes at a first axial distance from the combustion chamber, the plurality of vanes being located at a second axial distance from the combustion chamber. A second fuel port is provided through the center body at a third axial distance from the combustion chamber. The system further includes structure for producing a combustion instability frequency in the first combustor that is different from the combustion instability frequency in the second combustor.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
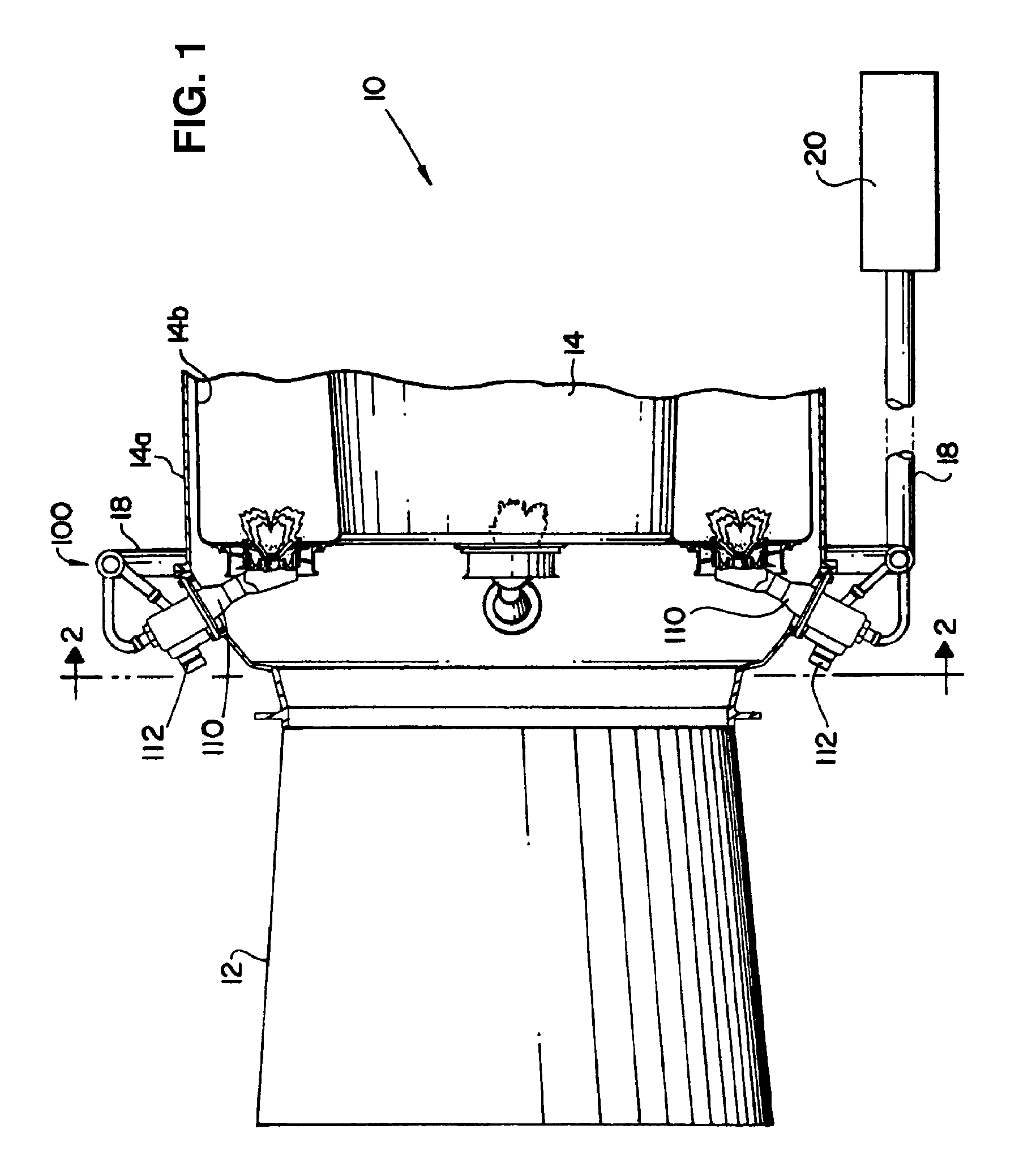
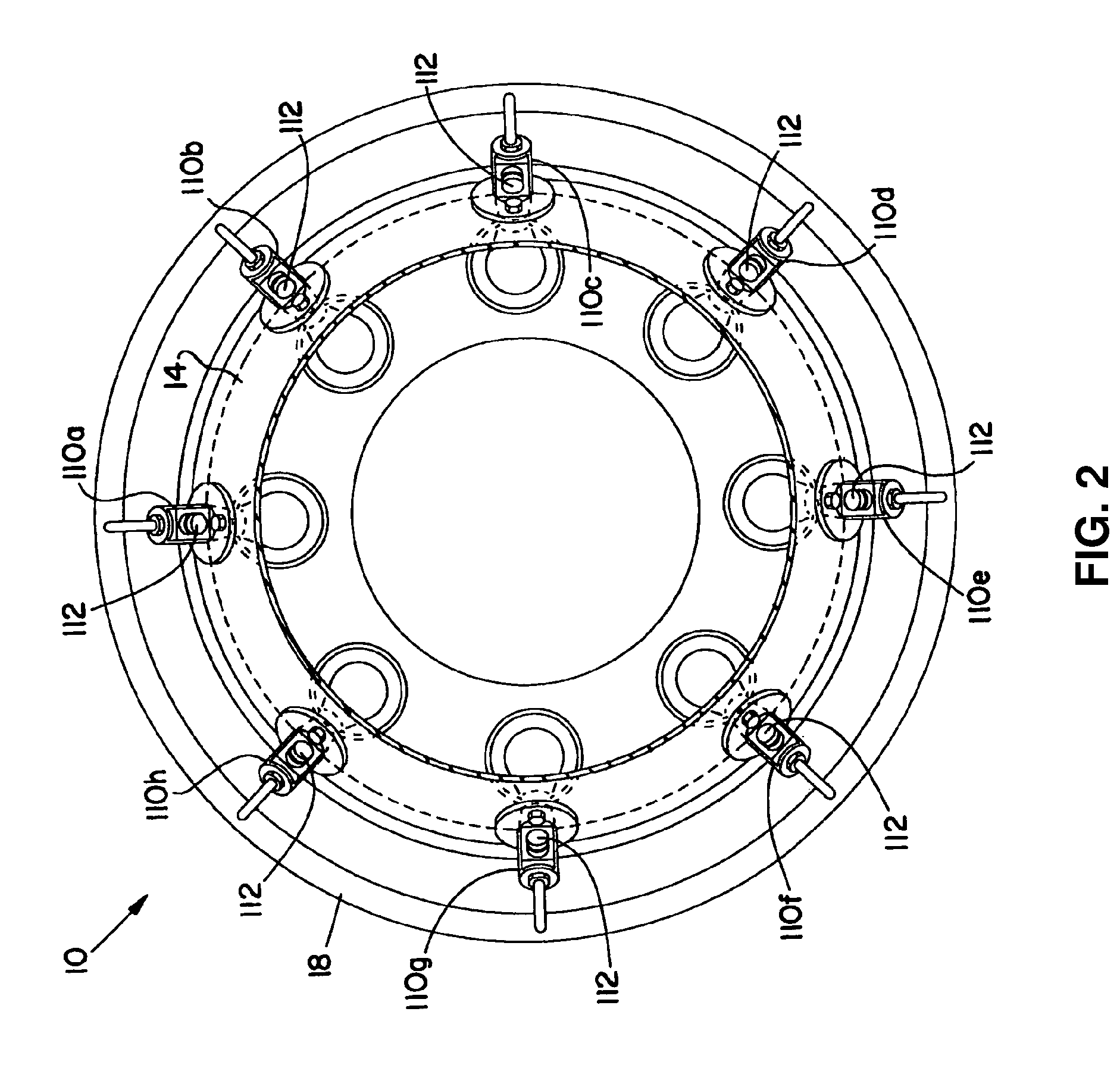
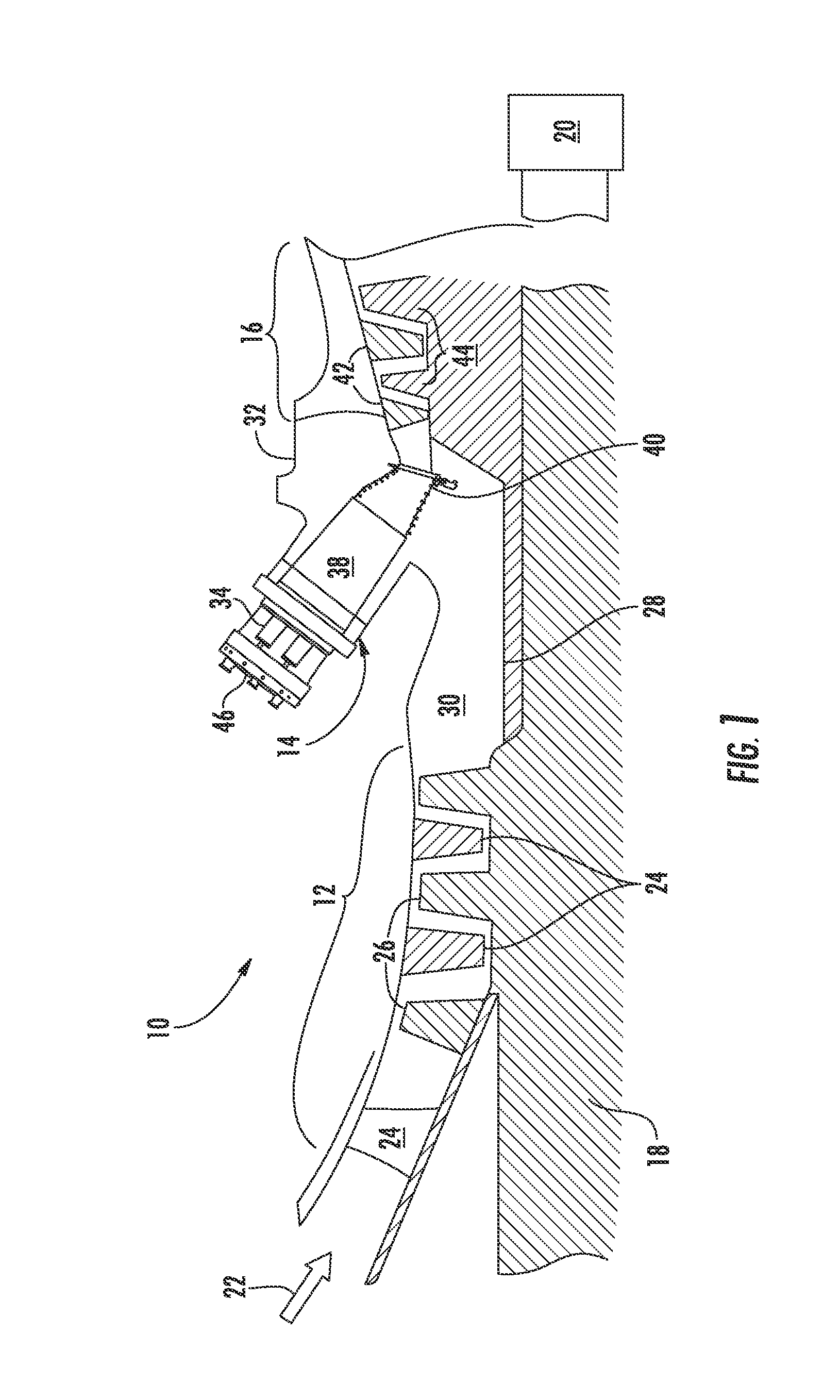
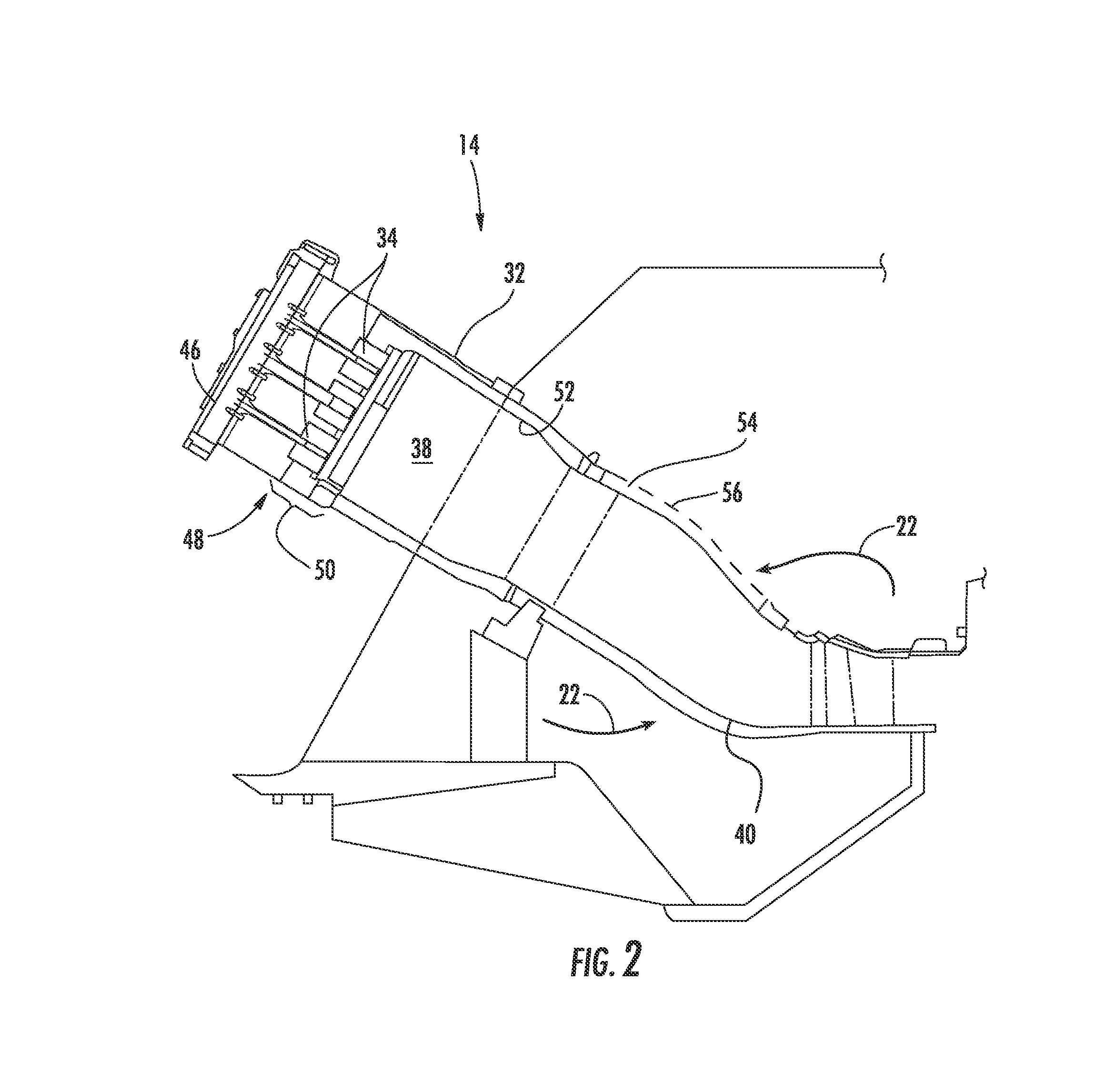
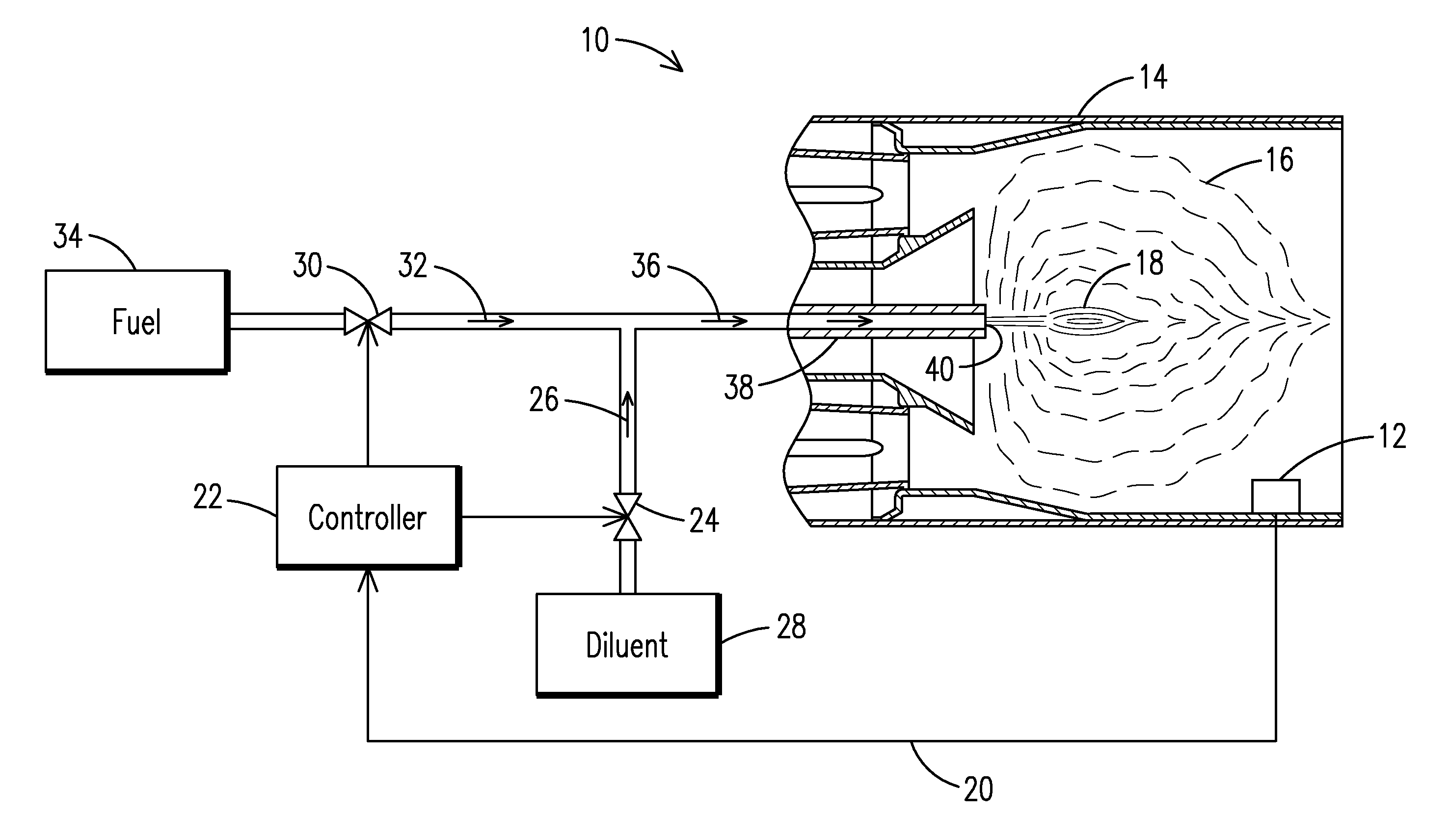
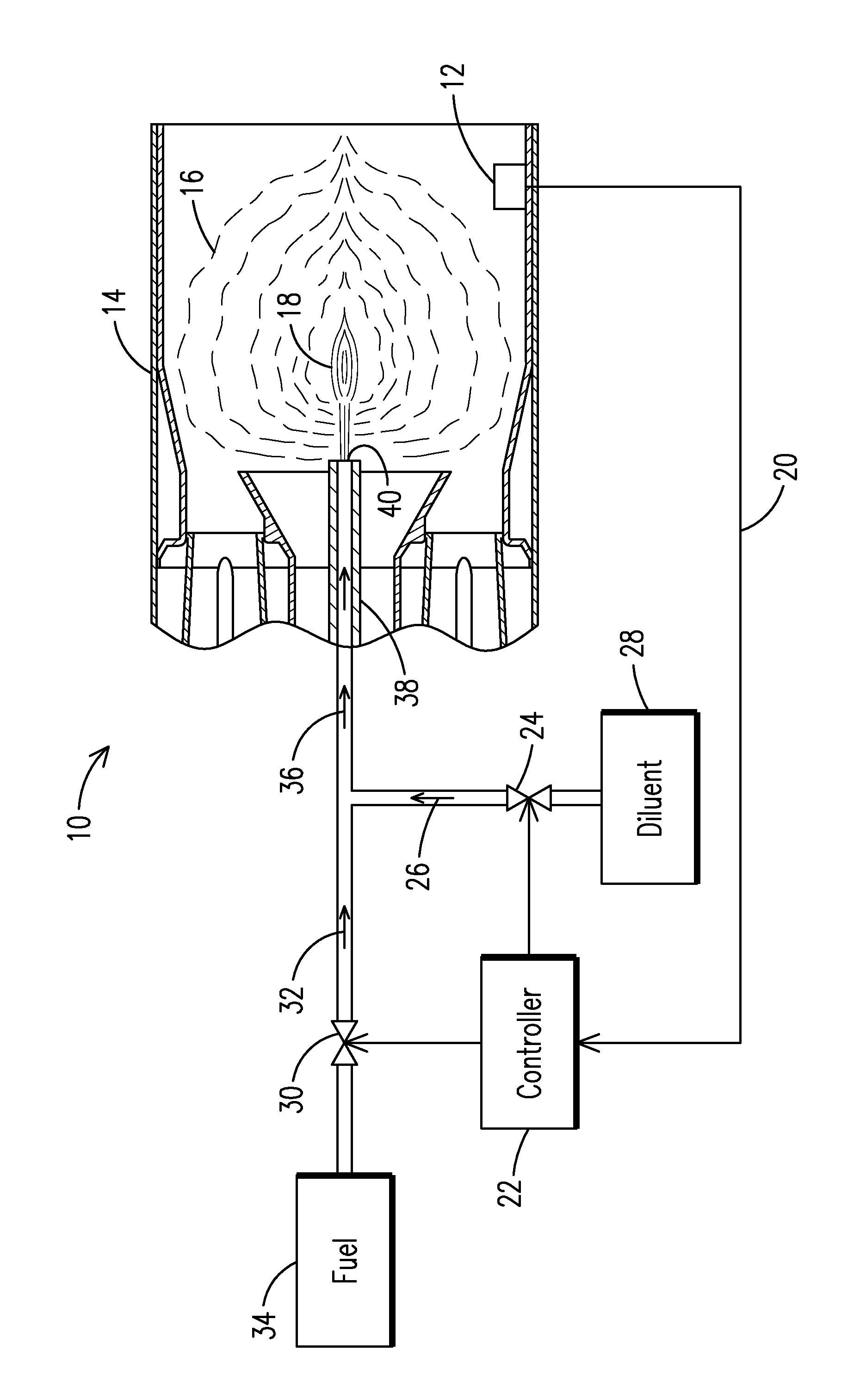
Utilizing a diluent to lower combustion instabilities in a gas turbine engine
ActiveUS20110300491A1Fuel supply regulationContinuous combustion chamberCombustion instabilityDiluent
A method of influencing combustion dynamics, including measuring a combustion dynamics parameter, and controlling a diluent flow (26) delivered to a fuel flow (32) upstream of a pilot burner fuel outlet (40) in response to the measured combustion dynamics parameter.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
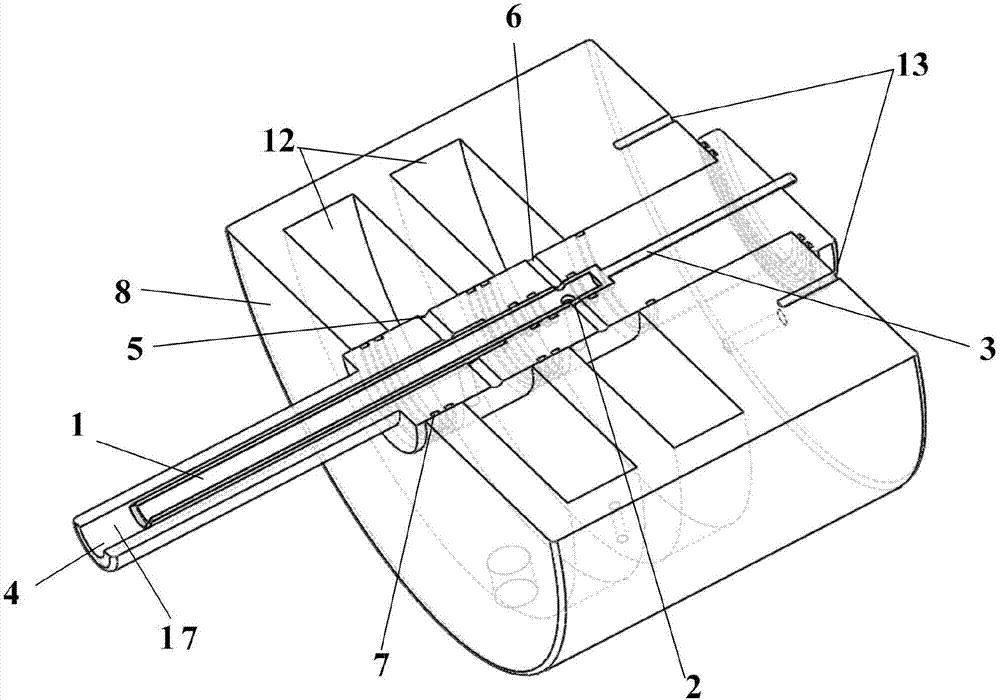
Afterburner structure based on self-excitation sweeping oscillation fuel nozzle
ActiveCN113280366AImprove atomization effectImprove uniformityContinuous combustion chamberEfficient propulsion technologiesRamjetCombustion instability
The invention provides an afterburner structure based on a self-excitation sweeping oscillation fuel nozzle. According to the fuel nozzle, under the condition of stable inlet fuel flow, the coanda effect of the fluid and the alternating feedback effect of the feedback channel, sweeping type oscillating jet flow with a certain frequency is formed at an outlet, so that the space uniformity of fuel injection is improved, on the basis that the structural complexity of an afterburner of an existing turbine engine and a ramjet combustion chamber of a subsonic combustion ramjet engine is not increased, the atomization performance and the oil-gas mixing uniformity of fuel oil in the afterburner / ramjet combustion chamber can be greatly improved, the combustion efficiency and the combustion instability of the engine are improved, meanwhile, the lengths of the afterburner and the subsonic combustion ramjet combustion chamber are shortened.
Owner:AERO ENGINE ACAD OF CHINA
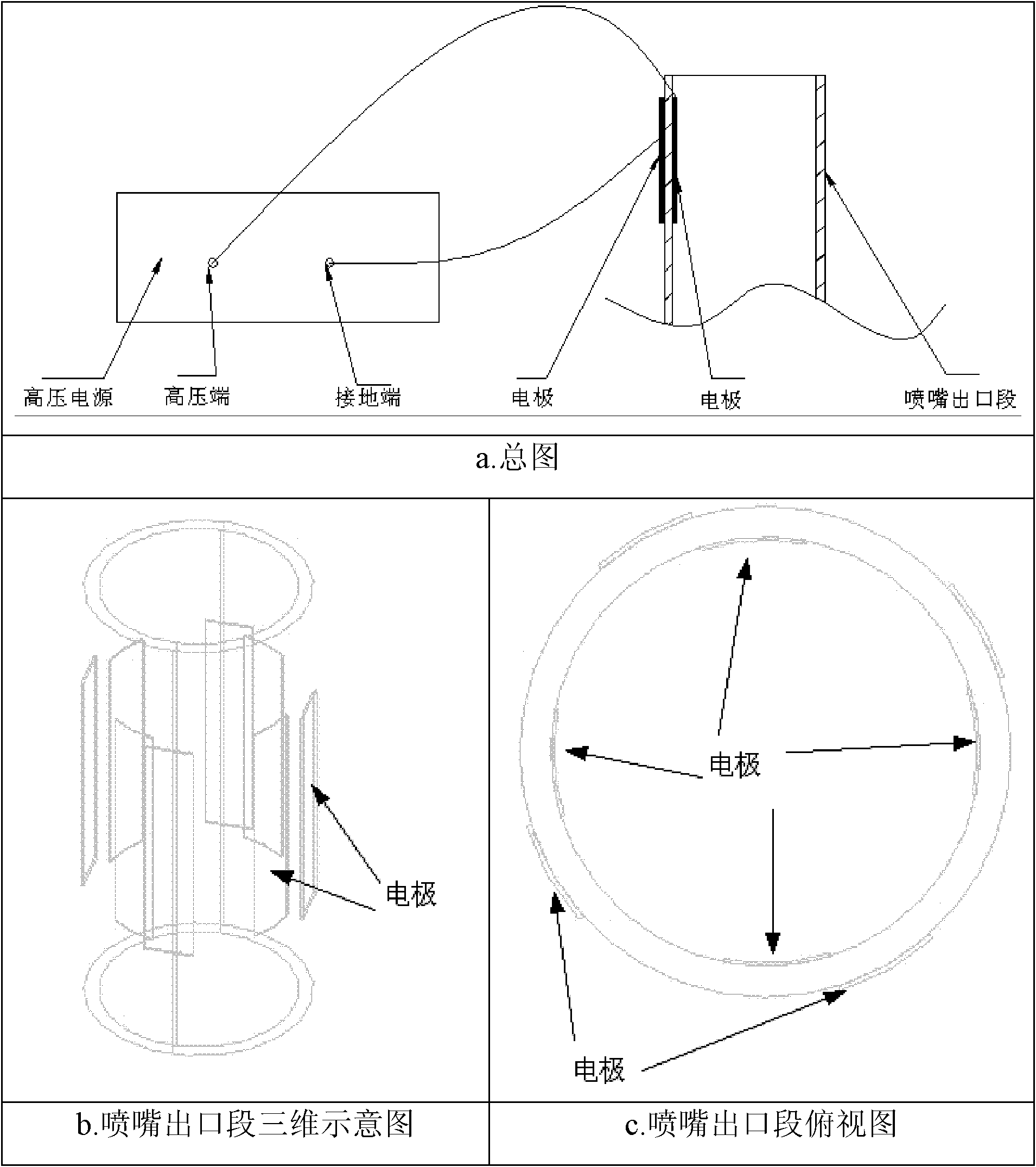
Coaxial direct-current plasma nozzle based on dielectric barrier discharge
ActiveCN107327354AEasy to replaceAccelerate evaporationRocket engine plantsCombustion instabilityElectricity
The invention discloses a coaxial direct-current plasma nozzle based on dielectric barrier discharge. The coaxial direct-current plasma nozzle comprises an inner metal cylinder, metal bars, an outer insulating cylinder, a propellant chamber, an external electrode and a high-voltage power supply, wherein the propellant chamber comprises a main through hole and two branch chambers; the outer insulating cylinder comprises a nozzle outlet part, a mounting part, an outer nozzle hole groove, an inner cylinder fixing groove and a metal bar groove; an inner propellant X through hole is formed in the inner metal cylinder. The coaxial direct-current plasma nozzle is provided with a main spraying runner for a propellant X and a circular seam spraying runner for a propellant Y. The metal bars are distributed in the metal bar groove and are electrically connected with the high-voltage power supply. The nozzle outlet part is covered with the external electrode, and the external electrode is grounded. The coaxial direct-current plasma nozzle can improve the evaporating and mixing process of fuel and an oxidizing agent in the traditional coaxial direct-current nozzle and can shorten ignition delay, broaden flameout limit and improve combustion instability.
Owner:PLA PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY OF CHINA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE AEROSPACE ENG UNIV
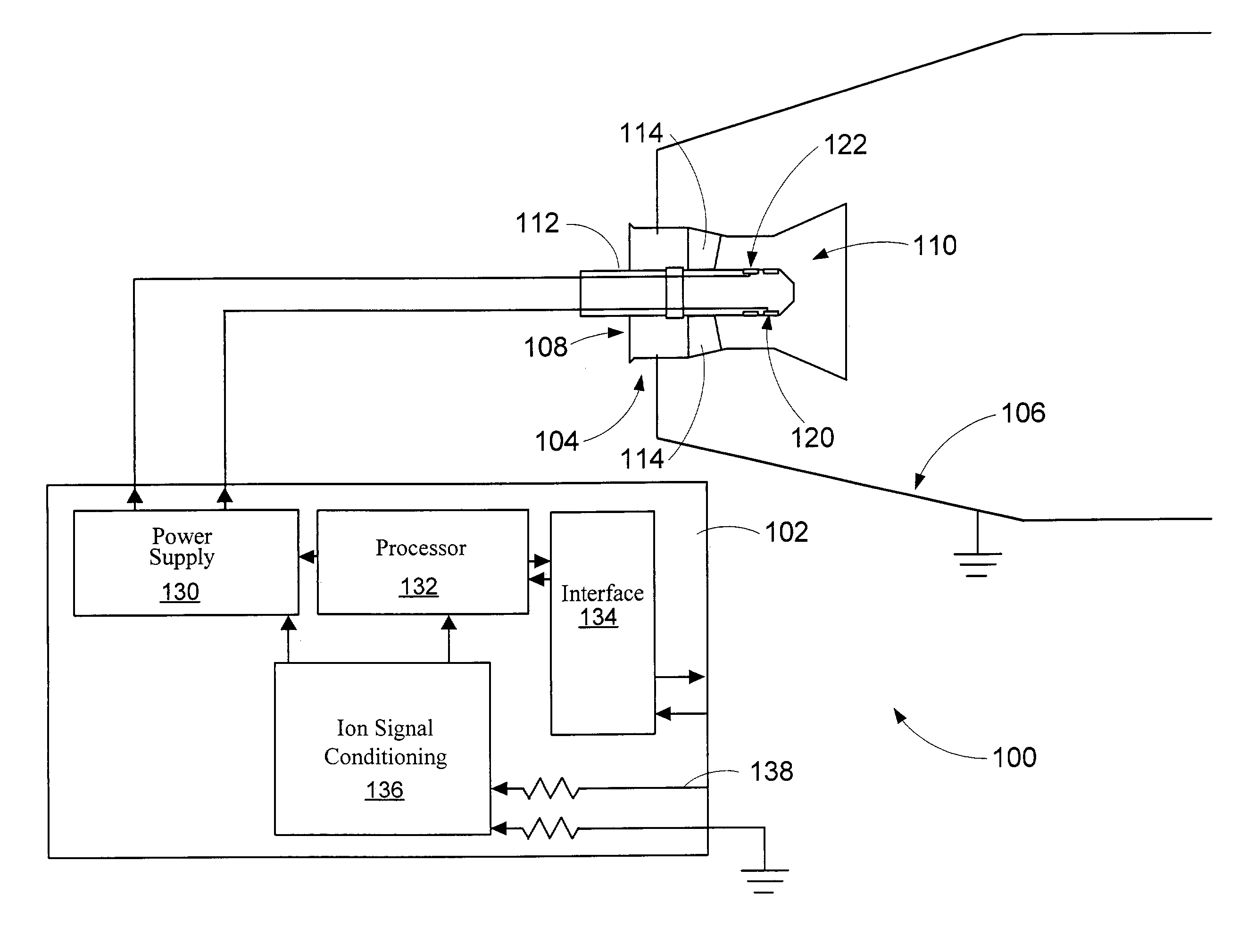
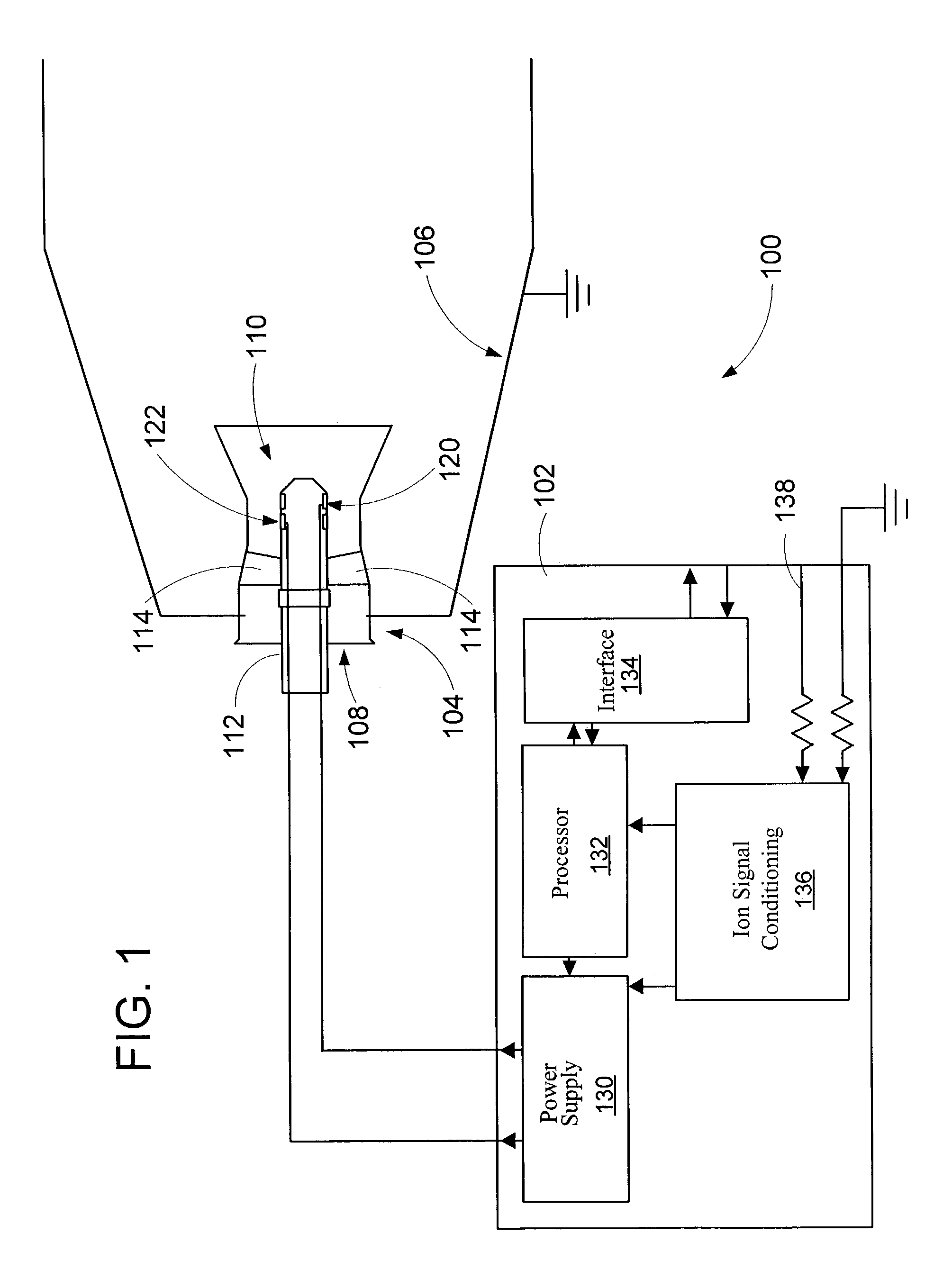
Method and apparatus for detecting combustion instability in continuous combustion systems
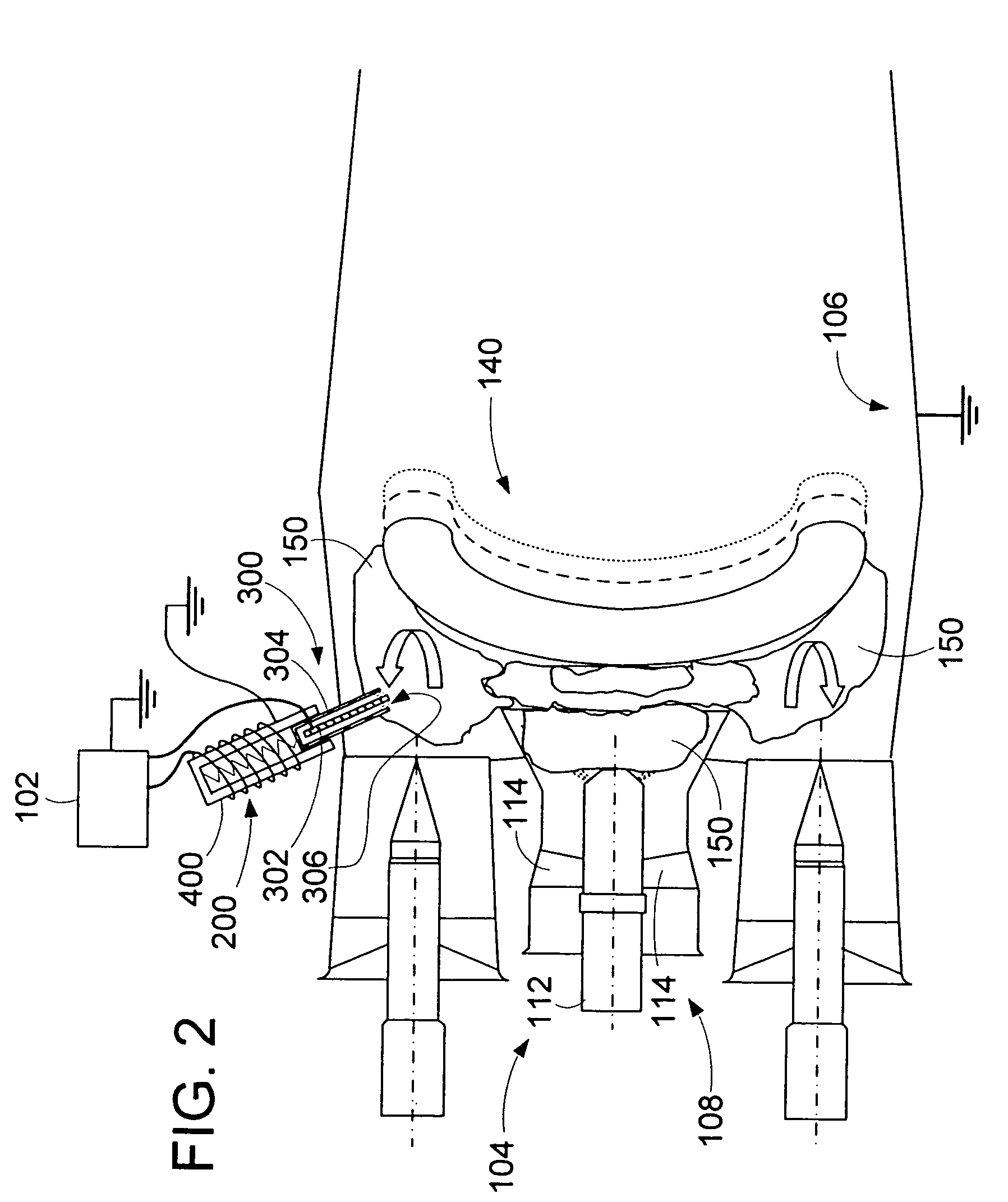
ActiveUS7096722B2Continuous combustion chamberElectric ignition installationCombustion instabilityElectricity
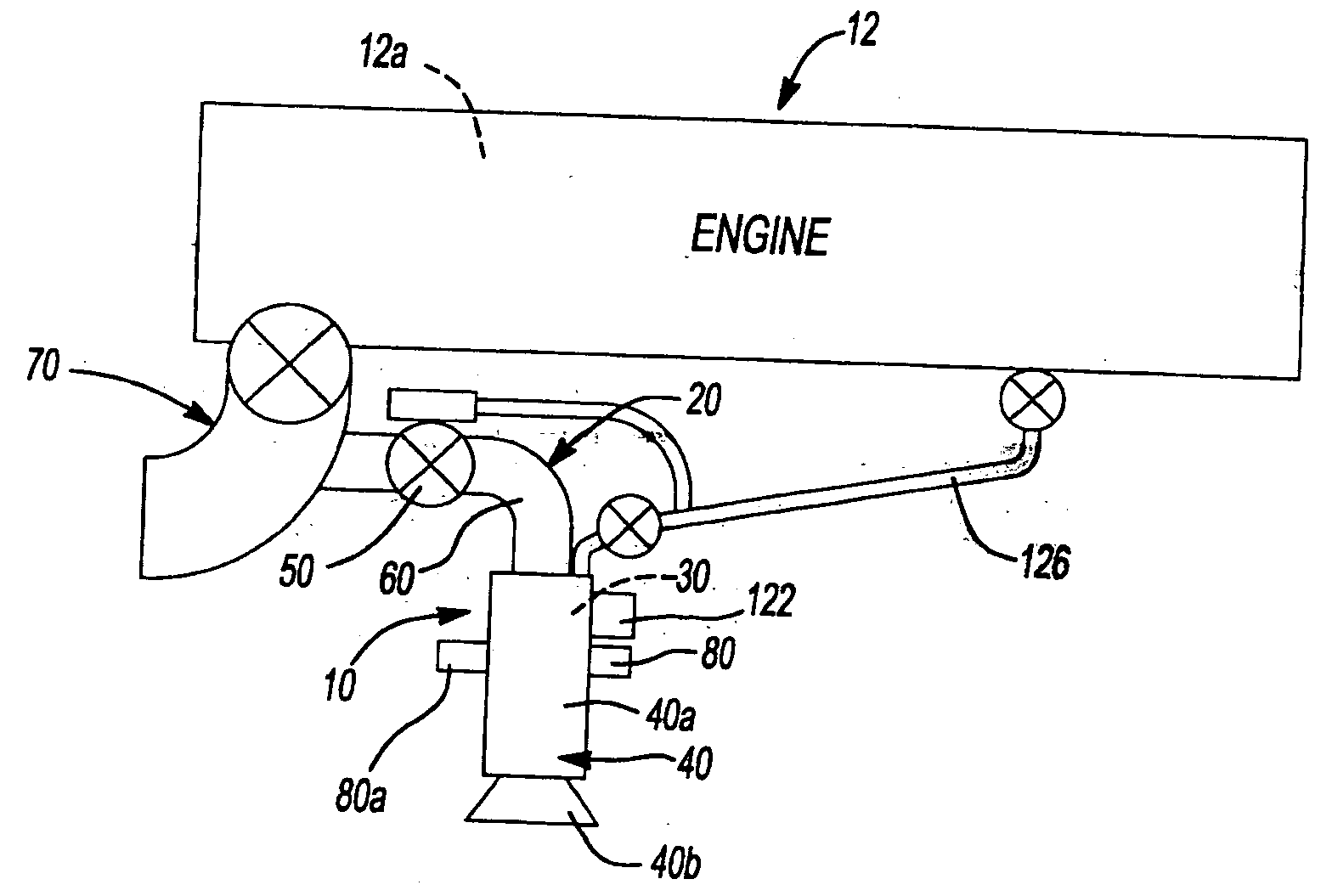
An apparatus and method to sense the onset of combustion stability is presented. An electrode is positioned in a turbine combustion chamber such that the electrode is exposed to gases in the combustion chamber. A control module applies a voltage potential to the electrode and detects a combustion ionization signal and determines if there is an oscillation in the combustion ionization signal indicative of the occurrence of combustion stability or the onset of combustion instability. A second electrode held in a coplanar but spaced apart manner by an insulating member from the electrode provides a combustion ionization signal to the control module when the first electrode fails. The control module broadcasts a notice if the parameters indicate the combustion process is at the onset of combustion instability or broadcasts an alarm signal if the parameters indicate the combustion process is unstable.
Owner:WOODWARD GOVERNOR CO
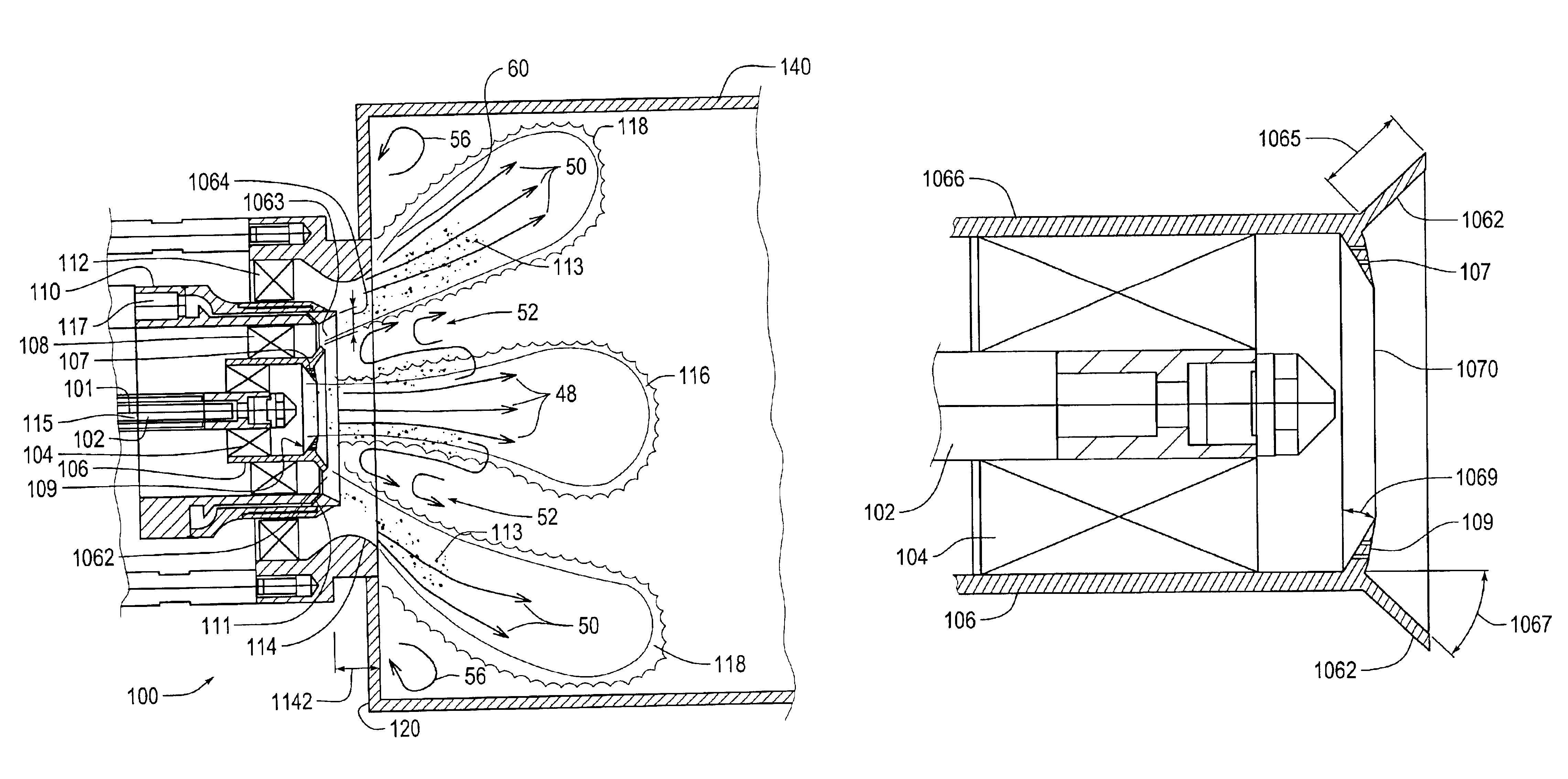
Air-fuel injection system for stable combustion
InactiveUS6908298B1Process stabilityFacilitate of combustionCombustion using gaseous and pulverulent fuelFuel supply regulationCombustion instabilityCombustion chamber
A method of and system for air-fuel injection for stable combustion in fuel combustors. It provides rapid mixing, continuous ignition and stable combustion under very fuel-rich and very fuel-lean conditions, mixtures that may even be beyond flammable limits. The rapid and intimate mixing are achieved by sizing, orienting and operating fuel and air orifices such that the reactant streams directly impinge, and the velocity head in the fluid in greater supply, in multiple orifices, is higher than the velocity head of the other reactant stream, by a factor of two (2) to five (5). The continuous ignition is achieved by preheating air to temperatures sufficiently high such that the resulting air-fuel mixture, after impingement and mixing, is above the fuel autoignition temperature. The stable combustion is achieved by designing the controlling orifice pressure drops and stream inertances to be higher for the reactant that is in short supply, relative to stoichiometric mixtures, such that a combustion chamber over-pressure causes the injected mixture ratio to move toward stoichiometric, in the direction of higher combustion temperatures and lower product densities. Under fuel-rich conditions the reactant in short supply is the air, and under fuel-lean conditions the reactant in short supply is the fuel. Appropriate ratios of these pressure drops and inertances are determined by dynamic analysis of potential modes of feed system-coupled combustion instability.
Owner:CASTLE LIGHT CORP
Autocorrelation theory-based engine instability prediction and assessment method
ActiveCN106709144AGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationCombustion instabilityCombustion chamber
The invention discloses an autocorrelation theory-based engine instability prediction and assessment method. The method comprises the steps of firstly filtering a pulsating pressure signal of a combustion chamber, separating out pressure oscillation of each order mode and performing autocorrelation calculation; secondly performing Hilbert transform on an autocorrelation result to obtain an outside envelope of the autocorrelation result; and finally fitting the outside envelope by applying a least square method to determine a first-order mode dissipation coefficient of an engine, and taking the first-order mode dissipation coefficient of the engine as an assessment tool of engine stability margin for predicting and assessing high-frequency combustion instability of the liquid rocket engine. According to the method, the engine can be subjected to instability quantitative prediction and assessment under the condition of not applying external force interference.
Owner:PLA PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY OF CHINA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE AEROSPACE ENG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com