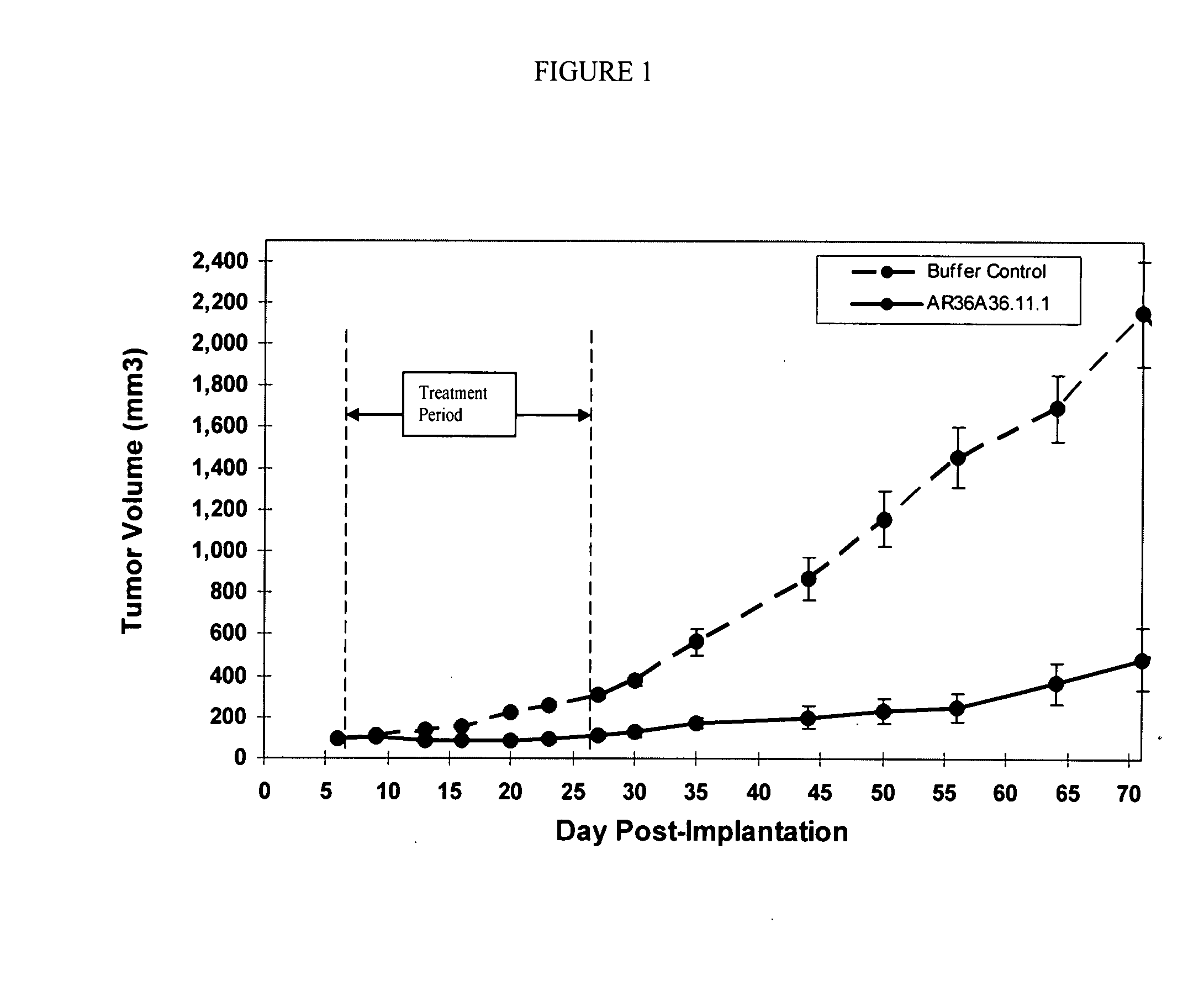
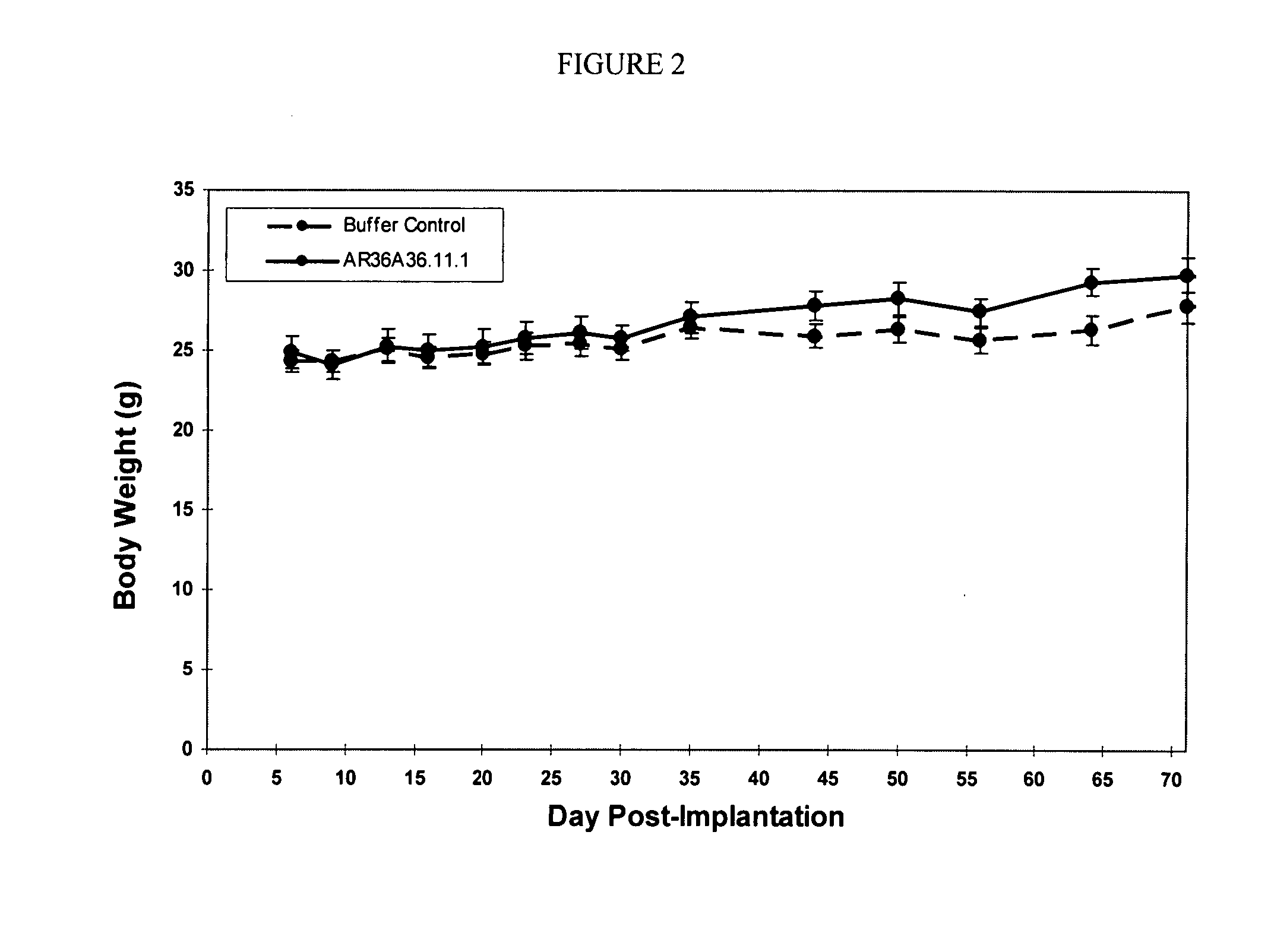
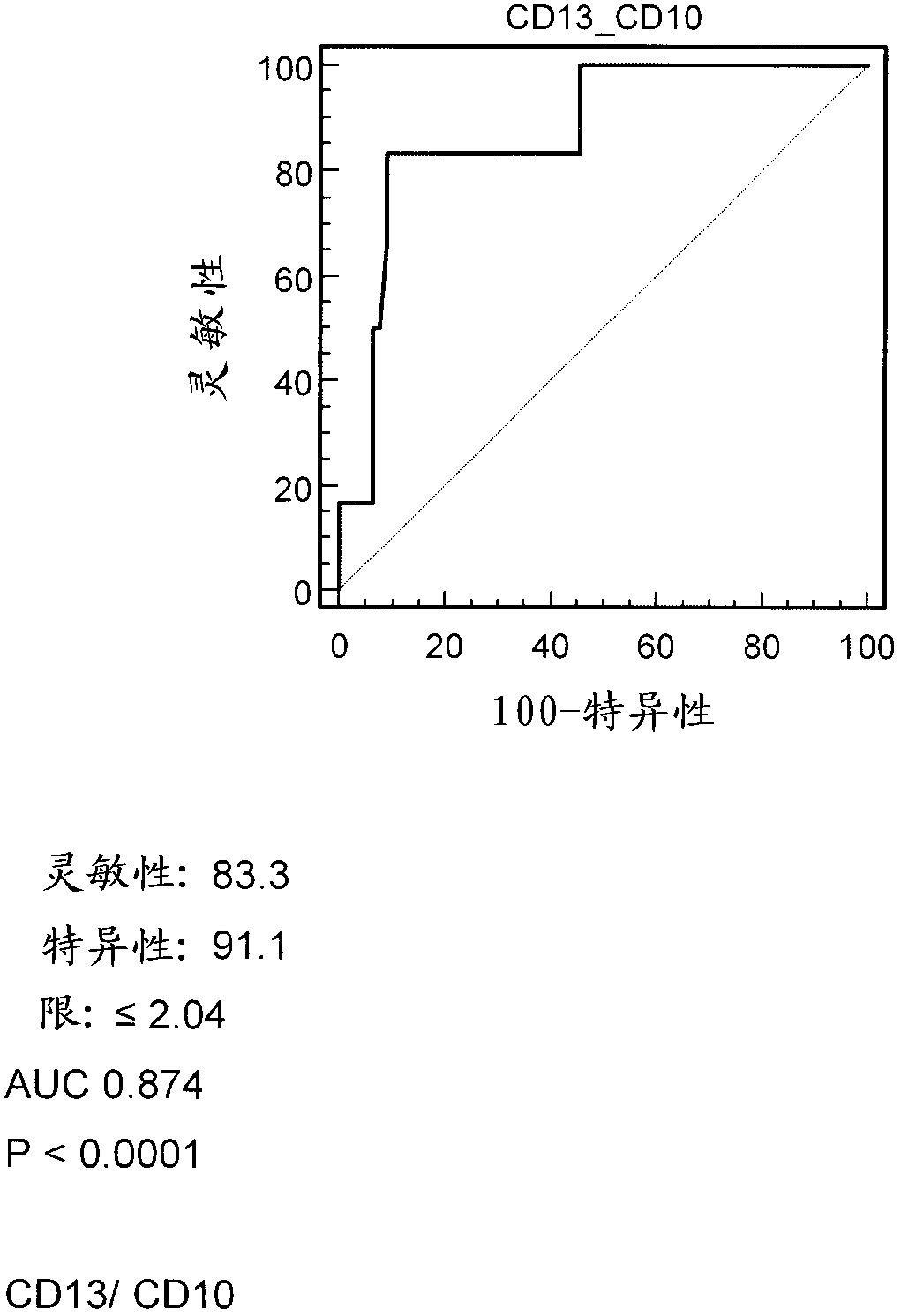
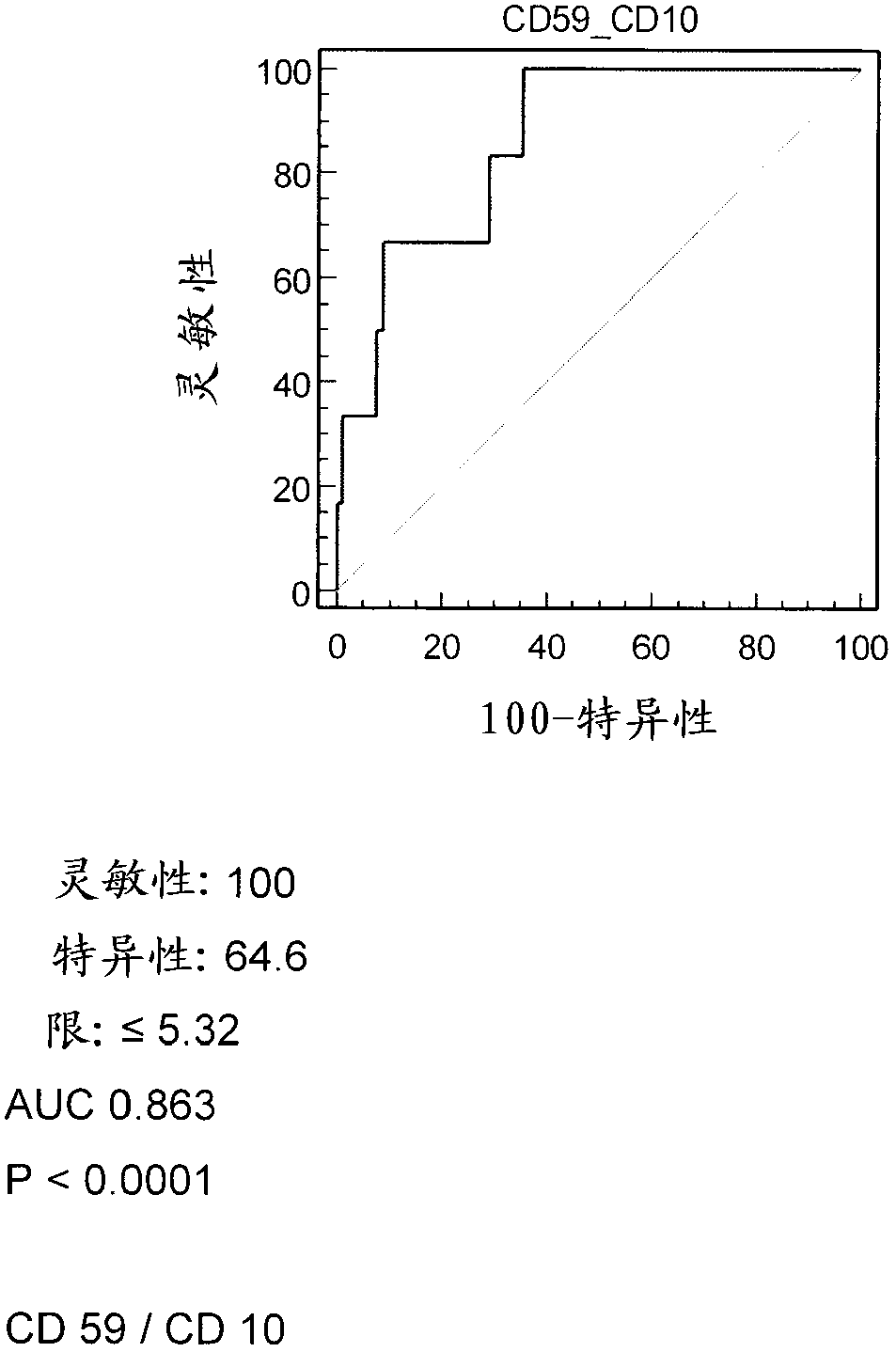
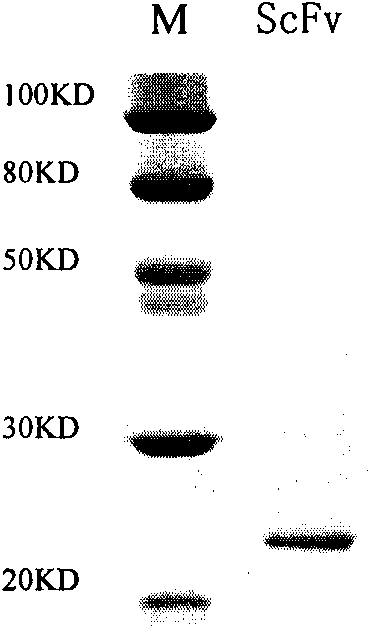Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
75 results about "CD59" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
CD59 glycoprotein, also known as MAC-inhibitory protein (MAC-IP), membrane inhibitor of reactive lysis (MIRL), or protectin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD59 gene. It belongs to the LY6/uPAR/alpha-neurotoxin protein family.
Identification and Isolation of Multipotent Cells From Non-Osteochondral Mesenchymal Tissue
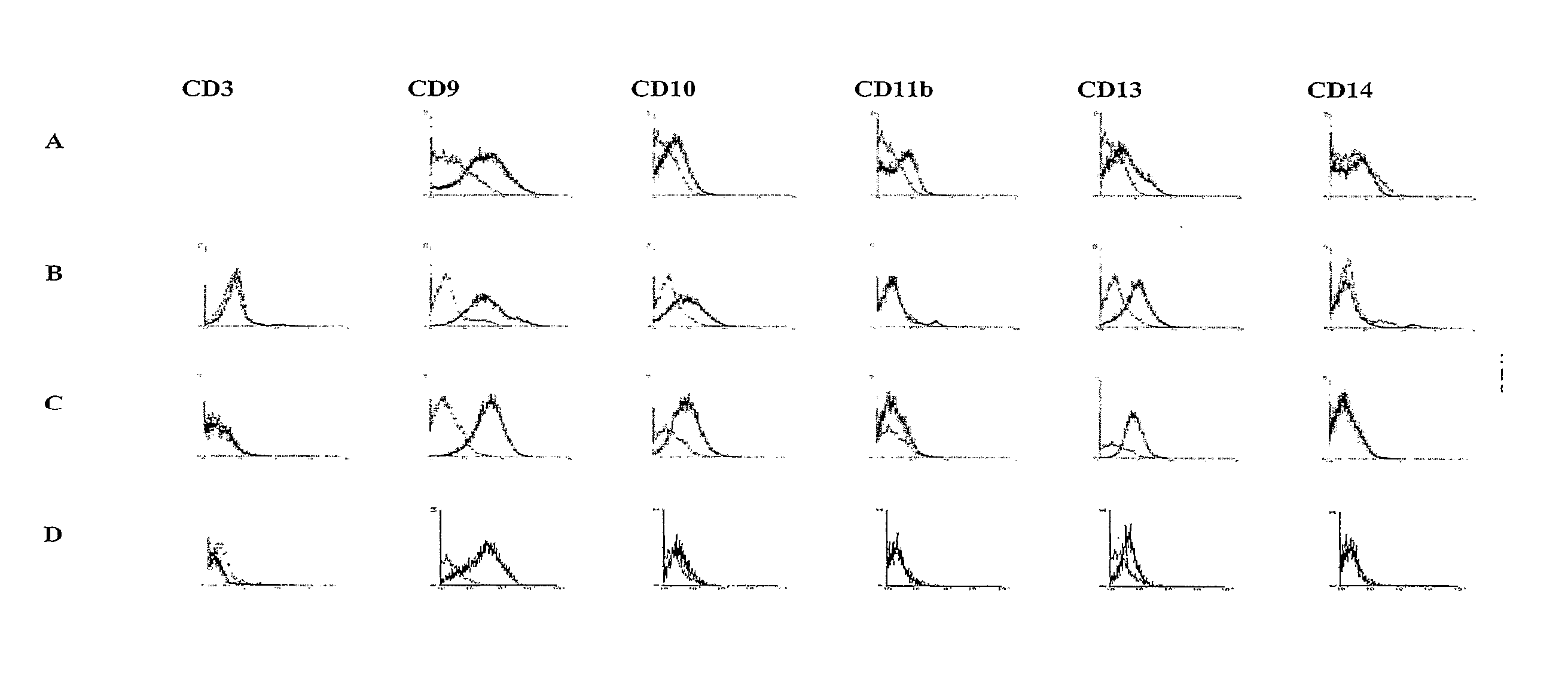
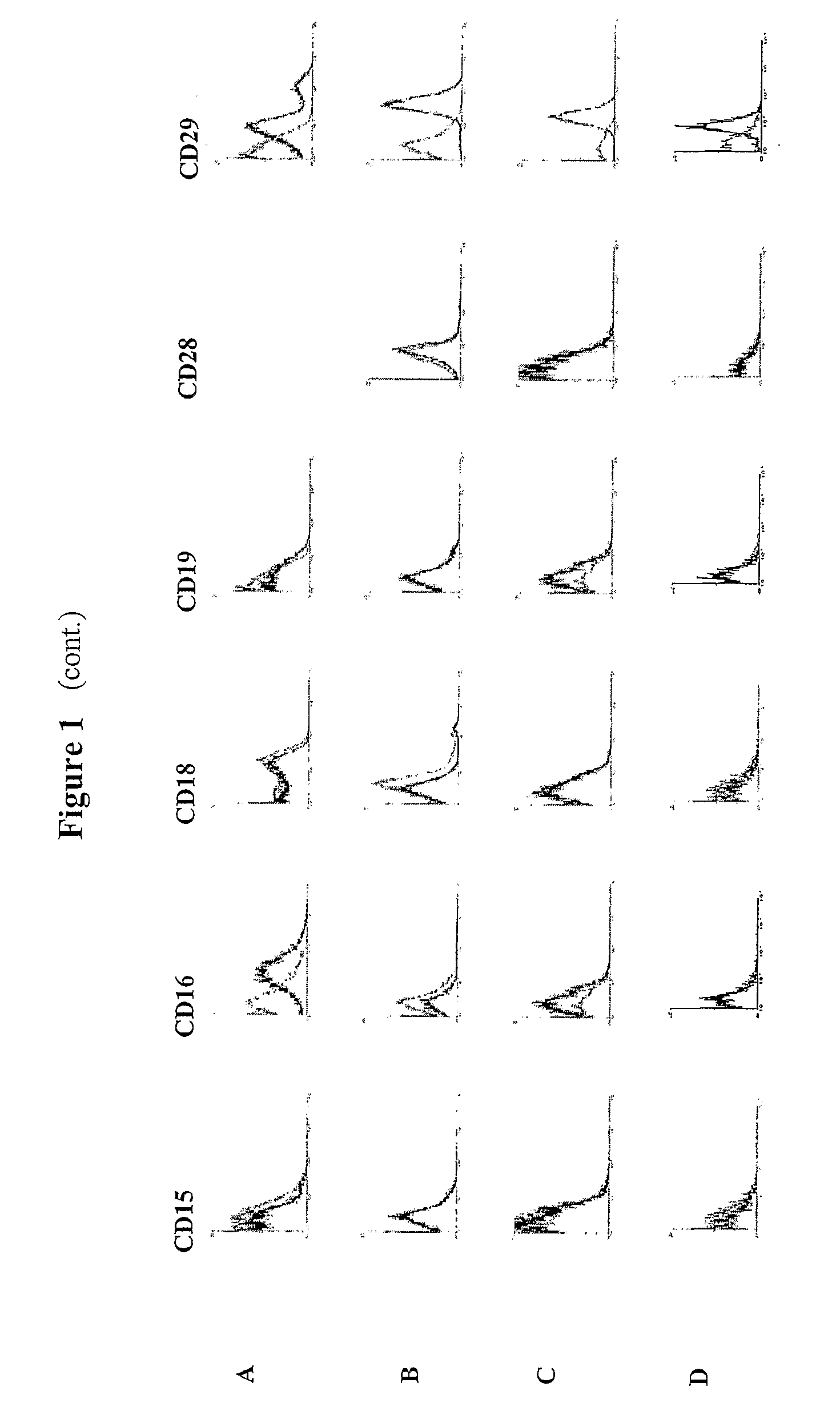
Identification and isolation of multipotent cells from non-osteochondral mesenchymal tissue. This invention relates to the identification and isolation of multipotent cells from non-osteochondral mesenchymal tissue. Specifically, it relates to an adult multipotent cell or a cell population or composition comprising said cell, isolated from non-osteochondral mesenchymal tissue, characterized in that it is positive for the following markers: CD9, CD10, CD13, CD29, CD44, CD49A, CD51, CD54, CD55, CD58, CD59, CD90 and CD105 and because it lacks expression of the following markers: CD11b, CD14, CD15, CD16, CD31, CD34, CD45, CD49f, CD102, CD104, CD106 and CD133.
Owner:AUTONOMOUS UNIVERSITY OF MADRID +1
Methods, products and treatments for diabetes
InactiveUS6835545B2Shorten the progressReduce riskMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymologyDiabetes mellitusCD59
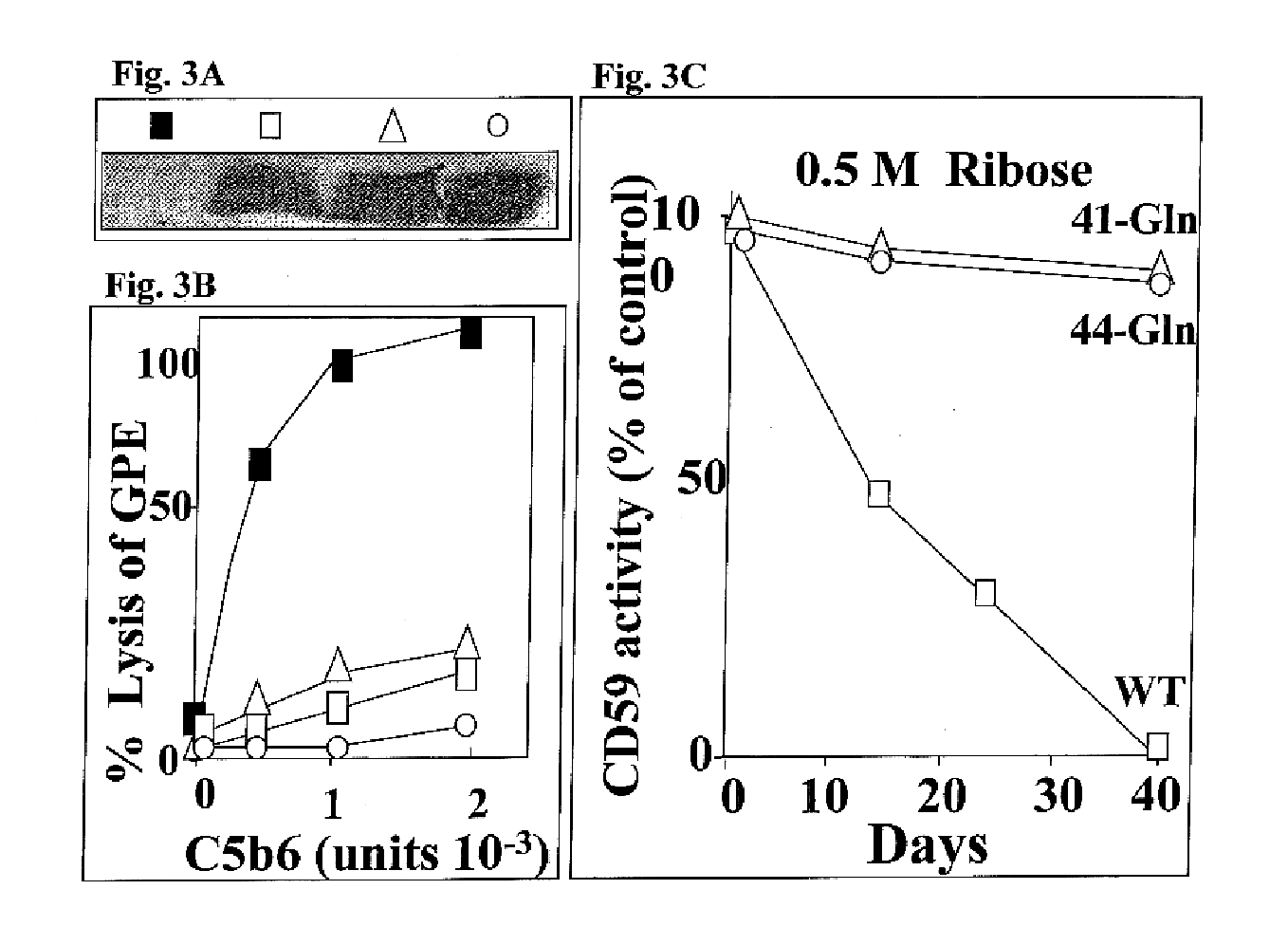
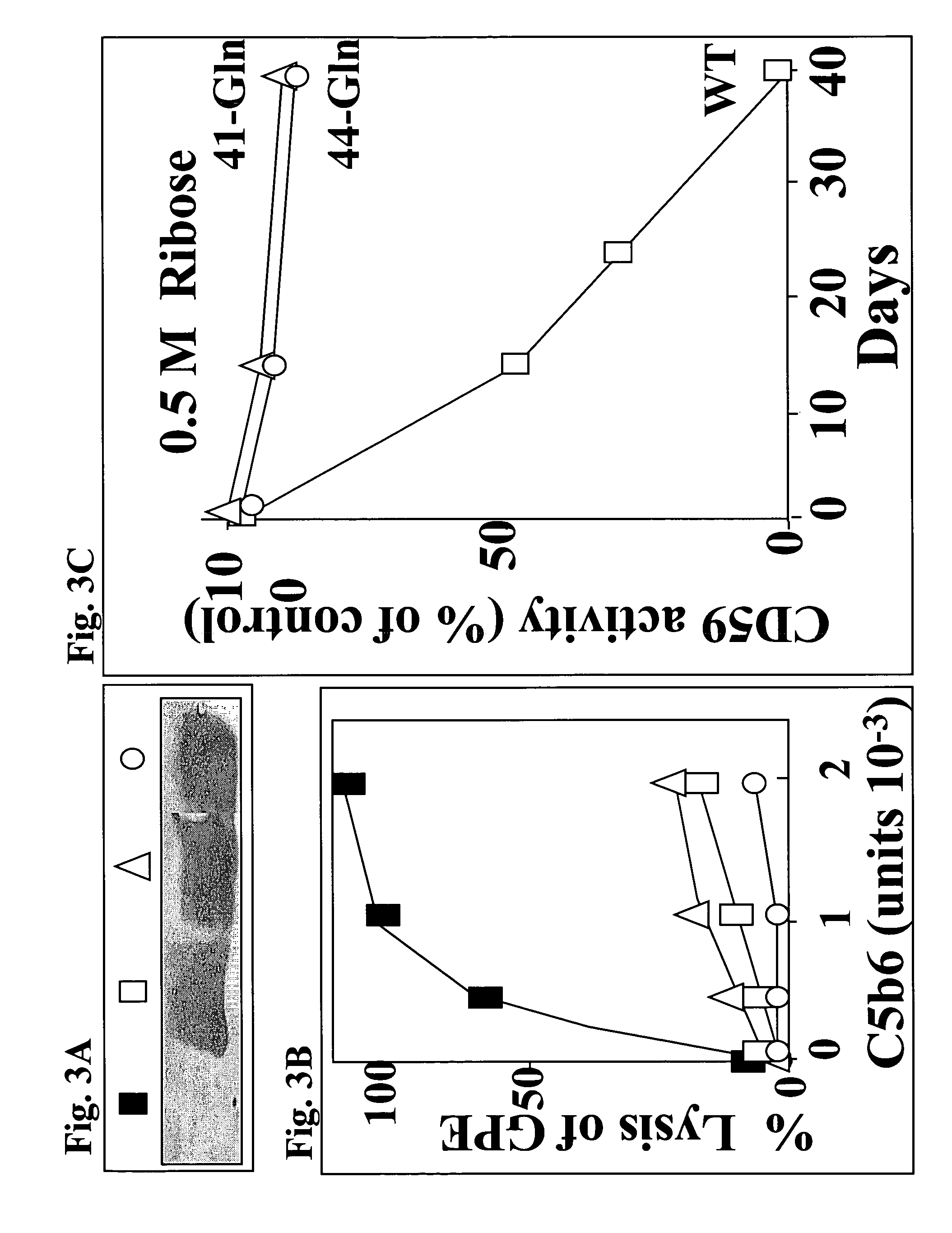
The invention involves assays, diagnostics, kits, and assay components for determining levels of K41-glycated CD59 in subjects. Treatments for subjects based upon levels of K41-glycated CD59 also are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
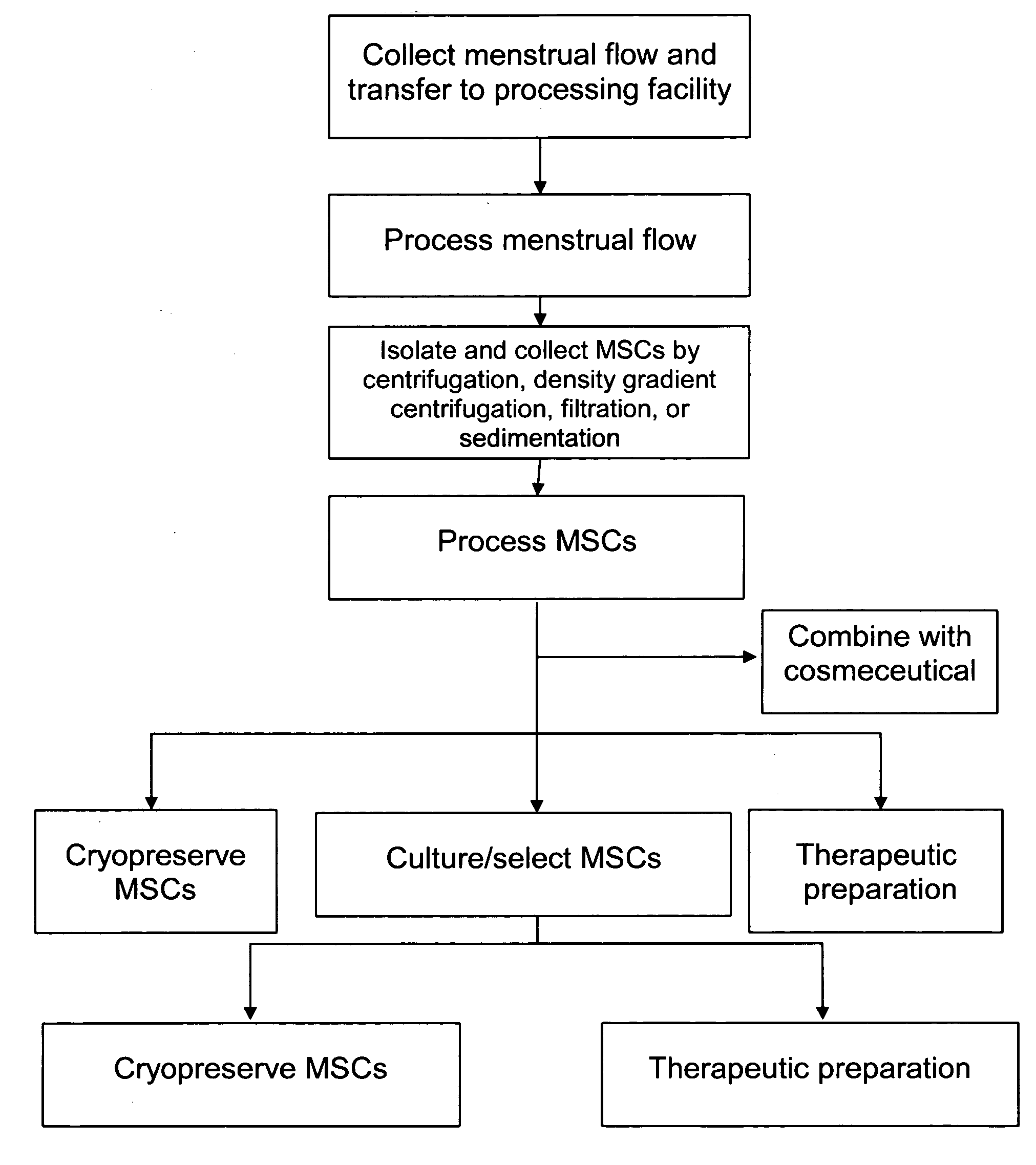
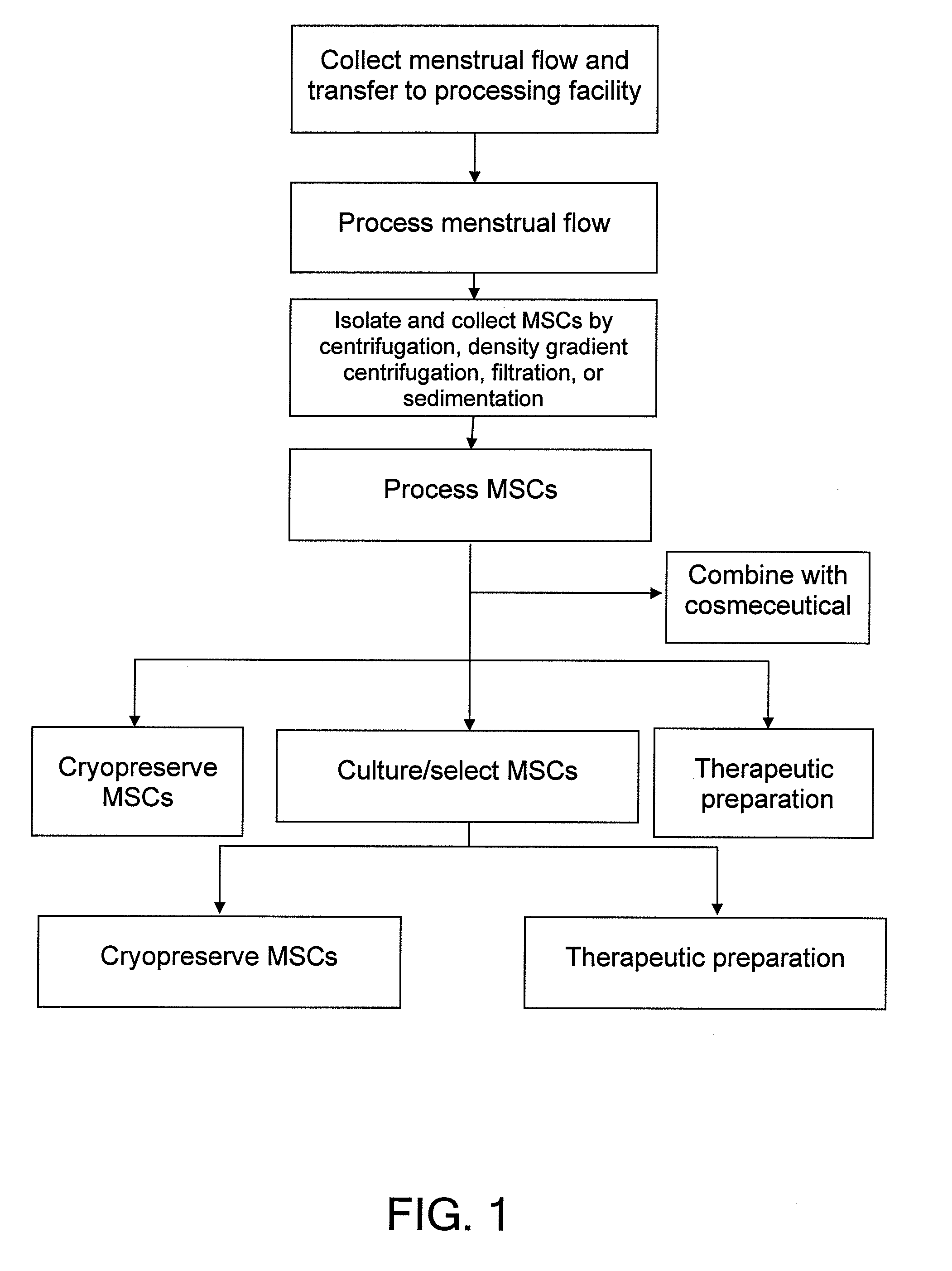
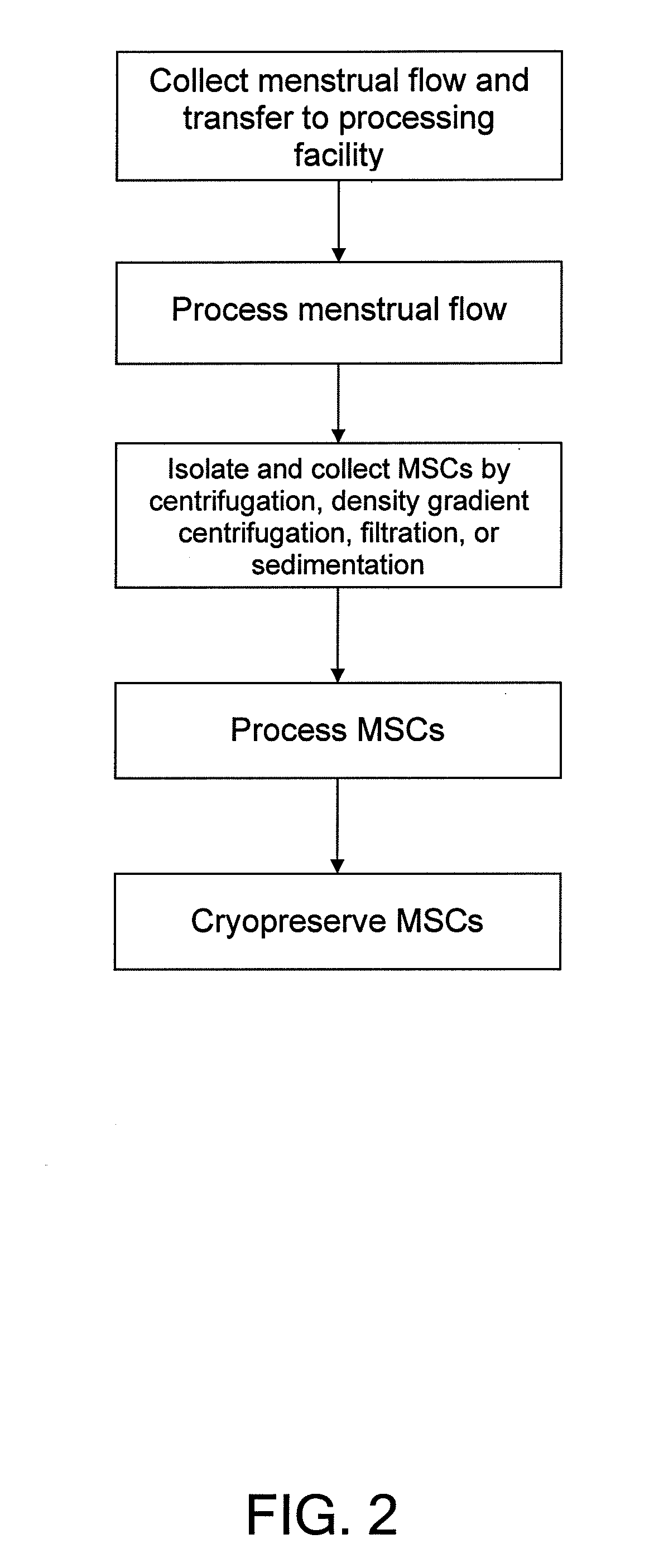
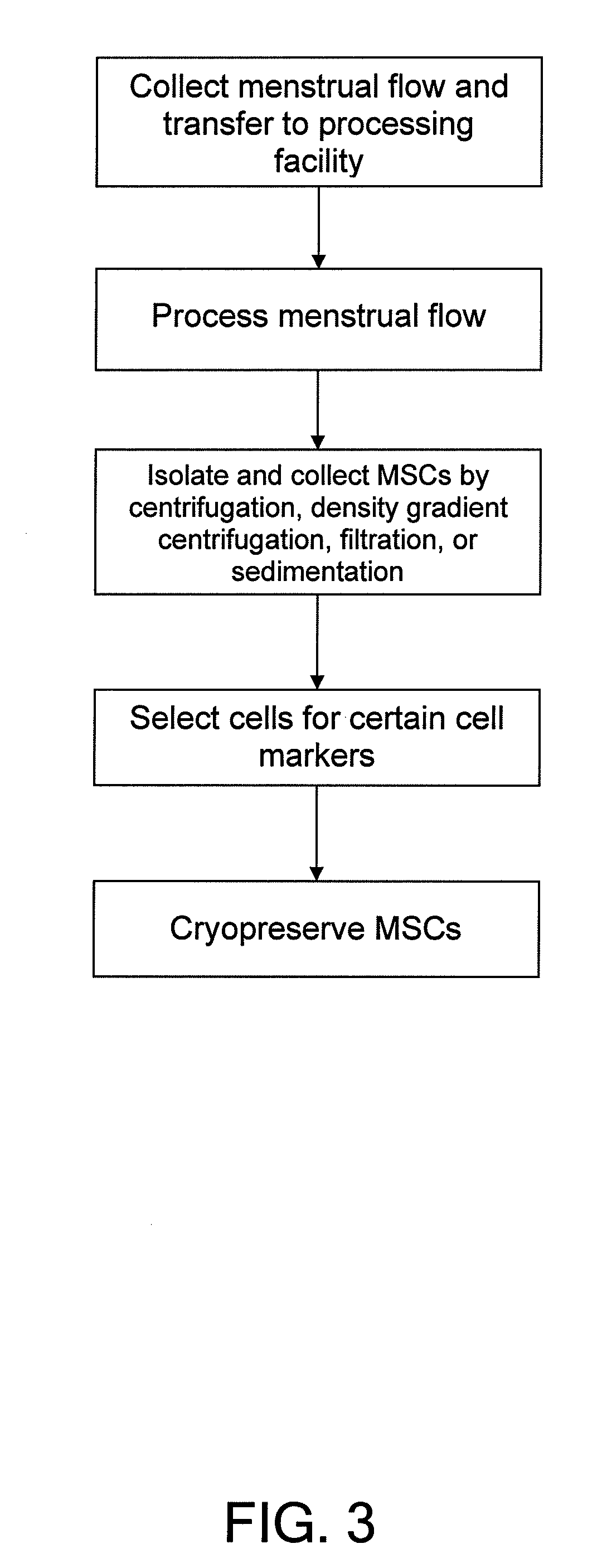
Procurement, isolation and cryopreservation of endometrial/menstrual cells
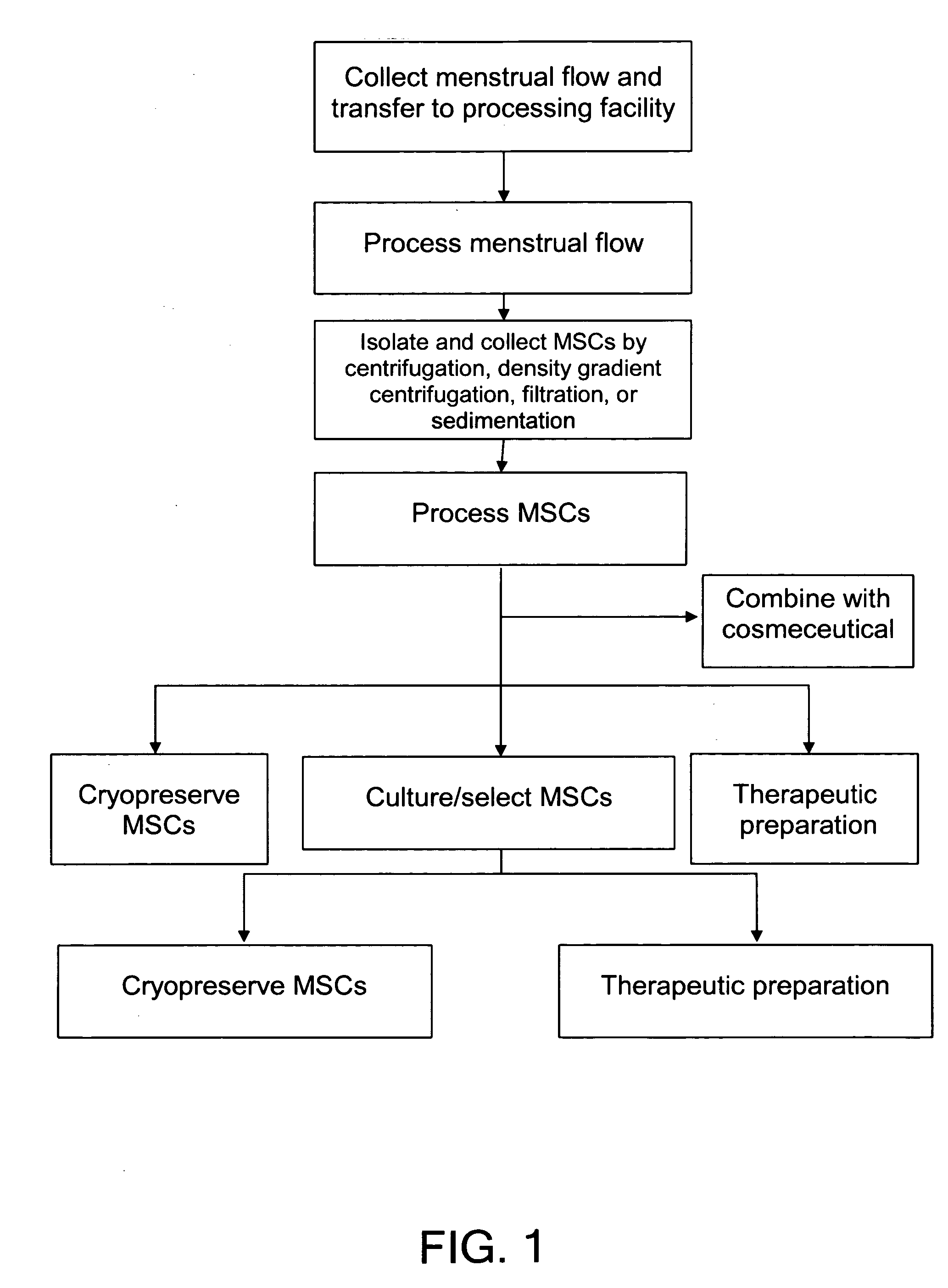
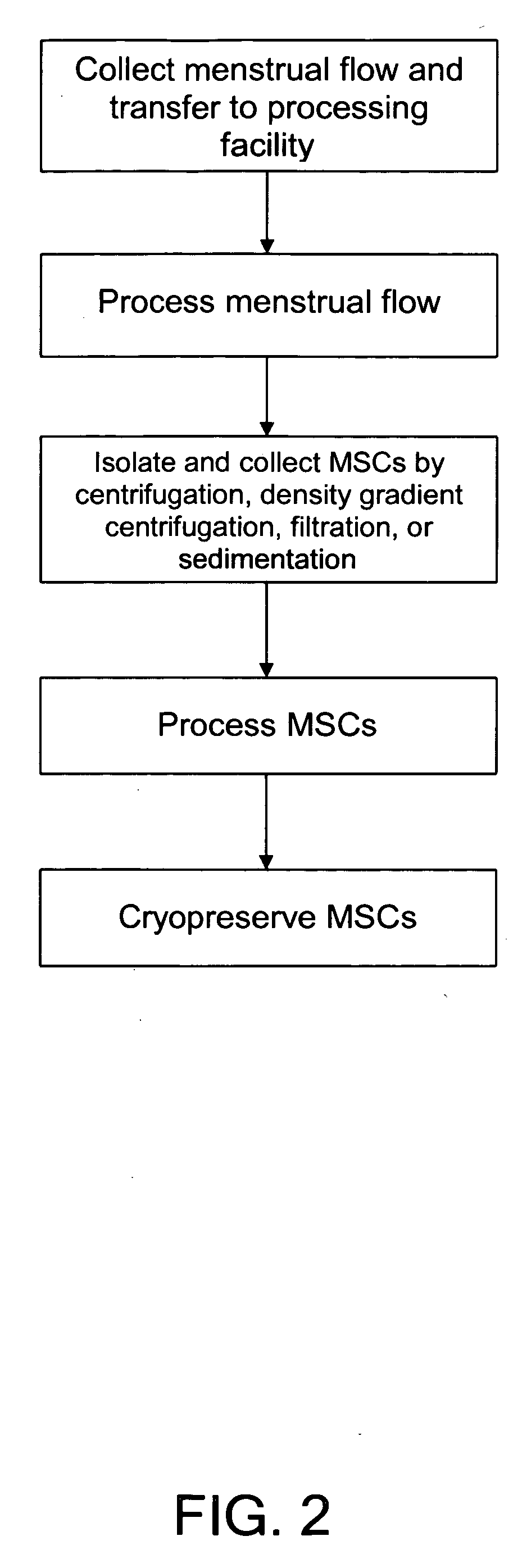
Compositions comprising menstrual stem cells (MSCs) and methods, processes, and system therefor are provided by the invention. MSCs are processed from menstrual flow collected during menses. MSCs may be cryopreserved, processed through various culturing and selection steps in preparation for cryopreservation, or processed for therapeutic or cosmeceutical use. Cryopreserved MSCs may be thawed in preparation for therapeutic and cosmeceutical use. MSCs express CD9, CD10, CD13, CD29, CD44, CD49e, CD49f, CD59, CD81, CD105, CD166, and HLA class I, and have low or no expression of CD3 and HLA class II.
Owner:CRYO CELL INTERNATIONAL INC
Methods, products and treatments for diabetes
The invention involves assays, diagnostics, kits, and assay components for determining levels of K41-glycated CD59 in subjects. Treatments for subjects based upon levels of K41-glycated CD59 also are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
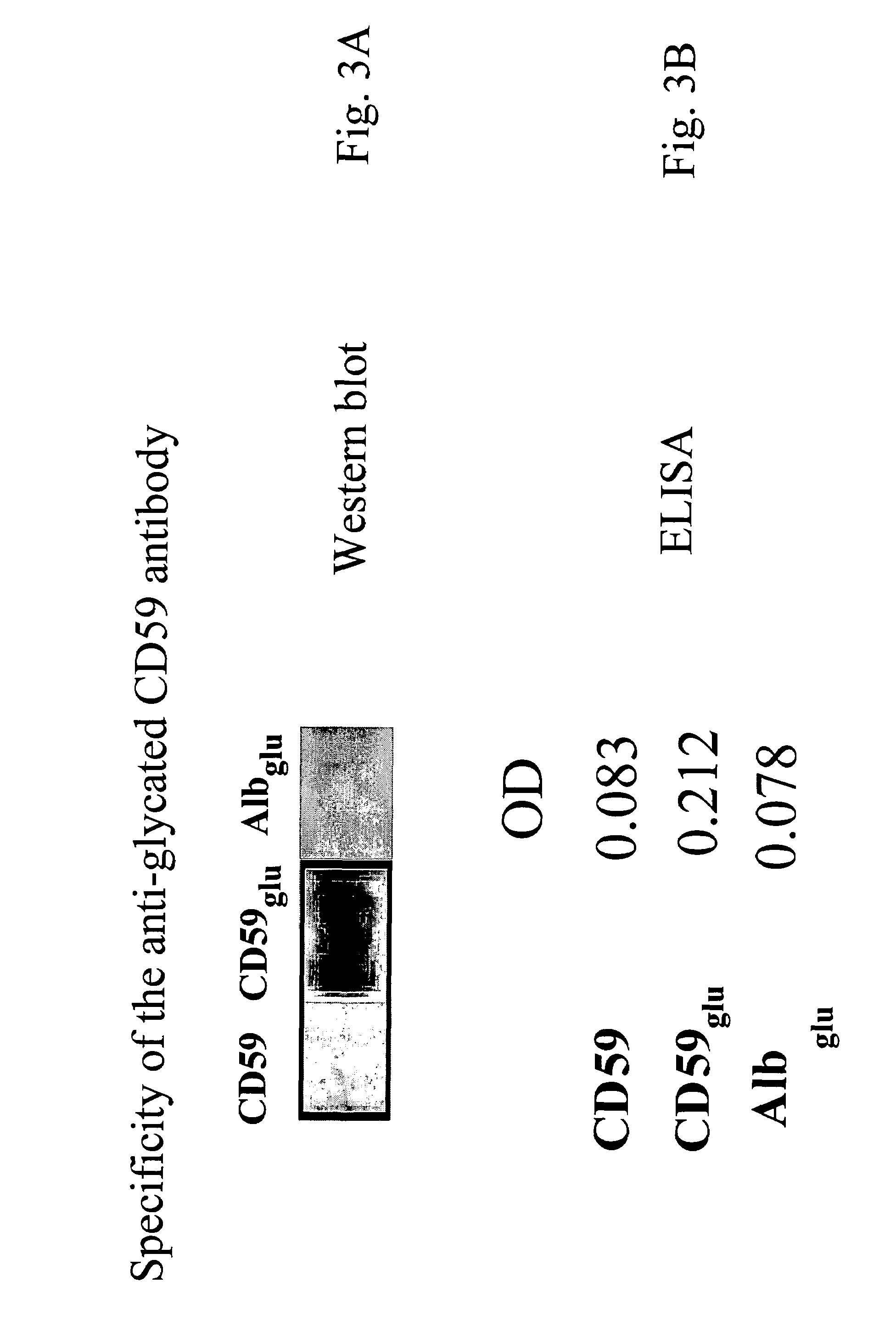
Anti-glycated CD59 antibodies and uses thereof
InactiveUS7439330B2Easy to analyzeImprove the level ofBiological testingFermentationDiabetes mellitusAntigen Binding Fragment
The invention includes antibodies or antigen-binding fragments thereof which bind specifically to glycated CD59, compositions containing one or a combination of such antibodies or antigen-binding fragments thereof, hybridoma cell lines that produce the antibodies, and methods of producing and using the antibodies or antigen-binding fragments thereof for diagnosis and treatment of diabetic conditions and diabetic-associated conditions.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Dental pulp marrow similar cells (DPMSC) and methods of isolating and using
InactiveUS20110158962A1Effective to ameliorateImprove isolationBiocideMetabolism disorderCD44Isolated population
The invention provides for isolated population of pulp marrow similar cells (DPMSCs) and methods for isolating and using these cells. The population of DPMSCs are highly homogenous for CD1O, CD29, CD13, CD44, CD49a, CD49d, CD59, CD73, CDw90, CD105, Oct-4 Isoform A and B, Nanog, Sox-2, and SSEA-4.
Owner:FOUND OF TRANSLATIONAL SCI +1
Cytotoxicity mediation of cells evidencing surface expression of CD59
InactiveUS20060140963A1Reduce the likelihood of problemsReduce the burden onBiological material analysisImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsWilms' tumorTumor cells
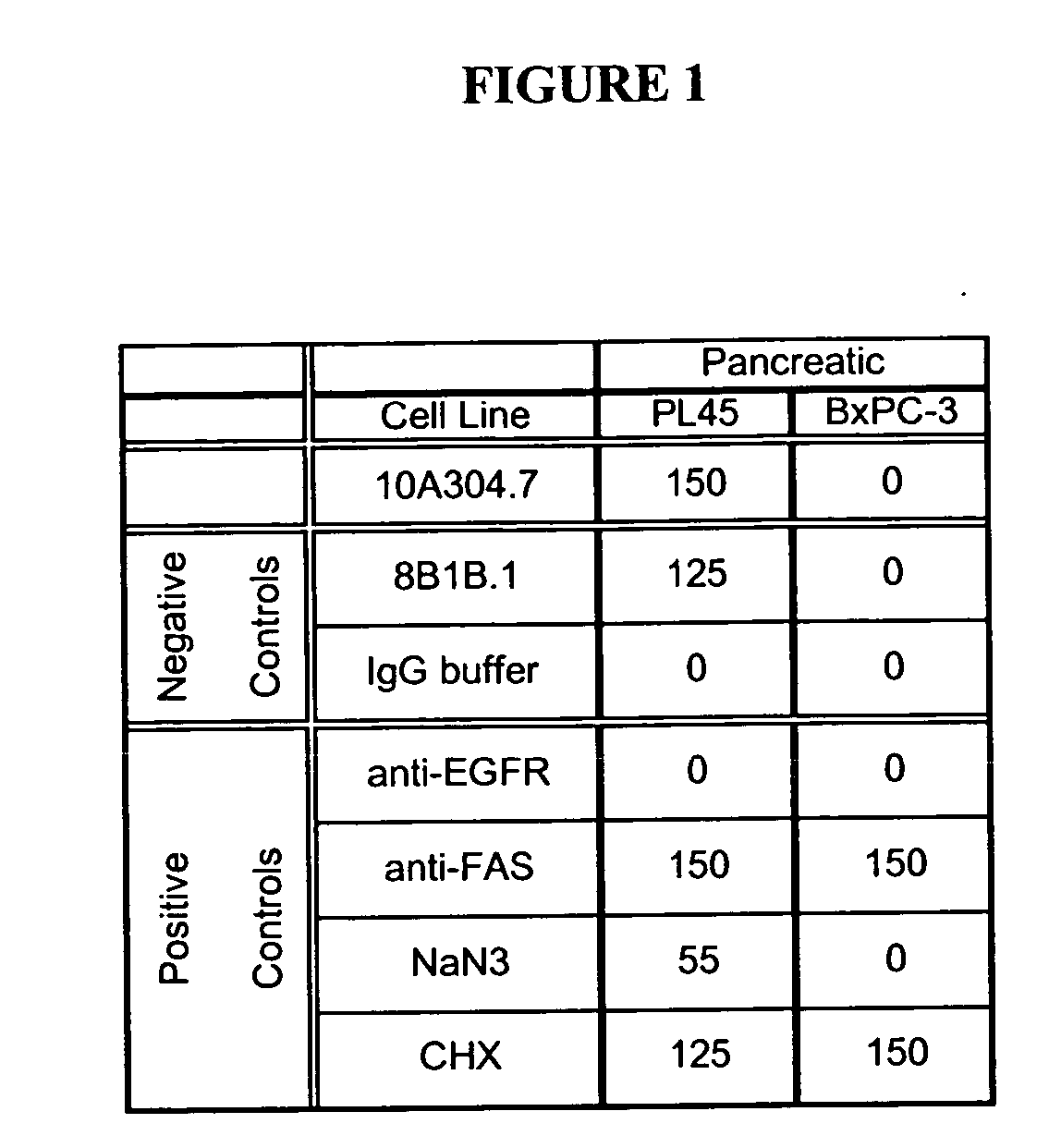
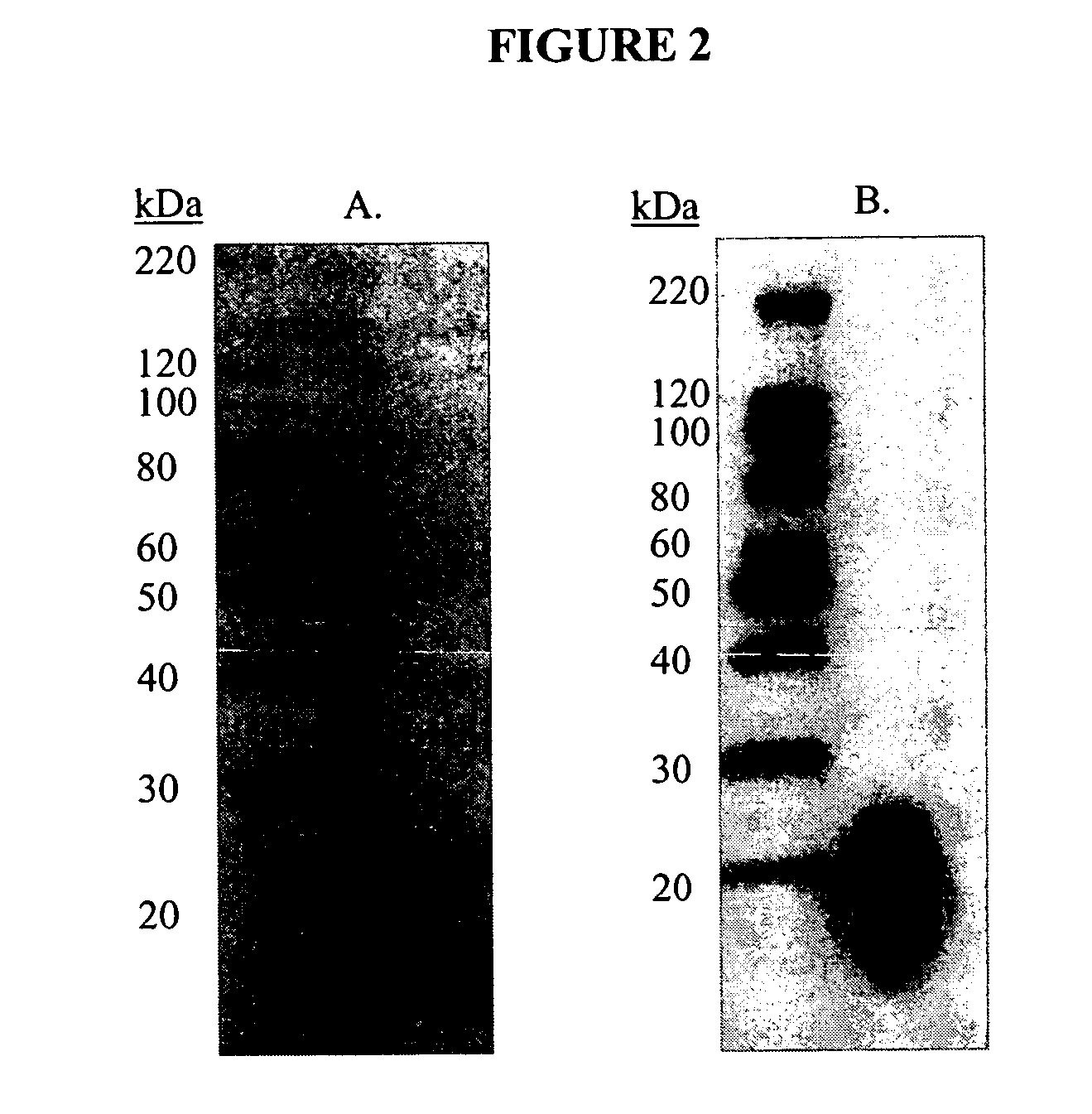
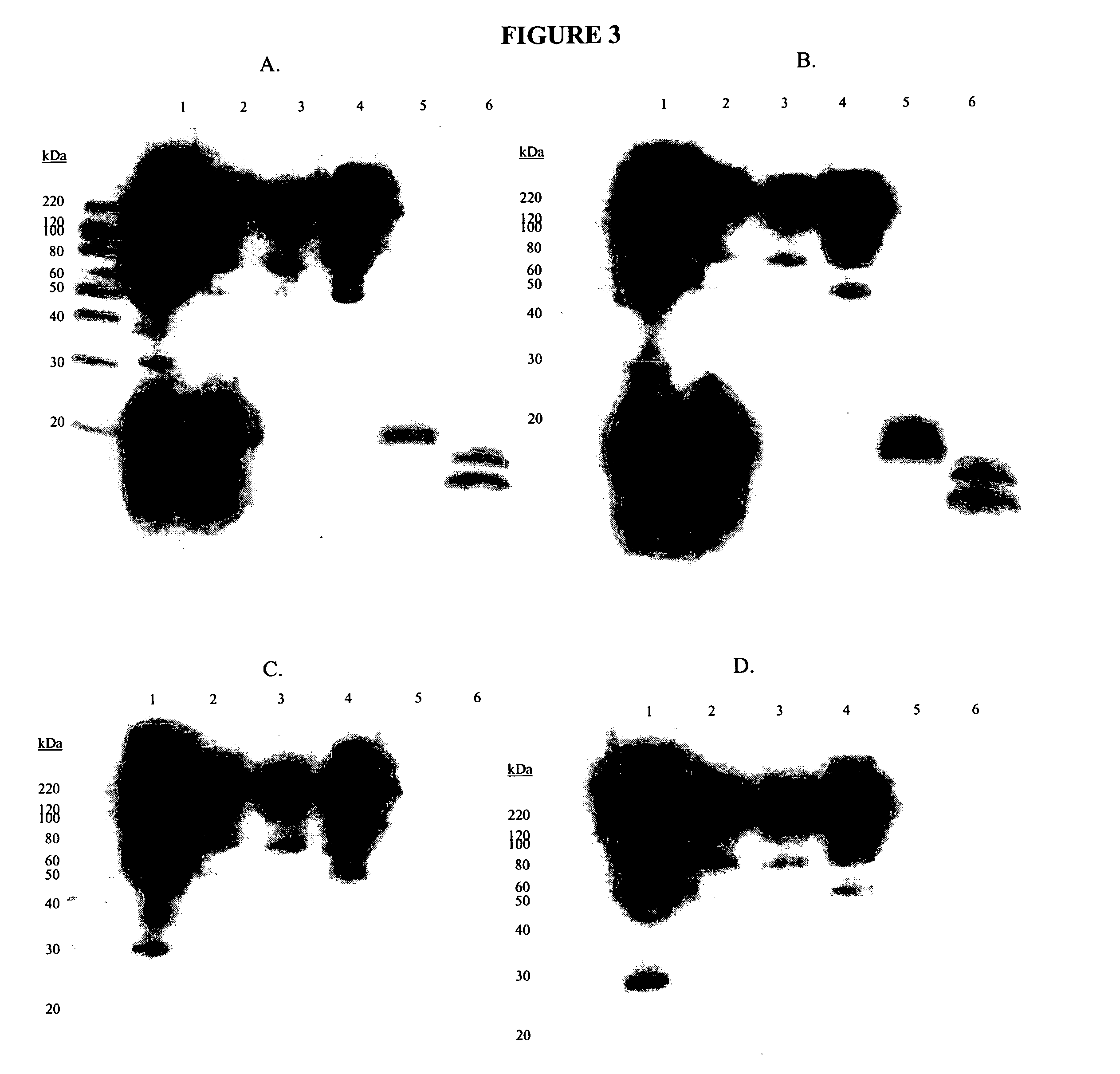
This invention relates to the diagnosis and treatment of cancerous diseases, particularly to the mediation of cytotoxicity of tumor cells; and most particularly to the use of cancerous disease modifying antibodies (CDMAB), optionally in combination with one or more chemotherapeutic agents, as a means for initiating the cytotoxic response. The invention further relates to binding assays which utilize the CDMAB of the instant invention.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE INC
Recombinant antibodies against cd55 and cd59 and uses thereof
ActiveUS20090053225A1Enhancing complement activationIncreased activationSugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against animals/humansCD20Region specific
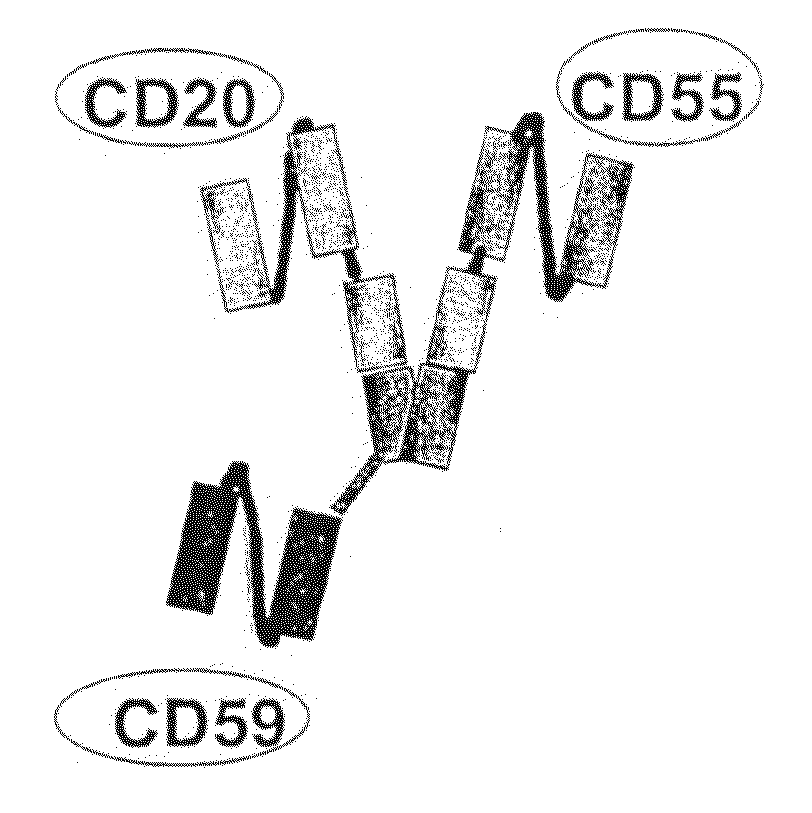
The present invention relates to recombinant antibody molecules and functional fragments thereof, useful for neutralizing the complement regulatory proteins CD55 and CD59, compositions comprising the recombinant molecules and methods of using the recombinant molecules for controlling complement resistance in cancer. The present invention further relates to heterodimeric diabody molecules comprising variable regions specific for CD55 / CD59 and CD20.
Owner:QUARK FARMACUITIKALS INC
Methods and materials for reducing cardiac xenograft rejection
ActiveUS20130111614A1Reducing cardiac xenograft rejectionIncreased durabilityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenGlycan
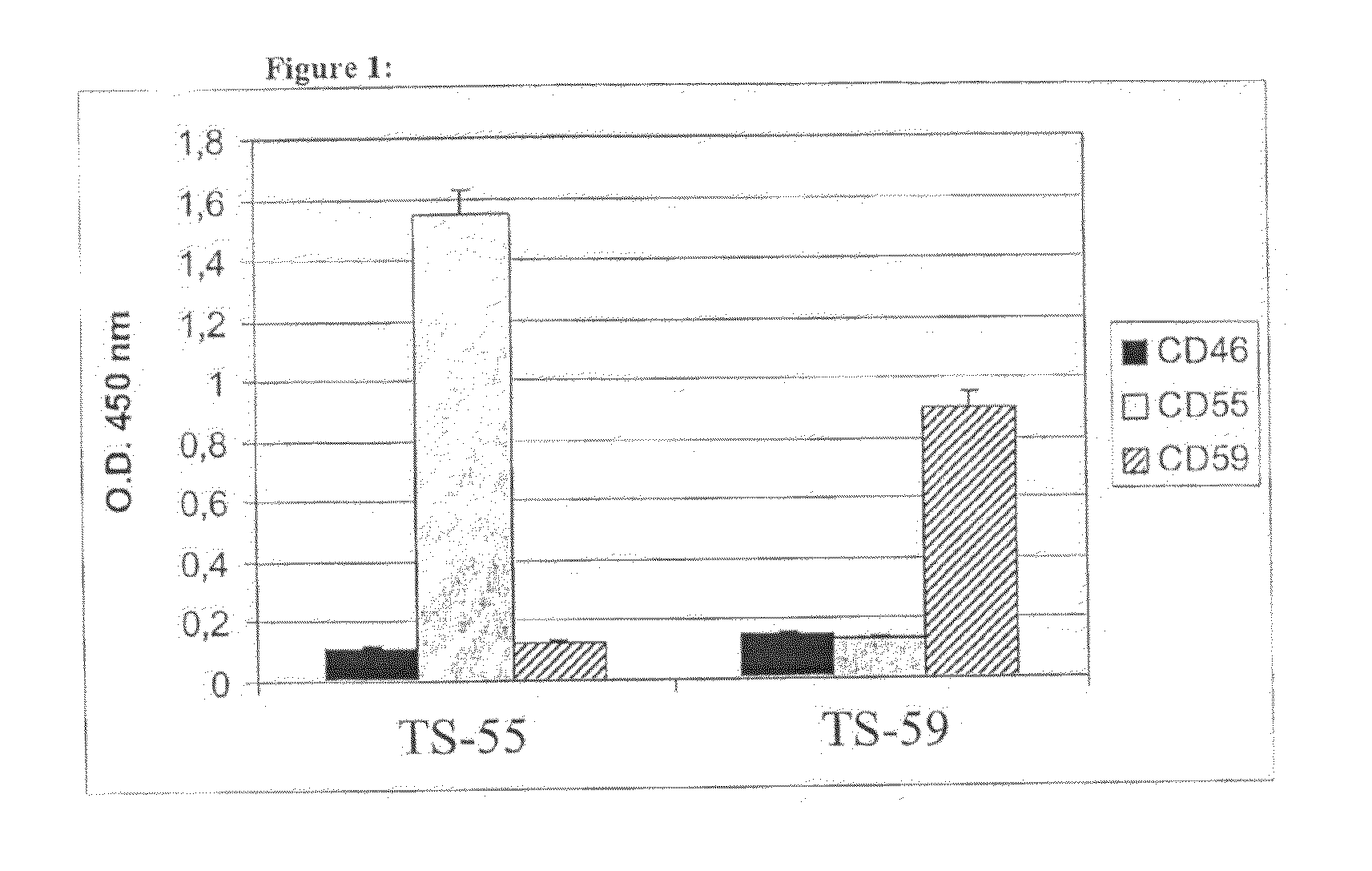
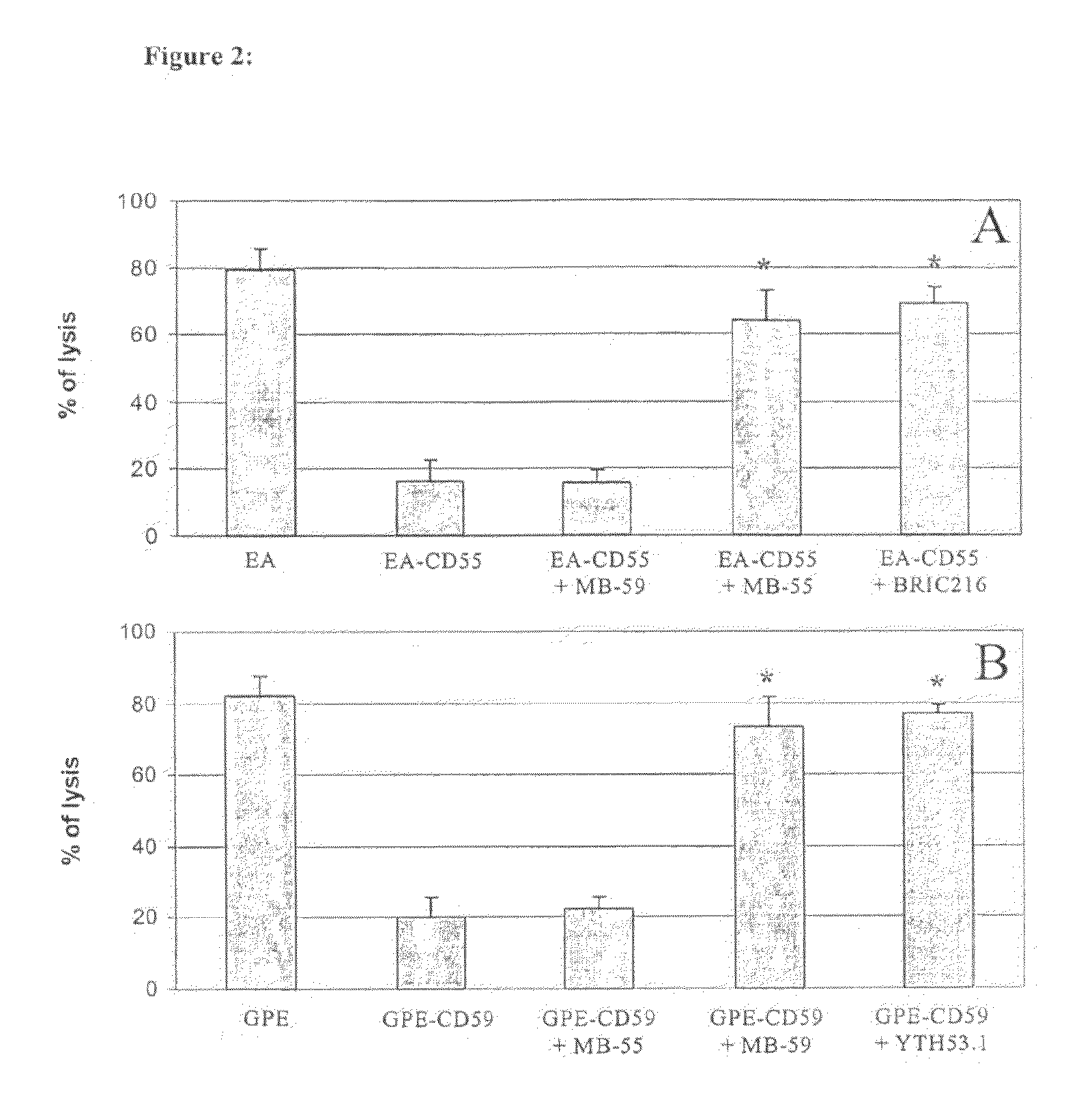
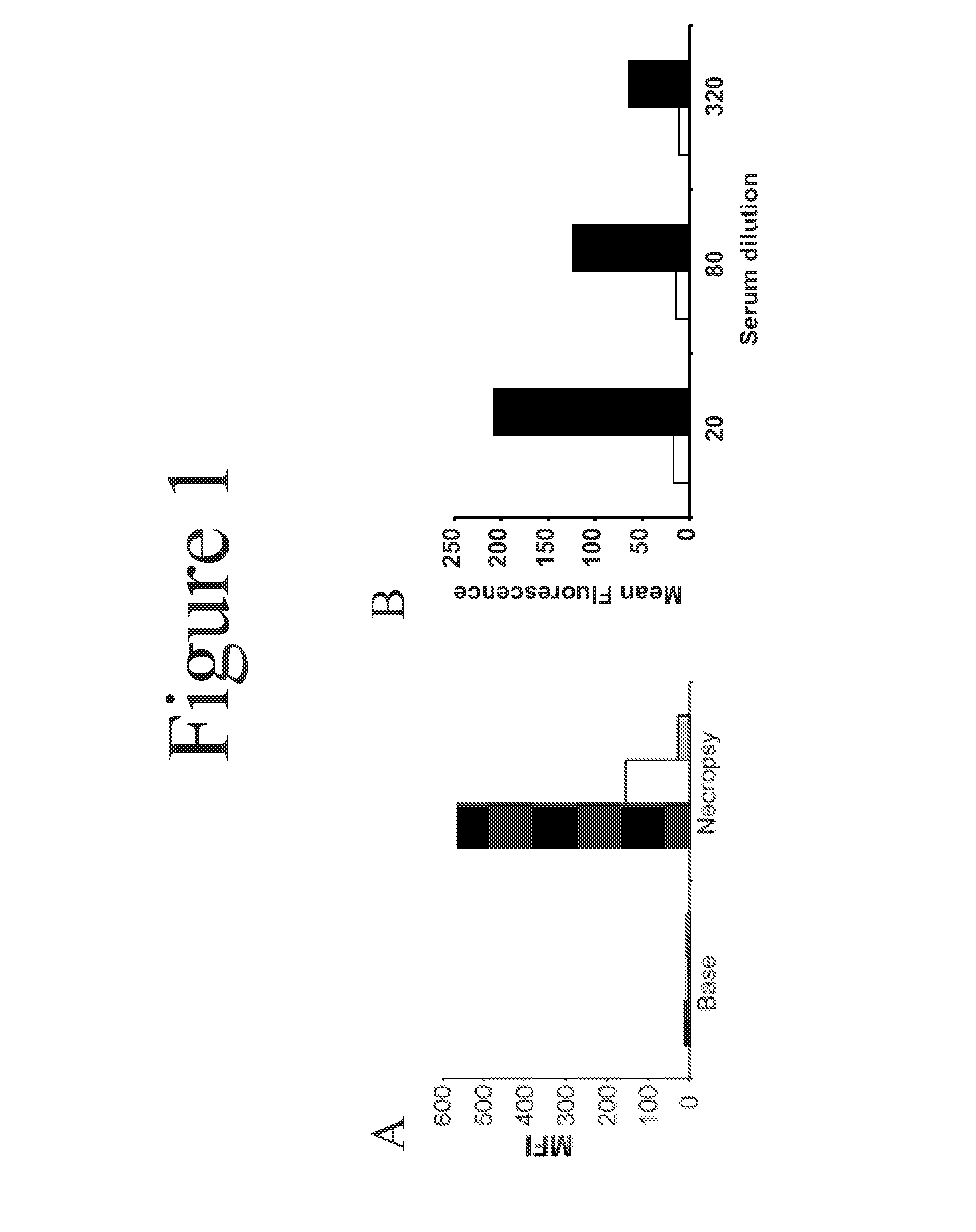
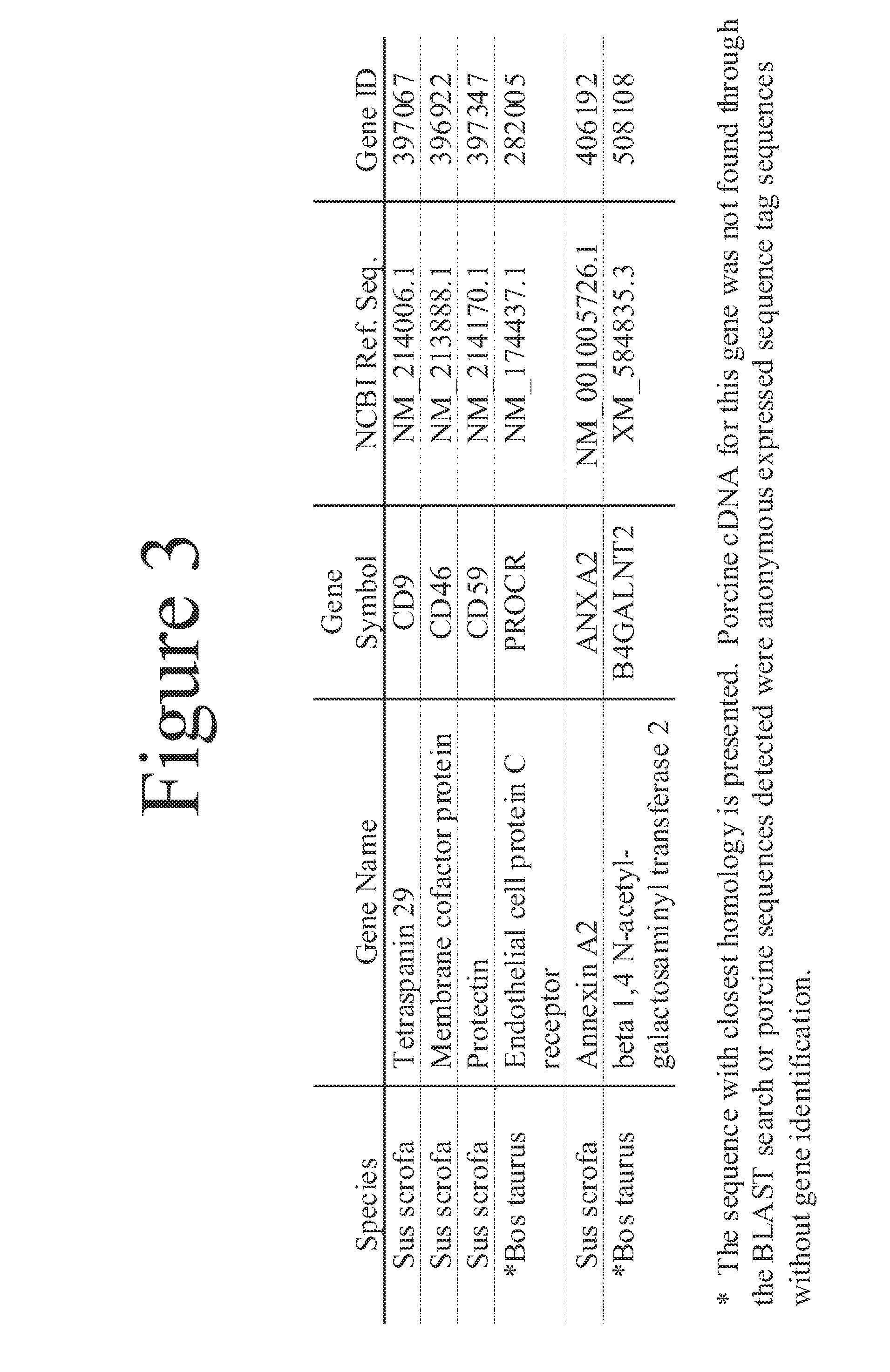
This document provides methods and materials involved in reducing cardiac xenograft rejection. For example, methods and materials for preparing transgenic pigs expressing reduced or no endogenous Sda or SDa-like glycans derived from the porcine β1,4 N-acetyl-galactosaminyl transferase 2 (B4GALNT2) glycosyltransferase and / or reduced or no endogenous α-Gal antigens, methods and materials for modifying the xenograft recipient's immunological response to non-Gal antigens (e.g. CD46, CD59, CD9, PROCR, and ANXA2) to reduce cardiac xenograft rejection, and methods and materials for monitoring the progress of xenotransplant immunologic rejection are provided.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Modified Organs and Cells for Xenotransplantation
InactiveUS20070089178A1Maintain integrityMaintaining viabilityBiocideGenetic material ingredientsHuman bodyGenetically engineered
Owner:RBC BIOTECH
Modified organs and cells for xenotransplantation
InactiveUS7166278B2Maintain integrityMaintaining viabilityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHeterograftsEngineered genetic
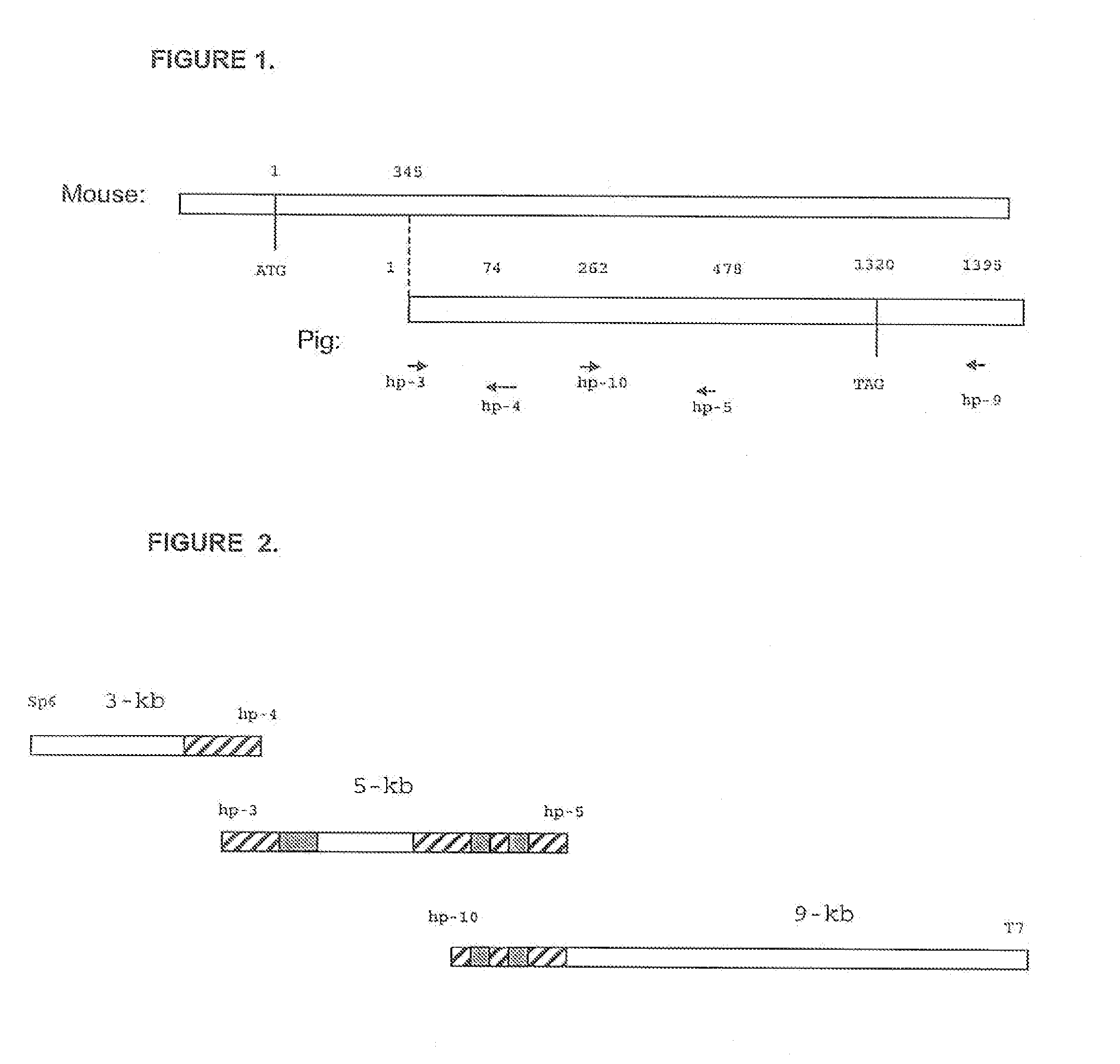
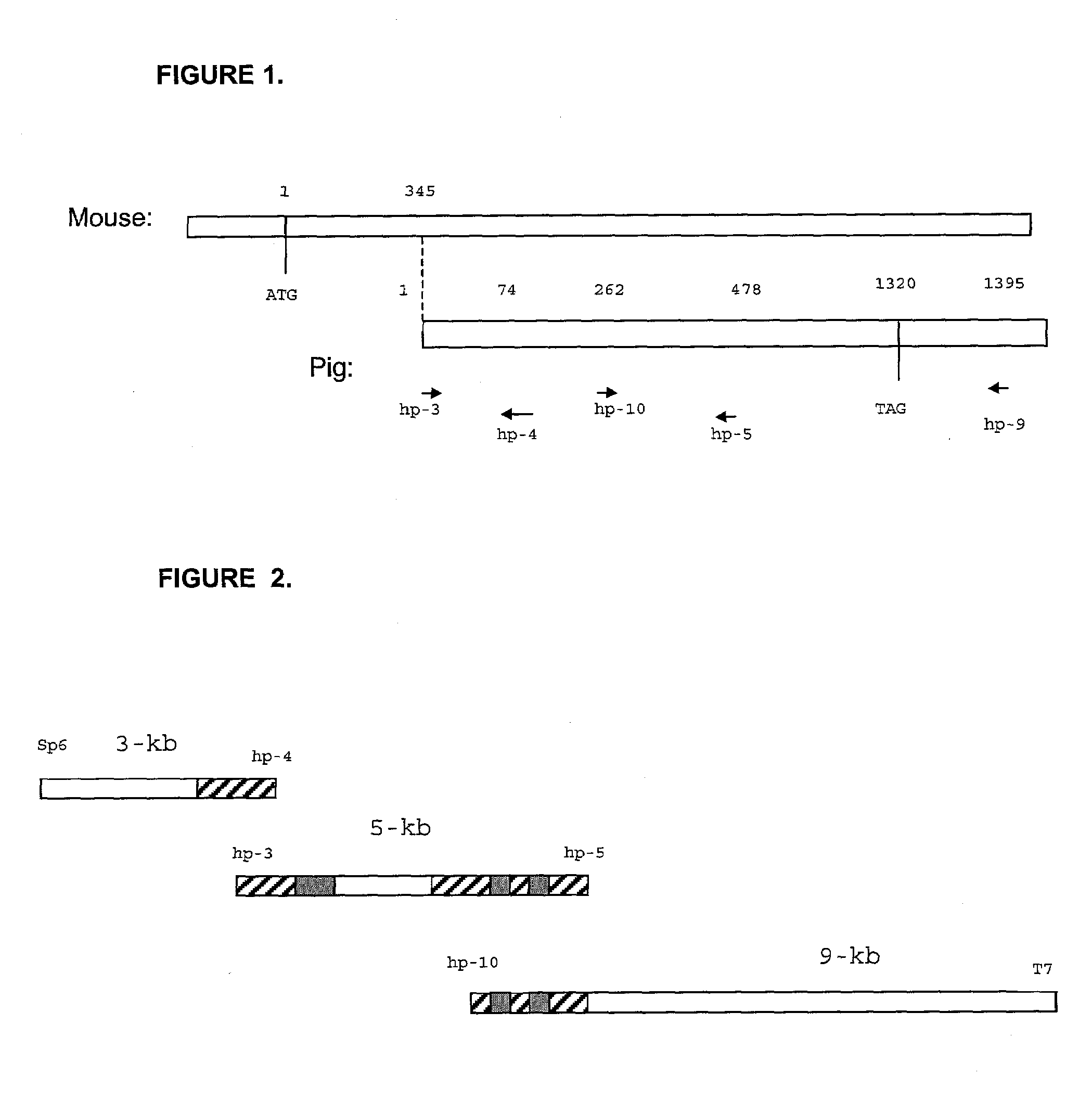
It has been discovered that there are at least two significant antigens present on the cells of animal species such as pigs that elicit an immune or inflammatory response immediately upon implantation into humans or contact with human serum. The first is an α-galactosyl (Gal) epitope, for example, Galα(1->3)Galβ(1->4)GlcNac (linear B type 2) or Galα(1->3) Galβ(1->4)Glc (linear B type 6). The second is an N-glycolylneuraminic acid (NeuGc) structure. By eliminating these epitopes, preferably by genetically engineering the animal so that the epitope is either not produced or is greatly reduced, or by chemical or enzymatic treatment of the animal's cells to remove the epitopes, it is possible to produce organs, tissues and cells suitable for xenotransplantation into humans. Cells can be rendered even more compatible by genetically engineering the animal to express a human complement regulatory protein (inhibitor), such as CD59, on its cells, or to express an excess of a pig complement regulatory protein.
Owner:RBC BIOTECH
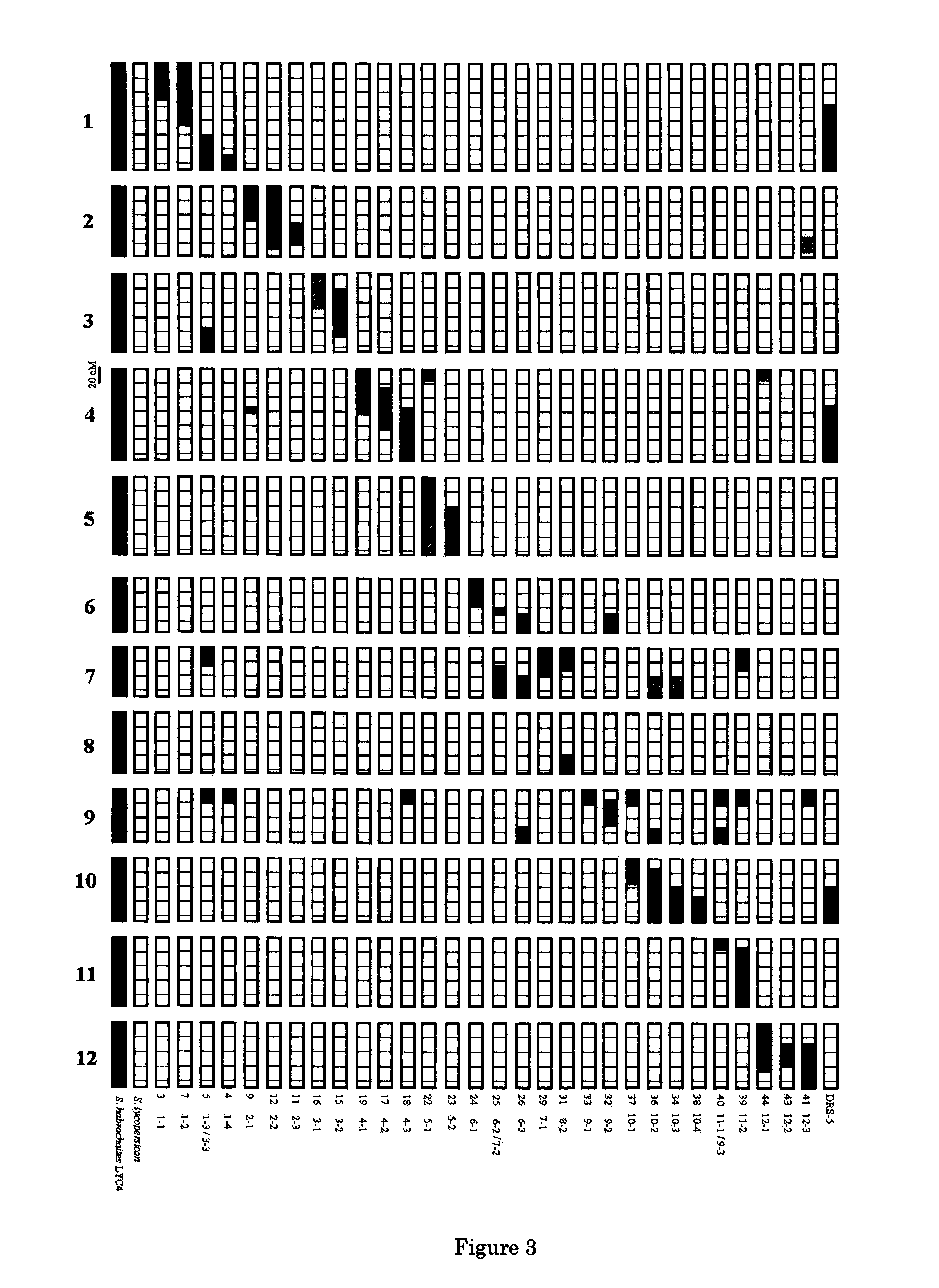
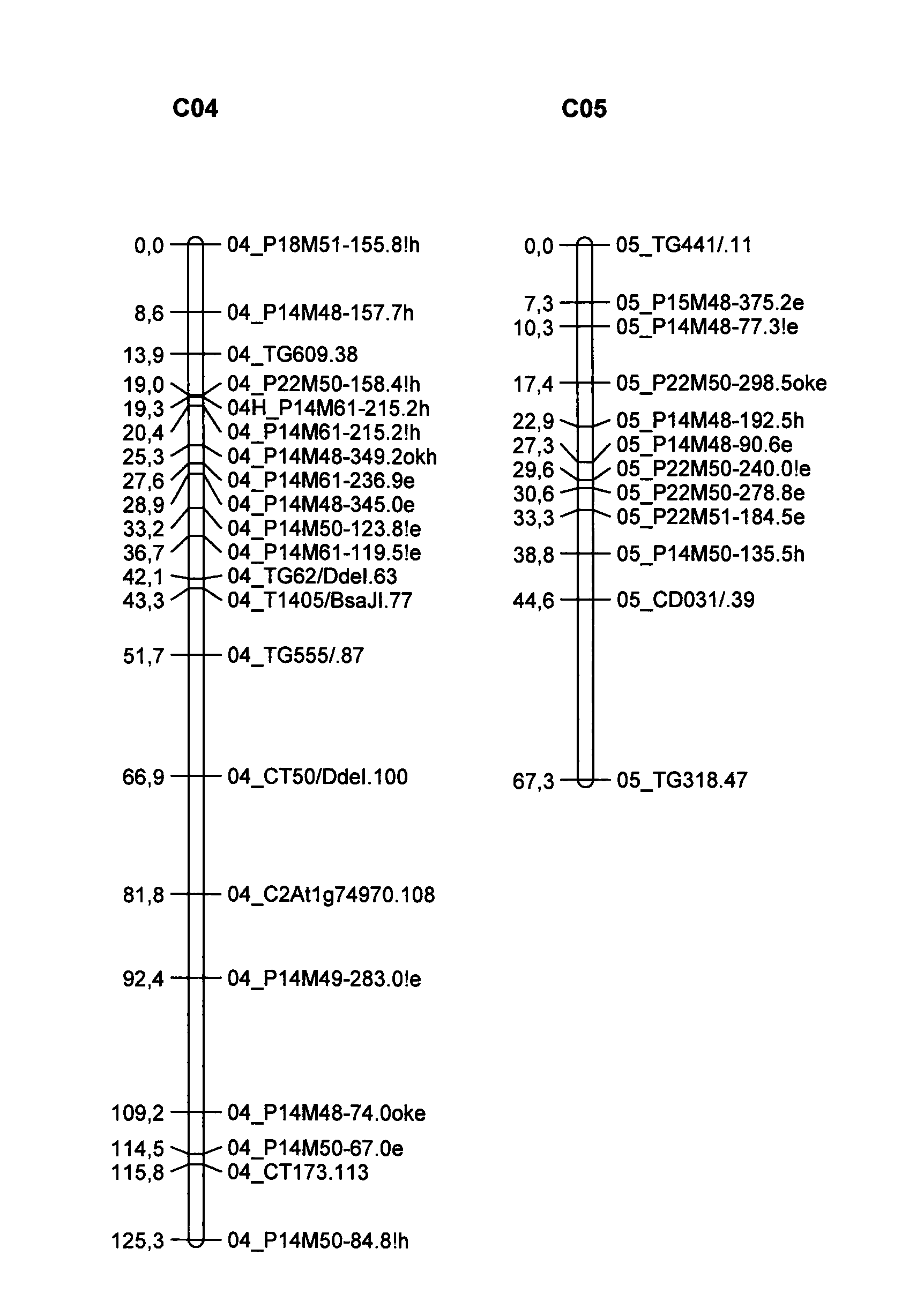
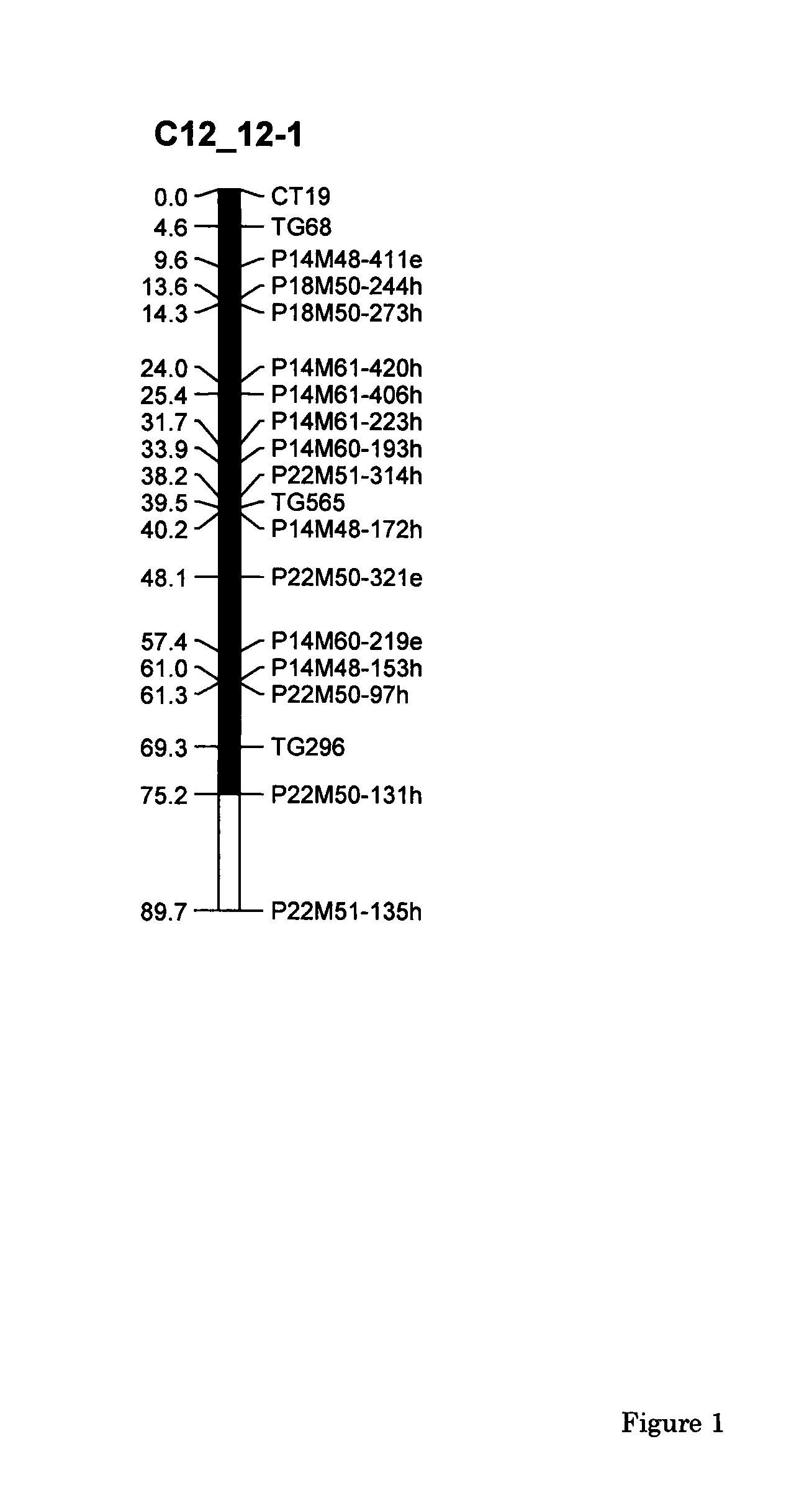
Parthenocarpic genetic elements derived from S. habrochaites
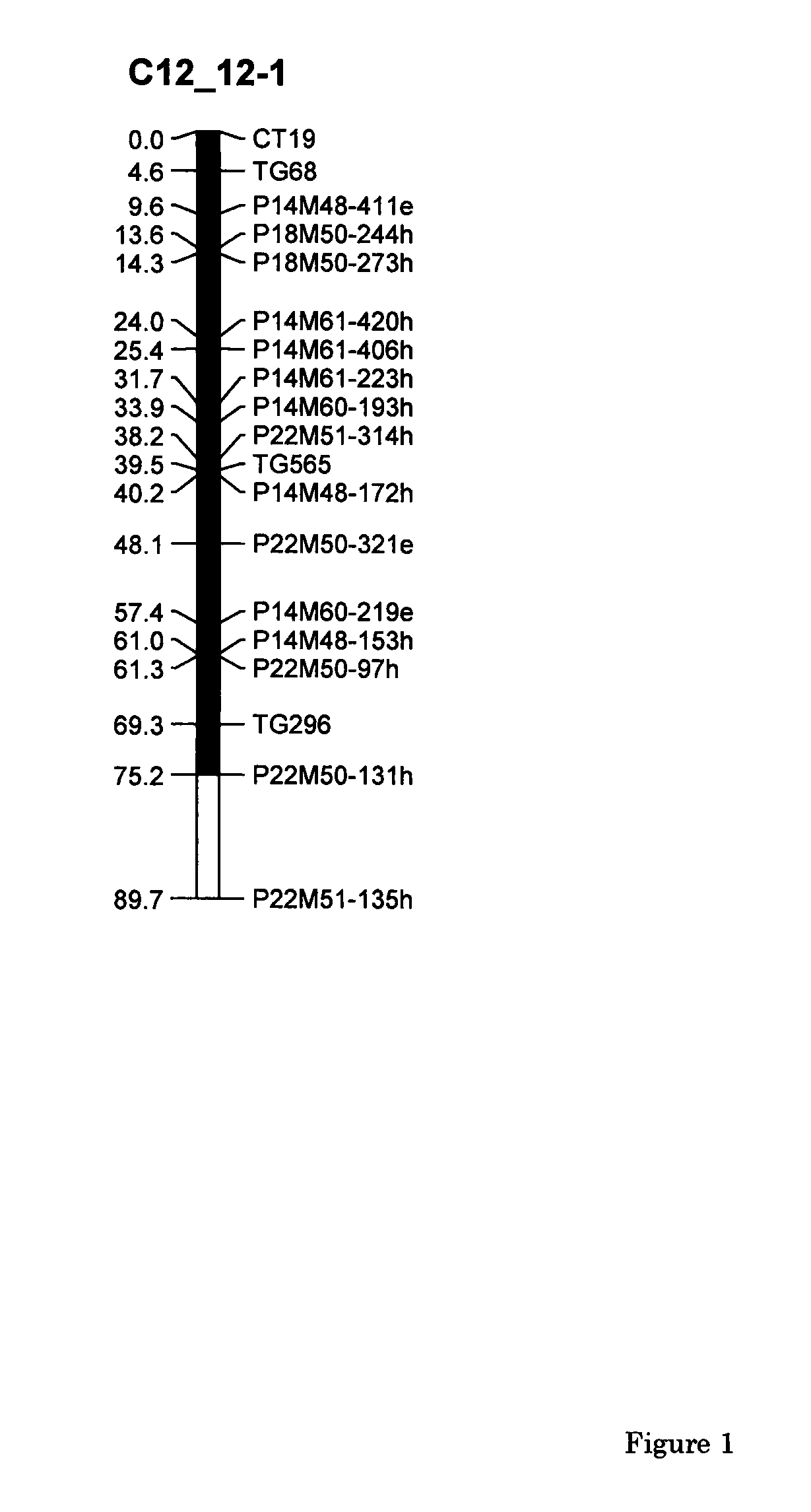
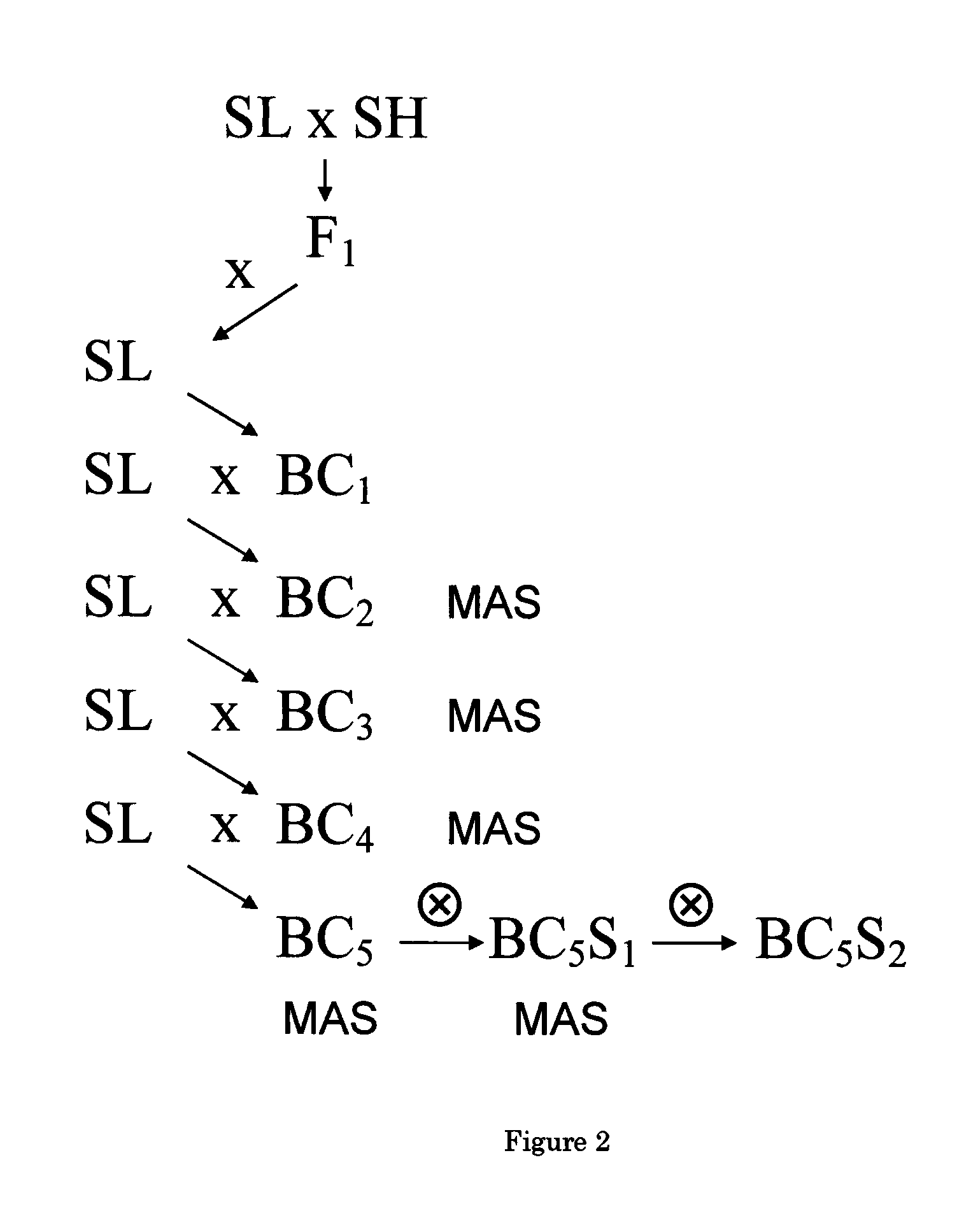
The present invention relates to a method of producing a parthenocarpic, and optionally male sterile, tomato plant comprising introgressing into said plant a genetic region from Chromosome 4, 5 and / or 12 of S. habrochaites LYC4 / 78, a representative sample of seed of which was deposited on 13 Nov. 2007 with the NCIMB under Accession number 41517, wherein the genetic region from Chromosome 4 of S. habrochaites LYC4 / 78 includes at least one marker selected from Marker CD59, RFLP Marker CT229, and COS Marker T1068, and wherein the genetic region from Chromosome 5 of S. habrochaites LYC4 / 78 includes at least one marker selected from COS Marker T1181, RFLP Marker TG441 and / or RFLP Marker CD31(A).
Owner:MONSANTO INVEST BV
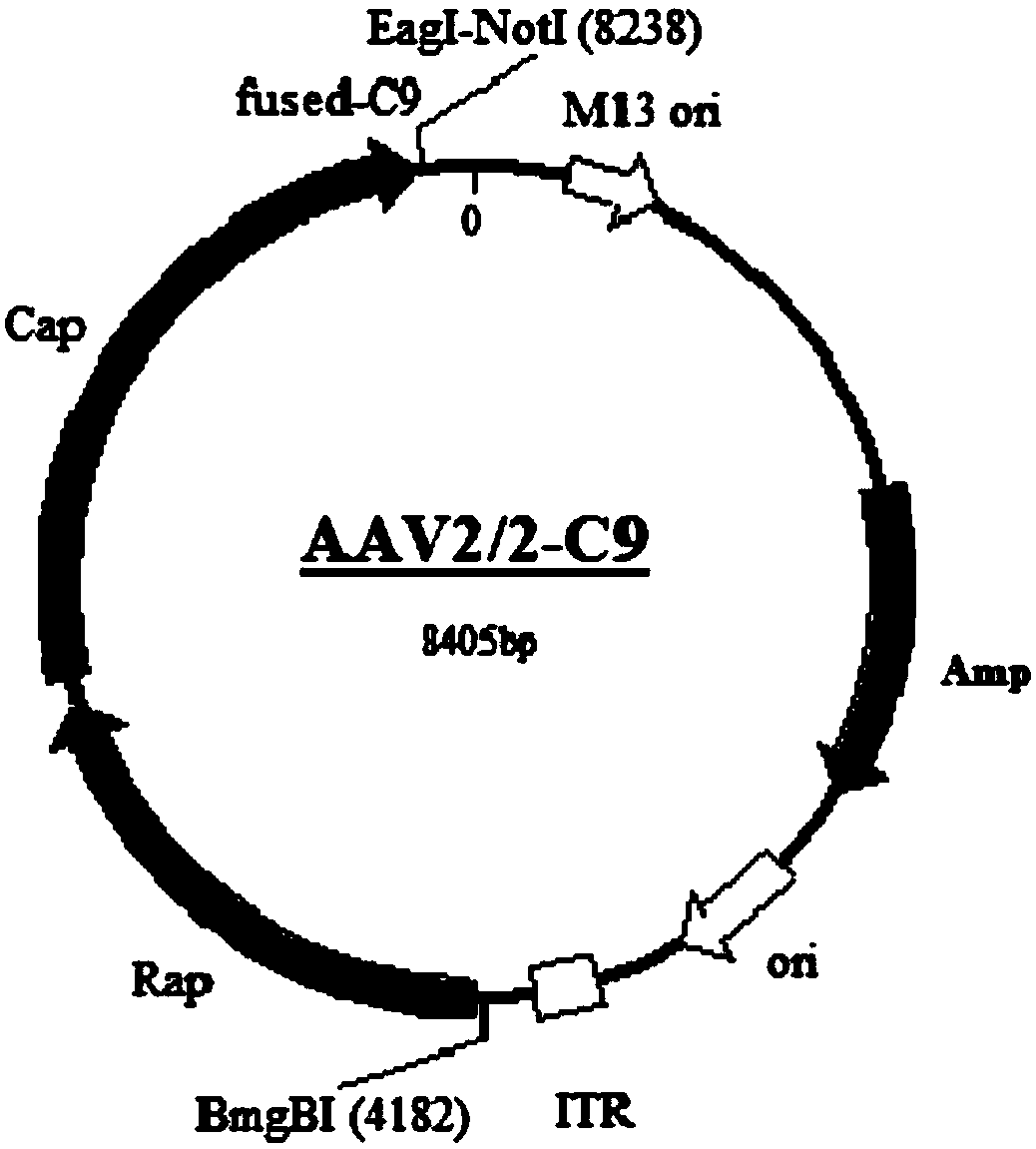
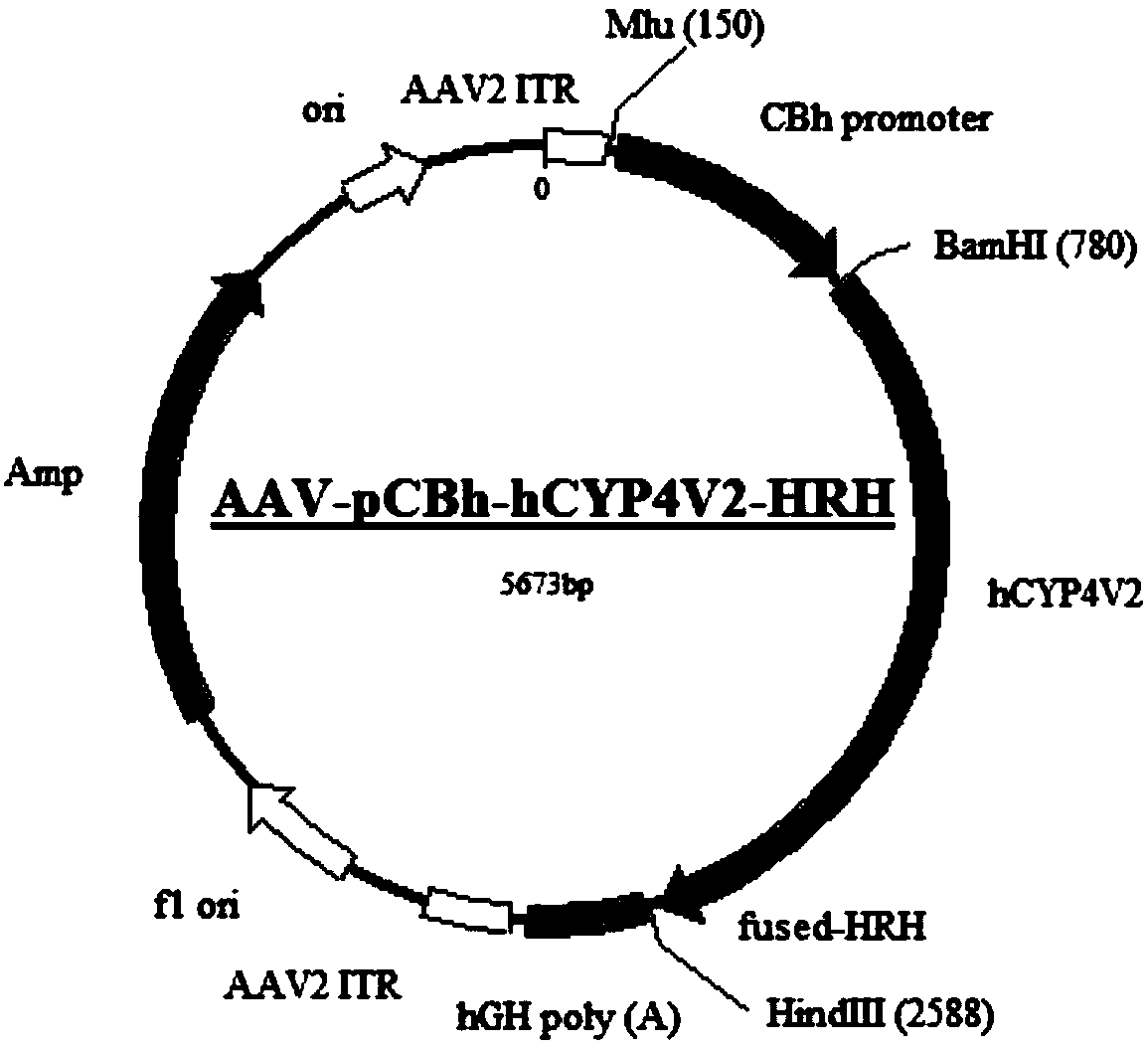
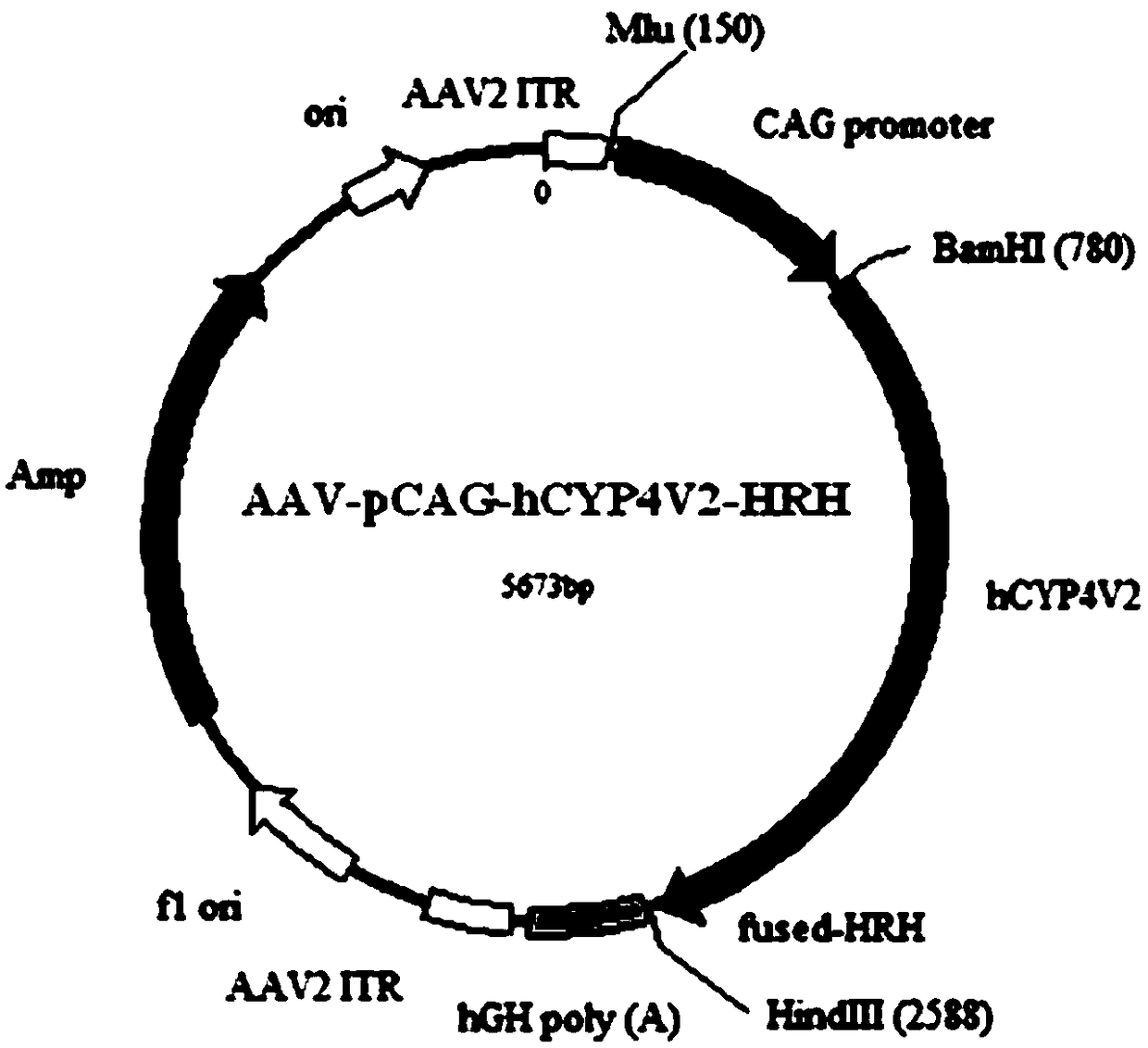
Gene carrier for treating or preventing bietti's crystalline dystrophy and application of gene carrier
The invention relates to a gene carrier for treating or preventing bietti's crystalline dystrophy (BCD) and application of the gene carrier. The gene carrier for treating or preventing bietti's crystalline dystrophy comprises a packaging plasmid and a carrier plasmid. The packaging plasmid is an AAV2 packaging plasmid where a gene sequence of anti-CD59 short-chain-polypeptide C9 is inserted; the carrier plasmid is an AAV carrier plasmid where a gene sequence of human cytochrome P450 superfamily protein CYP4V2, a gene sequence of anti-VEGF short-chain-polypeptide HRH and a starting sub sequenceare inserted. The AAV carrier can conduct fusion expression on C9 anti-CD59 short-chain-polypeptide to virus coat protein; coexpression of CYP4V2 and HRH can be achieved, protein function loss causedby CYP4V2 genic mutation in a RPE cell is compensated for, the normal function of the RPE cell can be effectively repaired, specificity antagonism of a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) can be achieved, and retinal atrophy caused by choroid hyperplasia is delayed. The invention further application of the gene carrier to preparation of medicine for treating or preventing bietti's crystalline dystrophy (BCD).
Owner:深圳泓熙生物科技发展有限公司
Parthenocarpic Genetic Elements Derived From S. Habrochaites
InactiveUS20100146656A1Microbiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesGenetic elementCD31
The present invention relates to a method of producing a parthenocarpic, and optionally male sterile, tomato plant comprising introgressing into said plant a genetic region from Chromosome 4, 5 and / or 12 of S. habrochaites LYC4 / 78, a representative sample of seed of which was deposited on 13 Nov. 2007 with the NCIMB under Accession number 41517, wherein the genetic region from Chromosome 4 of S. habrochaites LYC4 / 78 includes at least one marker selected from Marker CD59, RFLP Marker CT229, and COS Marker T1068, and wherein the genetic region from Chromosome 5 of S. habrochaites LYC4 / 78 includes at least one marker selected from COS Marker T1181, RFLP Marker TG441 and / or RFLP Marker CD31(A).
Owner:MONSANTO INVEST BV
Cytotoxicity mediation of cells evidencing surface expression of CD59
InactiveUS20080025977A1Raise the possibilityEfficient targetingDigestive systemBiological material analysisAbnormal tissue growthLymphatic Spread
This invention relates to the staging, diagnosis and treatment of cancerous diseases (both primary tumors and tumor metastases), particularly to the mediation of cytotoxicity of tumor cells; and most particularly to the use of cancerous disease modifying antibodies (CDMAB), optionally in combination with one or more CDMAB / chemotherapeutic agents, as a means for initiating the cytotoxic response. The invention further relates to binding assays, which utilize the CDMAB of the instant invention. The anti-cancer antibodies can be conjugated to toxins, enzymes, radioactive compounds, cytokines, interferons, target or reporter moieties and hematogenous cells.
Owner:ARIUS RES +1
Method and kit for cancer diagnosis
Owner:PROSTASOM
Recombinant antibodies against CD55 and CD59 and uses thereof
InactiveUS8034902B2Increased activationUseful in treatmentSugar derivativesArtificial cell constructsCD20Region specific
The present invention relates to recombinant antibody molecules and functional fragments thereof, useful for neutralizing the complement regulatory proteins CD55 and CD59, compositions comprising the recombinant molecules and methods of using the recombinant molecules for controlling complement resistance in cancer. The present invention further relates to heterodimeric diabody molecules comprising variable regions specific for CD55 / CD59 and CD20.
Owner:QUARK FARMACUITIKALS INC
Tumor angiogenesis associated genes and a method for their identification
InactiveUS20090035312A1Inhibit angiogenesisReduced microvessel densityOrganic active ingredientsFungiAbnormal tissue growthMouse tumor
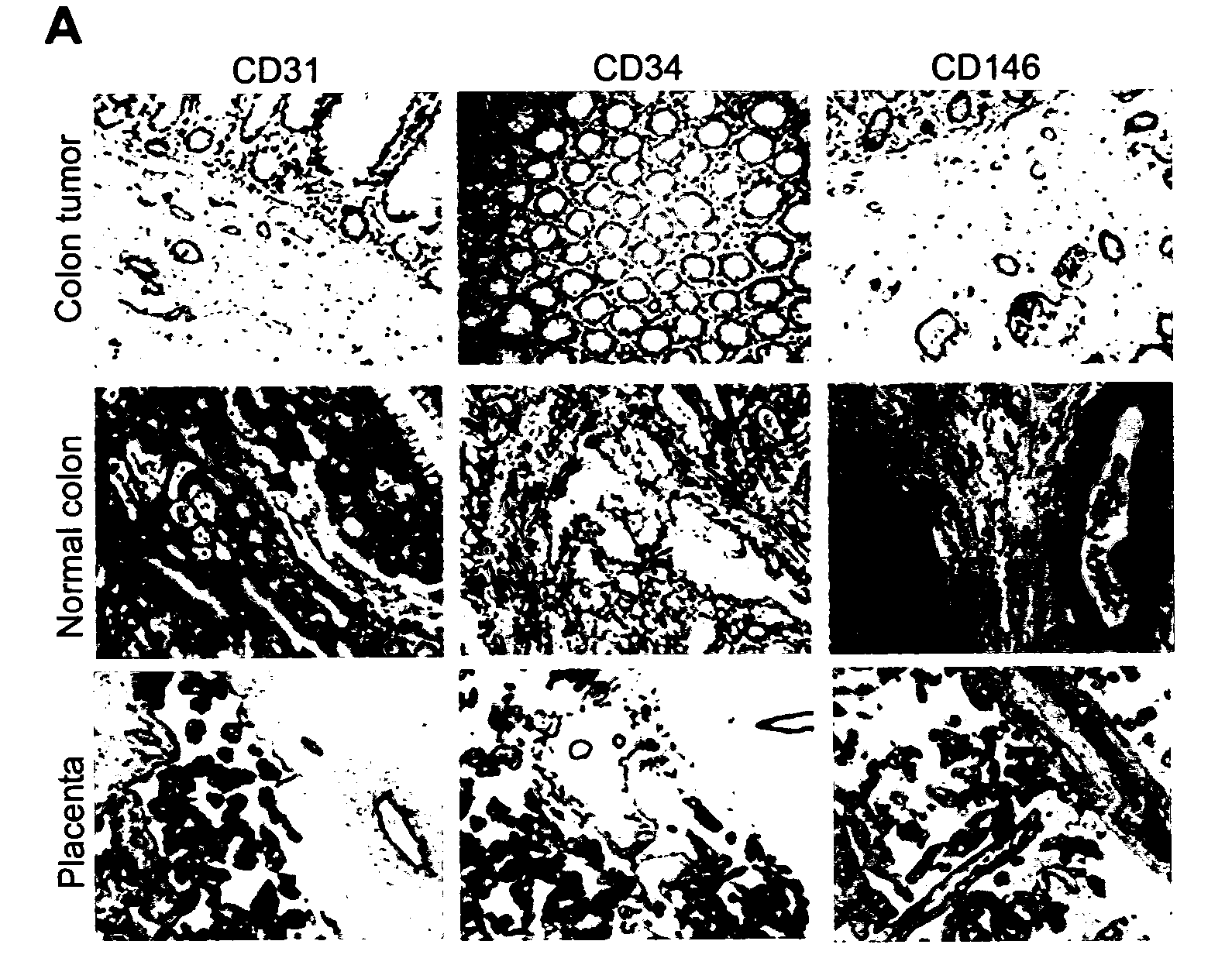
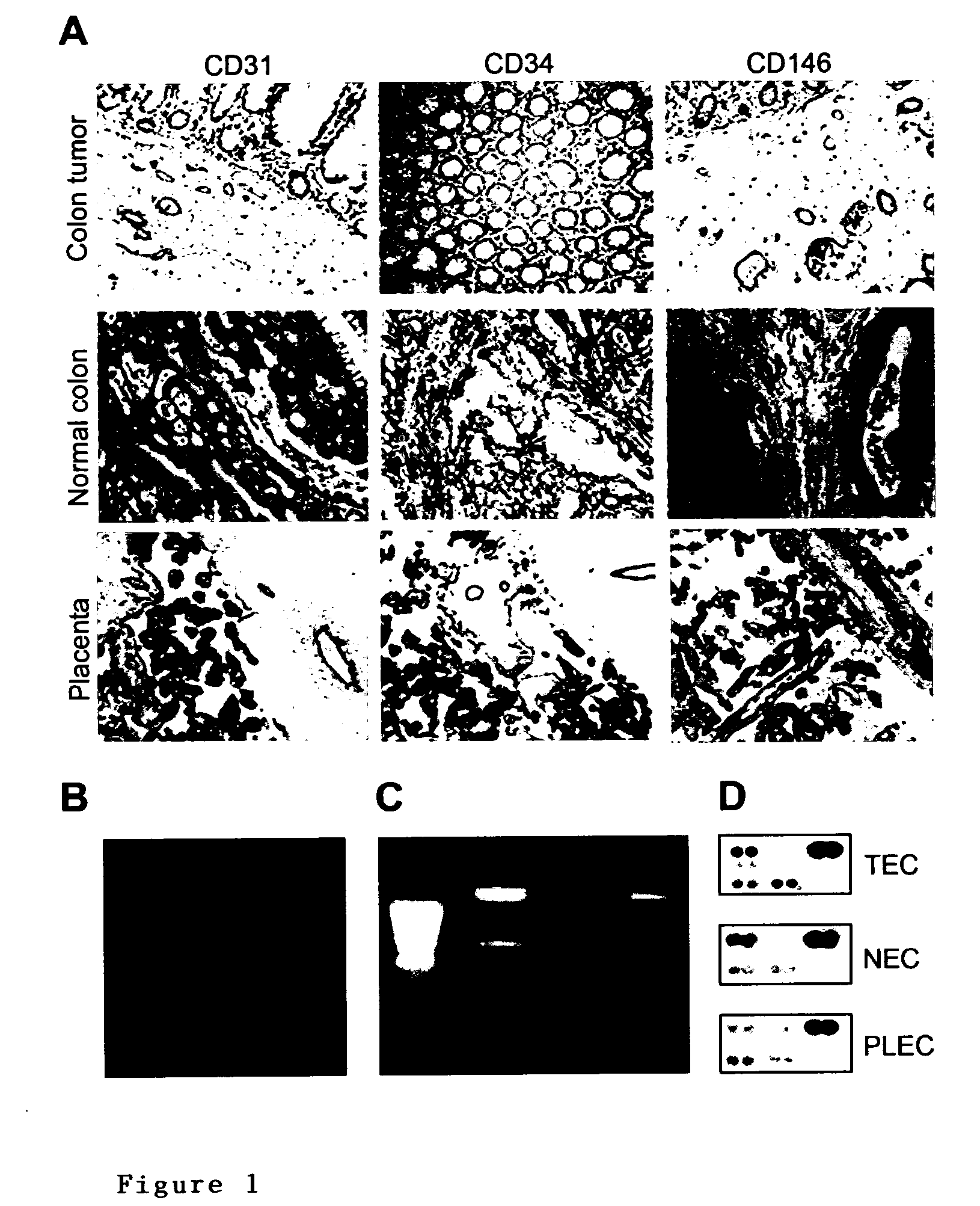
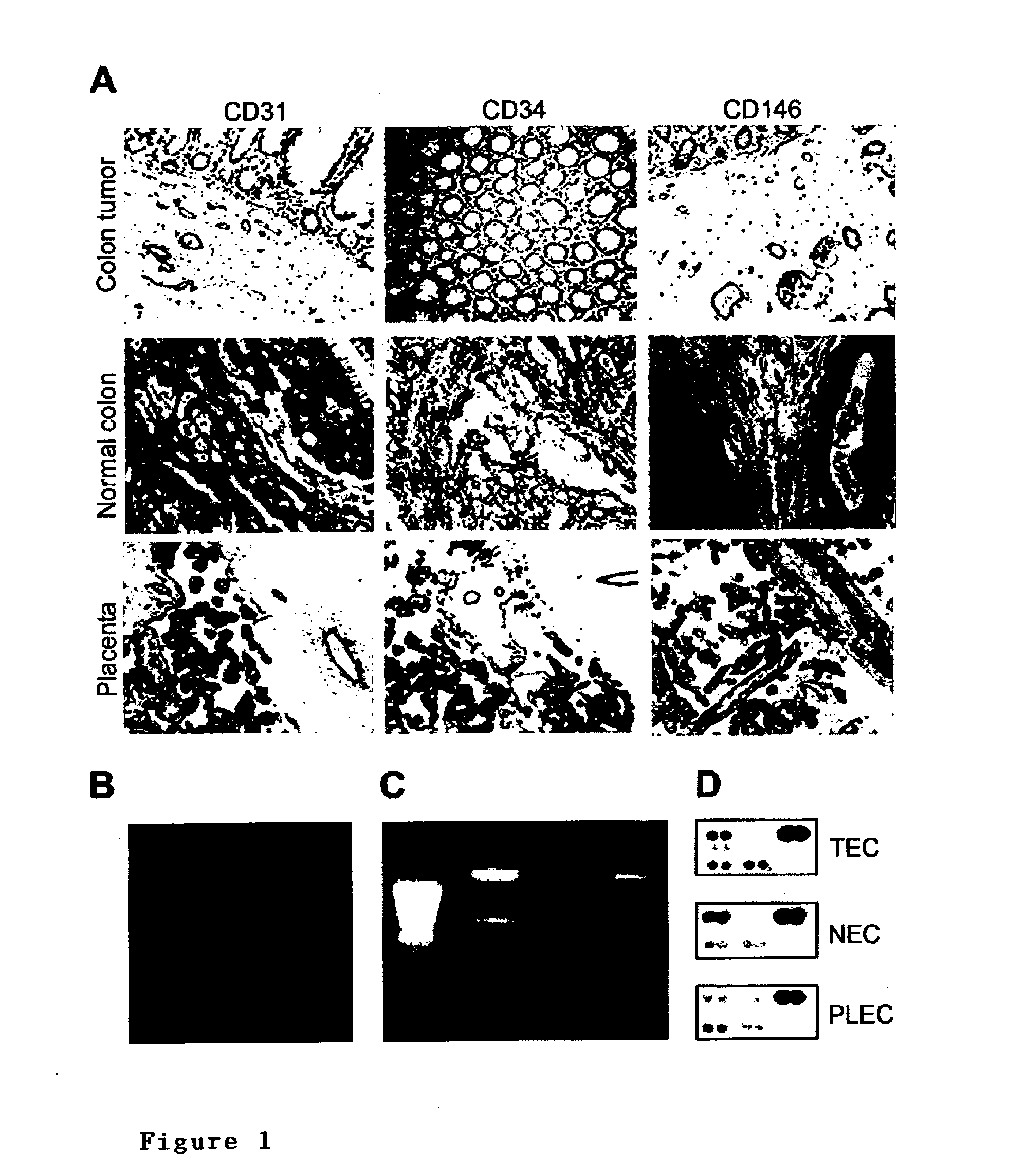
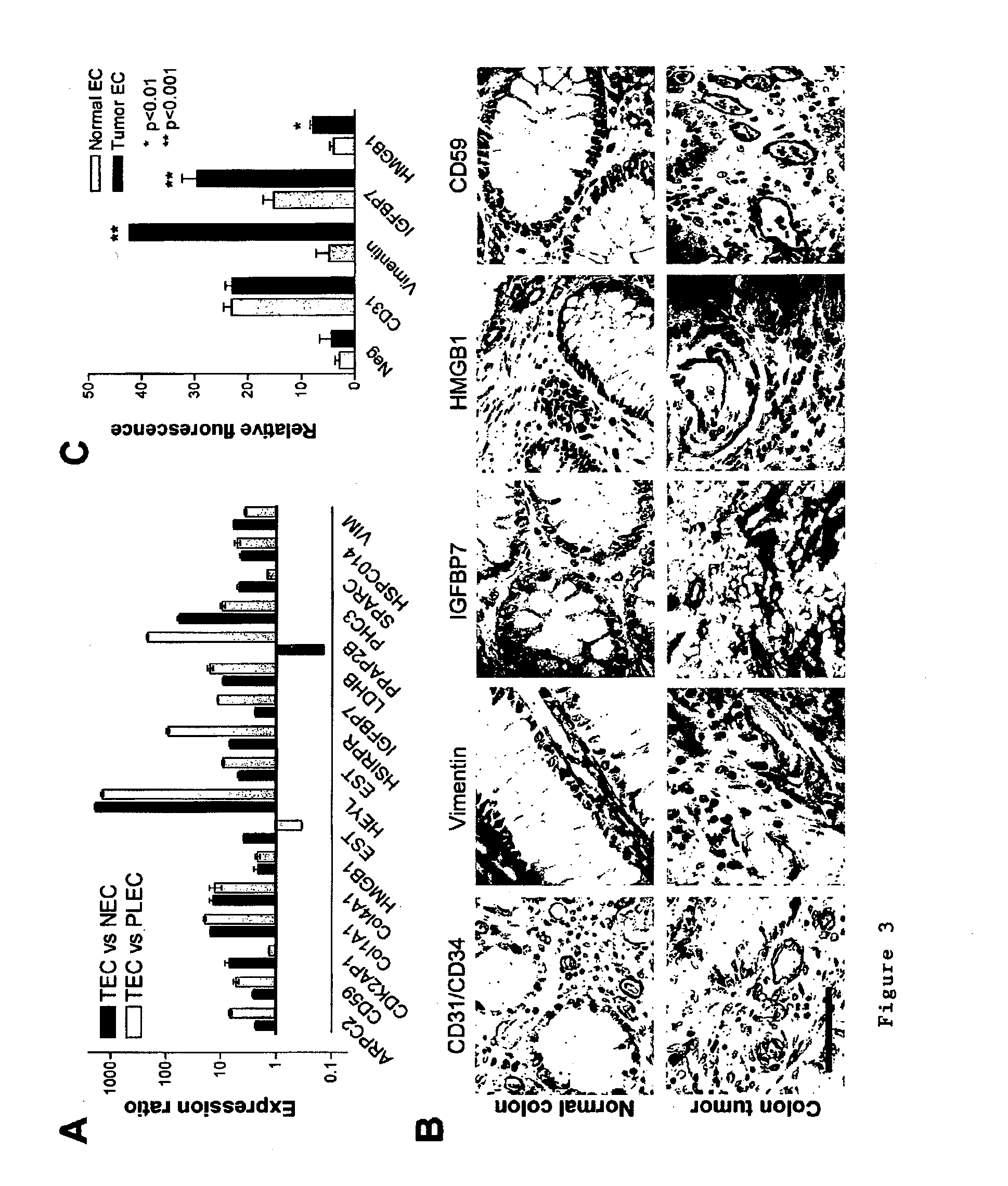
Methods of identifying specific target molecules for design of anti-angiogenic and vascular targeting approaches are disclosed. Transcriptional profiles of tumor endothelial cells were compared with that of normal resting endothelial cells, normal but angiogenically activated placental endothelial cells, and cultured endothelial cells. Although the majority of transcripts were classified as general angiogenesis markers, 17 genes were identified that show specific overexpression in tumor endothelium. Antibody targeting of four cell-surface expressed or secreted products (vimentin, CD59, HMGB1 and IGFBP7) inhibited angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Finally, targeting endothelial vimentin in a mouse tumor model significantly inhibited tumor growth and reduced microvessel density. The results demonstrate the utility of the identification and subsequent targeting of specific tumor endothelial markers for anticancer therapy.
Owner:MAASTRICHT UNIVERSITY
Mass spectrometric methods and products
ActiveUS7833725B2Rapid and reliable measureAccurate methodPeptidesBiological testingMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryBiology
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Surrogates of post-translationally modified proteins and uses thereof
ActiveUS9417248B2Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCompound specificDisease
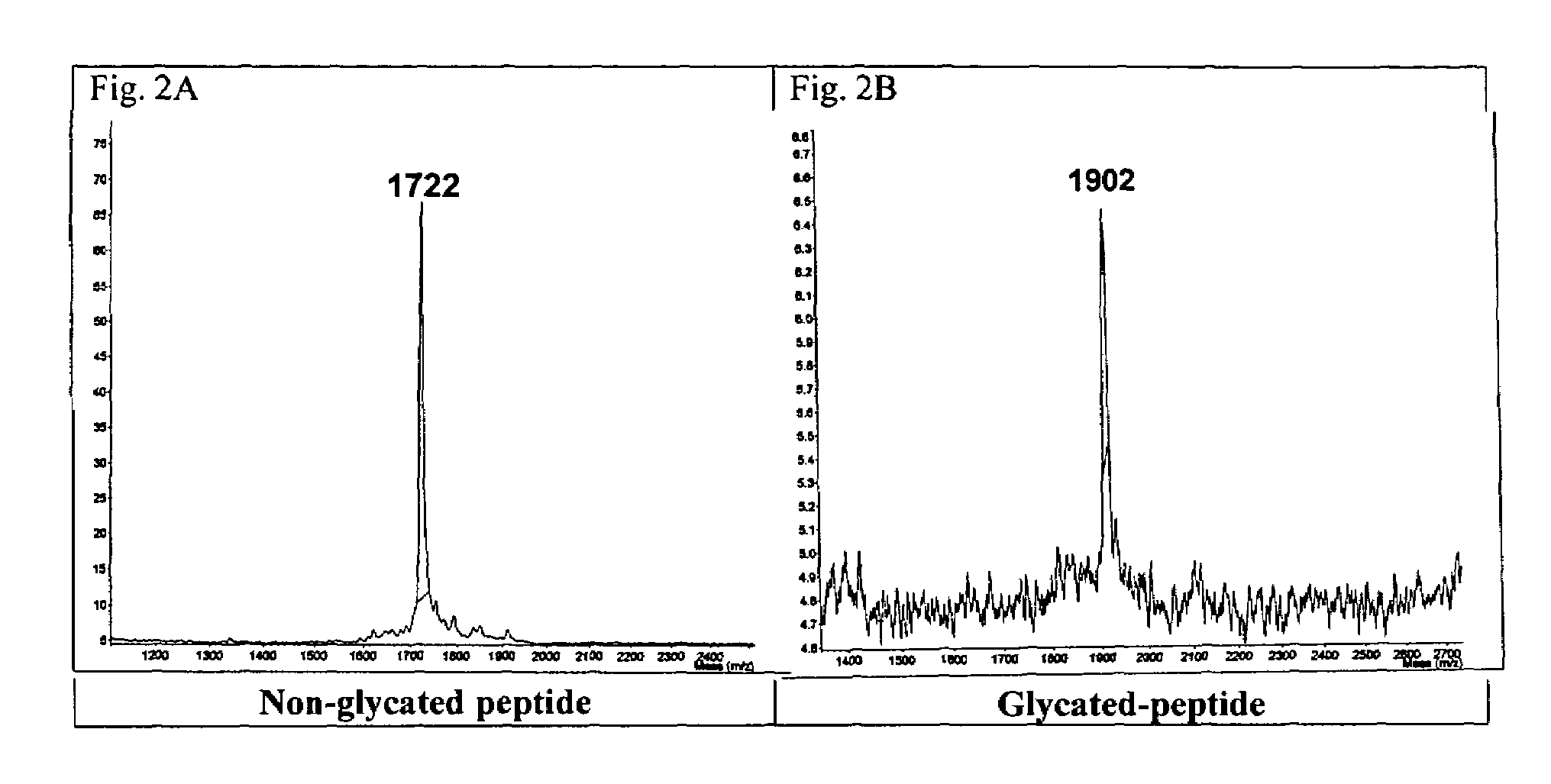
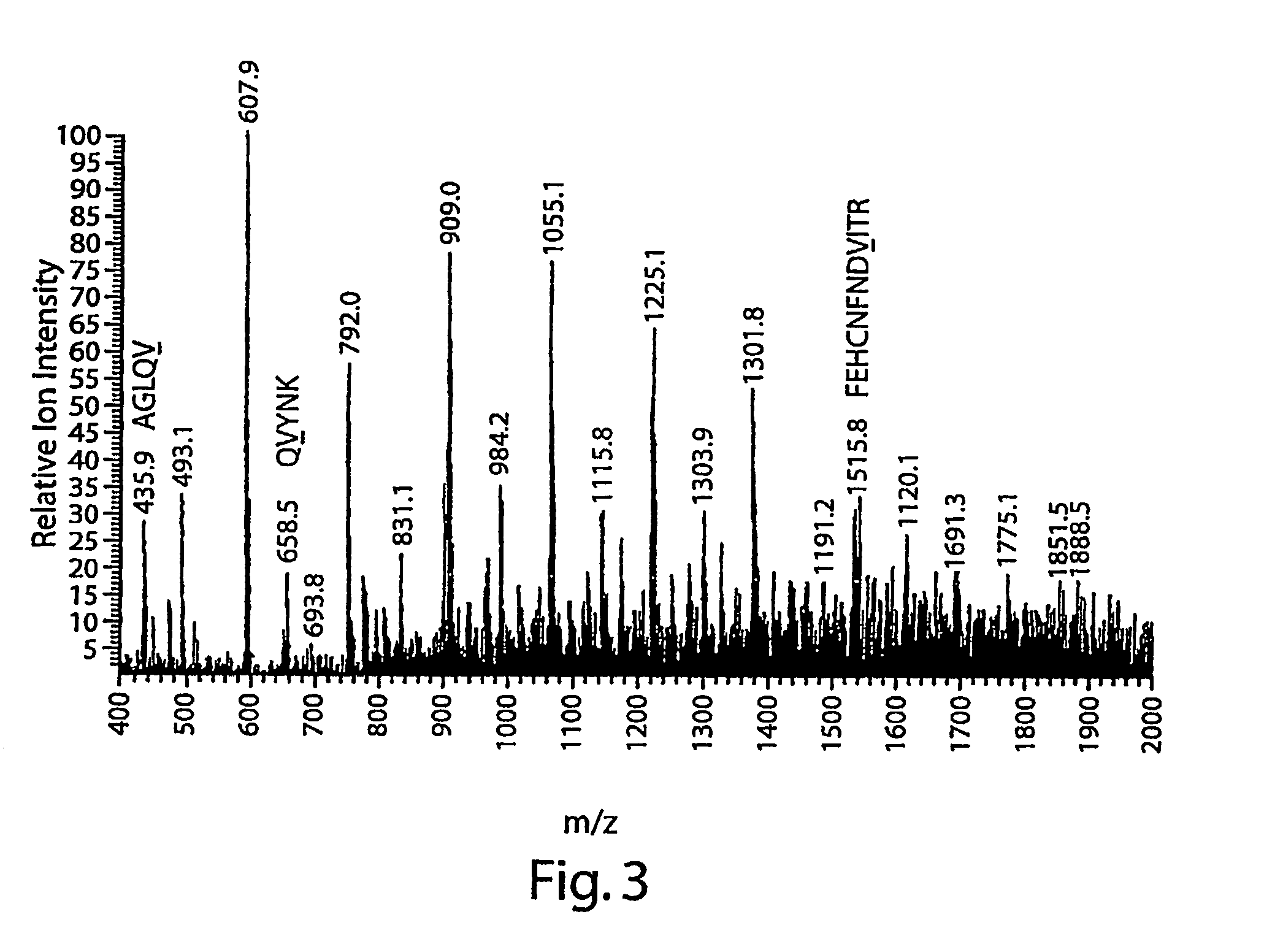
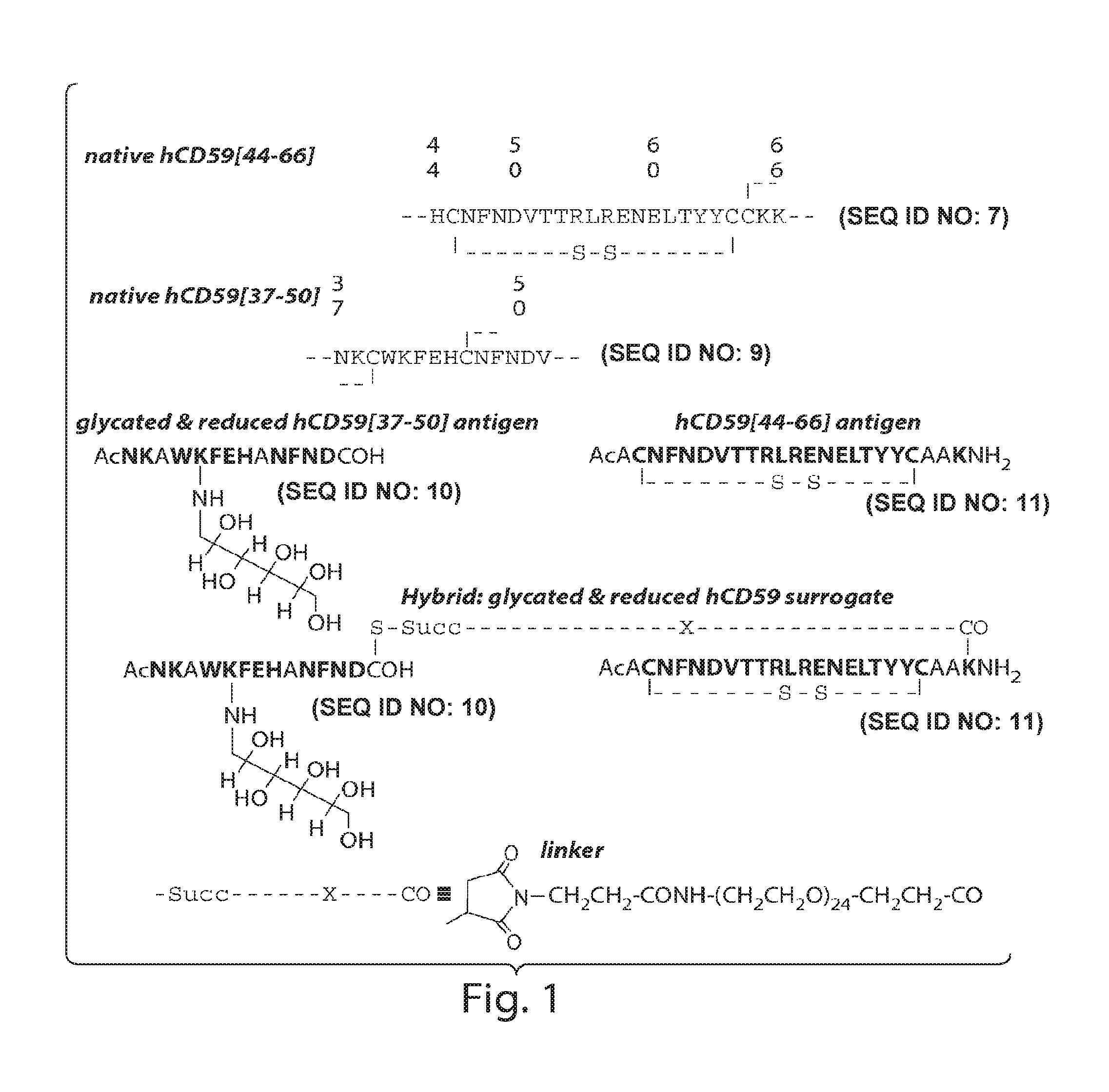
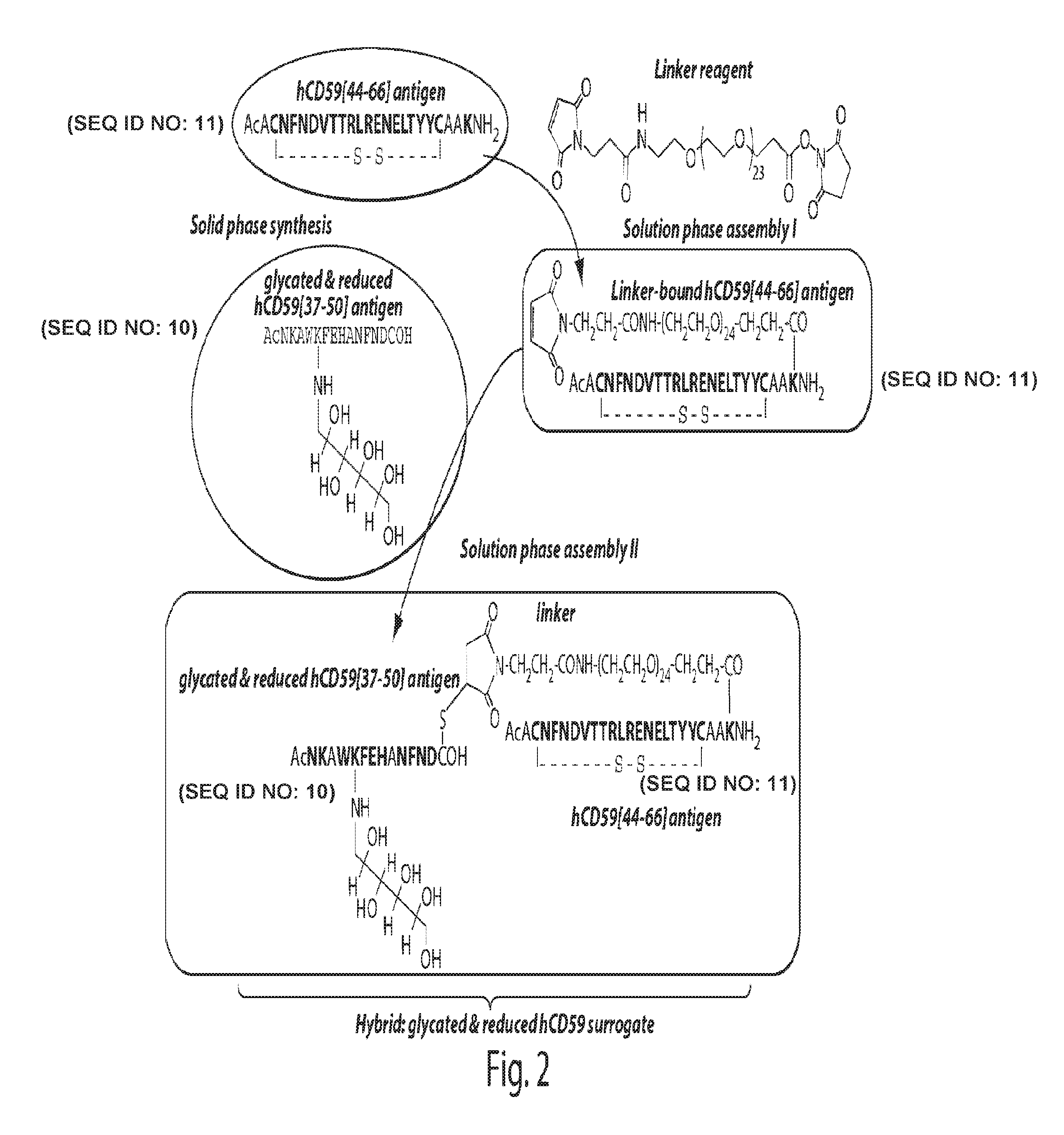
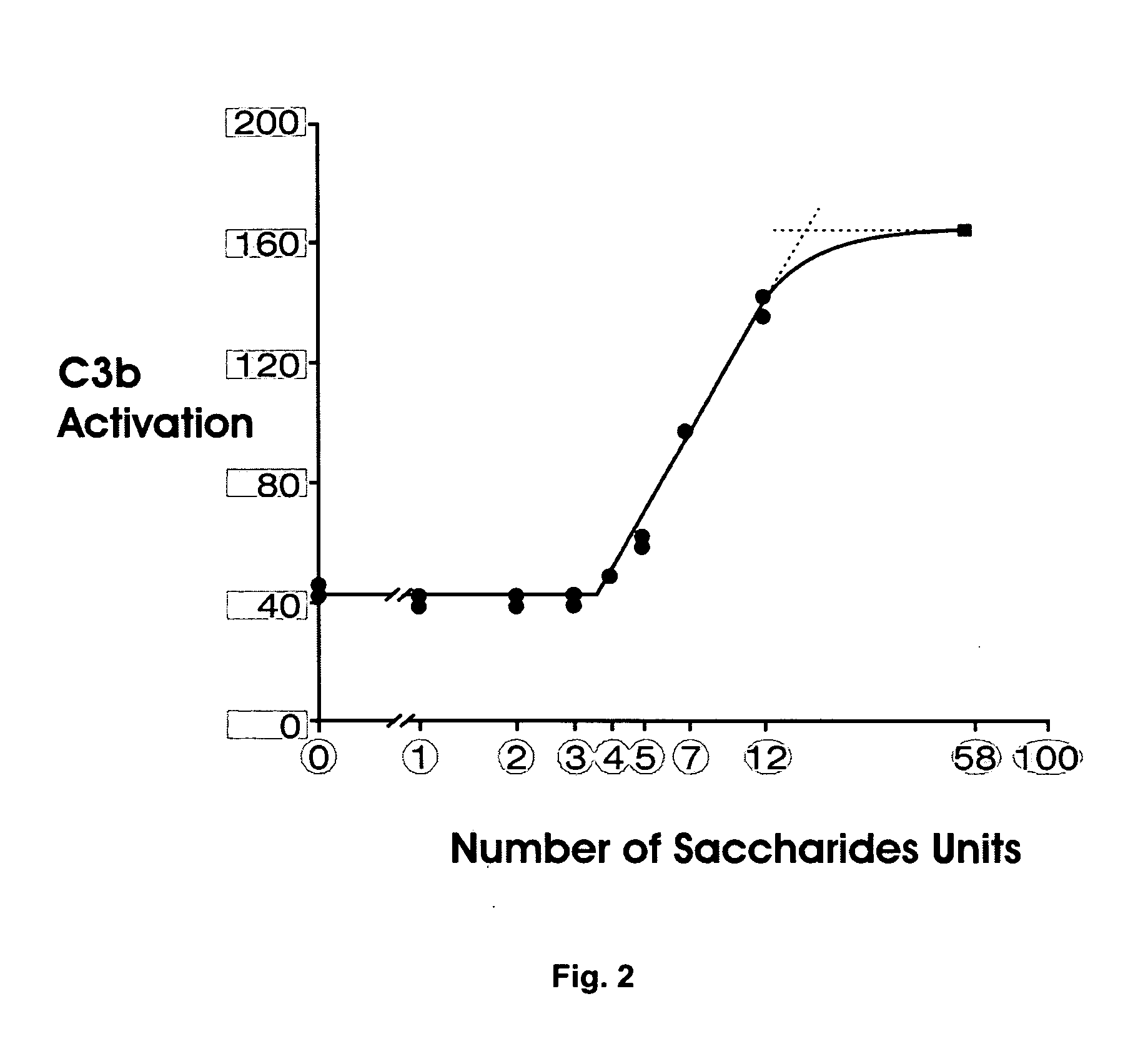
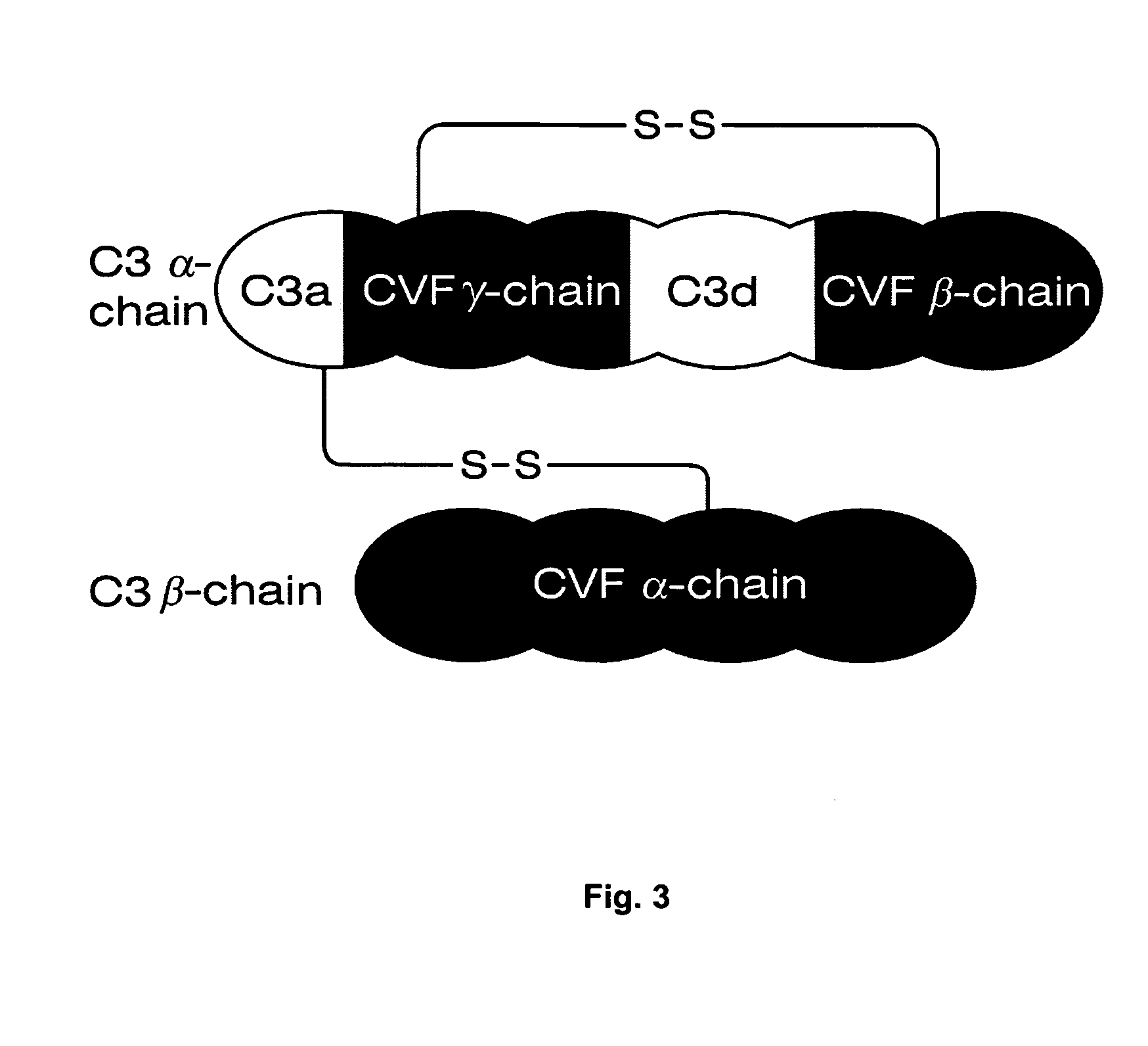
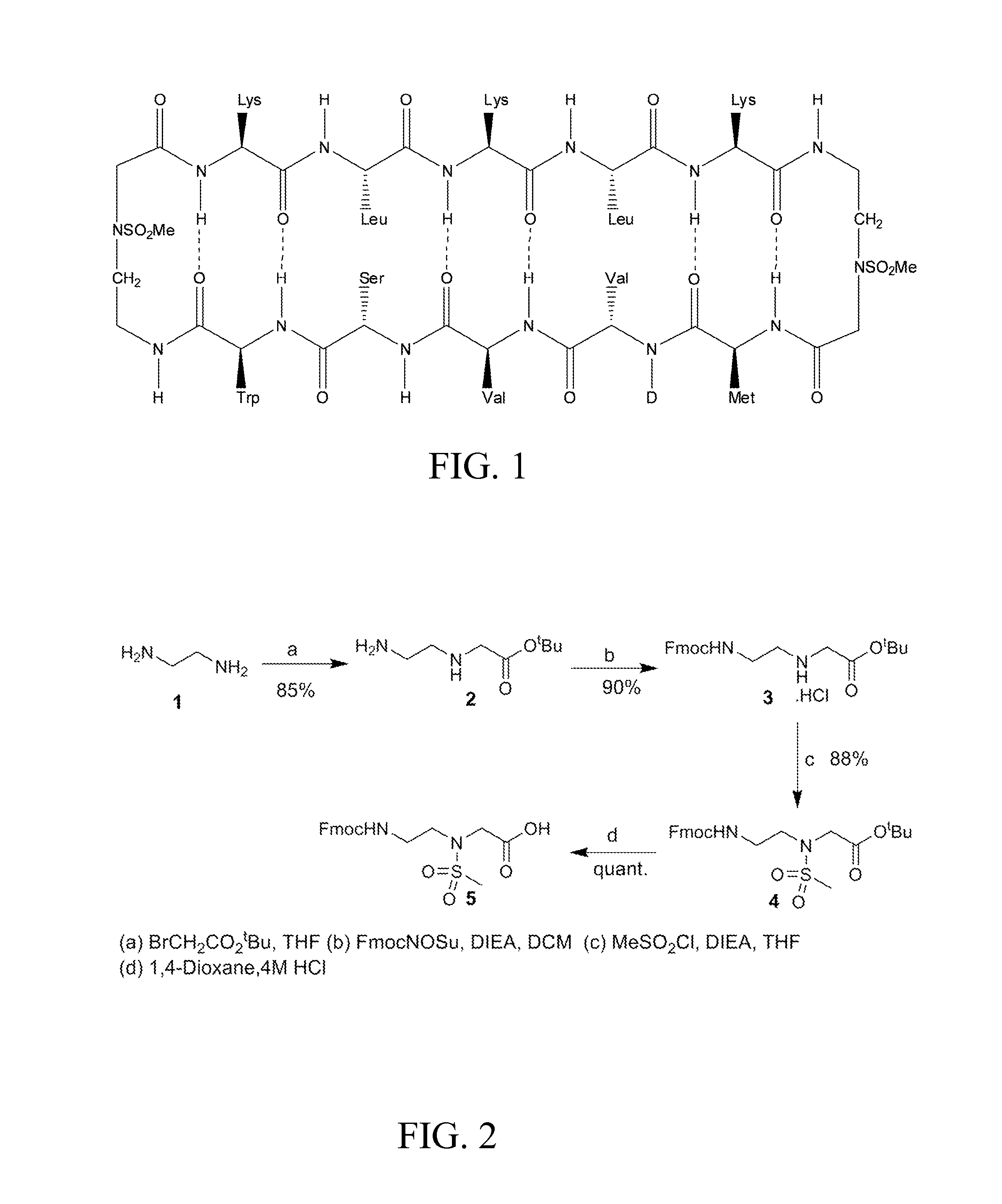
The present invention provides compounds that are surrogates of post-translationally modified proteins and uses thereof. Numerous diseases are associated with post-translationally modified proteins that are difficult to obtain in homogenous form and in quantities needed for immunization and use as convenient standards, calibrators, and / or reference compounds that facilitate the detection and analysis of endogenous post-translationally modified proteins. The surrogate compounds of the invention typically comprise antigenic epitopes (one of which carries a post-translational modification) that are tethered by a flexible and hydrophilic linker. The resulting compound behaves like a surrogate of the post-translationally modified protein because it preserves the character of the included antigens and allows recognition by specific antibodies targeting the individual antigens. The surrogate compounds may be prepared by covalently joining two or more polypeptide epitopes using one or more linkers, wherein at least one of the epitopes comprises a post-translational modification. In one aspect, the surrogate compounds of the invention comprise a C-terminal epitope and a glycated epitope of human CD59. The inventive methods allow quantification of the levels of glycated CD59 in the serum in human subjects, particularly those with diabetes or pre-diabetes. This technological platform of post-translationally modified protein surrogates can be applied to other diseases associated with post-translationally modified proteins (e.g., autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and systemic lupus erythematosus). In another aspect, the invention provides antibodies that bind specifically to the compounds of the invention and methods for producing such antibodies.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Fusion protein of anti-C3d targeted single-chain antibody and CD59, and application of fusion protein
ActiveCN110922489AExcellent antigen binding activityImprove survival ratePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAutoimmune conditionAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention discloses a fusion protein of a single-chain antibody of a human anti-complement C3d molecule and a complement inhibitor CD59. The antibody has excellent antigen binding activity. Biological distribution experiments prove that the fusion protein provided by the invention can be rapidly and highly aggregated at an arthritis part after entering a rheumatoid arthritis mouse model, and has an excellent anti-adhesion / anti-inflammation targeting inhibition effect. In treatment of MRL / lpr lupus erythematosus mice, the fusion protein provided by the invention can obviously improve the survival rate of the mice, and symptoms of proteinuria, glomerular score, interstitial inflammation, vasculitis, crescent / necrosis and the like of a treatment group are obviously improved, so that the fusion protein provided by the invention has an excellent application prospect in preparation of medicaments for treating autoimmune diseases.
Owner:BEIJING COMPLEMENT THERAPEUTICS LTD
Method of developing an immunogenic composition and HIV vaccine
InactiveUS20050112143A1Broad antigenic responseEasy to produceVirus peptidesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismImmune recognitionComplement factor I
An antigenic and immunogenic composition of predetermined inactivated strains of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is disclosed. Inactivation is through psoralen and ultraviolet radiation; the composition is rendered more effective by the removal of structural features of HIV that interfere with immune response. In particular, sialic acid is removed to enhance immune recognition of the composition and to impair Complement Factor H binding. CD55 and CD59 are also removed to prevent the binding of Complement Factor H. Determination of strains for inactivation may be though immunotherapeutic genotyping or probabilistic assessment of risk of exposure.
Owner:KARP NELSON M M D
Peptides for the treatment of cancer
Owner:H LEE MOFFITT CANCER CENT & RES INST INC +1
Mass Spectrometric Methods and Products
ActiveUS20100009378A1Rapid and reliable measureAccurate methodMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptidesAssayMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Antibody targeted complement inhibitor with anti-inflammatory action
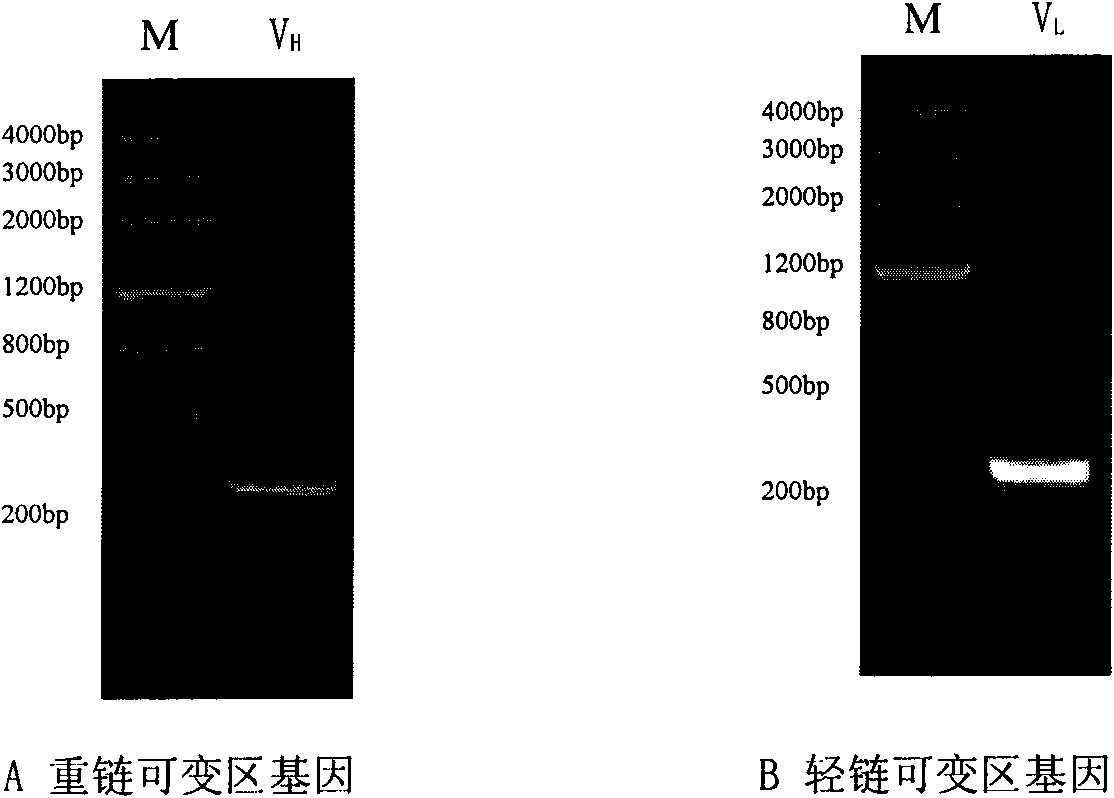
The invention discloses an anti-P-selectin single-chain antibody targeted complement inhibitor ScFv-CD59 and application thereof. The invention aims to provide an anti-P-selectin single-chain antibody targeted complement inhibitor ScFv-CD59 with specific targeting and the application thereof in preparing medicaments for treating systemic inflammations. The anti-P-selectin single-chain antibody targeted complement inhibitor ScFv-CD59 is a fusion protein obtained by connecting the amino terminal of the anti-P-selectin single-chain antibody ScFv with the complement inhibitor CD59 by using a connecting peptide. The experiment proves that the ScFv-CD59 can obviously improve the efficiency of inhibiting the complement-mediated cell cracking, can achieve high-degree accumulation at the immune injury part, can obviously inhibit the occurrence and degeneration of inflammations and can obviously reduce the side effect of infection caused by the complement inhibitor. Therefore, the ScFv-CD59 can be used as an active ingredient to be prepared into a novel gene engineering targeted protein medicament with a targeted P-selectin complement inhibitor for treating inflammations. The invention plays an important role in the pharmaceutical field and has wide application prospects.
Owner:INST OF PLA FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Agents and methods
InactiveCN104812413AVirus peptidesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCD43CD44
The invention provides an agent comprising: (i) a T cell antigen, and (ii) a binding partner for any of CD22, CD23, CD30, CD74, CD70, CD43, CD44, CD47, CD54, CD58, CD62L, CD95, HLA-DR, CD59, CD55, wherein, following binding of the agent to a cell that expresses any of CD22, CD23, CD30, CD74, CD70, CD43, CD44, CD47, CD54, CD58, CD62L, CD95, HLA-DR, CD59, CD55, the agent is internalised and the T cell antigen is presented on the surface of the cell in a form that can be recognised by a T cell.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BIRMINGHAM
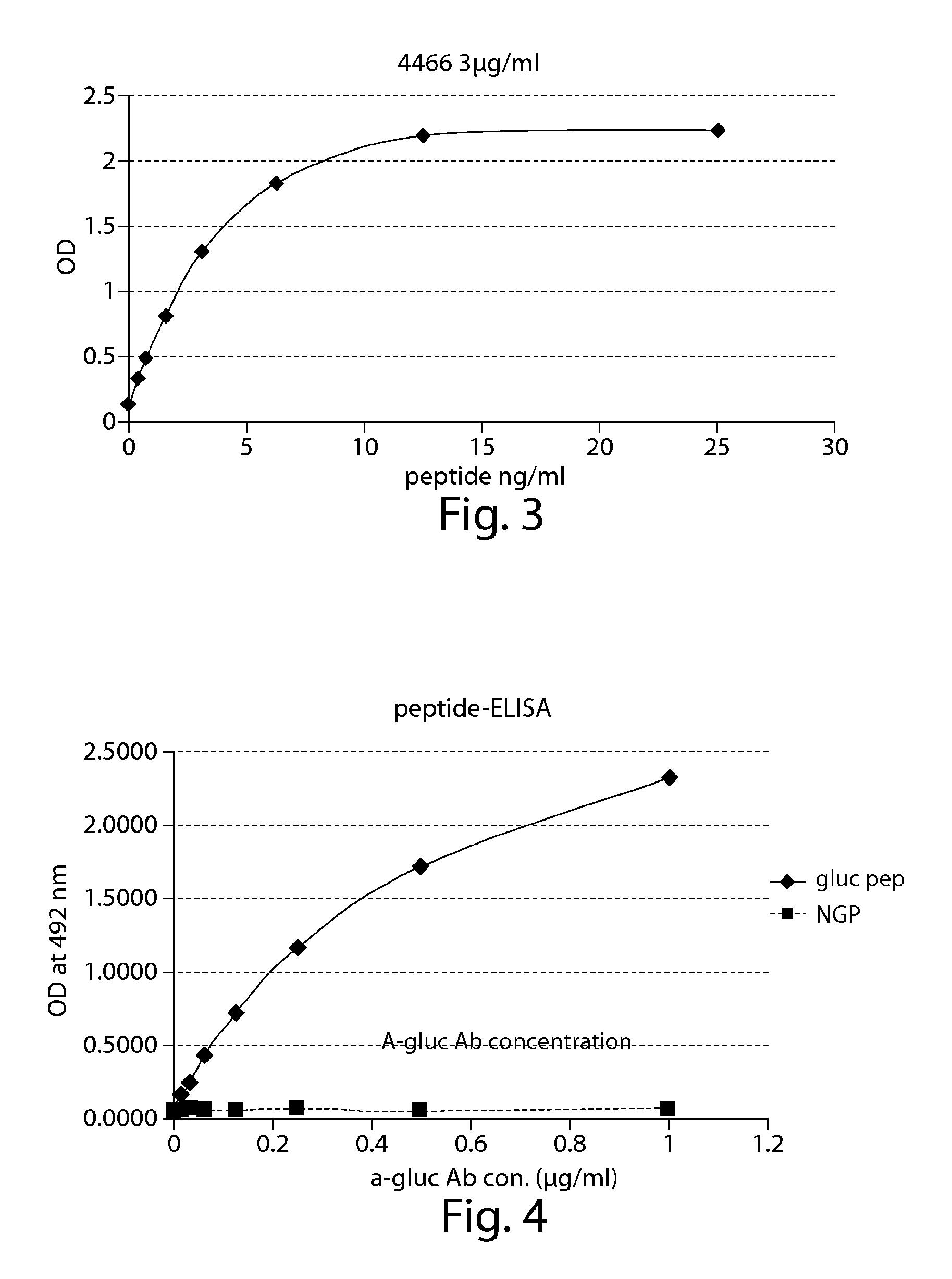
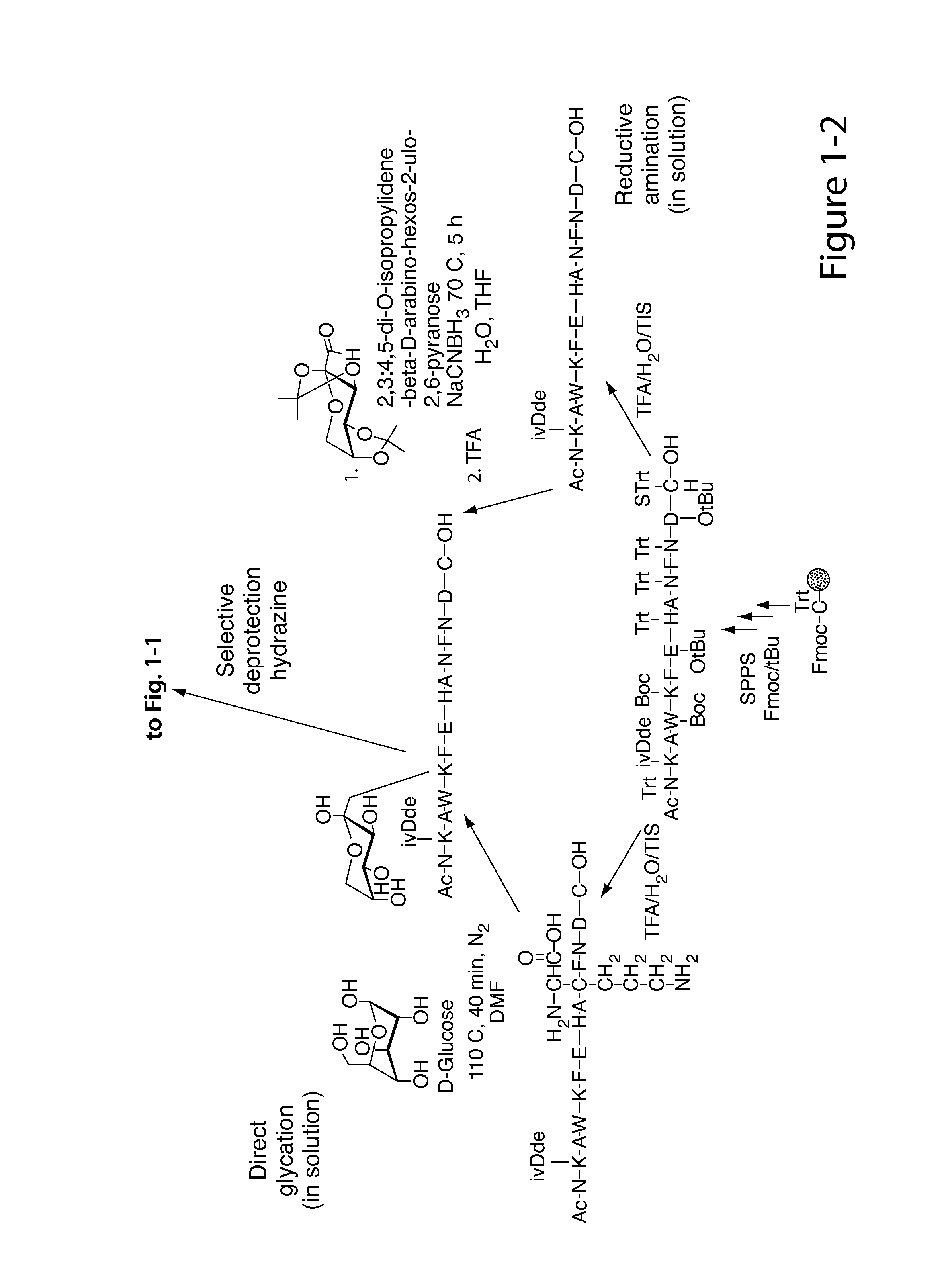
Glycated CD59 peptides, their preparation, and uses thereof
ActiveUS9068006B2Activation of and excessive and acceleratedExcessive and accelerated depositionPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsAntibody fragmentsPre diabetes
The present invention provides glycated Amadori products of the CD59 peptide and fragments thereof to be used as tools and among methods for the diagnosis and prognosis of pre-diabetes and diabetes. Certain aspects of the invention include glycated Amadori products of CD59 and fragments thereof to be used for the generation of antibodies and antibody fragments. Still other aspects of the invention include methodologies for the preparation of glycated Amadori products of CD59, fragments thereof, the inventive antibodies, and antibody fragments.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Procurement, Isolation, and Cryopreservation of Endometrial/Menstrual Cells
Compositions comprising menstrual stem cells (MSCs) and methods, processes, and system therefor are provided by the invention. MSCs are processed from menstrual flow collected during menses. MSCs may be cryopreserved, processed through various culturing and selection steps in preparation for cryopreservation, or processed for therapeutic or cosmeceutical use. Cryopreserved MSCs may be thawed in preparation for therapeutic and cosmeceutical use. MSCs express CD9, CD10, CD13, CD29, CD44, CD49e, CD49f, CD59, CD81, CD105, CD166, and HLA class I, and have low or no expression of CD3 and HLA class II.
Owner:CRYO CELL INTERNATIONAL INC
Epinephelus coioides antimicrobial peptide and application thereof
ActiveCN108892718AGrowth inhibitory activityEnriched gene poolPeptide/protein ingredientsAccessory food factorsIMMUNE STIMULANTSAntimicrobial peptides
The invention discloses an epinephelus coioides antimicrobial peptide. The antimicrobial peptide is epinephelus coioides CD59 protein, and has an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, or protein having an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, which is substituted, lost and / or added with one or more amino acids and / or is terminal modified and has the same or higher activity. Experiments prove that the epinephelus coioides antimicrobial peptide can be used for inhibiting the growth activity of vibrio alginolyticus, can be applied to preparation of immune stimulant or feed additivesfor fish, especially groupers, and has a wide application prospect. The CD59 gene sequence of the epinephelus coioides is obtained for the first time, can be used for enriching the gene pool of groupers, can be applied to preparation of recombinant protein, antibacterial and bacteriostatic additive and fish immune simulants, and provides new practice foundation for physiological immune researchesof epinephelus coioides.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Tumor angiogenesis associated genes and a method for their identification
InactiveUS20110229483A1Reduce redundancyPrevent amplification of highly abundant moleculesPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementAbnormal tissue growthMouse tumor
Crucial to designing anti-angiogenic and vascular targeting approaches is the identification of specific target molecules. We compared transcriptional profiles of tumor endothelial cells with that of normal resting endothelial cells, normal but angiogenically activated placental endothelial cells, and cultured endothelial cells. Although the majority of transcripts were classified as general angiogenesis markers, we identified 17 genes that show specific overexpression in tumor endothelium. Antibody targeting of four cell-surface expressed or secreted products (vimentin, CD59, HMGB1 and IGFBP7) inhibited angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Finally, targeting endothelial vimentin in a mouse tumor model significantly inhibited tumor growth and reduced microvessel density. Our results demonstrate the utility of the identification and subsequent targeting of specific tumor endothelial markers for anticancer therapy.
Owner:MAASTRICHT UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com