Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Acute mi" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Acute MI. Overview. A heart attack or acute myocardial infarction (MI) occurs when one of the arteries that supplies the heart muscle becomes blocked. Blockage may be caused by spasm of the artery or by atherosclerosis with acute clot formation.
Differentiating acute myocardial infarction from other ECG abnormalities
ActiveUS6979297B2Easy to detectElectrocardiographyCatheterECG abnormalityFirst myocardial infarction
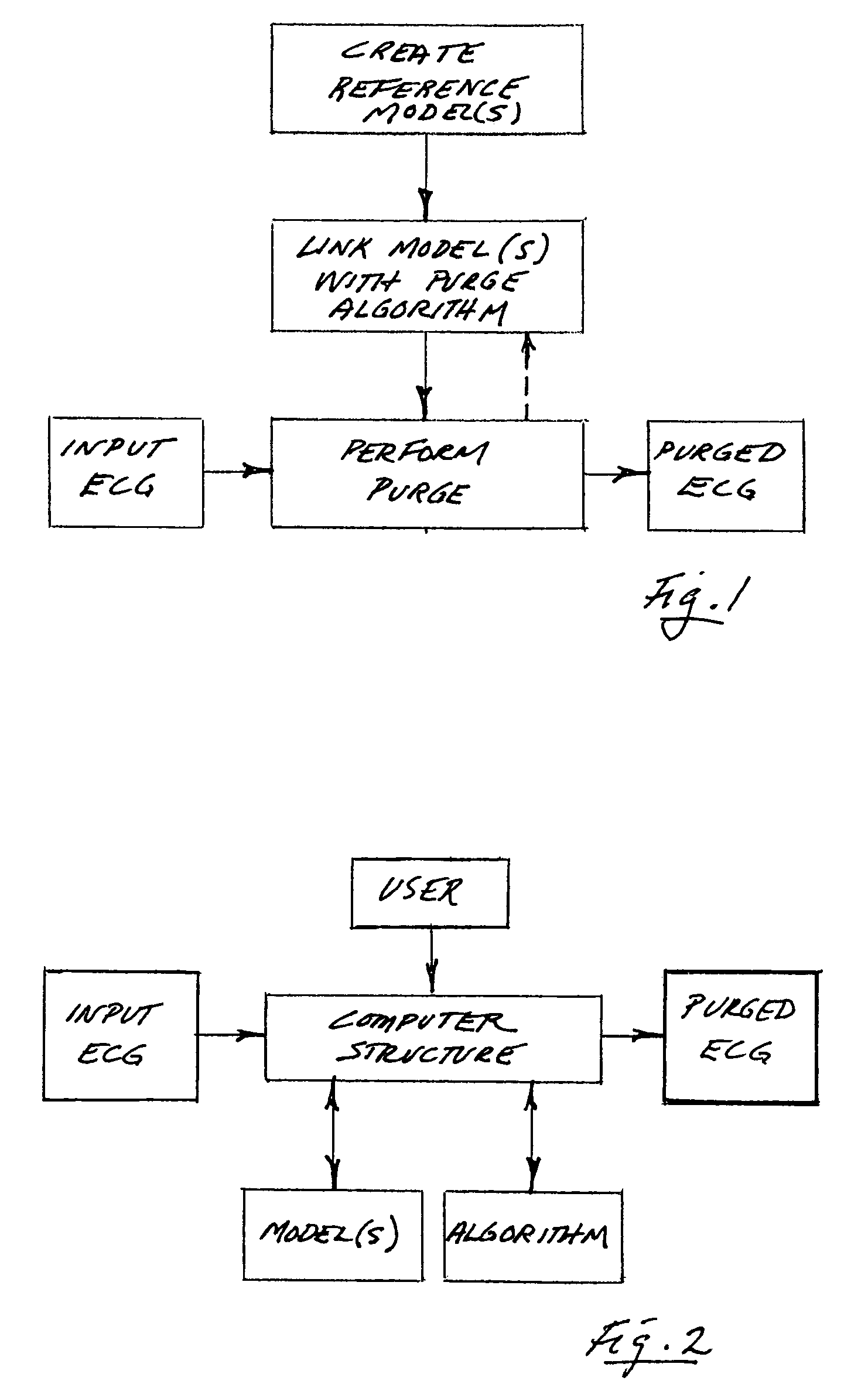
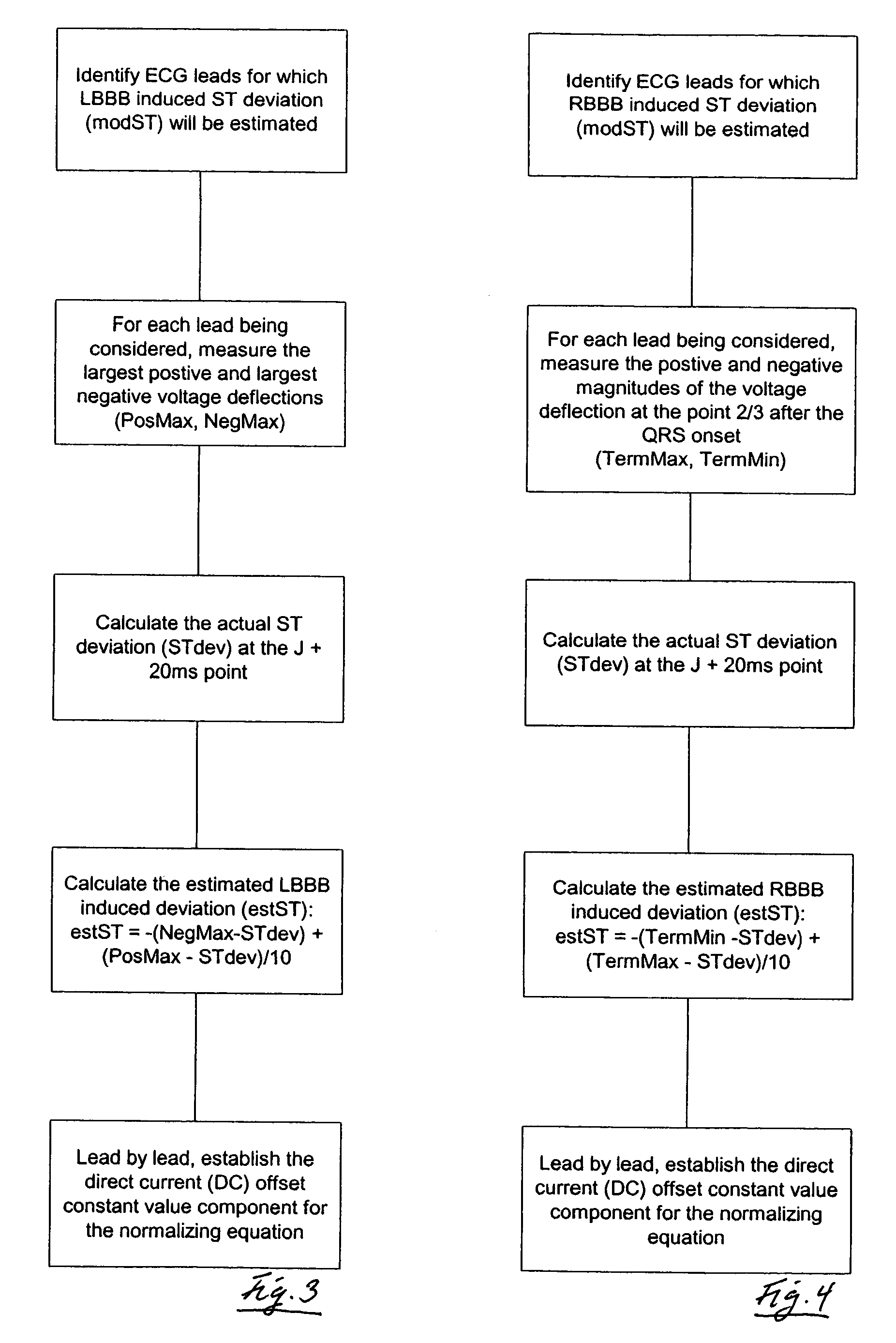
A method for differentiating acute myocardial infarction (AMI) from other ECG abnormalities. The method is performed by modeling selected ECG confounders that tend to obscure AMI evidence in the ECG waveform, and by purging a subject's ECG waveform of the effect(s) of these confounders through linking selected confounder models with an appropriate, computer-implementable purge algorithm.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
Diagnosis of acute myocardial, ischemic diseases
InactiveUS20060234304A1Enhance early detectionReduce morbidityDisease diagnosisBiological testingMedicineTest strips
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Non-invasive attached telemetering electrocardiographic recording method and system having ultra-long record period and ultra-high storage capacity
InactiveCN102485171AAchieve playbackRealize monitoringDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMass storageConvalescence
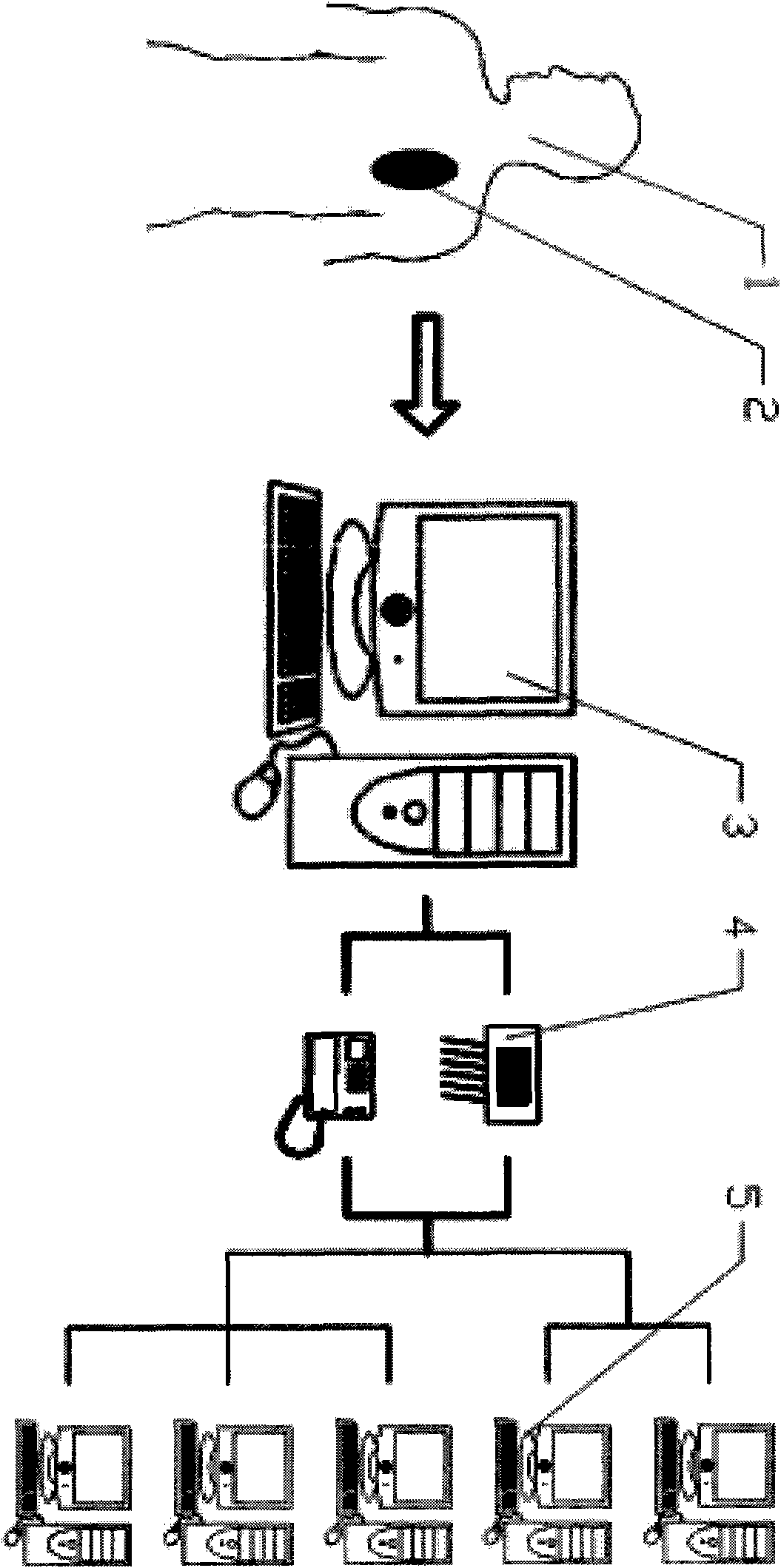
The invention relates to a non-invasive attached telemetering electrocardiographic recording method having an ultra-long record period and an ultra-high storage capacity. By using the method, characteristic values of electrocardiographic waves can be safely, stably and clearly acquired under the natural physiological state of a human body within a long period (more than 15 days), microvolt-level measurements of T-wave alternans can be acquired, and the collection, processing and high-capacity storage of electrocardiographic waves can be completed; and multiple electrocardiographic recording pasters can be used to realize the simultaneous recording of multi-channel body surface electrocardiograms, and a computer data processing and analysis system can complete the data monitoring and analysis, image display, data storage and printing and output of the recorded signals and realize the networking transmission of the electrocardiosignals. The clinical indications of the device include: symptoms related to suspected arrhythmia; determination of arrhythmia property, and completion of reasonably evaluating anti-arrhythmia treatment and monitoring myocardial ischemia; evaluation of anemic heart disease treatment measures; instructions to acute myocardial infarction patients before leaving hospital and during convalescence; and installation, detection and function assessment of sudden cardiac death and heart pacemakers.
Owner:杰升生物科技(上海)有限公司 +2
Combination treatment for acute myocardial infarction
InactiveUS20050255096A1Reduce mortalityBeneficial synergistic effect on the mortalityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsThrombusMortality rate
A combination therapy for the treatment of acute myocardial infarction comprises administering a combination of a thrombolytic agent and levosimendan or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof to a patient. The combination synergistically reduces mortality of patients with acute myocardial infarction.
Owner:ORION CORPORATION
Combination treatment with t-PA variant and low molecular weight heparin
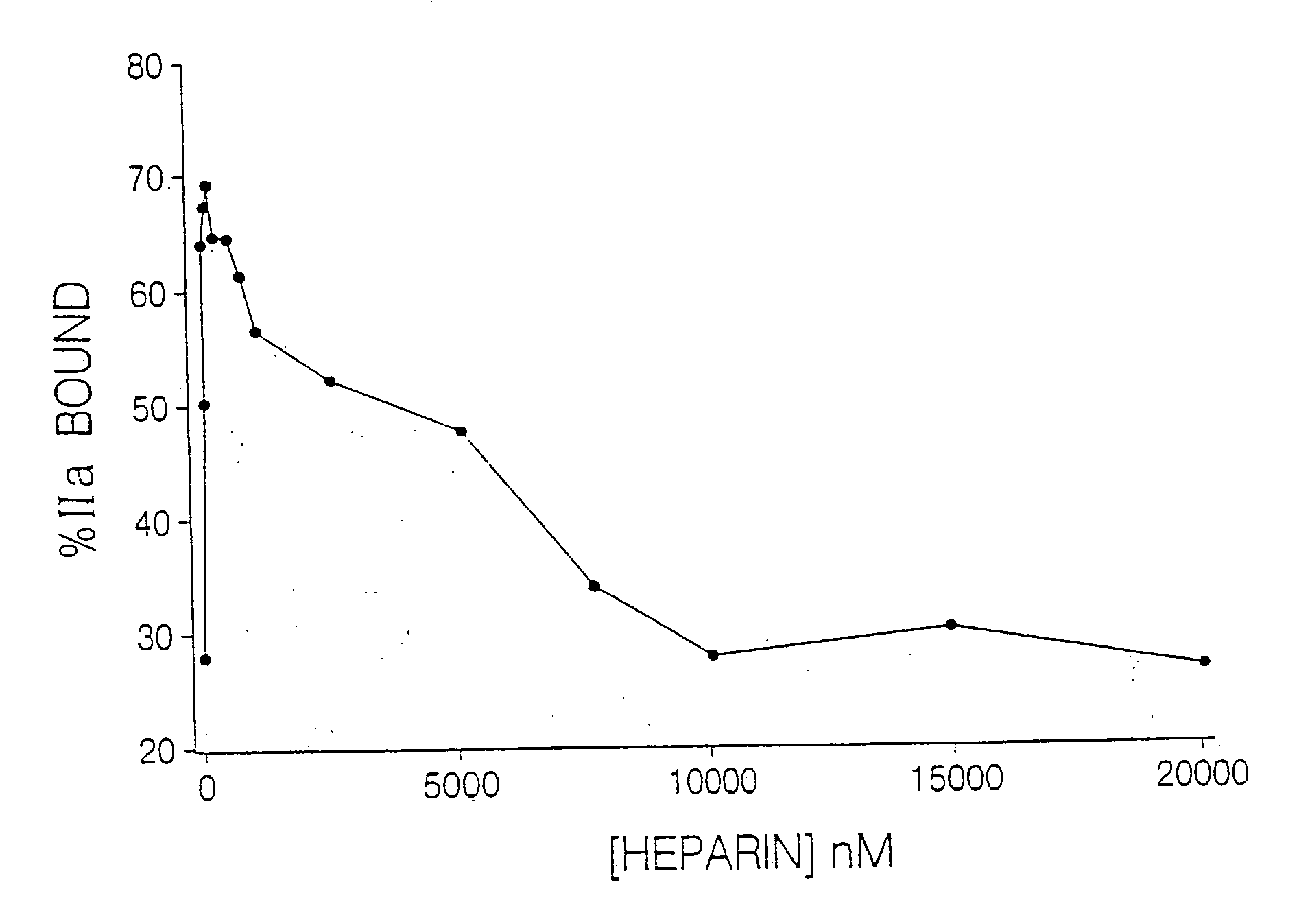
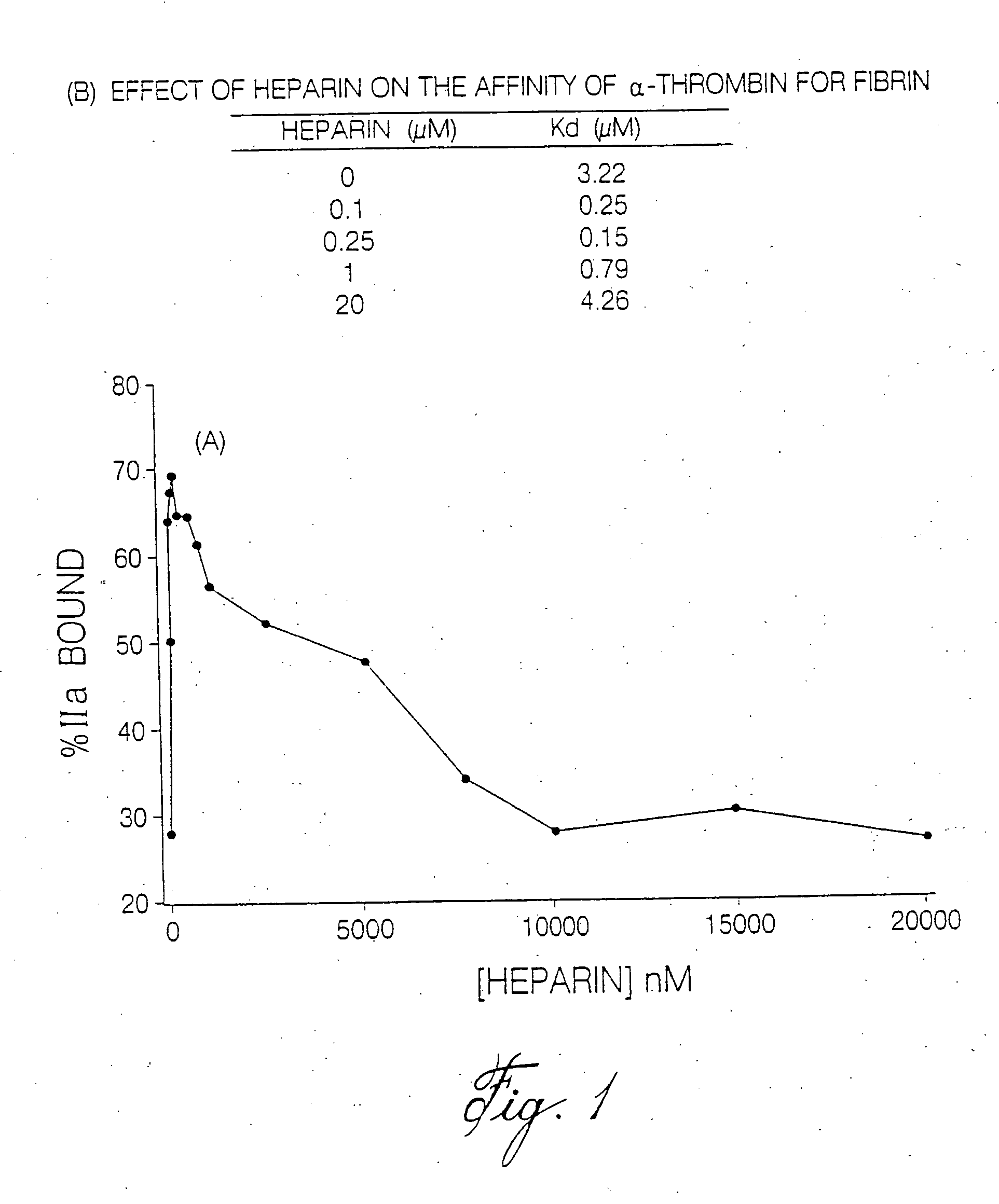
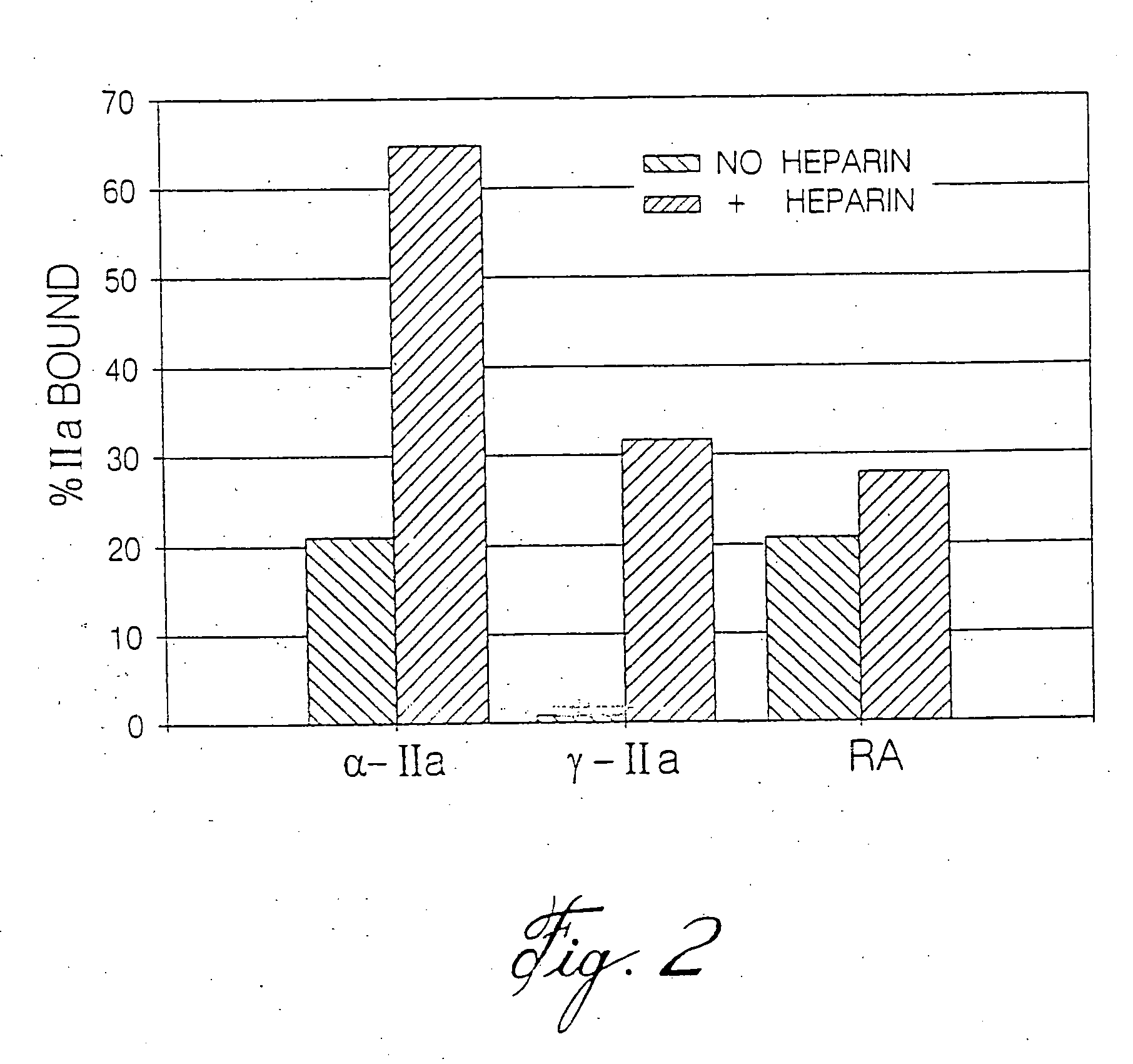
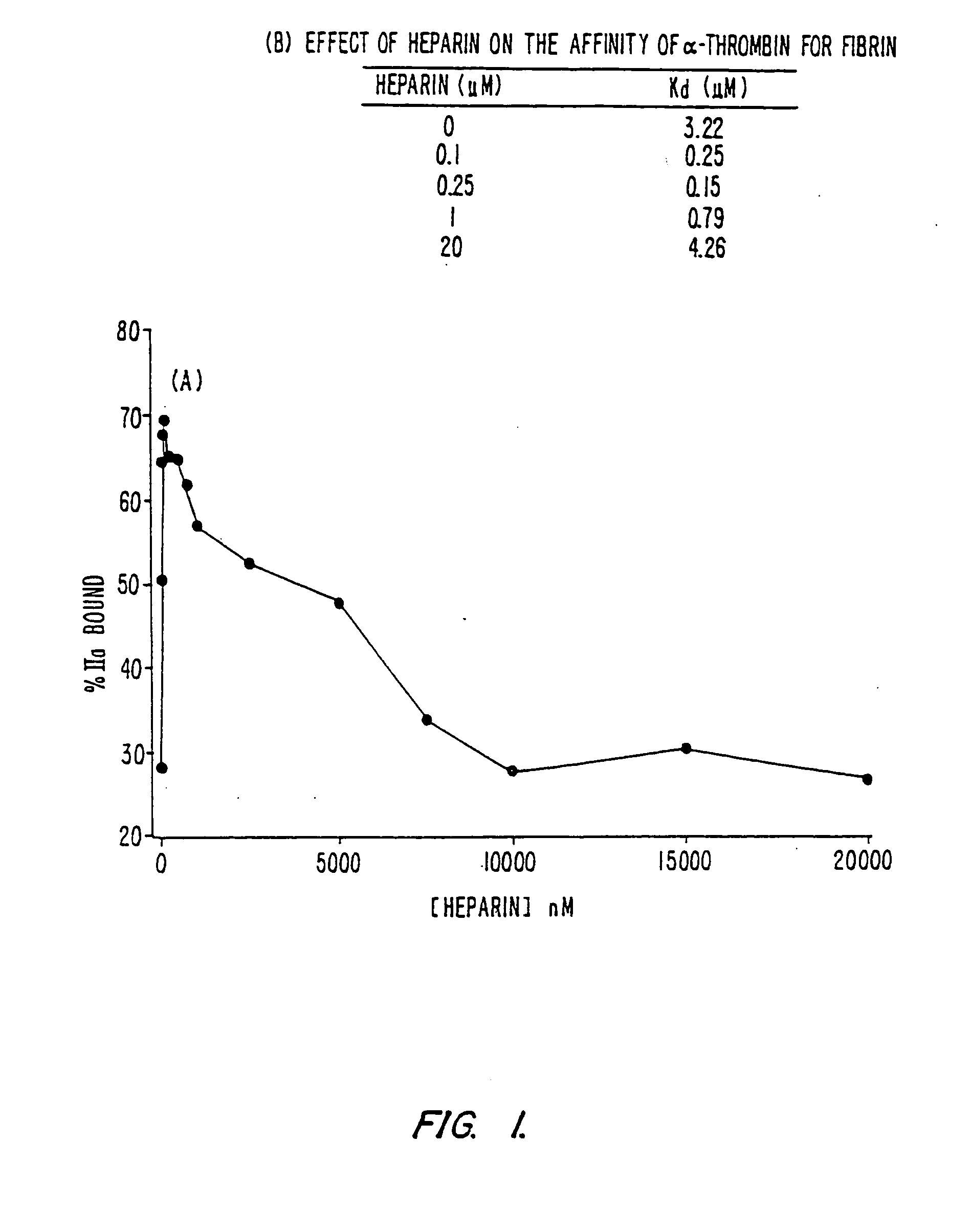
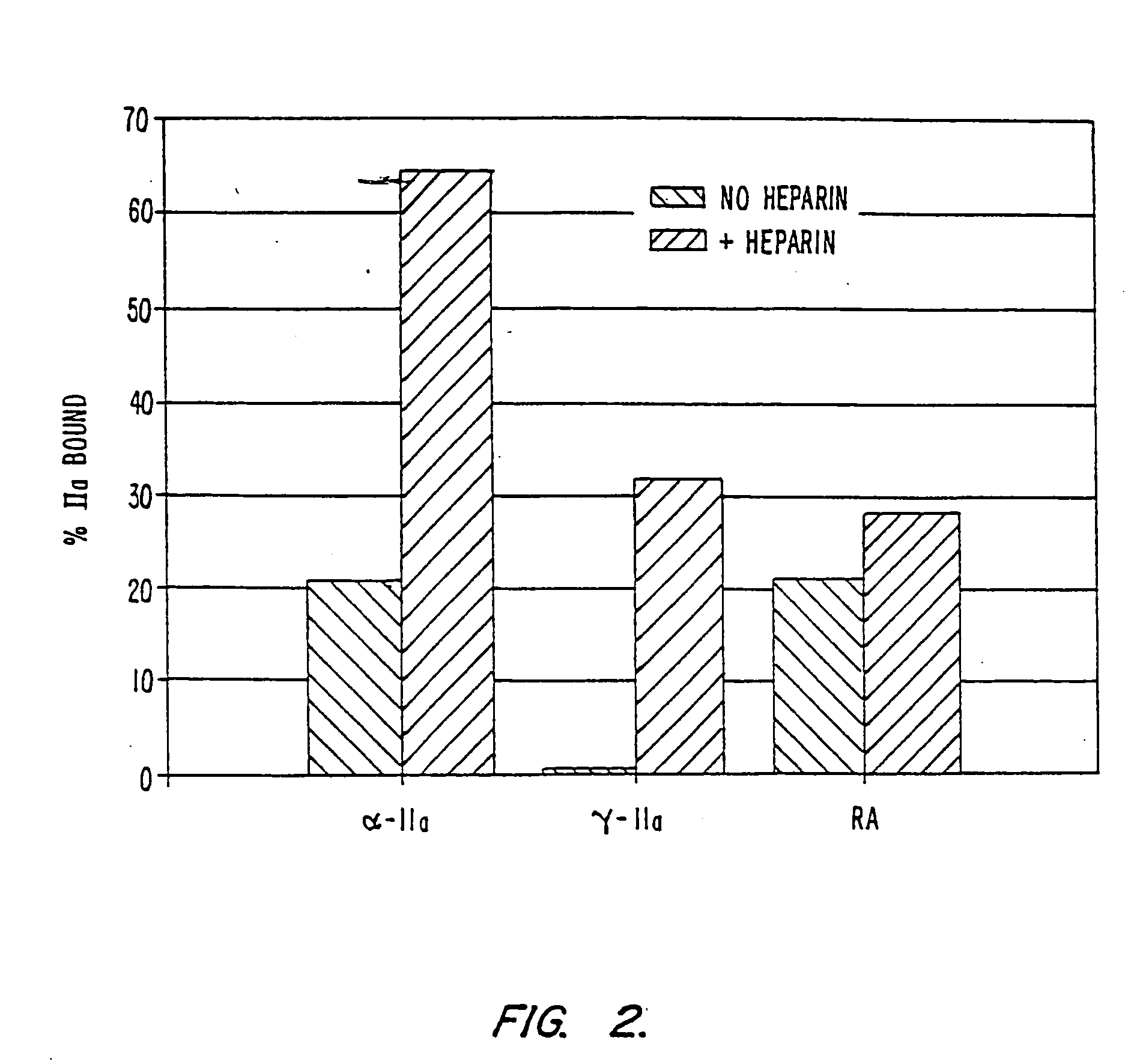
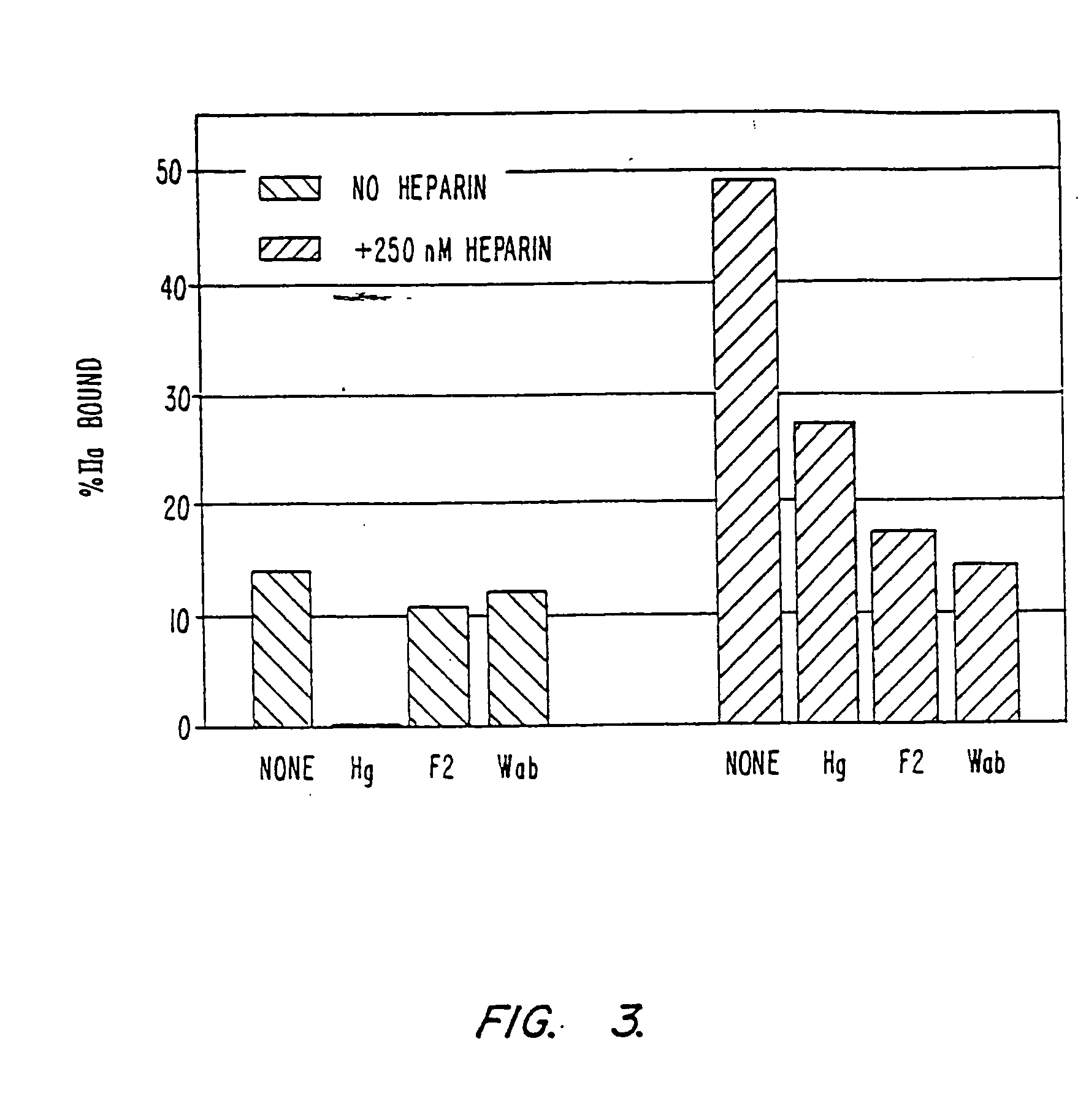
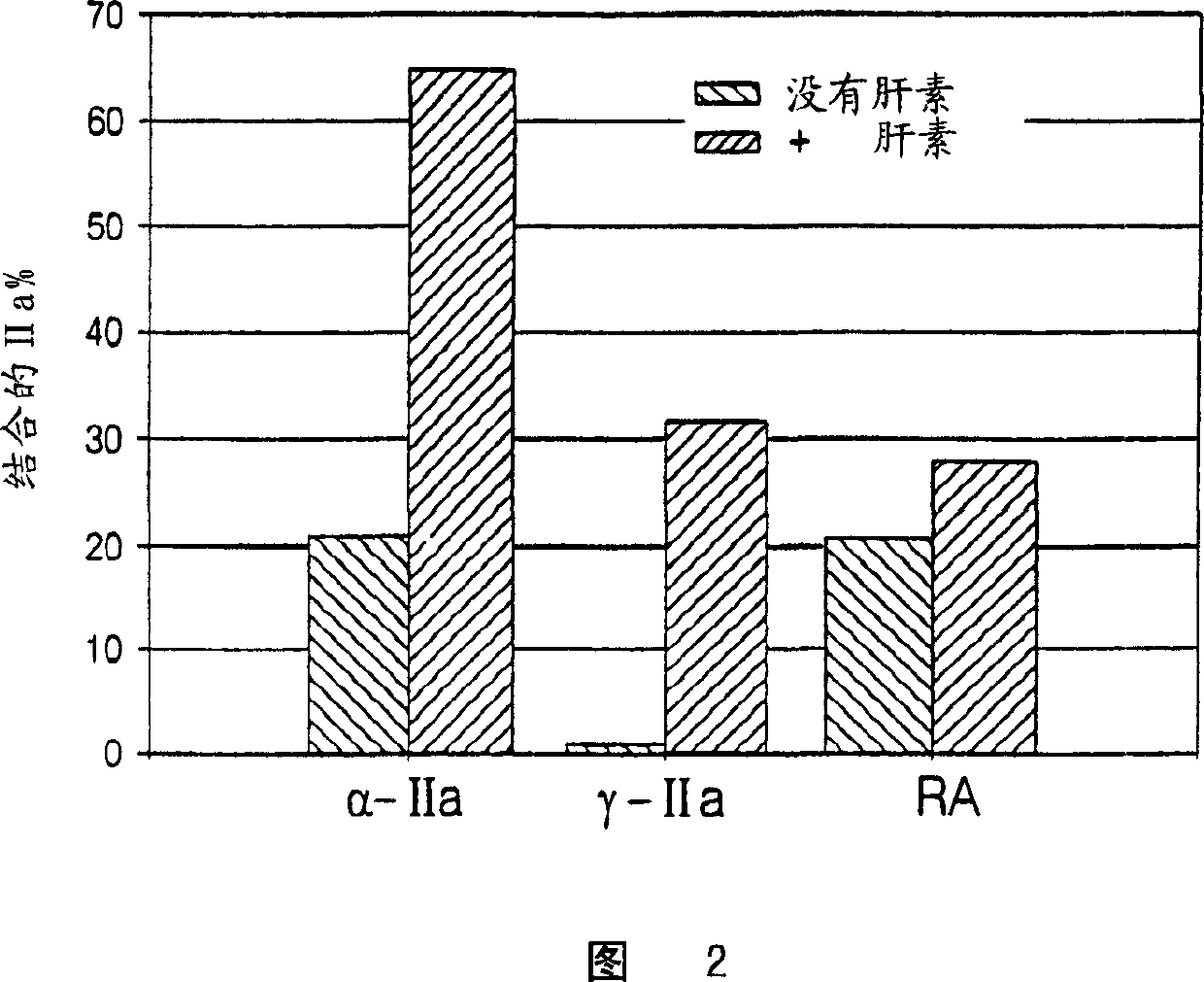
InactiveUS7084118B2Prolonged Circulatory Half-LifeRetained fibrin bindingData processing applicationsFibrinogenPLG - PlasminogenRegimen
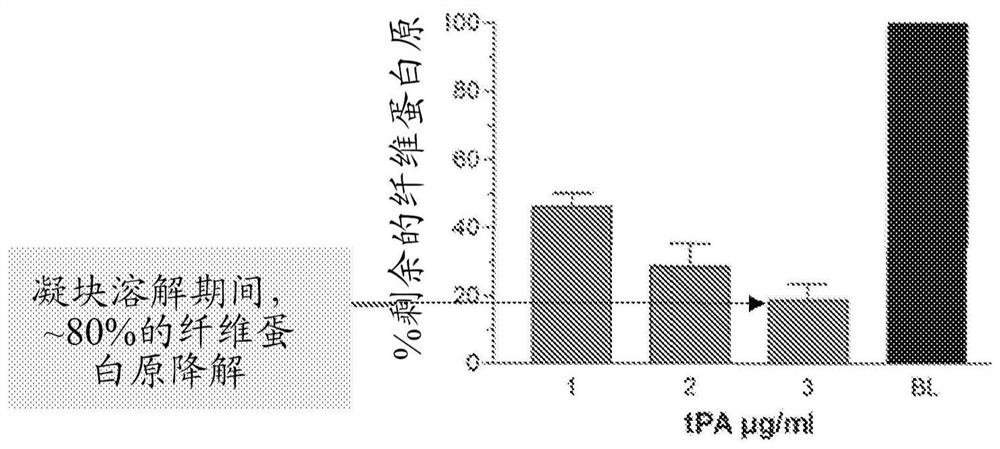
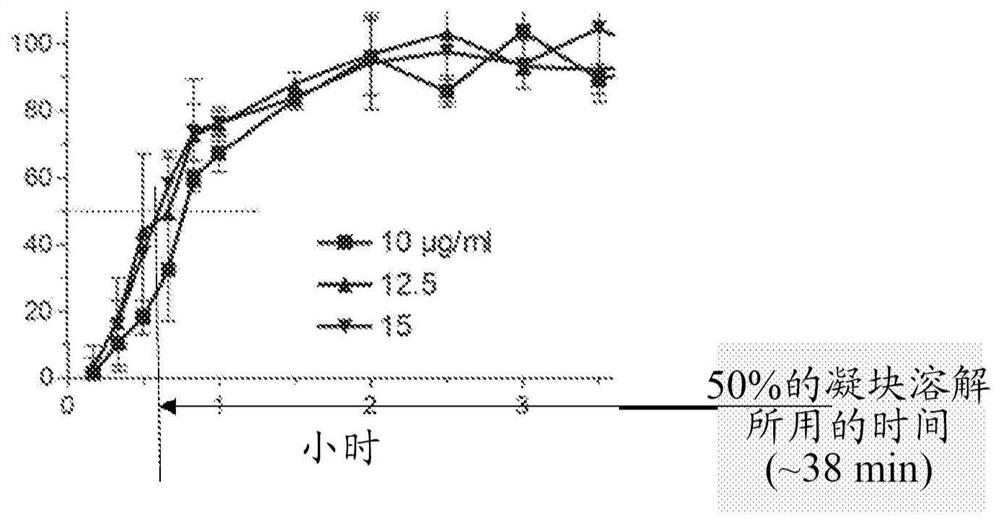
The invention concerns an improved therapeutic regimen for the treatment of thrombolytic disorders, such as acute myocardial infarction (AMI). In particular, the present invention concerns the treatment of thrombolytic disorders, e.g. AMI, with a combination of a tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) variant having improved fibrin specificity and extended plasma half-life when compared with wild-type human t-PA and a low molecular weight heparin.
Owner:AVENTIS PHARMA SA (US) +2
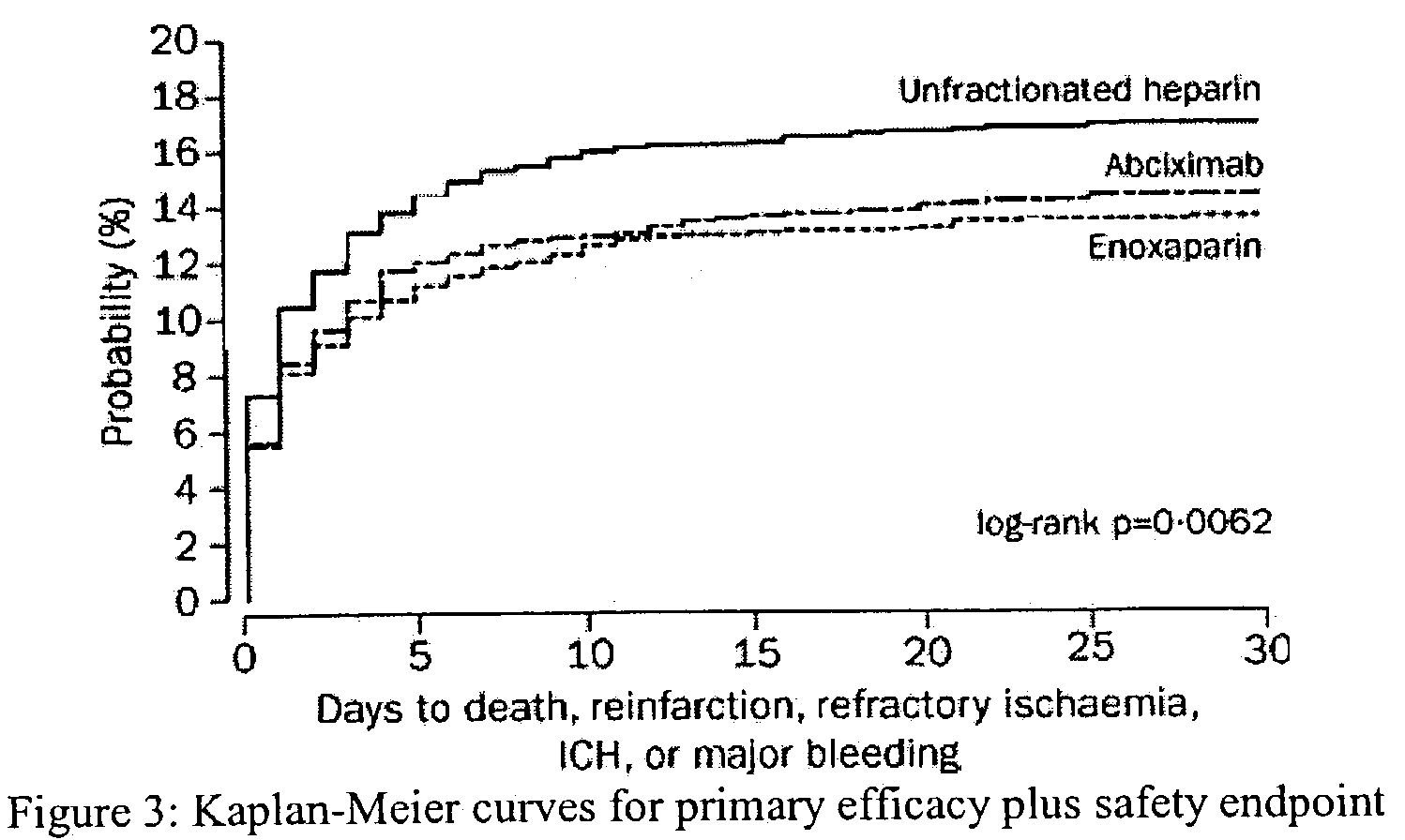
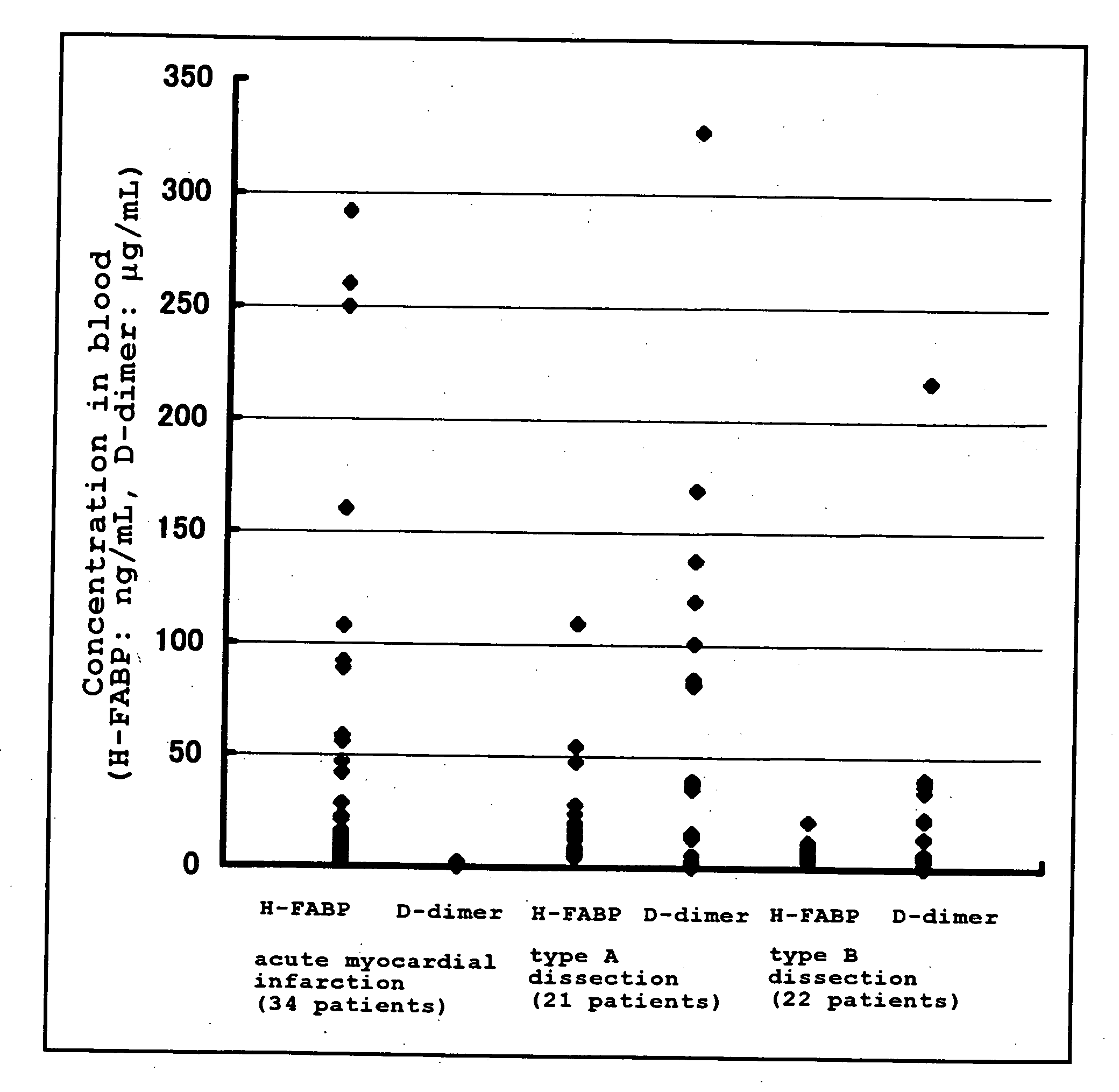
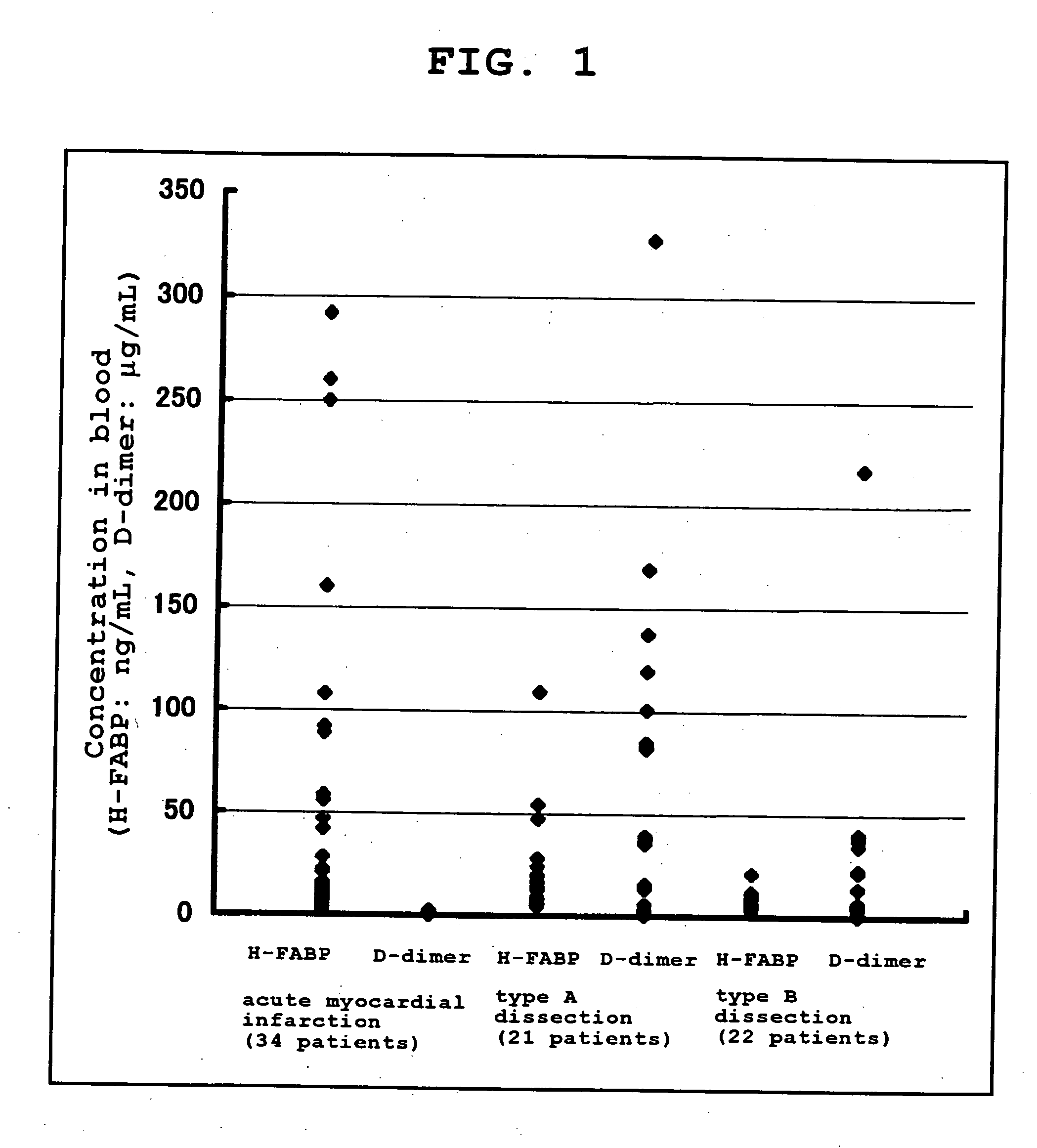
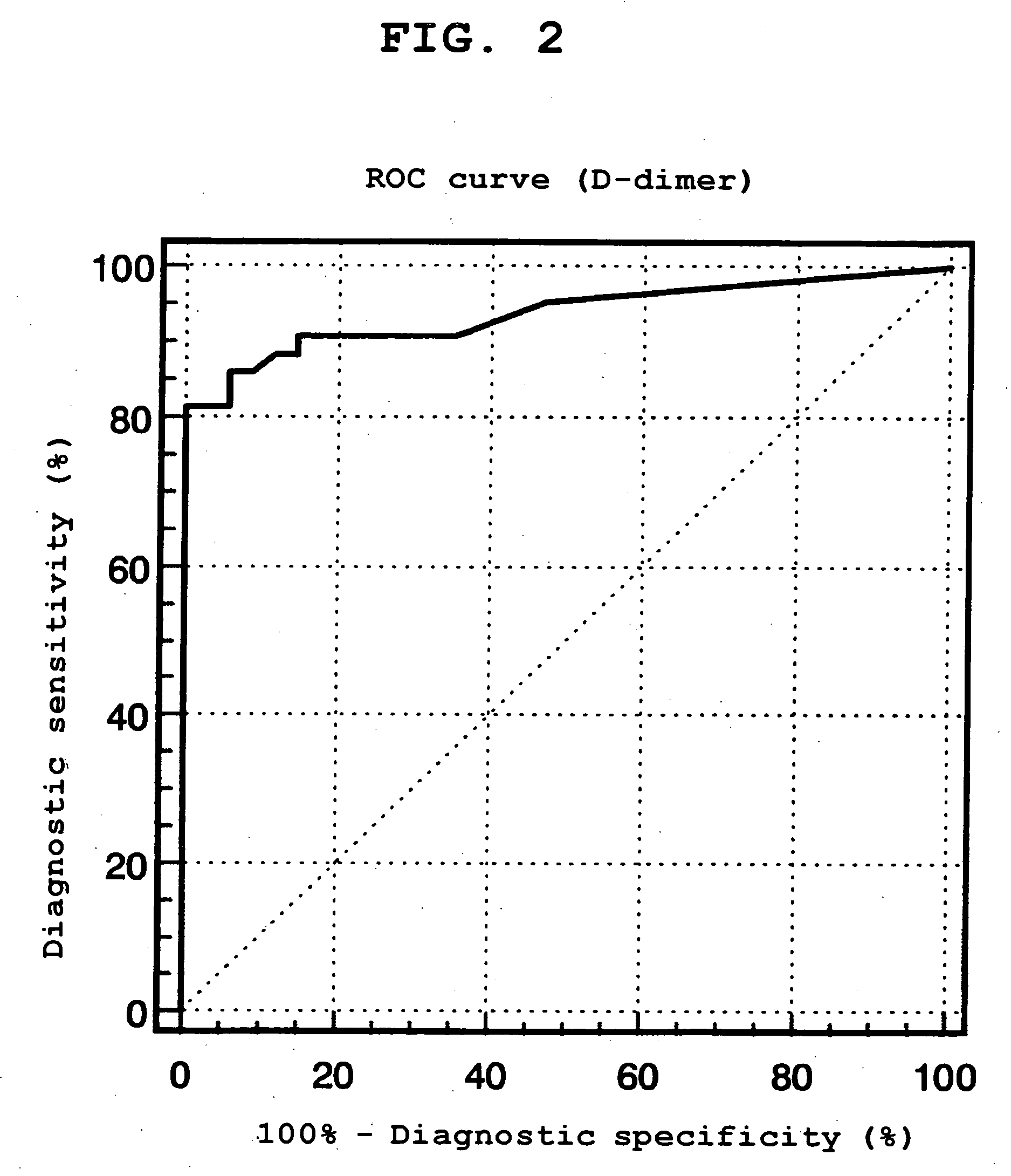
Method of Distinguishing Among Type a and Type B Acute Aortic Dissection and Acute Myocardial Infraction and Kit For Distinguishment
InactiveUS20080183062A1Highly accurately distinguishedDisease diagnosisDiagnostic recording/measuringAnatomyMyocardial infarction syndrome
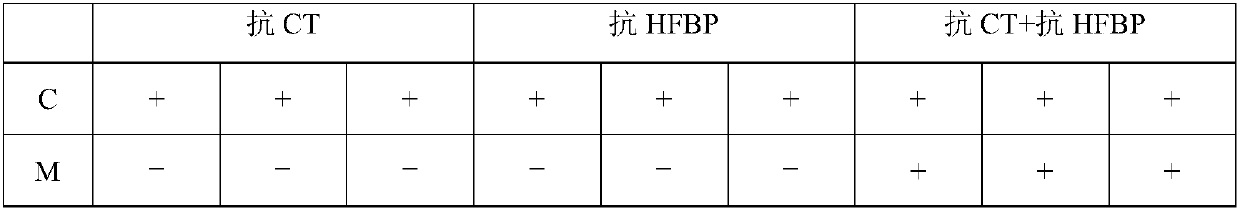
Provided is a method of distinguishing among Stanford type A acute aortic dissection, Stanford type B acute aortic dissection, and acute myocardial infarction, which are mutually similar in terms of clinical symptoms, and a kit for the distinguishment. Specifically, provided is a method of distinguishing among Stanford type A acute aortic dissection, Stanford type B acute aortic dissection, and acute myocardial infarction, which comprises detecting both D-dimer and H-FABP in blood separated from a person suspected of having acute aortic dissection and suspected of having acute myocardial infarction, and establishing the diagnosis on the basis of the concentrations detected, and a kit for the distinguishment.
Owner:SUMITOMO DAINIPPON PHARMA CO LTD
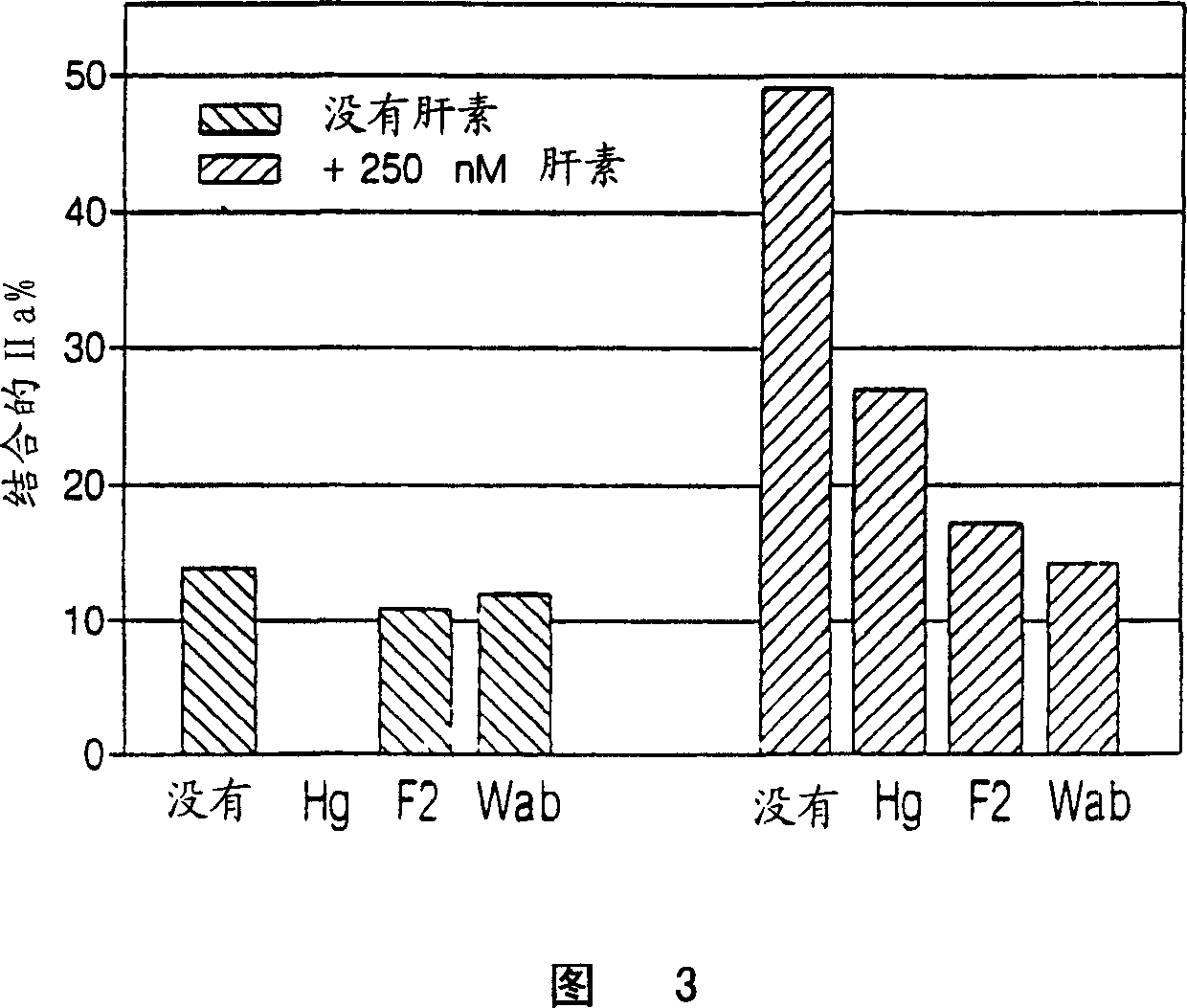
Heparin compositions that inhibit clot associated coagulation factors
InactiveUS20080119438A1Prevent reactivationAvoid generatingOrganic active ingredientsBlood disorderVenous bloodAngina
The present invention provides compositions and methods for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. More particularly, the present invention relates to modifying thrombus formation by administering an agent which, inter alia, is capable of (1) inactivating fluid-phase thrombin and thrombin which is bound either to fibrin in a clot or to some other surface by catalyzing antithrombin; and (2) inhibiting thrombin generation by catalyzing factor Xa inactivation by antithrombin III (ATIII). The compositions and methods of the present invention are particularly useful for preventing thrombosis in the circuit of cardiac bypass apparatus and in patients undergoing renal dialysis, and for treating patients suffering from or at risk of suffering from thrombus-related cardiovascular conditions, such as unstable angina, acute myocardial infraction (heart attack), cerebrovascular accidents (stroke), pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, arterial thrombosis, etc.
Owner:WEITZ JEFFREY I +1
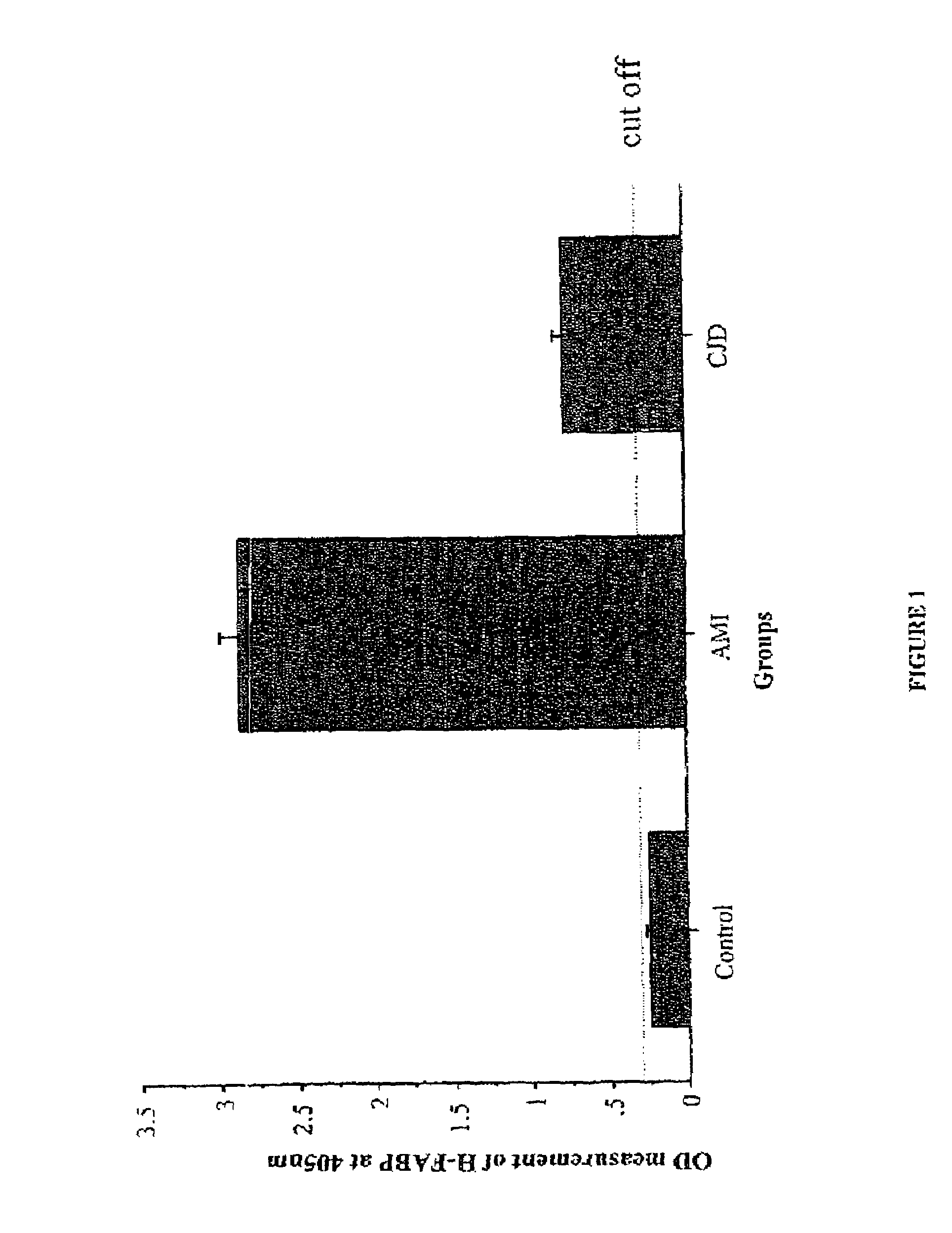
Diagnostic assay for transmissible spongiform encephalopathies
InactiveUS7368247B2Microbiological testing/measurementDepsipeptidesFatty acid bindingEnzyme immunoassays
Heart and brain fatty acid binding proteins (H-FABP, B-FABP) are markers for TSEs, especially CJD. The invention provides a diagnostic assay for either of these markers, preferably by enzyme immunoassay using a specific antibody thereto. Since H-FABP is also a marker for acute myocardial infarction (AMI), to distinguish CJD from AMI requires an assay specific to AMI, e.g. using troponin-1 or CK-MB as a marker, also to be carried out.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GENEVA
Method for diagnosing cardiac troponin I (cTn I) in semi-quantitative mode by employing double-indicatrix immunochromatography
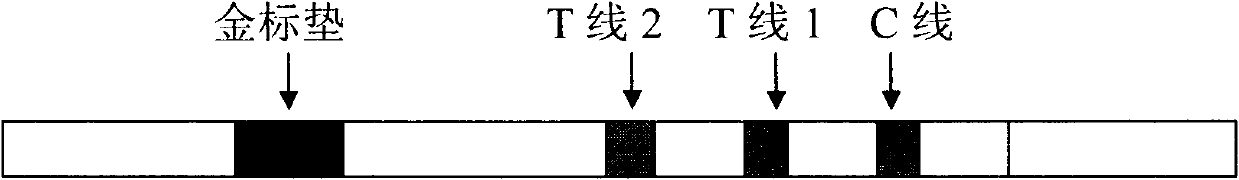
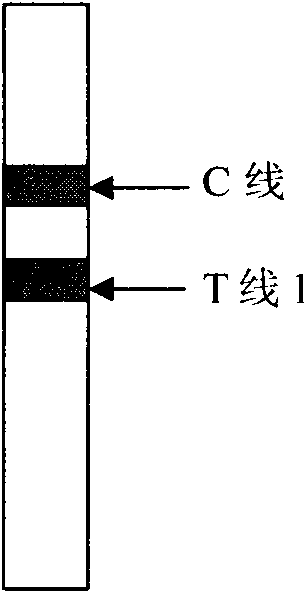
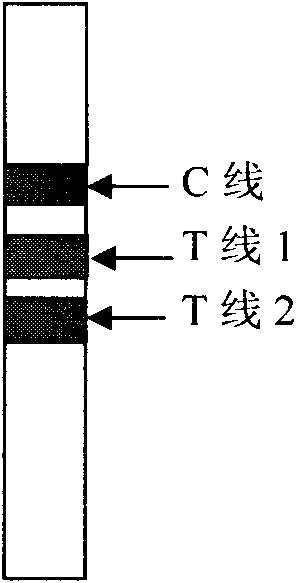
The invention discloses a detection method in the technical field of biological engineering, in particular a method for diagnosing cardiac troponin I (cTn I) in a semi-quantitative mode by employing double-indicatrix immunochromatography. Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is a serious disease in a coronary heart disease, is a common emergency among middle-aged and elderly people, and is high in death rate. According to statistics, one third to a half of patients die before being sent to a hospital. In the next 20 years, the AMI is a primary cause for death of the patients around the world. The cTn I is a reliable index which is currently acknowledged and has the highest specificity and the longest duration for myocardial infarction diagnosis. At present, cTn I detection methods which are commonly used in clinic comprise an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay method and a radioimmunoassay method, which are time-saving, labor-saving, difficult to popularize and high in cost. An immune colloidal gold technology is quickly developed in recent years and can be widely applied to detection of communicable diseases, early pregnancy and cancers. By employing colloidal gold immunochromatography, a quick detection method for the cTn I is established. By adoption of the method, a cTn I gray area of 1 to 5 ng / ml can be subjected to semi-quantitative detection.
Owner:正元盛邦(天津)生物科技有限公司
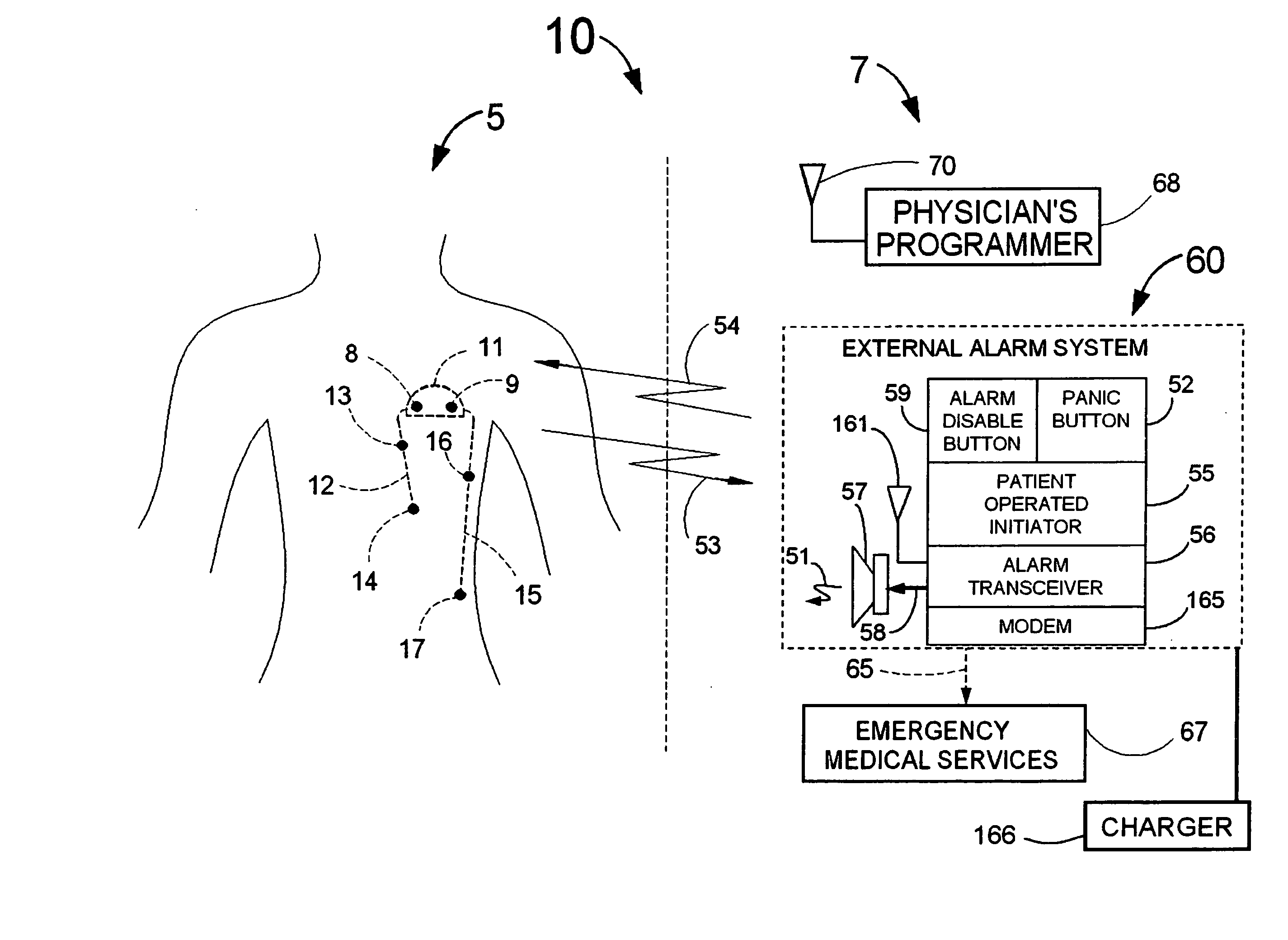
Means and method for the detection of cardiac events
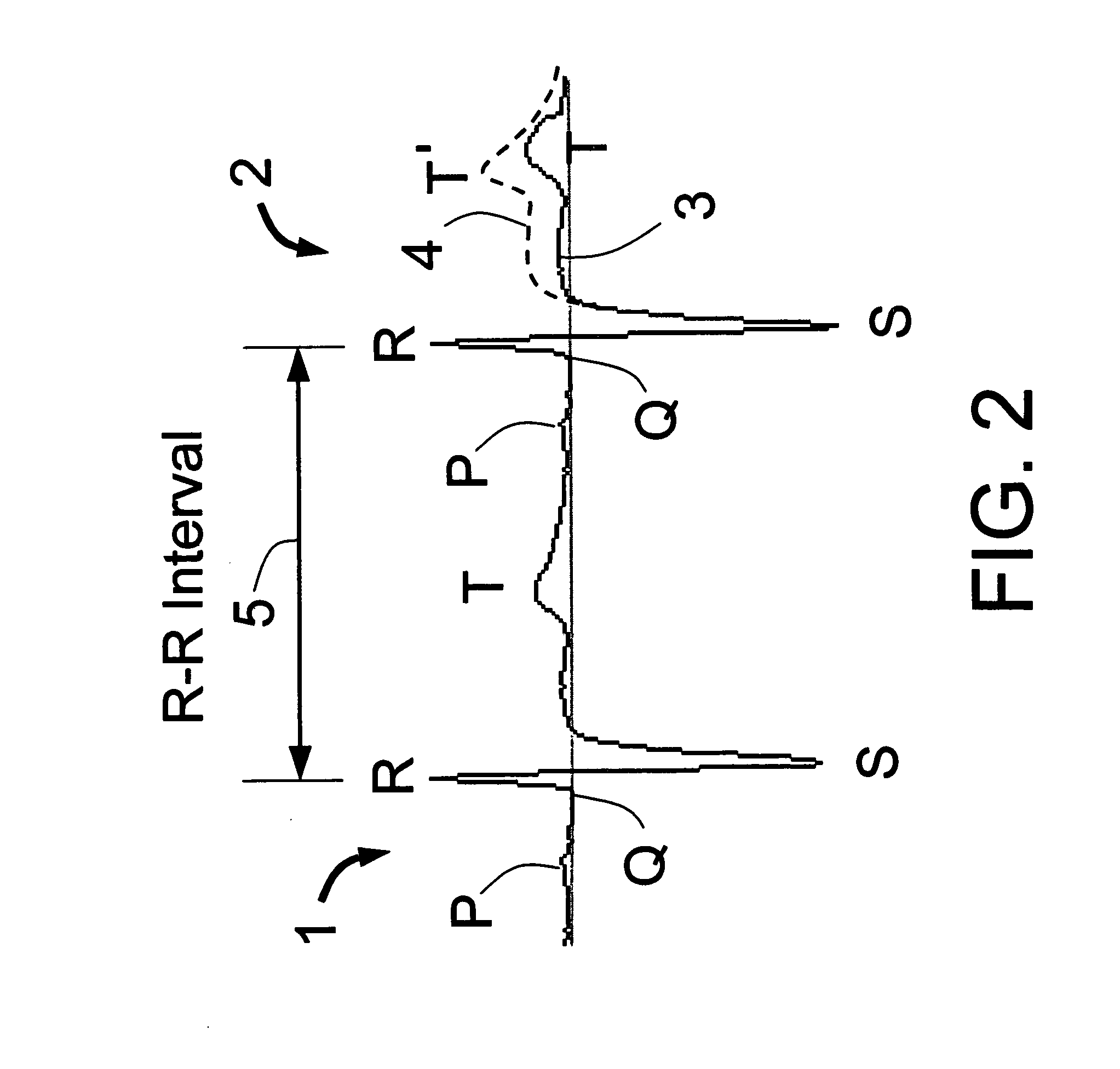
Disclosed is a system for the detection of cardiac events that includes an implanted device called a cardiosaver, a physician's programmer and an external alarm system. The system is designed to provide early detection of cardiac events such as acute myocardial infarction or exercise induced myocardial ischemia caused by an increased heart rate or exertion. The system can also alert the patient with a less urgent alarm if a heart arrhythmia is detected. Using different algorithms, the cardiosaver can detect a change in the patient's electrogram that is indicative of a cardiac event within five minutes after it occurs and then automatically warn the patient that the event is occurring. To provide this warning, the system includes an internal alarm sub-system (internal alarm means) within the cardiosaver and / or an external alarm system (external alarm means) which are activated after the ST segment of the electrogram exceeds a preset threshold.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
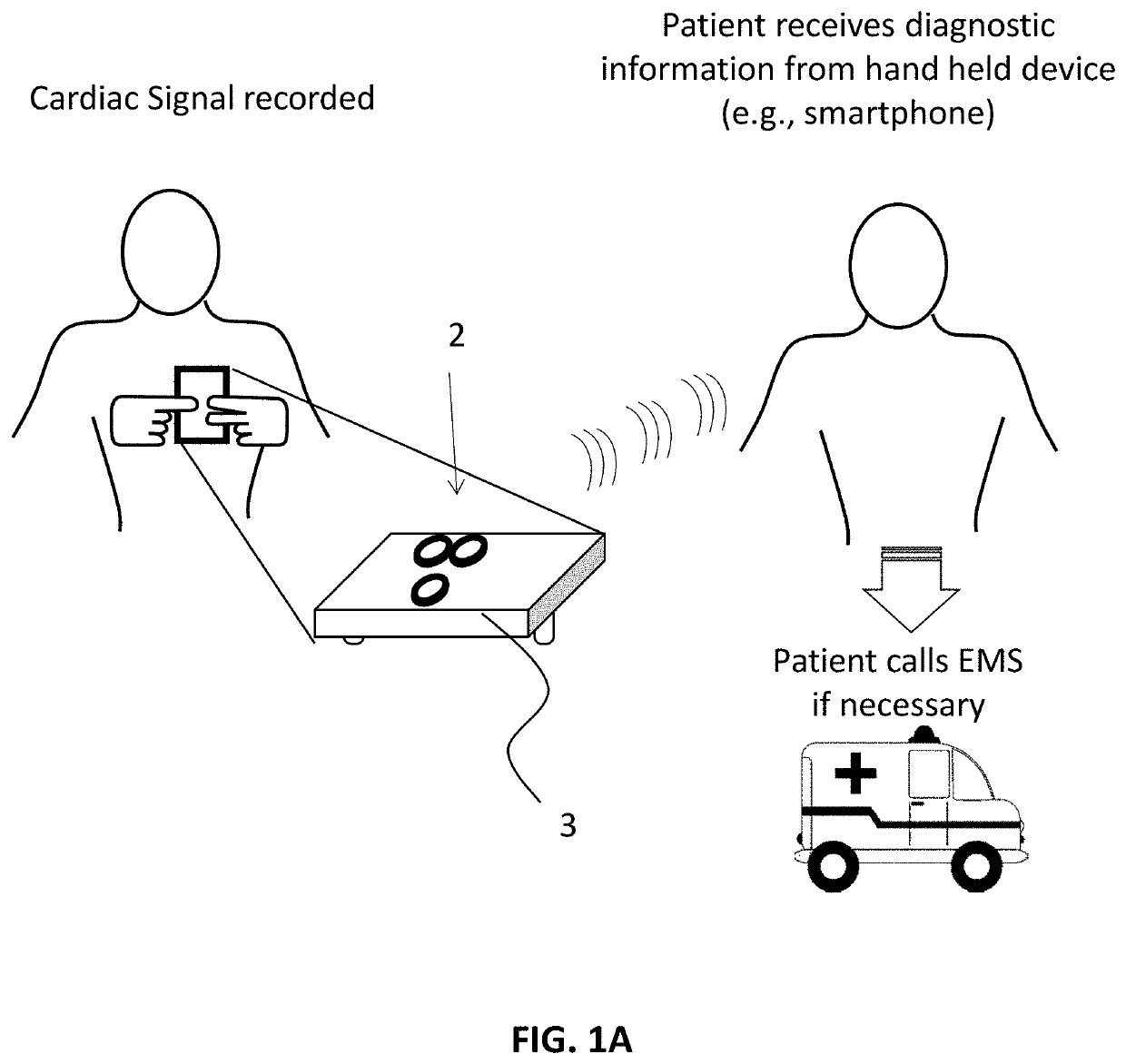
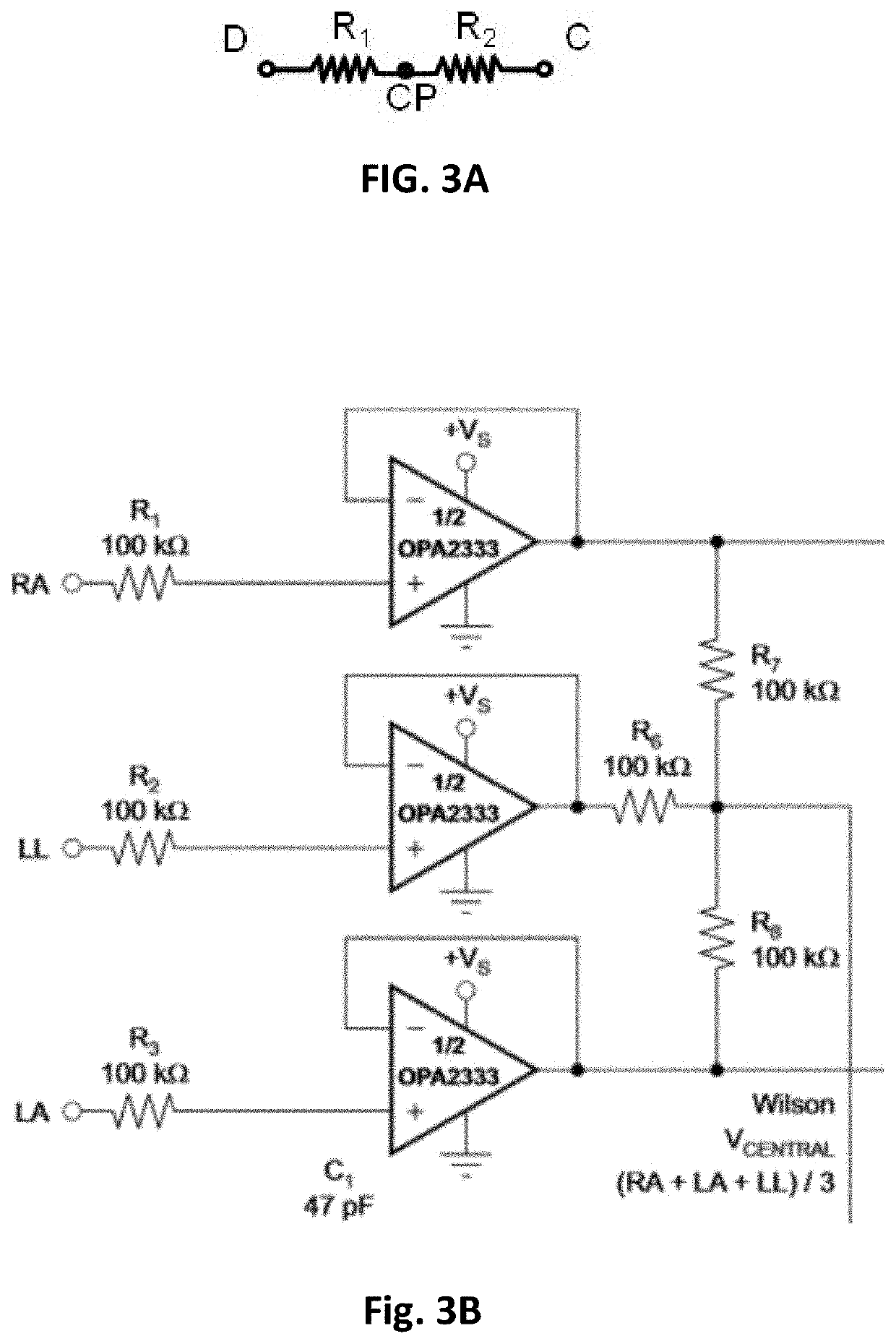
Electrocardiogram patch devices and methods
ActiveUS11071490B1Eliminate interferenceRemove noiseMedical automated diagnosisSensorsHeart disorderEcg lead
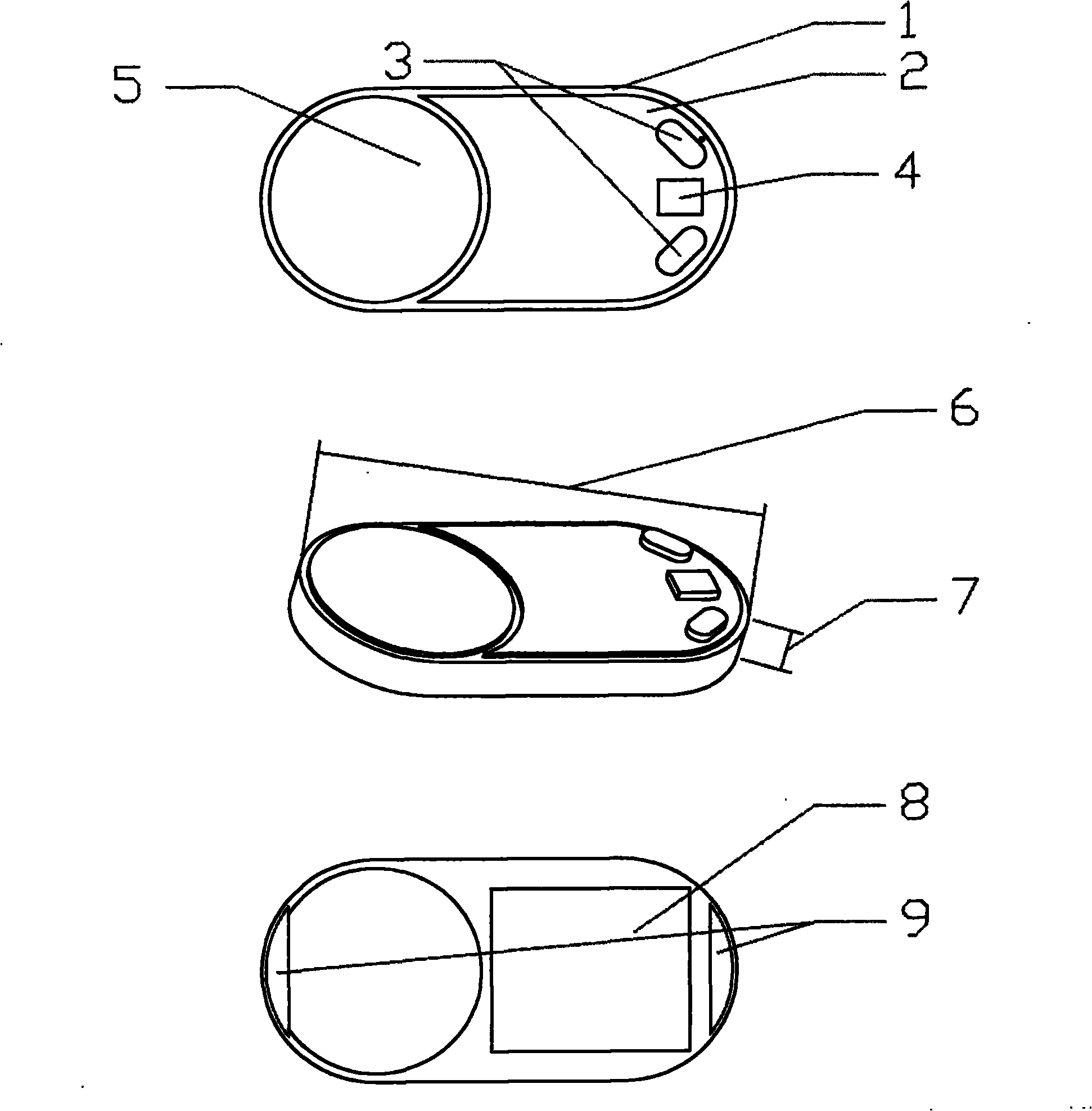
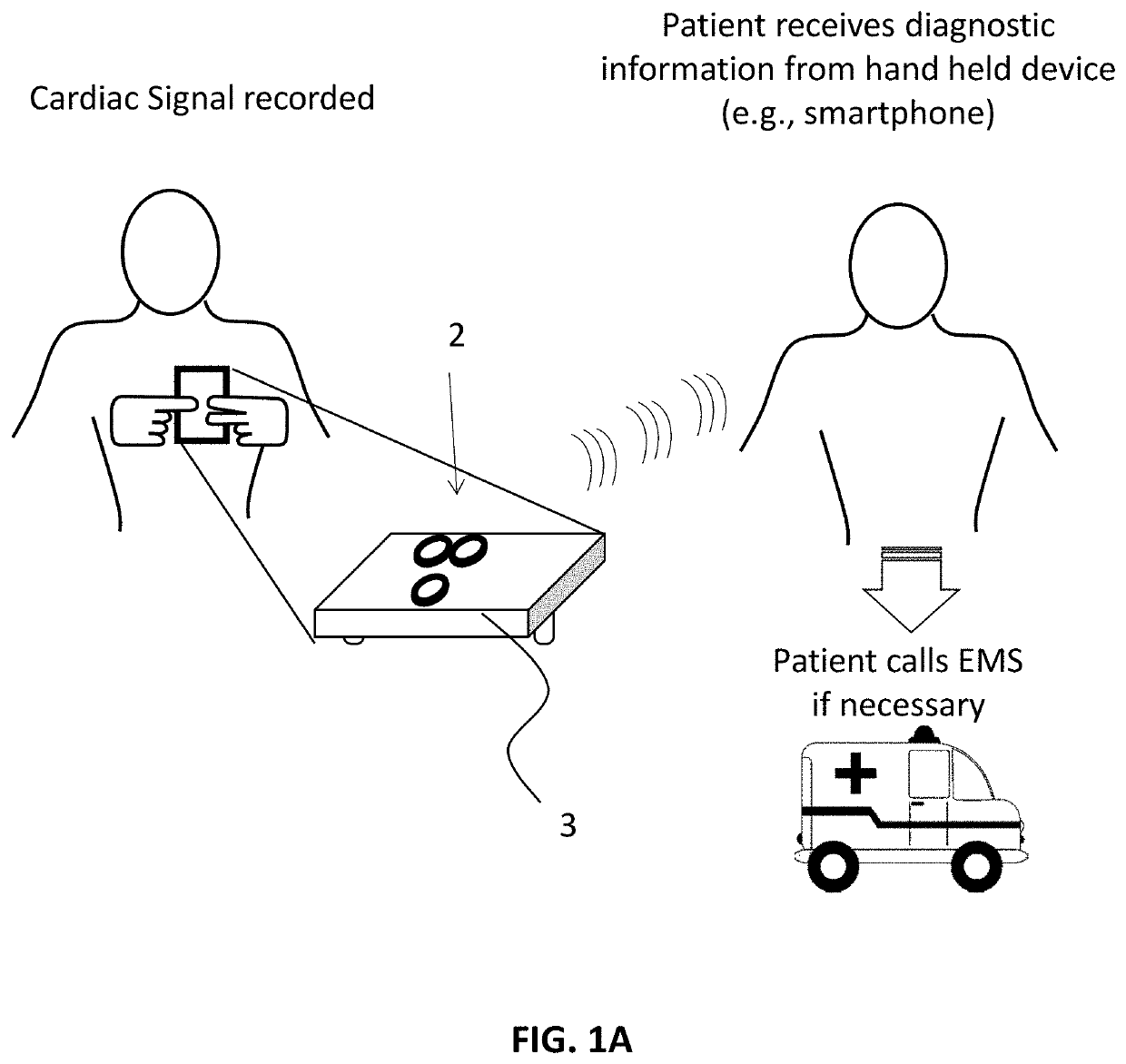
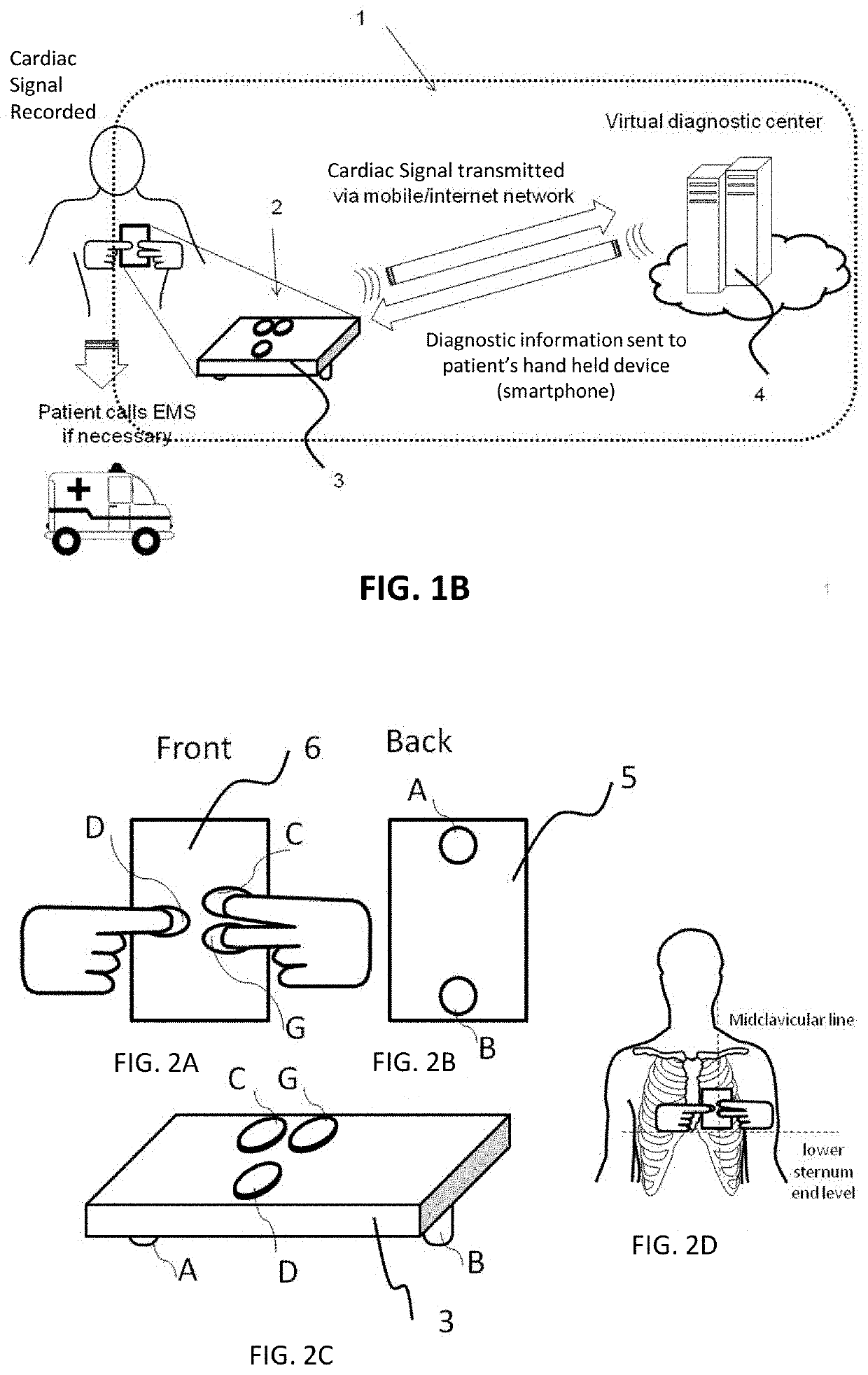
Methods and apparatuses, including devices and systems, for remote and detection and / or diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction (AMI). In particular, described herein are handheld and adhesive devices having an electrode configuration capable of recording three orthogonal ECG lead signals in an orientation-specific manner, and transmitting these signals to a processor. The processor may be remote or local, and it may automatically or semi-automatically detect AMI, atrial fibrillation or other heart disorders based on the analyses of the deviation of the recorded 3 cardiac signals with respect to previously stored baseline recordings.
Owner:HEARTBEAM INC
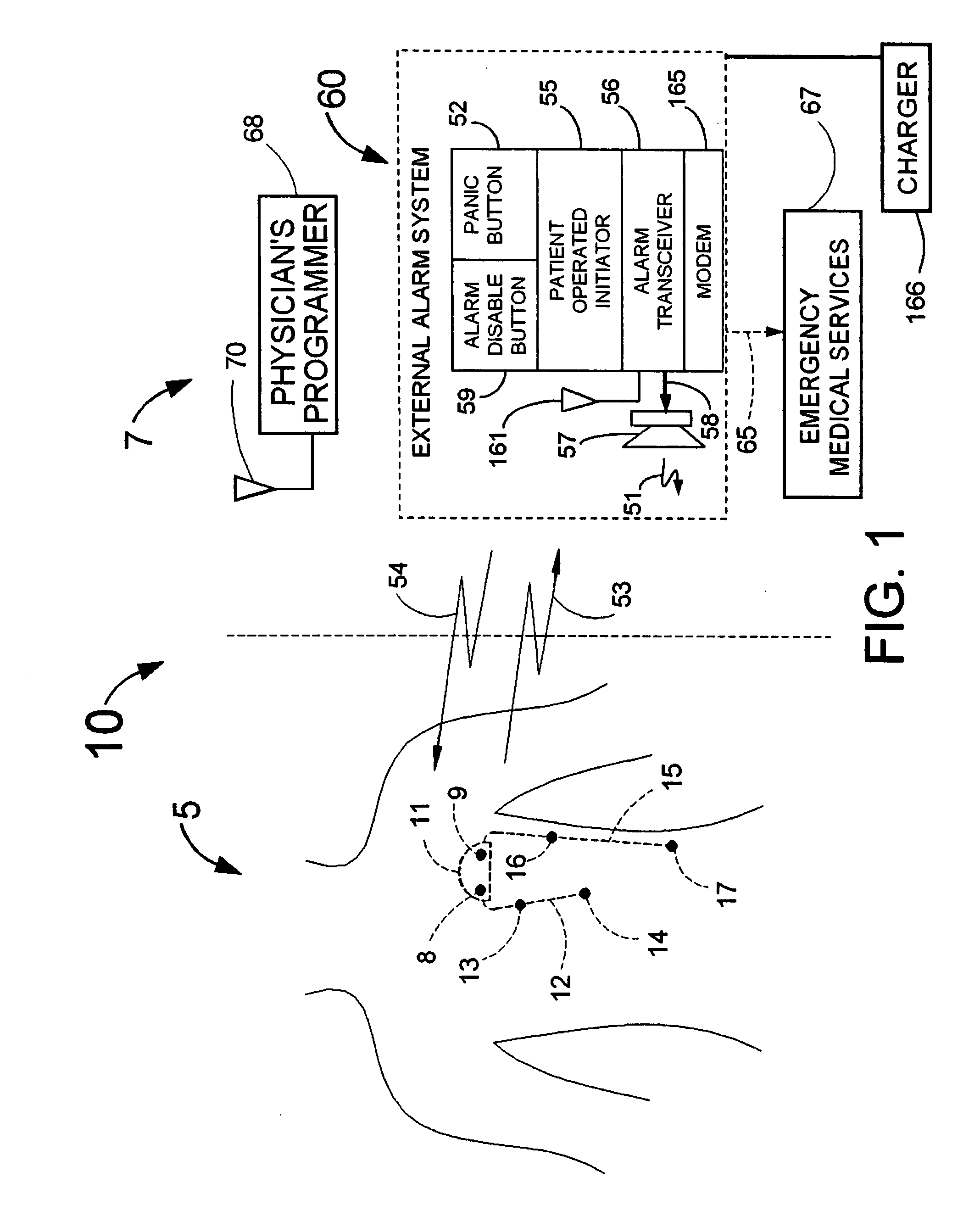
Means and method for the detection of cardiac events
Disclosed is a system for the detection of cardiac events that includes an implanted device called a cardiosaver, a physician's programmer and an external alarm system. The system is designed to provide early detection of cardiac events such as acute myocardial infarction or exercise induced myocardial ischemia caused by an increased heart rate or exertion. The system can also alert the patient with a less urgent alarm if a heart arrhythmia is detected. Using different algorithms, the cardiosaver can detect a change in the patient's electrogram that is indicative of a cardiac event within five minutes after it occurs and then automatically warn the patient that the event is occurring. To provide this warning, the system includes an internal alarm sub-system (internal alarm means) within the cardiosaver and / or an external alarm system (external alarm means) which are activated after the ST segment of the electrogram exceeds a preset threshold.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
Modified low molecular weight heparin that inhibits clot associated coagulation factors
InactiveUS20050032745A1Prevent reactivationPacify thrombusOrganic active ingredientsVenous bloodAngina
The present invention provides compositions and methods for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. More particularly, the present invention relates to modifying thrombus formation by administering an agent which, inter alia, is capable of (1) inactivating fluid-phase thrombin and thrombin which is bound either to fibrin in a clot or to some other surface by catalyzing antithrombin; and (2) inhibiting thrombin generation by catalyzing factor Xa inactivation by antithrombin III (ATIII). The compositions and methods of the present invention are particularly useful for preventing thrombosis in the circuit of cardiac bypass apparatus and in patients undergoing renal dialysis, and for treating patients suffering from or at risk of suffering from thrombus-related cardiovascular conditions, such as unstable angina, acute myocardial infarction (heart attack), cerebrovascular accidents (stroke), pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, arterial thrombosis, etc.
Owner:HAMILTON CIVIC HOSPITALS RESARCH DEV
Heparin compositions that inhibit clot associated coagulation factors
The present invention provides compositions and methods for treating cardiovascular disease. More specifically, the invention relates to thrombin by administering, inter alia, capable of (1) inactivating thrombin in the fluid phase by catalytic antithrombin and either binding to fibrin in a clot or binding to some other surface; and (2) Substances that inhibit thrombin production by antithrombin III (ATIII) catalyzing factor Xa inactivation to alter thrombus formation. The compositions and methods of the present invention are particularly useful for the prevention of thrombosis in cardiac bypass circulation and in patients undergoing renal dialysis, and for the treatment of patients with, or at risk of, cardiovascular disease associated with thrombosis In patients with thrombosis-related cardiovascular diseases such as unstable angina, acute myocardial infarction (heart attack), cerebrovascular accident (stroke), pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, arterial thrombosis, etc.
Owner:HAMILTON CIVIC HOSPITALS RESARCH DEV
Cmybp-c and MLC2 as diagnostic markers of cardiac injury
The invention relates to markers for acute myocardial infarction (AMI), particularly markers that may be used in the rapid and accurate diagnosis of AMI or reinfarction. A method of diagnosing cardiac injury comprising identifying an elevated concentration of cardiac myosin binding protein C (cMyBP-C) or a fragment thereof or myosin regulatory light chain 2 (MLC2) or a fragment thereof in a sample obtained from a subject.
Owner:KINGS COLLEGE LONDON
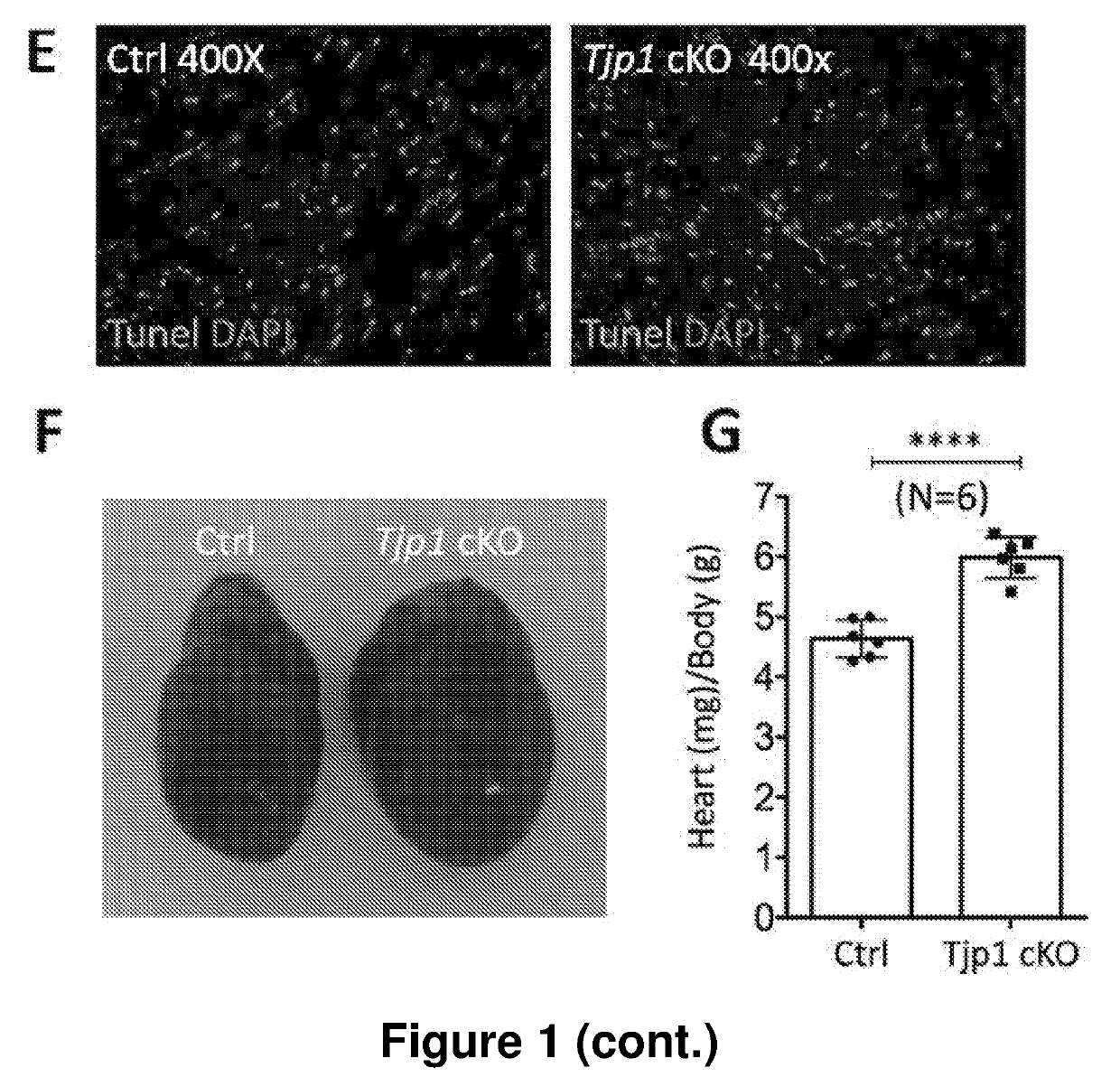
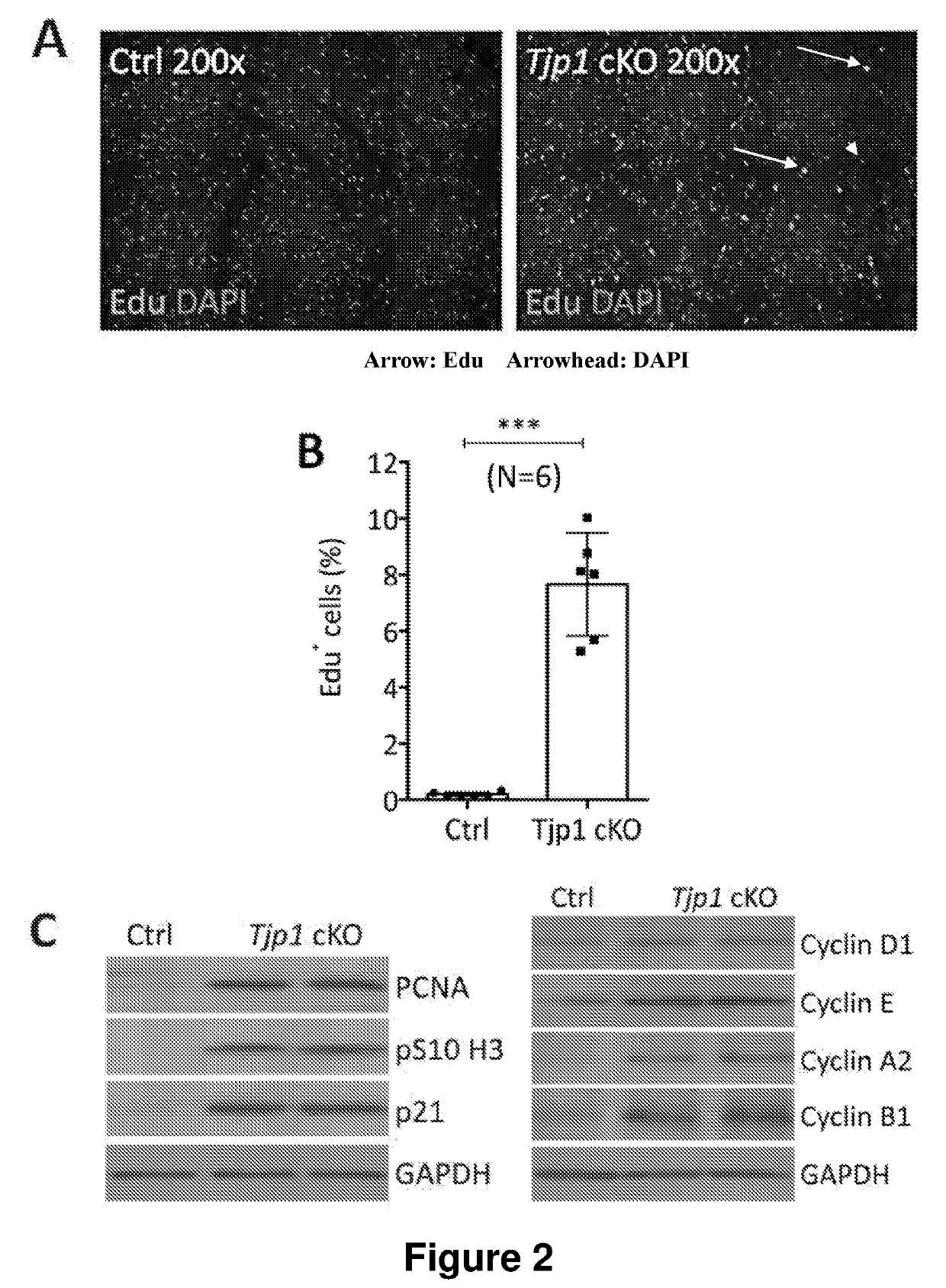
Modulation of tjp1 expression to regulate regeneration of heart cells
PendingUS20190256846A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsHeart muscle cell proliferationNeuregulin
The invention is a method for treating a heart disease, in particular acute myocardial infarction (AMI) in a subject comprising the step of administering to the subject a Tjp1 inhibitor, wherein administration of said Tjp1 inhibitor promotes cardiomyocyte proliferation. The invention further includes use of Tjp1 inhibitor in the manufacture of a medicament for a heart disease, a patch, and a nucleic acid encoding a Tjp1 inhibitor. In a particular embodiment, the Tjp1 inhibitor is a nucleic acid, i.e. an siRNA or shRNA of Tjp1. The invention also includes administration of said Tjp1 inhibitor in combination with Neuregulin-1 (NRG1), Fibroblast growth factor (FGF), Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) or Follistatin-like 1 (Fst1) and wherein said inhibitor is delivered in an adeno-associated virus of serotype 9 (AAV 9).
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES +1
Nourin molecular biomarkers diagnose angina patients with negative troponin
ActiveUS20200109454A1High sensitivityStrong specificityMedical simulationMedical data miningMolecular networkArtery diseases
The present invention provides a molecular network, devices, and assays for early diagnosis of angina patients experiencing acute chest pain with negative Troponin, and it reflects on disease progression and severity. The invention also allows for the diagnosis of angina in suspected patients with history of chest pain; differentiates between angina patients and acute myocardial infarction; as well as diagnose coronary artery disease patients from other non-cardiac and healthy individuals. The present invention indicates that the downregulation of Nourin IncCTB9H12.4 in coronary artery disease patients compared to non-cardiac and healthy controls, is significantly associated with upregulation of miR_106b and miR_137 resulting in overexpression of mRNA ANAPC11 and mRNA FTLH-17; respectively. Therefore, the invention provides a novel non-invasive good positive test to diagnose angina patients which also, has a good negative test to exclude chest pain non-angina patients and healthy individuals.
Owner:NOUR HEART
Novel prognostic biomarker in acute myocardial infarction
InactiveUS20150004625A1Immunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsPeptide/protein ingredientsPrognosticsPoor prognosis
Owner:GEMMATI DONATO
Electrocardiogram patch devices and methods
ActiveUS20210219902A1Eliminate interferenceRemove noiseMedical automated diagnosisSensorsHeart disorderEcg lead
Methods and apparatuses, including devices and systems, for remote and detection and / or diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction (AMI). In particular, described herein are handheld and adhesive devices having an electrode configuration capable of recording three orthogonal ECG lead signals in an orientation-specific manner, and transmitting these signals to a processor. The processor may be remote or local, and it may automatically or semi-automatically detect AMI, atrial fibrillation or other heart disorders based on the analyses of the deviation of the recorded 3 cardiac signals with respect to previously stored baseline recordings.
Owner:HEARTBEAM INC
Diagnostic methods for acute ischemic disease using activated hepcidin as an indicator
InactiveUS20100298159A1Accurate and simpler diagnosisLower noise measurementLibrary screeningDisease diagnosisDiagnosis earlyBlood concentration
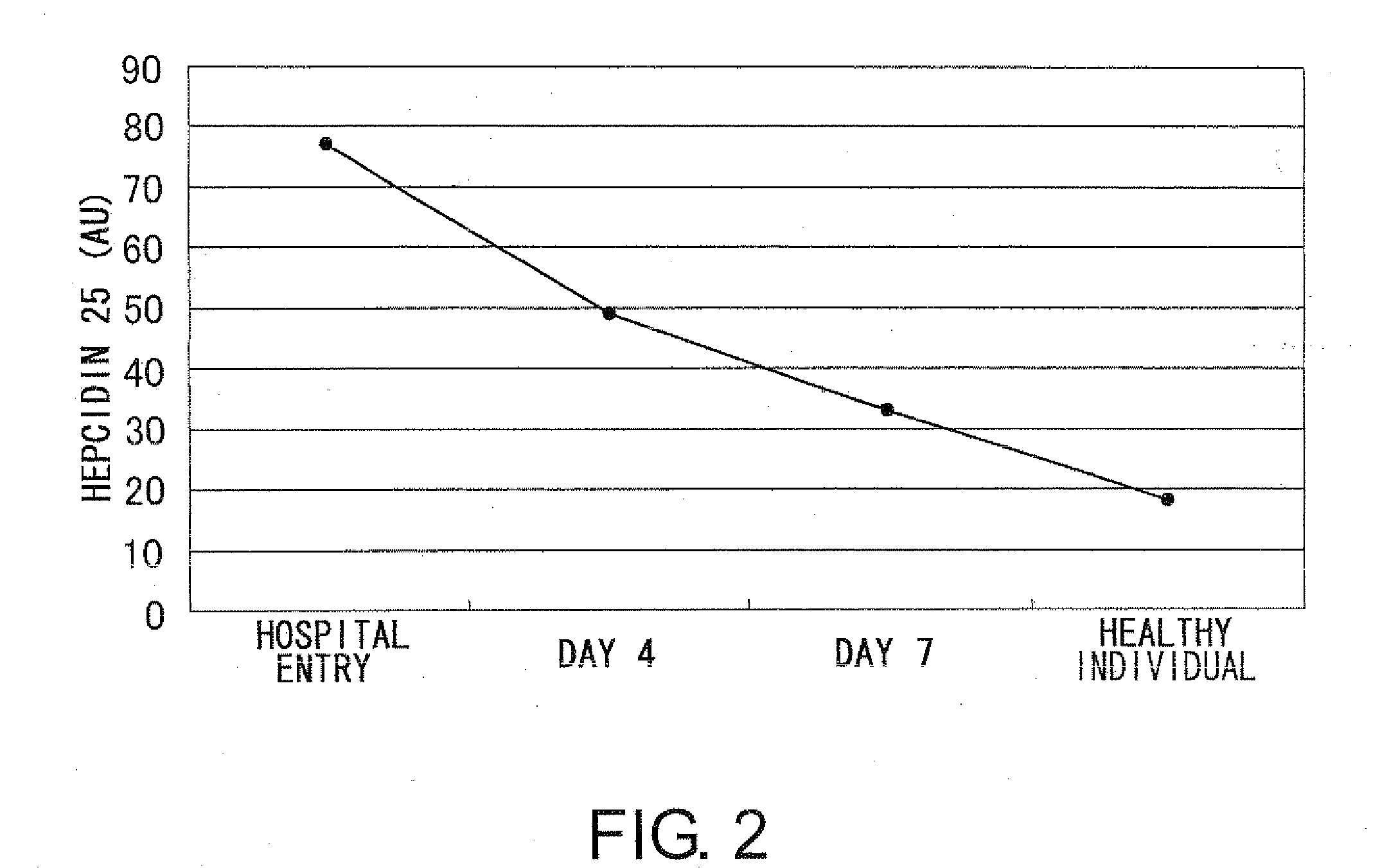
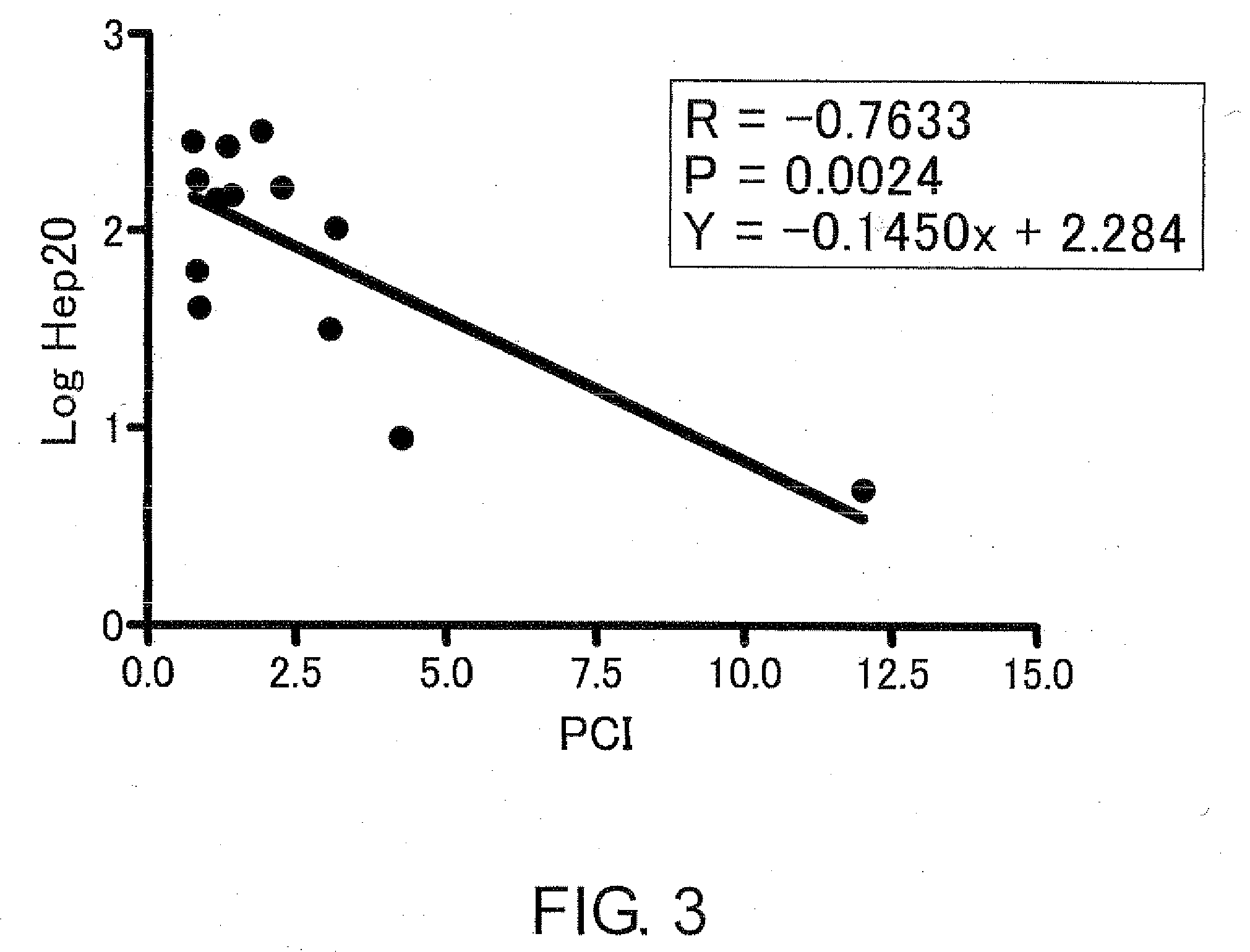
An objective of the present invention is to provide methods of testing for acute ischemic diseases using active hepcidin as an indicator, methods for determining the timing to administer an agent for treating the disease, and kits for these methods.To accomplish the above-mentioned objective, the present inventors analyzed the serum proteome patterns characteristic of acute myocardial infarction patients using SELDI-TOF-MS. As a result, it was found that hepcidin-20 has a very high correlation with acute myocardial infarction. Furthermore, the present inventors discovered that at the time of disease onset, the blood concentration of hepcidin-20 rises sharply in particular, and shows high levels within six hours, especially four hours of onset. The present invention enables early diagnosis of acute ischemic diseases.
Owner:TOMOSUGI NAOHISA
Method for reducing sepsis or cardiogenic shock associated with myocardial injury
InactiveUS20060263358A1Reduce morbidityImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAntibody ingredientsCardiogenic shockCoronary arteries
Methods of reducing sepsis or cardiogenic shock in patients experiencing myocardial injury are described. More specifically, this disclosure relates to the administration of a C5-C9 terminal complement inhibitor to patients who have had coronary artery bypass grafting or an acute myocardial infarction thereby reducing the incidence of sepsis.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Inhibition of ZD17-JNK interaction as therapy for acute myocardial infarction
PendingCN114599383APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseCardiac functioning
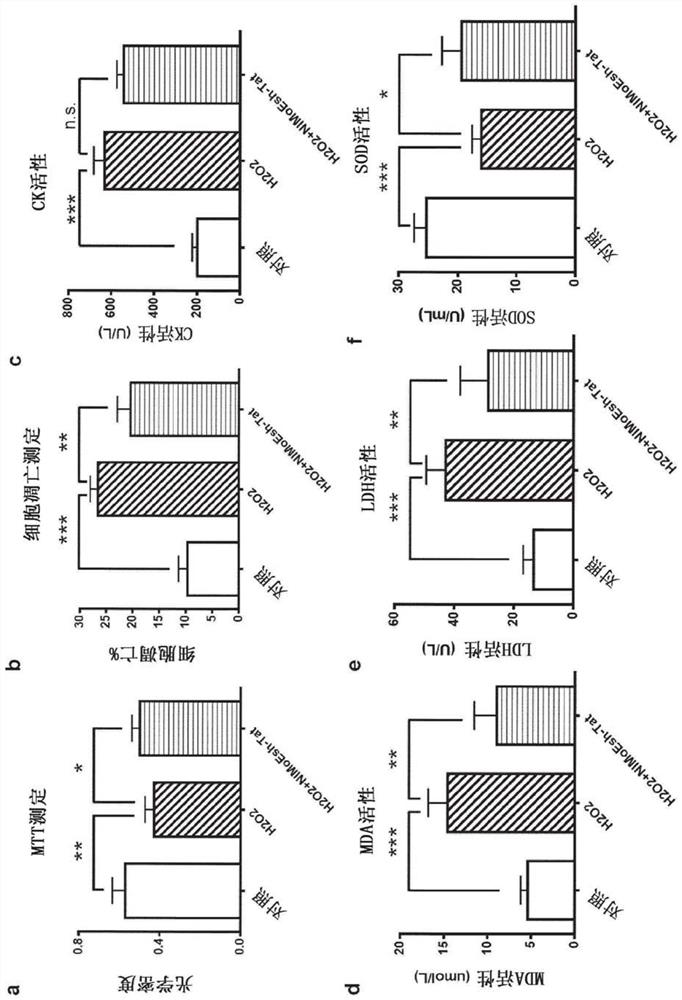
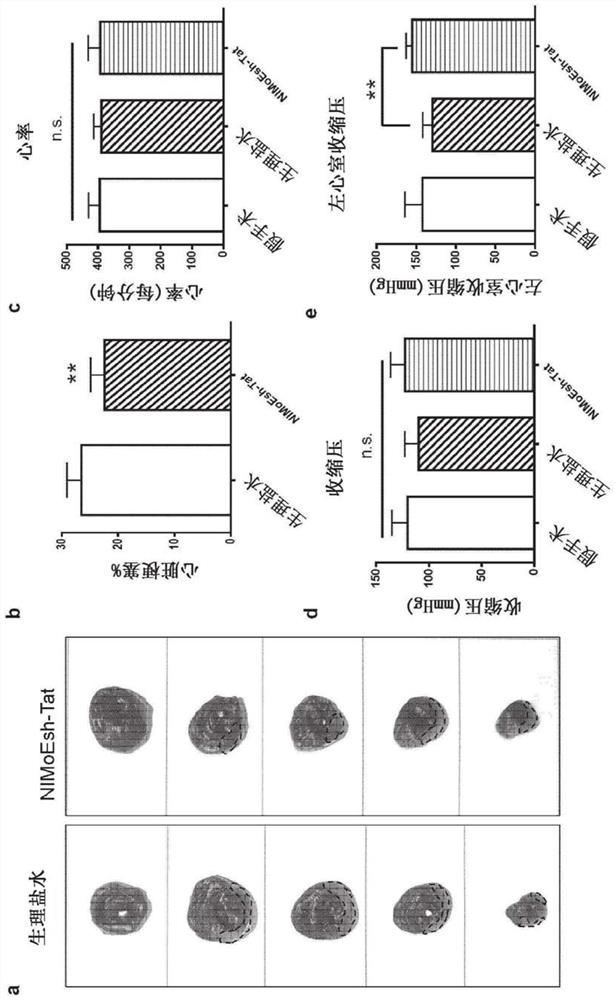
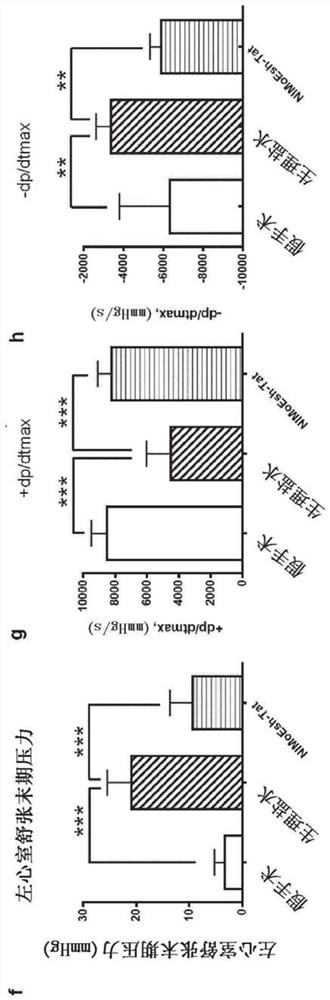
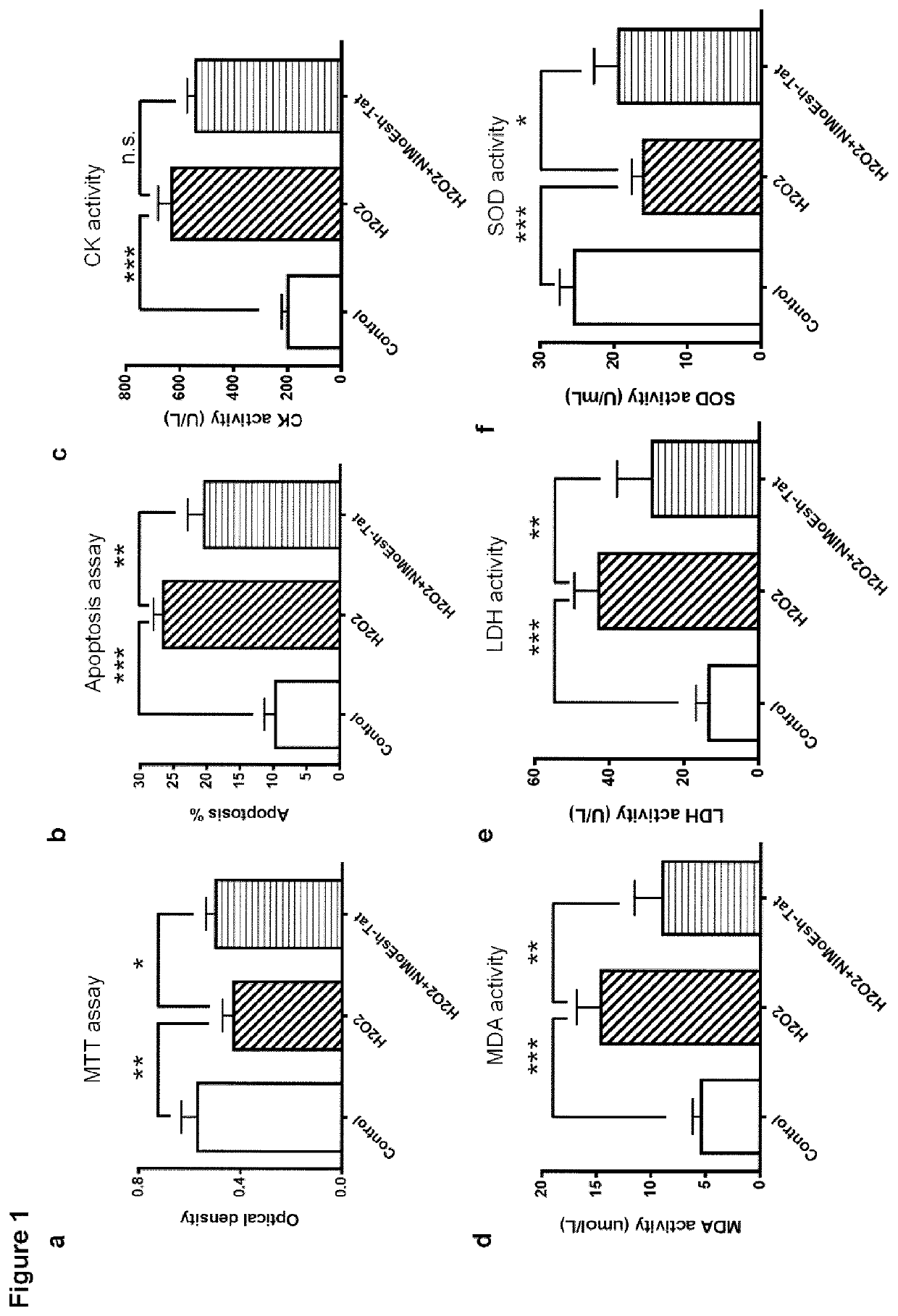
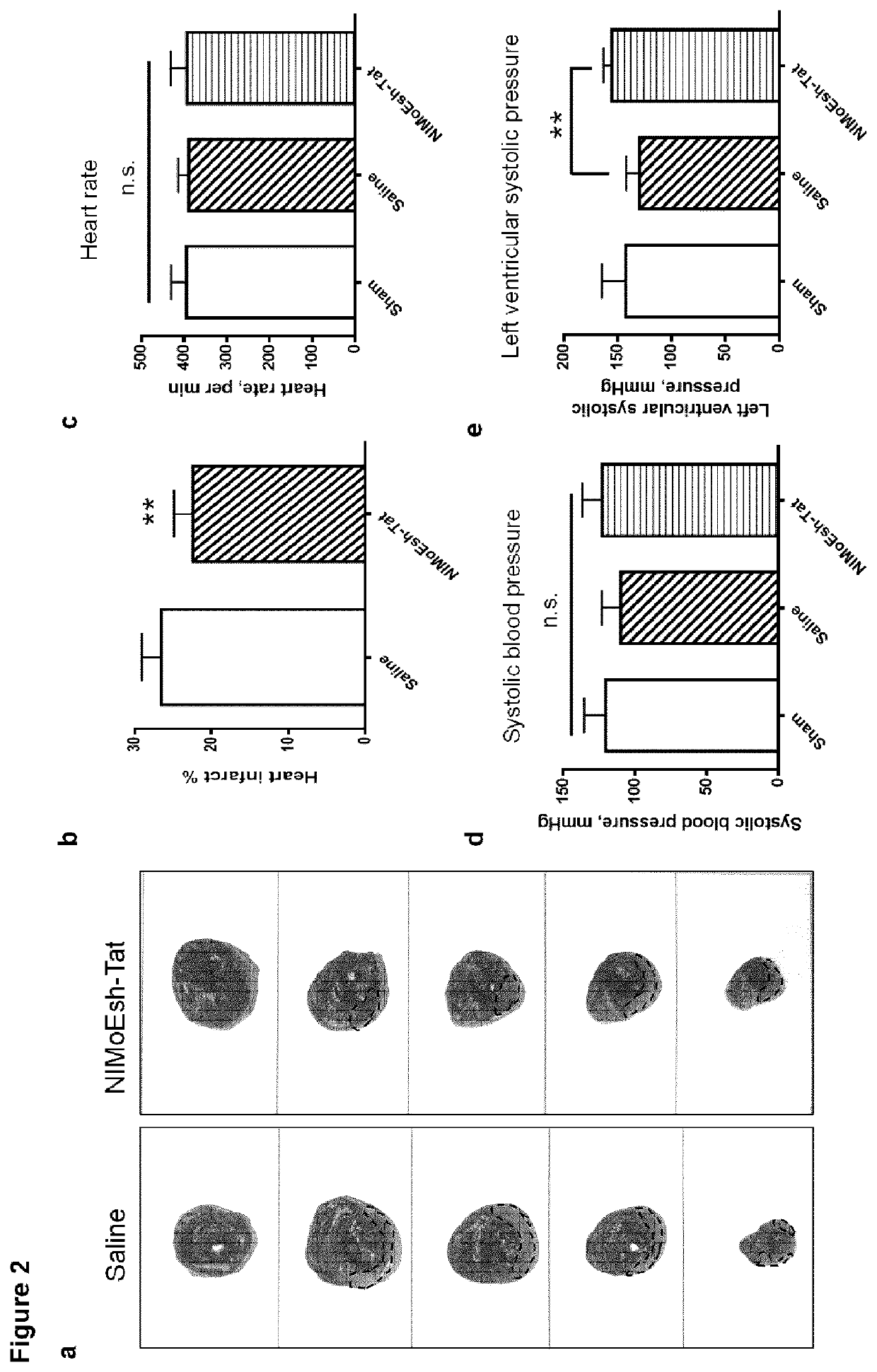
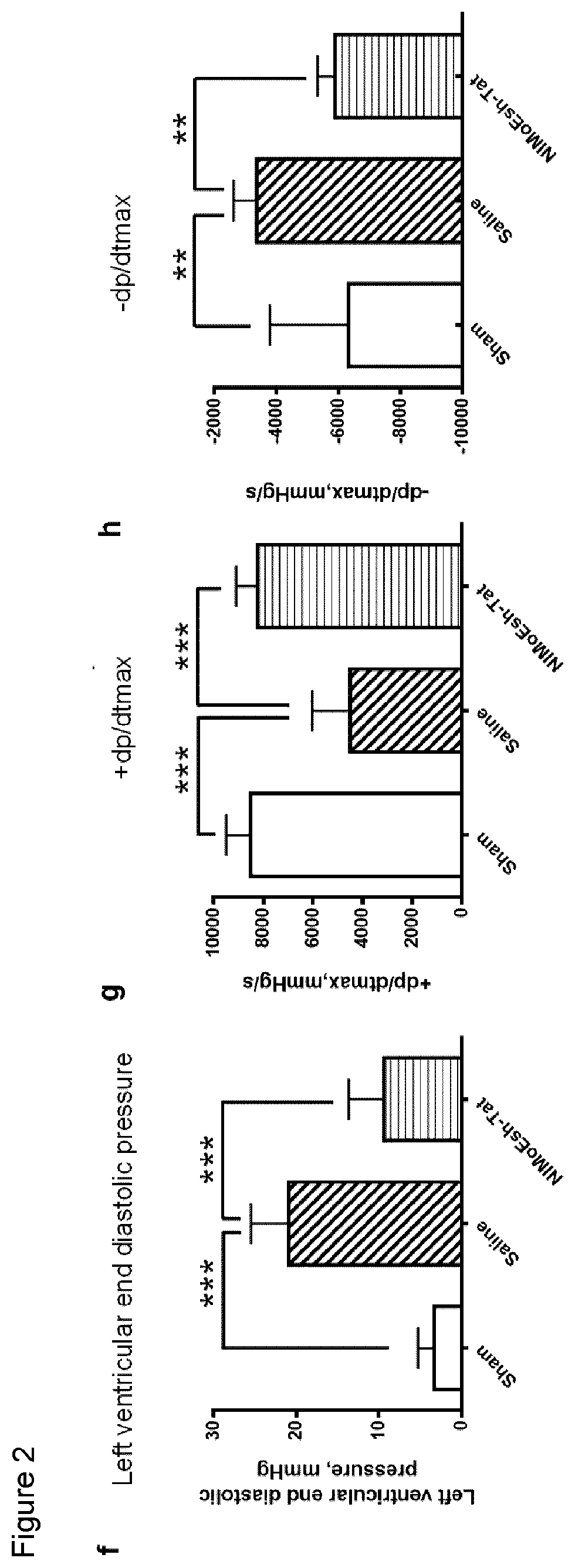
Disclosed herein are uses of a polypeptide comprising NIMoEsh for treating a disease or condition associated with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) in a subject in need thereof, uses of a polypeptide comprising NIMoEsh for restoring cardiac function following AMI in a subject in need thereof, uses of a polypeptide comprising NIMoEsh for reducing or preventing loss of cardiac function caused by AMI in a subject in need thereof, and uses of a polypeptide comprising NIMoEsh for treating a disease or condition associated with AMI in a subject in need thereof. The present invention relates to the use of a polypeptide comprising NIMoEsh for reducing AMI-induced cardiac tissue infarction in a subject in need thereof, and the use of a polypeptide comprising NIMoEsh for protecting myocardial cells from AMI-induced dysfunction in a subject in need thereof. Also disclosed herein are methods for such treatment, recovery, reduction or prevention, reduction and / or protection, as well as polypeptides comprising NIMoEsh for such treatment, recovery, reduction or prevention, reduction and / or protection.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Research method of MS-275 acting on acute myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury
PendingCN111575363AImprove the molecular mechanismCompounds screening/testingMicrobiological testing/measurementReperfusion injuryAcute myocardial ischaemia
The invention discloses a research method of MS-275 acting on acute myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury. The research method comprises the following steps: step I, performing ligation of an anterior descending branch of a left coronary artery of an SD male bandicoot to construct a bandicoot acute MI / RI model; step II, observing the action of the MS-275 in an MI / RI acute stage of the bandicoot;and step III, discussing a molecular mechanism of the MS-275 on bandicoot MI / RI protection action. According to the research, through constructing the bandicoot acute MI / RI model and combination within vivo and vitro experiments, the following research objectives are achieved: (1) observing the acetylation level of histone, and expression of HDAC1 and microRNA-210(miR-210) in cardiac muscle tissue of the bandicoot at the MI / RI acute stage; (2) confirming that the MS-275, a novel HDACI type selective depressant, has protection action on MI / RI of the bandicoot and influence on the acetylation level of the histone and expression of HDAC1 and miR-210 in tissue of a myocardial infarction region of the bandicoot subjected to myocardial ischemia reperfusion; and (3) disclosing a specific molecular mechanism that the MS-275 improves MI / RI of the bandicoot from the angle of miRNA epigenetic regulation, and providing an important theory and experiment basis for MI / RI treatment with HDACi.
Owner:THE SECOND XIANGYA HOSPITAL OF CENT SOUTH UNIV
One step cardiac test device
InactiveCN109561887AImprove accuracySurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsBlood markersHematological test
The invention provides a device for detecting diagnostic blood markers as early as half an hour upon an acute myocardial infarction symptoms onset.
Owner:NOVAMED
Methods and compositions for safe and effective thrombolysis
ActiveCN107073292BPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPharmacologyThrombolysis
Provided herein are methods, compositions and kits for safe and effective thrombolysis, eg, for the treatment of underlying stroke or acute myocardial infarction (AMI).
Owner:THROMBOLYTIC SCI
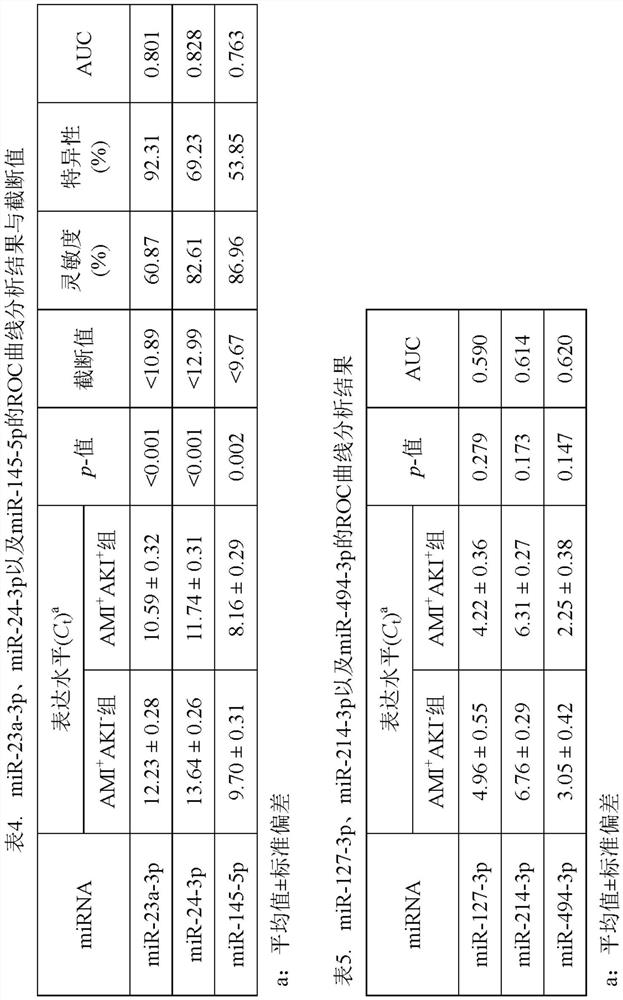
Products for predicting the risk of developing acute kidney injury in human subjects with acute myocardial infarction and uses thereof
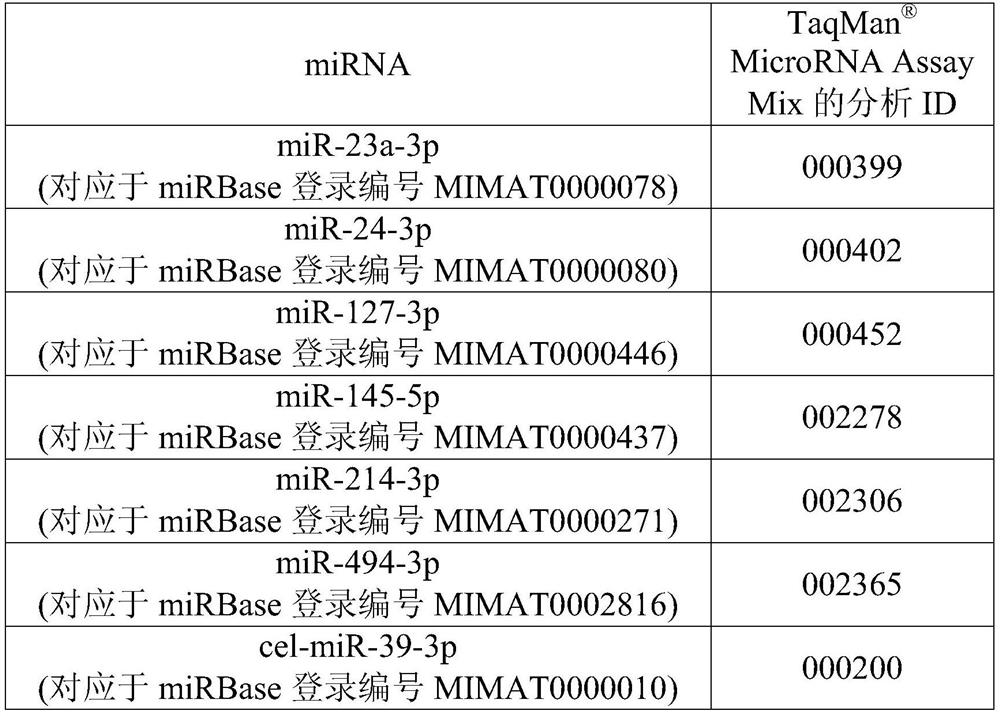
The present invention relates to methods for predicting the risk of developing acute kidney injury in a human individual with acute myocardial infarction. The present invention discloses a kit for predicting whether a human individual with acute myocardial infarction will develop acute kidney injury, wherein the kit comprises a reagent for detecting the expression level of miRNA selected from A group consisting of: miR-23a-3p, miR-24-3p, miR-145-5p, and combinations thereof. The present invention also discloses the use of the reagent supply for detecting the expression level of miRNA for the preparation of a kit for predicting whether a human individual with acute myocardial infarction will develop acute kidney injury.
Owner:CHUNG GUNG MEDICAL FOUNDATION LINKOU BRANCH +1
Inhibiting zd17-jnk interaction as a therapy for acute myocardial infarction
PendingUS20220362326A1Loss of functionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseCardiac functioning
Disclosed herein are uses of a polypeptide comprising NIMoEsh to treat a disease or condition associated with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) in a subject in need thereof, of a polypeptide comprising NIMoEsh to restore heart function after AMI in a subject in need thereof, of a polypeptide comprising NIMoEsh to reduce or prevent AMI-induced heart function loss in a subject in need thereof, of a polypeptide comprising NIMoEsh to reduce AMI-induced heart tissue infarct in a subject in need thereof, and of a polypeptide comprising NIMoEsh to protect cardiomyocytes against AMI-induced function loss in a subject in need thereof. Disclosed also herein are methods by which such treating, restoring, reducing or preventing, reducing, and / or protecting may be done, and a polypeptide comprising NIMoEsh for use in such treating, restoring, reducing or preventing, reducing, and / or protecting.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
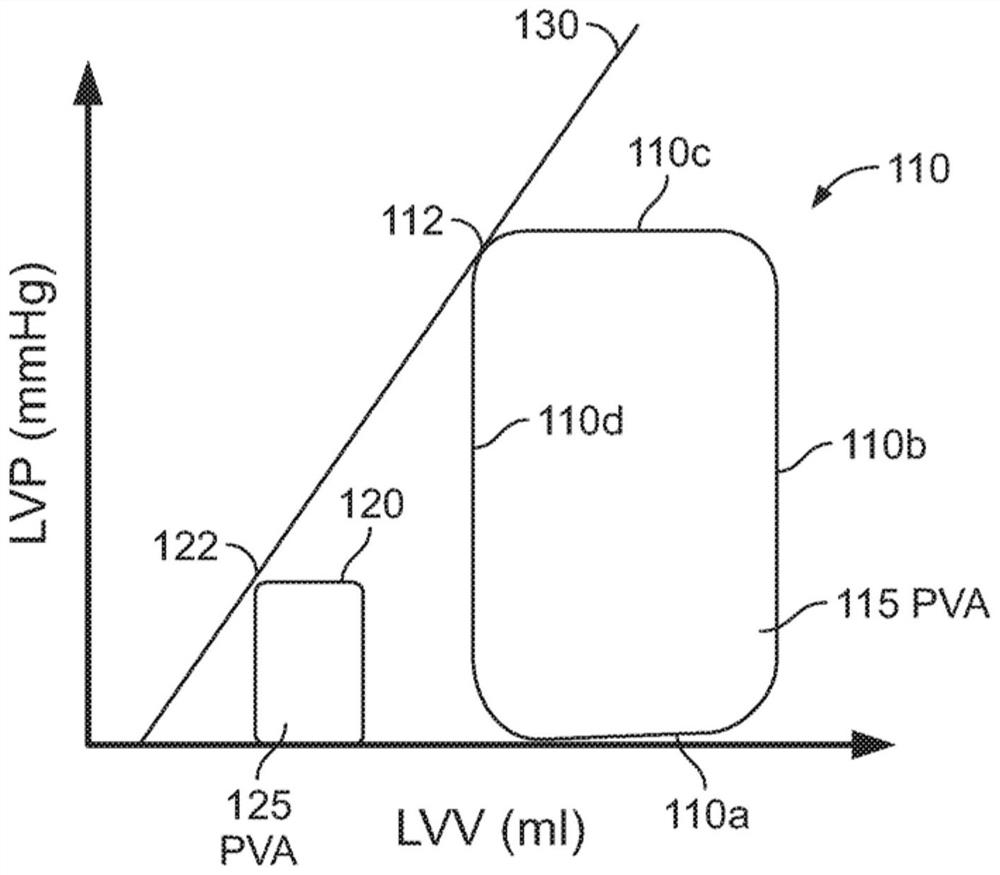
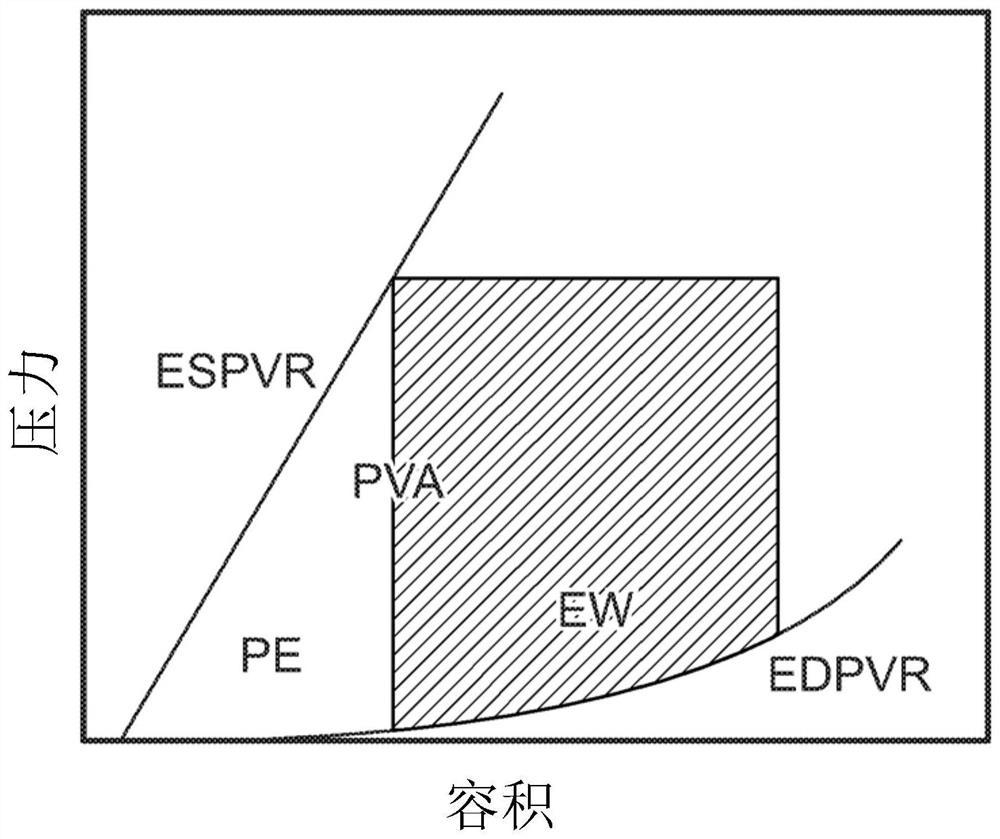
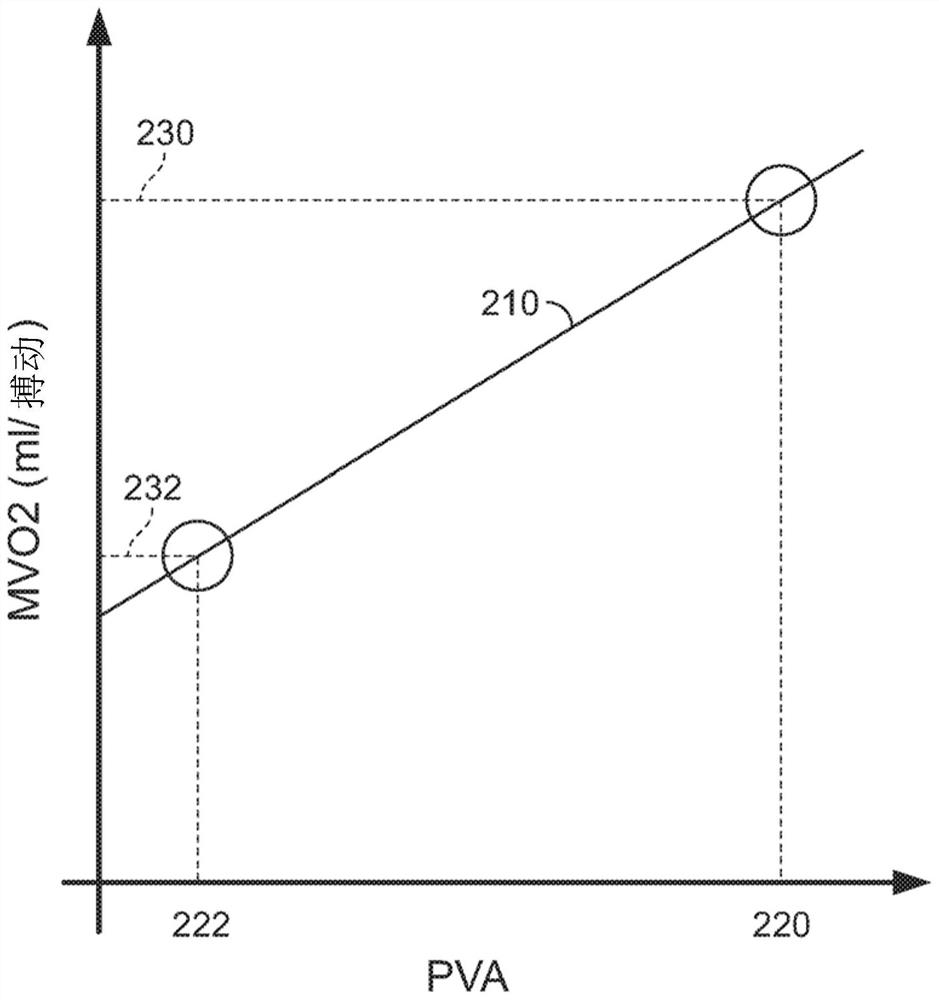
Systems and methods for controlling heart pump to minimize myocardial oxygen consumption
Various systems, devices, and methods are disclosed herein for healing acute myocardial infarction (AMI) patients using a heart, pump controlled in a maimer that maximizes mechanical unloading of the left ventricle in the presence of cardiovascular instability and minimizes myocardial oxygen consumption (MVO2) and consequentially infarct size to prevent the development of subsequent heart failure. In a closed feedback system, the system can include a sensor configured to generate an output used to measure or calculate a left ventricular systolic pressure (LSVP) within the left ventricle of a heart and a controller coupled to a heart, pump. The controller can be configured to measure or calculate the LVSP based on the output of the sensor and to control an operation of the heart pump to maximize mechanical unloading of the left ventricle based on the measured or calculated LVSP.
Owner:ABIOMED
Method of treatment and compounds for use therein
InactiveUS10328075B2Minimising the extent of ischaemia-reperfusion-induced myocardialCardiovascular disorderHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsProphylactic treatmentArtery occlusion
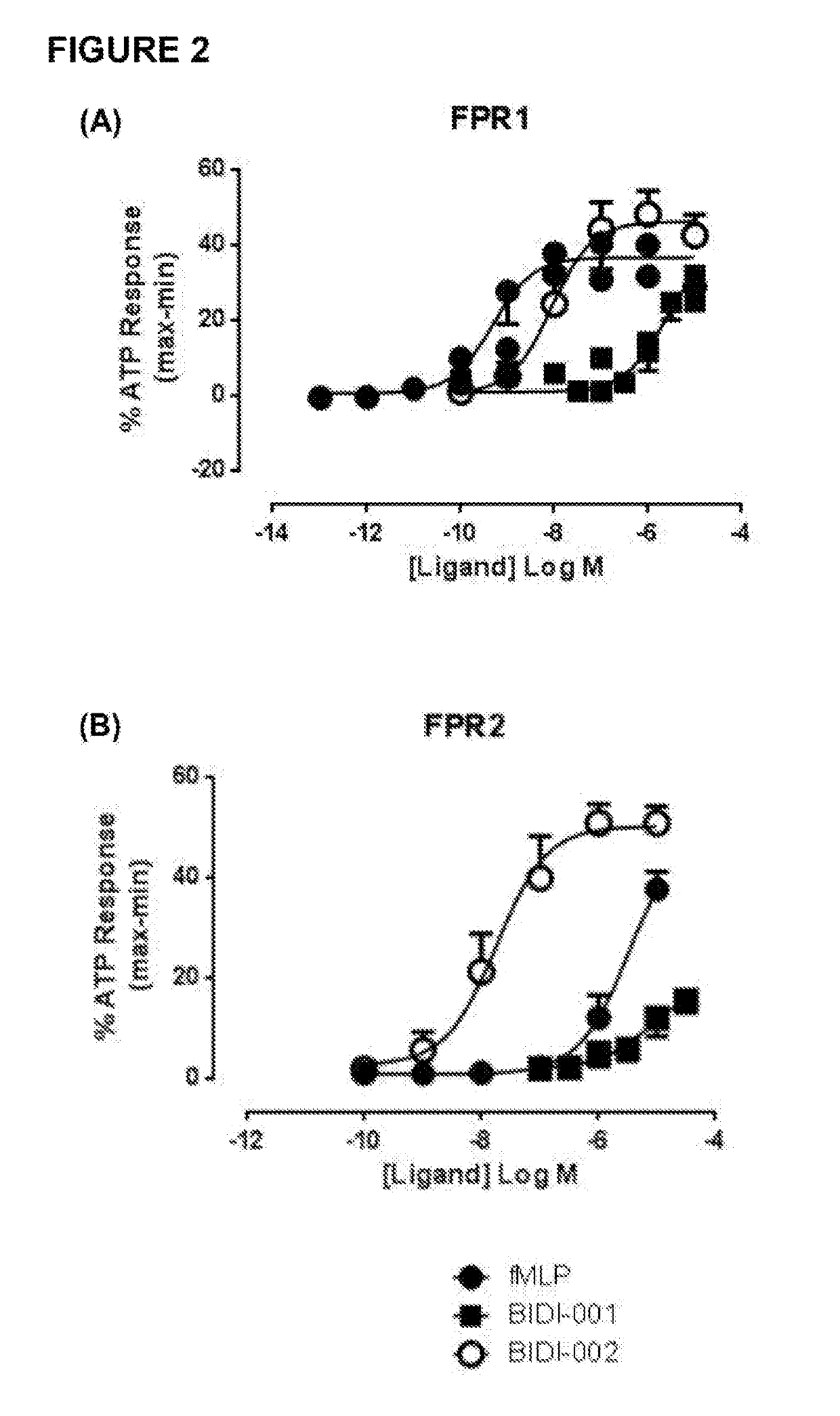
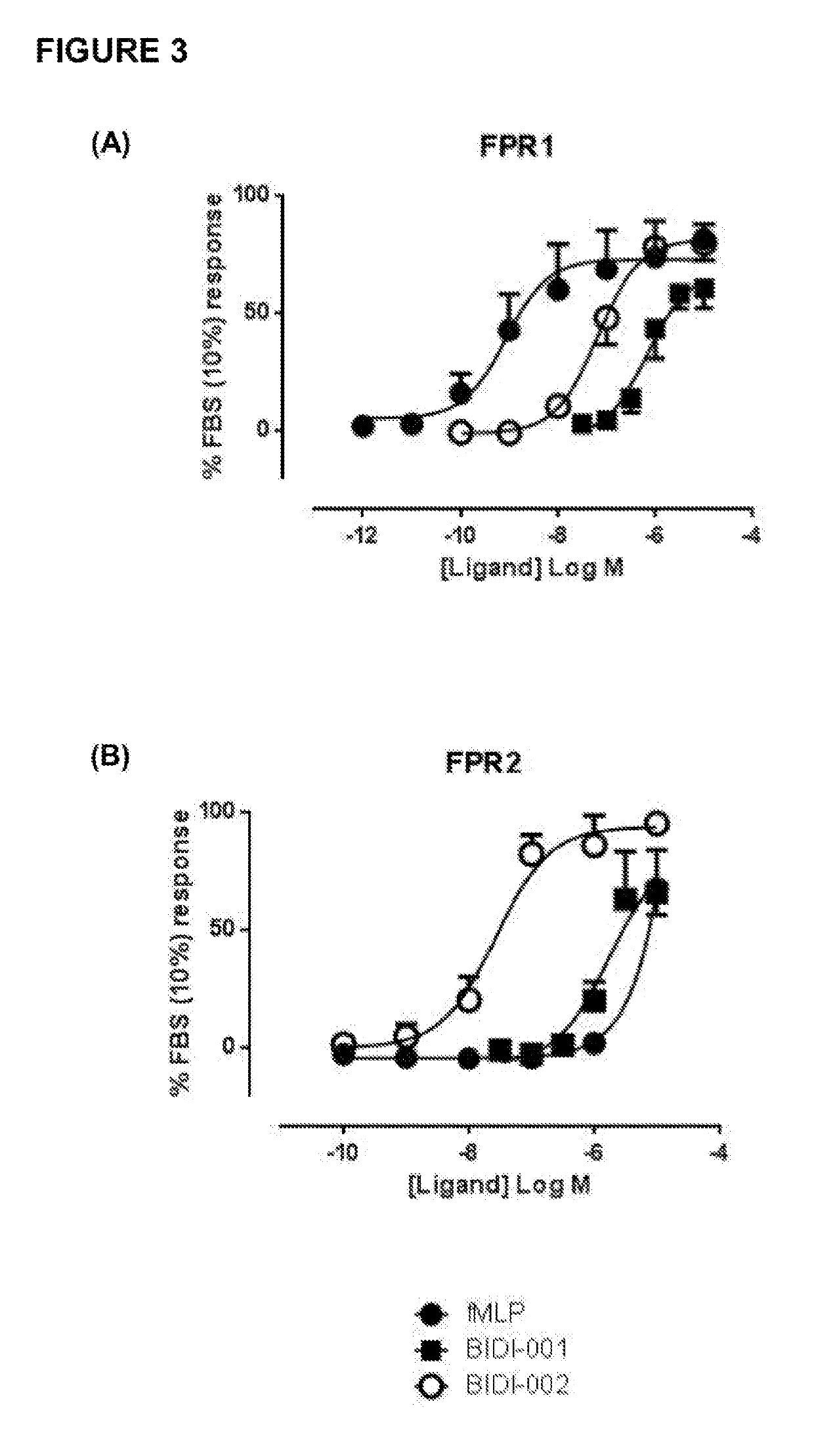
The present invention relates generally to a method of therapeutically or prophylactically treating ischaemia-induced myocardial tissue damage, in particular ischaemia-reperfusion-induced myocardial tissue damage. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method of reducing the extent of ischaemia-induced myocardial tissue damage in a mammal by selectively upregulating FPR1-mediated ERK signalling. The method of the present invention is useful, inter alia, in reducing the extent and / or severity of myocardial tissue damage associated with conditions characterized by myocardial ischaemia or myocardial ischaemia and reperfusion, such as acute myocardial infarction caused by atherosclerotic artery occlusion or blood clot-induced artery occlusion.
Owner:MONASH UNIV +1
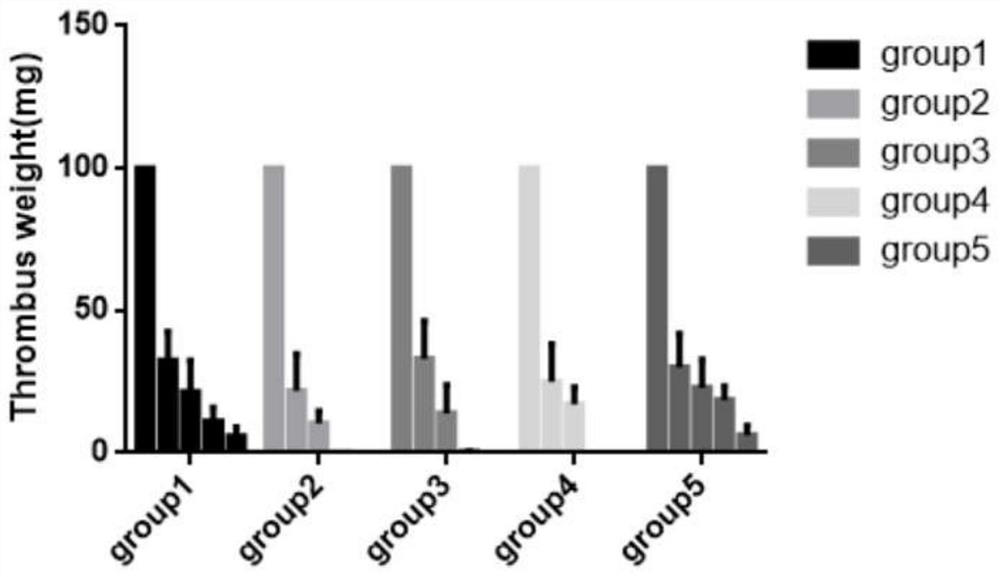
Method for extracting thrombus exosome of patient with acute myocardial infarction and application of thrombus exosome
ActiveCN113278584AReduce dosageHigh purityCell dissociation methodsMammal material medical ingredientsRadiologyThrombus
The invention relates to a method for extracting thrombus exosomes of patients with acute myocardial infarction and application, after thrombus is dissolved by using a method of mixing collagenase with pancreatin, exosomes in thrombus are successfully extracted by using an ultracentrifugation method, which is the first case at home and abroad, and compared with an existing method for extracting tissue exosomes by using collagenase, the method has the advantages that after the pancreatin is added, the use amount of collagenase is reduced, and the purity of the exosome is also improved.
Owner:GUIZHOU PROVINCIAL PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com