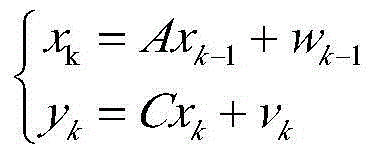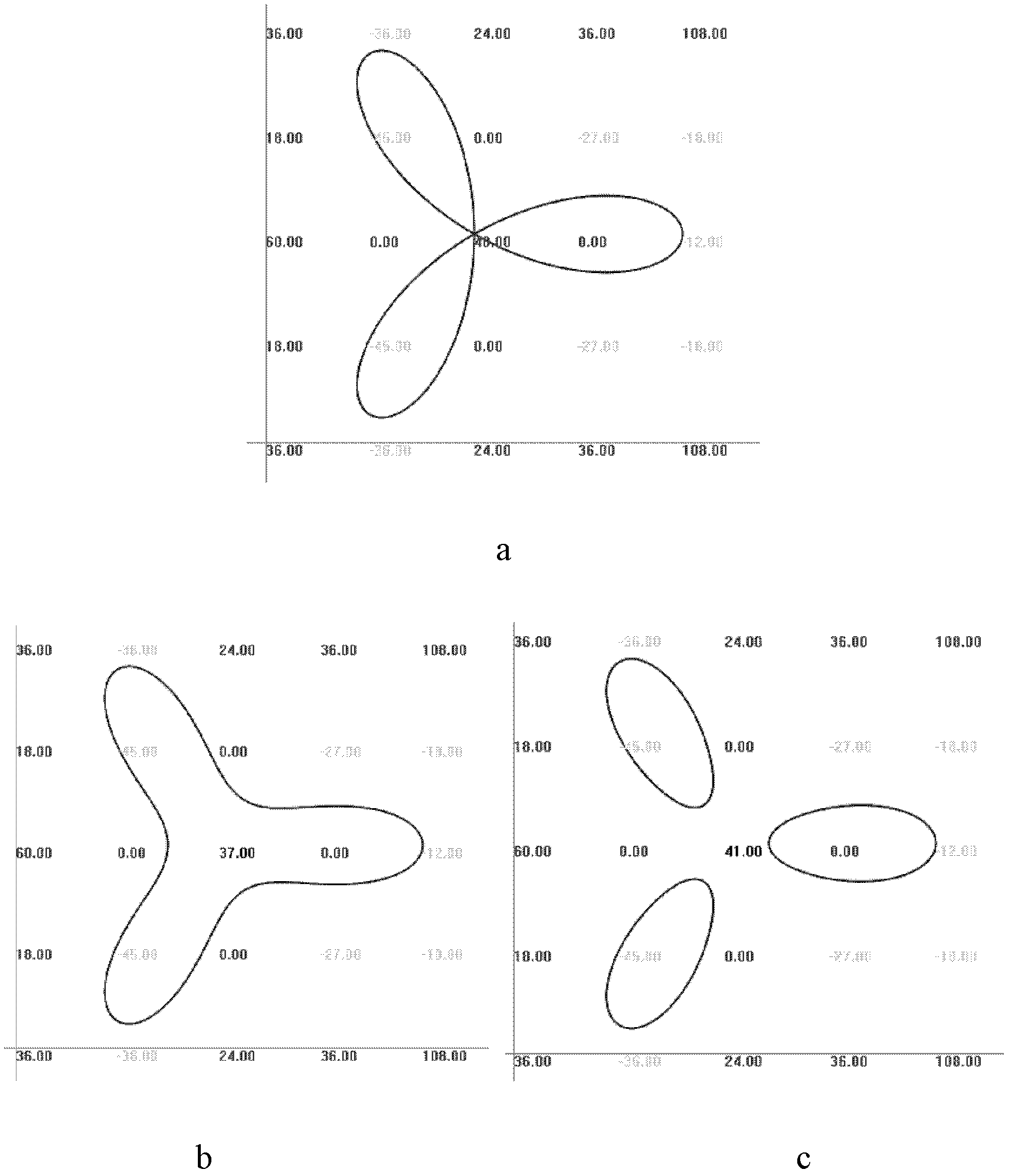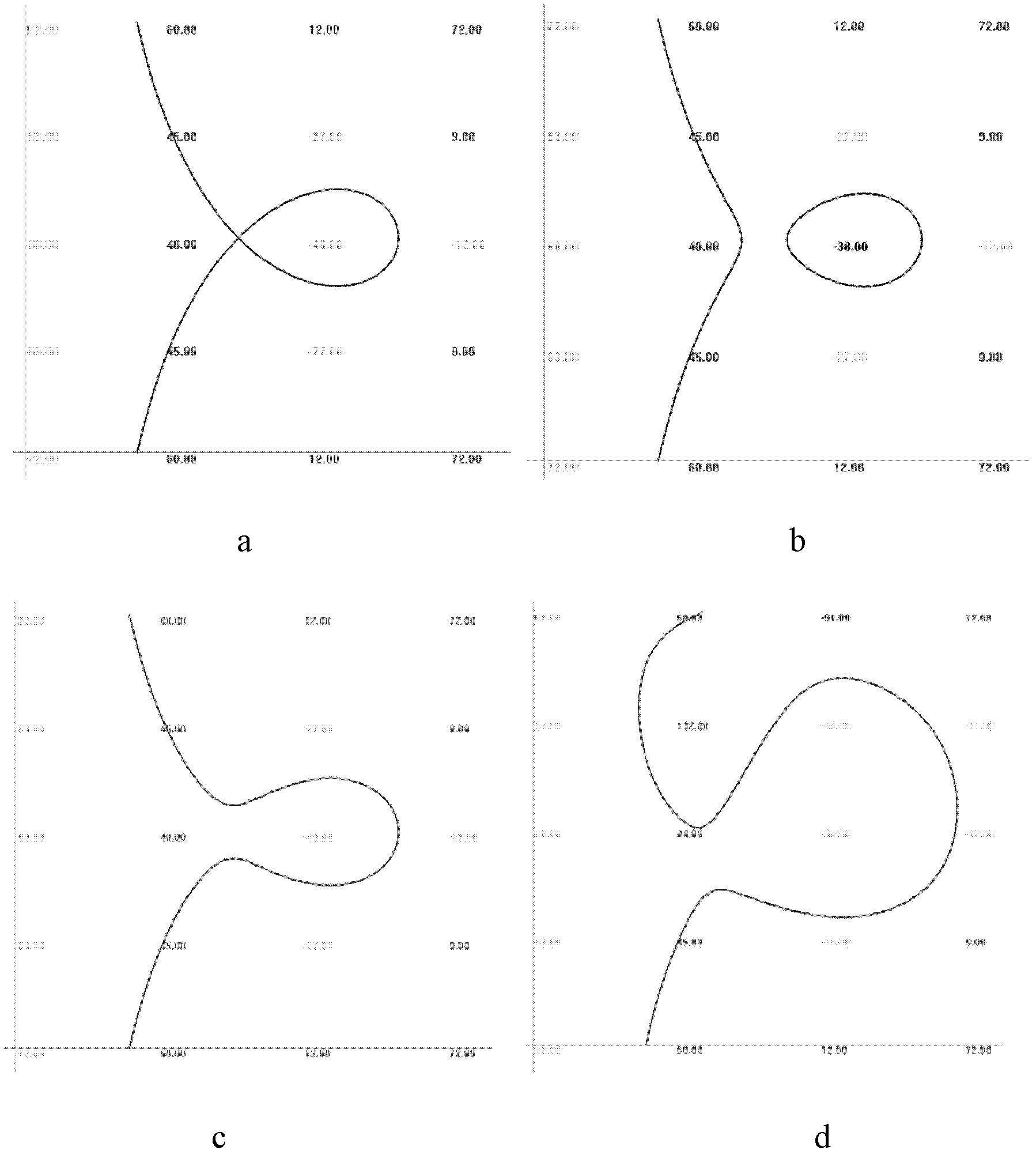Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
47 results about "Algebra of physical space" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
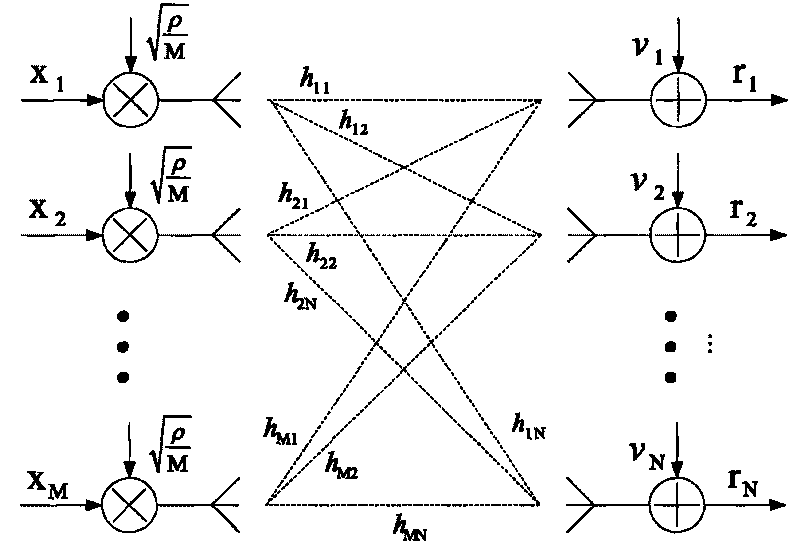
In physics, the algebra of physical space (APS) is the use of the Clifford or geometric algebra Cl3,0(R) of the three-dimensional Euclidean space as a model for (3+1)-dimensional spacetime, representing a point in spacetime via a paravector (3-dimensional vector plus a 1-dimensional scalar).
Geocoding method using multidimensional vector spaces
InactiveUS20060245572A1Interconnection arrangementsFuzzy logic based systemsFeature vectorData element
A process for evaluating and geocoding of GIS data elements utilizes a plurality of “locate” tests and a weighting scheme to express the match results as a multidimensional vector. Multiple inputs and data sources, as well as ambiguous and partial input data, are used to generate an output with improved precision by applying a weighting function to each input element and generating a set of test vectors (i.e., the input data element weighted by the known accuracy of the element / source). A sum of a plurality of tests is then generated as the “characteristic vector” of the test set. By using two (or more) different sets of test, two (or more) characteristic vectors are formed. Various well-known algebraic techniques can then be used to evaluate the results of each set of tests and select the “best match” result.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
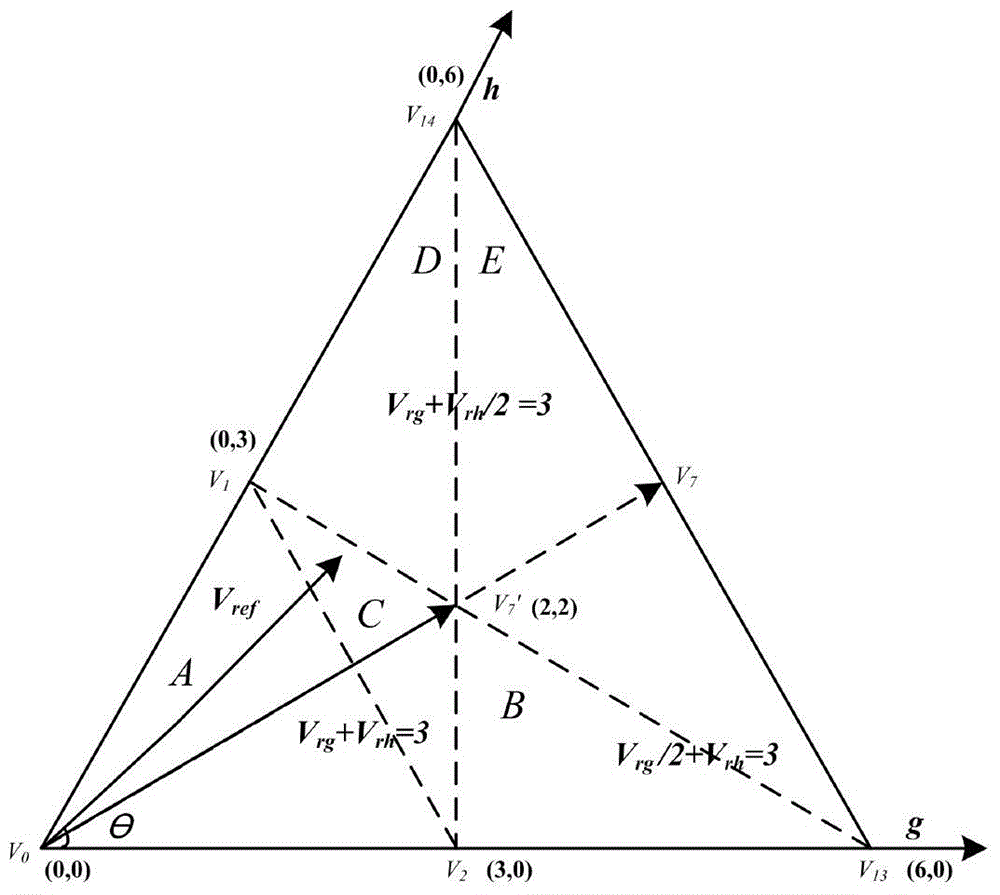
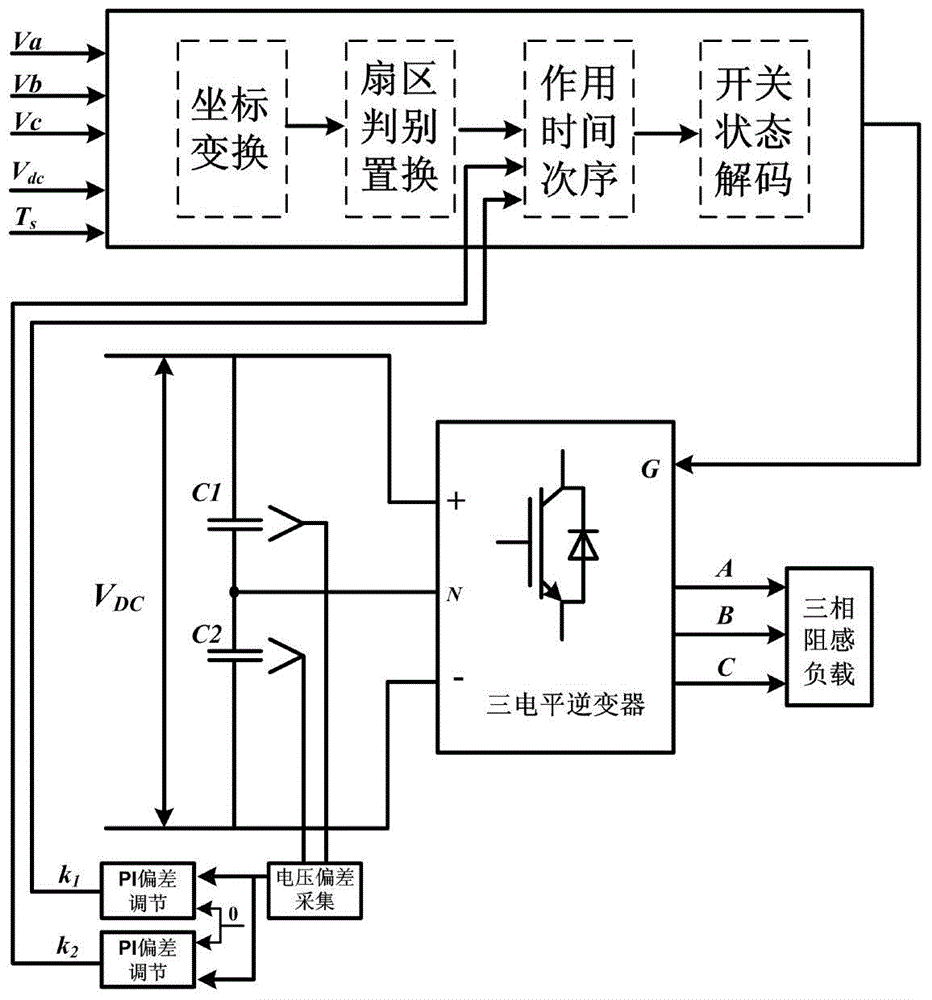
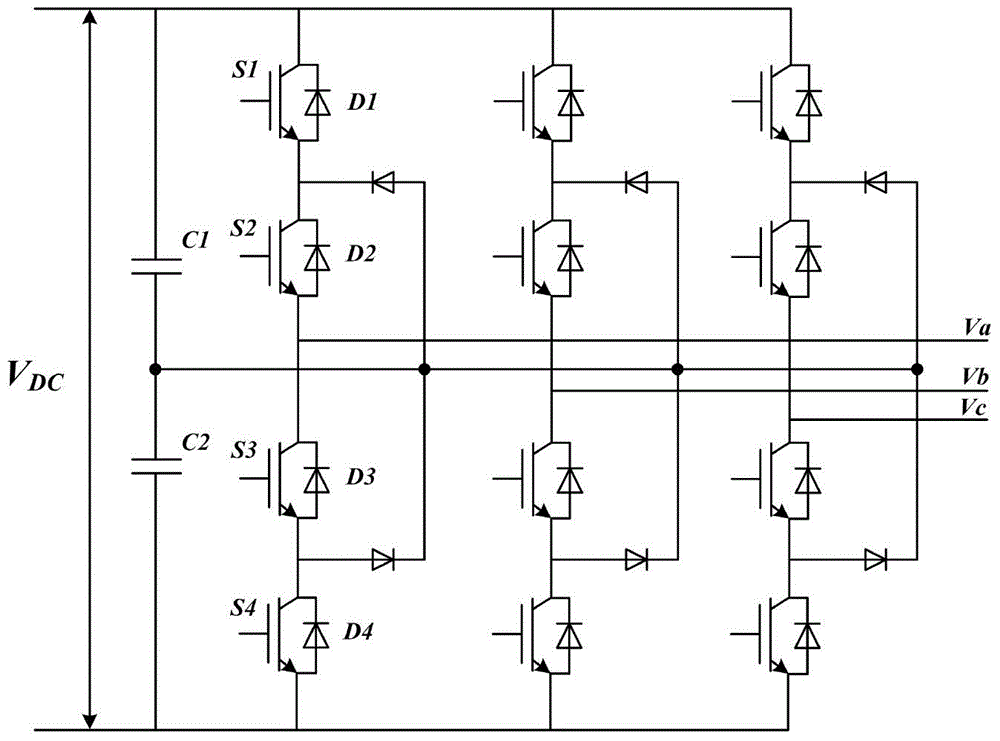
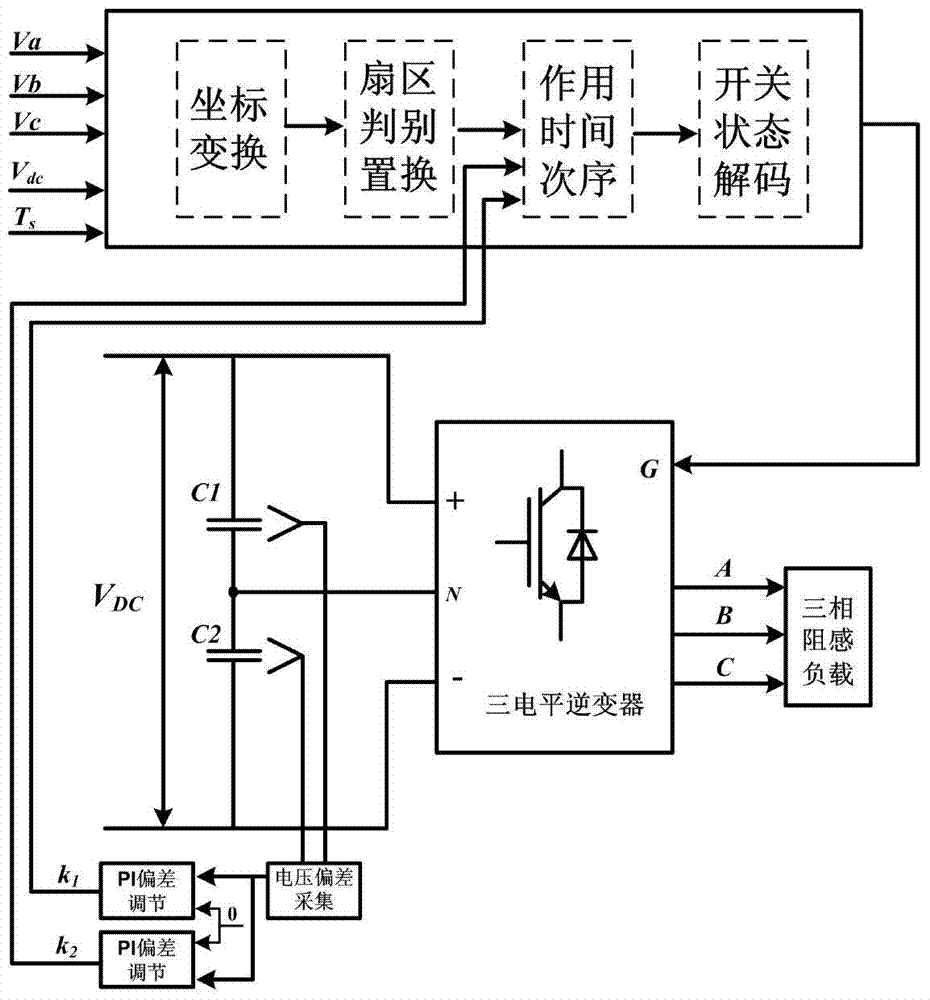
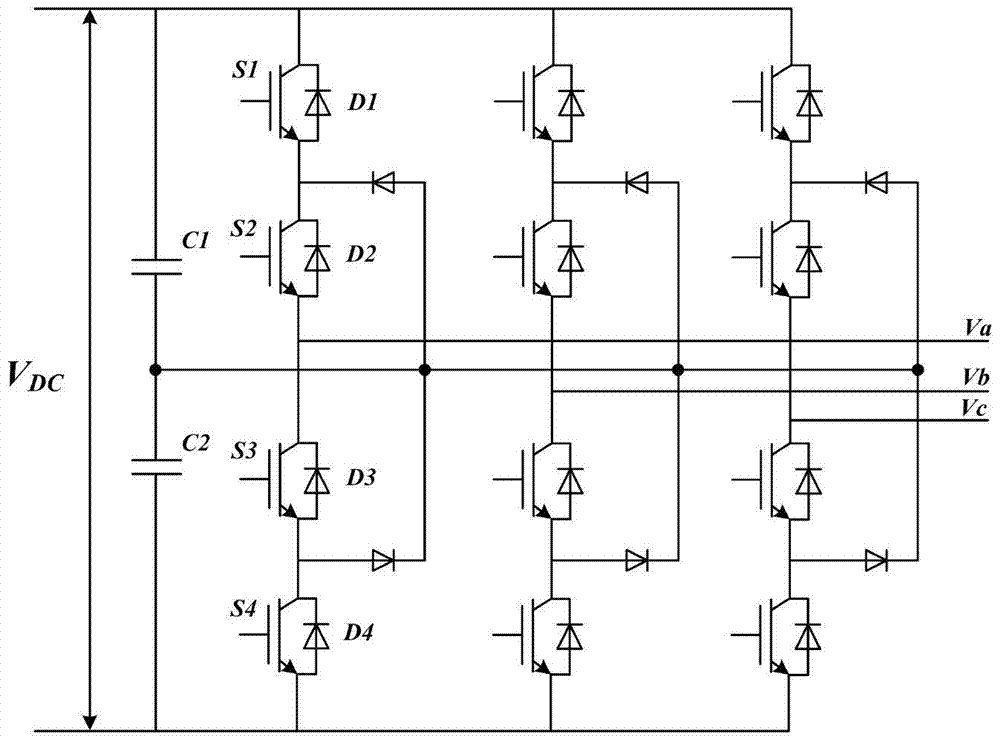
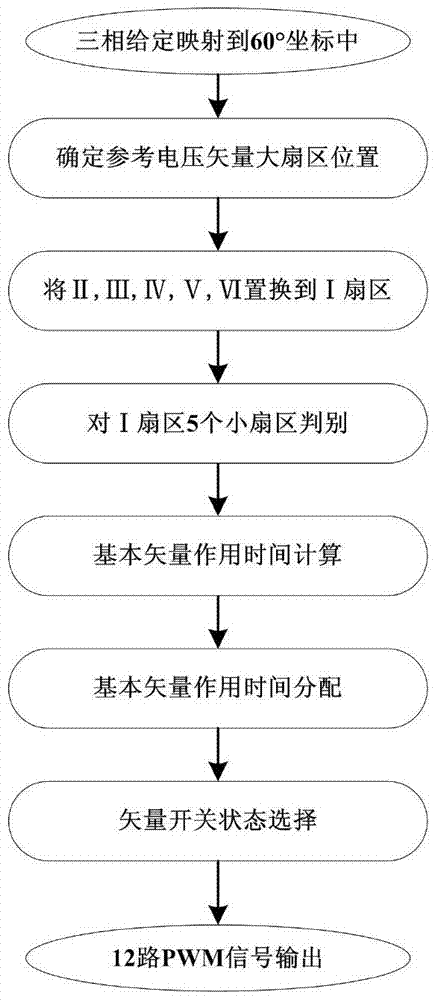
60degree coordinate system based virtual vector modulation algorithm of tri-level inverter
The invention relates to a 60degree coordinate system based virtual vector modulation algorithm of a tri-level inverter, belonging to the field of power and electronic application. According to the algorithm, virtual space vectors (VSVPWM) are mapped into a 60degree coordinate system via Clark / Park coordinate transformation so that basic vector coordinates are changed into simple algebraic coordinates, large and small sectors are discriminated according to logic judgment of linear coordinate equations, action time of three latest basic vectors are calculated via the algebraic coordinates in a volt-second balance principle, PWM signals are output in a nine-segment switching time sequence with a positive small vector at first, and action time of redundant small vectors is adjusted via closed-loop PI regulation according to two capacitance difference values. A lot of trigonometric function and irrational number operation in a traditional VSVPWM algorithm can be omitted, and the 60degree coordinate system based virtual vector modulation algorithm is characterized by being simple in calculation, high in instantaneity and easy to realize.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
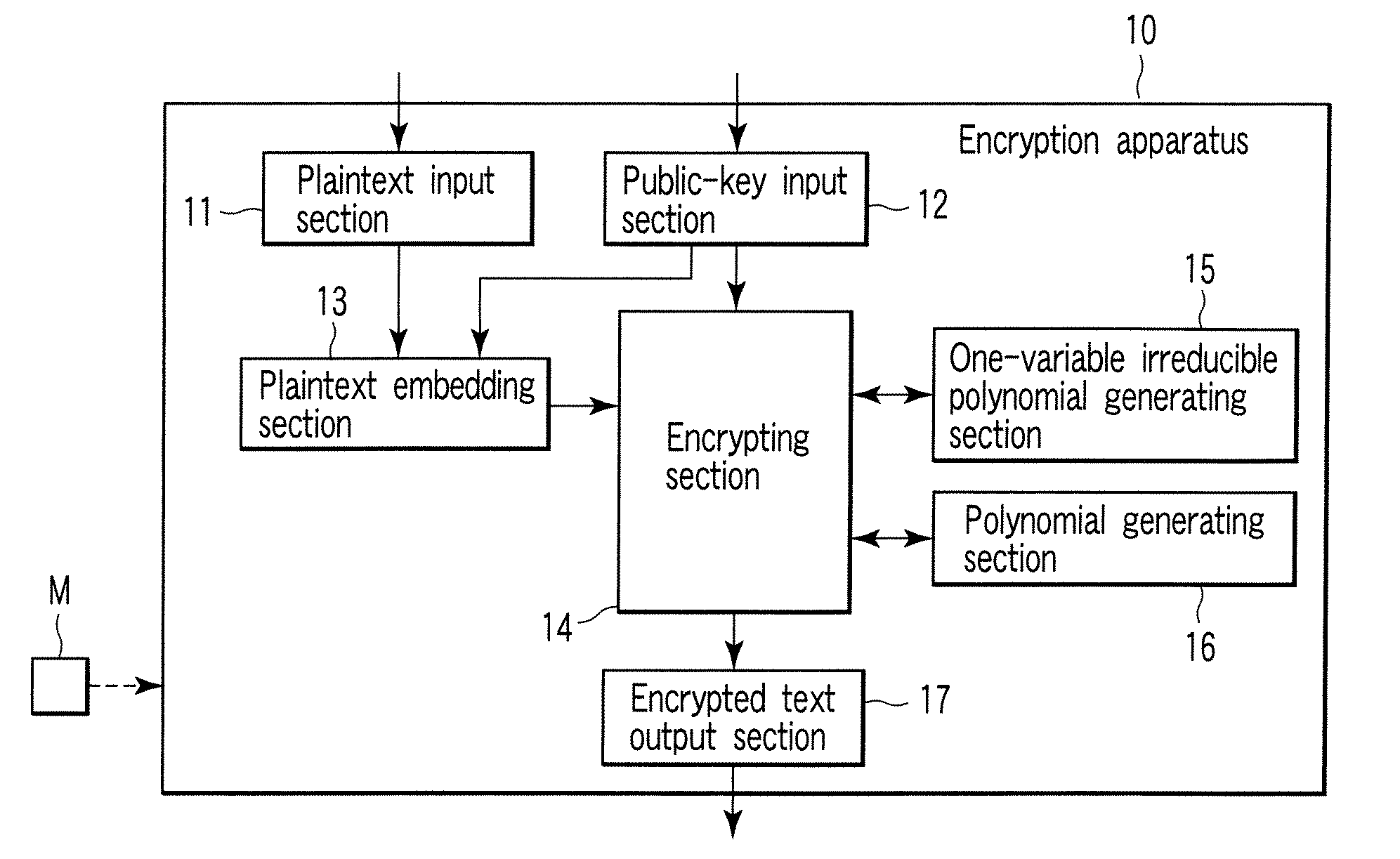
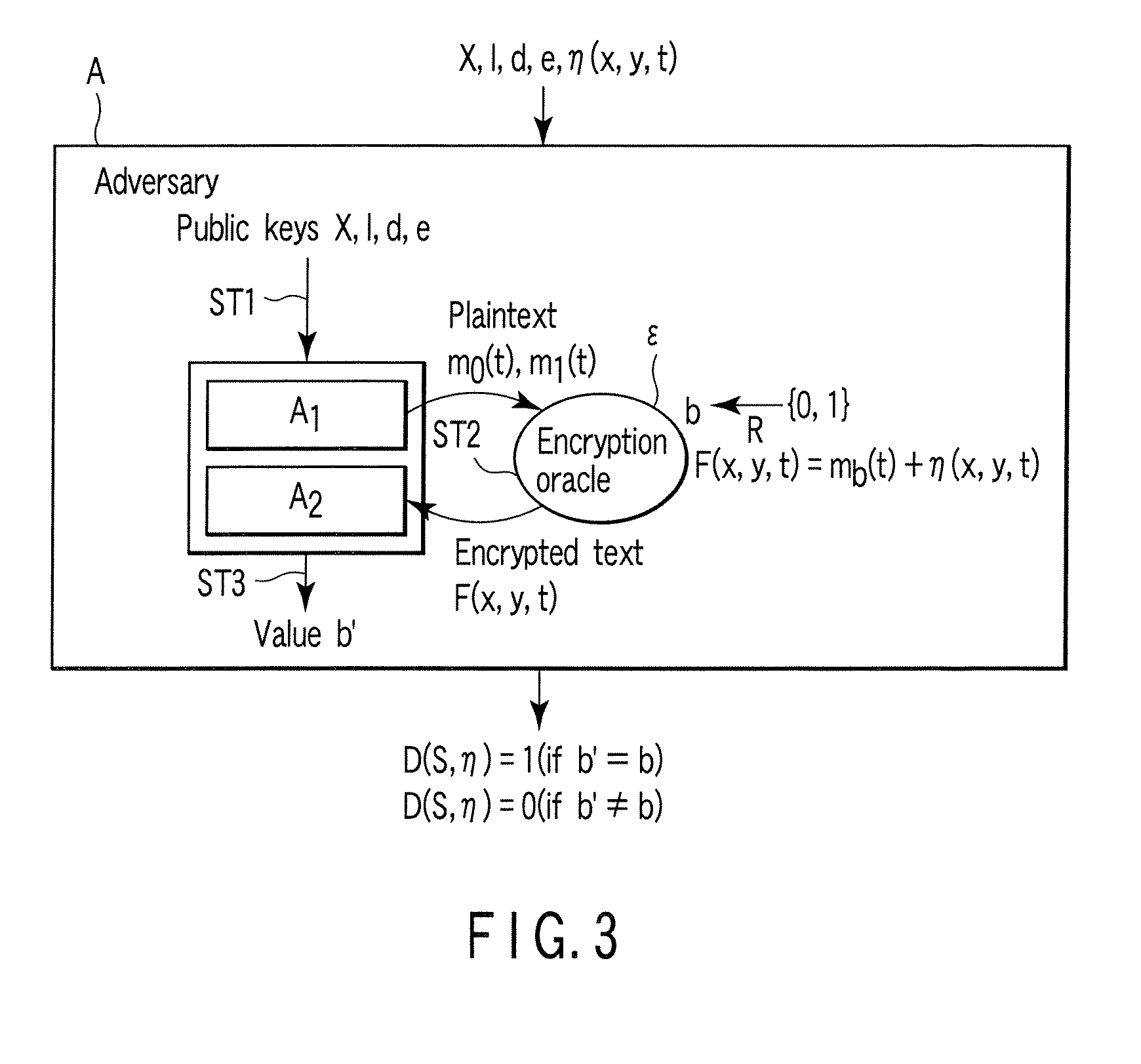
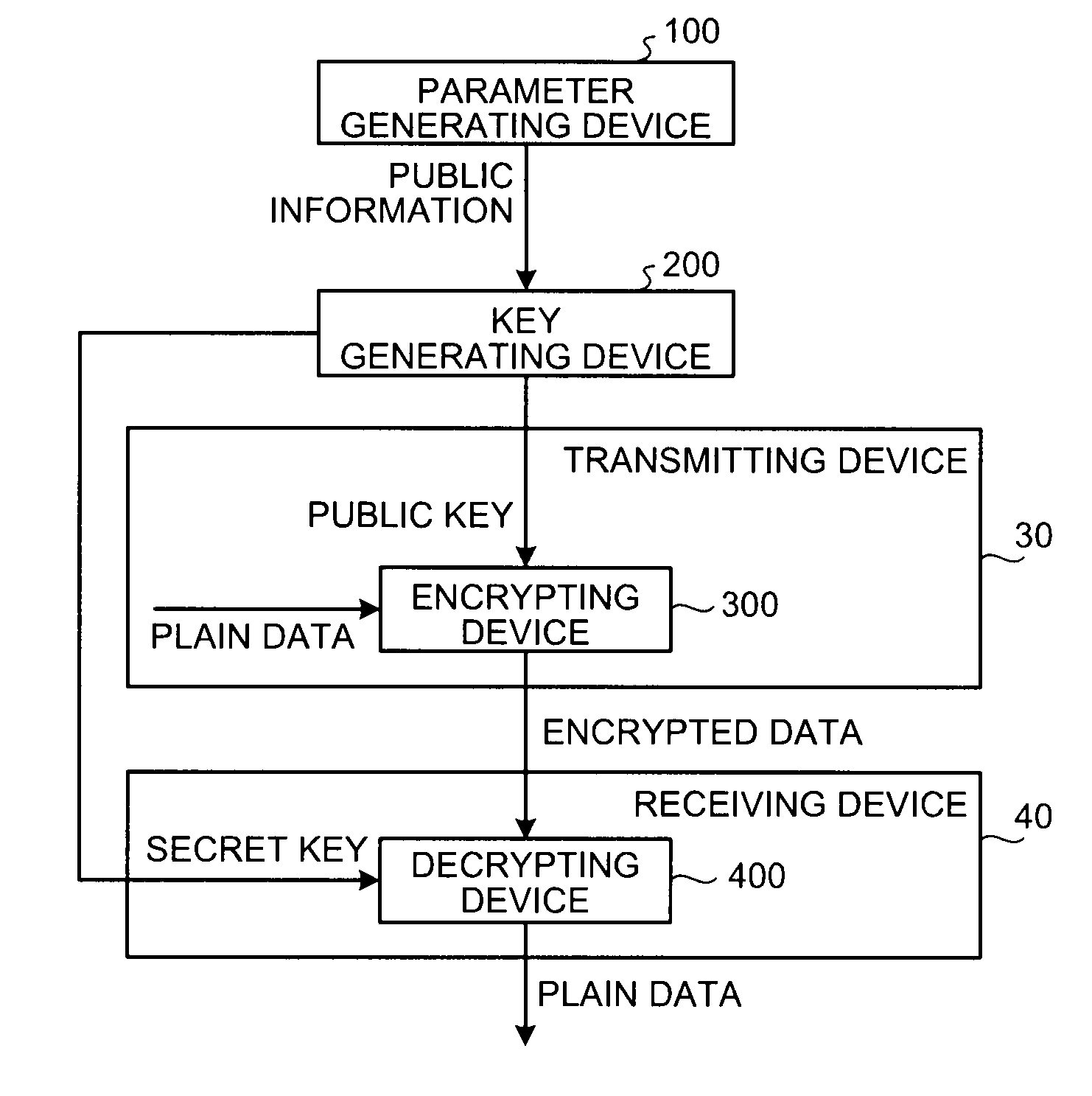
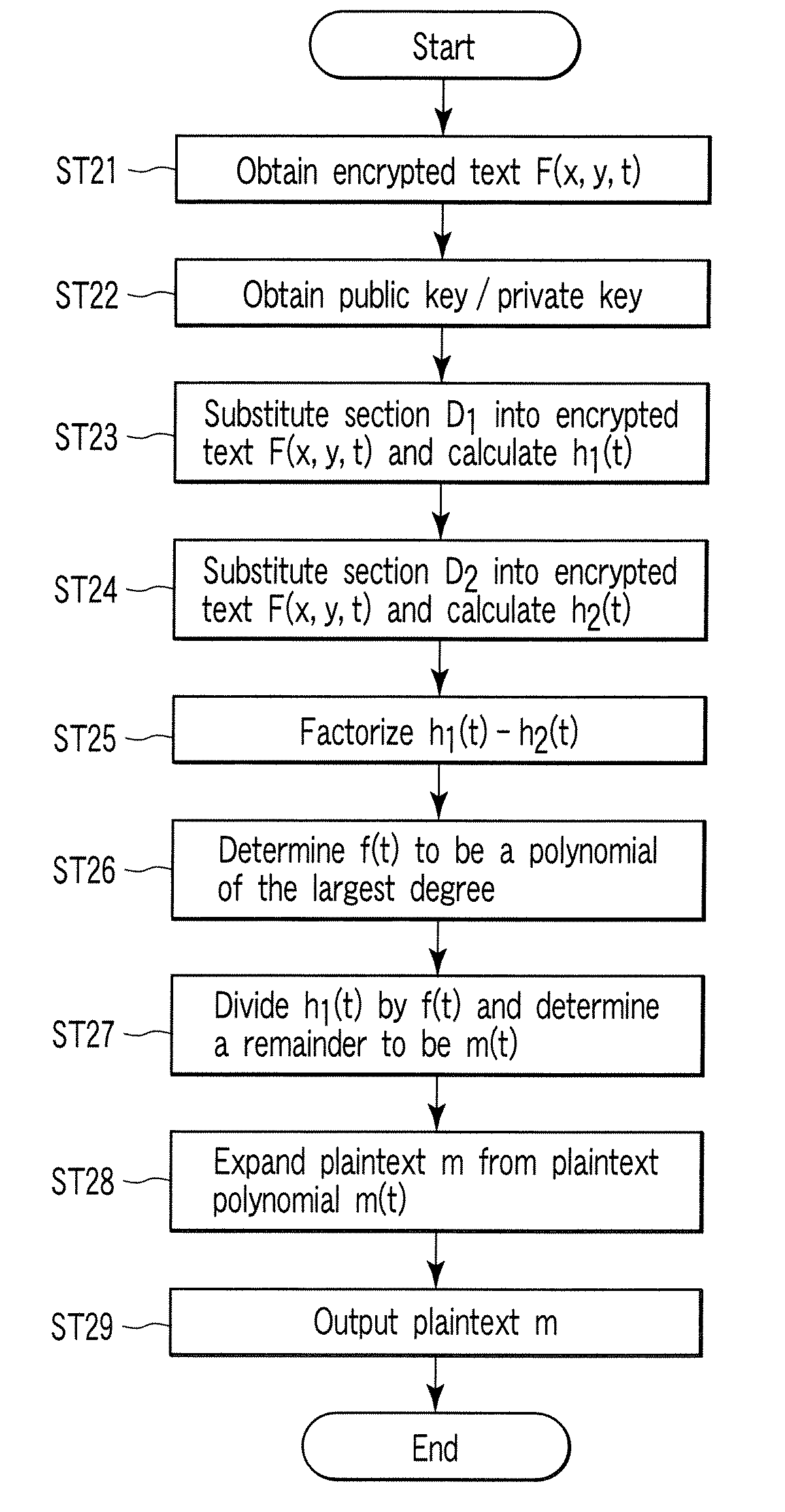
Encryption apparatus, decryption apparatus, and method
InactiveUS20070110232A1Public key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationPlaintextComputer hardware
A method whereby an encryption apparatus encrypts a message on the basis of a fibration X(x, y, t) serving as a public key when private keys are two or more sections corresponding to fibration X(x, y, t)=0 of an algebraic surface X, the method comprises embedding plaintext M obtained by concatenating the message to a random number as the coefficients of plaintext polynomial M(t) of degree l−1 or less, and generating encrypted text F=Epk(M, p, q, f, X) from the plaintext polynomial M(t) by an encrypting process of performing operations including at least one of addition, subtraction, and multiplication of random polynomials p(x, y, t), q(x, y, t), a random irreducible polynomial f(t) of degree l or more, and the fibration X(x, y, t) with respect to the plaintext polynomial M(t).
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Automatic elementary mathematic algebra type question answering method and system
InactiveCN107423286AImprove understandingEfficient use ofData processing applicationsSemantic analysisAlgorithmAlgebraic equation
The invention discloses an automatic elementary mathematic algebra type question answering method and system. The method comprises the following steps of: question input; question understanding: classifying each category of elementary mathematic algebra type questions and carrying out word segmentation and part-of-speech labelling on question texts; extracting a direct statement mathematic relationship by using a syntax-semantic hybrid model and adding an implicit type mathematic relationship according to question types so as to form an algebra relationship group; machine solution: distributing variables for entities in the formed algebra relationship group, converting the algebra relationship group into an algebra equation group, obtaining an entity-variable comparison table, and automatically solving the algebra equation group by a machine; and quasi-man answer generation: recovering semantic meanings of the variables in the algebra relationship group solution process according to solution sequences of the variables and the entity-variable comparison table, and combining the question texts to form a quasi-man answer process. According to the method and system, the automation degree of answering mathematic algebra type questions can be greatly improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
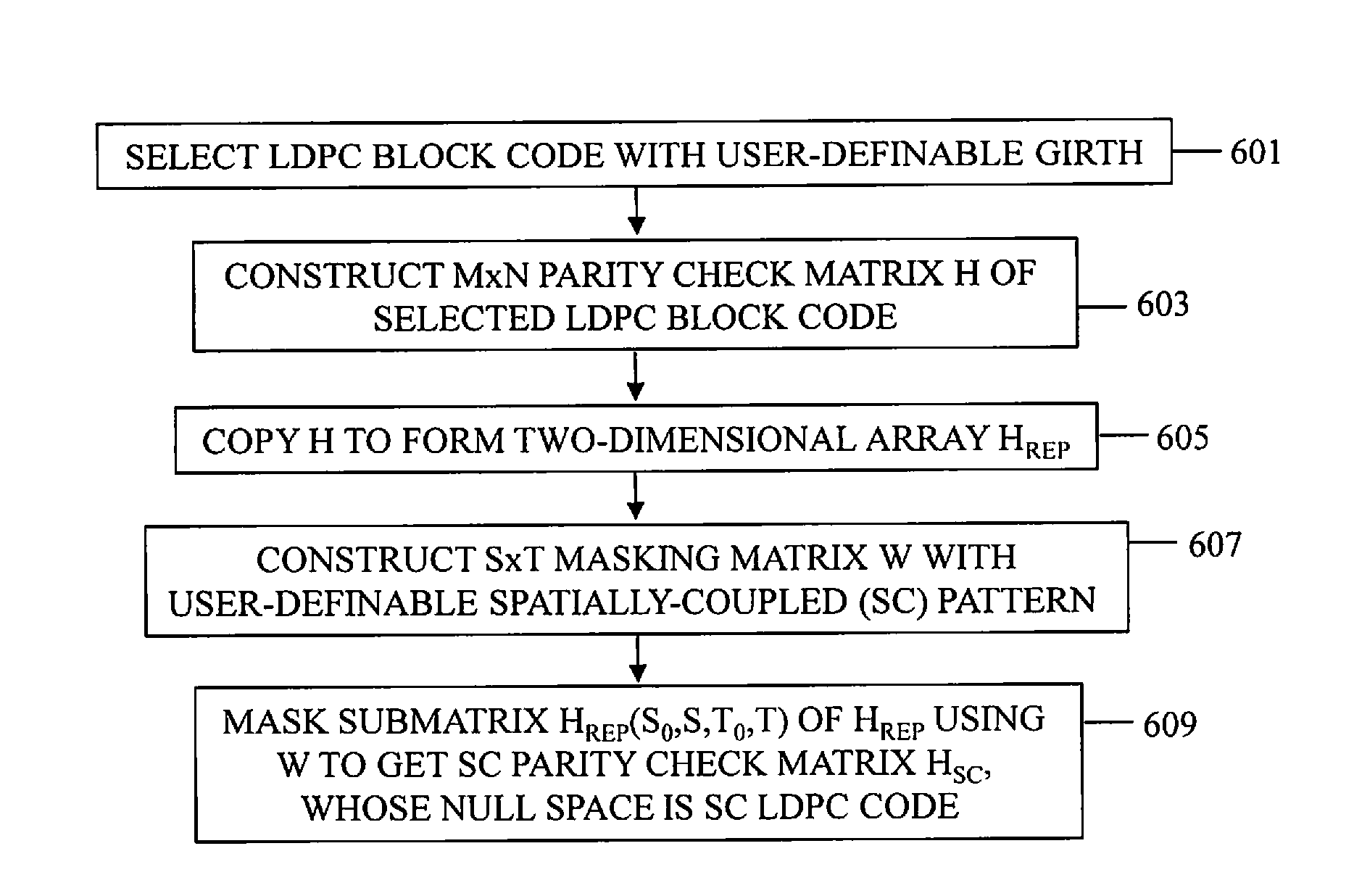
Method of and apparatus for generating spatially-coupled low-density parity-check code
InactiveUS20150155884A1Error correction/detection using convolutional codesError preventionBlock codeParity-check matrix
A method, apparatus, and non-transitory computer-readable recording medium for generating an algebraic Spatially-Coupled Low-Density Parity-Check (SC LDPC) code are provided. The method includes selecting an LDPC block code over a finite field GF(q) with a girth of at least 6; constructing a parity-check matrix H from the selected LDPC block code; replicating H a user-definable number of times to form a two-dimensional array Hrep; constructing a masking matrix W with a user-definable spatially-coupled pattern; and masking a sub-matrix of Hrep using W to obtain a spatially-coupled parity-check matrix HSC, wherein a null space of HSC is the algebraic SC LDPC code.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Geometrical optimal controller design method in tilt-rotor aircraft transition state switching process
ActiveCN108052008AAvoid singularity problemsUniqueness guaranteedAdaptive controlAttitude controlDynamic models
The invention provides a geometrical optimal controller design method in the tilt-rotor aircraft transition state switching process. The geometrical optimal controller design method aims at the problems of singularity, locality and the like of attitude control of a tilt-rotor aircraft in a Euclidean space, a Li group algebra in a Riemannian space is introduced, and through the combination of a Lagrangian function of a system and variation of an SO (3) tangent bundle, a Hamilton least principle is utilized to obtain global geometrical description of the tilt-rotor aircraft based on the SO (3) group. Through a built geometric switching dynamic model, the model problem of the tilt-rotor aircraft in a continuous space is converted into a nonlinear geometric optimal switching control problem. The algorithm can be applied to full-automatic unmanned driving and fuel economy of the tilt-rotor aircraft excessive switching process.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Decoding for algebraic geometric code associated with a fiber product
The present invention concerns a method of decoding a one-point algebraic geometric code defined on an algebraic curve represented by an equation in X and Z of degree 2μφ in Z, where φ is a strictly positive integer and μ an integer greater than 1, obtained by taking the fiber product of μ component algebraic equations, each of said component equations governing the unknown X and an unknown Yi, where i=0, . . . , μ−1, and being of degree 2φ in Yi. This method comprises the decoding of 2(μ−1)φ“clustered” codes, all defined on the same algebraic curve represented by one of said component equations. The invention also relates to devices and apparatuses adapted to implement this method.
Owner:CANON KK
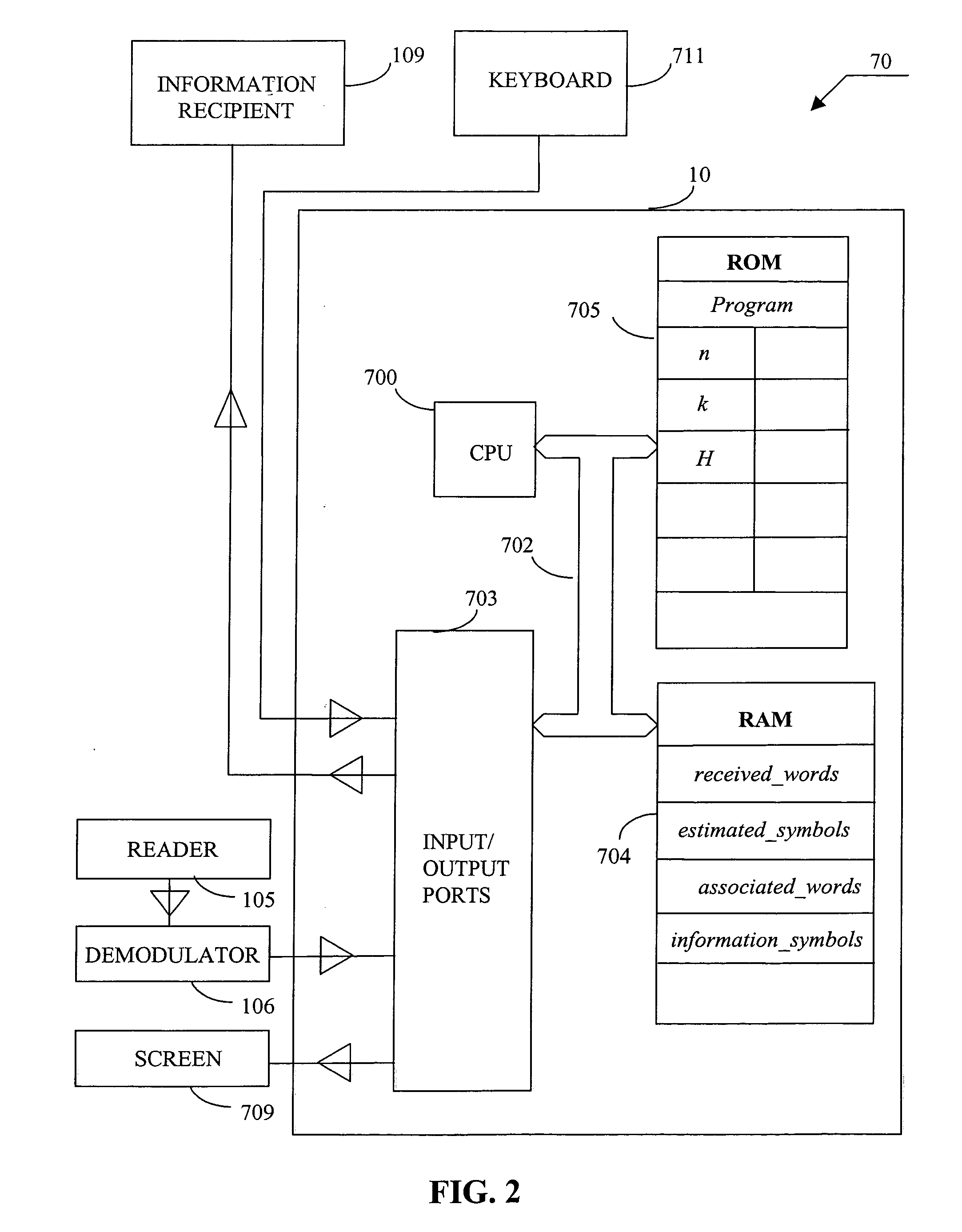
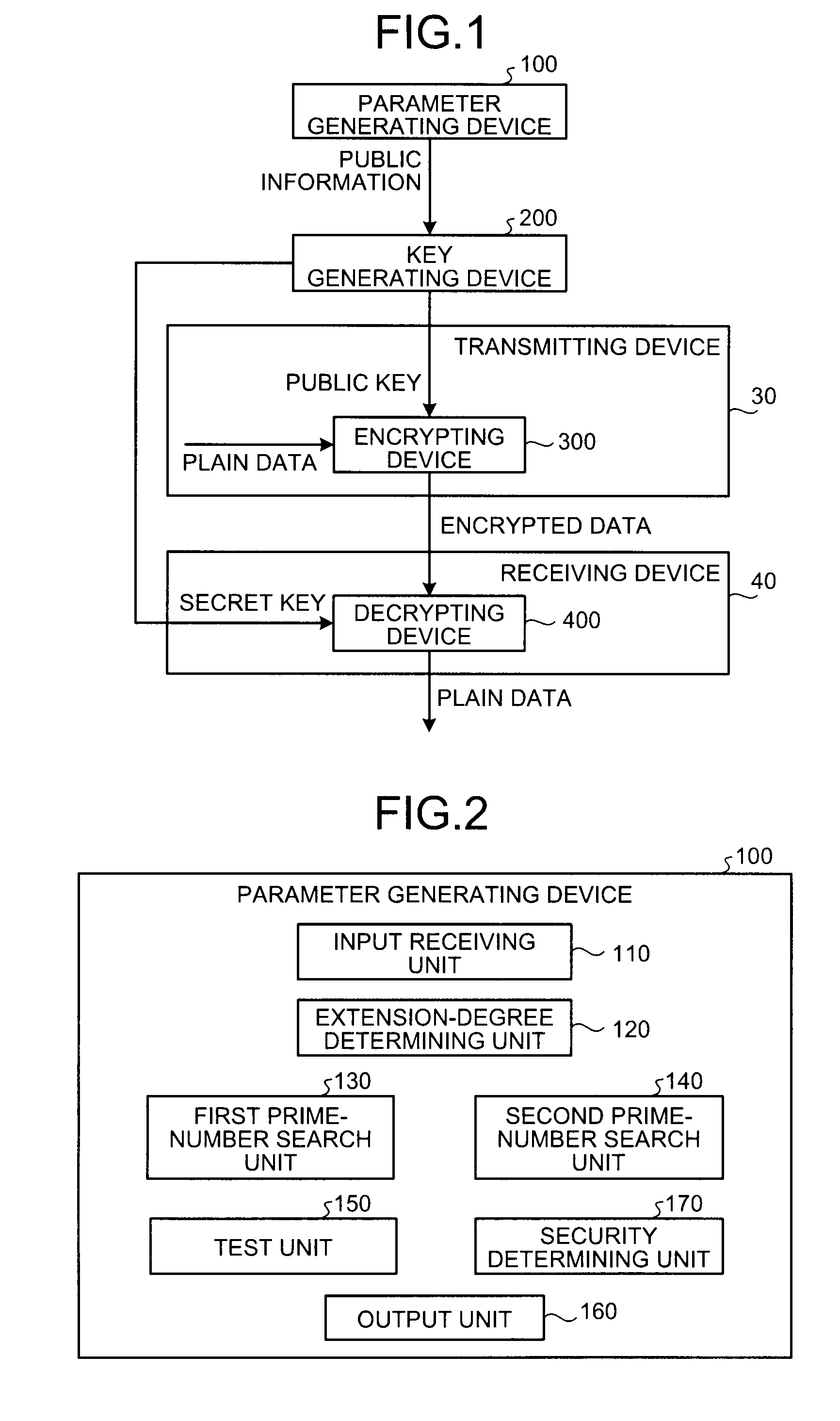
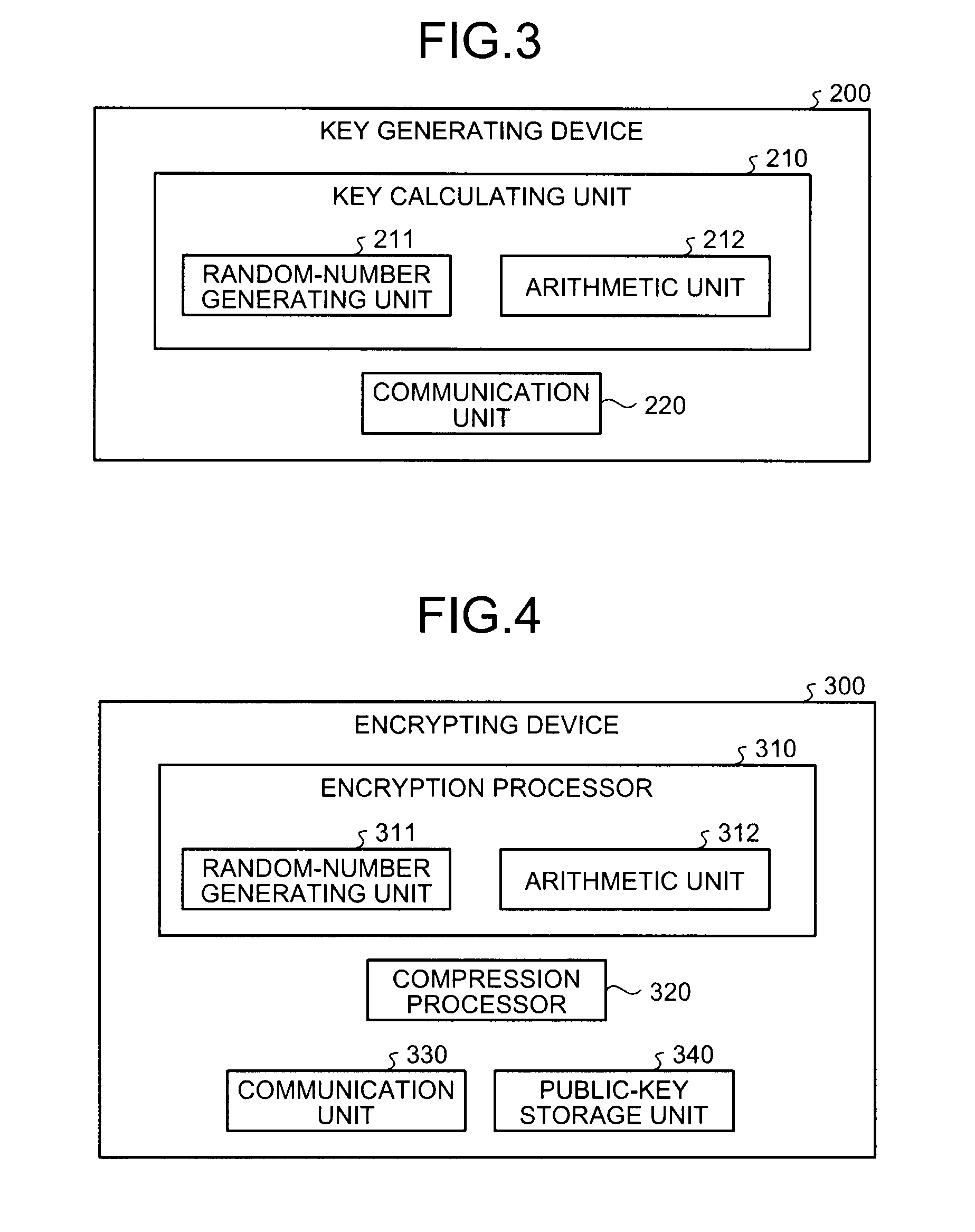
Parameter generating device and cryptographic processing system
InactiveUS20100046746A1Public key for secure communicationSecret communicationTheoretical computer sciencePublic key cryptosystem
A parameter generating device includes an input receiving unit that receives a degree n of an algebraic torus T including a group G in which a cryptosystem used in a torus-compressed public key cryptosystem is defined, a size W of a finite field F, and a size S of the group G, an extension-degree determining unit that determines an extension degree m of a finite field Fpm in which the algebraic torus T is defined, a first prime-number search unit that searches for a prime number p, a second prime-number search unit that searches for a prime number q, a test unit that checks whether a multiplication value nm is divisible by the prime number q, a security determining unit that determines that the cryptosystem is secure based on the multiplication value nm, and an output unit that outputs parameters when it is determined that the cryptosystem is secure.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Encoding method for low code rate LDPC code
InactiveCN101488760AReduce in quantityImprove performanceError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsComputation complexitySignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention discloses an encoding method of low bit-rate LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) code, including the following steps: step 1, matrixes H and H are respectively constructed, the H matrix is a diagonal matrix, H is an array matrix with q multiplied by 1 and consists of q end-around-shift permutation matrixes Q; the permutation matrix Q consists of b multiplied by b step permutation matrixes Q having row weight and line weight of 1, at most one element of 1 on each diagonal line and the rest elements of 0; step 2, an H matrix with the size of equal to bq multiplied b(q+1) is constructed; step 3, check vector c is constructed, c is equal to (p1, 1=1, 2, ..., M), p1 represents the value of any first check bit, and M is the length of check bit; step 4, according to the check vector c=(p1), the inputted information vector c is equal to (dj), and coded code word c=(cc) is obtained. In the method of the invention, an algebraic method used by end-around-shift value of Q permutation matrix leads belief propagation iterative decoding algorithm to be more easily realized in parallel; bidiagonal matrix structural characteristic of H matrix can encode low rate LDPC code in a recursion manner, and has linear time computing complexity. The simulation performance is superior to the performance of the existing low rate error correcting code, thereby being capable of reaching a signal noise ratio of 0.4 dB and having ratio compatibility.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Network community division method based on simulated annealing genetic algorithm
InactiveCN102663499AThe value of the objective function is largeDivision to achieveGenetic modelsNODALGenetics algorithms
The present invention discloses a network community division method based on simulated annealing genetic algorithm, and mainly solves problems of poor search capability and low division efficiency in present genetic algorithm. The network community division method based on simulated annealing genetic algorithm comprises the following realizing steps: (1) reading in a network diagram; (2) generating an adjacent matrix according to the network diagram; (3) initializing genetic algorithm parameters; (4) decoding chromosomes and calculating objective function values; (5) selecting chromosomes with relatively large objective function values to form a parental population; (6) crossing and varying chromosomes and generating new chromosomes to form progeny populations; (7) initializing simulated annealing algorithm parameters and implementing a local search; (8) obtaining a next parental population and performing iteration; (9) determining whether or not the iterative algebra reaches the largest algebra Gmax; if the iterative algebra reaches Gmax, then the iteration is terminated and the chromosome with the largest objective function value is output, and division of every node in the output chromosome is a final division result of nodes in the community. The network community division method based on simulated annealing genetic algorithm has advantages of strong search capability and high accuracy.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Encryption apparatus, decryption apparatus, and method
InactiveUS7773747B2Multiple keys/algorithms usagePublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwarePlaintext
A method whereby an encryption apparatus encrypts a message on the basis of a fibration X(x, y, t) serving as a public key when private keys are two or more sections corresponding to fibration X(x, y, t)=0 of an algebraic surface X, the method comprises embedding plaintext M obtained by concatenating the message to a random number as the coefficients of plaintext polynomial M(t) of degree l−1 or less, and generating encrypted text F=Epk(M, p, q, f, X) from the plaintext polynomial M(t) by an encrypting process of performing operations including at least one of addition, subtraction, and multiplication of random polynomials p(x, y, t), q(x, y, t), a random irreducible polynomial f(t) of degree l or more, and the fibration X(x, y, t) with respect to the plaintext polynomial M(t).
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
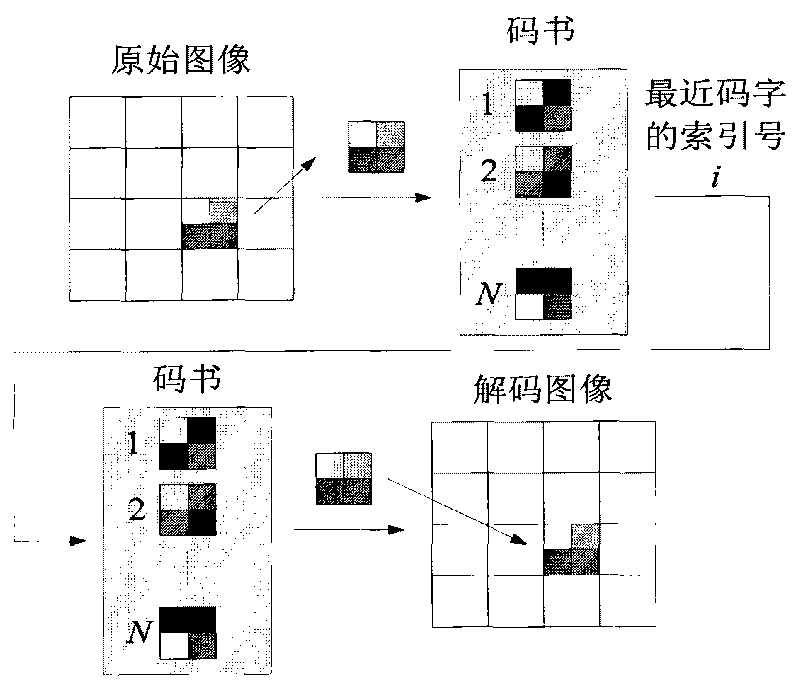
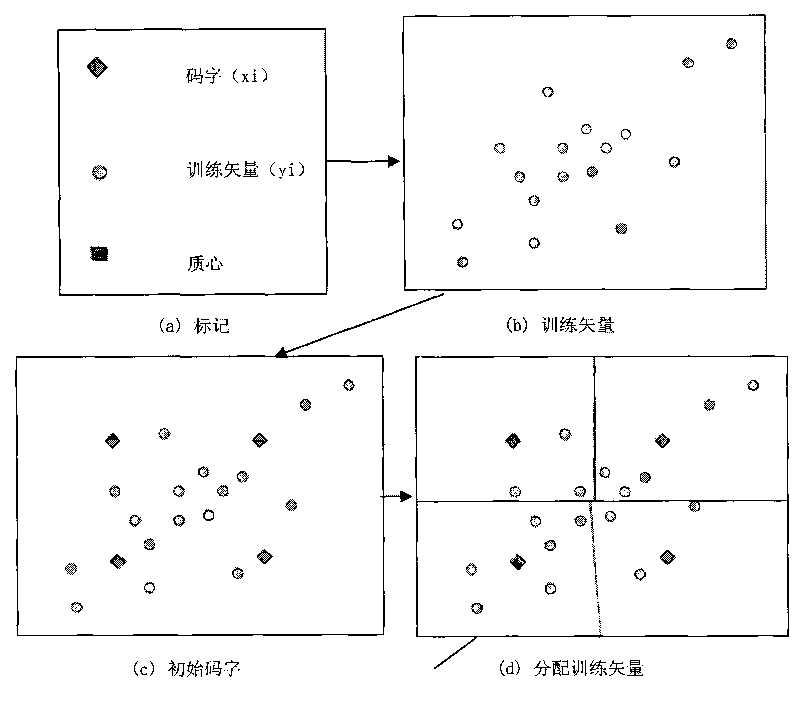
Neighborhood particle pair optimization method applied to image vector quantization of image compression
InactiveCN101710988AEasy to set upShort calculation timeTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationNeighborhood searchImage compression
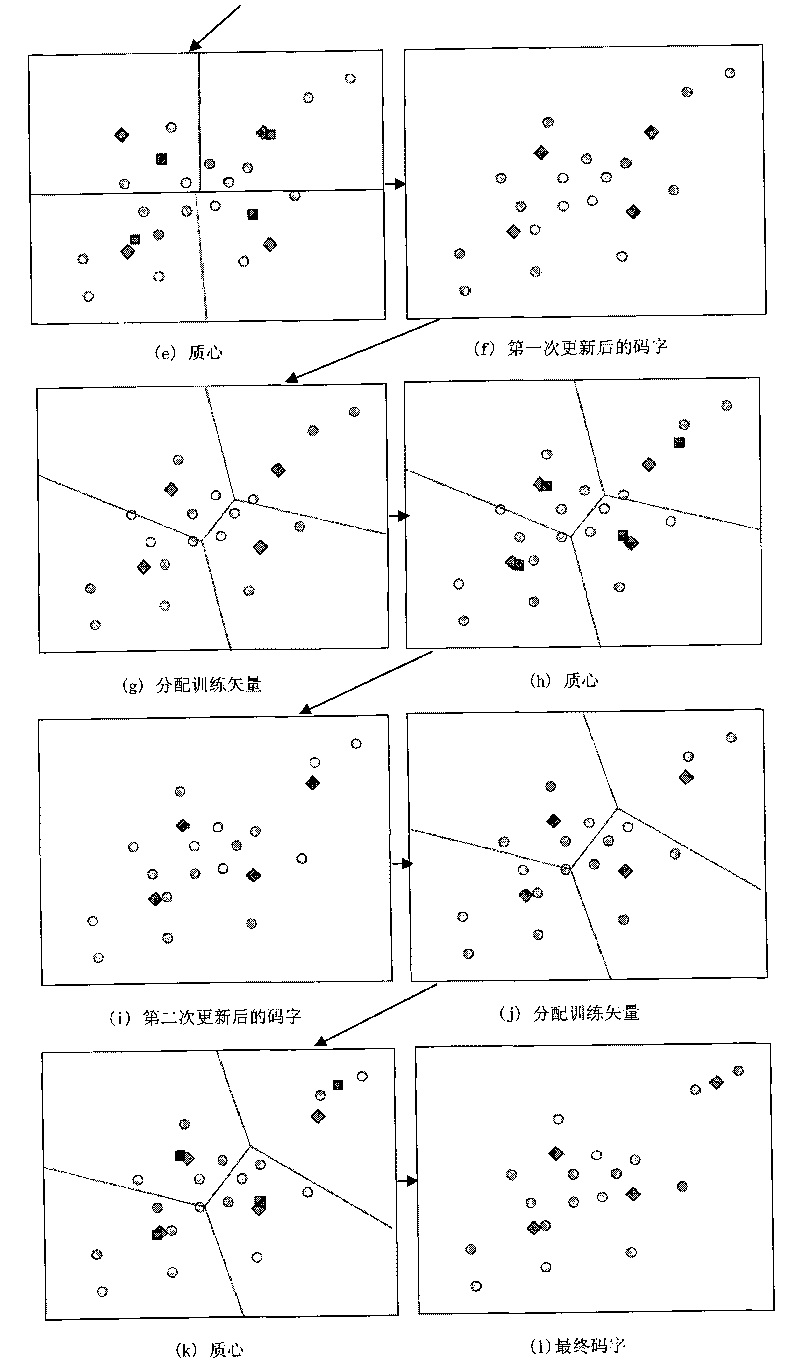
The invention relates to a neighborhood particle pair optimization method applied to image vector quantization of image compression. The method comprises that: code words are randomly selected from training vectors to form initial codebooks; each codebook is represented by one particle; two particles are randomly selected to form an initial particle pair; each particle is subjected to speed update and position update through a weighting PSO algorithm and is subjected to clustering operation through a K-means algorithm in each iteration; particle pair iterations of which iterative algebra is genmax are performed in total; in a jth particle pair iteration, the winner particle is named a jth-generation elite particle; a certain vector is randomly selected in a neighborhood of the jth-generation elite particle as a neighborhood particle to form a jth-generation neighborhood particle pair together with the jth-generation elite particle; and when j is equal to genmax, the elite particle is a genmax-generation elite particle which is a solution of the neighborhood particle pair optimization method. The method has the advantages of reducing the influence of initial codebook distribution on optimization results and significantly improving the quality of reconstructed images.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Control-limited minisatellite three-axis magnetic moment attitude control method based on algebraic Lyapunov equation
ActiveCN104881036AGuaranteed global asymptotic stabilityAttitude controlSystem matrixAlgebraic equation
Provided is a control-limited minisatellite three-axis magnetic moment attitude control method based on an algebraic Lyapunov equation. The invention relates to a control-limited minisatellite three-axis magnetic moment attitude control method based on an algebraic Lyapunov equation. The method is used to realize global stability of a minisatellite three-axis magnetic moment attitude control under control-limited conditions. The method comprises: step 1, establishing attitude kinematics and attitude kinetic models of control-limited minisatellite three-axis magnetic moment attitude control, to obtain a state-space equation; step 2, solving explicit solution P0 of the algebraic Lyapunov equation A<T>P0+P0A=-D<T>D, wherein A is a system matrix, D is a matrix in arbitrary dimensions, the system matrix A being critical stable or Lyapunov stable, ensuring the algebraic Lyapunov equation have a positive definite solution P0; step 3, and through the positive definite solution P0 of the algebraic Lyapunov equation, designing linear feedback control law under explicit control-limited conditions. The method is applied in the field of satellite control.
Owner:哈尔滨工业大学人工智能研究院有限公司
New WENO (Weighted Essentially Non-oscillatory) format construction method under trigonometric function framework
ActiveCN108763683AReduce truncation errorAvoid Unphysical OscillationsDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingShock waveAlgorithm
The invention discloses a new WENO (Weighted Essentially Non-oscillatory) format construction method under a trigonometric function framework. Compared with a classic essentially non-oscillatory format constructed through utilization of an algebraic polynomial, a weighted essentially non-oscillatory format constructed through utilization of a trigonometric function polynomial has the advantage that the weighted essentially non-oscillatory format is easier to simulate wave or high frequency oscillation problems, can obtain high order numerical precision can be obtained in a smooth area, and keeps essentially non-oscillatory property at shock wave and contact discontinuity locations. Even if the new TWENO format and the classic five-order WENO format employ information at the same five points, according to the new TWENO format, the lower global L<1> and L<infinite> norm truncation errors can be obtained. According to linear weights employed by the new TWENO format, the optimum solutiondoes not need to be obtained through burdensome numerical calculation, the linear weights can be set as any positive numbers satisfying the fact that the sum is 1. Compared with the classic WENO format, the new TWENO format has the advantages that the new TWENO format is simpler, has higher robustness and is easier to popularize to a high-dimensional space. According to the new TWENO format, a plurality of classic Euler problems are effectively and numerically simulated, and the effectiveness is sufficiently verified.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Real time field depth analogy method based on fuzzy partition of graphics processor
ActiveCN103093416AReduce trafficHigh speedImage enhancementProcessor architectures/configurationComputational scienceDepth of field
The invention discloses a real time field depth analogy method based on fuzzy partition of a graphics processor. The real time field depth analogy method based on the fuzzy partition of the graphics processor comprises the following steps of (1) converting a to-be-processed image into a file format which can be processed by a graphics processing unit (GPU), (2) processing specific information of the image, (3) carrying out partition blur processing to the image according to the specific information of the image, and deciding that the image adopts different fuzzy radius in different areas according to the specific information, and thus imitating a filed depth effect. Due to the facts that parallelism and programmable capacity of the GPU are fully used, a scene is saved as a texture in render, and a large amount of algebraic operation is transferred from a central processing unit (CPU) to the GPU, the real time field depth analogy method based on the fuzzy partition of the graphics processor not only releases the CPU, but also reduces amount of communication between the CPU and the GPU, and greatly improves imitation speed of the filed depth. Due to the fact that a partition fuzzy algorithm is directly used for processing an original image, a step of fusion of a traditional algorithm fuzzy image and the original image is saved, and accuracy of filed depth imitation is further improved. The image is clear and exquisite, close to a field depth effect picture which is shot by an actual camera, and the real time field depth analogy method based on the partition blur of the graphics processor is applicable to a virtual reality system.
Owner:CHENGDU SOBEY DIGITAL TECH CO LTD
Fluorescence molecular tomography reconstruction method based on alternative iterative operation
InactiveCN103393410AComprehensive measurement dataReduce morbidityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSteep descentAnatomical structures
The invention discloses a fluorescence molecular tomography reconstruction algorithm based on an alternative iterative operation, which is characterized in that a weighted algebraic reconstruction technique and a steepest descent method are used alternately for solving. The fluorescence molecular tomography reconstruction algorithm comprises the following steps that (1), measurement data is acquired; (2), a linear relationship between the measurement data and target distribution is established; (3), a 2 norm minimization problem with a constraint condition is constructed; and (4), the weighted algebraic reconstruction technique and the steepest descent method are used alternately for solving the minimization problem, and a target distribution diagram is obtained. According to the fluorescence molecular tomography reconstruction algorithm, based on a light transmission theory and a finite element method, prior information such as an optical characteristic parameter and an anatomical structure is used, multipoint excitation and multipoint measurement are adopted, and the measurement data is obtained as far as possible, so that the pathosis of the problem is reduced; the weighted algebraic reconstruction technique and the steepest descent method are used alternately for solving the problem, so that a reconstruction result of fluorescence molecular tomography is improved effectively; and the fluorescence molecular tomography reconstruction algorithm has an important application value in the fields of molecular imaging, reconstruction algorithms and the like.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Kalman filtering method for recursive estimation under condition that observation noise covariance matrix is unknown
The invention provides a Kalman filtering method for recursive estimation under the condition that an observation noise covariance matrix of a discrete time time-invariant system is unknown, wherein the method solves the problem of system state filtering estimation under the condition that the observation noise covariance matrix of the discrete time time-invariant system is completely unknown. The method includes the steps that (1) a new statistic sequence is built by means of an observation sequence; (2) a recursion formula of the covariance matrix of the new statistic sequence is calculated; (3) an estimation sequence (f(R)k)of the observation noise covariance matrix is calculated; (4) an estimation sequence of the covariance matrix is calculated, and then real-time estimation of the observation noise covariance matrix is calculated through an algebraic relation; (5) an estimation sequence substitution true value of the observation noise covariance matrix is put into a standard Kalman filtering method, and real-time state estimation of the system and a covariance matrix of state estimation deviation are calculated.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
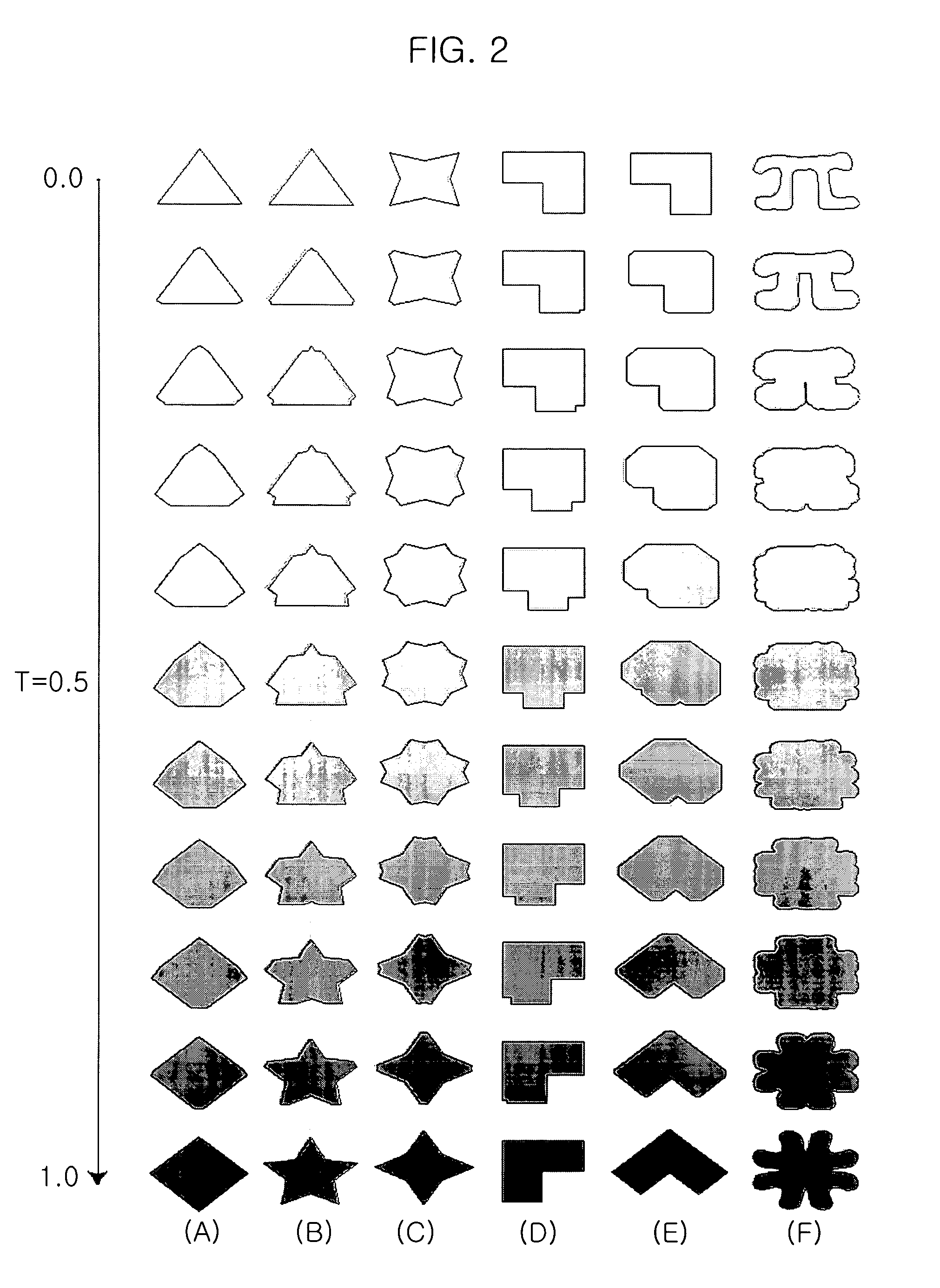
Method for morphing geometric shapes based upon direction map
InactiveUS7091995B2Smooth deformationFlat shapeImage enhancementGeometric image transformationMorphingAlgebra of physical space
The present invention provides a method for morphing different geometric shapes while not using algebraic characteristics and overcoming inefficiency of Minkowski sum computation. The method for geometric shape morphing by using direction map so as to smoothly morph more than two different geometric shapes includes the steps of: a) extracting each direction map of the geometric shape; b) merging the direction maps; c) scaling the merged direction map by group; and d) generating a polygon by using an inverse function of a direction map.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
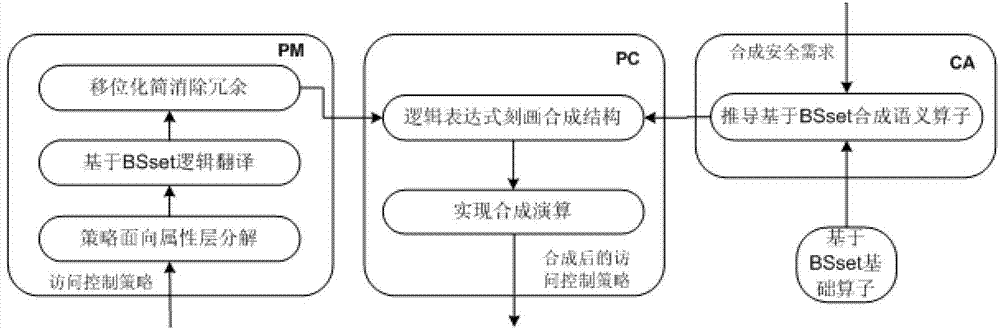
Access control policy synthesis method based on BSset (binary string set)
ActiveCN102932328AExtended Synthetic Semantic OperatorsSmall scaleTransmissionSynthesis methodsDecomposition
The invention discloses an access control policy synthesis method based on a BSset (binary string set). The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, defining elements of the BSset and a set operation rule based on a BS, performing attribute decomposition on an actual policy from an attribute restraint layer according to the definition, and separating the elements in the set to correctly express the policy with a logic expression based on the BS; then, performing semantic check and displacement fusion to eliminate the problems of rule redundancy and semantic conflicts; defining a logic synthesis operator based on the BSset according to actual security demands on the basis, and converting a synthesis mode into a logic expression; directly computing a synthesis result of a policy space based on binary modeling according to the logic expression through the characteristic of being directly taken as a data structure of the BS, wherein the synthesis result is taken as a policy algebra realization mechanism needing no logic conversion; and finally, translating the synthetic policy based on the BSset into an attribute policy.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
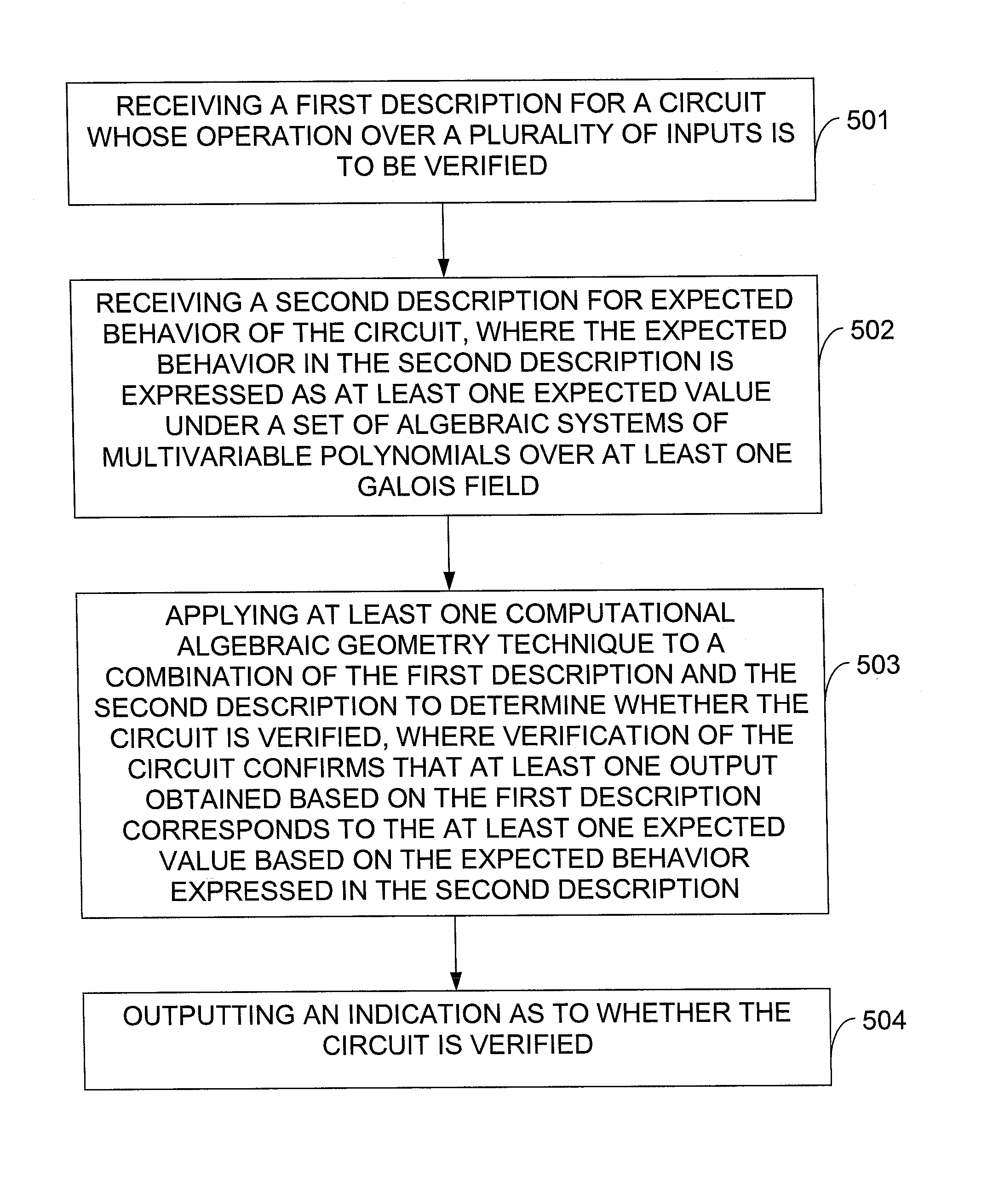
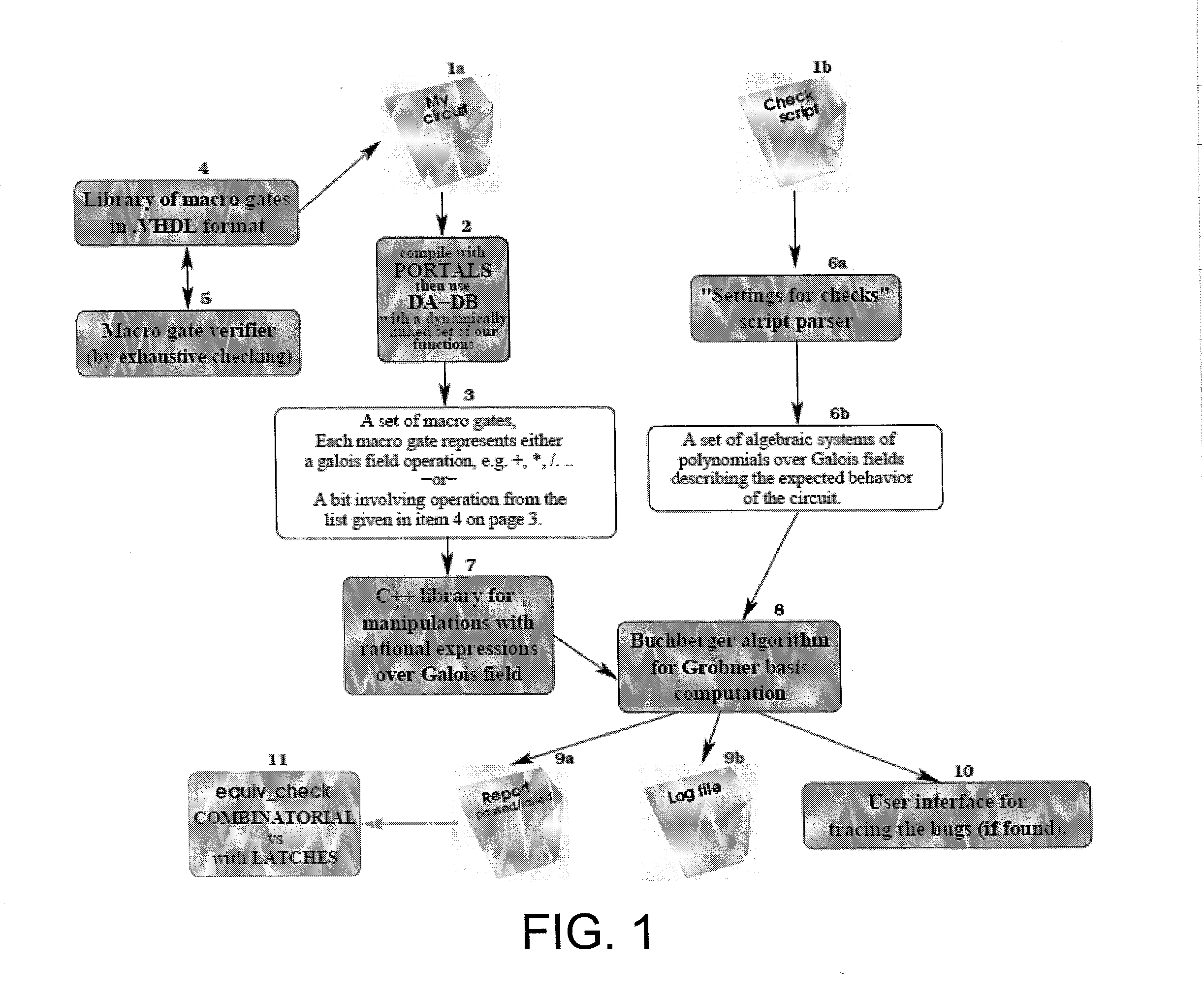
Circuit verification using computational algebraic geometry
InactiveUS20130198705A1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationTheoretical computer scienceMultivariable polynomials
In one exemplary embodiment of the invention, a method includes: receiving a first description for a circuit whose operation over a plurality of inputs is to be verified; receiving a second description for expected behavior of the circuit, where the expected behavior in the second description is expressed as a set of algebraic systems of multivariable polynomials over at least one Galois field; applying at least one computational algebraic geometry technique to a combination of the first description and the second description to determine whether the circuit is verified, where verification of the circuit confirms that at least one output obtained based on the first description corresponds to at least one expected value based on the expected behavior expressed in the second description; and outputting an indication as to whether the circuit is verified.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
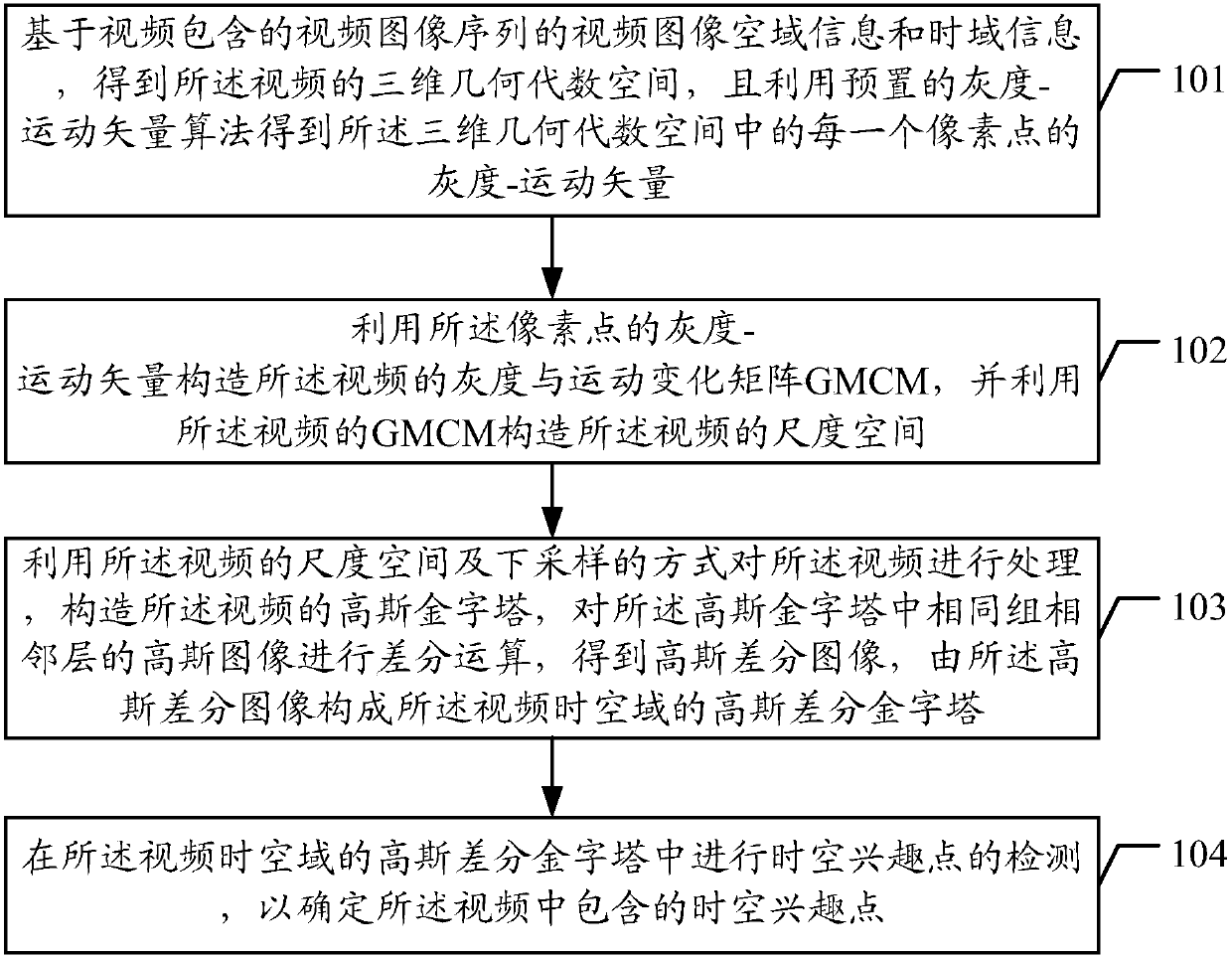
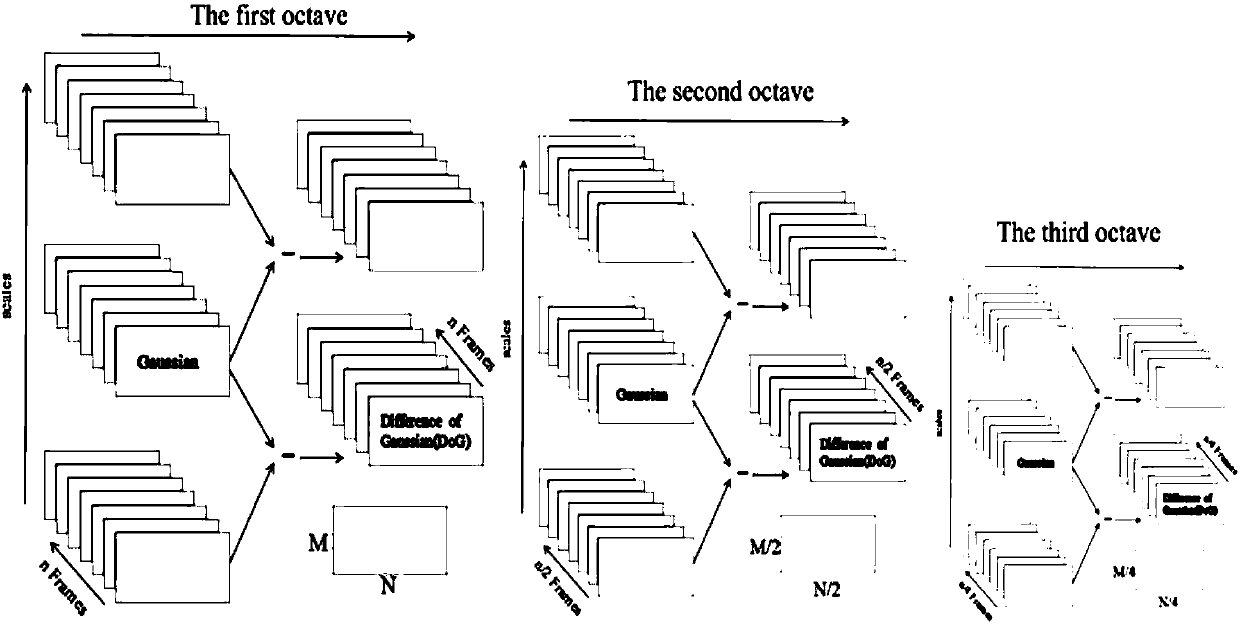
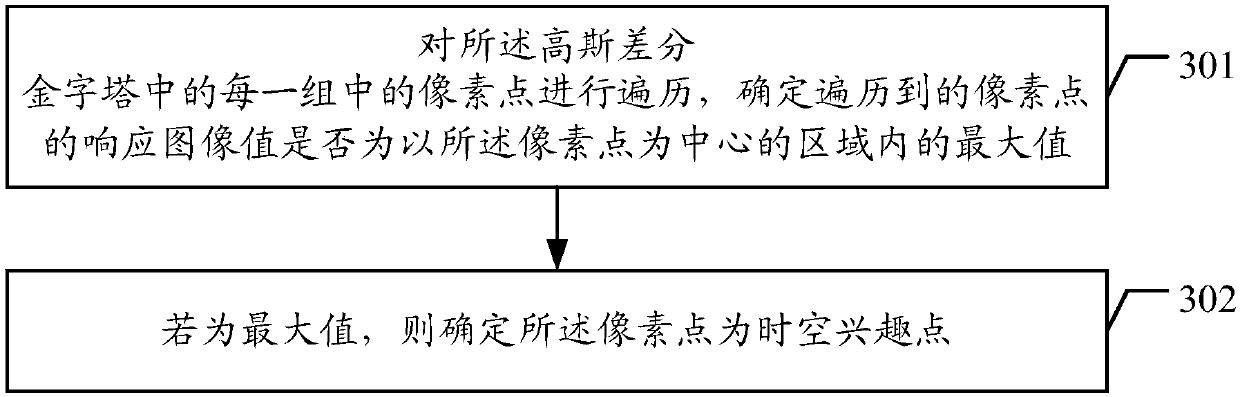
3D SIFT (3D Scale-invariant feature transform) framework-based detection method and device of spatio-temporal interest points (STIPs)
The invention discloses a 3D SIFT (3D Scale-invariant feature transform) framework-based detection method and device of spatio-temporal interest points (STIPs). The method and device combine gray information and motion change information. Compared with the prior art, the method constructs a GMCM (Gray and Motion Change Information Matrix) which is under a geometric algebra framework and contains the gray information and the motion change information, and constructs and obtains scale space through the GMCM; because the GMCM contains the gray information of pixels of a video in three-dimensional geometric algebraic space, and also contains the motion change information, the constructed and obtained scale space is related to the motion change information; and the scale space and a pyramid model constructed and obtained by utilizing the GMCM realize detection of the spatio-temporal interest points, the motion change information of the video on a time domain is fully utilized, and the repeatability, the robustness and other performance of the spatio-temporal interest points are enhanced.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Algebraic curve rasterization method based on pixel precision
InactiveCN102651137AMeet the requirements of real-time renderingQuick draw2D-image generationRelevant informationAlgorithm
The invention discloses an algebraic curve rasterization method based on pixel precision, comprising the following steps of: inputting an algebraic curve to be plotted and relevant information; limiting characteristic points of the curve into a pixel range to obtain a plurality of characteristic regions containing curve characteristic points; calculating crossed points of the curve and interfaces of the characteristic regions; constructing topology connecting information of the curve on the characteristic regions through the crossed points; determining the direction of the crossed points of the interfaces of the characteristic regions and utilizing a straight-line section to connect the adjacent characteristic regions to obtain a straight-line section fitting curve, wherein the straight-line section passes through the crossed points of the interfaces of the characteristic regions; and optimizing the straight-line section fitting curve, and plotting and displaying the curve. The algebraic curve rasterization method based on the pixel precision can obtain a high-quality curve through Newton iteration and guarantees the smoothness of the curve; and a numerical calculation process with complicated sub-resultant and high ordered equation rooting problems is omitted, and the curve can be conveniently plotted in real time.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
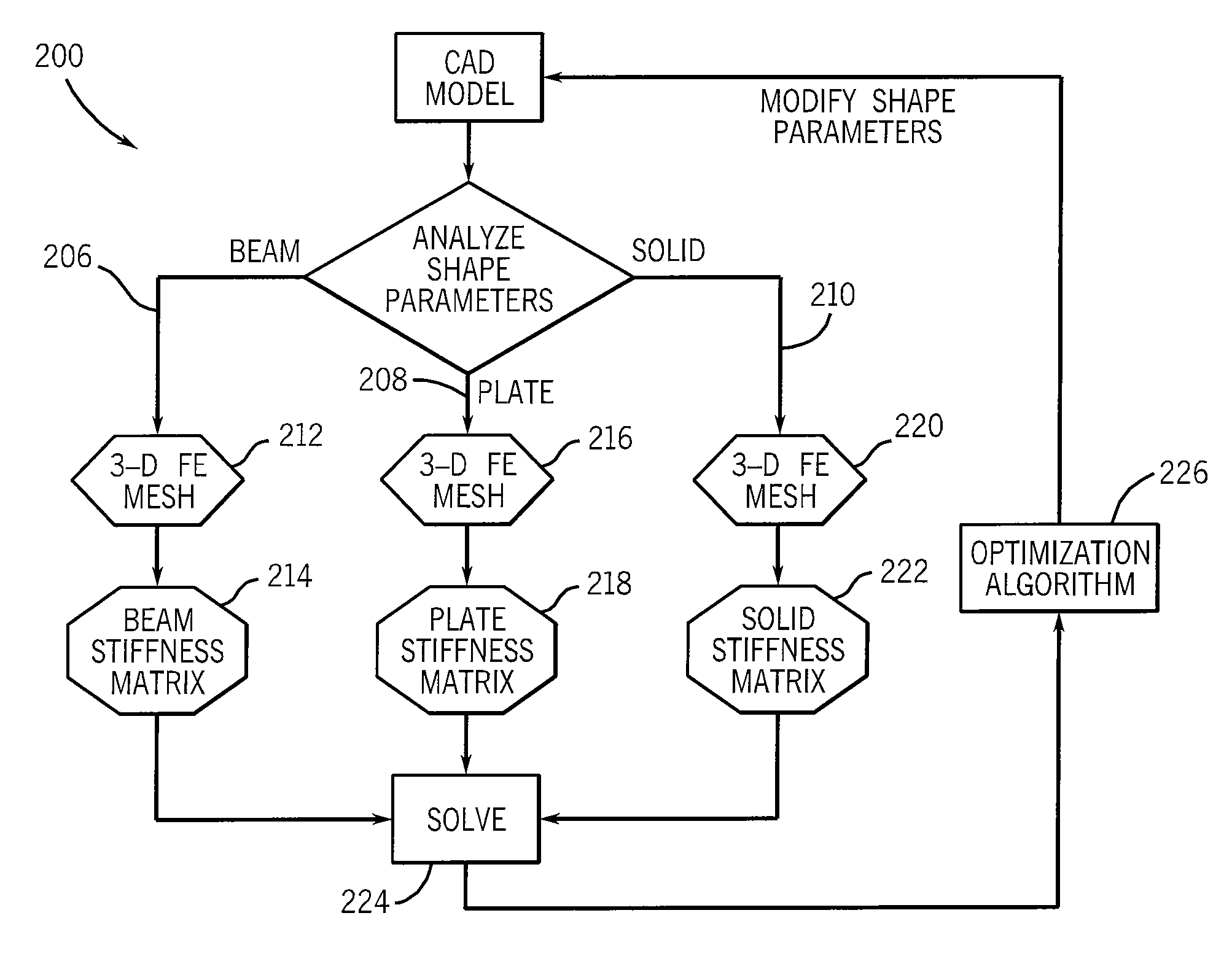
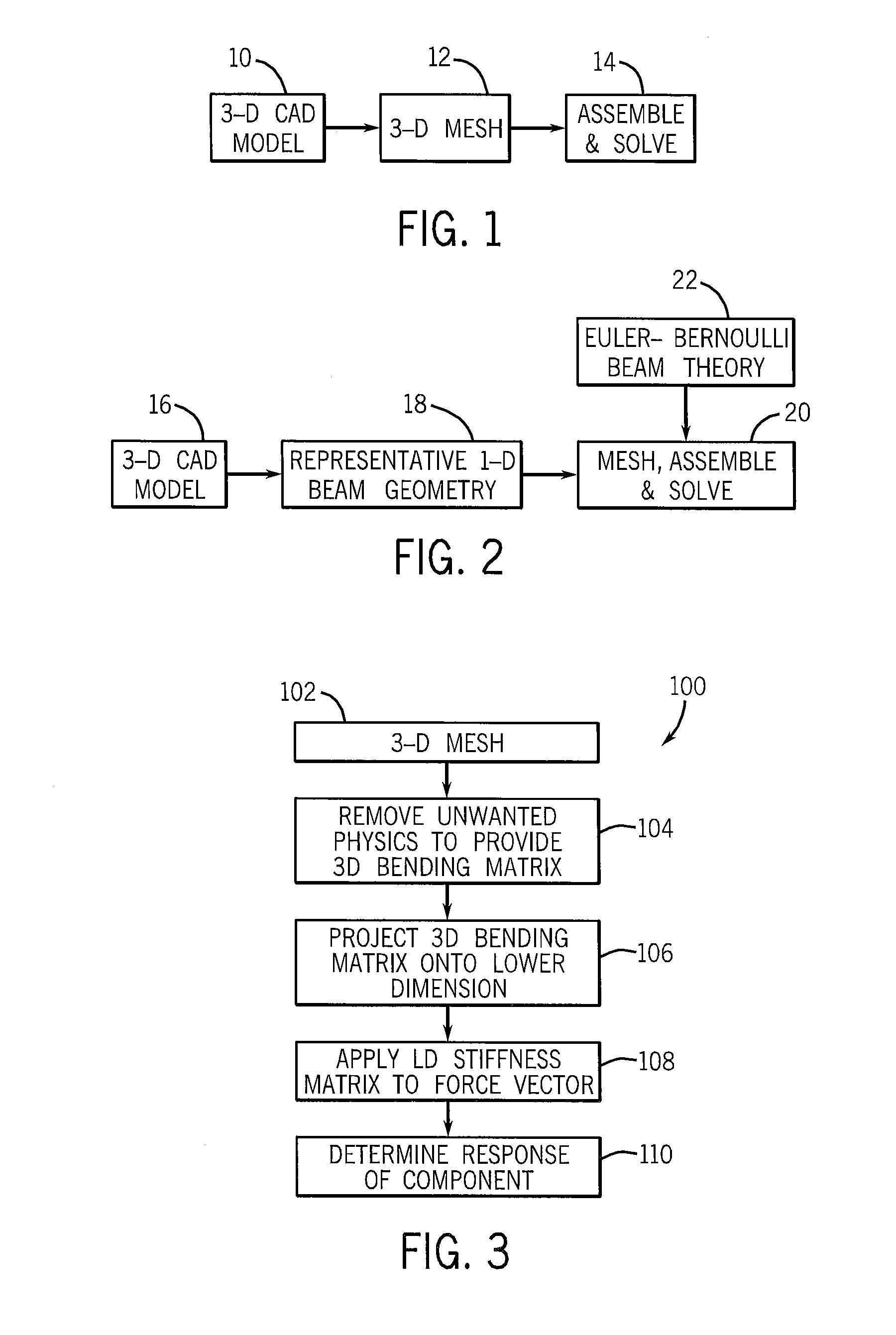
Method and system for analysis and shape optimization of physical structures using a computerized algebraic dual representation implicit dimensional reduction
ActiveUS8355893B2Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationData setDimensionality reduction
A method and system for simulating and analyzing the behavior of a structural component of a computerized model in response to a simulated event to determine an optimized shape for the component is disclosed. The shape is optimized using an implicit dimensional reduction rather than an explicit geometric replacement by discarding data of a 3D discretization that has little or no bearing on the performance of the component to a simulated event. The reduced dataset is then collapsed onto a lower dimension projection that is applied over a force vector that is representative of the simulated event to determine the behavior of the component to the simulated event. Optimization tools may then be used to modify the physical attributes of the component and performance of the component once again simulated until an optimized component is determined.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method for determining linear dispersion space-time codes for receiving antenna numberless than transmitting antenna number
InactiveCN101702643ASimple Coding Design ComplexityGood coding performanceSpatial transmit diversityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionLinear dispersionOrthogonal method
The invention relates to a method for determining linear dispersion space-time codes when the receiving antenna number is less than the transmitting antenna number. Large limitation exists in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, determining channel using times T (T is not less than M) and constructing layered matrices C1-CN; then constructing N stepped matrices U1-UN in T*T; constructing q=NT encoding matrices Aj, K in M*T, wherein the j is equal to 1 to T, the k is equal to 1 to N, the M is the transmitting antenna number, the N is the receiving antenna number, Aj, k is equal to P.Ck.diag (Uk(:, j)).Q, NT encoding matrices Aj, k are obtained together, and then the linear dispersion space-time codes are determined. The method adopts a trace orthogonal method to achieve approximately optimal channel volume and uses an algebraic method to obtain full set gains. The linear dispersion space-time codes determined in the method of the invention have simple encoding design complexity and simultaneously provide favorable encoding properties.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
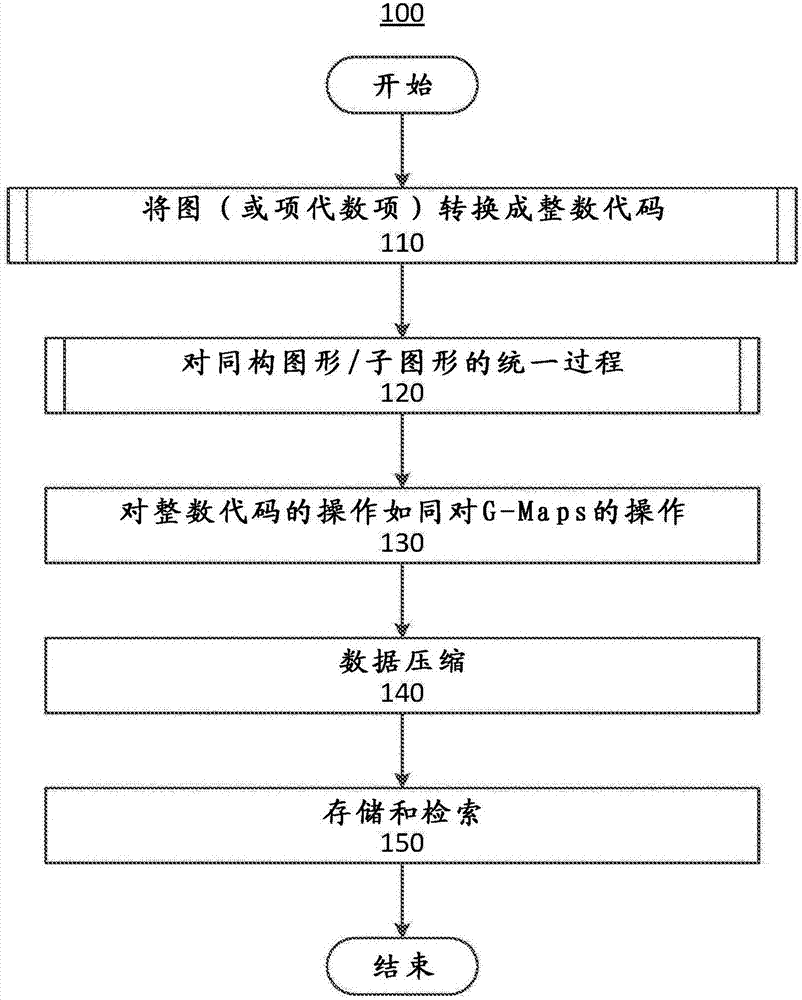
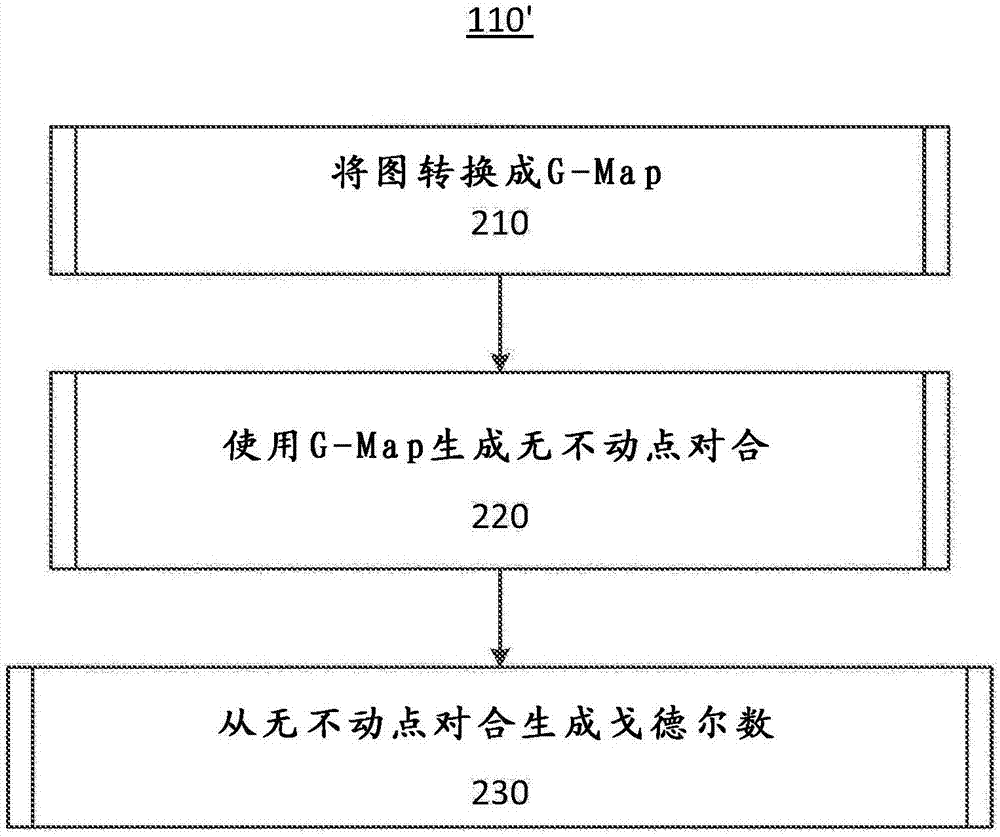
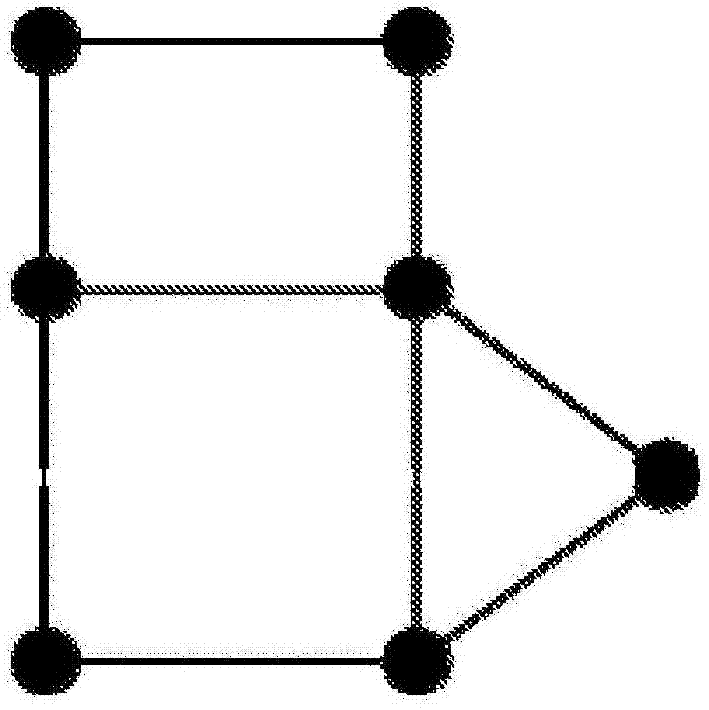
Apparatus and method for combinatorial hypermap based data representations and operations
A method and apparatus is provided for implementing combinatorial hypermaps (CHYMAPS) and / or generalized combinatorial maps (G-Maps) based data representations and operations, comprising: mapping term-algebras to tree-based numbers using a fast algorithm and representing a graph of the mapping structure as a CHYMAPS using reversible numeric encoding and decoding; generating a representation of CHYMAPS in a form optimized for sub-map (sub-graph) to map (graph) isomorphism and partial matching with a general matching process; performing operations on the CHYMAPS as operations on respective numerical representations; performing compression and decompression using a three bit self-delimiting binary code; and storing and retrieving codes.
Owner:KYNDI
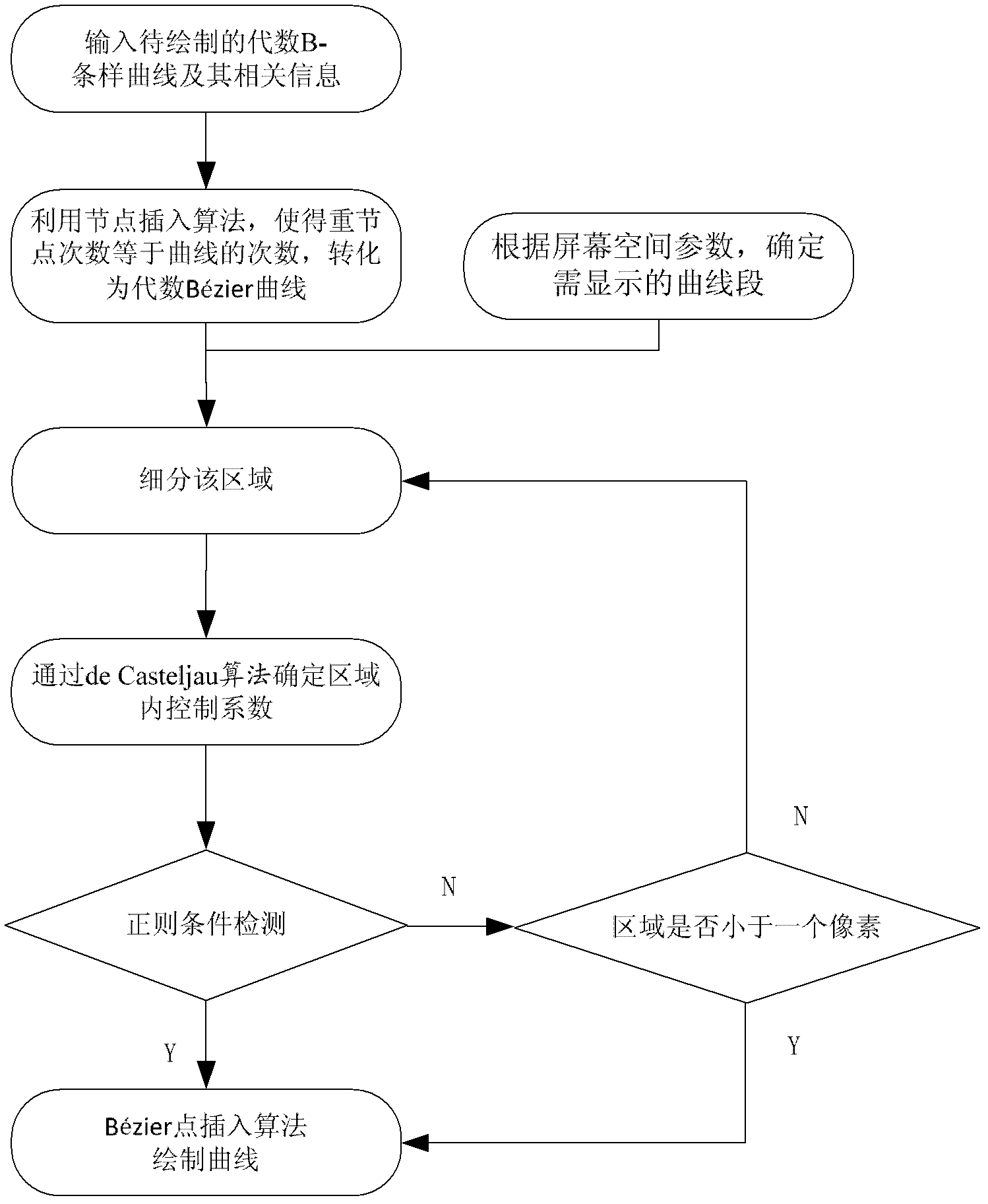
Rasterization method of algebraic B-spline curve based on regularization conditions
InactiveCN102663184AAvoid calculationAvoid numerical calculationsSpecial data processing applicationsComputational scienceGrating
The invention discloses a rasterization method of an algebraic B-spline curve based on regularization conditions. The rasterization method of the algebraic B-spline curve based on the regularization conditions includes the steps of inputting the algebraic B-spline curve to be drawn and relevant information; processing the curve in a fragmentation manner, and converting the processed curve into a piecewise algebraic Bezier curve; confirming a curve segment needing to be displayed according to screen space parameters; subdividing a region corresponding to the curve segment needing to be displayed to obtain a control coefficient of each sub-region curve; detecting whether each sub-region satisfies the regularization conditions or not; and as for one sub-region satisfying the regularization conditions or with the region area smaller than one pixel, drawing the curve in the sub-region and displaying the curve on a screen. The curve can be defined in a simple region, and precision of the pixel is higher. Characteristic points can be refined step by step to achieve the precision of the pixel, calculation of the characteristic points with high complexity of time and space is avoided, and real-time rasterization drawing of the algebraic B-spline curve with complex topology is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
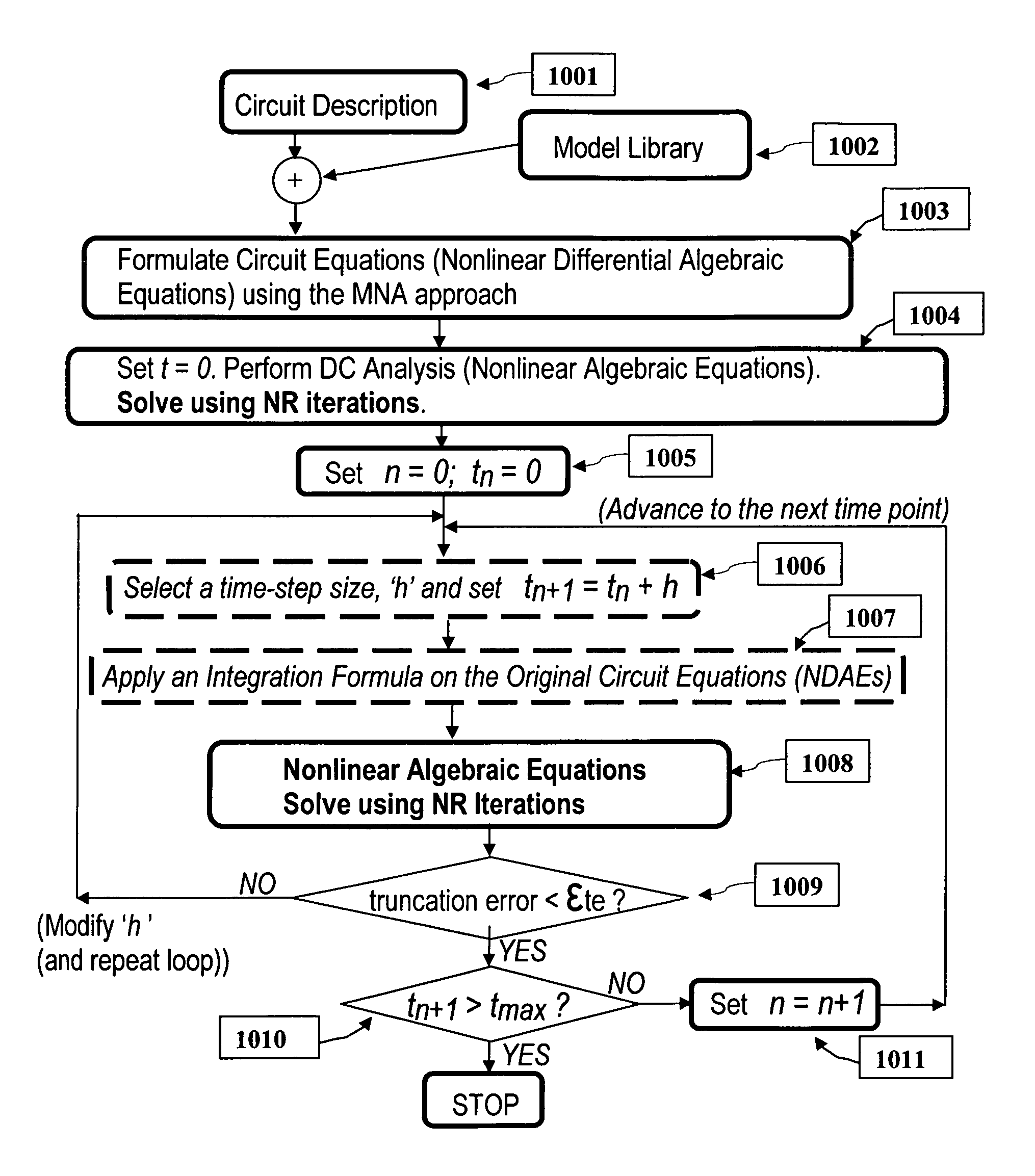
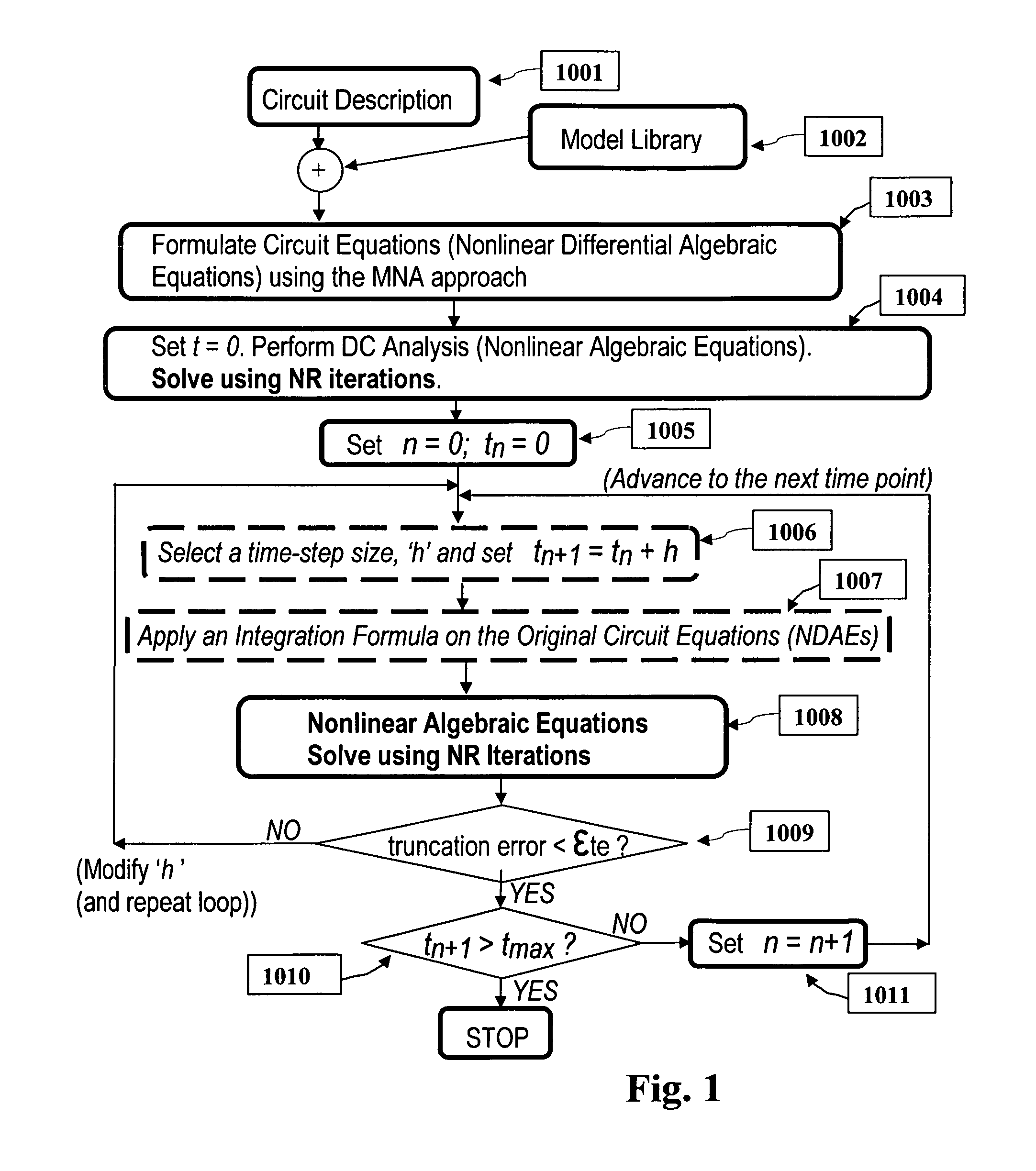
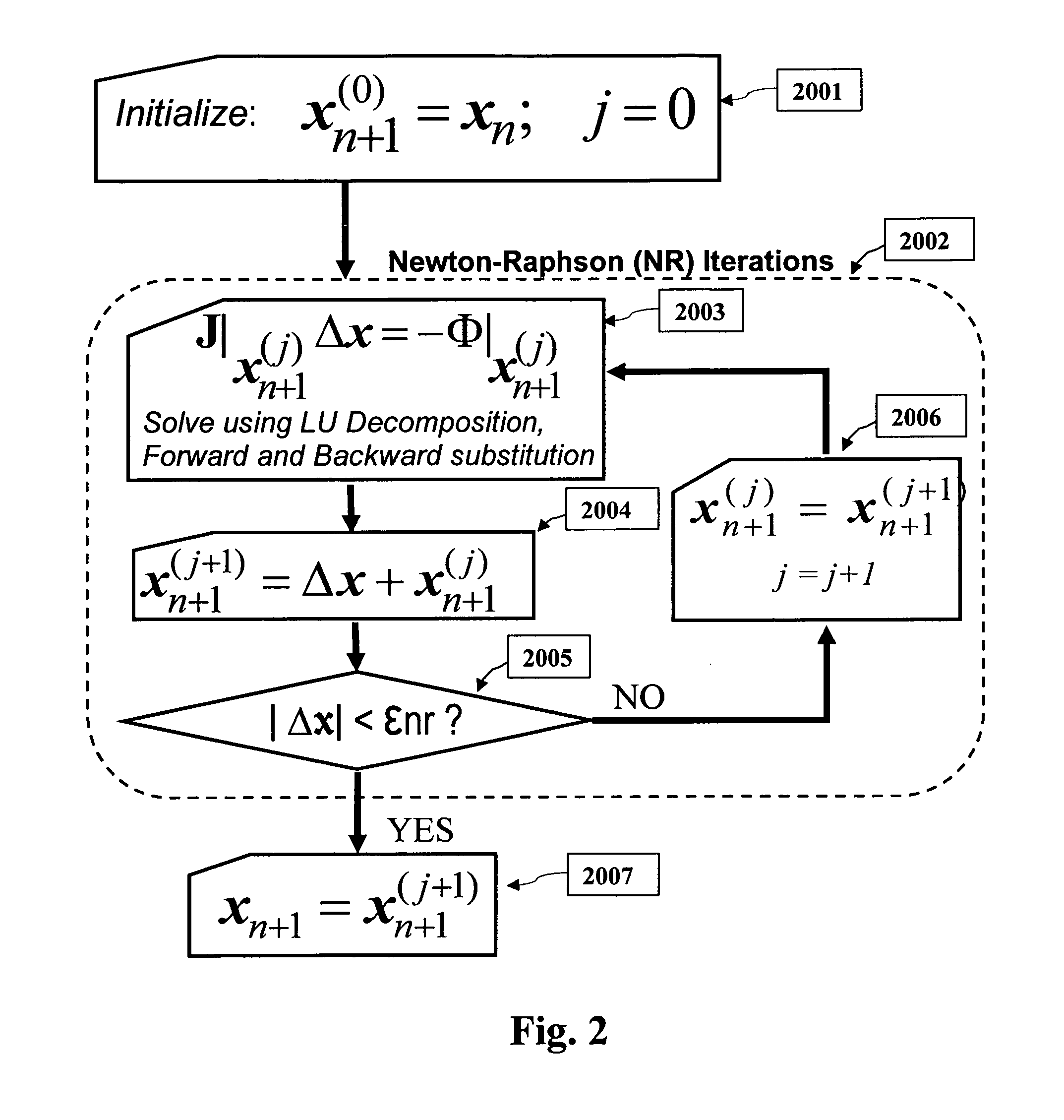
Parallel simulation of general electrical and mixed-domain circuits
InactiveUS8543360B2Computation can be minimizedMinimize overheadComputation using non-denominational number representationComputer aided designNODALDegree of parallelism
A new method for simulation of general electrical circuits on parallel computing platforms is disclosed. Parallel simulation of general time-domain circuits that are represented by nonlinear / linear differential algebraic equations is accomplished by partitioning them into smaller subcircuits via a novel combination of the companion form representation of the given circuit and an efficient form of node splitting, during Newton Raphson iterations, at any time point. The new invention formulates the interface vectors between partitions, through purely binary vectors, leading to a high degree of parallelism, scalability and reduced computational and communication costs for synchronizing the solutions between various partitions. Parallel platforms considered can be diverse such as (including but not restricted to) multicore CPUs, distributed systems of computers. The new invention also provides for scalable parallel simulation of mixed-domain formulations, such as (including but not restricted to), integrated circuits, electronic packages, PCBs, electromagnetic modules, MEMS and optical components etc.
Owner:OMNIZ DESIGN AUTOMATION CORP
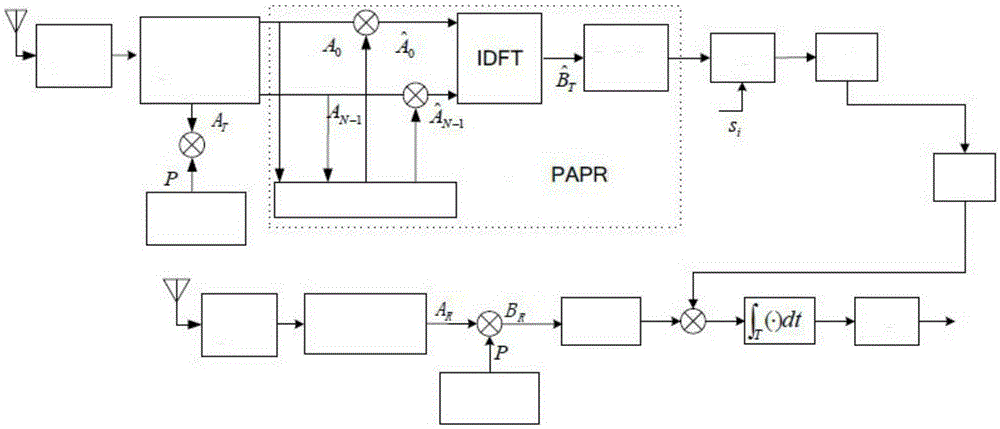
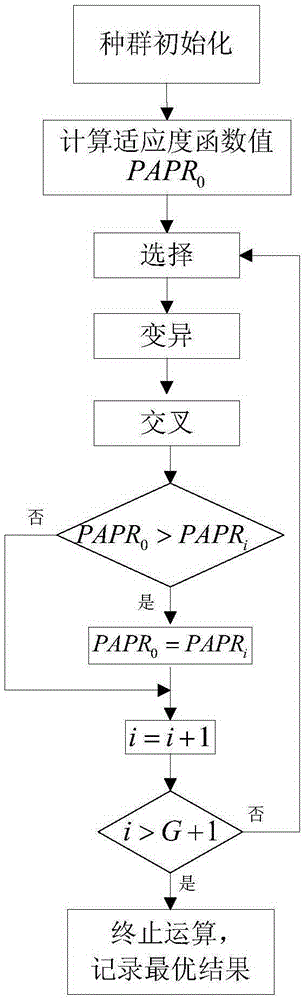
Method for reducing peak-to-average power ratio of transform domain communication system
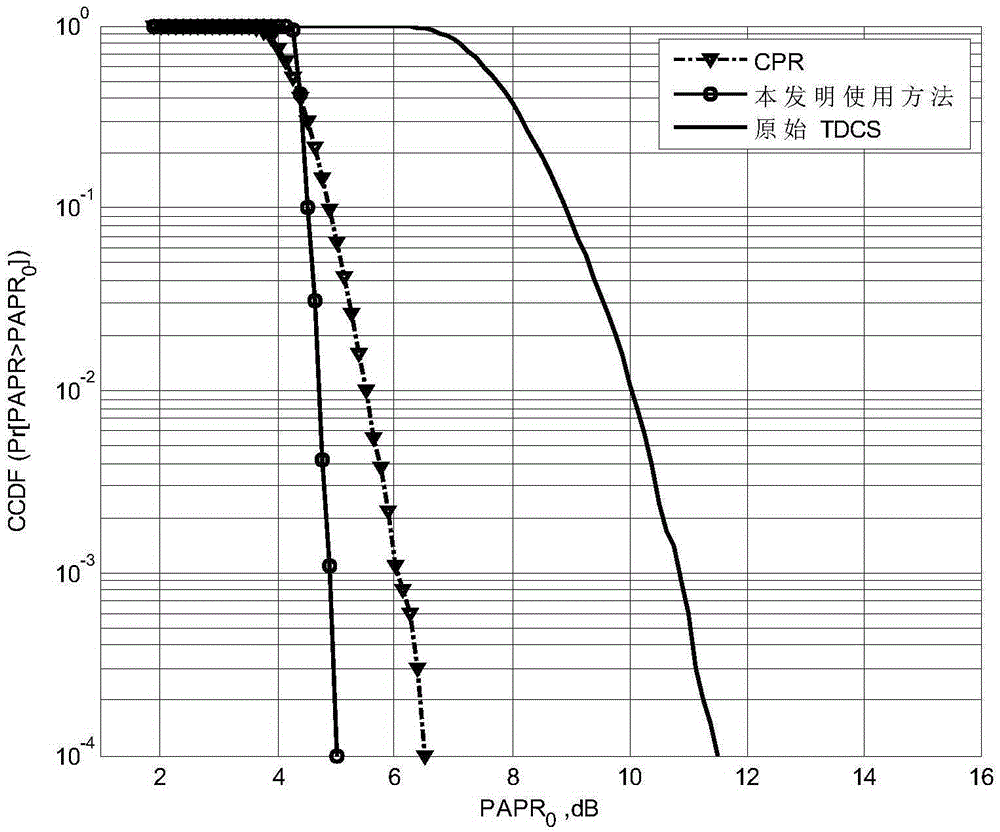
ActiveCN105306400AReduce peak-to-average power ratioChange spectrum magnitude vectorMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemGreek letter epsilon
The invention discloses a method for reducing a peak-to-average power ratio of a transform domain communication system. The specific method is as follows: 1) respectively setting an initial population number S, an upper population limit up, a lower population limit low, a variable coefficient F, a penalty function factor epsilon and a maximum generation G; 2) initializing the set populations, and respectively calculating a weighted basis function b0 and a fitness function PAPR0; 3) randomly selecting a part of generated population individuals; 4) varying the selected population individuals; 5) carrying out cross swap on the individuals in the varied population; 6) respectively calculating a weighted basis function bi and a fitness function PAPRi of a matrix Ti, comparing the size of PAPRi and PAPR0 in the step 2, and carrying out corresponding judgments; and 7) obtaining an optimal amplitude weighting factor vector (the expression is described in the specification) and a minimum peak-to-average ratio Pbest. The method disclosed by the invention is used for solving the problems of high complexity and weak orthogonality of the existing TDCS peak-to-average ratio inhibition method.
Owner:XIJING UNIV
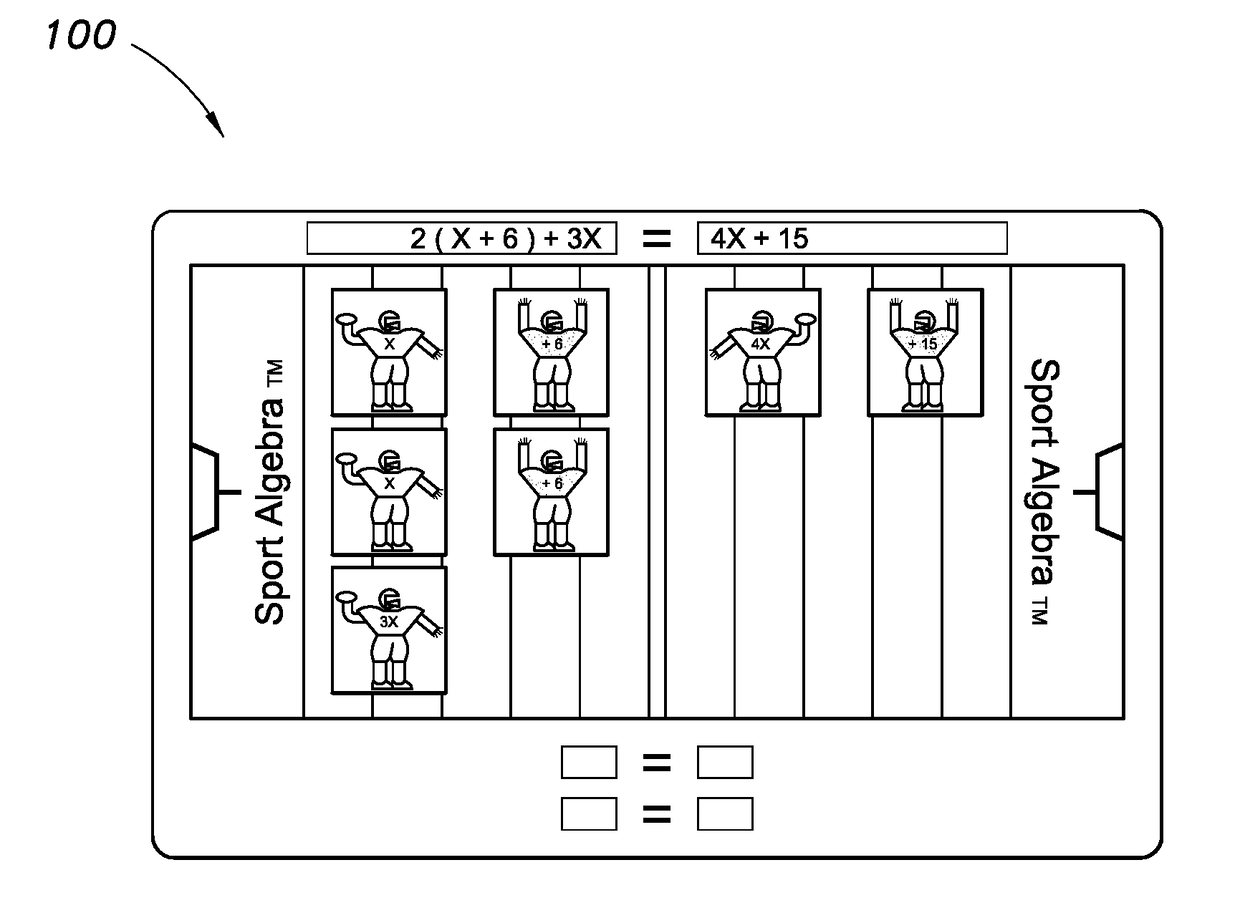
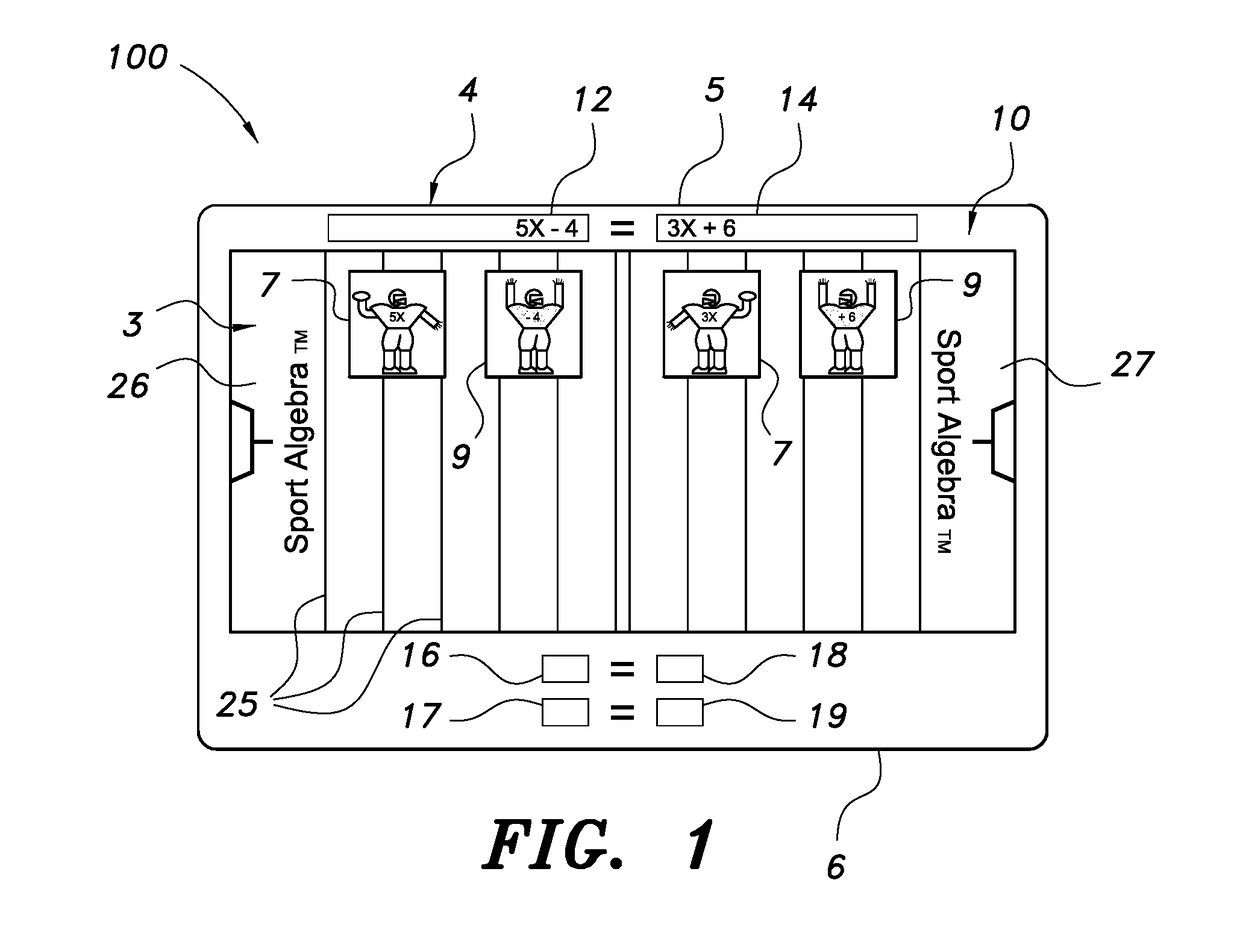
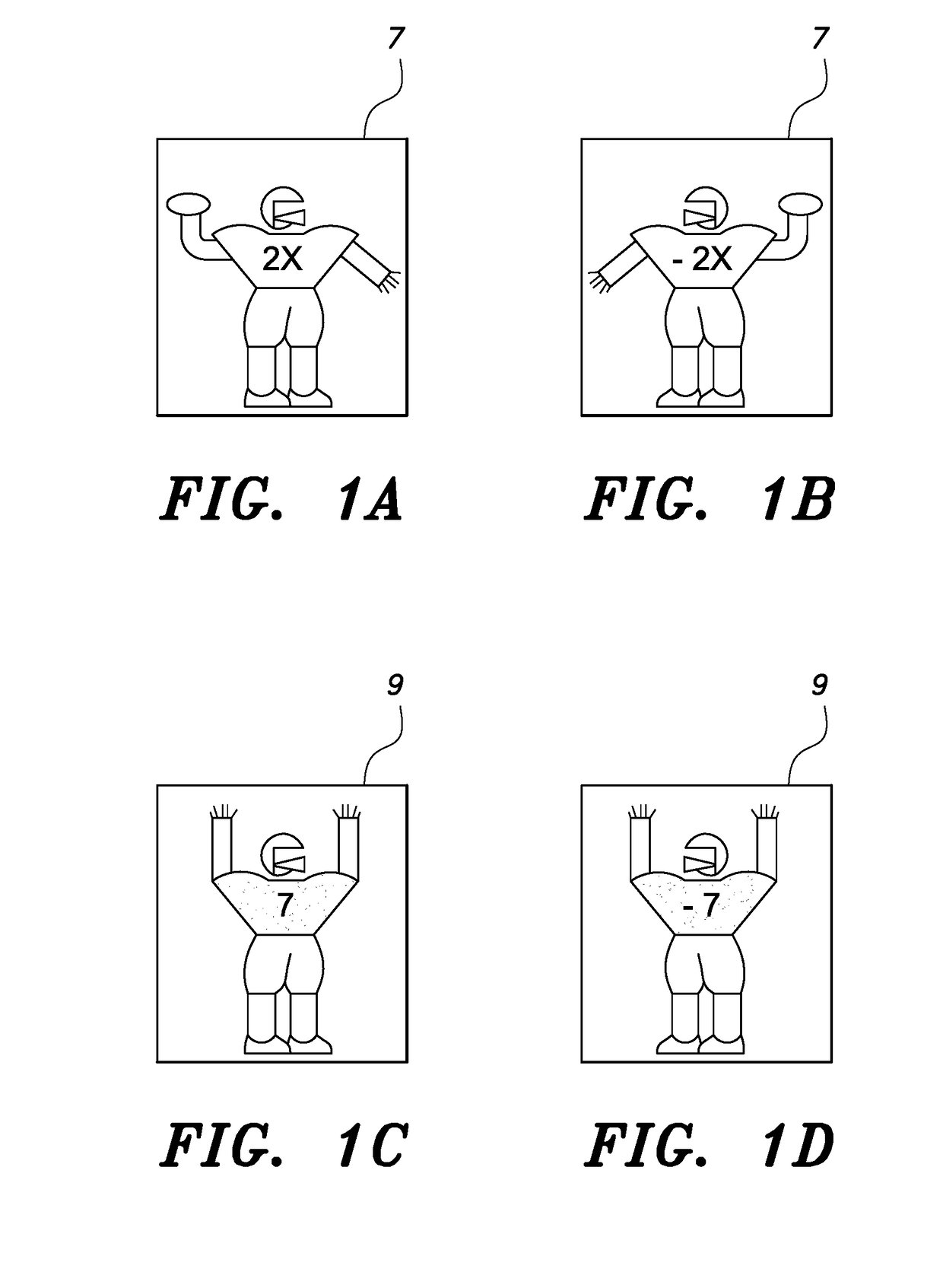
Visual and kinesthetic method and educational kit for solving algebraic linear equations involving an unknown variable
ActiveUS20180151090A1Accurate representationEasy to operateEducational modelsTeaching apparatusGraphicsAlgebraic solution
An educational kit for teaching mathematics includes easily manipulated elements, which serve as cognitive reinforcement during the learning process. These physical elements are used in conjunction with a set of grouping rules. The educational kit and corresponding grouping rules determine a model and process to represent both an algebraic linear equation and its algebraic solution. A simple element, such as an item / figure including a variable “X”, is used to denote the unknown quantity. An item / figure including a number is used to represent a numerical value. These items / figures contain the exact elements used to form the expressions of the linear equation and are not items / figures that simulate the elements that form the expressions of the equation. By the use of this educational kit and associated grouping, students learn to simplify a given linear algebraic equation to the point where the solution is obvious.
Owner:MATTHEWS JEFFREY B
Virtual vector modulation algorithm of three-level inverter based on 60° coordinate system
The invention relates to a 60degree coordinate system based virtual vector modulation algorithm of a tri-level inverter, belonging to the field of power and electronic application. According to the algorithm, virtual space vectors (VSVPWM) are mapped into a 60degree coordinate system via Clark / Park coordinate transformation so that basic vector coordinates are changed into simple algebraic coordinates, large and small sectors are discriminated according to logic judgment of linear coordinate equations, action time of three latest basic vectors are calculated via the algebraic coordinates in a volt-second balance principle, PWM signals are output in a nine-segment switching time sequence with a positive small vector at first, and action time of redundant small vectors is adjusted via closed-loop PI regulation according to two capacitance difference values. A lot of trigonometric function and irrational number operation in a traditional VSVPWM algorithm can be omitted, and the 60degree coordinate system based virtual vector modulation algorithm is characterized by being simple in calculation, high in instantaneity and easy to realize.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com